Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Conjugated polyelectrolyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
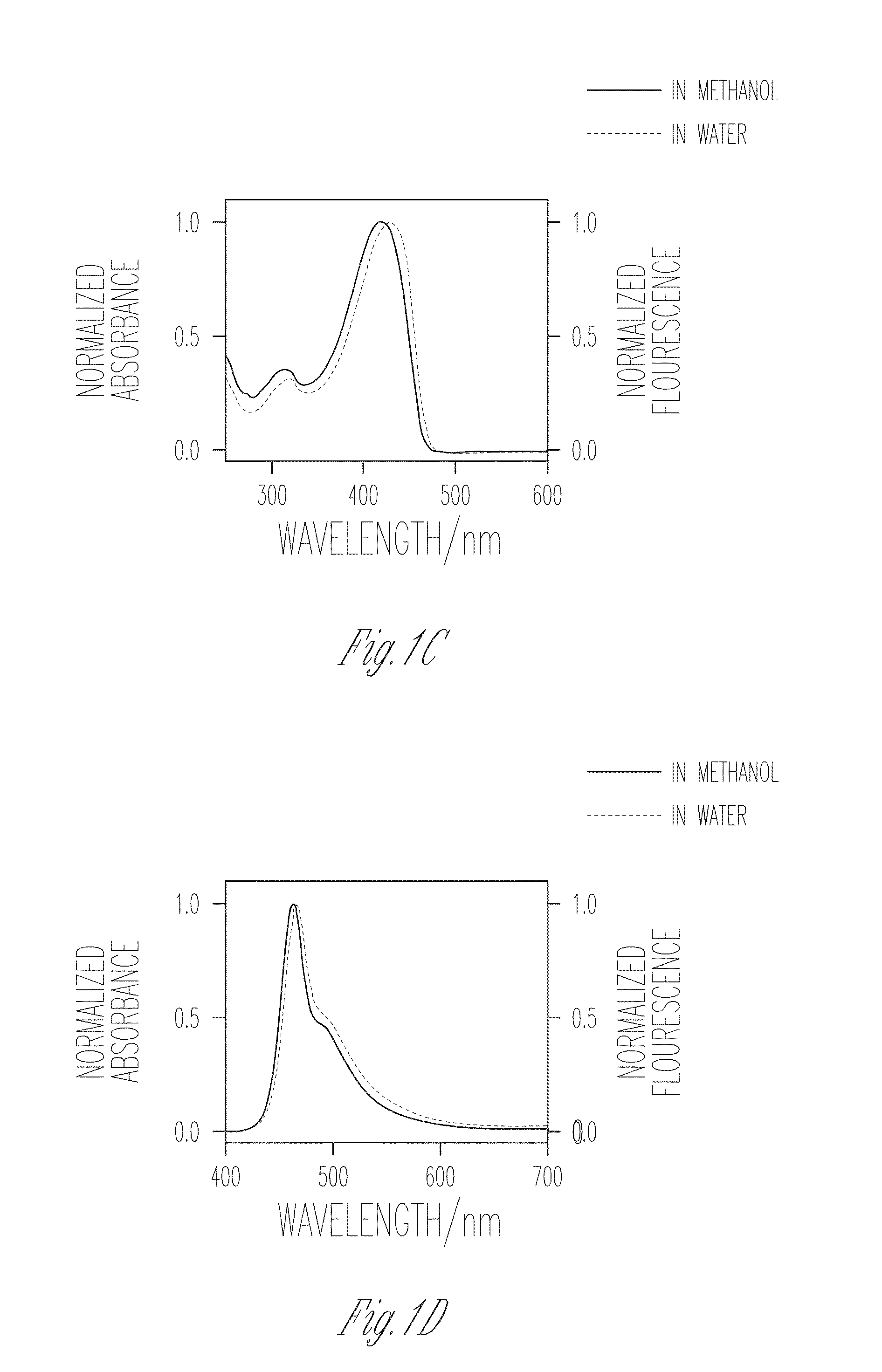
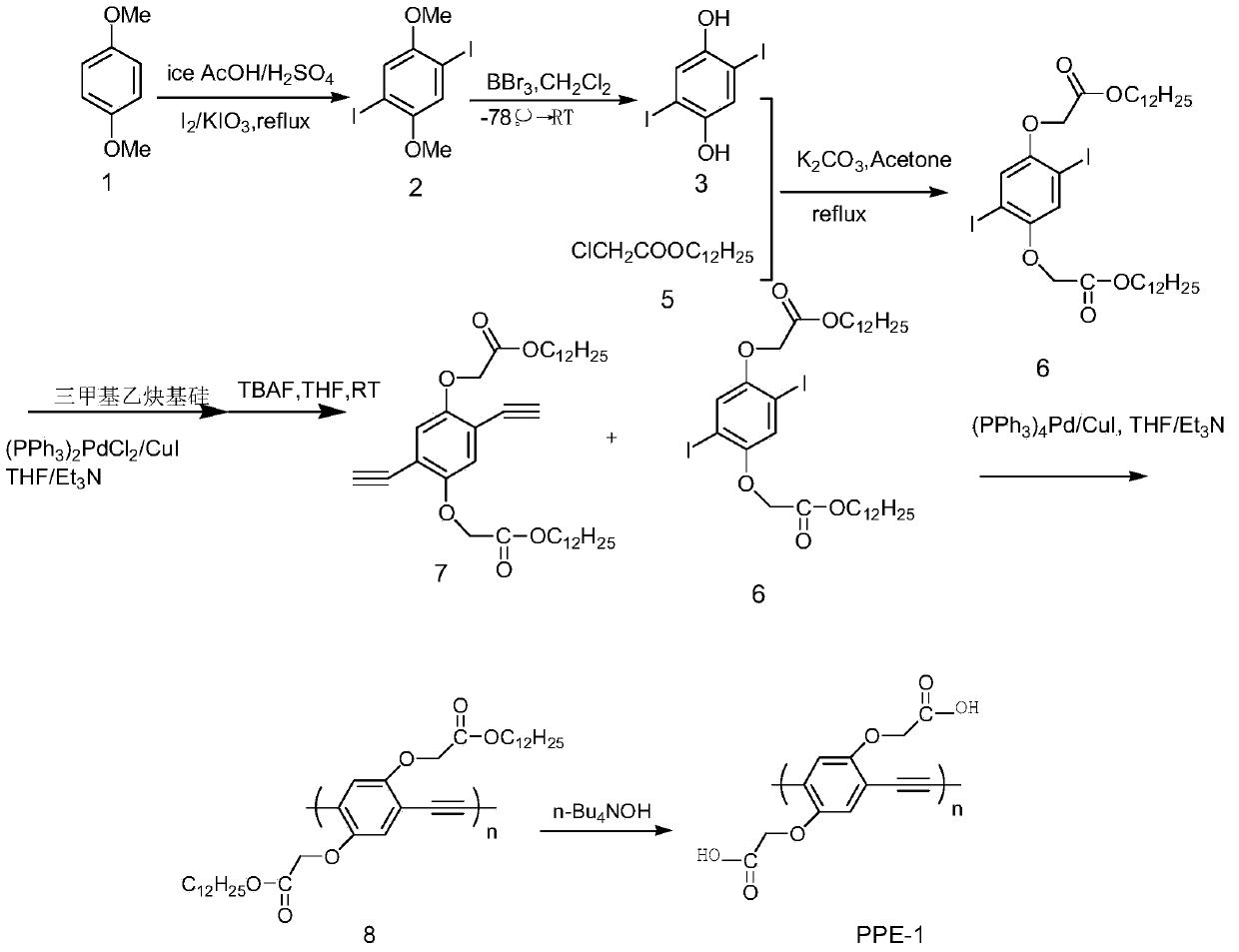
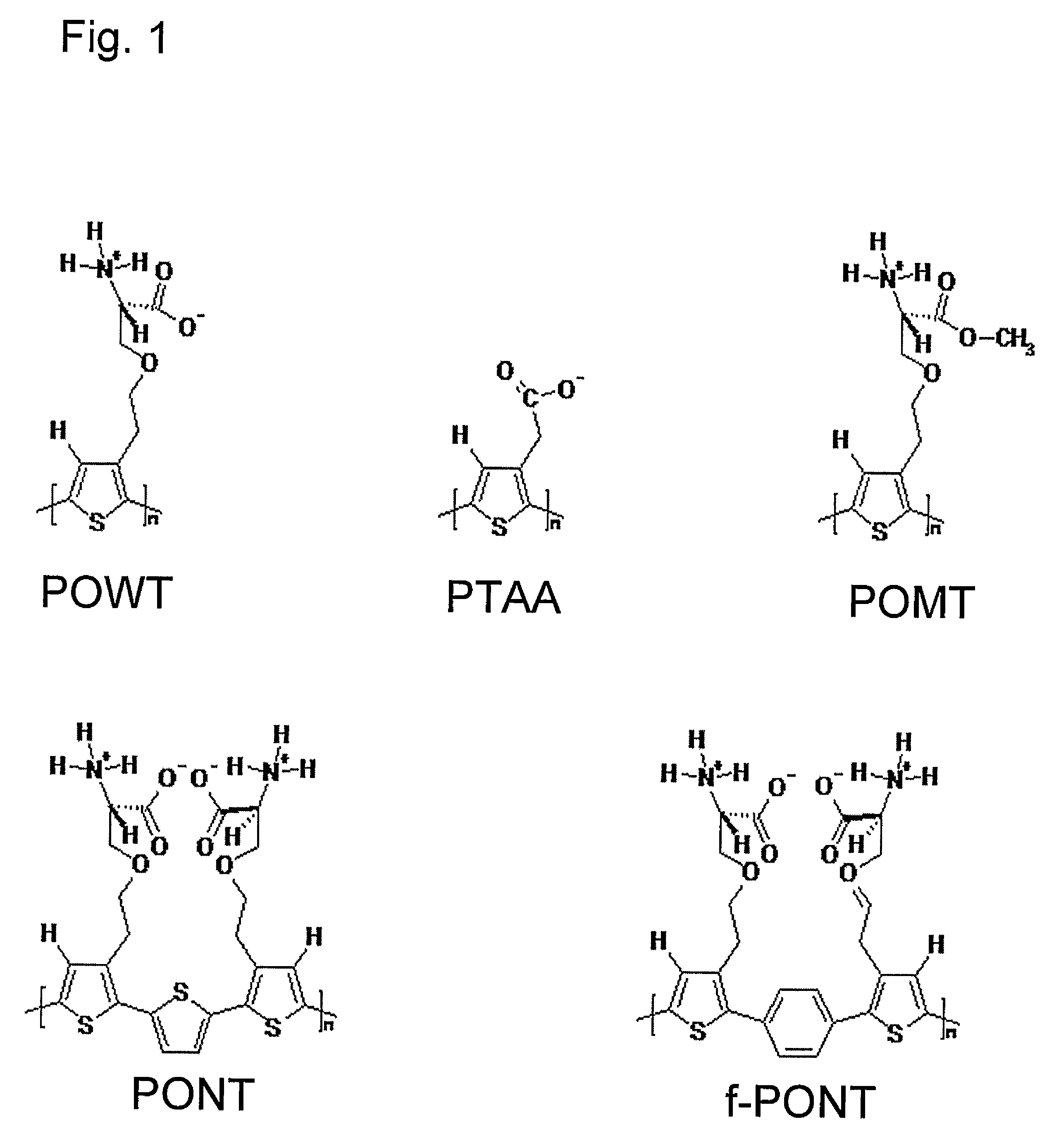
Conjugated polyelectrolytes (CPEs) are a class of polymeric materials that have emerged as important constituents in widely different, yet technologically relevant applications.
Methods for Determining Conformational Changes and Self-Assembly of Proteins
InactiveUS20080038751A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelf-assemblyConjugated polyelectrolyte
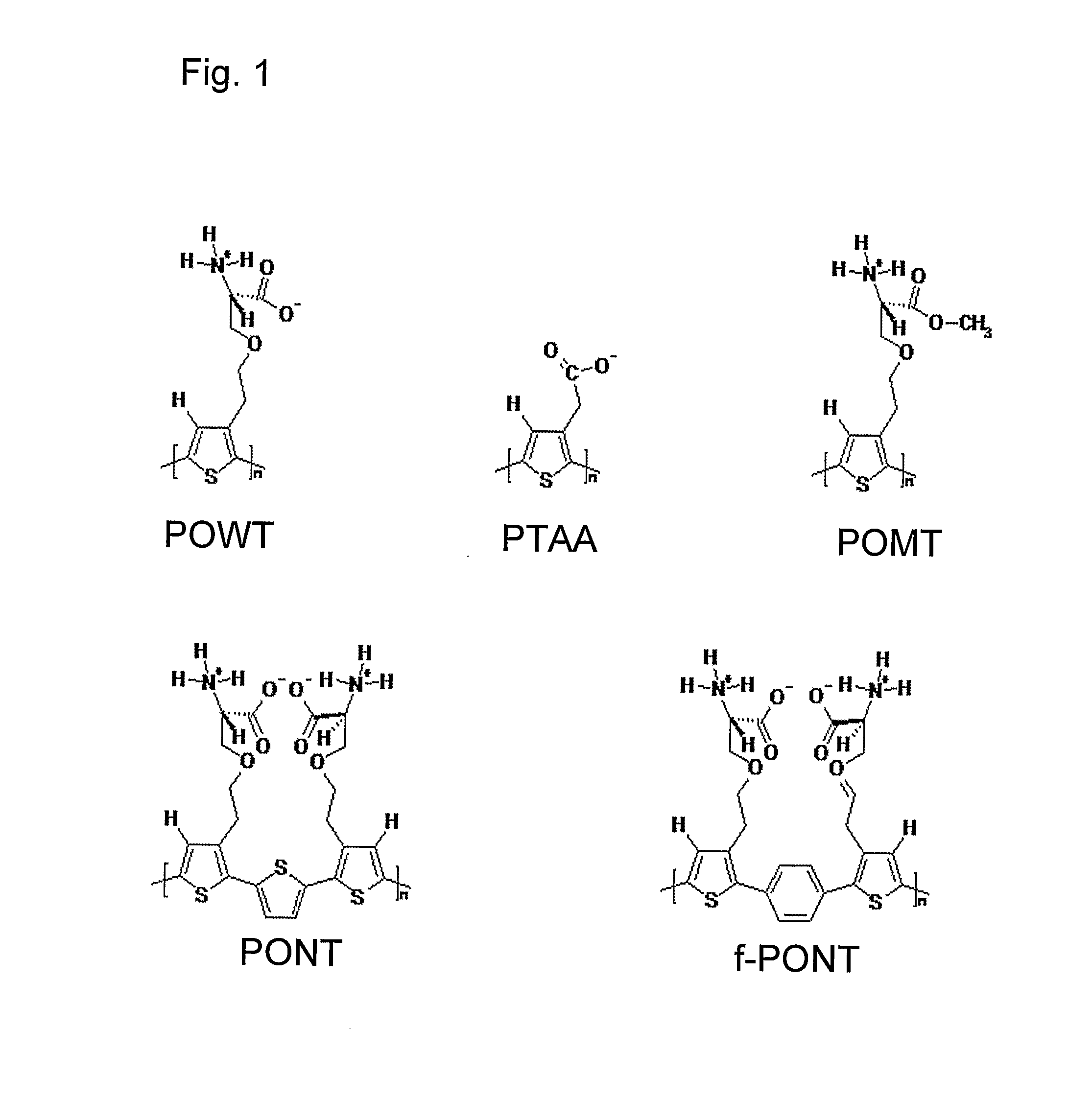
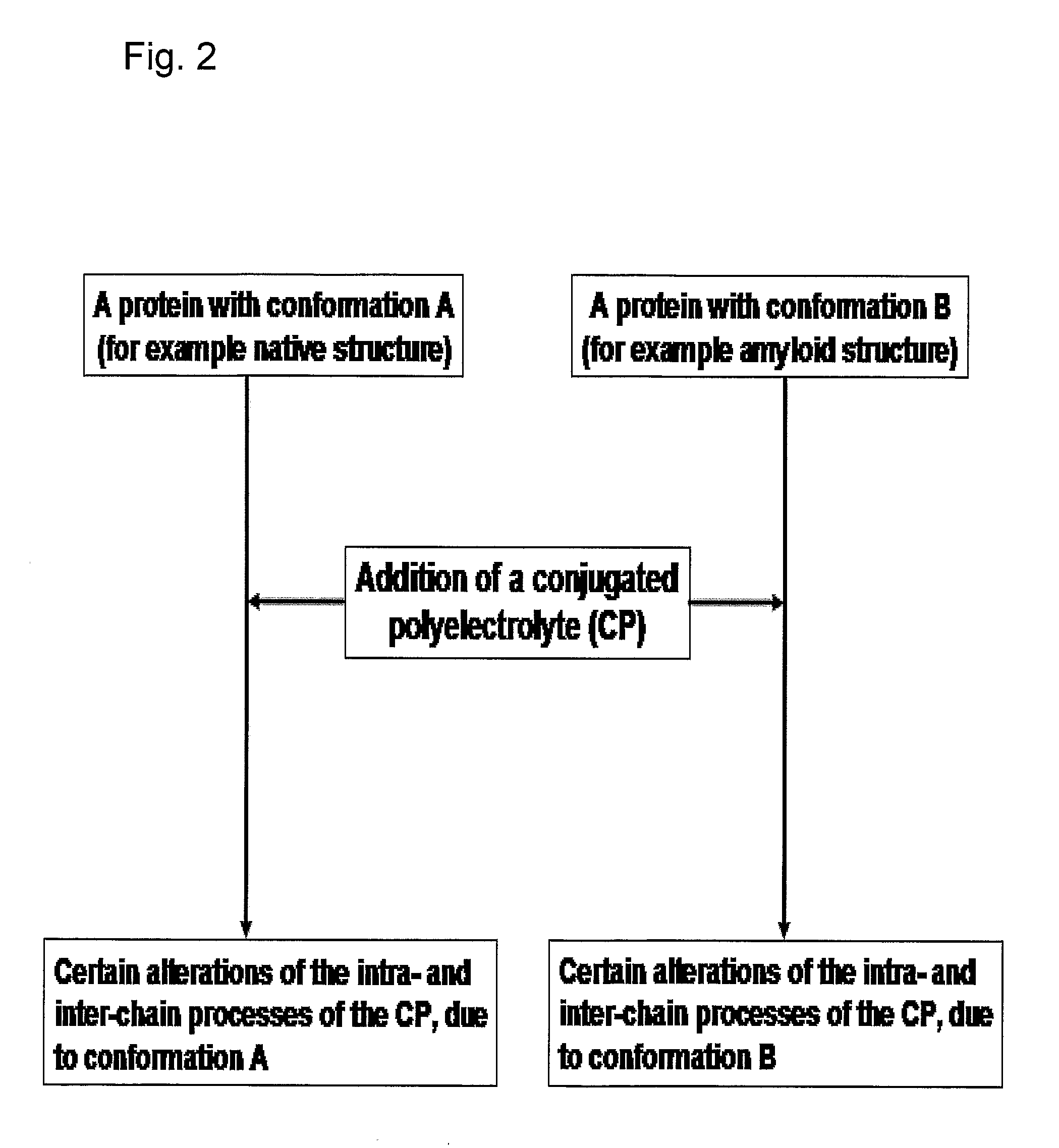
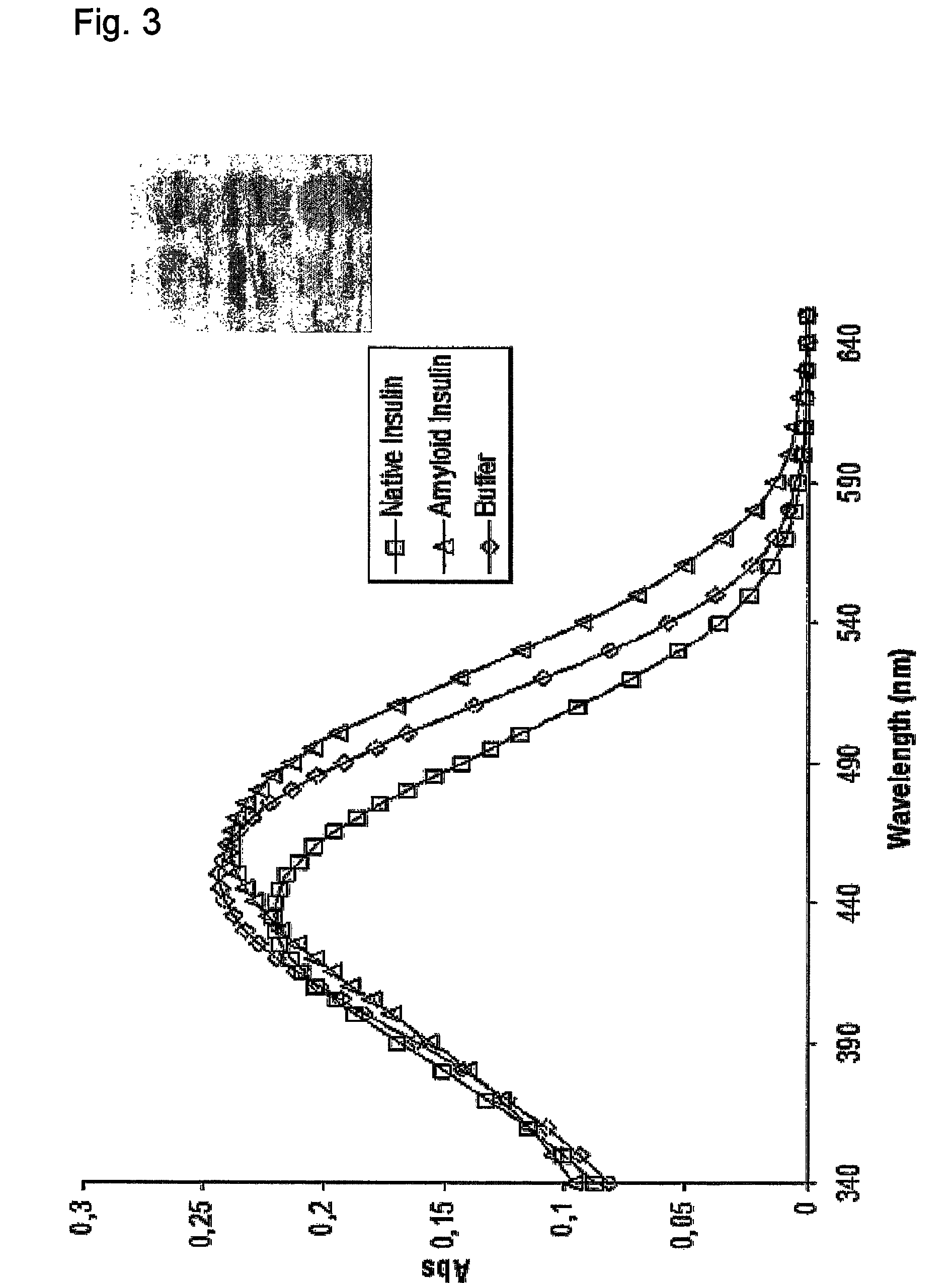
The invention relates to methods for measuring conformational changes and self-assembly / aggregation of proteins, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils, using conjugated polyelectrolytes. The conjugate polyelectrolyte is exposed to the protein whereby the conjugated polyelectrolyte and the protein of interest interact, and a change of a property of the polyelectrolyte in response to conformational changes of the protein is observed. The detected change is used to determine different conformations of the protein, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Surface Grafted Conjugated Polymers
ActiveUS20110159605A1High affinityInhibits fluorescenceCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationSilica particleCoupling
A surface grafted conjugated polyelectrolyte (CPE) is formed by coupling a CPE by a coupling moiety to the surface of a substrate. The substrate can be of any shape and size, and for many uses of the surface grafted CPE, it is advantageous that the substrate is a nanoparticle or microparticle. Surface grafted CPEs are presented that use silica particles as the substrate, where a modified silane coupling agent connects the surface to the CPE by a series of covalent bonds. Two methods of preparing the surface grafted CPEs are presented. One method involves the inclusion of the surface being modified by the coupling agent and condensed with monomers that form the CPE in a grafted state to the substrate. A second method involves the formation of a CPE with terminal groups that are complimentary to functionality that has been placed on the surface of the substrate by reaction with a coupling agent. The surface grafted CPEs are also described for use as biosensors and biocides.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Non-labeled ionic conjugated polyelectrolyte, synthetic method thereof and application to biological detection
InactiveCN103588960AThe test result is validGood water solubilityColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIridiumSolubility
The invention discloses design, detection application of non-labeled ionic conjugated polyelectrolyte. The non-labeled ionic conjugated polyelectrolyte has a structure shown as the general formula (I) shown in the description, and comprises a 9-substituted fluorenes unit and an acceptor unit Ar with electron-withdrawing characteristic, Ar is one substituent groups of benzo[d]thiadiazol, benzo[d]thiazol, thiazole, benzo[d]diazol, boron-dipyrromethene unit, iridium complex containing unit, metalloporphyrin containing unit, perylene bisimide, naphthalimide and the like, the ratio of fluorenes group to Ar (x:y) is 17:3-18:2, the side group comprises m+1 CH2 units, wherein Ion is one water-soluble groups such as quaternary ammonium group, carboxyl or sulfo group. The non-labeled ionic conjugated polyelectrolyte has extremely high solubility and stability, is applicable to multiple non-labeled biological detection, and is a brand-new sensing detection platform.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Patterning Method For Biosensor Applications And Devices Comprising Such Patterns
InactiveUS20070196819A1Material minimizationIncrease the areaMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFluorescencePatterned substrate
A patterned substrate for biosensing applications, wherein the pattern includes hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas, and selected ones of the areas include at least at least one reporter molecule, a property of which is detectable. A method of making a patterned substrate includes performing a stamping procedure to provide a pattern of hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas on a substrate of a suitable material. One step of the stamping procedure includes attaching at least one reporter molecule to at least selected ones of the areas, the fluorescence of the conjugated polyelectrolyte being detectable and which will change as a result of interaction with a biomolecule.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Conjugated polyelectrolyte capsules: light activated antimicrobials
Hollow conjugated polyelectrolyte (HCPE) microcapsules contain at least one conjugated polyelectrolyte and at least one other polyelectrolyte of complementary charge and the microcapsule has a hollow core. The conjugated polyelectrolyte is a polymer with a multiplicity of charged repeating units where a portion of the charged repeating units form a pi-conjugated sequence. The complementary polyelectrolyte is a polymer with a complementary charged repeating unit to the charged repeating units of the conjugated polyelectrolyte. The HCPE microcapsules can be formed by successively coating a sacrificial core with alternating layers of complementary polyelectrolytes, at least one of which is a conjugated polyelectrolyte. The sacrificial core can be removed to form the hollow center of a HCPE microcapsule. The HCPE microcapsules can be contacted with a medium containing microbes where the HCPE microcapsules associate with the microbes and efficiently kill the microbes when irradiated with light or other electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Indium tin oxide (ITO)-free quantum light emitting diode (QLED) and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN105140411AReduce usageGood light emitting effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerQuantum dot
The invention is applicable for the field of a quantum dot light emitting diode (QLED), and provides an indium tin oxide (ITO)-free QLED and a fabrication method thereof. The ITO-free QLED comprises a substrate carrier, a cathode layer, a first non-conjugated polyelectrolyte layer, an electron injection layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer, a hole transfer layer, a hole injection layer and an anode layer which are sequentially laminated, wherein the material of the anode layer is PEDOT:PSS (PH1,000). According to the fabrication method of the ITO-free QLED, the cathode layer, the first non-conjugated polyelectrolyte layer, the electron injection layer, the quantum dot light emitting layer, the hole transfer layer, the hole injection layer and the anode layer are sequentially fabricated on the substrate carrier.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Synthesis of water soluble doped conjugated polyelectrolytes for applications in organic electronics
InactiveUS20150075622A1Oxidation potentialEasy to takeElectrolytic capacitorsSolid-state devicesBackbone chainSolar battery
A method of fabricating a composition of matter, including fabricating one or more conjugated polyelectrolytes each comprising a donor-acceptor copolymer backbone and one or more anionic side groups, wherein the one or more conjugated polyelectrolytes are self doped. A solar cell comprising the doped CPE as a hole transport layer is also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Conjugated polyelectrolyte capsules: light activated antimicrobials
ActiveUS20110293470A1Low water solubilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsElectromagnetic radiationLight activated
Hollow conjugated polyelectrolyte (HCPE) microcapsules contain at least one conjugated polyelectrolyte and at least one other polyelectrolyte of complementary charge and the microcapsule has a hollow core. The conjugated polyelectrolyte is a polymer with a multiplicity of charged repeating units where a portion of the charged repeating units form a pi-conjugated sequence. The complementary polyelectrolyte is a polymer with a complementary charged repeating unit to the charged repeating units of the conjugated polyelectrolyte. The HCPE microcapsules can be formed by successively coating a sacrificial core with alternating layers of complementary polyelectrolytes, at least one of which is a conjugated polyelectrolyte. The sacrificial core can be removed to form the hollow center of a HCPE microcapsule. The HCPE microcapsules can be contacted with a medium containing microbes where the HCPE microcapsules associate with the microbes and efficiently kill the microbes when irradiated with light or other electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:STC UNM +1
PEDOT (poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)):PSS (poly(sodium-p-styrenesulfonate)) water dispersion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103937170AThe preparation method is simple and reliableHigh transparencyRoom temperatureOrganic semiconductor
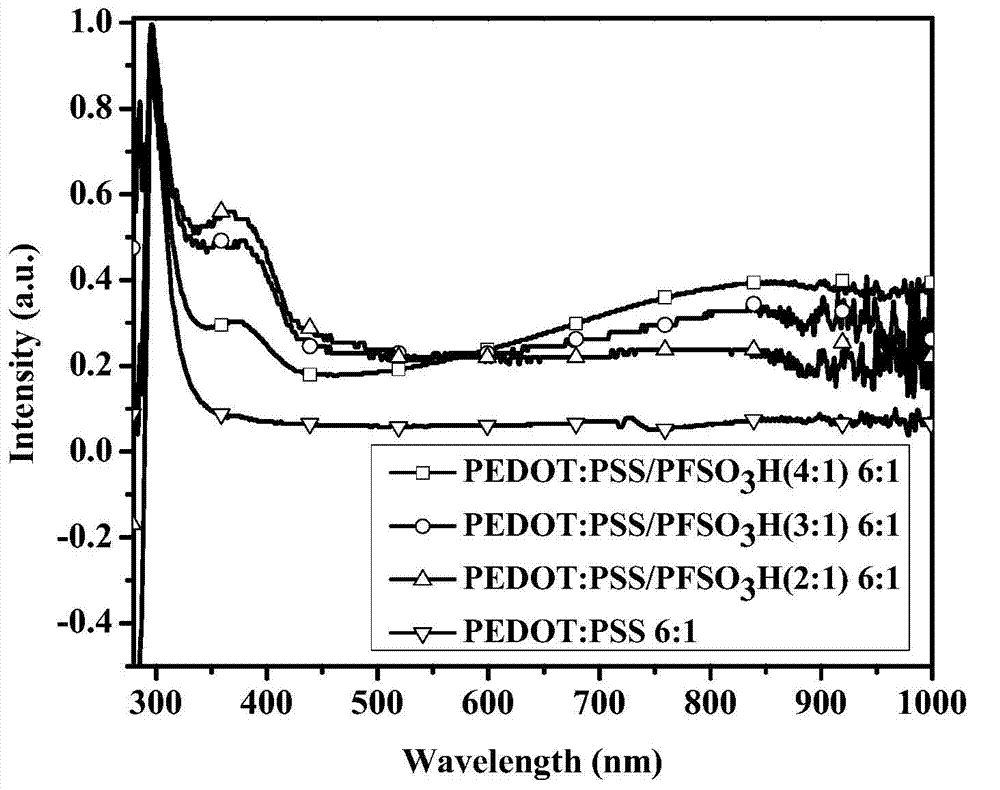
The invention relates to the technical field of organic semiconductors and in particular relates to a PEDOT (poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)):PSS (poly(sodium-p-styrenesulfonate)) water dispersion prepared by using sulfonic acid type conjugated polyelectrolyte as the template and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a sulfonic acid type anionic conjugated polymer, EDOT, PSS and deionized water to a reaction flask under the condition of room temperature and dissolving the materials by stirring the materials; then adding isopropanol, an initiator, a ferric iron catalyst and deionized water to react for 12-24 hours under the conditions of heating at 30-45 DEG C and stirring, thus obtaining a water dispersion; removing the supernatant after centrifuging the water dispersion, after repeating the operations three times, diluting the deionized water for precipitation and then carrying out ultrasonic dispersion for one hour, thus obtaining the PEDOT:PSS deep blue water dispersion with PFSO3H as the template. The PEDOT:PSS water dispersion prepared by the preparation method is simple and reliable in preparation method and has good repeatability. Films of the water dispersion have better transparency and higher electrical conductivity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Doping preferences in conjugated polyelectrolyte/single-walled carbon nanotube composites
InactiveUS20170069814A1Improve solubilityThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric device junction materialsPolymer scienceCarbon nanotube
A method of fabricating a doped composite including combining one or more carbon nanotubes with one or more Conjugated Polyelectrolytes (CPEs) to form a composite, wherein charge transfers between one or more of the CPEs and one or more of the carbon nanotubes, and the CPEs and / or a relative content of the carbon nanotubes in the composite are selected to obtain the composite that is n-type or p-type doped.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Surface grafted conjugated polymers
Owner:STC UNM +1
Cationic conjugated polyelectrolyte electron injection layers altered with counter anions having oxidative properties
InactiveUS20100096656A1Improve performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron injectionPolymer light emitting diodes
Counter anions having oxidative properties alter the performance of solution processed multilayer polymer light emitting diodes (PLEDs) that use cationic conjugated polyelectrolytes (CPEs) as electron injection layers (EILs). In some versions, PLEDs with poly(2-methoxy-5-(2′-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylene vinylene) (MEH-PPV) emissive layers and cationic CPE EILs are altered with halide counter anions to exhibit a systematic increase in device performance. Exemplary oxidative counter anions are halide counter anions with F−>Cl−>Br−>I− in terms of device performance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Conjugated polyelectrolytes and methods of using the same
Various embodiments disclosed relate to conjugated polyelectrolytes and methods of using the same. Various embodiments provide a conjugated polyelectrolyte including a subunit having the structure —R1—Y—R2—Z—. At each occurrence, R1 is independently chosen from 1,4-bonded phenylene substituted by —X—R3—R4 j times and 2,5-bonded thiophene substituted by —X—R3—R4 j times. At each occurrence, Y is independently chosen from a bond and —C≡C—. At each occurrence, R2 is independently chosen from a bond, a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene, thiophenylene, azulenylene, heptalenylene, biphenylene, indacenylene, fluorenylene, phenanthrenylene, triphenylenylene, pyrenylene, naphthacenylene, chrysenylene, biphenylenylene, anthracenylene, and naphthylene. At each occurrence, Z is independently chosen from a bond and —C≡C—. The variables j, R3, and R4 are as defined herein.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Complementary conjugated polyelectrolyte complexes as electronic energy relays
ActiveUS20190006545A1Light-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureArtificial photosynthesisElectronic energy transfer
The present invention generally relates to artificial photosystems and methods of their use, for example in artificial photosynthesis, wherein the artificial photosystems comprise one or more light-harvesting antenna (LHA) comprising a conjugated polyelectrolyte (CPE) complex (CPEC) comprising a donor CPE and an acceptor CPE, wherein the donor CPE and acceptor CPE are an electronic energy transfer (EET) donor / acceptor pair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sensor array and application of sensor array to aided identification of metal ions
ActiveCN104198451AAmplify the response signalLow costColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSensor arraySpecific detection
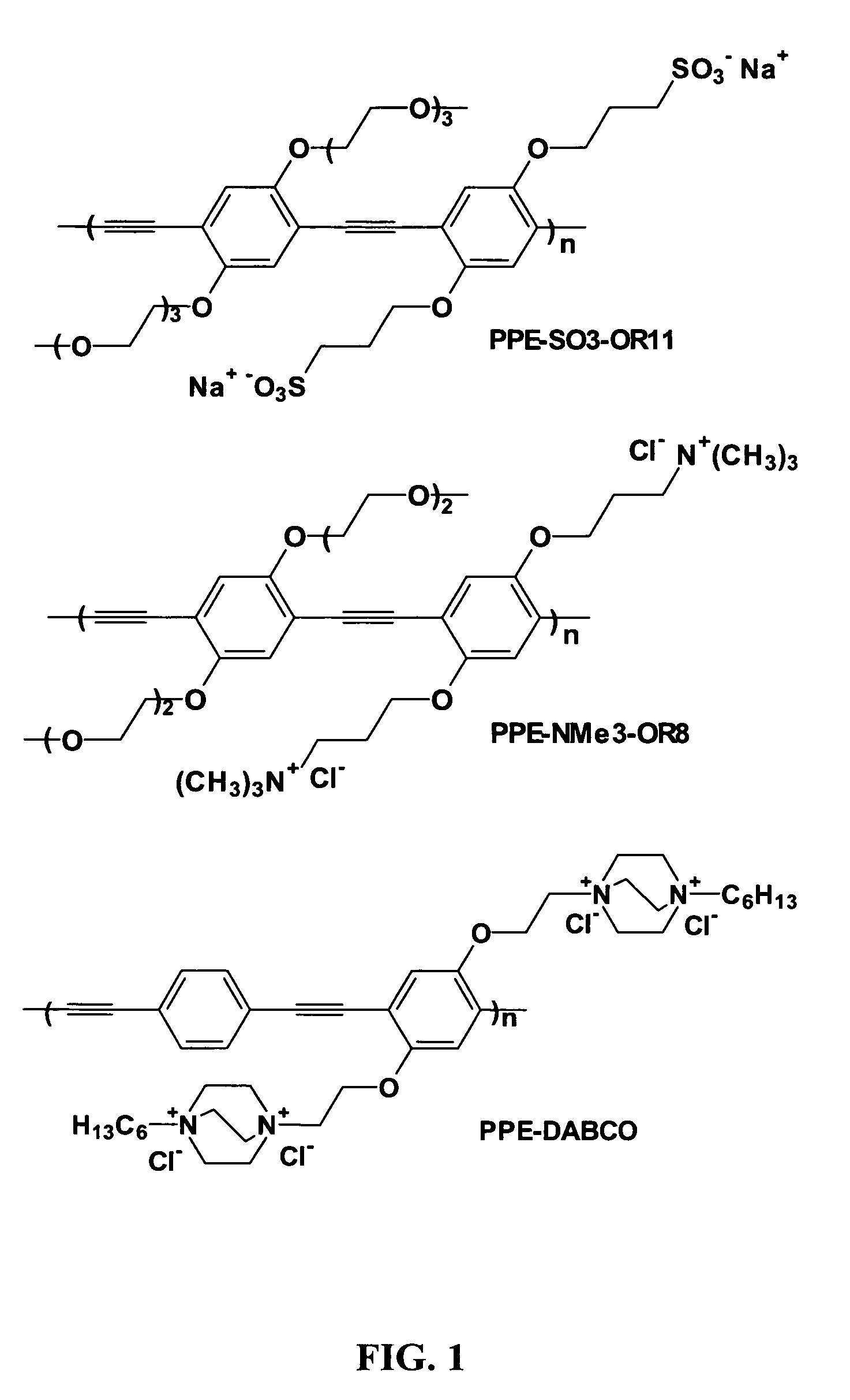
The invention provides a sensor array and an application of the sensor array to aided identification of metal ions. The sensor array comprises a probe array, wherein the probe array is formed by the following four types of conjugated polyelectrolytes, namely a conjugated polyelectrolyte shown in a formula I, a conjugated polyelectrolyte shown in a formula II, a conjugated polyelectrolyte shown in a formula III and a conjugated polyelectrolyte shown in a formula IV. Due to the adoption of the special photo-physical property of the conjugated polyelectrolytes, reaction signals can be amplified; the four types of conjugated polyelectrolytes are combined to form an array sensor; as each type of conjugated polyelectrolyte has different quenching efficiencies for different metal ions, the collected signals are arranged in sequence; data is processed to obtain a fluorescence intensity ratio in a columnar graph; each type of metal ions has different characteristic graphs; compared with the ordinary specific detection on one type of metal ions by virtue of one probe, the sensor array has the advantages that neither complex molecular design and synthesis nor modification of some fluorophores is needed, and the cost and operation complexity are greatly reduced. The formula I, the formula II, the formula III and the formula IV are as shown in specification.
Owner:深圳市乾康医药科技有限公司
Quaternary phosphonium salt group-containing conjugated polyelectrolyte and its use in organic photoelectric device
InactiveCN105237745AExcellent charge extraction performanceImprove fill factorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphonium saltAlcohol
The invention relates to a quaternary phosphonium salt group-containing conjugated polyelectrolyte and its use in an organic photoelectric device. The quaternary phosphonium salt group-containing conjugated polyelectrolyte comprises five parts A, B, R, R1 and X<->. The part A is a conjugated unit component containing a quaternary phosphonium salt group at a side chain. The part B is a conjugated unit copolymerized with the part A. The part R is a group surrounded by phosphine positive ions. The part R1 is a connection unit for connecting the conjugated unit A and the phosphine positive ion. The part X<-> is a negative ion corresponding to the phosphine positive ion. The conjugated polyelectrolyte can be used for processing of a strong polar solvent such as alcohol and is suitable for making of multilayer photoelectric devices. The quaternary phosphonium salt group-containing conjugated polyelectrolyte can be used as a cathode interface modification material in a photovoltaic device and improve device performances.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Production method of novel fluorescent biosensor for bacillus coli detection
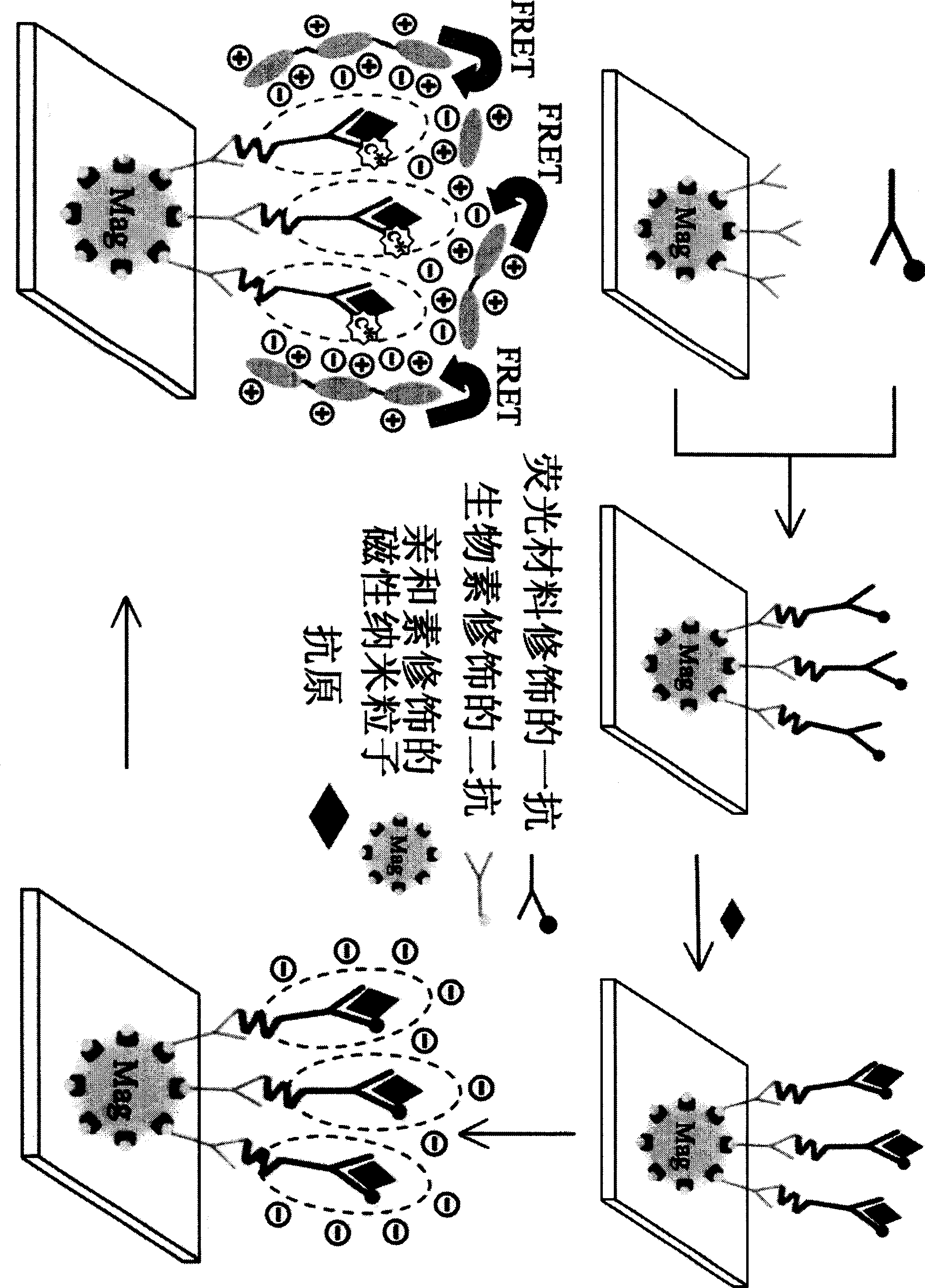
InactiveCN101470113AAchieve ultra-sensitive identificationSimple methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliElectricity
The invention relates to a super sensitivity fluorescence biosensor, for using magnetic practical to load antibodies and capture antigens, using water soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte to induce fluorescence amplification to check Escherichia coli O157: H7, which first utilizes magnetic particles to capture Escherichia coli O157: H7 antigens, to generate an antigen antibody unity with fluorescence labels; adds water soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte to induce and act with electrostatics, to recognize the super-molecules between the antigen antibody unity and the conjugated polyelectrolyte to form a super-molecule fluorescence composite system; exciting the fluorescence composite via the light or electricity of the conjugated polyelectrolyte, to induce the super fluorescence amplification of thousands and millions level of the prior fluorescence label signals, thereby forming a super sensitivity fluorescence biosensor. The biosensor system is based on the fluorescence sensitivity raising and efficiency raising effect of water soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte, which can be applied for fast super sensitivity detection on acute infectious disease as Escherichia coli O157: H7.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH +3
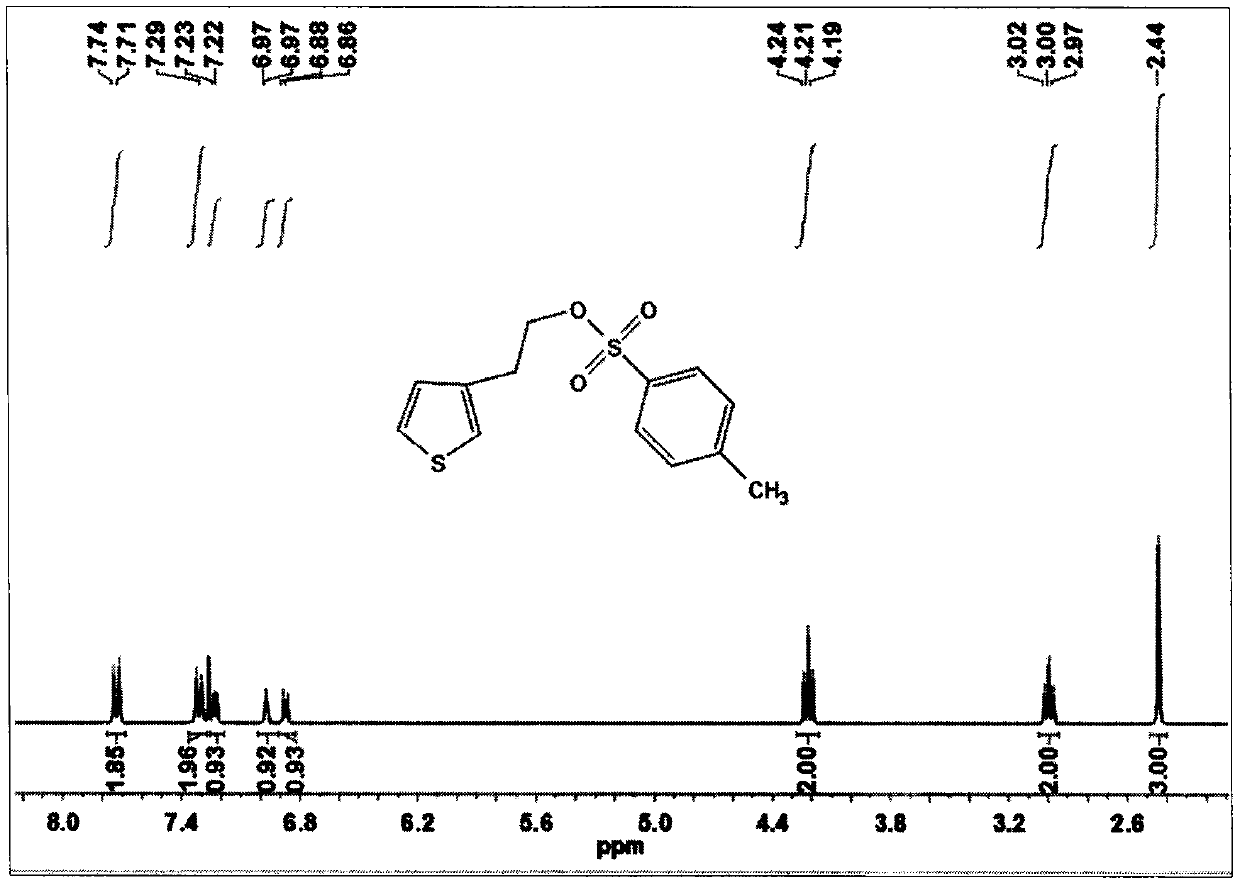
Conjugated polyelectrolyte for fluorine ion detection, preparation of conjugated polyelectrolyte and application of conjugated polyelectrolyte
ActiveCN105295009AGood selectionLaunch does not affectFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityIridium
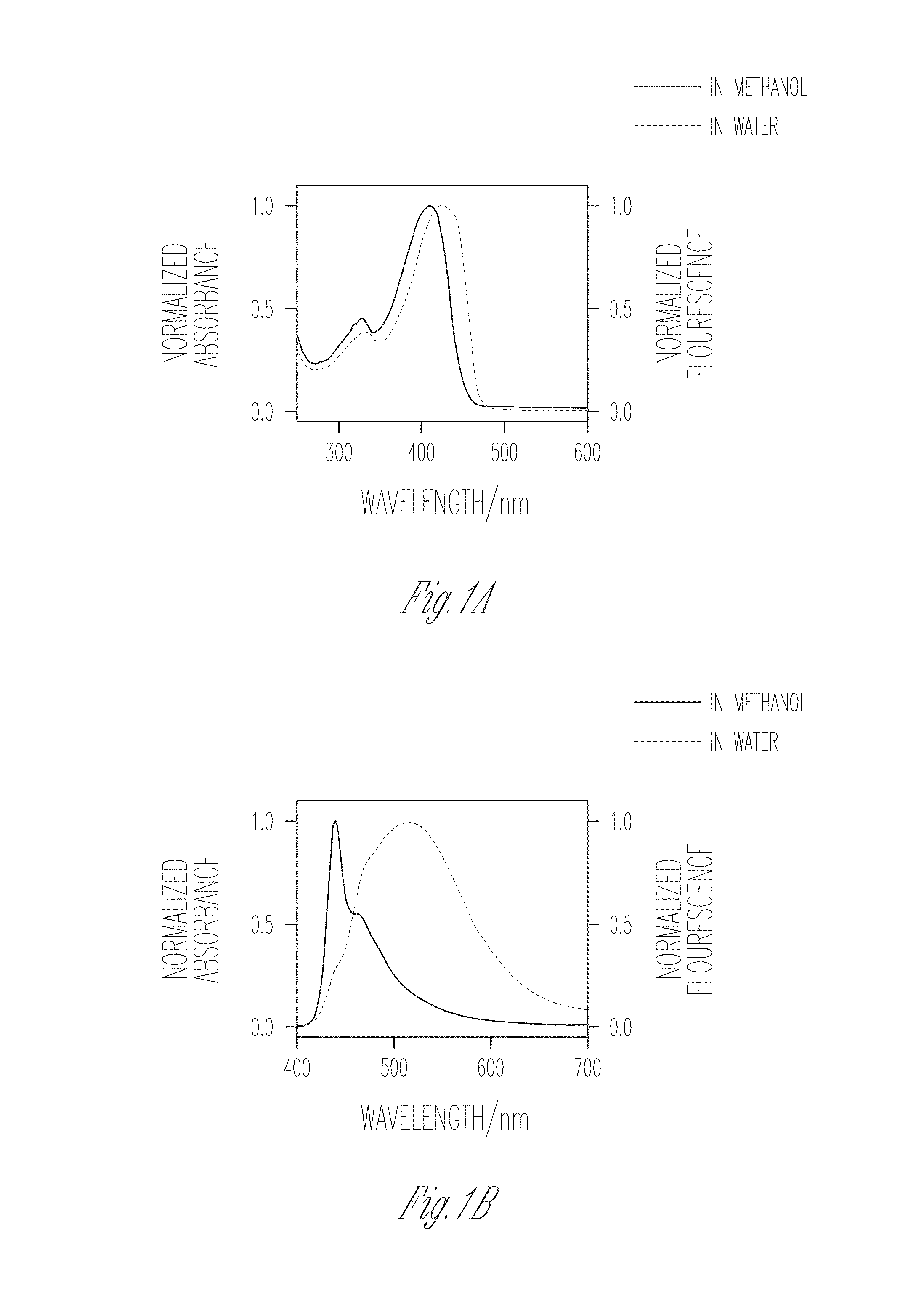
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorine ion detection and conjugated polyelectrolyte, and particularly relates to a conjugated polyelectrolyte capable of being used for fluorine ion detection, a preparation method of the conjugated polyelectrolyte and application of the conjugated polyelectrolyte to the field of fluorine ion chemicobiological sensors. The conjugated polyelectrolyte provided by the invention has a main chain structure of the conjugated polymers and an iridium complex substituting structure; through the main chain structure of the conjugated polymers, blue fluorescence can be emitted under the ultraviolet ray irradiation; through the iridium complex structure, red phosphorescence can be emitted under the visible light irradiation. The fluorine ions can promote the Si-O bound fracture in the iridium complex, so that the red light emission of the iridium complex quenches. The conjugated polyelectrolyte provides the possibility for building the chemicobiological sensors for high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of the fluorine ions. Meanwhile, better water solubility and biocompatibility are realized; the detection on the fluorine ions in the water solution and in the cells can be realized. The molecular formula of the conjugated polyelectrolyte is shown as the formula provided by the accompanying drawing, wherein the Ar is selected from the following substances shown as the accompanying drawing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Methods for determining conformational changes and self-assembly of proteins
The invention relates to methods for measuring conformational changes and self-assembly / aggregation of proteins, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils, using conjugated polyelectrolytes. The conjugate polyelectrolyte is exposed to the protein whereby the conjugated polyelectrolyte and the protein of interest interact, and a change of a property of the polyelectrolyte in response to conformational changes of the protein is observed. The detected change is used to determine different conformations of the protein, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Conjugated polyelectrolytes and methods of using the same
Various embodiments disclosed relate to conjugated polyelectrolytes and methods of using the same. Various embodiments provide a conjugated polyelectrolyte including a subunit having the structure —R1—Y—R2—Z—. At each occurrence, R1 is independently chosen from 1,4-bonded phenylene substituted by —X—R3—R4 j times and 2,5-bonded thiophene substituted by —X—R3—R4 j times. At each occurrence, Y is independently chosen from a bond and —C≡C—. At each occurrence, R2 is independently chosen from a bond, a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene, thiophenylene, azulenylene, heptalenylene, biphenylene, indacenylene, fluorenylene, phenanthrenylene, triphenylenylene, pyrenylene, naphthacenylene, chrysenylene, biphenylenylene, anthracenylene, and naphthylene. At each occurrence, Z is independently chosen from a bond and —C≡C—. The variables j, R3, and R4 are as defined herein.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Methods for detection of pathogenic prion proteins associated with prion diseases, using conjugated polyelectrolytes
InactiveUS20090197343A1Disease diagnosisBiological testingRadiation exposureElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of a pathogenic prion species in a sample comprising the steps—bringing the sample in contact with at least one conjugated polyelectrolyte (CPE)—irradiating the CPE with electromagnetic radiation—measuring the radiation emitted or absorbed by the CPE at at least one wavelength, and—comparing the measured emitted or absorbed radiation to at least one reference value corresponding to the CPE interacting with a known prion species. Optionally, the emitted or absorbed radiation is measured at least two wavelengths and a ratio is formed of the values of the measured radiation. The method facilitates differentiation between different strains of pathogenic prion species. The invention also relates to devices for performing the method.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Benzobithiadiazole-containing n-type water/alcohol soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN112646129AStable n-type conductivityImprove collection effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solar cellSide chain
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials, and discloses abenzobithiadiazole-containing n-type water / alcohol soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte as well as preparation and application thereof. The structure of the benzobithiadiazole-containing n-type water / alcohol soluble conjugated polyelectrolyte is shown as a formula I, A or B is a side chain with a water-alcohol soluble strong polar group, and at least one of A and B is a side chain with a water-alcohol soluble strong polar group, wherein x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.5 and is not 0, and n is a positive integer of 1-2000. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the conjugated polyelectrolyte. The conjugated polyelectrolyte disclosed by the invention has air-stable n-type conductivity, has extremely weak absorption in a visible light region, and does not influence light absorption of an active layer when being applied to an organic solar cell device; meanwhile, the conjugated polyelectrolyte disclosed by the invention has water / alcohol solubility and can be processed by a solution. The method is simple and easy to implement. The conjugated polyelectrolyte disclosed by the invention is used for preparing a photoelectric device and is used as an electron transport layer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
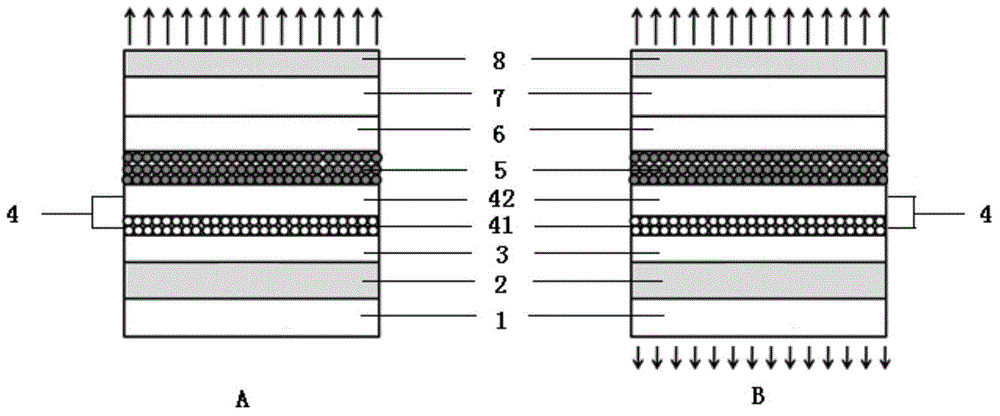
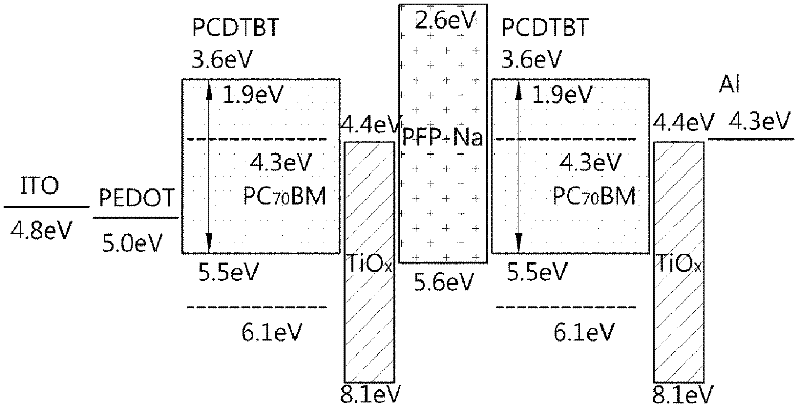
Multilayer organic solar cell using a polyelectrolyte layer, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN102396072AImprove efficiencyBroaden your optionsElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsConjugated polyelectrolyte
The invention relates to a multilayer organic solar cell using a polyelectrolyte layer, and to a method for manufacturing same. The multilayer organic solar cell comprises a first electrode, a first organic photoactive layer, a recombination layer, a second organic photoactive layer, and a second electrode. The recombination layer includes an n-type semiconductor material layer and a conjugated polyelectrolyte layer.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Conjugated polyelectrolyte, and preparation method therefor and biological application thereof
InactiveCN105348493ADecreased fluorescence intensityLittle change in contentMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureBrightness perception
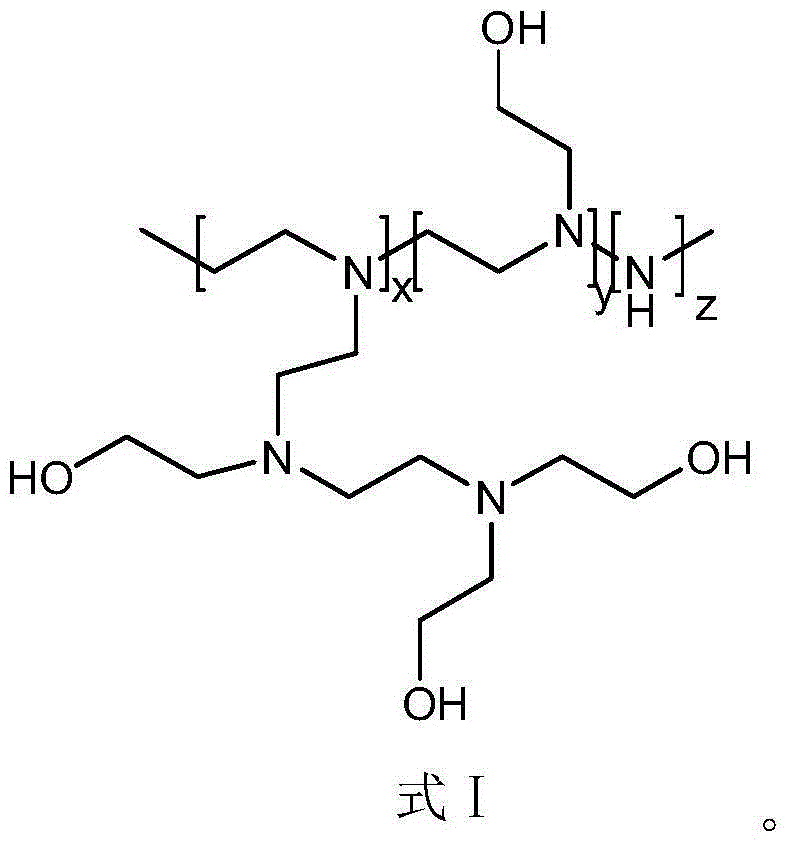
The present invention provides a conjugated polyelectrolyte, and a preparation method therefor and a biological application thereof. The conjugated polyelectrolyte has a chemical structure as shown in the formula I, wherein m is an integer whose value is 2-12, n is an integer whose value is 10-100, and Et is an ethly. The conjugated polyelectrolyte has good cell compatibility, low toxicity and excellent optical physical properties (such as high brightness and high optical stability), and is sensitive to ATP response, and can be effectively used for cell imaging or ATP semi-quantitative detection. The formula I is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Application of amino acid group-containing zwitterionic conjugated polyelectrolyte with hole transporting property
ActiveCN110408008ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityOrganic solar cell
An amino acid group-containing zwitterionic conjugated polyelectrolyte developed in the invention has the advantages of high stability, good solubility and energy level matching, has obvious advantages in perovskite solar cells than a conventional hole transport material PEDOT:PSS, and has potential and broad application prospects in the electronic fields such as perovskite solar cells, organic solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
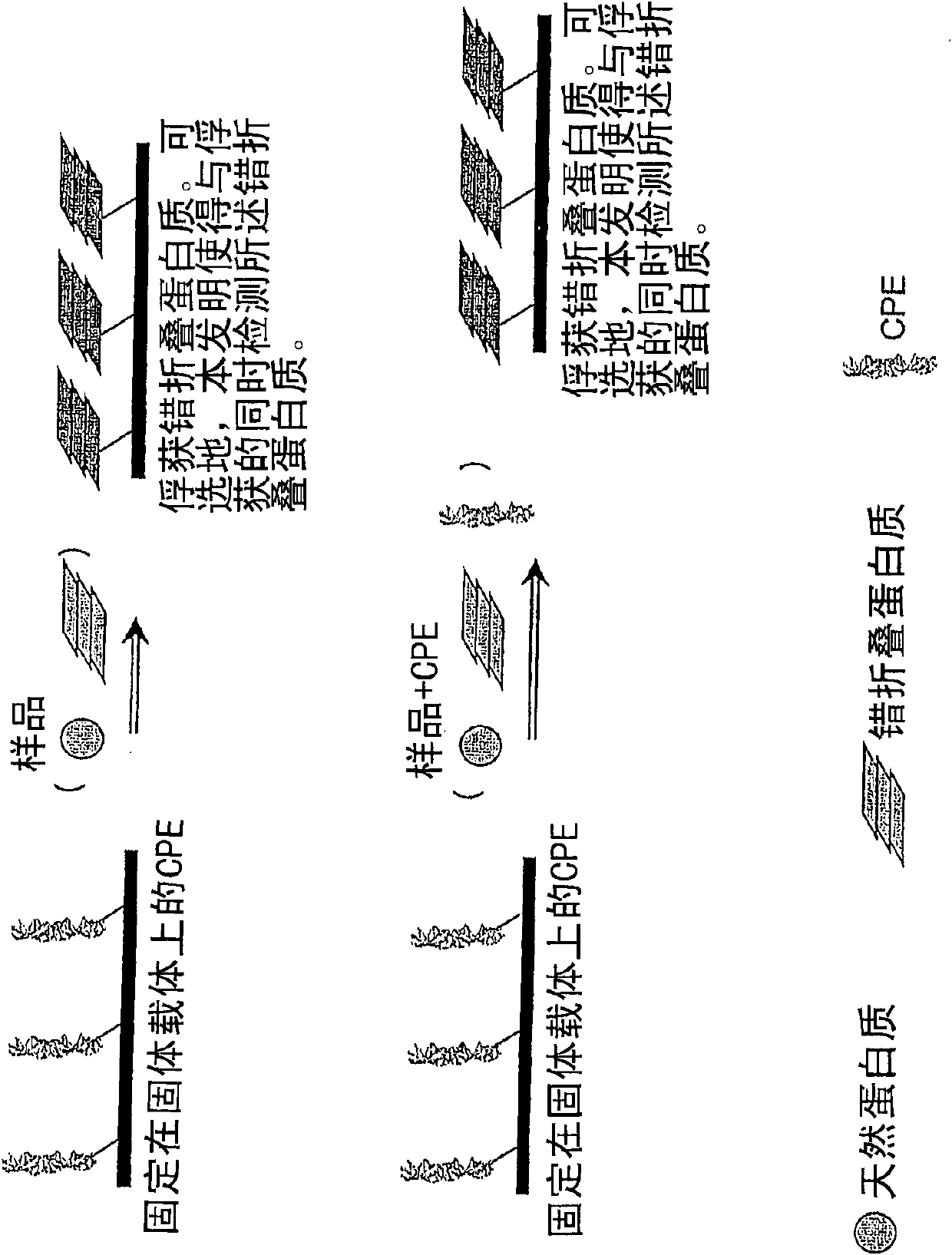
Medicamentous application of CPE (Conjugated Polyelectrolyte)
The invention relates to application of a CPE (Conjugated Polyelectrolyte) as a novel therapeutic agent which takes effect by interfering the formation of misfolding, pathological or rogue proteins or capturing the misfolding, pathological or rogue proteins in vivo.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX PHARMA
Binding of pathological forms of proteins using conjugated polyelectrolytes
InactiveCN101784559ANervous disorderPeptide preparation methodsNormal proteinProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a method for separation of an aggregated misfolded protein from an environment comprising a non-aggregating normal form of the protein, comprising contacting both said misfolded and normal protein with a conjugated polyelectrolyte (CPE) and separating the CPE / protein complex from the other constituents of the sample.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Perylene grafted poly (4-vinylpyridine), synthesis thereof and preparation of fluorescent probe
InactiveCN103897085AEnhanced Fluorescence Energy Resonance Transfer EfficiencyIncreased resonance transfer efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionCationic polyelectrolytes
The invention relates to perylene grafted poly (4-vinylpyridine), synthesis thereof and preparation of a fluorescent probe, and belongs to the fields of functional polymer technology, analytical chemistry and bioanalytical chemistry. The synthesis method comprises the steps of: grafting perylene A bromine onto poly (4-vinylpyridine); protonizing the product by using iodomethane to obtain perylene grafted poly (4-vinylpyridine) PFPM cationic polyelectrolyte. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the fluorescent probe by using perylene grafted poly (4-vinylpyridine). The synthesis method of the dis-conjugated polyelectrolyte PFPM disclosed by the invention is easy to operate; when DNA is added in the PFPM solution to form a composite probe, PFPM is aggregated, and the fluorescence intensity is increased. According to the invention, a dual detection mechanism of intercalation and aggregation-induced emission is provided, is not previously reported and has good reference meaning to future researches.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Conjugated polyelectrolyte photoelectric material and applications thereof in polymer light-emitting diodes
ActiveCN102977344BNo acid corrosionConducive to large-scale industrializationOrganic chemistryHole injection layerSide chain
The invention discloses a conjugated polyelectrolyte photoelectric material and applications thereof in polymer light-emitting diodes. A side chain of the conjugated polyelectrolyte photoelectric material disclosed by the invention is provided with quaternary ammonium salt polar groups, so that the material can be dissolved in polar solvents such as methanol and ethanol, but is insoluble in solvents such as toluene and the like. The conjugated polyelectrolyte photoelectric material can be used as a hole-injection layer material to be applied to polymer light-emitting diodes.
Owner:HAIMEN BIWEI INTPROP SERVICE CO LTD
Conjugated-nonconjugated n-type polyelectrolytes and their applications in organic optoelectronic devices
ActiveCN105384930BImprove mobilityImprove conductivityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesOrganic chemistryPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to conjugated-non-conjugated N-type polyelectrolyte and its application in organic photoelectric devices. The conjugated-non-conjugated N-type polyelectrolyte has A, B and X ‑ Three components, A is a conjugated unit component, B is a non-conjugated alkyl chain containing one or more quaternary ammonium salt groups, X ‑ It is the negative ion corresponding to the nitrogen positive ion on the B component quaternary ammonium salt. The polyelectrolyte can be processed with strong polar solvents such as alcohol, and is suitable for making complex multilayer photovoltaic devices. The conjugated-non-conjugated polyelectrolyte can be used as a cathode interface modification material in organic photoelectric devices to improve device performance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com