Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Metastatic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metastatic Cancer Cell. Abstract. Metastasis is the result of cancer cell adaptation to a tissue microenvironment at a distance from the primary tumor. Metastatic cancer cells require properties that allow them not only to adapt to a foreign microenvironment but to subvert it in a way that is conducive to their continued proliferation and survival.
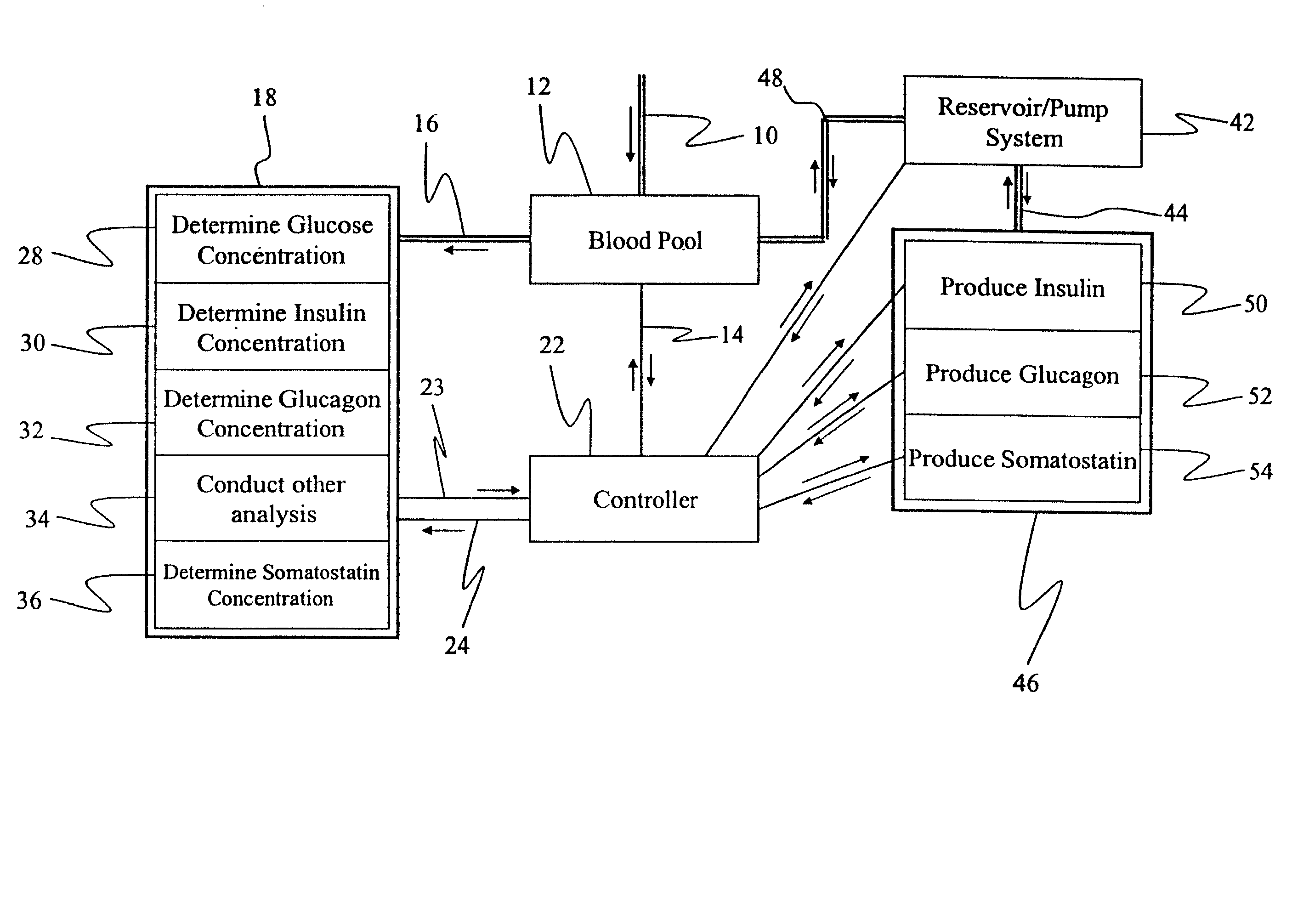
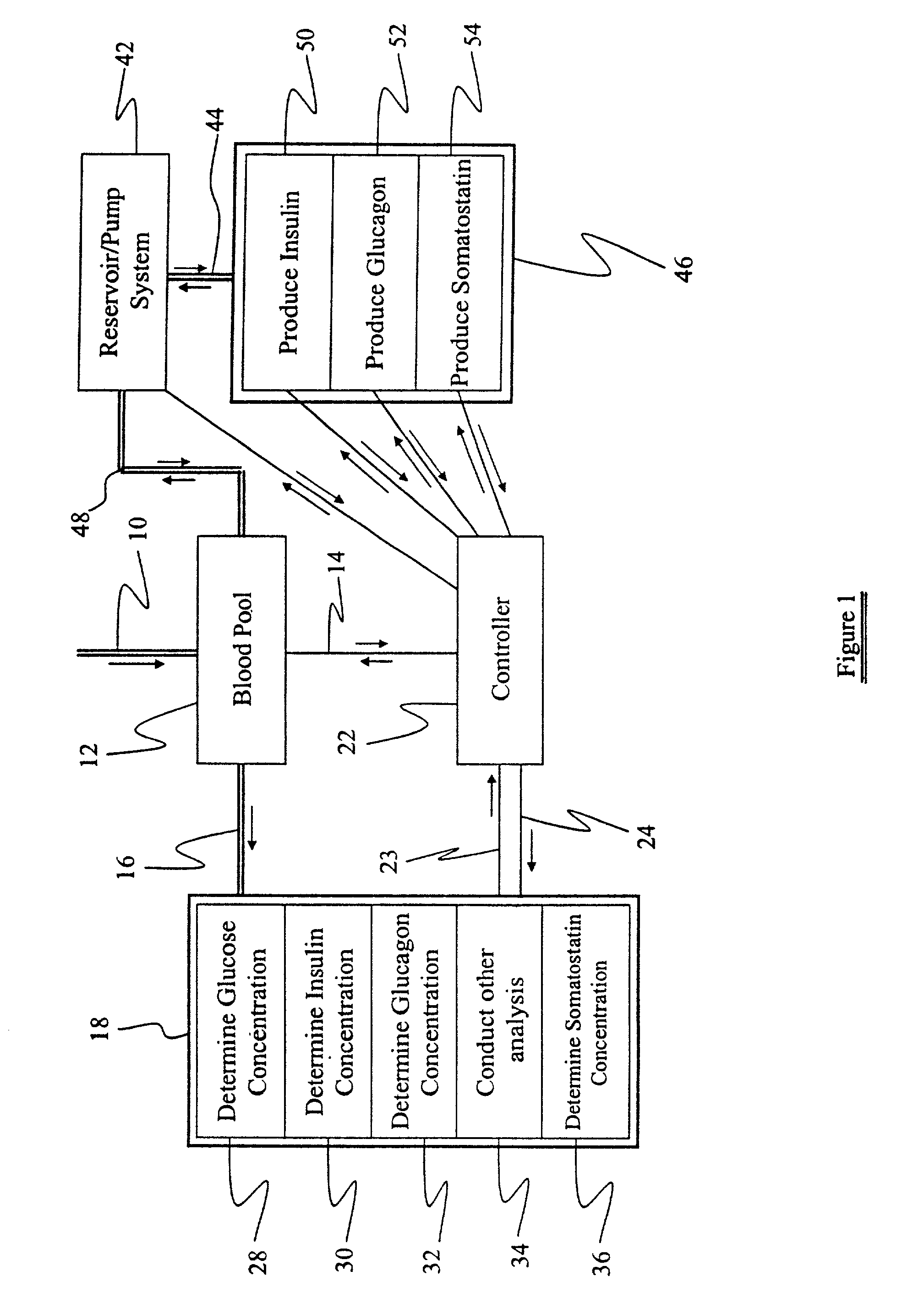
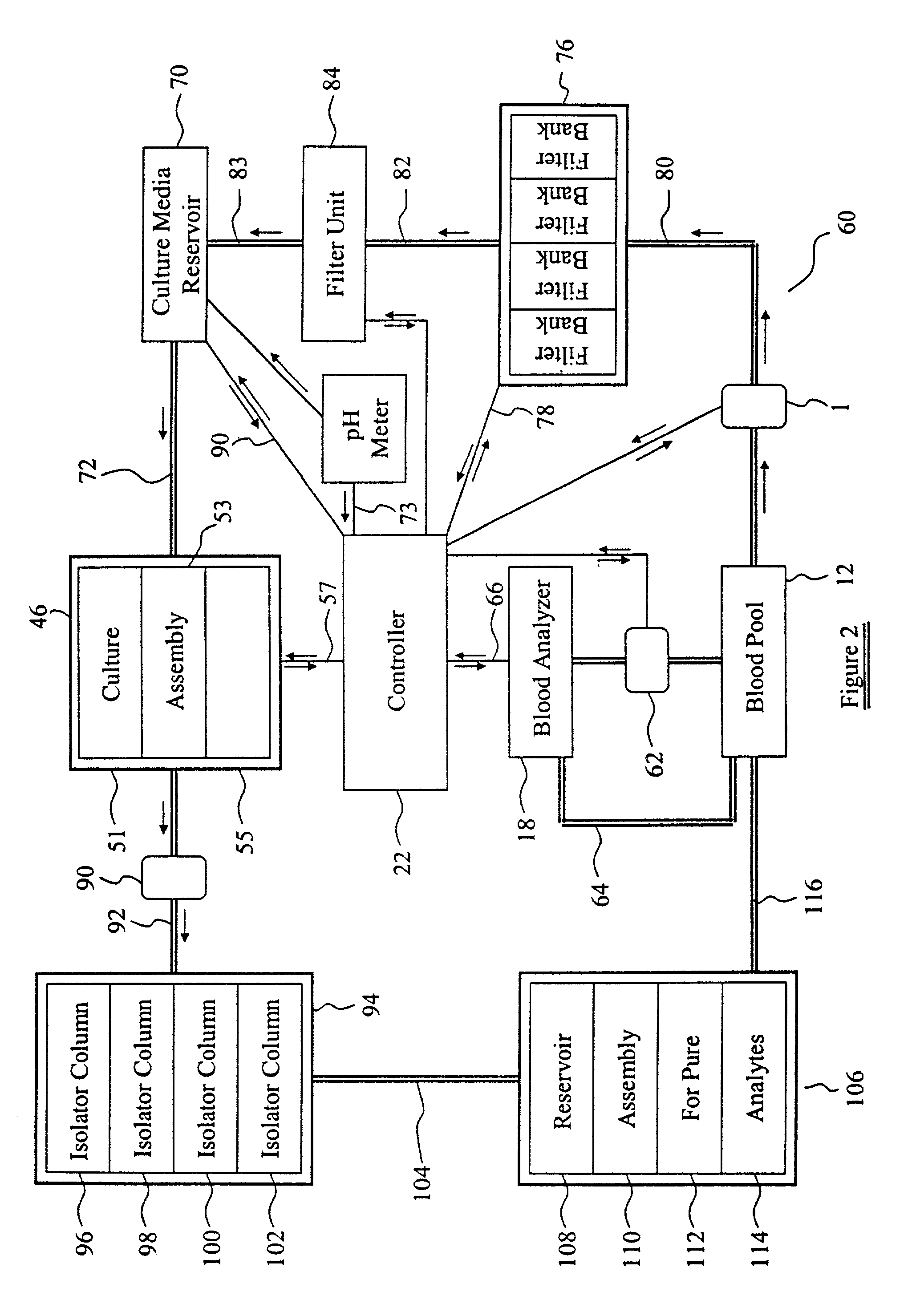
Process for identifying cancerous and/or metastatic cells of a living organism
InactiveUS7244232B2Compounds screening/testingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiological bodyCancer cell
Owner:BIOMED SOLUTIONS
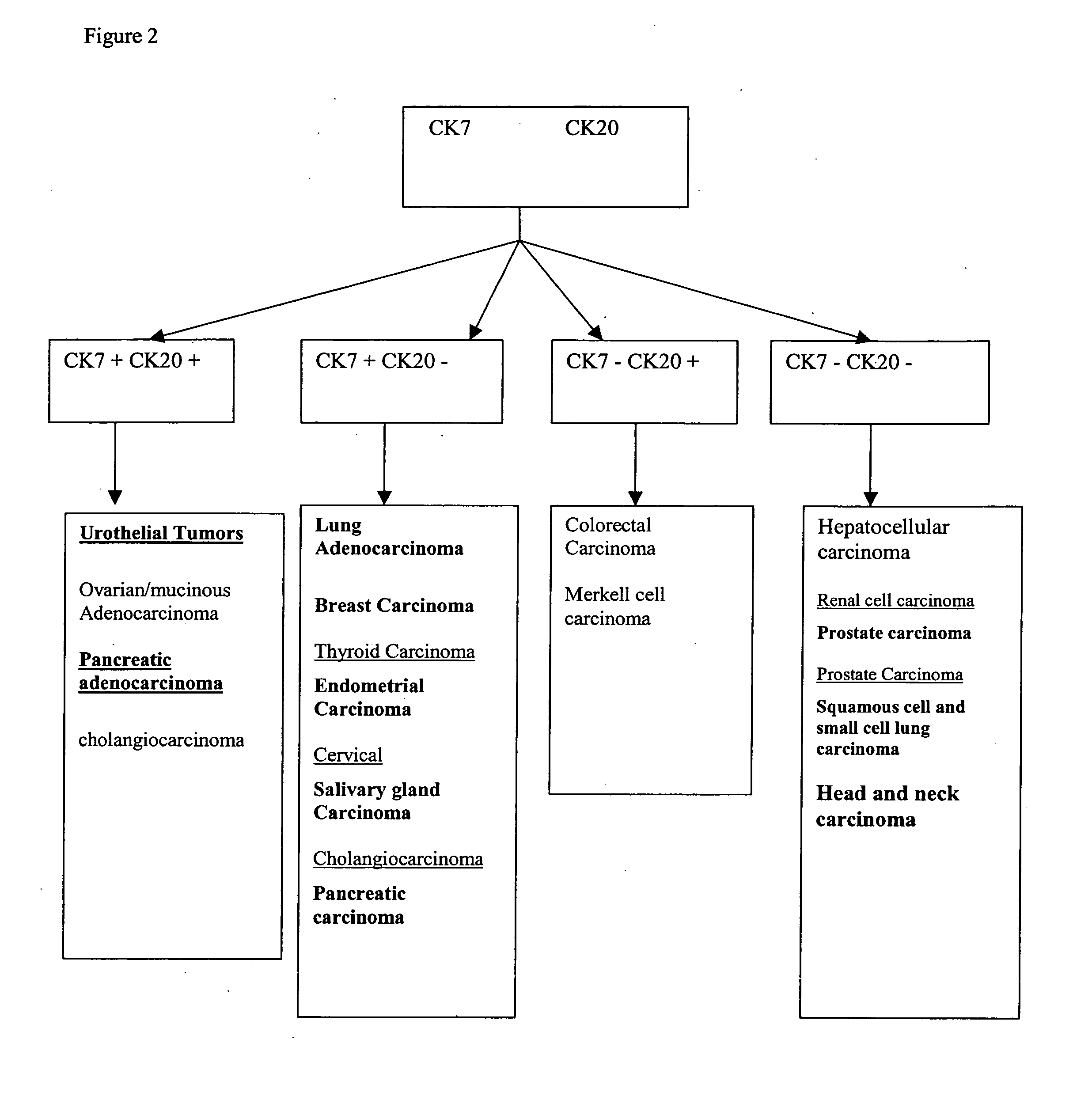
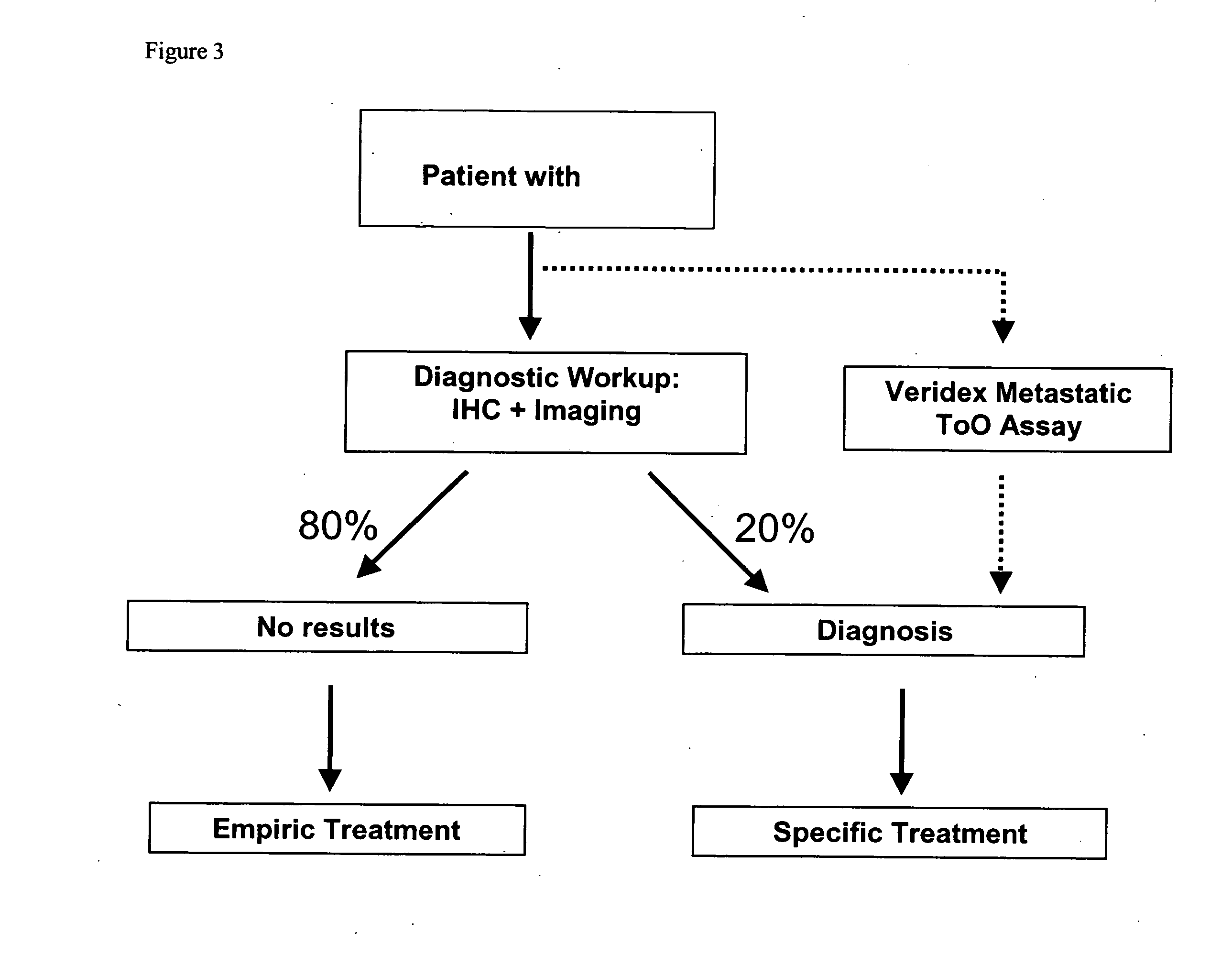
Methods and materials for identifying the origin of a carcinoma of unknown primary origin
InactiveUS20070065859A1High sensitivityStrong specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadHigh probability
The present invention provides a method of identifying origin of a metastasis of unknown origin by obtaining a sample containing metastatic cells; measuring Biomarkers associated with at least two different carcinomas; combining the data from the Biomarkers into an algorithm where the algorithm normalizes the Biomarkers against a reference; and imposes a cut-off which optimizes sensitivity and specificity of each Biomarker, weights the prevalence of the carcinomas and selects a tissue of origin determining origin based on highest probability determined by the algorithm or determining that the carcinoma is not derived from a particular set of carcinomas; and optionally measuring Biomarkers specific for one or more additional different carcinoma, and repeating the steps for additional Biomarkers.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Sequences for targeting metastatic cells
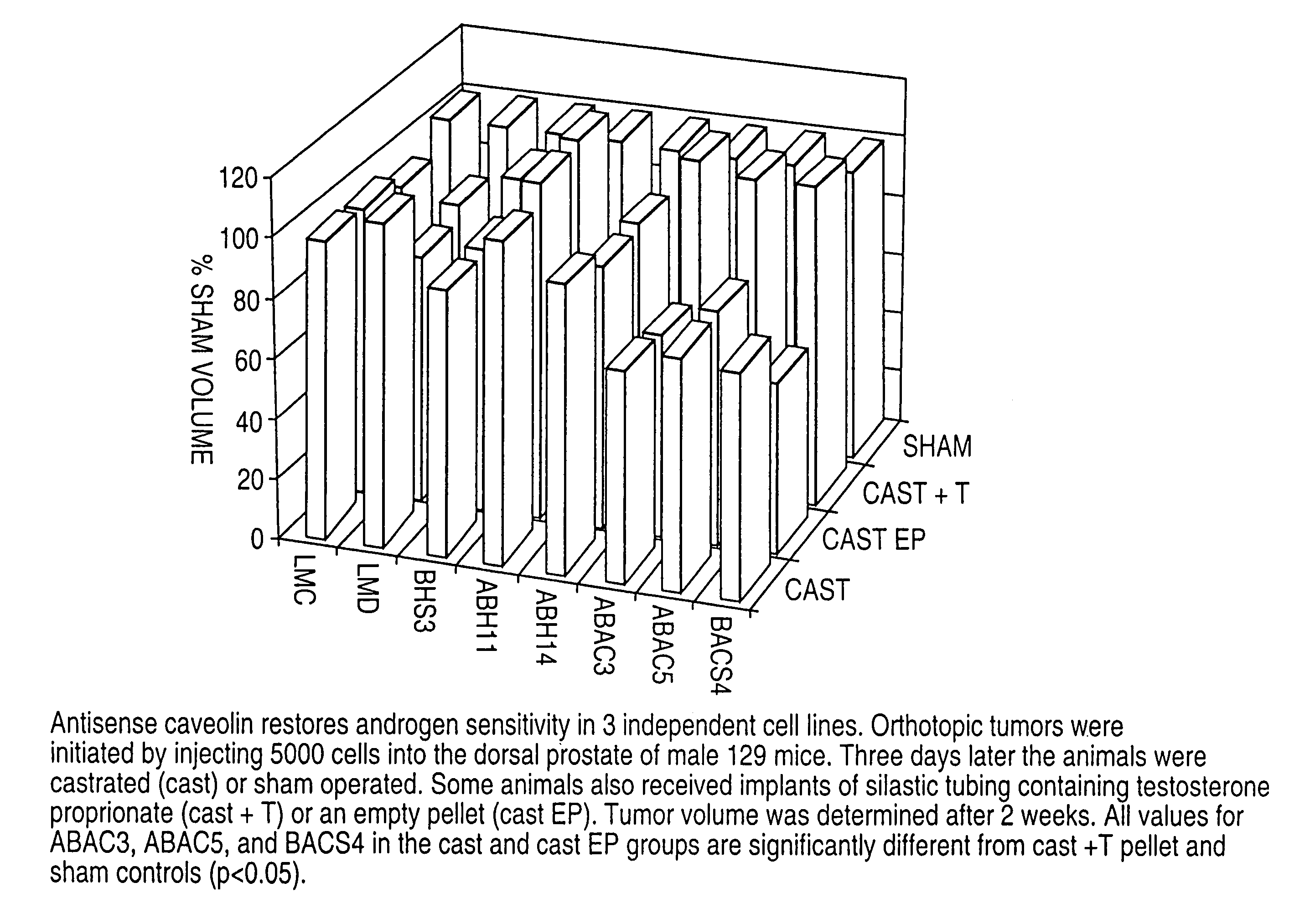
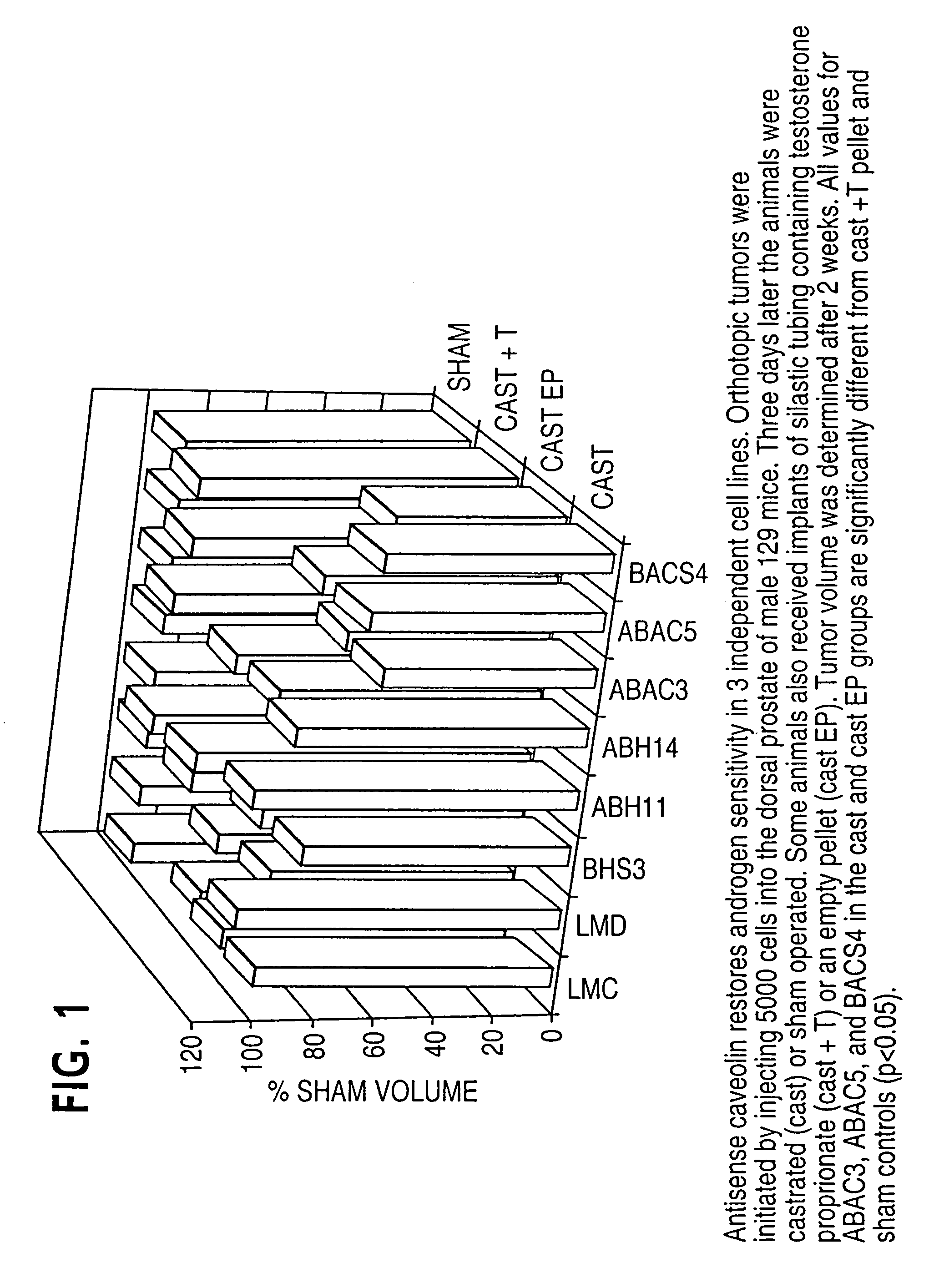
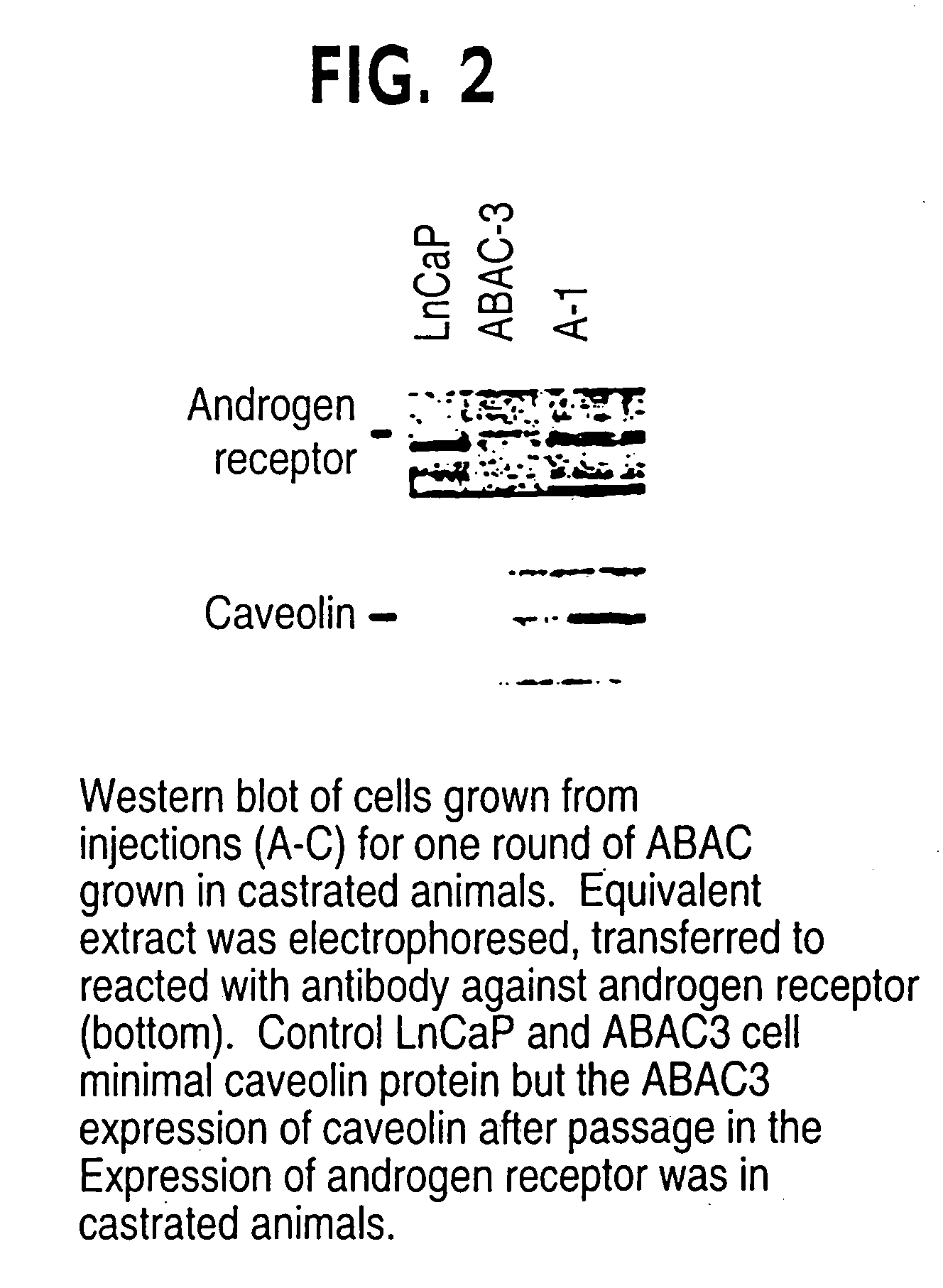
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of metastatic diseases using metastatic sequences, such as caveolin, to target metastatic cells. According to the methods of the present invention, certain cancers, including metastatic prostate cancer, may be treated by therapies which suppress expression of the caveolin gene. The present invention relates to biological technologies designed to block the activity of caveolin or the function of caveolae, including vector delivery of antisense caveolin sequences, the use of anti-caveolin antibodies, the use of promoters, and other approaches targeting the expression of caveolin.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
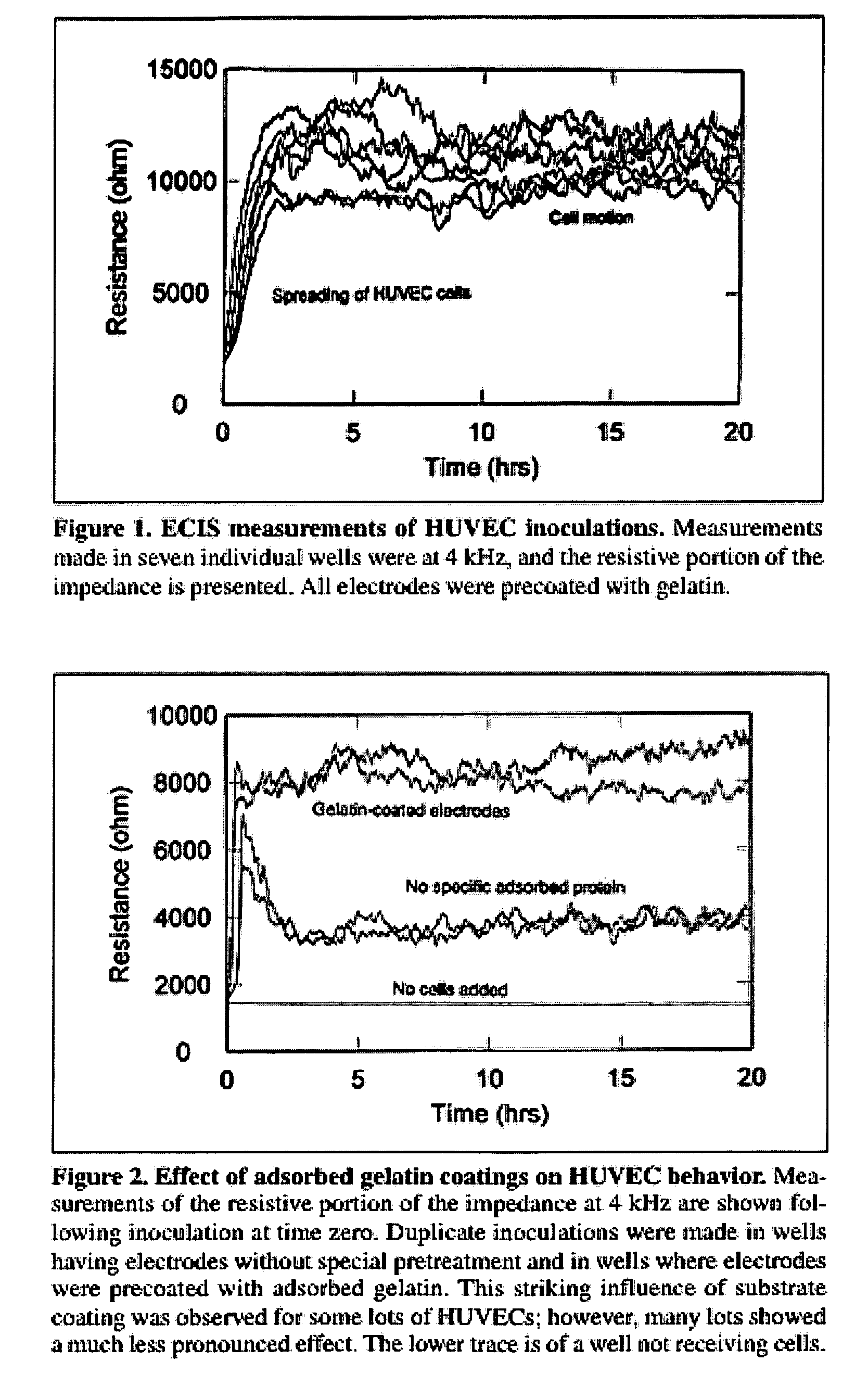
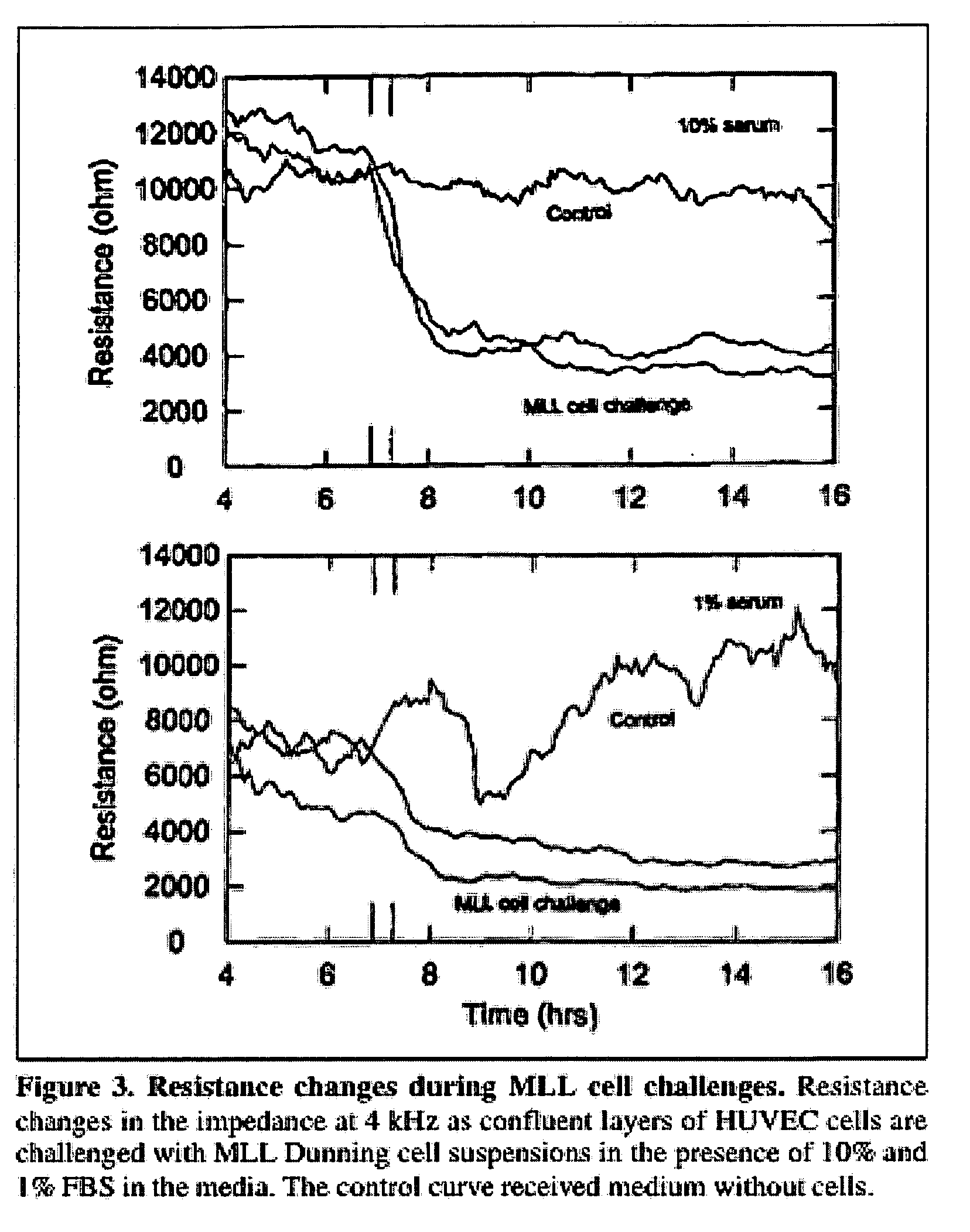
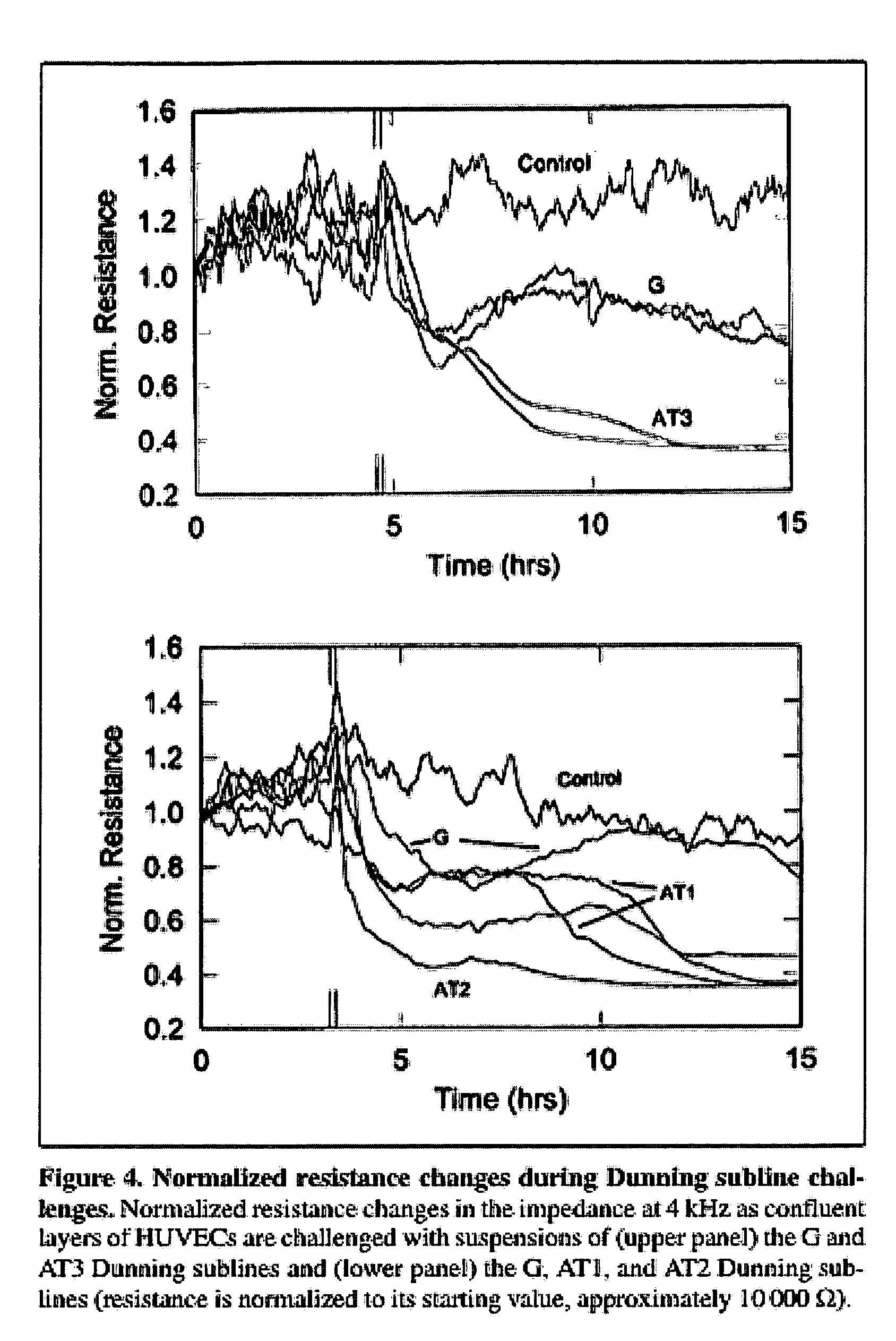
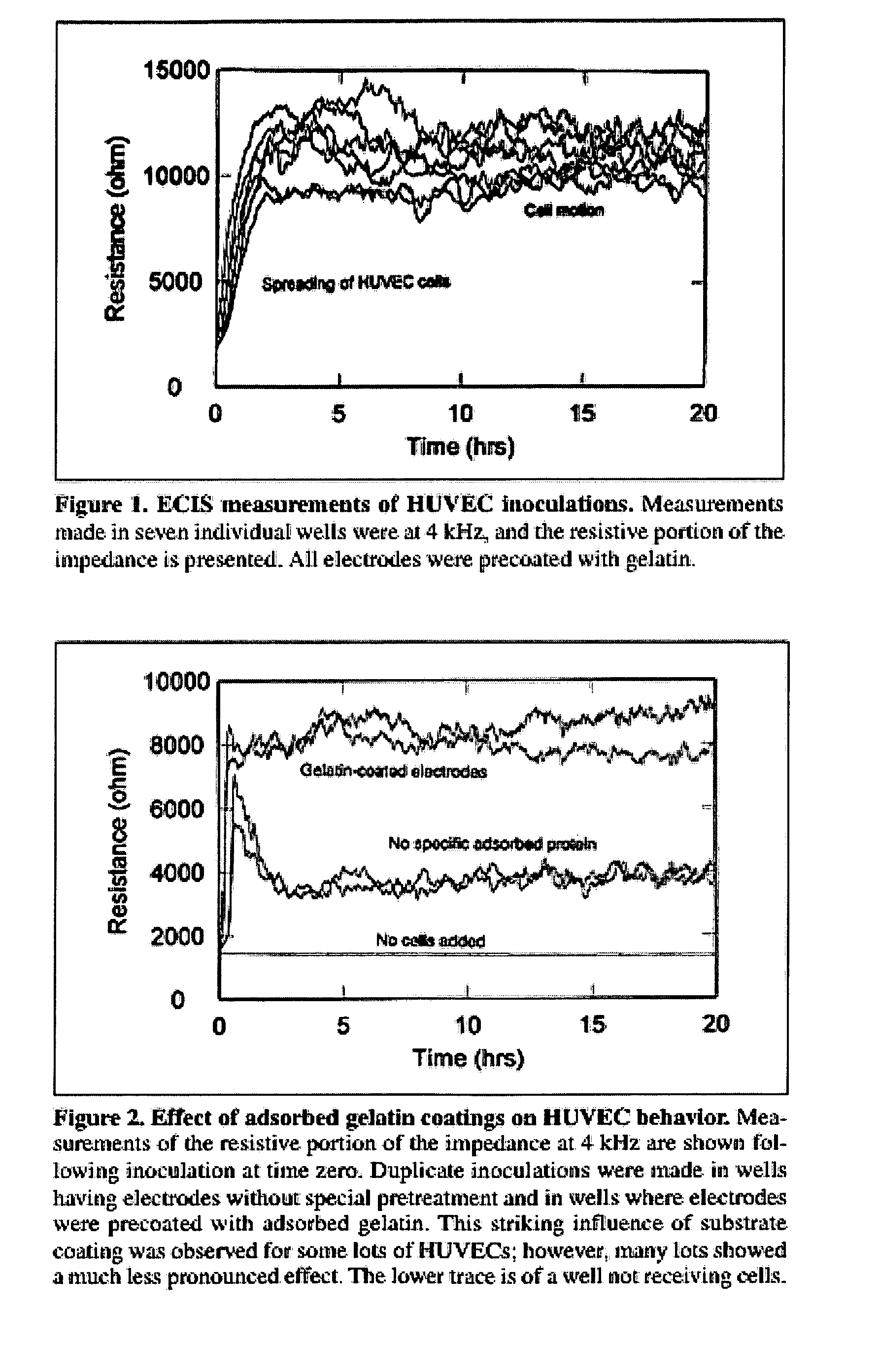
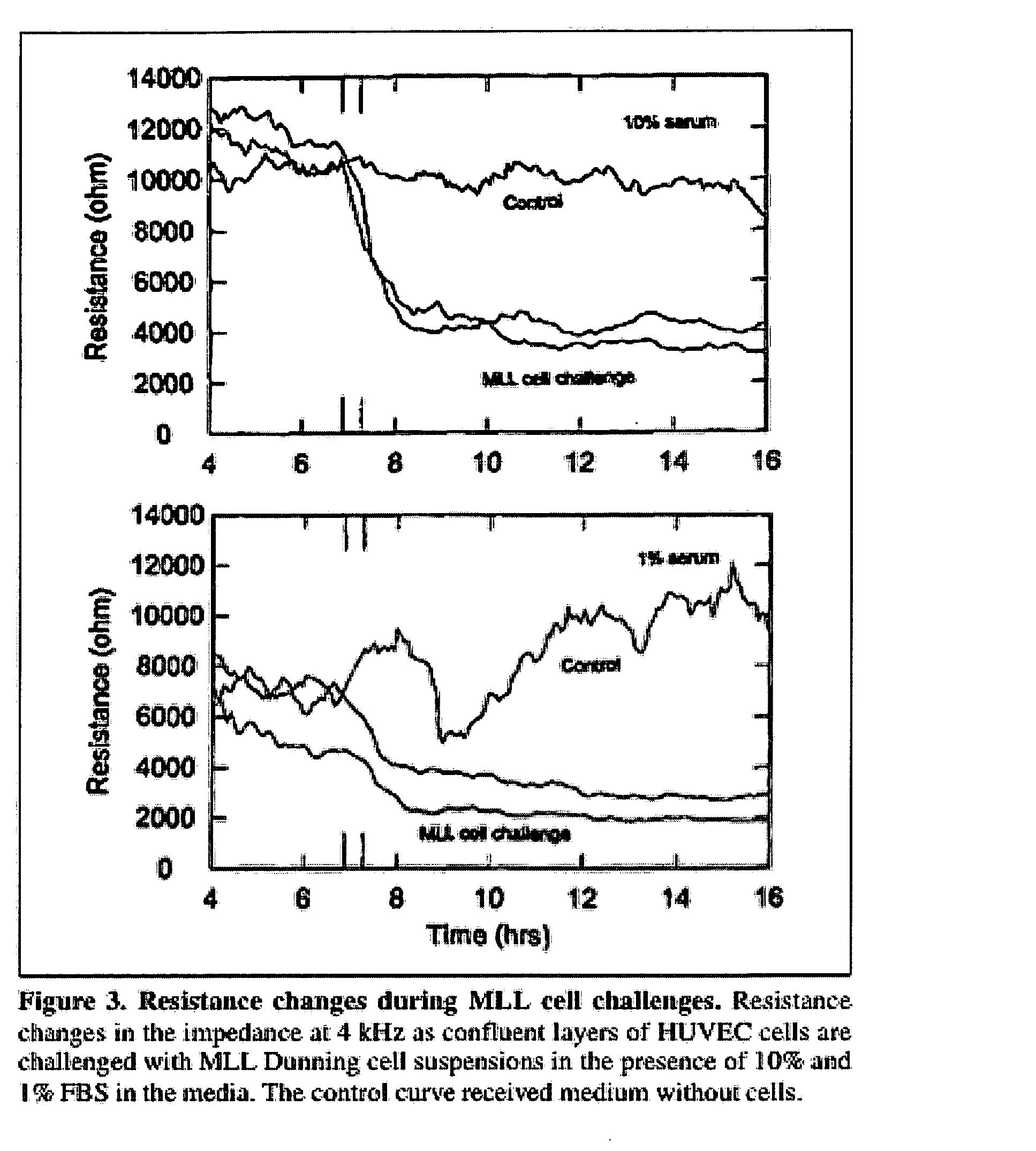
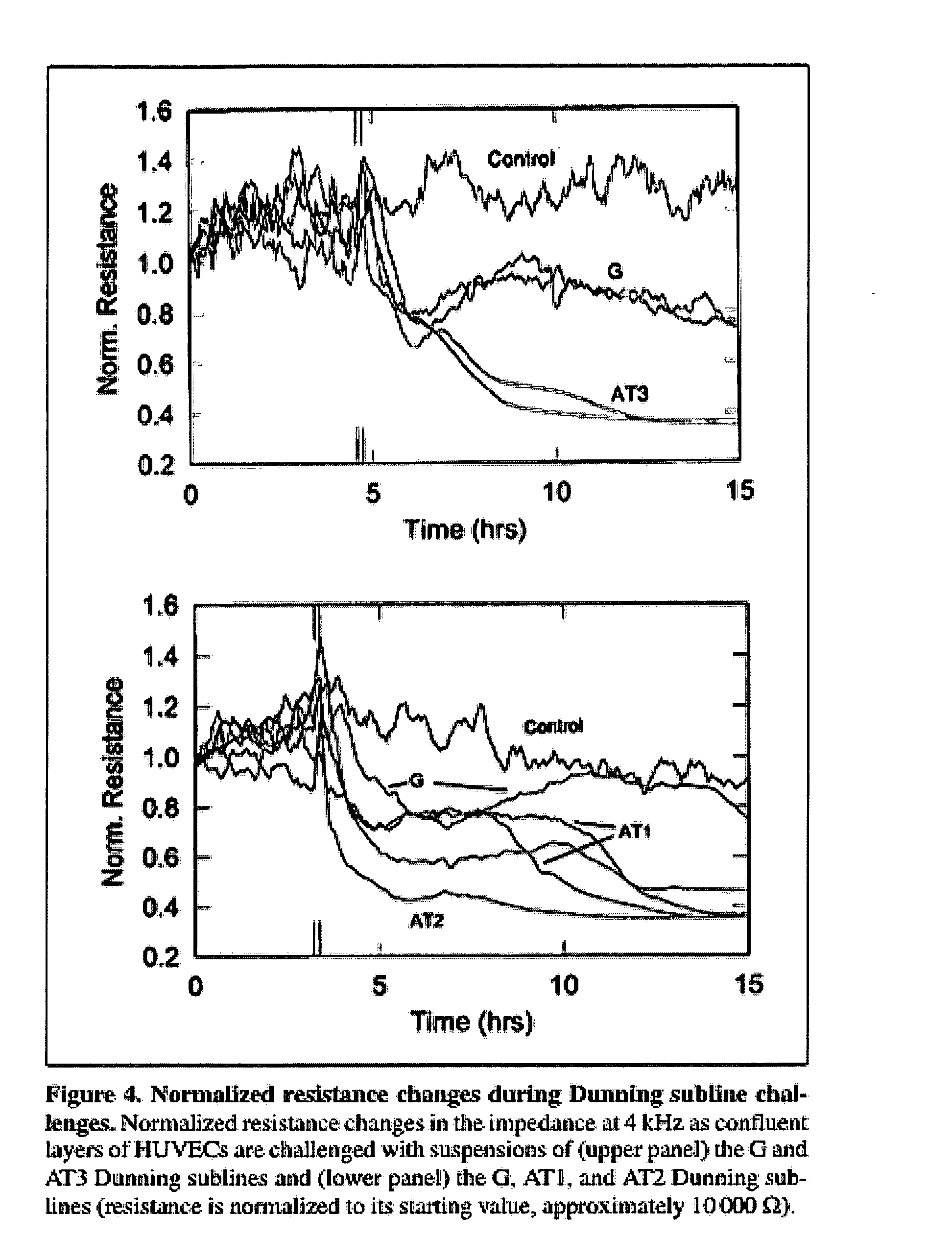
Real-time impedance assay to follow the invasive activities of metastatic cells in culture
The present invention provides methods for the assessment of the metastatic potential of cells by measuring the effect of the cells on the impedance of an electrode. Accordingly, the present invention similarly provides methods for establishing indicators of metastatic potential based on a cell's effect on impedance. Such methods may be employed in vitro or in vivo. In some embodiments, the electrode is coated with endothelial or epithelial cells.
Owner:APPLIED BIOPHYSICS
System and device for characterizing cells
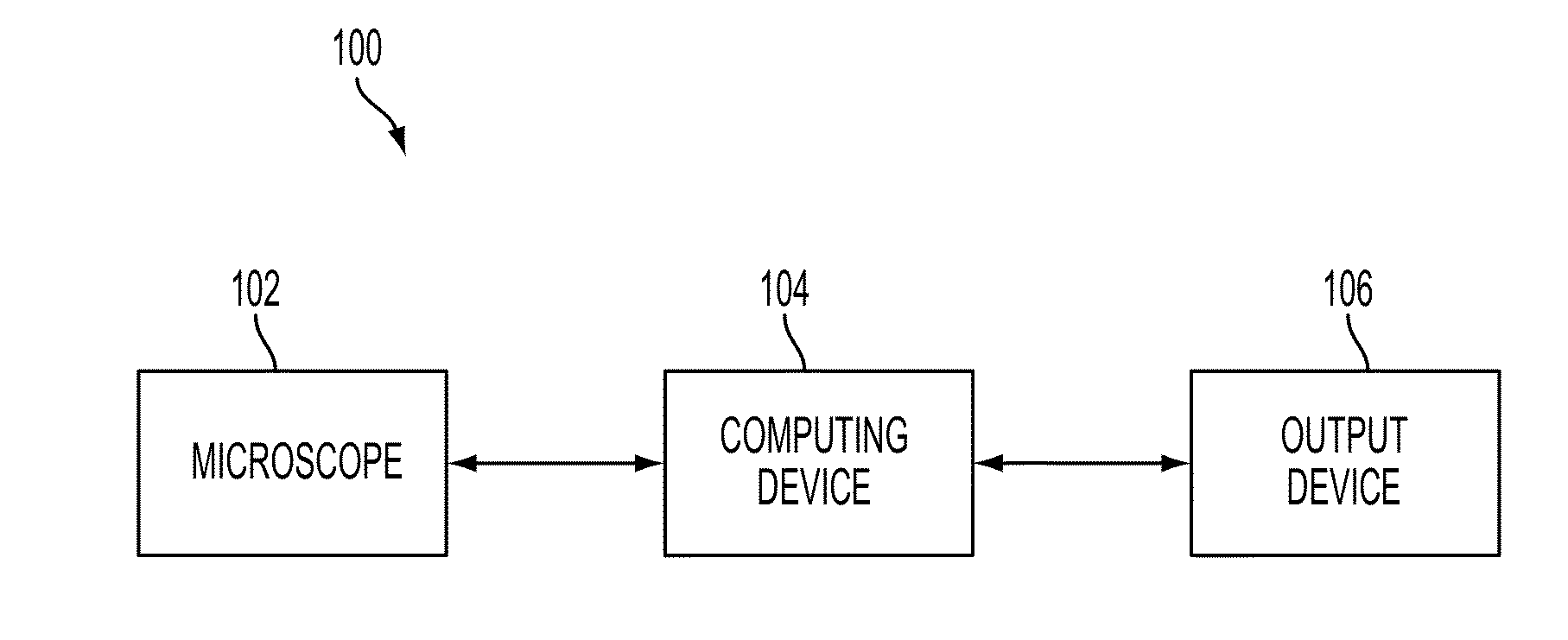
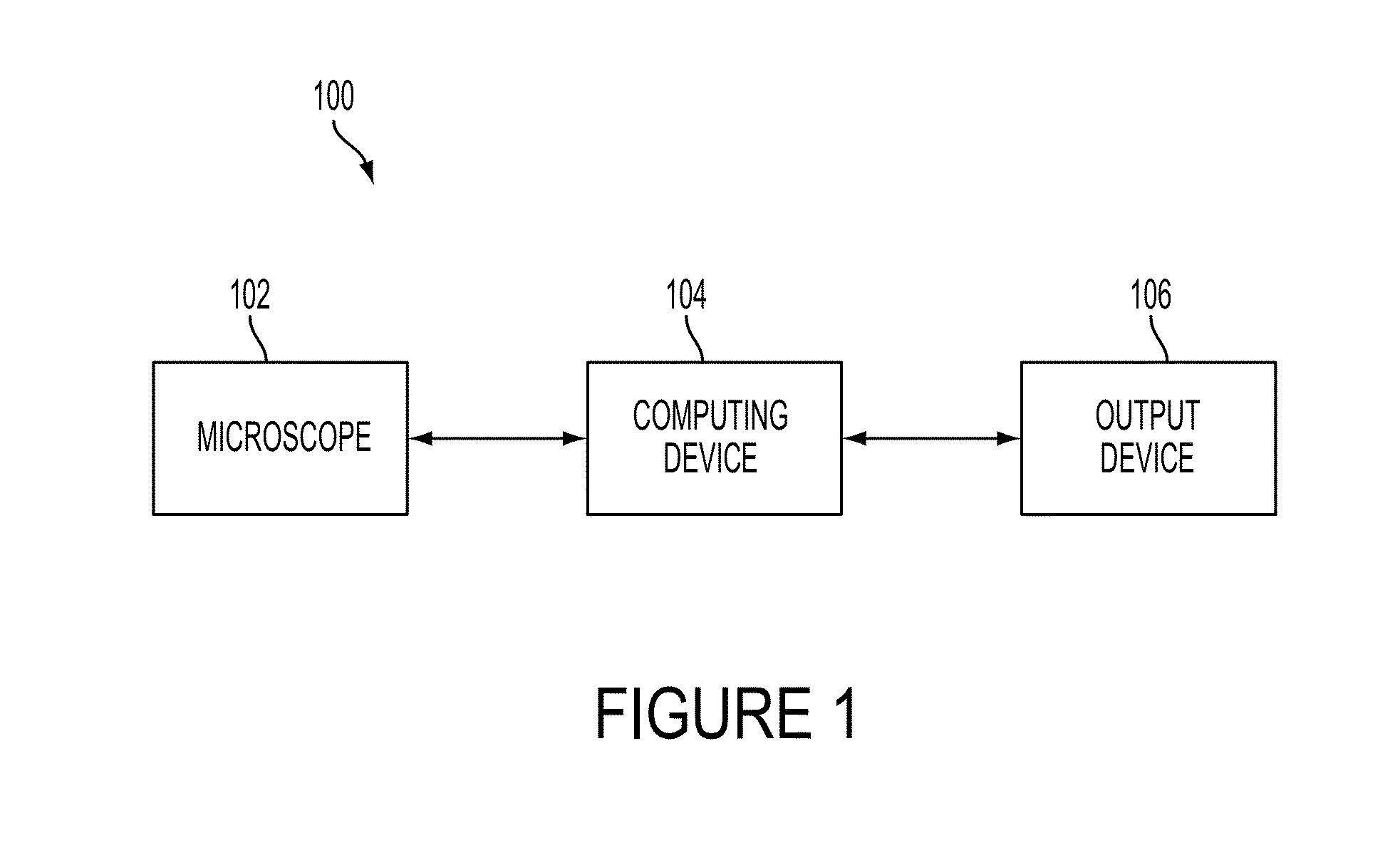
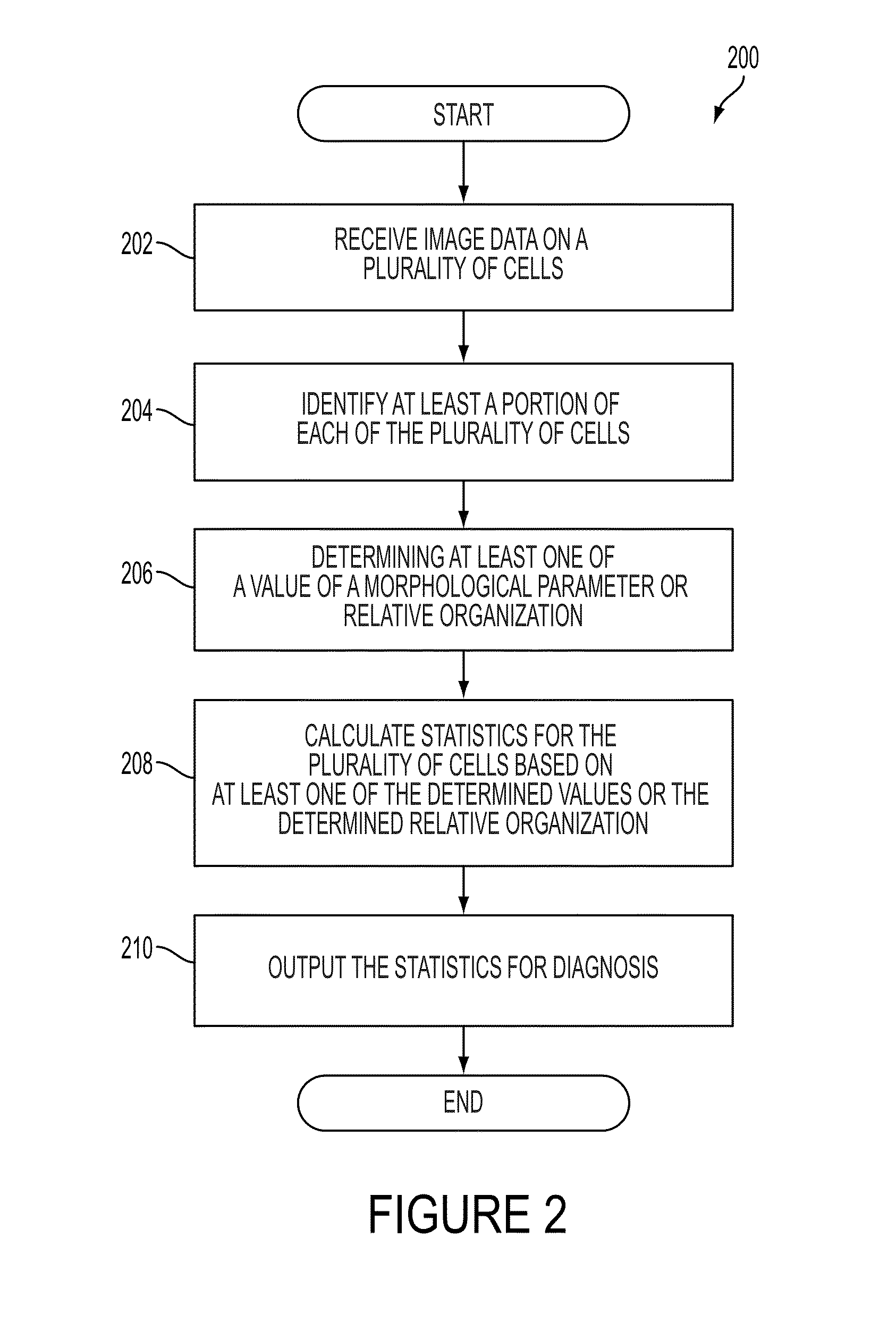
A diagnostic device includes a microscope configured to obtain image data on a plurality of cells and a computing device. The computing device is configured to receive the image data, identify at least a portion of each of the plurality of cells based on the received image data, determine at least one of a value of a morphological parameter for each identified at least a portion of the plurality of cells or a relative organization among the identified at least a portion of the plurality of cells, and calculate statistics for the plurality of cells based on the at least one of the determined values of the morphological parameter or the determined relative organization, the statistics including information suitable for distinguishing metastatic cells from non-metastatic cells. The diagnostic device further includes an output device configured to output the statistics for diagnosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Regulatory b cells and their uses
ActiveUS20130136754A1Increase productionImprove the level ofBiocideSnake antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAutoimmune responses
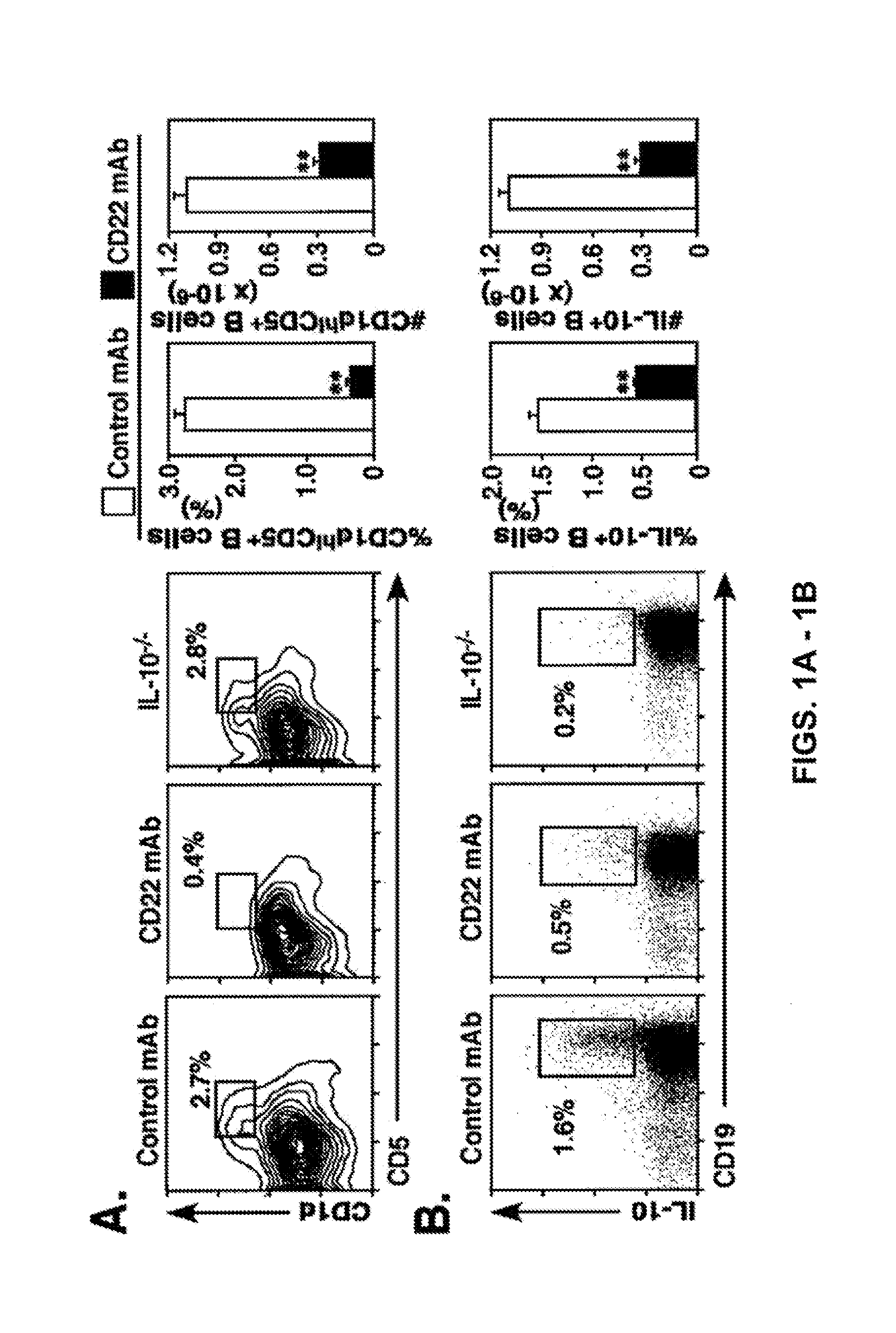
The present invention relates to a distinct B cell subset, B10 cells, that regulate T cell mediated inflammatory responses through the secretion of interleukin-10 (IL-10). The invention also relates to the use of B10 cells in the manipulation of immune and inflammatory responses, and in the treatment of disease. Therapeutic approaches involving adoptive transfer of B10 cells, or expansion of their endogenous levels for controlling autoimmune or inflammatory diseases and conditions are described. Ablation of B10 cells, or inhibition of their IL-10 production can be used to upregulate immunodeficient conditions, ameliorate infectious diseases and / or to treat tumors / cancer. Diagnostic applications are also encompassed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Methods for Detecting Minimum Residual Disease
The present invention features methods and compositions for identifying markers of minimum residual disease (MRD), as well as markers of metastatic cells. The present invention further provides methods for detecting MRD and metastatic cell in a subject.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Analysis of single cell mechanical phenotyping for metastatic detection
The present invention relates to a method and system for analyzing mechanical signatures of a plurality of cells for metastatic detection. Specifically, a data set characterized by at least one metric (such as Brillouin frequency shift and / or Brillouin linewidth) representing a cell mechanical signature is acquired for the plurality of cells by using a label-free Brillouin spectroscopy. A merit function is calculated based on one or more statistical characteristics of the data set, such as sensitivity and specificity. Then, the plurality of cells can be classified to detect metastatic cells based on mechanical signatures provided by the data set and an optimal metric value delivering maximum to the merit function.
Owner:CANON USA
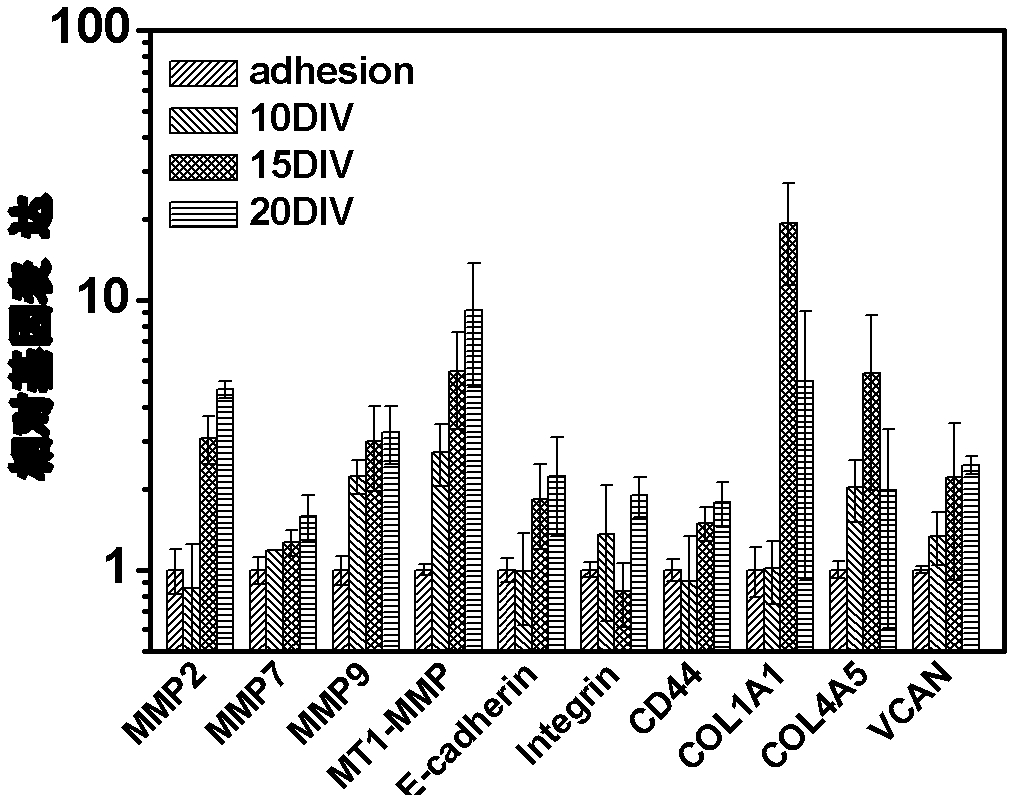
Human tumor invasion and metastasis histioid in vitro three-dimensional model and construction and evaluation thereof
InactiveCN103160468AKeep aliveSimulation excellentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsHuman tumorHydrogel scaffold
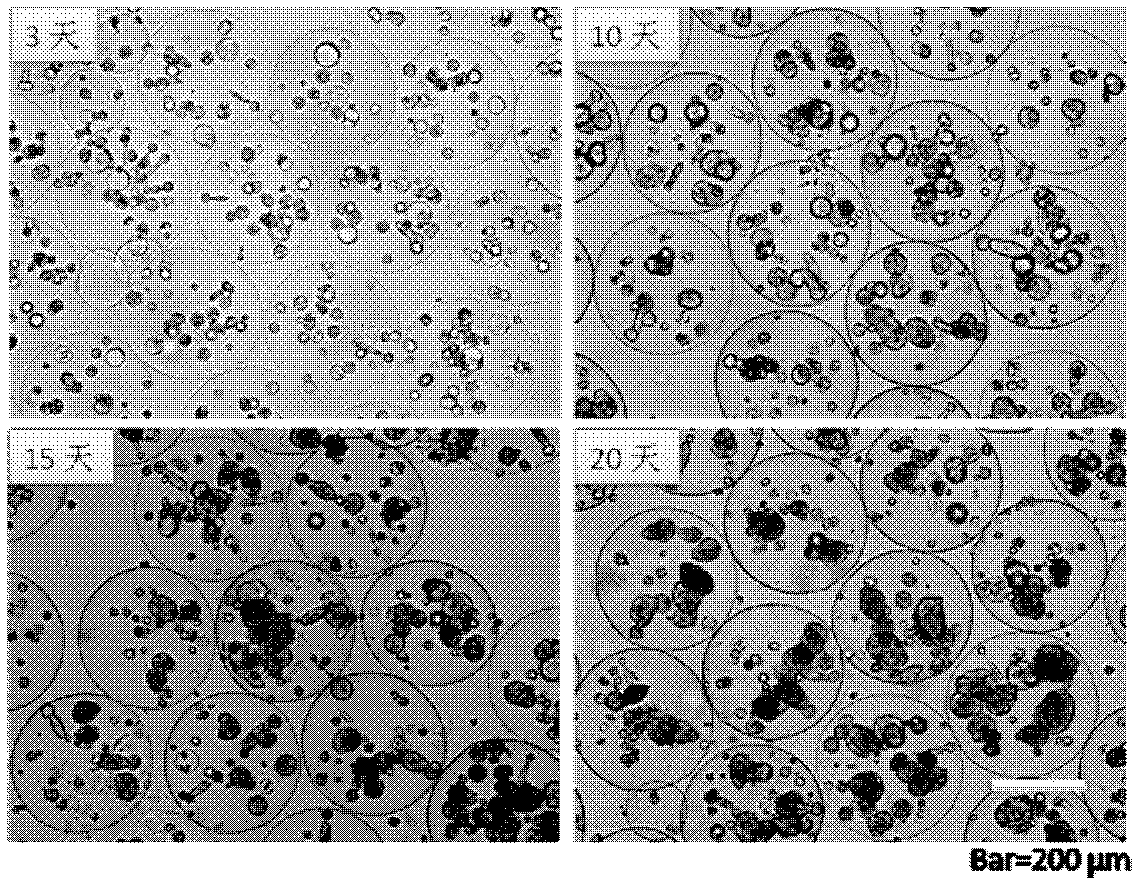
The invention discloses an in vitro model simulating human tumor metastasis. Cells in the model have a tumor high metastasis character. The model is constructed by building of a micro spherical hydrogel support frame by tumor high metastasis cells, building of a tumor cell in vitro metastasis model and identifying of the constructed tumor cell in vitro metastasis model. The model can grow in a three-dimensional culturing cell in a clustering mode, and tumor cell biological behaviors in metastasis can be detected. The model has important value in studying of a clinical tumor metastasis mechanism and controlling of screening of metastasis medicine and can be taken as a technical platform for manufacturing anti-tumor metastasis gene vaccines and building screening of anti-tumor metastasis medicine.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human liver cancer high-transfer cell strain with stable expression of fluorescent protein and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101381706AAvoid pollutionImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCarcinoma cell lineCancer cell
The invention belongs to the field of micro-organism animal cell line and relates to a human hepatoma cell line which can emit high-intensity red or green fluorescence and has high transferring ability of lung and lymph node metastasis, and a method for establishing the same. The method comprises the following steps: using the human hepatoma cell line HCCLM3 and HCCLM6 which have high transferring ability of the lung and lymph node metastasis as mother cells, performing cotransfection on plasmid DNA of 239 cells through slow virus packaging plasmids to obtain false slow virus particles by expressing red or green fluorescent protein genes through eucaryon, and infecting liver cancer cell strains of the mother cells to obtain the chromosome integrated hepatoma cell line which has high transferring ability of the lung and lymph node metastasis and can stably expressing the red or the green fluorescence. The human hepatoma cell line which has high transferring ability of the lung and lymph node metastasis in vitro can be applied to the tracer studies on tumor cells, the molecular mechanism studies on the recurrence and transferring of liver cancer, as well as the pre-clinical drug efficacy studies on new anti-tumor drugs, thus the human hepatoma cell line has wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
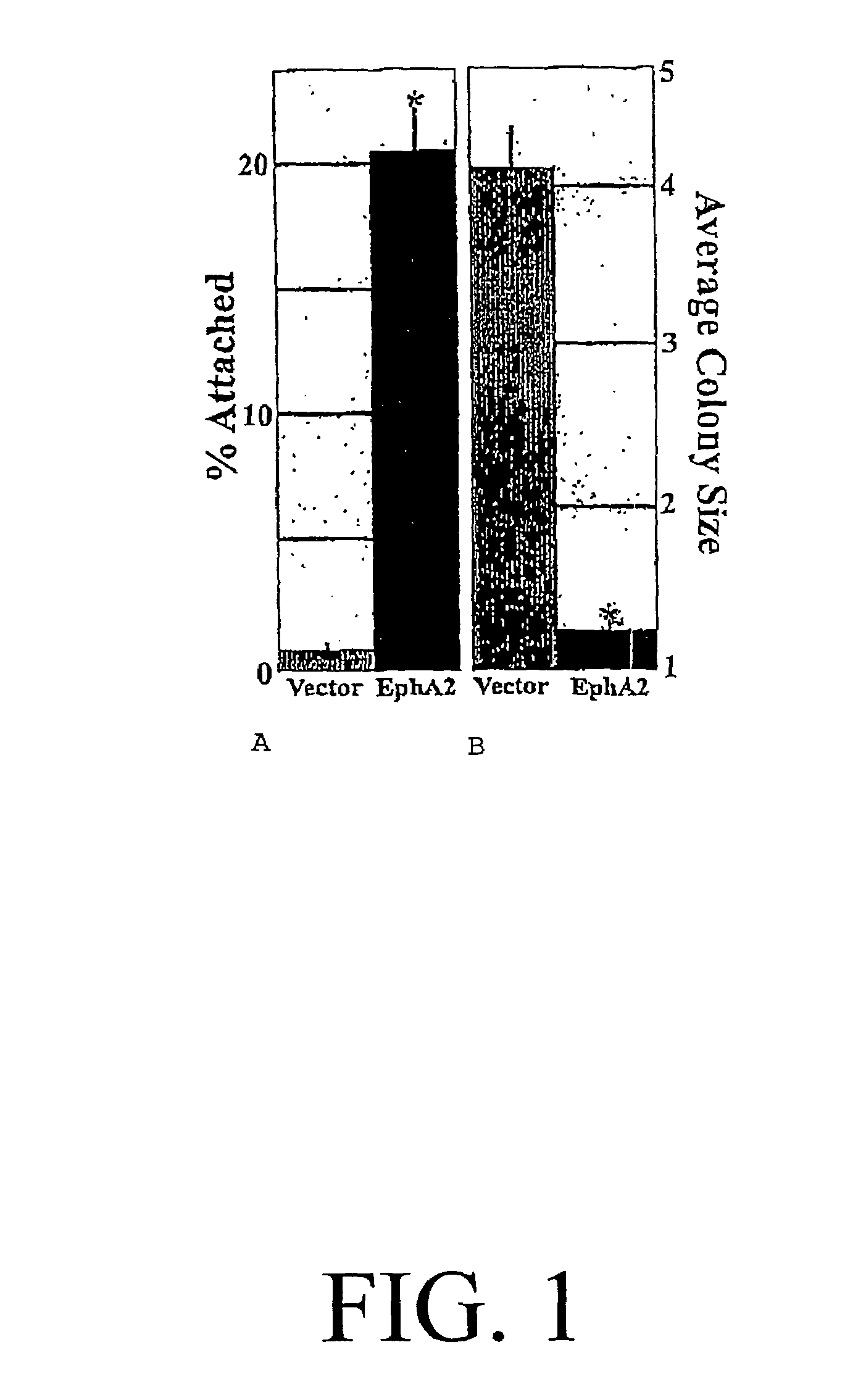
EphA2 monoclonal antibodies and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS7402298B1Avoid collateral damageInhibit growthBiocideAntibody ingredientsCancer cellExtracellular Structure
The invention provides a monoclonal antibody, a fragment thereof, or a molecular complex thereof that binds to an extracellular domain of an EphA2 receptor molecule, wherein binding of the monoclonal antibody or fragment thereof to the EphA2 receptor molecule present in the membrane of a cancer cell favorably alters activity of the EphA2 receptor molecule. The invention further relates to methods of making and using the monoclonal antibodies, fragments, and molecular complexes regarding the same. The monoclonal antibodies of the present invention target the extracellular domain of EphA2 and operate to redirect the function of EphA2 to selectively block the growth and invasiveness of metastatic cells. The invention thus makes possible therapeutic strategies that optimally target metastatic cells while preventing collateral damage to normal tissues.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Real-time impedance assay to follow the invasive activities of metastatic cells in culture
The present invention provides methods for the assessment of the metastatic potential of cells by measuring the effect of the cells on the impedance of an electrode. Accordingly, the present invention similarly provides methods for testing the efficacy of anti-cancer therapies and for establishing indicators of metastatic potential based on a cell's effect on impedance. Such methods may be employed in vitro or in vivo. In some embodiments, the electrode is coated with endothelial or epithelial cells. A first aspect of the invention provides a method of assessing a metastatic potential of a cell comprising the steps of providing an electrode coated with a plurality of substrate cells, obtaining a first measurement of at least one electrical property of the coated electrode, contacting the electrode with at least one test cell, obtaining a second measurement of at least one electrical property of the coated electrode, and comparing the first and second measurements.
Owner:APPLIED BIOPHYSICS
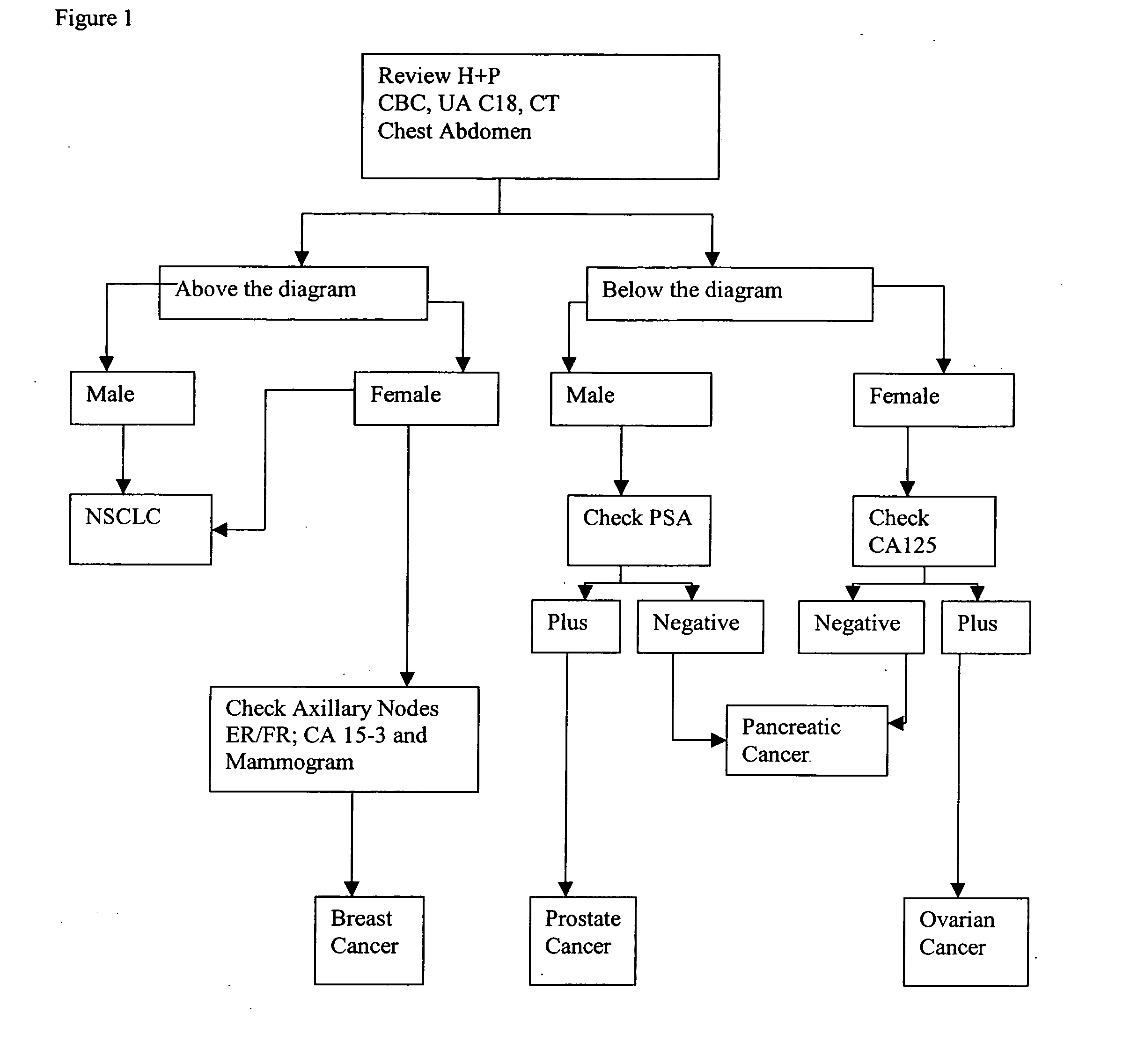
Methods for diagnosing pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS20080050726A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadHigh probability
The present invention provides a method of identifying origin of a metastasis of unknown origin by obtaining a sample containing metastatic cells; measuring Biomarkers associated with at least two different carcinomas; combining the data from the Biomarkers into an algorithm where the algorithm normalizes the Biomarkers against a reference; and imposes a cut-off which optimizes sensitivity and specificity of each Biomarker, weights the prevalence of the carcinomas and selects a tissue of origin determining origin based on highest probability determined by the algorithm or determining that the carcinoma is not derived from a particular set of carcinomas; and optionally measuring Biomarkers specific for one or more additional different carcinoma, and repeating the steps for additional Biomarkers.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
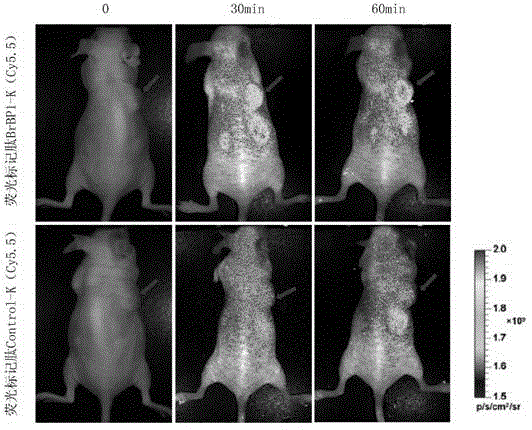
Polypeptide in specific binding with breast cancer brain metastases cells
ActiveCN103145803AImprove anti-tumor effectSmall molecular weightPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsTumor targetSorbent
The invention discloses BrBP1 polypeptide in specific binding with breast cancer brain metastases cells, and further relates to a preparation method of the polypeptide. The method includes: by utilization of phage display technology, carrying out a plurality of rounds of whole-cell depletion screening, and screening out phage clones bound with a breast cancer brain metastases cell line; randomly picking out a plurality of the phage clones, and selecting strongly positive phage clones with a cell enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) method; and after increasing the strongly positive phage clones, carrying out sequencing, and synthesizing the tested BrBP1 polypeptide in a manual mode. The polypeptide can be applied to preparation of medicine used for curing breast cancer brain metastases and kits used for early-stage diagnosis of the breast cancer brain metastases. The polypeptide can be synthesized with a manual method, is small in molecular weight, high in activity, strong in penetrating power, high in affinity and specificity and low in toxicity, has good tumor-targeting performance inside and outside a body, can also be internalized to enter cells, and is suitable for being used as vectors for targeted therapy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
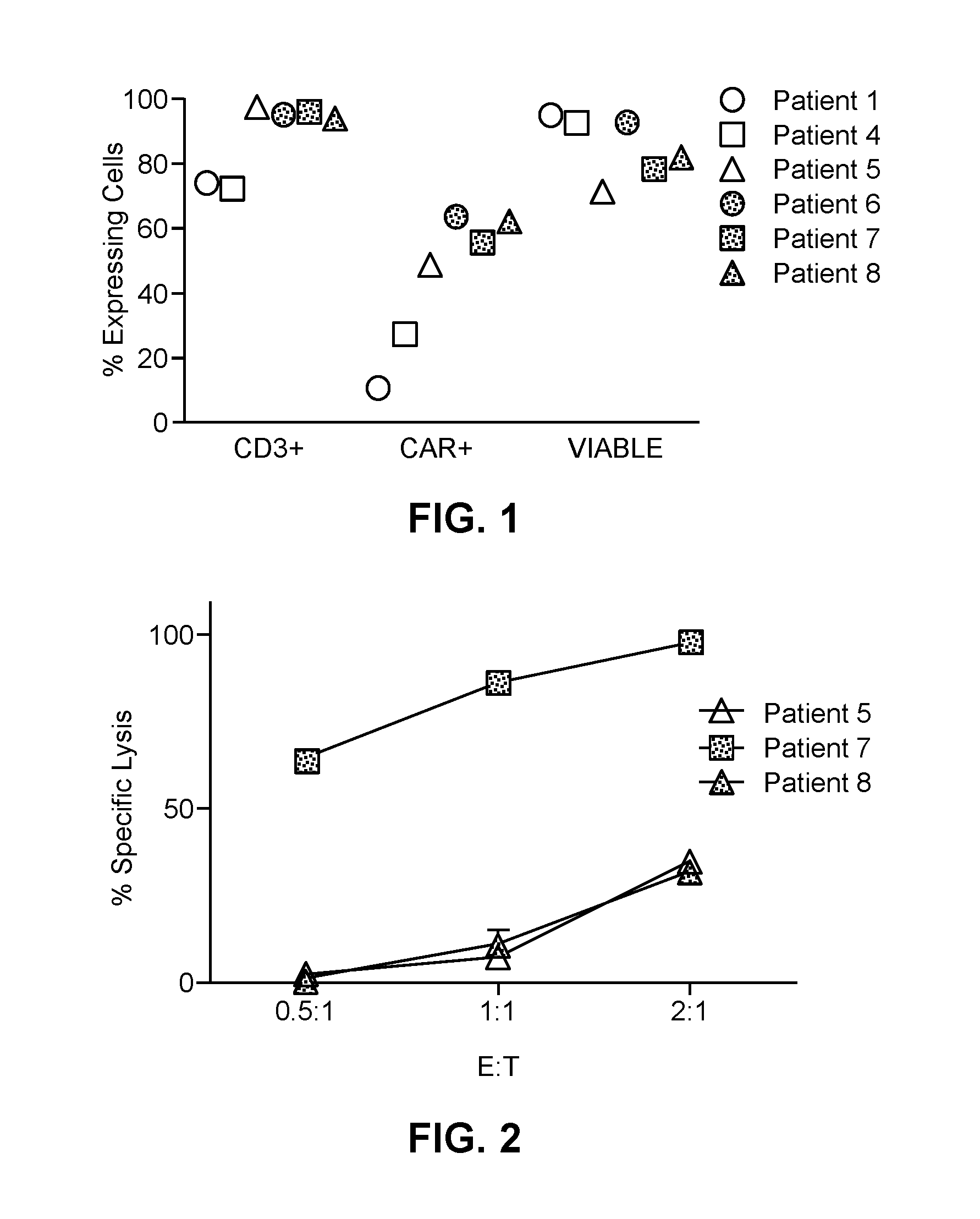
Hepatic arterial infusion of car-t cells
ActiveUS20160303166A1Reduce tumor burdenReduce the burden onPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyLymphatic SpreadCo administration
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of liver metastases in a subject. The methods include hepatic arterial infusion (HAI) of chimeric antigen receptor modified T cells (CAR-T) which are highly specific for tumor antigens such as carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). The HAI method is optimized to maximize exposure of the modified cells to the metastatic cells while minimizing exposure to healthy cells. The methods include co-administration of a second therapeutic agent, such as IL-2.
Owner:PROSPECT CHARTERCARE RWMC LLC
Methods for detecting minimum residual disease
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Highly metastatic model of human melanoma, cell subline, creation methods, and dynamic detection of metastasis
InactiveCN102067828AMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsMetastatic melanomaLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a highly metastatic model of human melanoma, a highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma, creation methods for the highly metastatic model and the highly metastatic cell subline, and the dynamic detection of metastasis. The subcutaneously-transplanted mouse highly metastatic model and the corresponding cell subline are established in an in-vivo screening way in a mouse with severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) by using mouse lung metastasis, namely human malignant melanoma cell strain A375 pulmonary metastasis, wherein the highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma is A375sci, and has a human tumor cell karyotype; and 60 to 75 hypo-triploid-dominated chromosomes are acrocentric and have a heteroploid karyotype. The cell subline has the two routes of metastasis of blood trails and lymph. The in-vivo screening of the highly-metastatic model is performed by using animals with severe immune deficiency, and is expressed and applied in nude mice. A method for detecting Alu genes by using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is simple, highly sensitive and highly specific, and can be used for detecting organ metastasis, particularly micrometastasis, in a human tumor animal-xenotransplantation model.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Antiproliferative activity of G-rich oligonucleotides and method of using same to bind to nucleolin
InactiveUS20080318887A1Organic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthMetastatic cell
Compositions and methods for modulating tumor proliferation in an individual are provided. The methods employ nucleolin-binding agents, such as aptamers. The aptamers of the present invention can be used to modulate the proliferation of malignant, dysplastic, hyperproliferative, and / or metastatic cells through interference with molecular interactions and functions of nucleolin in the tumor cell.
Owner:ADVANCED CANCER THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of cancer
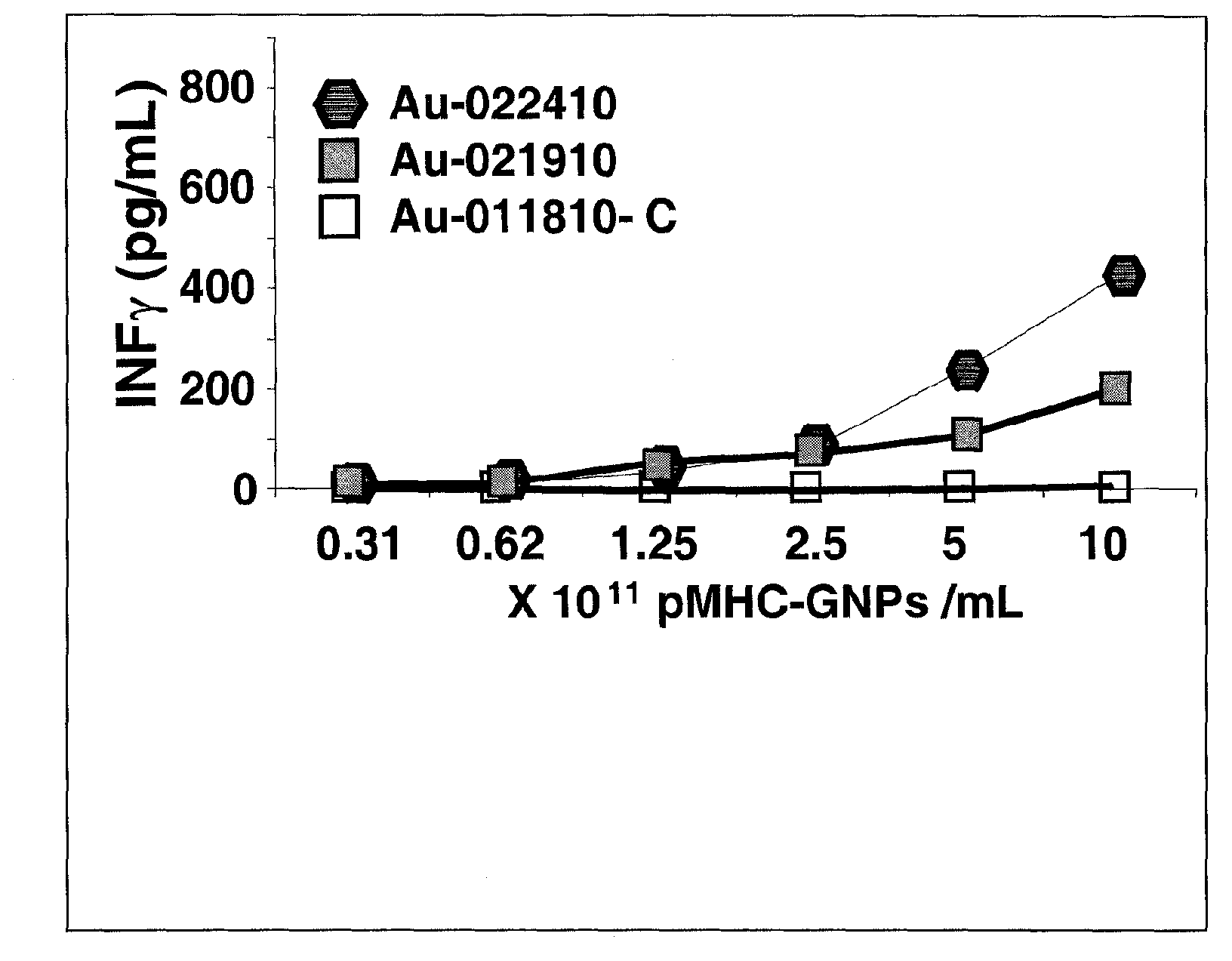
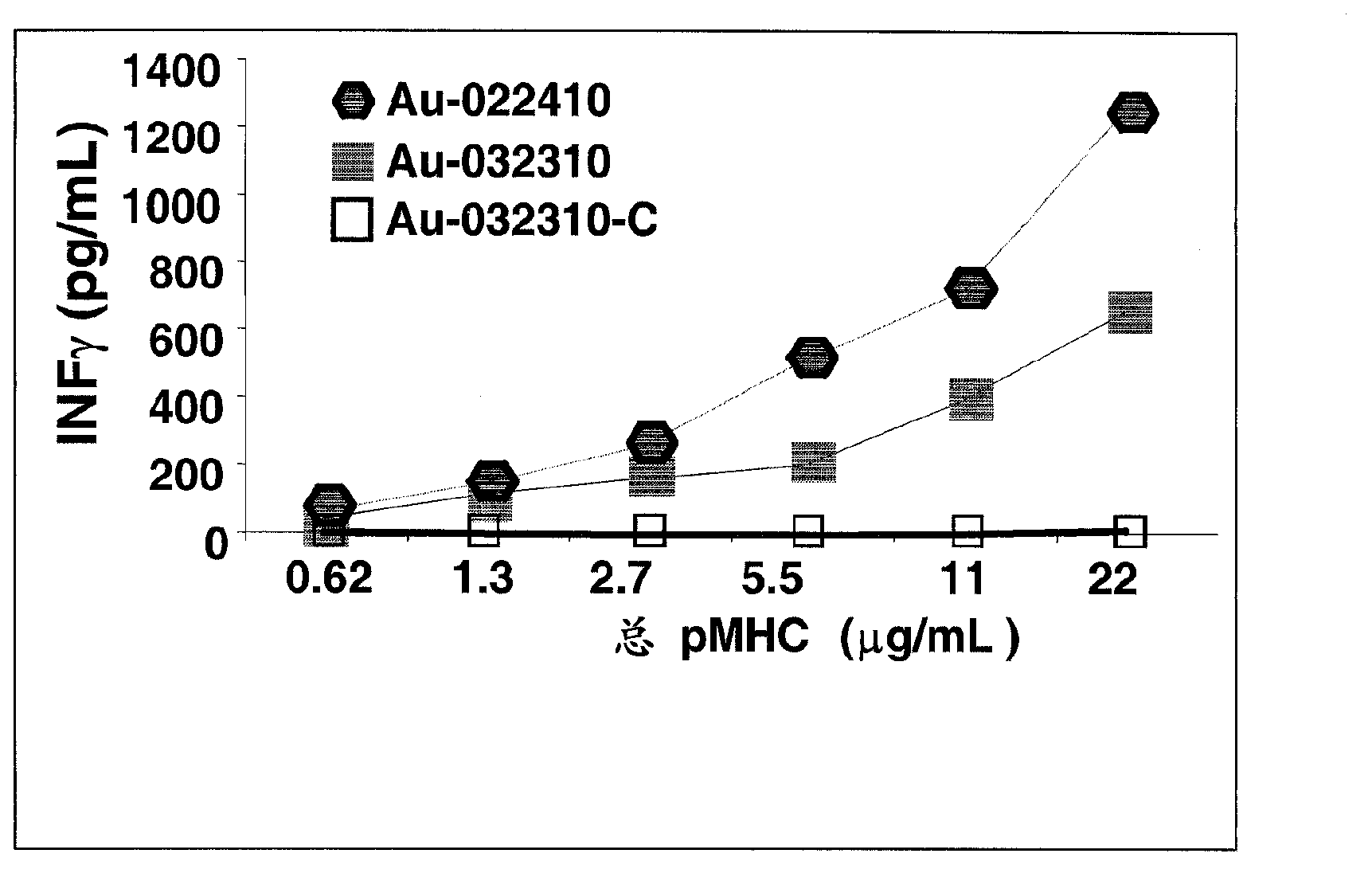
Conventional cancer immunotherapy falls short at efficiently expanding T cells that specifically target cancerous cells in numbers sufficient to significantly reduce the tumor size or cancerous cell number in vivo. To overcome this limitation, provided herein are nanoparticles coated with MHC class I and / or class II molecules presenting tumor-specific antigens and co-stimulatory molecules and their use to expand antigen-specific anti-tumorigenic T cellsto levels not achieved in current immunotherapeutic techniques. These antigen-specific anti-tumorigenic T cells include cytotoxic T cells, effector T cells, memory T cells, and helper T cells that are necessary to initiate and maintain a substantial immune response against metastatic or non- metastatic cancerous, pre-cancerous, or neoplastic cells in vivo.; The present invention describes a systemic approach to targeting cancerous or pre-cancerous cells that are circulating cells, as in lymphomas, migratory metastatic cells, and solid tumors.
Owner:UTI LLP
HLJ1 gene expression
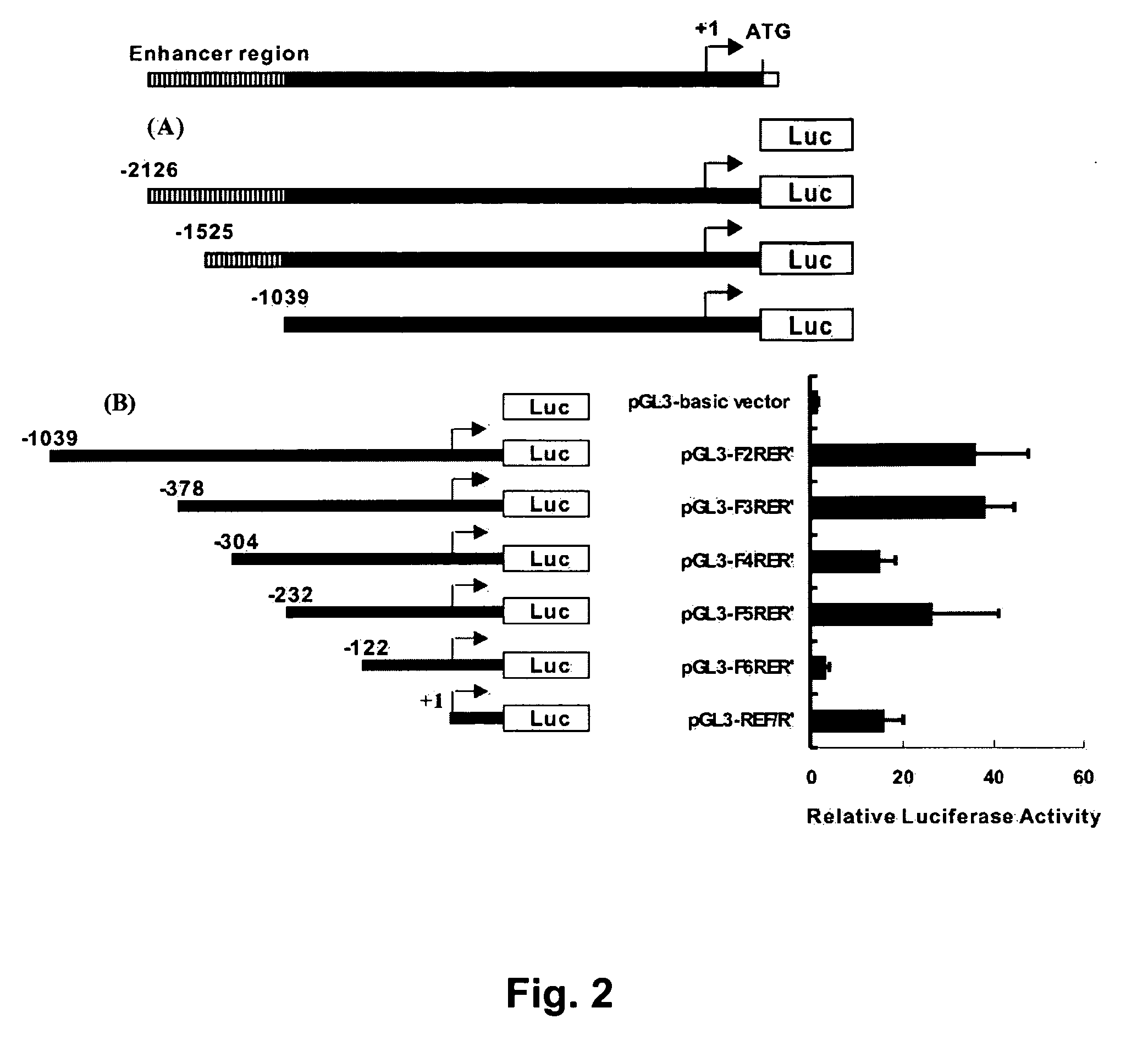
InactiveUS20060194235A1Increase transcriptionSlow metastasisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionTumour suppressor genePromoter activity
The human HLJ1 tumor suppressor gene is herein defined as regulated by promoter, enhancer, and silencer regions. HLJ1 promoter activity and gene expression are inversely correlated with metastatic ability. HLJ1 is highly expressed, and inducible, in cells with low metastatic ability and expressed to a lesser extent in highly metastatic cells. HLJ1 gene expression suppressed the growth of human lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. It also impeded the motility of human adenocarcinoma cells and reduced the anchorage-independent growth capacity and invasiveness of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma cells. The degree to which human lung adenocarcinoma patients express HLJ1 predicts their survival prognosis and their probability of relapse.
Owner:NAT HEALTH RES INSTITUES
Biology activity determination method of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN103792200AWide applicabilityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsSolubilityStaining
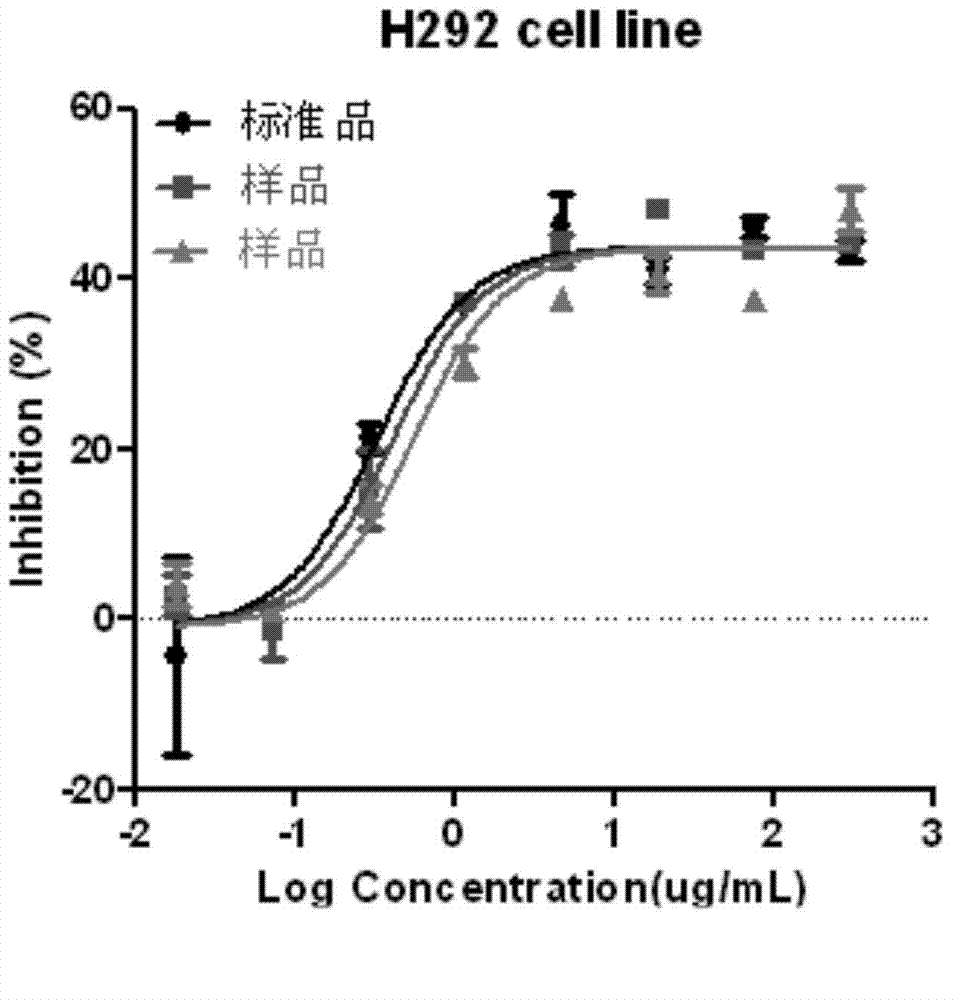
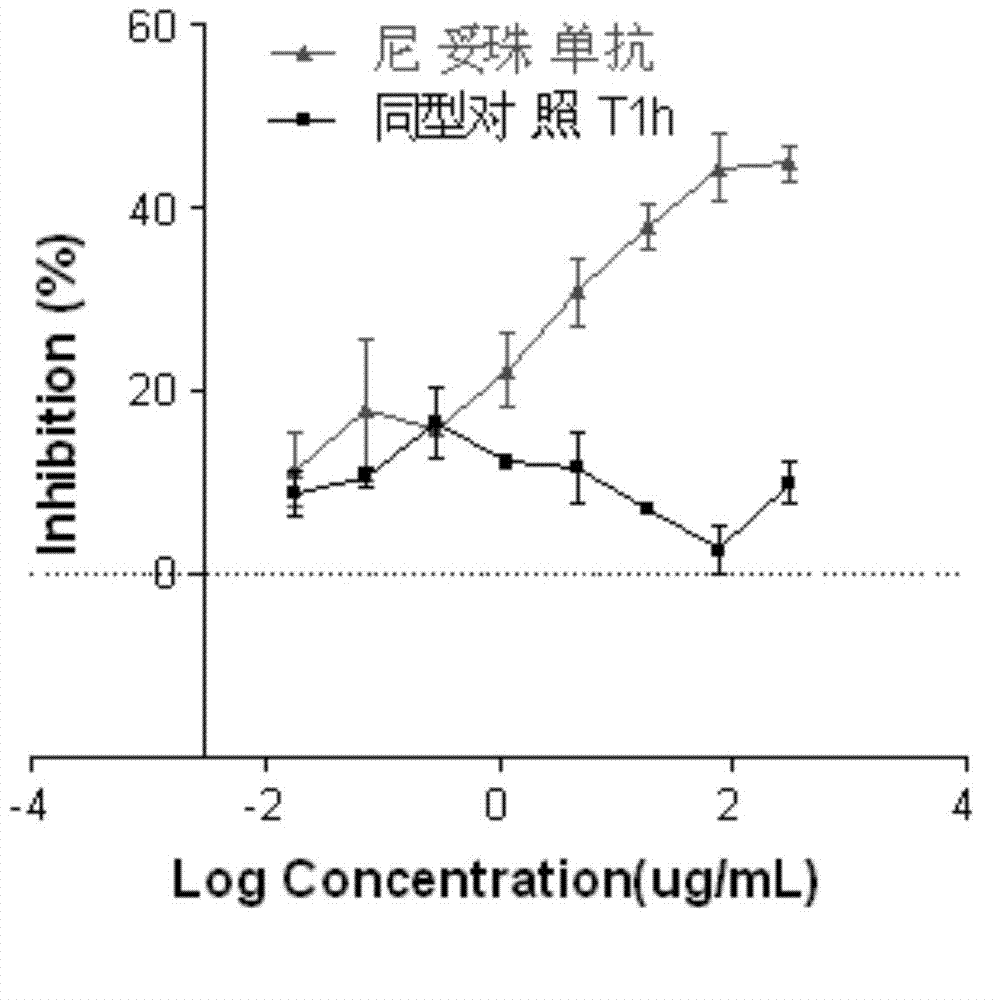
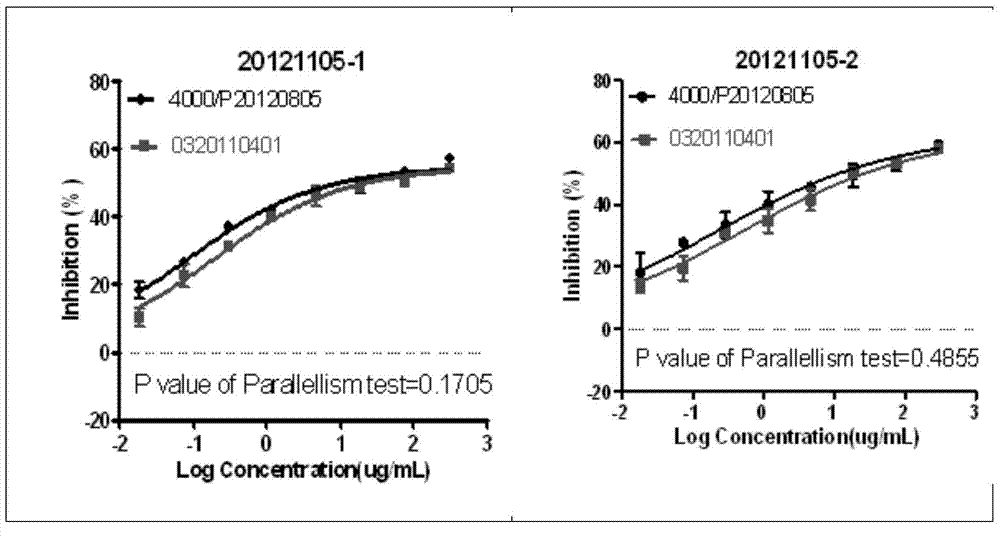
The invention discloses a biology activity determination method of a monoclonal antibody of a recombined anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor. The method comprises the following steps: incubating human lung cancer-lymph node metastasis cells H292 and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody with different concentrations; adding a cell counting dye reagent CCK-8; determining the light absorption value of stained vital cells through a microplate reader; processing experiment data through a computer program; calculating the biology activity of an anti-EGFR sample relative to an anti-EGFR standard. According to the invention, a cell strain with the detected cells H292 is applicable to antibodies with different affinities, the cell culture time is short, and the needed cell quantity is less; staining fluid of an MTT colorimetric method is improved, CCK-8 staining fluid is used, the product solubility is good, further solution treatment is not needed, the detection result can be detected at different time after the staining fluid is added, the developing result is stable, and the quality is controllable. The biology activity determined by the method is related to clinical effects, thus meeting the relevant technical requirement of FDA.
Owner:BIOTECH PHARMA CO LTD
Antiproliferative activity of G-rich oligonucleotides and method of using same to bind to nucleolin
Compositions and methods for modulating tumor proliferation in an individual are provided. The methods employ nucleolin-binding agents, such as aptamers. The aptamers of the present invention can be used to modulate the proliferation of malignant, dysplastic; hyperproliferative, and / or metastatic cells through interference with molecular interactions and functions of nucleolin in the tumor cell.
Owner:ADVANCED CANCER THERAPEUTICS
Arylquinoline, arylquinolone and arylthioquinolone derivatives and use thereof to treat cancer
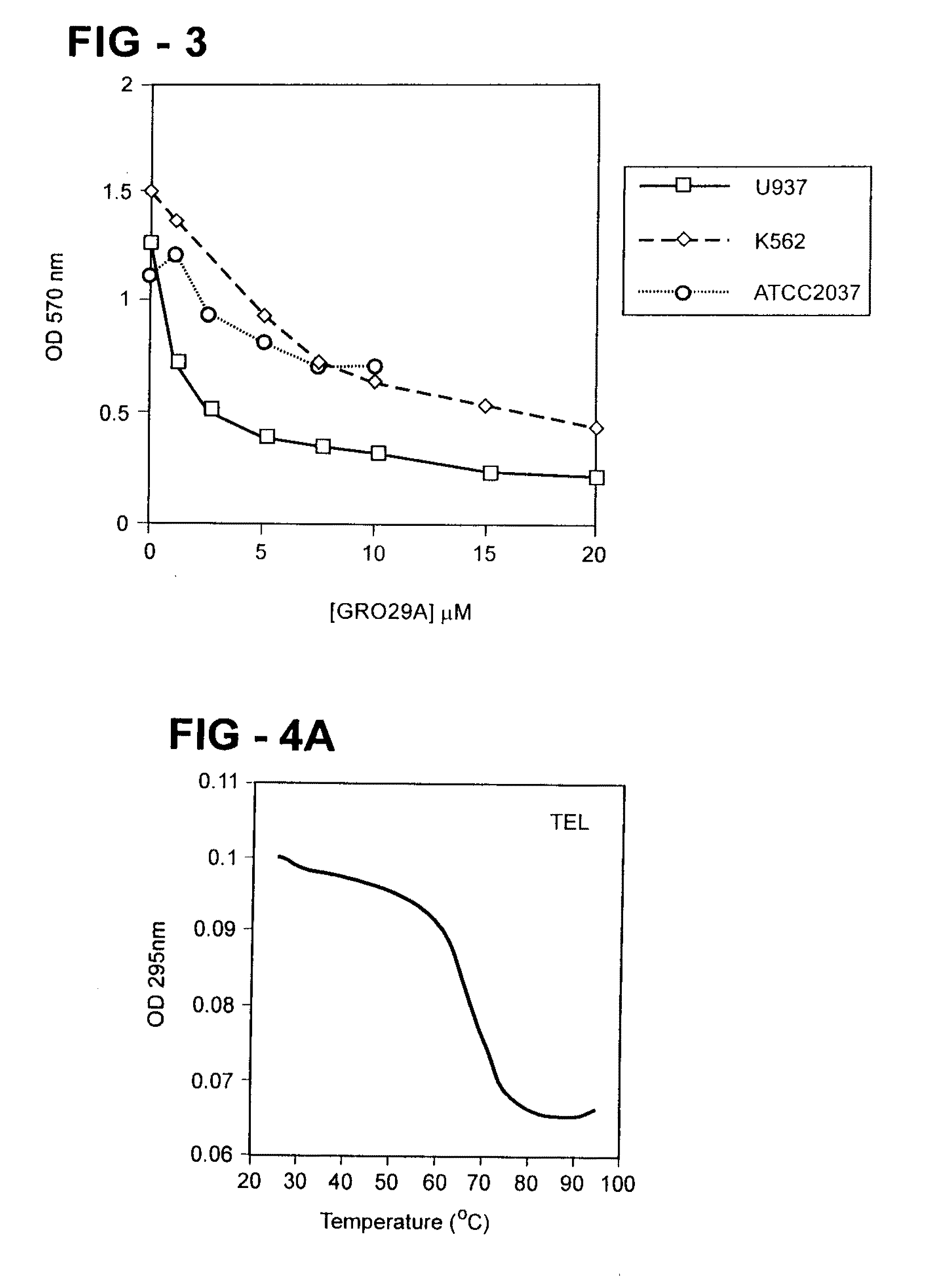
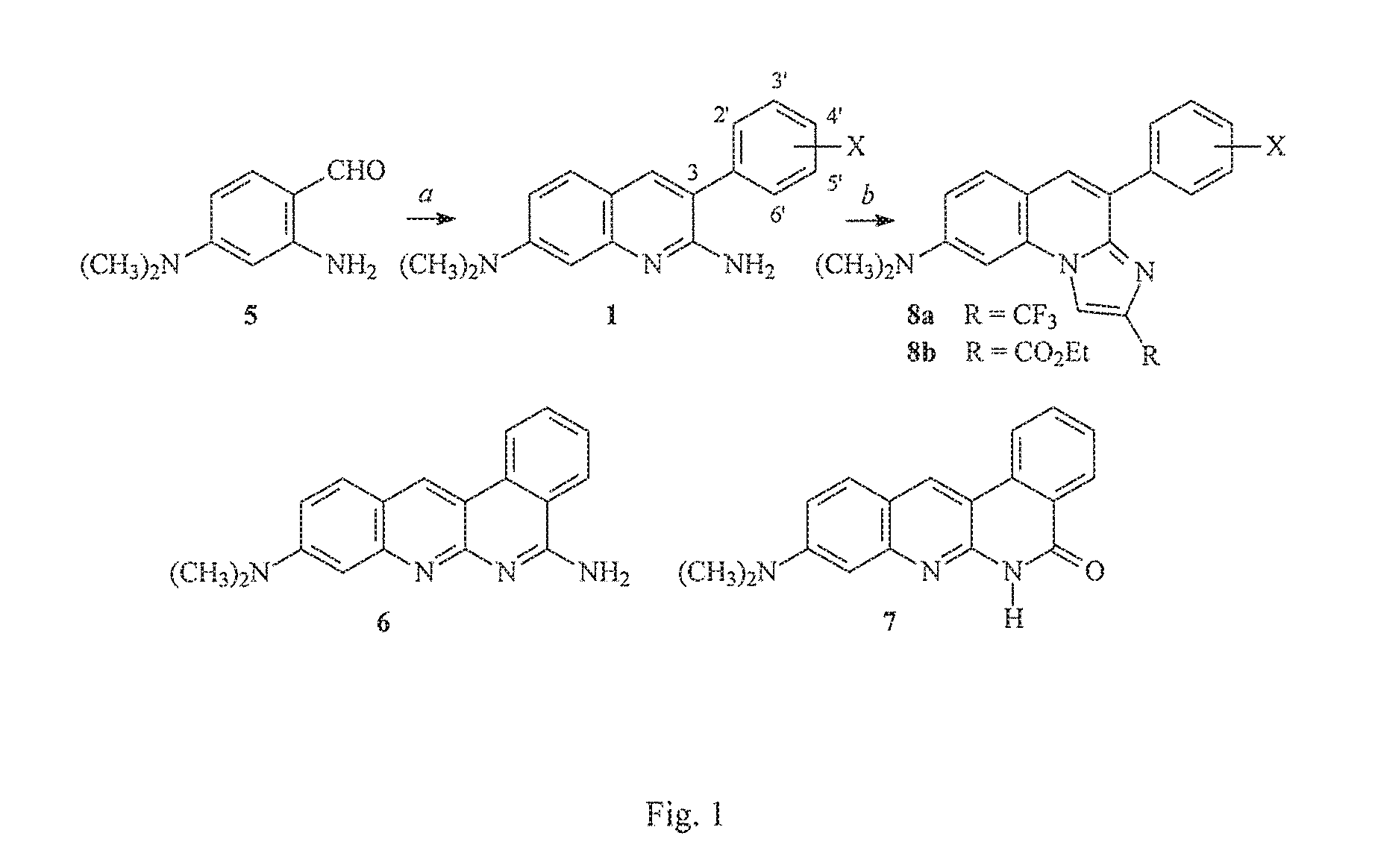
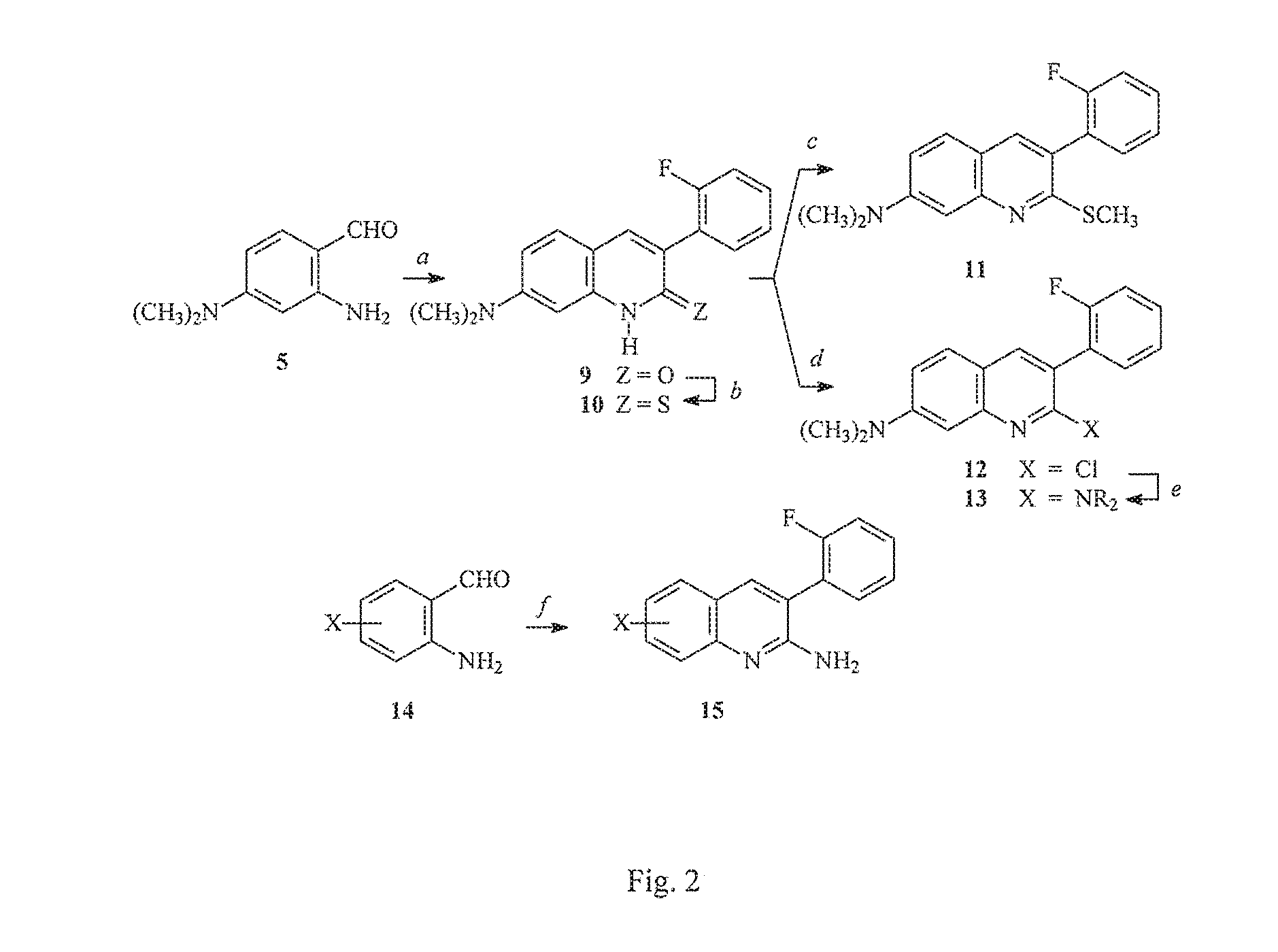
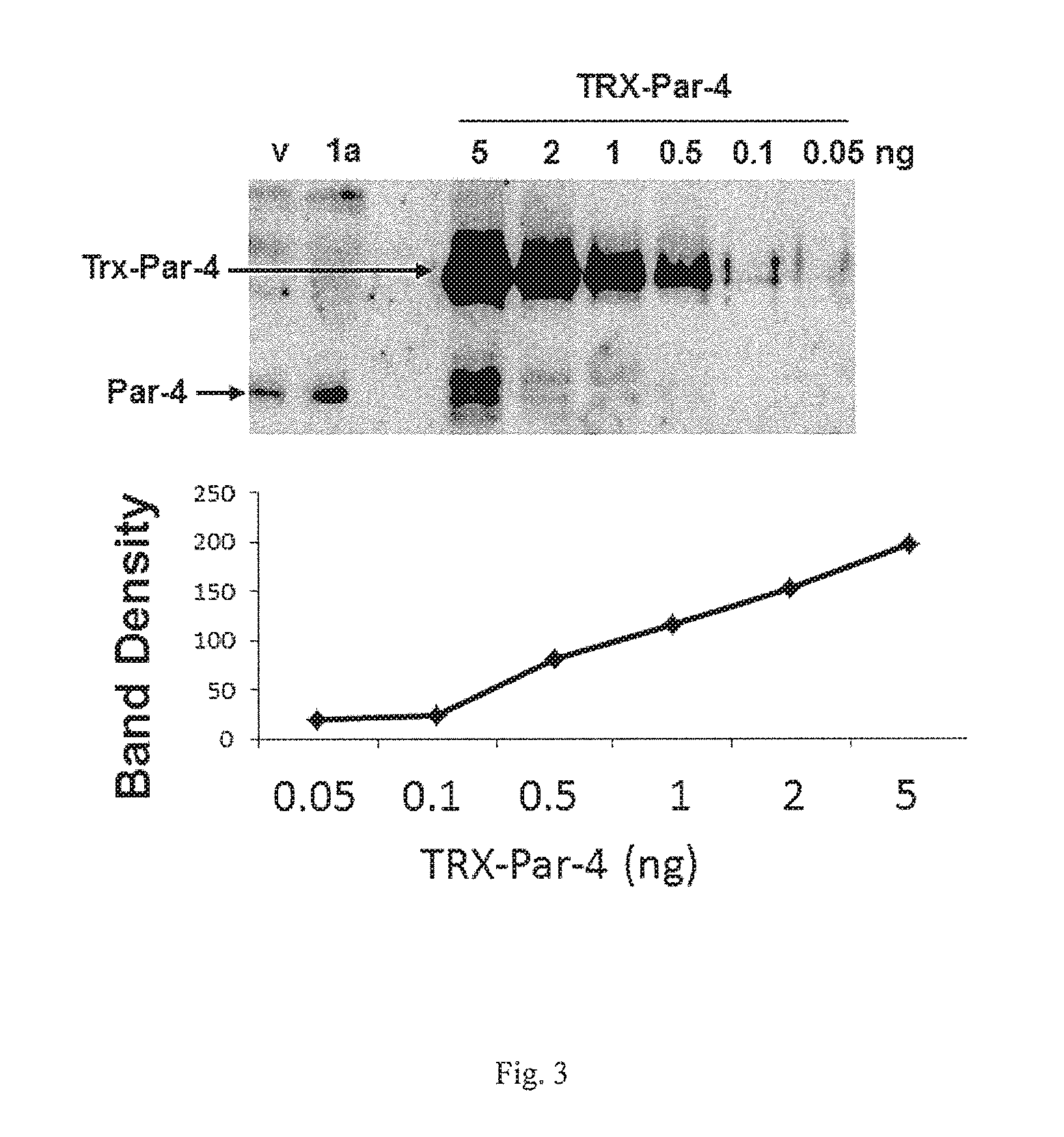
Arylquinoline derivatives and their use for treating cancer or cancer metastasis is disclosed. The compounds of the subject technology promote cells to secrete a pro-apoptotic tumor suppressor, i.e., prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4), which in turn promote apoptosis in cancer cells or metastatic cells.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Tumor specific antibodies and uses therefor
ActiveCN103492417AOrganic active ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsAntiendomysial antibodiesTumor-Specific Antibody
Provided are isolated antibodies, and fragments and derivatives thereof, which bind to tumor antigens. Also provided are compositions and delivery agents that include the disclosed antibodies and fragments and derivatives thereof; cells that produce the same; methods for producing the same; methods of using the same for detecting, targeting, and / or treating tumors and / or metastatic cells derived therefrom and / or tumor stem cells; and methods for predicting the recurrence of cancer in a subject.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
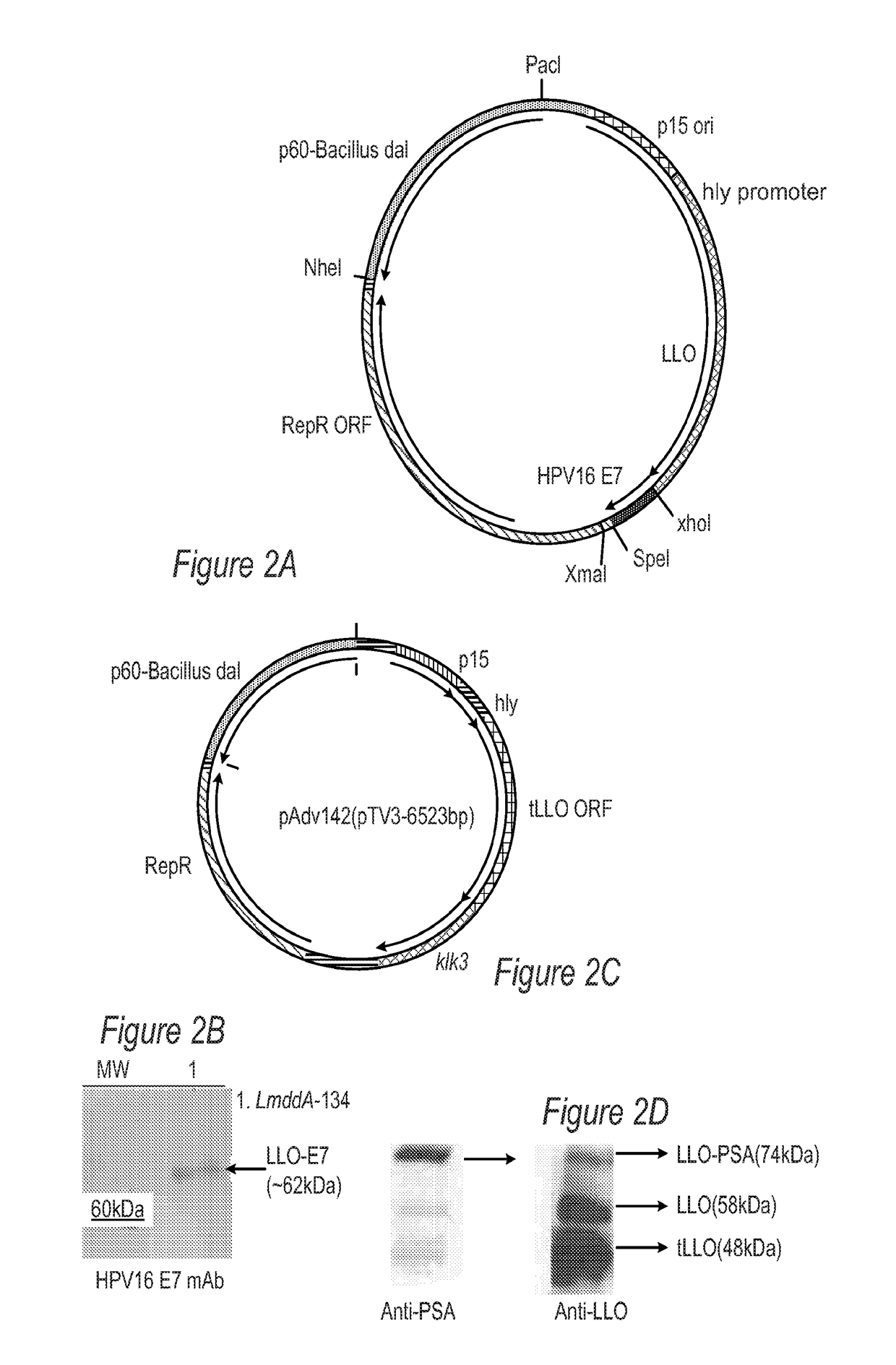
Combination Therapies With Recombinant Listeria Strains
InactiveUS20180153974A1Enhanced anti-tumor T cell responseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusion with degradation motifTransfer cellGenus Listeria
The disclosure is directed to compositions comprising an oncolytic virus, chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR T cells), a therapeutic or immunomodulating monoclonal antibody, a targeting thymidine kinase inhibitor (TKI), or an adoptively transferred cells incorporating engineered T cell receptors, and a live attenuated recombinant Listeria strain comprising a fusion protein of a Truncated LLO, a truncated ActA or a PEST-sequence peptide fused to a tumor-associated antigen. The disclosure is further directed to methods of treating, protecting against, and inducing an immune response against a tumor, comprising the step of administering the same, with or without an additional radiation therapy treatment.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Method for preparing breast cancer bone metastasis organs
InactiveCN111019903AIncrease success rateCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOncologyMetastatic cell
The invention relates to a method for preparing breast cancer bone metastasis organs, which comprises the following steps: mixing breast cancer bone metastasis cells, feeder layer cells, a temperature-sensitive hydrogel and a first culture medium, and culturing to obtain breast cancer bone metastasis organs; wherein the feeder layer cells comprise bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells without a proliferation function. By means of the technical scheme, the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells without the proliferation function are used as feeder layer cells for breast cancer bone metastasis organ culture, and the success rate of breast cancer bone metastasis organ culture through the method is high.
Owner:北京科途医学科技有限公司
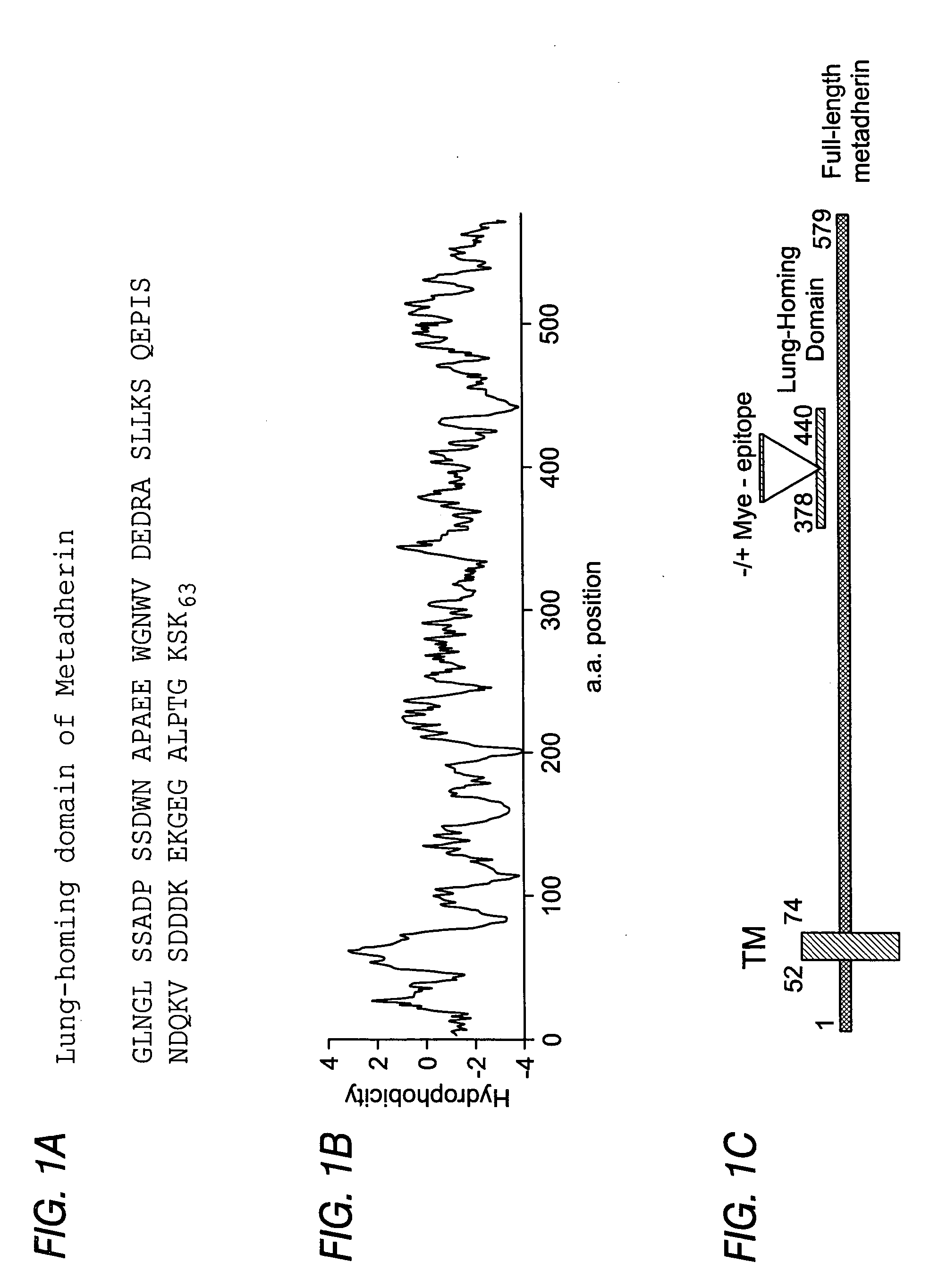
Metadherin polypeptides, encoding nucleic acids and methods of use
InactiveUS20050208057A1Compound screeningTumor rejection antigen precursorsLymphatic SpreadLung tissue
Metadherin, a protein that controls metastasis, and variants of metadherin are described. DNA sequences encoding the same and methods of production are described. Therapies involving the application of metadherin, binding agents that bind to metadherin, such as antibodies, and expression modulating agents, such as siRNA, are described. The use of metadherin or metadherin variants for delivering desired substances to particular lung tissue is described. A method of diagnosing metastatic cells based on the presence of metadherin is described.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Fluorescence labeled human triple-negative breast cancer osseous metastasis cell line
ActiveCN111593026ARealize visualizationAchieve traceabilityMicroorganism based processesPeptidesCell bodiesOncology
The invention provides a fluorescence labeled human triple-negative breast cancer osseous metastasis cell line. The fluorescence labeled human triple-negative breast cancer osseous metastasis cell line is prepared with a method as follows: a human triple-negative breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 is cultured; a lentivirus carrier containing RFP (red fluorescence protein) is amplified, and an RFP labelled MDA-MB-231 cell is prepared; the RFP-MDA-MB-231 cell is transplanted to the fourth pair breast fat pad position of a nude mouse and grows into tumor; shin bone of a hind limb is taken after 4-6 weeks, bone marrow is flushed with a buffer solution and digested with collagenase, a single cell from the bone marrow is obtained, in-vitro culture amplification is performed, and red fluorescence cells are sorted with a flow cytometry; through tumor formation screening in a body of the nude mouse, the red fluorescence labelled MDA-MB-231 human triple-negative breast cancer osseous metastasis cellline is obtained. The human triple-negative breast cancer osseous metastasis cell line has the characteristics of osseous metastasis, is labelled by fluorescent protein and realizes visualization andtraceability.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Antiproliferative activity of g-rich oligonucleotides and method of using same to bind to nucleolin
Compositions and methods for modulating tumor proliferation in an individual are provided. The methods employ nucleolin-binding agents, such as aptamers. The aptamers of the present invention can be used to modulate the proliferation of malignant, dysplastic, hyperproliferative, and / or metastatic cells through interference with molecular interactions and functions of nucleolin in the tumor cell.
Owner:ADVANCED CANCER THERAPEUTICS
Treatment of cancer/inhibition of metastasis
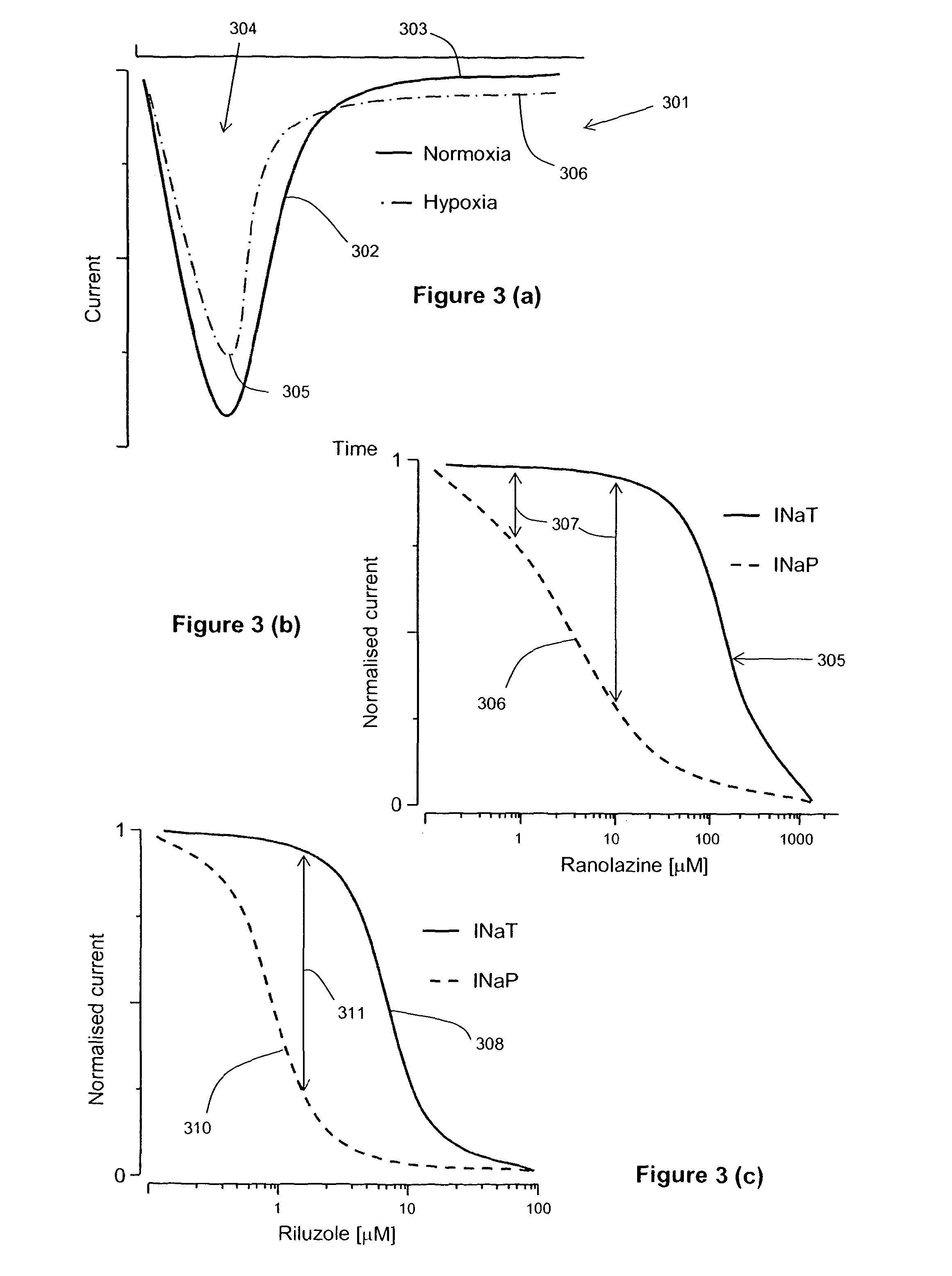
Substances and methods are disclosed for reducing or preventing metastatic behaviour in VGSC expressing cancer by the effect of at least reducing the persistent part of the voltage gated sodium channel current without eliminating the transient part. Inhibition of metastatic cell behaviours such as detachability, lateral motility, transverse migration and invasiveness is demonstrated using the known drugs ranolazine and riluzole.
Owner:DJAMGOZ MUSTAFA B A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com