Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Nanostructured membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multispectral plasmonic crystal sensors
InactiveUS20080212102A1Enhanced local plasmonic field distributionImproved field distributionSolid-state devicesScattering properties measurementsCouplingCrystal structure
The present invention provides plasmonic crystals comprising three-dimensional and quasi comprising three-dimensional distributions of metallic or semiconducting films, including multi-layered crystal structures comprising nanostructured films and film arrays. Plasmonic crystals of the present invention include precisely registered and deterministically selected nonplanar crystal geometries and spatial distributions providing highly coupled, localized plasmonic responses in thin film elements and / or nanostructures of the crystal. Coupling of plasmonic responses provided by three-dimensional and quasi-three dimensional plasmonic crystal geometries and structures of the present invention generates enhanced local plasmonic field distributions useful for detecting small changes in the composition of an external dielectric environment proximate to a sensing surface of the plasmonic crystal. Plasmonic crystal structures of the present invention are also useful for providing highly localized excitation and / or imaging of fluorophores proximate to the crystal surface.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Multi-wavelength optical devices and methods of using same
Owner:VALENCELL INC
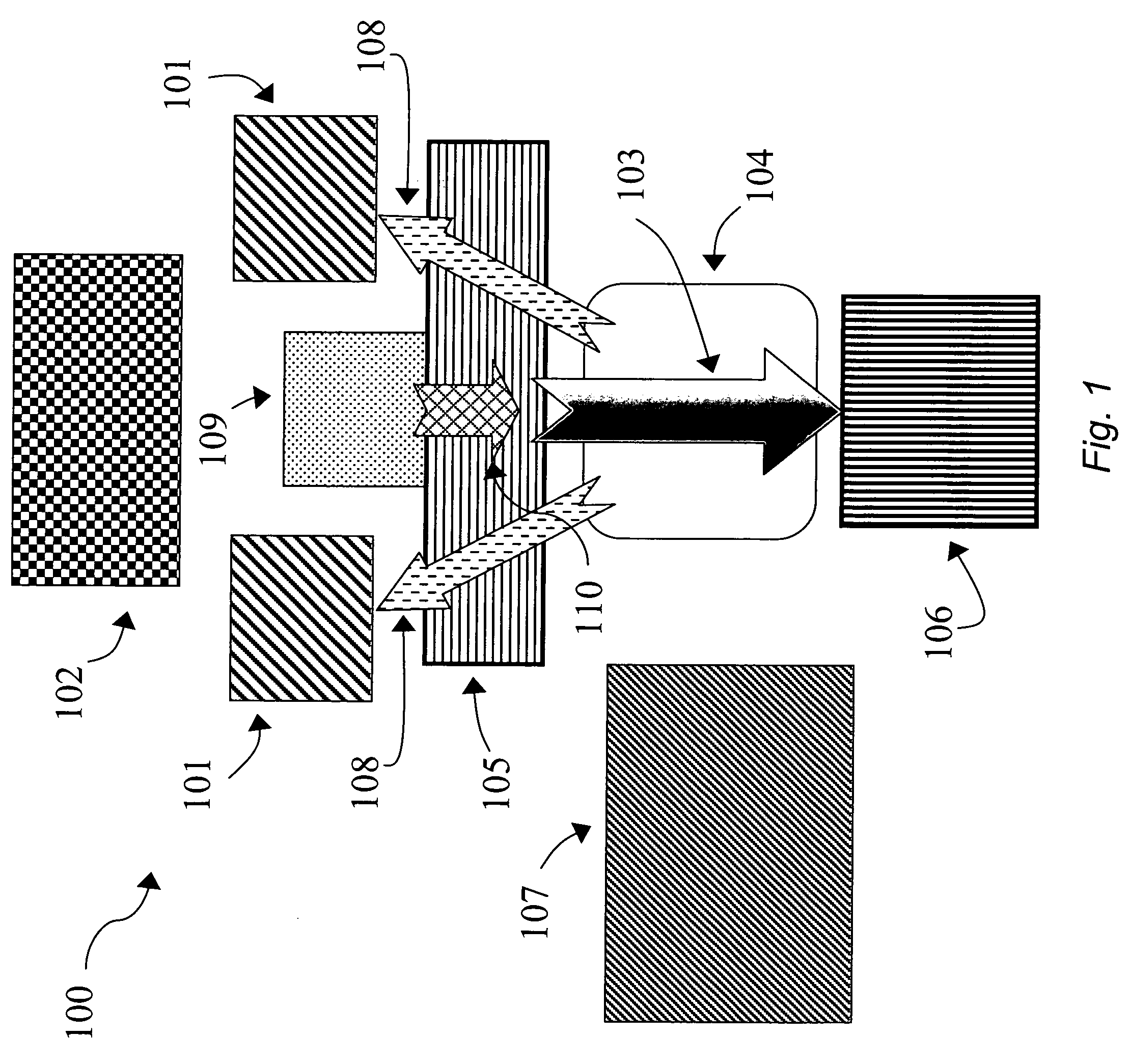
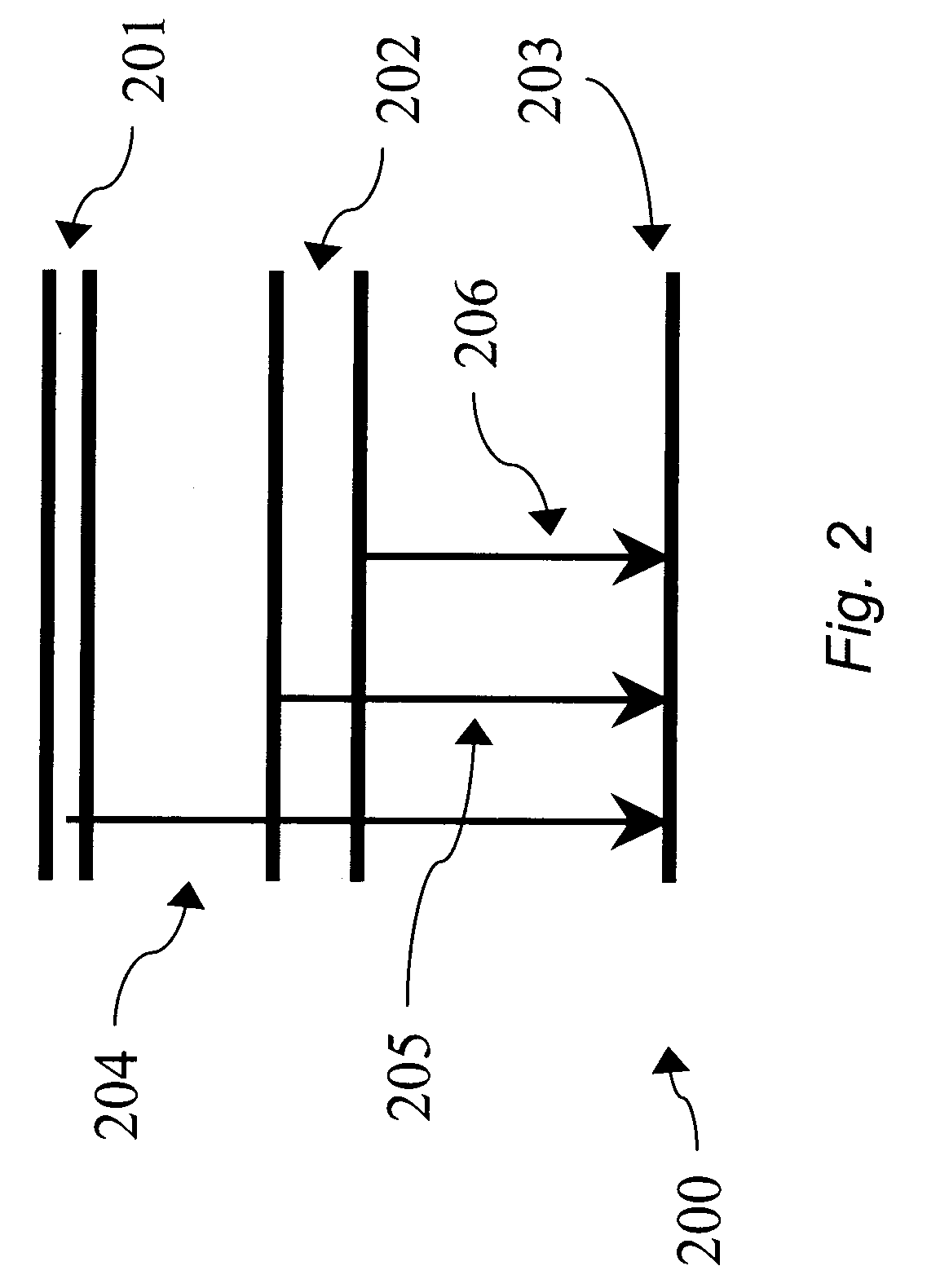
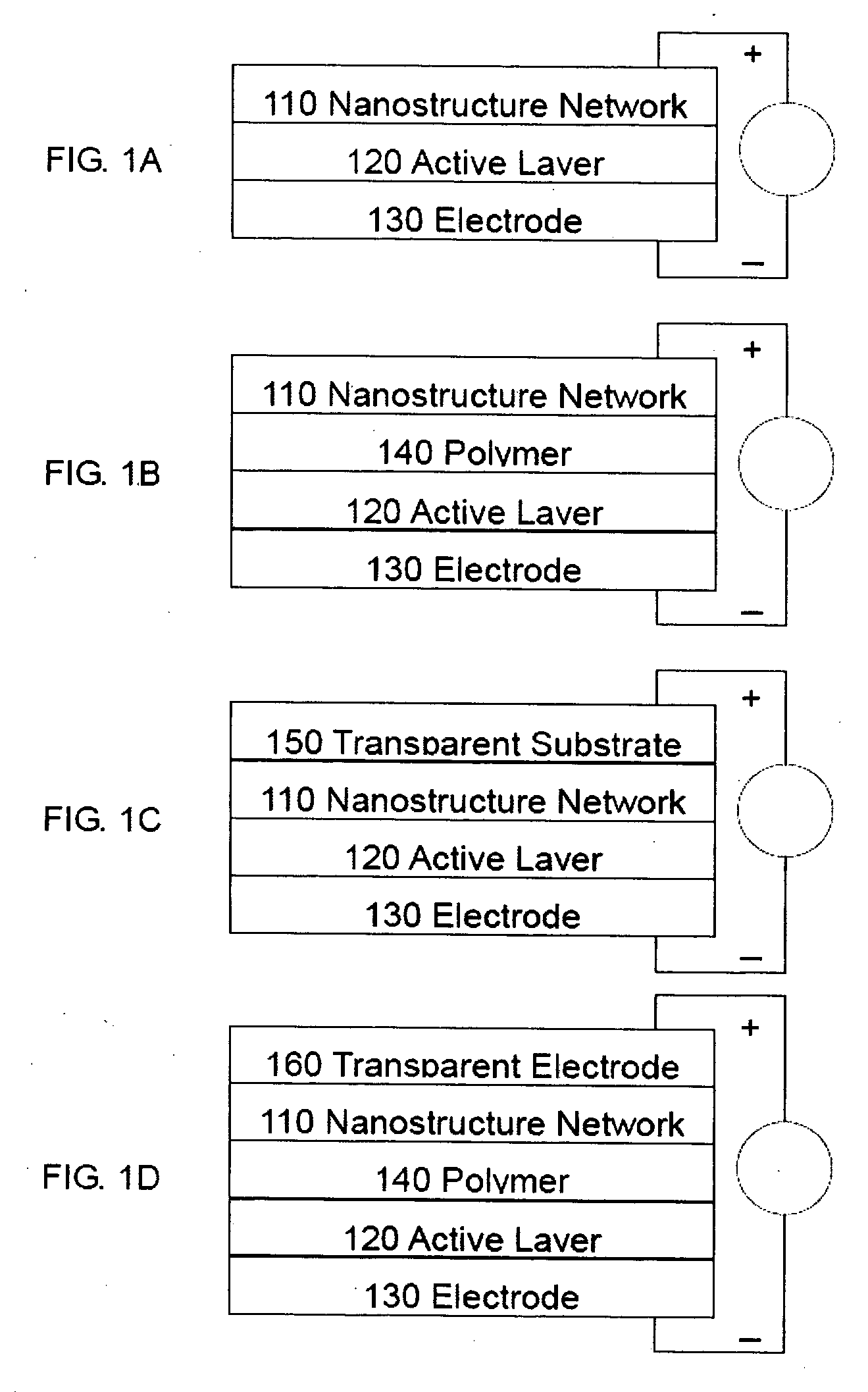
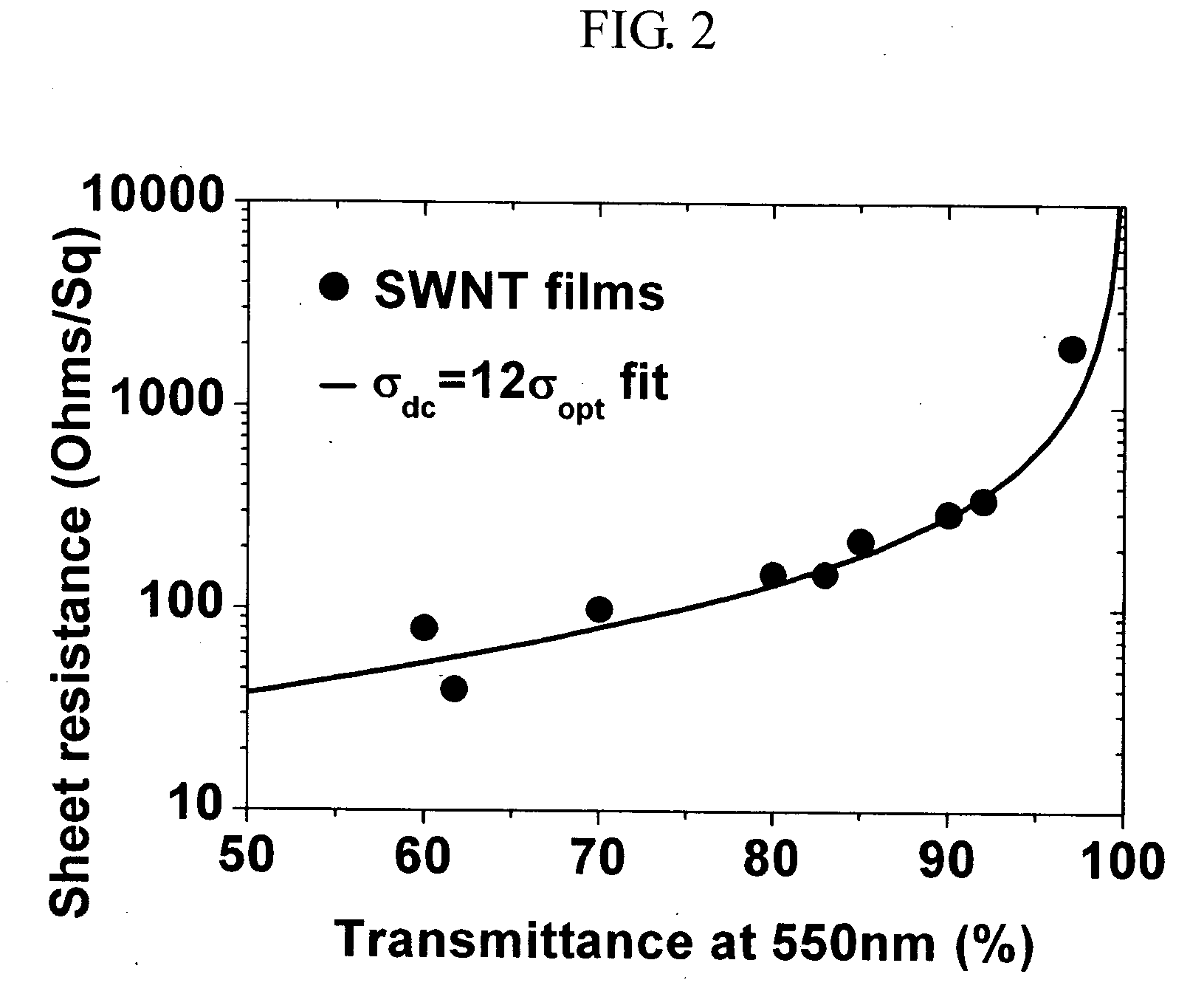
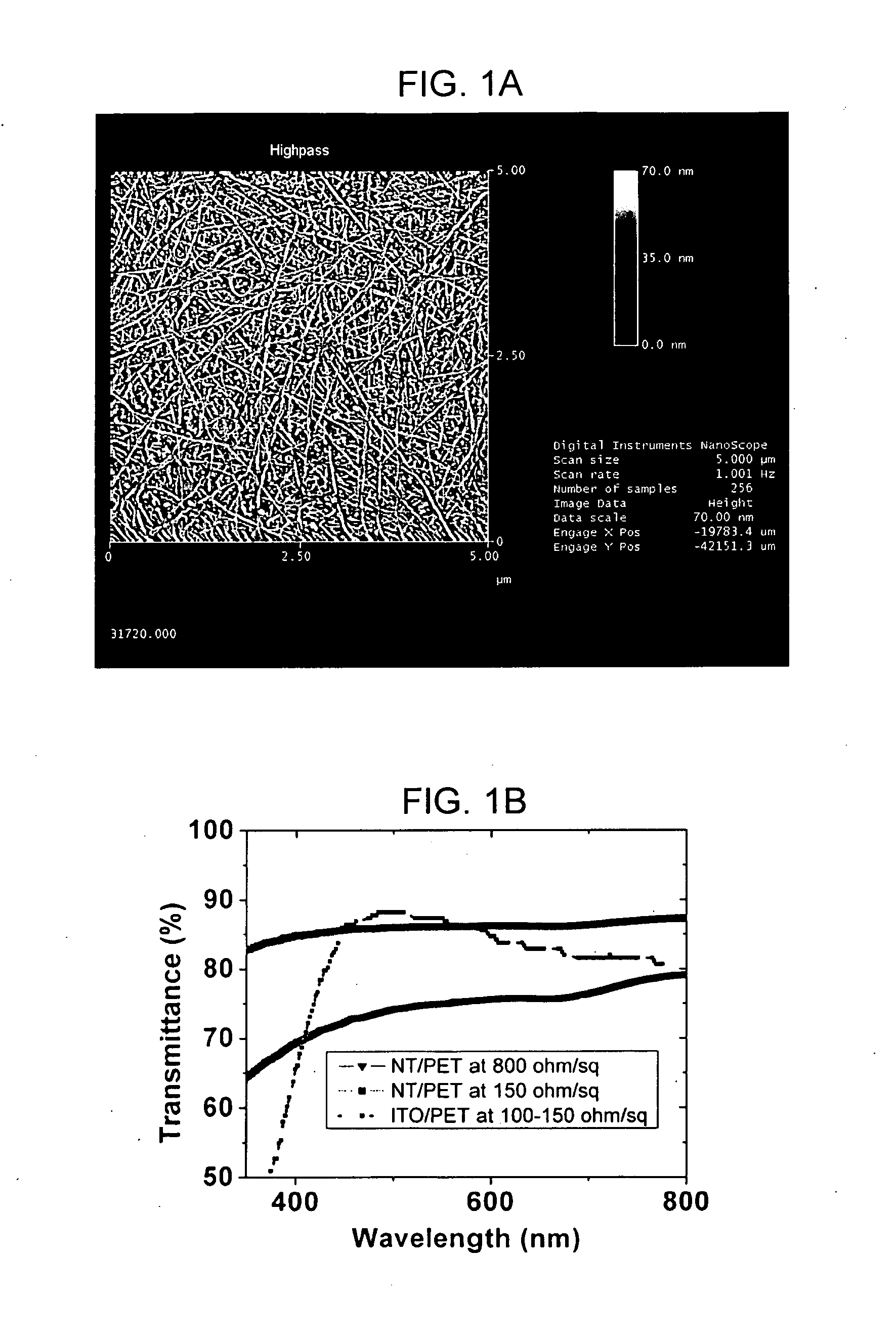
Transparent electrodes formed of metal electrode grids and nanostructure networks
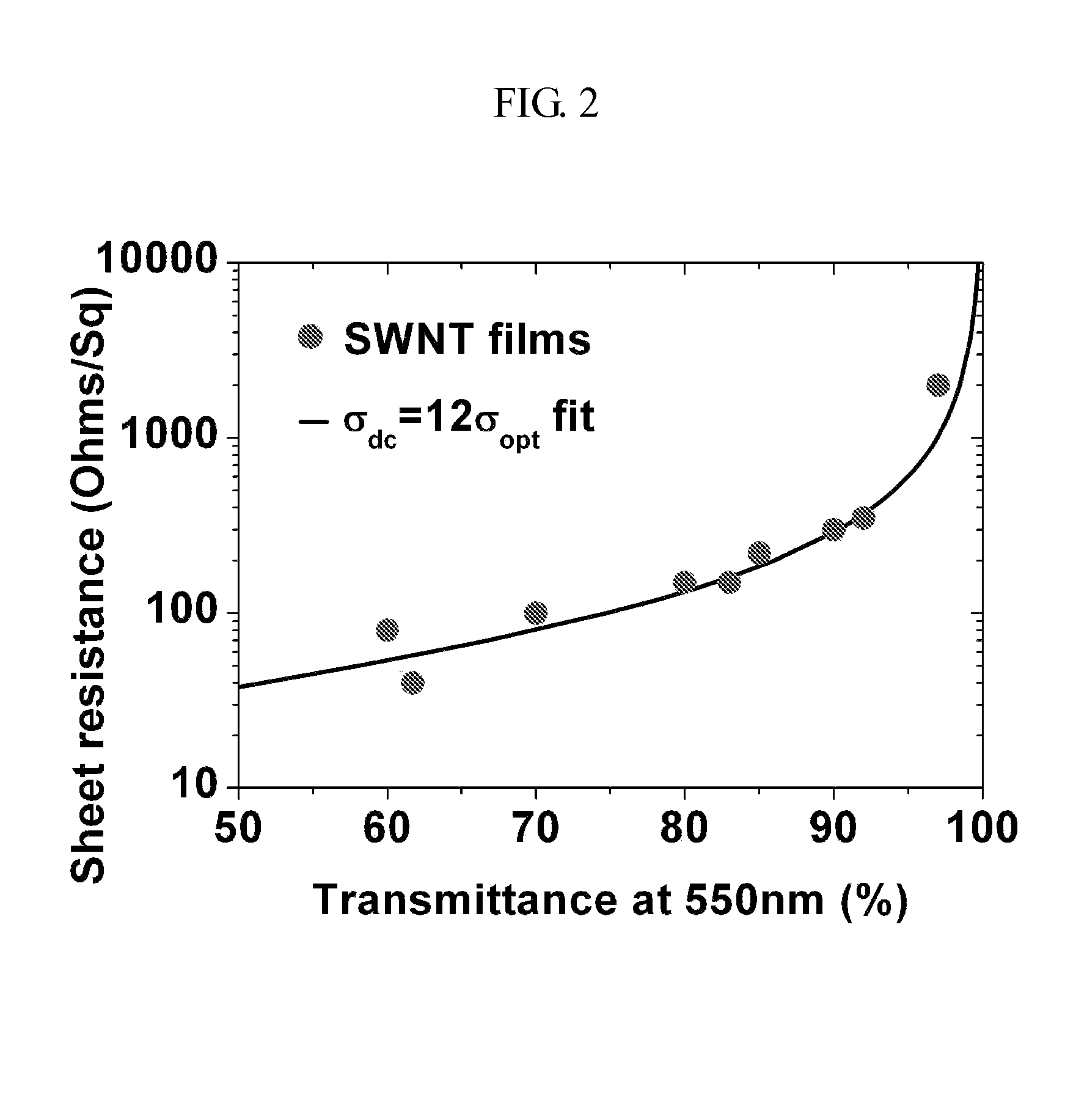
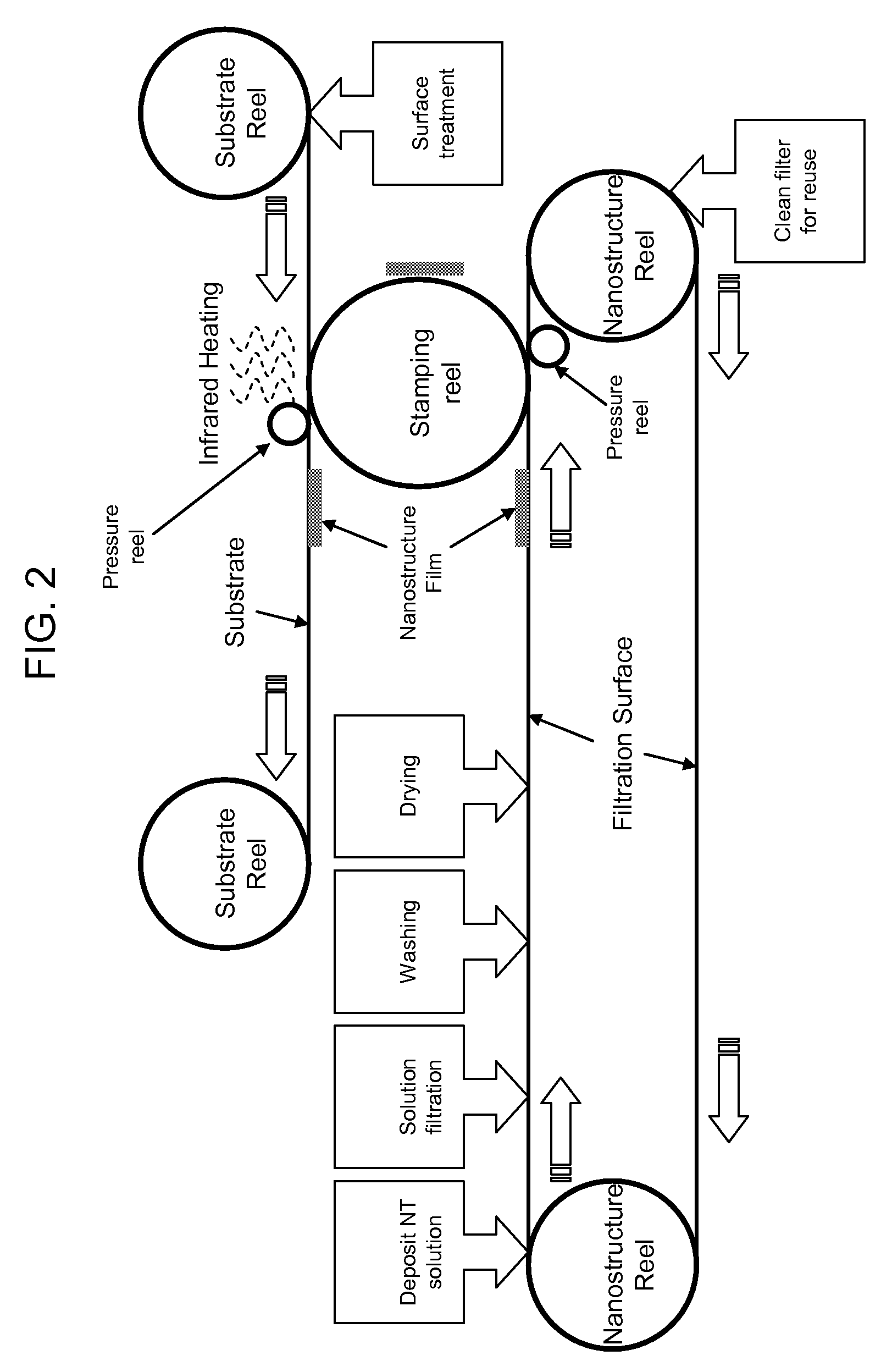
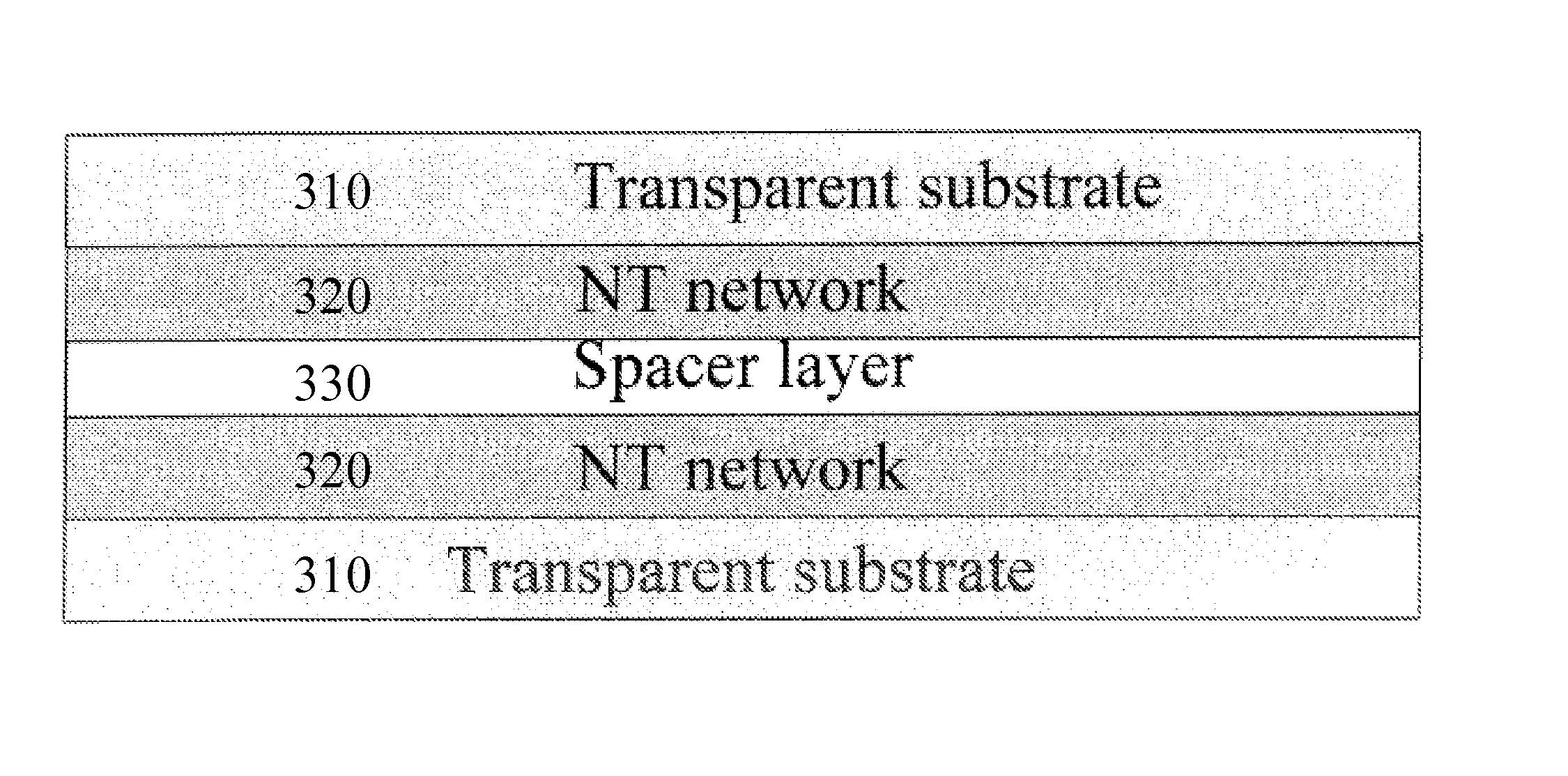
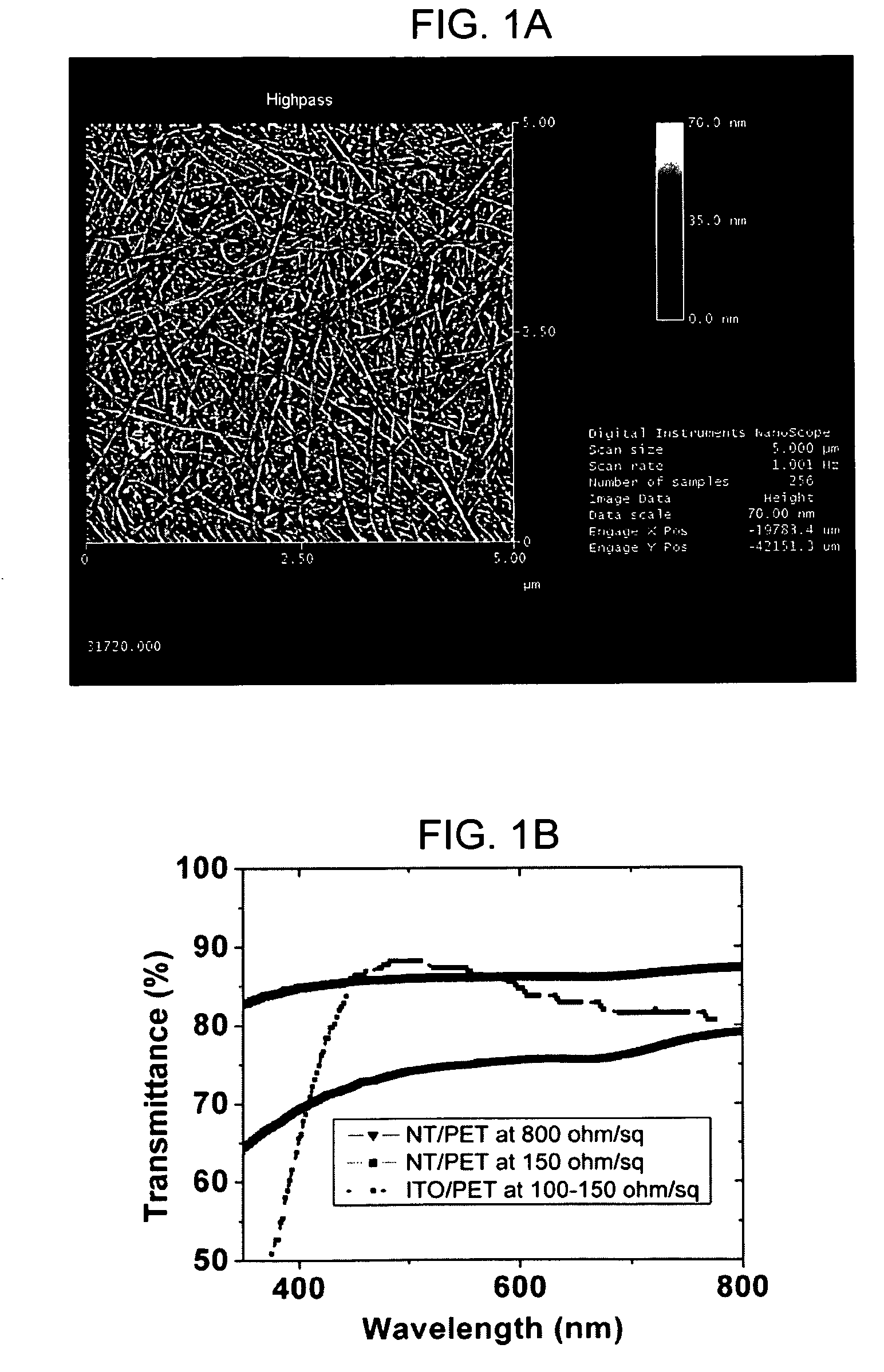
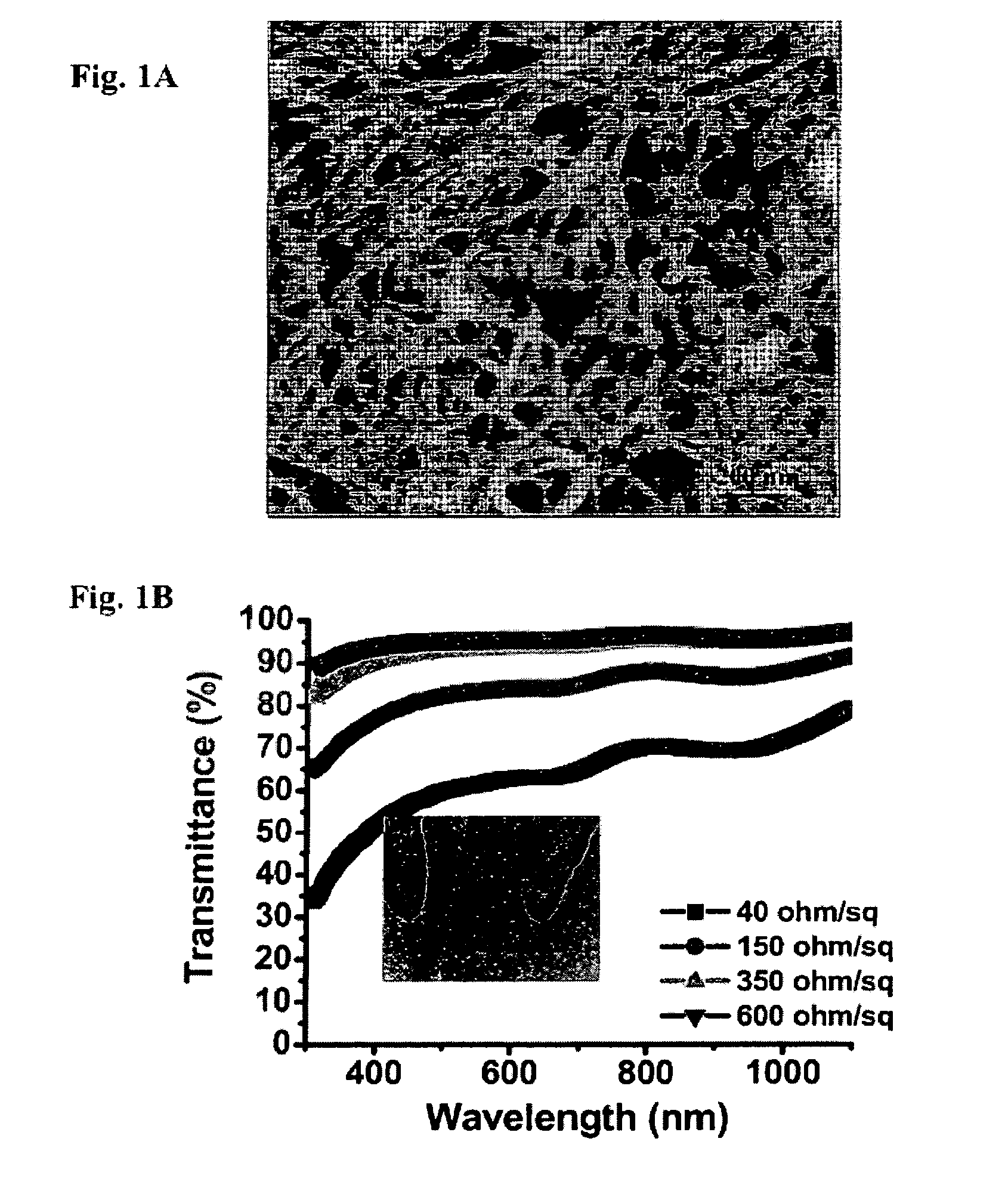
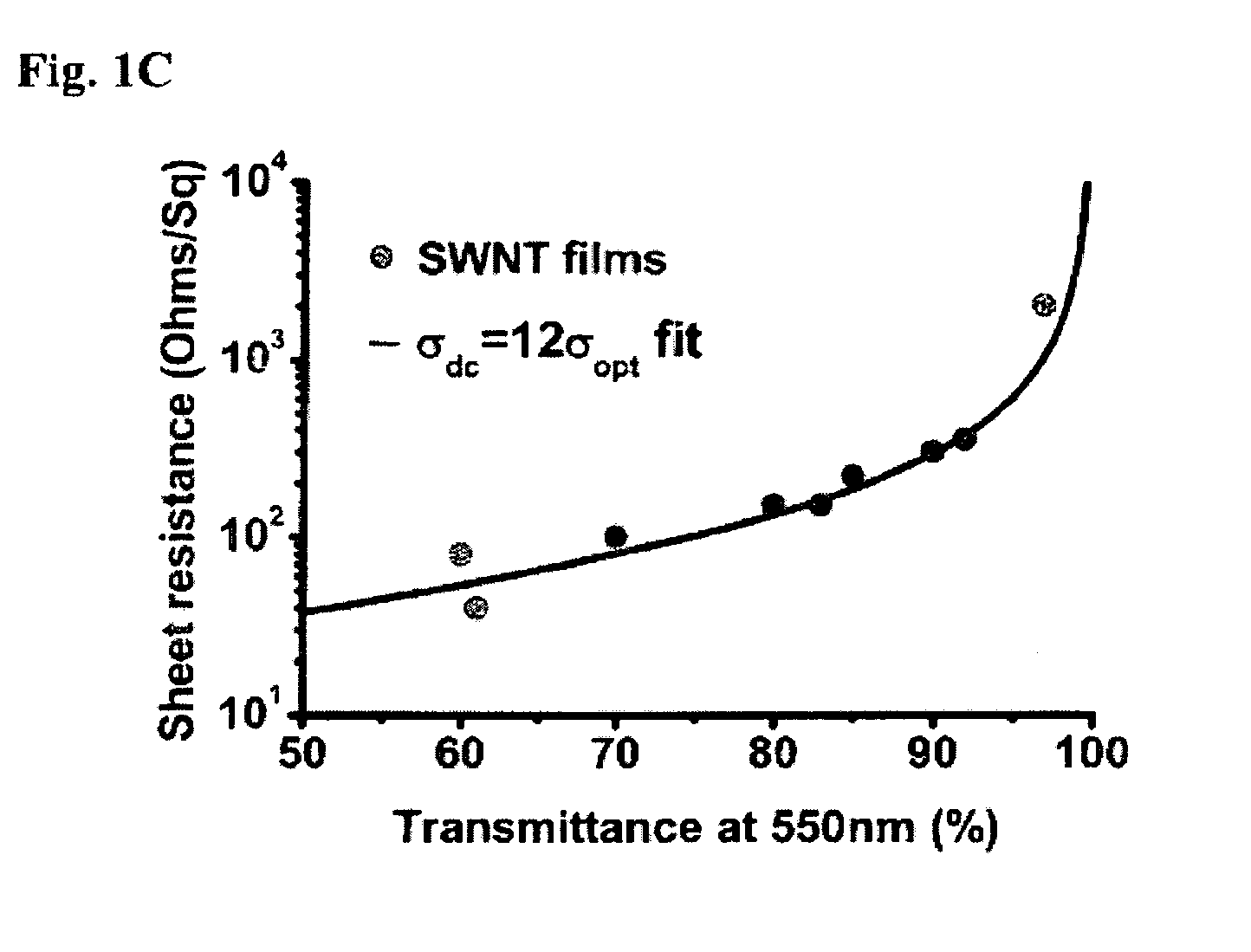
An optoelectronic device comprising at least one nanostructure-film electrode is discussed. The optoelectronic device may further comprise a different material, such as a polymer, to fill pores in the nanostructure-film. Additionally or alternatively, the optoelectronic device may comprise an electrode grid superimposed on the nanostructure-film.
Owner:UNIDYM +1
Compliant and nonplanar nanostructure films
ActiveUS20080317982A1Envelopes/bags making machineryLiquid surface applicatorsPlanar substrateNanostructure
A coated substrate comprising a nanostructure film formed on a non-planar substrate is described. The coated substrate may further be compliant, optically transparent and / or electrically conductive. Fabrication methods thereof are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solar cell with nanostructure electrode
An optoelectronic device comprising at least one nanostructure-film electrode and fabrication methods thereof are discussed. The optoelectronic device may further comprise a different material to fill in porosity in the nanostructure-film. Additionally, the optoelectronic device may be a solar cell, comprising at least one of a variety of photosensitive active layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
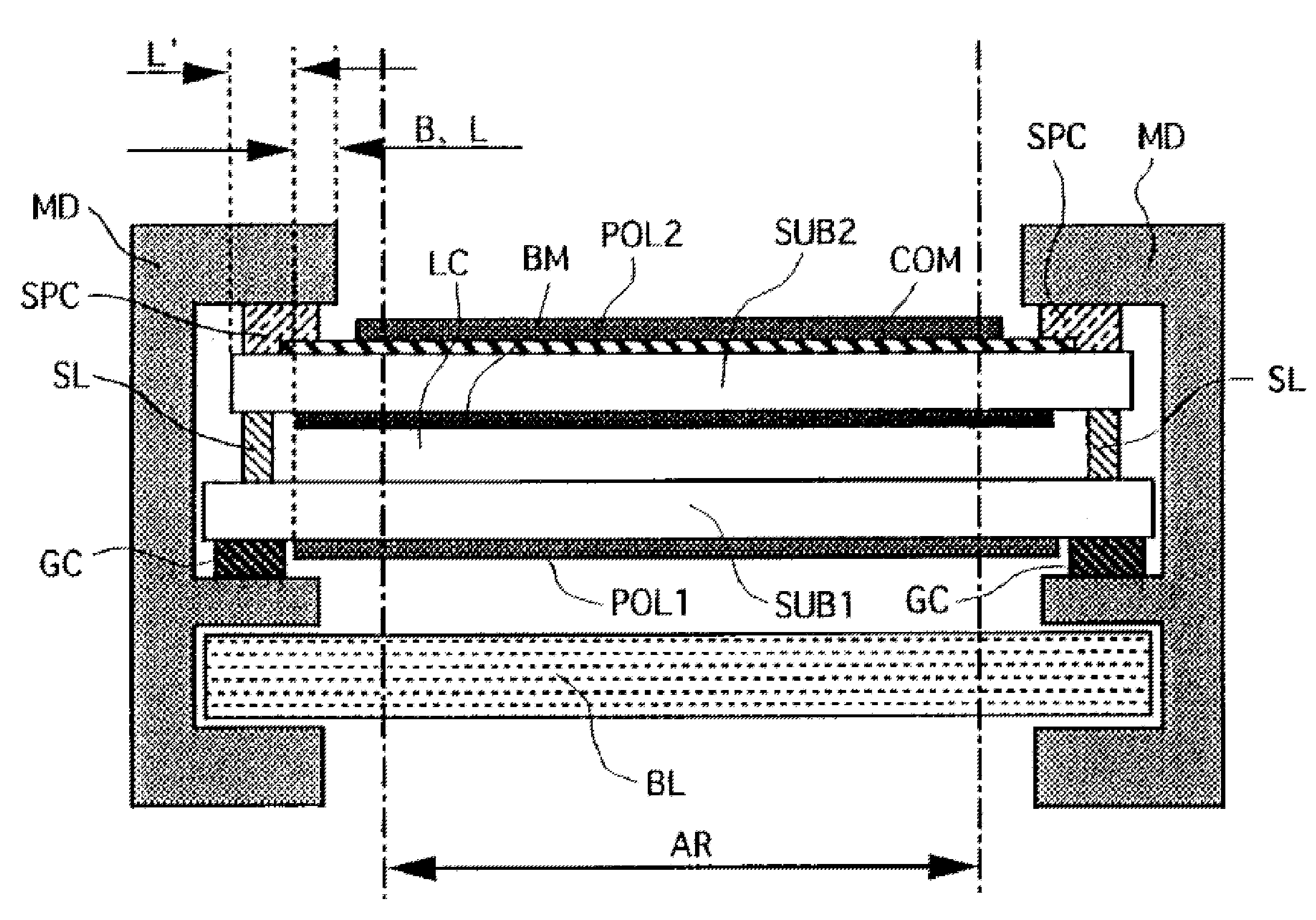
Nanostructure-Film LCD Devices
ActiveUS20090147167A1Extraordinary strengthExtraordinary electrical conductivityLiquid crystal compositionsSolid-state devicesNano structuringLiquid-crystal display
This invention relates to an LCD device comprising an electrically conductive and optically transparent nanostructure film deposited adjacent to or forming a part of at least one of a) a layer comprising triacetyl cellulose (TAC), b) a polarizing layer, c) an adhesive layer, d) a protective layer, e) an anti-glare layer f) an anti-reflective layer, or g) an antistatic layer. One embodiment is a device comprising an in plane switching (IPS) liquid crystal display (LCD) and a nanostructure film, wherein the film is electrically conductive, and wherein the film is optically transparent.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
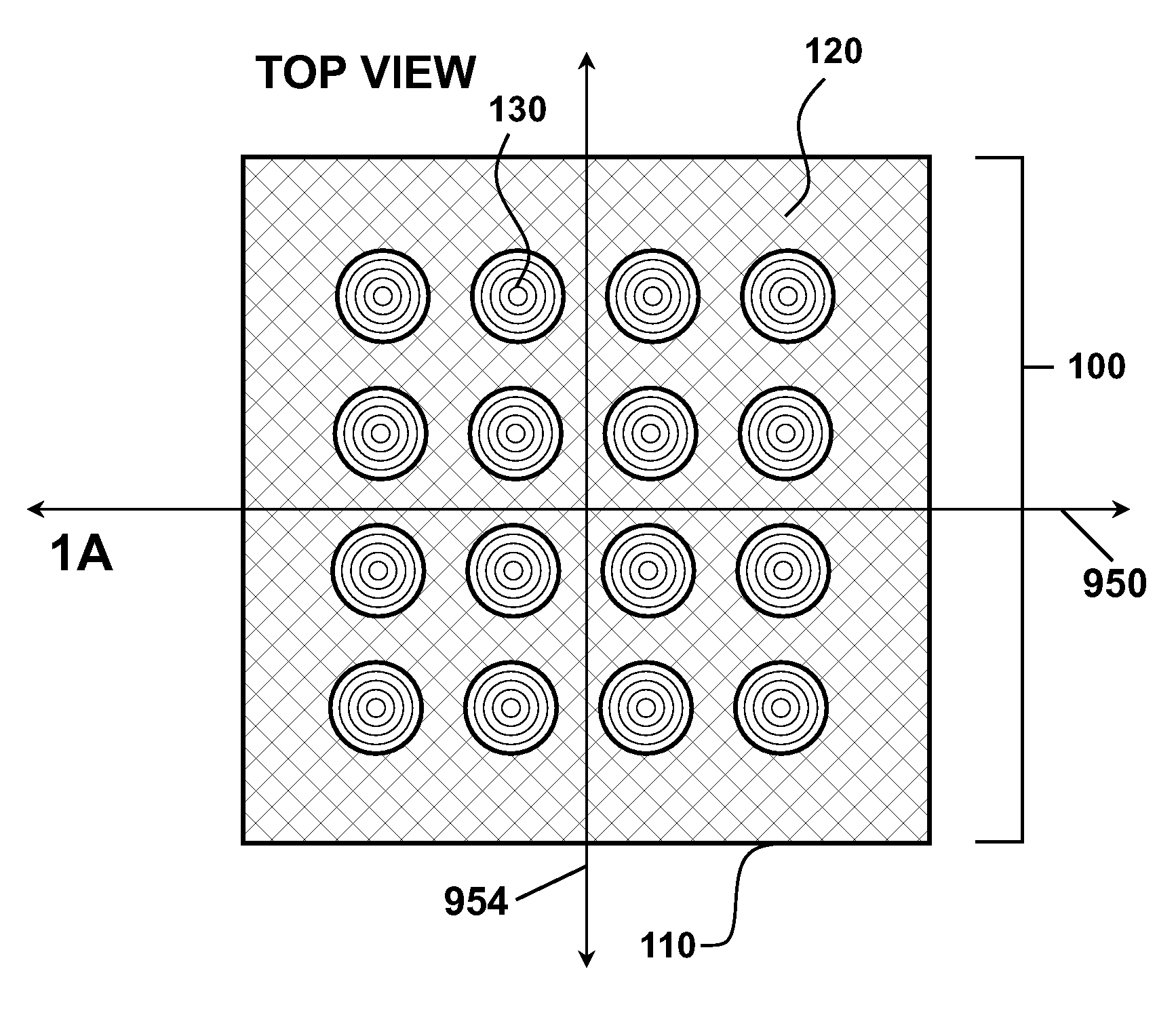
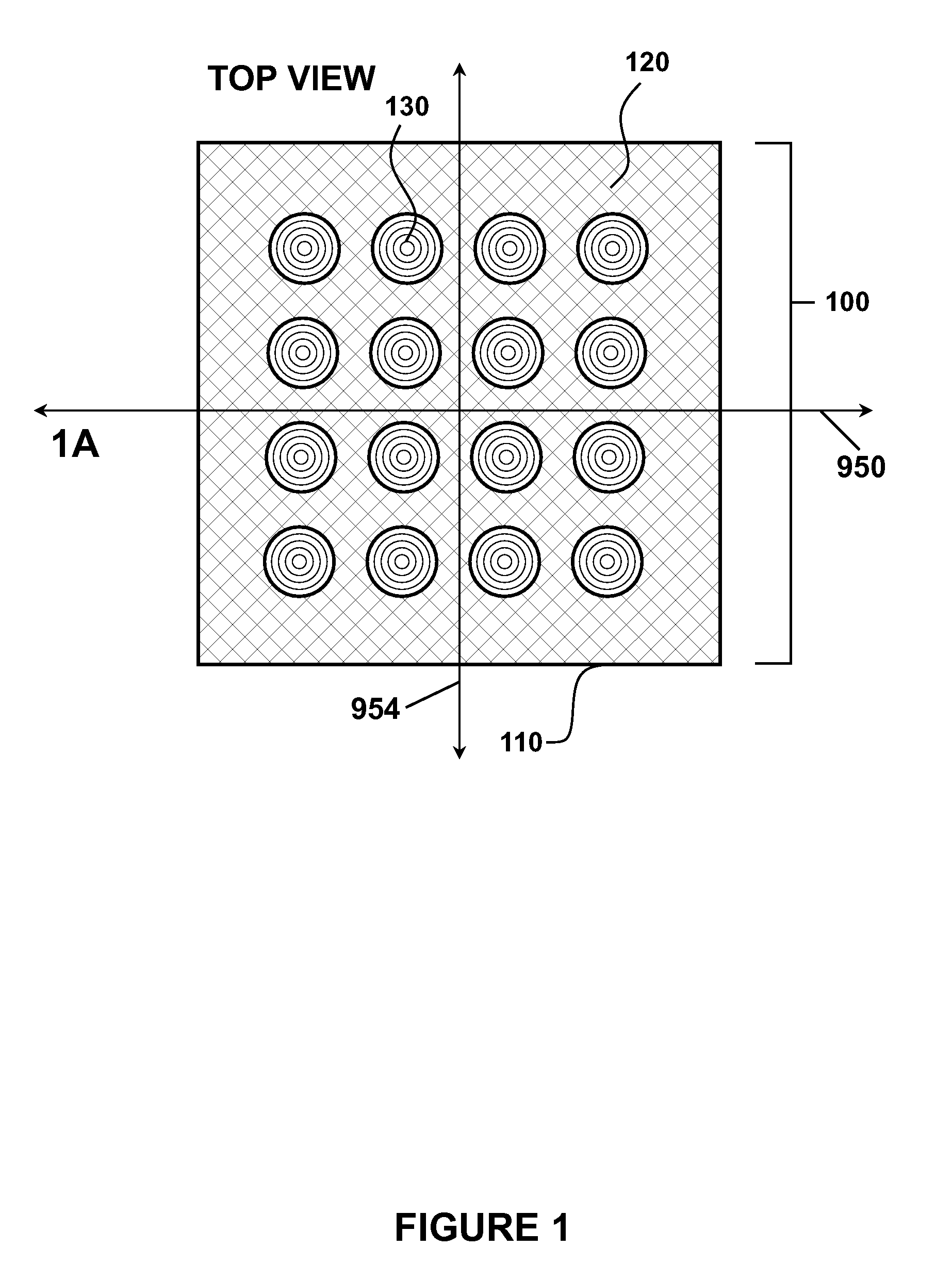
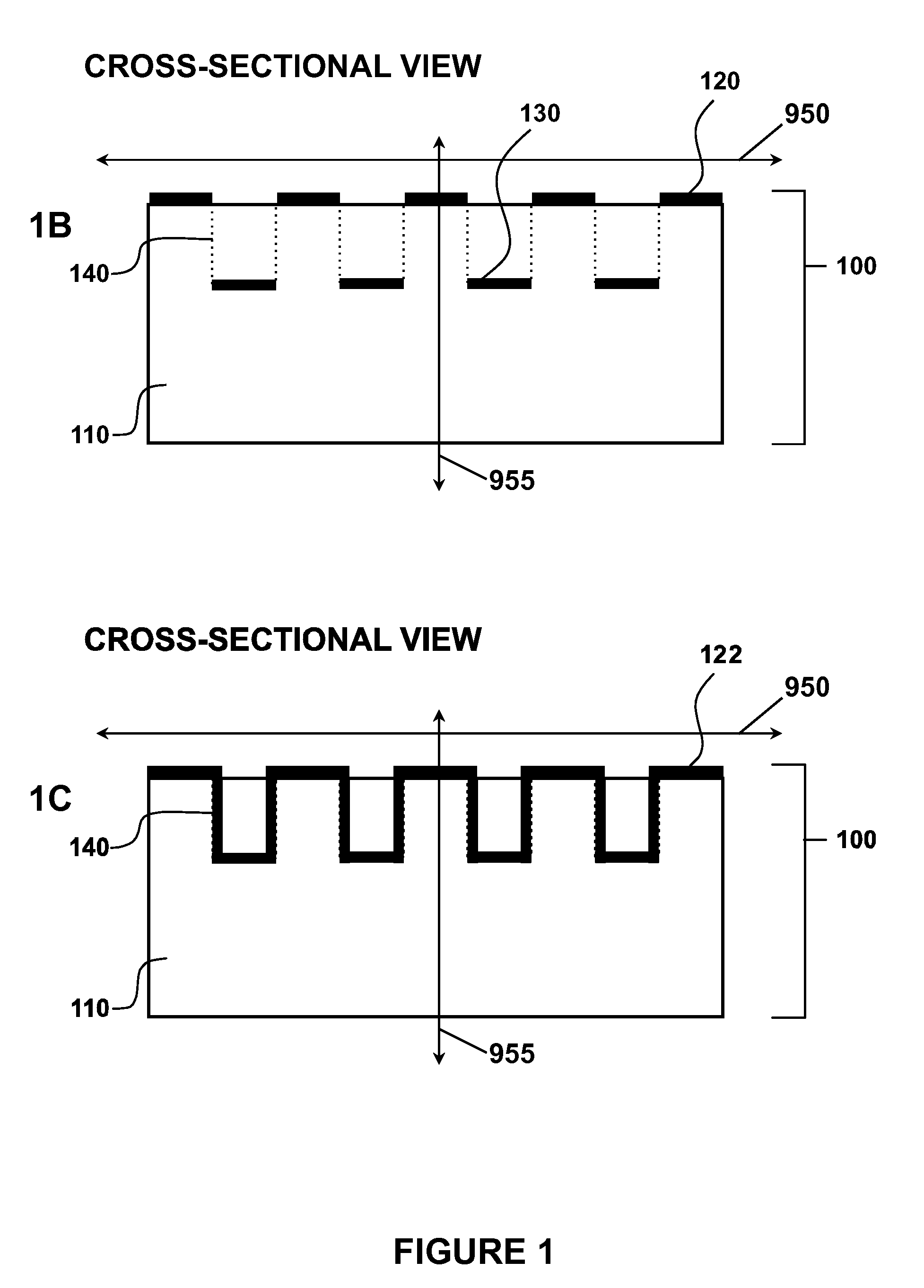
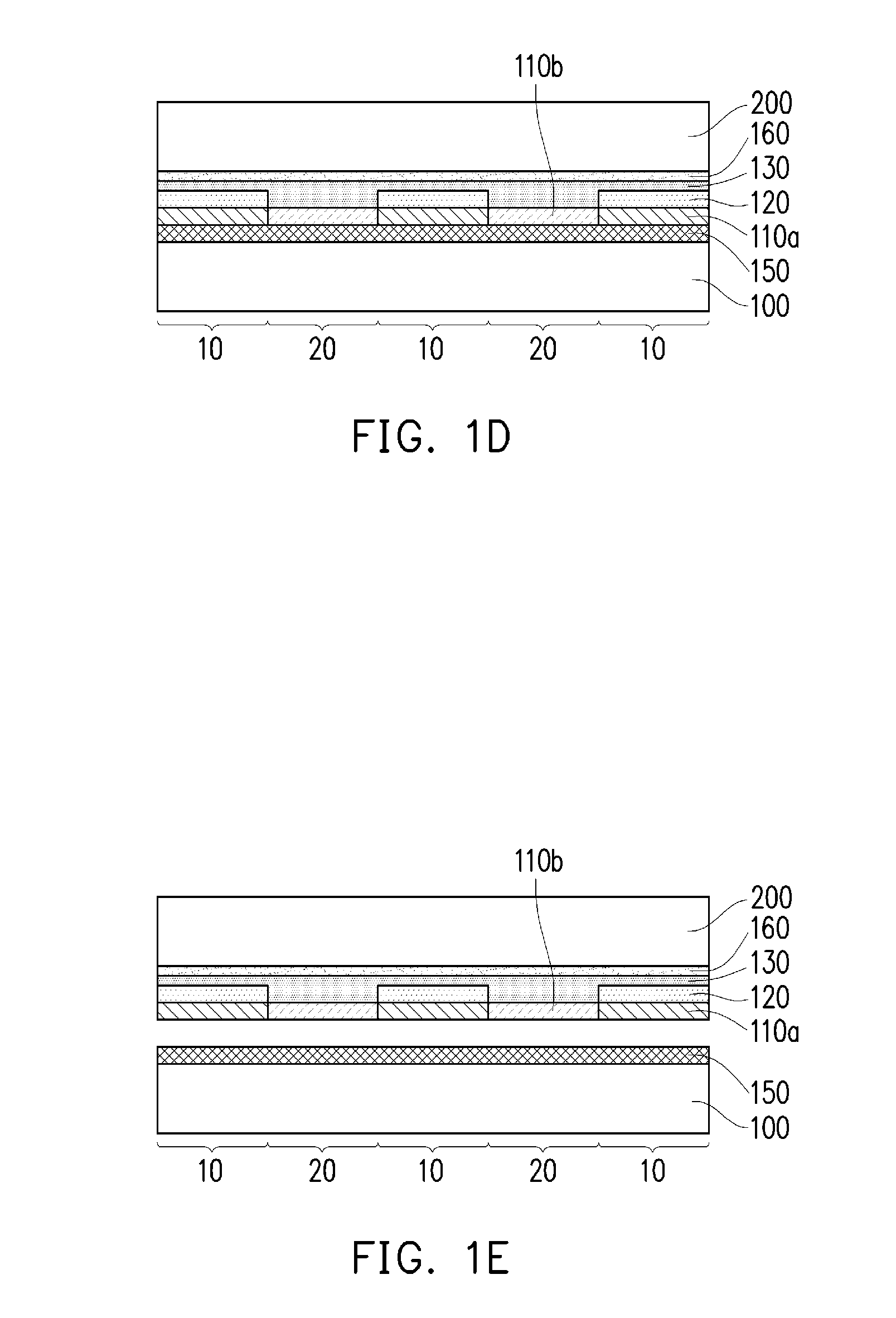
Efficient 3-D nanostructured membranes
ActiveUS20050204920A1Improve permeabilityHigh selectivitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesNanostructureNanostructured membrane
There is provided a high efficient gas separation membrane of two or more layers, which comprises a separating layer of 3-dimensional nanostructure and a supporting layer, wherein the 3-dimensional nanostructure can maximize a surface area per unit permeation area.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
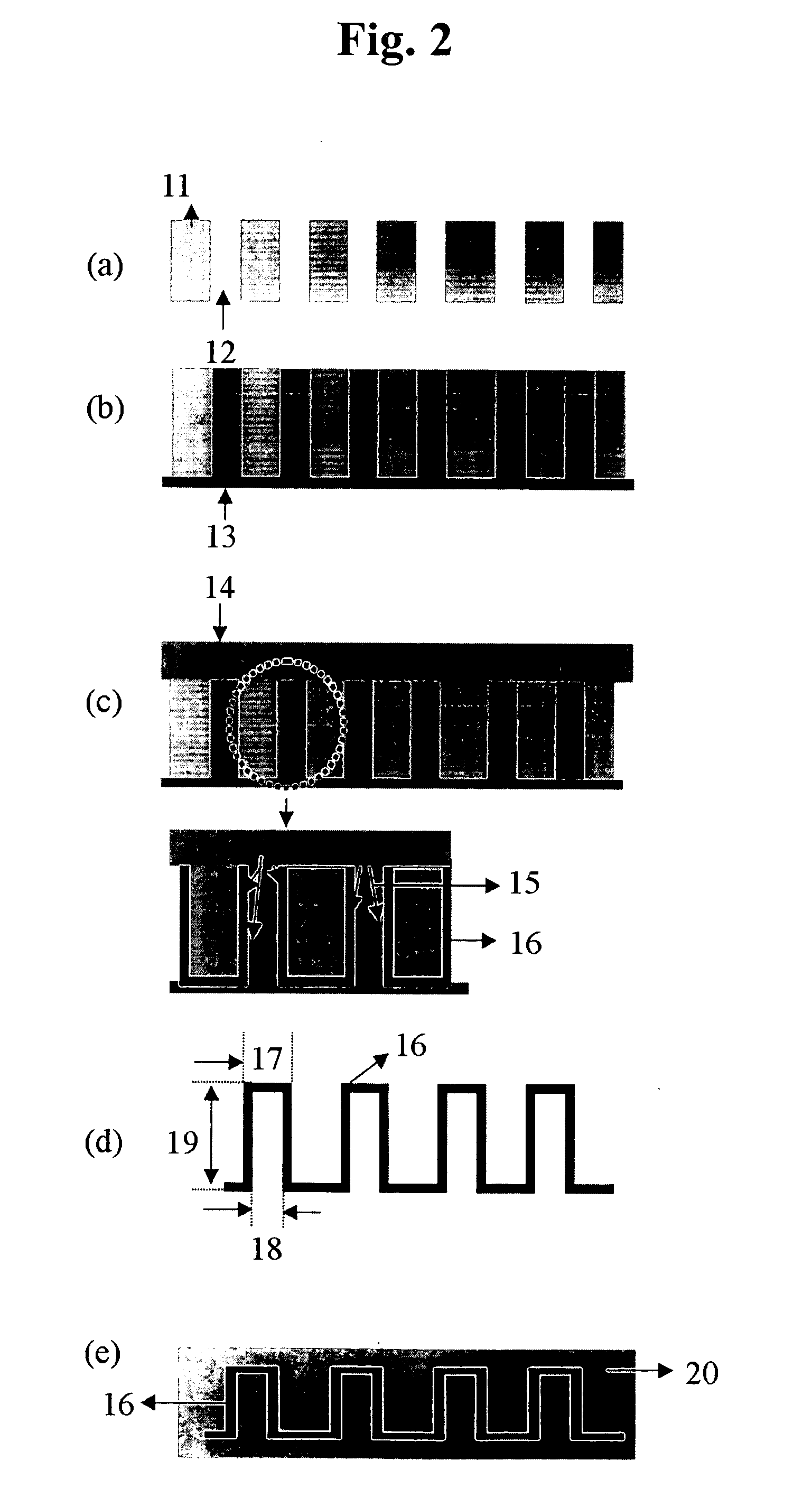
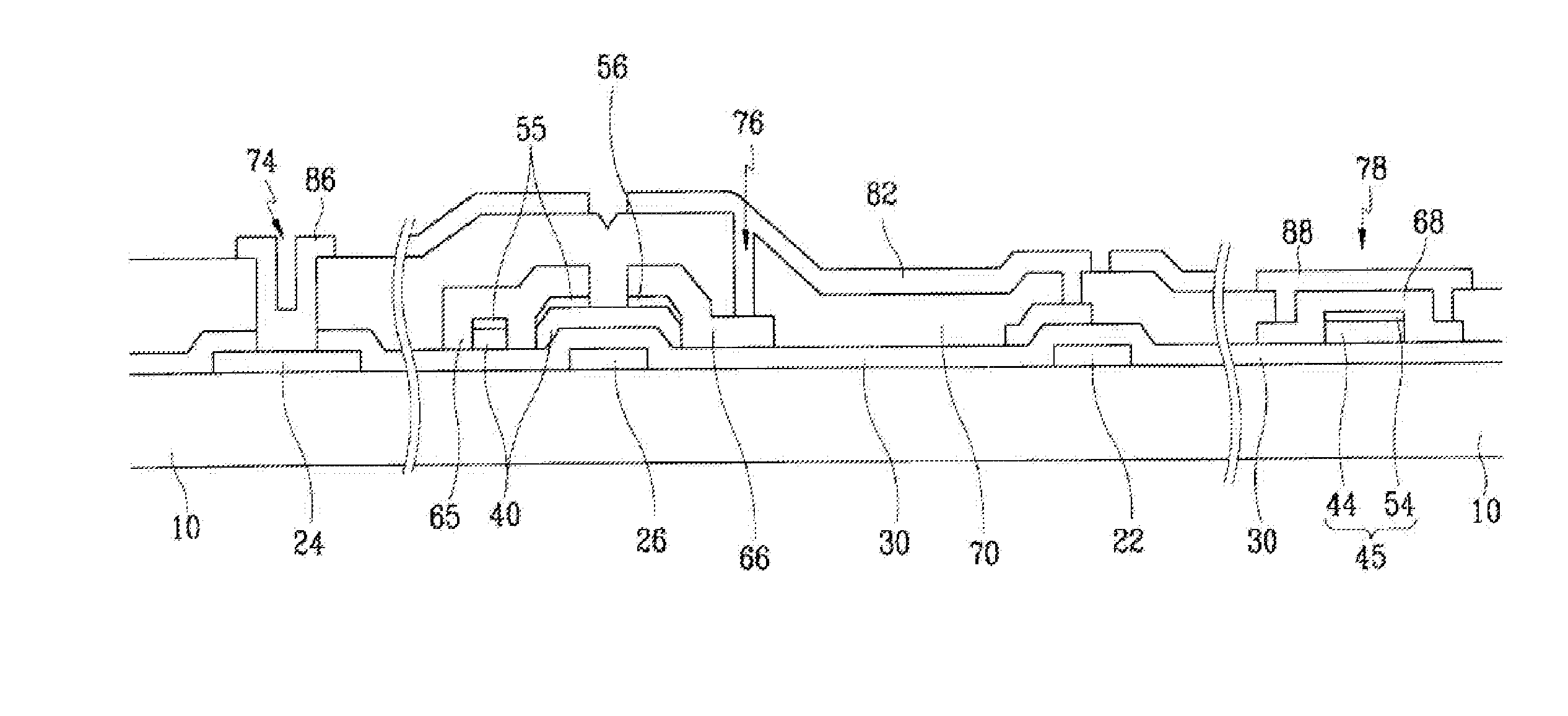
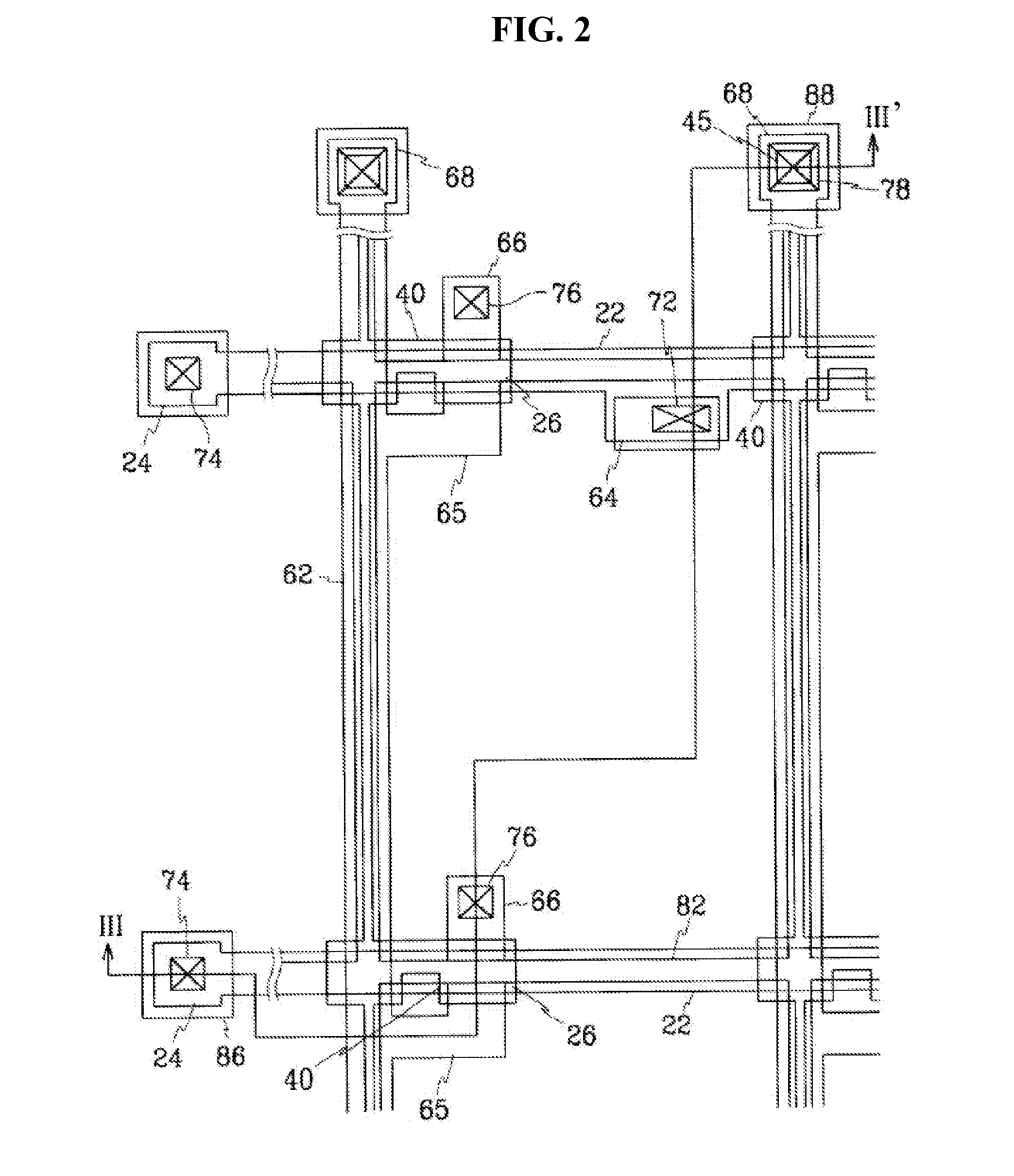
Transparent and Conductive Nanostructure-Film Pixel Electrode and Method of Making the Same
ActiveUS20080157080A1Reduce in quantityCostMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsActive matrixEngineering
A pixel electrode is provided, comprising a nanostructure-film deposited over an active matrix substrate, such that the pixel electrode makes electrical contact with an underlying layer. Similarly, auxiliary data pads and auxiliary gate pads are provided, which also comprise nanostructure-films deposited over an active matrix substrate, such that they make electrical contact with underlying layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
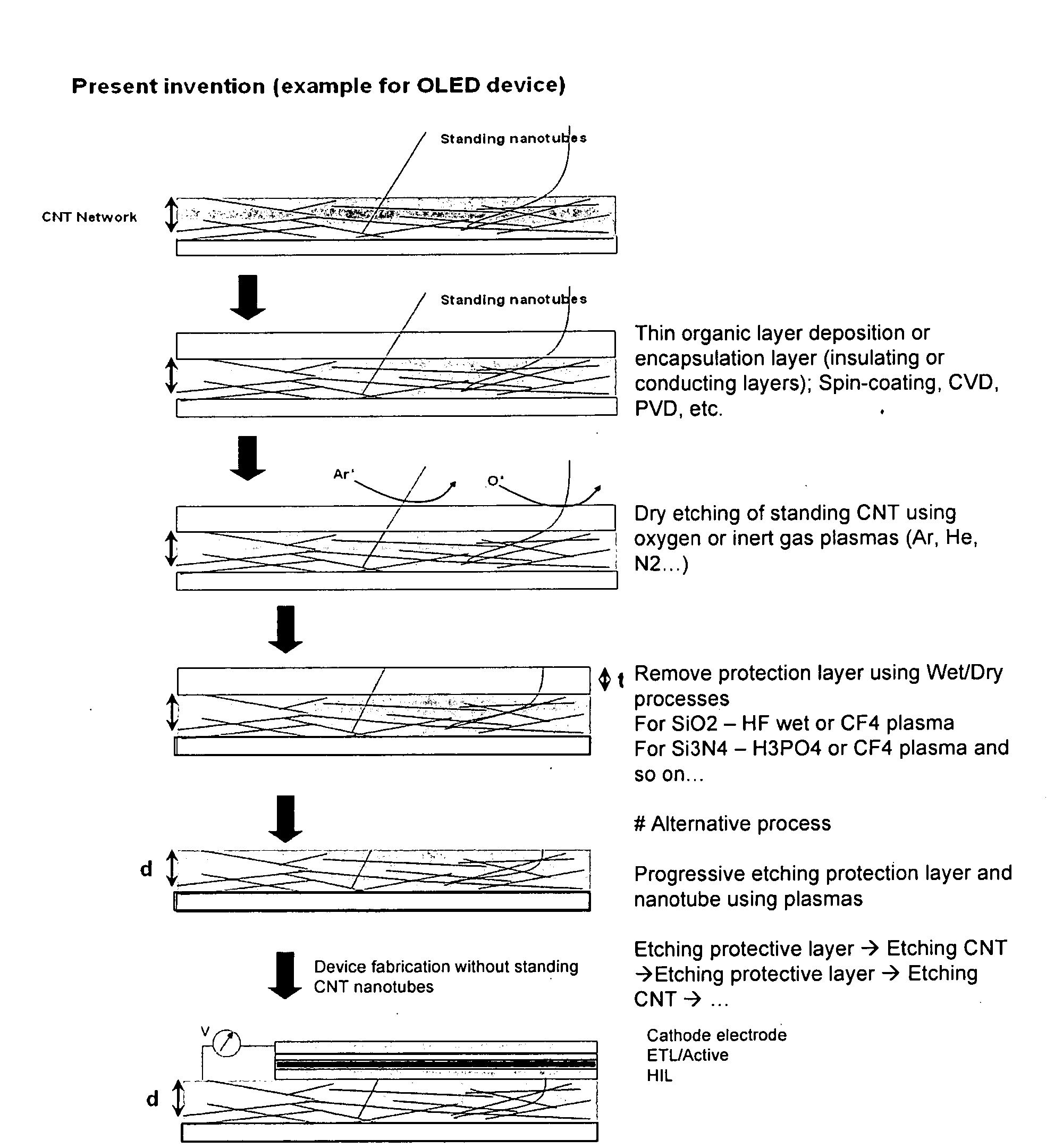
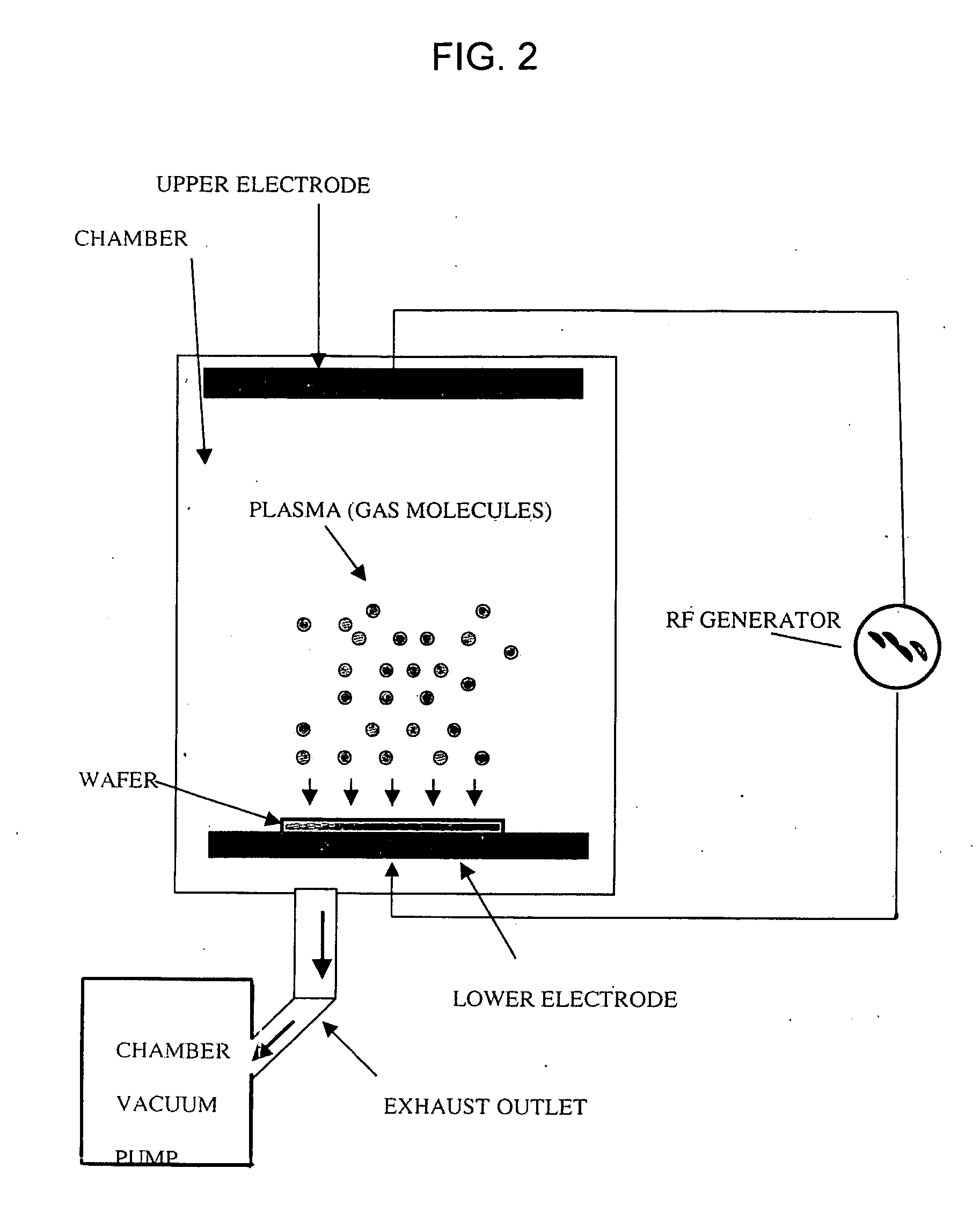
Inert gas etching
A method of patterning a nanostructure film using a plasma is described. The nanostructure film may substantially comprise carbon and / or carbon nanotubes. The plasma may comprise an inert gas. The plasma may be applied to the nanostructure film at close to atmospheric pressure and room temperature.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic electroluminesence device
InactiveCN1527648AImprove luminous efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesQuantum efficiencyCoupling
The present invention reveals organic electroluminescence device in the structure capable of preventing degradation of outer quantum efficiency of the organic electroluminescence assembly caused by surface plasma sub-resonance. The organic electroluminescent device has organic electroluminescence light leading out layer in nano structure of dielectric material or organic material and metal grains in nano size. The nano structure film layer may resonate with surface plasma in the assembly to form coupling, so that the light falling into the assembly may be taken out from the assembly to raise the light-emitting efficiency of the organic electroluminescence device effectively.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for preparing porous titanium filtering material surface functionalization nano-structure film
InactiveCN101122041AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyImprove featuresSemi-permeable membranesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingNano structuringAlloy
The invention provides a method of preparing a functional nano structure film of the surface of a multi-hole titanium filtering material. The method is to deoil and clean the surface of a micro-hole alloy titanium slice and use the slice as the anode, use the inorganic or organic solution with fluorinion as the electrolyte, and a platinum electrode as the cathode, conduct anodic oxidation to a multi-hole titanium sample, and then anneal in the high temperature range of 430 to 600DEG C, so as to obtain a 1 to 120Mu m thick TiO2 nano structure array film on the multi-hole metal titanium. A composite structure prepared by the invention has functions and effects of photocatalysis organic sewage treatment, filtering and separation. Meanwhile, the titanium dioxide structure grows from the basal in situ, so that interfaces are firmly adhered, and preparation and loading of the photochemical catalyst can be completed at a time.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Patterned conductive film, method of fabricating the same, and application thereof
ActiveUS20150047885A1Improve conductivityLow costMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsNano structuringNanometre
Provided is a patterned conductive film may include a conductive interconnected nano-structure film. The conductive interconnected nano-structure film may include a first region and a second region adjacent to the first region. A conductivity of the first region may be at least 1000 times a conductivity of the second region.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
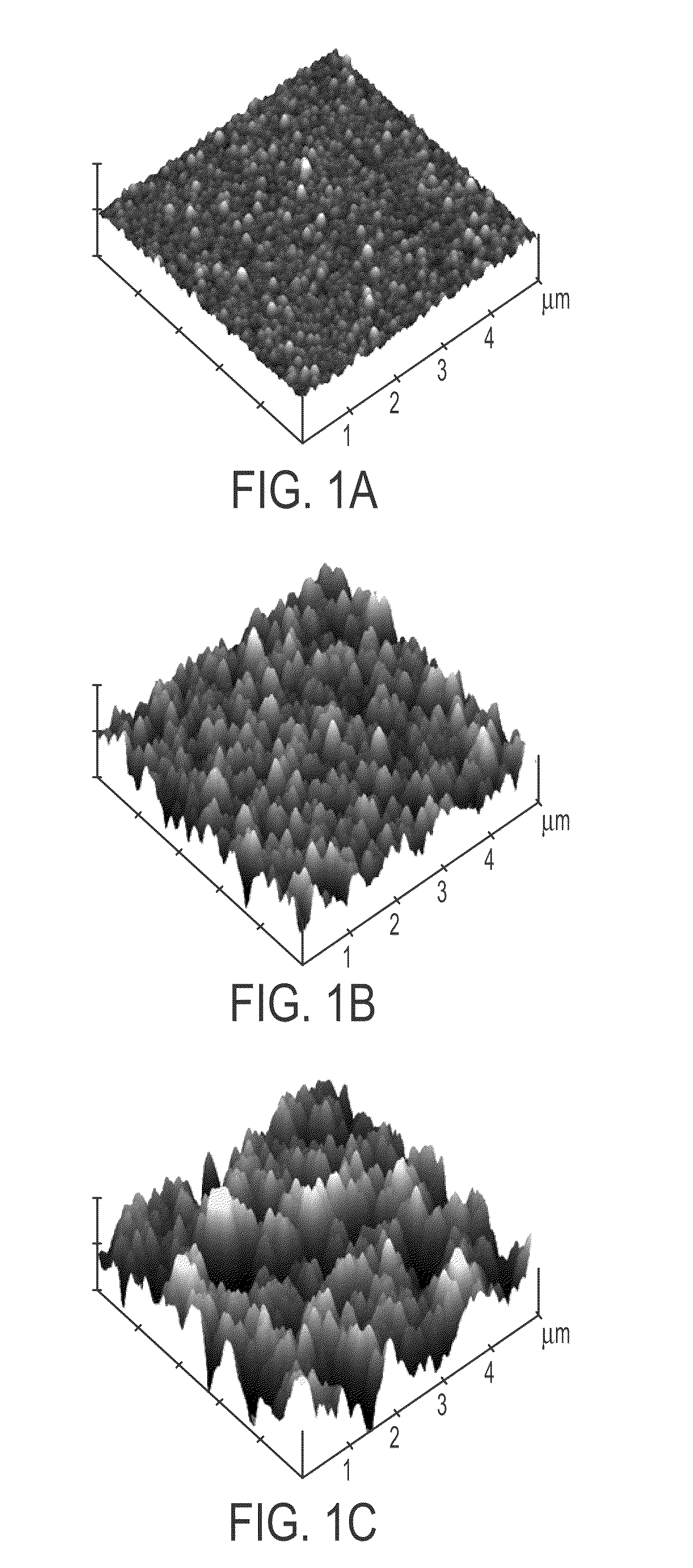
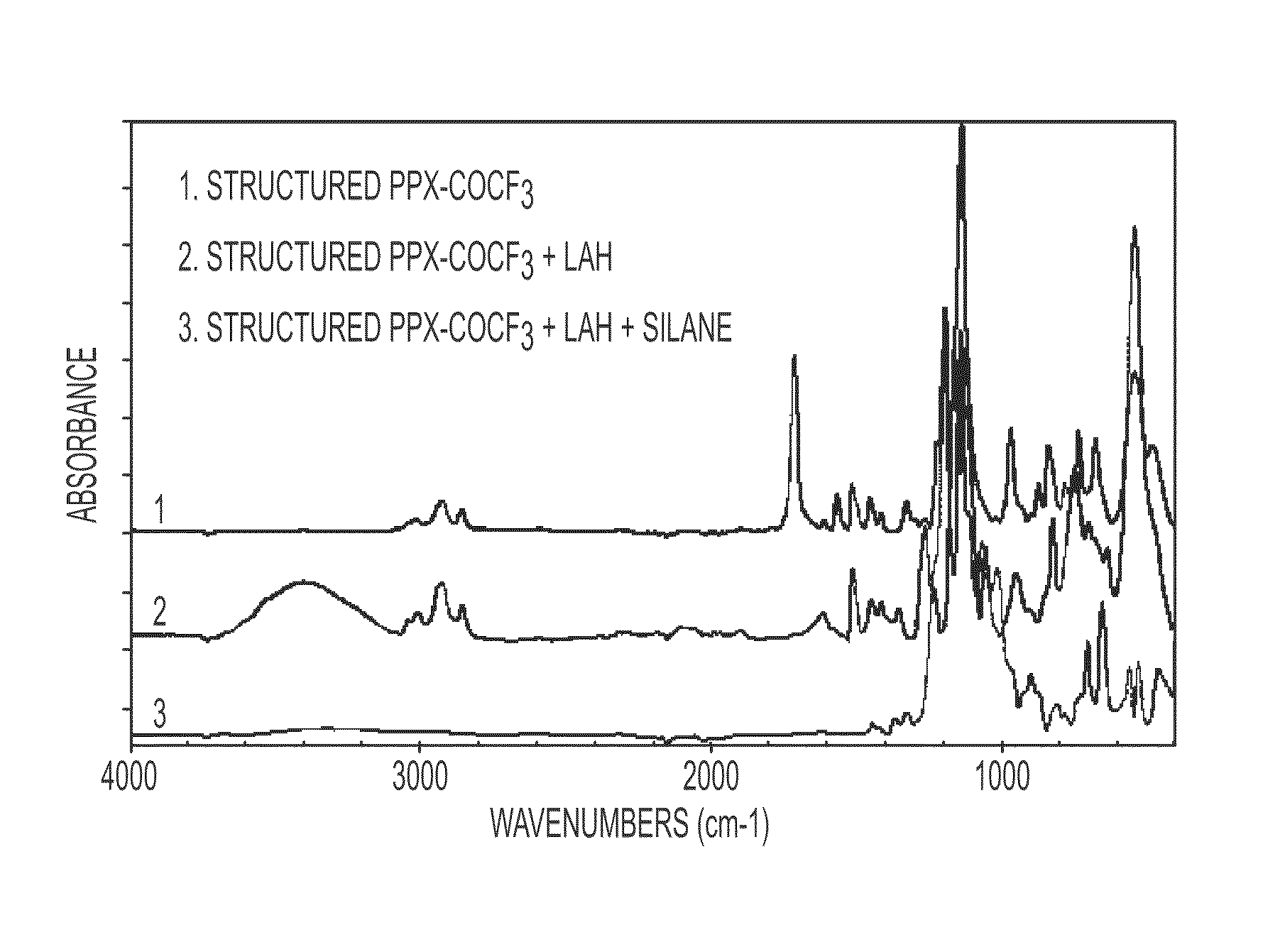
Hydrophobic nanostructured thin films
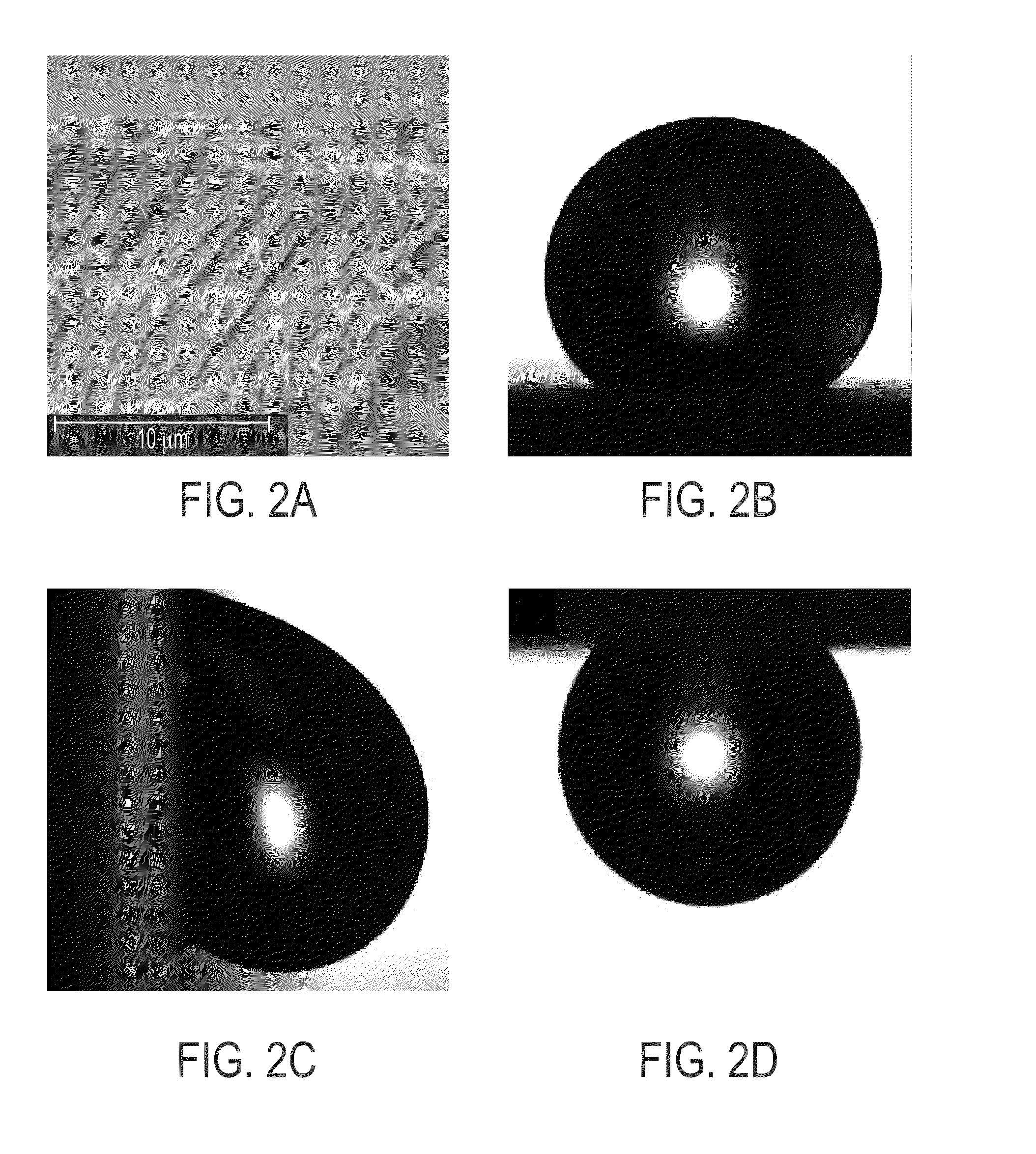
Provided herein are the polymers shown below. The value n is a positive integer. R1 is an organic group, and each R2 is H or a chemisorbed group, with at least one R2 being a chemisorbed group. The polymer may be a nanostructured film. Also provided herein is a method of: converting a di-p-xylylene paracyclophane dimer to a reactive vapor of monomers; depositing the reactive vapor onto a substrate held at an angle relative to the vapor flux to form nanostructured poly(p-xylylene) film; reacting the film with an agent to form hydrogen atoms that are reactive with a precursor of a chemisorbed group, if the film does not contain the hydrogen atoms; and reacting the hydrogen atoms with the precursor. Also provided herein is a device having a nanostructured poly(p-xylylene) film on a pivotable substrate. The film has directional hydrophobic or oleophobic properties and directional adhesive properties.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
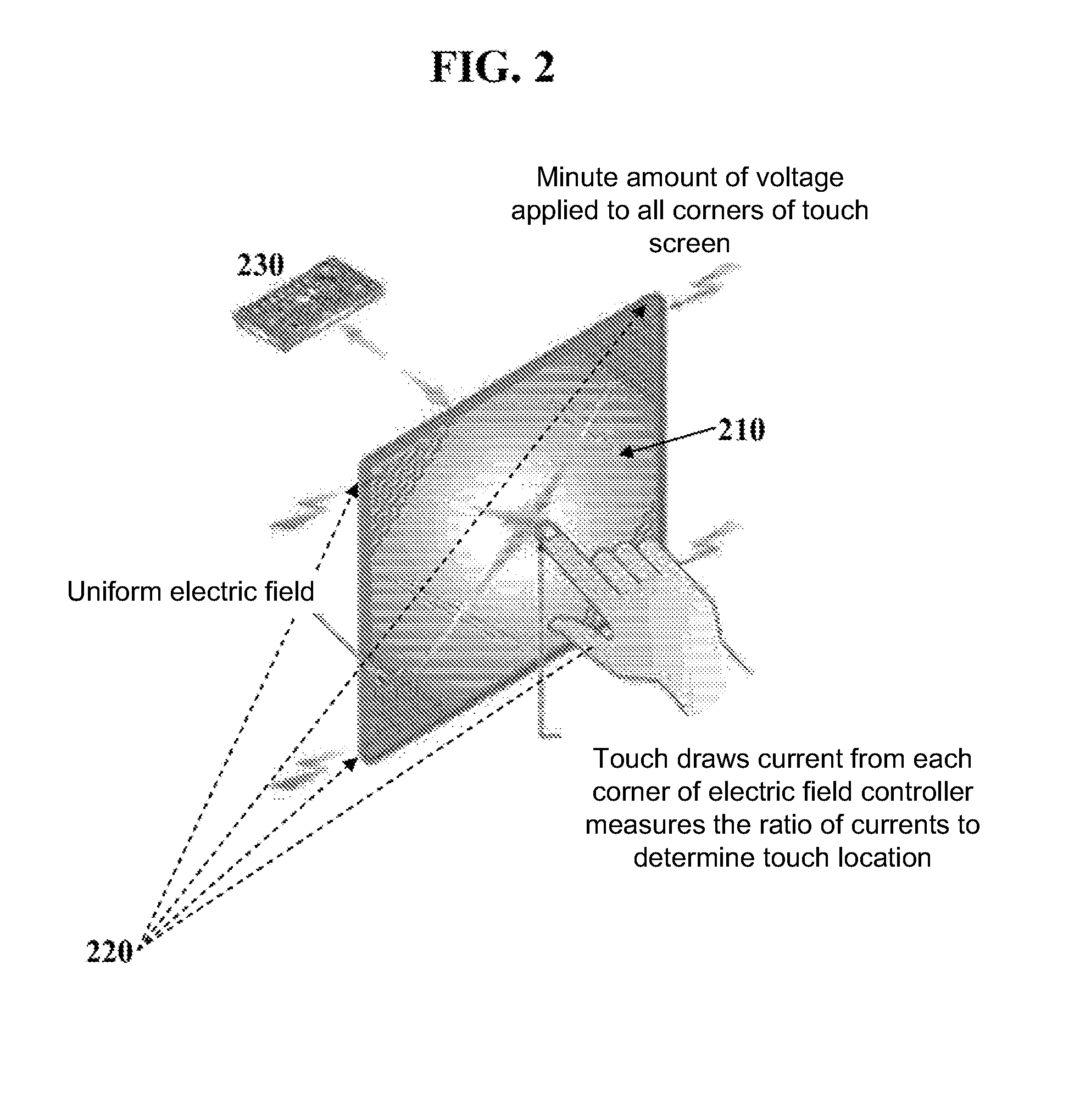
Touch screen devices employing nanostructure networks
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multipoint nanostructure-film touch screen
A touch screen comprising at least one nanostructure film and capable of detecting multiple touches occurring at the same time at distinct locations in a plane of the touch screen is described. The touch screen may comprise a sensing layer, a driving layer and / or a shielding layer. At least one of these layers may comprise a nanostructure film, and at least two of these layers may be formed on a common substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing a large continuous oriented nanostructured mixed metal oxide film
InactiveUS20080108498A1Small sizeHighly preferred orientationOther chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPresent methodNanoparticle
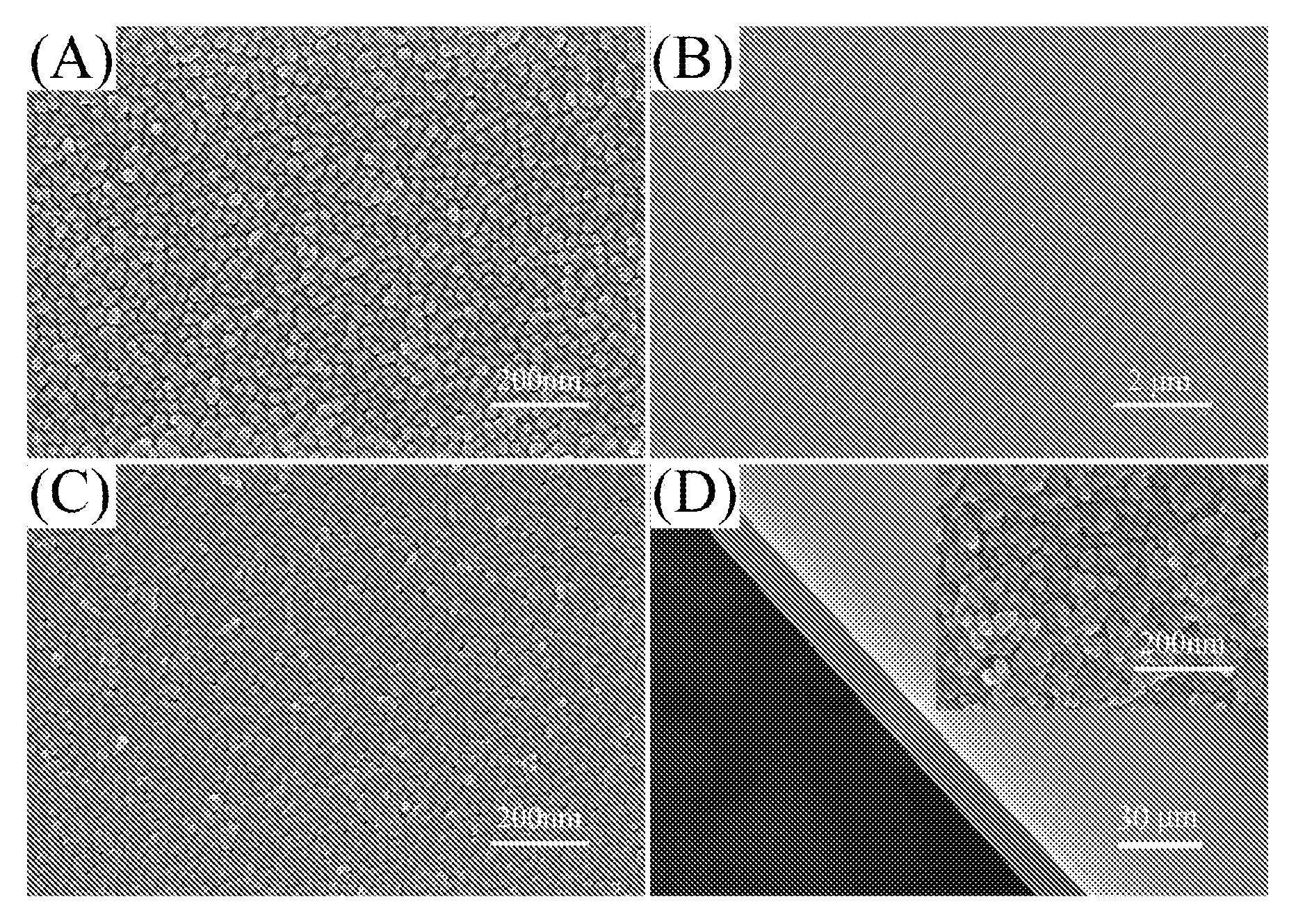
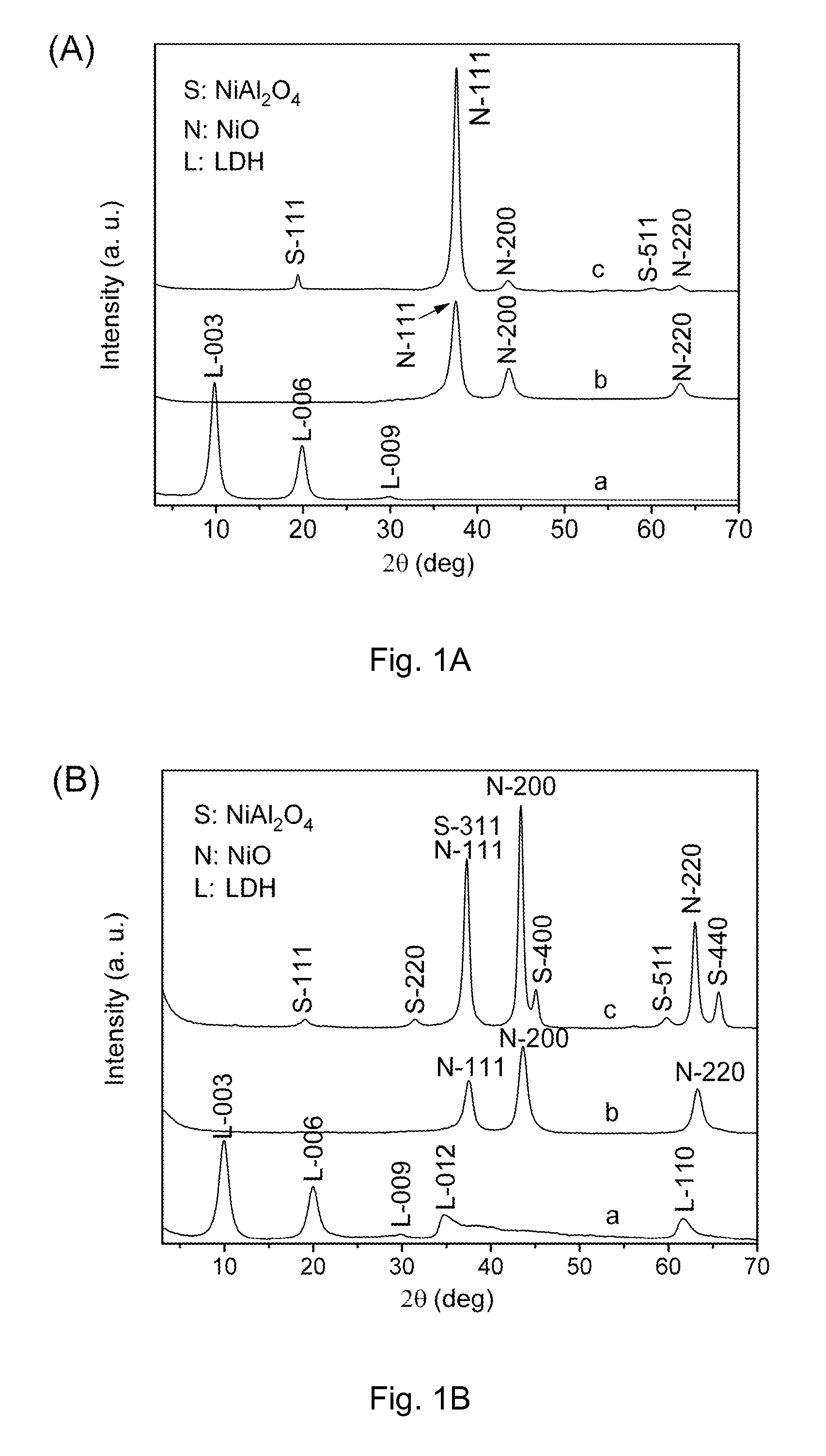
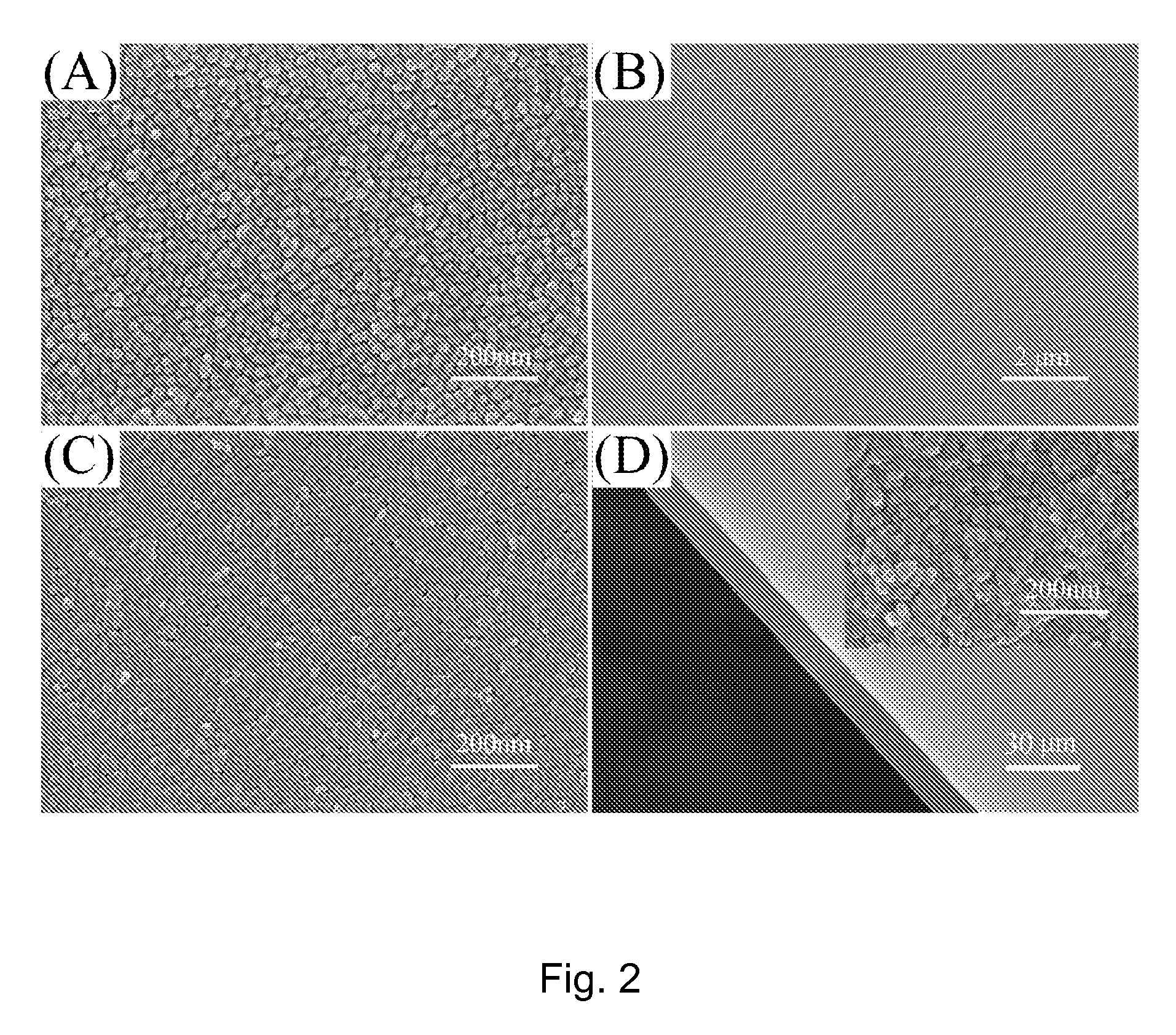
This invention provides a general method for preparing a large oriented nanostructured mixed metal oxide (MMO) film comprising the steps of (a) preparing a highly (00l)-oriented LDH film, and (b) calcining the LDH film at a temperature of 300° C. to 1300° C. for 10 min to 36 h to obtain an oriented nanostructured MMO film. In the oriented MMO film, MMO nanoparticles are densely packed and form defect-free films which have high thermal stability. The major advantage of the present method is that it can be used for mass-production of large continuous oriented nanostructured MMO films without using any templates, lattice-matched single-crystalline substrates and / or expensive equipment, and the composition of the prepared MMO films can be readily adjusted by changing the composition of the LDHs fims as the precursor.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
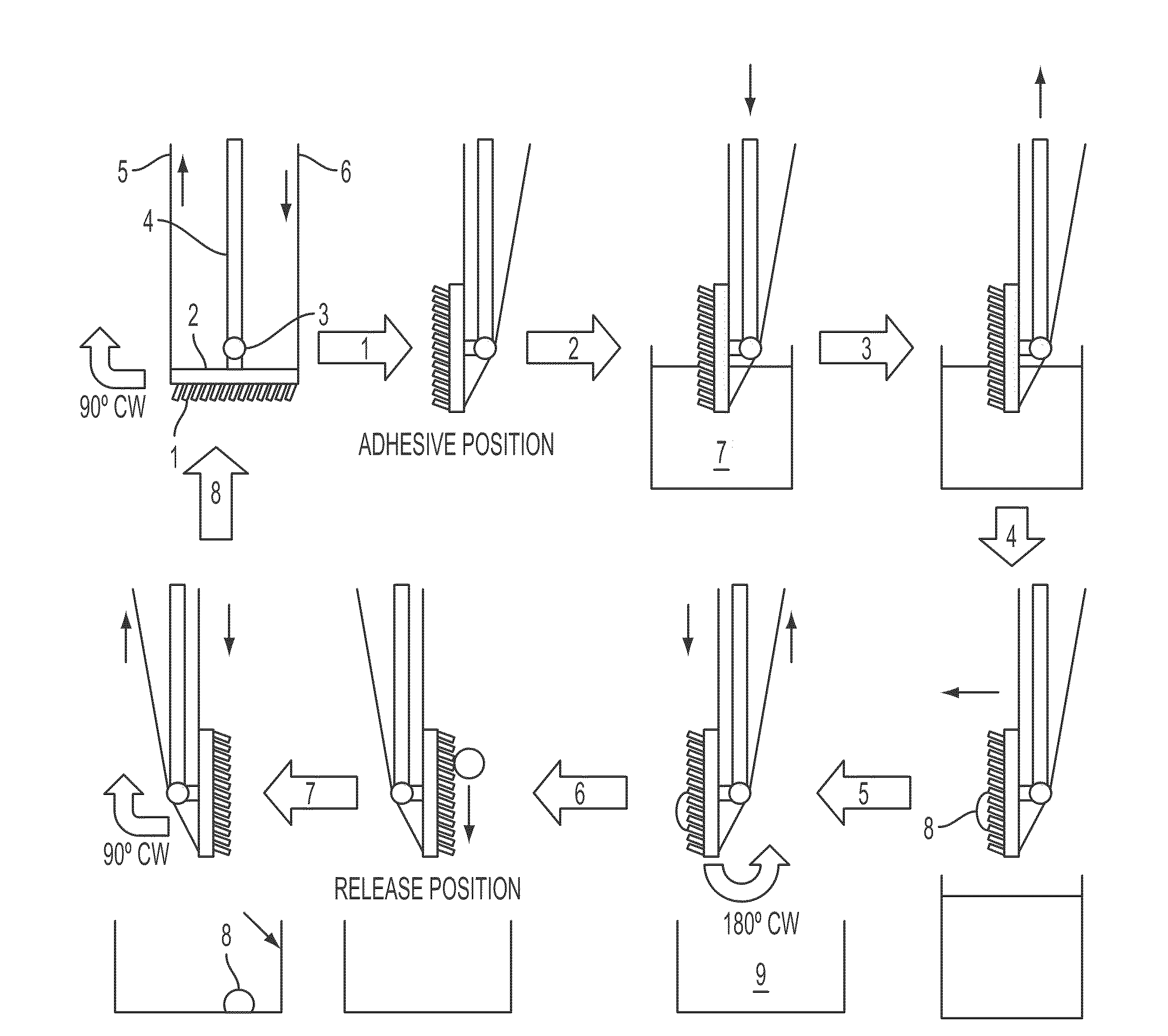
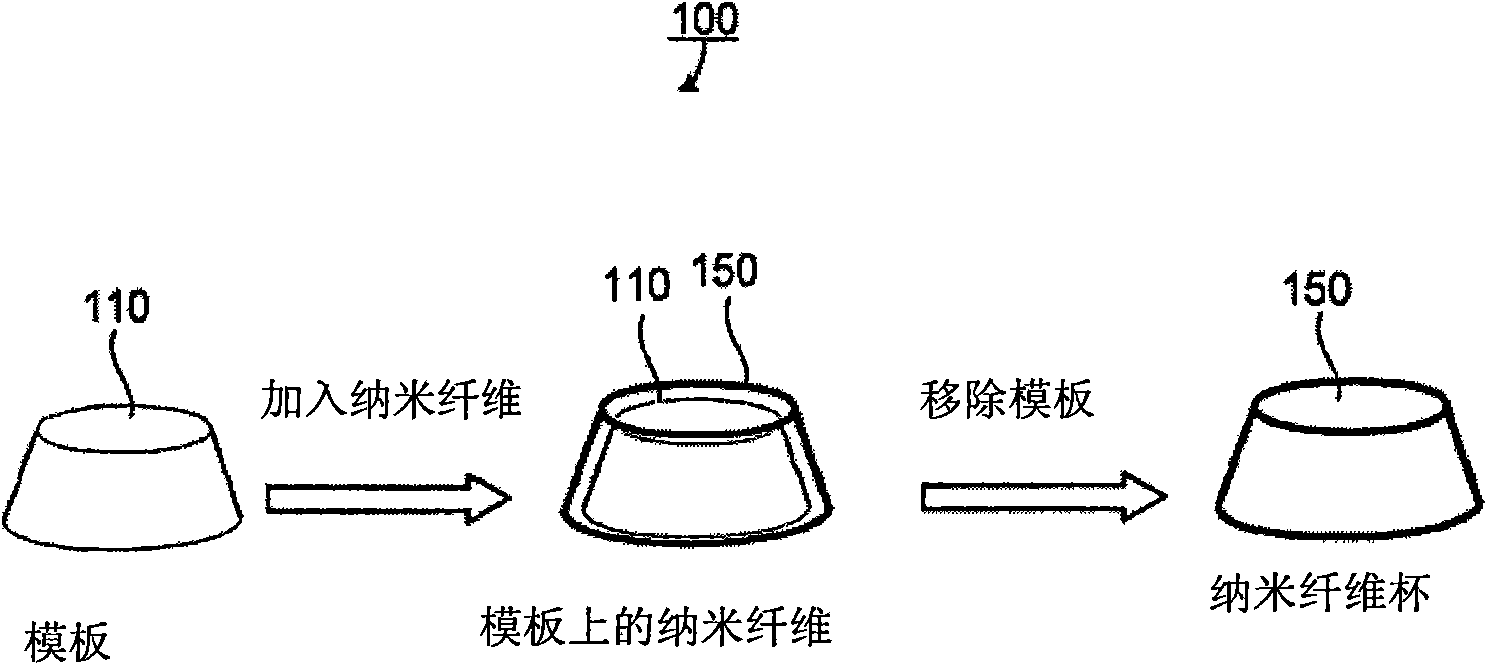
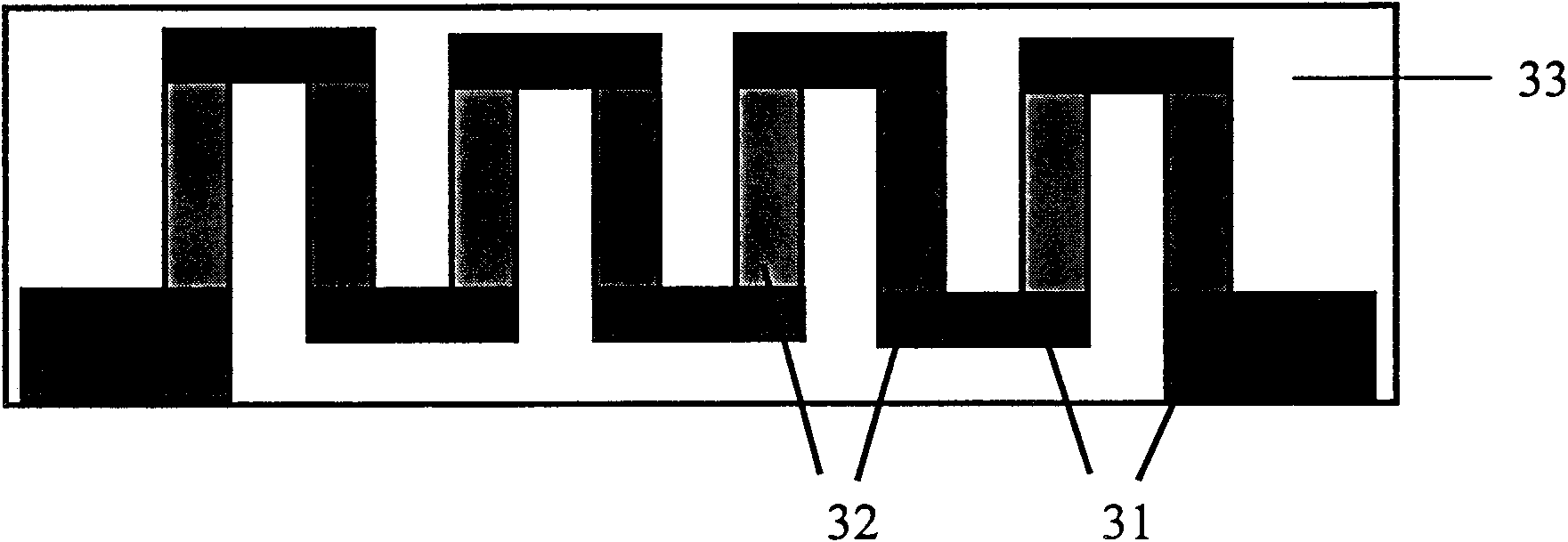
Implantable biosensor from stratified nanostructured membranes
ActiveUS7863038B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectronic componentBiological activation
A new class of biosensors and methods for making and using same are disclosed. The biosensors are multi-layered membrane composites, where at least one layer is prepared by the layer-by-layer process and at least one layer is responsive to changes is a property of a biological system such as changes in the concentration of an atom, ion, molecule or molecular assembly. Because the biosensors are multi-layered, a single biosensor is capable monitor a number of different properties of a biological system simultaneously. The biosensors are monitored by systems that impinge an excitation waveform on the biosensors and analyze a reflected and / or a transmitted resultant waveform. Additionally, the biosensors can be associated with field activated electronic components so that implantable, self-contained analytical devices can be constructed and monitored by field generators, where data is transmitted to an analyzer after field activation.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
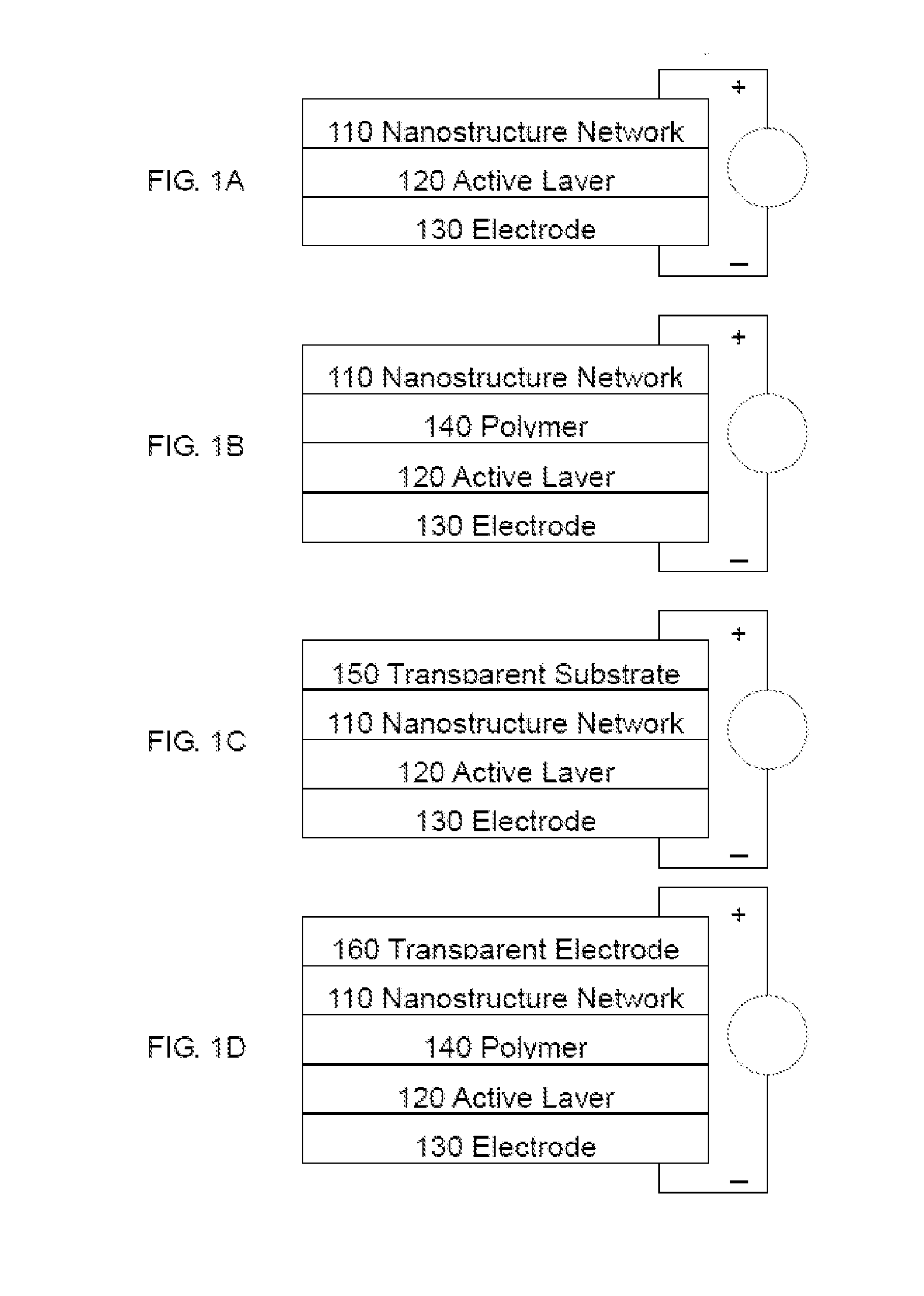
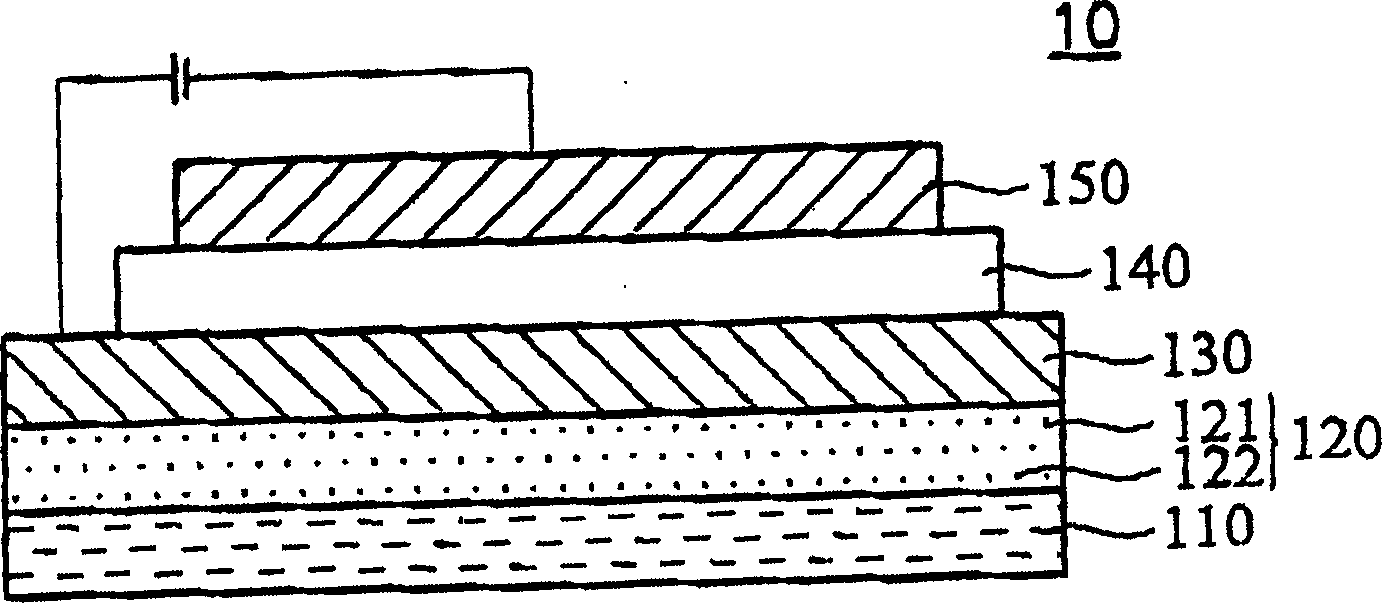
Organic light-emitting diodes with nanostructure film electrode(s)
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) comprising at least one nanostructure-film electrode, and fabrication methods thereof are discussed. The nanostructure-film is preferably transparent, and may be deposited on a preferably-transparent substrate using a variety of techniques. A different material may be used to planarize the nanostructure-film and / or otherwise improve OLED performance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Preparation method for high-sensitivity amperometric glucose sensor
InactiveCN102645463AIncrease surface areaImprove electrocatalytic performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityGlucose sensors
The invention relates to a preparation method for a high-sensitivity amperometric glucose sensor. Alpha-Ni(OH)2 sol and a nanostructured membrane are first prepared, cut FTO (fluorine-doped tin oxide) electrodes are then ultrasonically washed sequentially with isopropanol and methanol for 15 minutes, and are dried in the air, and under the rotational speed of 2500rpm, the spin-coating method is adopted to spin-coat the prepared Alpha-Ni(OH)2 sol on each electrode within 1.0cm2 of limited area for 2 minutes; finally, the electrode is dried under vacuum for 24 hours and then roasted under 240 DEG C for 30 minutes, and thereby the nanostructured membrane-modified electrochemical sensor formed by Alpha-Ni(OH)2 is obtained. Cyclic voltammetry and flow injection analysis indicate that the sensor shows enlarged surface area and enhanced electrocatalytical property.
Owner:WUXI BAILING SENSING TECH
Electrochromic compounds
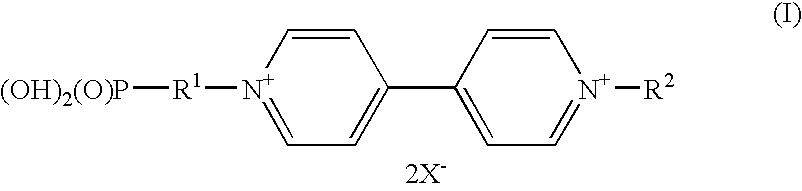
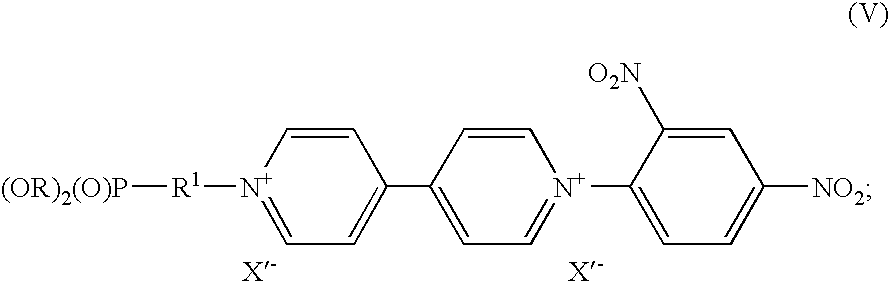
InactiveUS20090259042A1Improve stabilityImprove solubilityPhosphorus organic compoundsTenebresent compositionsPhotochemistryElectrochromic devices
The invention concerns electrochromic compounds of the general formula I. These compounds may be used in electrochromic devices, especially electrochromic devices comprising nanostructured films.
Owner:NTERA LTD (IE)
Hydrophobic nanostructured thin films
Provided herein are the polymers shown below. The value n is a positive integer. R1 is an organic group, and each R2 is H or a chemisorbed group, with at least one R2 being a chemisorbed group. The polymer may be a nanostructured film. Also provided herein is a method of: converting a di-p-xylylene paracyclophane dimer to a reactive vapor of monomers; depositing the reactive vapor onto a substrate held at an angle relative to the vapor flux to form nanostructured poly(p-xylylene) film; reacting the film with an agent to form hydrogen atoms that are reactive with a precursor of a chemisorbed group, if the film does not contain the hydrogen atoms; and reacting the hydrogen atoms with the precursor. Also provided herein is a device having a nanostructured poly(p-xylylene) film on a pivotable substrate. The film has directional hydrophobic or oleophobic properties and directional adhesive properties.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Synthesis of nanotopographic biomimetic membranes for tissue culture, engineering and prosthetics applications
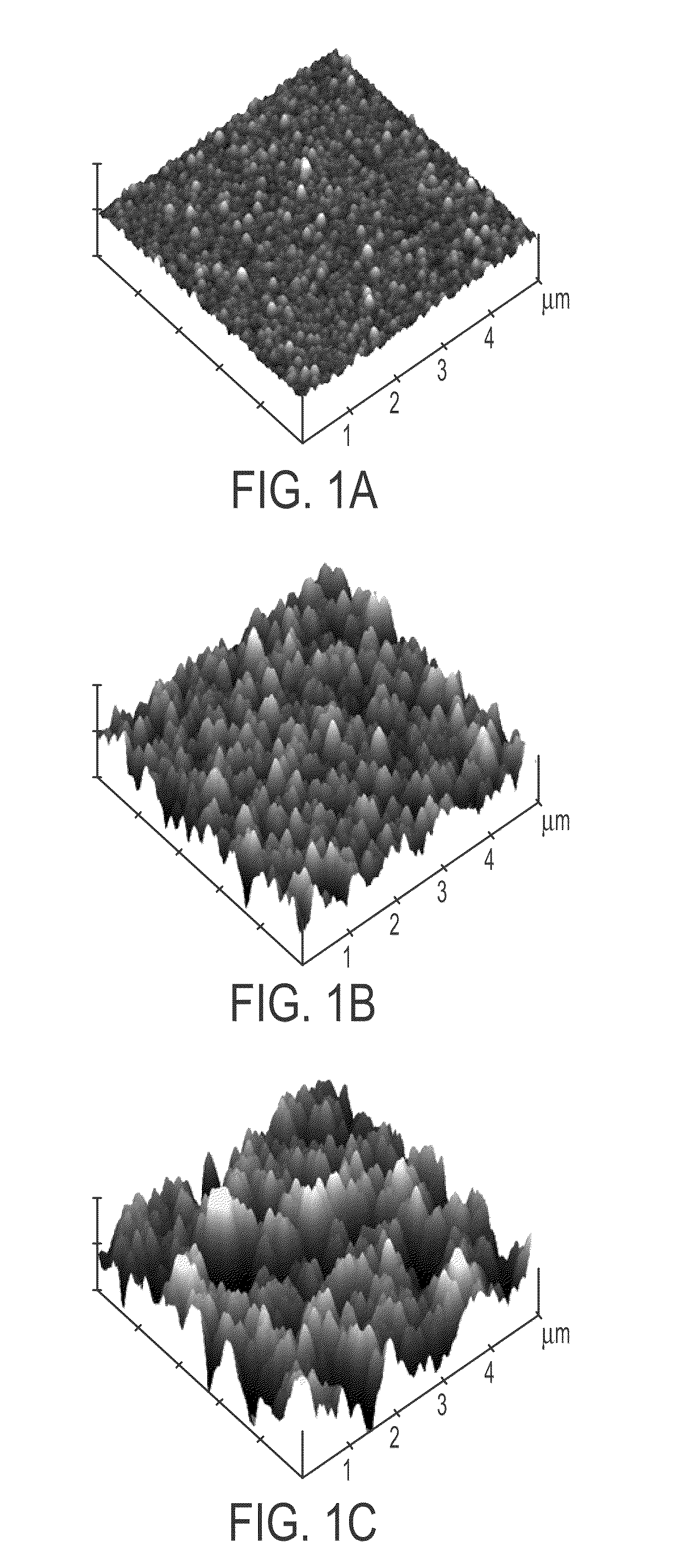
The present invention provide methods for preparing nanostructured membranes. The methods include: providing a substrate with a charged silanized surface; forming a multilayered membrane containing at least two polyelectrolytes; inducing polyelectrolyte phase separation; crosslinking the multilayered membrane; and covalently linking the multilayered membrane to the silanized surface. Methods for fabricating membrane replicas are also disclosed, as well as devices such as cell- and tissue-culture substrates that contain the membranes and membrane replicas. Resulting materials exhibit topographic features and compliance of the extracellular matrix in vivo.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
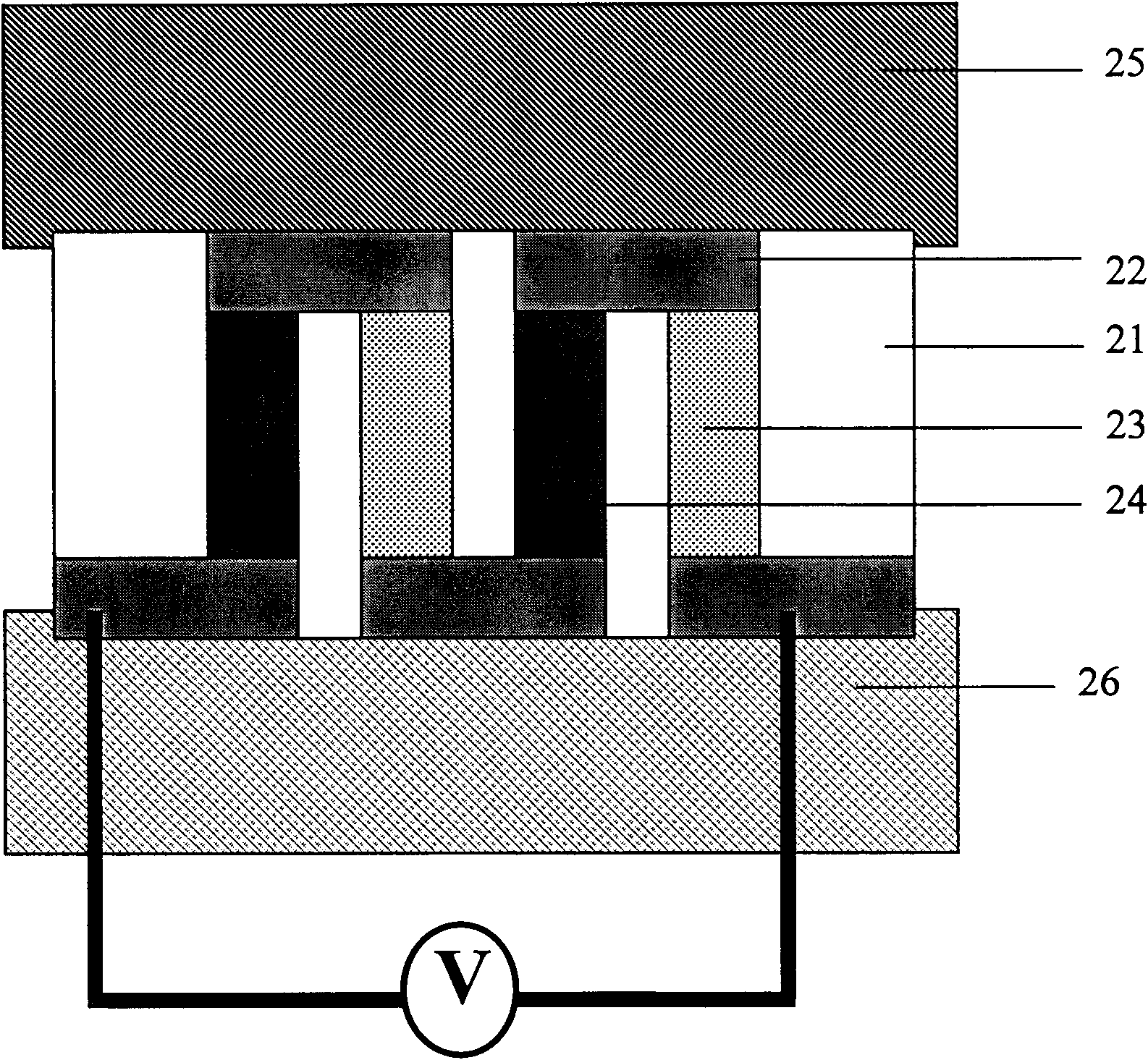
Composite field emission source
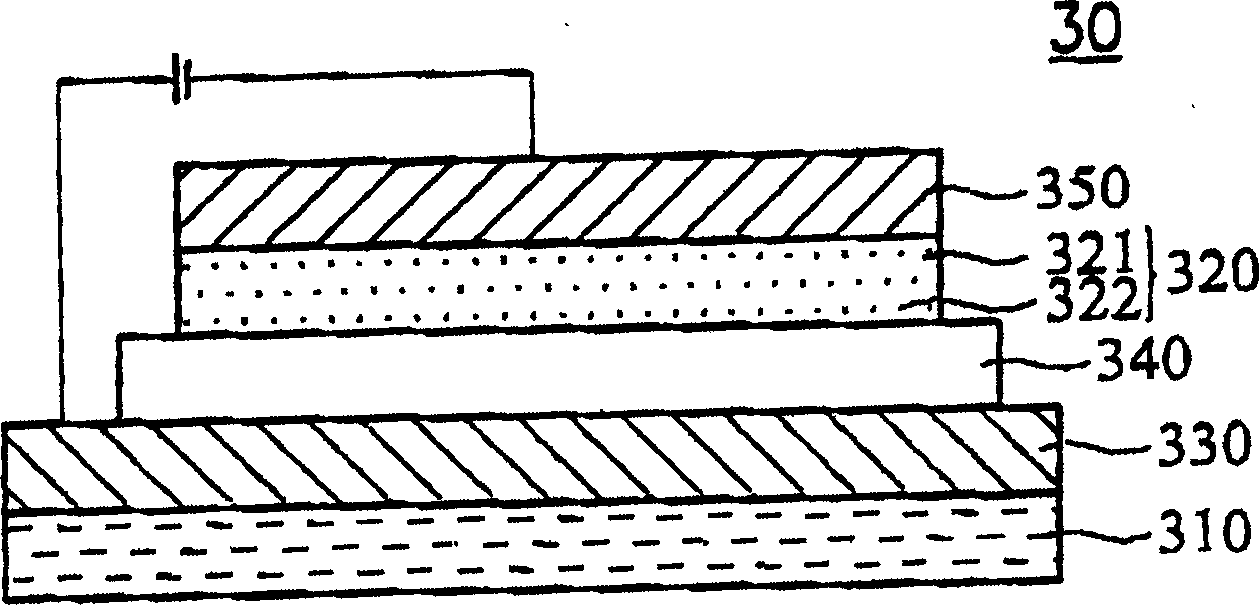
ActiveUS8080929B2Avoid problemsReducing a turn-on fieldDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsSputteringComposite field
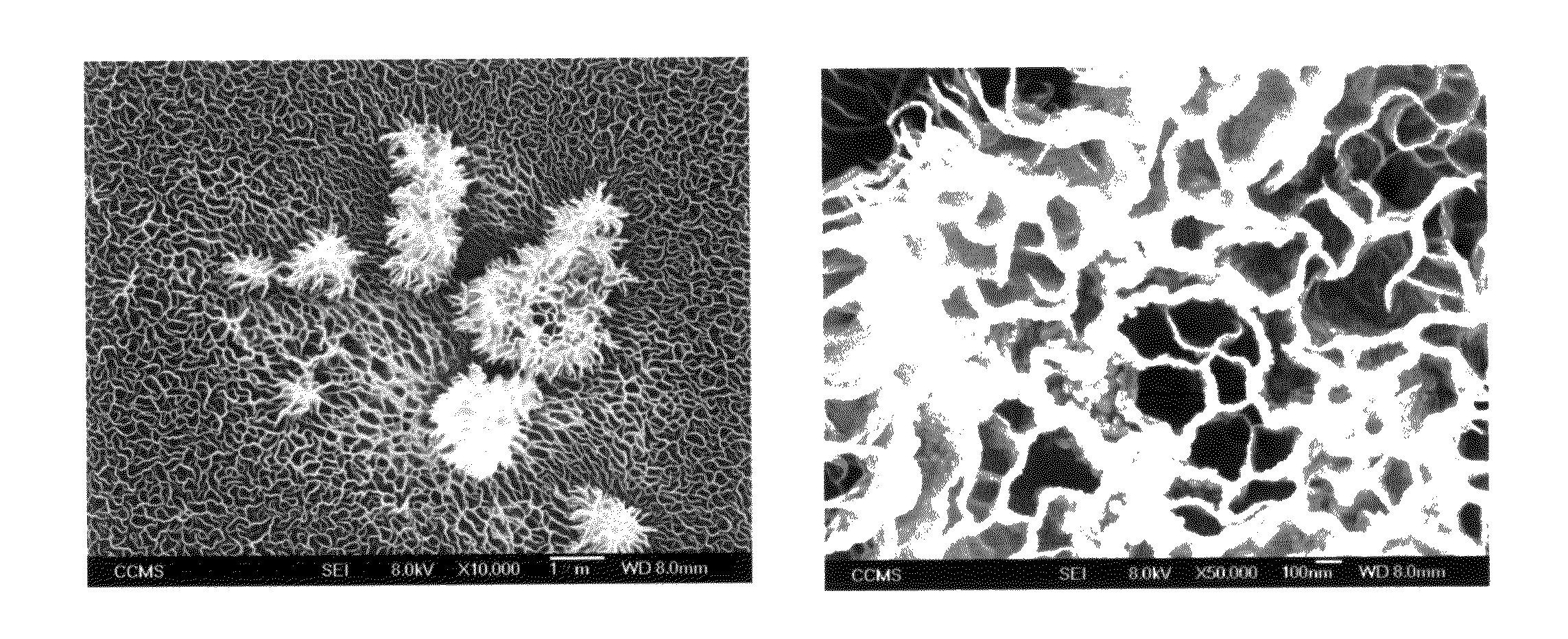
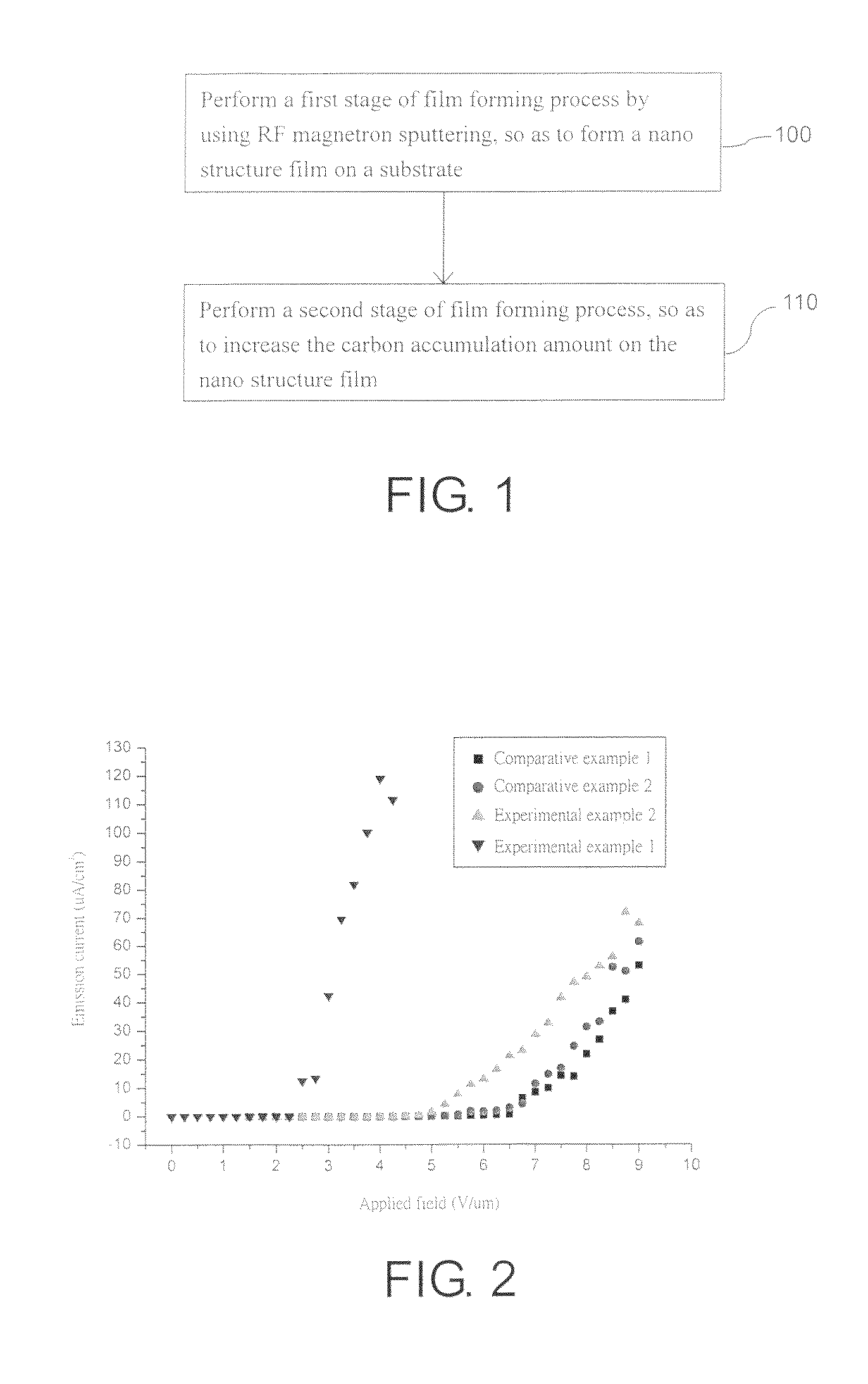
A method of fabricating a composite field emission source is provided. A first stage of film-forming process is performed by using RF magnetron sputtering, so as to form a nano structure film on a substrate, in which the nano structure film is a petal-like structure composed of a plurality of nano graphite walls. Afterward, a second stage of film-forming process is performed for increasing carbon accumulation amount on the nano structure film. Therefore, the composite field emission source with high strength and nano coral-like structures can be obtained, whereby improving the effect and life of electric field emission.
Owner:TATUNG UNIVERSITY +1
Tio2 nanostructures, membranes and films, and methods of making same
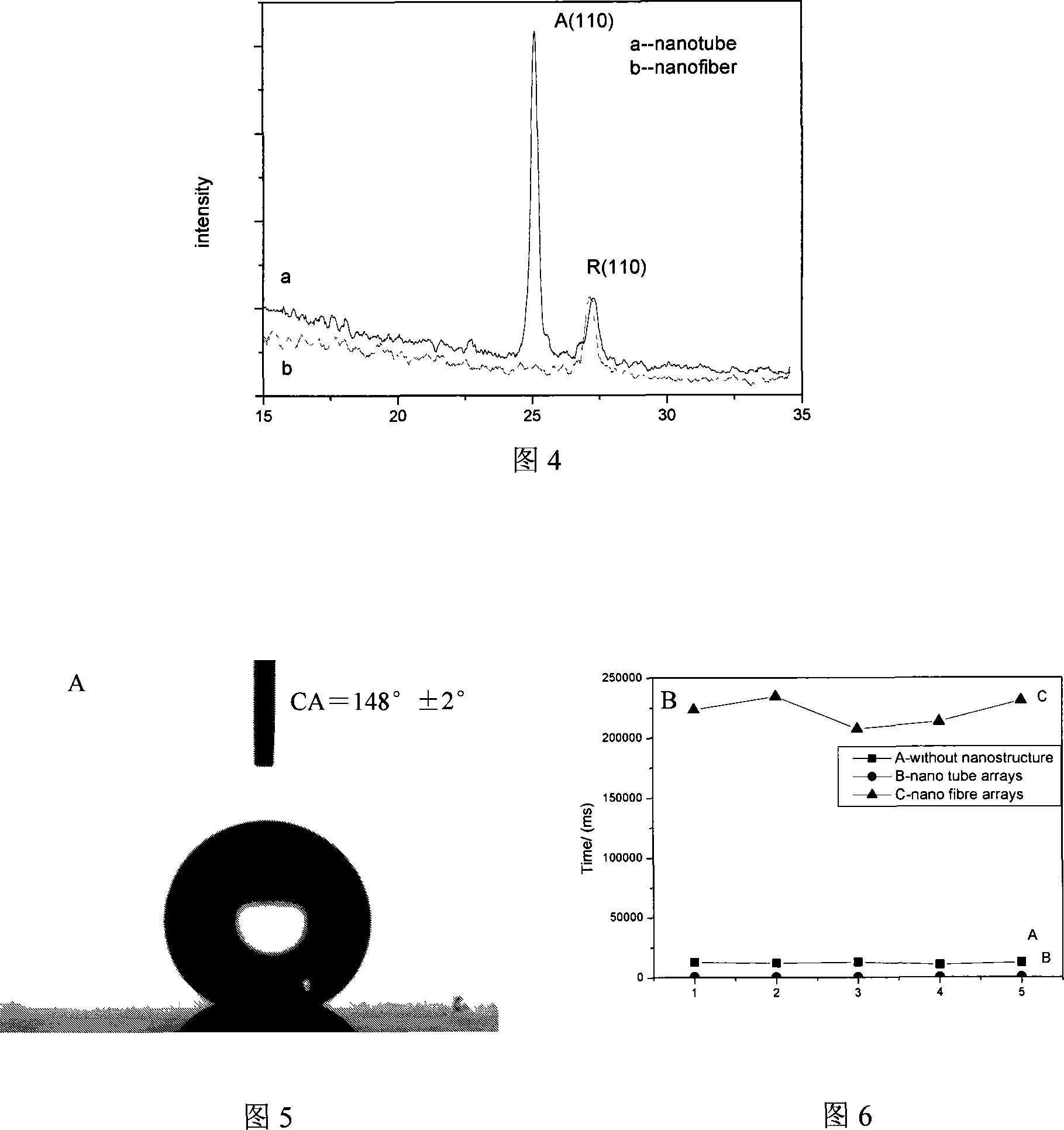
One aspect of the present invention relates to a method for synthesizing macro-sized nanostructures. The method in one embodiment comprises the steps of mixing an amount of TiO2 powders with a volumeof an alkali or alkaline solution to form a mixture, and heating the mixture at a temperature higher than 160 0C for a period of time effective to allow TiO2-containing, macro-sized nanostructures toform, wherein the TiCh-containing, macro-sized nanostructures form in an environment that has no presence of a substrate that comprises Ti. These TiO2-containing, macro-sized nanostructures can be utilized to form a free standing membrane, and / or a three- dimensional (3D) structure.
Owner:阿肯色州大学技术发展基金会
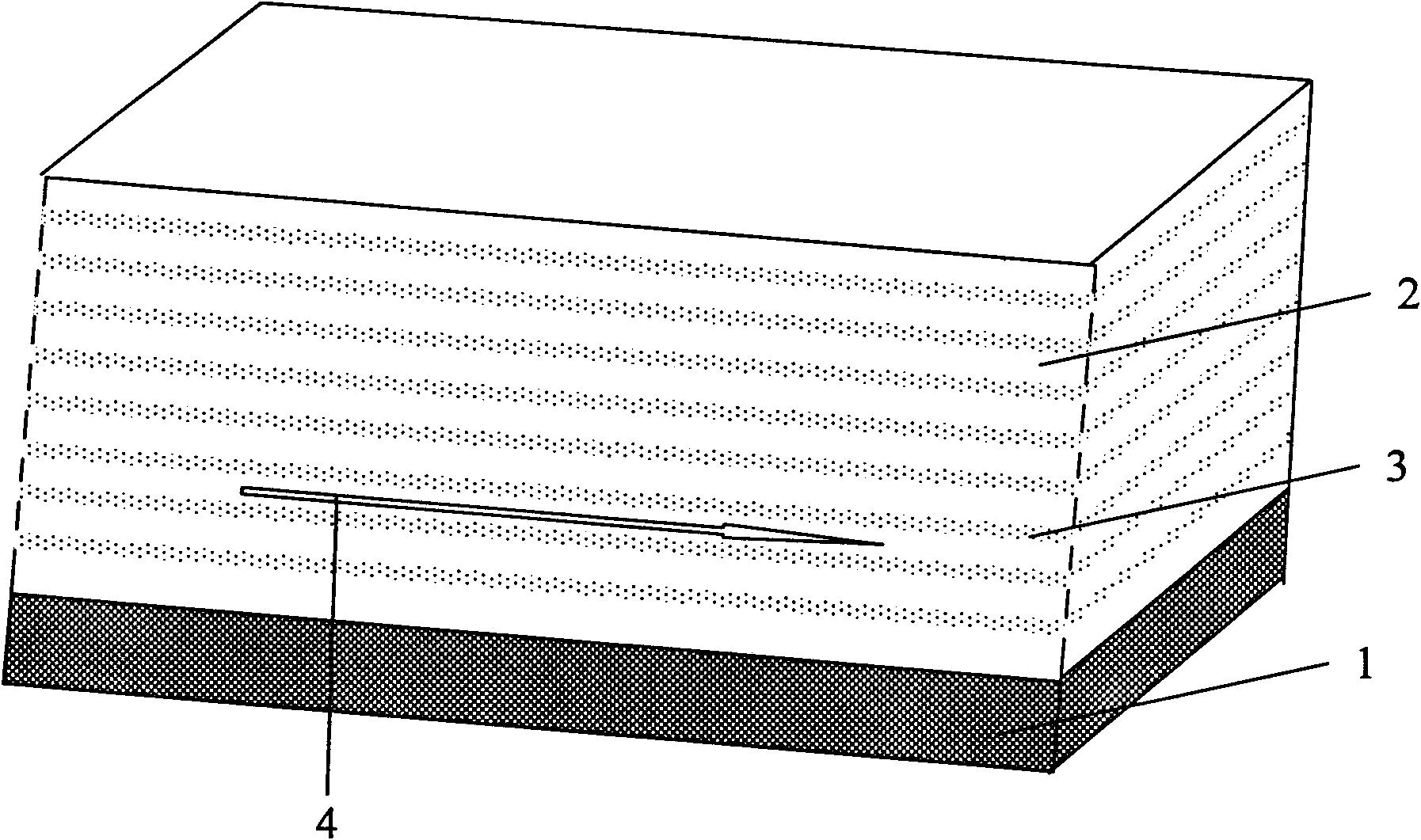
Nanostructured thermoelectric material and device and production method thereof
InactiveCN101969096AHigh crystallinityOvercoming the reduced case of quantum confinement effectsThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric materialsNano structuring
The invention discloses a nanostructured thermoelectric material, a nanostructured thermoelectric device and a production method thereof. The thermoelectric material comprises an insulating substrate and a nanostructured thermoelectric membrane, wherein the nanostructured thermoelectric membrane is composed of at least two nano-thickness thermoelectric material layers and at least two phonon scattering layers, and the thermoelectric material layers and the phonon scattering layers are overlapped alternately. The thermoelectric material can be a p-type thermoelectric material or an n-type thermoelectric material, which depends on the type of charge carrier of the thermoelectric material layers. Connecting electrodes are plated between the thermoelectric membranes of a p-type nanostructured thermoelectric material and a n-type nanostructured thermoelectric material so as to form a thermoelectric pair; and then a plurality of thermoelectric pairs are connected in parallel or in series so as to form the thermoelectric device. The nanostructured thermoelectric material of the invention has the advantages of good thermal stability, high nanostructured membrane deposition efficiency, high thermoelectric conversion efficiency, and lower cost; and the nanostructured thermoelectric device has the advantages of simple structure, easy preparation, low internal resistance, and great practical value in the fields such as refrigeration / calorification or temperature differential power generation, and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nanostructured and nanoporous film compositions, structures, and methods for making the same
InactiveCN1703286AHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingNanoporous membraneNanostructure
This invention comprises methods for making nanostructured and nanoporous thin film structures of various compositions. These films can be directly patterned. In these methods, precursor films are deposited on a surface and different components of the precursor film are reacted under selected conditions, forming a nanostructured or nanoporous film. Such films can be used in a variety of applications, for example, low k dielectrics, sensors, catalysts, conductors or magnetic films. Nanostructured films can be created: (1) using one precursor component and two reactions, (2) using two or more components based on differential rates of photochemical conversion, (3) using two precursors based on the thermal sensitivity of one precursor and the photochemical sensitivity of the other, and (4) by photochemical reaction of a precursor film and selected removal of a largely unreacted component from the film.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
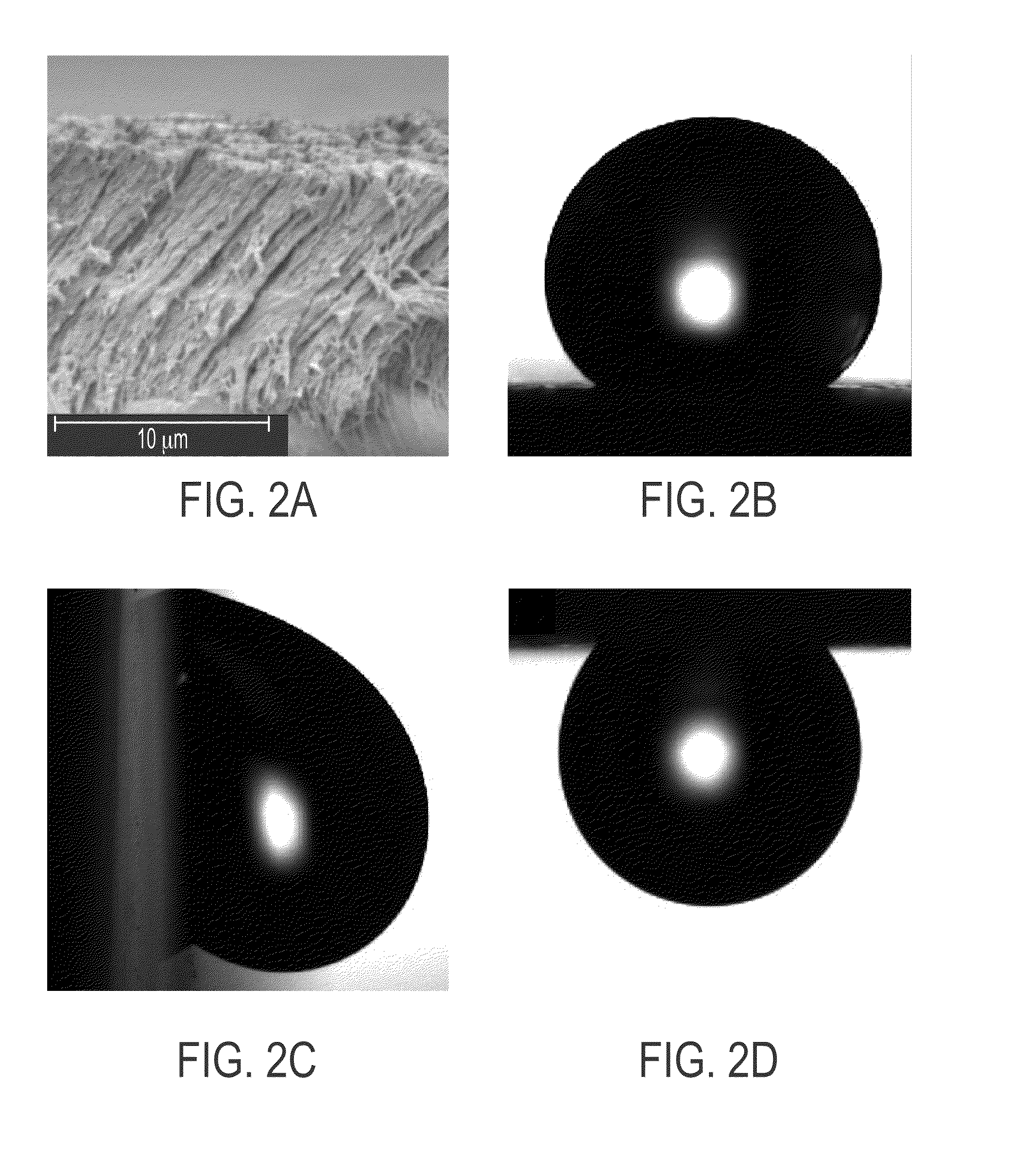
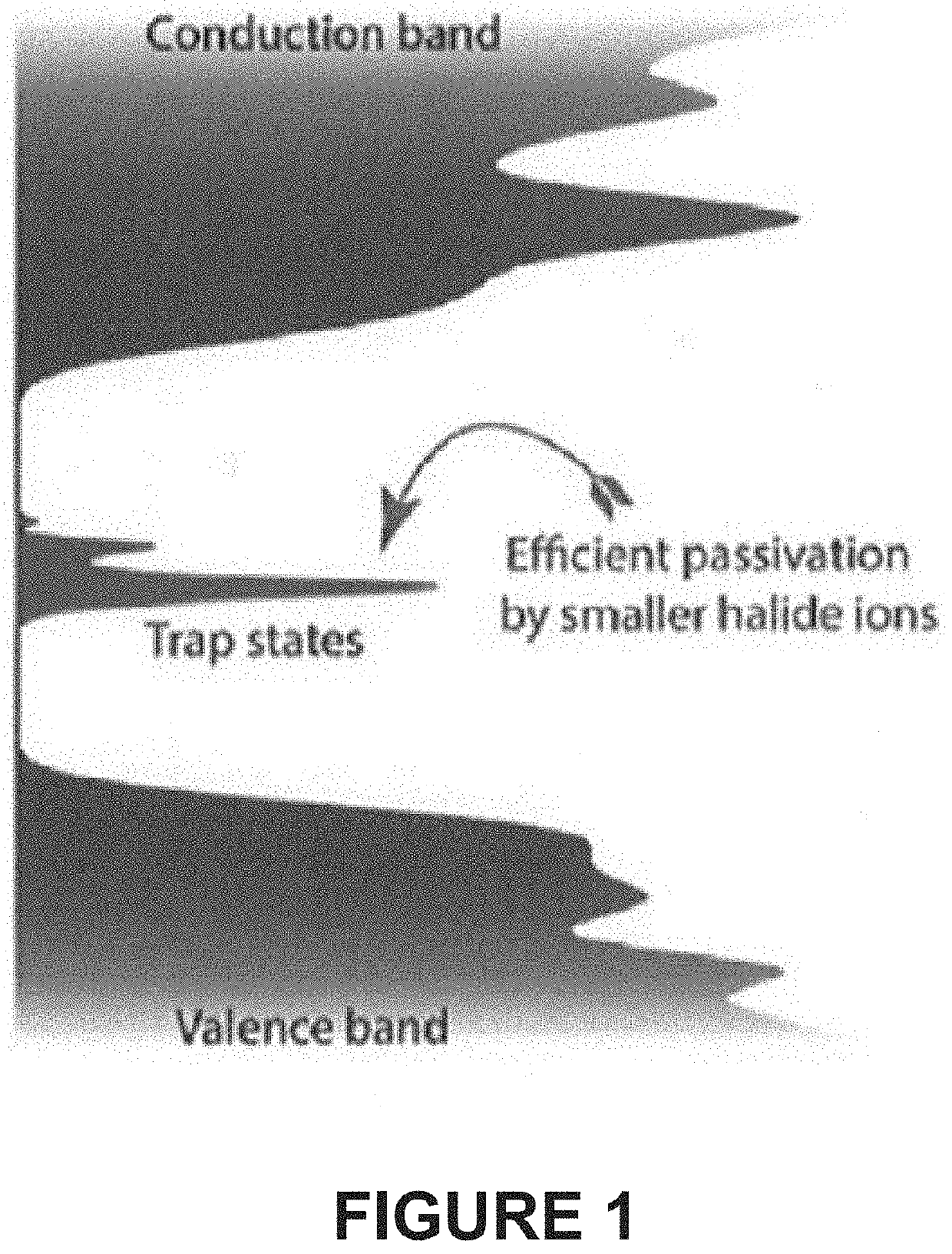
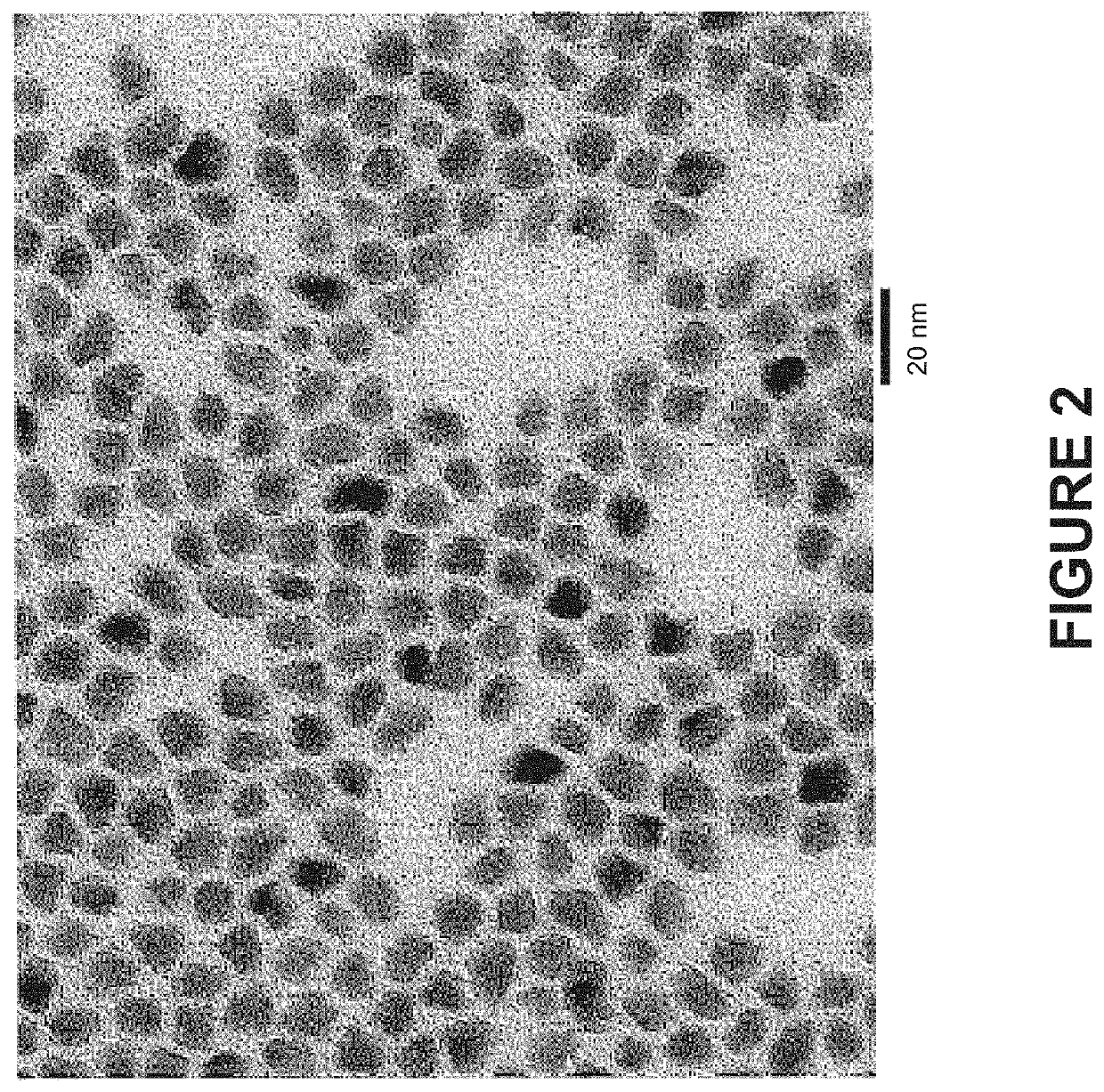
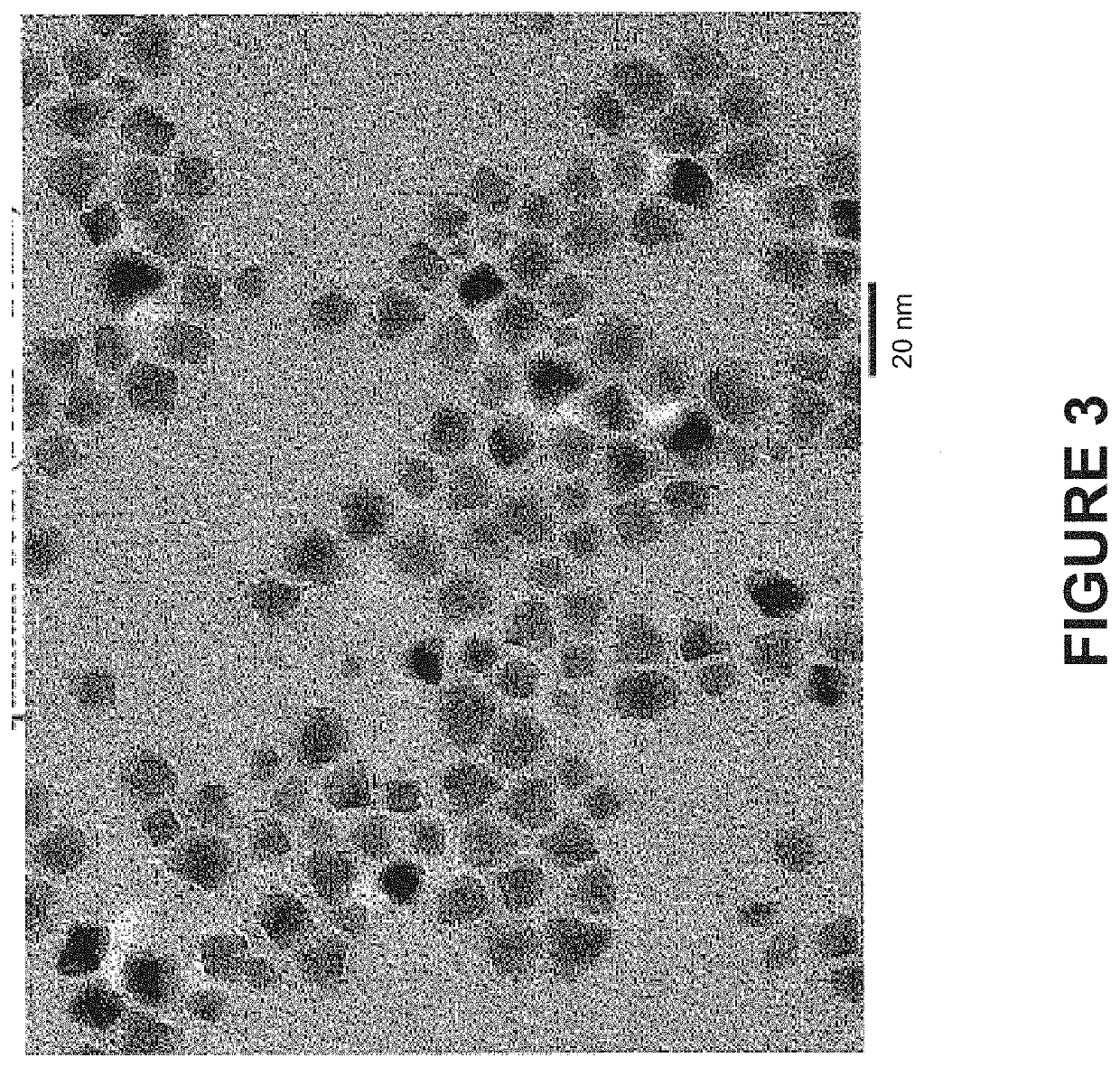
Blue-emitting nanocrystals with cubic shape and fluoride passivation
This disclosure pertains to the field of nanotechnology. The disclosure provides methods of preparing nanostructures with fluoride passivation. The disclosure also provides methods of preparing nanostructures with fluoride and amine passivation. The nanostructures have high quantum yield, narrow emission peak width, tunable emission wavelength, and colloidal stability. Also provided are nanostructures prepared using the methods. And, nanostructure films and molded articles comprising the nanostructures are also provided.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
Thin film-based compact absorption cooling system
ActiveUS20140238072A1Low costSmall sizeClimate change adaptationEnergy efficient heating/coolingDesorptionNanofiber
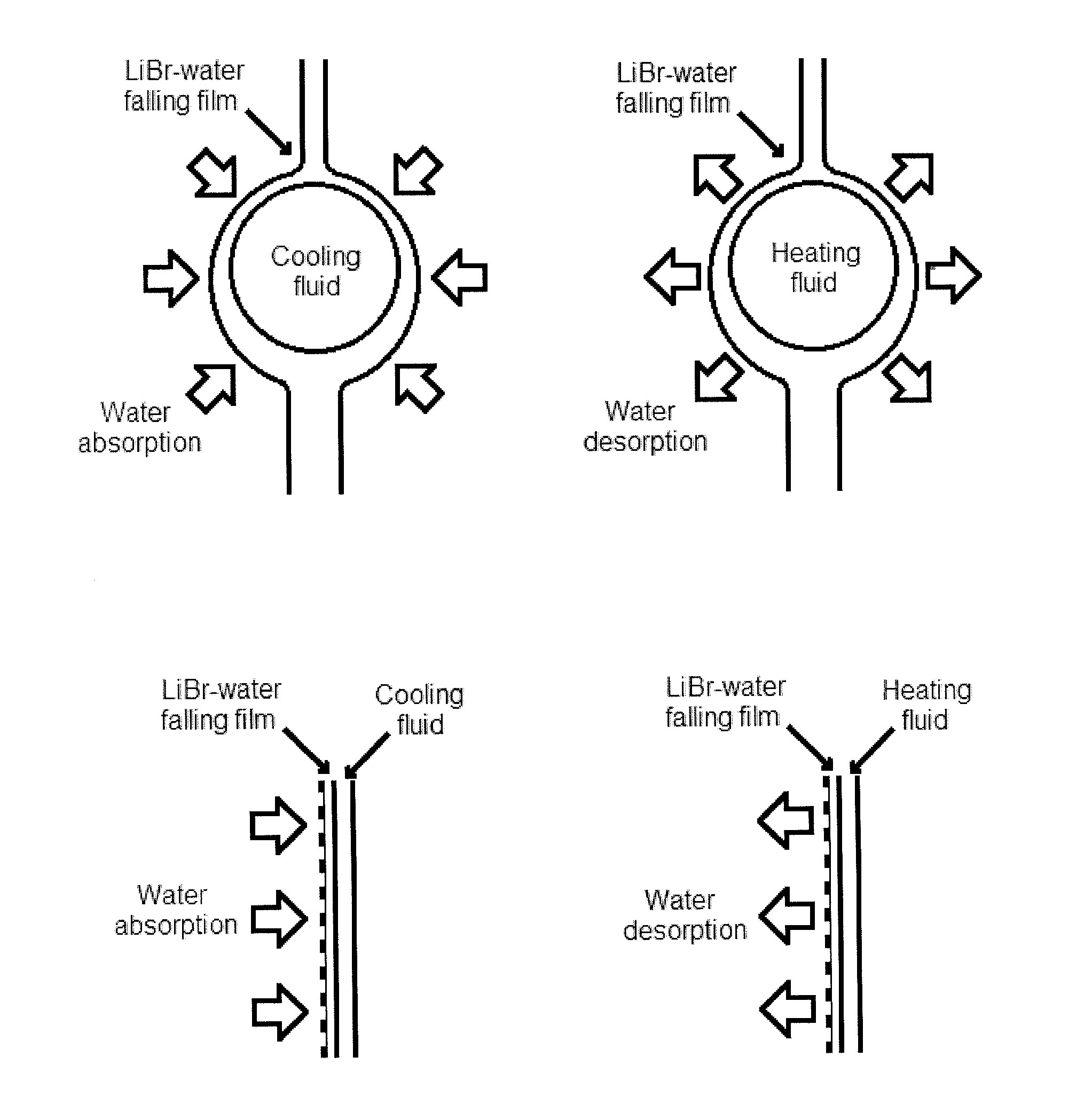
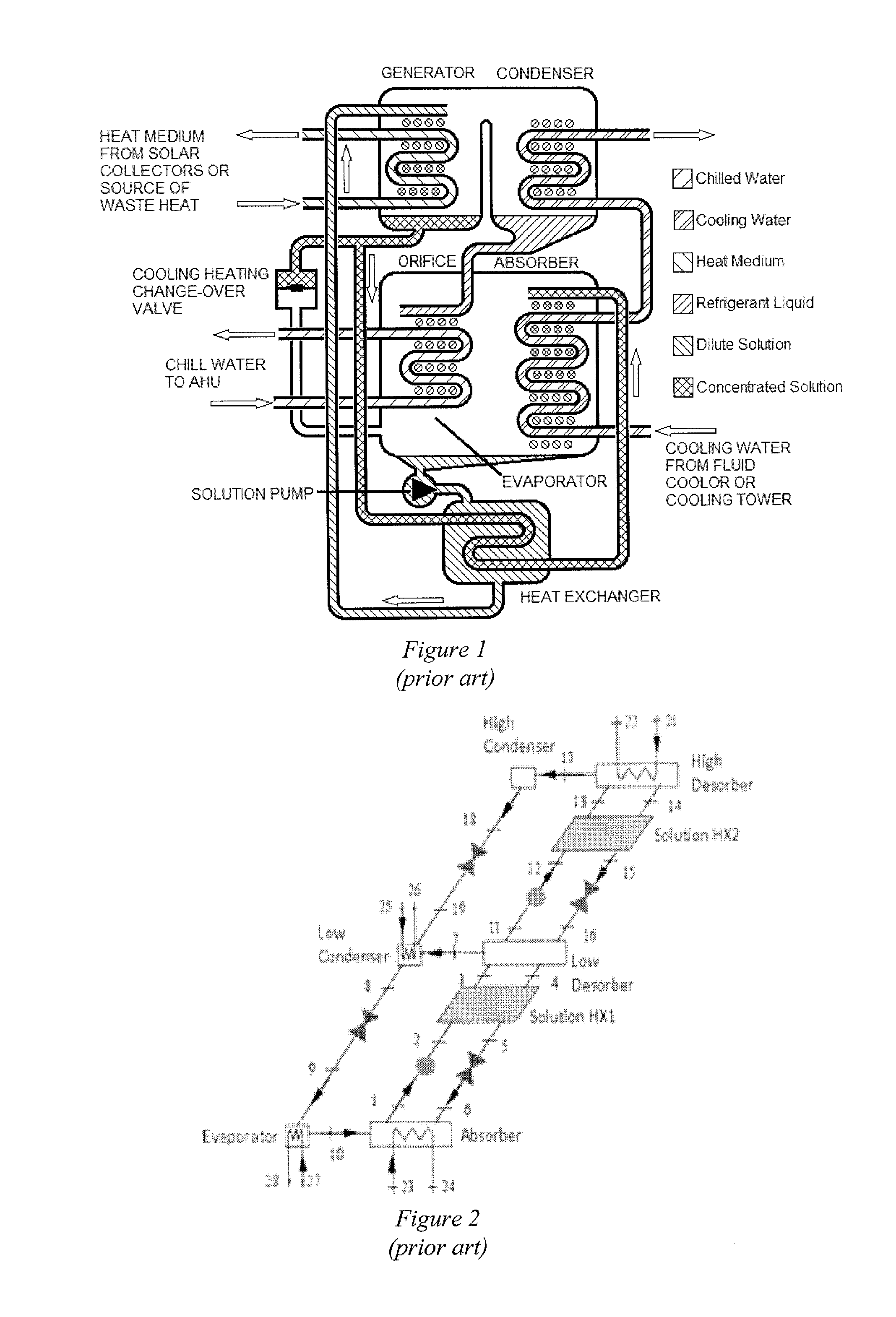
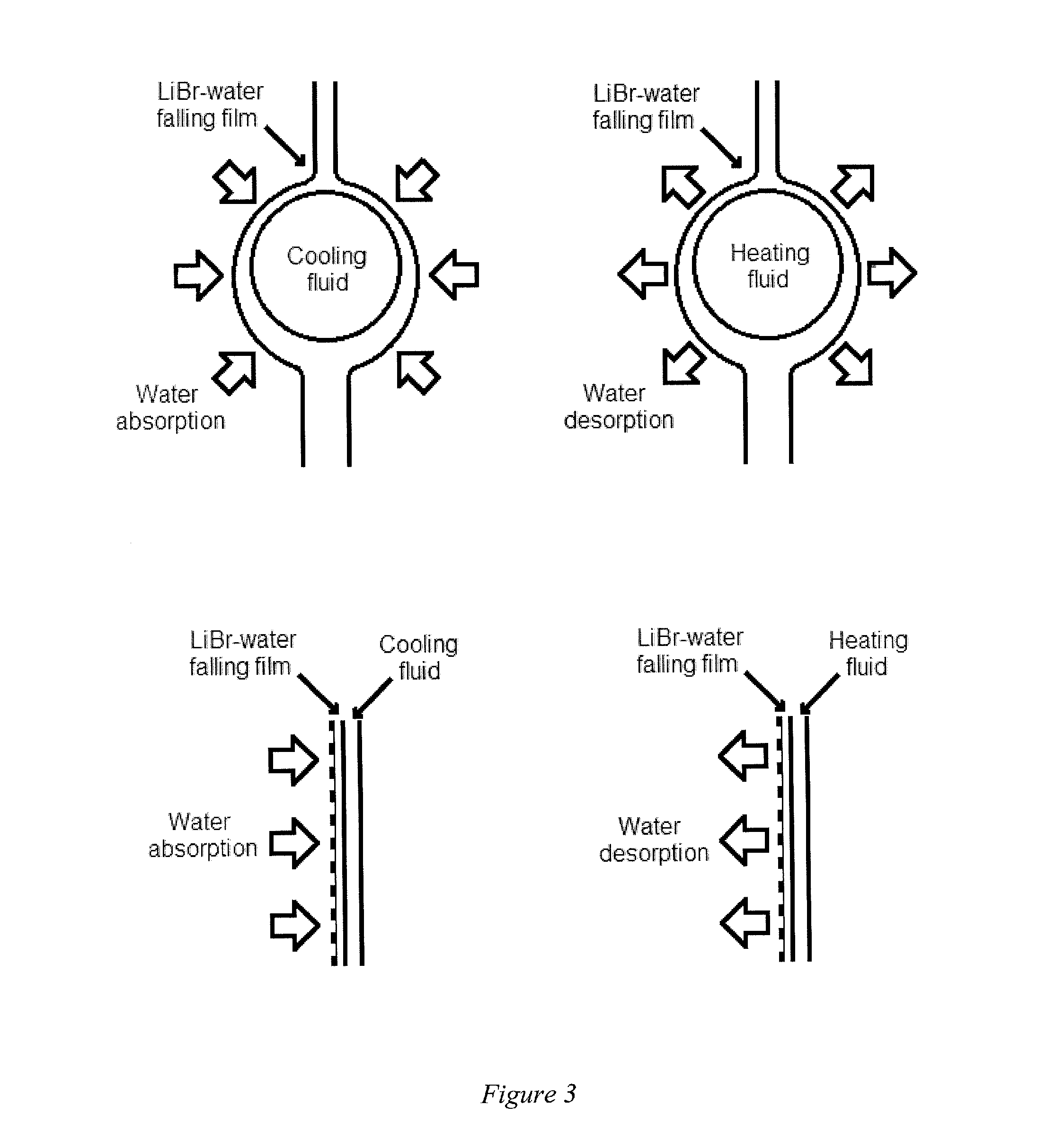
An exchanger for absorption or desorption of a refrigerant employs an ultra thin film (UTF) of a refrigerant solution constrained to a channel by a permeable membrane. The UTF has a thickness of about 250 μm or less. The permeable membrane can be a nanostructured membrane, such as a membrane of nanofibers. The exchangers can be employed in an absorption refrigeration system (ARS) that use waste heat or solar heaters permitting the ARS to be less than one tenth the volume and mass of a conventional ARS.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Patterned conductive film, method of fabricating the same, and application thereof
Provided is a patterned conductive film may include a conductive interconnected nano-structure film. The conductive interconnected nano-structure film may include a first region and a second region adjacent to the first region. A conductivity of the first region may be at least 1000 times a conductivity of the second region.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Method for manufacturing solar cell with nano-structural film
InactiveUS20150333195A1Increase routeReduce light reflectivityPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolystyreneSolar cell
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a solar cell with a nanostructural film, including steps of treating a glass substrate with UV ozone, uniformly coating a polystyrene nanospherical layer containing plural nanospheres on the surface of the glass substrate and curing the polystyrene nanospherical layer for adhesion onto the glass substrate, forming a first optical layer on the surface of the polystyrene nanospherical layer, curing and releasing the first optical layer from the polystyrene nanospherical layer to obtain a concave spherical nanostructured film, and finally affixing the concave spherical nanostructured film on the surface of a solar cell to manufacture a solar cell with nanostructure after curing by baking.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com