Fermentation method for producing nitrite reductase
A technology of nitrite and reductase, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, methods using microorganisms, oxidoreductase, etc., can solve problems such as excessive nitrite, and achieve the effect of increasing production, broad prospects and safety advantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Acclimatization and purification of strains.
[0035] 1. Acclimatization of strains
[0036] Add 0.01%~0.1% NaNO to the fermentation medium 2 , inoculated into the fermentation medium according to the inoculum amount of 2% of the volume of the fermentation broth, and cultured at 25-30° C. for 36-48 hours.
[0037] Fermentation medium: glucose 2g, peptone 1g, yeast powder 0.4g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g, beef powder 0.8g, magnesium sulfate 0.02g, sodium acetate 0.5g, triammonium citrate 0.2g, manganese sulfate 0.005g, spit Temperature-80 0.1g, distilled water 1L, pH6.2±0.2, sterilized by high-pressure steam at 121℃ for 30min.
[0038] 2. Purification of Strains
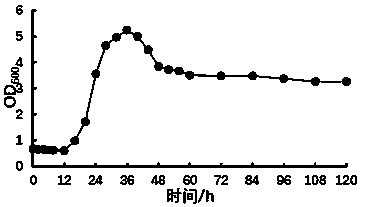
[0039] According to the conventional method for isolation of pure microorganisms, the domesticated strains are placed at 30°C for 48-72h. Inoculate into a new solid medium for selection of Lactobacillus plantarum, repeat at least 10 times, and purify colonies. Fermentation test was carried out in ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Isolation and identification of purified strains:
[0044] (1) Bacteria and colony morphological characteristics of the purified strain
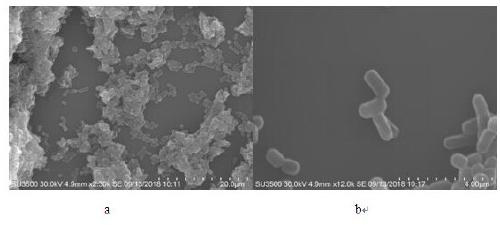
[0045] The morphological characteristics of the colony are: the colony is white, opaque, smooth, with neat edges and easy to pick. The biological characteristics of the strain were preliminarily identified by simple staining, Gram staining, capsule staining, and spore staining. Lambert-negative, non-capsulated, non-spore-forming, non-flagellate, such as figure 1 shown.
[0046] Genetic Traits:
[0047] The 16S rRNA whole gene base sequence of the purified strain is SEQ ID NO.1; the total 16S rRNA gene sequence of the strain is 1483bp (Genbank accession number: MH596000.1);
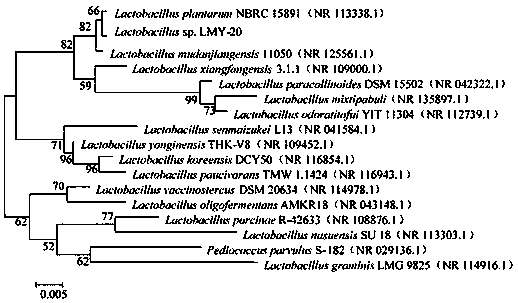
[0048] The strain has similarities with Lactobacillus plantarum, and its 16S rRNA sequence was systematically analyzed with Mega5.0 software, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by Neigbor-Joining method to show that this strain and Lactobacillus plantarum...
Embodiment 3
[0050] (1) Culture medium preparation:
[0051] ① Solid seed medium: glucose 2g, peptone 1g, yeast powder 0.4g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g, beef powder 0.8g, magnesium sulfate 0.02g, sodium acetate 0.5g, triammonium citrate 0.2g, agar 2g, distilled water 1L, pH6.2±0.2, autoclaved at 121℃ for 30min;
[0052] ②Liquid seed medium: glucose 2g, peptone 1g, yeast powder 0.4g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g, beef powder 0.8g, magnesium sulfate 0.02g, sodium acetate 0.5g, triammonium citrate 0.2g, distilled water 1L, pH6 .2±0.2, 121°C high pressure steam sterilization for 30min;
[0053] ③Fermentation medium: glucose 2g, peptone 1g, yeast powder 0.4g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2g, beef powder 0.8g, magnesium sulfate 0.02g, sodium acetate 0.5g, triammonium citrate 0.2g, manganese sulfate 0.005g, Tween-80 0.1g, distilled water 1L, pH6.2±0.2, sterilized by high pressure steam at 121℃ for 30min.
[0054] ④ Inoculate the strain on a solid seed medium according to a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com