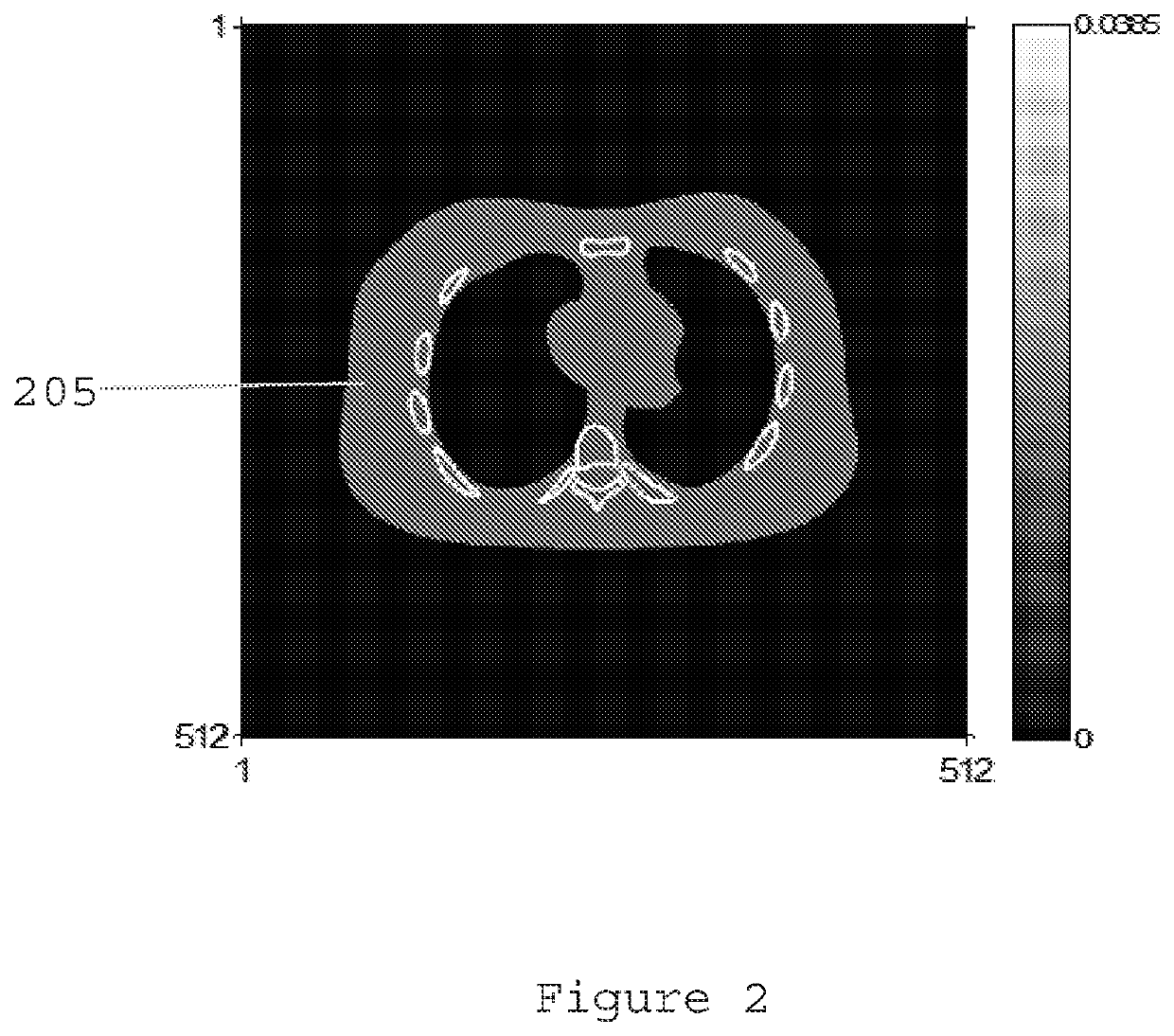
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Computed tomography colography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-parameter X-ray computed tomography
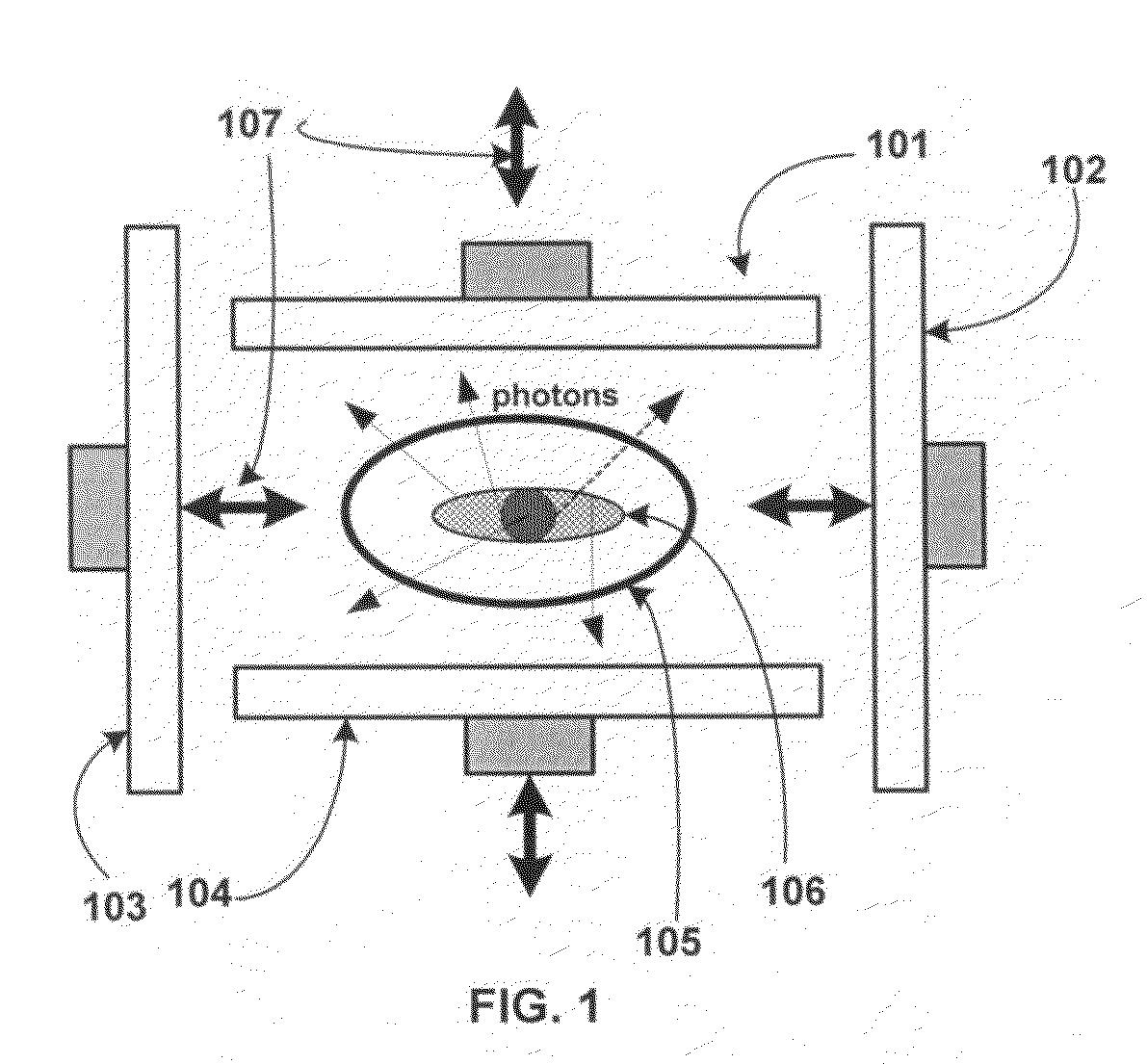
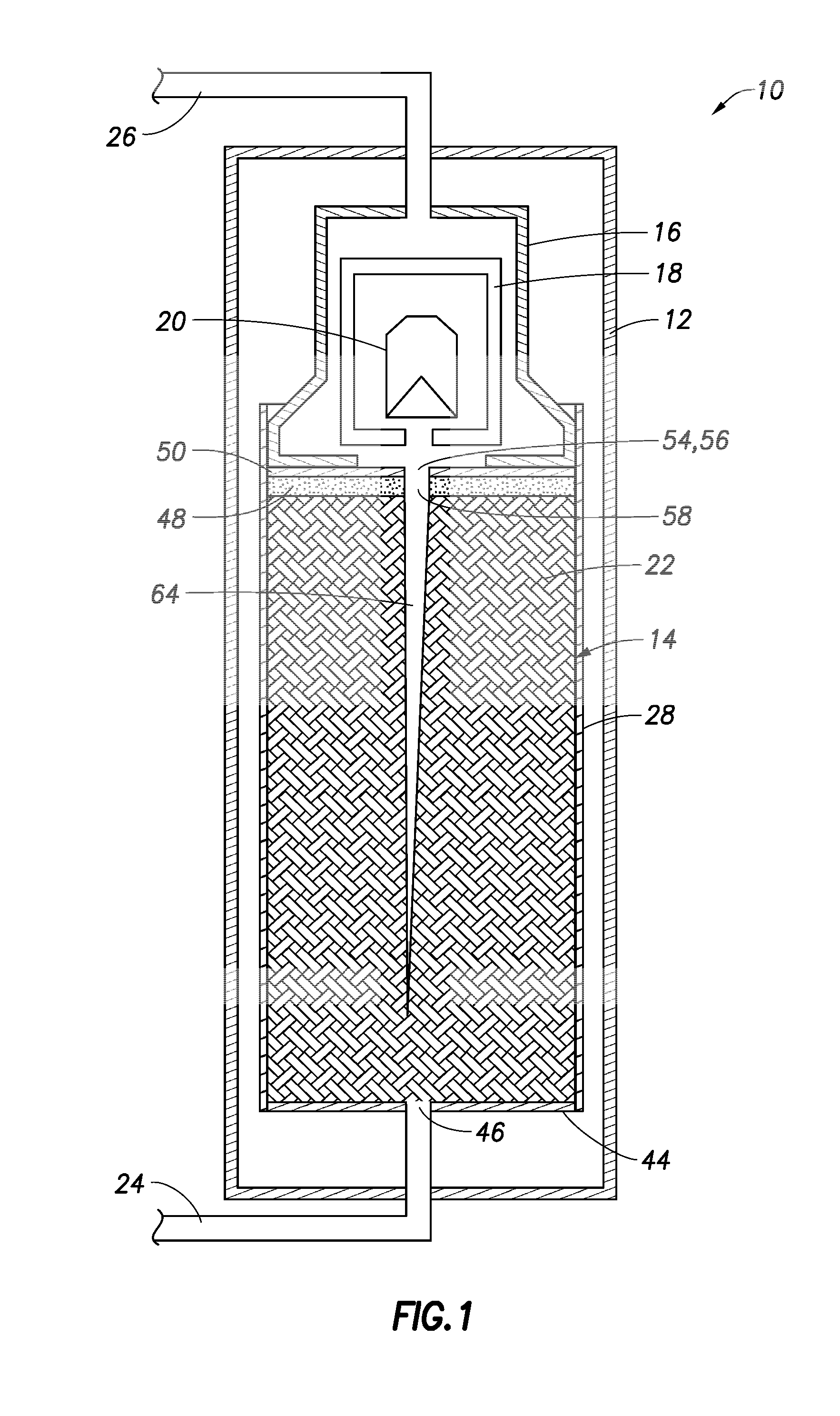
ActiveUS8121249B2Eliminate crosstalkIncrease sampling rateRadiation/particle handlingTomographyData setX-ray
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
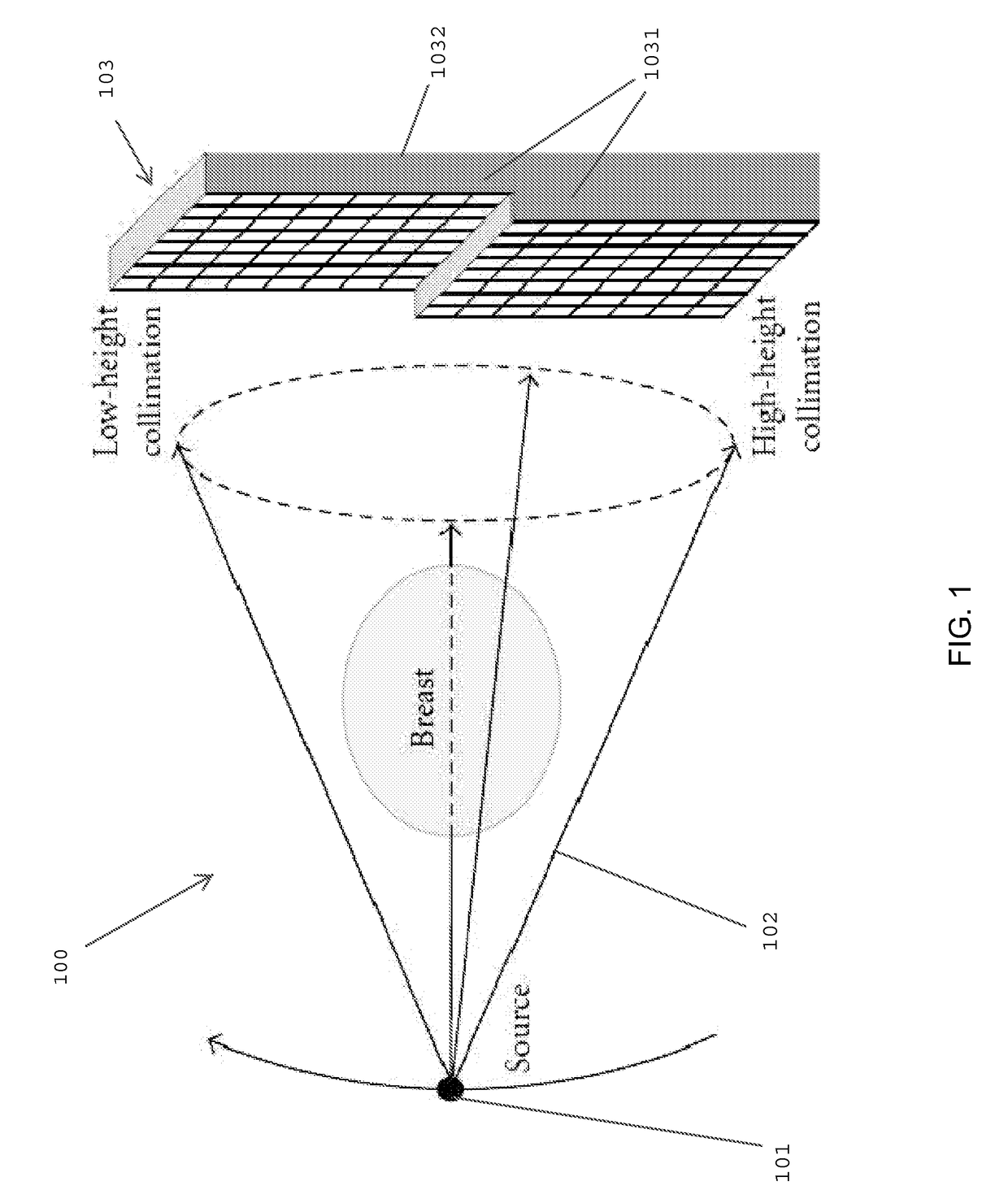
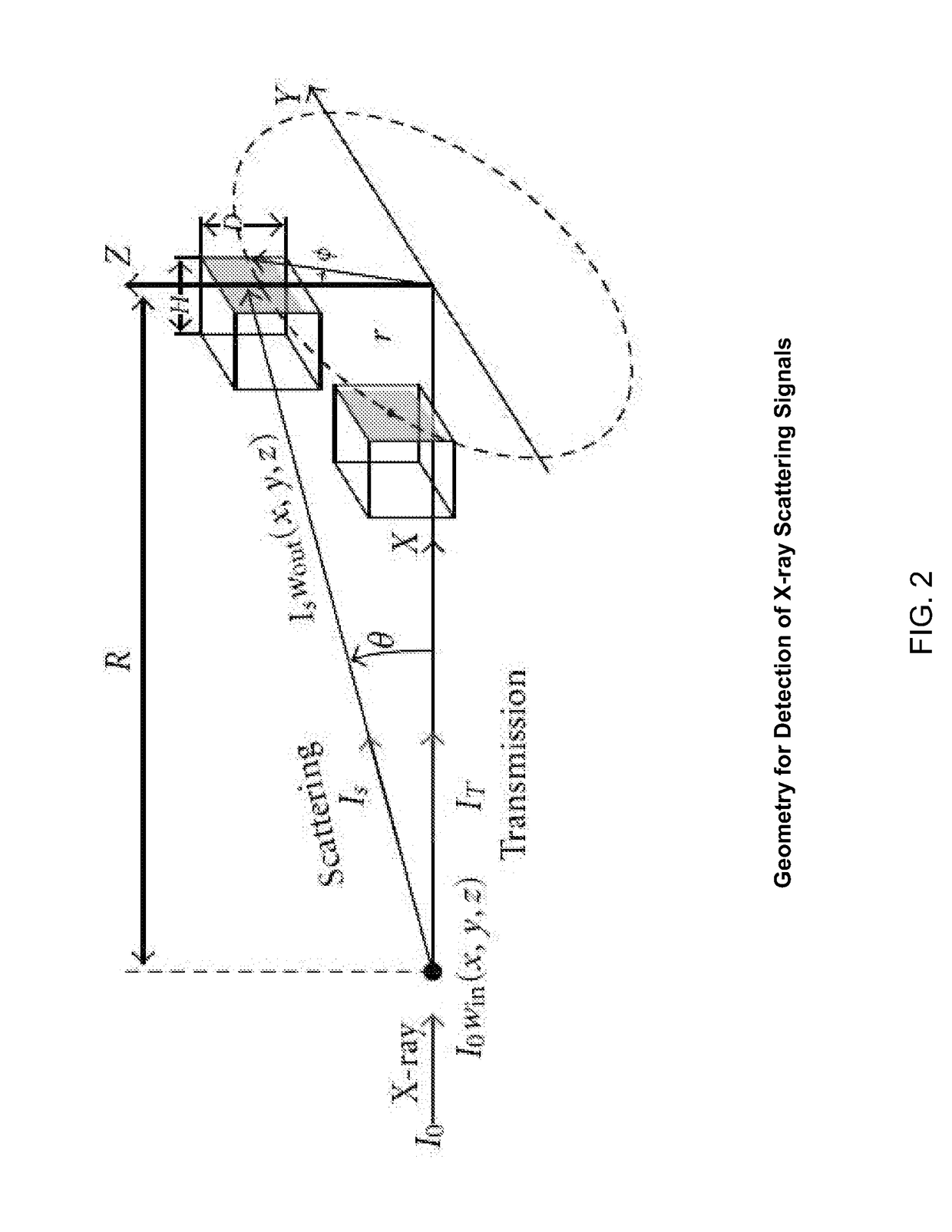
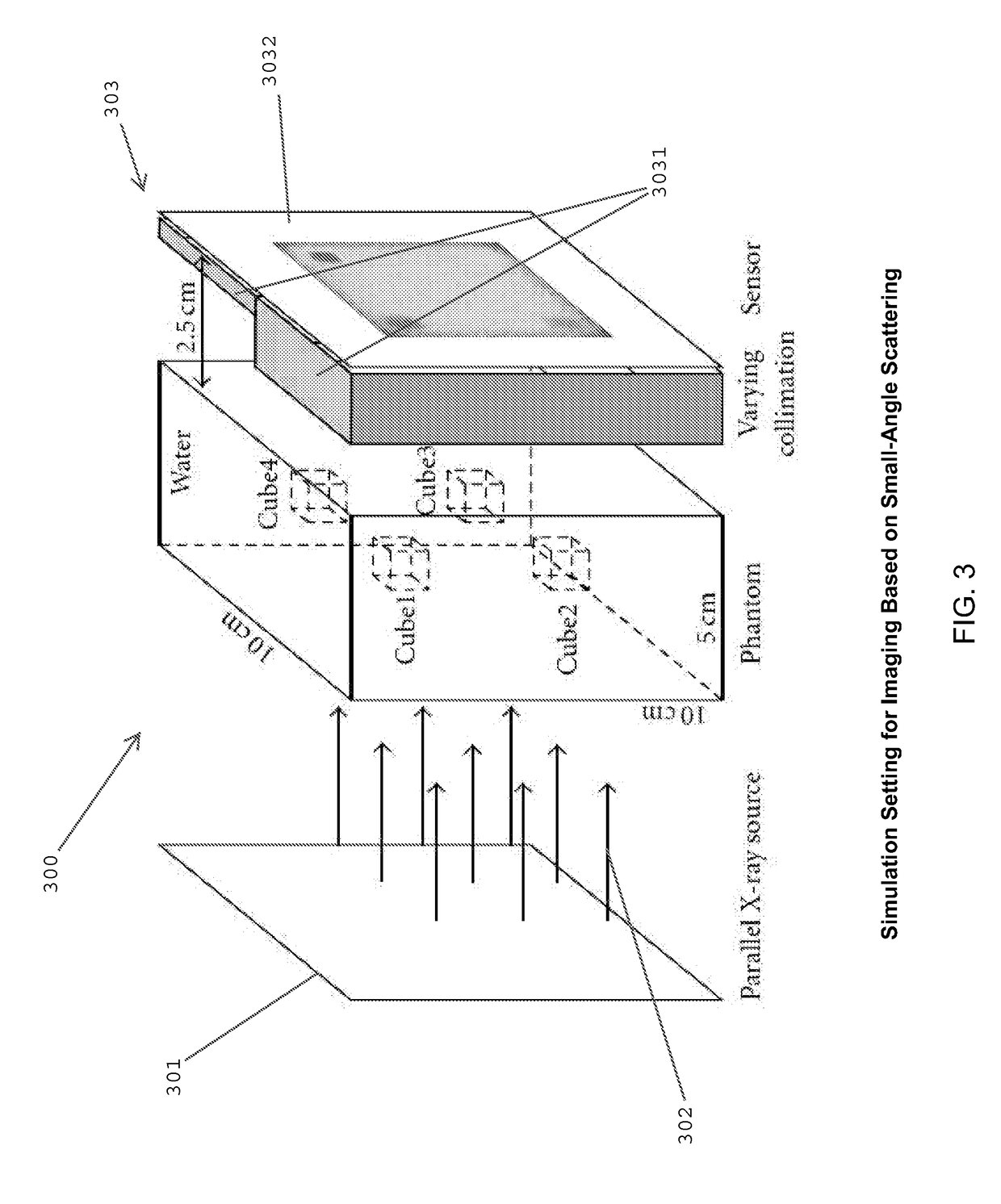
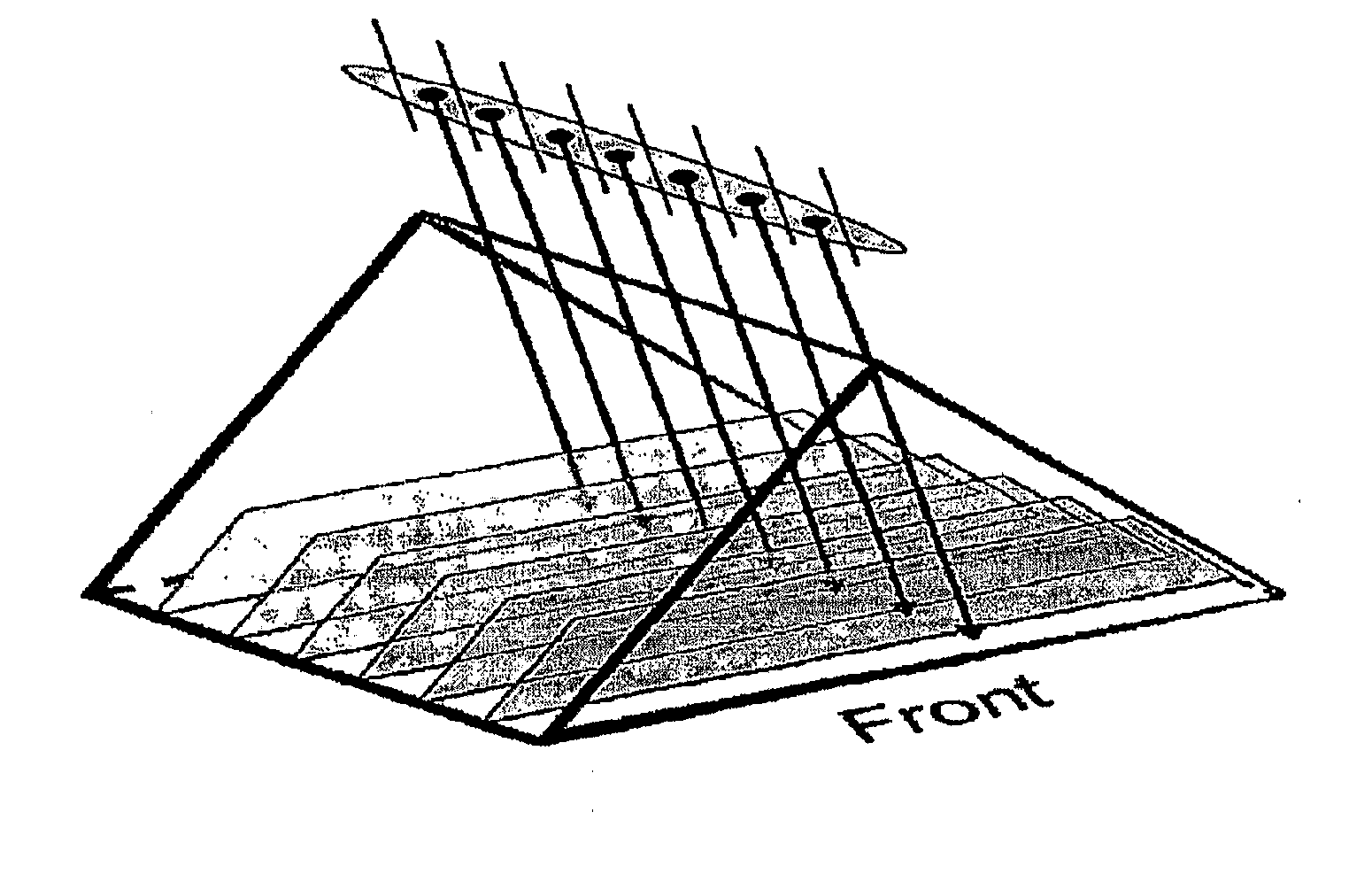
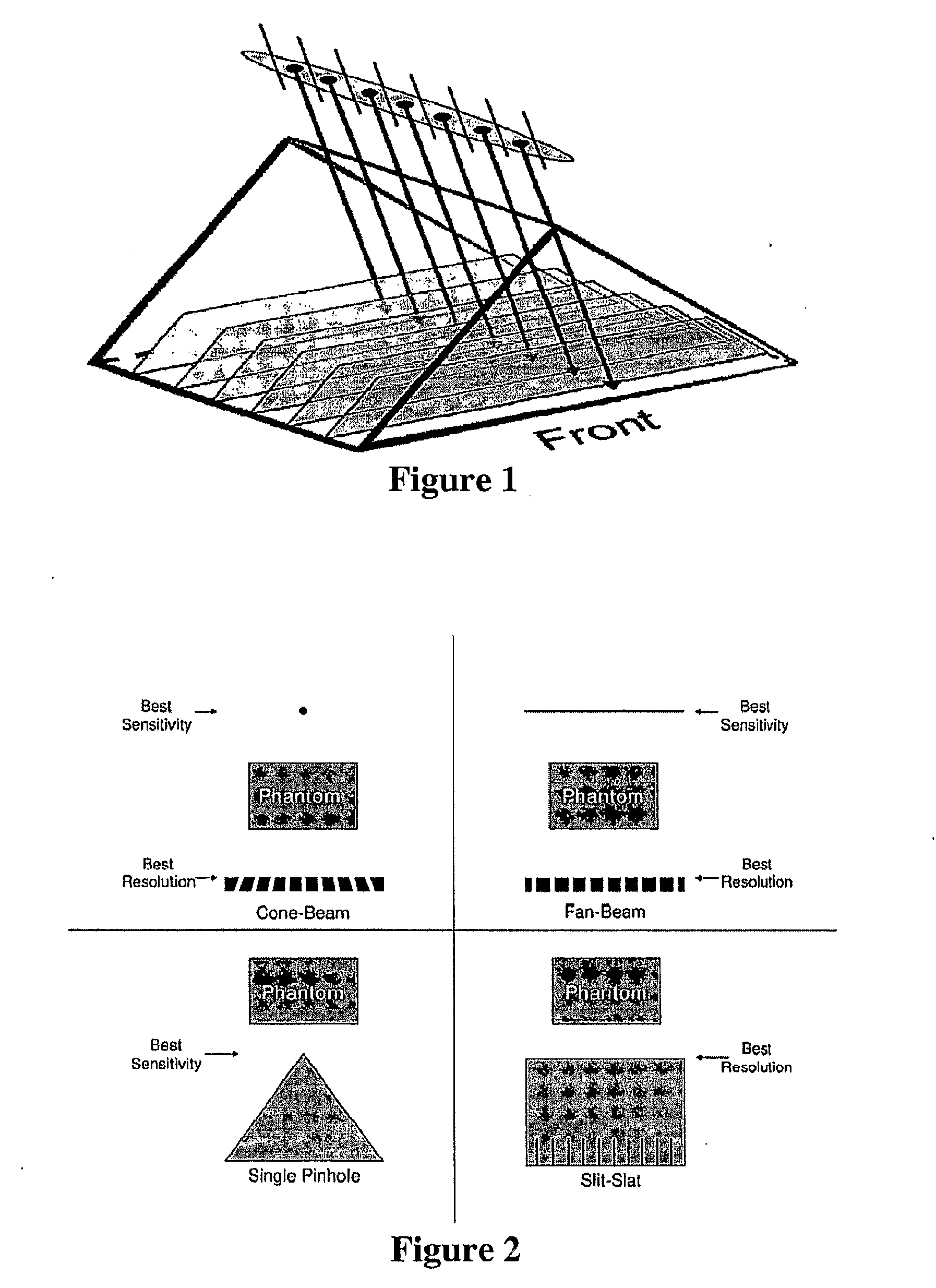
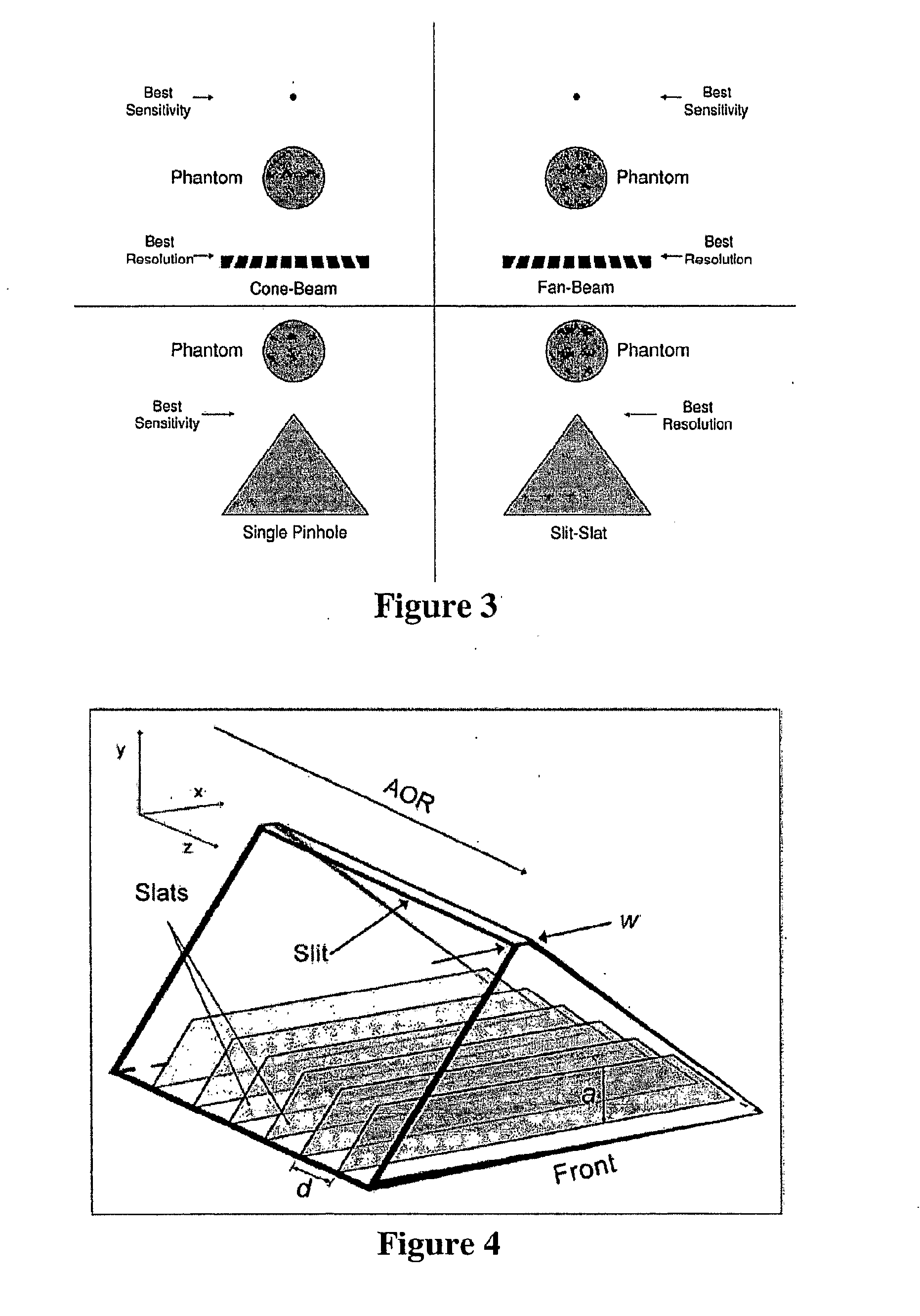
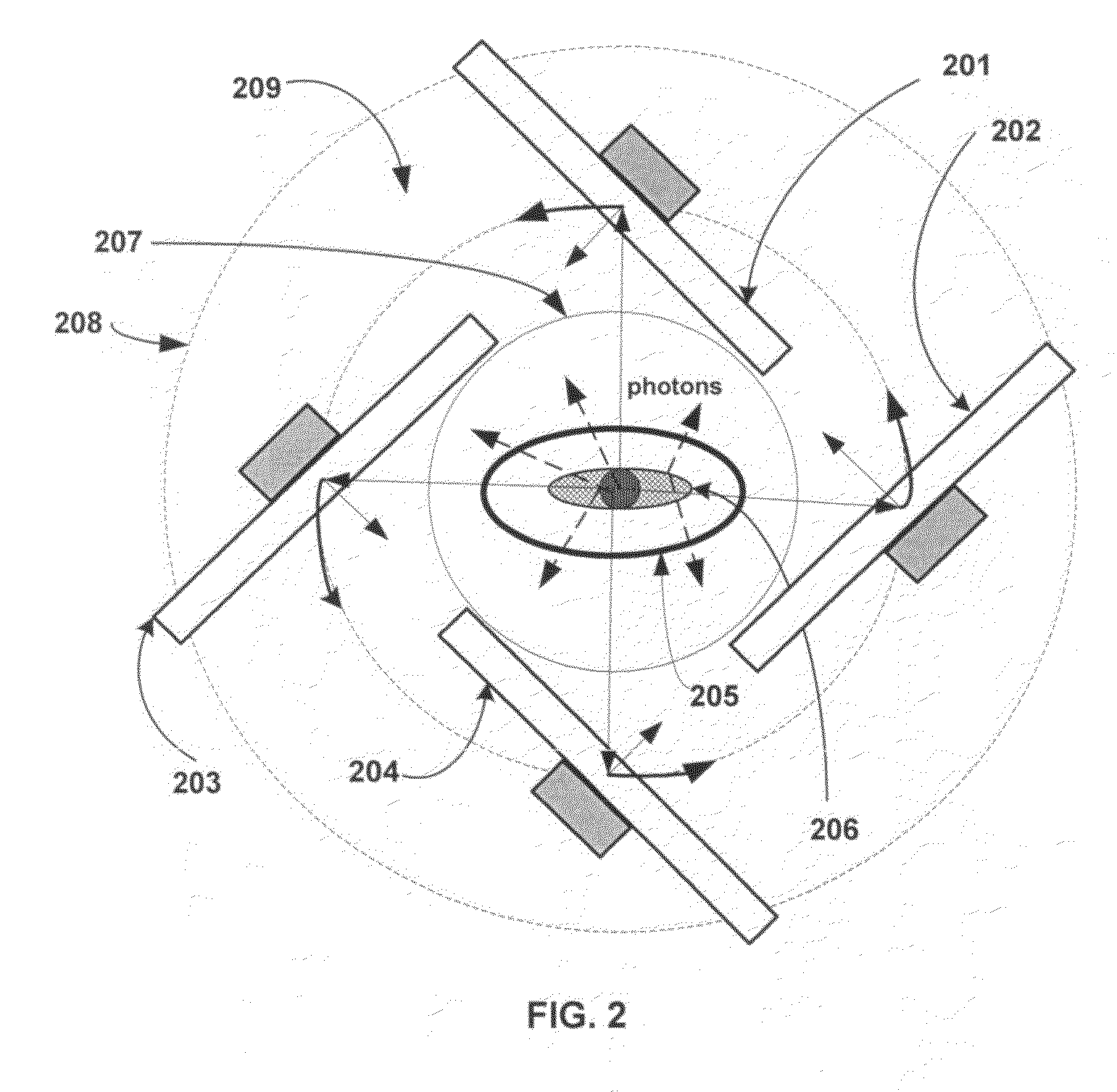
Slit-slat collimation
ActiveUS7831024B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionSingle-photon emission computed tomography
This invention is directed to a collimator and collimation techniques. Specifically, the invention is directed to a collimator and method for collimation wherein the collimator combines the resolution and sensitivity properties of pinhole Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging with the 2D complete-sampling properties of fan-beam collimators.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
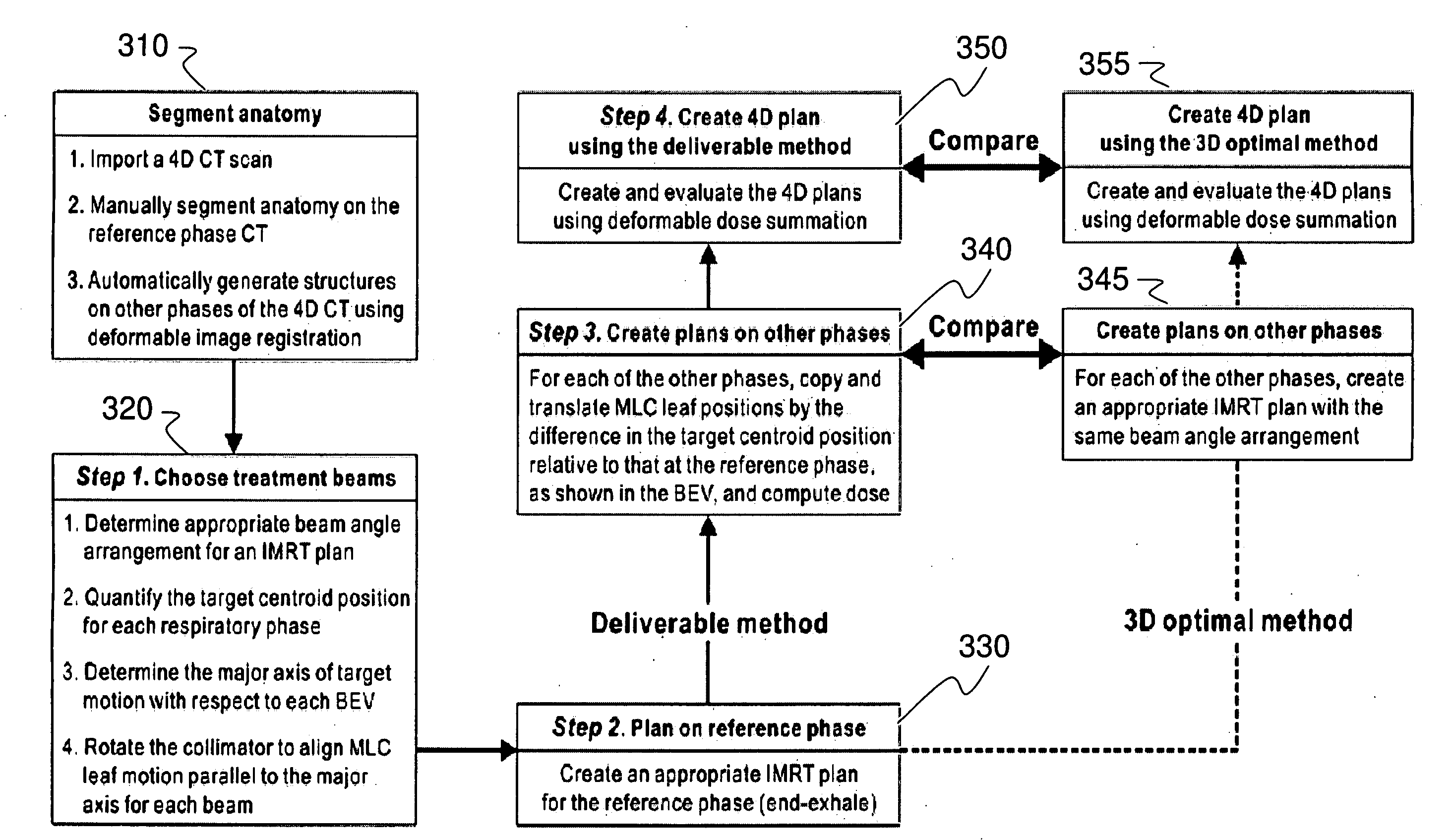
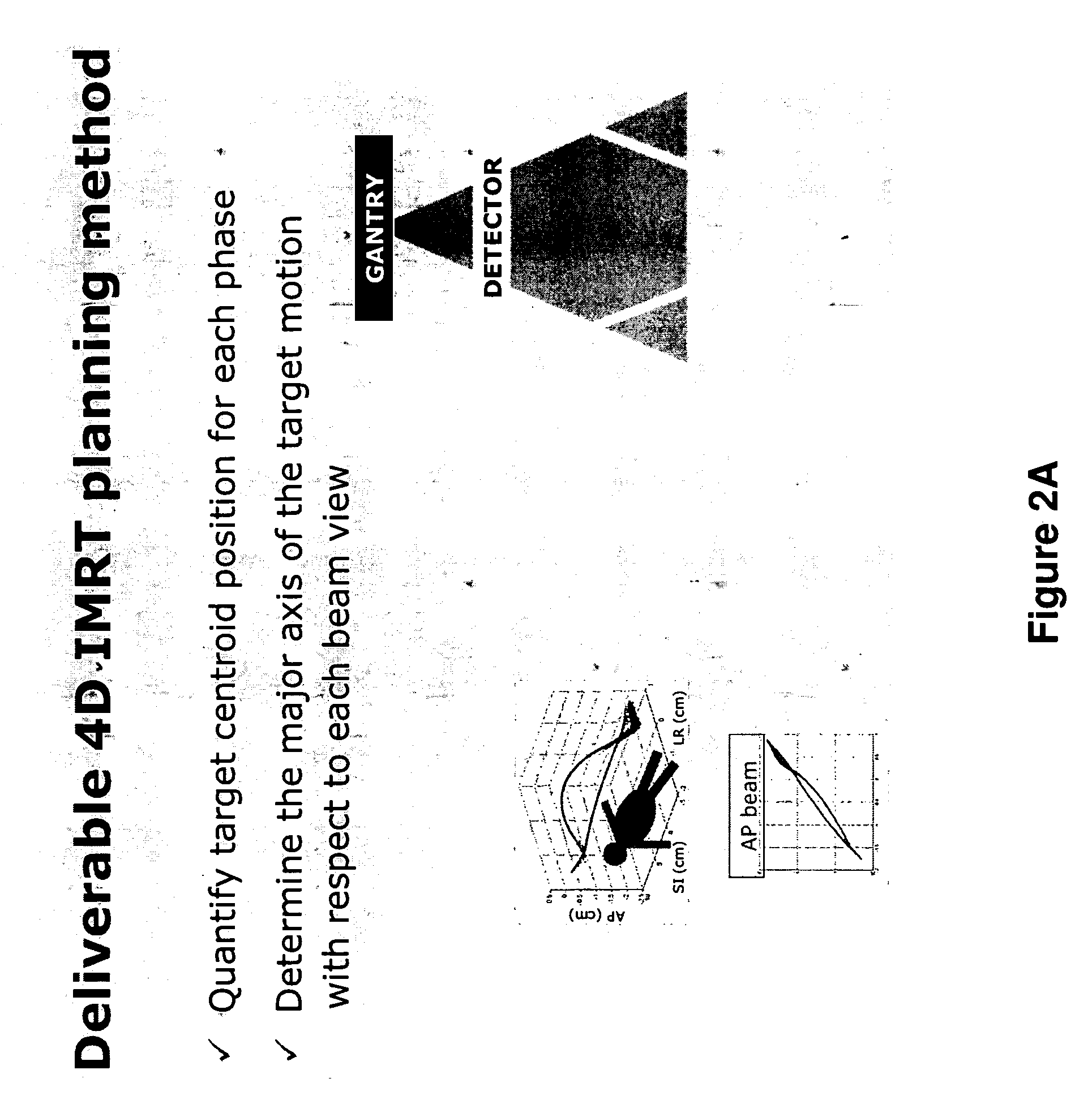
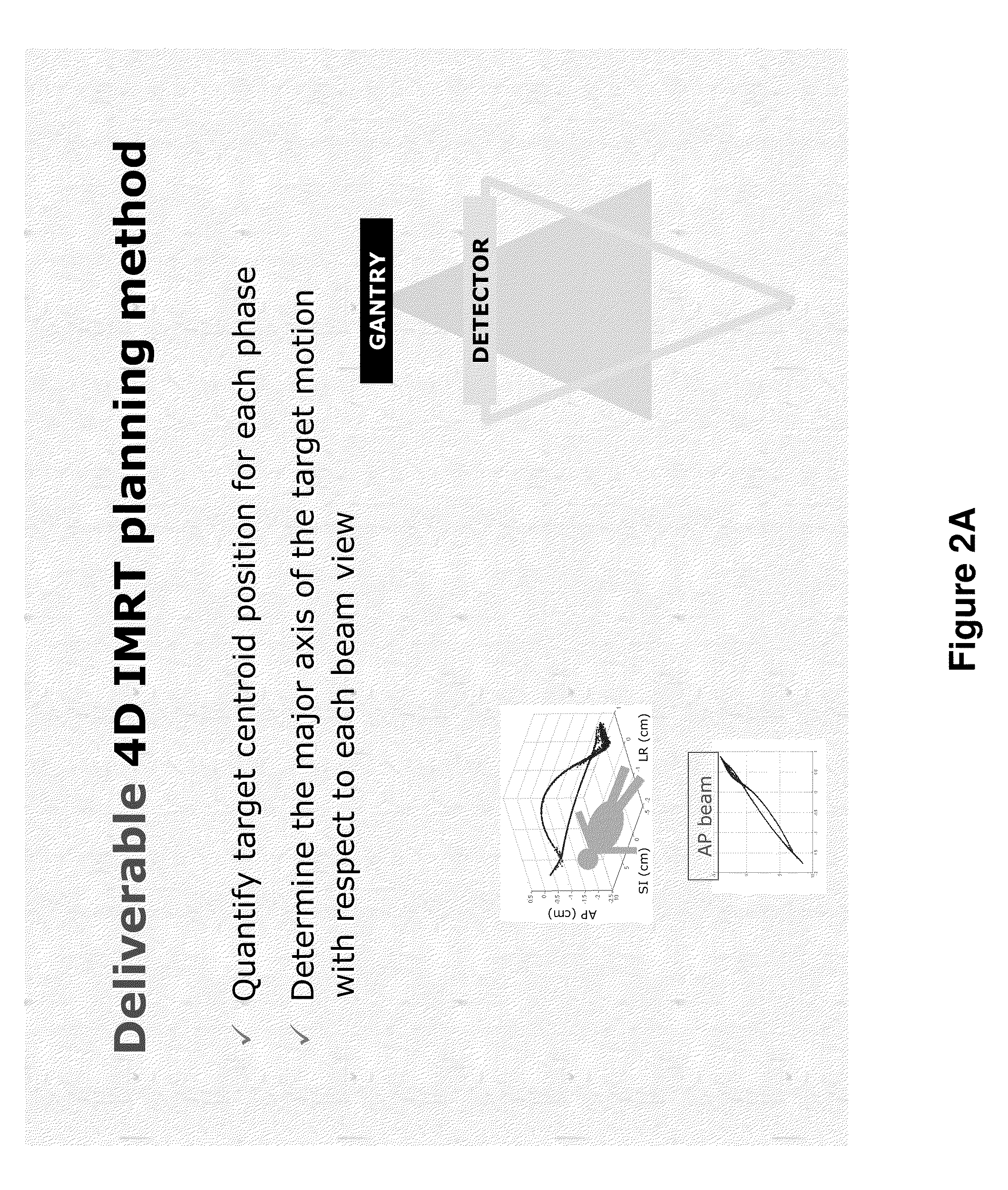
Method and system for four dimensional intensity modulated radiation therapy for motion compensated treatments
InactiveUS20090041188A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresTumour volume
A deliverable four dimensional (4D) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning method is disclosed, for delivery using a linear accelerator with a dynamic multi-leaf collimator (DMLC). A 4D computed tomography (CT) scan is used for segmenting tumor anatomy on a reference phase of periodic motion of the tumor. Deformable registration of the 4D CT data is used to generate corresponding anatomical structures on other phases. Preferably, the collimator for each beam position is aligned using the gross tumor volume (GTV) centroid motion corresponding to the periodic motion of the tumor, as determined from the two dimensional (2D) projection of a given beam position. A deliverable IMRT plan is created on the 4D CT image set in which the MLC leaf positions and beam on / off status can vary as a function of respiratory phase by solving a four dimensional optimization problem. The mechanical constraints of the MLC leaves are included in the optimization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
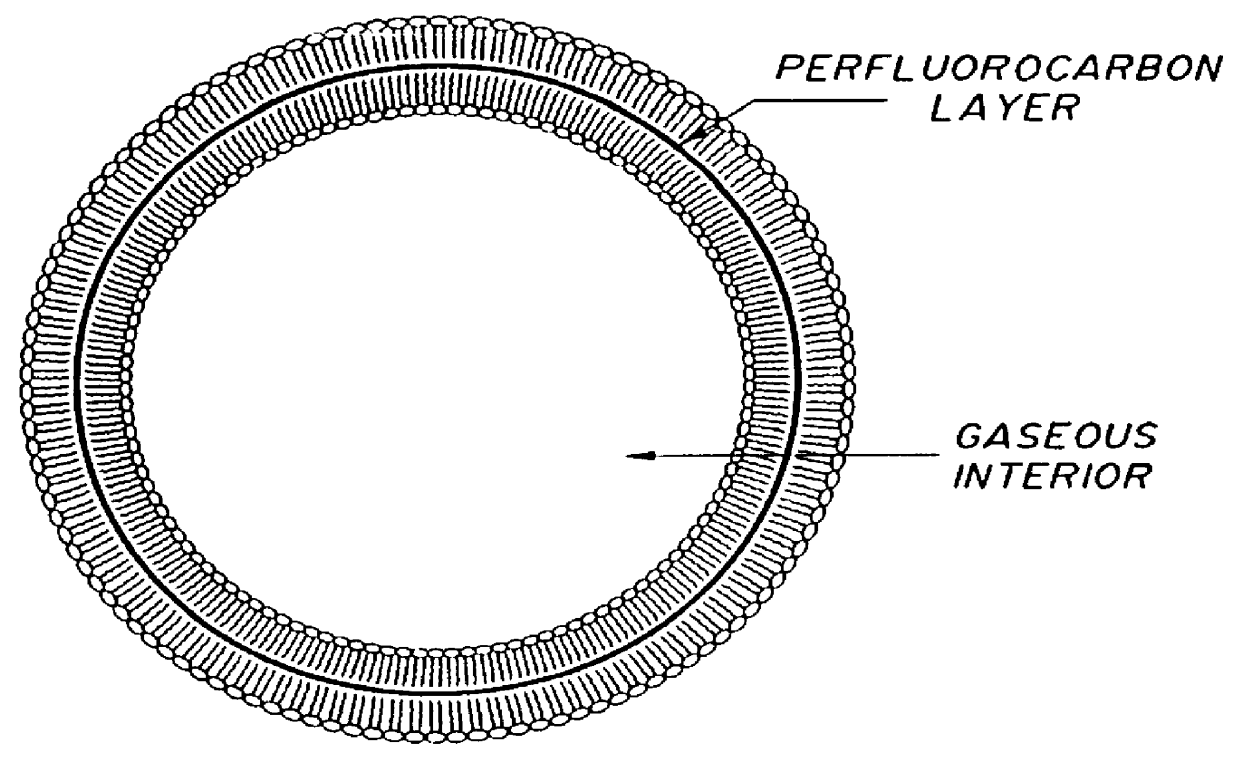
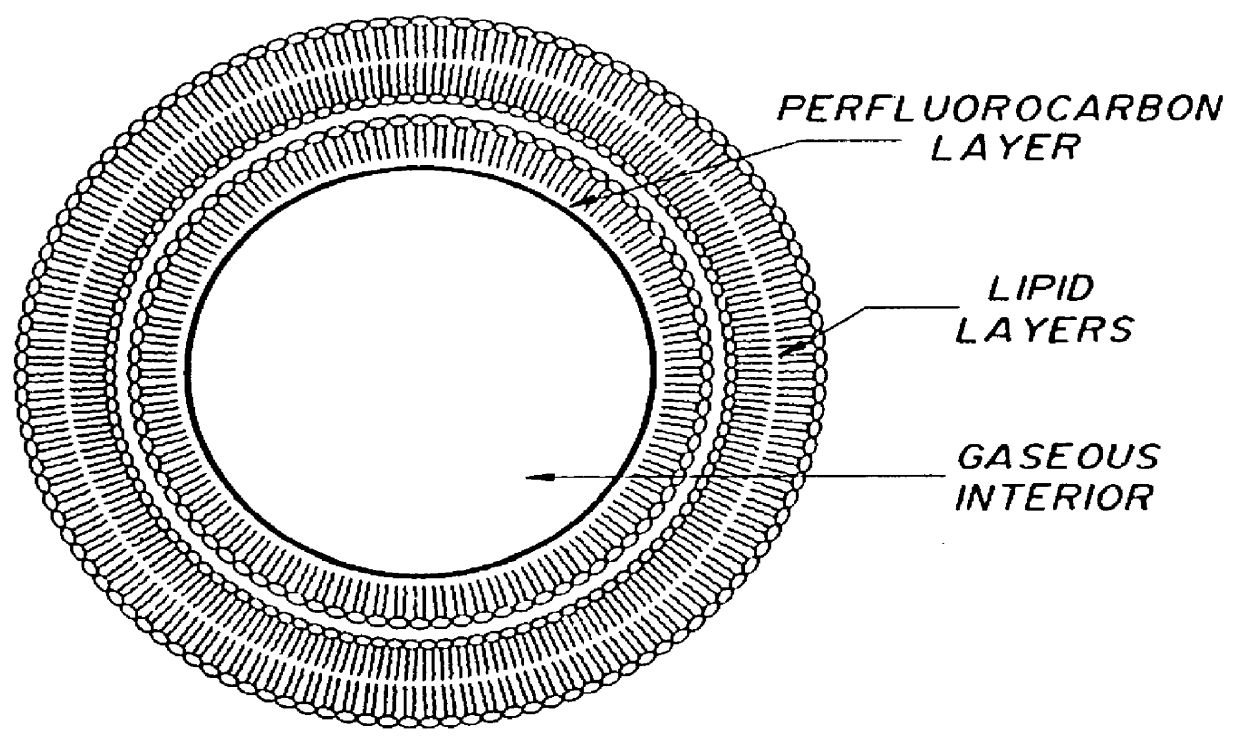
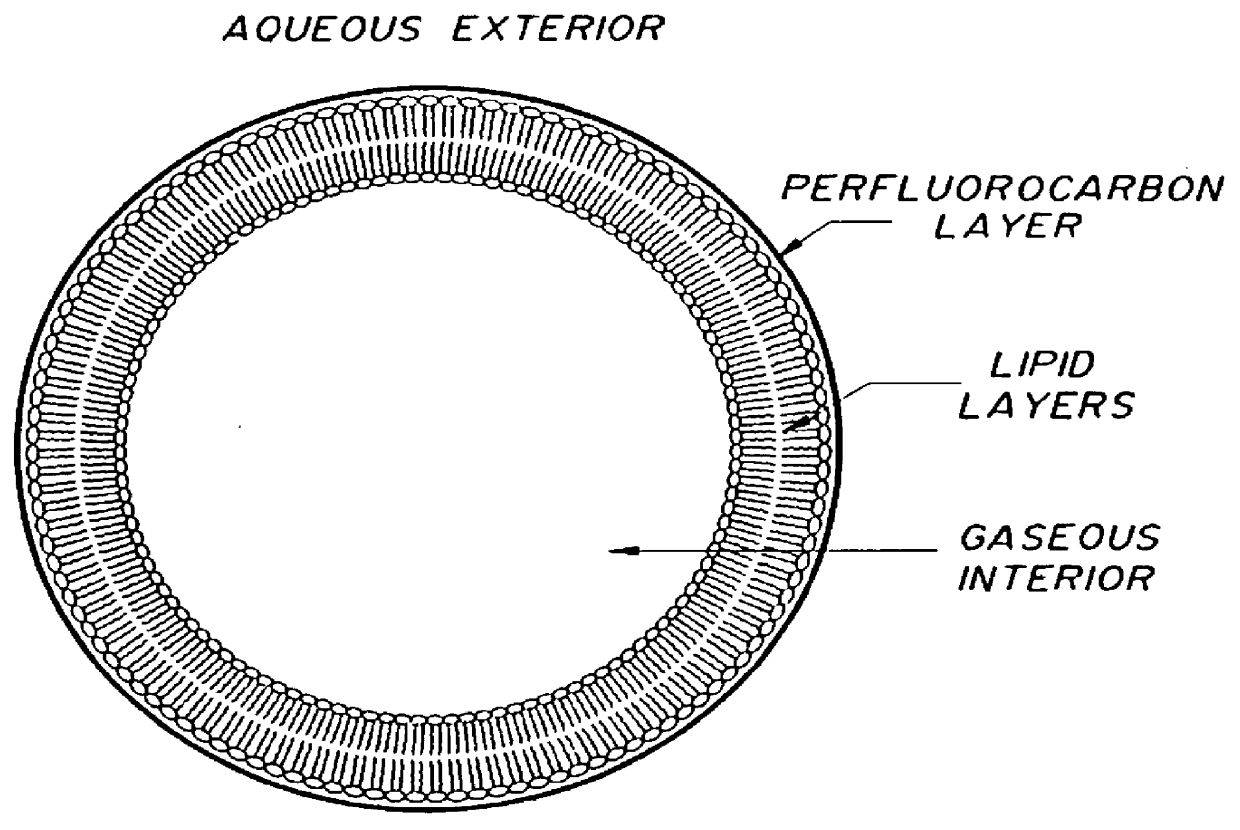
Method of computed tomography using fluorinated gas-filled lipid microspheres as contrast agents
InactiveUS6117414ALow densityEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryLipid formationFluorinated gases
Novel gas filled microspheres useful as computed tomography (CT) contrast agents. The microspheres are prepared from a gas and / or a gaseous precursor, and one or more stabilizing compounds.
Owner:IMARX THERAPEUTICS
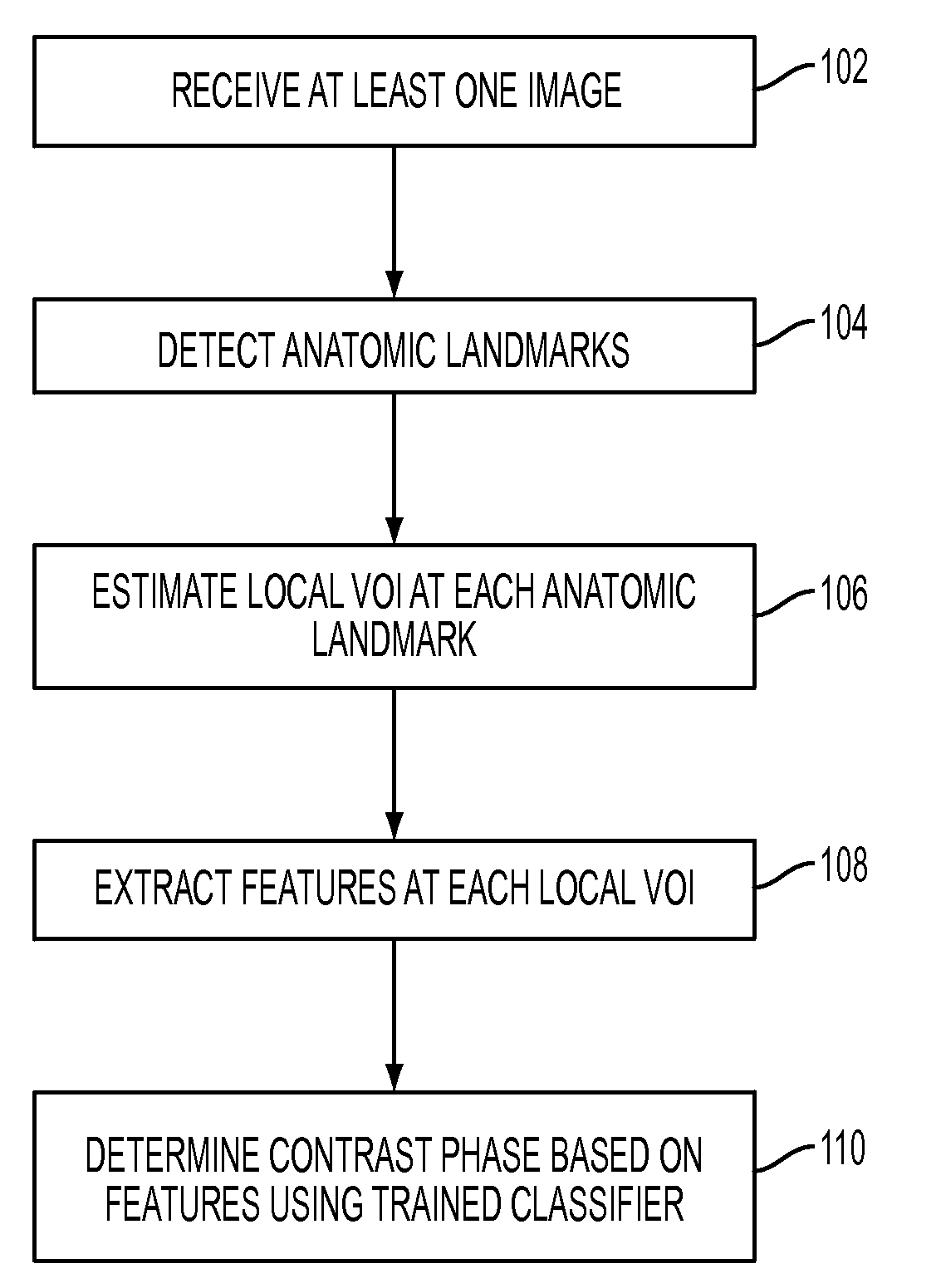
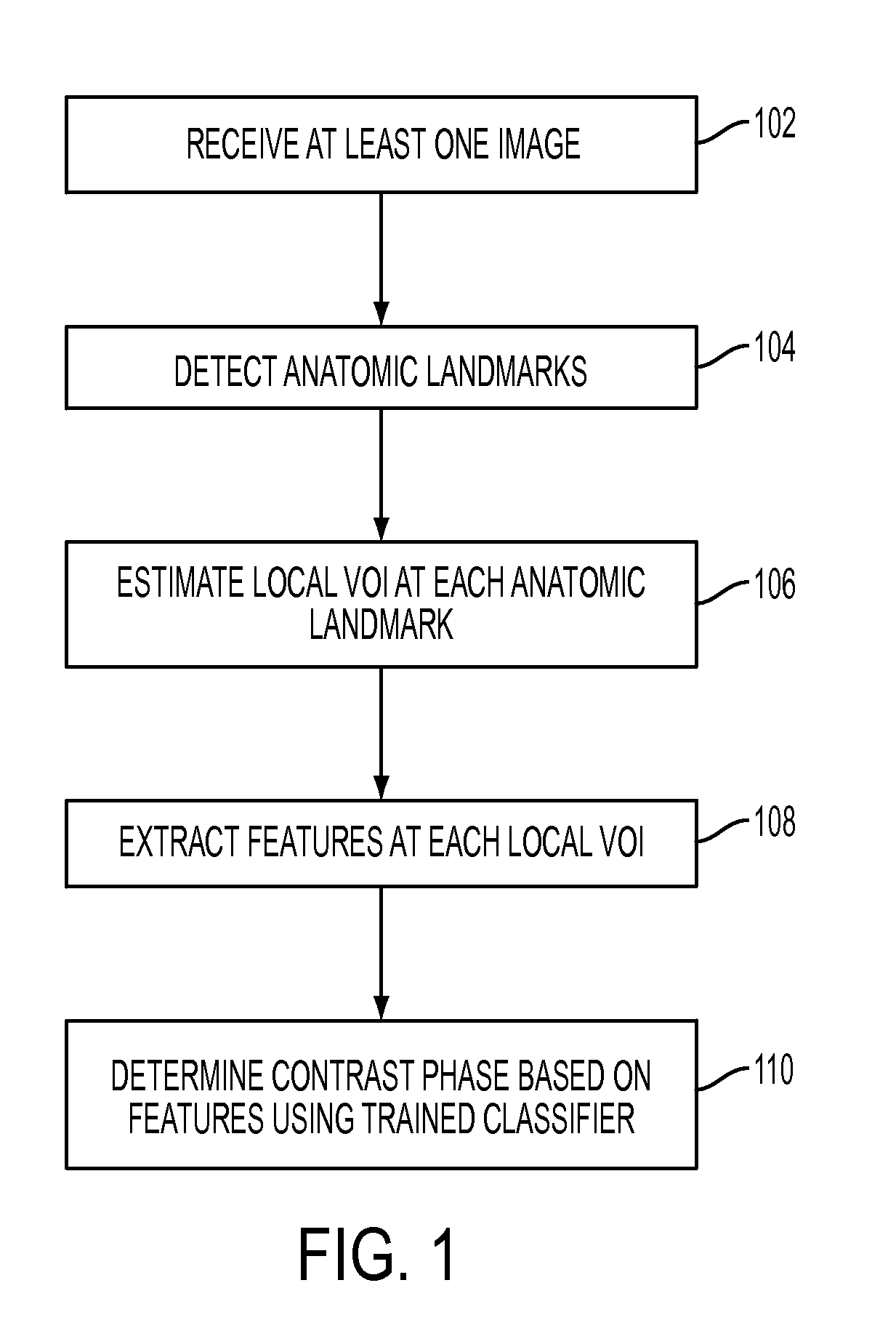
Method and System for Automatic Contrast Phase Classification
A method and system for classifying a contrast phase of a 3D medical image, such as a computed tomography (CT) image or a magnetic resonance (MR) image, is disclosed. A plurality of anatomic landmarks are detected in a 3D medical image. A local volume of interest is estimated at each of the plurality of anatomic landmarks, and features are extracted from each local volume of interest. The contrast phase of the 3D volume is determined based on the extracted features using a trained classifier.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
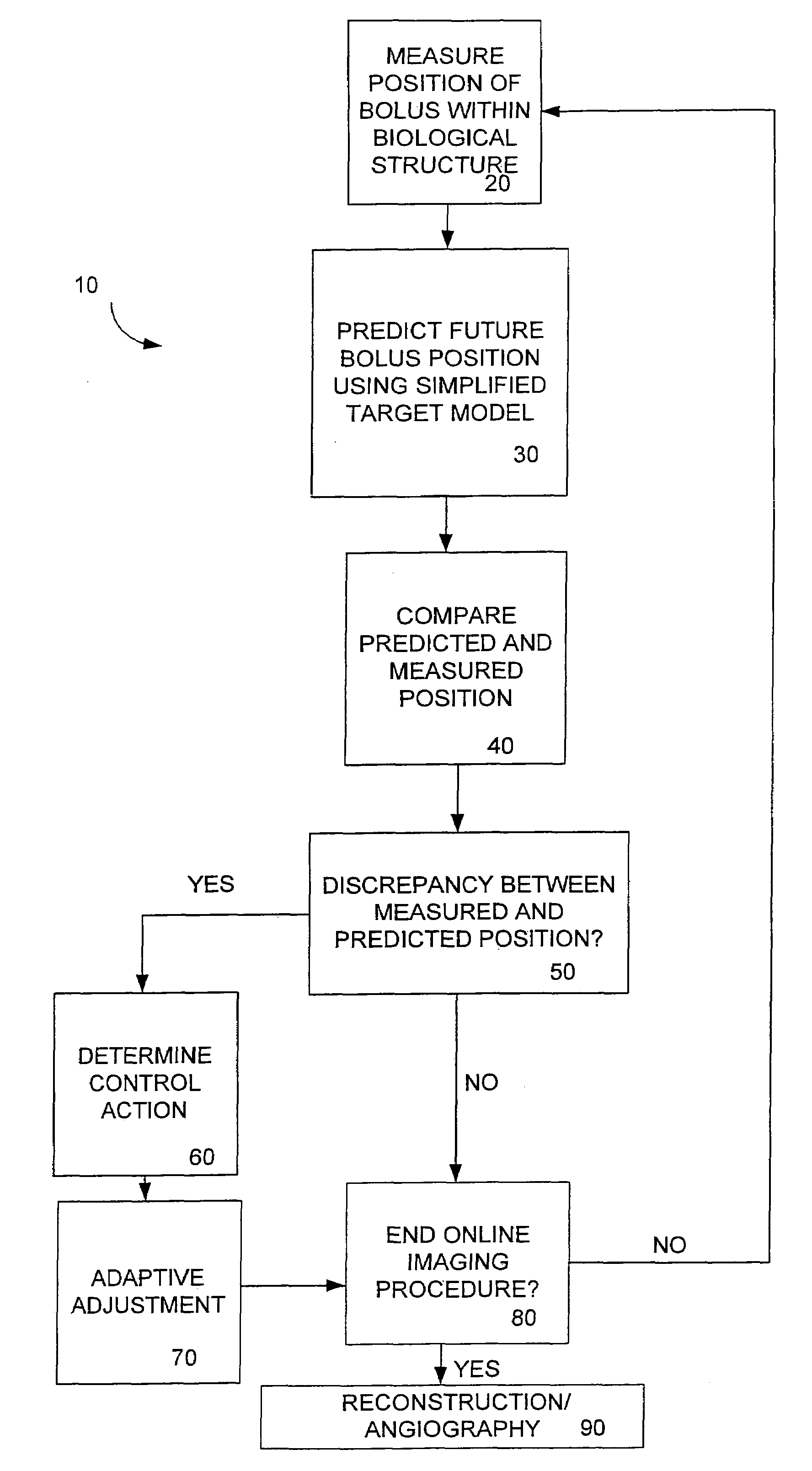
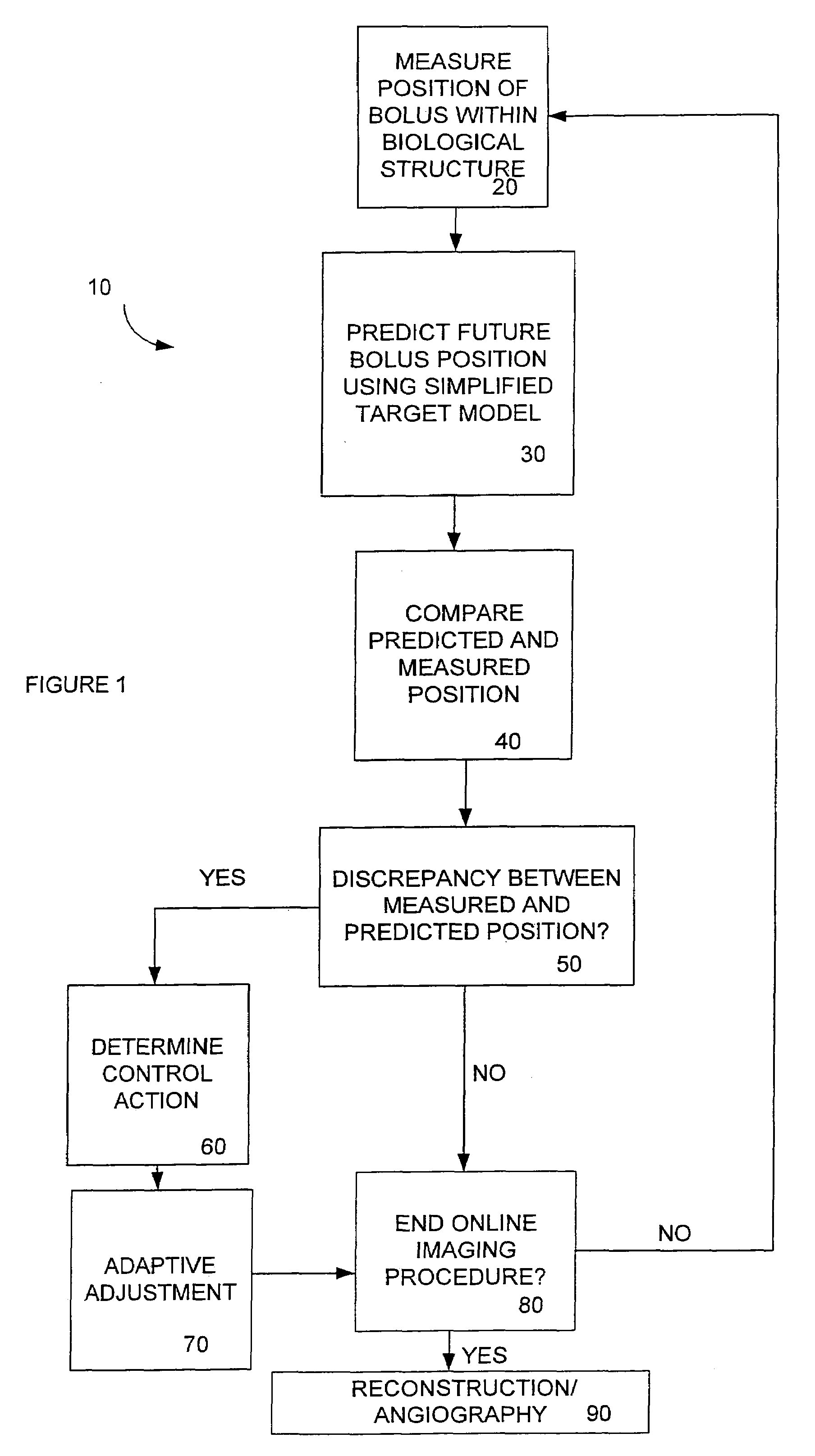
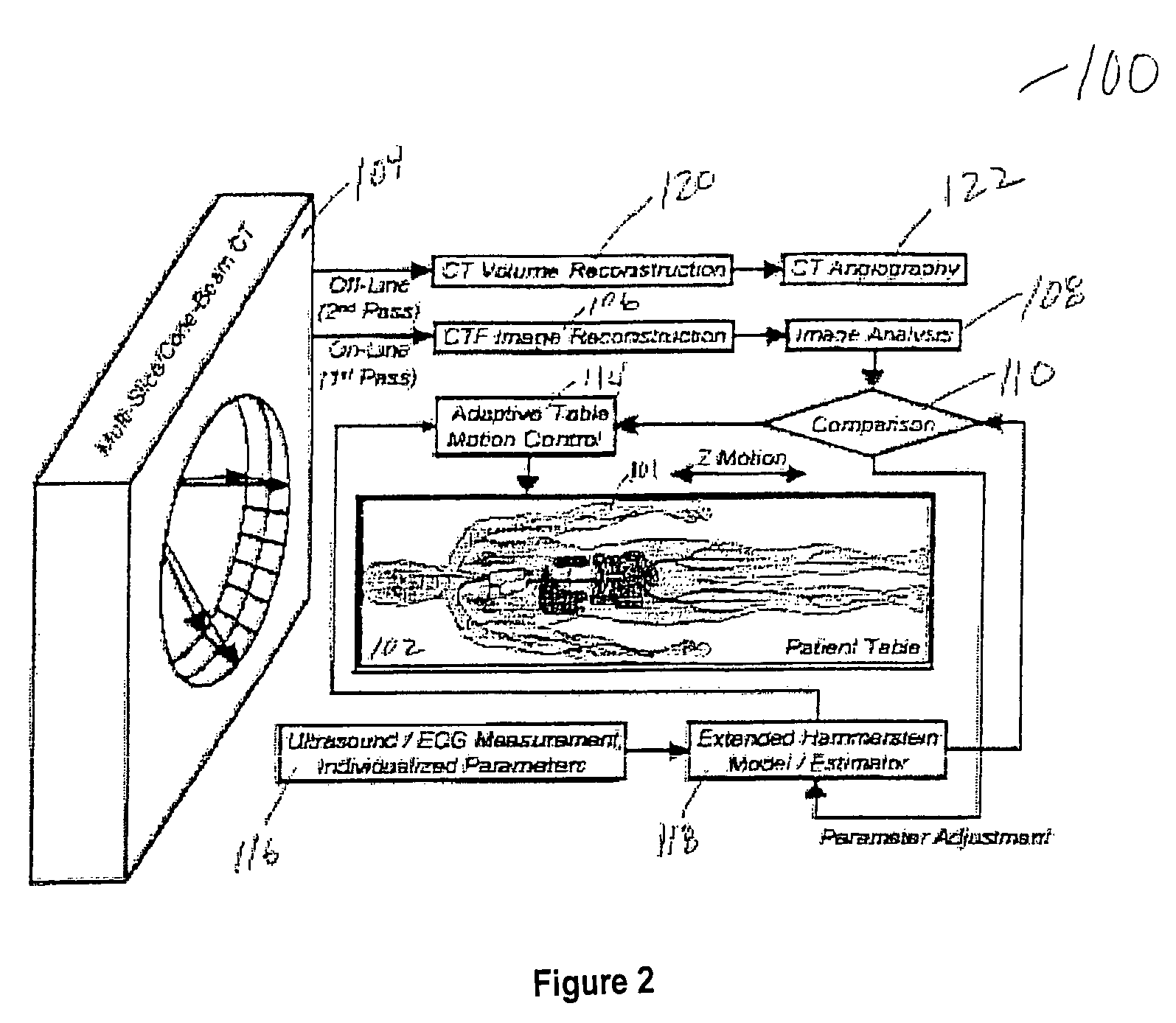
System and method for adaptive bolus chasing computed tomography (CT) angiography
InactiveUS7522744B2Increase contrastMedical simulationImage enhancementContrast levelContrast enhancement
A method of utilizing bolus propagation and control for contrast enhancement comprises measuring with an imaging device a position of a bolus moving along a path in a biological structure. The method further comprises predicting a future position of the bolus using a simplified target model and comparing the predicted future position of the bolus with the measured position of the bolus. A control action is determined to eliminate a discrepancy, if any, between the predicted position of the bolus and the measured position of the bolus and the relative position of the imaging device and the biological structure is adaptively adjusted according to the control action to chase the motion of the bolus.
Owner:IOWA RES FOUND UNIV OF
Slit-slat collimation
ActiveUS20090304150A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionPhoton
This invention is directed to a collimator and collimation techniques. Specifically, the invention is directed to a collimator and method for collimation wherein the collimator combines the resolution and sensitivity properties of pinhole Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging with the 2D complete-sampling properties of fan-beam collimators.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and system for four dimensional intensity modulated radiation therapy for motion compensated treatments
InactiveUS7835493B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionTumour volumeAnatomical structures
A deliverable four dimensional (4D) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning method is disclosed, for delivery using a linear accelerator with a dynamic multi-leaf collimator (DMLC). A 4D computed tomography (CT) scan is used for segmenting tumor anatomy on a reference phase of periodic motion of the tumor. Deformable registration of the 4D CT data is used to generate corresponding anatomical structures on other phases. Preferably, the collimator for each beam position is aligned using the gross tumor volume (GTV) centroid motion corresponding to the periodic motion of the tumor, as determined from the two dimensional (2D) projection of a given beam position. A deliverable IMRT plan is created on the 4D CT image set in which the MLC leaf positions and beam on / off status can vary as a function of respiratory phase by solving a four dimensional optimization problem. The mechanical constraints of the MLC leaves are included in the optimization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
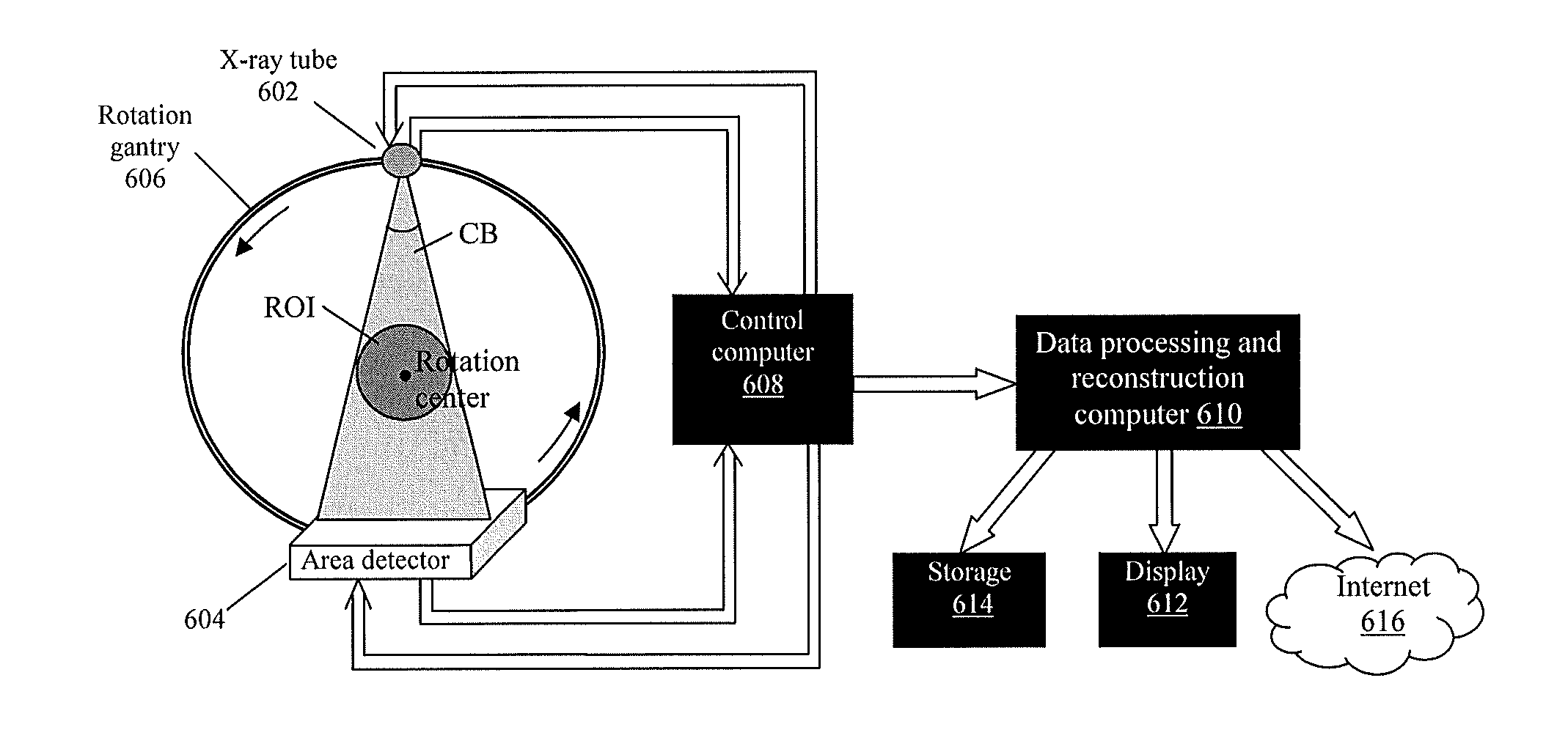
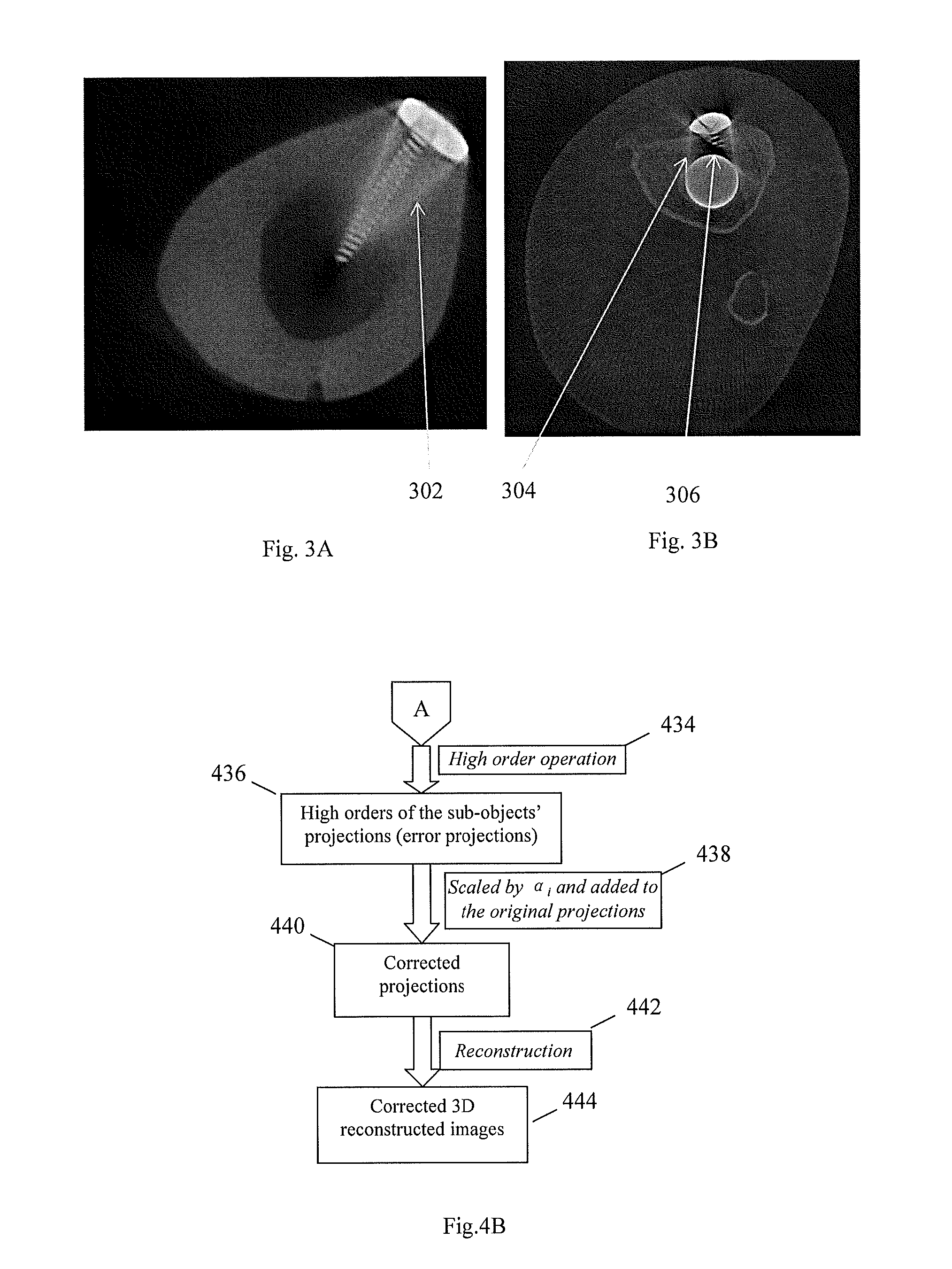
Method and apparatus for 3d metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam ct imaging
ActiveUS20120008845A1Accurate reconstruction imageHigh artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
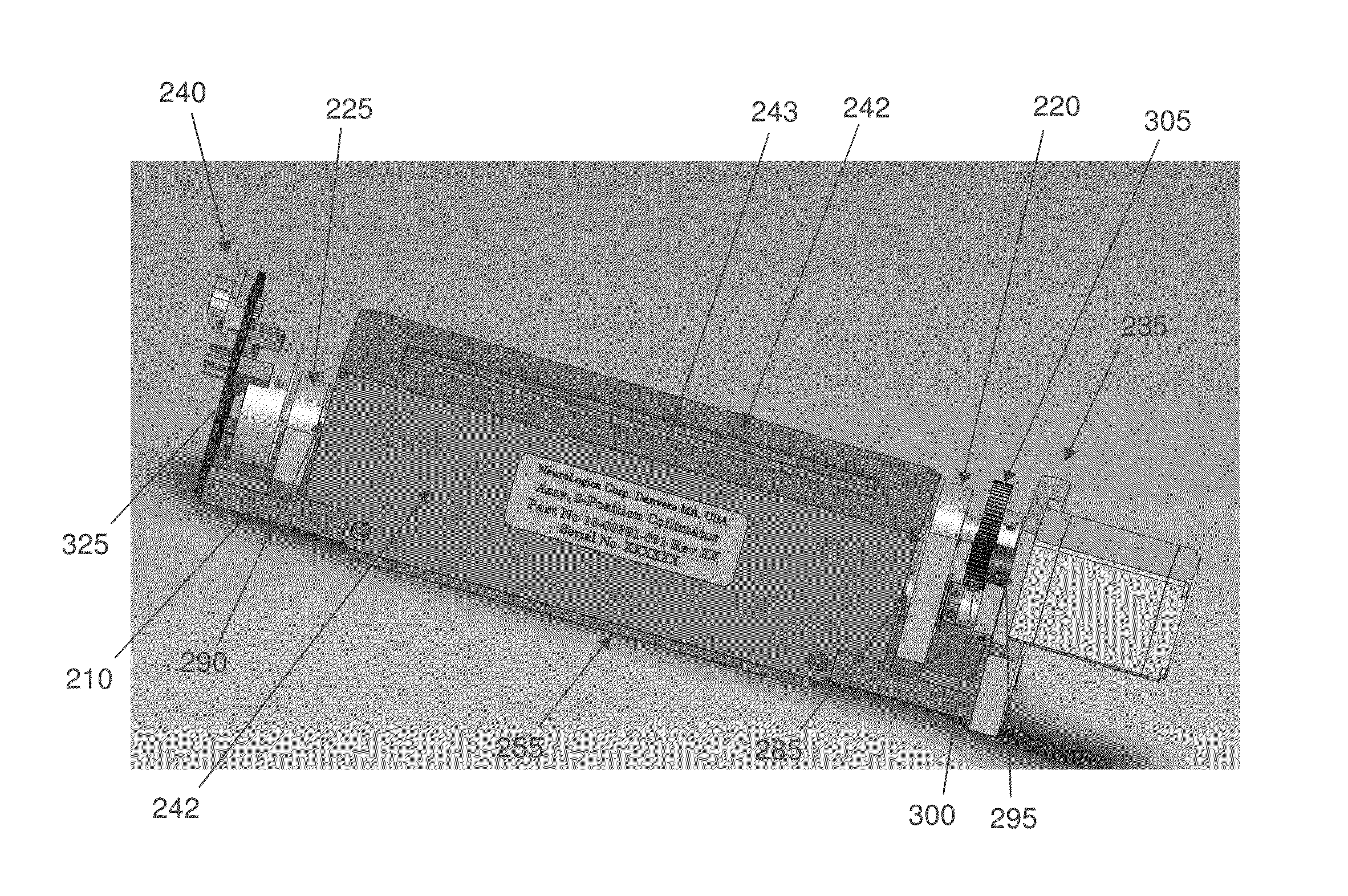
Computerized tomography (CT) imaging system with multi-slit rotatable collimator
ActiveUS20140140471A1Fast and simple and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayTomography
Apparatus for collimating an X-ray beam, the apparatus comprising:a multi-slit rotatable collimator comprising:a semi-tubular structure extending coaxially along a longitudinal axis, the semi-tubular structure being formed out of an X-ray impermeable material;at least one slit formed in the semi-tubular structure, wherein the at least one slit extends parallel to the longitudinal axis of the semi-tubular structure;a mount for rotatably supporting the semi-tubular structure in the path of an X-ray beam; anda drive mechanism for selectively rotating the semi-tubular structure about the longitudinal axis of the semi-tubular structure, whereby to selectively (i) position the at least one slit in the path of the X-ray beam so as to tailor the X-ray beam to the width of the at least one slit, and (ii) position a solid portion of the semi-tubular structure in the path of an X-ray beam so as to block an X-ray beam.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
Method for improving imaging quality of limited-angle CT through combination of ultrasonic image
InactiveCN103455989AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationImaging quality
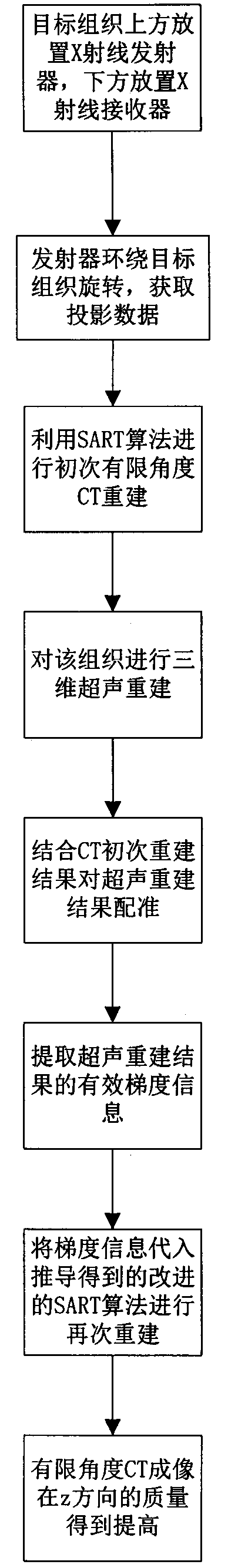
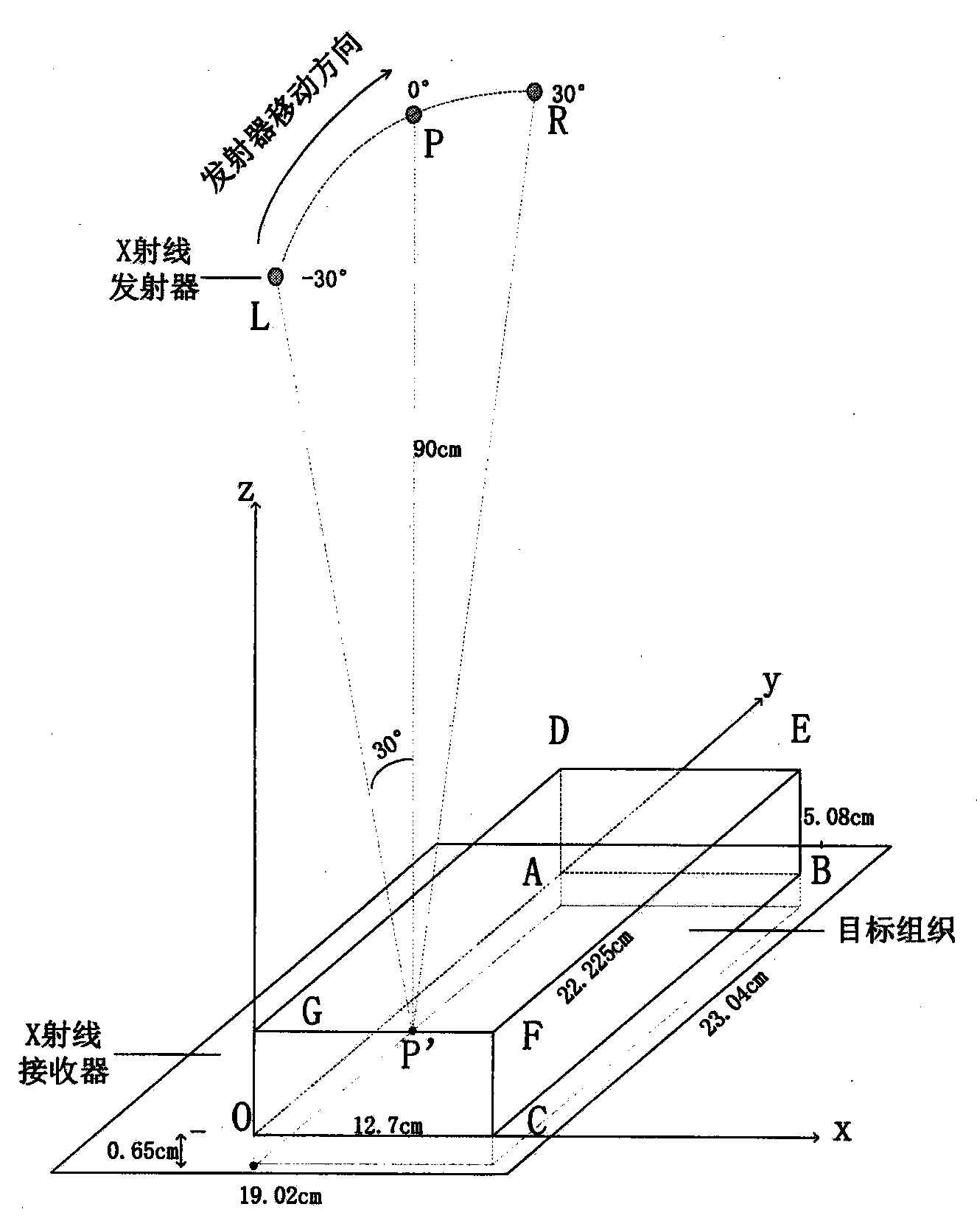
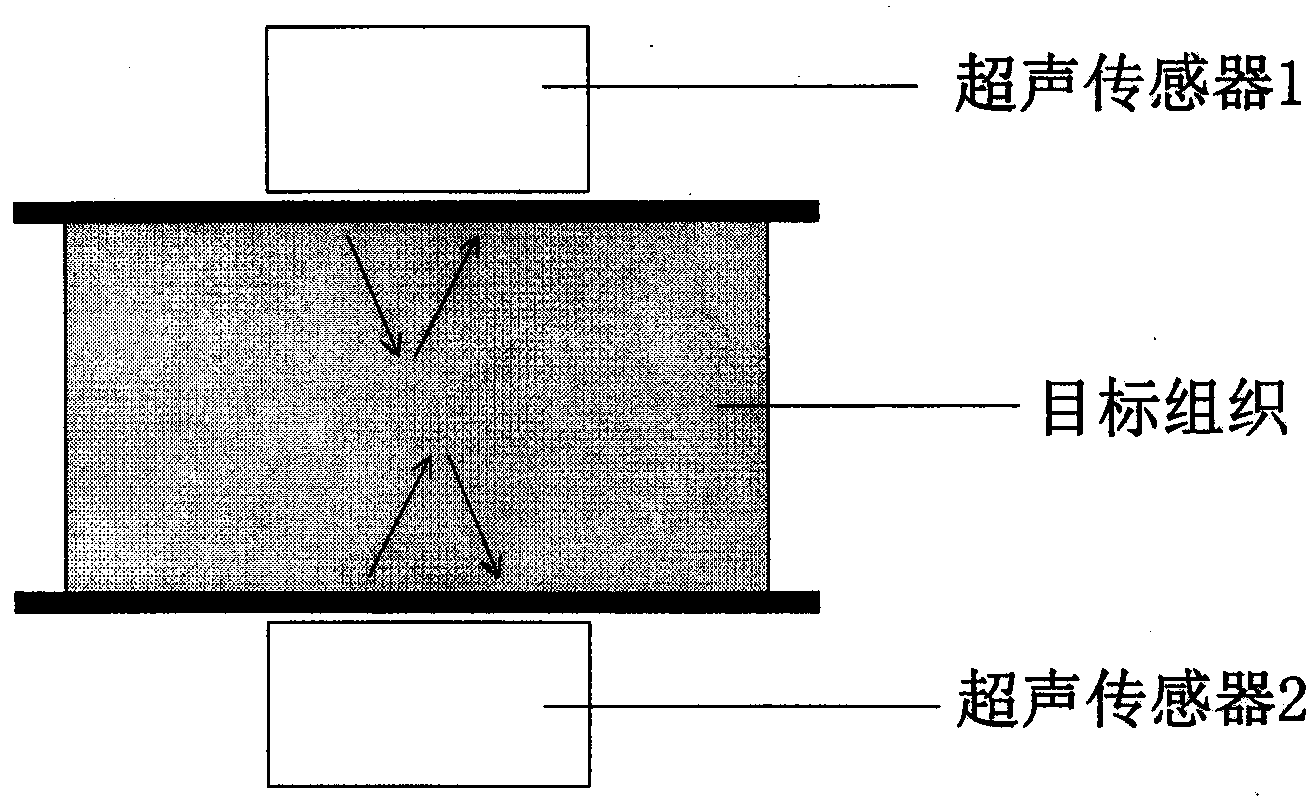
The invention discloses a method for improving the imaging quality of limited-angle CT (Computed Tomography). The method comprises the following steps that an X-ray emitter and an X-ray receiver are arranged above target tissue and below the target tissue respectively; the emitter is made to move around the tissue and emit X rays within a limited angle, and meanwhile, projection data are collected; primary reconstruction is conducted by the utilization of a synchronous algebraic reconstruction technology; a three-dimensional ultrasonic image of the tissue is obtained; registering is conducted on the ultrasonic image through the combination of a primary CT reconstruction result; effective gradient information of the ultrasonic image is extracted, an improved synchronous algebraic reconstruction technology is used for conducting reconstruction again and an limited-angle CT imaging result with quality improved is obtained. According to the method for improving the imaging quality of the limited-angle CT, the characteristic that ultrasonic imaging is clear at the edge of the z direction is utilized, the problems that the limited-angle CT reconstruction result is serious in image artifact and fuzzy in boundary in the z direction, and innovation is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System and method for artifact reduction of computed tomography reconstruction leveraging artificial intelligence and a priori known model for the object of interest
PendingUS20220035961A1Reduce artifactsComplicated processingGeometric CADImage enhancementPattern recognitionAlgorithm
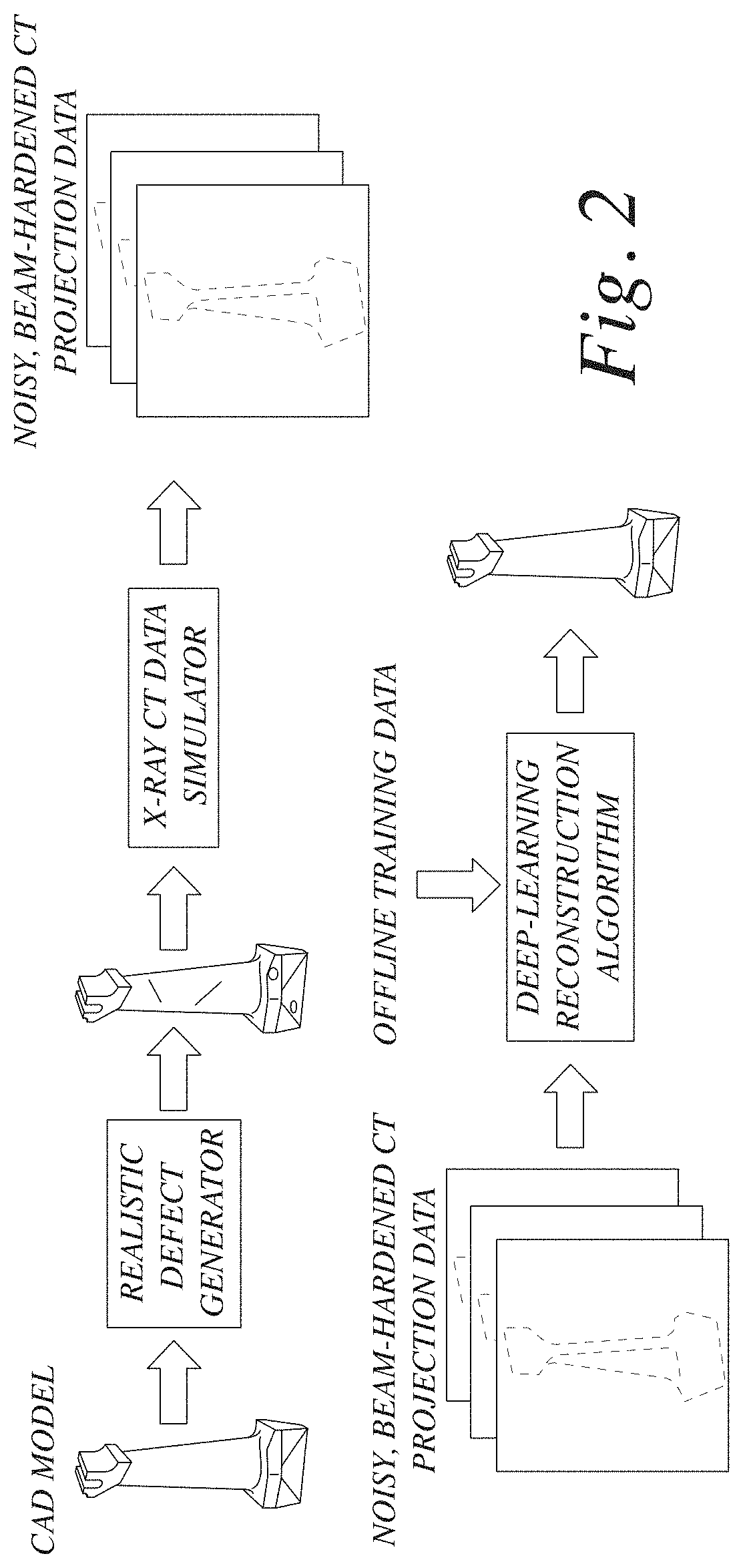
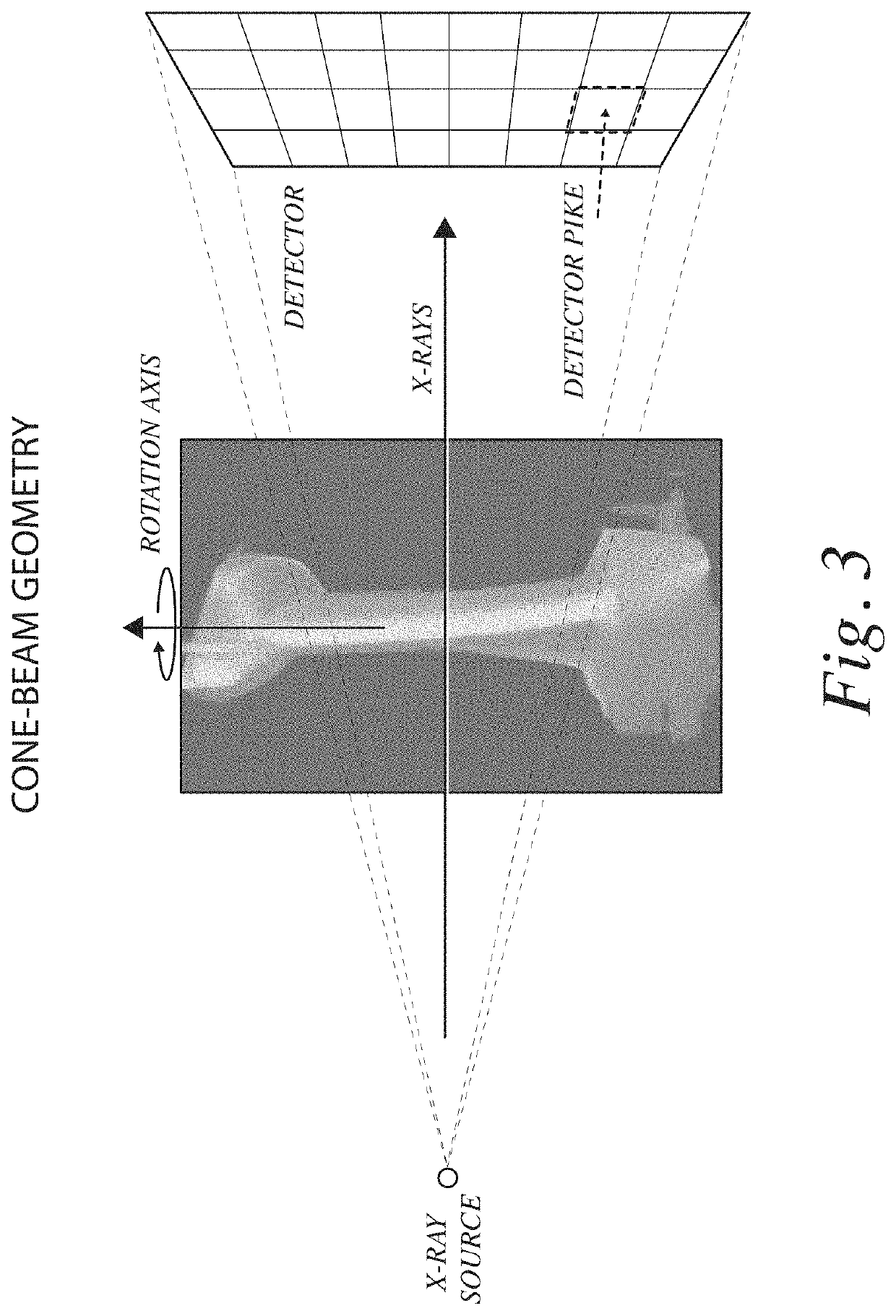
Nondestructive evaluation (NDE) of objects can elucidate impacts of various process parameters and qualification of the object. Computed tomography (CT) enables rapid NDE and characterization of objects. However, CT presents challenges because of artifacts produced by standard reconstruction algorithms. Beam-hardening artifacts especially complicate and adversely impact the process of detecting defects. By leveraging computer-aided design (CAD) models, CT simulations, and a deep-neutral network high-quality CT reconstructions that are affected by noise and beam-hardening can be simulated and used to improve reconstructions. The systems and methods of the present disclosure can significantly improve the reconstruction quality, thereby enabling better detection of defects compared with the state of the art.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Biodegradable computed tomography contrast agents
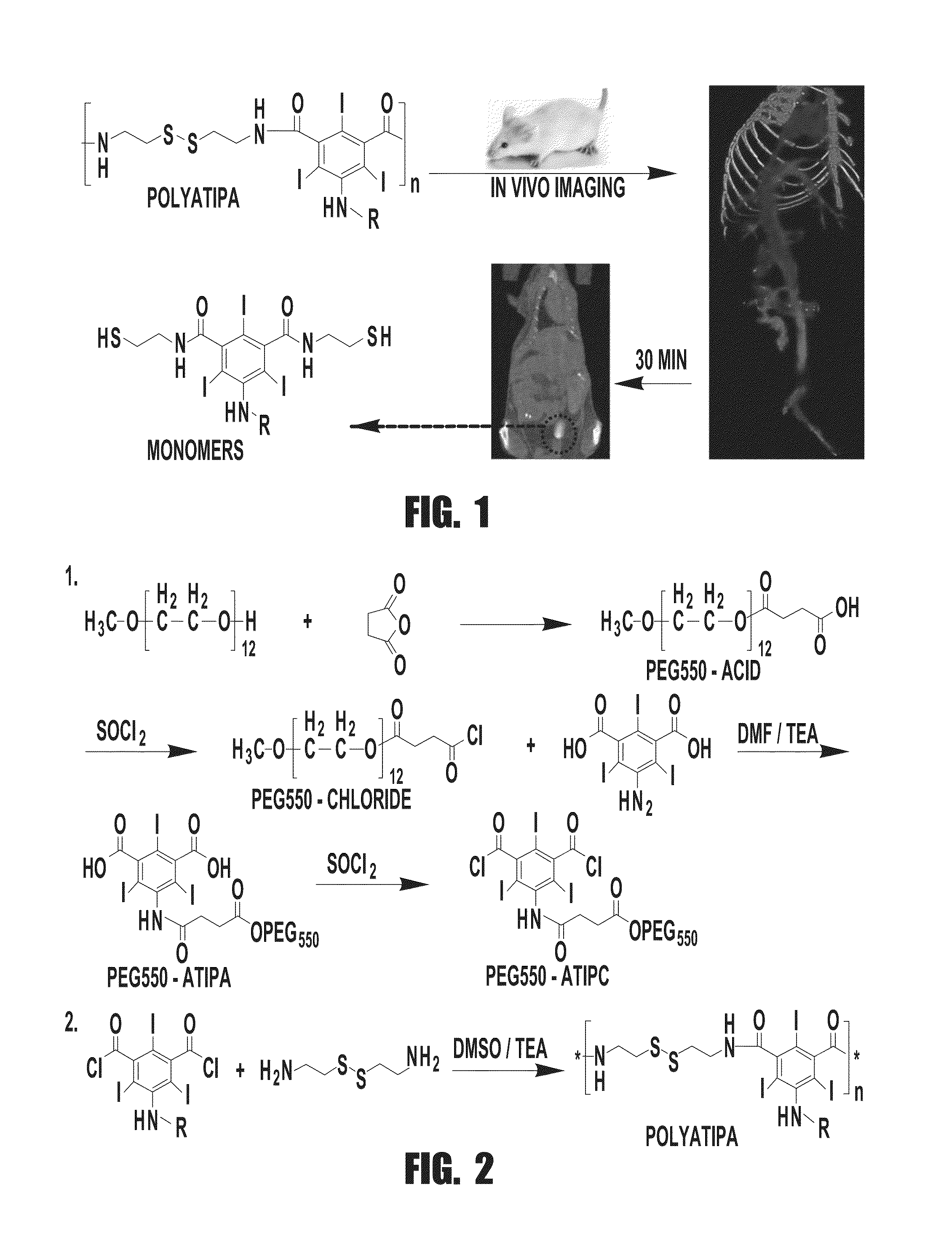
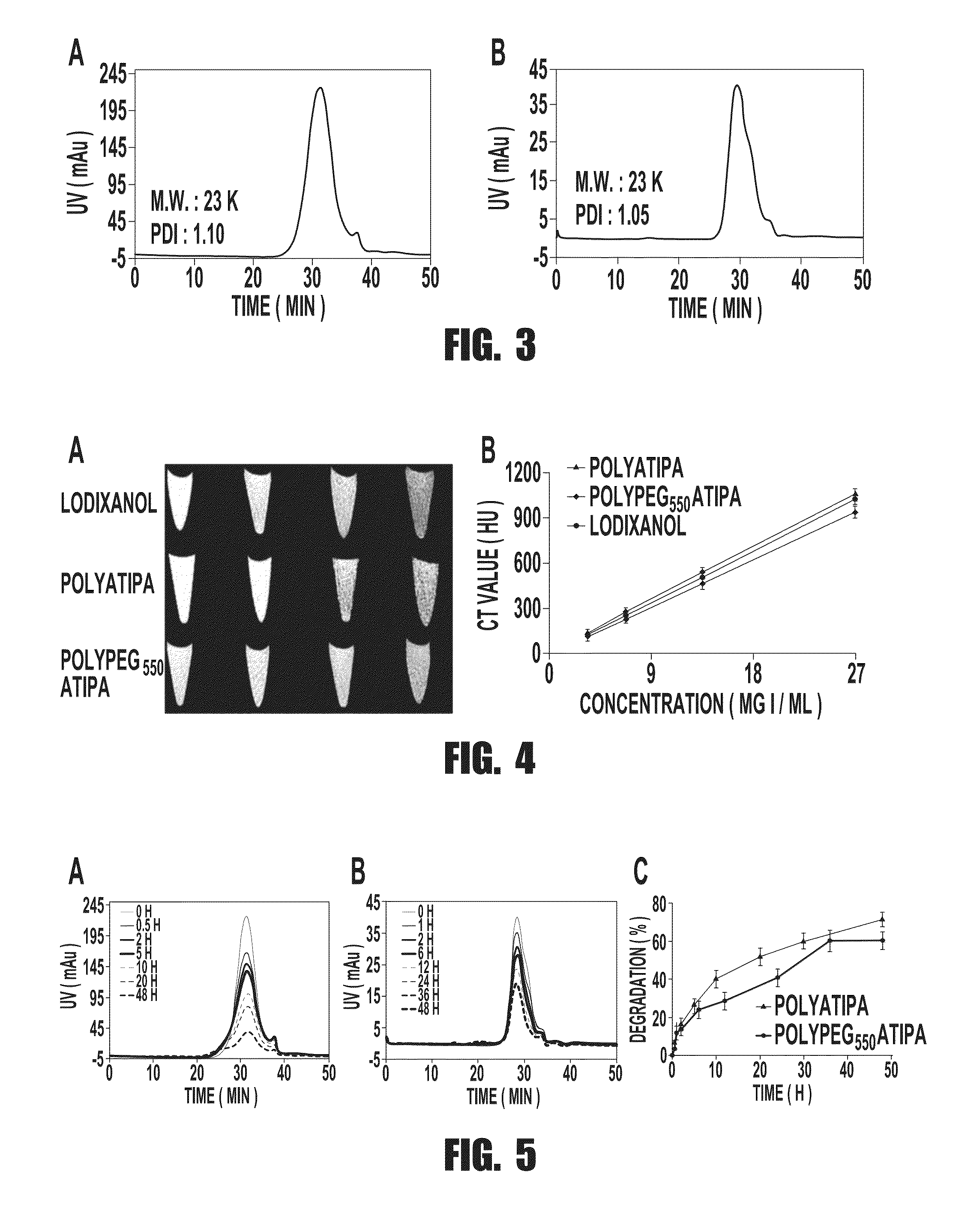
ActiveUS20150119706A1Improve pharmacokineticsImprove securityThiol preparationX-ray constrast preparationsSufficient timeX-ray
Biodegradable computed tomography (CT) contrast agents comprising a polyiodinated aryl contrast agent that is crosslinked by an organic disulfide are described herein. The contrast agents can be used to image a tissue region by administering an effective amount of the biodegradable CT contrast agent to a subject, allowing a sufficient amount of time for the biodegradable CT contrast agent to enter the tissue region, and performing x-ray computed tomography imaging of the tissue region of the subject.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
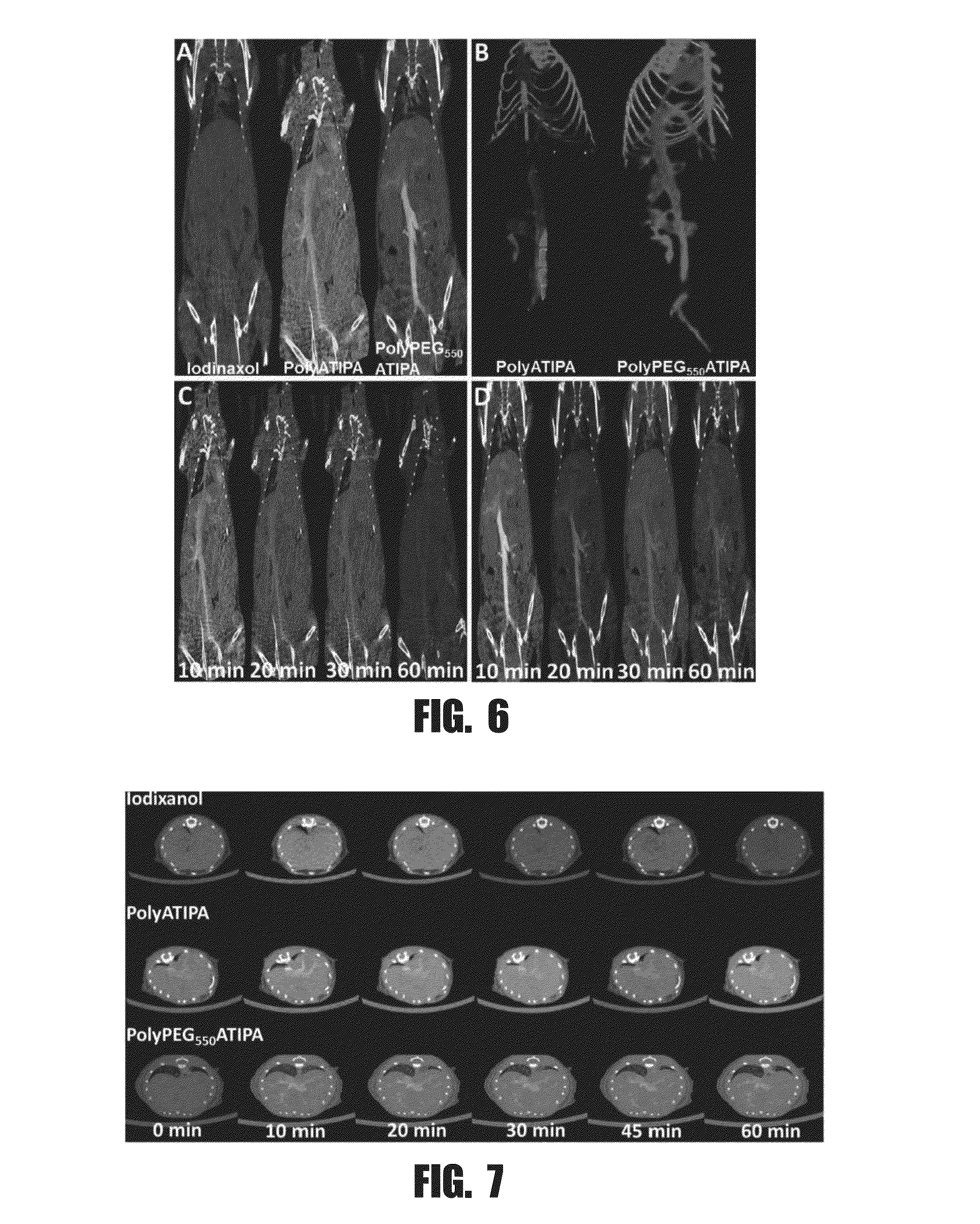
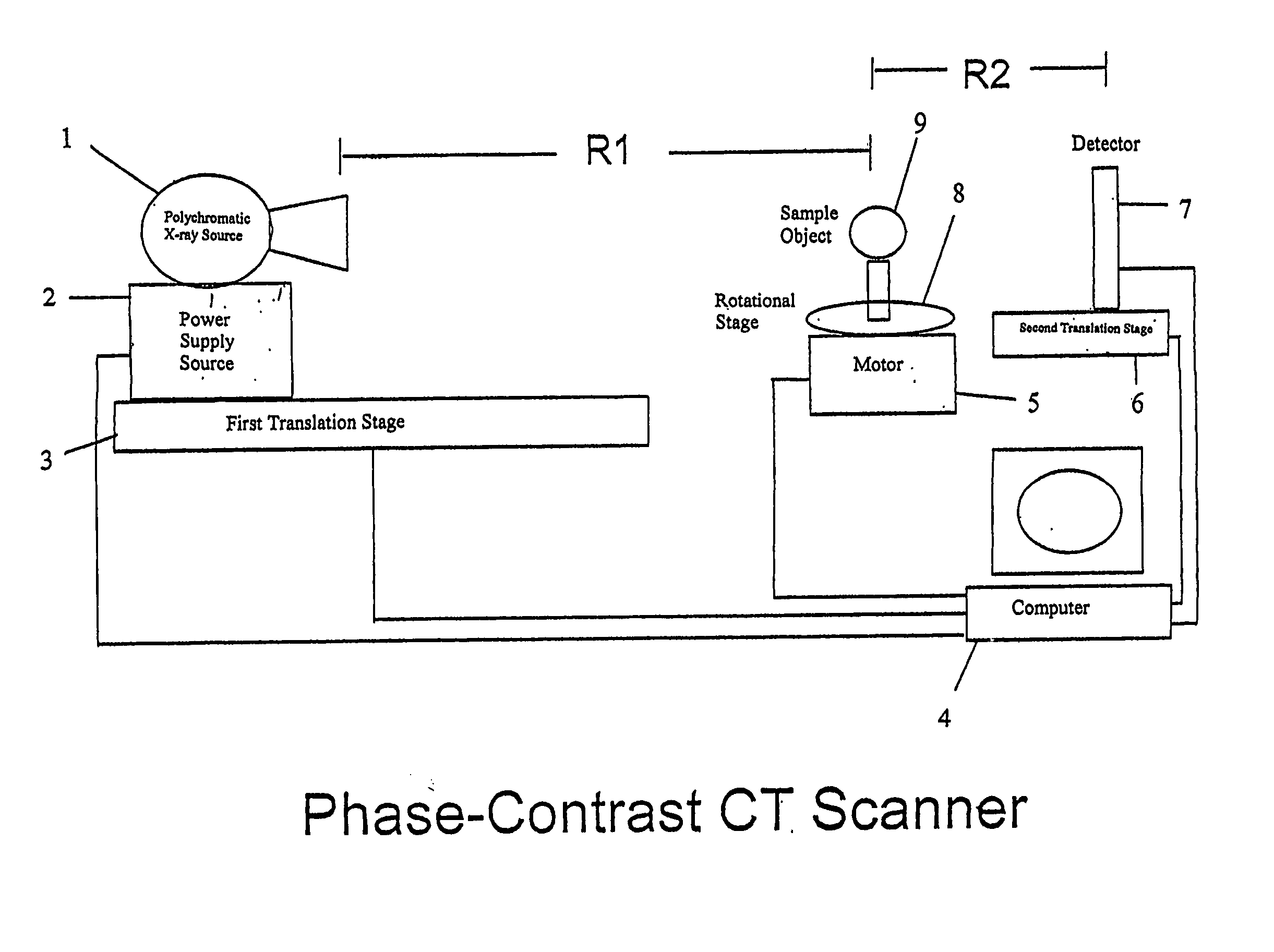
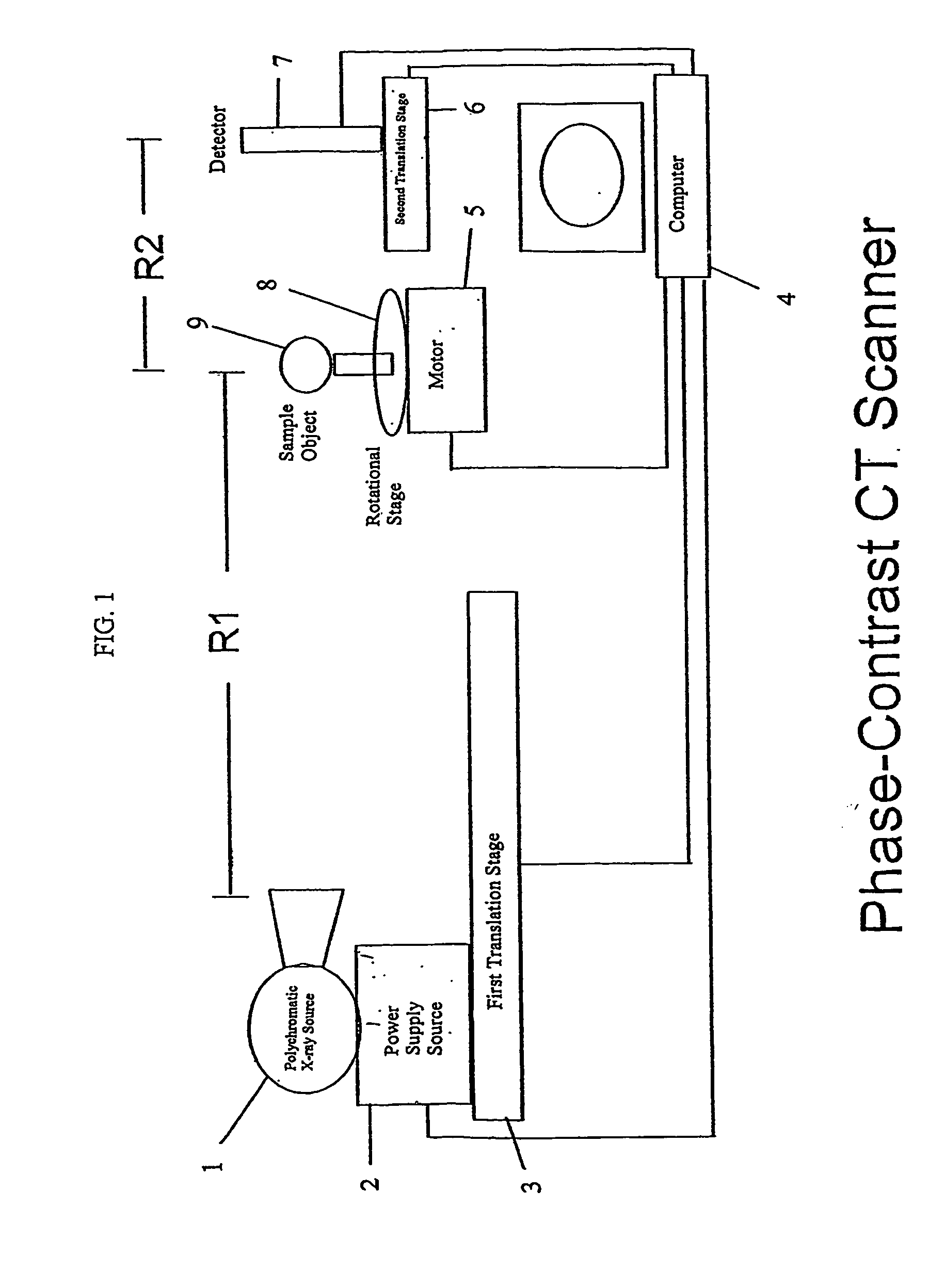
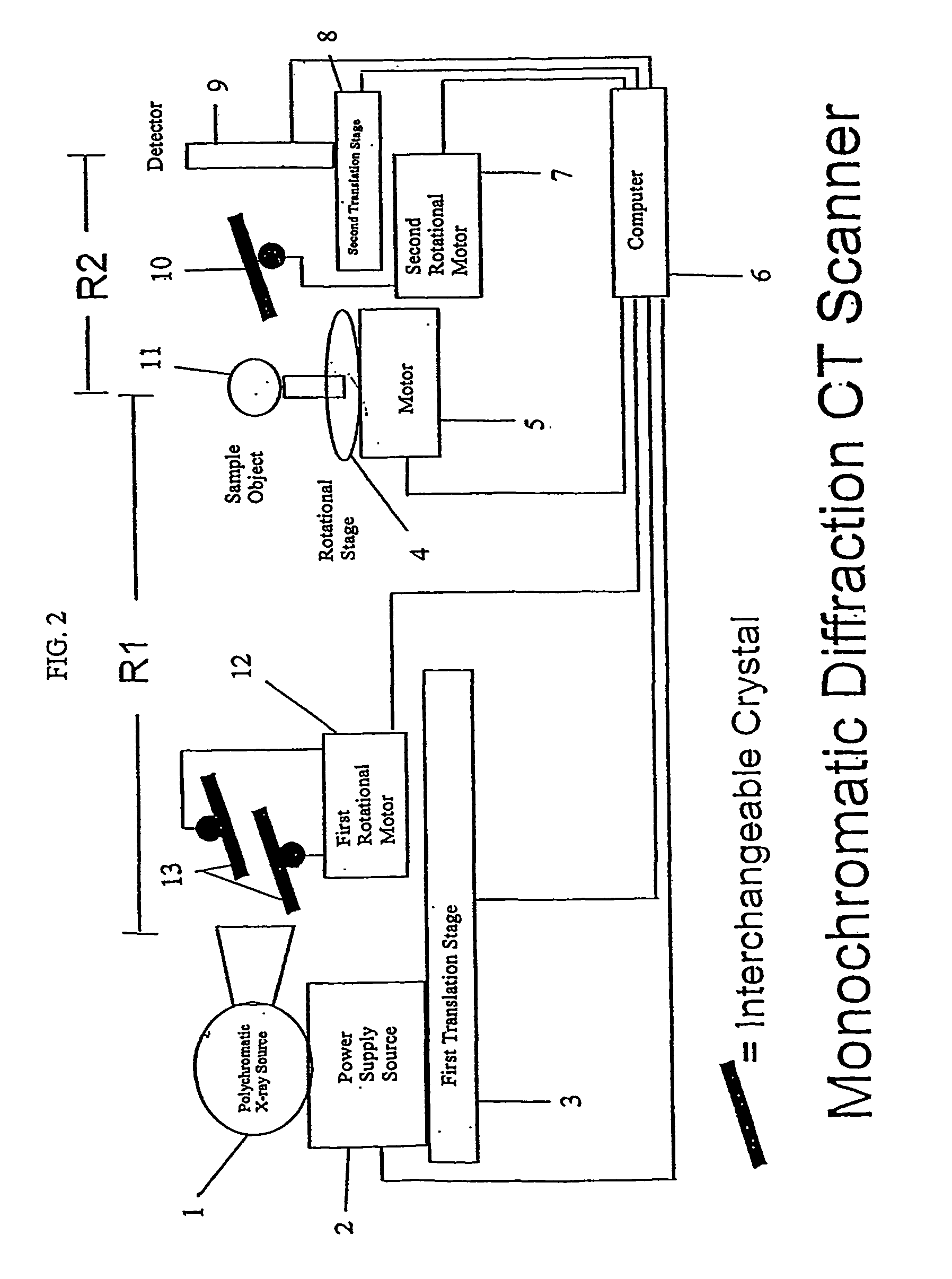
Phase-contrast enhanced computed tomography
InactiveUS20050129169A1Imaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhysicsComputed tomography scanner
A phase-contrast x-ray computed tomography scanner, a monochromatic diffraction computed tomography scanner, a rotatable monochromatic diffraction computed tomography scanner, and a combination phase-contrast and monochromatic computed tomography scanner are provided. In addition, a method of identifying an unknown sample is provided.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
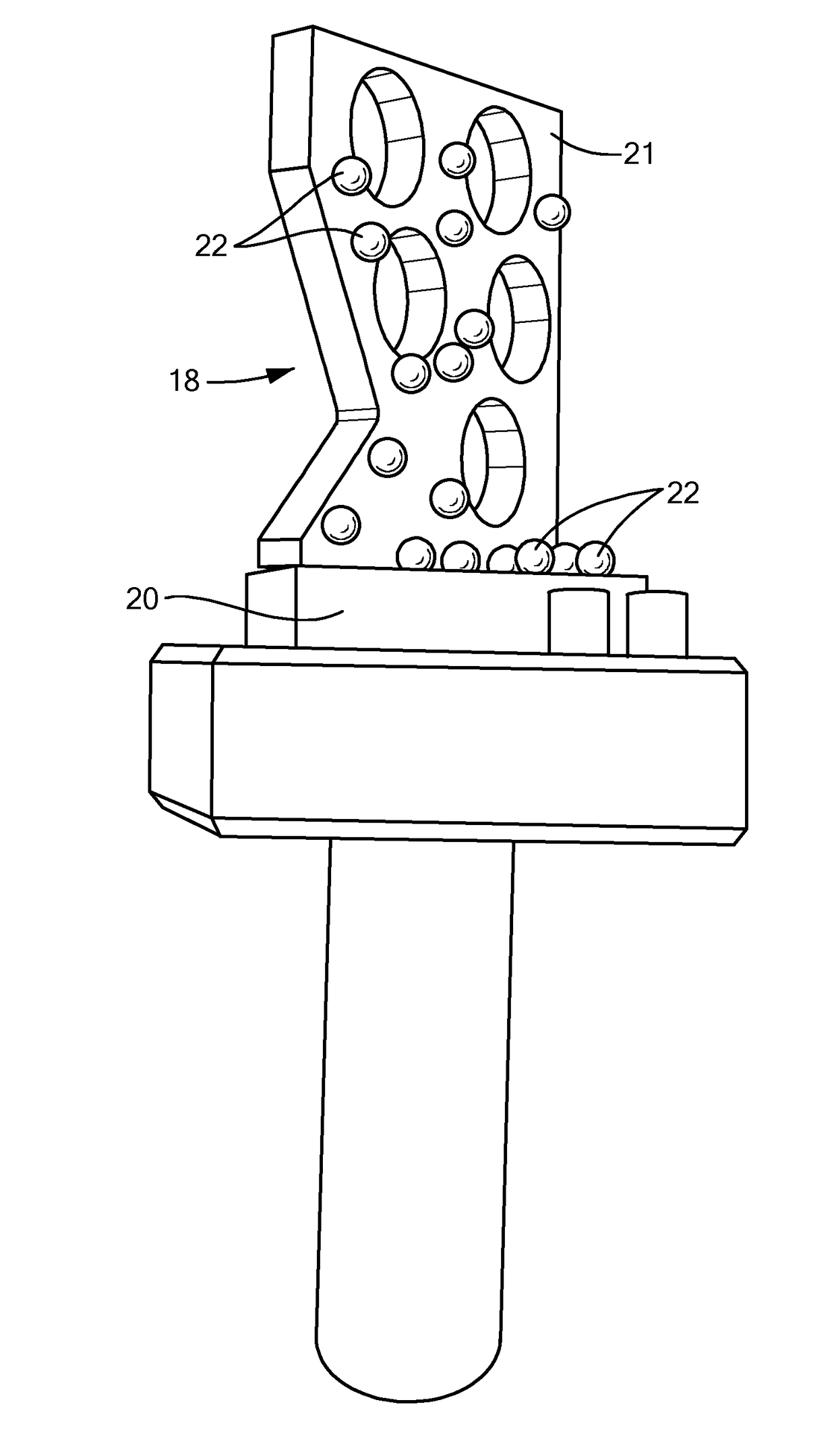
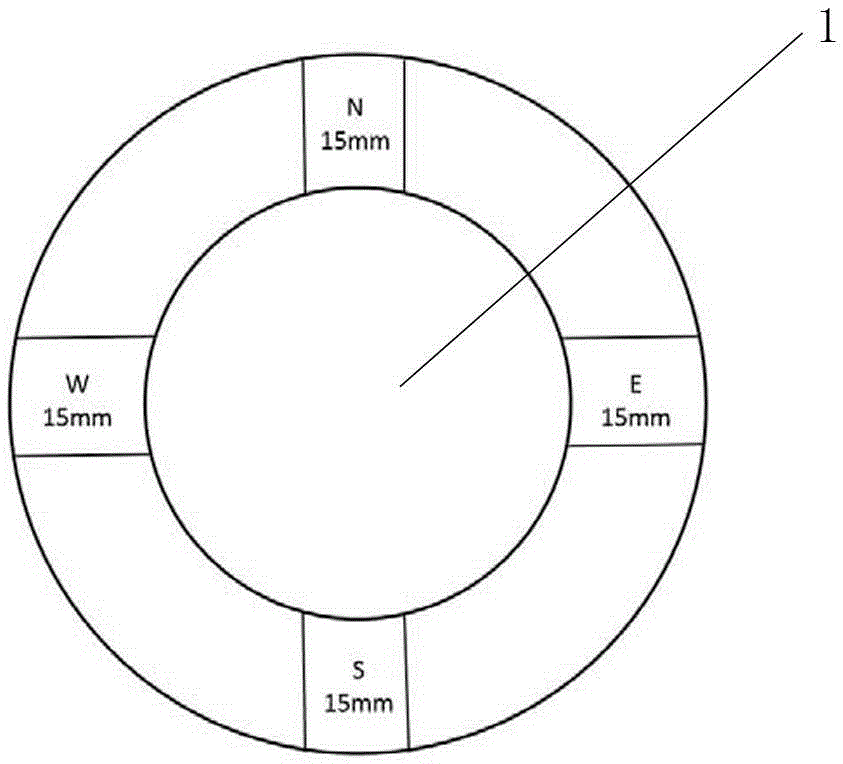
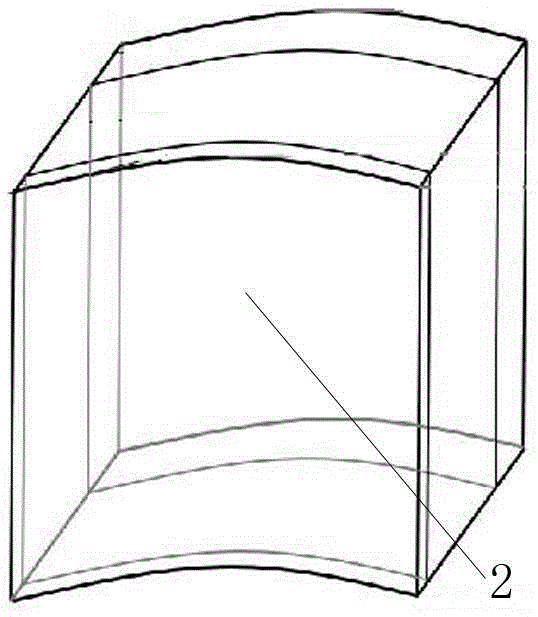
Three-dimensional computed tomography gauge
ActiveUS20170112462A1Reduce distractionsEnsure uniformityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation measurementFractographyComputed tomography
A method of calibrating an x-ray computed tomography machine provides an x-ray computed tomography machine having calibration settings, and uses the x-ray computed tomography machine to produce a gauge reconstruction. The gauge has a first base supporting two or more objects, and a second base supporting two or more objects. The first base and the second base form a perpendicular configuration, and each of the plurality of objects is secured on at least one of the first base and the second base. Each of the objects has a center, and the distance between the centers of each object is known. The method then measures the distance between at least two objects to produce measured center distance values, compares the measured center distance values against the known center distance values, and uses the comparison to determine if there is a distance error in the gauge reconstruction.
Owner:HEXAGON METROLOGY INC
Out of plane artifact reduction in digital breast tomosynthesis and CT
ActiveUS9449403B2Avoid on-line computationHigh possible contrastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAngular rangeNuclear medicine
Reduction of artifacts in digital breast tomosynthesis and in computed tomography. Because of the limited angular range acquisition in DBT the reconstructed slices have reduced resolution in z-direction and are affected by artifacts. Out-of-plane blur caused by dense tissue and large masses complicates 3D visualization and reconstruction of thick slices volumes. The streak-like out-of-plane artifacts caused by calcifications and metal clips distort the true shape of calcification, an important malignancy predictor. Microcalcifications could be obscured by bright artifacts. The technique involves reconstructing a set of super resolution slices and predicting the “artifact-free” voxel intensity based on the corresponding set of projection pixels using a statistical model learned from a set of training data. The resulting reconstructed images are de-blurred and streak artifacts are reduced, visibility of clinical features, contrast and sharpness are improved, 3D visualization and thick-slice reconstruction is possible without the loss of contrast and sharpness.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
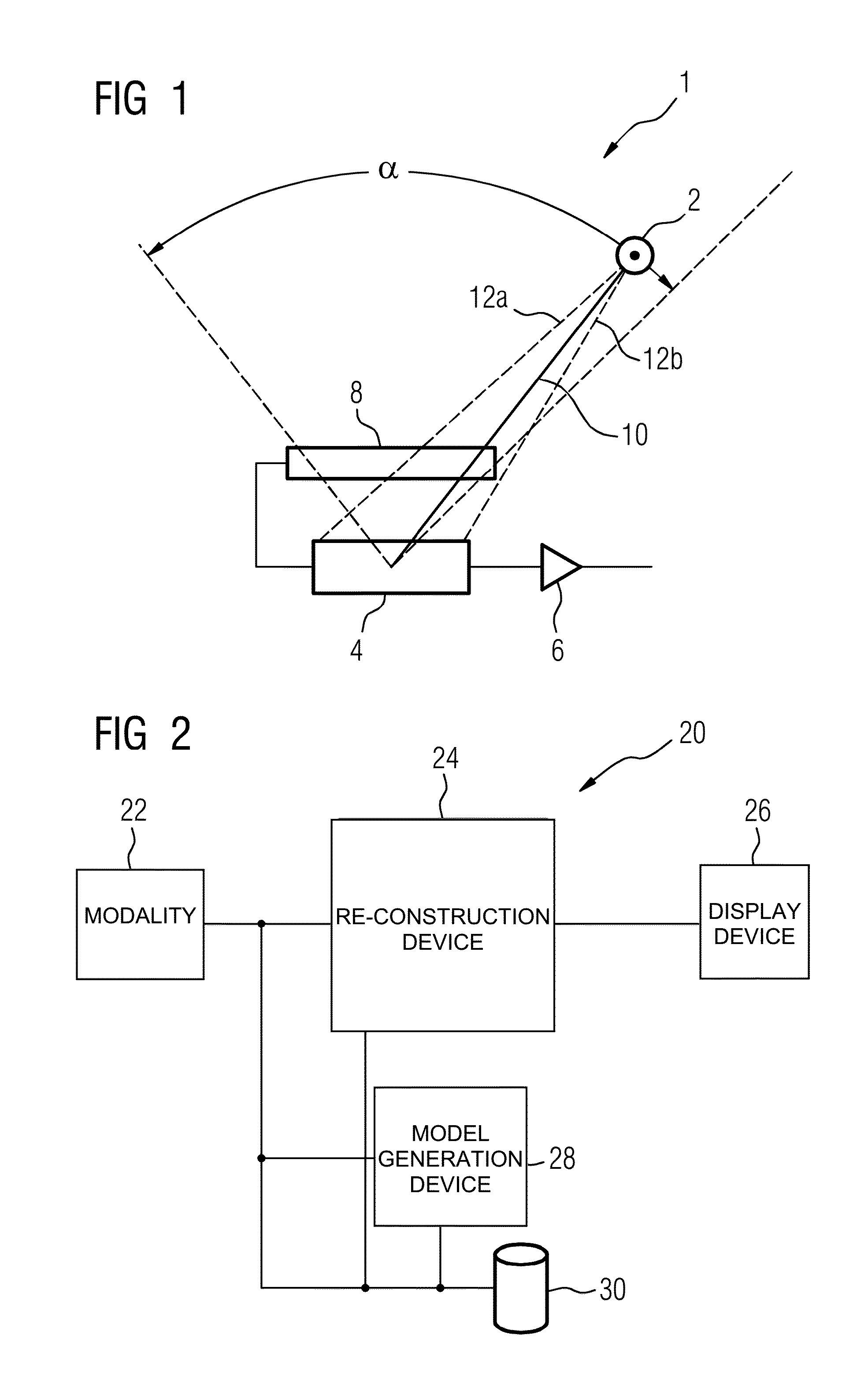
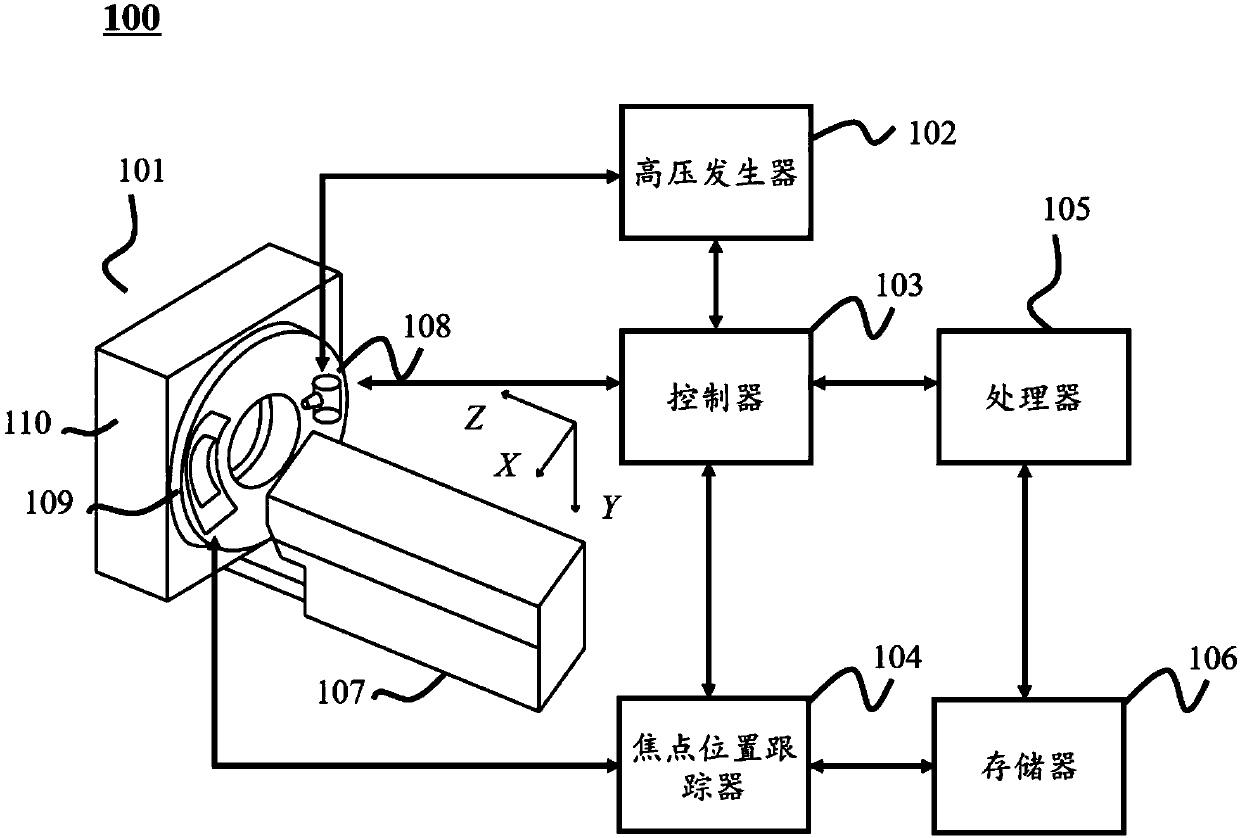
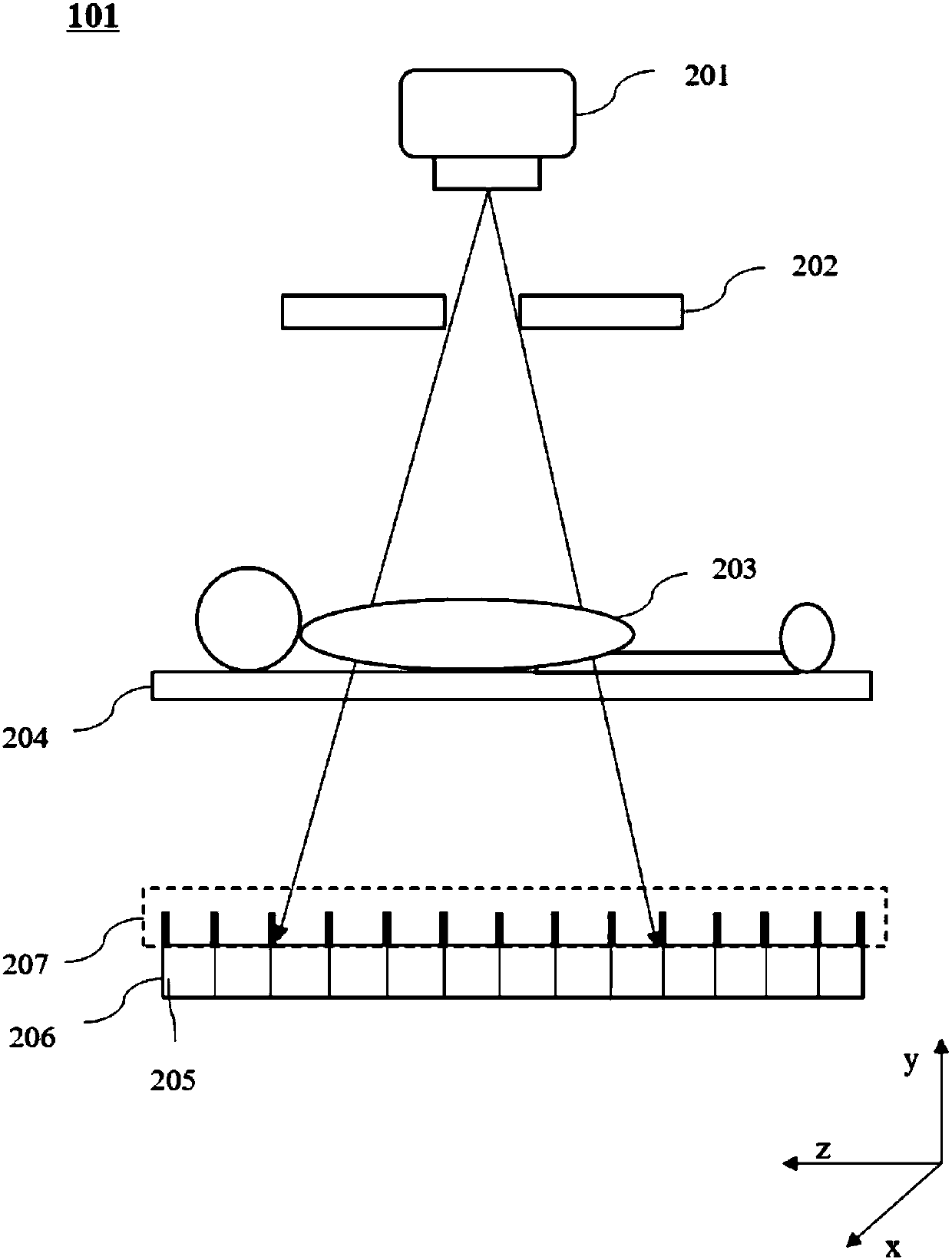
Collimator, imaging equipment, focal position tracing method and correcting method
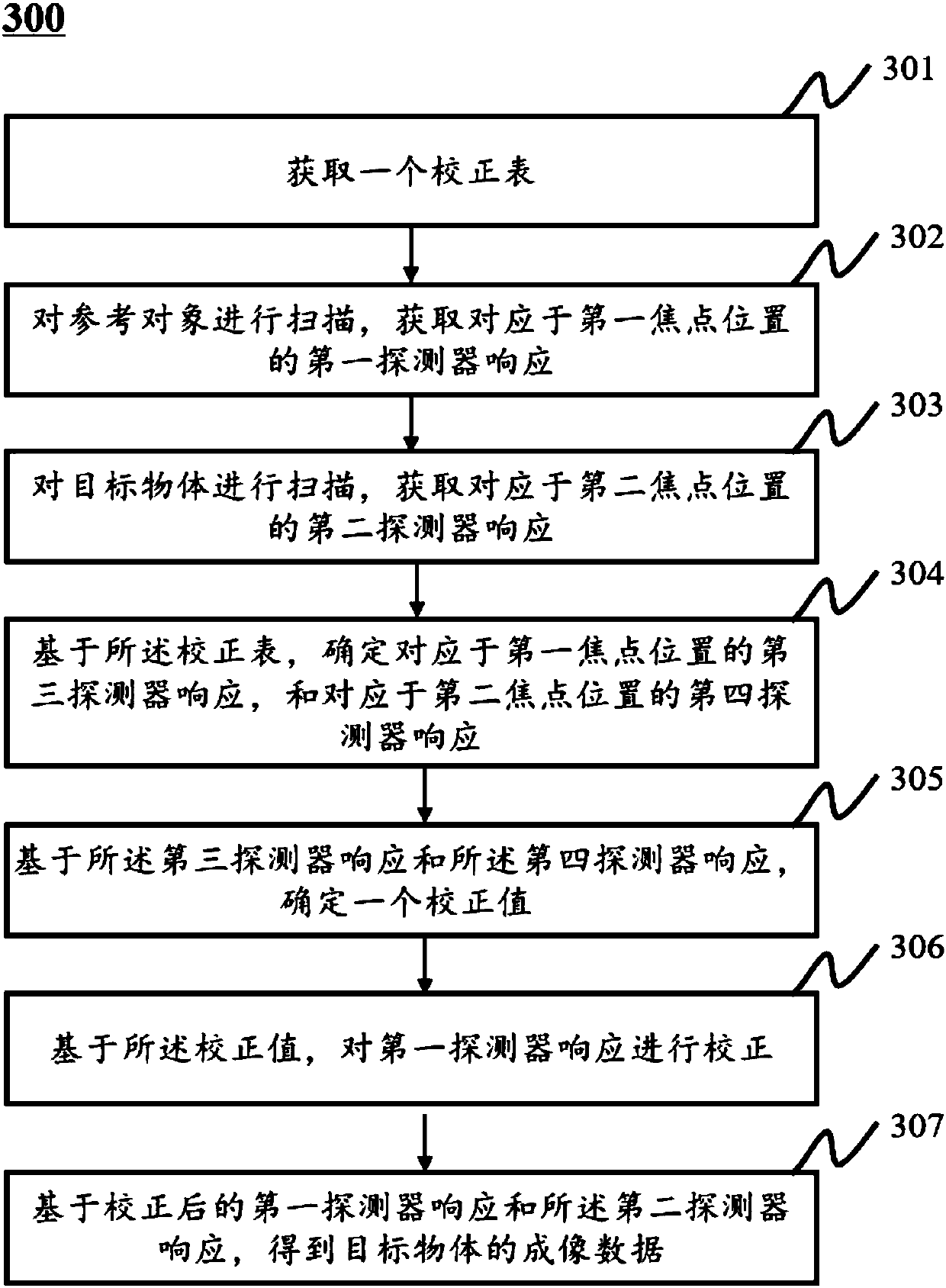
ActiveCN107582089AIncrease profitGuaranteed image qualityRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsImaging qualityFocal position
The invention discloses a computed tomography data correcting method. The method includes the steps that a reference object is scanned, and first detector response corresponding to the first focal position is obtained; the target object is scanned, and second detector response corresponding to the second focal position is obtained; a correction table is inquired, third detector response corresponding to the first focal position and fourth detector response corresponding to the second focal position are determined, and the correction table comprises the corresponding relation between differentfocal positions and detection response; based on the third detector response and the fourth detector response, the first detector response is corrected; imaging data corresponding to the target objectis obtained based on the first detector response and the second detector response obtained after correction. By correcting computed tomography data, image artifacts caused by focal position offset are reduced or eliminated, and imaging quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System and method for reducing or eliminating streak artifacts and illumination inhomogeneity in CT imaging
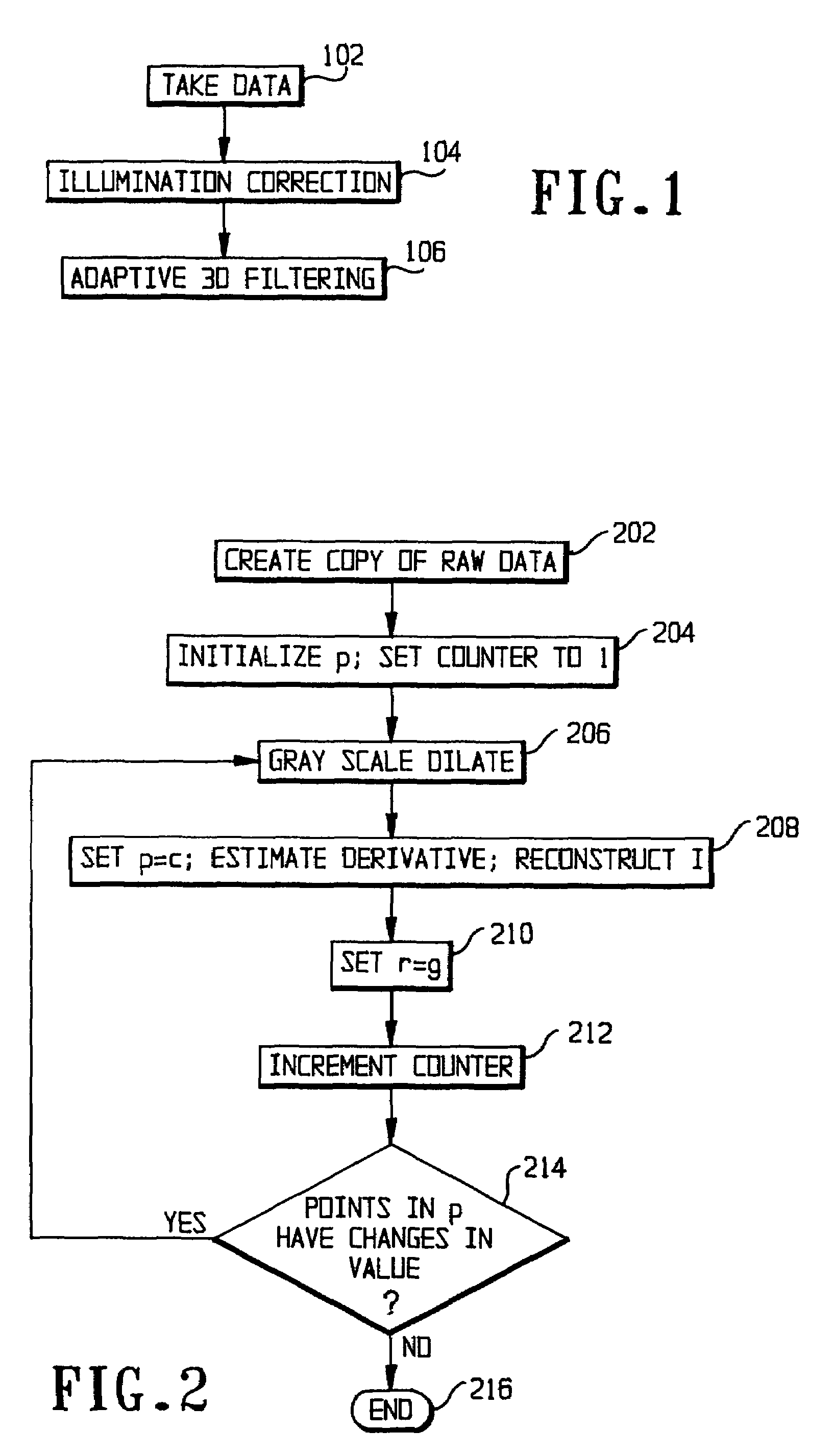
InactiveUS7406211B2Reduce and eliminate streak artifactImage enhancementImage analysisImage contrastGray scale morphology
In CT (computed tomography) images, streak artifacts caused by the presence of metal implants and inhomogeneous estimation of tissue density are reduced or eliminated. The algorithm has two basic steps: 1) illumination correction and 2) adaptive 3D filtering. The algorithm starts by estimating the direction of the streak and the degree of inhomogeneous densities by gray scale morphology dilatation. Then, it proceeds to estimate the correct densities based on the estimations and to reduce the streak by an adaptive 3D filtering whose parameters depend on the streak direction and the local image contrast.
Owner:VIRTUALSCOPICS
Method of and system for classifying objects using histogram segment features of multi-energy computed tomography images
InactiveUS7474786B2Character and pattern recognitionNuclear radiation detectionLow-pass filterPeak value
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Method for quickly detecting water content of bamboo on basis of X-ray CT (computed tomography) technology
InactiveCN105403578AEasy to detectNon-destructive testingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCt technologyTomography
The invention belongs to a method for quickly detecting the water content of bamboo on the basis of an X-ray CT (computed tomography) technology. The method comprises steps as follows: standard specimens for detecting the water content of to-be-detected bamboo are selected as required; the manufactured specimens are put into dryers containing different saturated salt solutions, the mass of the specimens in different water content gradient states and the mass of the totally dry specimens are weighed according to Testing Methods for Physical and Mechanical Properties of Bamboos GB / T 15780-1995 when the water content of the specimens is stable and does not change, the specimens in different water content states are subjected to CT scanning in the axial direction of moso bamboo by means of the X-ray CT technology, appropriate scanning parameters are selected according to different bamboo species, the number of scanned layers is determined according to the thickness of the scanned layer and the interval between the adjacent layers, a fitting equation is established according to a fitting curve, and the water content of the to-be-detected sample is calculated. The method is environment-friendly and efficient, can be used for detecting the water content of the bamboo conveniently, quickly and intactly and has the advantages of accuracy, environment-friendliness, low cost and simplicity and convenience in operation.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
X-ray imaging systems and methods, and methods of manufacture of collimators for use therein
ActiveUS20190290224A1Excellent mechanical propertiesImprove toughnessHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsComputed tomographyImaging quality
Provided herein are x-ray imaging systems, methods of x-radiography, and methods of manufacture of collimators suitable for use in x-ray imaging systems and methods of x-radiography. The systems, methods and devices proposed here may assist in providing for improved magnification of x-rays in an x-ray imaging system with improved image quality compared to known systems. It may find applications in a variety of x-ray applications, for example x-ray CT (Computed Tomography) and 2D projectional radiography for e.g. non-destructing testing purposes.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
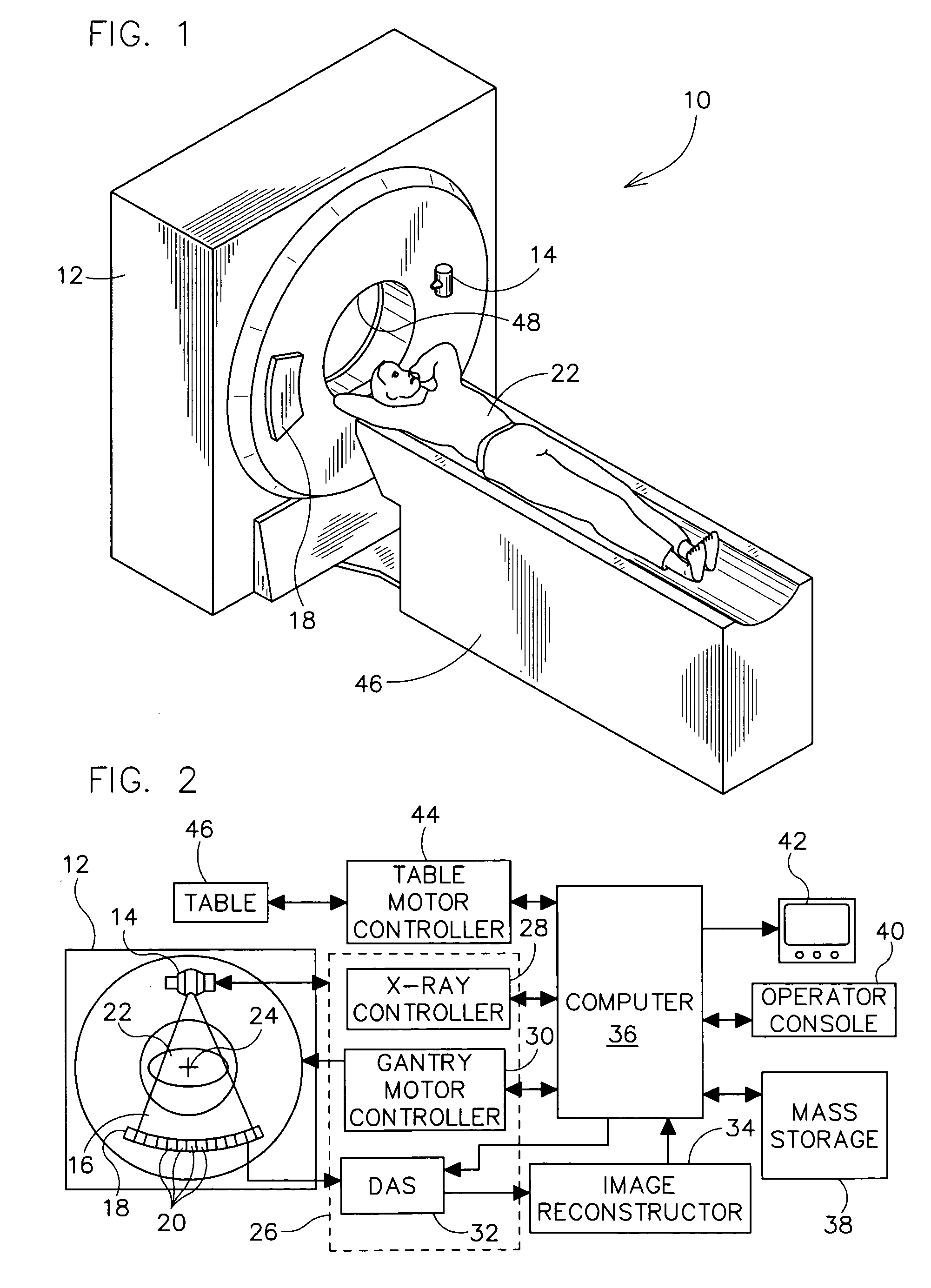
Gain correction for a CT system
ActiveUS7734004B2Reduce errorsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNuclear medicinePerformed Imaging
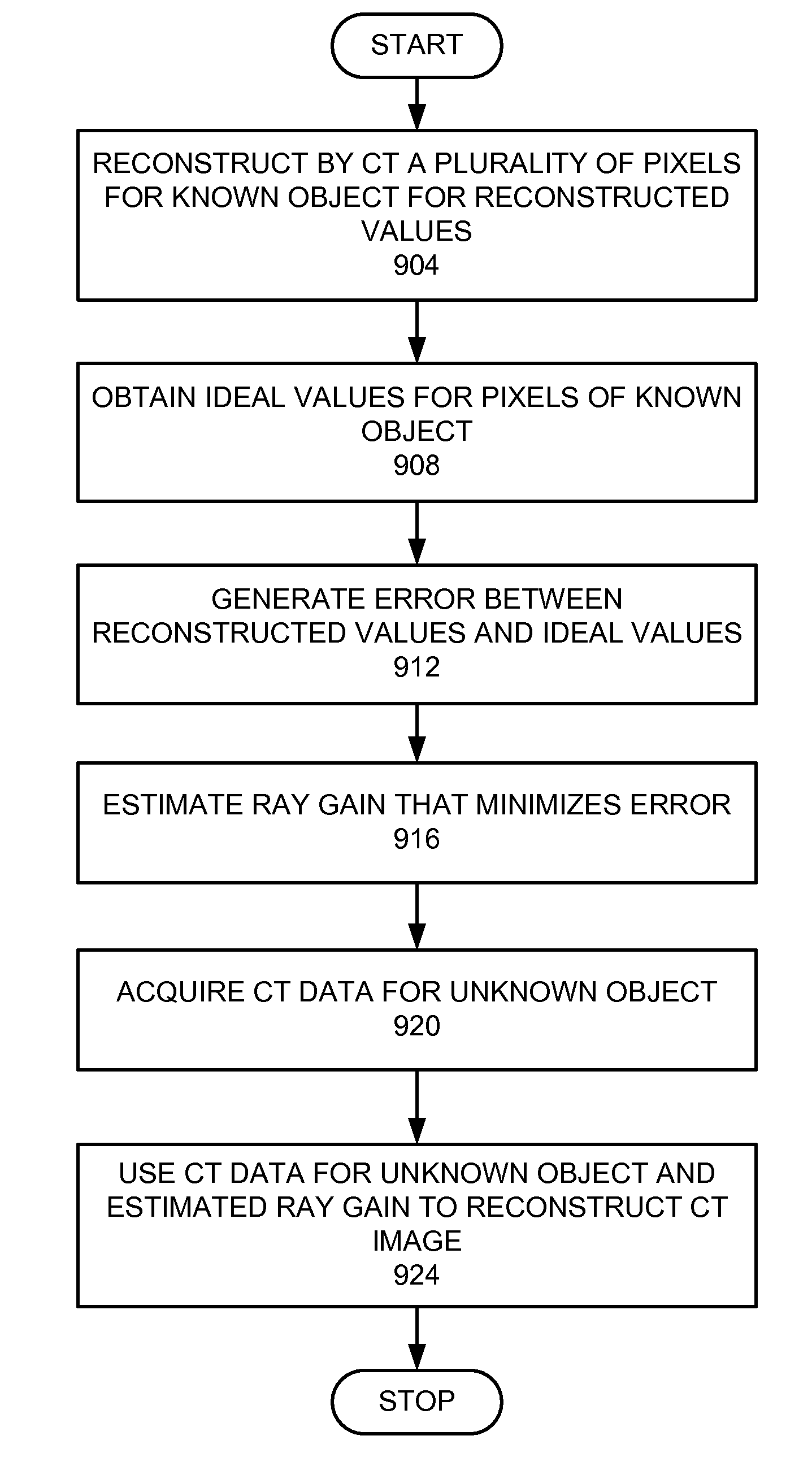
A method for imaging unknown objects in a computed tomography (CT) system, comprising determining ray gain for a known object is provided. A CT reconstruction is performed with the known object to obtain reconstructed values. Ideal values are obtained for pixels of the known object. An error related to a difference between the reconstructed values and the ideal values is generated. A ray gain is estimated that reduces the error.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for high-sensitivity single-photon emission computed tomography
InactiveUS8008625B2High sensitivityReduce total usageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSingle photon emission computerized tomographyPhoton emission
A method and apparatus are disclosed for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The apparatus includes a two-dimensional (2D) gamma detector array that moves to different positions in a three-dimensional (3D) volume space near an emission source and records a data vector g. In particular, the 3D volume space in which emission data g is measured extends substantially along a radial direction r pointing away from the emission source and each photon detector element in the 2D gamma detector array is provided with a very large collimator aperture. Data g is related to the 3D spatial density distribution f of the emission source, noise vector n, and a system matrix H of the SPECT / PET apparatus through the linear system of equations g=Hf+n. This equation is solved for f by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
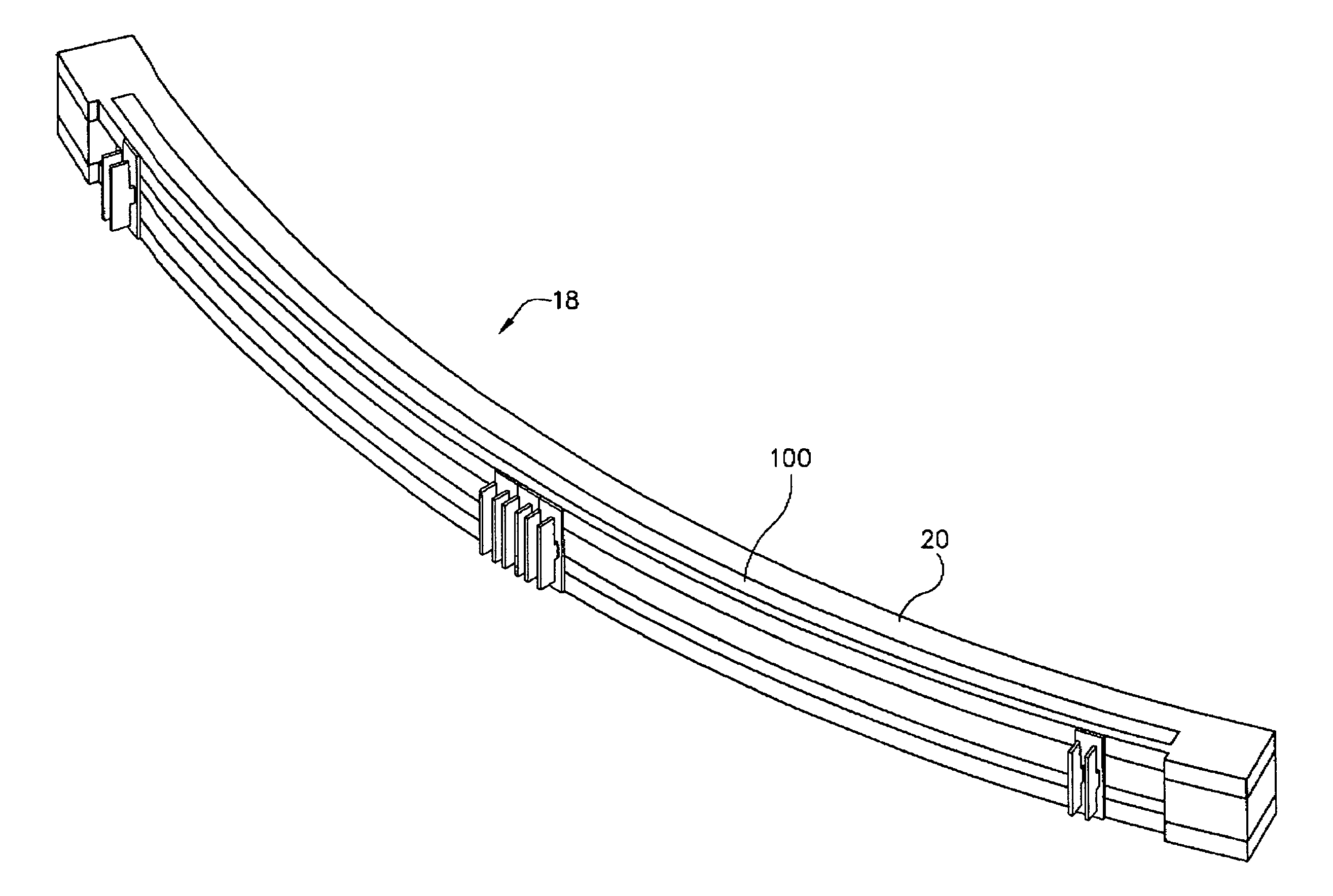
Self regulating detector rail heater for computed tomography imaging systems
ActiveUS7161157B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingEngineeringRadiative heating
The present application discloses an x-ray detector for use in a computed tomography (CT) imaging system. The x-ray detector assembly comprises an array of detector cells coupled between detector rails. The present invention provides a self regulating heating element having a body that, when current is passed therethrough, radiates heat until a specific reference temperature is reached, at which point the resistance of the PTC heater increases, thus reducing the current through the PTC heater, and, as a result, the radiative heating of the PTC heater.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System, method and computer-accessible medium for ultralow dose computed tomography image reconstruction
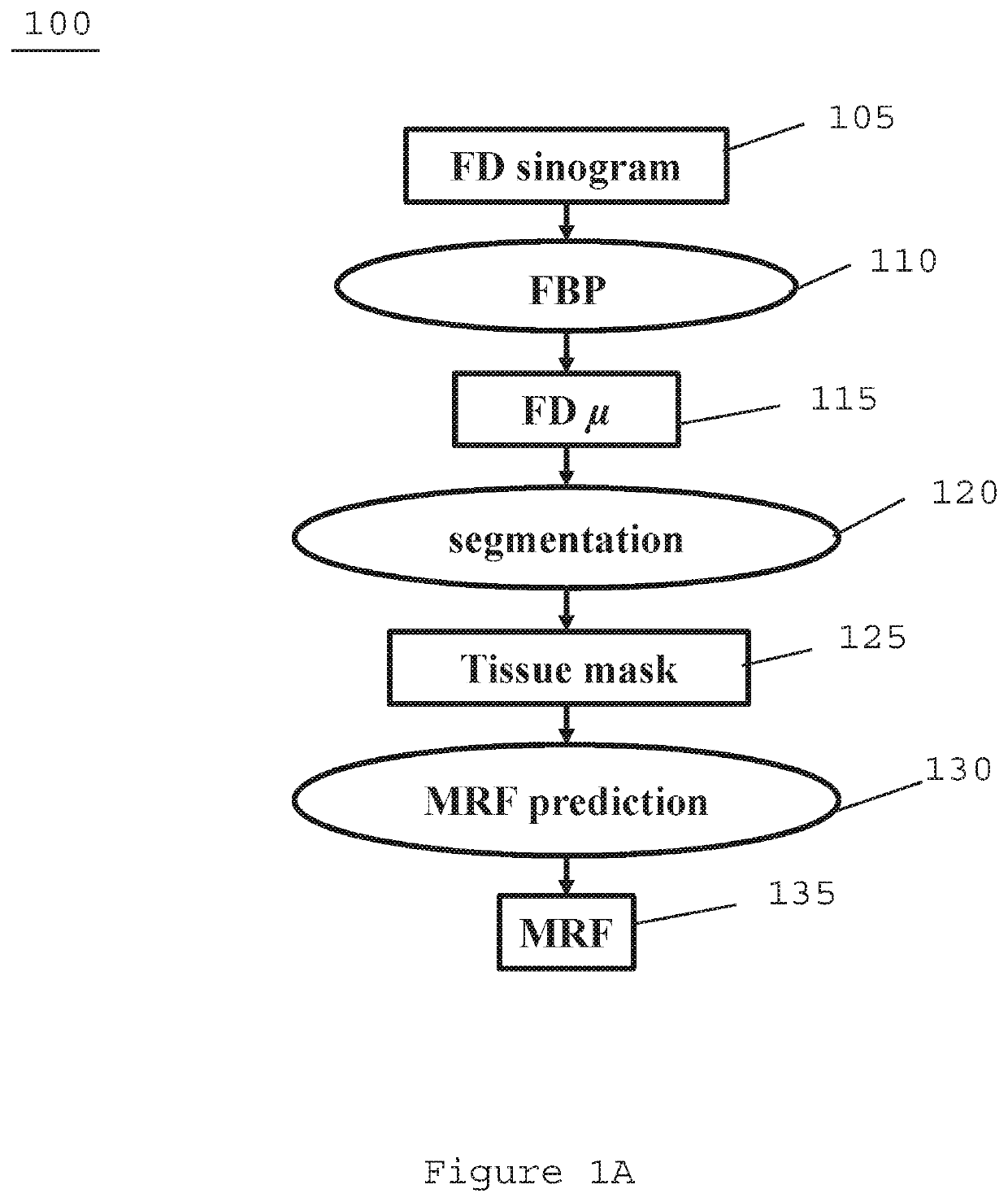
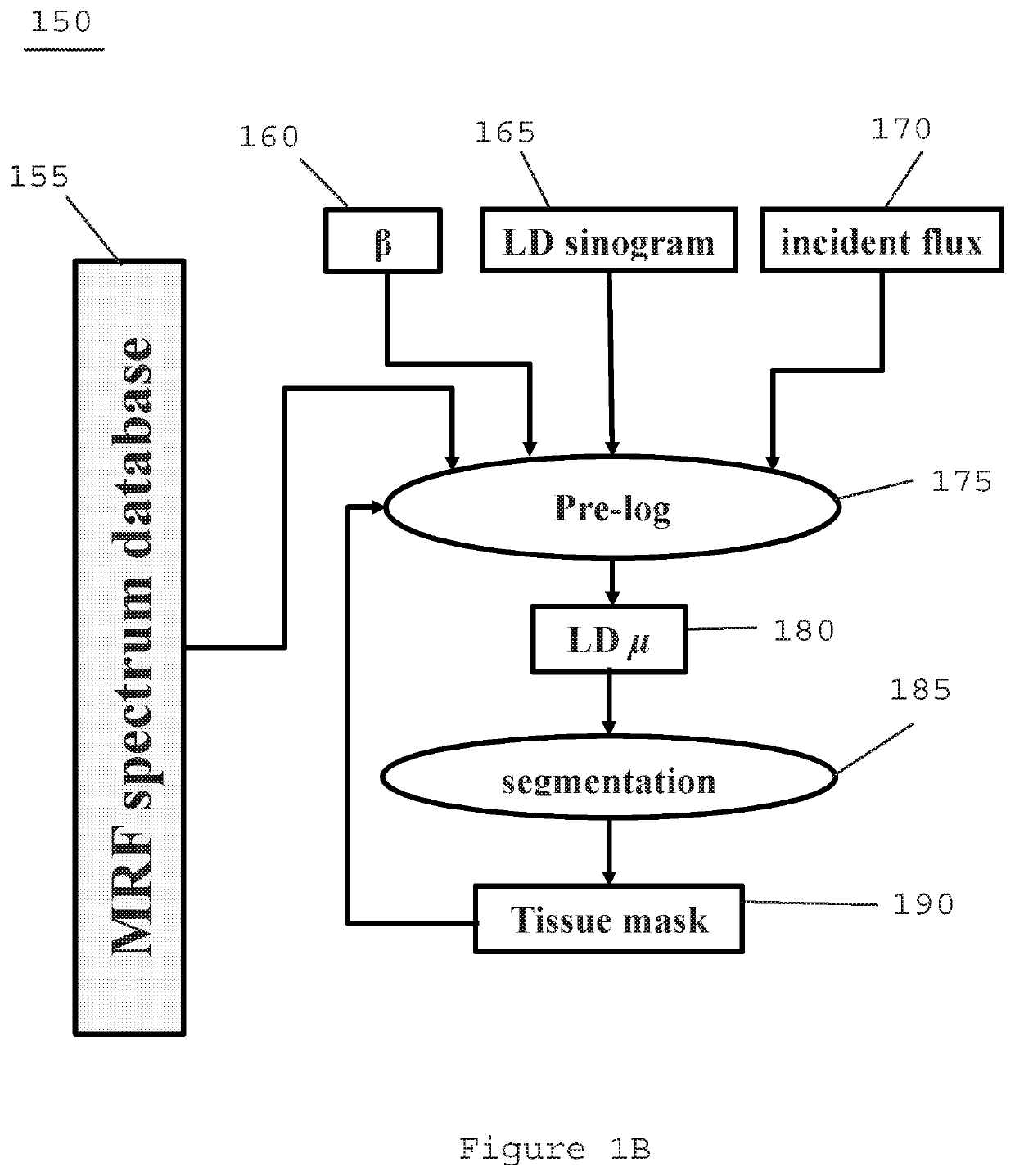
An exemplary system, method, and computer-accessible medium for generating computed tomography (“CT”) image(s) of a subject(s) can be provided which can include receiving low dose CT imaging information for the subject(s), where the low dose CT imaging information can be based on a radiation dose of less than about 50 mAs, receiving a priori CT image data, and generating the CT image(s) based on the low dose CT imaging information and the a priori CT image data. A further CT images(s) can be generated based on the CT image(s) and the a priori CT image data. The a priori CT image data can include a set of Markov Random Field (MRF) coefficients derived from high dose or full dose CT image data.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Determining Perforation Tunnel Impairment Productivity Using Computed Tomography
Disclosed is a method of testing the effectiveness of perforations and well treatments to enhance production, wherein tomographic image data is collected while fluid flow tests are conducted on a formation sample and thereafter three dimensional images are created and analyzed.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
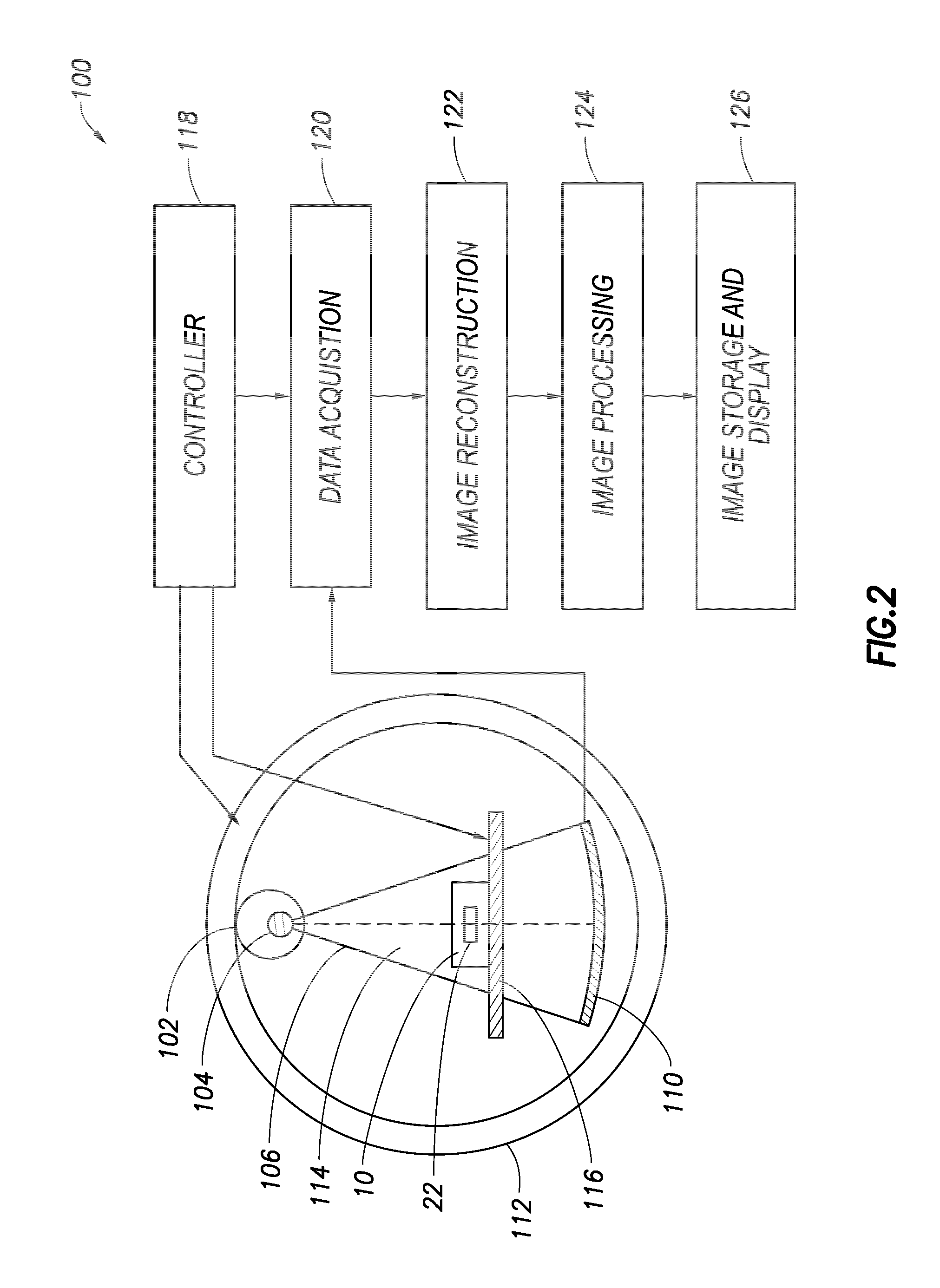
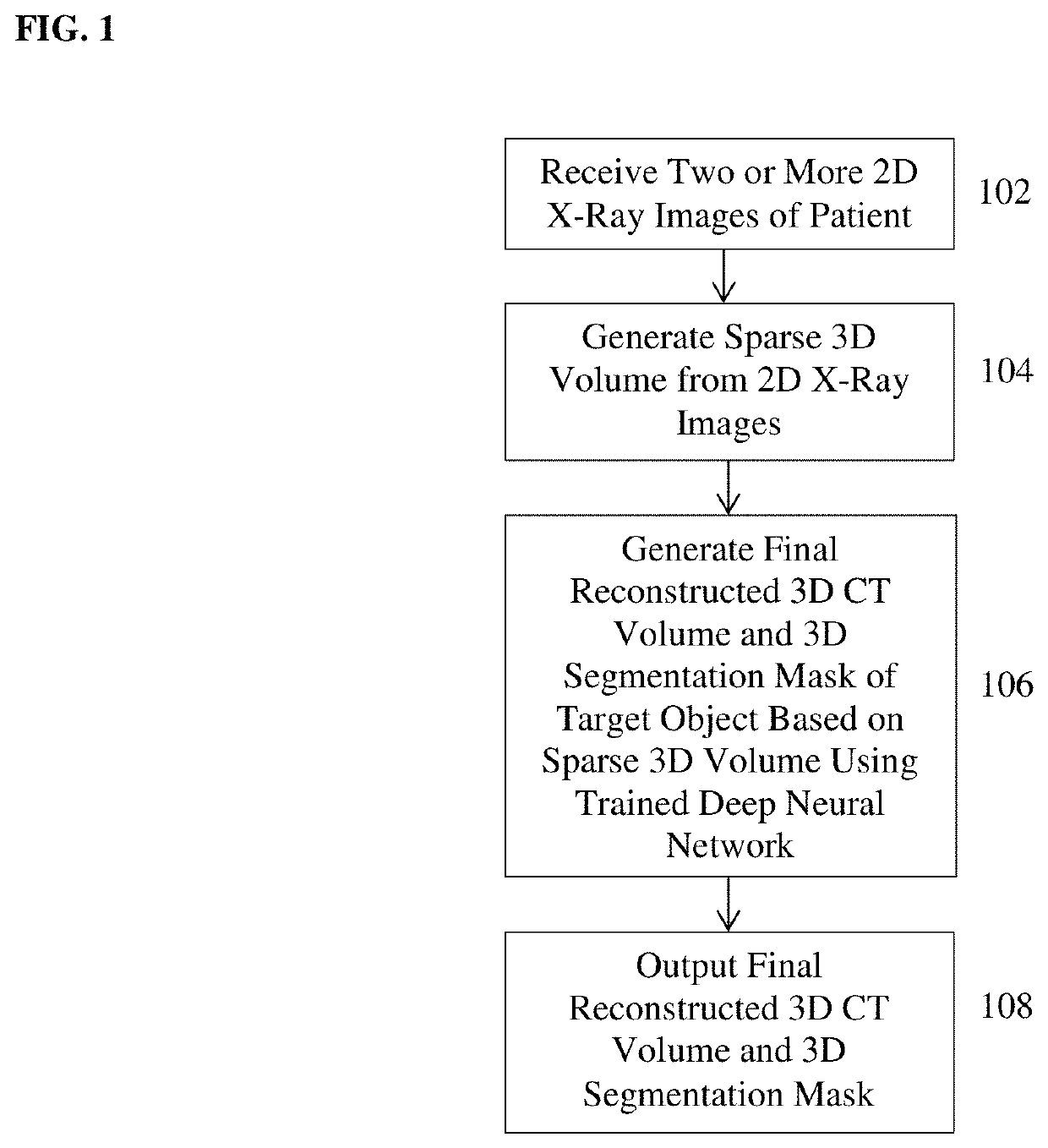
Method and system for 3D reconstruction of X-ray CT volume and segmentation mask from a few X-ray radiographs
A method and apparatus for automated reconstruction of a 3D computed tomography (CT) volume from a small number of X-ray images is disclosed. A sparse 3D volume is generated from a small number of x-ray images using a tomographic reconstruction algorithm. A final reconstructed 3D CT volume is generated from the sparse 3D volume using a trained deep neural network. A 3D segmentation mask can also be generated from the sparse 3D volume using the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Elongate Implant Containing a Structurally Encoded Pin, Carrier and Reading System Therefor
ActiveUS20180064506A1Process economyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInternal osteosythesisPositron emissionComputed tomography
A carrier for retaining a plurality of implants each comprising a structurally encoded pin, the structurally encoded pin having a shape or surface characteristics discernable by an imaging modality such as x-ray, fluoroscopy, computed tomography, electromagnetic radiation, ultrasound, visible light, UV light, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography and neutron imaging, from outside the carrier, the shape or surface characteristics representing structurally encoded data. The invention further discloses a carrier for viewing a plurality of implants, and associated reading systems for reading a plurality of implants. Finally, the invention discloses methods for reading a plurality of implantable devices retained within a carrier.
Owner:KIESER BRIAN +2
Method for artifact reduction using monoenergetic data in computed tomography
ActiveUS10573030B2Increase contrastReduce contrastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setTomography
A method for artifact correction in computed tomography, the method including: (1) acquiring a plurality of data sets associated with at least one low X-ray energy, and at least one high X-ray energy; (2) generating a plurality of preliminary images from the plurality of data sets; (3) identifying sources of an artifact source image; (4) forward projecting the artifact source image to produce artifact source data; (5) selecting and combining the plurality of data sets acquired in order to produce a new subset of data associated with the artifact, whereby to produce artifact reduced data; (6) generating a repaired data set to keep data sets associated with the low X-ray energy in artifact-free data and to introduce data sets associated with the high X-ray energy in regions impacted by an artifact; and (7) generating a final reduced artifact image from the repaired data set.
Owner:PHOTO DIAGNOSTIC SYST INC
System and method for beam hardening correction (BHC) in computed tomography (CT) image reconstruction
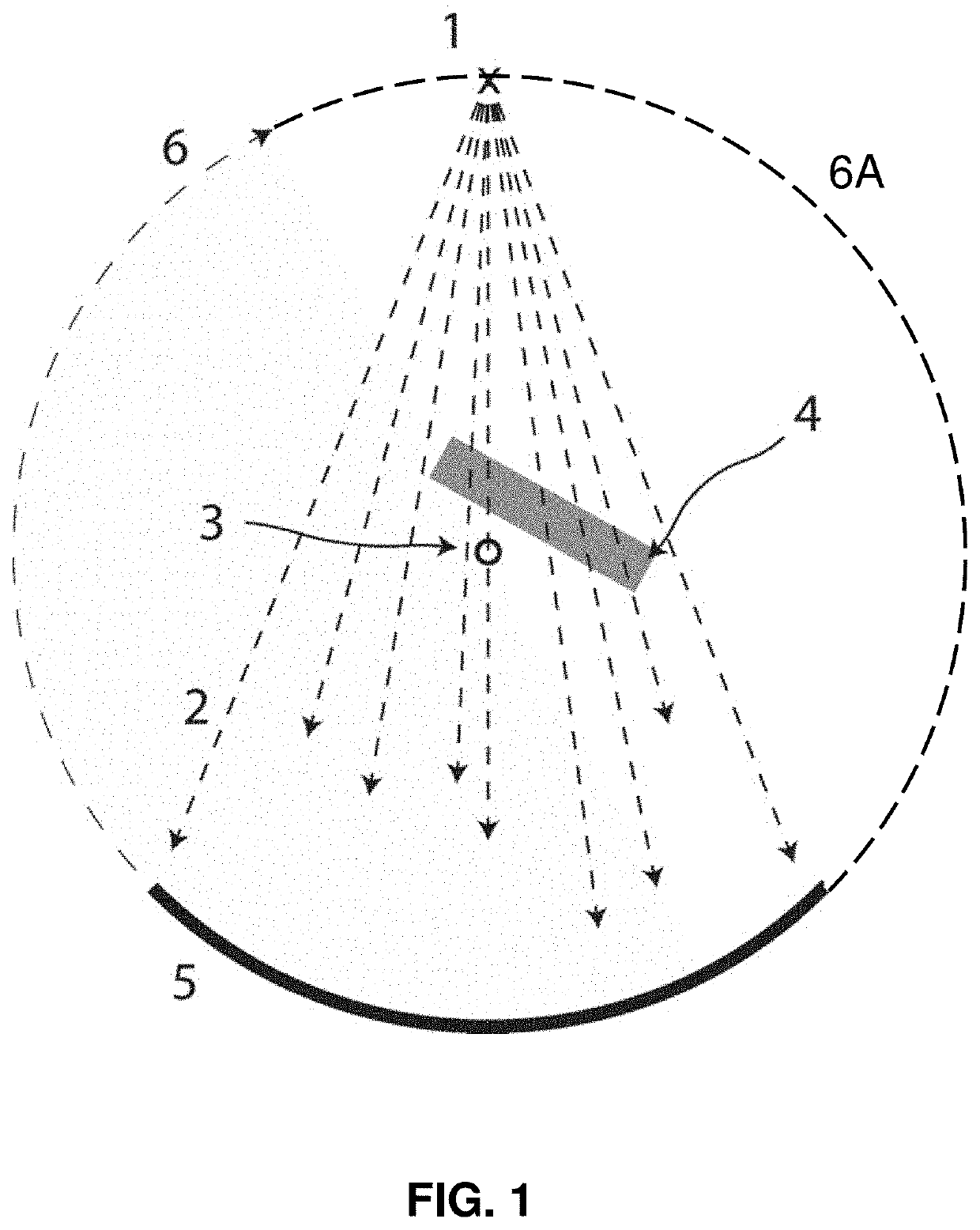
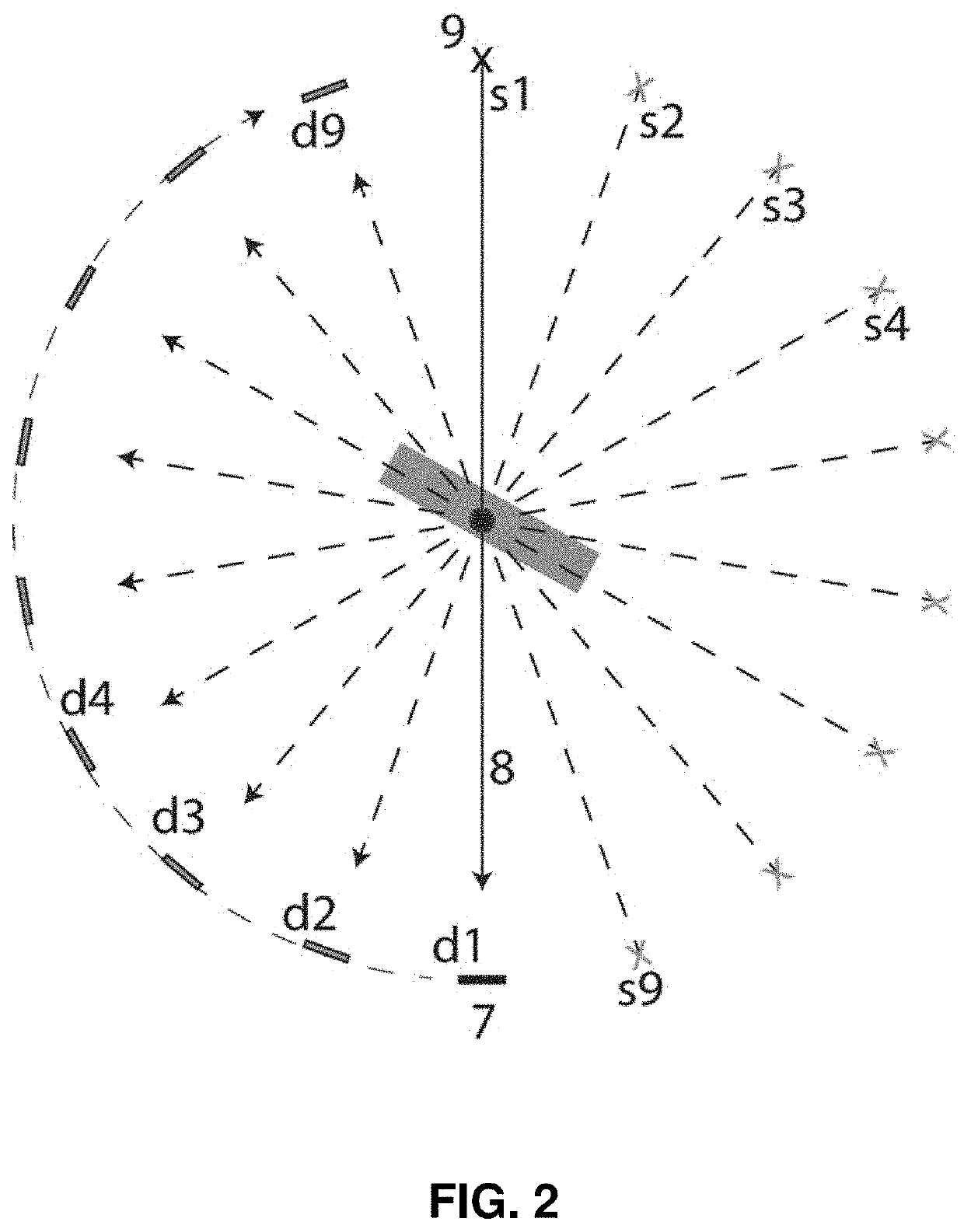
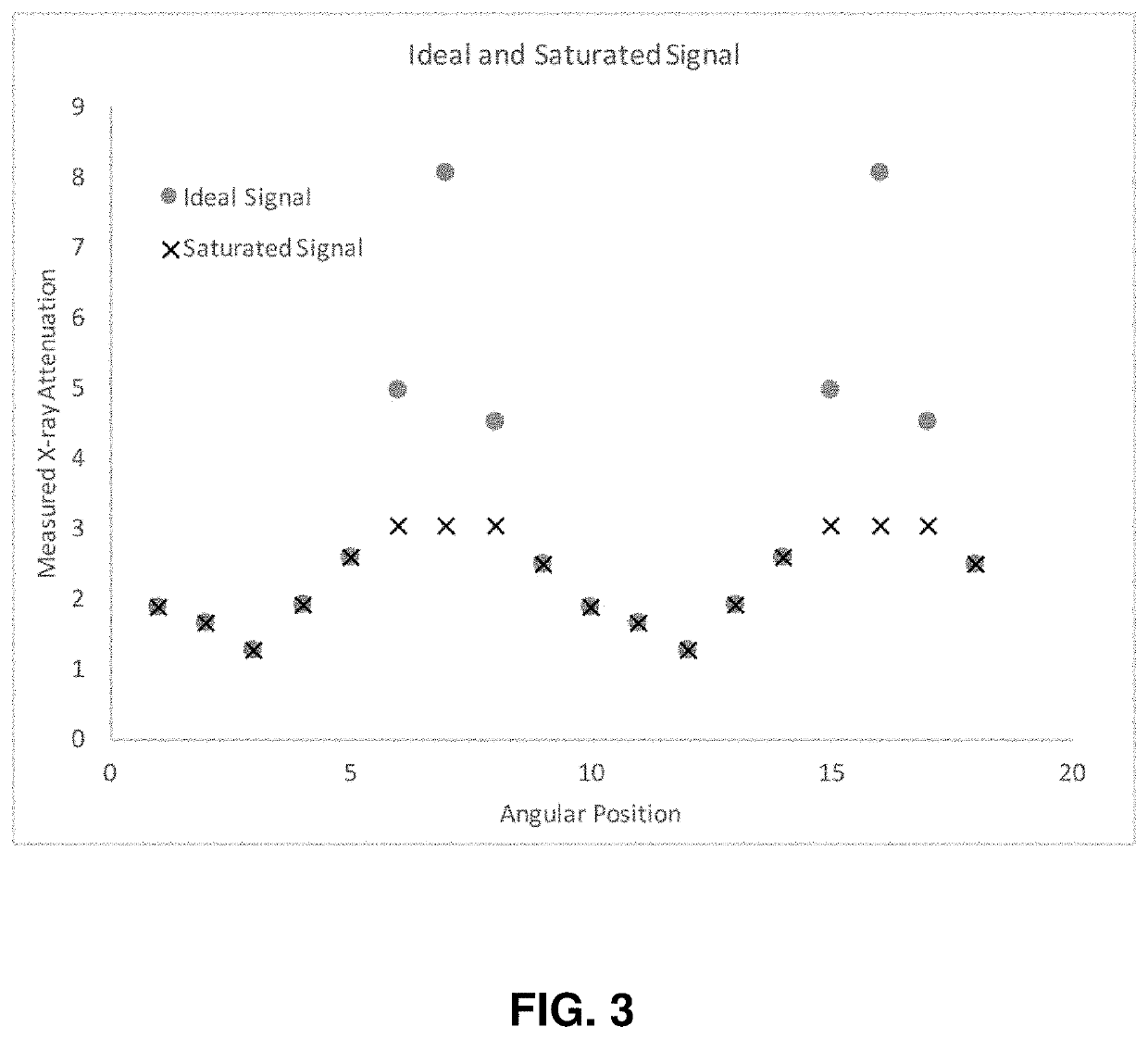
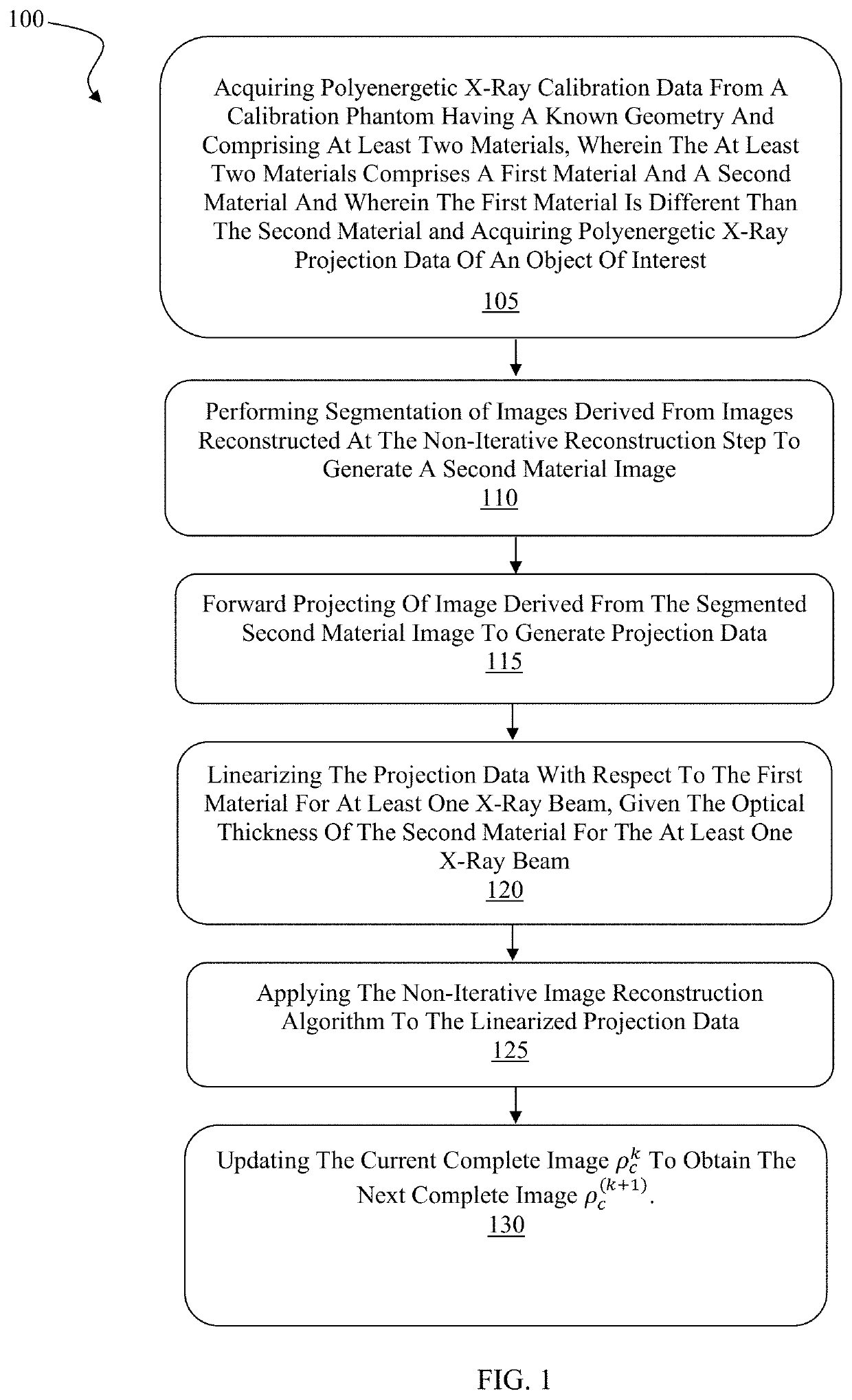
InactiveUS20200342640A1Reduces beam hardening artifactReconstruction from projectionImage analysisRadiologyBeam hardening
An improved system and method for the reduction of beam hardening artifacts in CT image reconstruction based on polyenergetic x-ray projection data and polyenergetic x-ray calibration data from a known calibration phantom.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com