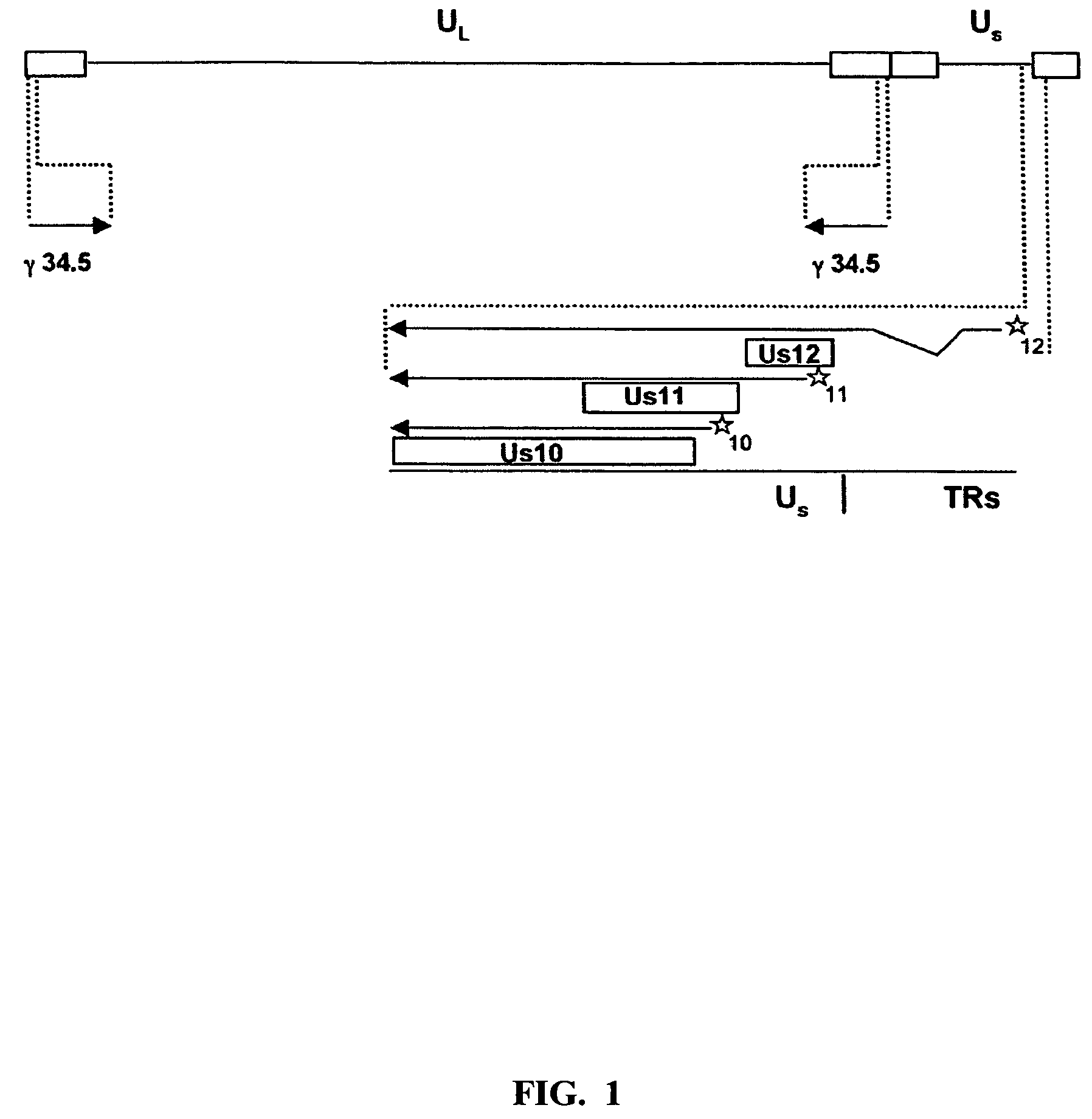
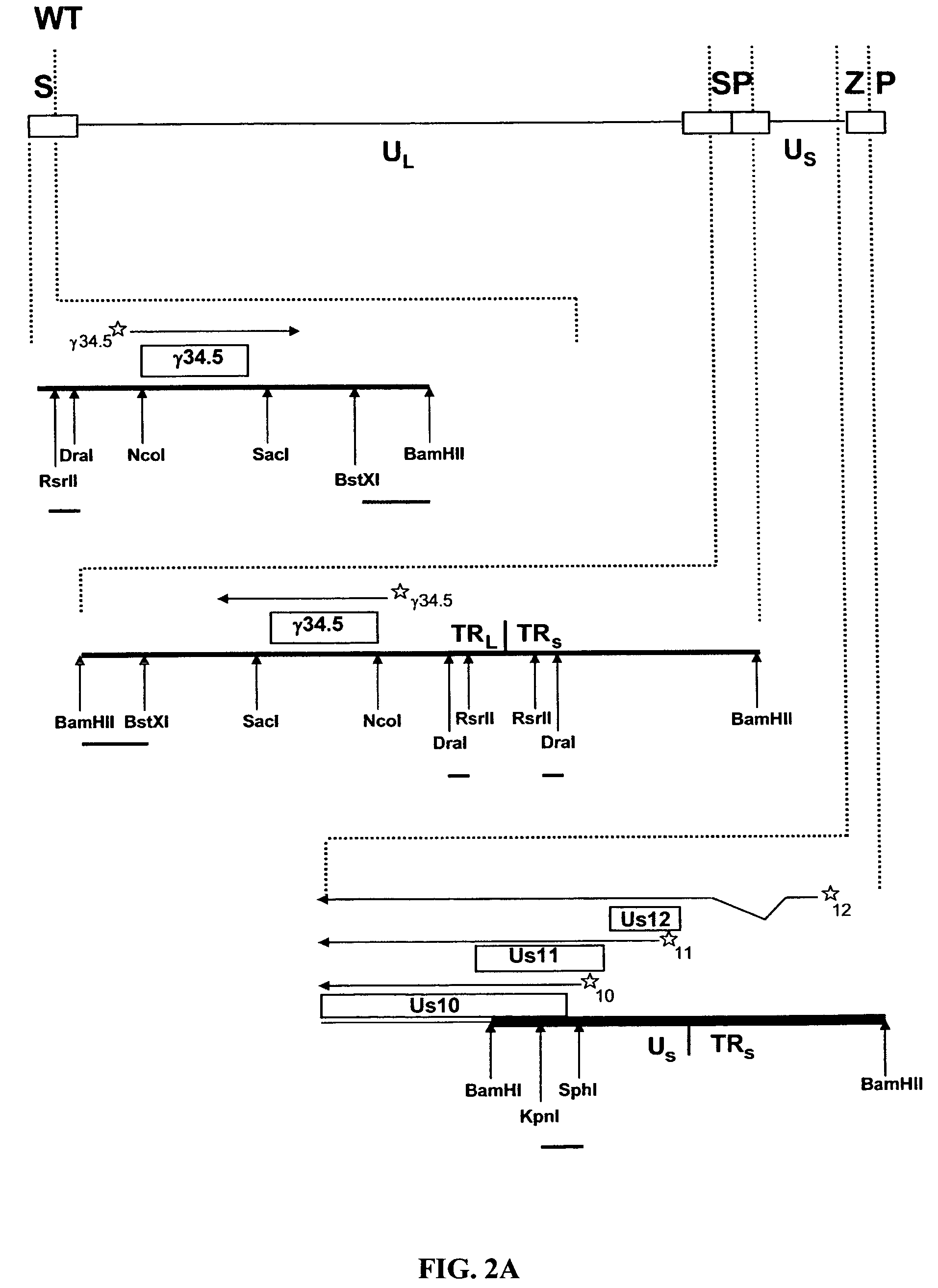
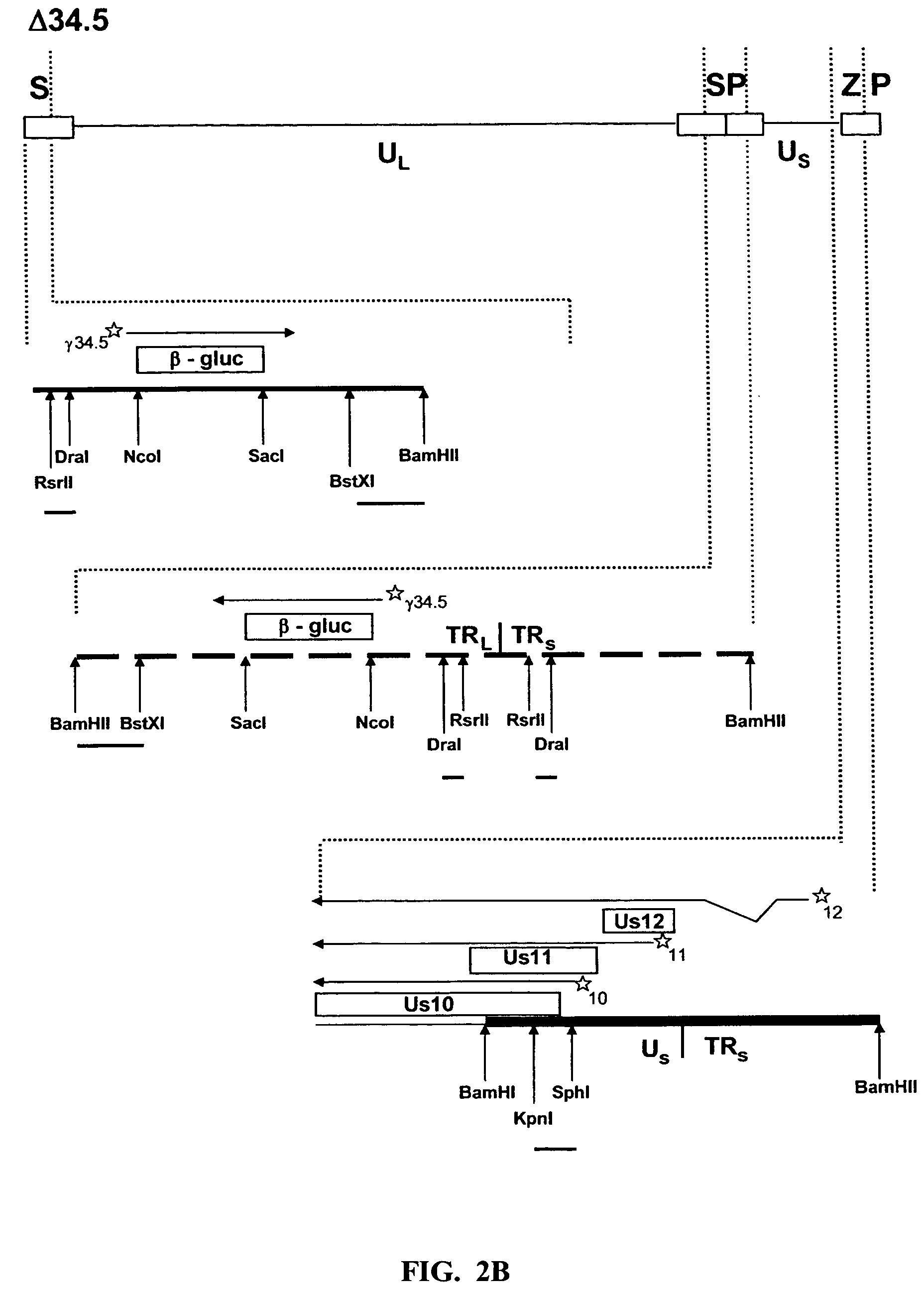
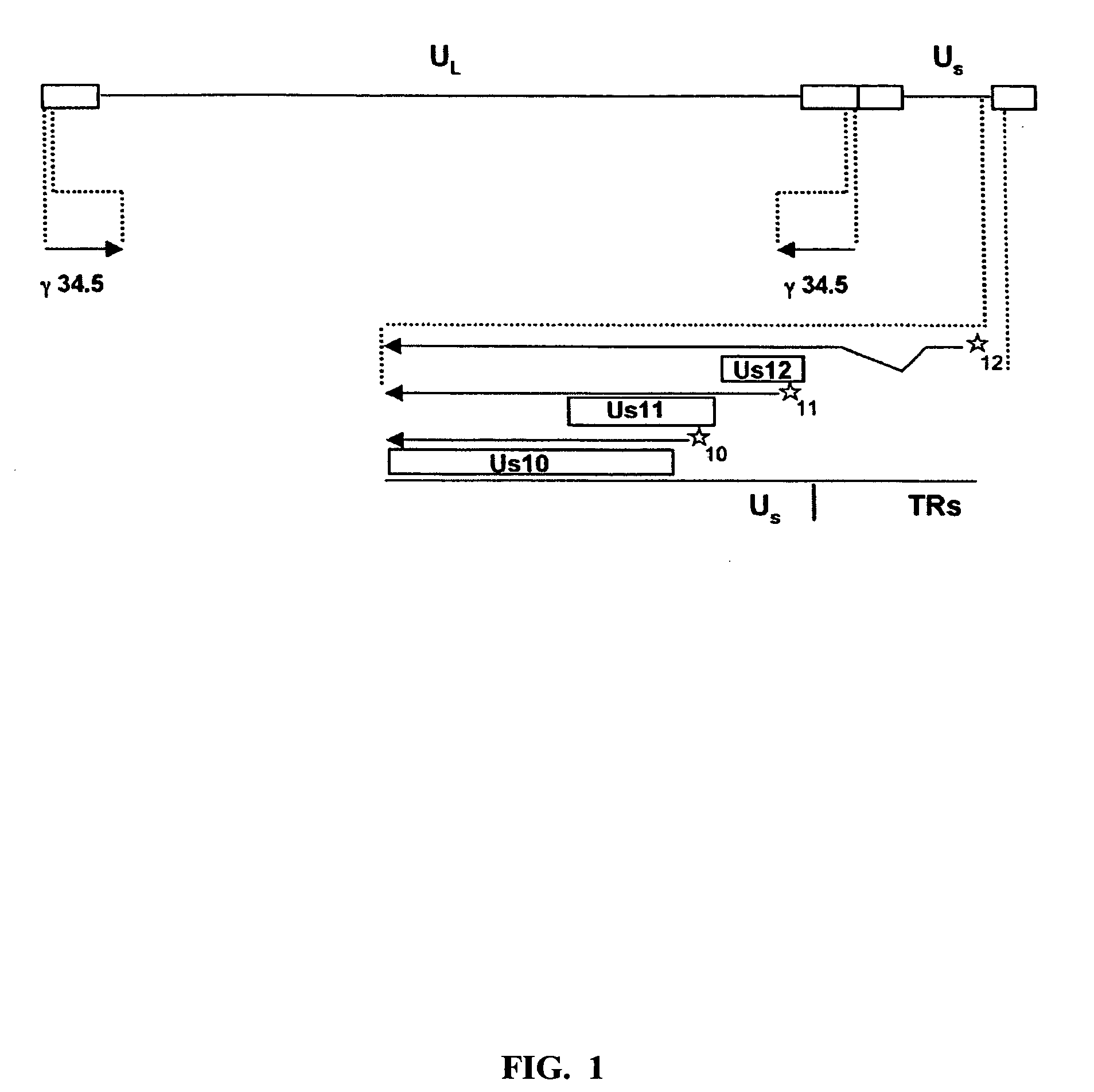
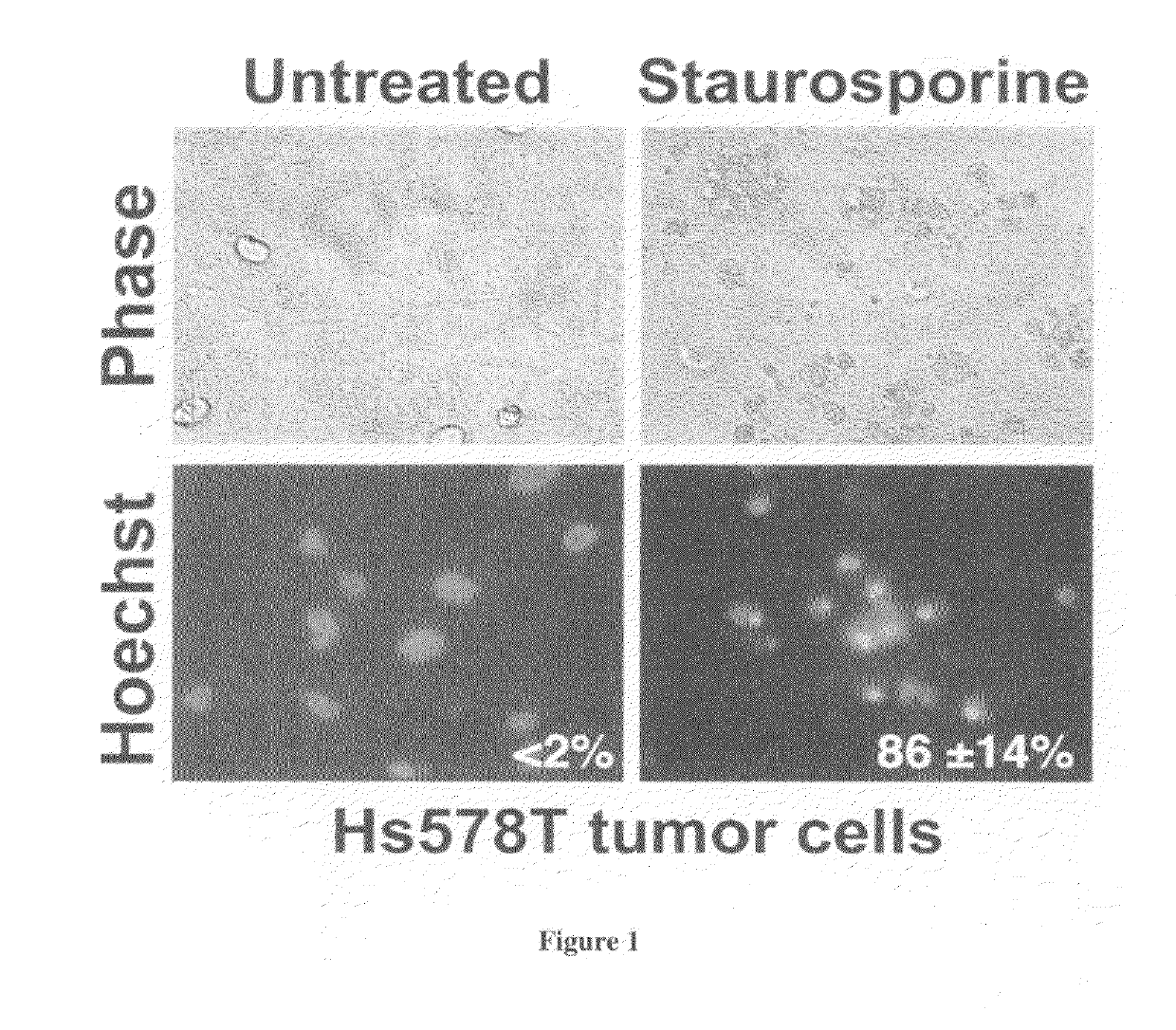
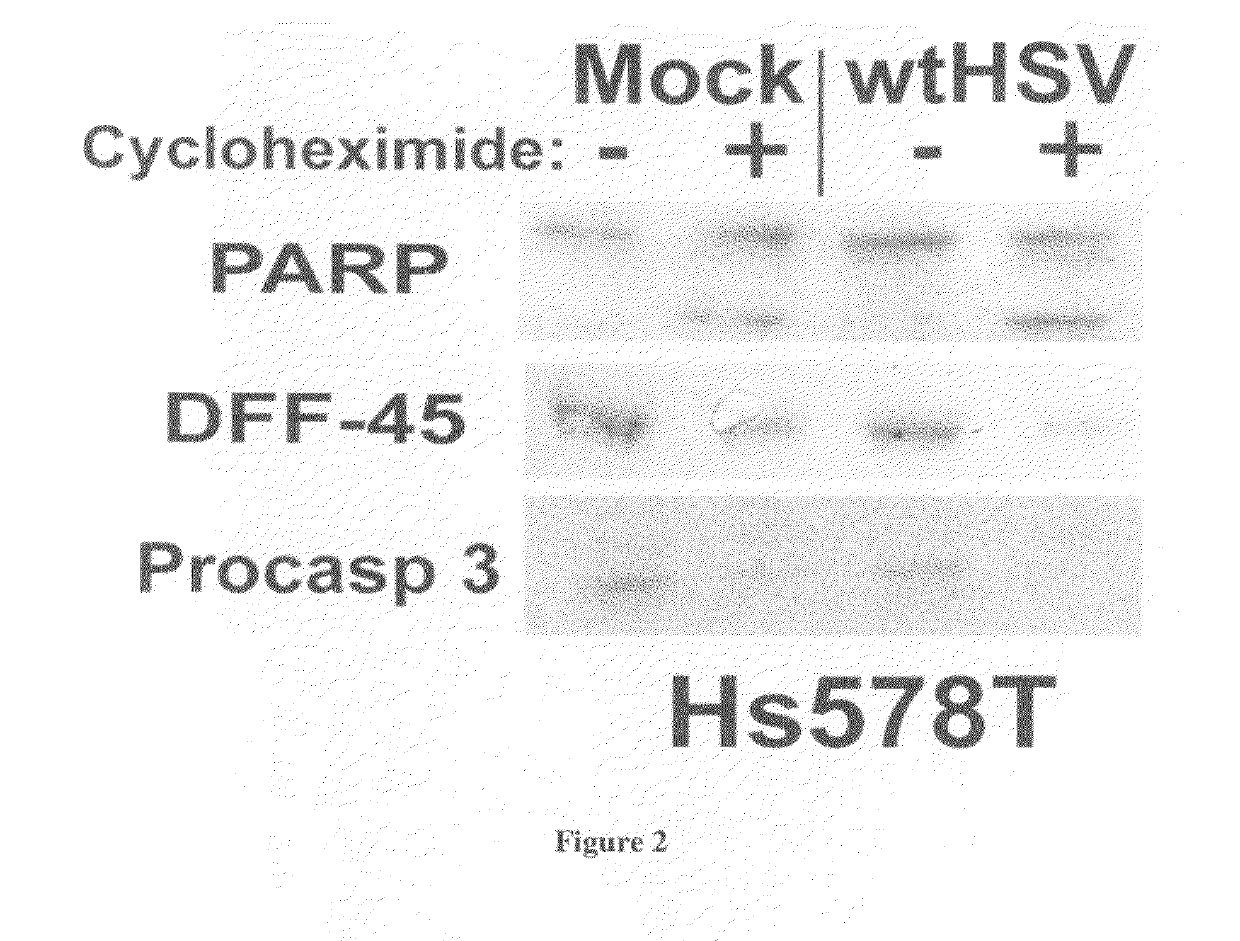
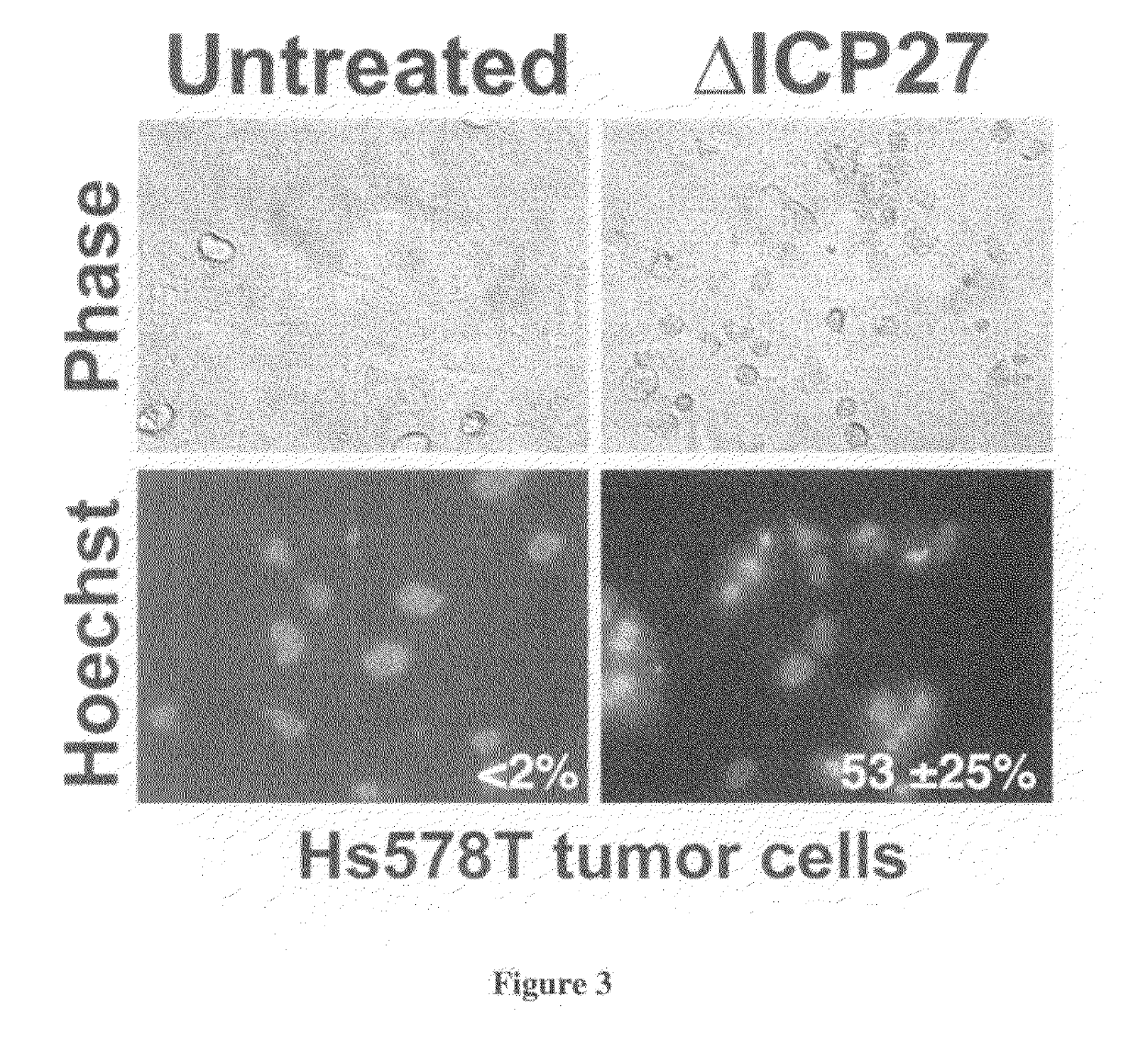
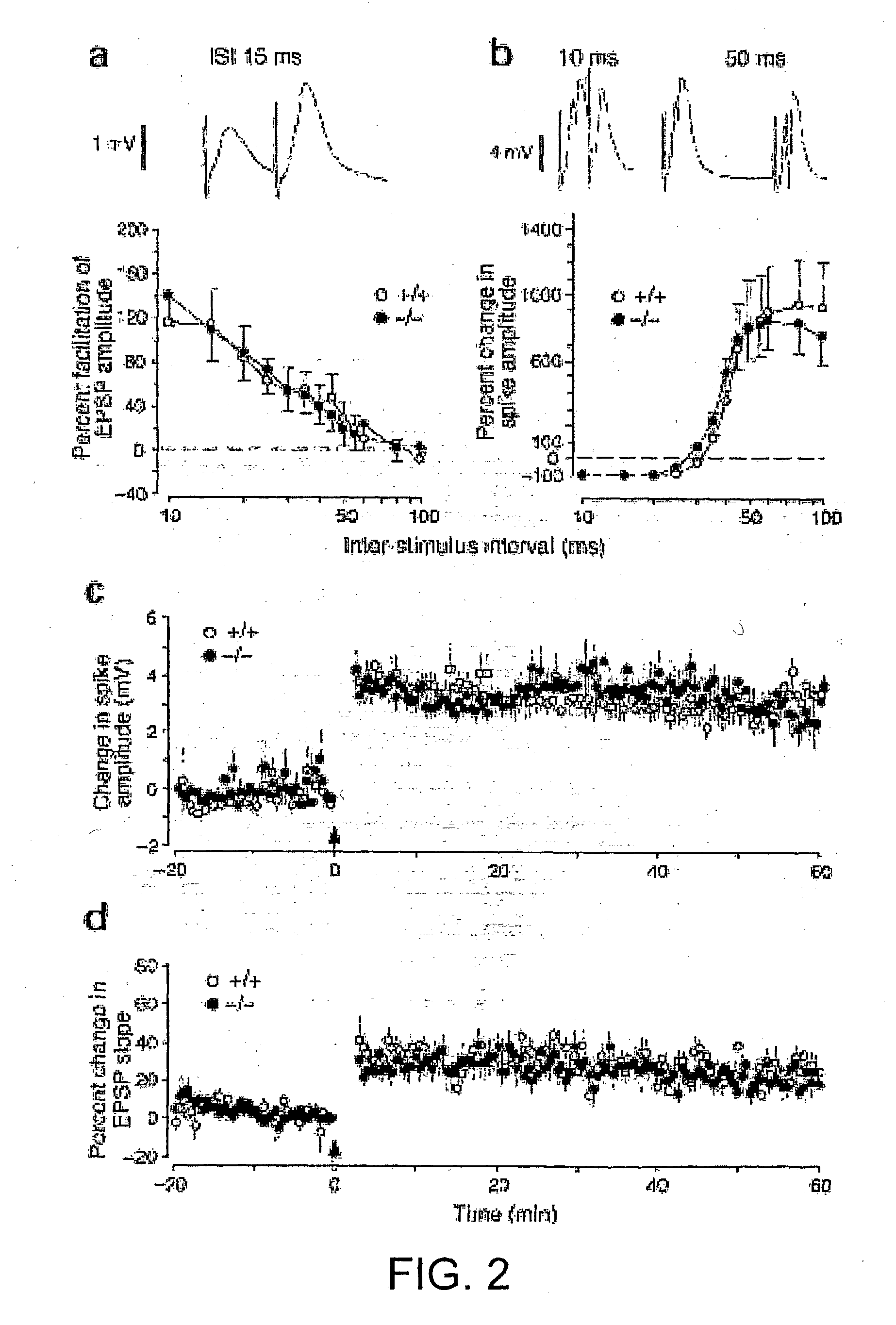
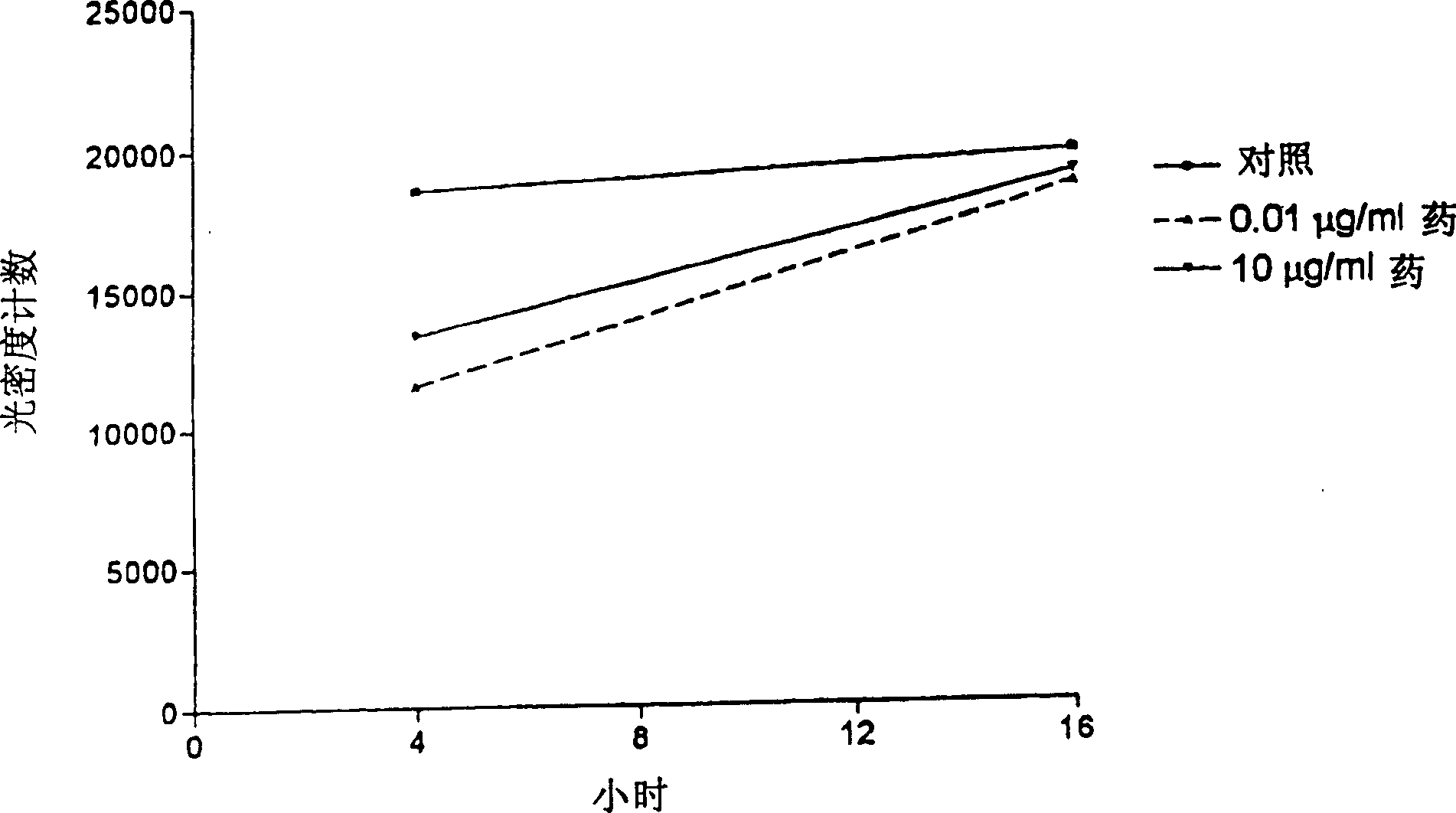
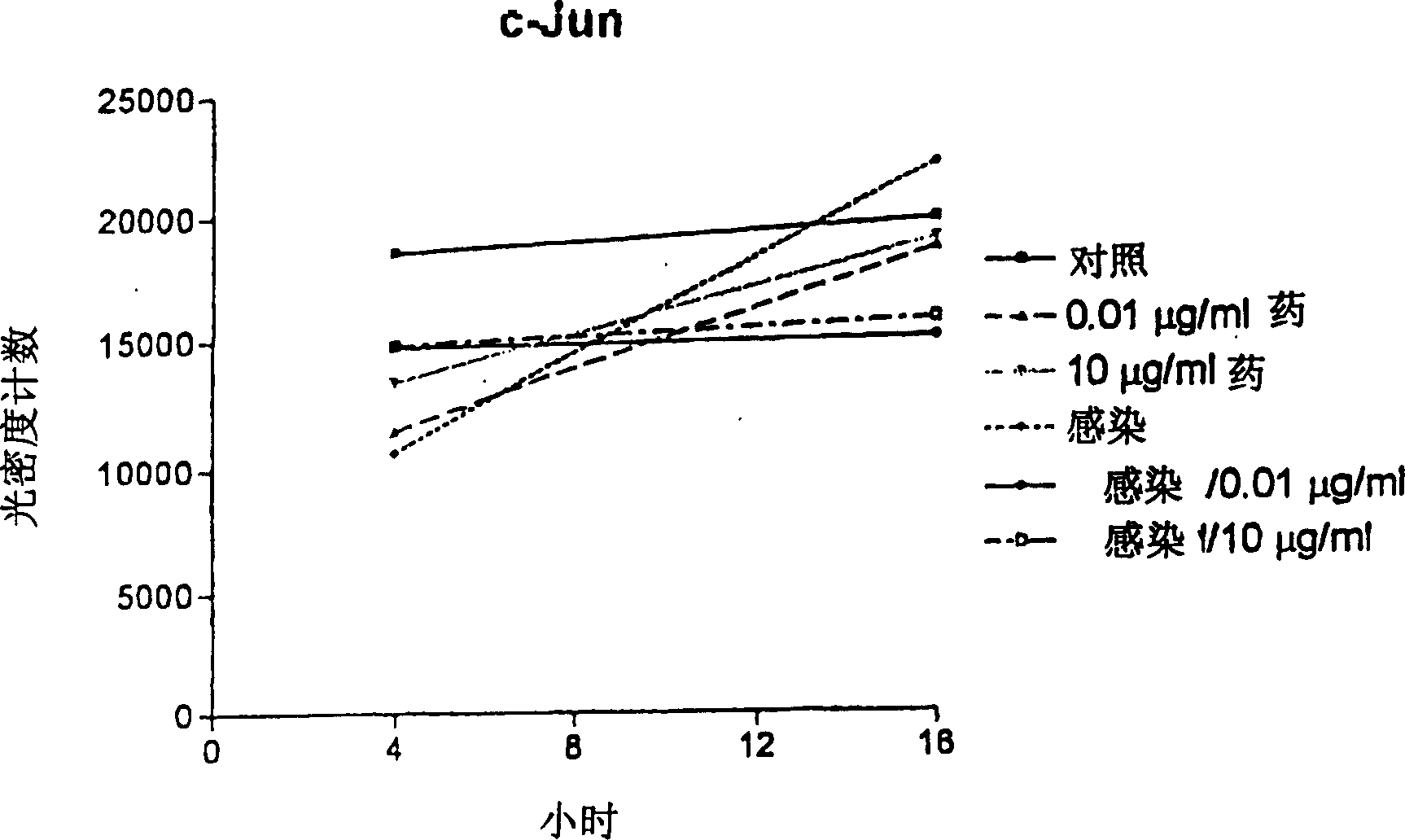
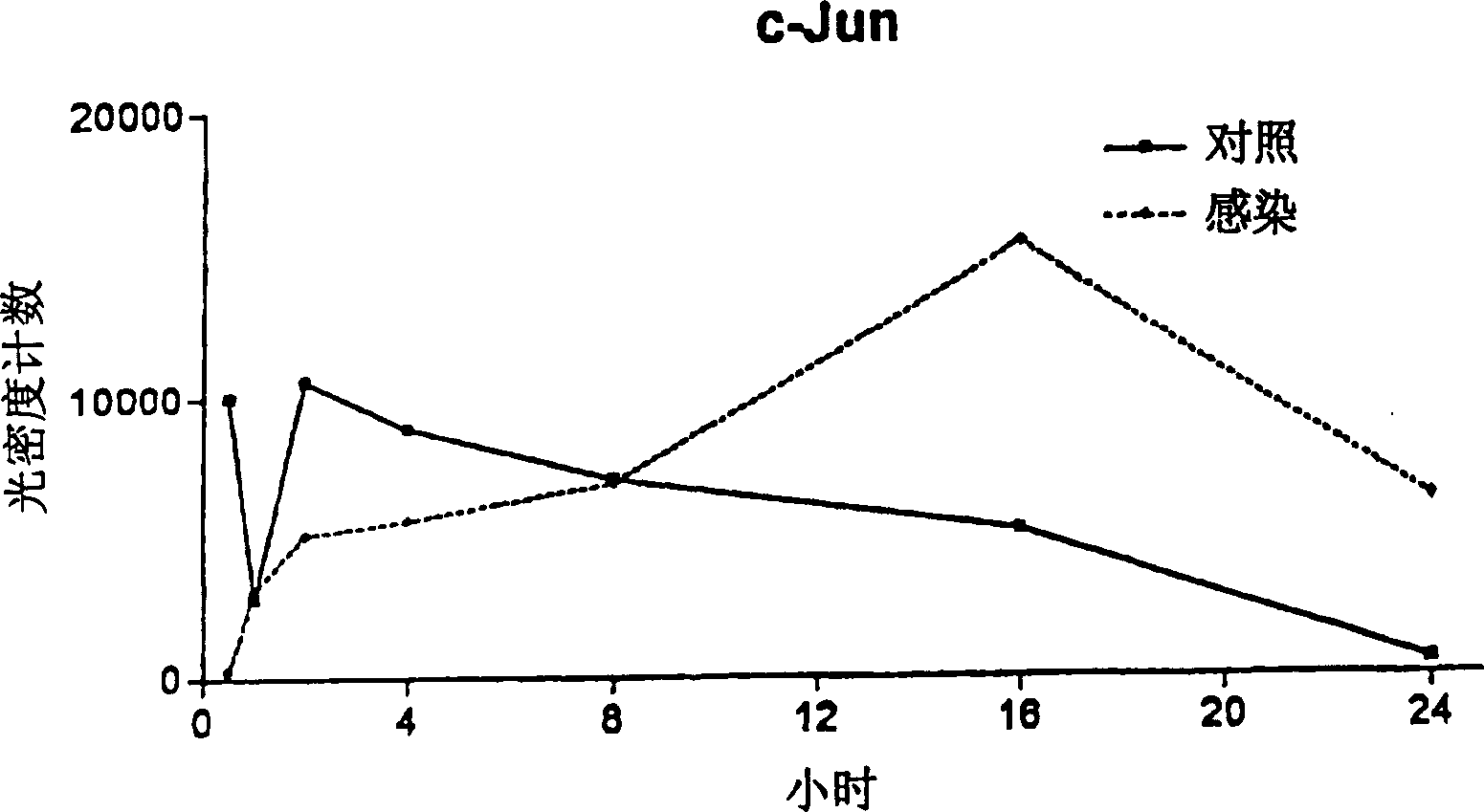
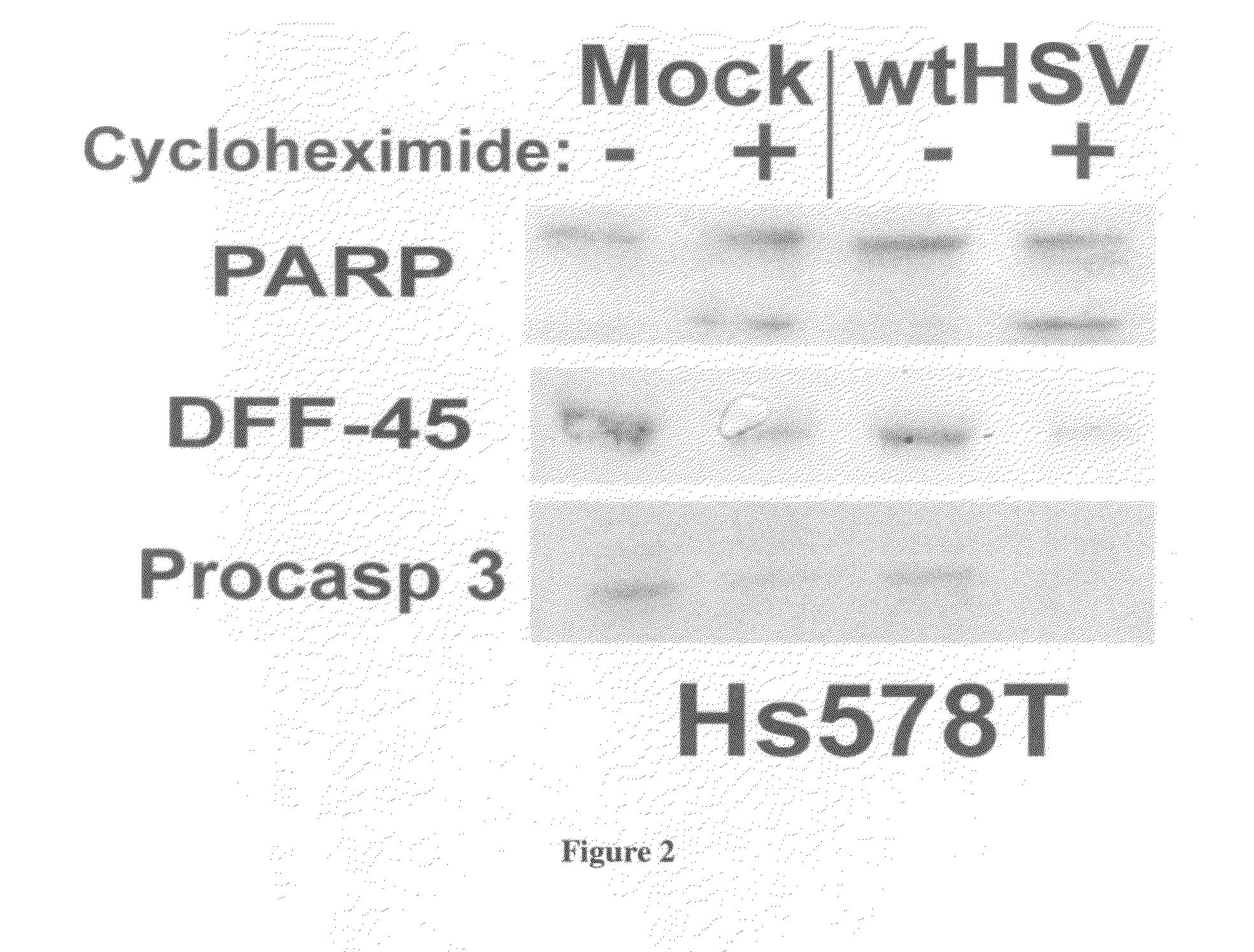Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Early response gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immediate early genes (IEGs) are genes which are activated transiently and rapidly in response to a wide variety of cellular stimuli. They represent a standing response mechanism that is activated at the transcription level in the first round of response to stimuli, before any new proteins are synthesized.
Virulent oncolytic herpes simplex virus strains engineered to counter the innate host response
ActiveUS7731952B2Preserving abilityContinual and sustained deliveryBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAutoimmune responsesHost response
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Avirulent oncolytic herpes simplex virus strains engineered to counter the innate host response
ActiveUS20060039894A1Preserving abilityContinual and sustained deliveryBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
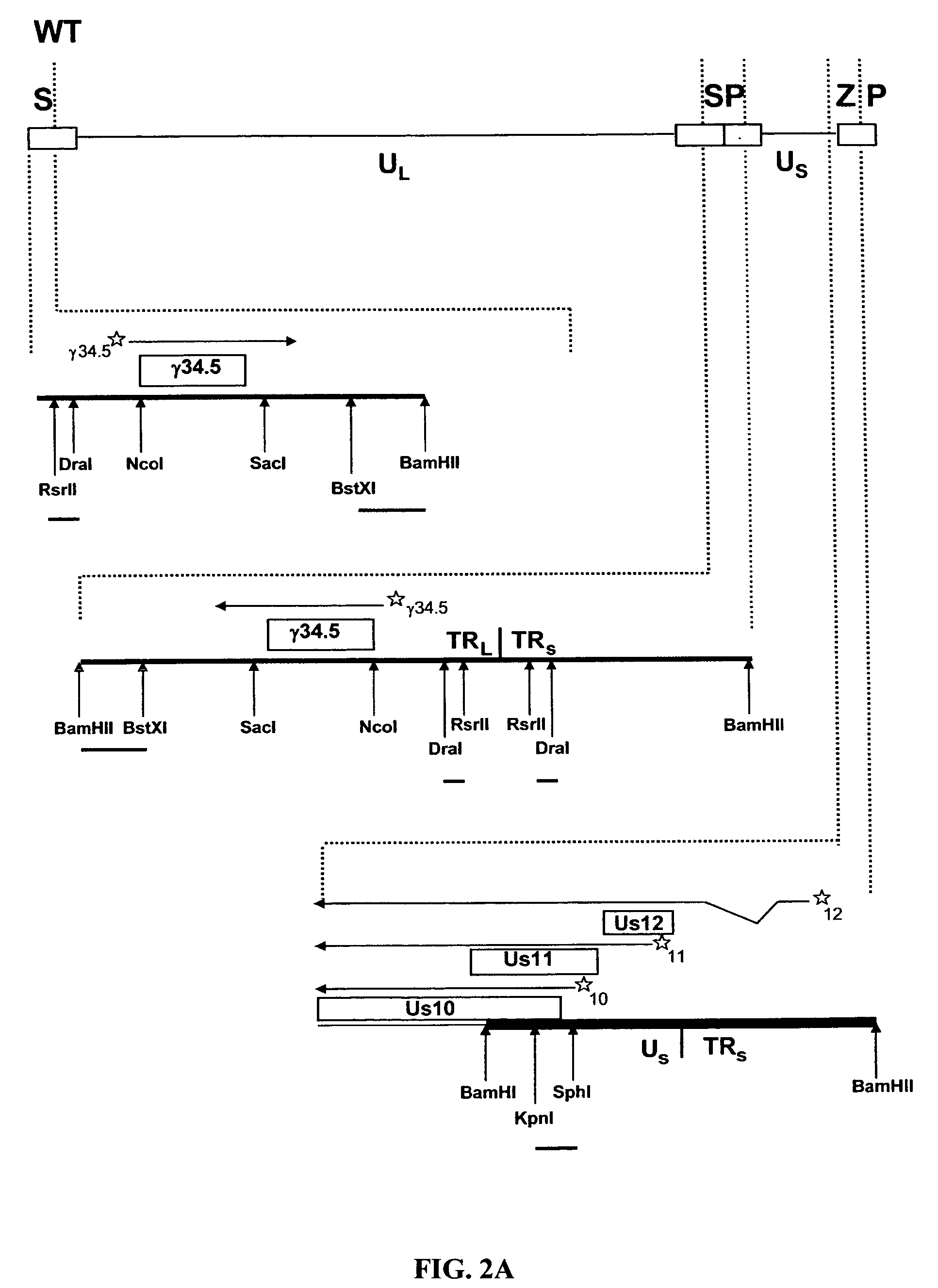
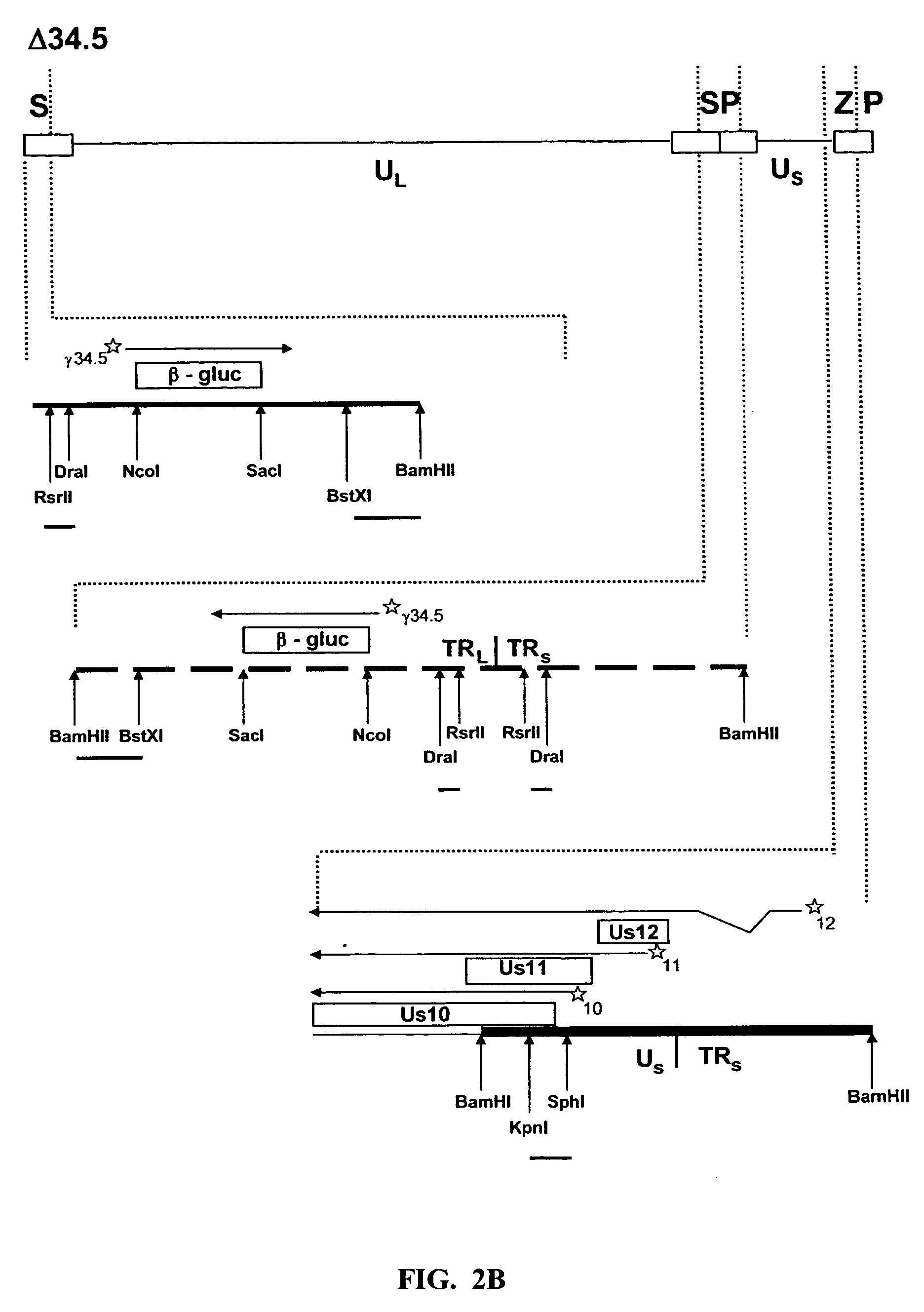
The present invention relates to an avirulent, oncolytic herpes simplex virus modified from a wild-type herpes simplex virus so that both γ134.5 genes of the virus have been deleted and each replaced with an interferon-resistance gene that is expressed as an immediate-early gene. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition that includes the modified herpes simplex virus of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle for in situ administration to tumor cells. Also provided in the present invention are methods for killing tumor cells in a subject and for immunizing a subject against an infectious disease, cancer, or an autoimmune disease that involve administering to a subject the modified avirulent, oncolytic herpes simplex virus of the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
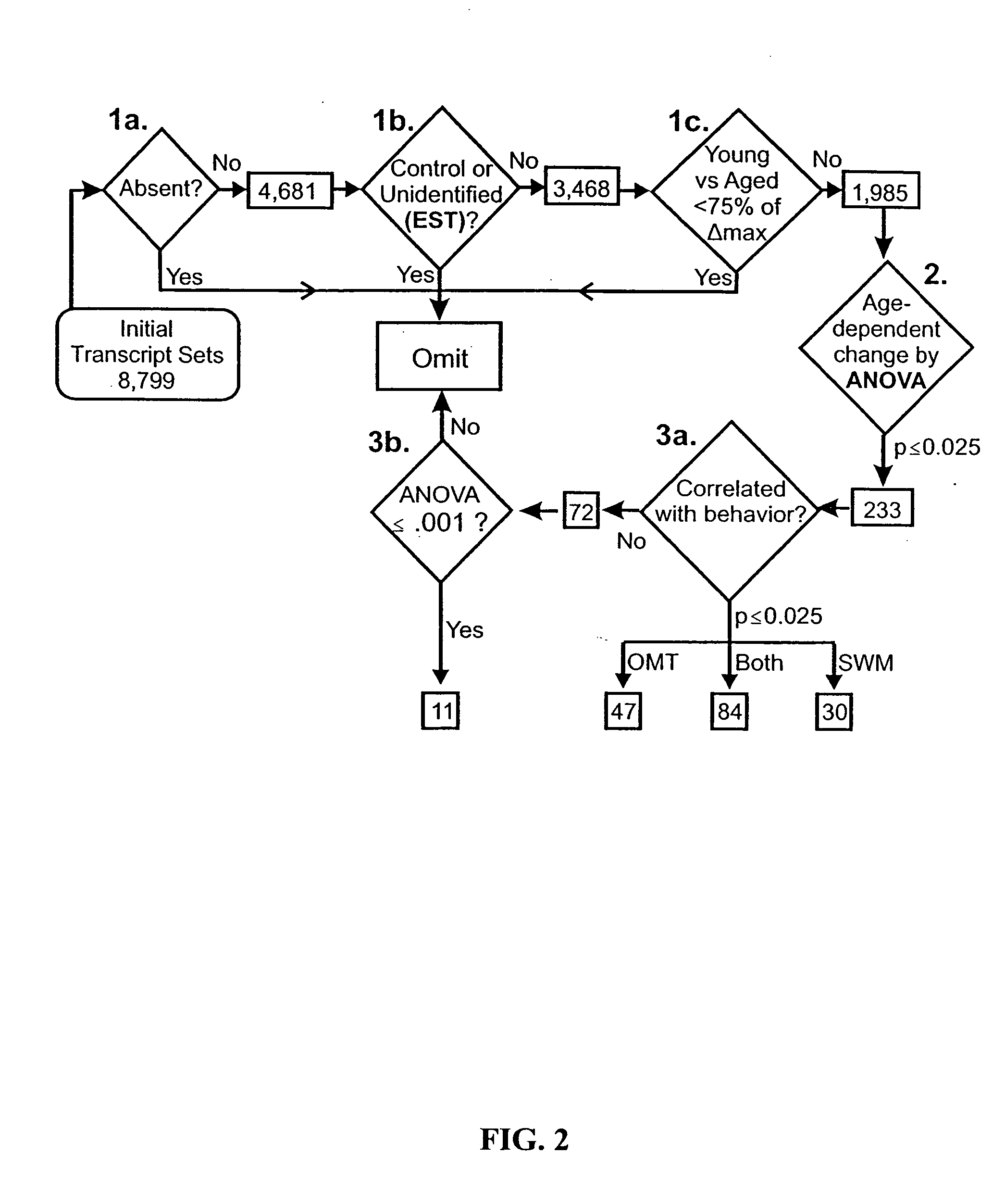
Gene expression profile biomarkers and therapeutic targets for brain aging and age-related cognitive impairment
InactiveUS20050071088A1Increase neuronal vulnerabilityImprove lipid metabolismMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAntigenDisease cause
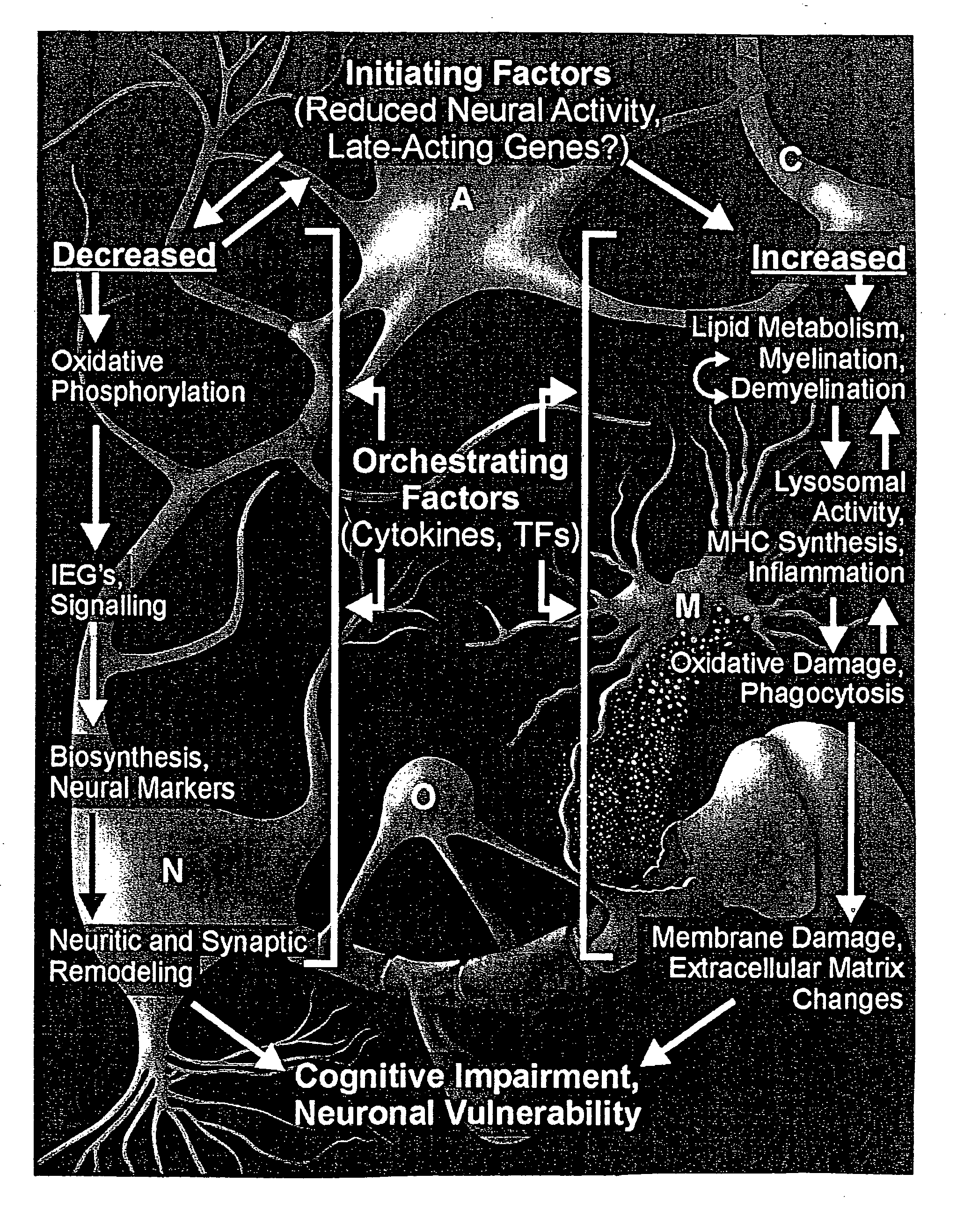
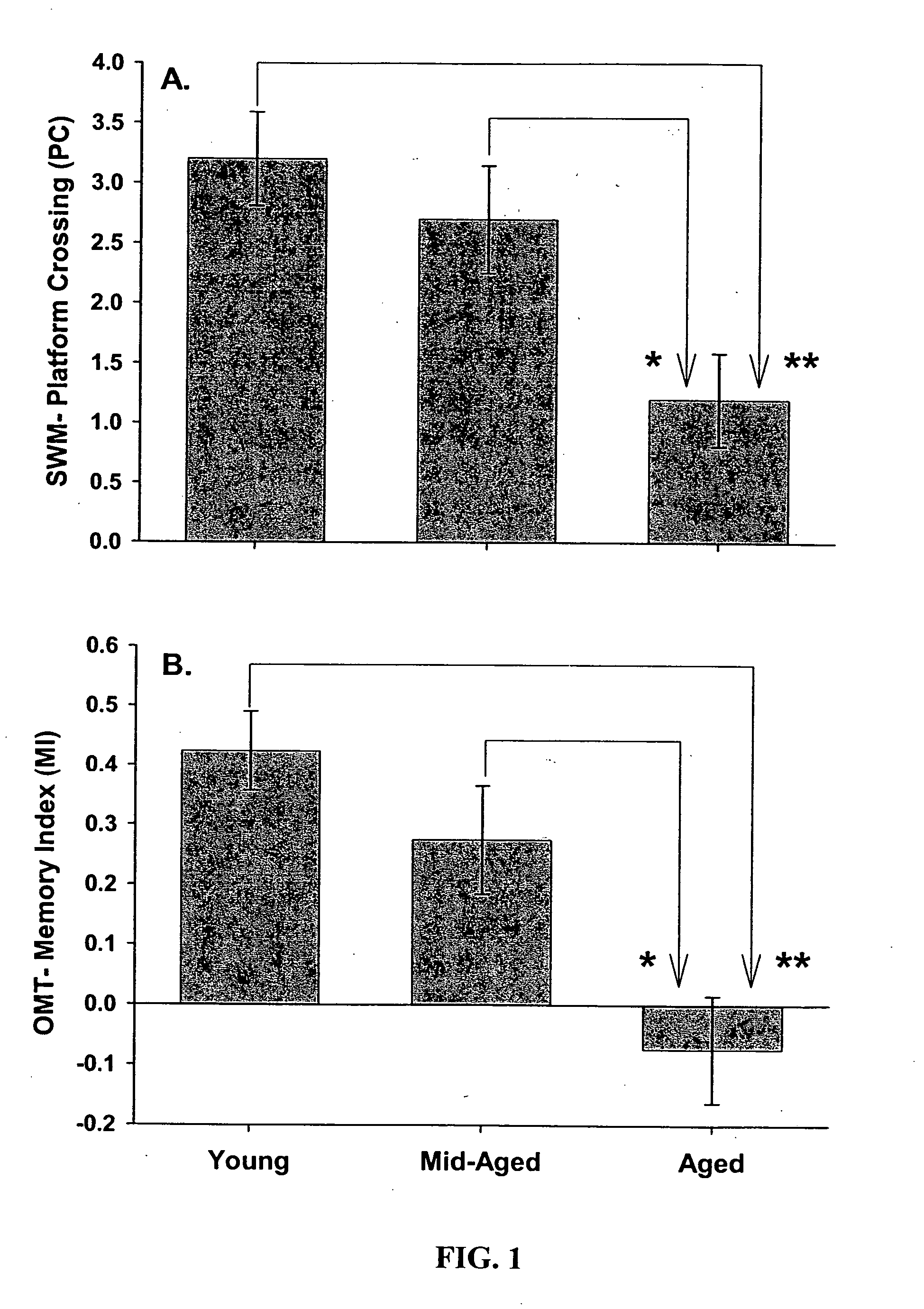
A statistical and functional correlation strategy to identify changes in cellular pathways specifically linked to impaired cognitive function with aging. Analyses using the strategy identified multiple groups of genes expressed in the hippocampi of mammals, where the genes were expressed at different levels for several ages. The aging changes in expression began before mid-life. Many of the genes were involved in specific neuronal and glial pathways with previously unrecognized relationships to aging and / or cognitive decline. The processes identified by the strategy suggest a new hypothesis of brain aging in which initially decreased neuronal activity and / or oxidative metabolism trigger separate but parallel genomic cascades in neurons and glia. In neurons, the cascade results in elevations in calcium signaling and reductions of immediate early gene signaling, biosynthesis, synaptogenesis and neurite remodeling. In contrast, glia undergo increased lipid metabolism and mediate a cycle of demyelination and remyelination that induces antigen presentation, inflammation, oxidative stress and extracellular restructuring. These identified genes and the proteins they encode can be used as novel biomarkers of brain aging and as targets for developing treatment methods against age-related cognitive decline, Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Genetically stable recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (RMVA) vaccines and methods of preparation thereof
ActiveUS20100316667A1Elicit immune responseVectorsSugar derivativesHeterologousModified vaccinia Ankara
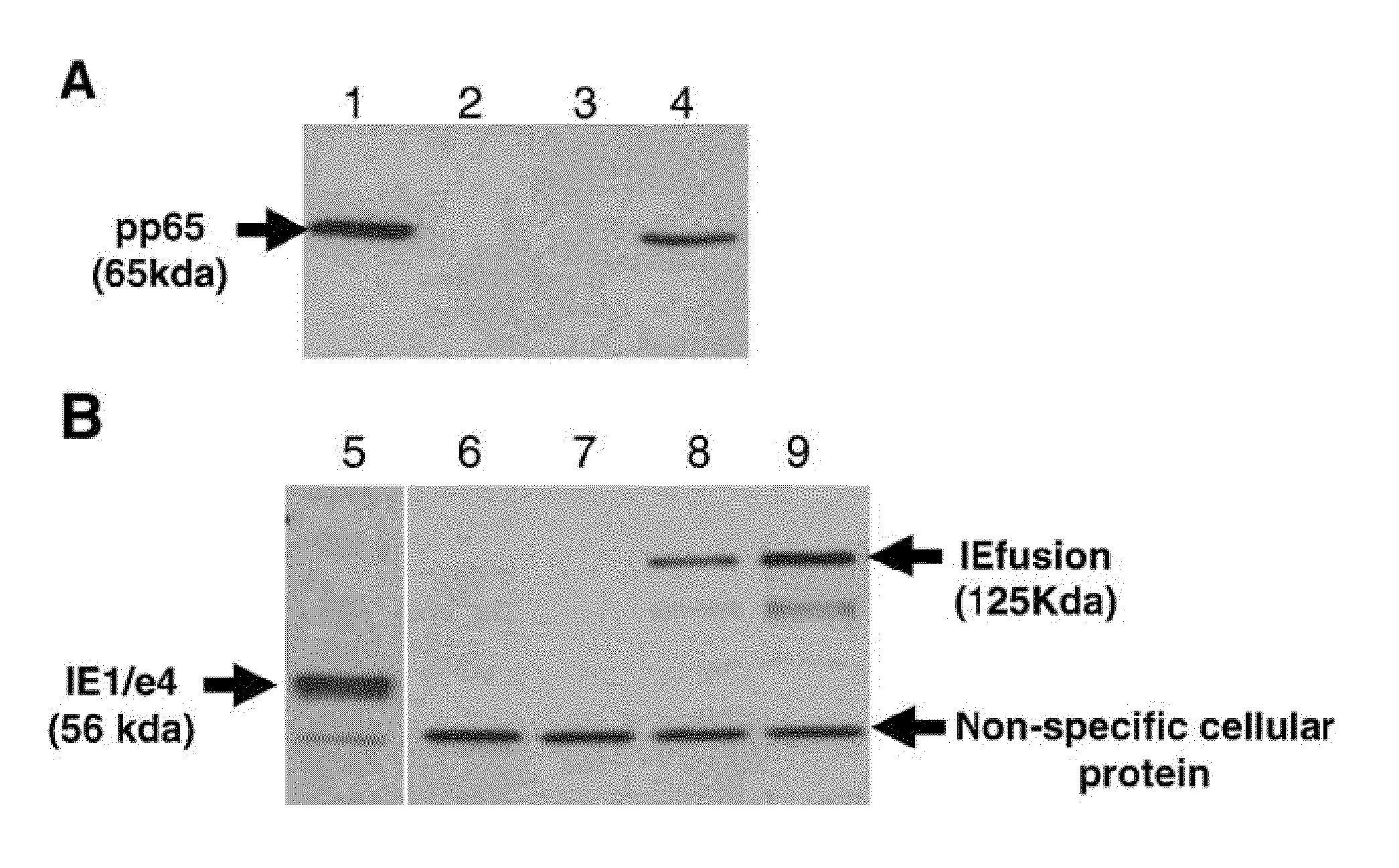
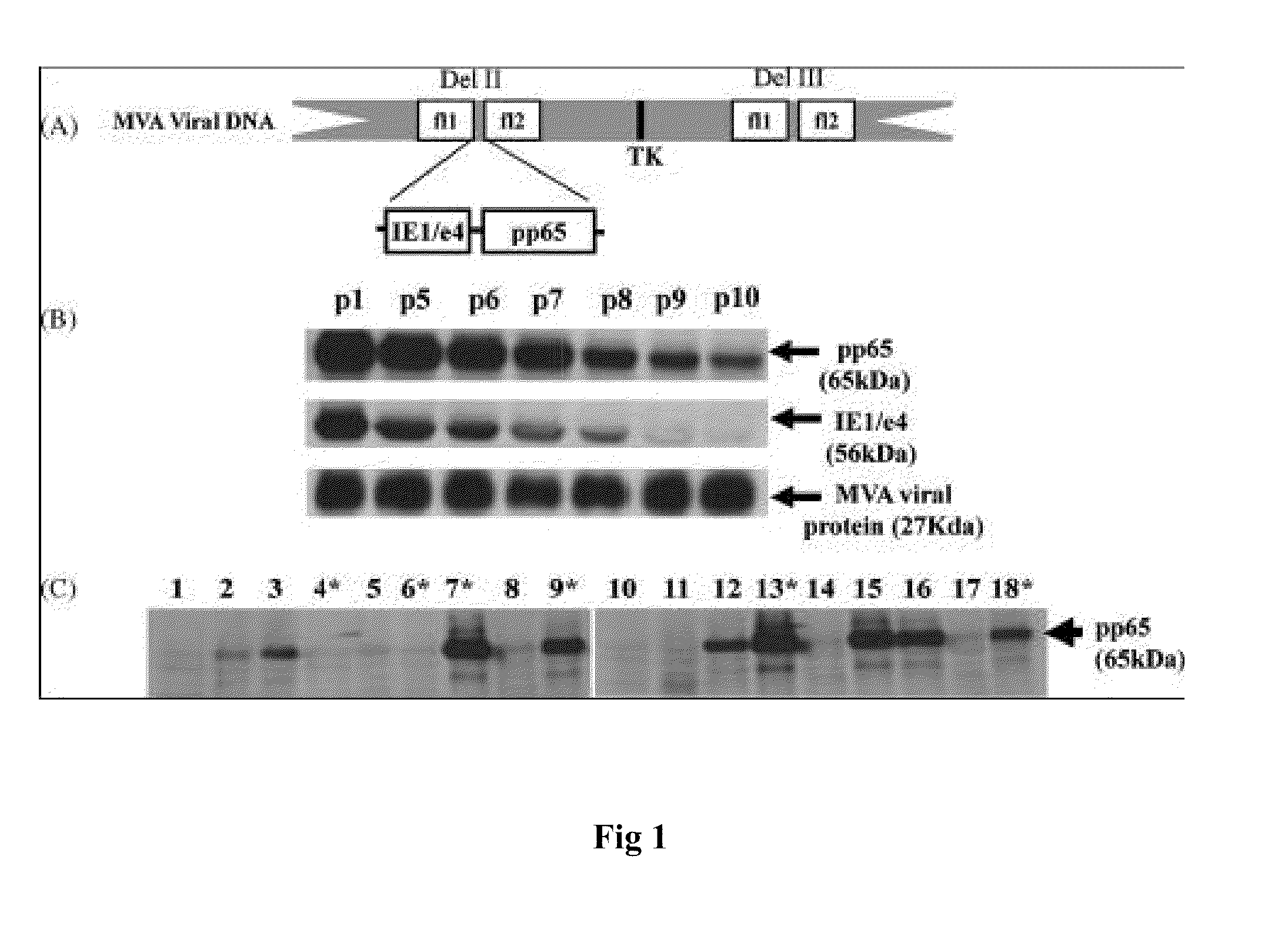
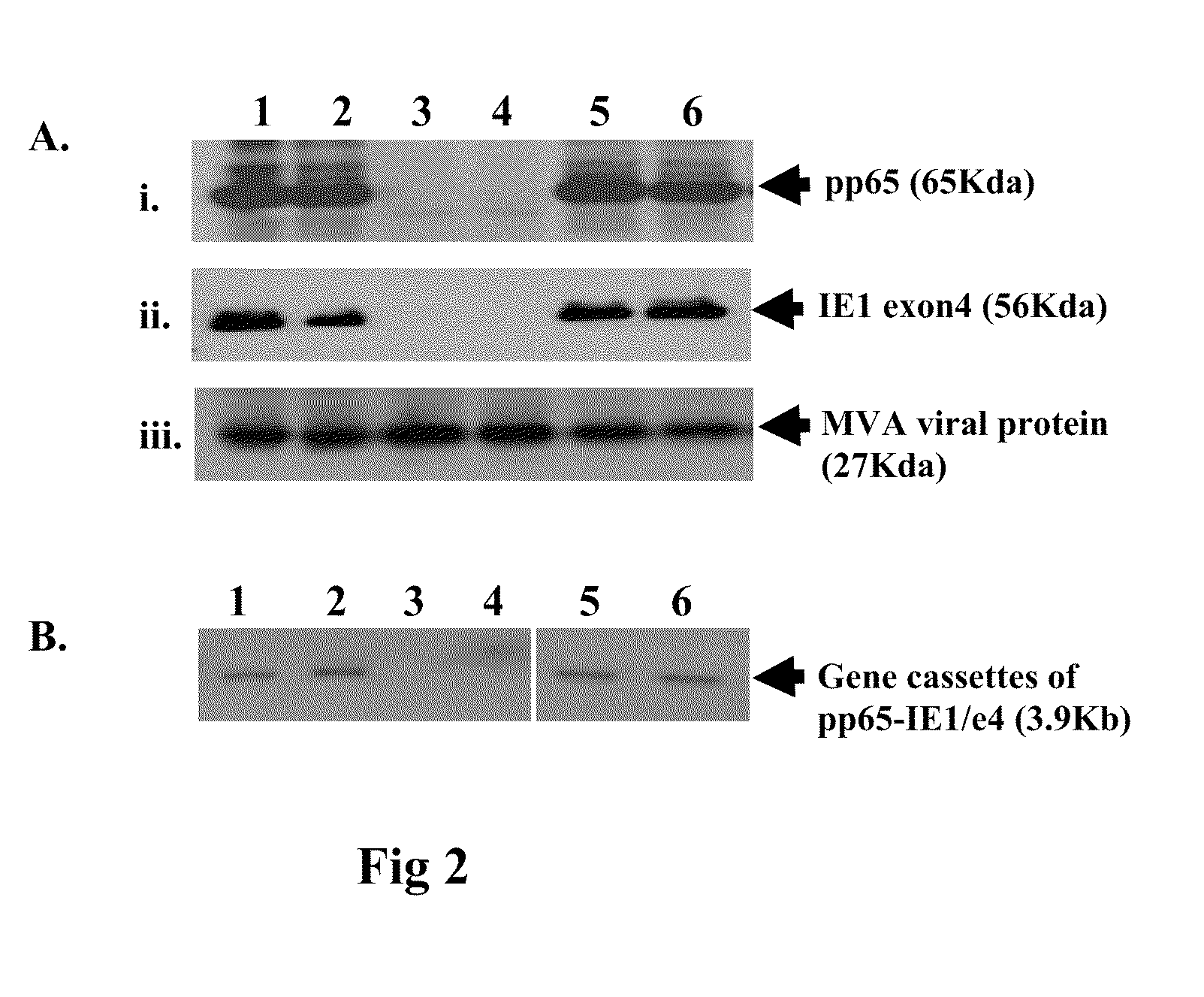
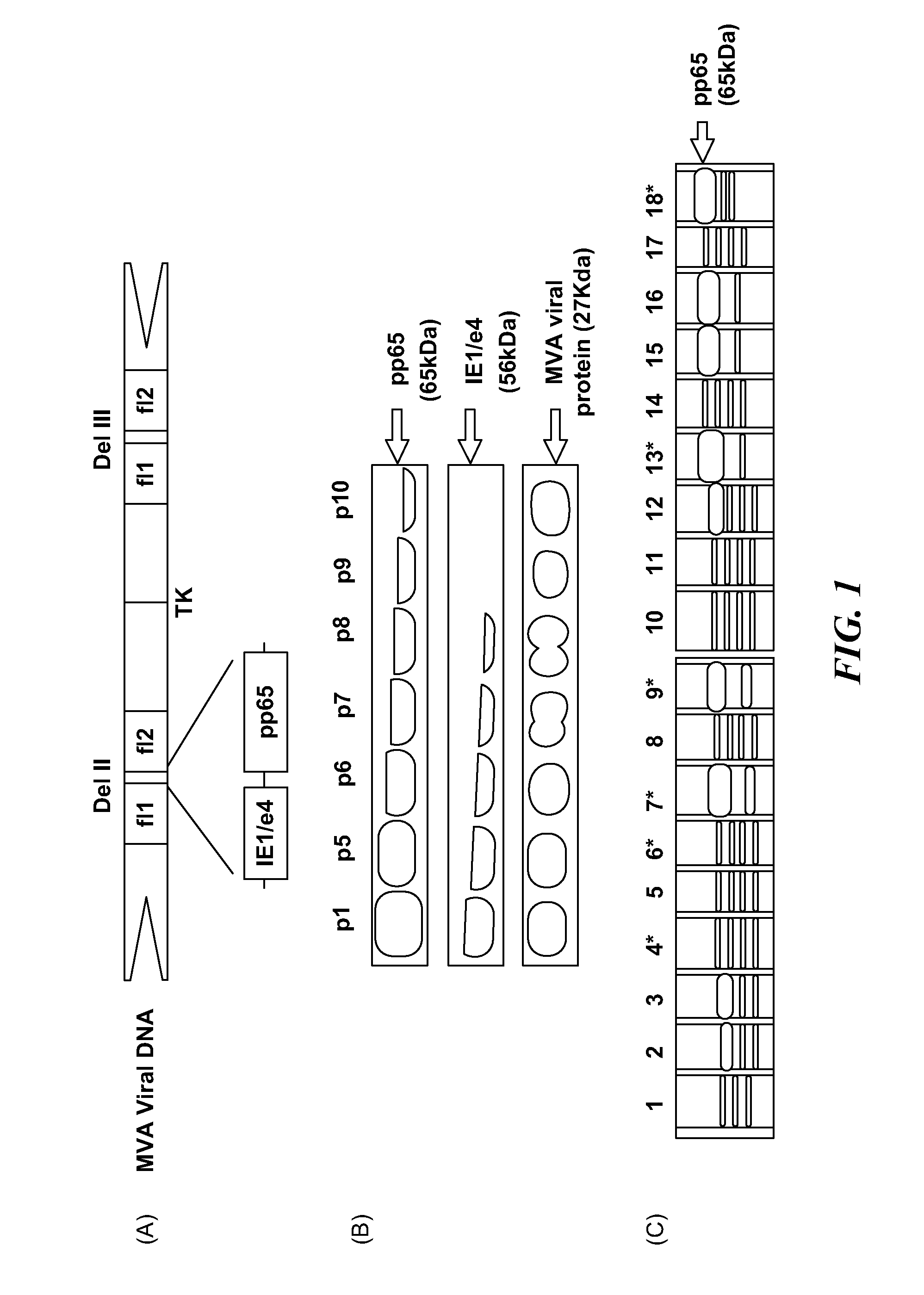
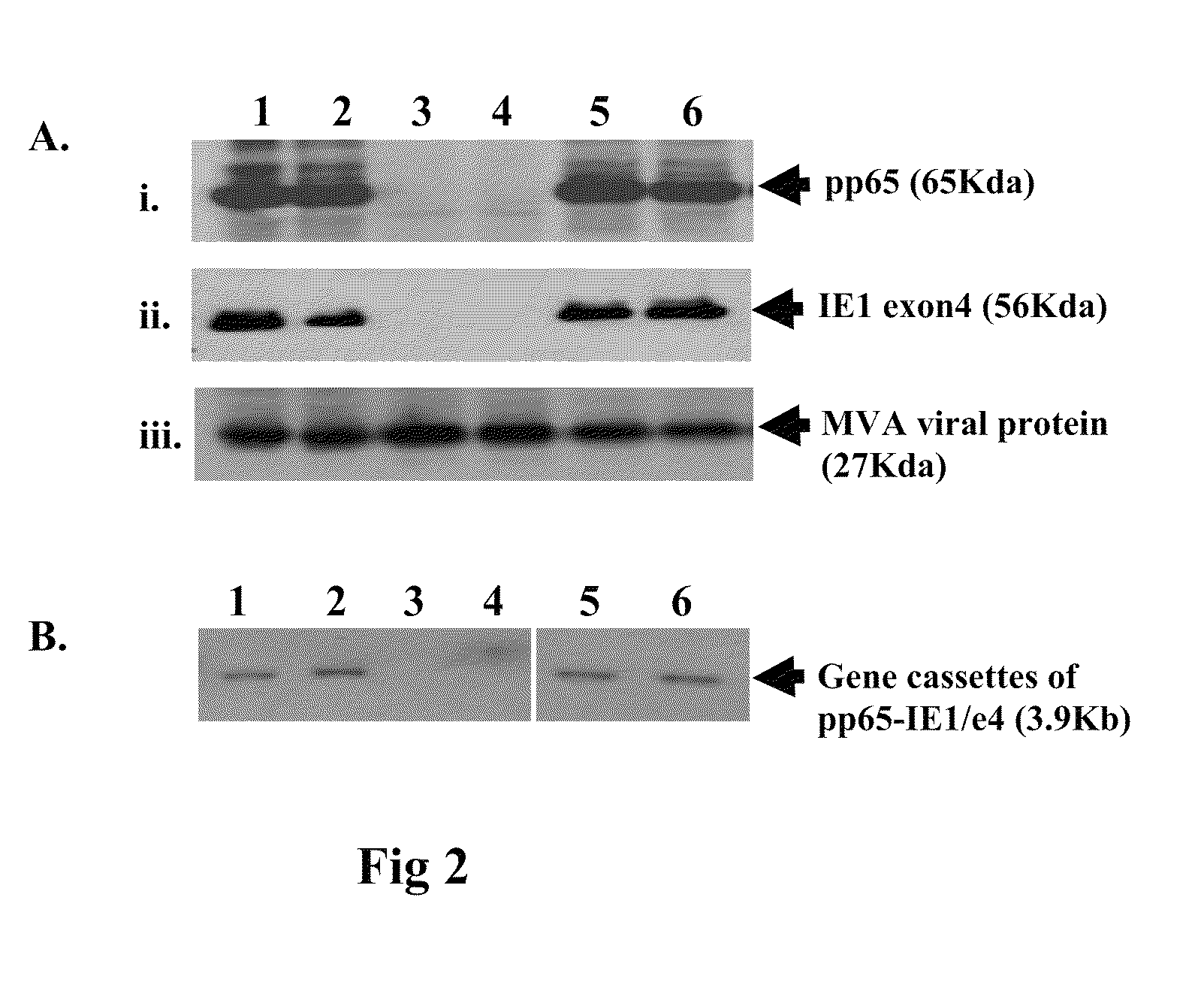
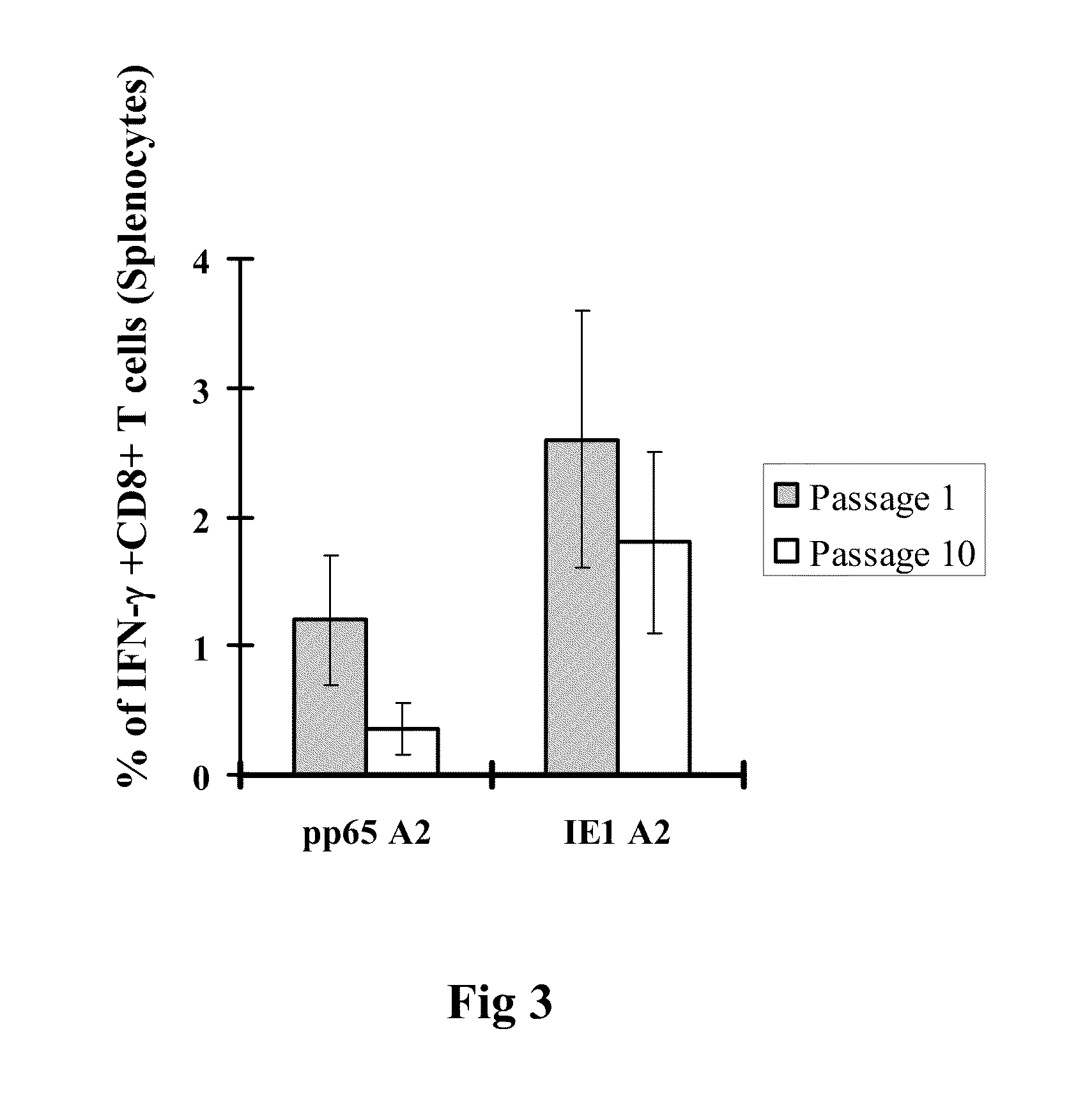
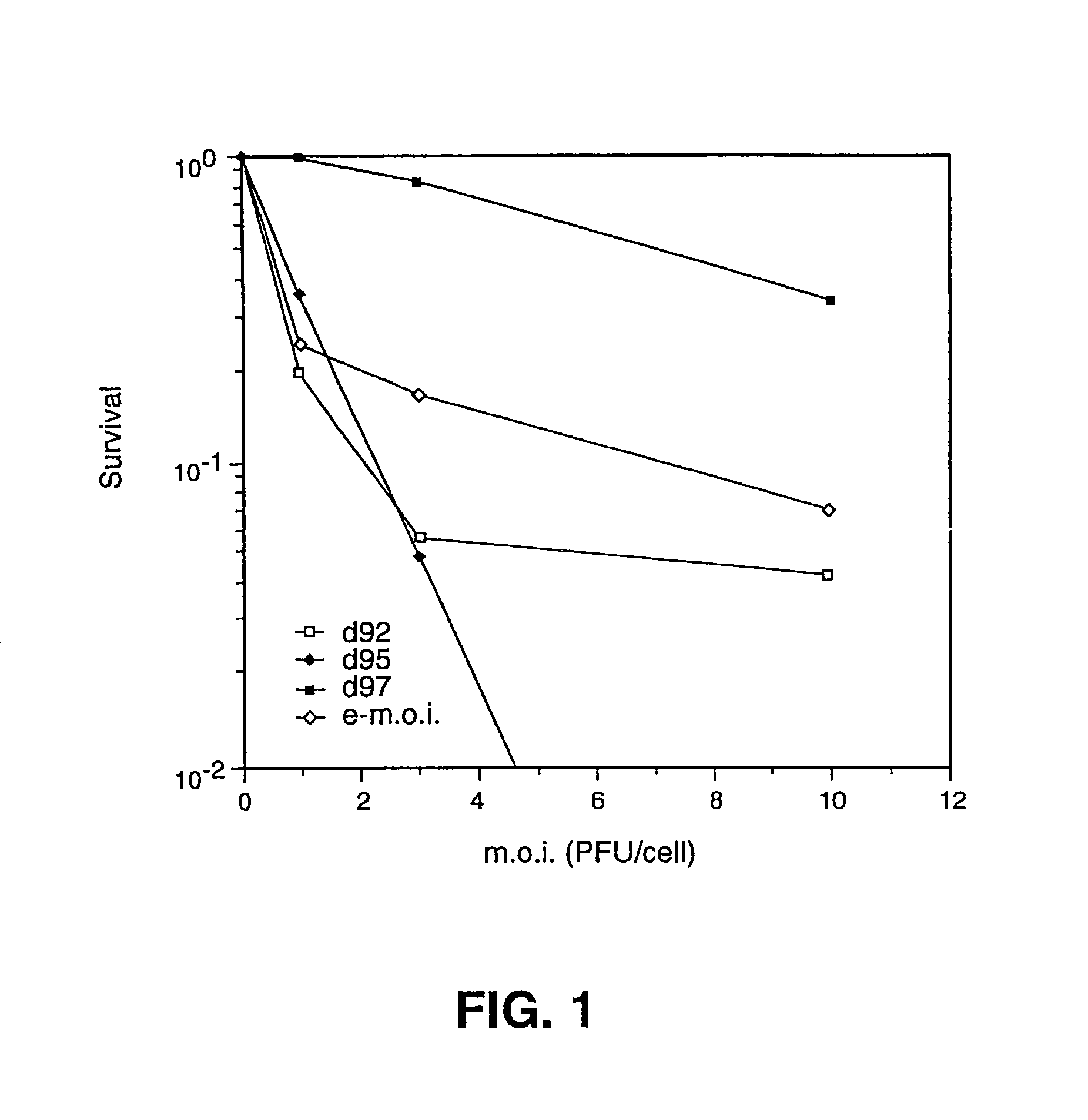
A vaccine comprising an immunologically effective amount of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (rMVA) virus which is genetically stable after serial passage and produced by a) constructing a transfer plasmid vector comprising a modified H5 (mH5) promoter operably linked to a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous foreign protein antigen, wherein the expression of said DNA sequence is under the control of the mH5 promoter; b) generating rMVA virus by transfecting one or more plasmid vectors obtained from step a) into wild type MVA virus; c) identifying rMVA virus expressing one or more heterologous foreign protein antigens using one or more selection methods for serial passage; d) conducting serial passage; e) expanding an rMVA virus strain identified by step d); and f) purifying the rMVA viruses from step e) to form the vaccine. One embodiment is directed to a fusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) protein antigen comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding two or more antigenic portions of Immediate-Early Gene-1 or Immediate-Early Gene-2 (IEfusion), wherein the antigenic portions elicit an immune response when expressed by a vaccine.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Genetically stable recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (rMVA) vaccines and methods of preparation thereof
A vaccine comprising an immunologically effective amount of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (rMVA) virus which is genetically stable after serial passage and produced by a) constructing a transfer plasmid vector comprising a modified H5 (mH5) promoter operably linked to a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous foreign protein antigen, wherein the expression of said DNA sequence is under the control of the mH5 promoter; b) generating rMVA virus by transfecting one or more plasmid vectors obtained from step a) into wild type MVA virus; c) identifying rMVA virus expressing one or more heterologous foreign protein antigens using one or more selection methods for serial passage; d) conducting serial passage; e) expanding an rMVA virus strain identified by step d); and f) purifying the rMVA viruses from step e) to form the vaccine. One embodiment is directed to a fusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) protein antigen comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding two or more antigenic portions of Immediate-Early Gene-1 or Immediate-Early Gene-2 (IEfusion), wherein the antigenic portions elicit an immune response when expressed by a vaccine.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Herpes simplex virus strains
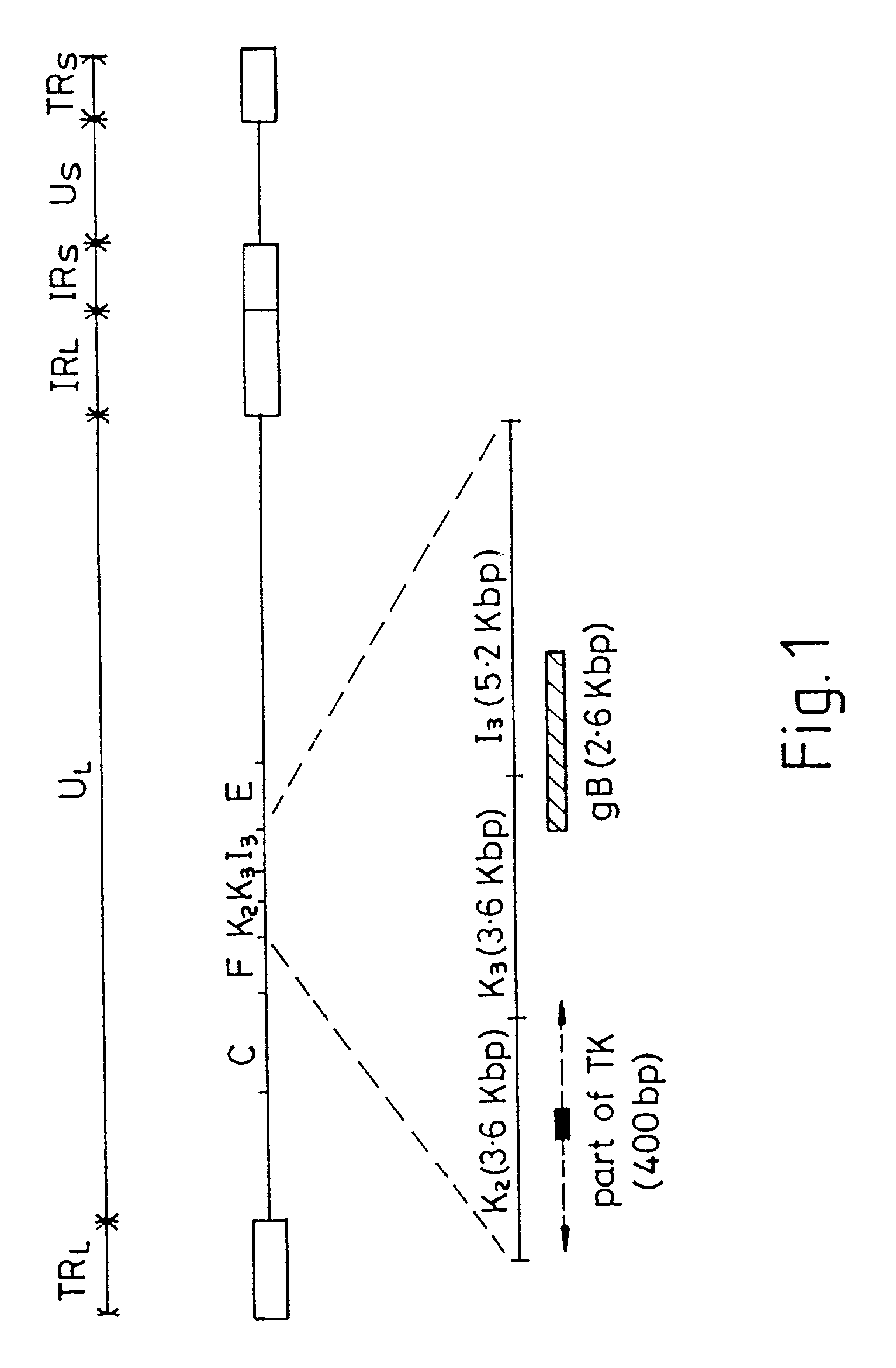
InactiveUS7078029B2Reduction in wild-type reversionInterference minimizationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene productEarly response gene
The present invention provides an HSV having a genome with a mutation of a TAATGARAT sequence such that, in the presence of a ICP4 gene product, a native immediate early gene is expressed from the genome with delayed kinetics, the genome having a further inactivating mutation of each of the genes encoding ICP4.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Replication incompetent herpes viruses for use in gene therapy
InactiveUS6821753B2Minimize the possibilityReduced activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseGene delivery
Use of a replication incompetent herpes virus capable of delivering a gene to multiple connected sites within the nervous system, which virus comprises: (a) a mutation which prevents or reduces the expression of at least two immediate early genes; and (b) a heterologous gene operably linked to a promoter active during herpes virus latency; in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a central nervous system disorder, a method of determining whether a gene has an effect on a phenotype associated with a central nervous system disorder and in a method of treatment of a disorder of the central nervous system are described.
Owner:BIOVEX LTD
Replication incompetent herpes viruses for use in gene therapy
InactiveUS20030082142A1Minimize the possibilityReduced activityBiocideNervous disorderGene deliveryHeterologous
Use of a replication incompetent herpes virus capable of delivering a gene to multiple connected sites within the nervous system, which virus comprises: (a) a mutation which prevents or reduces the expression of at least two immediate early genes; and (b) a heterologous gene operably linked to a promoter active during herpes virus latency; in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a central nervous system disorder, a method of determining whether a gene has an effect on a phenotype associated with a central nervous system disorder and in a method of treatment of a disorder of the central nervous system are described.
Owner:BIOVEX LTD
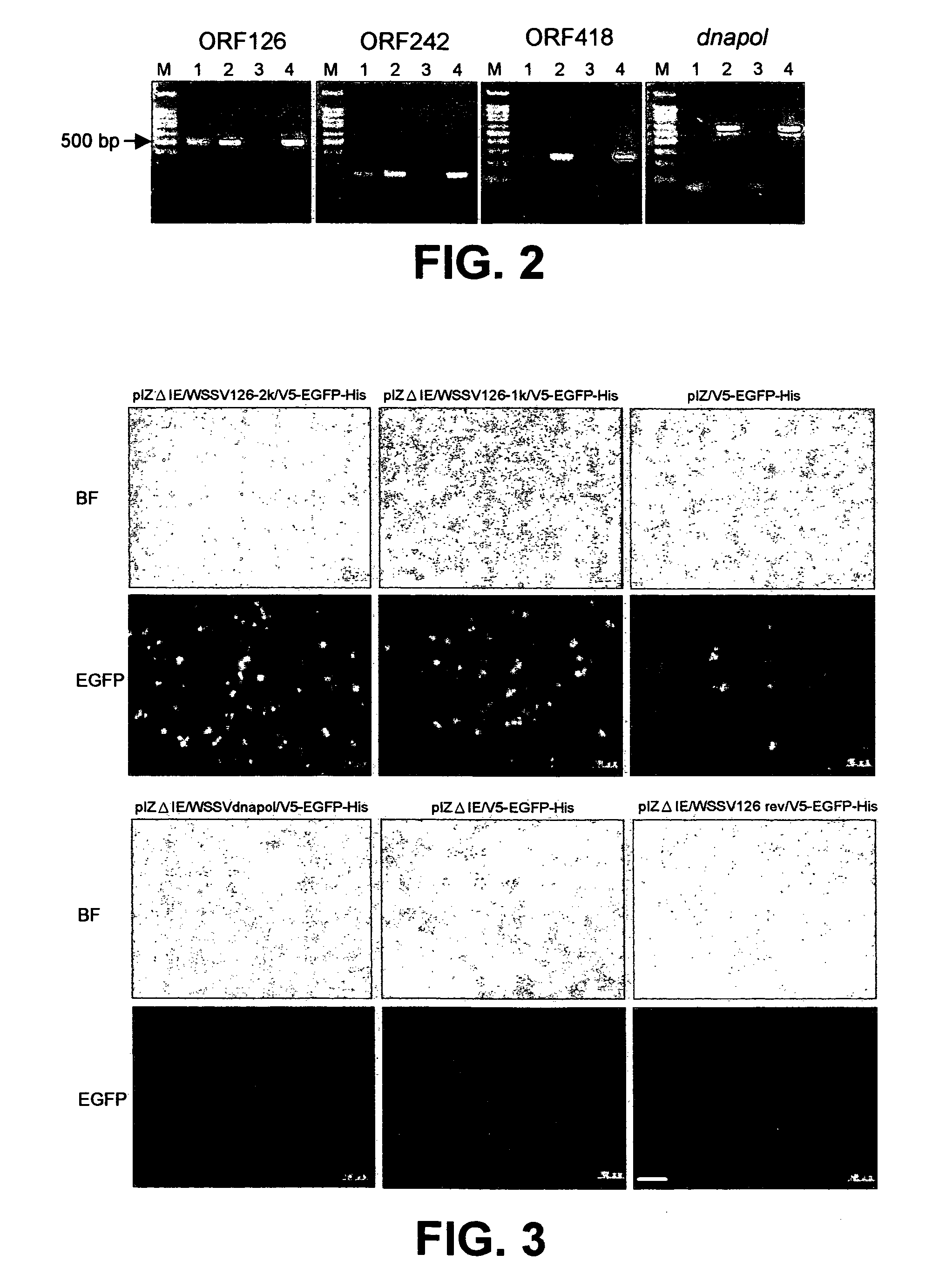
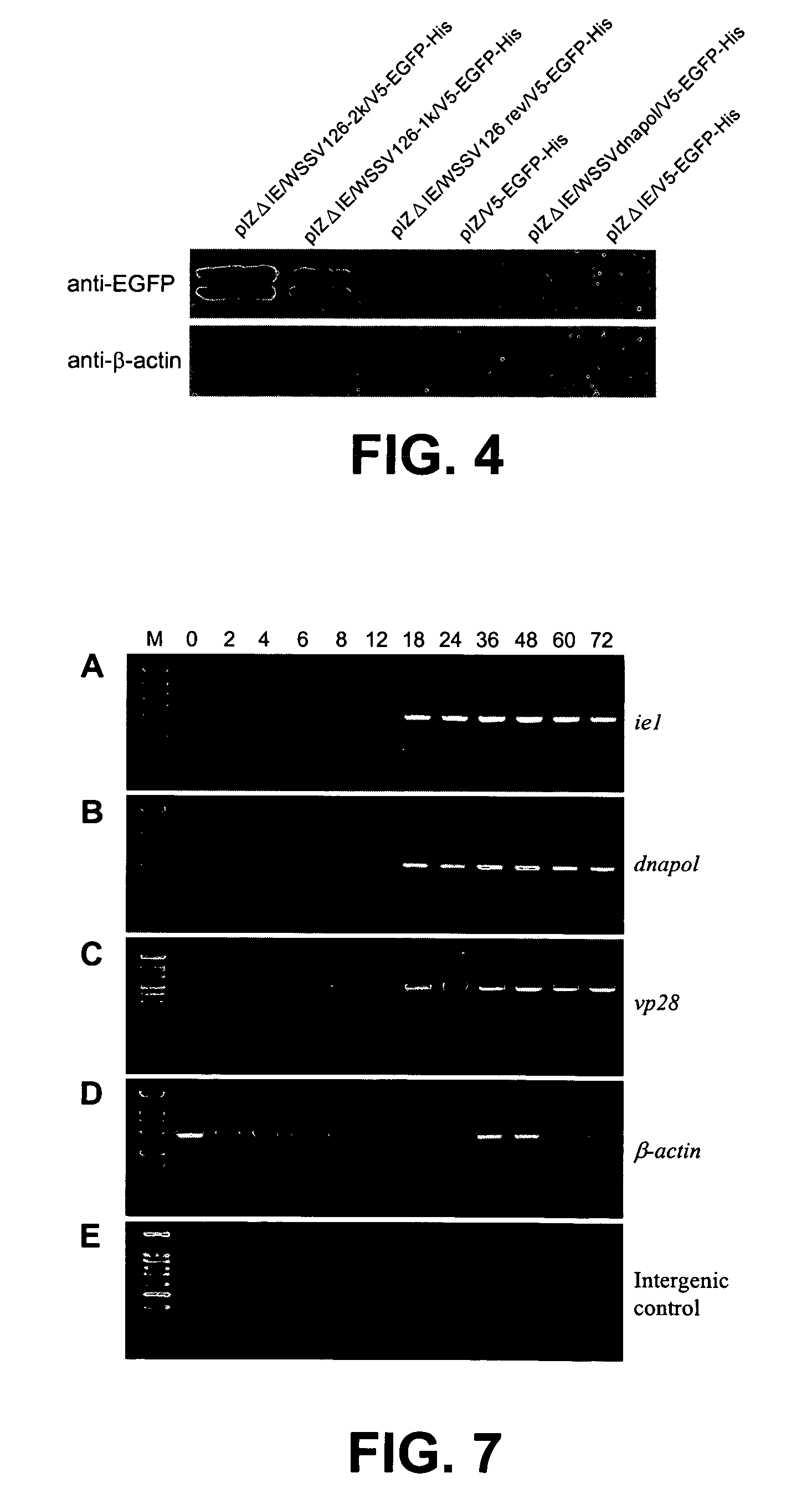
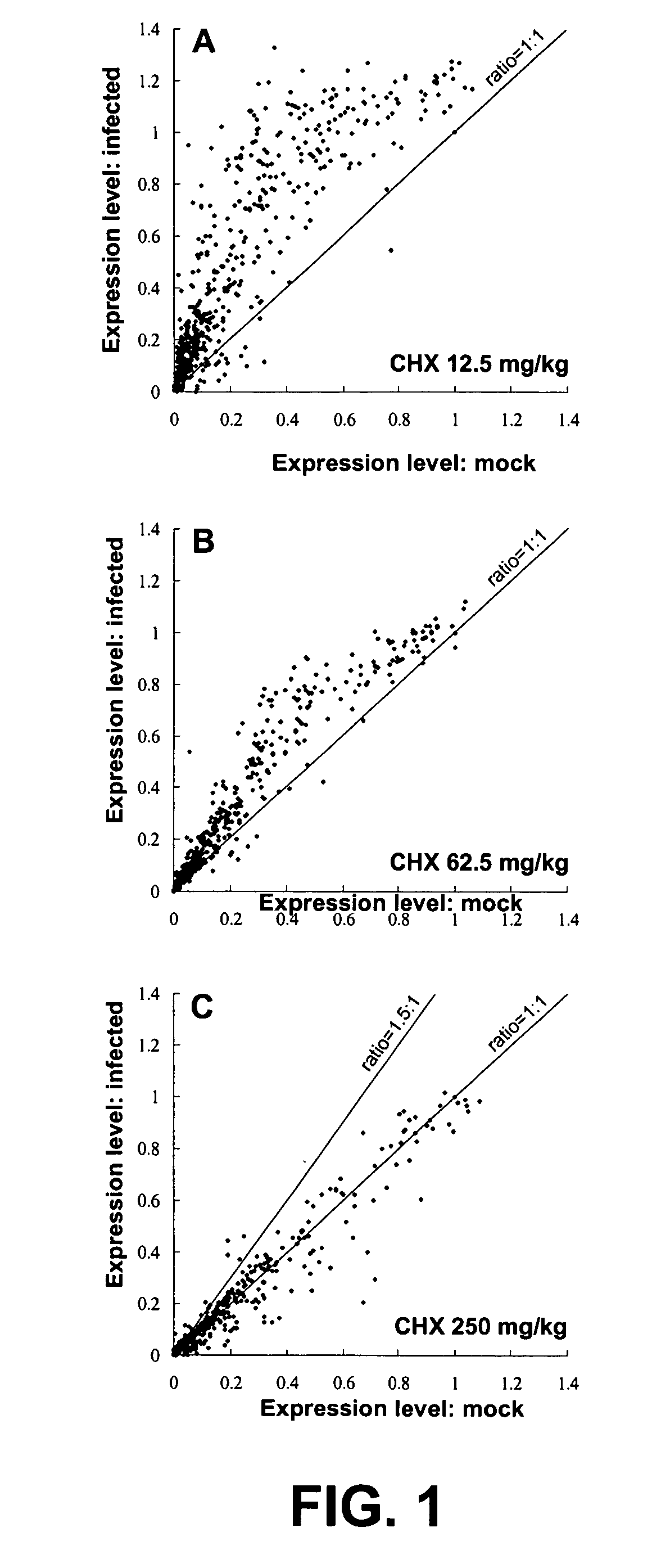
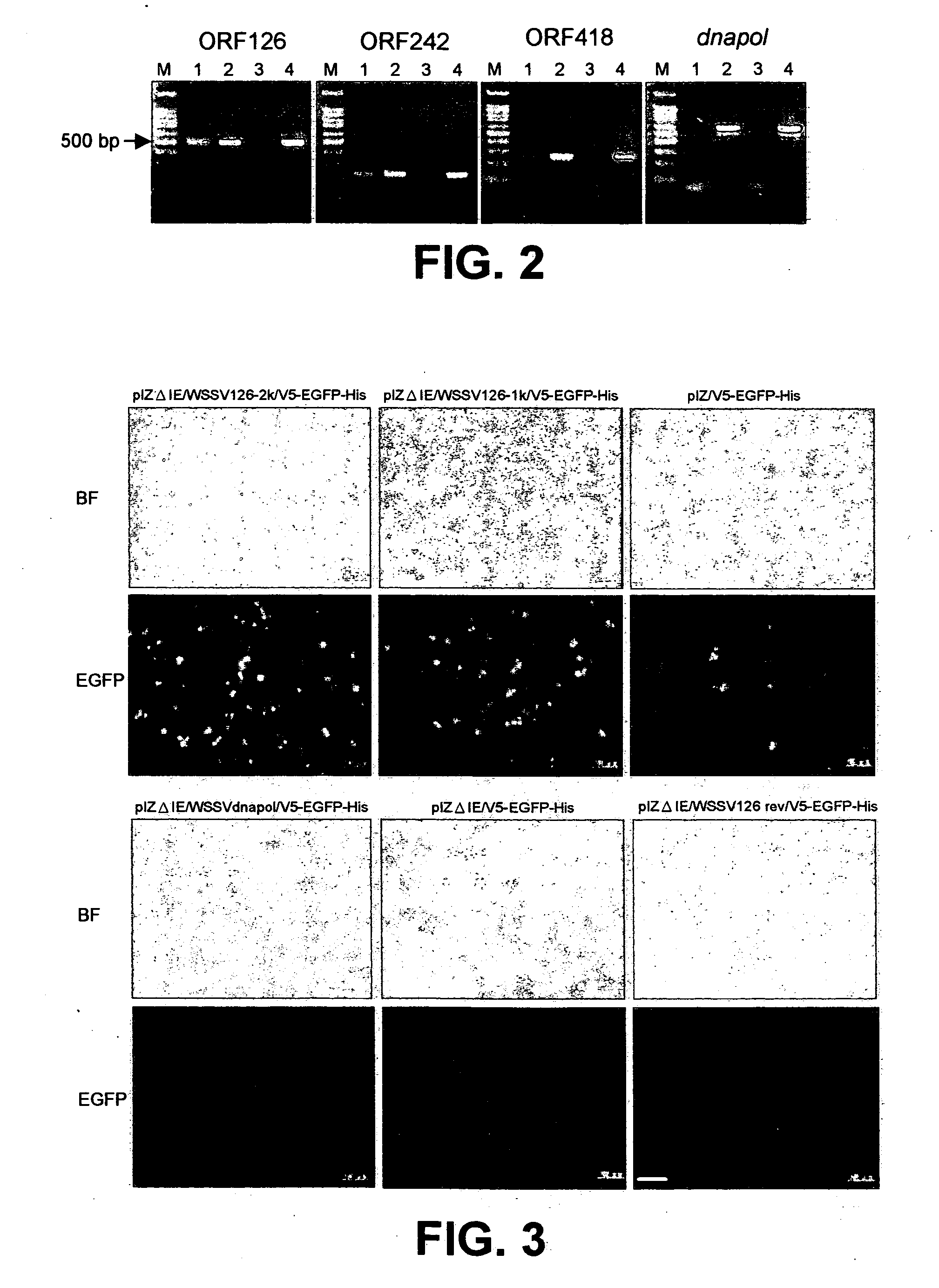
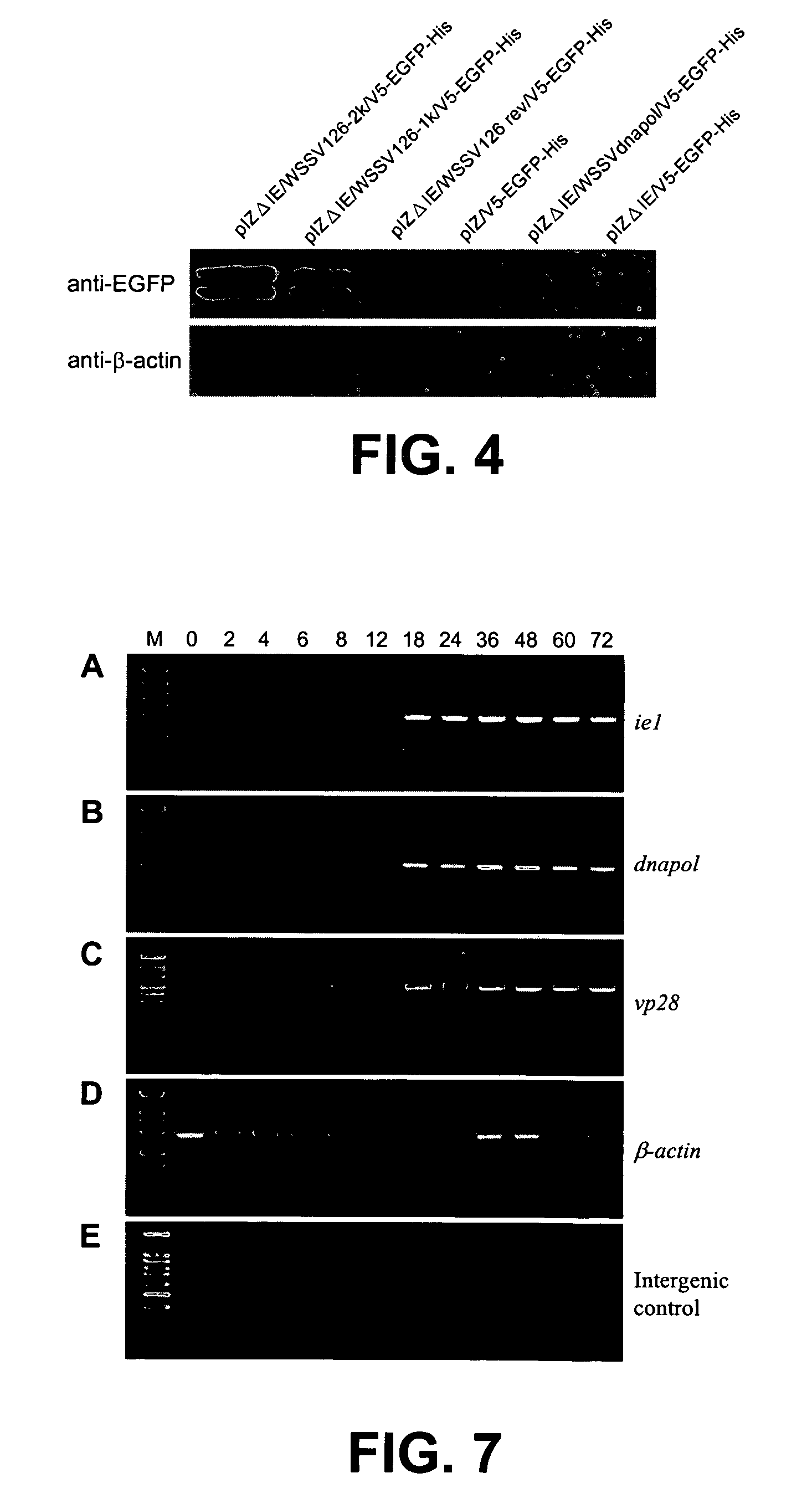
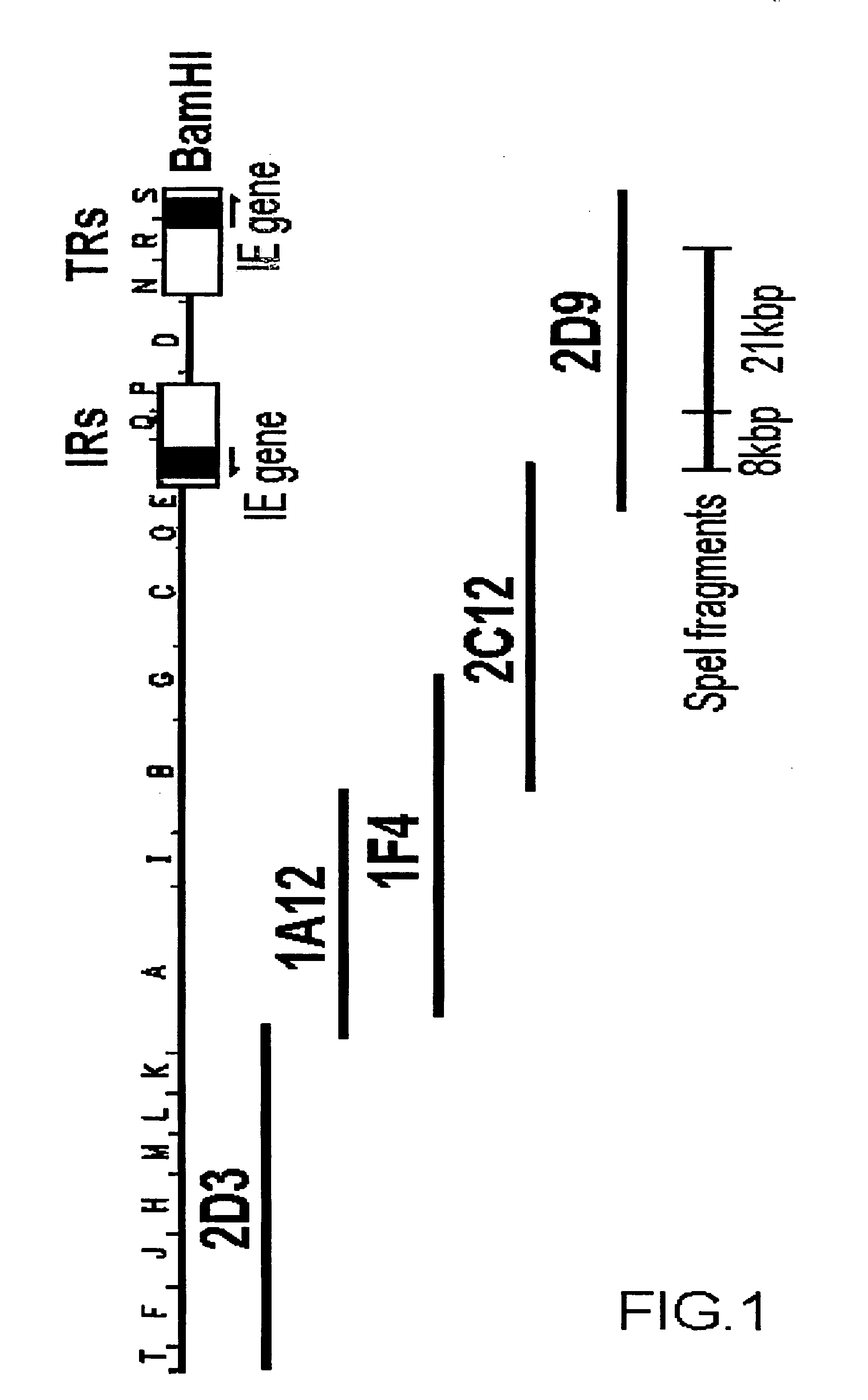
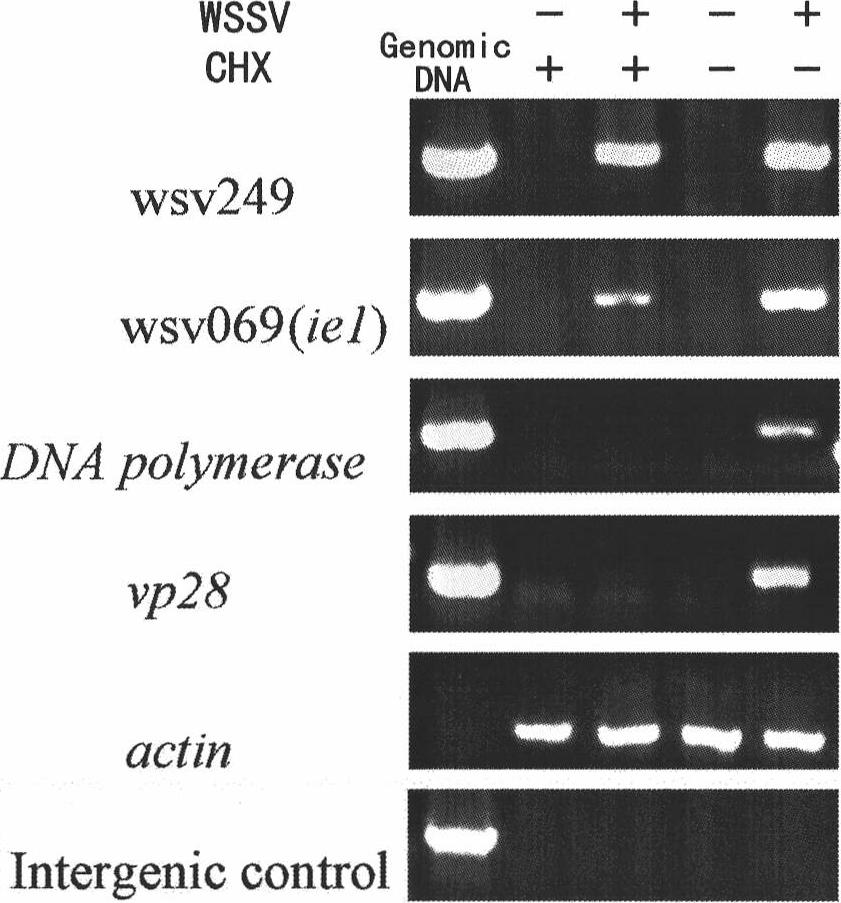
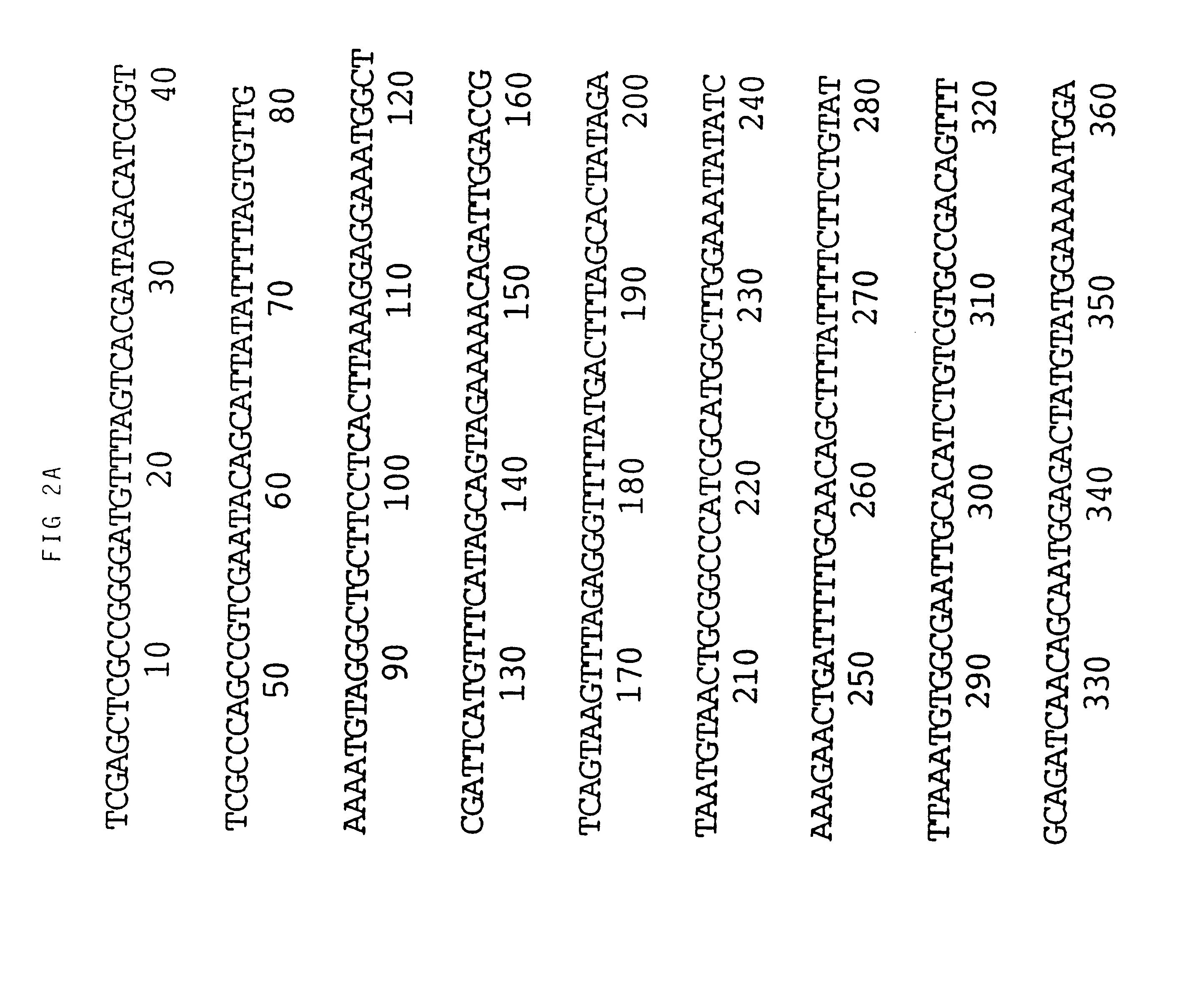
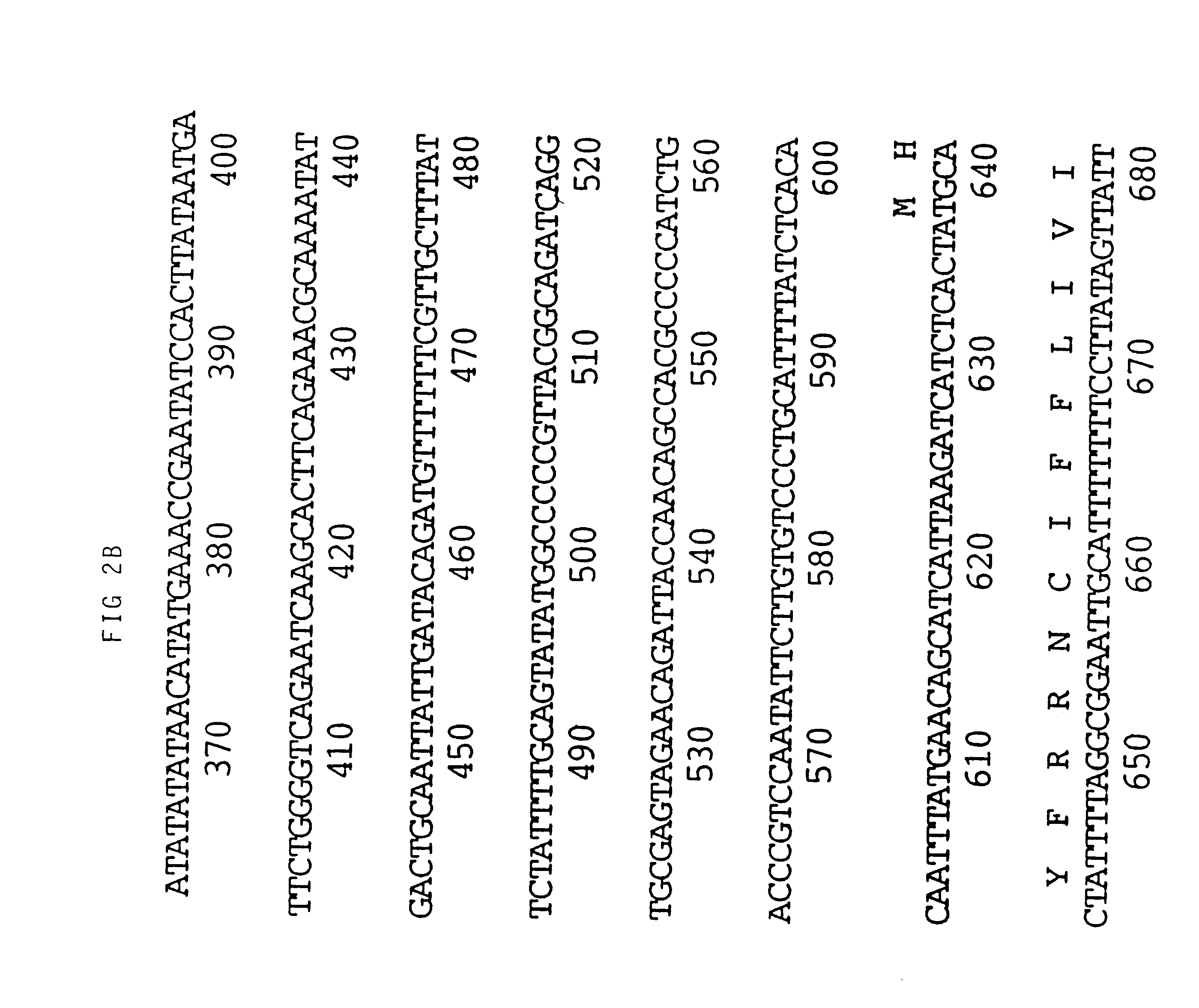
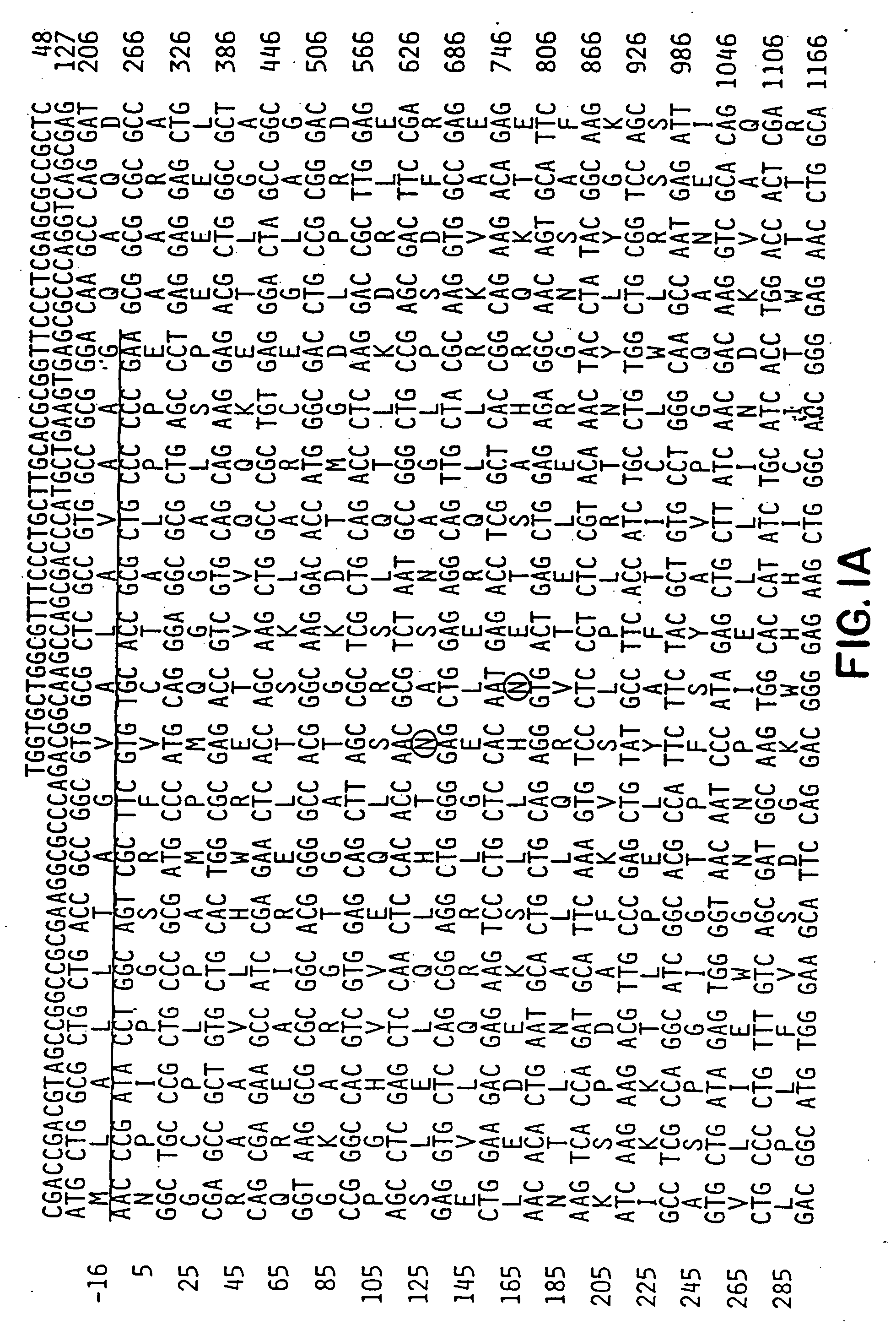
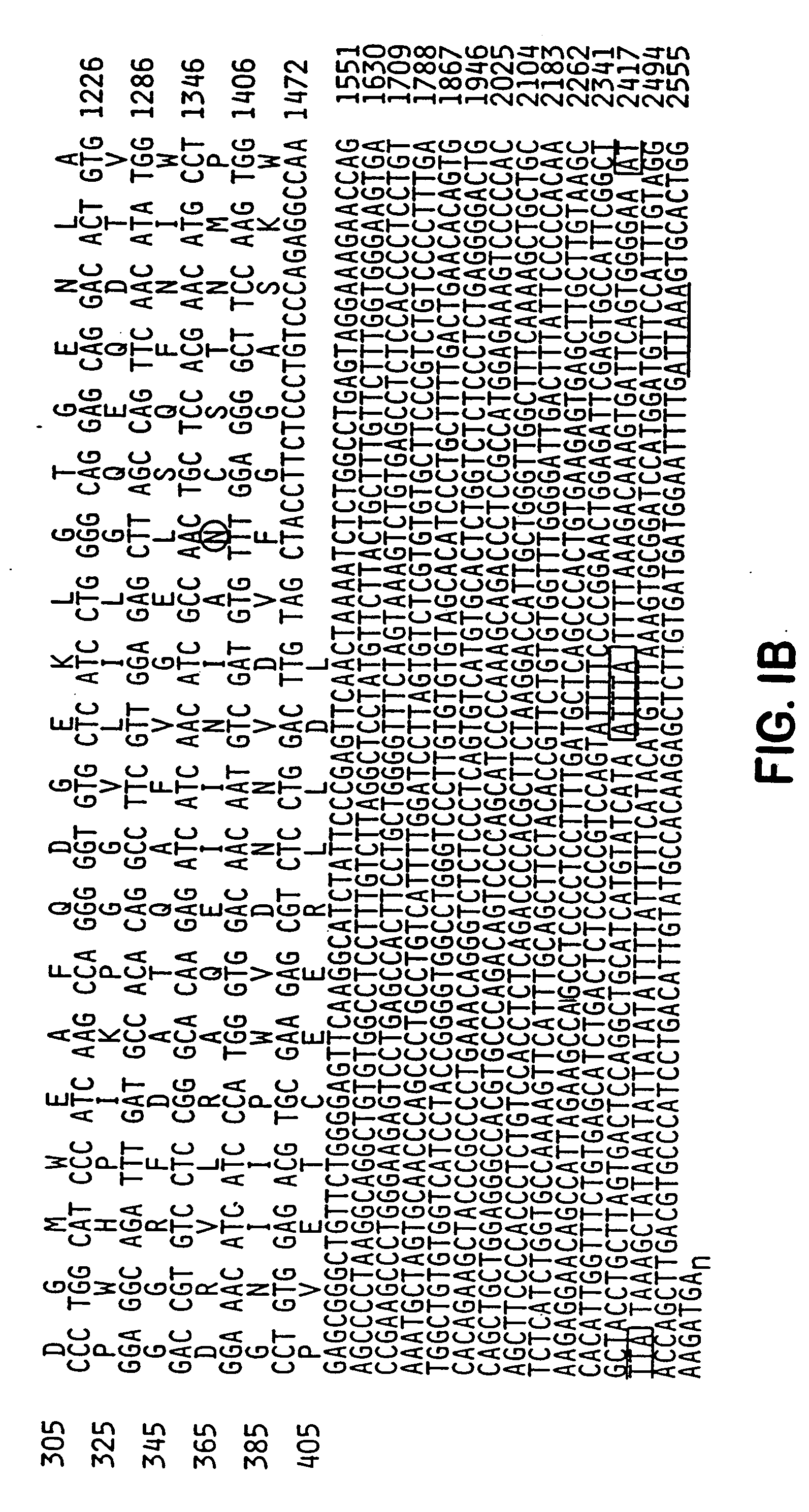
Promoter sequences from WSSV immediate early genes and their uses in recombinant DNA techniques
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Promoter sequences from WSSV immediate early genes and their uses in recombinant DNA techniques
Disclosed herein are isolated promoter-regulatory regions from a newly identified WSSV immediate early (IE) gene, ie1 (immediate early gene #1), which exhibit promoter activity to drive the transcription of a target gene in non-native host cells. The isolated promoter-regulatory regions can be used in the construction of a variety of recombinant expression vectors for transforming a broad spectrum of host cells.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
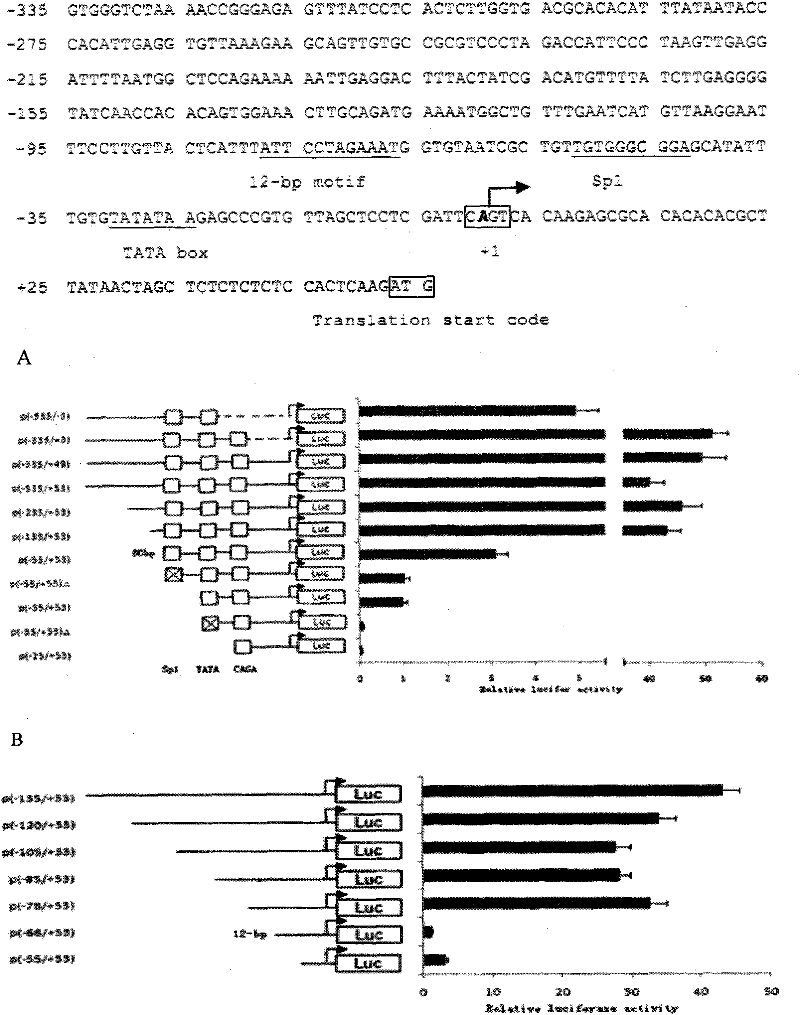
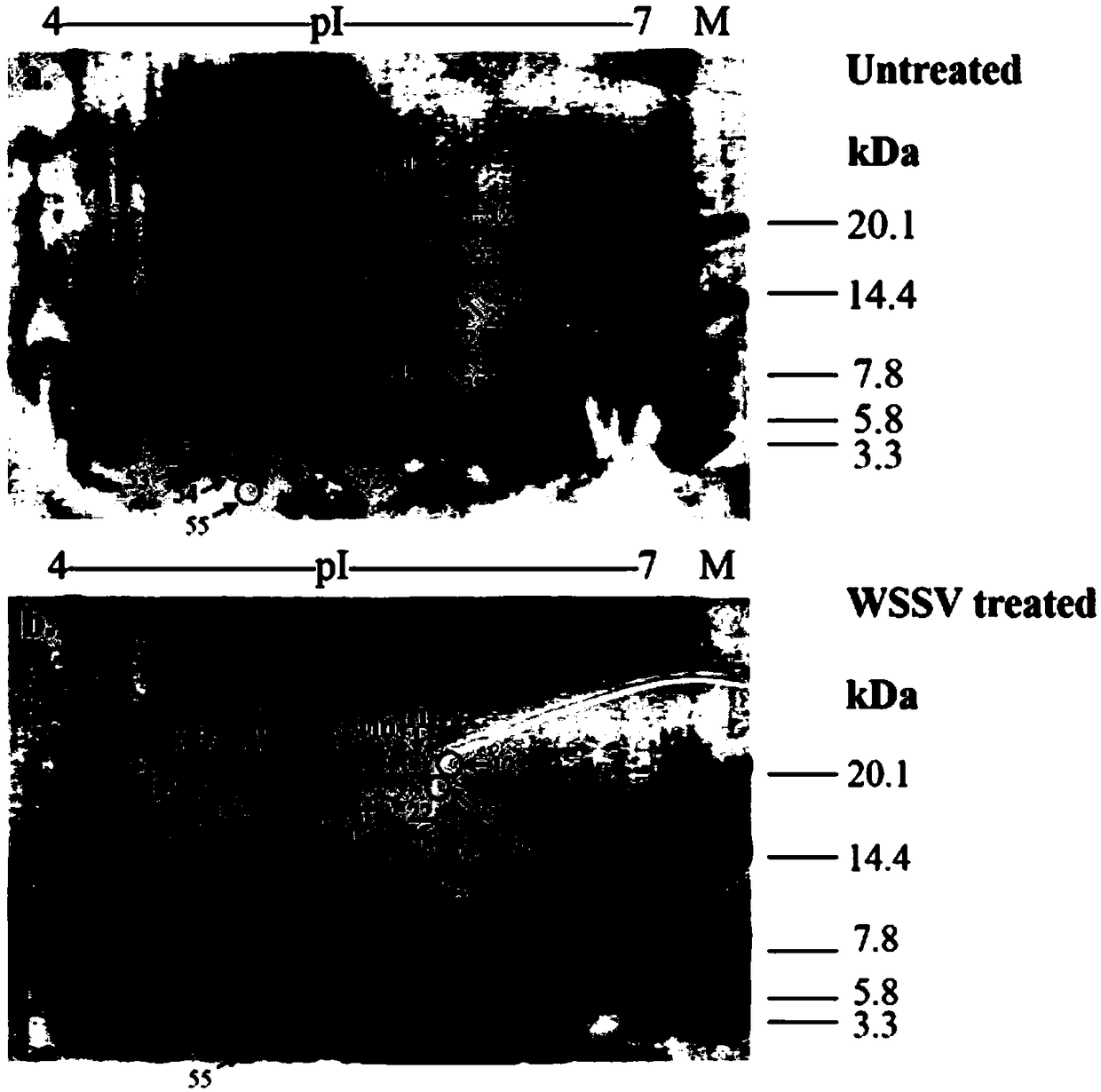
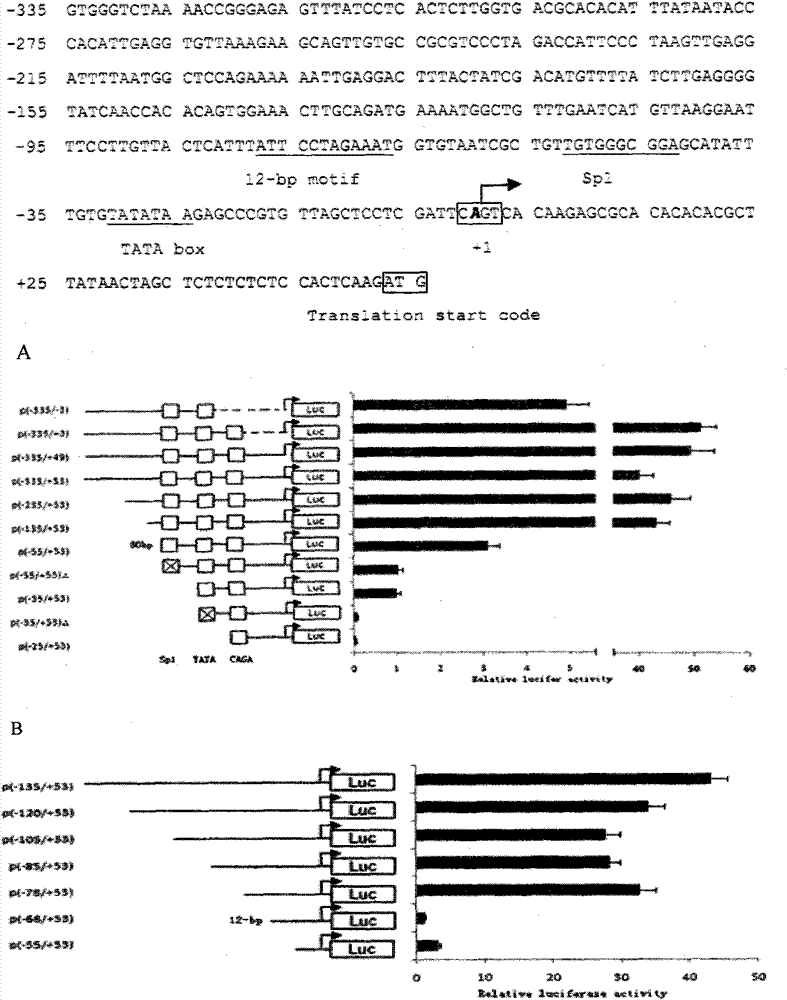
Main cis-acting element of shrimp white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) iel promoter and transcription factor combined with same and application
InactiveCN102174518APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEffective actionWhite spot syndrome
The invention discloses a main cis-acting element of a shrimp white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) iel promoter and a transcription factor combined with the same and application. In the invention, by starting from transcriptional regulation of WSSV iel and carrying out structural and functional analysis on the promoter of the WSSV iel through deletion and mutation, a 12-bp DNA is found to be the maincis-acting element of the WSSV iel and is a crucial factor for the high expression of the iel. In the invention, a DNA affinity chromatography method is used for purifying a protein combined with a DNA segment from a nucleus protein Sf9, the protein is identified to be PHB2 (Poly-Beta-Hydroxybutyrate 2) through biological mass spectrometry, and the interaction between the protein and the DNA segment is proved to be specific by an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Experiment results prove that PHB2 serves as a transcription factor and is specifically combined with a 12-bp DNA sequence of the iel promoter to start WSSV immediate early gene transcription so as to further regulate the replication of the WSSV, and can be used as an effective action target of medicaments for screening medicaments for resisting the shrimp WSSV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
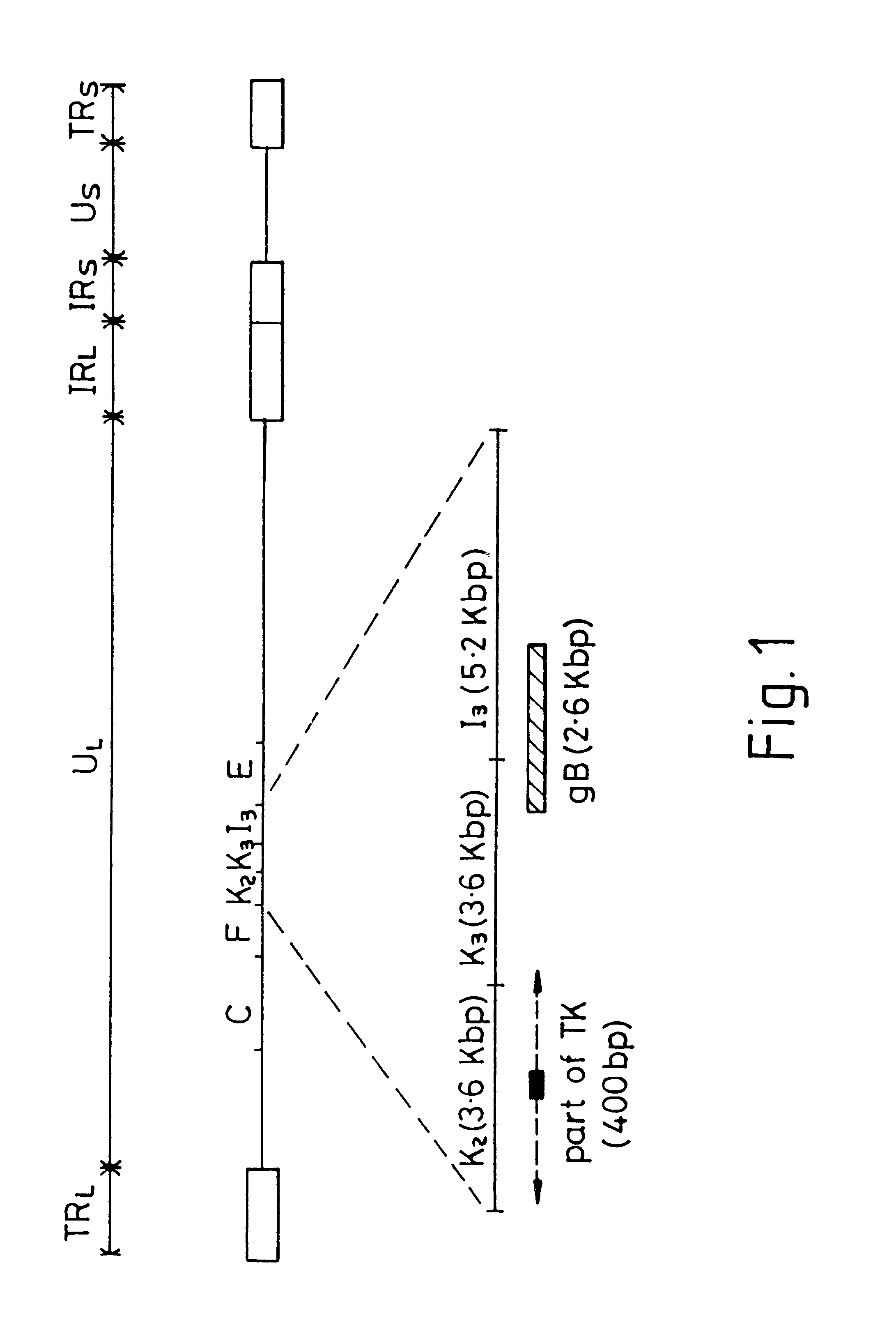
Attenuated equine herpesvirus
InactiveUS7060282B1Reduced virulenceViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesVirulent characteristicsViral Genes
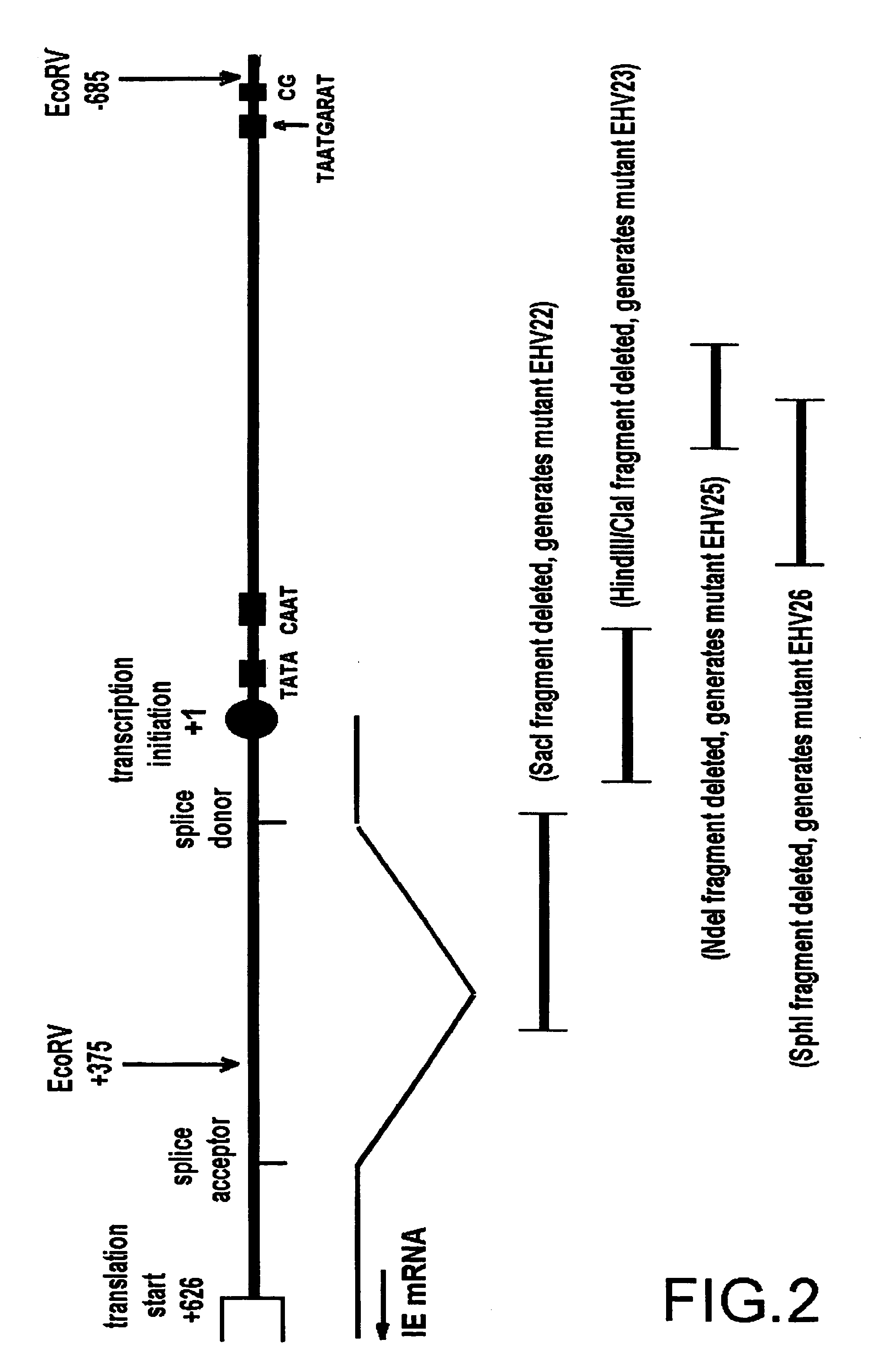
The present invention relates to novel Equine herpesvirus (EHV) mutants comprising one or more deletions, substitutions, or insertions in the endogenous promoter region of an essential viral gene, preferably the immediate early gene of EHV. The EHV mutants are stable and have reduced virulence, which makes them very suitable for use in a live vaccine. The invention furthermore relates to live vaccines comprising said EHV mutants, to DNA sequences and vectors harbouring a mutated EHV sequence, to host cells transfected with said DNA or vectors. The invention also relates to a method of attenuating EHV in general, and EHV-1 in particular.
Owner:INTERVET INT BV
Nucleic acid constructs
A nucleic acid construct comprising a chimeric promoter sequence and a cloning site for inserting a coding sequence operably linked to the chimeric promoter, wherein the chimeric promoter sequence includes: (a) hCMV immediate early promoter sequence (b) exon 1 and at least a part of exon 2 of the hCMV major immediate early gene; (c) replacing a heterologous intron in the intron A region of the hCMV major immediate early gene.
Owner:POWDER JECT VACCINES INC
Synthetic Herpes Simplex Viruses Type-1 for Treatment of Cancers
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Universal strong promoter among species derived from white spot syndrome virus and application thereof
InactiveCN101818149AImprove efficiencyImprove general performanceVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsProtein targetWhite spot syndrome
The invention relates to a universal strong promoter among species derived from white spot syndrome virus and an application thereof. The invention provides the universal strong promoter among the species derived from the white spot syndrome virus, two primers of the strong promoter, an expression vector of the strong promoter and recombinant host cells of the expression vector. The promoter is an immediate early gene promoter of the white spot syndrome virus and can high-efficiently start the expression of downstream genes in insect cells, mammalian cells and the white spot syndrome virus host cells (including cells of crayfish and shrimp). The recombinant host cells are obtained by transfection of the expression vector containing the universal strong promoter among the species derived from the white spot syndrome virus in the host cells, and the recombinant host cells can express target protein genes controlled by the universal strong promoter among the species derived from the white spot syndrome virus.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
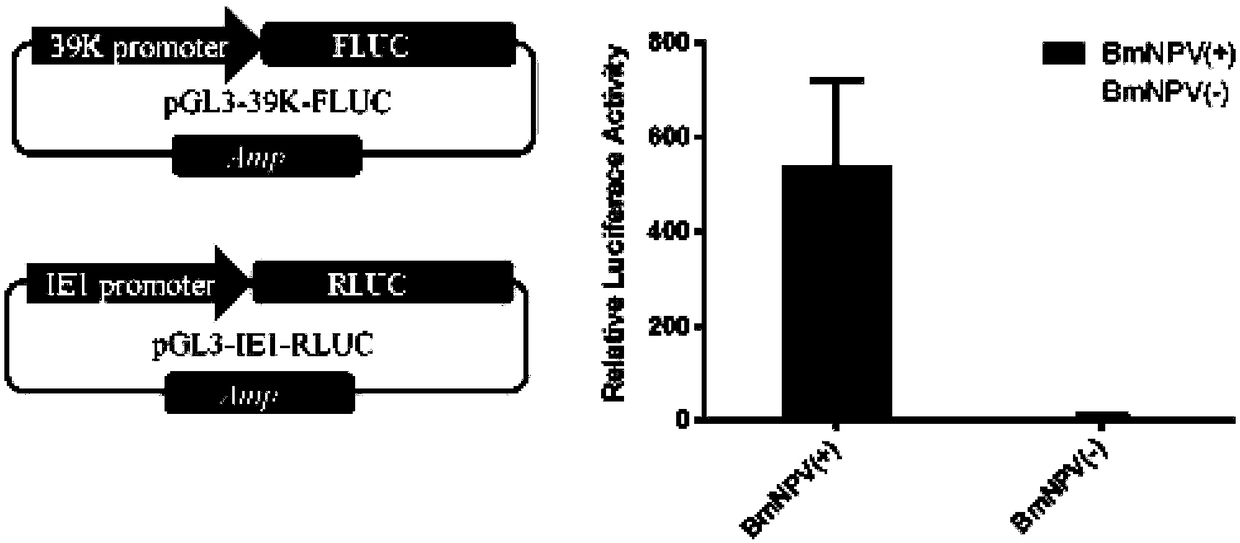
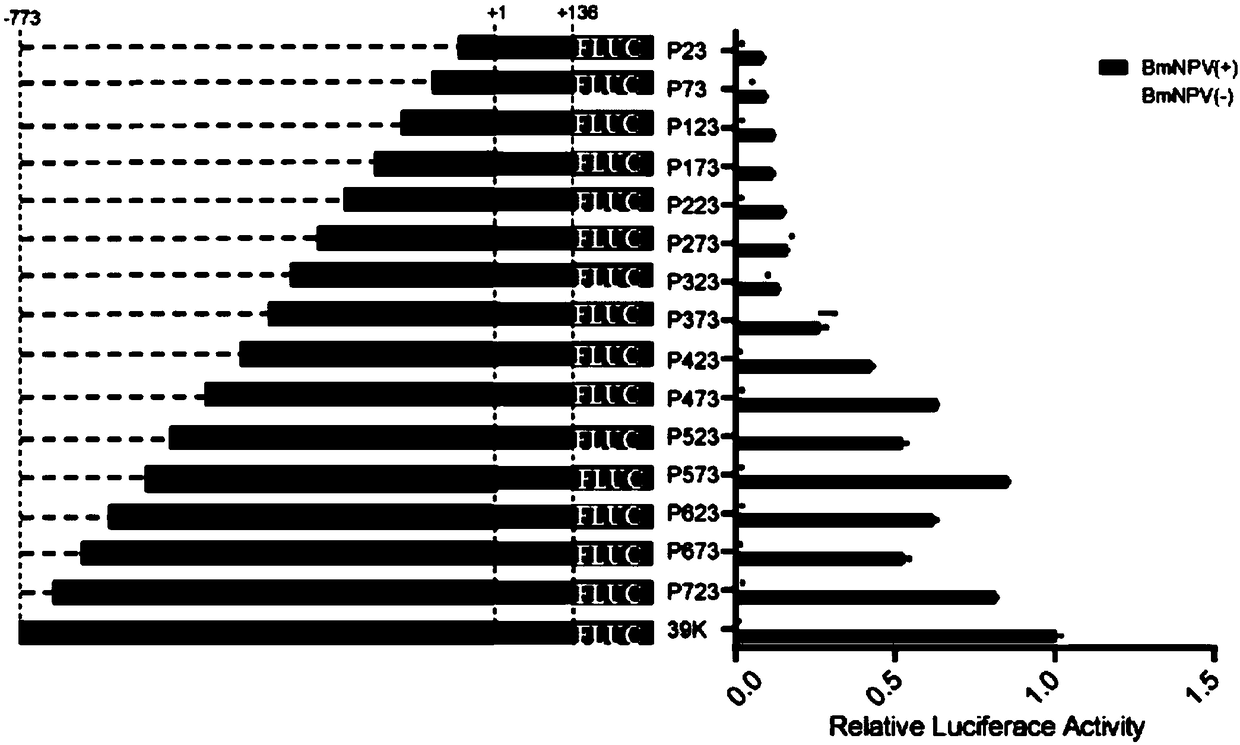
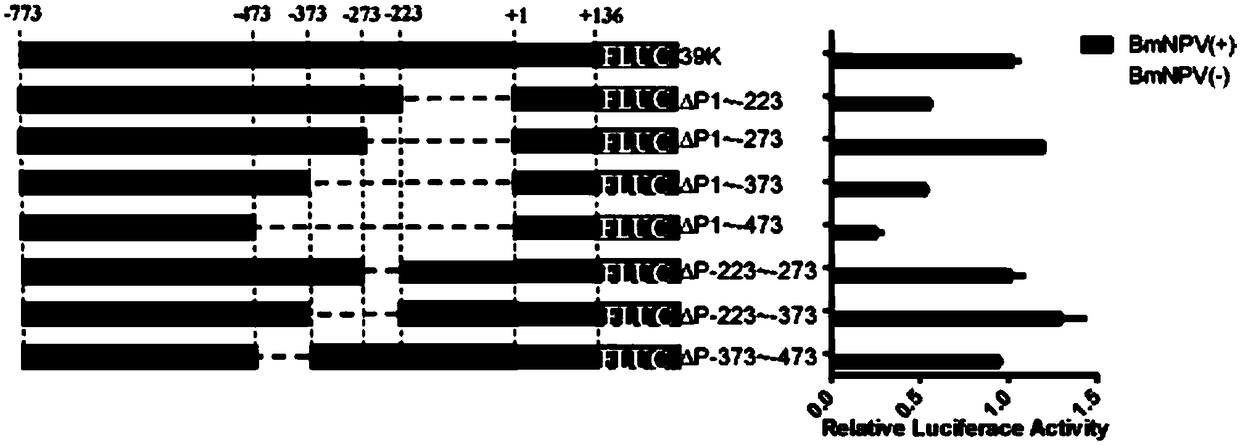
Bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus (BmNPV) inducible 39K promoter, and recombinant vector and application thereof
ActiveCN108998455AShorten the lengthEnhance induction activityFermentationDsDNA virusesBombyx moriGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a BmNPV inducible 39K promoter, and a recombinant vector and application thereof. The promoter uses the optimal sequence of a promoter of the BmNPV delayed early gene 39K as aparental promoter; the optimal sequence is gradually truncated and analyzed to reduce the length of the promoter, and a recombinant promoter is constructed and still has strong BmNPV induced promoteractivity; and it is verified that the immediate early gene IE-1 protein of BmNPV can transcribe and bind to the 39K (-310 to -355) region so as to induce the expression of the 39K promoter. Accordingto the invention, the region is used for constructing different synthetic inducible promoters, and the inducible expression activity of 39K and other different promoters can be efficiently improved;and the synthetic inducible promoter are applicable to molecular biological theory analysis such as gene function analysis, the application research on the expression system of BmNPV and the improvement of Bombyx mori varieties via the genetic engineering technology.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6204045B1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiHeterologousLaryngotracheitis virus
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TX (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
Anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 from blood blue protein of penaeus vannamei and application thereof
ActiveCN108976298APrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAntimicrobial peptidesLate gene
The invention relates to an anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 from blood blue protein of penaeus vannamei. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; the coding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2; the short peptide LvHcS52 can obviously inhibit the WSSV immediate early gene wsv069 and late stage gene wsv421 transcription at both the animal level and the in vitro cell level; meanwhile, the WSSV proliferation can also be obviously inhibited in the body; the STAT signal path in the prawn blood cells can be activated; the transcription of the downstream antimicrobial peptide of the signal path can be triggered so that the anti-WSSV function is achieved. The anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 provided by the invention can be used as a preparation for inhibiting WSSV, and can be added into feed as additives so as to improve the anti-WSSV capability of the penaeus vannamei.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
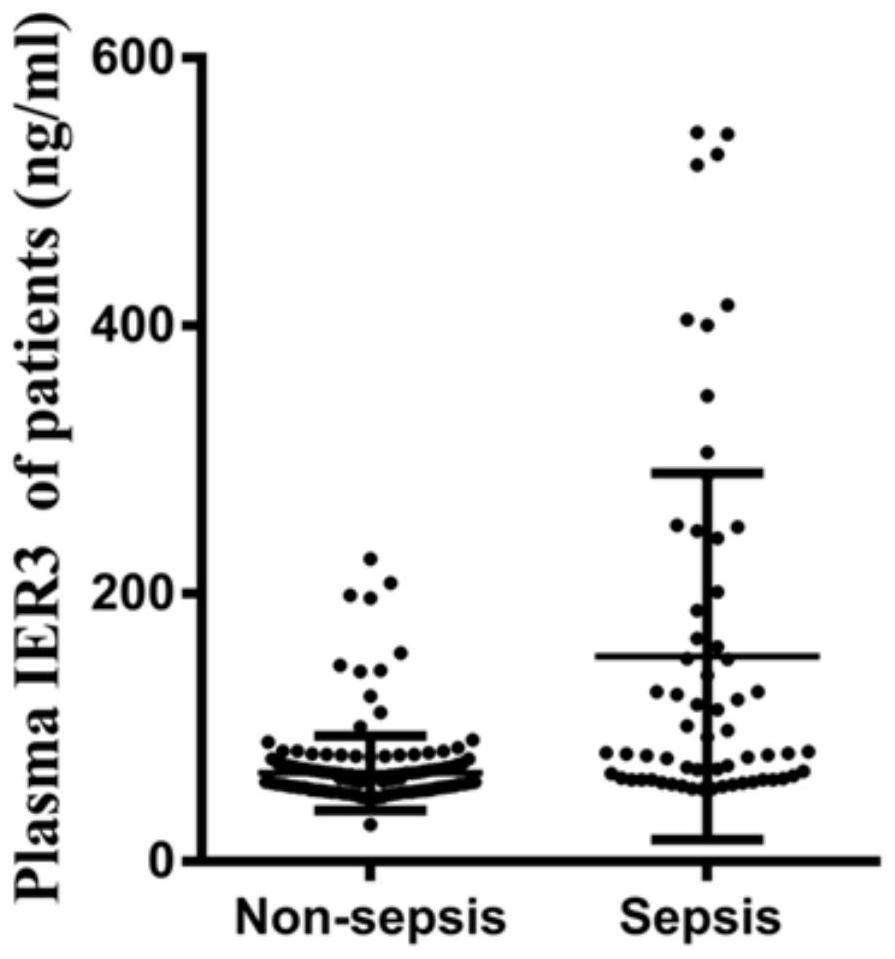
Application of IER3 as biomarker in early prediction of sepsis
PendingCN112011603AGood early predictive valueReduce incidenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisEarly predictionIntervention treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of an early response gene 3 (IER3) as a biomarker in a reagent or a kit for early prediction of sepsis. The IER3 is adopted as a biomarker, and crowd experiments prove that the IER3 level of plasma of a patient suffering from severe trauma sepsis is remarkably higher than that of a patient without sepsis. By detecting the plasma IER3 level, early prediction is conducted on the sepsis occurrence risk of a severely wounded patient so as to give individualized interventional therapy, the occurrence rate of post-traumatic sepsis can be reduced, and the important clinical application value can be achieved for improving prognosis of the severely wounded patient.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军特色医学中心
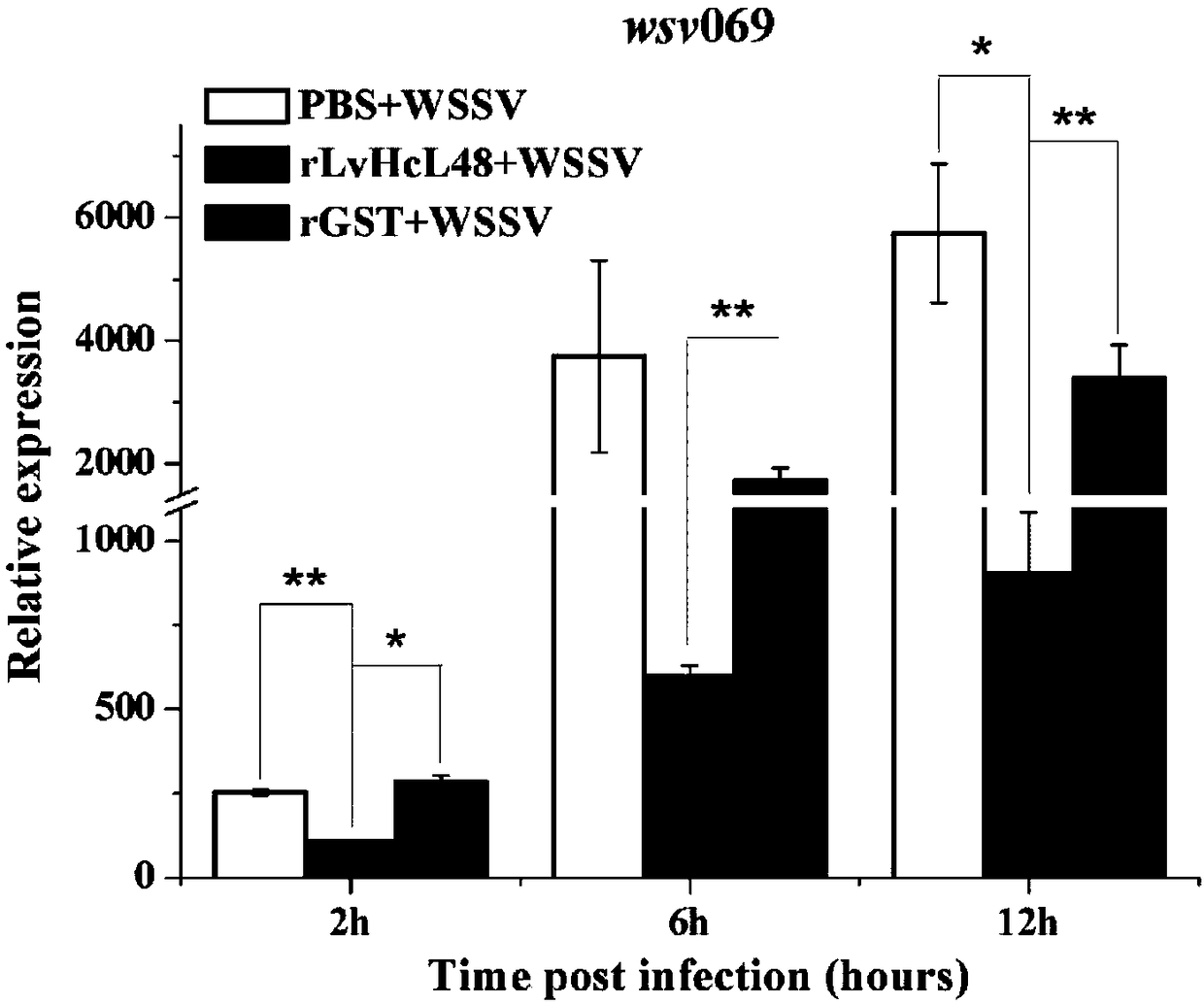
Anti-WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) peptide LvHcL48 derived from litopenaeus vannamei hemocyanin and application thereof
ActiveCN108840925APrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory food factorsWhite spot syndromeIn vivo
The invention relates to an anti-WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) peptide LvHcL48 derived from litopenaeus vannamei hemocyanin. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the coding genes are shown as SEQ ID NO:2. Regardless of the animal level or in-vitro cell level, the oligopeptide LvHcL48 disclosed by the invention can achieve effects of obviously inhibiting transcription of immediate early genes wsv069 and late genes wsv421 of the WSSV and further obviously inhibiting proliferation of the WSSV in vivo; the peptide LvHcL48 can further interact with the most important outer membrane protein VP28 of the WSSV, and is possibly an action mechanism for achieving effects. The anti-WSSV peptide LvHcL48 disclosed by the invention can serve as a preparation for inhibiting the WSSV, andcan serve as an additive to be added into feed so as to be expected to improve the WSSV resistance of the litopenaeus vannamei.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Viral nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS20010024817A1Improved vaccineOrganic active ingredientsFungiLaryngotracheitis virusInsertion site
Various genes of herpes virus of turkeys (HVT), Marek's disease virus (MDV) and infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) have been identified as non-essential regions (and candidates for insertion sites for foreign genes) and / or as antigen-encoding regions. The former include the HVT homologue of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) gC gene, the TK (thymidine kinase) region of MDV or ILTV, ORF3 of ILTV (as defined herein), the ribonucleotide reductase (large subunit) gene of ILTV, MDV or HVT and the ribonucleotide reductase (small subunit) gene of MDV. The antigen-encoding regions include the HVT homologues of the HSV gB, gC and gH genes, the ILTV homologue of HSV gB, ORF2 of ILTV, and the HVT homologue of the HSV-1 immediate early genes IE-175 and IE-68. Manipulation of these genes allows vaccines to be prepared comprising attenuated virus or virus carrying heterologous antigen-encoding sequences.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
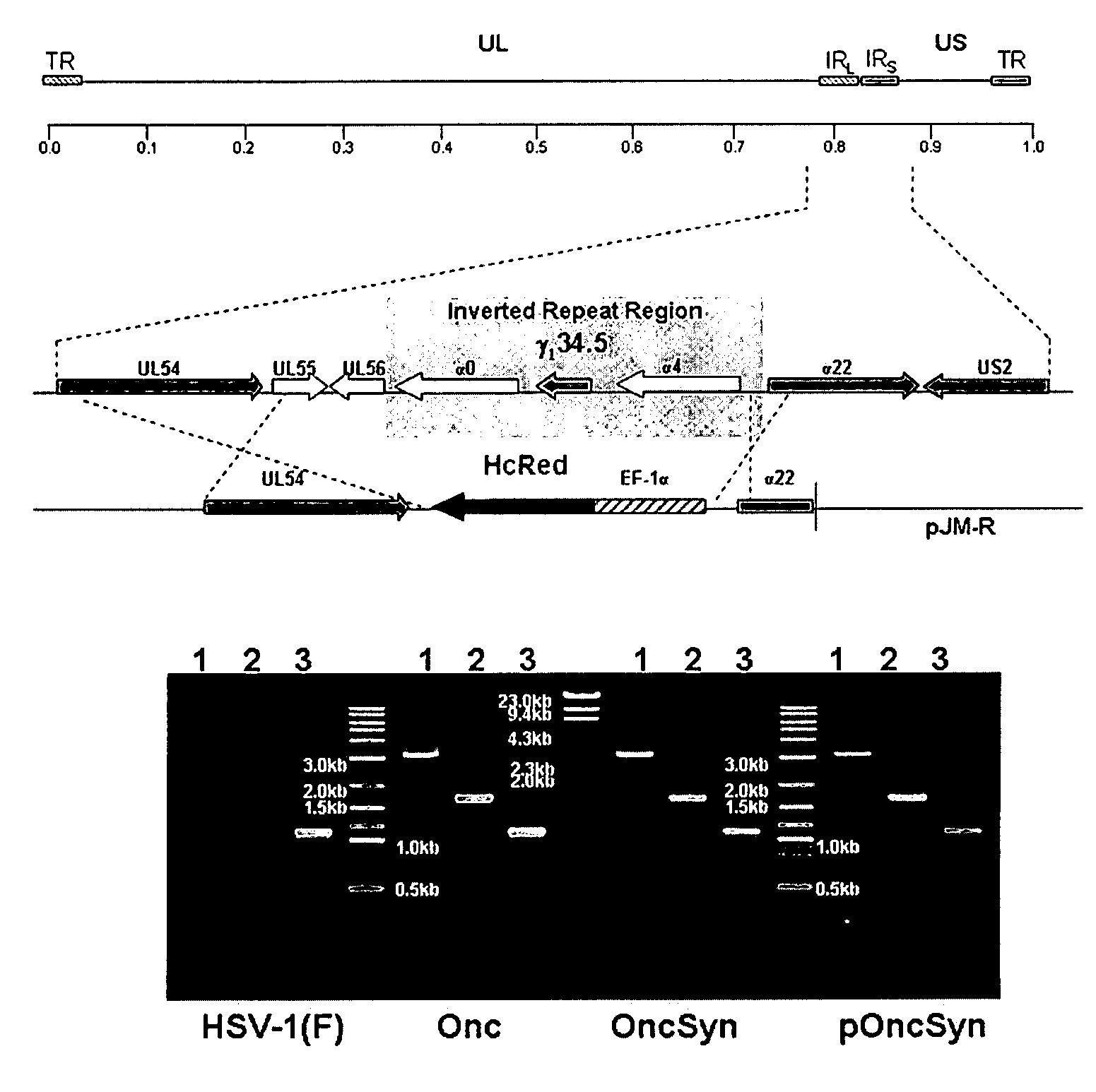
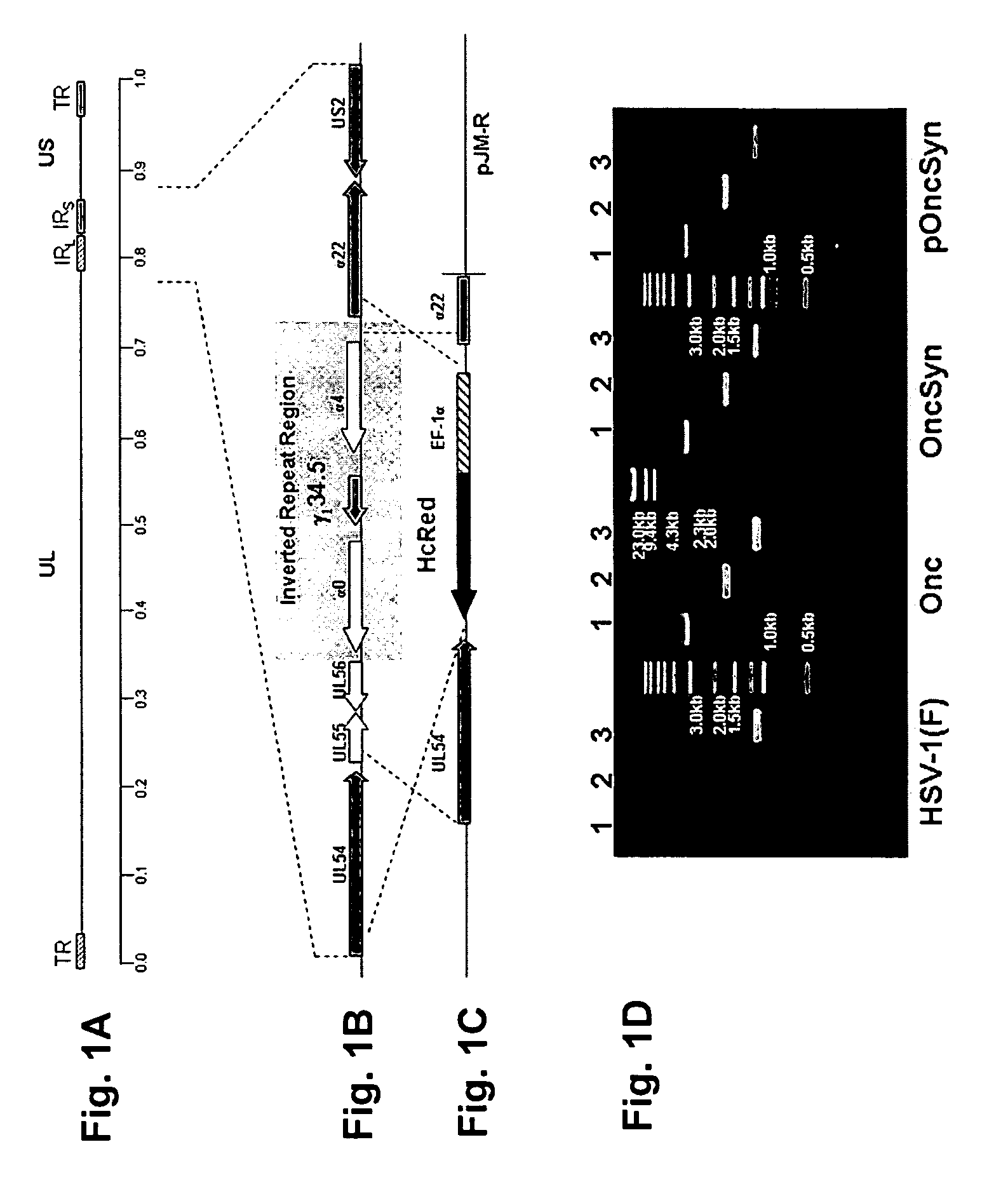
Synthetic herpes simplex viruses type-1 for treatment of cancers
ActiveUS8586028B2High replicationHigh spreadBiocideGenetic material ingredientsViral glycoproteinCancer cell
A recombinant herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1) has been constructed that carries a deletion of one of the two viral γ1 34.5 genes and other immediate early genes, which render the virus able to selectively replicate in cancer cells but not efficiently replicate in normal cells, and in which specific mutations have been introduced to enable the virus to spread among cancer cells by virus-induced fusion. Specifically, syncytial mutations have been introduced in the genes coding for glycoprotein B and glycoprotein K of the virus, enabling high replication and spread of the virus in cancer cells in the presence of substantially lower amounts of γ1 34.5 protein, which is required for optimum infectious virus produced and virus-induced cell fusion. These altered viruses or the isolated bacterial chromosomes could be used to treat various cancers including breast, liver, colon, and other tissues.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Enhancer for promoter, and use thereof
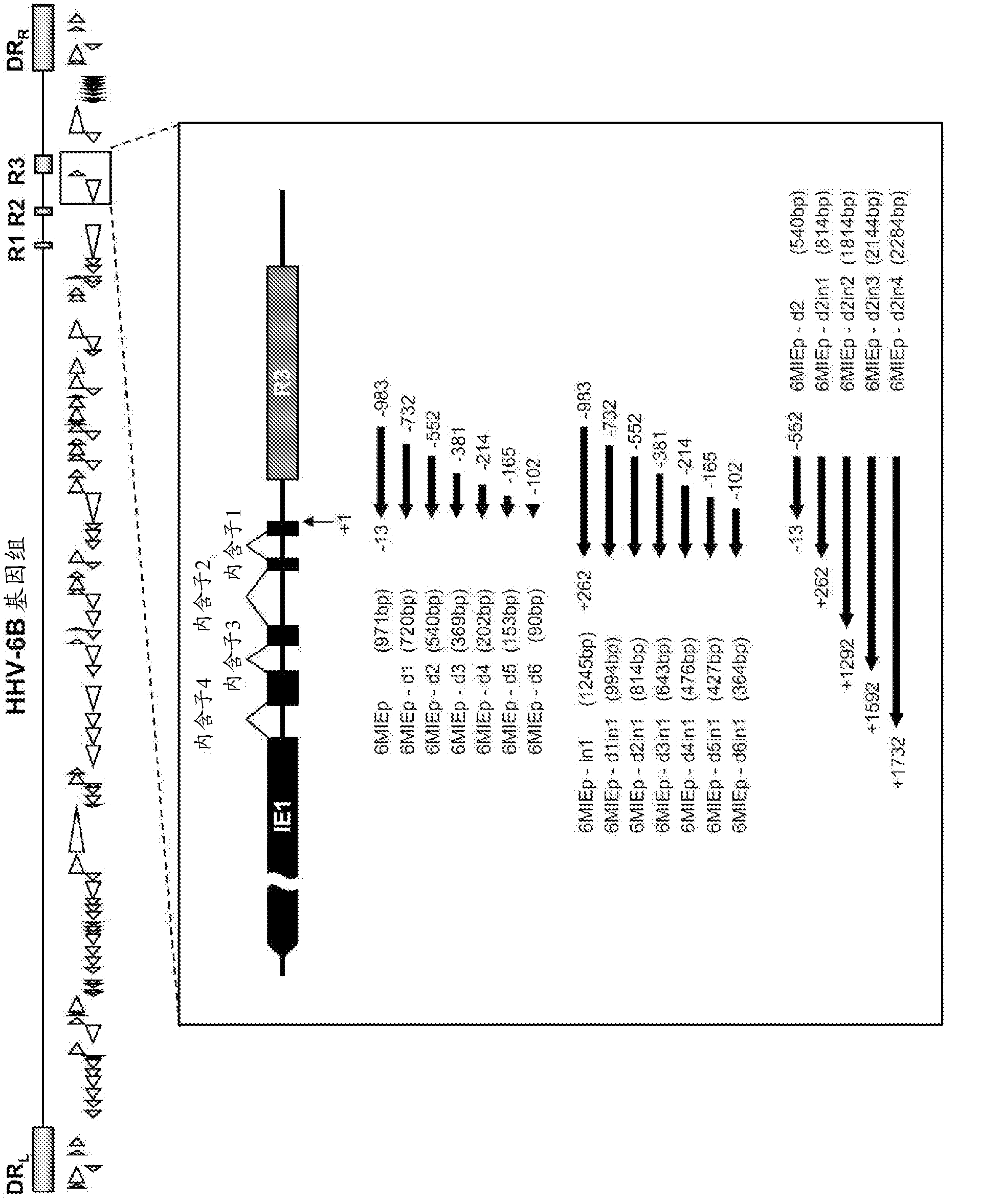
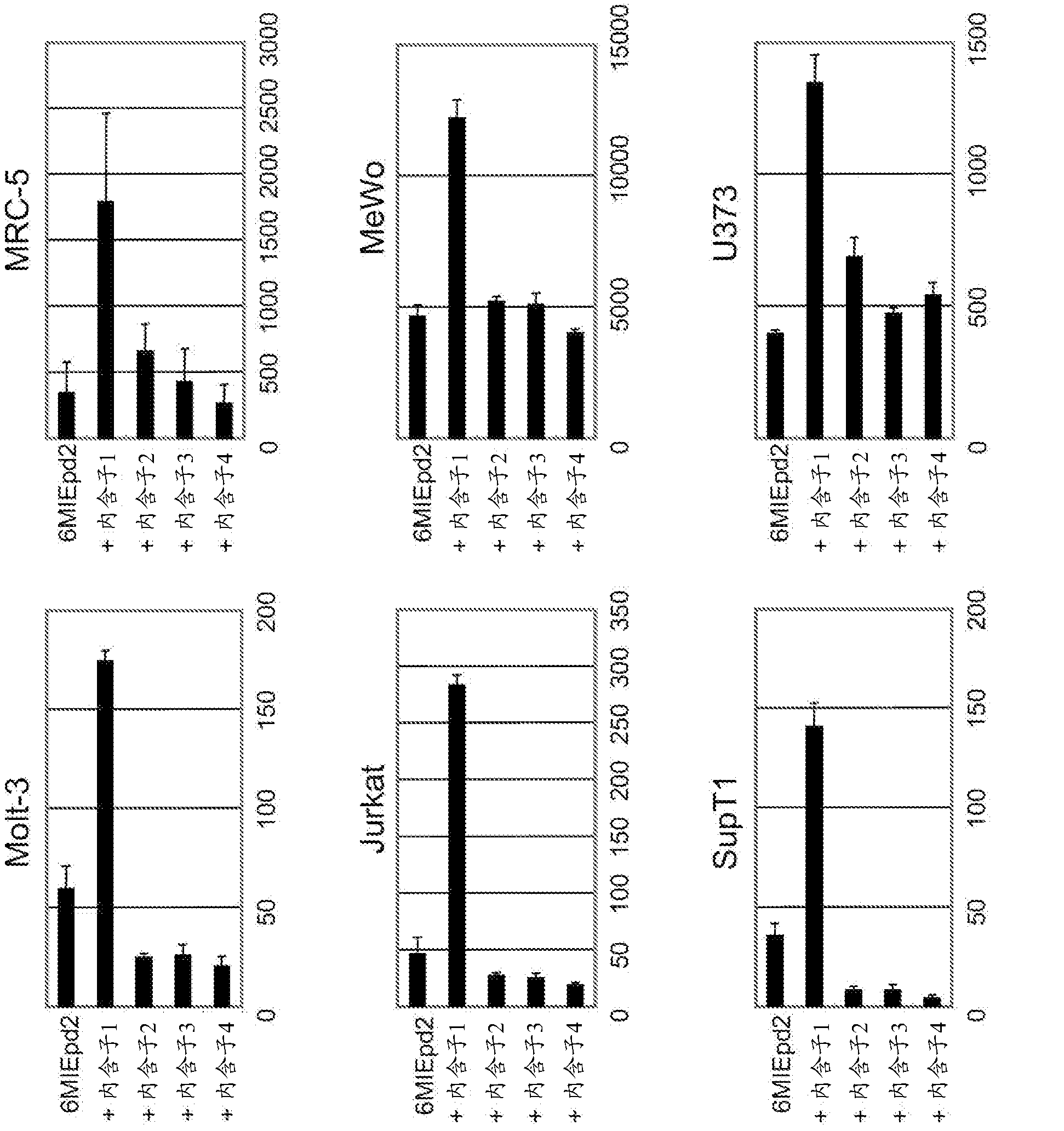
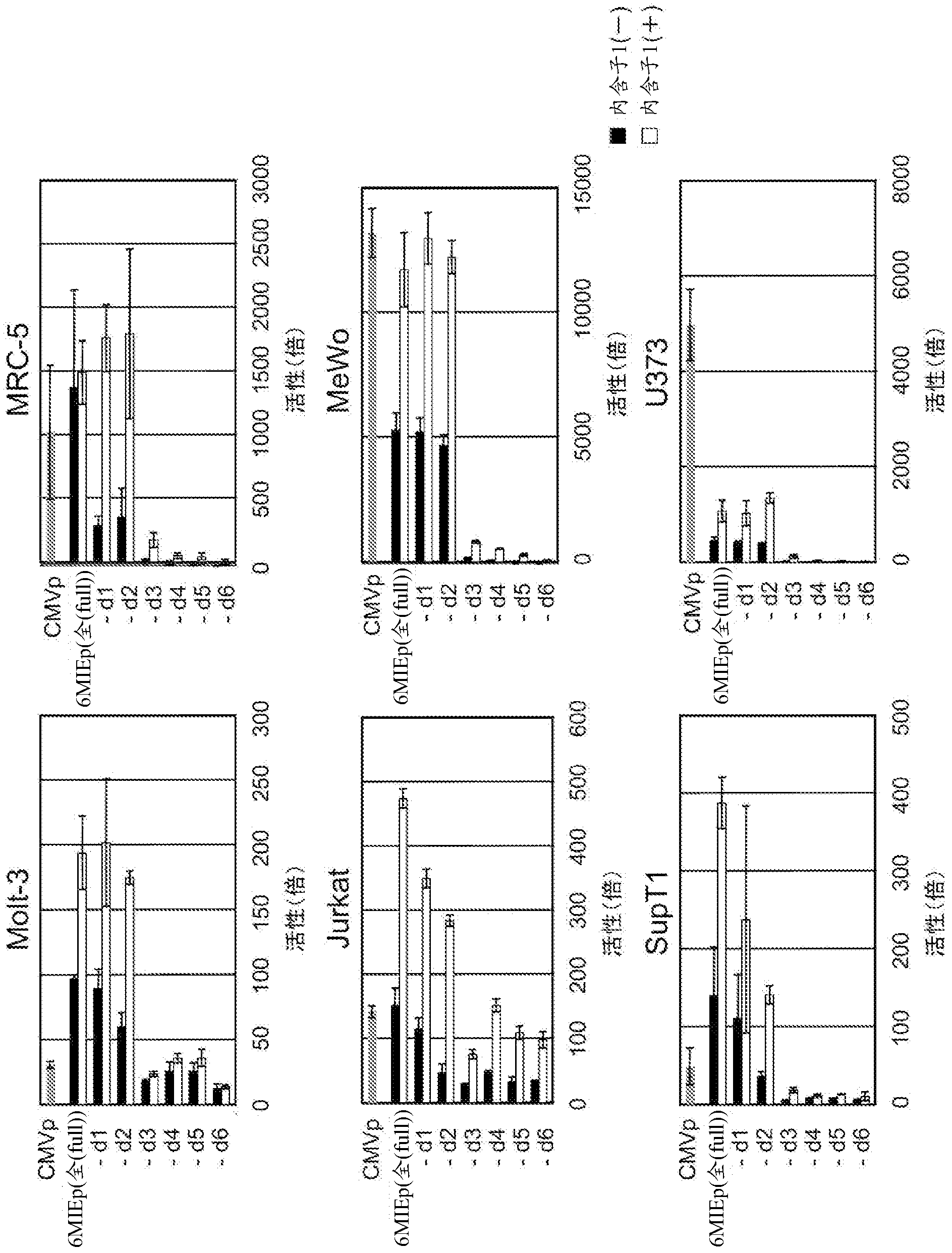
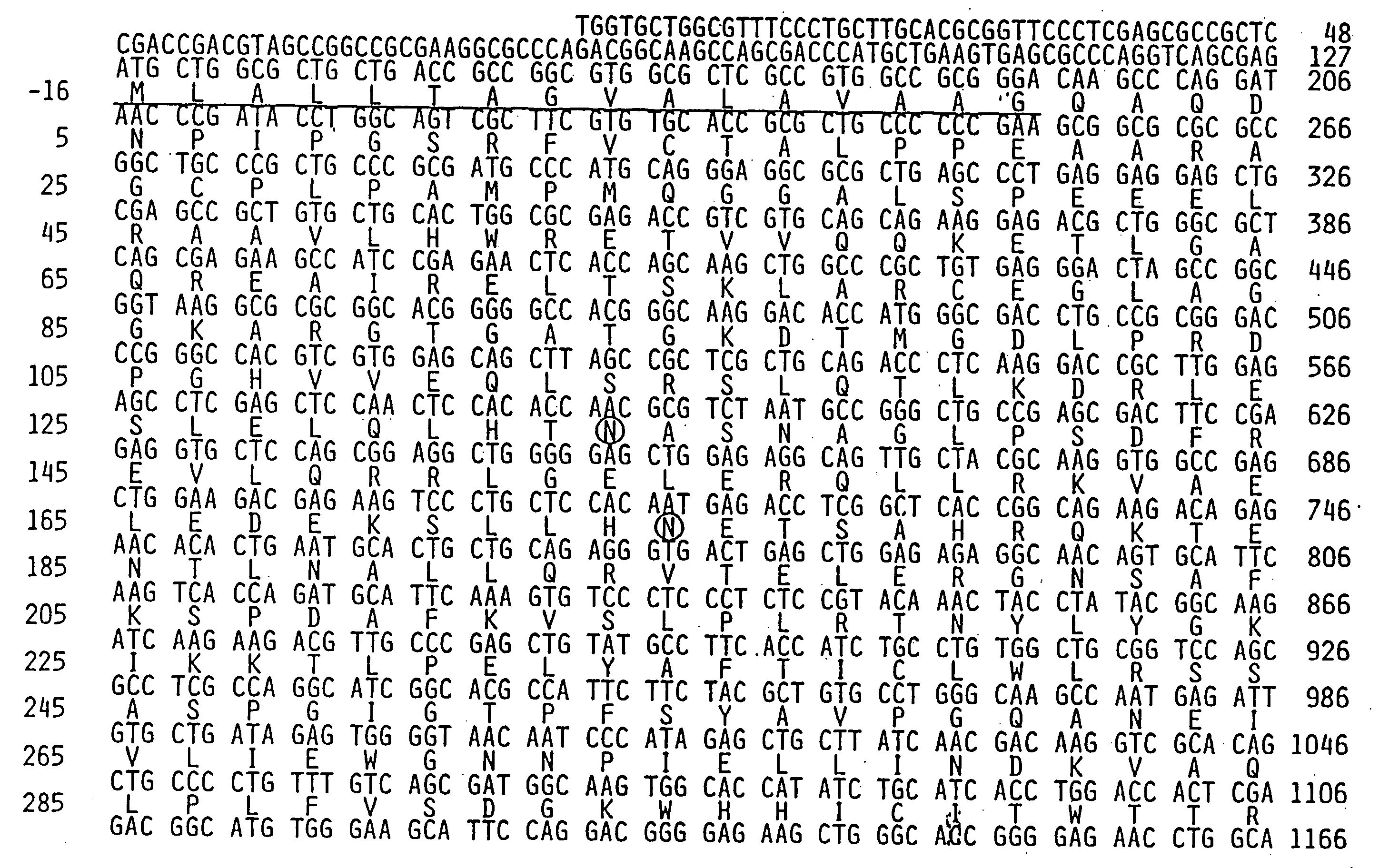
Disclosed is an enhancer for a viral promoter such as a promoter that can induce expression selectively and strongly in immunocompetent cells (e.g., lymphocytes) or blood cells. It is found unexpectedly that an intron has the above-mentioned enhancer activity. Thus, it is found that an enhancer for a promoter, which comprises an intron sequence for a major immediate early gene (MIE) of human herpes virus-6 (HHV-6) (particularly HHV-6B) or a fragment of the intron sequence, has a potent promoter activity.
Owner:NAT INST OF BIOMEDICAL INNOVATION HEALTH & NUTRITION +1
Method for identifying compounds which affect synaptogenesis
InactiveUS20080233571A1Increase the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSynaptogenesisPolynucleotide
A method is provided for identifying a compound which affects the formation of AMPA receptors into aggregates. A method is also provided for identifying a compound which affects the formation of synaptic connections. A method is provided for identifying a compound that modulates immediate early gene expression. A method is further provided for increasing the number of excretory synapses of a neuron, including introducing into the neuron a polynucleotide sequence encoding a Narp operatively linked to a promoter, or a Narp polypeptide, thereby increasing the number of excretory synapses of the neuron. A method is provided for treating a subject with a disorder associated with a decrease in a function or expression of Narp, including administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound that augments Narp function or expression. A method is provided for treating a subject with a disorder associated with an increase in a function or expression of Narp, including administering to the subject a therapeutically effective of a compound that inhibits Narp function or expression. A method is provided for treating a patient having or at risk of having a disorder associated with decreased Narp expression. The method includes introducing into a cell of a patient having a disorder associated with decreased Narp expression or function a polynucleotide sequence encoding a Narp polypeptide operatively linked to a promoter. A method is provided for treating a subject having a deficiency in a neuron's immediate early gene responsiveness to a stimulus. The method includes administering a nucleic acid encoding a Narp polypeptide to said subject, wherein the administration results in amelioration of the deficiency.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Main cis-acting element of shrimp white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) iel promoter and transcription factor combined with same and application
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method of determining susceptibility of a tumor cell to a chemotherapeutic agent: novel use of herpes
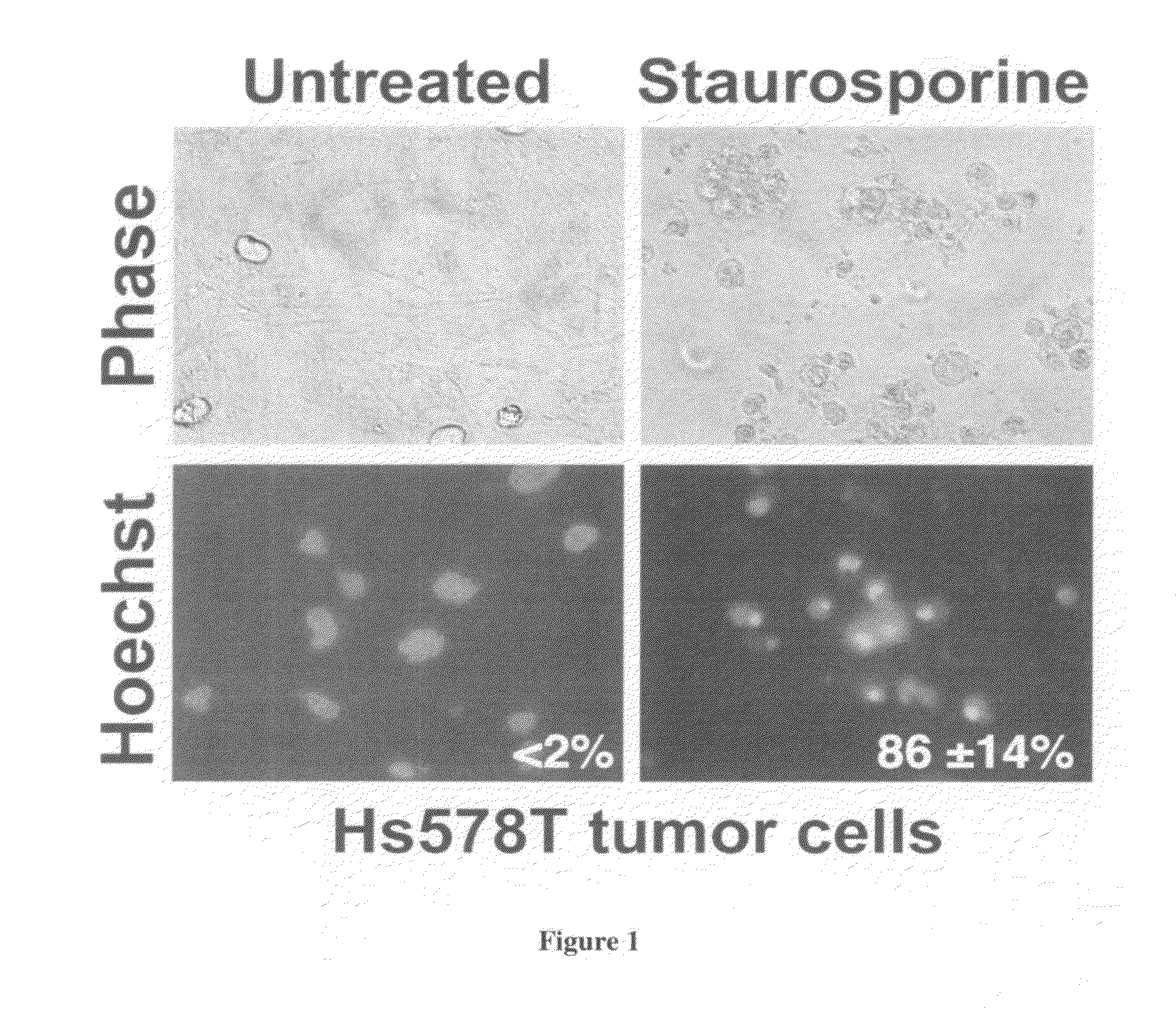
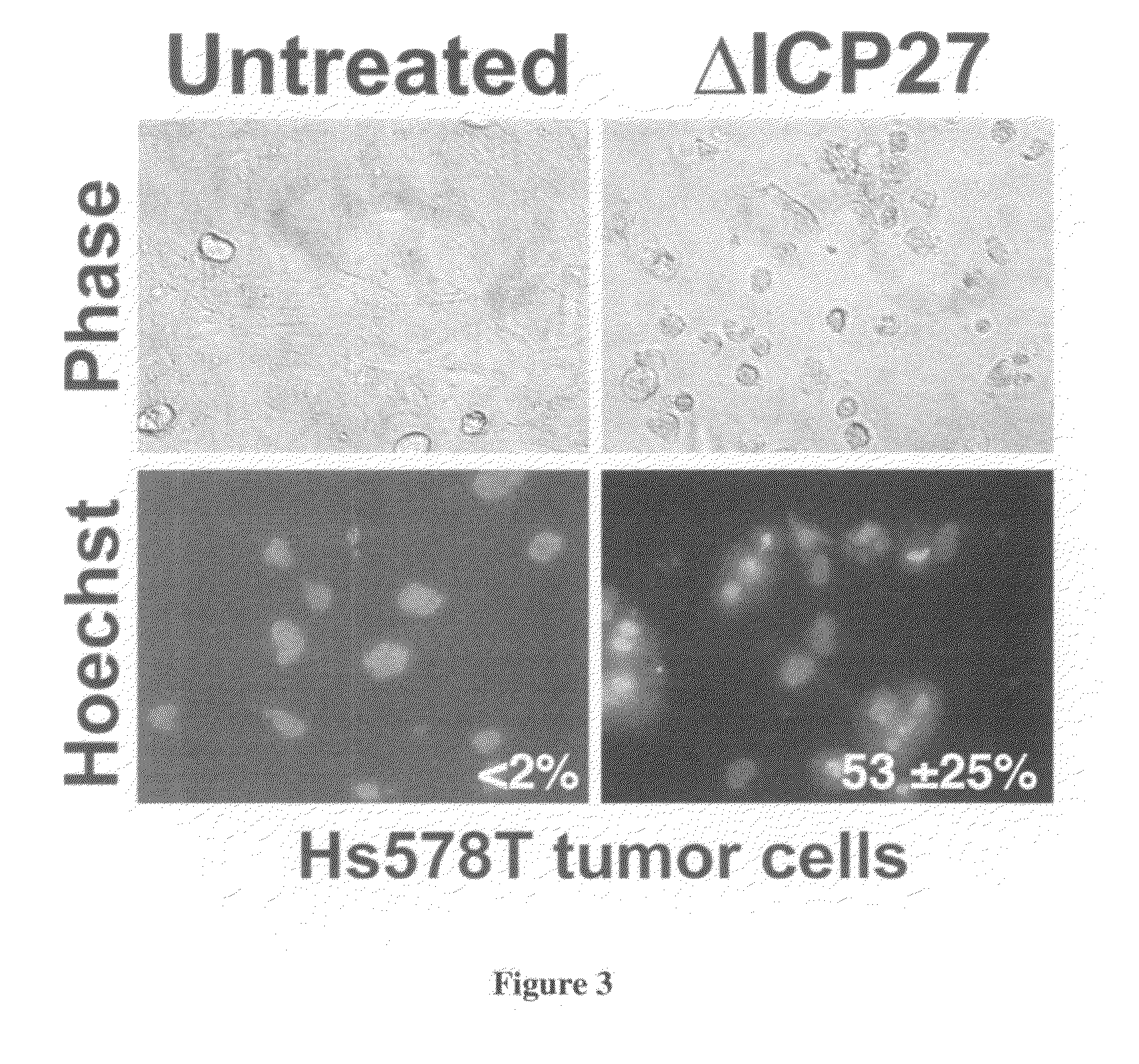
InactiveUS20090325146A1Broaden applicationRapid and non-invasive and reliable assayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisApoptosisWilms' tumor
The present invention provides a method of determining if a tumor cell is susceptible to killing by a chemotherapeutic agent, comprising: (a) providing a tumor cell; (b) infecting said tumor cell with a herpes simplex virus or a herpes simplex virus defective in an immediate early gene selected from the group consisting of ICP27, ICP4, and ICP22; and (c) determining the presence of apoptotic killing of said tumor cell, wherein the presence of apoptotic killing is indicative of susceptibility to said chemotherapeutic agent. Chemotherapeutic agent may include doxorubicin, etoposide, paclitaxel, cisplatin, or 5-fluorouracil. The present invention also provides a herpes simplex virus promoter construct having a lacZ gene to assess tumor resistance to chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Method of determining susceptibility of a tumor cell to a chemotherapeutic agent: novel use of herpes simplex virus
InactiveUS8778331B2Rapid and non-invasive and reliable assayConveniently determinedBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementApoptosisWilms' tumor
The present invention provides a method of determining if a tumor cell is susceptible to killing by a chemotherapeutic agent, comprising: (a) providing a tumor cell; (b) infecting said tumor cell with a herpes simplex virus or a herpes simplex virus defective in an immediate early gene selected from the group consisting of ICP27, ICP4, and ICP22; and (c) determining the presence of apoptotic killing of said tumor cell, wherein the presence of apoptotic killing is indicative of susceptibility to said chemotherapeutic agent. Chemotherapeutic agent may include doxorubicin, etoposide, paclitaxel, cisplatin, or 5-fluorouracil. The present invention also provides a herpes simplex virus promoter construct having a lacZ gene to assess tumor resistance to chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
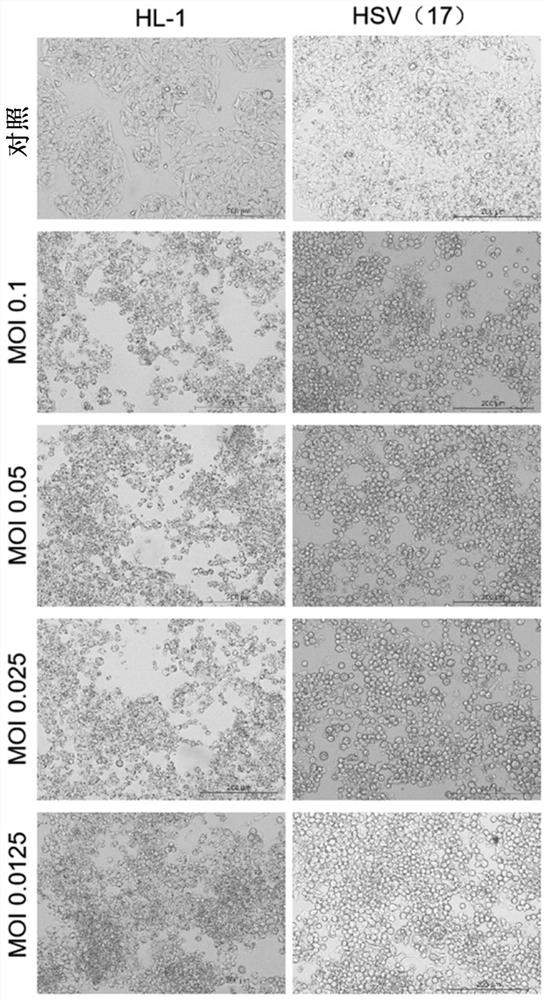
Non-reproductive recombinant herpes virus and use thereof
The application relates to a non-reproductive herpes simplex virus. One or more immediate early genes are knocked out or destroyed, and thus, reproduction capability is lost; and the herpes simplex virus is derived from a herpes simplex virus with an accession number of CCTCC V201810 or descendants thereof. The invention further relates to a composition containing the virus and a viral culture of the composition.
Owner:BEIJING WELLGENE CO LTD
Synaptic transmission assay
InactiveUS20040076989A1Increased rates of presynaptic neurotransmitter releaseCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSynapseEarly response gene
The invention relates to a method for assessing the ability of a test compound or mixture of test compounds to modulate LTP induction by measuring the modulation of immediate early gene expression in response to the compound or mixture of compounds.
Owner:ALAN FINE NAT INST FOR MEDICAL RES
A method for treating viral diseases and other disorders by altering immediate gene expression through administration of peptide T
A method for inhibiting viral replication and for treating neurotrophic conditions by modulating / suppressing immediate early gene expression in a host cell comprising administering a modulating / suppressing effective amount of formula (I) in a physiologically suitable carrier The peptide or its derivatives: Ra-Ser-Thr-Thr-Thr-Asn-Tyr-Rb, Ra represents the amino terminal residue Ala or D-Ala and Rb represents the carboxyl terminal residue Thr or Thr amide, the formula ( I) Peptide derivatives add a Cys residue at one or both ends of the amino and carboxyl groups, or a peptide or derivatives of the formula (II): R1-R2-R3-R4-R5, R1 is the amino-terminal residue Thr, Ser, Asn, Glu, Arg, Ile or Leu, R2 is Thr, Ser or Asp, R3 is Thr, Ser, Asn, Arg, Gln, Lys or Trp, R4 is Tyr and R5 is preferably the carboxy-terminal residue Thr , Arg or Gly, the derivative of the peptide of formula (II) has the corresponding D-amino acid as the amino terminal residue, and / or the corresponding amide derivative as the carboxyl terminal residue, and / or at the amino and carboxyl terminal A Cys residue is appended to one or both ends of .
Owner:ADVANCED IMMUNI T
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com