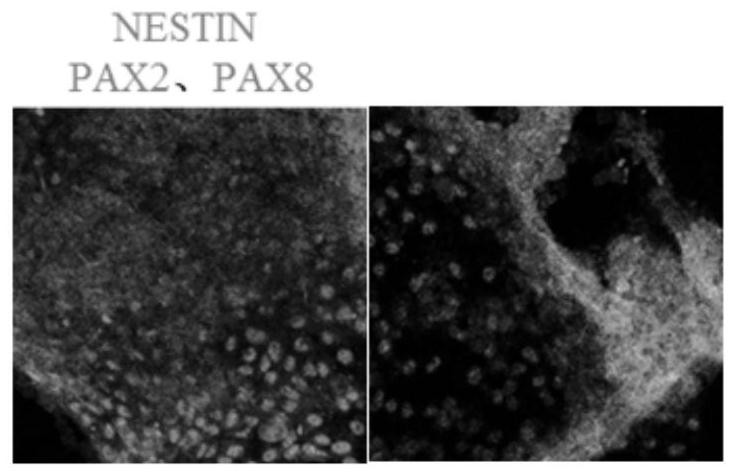
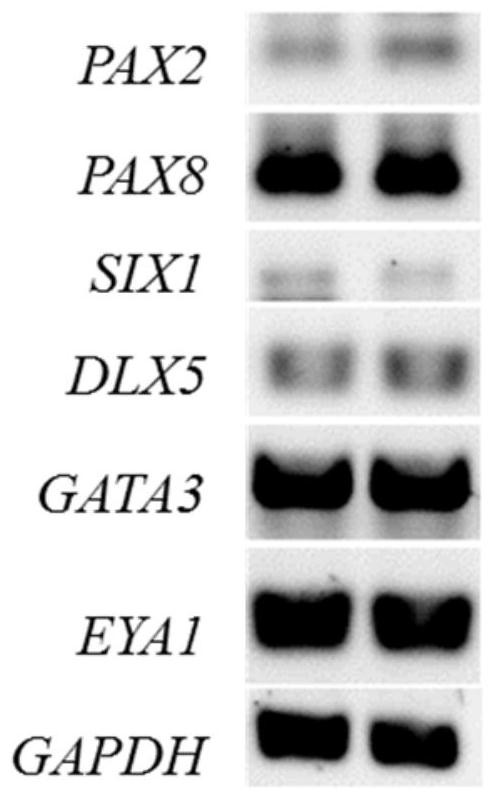
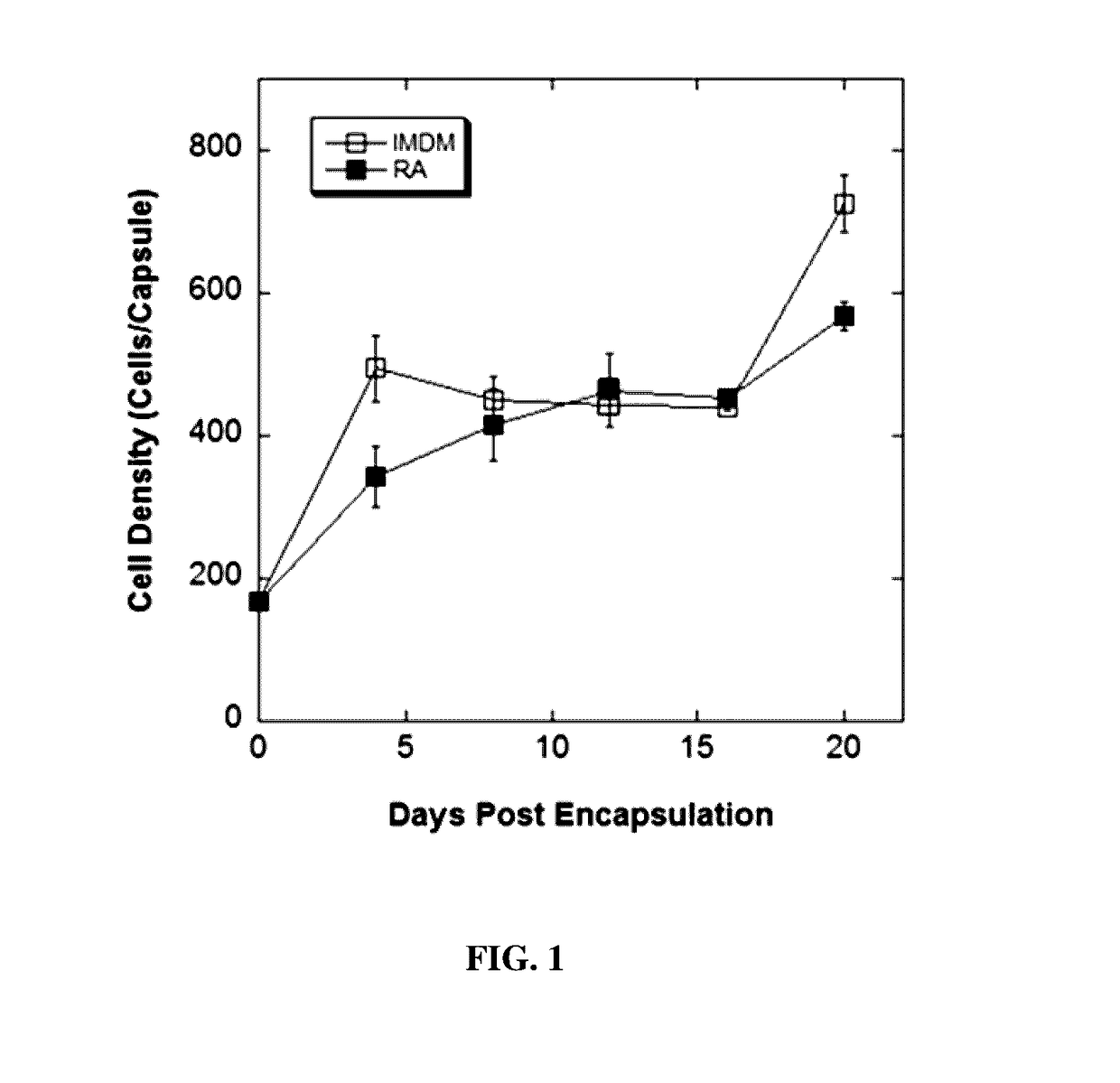
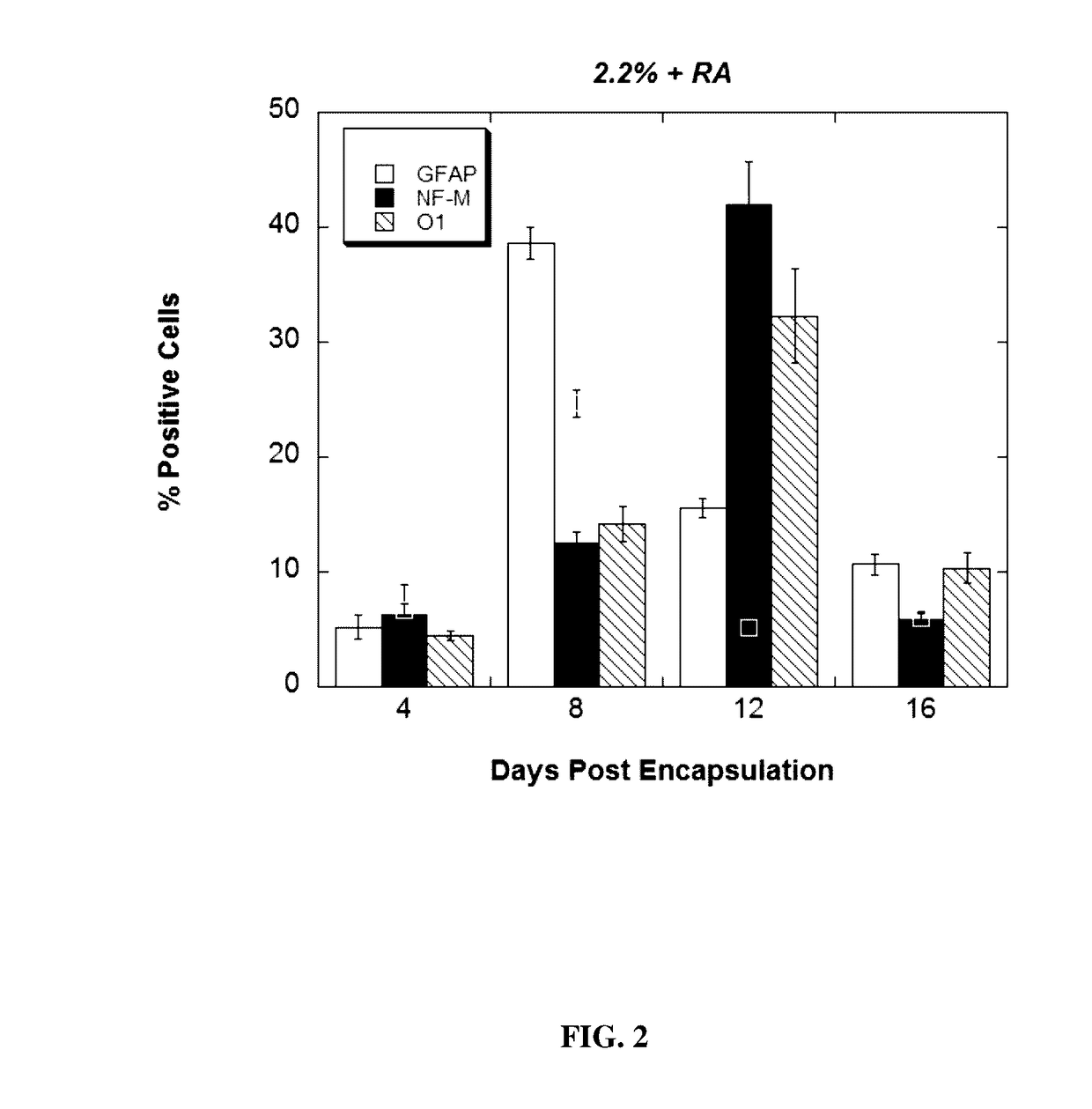
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Cell differentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
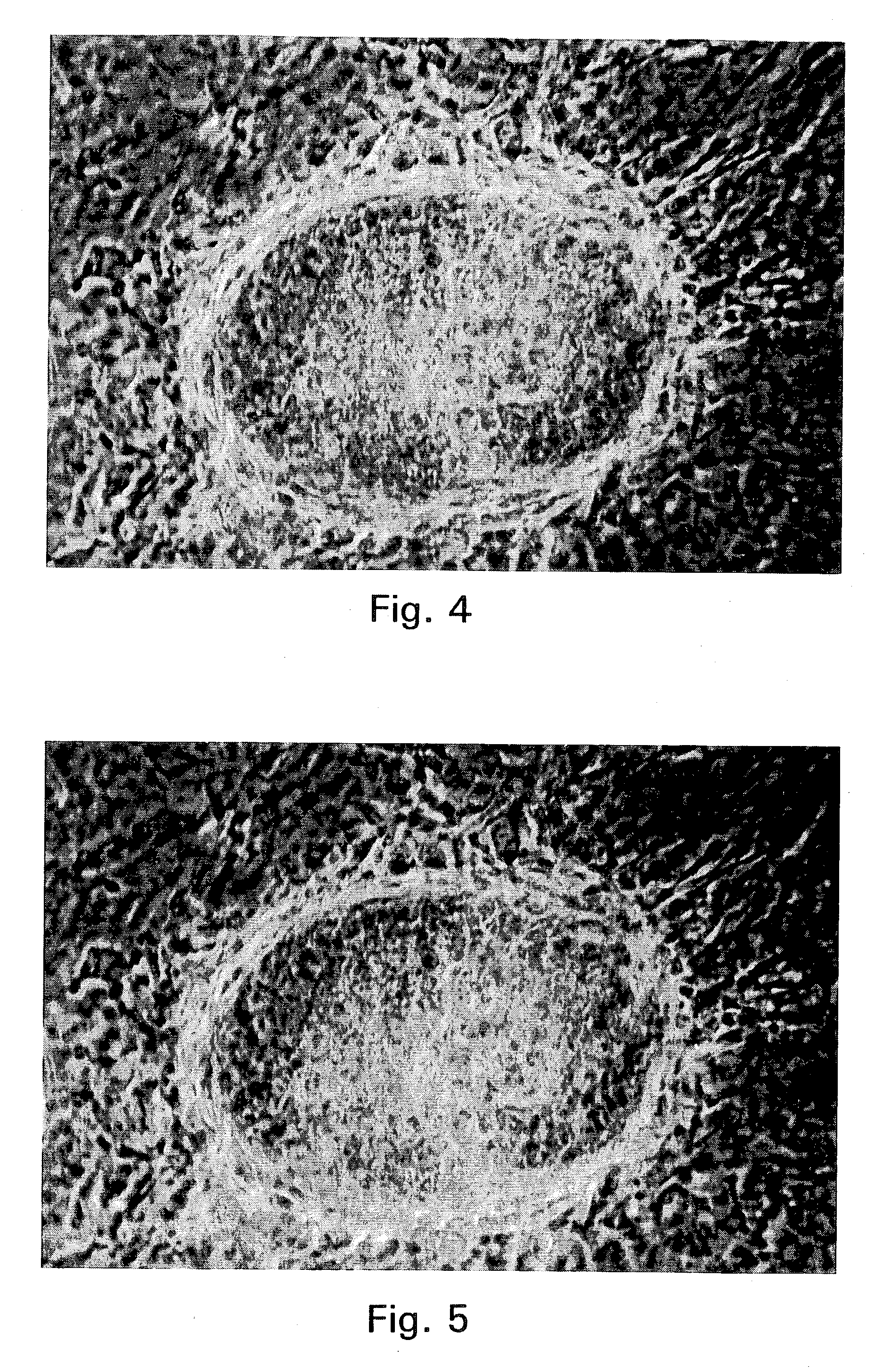
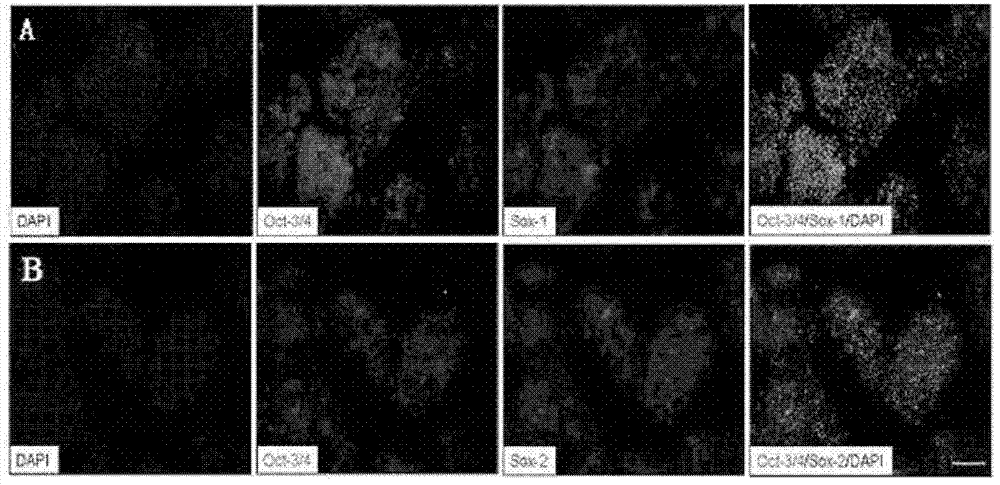
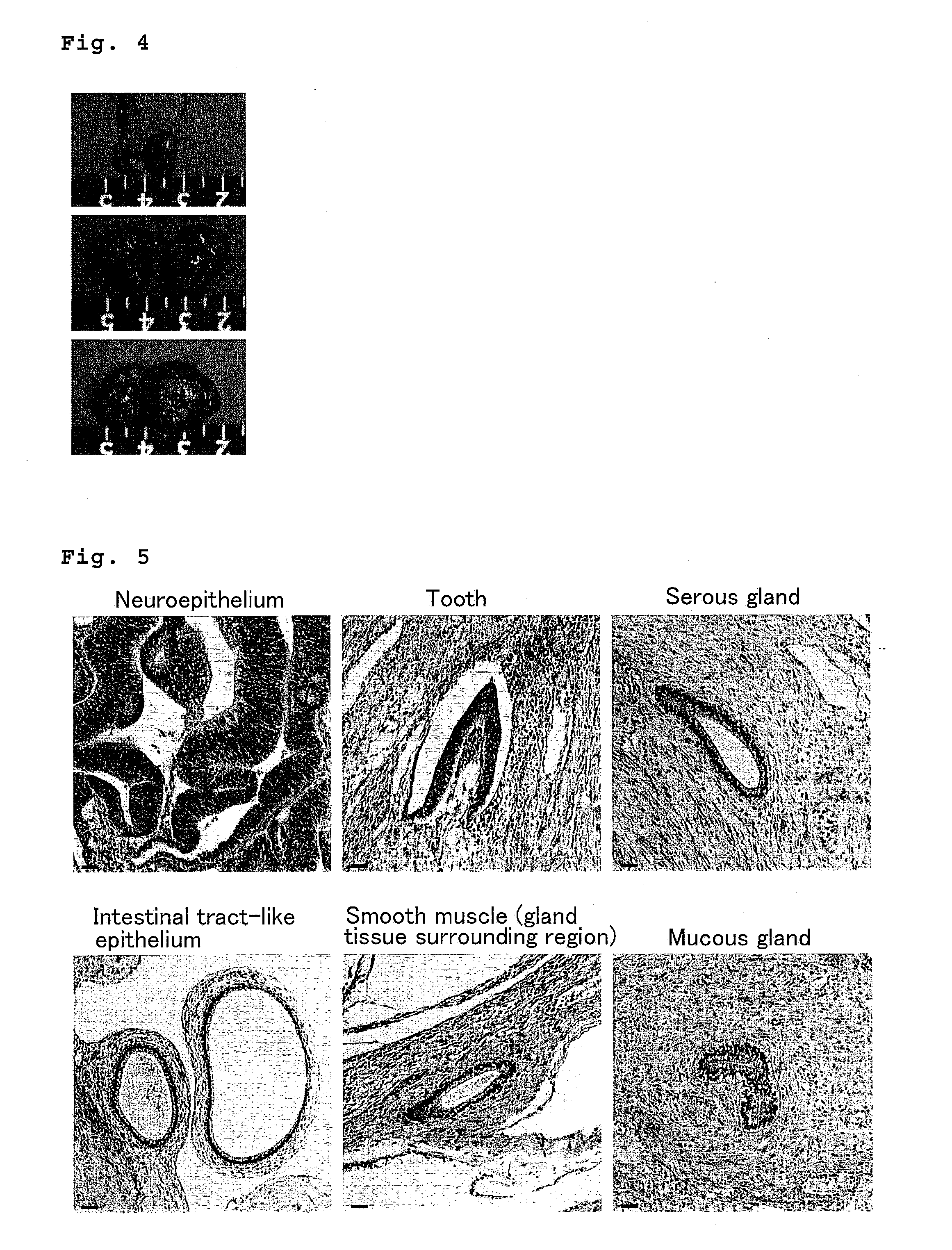
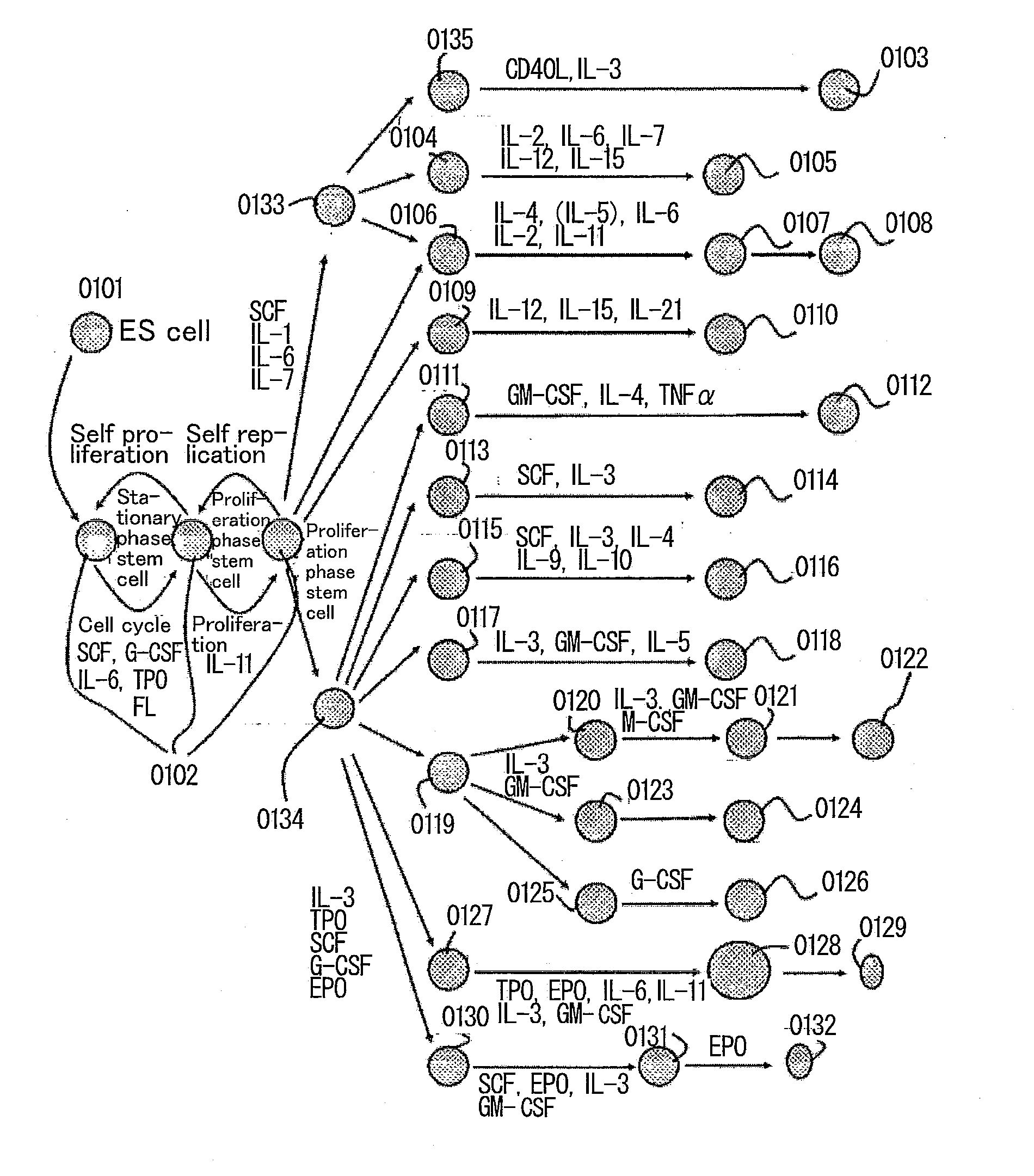
Cell differentiation is the process by which genetically identical cells of an embryo become specialized or the process by which stable differences arise between cells of the embryo.
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
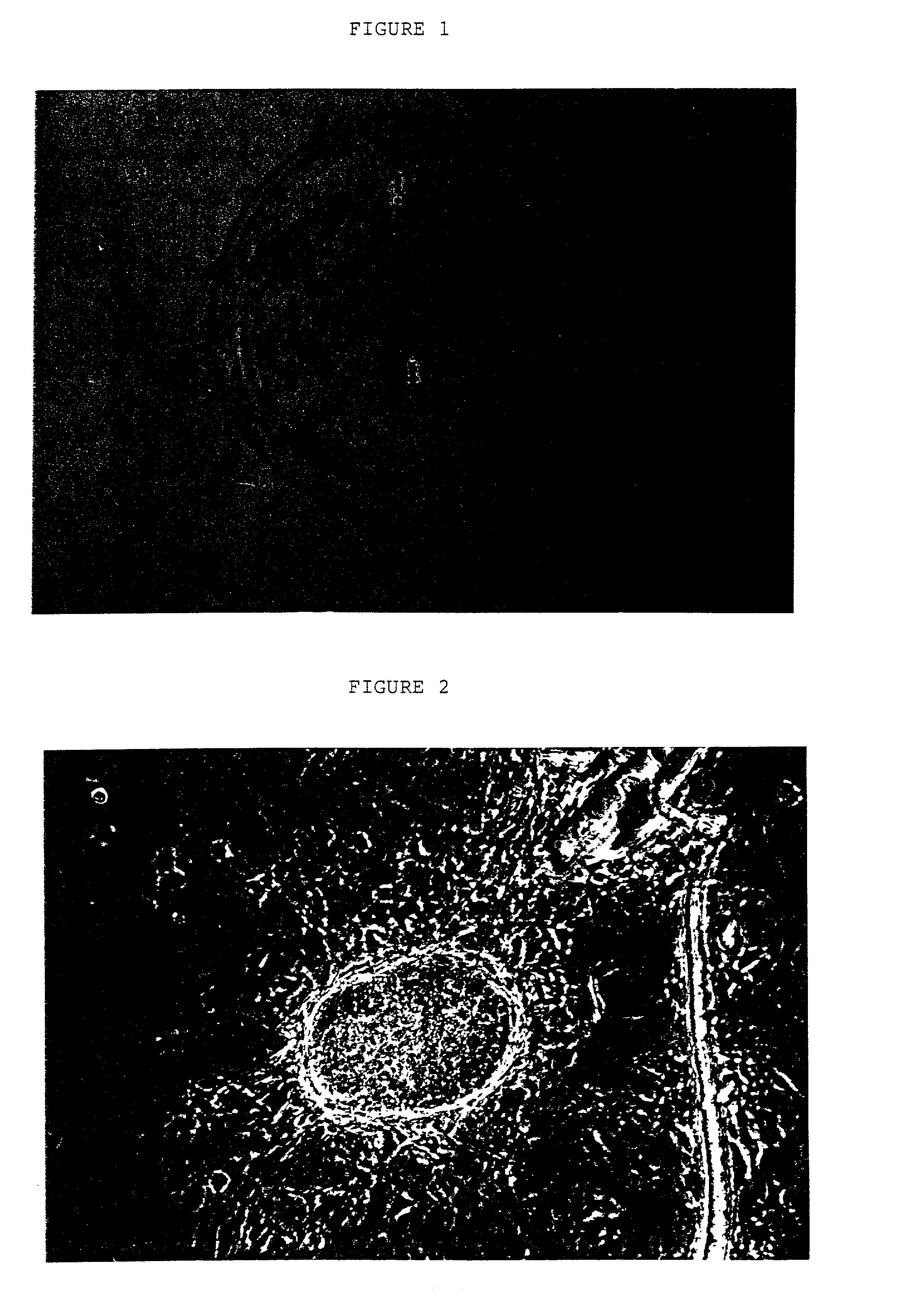
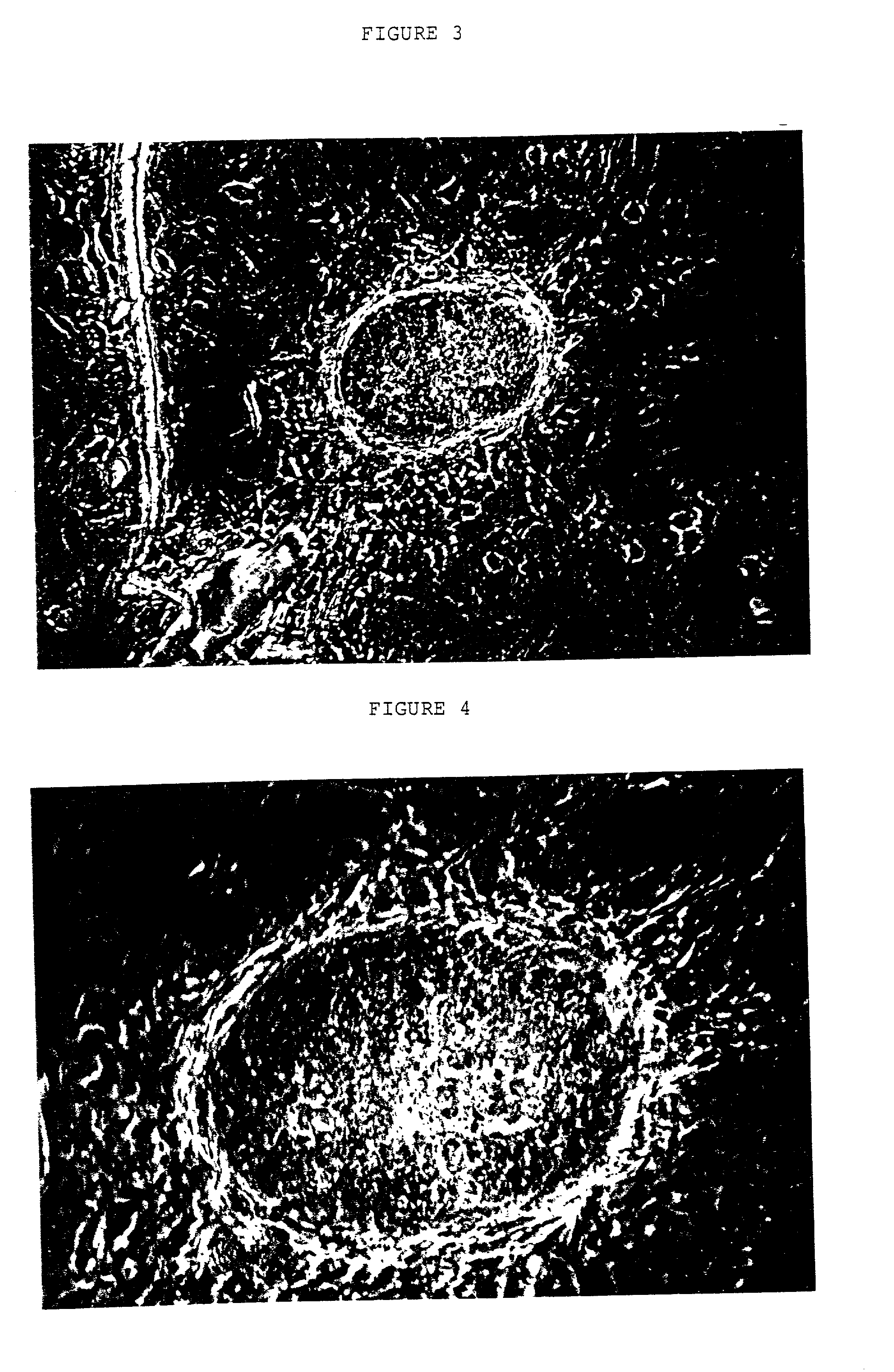
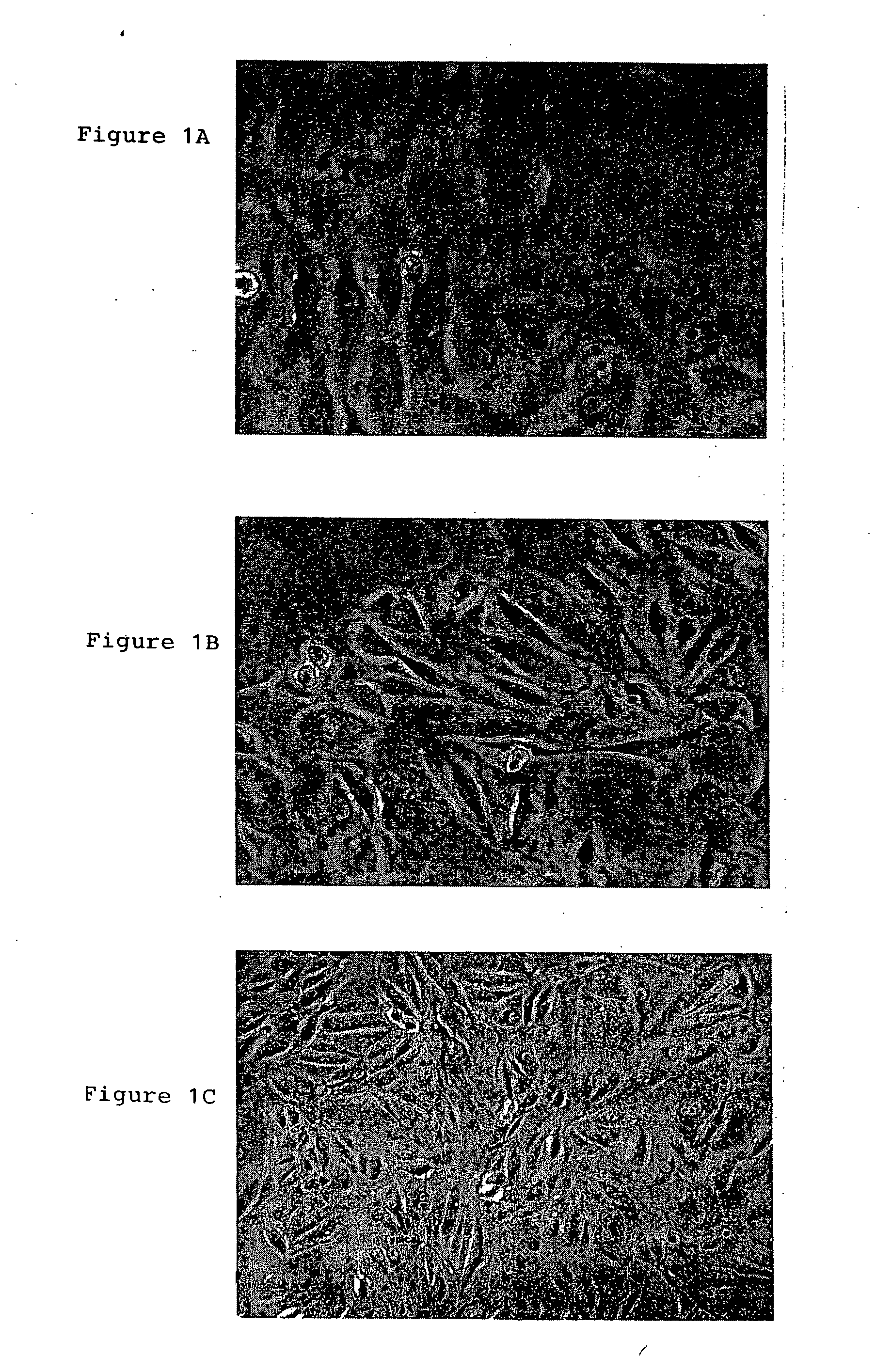
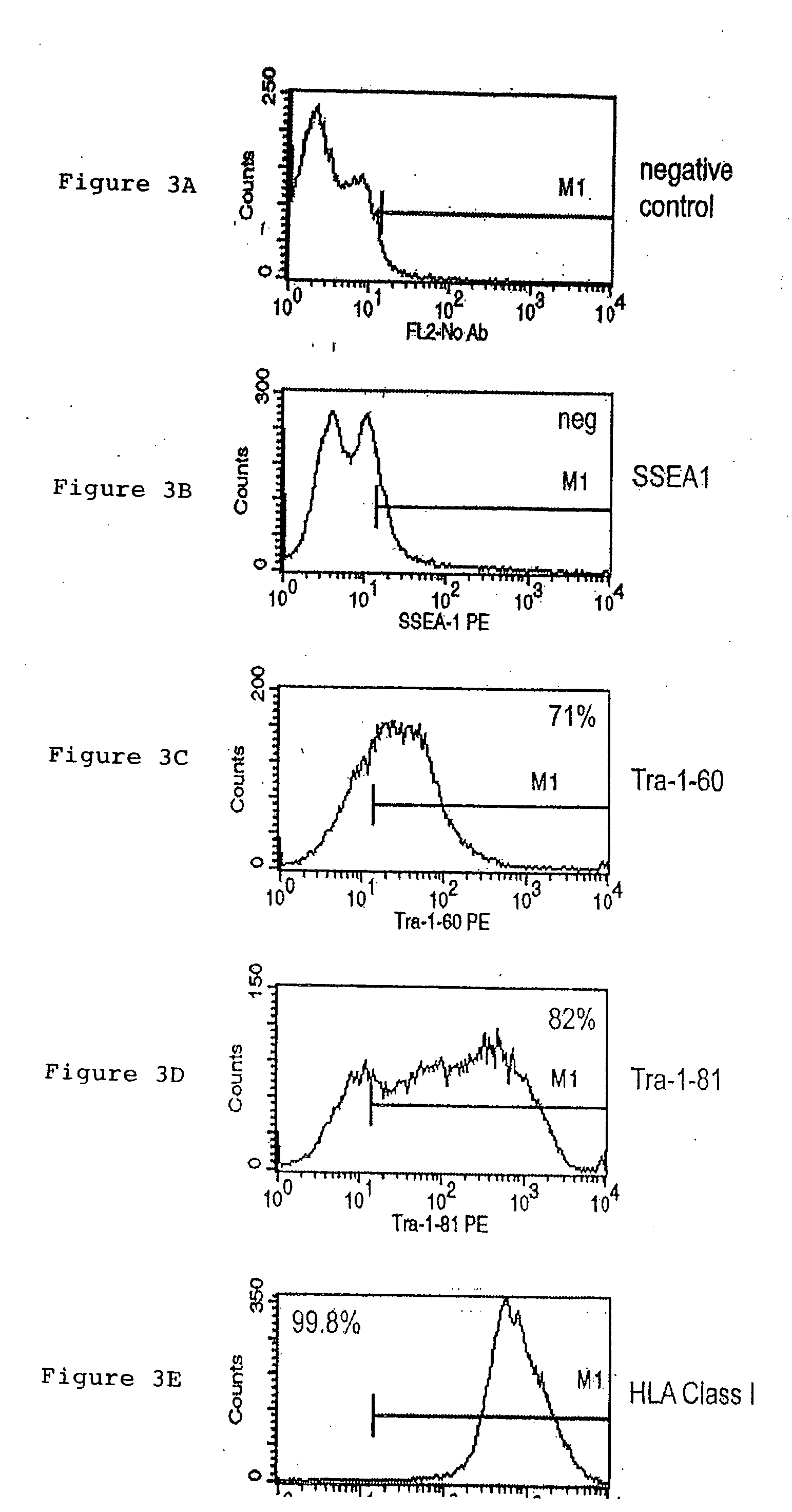
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production of reprogrammed cells with restored potential
InactiveUS20070032447A1Reduce in quantityDifferentiation potential in differentiatedBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsNuclear transferGenome
A method for treating cells and / or nuclear transfer units and / or stem cells in culture with such compounds, individually or in combinations, is described. The method results in a globally hypomethylated genome and a restoration of cell differentiation and / or developmental potential, or potentiality. In addition, a method for the in vitro production of reprogrammed cells which have had differentiation potential (totipotential, pluripotential, or multipotential) restored by demethylating the genome is described.
Owner:NUPOTENTIAL INC
Conditionally immortalized long-term stem cells and methods of making and using such cells
ActiveUS20100297763A1Inhibit apoptosisPromotes proliferationVirus peptidesApoptosis related proteinsDiseaseStudy methods
Disclosed are methods for conditionally immortalizing stem cells, including adult and embryonic stem cells, the cells produced by such methods, therapeutic and laboratory or research methods of using such cells, and methods to identify compounds related to cell differentiation and development or to treat diseases, using such cells. A mouse model of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cells and methods related to such mouse model are also described.
Owner:NAT JEWISH HEALTH +1
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation and methods for enhancing embryonic development by genetic alteration of donor cells or by tissue culture conditions
InactiveUS20030229908A1Good curative effectIncrease productionNew breed animal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEmbryo
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of differentiated donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation. Also, methods for improving nuclear transfer efficiency by genetically altering donor cells to inhibit apoptosis, select for a specific cell cycle and / or enhance embryonic growth and development are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Generation of neural stem cells from undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050255589A1Improve portabilityPotent in vivoNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorNeural cell
The present invention relates to the generation of neural cells from undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. In particular it relates to directing the differentiation of human ES cells into neural progenitors and neural cells and the production of functioning neural cells and / or neural cells of a specific type. The invention also includes the use of these cells for the treatment of neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ES CELL INT
Aging-resistant eye cream
InactiveCN104586666AEliminate melaninPromote regenerationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycerolCell differentation
Owner:GUANGZHOU EUROVMY BIOLOGICAL TECH
Cell differentiation of adipose-derived precursor cells
The present invention provides a simple method for controlled differentiation of adipose-derived precursor cells. A method is provided for preparing a differentiated cell. The method comprises A) obtaining a mixture by mixing a) an adipose-derived precursor cell and b) a differentiated cell corresponding to a desired site; and B) culturing the mixture under sufficient conditions which allow the adipose-derived precursor cell to differentiate. The present invention also provides a composition for cell implantation comprising a) an adipose-derived precursor cell and b) a differentiated cell corresponding to a desired site.
Owner:BIOMASTER
Method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve cells through in vitro induction
InactiveCN102899285APromote partial recoveryPromote regenerationNervous disorderMammal material medical ingredientsOLIG2Conceptus
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and relates to a method for differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve cells through in vitro induction, especially to a method for induction of Olig2<+>-GFP<+>-mES nerve cell differentiation through a purine derivative Purmorphamine, and uses thereof. According to the present invention, an embryoid body mediated nerve induction method is adopted, Olig2-GFP<+>-mES is adopted as a cell model, a purine derivative Purmorphamine and all-trans retinoic acid are combined to carry out directed induction on the Olig2-GFP<+>-mES cells to obtain spinal motor neurons and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells through differentiation; experiment results show that the Purmorphamine can be used as a substitute of SHH, can effectively induce Olig2<+>-GFP<+>-mES differentiation to obtain high purity and function spinal motor neurons and oligodendroglial cells, and can cause expression changes of related genes; and transplant experiment results show that the induced nerve cells can promote partial function and morphology restoration after rat spinal cord injury, and have effects of spinal cord injury regeneration promotion and function reconstruction.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
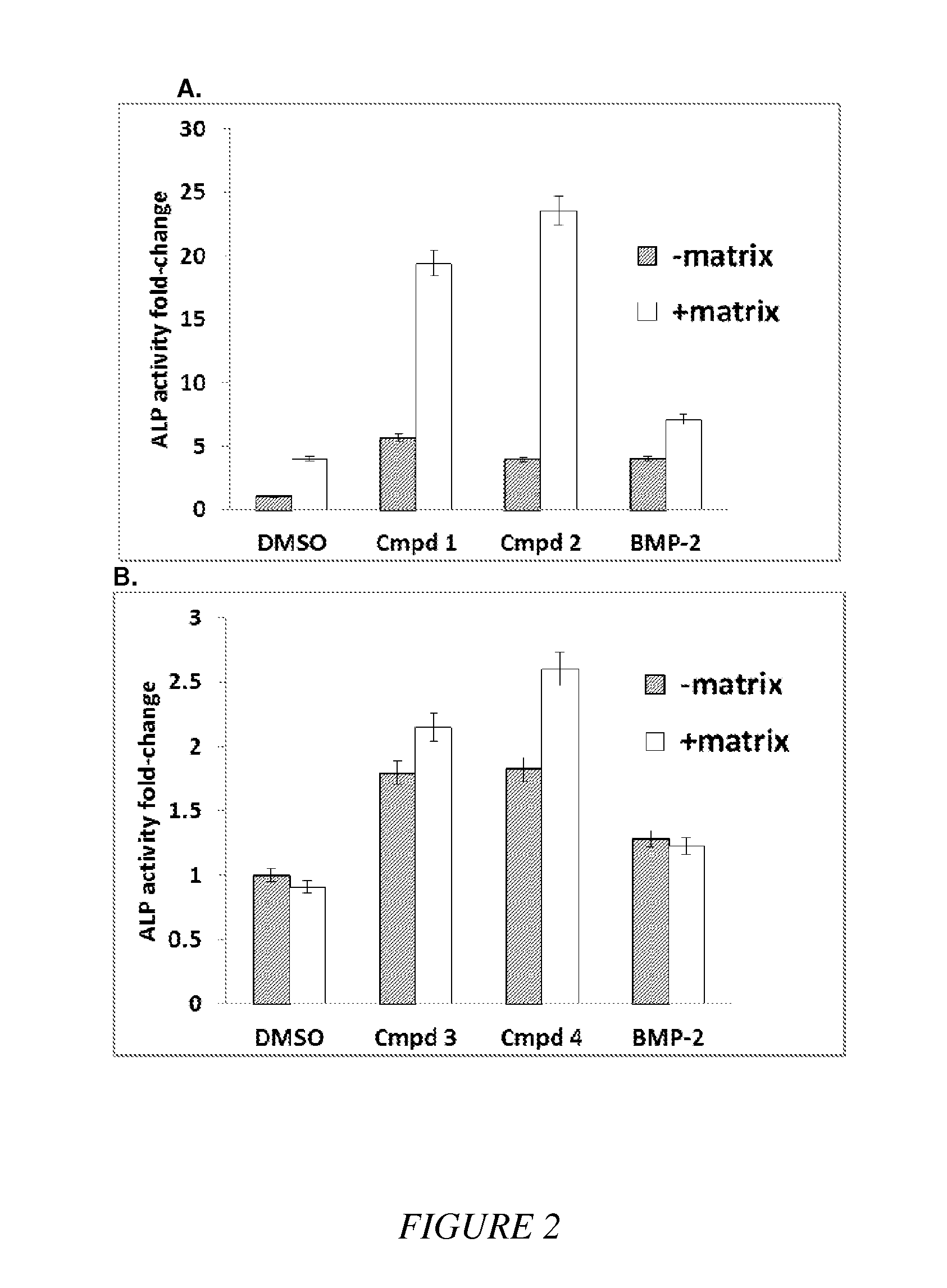
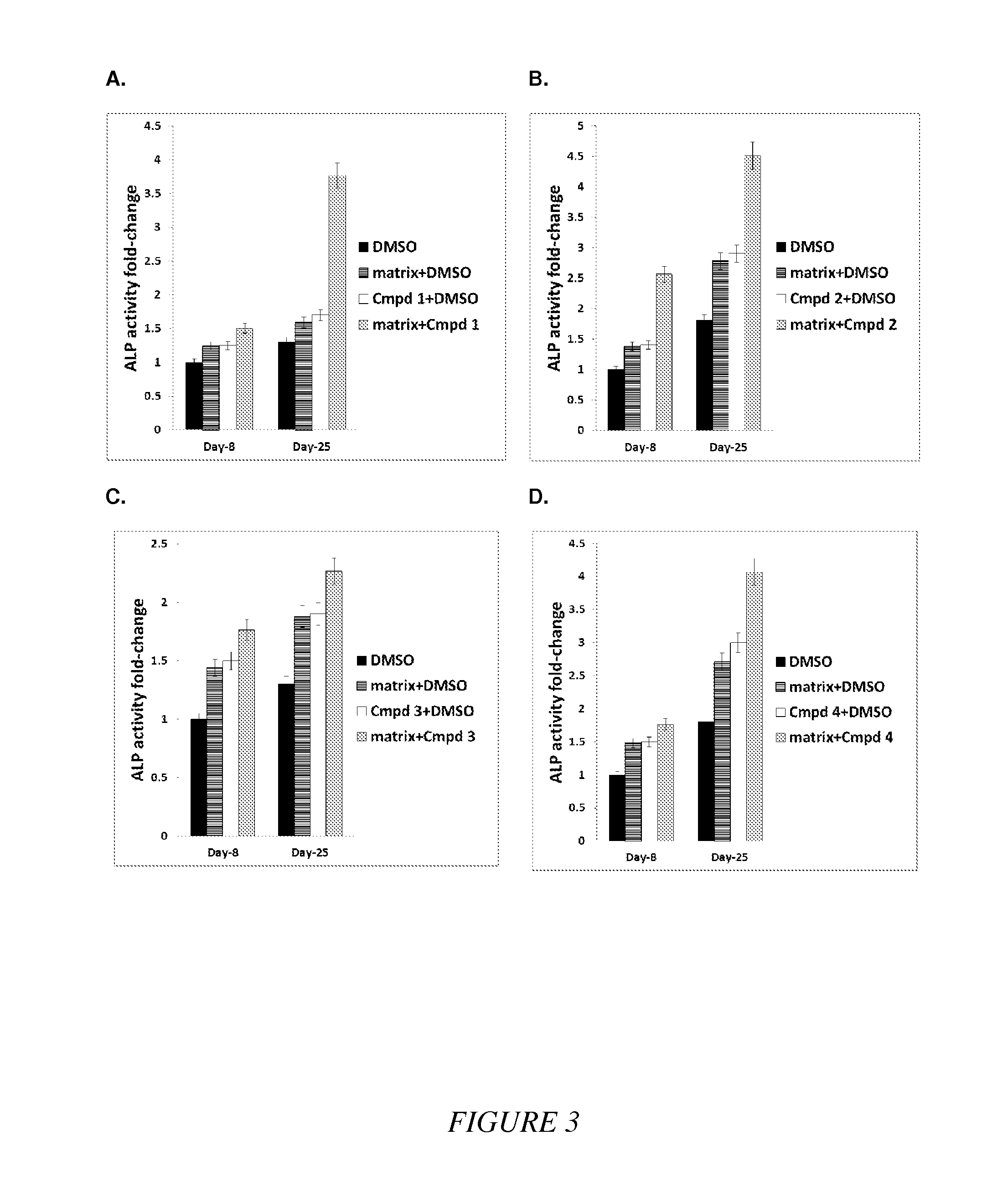
Compounds and matrices for use in bone growth and repair
Compositions of small molecules, matrices, and isolated cells including methods of preparation, and methods for differentiation, transdifferentiation, and proliferation of animal cells into the osteoblast blast cell lineage were described. Examples of osteogenic materials that were administered to cells or co-cultured with cells are represented by compounds of Formula II, IV, and VI independently or preferably in combination with a matrix to afford bone cells. Small molecule-stimulated cells were also combined with a matrix, placed with a cellular adhesive or material carrier and implanted to a site in an animal for bone repair. Matrix pretreated with compounds of Formula II, IV, and VI were also used to cause cells to migrate to the matrix that is of use for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:HUMAN BIOMOLECULAR RES INST
B cell-derived ips cells and application thereof
InactiveUS20110231944A1Low costLow cost productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsMonoclonal antibodyImmunodeficient Mouse
Provided are a B cell-derived iPS cell generated using a convenient technique, a technology for providing a human antibody at low cost using the iPS cell, an immunologically humanized mouse prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell, and the like. Also provided are a cloned cell obtained by contacting a B cell with nuclear reprogramming factors excluding C / EBPα and Pax5 expression inhibiting substances, particularly nucleic acids that encode Oct3 / 4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc, wherein the cloned cell has an immunoglobulin gene rearranged therein and possesses pluripotency and replication competence (B-iPS cell). Still also provided are a method of producing a monoclonal antibody against a specified antigen, comprising recovering an antibody from a culture of B cells obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell derived from a B cell immunized with the specified antigen, and a method of generating an immunologically humanized mouse, comprising transplanting to an immunodeficient mouse a human immunohematological system cell obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell.
Owner:RIKEN
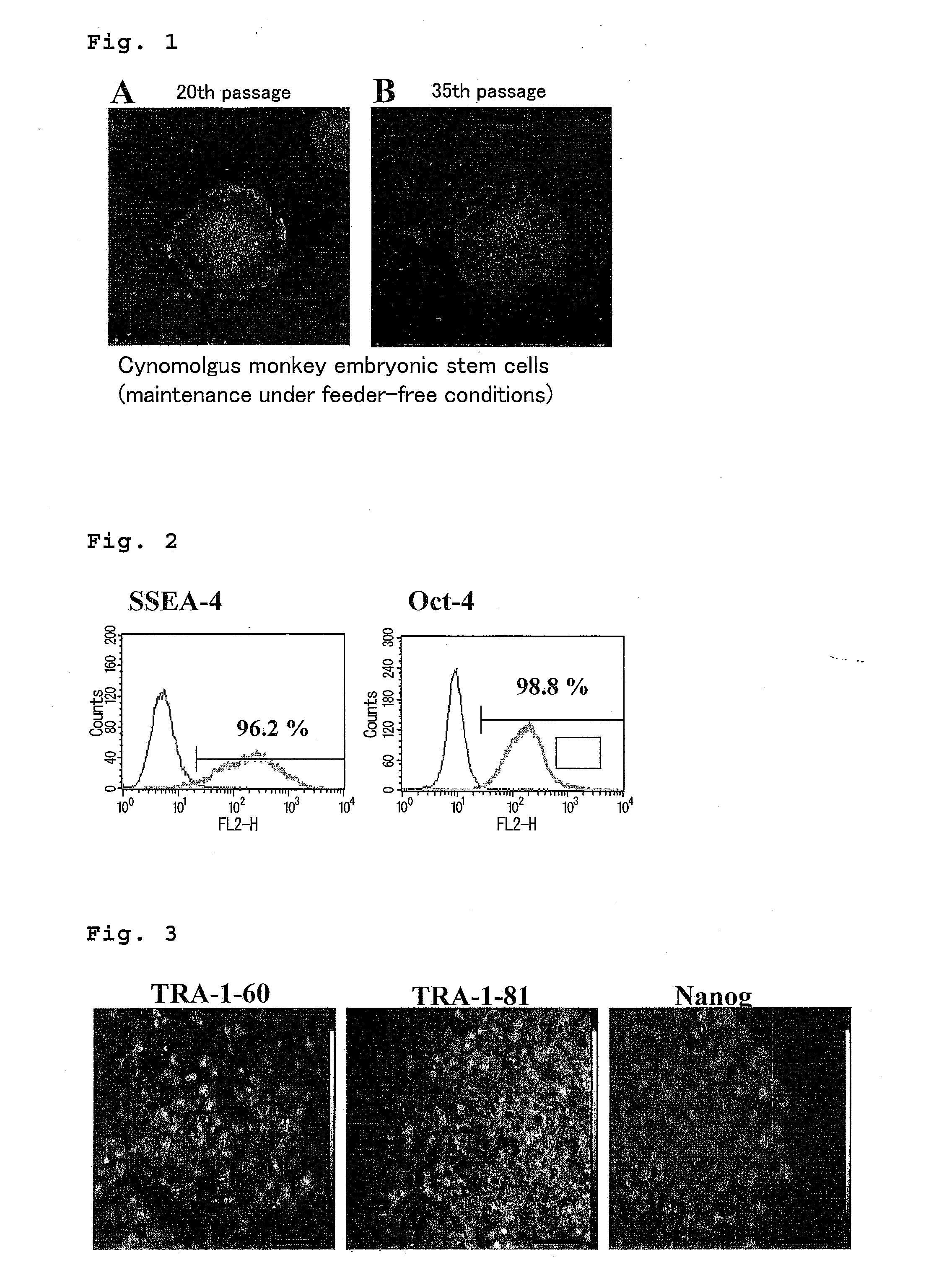
Method for culturing and subculturing primate embryonic stem cell, as well as method for inducing differentiation thereof
InactiveUS20110151554A1Safely culturedLow costCell dissociation methodsCulture processCell-Extracellular MatrixVascular endothelium
The present invention provides a method for subculturing primate embryonic stem cells, and a method for inducing differentiation of the same cell into a vascular endothelial cell and a blood cell. The present invention provides a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a medium containing a protein component without using feeder cells and cytokines in a container coated with an extracellular matrix, detaching colonies of the resulting embryonic stem cells in the presence of a cytodetachment agent, and plating the colonies in the similar medium, and a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a serum-containing or not containing medium in the presence of cytokine, adhesion-culturing the resulting embryoid body or embroyid body-analogous cellular aggregate in the presence of a cytokine to obtain specific precursor cells, and separating non-adherent cells and adherent cells from the specific precursor cells to obtain blood cells and vascular endothelial precursor cells.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GLOBAL HEALTH & MEDICINE +2
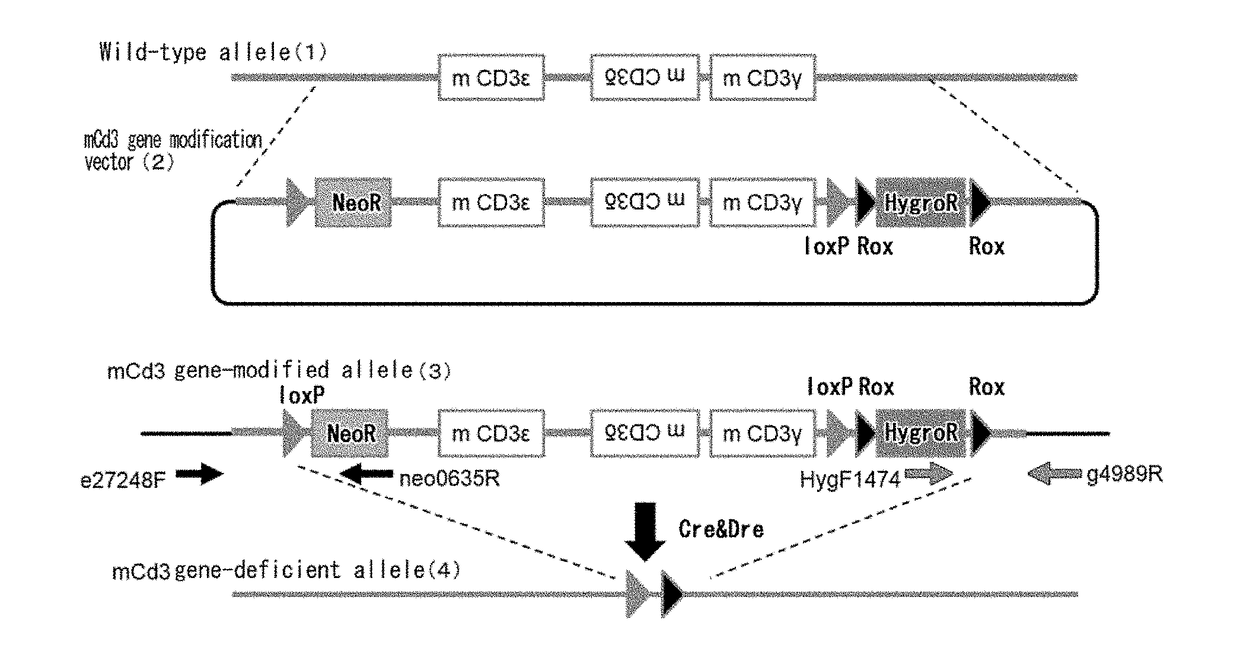
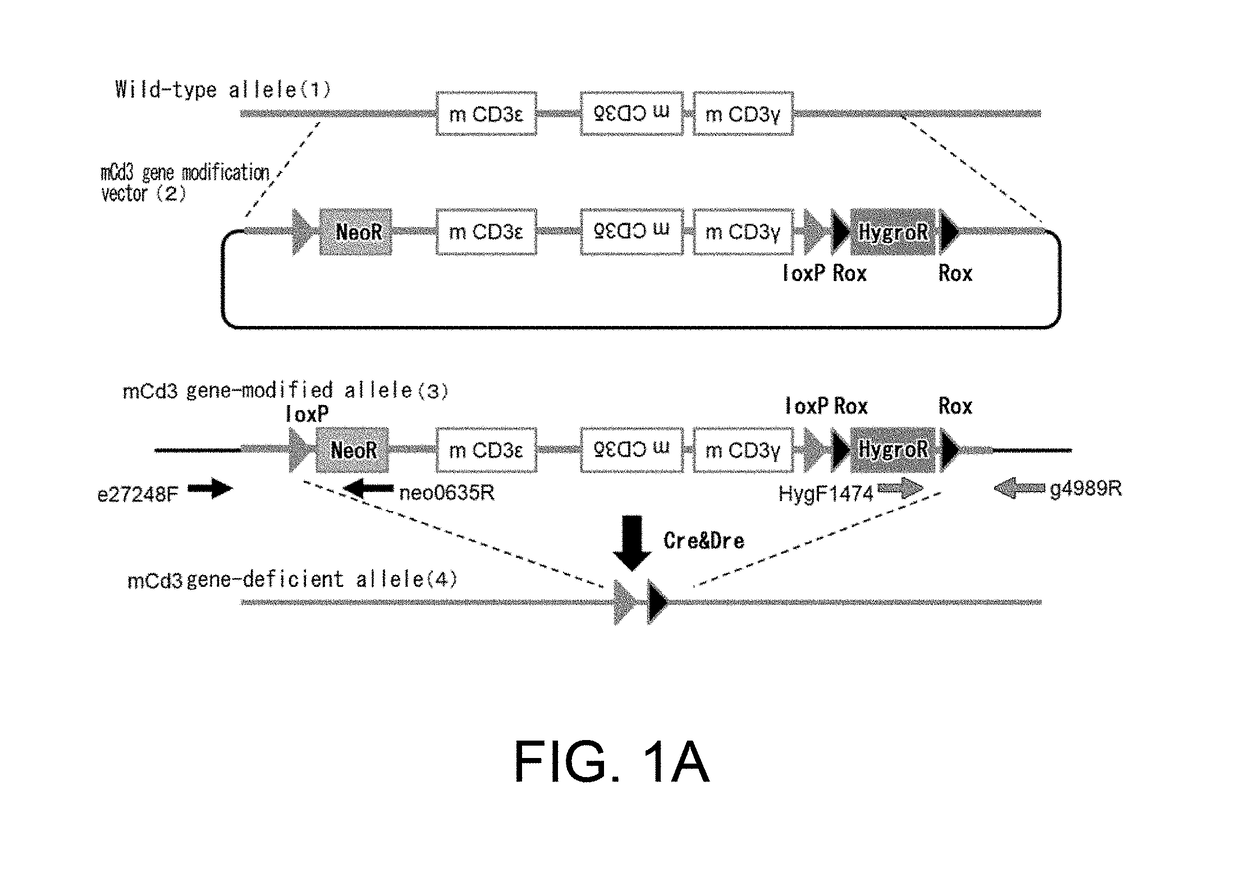
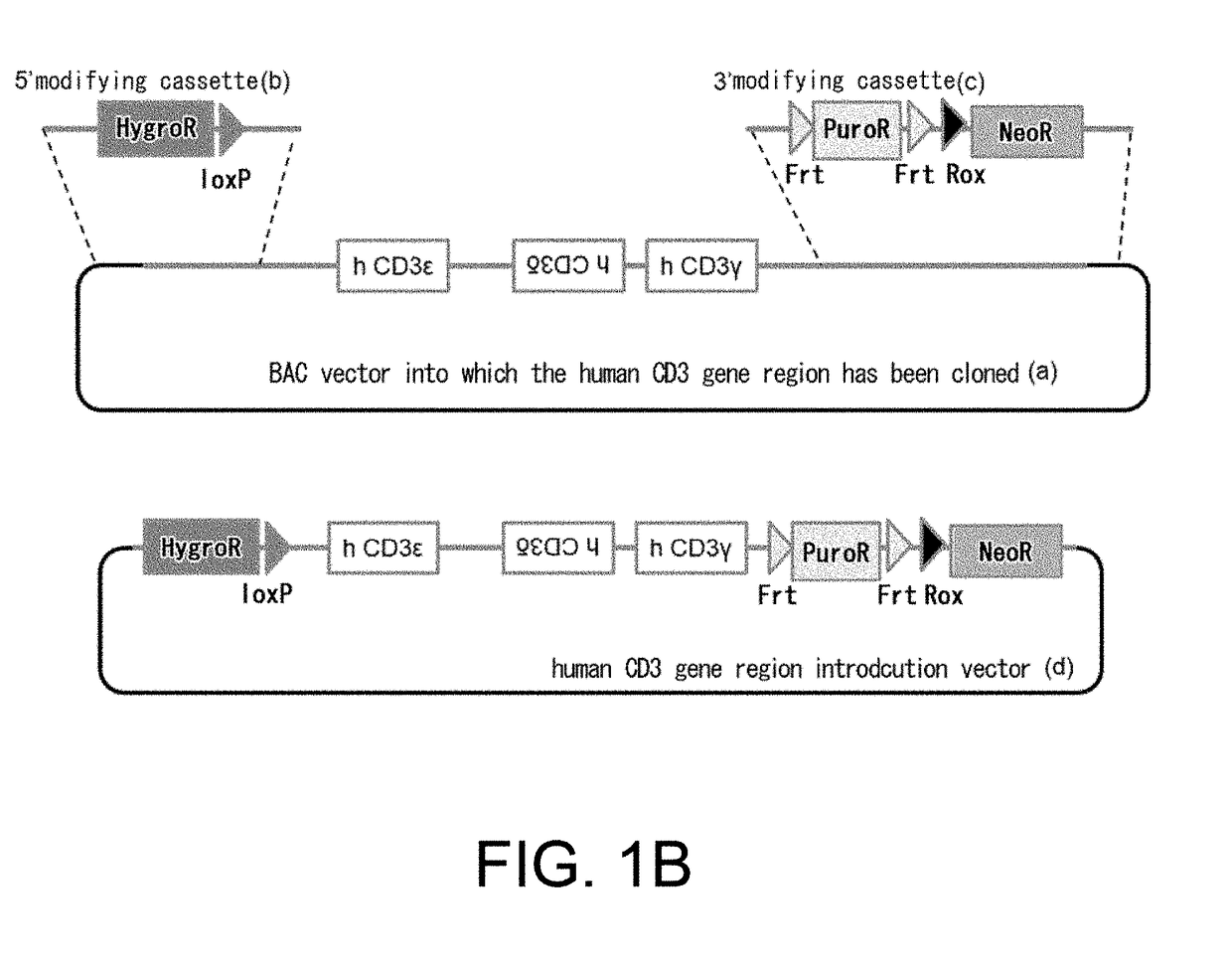
Non-human animal having human cd3 gene substituted for endogenous cd3 gene
ActiveUS20180192623A1Appropriately evaluatedImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulinsMature T-CellT cell
The present invention provides genetically modified non-human animals which are deficient in at least one or more types of CD3 genes selected from the group consisting of endogenous CD3ε, CD3δ, and CD3γ in its genome and functionally express at least one or more types of human CD3 genes selected from the group consisting of human CD3ϵ, CD3δ, and CD3γ. In the genetically modified non-human animals of the present invention, mature T cell differentiation and production can take place, and immunocompetent cells including T cells can exert their functions. The genetically modified non-human animals of the present invention enable efficient evaluation and screening in the development of therapeutic agents and therapeutic methods that use human CD3-mediated targeted drugs.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for inducing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells of human embryo livers into islet beta-like cells and stably expressing insulin and special induced liquid thereof
InactiveCN101580818AOvercome the instability of expression and other deficienciesAvoid Biosecurity ConcernsTissue cultureFermentationCell massEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells of human embryo livers into islet beta-like cells and stably expressing insulin and special induced liquid thereof. The method comprises the following steps: separating, purifying and amplifying mesenchymal stem cells of human embryo livers; then taking out cells formed after the third generation and inducing the cells by the special induced liquid to obtain islet beta-like cell mass capable of expressing the insulin stably. The induced liquid can be obtained by adding TAT-PDX1 fusion protein in cell culture fluid. The method can realize in-vitro induction of mesenchymal stem cells of human embryo livers into islet beta-like cells capable of secreting the insulin stably. When transplanted in the body of a diabetic patient, the obtained islet beta-like cells can further adjust blood sugar level so as to realize cell therapy of diabetes. Therefore, research in the field has broad clinic application prospect and can bring greater economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
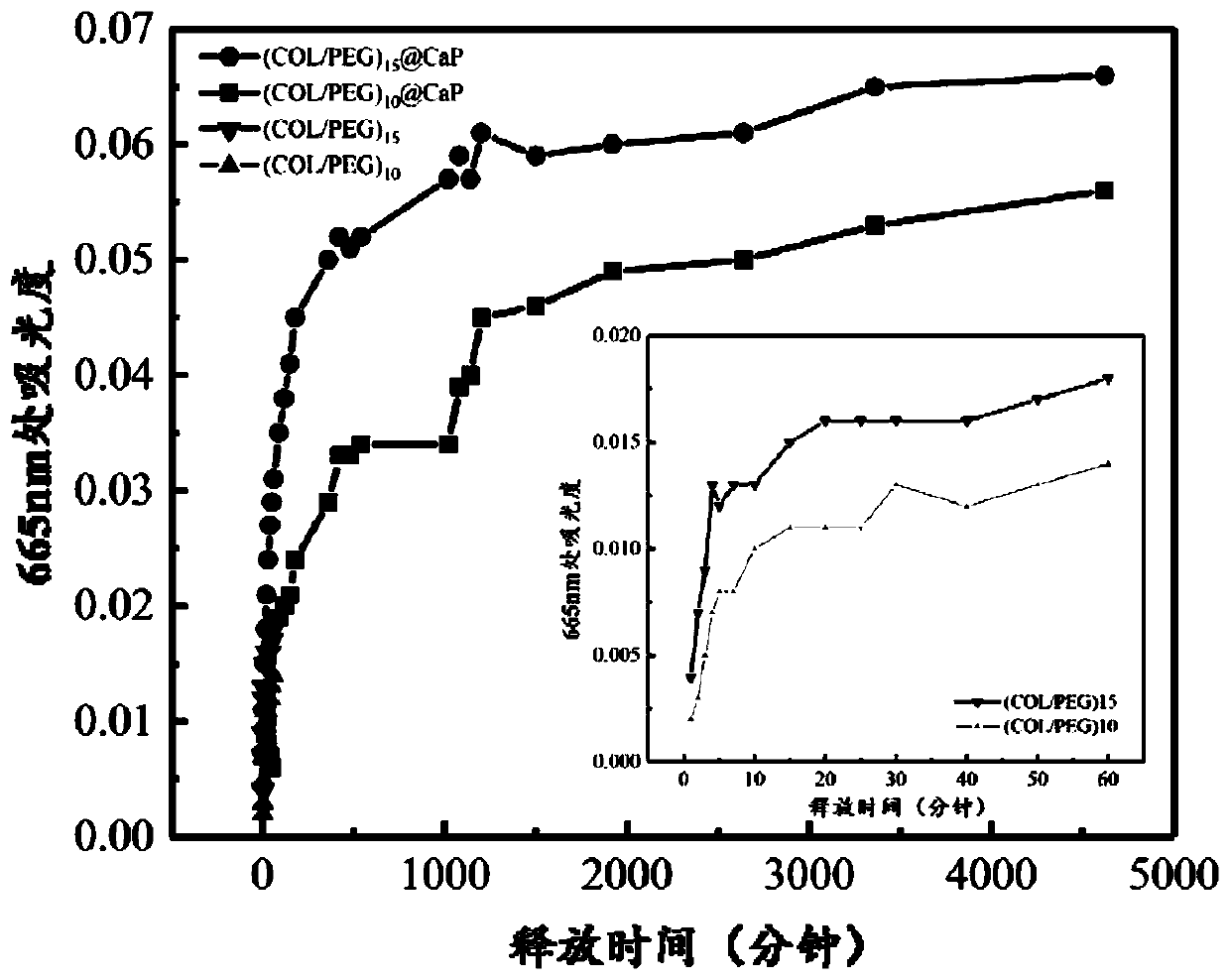
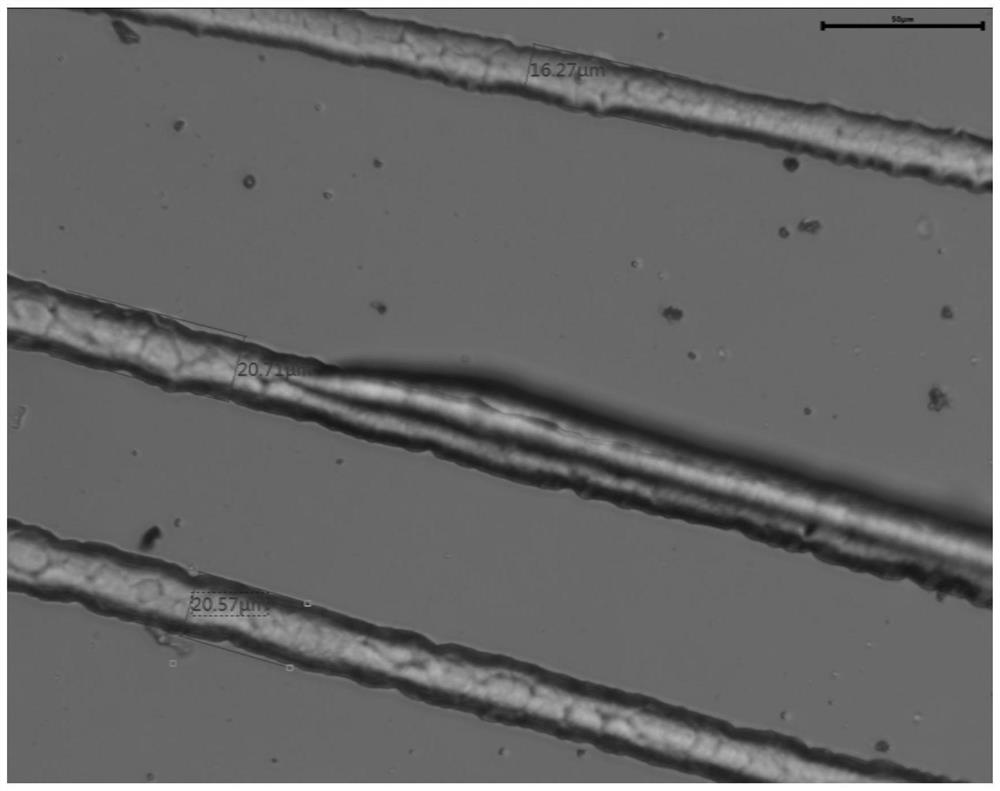
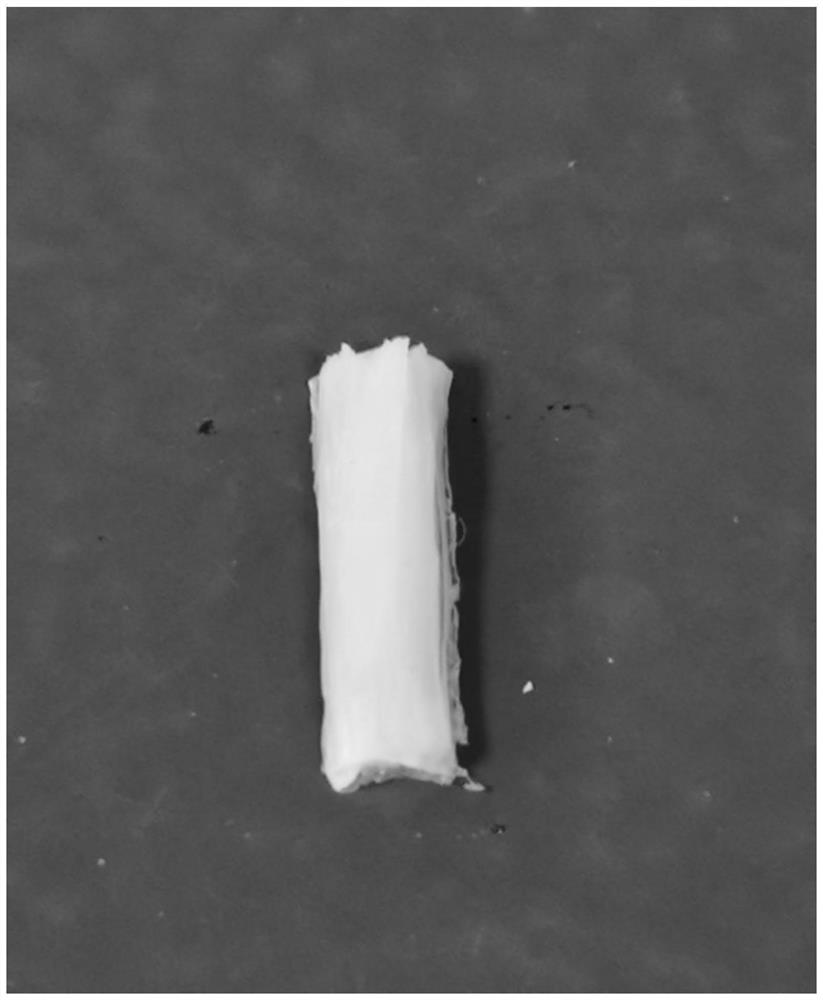
Preparation method of COL/PEG@CaP biomineralization multilayer film
InactiveCN110734646AImprove biotoxicityGood biocompatibilityCoatingsProsthesisMultilayer membraneCell differentation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a COL / PEG@CaP biomineralization multilayer film. According to the preparation method, titanium alloy is taken as a substrate, the surface adhesiveness of the titanium alloy is improved with PDA; on the PDA modified titanium alloy substrate, COL and PEG are taken as polyelectrolytes, layer-by-layer self-assembly technology is adopted to prepare a COL / PEG self-assembled multilayer film; and at last, the COL / PEG@CaP biomineralization multilayer film is prepared through biomineralization. The COL / PEG@CaP biomineralization multilayer film prepared bythe invention can effectively improve the biotoxicity of inorganic particles in vivo; the preparation process is simple, low in cost, short in period and suitable for mass production, and has a wide application prospect; the prepared (COL / PEG)@CaP mineralized film has the functions of drug loading and release, osteoblast directional differentiation control and cell differentiation degree detection, and has a wide application prospect in the field of tissue engineering.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Compositions and methods for neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells
The present invention provides compositions and methods for human neural cell production. More particularly, the present invention provides cellular differentiation methods employing an essentially serum free MEDII conditioned medium for the generation of human neural cells from pluripotent and multipotent human stem cells.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Spinal cord injury repair material and preparation method of tissue engineering scaffold
ActiveCN113181428AGood repeatabilityEasy to prepareTissue regenerationProsthesisSpinal cord lesionSpinal cord
The invention relates to the technical field of regenerative medicine, in particular to a spinal cord injury repair material and a preparation method of a tissue engineering scaffold. The spinal cord injury repair material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10 to 40 parts of water-soluble polymer material, 5 to 20 parts of spinal cord biological material, 10 to 20 parts of hydrogel and 0 to 5 parts of medicine. According to the spinal cord injury repair material, the polycaprolactone with good water solubility is used as the high polymer material fiber, the polycaprolactone and a hydrogel material are easy to obtain as raw materials, the micron fiber forming ink prepared from the polycaprolactone is simple to prepare, a medicine for regulating and controlling the differentiation of neuronal stem cells can be loaded in situ, and the spinal cord removal cell biological material can provide a similar growth environment for the neural stem cells, so that the survival time of the neural stem cells is prolonged, the neural stem cells are guided and promoted to differentiate into the neuronal cells, and the prepared tissue engineering scaffold is relatively good in repeatability.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF YOUJIANG MEDICAL UNIV FOR NATTIES +1
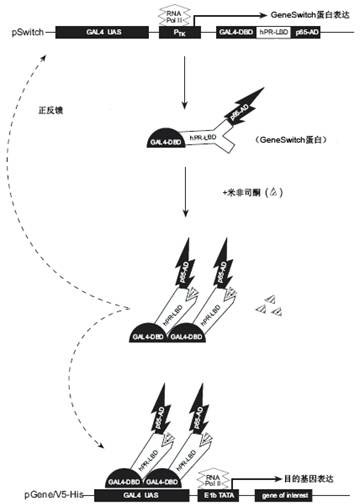
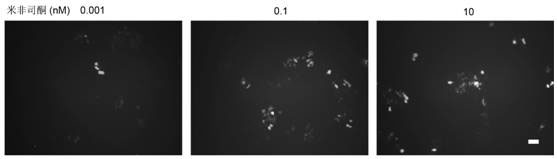
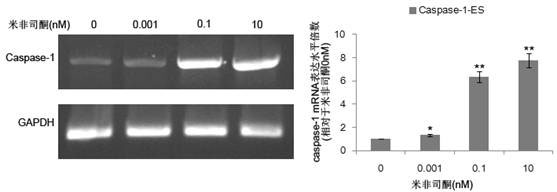
Caspase-1-ES cell line induced by mifepristone
InactiveCN102424818ADoes not affect differentiation potentialReduce the risk of transplantation tumorNervous disorderAntipyreticIntracellularCaspase
The invention relates to a caspase-1-ES cell line induced by mifepristone. The collection number of the caspase-1-ES cell line is CCTCC No.C201193. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the cell line. The invention has the advantages that: caspase-1 is transferred into an embryonic stem (ES) cell for the first time, and the differential potential of the cell is not influenced; the caspase-1 is highly expressed in the ES cell for the first time, it is proved that activated caspase-1 initiates DNA damage to cause death of undifferentiated caspase-1-ES cells in vitro, and a risk of nodule formation caused by ES cell transplantation is reduced; it is discovered that the highly expressed caspase-1 in the differentiated ES cell does not obviously influence the cell for the first time, and the treatment effect of the ES cell is maintained; and the safety of embryonic stem cell transplantation is improved, the effect of treating parkinson disease and other neurologic diseases is remained, and the caspase-1-ES cell line can be widely applied to stem cell transplantation.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method for inducing selectively suppressed immune response to transplanted tissue or cells
InactiveUS7625557B2Raise the possibilitySuppress immune rejectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompounds screening/testingAbnormal tissue growthDendritic cell
Transimmunization methods incorporating skin immunologic challenges are described for either selectively suppressing the immune response of recipients of transplanted tissue or cells or monitoring induced anti-cancer immunity. In one embodiment, skin from the transplant donor is allografted to the transplant recipient to induce an immunological response to the transplanted skin. A quantity of blood is taken from the recipient and treated to render the T cells in the blood apoptotic and to induce differentiation of blood monocytes into dendritic cells. The treated blood is incubated and administered to the recipient to induce formation of suppressor T cell clones which reduce the number of T cells attacking the transplanted tissue or organ. This tolerogenic approach can be complemented by also feeding the immature dendritic cells apoptotic or necrotic cells from the organ donor. In a second embodiment, dendritic cells loaded with tumor antigens are injected intradermally to monitor the anti-cancer immunity induced by Transimmunization.
Owner:YALE UNIV
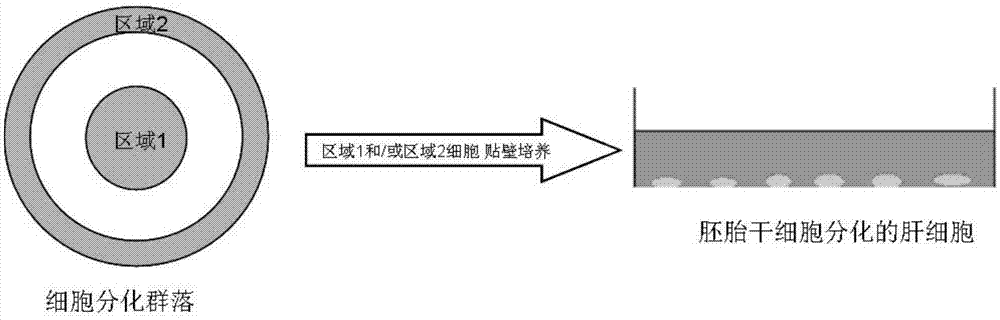
Sorting method of hepatocytes of which embryonic hepatic cells are differentiated
InactiveCN105441382AProtective functionAvoid damageCulture processArtificial cell constructsRound cellConceptus
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell culture, and in particular relates to a sorting method of hepatocytes of which embryonic hepatic cells are differentiated. According to the sorting method, the embryonic hepatic cells are cultured into embryoid bodies in a shaking or suspension culture mode, then the embryoid bodies are cultured in an adherent culture mode, so as to gradually grow and differentiate into round differentiated cell communities, and cells in a specific area are selected to be sorted in a specific period and are cultured again in the adherent culture mode according to spatial distribution regularities of the differentiated hepatic cells in the round cell communities. In the process of adherent culture, according to a cell differentiation situation, EGFs (Epidermal Growth Factor), TGFs (Transforming Growth Factor), HGFs (Hepatocyte Growth Factor), OSMs and the like are selected as hepatic growth factors in the process that the embryoid bodies are differentiated into the hepatocytes, so as to promote the hepatocytes to differentiate, the whole sorting process has the advantages of simplicity in operation and low cost, cellular damage can be obviously reduced, compared with the prior art, the hepatic cell differentiation rate is greatly increased, the sorted cells grow with good conditions, and the cell purity and the cell functional requirements of hepatocyte transplantation can be satisfied.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
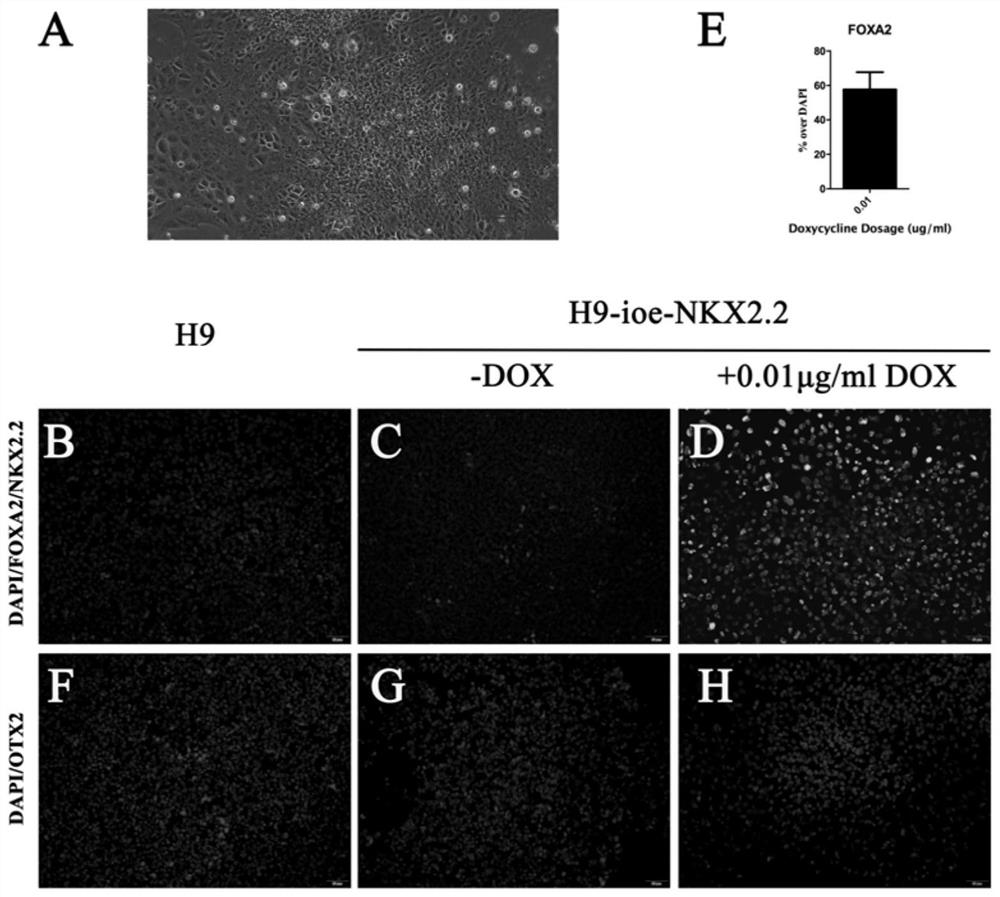
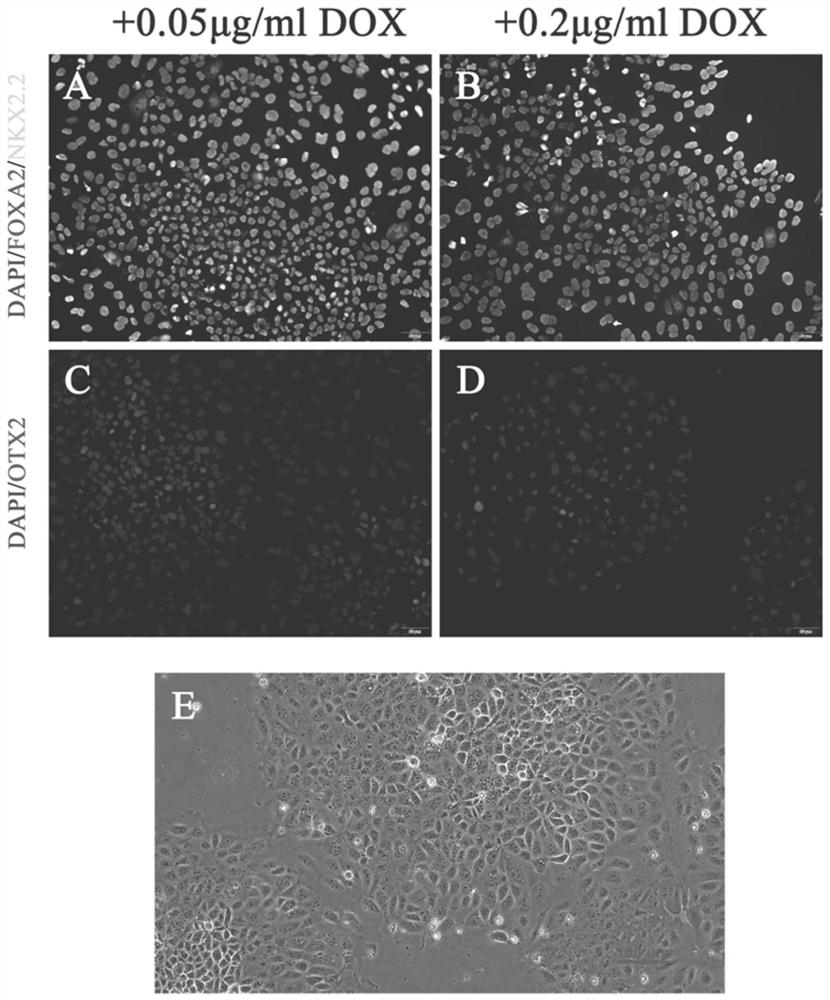
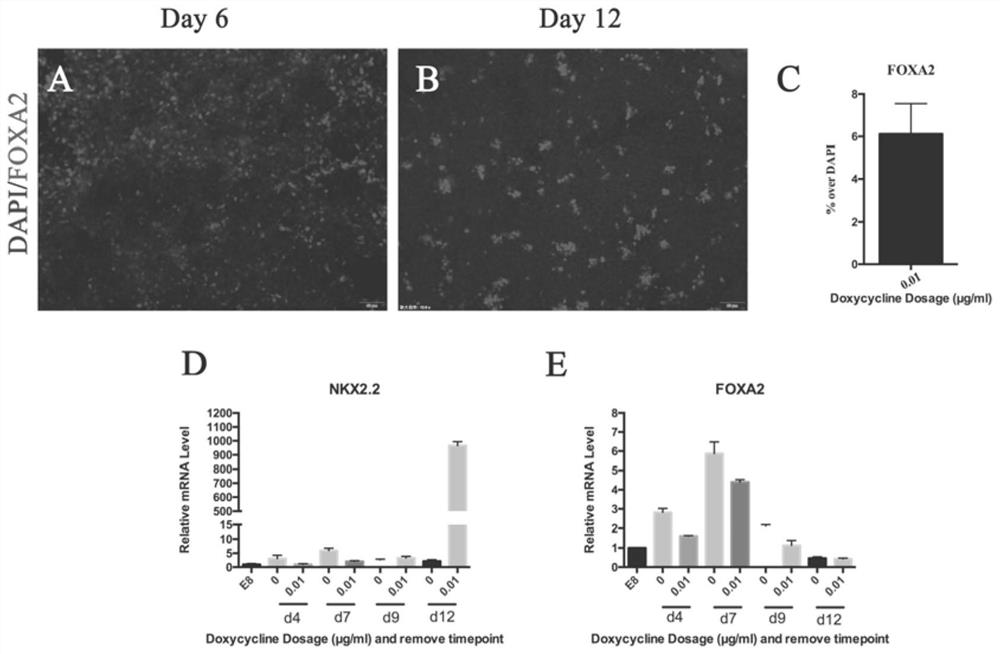
Method for obtaining human Floor Plate cells and application of human Floor Plate cells
ActiveCN113493773AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsBrain developmentCell differentation
The invention provides a method for obtaining human Flooor Plate (FP) cells in vitro. The method comprises the following steps: a human embryonic stem cell line H9 is modified through a gene, and an NKX2.2-CDS region and an inducible Tet-on expression system are inserted into a human chromosome 19 to obtain a human embryonic stem cell line H9-iOE-NKX2.2, of which the NKX2.2 expression level accurately depends on exogenous DOX dosage; and on the basis of H9-iOE-NKX2.2, the H9-iOE-NKX2.2 is cultured for 12 days by using a specific nerve induction culture medium, and meanwhile, the expression of NKX2.2 is induced at a low level in the first 6 days. According to the invention, the functional human Floor Plate cells secreting SHH can be rapidly obtained, and the human Floor Plate cells obtained by differentiation can be applied to in-vitro research of human neural circuit constitution, treatment of various brain development disorder diseases caused by FP cell abnormality and expansion of in-vitro brain cell differentiation methods.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
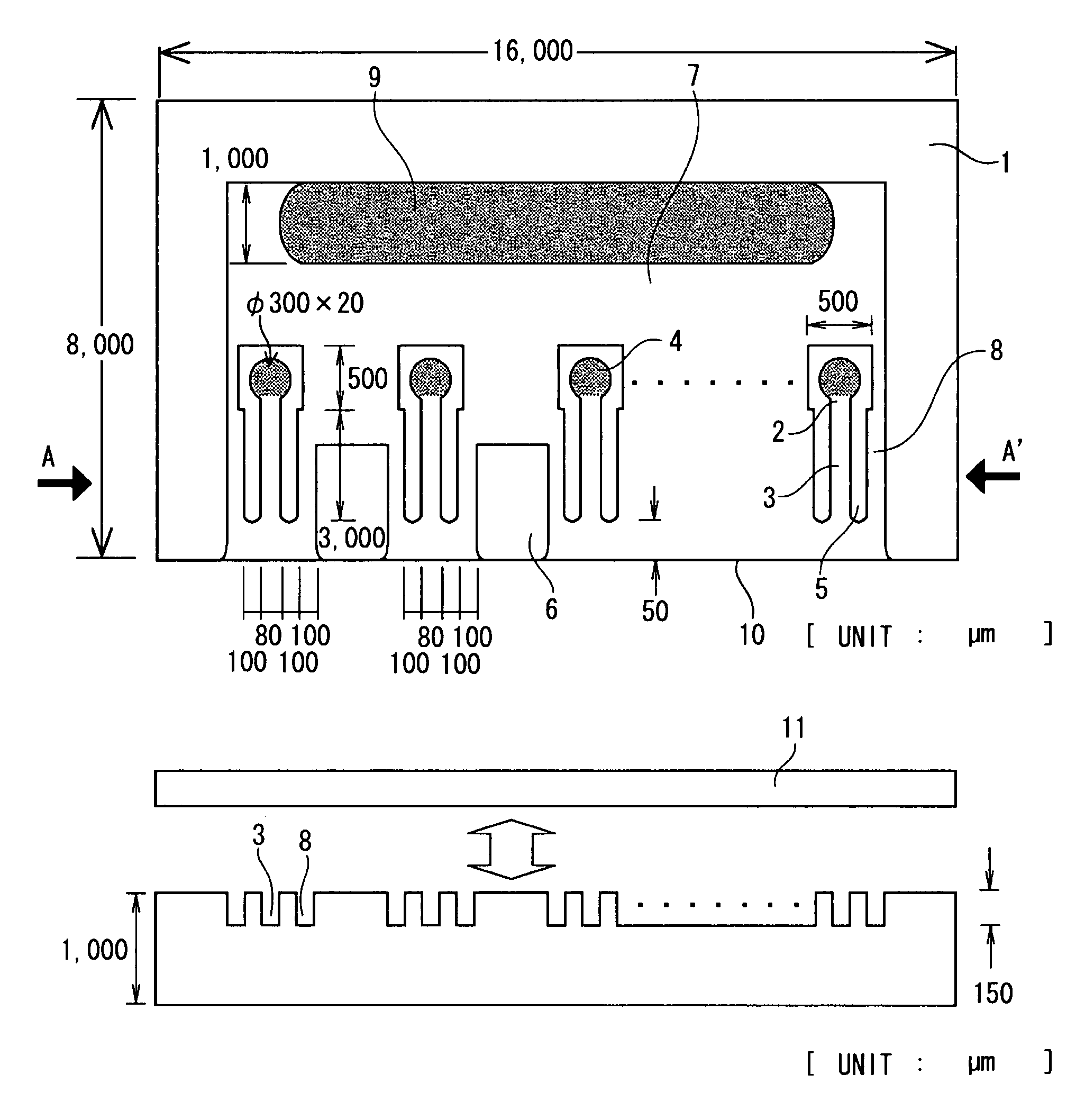
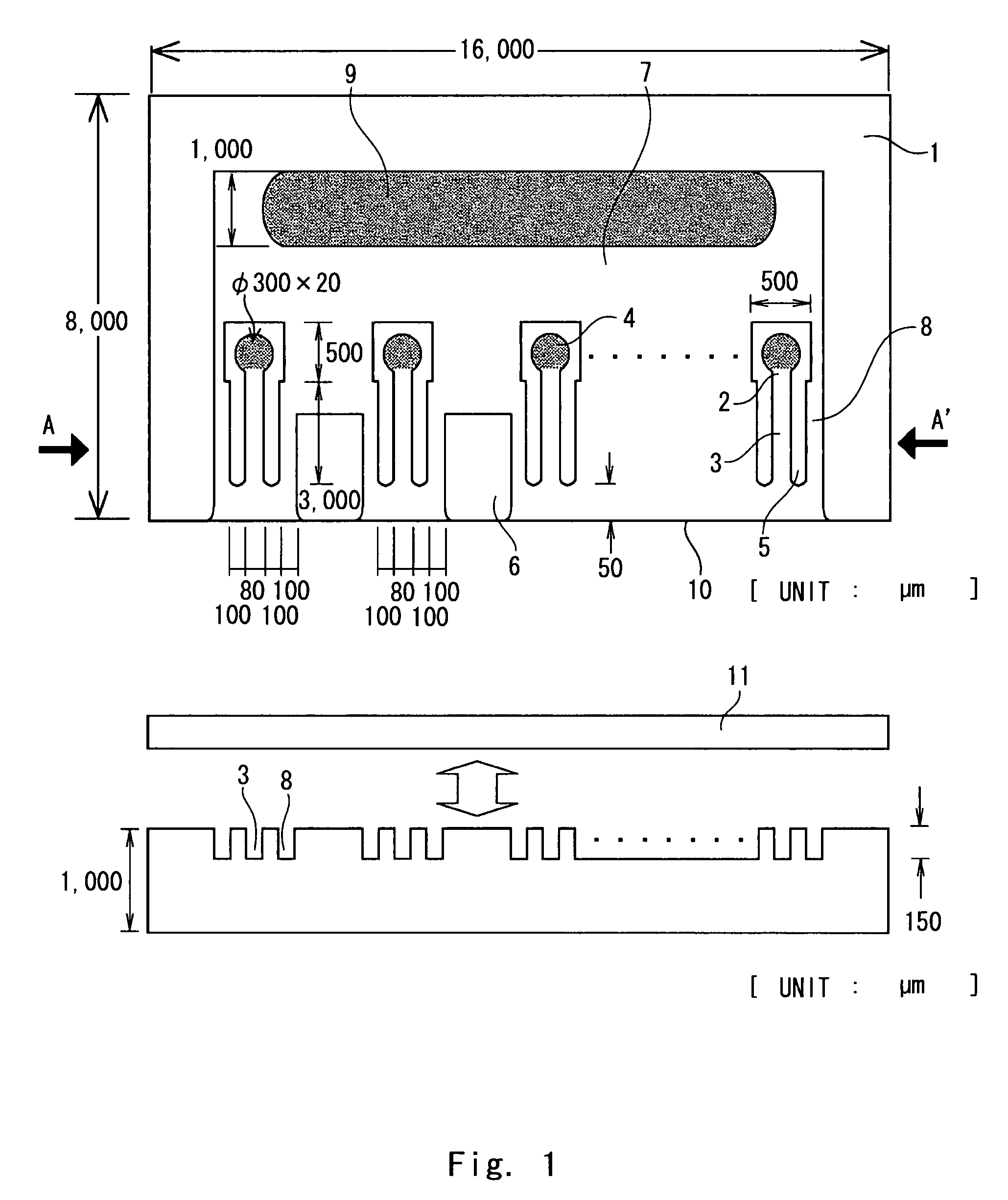
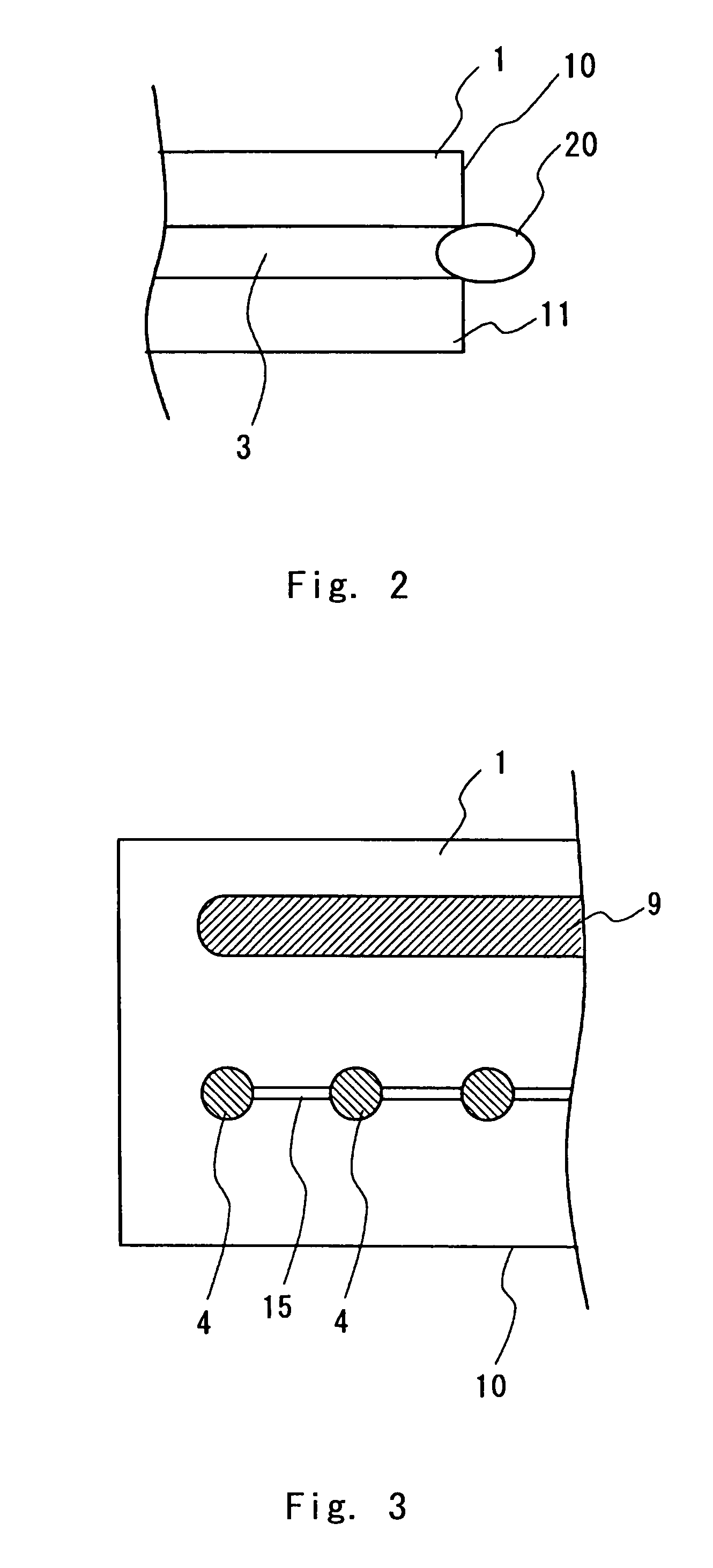
Microchannel array
InactiveUS7432110B2Increase speedFlow mixersTransportation and packagingCell differentationEngineering
A microchannel array according to the present invention includes a first substrate 1, and a second substrate 11 bonded to the first substrate 1. Two sets, that is, a set of a first through-hole 9, a first recess 7, and a first groove 8 and a set of a second through-hole 4, a second recess 2, and a second groove 3 are formed on the first substrate 1. The different sets are separated by a partition 5. A cell differentation / proliferation speed after micro-injection can be increased by using such microchannel array.
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG +2
Method for directionally differentiating induced multipotent stem cells into inner ear hair cell-like cells
ActiveCN112852715APossesses electrophysiological functions of hair cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsCulture processInduced pluripotent stem cellSaccule
The invention provides a method for directionally differentiating induced multipotent stem cells into inner ear hair cell-like cells. A culture medium with definite chemical components is mainly utilized, small molecule compounds are added at proper time to induce and differentiate iPSC into inner ear progenitor cells, and then the inner ear progenitor cells and chick embryo elliptical capsule cells are co-cultured, so that the inner ear hair cell-like cells are obtained. According to the method, the induced multipotent stem cells can be effectively and directionally differentiated into the inner ear hair cell-like cells, and the inner ear hair cell-like cells obtained through differentiation have cilia bundle structures, express inner ear hair cell specific proteins and have hair cell electro-physiological functions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lineage differentiation of encapsulated embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20170100436A1Reduce aggregationIncrease differentiationNervous disorderNervous system cellsDiseaseCell differentation
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Engineering antibody against CD44 for inducing leukemia cell differentation and necrosis
InactiveCN1552735AReduce manufacturing costShort build cycleAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCD44Monoclonal antibody
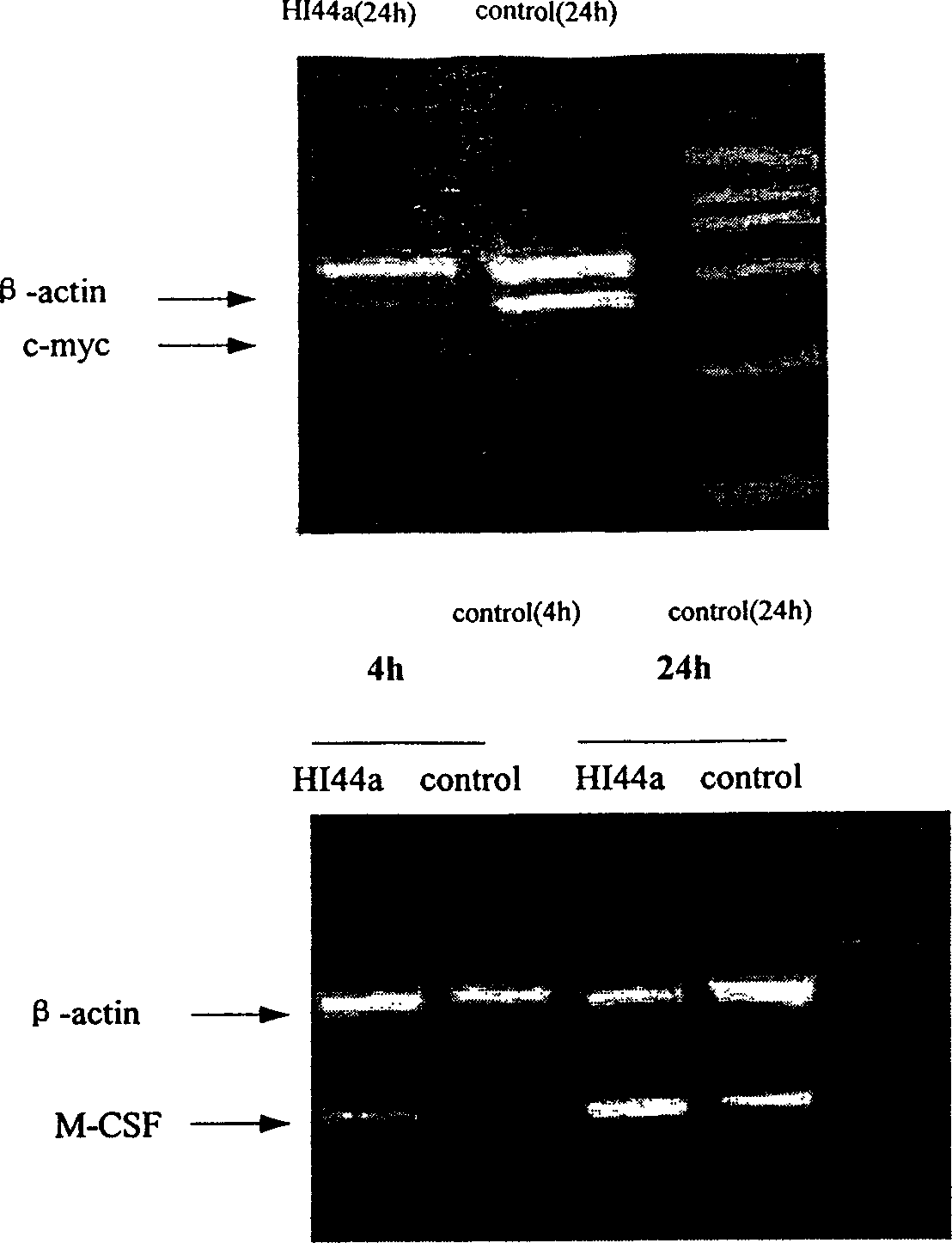
An engineering antibody CD44 for inducing the differentiation and wither of leukemia cells, the gene in the heavy chain and light chain variable region of monoclonal antibody HI44a of CD44, the polypeptide coded by said gene, the carrier containing said gene, and the application of said gene and polypeptide in preparing medicines for diagnosing and treating leukemia and disclosed.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Cell transplantation culture method for forming bone tissue in vivo
The invention relates to a cell transplantation culture method for forming bone tissue in vivo. The method is characterized in that a three-dimensional matrix BD Matrigel with fast degradation performance is employed to provide a three-dimensional structure for osteogenous seed cells to grow in vivo, so that an osteoid tissue structure can form in osteogenous seed cells. At the same time, BD Matrigel has certain dissolving capacity, corresponding growth factors or small molecular compounds and the like can be added at the early stage of cell transplantation so as to provide a microenvironment suitable for cell differentiation and survival at the early stage of in-vivo growth of the transplanted cells. The method provided by the invention can also be used for transplantation of various cells in tissue engineering, brings convenience to basic research, and brings prospects for clinical application.
Owner:YUNNAN JICI INSITUTE FOR REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
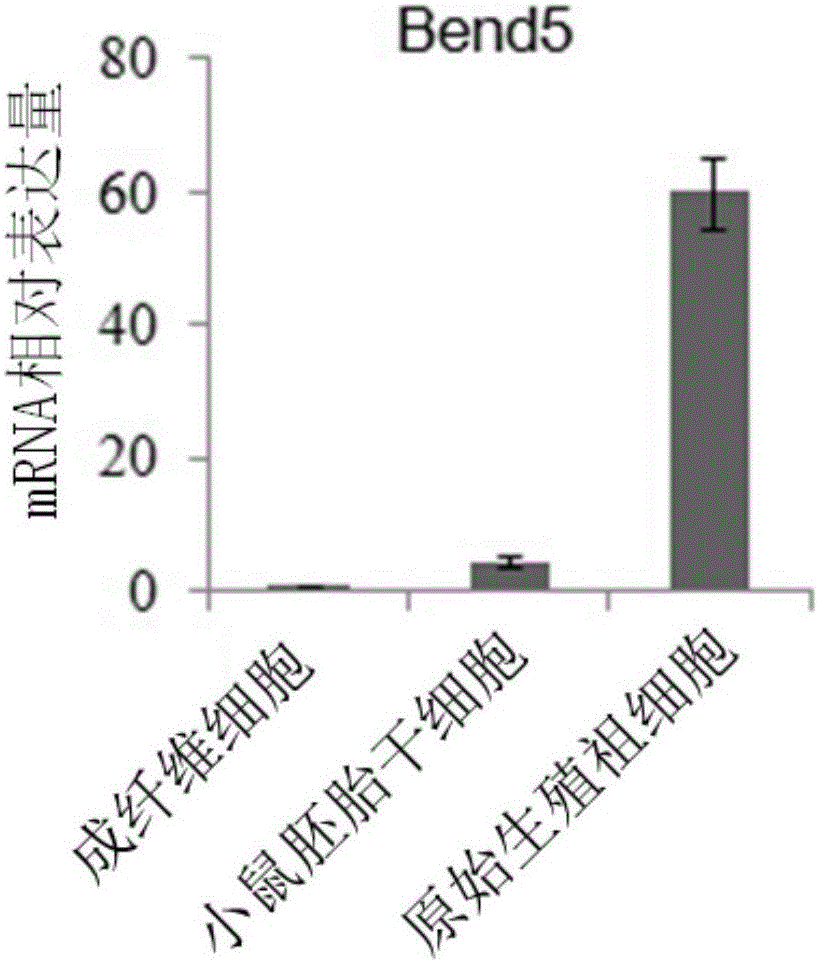
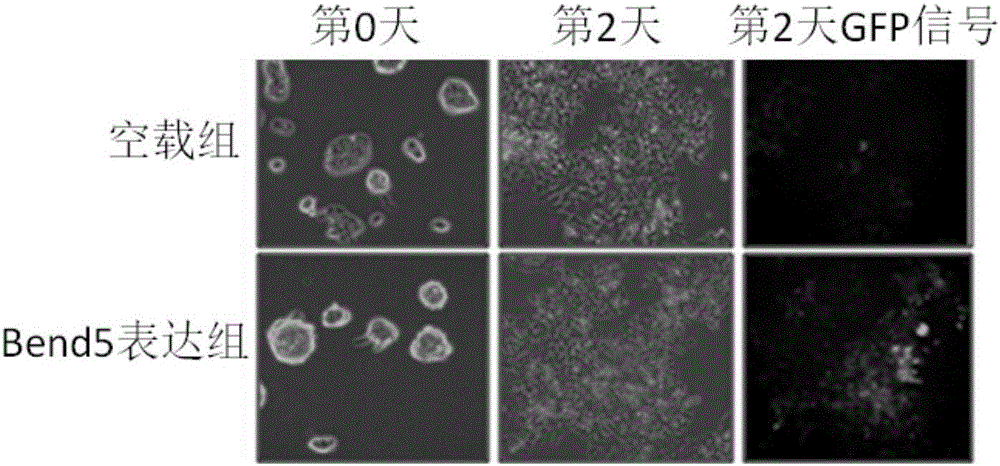
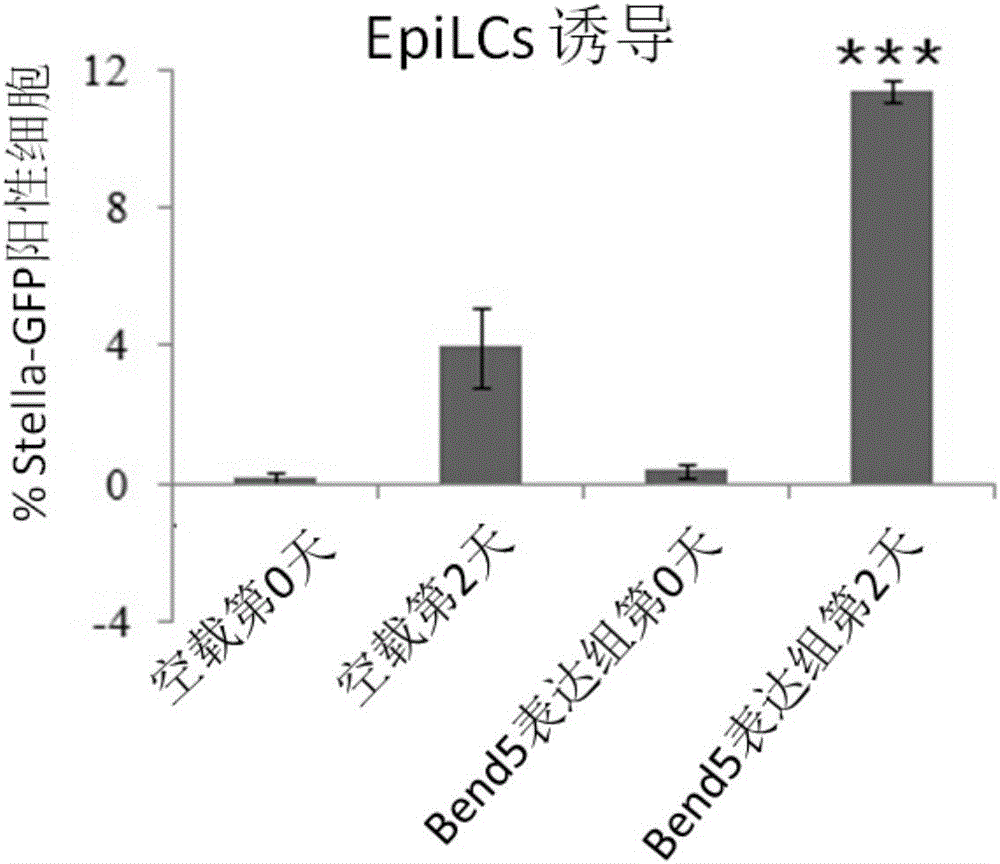
Application of Bend5 protein to acceleration of induced differentiation of embryonic stem cells to into primitive reproductive progenitor-like cells
ActiveCN106011051APromote differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsCell culture active agentsCell differentationMouse Embryonic Stem Cell
The invention discloses application of Bend5 protein to acceleration of induced differentiation of embryonic stem cells into primitive reproductive progenitor-like cells. An amino acid sequence of the Bend5 protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. A primary structure of the protein comprises a Coiled-coil structure domain and a BEN structure domain. Specifically, excessive expression of the Bend5 can accelerate differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into similar ectoderm-like cells; the excessive expression of the Bend5 also can accelerate differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into primitive reproductive progenitor-like cells. Furthermore, research results show that transcription factor protein Bend5 is combined with Stella gene with dependence on BEN structure domain protein, and Tet1 and Oct4 are recruited to activate expression of the Stella gene, so that the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into primitive reproductive progenitor-like cells can be accelerated. The Bend5 protein has a good application prospect in treatment of infertility.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
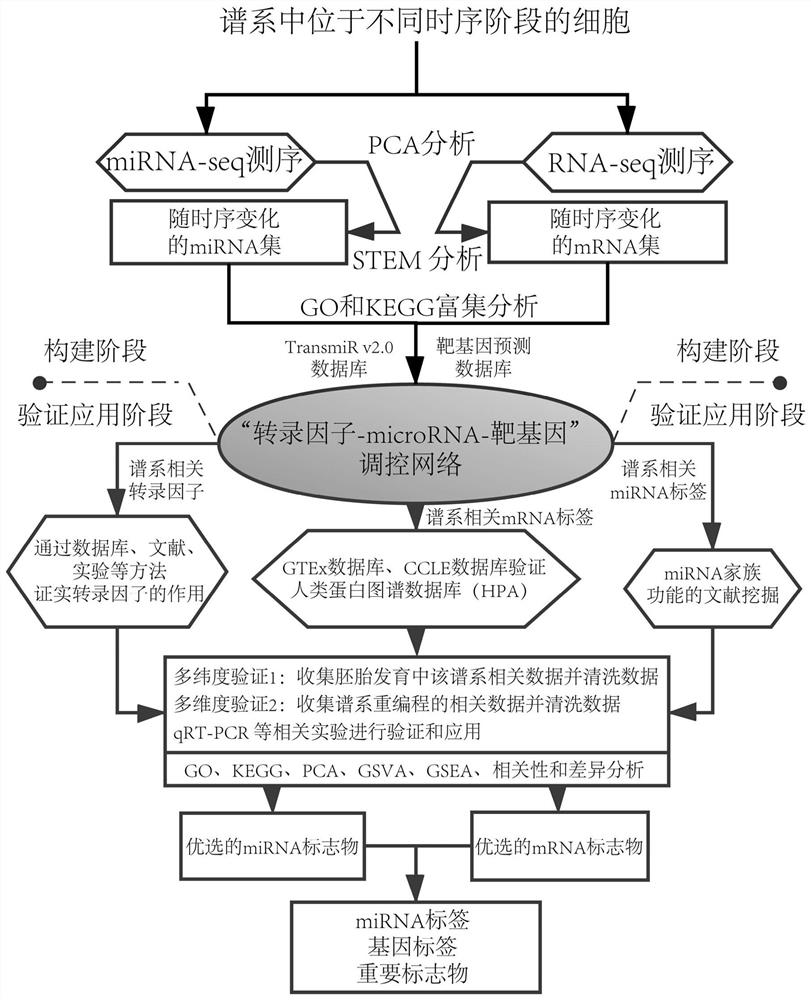
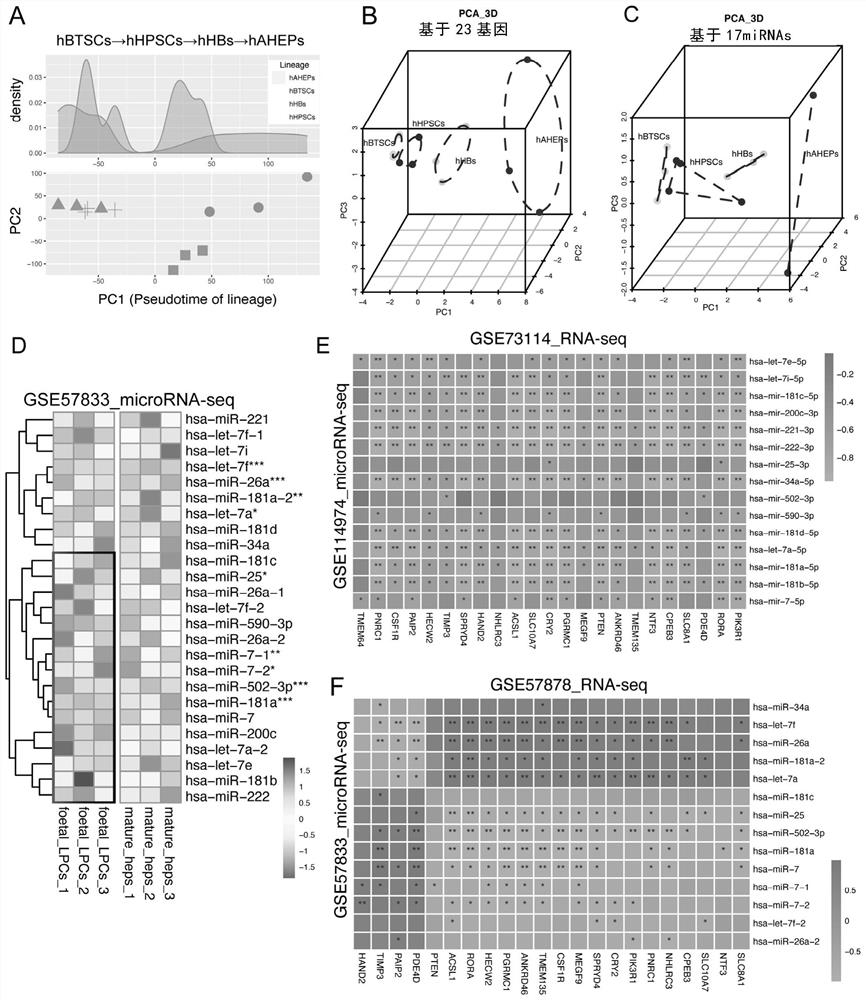
Marker for evaluating hepatic lineage cell maturity, biomics kit and construction method
ActiveCN113106160AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCell differentationCellular development
The invention provides a marker for evaluating hepatic lineage cell maturity, a biomics kit and a construction method. According to the invention, a microRNA set and a gene set which have time sequence characteristics and have a regulatory relationship in cell development are elaborated from a new perspective for the first time, a transcription factor-microRNA-target gene regulatory network related to hepatocyte differentiation and maturation regulation is established, and a gene tag and a microRNA tag of hepatolineage specificity are obtained, wherein these tags or combinations thereof can be used as potential new markers for hepatic lineage cells. The invention also provides a biomics kit for the hepatic lineage cells, and a new scheme is provided for large-scale amplification of stable hepatic lineage cells and monitoring of in-vitro culture states of the hepatic lineage cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
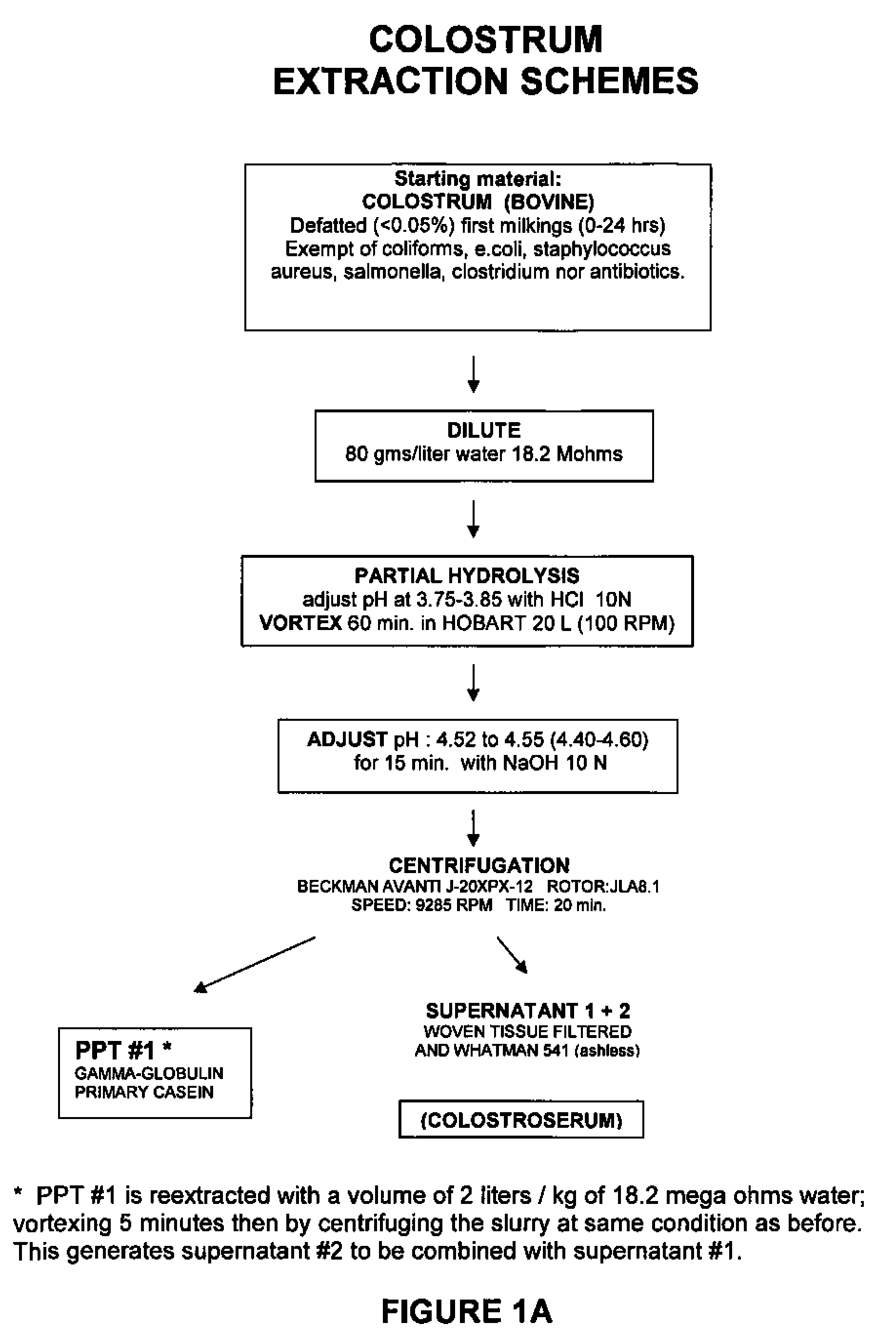
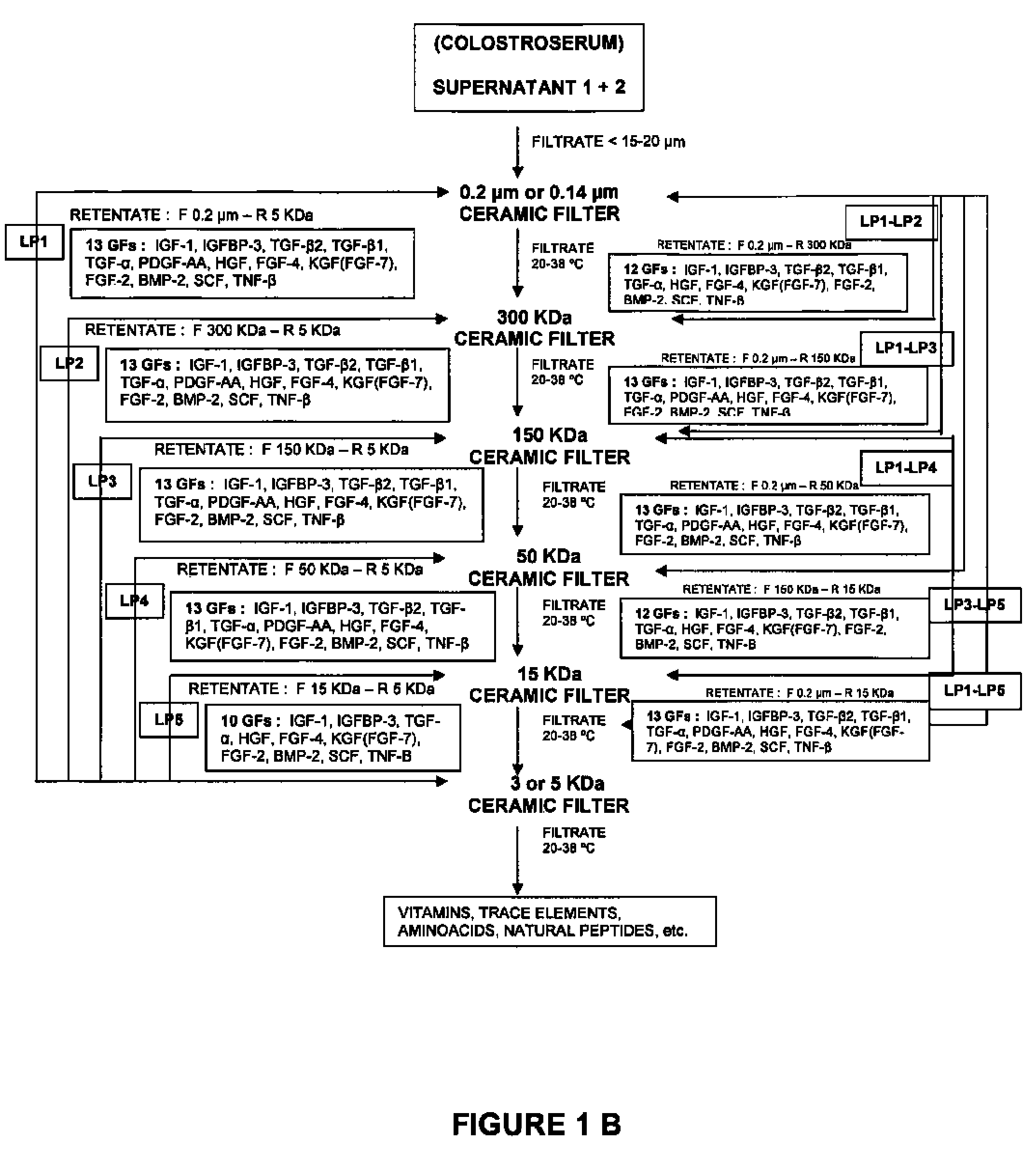
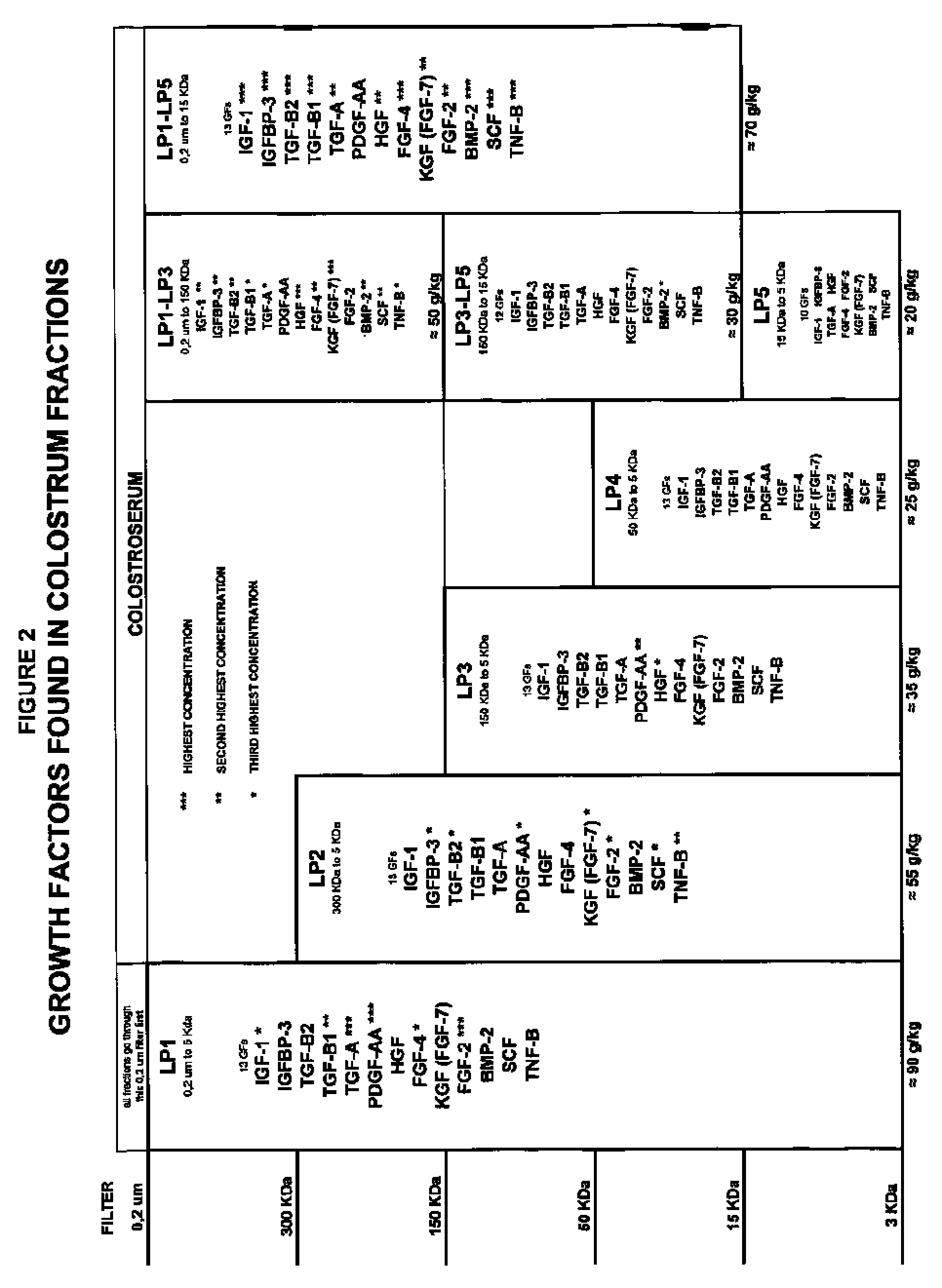
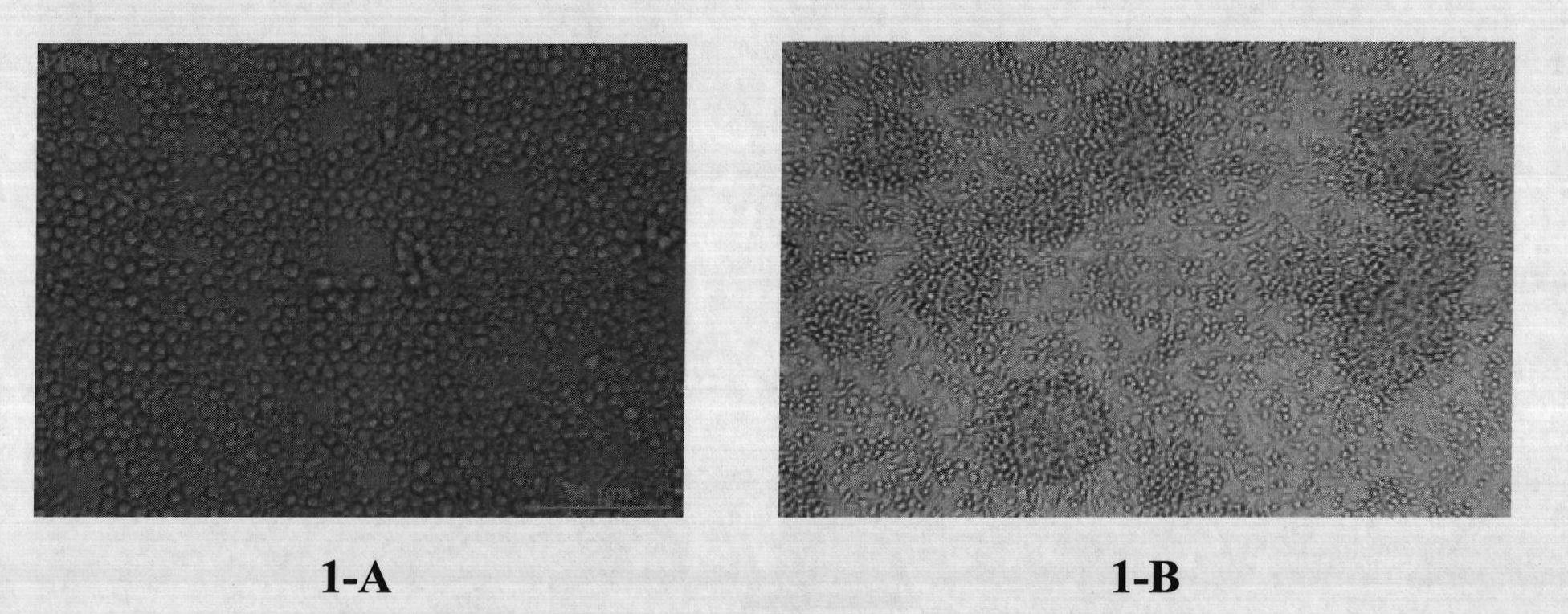
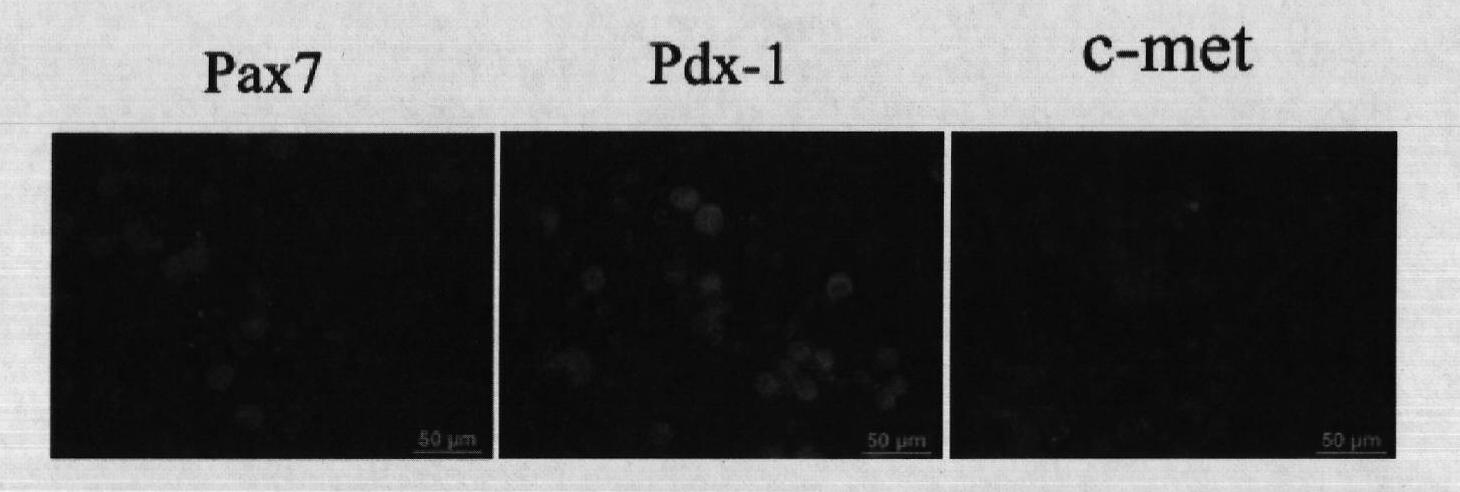
Isolation of growth and differentiating factors from colostrum
The present invention concerns a novel process for isolating growth and differentiating factors present in colostrum, all in a natural way. This process is characterized by maturation steps (controlled mild acid hydrolysis) and physical steps (molecular filtration) which optimize recovery of measured growth factors and their ability to entice a response on human cells. Advantageously, this process allows the derivation and isolation of growth and differentiating factors with highly disparate sizes (or molecule weights) in pools. These pools can be used in select and varied ways, including cosmetic, cosmeceutical, nutraceutical, dermatological, pharmaceutical, medical and veterinary applications. It can also be used as a replacement to fetal calf serum to promote cell proliferation, and above all, cell differentiation.
Owner:NEXCELL BIOSCI
Method and kit allowing reverse differentiation of human somatic cells for generation of autologous pancreatic stem cells and autologous pancreas islet, and application thereof
InactiveCN102399740AAddressing critical deficitsImprove securityNervous disorderPancreatic cellsCell specificDisease
The invention provides a method allowing reverse differentiation of human somatic cells for generation of autologous pancreatic stem cells and autologous pancreas islet. The method is as follows: culture solutions containing extractives of different plants and different protein components are used to culture human somatic cells step by step, which enables the somatic cells to generate autologous pancreatic stem cells through reverse differentiation, and autologous pancreas islet is generated through further culture. The method provided in the invention enables the first generation of autologous pancreatic stem cells and autologous pancreas islet at a magnitude order of tens of billions to be generated within two to three weeks. The plant and protein-induced human autologous pancreatic stem cells have similar cell specific phenotypes and a plurality of cell differentiation capability as those of human natural pancreatic stem cells; the autologous pancreatic stem cells and autologous pancreas islet cells have immense potential both in the application field of treatment of pancreatic diseases like insulin deficiency type diabetes and in the engineering field of autologous pancreatic tissue; the invention is also applicable to establishment of novel autologous pancreatic stem cell libraries and long-term permanent preservation of autologous pancreatic stem cells.
Owner:林雄斌
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com