Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
494 results about "Mineral deposit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
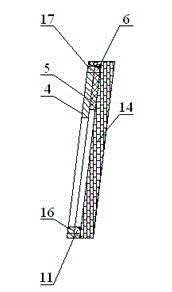
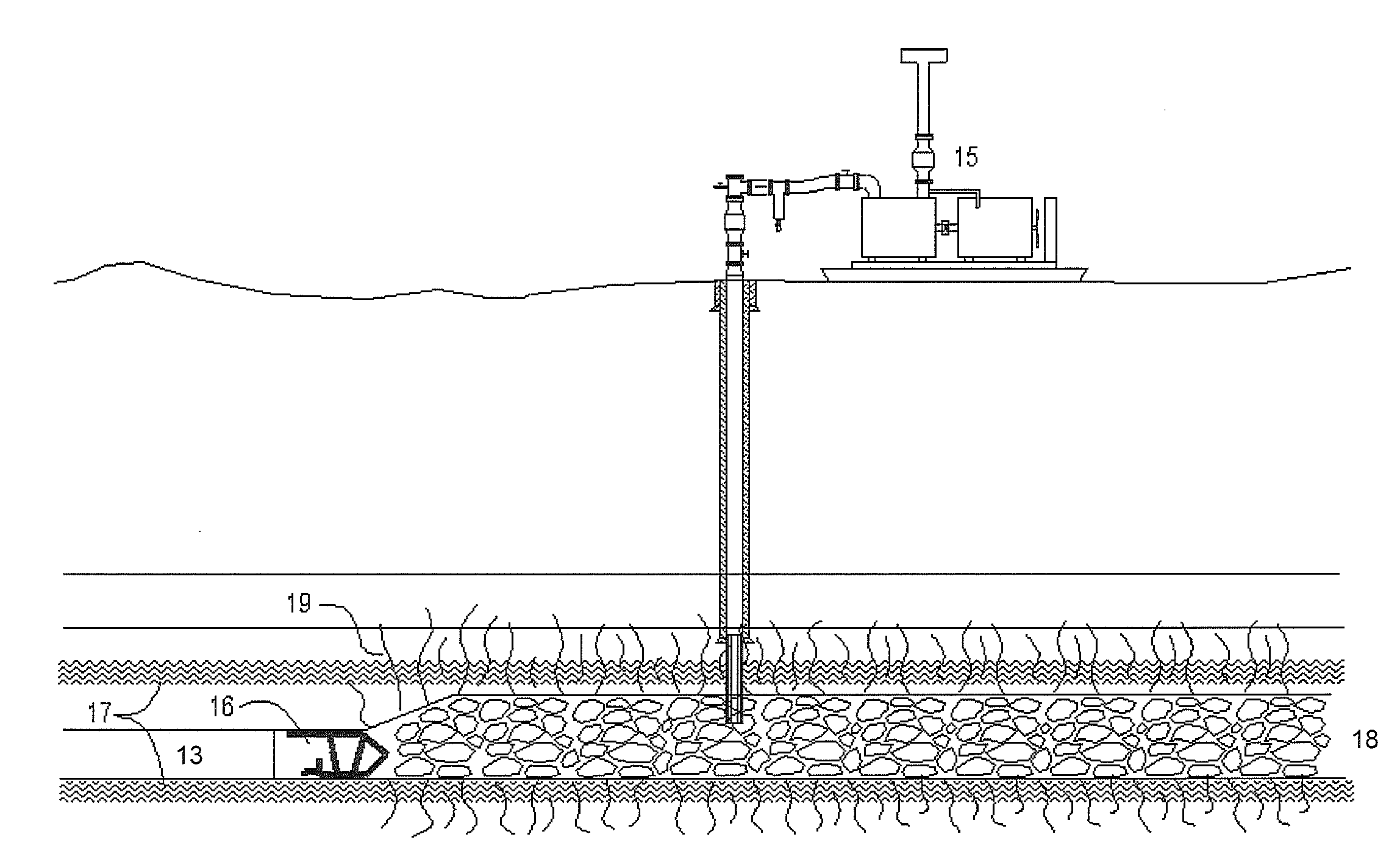
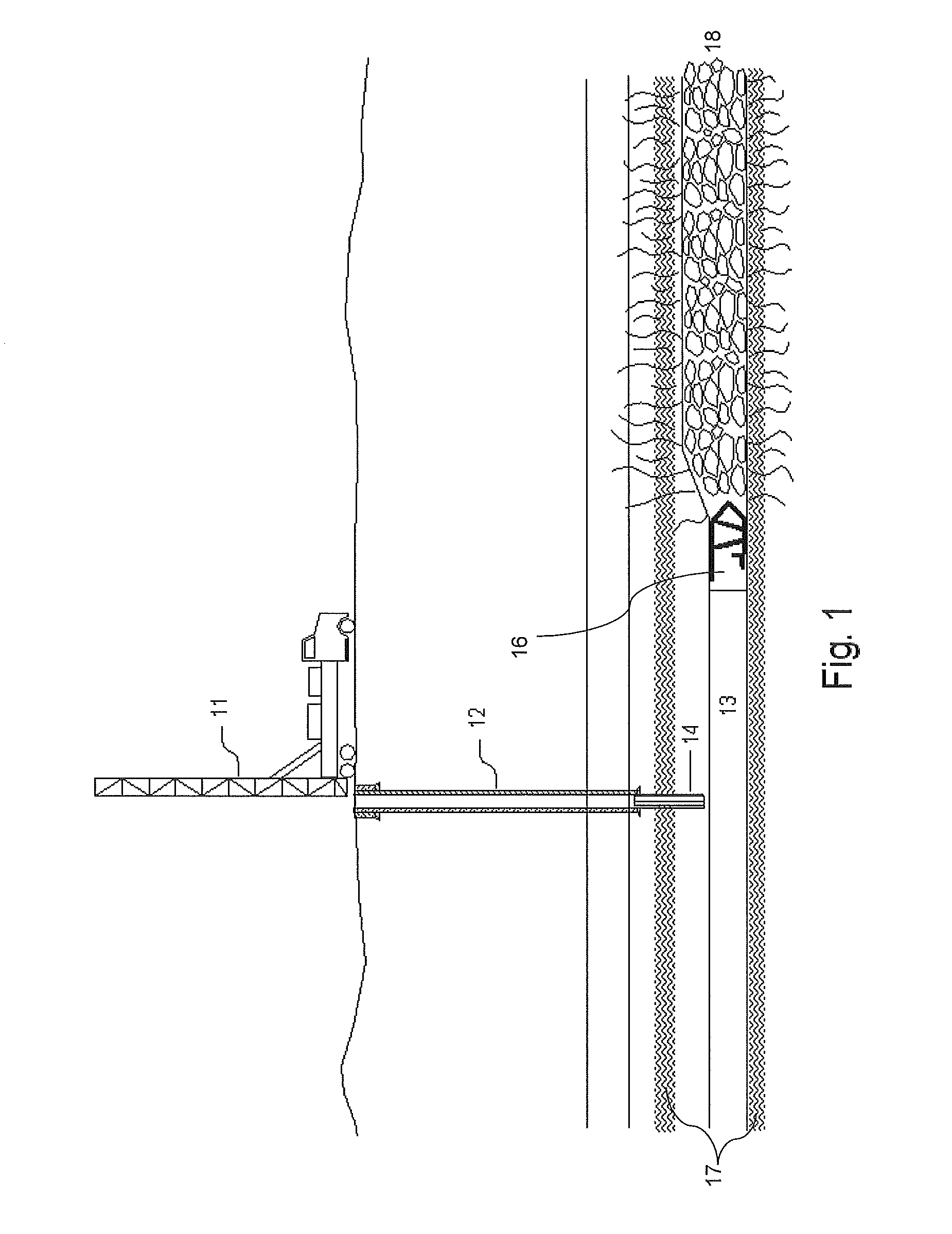
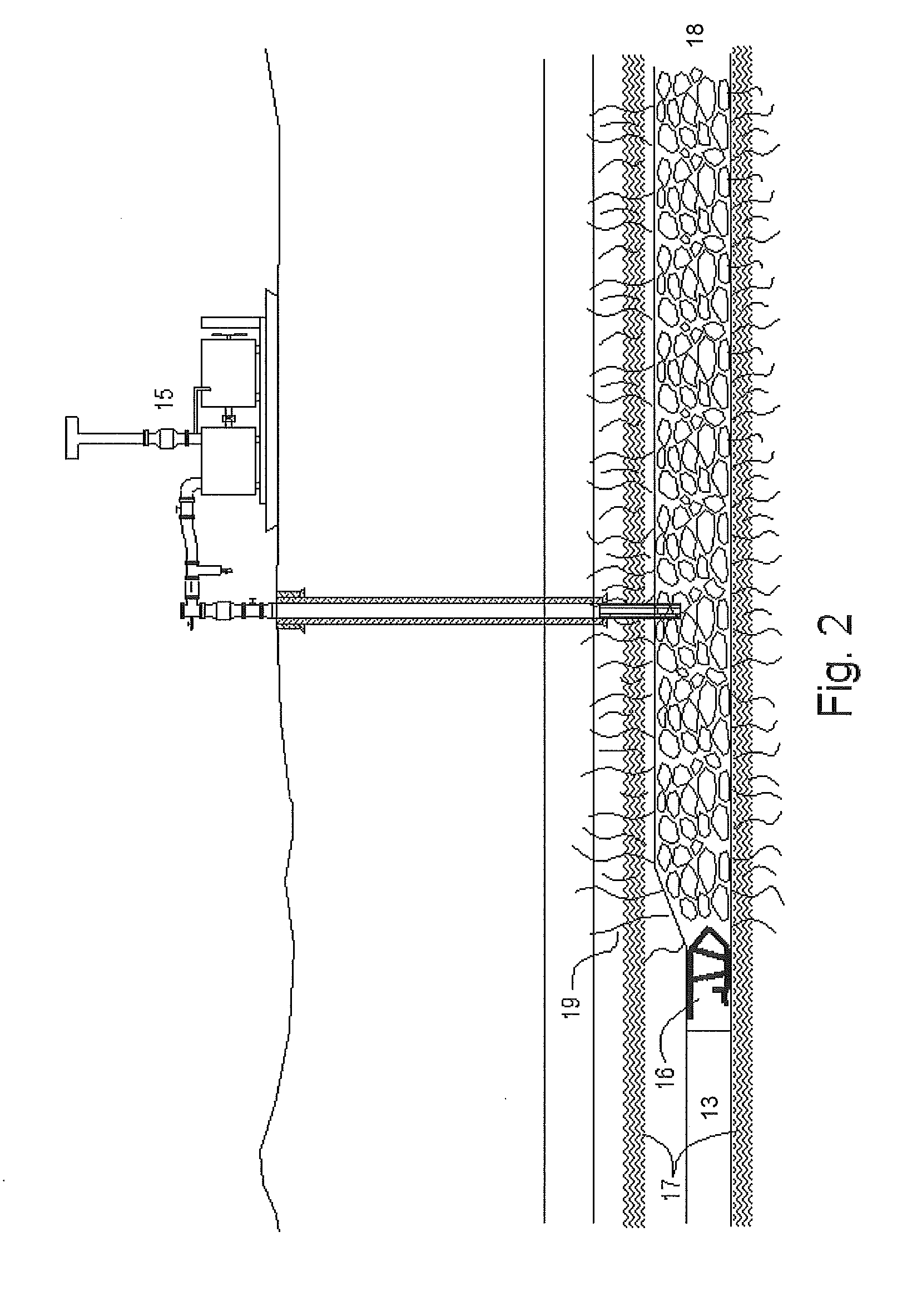
Mineral deposits in the crust of weathering (iron and nickel ores and other residua) may have a mantle-like, platelike, pocket, or vein form. Deposits of endogenous beds of copper, lead, zinc, tungsten, tin, and gold usually occur in veins; they may also occur in the form of lenses, pipes, stocks,...
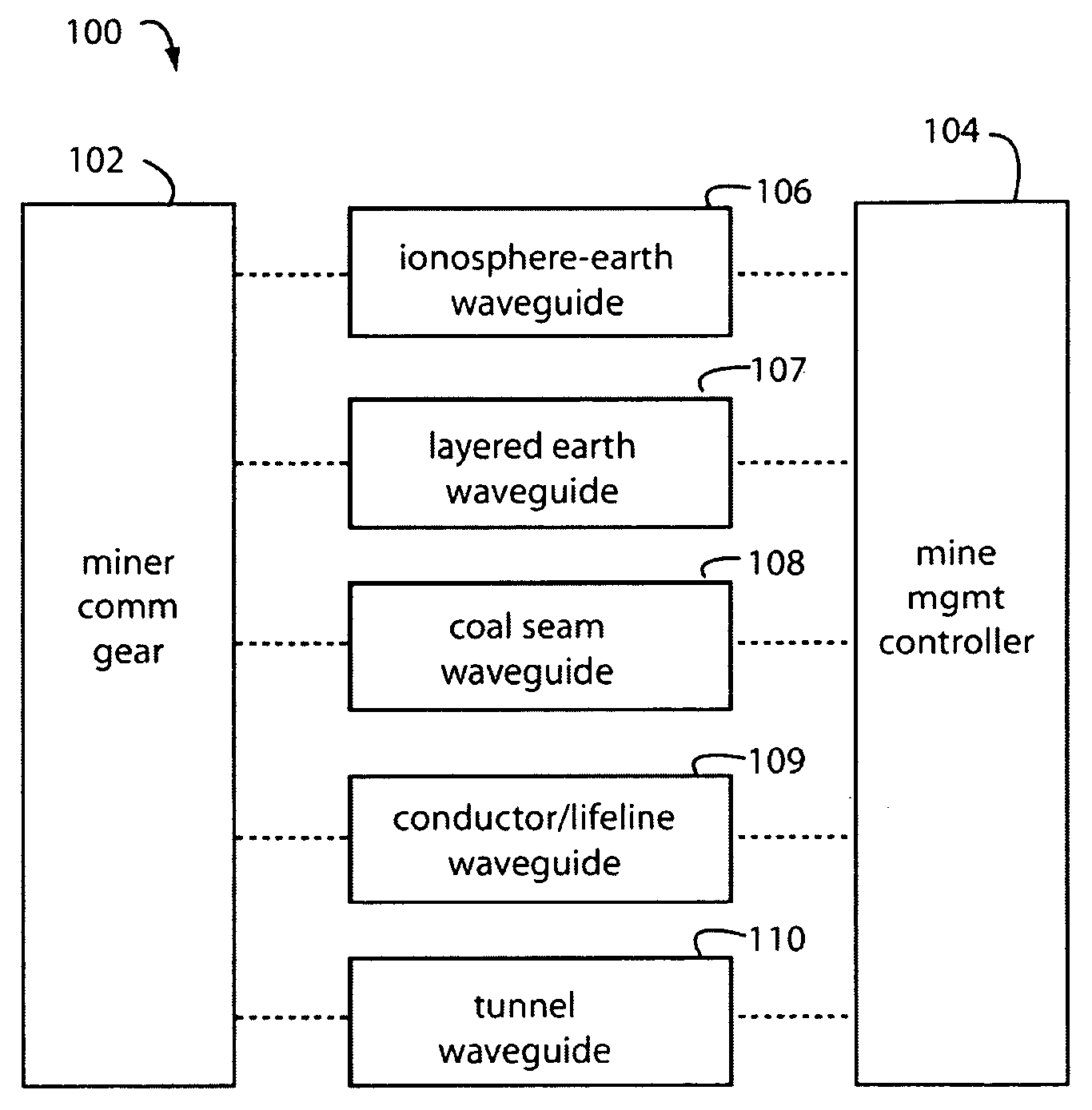
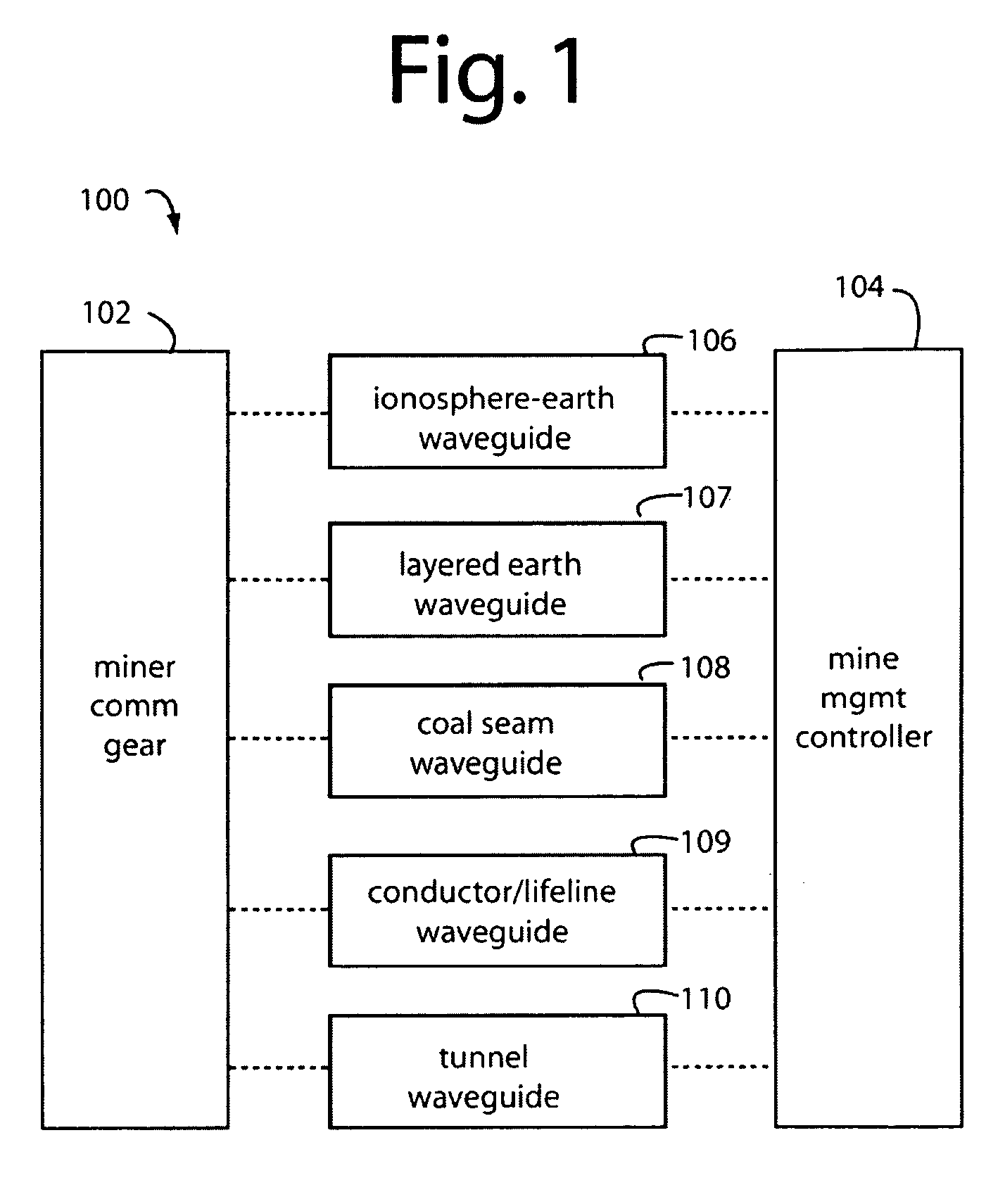
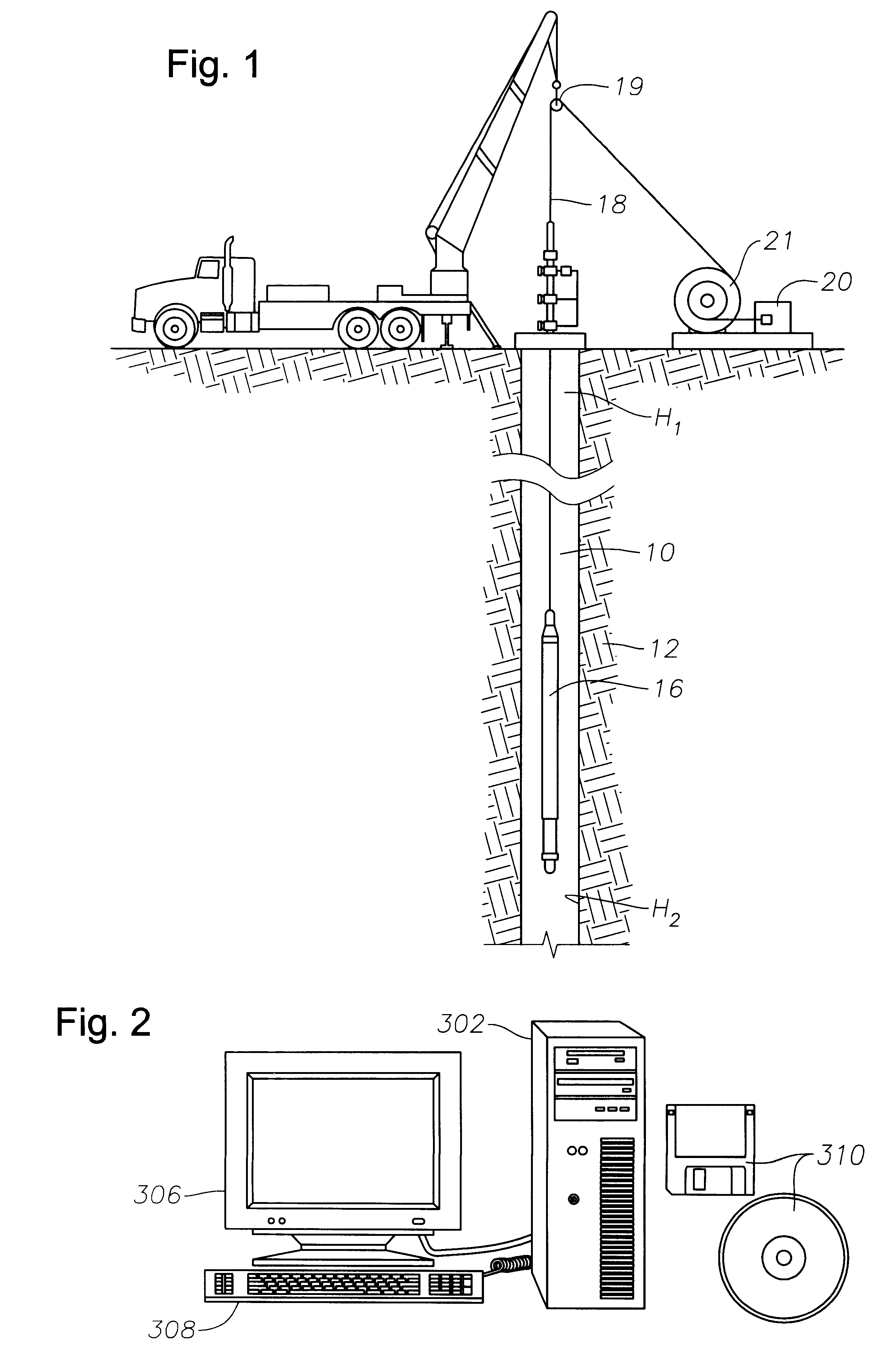
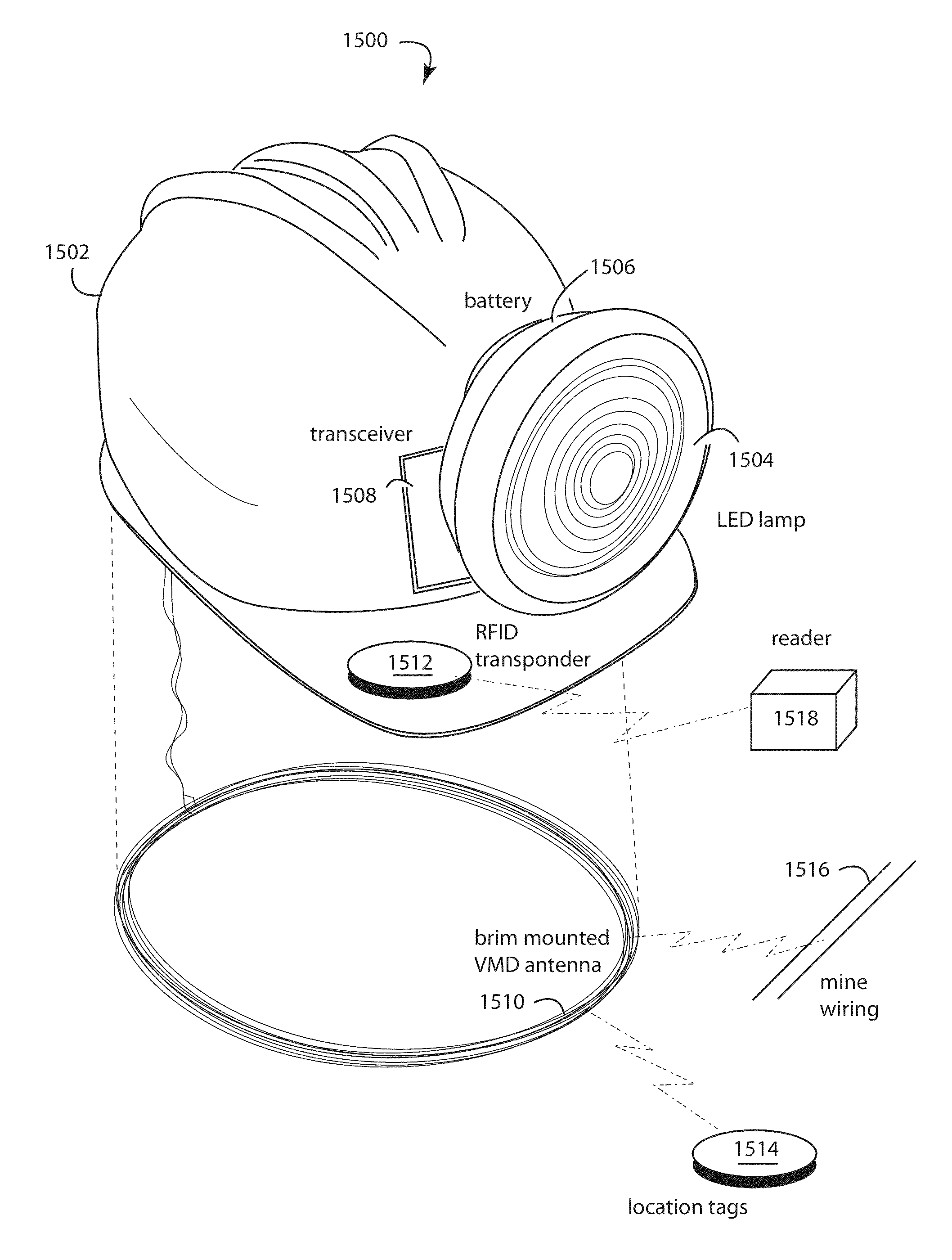
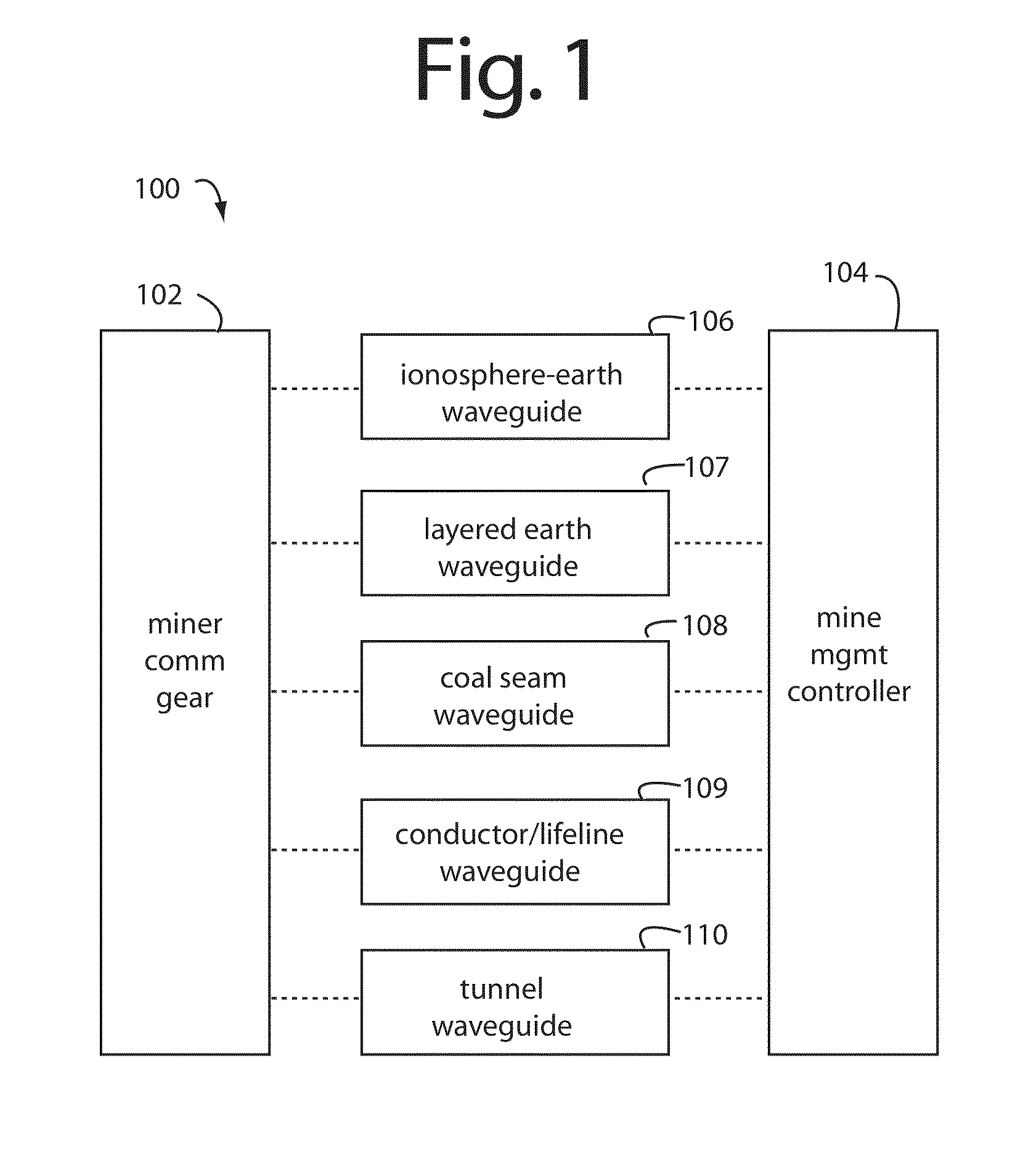
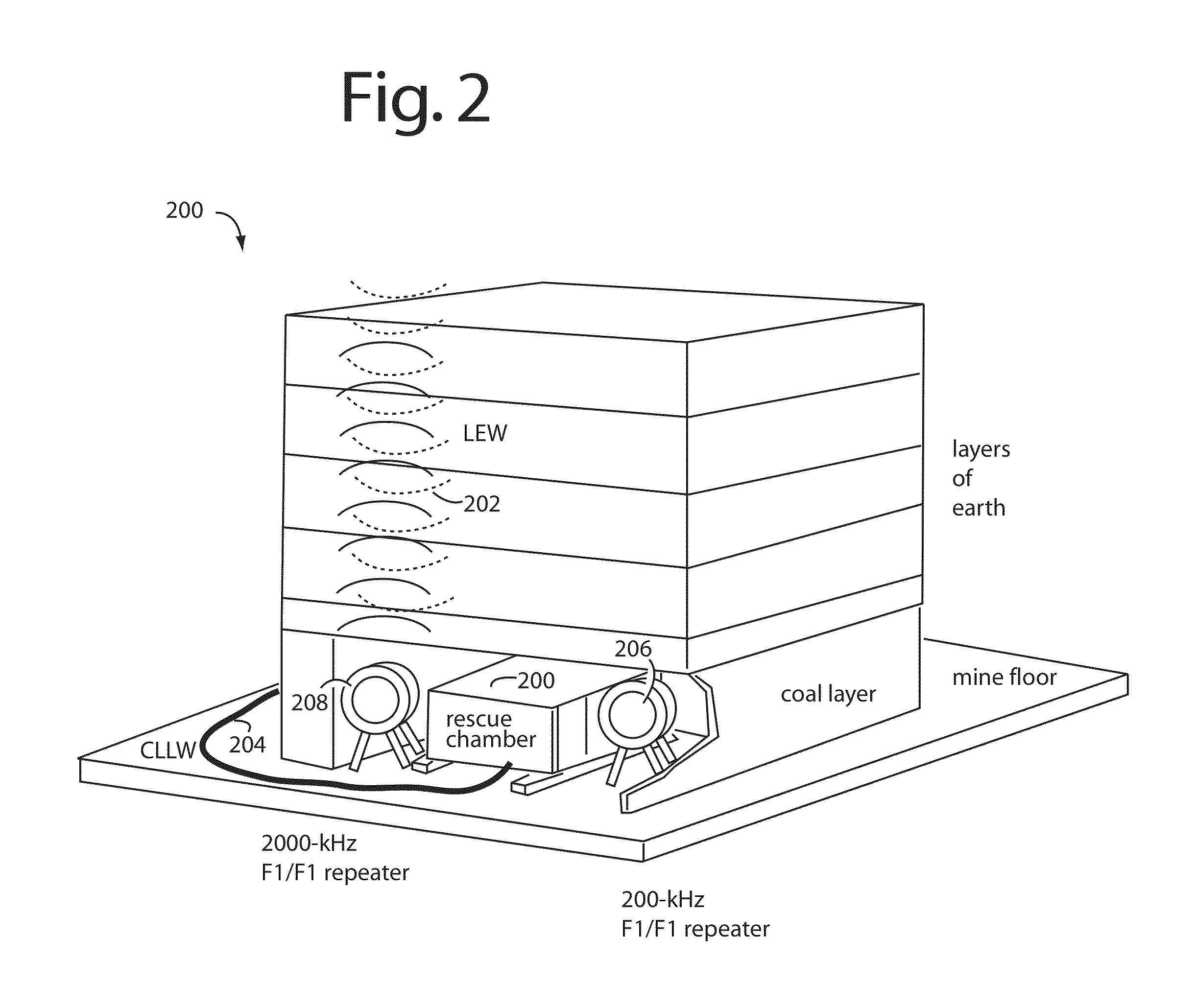
Underground radio communications and personnel tracking system
InactiveUS20090140852A1Function providedSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionElectric signalling detailsTransceiverElectrical conductor
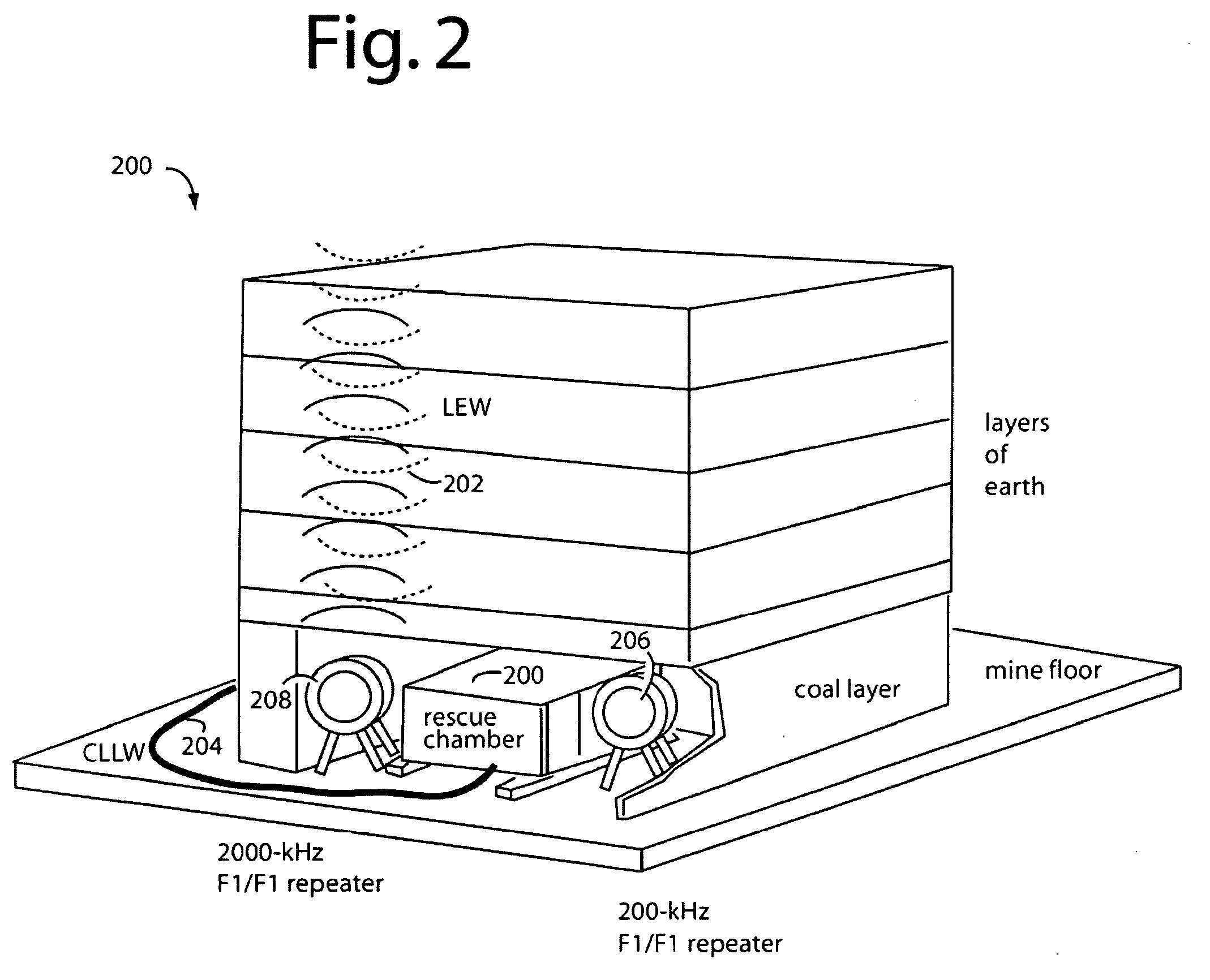
An underground radio communications and personnel tracking system uses a portable communications device worn by a miner when underground in a mine. A cap-lamp transceiver provides voice and text communication on ultra-low frequency (ULF) to ultra-high frequency (UHF) carrier frequencies and modulation adapted by programming of a software defined radio to making selective and agile radio contacts via through-the-earth, conductor / lifeline, coal seam, tunnel, and ionosphere / earth-surface waveguides for transmission of electromagnetic waves. These waveguides comprise layered earth coal and mineral deposits, and manmade mining complex infrastructures which serendipitously form efficient waveguides. Ultra-Low Frequency F1 / F1 repeaters are placed underground in the mine, and providing for extended range of communication of the cap-lamp transceiver with radios and tracking devices above ground of the mine.
Owner:STOLAR
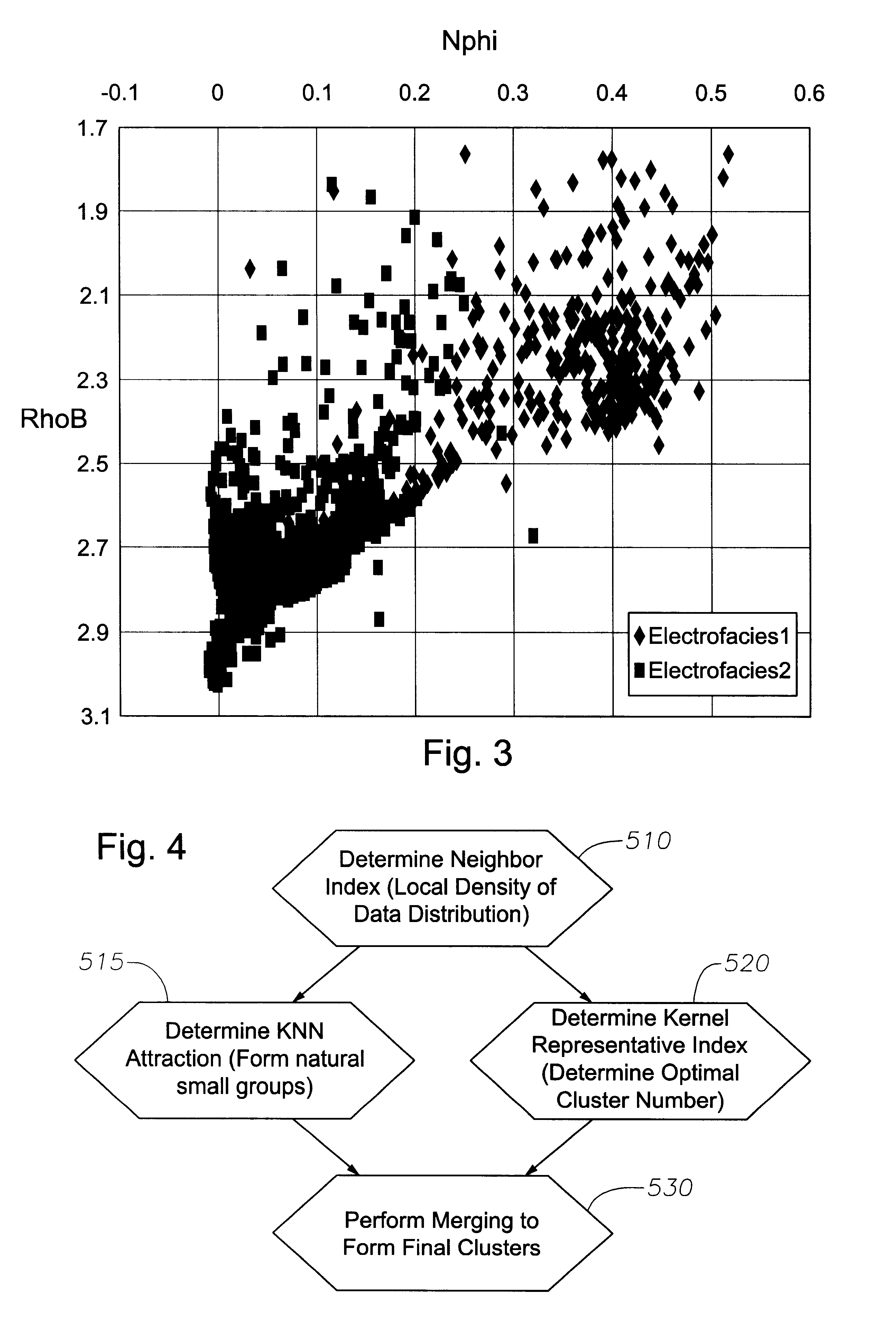
Multi-resolution graph-based clustering
InactiveUS6295504B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCharacter and pattern recognitionReference sampleData set
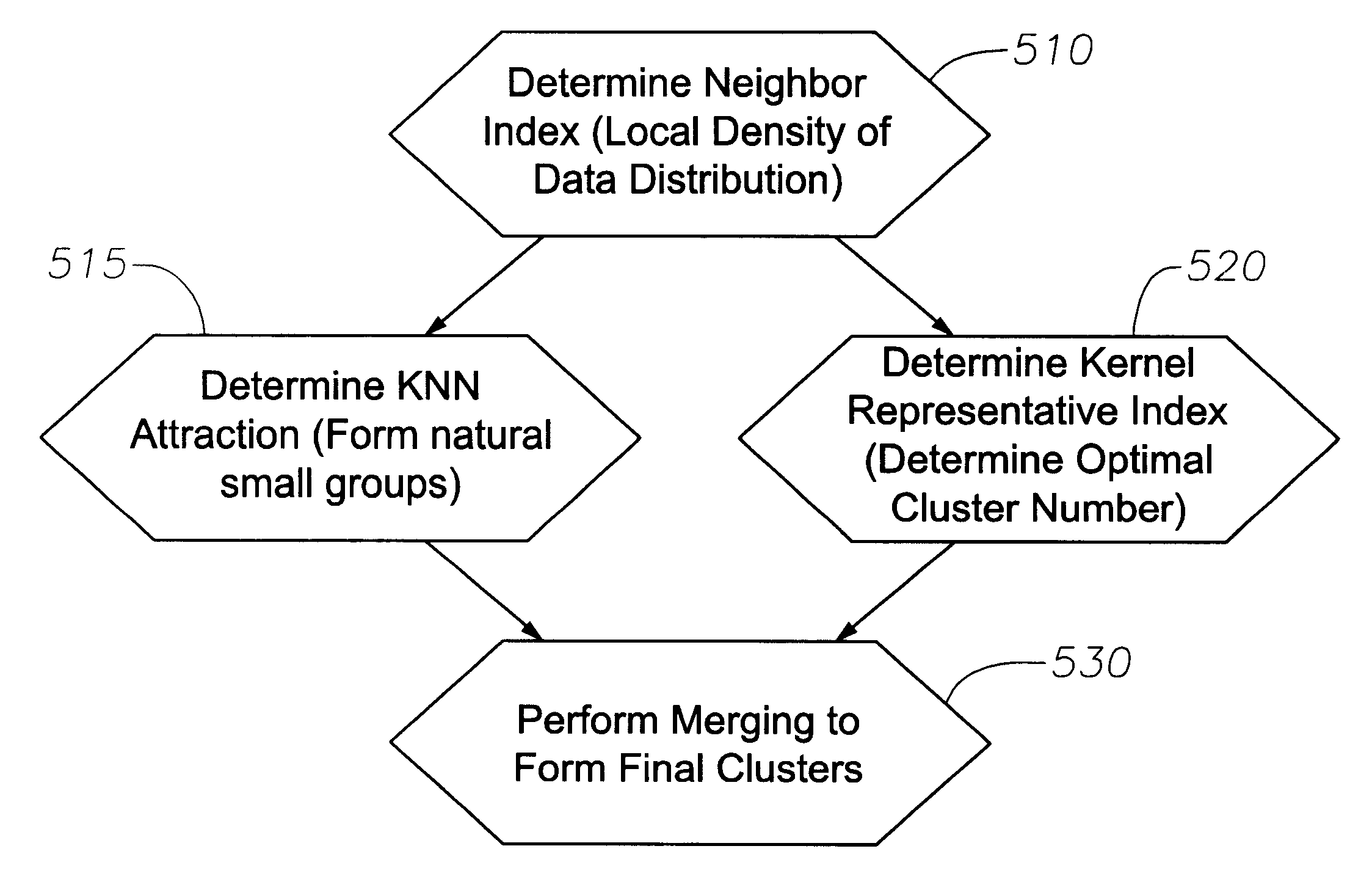
An apparatus and method for obtaining facies of geological formations for identifying mineral deposits is disclosed. Logging instruments are moved in a bore hole to produce log measurements at successive levels of the bore hole. The set of measurements at each such level of the bore hole interval is associated with reference sample points within a multidimensional space. The multidimensional scatter of sample points thus obtained is analyzed to determine a set of characteristic modes. The sample points associated with characteristic modes are grouped to identify clusters. A facies is designated for each of the clusters and a graphic representation of the succession of facies as a function of the depth is thus obtained. To identify the clusters, a "neighboring index" of each log measurement point in the data set is calculated. Next, small natural groups of points are formed based on the use of the neighboring index to determine a K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) attraction for each point. Independently of the natural group formation, an optimal number of clusters is calculated based on a Kernel Representative Index (KRI) and based on a user-specified resolution. Lastly, based on the data calculated from the prior steps, final clusters are formed by merging the smaller clusters.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
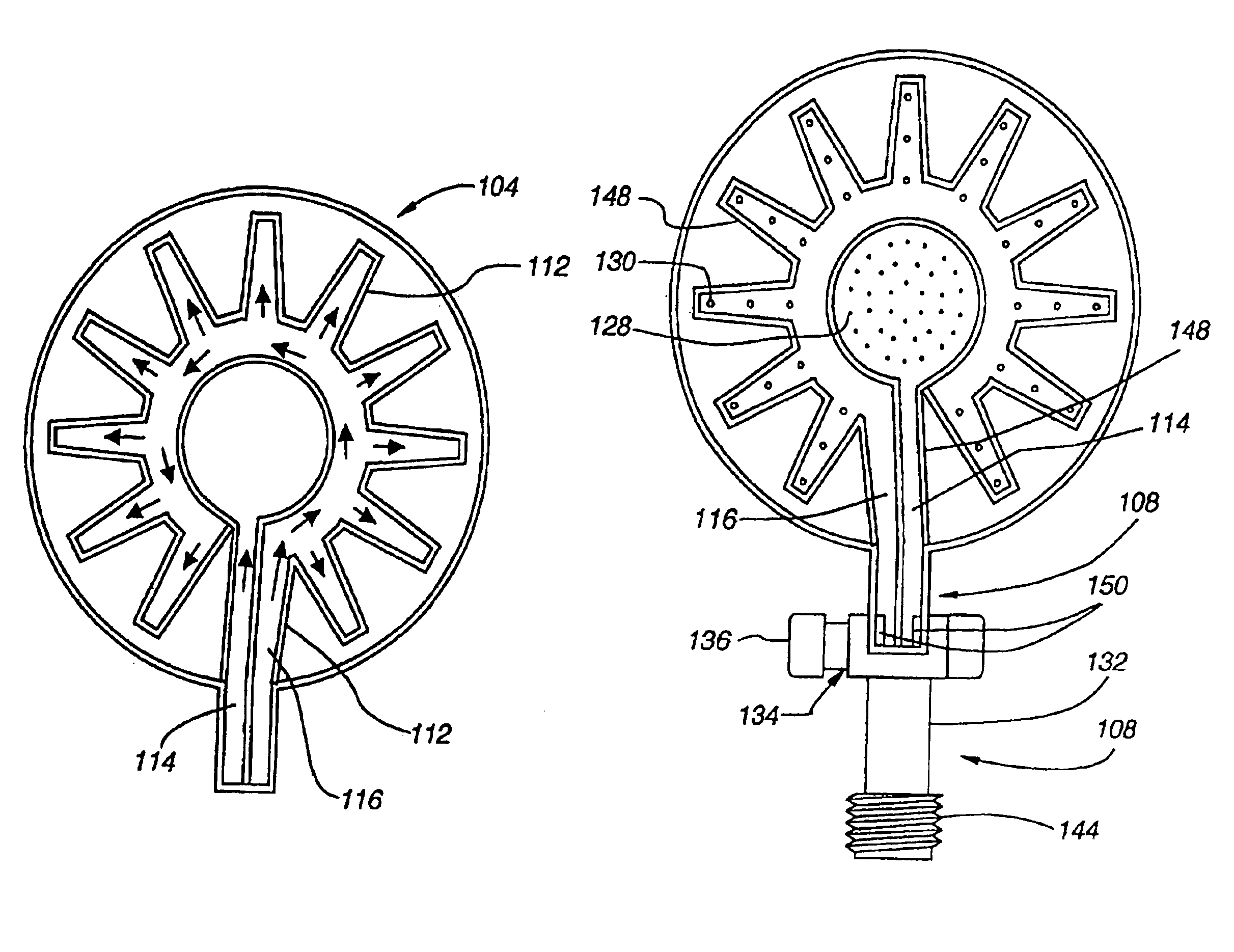
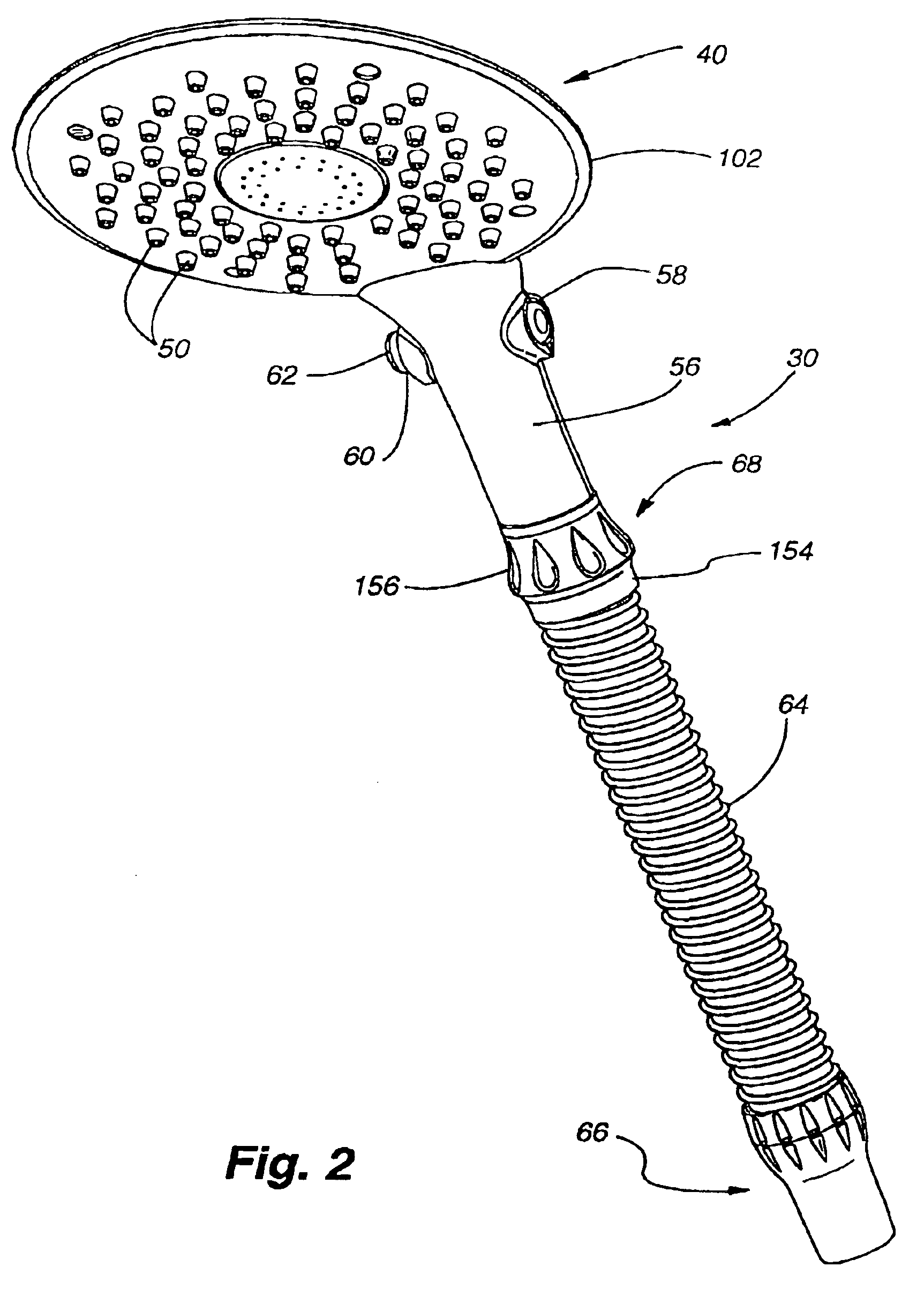
Shower head assembly
A shower head having a plurality of nozzles capable of attachment to a flexible shower arm. The shower head has a unique nozzle construction that allows for the manipulation of an external flexible nozzle to remove mineral deposits and has an internal, rigid nozzle structure for efficiently forming an aesthetically pleasing water stream. The shower head may have two available flow configurations which are selectable by a valve.
Owner:WATER PIK INC
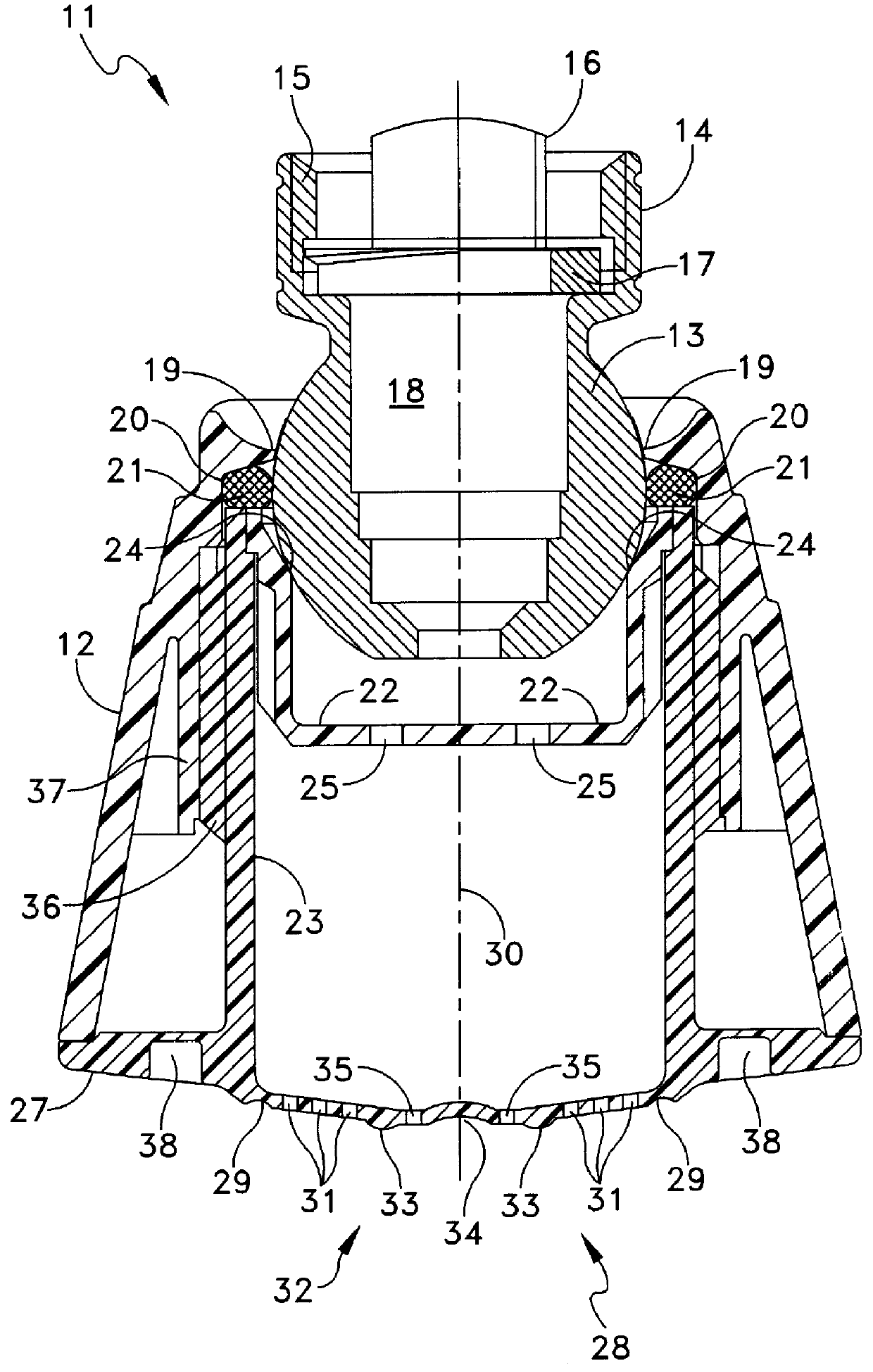
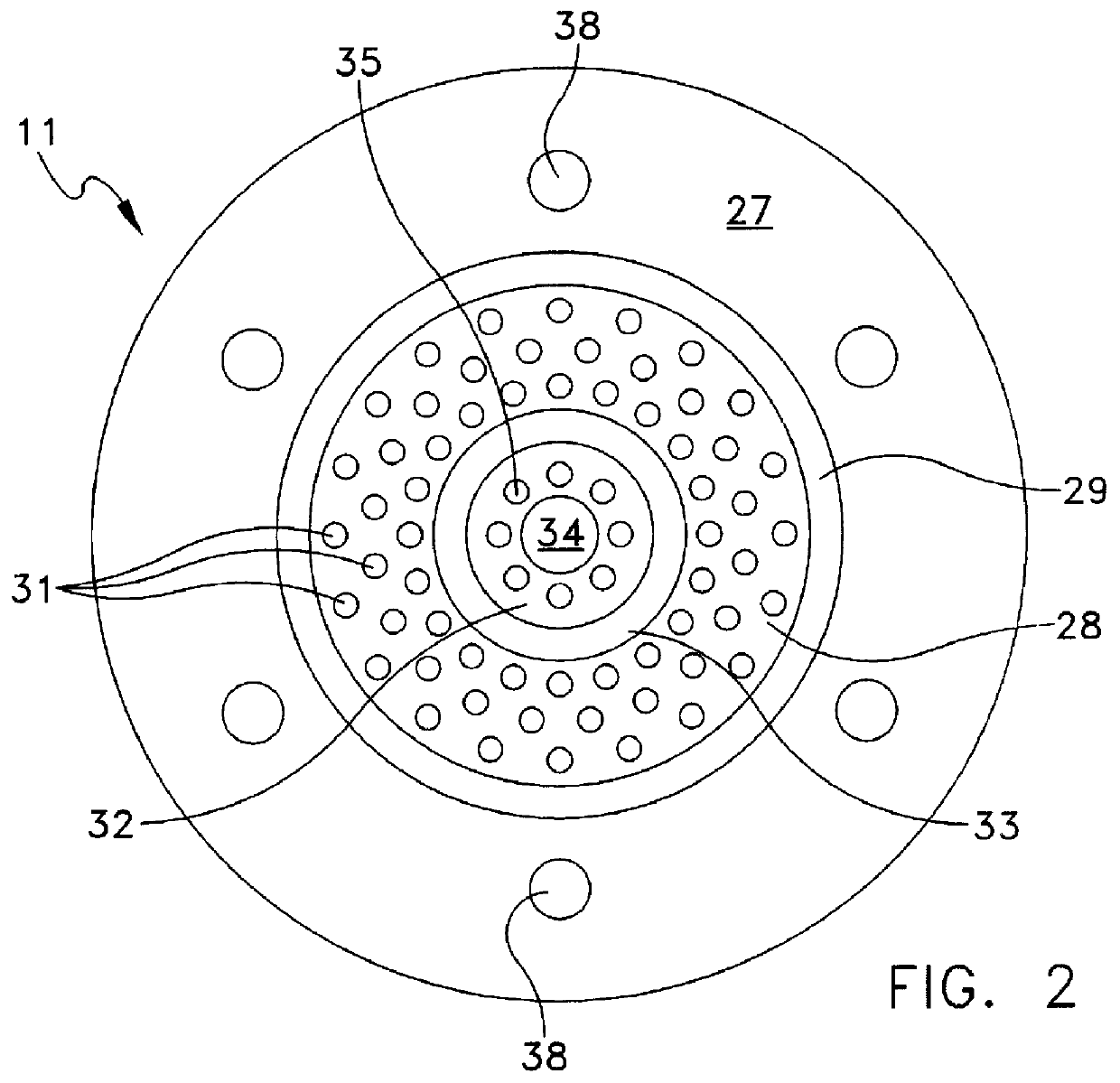
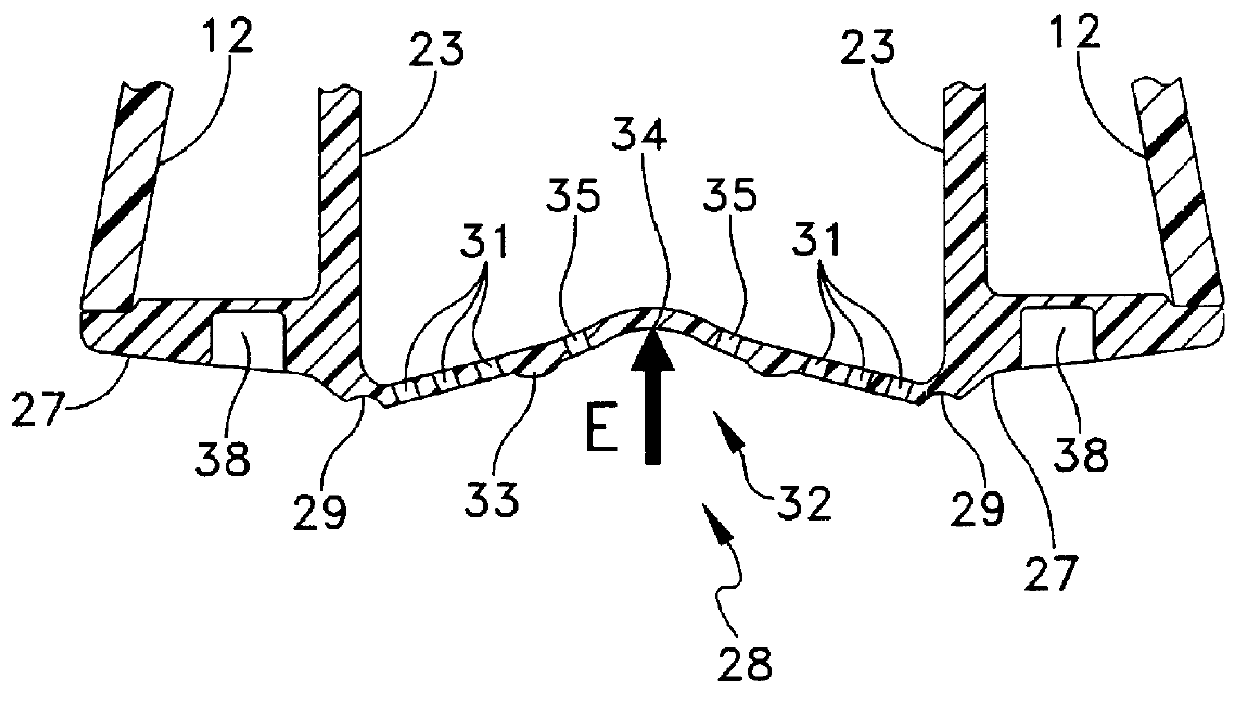
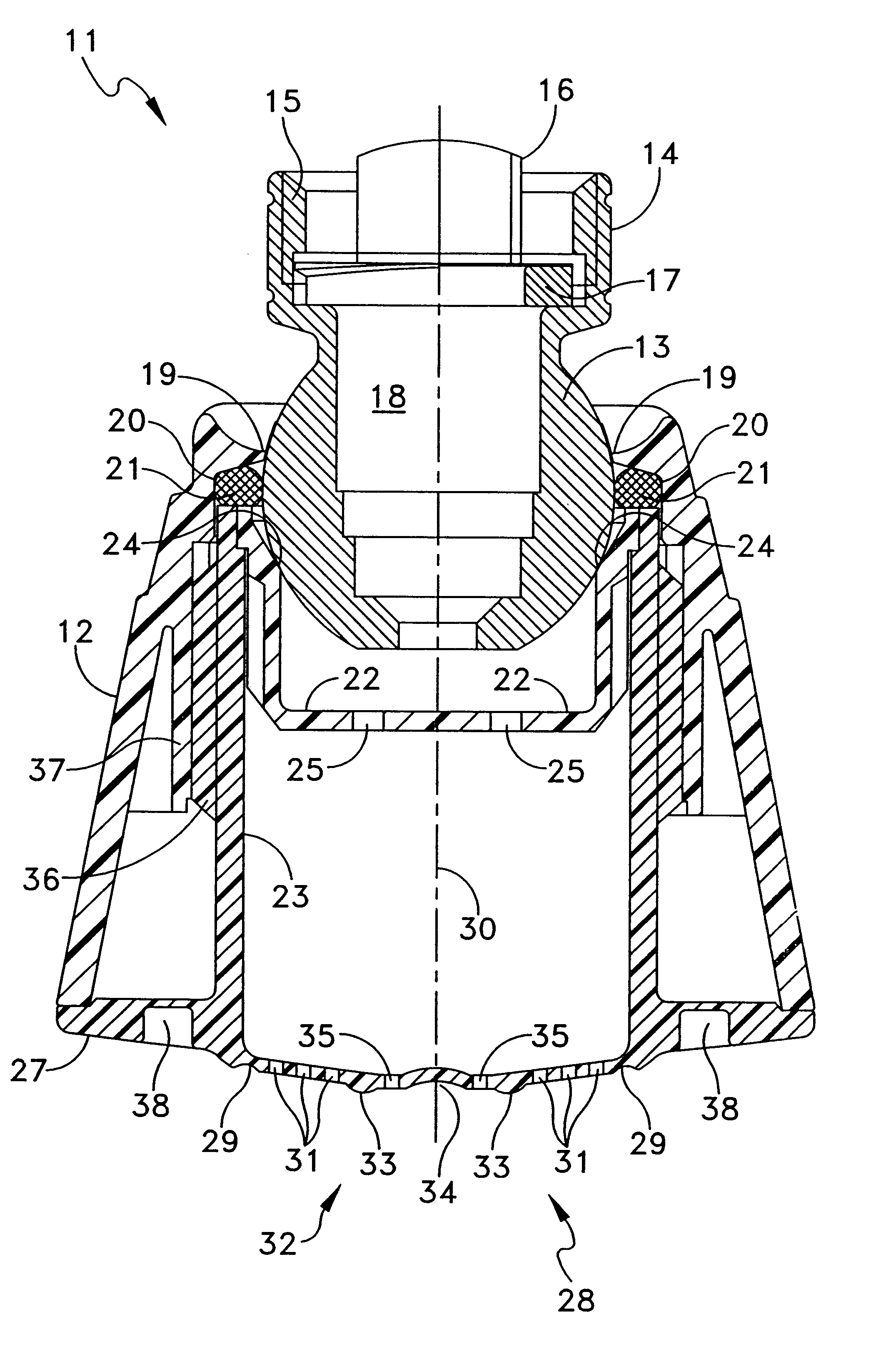
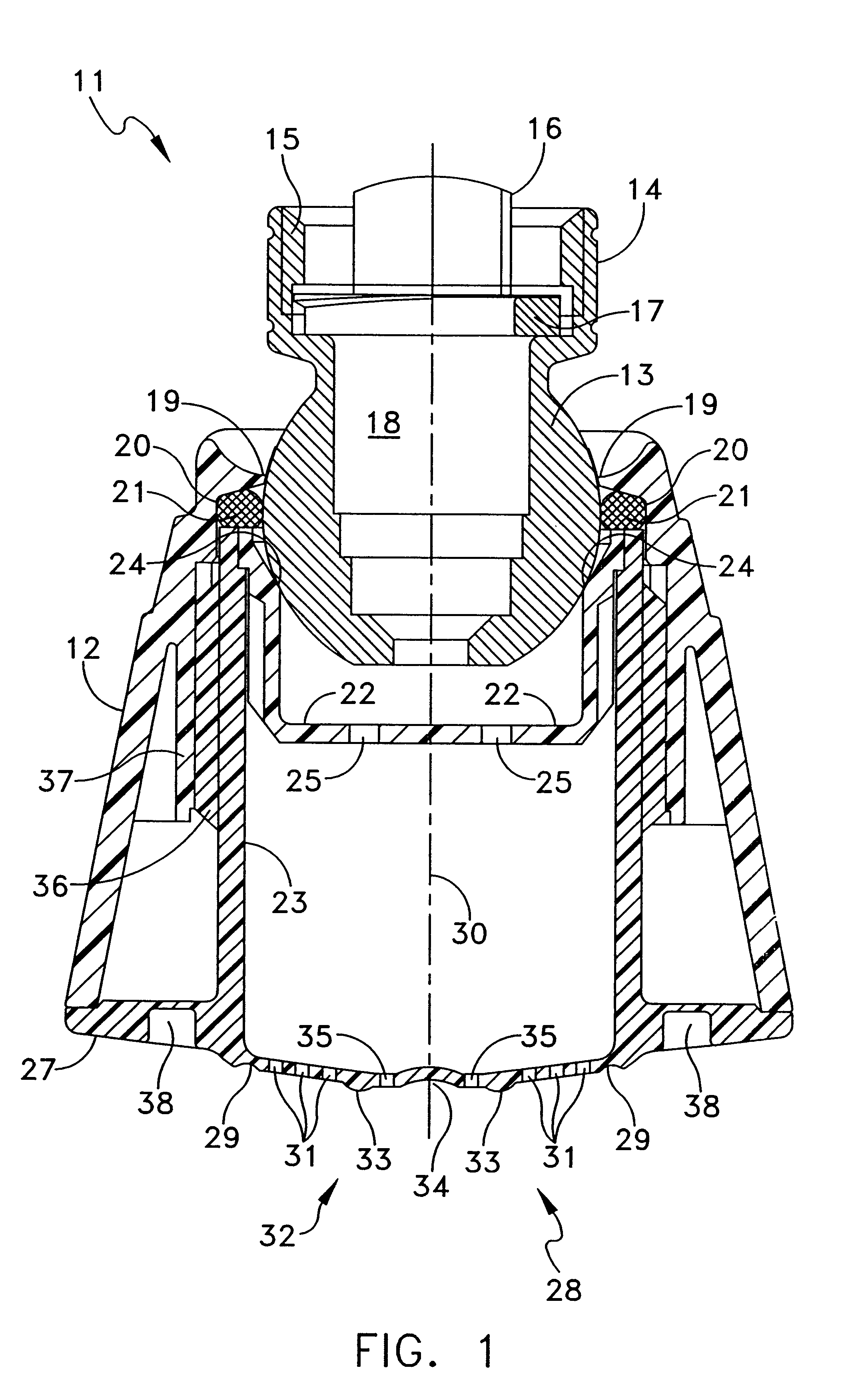
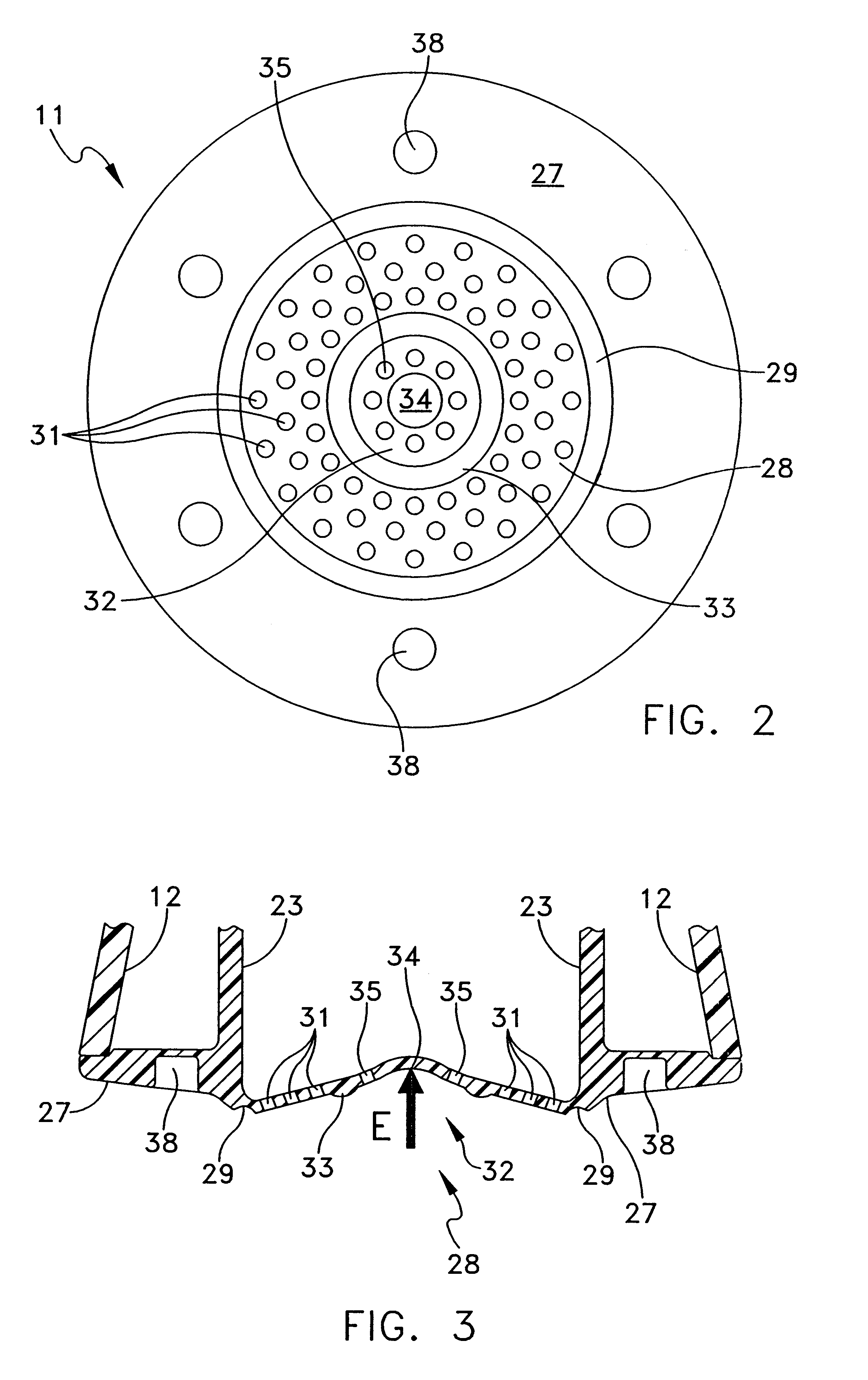
Shower device having a resiliently depressible jet disk for removing mineral deposits
A shower device having a flexible, flat jet or spray disk is created, in which at least one surface zone is curved outwards and on exceeding a specific pressing in force (E) exerted thereon springs round suddenly with the curvature inwards into a space located behind it and automatically springs back to the starting position when the force is relieved. As a result of the springing or springing round, it is possible to detach lime deposits from the jet disk.
Owner:HANS GROHE GMBH & CO KG
Shower device having a resiliently depressible jet disk for removing mineral deposits
A shower device having a flexible, flat jet or spray disk is created, in which at least one surface zone is curved outwards and on exceeding a specific pressing in force (E) exerted thereon springs round suddenly with the curvature inwards into a space located behind it and automatically springs back to the starting position when the force is relieved.As a result of the springing or springing round, it is possible to detach lime deposits from the jet disk.
Owner:HANS GROHE GMBH & CO KG
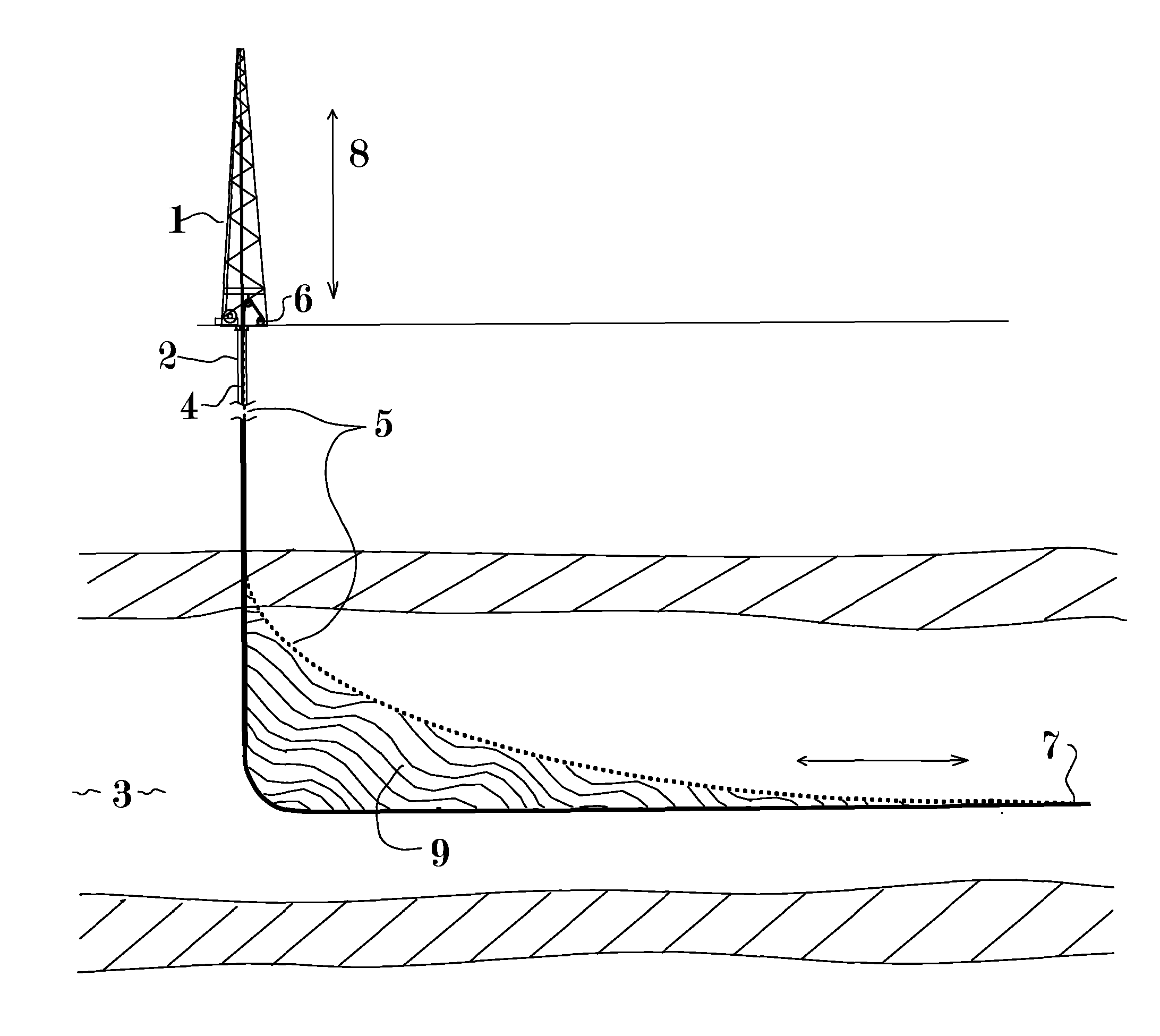
Method and Apparatus for Increasing Well Productivity
InactiveUS20110247816A1Increase productivityRate of flow of resources between the formation and the well is substantially increasedEarth drilling toolsFluid removalEnvironmental issueFlow limitation
This patent application discloses method and apparatus to cut an extended slot connecting a well to a substantial cross section of a desired producing formation whereby material can flow freely between the formation and the wellbore and at least partially overcome the flow limitations of low permeability formations without the environmental issues associated with hydraulic fracturing. It is further disclosed that the connection between said slot and the formation may be further enhanced by explosive or combustive processes that rapidly generate gas pressure within the large surface area of the slot, thereby changing its characteristics and forcing open additional fractures into the cross section of formation exposed to the slot. The method may significantly increase the recoverable percentage of natural gas from low permeability deposits such as shale and coal.
Owner:CARTER JR ERNEST E
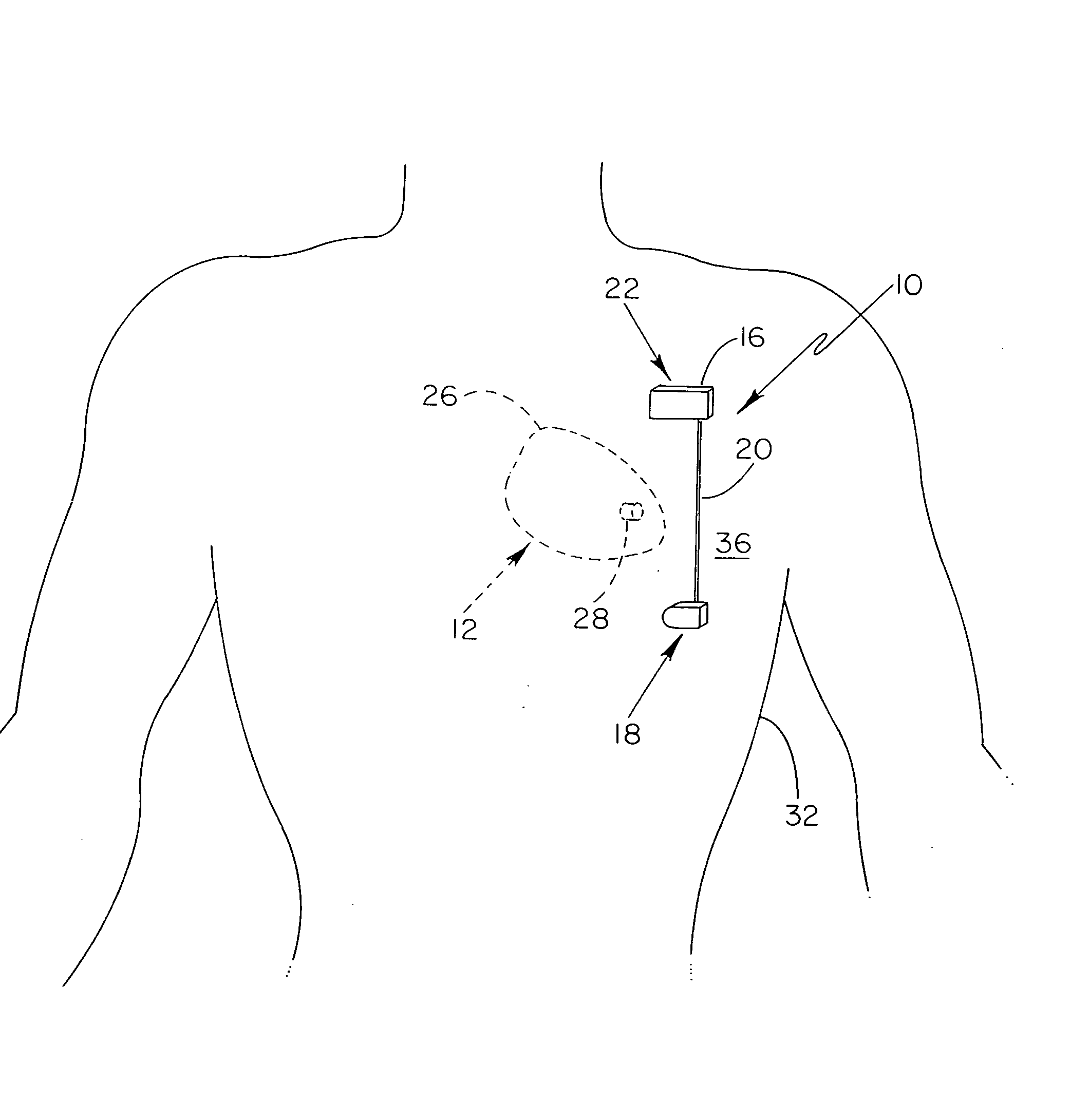
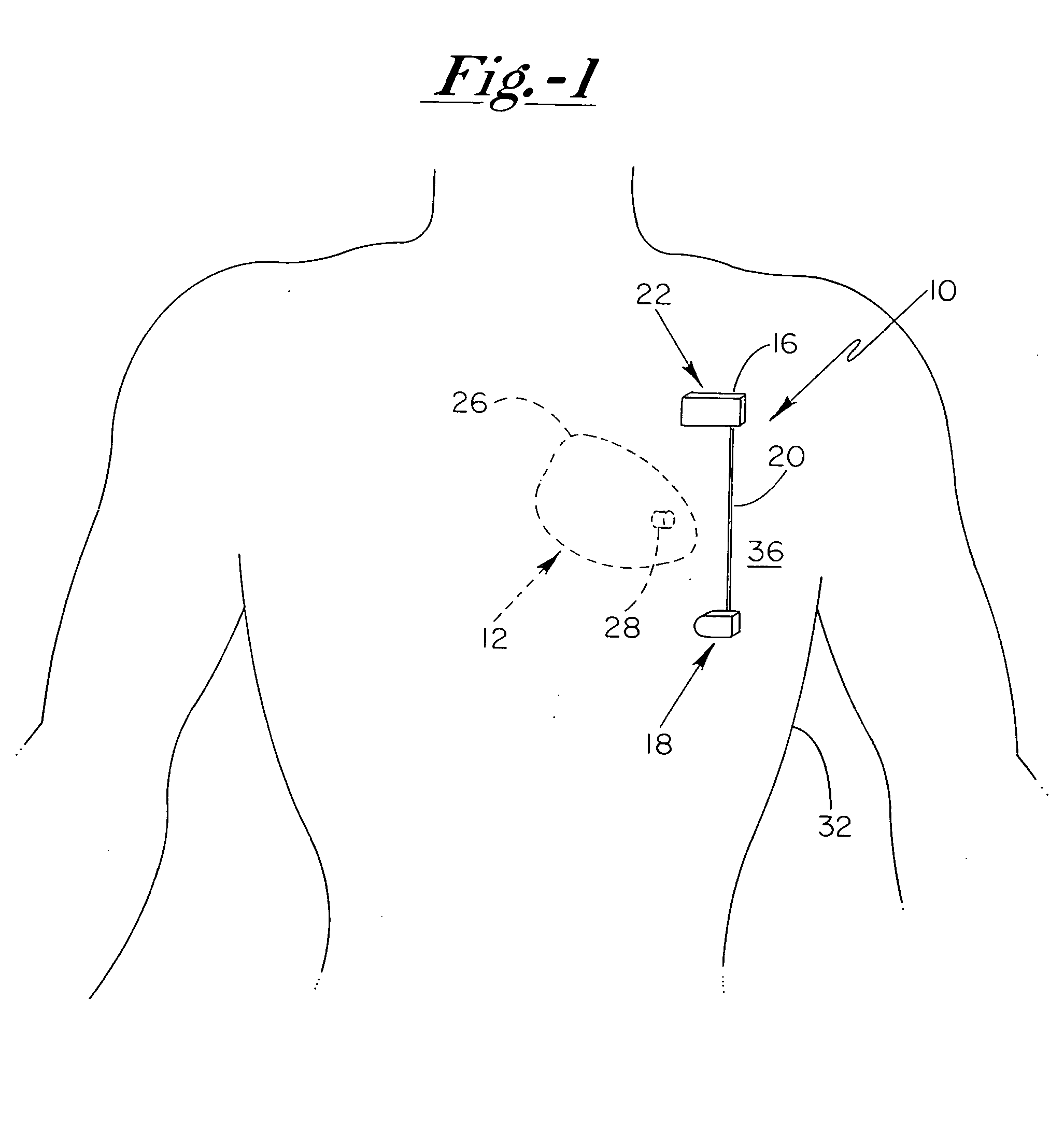
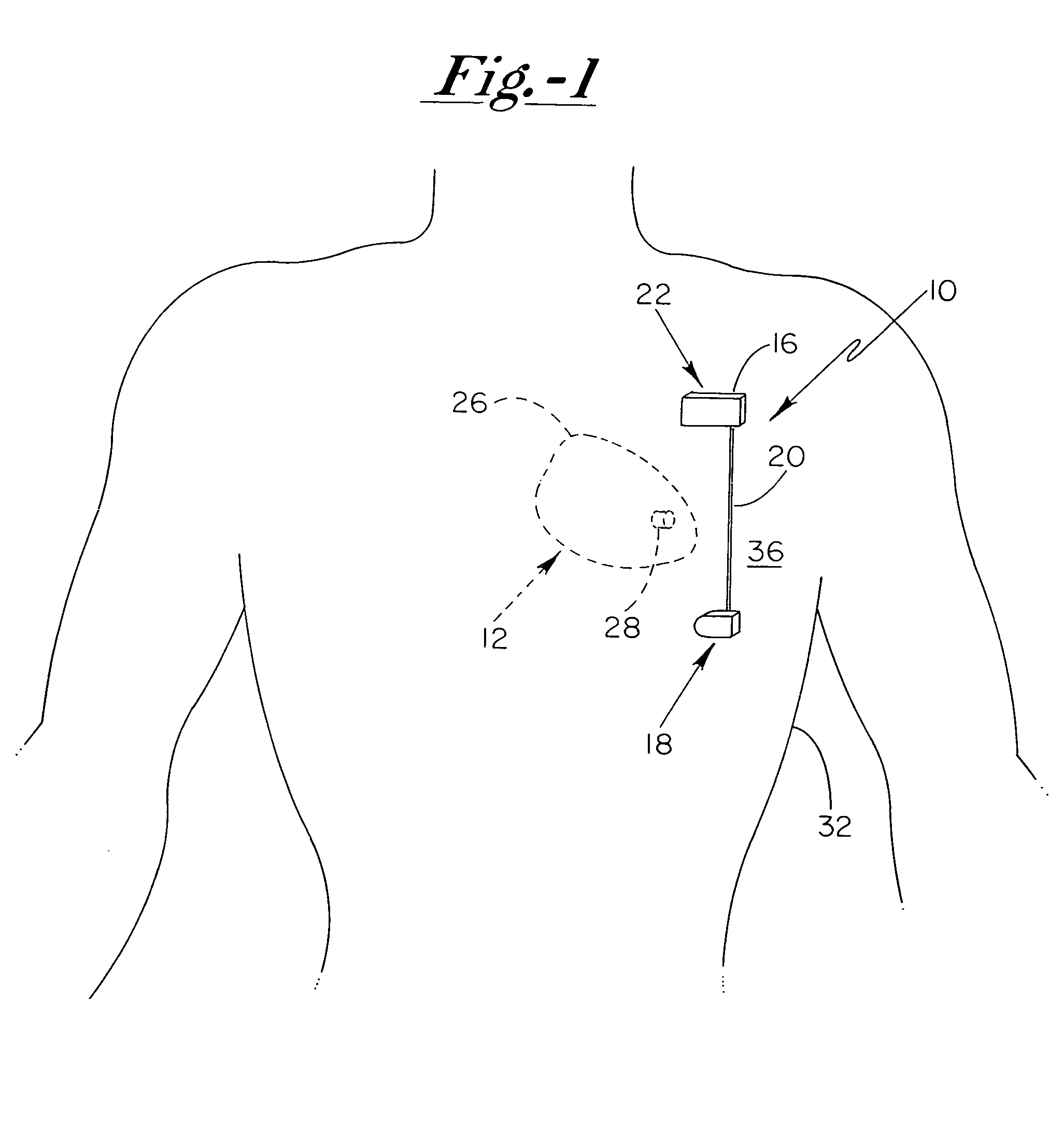
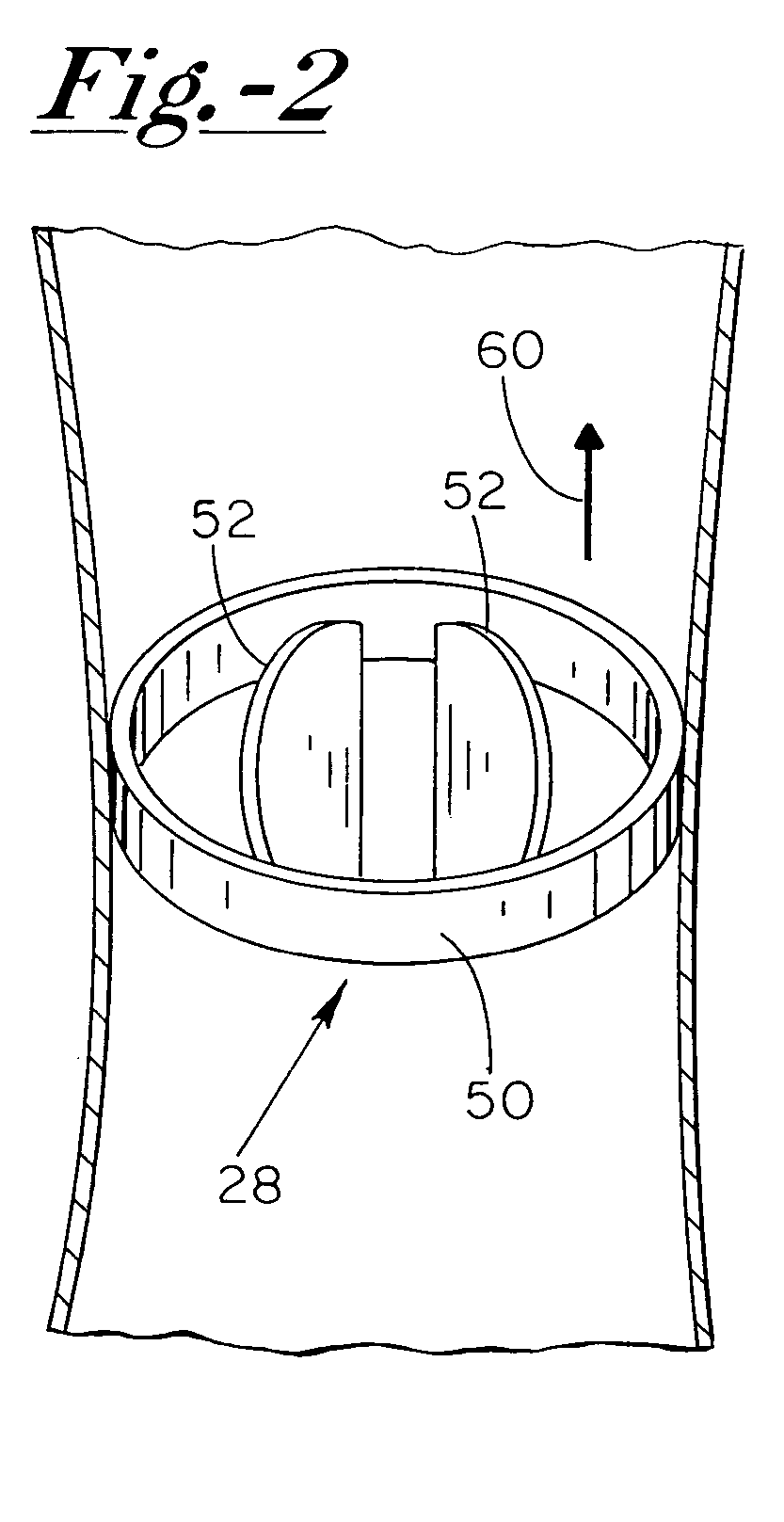
Anti-coagulation and demineralization system for conductive medical devices
ActiveUS20060009804A1Prevention and elimination of blood component depositElectrotherapyArtificial respirationThoracic structureElectricity
A system for minimizing and / or eliminating coagulative or mineral deposits on respective blood-contacting surfaces of implanted medical devices includes an implantable system having a current generating device that is electrically coupled to at least first and second electrodes for developing a current therebetween. The at least first and second electrodes are disposed across a patient's thoracic cavity in a manner so that a particular implanted medical device having at least a portion thereof that is fabricated from an electrically conductive material is disposed in a path substantially between such electrodes, thereby focusing the generated electrical current at the electrically conductive portion of the implanted medical device for therapeutic treatment thereat.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Electrolytic system and method for enhanced release and deposition of sub-surface and surface components
ActiveUS20080115930A1Maximize extraction efficiencyOperating cost structureCellsPolycrystalline material growthElectrolysisCarrier fluid
The present electrolytic system and method for extracting components includes a means for providing a carrier fluid; a means for providing a pair of electrodes interposed by a permeable membrane to create a first channel and a second channel; a means for flowing the carrier fluid through the first and second channel; a means for applying a voltage to the pair of electrodes to produce a first ionized carrier fluid in the first channel and a second ionized carrier fluid in the second channel; a means for injecting at least one of the first ionized carrier fluid and the second ionized carrier fluid into the subsurface reservoir to release the components; and a means for recovering the at least one of the first ionized carrier fluid and the second ionized carrier fluid and the components from a subsurface strata or ex-situ mineral deposit.
Owner:STRATEGIC RESOURCE OPTIMIZATION
Scale removal
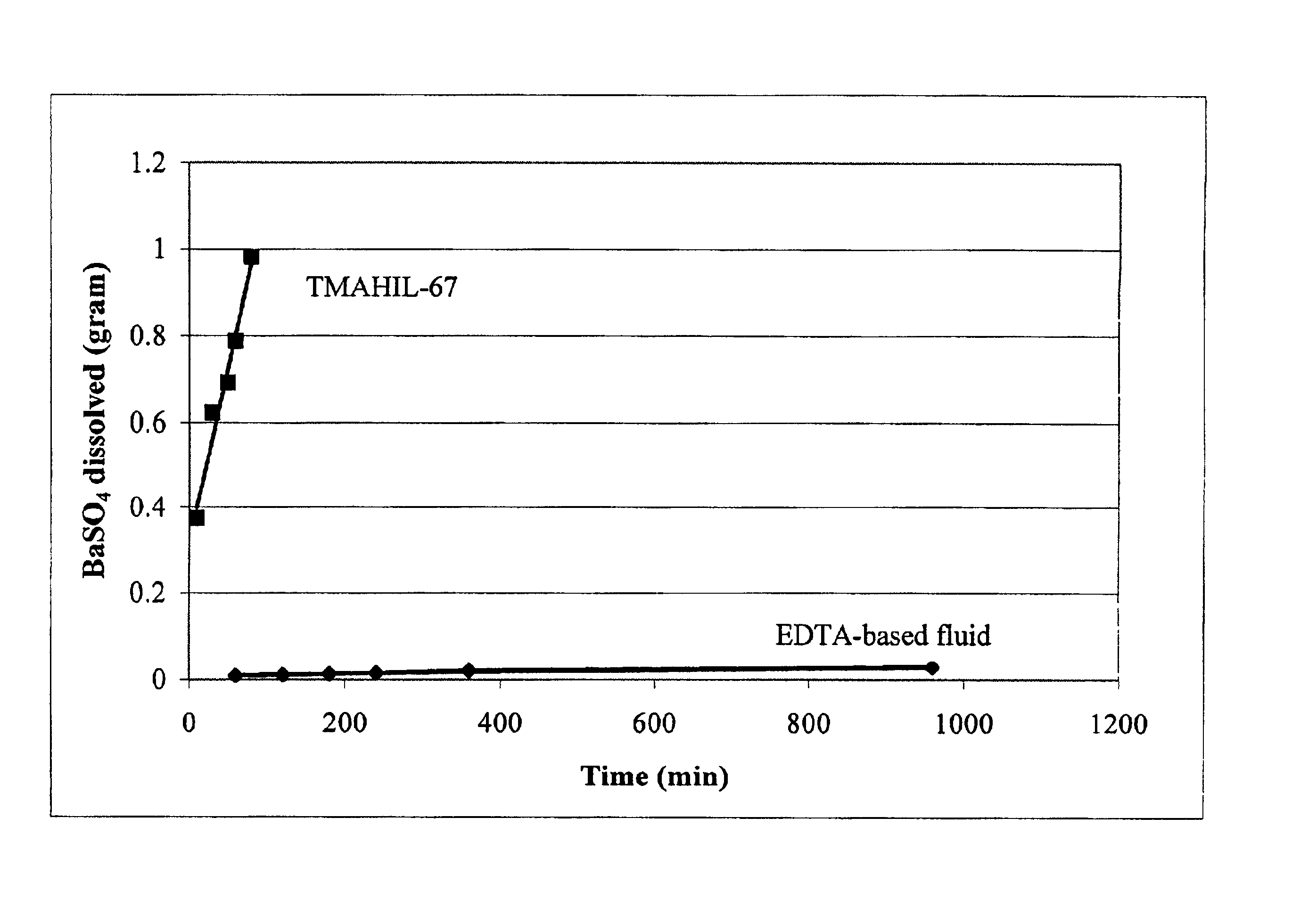
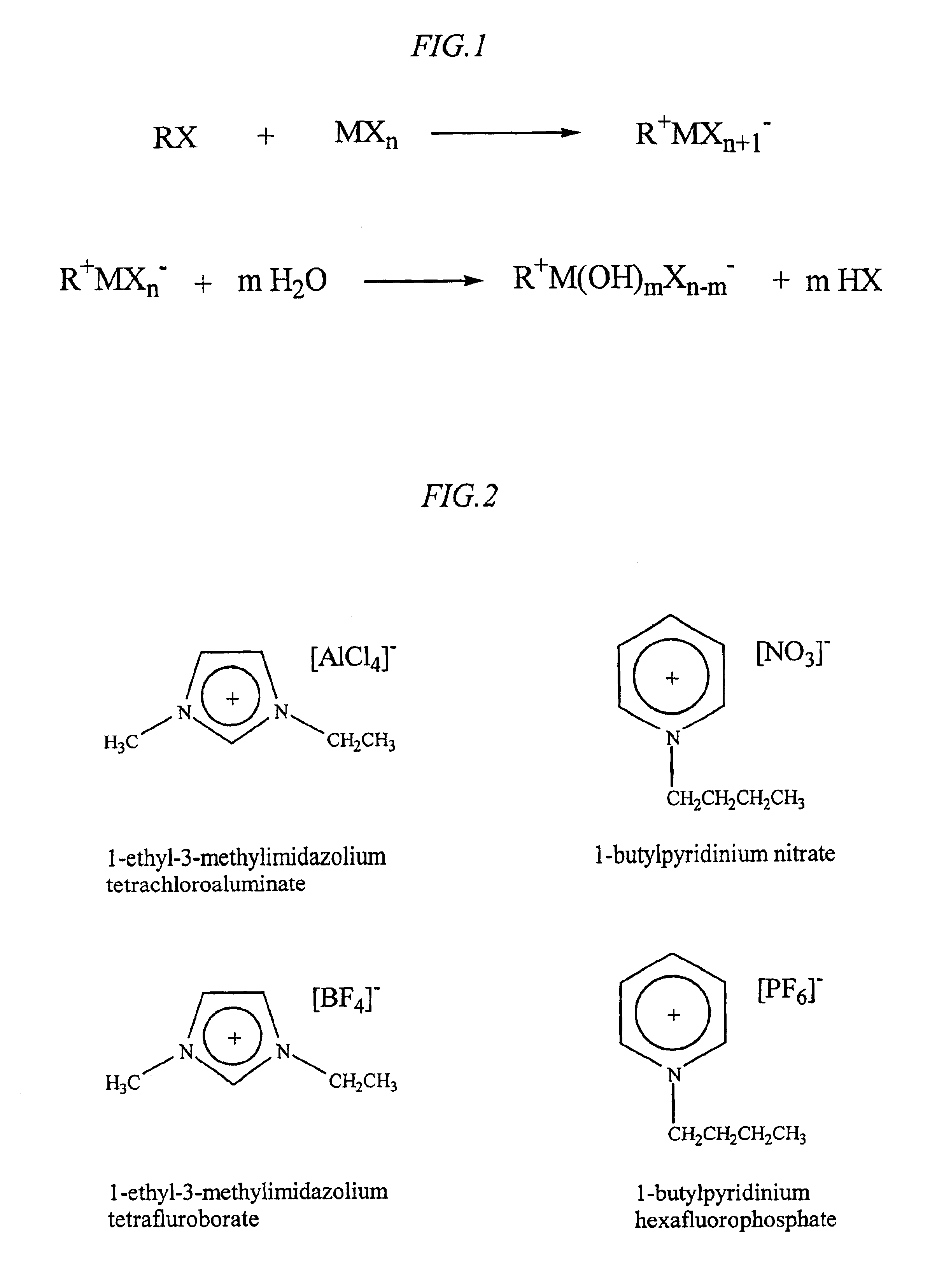
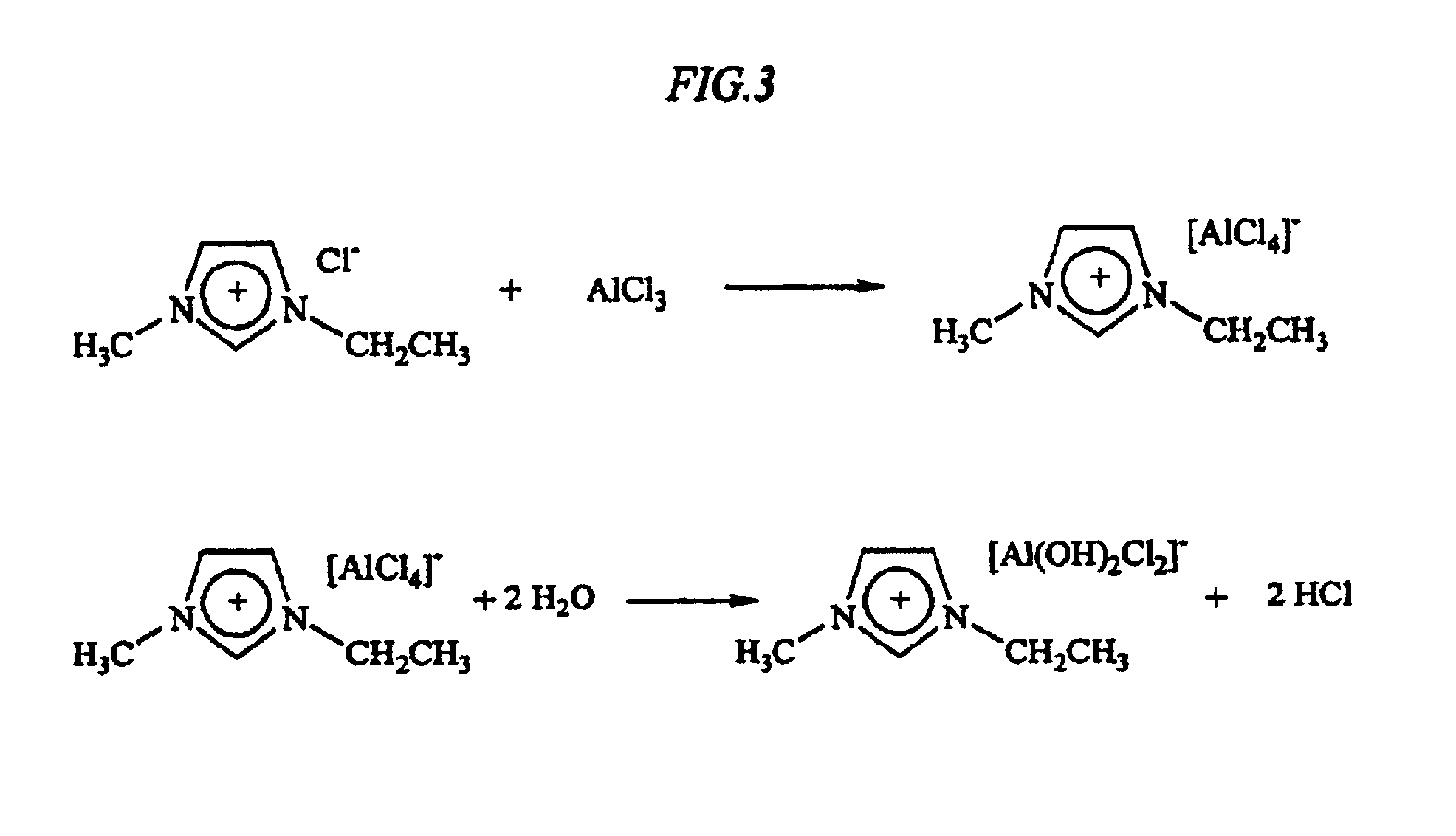
A method for treating a wellbore (or well casing) and the contiguous wellbore area to remove scale (mineral deposits comprised of, e.g., BaSO4, CaCO3, etc.) in the context of hydrocarbon recovery and other applications is disclosed, said method including contacting the scale with a fluid comprised of an ionic liquid or liquids.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
High-altitude permafrost region porphyry type copper polymetallic mine exploration technology combination method
InactiveCN103852807AImprove exploration efficiencyNarrow down the scope of prospectingGeological measurementsPetrochemistryRegional geology
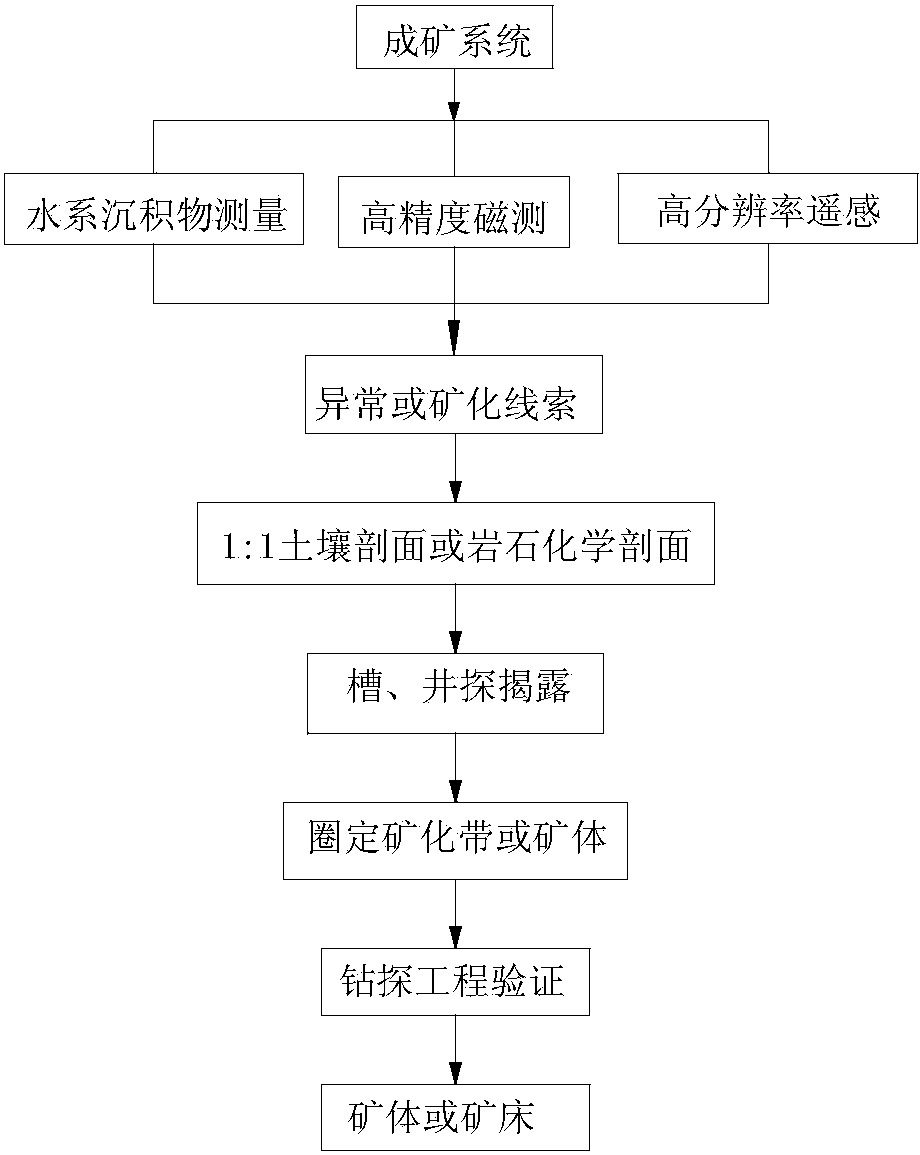
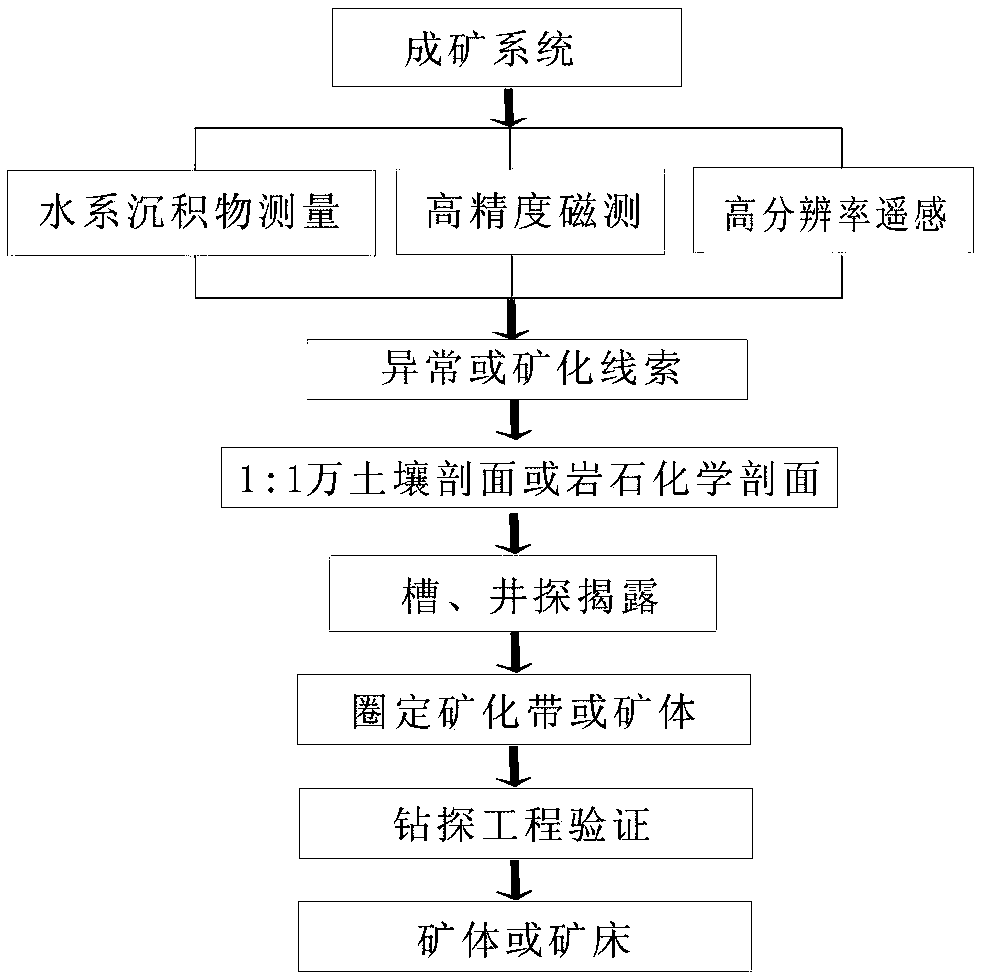
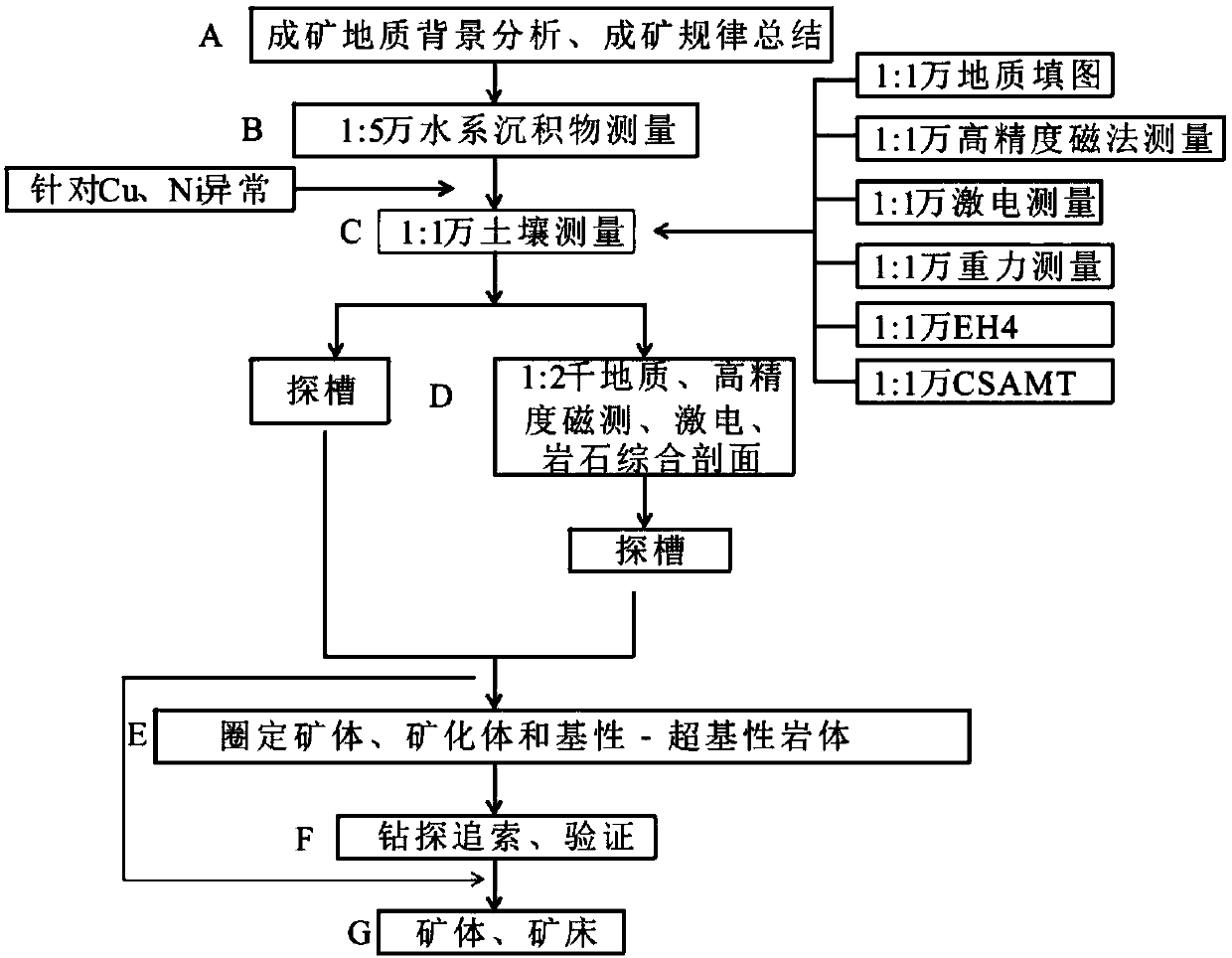
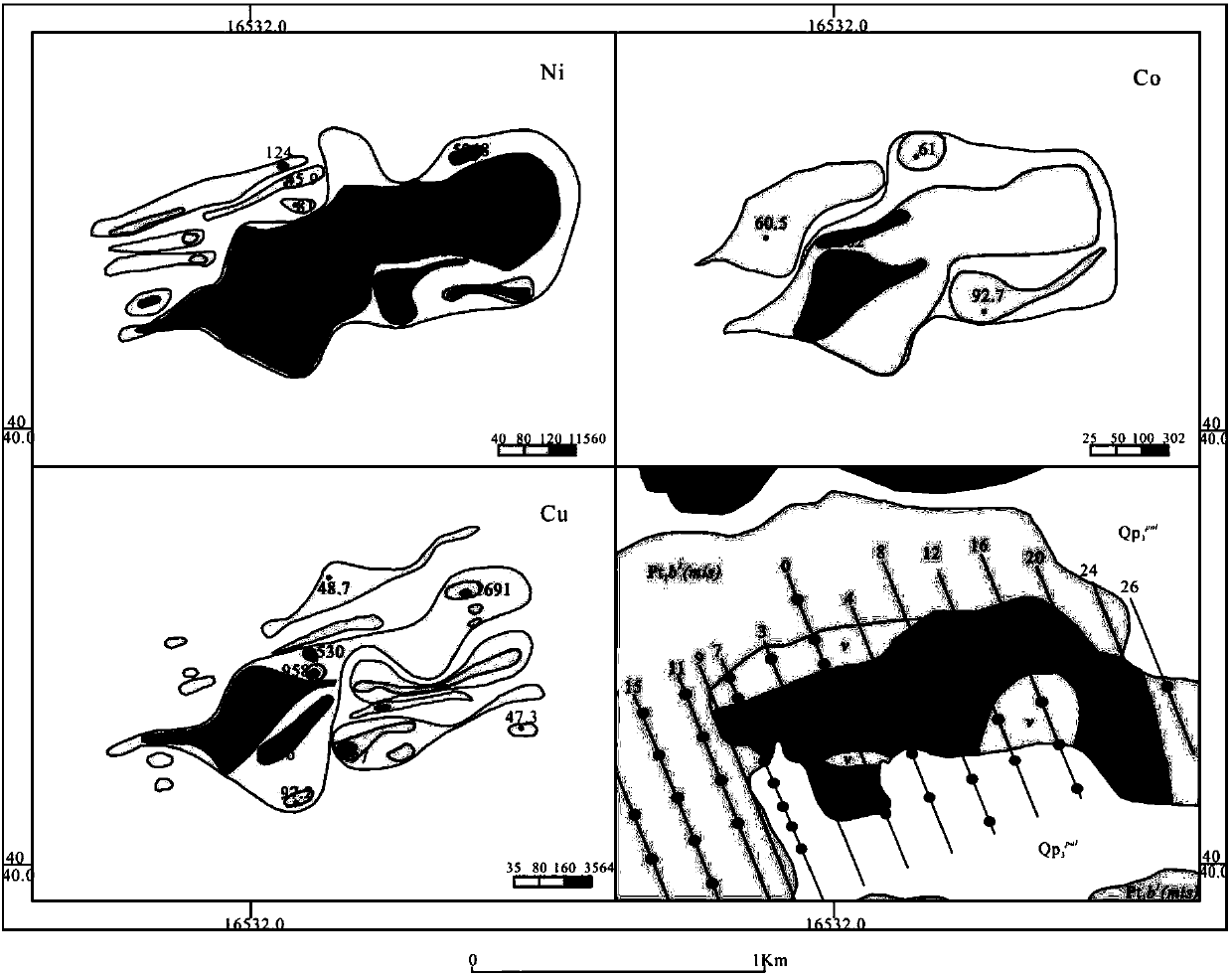
The invention discloses a high-altitude permafrost region porphyry type copper polymetallic mine exploration technology combination method which can improve the prospecting success rate. The method includes the following steps: A, determining a metallogenic system as a collision orogenic metallogenic system in cooperation with a collision orogenic regional geological background according to the output spatial-temporal characteristics of a permafrost region porphyry type copper molybdenum mine typical mineral deposit and numerous mineral occurrences; B, measuring stream sediments with the aim of observing geochemical halos on the upper portion of a porphyry body mineral body, defining a magnetic abnormity region through high-accuracy magnetic measurement, and defining a remote sensing predicting region with the aim of forecasting mineral resources such as copper, lead and zinc through high resolution remote sensing; C, conducting 1:1 soil profile or petrochemistry profile, groove and well exploratory exposure on explored abnormal or mineralization clues; D, defining a mineralized region or the mineral body; E, verifying the defined mineralized region or mineral body through drilling; F, determining the mineral body or the mineral deposit. By means of the method, the prospecting working period of a porphyry type copper molybdenum mineral region can be shortened, and meanwhile numerous metal mineral bodies can be explored.
Owner:青海省地质矿产研究所
Method of treating a glazing panel
InactiveUS20050132558A1Avoid breakingReduce the amount requiredCondensed water formation preventionMetal working apparatusEngineeringGlass sheet
The present invention relates to a method of treating a glazing panel from an inside location. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method of treating glazing panels used in windows and patio doors. Initially, an orifice is formed on both the inside and outside panes on windows and on the side and outside frames of patio doors. Then, particulate matter such as dirt, dust, and mineral deposits are purged from the enclosed volume of the glazing panel by applying a cleaning solution via the orifice. Next, a valve is attached to the outside pane / frame to cover the orifice whereby the valve is designed to reduce the amount of precipitation or matter from entering while allowing air to exit the glazing panel. Finally, a seal is used to cover the orifice on the inside pane or side frame to ensure that the building air does not enter the interior of the glazing panel. The method can also be used to treat windows for high altitude transport, or to prevent explosion in the presence of intense heat.
Owner:HENNESSY DENIS JOHN +1
Cap-lamp and communications support system
An underground radio communications and personnel tracking system uses a cap-lamp worn by a miner when underground in a mine. A cap-lamp transceiver provides voice and text communication on ultra-low frequency (ULF) to ultra-high frequency (UHF) carrier frequencies and modulation adapted by programming of a software defined radio to making selective and agile radio contacts via through-the-earth, conductor / lifeline, coal seam, tunnel, and ionosphere / earth-surface waveguides for transmission of electromagnetic waves. These waveguides comprise layered earth coal and mineral deposits, and manmade mining complex infrastructures which serendipitously form efficient waveguides. Ultra-Low Frequency F1 / F1 repeaters are placed underground in the mine, and providing for extended range of communication of the cap-lamp transceiver with radios and tracking devices above ground of the mine.
Owner:STOLAR
Remote sensing electric field exploration system
InactiveUS7002349B2Maximize effectivenessLow costAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesElectric/magnetic detection for transportMotion detectorElectric field sensor
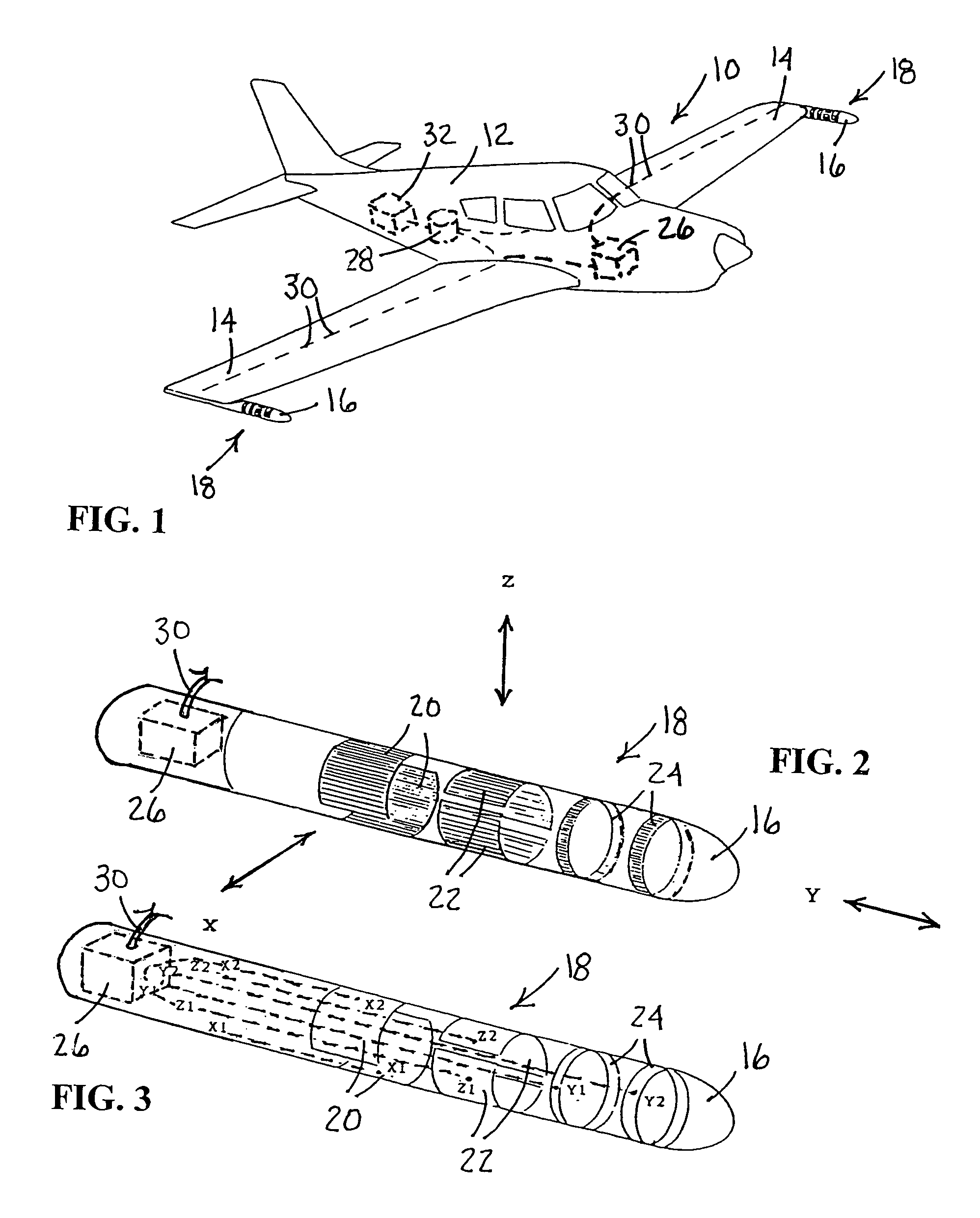
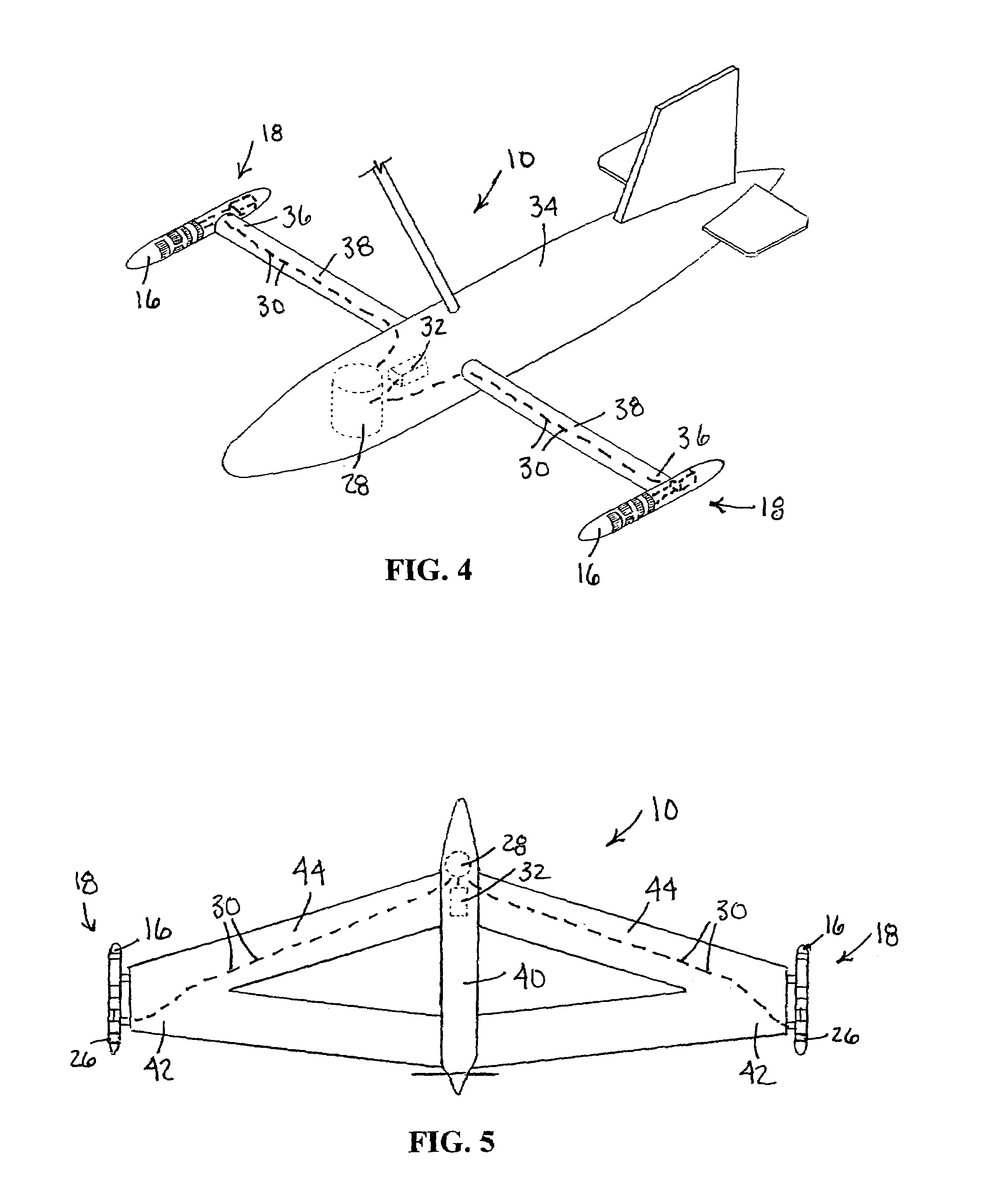
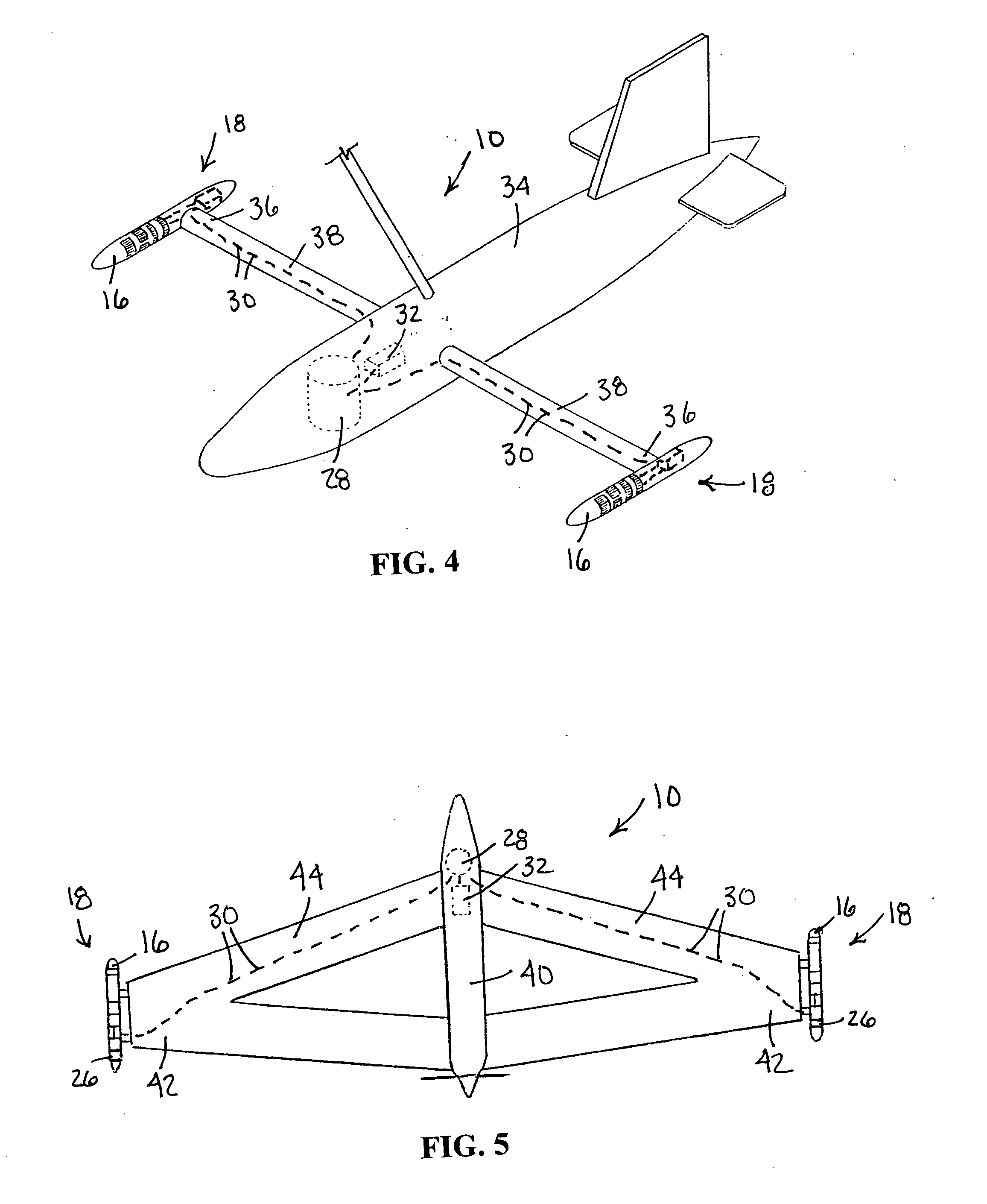
An airborne exploration system used with an aircraft for shallow and deep exploration for oil and gas, mineral deposits and aquifers. The survey system uses natural electromagnetic EM fields as an energy source. The exploration system includes a pair of aerodynamic housing pods adapted for mounting on wing tips of the aircraft. The housing pods include electric field sensors with three orthogonal electric dipoles oriented along an X, Y and Z axis. An optional third set of orthogonal electric dipoles can be mounted in the tail of the aircraft. The field sensors are electrically attached to angular motion detectors mounted inside housing pods. The motion detectors are used for compensating for errors caused by angular motion of the aircraft when in the presence of strong electric field gradients. The system also includes a total field magnetometer mounted in the aircraft. The various filtered outputs of the magnetometer are used to provide phase and amplitude references for the similarly filtered and angular motion corrected outputs of the electric field sensors. The electric field data when normalized and phase referenced against the magnetic field data provides valuable geological and geophysical information related to the subsurface flow of telluric currents.
Owner:TELLURIC EXPLORATION
Coarse-to-fine self-organizing map for automatic electrofacies ordering
InactiveUS6477469B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDigital computer detailsElectricityOutcrop
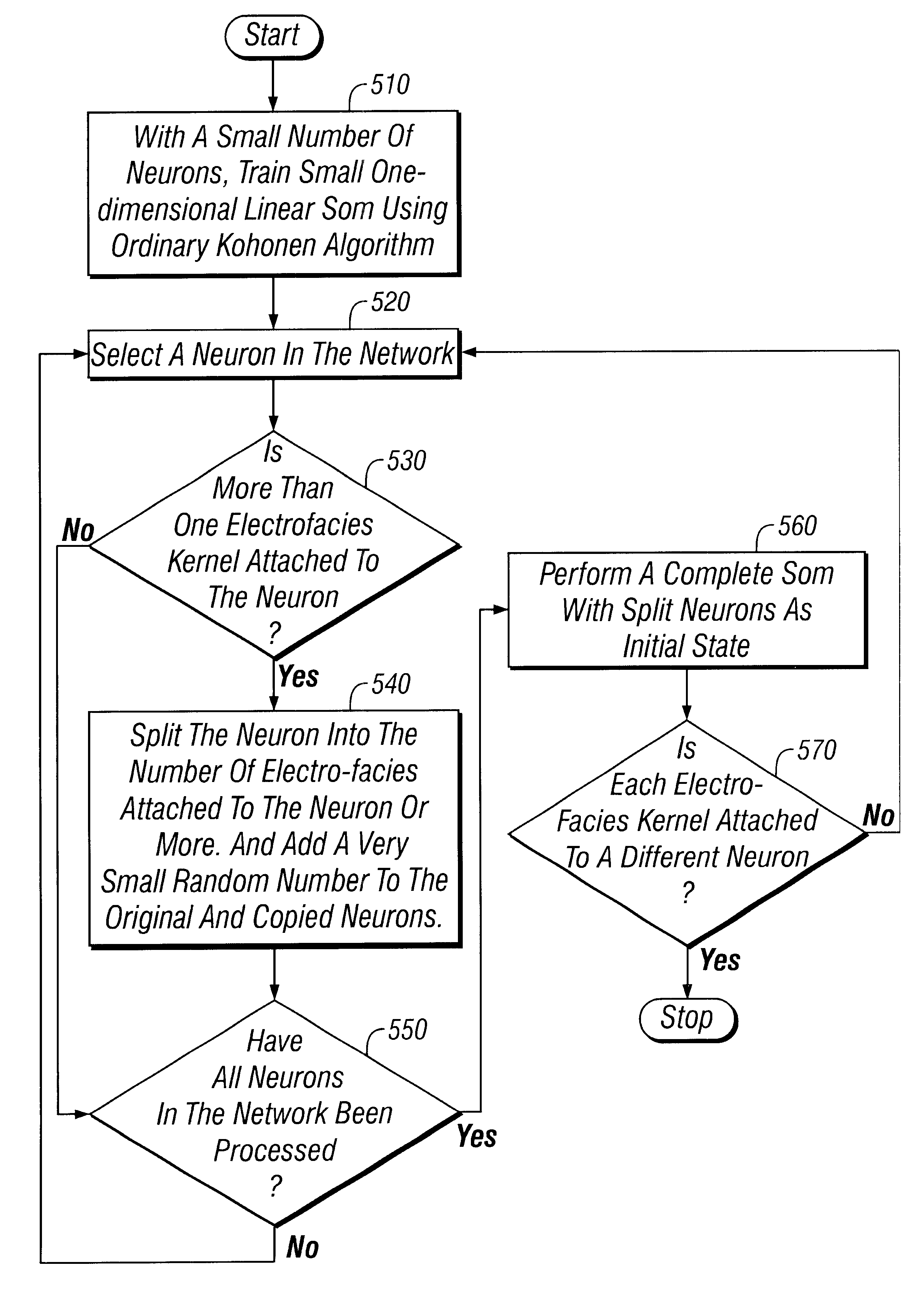
A method for ordering electrofacies to assist in identification of mineral deposits is disclosed. Automated ordering of electrofacies allows geologists to draw inferences about the geological settings in which sediment deposit occurred without directly examining core samples or outcrops. The electrofacies order is determined by (a) training a one-dimensional linear self-organizing map to form an initial neural network that includes a plurality of neurons. The number of neurons is small in comparison to the number of electrofacies kernels (i.e., not greater than one-third the number of electrofacies kernels). (b1) A neuron is selected from the initial neural network. In the next step (b2), the processor determines if more than one electrofacies kernel is attached to the neuron. (b3) If more than one electrofacies kernel is attached to the neuron, then the neuron is split into the number of electrofacies kernels attached to the neuron. (c) Steps (b1)-(b3) are repeated until all neurons in the initial neural network have been processed. In the next step, (d) a self-organizing map is trained to form a final neural network using the split neurons in the initial neural network as initial state. (e) Steps (b1)-(d) are repeated if more than one electrofacies kernel is attached to a neuron with the initial neural network equal to the final neural network. In the last step (f), each electrofacies kernel corresponding to a neuron in the final neural network is correlated to an order number.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC +1
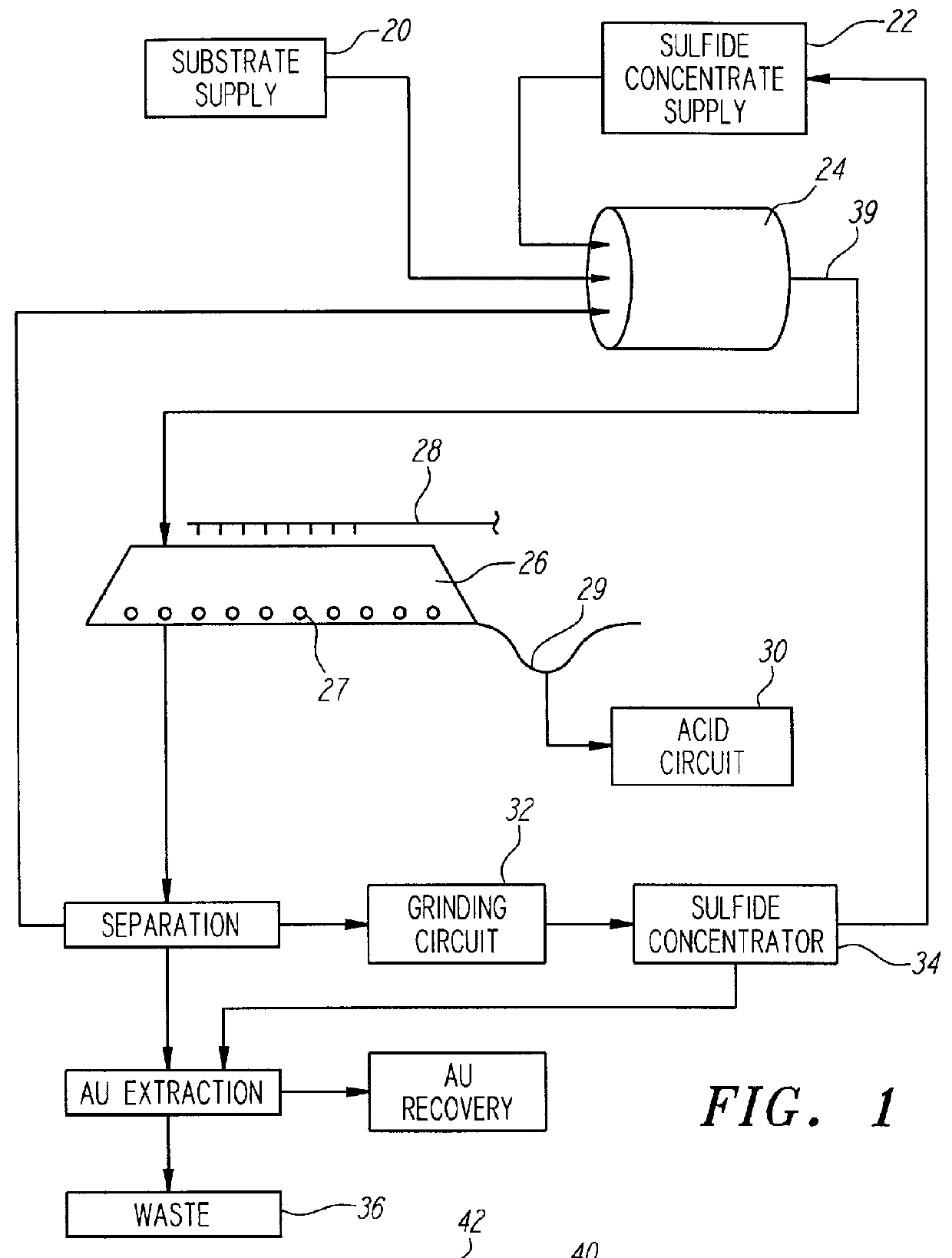
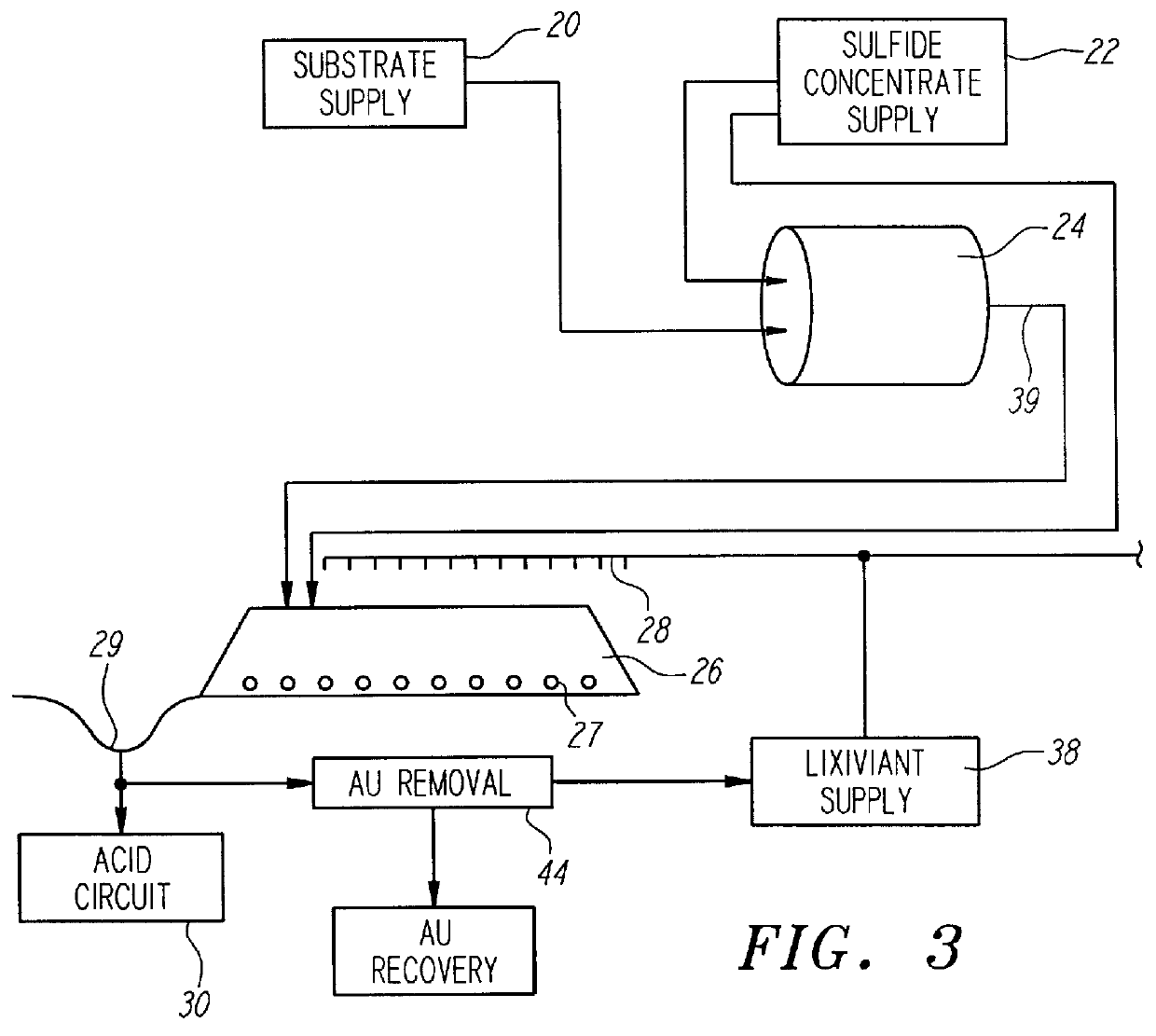
Nonstirred bioreactor for processing refractory sulfide concentrates and method for operating same
InactiveUS6083730AReduced pHIncrease equipment costSolvent extractionContaminated soil reclamationSulfide mineralsMetallic sulfide
A method of biooxidizing sulfide minerals in a nonstirred bioreactor is provided. According to the disclosed method, a concentrate of sulfide minerals is coated onto a substrate, such as coarse ore particles, lava rock, gravel or rock containing mineral carbonate as a source of CO2 for the biooxidizing bacteria. After the sulfide minerals are coated onto the substrate, a heap is formed with the coated substrates or the coated substrates are placed within a tank. The sulfide minerals are then biooxidized to liberate the metal value of interest. Depending on the particular ore deposit being mined, the sulfide mineral concentrates used in the process may comprise sulfide concentrates from precious metal bearing refractory sulfide ores or they may comprise sulfide concentrates from metal sulfide type ores, such as chalcopyrite, millerite or sphalorite. The distinction being that in the former, the metal of interest is a precious metal occluded within the sulfide minerals, whereas in the latter, the metal to be recovered is copper, nickel or zinc and is present as a metal sulfide in the sulfide concentrate.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
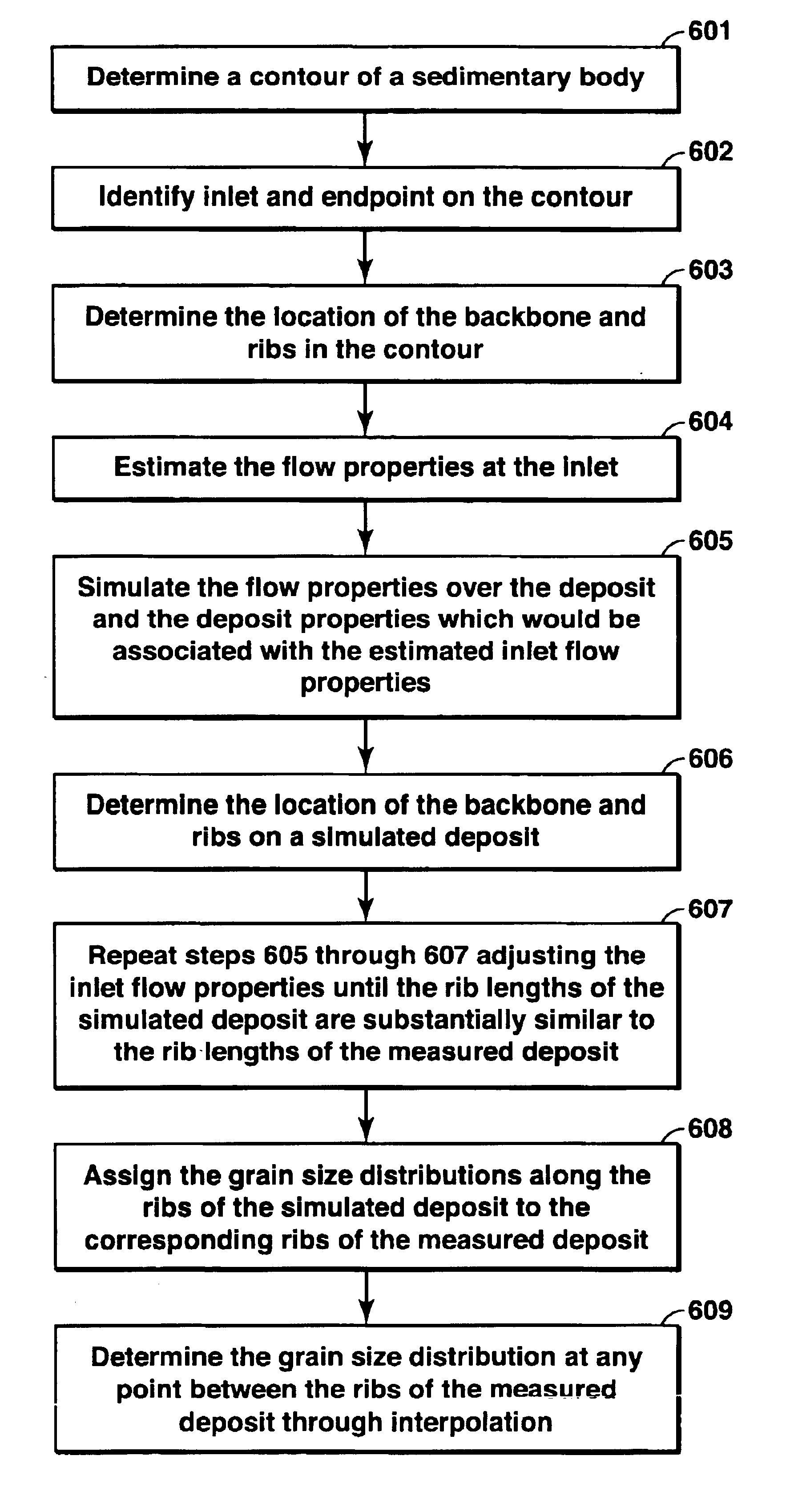
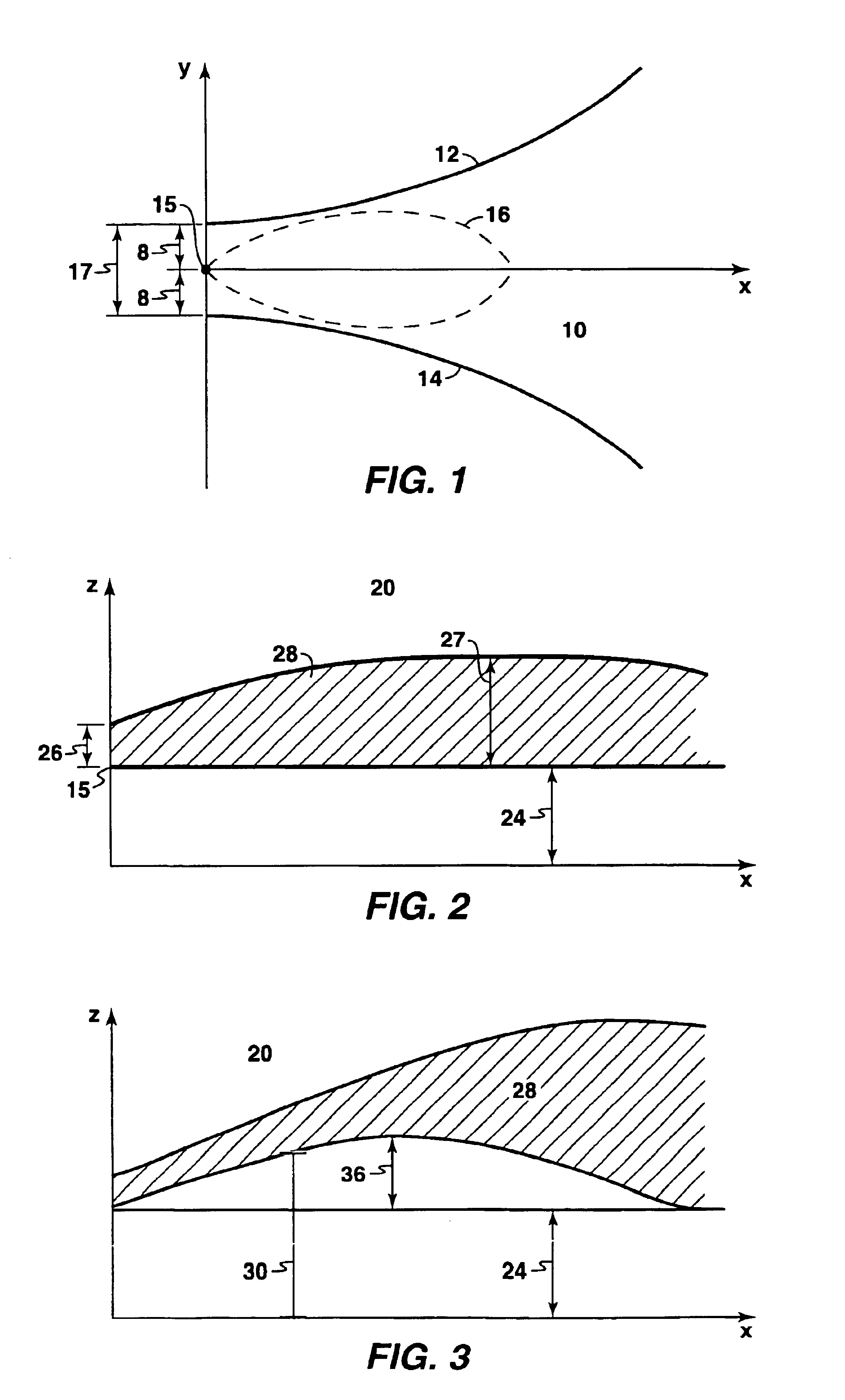
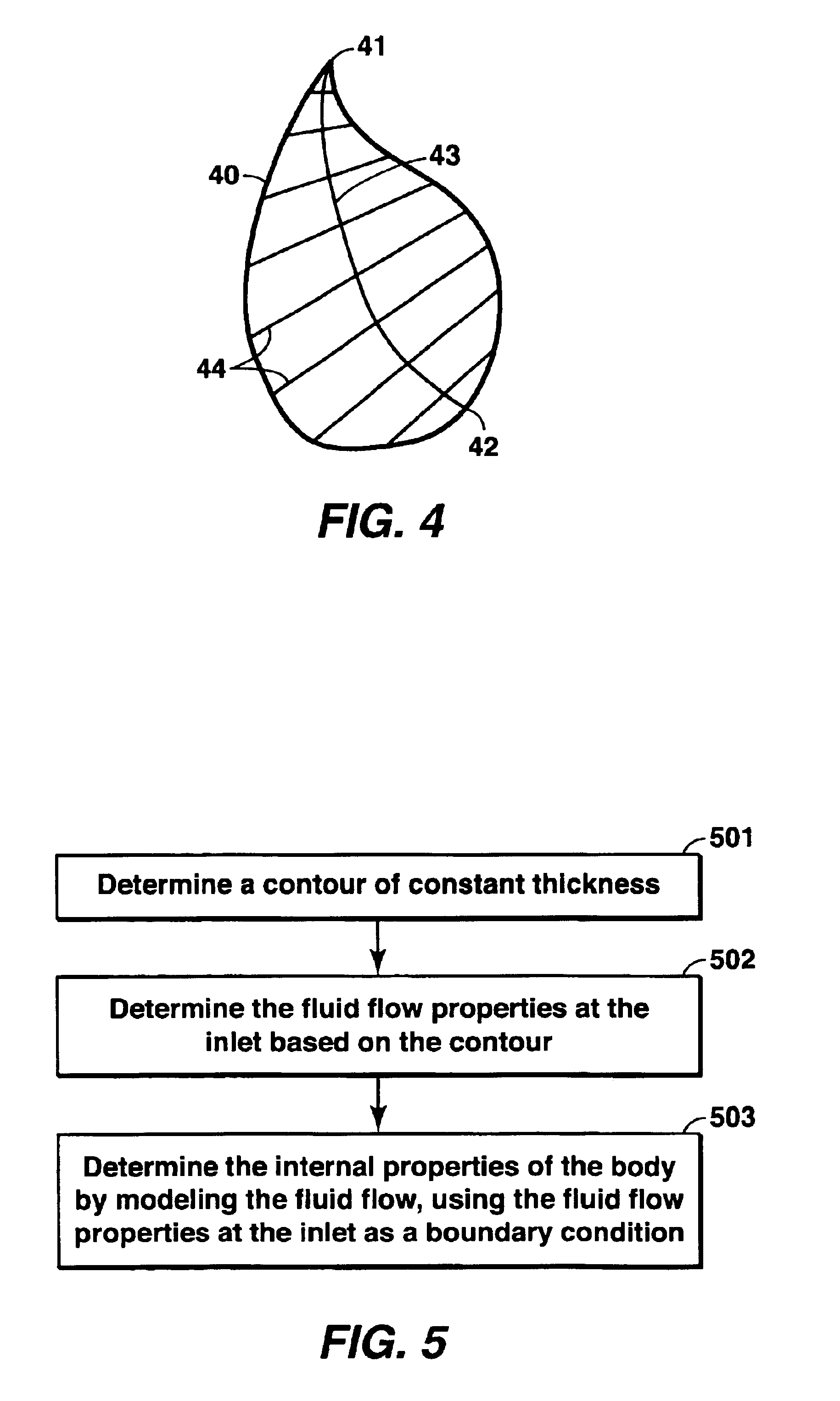
Method for predicting properties of a sedimentary deposit from a thickness contour of the deposit
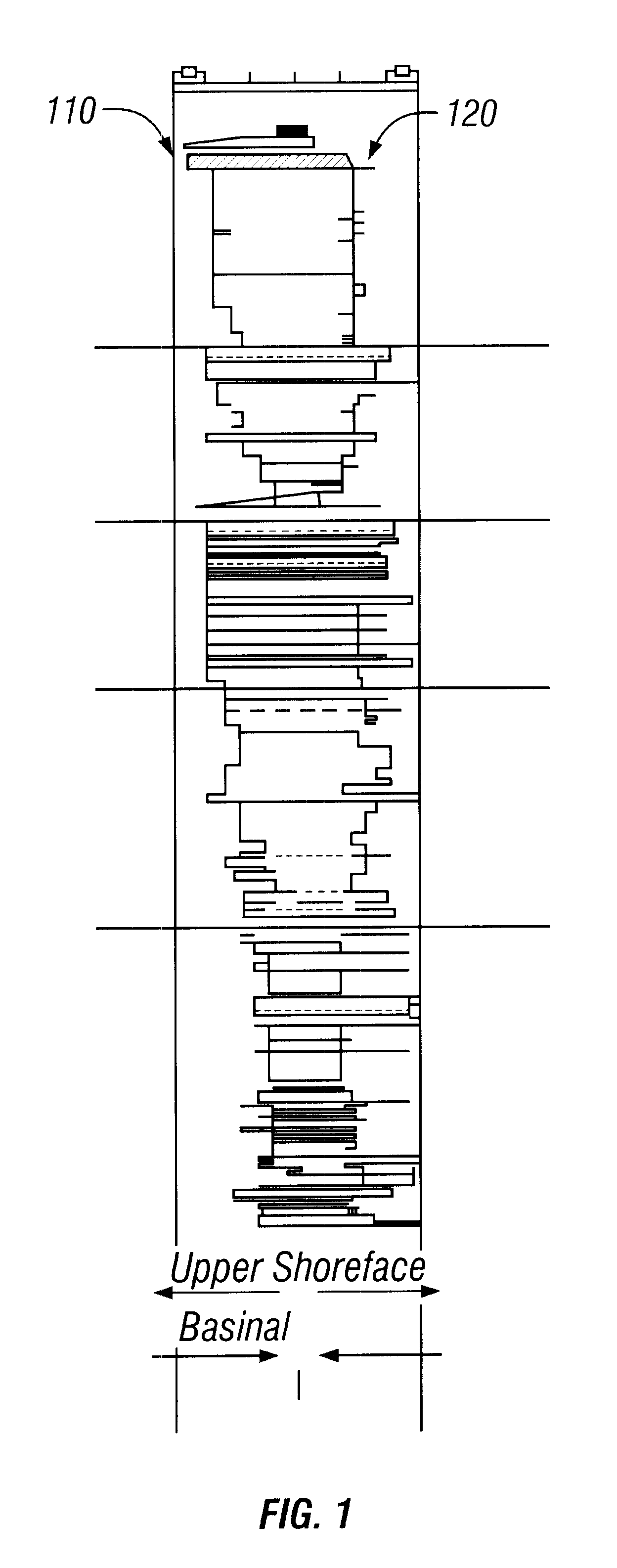
ActiveUS6885941B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSedimentMineral deposit
The properties of a water-lain sedimentary deposit may be predicted at any location from a contour of constant deposit thickness. One embodiment of the method comprises (a) determining an outline of constant deposit thickness in a measured deposit, (b) determining the fluid flow properties at the inlet of the measured deposit, (c) determining a property of the deposit at any point inside the deposit from modeling the fluid flow. The properties of the deposit at any point may include the thickness of the sediment body, the size of the body, the shape of the body, and the grain size distribution at each point within the body, and any combination thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
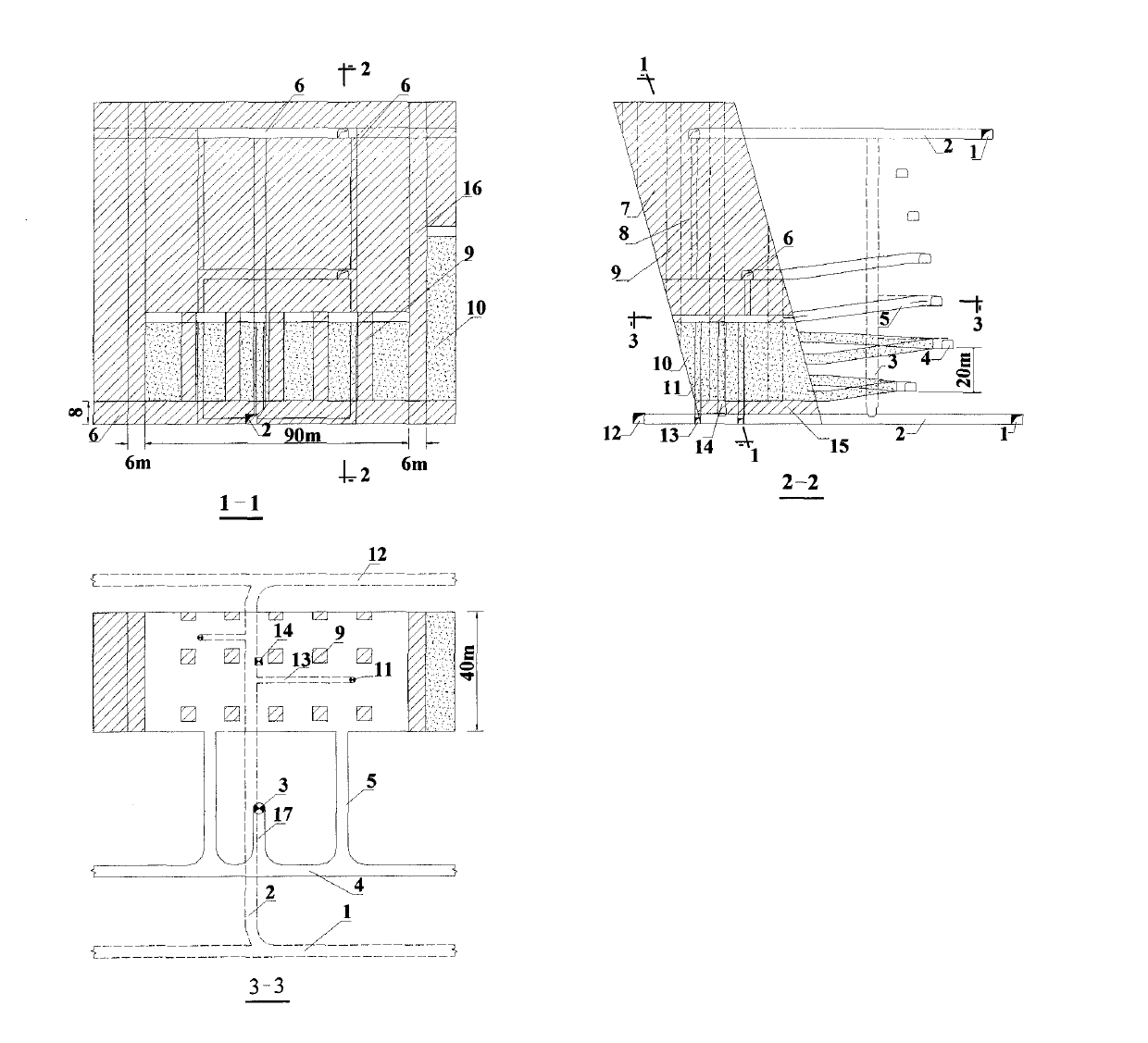
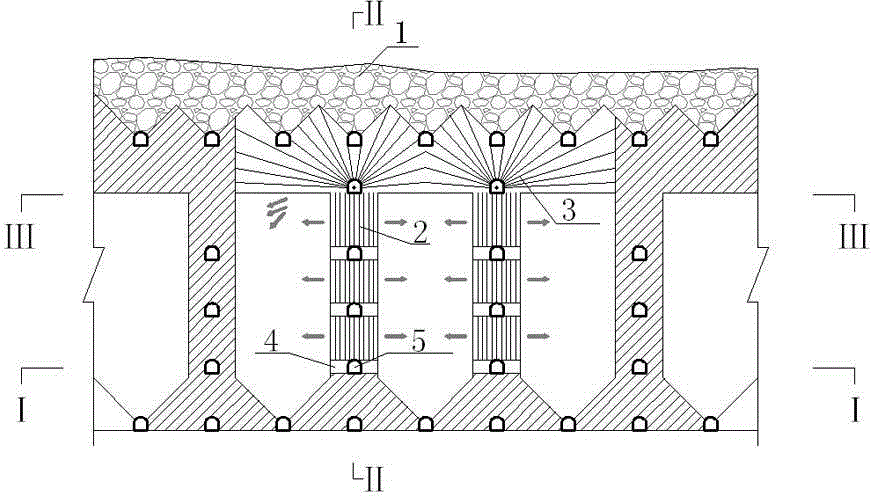
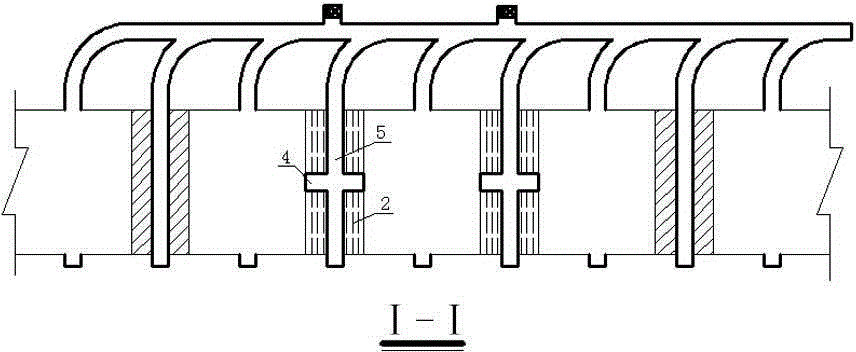
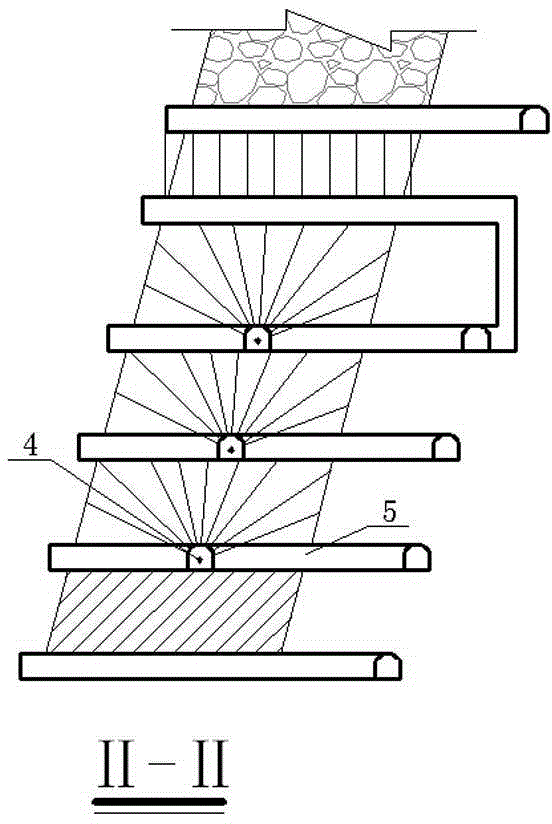
Point pillar type full-ore-deposit middle-section-free upward high-layering continuous propelling fill mining method
ActiveCN102392641AImprove stope production capacityRaw ore cost reductionUnderground miningSurface miningMechanical engineeringMineralogy
The invention relates to an underground mining technology, in particular to a point pillar type full-ore-deposit middle-section-free upward high-layering continuous propelling fill mining method. In the technical scheme, large panel mining is adopted; point pillars are reserved in a stope; an accurate mining project is arranged on rock; the height of a slice drift is 20 meters; light exposure roof control is adopted; the layering height is increased to 7.5-8 meters; a headspace of 2 meters is reserved after every filling for serving as the operating space of a next layer; no middle section lane or roof and bottom pillars are reserved; and continuous propelling and mining of a full ore deposit from bottom to top layer after layer is adopted. The method has the beneficial effects that: the middle section exploration and transportation work amount is reduced, the slice drift work amount is reduced, the layering height is increased, and the mining efficiency is increased; a full-ore-deposit upward continuous propelling fill mining process is adopted, so that the continuity of a milling, filling and discharging process is enhanced, the using amount of cement is reduced greatly, and thefilling cost is reduced; and the problems of large quantity of layering filling times, low mining efficiency and high cost are solved.
Owner:中钢矿业开发有限公司 +1
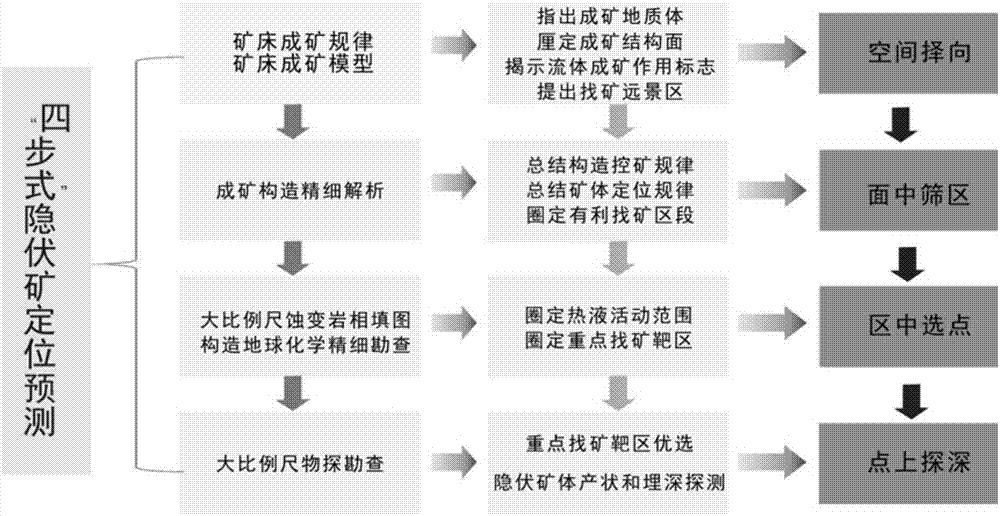
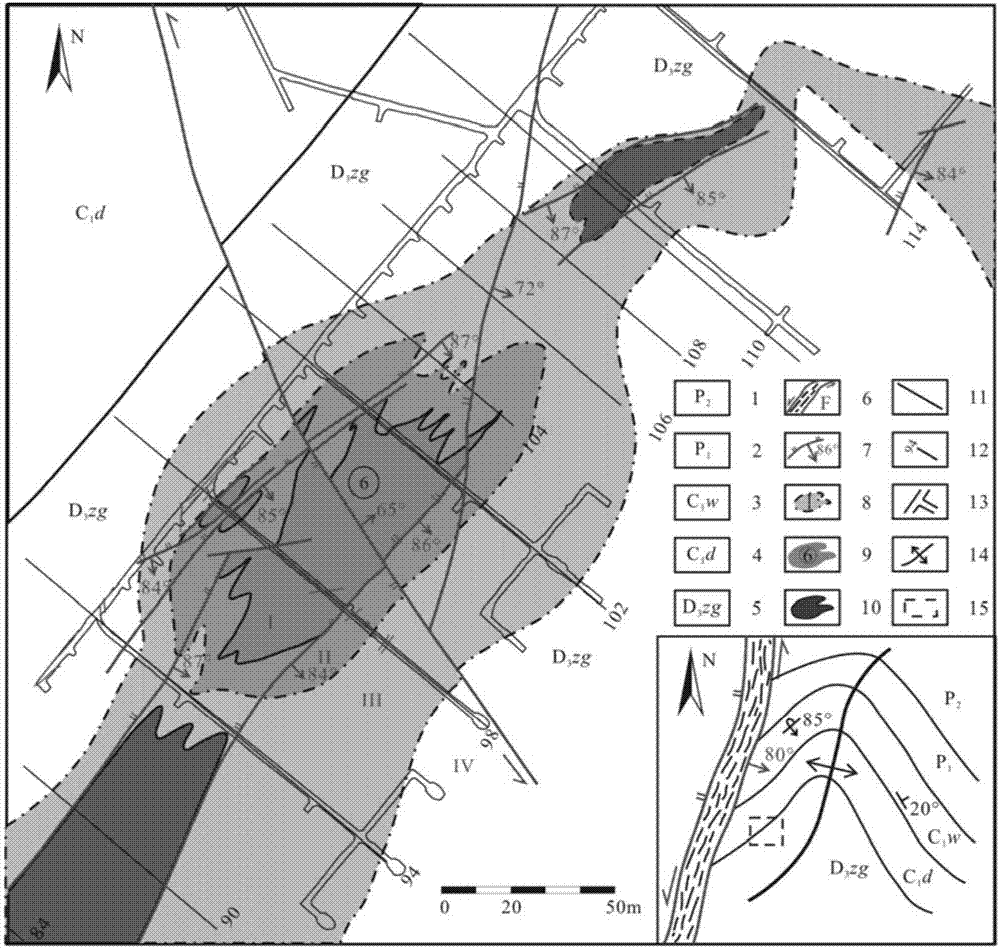
'Four-step' large-scale method for locating and detecting deep hydrothermal ore deposits or ore bodies
ActiveCN107346038AEliminate the influence of unfavorable factors such as large electromagnetic interferenceWide range of applicationsGeological measurementsLocation predictionMaterials science
The invention discloses a 'four-step' large-scale method for locating and detecting deep hydrothermal ore deposits or ore bodies. Deep ore deposits or ore bodies are directly located and detected through four stages, namely, ore deposit forming rule research, fine analysis of ore forming structure, altered lithofacies mapping and structural geochemical fine exploration, and geophysical deep detection and concealed ore location prediction. The method is based on a large-scale (1:200-1:50000) progressive deep-buried ore deposit or ore body location and detection technology integrating 'ore deposit model prediction, structure prediction, altered lithofacies mapping and structural geochemical fine exploration, and geophysical exploration'. A systematic deep ore exploration technology is realized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
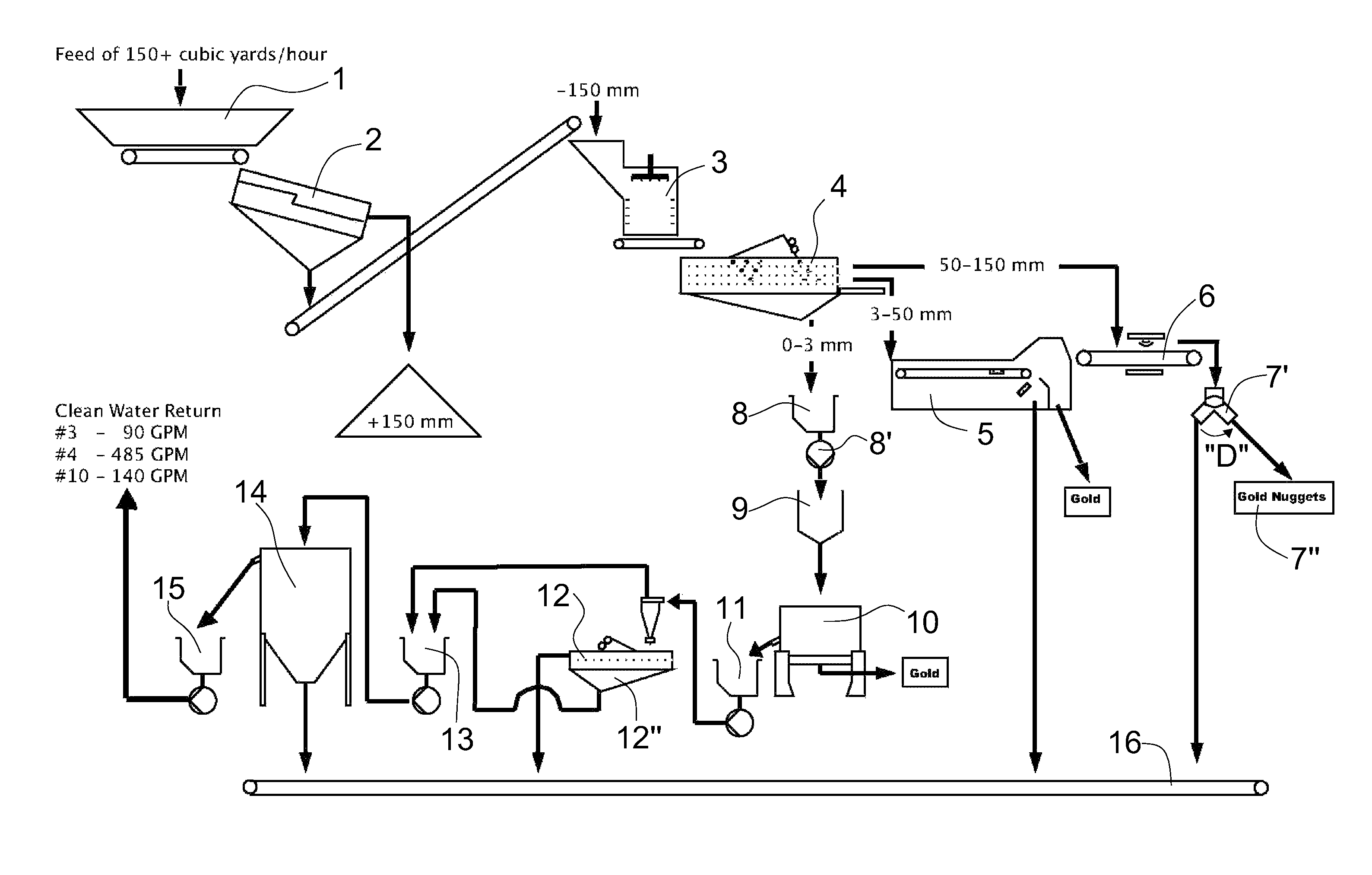
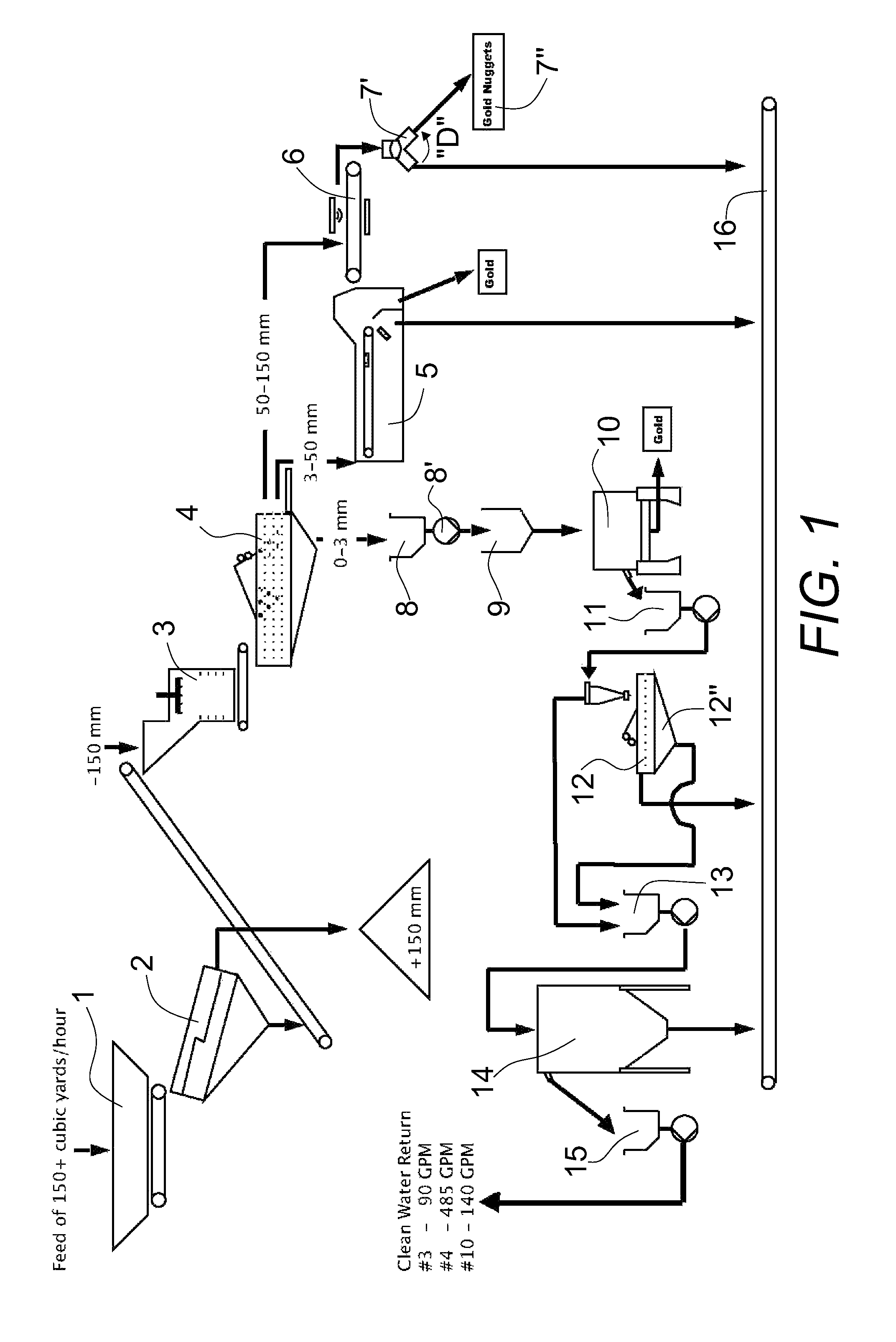
Methods and systems for recovering alluvial gold
Various embodiments of methods and systems are provided for mining alluvial gold deposits. The methods can comprise collecting feed from alluvium and washing the feed at high pressure. The feed can be separated into a plurality of separate fractions. At least one fraction is transferred to a metal sensor system using a conveyer, wherein when gold is detected in a piece of the fraction, an air blast can be targeted and delivered at the piece, with the air blast diverting the piece to a receiving container.
Owner:QUINCY FROST INVESTMENTS INC
Anti-coagulation and demineralization system for conductive medical devices
A system for minimizing and / or eliminating coagulative or mineral deposits on respective blood-contacting surfaces of implanted medical devices includes an implantable system having a current generating device that is electrically coupled to at least first and second electrodes for developing a current therebetween. The at least first and second electrodes are disposed across a patient's thoracic cavity in a manner so that a particular implanted medical device having at least a portion thereof that is fabricated from an electrically conductive material is disposed in a path substantially between such electrodes, thereby focusing the generated electrical current at the electrically conductive portion of the implanted medical device for therapeutic treatment thereat.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
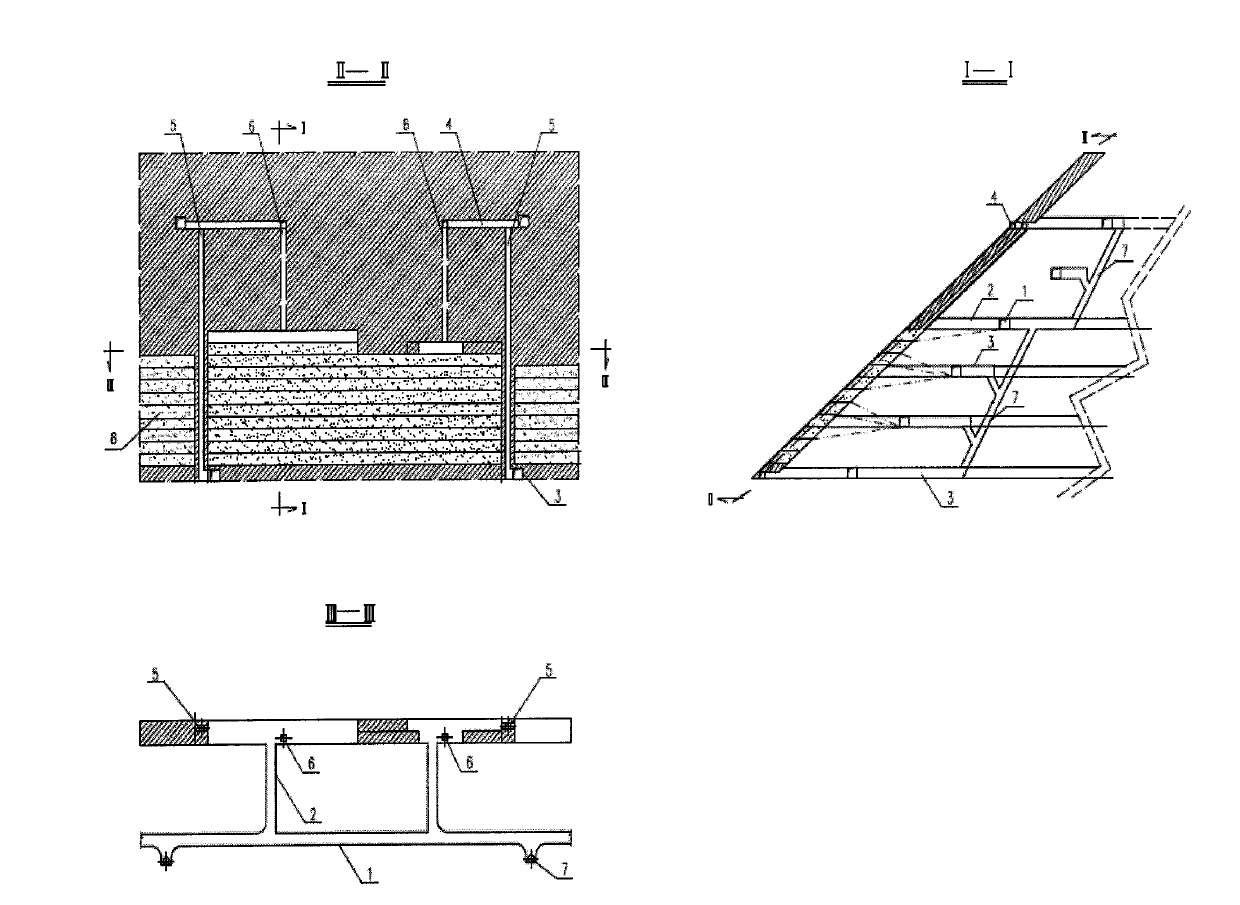
Filling mining method of gently inclined thin mineral deposit with soft roof
InactiveCN103147761AEnsure safetyAvoid mixingUnderground miningSurface miningEarth surfaceMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a filling mining method of a gently inclined thin mineral deposit with a soft roof. The technical scheme of the invention is as follows: the filling mining method comprises the steps of firstly dividing the mineral deposit into panels, dividing the panels into strips, arranging preliminary mining and cutting laneways; then getting rid of soft roofs (5) and mining bodies (4) of the mined strips by blasting: and then filling: filling an empty area formed after mining the strip N-2 with waste rocks produced by getting rid of the soft roofs (5) of the strips N and N+1 by grouting, with the filling width being half of the width of the strips, when filling the strip N-2 with the waste rocks by grouting for 10-20m, starting to fill an empty area formed after mining the strip N-3 and the other half of an empty area formed after mining the strip N-4 with one half filled with the waste rocks by grouting with tailings, and enabling the tailing filling to lag behind the waste rock filling by grouting for 10-20m in the filling process, wherein N=2k+1, and k is an integer which is greater than or equal to 2. The filling mining method can improve the production capacity simultaneously while ensuring the stope operation safety and protecting the ground surface environment, and has the advantages of high recovery ratio, and low dilution rate, boulder yield and cost.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mining method for co-extraction of non-combustible ore and mine methane
ActiveUS20090315388A1Safer working environment undergroundAvoid excessive dilutionDisloding machinesUnderground miningMineralogyMethane
Mining method for co-extraction of non-combustible ore and mine methane A method for co-extracting non-combustible ore (e.g., trona) and methane from an underground formation comprising at least one methane-bearing layer and a non-combustible ore bed having a rock roof, comprising:providing a well having a downhole end positioned above the ore bed roof;mining an ore region from an initial cavity and removing the mined ore, thereby creating a subsequent cavity;advancing the mining step to another ore region from the subsequent cavity;allowing the roof of the initial cavity to cave so as to create a gob;repeating the mining, advancing and caving steps, the caving being effective in generating fluid communication between the gob and the well downhole end and in fracturing the methane-bearing layer so as to release methane into the gob; andrecovering a gob gas comprising released methane through the well to the surface.
Owner:SOLVAY CHEM INC
Geophysical technique for mineral exploration and discrimination based on electromagnetic methods and associated systems
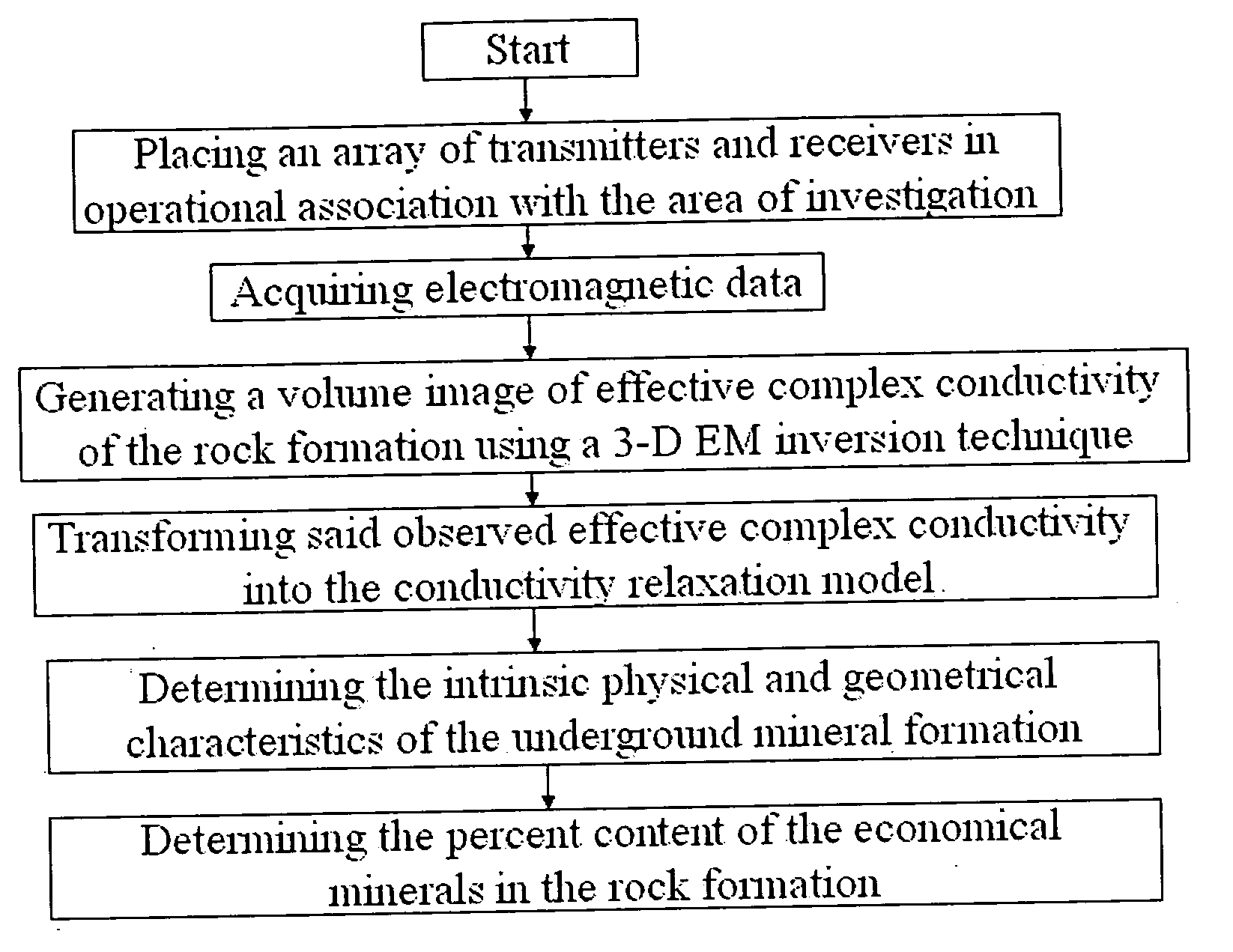
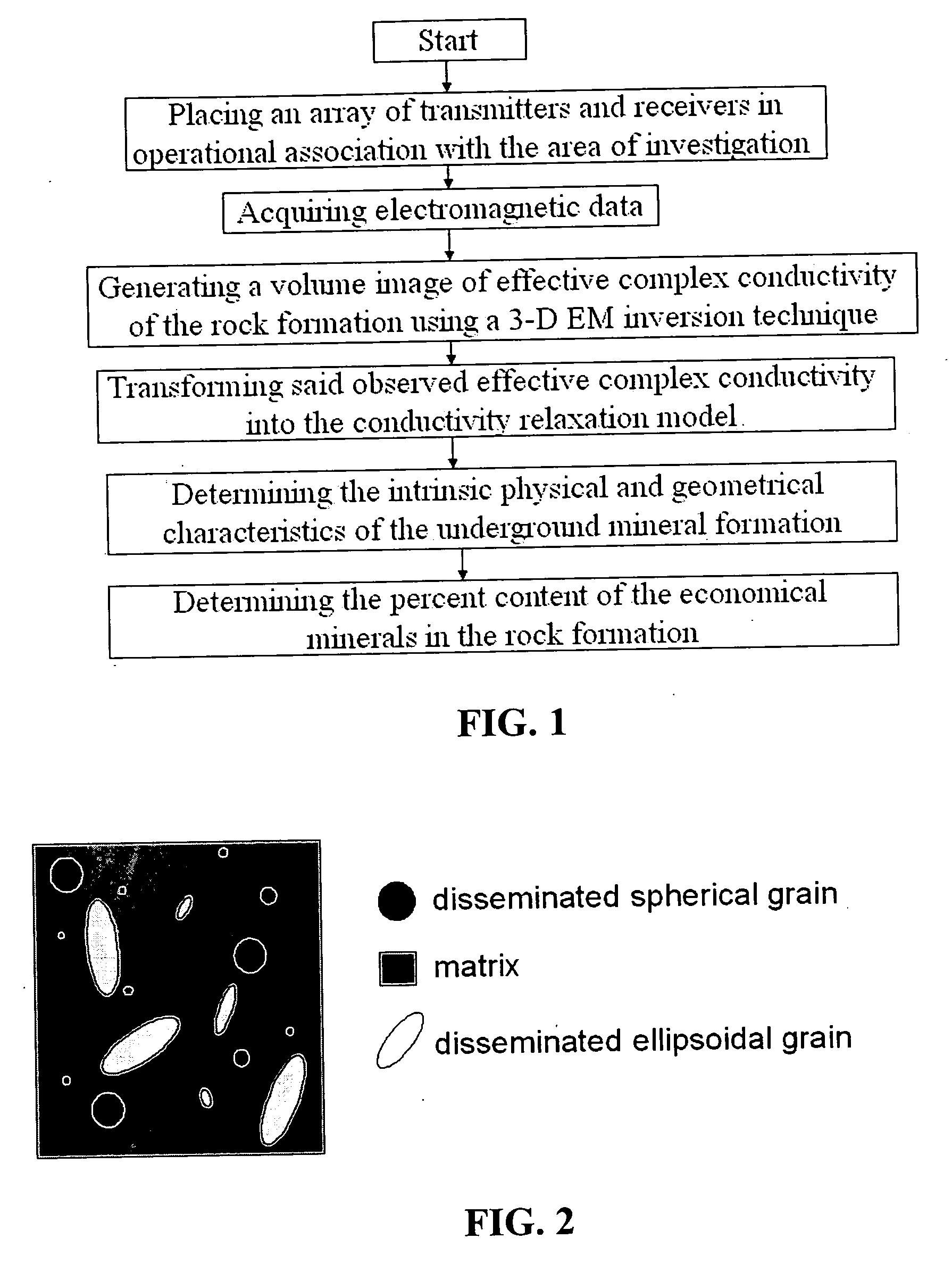
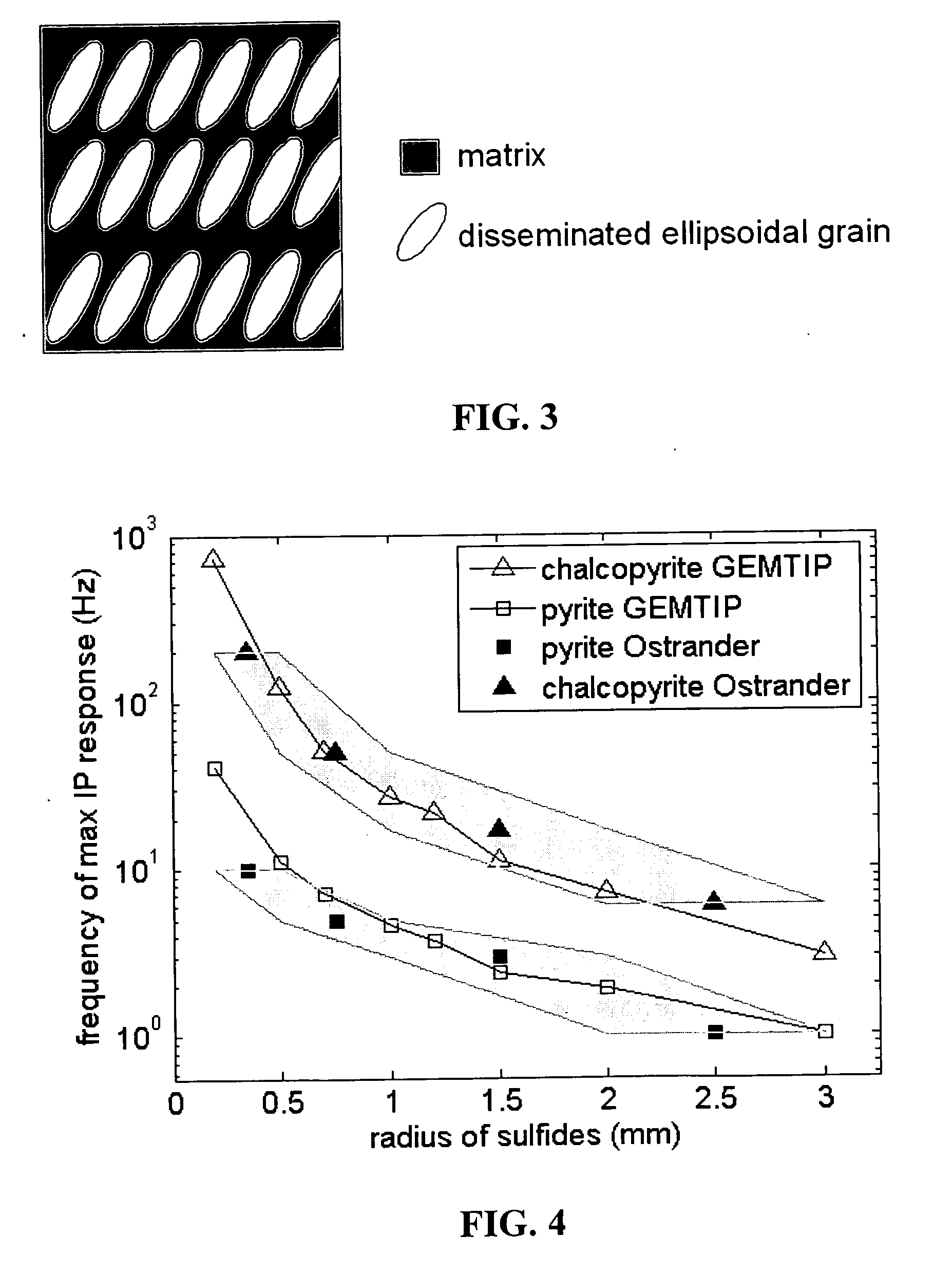
ActiveUS20070061080A1Realistic representationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingAnalytical expressionsMicroscopic scale
Mineral exploration needs a reliable method to distinguish between uneconomic mineral deposits and economic mineralization. A method and system includes a geophysical technique for subsurface material characterization, mineral exploration and mineral discrimination. The technique introduced in this invention detects induced polarization effects in electromagnetic data and uses remote geophysical observations to determine the parameters of an effective conductivity relaxation model using a composite analytical multi-phase model of the rock formations. The conductivity relaxation model and analytical model can be used to determine parameters related by analytical expressions to the physical characteristics of the microstructure of the rocks and minerals. These parameters are ultimately used for the discrimination of different components in underground formations, and in this way provide an ability to distinguish between uneconomic mineral deposits and zones of economic mineralization using geophysical remote sensing technology.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH +1
Mining method of nearly horizontal mineral deposit of opencast coal field by casting and internally dumping
InactiveCN103470262AReduce effluxShort distanceUnderground miningSurface miningOpen-pit miningCoal field
The invention relates to a mining method of a nearly horizontal mineral deposit of an opencast coal field by casting and internally dumping and belongs to the mining method of the opencast coal field. The mining method comprises the following steps: (1) dividing a strip mine into a plurality of mining regions, mining overburdened materials of a first strip region, and stacking the overburdened materials outside an opencast mining limit; (2) dividing an overburdening table into one or more tables to be mined; (3) discharging the overburdened materials of a second strip region into a worked-out section of the first strip region after a mineral deposit exposed in the first strip region is mined, and transporting mined mineral products out of a mining field through entering-exiting channel transporting passages arranged on two sides of a channel or the middles of the strip regions. The mining method has the advantages that as the overburdened materials can be discharged and abandoned in the worked-out section, the occupied land of an externally-dumped soil site can be saved; the mining method is environment-friendly and is capable of restoring the land influenced by the mining operation during mining; abandoned and unserviceable lands in barren and mountainous mines can be changed into usable lands.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Remote sensing electric field exploration system
InactiveUS20050285598A1Low costMaintenance requirement is minimalAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAcoustic wave reradiationAviationMotion detector
An airborne exploration system used with an aircraft for shallow and deep exploration for oil and gas, mineral deposits and aquifers. The survey system uses natural electromagnetic EM fields as an energy source. The exploration system includes a pair of aerodynamic housing pods adapted for mounting on wing tips of the aircraft. The housing pods include electric field sensors with three orthogonal electric dipoles oriented along an X, Y and Z axis. An optional third set of orthogonal electric dipoles can be mounted in the tail of the aircraft. The field sensors are electrically attached to angular motion detectors mounted inside housing pods. The motion detectors are used for compensating for errors caused by angular motion of the aircraft when in the presence of strong electric field gradients. The system also includes a total field magnetometer mounted in the aircraft. The various filtered outputs of the magnetometer are used to provide phase and amplitude references for the similarly filtered and angular motion corrected outputs of the electric field sensors. The electric field data when normalized and phase referenced against the magnetic field data provides valuable geological and geophysical information related to the subsurface flow of telluric currents.
Owner:TELLURIC EXPLORATION
Method and process for the systematic exploration of uranium in the athabasca basin
InactiveUS20090028000A1Enhance subsurface imageImprove interpretationSeismic signal processingGeophoneAcoustic wave
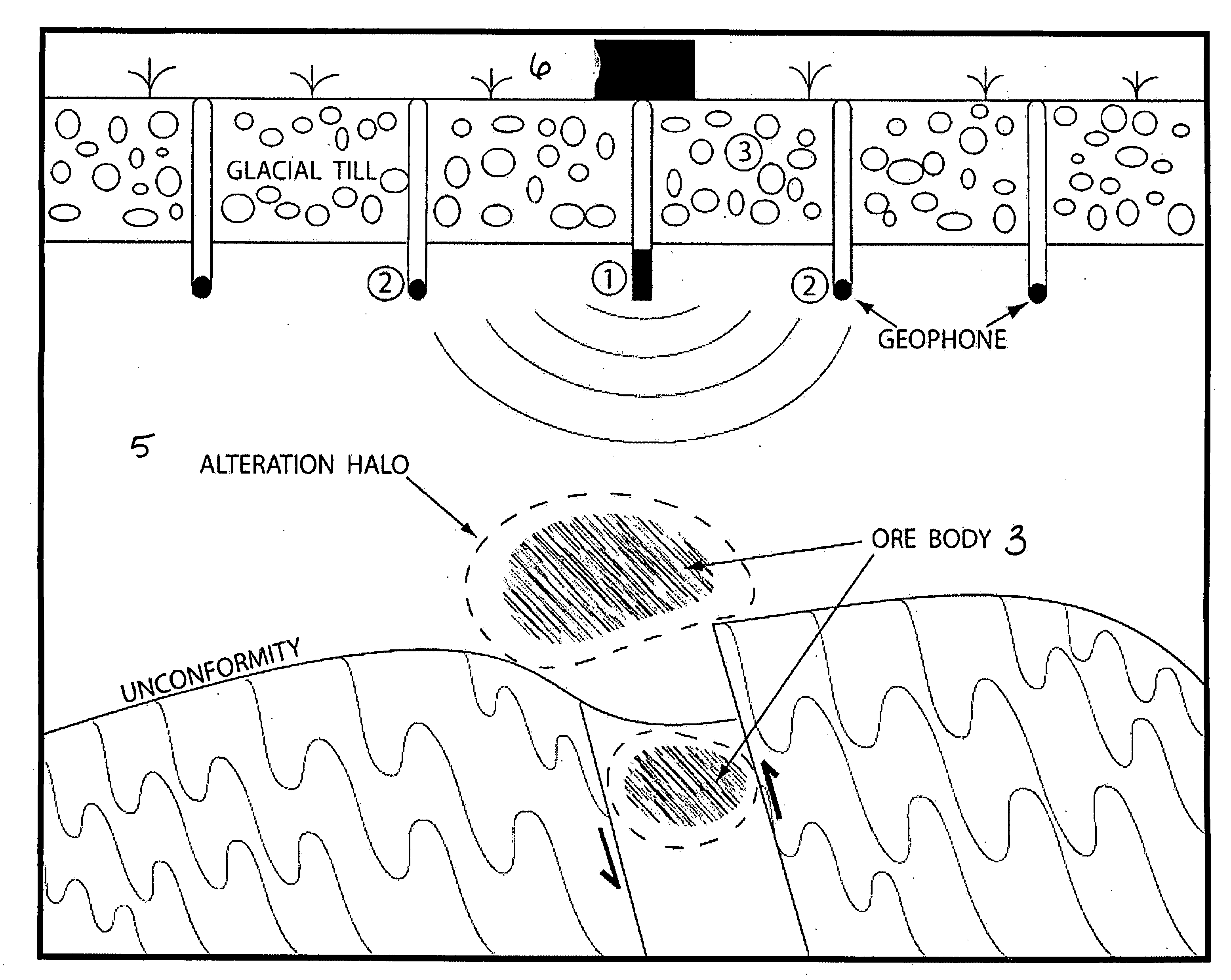
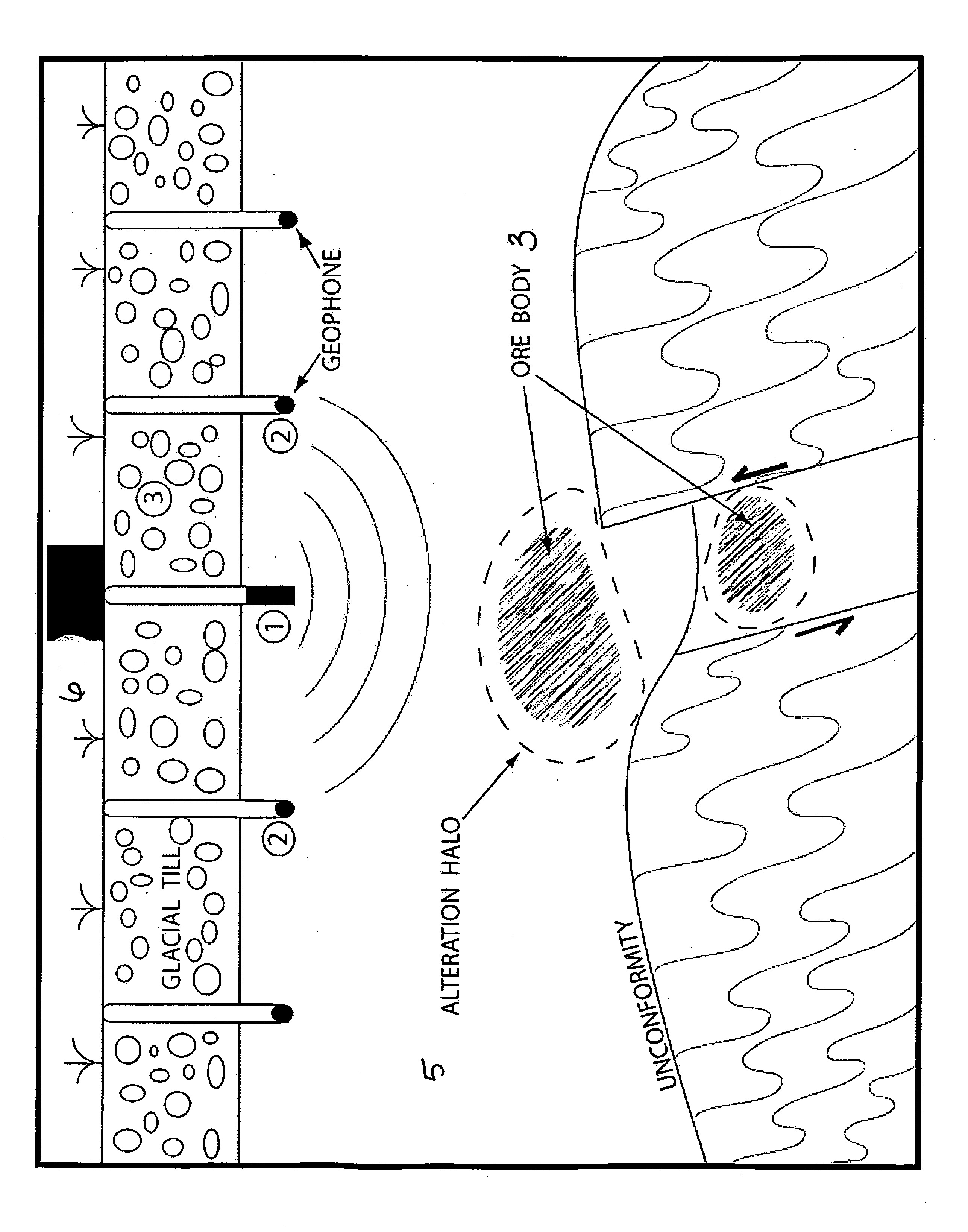
A method for the identification of metallic deposits in a rock formation is provided. The method for the identification includes the steps of providing an acoustic source for generating frequencies to produce acoustic waves, arranging at least one geophone optimized to detect the frequencies and oriented to enhance reflection planes from faults and fractures associated with an ore body in a rock formation and locating the acoustic source and at least one geophone in at least one shallow bore hole beneath unconsolidated surface material of the rock formation. The method further includes the steps of directing the acoustic waves to an underlying rock formation to generate seismic reflection data and processing the seismic reflection data by altering the frequency and the amplitude to identify unique seismic attributes that allow detection of at least one metallic deposit or ore body in the rock formation.
Owner:OBRIEN THOMAS B
Cenozoic magmatic copper polymetallic ore prospecting method
InactiveCN108761564AGreat Prospecting BreakthroughEarth material testingGeological measurementsPetrochemicalCenozoic
The invention discloses a cenozoic magmatic copper polymetallic ore prospecting method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a magmatic zone or an abnormal area (zone) according to magmatic ore deposit and spot output space-time and geological background; preliminarily determining prospecting targets and target classification by virtue of stream sediment measurement; selecting zones having excellent copper mineralization or molybdenum mineralization or excellent abnormality in target classification for performing magnetic survey verification, and determining a first precedencetarget area or a first abnormal area; determining a second precedence target area or a second abnormal area in the first precedence target area or the first abnormal area by adopting high resolutionremote sensing; performing on-the-spot survey inspection on the second precedence target area or the second abnormal area, and finding out a geologic abnormal area (zone) or a mineralization clue area; performing soil profile or petrochemical profile measurement according to 1:10000, and determining the ore-bearing geological body position on the surface and mineralized body features; performing shallow exposure recourse to control the specific location and shape of the mineralized zone or mineralized body by utilizing trenching; and determining the depth grade thickness scale and occurrence conditions of the mineralized body by utilizing drilling, and discovering the metal ore or ore deposit.
Owner:青海省地质调查院
Mining method for transitioning underground ore bodies from open stope mining method to caving mining method
ActiveCN104405395ASolve recycling povertySolve problems such as large loss rateUnderground miningSurface miningMineral SourcesEconomic benefits
The invention provides a mining method for transitioning underground ore bodies from an open stope mining method to a caving mining method, and aims at solving the problems of low working safety, large ore recycling lean loss rate, complicated construction organization and the like in a transitioning period of the two mining methods in the prior art. The mining method comprises the steps: 1, dividing regions, determining a critical exposure area, determining a stopping region and determining a region stopping sequence; 2, recycling interparietal columns; 3, generating waste stone coverage layers; 4, recycling ore pillars in adjacent regions; 5, drawing ores; 6, recycling a bottom structure. The mining method has the benefits that the potential safety and the problems of ore recycling lean loss rate and the like in a mutual transitioning process of the two mining methods are solved, and conditions are created for comprehensively using ore resources, prolonging the service life of a mine and enhancing the total economic benefit of an ore deposit.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
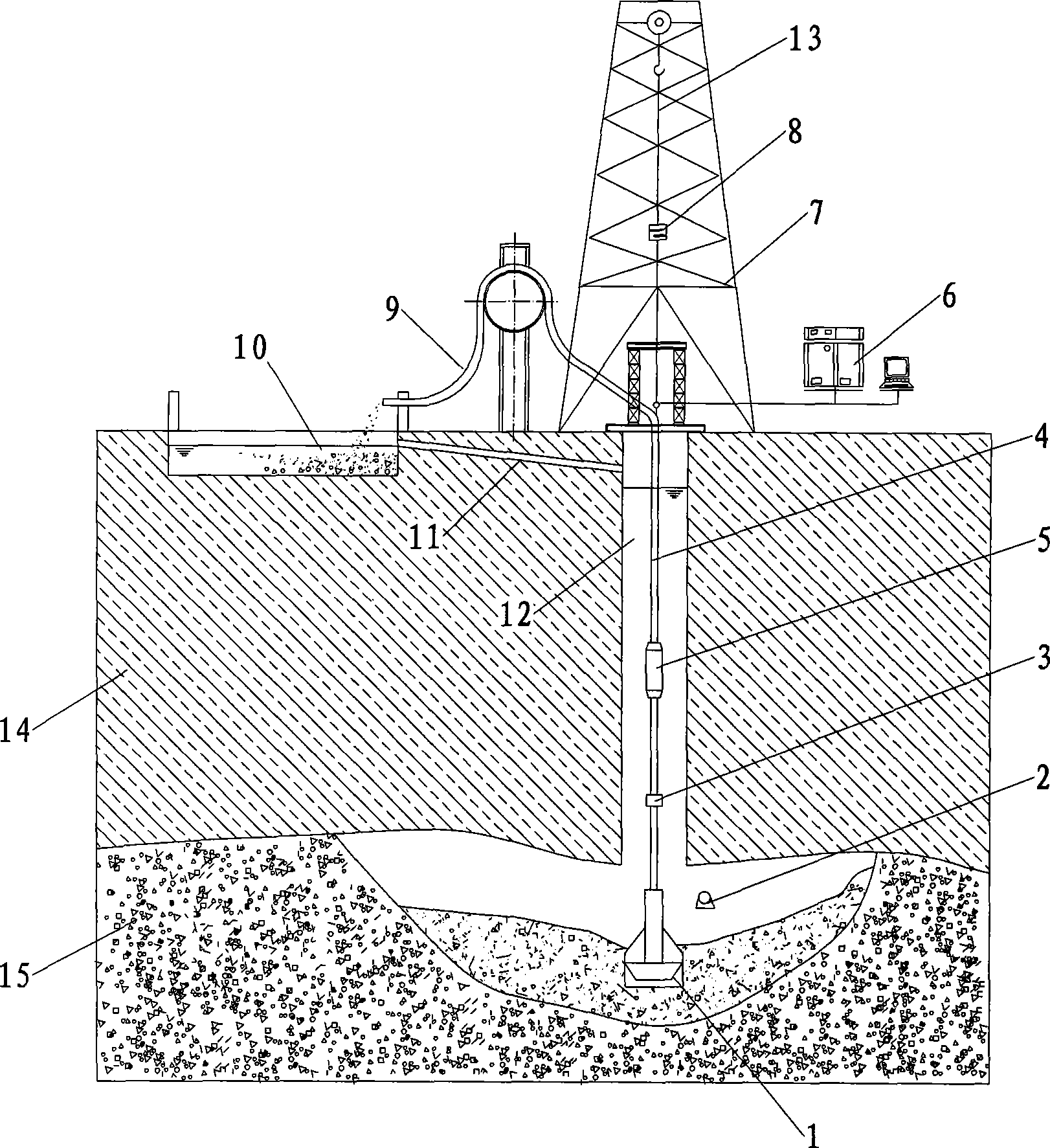
An underwater mining method and its devices
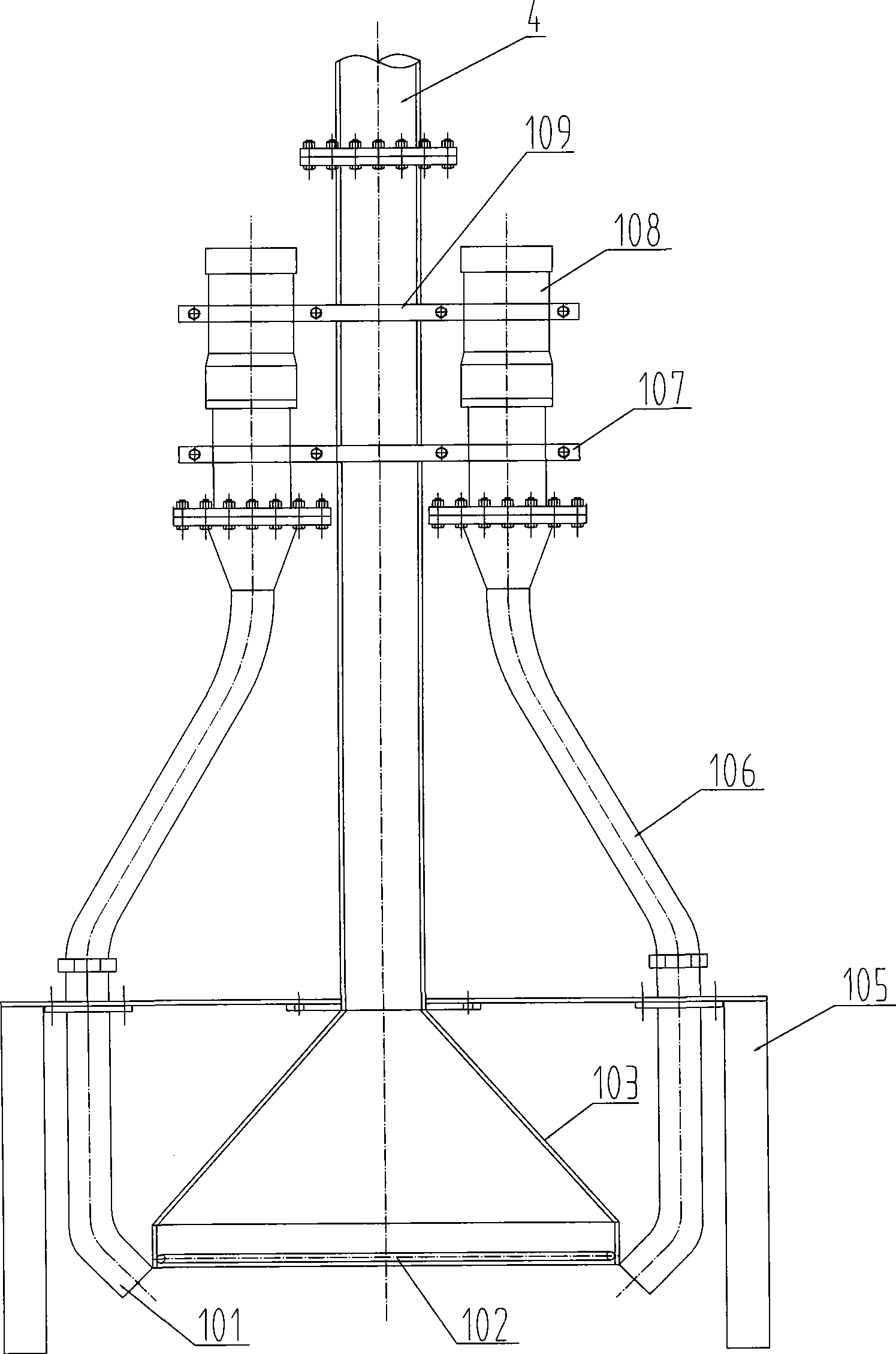
An underwater mining method and its devices, with the following steps: (1) rock breaker or other blasting methods are used to break the underwater mineral deposit into the ore particle size that meets the transport requirement of the lift pipe; (2) the lift pipe, lift pump and hydraulic mineral sucker are arranged in the shaft. When the sucker touches the bottom, the lift pump will be started to convey clear water; (3) the sucker keeps the ore particles at the inlet of the lift pipe in a suspended state; (4) the ore particles are lifted to the ore storage tank on the ground; (5) the ore settles in the tank. The deslimed clear water is discharged into the shaft; (6) the remote control station is responsible for monitoring and control; (7) after mining is finished, the hydraulic mineral sucker will be stopped. When clear water comes out of the outlet of conveying pipe, the lift pump may be shut down. This system consists of hydraulic mineral sucker, underwater space probe, lift pipe, lift pump, remote control station, conveying pipe and mineral storage tank on the ground. The present invention has the following main advantages: simple and compact structure, easy operation, high safety and high mining efficiency.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Magma type copper-nickel ore exploration method
InactiveCN107589472AImprove exploration efficiencyNarrow down the scope of prospectingGeological measurementsMagmaSediment
The invention discloses a magma type copper-nickel ore exploration method. The magma type copper-nickel ore exploration method comprises steps of A, analyzing a geological setting of an ore-forming process of a magma type copper-nickel mineral deposit and summarizing its ore-forming pattern, B, carrying out 1:50000 stream sediment measurement with an aim to observe a geochemical halo on the upperpart of a rock mass, marking abnormities of Cu and Ni, C, performing 1:10000 soil measurement by targeting an area where the Cu and Ni are abnormal, D performing trenching reveal on abnormalities anda mineralized clue or performing 1:2000 geologic measurement, high accuracy magnetic survey, induced polarization sounding and rock comprehensive profile measurement and revealing through trenching engineering, E, marking ore bodies, mineralized bodies and basic and ultra-basic rock bodies, F, using drilling to perform verification on the marked ore bodies or mineralized bodies, and G, determiningthe ore body or the mineral deposit. The magma type copper-nickel ore exploration method can improve a success rate of ore prospecting, can effectively shorten a construction period of ore prospecting and can find various kinds of metal mineral bodies.
Owner:青海省第三地质矿产勘查院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com