In-vivo implant capable of promoting endothelial cell adhesion and differentiation
A technology of implants and endothelial cells in vivo, applied in the field of implants in vivo, can solve the problems of increased thrombus, achieve the effects of preventing restenosis, better therapeutic effect, and increased implant stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
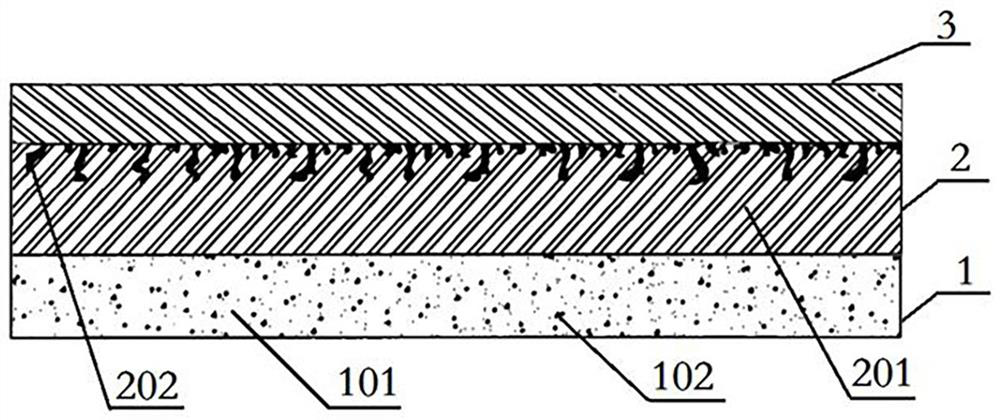
[0023] see attached figure 1 As shown, an in vivo implant that promotes endothelial cell adhesion and differentiation consists of a carrier and a support and includes an inner region 3, an outer region 1, and an intermediate region 2 sandwiched between the inner region 3 and the outer region 1 , the thickness of the middle area 2 is greater than the thickness of the outer area 1, the thickness of the outer area 1 is greater than the thickness of the inner area 3, the middle area 2 and the inner area 3 together constitute the support of the implant, forming the The inner area 3 of the support body is made of degradable material, which can strongly support the implant as a whole. An intermediate area 2 is integrally formed on the outside of the inner area 3, and the intermediate area 2 is made of degradable material. The material 201 is compounded with the first drug 202, and a layer of carrier is sprayed on the periphery of the middle region 2 to form the outer region 1. The ca...
Embodiment 2
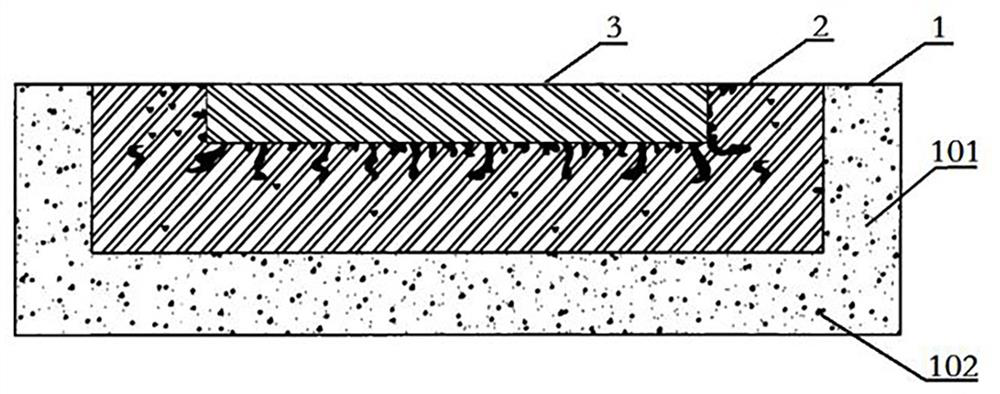
[0034] The structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that in this embodiment, as figure 2 As shown, when the implant is a sheet-like structure, its layers can also be folded and wrapped up at the edges after being stacked, that is, the peripheral edges of the outer region 1 are folded upward to wrap the outer edges of the middle region 2, and the middle region The peripheral edges of 2 are folded upward to wrap the outer edges of the inner region 3, and finally an implant with smooth upper and lower surfaces is formed.
[0035] When the degradable material is a polymer of degradable biopolymer materials, degradable magnetic nanoparticles with Fe3O4 as the main material can also be added to the constituent materials of the inner region 3 of the implant, and the degradable magnetic nanoparticles can be made by an external magnetic field. Nanoparticles generate a thermal effect, which in turn can heat up the interior of the imp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com