Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1400 results about "Normal platelet morphology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The normal range (99% of population analyzed) for platelets in healthy Caucasians is 150,000 to 450,000 per cubic millimeter (a mm3 equals a microliter). or 150–400 × 109 per liter. The normal range has been confirmed to be the same in the elderly and Spanish populations.
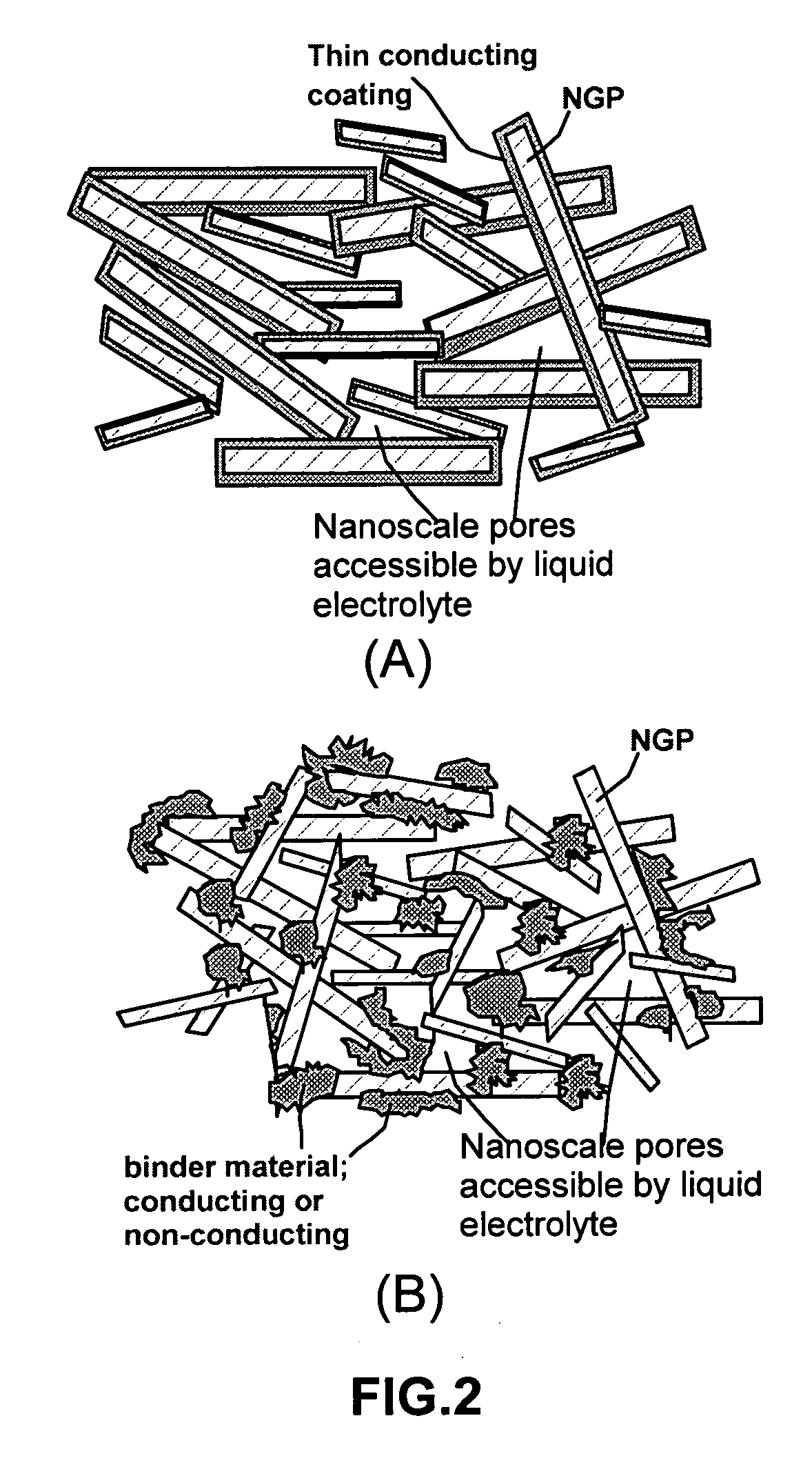
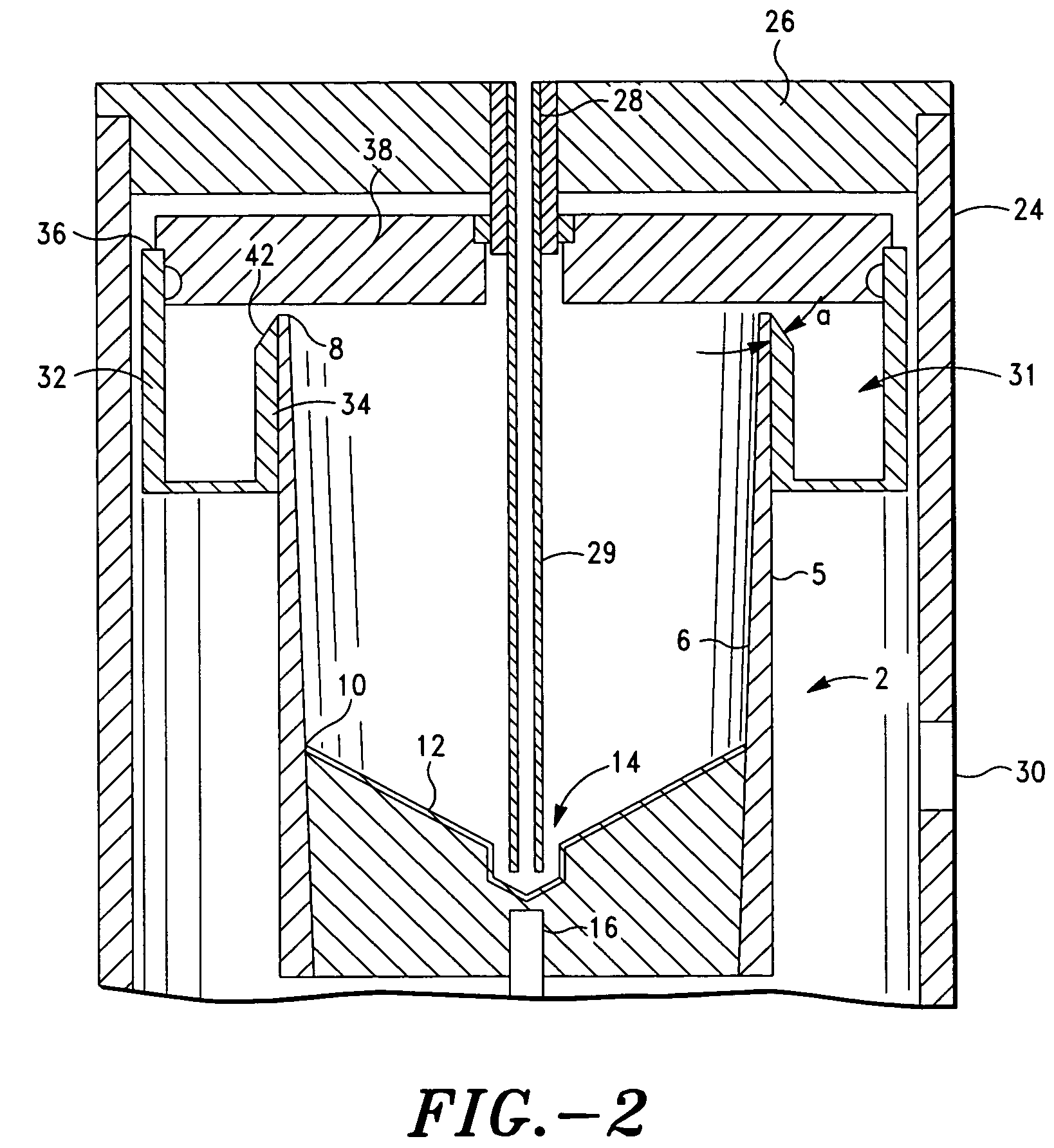
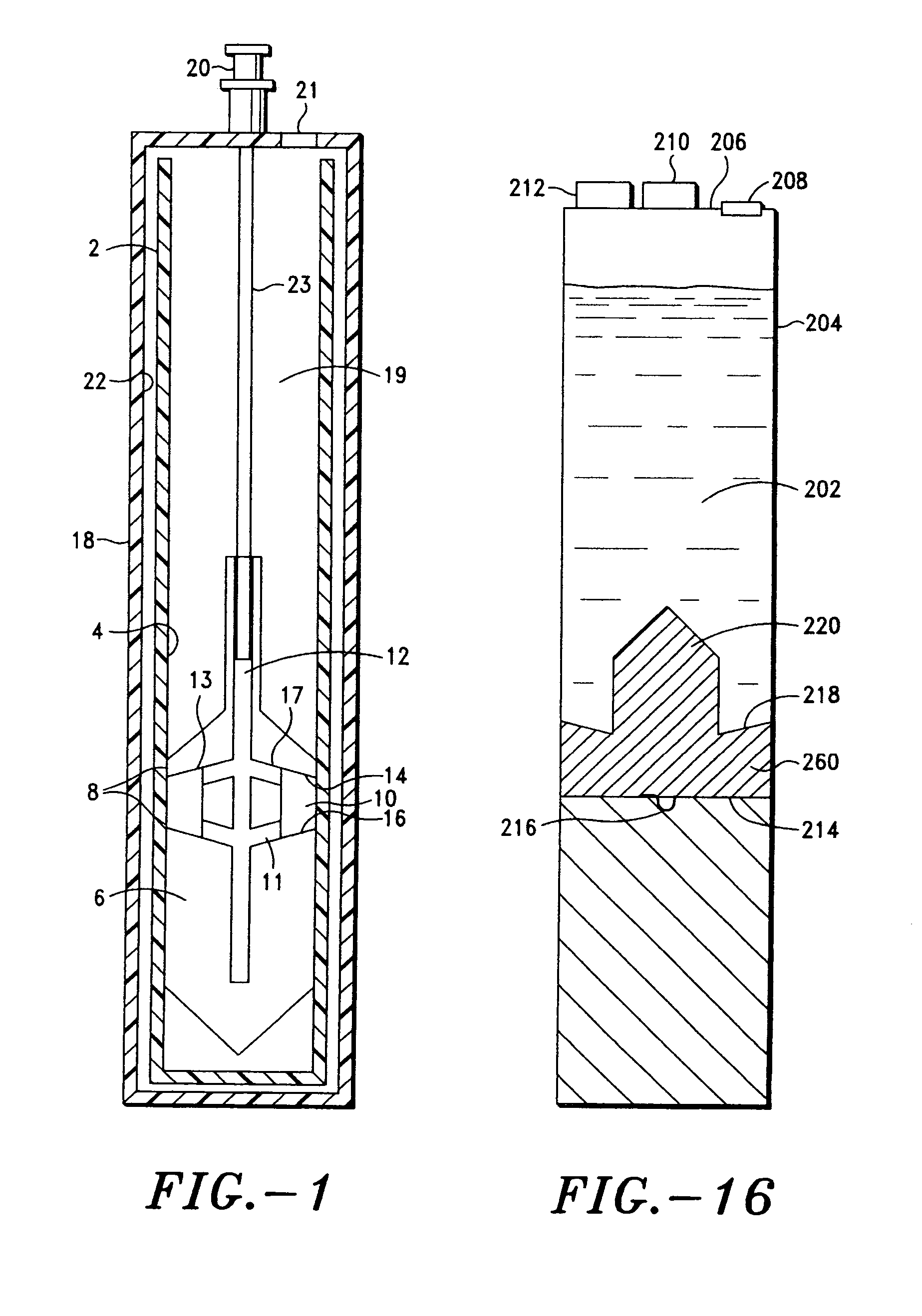
Process for producing nano-scaled platelets and nanocompsites
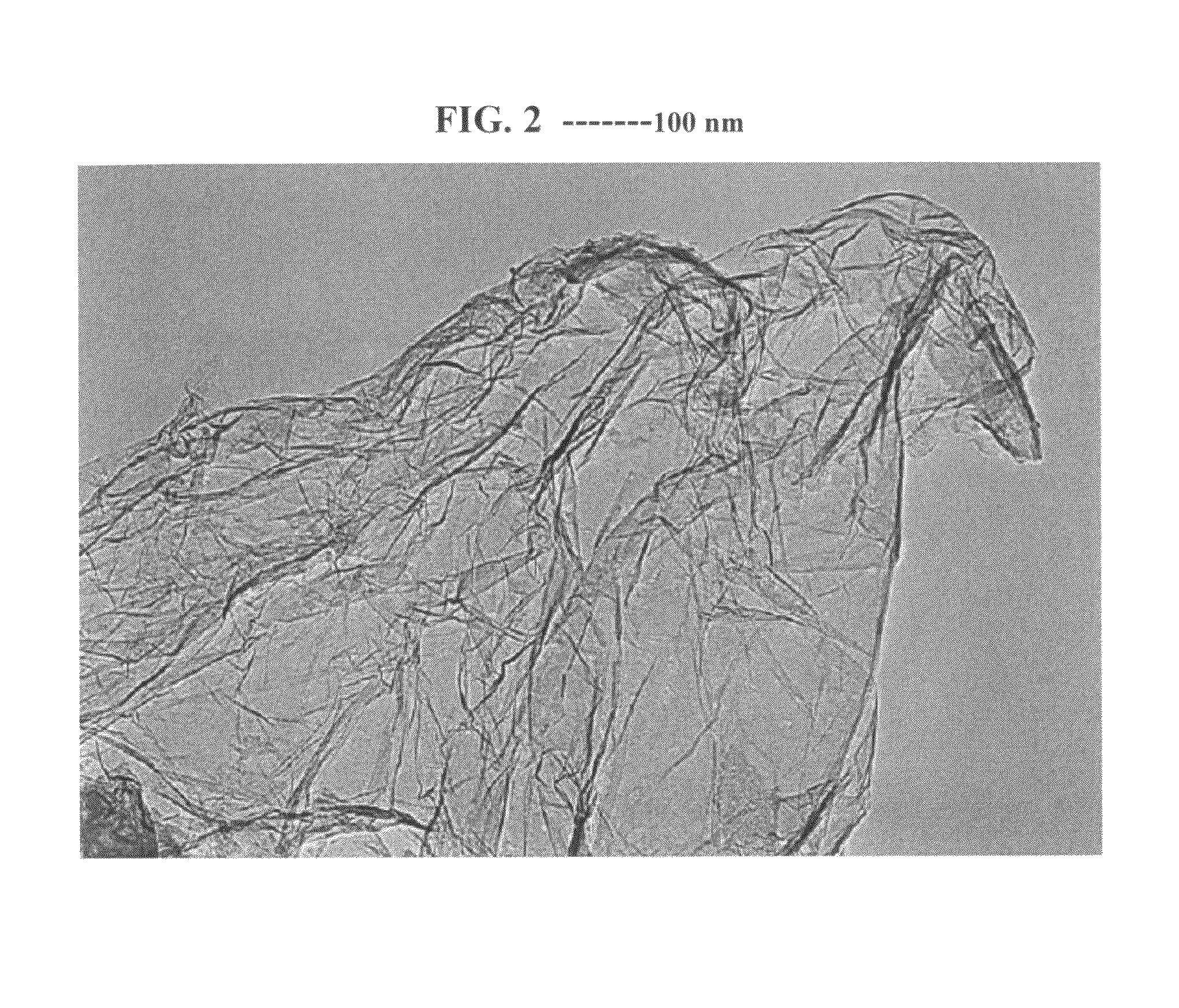
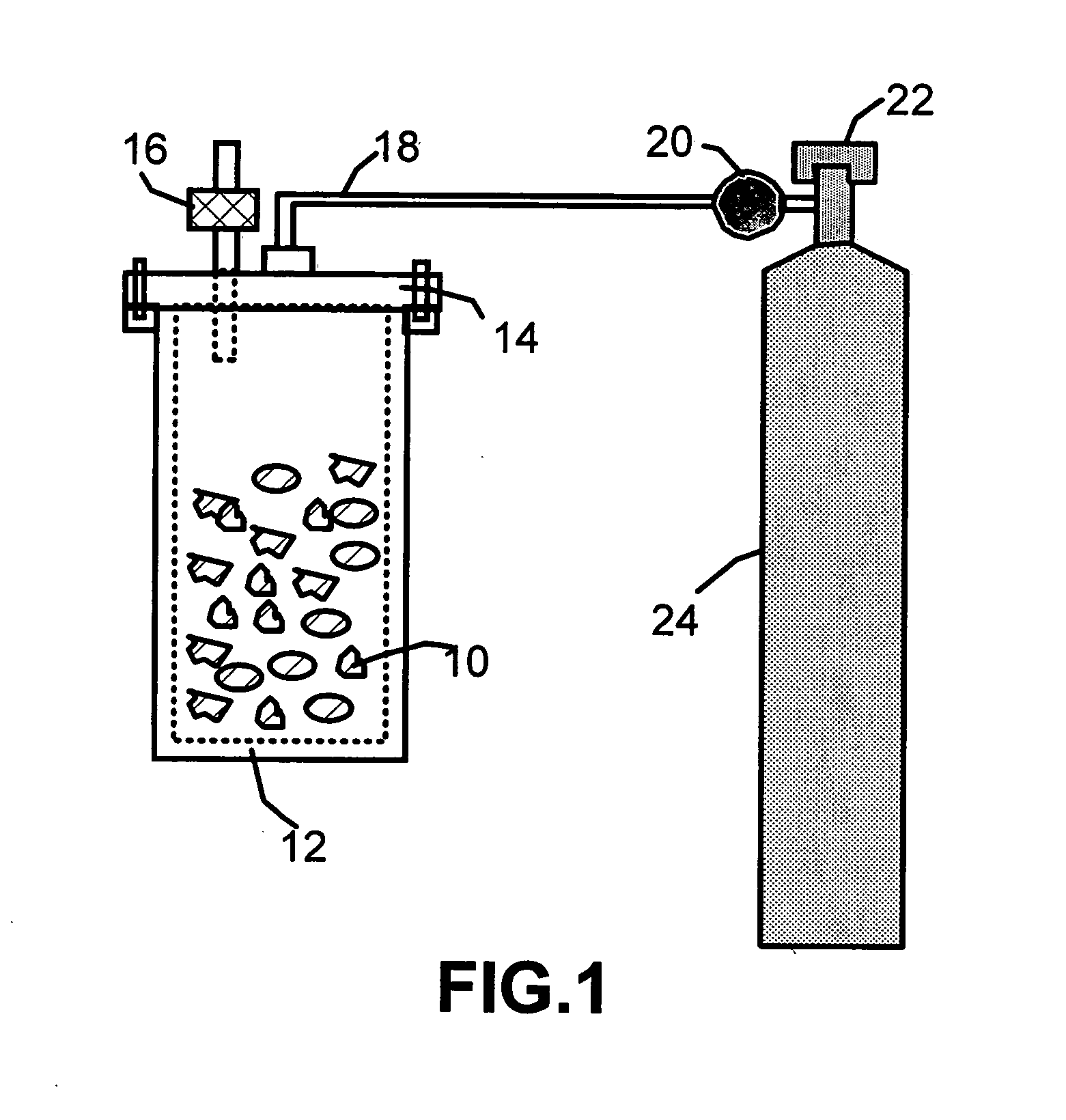
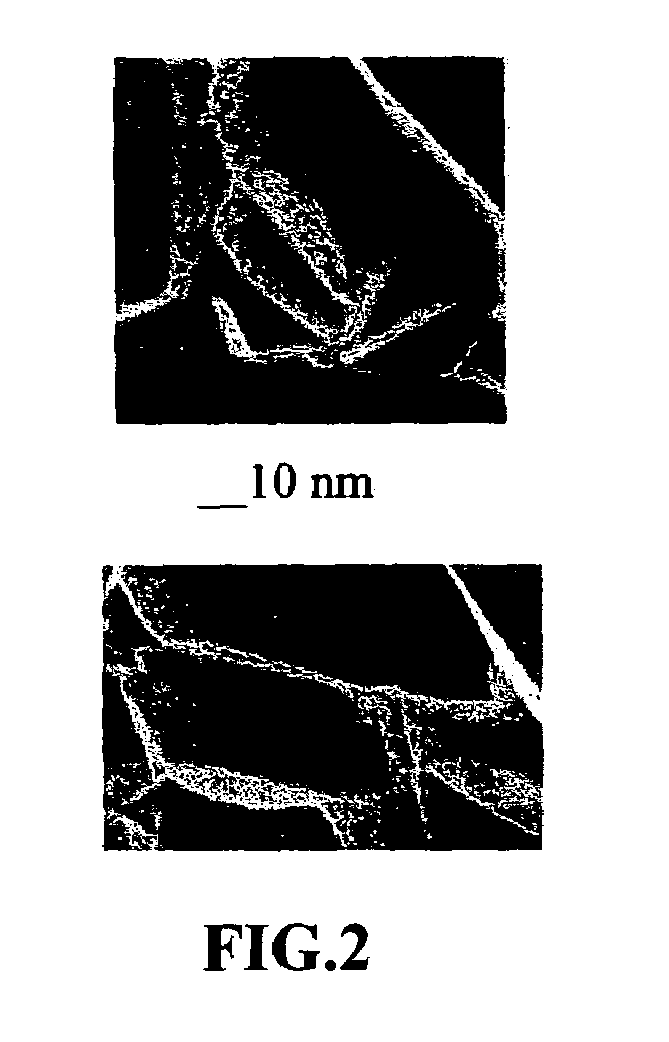
Disclosed is a process for exfoliating a layered material to produce nano-scaled platelets having a thickness smaller than 100 nm, typically smaller than 10 nm, and often between 0.34 nm and 1.02 nm. The process comprises: (a) subjecting a layered material to a gaseous environment at a first temperature and first pressure sufficient to cause gas species to penetrate between layers of the layered material, forming a gas-intercalated layered material; and (b) subjecting the gas-intercalated layered material to a second pressure, or a second pressure and a second temperature, allowing gas species to partially or completely escape from the layered material and thereby exfoliating the layered material to produce partially delaminated or totally separated platelets. The gaseous environment preferably contains only environmentally benign gases that are reactive (e.g., oxygen) or non-reactive (e.g., noble gases) with the layered material. The process can also include dispersing the platelets in a matrix material to form a nanocomposite.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
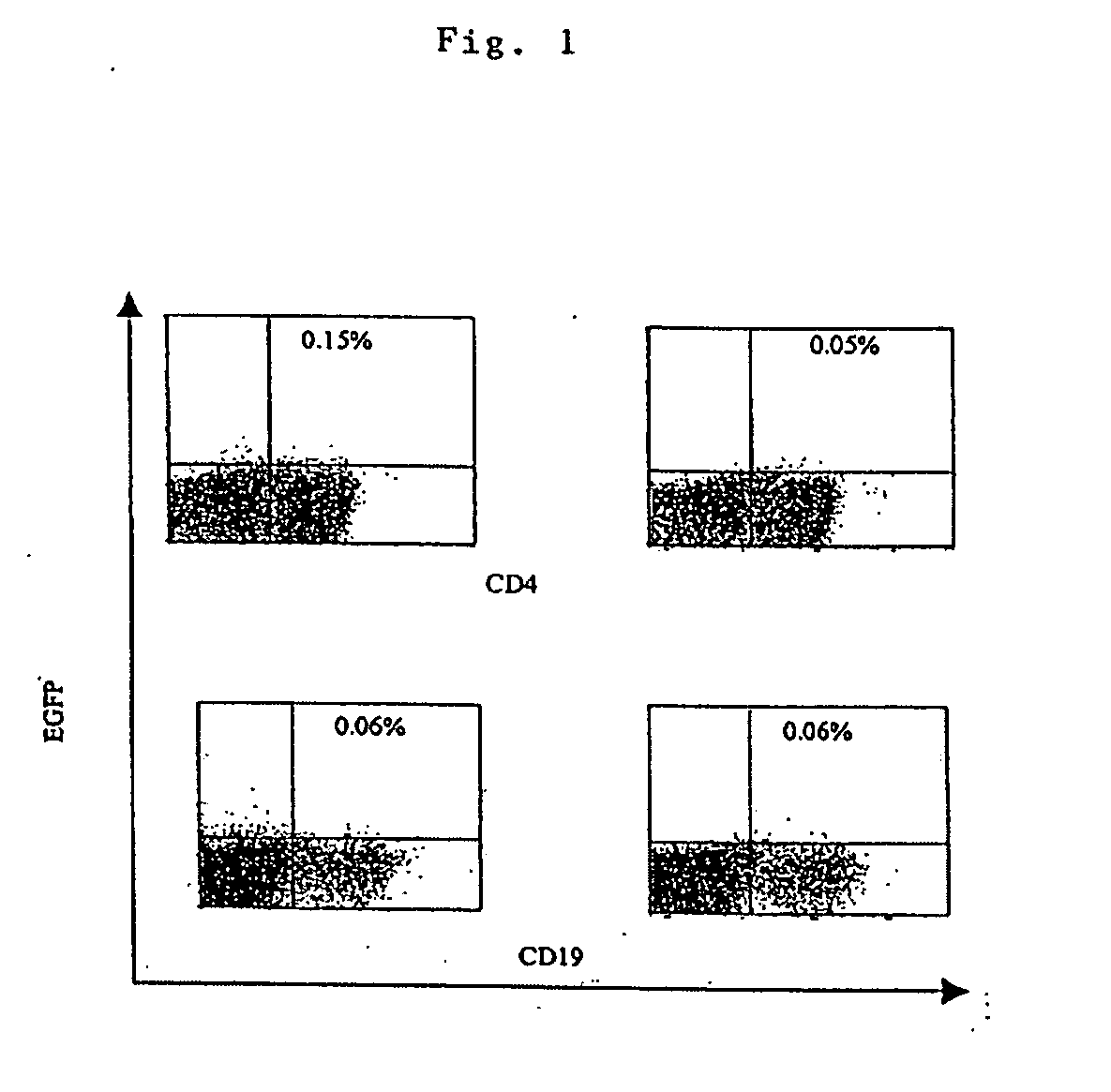
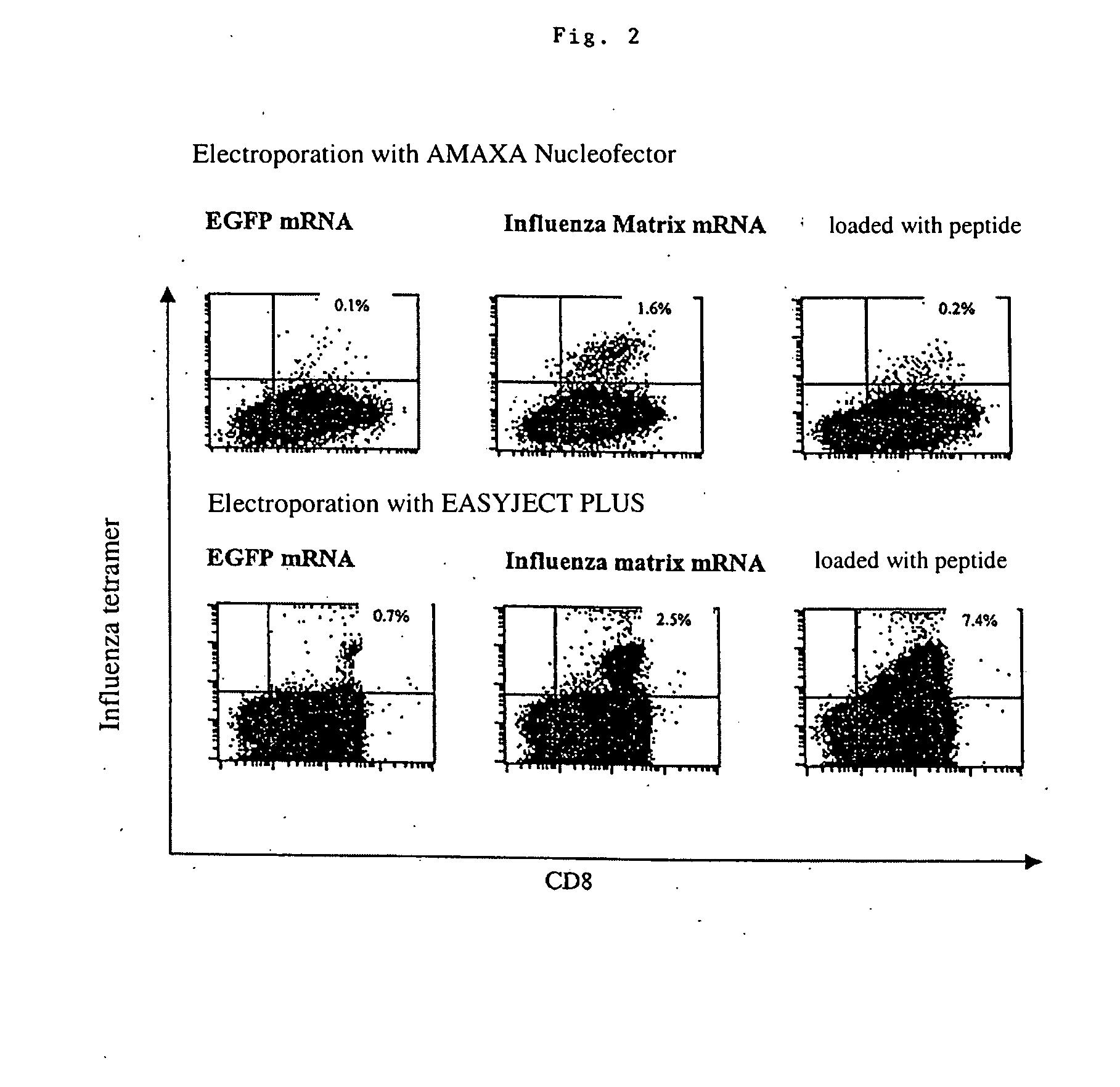
Transfection of blood cells with mRNA for immune stimulation and gene therapy
InactiveUS20060188490A1Improve stabilityIncrease transfectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAntigenCancer prevention
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing blood cells or haemopoietic cells, e.g. red blood cells (erythrocytes), granulocytes, mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and / or blood platelets, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and / or vehicle, wherein the cells are transfected with at least one mRNA comprising at least one region coding for at least one antigen. The invention further discloses a method of preparing the aforesaid pharmaceutical composition and the use of blood cells transfected in this way for the preparation of drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for immune stimulation against the antigens encoded by the mRNA. The subjects according to the invention are used especially for the therapy and / or prophylaxis of carcinoses or infectious diseases and can also be employed in gene therapy.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
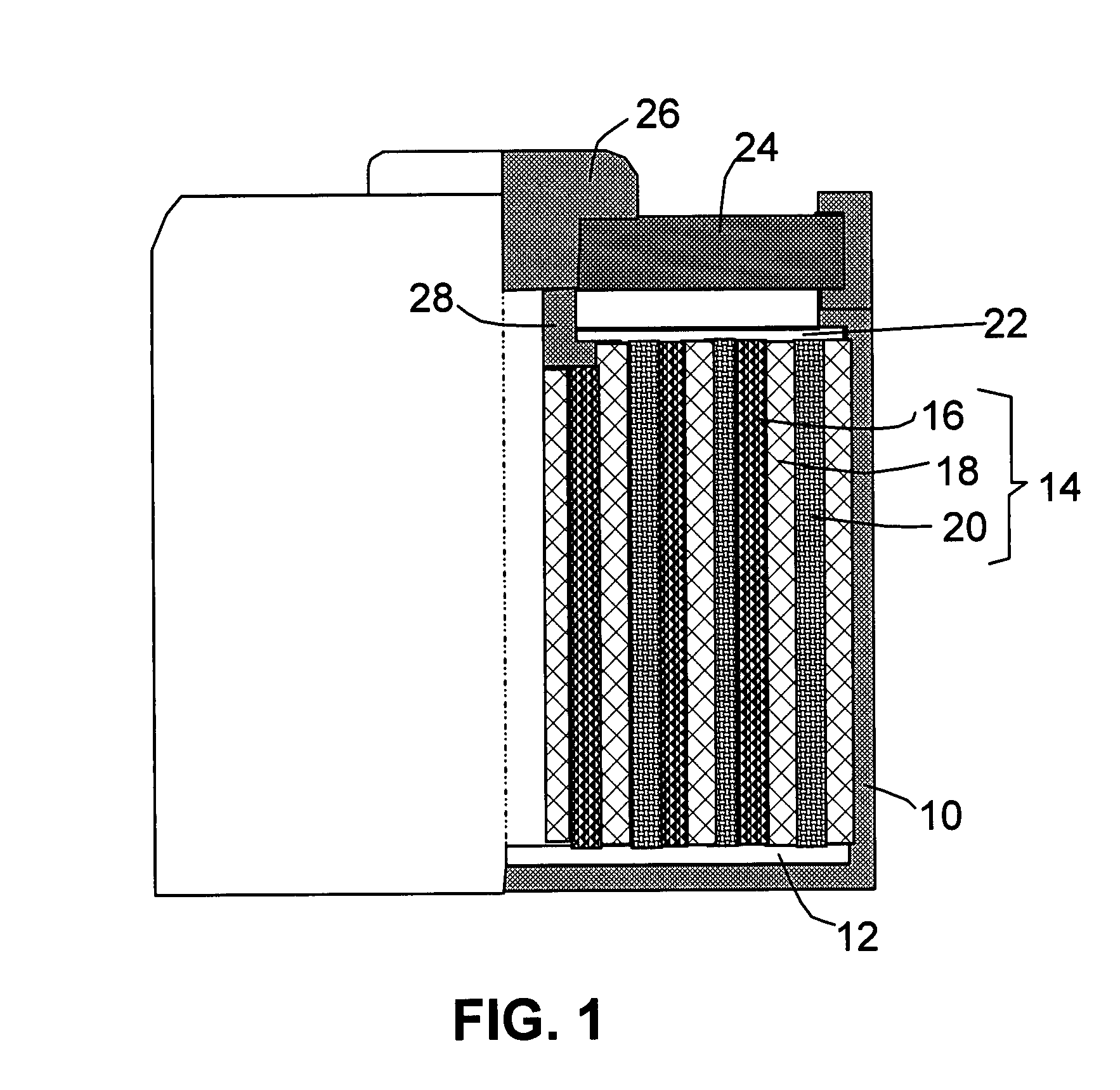
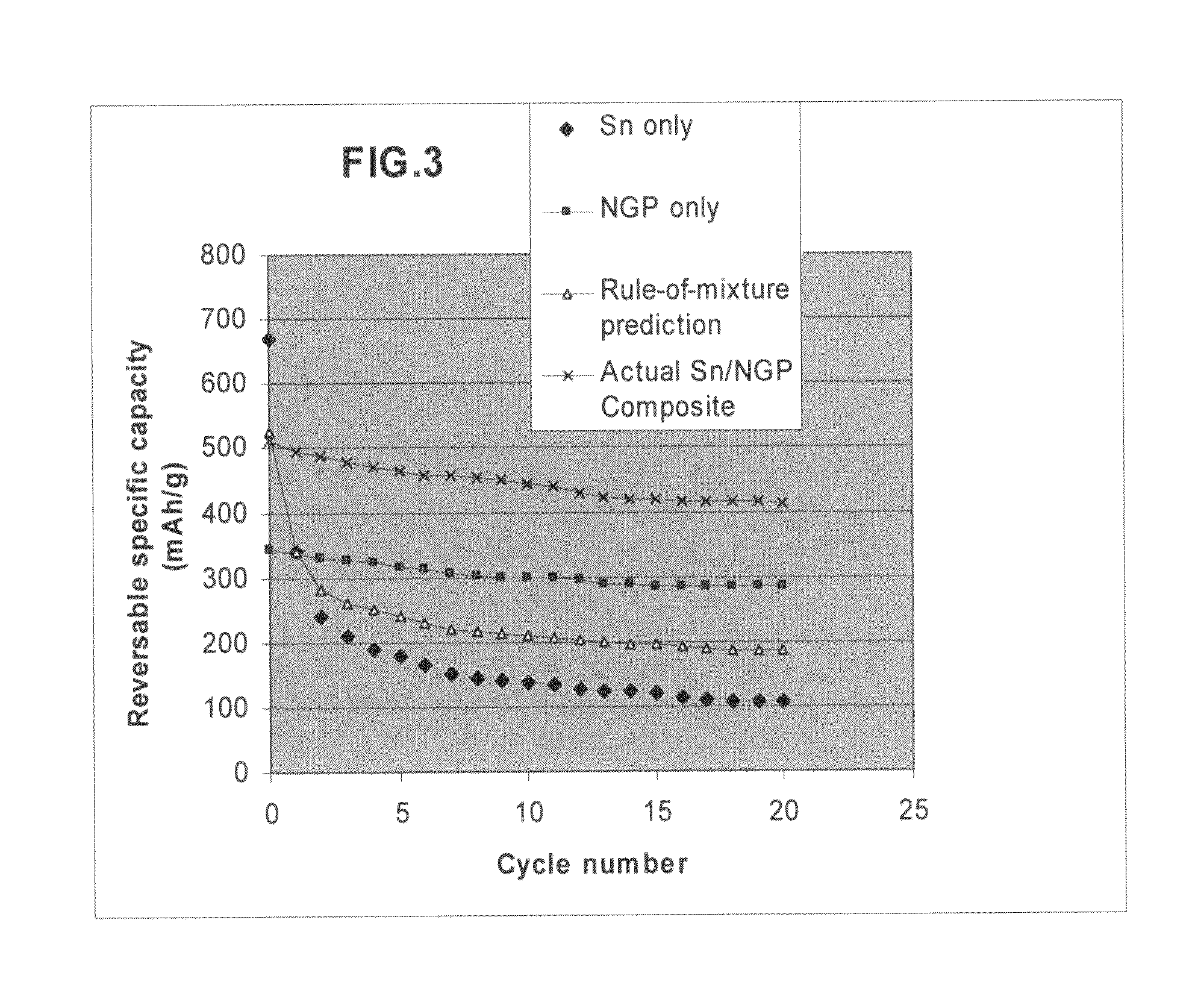
Nano graphene platelet-base composite anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS7745047B2Improve conductivityLower internal resistanceAlkaline accumulatorsElectrolytic capacitorsGraphiteGraphene
The present invention provides a nano-scaled graphene platelet-based composite material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing lithium ions; and (b) a plurality of nano-scaled graphene platelets (NGPs), wherein a platelet comprises a graphene sheet or a stack of graphene sheets having a platelet thickness less than 100 nm; wherein at least one of the particles or coating is physically attached or chemically bonded to at least one of the graphene platelets and the amount of platelets is in the range of 2% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating in the range of 98% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
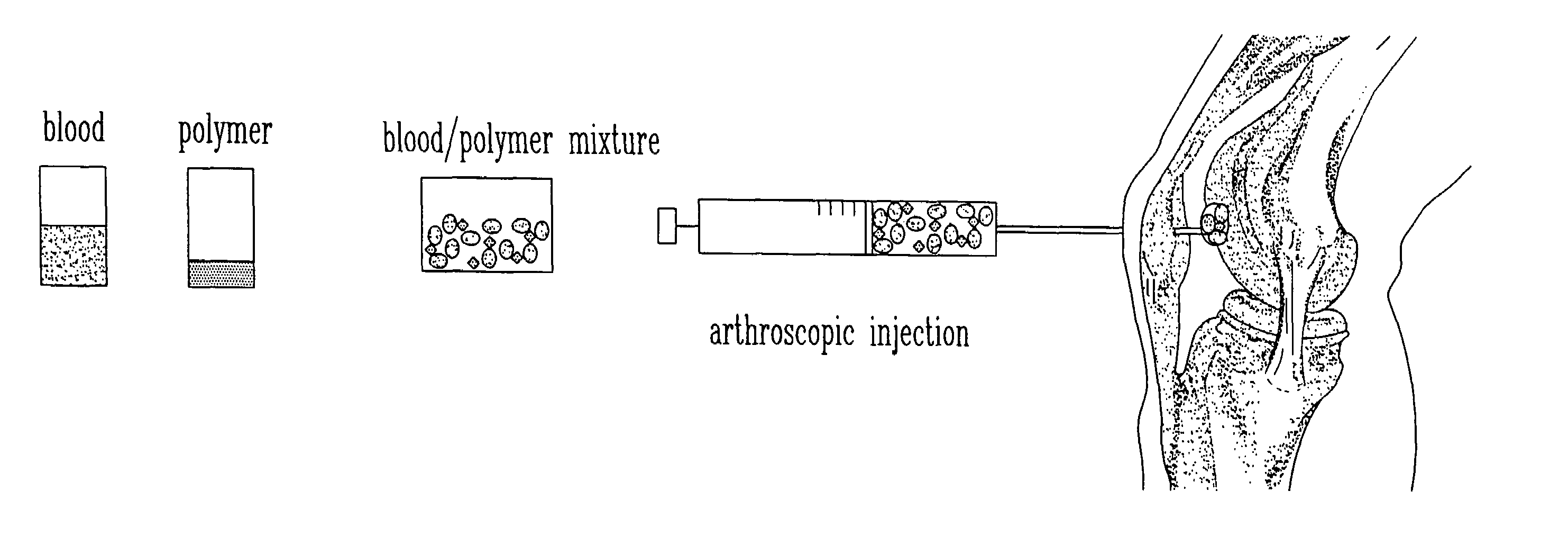
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Method of rendering a mechanical heart valve non-thrombogenic with an electrical device
InactiveUS20050021134A1Reduce and eliminate clottingEasy accessElectrotherapyHeart valvesThrombusElectrical devices
A mechanical device for implantation into a patient's body is designed or modified to be electrically charged to prevent coagulation on the device, thereby extending the life of the device and alleviating the need for the patient to utilize anticoagulant therapy. The device may be a heart valve and is electrically charged by being connected to a power source. The power source is preferably a battery pack implanted in the body and is connected to the device by connector wires. The charge applied to the device may be negative or positive, as long as it helps to repel platelets and / or red blood cells from the device in order to help prevent coagulation on one or more surfaces of the device.
Owner:JS VASCULAR
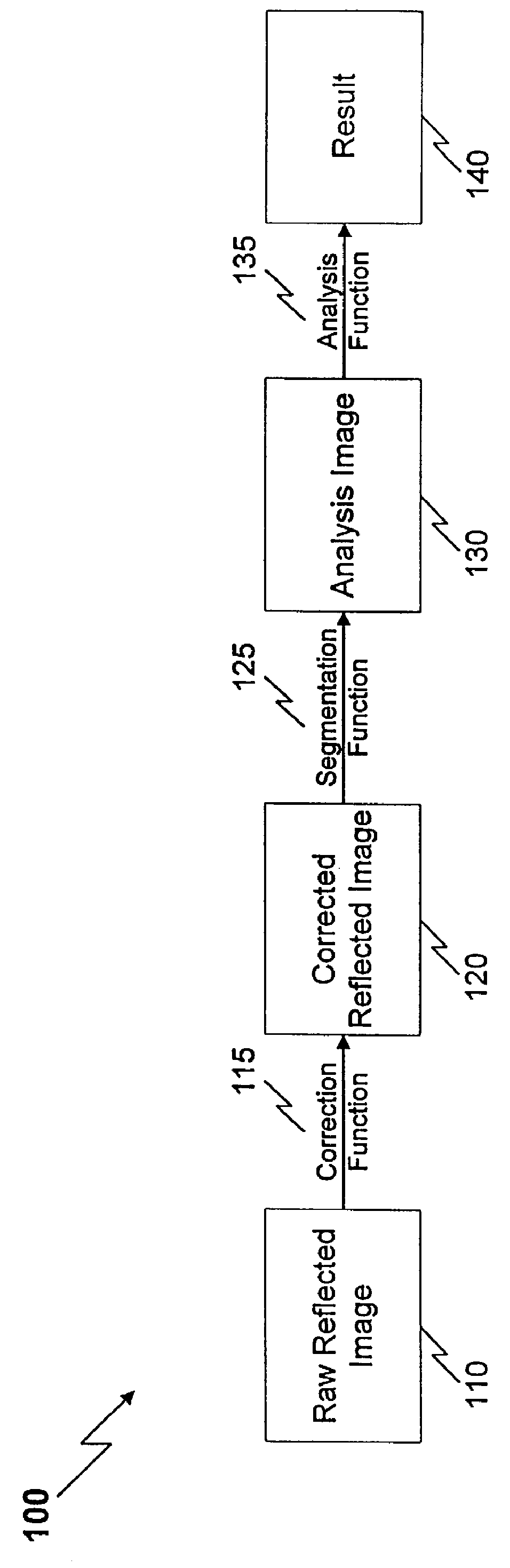
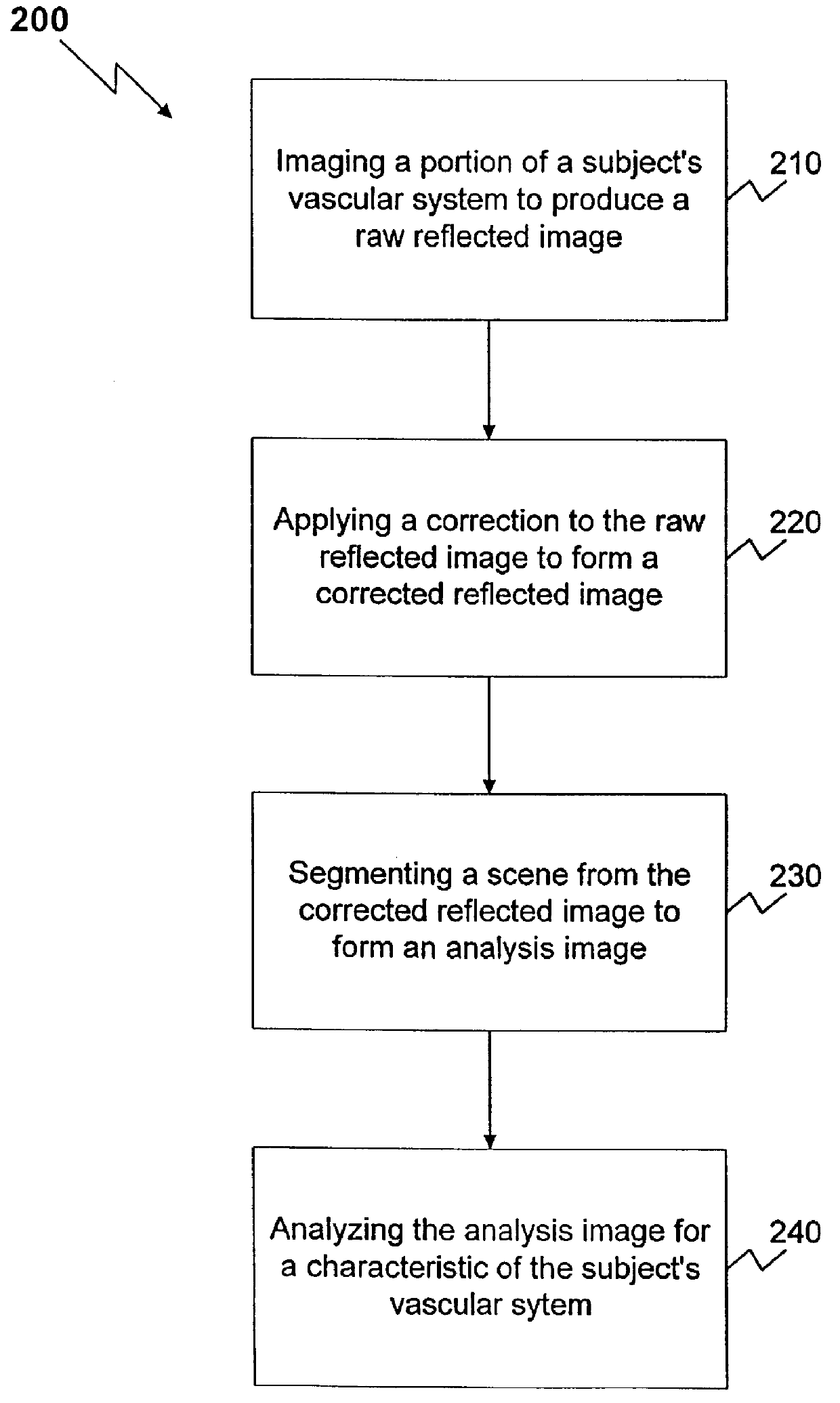
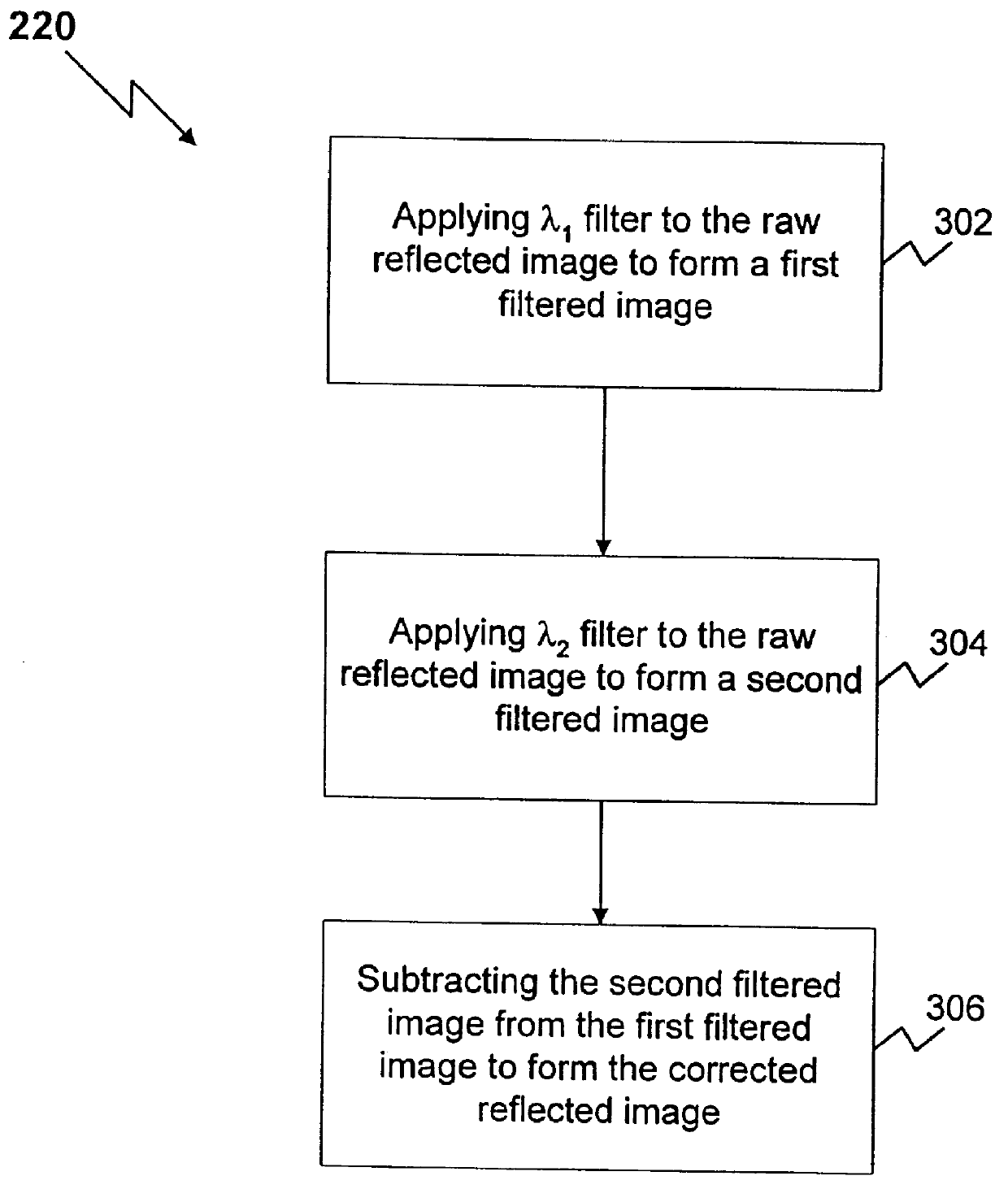
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis
InactiveUS6104939AQuick measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsWhite blood cellPolarizer
Method and apparatus for reflected imaging analysis. Reflected imaging is used to perform non-invasive, in vivo analysis of a subject's vascular system. A raw reflected image (110) is normalized with respect to the background to form a corrected reflected image (120). An analysis image (130) is segmented from the corrected reflected image to include a scene of interest for analysis. The method and apparatus can be used to determine such characteristics as the hemoglobin concentration per unit volume of blood, the number of white blood cells per unit volume of blood, a mean cell volume, the number of platelets per unit volume of blood, and the hematocrit. Cross-polarizers can be used to improve visualization of the reflected image.
Owner:INTPROP MVM
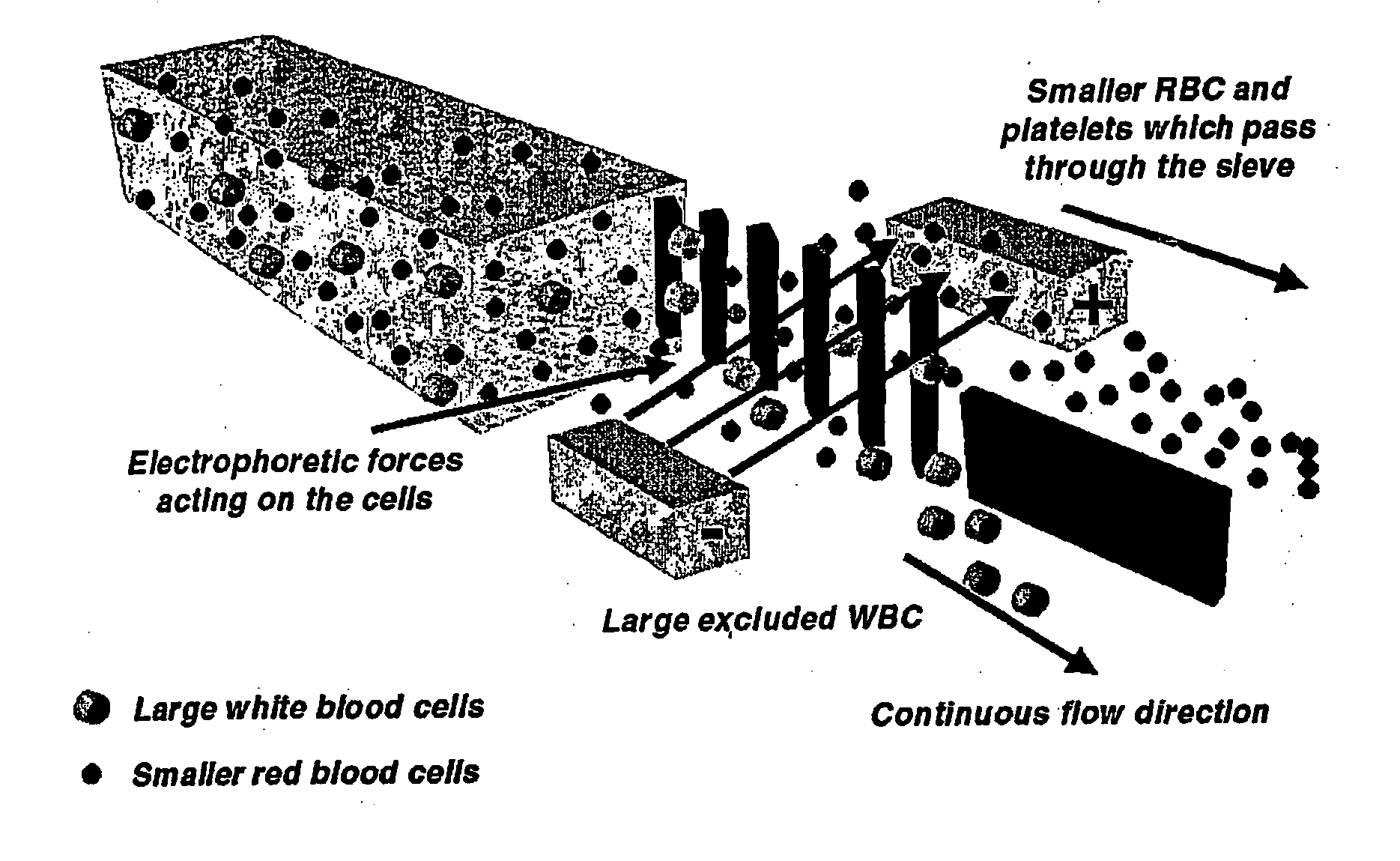
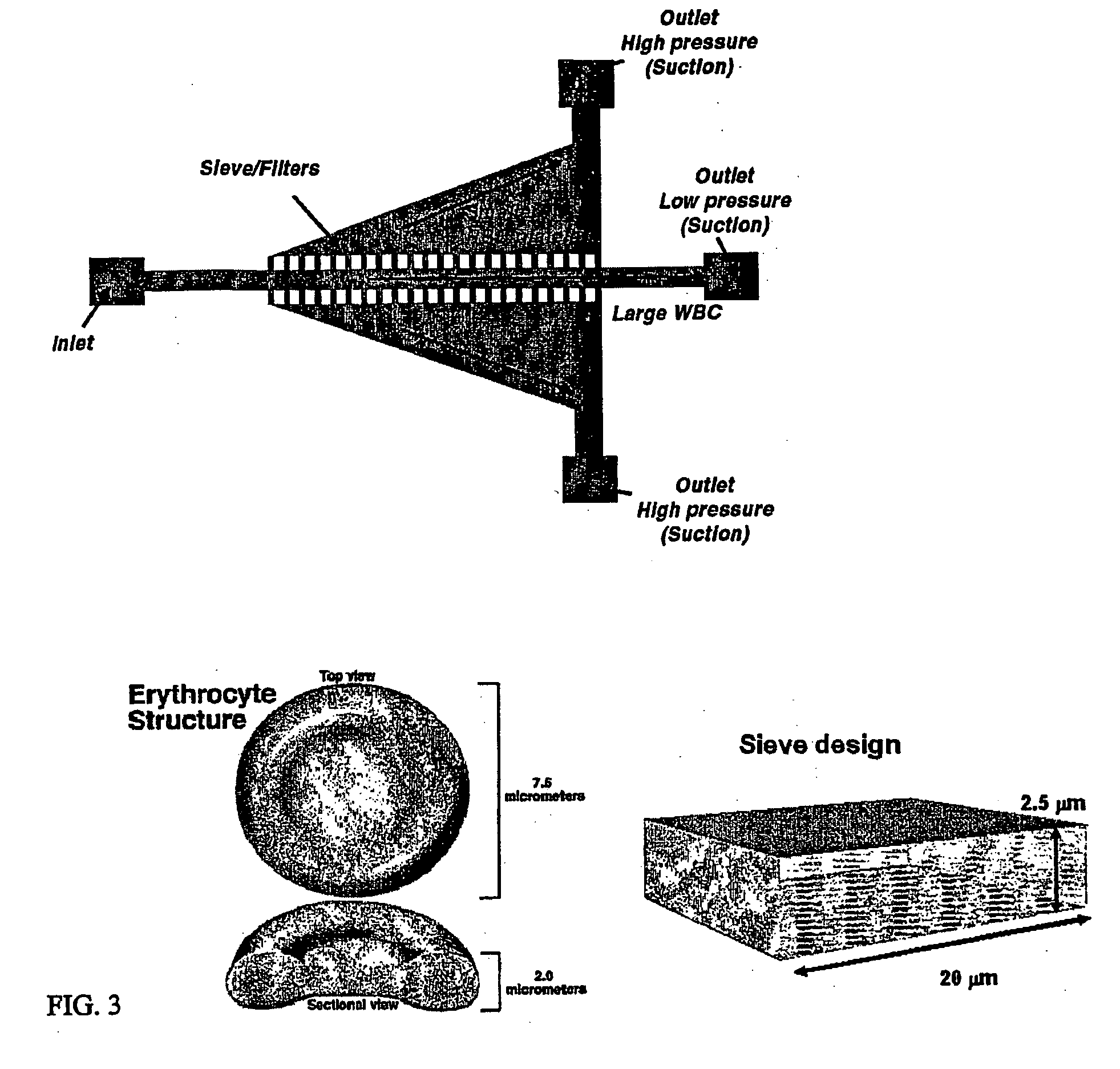
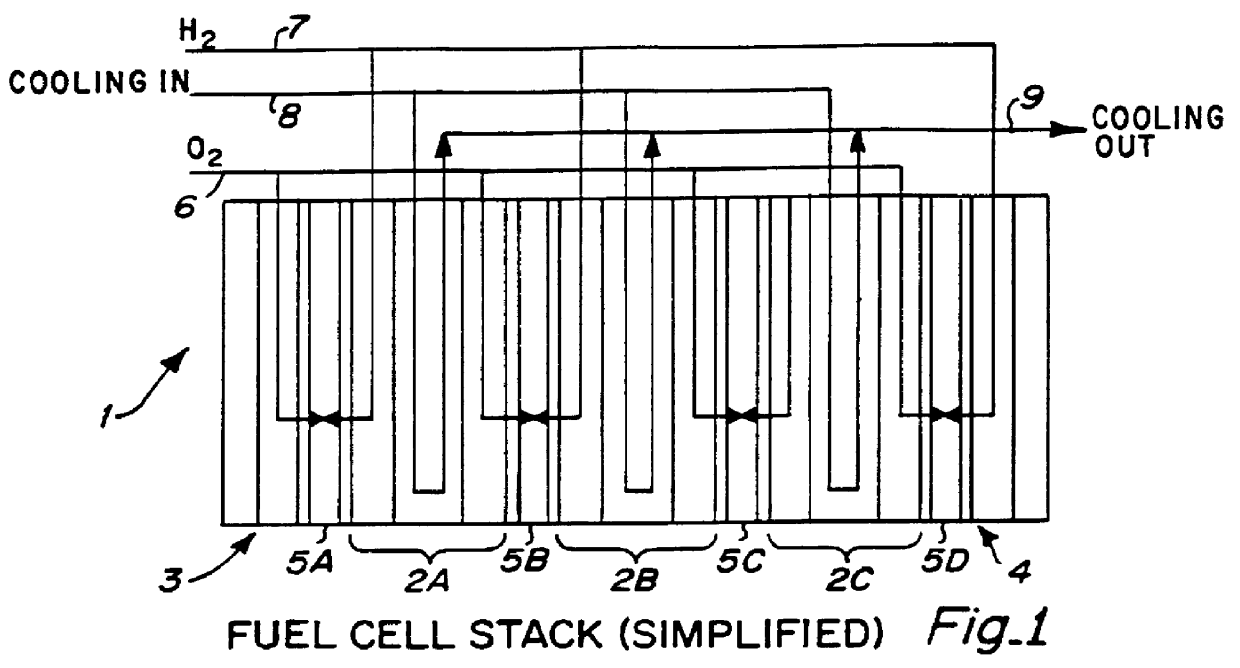
Microfluidic systems for size based removal of red blood cells and platelets from blood
The invention features devices and methods for enriching a sample in one or more desired particles. An exemplary use of these devices and methods is for the enrichment of cells, e.g., white blood cells in a blood sample. In general, the methods of the invention employ a device that contains at least one sieve through which particles of a given size, shape, or deformability can pass. Devices of the invention have at least two outlets, and the sieve is placed such that a continuous flow of fluid can pass through the device without passing through the sieve. The devices also include a force generator for directing selected particles through the sieve. Such force generators employ, for example, diffusion, electrophoresis, dielectrophoresis, centrifugal force, or pressure-driven flow.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
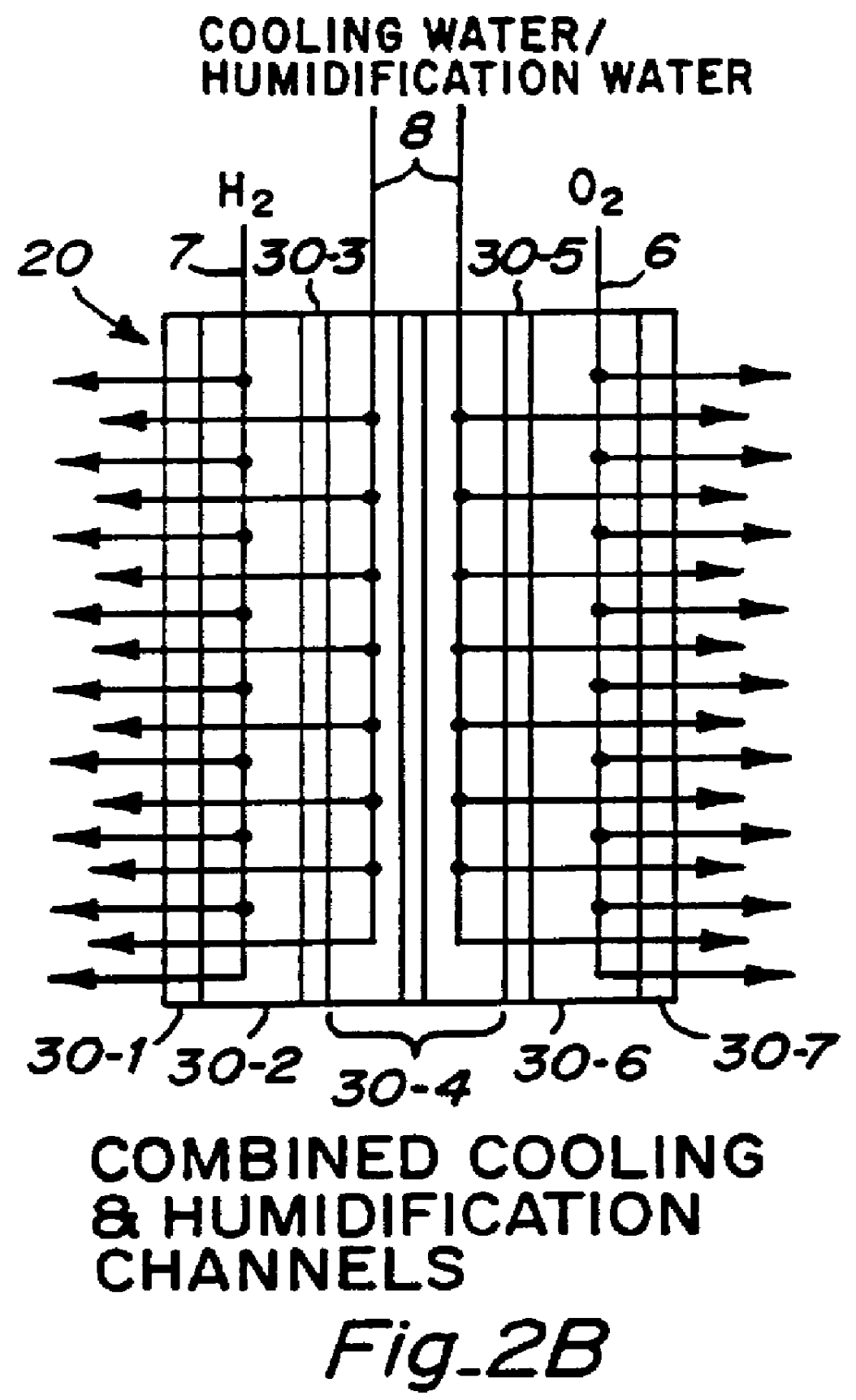
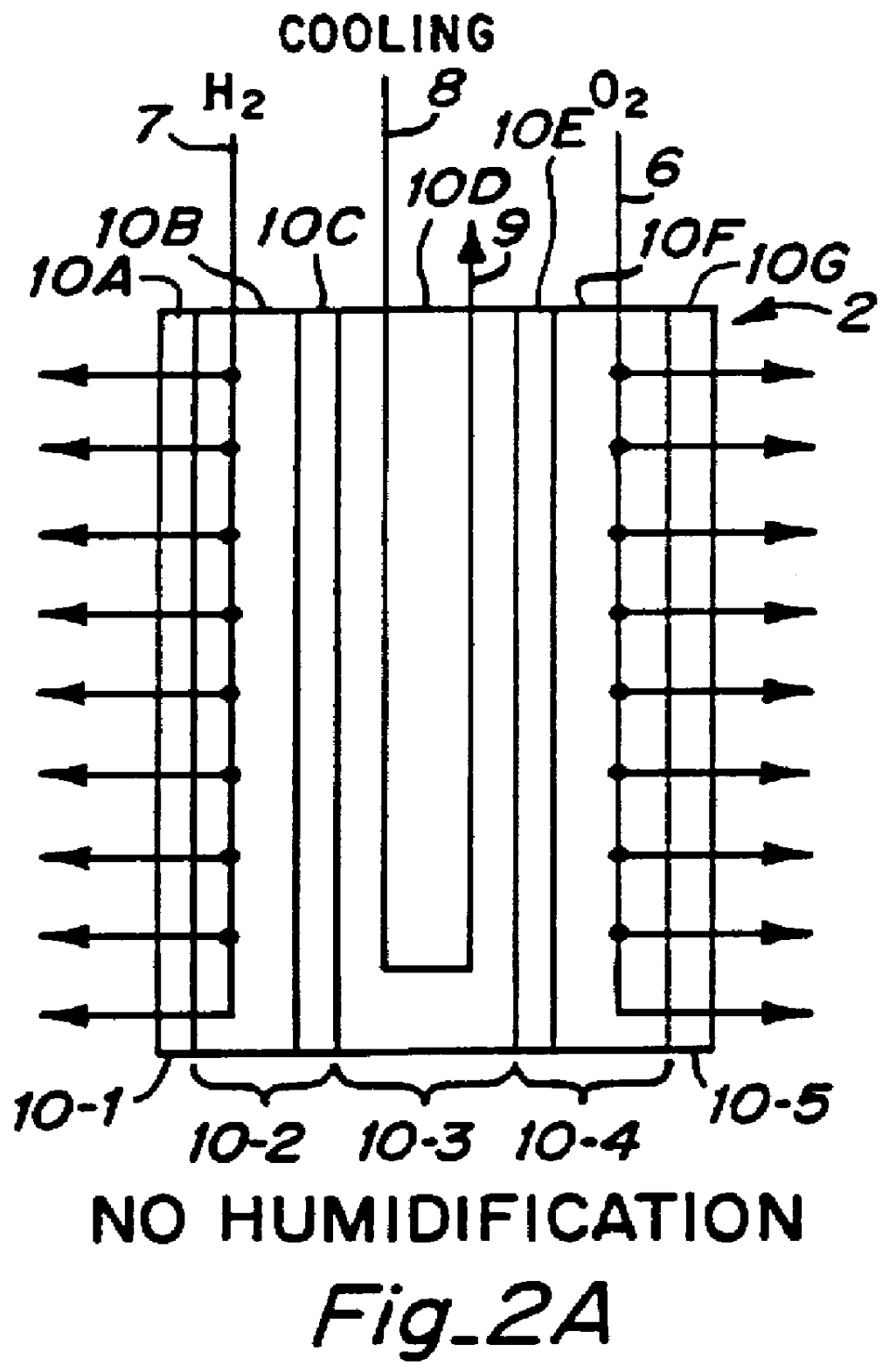
Fuel cell platelet separators having coordinate features
InactiveUS6051331ASimple designEvenly distributedSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingLaser etchingFuel cells
PCT No. PCT / US95 / 13325 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Oct. 10, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 12316 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 25, 1996Fuel cell stacks comprising stacked separator / membrane electrode assembly fuel cells in which the separators comprise a series of thin sheet platelets, having individually configured serpentine micro-channel reactant gas humidification active areas and cooling fields therein. The individual platelets are stacked with coordinate features aligned in contact with adjacent platelets and bonded to form a monolithic separator. Post-bonding processing includes passivation, such as nitriding. Preferred platelet material is 4-25 mil Ti, in which the features, serpentine channels, tabs, lands, vias, manifolds and holes, are formed by chemical and laser etching, cutting, pressing or embossing, with combinations of depth and through etching preferred. The platelet manufacturing process is continuous and fast. By employing CAD based platelet design and photolithography, rapid change in feature design can accommodate a wide range of thermal management and humidification techniques. One hundred H2-O2 / PEM fuel cell stacks of this IFMT platelet design will exhibit outputs on the order of 0.75 kW / kg, some 3-6 times greater than the current graphite plate PEM stacks.
Owner:H POWER
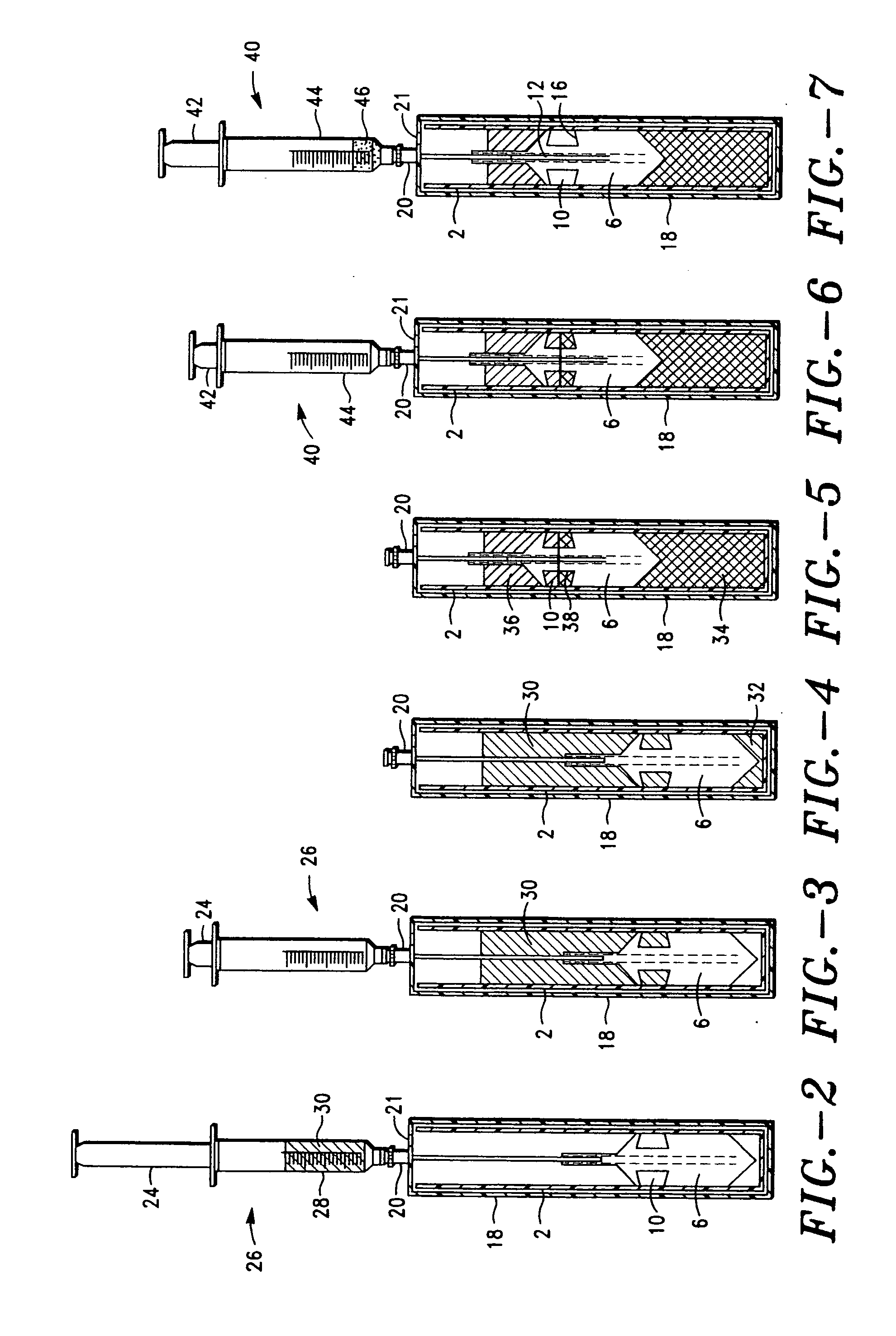
Method and apparatus for collecting hyperconcentrated platelets
InactiveUS6022306AOther blood circulation devicesDispersed particle separationParticle flowPlatelet product
The instant invention relates to a method and the apparatus for collecting a hyperconcentrated platelet product. A fluid containing platelets and other particles flows into a fluid chamber at a flow rate. The flow rate of the fluid is selected to retain the majority of the platelets in the fluid chamber in a saturated bed. The platelets are collected from the fluid chamber without collecting the other particles to form a hyperconcentrated other particle reduced platelet product.
Owner:CARIDIANBCT
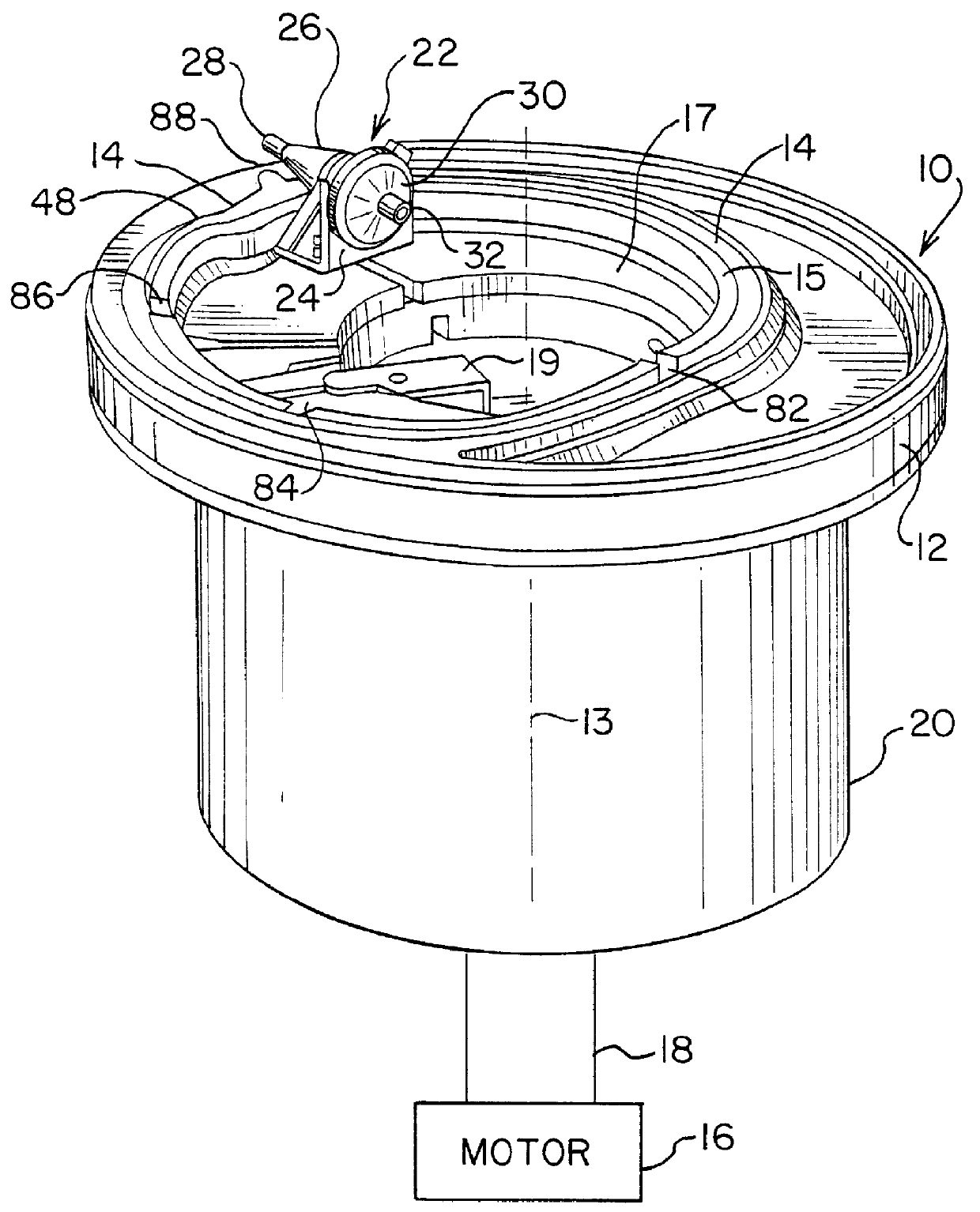
Method and apparatus for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS20060175242A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingFiberRed blood cell
The PRP separator-concentrator of this invention is suitable for office use or emergency use for trauma victims. The PRP separator comprises a motorized centrifugal separation assembly, and a concentrator assembly. The centrifugal separator assembly comprises a centrifugal drum separator that includes an erythrocyte capture module and a motor having a drive axis connected to the centrifugal drum separator. The concentrator assembly comprises a water-removal module for preparing PRP concentrate. The centrifugal drum separator has an erythrocyte trap. The water removal module can be a syringe device with water absorbing beads or it can be a pump-hollow fiber cartridge assembly. The hollow fibers are membranes with pores that allow the flow of water through the fiber membrane while excluding flow of clotting factors useful for sealing and adhering tissue and growth factors helpful for healing while avoiding activation of platelets and disruption of any trace erythrocytes present in the PRP.
Owner:HANUMAN +1
Process for producing nano-scaled graphene platelet nanocomposite electrodes for supercapacitors
ActiveUS20090092747A1Increase the areaImprove conductivityElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesHigh capacitanceCvd graphene
A process for producing meso-porous nanocomposite electrode comprising nano-scaled graphene platelets. The process comprises: (A) providing nano-scaled graphene platelets, wherein each of the platelets comprises a single graphene sheet or a stack of multiple graphene sheets, and the platelets have an average thickness no greater than 100 nm (preferably less than 5 nm and most preferably less than 2 nm in thickness); (B) combining a binder material, the graphene platelets, and a liquid to form a dispersion; (C) forming the dispersion into a desired shape and removing the liquid to produce a binder-platelet mixture; and (D) treating the binder material under a desired temperature or radiation environment to convert the binder-platelet mixture into a meso-porous nanocomposite electrode, wherein the platelets are bonded by the binder and the electrode has electrolyte-accessible pores characterized in that the nanocomposite has a surface area greater than about 100 m2 / gm (preferably greater than 200 m2 / gm, more preferably greater than 500 100 m2 / gm, and most preferably greater than 1,000 m2 / gm). A supercapacitor featuring such a nanocomposite exhibits an exceptionally high capacitance value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Devices and methods for interstitial injection of biologic agents into tissue
The current invention discloses a method for treating infracted / ischemic injury to a myocardium by injecting a substance into the myocardium. The injected substance helps to prevent negative adaptive remodeling by providing mechanical reinforcement or mechanical reinforcement combined with biological therapy. A number of substances for injection are disclosed, including multi component substances such as platelet gel, and other substances. The substances disclosed may contain additives to augment / enhance the desired effects of the injection. The invention also discloses devices used to inject the substances. The devices can include means for ensuring needles do not penetrate beyond a desired depth into the myocardium. The devices can also include needles having multiple lumens such that the components of the platelet gel will be combined at the injection site and begin polymerization in the myocardium.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for separation of particles suspended in a liquid from the liquid in which they are suspended
InactiveUS20100078384A1Improve concentrationAvoid turbulenceSemi-permeable membranesLiquid separation by electricityUltrasonic sensorCompressibility
A method for separating, or removing, particulate material, e.g., blood cells, from a sample of fluid, e.g., whole blood of a patient, in which the particulate material is suspended. In the case of separating blood cells from blood plasma or blood serum, the resulting samples of blood plasma or blood serum can be used for in vitro diagnostic applications. In normal practice, a whole blood sample of a patient are provided and then introduced into an apparatus that contains a flow channel. An acoustic field, which contains acoustic standing waves from external ultrasonic transducers, is located within the flow channel. Laminar flow is maintained in the flow channel. Blood cells and platelets are separated from blood plasma or blood serum at the end of the flow channel and collected. The method described herein allows fluid components to differentially migrate to areas of preferred acoustic interaction. The parameters that affect separation of particles are size, density, compressibility of the particles, and the fluid surrounding the particles.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
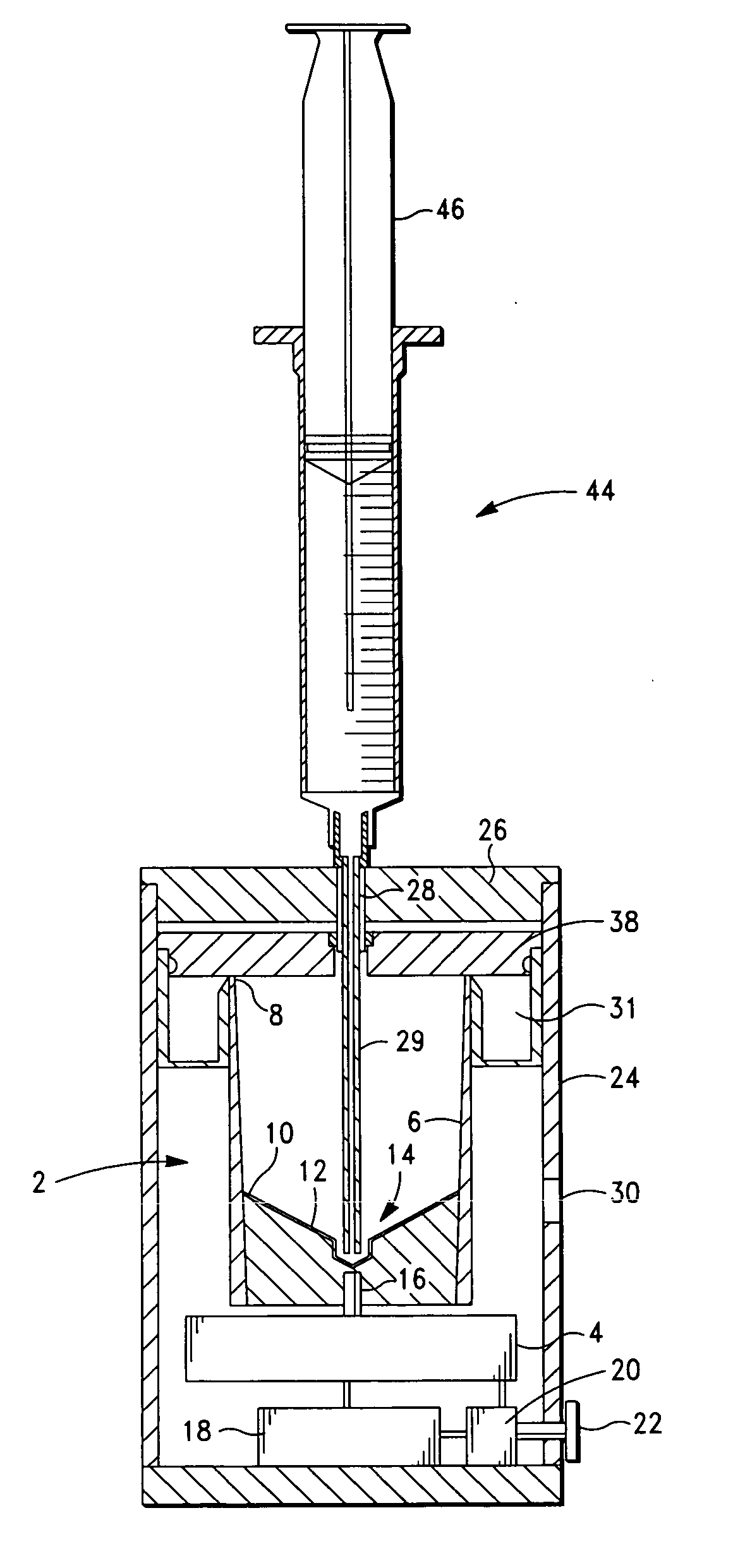
Method and apparatus for preparing platelet rich plasma and concentrates thereof
ActiveUS7708152B2Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingFiberRed blood cell
The PRP separator-concentrator of this invention is suitable for office use or emergency use for trauma victims. The PRP separator comprises a motorized centrifugal separation assembly, and a concentrator assembly. The centrifugal separator assembly comprises a centrifugal drum separator that includes an erythrocyte capture module and a motor having a drive axis connected to the centrifugal drum separator. The concentrator assembly comprises a water-removal module for preparing PRP concentrate. The centrifugal drum separator has an erythrocyte trap. The water removal module can be a syringe device with water absorbing beads or it can be a pump-hollow fiber cartridge assembly. The hollow fibers are membranes with pores that allow the flow of water through the fiber membrane while excluding flow of clotting factors useful for sealing and adhering tissue and growth factors helpful for healing while avoiding activation of platelets and disruption of any trace erythrocytes present in the PRP.
Owner:HANUMAN +1
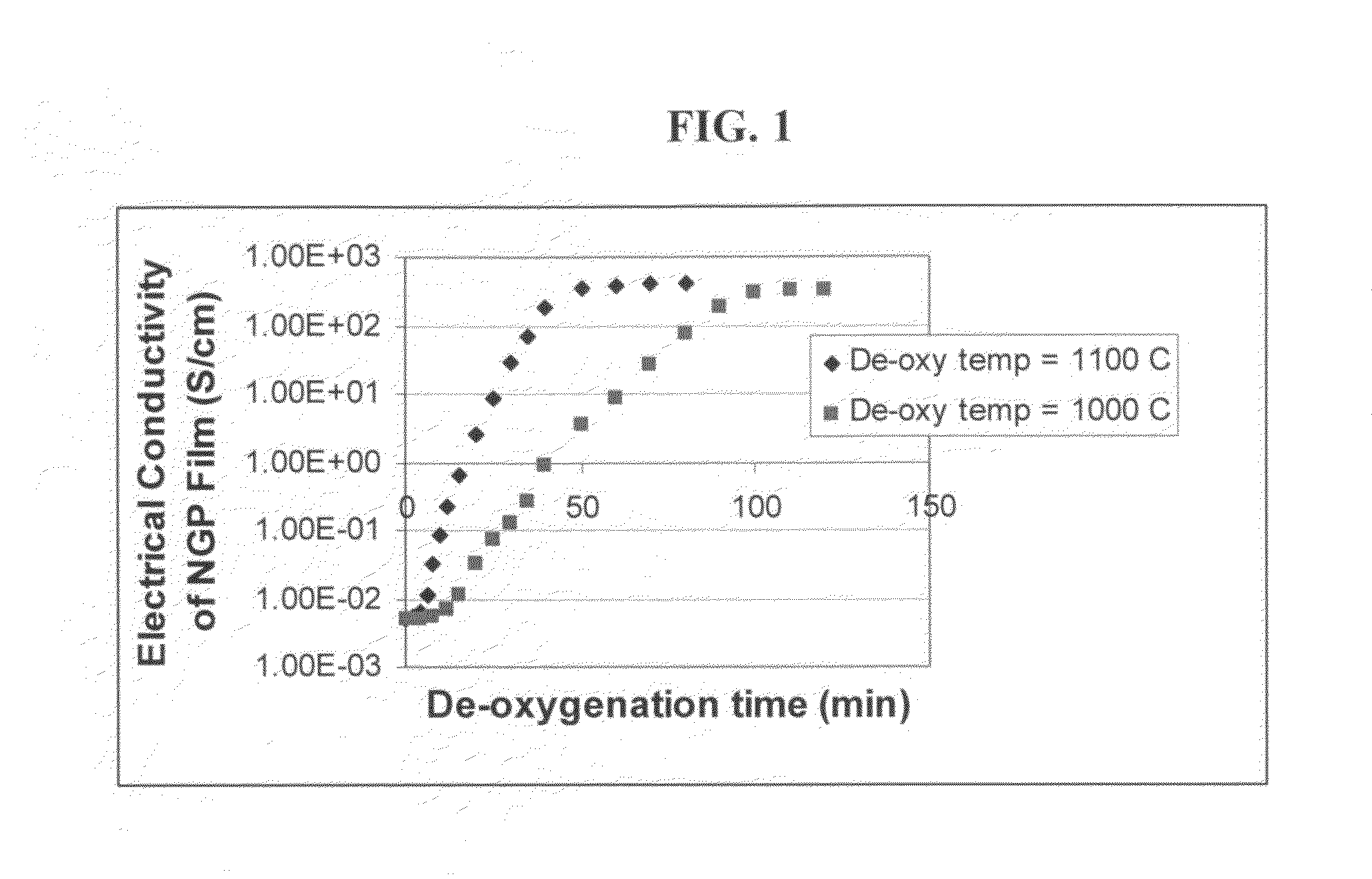
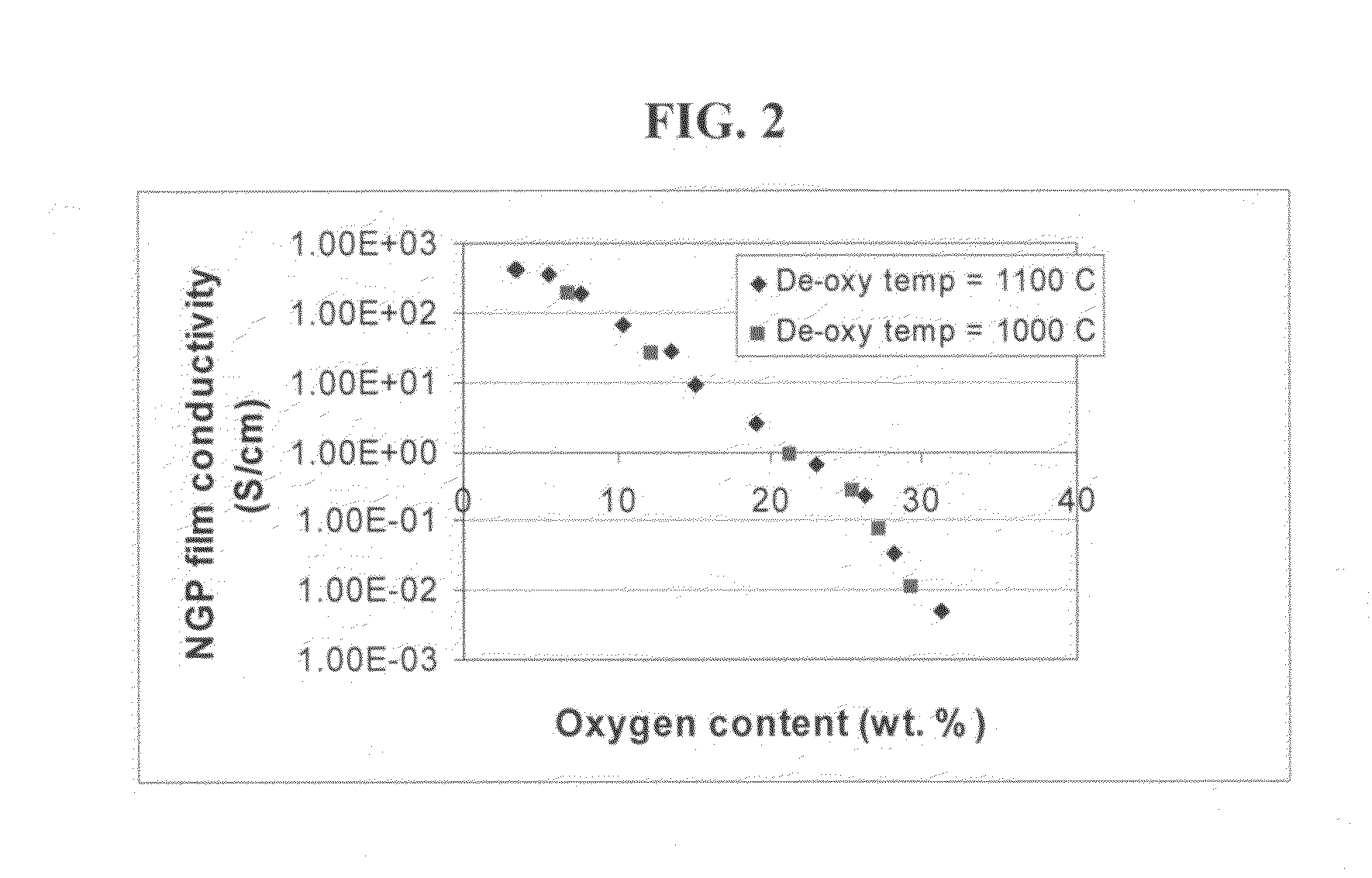
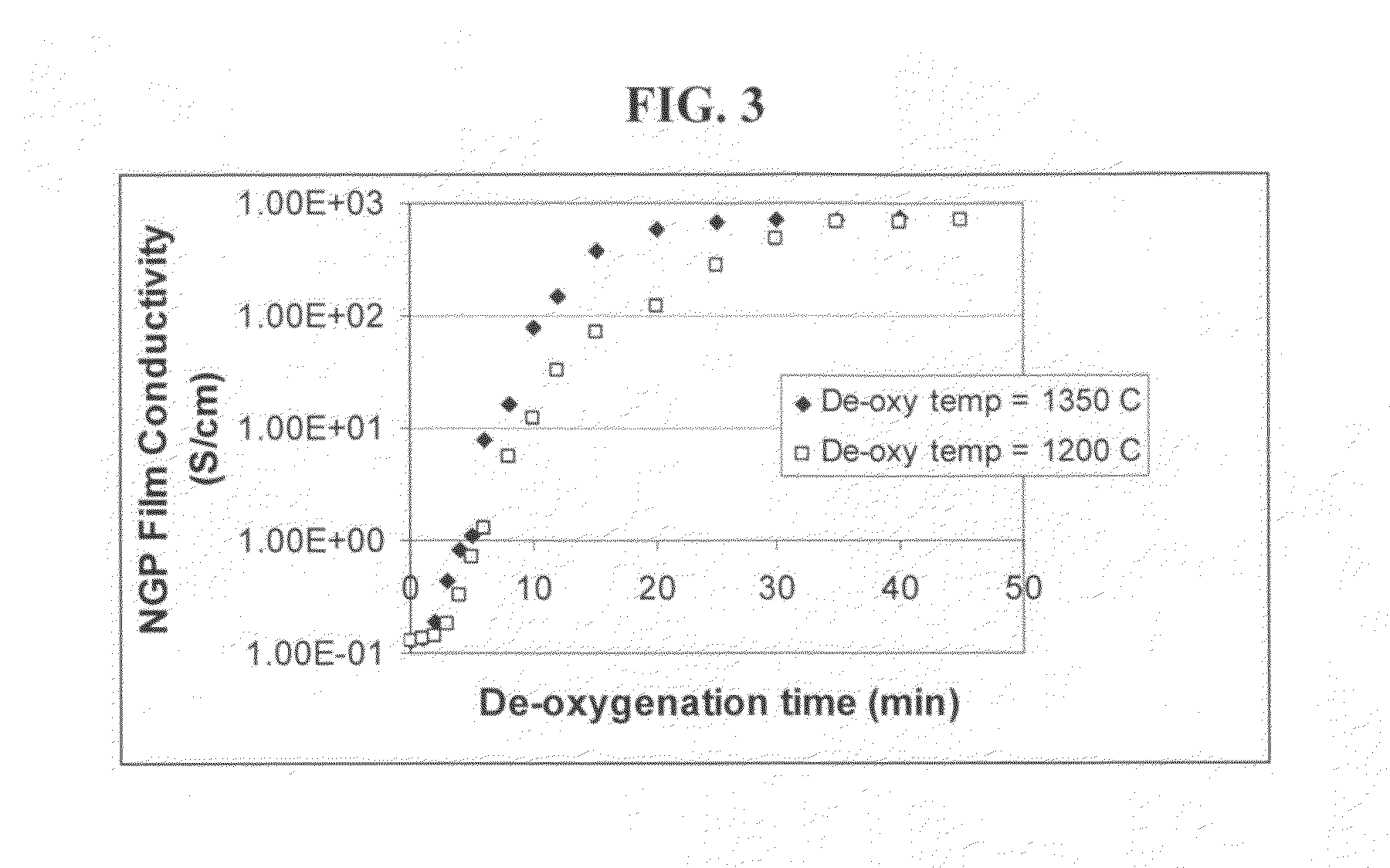
Process for producing dispersible Nano Graphene Platelets from oxidized graphite
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are dispersible and conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) or graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GIC or GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time to obtain the desired dispersible nano graphene platelet with an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight, preferably below 20% by weight, further preferably between 5% and 20% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Doped spherically-shaped supported catalyst and process for hydrotreating and hydroconverting metal-containing oil fractions
ActiveUS20050211603A1Catalytic crackingCatalyst activation/preparationCatalytic metalSilicon dioxide
The present invention concerns a catalyst for hydrotreating and / or hydroconverting heavy metal-containing hydrocarbon feeds, said catalyst comprising a support in the form of beads based on alumina, at least one catalytic metal or a compound of a catalytic metal from group VIB (column 6 in the new periodic table notation), optionally at least one catalytic metal or compound of a catalytic metal from group VIII (columns 8, 9 and 10 of the new periodic table notation), with a pore structure composed of a plurality of juxtaposed agglomerates, each formed by a plurality of acicular platelets, the platelets of each agglomerate being generally radially orientated with respect to each other and with respect to the center of the agglomerate. The catalyst also comprises at least one doping element selected from the group constituted by phosphorus, boron, silicon (or silica which does not belong to that which could be contained in the selected support) and halogens. The invention also concerns the use of said catalyst in converting metal-containing feeds.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
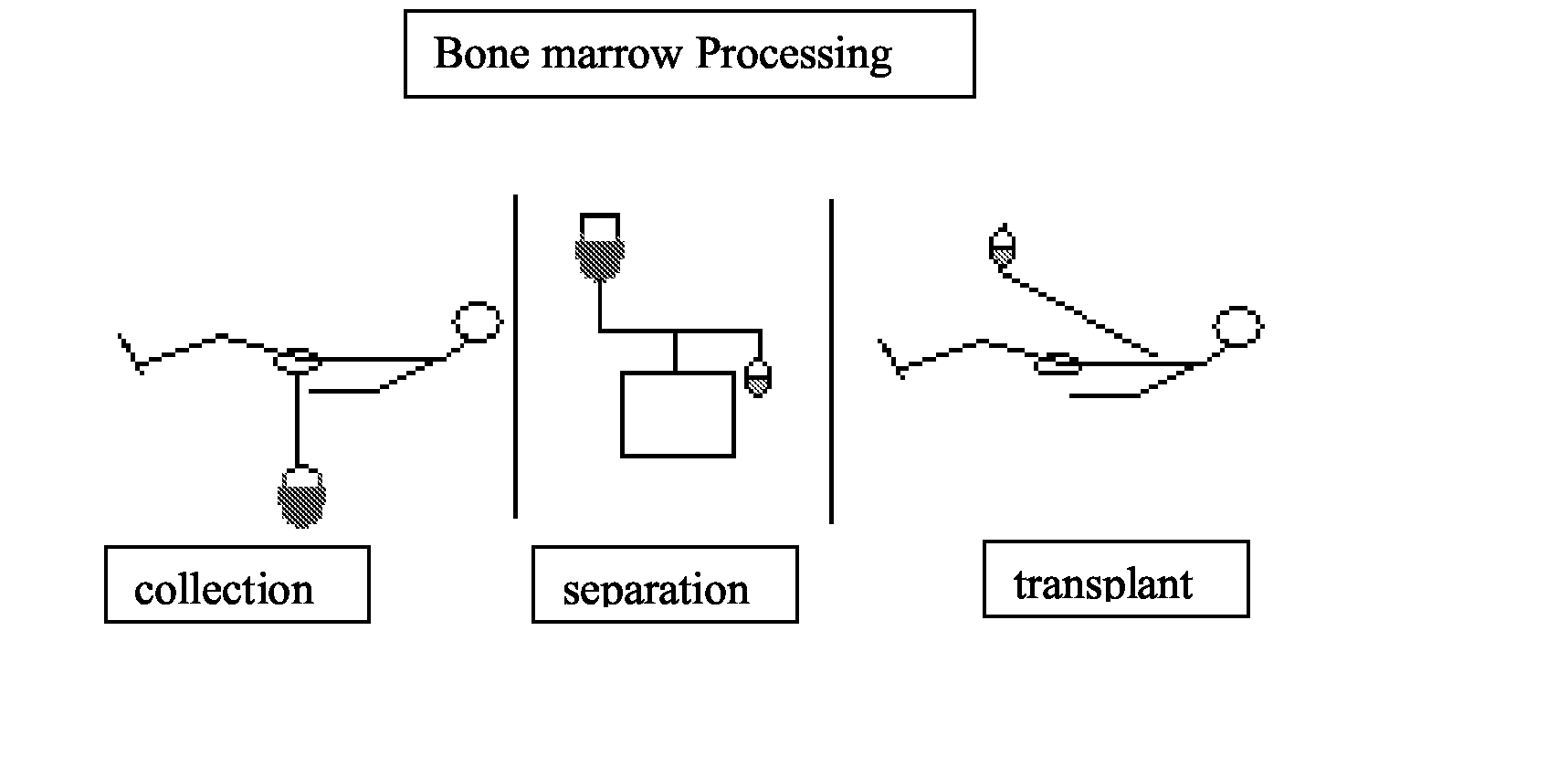
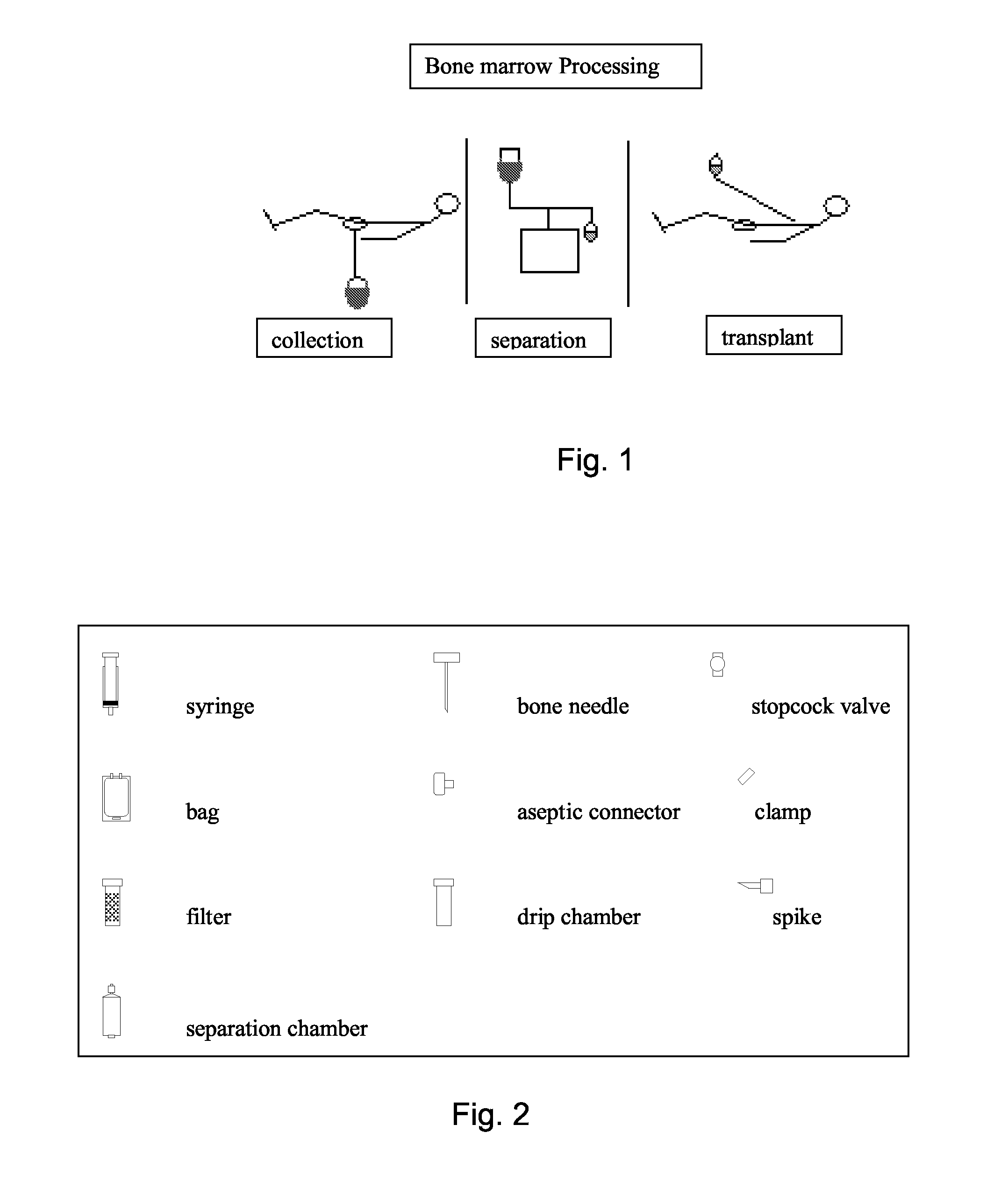
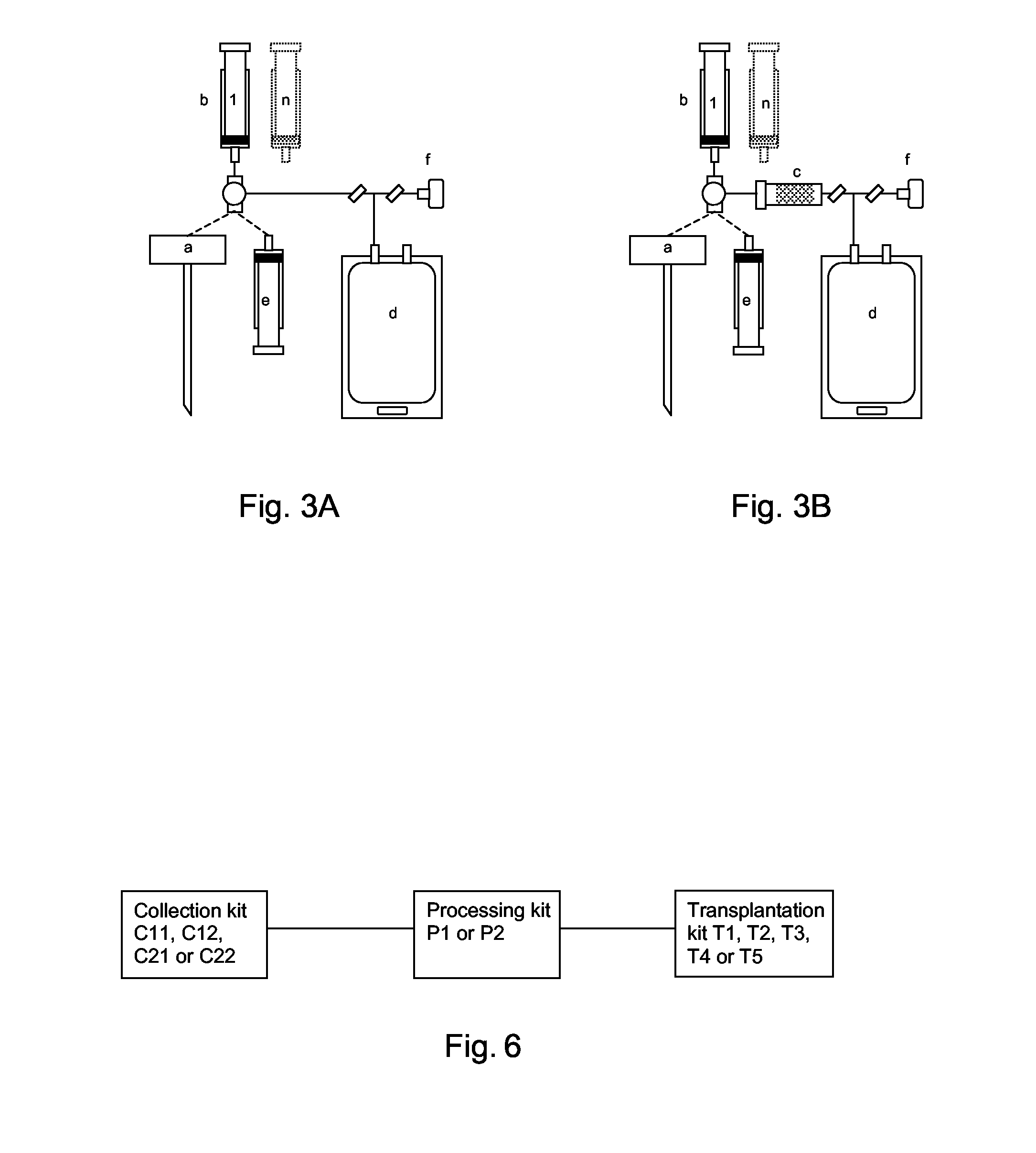
Integrated System for Collecting, Processing and Transplanting Cell Subsets, Including Adult Stem Cells, for Regenerative Medicine
InactiveUS20080171951A1Accurate collectionMinimize risk of contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderFluid transportTissue repair
A system for the extraction, collection, processing and transplantation of cell subsets, including adult stem cells and platelets, in particular for tissue repair in regenerative medicine, comprises a set of disposable fluid-transport elements that are pre-connected or that include aseptic connectors for making interconnections between them in an aseptic manner or are adapted to be aseptically connected. The set usually includes three kits of disposable sterile elements, a collection kit, a processing kit, and a transplantation kit packaged in a blister pack on a support such as a tray, having one compartment for receiving each inter-connectable kit of the set. The set includes an extracting device, for example including a needle for bone puncture or vein puncture, for extracting bone marrow or other sources of cell subsets from a patient.
Owner:BIOSAFE SA
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS20060029578A1Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
The present invention relates to a new method for repairing human or animal tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, ligament, tendon, bone, skin, cornea, periodontal tissues, abscesses, resected tumors, and ulcers. The method comprises the step of introducing into the tissue a temperature-dependent polymer gel composition such that the composition adhere to the tissue and promote support for cell proliferation for repairing the tissue. Other than a polymer, the composition preferably comprises a blood component such as whole blood, processed blood, venous blood, arterial blood, blood from bone, blood from bone-marrow, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta blood, erythrocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin and platelet rich plasma. The present invention also relates to a new composition to be used with the method of the present invention.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
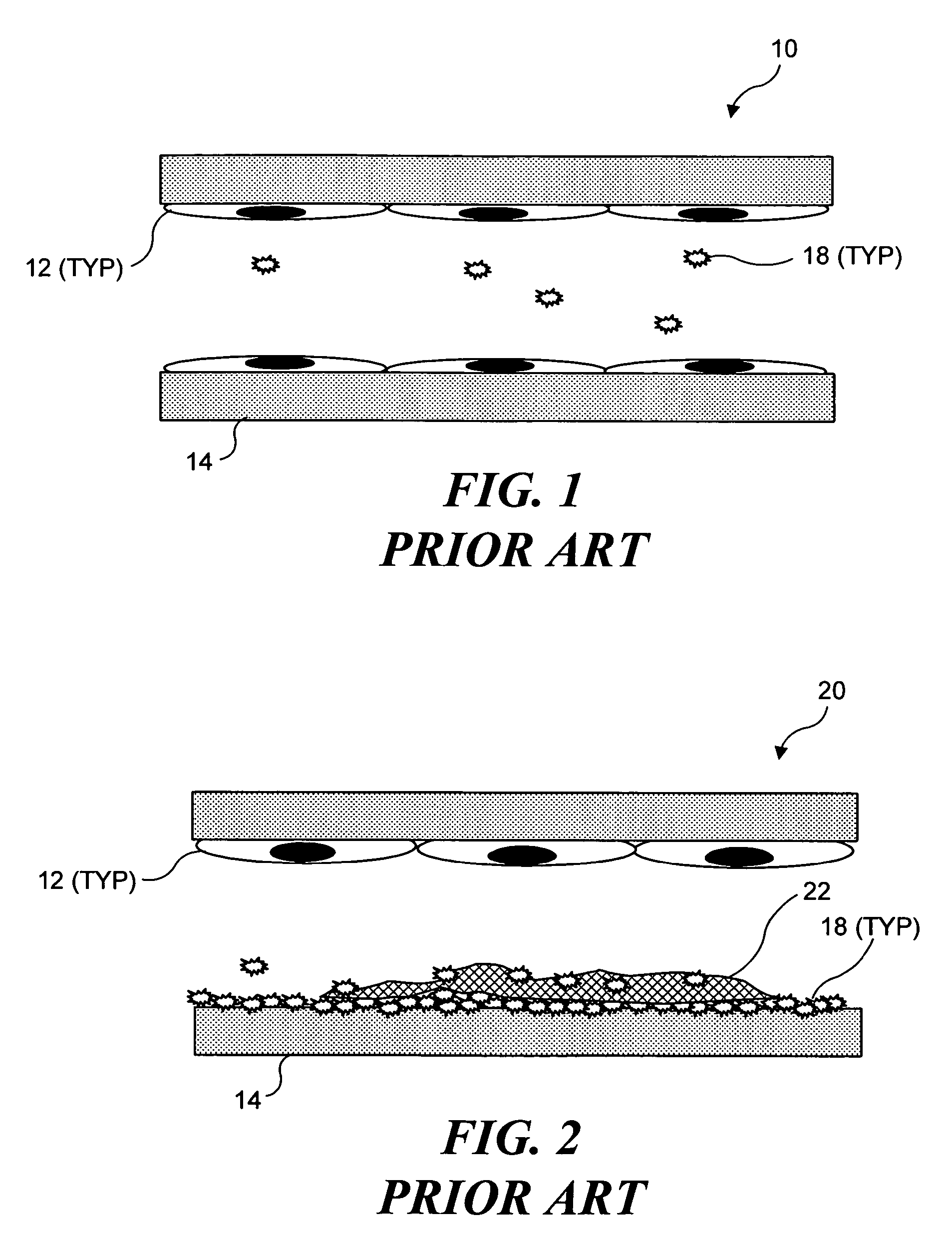
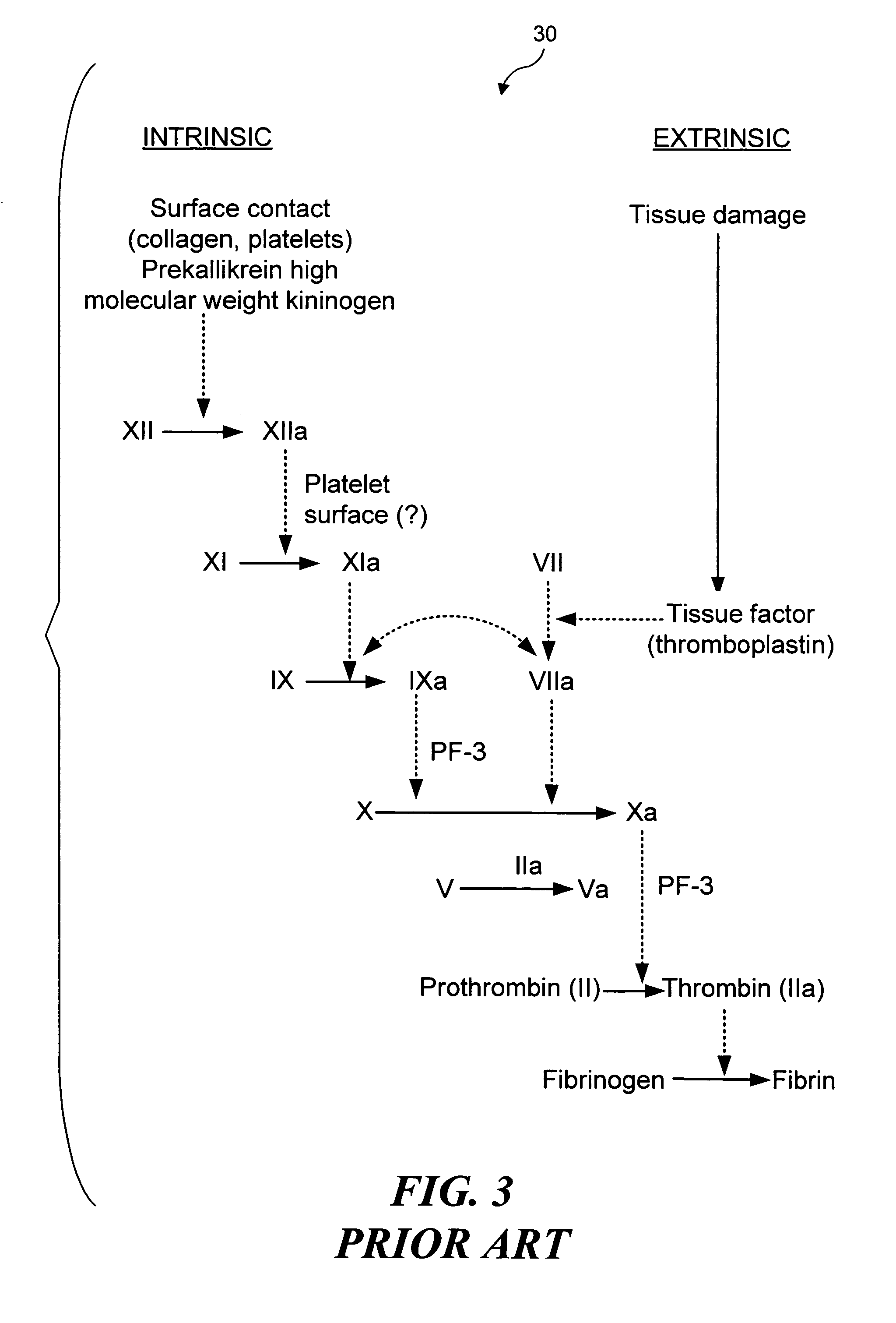
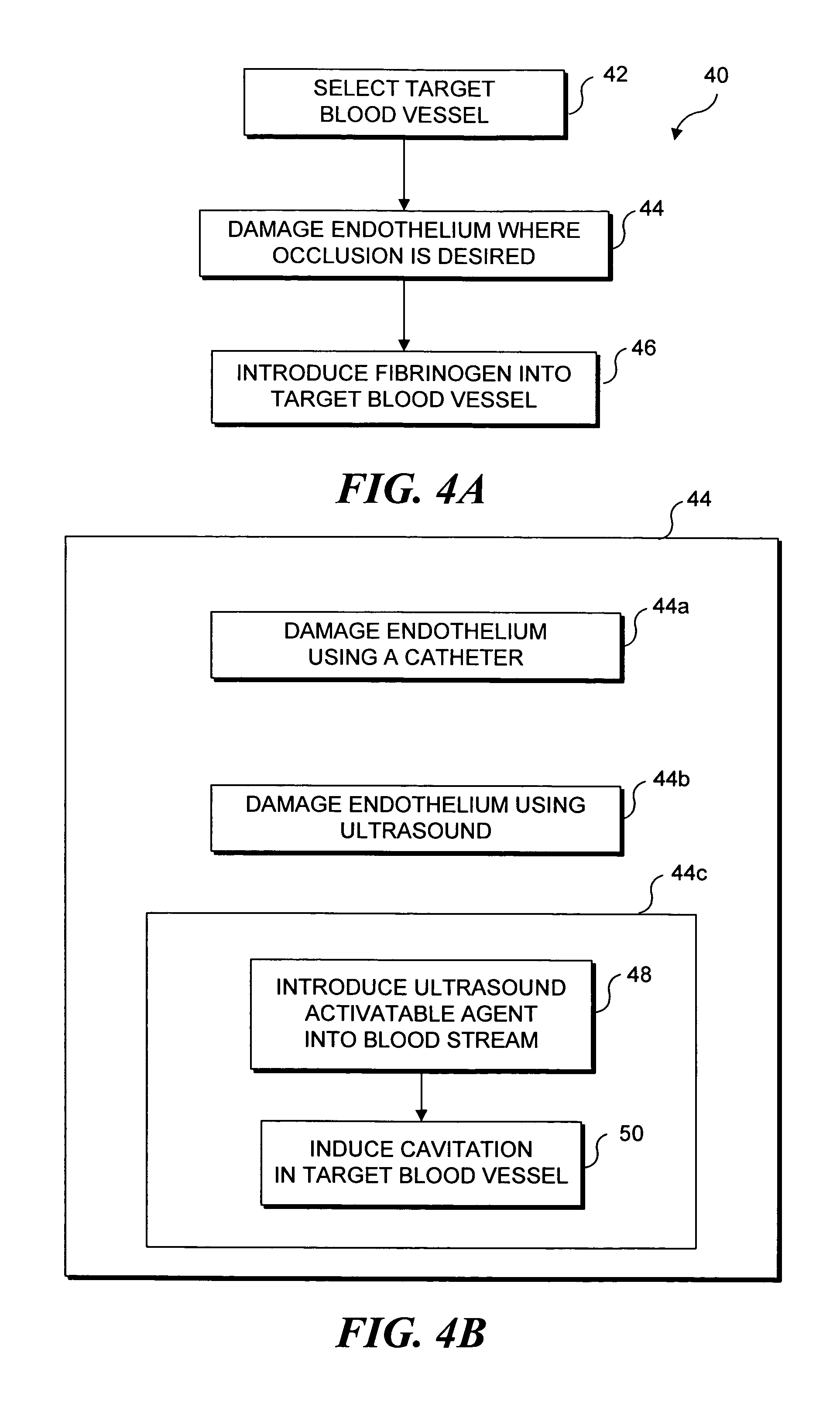
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS7591996B2Eliminate heat damageFew techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
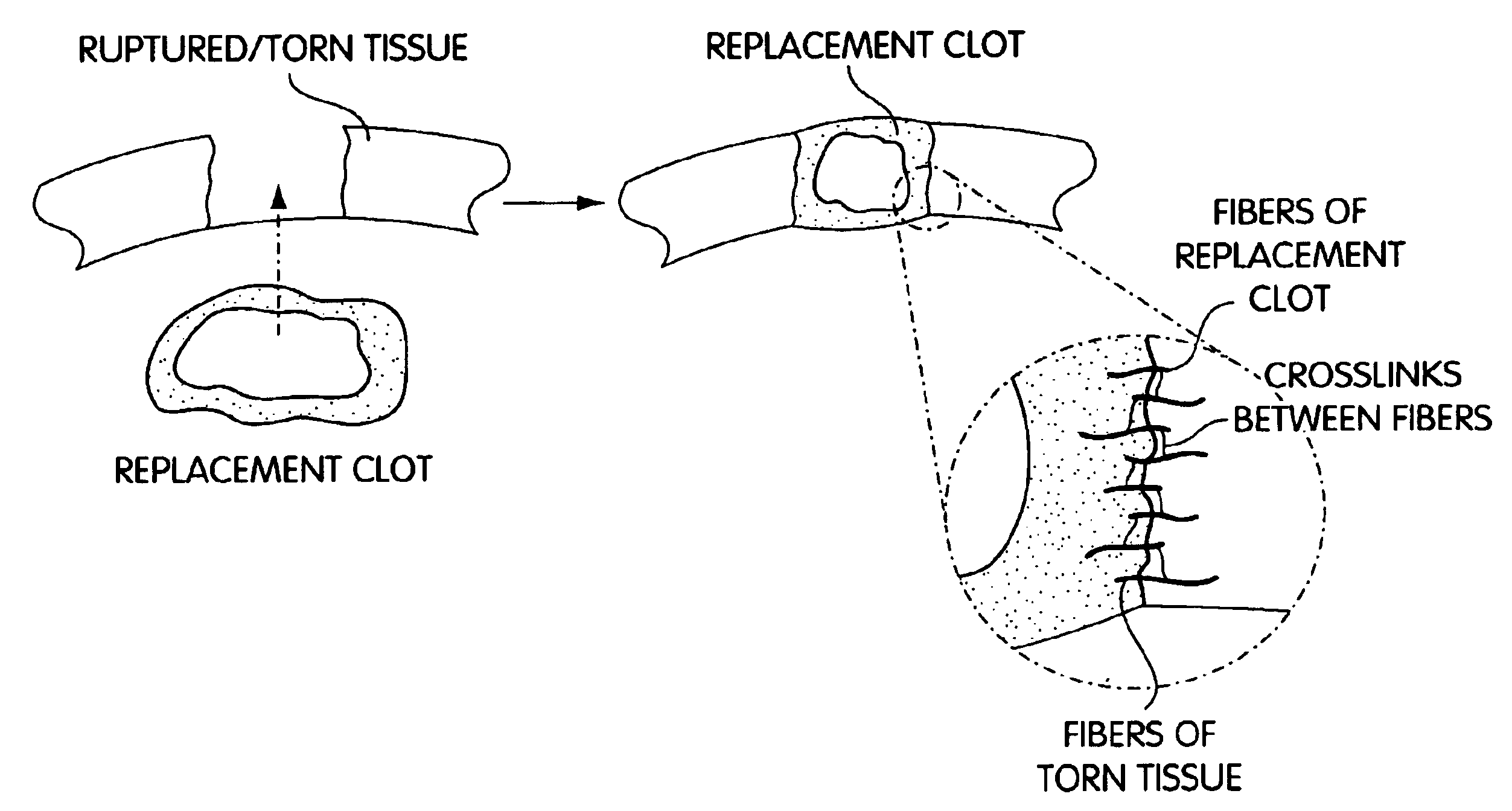
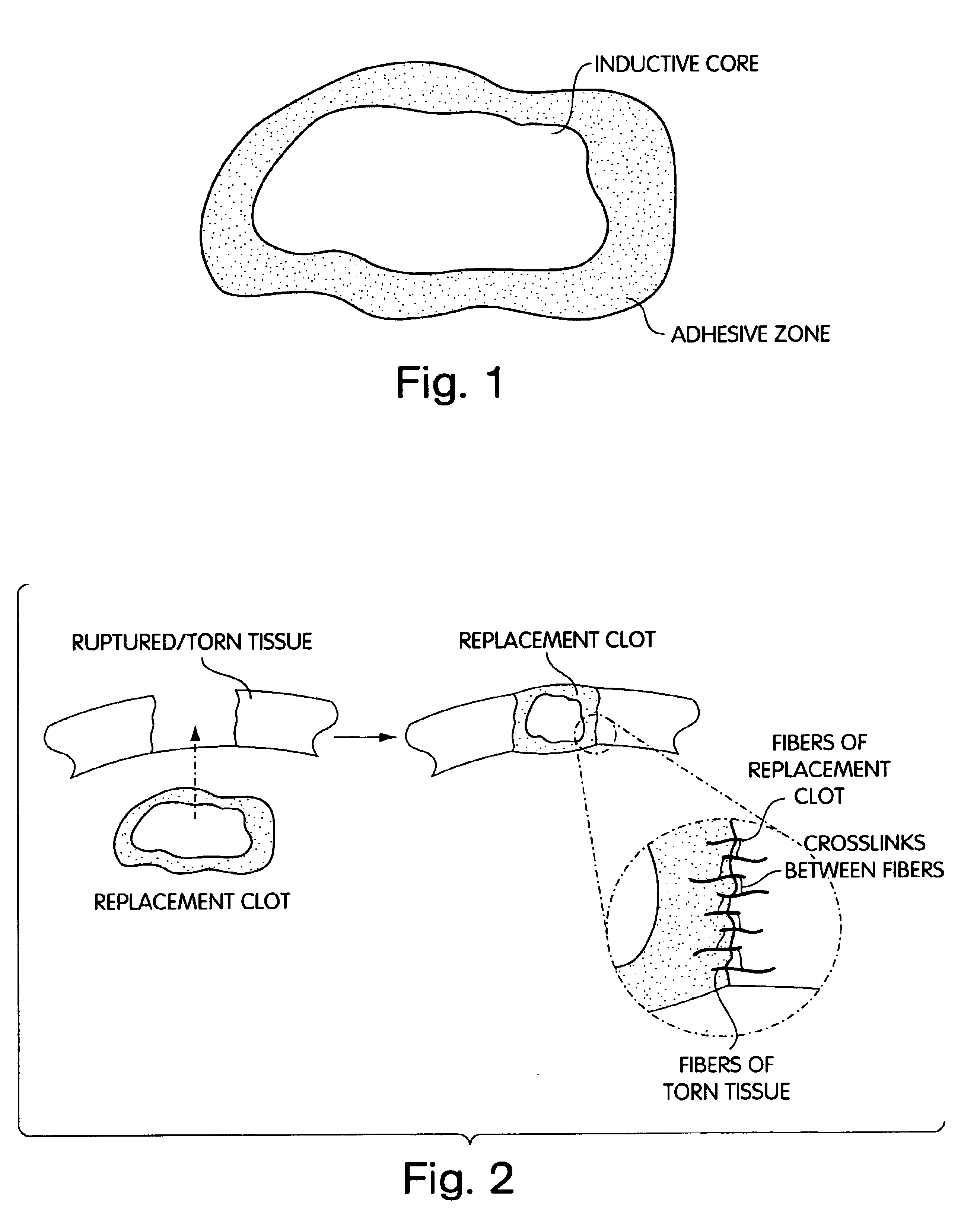
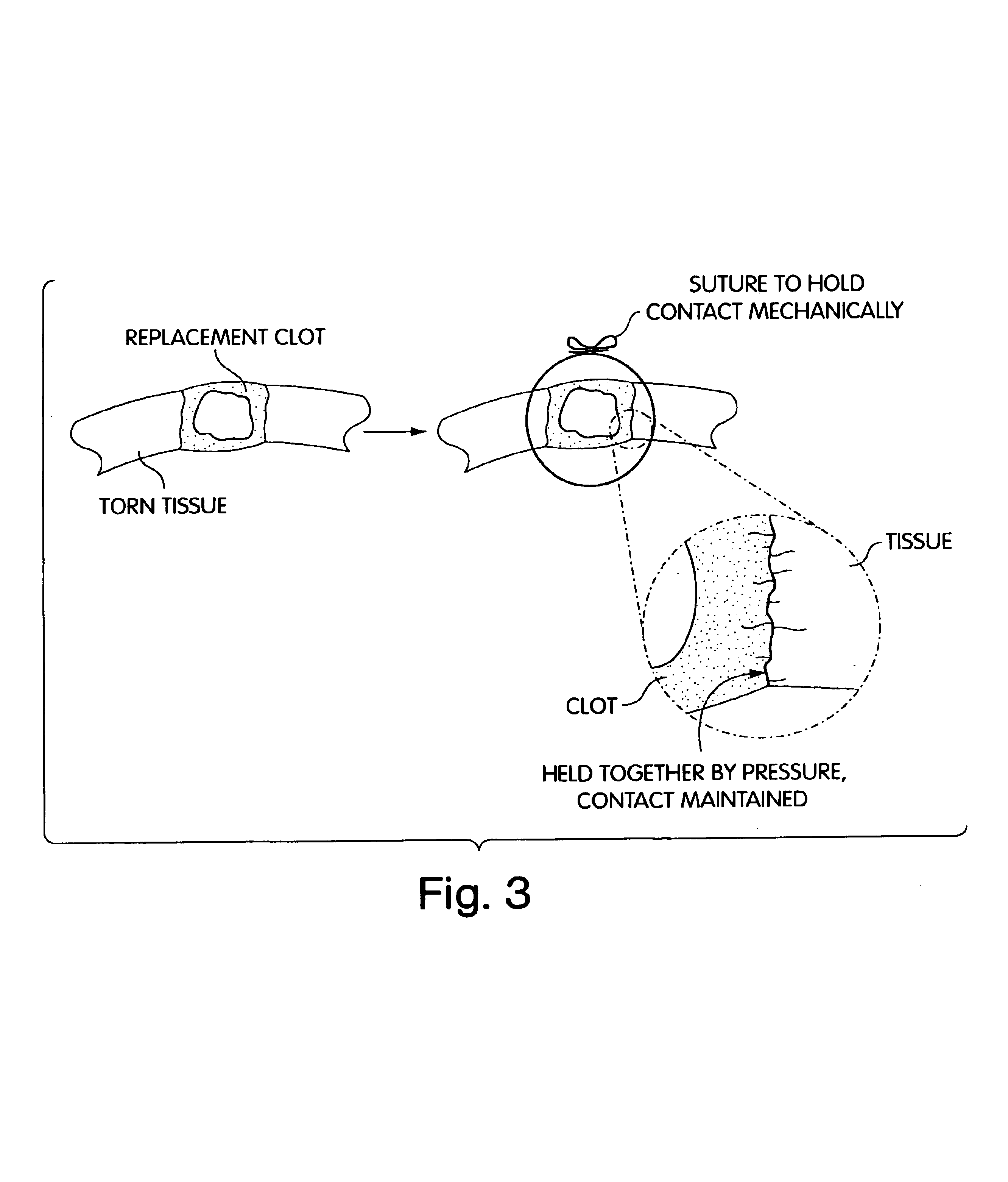
Biologic replacement for fibrin clot
InactiveUS6964685B2Increase contactResists premature degradationSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsExtra-ArticularExtracellular proteins
The invention provides compositions and methods for repairing intra-articular and extra-articular tissue including ligament, meniscus, cartilage, tendon, and bone. The method includes contacting the ends of an injured tissue from a patient with a composition. The repair composition includes soluble type 1 collagen, a platelet, and at least one of an extracellular protein and a neutralizing agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Methods and apparatus for isolating platelets from blood
InactiveUS20050186120A1Simple and fast preparationIncrease productionMedical devicesLaboratory glasswaresMedicineRed blood cell
A platelet collection device comprising a centrifugal spin-separator container with a cavity having a longitudinal inner surface. A float in the cavity has a base, a platelet collection surface above the base, an outer surface. The float density is below the density of erythrocytes and above the density of plasma. The platelet collection surface has a position on the float which places it below the level of platelets when the float is suspended in separated blood. During centrifugation, a layer of platelets or buffy coat collects closely adjacent the platelet collection surface. Platelets are then removed from the platelet collection surface. Movement of a float having a density greater than whole blood through the sedimenting erythrocytes releases entrapped platelets, increasing the platelet yield.
Owner:DORIAN RANDEL +2
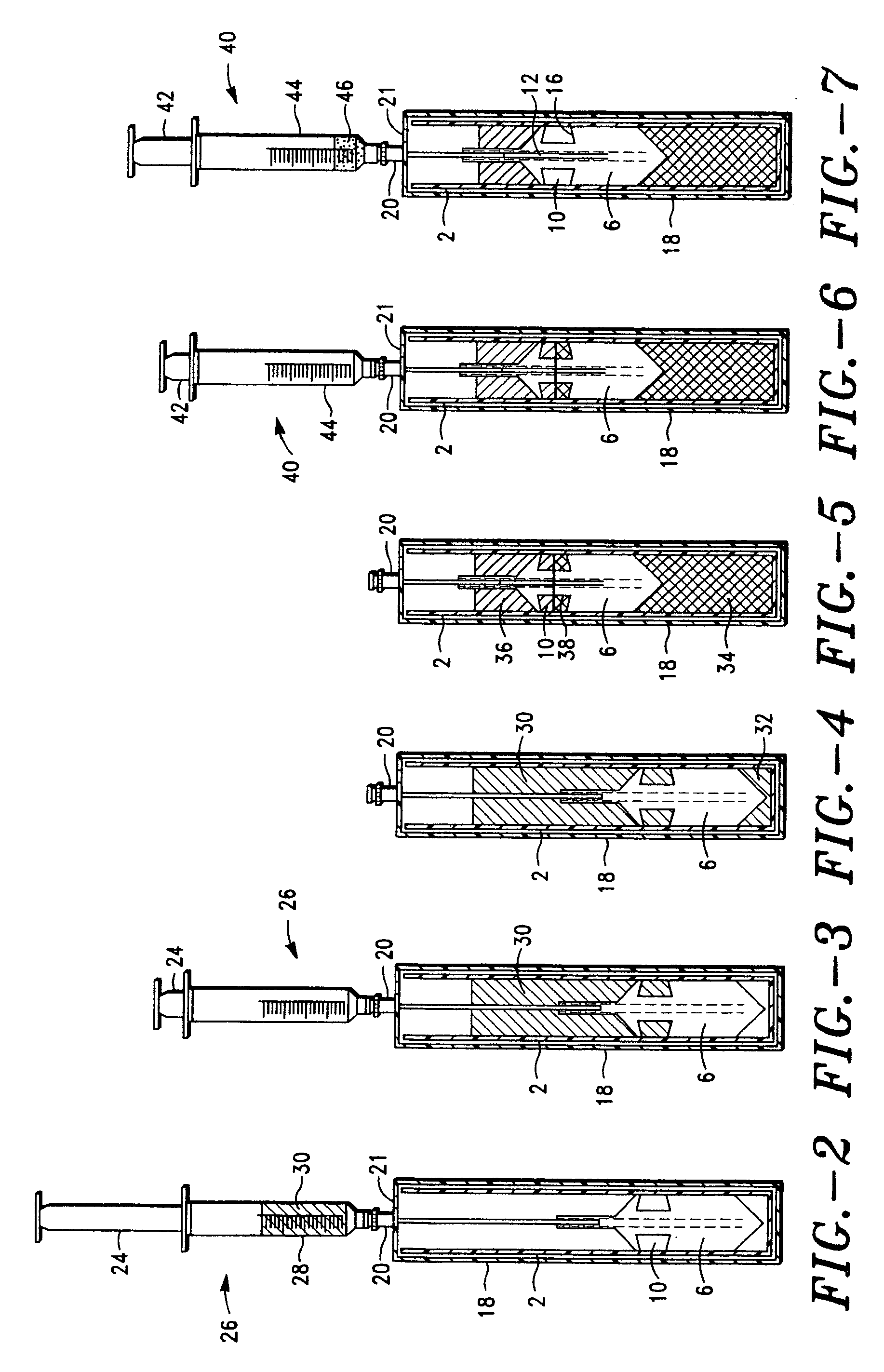
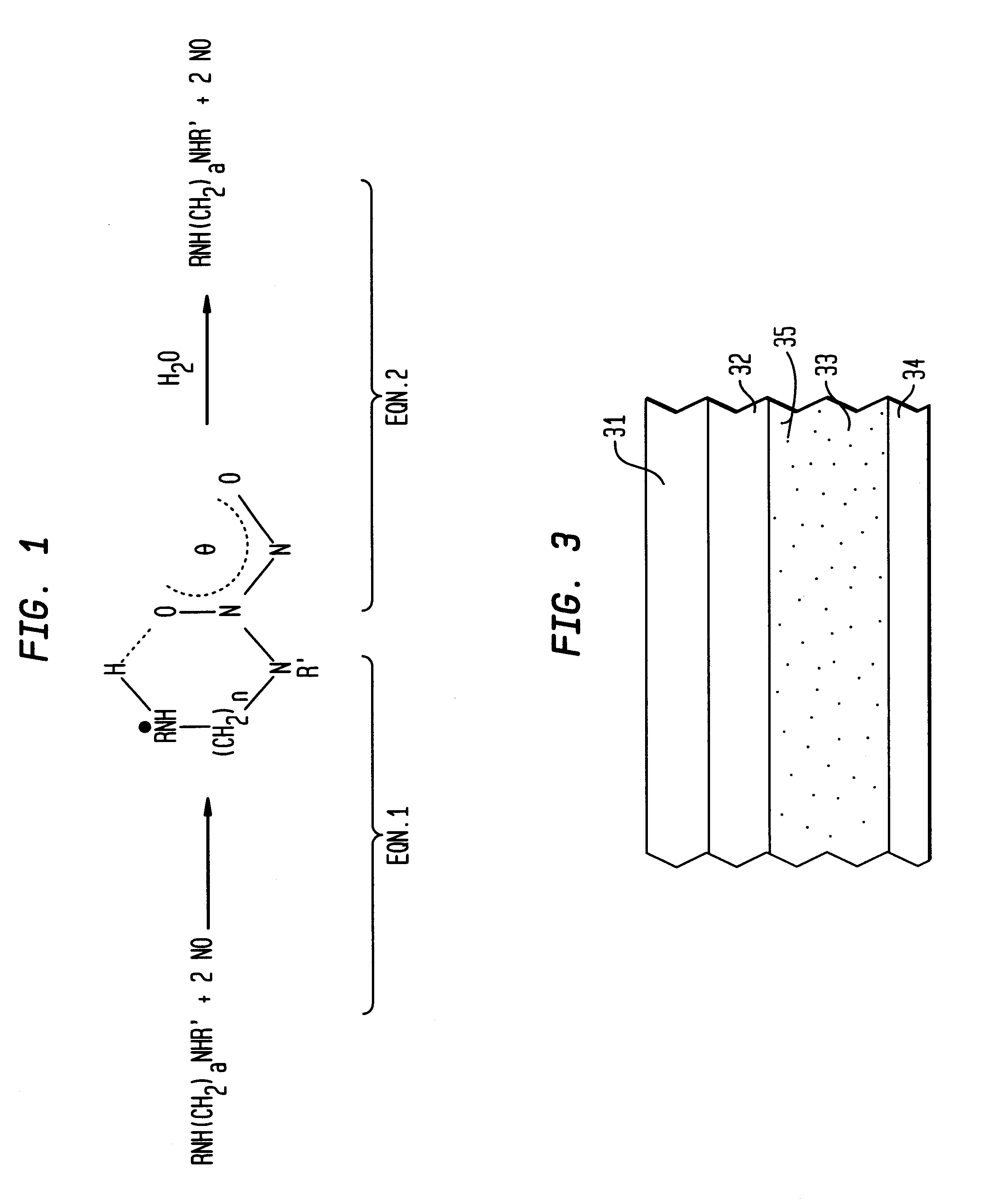
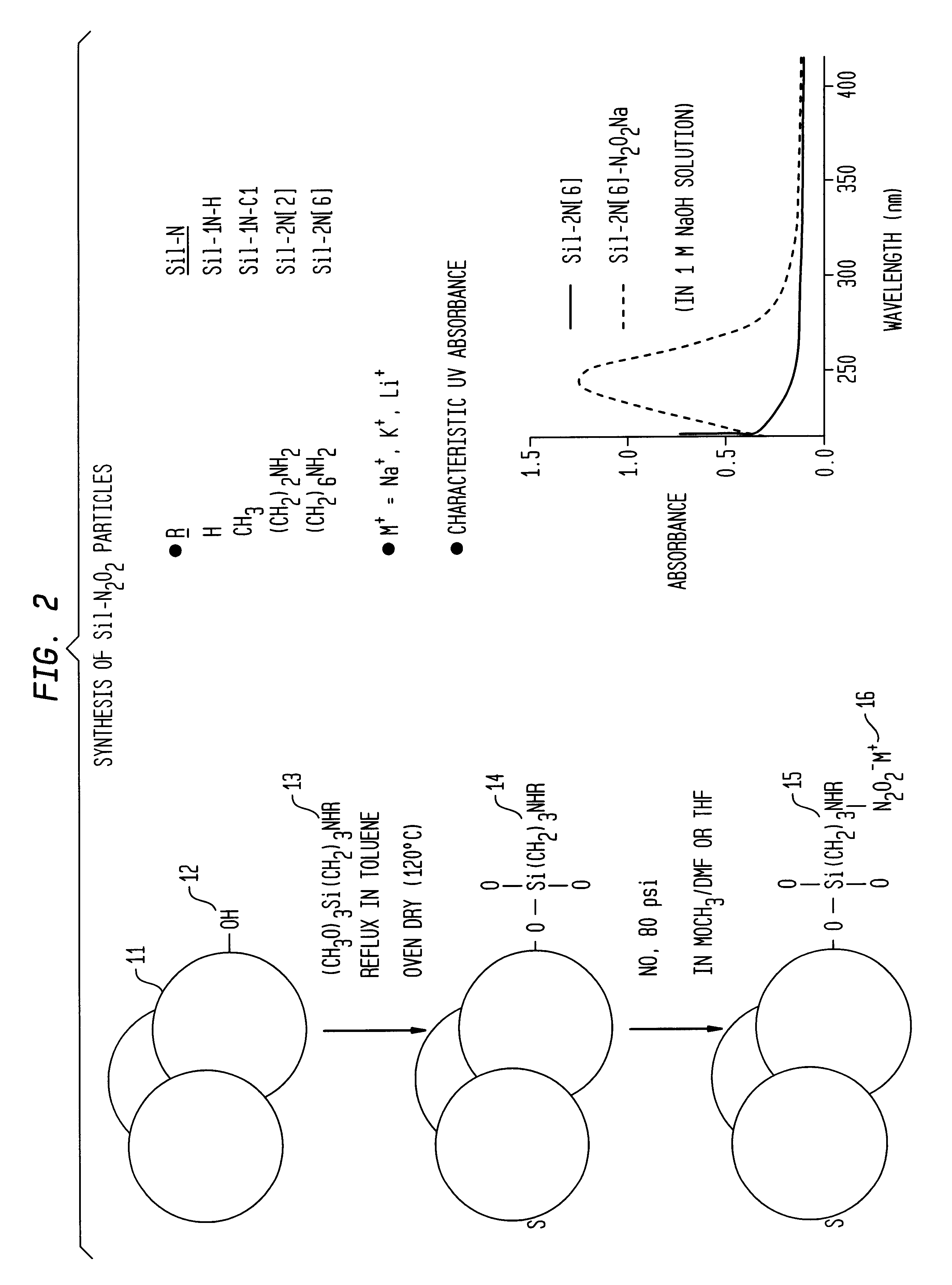
Nitric oxide-releasing polymers incorporating diazeniumdiolated silane derivatives
InactiveUS6841166B1Reduce activationReduce aggregationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsPolymeric surfaceSilanes
Biocompatible polymeric materials capable of providing in situ release of nitric oxide (NO) included diazeniumdiolated fumed silica as a filler in a multilayer polymer structure to release NO upon contact with water (blood). The blood-contacting polymer surface is preferably multi-layered so that the NO-releasing layer, containing the diazeniumdiolated fumed silica, is shielded from blood contact by one or more top (or base) coats. When in contact with blood, the NO released at the surface of the polymer prevents platelet activation and adhesion to the surface, thereby reducing platelet consumption, risk of thrombus formation and other clinical complications associated with interactions between blood and foreign materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method and system for microfluidic manipulation, amplification and analysis of fluids, for example, bacteria assays and antiglobulin testing
A microfluidic system for isolation and amplification of DNA or RNA from aqueous solutions and detection of the DNA or RNA on a lateral flow detection strip, including a disposable microfluidic card for use in analysis of bacteria in platelets and an analysis of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) in urine. The card will include an embedded membrane that filters out cells and cellular debris. Any biological debris on the membrane will be lysed and the DNA or RNA amplified via PCR amplification protocol, including appropriate reagents and thermal cycling conditions. The amplified DNA or RNA are transferred to a lateral flow detection strip for a visual diagnostic read out. An alternate embodiment includes a microfluidic card for use in typing antiglobulin assays.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Methods and apparatus for isolating platelets from blood
InactiveUS20050196874A1Simple and fast preparationIncrease productionSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMedicineRed blood cell
A platelet collection device comprising a centrifugal spin-separator container with a cavity having a longitudinal inner surface. A float in the cavity has a base, a platelet collection surface above the base, an outer surface. The float density is below the density of erythrocytes and above the density of plasma. The platelet collection surface has a position on the float which places it below the level of platelets when the float is suspended in separated blood. During centrifugation, a layer of platelets or buffy coat collects closely adjacent the platelet collection surface. Platelets are then removed from the platelet collection surface. Movement of a float having a density greater than whole blood through the sedimenting erythrocytes releases entrapped platelets, increasing the platelet yield.
Owner:HANUMAN
Separation of platelets from whole blood for use as a healant
InactiveUS7011852B2Rapidly and conveniently and cost-effectively harvestEliminate useSurgical adhesivesMammal material medical ingredientsFiltrationBlood plasma
Owner:MOHAMMAD S FAZAL +1
Method and apparatus for detecting and counting platelets individually and in aggregate clumps
ActiveUS7929121B2Accurate countShorten the counting processBiological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceGranularity
A method for enumerating platelets within a blood sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: 1) depositing the sample into an analysis chamber adapted to quiescently hold the sample for analysis, the chamber defined by a first panel and a second panel, both of which panels are transparent; 2) admixing a colorant with the sample, which colorant is operative to cause the platelets to fluoresce upon exposure to one or more predetermined first wavelengths of light; 3) illuminating at least a portion of the sample containing the platelets at the first wavelengths; 4) imaging the sample, including producing image signals indicative of fluorescent emissions from the platelets, which fluorescent emissions have an intensity; 5) identifying the platelets by their fluorescent emissions, using the image signals; 6) determining an average fluorescent emission intensity value for the individual platelets identified within the sample; 7) identifying clumps of platelets within the sample using one or more of their fluorescent emissions, area, shape, and granularity; and 8) enumerating platelets within each platelet clump using the average fluorescent emission intensity value determined for the individual platelets within the sample.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
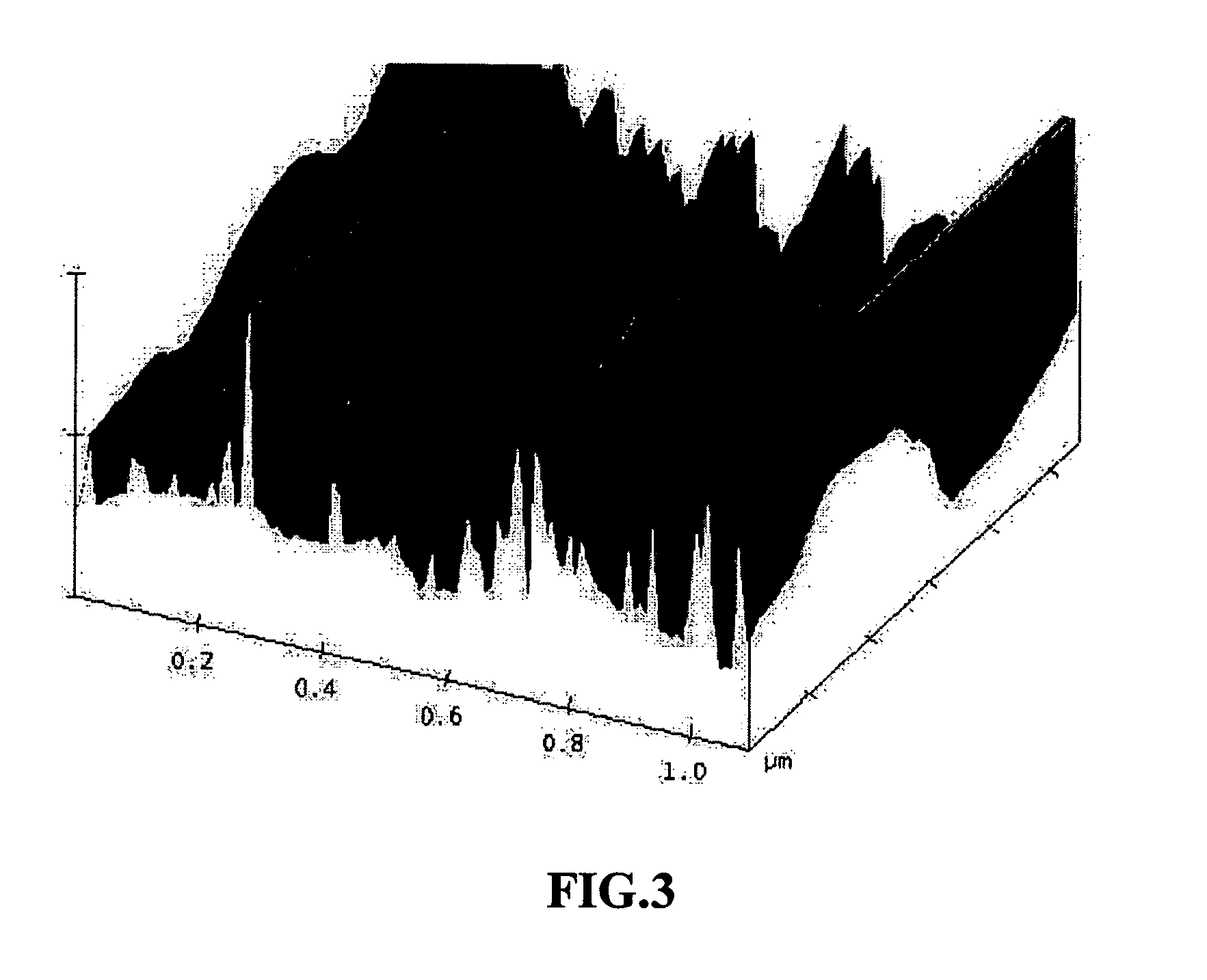
Production of ultra-thin nano-scaled graphene platelets from meso-carbon micro-beads
ActiveUS20090169467A1Improve permeabilityPromote quick completionMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentFiberMetallurgy
A method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets (NGPs) having an average thickness no greater than 50 nm, typically less than 2 nm, and, in many cases, no greater than 1 nm. The method comprises (a) intercalating a supply of meso-carbon microbeads (MCMBs) to produce intercalated MCMBs; and (b) exfoliating the intercalated MCMBs at a temperature and a pressure for a sufficient period of time to produce the desired NGPs. Optionally, the exfoliated product may be subjected to a mechanical shearing treatment, such as air milling, air jet milling, ball milling, pressurized fluid milling, rotating-blade grinding, or ultrasonicating. The NGPs are excellent reinforcement fillers for a range of matrix materials to produce nanocomposites. Nano-scaled graphene platelets are much lower-cost alternatives to carbon nano-tubes or carbon nano-fibers.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Platelet suspensions and methods for resuspending platelets
Platelet suspensions and methods for resuspending platelet concentrates are disclosed. The platelet concentrates are resuspended by combining a platelet concentrate with a hypertonic solution of either sodium chloride or potassium chloride. The resuspended platelets may be stored and / or administered to a patient.
Owner:FENWAL
Spacer-modified nano graphene electrodes for supercapacitors
ActiveUS20110157772A1Increase surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid electrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceSupercapacitor
A surface-modified nano graphene platelet (NGP), comprising: (a) a nano graphene platelet having a thickness smaller than 10 nm; and (b) discrete, non-continuous, and non-metallic bumps or nodules bonded to a surface of the graphene platelet to serve as a spacer. When multiple surface-modified NGP sheets are stacked together to form an electrode, large numbers of electrolyte-accessible pores are formed, enabling the formation of large amounts of double layer charges in a supercapacitor, which exhibits an exceptionally high specific capacitance.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com