Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Hyponitrite reductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a hyponitrite reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of hydroxylamine H₂NOH by the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide cation (NAD⁺) into hyponitrous acid HON=NOH: 2 H₂NOH + 2 NAD⁺ ⇌ HON=NOH + 2 NADH + 2 H⁺ This systematic name of this enzyme class hydroxylamine:NAD+ oxidoreductase. It is also called NADH2:hyponitrite oxidoreductase. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on other nitrogenous compounds as donors with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
Preparation method of nitrite reductase and enzyme product thereof
InactiveCN101597598AImprove stabilityImprove safety and qualityMicroorganism based processesAnimal feeding stuffFood poisoningSephadex gels
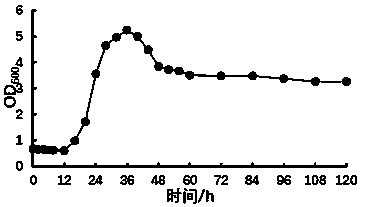
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrite reductase, comprising the following steps: inoculating lactobacillus in a MRS culture medium to culture a first generation strain and then to culture a second generation strain; inoculating the second generation strain in a MRS fermentation culture medium to culture for 30-48h; adding sodium nitrite solution in the fermentation solution to culture for 16-32h; collecting precipitate; adding buffer solution in precipitate to fully suspend the fermentation liquor precipitate, adding lysozyme solution and treating the mixture by ultrasonication to obtain broken cell solution, collecting supernatant; filtrating the supernatant and collecting the filtrate; separating the filtrate with a sephadex chromatographic column to obtain precipitate, namely, nitrite reductase and adding 10-50% of starch in the precipitate to obtain the enzyme product. The enzyme preparation prepared by the method can be used to remove the residue of nitrite in food, feed and environment, improves the food safety and quality and prevents the poisoning, cancer and the like caused by nitrite.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Bacillus cereus and application thereof to preparation of nitrite reductase
ActiveCN104212739AWide variety of sourcesFermented enzyme stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus cereusHigh activity
The invention discloses a Bacillus cereus and application thereof to preparation of nitrite reductase. The Bacillus is isolated from thick broad-bean sauce, and is identified as Bacillus cereus LJ01, which has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in June 19, 2014 and has a preservation number CGMCC No.9360. The strain LJ01 is used for the preparation of nitrite reductase (NiR); NiR extracted from Bacillus cereus LJ01 has high activity; and conditions for NiR to degrade nitrite are simple. The conditions disclosed by the invention can reduce NiR enzyme activity loss to obtain high purity NiR; and NiR provides a novel method for solving the problem of nitrite in three fields of fermented vegetables, meat products and aquaculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of nitrite reductase of lactobacillus casei subsp rhamnosus
InactiveCN104212775AProduces stable NiRWide variety of sourcesMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesLactobacillus casei subsp rhamnosusNitrite reductase
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrite reductase of lactobacillus casei subsp rhamnosus. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying inductive culture of nitrite reductase on lactobacillus casei subsp rhamnosus 6013; adding an enzyme protective agent to extract coarse nitrite reductase when the wall is broken; after carrying out vacuum-freezing and drying, finally preparing pure nitrite reductase sequentially through anion exchange chromatography and / or sephadex chromatography. The activity of NiR extracted from lactobacillus casei subsp rhamnosus is high and the condition for degrading nitrite reductase by NiR is simple. According to the disclosed condition, the enzyme activity loss of NiR is less, and the obtained NiR is high in purity and can be used for solving problem of nitrite in three fields such as vegetable fermentation, meat products and aquatic water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for degrading nitrites in foods
The invention discloses a method for degrading nitrites in foods. The method comprises the following steps of adding nitrite reductase in food sauce, performing standing for reaction for 6-12h at the temperature of 27-37 DEG C, then regulating a pH value with an organic acid to 2.0-5.5, and performing standing for reaction for 4-12h at the temperature of 20-37 DEG C, wherein a nitrite reductase gene is from edible bacteria. According to the method provided by the invention, by adopting a method for degrading sodium nitrite by adopting a crude enzyme solution firstly and then adopting the organic acid, and compared with a mode of singly using the organic acid or the nitrite reductase, the method has a good effect; the degradation rate of the sodium nitrite is calculated by determining the concentration of the nitrite in the system with a naphthylethylenediamine hydrochloride method to reach 90 percent or above; and the method can be used for degrading high-nitrite foods with a pH value larger than 5.0, such as pickles.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of nitrite reductase and method for preparing nitrite reductase preparation
InactiveCN101230337AHigh temperature resistantHave physical and mental healthMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCulture fluidFood safety
The invention discloses a preparation method of preparing nitrite reductase and preparing the preparation of the nitrite reductase, which belongs to the preparing technology field of biologic enzyme and enzyme preparation. Bacillus megatherium which can produce nitrite reductase is activated and prepared into seed, the obtained seed culture fluid is inoculate into a liquid ferment substrate by 1-10 percent of inoculation dosage; the initial pH value is 5.0-7.5, at 25-40 DEG C and 100-240r / min of rotation speed, after 20-36 hours of constant temperature cultivation, bacterial suspension is produced. Re-suspending the bacterial suspension by phosphate buffer can produce thalli. After the thalli is smashed by ultrasonic, the supernatant fluid is frozen and centrifugated, and then the rough enzyme solution is obtained. Nitrite reductases of different consistences and purities can be obtained after the rough enzyme solution is separated and purified. Liquid enzyme preparation can be prepared after enzyme protecting solute is added in the nitrite reductase. The enzyme activity of nitrite reductase preparation produced by using the invention is 4000-8000U / mL. The preparing method is simple, the production period is short, and public food safety can be maintained.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for degrading nitrite in salted fish through enzymic method
ActiveCN103750409APromote decompositionFacilitate functioningFood dryingFood preparationCold airFresh fish
The invention discloses a method for degrading nitrite in salted fish through an enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) washing fresh fish or frozen fish, salting the fish with salt, taking out the fish, rinsing with clean water, and draining; (2) adding nitrite reductase into the salted fish, wherein the addition amount of the nitrite reductase is 0.8-1.6g per kg of fish, and the enzymatic activity of the nitrite reductase is 3,500-4,500U / g; (3) airing the fish treated with an enzyme solution on a drying rack for 1-2 hours, putting the fish in a low-temperature heat pump dryer or cold-air drying equipment at the temperature of 28-35 DEG C, and airing the fish until the moisture content of the fish body is 35-45 percent. According to the method, the content of the nitrite generated in the process of processing the salted fish can be effectively reduced, the taste and quality of the salted fish products are kept, and the safety of the salted fish products is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
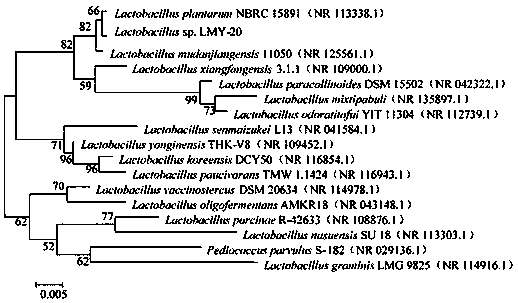
Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, protein coded by gene and applications of protein
PendingCN109609524AEfficient degradationHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNitrite reductase
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, a protein coded by the gene and applications of the protein, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. In the present invention, the nitrite reductase gene in lactobacillus plantarum is cloned by a PCR technology and induced to express in escherichia coli, and affinity chromatography purification is utilized to obtain a high-purity recombinant protein. The high-purity protein purified by the method of the invention can effectively degrade nitrite in food, and the structure and properties of the protein can be studied.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, protein encoded by lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene and preparation method of protein
InactiveCN104152469AHigh puritySolve the problem of isolating nitrite reductase with higher purityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesAntigenEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, protein encoded by the lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene and a preparation method of the protein. A nucleotide sequence of the lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. A gene sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 is cloned to a prokaryotic expression vector pET-32a(+); inducible expression is carried out in recombinant escherichia coli; high-purity recombinant protein is obtained by affinity chromatography purification. By using the high-purity protein purified by the method disclosed by the invention, nitrite can be effectively degraded, an enzymic preparation can be produced, the nitrite in food can be effectively degraded, and the protein can also be applied to preparation of a lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase antibody as an antigen, and can be applied to research of structure and property of the antibody.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
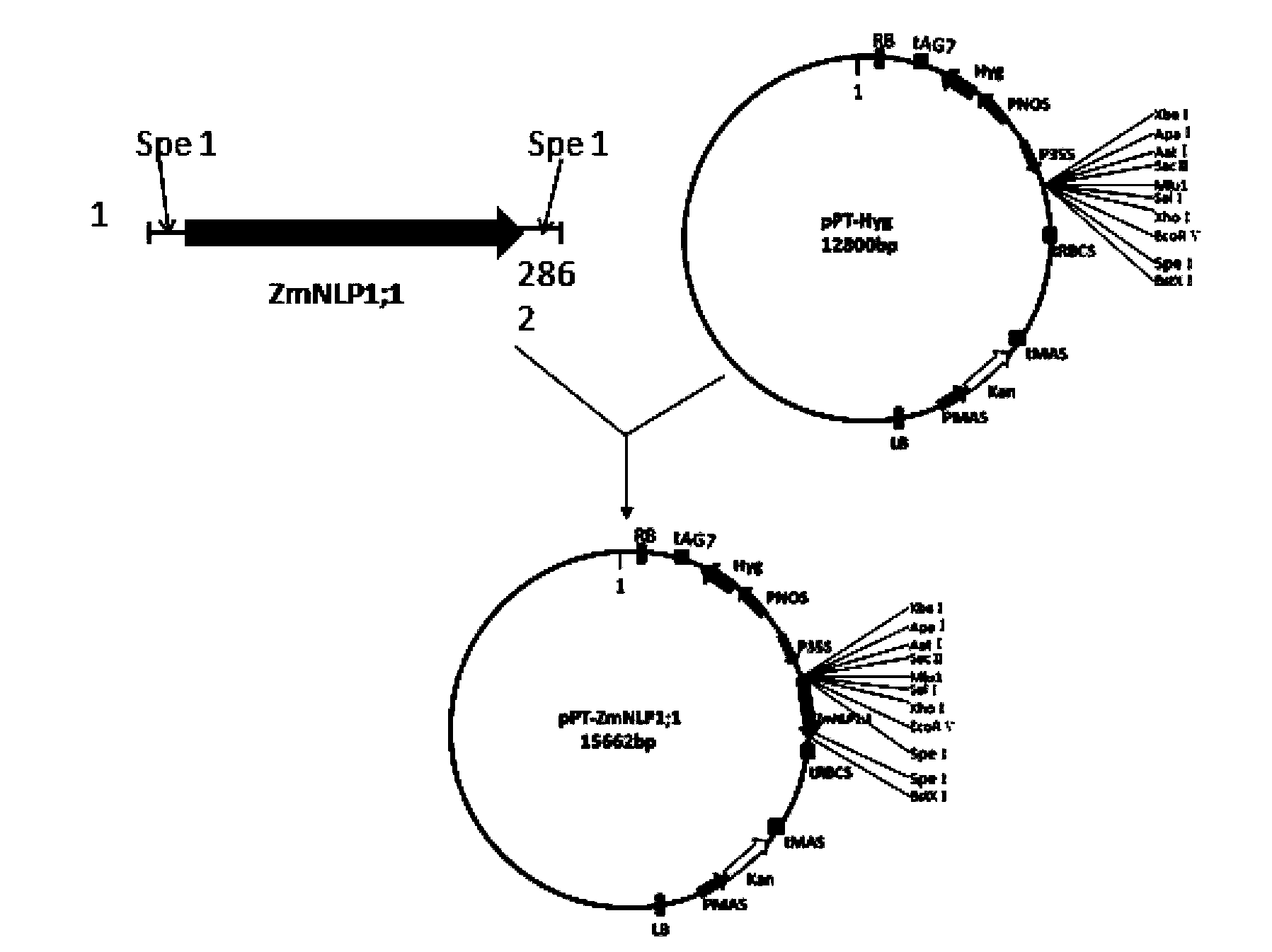
Transcription factor ZmNLP4 derived from corn and application thereof
ActiveCN107602683AIncrease biomassIncrease the content of amino acidsPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideLateral root
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and provides a transcription factor ZmNLP4 derived from corn and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a coded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with a receptor Arabidopsis, the Arabidopsis in which the transcriptionfactor is transferred has the advantages that the total biomass is obviously increased, the content of in-vivo amino acids and total nitrogen is increased, the main root length and quantity of lateral roots are obviously increased, the yield per plant is obviously increased, and the expressions of nitrate transporters, nitrate reductase genes and nitrite reductase genes are obviously increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
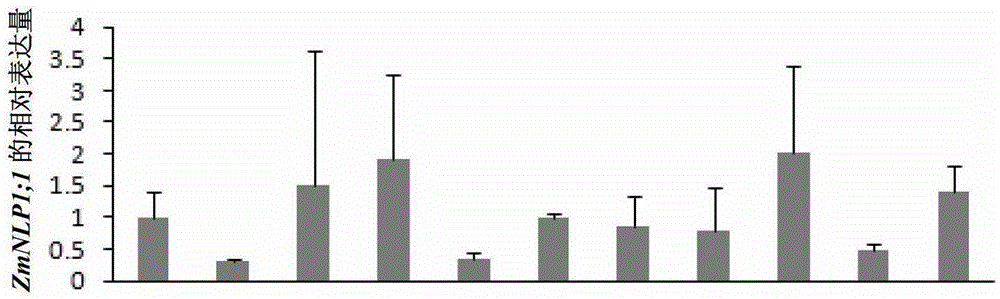
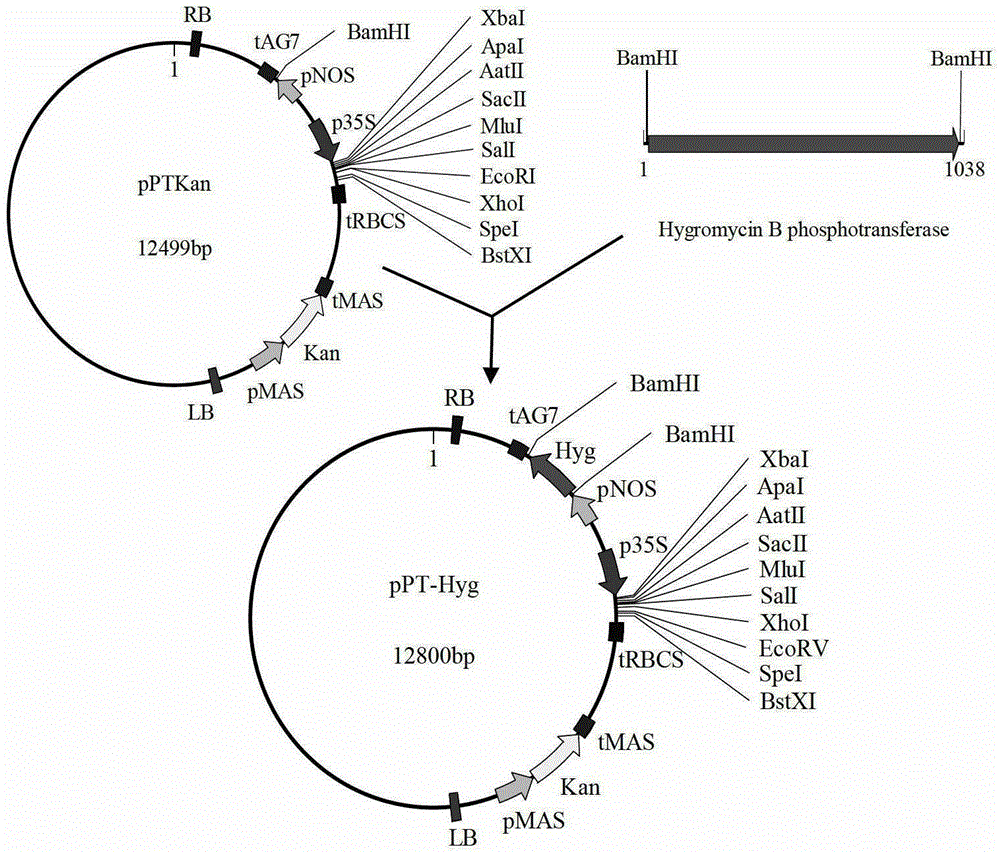
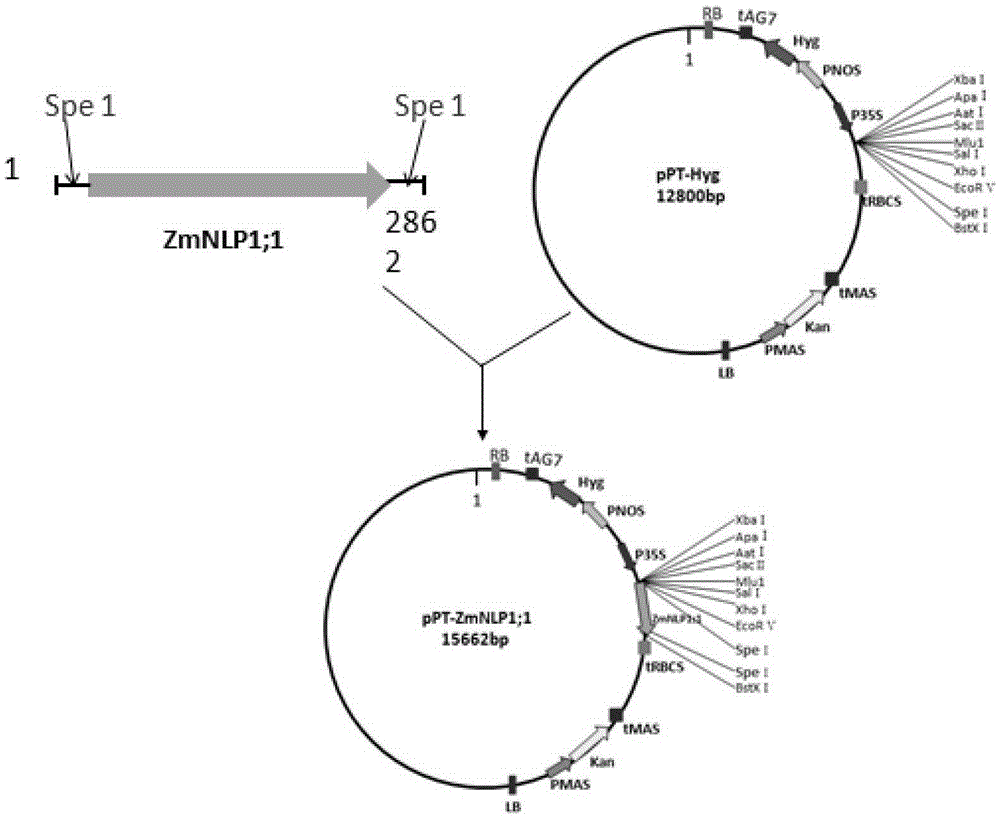
Transcription factor derived from corn and new use of coding gene thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor derived from corn and new use of a coding gene thereof. The new use provided by the invention is a method using a coding nucleic acid molecule of ZmNLP1;1 to cultivate a transgenic plant. The method is a method for cultivating the transgenic plant with at least one characters of the following 1)-4): 1) aboveground biomass is higher than that of a receptor plant; 2) after induction of a nitrate, the nitrate transport protein gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; 3) after induction of the nitrate, nitrate reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and 4) after induction of the nitrate, nitrite reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and the method comprises a step for introducing a ZmNLP1;1 gene into the receptor plant; and the ZmNLP1;1 gene codes a protein shown in SEQ ID No.2. Experiments show that, in the condition of using nitric nitrogen (NO<3->) as a sole nitrogen source, the aboveground biomass and the total biomass of arabidopsis transgenic with the ZmNLP1;1 gene are increased significantly compared with that of receptor arabidopsis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
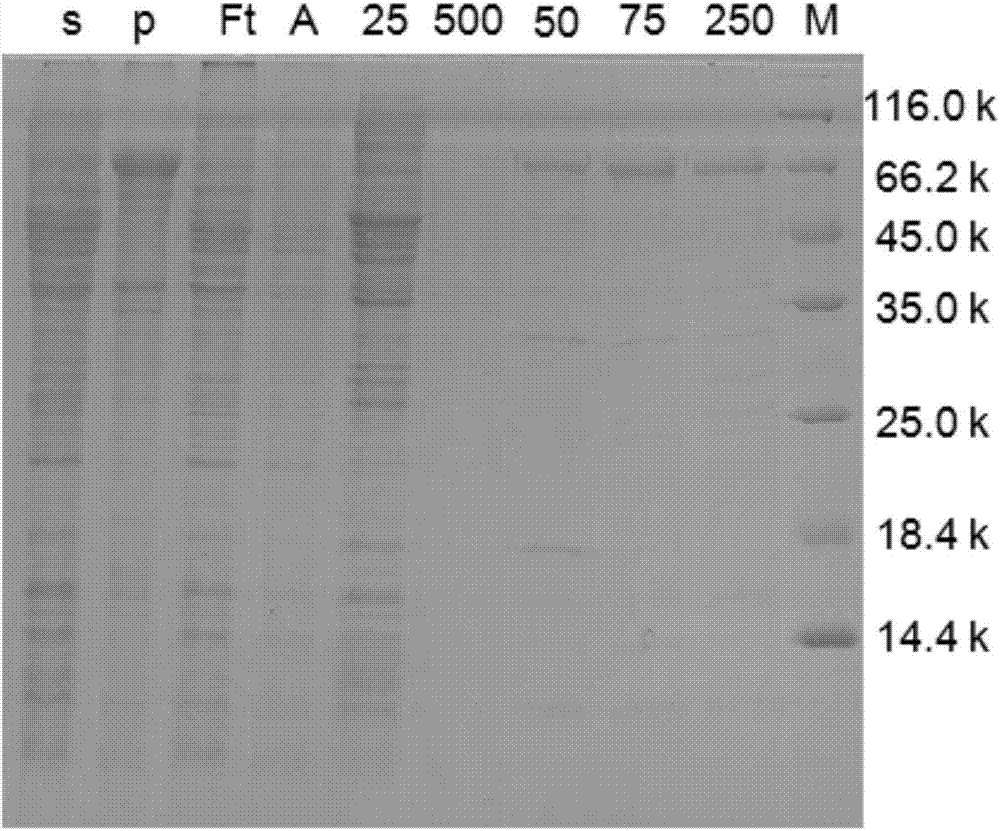
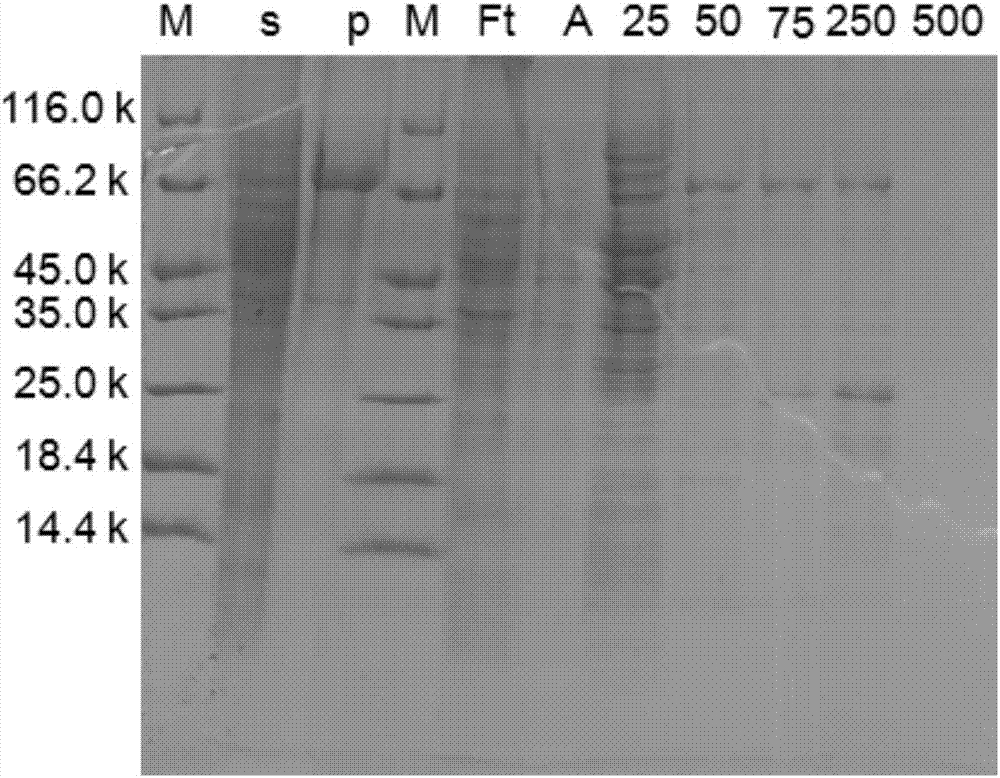
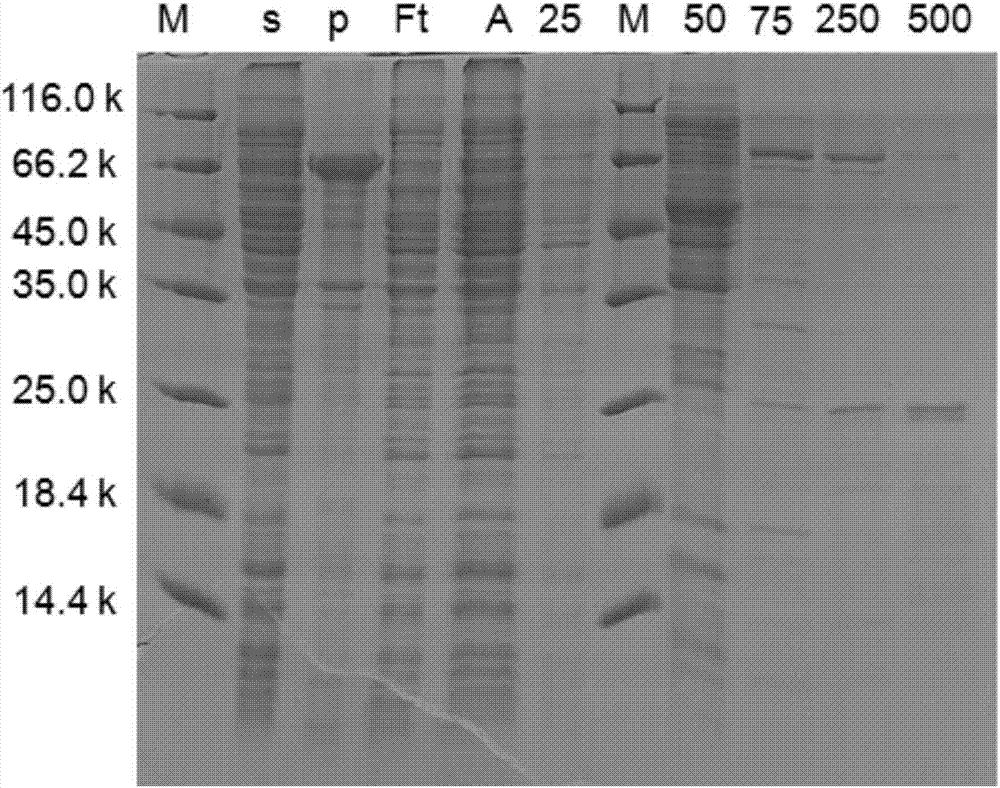
Recombinant nitrite reductase and construction method thereof
The invention discloses recombinant nitrite reductase and a construction method of the recombinant nitrite reductase. An NiR (nitrite reductase) gene in bacillus cereus LJ01 is amplified by adopting the PCR technology, the amplified gene is cloned to a carrier, an expression host strain is transformed, recombinant bacteria induced by IPTG is added, shaking culture is carried out at 16-37 DEG C, fermentation liquor is centrifugalized, bacterial sludge is taken, resuspending is carried out, high-pressure grinding is carried out, and crude enzyme liquid is extracted, wherein the bacillus cereus LJ01 is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC NO.9360. According to the technical scheme, the NiR gene is cloned, the cloned gene is expressed in a large amount in a host cell, meanwhile, the recombinant protein is provided with a specific label through plasmids, so that the purification process is simplified, and the extraction amount of NiR is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for regulating microbial denitrifying florae on basis of combination of powdered activated carbon and organic matter
PendingCN108178324AAdapt and stabilizeRaise the ratioBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeCommunity structure
The invention relates to a method for regulating microbial denitrifying florae on the basis of combination of powdered activated carbon and organic matter. According to the method, after activated anammox sludge, anaerobic granular sludge and activated carbon powder are added to an SAMBR, to-be-treated wastewater is introduced, the organic matter is added, and the microbial denitrifying florae areregulated. The method has the following advantages: microbial community structure in the anammox process can be domesticated effectively, and nitrogen-containing wastewater containing the organic matter can be removed from the domesticated activated sludge; proteobacteria becomes dominant phylum, relative content of predicted genes related to nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase and other enzymes throughout a denitrification pathway in a nitrogen circulation pathway is increased remarkably, the whole denitrification process is enhanced, and the anammox process can adapt to the wastewatercontaining the organic matter.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104152393AGuaranteed purityStable biological activityBacteriaClimate change adaptationNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention relates to engineering bacteria based on nitrite reductase and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria in the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: by taking streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA as a template, performing PCR amplification with a primer containing enzyme cutting sites to sequentially obtain nucleotide sequences for encoding nitrite reductase large-subunits and nitrite reductase small subunits; sequentially connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplification to a coexpression vector pETDuet-1, and finally obtaining a recombinant coexpression vector pETDuet-NC-ND; and transforming the nitrite reductase expression vector into an Escherichia coli expression strain. Aiming at the defects that the application range and effect are severely limited because most of the nitrite reductases are intracellular enzymes in a living body and the expression quantity is low in the prior art, the engineering bacteria can realize great in-vitro expression synthesis of the nitrite reductase by using genetic engineering means and has high significance for rapidly repairing secondary salinization soil and realizing precision agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bacillus megaterium co-expression vector for nitrite reductase and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103614404AExpression guaranteeLimit use effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEscherichia coliBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a bacillus megaterium co-expression vector for nitrite reductase and a construction method thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the co-expression vector, all genome sequences of bacillus megaterium are determined and serve as a template, gene sequences containing restriction enzyme cutting sites, namely a large subunit (Bm-Nas D) and a small subunit (Bm-Nas E) of nitrite reductase, are amplified according to designed PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers and are sequentially connected to the co-expression vector pETDuet-1, and positive clones of Escherichia coli DH5alpha containing target gene fragments are selected by a colony PCR technology. The co-expression vector has the advantages that the defect in the prior art that the use effect is seriously restricted due to the fact that the expression level of the gene sequence of the small subunit of nitrite reductase in natural bacillus megaterium is very low is overcome, and the genetic expression level is increased greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing nitrite reductase from flammulina velutipes
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
Bacillus cereus NiR (nitrite reductase), gene and application
InactiveCN105063066AHigh purityAddressing Purity IssuesWater contaminantsEnzymesEscherichia coliNitrite reductase
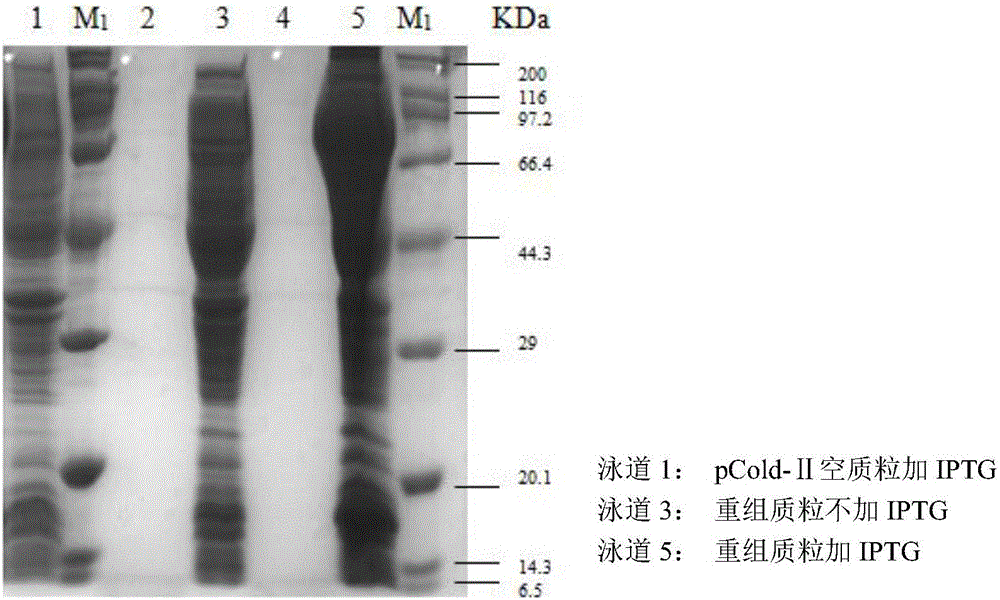
The invention discloses a Bacillus cereus NiR (nitrite reductase), a gene and an application. The NiR gene in Bacillus cereus LJ01 is cloned and induced for expression in Escherichia coli with the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, cells of blank-plasmid-containing BL21 subjected to IPTG (isopropyl beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside) induction, recombinant-plasmid-containing BL21 subjected to induction without IPTG and recombinant-plasmid-containing BL21 subjected to IPTG induction are subjected to ultrasonic crushing for extraction of crude enzymes, SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is performed on the crude enzymes for detection of recombinant protein expression, high-purity recombinant protein is obtained through affinity chromatography purification, and the problem about separation of NiR with higher purity and content from the Bacillus cereus is solved. A large amount of NiR recombinant protein can be used for degrading nitrite in food, non-acid environments and aquatic water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Aspergillus parasiticus and applications thereof in preparation of nitrite reductase, nitrite reductase gene and genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN104312925AReduce energy consumptionPromote degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesNitrite reductaseGenetically engineered
Aspergillus parasiticus and applications thereof in preparation of nitrite reductase, a nitrite reductase gene and a genetically engineered bacterium containing the nitrite reductase are disclosed. The accession number of the aspergillus parasiticus is CCTCC M2013662. The aspergillus parasiticus has characteristics of high efficiency, low energy consumption, good nitrite degradation effects, and rapid and reliable degradation is provided, and can be well applied in preparation of the nitrite reductase, preparation of the nitrite reductase gene and preparation of the genetically engineered bacterium containing the nitrite reductase.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
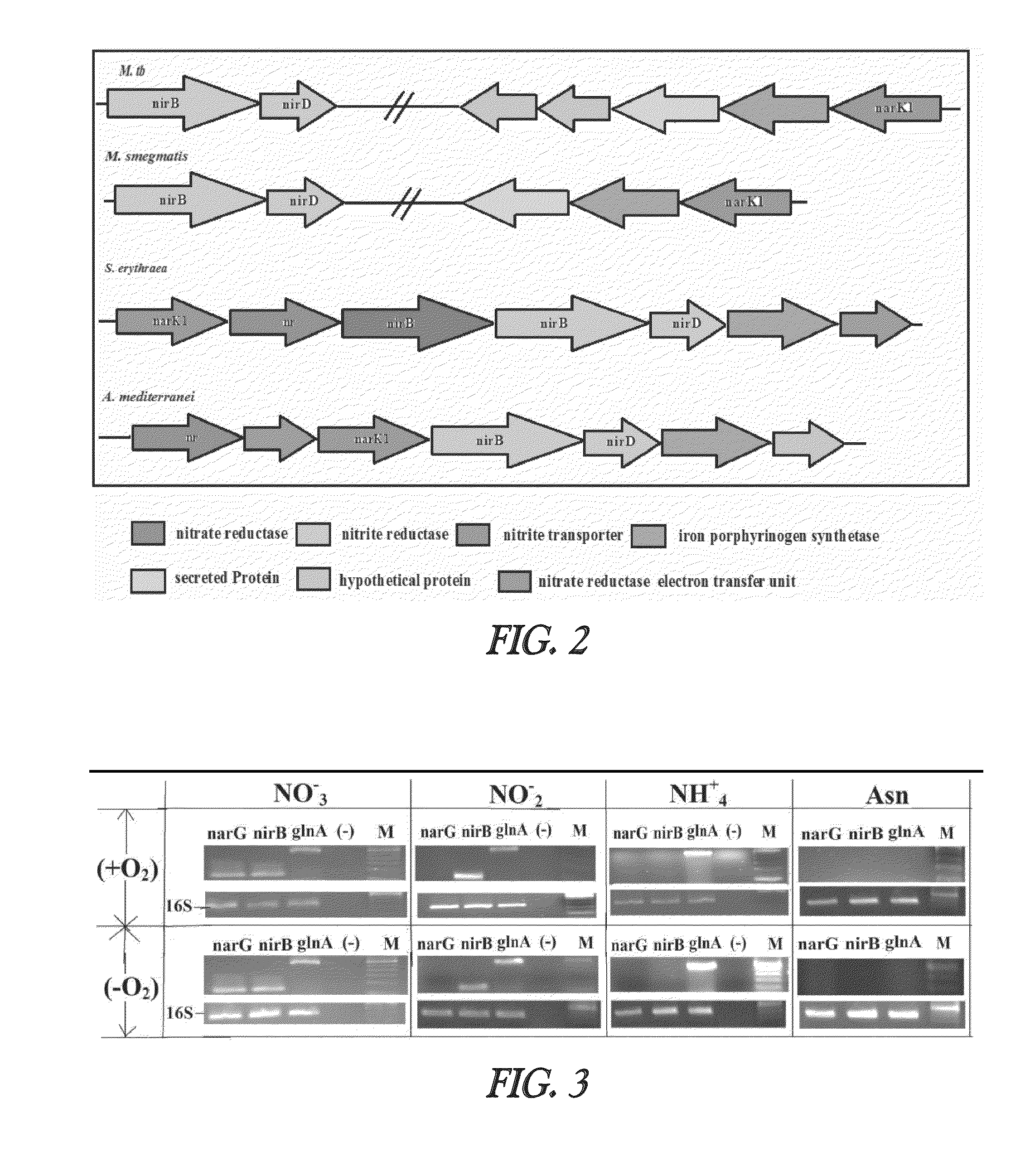
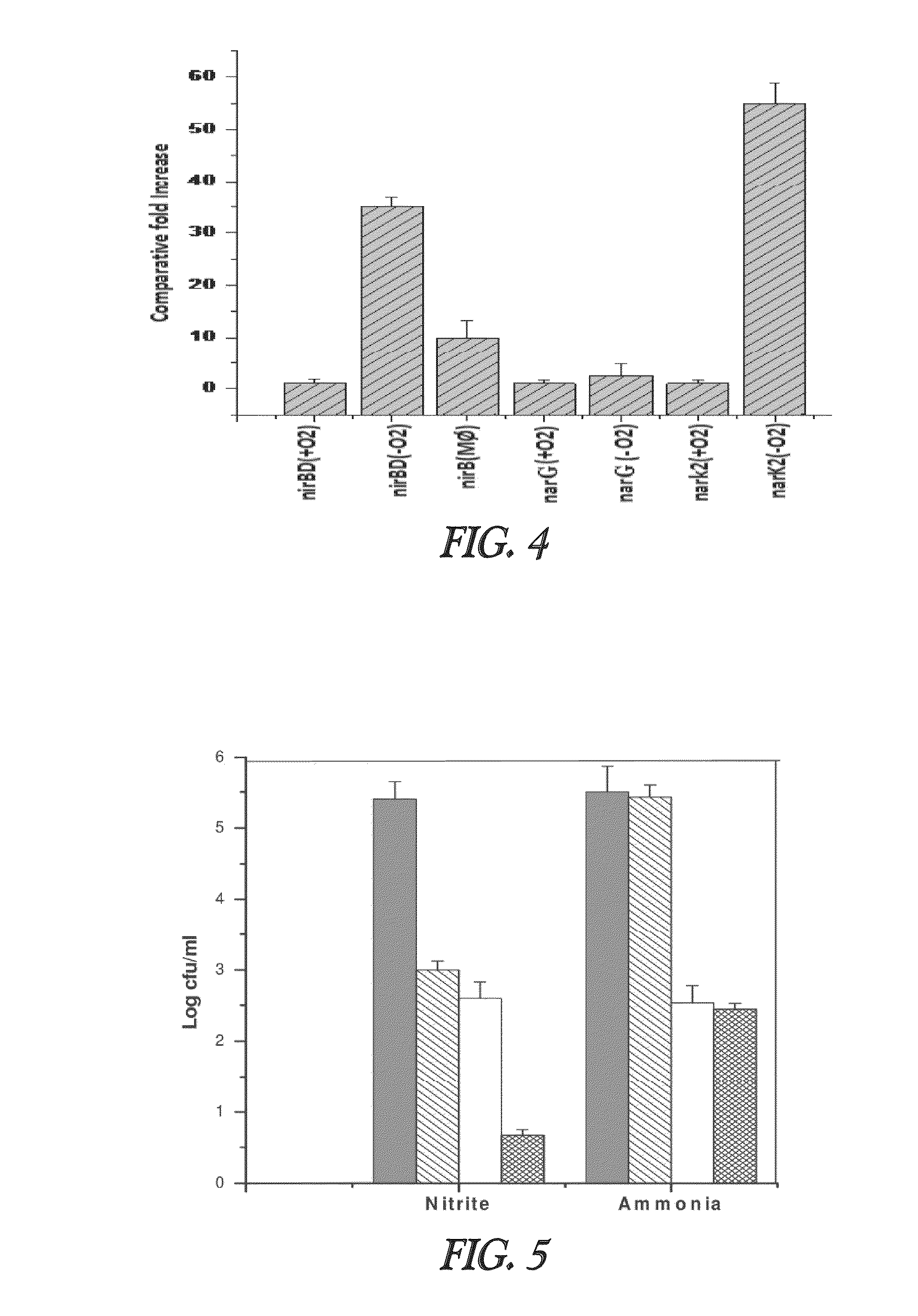
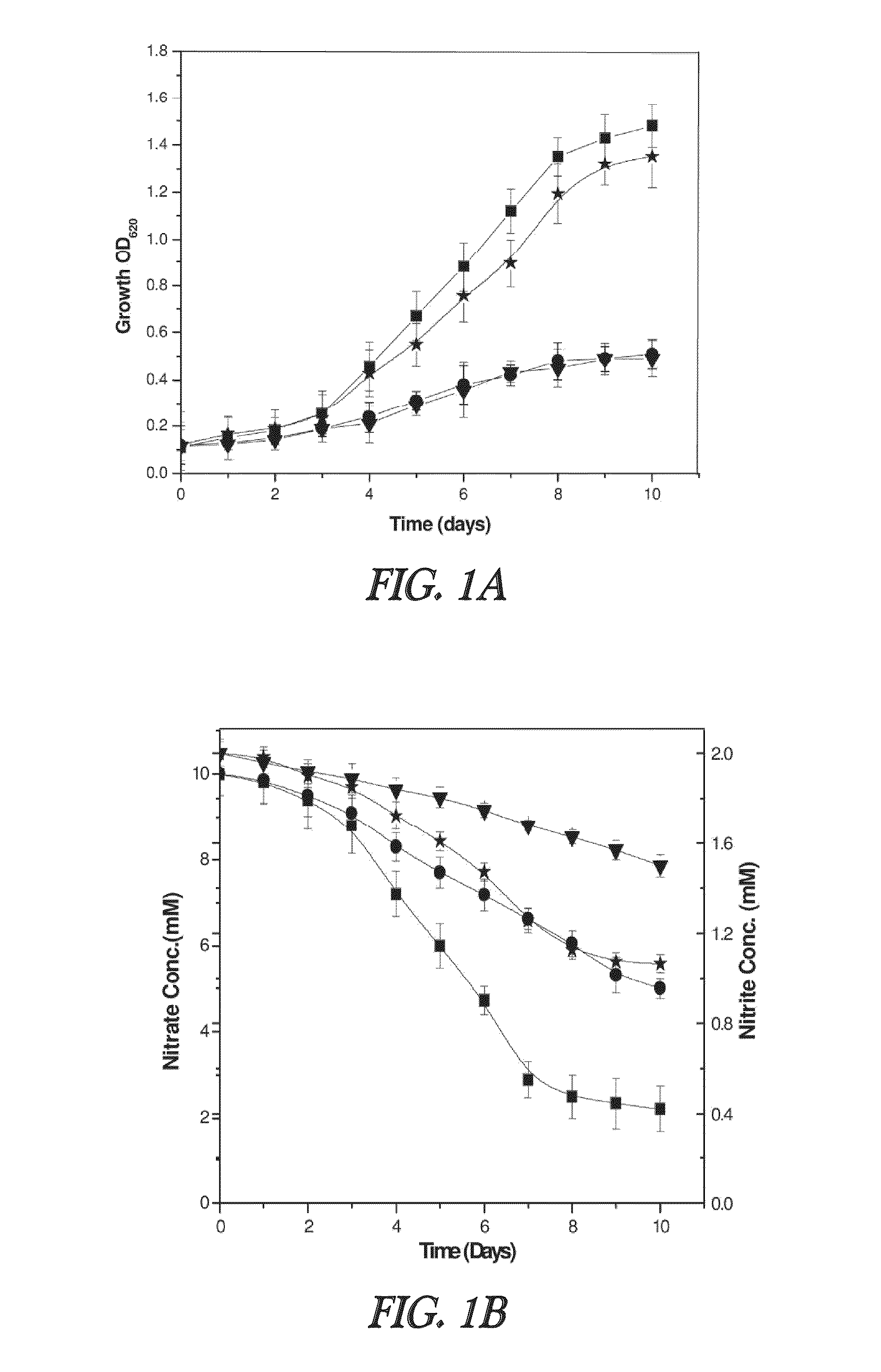
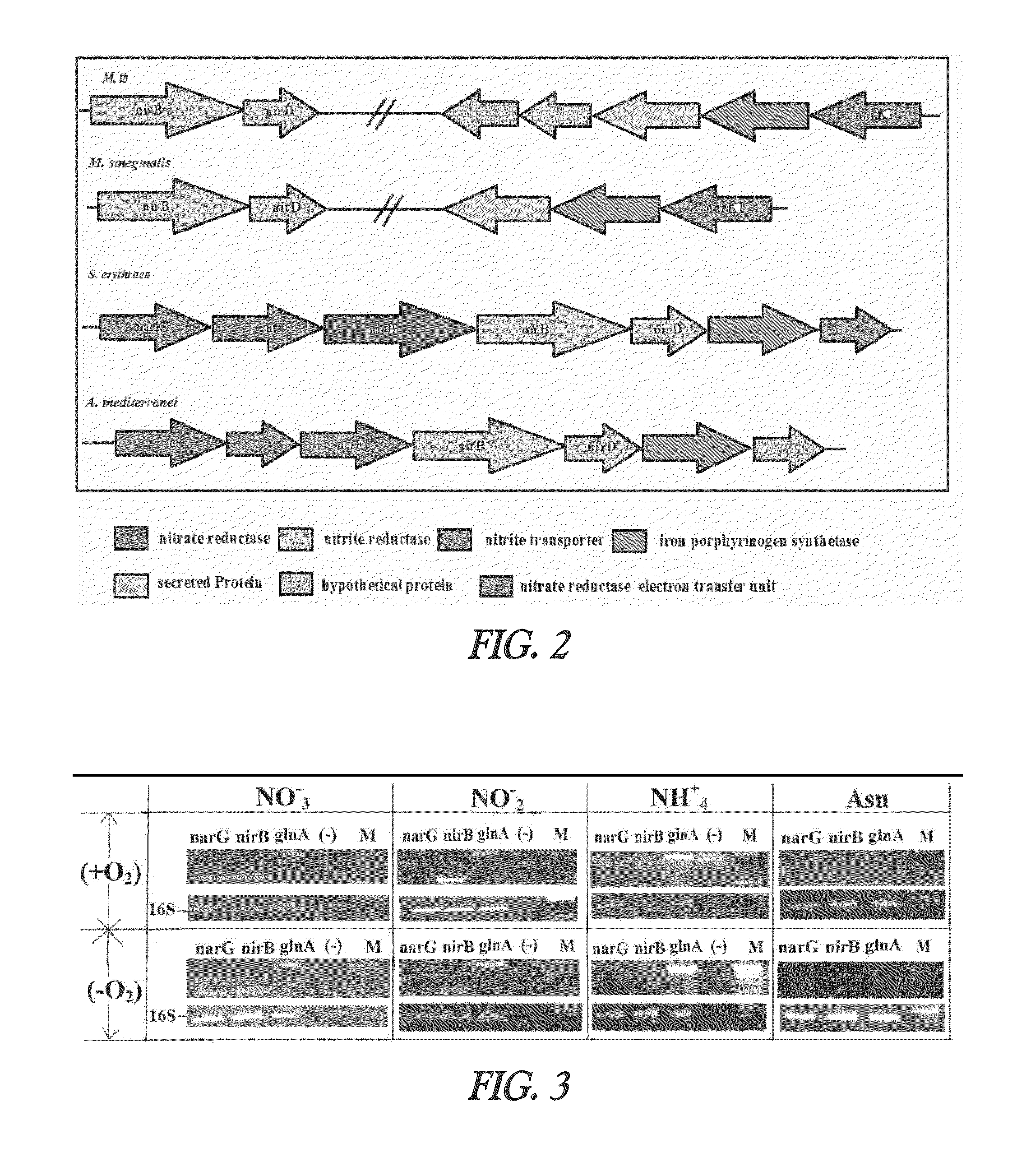
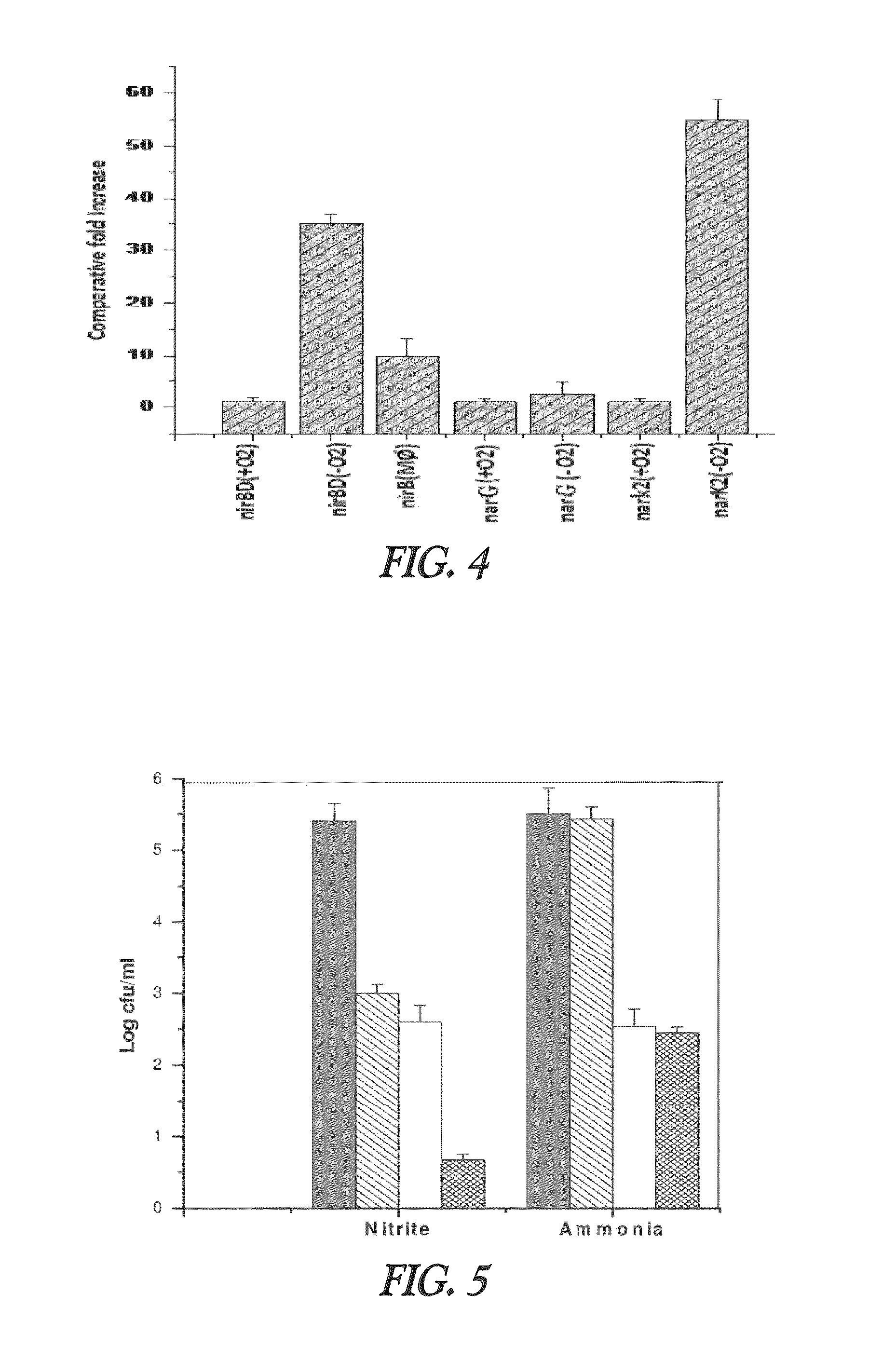
Nitrite-reductase (NIRB) as potential Anti-tubercular target and a method to detect the severity of tuberculosis disease
ActiveUS20140242626A1Improve survivalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseMedicine
The present invention discloses functional nitrite reductase as a potential drug target for anti-tubercular drug development. The present invention also relates to the development of an easy method for identification of nitrite in clinical samples as well as its correlation with the severity of the disease. Presence of active as well as dormant / latent stages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) could be identified from nitrite in clinical samples like sputum of potential TB patients.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Heterotrophic nitrification engineering bacteria capable of achieving nitrite nitrogen accumulation and building method thereof
InactiveCN106148377AAccumulation of influenceLong-term stable short-range nitrification effectBacteriaOxidoreductasesNitrationBacterial strain
The invention provides a building method of heterotrophic nitrification engineering bacteria capable of achieving nitrite nitrogen accumulation. The building method comprises the steps that 1, heterotrophic nitrification bacteria with NO2--N as the main nitration product are selected as test bacteria; 2, whole genome sequence sequencing analysis is carried out on the test bacteria, the positions of sequences of nitrite reductase genes to be deleted and all homologous genes in gene sequences are recognized and determined; 3, the PCR technology is utilized for amplifying recognized nitrite reductase gene sequences to obtain a homologous arm sequence, the homologous arm sequence is linked to a carrier with marker genes to form donor strains, the donor strains and test bacteria are subjected to inoculated culture, and finally a specific site expression method of marker genes is adopted for obtaining bacterial strains with nitrite reductase genes successfully deleted; 4, operations in the step 3 are repeated till all the homologous genes are successfully deleted, and finally the heterotrophic nitrification engineering bacteria capable of achieving NO2--N accumulation are obtained.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
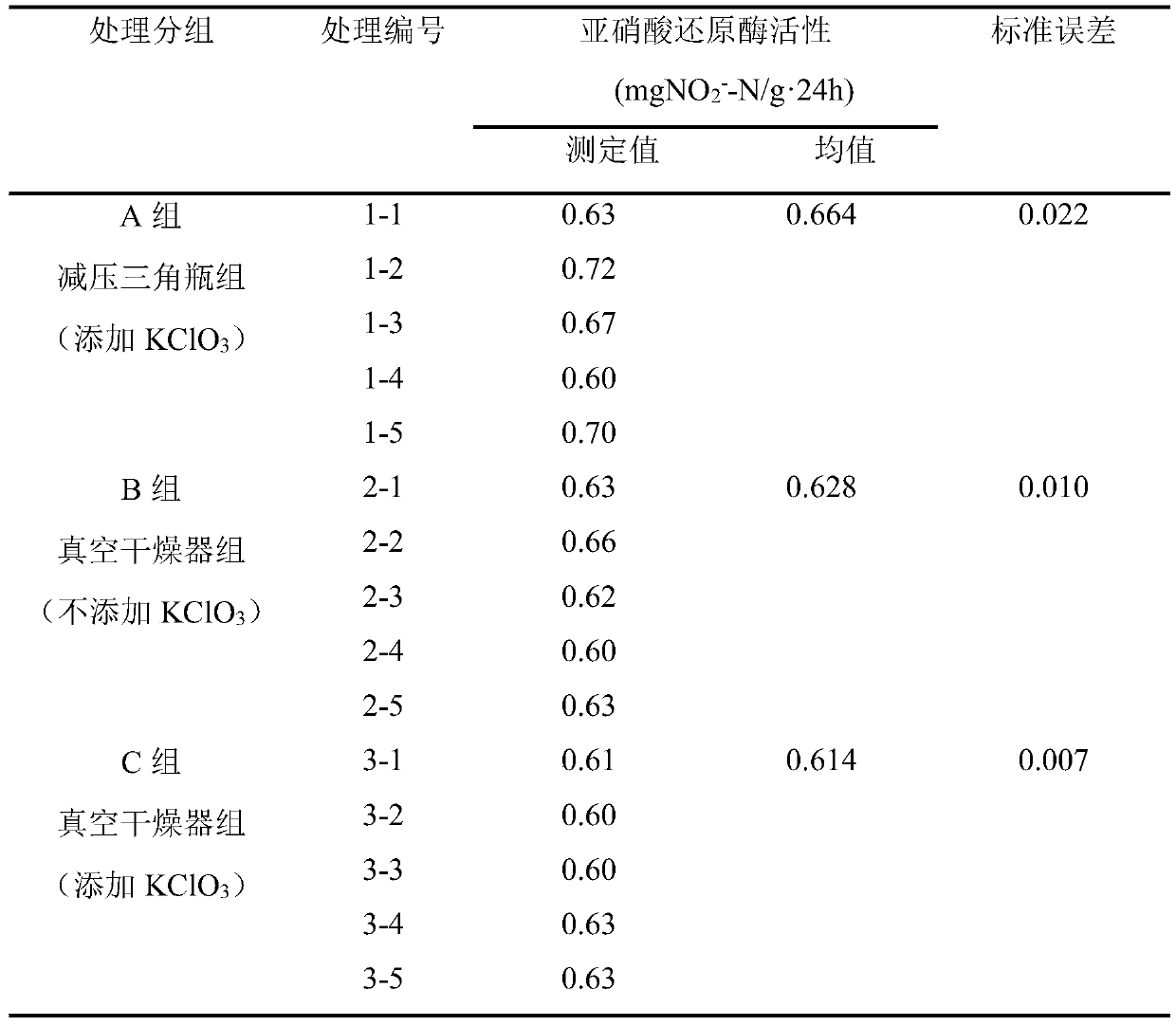
Improved determination method of nitrite reductase
PendingCN111474127AEnsure consistencyReduce the differenceColor/spectral properties measurementsSulfanilic acidNitrite reductase
The invention discloses an improved determination method of nitrite reductase in soil. In the presence of a hydrogen donor and under anaerobic conditions, nitrite reacts with a sulfanilic acid-alpha-naphthylamine reagent to determine the variation of NO2<->-N before and after enzymatic reaction so as to represent the activity of nitrite reductase. A vacuum dryer is adopted to replace a decompression triangular flask to serve as a culture container, so that the culture environment is anaerobic, the operation process can be simplified, and data errors caused by culture condition differences arereduced. Meanwhile, a certain amount of KClO3 is added during testing and standard curve preparation, so that NO2<-> can be inhibited from being oxidized into NO3<->, the loss of NO2<-> is reduced, and the data accuracy is improved. The method disclosed by the invention is high in reproducibility, simple and feasible, and capable of reducing errors, so that the stability of a measurement result between parallel processing is higher, and the measurement result is closer to a real value.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Nitrite-reductase (NIRB) as potential anti-tubercular target and a method to detect the severity of tuberculosis disease
The present invention discloses functional nitrite reductase as a potential drug target for anti-tubercular drug development. The present invention also relates to the development of an easy method for identification of nitrite in clinical samples as well as its correlation with the severity of the disease. Presence of active as well as dormant / latent stages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) could be identified from nitrite in clinical samples like sputum of potential TB patients.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for kluyveromyces lactis eukaryotic expression of nitrite reductase gene in lactobacillus plantarum
The invention discloses a method for kluyveromyces lactis eukaryotic expression of a nitrite reductase gene in lactobacillus plantarum. The method has the advantages that a lactobacillus plantarum genome is taken as a template, a specific primer is designed to amplify the sequence of the nitrite reductase gene, enzyme cutting sites are introduced into the two ends of the specific primer respectively and subcloned into an expression vector pKLAC2 to construct a recombinant plasmid, after enzyme cutting linearization, kluyveromyces lactis is electrotransformed, positive clone transformants are screened, finally, seed culture and liquid fermentation culture are carried out, a supernatant of a fermentation liquid is taken, and a nitrite reductase expression product is obtained. The method forthe kluyveromyces lactis eukaryotic expression of the nitrite reductase gene in the lactobacillus plantarum has the advantages that prepared recombinant nitrite reductase has higher enzyme activity, the enzyme activity is stable, a foundation is laid for the industrial production of the nitrite reductase, and the method can be used for the fields of food, medicine and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
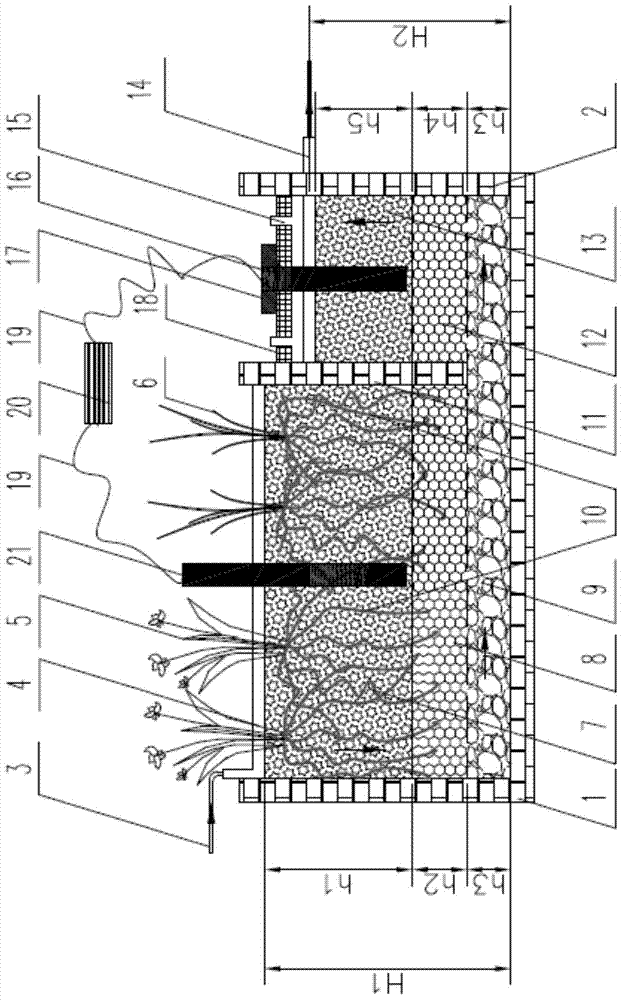
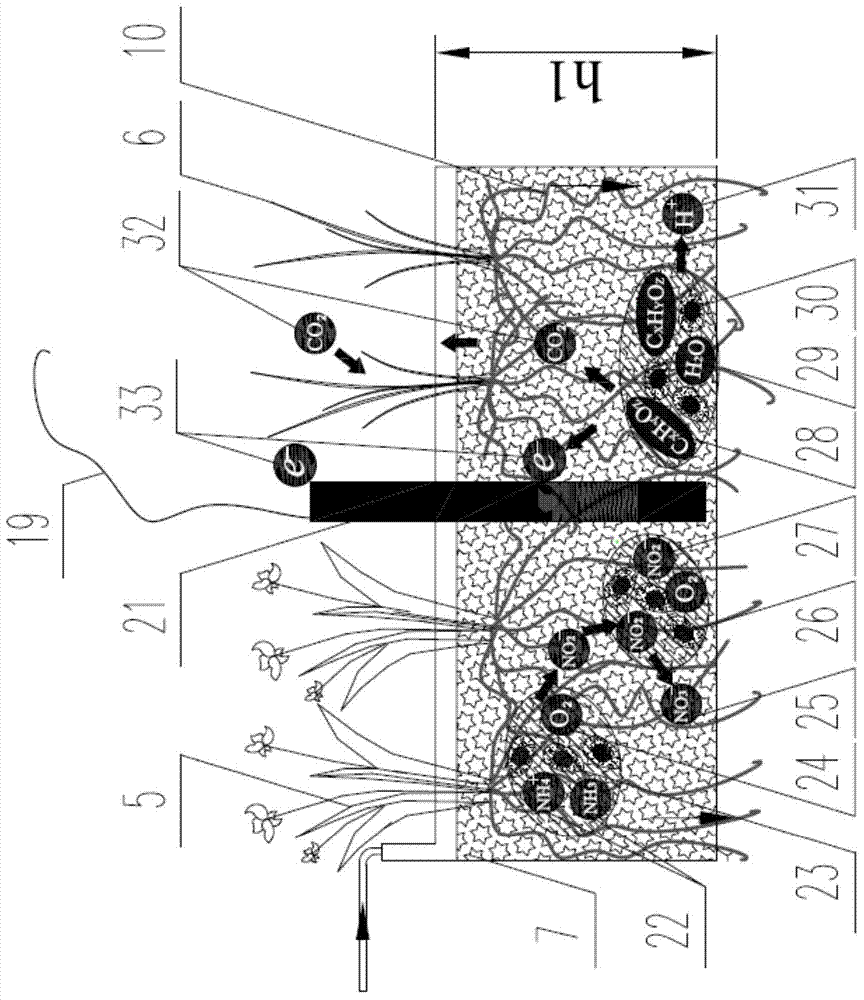
Method for improving denitrification of integrated vertical flow constructed wetlands
ActiveCN103466801BAchieve removalImprove denitrification effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesEnergy based wastewater treatmentConstructed wetlandNitrous-oxide reductase
The invention discloses a method for improving denitrification of integrated vertical flow constructed wetlands. The method for improving the denitrification of the integrated vertical flow constructed wetlands comprises the steps that (I) waste water enters a surface conductive filler layer and a middle nonconductive filler layer of a downstream pool in sequence, and ammonia nitrogen in the waste water is oxidized and becomes nitrate nitrogen under the action of the aerobic denitrifying bacteria and nitrifying bacteria; (II) the waste water obtained through the step (I) enters a communication layer of the downstream pool, a communication layer of an upstream pool, a middle nonconductive filler layer of the upstream pool in sequence, and the nitrate nitrogen in the waste water is reduced to nitrogen through a heterotrophic mode under the action of nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase and nitrous oxide reductase; (III) the water obtained through the step (II) enters a surface conductive filler layer of the upstream pool, and the nitrate nitrogen in the waste water is reduced to nitrogen through a heterotrophic mode under the action of electrochemical autotrophic denitrification; (IV) the denitrified waste water obtained through the step (III) finally flows out through water outlet collecting pipes. The method is simple and convenient to operate and capable of obviously improving the denitrification effect of the integrated vertical flow constructed wetlands.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
A method for enzymatically degrading nitrite in salted fish
ActiveCN103750409BPromote decompositionFacilitate functioningFood dryingFood preparationCold airFresh fish
The invention discloses a method for degrading nitrite in salted fish through an enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) washing fresh fish or frozen fish, salting the fish with salt, taking out the fish, rinsing with clean water, and draining; (2) adding nitrite reductase into the salted fish, wherein the addition amount of the nitrite reductase is 0.8-1.6g per kg of fish, and the enzymatic activity of the nitrite reductase is 3,500-4,500U / g; (3) airing the fish treated with an enzyme solution on a drying rack for 1-2 hours, putting the fish in a low-temperature heat pump dryer or cold-air drying equipment at the temperature of 28-35 DEG C, and airing the fish until the moisture content of the fish body is 35-45 percent. According to the method, the content of the nitrite generated in the process of processing the salted fish can be effectively reduced, the taste and quality of the salted fish products are kept, and the safety of the salted fish products is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
A kind of electron donor protein of Lactobacillus casei degrading nitrite and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105039470BWide variety of sourcesReduce manufacturing costWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryCulture fluidElectron donor
The invention discloses a nitrite-degrading electron donor protein obtained from lactobacillus casei and a preparation method thereof and application. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) cultivating and preparing lactobacillus casei subsp.rhamnosus into a seed solution, inoculating the lactobacillus casei subsp.rhamnosus to an induction medium A, performing static induced cultivation to obtain an induced working leavening agent; (2) inoculating the induced working leavening agent to an induction medium B, and performing static induced cultivation to obtain a culture solution containing the electron donor protein for degrading nitrite; (3) centrifuging the culture solution containing the electron donor protein for degrading nitrite, performing cleaning and centrifugation, and obtaining bacteria; (4) adding an electron donor protein buffer solution to the bacteria, adding lysozyme, performing cell disruption after uniform mixing, obtaining supernatant of a centrifuged cell disruption solution, wherein the supernatant is an electron donor crude protein fluid for degrading nitrite; and obtaining the electron donor protein by purifying the crude protein fluid. A mixed solution of the electron donor protein and nitrite reductase can quickly degrade nitrite.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Anammox bacterium nitrite reductase expression vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN104498518AHigh expressionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNitrite reductaseFunctional activity
The invention relates to an anammox bacterium nitrite reductase expression vector and a construction method thereof. The recombinant engineering strain has a base sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 1. According to the recombinant engineering strain disclosed by the invention, the expression level and functional activity of the gene are greatly improved, so that the application of anammox bacterium nitrite reductase to an anaerobic ammonia oxidation process is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
A bacillus amyloliquefaciens nitrite reductase, a gene and applications
InactiveCN106244603AHigh purityResolve separabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefaciens nitrite reductase, a gene and applications, and belongs to the field of biological engineering. The nitrite reductase gene of bacillus amyloliquefaciens H47 is cloned by utilizing a PCR technique and subjected to inducible expression in escherichia coli, and a high-purity recombinant protein is obtained by purification utilizing affinity chromatography. A foundation is laid for researching enzymatic properties of the reductase, researching the nitrite degrading route of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens H47 and improving the nitrite degrading rate of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens H47. NiRBD in the bacillus amyloliquefaciens H47 is one of nitrite reductases, reduces nitrites into ammonium, can be applied for degrading nitrites in ensilage for ruminants and can be used for degrading nitrites in kitchen waste fermented fertilizers.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A new use of a maize-derived transcription factor and its coding gene
The invention discloses a transcription factor derived from corn and new use of a coding gene thereof. The new use provided by the invention is a method using a coding nucleic acid molecule of ZmNLP1;1 to cultivate a transgenic plant. The method is a method for cultivating the transgenic plant with at least one characters of the following 1)-4): 1) aboveground biomass is higher than that of a receptor plant; 2) after induction of a nitrate, the nitrate transport protein gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; 3) after induction of the nitrate, nitrate reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and 4) after induction of the nitrate, nitrite reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and the method comprises a step for introducing a ZmNLP1;1 gene into the receptor plant; and the ZmNLP1;1 gene codes a protein shown in SEQ ID No.2. Experiments show that, in the condition of using nitric nitrogen (NO<3->) as a sole nitrogen source, the aboveground biomass and the total biomass of arabidopsis transgenic with the ZmNLP1;1 gene are increased significantly compared with that of receptor arabidopsis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fermentation method for producing nitrite reductase
InactiveCN109679930AIncrease productionEliminate residueMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism separationFood safetyNitrite reductase
The invention relates to the technical field of microbiology, enzyme engineering, fermentation engineering and biochemistry, in particular to a bacterial strain for producing nitrite reductase and a fermentation method thereof. After the bacterial strain of lactobacillus plantarum (the preservation number is CGMCC NO.1.12935) is domesticated and purified; the nitrite reductase is produced throughfermentation. After the bacterial strain is domesticated and purified, the yield of the nitrite reductase produced by bacteria through stable fermentation is improved; nitrite in food and feed can beeliminated. From the food safety angle, the lactobacillus nitrite reductase is developed for reducing and eliminating the residue of nitrite in food; wide prospects and safety advantages are realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com