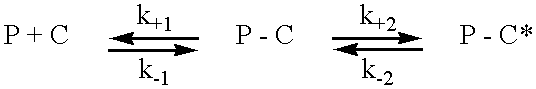Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Calcium dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Calcium-Dependent Chloride Channel (Ca-ClC) proteins (or calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCCs), are heterogeneous groups of ligand-gated ion channels for chloride that have been identified in many epithelial and endothelial cell types as well as in smooth muscle cells.
Modified ligands of calcium-dependent binding proteins
InactiveUS6316409B1High affinityImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWild typeCalcium dependent
The present invention relates to ligands capable of binding a calcium dependent binding protein, that comprise an amino acid sequence corresponding to that of a wild type ligand for the calcium dependent binding protein with modification which results in enhanced affinity of the ligand for the calcium dependent binding protein.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Compositions And Methods For Treating Toxoplasmosis, Cryptosporidiosis, And Other Apicomplexan Protozoan Related Diseases
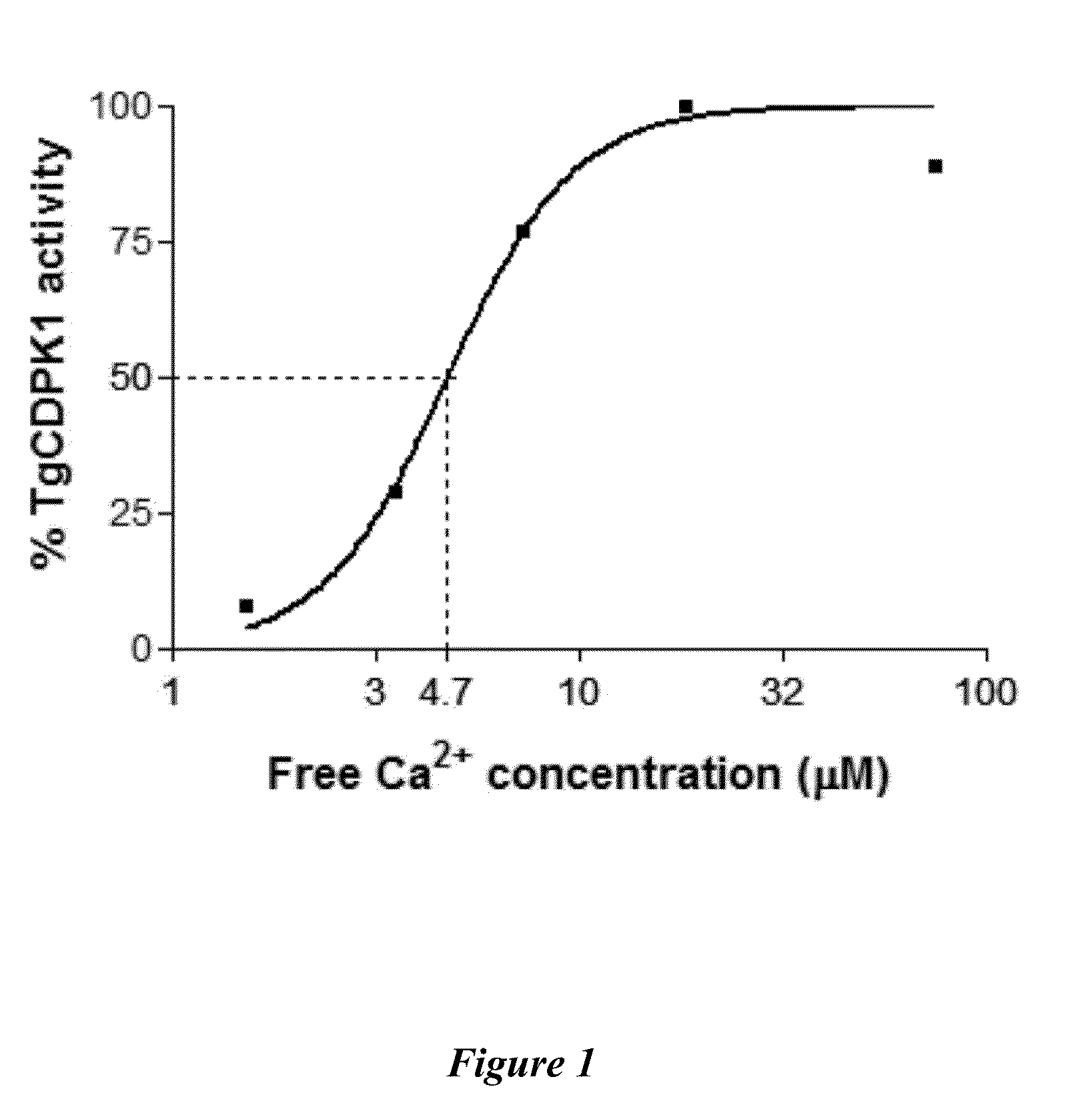
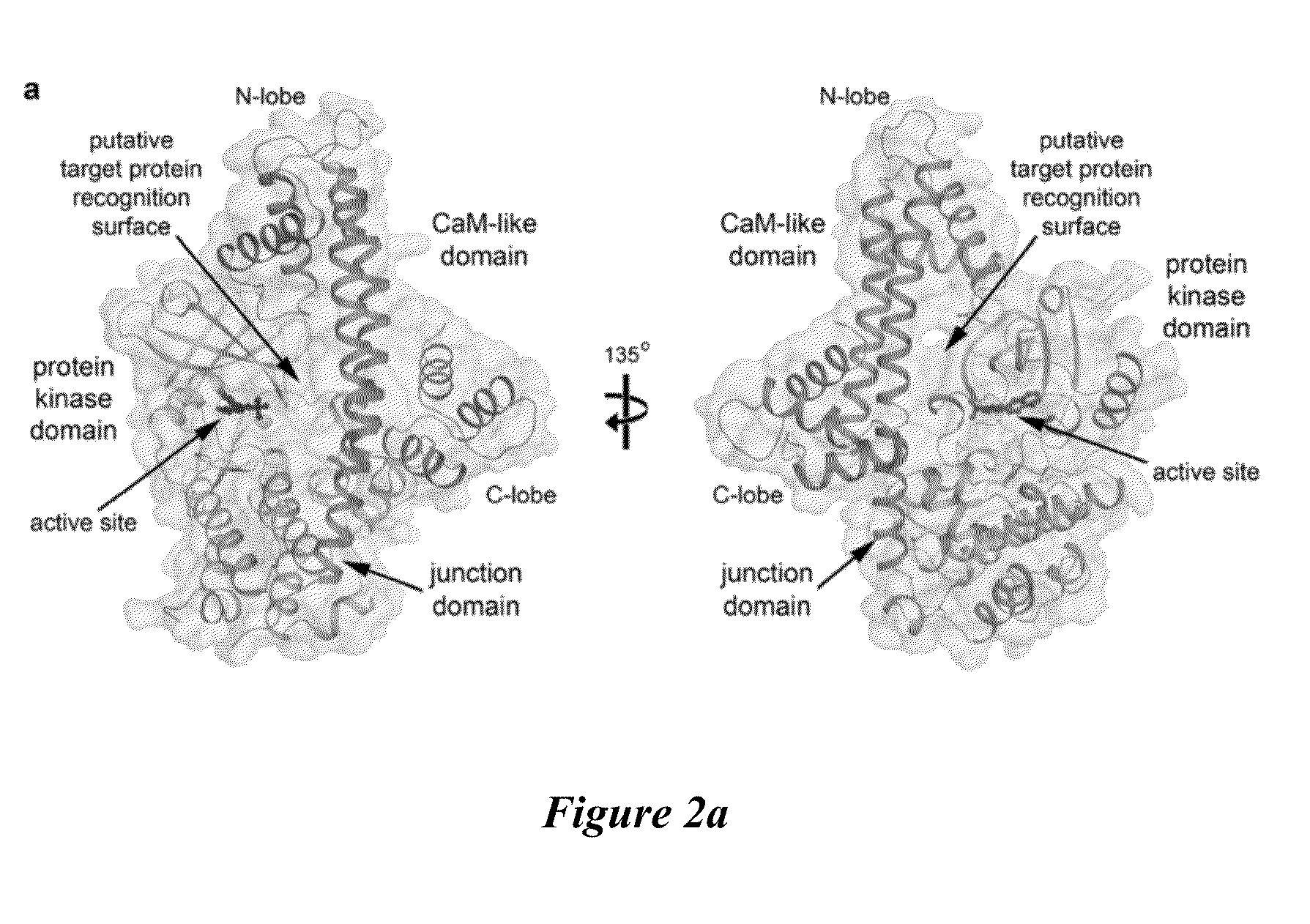
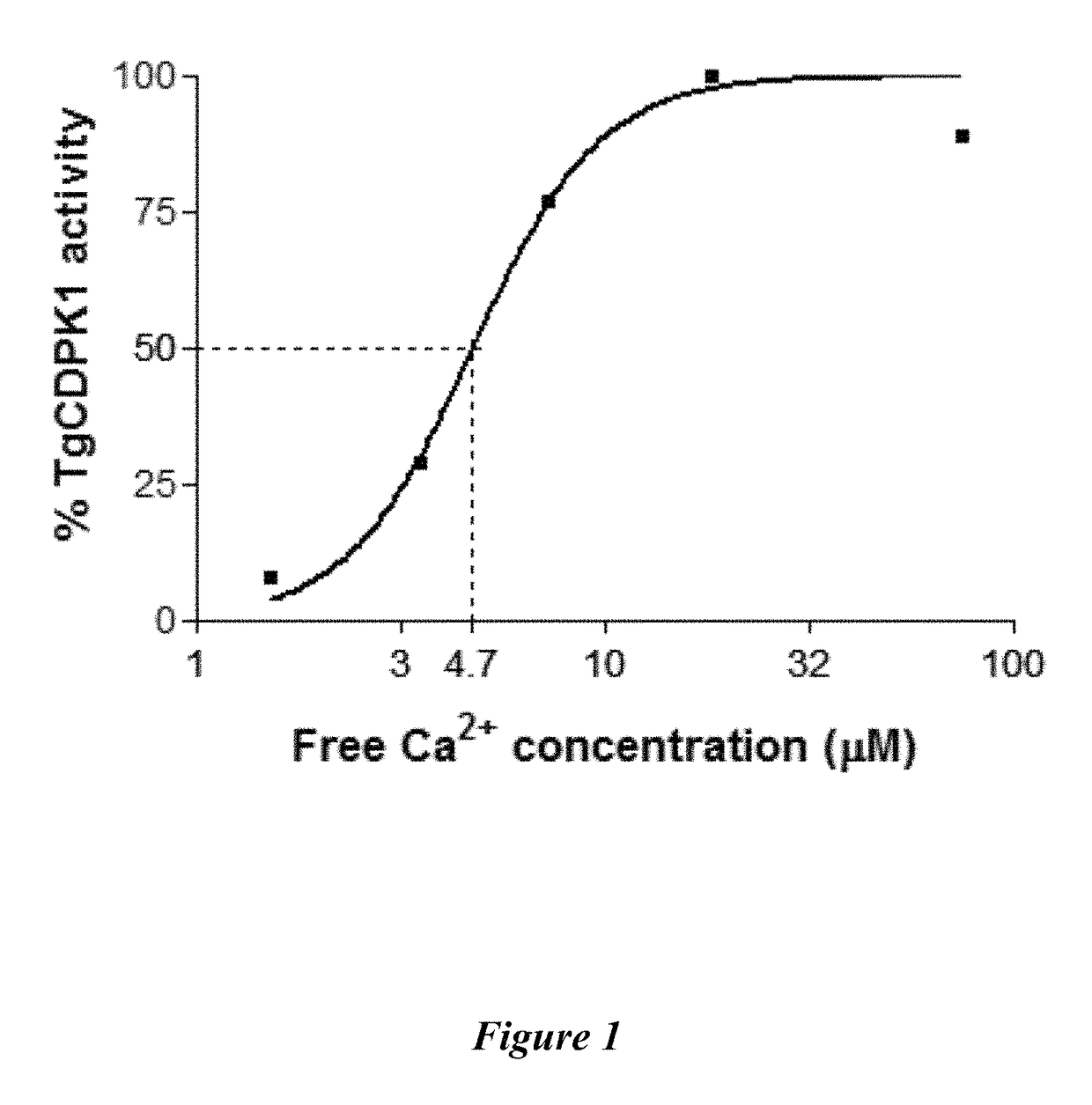
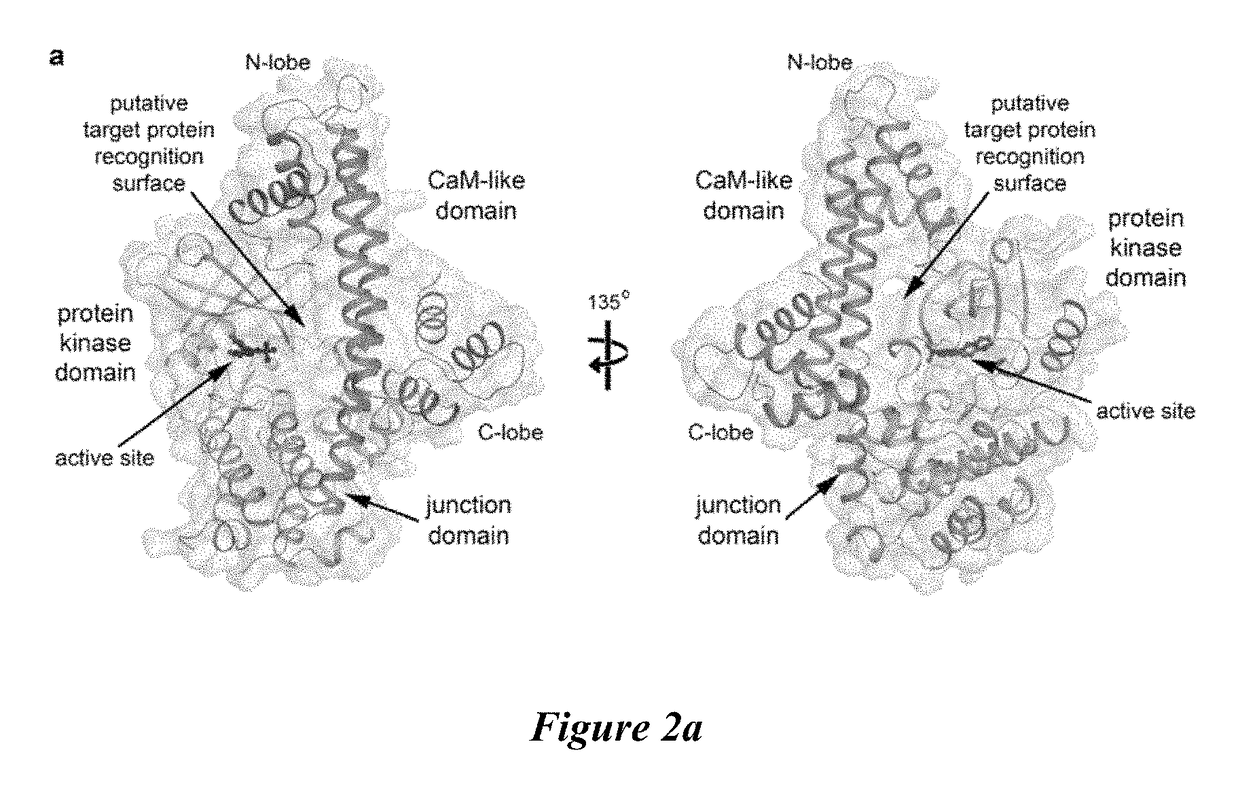
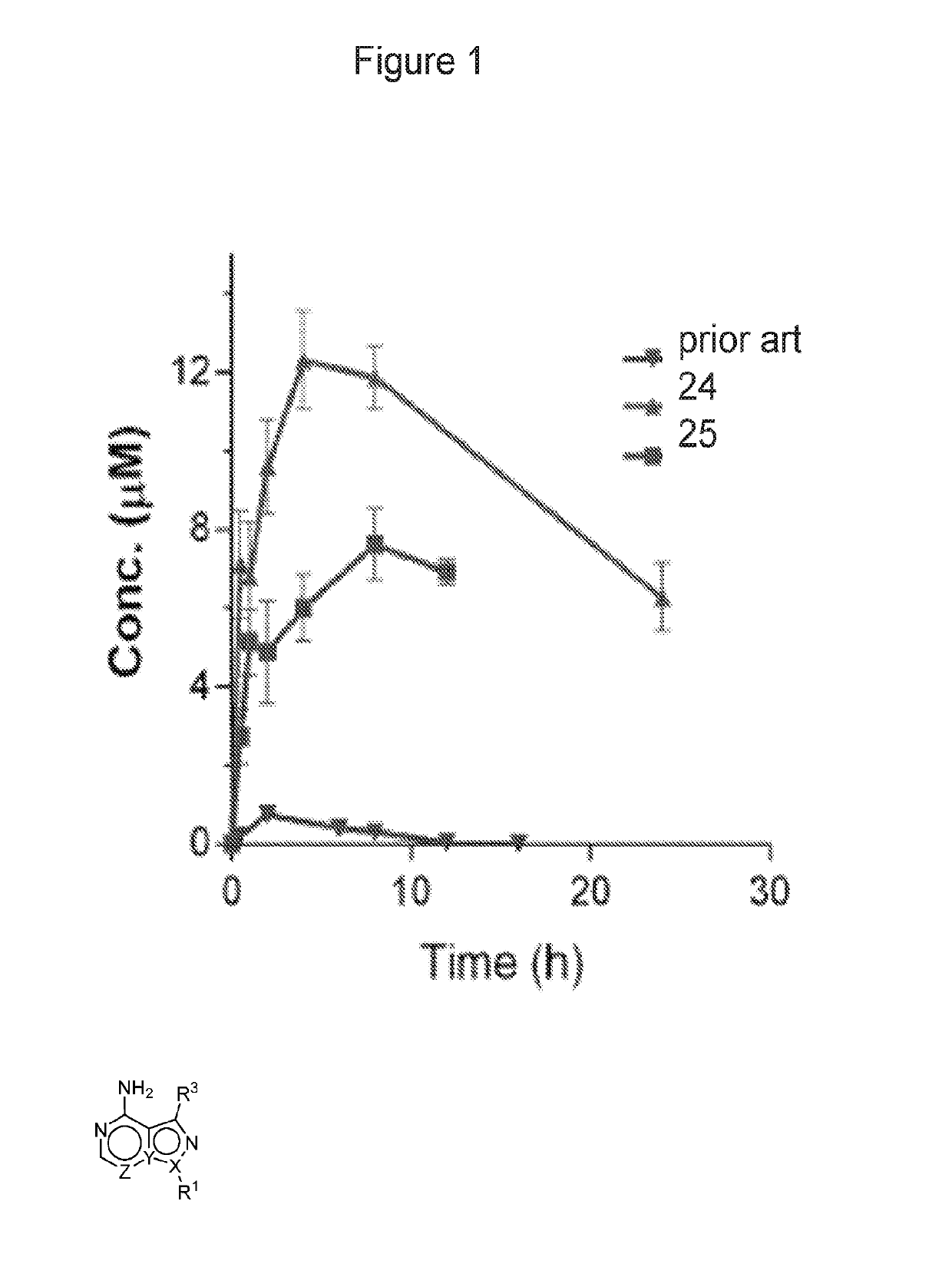
Compositions and methods for the treatment of toxoplasmosis, caused by the infectious eukaryotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) and for the treatment of cryptosporidiosis, caused by the infectious eukaryotic parasites Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum) and Cryptosporidium hominus (C. hominus) are described. In particular, the present disclosure is directed to compositions and methods for inhibiting either T. gondii calcium dependent protein kinases (TgCDPKs) or C. parvum and C. hominus calcium dependent protein kinases (CpCDPKs) using pyrazolopyrimidine and / or imidazo[1,5-a]pyrazine inhibitors, of the formula,wherein the variables X, Y, Z, L, R1, and R3 are defined herein.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Annexin a2 as immunological target
InactiveUS20110293608A1Prevent intrusionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAntigenCalcium-dependent phospholipid binding
AnnexinA2 (ANXA2), a member of the Annexin family of calcium-dependent, phospholipid binding proteins, is one of a panel of identified antigens recognized by the post-vaccination sera of patients who demonstrated prolonged disease-free survival following multiple vaccinations. AnnexinA2 is abundantly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinomas and cell surface / membrane AnnexinA2 increases with the progression from premalignant lesions to invasive pancreatic adenocarcinomas. The cytoplasmic to cell surface translocation of AnnexinA2 expression is critical for pancreatic cancer cell invasion. In addition, phosphorylation of AnnexinA2 at Tyrosine 23 is important for its localization to the cell surface and for the invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Finally, loss of AnnexinA2 leads to the loss of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Nucleic acid molecules encoding annexins from plants
InactiveUS20050089872A1Improvement of resistance to environmental damageResist damageImmunoglobulinsFermentationAbscisic acidAnnexin
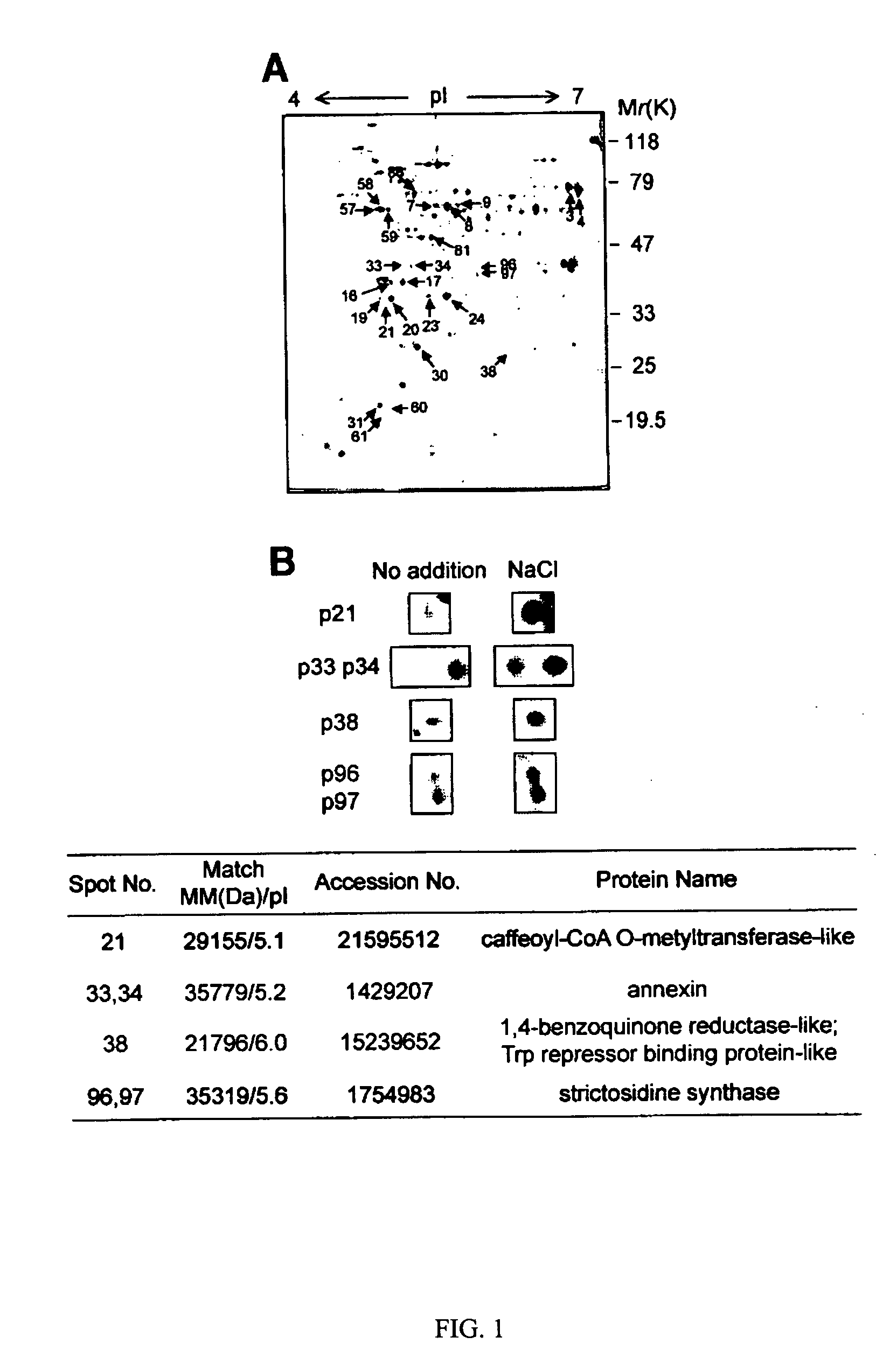
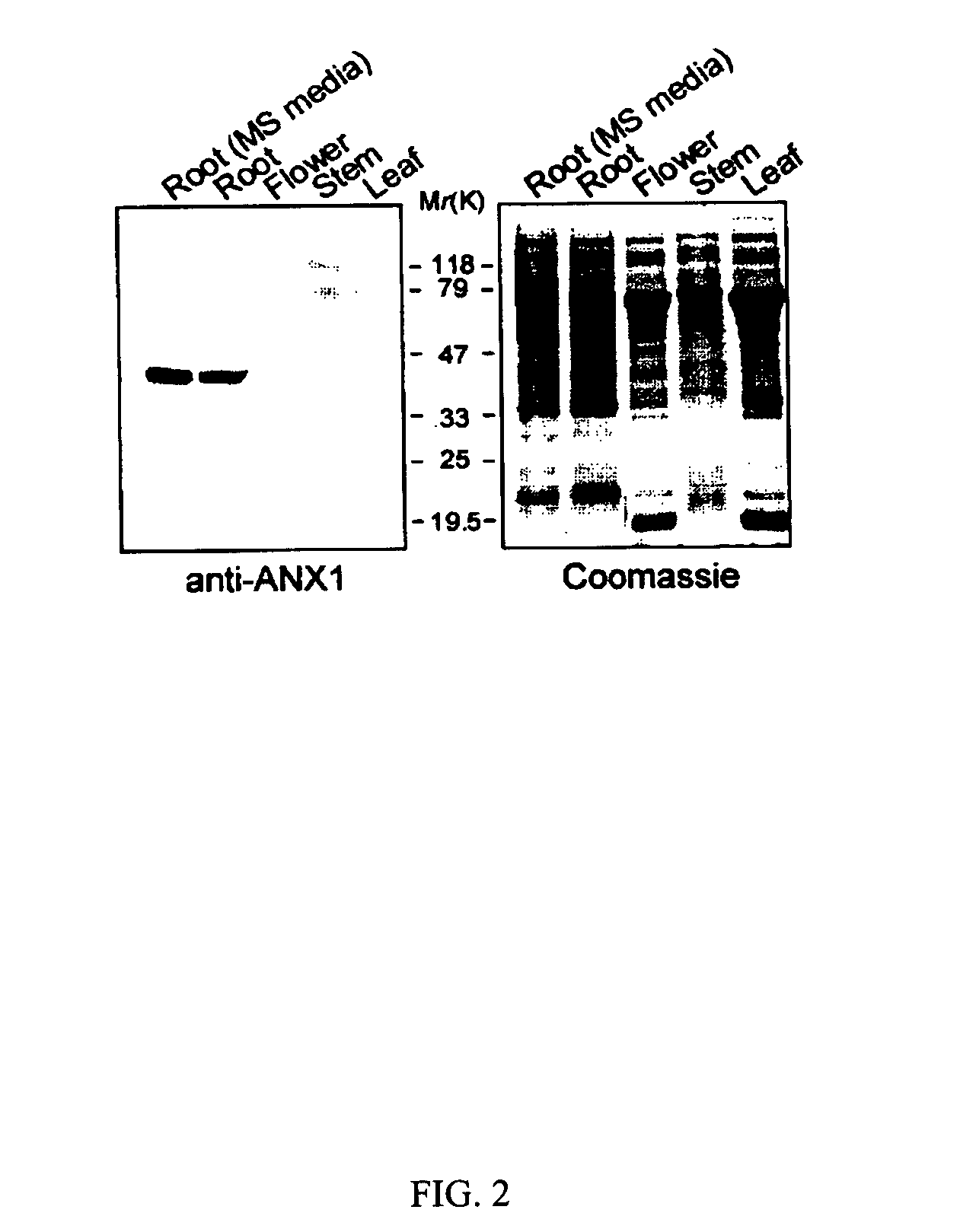
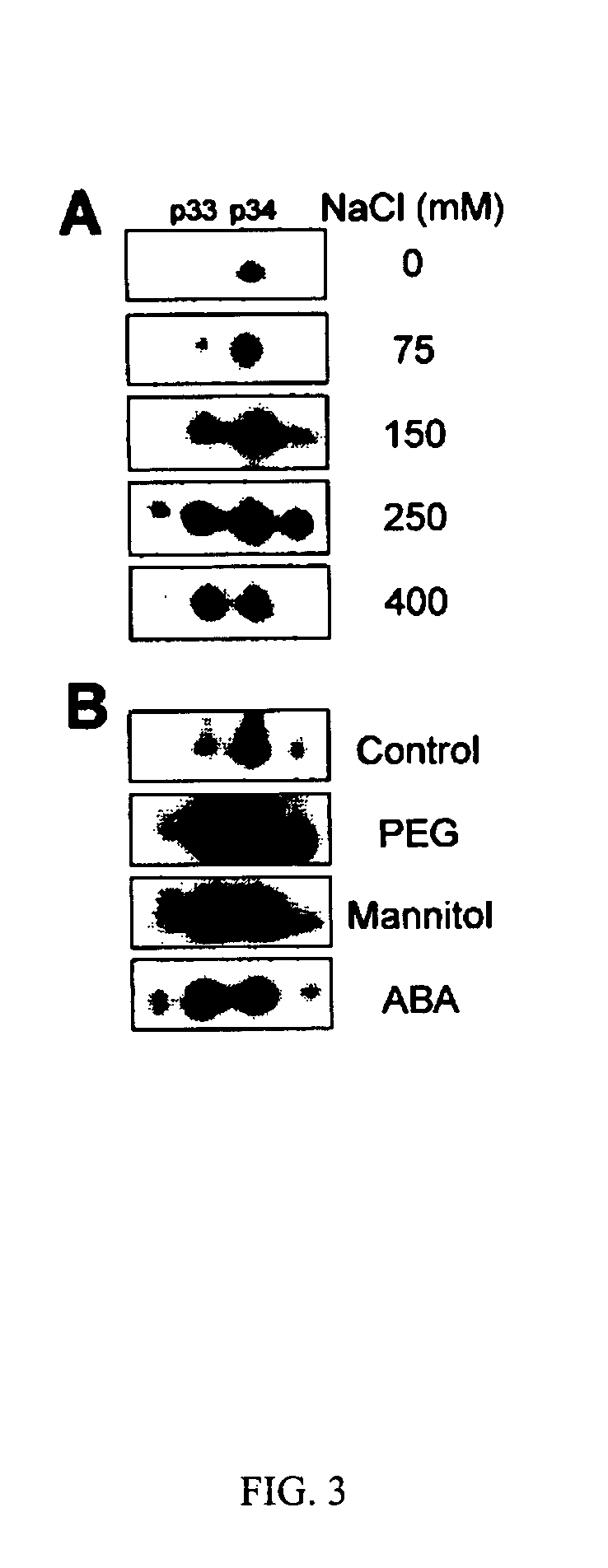
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules encoding annexin 1 (ANX1) and annexin 4 (ANX4) that belong to a multigene family of calcium-dependent membrane binding proteins. ANX1 and ANX4 are inducible by abscisic acid (ABA), salt and other various stress treatments. The anx1 and anx4 mutant plants are characterized by their hypersensitivity to salt and ABA during seed germination and early seedling growth. The invention can be utilized to generate transgenic plants that are tolerant to environmental stress.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Human calcium dependent proteases, polynucleotides encoding the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6716614B1Increased white blood cell countHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaPharmacogenomicsNucleotide
Novel human polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences are disclosed that can be used in therapeutic, diagnostic, and pharmacogenomic applications.
Owner:LEXICON GENETICS INC (US)
Microorganism of the genus Lactobacillus capable of binding to S. mutans and compositions comprising the same
The present invention relates to a microorganism belonging to the group of lactic acid bacteria characterized in that it is capable of specifically binding to Streptococcus mutans, wherein the specific binding is (i) resistant to heat treatment; and / or (ii) resistant to protease treatment; and / or (iii) calcium-dependent; and / or (iv) formed within a pH range between 4.5 and 8.5; and / or (v) formed in the presence of saliva. Preferably, the specific binding can be assayed as follows: (a) growing said microorganism to stationary phase; (b) mixing said microorganism with Streptococcus mutans which has been grown to stationary phase; (c) incubating the mixture obtained in step (b) under conditions allowing the formation of aggregates of said microorganism and Streptococcus mutans and (d) detecting aggregates by the occurrence of a pellet. Another aspect of the present invention is an analog or fragment of said microorganism which is thermally inactivated or lyophilized, wherein said analog or fragment retains the capability of specifically binding to Streptococcus mutans. In addition, the present invention encompasses compositions and additives for food, feed or drinks comprising the microorganism belonging to the group of lactic acid bacteria which specifically bind to Streptococcus mutans or an analog or fragment thereof. Moreover, uses of said microorganism or said analog or fragment thereof for the preparation of an anticariogenic or pharmaceutical composition or anticariogenic food or feedstuff as well as methods for producing said compositions or food or feedstuff are provided by the present invention.
Owner:BASF AG
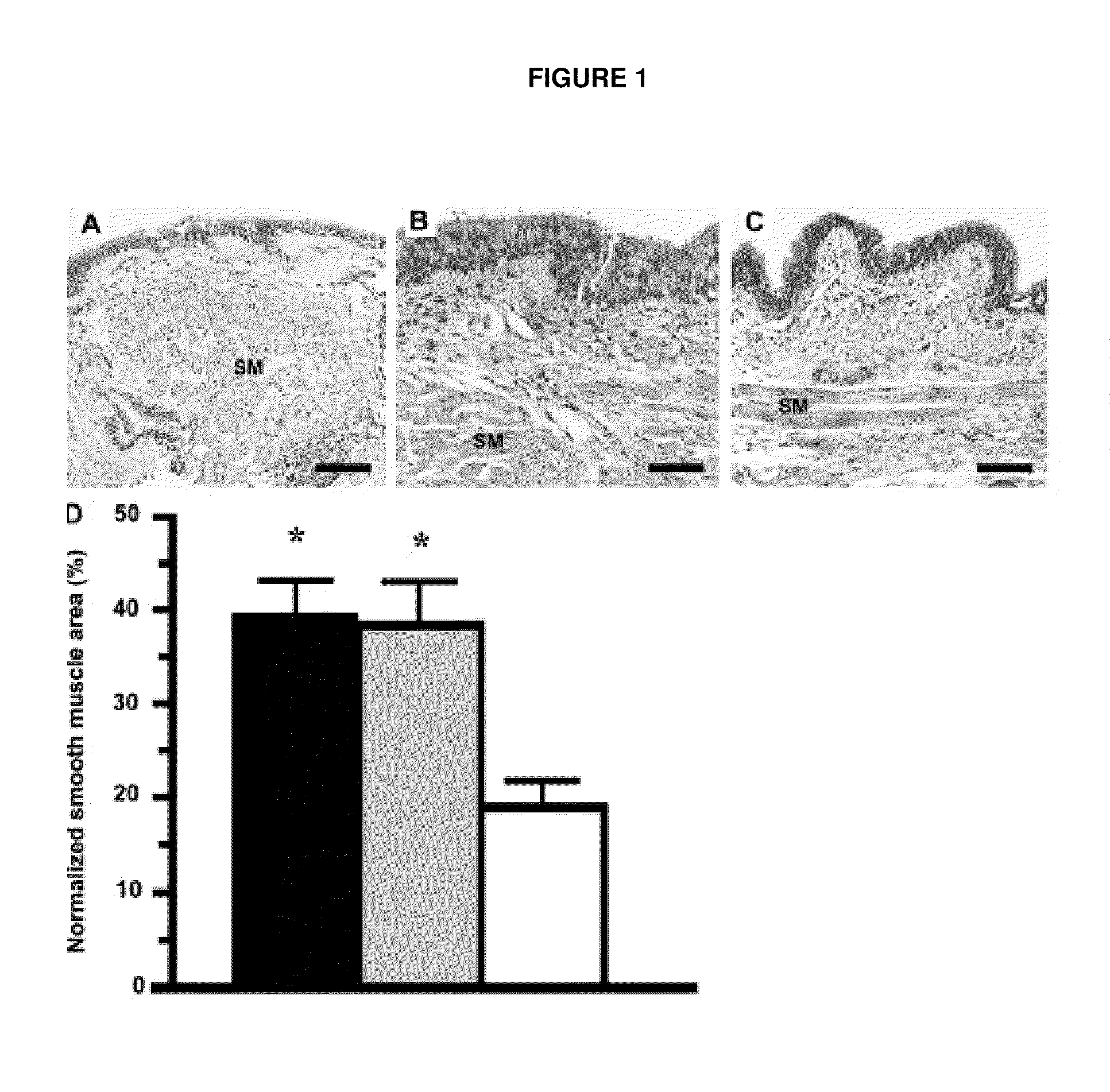
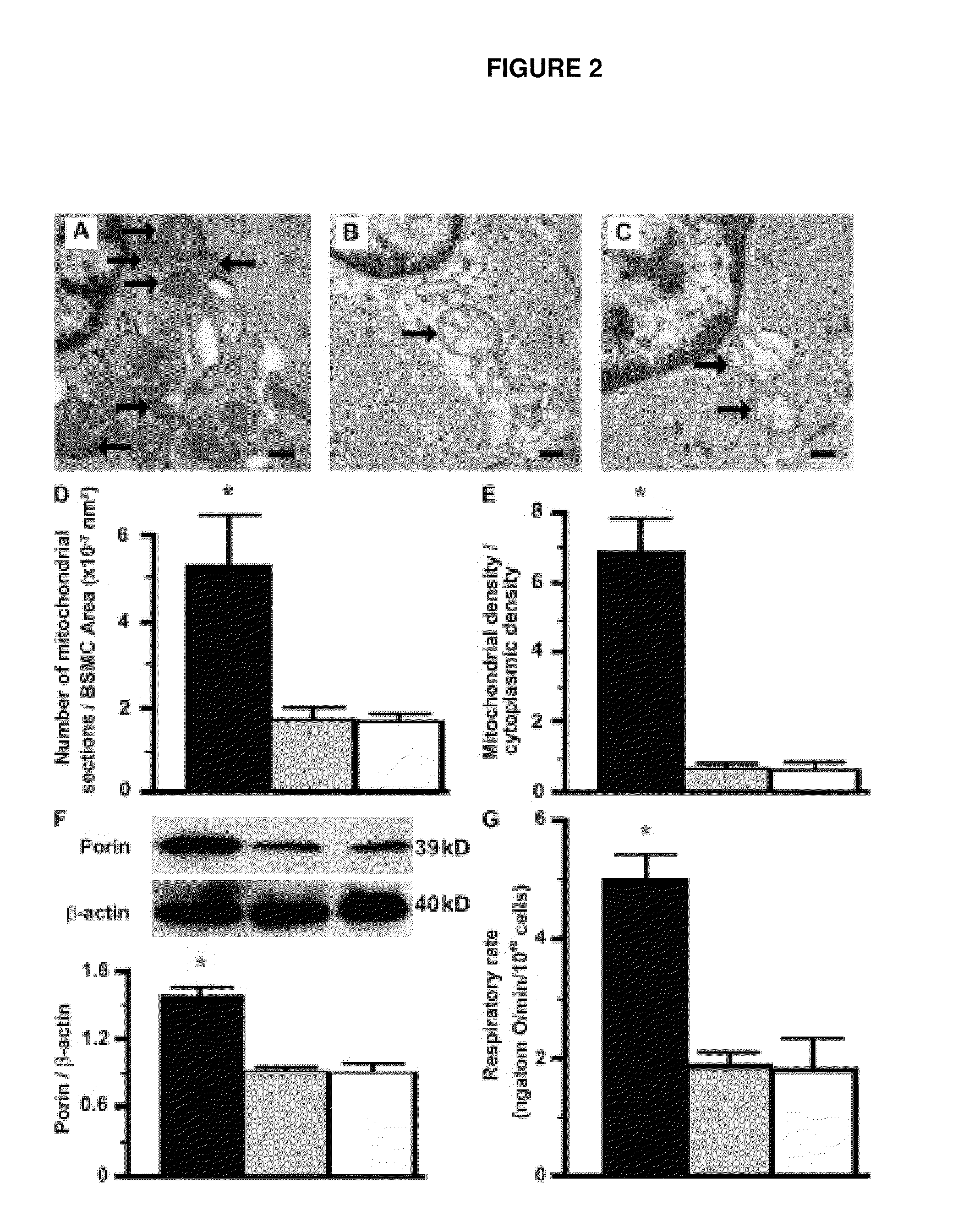
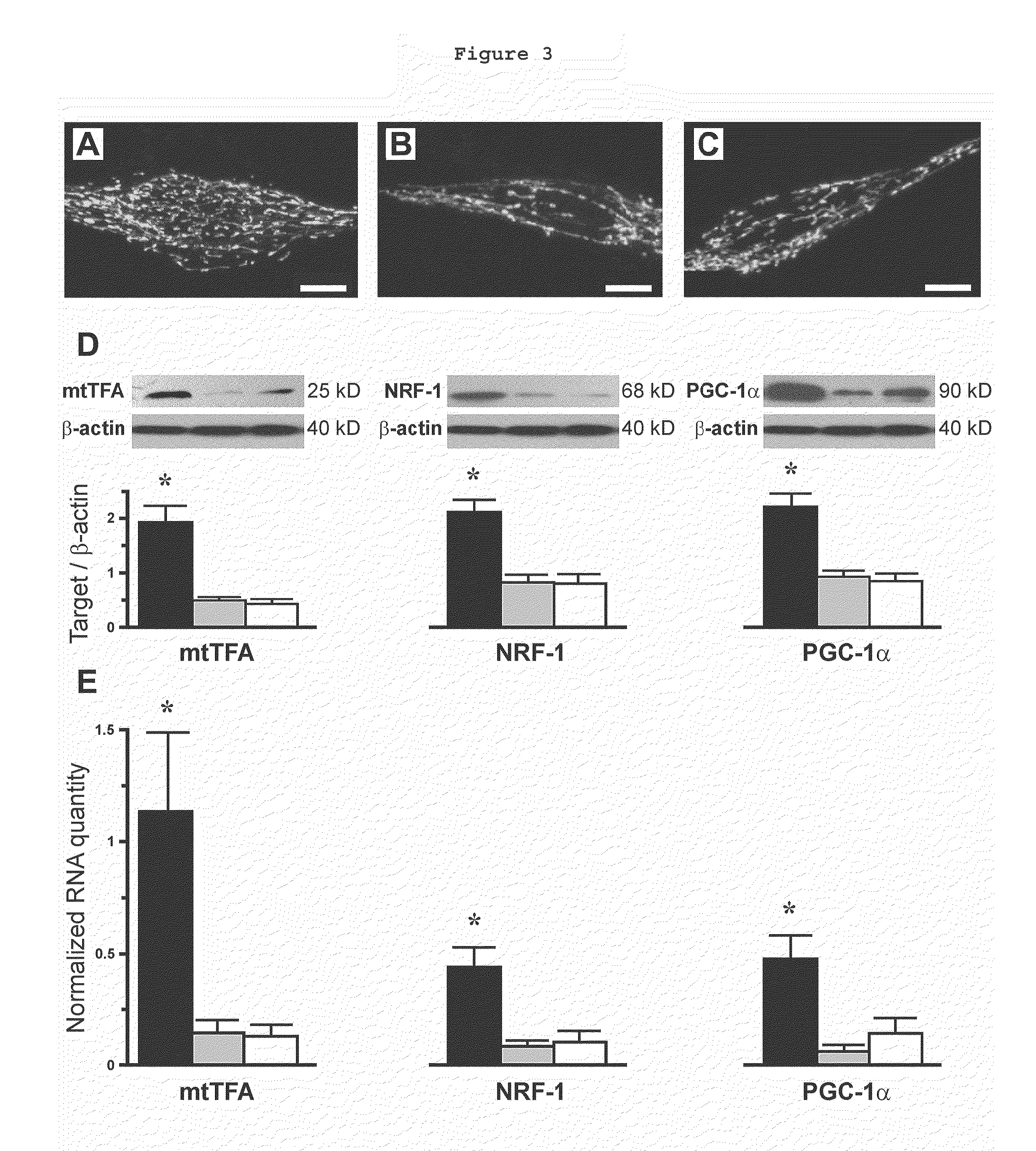
Bronchial smooth muscle remodeling involves calcium-dependent enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis in asthma
InactiveUS20090318413A1Prevent proliferationInhibit expressionBiocideAnimal repellantsSmooth muscleMedicine
The present invention thus provides a method of inhibiting bronchial smooth muscle remodeling in asthma, comprising the step of administering to a subject having asthma an agent that inhibits calcium-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis.
Owner:UNIV VICTOR SEGALEN BORDEAUX 2
Method for enzymatic treatment of textiles such as wool
InactiveUS20030154555A1Good dimensional stabilityImprove yarn strengthPhysical treatmentWrinkle resistant fibresFiberActive agent
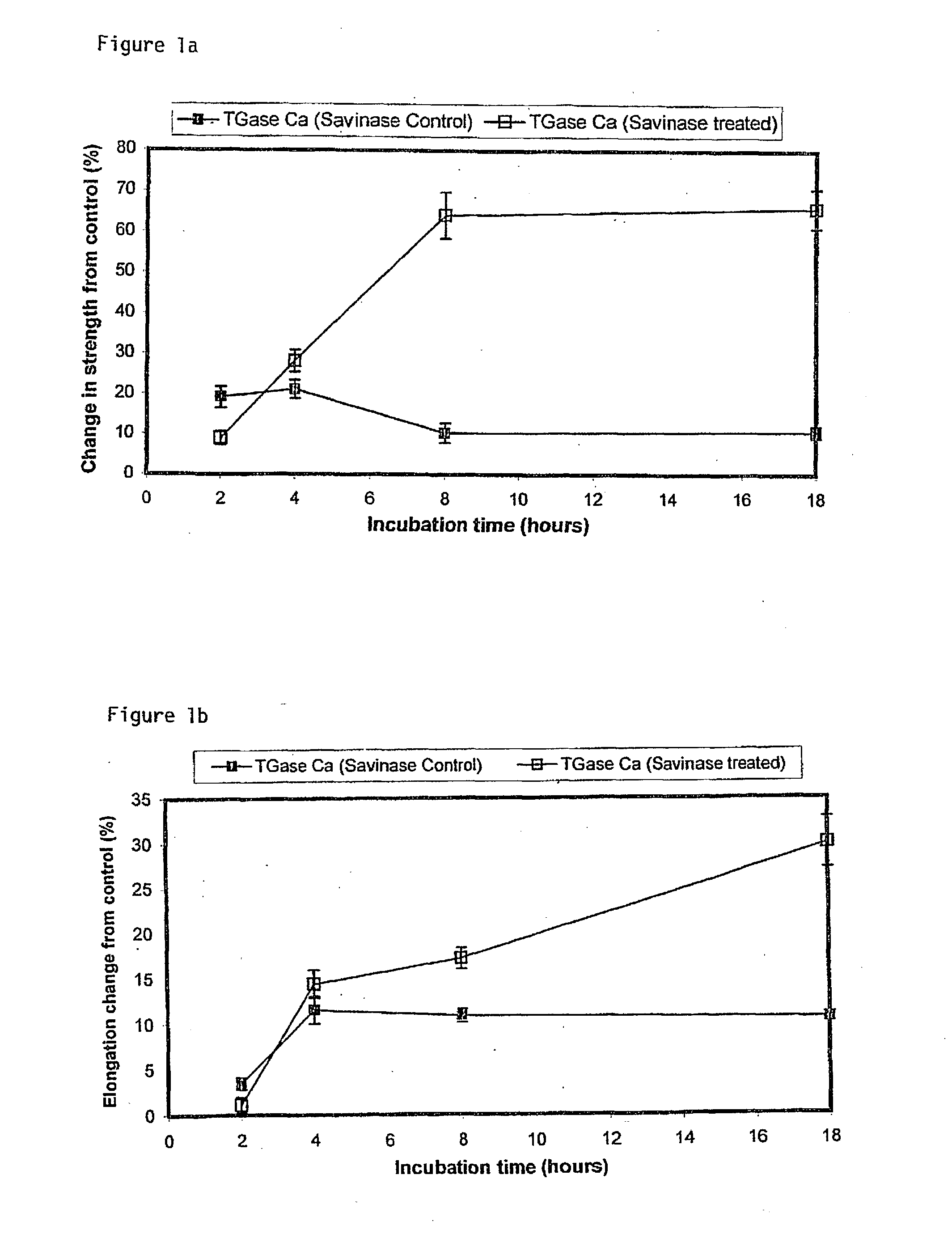
The application provides a method of treating fibrous textile goods comprising treating the fibrous textile goods with an enzyme. This enzyme can be used to covalently link one or more active functional compounds to the fibres and / or to trap one or more acitve functional compound within an inter-fibre matrix and / or within an intra-fibre matrix formed by the action of the enzyme. Preferably, the enzyme is a traglutaminase, especially a calcium-dependent transglutaminase. The enzyme may be used to add primary-amine containing active agents to the textile goods and also for the addition of proteins or peptides that have functional groups linked to them.
Owner:NOTTINGHAM TRENT UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for treating toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidiosis, and other apicomplexan protozoan related diseases
Compositions and methods for the treatment of toxoplasmosis, caused by the infectious eukaryotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) and for the treatment of cryptosporidiosis, caused by the infectious eukaryotic parasites Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum) and Cryptosporidium hominus (C. hominus) are described. In particular, the present disclosure is directed to compositions and methods for inhibiting either T. gondii calcium dependent protein kinases (TgCDPKs) or C. parvum and C. hominus calcium dependent protein kinases (CpCDPKs) using pyrazolopyrimidine and / or imidazo[1,5-a]pyrazine inhibitors, of the formula,wherein the variables X, Y, Z, L, R1, and R3 are defined herein.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
High alkaline protease and use thereof
InactiveUS8153413B2Good alkali resistanceImprove the immunitySugar derivativesBacteriaSitus inversusAmino acid
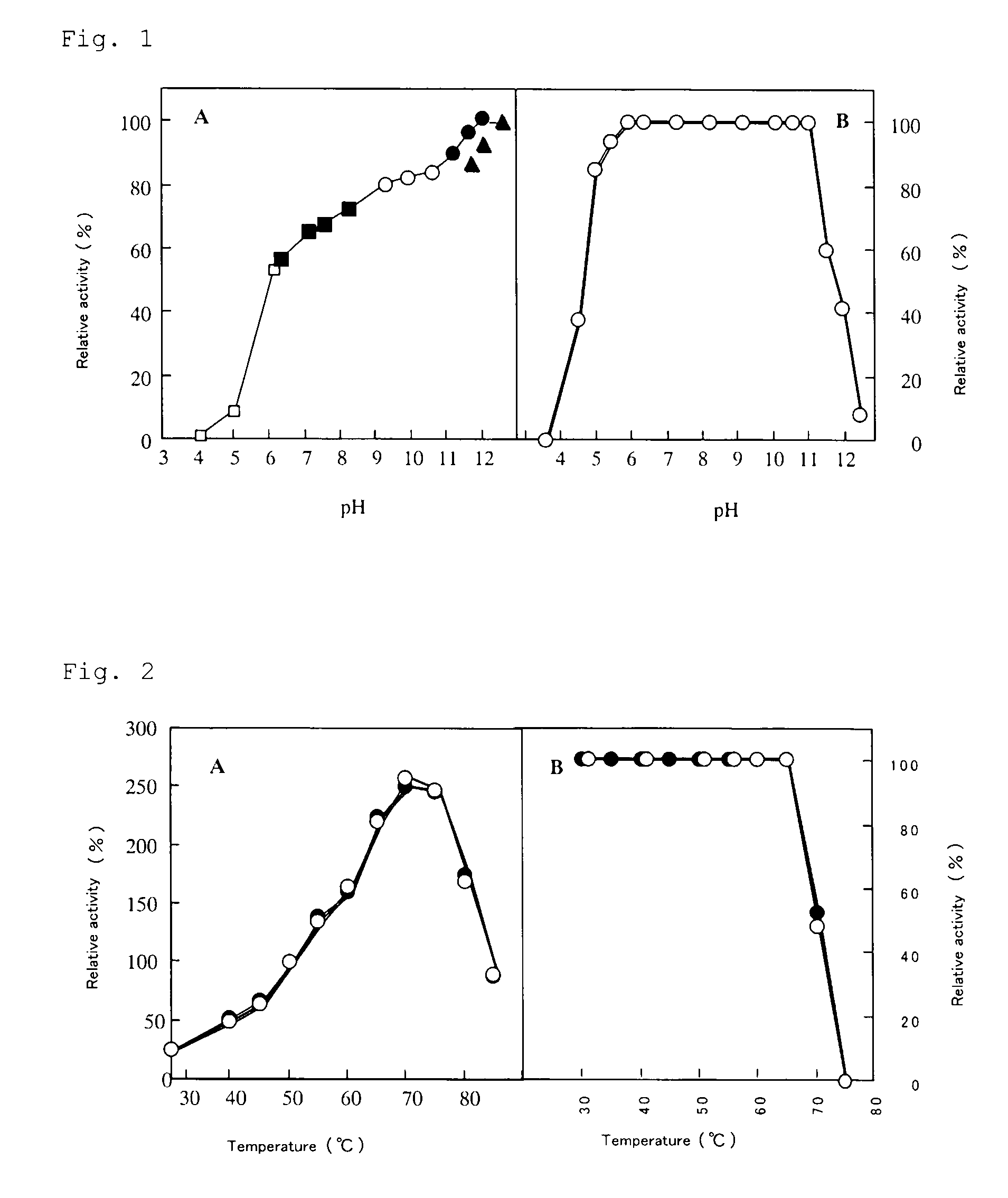
The invention aims to provide a novel alkaline protease having peculiar properties such as high alkali activity, resistance to surfactants and calcium-dependent thermostability and exhibiting excellent performance in highly alkaline detergents, and a gene coding for the amino acid sequence thereof. There is provided an alkaline protease with such properties that an active pH range is from 5 to 13, an optimum pH is approximately 12.6, an optimum temperature is 70° C., no activity drop by heating is observed up to 65° C. at pH 10 and the optimum temperature and the thermostability are not affected by Ca2+ ions. Specifically, there is provided, for example, an alkaline protease having an amino acid sequence constituting a mature enzyme as represented by SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence resulting from deletion, substitution, situs inversus arrangement, addition or insertion of a part of amino acids thereof, or derived from Alkaliphillus transvaalensis. The protease cleaves 26 peptide bonds among 29 peptide bonds of acidic insulin B-chain.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
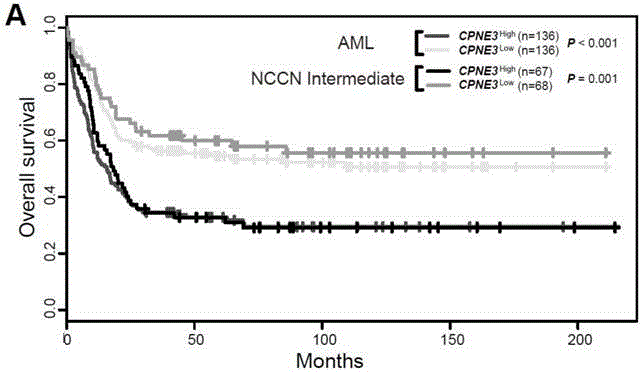
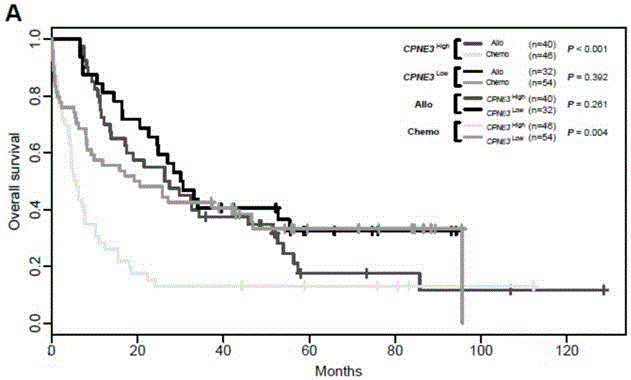
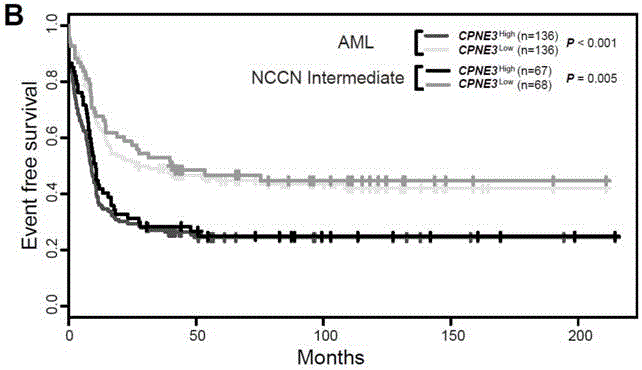
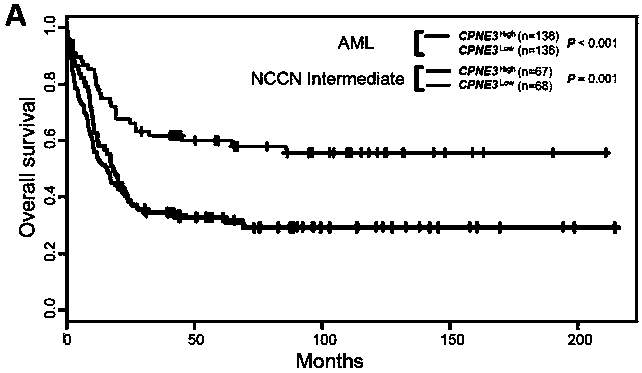
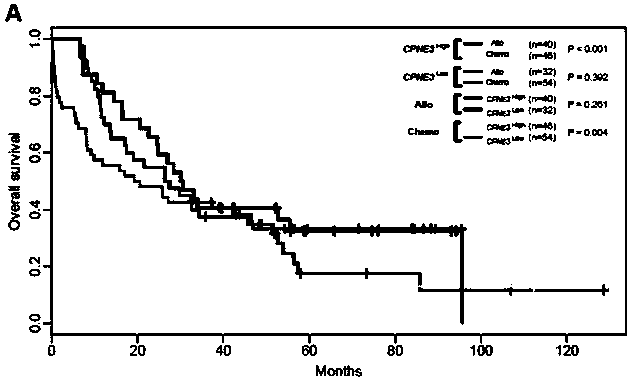
Kit for adult AML (acute myeloid leukemia) risk stratification and clinical prognosis evaluation and application of CPNE3
ActiveCN106244675ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMyeloid leukemiaClinical prognosis
The invention provides a kit for adult AML (acute myeloid leukemia) risk stratification and clinical prognosis evaluation and an application of CPNE3, namely a gene chip and the kit for conducting risk stratification or clinical prognosis evaluation on patients with adult AML, wherein primer pairs of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins copine III genes are used, and the sequences of one of the primer pairs are shown as agactcccacgaaactcagg (SEQ ID NO:2) and ctgtgcgctcaacctcatac (SEQ ID NO:3) or complementary sequences thereof, and the primer pairs are used for detecting the expression level of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins in adult AML cells or tissues.
Owner:石金龙
Means and Methods for Preventing and/or Treating Caries
The present invention relates to a microorganism belonging to the group of lactic acid bacteria capable of specifically binding to Streptococcus mutans, wherein the specific binding is (i) resistant to heat treatment; (ii) resistant to protease treatment; (iii) calcium-dependent; (iv) formed within a pH range between 4.5 and 8.5; and / or (v) formed in the presence of saliva. The present invention is also relates to an analog or fragment of the microorganism which is thermally inactivated or lyophilized, wherein the analog or fragment retains the capability of specifically binding to Streptococcus mutans. The invention further encompasses compositions and additives for food, feed or drinks comprising the microorganism or an analog or fragment thereof. Also provided is uses of the microorganism or an analog or fragment thereof for the preparation of an anticariogenic or pharmaceutical composition or anticariogenic food or feedstuff as well as methods for producing the compositions or food or feedstuff.
Owner:BASF AG
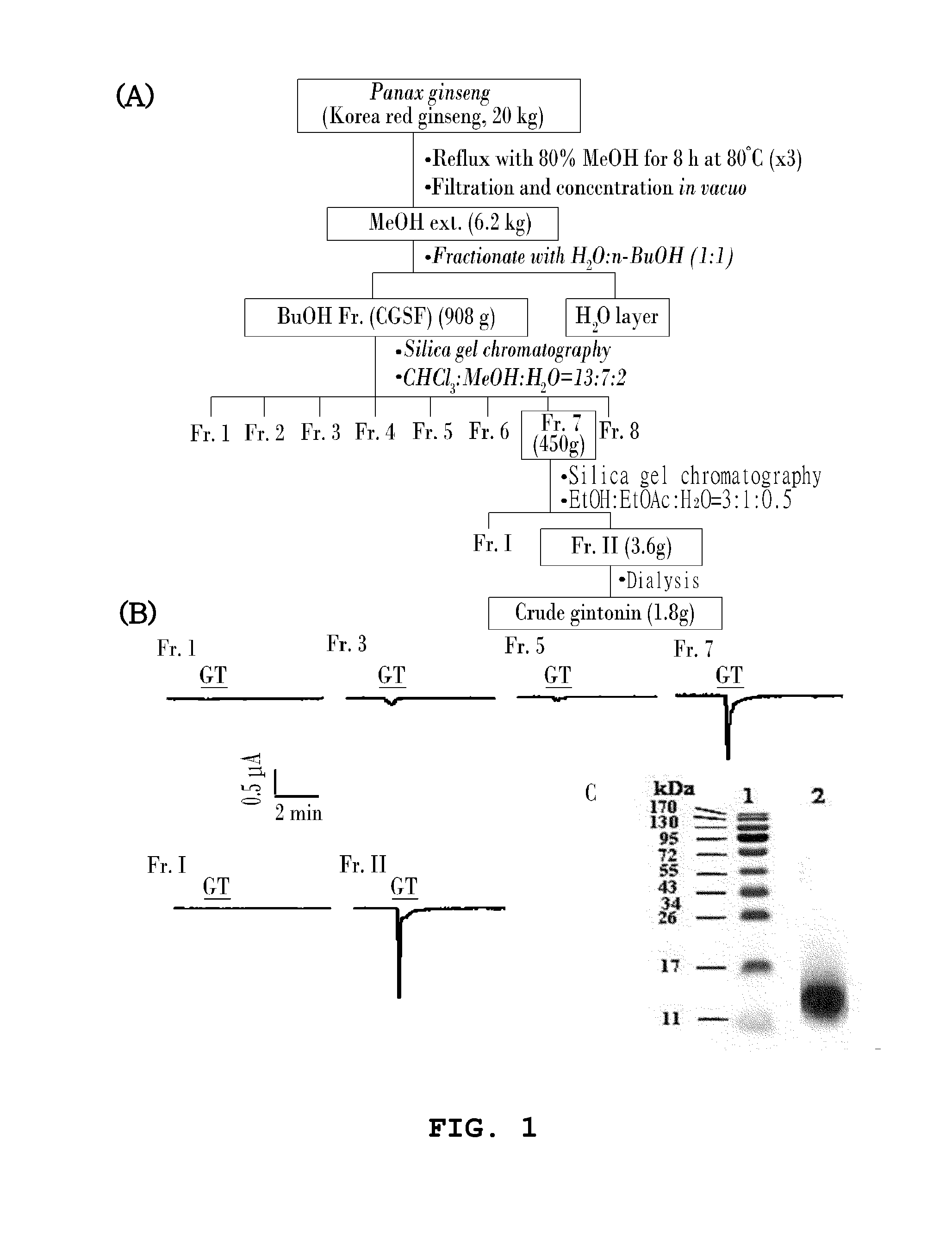
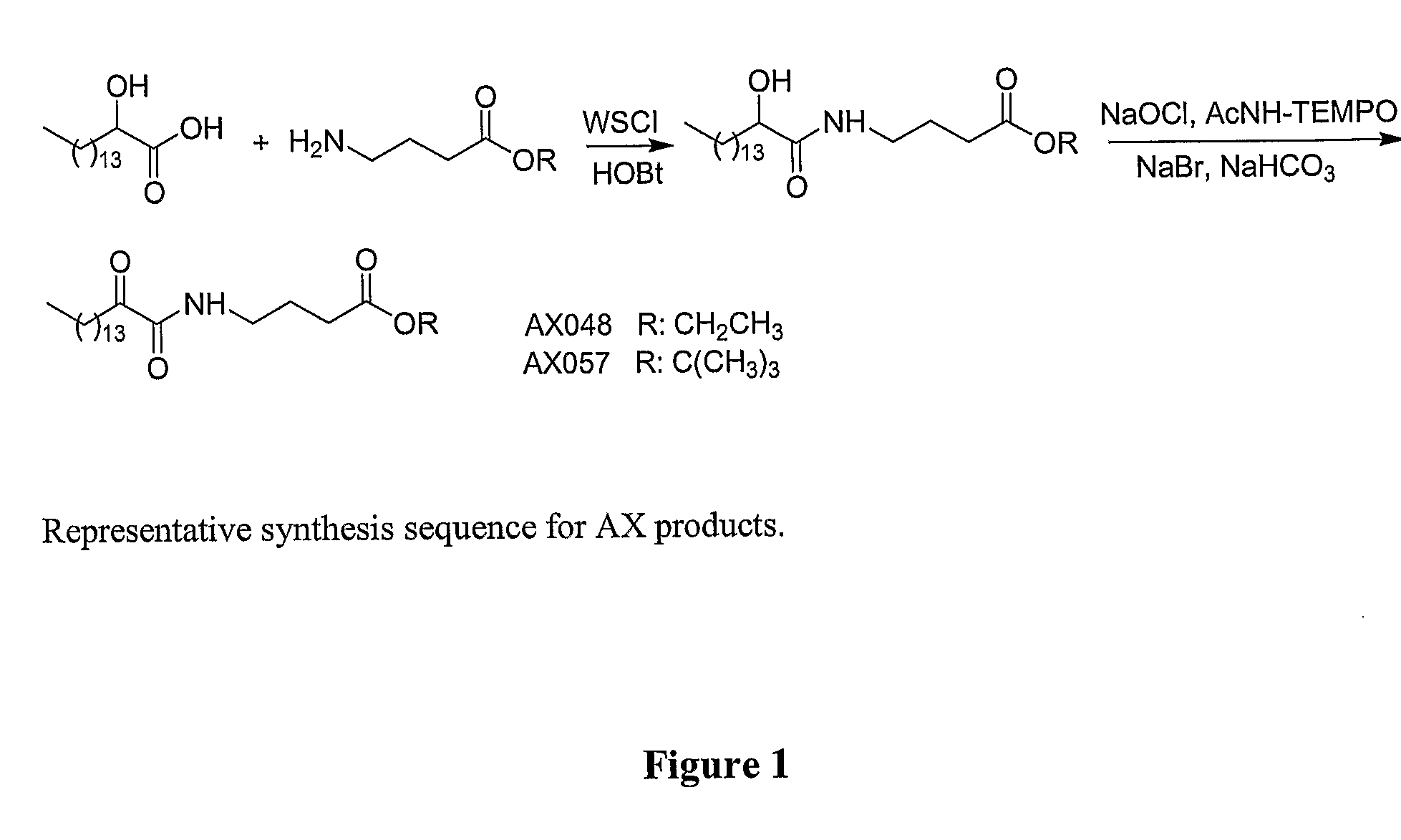
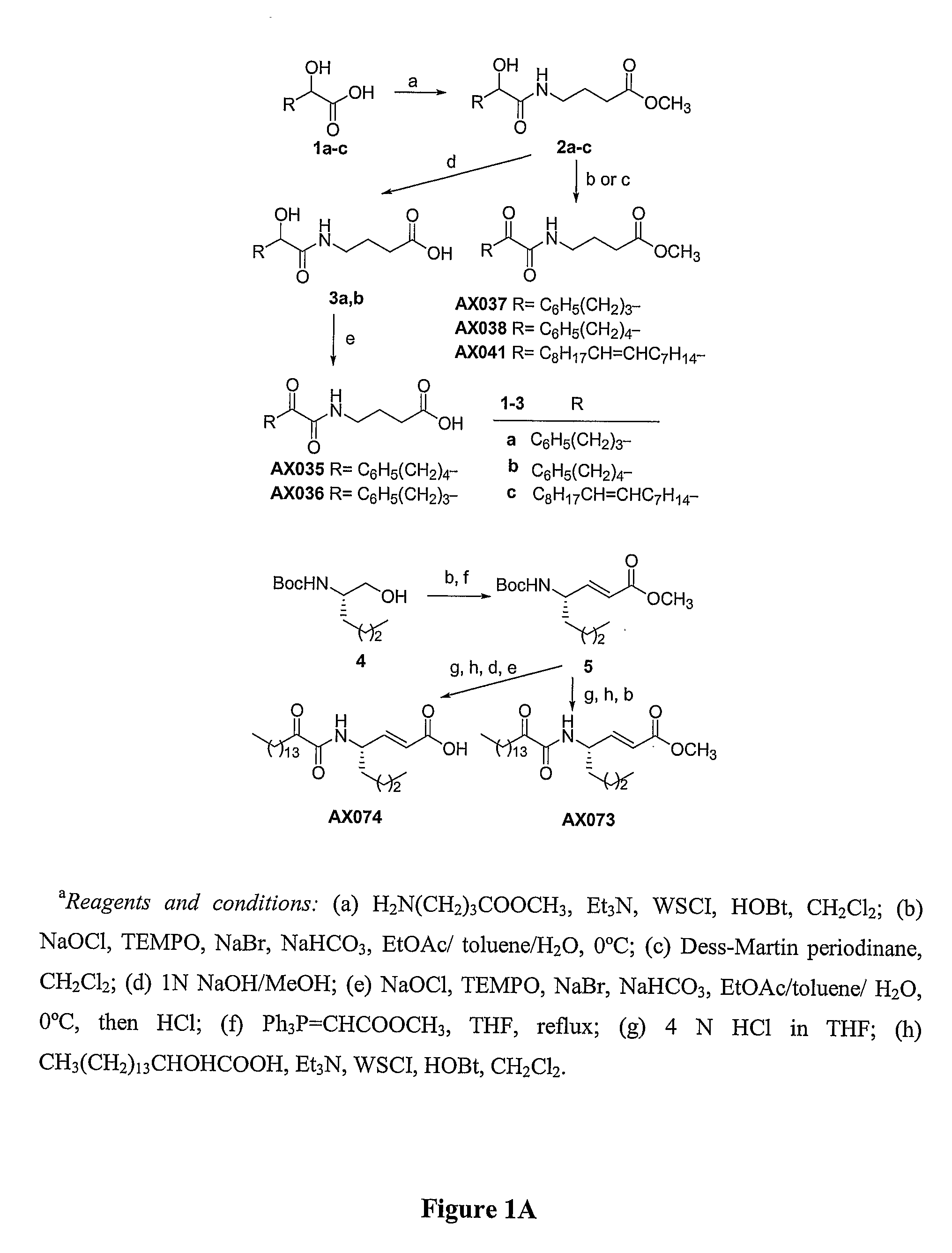
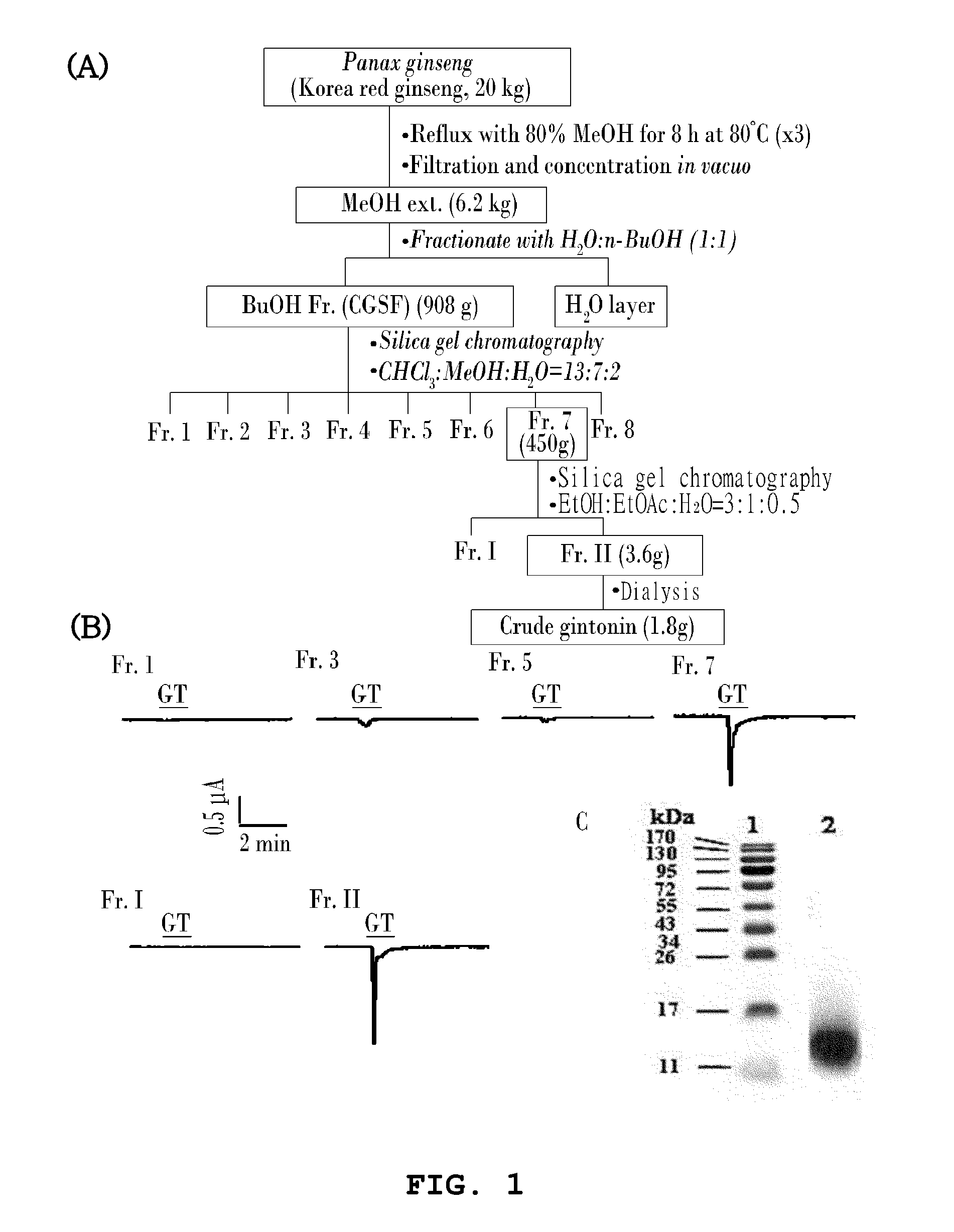
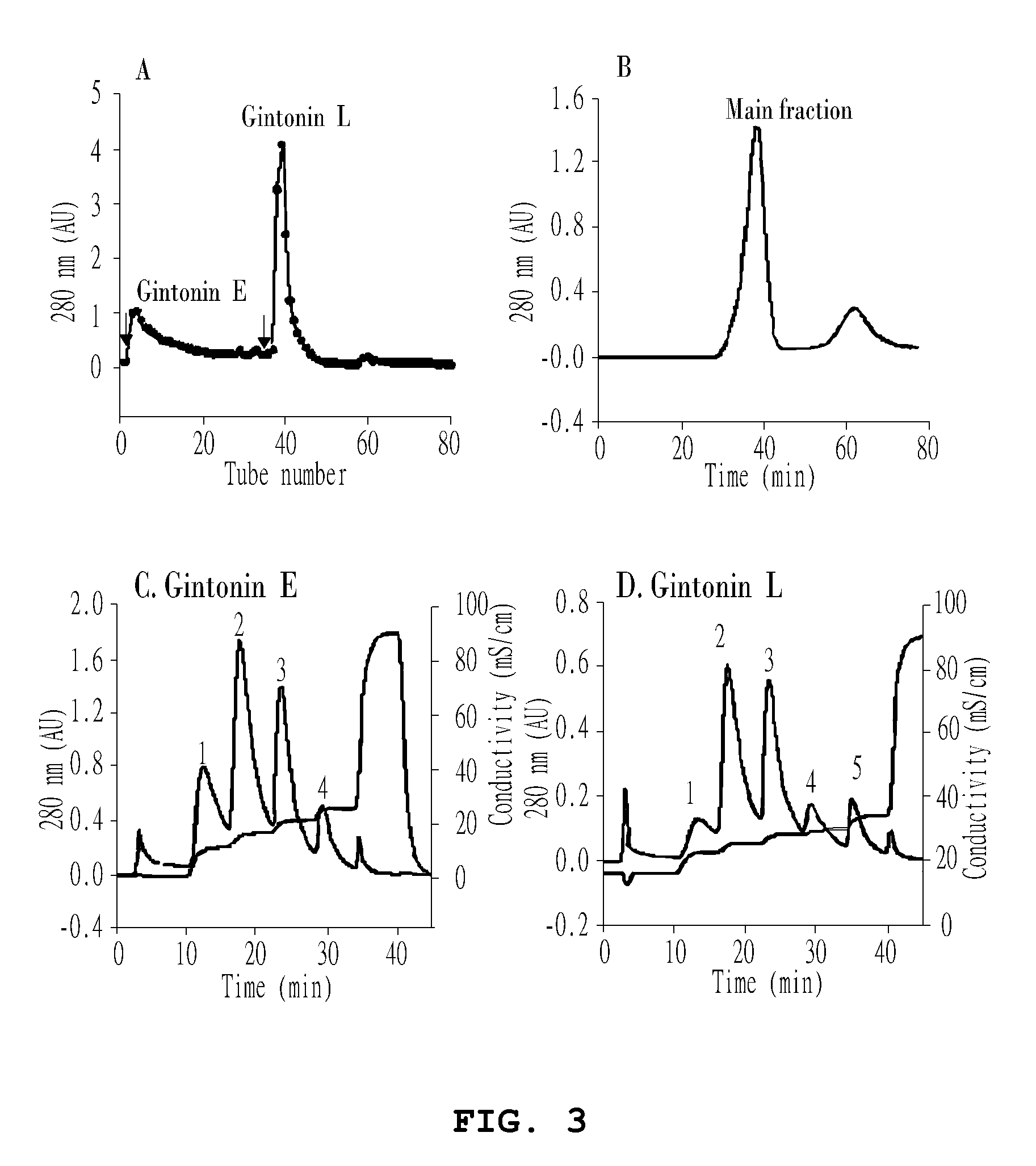
Method for preparing gintonin, which is a novel glycolipoproetin from panax ginseng, and gintonin, which is a novel glycolipoprotein, prepared by the method
ActiveUS20120165266A1Prevention and treatmentPrevention and treatment of calcium deficiencyBiocideNervous disorderAngiogenesis growth factorChloride channel
Disclosed are the novel glycolipoprotein gintonin isolated and identified from ginseng, a method for preparing the same, and uses thereof. Gintonin causes a transient increase in intracellular free Ca2+ level, which in turn activates endogenous Ca2+-activated chloride channel to elevate intracellular calcium levels. Therefore, the novel glycolipoproteins are useful in the therapy and prophylaxis of calcium deficiency-associated diseases as well as effectively inducing calcium-dependent physiological activities, including adaptogenic activity, immunostimulatory activity, aphrodisiac activity, neuroprotection and neuroactivation, angiogenesis, and antidiabetic activity.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV HLDG
Systemic and Intrathecal Effects of a Novel Series of Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors on Hyperalgesia and Spinal Pge2 Release
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) forins are expressed in spinal cord whose inhibition induces a potent antihyperalgesia. PLA2 inhibitor compounds are provided that include a common motif consisting of a 2-oxoamide with a hydrocarbon tail and a four carbon tether. The compounds block Group IVA calcium dependent PLA2 (cPLA2) and / or Group VIA calcium independent PLA2 (iPLA2) and / or Group V secreted PLA2 (sPLA2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
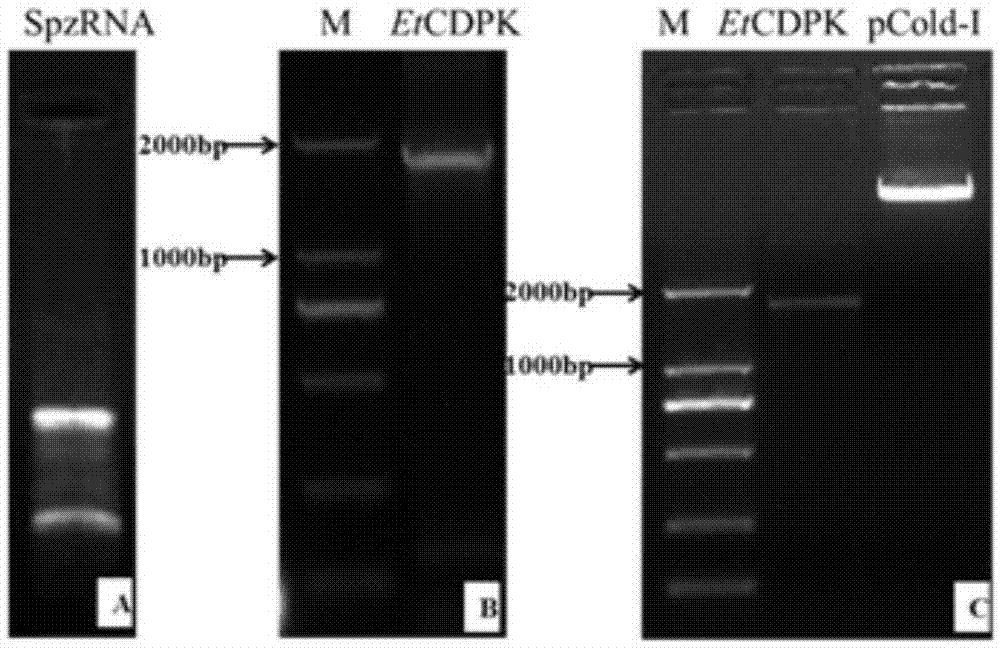
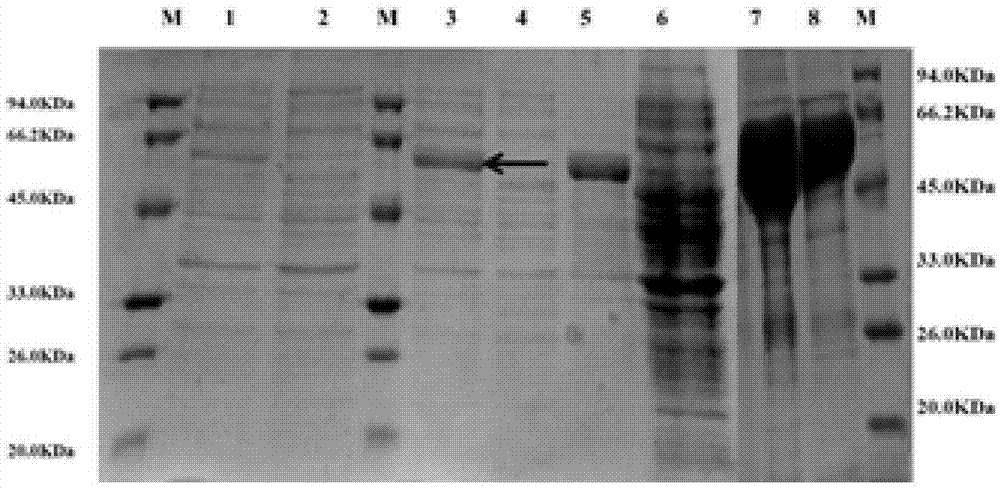
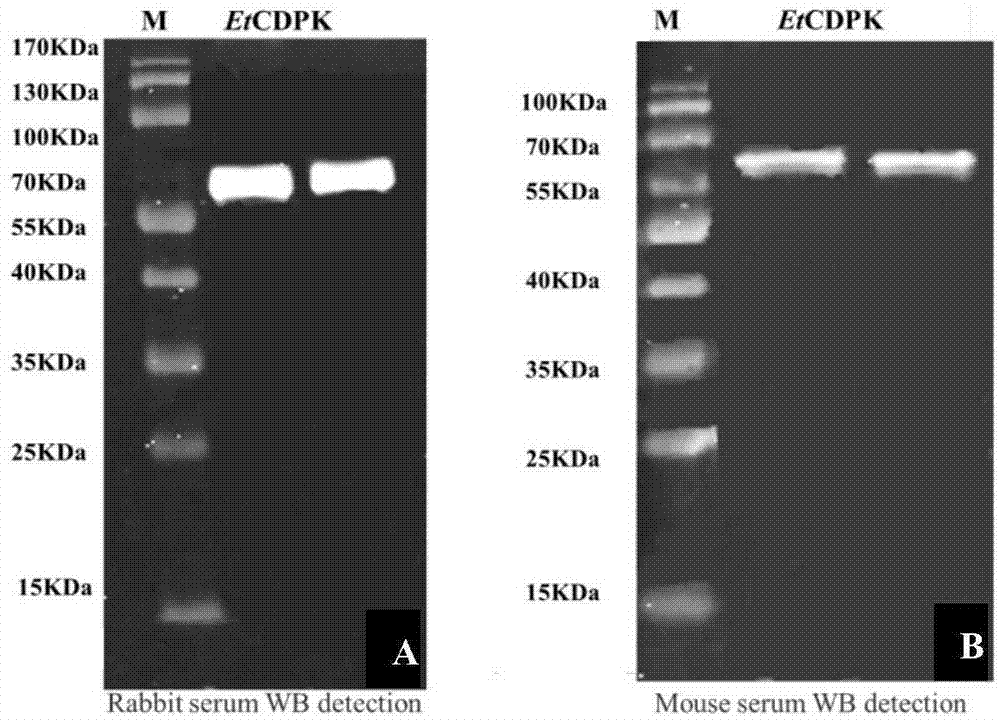
Eimeria tenella calcium-dependent protein kinases 4 gene, and applications thereof
InactiveCN106854653AInhibitionGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSporeCalcium-dependent protein kinase
The invention discloses an eimeria tenella gene, and more specifically discloses eimeria tenella calcium-dependent protein kinases 4 gene. The nucleotide sequence is disclosed in SEQ ID NO.1. The eimeria tenella calcium-dependent protein kinases 4 gene is a high expression gene at eimeria tenella spore period, is related to invading of sporozoite into host cells, and possesses relatively high application value in development of novel vaccines or novel drugs used for inhibiting invading of sporozoite into host cells and blocking eimeria tenella life history.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compositions and methods for treating toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidiosis and other apicomplexan protozoan related diseases
The present disclosure is directed to compositions and methods for inhibiting either Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) calcium dependent protein kinases (TgCDPKs) or Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum) and Cryptosporidium hominus (C. hominus) calcium dependent protein kinases (CpCDPKs) using pyrazolopyrimidine and / or imidazo[1,5-α]pyrazine inhibitors, of the Formula (I), wherein the variables X, Y, Z, R1, and R3 are defined herein.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
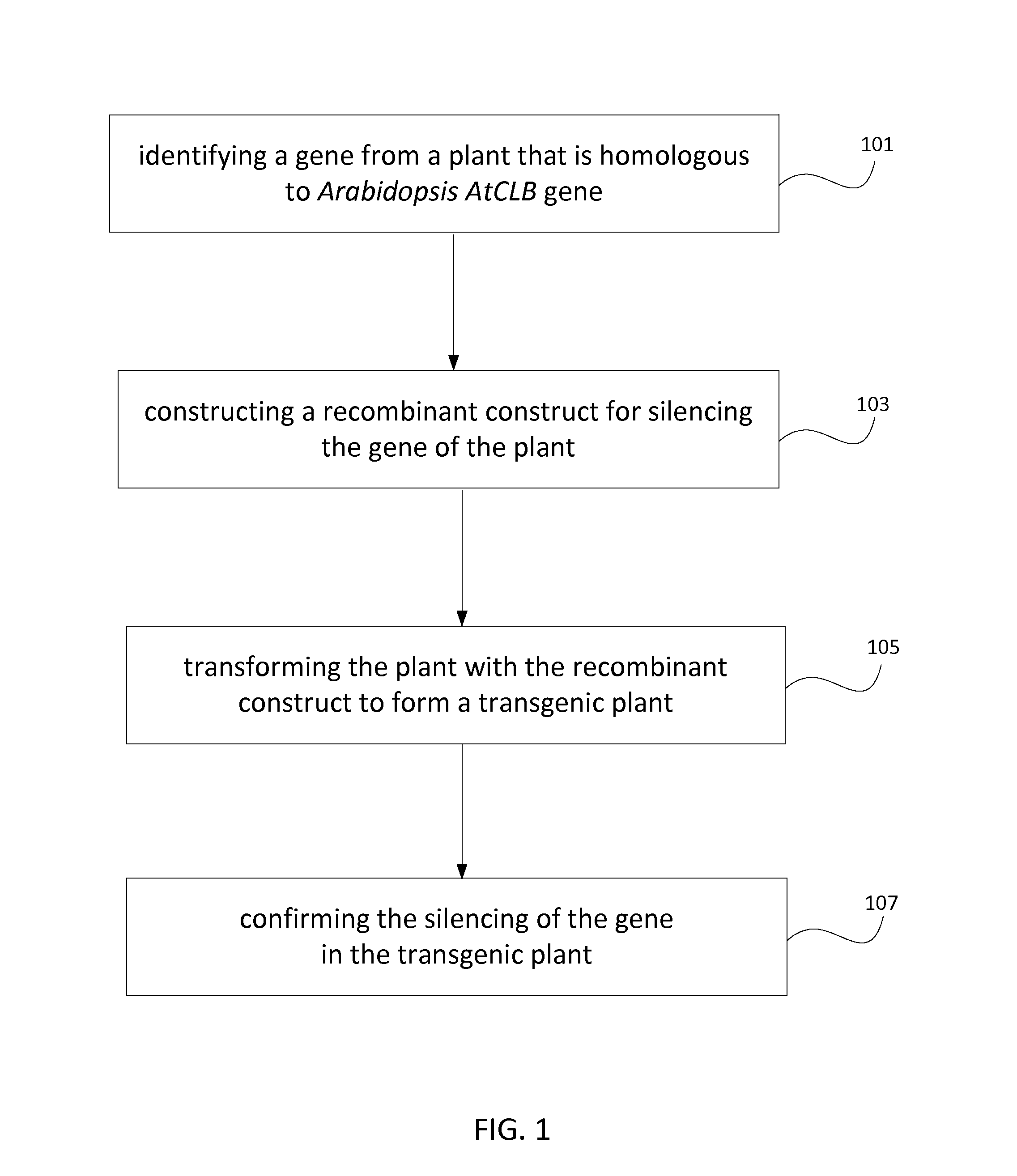
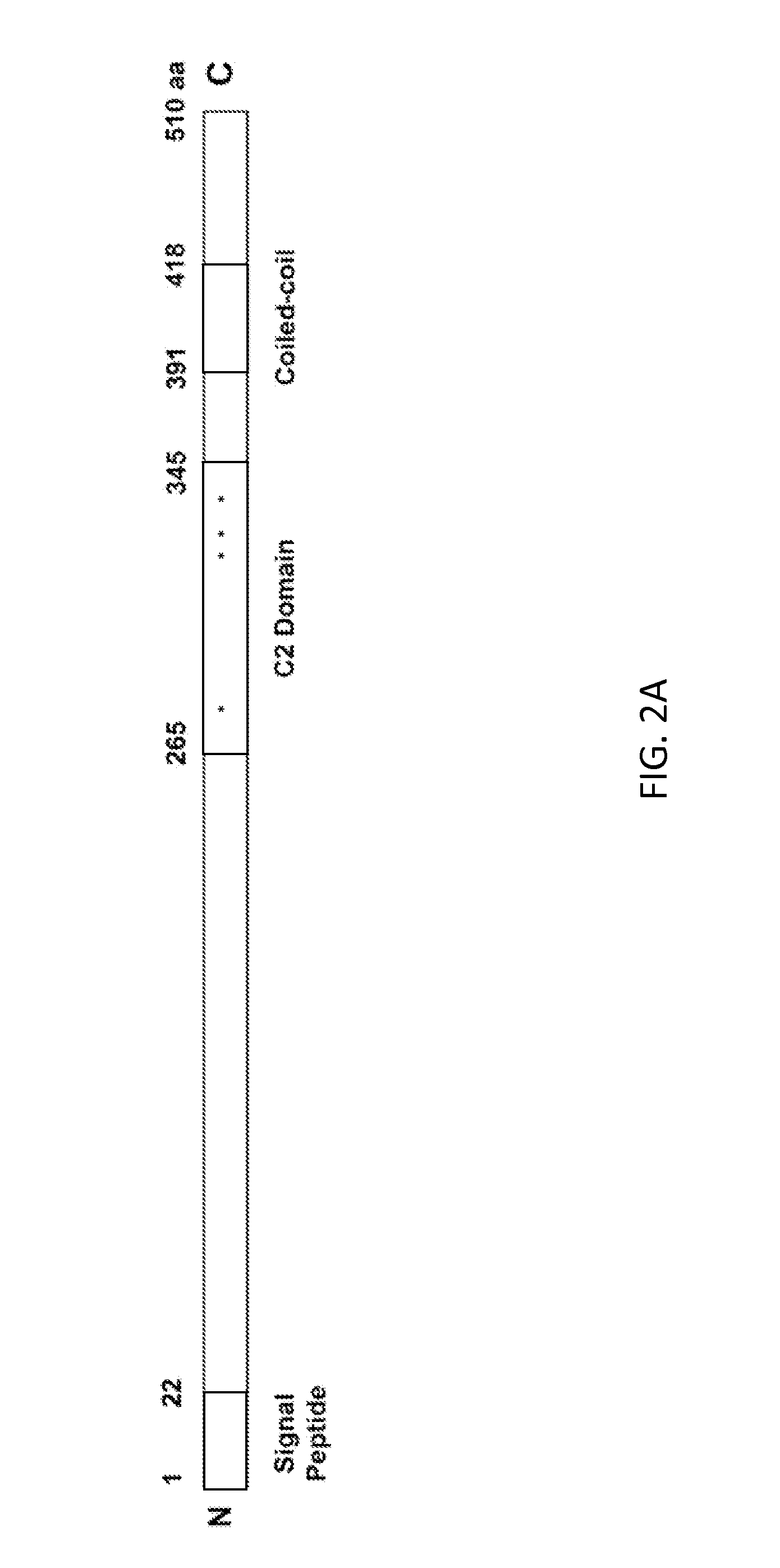
Method for producing stress tolerant transgenic plant by silencing a gene encoding calcium-dependent lipid-binding protein with c2 domain and applications of the same
InactiveUS20140082767A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationNucleotideLipid binding
A transgenic plant includes a first gene having a first polynucleotide and a recombinant construct having a second polynucleotide. The first polynucleotide is homologous to a Atclb gene fragment represented by nucleotide acids 963-1205 of SEQ ID NO:1. The first polynucleotide encodes a C2-like domain, and the Atclb gene fragment encodes a C2 domain represented by amino acids 265-345 of SEQ ID NO:2. The C2-like domain is homologous to the C2 domain. The second polynucleotide has at least 90% identity to the first polynucleotide or a sequence complimentary to the first polynucleotide. The recombinant construct is configured to silence the first gene such that the transgenic plant is tolerant to abiotic stress. A method to produce the transgenic plants.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method for preparing gintonin, which is a novel glycolipoproetin from panax ginseng, and gintonin, which is a novel glycolipoprotein, prepared by the method
ActiveUS8563052B2Prevention and treatmentPrevention and treatment of calcium deficiencyBiocideNervous disorderChloride channelAngiogenesis growth factor
Owner:KONKUK UNIV HLDG
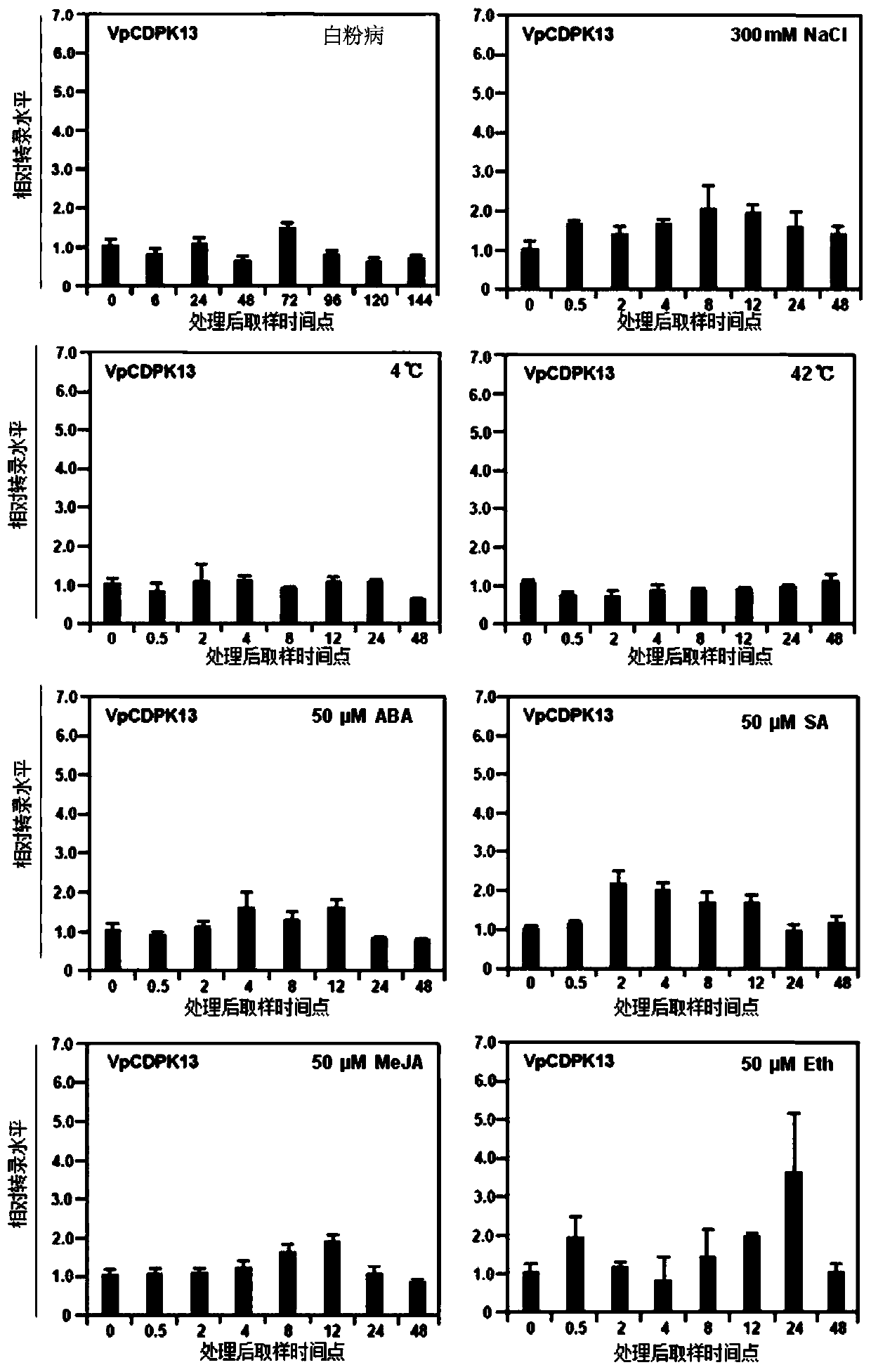
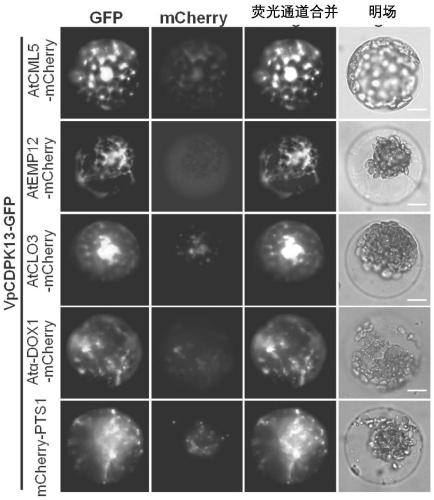
Powdery mildew resistant grape calcium dependent protein kinase gene VpCDPK13 and application thereof
ActiveCN111197035AImprove powdery mildew resistanceStrongly inhibit growthTransferasesGenetic engineeringVitis viniferaCalcium-dependent protein kinase
The invention discloses a Chinese wild East China grape Baihe-35-1 calcium-dependent protein kinase gene VpCDPK13 and an application thereof. The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, inparticular to the field of grape disease-resistant breeding. The calcium-dependent protein kinase gene VpCDPK13 is separated from the disease-resistant Chinese wild East China grape Baihe-35-1 plantgenome through a gene cloning technology, and is transferred into a powdery mildew susceptible grape plant to obtain a powdery mildew resistant transgenic grape plant, so that the powdery mildew resistance of grapes is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
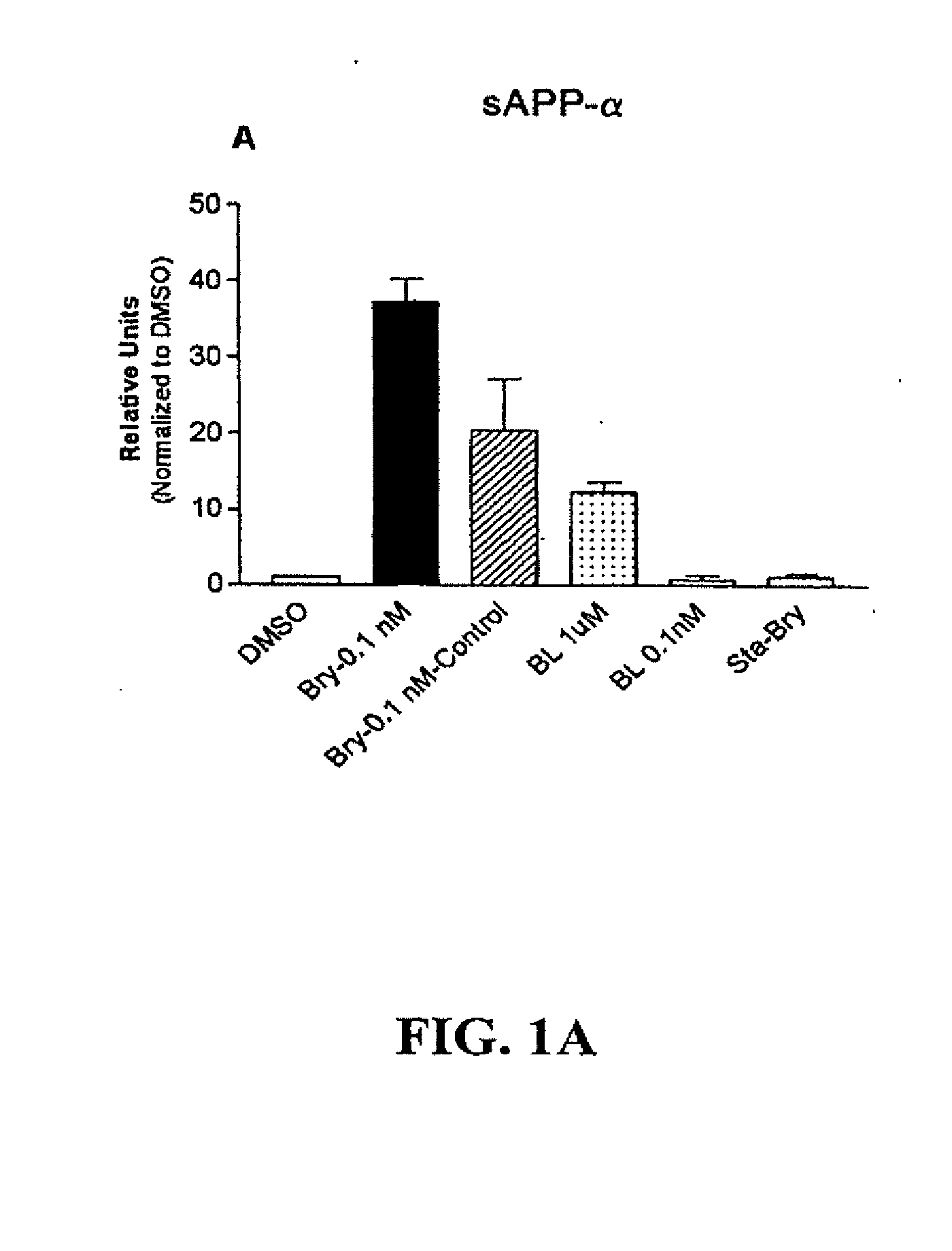
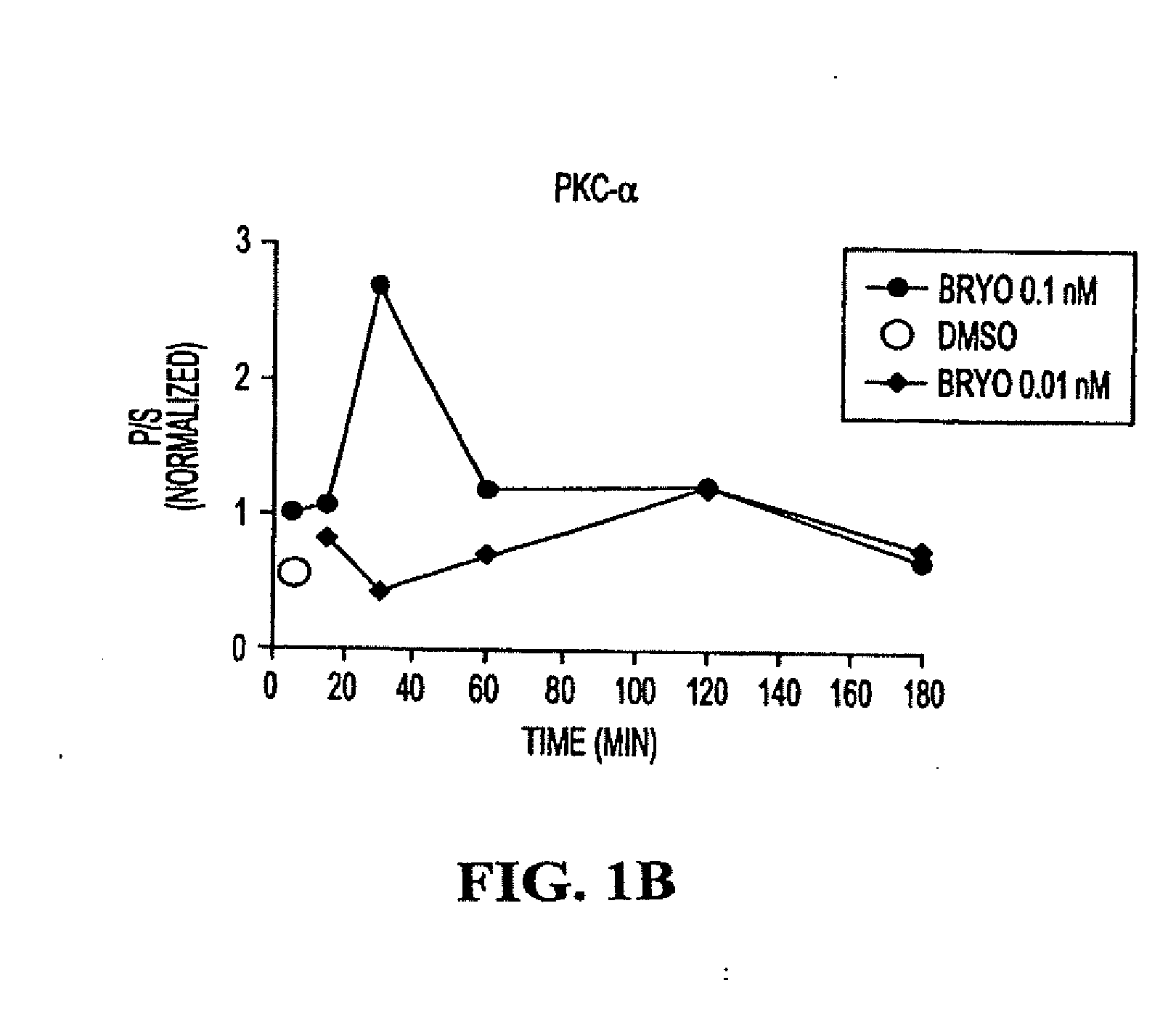
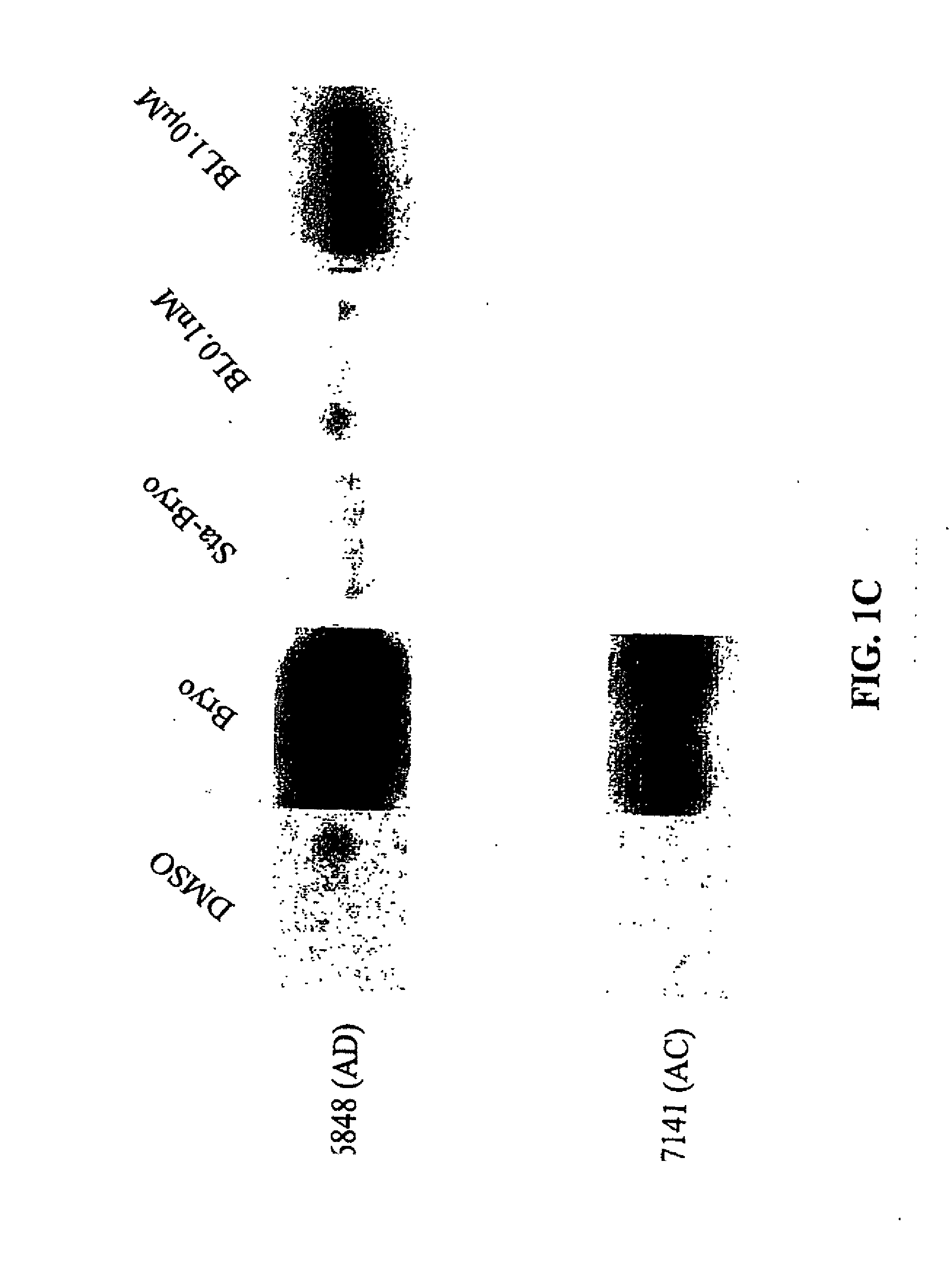
PCK ACTIVATION AS A MEANS FOR ENHANCING sAPPa SECRETION AND IMPROVING COGNITION USING BRYOSTATIN TYPE COMPOUNDS
InactiveUS20110196028A1Inhibit aggregationImprove/enhance cognitive abilityBiocideNervous disorderChemical reactionSignalling molecules
This invention provides a method for isolating and identifying proteins participating in protein-protein interactions in a complex mixture. The method uses a chemically reactive supporting matrix to isolate proteins that in turn non-covalently bind other proteins. The supporting matrix is isolated, and the non-covalently bound proteins are subsequently released for analysis. Because the proteins are accessible to chemical manipulation at both the binding and release steps, identification of the non-covalently bound proteins yields information on specific classes of interacting proteins, such as calcium-dependent or substrate-dependent protein interactions. This permits selection of a subpopulation of proteins from a complex mixture on the basis of specified interaction criteria. The method has the advantage of screening the entire proteome simultaneously, unlike two-hybrid systems or phage display methods which can only detect proteins binding to a single bait protein at a time. The method is applicable to the study of protein-protein interactions in biopsy and autopsy specimens, to the study of protein-protein interactions in the presence of signaling molecules, pharmacological agents or toxins, and for comparison of diseased and normal tissues or cancerous and untransformed cells.
Owner:BLANCHETTE ROCKEFELLER NEUROSCI INST
Eimeria tenella calcium-dependent protein kinase gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an eimeria tenella gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene coded calcium-dependent protein kinase comprises a DNA sequence for coding an SEQ ID NO.1 amino acid sequence or a DNA sequence for coding an amino acid sequence with calcium-dependent protein kinase activity obtained by deleting, adding, inserting or replacing one or a plurality of amino acids in the SEQ ID NO.1amino acid sequence. The invention also discloses a protein coded by the gene. The eimeria tenella gene is a new gene highly expressed in a sporozoite phase of the eimeria tenella, and is related to the invasion of a to a host cell. The gene has high application value in developing new vaccines or new medicines for inhibiting the invasion of the sporozoite to the host cell and blocking the life cycle of the eimeria tenella.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods of determining polypeptide structure and function
The present invention provides methods for determining the structure and / or function of one or more domains of a cation-dependent (and preferably calcium-dependent) polypeptide (particularly a calcium-dependent enzyme, which may be a protease such as calpain) in the presence of one or more cations. The invention further provides methods for identifying a ligand having the ability to bind to one or more ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of a cation-dependent (and preferably calcium-dependent) polypeptide, and ligands identified by these methods. The invention also provides methods of treating or preventing physical disorders in animals using these ligands.
Owner:ELCE JOHN S +4
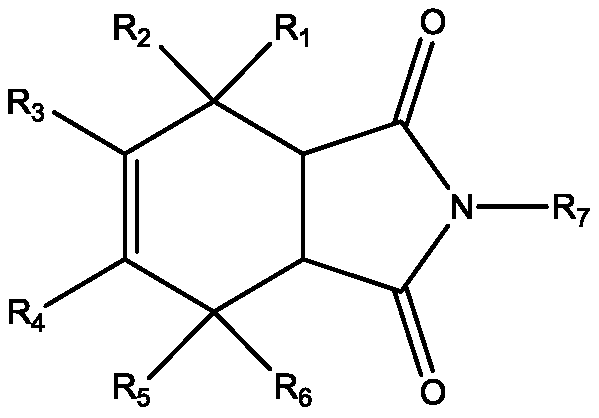
A new application of isoindole-1,3-dione compound
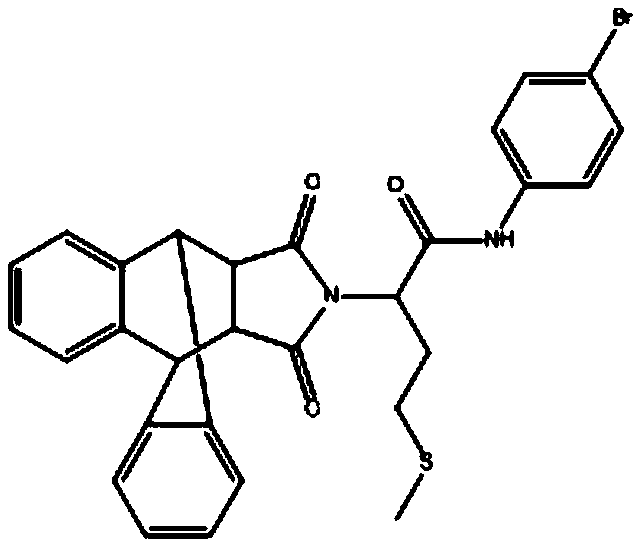
InactiveCN106806366BOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsDiketonePROTOZOAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
The invention provides application of a novel skeleton compound in preparing drug for preventing and treating parasitic infection disease. The novel skeleton compound can be used as calcium-dependent protein kinase. The invention discloses an isoindole-1, 3-diketone compound which has effect of inhibiting activity of the calcium-dependent protein kinase, can be used for preparing the drug for preventing or / and treating protozoal infectious disease and has potential application prospect in acute and chronic parasitic disease. Comparison tests show that the isoindole-1, 3-diketone compound has obvious higher activity in inhibiting CDPK1 than a pyrazolopyrimidine compound NM-PP1.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Novel human calcium dependent proteases, polynucleotides encoding the same, and uses thereof
Owner:DONOHO GREGORY +5
Systemic and intrathecal effects of a novel series of phospholipase a2 inhibitors on hyperalgesia and spinal pge2 release
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) forins are expressed in spinal cord whose inhibition induces a potent antihyperalgesia. PLA2 inhibitor compounds are provided that include a common motif consisting of a 2-oxoamide with a hydrocarbon tail and a four carbon tether. The compounds block Group IVA calcium dependent PLA2 (cPLA2) and / or Group VIA calcium independent PLA2 (iPLA2) and / or Group V secreted PLA2 (sPLA2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
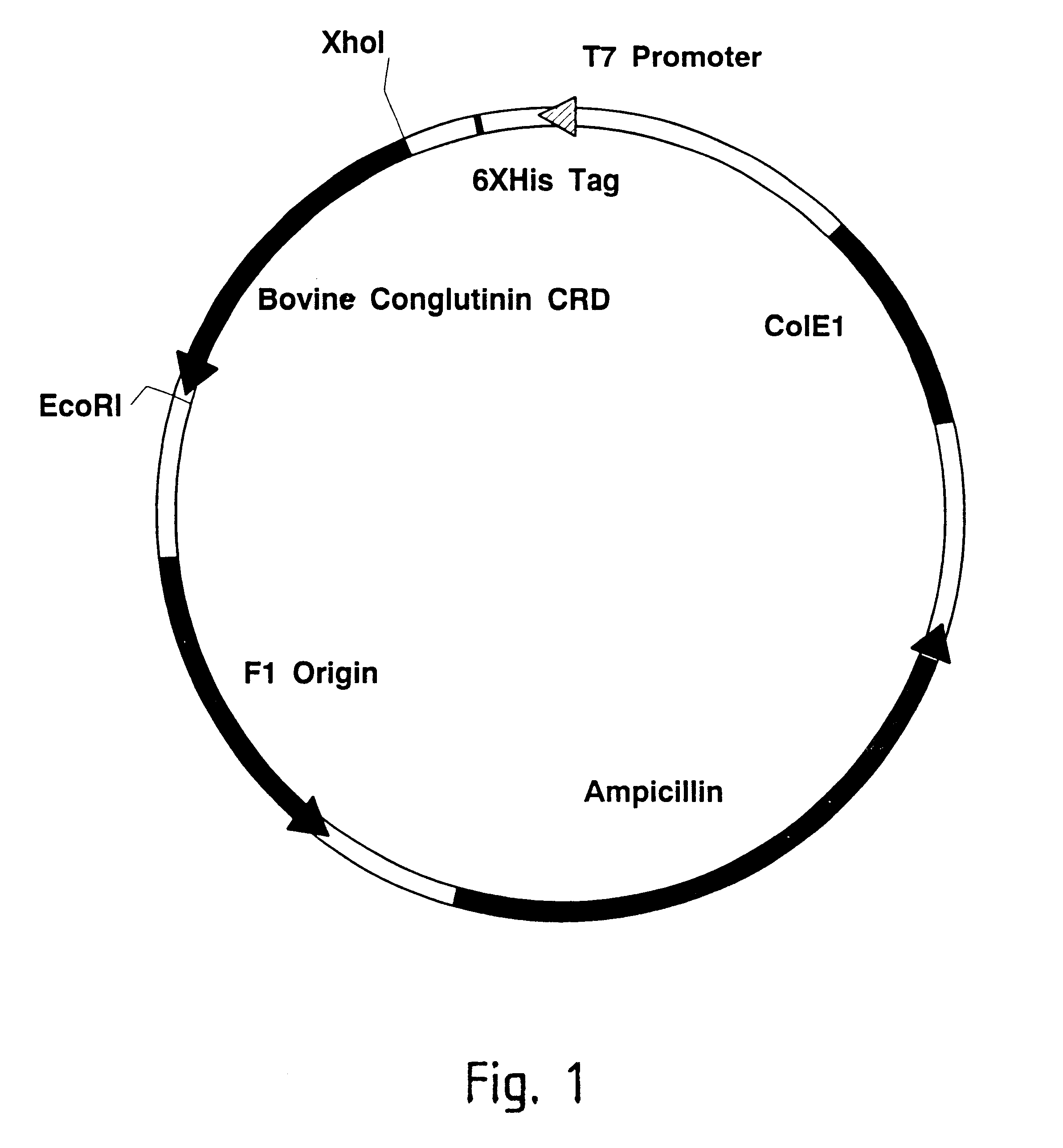
Methods for detecting anti-viral activity of calcium-dependent lectins
A recombinant conglutinin which contains a collagen region consisting of six amino acids containing two amino acid sequences Gly-Xaa-Xaa (SEQ ID NO:3, wherein Xaa stands for a protein-constituting amino acid), the neck region of natural conglutinin and the sugar chain recognition region of natural conglutinin, has an antiviral activity (virus neutralizing activity), and is expected to be applicable to drugs; and a process for detecting anti-influenza A virus activity of a mannose-binding protein (MBP) or a human mannose-binding protein (hMBP) involving the step of treating influenza A virus-infected cells with the MBP or hMBP and measuring the level of the suppression of the budding of the virus in the virus-infected cells. An MBP and an hMBP having an anti-influenza A virus activity are disclosed.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Method and compositions for the identification of agents that have a potential effect against chronic inflammatory diseases
The present invention is based on two important experimental observations: The first observation is that increased extracellular concentrations of ionized calcium are found in erosive arthritis and stimulate monocytic IL-1β release via the CaSR and GPRC6A. Simultaneous stimulation of monocytes with calcium ions and selected TLR ligands results in a 20-fold increased IL1β response compared to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) alone. During the crosstalk between GPCR and TLR signaling, phospholipase C is activated, which triggers calcium dependent potassium channels, resulting in potassium efflux, caspase-1 activation and IL-1β release. The amplification of IL1β secretion at sites of locally increased calcium ion concentrations aggravates rheumatoid arthritis. The second important observation is that both CaSR and GPRC6A, are highly expressed in the synovial membrane of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but expression of GPRC6A, but not of CaSR, is lower in patients with osteoarthritis (s. FIG. 1). The latter is generally not accompanied by inflammation. Thus, expression of GPRC6A appears to be upregulated in chronic inflammatory situations. Based on these experimental observations the invention provides a method and compositions for the identification of agents that have a potential effect against chronic inflammatory conditions, in particular erosive arthritis and atherosclerosis.
Owner:UNIV LEIPZIG
Method for isolating subpopulations of proteins that engage in protein-protein interactions
InactiveUS20060275821A1FocusReduce signal to noise ratioDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsRNA-Protein InteractionChemical reaction
The invention provides a method for isolating and identifying proteins participating in protein-protein interactions in a complex mixture. The method uses a chemically reactive supporting matrix to isolate proteins that in turn non-covalently bind other proteins. The supporting matrix is isolated, and the non-covalently bound proteins are subsequently released for analysis. Because the proteins are accessible to chemical manipulation at both the binding and release steps, identification of the non-covalently bound proteins yields information on specific classes of interacting proteins, such as calcium-dependent or substrate-dependent protein interactions. This permits selection of a subpopulation of proteins from a complex mixture on the basis of specified interaction criteria. The method has the advantage of screening the entire proteome simultaneously, unlike two-hybrid systems or phage display methods which can only detect proteins binding to a single bait protein at a time. The method is applicable to the study of protein-protein interactions in biopsy and autopsy specimens, to the study of protein-protein interactions in the presence of signalling molecules, pharmacological agents or toxins, and for comparison of diseased and normal tissues or cancerous and untransformed cells.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
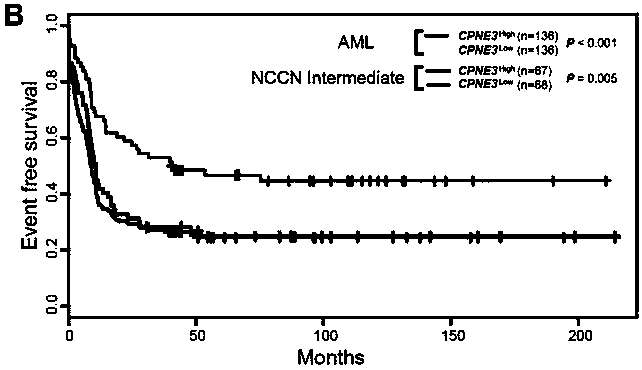
Adult AML risk stratification and clinical prognosis assessment kit and application of cpne3
ActiveCN106244675BNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical prognosisAcute myeloid leukemias
The invention provides a kit for adult AML (acute myeloid leukemia) risk stratification and clinical prognosis evaluation and an application of CPNE3, namely a gene chip and the kit for conducting risk stratification or clinical prognosis evaluation on patients with adult AML, wherein primer pairs of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins copine III genes are used, and the sequences of one of the primer pairs are shown as agactcccacgaaactcagg (SEQ ID NO:2) and ctgtgcgctcaacctcatac (SEQ ID NO:3) or complementary sequences thereof, and the primer pairs are used for detecting the expression level of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins in adult AML cells or tissues.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Pyrimidine derivative
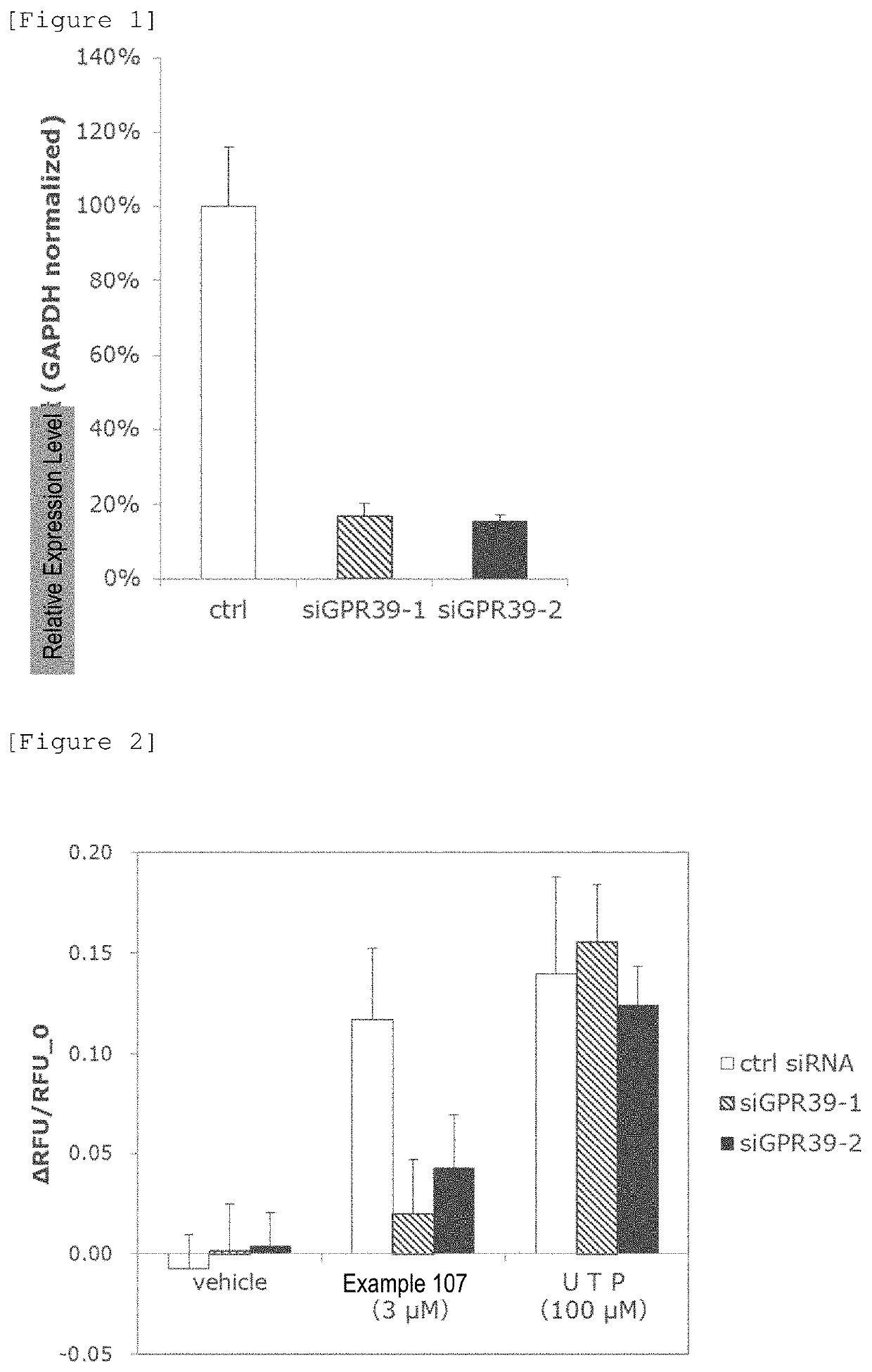
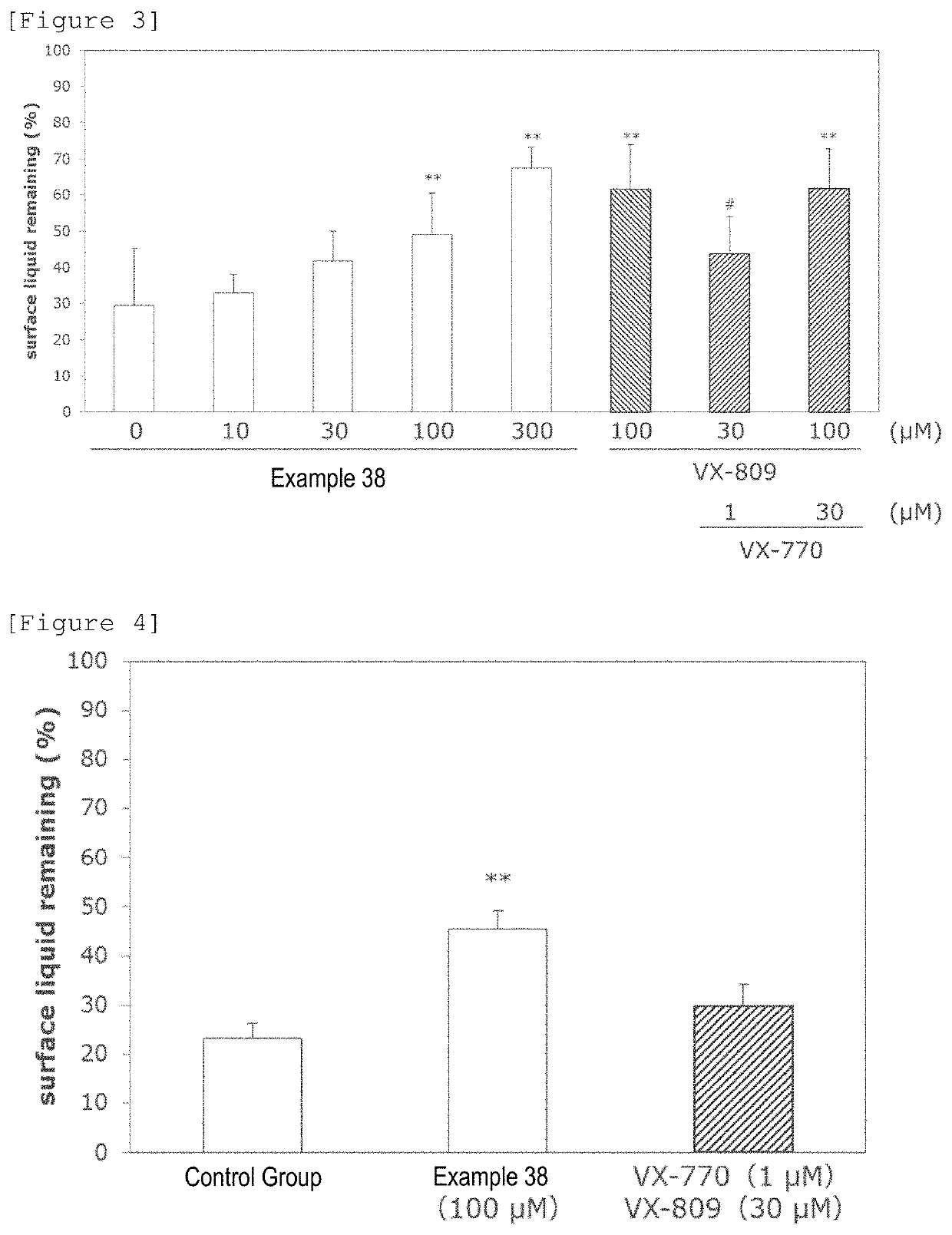
Cystic fibrosis is developed through mutation of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator (CFTR), which is one type of chloride channel. An object of the present invention is to provide compounds effective in the treatment of cystic fibrosis that open a chloride channel different from CFTR, which is the cause of the disease, and do not depend on CFTR.Compounds of the present invention are compounds or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof that open calcium dependent chloride channels (CaCCs) via G-protein coupled receptor 39 (GPR39) agonism to have strong chloride ion-secretory action, and are represented by the following general formula (I):General formula (I):wherein,X represents a carboxyl group or a tetrazolyl group;Q represents a C1-C3 alkylene group, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, etc.;G represents a phenyl group where the phenyl group may have 1 to 3 substituents independently selected from the group consisting of a halogen atom, a cyano group, a C1-C6 alkyl group, etc.;R1 represents a C1-C6 alkyl group, etc.;R2 represents a C1-C6 alkyl group that may have 1 to 3 substituents independently selected from the following group A, or a group selected from the following group B:Group A: a phenyl group and a pyridyl group, wherein the phenyl group and the pyridyl group may have 1 to 3 substituents independently selected from the following group D;Group B: —OH, —O-M, —SH, —S-M, —NH2, —NH-M, and —N-M2, wherein M is a C1-C6 alkyl group that may have 1 or 2 substituents independently selected from the following group C, or a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group that may have 1 or 2 substituents independently selected from the following group C;Group C: a halogen atom, a cyano group, a phenyl group, a pyridyl group, etc., wherein the phenyl group and the pyridyl group may have 1 to 3 substituents independently selected from the following group D; andGroup D: a halogen atom, a cyano group, a C1-C6 alkyl group, etc.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com