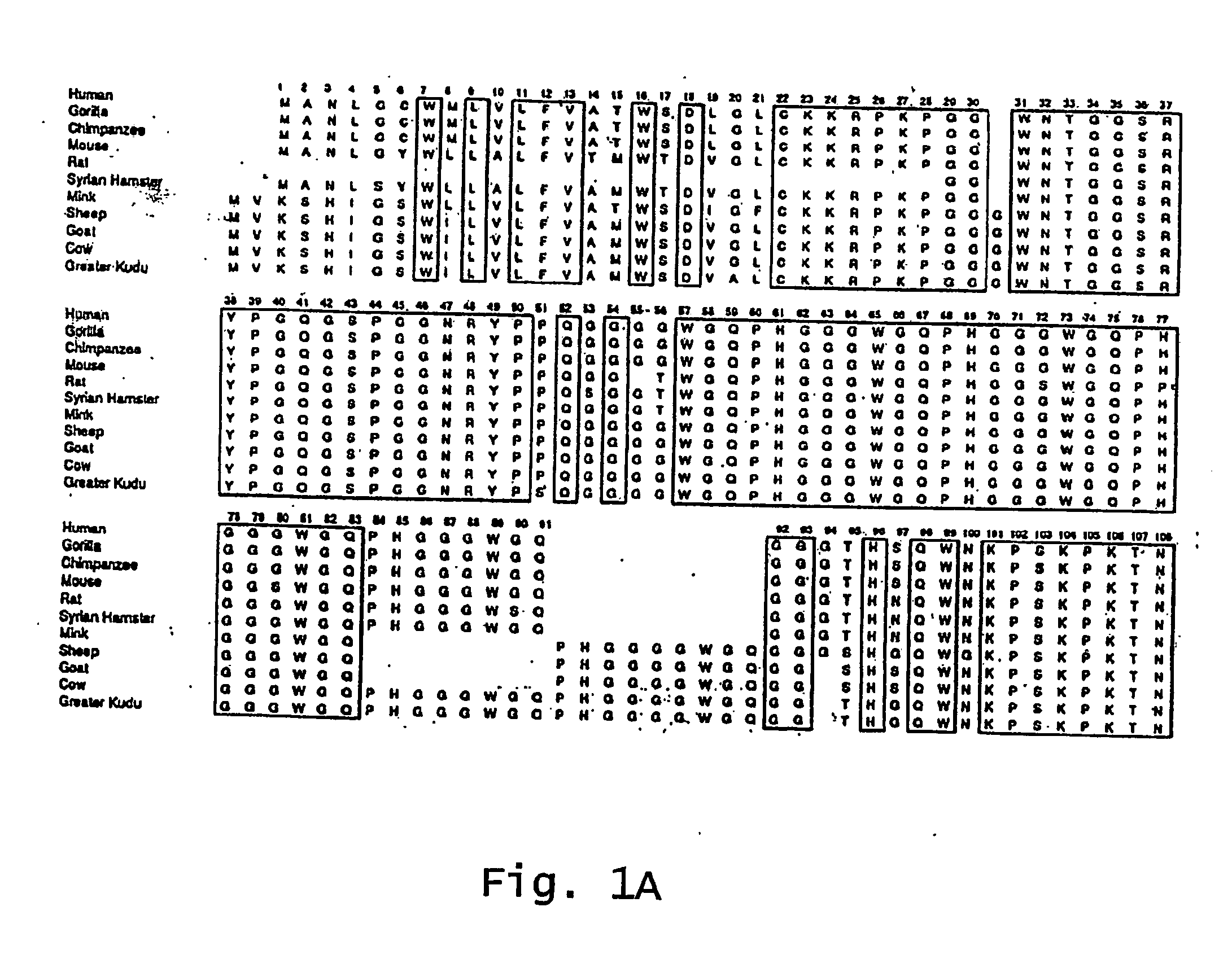
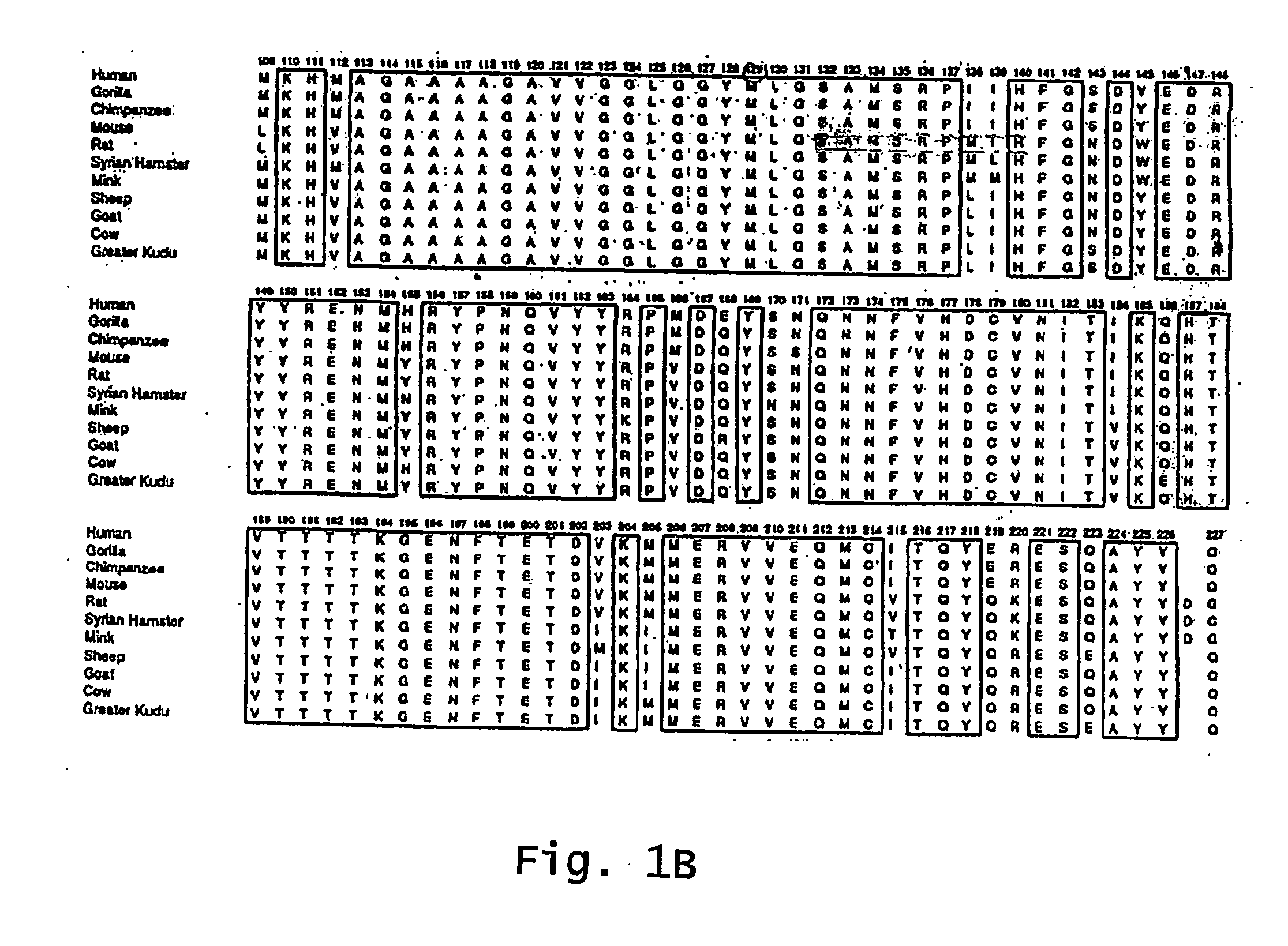
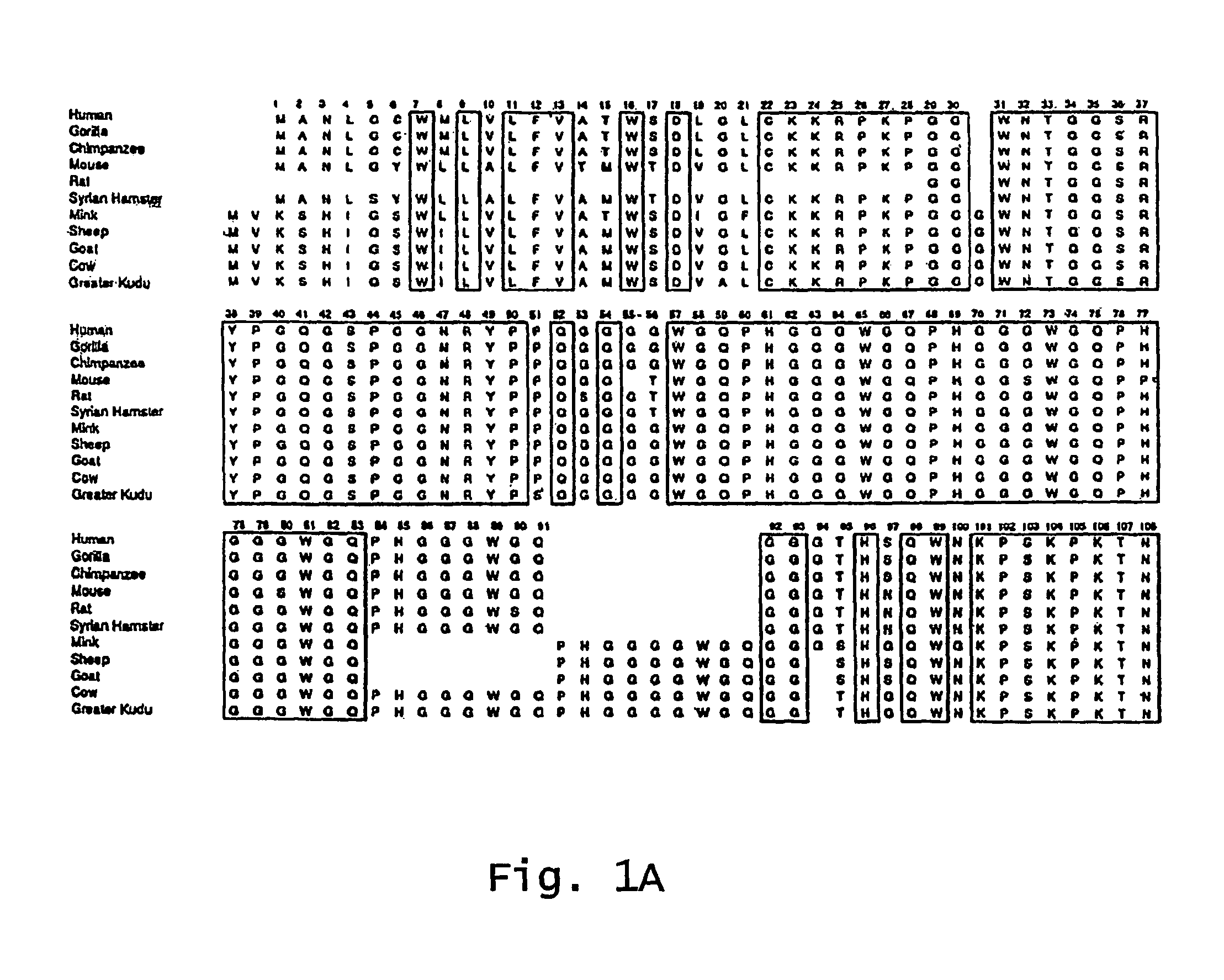
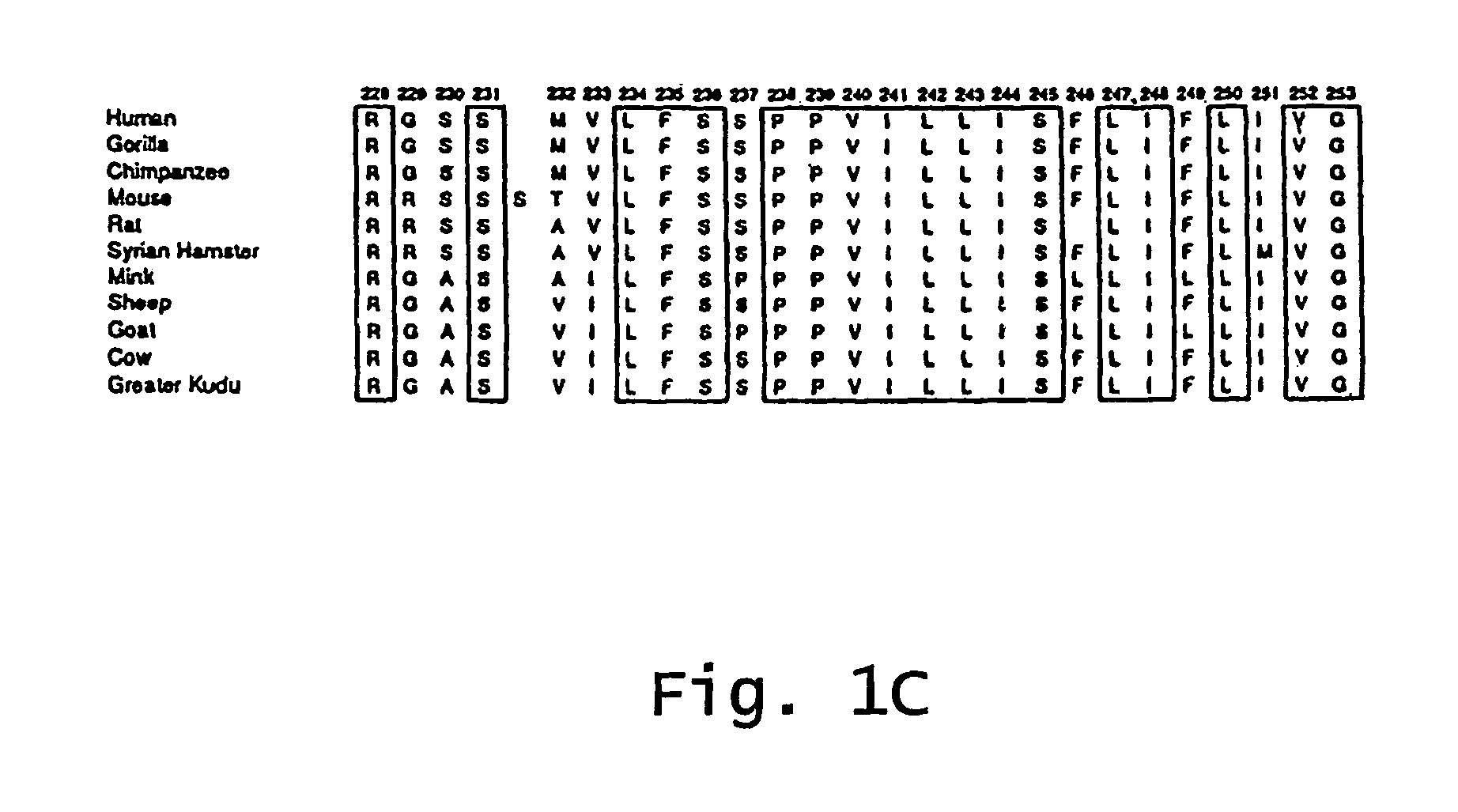
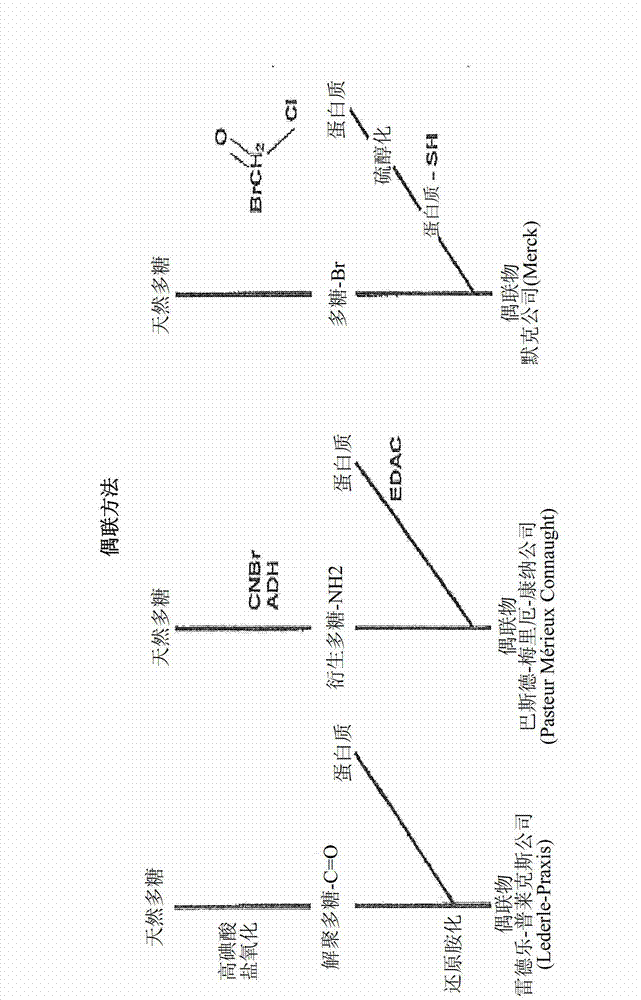
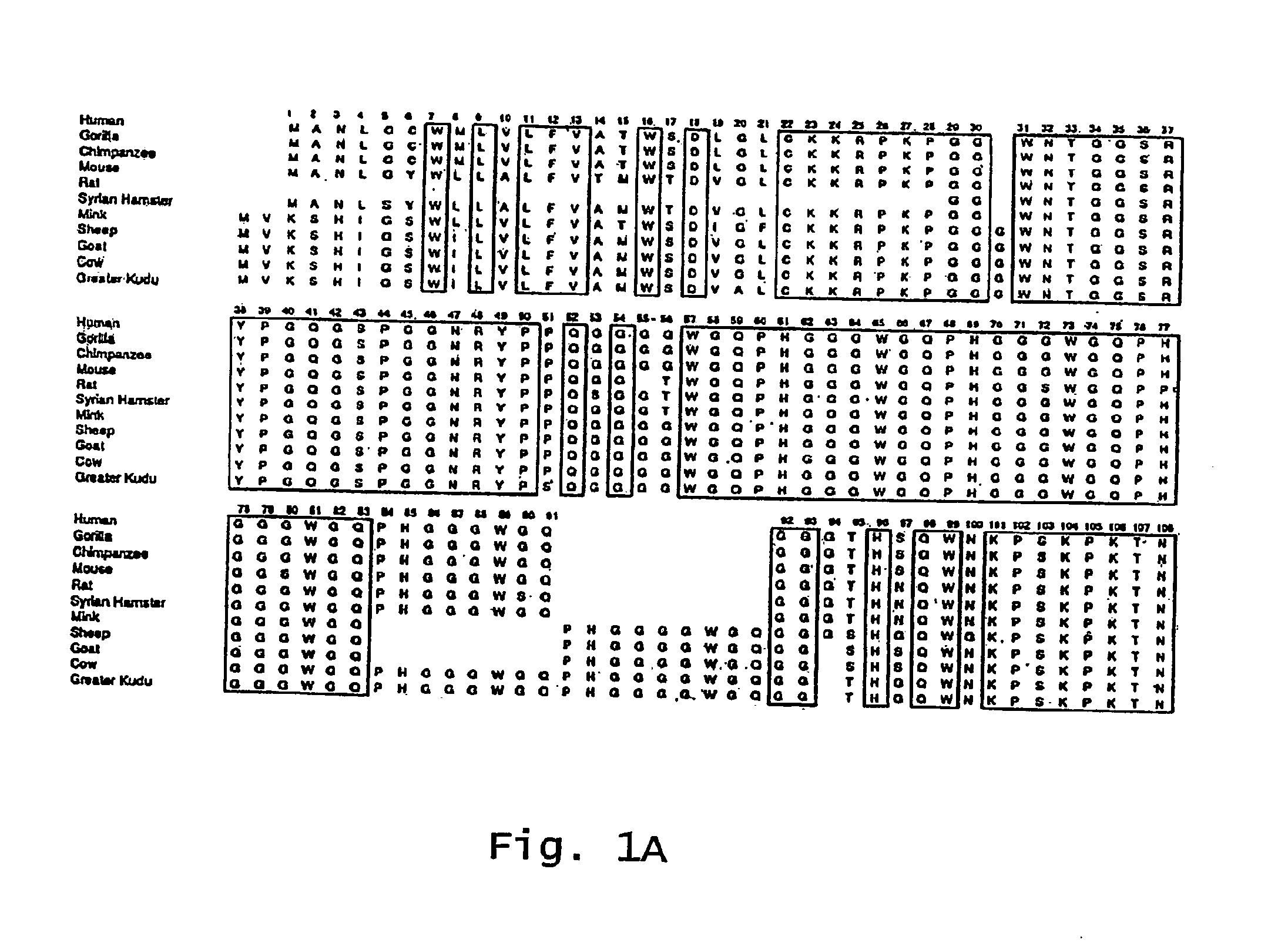
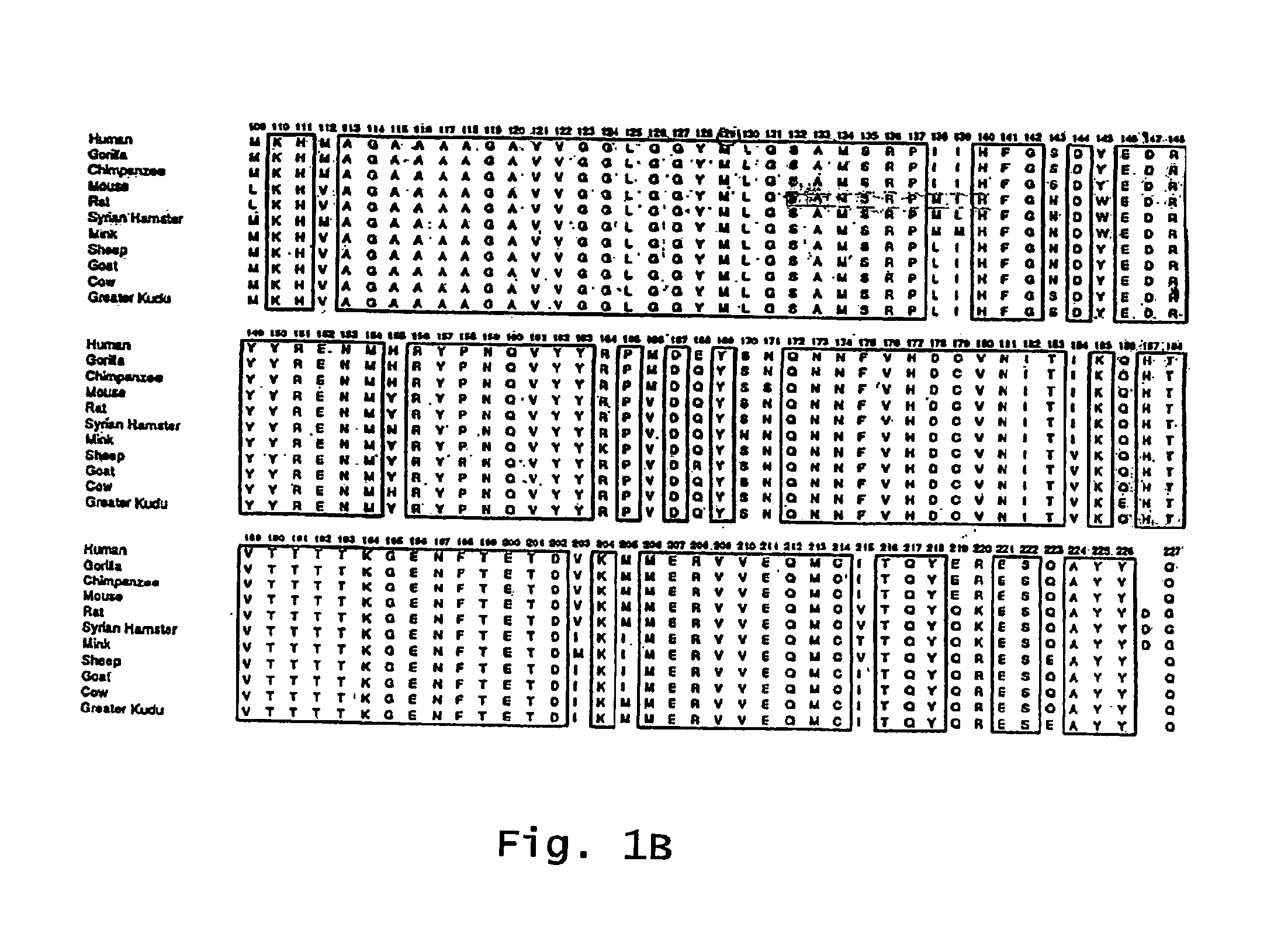
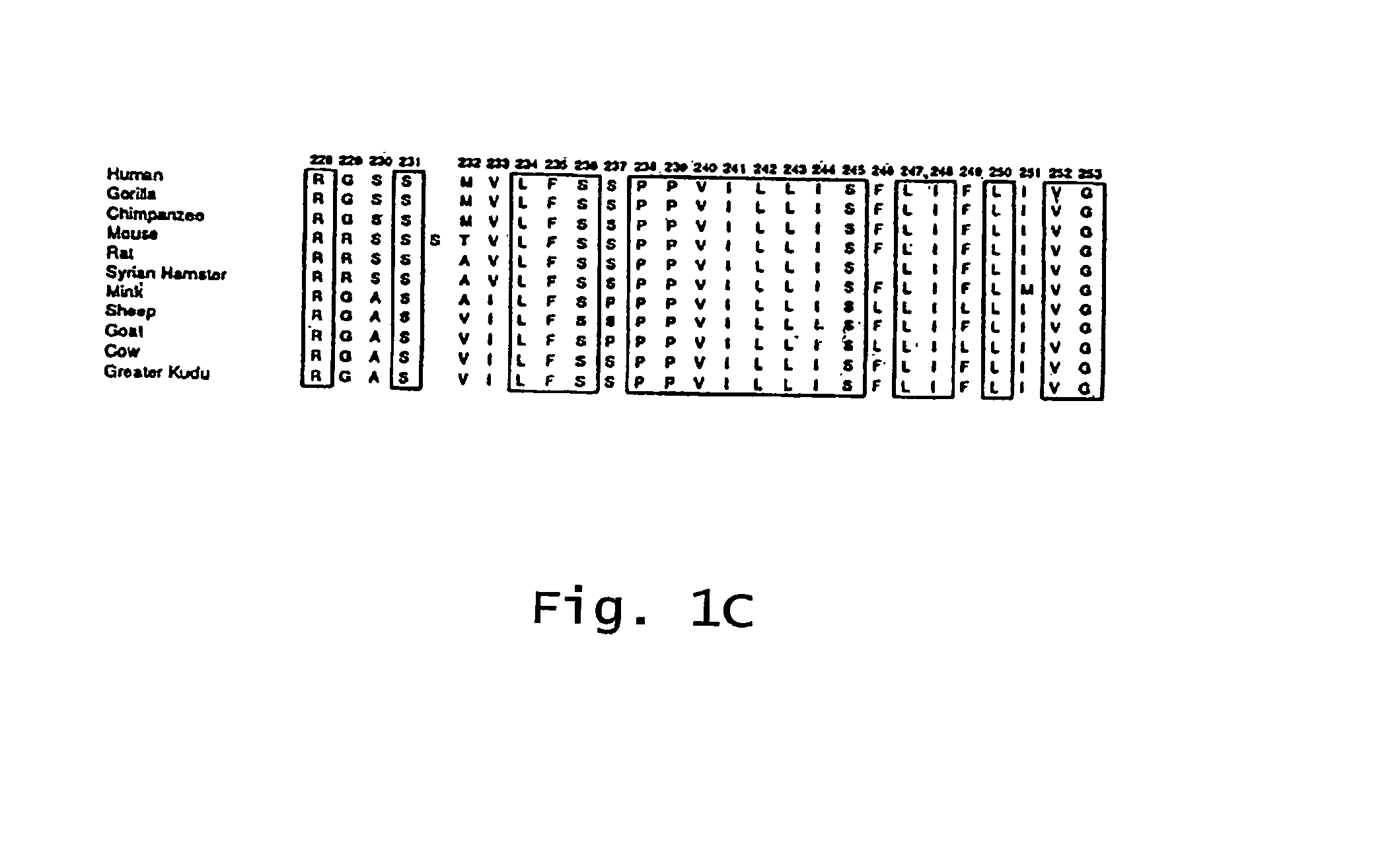
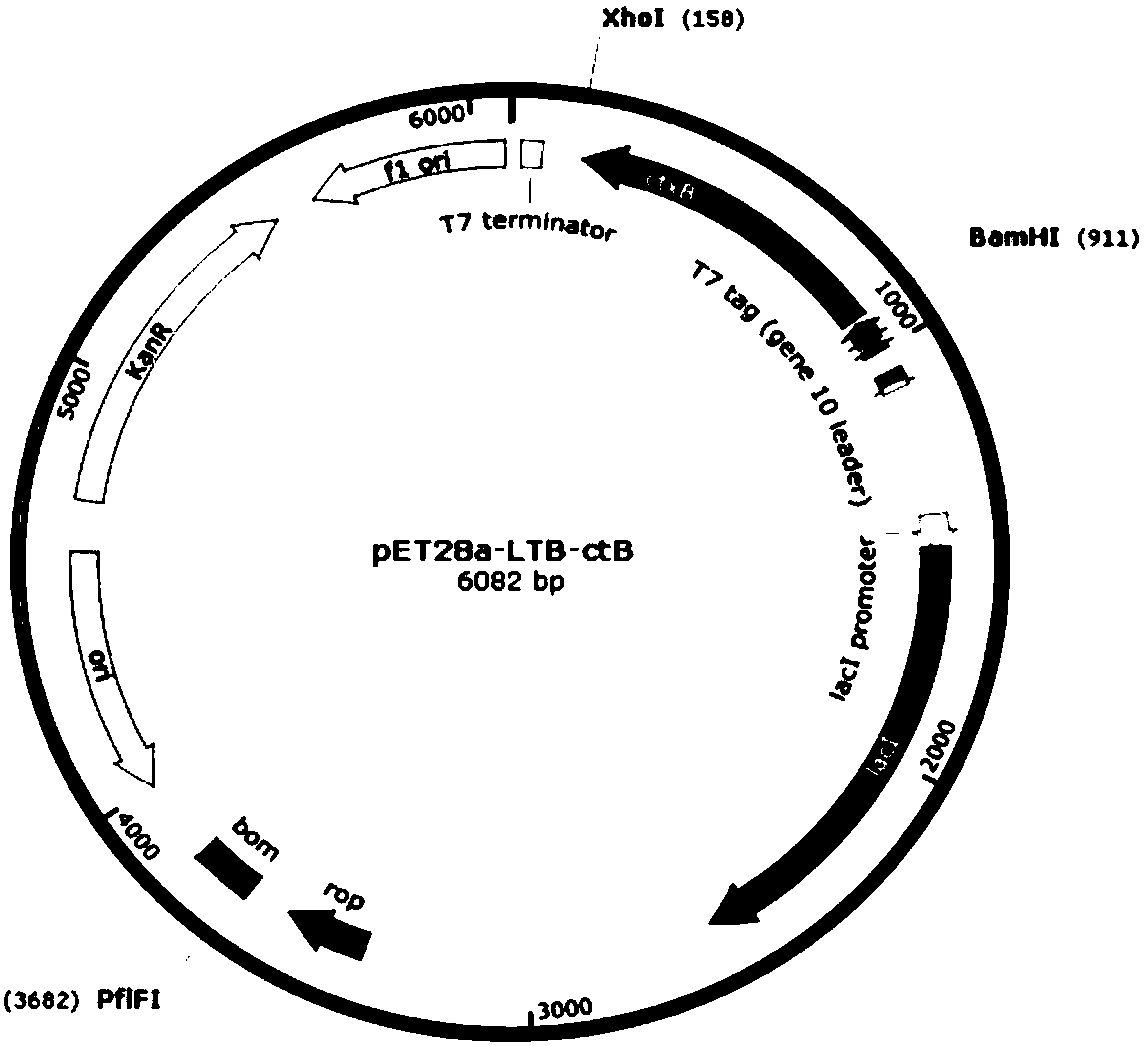
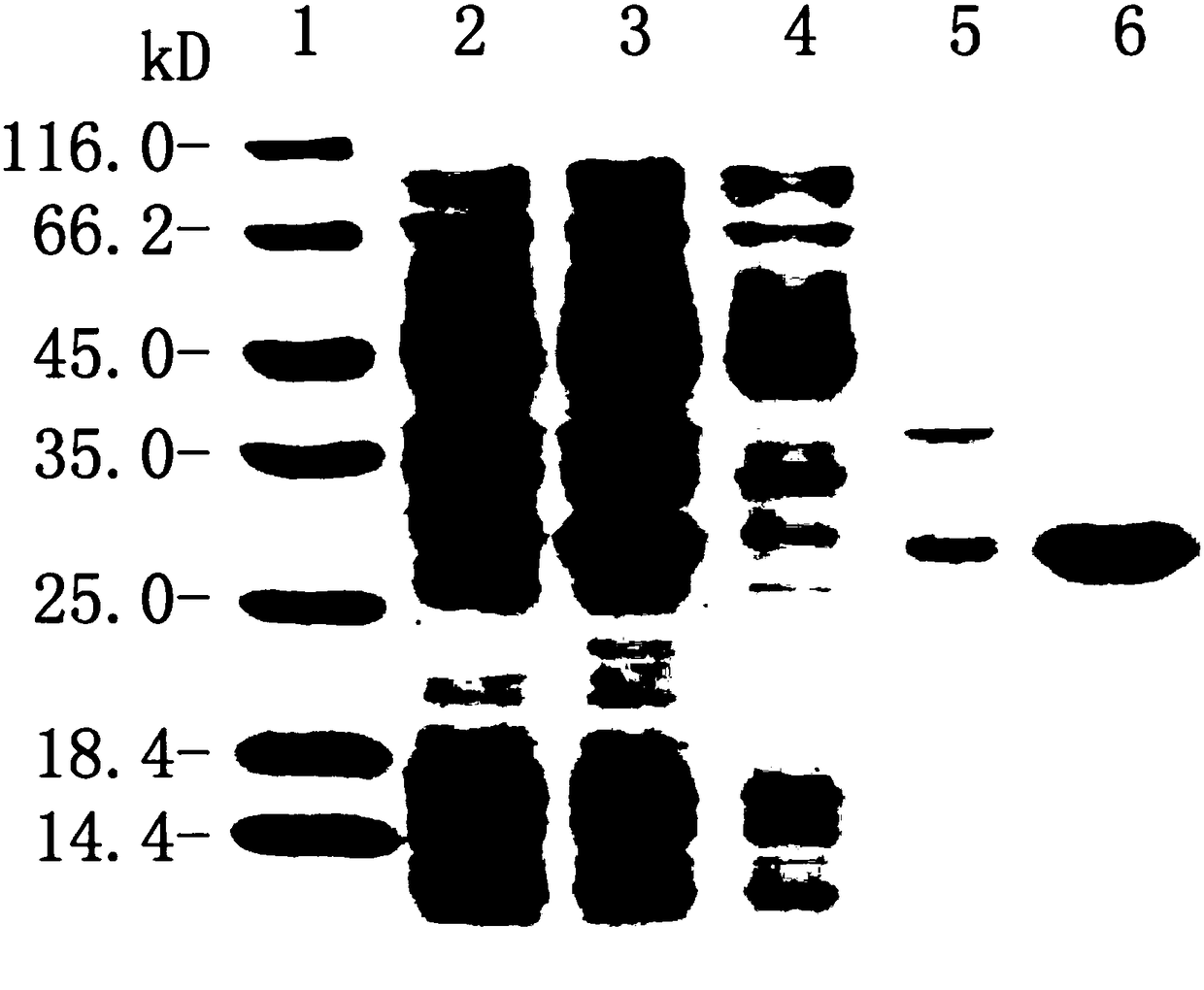
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Heat-labile enterotoxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heat-labile enterotoxin is a type of labile toxin found in Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus.
Mutant enterotoxin effective as a non-toxic oral adjuvant
InactiveUS6019982AEnhance immune responseLack of activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
Methods and compositions are provided herein for the use of a novel mutant form of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin which has lost its toxicity but has retained its immunologic activity. This enterotoxin is used in combination with an unrelated antigen to achieve an increased immune response to said antigen when administered as part of an oral vaccine preparation.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Mutant enterotoxin effective as a non-toxic adjuvant
InactiveUS6436407B1Low toxicityLack of activityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenHeat-labile enterotoxin
Methods and compositions are provided herein for the use of a novel mutant form of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin which has lost its toxicity but has retained its immunologic activity. This enterotoxin is used in combination with an unrelated antigen to achieve an increased immune response to said antigen when administered as part of a vaccine preparation.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Mucosal immunization to prevent prion infection
Vaccines against prion disease eliciting a humoral immune response when administered mucosally are described. The vaccines comprise a prion protein, a prion protein fragment, or a non-amyloidogenic prion protein homolog and an adjuvant suitable for inducing a humoral immune response after mucosal administration. Suitable adjuvants include cholera toxin subunit B, heat-labile enterotoxin and aluminum hydroxide. Alternatively, the vaccine comprises a vector encoding a prion protein, fragment, or homolog in an attenuated Salmonella host. The vaccines can be used to prevent or treat prion disease in humans and other mammals.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition of escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin adjuvant and methods of use
InactiveUS6413523B1Enhance immune responseLow toxicityBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsSerum igeAdjuvant
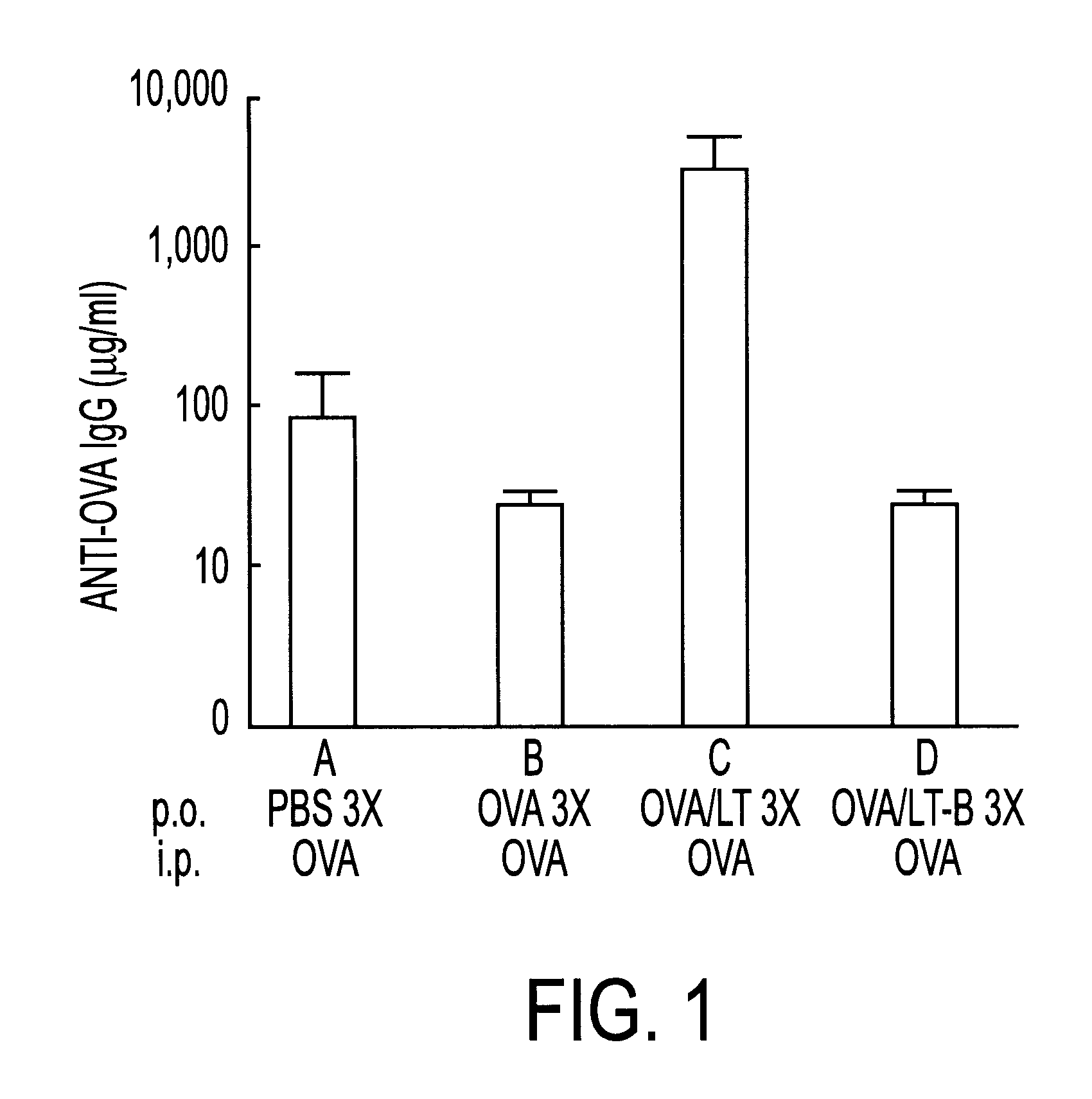
Novel immunoregulatory utilities of Escherichi coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) are disclosed. This enterotoxin can be used in combination with an unrelated antigen to achieve a higher immune response to said antigen when administered as part of an oral vaccine preparation. By way of example, the efficacy of oral adjuvant therapy of LT in the development of immunological protection against herpes simplex virus was examined. In addition, the ability of LT to influence the induction and maintenance of tolerance in animals primed orally with two unrelated protein antigens administered simultaneously, OVA and BSA was examined. Simultaneous administration of LT with OVA was shown to prevent the induction of tolerance to OVA and to increase the serum anti-OVA IgG response to 30-90 fold over PBS primed and OVA primed animals, respectively.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
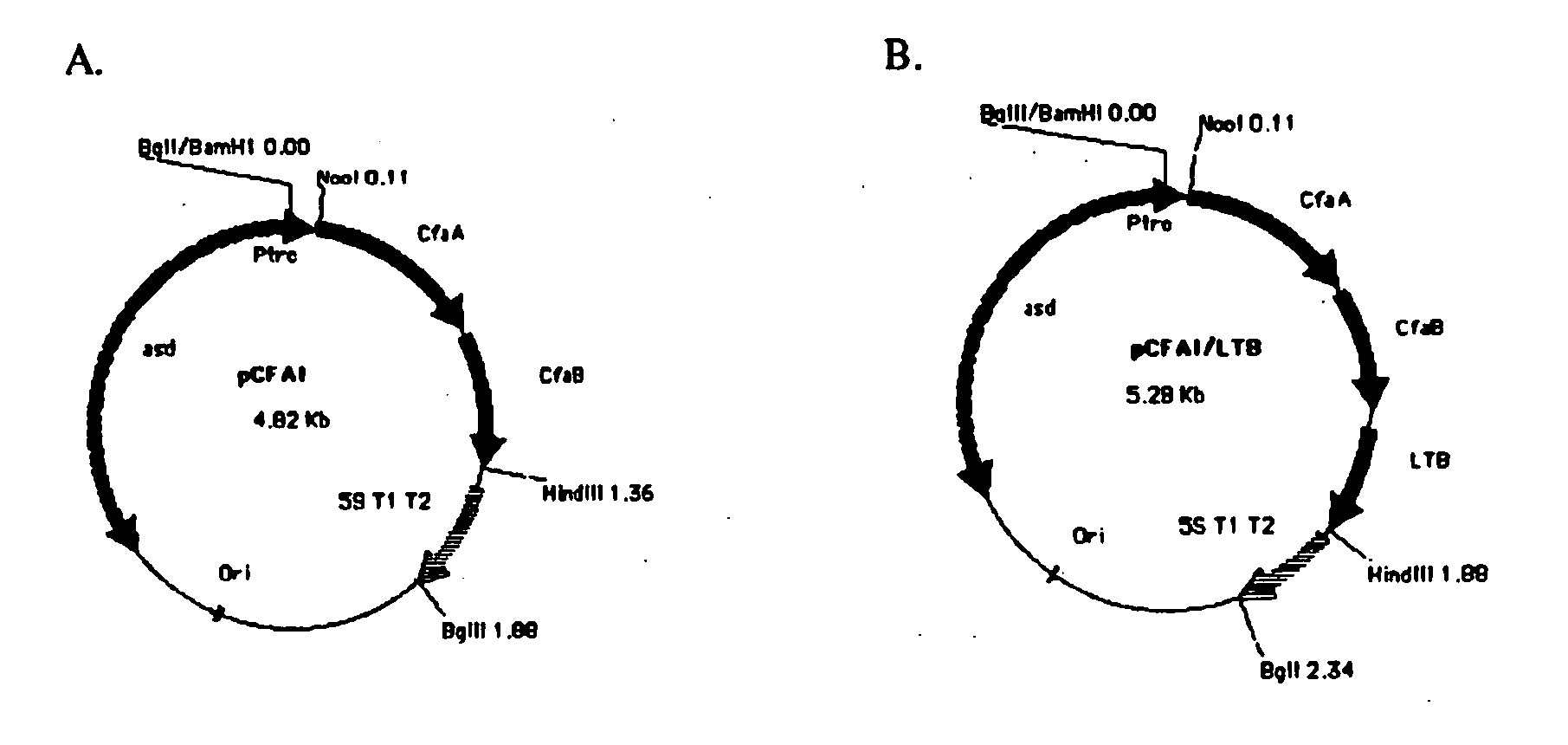
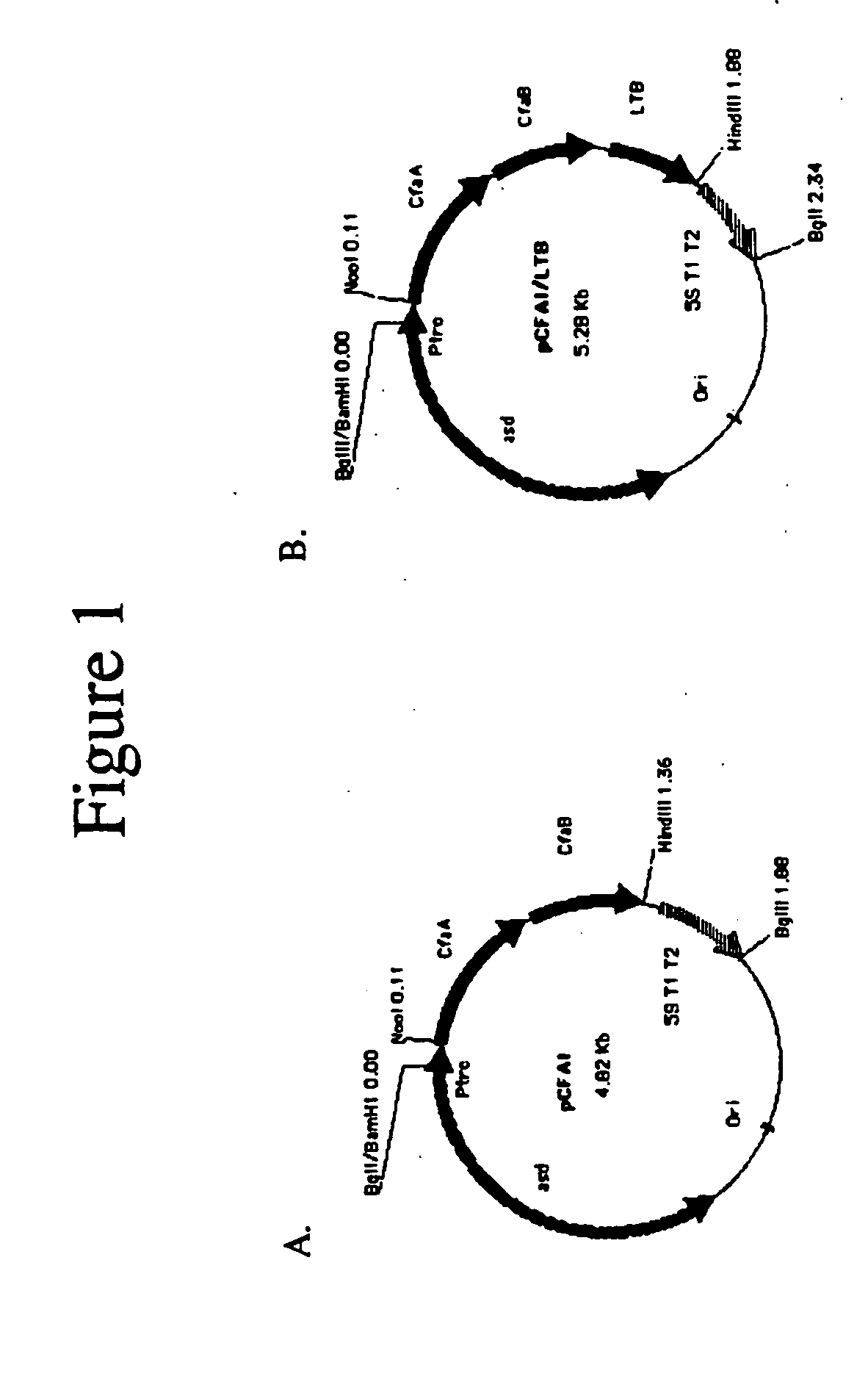
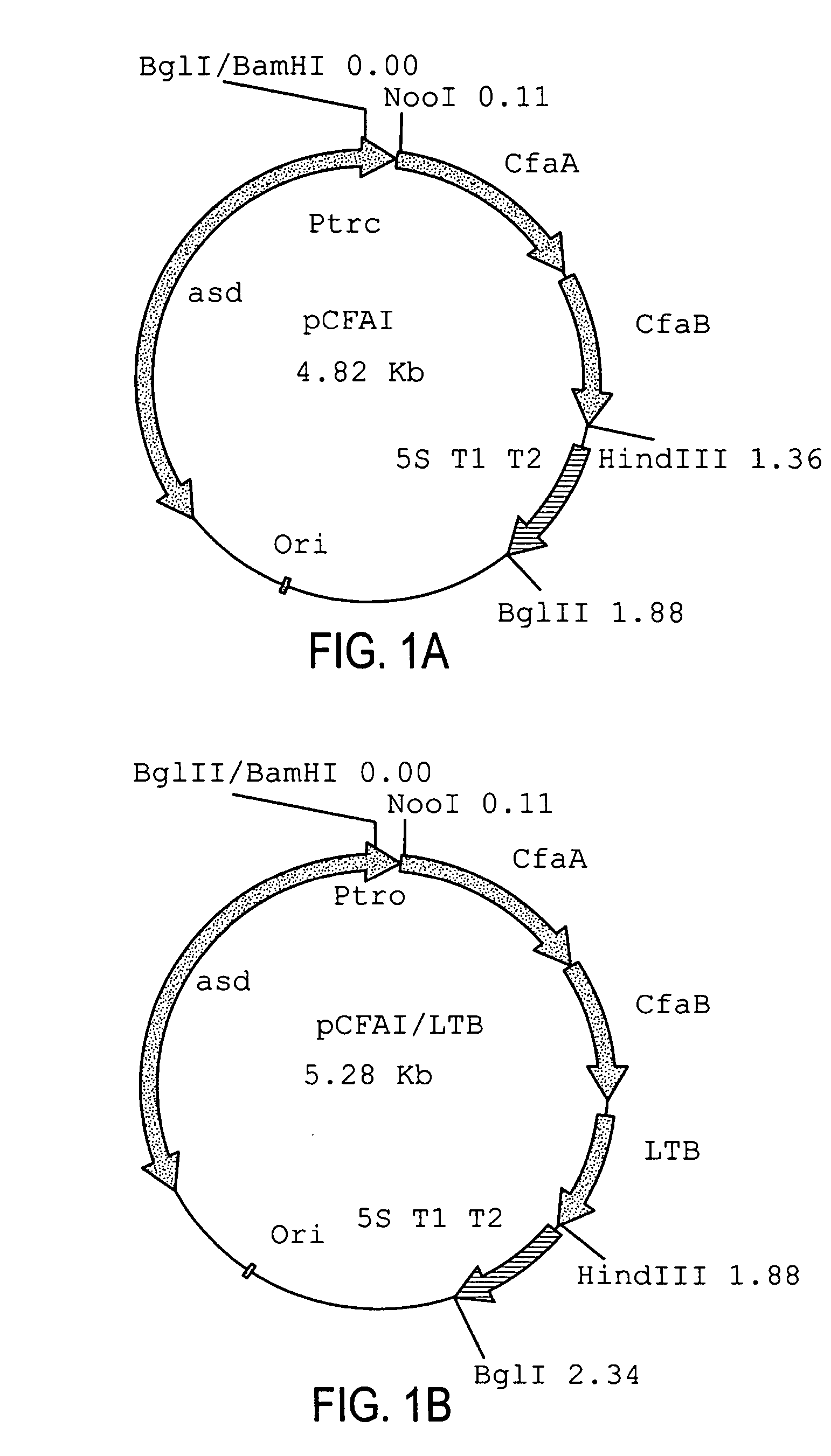
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (cfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E.coli
ActiveUS20070237791A1Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
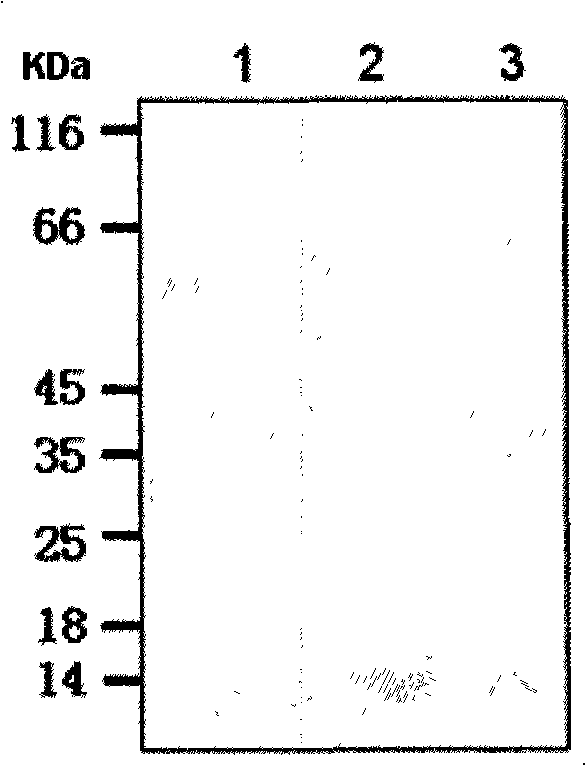
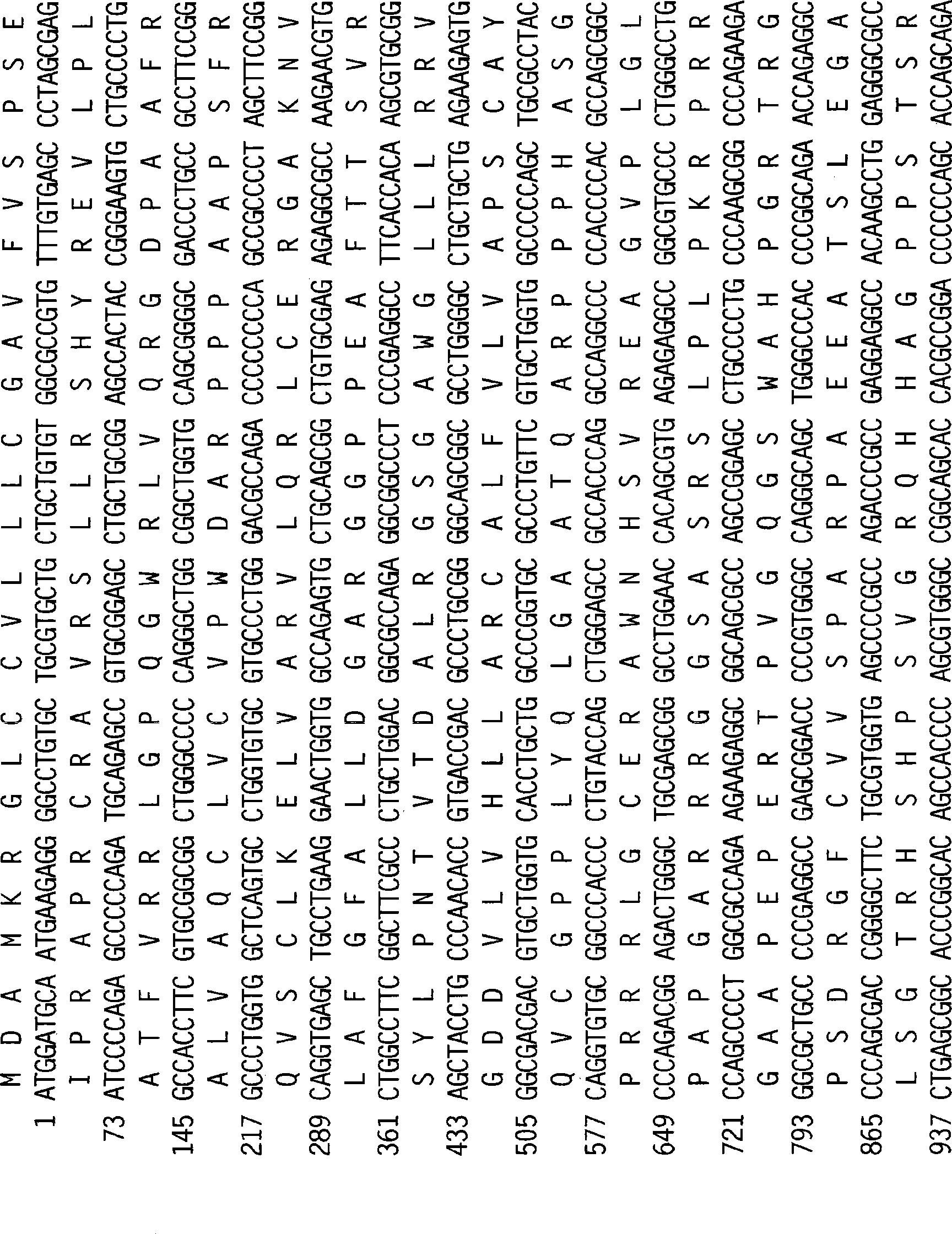
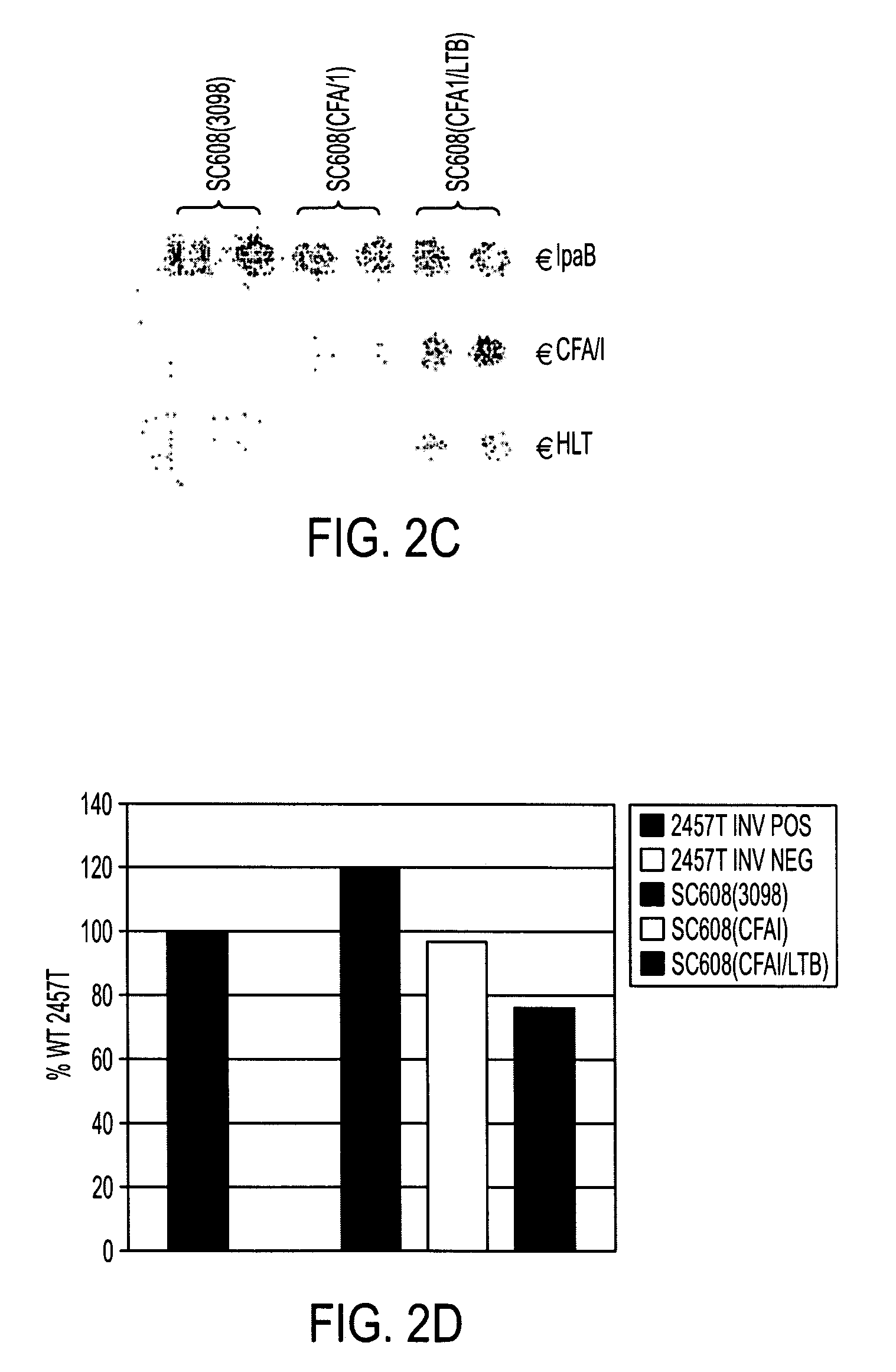
With the goal of creating a combination vaccine against Shigella and other diarrheal pathogens we have constructed a prototype vaccine strain of Shigella flexneri 2a (SC608) that can serve as a vector for the expression and delivery of heterologous antigens to the mucosal immune system. SC608 is an asd derivative of SC602, a well-characterized vaccine strain, which has recently undergone several phase 1 and 2 trials for safety and immunogenicity. Using non-antibiotic asd-based plasmids, we have created novel constructs for the expression of antigens from enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), including CFA / I (CfaB and CfaE) and the B-subunit from heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) in Shigella vaccine strain SC608. Heterologous protein expression levels and cellular localization are critical to immune recognition and have been verified by immunoblot analysis. Following intranasal immunization (SC608(CFAI) and SC608(CFAI / LTB) of guinea pigs, serum IgG and IgA immune responses to both the Shigella LPS and ETEC antigens can be detected by ELISA. In addition, ELISPOT analysis for ASCs from cervical lymph nodes and spleen showed similar responses. All vaccine strains conferred high levels of protection against challenge with wild-type S. flexneri 2a using the Sereny test. Furthermore, serum from guinea pigs immunized with SC608 expressing CfaB and LTB contained antibodies capable of neutralizing the cytological affects of heat-labile toxin (HLT) on Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. These initial experiments demonstrate the validity of a multivalent invasive Shigella strain that can serve as a vector for the delivery of pathogen-derived antigens.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Respiratory syncytial virus sub-units vaccine, preparation and application
InactiveCN101264323ALimit developmentEnhance cellular immune responseDepsipeptidesAntiinfectivesEscherichia coliCtl epitope
The invention relates to a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine, and the preparation method and application, in particular to an application of escherichia coli to express and recombinant respiratory syncytial virus G protein and mutation G protein, and preparation vaccine with nontoxic typed escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin, for human or animal preventive inoculation, and for respiratory syncytial virus resistance, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The respiratory syncytial virus vaccine is characterized in that: the respiratory syncytial virus subunits vaccine comprises lopped respiratory syncytial virus RSV protein G, and further comprises nontoxic typed escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin LT adjuvant. The vaccines are lopped respiratory syncytial virus RSV protein G containing amino acid between aa130 and 230 of the original G protein, and substitutes the amino acid CAWIC (CX3C module ordered) between aa182 and 186 with the amino acid YLEKESIYY (CTL epitope) on the RSV M protein, forming the GCIL protein. The respiratory syncytial virus vaccine has the advantages of remarkable practical significance for preventing human respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Telomerase reverse transcriptase fusion protein, nucleotides encoding it, and uses thereof
Polynucleotides encoding telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) fusion proteins are provided, the TERT fusion proteins comprising a TERT protein, or functional variant thereof, fused to a substantialportion of the B subunit of heat labile enterotoxin (LTB). TERT variants useful in TERT-LTB fusion proteins of the invention comprise mutations that function to eliminate telomerase catalytic activity. The polynucleotides of the present invention can elicit an immune response in a mammal, which, in preferred embodiments, is stronger than the immune response elicited by a wild-type TERT. TERT expression is commonly associated with the development of human carcinomas. The present invention provides compositions and methods to elicit or enhance immunity to the protein product expressed by the TERT tumor-associated antigen, wherein aberrant TERT expression is associated with a carcinoma or its development. This invention specifically provides adenoviral vector and plasmid constructs carryingpolynucleotides encoding TERT fusion proteins and TERT variants and discloses their use in vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for preventing and treating cancer.
Owner:IST DI RICERCHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE P ANGELETTI
Saccharide derivatives
Disclosed are novel saccharide derivatives which inhibit binding of toxins, such as heat-labile enterotoxin or cholera toxin, to their receptors either in vitro or in vivo. Additionally, disclosed are compounds which inhibit binding of enterovirulent organisms (e.g., bacteria, virus, fungi, and the like), such as Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli, to their cell surface receptors.
Owner:SYNSORB BIOTECH INC
Gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 infection and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection and a preparation method thereof. The inflection comprises multiple diseases related with the nervous system such as hand-foot-and-mouth disease, paralytic diseases of sterile meningitis, cephalitis and poliomyelitis and the like. Escherichia coli labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) is used as an immunological enhancement adjuvant, two fragments of linear neutralizing epitope SP55 and SP70 in EV71 virus coat protein VP1 are used as antigens, prokaryotic expression plasmids of LTB-SP55-SP70 fusion genes are constructed by using gene engineering technology, the plasmids are expressed in escherichia coli, and a recombinant expression product is purified for preparing the EV71 virus gene engineering vaccine.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所 +1
Constructing genetic engineering Vaccine of adhesin of confluent Helicobacter pylor and preparation method
InactiveCN1563388ANumber of consistent peaksGood attentionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliAdjuvant
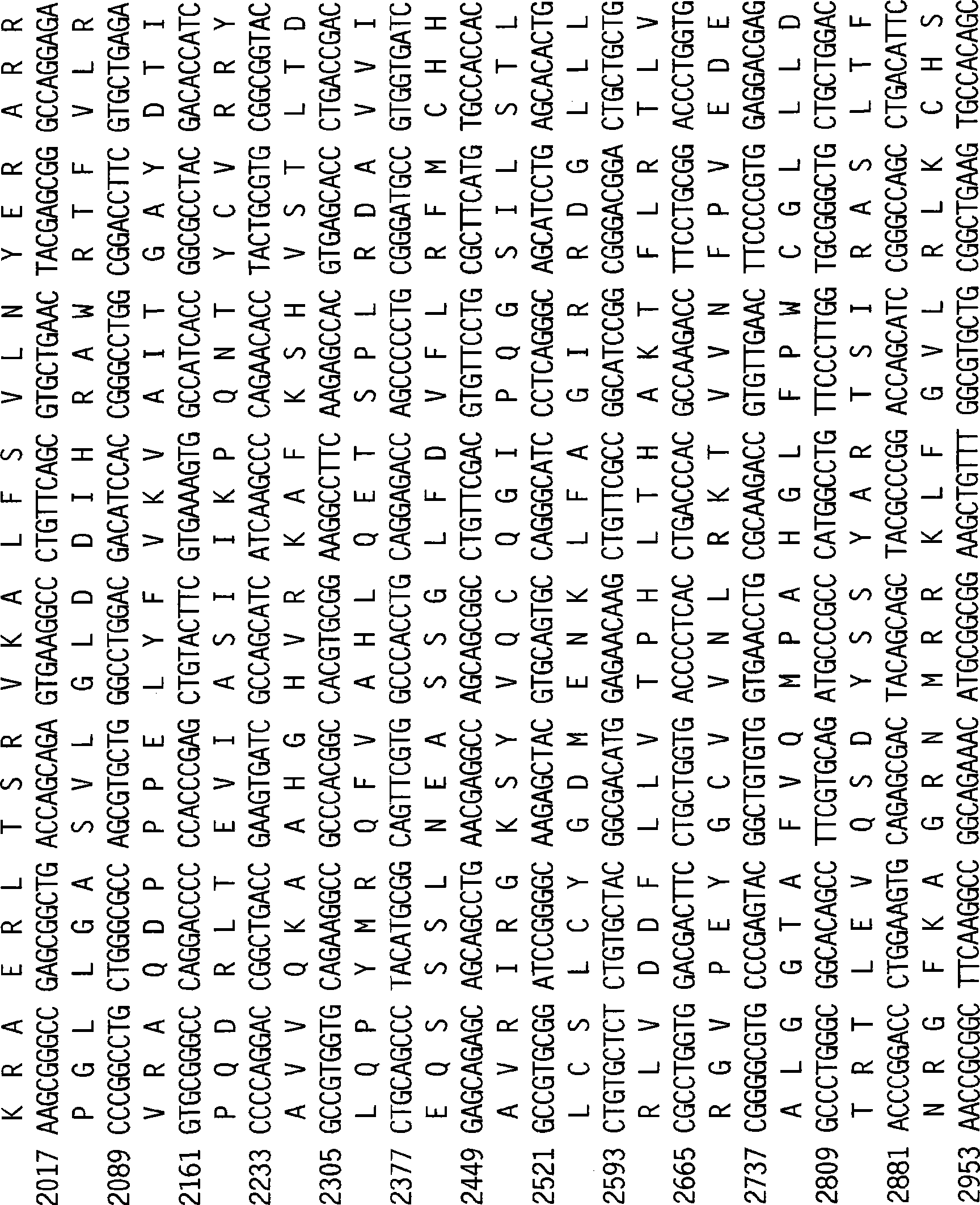
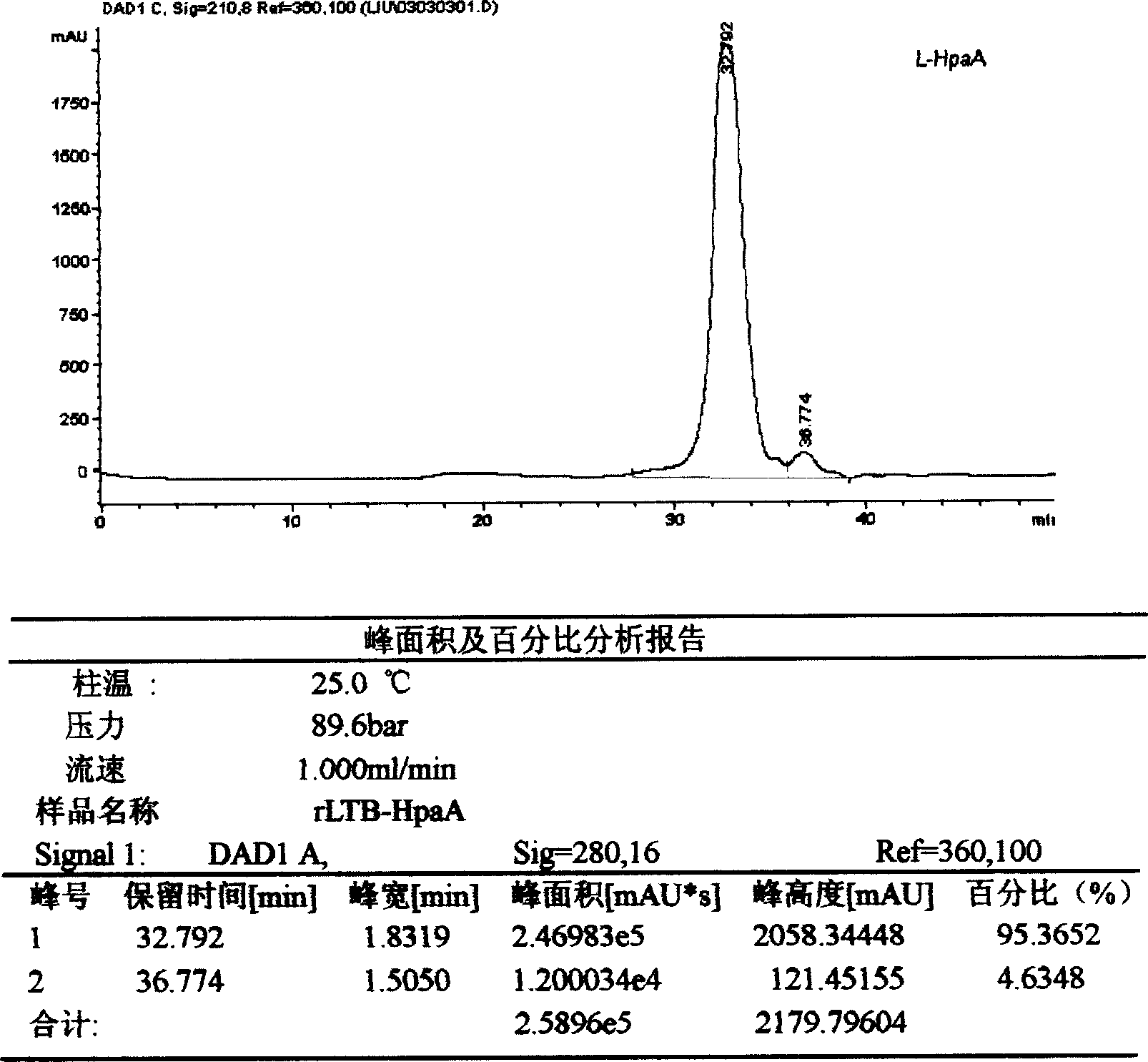
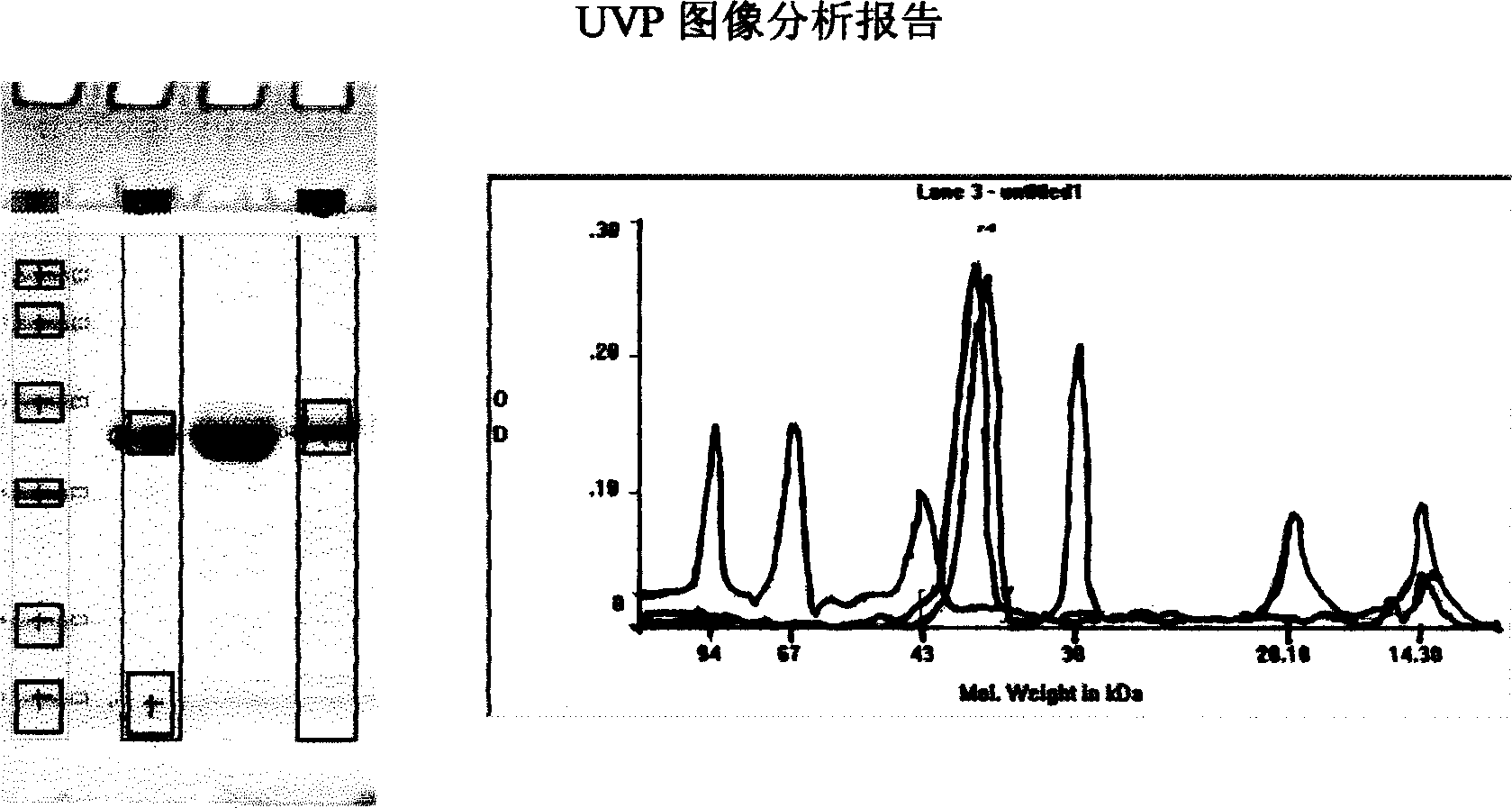
This invention discloses the construction of a fused poloric spirillum adhesion gene engineered bacterial vaccine characterizing that the adhesion HpaA is used to construct an adjuvant fused engineered vaccine of poloric spirillum adhesion and colibacillus heat-labile enterotoxin B sub unit or cholear toxin B sub unit intramolecular to get large quantity of necessary vaccine proteins by high density fermentation, occlusion body extraction, renaturation and purification to be proprared to peroral, injection and spray agents.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Epitope delivery system with Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin B subunits serving as carriers
The invention relates to design techniques of an antigenic epitope delivery system and preparation purification techniques, and relates to application of the antigenic epitope delivery system to epitope vaccine development and preparation. An epitope delivery system with Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin B subunits serving as carriers is characterized in that Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin B (LTB) subunits are connected with specific peptides by means of recombinant DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) technology, and then the corresponding B lymphocyte epitope or T lymphocyte epitope is connected to the LTB subunits. According to experiments, the B lymphocyte epitope carried by the antigenic epitope delivery system can effectively impel animals to generate antibodies aiming at the epitope; and the T lymphocyte epitope carried by the antigenic epitope delivery system can effectively impel animals to generate CD8 lymphocyte cells aiming at the epitope. Therefore, the antigenic epitope delivery system can play a significant role in development of epitope vaccines.
Owner:冯强
Minigene
The present invention provides minigenes suitable as a prophylactic or therapeutic vaccine against conditions such as cancer, infectious diseases or autoimmune diseases, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the minigene. The minigenes of the present invention comprise (a) a human tissue plasminogen signal peptide; (b) at least one T-cell epitope; and (c) an E. coli heat labile enterotoxin B subunit; wherein the at least one T-cell epitope is linked to the rest of the minigene, and to any other epitopes, by furin sensitive linkers. In some embodiments of the invention, the minigene comprises T-cell epitopes from one or more of CEA, her-2 / neu and hTERT. Also provided herein are immunogenic peptide epitopes of CEA, her-2 / neu and hTERT, as well as immunogenic peptide analogs, and pharmaceutical compositions and vaccines comprising one or more of said peptides and analogs for prophylaxis and / or treatment of cancer or other disorder. Methods of inducing an immune response in a patient, in addition to methods of treatment using the minigenes, immunogenic peptides, and peptide analogs disclosed herein are also provided.
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
Purifying process for oral recombinant helicobacter pylori vaccine
InactiveCN104962541AHigh purityEase of industrial productionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliProtein target
The invention discloses a purifying process for an oral recombinant helicobacter pylori vaccine. The effective component of the vaccine is fusion protein of Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) and urase subunit B (UreB). LTB-UreB vaccine protein with high purity is obtained by subjecting a collected fermented genetically-engineered bacterium expressing the LTB-UreB fusion protein to high pressure bacterium breaking, washing, cleavage, anion-exchange column chromatography, ultrafiltration, gel filtration chromatography, etc. The purifying process has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency, good repeatability, high yield and easy realization of industrial production; the obtained target protein has a purity of more than 98% according to detection results of high performance liquid chromatography; and animal test proves that the oral recombinant helicobacter pylori vaccine protein prepared by using the purifying process has good immunocompetence and immunoprotectivity.
Owner:CHONGQING KANG WEI BIOTECH
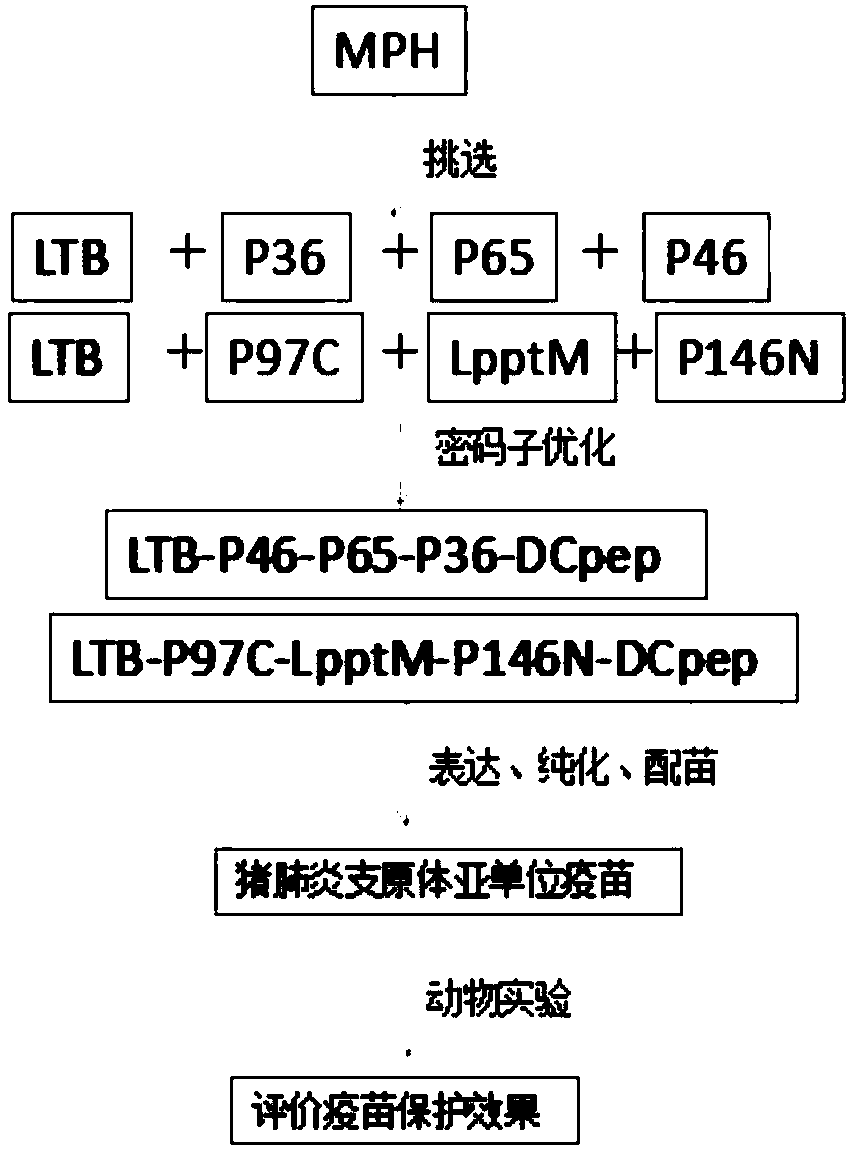
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae subunit vaccine and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109678968AFor proper foldingPreserve immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliDendritic cell
The invention provides a mycoplasma hyopneumoniae subunit vaccine and a preparation method and application thereof. A plurality of antigenic proteins of mycoplasma are connected by a flexible Linker and expressed as a chimeric protein, and the proteins are mutually unaffected, and can retain respective immunogenicity. The mucosal immune protection effect of the vaccine is greatly enhanced by adding the escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit and the dendritic cell-inducing peptide to the chimeric protein. The invention also relates to a preparation method of a mycoplasma hyopneumoniae chimeric antigen and application of the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae chimeric antigen to the subunit vaccine for preventing mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection. The mycoplasma chimeric antigen is expressed in bacillus megaterium and can be used for industrial preparation of safe mycoplasma hyopneumoniae subunit vaccines.
Owner:WUHAN KEQIAN BIOLOGY CO LTD
Mucosal immunization to prevent prion infection
Vaccines against prion disease eliciting a humoral immune response when administered mucosally are described. The vaccines comprise a prion protein, a prion protein fragment, or a non-amyloidogenic prion protein homolog and an adjuvant suitable for inducing a humoral immune response after mucosal administration. Suitable adjuvants include cholera toxin subunit B, heat-labile enterotoxin and aluminum hydroxide. Alternatively, the vaccine comprises a vector encoding a prion protein, fragment, or homolog in an attenuated Salmonella host. The vaccines can be used to prevent or treat prion disease in humans and other mammals.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Treating allergy with detoxified e. coli heat-labile enterotoxin
ActiveUS20110236424A1Effective treatmentBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliE coli heat stable toxin
A method for treating allergy with a pharmaceutical composition containing a detoxified E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin, and, optionally, an allergen.
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY
Chlamydia vaccines
Vaccine preparations are provided for the prevention of Chlamydia infections comprising a major outer membrane protein from chlamydia and a mucosal adjuvant such as a combination of QS21 and 3D-MPL, or chlorea Toxin or Heat labile enterotoxin. Such preparations provide protection from Chlamydia induced fertility.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (CfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E. coli
ActiveUS7759106B2Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Design and preparation method and application of echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine LTB-Emy162
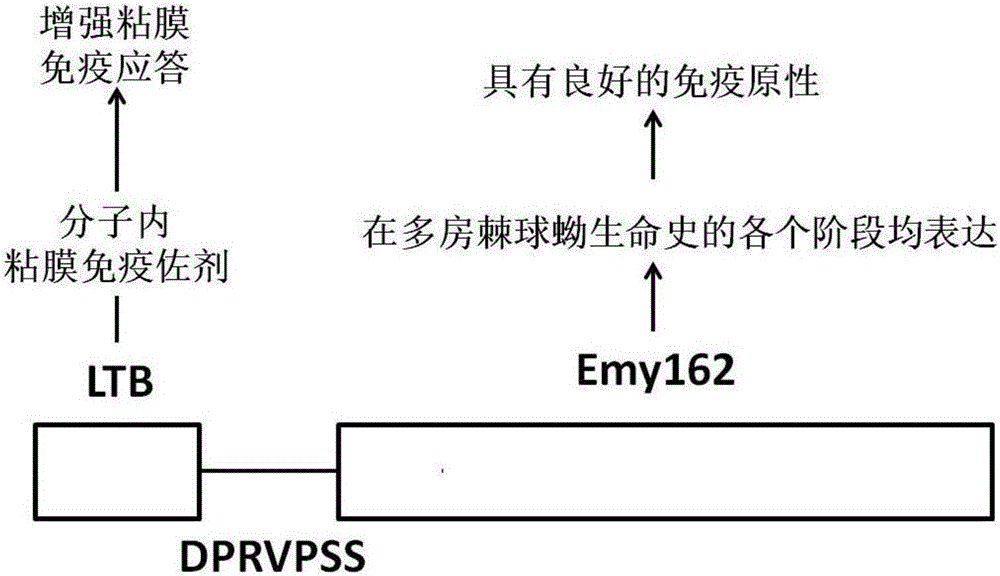
ActiveCN106581667AImprove securityIncrease productionBacteriaAntiparasitic agentsEscherichia coliDisease
The invention relates to a design and preparation method and an application of an echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine LTB-Emy162. The active component of the echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine LTB-Emy162 is a polypeptide, which is mainly composed of an echinococcus multilocularis antigen protein Emy162 amino acid sequence and a mucosal immunoadjuvant E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) amino acid sequence. In the invention, the gene sequence of the echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine LTB-Emy162 is synthesized through gene synthesis technology, the gene sequence is then linked to an expression vector through dual enzyme-cut, the expression vector then is converted into Arctic Express to perform expression of fusion protein, after purification of the protein, the echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine LTB-Emy162 is produced. The echinococcus multilocularis subunit vaccine can induce body to generate T-cell and B-cell immunologic response of the echinococcus multilocularis and humoral immune response of a high-titer specific antibody, and can be applied in prevention and therapy of echinococcus multilocularis infection related diseases.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIVERSITY
Fusion protein containing mycoplasma hyopneumoniae antigen, vaccine composition and application
ActiveCN107868130AImprove protectionImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmune effectsMycoplasma
The invention relates to a fusion protein. The fusion protein comprises enterotoxigenic escherichia coil heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit and mycoplasma hyopneumoniae antigen protein in a sequence from an N end to a C end. The invention also relates to a vaccine composition prepared from the fusion protein and an application thereof. The vaccine composition provided by the invention can achieve the immune effect of the commercial inactivated vaccine or better immune effect after one-time immunization.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
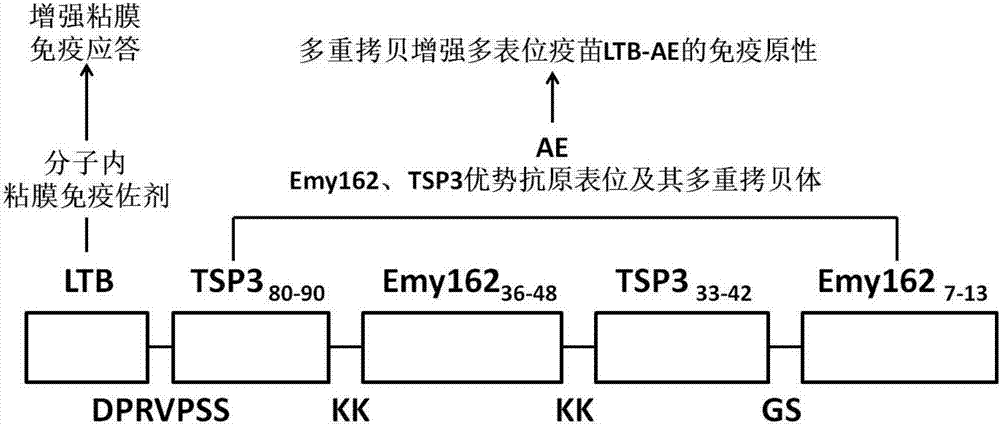
A design, preparing method and applications of an echinococcus multilocularis multi-epitope vaccine LTB-AE
The invention relates to a design, preparing method and applications of an echinococcus multilocularis multi-epitope vaccine LTB-AE. An active component of the multi-epitope vaccine LTB-AE is a polypeptide. The polypeptide mainly comprises an echinococcus multilocularis multi-epitope peptide AE, and a mucosal immune adjuvant that is an escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB). A gene sequence of the multi-epitope vaccine LTB-AE is synthesized mainly by a gene synthesis technique, and is connected to an expression vector through double digestion, then the expression vector is converted into arctic express to perform expression of a fusion protein, and after the protein is purified, the multi-epitope vaccine LTB-AE is obtained. The multi-epitope vaccine can induce a body to generate immune responses and high-titer specific antibody humoral immune responses to echinococcus multilocularis T cells and B cells, and can be used for preventing and treating echinococcus multilocularis infection related disease.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIVERSITY
Eukaryon expression of coli heat-sensitive toxin B subunit
InactiveCN1746308AImprove expression levelCorrect cutting and processingFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliProtein target
An eucaryotic expression of E.coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit, LT-B is prepared by defining nucleic acid endoenzyme site, connecting LT-B nucleic acid sequence with pPICZ alpha A to obtain recombinant expression carrier, inducing recombinant expression carrier into Pichiapastoris X-33 or KM71, and fermentation expressing to obtain target protein LT-B. It has high economical value.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for preparing heat-labile enterotoxin of E, coli
InactiveCN1821398ADoes not affect translatioDoes not affect synthesis speedFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The present invention discloses the preparation process of heat labile enterotoxin of E. coli, and the preparation process has intracellular expression or secretory expression of LT or LTB in yeast cell. Exogenously expressing LT and its mutant or subunit in eukaryotic yeast cell has greatly raised expression level. The present invention constitutes multicopy LT or LTB subunit expression kit, has increased gene dosage of LT or LTB in yeast, LT or LTB gene recombination following alcohol dehydrogenase promoter as the powerful promoter of Pichia yeast expression vector, methanol induced high expression of exogenous protein in yeast cell and thus raised expression level of LT and its mutant or LTB in yeast cell, simple post purification and safe clinical application. The present invention has low production cost and high target protein yield, and is significant in the scale production and clinical application of mucous membrane adjuvant.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polysaccharide conjugation with detoxified E. COLI heat labile enterotoxin (LT) used as vaccine
InactiveCN102858370AAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliConjugate vaccine
A detoxified recombinant E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin mutant, LTS61K, is employed as a carrier protein to conjugate polysaccharide. The LTS61K contains a mutated mature sub-unit A (LTA) that includes lysine at amino acid position 61 and a wild-type mature sub-unit B (LTB). Various types of bacterial capsular polysaccharide antigens were chemically conjugated with the LTS61K protein by a reductive amination reaction. The conjugated polysaccharide-LTS61K products were physically, chemically and biochemically identified as soluble form. Rabbits were immunized intramuscularly to determine the immunogenicity of conjugated vaccines by ELISA to detect anti- polysaccharide antigen IgG titers and serum bactericidal assay thereby determining the functional activity of the antibodies.; Study results show that conjugated polysaccharide-LTS61K vaccines induce higher polysaccharide-specific IgG titers and greater bactericidal activity in sera than that of polysaccharide alone or polysaccharide mixed with LTS61K. The presence of anti-LTS61K serum IgG antibody alleviates travel diarrhea caused by E. coli (ETEC enterotoxigenic E. coli).
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY
Mucosal immunization to prevent prion infection
Vaccines against prion disease eliciting a humoral immune response when administered mucosally are described. The vaccines comprise a prion protein, a prion protein fragment, or a non-amyloidogenic prion protein homolog and an adjuvant suitable for inducing a humoral immune response after mucosal administration. Suitable adjuvants include cholera toxin subunit B, heat-labile enterotoxin and aluminum hydroxide. Alternatively, the vaccine comprises a vector encoding a prion protein, fragment, or homolog in an attenuated Salmonella host. The vaccines can be used to prevent or treat prion disease in humans and other mammals.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Telomerase reverse transcriptase fusion protein, nucleotides encoding it, and uses thereof
Polynucleotides encoding telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) fusion proteins are provided, the TERT fusion proteins comprising a TERT protein, or functional variant thereof, fused to a substantial portion of the B subunit of heat labile enterotoxin (LTB). TERT variants useful in TERT-LTB fusion proteins of the invention comprise mutations that function to eliminate telomerase catalytic activity. The polynucleotides of the present invention can elicit an immune response in a mammal, which, in preferred embodiments, is stronger than the immune response elicited by a wild-type TERT. TERT expression is commonly associated with the development of human carcinomas. The present invention provides compositions and methods to elicit or enhance immunity to the protein product expressed by the TERT tumor-associated antigen, wherein aberrant TERT expression is associated with a carcinoma or its development. This invention specifically provides adenoviral vector and plasmid constructs carrying polynucleotides encoding TERT fusion proteins and TERT variants and discloses their use in vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for preventing and treating cancer.
Owner:MSD ITAL
Antigen chimera, antigen composition, vaccine, method of preparing the same and cassette thereof
ActiveUS20160368951A1Improving immunogenicityIncrease volumeAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliPentamer
The present invention provides an antigen chimera, comprising: a fusion protein of an antigen and a mucosal immune adjuvant protein monomer capable of forming a multimer; and the mucosal immune adjuvant protein monomer capable of forming the multimer; wherein the mucosal immune adjuvant protein monomer capable of forming the multimer is one selected from cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB), the multimer is a pentamer, and in the chimera the molar ratio between the fusion protein and the mucosal immune adjuvant protein monomer capable of forming multimers is 1:4. In the present invention, a characteristic that a mucosal immune adjuvant protein can form a pentamer is used to form a chimeric structure, so as to form an antigen having a higher potency. Moreover, a mucosal immune adjuvant protein is used to improve an immune effect, so as to improve an effect of enhancing antigen immunogenicity. In addition, the chimeric protein antigen formed with the recombined antigen of the present invention stimulates a mucous membrane to produce secretory IgA and induce the occurrence of mucosal immunity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED CELL BIOTECH
Pneumococcus combined vaccine using recombinant vector protein and preparation method of pneumococcus combined vaccine
ActiveCN108339115AEnhance immune responseStructurally elasticAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
Owner:BRAVOVAX +1
Recombinant DNA, plasmid, transformed microorganism and vaccine protein for prevention and therapy of urinary tract infection
Disclosed is a novel vaccine against Escherichia coli (E. coli) responsible for urinary tract infections. The vaccine is a recombinant chimeric protein which is prepared by linking by genetic recombination a gene encoding an antigenic determinant of uropathogenic E. coli to a CTXA2B gene encoding nontoxic A2 and B subunits of Vibrio cholerae cholera toxin (CTX) or a LTXA2B gene encoding nontoxic A2 and B subunits of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin, wherein a translation product of the CTXA2B or LTXA2B gene serves as an immunogenic adjuvant stimulating mucosal immune responses, expressing the resulting recombinant gene in E. coli, and isolating and purifying an expressed recombinant fusion protein. The recombinant chimeric protein is useful as an oral vaccine with mild side effects and excellent vaccination efficiency against uropathogenic E. coli. Thus, the chimeric vaccine protein can remarkably reduce recurrence of urinary tract infections, prevent occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and replace the conventional chemotherapy for urinary tract infections. Also, the chimeric vaccine protein has other advantages of being capable of being produced and commercialized in a short period with relatively low costs, and being easily modified by replacing its genetic constituents with other genes to provide various vaccines.
Owner:SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY
Mutated e. coli heat-labile enterotoxin
This invention relates to a mutant E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) subunit A that can be used as an adjuvant. This subunit A mutant contains an amino acid substitution at a position correspondingto position 61 of a wild-type LT. An LT containing this mutated subunit A exhibits reduced toxicity compared to its wild type counterpart.
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com