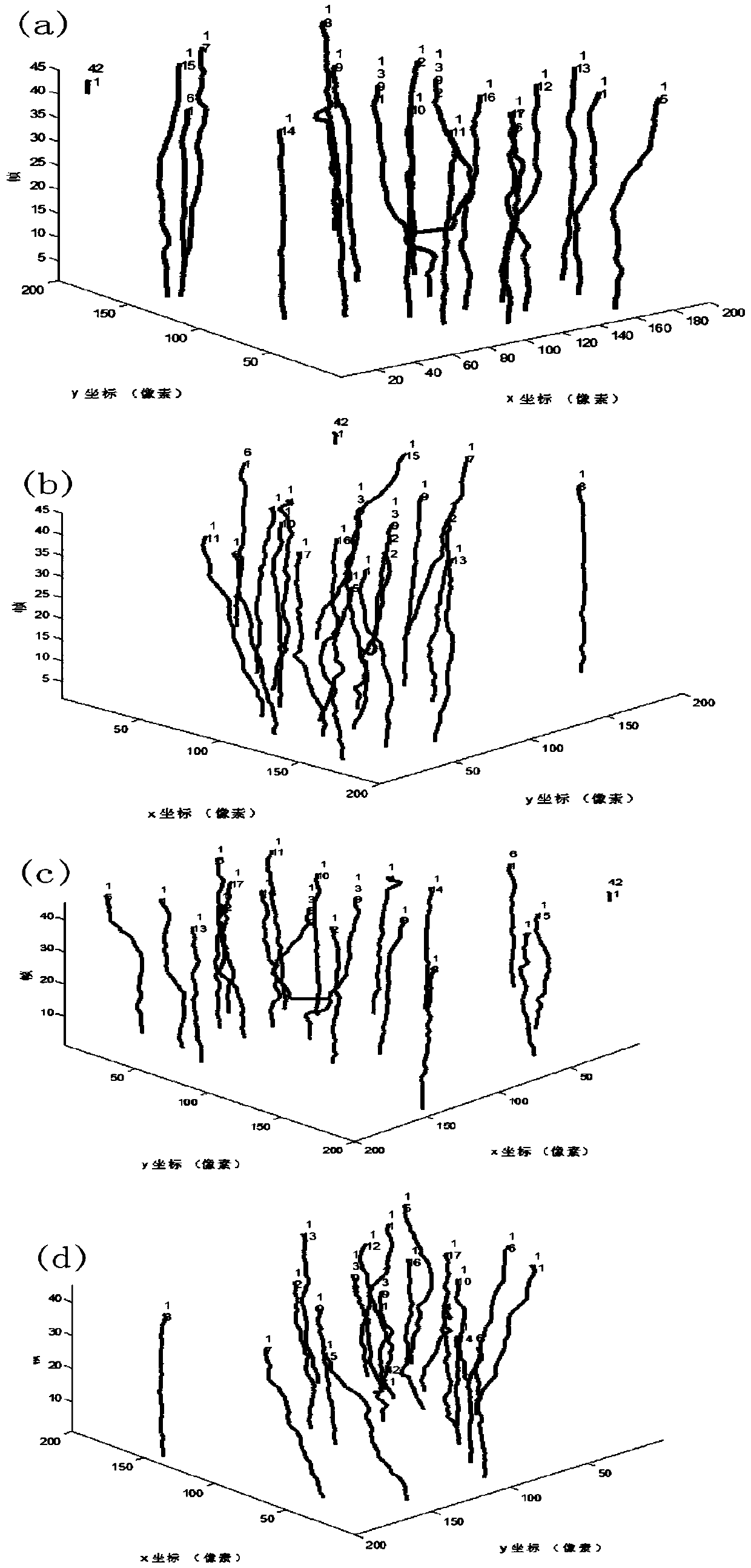
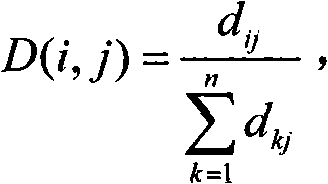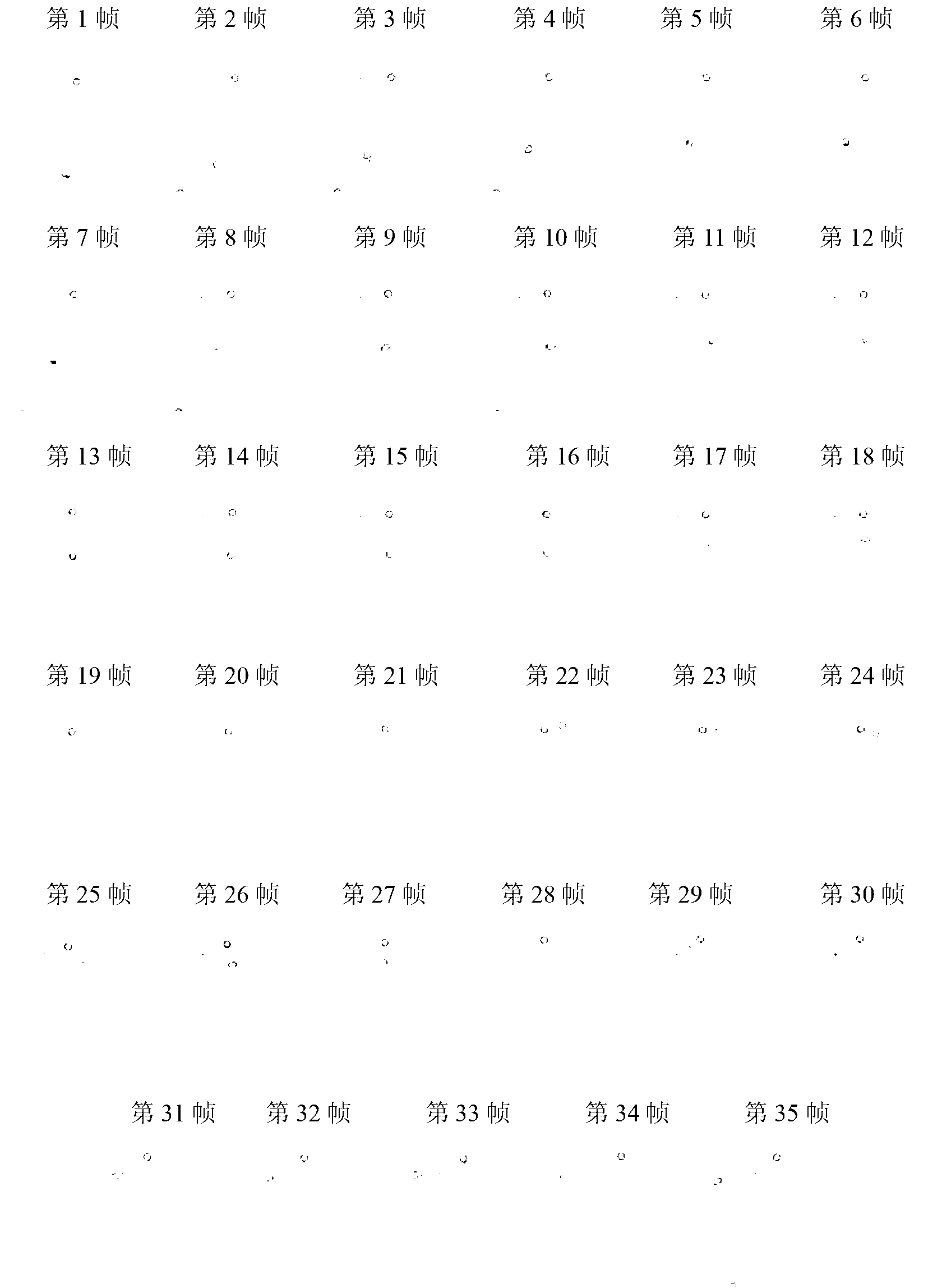Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Cell tracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoparticle loaded stem cells and their use in MRI guided hyperthermia
InactiveUS20120283503A1Enhanced MR propertyEnough timeElectrotherapyMedical devicesMri guidedMagnetite Nanoparticles
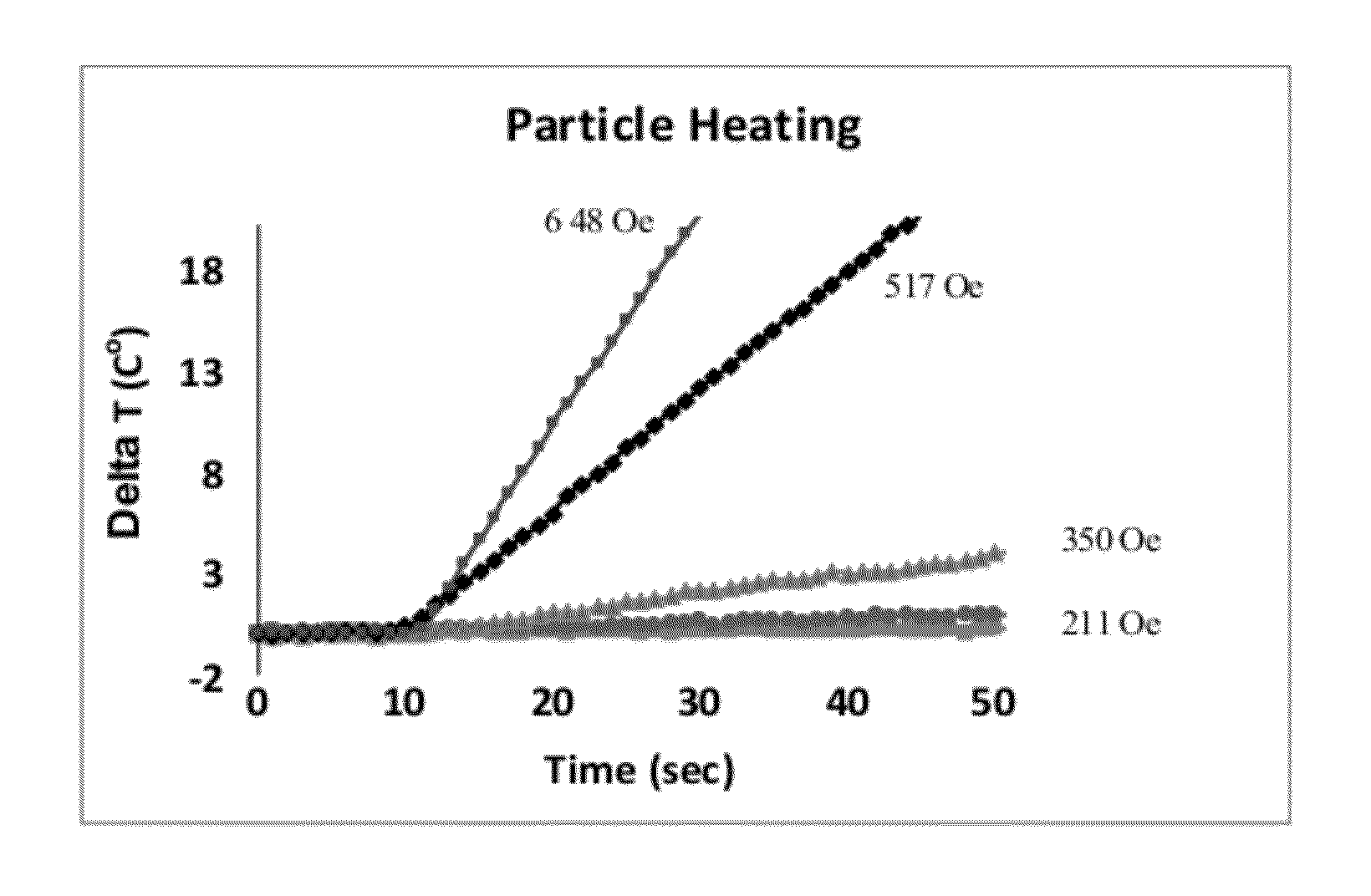
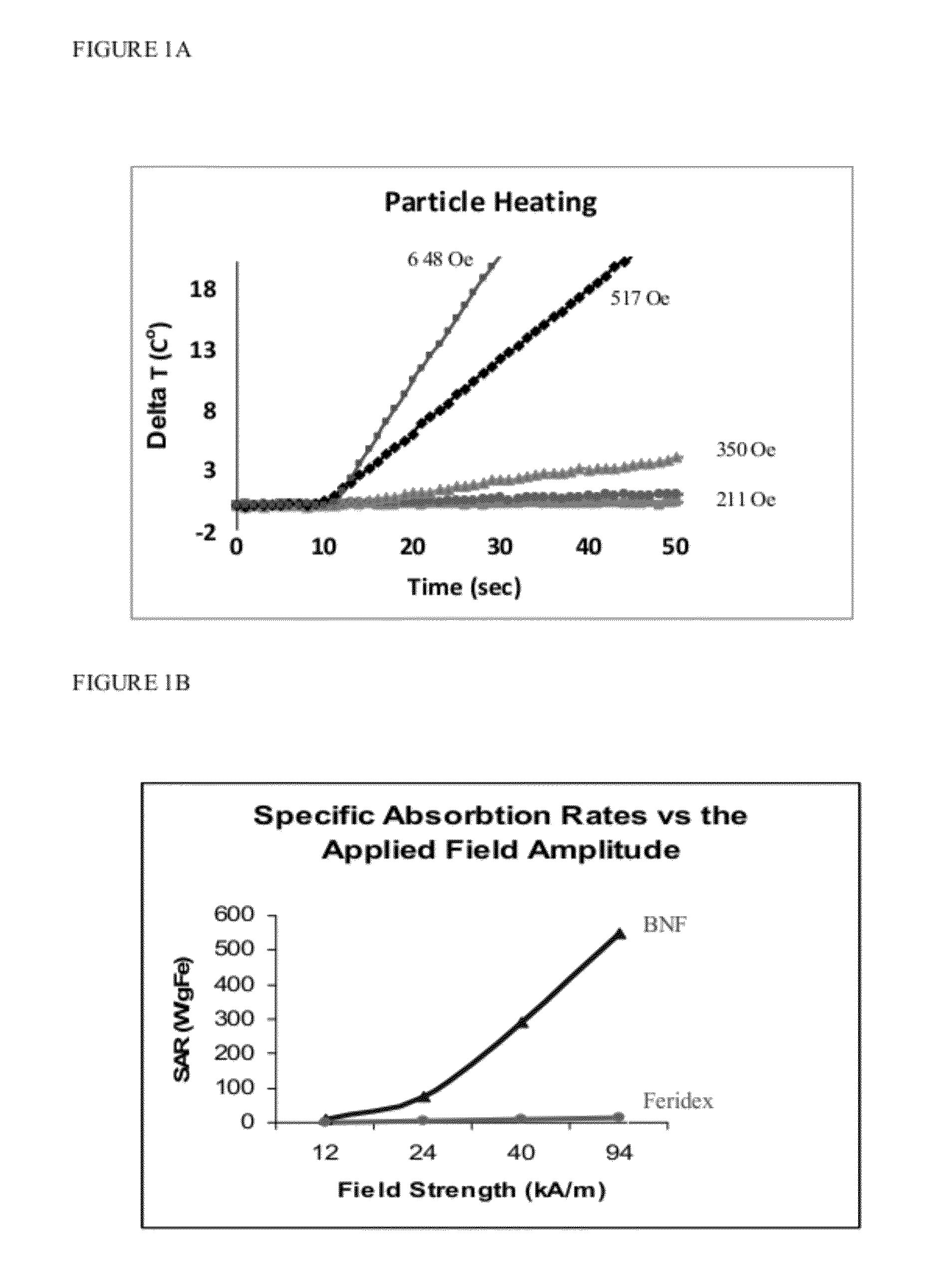
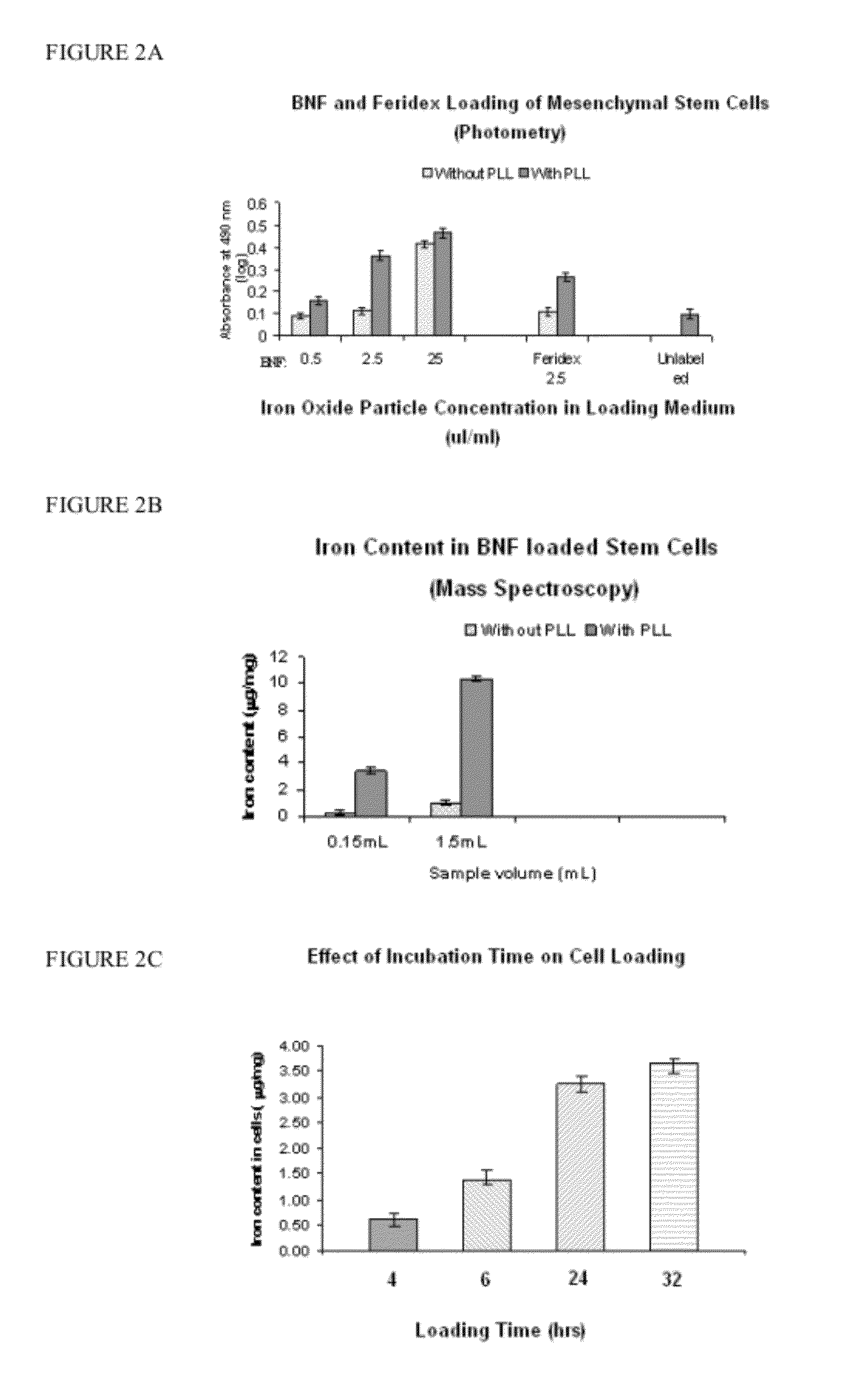
The present invention provides stem cells loaded with bi-functional magnetic nanoparticles (nanoparticle-loaded stem cells (NLSC)) that both: a) heat in an alternating magnetic field (AMF); and b) provide MRI contrast enhancement for MR-guided hyperthermia. The nanoparticles in the NLSC are non-toxic, and do not alter stem cell proliferation and differentiation, the nanoparticles do however, become heated in an alternating magnetic field, enabling therapeutic applications for cancer treatment. NLSC can deliver hyperthermia to hypoxic areas in tumors for sensitization of those areas to subsequent treatment, thus delivering therapy to the most treatment-resistant tumor regions. The heating of diseased tissue either results in direct cell killing or makes the tumor more susceptible to radio- and / or chemotherapy. The NLSC of the present invention can be used for MR image-guided hyperthermia in oncology, in stem cell research for cell tracking and heating, and for elimination of mis-injected stem cells.
Owner:OSTROVSKA LYUBOV PHD
Emissive species for clinical imaging
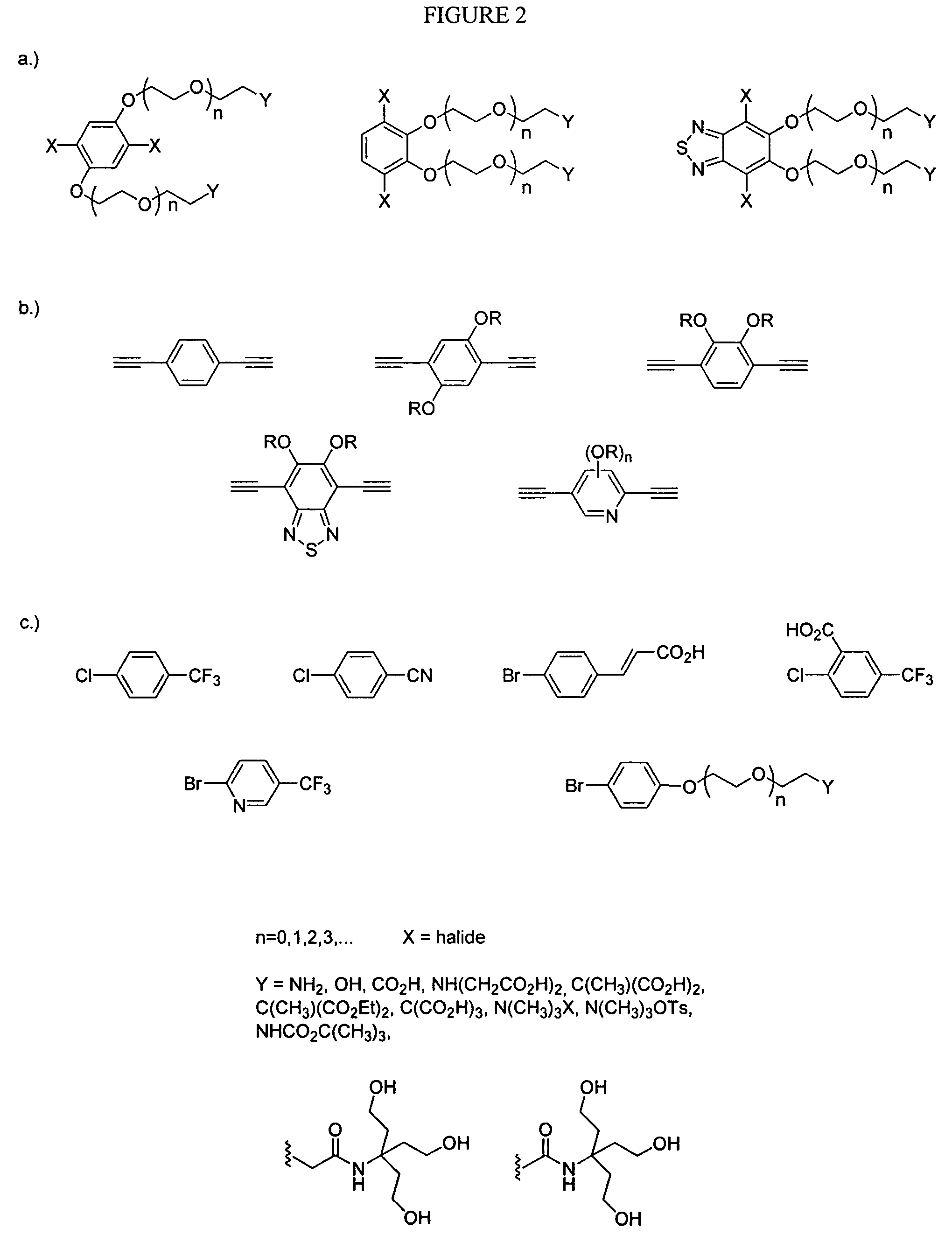
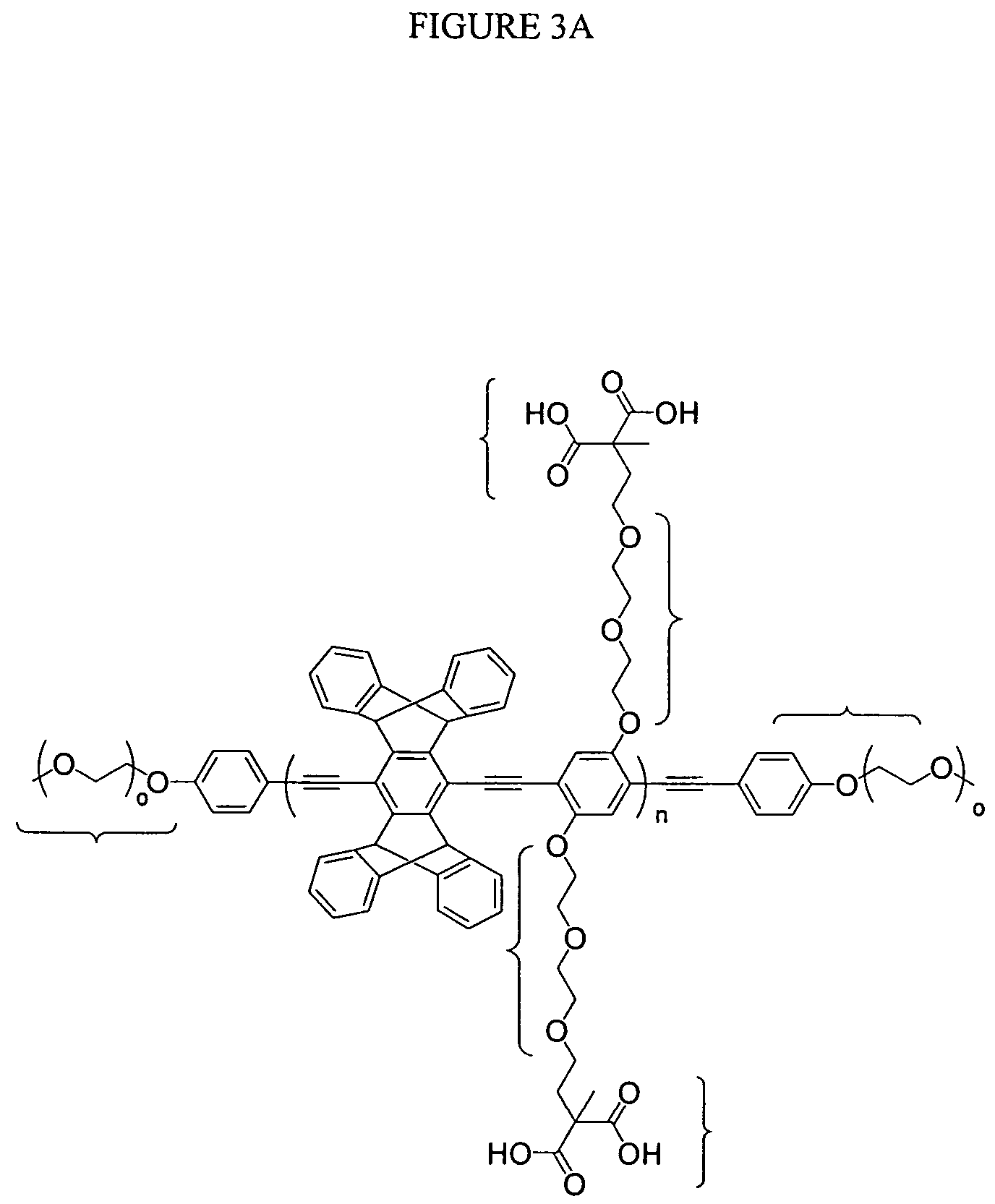
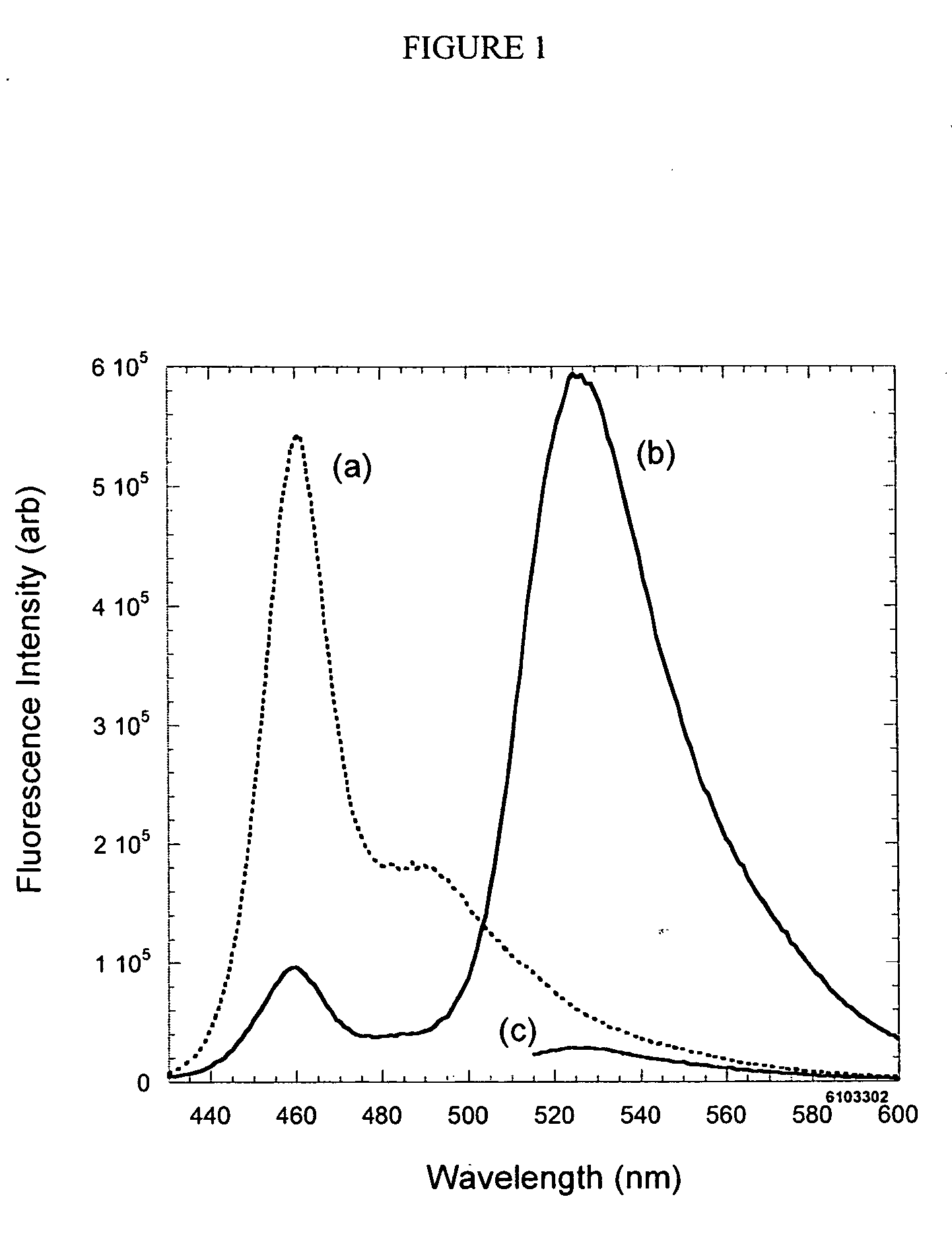
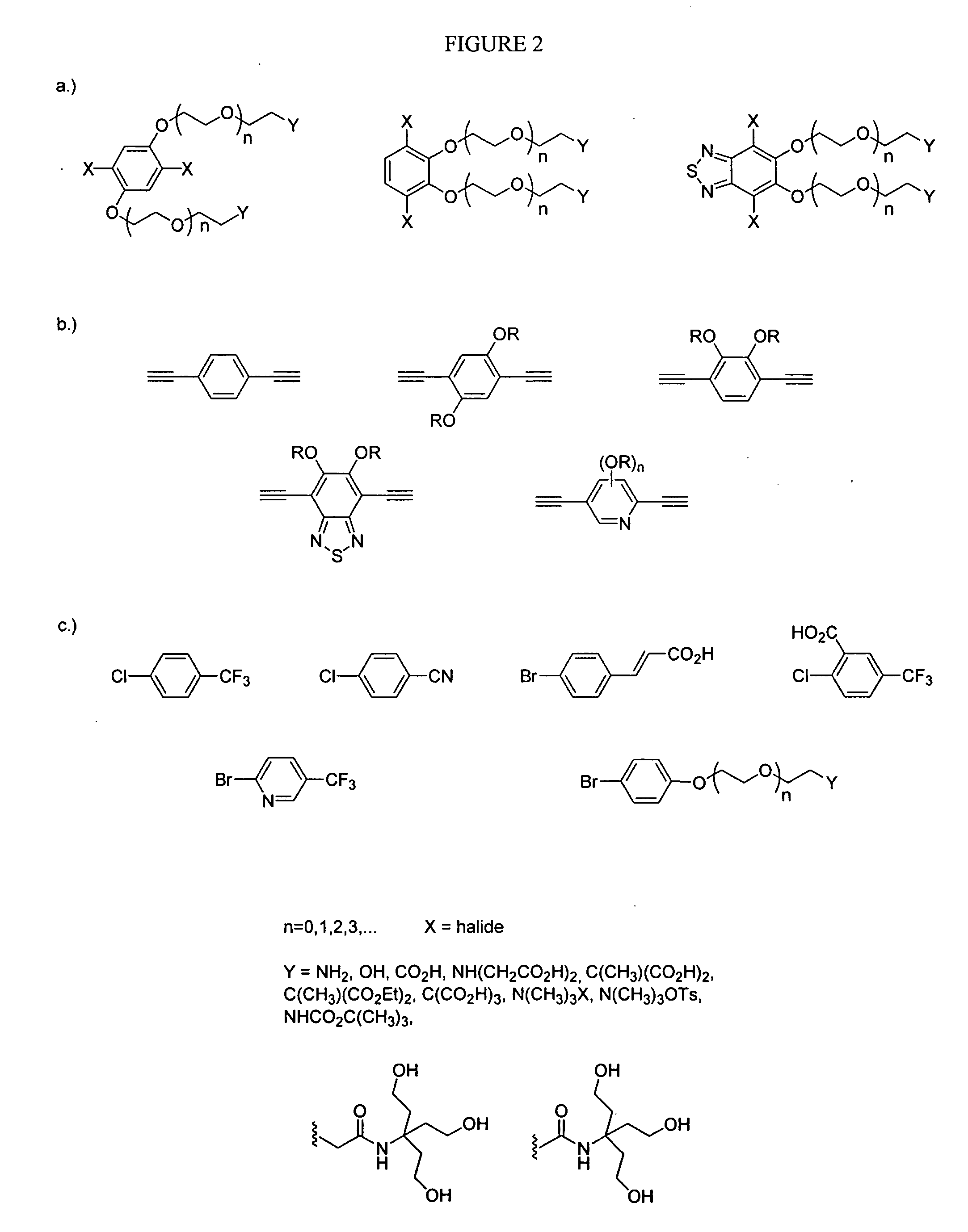
InactiveUS7521232B2Relaxes constraintMinimize interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureOligomerNormal cell
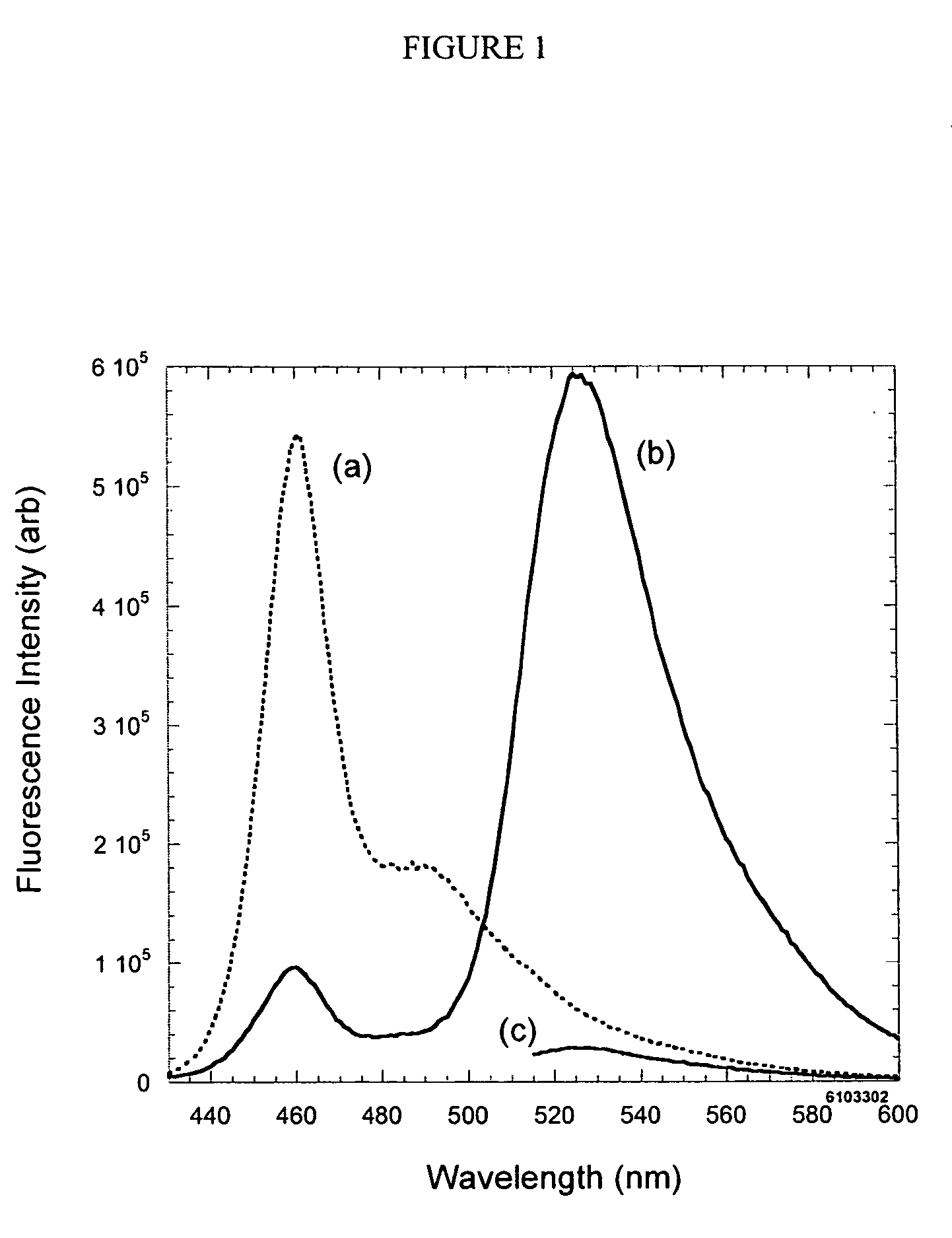
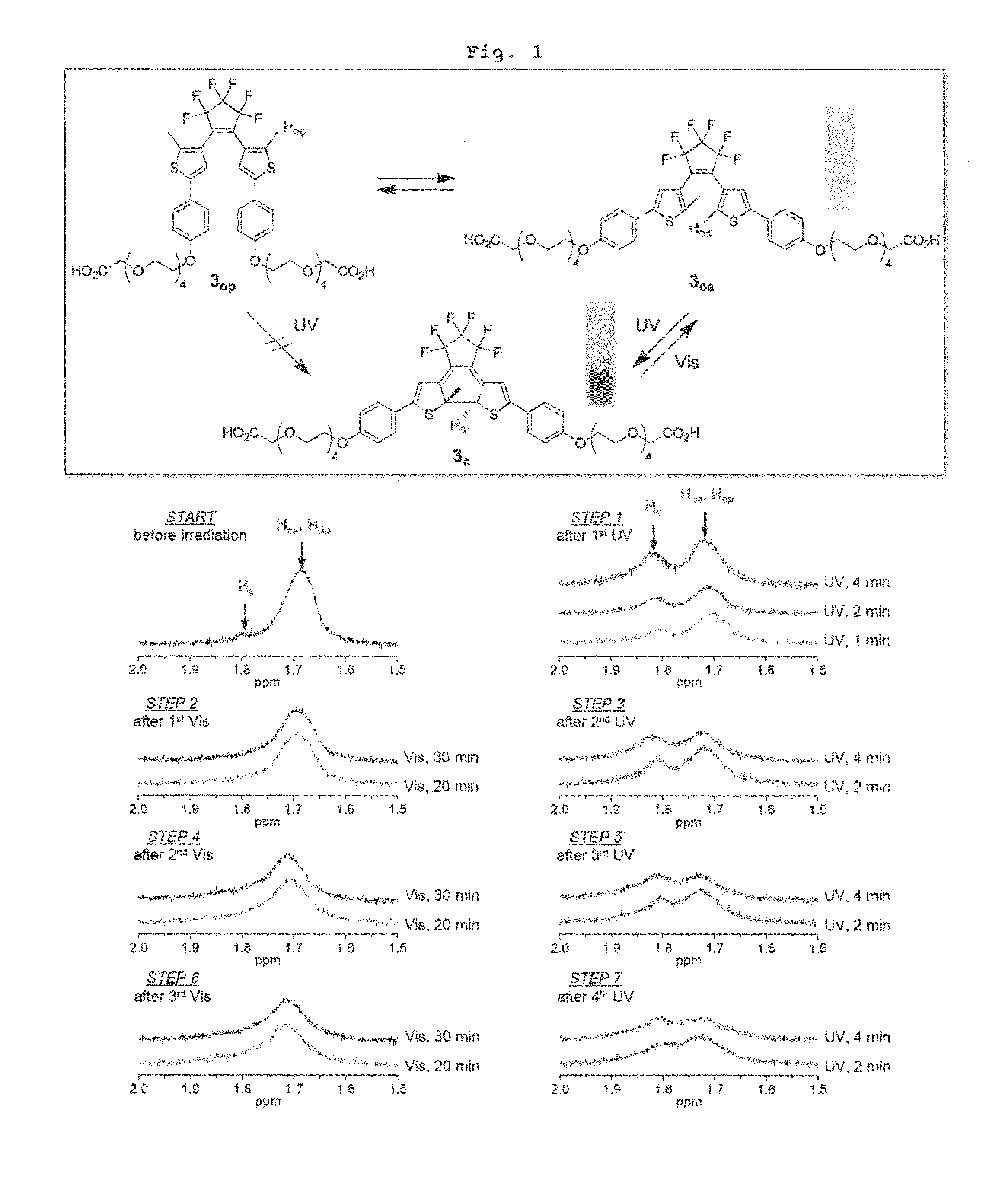
The present invention relates to materials and methods useful in the study of cells and species associated with cells. Materials of the present invention may include emissive, photostable organic molecules (e.g., conjugated polymers, conjugated oligomers) that are appropriately functionalized to interact with a cell with essentially no disruption in normal cell functioning. The present invention may be useful in, for example, cell imaging, cell tracking, in vivo monitoring of cellular events, drug delivery, and determination of biological species. In one embodiment, a conjugated polymer or oligomer may be internalized into a cell and may exhibit a strong and stable emissive signal, allowing the cell to be monitored under extensive microscopic conditions for extended periods of time.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Emissive species for clinical imaging
InactiveUS20070281289A1Minimize interactionRelaxes constraintMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureMicroscopic scaleBiological species
The present invention relates to materials and methods useful in the study of cells and species associated with cells. Materials of the present invention may include emissive, photostable organic molecules (e.g., conjugated polymers, conjugated oligomers) that are appropriately functionalized to interact with a cell with essentially no disruption in normal cell functioning. The present invention may be useful in, for example, cell imaging, cell tracking, in vivo monitoring of cellular events, drug delivery, and determination of biological species. In one embodiment, a conjugated polymer or oligomer may be internalized into a cell and may exhibit a strong and stable emissive signal, allowing the cell to be monitored under extensive microscopic conditions for extended periods of time.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
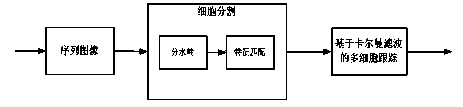
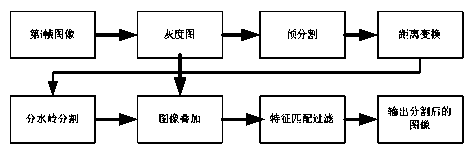
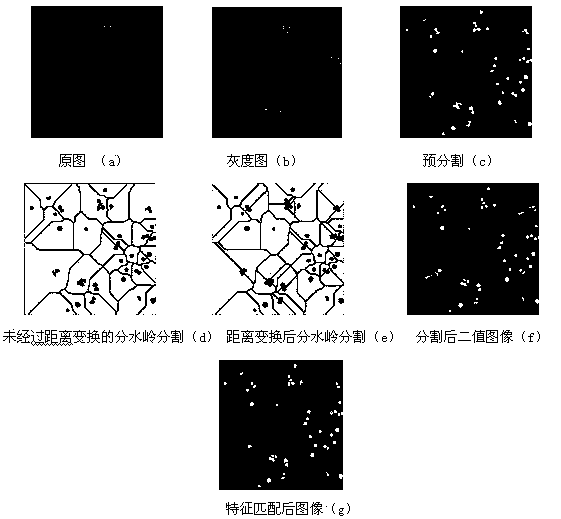
Method for synchronously tracking multiple cells in high-adhesion cell environment
InactiveCN103559724AEffective segmentationHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCell synchronizationCell segmentation
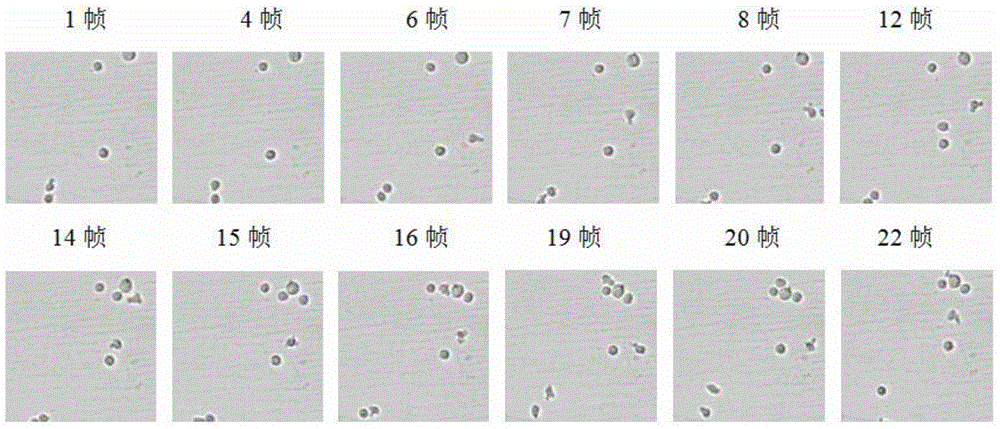
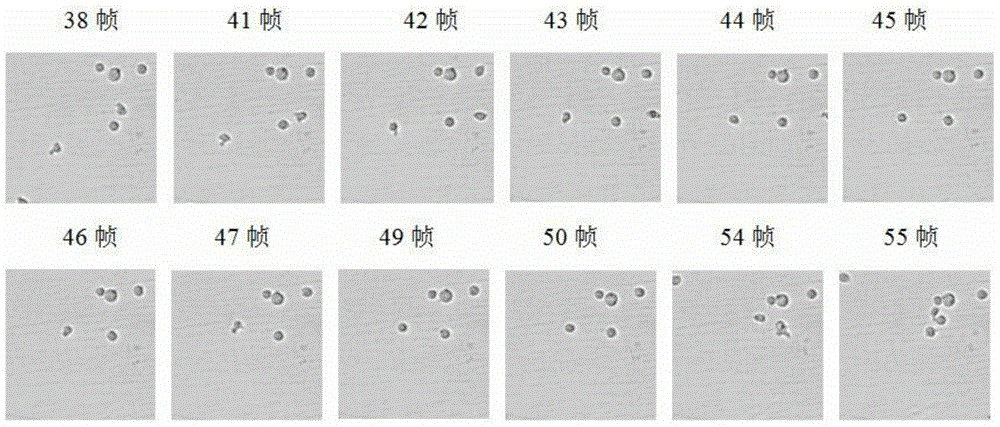
The invention belongs to the field of cell tracking, and discloses a method for synchronously tracking multiple cells in a high-adhesion cell environment. In a cell sequence image, how to divide and synchronously track the cells is an unsolved problem, and especially the problem of tracking and dividing the cells under the high-adhesion condition urgently needs to be solved. An improved dividing algorithm based on watersheds and multi-feature matching is firstly provided to achieve cell dividing, then a motion model suitable for Kalman filtering is built, the multi-feature matching is added to achieve cell predication and tracking. Through experimental verification, the method is effective, the average effective rate of dividing sequence frame cells is 94.4%, and the tracking effect is superior to that of the tracking method in the prior art.
Owner:苏州相城常理工技术转移中心有限公司
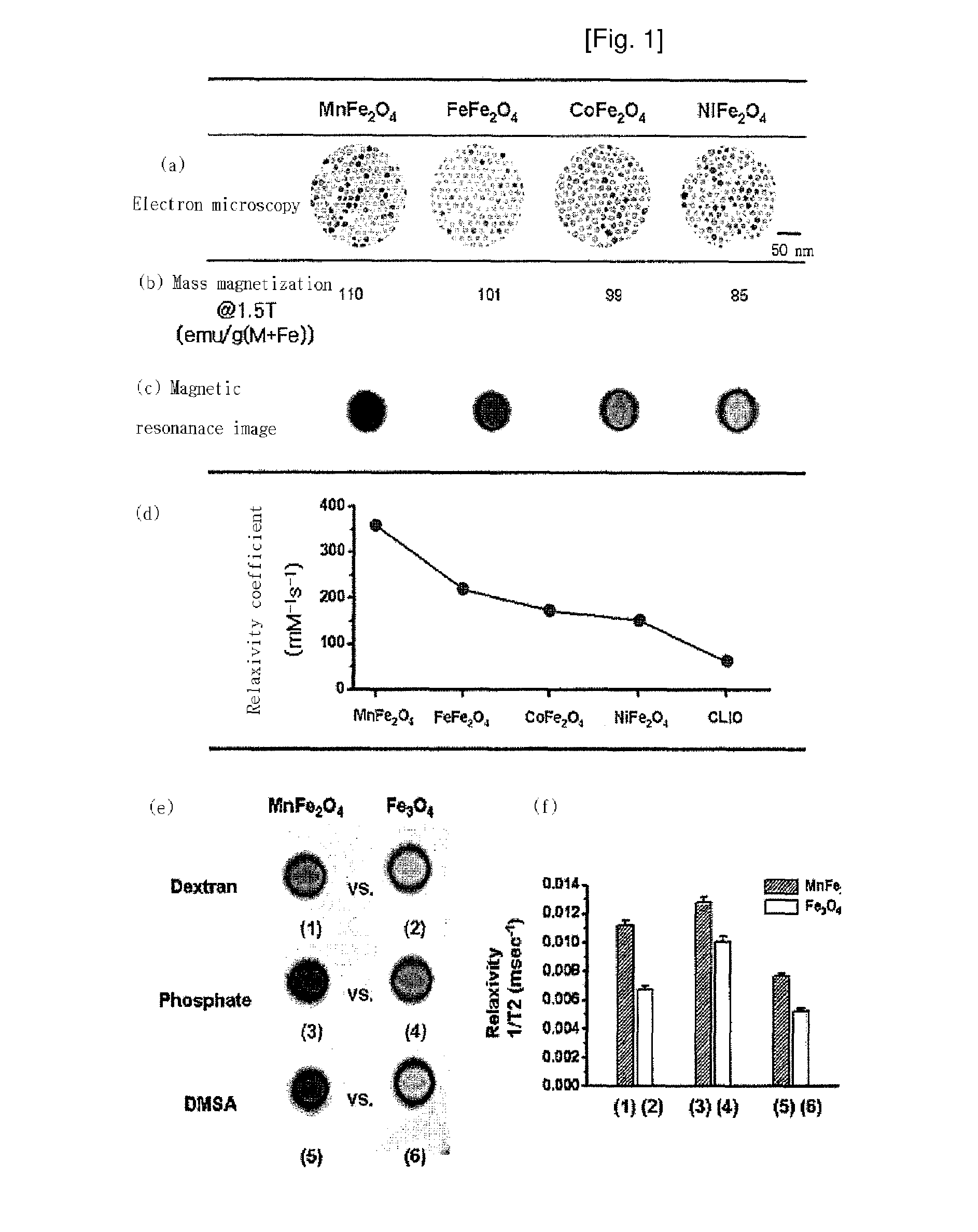
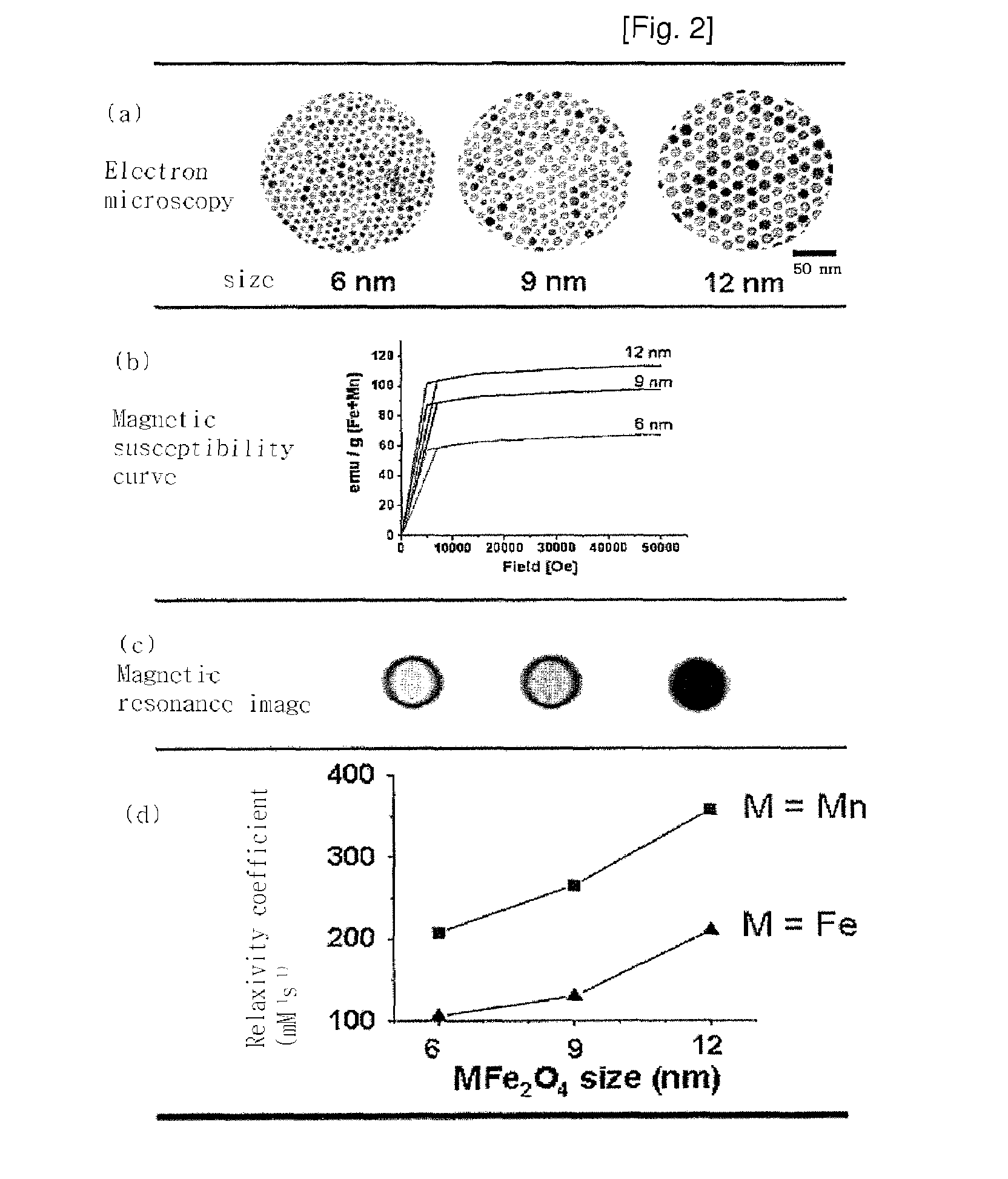
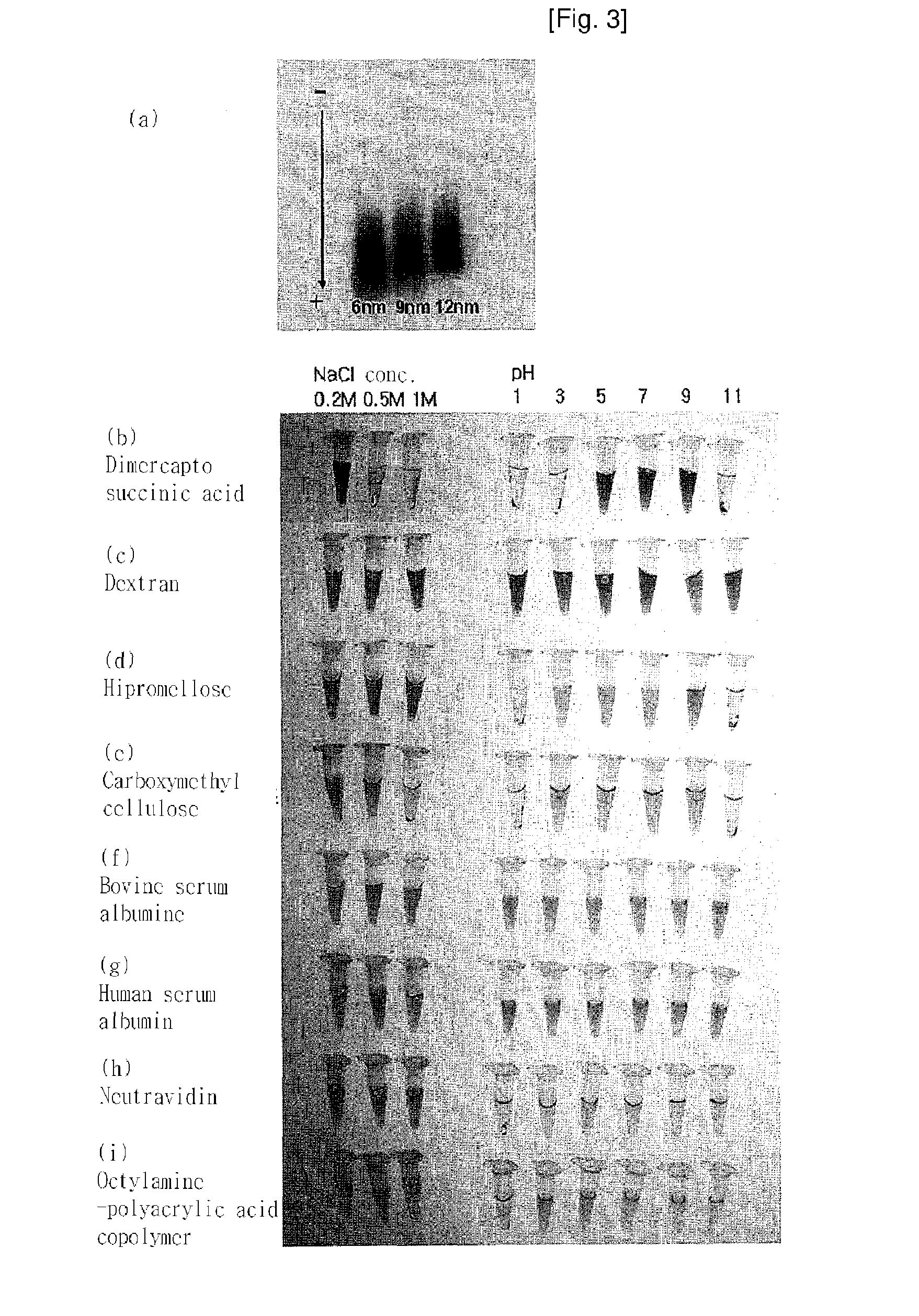
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents containing water-soluble nanoparticles of manganese oxide or manganese metal oxide
InactiveUS20090220431A1Uniform sizeImprove magnetic propertiesPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyElemental compositionMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates to a manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent, which is characterized in that: The core of it comprises 1 to 1000 nm-sized manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles which include MnO a (0<a<5) or MnMbOe (wherein M is at least one metal atom selected from the group consisting of a Group 1 or 2 element such as Li, Na, Be, Ca, Ge, Mg, Ba, Sr and Ra, a Group 13 element such as Ga and In, a transition metal element such as Y, Ta, V, Cr, Co, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Cd and Hg, and lanthanide or actinide group elements such as La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb, 0<b<5 and 0<c<10); preferably MnM′dFeeOf (wherein M′ is at least one metal atom selected from the group consisting of a Group 1 or 2 element such as Li, Na, Be, Ca, Ge, Mg, Ba, Sr and Ra, a Group 13 element such as Ga and In, a transition metal element such as Y, Ta, V, Cr, Co, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Cd and Hg, and lanthanide or actinide group elements such as La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb, 0<d<5, 0<e<5, and 0<f<15). In addition, the nanoparticles include water-soluble manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles which is characterized in that they are soluble in water themselves or stable in an aqueous media as being coated with a water-soluble ligand and they possess enhanced magnetic properties and MRI contrast effect. Also the water soluble manganese-containing metal oxide nanoparticles are coupled with an bioactive material such as chemical molecules or bio-functional molecules, and thus the nanoparticles can be used as an MRI contrast agent for target specificity and cell tracking.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
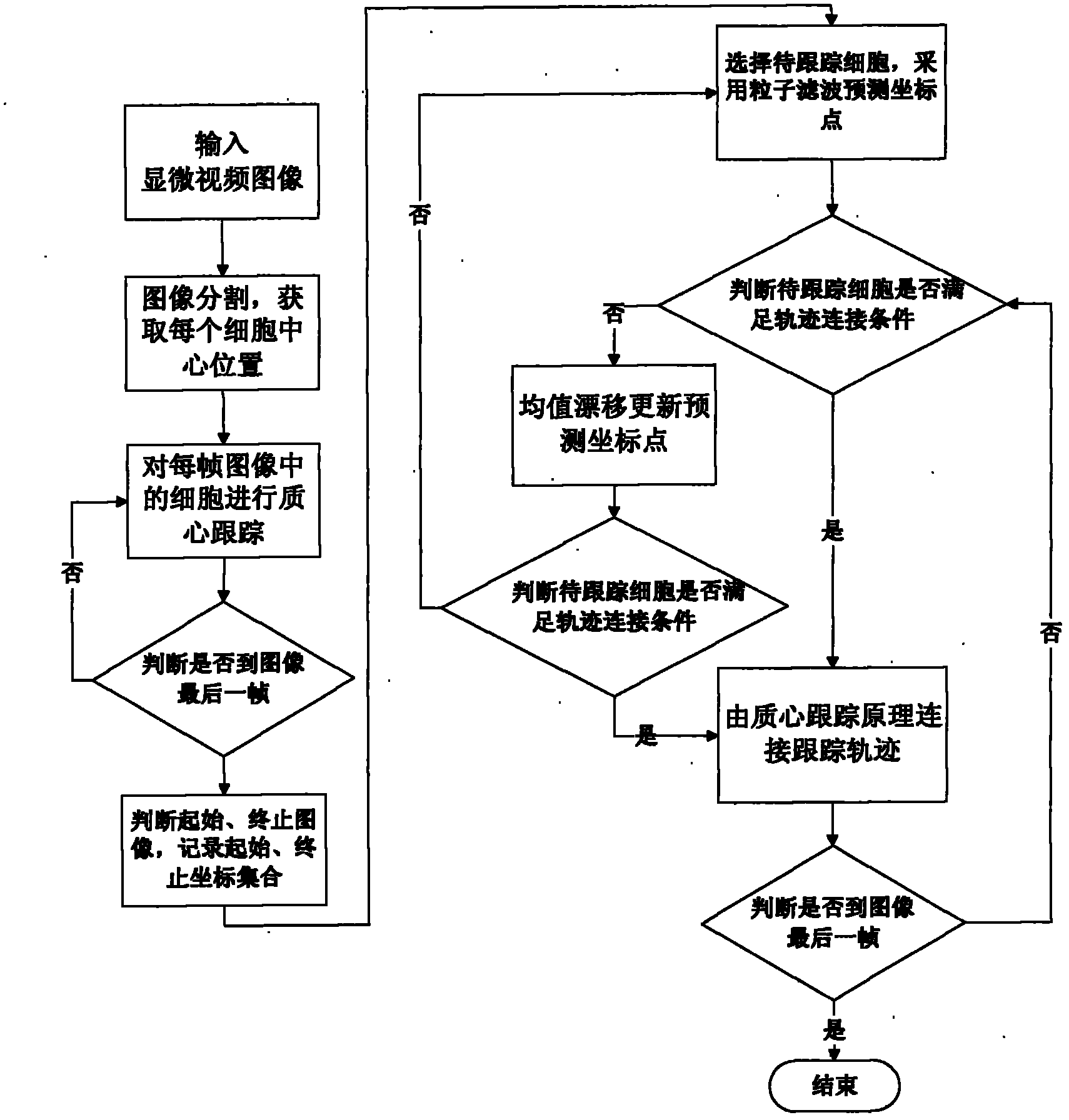
Centroid tracking framework based particle filter and mean shift cell tracking method
The invention discloses a centroid tracking framework based particle filter and mean shift cell tracking method, which mainly solves the problem of low accuracy rate of the traditional cell tracking method. The cell tracking method comprises the following steps of: performing binary segmentation to a video image, and extracting the central position of each cell; tracking the centroid of the cell, and recording the tracking trace of the cell; respectively recording the starting coordinates and the terminating coordinates of the trace into a starting coordinate set and a terminating coordinate set, and selecting a cell to be tracked; further predicting the trace of the cell to be tracked by using particle filter to obtain a predicted coordinate point in the next frame of image; selecting the subsequent tracking trace of the cell to be tracked by using the mean shift method in good time according to the predicted coordinate point; and circulating the steps of prediction and selection till the last frame of image, and completing the tracking of all cells. Compared with other traditional tracking methods, the cell tracking method has improvement in the aspects of tracking effect and accuracy rate and can be used for analyzing motor cells in a medical microscope video image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for neighbor cell tracking
ActiveUS20150139190A1Wireless commuication servicesHigh level techniquesCommunications systemComputer terminal
The client terminals in a mobile wireless communication system typically continually search and keep track of the neighbor cells surrounding the cell from which it may be receiving service. Keeping track of neighbor cells by the client terminal may require periodic measurements on the neighbor cells and these measurements contribute to power consumption in the client terminal. The power consumption for neighbor cell measurements is an important factor when the client terminal either actively receiving service from the network or in standby mode when the client terminal is not actively receiving service from the network. A method and apparatus are presented that enable the client terminal to keep track of the neighbor cells with reduced measurements and thereby with reduced power consumption.
Owner:MBIT WIRELESS
Automatic tracking method for video frequency microscopic image cell
InactiveCN101144784AImage enhancementMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscopic imageDynamic models
The invention relates to an automatic cell tracking method for a video microscope image. The existing tracking method has lower degree of automation, and can not adapt to the complex polytropism of the cell movement form and the multi-cell movement tracking. The invention comprises the steps that the abstained video microscope image of the cell movement is enhanced frame by frame; and a target cell is extracted form the enhanced cell movement image to establish the dynamic model of the cell movement for tracking moving target cell. On the basis of analyzing the characteristics of the cell movement and the noise and interference characteristics in the image, the invention adopts the method of dynamic system modeling and stochastic modeling, and through recursing Bayesian filtering and the data connectivity technology, to track the movement trajectory of the cell, and thereby, the automation degree is high, as well as the processing capability is strong.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
7-hydroxycoumarin-based cell-tracking reagents
ActiveUS9400273B1Bright fluorescence intensityUniform cell stainingOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCell stainingBiochemistry
Described herein are compounds, methods, and kits for long-term tracking of cell proliferation, differentiation, and / or function. The compounds of the present invention are novel cell-tracking reagents, efficiently excitable with a 405-nm violet laser, that provide bright fluorescence intensity, uniform cell staining, and good retention within cells as well as low toxicity toward cells.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
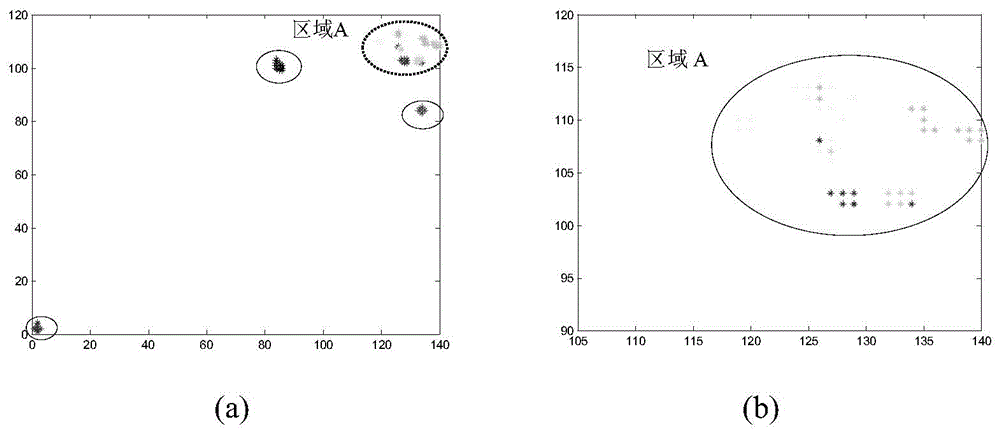
Variable density cell tracking method based on multi-mode ant colony system
ActiveCN105279768AImplement automatic trackingImprove tracking stabilityImage analysisInitial distributionDensity change
The present invention provides a variable density cell tracking method based on a multi-mode ant colony system. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a plurality of frames of continuous original grey-scale maps of a variable density cell, selecting one frame of the original grey-scale map as a current frame, calculating an average likelihood score of pixels in the current frame of the original grey-scale map, and placing ants in regions where the cells might appear according to a calculation result, thus to obtain generator ant colony initial distribution. The method provided by the present invention has the beneficial effects that automatic tracking of cell density changing situations (especially a cell concentrating situation) caused by movements, collision and fission can be realized, all cyto-dynamics characteristic parameters such as a track and speed are given, and automatic tracking of variable density cells caused by entering or leaving a view can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU SAIKANG MEDICAL EQUIP
Feature associated cell tracking method based on centroid tracking frame
InactiveCN101950424AOvercoming the disadvantage of tracking failureImprove accuracyImage analysisCurrent cellBinary segmentation
The invention discloses a feature associated cell tracking method based on a centroid tracking frame, which mainly solves the problem of low correct rate of the current cell tracking method. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out binary segmentation on a video image and extracting the central position of each cell; carrying out centroid tracking on the cells and recording the tracking path of the cells; respectively recording the origin coordinate and the terminal coordinate of the path into an origin coordinate set and a terminal coordinate set, selecting a cell to be tracked, and selecting a cell to be associated from a neighborhood matching area of the cell to be tracked; carrying out feature association on the cell to be tracked and the cell to be associated by a feature associating method and updating the path of the cell to be tracked; and finally, cycling the steps to the image at the last frame to finish tracking all the cells. Compared with other traditional tracking methods, the invention is improved in the aspects of the tracking effect and correct rate, and can be used for analyzing motor cells in medical microscopic video images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
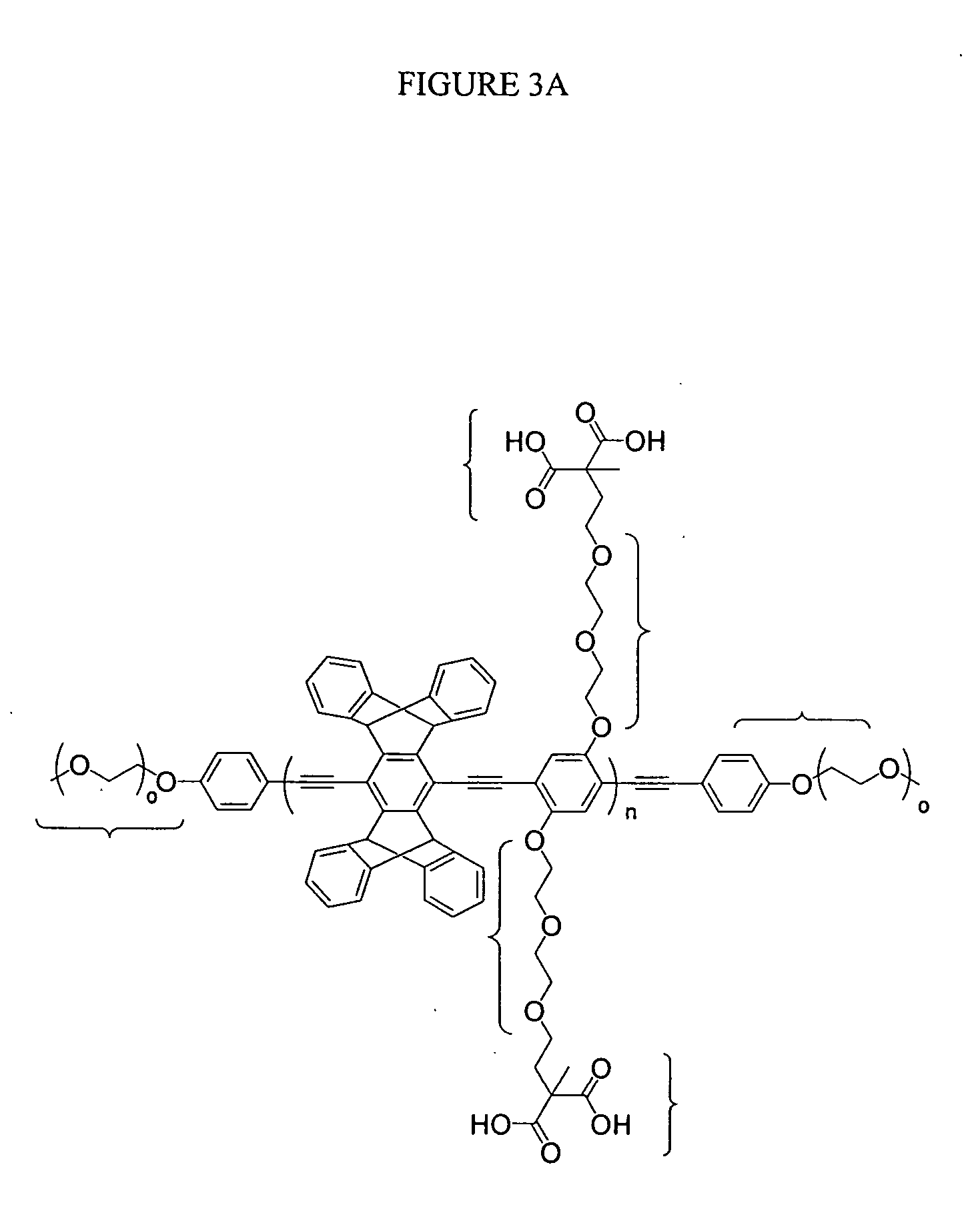
Polyethylenimine-aliphatic polyester graft polymer as well as preparation method and nanometer particle thereof
InactiveCN103172845ALow toxicityImprove efficacyPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyesterPolymer science
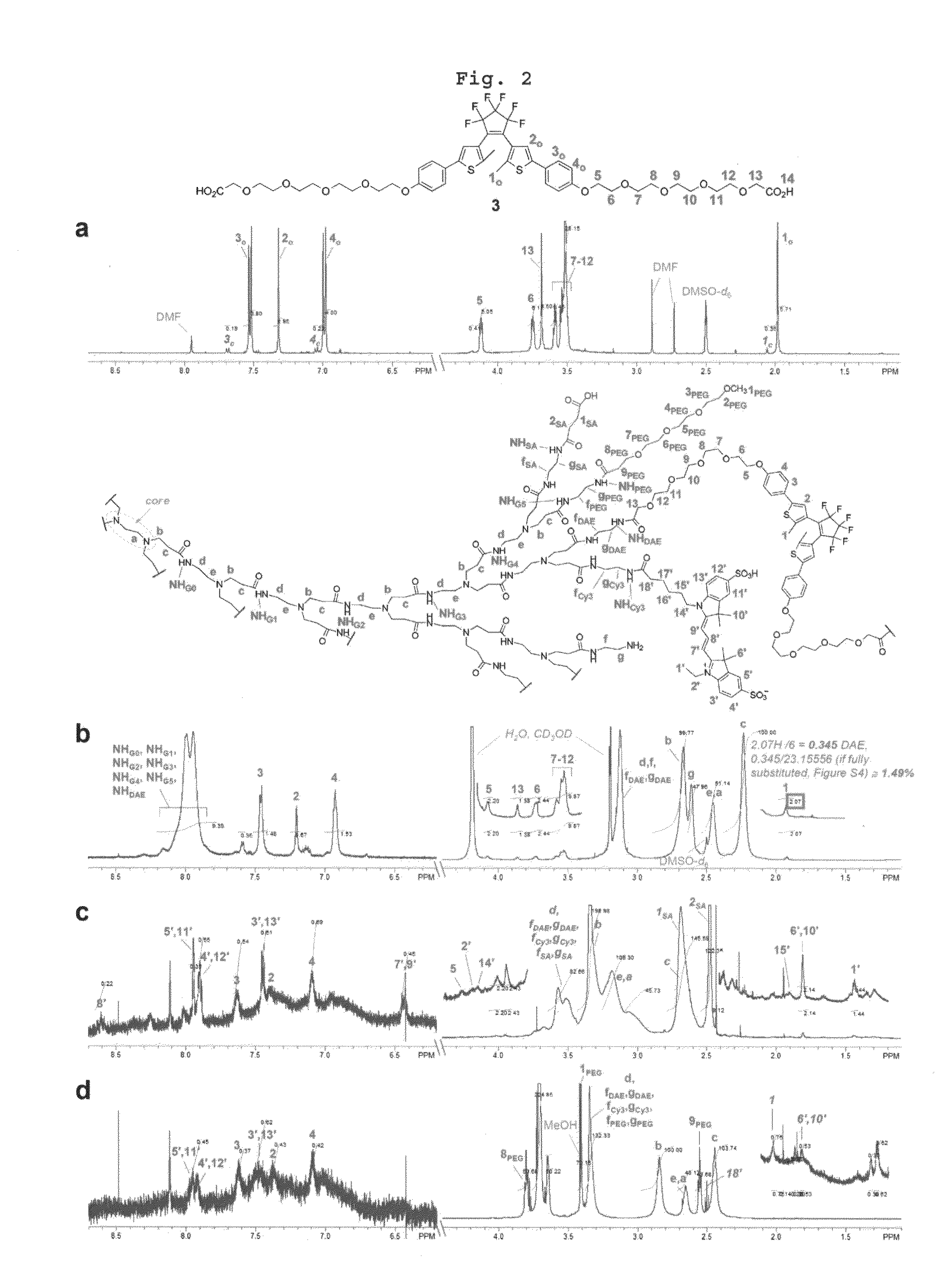
The invention discloses a polyethylenimine-aliphatic polyester graft polymer as well as a preparation method of the polyethylenimine-aliphatic polyester graft polymer and a preparation method of a nanometer particle. The polyethylenimine-aliphatic polyester graft polymer has a structure as shown in formula (1), wherein a is an integral number from 10 to 500, b is the integral number from 10 to 500, R1-R3 are independently selected from one or more of the structures as shown in formula (2) to formula (4), n is the integral number from 12 to 240, x is the integral number from 12 to 240 and y is the integral number from 12 to 240. The polyethylenimine-aliphatic polyester graft polymer provided by the invention has excellent fluorescence performance and biocompatibility, and has extensive application in the medicine loading field and the cell tracking field.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
PSO based multi-cell position outline synchronous accurate tracking system
ActiveCN104063880AAccurate trackingImprove tracking stabilityImage analysisEngineeringParticle swarm algorithm
The invention provides a particle swarm optimization based multi-cell position and outline synchronous accurate tracking system which comprises three main modules including a PSO based tracking module, a PSO based discovery module and a PSO based outline module. For existing-cell tracking, the PSO based tracking module obtains an initial state of a cell in a current frame on the basis of an existing-cell prior state, then calculates a cell outline through the PSO based outline module and meanwhile achieves accurate tracking by utilizing the iterative mass center updating process. For newly-emerging cell tracking, the PSO based discovery module discovers the position of a new cell in a whole image through appropriate particle swarm initialization and searching mechanism and further obtains the cell outline.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Magnetic resonance method for the detection and imaging of susceptibility related magnetic field distortions
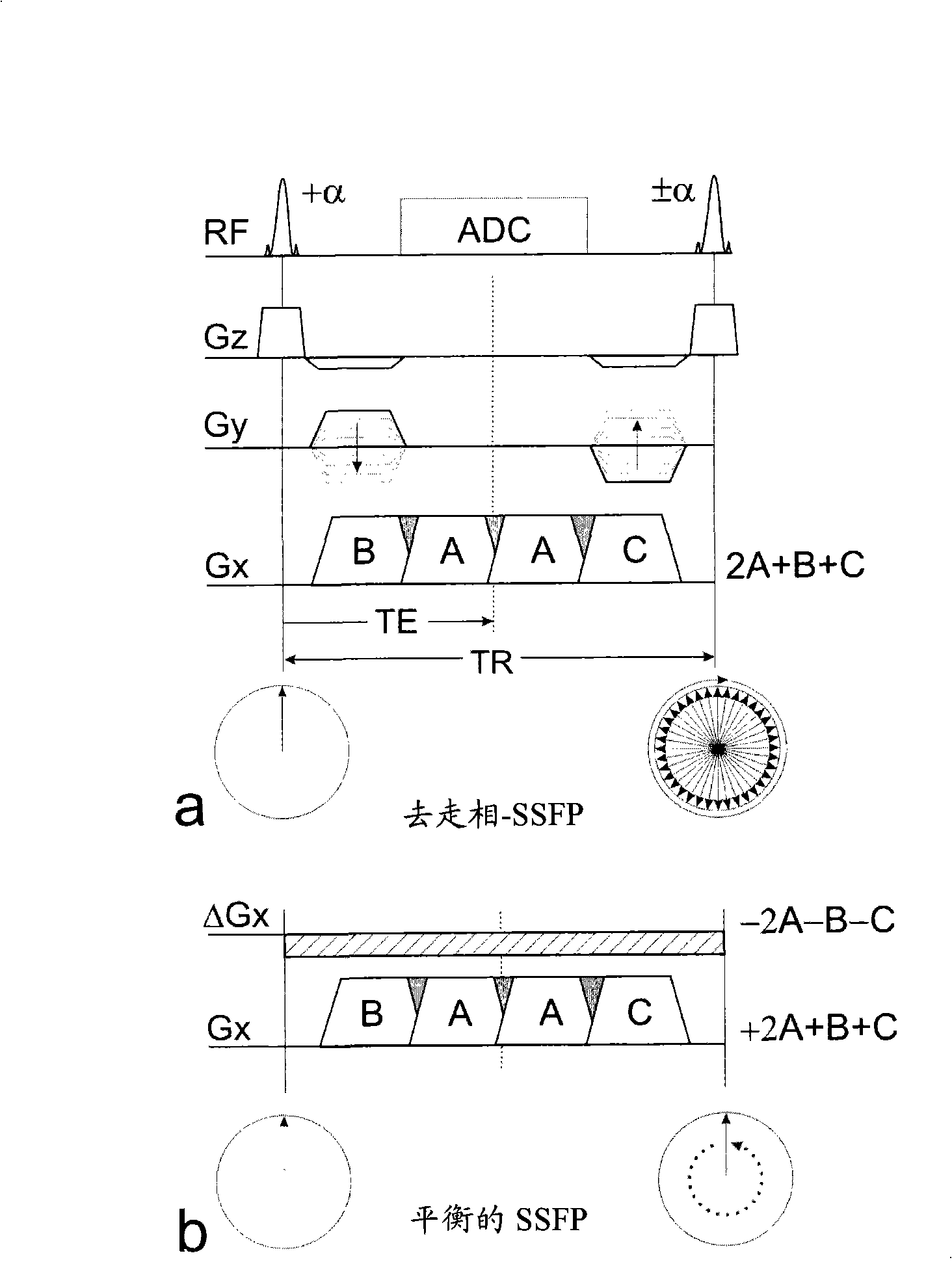
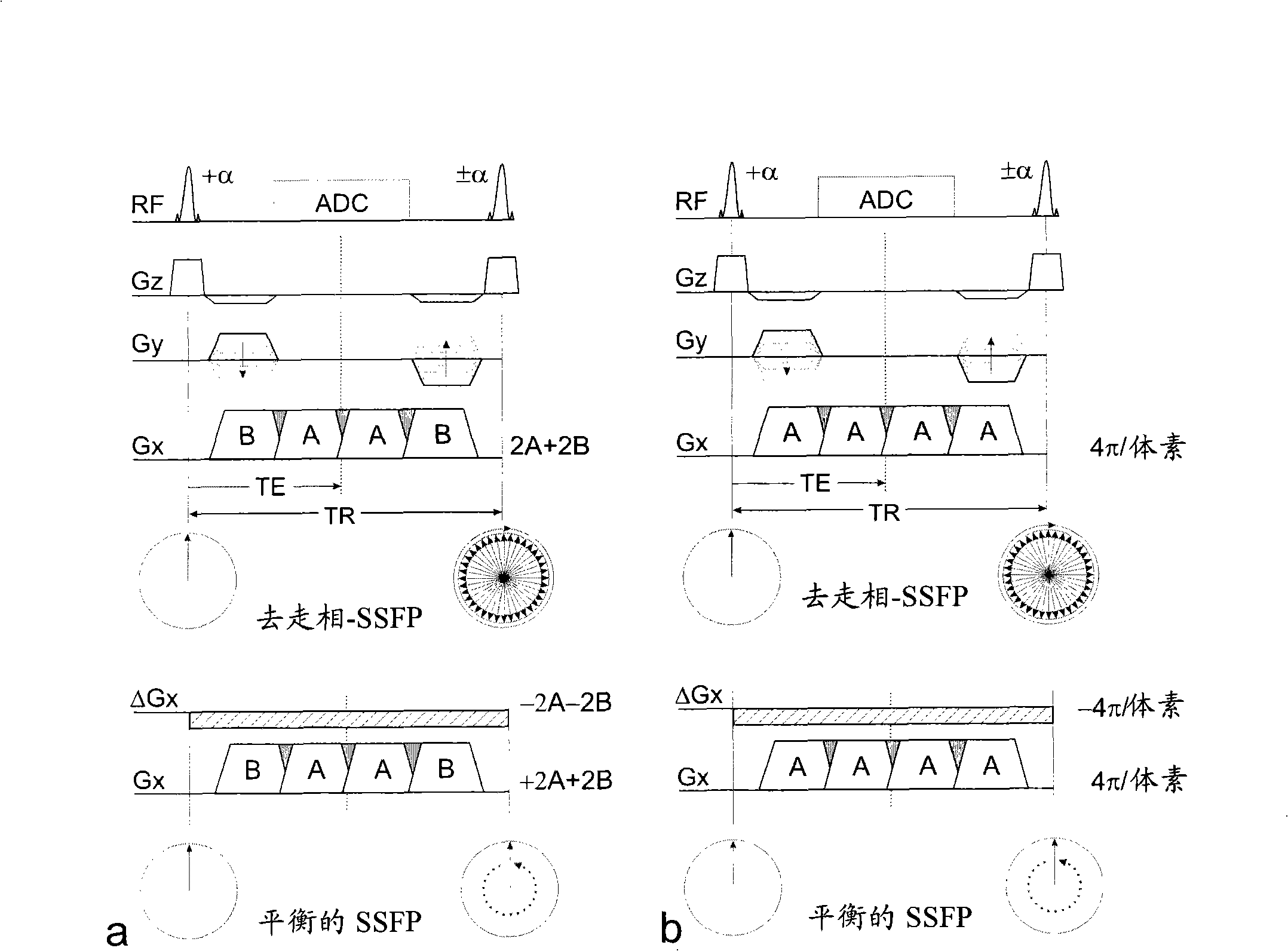
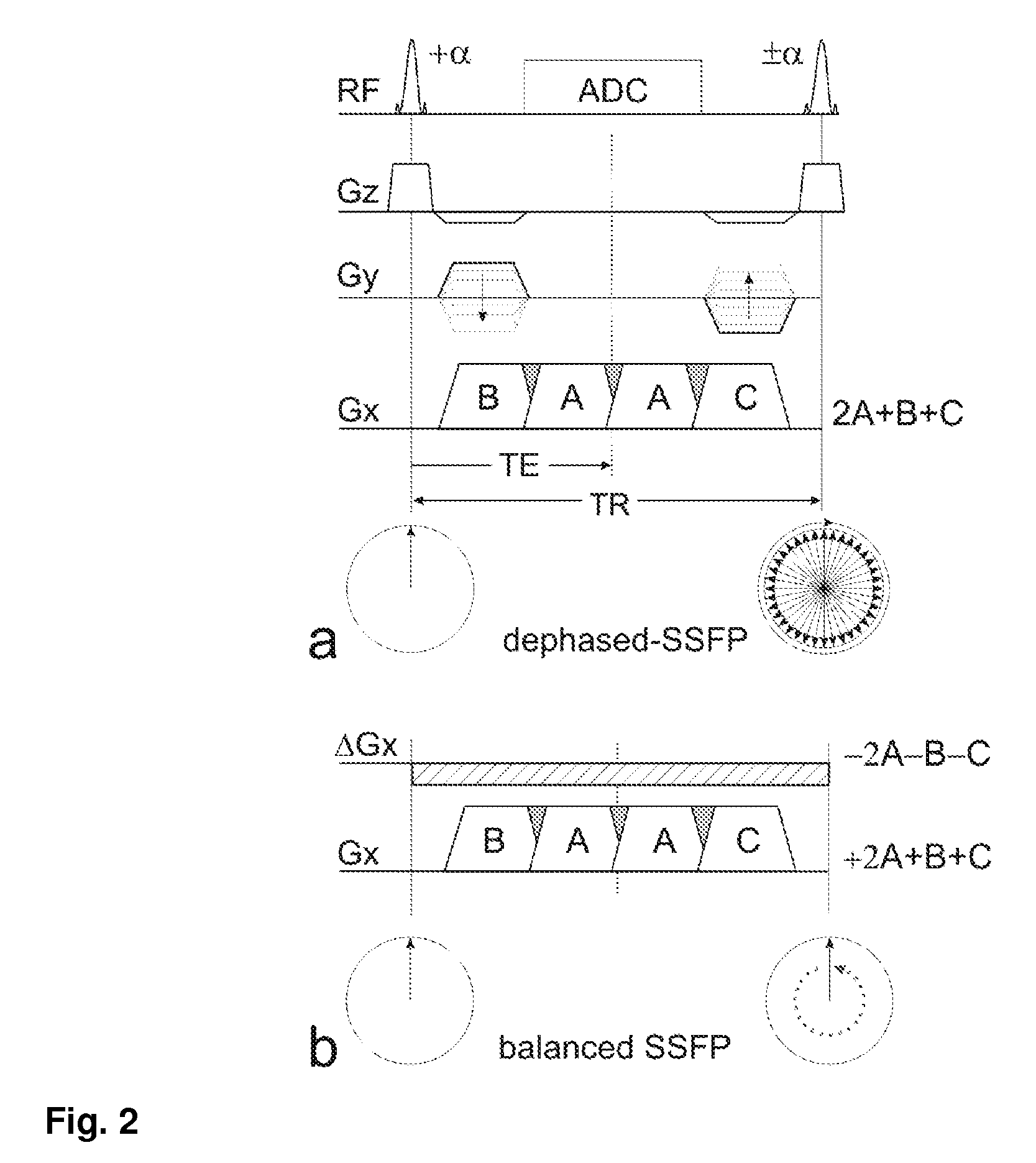
Disclosed are methods and apparatuses for generating susceptibility-related contrast images, as induced, e.g., by marker material interventional devices used for passive MR-guided interventions, or by particles or cells loaded with marker materials used for molecular imaging, cell-tracking or cell-labeling. Near a local magnetic field perturber a positive contrast signal emanates from local gradient compensation to form, e.g., a balanced SSFP type of echo, whereas everywhere else echoes are shifted outside of the data acquisition window.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Magnetic resonance non-balanced-SSFP method for the detection and imaging of susceptibility related magnetic field distortions
Disclosed are methods and apparatuses for generating susceptibility-related contrast images, as induced, e.g., by marker material interventional devices used for passive MR-guided interventions, or by particles or cells loaded with marker materials used for molecular imaging, cell-tracking or cell-labeling. Near a local magnetic field perturber a positive contrast signal emanates from local gradient compensation to form, e.g., a balanced SSFP type of echo, whereas everywhere else echoes are shifted outside of the data acquisition window.
Owner:BASEL UNIV OF
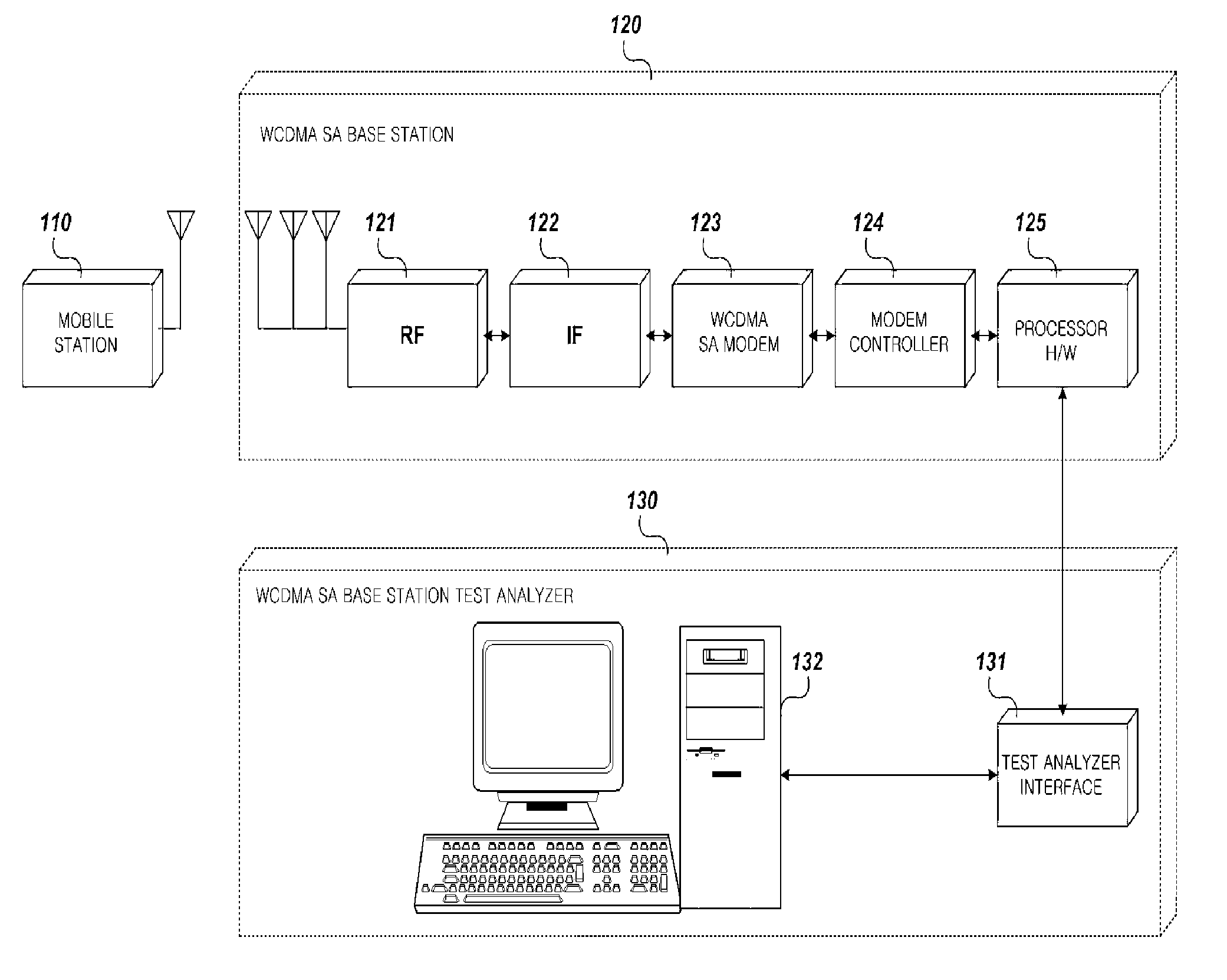
Apparatus and method for testing and analyzing base station with smart antenna, and protocol structure
InactiveUS20070202918A1Effective functionImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentSmart antennaCyclic prefix
Disclosed is a downlink signal configuring method and device, and synchronization and cell search method and device using the same in a mobile communication system. A downlink frame has plural symbols into which pilot subcarriers are distributively arranged with respect to time and frequency axes. Initial symbol synchronization and initial frequency synchronization are estimated by using a position at which autocorrelation of a cyclic prefix of a downlink signal and a valid symbol of the downlink is maximized, and cell search and integer-times frequency synchronization are estimated by using pilot subcarriers included in the estimated symbol. Fine symbol synchronization, fine frequency synchronization, and downlink frame synchronization is estimated by using an estimated cell search result. Downlink frequency and time tracking is performed, cell tracking is performed by using a position set of pilot subcarriers inserted into the downlink frame, fine symbol synchronization tracking and fine frequency synchronization tracking are repeated by using the pilot subcarriers to perform the frequency and time tracking of the downlink frame.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Ant colony neighbor cell tracking system based on cooperation and competition mode and application thereof
ActiveCN103955946AImplement automatic trackingImprove tracking stabilityImage analysisBiological modelsAlgorithmNear neighbor
The invention discloses an ant colony neighbor cell tracking system based on a cooperation and competition mode and application thereof. The system includes an initial ant colony distribution and rough classification module, a multi-ant-colony decision module and a fusion and deletion module. The initial ant colony distribution and rough classification module uses an approximate median method to extract a foreground image of cells so as to obtain initial ant colony distribution and then uses a K-mean-value clustering method to roughly divides the ant colony into N groups of sub-ant colonies. The multi-ant-colony decision module constructs a cell position estimation module, which is under the common action of N independent sub-pheromone fields and total pheromone fields, on the cooperation and competition mode. The fusion and deletion module performs multi-cell position estimation based on pheromone field construction through combination of similar sub-ant-colonies and removal of false targets caused by clutter and uses a nearest neighbor method which is easy to realize to perform cell correlation and obtain cell motion trails and kinetic parameters. The ant colony neighbor cell tracking system based on the cooperation and competition mode is capable of realizing neighbor multi-cell kinetic parameter estimation under a low-contrast-ratio cell image sequence, that is, under conditions that neighbor multi-cell kinetic characteristics are different, cells are deformed and time variance happens in cell number and the like, on the basis that no cell detection module or large quantity of cell training samples are needed, through cooperation and competition of an ant cluster system, problems of neighbor multi-cell multi-parameter estimation and tracking are solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
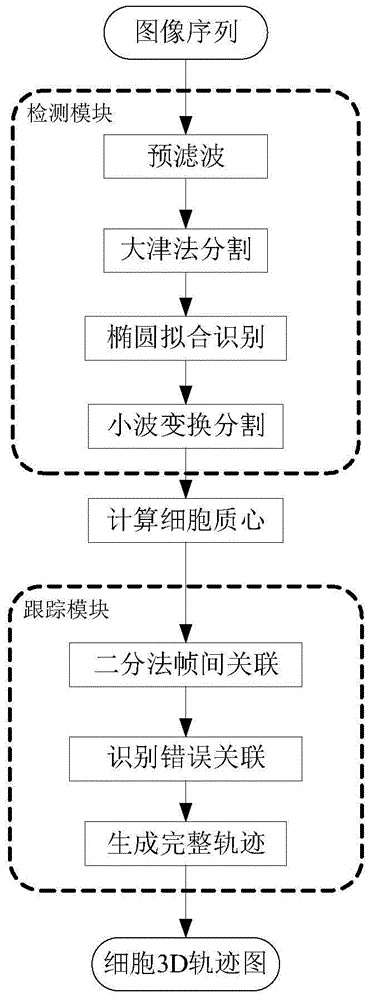
Cell tracking method based on global and local optimum
ActiveCN105678810ANo initialization requiredWithout human interventionImage enhancementImage analysisCell divisionLocal optimum
The invention discloses a cell tracking method based on global and local optimum. According to the method, independent regions are obtained through initial segmentation by means of ellipse fitting, and adherent cells in need of segmentation are identified; then a wavelet transformation method is used to carry out further segmentation; the center of mass of each cell subjected to segmentation is calculated and used as a unique characteristic of the cell; a bipartite graph matching method is used for inter-frame correlation of the cells, then cell shifting-in, shifting-out, division and shielding events are identified, matching is iterated and incomplete cell track segments are obtained; and through analysis, identification and correction of cell track segments, finally a complete cell track is generated based on local optimum. The method utilizes cell location information to achieve sub-cell relation of cell division and has good effect on different data sets.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Satellite communication system using linear cell tracking
InactiveUS7171158B2Eliminate overheadAntennas is relatively simpleCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsSystem capacityPeak value
An improved satellite communication device and system are provided. The satellite communication device uses yaw or roll-yaw steering to linearize angular track of uplink cells; one-dimensional linear “ratcheting” in an uplink antenna to maintain resource allocation of uplink cells along antenna columns; phased-array downlink antennas which can track earth-fixed downlink cells while compensating for the yaw (or roll-yaw) satellite steering; and variable rate TDMA service among downlink cells in a footprint. As a result, system overhead for performing new resource allocations between satellite handovers is minimized, thereby reducing resource management and increasing system capacity. Flexible bandwidth / capacity assignment of both uplink and downlink resources to earth locations via linear cell ratcheting, uplink RF peaking switch, and data-driven variable-TDMA downlink phased-arrays, is provided.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
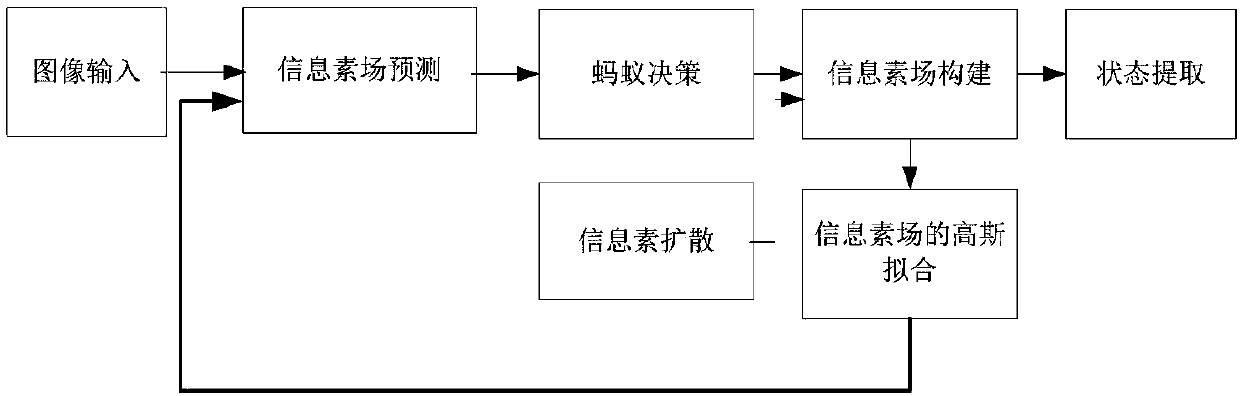
Pheromone prediction-based ant colony multi-cell tracking system
ActiveCN107871156ATroubleshoot tracking issuesEasy to trackBiomolecular computersArtificial lifeAlgorithmDecision taking
The invention discloses a pheromone prediction-based ant colony multi-cell tracking system. The system comprises four modules: a pheromone field prediction module, an ant decision module, a pheromonefield Gaussian fitting module and a state estimation module. Through analysis of the modules, multi-cell tracking is realized. After an original picture is input, based on a cell pheromone field Gaussian fitting result of a previous frame, pheromone field prediction is performed by utilizing a Gaussian mixture model; a pheromone field is constructed by utilizing a bell curve-based pheromone diffusion model in a pheromone gradient-based ant working mode; and through a K-mean clustering method, cell position estimation is performed after removal of a false target caused by clutters, and finallyassociation is performed by utilizing cell distance features to obtain cell motion tracks, thereby realizing the multi-cell tracking.
Owner:JIANGSU SAIKANG MEDICAL EQUIP
Method of dynamic cell tracking in a sample
ActiveUS20120070060A1Improve cell tracking accuracyImprove tracking accuracyImage analysisAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsCell divisionAlgorithm
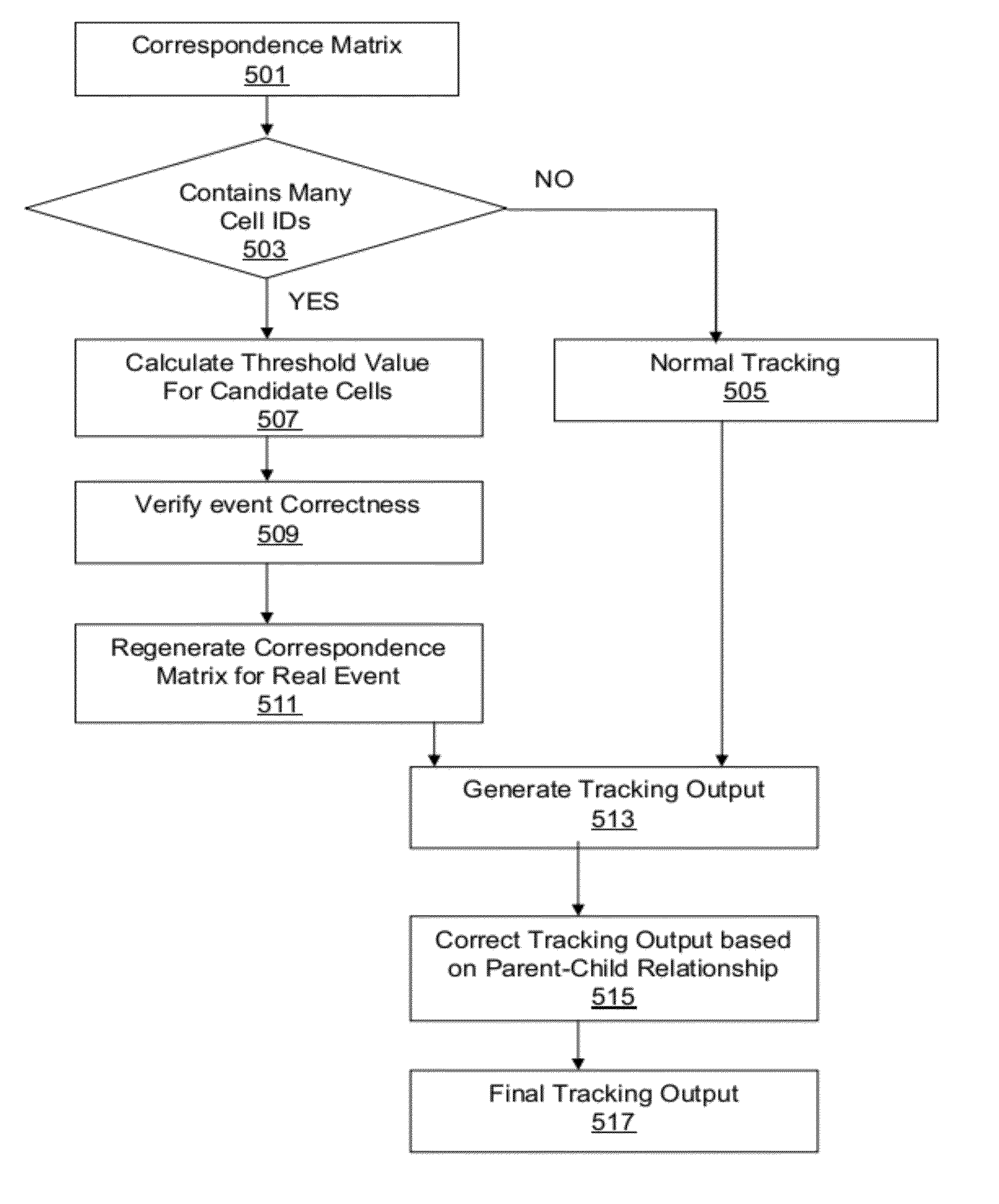
This invention provides a method of dynamic cell tracking in a sample comprising the steps of, generating a correspondence measure between cells in two consecutive time-elapsed images of a sample, evaluating said correspondence measure to generate events linking individual cells in the two images, the events being selected from the group: unchanged, cell removal, cell migration, cell collision and cell division, and providing a tracking output of events linking individual cells in the two images. In the invention, the step of establishing linking events involves verifying the correctness of generated cell collision and cell division events, by calculating an adaptive threshold value for each such event and comparing the threshold value with an event parameter. There is further provided a system for dynamic cell tracking in a sample.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
United multi-cell tracking method based on label ant colony
ActiveCN110598830ATroubleshoot match build issuesIncreased splitting accuracyArtificial lifeComplex mathematical operationsRecovery methodRestoration method
The invention discloses a united multi-cell tracking method based on a label ant colony. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating a group of cell candidate ant colonies in a current frame by adopting a label-free scouting ant colony, constructing a bipartite graph on the basis of the cell candidate ant colonies, and forming the bipartite graph by a cell state estimated in theprevious frame and the currently generated cell candidate ant colonies; secondly, optimally realizing inter-frame matching by utilizing the label ant colony and taking track optimal sub-mode distribution as a target function, wherein the multi-cell state is obtained by multi-Bernoulli parameters approximate to the evolved label ant colony, and the spectrum tree of the cells is obtained by extracting a track pheromone field on inter-frame matching determined by the spectrum tree; finally, providing a four-step flight path recovery method for flight path breakage so as to realize correlation between broken flight paths. According to the method, the spectrum coefficient of the cell can be extracted by utilizing the track pheromone, and the state of the cell is estimated by utilizing the foodpheromone; compared with the prior art, the cell division accuracy and recall rate are obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SAIKANG MEDICAL EQUIP
High density cell tracking method based on topological constraint and Hungarian algorithm
The invention provides a high density cell tracking method based on topological constraint and a Hungarian algorithm, which comprises: (1) segmenting a cell image sequence by using an image segmentation method which combines a level set algorithm and a local gray threshold process, and initially labeling segmented cells in each frame; (2) according to distance limitation, establishing a tracking search region for a cell to be matched in the kth frame in the k+1th frame, and listing the cells in the region as candidate cells; (3) establishing a coefficient matrix Q, and if a cell j in the k+1th frame is the candidate cell of a cell i in the kth frame, performing data association according to topological constraint to calculate the similarity Qij of the cell j, or assigning a larger value to the similarity of the cell j; (4) performing transformation on the coefficient matrix by using the Hungarian algorithm to find out independent zero elements, wherein the cells represented by the rows of the zero elements are matched; (5) finding out rows in which there are no zero elements after matrix transformation, and taking the cells corresponding to the rows into consideration respectively; and (6) adding 1 to the k, jumping to the step 2, and repeating the steps till the last frame of the image sequence. The method can realize high-efficiency cell tracking.
Owner:DONGGUAN BOALAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Cell division identification method
ActiveCN102722717AImprove recognition rateAvoid difficultiesImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a cell division identification method. The method comprises the following steps of: learning a first optimum dictionary through a first training set and a target function; sparsely decomposing the first training set through the first optimum dictionary, and acquiring first optimum sparse decomposition coefficients which correspond to all first vision characteristic vectors; acquiring a trained dividing cell model through the first optimum sparse decomposition coefficients which correspond to a positive sample and a negative sample; and acquiring second optimum sparse decomposition coefficients of new test data, inputting the second optimum sparse decomposition coefficients into the trained dividing cell model, and acquiring an output result, wherein the type of the output result is marked as 1, the new test data comprise a dividing cell area, and when the type of the output result is marked as 0, the new test data do not comprise the dividing cell area. By adoption of the cell division identification method, the difficulty in target characteristic extraction of a non-rigid body is overcome, identification of a cell division behavior is independent of cell tracking and time sequence deduction models, influence of computation complexity can be remarkably reduced, and the identification rate of cell division is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reversible Fluorescence Photoswitch based on Dye-Crosslinked Dendritic Nanoclusters for High-Contrast Imaging of Living Biological Systems
The present invention relates to a reversible fluorescence photoswitch based on the dye-crosslinked dendritic nanoclusters for high-contrast imaging of living biological systems. The dendritic nanocluster according to the present invention consists of two or more dendrimers crosslinked each other to have a globular shape overall, and thereby enhancing the fluorescence intensity and improving the detection sensitivity of the monomeric dendrimers. In addition, the dendritic nanocluster according to the present invention was found to internalize into a living zebrafish by both skin permeation and microinjection, independently. Further, the dendritic nanocluster according to the present invention showed low toxicity and thus it could be useful for both in vivo and in vitro imaging as well as the ex vivo cell tracking applications.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Multicellular multi-parameter joint estimation and accurate tracking system based on ant colony system
ActiveCN103268617AAchieve precise trackingAccurate Joint TrackingImage analysisBiological modelsGray levelLow contrast
The invention provides a multicellular multi-parameter joint estimation and accurate tracking system based on an ant colony system, and belongs to the field of cell tracking, wherein parameters include positions, speed, outlines and the like. Initial position distribution of an ant colony is generated due to the fact that a corresponding local area gray level variance of each gray image is defined. Two information pixel fields which work in parallel and are mutually independent are built on the basis, wherein the pixel fields comprise a position field and an outline field. A bounded ant colony decision making system is respectively built on a cell position estimation module and a cell outline estimation module. Finally, important parameters such as positions, speed and outlines of cells are precisely estimated. Therefore, accurate tracking of multiple cells is achieved. By means of mutual cooperation of the bounded heuristic type ant colony systems, a cell detection module is needless, a large number of cell training samples are needless, and the joint estimation and tracking problems of multicellular kinetic parameters and multicellular outlines in a low-contrast cell image sequence are solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Stem cell tracking method based on deep learning
InactiveCN108256408AReal-time tracking hasImprove recognition accuracyAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMicroscopic imageNerve network
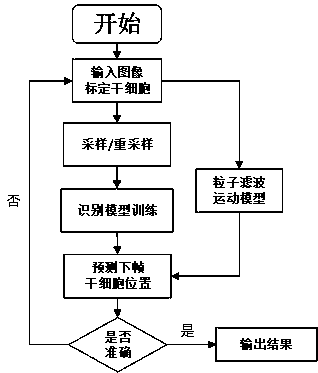
The invention discloses a stem cell tracking method based on the deep learning technology and a stem cell tracking system based on the deep learning technology. The method / system comprises the steps that 1: a cell tracking algorithm based on the deep learning technology is put forward; 2: a cell division detection algorithm based on the deep learning technology is put forward; and 3: a set of stemcell real-time tracking and division detection system is established. The invention relates to the fields of deep learning, cell tracking, division detection and the neural network. According to themethod, automatic tracking of stem cell movement and division time detection of the movement process can be realized by using the image analysis technology based on deep learning by aiming at stem cell microscopic image input based on the stem cell to be observed calibrated by the first frame so as to provide the great analysis tool for the stem cell research work. Real-time automatic tracking method of stem cell movement can be realized so that the method and the system have great generalization and tracking accuracy and can be applied to the tracking task of other types of cells through proper adjustment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation and application of double-fluorescent polymer quantum dot material
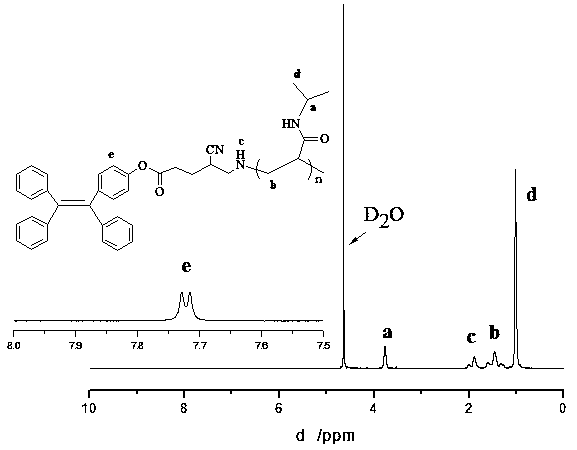
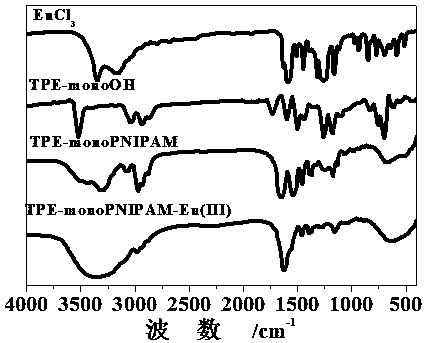
ActiveCN108504348AGood dual fluorescent propertiesNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytoplasmComputational chemistry
The invention discloses a double-fluorescent polymer quantum dot material. A hydrophobic TPE blue chromophore with an AIE (Aggregation-Induced Emission) property and amphiphilic PNIPAM (Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)) are covalently connected together to self-assemble a polymer quantum dot TPE-monoPNIPAM with a nano-scale; then the polymer quantum dot is coordinated with Eu(III) to prepare TPE-monoPNIPAM-Eu(III); the polymer quantum dot has very good double-fluorescent property, aggregation-induced emission property and temperature-sensitive property. A Hela cell staining result shows that the polymer quantum dot can be used for staining cytoplasm very well and is aggregated in the cytoplasm so as to generate high-brightness fluorescent light; blue and red composite light can be generated under different excitation wavelengths; especially, bright blue light can be generated under the excitation of light with the wavelength of 365nm and high-brightness red light is generated under the excitation of light with the wavelength of 395nm; the double-fluorescent polymer quantum dot material can be applied to the fields of biology better, such as cell imaging and cell tracking.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Carboxylation chitosan nano-fluorescence probe with aggregation-induced emission characteristic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106243244AEndocytosisUniform sizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsDispersityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a carboxylation chitosan nano-fluorescence probe with aggregation-induced emission characteristic. A preparation method of the probe comprises the following main steps: labeling tetraphenylethylene fluorescence molecule (TPE) to a carboxylation chitosan chain (NCS) to obtain TPE-NCS with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristic; and using sodium polyphosphate by an ion-crosslinking method to prepare TPE-NCS nanoparticles. The prepared nano-fluorescence probe has good dispersity in an aqueous solution, and has aggregation-induced emission characteristic. In comparison with a traditional fluorescence probe, the nano-fluorescence probe has advantages of high sensitivity, good light stability, no fluorescence spectra shift, stable and uniform nanoparticle size, easy storage and the like. Due to inherent characteristics of carboxylation chitosan, the probe of the invention has good biocompatibility, long retention of body circulation and good dispersity within a wide pH range, and could be used in fields of long-period cell tracking, pathological monitoring, drug metabolism detection, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
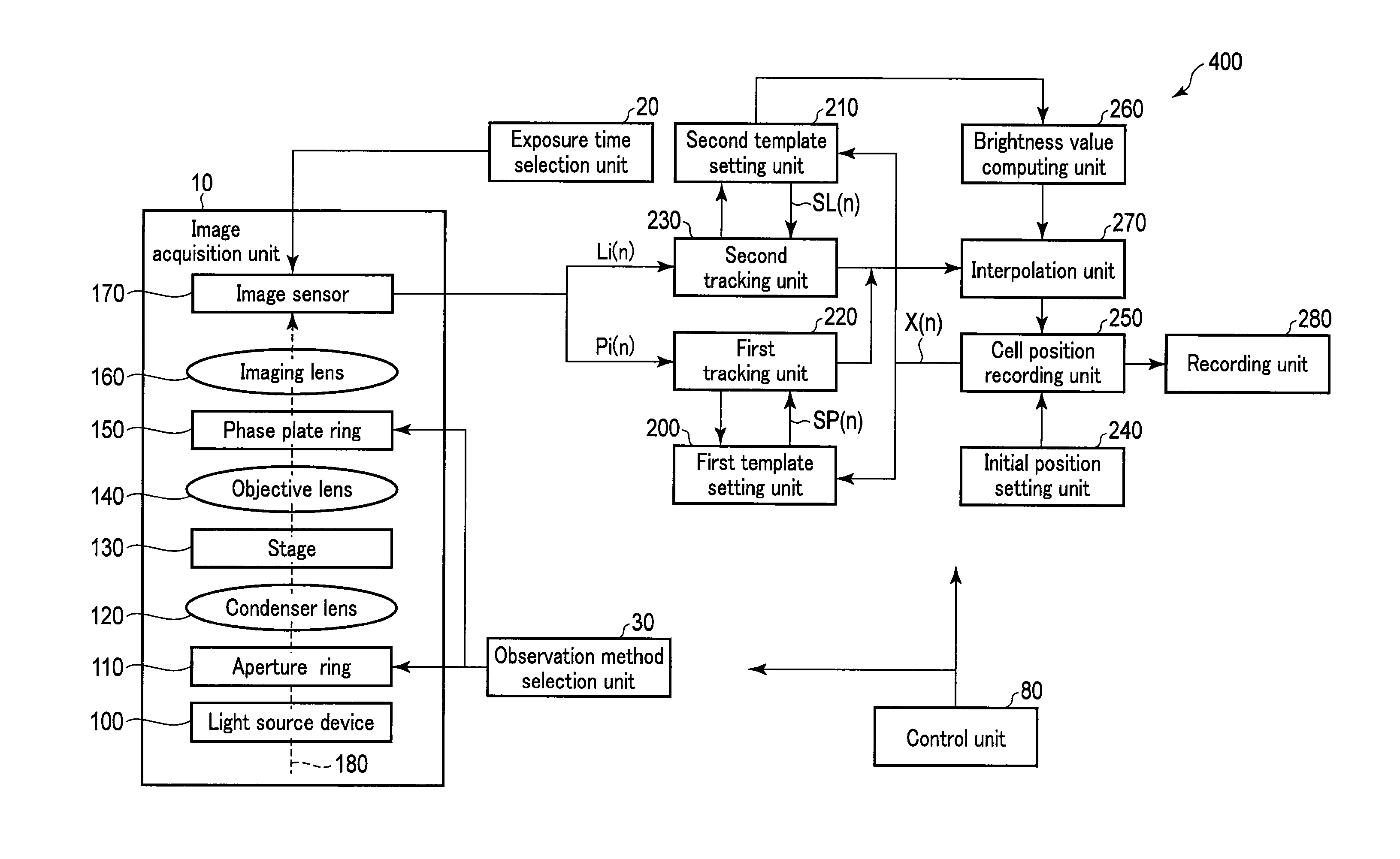
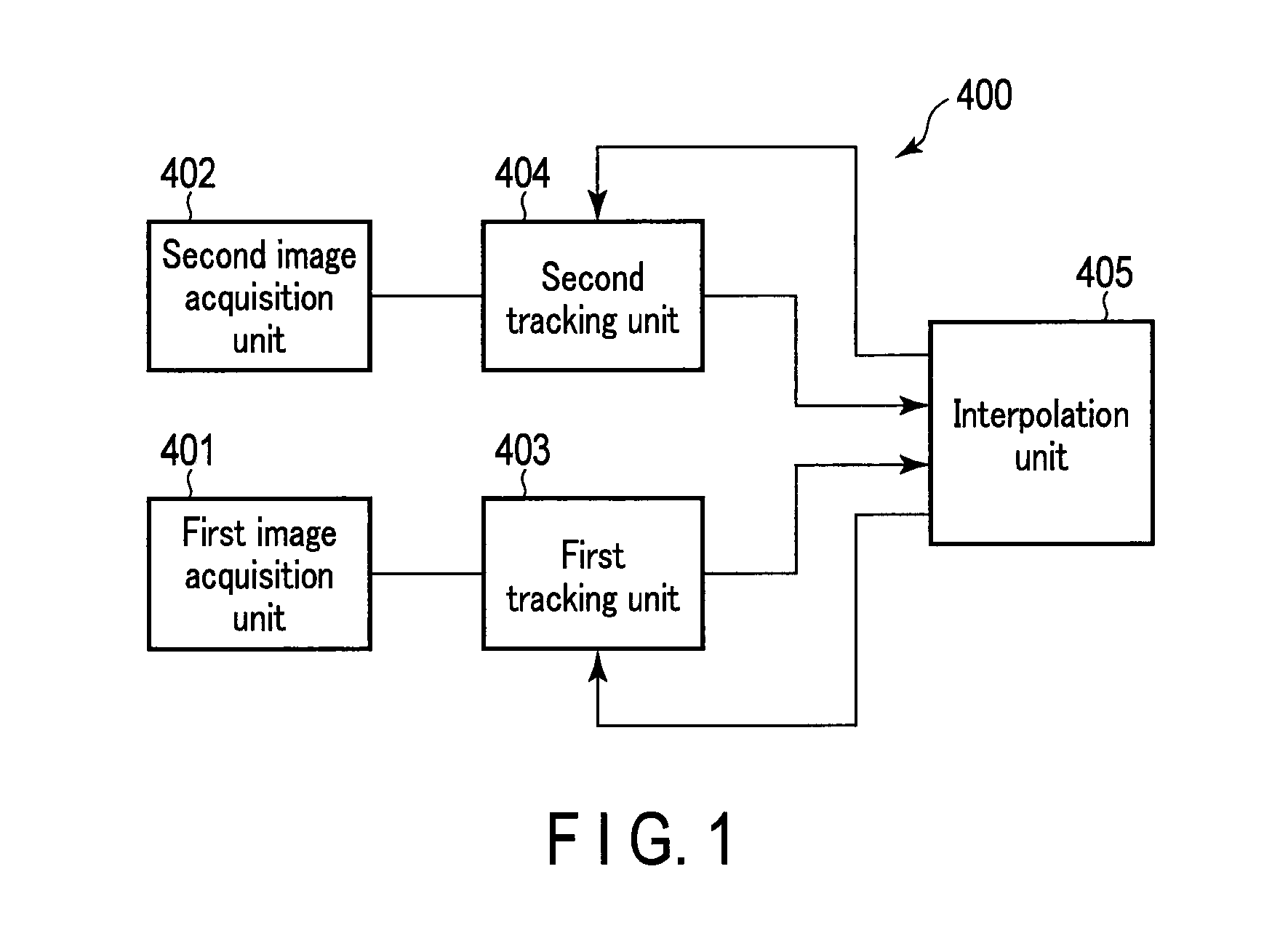
Cell Tracking Device and Method, and Storage Medium Non-Transitory Storing Computer-Readable Cell Tracking Programs
A cell tracking device includes first and second image acquisition units, first and second tracking units and an interpolation unit. The first image acquisition unit picks up images of a cell under a short-time exposure condition at points in time to capture short-time exposure images. The second image acquisition unit picks up images of the cell under a long-time exposure condition to capture long-time exposure images, each image of the cell under the long-time exposure condition being picked up within each interval between the points in time. The first tracking unit tracks the cell based upon the short-time exposure images. The second tracking unit tracks the cell based upon the long-time exposure images. The interpolation unit interpolates a tracking result obtained by the second tracking unit with a tracking result obtained by the first tracking unit.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com