Polyethylene glycol bipolymer with endothelial cell selectivity and preparation method and application method of composite coating
A polyethylene glycol and binary copolymer technology, which is applied in the interdisciplinary field, can solve the problems of reducing the migration and proliferation ability of endothelial cells, increasing the risk of late thrombosis, and destroying the vascular endothelial layer, so as to achieve the realization of in situ endothelial cells in vivo. Capture capability, maintain non-specific impedance performance, wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Binary Copolymer
[0045]
[0046] (1.1) Dissolve 0.5 g of the biocompatible monomer PEGMA (n=19) of the cell glycocoating biomimetic, and 1.5 g of the polymerizable monomer GMA containing reactive functional groups with 30 ml of ethanol to obtain solution A;
[0047] (1.2) 0.04g initiator AIBN is added in solution A to obtain solution B;
[0048] (1.3) Deoxygenate solution B with argon for 30 minutes, heat to 60°C, and react for 24 hours;
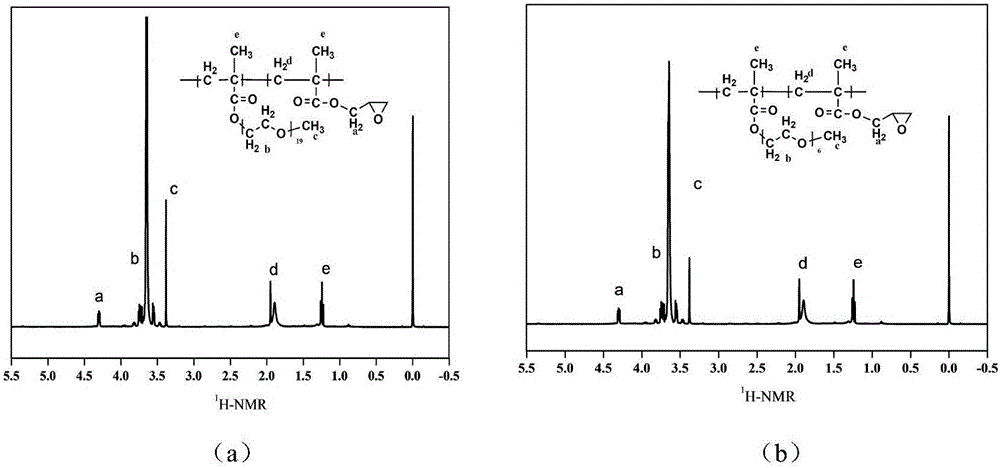
[0049] (1.4) The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the glacial ether was precipitated twice to obtain the polyethylene glycol binary copolymer PEGMA-GMA with endothelial cell selectivity. NMR results confirmed that the obtained product had the expected structure. Such as figure 1 (a) shown.
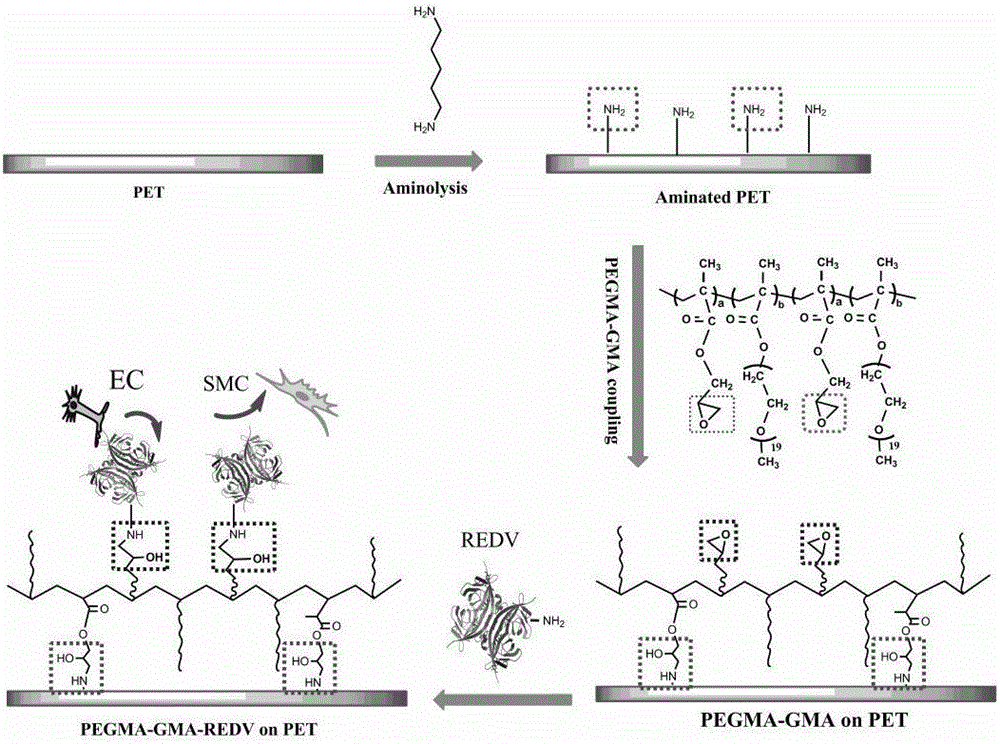
[0050] (2) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Composite Coating
[0051](2.1) Dissolving the endothelial cell-selective polyethyl...
Embodiment 2
[0061] (1) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Binary Copolymer
[0062]
[0063] (1.1) Dissolve 0.8 g of the biocompatible monomer PEGMA (n=6) of the cell glycocoating biomimetic, and 1.6 g of the polymerizable monomer GMA containing reactive functional groups in 50 ml of ethanol to obtain solution A;
[0064] (1.2) 0.048g initiator AIBN is added in solution A to obtain solution B;
[0065] (1.3) Deoxygenate solution B with argon for 20 minutes, heat to 70°C, and react for 36 hours;
[0066] (1.4) The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the glacial ether was precipitated twice to obtain the polyethylene glycol binary copolymer PEGMA-GMA with endothelial cell selectivity. NMR results confirmed that the obtained product had the expected structure. Such as figure 1 (b) shown.
[0067] (2) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Composite Coating
[0068] (2.1) Dissolving the endothelial cell-selective polyethyle...
Embodiment 3
[0078] (1) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Binary Copolymer
[0079]
[0080] (1.1) Dissolve 2 g of the biocompatible monomer PEGMA (n=30) of the cell glycoside biomimetic, and 1 g of the polymerizable monomer GMA containing reactive functional groups with 70 ml of ethanol to obtain solution A;
[0081] (1.2) Add 0.01g initiator AIBN to solution A to obtain solution B;
[0082] (1.3) Deoxygenate solution B with argon for 20 minutes, heat to 80°C, and react for 48 hours;
[0083] (1.4) The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the glacial ether was precipitated twice to obtain the polyethylene glycol binary copolymer PEGMA-GMA with endothelial cell selectivity. NMR results confirmed that the obtained product had the expected structure.
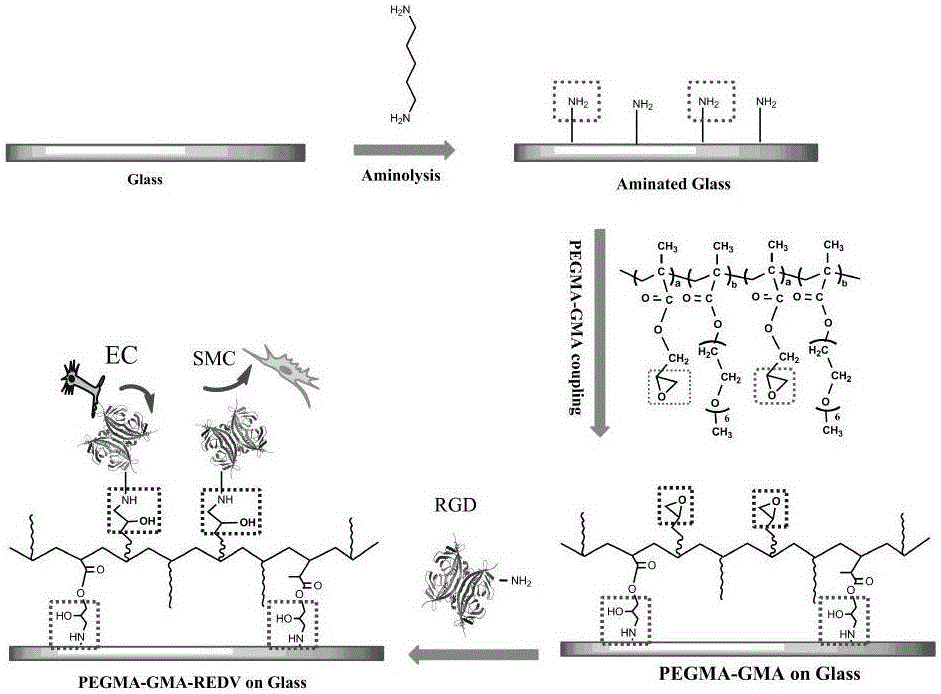
[0084] (2) Preparation of Endothelial Cell Selective Polyethylene Glycol Composite Coating
[0085] (2.1) Dissolving the endothelial cell-selective polyethylene glycol binary copolymer PEGMA-GMA in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com