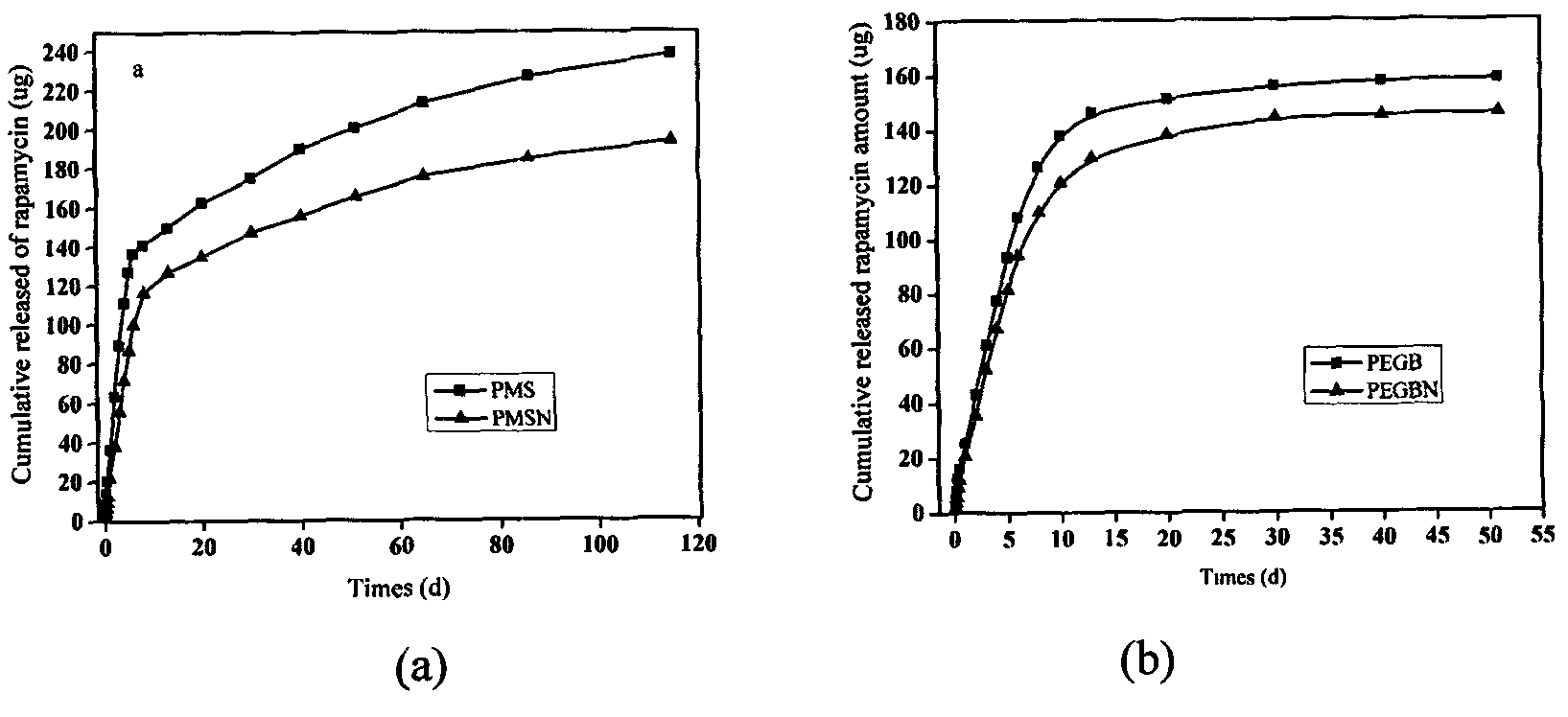
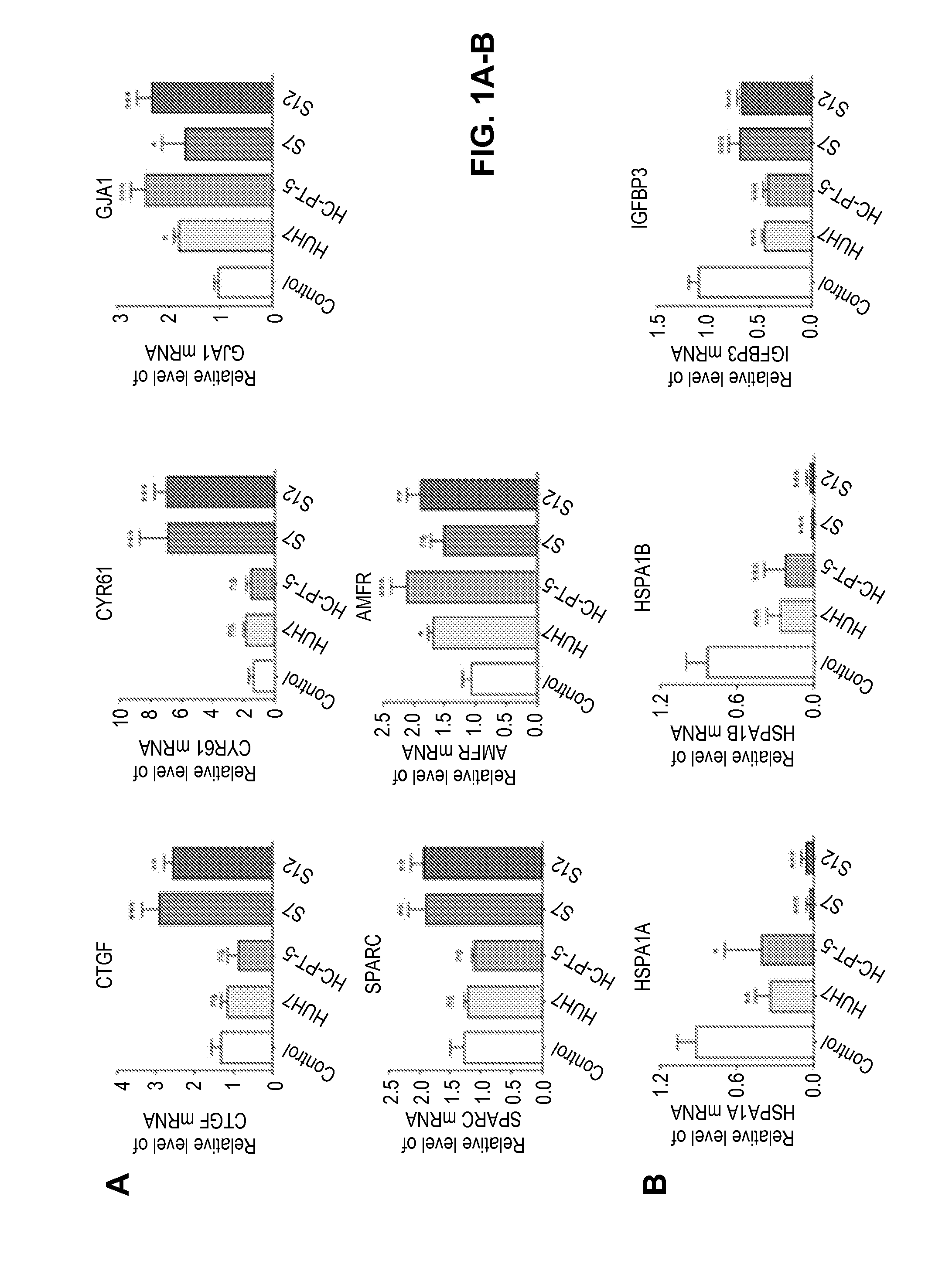
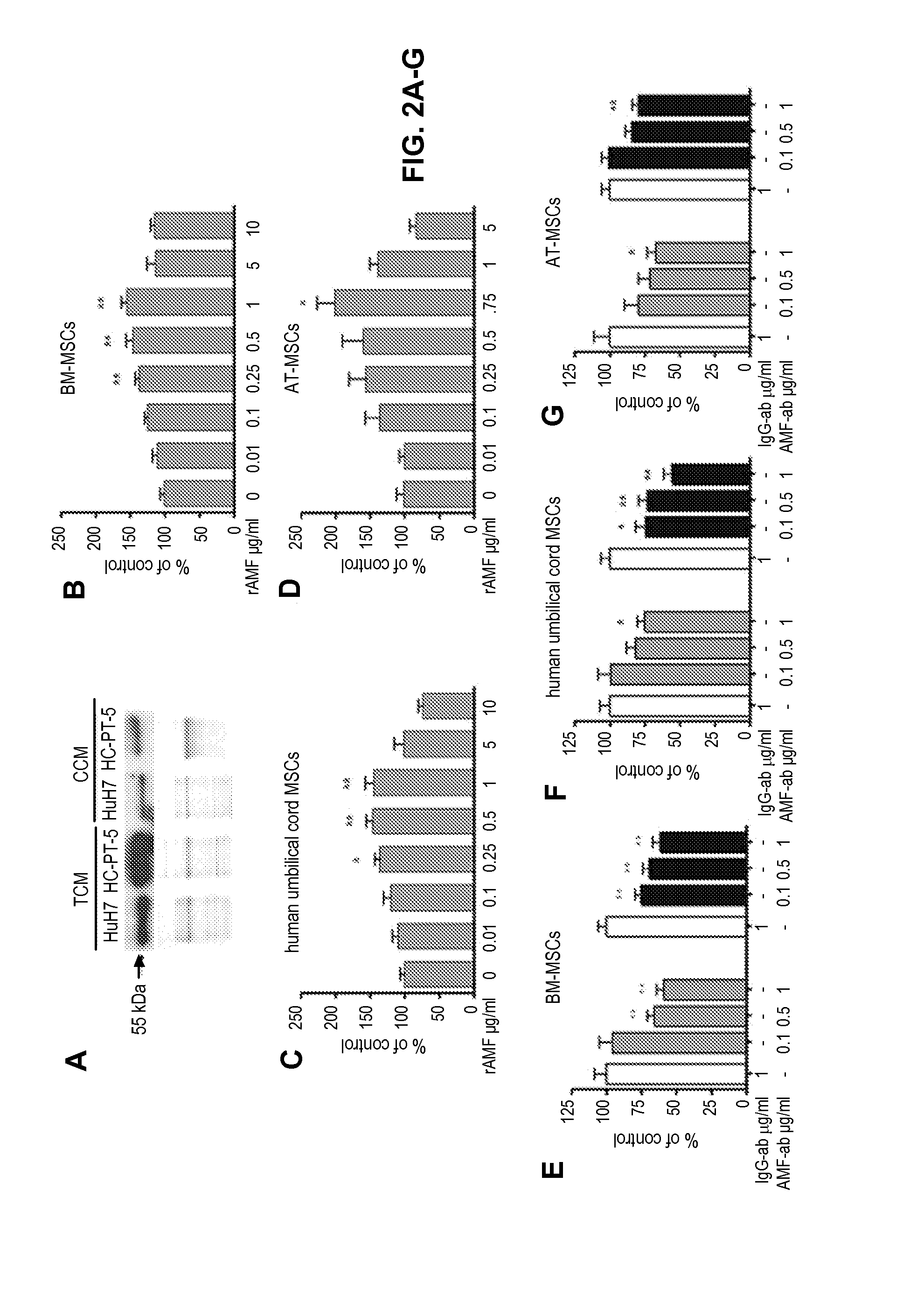
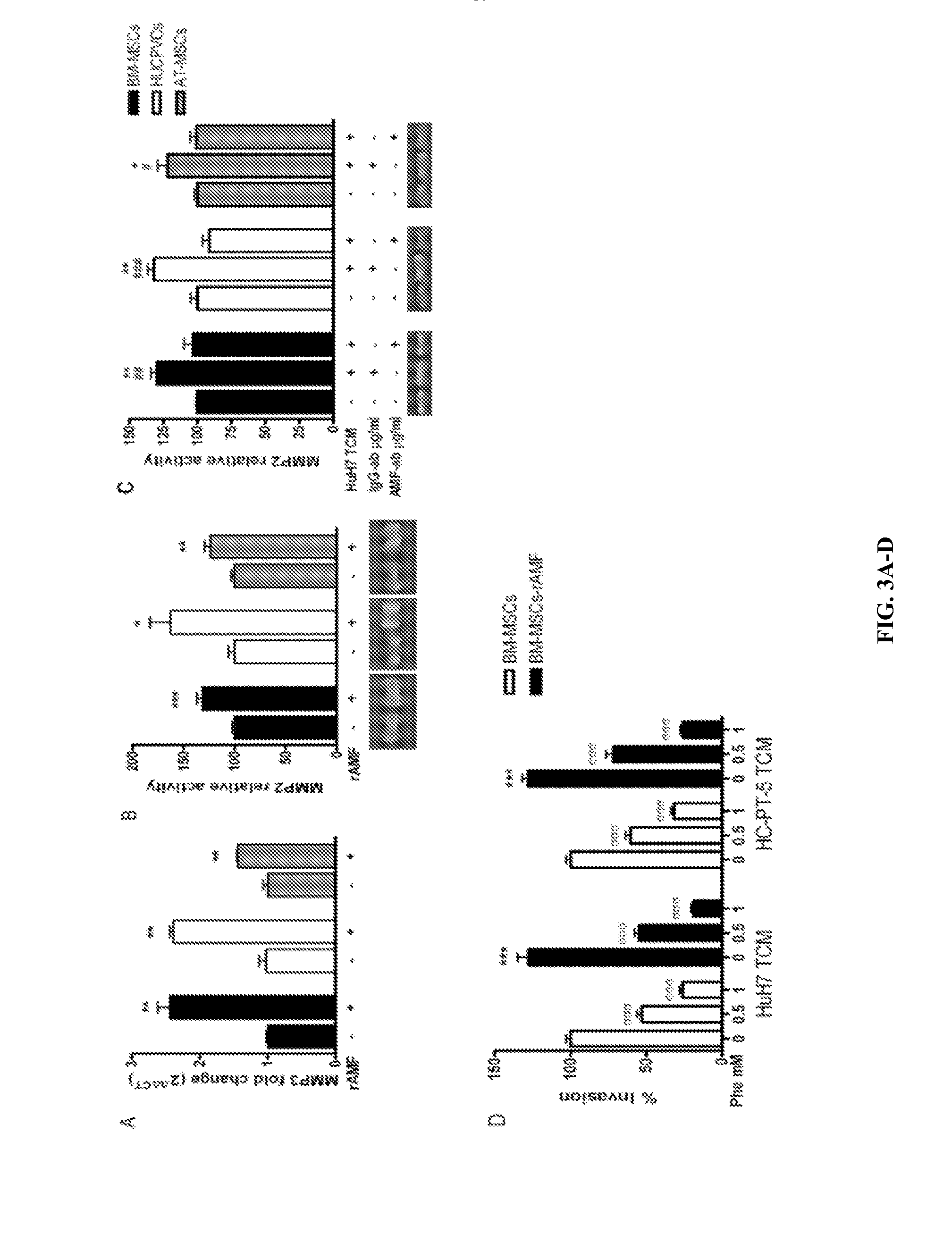
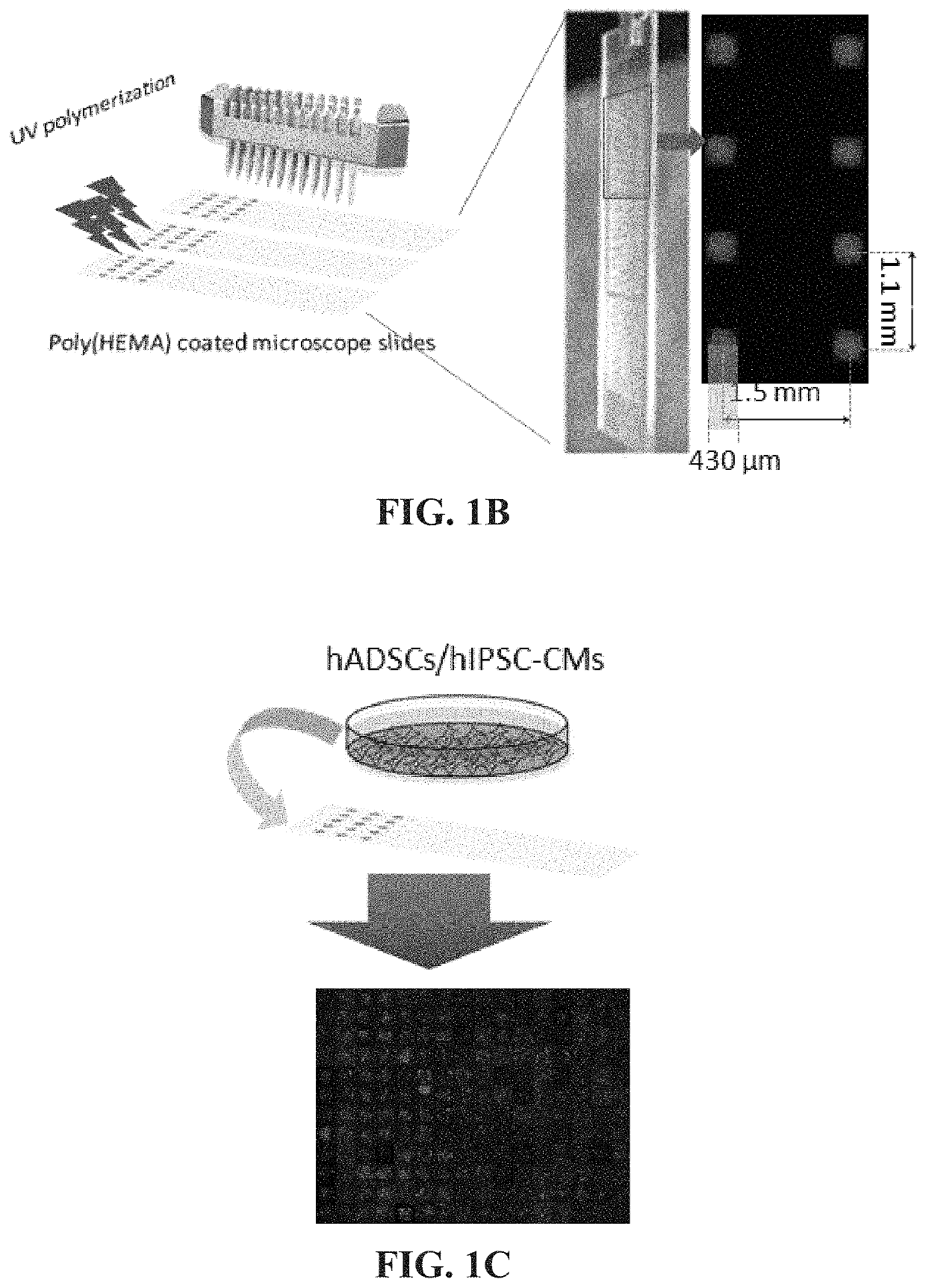
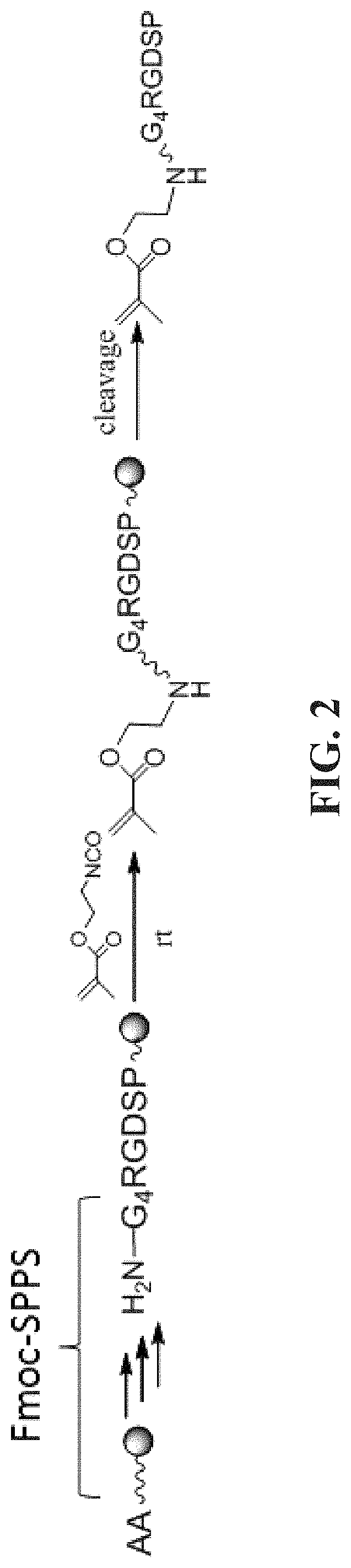
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Endothelial cell-cell adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The attachment of an endothelial cell to another endothelial cell via adhesion molecules. [GOC:BHF]
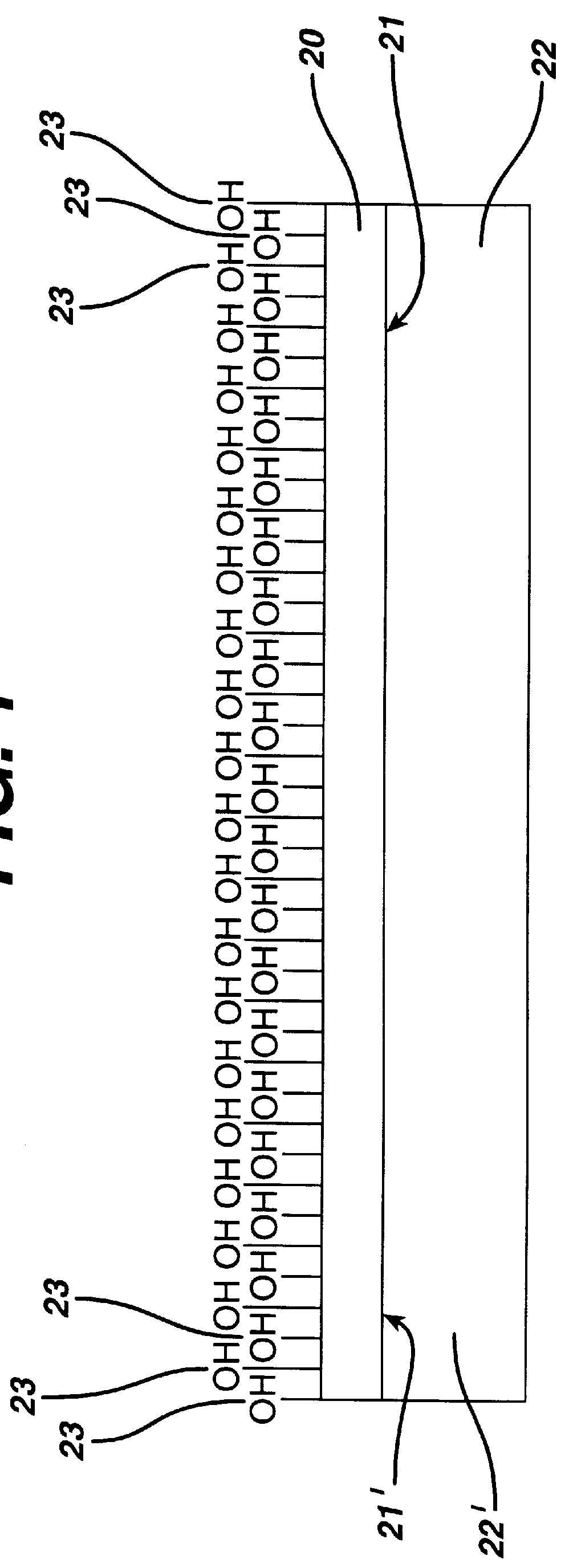
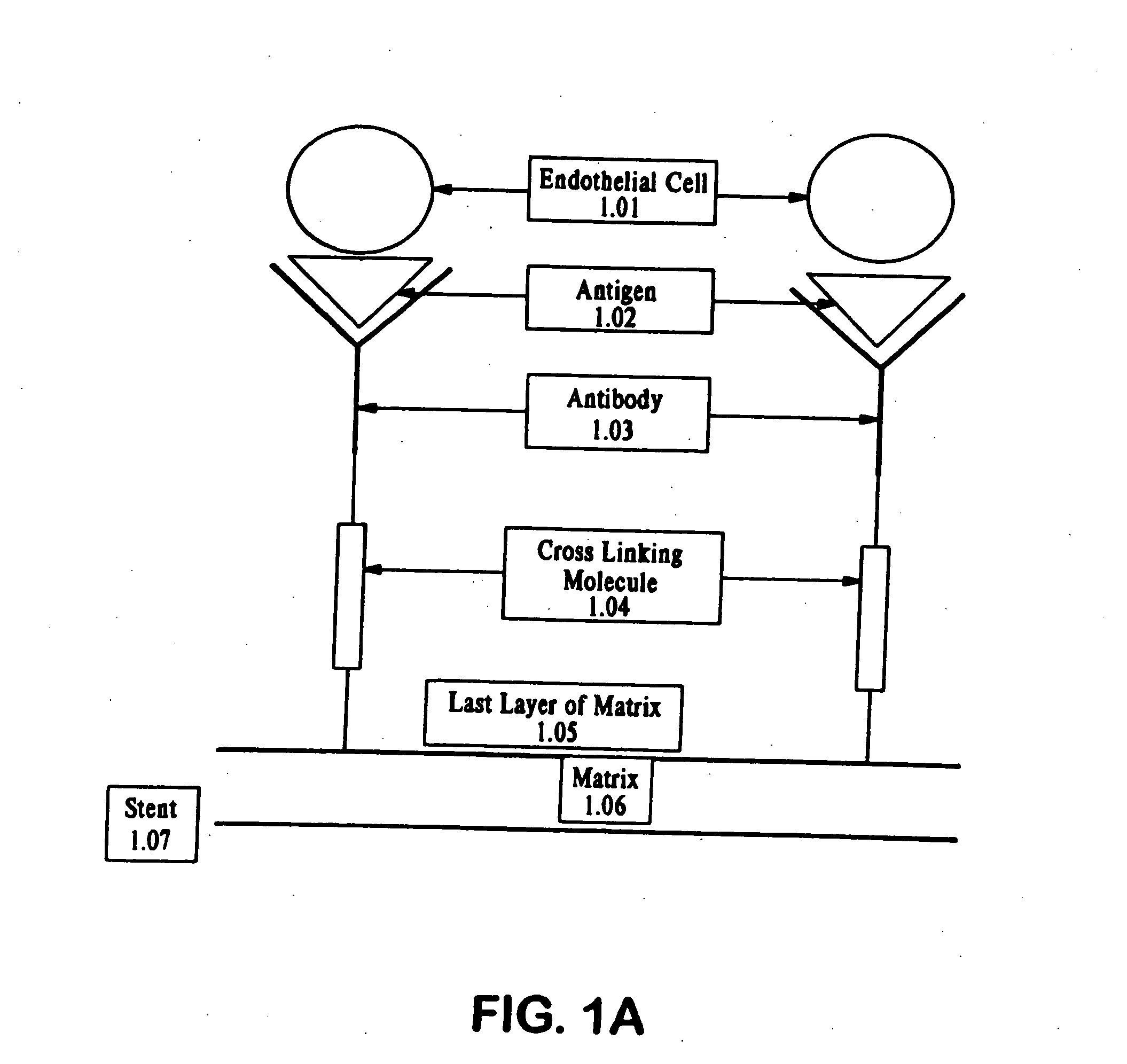
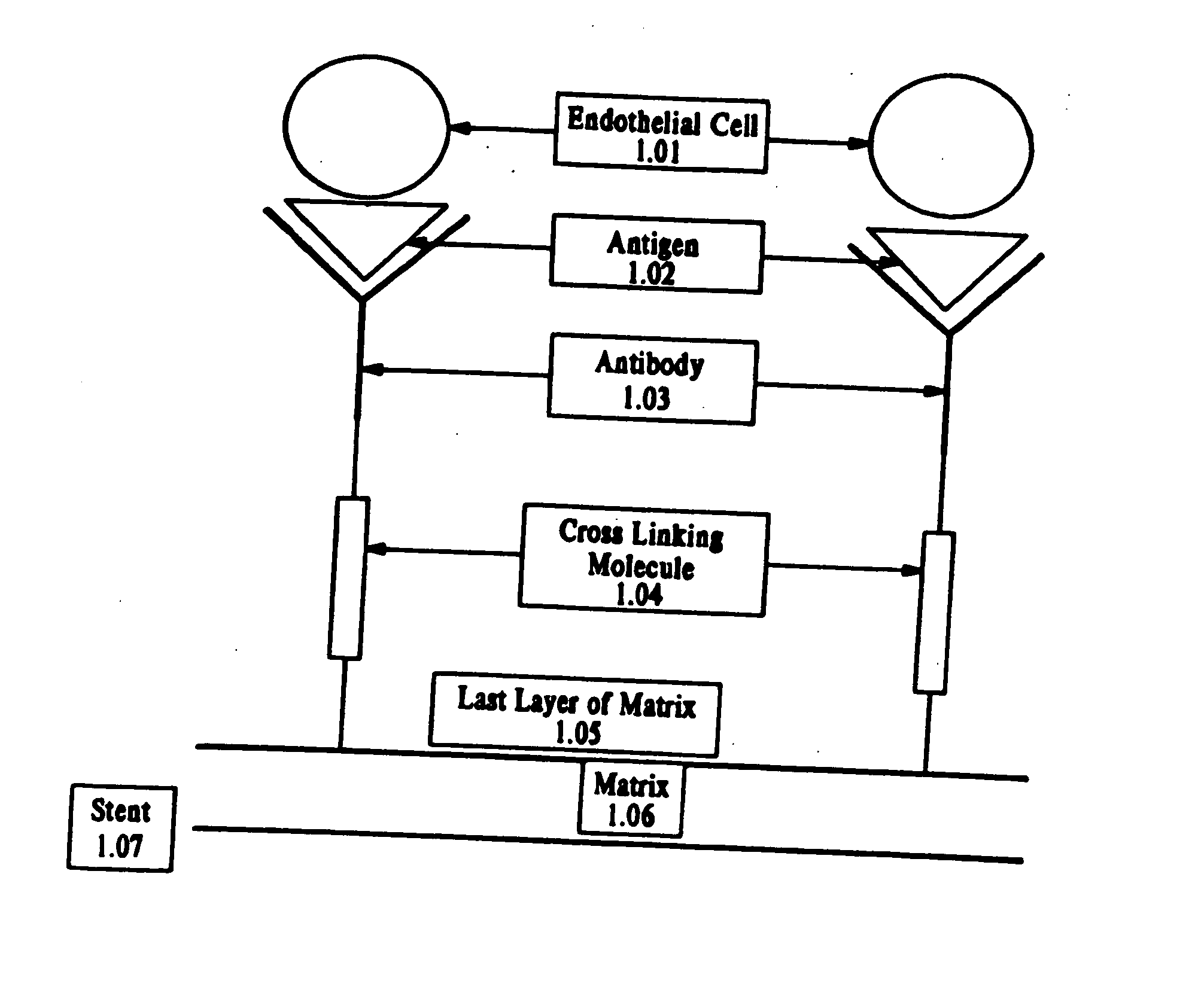
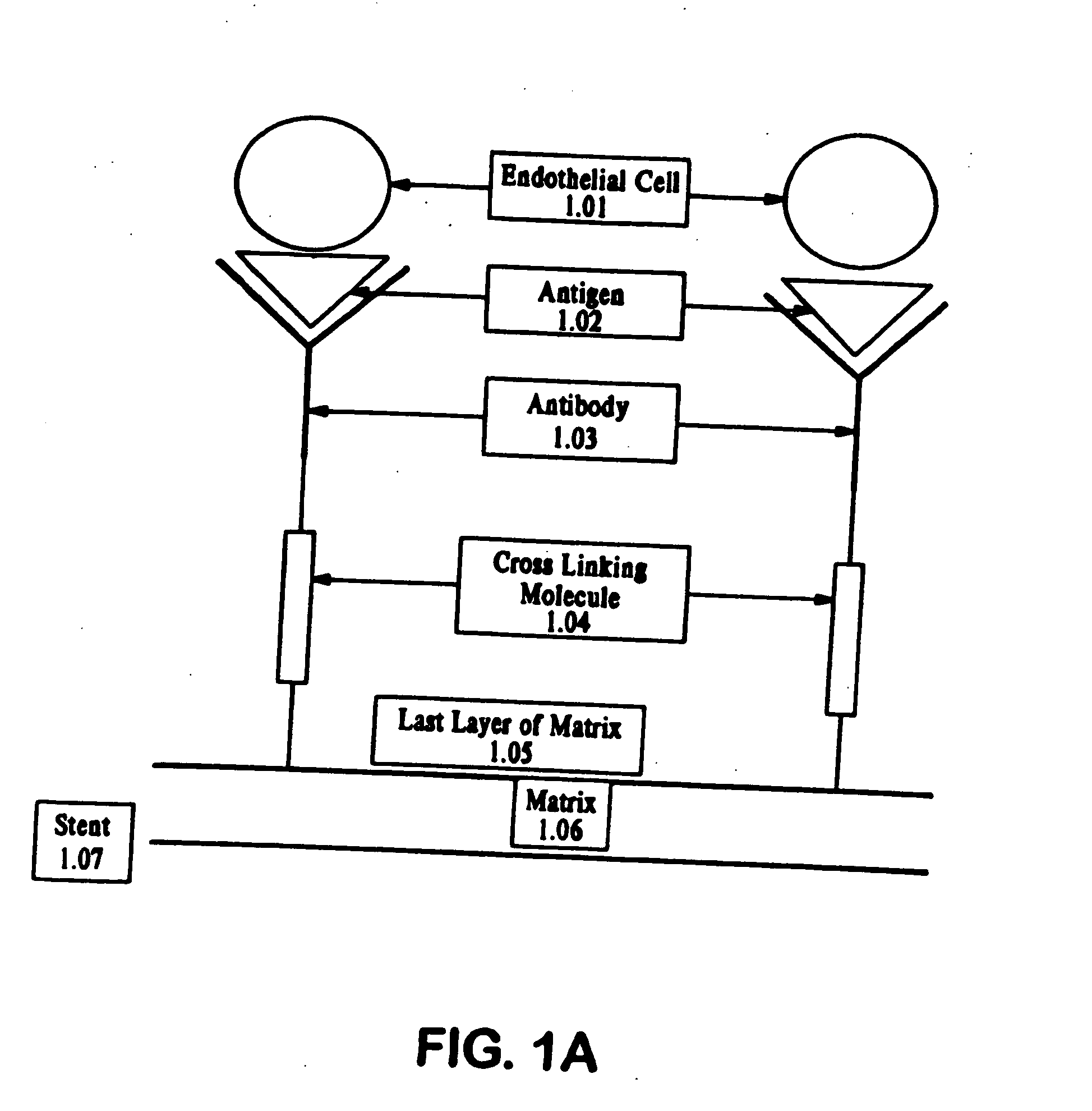
Method of coating an intravascular stent with an endothelial cell adhesive five amino acid peptide
InactiveUS6140127APromoting cell attachmentRestore patencyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell specificArginine
Endothelial cell attachment to an intravascular stent is promoted by coating the stent with an endothelial cell specific adhesion peptide. Coating is preferably carried out by activating the intravascular stent using plasma glow discharge, applying on the stent a layer or plurality of layers of a polymer such as poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate), applying a tresylation solution containing pyridine and tresyl chloride, and applying a five amino acid peptide having the sequence glycine-arginine-glutamic acid-aspartic acid-valine.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
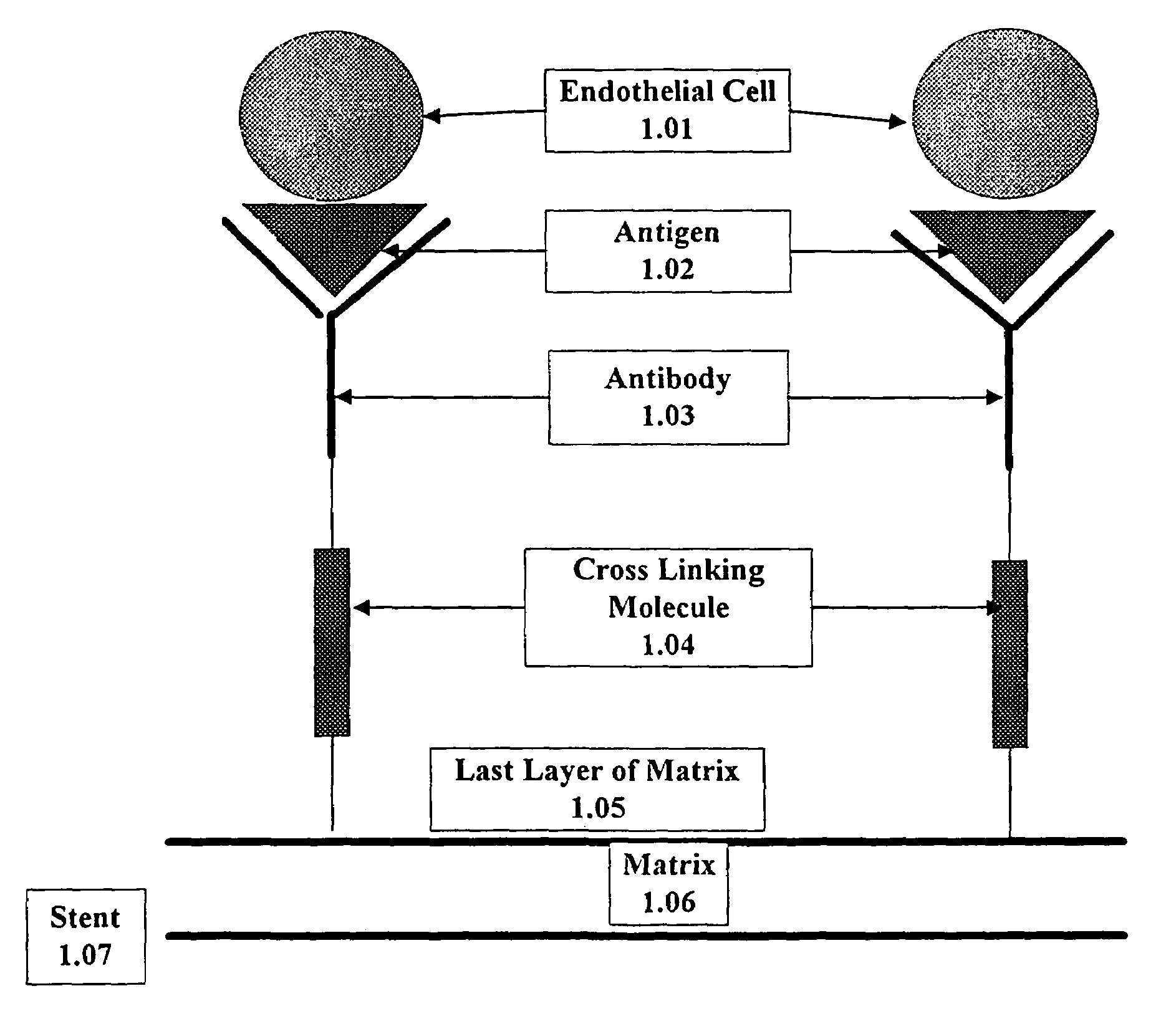
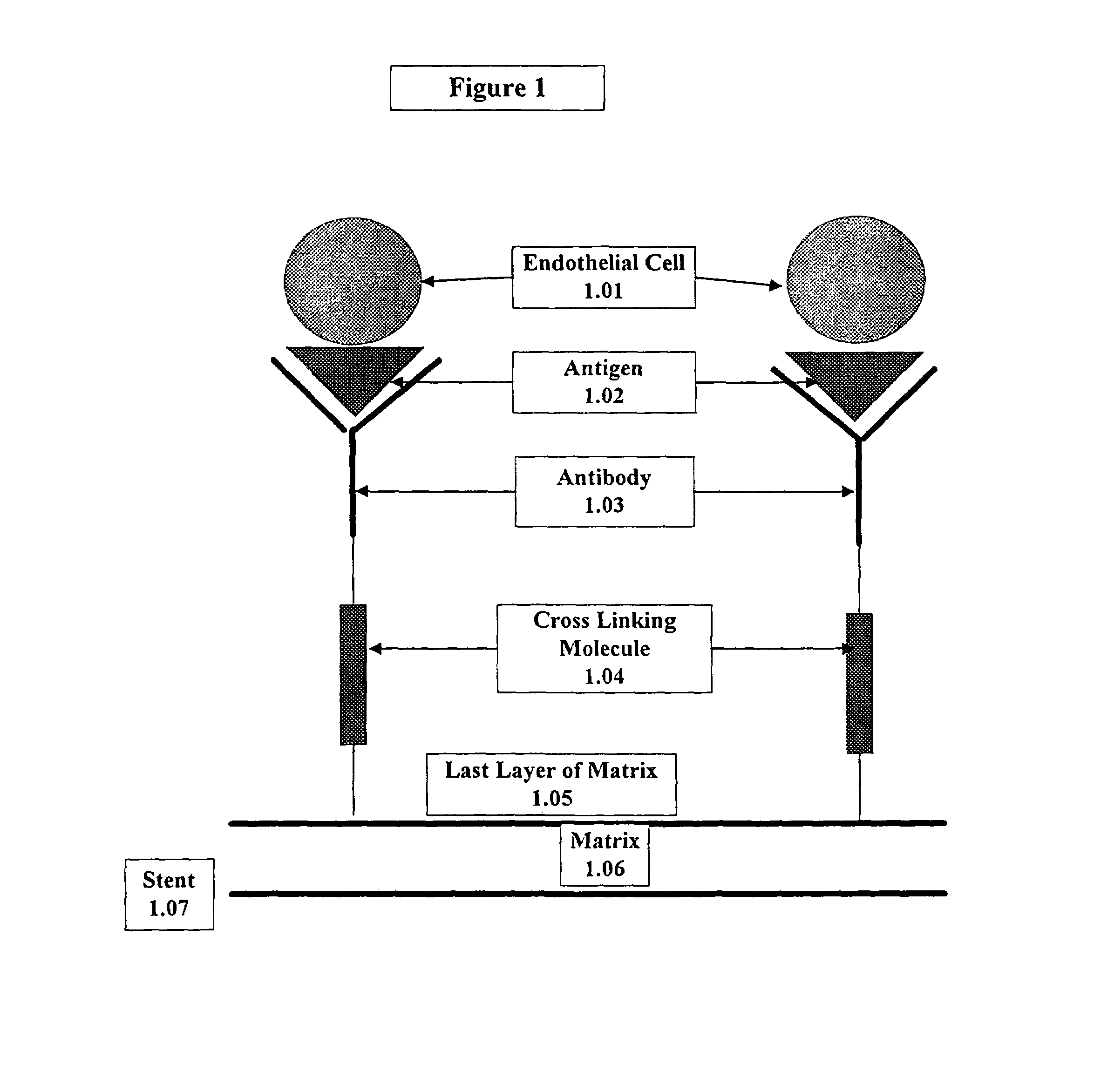
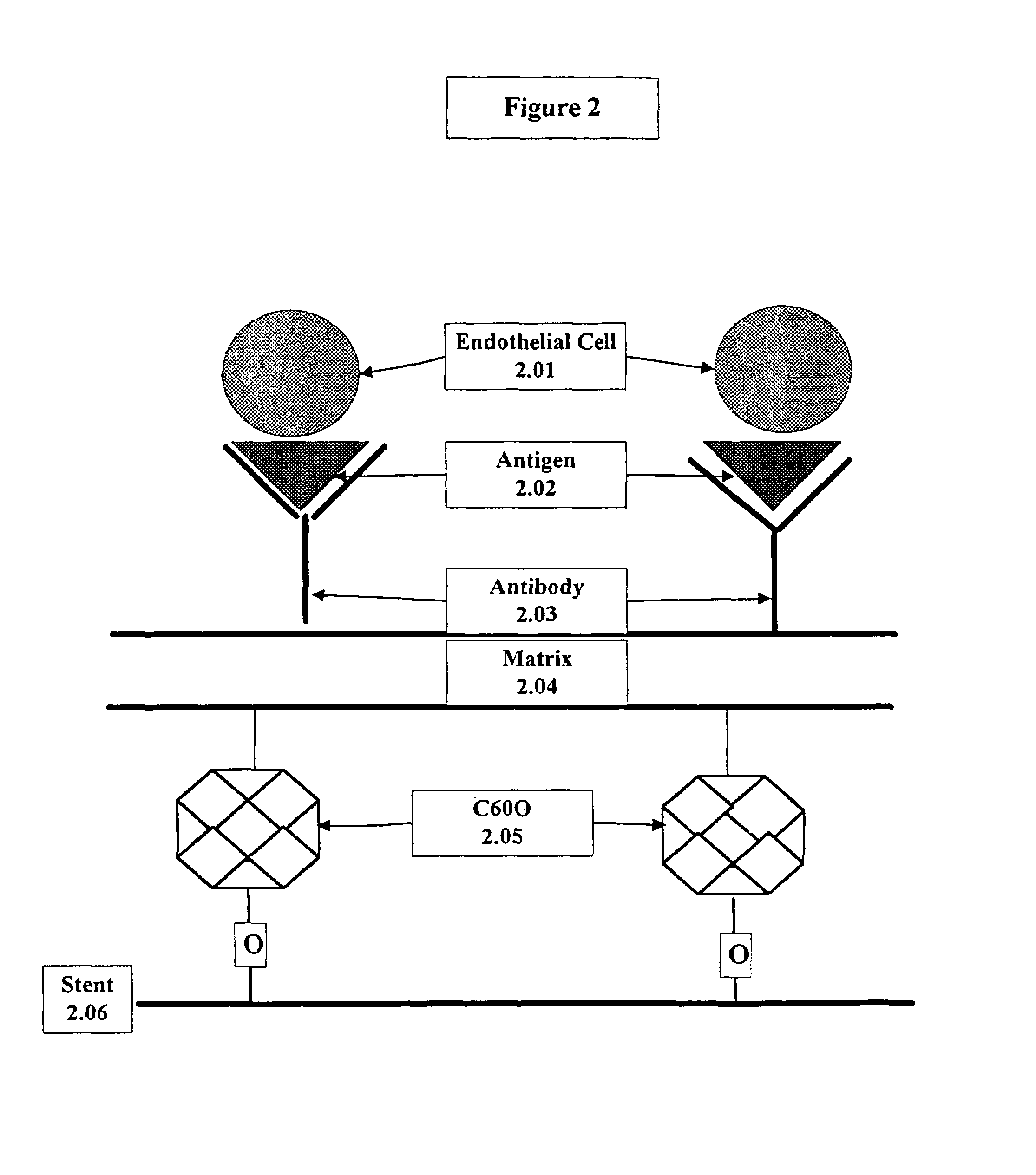
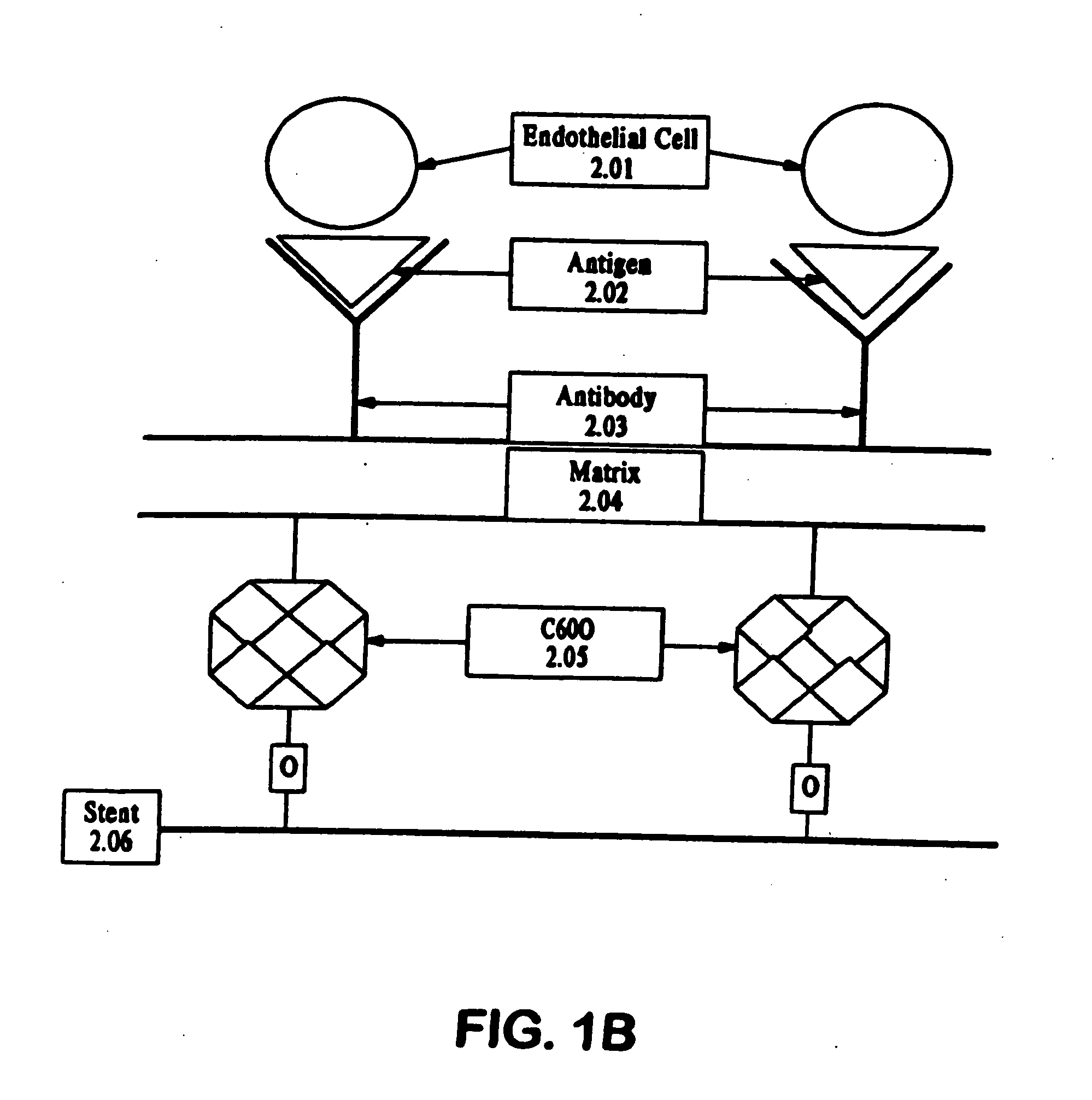
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
InactiveUS7037332B2Prevent restenosisMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsCell Surface AntigensPercent Diameter Stenosis
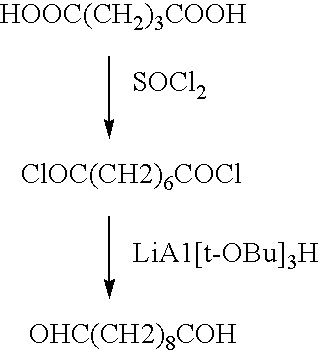
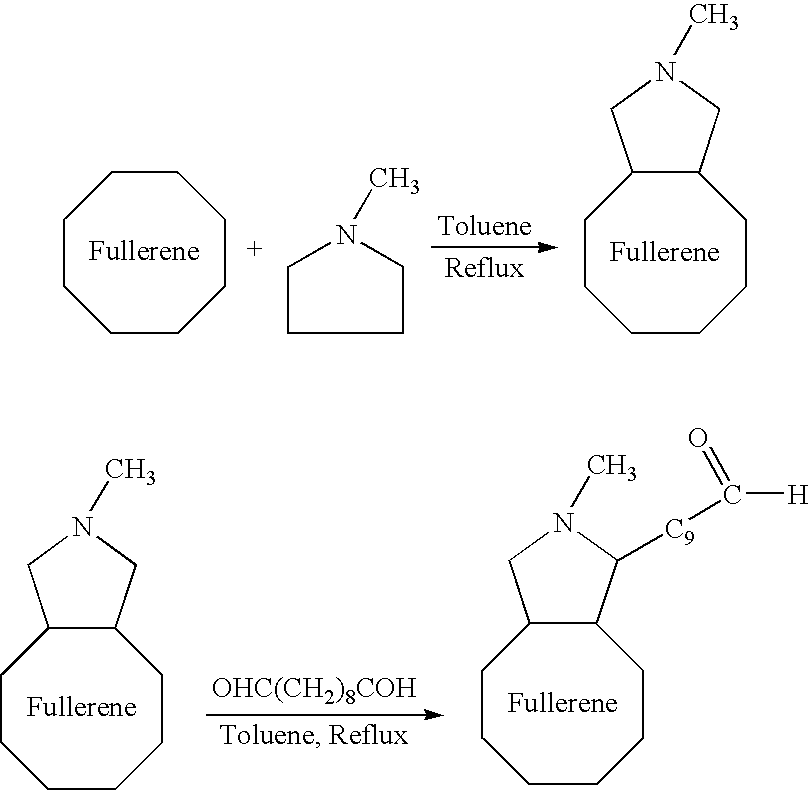
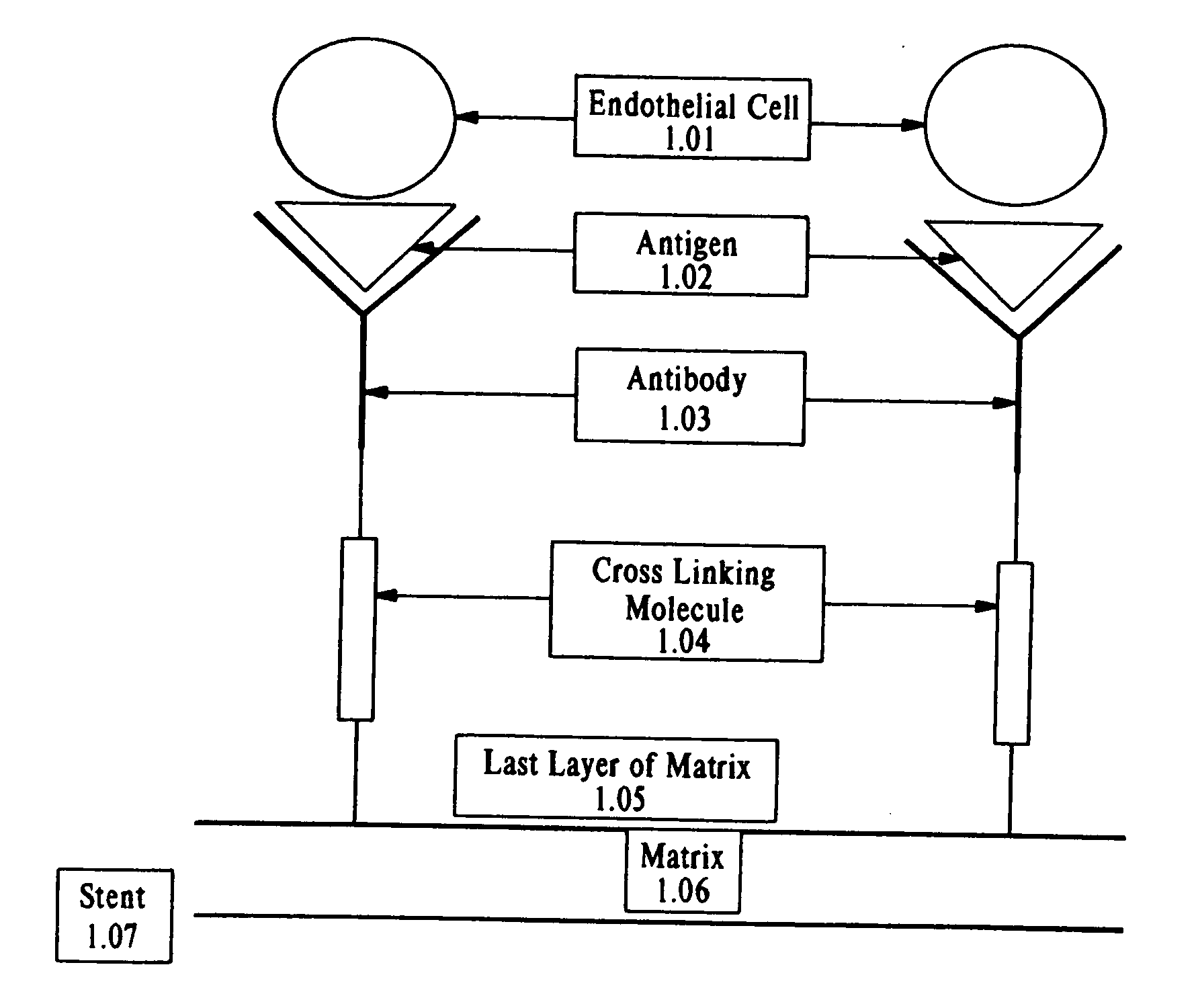
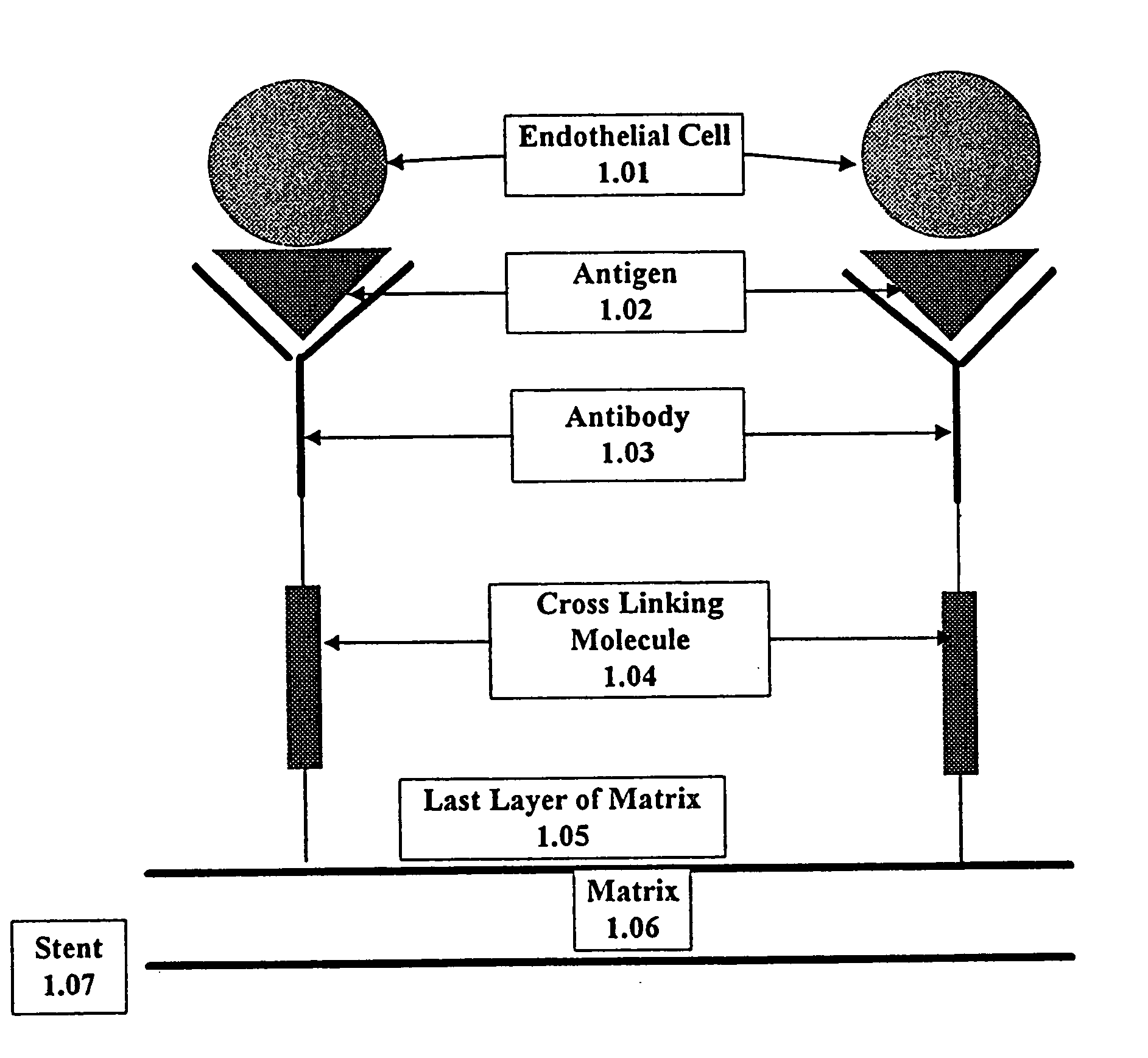
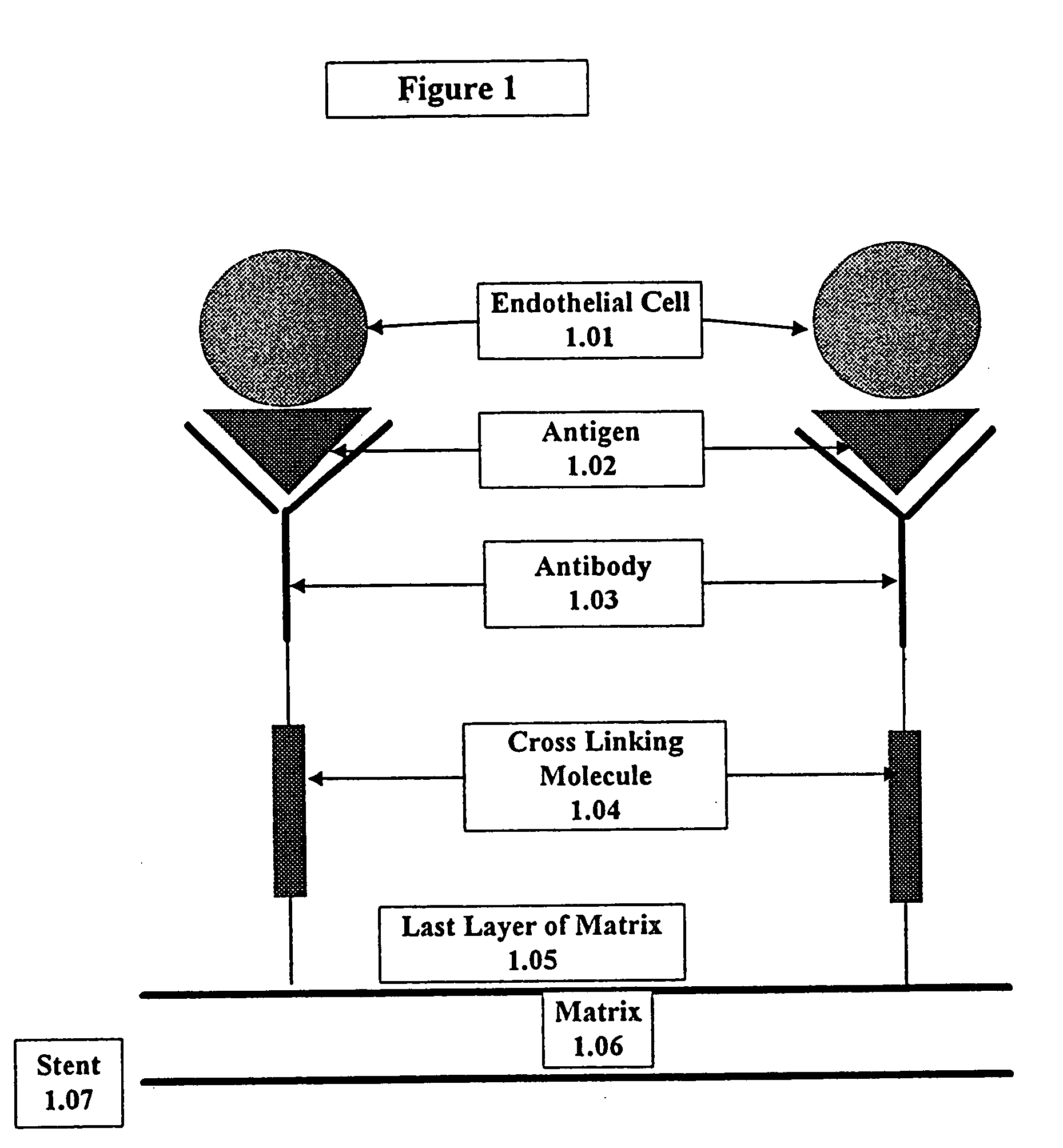
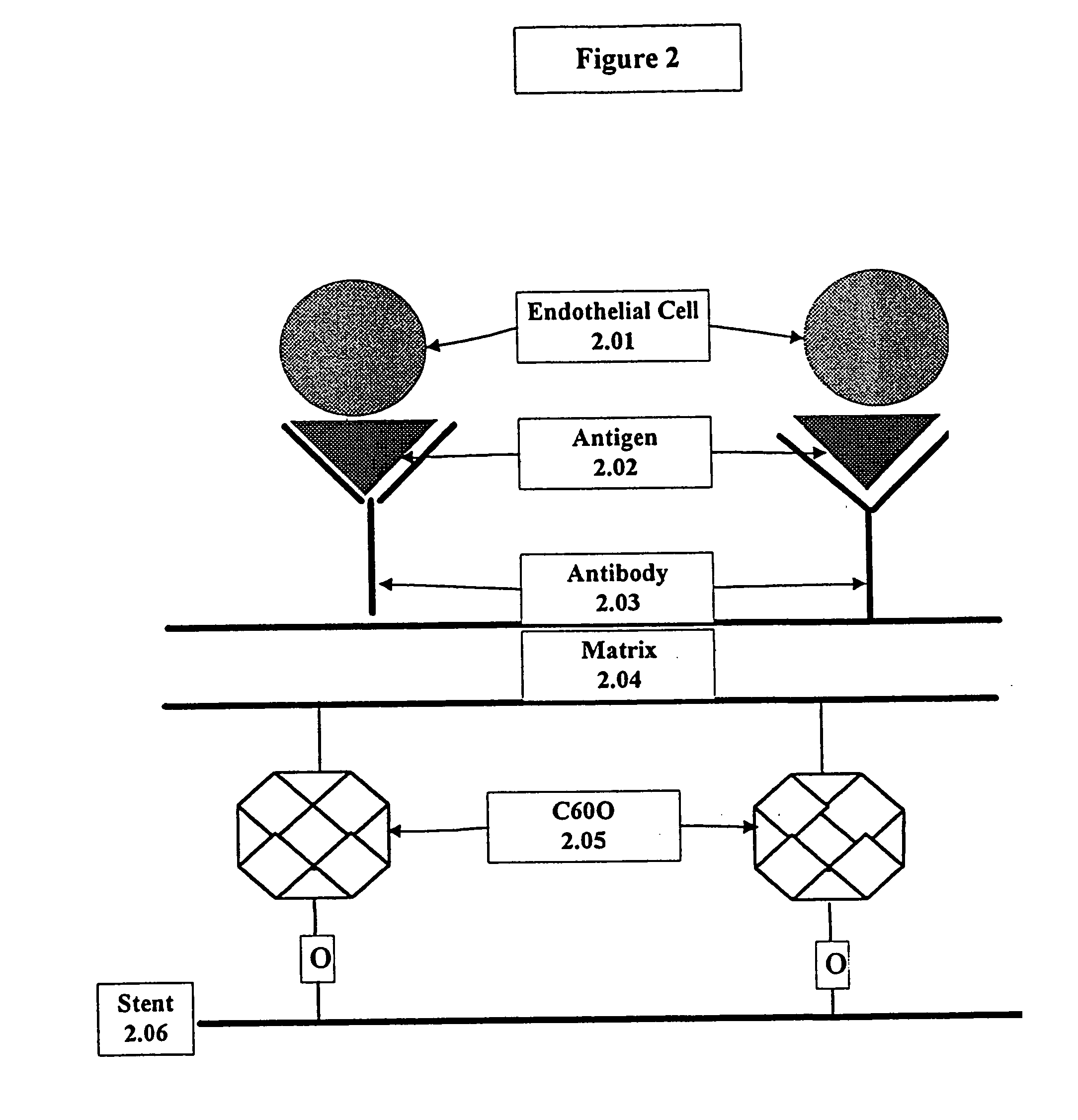
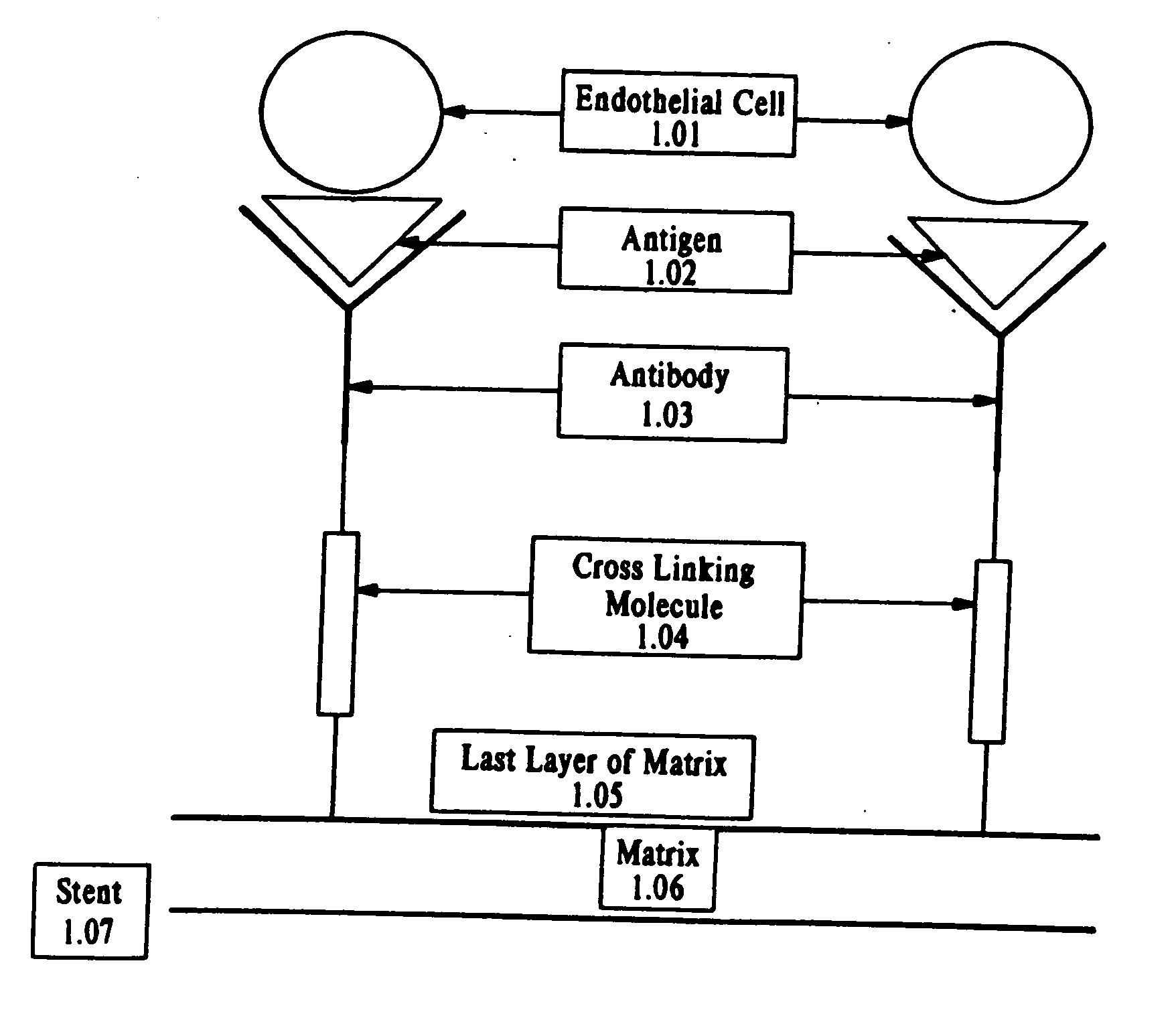
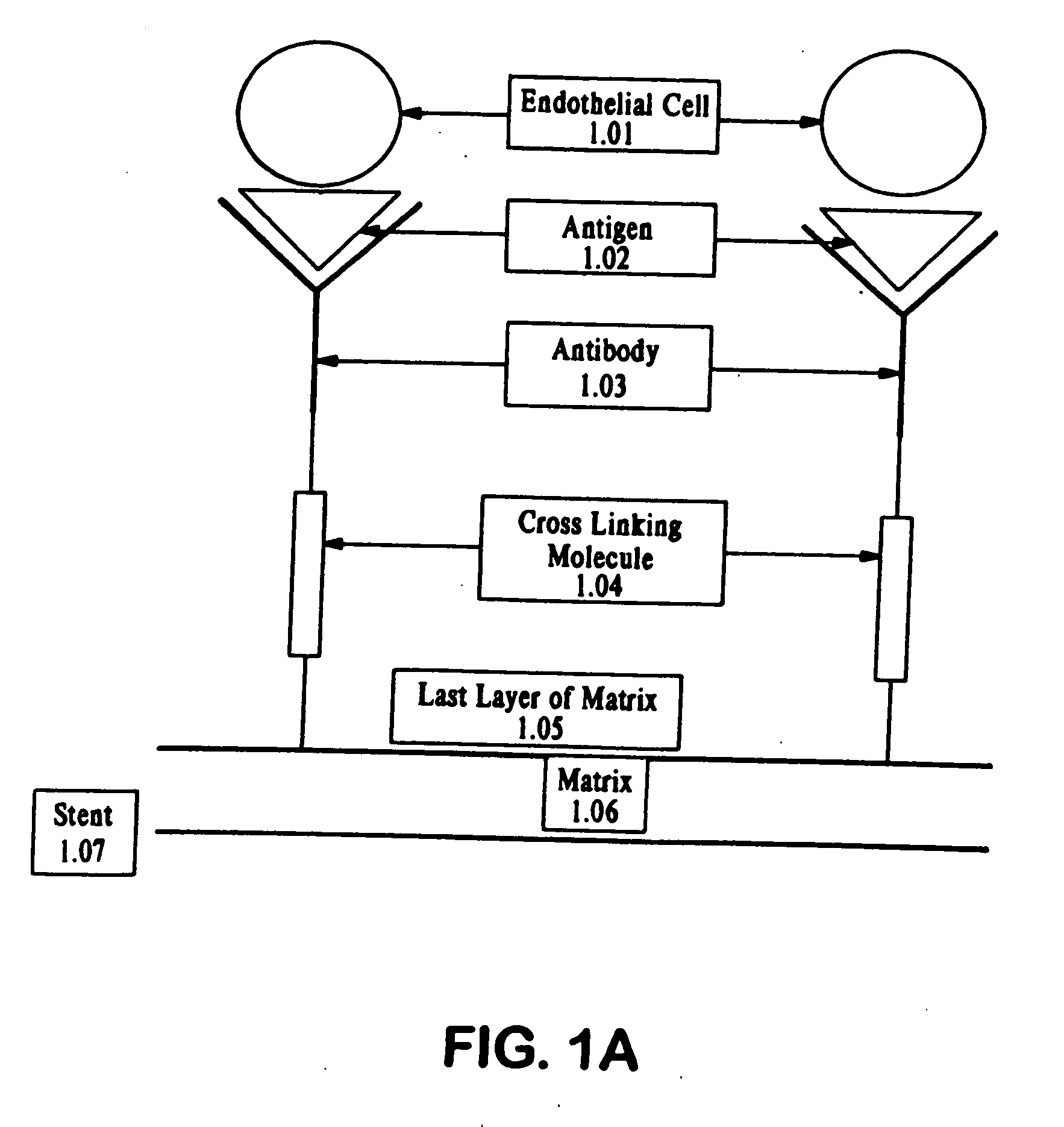
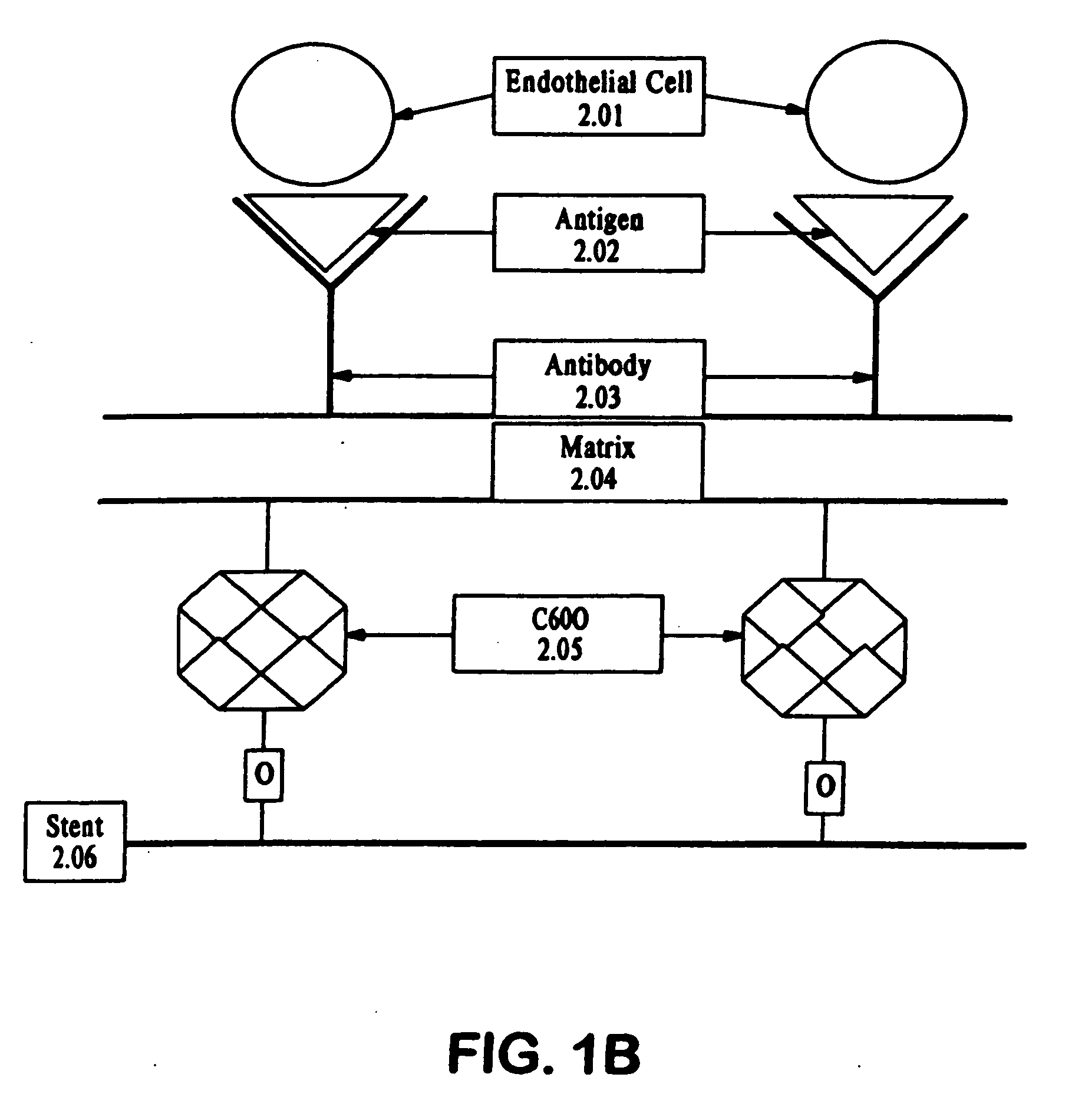
A medical device coated with one or more antibodies and one or more layers of a matrix is disclosed. The antibodies or fragments thereof react with an endothelial cell surface antigen. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for producing the medical device. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of a synthetic material, such as a fullerene, or a naturally occurring material. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote the adherence of cells captured in vivo on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. By facilitating adherence of cells to the surface of the medical device, the disclosed methods and compositions will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
InactiveUS20050043787A1Prevent restenosisPreventing other thromboembolic complicationMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPolyethylene glycol
This invention provides compositions and methods for producing a medical device coated with a matrix and an antibody which reacts with an endothelial cell antigen. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of synthetic material, such as polyurethane, poly-L-lactic acid, cellulose ester or polyethylene glycol. In another embodiment, the matrix is composed of naturally occurring materials, such as collagen, fibrin, elastin, amorphous carbon. In a third embodiment, the matrix may be composed of fullerenes. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote adherence of endothelial cells on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the endothelial cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. Methods of preparing such composition and methods of treating a mammal with atherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstruction are disclosed. By facilitating adherence of endothelial cells to the surface of the medical device, the methods and compositions of this invention will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
InactiveUS20070055367A1Improved prognosisInhibit intimal hyperplasiaMaterial nanotechnologyStentsAntigenProgenitor
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUS MEDICAL TECH +1
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
InactiveUS20070042017A1Inhibit intimal hyperplasiaImproved prognosisMaterial nanotechnologySurgeryProgenitorAntigen
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence and differentiation
InactiveUS20070196422A1Improved prognosisPrevent restenosisStentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenVascular obstruction
Compositions and methods are provided for producing a medical device such as a stent, a stent graft, a synthetic vascular graft, heart valves, coated with a biocompatible matrix which incorporates antibodies, antibody fragments, or small molecules, which recognize, bind to and / or interact with a progenitor cell surface antigen to immobilize the cells at the surface of the device. The coating on the device can also contain a compound or growth factor for promoting the progenitor endothelial cell to accelerate adherence, growth and differentiation of the bound cells into mature and functional endothelial cells on the surface of the device to prevent intimal hyperplasia. Methods for preparing such medical devices, compositions, and methods for treating a mammal with vascular disease such as restenosis, artherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstructions are disclosed.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
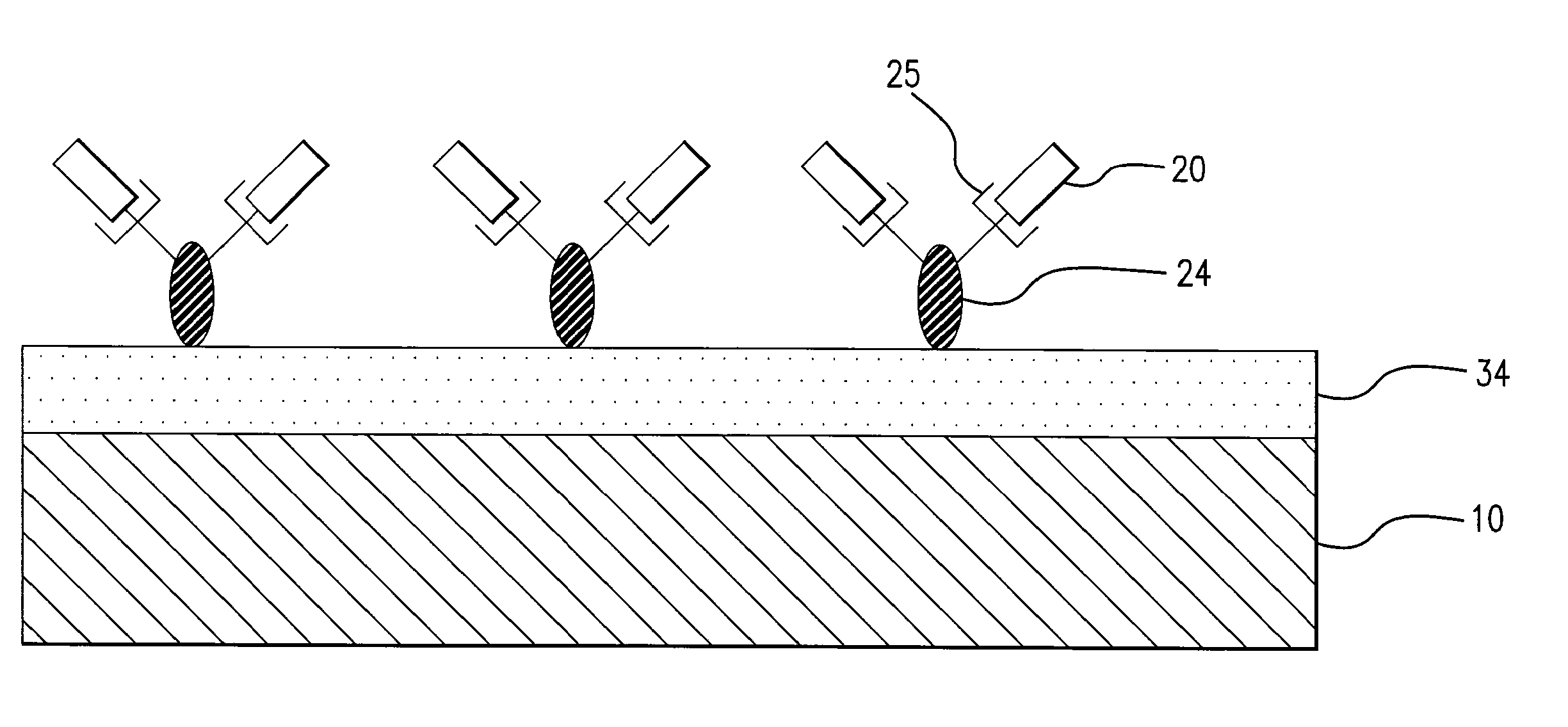
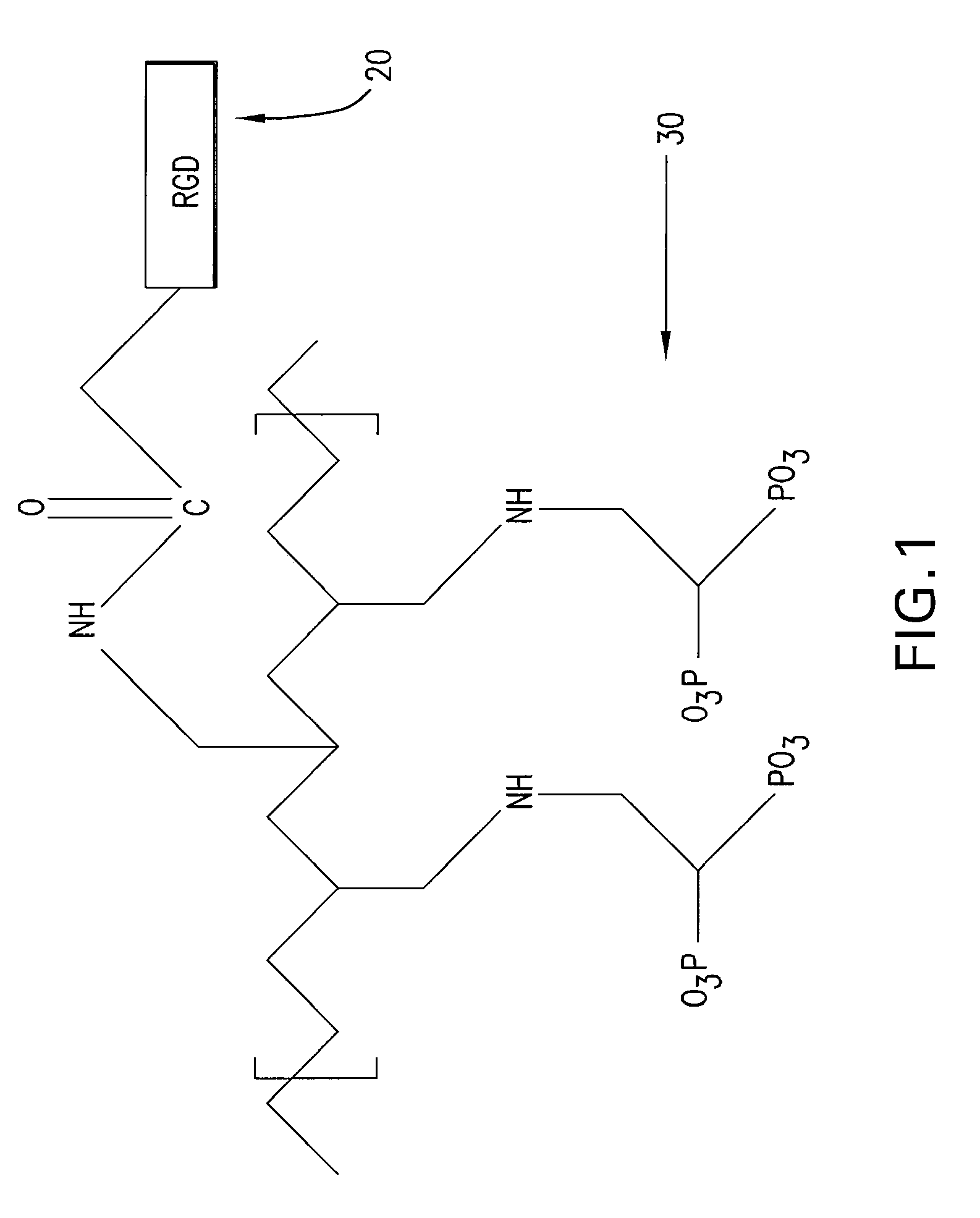
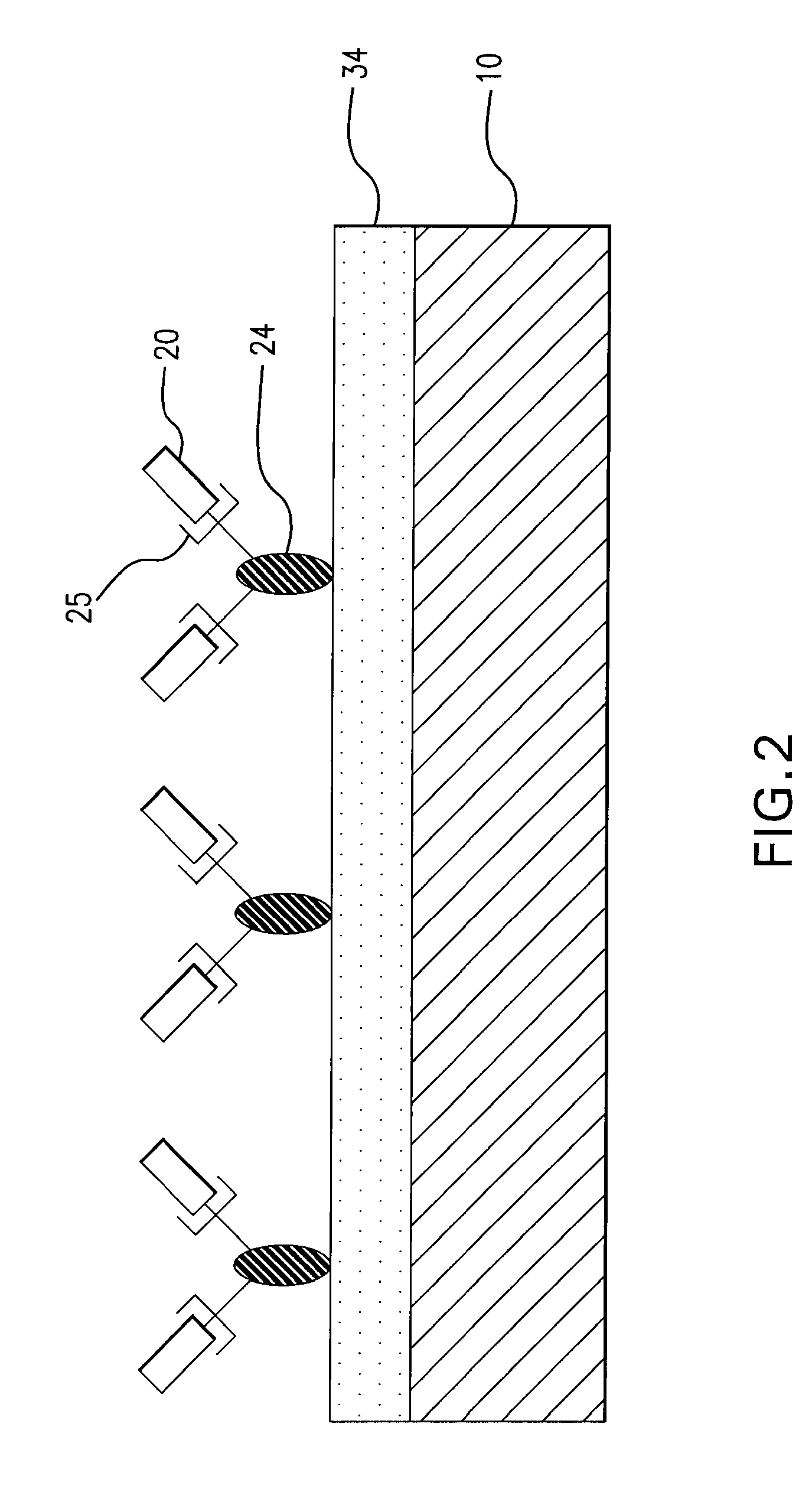
Medical devices having a coating for promoting endothelial cell adhesion
A medical device having a coating of cell adhesion polypeptides to enhance endothelial cell adhesion onto the medical device. The cell adhesion polypeptides may be any of the proteins of the extracellular matrix which are known to play a role in cell adhesion or derivative peptides such as RGD or YIGSR. The polypeptides may be incorporated into the backbone of a polymer such as polyurethane, or grafted onto a polymer such polybisphosphonate. The polypeptides may also be carried on antibodies or displayed on bacteriophages. The polypeptides may also be modified to have adhesive amino acid sequences. In certain embodiments, the medical device further comprises a temporary barrier that protects the polypeptides from biofouling. The temporary barrier may be formed of a biodegradable polymer and be constructed as a coating over the polypeptides or as a plurality of micelles encapsulating the polypeptides. In certain embodiments, the polypeptides may be coated onto the medical device in such a manner as to form a monolayer of the polypeptides.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
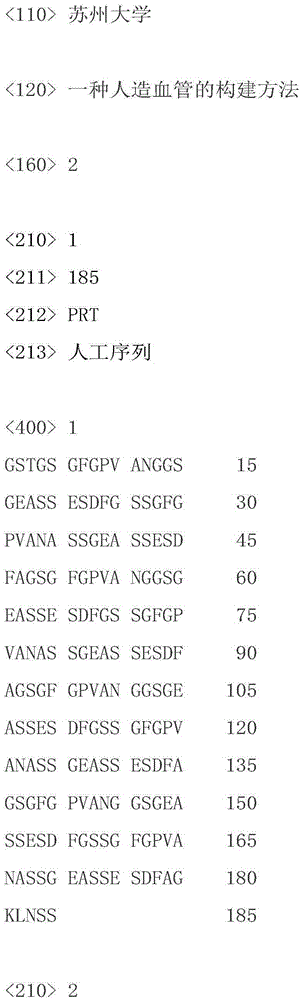
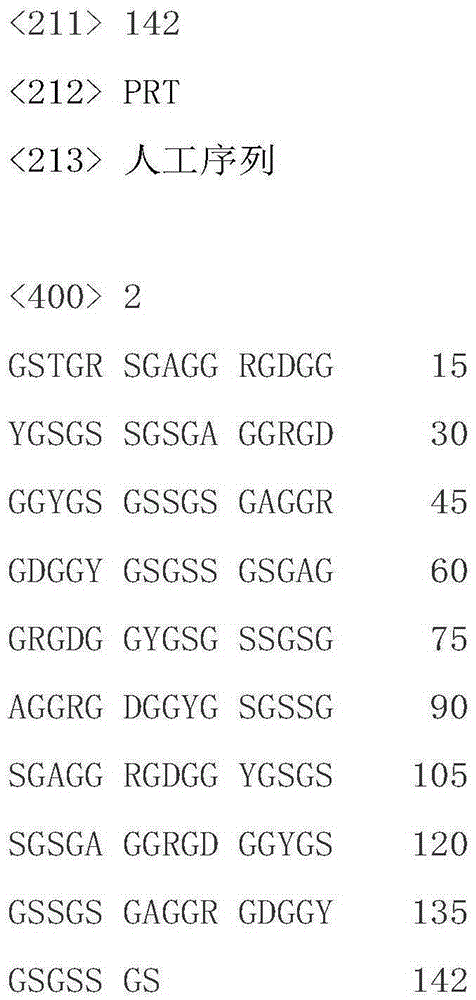
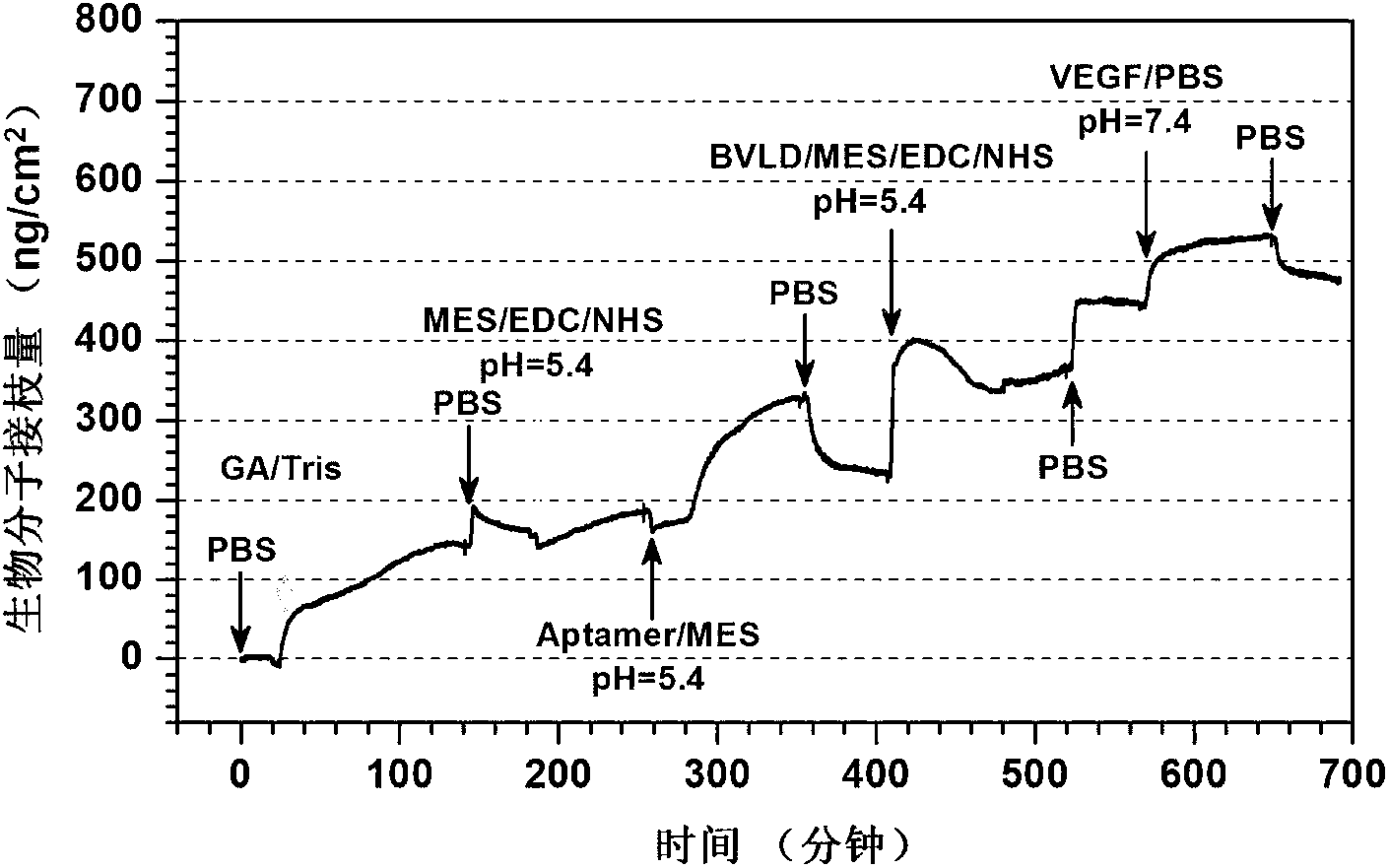
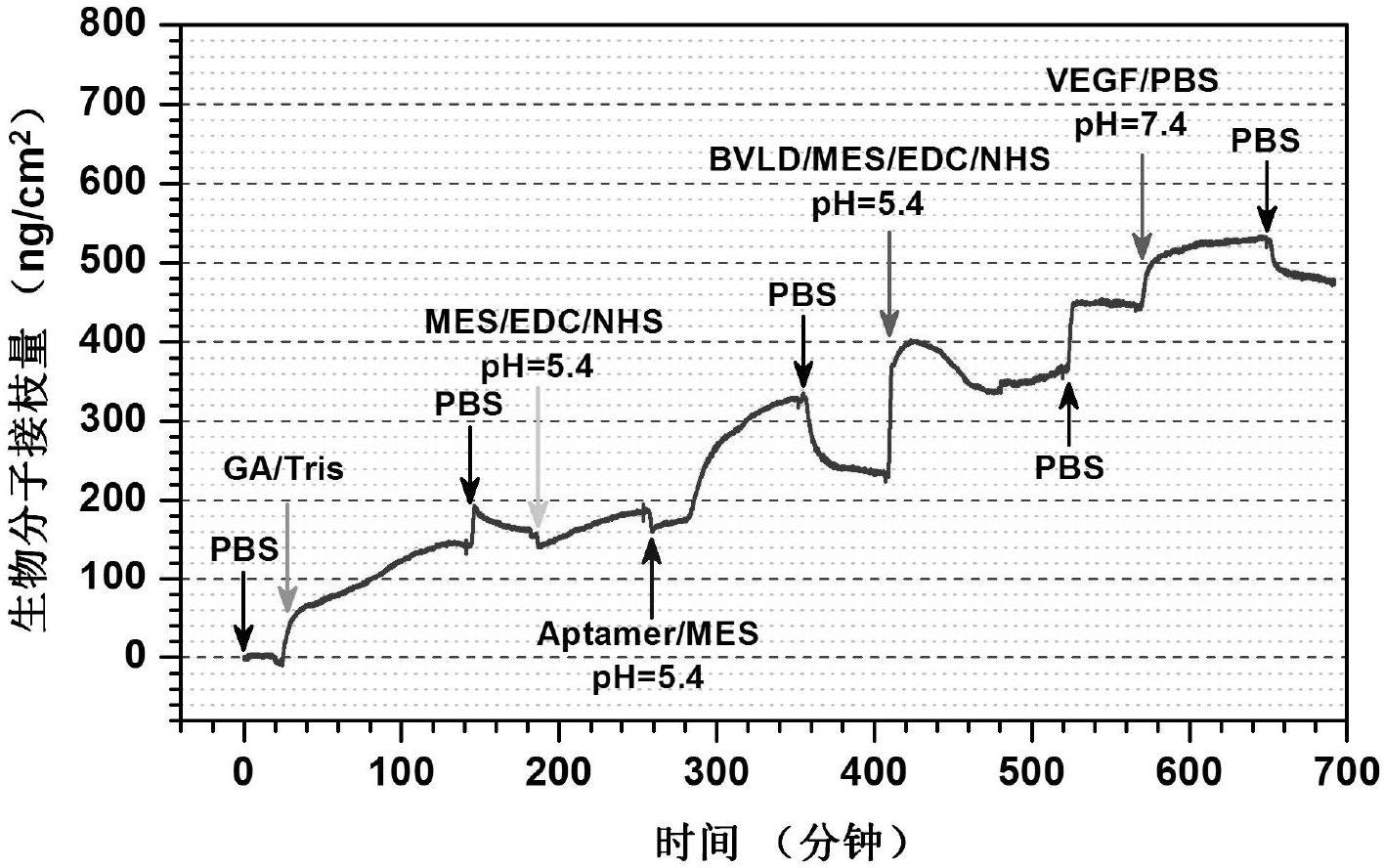
Construction method of artificial blood vessel
The invention discloses a construction method of an artificial blood vessel, and the method particularly includes the step that both the interior and the exterior of a polyester knitting tube are evenly coated with regenerated silk fibroin introducing two types of functional peptides. According to one of the functional peptides, the chain side base contains a great number of hydrophilic carboxy groups, and the acidic amino acid and molecules of the peptide are of electronegativity; the other peptide contains eight RGD and promotes cell adhesion. The two types of peptides come from expressions of living bodies, the sequences are analogues from natural protein, no toxicity or irritation exists, the molecular weight is singular, the peptides and the silk fibroin can be arranged on a polyester pipe in a covalent binding and coated mode, the hydrophilic performance and electronegativity are provided for the artificial blood vessel continuously and stably, endothelialization is promoted, harm to cells is lowered, and thrombus blockage caused by proteinosis and blood cell aggregation is prevented. The constructed artificial blood vessel has good biocompatibility and has an electronegative membrane layer similar to a natural blood vessel and a microenvironment for promoting adhesion growth of endothelial cells, and accordingly it is beneficial to protect blood cells and prevent thrombus from forming.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of biomedical materials of multiclass functional group rich in amino group, carboxyl group and benzoquinonyl group
InactiveCN102698322ADensity regulationEffective combinationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingGallic acid esterEndothelial cell-cell adhesion
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomedical materials of a multiclass functional group rich in amino groups, carboxyl groups and benzoquinonyl groups. The multiclass functional group rich in the amino groups, the carboxyl groups and the benzoquinonyl groups is constructed on the surface of a biomedical substrate material, the steps comprise soaking the substrate material in alkalinity Tris buffered solution of gallic acid with the concentration of 10ng / ml-20ng / ml in an environment rich in the amino groups, and reacting for 15min-30days to be sufficiently washed to obtain the biomedical material containing multiple functional groups. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple in operation, soft in reaction condition, easy to apply and controllable in functional group density process. Followed manufactured implantation instruments have good anticoagulation, endothelial cell adhesion, proliferation and migration functions are promoted, smooth muscle cell adhesion and proliferous functions are obviously restrained, and in-situ rapid induction endothelium functionalization of intravascular stents, intravascular stents and tissue engineering scaffolds which induce capillaries to form is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
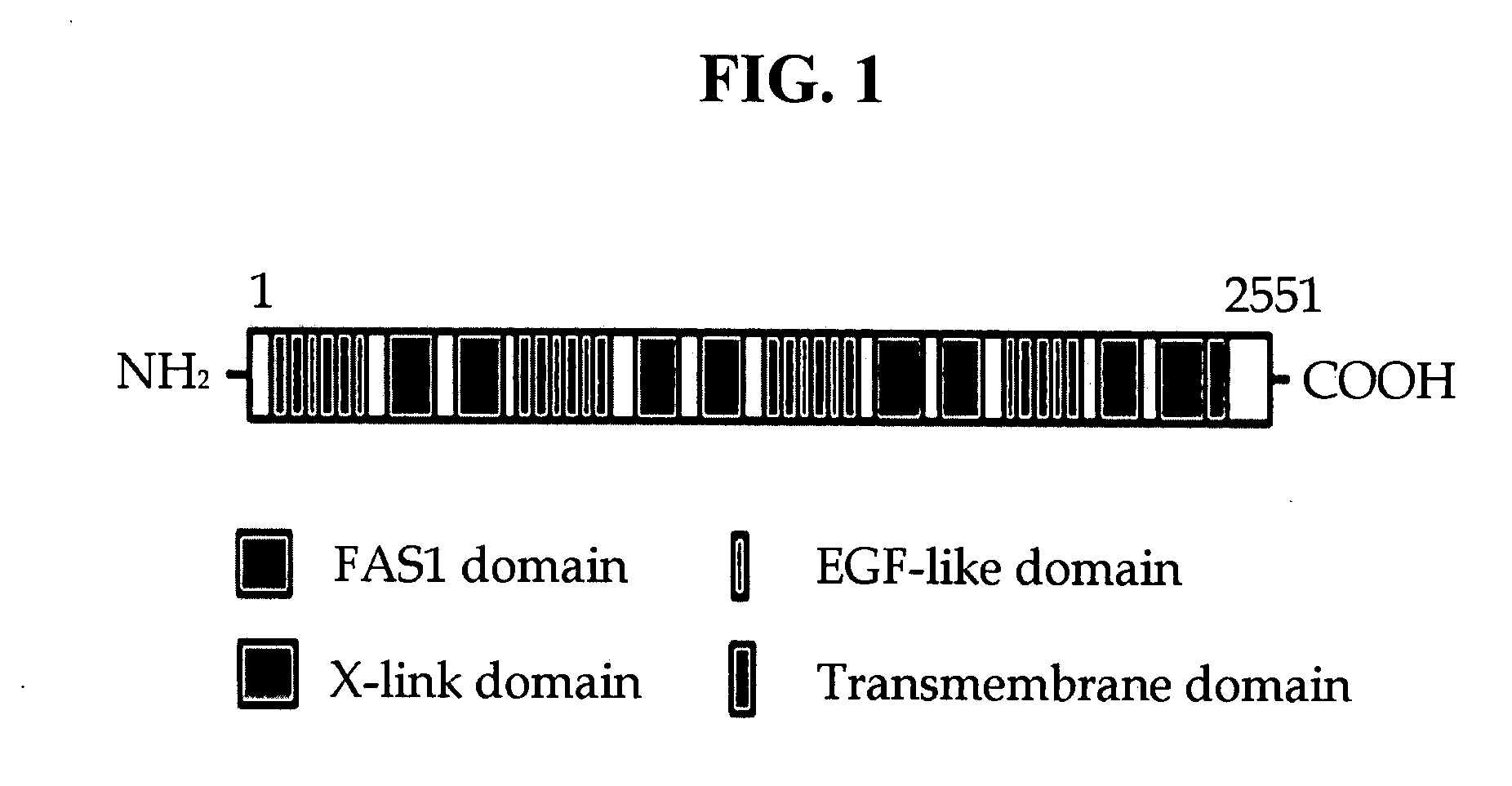
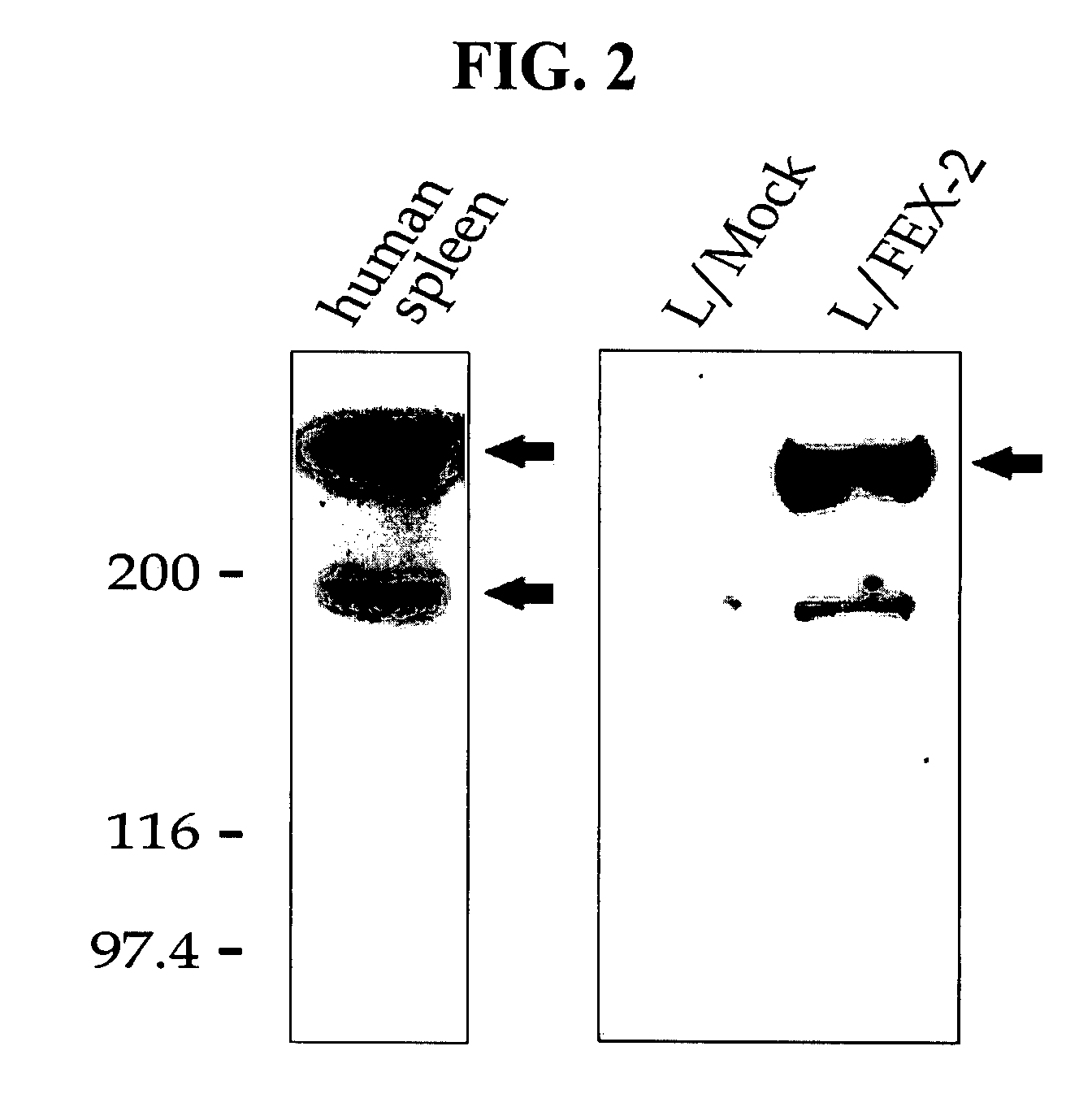
Method and pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating diseases associated with inflammation
The present invention relates to a method and pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating inflammatory diseases. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for inhibiting lymphocyte adhesion to an endothelial cell, or a method for treating an inflammatory disease, which comprises administering to a subject in need thereof an inhibitor against lymphocyte adhesion to a FEX-2 polypeptide. A pharmaceutical composition comprising the inhibitor against lymphocyte adhesion to a FEX-2 polypeptide, and the use of the inhibitor against lymphocyte adhesion to a FEX-2 polypeptide are also disclosed. Further, a method for screening a medicament for inhibiting lymphocyte adhesion to a FEX-2 polypeptide or a medicament for treating an inflammatory disease, which comprises a step of selecting an inhibitor against lymphocyte adhesion to a FEX-2 polypeptide, is disclosed.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Coating and material to promote vascular intimal repairing, preparation method of material and medical product
InactiveCN109966565APromote repairImprove adhesionSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMetal-organic frameworkMedical product
The invention relates to the field of biomedical materials and provides coating to promote vascular intimal repairing. An amino-containing polypeptide and a copper-based MOF (metal-organic framework)are grafted to the surface of the coating; the amino-containing polypeptide is capable of specifically promoting adhesion of endothelial cells. A material to promote vascular intimal repairing comprises a substrate material; the coating to promote vascular intimal repairing is attached to the surface of the substrate material. A preparation method of the material to promote vascular intimal repairing comprises coating the surface of the substrate material with the copper-based MOF and the coating which the amino-containing polypeptide is grafted to; the amino-containing polypeptide can specifically promote adhesion of the endothelial cells; a medical product is made with the above material to promote vascular intimal repairing. All the coating, the material and the medical product providedherein can specifically promote adhesion and growth of endothelial cells, and reduce damage to the endothelial cells in a peroxidation micro environment.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
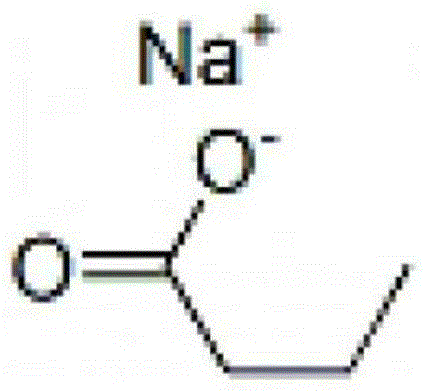
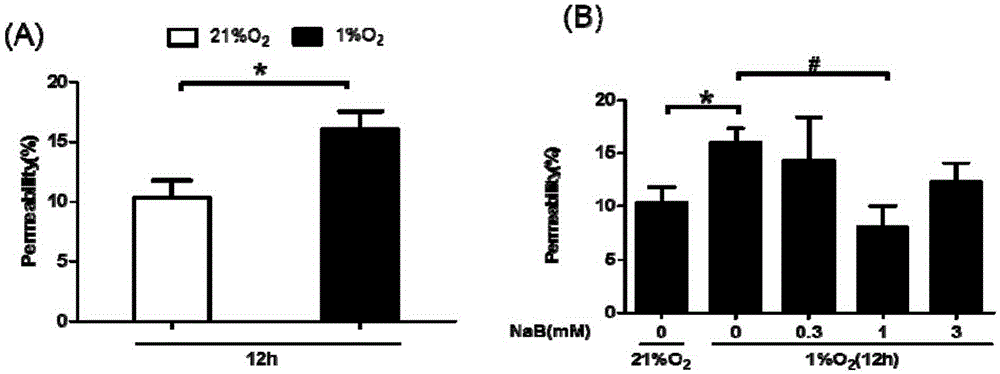
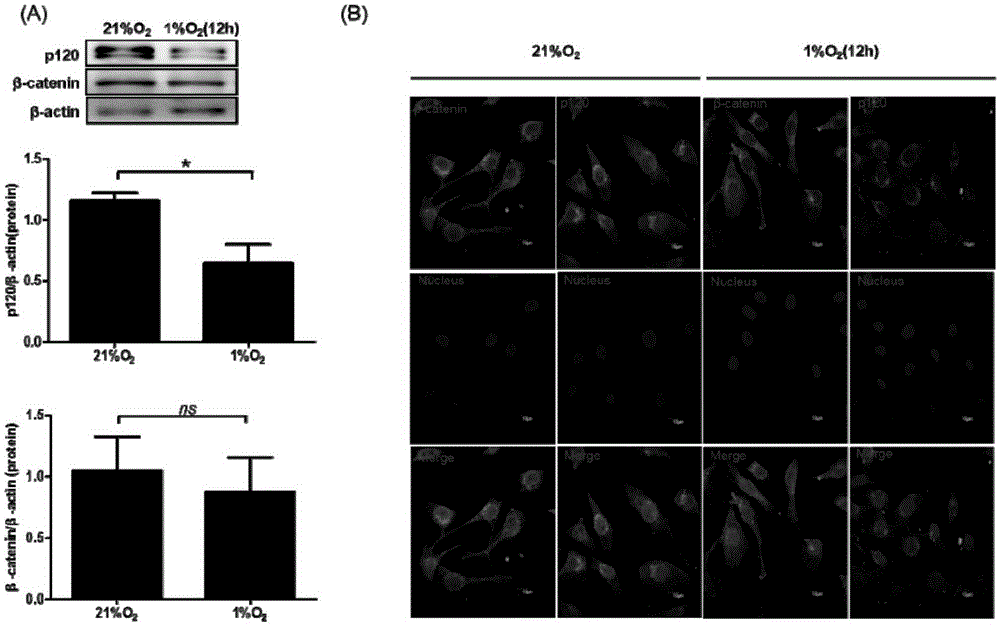
Application of sodium butyrate in preventing and curing high permeability of blood vessels and relevant diseases
InactiveCN105395533AStable in natureImprove permeabilityNervous disorderRespiratory disorderDiseaseVascular endothelium permeability
The invention discloses application of sodium butyrate in preparing medicine used for treating and restraining diseases or symptoms relevant to blood vessel permeability enhancement or postponing outbreak of the diseases or symptoms or abating the caused diseases or symptoms. The sodium butyrate can increase the expression of vascular endothelial cell adherent junction gap-associated protein p120 on the oxygen deficit condition, endothelial cell adherent junction stability is kept, and blood vessel endothelium permeability is restrained from being increased on the oxygen deficit condition; the sodium butyrate is soluble in an aqueous solution and stable in property, and not matter dry powder or the aqueous solution can be preserved at normal temperature. The sodium butyrate can be completely and directly absorbed by the intestinal tract, secondary degradation is avoided, and the price is low.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Endothelial cell selective composite coating material used for cardiovascular stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102210890AImprove performanceConducive to loadSurgeryCoatingsCardiovascular stentCell selectivity
The invention discloses an endothelial cell selective composite coating material used for a cardiovascular stent and a preparation method thereof. The coating comprises a medicament-carrying polymer substrate layer and a polymer outer layer for fixing a biological activity molecule, wherein a substrate layer material is obtained by copolymerizing a biocompatible monomer containing a cell membrane biomimetic structure and a polymerizable monomer containing a hydrophobic function group, and then a polymer solution and a medicament solution are co-mixed to construct the substrate layer of the stent; and the polymer outer layer is obtained by copolymerizing the biocompatible monomer containing a cell membrane biomimetic structure, the polymerizable monomer containing the hydrophobic function group and a polymerizable monomer containing a reactive activity function group, then the biological activity molecule for promoting endothelial cell adhesion is introduced through a surface fixing method so that the coating has endothelial cell selectivity. The composite coating material used for a cardiovascular stent coating can maintain non-specificity impedance performance of a stent surface and realize capturing capability of the in vivo endothelial cell in situ; and the obtained coating structure is stable, can adapt an internal environment of a human body, and has favorable application prospect in treating cardiovascular restenosis and cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions and methods for increasing mesenchymal stromal cell migration to tumors
InactiveUS20160220612A1Promote migrationImprove adhesionGenetically modified cellsUnknown materialsAbnormal tissue growthStromal cell
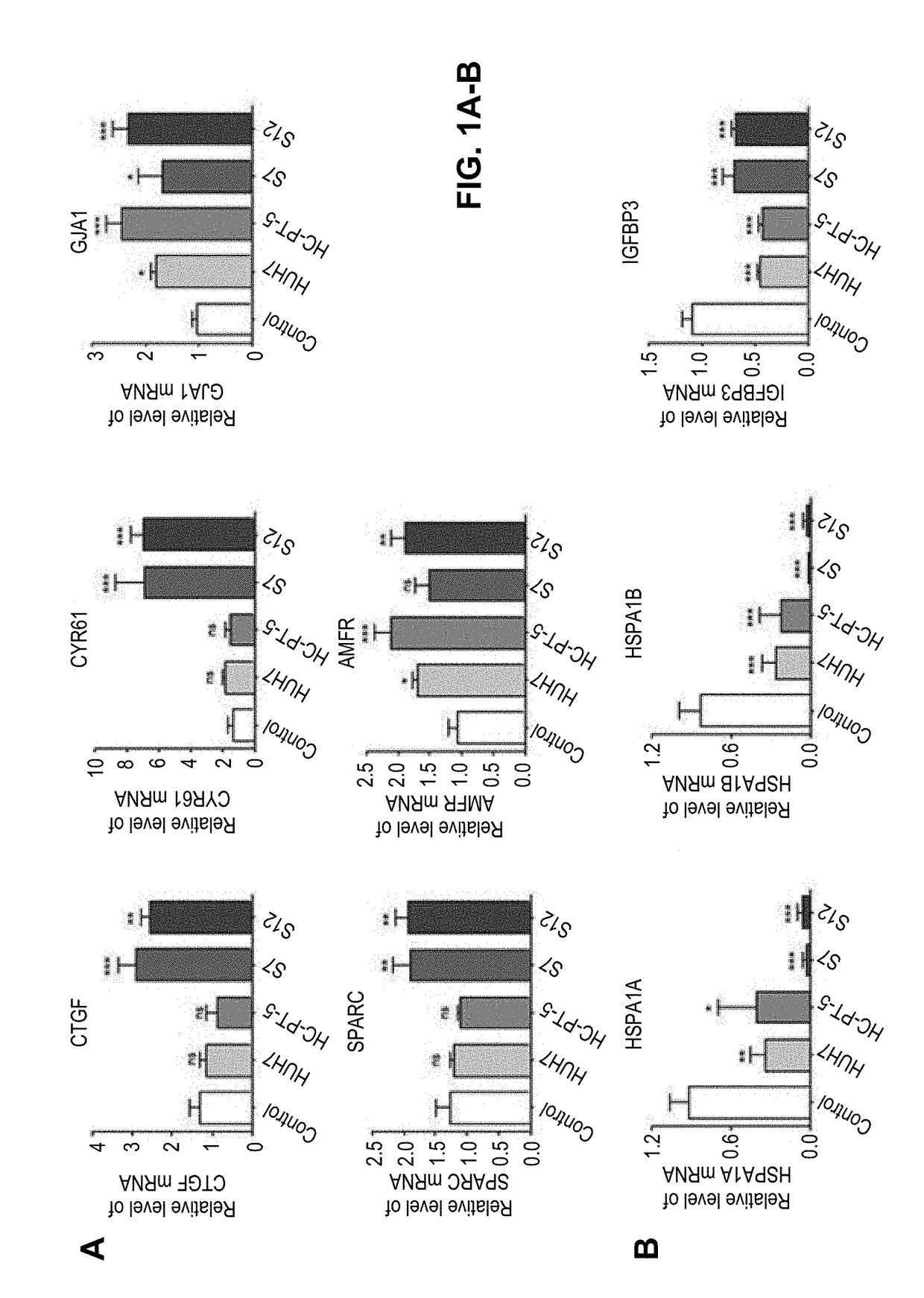
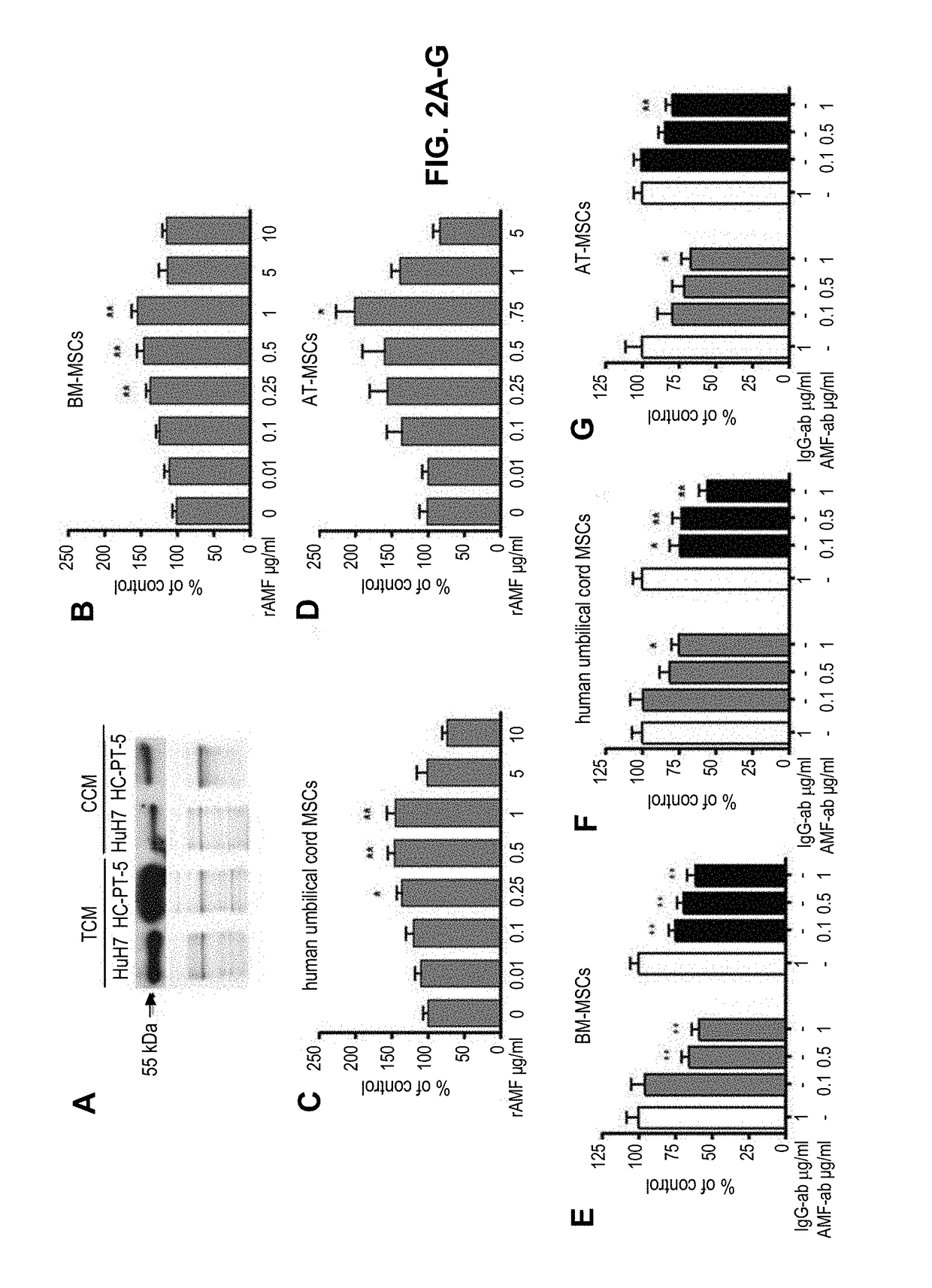
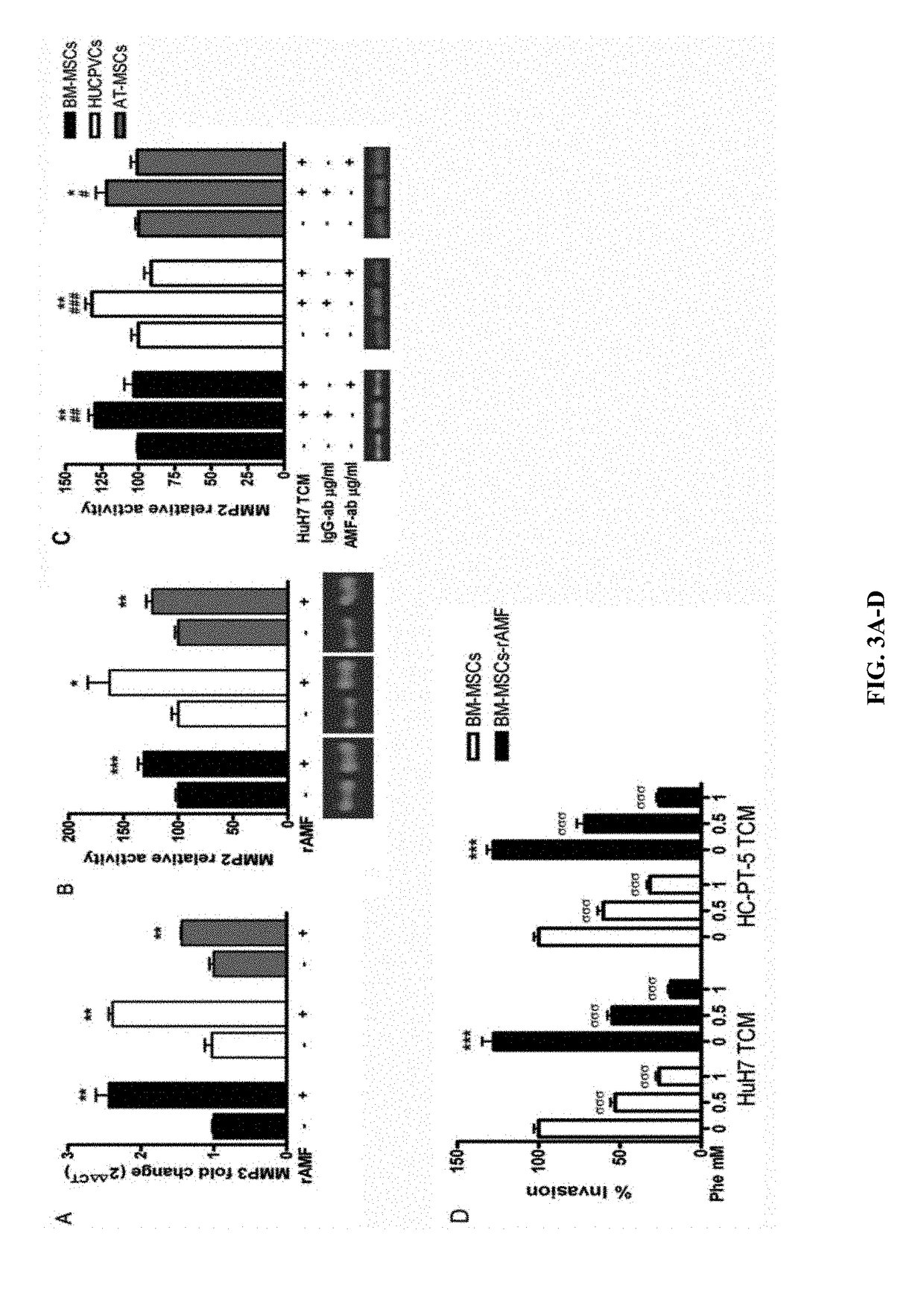
The present application is directed to compositions and methods for treating a subject with cancer and / or increasing migration of a mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) stimulated with a recombinant autocrine motility factor (rAMF) to a tumor or a tumor cell, e.g. hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In addition, methods for increasing adhesion of MSCs to endothelial cells with rAMF are disclosed. In some embodiments, the MSCs comprise a therapeutic agent, e.g., an anti-tumor agent.
Owner:ROSIVO LLC +3
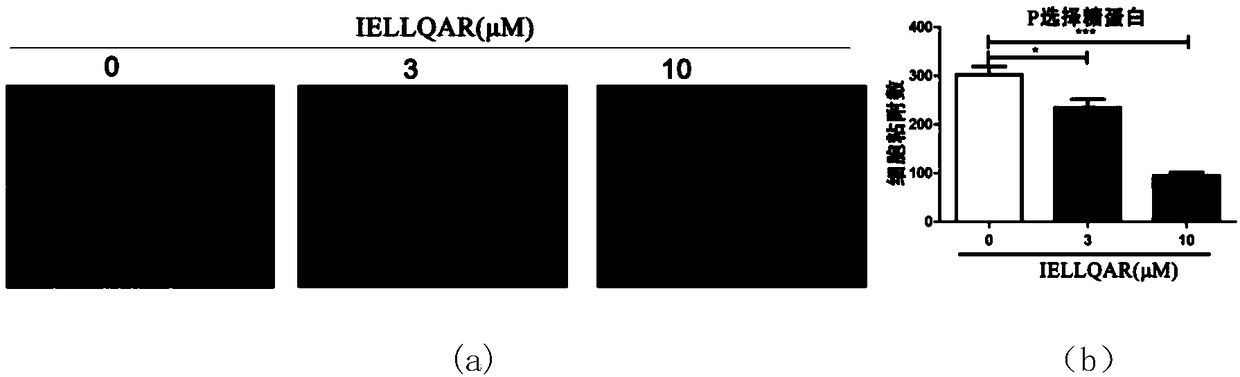
Application of IELLQAR as medicine for preventing and treating atherosclerosis diseases
ActiveCN109106940ADelay progressReduce infiltrationPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderInflammatory factorsAtheroma
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Polyethylene glycol bipolymer with endothelial cell selectivity and preparation method and application method of composite coating
InactiveCN105713152AThe synthesis method is simpleHigh reactivitySurgeryCoatingsCell selectivityPolythylene glycol
The invention relates to a polyethylene glycol bipolymer with endothelial cell selectivity and a preparation method and an application method of a composite coating. The polyethylene glycol bipolymer is synthesized by a cellular carbohydrate coat-bionic biocompatible monomer and a polymerizable monomer containing reactive active functional groups through a free radical polymerization method, and bioactive molecules for promoting endothelial cell adhesion is introduced through a surface fixing method to enable the coating to have endothelial cell selectivity. The polyethylene glycol composite coating with excellent reactivity is capable of keeping non-specificity impedance performance of stent surfaces and achieving in-vivo in-situ endothelial cell capture capability, is stable in structure and can be applicable to an internal environment of a human body, thereby having a promising prospect on cardiovascular restenosis, cancers and the like.
Owner:HUANGHUAI UNIV
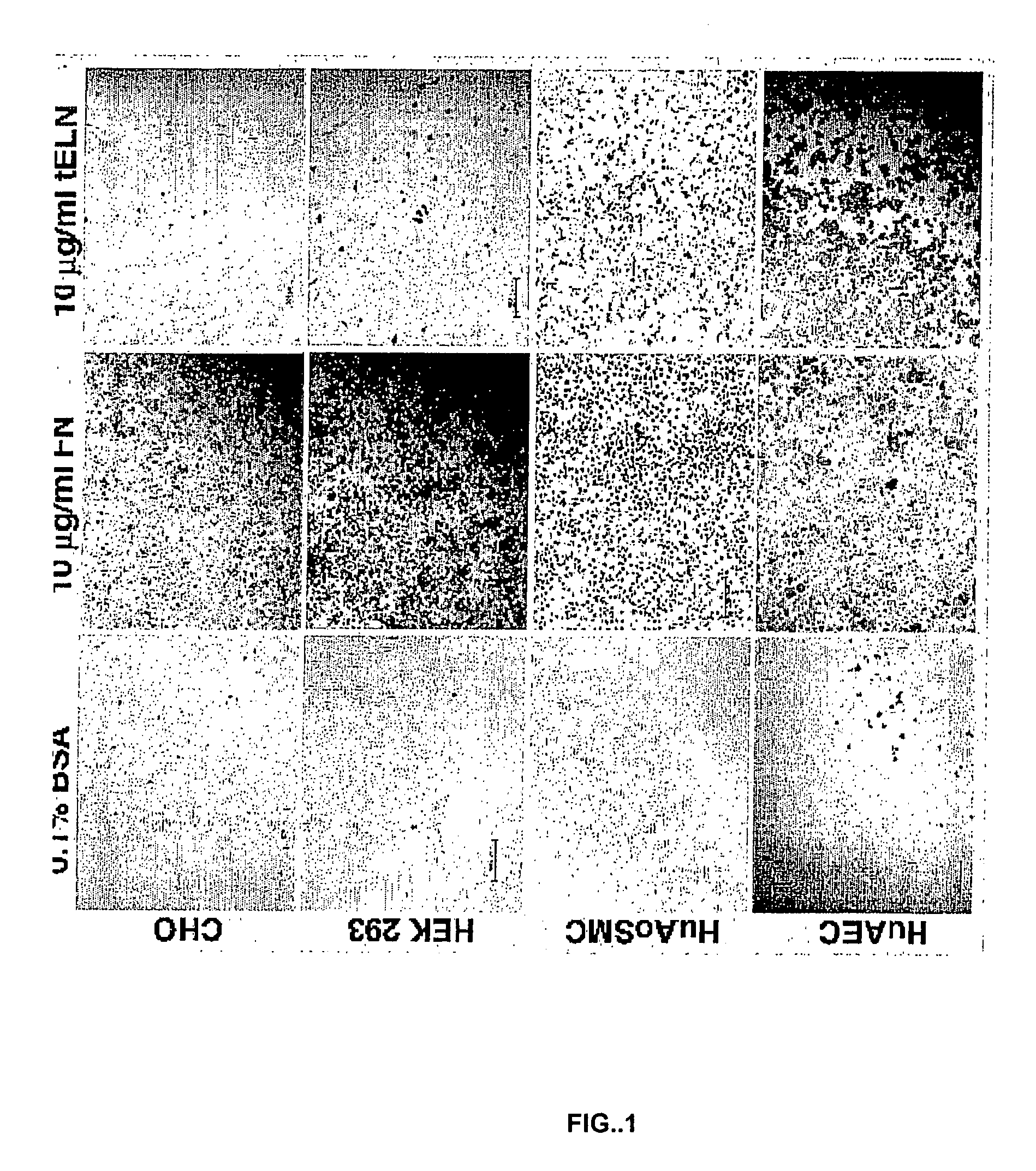
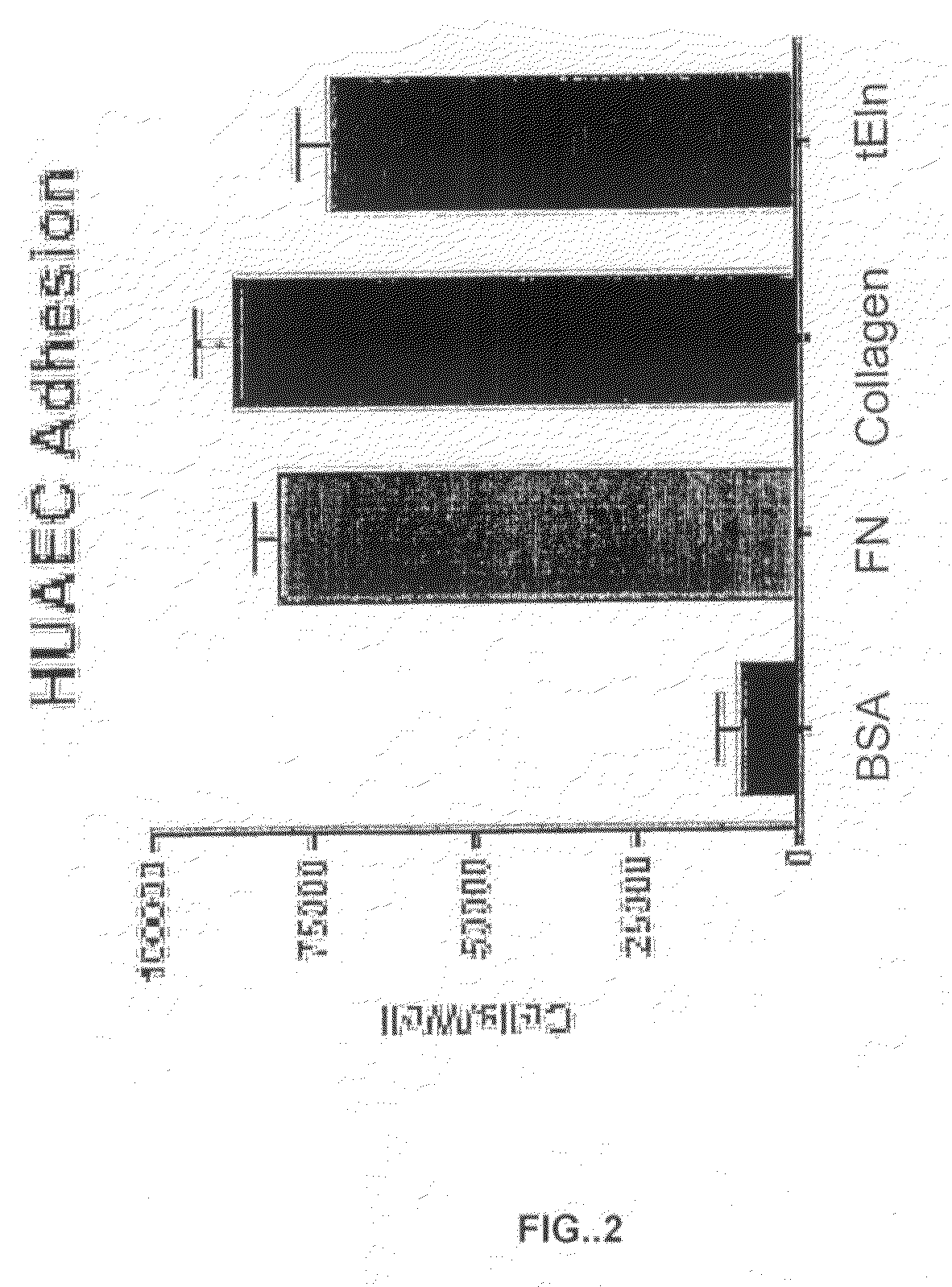
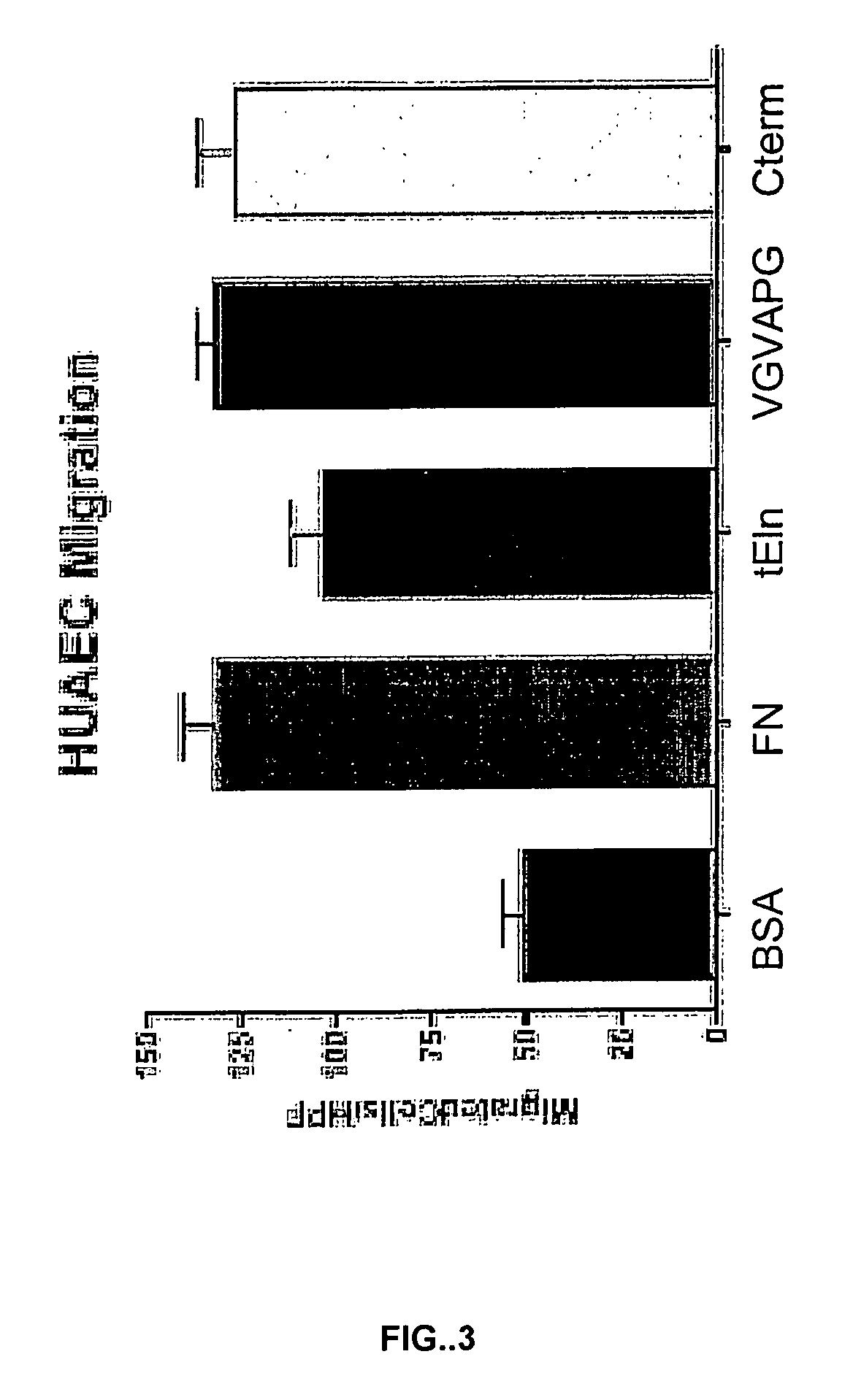
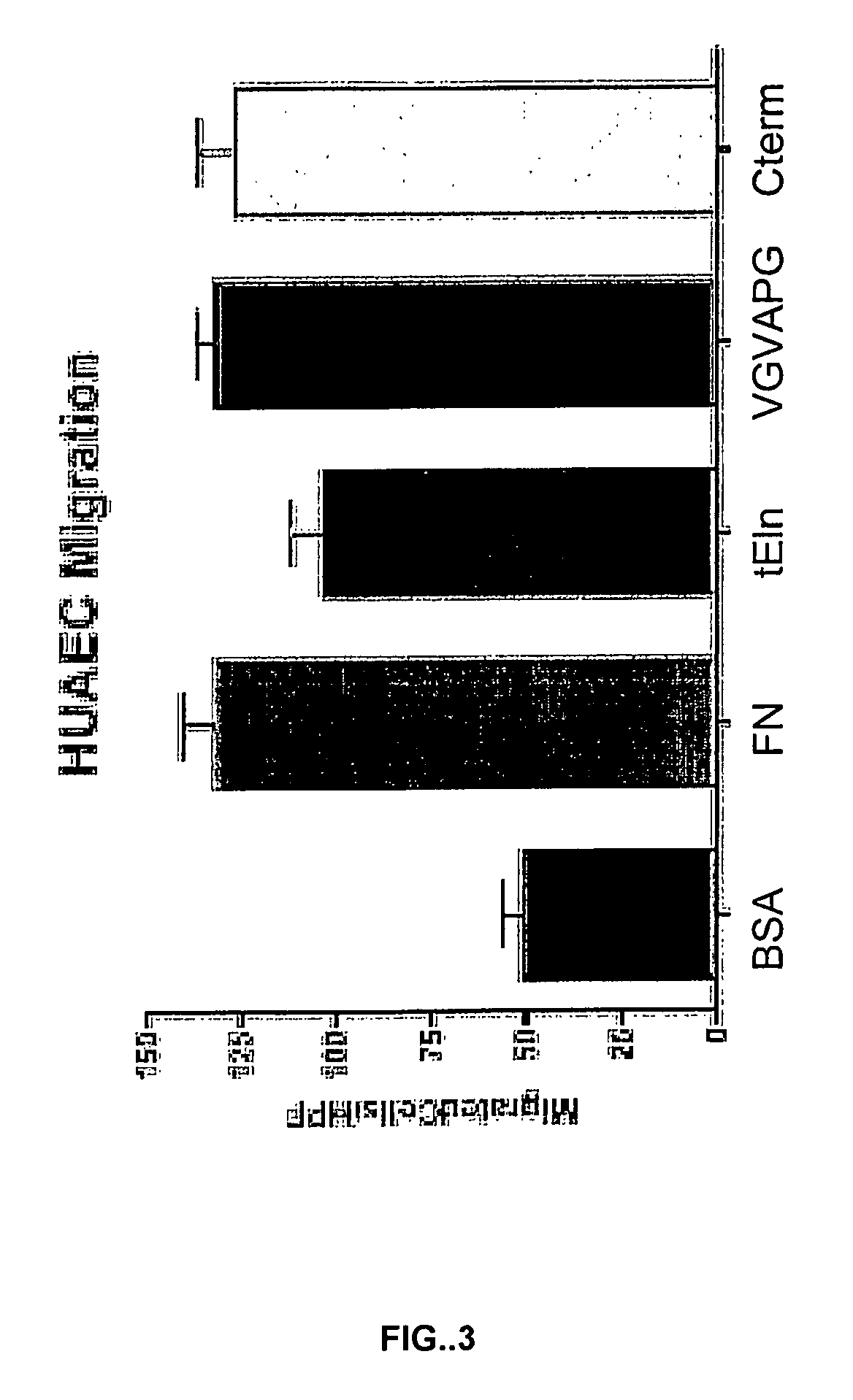
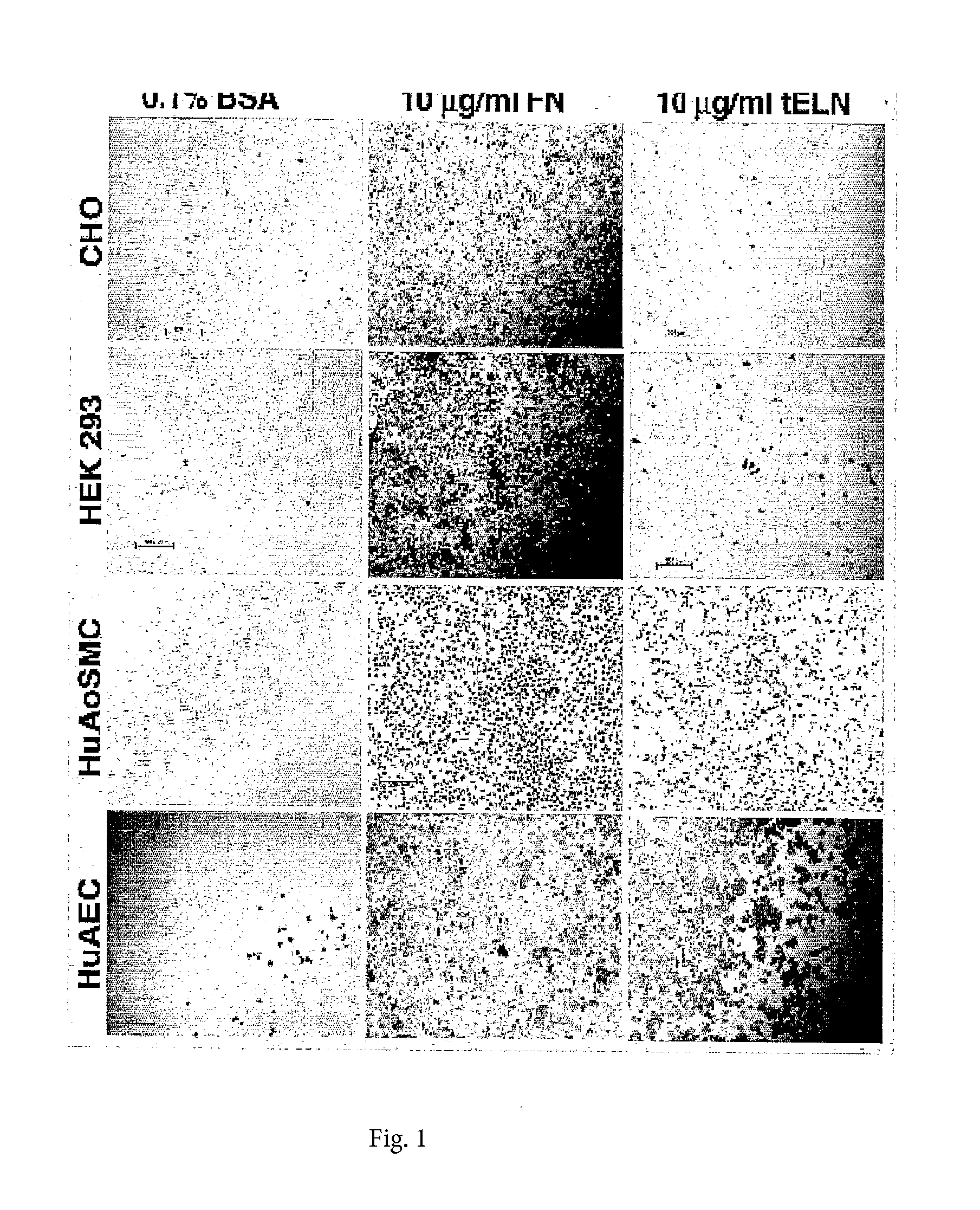
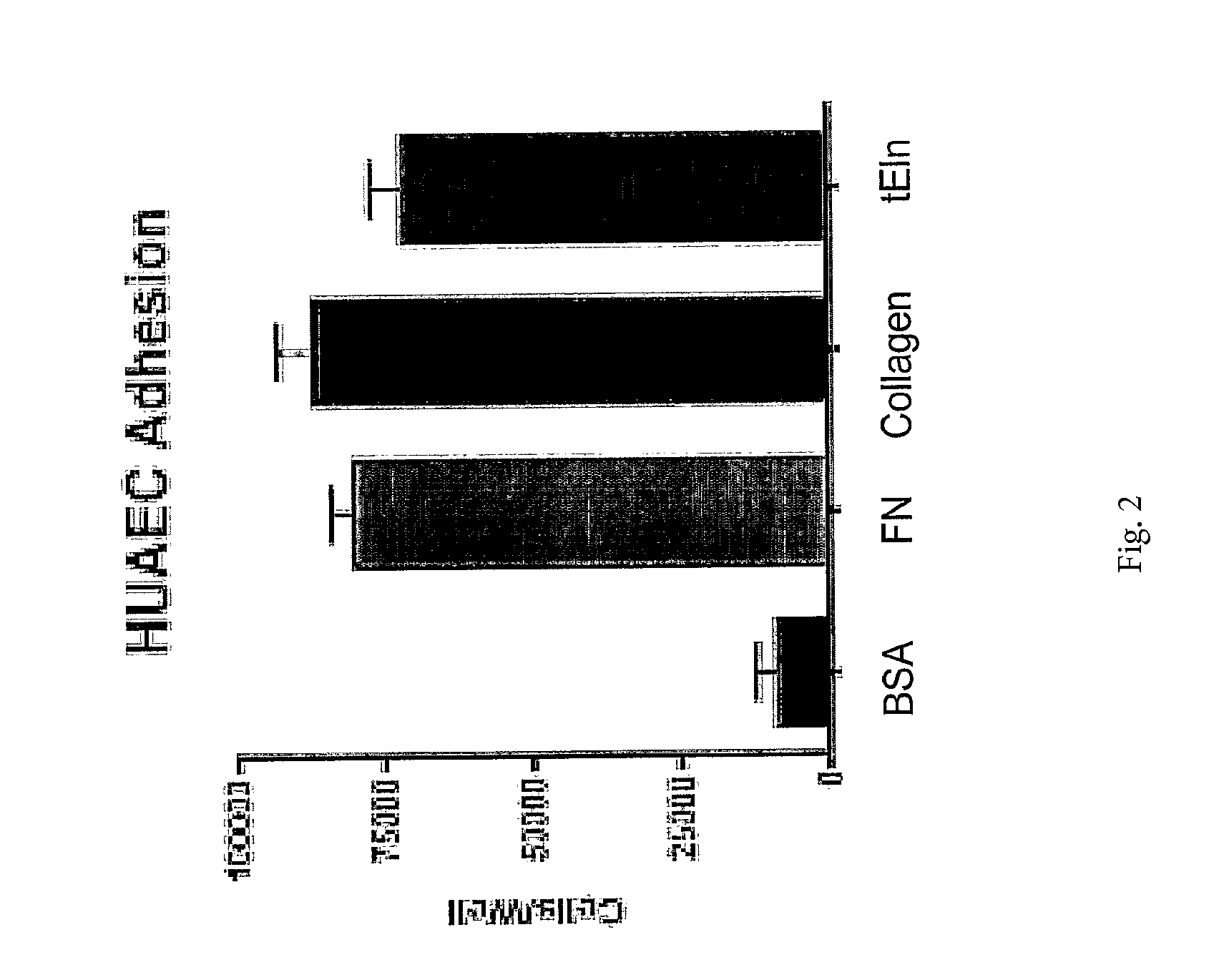
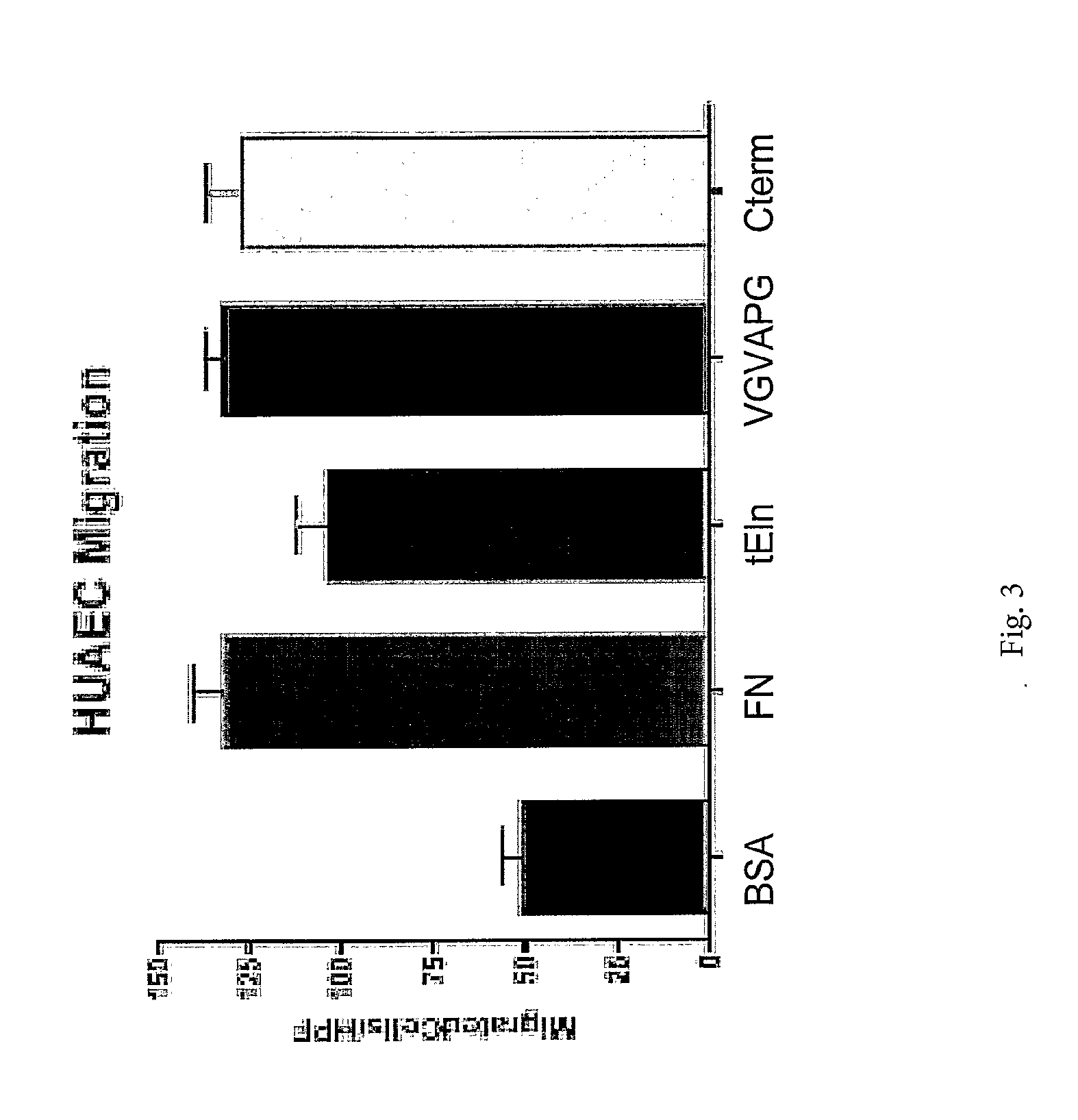
Tropoelastin for Promoting Endothelial Cell Adhesion or Migration
InactiveUS20090280152A1Promote endothelial adhesionModulating adhesionElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAdhesion processTropoelastin
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
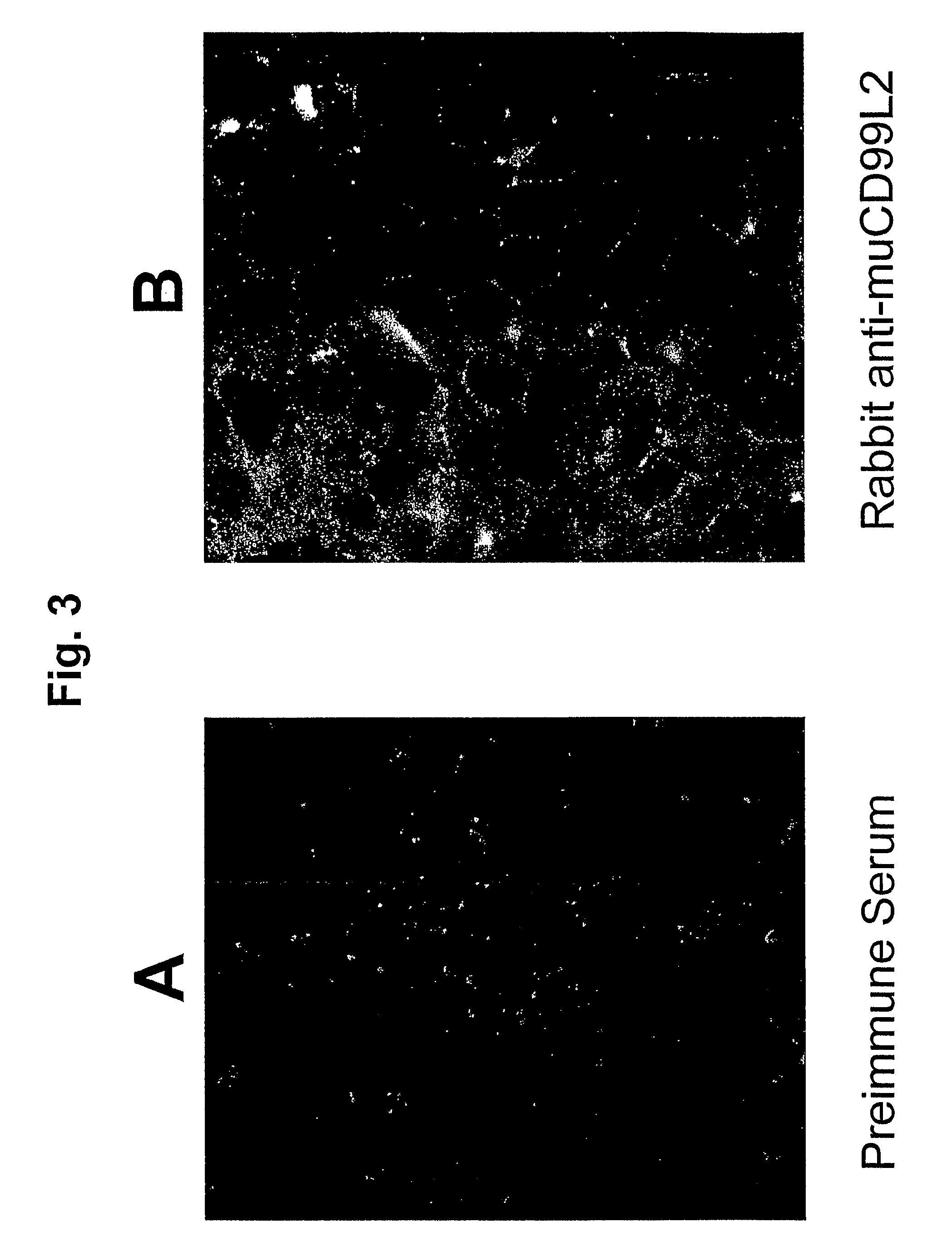
Methods of inhibiting transendothelial migration of neutrophils and monocytes with anti-CD99L2 antibodies
ActiveUS8088382B2Inhibits leukocyte bindingInhibits leukocyte transmigrationAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAdhesion processWhite blood cell
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
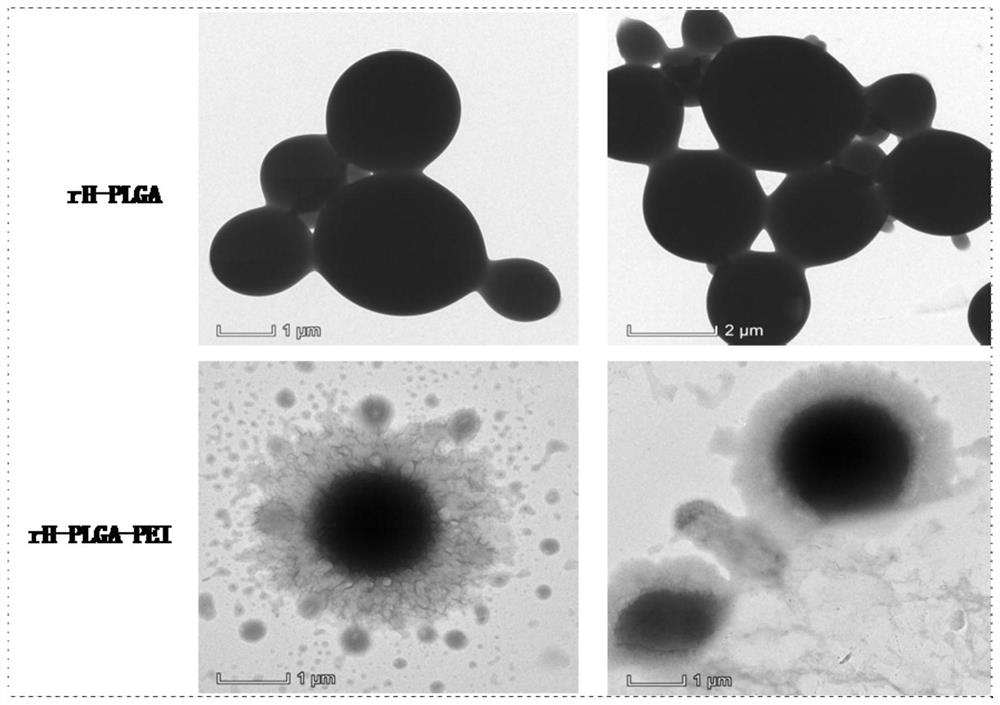
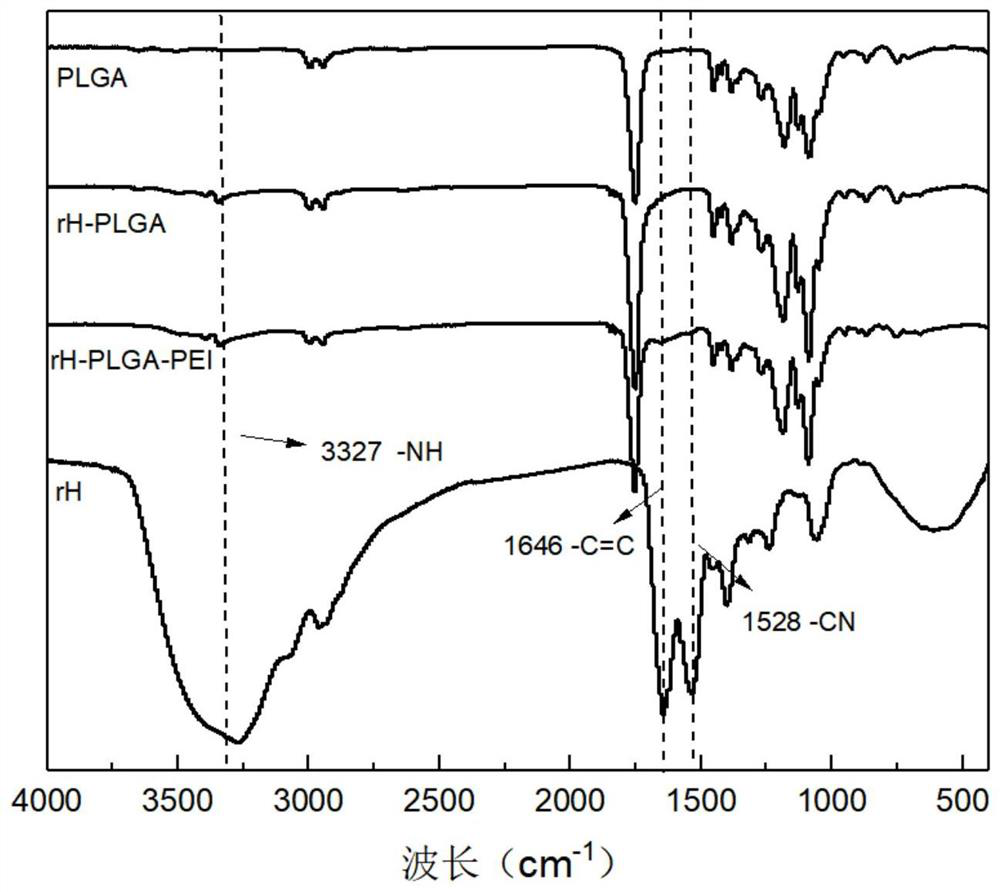
rH-PLGA/PEI microsphere and dopamine modified small-caliber intravascular stent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112870435AImprove adhesionPromote proliferationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingTissue repairVascular tissue
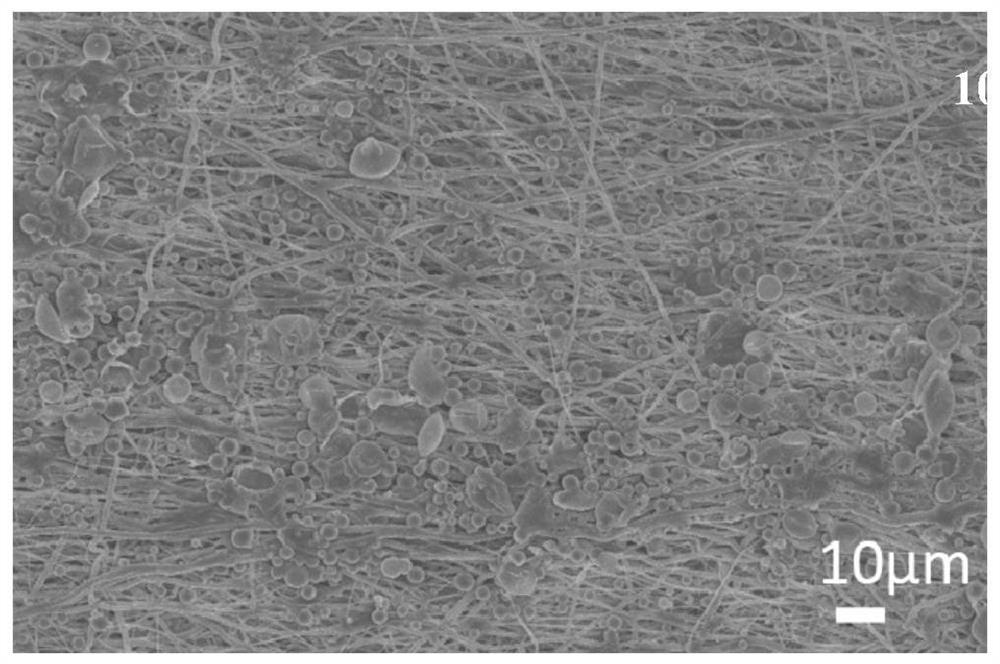
The invention discloses a rH-PLGA / PEI microspheres and dopamine modified small-caliber intravascular stent material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a PCL nanofiber scaffold as a substrate by using an electrostatic spinning technology, depositing a layer of dopamine on the surface of the PCL nanofiber scaffold, and loading PLGA / PEI microspheres wrapped with hirudin on PCL nanofibers by using the adhesion of the dopamine to obtain the small-caliber intravascular stent material. According to the method, hirudin, PLGA / PEI microspheres and dopamine are combined, the obtained stent can prevent thrombus and promote rapid endothelialization and revascularization for a long time, the process is simple and feasible, and repeatability is good. The small-caliber intravascular stent has good biocompatibility, and the vascular tissue repair speed and quality are accelerated by utilizing the promotion effect and anticoagulant effect of hirudin on endothelial cell adhesion and proliferation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tropoelastin for promoting endothelial cell adhesion or migration
InactiveUS9005356B2Treating and preventing restenosis or thrombosisImprove adhesionElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsTropoelastinEndothelial cell-cell adhesion
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Tropoelastin for Promoting Endothelial Cell Adhesion or Migration
ActiveUS20150151028A1Treating and preventing restenosis or thrombosisImprove adhesionElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAdhesion processTropoelastin
The invention provides methods, compositions, and devices for promoting adhesion or migration of endothelial cell.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for increasing mesenchymal stromal cell migration to tumors
ActiveUS20190022143A1Genetically modified cellsUnknown materialsStromal cellHepatocellular carcinoma
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET
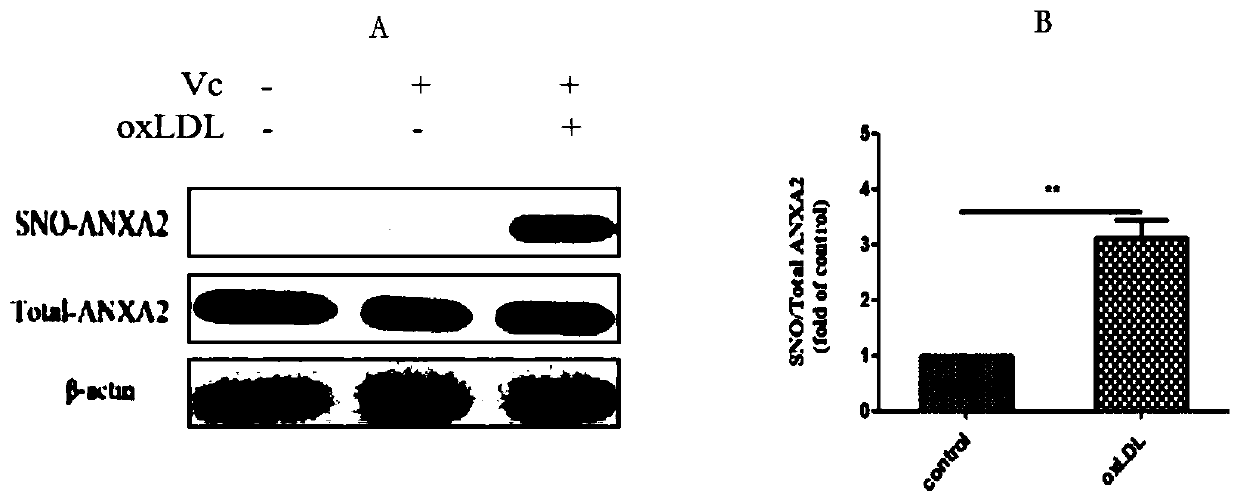
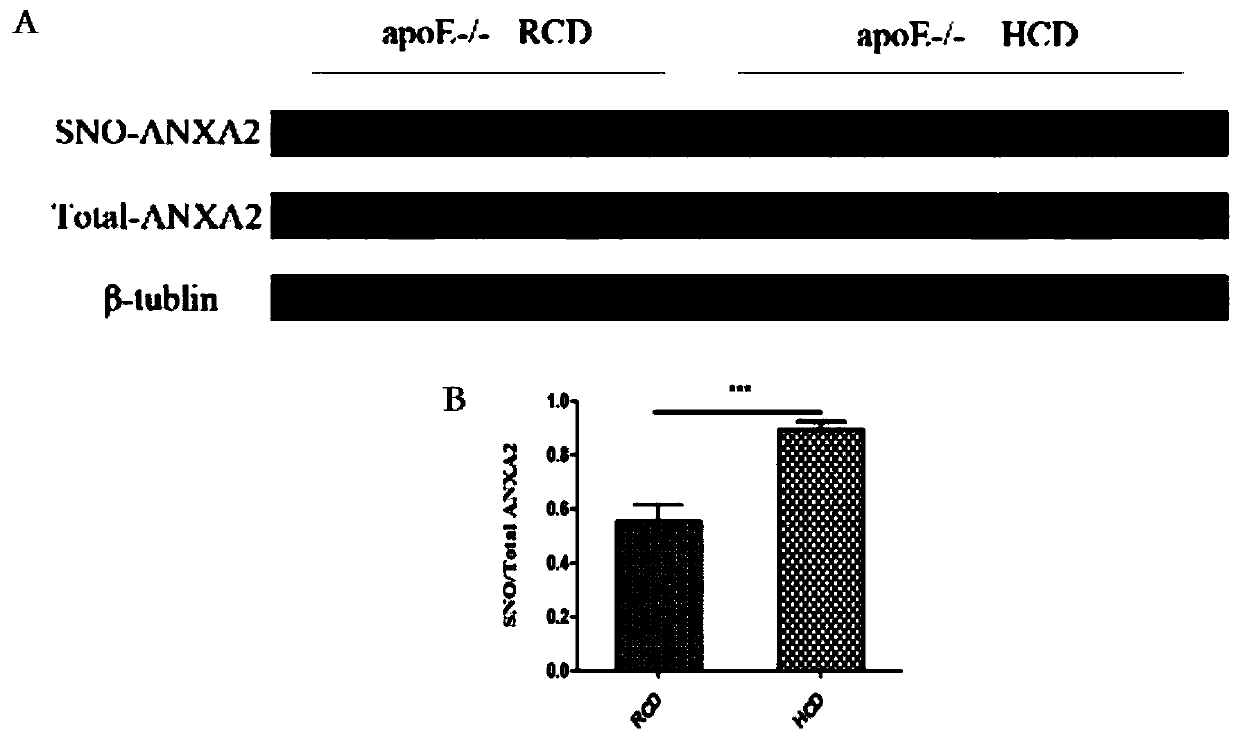
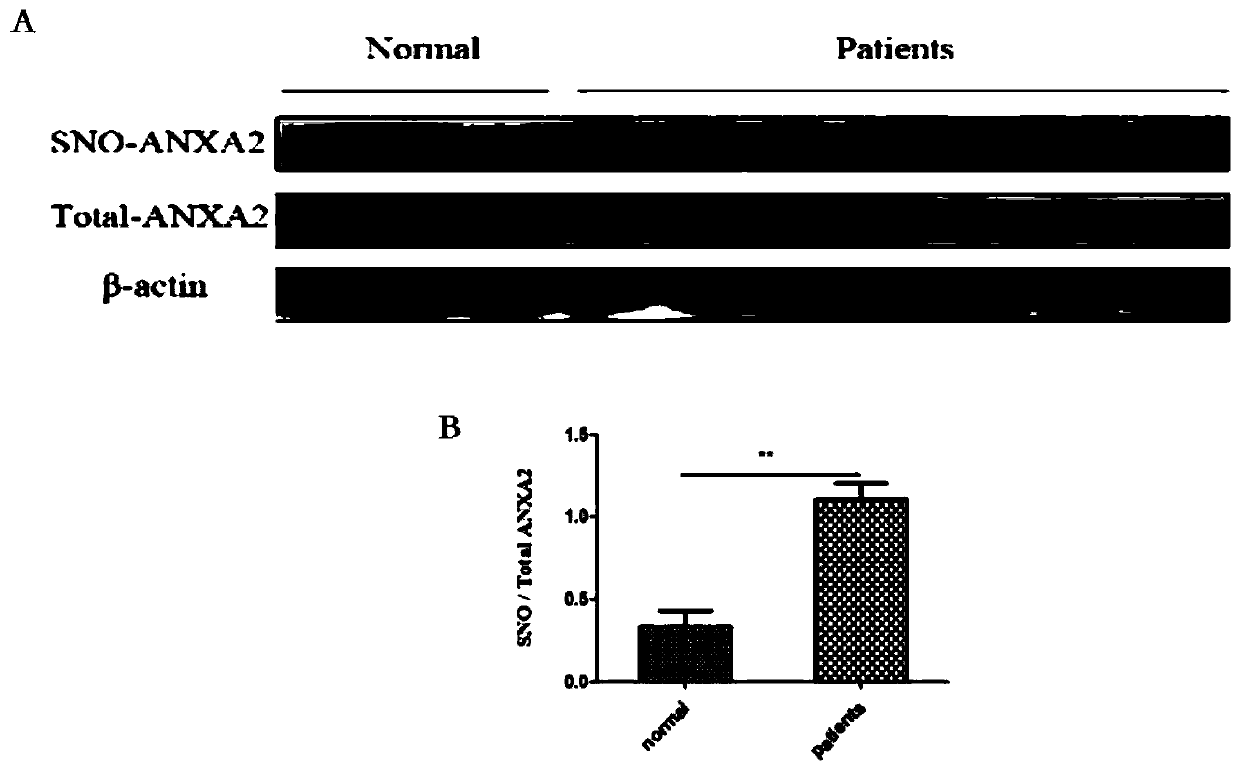
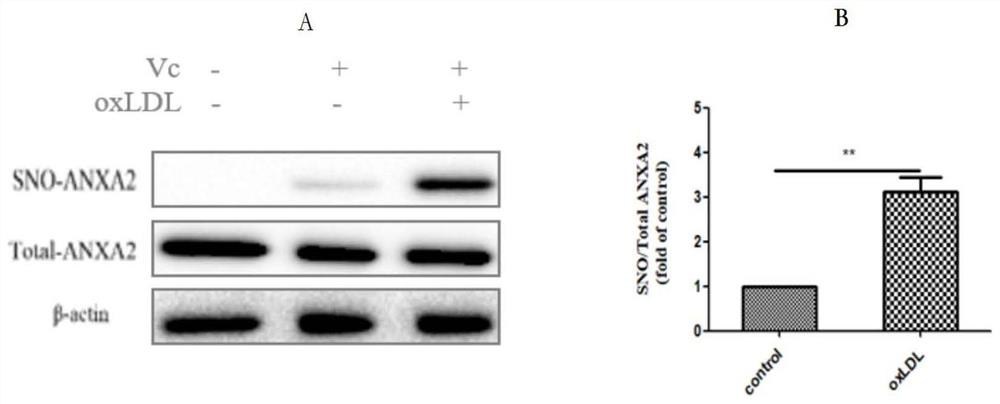
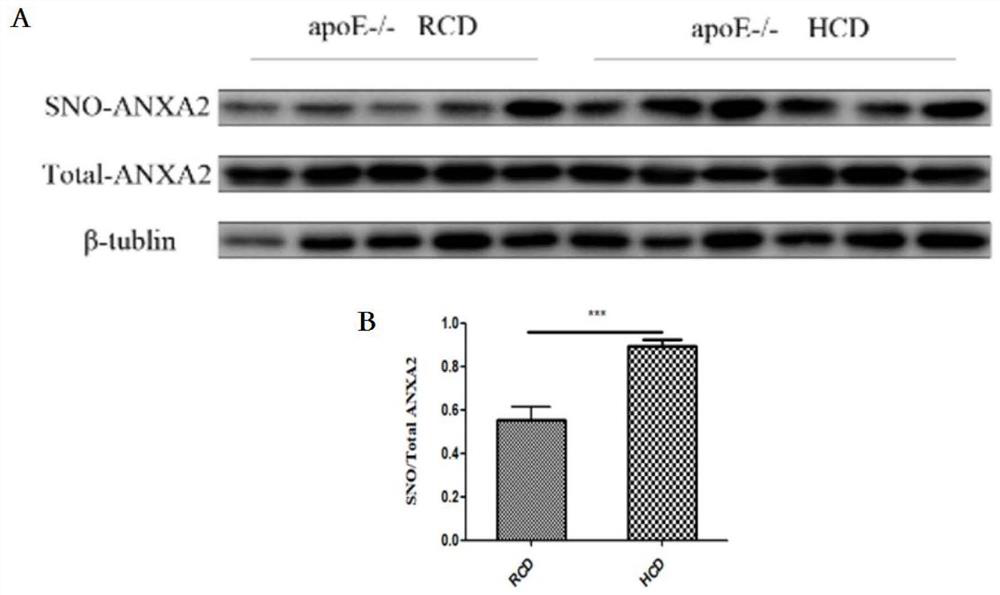
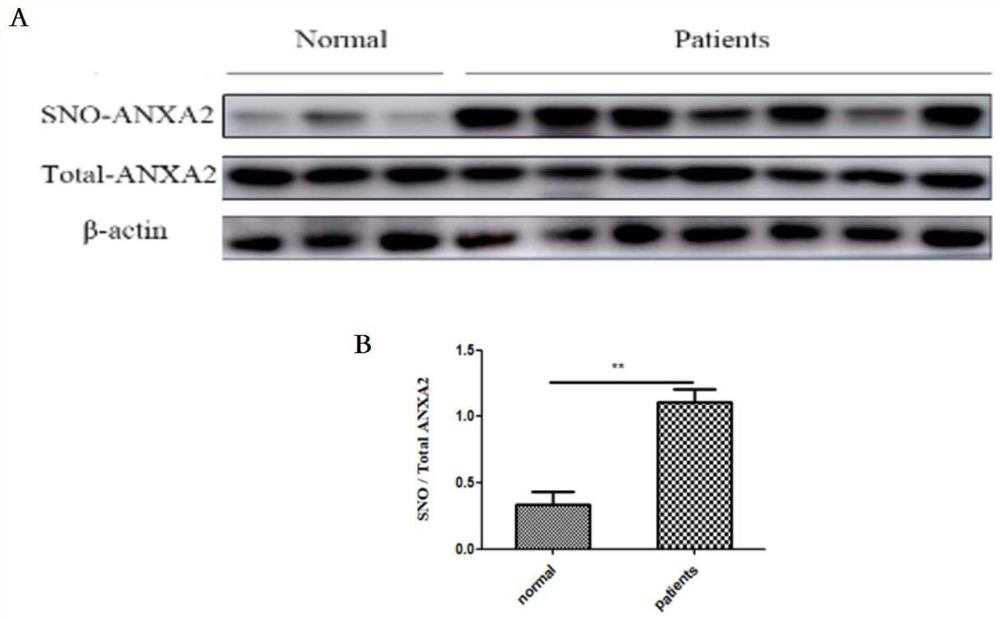
Medical use of thiol and nitrosylation modification of intervention annexin A2 (ANXA2)
ActiveCN110025787APrevent atherosclerosisImportant medicinal valueUnknown materialsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseBlood Vessel Tissue
The invention provides an application of thiol and nitrosylation modification of intervention annexin A2 (ANXA2) to preparation of medicines for preventing and treating atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases, and relates to the field of the cardiovascular system. The thiol and nitrosylation modification level of ANXA2 in blood vessel tissue of animals suffering from atherosclerosis is increased. At cell level, a Cys133 site of mutation ANXA2 can restrain increase of adhesive attachment of THP1 cells and endothelial cells caused by oxLDL, and reduce mRNA level of ICAM1 and VCAM1. At animal level, the Cys133 site of mutation ANXA2 can restrain increase of atherosclerotic plaque caused by high fat diet, reduce mRNA level of ICAM1 and VCAM1 and vascular endothelial dilatation functionsand improve the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases. According to the application of the invention, a new preparation method of medicines for preventing and treating the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases is developed, and meaningful reference is provided for preventing and treating the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
In-vivo implant capable of promoting endothelial cell adhesion and differentiation
ActiveCN114699567APrevent proliferationMeet individual needsSurgeryTissue regenerationAntiendomysial antibodiesEndothelial cell-cell adhesion
The invention discloses an in-vivo implant capable of promoting adhesion and differentiation of endothelial cells, an internal area of the implant is made of a degradable material and plays a role in throughout and always supporting the implant, a middle area is formed by compounding the degradable material and a first drug, and an external area is formed by compounding an organic polymer material and a second drug and plays a role in throughout and always supporting the implant. The first medicine is an anti-restenosis medicine for inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation, the second medicine is a specific endothelial progenitor cell antibody capturing medicine, and the proportion of the second medicine in an external area is gradually changed, so that the adhesion and differentiation capabilities of endothelial cells around a tissue injury part are improved, and the tissue injury effect is improved. And meanwhile, after the expected repairing purpose is achieved, the slow release of the first medicine is utilized to inhibit the cell proliferation so as to prevent the occurrence of restenosis. The variable stacking form can adapt to the structural characteristics of the human body, the requirements of different patients and different implantation positions are met, the operation is safer and more reliable, and the postoperative curative effect is better.
Owner:开封市卫生学校
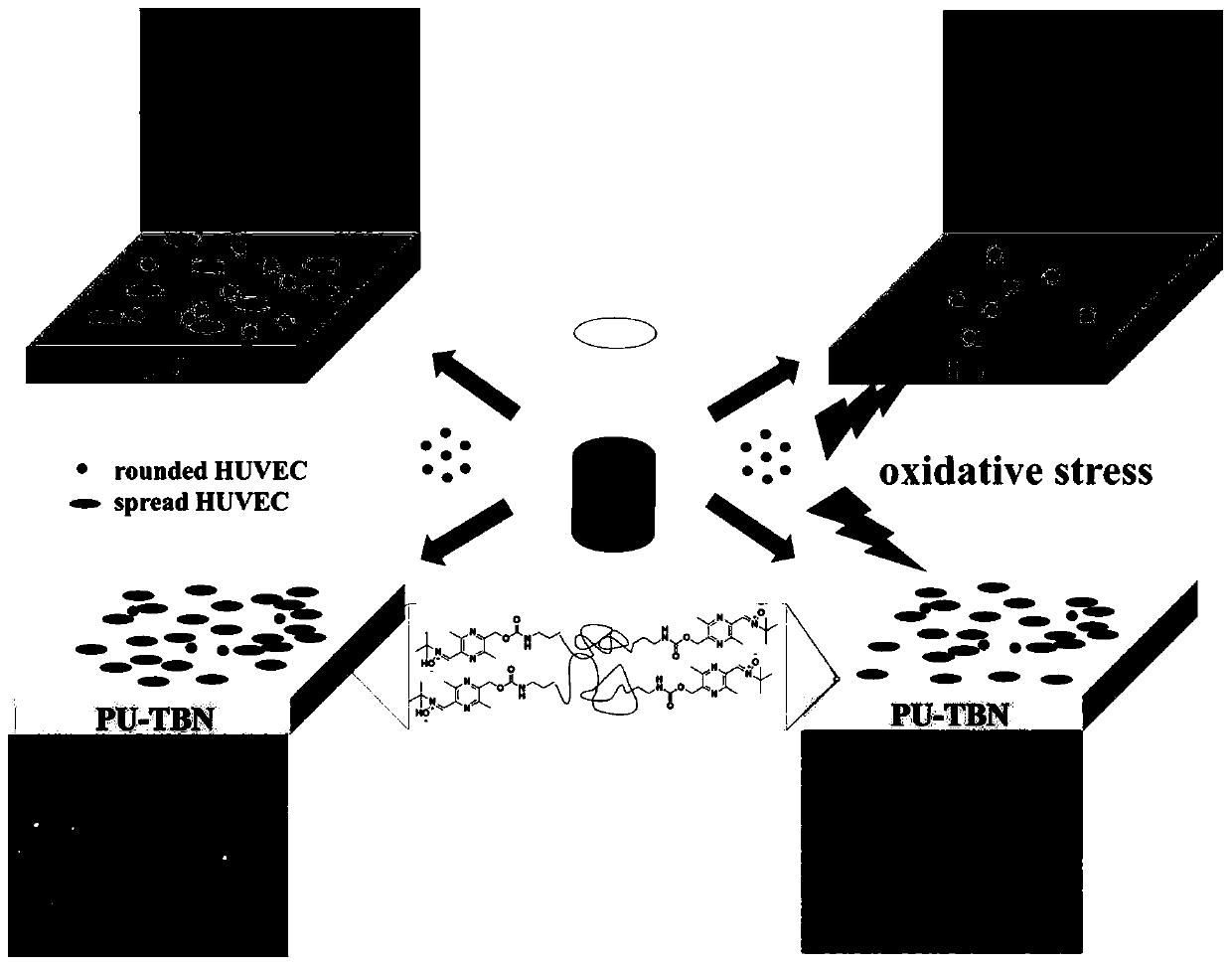
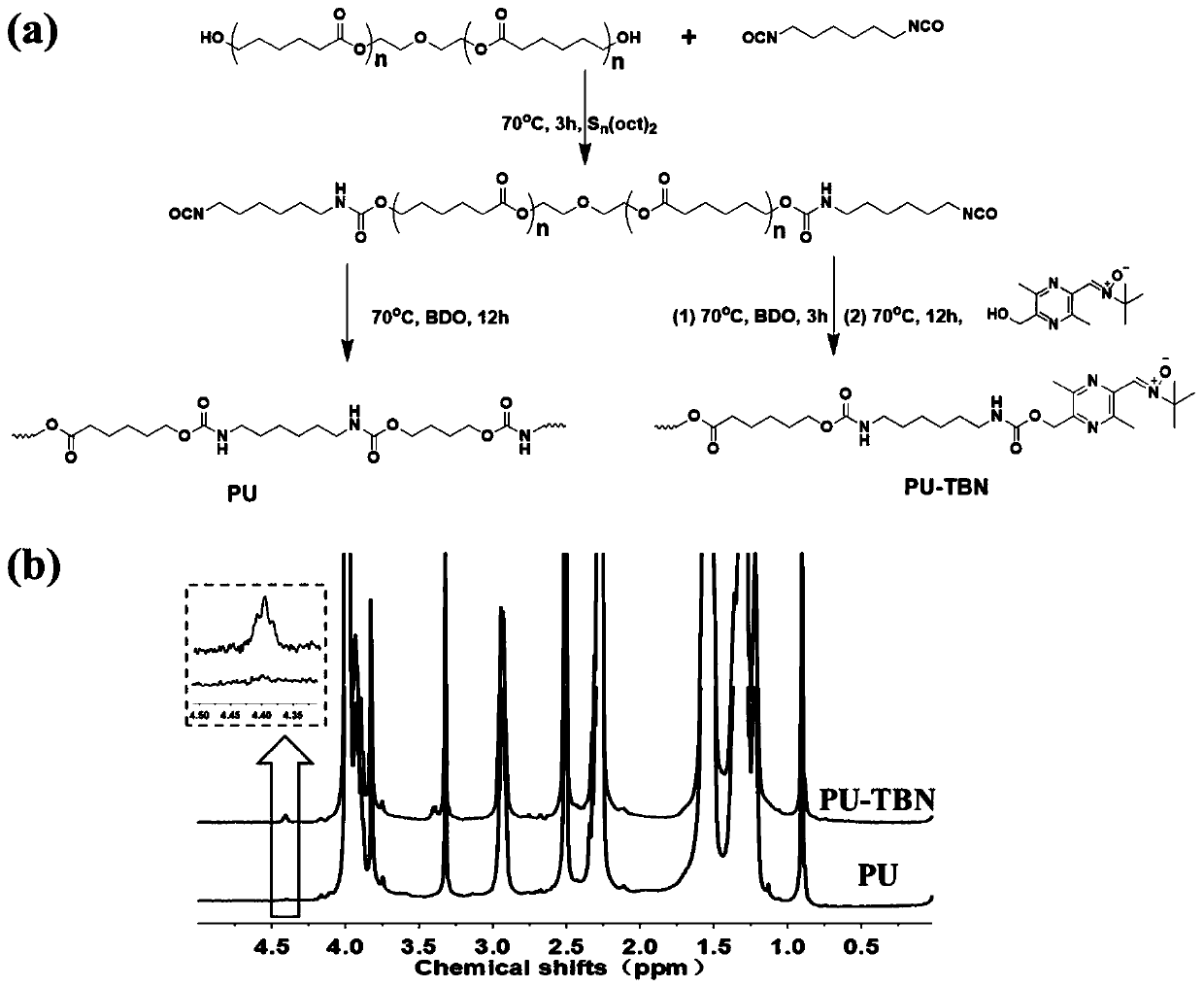
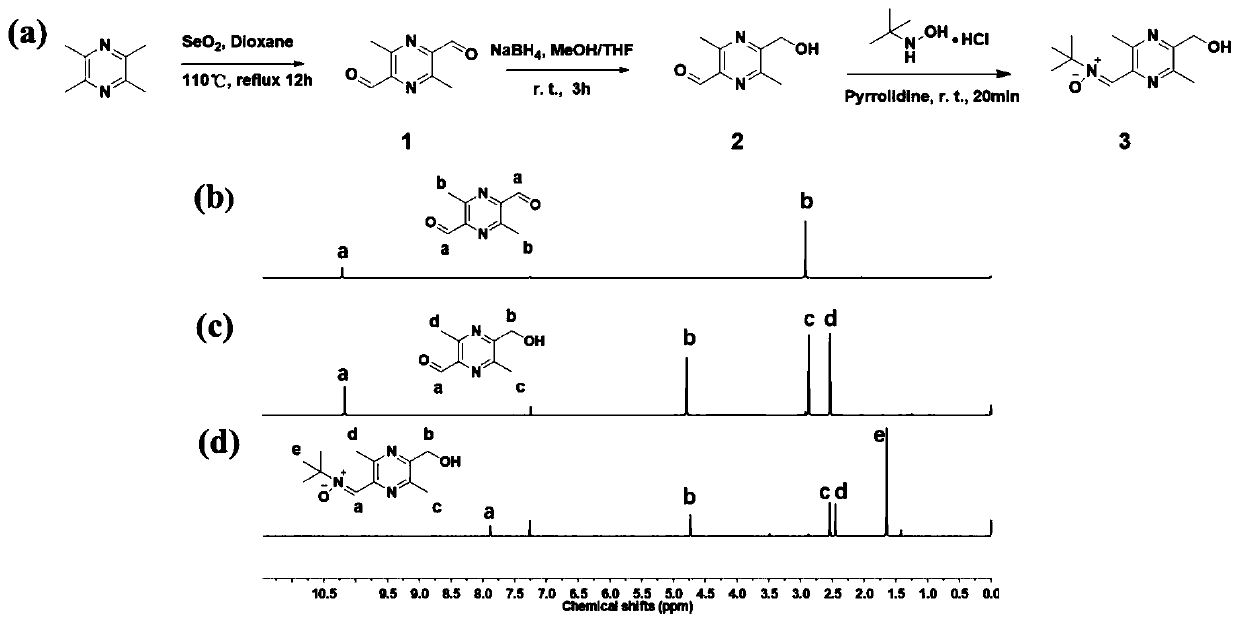
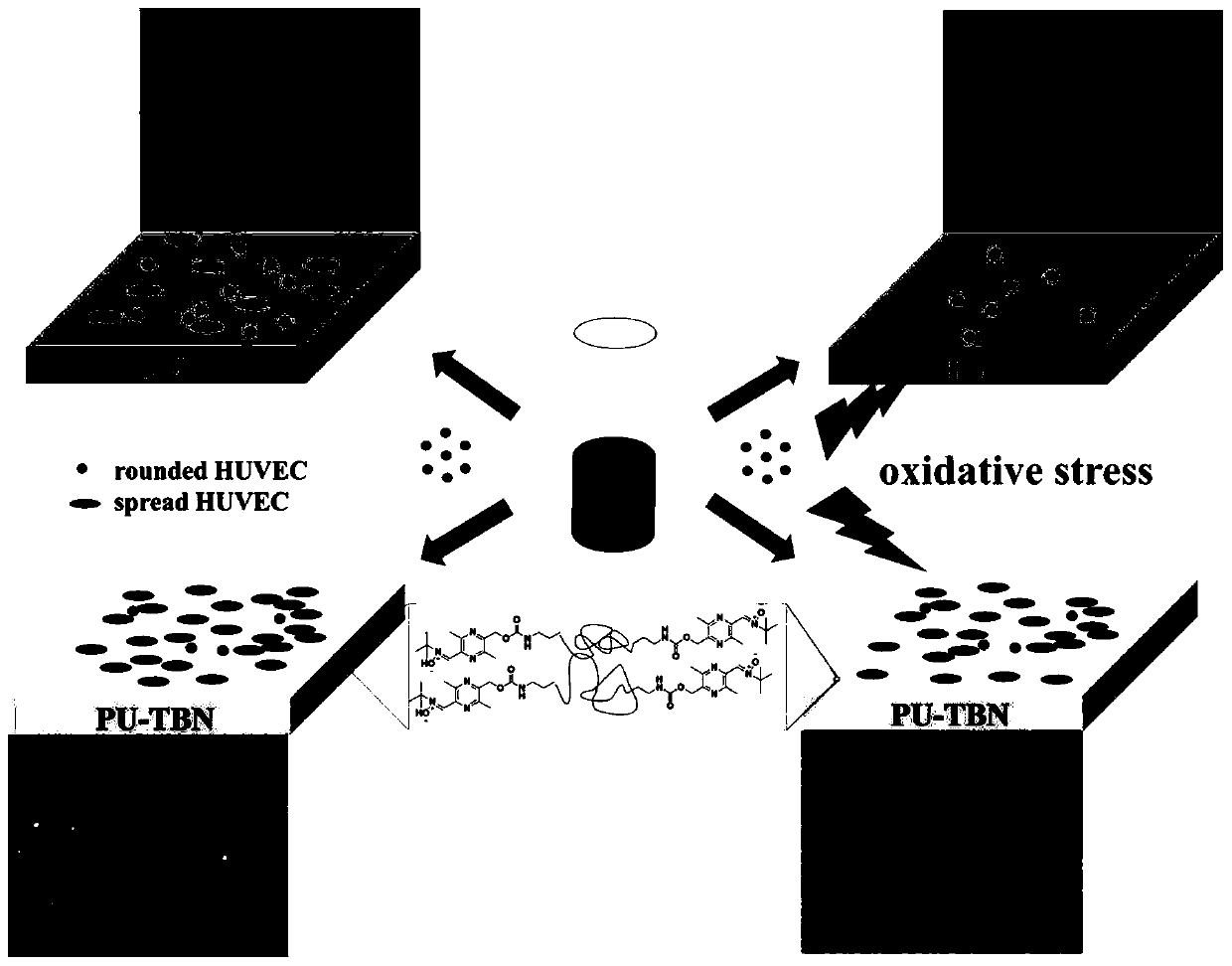
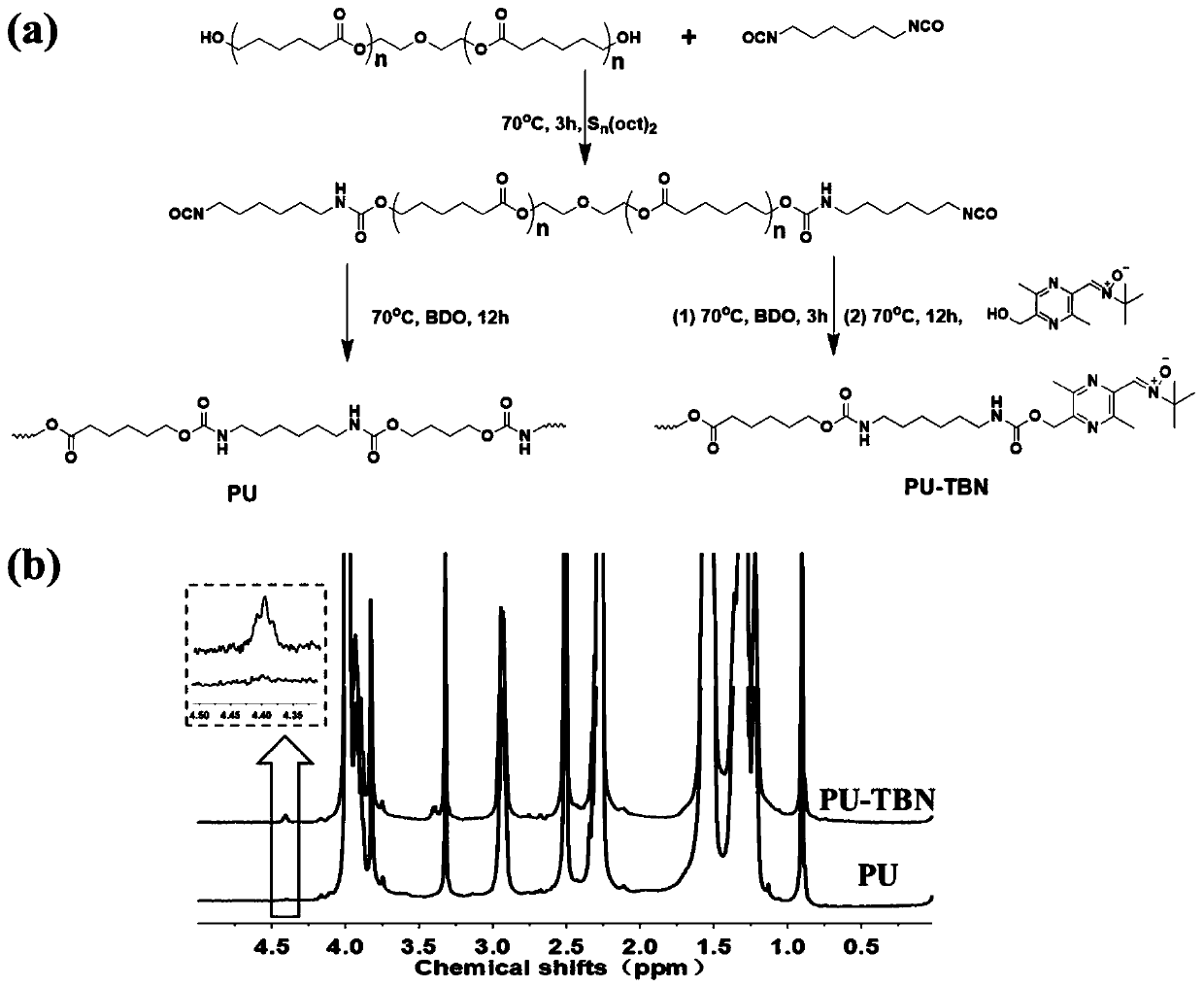
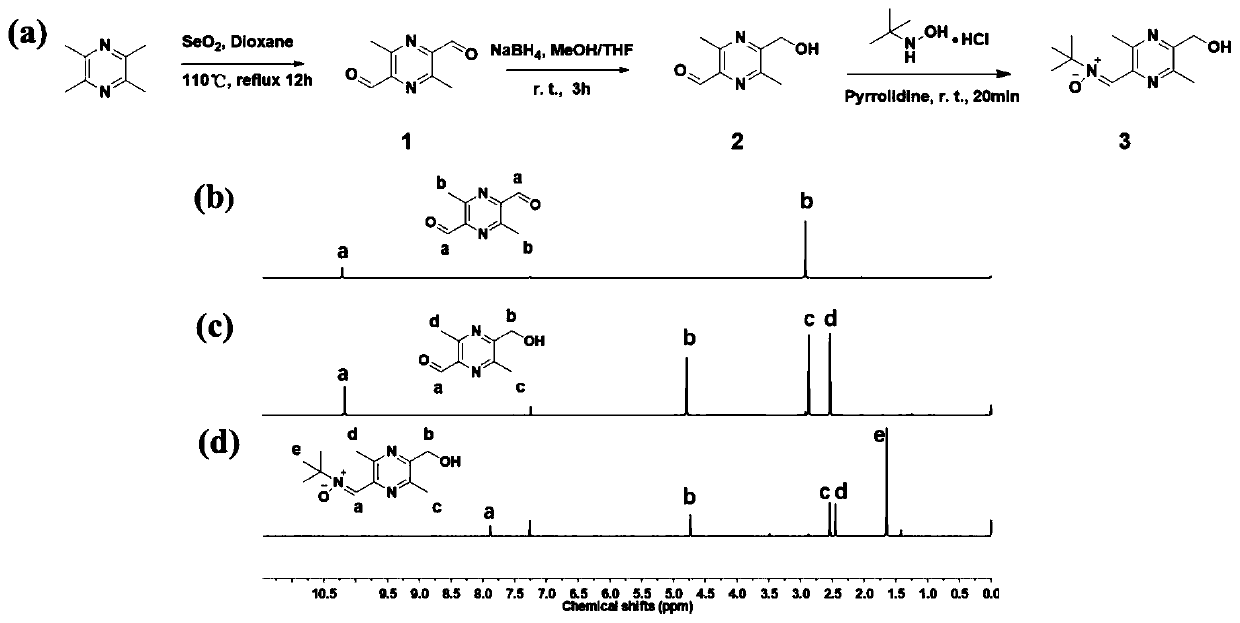
Bifunctional polyurethane and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110283296BImprove mechanical propertiesStrong structural designProsthesisPolymer scienceBifunctional
The invention relates to difunctional polyurethane and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biologic medical materials. The technical problem that an existing blood vessel material cannot eliminate oxidative stress of a blood vessel implant part is solved. The difunctional polyurethane contains a ligustrazine-nitrone group, and the structural formula of the ligustrazine-nitrone group is shown in the formula I. According to the difunctional polyurethane, by introducing a polyurethane molecular chain (tail end) into the ligustrazine-nitrone group with the dual functions of anti-oxidant and endothelial cell sticking promotion, the dual functions of polyurethane anti-oxidation and endothelial cell sticking promotion are given, adhesion and multiplication of endothelial cells can be effectively promoted, and the normal functions of the endothelial cells are promoted under the oxidation stress environment.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Difunctional polyurethane and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110283296AGood mechanical propertiesStrong structural designProsthesisOxidative stressStructural formula
The invention relates to difunctional polyurethane and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biologic medical materials. The technical problem that an existing blood vessel material cannot eliminate oxidative stress of a blood vessel implant part is solved. The difunctional polyurethane contains a ligustrazine-nitrone group, and the structural formula of the ligustrazine-nitrone group is shown in the formula I. According to the difunctional polyurethane, by introducing a polyurethane molecular chain (tail end) into the ligustrazine-nitrone group with the dual functions of anti-oxidant and endothelial cell sticking promotion, the dual functions of polyurethane anti-oxidation and endothelial cell sticking promotion are given, adhesion and multiplication of endothelial cells can be effectively promoted, and the normal functions of the endothelial cells are promoted under the oxidation stress environment.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Blocking leukocyte emigration and inflammation by interfering with CD99l2
InactiveCN101437539BInhibit bindingInhibition shiftAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsWhite blood cellTherapeutic treatment
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Medicinal application of interfering with annexin a2 sulfhydryl nitrosylation modification
ActiveCN110025787BPrevent atherosclerosisImportant medicinal valueUnknown materialsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseBlood Vessel Tissue
The invention provides an application of thiol and nitrosylation modification of intervention annexin A2 (ANXA2) to preparation of medicines for preventing and treating atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases, and relates to the field of the cardiovascular system. The thiol and nitrosylation modification level of ANXA2 in blood vessel tissue of animals suffering from atherosclerosis is increased. At cell level, a Cys133 site of mutation ANXA2 can restrain increase of adhesive attachment of THP1 cells and endothelial cells caused by oxLDL, and reduce mRNA level of ICAM1 and VCAM1. At animal level, the Cys133 site of mutation ANXA2 can restrain increase of atherosclerotic plaque caused by high fat diet, reduce mRNA level of ICAM1 and VCAM1 and vascular endothelial dilatation functionsand improve the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases. According to the application of the invention, a new preparation method of medicines for preventing and treating the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases is developed, and meaningful reference is provided for preventing and treating the atherosclerosis related blood vessel diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Bi-functional arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptides and methods to promote angiogenesis
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com