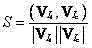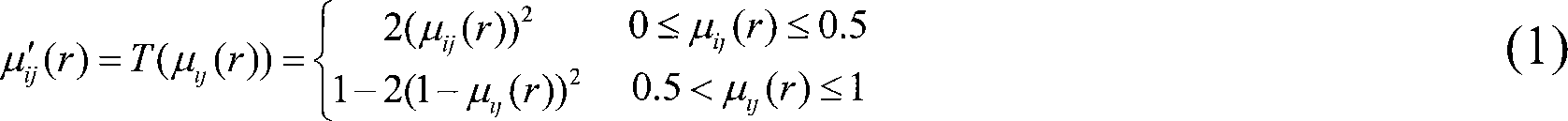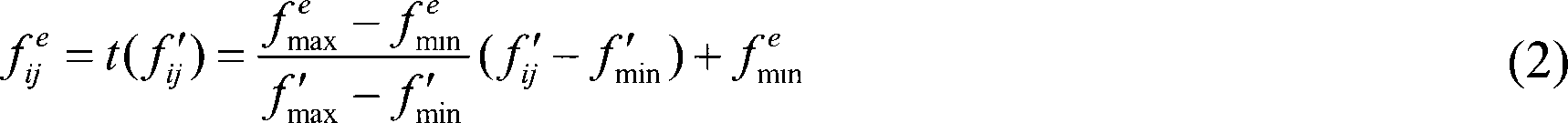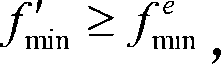Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
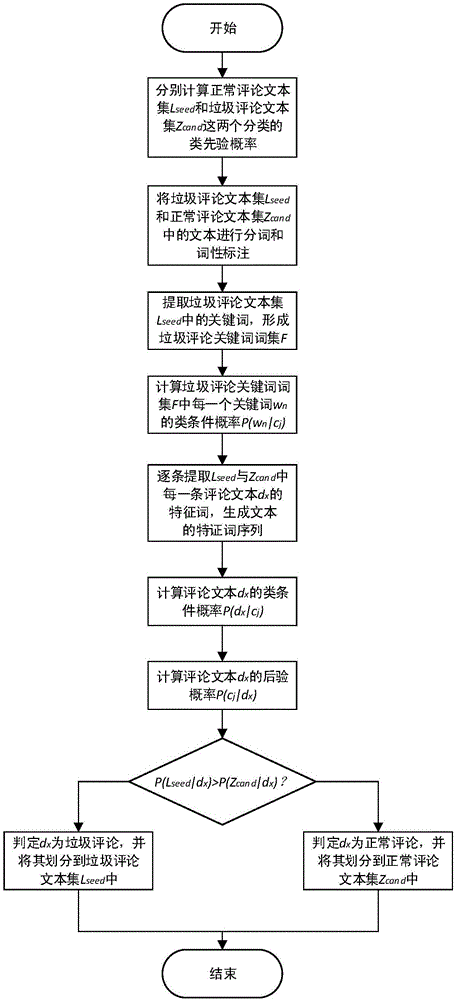
97 results about "Bayesian filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Bayesian filter is a program that uses Bayesian logic , also called Bayesian analysis, to evaluate the header and content of an incoming e-mail message and determine the probability that it constitutes spam . Bayesian logic is an extension of the work of the 18th-century English mathematician Thomas Bayes.
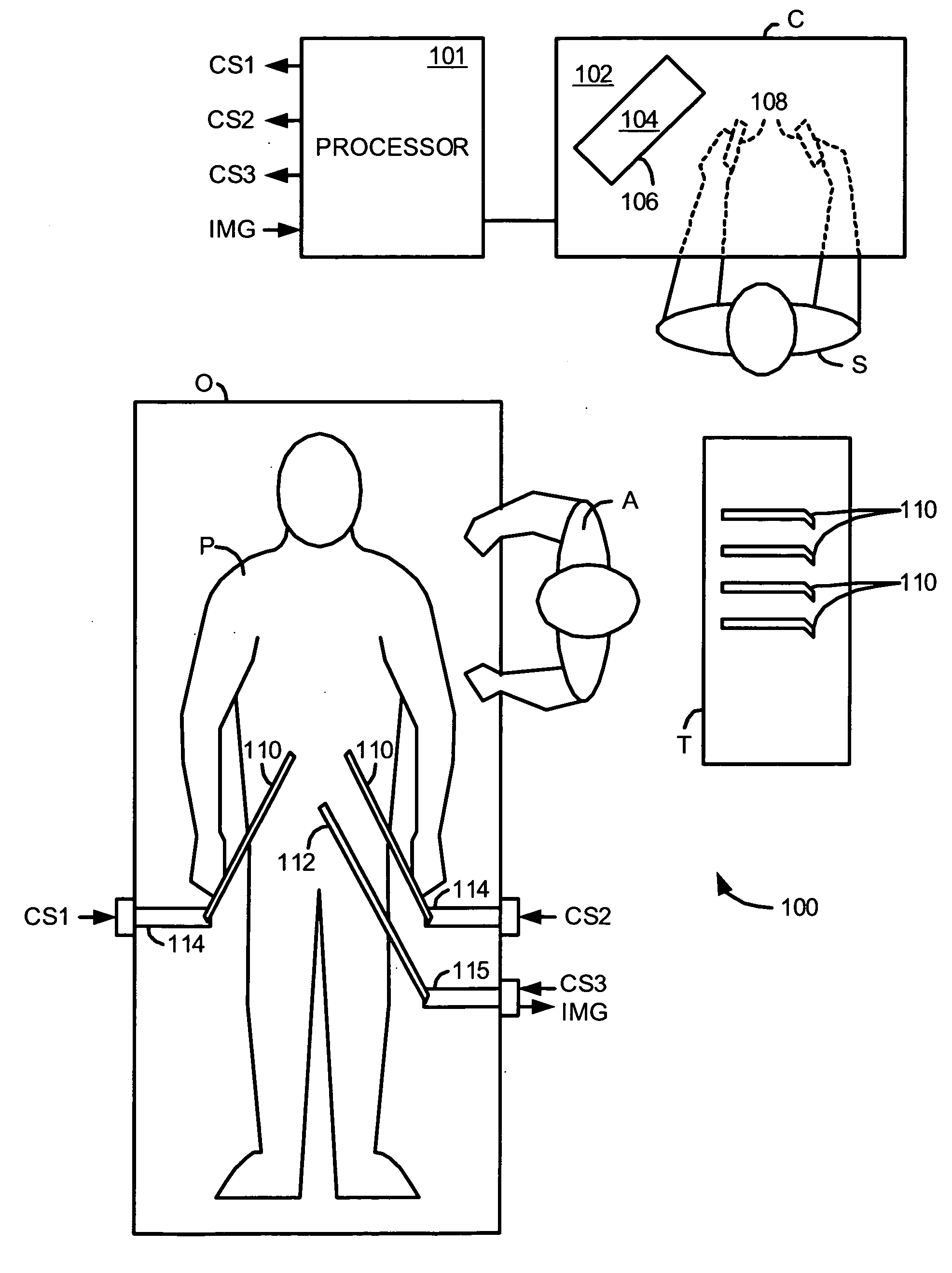
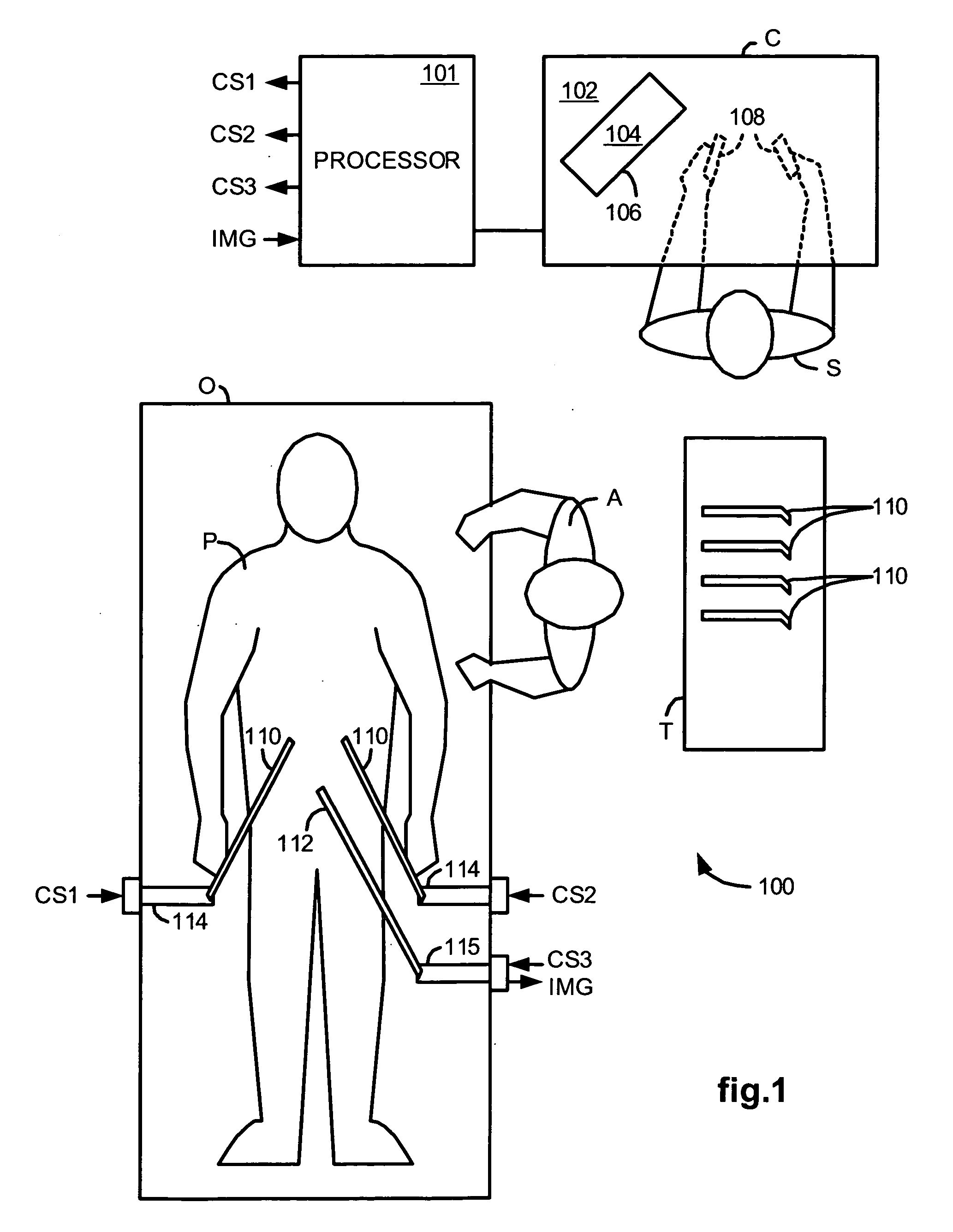
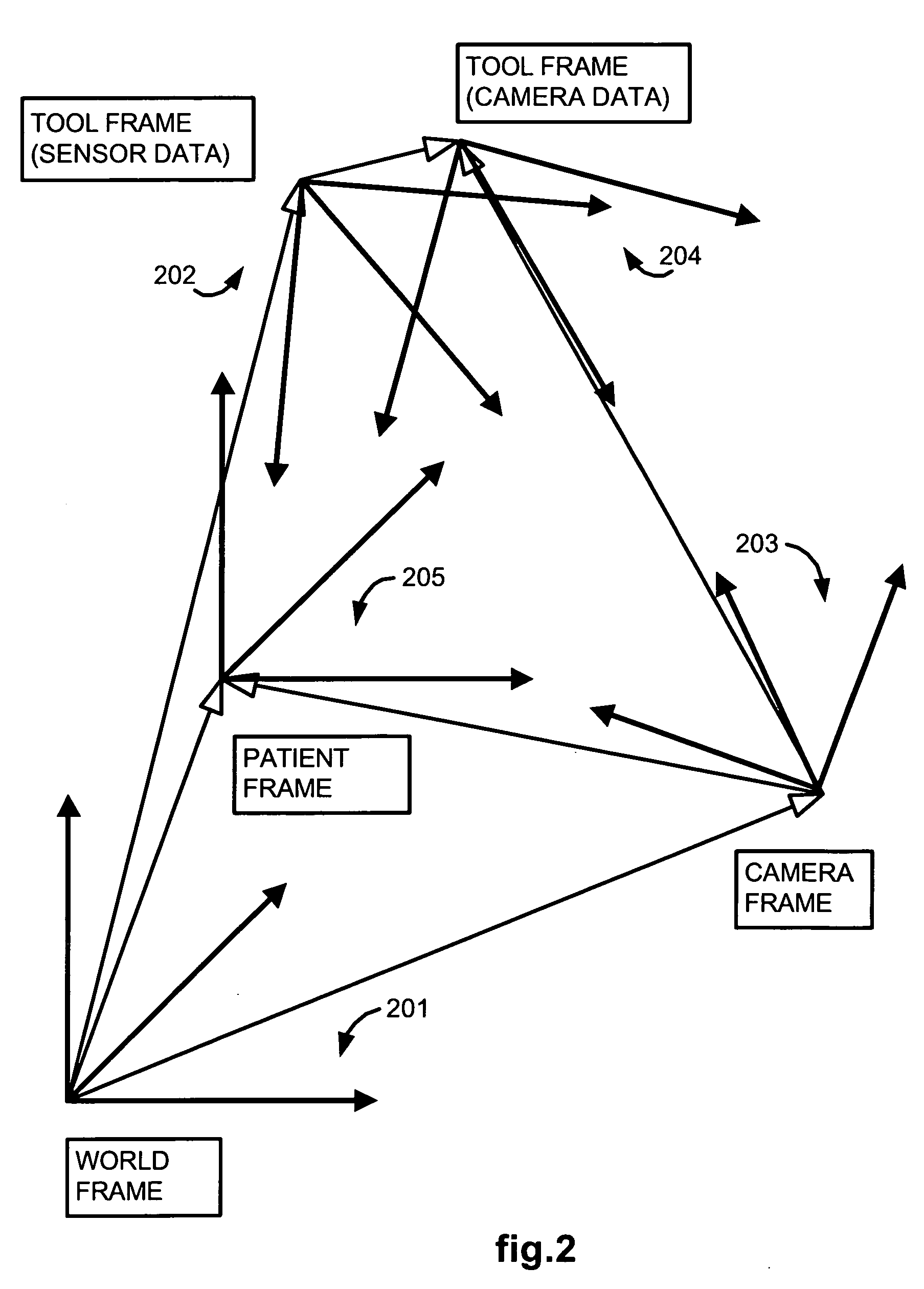
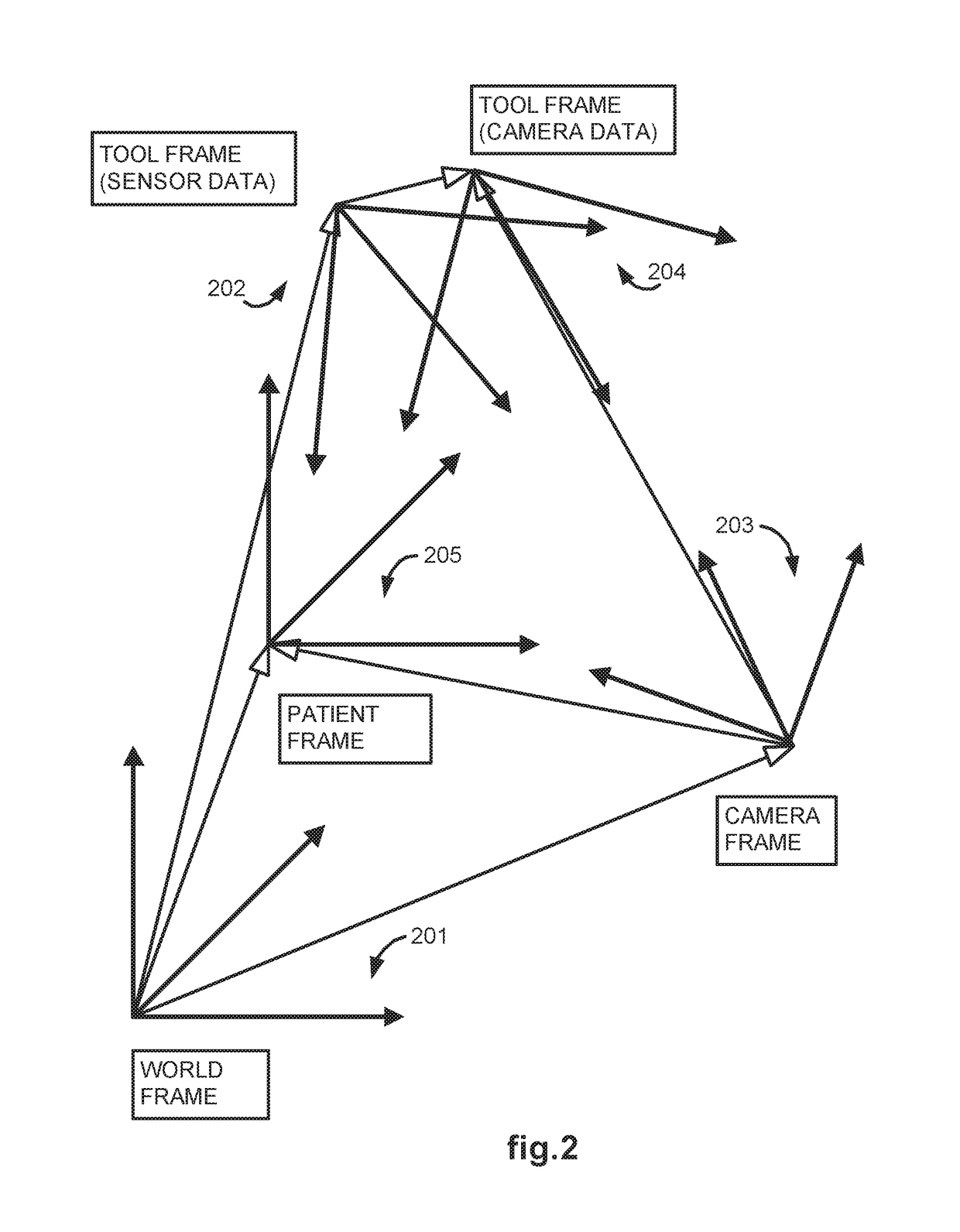
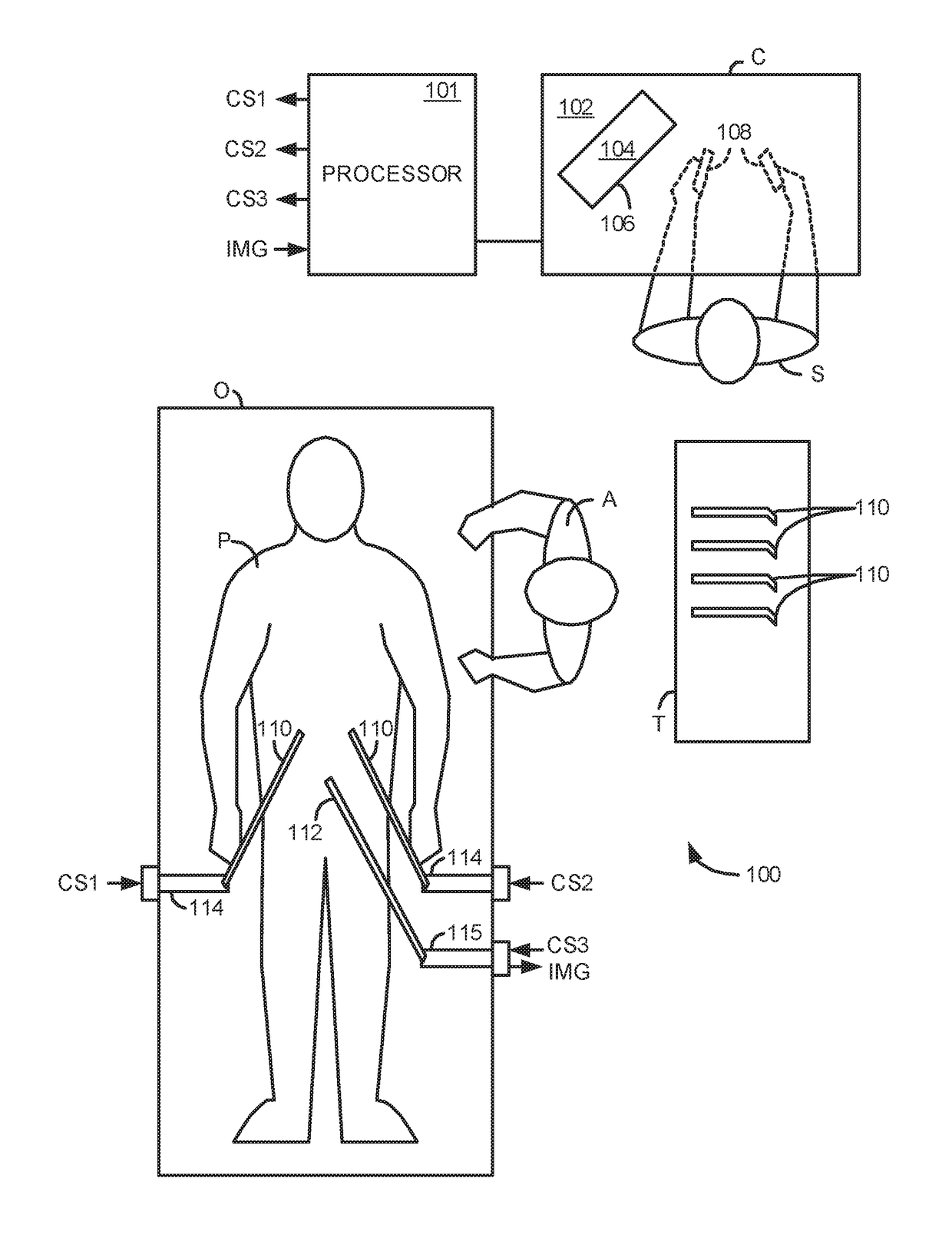
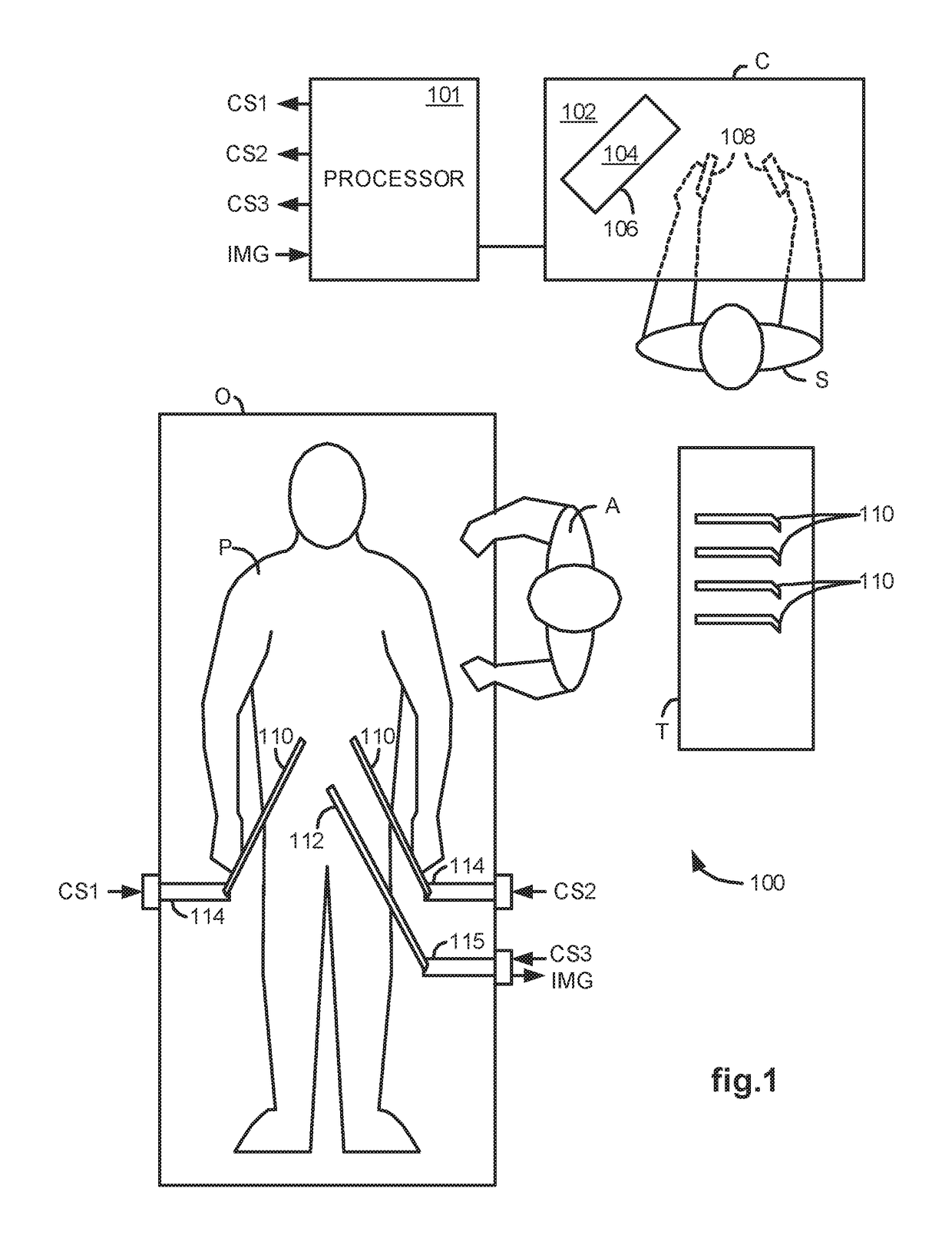
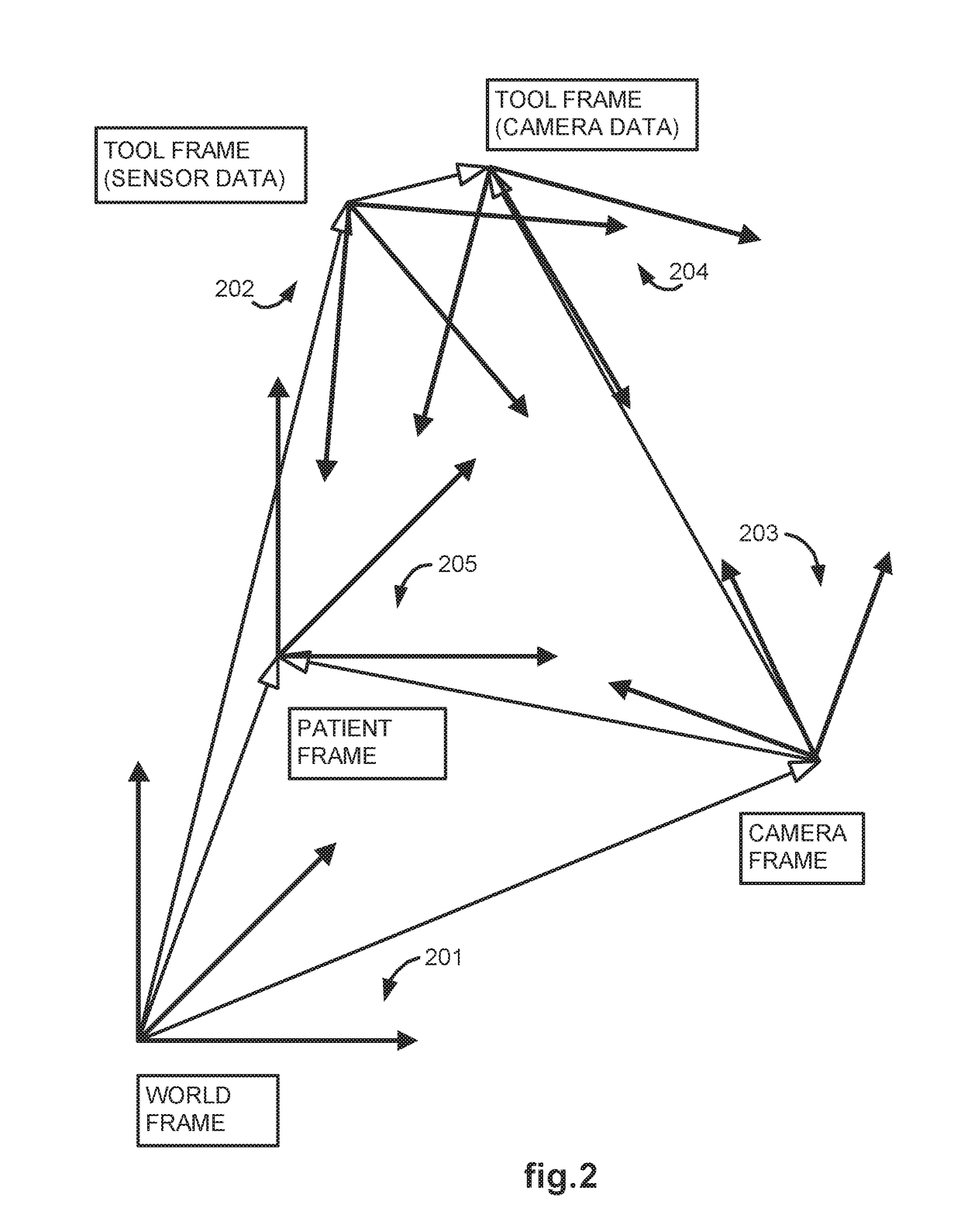
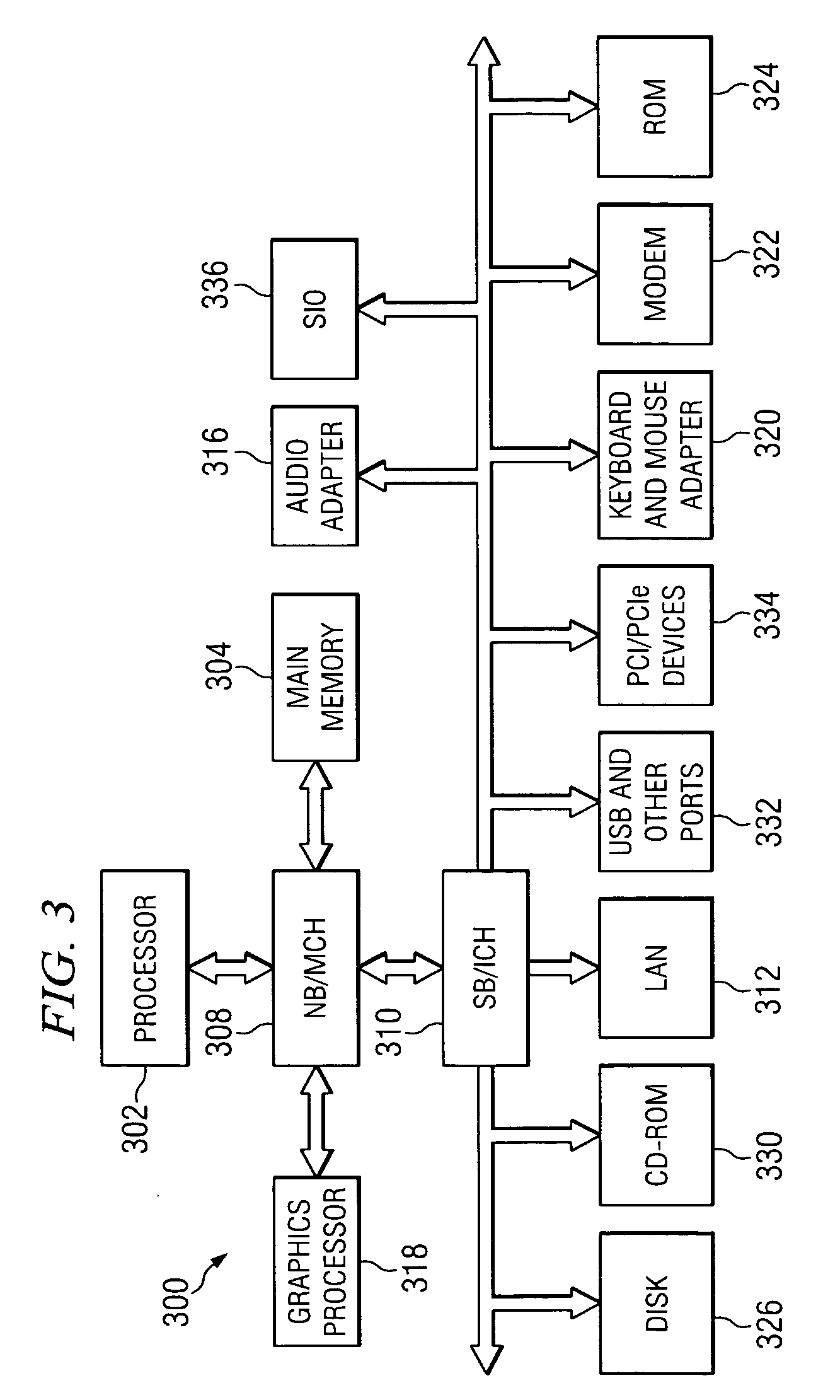
Methods and system for performing 3-D tool tracking by fusion of sensor and/or camera derived data during minimally invasive robotic surgery
ActiveUS20060258938A1Easy to distinguishFacilitate communicationSurgical navigation systemsLaproscopesTriangulationExternal camera
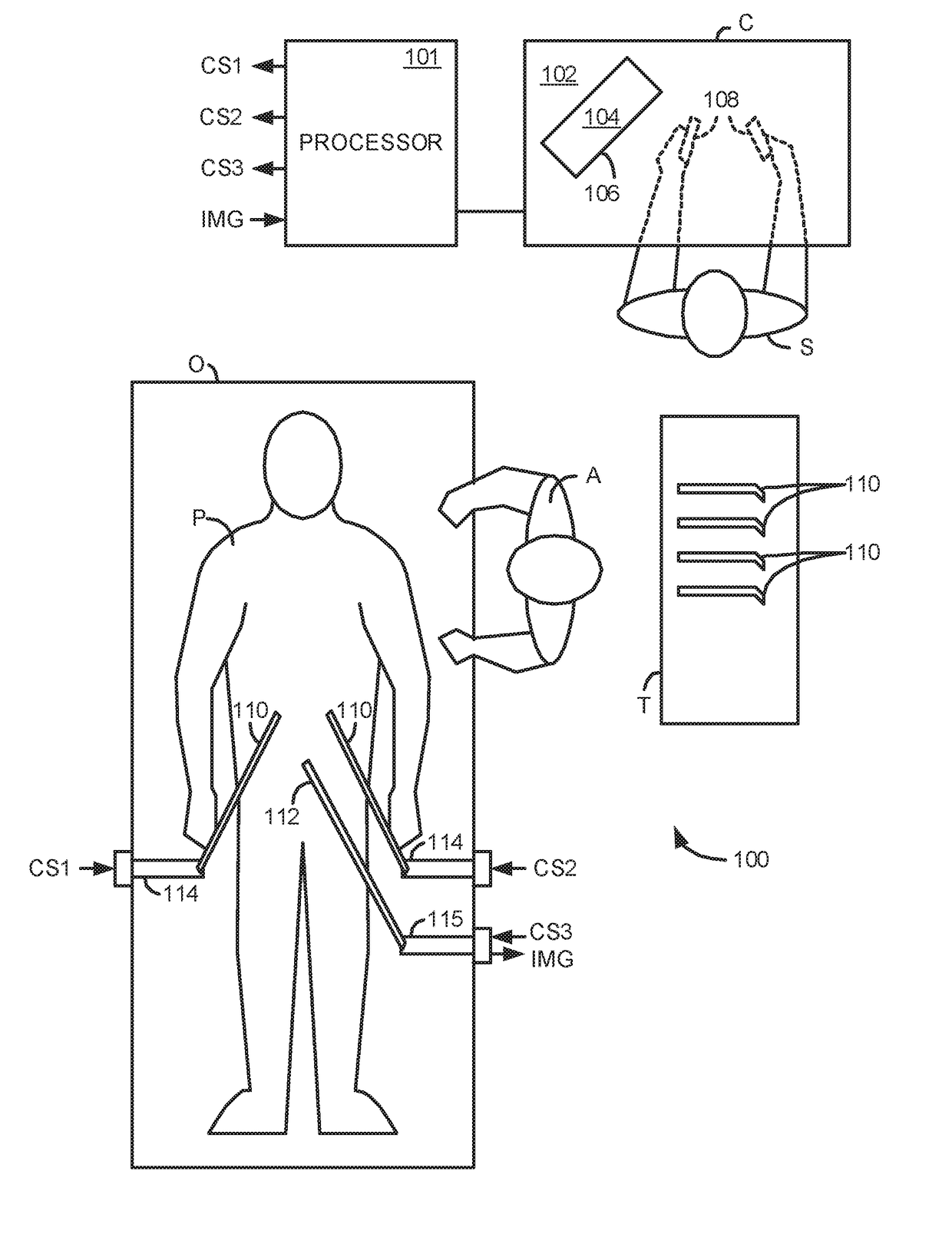
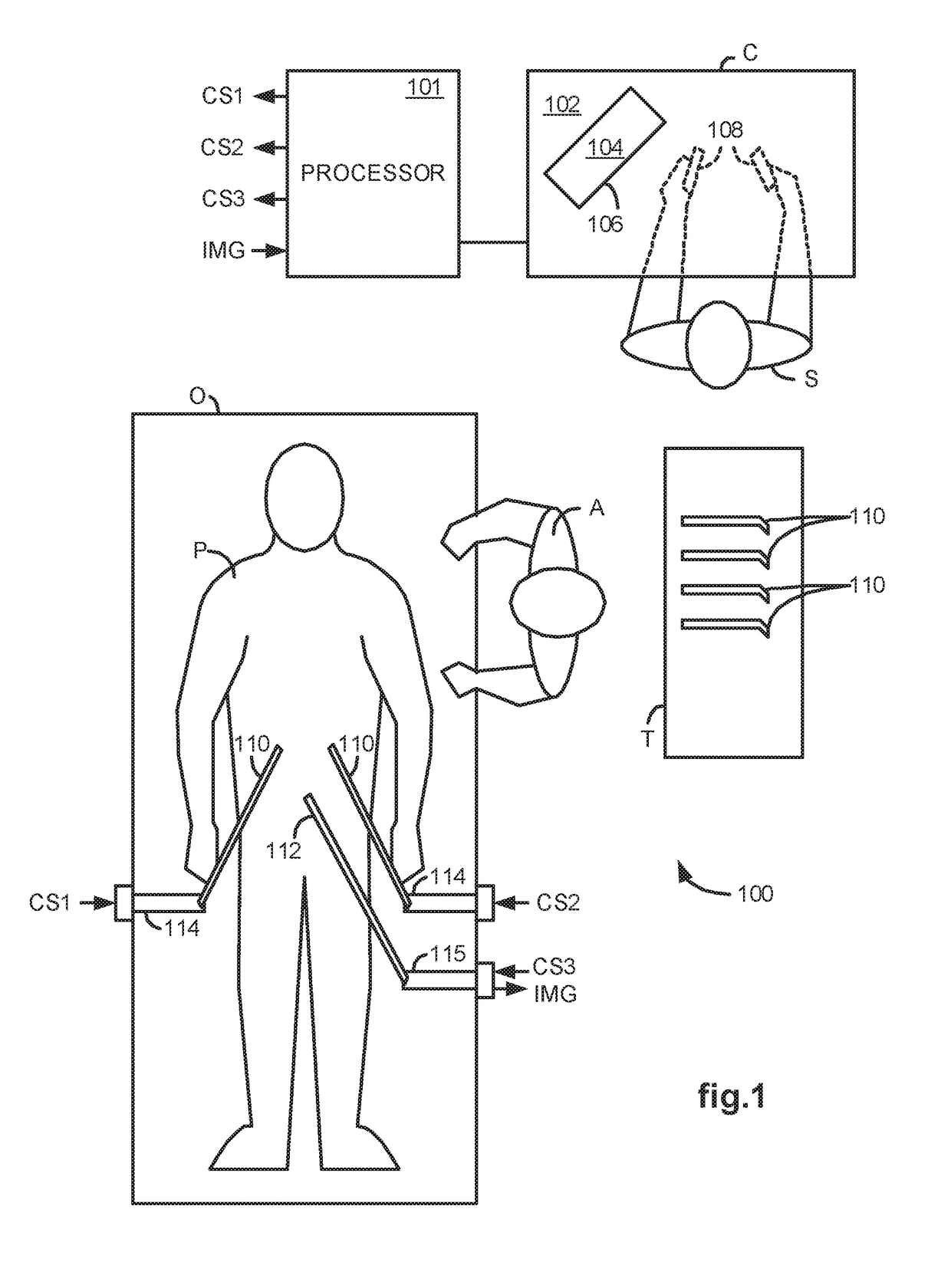
Methods and system perform tool tracking during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Tool states are determined using triangulation techniques or a Bayesian filter from either or both non-endoscopically derived and endoscopically derived tool state information, or from either or both non-visually derived and visually derived tool state information. The non-endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from sensor data provided either by sensors associated with a mechanism for manipulating the tool, or sensors capable of detecting identifiable signals emanating or reflecting from the tool and indicative of its position, or external cameras viewing an end of the tool extending out of the body. The endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from image data provided by an endoscope inserted in the body so as to view the tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
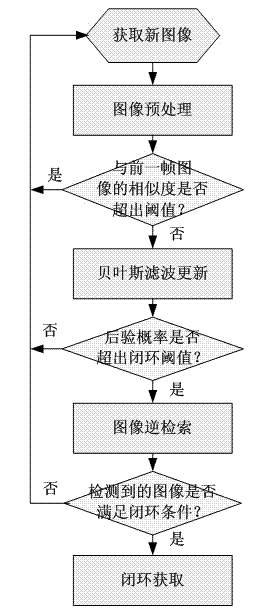
Image appearance based loop closure detecting method in monocular vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping)
InactiveCN102831446AReduce the amount of calculationLower requirementCharacter and pattern recognitionPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingVisual perception
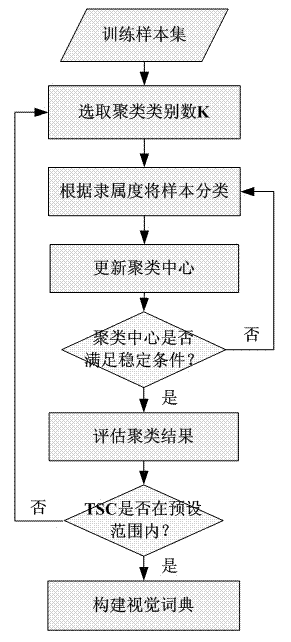
The invention discloses an image appearance based loop closure detecting method in monocular vision SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping). The image appearance based loop closure detecting method includes acquiring images of the current scene by a monocular camera carried by a mobile robot during advancing, and extracting characteristics of bag of visual words of the images of the current scene; preprocessing the images by details of measuring similarities of the images according to inner products of image weight vectors and rejecting the current image highly similar to a previous history image; updating posterior probability in a loop closure hypothetical state by a Bayesian filter process to carry out loop closure detection so as to judge whether the current image is subjected to loop closure or not; and verifying loop closure detection results obtained in the previous step by an image reverse retrieval process. Further, in a process of establishing a visual dictionary, the quantity of clustering categories is regulated dynamically according to TSC (tightness and separation criterion) values which serve as an evaluation criterion for clustering results. Compared with the prior art, the loop closure detecting method has the advantages of high instantaneity and detection precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Methods and System for Performing 3-D Tool Tracking by Fusion of Sensor and/or Camera Derived Data During Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
ActiveUS20170079725A1Easy to distinguishFacilitate communicationSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesTriangulationExternal camera
Methods and system perform tool tracking during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Tool states are determined using triangulation techniques or a Bayesian filter from either or both non-endoscopically derived and endoscopically derived tool state information, or from either or both non-visually derived and visually derived tool state information. The non-endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from sensor data provided either by sensors associated with a mechanism for manipulating the tool, or sensors capable of detecting identifiable signals emanating or reflecting from the tool and indicative of its position, or external cameras viewing an end of the tool extending out of the body. The endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from image data provided by an endoscope inserted in the body so as to view the tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
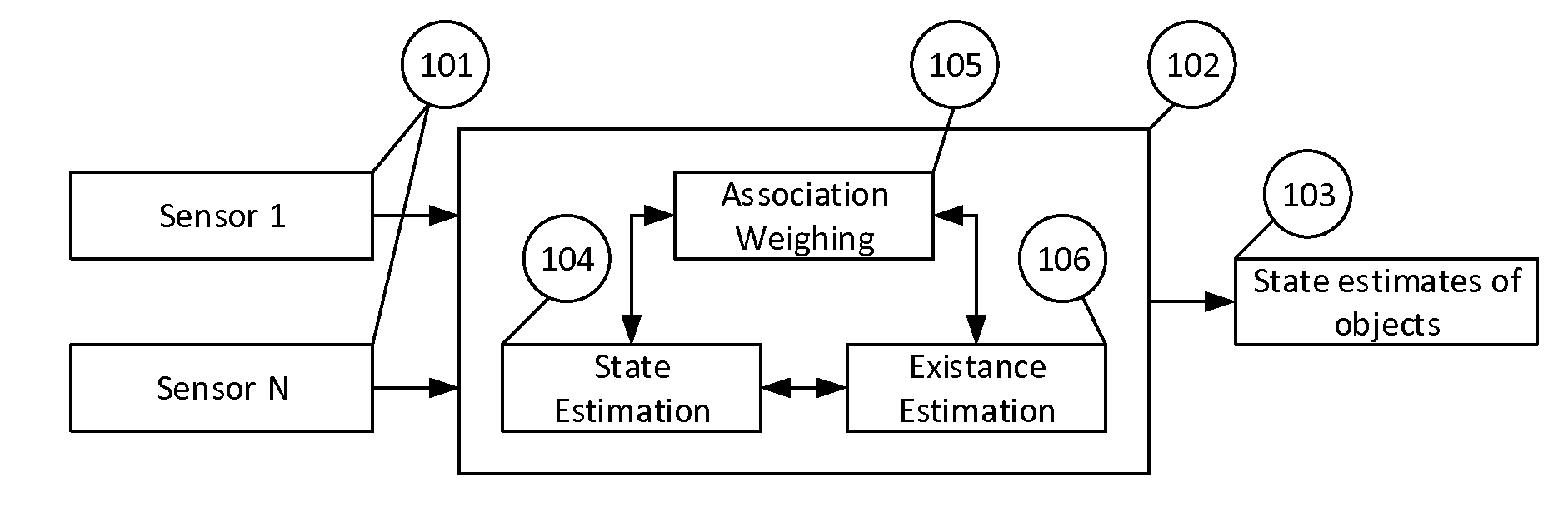
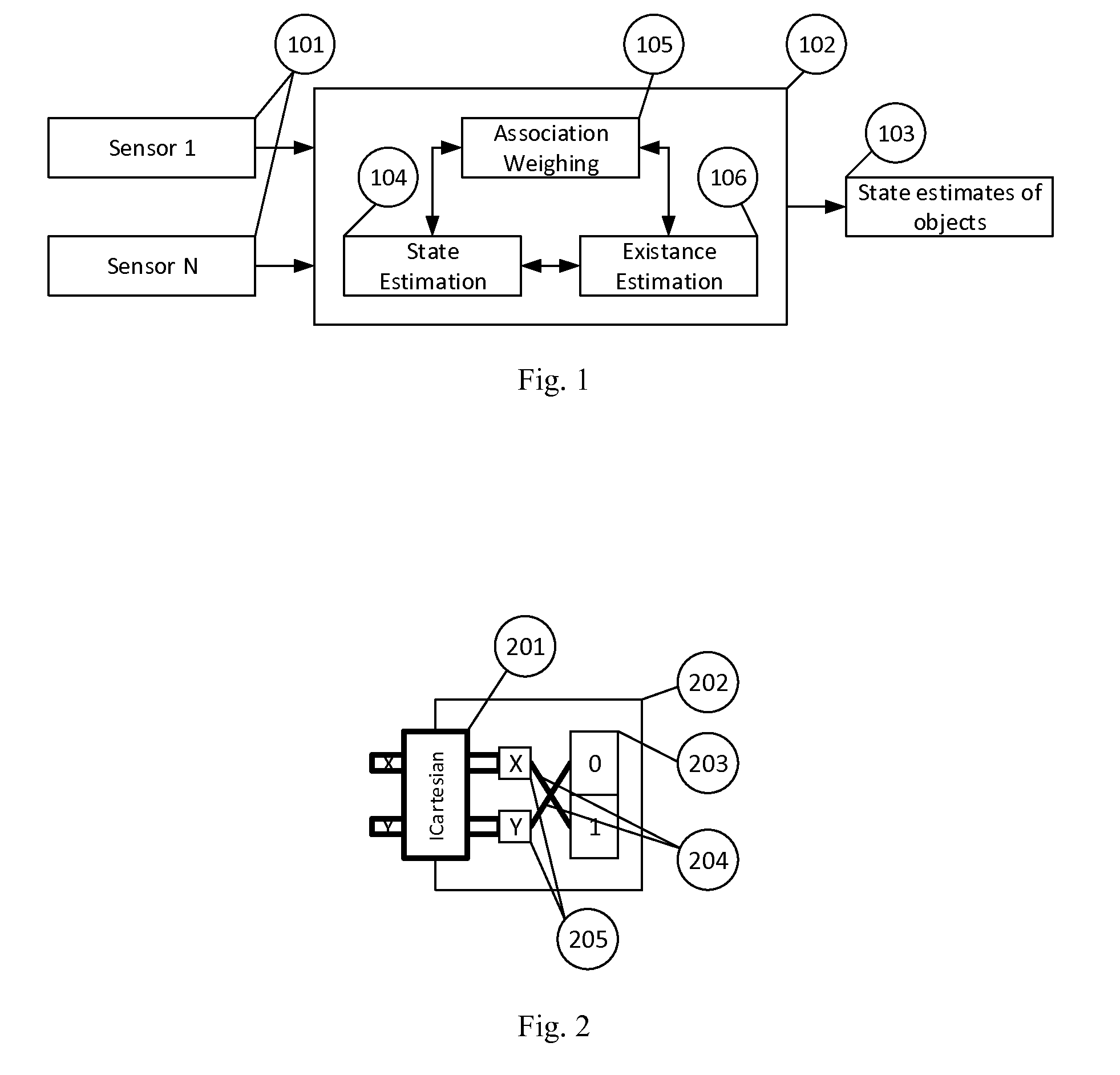
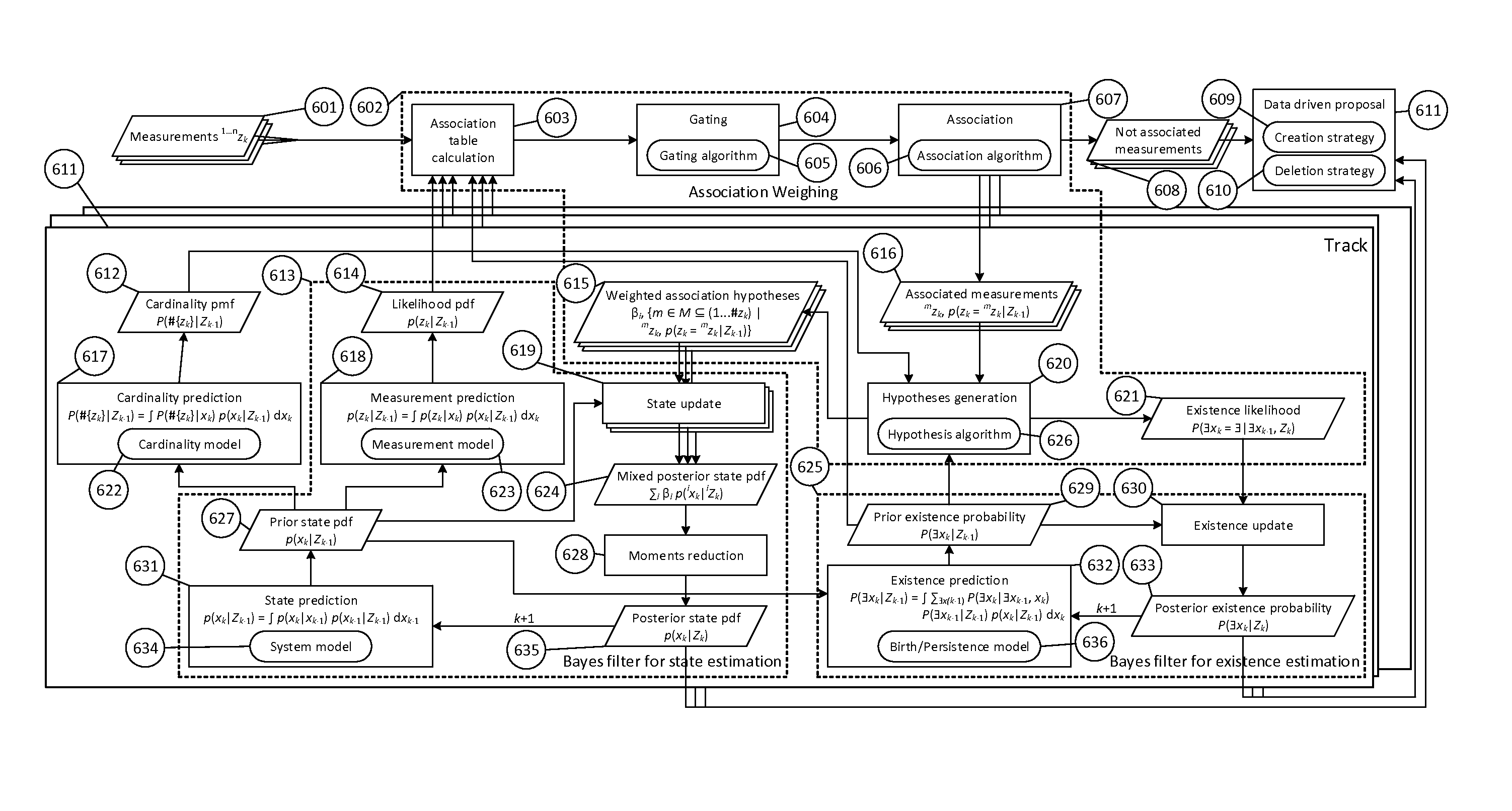
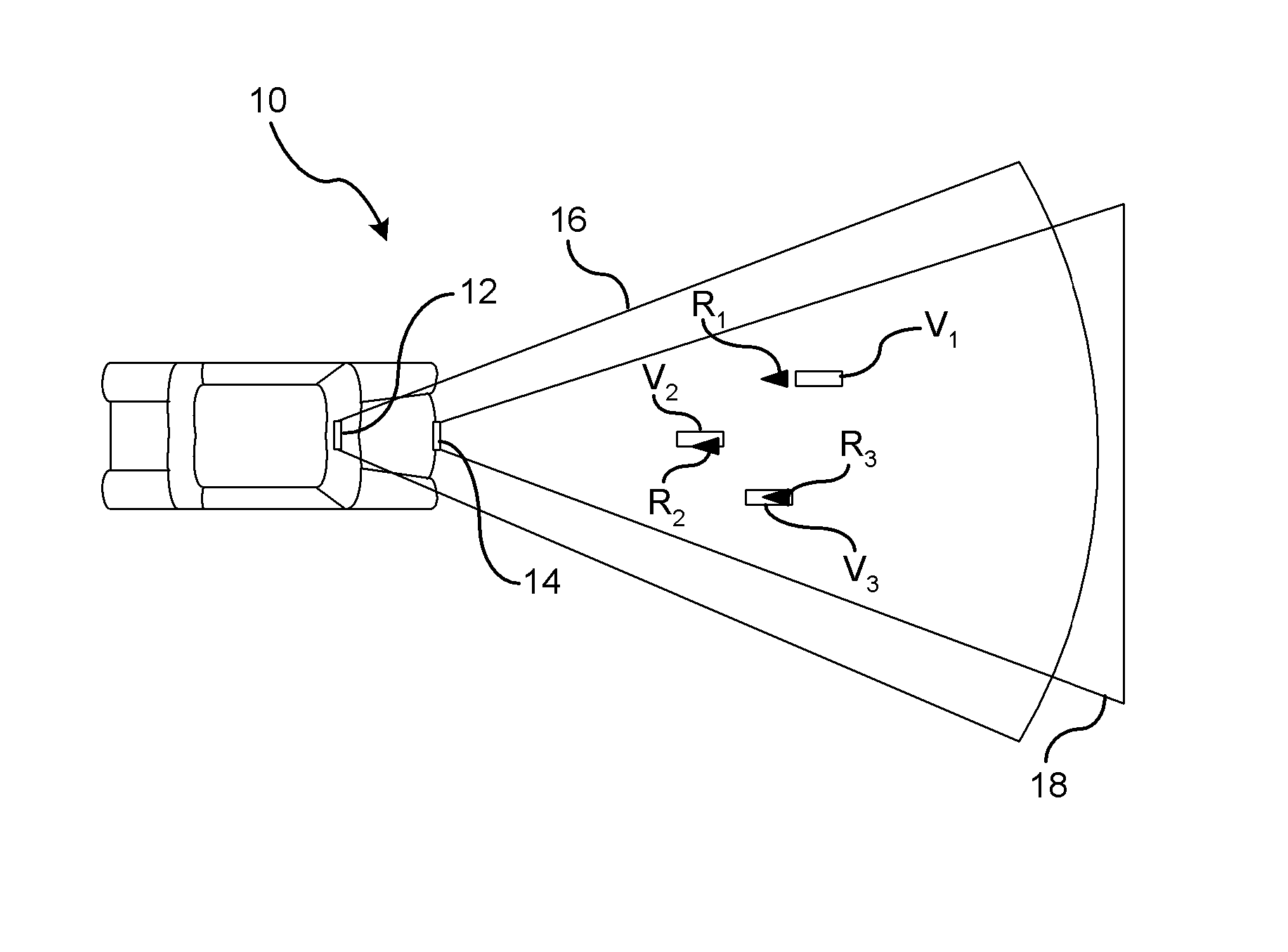
Method and apparatus for the tracking of multiple objects
ActiveUS20140324339A1Simple designNavigation instrumentsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer scienceBayesian filtering
Tracking systems using multi-object-tracking (MOT) combine data from a plurality of sensors (101) to derive a state estimate of one or more objects (103) are described. The interfaces to the sensors (101) are such that different ones of the sensors (101) can be used. The tracking (102) in the system consists of different blocks for state estimation (104), object's existence estimation (106), and data association (105). To utilize the data of a sensor, the sensor data and the system which is observed is modeled using the Bayesian filtering framework. All interfaces of the system, i.e. the interfaces between the sensors (101) and the MOT system as well as of the blocks in the MOT are of a characteristic that ensures that only compatible models are used with each other already when designing the system
Owner:BASELABS
Methods and System for Performing 3-D Tool Tracking by Fusion of Sensor and/or Camera Derived Data During Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
ActiveUS20170079726A1Easy to distinguishFacilitate communicationSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesTriangulationExternal camera
Methods and system perform tool tracking during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Tool states are determined using triangulation techniques or a Bayesian filter from either or both non-endoscopically derived and endoscopically derived tool state information, or from either or both non-visually derived and visually derived tool state information. The non-endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from sensor data provided either by sensors associated with a mechanism for manipulating the tool, or sensors capable of detecting identifiable signals emanating or reflecting from the tool and indicative of its position, or external cameras viewing an end of the tool extending out of the body. The endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from image data provided by an endoscope inserted in the body so as to view the tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
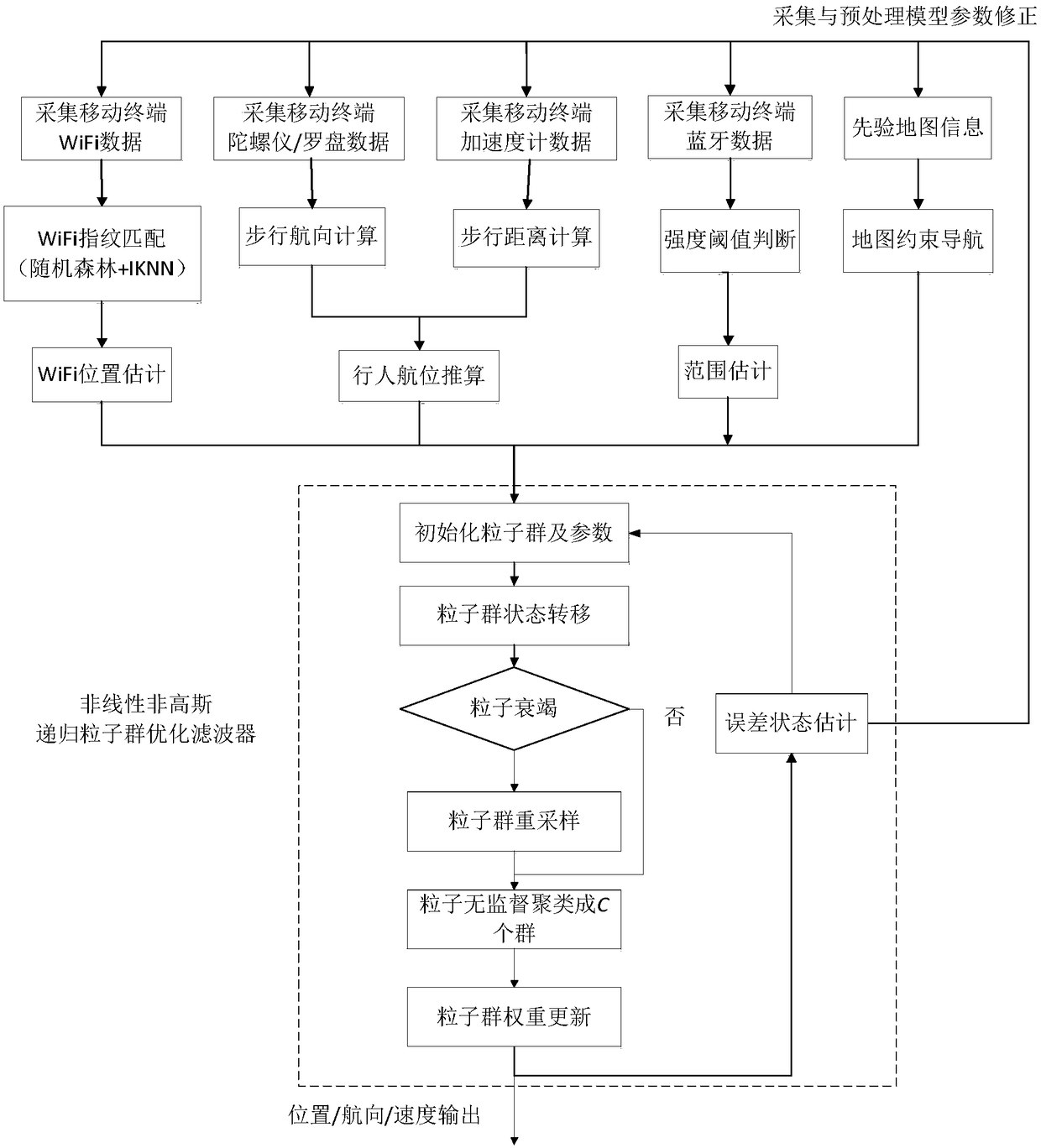
Method for estimating indoor pedestrian combination poses based on multi-particle swarm optimized
ActiveCN109298389ASuppress cumulative errorSmall amount of calculationPosition fixationPattern recognitionComputer vision
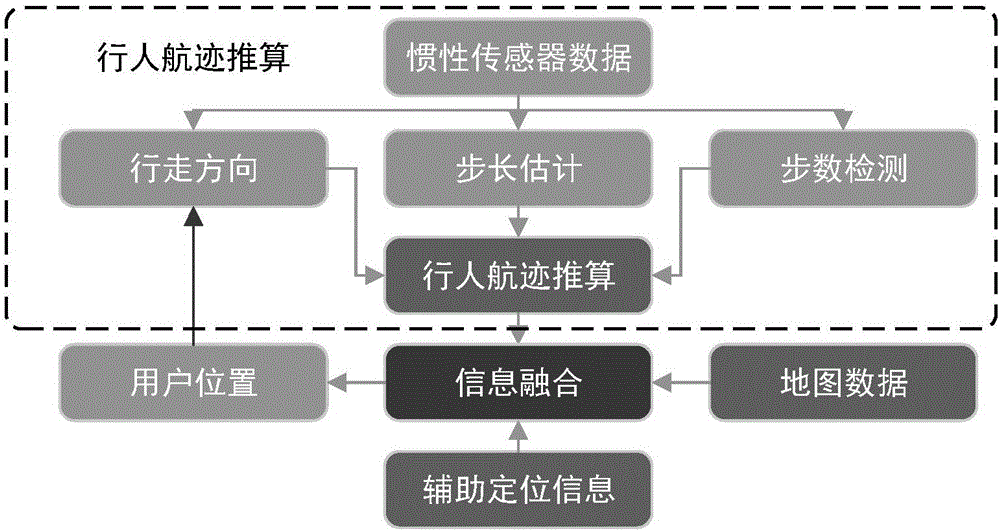
The invention discloses a method for estimating indoor pedestrian combination poses based on a multi-particle swarm optimized. The method comprises the following steps of: using a WiFi-RSS fingerprintidentification method to obtain a WiFi positioning result; using a micro-inertial sensor pedestrian trajectory reckoning method to obtain a pedestrian poses result; using a Bluetooth signal strengthconstraint method to constrain the pedestrian movement range to determine whether the pedestrian is within the communication range of nodes; using a map matching method of the indoor map to constrainthe WiFi positioning result and a pedestrian track reckoning result; using a multi-particle swarm recursive Bayesian filtering method to perform nonlinear non-Gaussian data fusion on the WiFi positioning result, the pedestrian poses result, the pedestrian movement range constraint result, and the map matching method result; finally, obtaining the pedestrian position poses information. According tothe method for estimating the indoor pedestrian combination poses based on the multi-particle swarm optimized, the multi-source information of WiFi-RSS fingerprint, PDR, and MM is fused, and gross and cumulative errors of a filter are eliminated by using the Bluetooth information. The multi-source information fusion is used to optimize the weight and distribution of the particle swarm to improvethe accuracy, reliability, and real-time capability of the indoor pedestrian poses estimation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
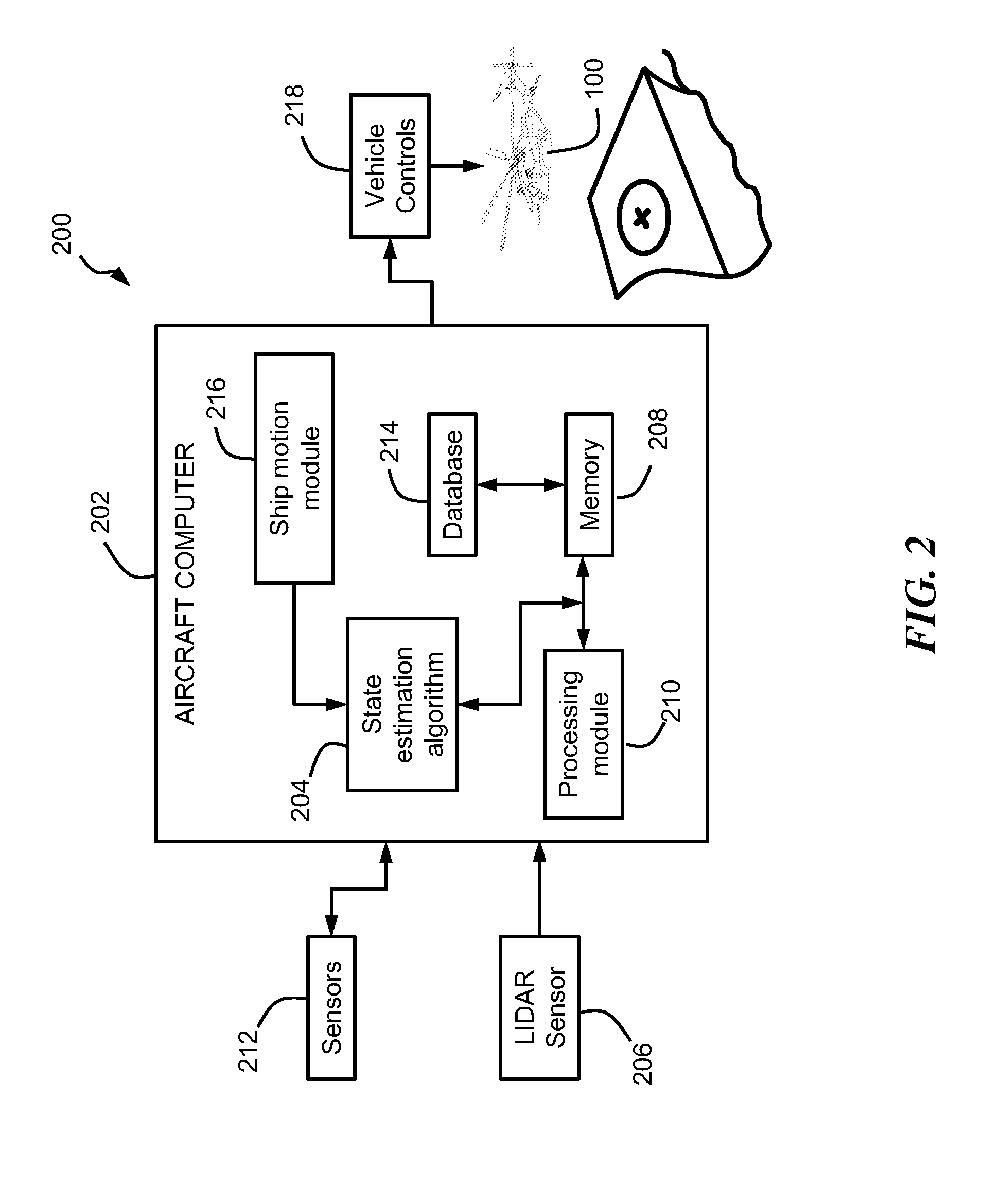
Lidar-based shipboard tracking and state estimation for autonomous landing
ActiveUS20160009410A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAircraft landing aidsElevation angleVertical plane
A system and method for state estimation of a surface of a platform at sea, includes receiving sensor signals indicative of LIDAR data for the platform; applying a Bayesian filter to the LIDAR data for a plurality of hypotheses; determining vertical planes representing azimuth and elevation angles for the LIDAR data; applying a robust linear estimation algorithm to the vertical planes; and determining candidate points in response to the applying of the robust linear estimation algorithm.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
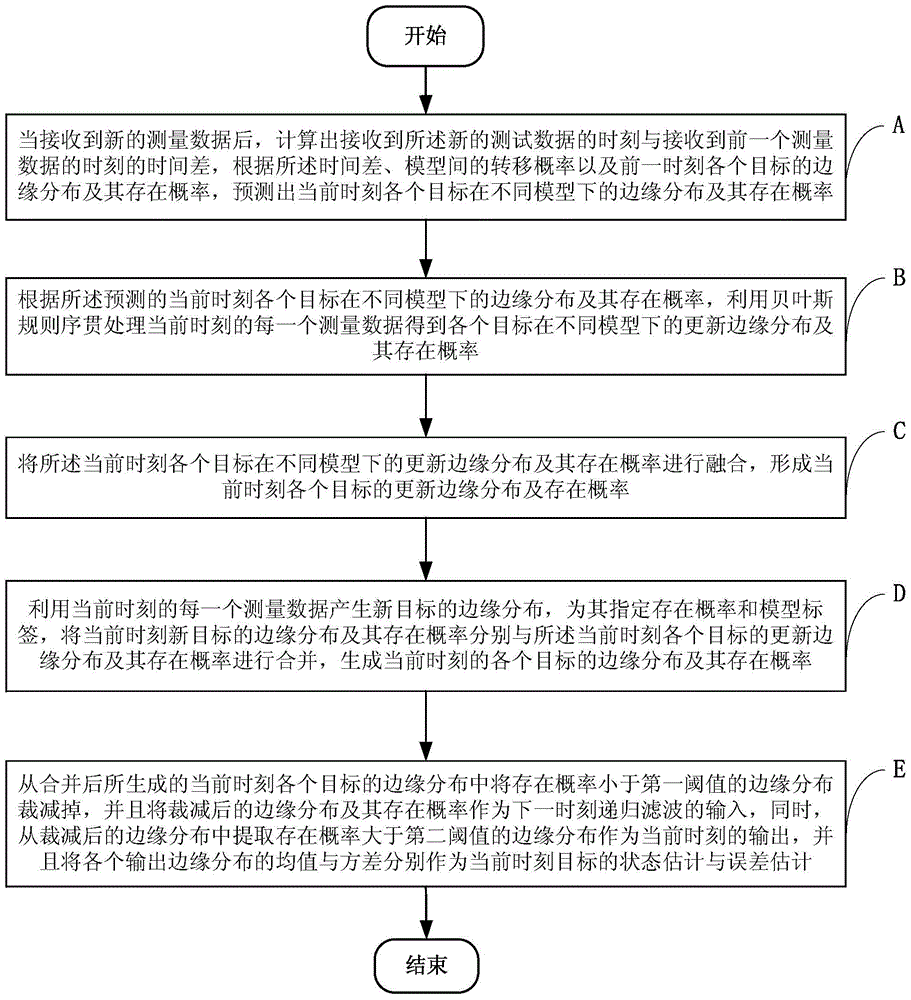
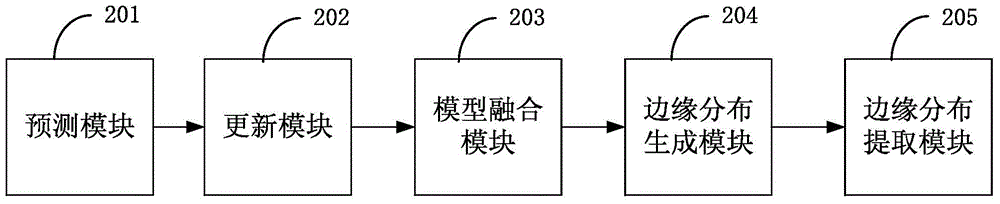
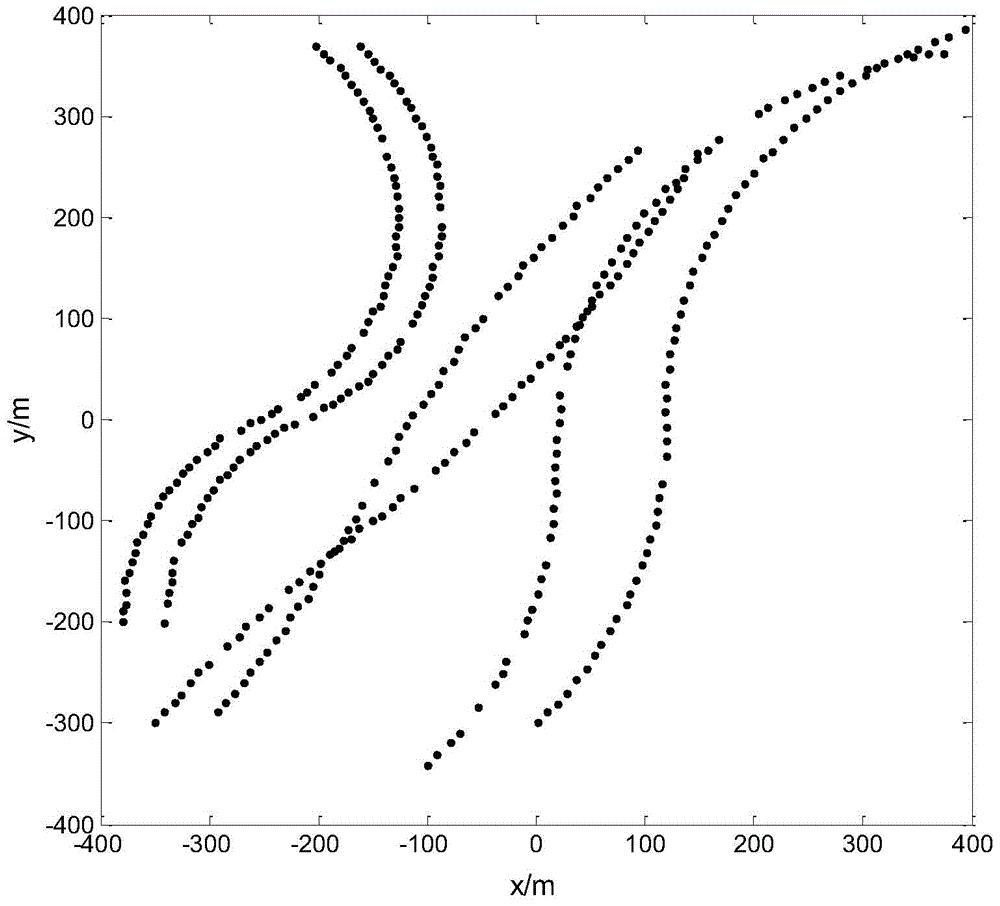
Multi-target tracking method and tracking system based on sequential Bayes filtering
InactiveCN105719312AGuaranteed real-timeSolving the Tracking Problem of Multiple Maneuvering TargetsImage analysisMulti target trackingComputer science
The invention relates to multi-sensor information fusion technology, and provides a multi-target tracking method based on sequential Bayes filtering. The tracking method comprises steps of predicting edge distribution of all targets in different models and existence probability thereof; according to the predicted edge distribution and the existence probability thereof, using the Bayes principle for processing so as to obtain updated edge distribution and existence probability thereof; fusing the updated edge distribution and the existence probability thereof so as to form updated edge distribution and existence probability thereof at present; combining the edge distribution and existence probability thereof of a new target with the updated edge distribution and the existence probability thereof so as to generate edge distribution and the existence probability thereof at preset; and cutting the edge distribution whose existence probability is smaller than a first threshold, and existing and outputting the edge distribution whose existence probability is larger than a second threshold value. In this way, real-time performance of data processing is ensured and a tracking problem for a multi-maneuvering object whose moving modes are transformed among different models is effectively solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
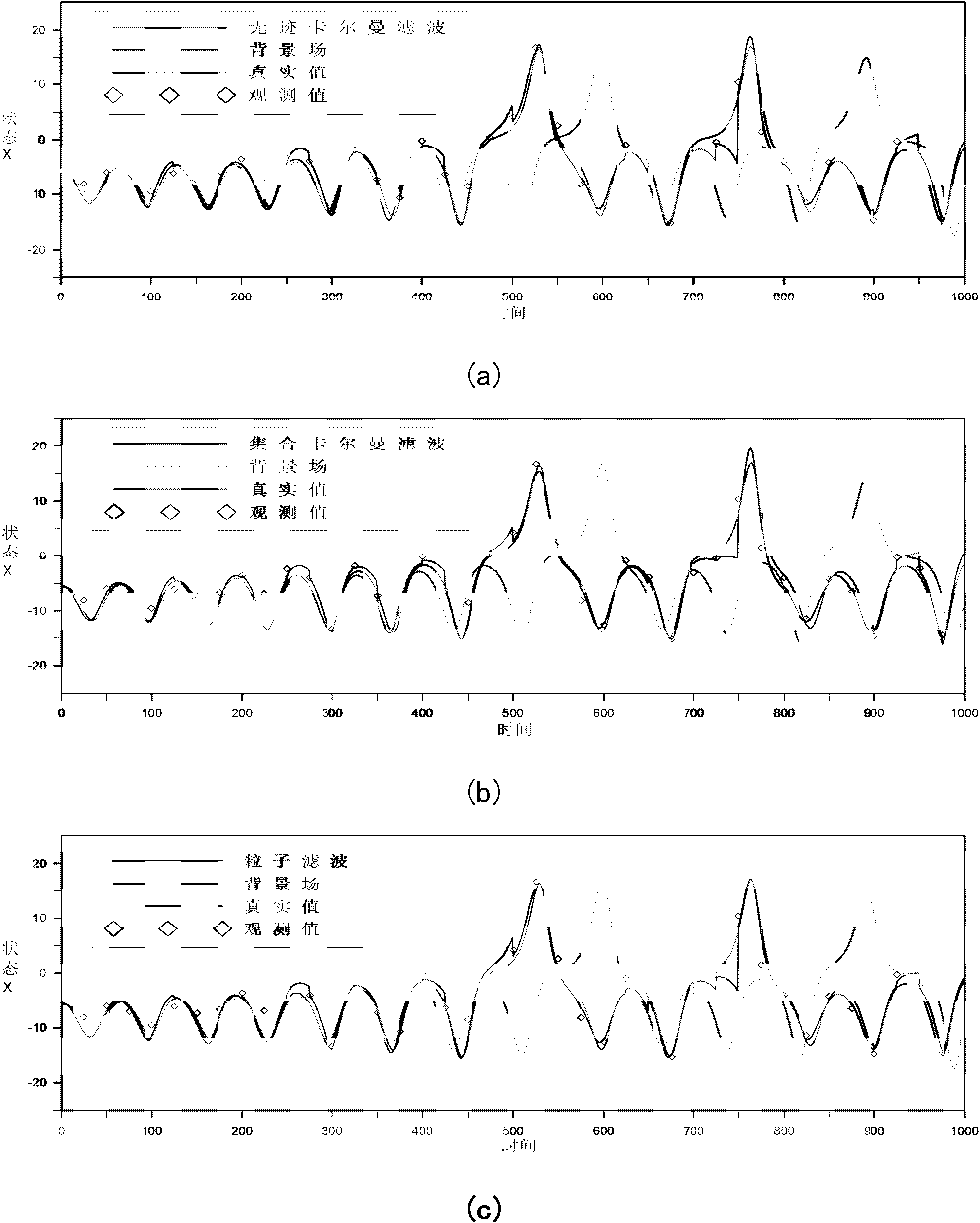
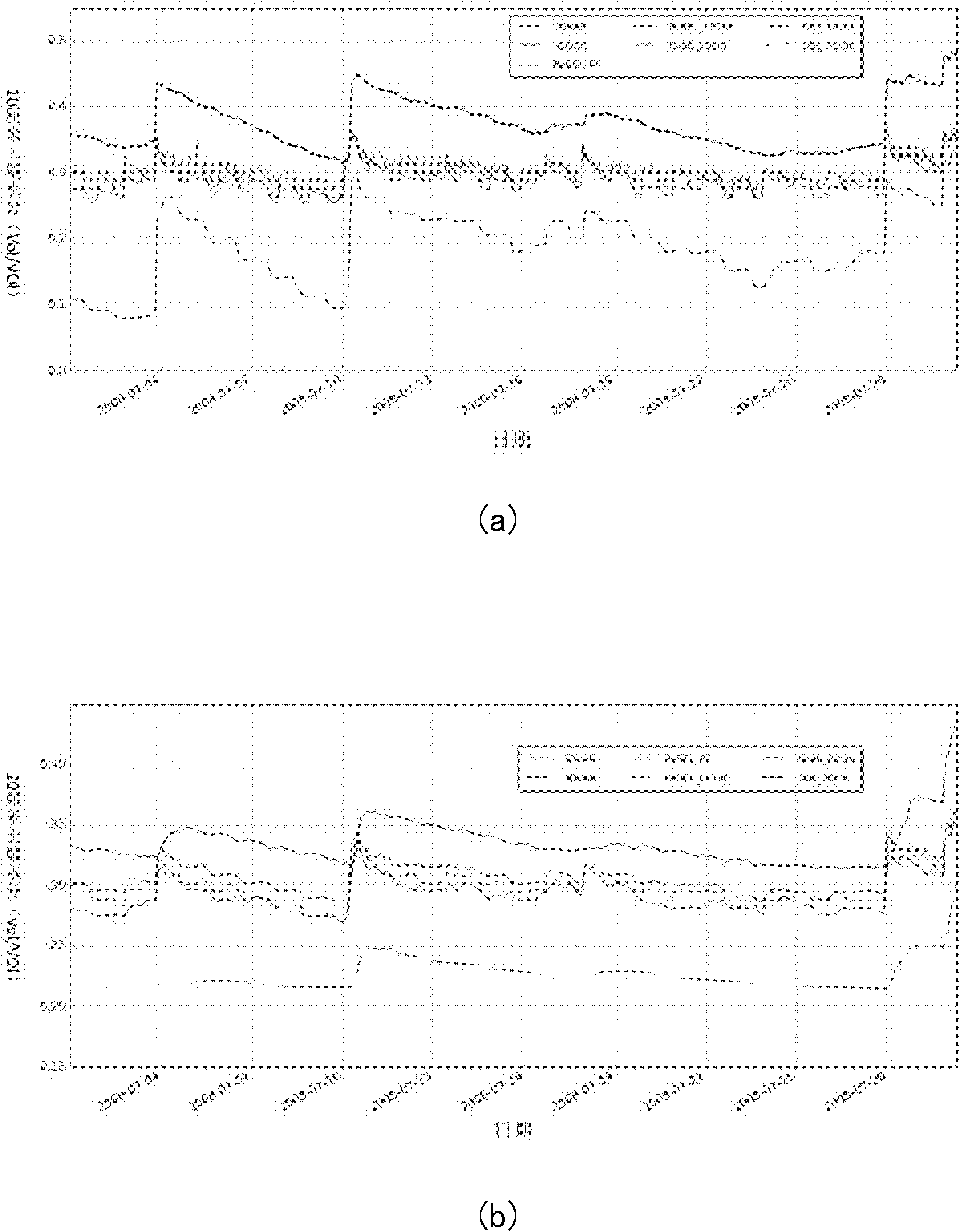
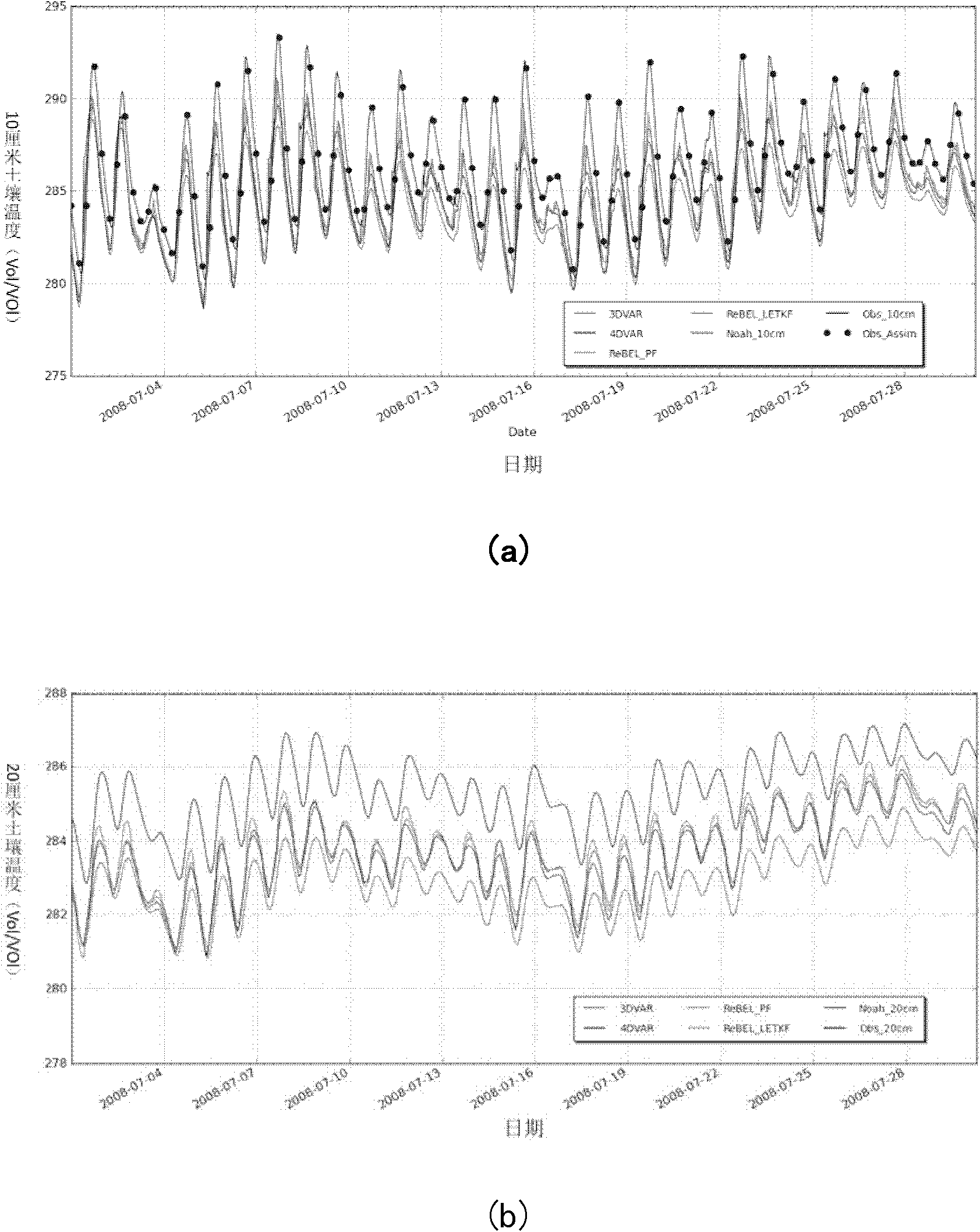
Bayesian fitering-based general data assimilation method
InactiveCN102737155AFast operationSimulator controlSpecial data processing applicationsValue setProcess information
The invention discloses a bayesian fitering-based general data assimilation method. The method comprises the steps of: inputting an initial value set into an analysis model in a prediction step so as to obtain a prediction set value; calculating prediction error covariance matrix by using set kalman filtering in an updating step, and updating each prediction set according to the observation value and kalman gain matrix; or, calculating importance weight of each set sample by adopting particle filtering through set prediction value, calculating the number of effective particles by utilizing normalization importance, resampling the set according to the weight to obtain updated analysis value and analysis set; or, calculating prediction error covariance matrix by adopting unscented kalman filtering, and updating each prediction set according to the observation value and kalman gain matrix; conducting next prediction and assimilation by taking the updated analysis set as the initial values of the analysis model, and repeating the prediction step and the updating step. The method can enable Earth remote-sensing observation information and land surface process model information to be effectively integrated, thus forming a land surface process information prediction system with small errors.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
Position localization using visible light communication
Visible-light communication (VLC) is an optical wireless communication technique that uses light emitting diodes (LEDs) or other optical sources to transmit information to a user equipment (UE) device. An optically-based location determination approach, such as using VLC infrastructure, can meet a desire for location-based services where use of VLC can provide a solution to an indoor localization or navigation problem. A fingerprinting approach can include use of an optical received signal strength (RSS) or other information (e.g., an image of a scene) to generate a spatial fingerprint map of an area. A later-received RSS on the UE device and the prior-generated fingerprint map representative of RSS can be received, and a fingerprint map and RSS observations can be provided as inputs to a Bayesian filter, such as an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) or a Particle Filter, to provide an estimated position for the UE device.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Indoor positioning method and positioning device based on multi-source information fusion
ActiveCN106412826ALess susceptible to interferenceLow costWireless commuication servicesLocation information based serviceComputer sciencePedestrian
The invention discloses an indoor positioning method and positioning device based on multi-source information fusion. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring information map information, dispersing the indoor map information as a plurality of uniform lattice points to obtain the latticed indoor map information, and establishing connectivity among the dispersed lattice points; acquiring pedestrian track plotting information obtained by a mobile terminal based on user walking so as to obtain change information with the probability on the plurality of uniform lattice points according to the indoor map information and the pedestrian track plotting information; and acquiring assistant positioning information to modify the probability on different lattice points, and then fusing the latticed indoor map information, the pedestrian track plotting information and the assistant positioning information through the Bayesian filtering to finish the indoor positioning. Through the adoption of the positioning method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the indoor map information, the pedestrian track plotting information and the assistant positioning information can be fused to realize the aim of high-precision indoor positioning; not only is the positioning precision improved, but also the positioning efficiency is improved; and the positioning is simple and easy to realize.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
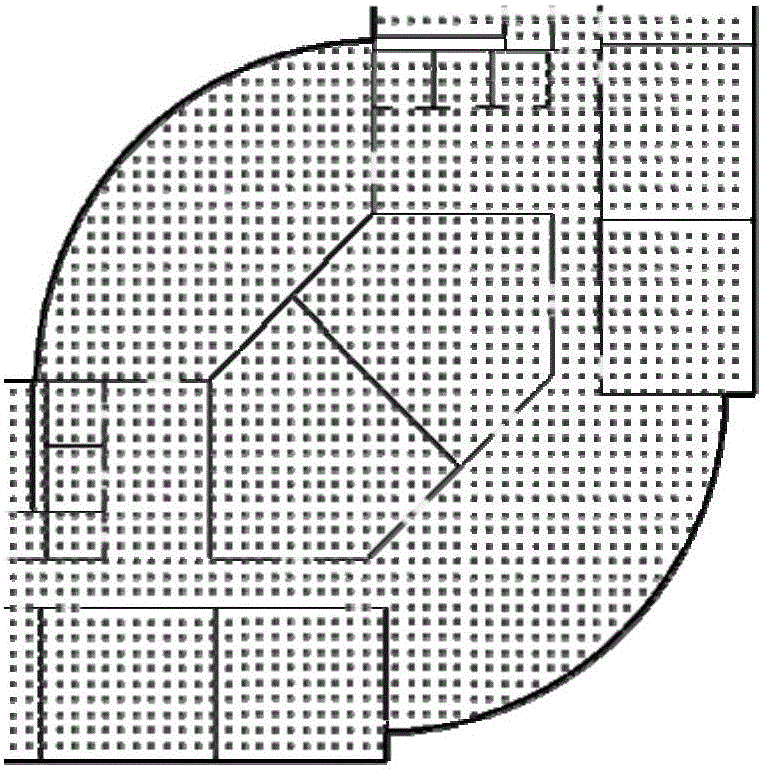
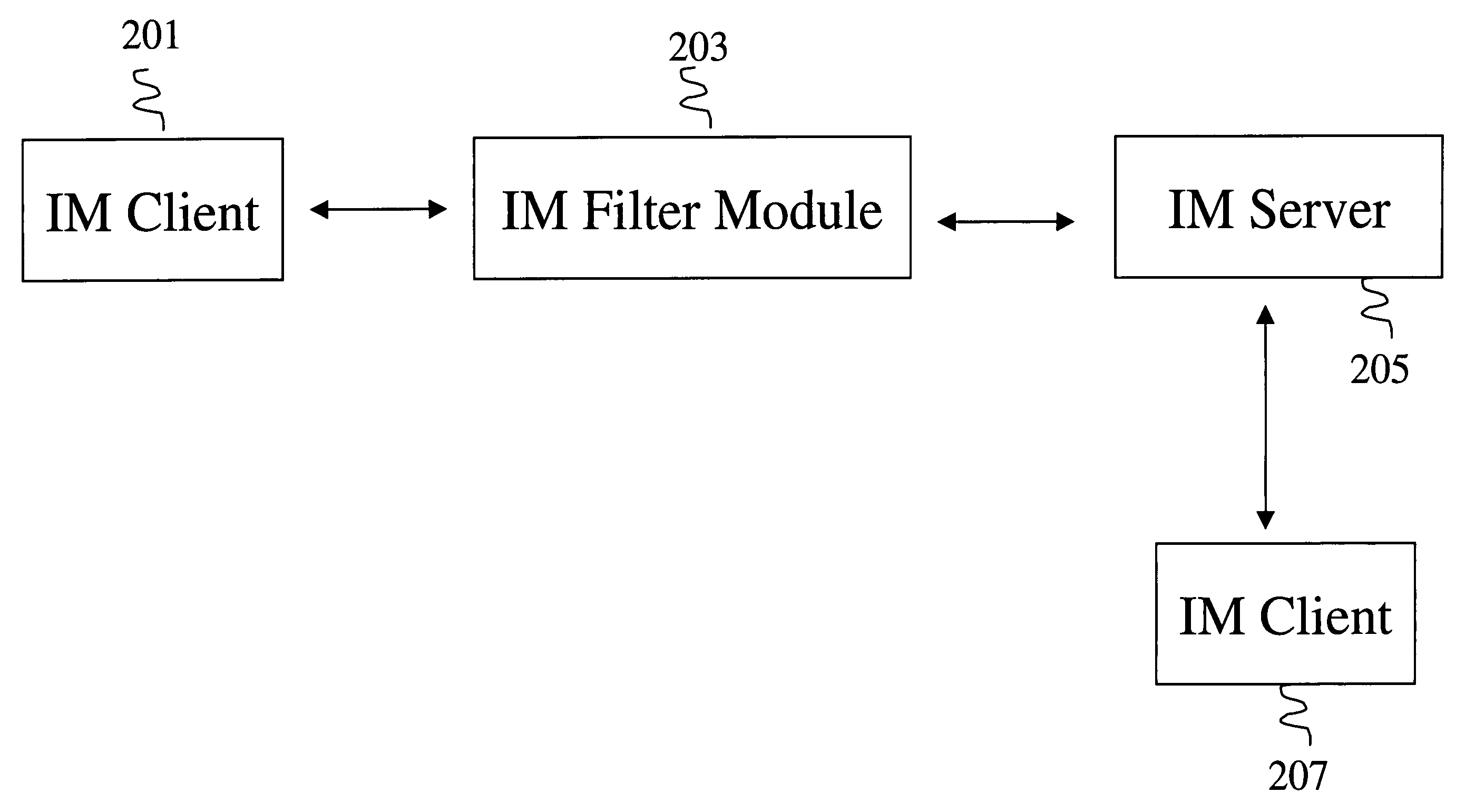
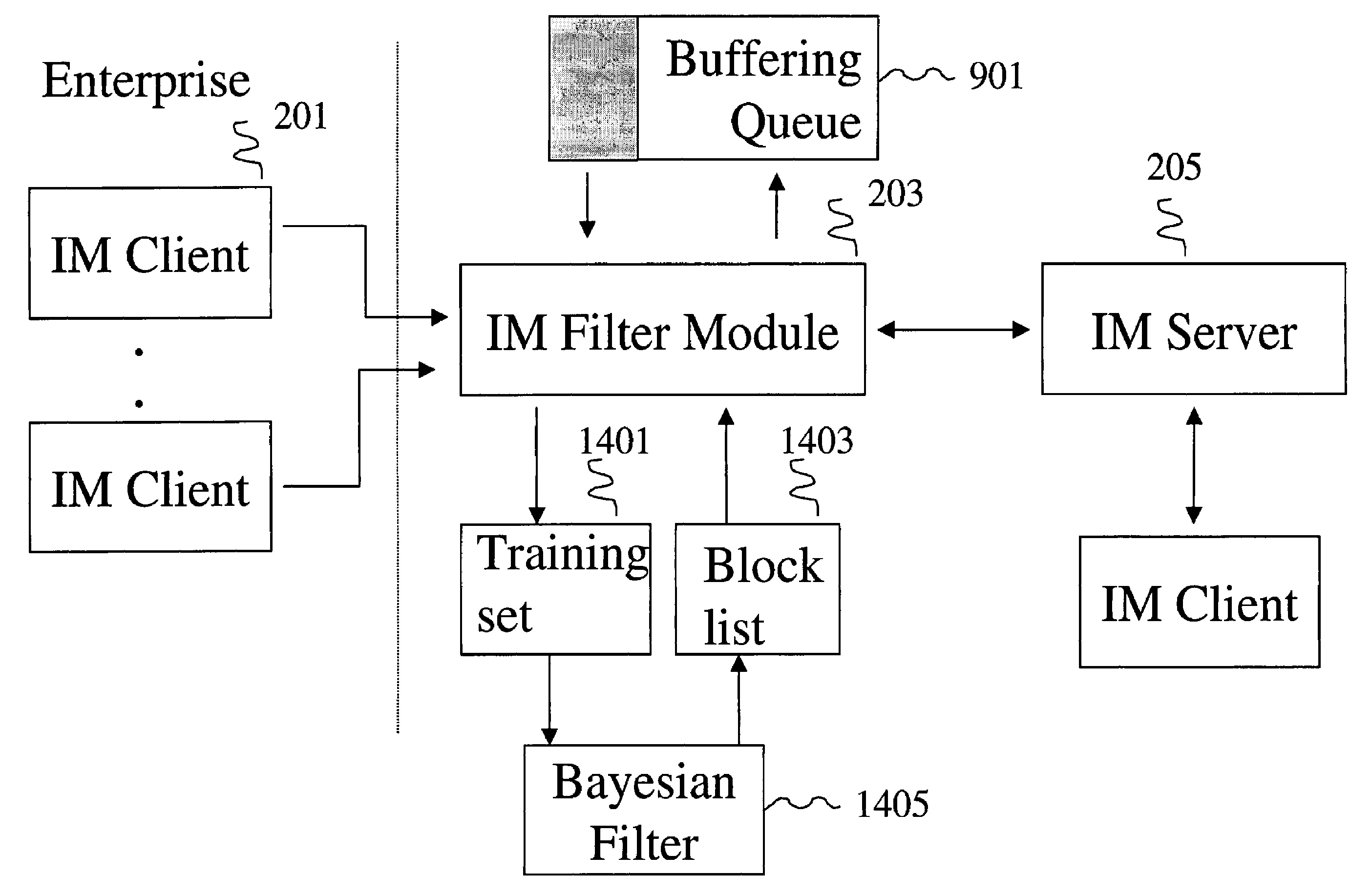
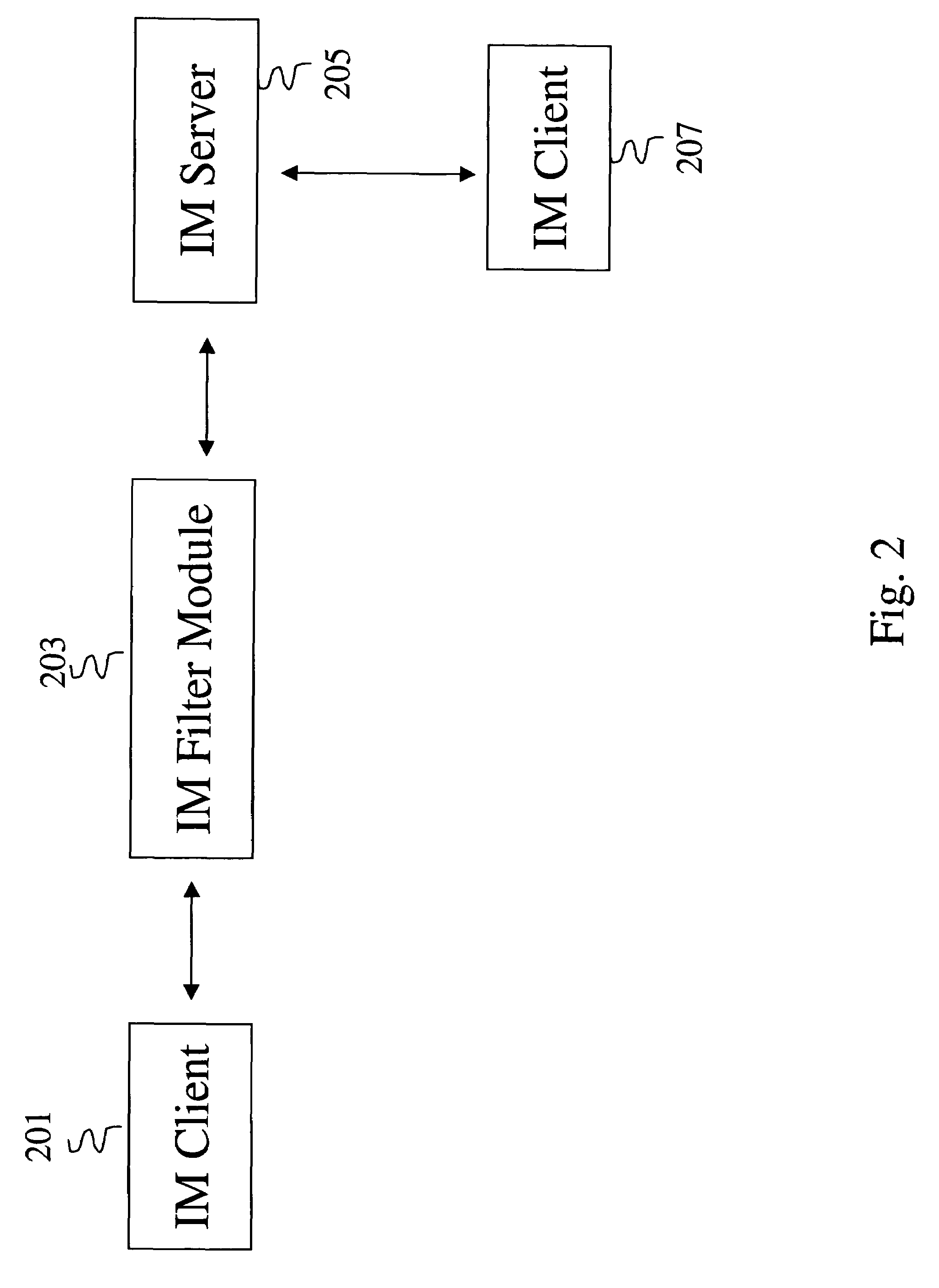
Methods and systems for detecting and preventing the spread of malware on instant messaging (IM) networks by using Bayesian filtering
InactiveUS20070006026A1Avoid spreadingMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionMalwareClient-side
Methods and systems for reducing the spread of malware in communication between an instant message (IM) client and an IM server are described. An IM filter module (IM FM) is configured to analyze messages exchanged between an IM server and an IM client. The IM FM also identifies one or more messages as possibly containing malware among the exchanged messages and assigns a confidence level to each identified message. A confidence level represents a probability of a message containing malware. A Bayesian filter is configured to train itself using the identified messages and the confidence levels and adjust the confidence levels. A feedback training mechanism for the Bayesian filter is also included. In particular, the IM FM examines additional messages exchanged between the IM server and IM client, identifies one or more messages as possibly containing malware among the additional messages using the adjusted confidence values. The IM FM also assigns a confidence level to each additionally identified message. The Bayesian filter is further configured to re-train itself using the identified messages, the additionally identified messages, and the confidence levels and adjust the confidence levels.
Owner:CA TECH INC
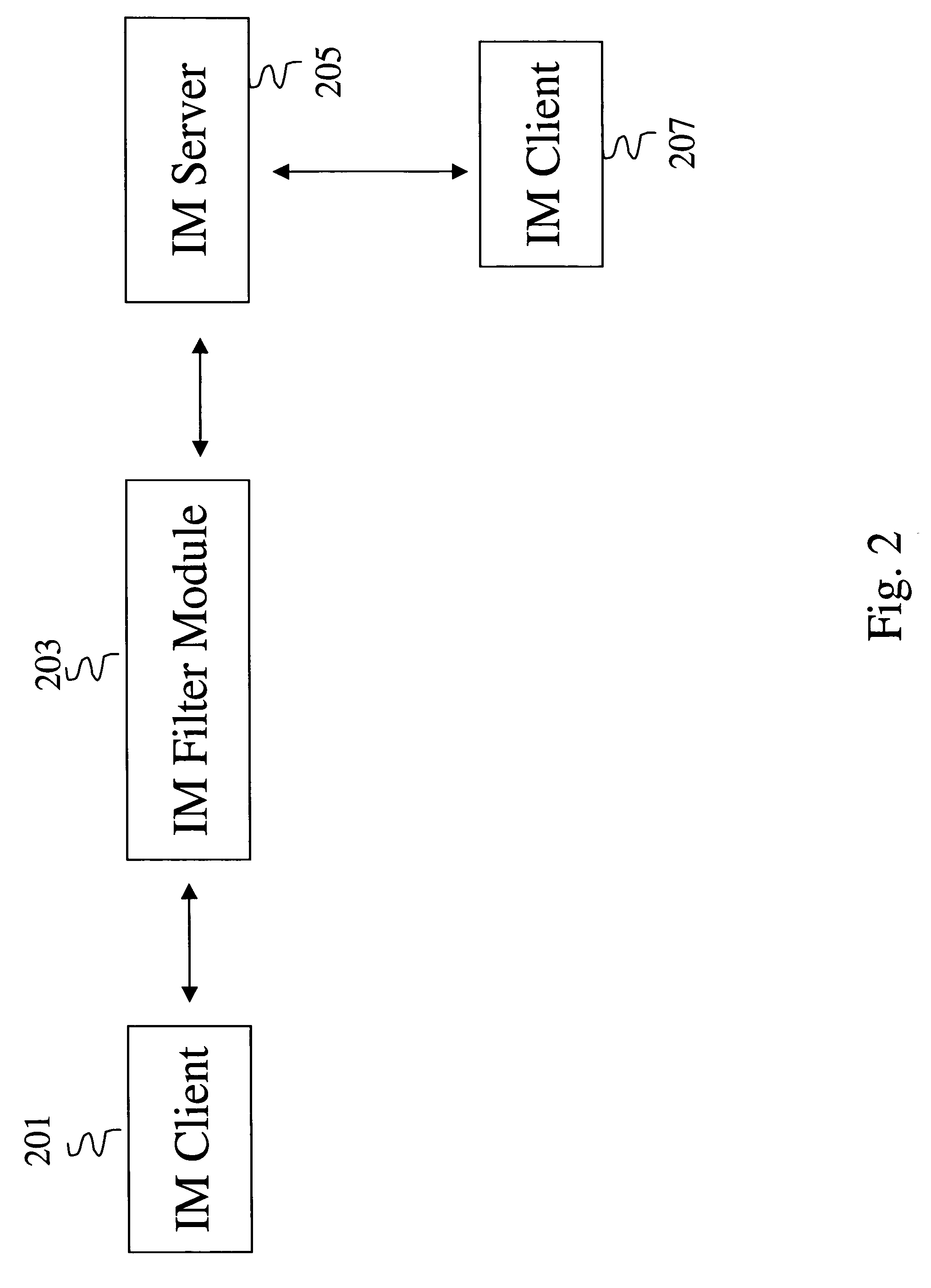
System and method for intrusion decision-making in autonomic computing environments
InactiveUS20050278178A1Recognize disadvantageSpeech analysisComputer security arrangementsData miningSecurity policy
A mechanism is provided for performing intrusion decision-making using a plurality of approaches. Detection approaches may include, for example, signature-based, anomaly-based, scan-based, and danger theory approaches. When event information is received, each approach produces a result. A consensus of each result is then reached by using, for example, Bayesian Filtering. A corpus is kept for each approach. An intrusion corpus keeps combinations of the corpora for all of the approaches that constitute intrusions. A safe corpus keeps combinations of the corpora for all of the approaches that do not constitute an intrusion. The corpora for the approaches may be pre-defined according to security policies and the like. The intrusion corpus and the safe corpus may be trained using scores that are determined using the detection approaches.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for the tracking of multiple objects
ActiveUS8954272B2Navigation instrumentsFuzzy logic based systemsMulti target trackingComputer science
Owner:BASELABS
Automatic tracking method for video frequency microscopic image cell
InactiveCN101144784AImage enhancementMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscopic imageDynamic models
The invention relates to an automatic cell tracking method for a video microscope image. The existing tracking method has lower degree of automation, and can not adapt to the complex polytropism of the cell movement form and the multi-cell movement tracking. The invention comprises the steps that the abstained video microscope image of the cell movement is enhanced frame by frame; and a target cell is extracted form the enhanced cell movement image to establish the dynamic model of the cell movement for tracking moving target cell. On the basis of analyzing the characteristics of the cell movement and the noise and interference characteristics in the image, the invention adopts the method of dynamic system modeling and stochastic modeling, and through recursing Bayesian filtering and the data connectivity technology, to track the movement trajectory of the cell, and thereby, the automation degree is high, as well as the processing capability is strong.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Enhanced data association of fusion using weighted bayesian filtering
ActiveUS20130236047A1Great confidenceRobust and accurate associationScene recognitionImage acquisitionField of viewMachine learning
A method of associating targets from at least two object detection systems. An initial prior correspondence matrix is generated based on prior target data from a first object detection system and a second object detection system. Targets are identified in a first field-of-view of the first object detection system based on a current time step. Targets are identified in a second field-of-view of the second object detection system based on the current time step. The prior correspondence matrix is adjusted based on respective targets entering and leaving the respective fields-of-view. A posterior correspondence matrix is generated as a function of the adjusted prior correspondence matrix. A correspondence is identified in the posterior correspondence matrix between a respective target of the first object detection system and a respective target of the second object detection system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Density morphing and mode propagation for Bayesian filtering
ActiveUS20050038638A1Reduce in quantityGenerate numberSimulator controlCharacter and pattern recognitionMorphingState model
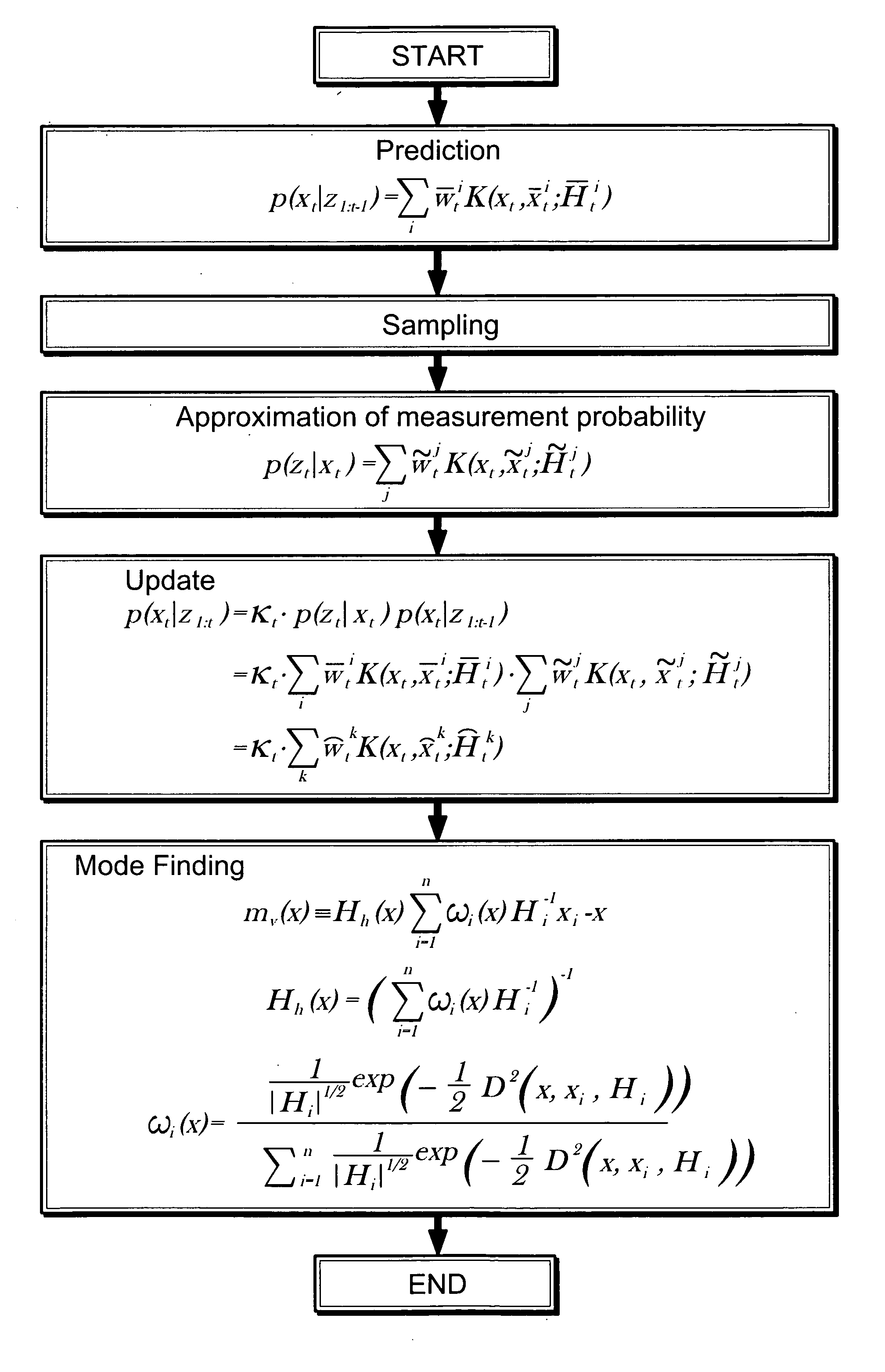
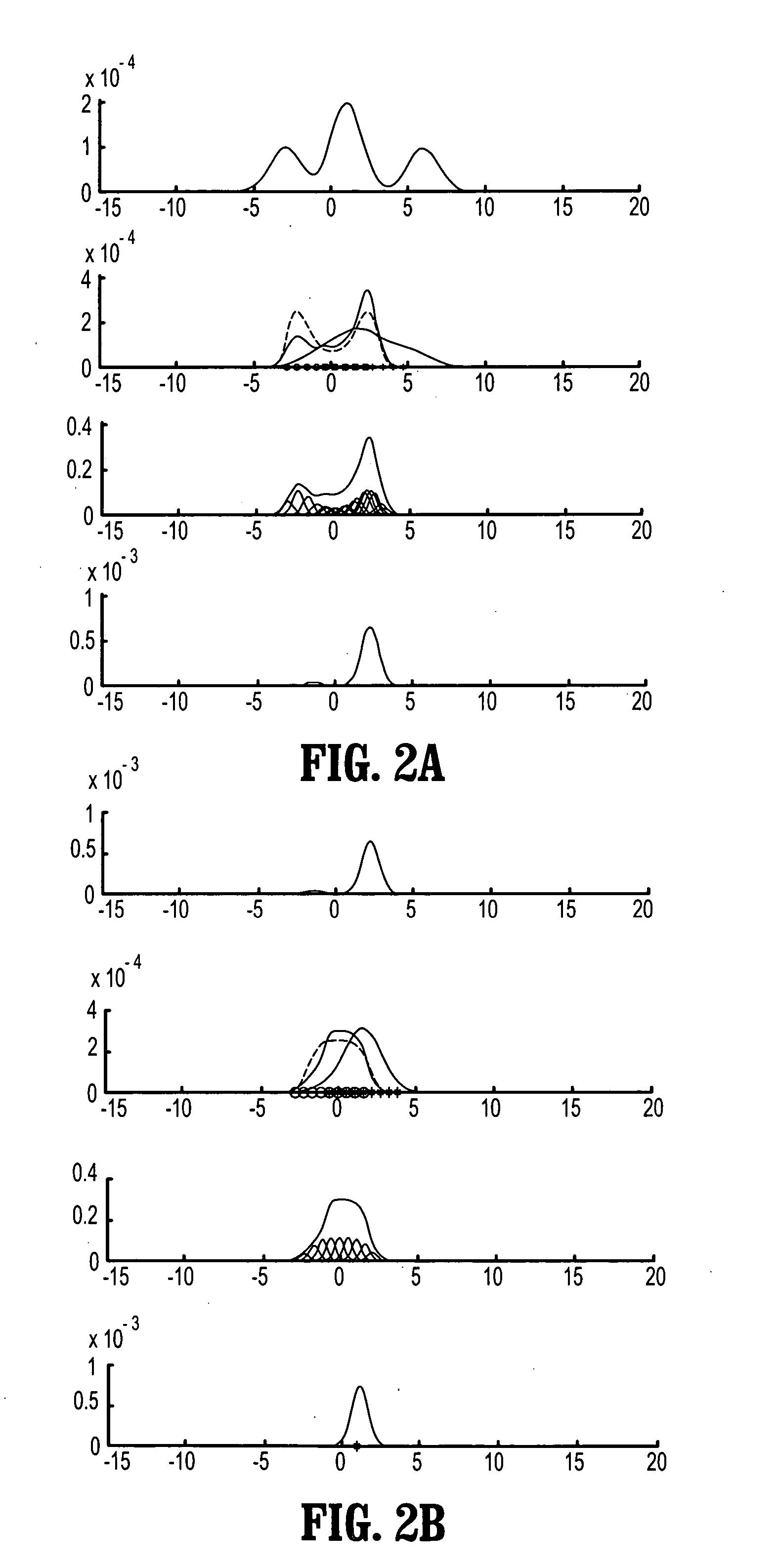
A system and method for modeling a dynamic system using Bayesian filtering, includes a prediction module to predict a state model of the dynamic system, the prediction module generates a prediction density having at least one mode, the state model includes a conditional density function including at least one kernel. Approximating module approximates a measurement probability from a sample set through at least one kernel and an update module updates the conditional density function using the measurement probability and the prediction density. A mode finding and mixture reduction module reduces the number of kernels in the conditional density function.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
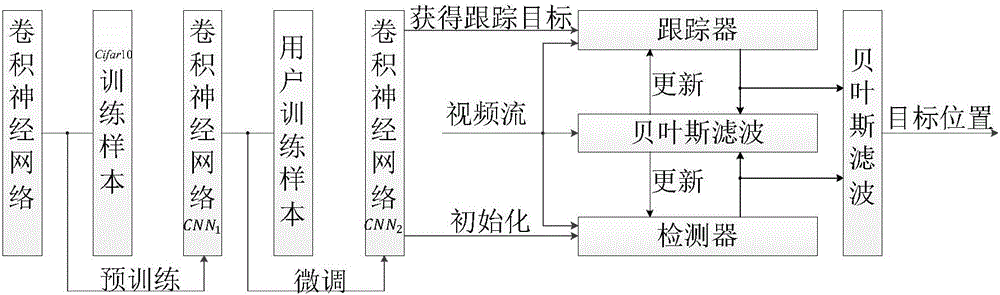
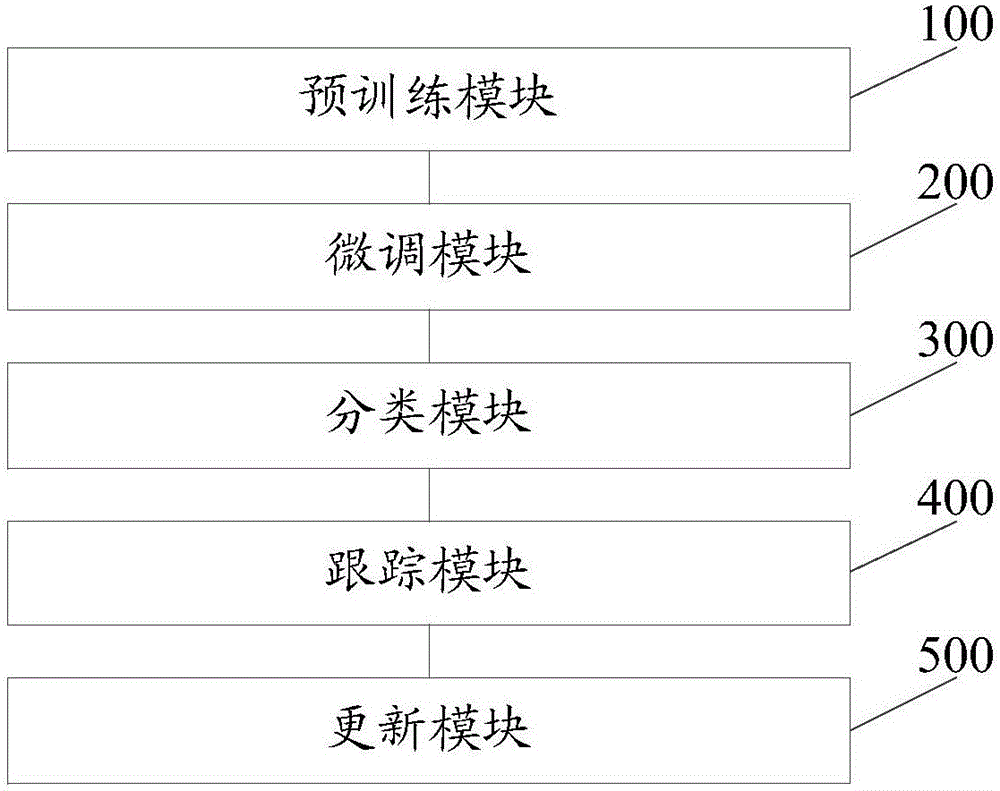
A tracking method and system based on a convolutional neural network and a Bayesian filter
The invention provides a tracking method and system based on a convolutional neural network and a Bayesian filter. The method comprises the steps of based on preset training sets, performing pre-training on a convolutional neural network to obtain a primary model of the convolutional neural network; receiving a video stream with a tracking target input by a user, performing tracking on the tracking target in the video stream via the primary model and performing fine adjustment on the parameters of the primary model by using the fine adjustment technology to obtain the final model of the convolutional neural network; receiving a monitoring video stream with the tracking target input by the user, performing identification and tracking on the tracking target in the monitoring video stream automatically via a post-substitution TLD algorithm and updating a target model set and a background set via a Bayesian filter. By training a convolutional neural network to generate a final model, a tracking target can be identified automatically in a monitoring video stream; samples can be updated by using a Bayesian filter, so that long time tracking of targets is realized and the operation experience of users is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Methods and systems for detecting and preventing the spread of malware on instant messaging (IM) networks by using Bayesian filtering
InactiveUS7577993B2Avoid spreadingMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionClient-sideMalware
Methods and systems for reducing the spread of malware in communication between an instant message (IM) client and an IM server are described. An IM filter module (IM FM) is configured to analyze messages exchanged between an IM server and an IM client. The IM FM also identifies one or more messages as possibly containing malware among the exchanged messages and assigns a confidence level to each identified message. A confidence level represents a probability of a message containing malware. A Bayesian filter is configured to train itself using the identified messages and the confidence levels and adjust the confidence levels. A feedback training mechanism for the Bayesian filter is also included. In particular, the IM FM examines additional messages exchanged between the IM server and IM client, identifies one or more messages as possibly containing malware among the additional messages using the adjusted confidence values. The IM FM also assigns a confidence level to each additionally identified message. The Bayesian filter is further configured to re-train itself using the identified messages, the additionally identified messages, and the confidence levels and adjust the confidence levels.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method for localization of nodes by using partial order of the nodes
InactiveUS20110105161A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationKaiman filterBayesian filtering
The present invention relates to a new method for localization, i.e. finding positions and orientations of nodes communicating in wireless networks. The method is based on using directional information (angle-of-arrival, AOA), and optionally distance information, combined with estimation by recursive filters such as e.g, Kaiman filters, recursive least squares filters, Bayesian filters, or particle filters. The method expresses the localization problem as set of linear equations and ensures stability and convergence by imposing a partial order on the nodes.
Owner:LOCUSENSE
Slam method and Slam device based on prior information
ActiveCN107607107AHigh precisionConstrained global consistencyNavigation instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsRadar observationsPattern recognition
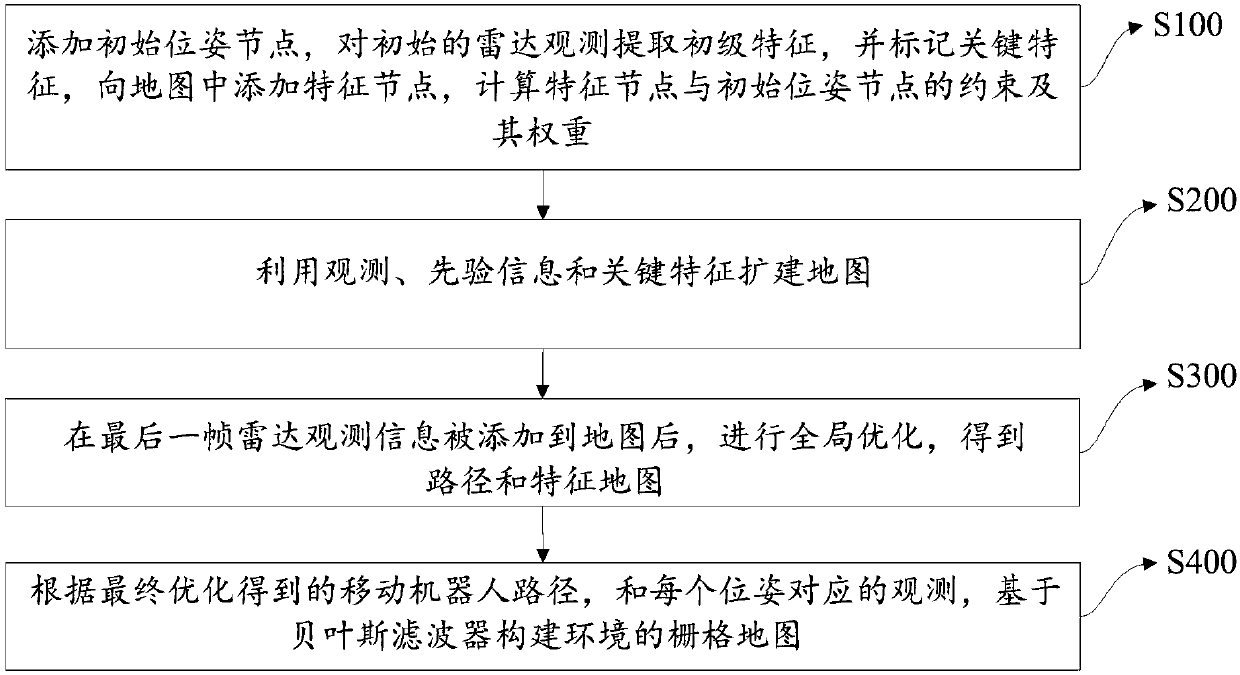
The invention provides a Slam method based on prior information. The method includes the steps of: 1) adding an initial pose node, extracting primary feature of initial radar observation, marking keyfeatures, adding a feature node to a map, and calculating the constraint and weight of the feature node and the initial pose node; 2) extending the map by means of observation, the prior information and the key features; 3) when the last frame of radar observation information is added to the map, performing global optimization to obtain a route and a feature map; 4) establishing a raster map of the environment on the basis of a Bayesian filter according to the route, which is obtained through the final optimization, of a movable robot and observation corresponding to every pose. The prior information is introduced through the expandable feature hierarchy, so that the method can adapt different environments and prior information in different types; besides the structural features, the key features are also considered, and the framework and size of the environment are further constrained by means of the extra constraint among the key features, thus reducing accumulated error.
Owner:STANDARD ROBOTS CO LTD
Lamb wave damage location method based on non-linear unscented Kalman filtering algorithm
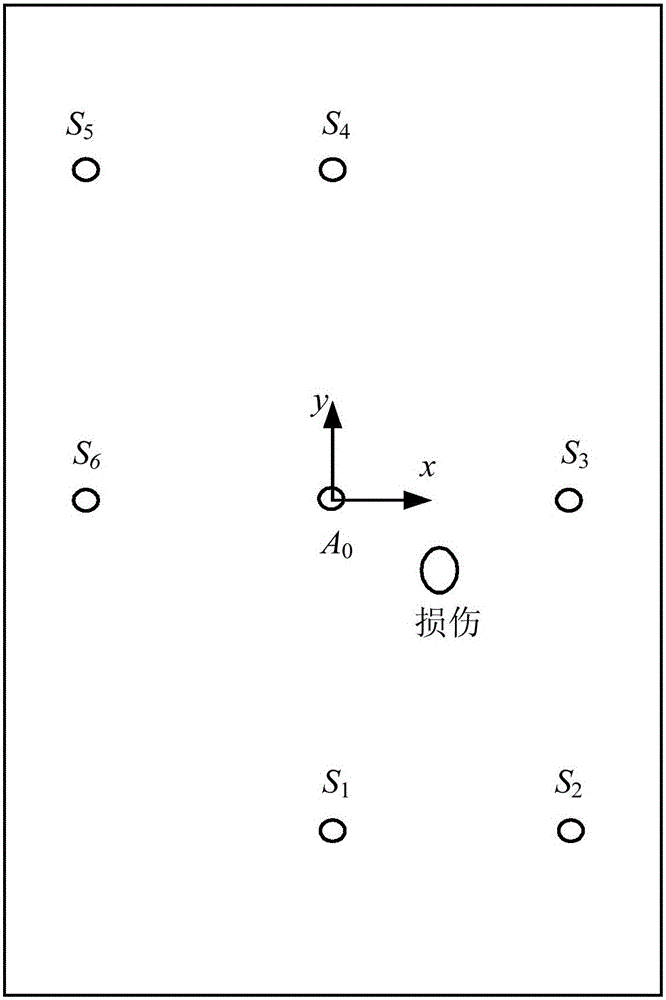
InactiveCN106093207ARealize the solutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPropagation timeBayesian filtering
The invention discloses a lamb wave damage location method based on a non-linear unscented Kalman filtering algorithm. The method includes the steps that multiple (at least four) piezoelectric sensors for exciting and receiving ultrasonic lamb waves are arranged on a damage-containing isotropous planar structure; the damage position is recognized and converted into a Bayes filtering problem, a state vector evolution systematic equation and a non-linear measurement equation are set up, the propagation time of the lamb waves scattered by damage on routes of all exciting sensors and all receiving sensors is used as known measurement quantity, and the damage center position and the lamb wave speed are used as unknown state variables. The non-linear unscented Kalman filtering algorithm is adopted for iterative estimation, and therefore damage location and solution of lamb wave speed are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
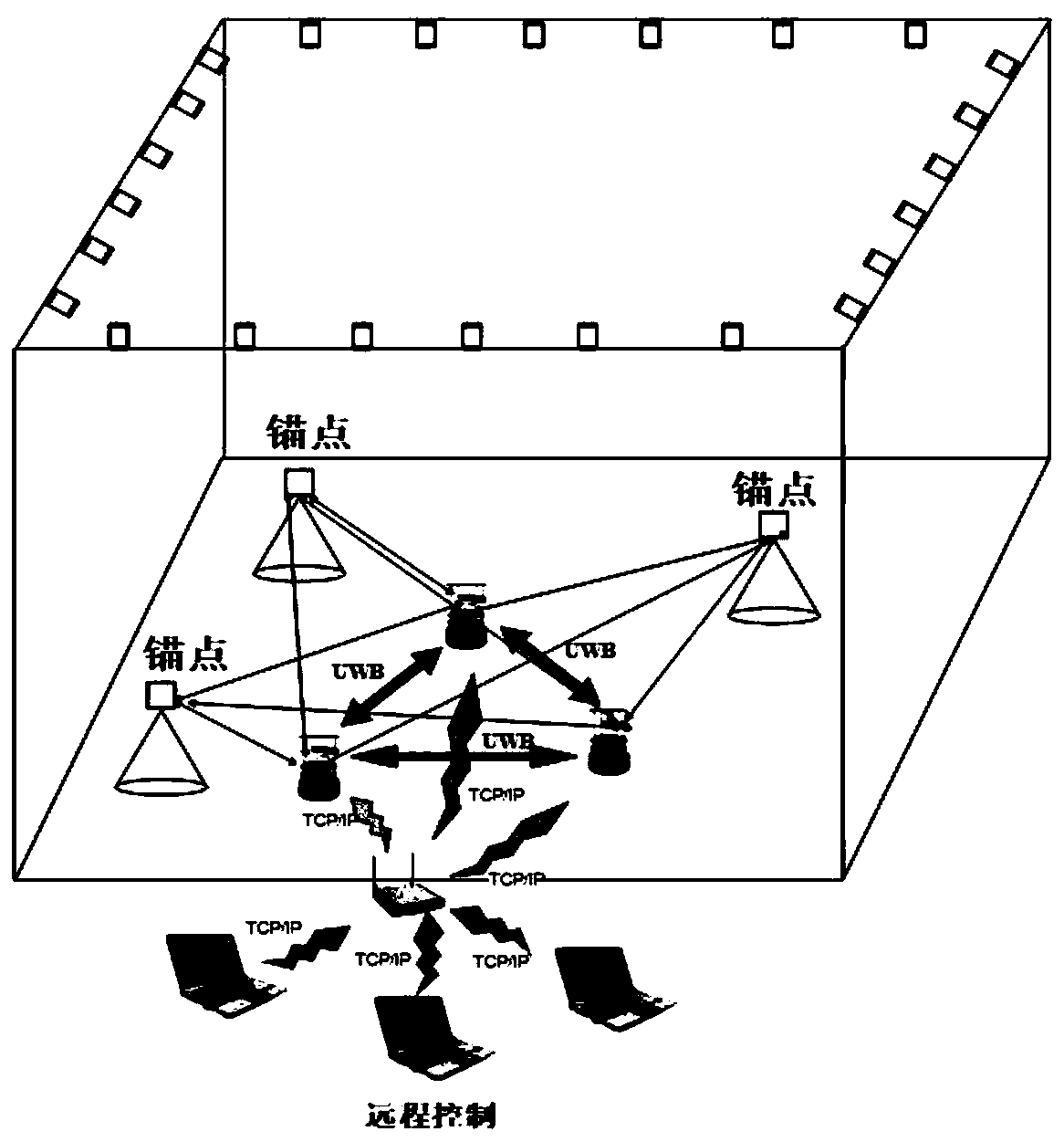
Multi-mobile-robot high-precision collaborative tracking method based on ultra-wideband technology
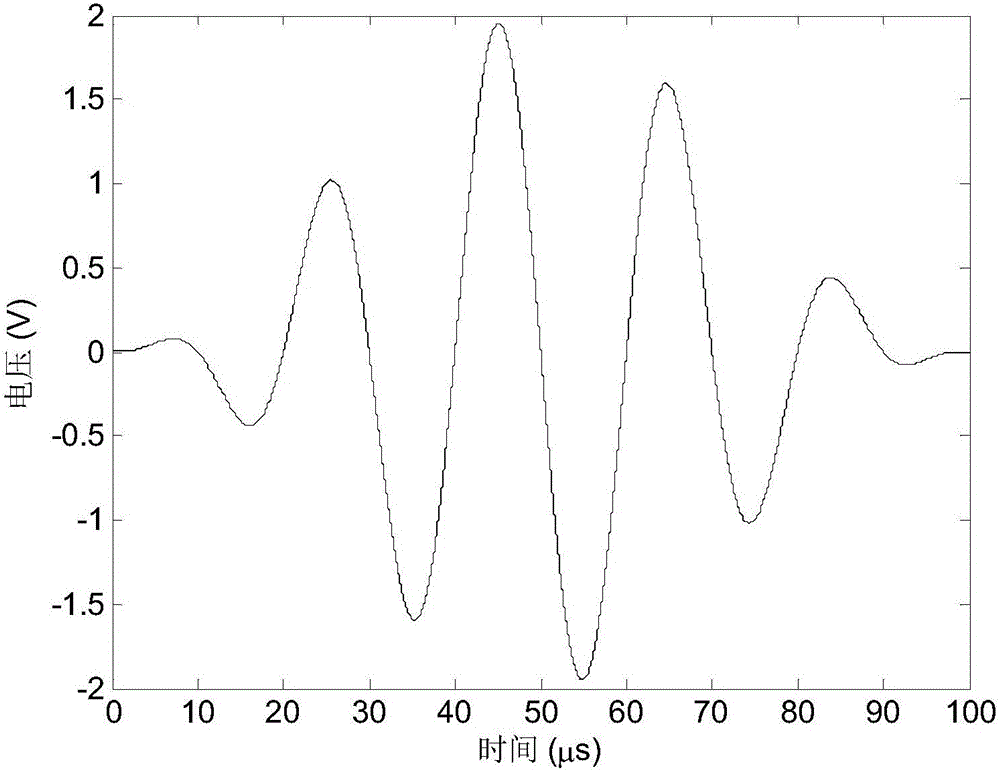
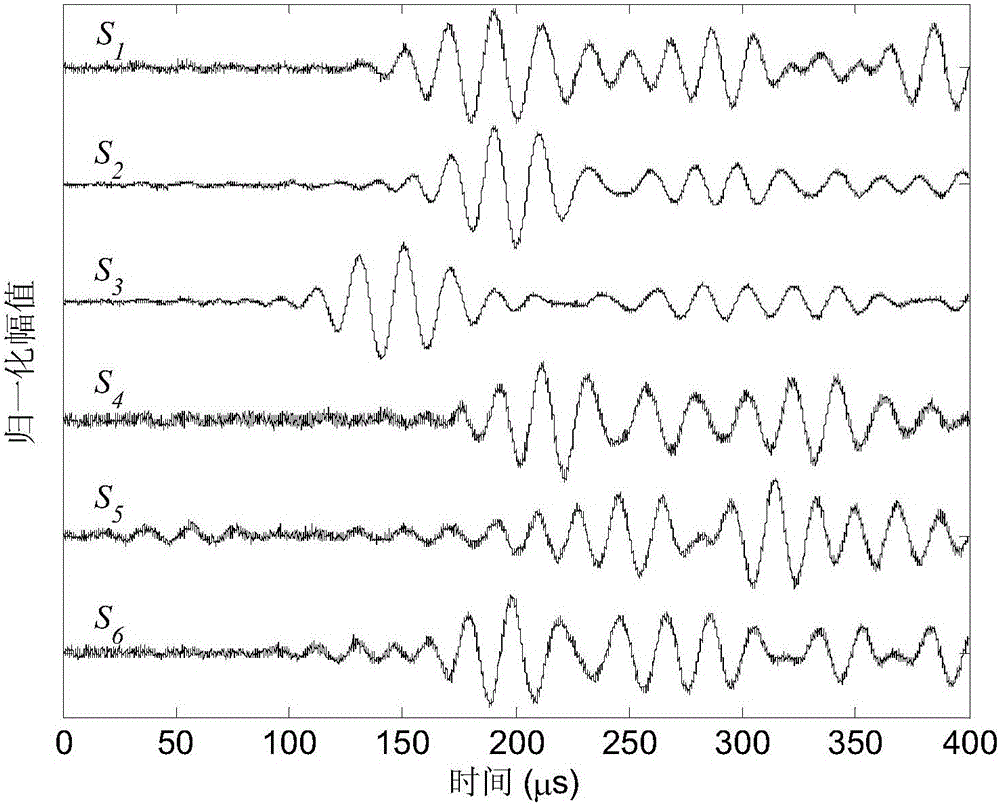
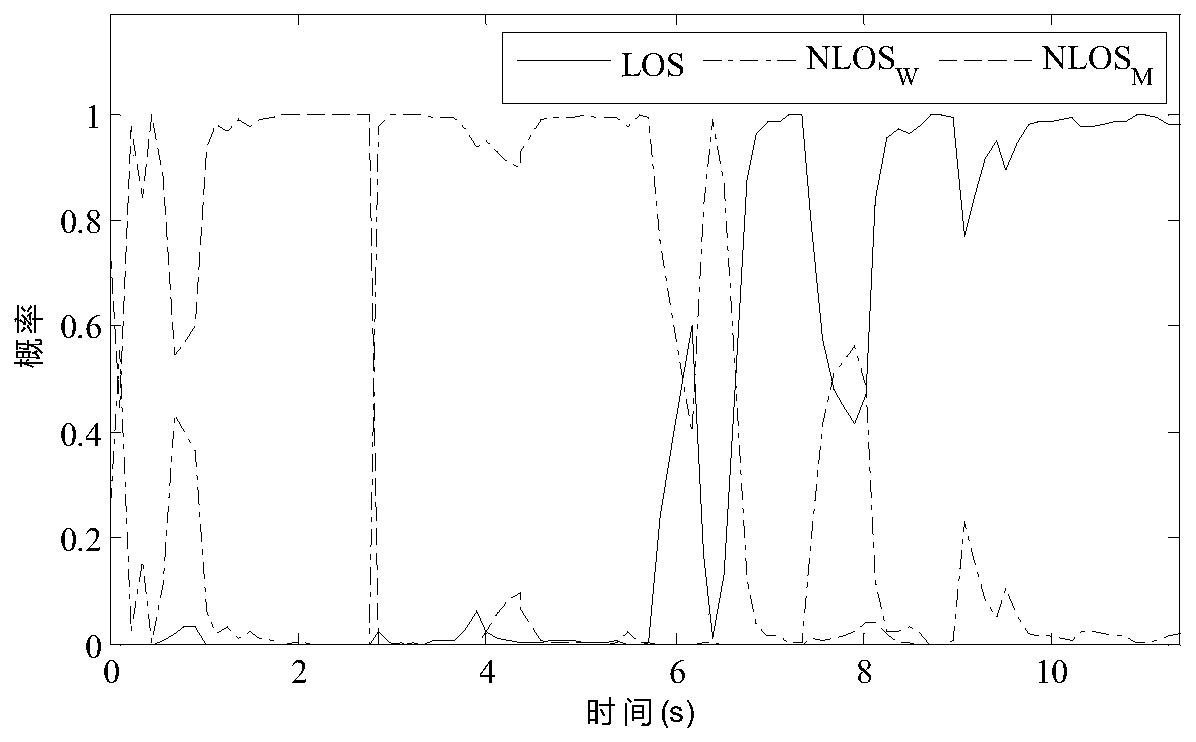
ActiveCN110244715AImprove ranging accuracyImprove data transfer ratePosition/course control in two dimensionsUltra-widebandParticle filtering algorithm
The invention discloses a multi-mobile-robot high-precision collaborative tracking method based on an ultra-wideband technology. The method comprises the following steps: a multi-mobile-robot collaborative tracking experiment platform is built under an ROS; a multi-node ranging network is built through an ultra-wideband sensor, and information of the distances between robots and between the robots and an anchor point is obtained at the same time; an ultra-wideband ranging error weakening algorithm based on Bayesian filtering is provided for effectively weakening LOS and NLOS errors of obtained ranging values to restore real distance values; position information of the mobile robots is estimated by adopting a cooperative tracking algorithm, namely, a collaborative particle filtering algorithm based on Gibbs sampling; and real tracks of corresponding motions of the robots are obtained by adopting an OptiTrack motion capturing system, and a collaborative tracking algorithm is evaluated. The LOS and NLOS errors in a complex environment can be effectively weakened; the restored distances are real; the position information of each robot at any moment can be accurately determined; and multi-robot collaborative tracking is realized.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
SMC (Sequential Monte Carlo) algorithm based acoustic emission source location method
ActiveCN104914167AAchieve positioningMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesState variableAcoustic emission
The invention discloses an SMC (Sequential Monte Carlo) algorithm based location method. The method comprises the following steps: distributing not less than four sensors for receiving acoustic emission signals emitted by an acoustic emission source on acoustic emission sources of an isotropic planar structure; converting acoustic emission source location into bayesian filtering, building a system equation and a measurement equation respectively, using Poda moment between each sub-sensor and a main sensor as a known measurement quantity and taking a source position and the wave velocity as unknown state variables. The SMC simulation algorithm is adopted to perform iterative estimation on unknown status variables due to lack of analytical solution, and an acoustic emission source is located under the influence of uncertain factors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
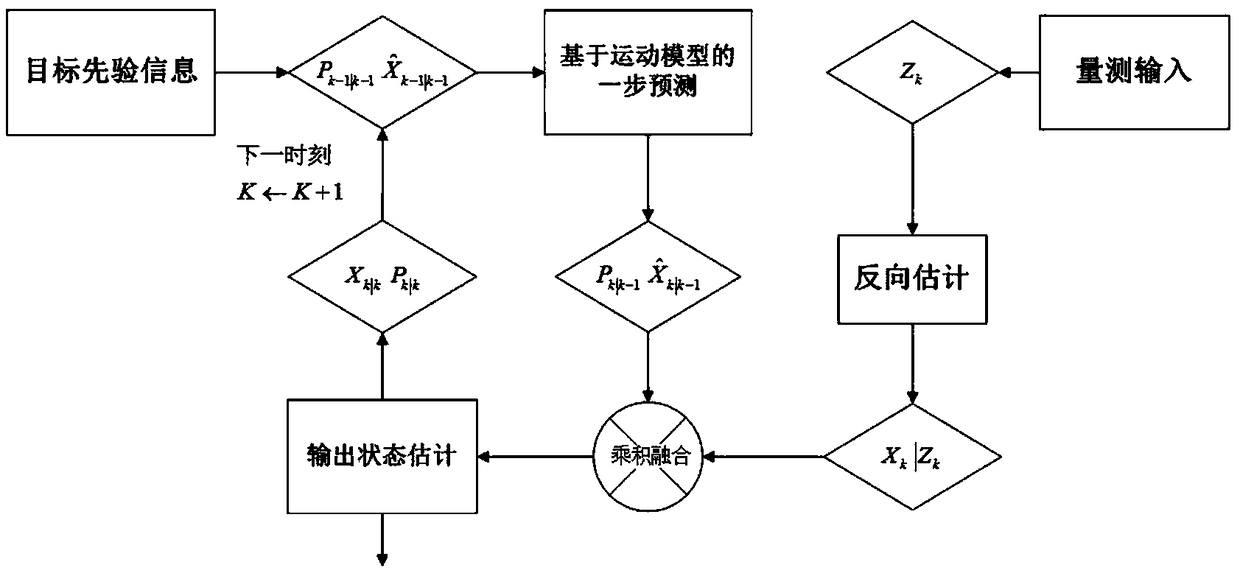
A Bayesian filter target tracking algorithm
ActiveCN109284677AEfficient integrationHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsFixation point
The invention discloses a Bayesian filter target tracking algorithm. The method includes: 1. the target state one-step prediction estimation of the next moment is obtained through a motion model basedon the target state optimal estimation of a k-1 moment; 2, the range information and angle information of the target relative to the radar are converted into the Cartesian coordinate position information of the target by the fixed-point sampling non-linear transformation method of random variable after the observation value of the target at the time k is obtained by the radar observation station.3, the two parts of the target state one-step prediction prior information and the radar observation inverse estimation likelihood function are combined through product fusion according to the probability likelihood product rule, and finally the posterior estimation of the target state at time k is obtained, and after the target state is stored, the moment is updated and the next iteration turn is entered. The invention has the characteristics of higher precision, better robustness and more concise algorithm structure, and has high practical value in radar, multi-sensor, maneuver and multi-target tracking.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
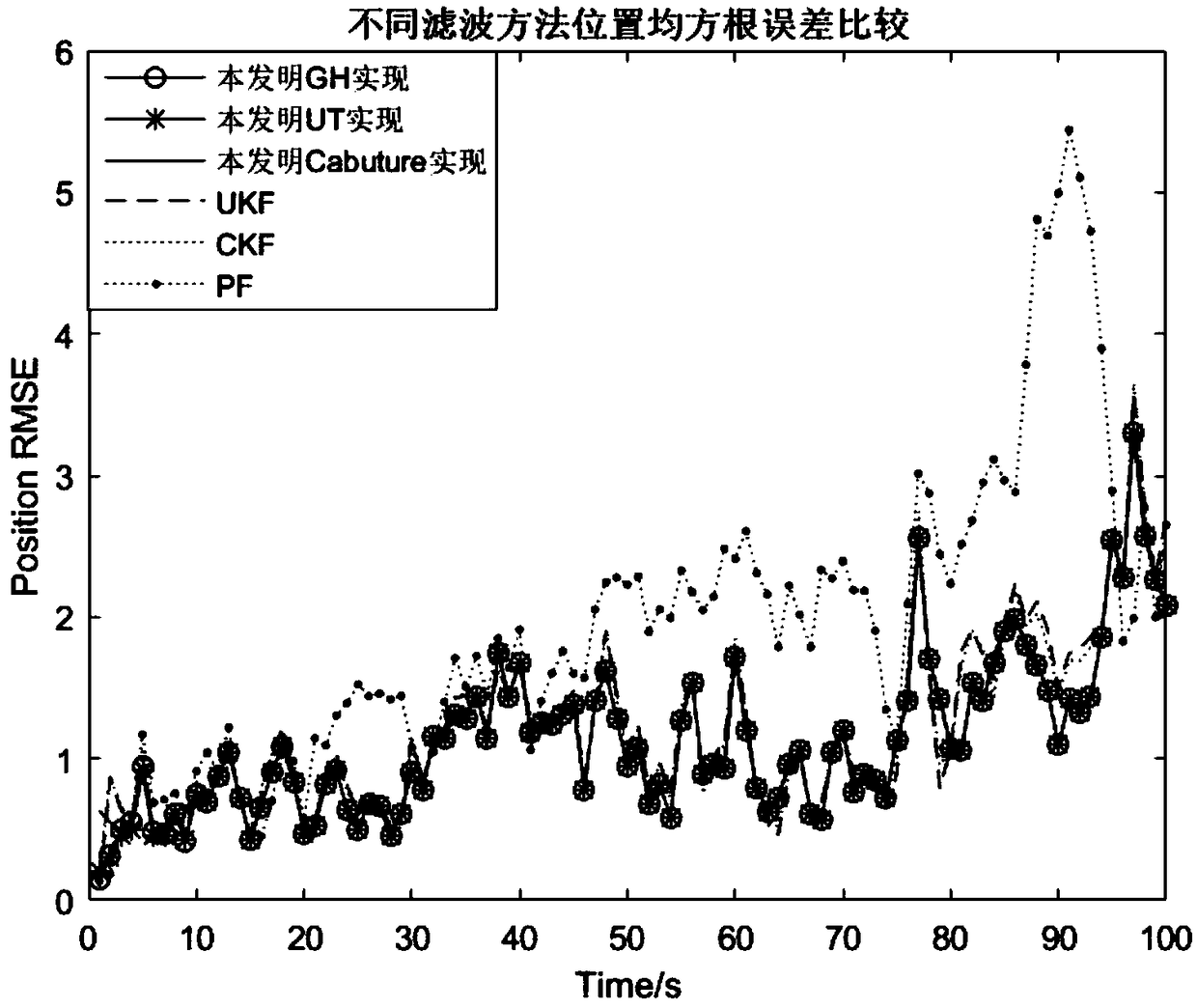
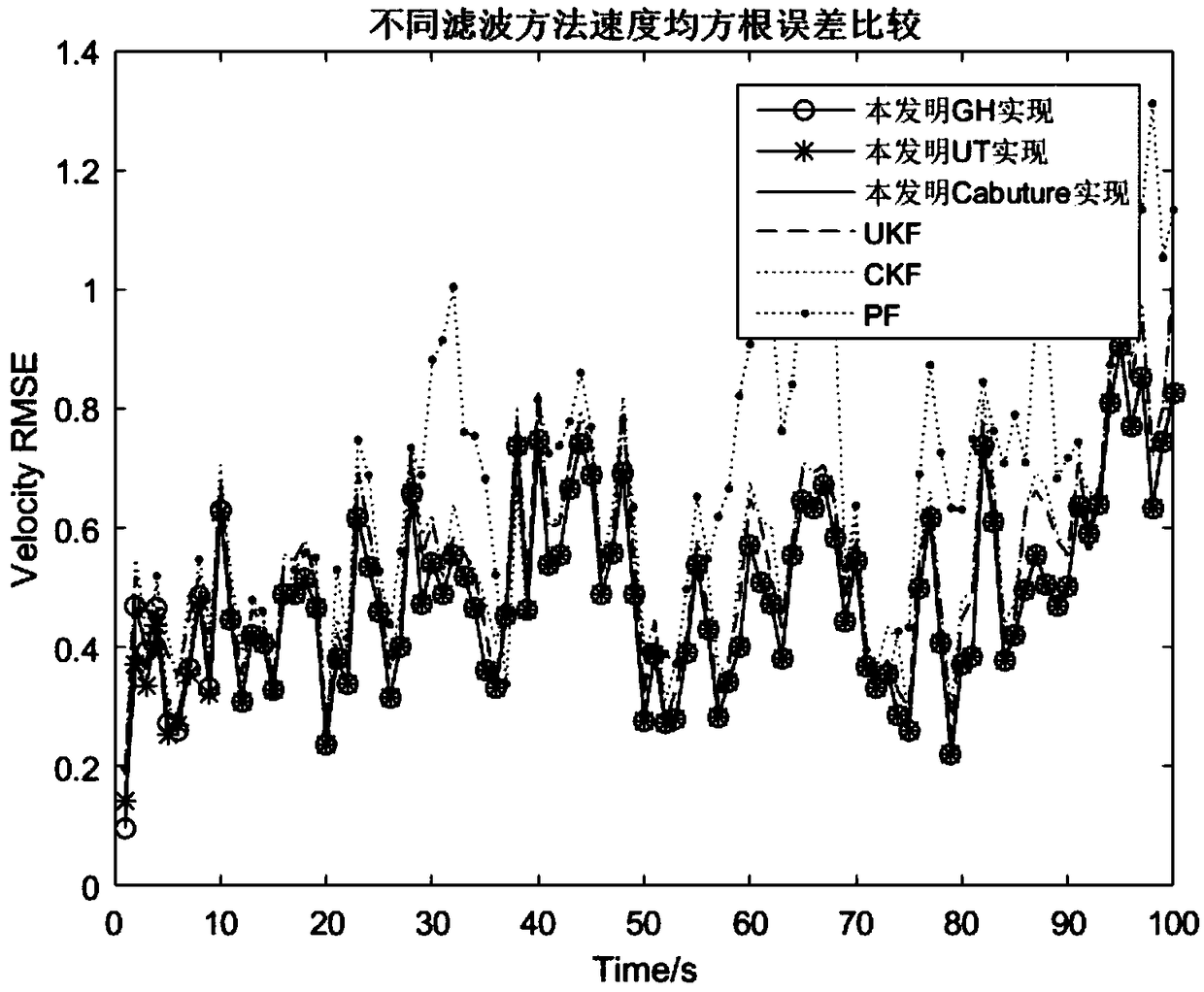
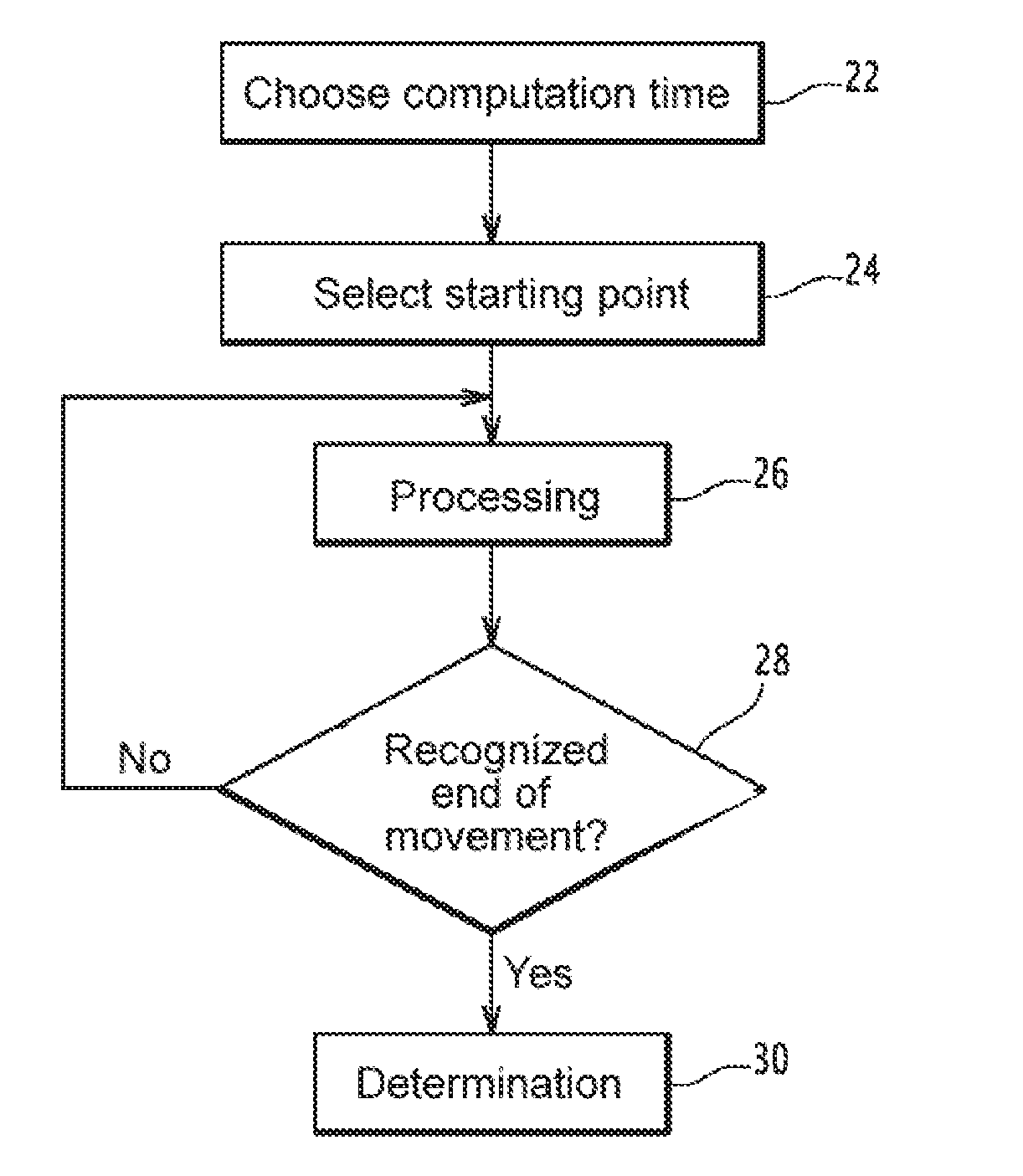
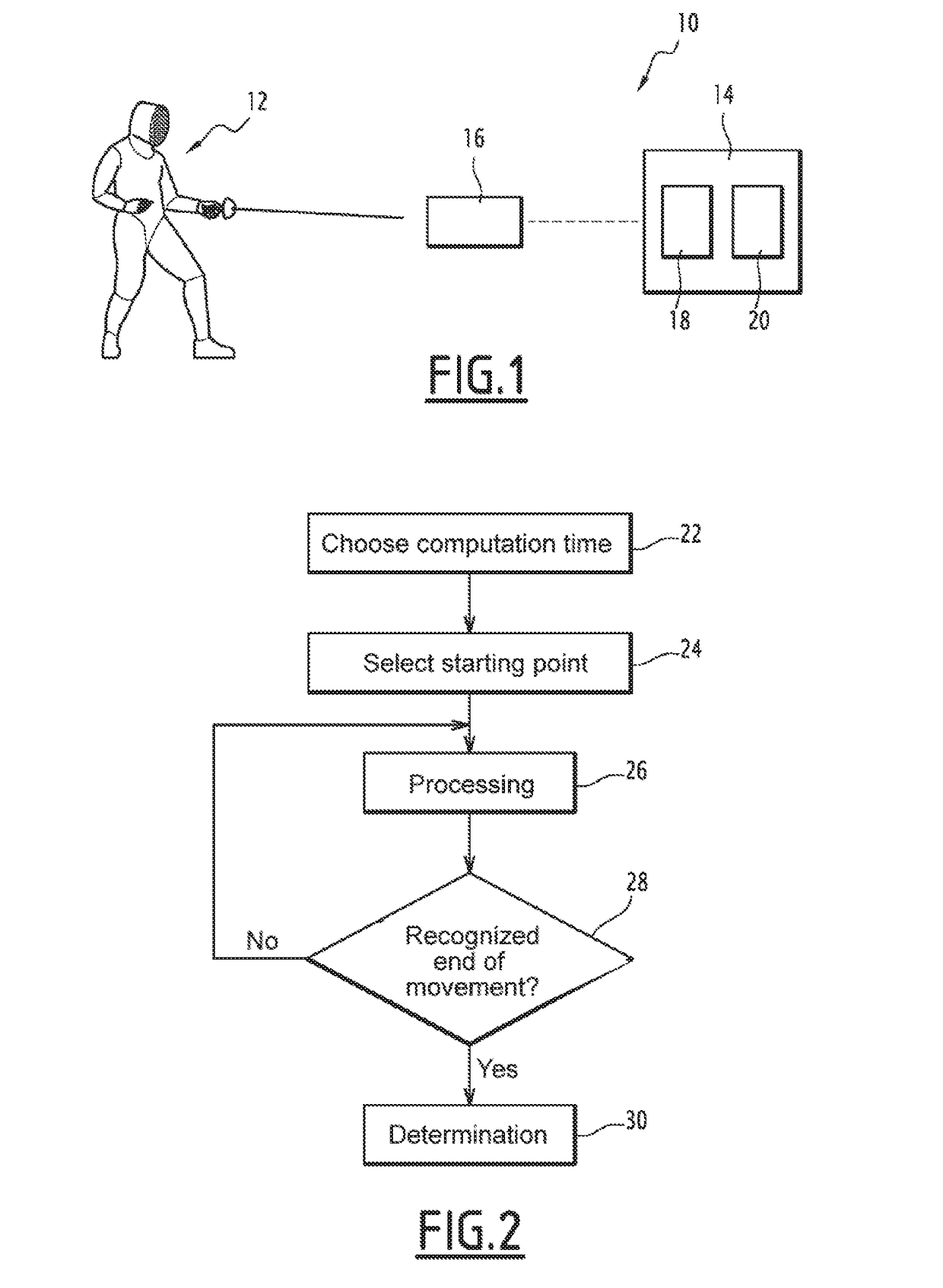
Method of identifying a movement by quantified recursive bayesian filtering
InactiveUS20170147872A1Character and pattern recognitionVideo gamesKinematicsTheoretical computer science
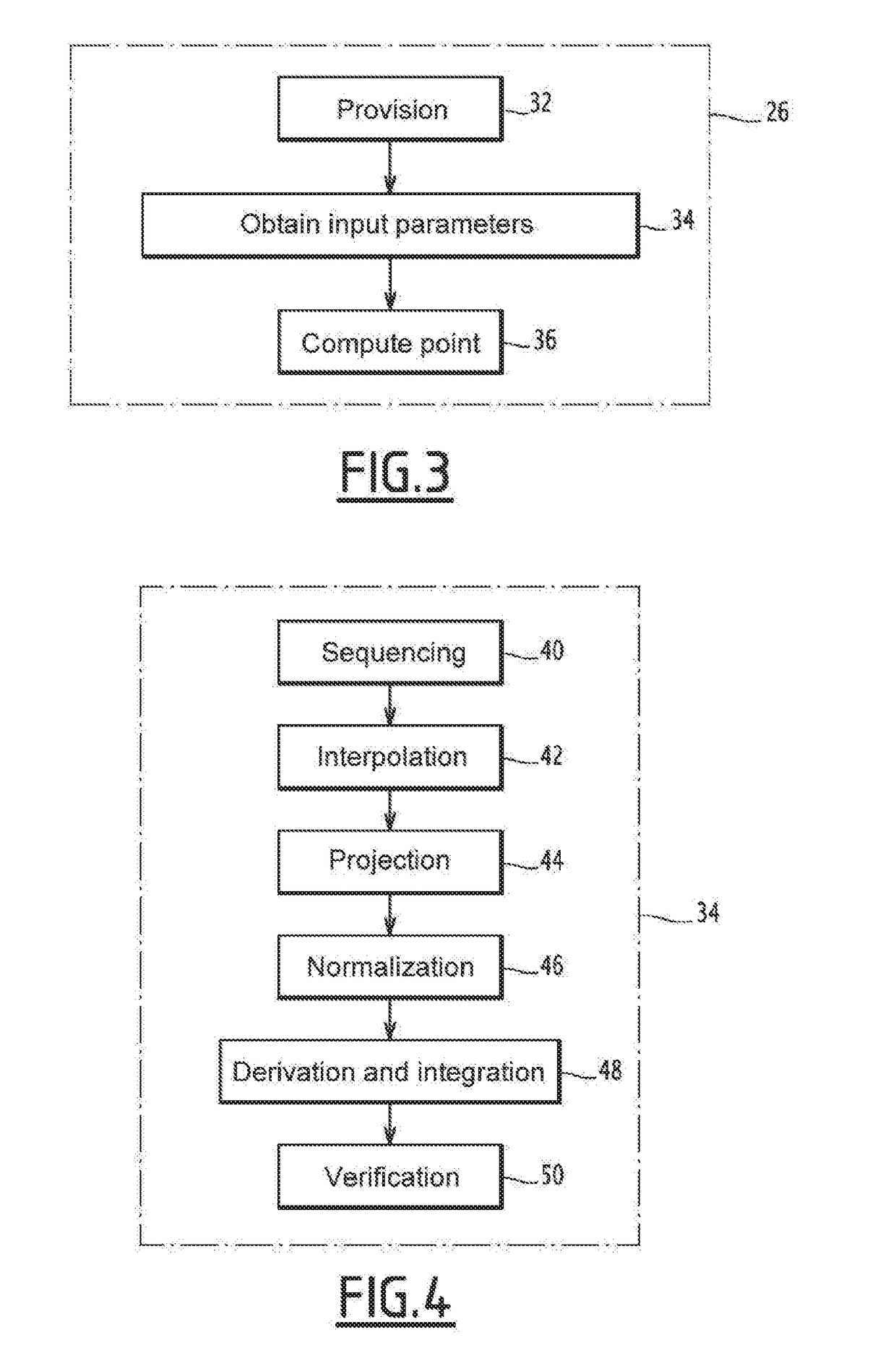
The invention relates to a method for analyzing a movement by a human being, the method including the following steps:selecting an initial probability function,processing,recognizing the end of the movement to be analyzed when a criterion is verified, the processing step being iterated for as long as the criterion is not verified,determining a piece of information regarding the movement to be analyzed,each iteration of the processing step comprising a step for:providing a set of characteristic parameters relative to the movement to be analyzed during the chosen computing time interval,computing a point, the computed point belonging to a reference kinematic and making a function depending on the a posteriori conditional probability function extremal,the determination step taking into account the points computed upon each iteration of the processing step.
Owner:MAROY
Knee osteoarthritis motion monitoring method based on Android system
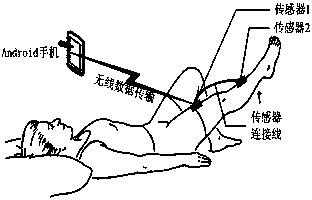
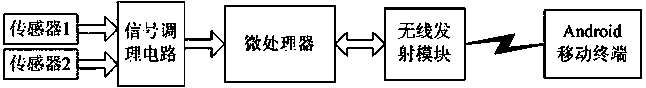
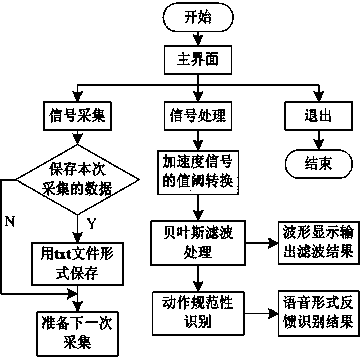
The invention relates to the field of knee osteoarthritis motion monitoring, in particular to a knee osteoarthritis motion monitoring method based on an Android system. The method is characterized in that signals of acceleration sensors worn on thighs and shanks of a human body are collected through a wireless collection device, the signals are transmitted to an Android mobile terminal in a wireless transmission mode, by means of a signal processing system arranged on the Android mobile terminal, the collected acceleration signals are filtered in a Bayesian filtering algorithm, and motion standardization is recognized through a rule induction method. By means of the method, nonstandard motions of a patient during sports can be well recognized, and application requirements of motion monitoring can be well met.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
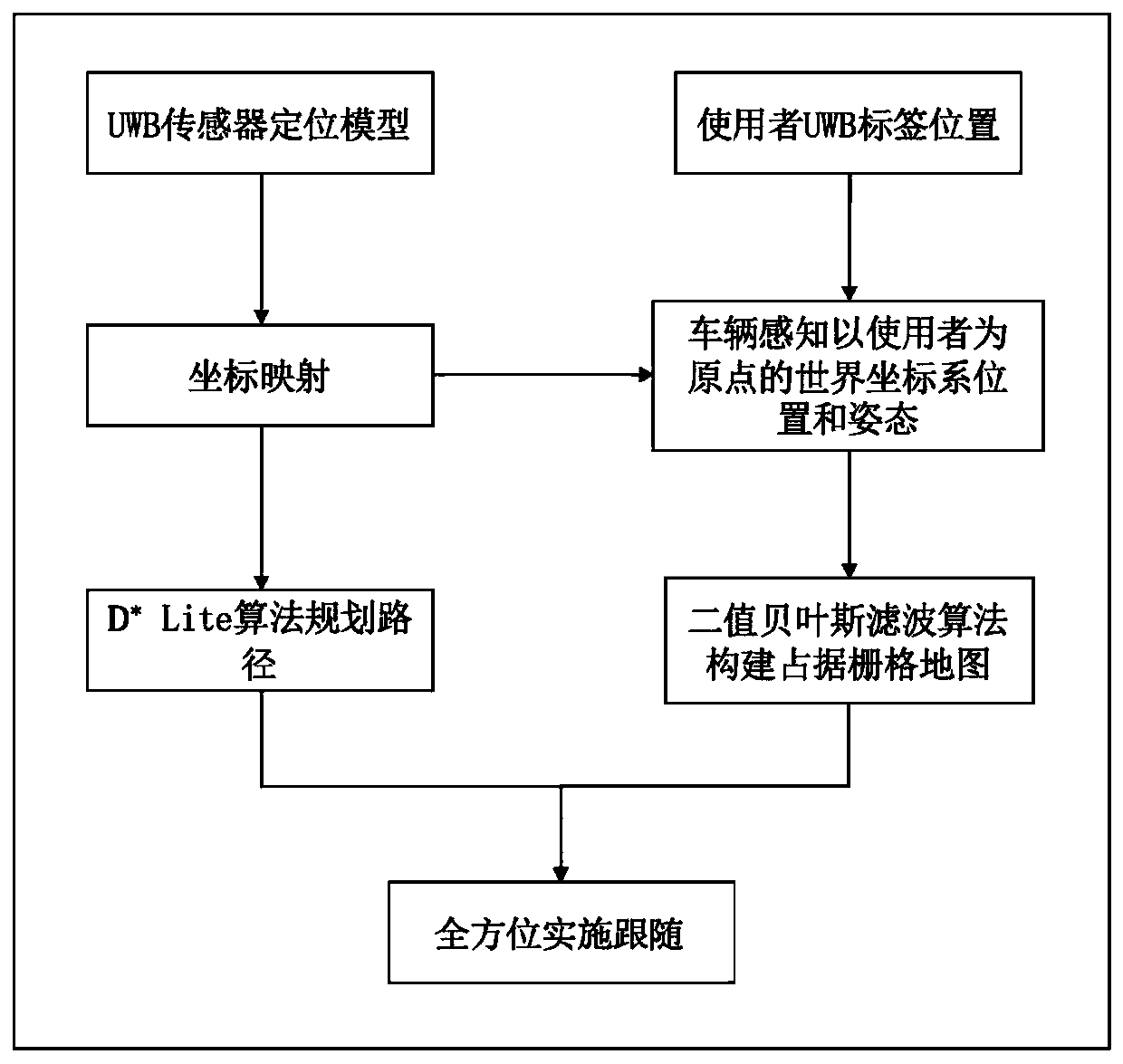
Vehicle omni-directional following method based on UWB and laser radar sensor
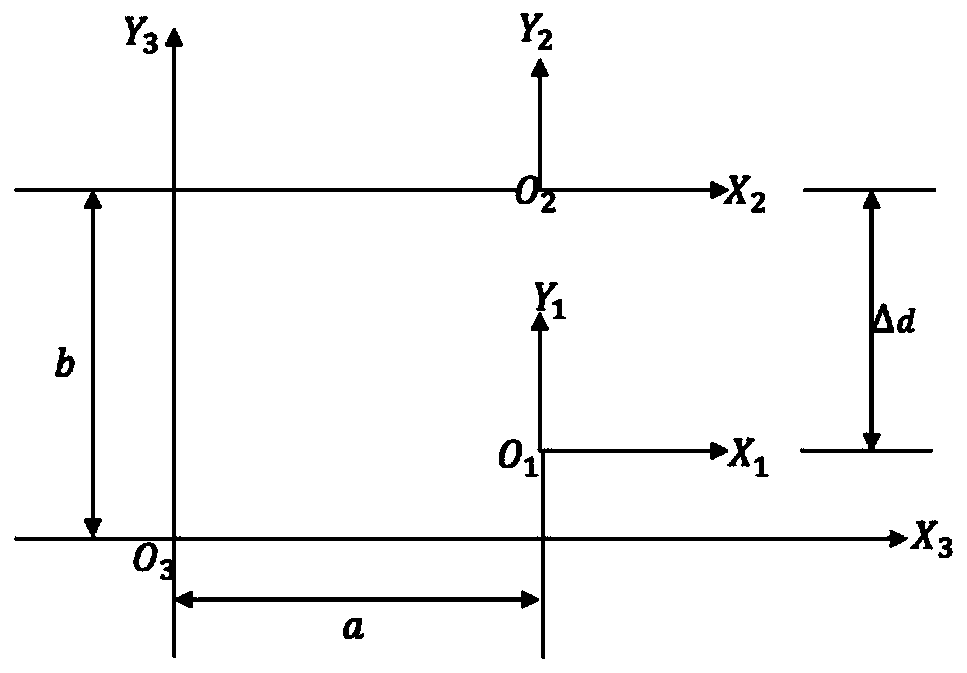
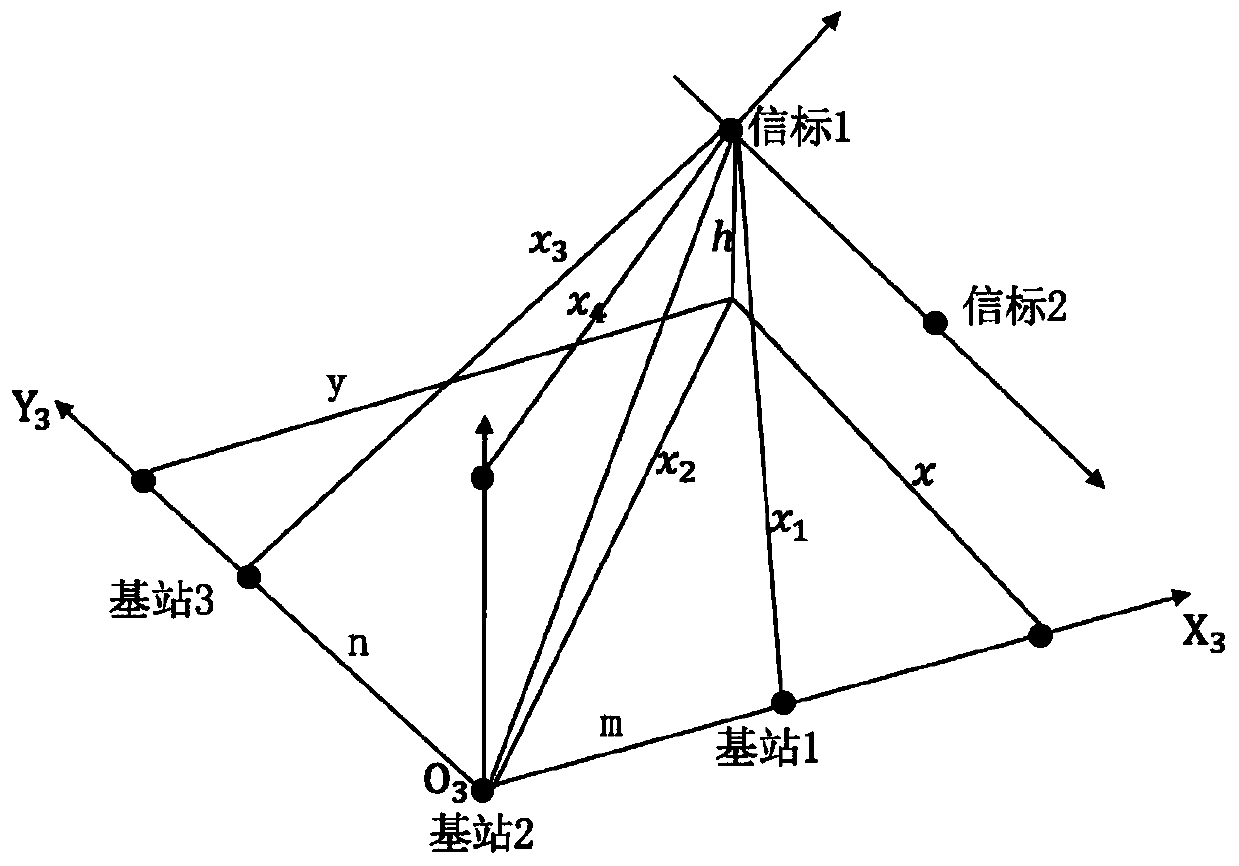
ActiveCN111240341AFollow up in real timeImprove mapping accuracyAutonomous decision making processParticular environment based servicesObstacle avoidance algorithmGenetics algorithms
The invention discloses a vehicle omni-directional following method based on UWB and a laser radar sensor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a vehicle coordinate system,a laser radar coordinate system and a UWB sensor coordinate system, establishing a world coordinate system, and performing coordinate mapping between the world coordinate system and the vehicle coordinate system; then, enabling the vehicle to sense the position and posture of the vehicle in a world coordinate system with an artificial origin in real time; acquiring obstacle information by using the laser radar sensor, converting coordinates of an obstacle in a laser radar coordinate system into coordinates in the vehicle coordinate system, and constructing an occupied grid map by using a binary Bayesian filtering algorithm; and finally, enabling the vehicle to realize real-time following in any direction based on an occupied grid map and an automatic following and obstacle avoidance algorithm based on a parallel genetic algorithm. The method is simple in algorithm and high in positioning precision, and can realize omnibearing real-time following of the autonomous vehicle around the user.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
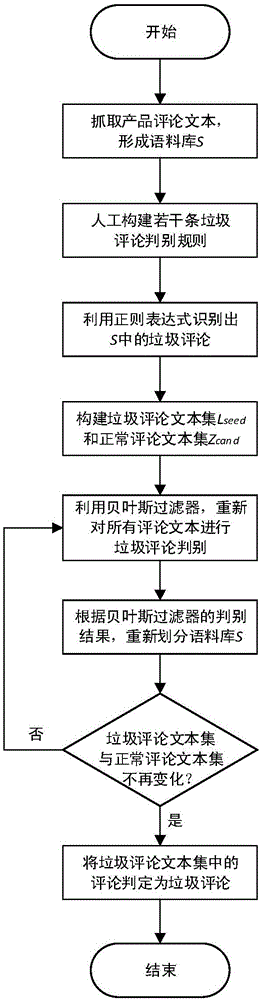
Method for filtering comment spam based on bidirectional iteration and automatically constructed and updated corpus
InactiveCN105068986AReduce labor costsImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsBayesian filteringMultimedia
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Enhanced positioning system using hybrid filter background
The disclosure generally relates to an enhanced positioning system and method using a combination or hybrid filter. In one embodiment, Time-Of-Flight (ToF) measurements are used to determine an approximate location for a mobile device in relationship to one or more Access Points. The ToF combined with known and unknown variables are then processed through a hybrid filter system to determine location of the mobile device. The hybrid filter system may include a Kalman Filter (KF) for processing linear models and generally Gaussian noise distribution. The KF assumes that the state probability of mobile device location is Gaussian. Such variables include, for example, WiFi ToF bias. The hybrid filter system may include a Bayesian Filter (BF) for processing variables having non-Gaussian noise distribution and non-linear models. Such variables include, for example, the coordinates of the mobile device. A probability determination from each of the KF and BF is then applied to estimate the mobile device location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com