Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Chloramphenicol Resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonsusceptibility of bacteria to the action of CHLORAMPHENICOL, a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis in the 50S ribosomal subunit where amino acids are added to nascent bacterial polypeptides.
Recombinant vector for eliminating activity of kanamycin drug resistance gene and building method of recombinant vector
InactiveCN105463003AInhibitory activityHigh copy numberNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionNovel geneOrganism
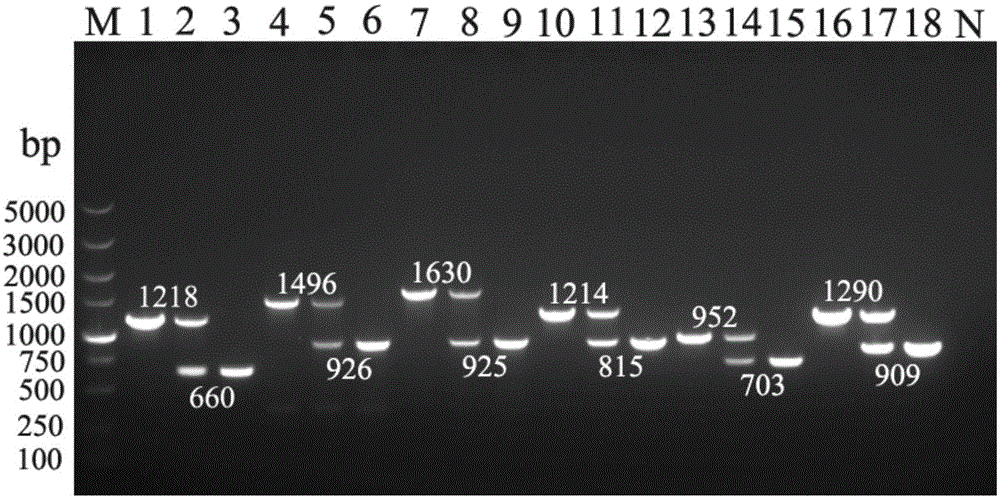
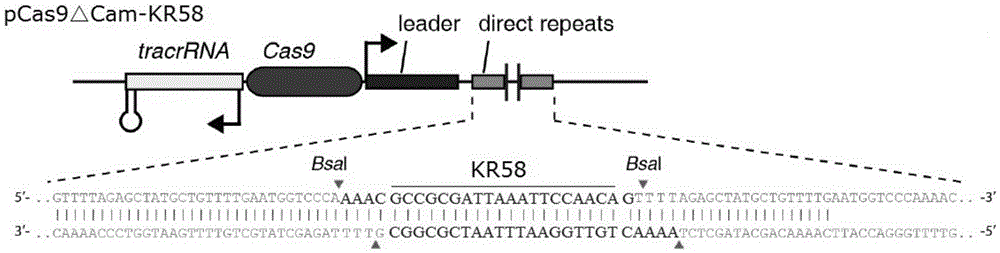
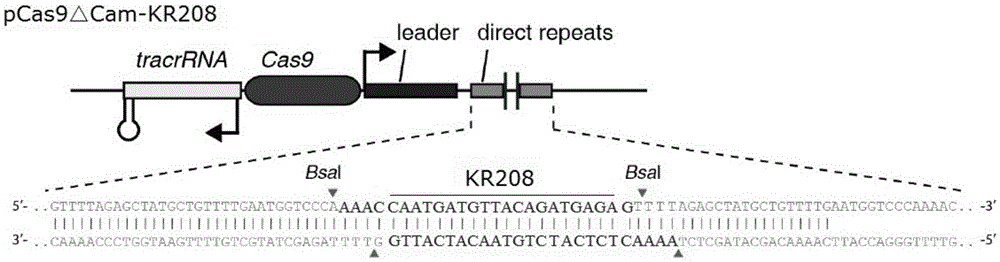
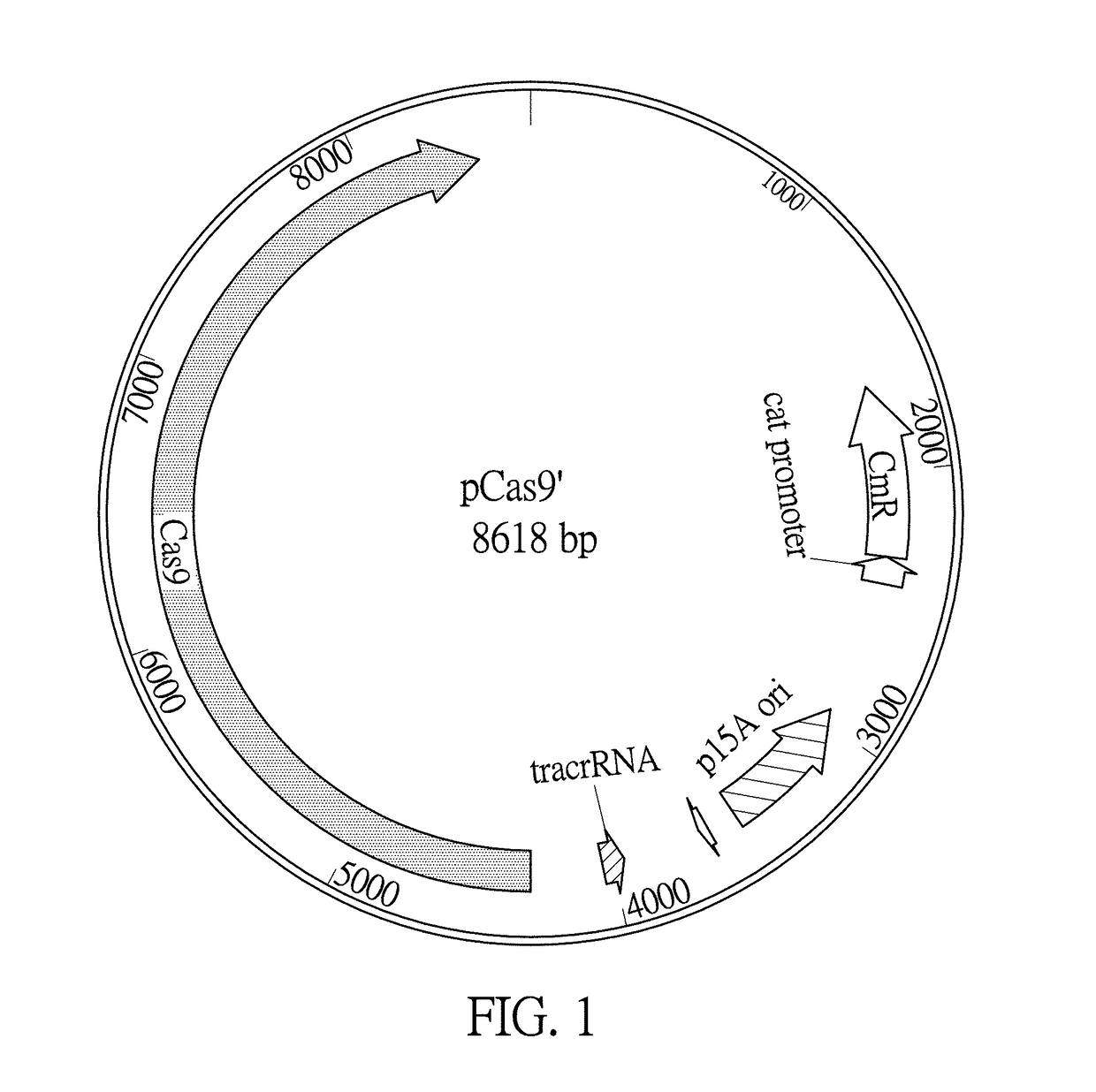
The invention provides a recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of a kanamycin drug resistance gene, and aims at eliminating drug resistance germs in organisms and solving the problem of kanamycin drug resistance of the germs. The recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of the kanamycin drug resistance gene is characterized by comprising a pCas9 vector subjected to chloramphenicol resistance elimination and a gRNA nucleotide sequence KR58 or KR208 aiming at a kanamycin resistance gene kan; the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR58 is GCCGCGAT TAAATTCCAACA, and the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR208 is CAATGATG TTACAGATGAGA. A building method of the recombinant vector mainly comprises the steps of carrying intergenic region nucleic acids by a novel gene editing tool CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system; removing a chloramphenicol resistance gene on the recombinant vector; transforming the gene into vaccine vector bacteria such as attenuated salmonella typhimurium; performing co-culture on the recombinant bacteria and the kanamycin drug resistance gene so that the recombinant vector in the recombinant bacterium cell enters the kanamycin drug resistance bacteria in an engaging mode. The activity of the kanamycin resistance gene kan is effectively inhibited, so that the original drug resistance bacterium cannot grow on a kanamycin culture medium.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Cas9 plasmid, genome editing system and method of escherichia coli
ActiveUS20170226522A1Improve efficiencyImprove fidelityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliGenome editing
A Cas9 expression plasmid, a genome editing system and a genome editing method for Escherichia coli are provided. The Cas9 expression plasmid includes a tracrRNA sequence, a Cas9 gene and a chloramphenicol resistance gene (CmR). The Cas9 expression plasmid is applied to CRISPR / Cas-coulped λ-red recombineering system for editing genomes of E. coli with high efficiency.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis strain for excreting nattokinase at high efficiency and preparation technology of high-purity nattokinase
InactiveCN107058204AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRestriction enzyme digestionDigestion
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis strain for excreting nattokinase at high efficiency. An aprN gene of bacillus subtilis NK is amplified by a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique; codons of initial thirty amino acids are optimized according to the codon preference of the bacillus subtilis, a recombination expression plasmid pHT01-aprN is established, and the correctness is verified through the restriction enzymes digestion, PCR amplification and sequencing. The recombination expression plasmid pHT01-aprN is imported into the bacillus subtilis 168 by an electric shocking method, and is performed with resistance screening by adopting chloramphenicol, so as to obtain engineering bacteria. After the fermenting condition is optimized, and the expression is induced by IPTG, the highest enzyme activity in a shake culture fermenting liquid is 289U / ml; the highest enzyme activity in a high-density fermenting liquid is 7778U / ml; the highest enzyme activity of a nattokinase preparation prepared by affinity column chromatography is 981731U / g.
Owner:上海诺金科生物科技有限公司
Single-resistance escherichia coli-bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN104232675AEasy genetic manipulationEase of plasmid transformationBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliAgricultural science
The invention discloses a single-resistance escherichia coli-bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector and application thereof. The bacillus subtilis shuttle expression vector provided by the invention comprises the following elements: a bacillus subtilis formed strong promoter P43, a sequence which encodes signal peptide, multiple cloning sites, an antibiotics resistance gene (kalamycin or chloramphenicol), a bifunctional promoter sequence which can start resistance gene expression of kalamycin or chloramphenicol in escherichia coli and bacillus subtilis, and copy homing sequences of bacillus subtilis and escherichia coli. The expression vector disclosed by the invention not only can be stably copied in escherichia coli, but also can be stably copied in bacillus subtilis, and expresses homologous and heterologous proteins. All vectors just contain one resistance gene, the plasmid of which is less than 400bp, so that gene operation and plasmid conversion are easy to carry out, and the conversion ratio is high. Besides the expression vector of an exogenous gene, the vector can be further used for screening promoters and constructing a gene knock-out vector.
Owner:WUHAN RUIHENGDA BIOLOGICAL ENG
Universal gene-knockout suicide vector for vibrios and application thereof
InactiveCN105063073AStrong lethal effectWide range of lethal objectsBacteriaHybrid cell preparationAgricultural scienceRestriction enzyme digestion
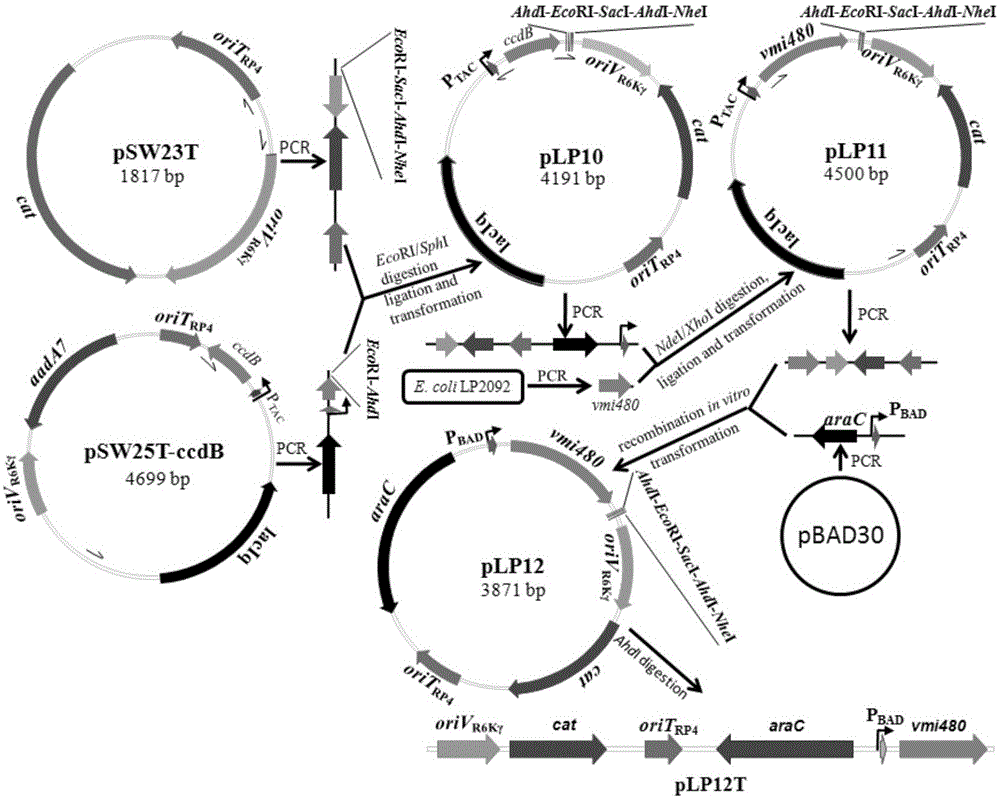
The invention discloses a universal gene-knockout suicide vector for vibrios and a construction method theroef and provides an application thereof in gene knockout of the vibrios. The universal gene-knockout suicide vector pLP12 is a ring-shaped vector and comprises a PBAD promoter, a repressor protein gene araC, an RP4 transferring initiation site, a chlorampenicol resistant gene, an R6K duplicating initiation site, a multiple-cloning-site area and a lethal gene vmi480; the multiple-cloning-site area at least contains two AhdI restriction enzyme digestion sites; the suicide vector pLP12 is subject to AhdI restriction enzyme digestion to form linearized suicide vector pLP12T. The universal gene-knockout suicide vector adopts entirely-new reverse selection genes vmi480 and is used for replacing the common sacB gene. Foreign fragments carried by the pLP12T are transferred to vibrio cells to be mutated by a jointing mode, under the pressure of antibiotics and reverse selection of products of lethal gene vmi480, first-time homologous recombination and second-time homologous recombination are carried out on the vibrios successively, and finally the mutant strain with deletion of target genes is generated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for homologous recombining by using spirulina and expressing human gene
InactiveCN1528902AImprove conversion rateEasy to detectOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHuman bodyRecombinant expression
The invention refers to a method for reconstructing the cloned and constructed human body tumor death factor TRAIL gene expression carrier into spirulina gene group to be expressed stably with gene gun. The special components of the reconstructed TRAIL expression carrier include resistant mark gene expression box CAT, chlorophyll body photosynthetic gene promotor and ender, spirulina homologous segment, TRAIL gene segment without coding film combining part, the expression system also includes characters of primary nucleus and eukarya. The invention sets suitable striking parameter, uses gene gun to guide the reconstructed expression carrier into spirulina silk body, and through several times of sifting of chloramphenicol with incremental density and molecular biology testing, the invention gets spirulina converter of TRAIL gene. The invention applies to spirulina reconstruction and human body gene expression, it also applies to reconstruct and express other primary nucleolus and eukarya.
Owner:广东梅雁蓝藻有限公司
Enhance-like element gene for enhancing foreign protein expression and application of gene
InactiveCN102965375AIncreased expression level propertiesIncrease resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBacterial strainCapsid
The invention discloses an enhance-like element gene ER1 for enhancing foreign protein expression in prokaryotic cells. The enhance-like element gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (Sequence Identity No) or a truncated sequence of the nucleotide sequence, wherein the gene sequence is screened by establishing a fusion expression reporter gene recombinant vector; the fusion reporter gene consists of major capsid protein L1 gene of human papilloma virus and chloramphnicol acetyltransferase (CAT); the gene fragments to be selected are linked with the sieving recombinant vector and is transformed so as to establish a gene library; and the recombinant bacterial strain containing the enhance-like element gene sequence is screened based on the chloramphenicol resistance, so as to obtain the enhance-like element sequence which can improve the activity of chloramphenicol of the fusion reporter gene of the strain and promotes the foreign protein expression.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enhanced subsample gene capable of improving expression of foreign protein and application thereof
InactiveCN103602684AIncrease resistanceImprove practicalityVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationCapsidChloramphenicol Acetyl Transferase Gene
The invention discloses an enhanced subsample gene capable of improving expression of foreign protein in a prokaryotic cell. The gene has a nucleotide sequence or a truncated sequence thereof shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The gene is screened by constructing a fusion expression report gene recombinant carrier. The fusion expression report gene consists of a truncated sequence L11 of a main capsid protein L1 of a human papilloma virus and a chloramphnicol acetyl transferase gene (CAT). A to-be-screened gene segment and the recombinant carrier for screening are connected and converted for constructing a gene library, and a recombinant strain comprising the gene sequence of the enhanced subsample is screened by improving the resistance of chloramphnicol, so that the enhanced subsample sequence is obtained. The sequence can be used for improving the resistance of chloramphnicol of the fusion expression report gene recombinant carrier and the expression level of the foreign protein.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chloramphenicol resistance selection in Bacillus licheniformis
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Red fluorescein detection method for nisin, and indicator bacterium and recombinant plasmid thereof
InactiveCN102071210ARapid detection of nisin contentDetection of nisin contentMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyFluorescein
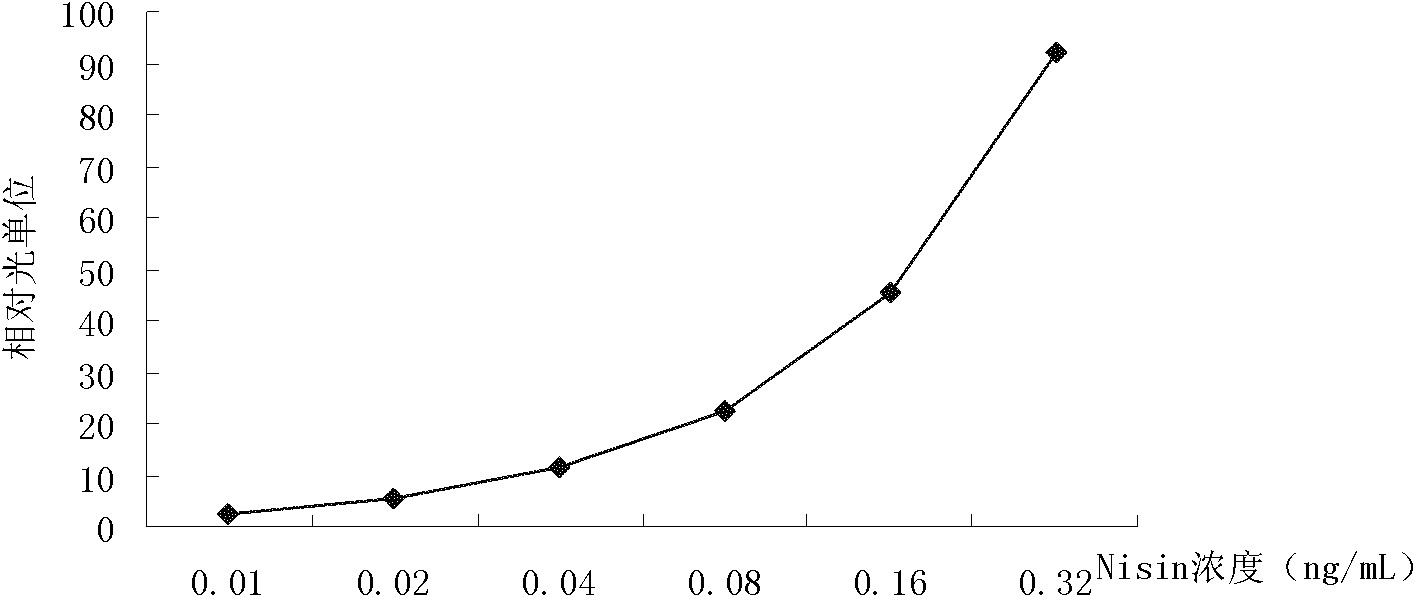
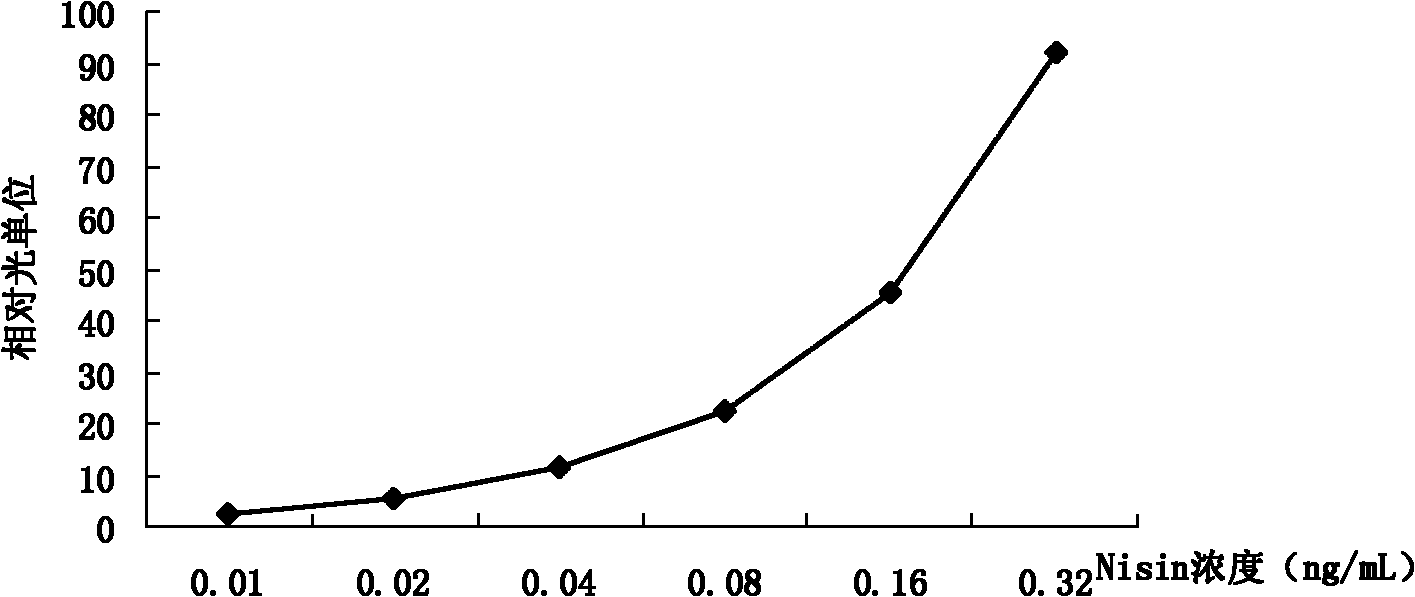
The invention relates to a red fluorescein detection method for nisin, and an indicator bacterium and recombinant plasmid thereof. A recombinant plasmid vector is used for converting host Streptococcus lactis NZ9000 to obtain a gene engineering indicator bacterium strain which can respond to nisin to generate red fluorescein. The recombinant plasmid vector contains a red luciferase cobA gene controlled by an inducible strong promoter PnisA, and a chloramphenicol resistance gene. The gene engineering indicator bacterium TD304 constructed by the invention can be used for quickly detecting the content of nisin in a nisin fermentation liquid, thereby providing scientific parameters for establishing an optimal terminating point for fermenting production of nisin; and the gene engineering indicator bacterium TD304 can also be used for quickly detecting the content of nisin in water, food and milk beverages.
Owner:天津艾玛斯特生物科技有限公司
Staphylococcus aureus mutant strain, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103333849ABiological properties are stableLow toxicityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
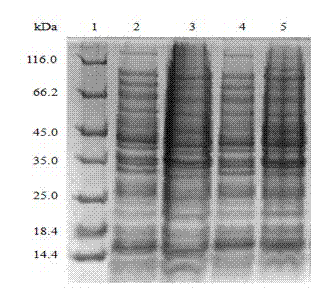
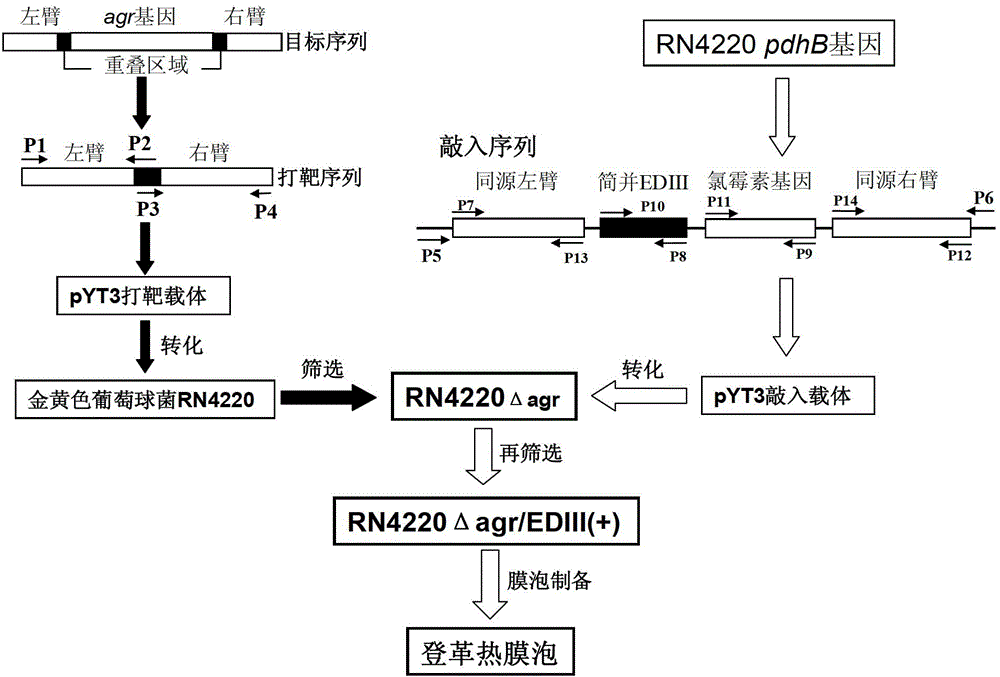
The invention discloses a staphylococcus aureus mutant strain, and a preparation method and applications thereof in general. The preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No.7583. The preparation method comprises following steps: performing gene knockout of agr gene, which is used for encoding a global regulatory factor (Agr) and is in staphylococcus aureus RN 4220 strain chromosomes, by application of homologous recombination; implanting a degenerate sequence used for encoding dengue virus envelope E protein EDIII region to 3' terminal of RN4220 pdhB gene, which is used for encoding pyruvate dehydrogenase beta-subnit ,by application of homologous recombination; implanting chloramphenicol resistant encoding gene at the back of EDIII; and then performing nucleotide sequencing for identification. The mutant strain of the invention is taken as engineering bacteria, and after fermentation, bacterial membrane vesicles containing dengue virus EDIII recombinant protein are purified from obtained fermentation supernatant. The dengue virus membrane vesicles produced by bacteria are used as a vaccine in prevention of infectious disease caused by dengue virus.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
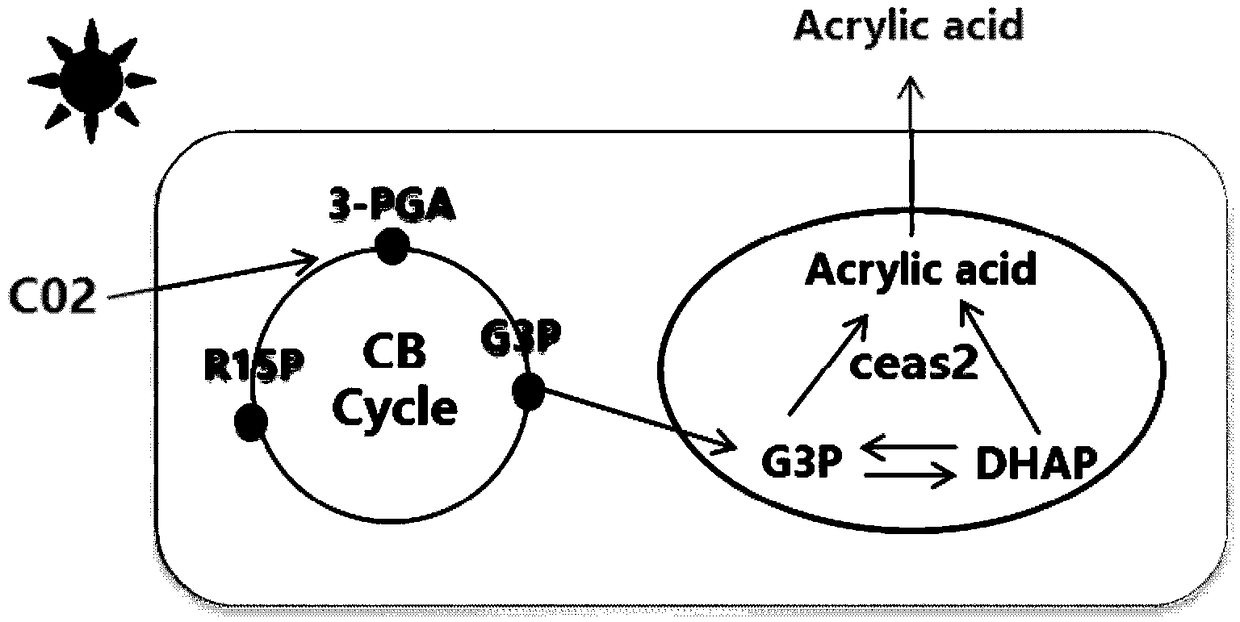
Method for synthesizing acrylic acid from cyanobacteria
InactiveCN108728474AEasy to buildReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
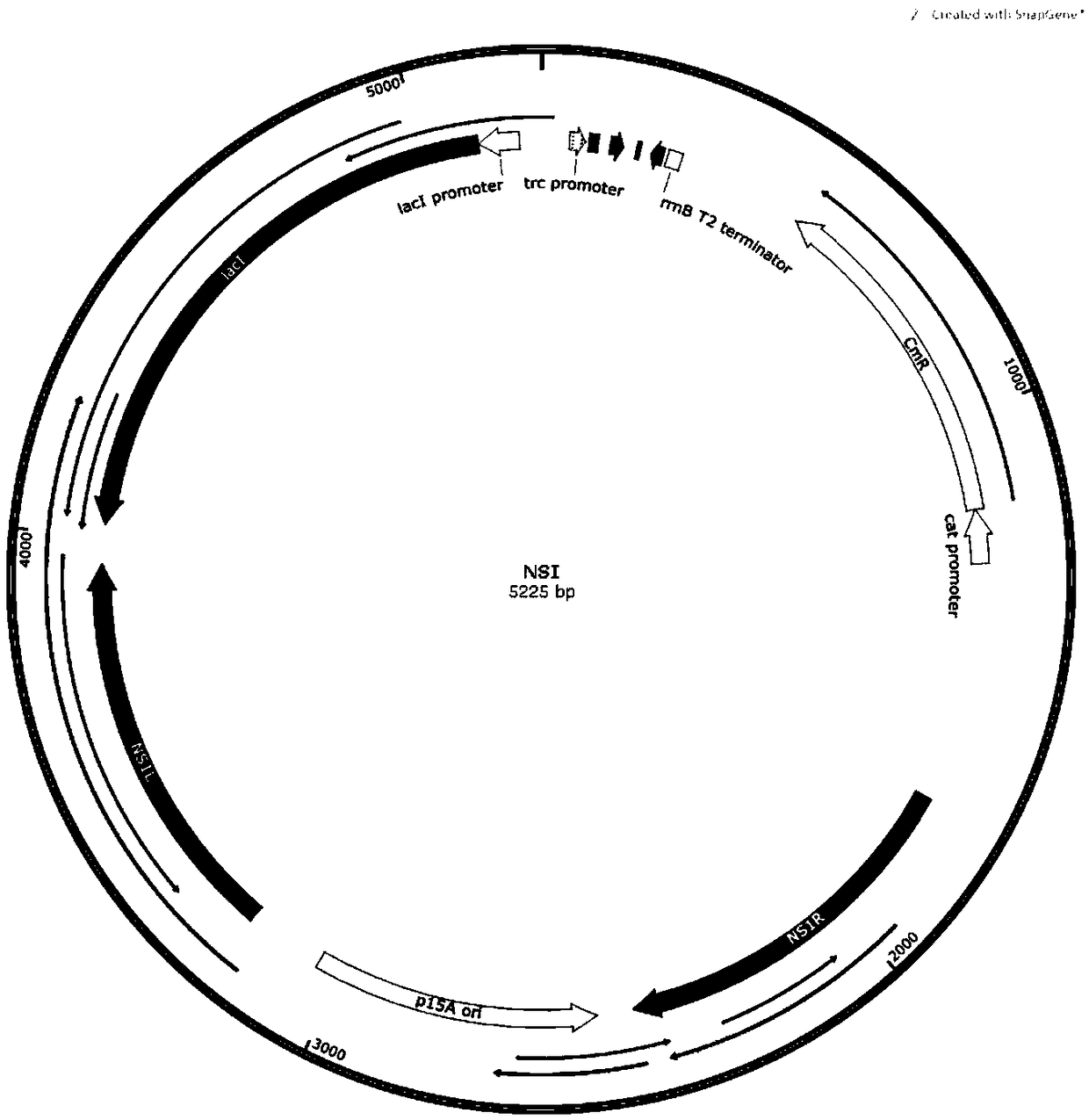
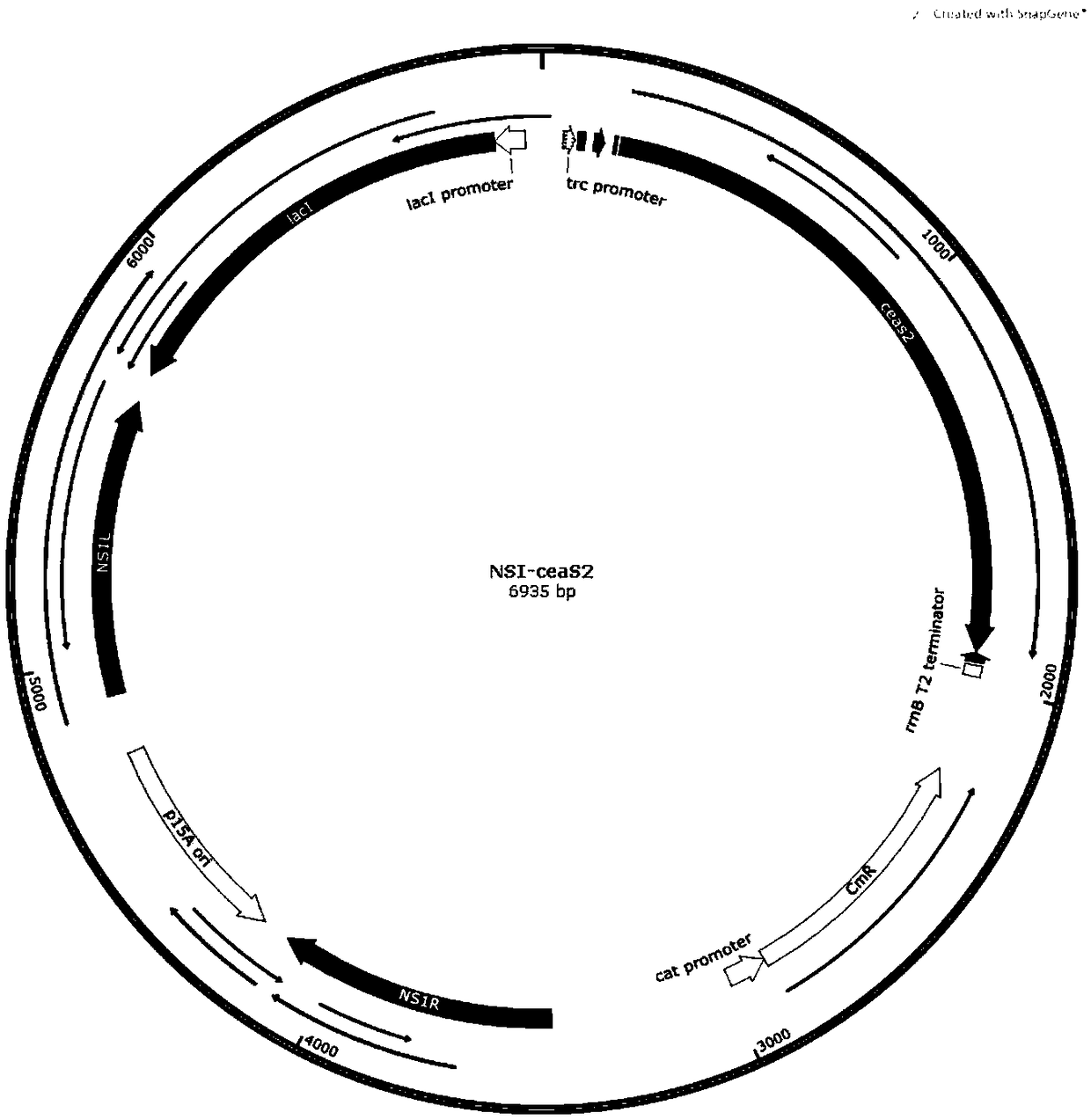
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing acrylic acid from cyanobacteria. The method comprises the following steps: 1), firstly, based on an NSI gene of cyanobacteria Syn7942, constructing an integrated vector NSI, and recombining to obtain a vector NSI-ceaS2; 2), transforming the recombinant vector NSI-ceaS2 into cyanobacteria Syn7942 cells, and then preliminarily screening out monoclonal transgenic cyanobacteria Syn7942 through a chloramphenicol solid culture medium; 3), transferring the screened monoclonal transgenic cyanobacteria Syn7942 to a liquid culture medium with chloramphenicol resistance, and after the cyanobacteria grow out, extracting a cyanobacteria genome for PCR verification of a target gene; 4), transferring the successfully verified monoclonal transgenic cyanobacteria Syn7942 to the liquid culture medium for culture, and when the cyanobacteria grow till OD730 is greater than or equal to 1, adding IPTG for inducing expression of a gene ceaS2, and catalytically synthesizing the acrylic acid by an enzyme by using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) or dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) produced by photosynthesis of the cyanobacteria as a substrate; 5), performing separation and purification. By the method, when the acrylic acid is synthesized through transformation of the cyanobacteria as substrate organisms, only sunlight and moisture and the like are required as production raw materials, production equipment and a production environment are easy to construct, and high electricity consumption is not required, so that the production cost of the methodprovided by the invention is greatly lower than those of other production methods.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
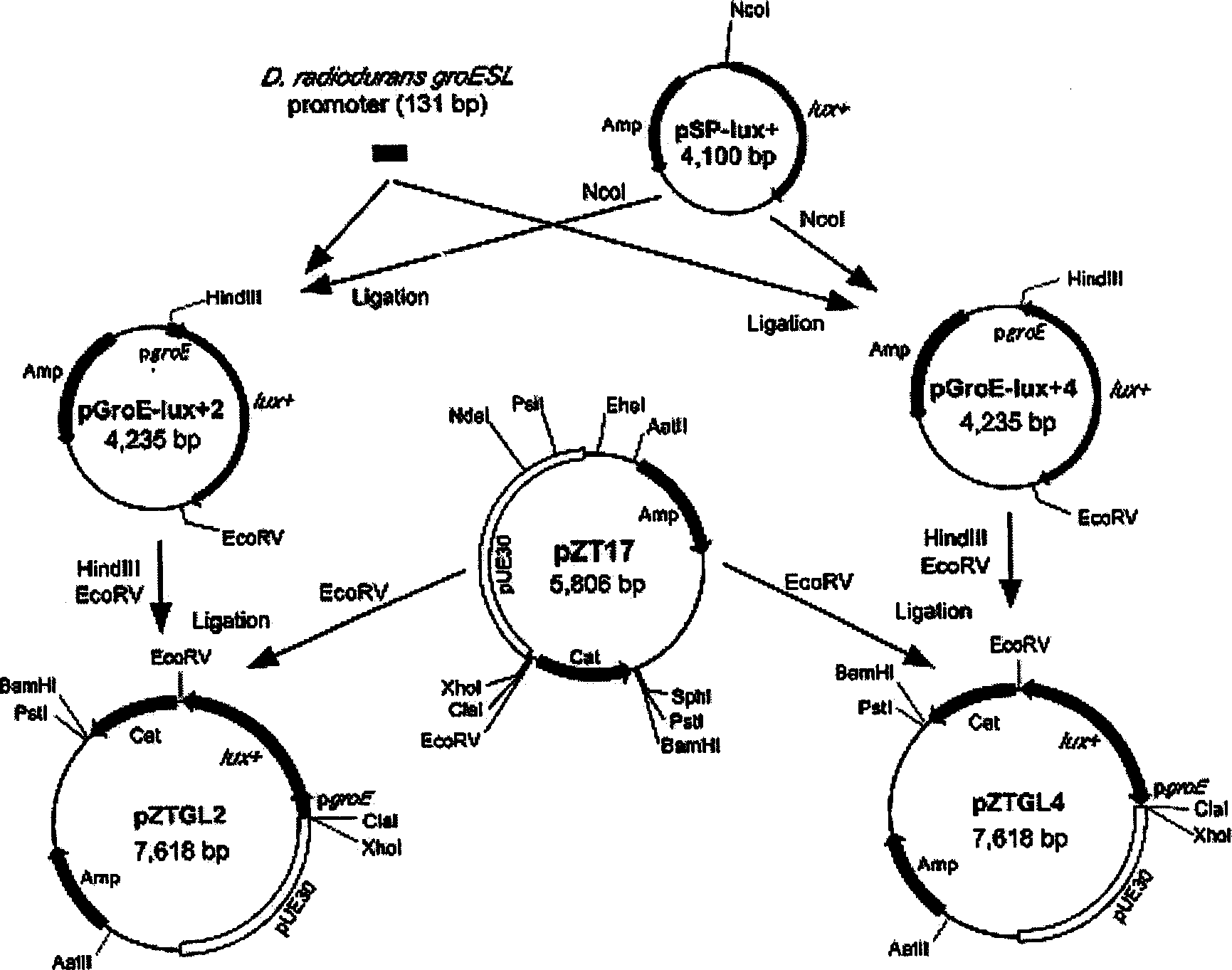
Method for preparing radio-resistant bacterium having luciferase activity
InactiveCN101113426AHigh luciferase activityMonitor impact in real timeBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliDeinococcus grandis
The invention relates to a preparation method of radioresistant bacterium that contains the activity of luciferase. The invention takes plasmids originating from radioresistant bacterium deinococcus radiopugnans as a base to recompose with plasmids that can ensure self-duplication in escherichia coli to form a shuttle carrier. The carrier is recomposed with DNA fragments in the luciferase gene lux field that originates from into host DNA of photinus pyralis from North America into plasmids with luciferase genes. Then the plasmids are introduced into bacterial of a radioresistant bacterium family, deinococcus grandis are transformed by the constructed plasmids to get chloramphenicol resistant strains. The radioresistant bacterium prepared by the method of the invention can be used in various fields of outdoor opening and close environments. The carrier has the luciferase genes, thereby having better application value to real-time supervision and control on the propagation, distribution and influence to the environment of the recomposed transformants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dual-specificity monoclonal antibody for resisting chloramphenicol and apramycin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103087195AStable traitsHigh detection sensitivityHybrid immunoglobulinsBispecific monoclonal antibodyChloramphenicol Resistance
The invention discloses a dual-specificity monoclonal antibody for resisting chloramphenicol and apramycin as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biotechnology. The dual-specificity monoclonal antibody simultaneously has specificity for the chloramphenicol and the apramycin. The preparation method of the dual-specificity monoclonal antibody comprises the steps of: synthesizing haptens and artificial antigens of the chloramphenicol and the apramycin; preparing and secreting chloramphenicol resistance hybridoma cell strains by using the artificial antigens of the chloramphenicol; preparing and secreting apramycin resistance hybridoma cell strains by using artificial antigens of the apramycin; fusing the chloramphenicol resistance hybridoma cell strains and the apramycin resistance hybridoma cell strains, then screening to obtain tetrasomic hybridoma cells which secrete the dual-specificity monoclonal antibody for resisting chloramphenicol and apramycin. The dual-specificity monoclonal antibody obtained by the method has stable character and high detection sensitivity and can be produced in large quantities; and an ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) analytical method is established by using the antibody and provides technological base for rapid detection of the chloramphenicol and apramycin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
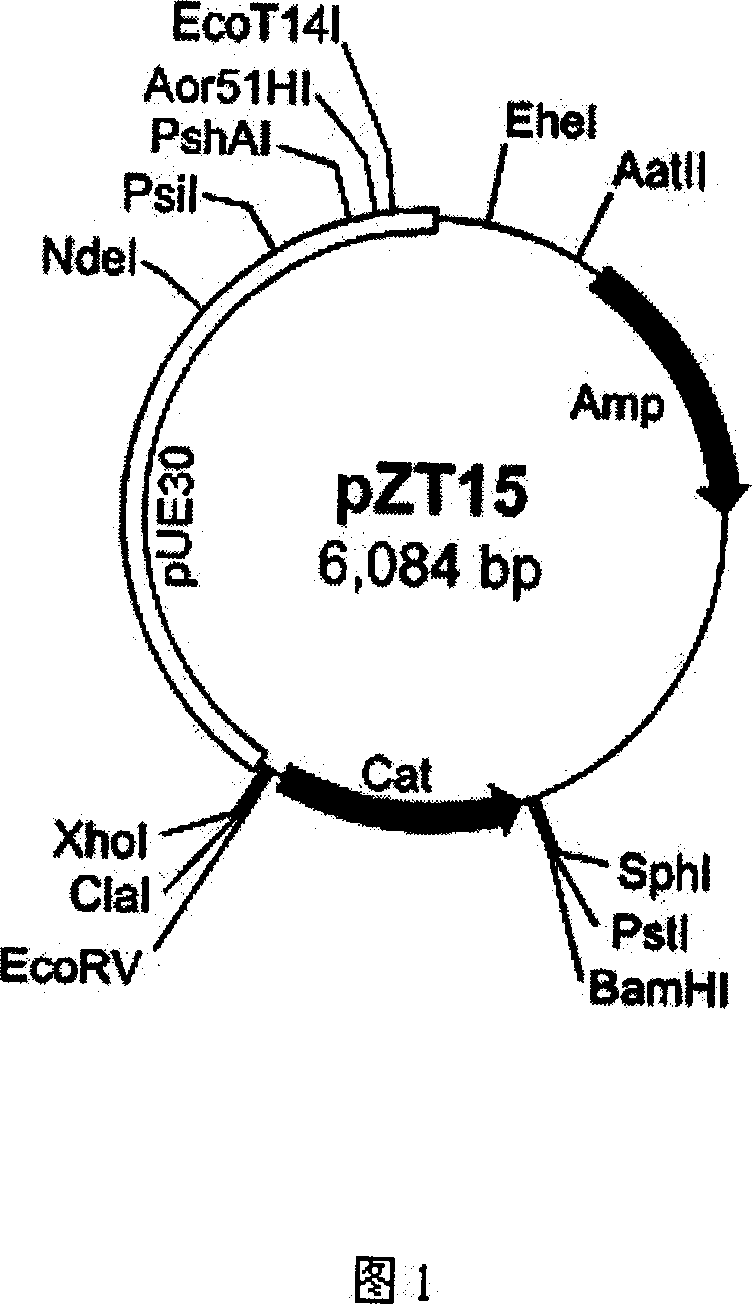
Modified entry vector pRMG-C and application thereof
InactiveCN106222168AReduce experiment costExpensive to fixNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionChloramphenicol ResistanceMultiple cloning site
The invention provides a modified entry vector pRMG-C and application thereof. A commercial cloning vector serves as the framework of the modified entry vector pRMG-C, and a section of artificially synthesized sequence is added and comprises recombinase recognition sites attL1 and attL2 and a section of multiple cloning sites in the middle; besides, an ampicillin resistance gene is replaced with a chloramphenicol resistance gene. A peanut ethylene signal pathway key gene AhETR1 is subcloned to pRMG-C with the seamless cloning technology, then AhETR1 is recombined to various vectors through an LR reaction, and it is proved that the entry vector pRMG-C can be applied to the LR reaction without digestion. By means of the entry vector pRMG-C, the problem that an adopted commercial entry vector is expensive is solved, and the tedious steps of digestion and the like are omitted; the entry vector pRMG-C has important application value.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Zymomonas mobilis gene engineering bacterium capable of producing isobutanol and construction method of zymomonas mobilis gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102876625AUnique ED PathwayHigh isobutanol toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsobutanolStaphylococcus lactis
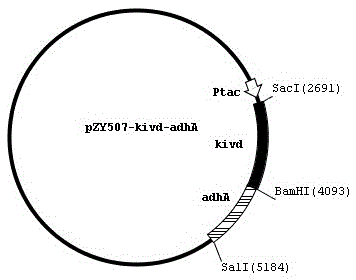
The invention relates to a zymomonas mobilis gene engineering bacterium capable of producing isobutanol and a construction method of the zymomonas mobilis gene engineering bacterium. A 2-ketoisovalerate decarboxylase (kivd) gene and an alcohol dehydrogenase (adhA) gene in Lactococcus lactis 1.2829 can be obtained through cloning and connected to plasmid pZY507 with chloramphenicol resistance for construction to obtain recombinant plasmid pZY507KA, the recombinant plasmid is electro-transformed into zymomonas mobilis, and bacterial strains with chloramphenicol resistance are screened to be the target engineering bacterium. The obtained gene engineering bacterium can decompose glucose to synthesize the isobutanol after the engineering bacterium is induced, a zymomonas mobilis fermentation method is firstly used for producing the isobutanol, and simultaneously, huge potential and values of the zymomonas mobilis are shown.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
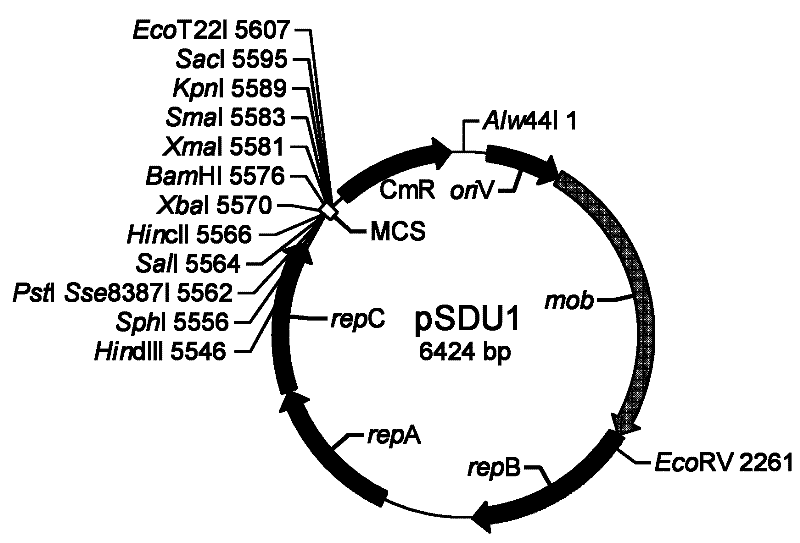
Small shuttle plasmid pSDU1 with chloramphenicol resistant gene for Acidithiobacillus caldus
InactiveCN102250939AGreat application potentialImprove carrying capacityVector-based foreign material introductionTransformation efficiencyCloning Site
The invention discloses a small shuttle plasmid pSDU1 with a chloramphenicol resistant gene for Acidithiobacillus caldus, which consists of a replicor oriV, an auto-replicating protein gene rep, a conjugational transfer gene mob, a chloramphenicol resistance selection gene cat and a multiple cloning site (MCS). The plasmid pSDU1 uses chloramphenicol resistance as a selection marker and has higher conversion efficiency; the multiple cloning sites of the plasmid pSDU1 are introduced, and the use is convenient; the oriV, rep and mob parts of the plasmid pJRD 215 is used, so higher stability is achieved; and the length of the plasmid is only 6.4kbp and the bearing capacity of the plasmid is higher, which indicate the plasmid has a huge application potential in molecular biological research and genetic engineering modification of the Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
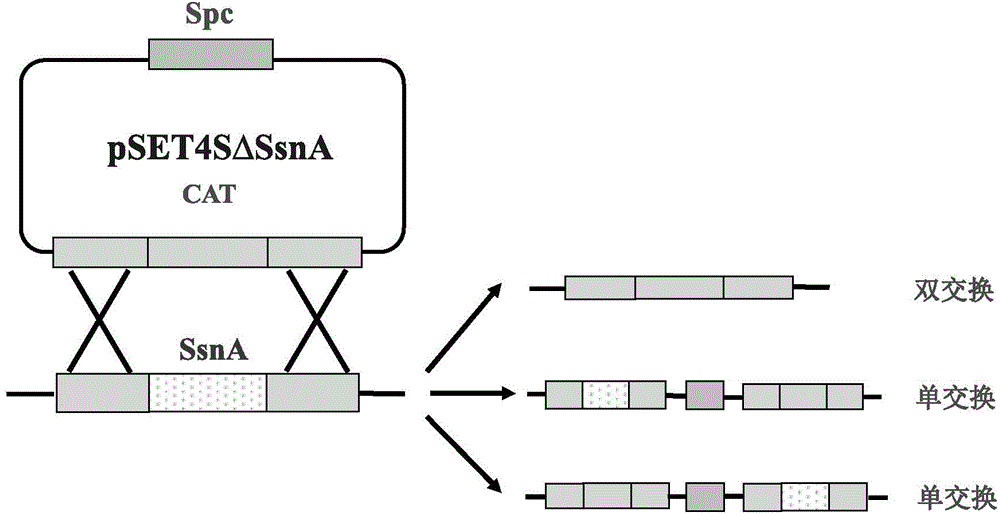
Streptococcussuis serotype 2 SsnA gene knockout mutant strain, and preparation method and application of mutant strain
InactiveCN104611282AReduced toxicityReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProtective antigenAntigen
The invention discloses a streptococcussuis serotype 2 SsnA gene knockout mutant strain, and a preparation method and an application of the mutant strain. The mutant strain is formed by substituting an SsnA gene in a streptococcussuis serotype 2 SS2-GD01 strain with a chloramphenicol resistant gene cassette CAT. The mutant strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2014539 on October 31, 2014. The growth characteristic of the SS2-GD01 SsnA strain is similar to a wild strain; the adhesion and invasion capacity of the SS2-GD01 SsnA strain on an Hep-2 cell in vitro is obviously reduced; the virulence of the SS2-GD01 SsnA strain is obviously reduced compared with the wild strain; SsnA participates in a pathopoiesis process of streptococcussuis serotype 2 and is a new virulence correlation factor; and the mutant strain provides an important clue for screening of protective antigens of multivalent subunit vaccine, and can be applied to research and development of streptococcussuis serotype 2 attenuated vaccine.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HEALTH GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
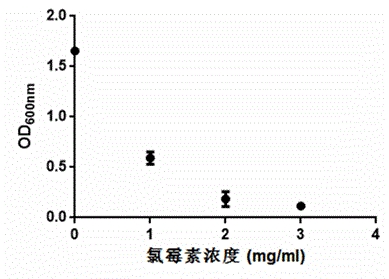
Pichia pastoris expression vector taking chloramphenicol as screening marker and application thereof
InactiveCN104388461AAvoid cumbersome configurationEasy to manufactureFungiVector-based foreign material introductionForeign proteinChloramphenicol Resistance
The invention discloses a pichia pastoris expression vector taking chloramphenicol as a screening marker, particularly a pichia pastoris screening system based on chloramphenicol. The invention reveals a fact that chloramphenicol has an obvious inhibitory effect on pichia pastoris GS115 so that pichia pastoris cannot grow on a YPG resistant solid medium containing chloramphenicol; and based on the fact, a pichia pastoris screening system using chloramphenicol as a screening antibiotic is established. Pichia pastoris is screened by using a vector containing chloramphenicol resistance gene CAT, as well as pichia pastoris electroporation transformation competence prepared by a method disclosed by the invention and a chloramphenicol screening solid medium; EGFP is used as a reporter gene; after pichia pastoris is transformed, green fluorescence can be observed under a fluorescence microscope, which means that the vector and the screening system can be effectively used for transformation and screening of pichia pastoris and expression of foreign protein.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of isobutanol-producing Zymomonas mobilis genetically engineered bacteria and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102876625BUnique ED PathwayHigh isobutanol toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsobutanolChloramphenicol Resistance
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Shuttle vector between antiradiation bacterium and colibacillus and its construction process
InactiveCN1986816AHigh luciferase activityMonitor impact in real timeVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesBiotechnology
The present invention is shuttle vector between antiradiation bacterium and colibacillus and its preparation process. Antiradiation bacterium Deinococcus radiopugnans originated plasmid and the colibacillus plasmid capable of being auto replicated are recombined to constitute the shuttle vector. The shuttle vector is recombined with the DNA segment possessing luciferase gene lux originated from host DNA of Photinus pyralis to constitute plasmid with luciferase gene, the plasmid is introduced into antiradiation bacterium, and the constituted plasmid is used in converting Deinococcus grandis to obtain bacterium strain with chloromycetin resistance. The shuttle vector can auto replicate in antiradiation bacterium and colibacillus and may be introduced into antiradiation bacterium. It may be used in various kinds of field environments and possesses luciferase gene.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
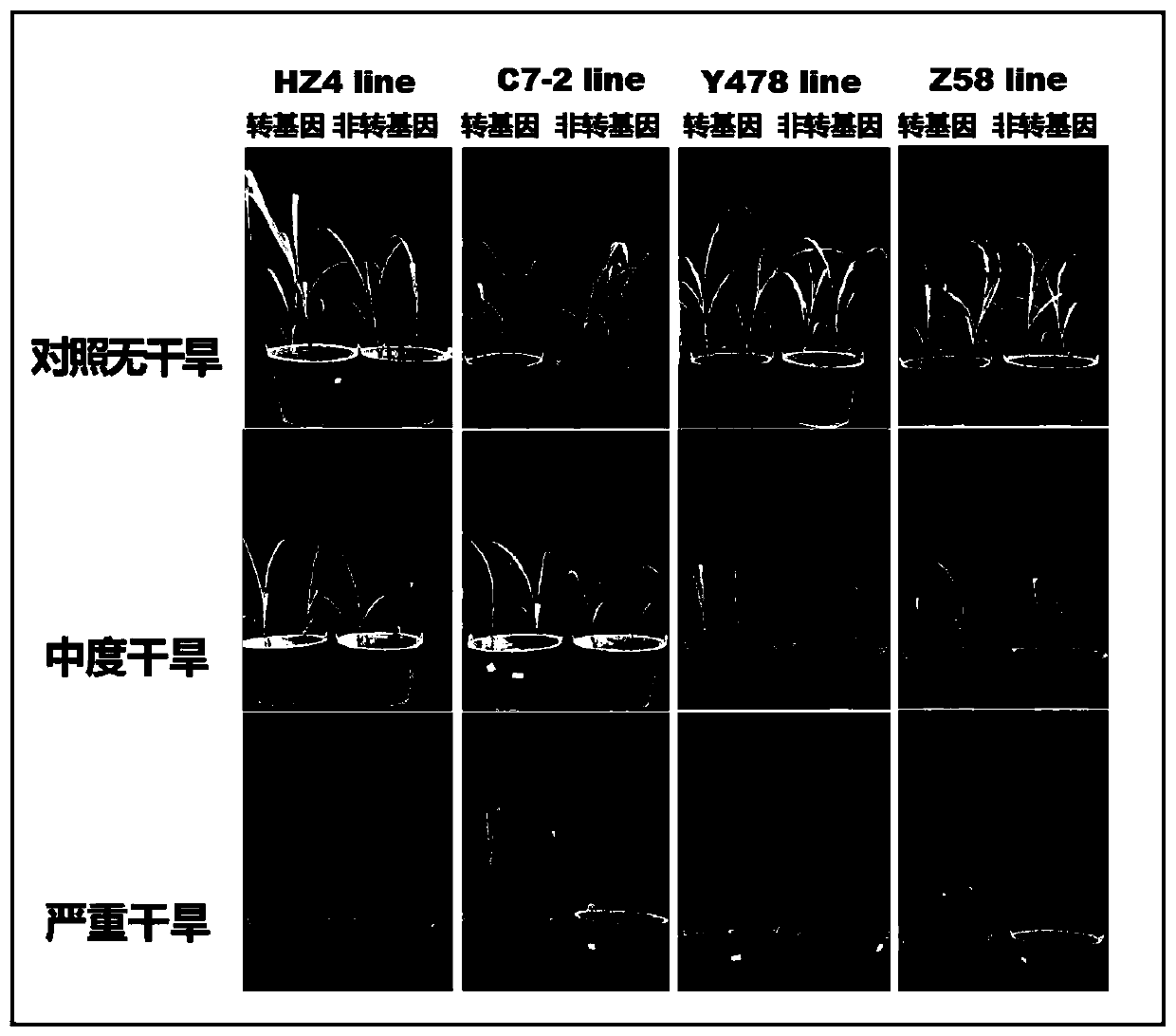
Protein capable of enhancing plant drought resistance and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110607309AStrong drought resistancePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringChloramphenicol ResistanceTransgenic technology
The invention provides a gene capable of enhancing plant drought resistance, a protein encoded by the gene and application of the protein in acquirement of high-drought-resistance corn by using a transgenic technology. Transgenic corn plants are obtained by introducing the gene into corn through a recombinant eukaryotic expression vector taking chloramphenicol resistance and herbicide resistance Basta as selection markers. The invention provides the gene capable of enhancing plant drought resistance, the protein encoded by the gene and application of the protein in cultivation of high-drought-resistance corn, and the gene is introduced into corn plants through an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method so as to obtain transgenic corn. Compared with an untransformed corn variety, the transgenic corn plants have relatively strong drought resistance.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Shuttle vector beneficial to construction of long fragment DNA and preparing method and application thereof
PendingCN106497955AIncrease concentrationHigh plasmidNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention relates to a shuttle vector beneficial to construction of long fragment DNA and a preparing method and application thereof. The shuttle vector is capable of shuttling back and forth in saccharomyces cerevisiae and escherichia coli, and has a saccharomyces cerevisiae replication origin oriV and an escherichia coli replication origin ori2, both the oriV and the ori2 are low-copy replication origins, and the shuttle vector can conduct stable replication in both the saccharomyces cerevisiae and the escherichia coli, a screening label in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is HIS3, and the screening label in the escherichia coli is chlorampenicol resistance. According to the shuttle vector beneficial to the construction of long fragment DNA and the preparing method and application thereof, the constructed saccharomyces cerevisiae-escherichia coli shuttle vector (named pSynoYAC0) is capable of being successfully assembled in a yeast system, however, plasmid extracted from the saccharomyces cerevisiae has poor quality, while the plasmid extracted from the escherichia coli has high quality, thus further experiment demands such as sequencing and enzyme digestion can be satisfied. The shuttle vector is also capable of conducting replication in the escherichia coli, and the replication belongs to a single copy; meanwhile, the shuttle vector is capable of existing stably in the replication process, thus the vectors meeting the demands can be obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
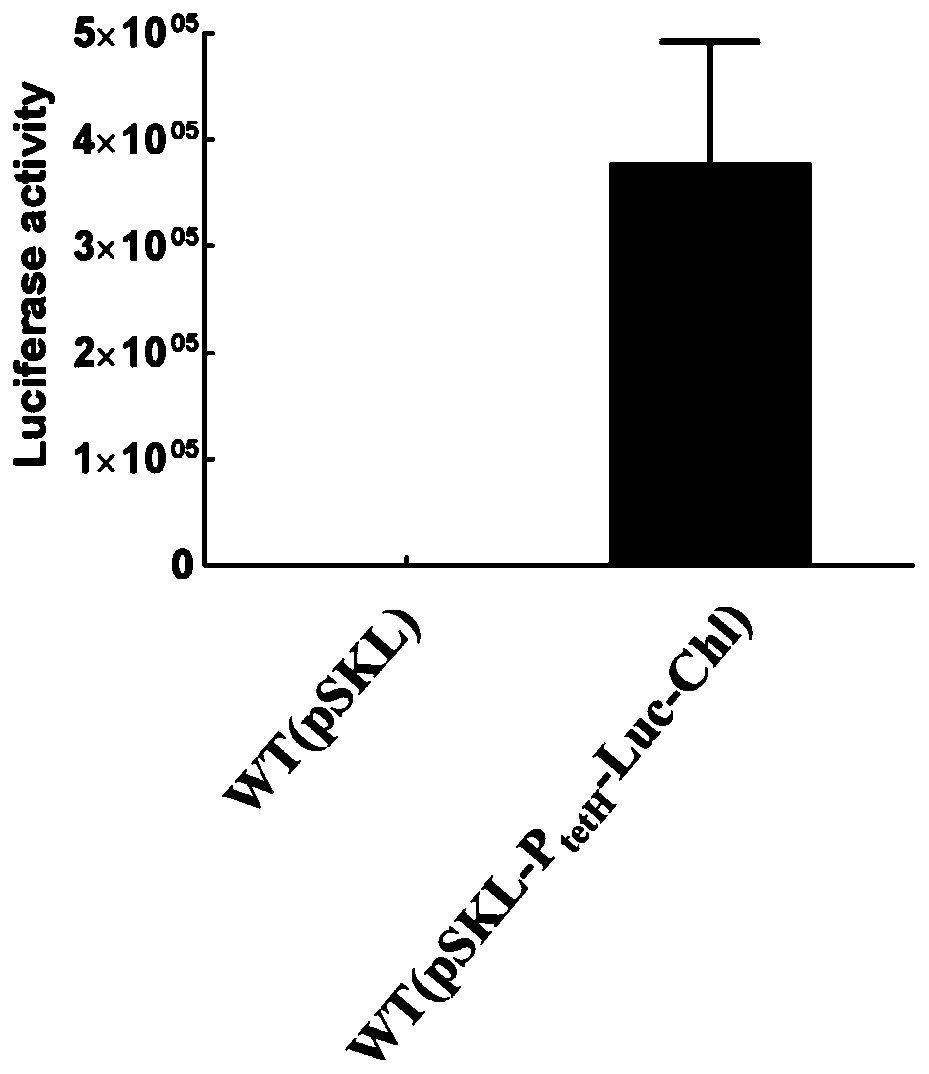
Recombinant plasmid and application of same in identification of gene expression of thiobacillus aeruginosa
PendingCN110257413AReduce sizeEasy genetic manipulationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideFluorescence
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid containing a tetH promoter, a firefly luciferase gene luc, a chloramphenicol resistance gene cat, a replicator oriV, a junction transfer gene mob, replication protein genes repA, repB and repC and a Kanamycin resistance gene Kanr element, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention further discloses an application of the recombinant plasmid in identification of gene expression of thiobacillus aeruginosa, luciferase activity of recombinant bacteria is detected after establishment, and the intensity of gene expression of thiobacillus aeruginosa is determined according to the size of the fluorescence value. The method has the advantages of low background, high sensitivity, simple operation, high repeatability and accuracy; establishment of engineering bacteria with stress resistance and high efficiency leaching, for realizing the screening of the efficient promoters and the identification of the gene expression intensity in the thiobacillus autotrophic bacteria has the theoretical guiding significance and the practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods and compositions for recombination a gene-deficient strains of agrobacterium tumefaciens
ActiveUS20160068851A1BacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesResistant genesChloramphenicol Resistance
The present disclosure provides novel compositions and methods for the production and use of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains (for example LBA4404) that are deficient in RecA activity relative to the parent strain. Combinations with other gene-deficient-strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens are also disclosed. Specifically, two exemplary s recA minus strains, UIA777 where chloramphenicol resistant gene disrupting the recA gene and UIA770 where kanamycin resistant gene disrupting the recA gene are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
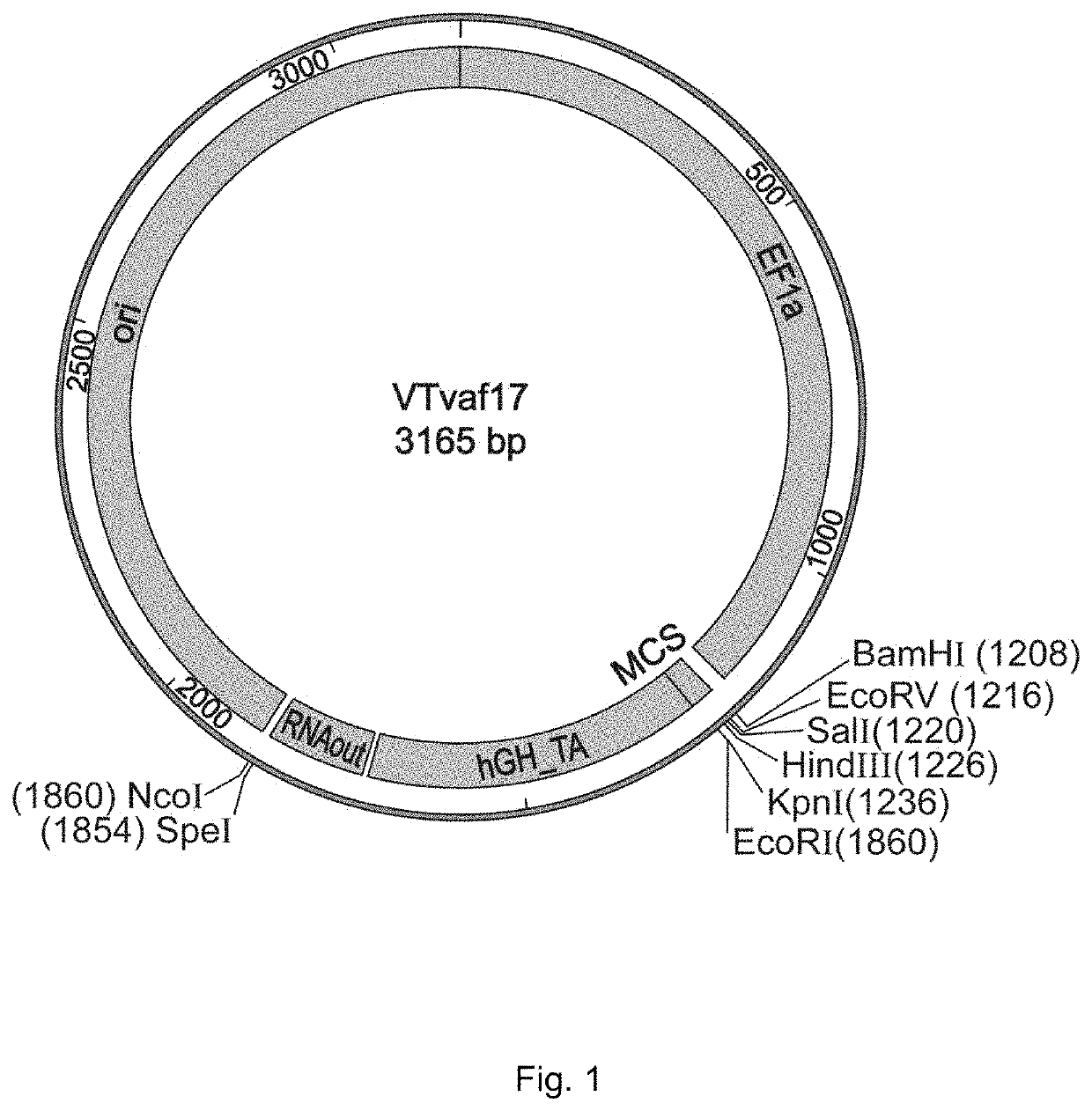
GENE THERAPY DNA VECTOR VTvaf17, METHOD OF PRODUCTION; ESCHERICHIA COLI STRAIN SCS110-AF, METHOD OF PRODUCTION; ESCHERICHIA COLI STRAIN SCS110-AF/VTvaf17 BEARING GENE THERAPY DNA VECTOR VTvaf17, METHOD OF PRODUCTION
ActiveUS20200385743A1Increase productionHydrolasesMicroorganismsOrigin of replicationElectroporation
Disclosed is a gene therapy DNA vector VTvaf17 for genetic modification of animal and human cells having SEQ ID No. 1, and methods for its synthesis, involving constructing vectors containing a promoter region of human elongation factor EF1A, a polylinker with sites for restriction endonucleases, a transcription terminator, a polyadenylation sequence of human growth factor, a regulatory element of transposon Tn10 allowing for antibiotic-free positive selection, an origin of replication, and a kanamycin resistance gene. Escherichia coli strain SCS110-AF is also provided by the present invention. The method for creating the strain involves constructing a linear DNA fragment containing regulatory element of transposon Tn10, a levansucrase gene, sacB, a chloramphenicol resistance gene, and two homologous sequences. The E. coli cells are transformed by electroporation and clones surviving chloramphenicol are chosen. The invention further discloses Escherichia coli strain SCS110-AF / VTvaf17, which carries DNA vector VTvaf17, and methods for its synthesis.
Owner:CELL & GENE THERAPY LTD
Escherichia coli-streptomycete shuttle-type BAC vector and construction method
InactiveCN104046648AOvercoming difficult conversionOvercoming problems with the strict restriction system of StreptomycesVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousEscherichia coli
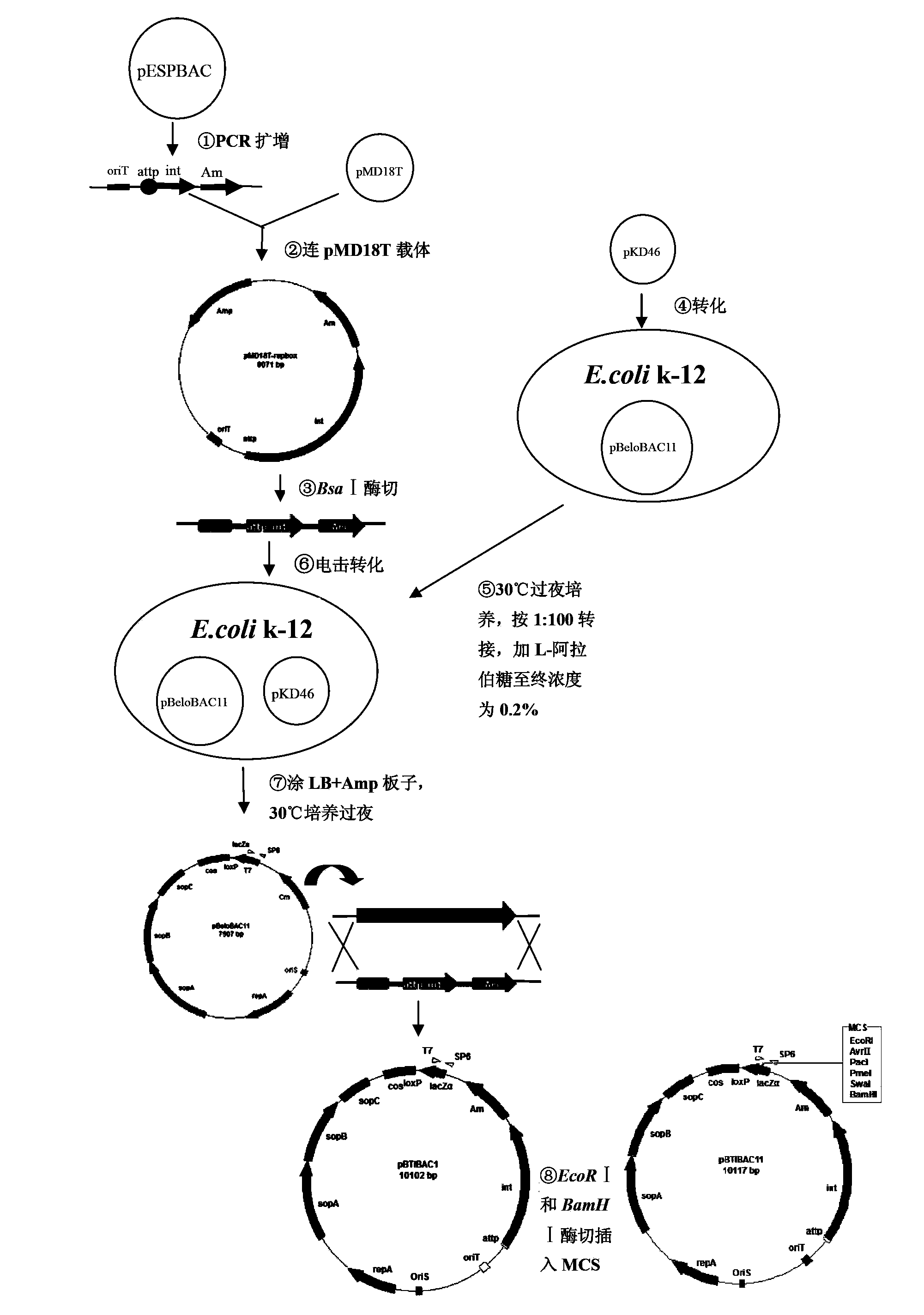
The invention relates to an escherichia coli-streptomycete shuttle-type BAC vector and its construction method. The BAC carrier contains multiple cloning sites (MCS), an Am resistant gene, an intergrase gene int, an integrate site attp, conjugal transfer fragments oriT and oriS, a repA gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC sequence, a cos site and a loxP site of replication region of the BAC vector. Beginning with pBeloBAC11, a Red homologous recombination technology is used to replace the above chloramphenicol resistant gene with DNA fragment of oriT-attp-int-Am for conjugal transfer (oriT), site-specific integration (attp-int) and resistance screening (Am) so as to obtain a vector pBTIBAC1. Thus, a foundation is established for realizing heterogeneous expression of large fragments of gene clusters in streptomycete.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Formylation gene cassette knockout mutant of Escherichia coli DH5alpha and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109694839AEasy to operateIntegrity guaranteedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliProtein C
The invention discloses a formylation gene cassette knockout mutant of Escherichia coli DH5alpha and a construction method thereof. The construction method utilizes a lambdaRed homologous recombination technology to simultaneously perform gene knockout on the gene fmt encoding the methionine-tRNA transformylase on the Escherichia coli E.coli DH5alpha chromosome and the gene def encoding the peptide deformylase, and PCR product electrophoresis and sequencing identification confirm that the obtained strain is a knockout mutant. The construction method of the invention is simple, an expression frame of other proteins on the genome is not changed, and the knock-in replacement of the chloramphenicol resistance gene facilitates the preservation of the strain and is beneficial for subsequent application. The constructed formylation gene knockout mutant of Escherichia coli DH5alpha completely eliminates the influence of PDF from the gene level, and can be used as the original material for studying the physiological process of formylation and deformylation, and the samples are provided for proteomics and metabolomics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Converted attenuated listeria introducing EB virus LMP2A nucleotide sequence and vaccine of converted attenuated listeria
InactiveCN104073460AImprove securityImprove reliabilityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaNucleotideNasopharyngeal cancer
The invention discloses a converted attenuated listeria introducing the sequence of EB virus LMP2A nucleotide and a vaccine of the converted attenuated listeria, wherein the EB virus LMP2A nucleotide is positioned on a p1565 shuttle plasmid, and replicated and expressed on the attenuated listeria or the offspring of the attenuated listeria; the vaccine provided by the invention is of relatively high security and reliability, so that the vaccine has no obvious damage effects on various tissues and organs; meanwhile, the attenuated listeria without chloramphenicol resistance can avoid that chloramphenicol drug resistance occurs during a curing process of a nasopharynx cancer patient.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Promoter-like gene for efficiently promoting and expressing heterologous protein and application thereof
ActiveCN107475257AImprove practicalityImprove abilitiesAcyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideProtein C
The invention discloses a constitutive promoter-like gene VP2 which is found from a eukaryotic cell African green monkey kidney cell (Vero) and can be used for promoting heterologous protein expression in a prokaryotic cell, and a truncating sequence Vh2 of the constitutive promoter-like gene VP2. A nucleotide sequence of the promoter-like gene VP2 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; the nucleotide sequence of the truncating sequence is shown as 60bp to 107bp in SEQ ID NO: 1; the gene is constructed to form an expression reporter gene chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) gene recombinant vector for screening; the screened vector and a gene segment to be screened are recombined, and a gene library is constructed; a promoter-like sequence is obtained by a recombinant strain containing a promoter-like gene sequence through a method for screening the resistance of chloramphenicol; the sequence can be used for efficiently starting and expressing heterologous protein in the prokaryotic cell.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com