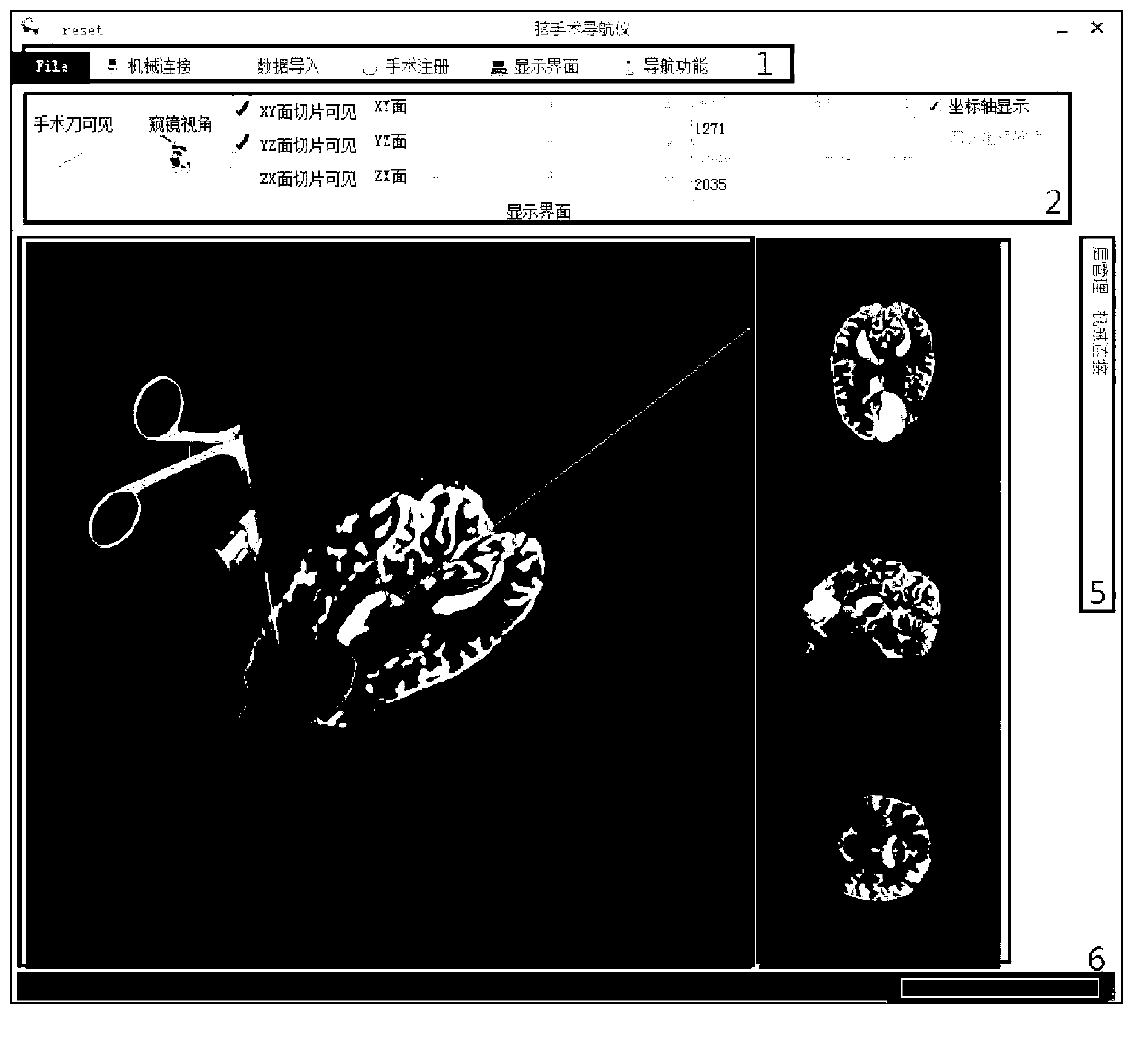
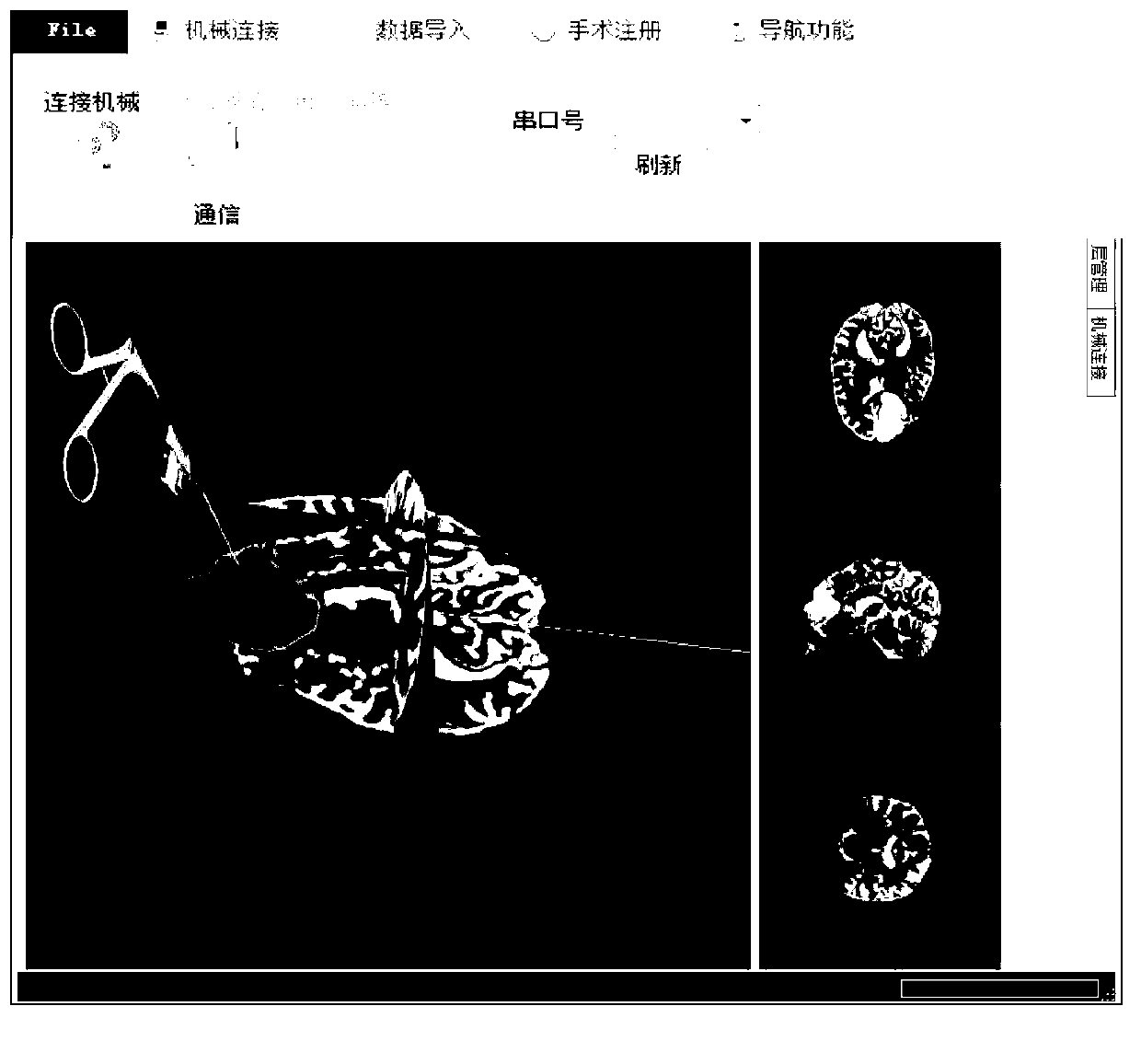
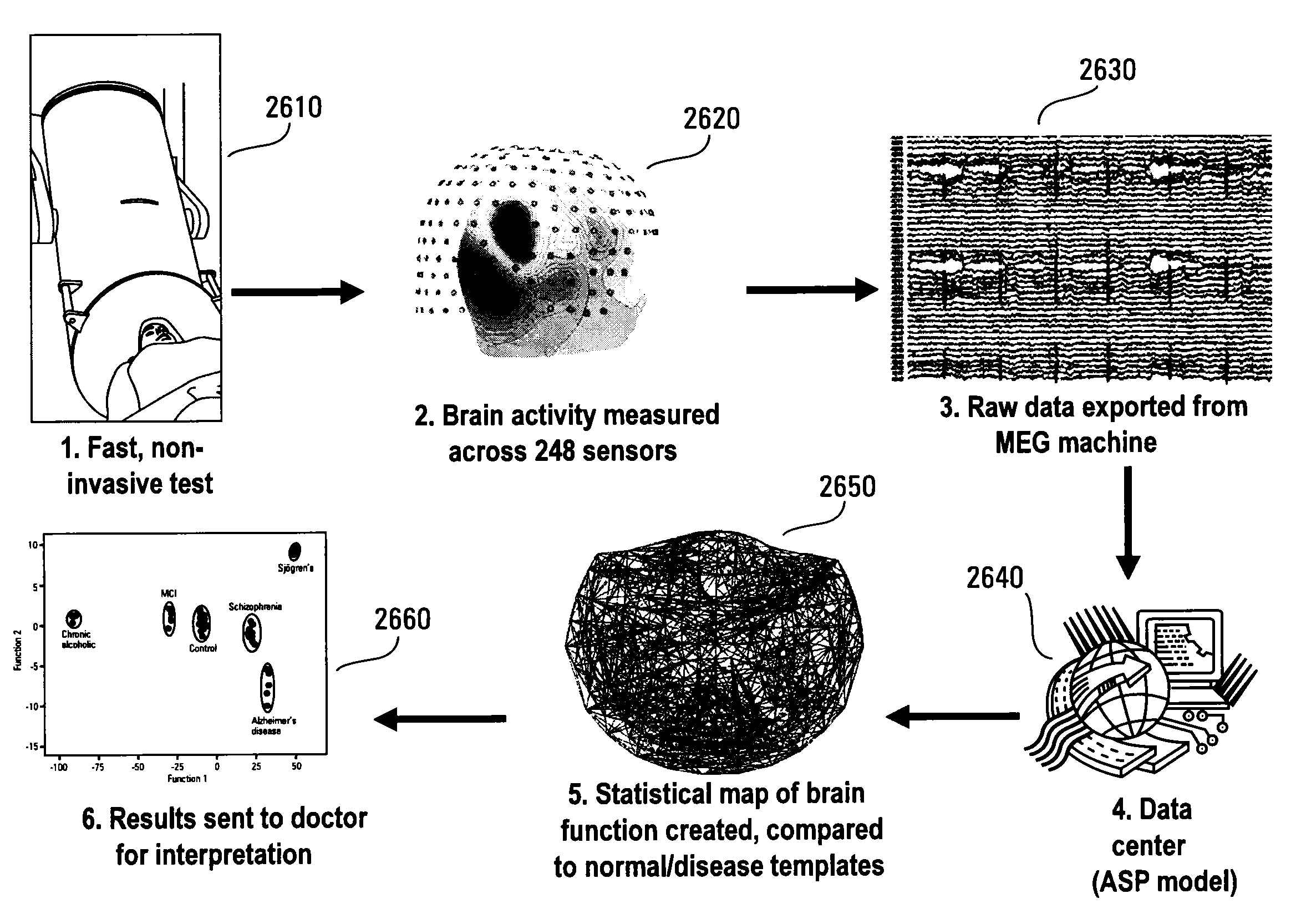
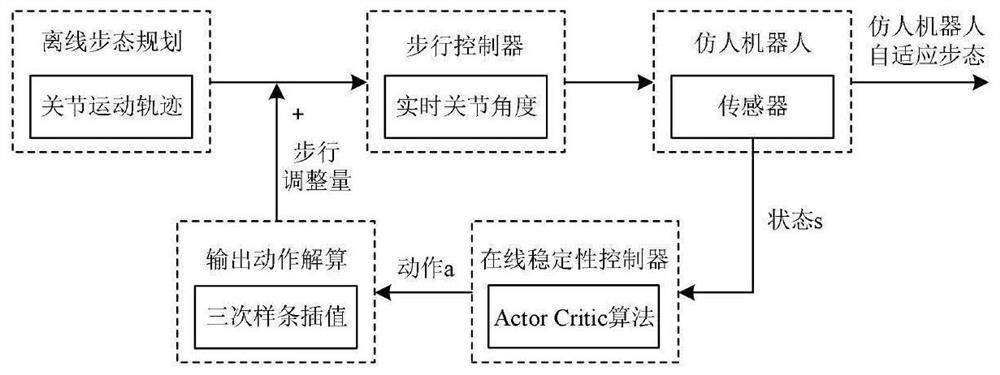
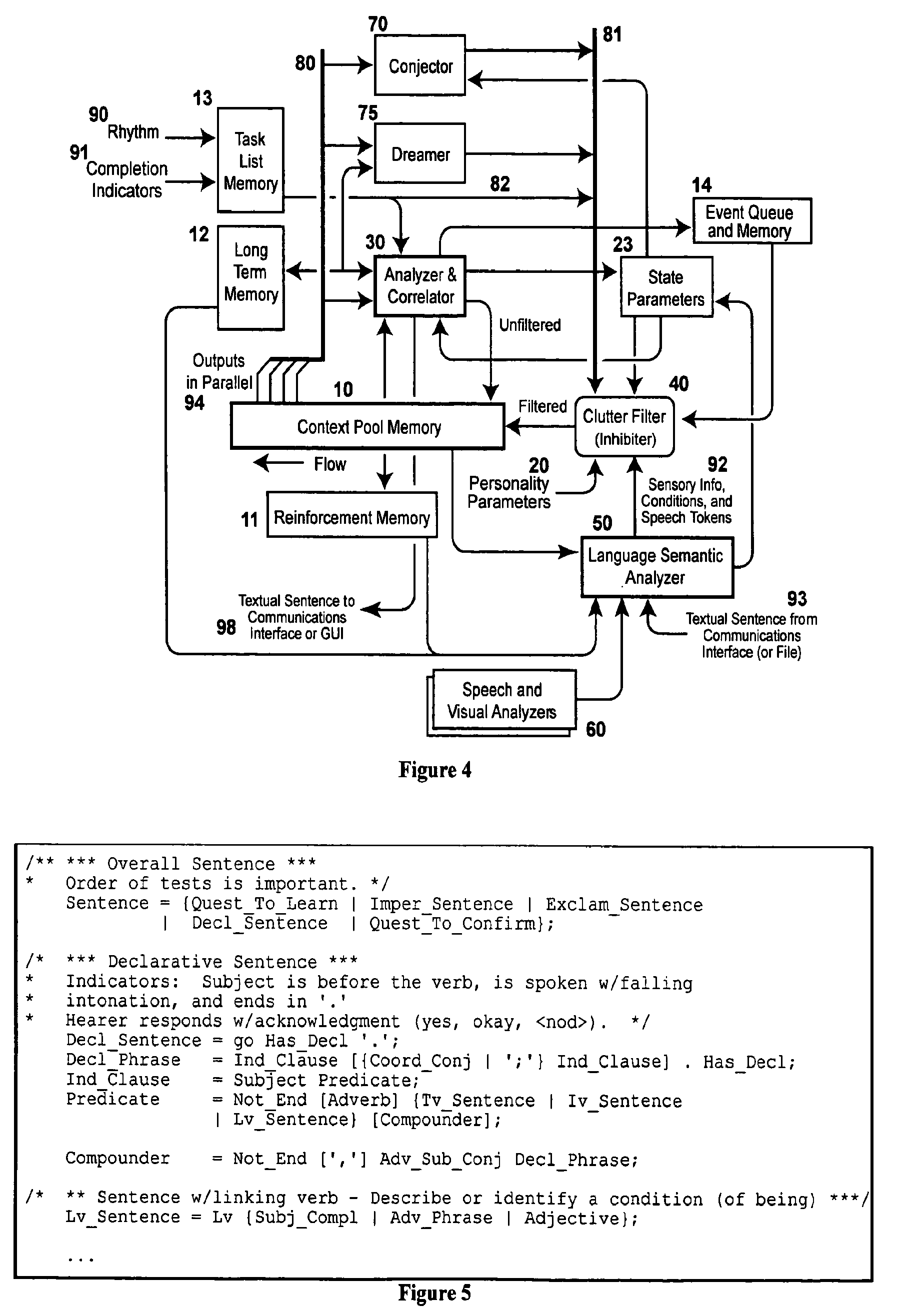
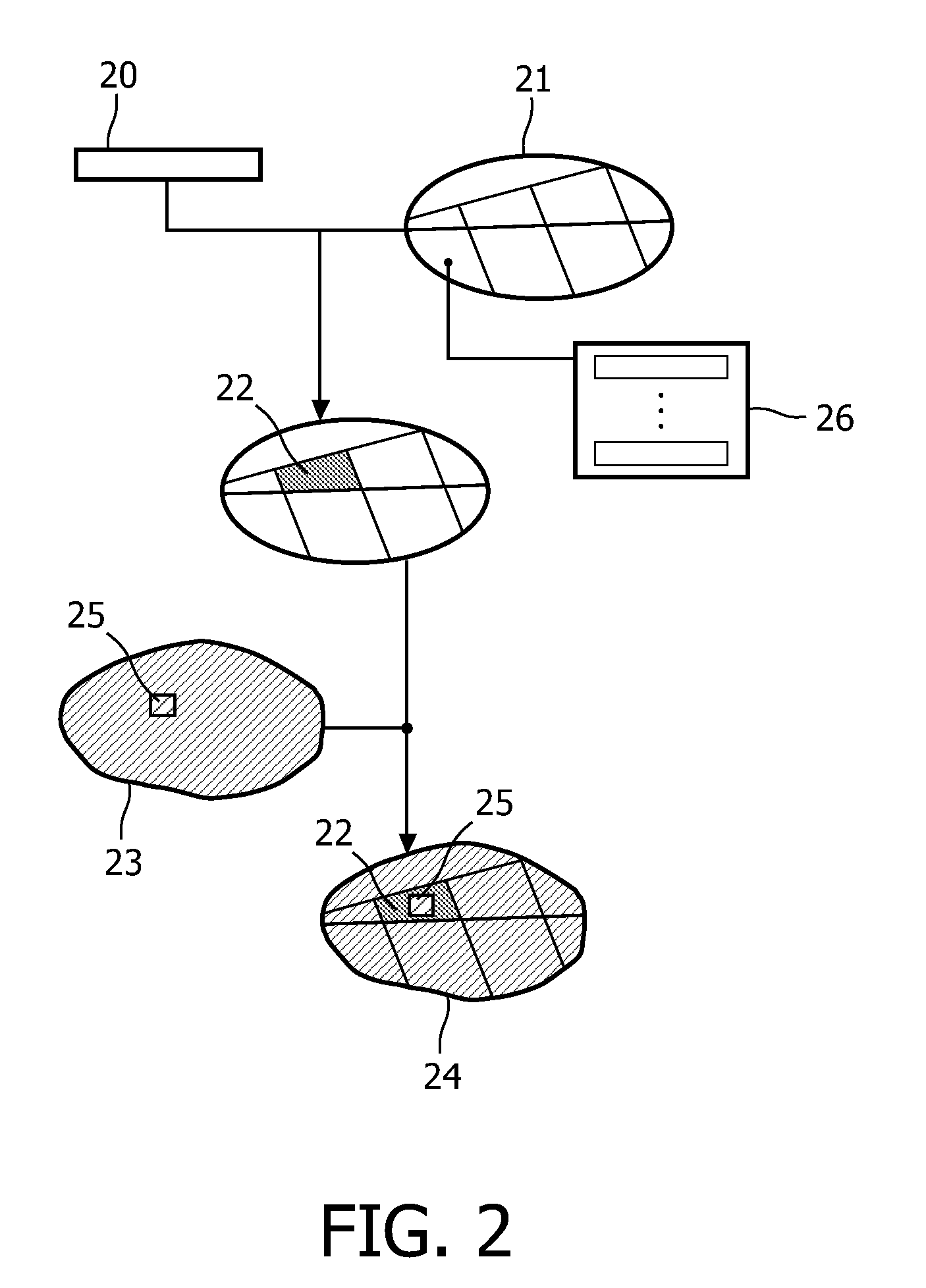
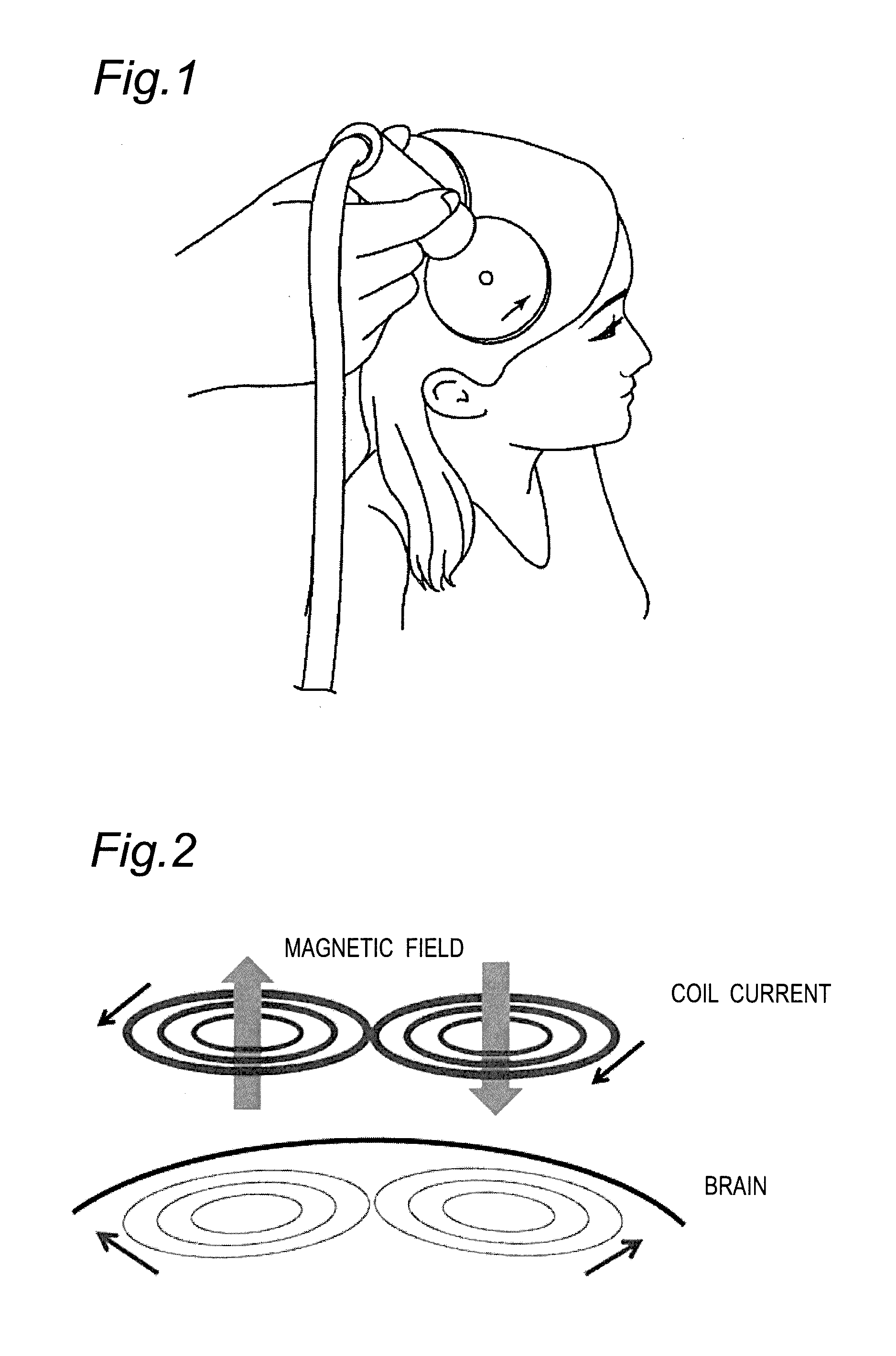
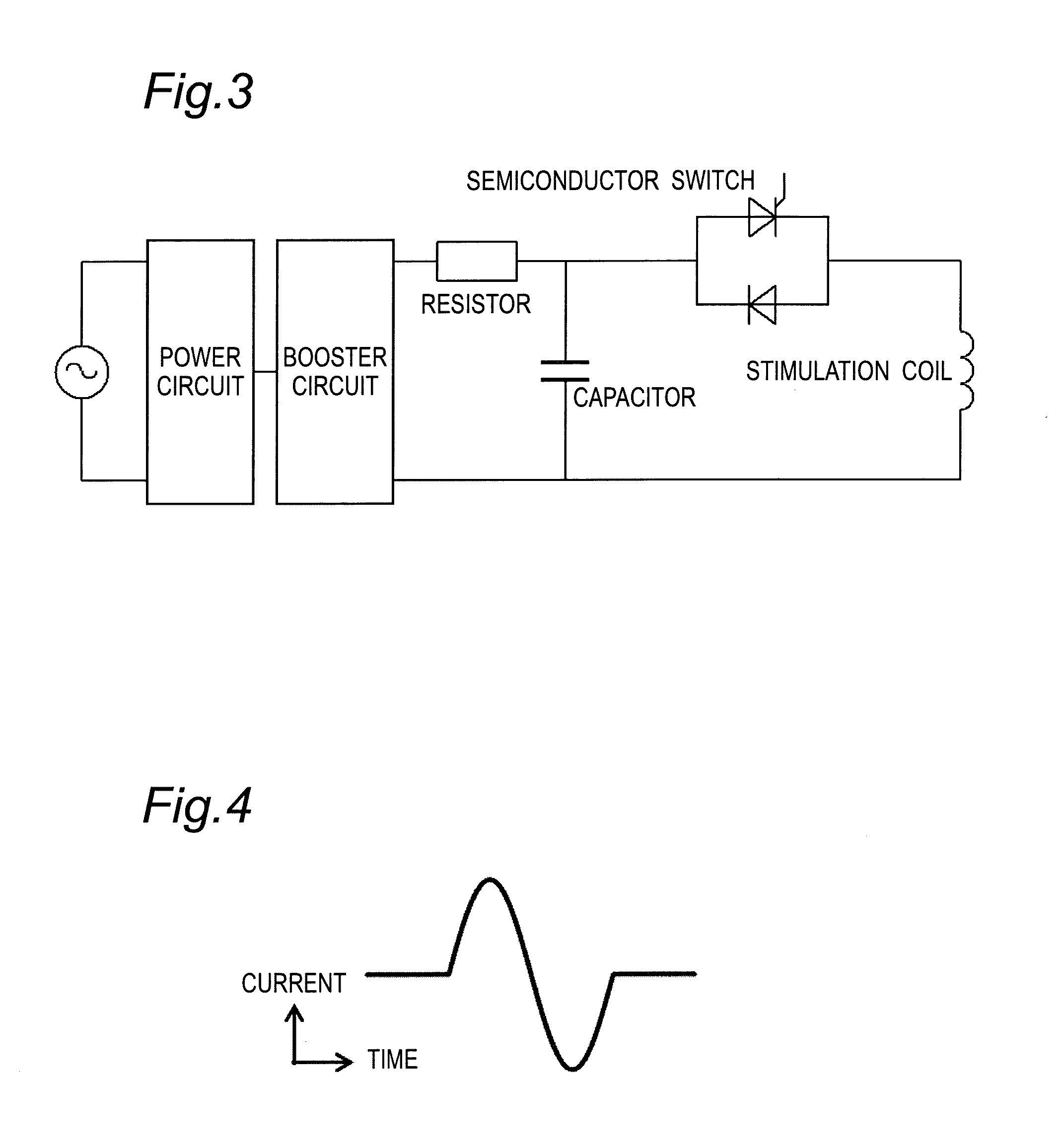
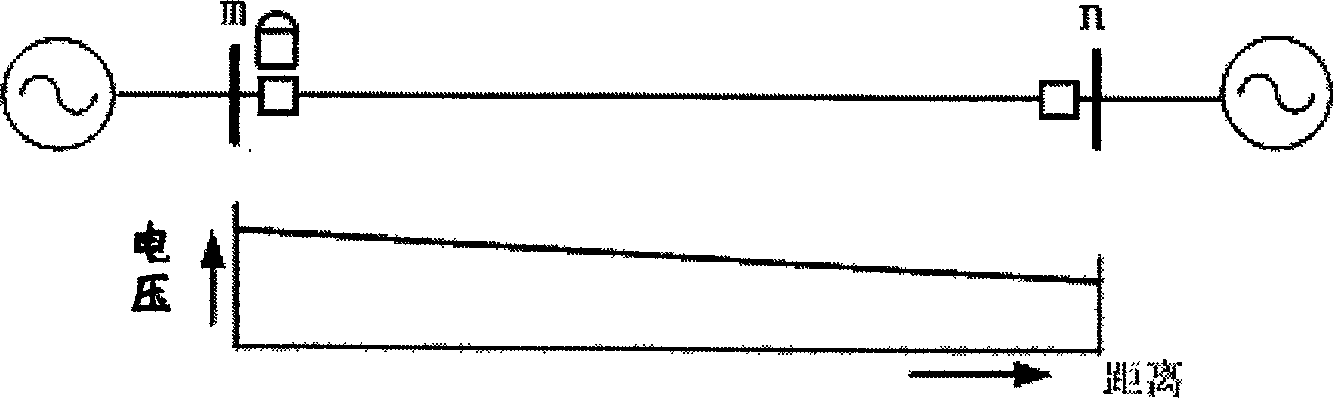Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Brain model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Analysis of brain patterns using temporal measures
ActiveUS20080091118A1Low costImprove throughputElectroencephalographyMedical simulationBrain pathologiesAlgorithm
A set of brain data representing a time series of neurophysiologic activity acquired by spatially distributed sensors arranged to detect neural signaling of a brain (such as by the use of magnetoencephalography) is obtained. The set of brain data is processed to obtain a dynamic brain model based on a set of statistically-independent temporal measures, such as partial cross correlations, among groupings of different time series within the set of brain data. The dynamic brain model represents interactions between neural populations of the brain occurring close in time, such as with zero lag, for example. The dynamic brain model can be analyzed to obtain the neurophysiologic assessment of the brain. Data processing techniques may be used to assess structural or neurochemical brain pathologies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
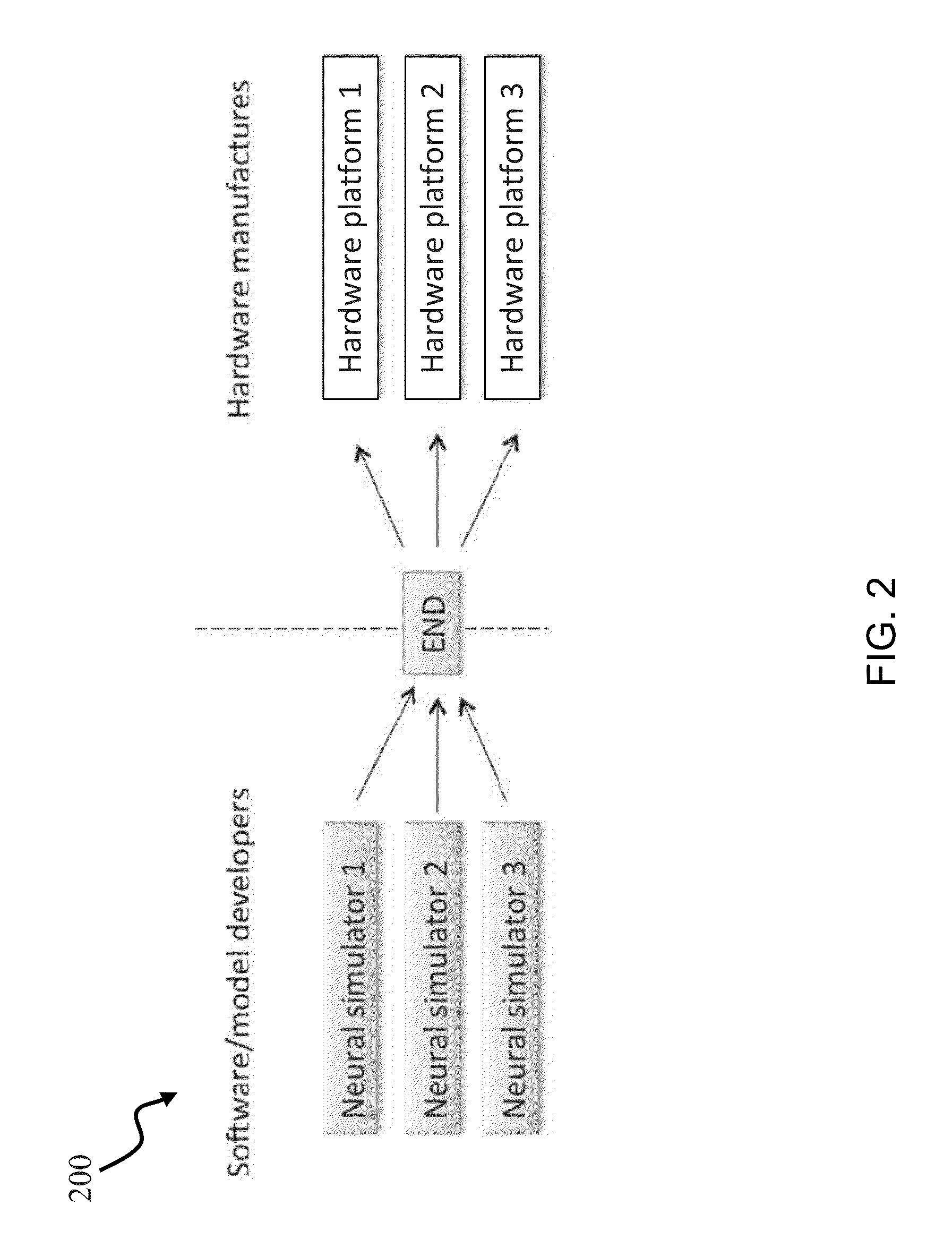
Elementary network description for efficient link between neuronal models and neuromorphic systems
A simple format is disclosed and referred to as Elementary Network Description (END). The format can fully describe a large-scale neuronal model and embodiments of software or hardware engines to simulate such a model efficiently. The architecture of such neuromorphic engines is optimal for high-performance parallel processing of spiking networks with spike-timing dependent plasticity. The format is specifically tuned for neural systems and specialized neuromorphic hardware, thereby serving as a bridge between developers of brain models and neuromorphic hardware manufactures.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
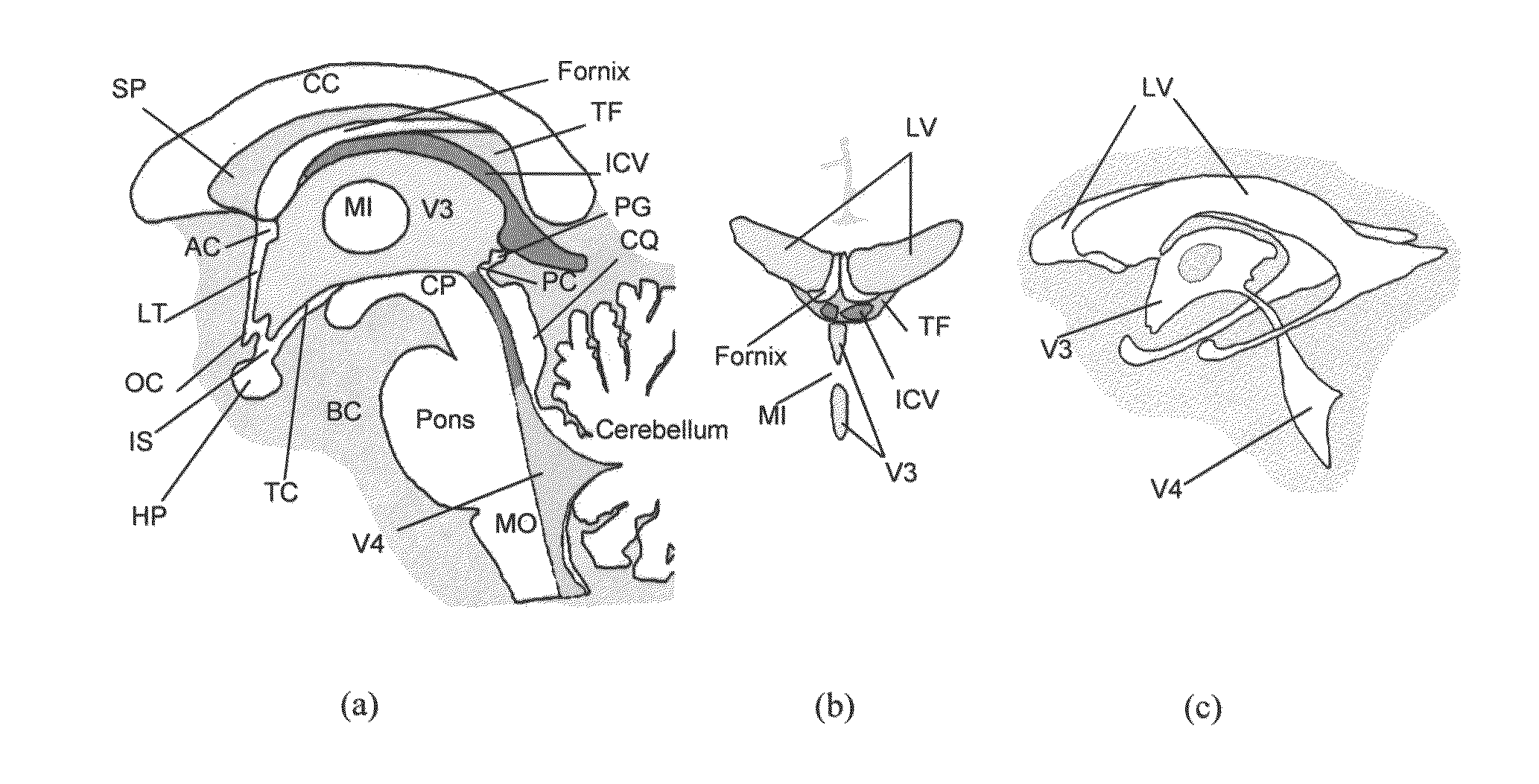
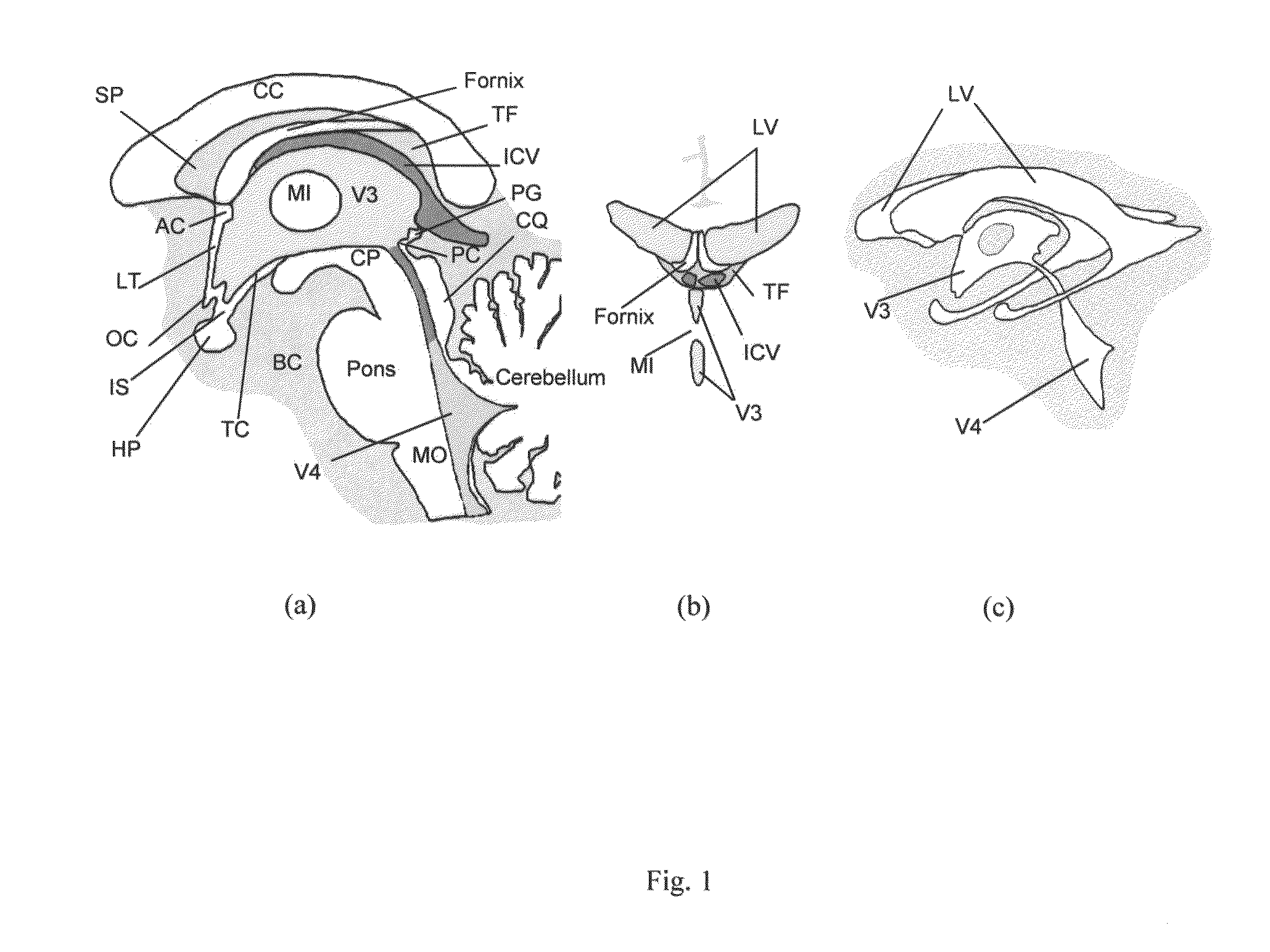
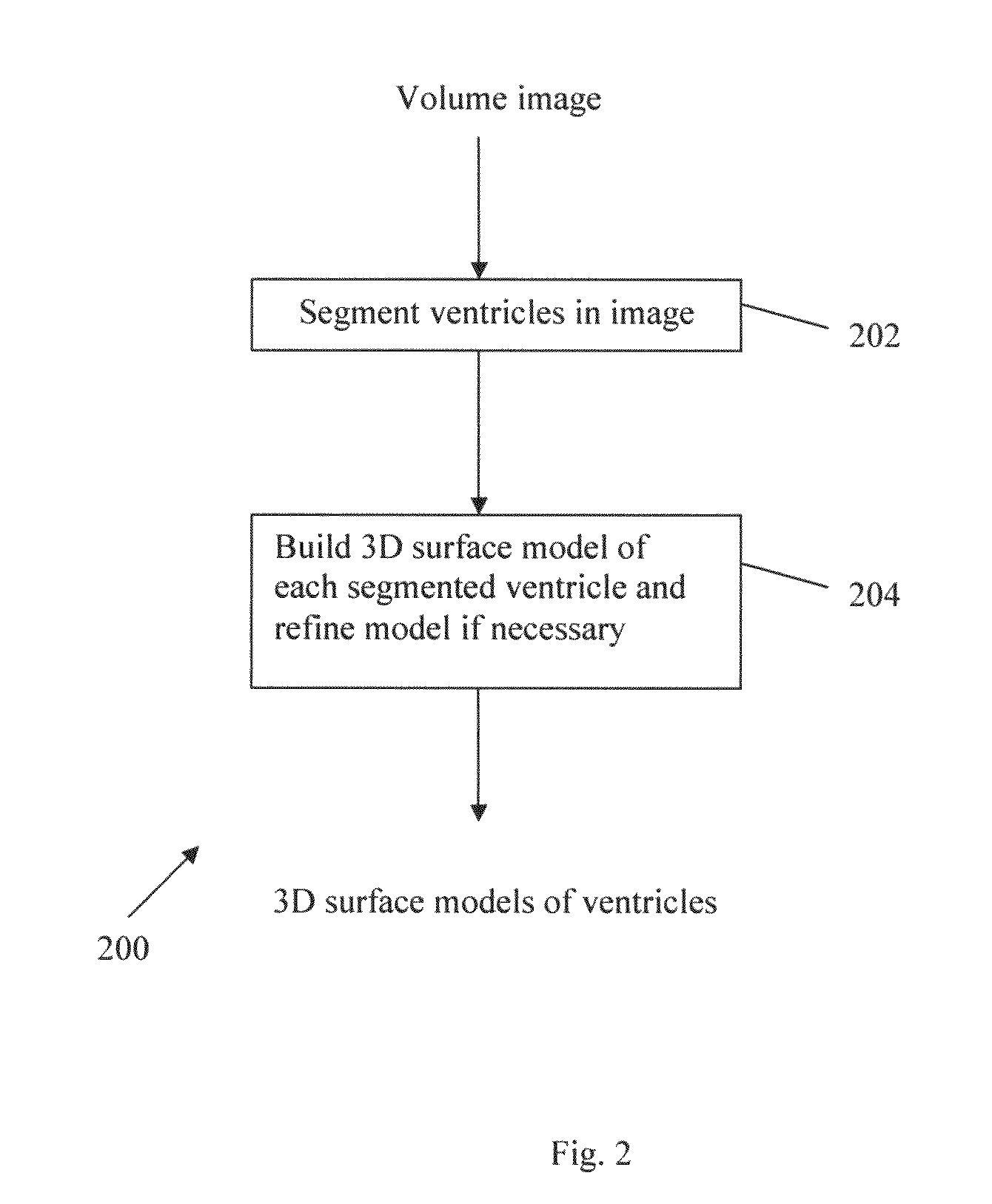
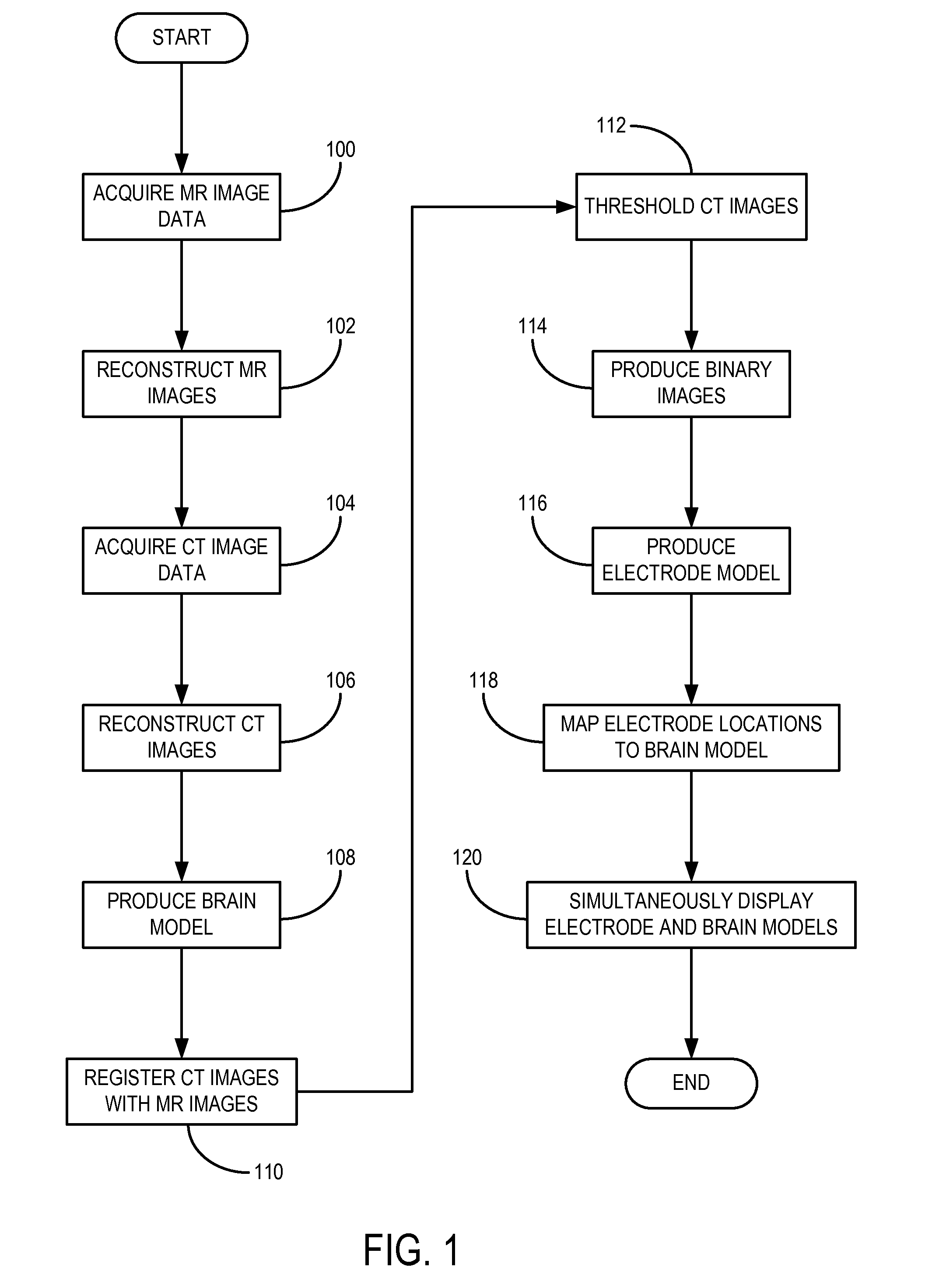
Method and system for anatomy structure segmentation and modeling in an image
A method is proposed for segmenting one or more ventricles in a three-dimensional brain scan image (e.g. MR or CT). The image is registered against a brain model, which ventricle models of each of the one or more ventricles. Respective regions of interest are defined based on the ventricle models. Object regions are first obtained by applying region growing procedure in the regions of interest, and then trimmed based on anatomical knowledge. A 3D surface model of one or more objects is constructed within a 3D space from the segmented structure. A 3D surface is edited and refined by a user selecting amendment points in the 3D space which are indicative of missing detail features. A region of the 3D surface near the selected points is then warped towards the amendment points smoothly, and the modified patch is combined with the rest of the 3D surface yields the accurate anatomy structure model.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
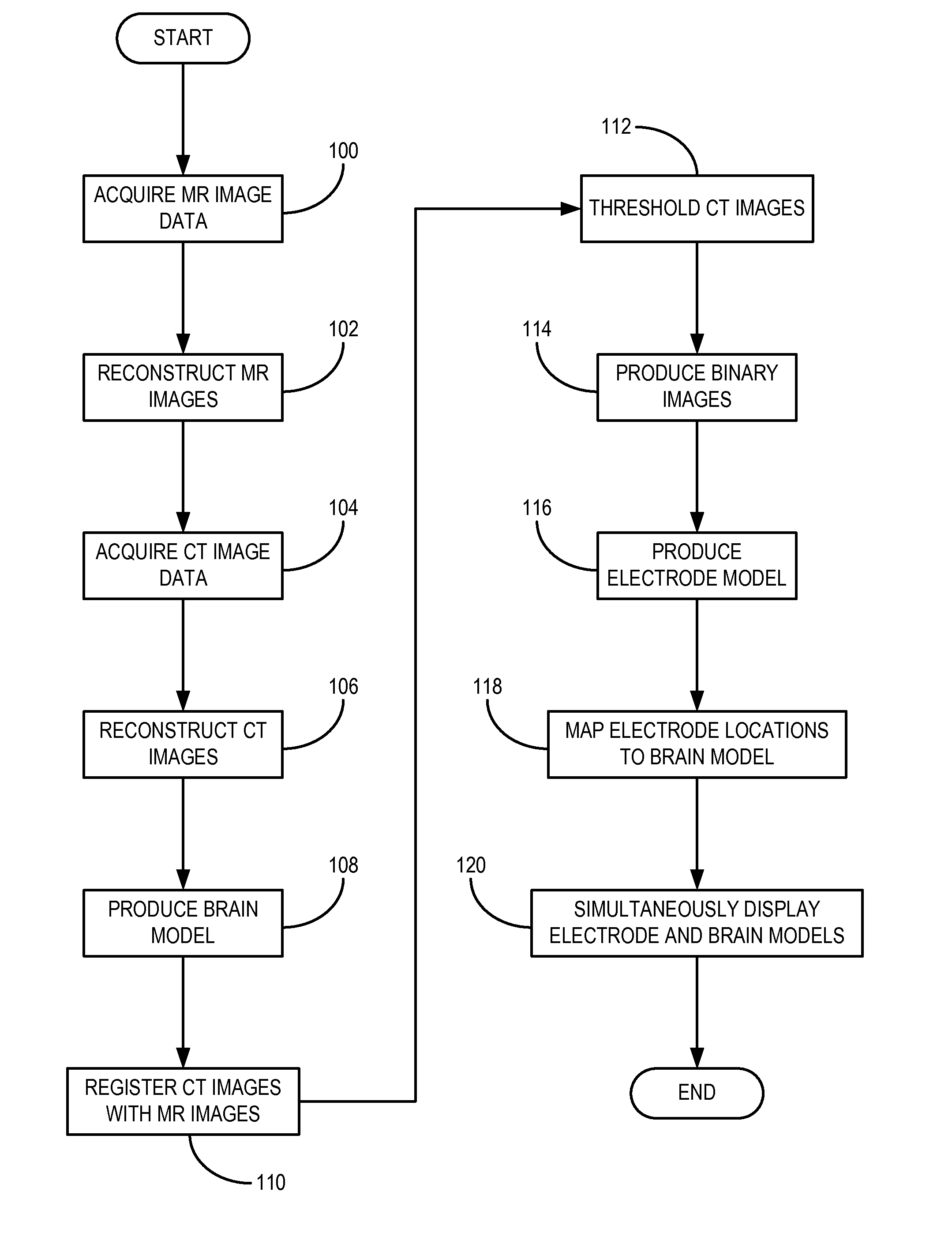
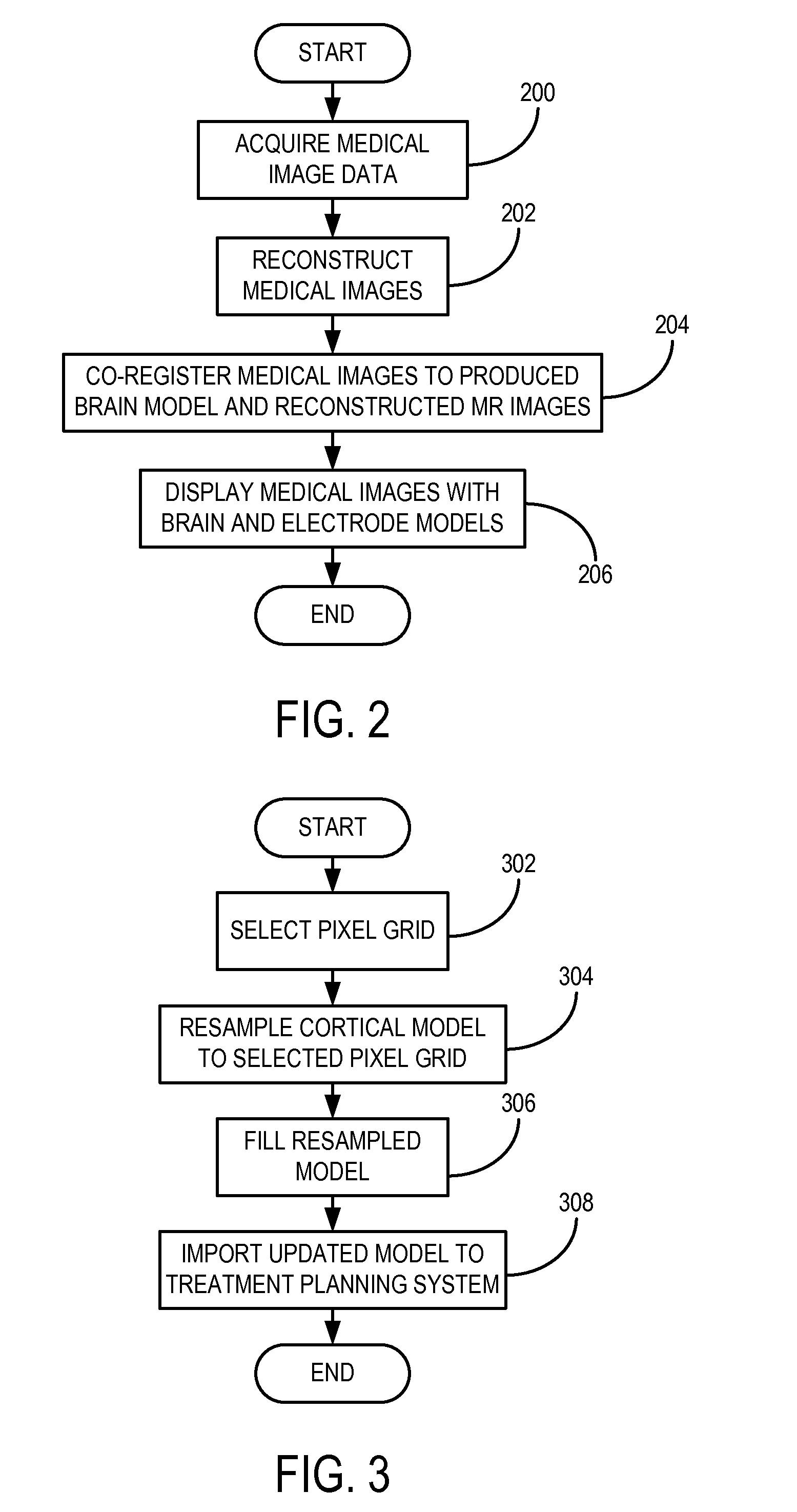
Method for Determining Locations of Implanted Electrodes with Medical Images
ActiveUS20120271151A1Overcomes drawbackError minimizationElectroencephalographyComputerised tomographsSurgical operationBrain section
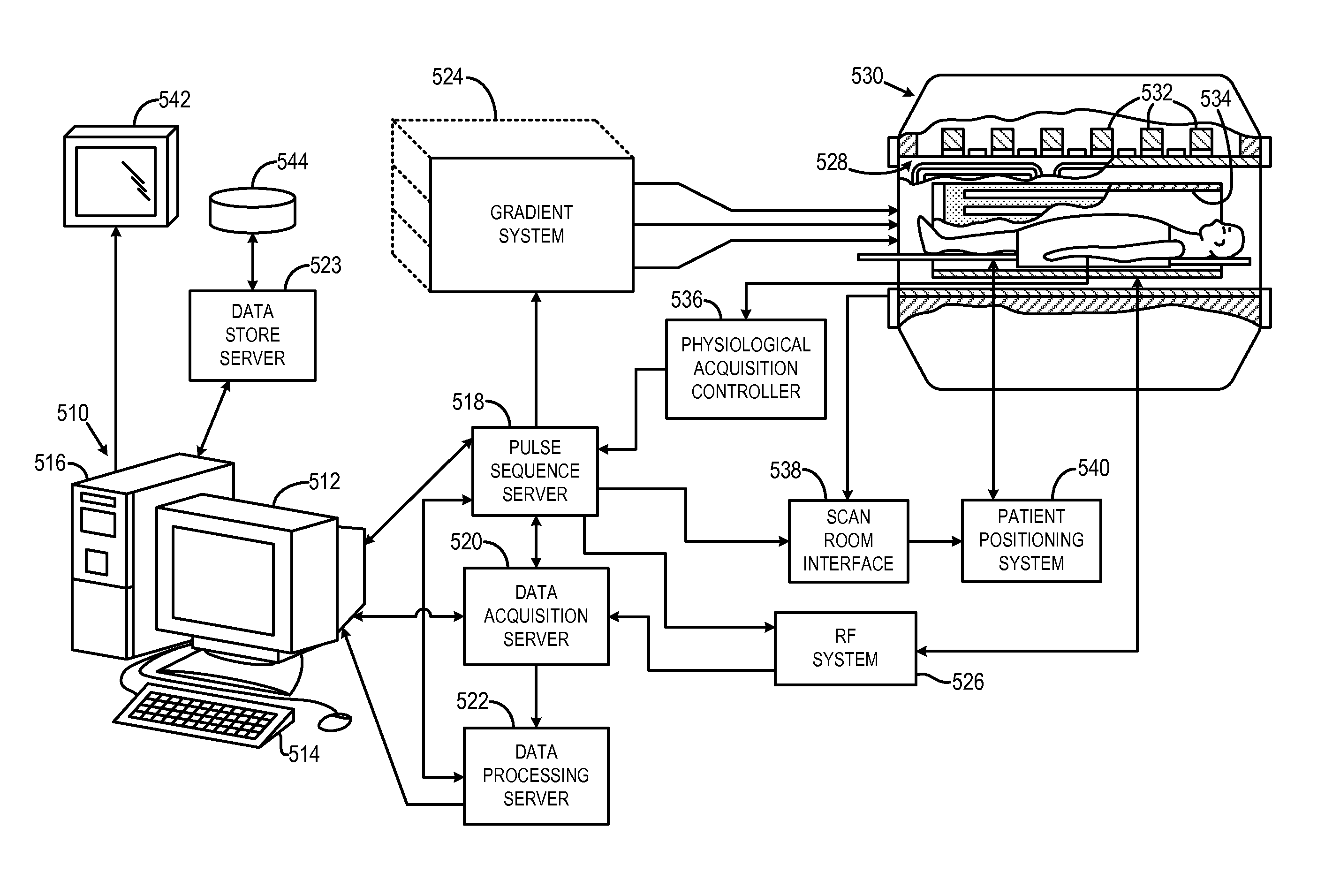
A method for accurate localization and visualization of implanted electrodes, such as implanted intracranial electrodes, is provided. More particularly, a realistic representation of intracranial electrode positions on patient-specific post-implantation MRI brain renderings is obtained. The resulting computer models provide an accurate depiction of electrode locations on three-dimensional brain renderings that are suitable for use in surgical planning of resection boundaries around, for example, epileptic zones. Electrodes placed inter-hemispherically are also visible with this method. In addition, a method for creating electrode “shadows” cast upon the brain model surface is provided. These electrode shadows are useful for estimating cortical areas sampled by iEEG and for locating electrodes that may straddle sulci and contact two adjacent cortical gyri.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
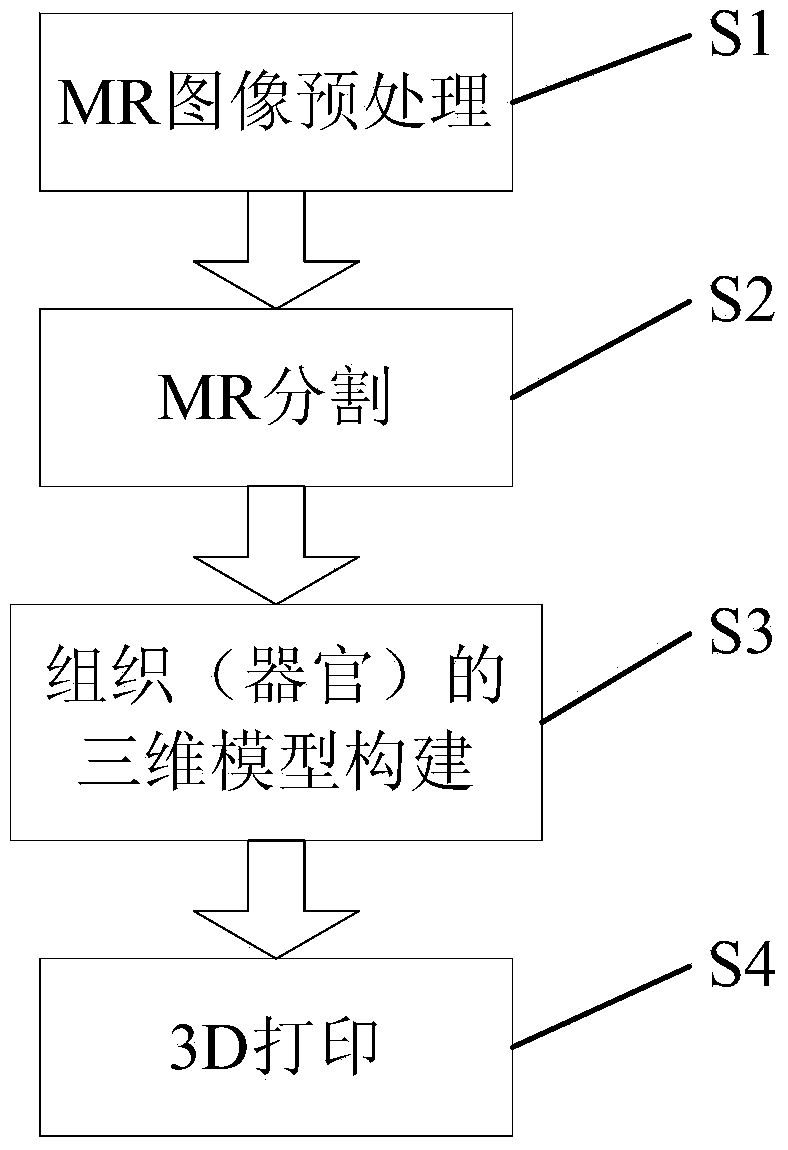
Method for 3D printing of head and brain models with multiple materials at low cost
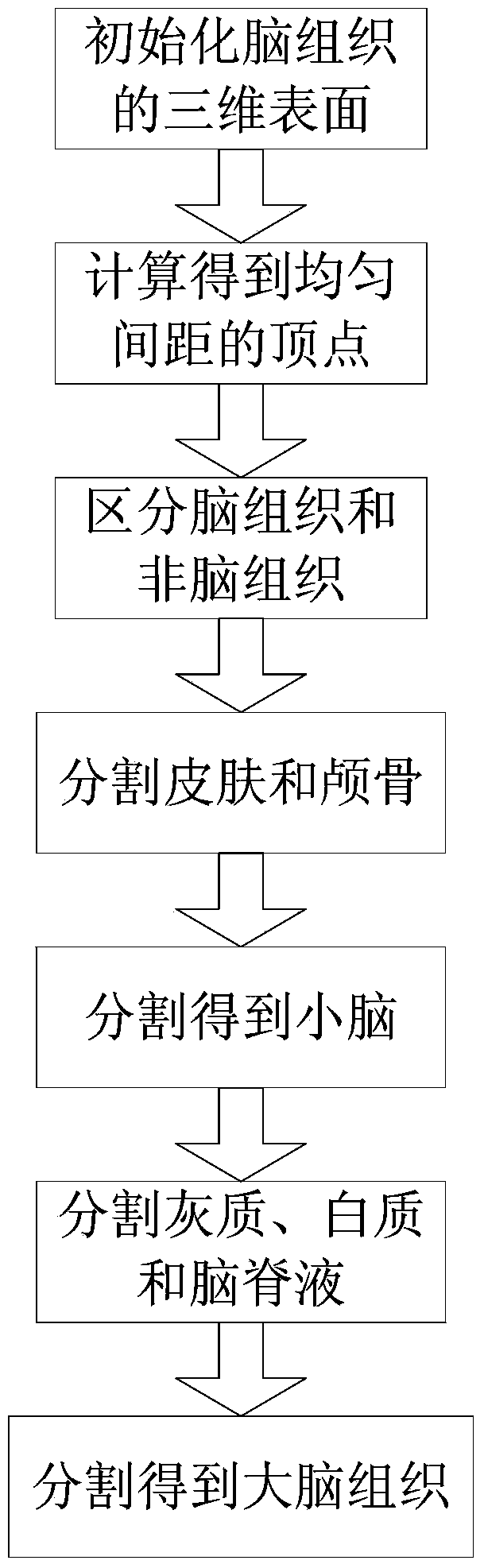
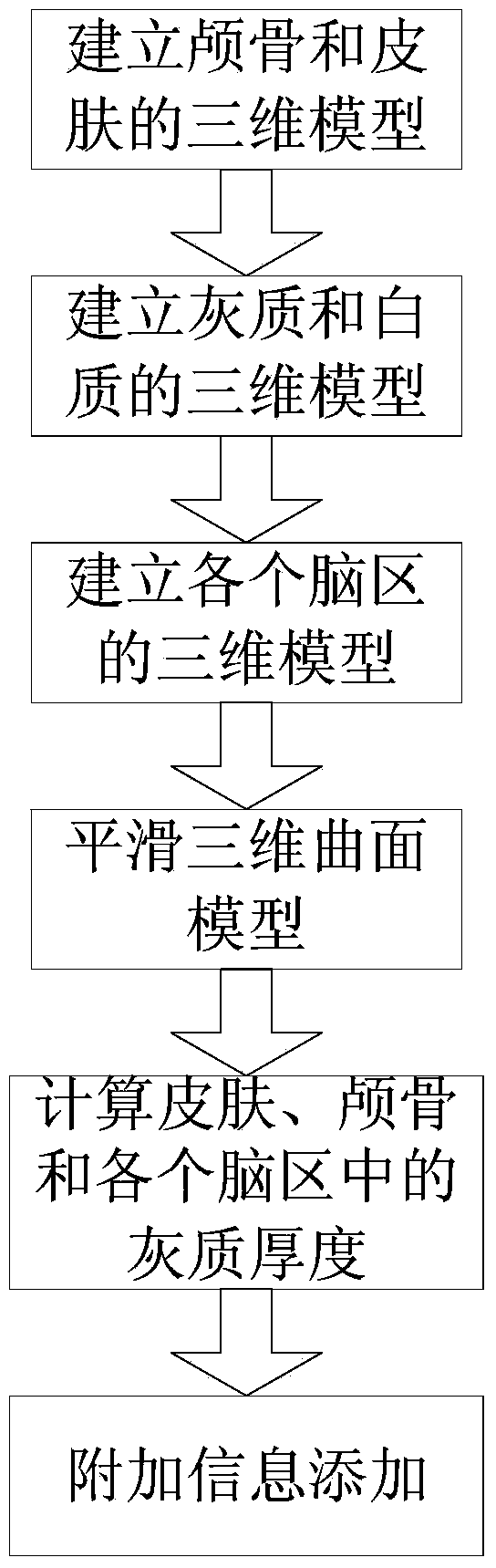
The invention provides a method for 3D printing of head and brain models with multiple materials at low cost. The method includes the steps that an MR image is used, a three-dimensional model is quickly established for brain tissue, different tissue / organs of a brain are printed by the adoption of a 3D printing method in a regional / layered mode, and skull and skin of a left hemisphere and skull and skin of a right hemisphere are printed respectively. Specifically, the method includes the steps of (1) preprocessing the MR image, (2) segmenting and extracting different tissue / organs in the image, (3) establishing the three-dimensional model for the brain tissue / organs and (4) converting the three-dimensional model into cross section data, selecting printing materials and carrying out 3D printing. The three-dimensional model can be precisely established for the brain tissue on the basis of precise segmentation of the MR image, a regional / layered printing mode is used according to distribution characteristics of tissue / organs, a multi-material 3D printing process is converted into a repeated single-material 3D printing process, the requirements for a 3D printer are reduced, and printing cost of the brain model is greatly reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Full-scale distributed whole brain simulation system based on brain-like pulse neural networks
InactiveCN108182473AImplement a custom applicationEffective simulationPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsScripting languageNerve network
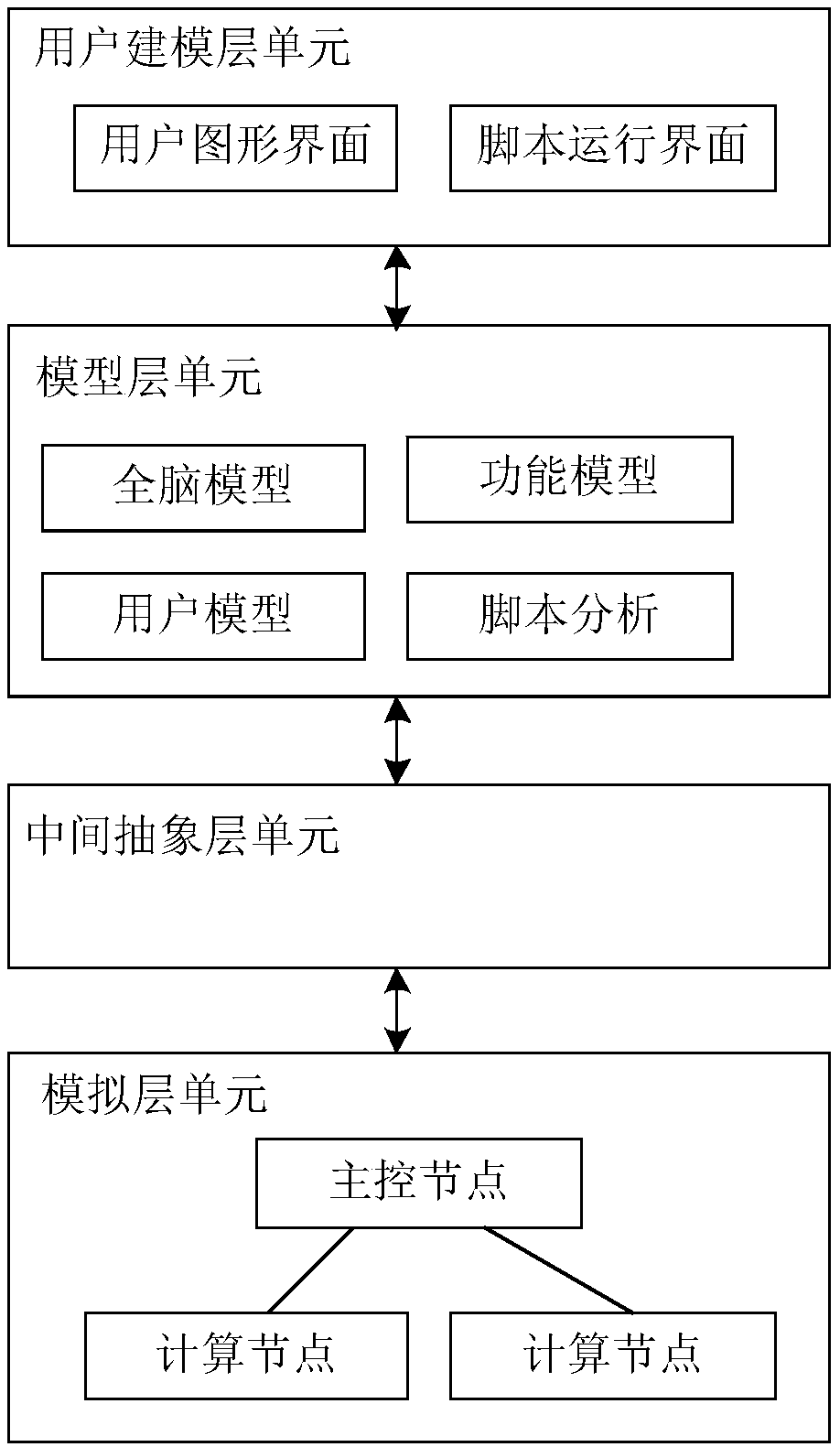
The invention relates to the field of brain-like neural networks, provides a full-scale distributed whole brain simulation system based on brain-like pulse neural networks, and aims to solve problemsof lack of multiple scales and multiple scale modeling methods in brain-like simulation and modeling and simulation coupling. The system comprises a user modeling layer unit, a model layer unit, an intermediate abstract layer unit and a simulation layer unit. In the user modeling layer unit, users can perform modeling based on a whole brain model by employing a modeling script language; in the model layer unit, the system saves a built-in model and a user-built model and converts the model to intermediate abstraction; in the intermediate abstract layer unit, the system combines the intermediate abstraction and converts the abstraction to a runtime format; and in the simulation layer unit, the system reads the runtime format to simulate operation and interacts with the users in real time. According to the system, the modeling and simulation of neural network models of multiple scales can be realized in multiple scales, and the portability of the brain-like models is improved with the combination of the hardware design.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Analogue operation training system
ActiveCN103280144AAvoid damagePrevent functional nerve damageEducational modelsDaily operationManufacturing technology
The invention discloses an analogue operation training system, and belongs to the field of cross-over studies coalescing a plurality of subjects such as an information technology, an automation technology and a machinery manufacturing technology. The analogue operation training system can be used for operation path planning before an operation and the daily operation training of a physician. Analogue operation software is developed, a brain model can be established according to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and a virtual operation can be performed based on the brain model in a computer virtual space; an operation operator is designed, and has six degrees of freedom, and the operating principle for the operation operator is the same as that of a ventriculoscope operating knife, so that real sense of operation is ensured; a field programmable gate array (FPGA)-based multi-path data acquisition system is designed, and can be used for acquiring six paths of coder data in real time, so that the system is high in real-time performance; and the system is high in brain model accuracy, real-time tracking performance, operation realism and automation degree and low in development cost.
Owner:杭州博医微视科技有限公司
Analysis of brain patterns using temporal measures
ActiveUS9101276B2Improve throughputLow costMedical simulationElectroencephalographyBrain pathologiesNeurochemistry
A set of brain data representing a time series of neurophysiologic activity acquired by spatially distributed sensors arranged to detect neural signaling of a brain (such as by the use of magnetoencephalography) is obtained. The set of brain data is processed to obtain a dynamic brain model based on a set of statistically-independent temporal measures, such as partial cross correlations, among groupings of different time series within the set of brain data. The dynamic brain model represents interactions between neural populations of the brain occurring close in time, such as with zero lag, for example. The dynamic brain model can be analyzed to obtain the neurophysiologic assessment of the brain. Data processing techniques may be used to assess structural or neurochemical brain pathologies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Online stably controlled humanoid robot based on bionic reinforcement learning type cerebellum model
ActiveCN112060082AImprove stabilityImprove balanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorArtificial lifeSimulationNerve cells
The invention relates to an online stably controlled humanoid robot based on a bionic reinforcement learning type cerebellum model and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. In order to solve the problem of improving the stabilizing and balancing abilities of the humanoid robot in a walking process, the humanoid robot comprises an apparatus for planning an offline gait of the humanoid robot anda cerebellum model controller, wherein the apparatus output makes the humanoid robot tracks a joint movement locus generated offline to have the walking ability; and the cerebellum model controller, responding to the offline gait, comprises a state encoding module, a cerebellum model, an inferior olive feeding module and a motion mapping module, wherein the state encoding module adjusts an activated state of PF according to state information collected by a sensor of the humanoid robot, the inferior olive feeding module modifies a behavior selection probability and a cerebellum nerve cell storage weight based on evaluation information fed back by an environment, and the motion mapping module adjusts actions of the robot according to output of a functional module. The online stably controlled humanoid robot has an effect of improving the stabilizing and balancing abilities of the humanoid robot in the walking process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Full-simulation neurosurgery surgery platform based on 3D printing and breath cyclic reconstruction
InactiveCN106228883AAnticipate sudden emergenciesImplement simulation exercisesEducational modelsNeurosurgeryDissection
The present invention discloses a full-simulation neurosurgery surgery platform based on 3D printing and breath cyclic reconstruction. The full-simulation neurosurgery surgery platform comprises an operation platform used for neurosurgery dissection, a liquid circulation power system for forming a flowing liquid pressure system according to the clinical breath heart rate and the blood pressure and a detachable modular enclosed brain model possessing the blood vessel nerve brain tissues. A three-dimension fixing head rack is installed on the operation platform, the brain model is fixed on the three-dimension fixing head rack and is equipped with a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet, and the liquid circulation power system is equipped with a power output port and a power input port, wherein the power output port of the liquid circulation power system is communicated with the liquid inlet of the brain model via a catheter, and the liquid outlet of the brain model is communicated with the power input port of the liquid circulation power system. The advantages of the present invention are that: the medical care personnel can simulate and train by the full-simulation neurosurgery surgery platform based on the 3D printing and breath cyclic reconstruction, various emergent emergency situations of a real case during an operation process can be predicted effectively, and the omnibearing clinic simulation and the simulation exercise are realized, so that a training effect is more effective.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Analysis of brain patterns using temporal measures
InactiveCN101583308AOvercoming the shortcomings of subjective evaluationLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBrain pathologiesAlgorithm
A set of brain data representing a time series of neurophysiologic activity acquired by spatially distributed sensors arranged to detect neural signaling of a brain (such as by the use of magnetoencephalography) is obtained. The set of brain data is processed to obtain a dynamic brain model based on a set of statistically-independent temporal measures, such as partial cross correlations, among groupings of different time series within the set of brain data. The dynamic brain model represents interactions between neural populations of the brain occurring close in time, such as with zero lag, for example. The dynamic brain model can be analyzed to obtain the neurophysiologic assessment of the brain. Data processing techniques may be used to assess structural or neurochemical brain pathologies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
A method and system for three-dimensional reconstruction and display interaction of medical image of brain tumor
InactiveCN109157284AImprove diagnostic efficiencyAugmented virtual realityImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceBrain section
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image three-dimensional reconstruction, in particular to a brain tumor medical image three-dimensional reconstruction display interaction methodand a system, comprising the following steps: acquiring a plurality of medical diacom images, preprocessing each medical diacom image to obtain a preprocessed image; According to the pre-processed images, the three-dimensional model of brain can be obtained by three-dimensional modeling. The brain tumor information was obtained by analyzing the three-dimensional brain model, and the brain tumor resection scheme was recommended according to the brain tumor information. According to the operation instruction, the tumor resection was simulated on the three-dimensional brain model, and the wholeoperation process was simulated by the doctor through the naked eye 3D display, and the operation was reminded according to the doctor's intraoperative operation. The invention constructs a three-dimensional model of the brain through the medical image of the brain tumor and simulates the operation, the human-computer interaction process is displayed through the naked eye 3D display, the sense ofvirtual reality is enhanced, and the analysis of the brain tumor is a scheme for the doctor to remove the tumor, thereby improving the diagnosis efficiency of the doctor.
Owner:广州狄卡视觉科技有限公司
Method of emulating human cognition in a brain model containing a plurality of electronically represented neurons
A method of emulating the human brain with its thought and rationalization processes is presented here, as well as a method of storing human-like thought. The invention provides for inclusion of psychological profiles, experience and societal position in an electronic emulation of the human brain. This permits a realistic human-like response by that emulation to the people and the interactive environment around it.
Owner:NEURIC TECH
Cort_x: a dynamic brain model
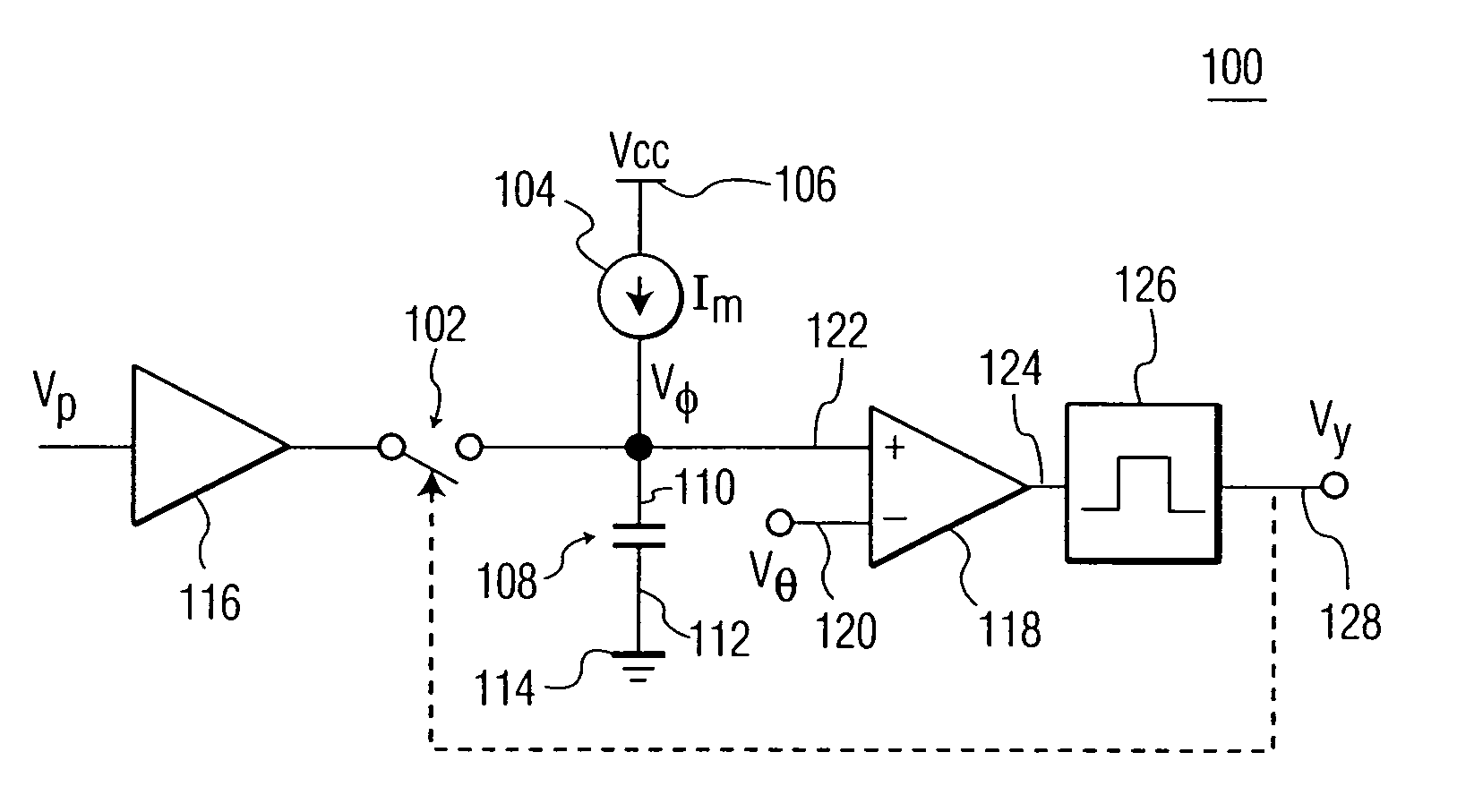
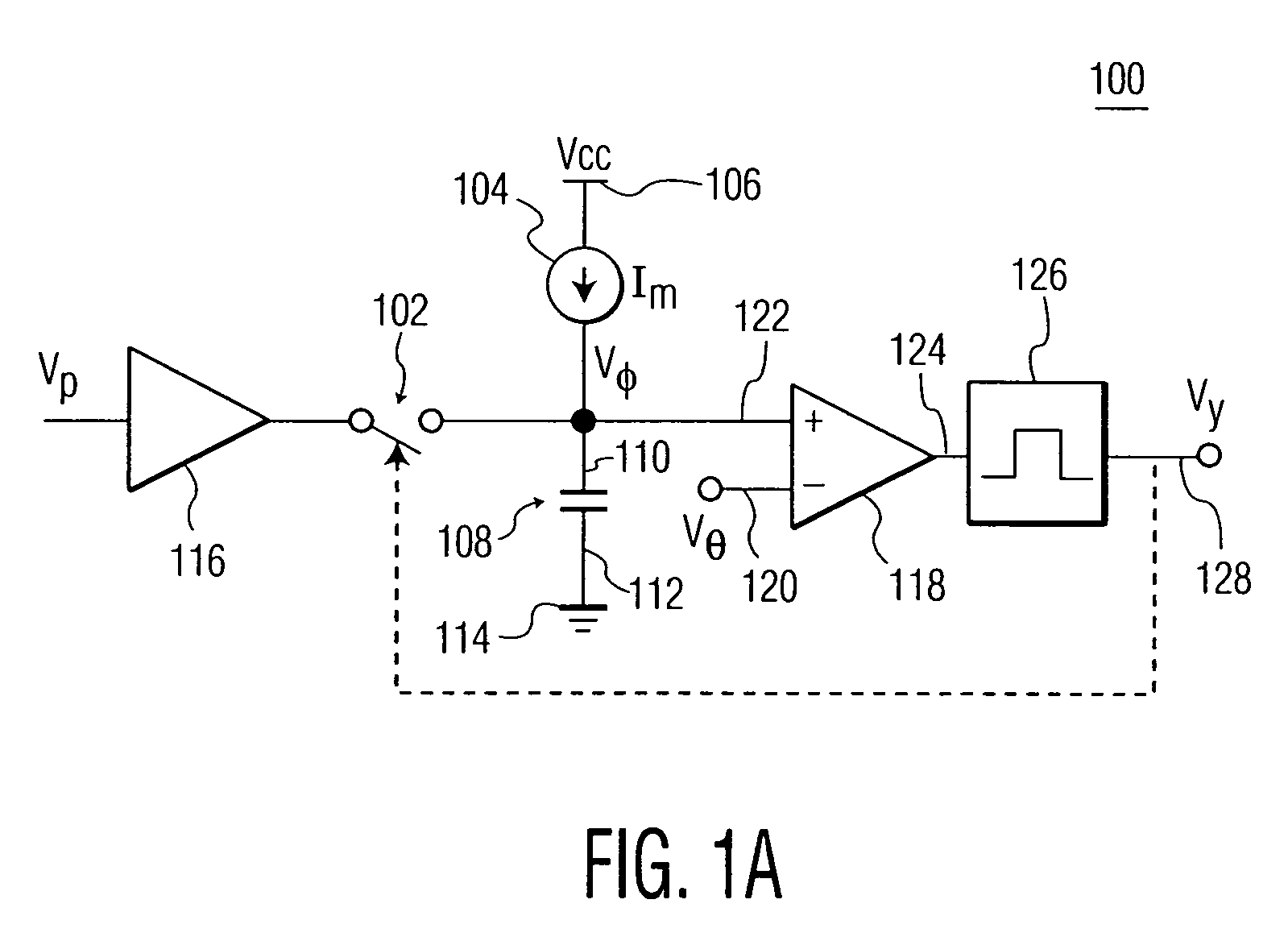
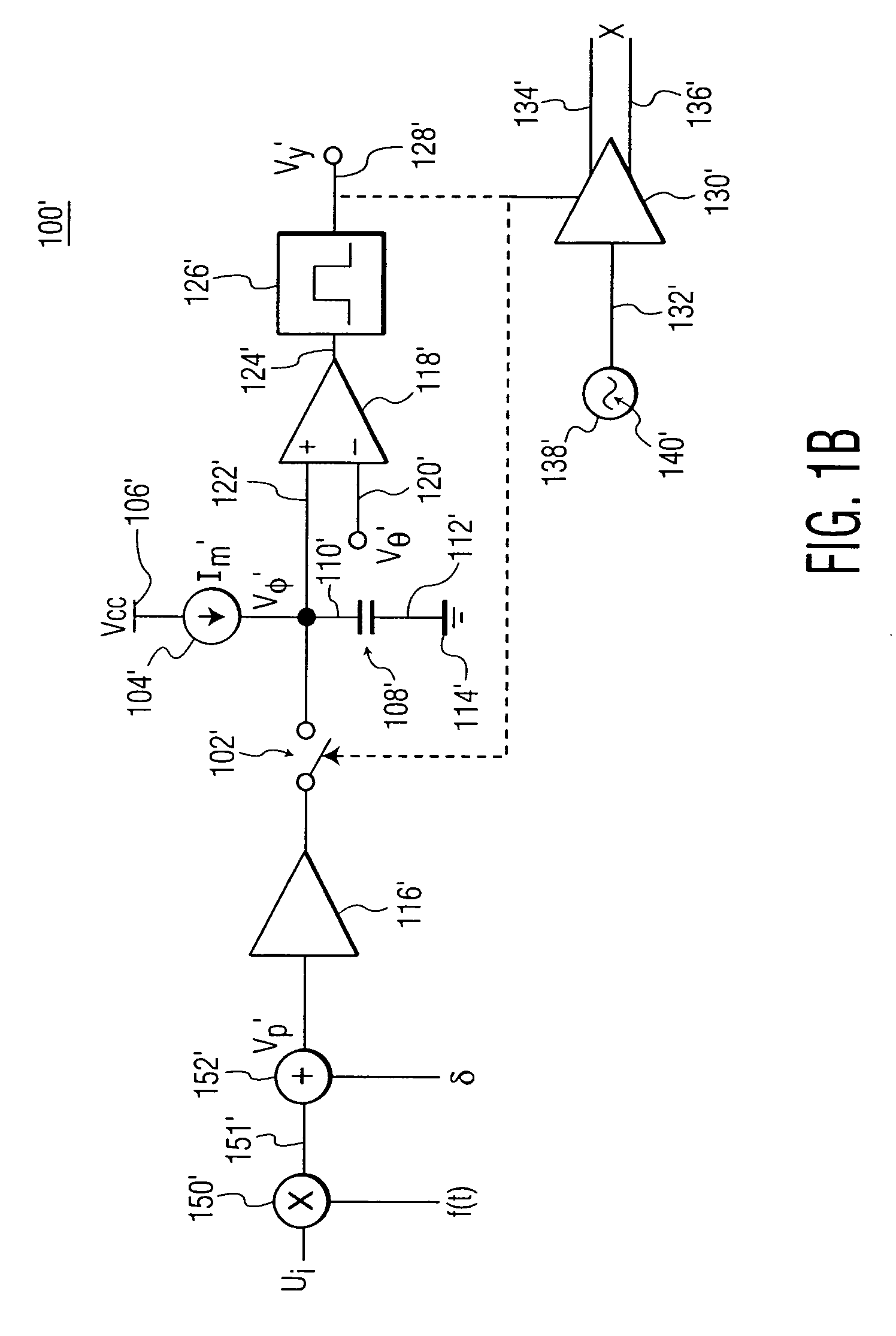
InactiveUS20060271342A1Digital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationCapacitanceCapacitor voltage
A cortical column emulation circuit includes a capacitor which is coupled at a first end to a source of reference potential by a switch, a current source coupled to the first end of the capacitor for charging the capacitor when the switch is open to develop a capacitor voltage between the first end and the second end of the capacitor; and a comparator which compares the voltage across the capacitor to a threshold potential and generates a pulse signal when the capacitor voltage is greater than the threshold voltage. The pulse signal closes the switch to connect the first end of the capacitor to the source of reference potential. A set of cortical column emulation circuits may be coupled together by an adaptive coupling to form a cortical region emulation circuit. The adaptive coupling circuit weights an input stimulus and a plurality of state vector elements by variable coupling coefficients.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Distance measuring method based on Bergeron model for power transmission line
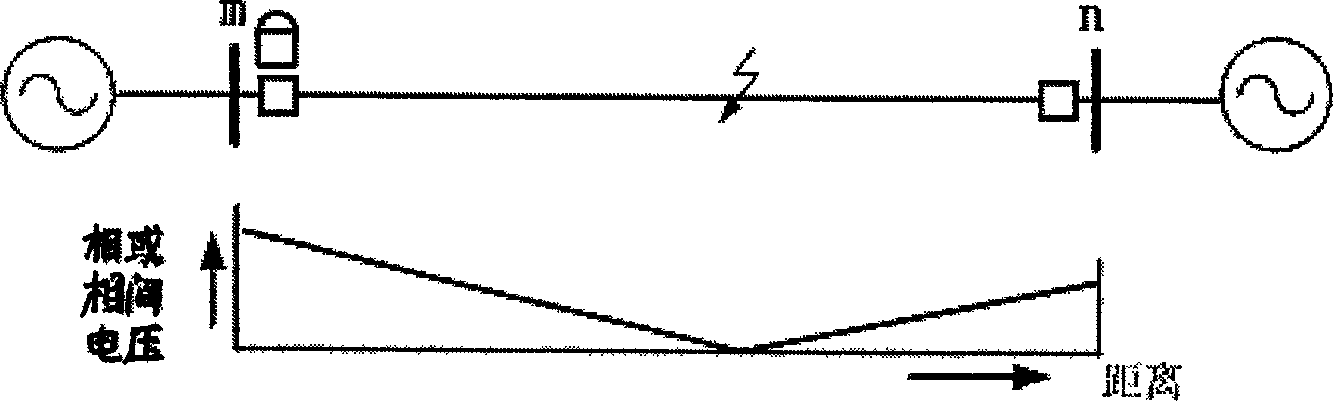
The invention relates to a power transmission wire fault distance-measuring and protecting method, which comprises the following steps: using phase-choosing unit to choose the fault phase when it occurs the wire fault, ascertaining the computing step-length by the wire length and accuracy, adopting Brain model to compute the step-length of the fault phase voltage or between the fault phases to obtain the voltage of each point of the wire, looking for the minimum voltage point of the wire to obtain the fault point.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for determining locations of implanted electrodes with medical images
ActiveUS8666478B2Error minimizationElectroencephalographyCharacter and pattern recognitionIntracranial electrodesComputer vision
A method for accurate localization and visualization of implanted electrodes, such as implanted intracranial electrodes, is provided. More particularly, a realistic representation of intracranial electrode positions on patient-specific post-implantation MRI brain renderings is obtained. The resulting computer models provide an accurate depiction of electrode locations on three-dimensional brain renderings that are suitable for use in surgical planning of resection boundaries around, for example, epileptic zones. Electrodes placed inter-hemispherically are also visible with this method. In addition, a method for creating electrode “shadows” cast upon the brain model surface is provided. These electrode shadows are useful for estimating cortical areas sampled by iEEG and for locating electrodes that may straddle sulci and contact two adjacent cortical gyri.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
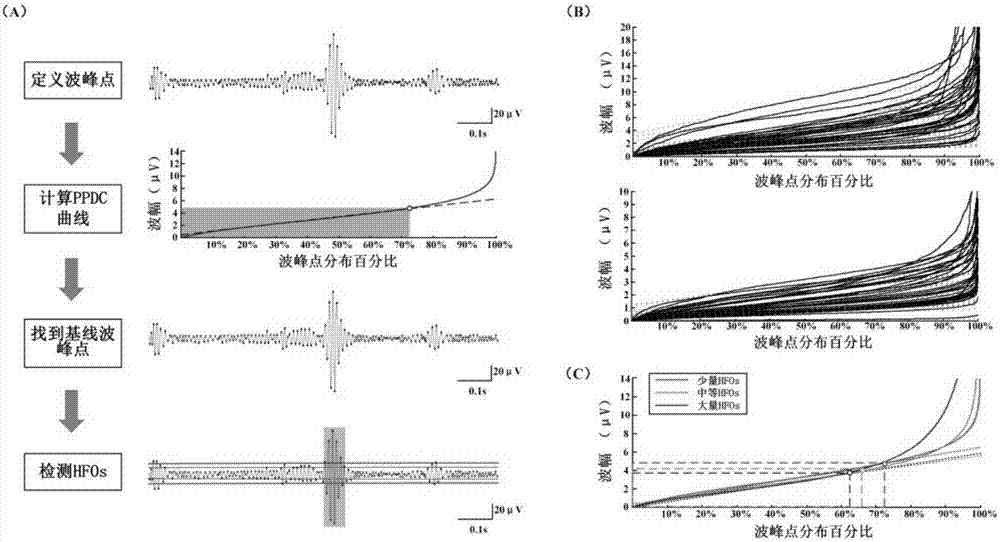
High-frequency oscillation automatic detection system based on calculation of baseline of maximum peak point distribution
InactiveCN107463908AAccurate measurementHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceComputed tomography
The present invention relates to a high-frequency oscillation automatic detection system based on calculation of a baseline of maximum peak point distribution. The system consists of the following modules: a high-frequency oscillation automatic detection module (1), an individualized brain model preparation module (2), and a result integration and report output module (3). The high-frequency oscillation automatic detection module (1) obtains data from an original electroencephalogram of a patient, and after carrying out calculation to obtain a baseline by using an algorithm of calculating a dynamic baseline based on a maximum distribution peal point, obtains a data result; the individualized brain model preparation module (2) obtains data from a nuclear magnetic resonance and CT scanning result, combines the data with the data result obtained by the high-frequency oscillation automatic detection module (1) to draw an individualized brain model jointly; and the result integration and report output module (3) outputs a clinical test report.
Owner:杨小枫 +2
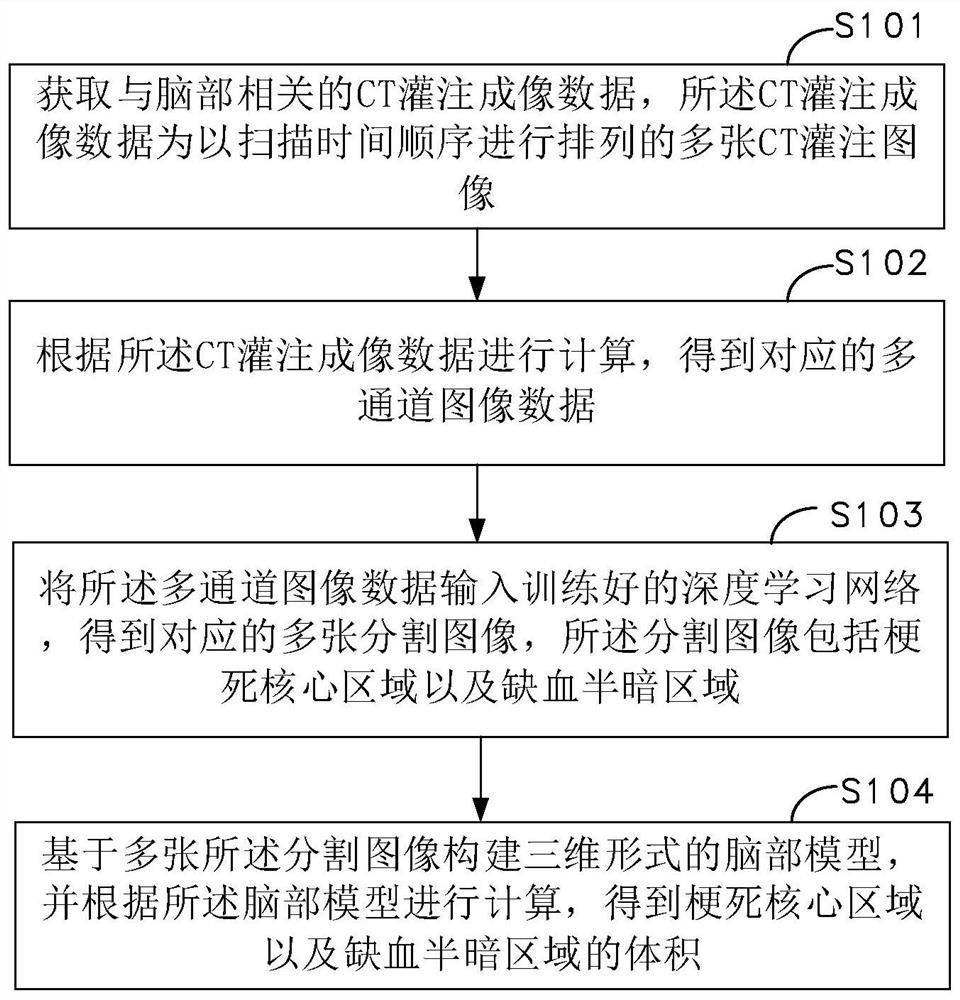
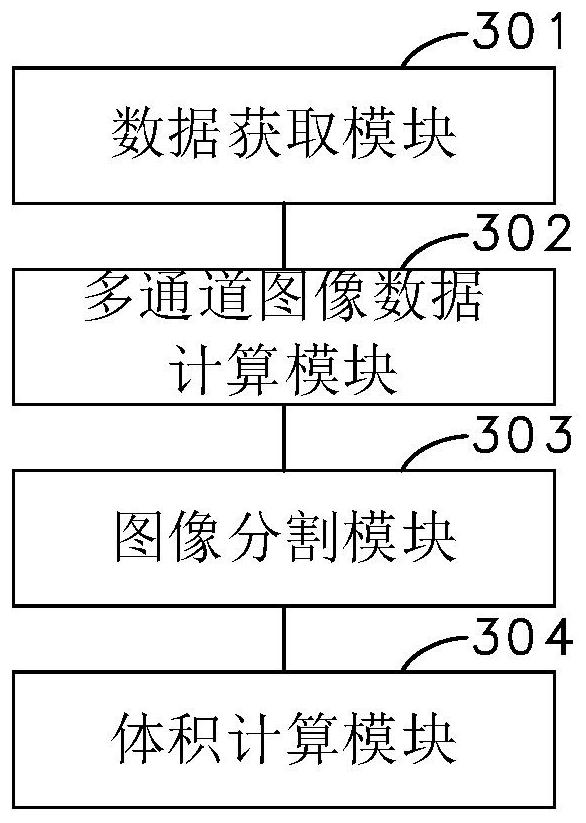
Brain lesion area volume obtaining method and device based on deep learning, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112435212AHigh precisionIncrease computing speedImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyBrain lesions
The invention relates to a brain lesion area volume obtaining method and device based on deep learning, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring CTperfusion imaging data related to the brain, wherein the CT perfusion imaging data are a plurality of CT perfusion images arranged according to a scanning time sequence; calculating according to the CT perfusion imaging data to obtain corresponding multi-channel image data; inputting multi-channel image data into the trained deep learning network, and obtaining a plurality of corresponding segmented images, wherein each segmented image comprises an infarction core region and an ischemia semi-dark region; and constructing a brain model in a three-dimensional form based on the plurality of segmented images, and performing calculation according to the brain model to obtain volumes of the infarction core region and the ischemia semi-dark region. By adopting the method, the accuracy and the calculation speed can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARTERYFLOW TECH CO LTD
Distributed large data real-time processing system and method based on left and right brain model
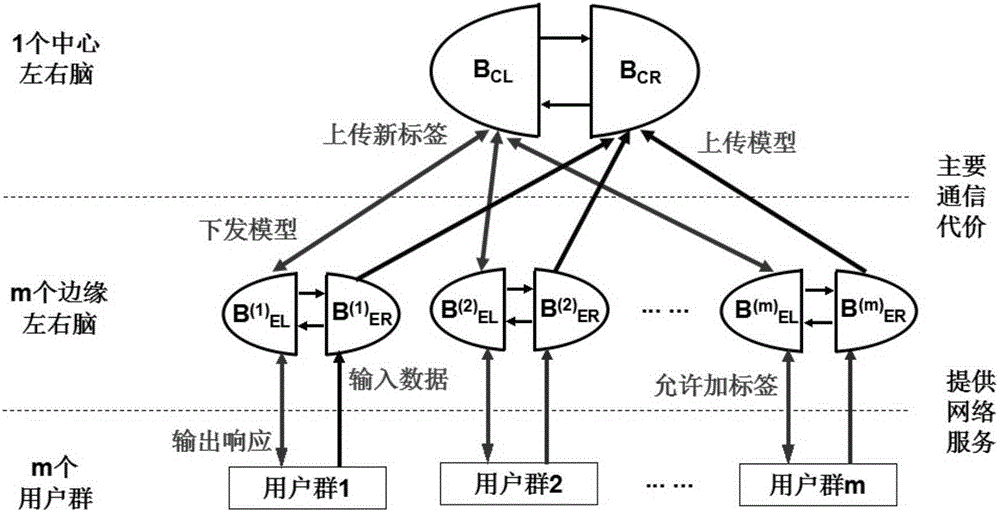
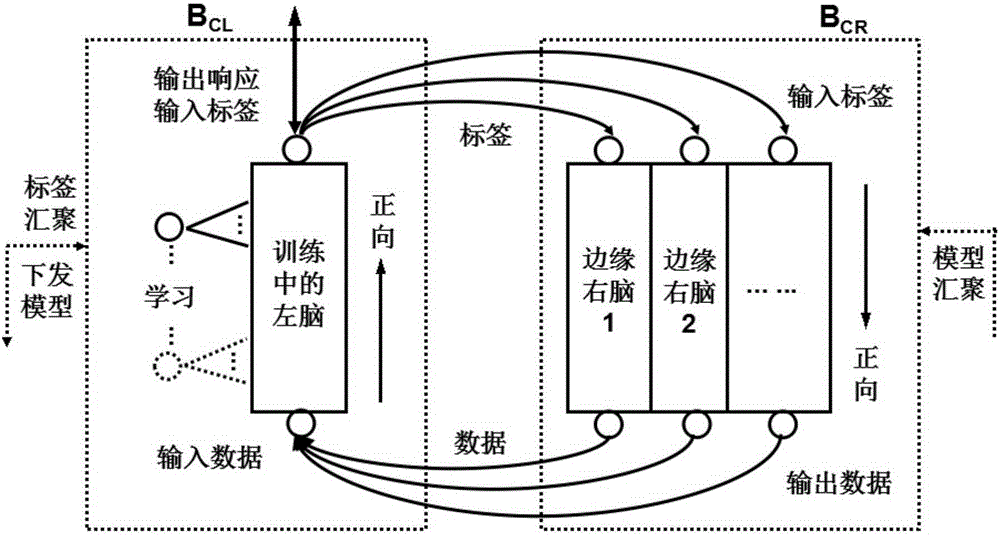
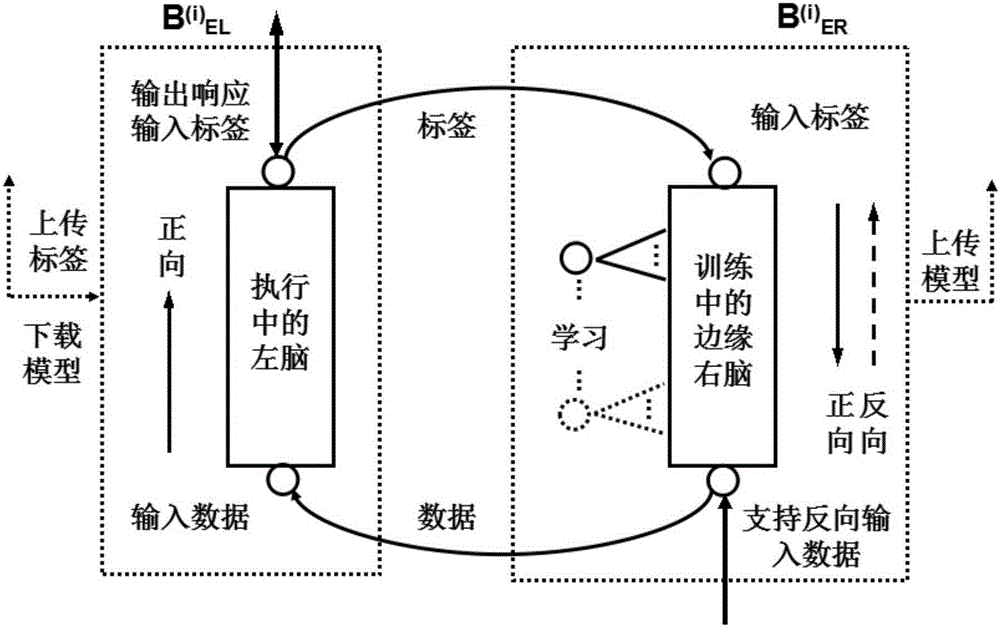
InactiveCN106339072AReal-time processingImprove transmission costInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingEdge serverTime processing
The invention relates to a distributed large data real-time processing system based on a left and right brain model comprising an edge left-brain module set {B(i)EL} consisting of m edge left-brain modules, an edge right-brain module set {B(i)ER} consisting of m edge right-brain modules, a central left-brain module BCL and a central right-brain module BCR, wherein 1<=i<=m, m is the number of edge servers; an ith user group is bidirectionally connected with an ith edge left-brain module B(i) EL; an ith user group is unidirectionally connected to an ith edge right-brain module B(i) ER; the i th edge left-brain module B(i) EL is bidirectionally connected with the ith edge right-brain module B(i) ER; the central left-brain module BCL is bidirectionally connected with the ith edge left-brain module B(i) EL; the ith edge right-brain module B(i) ER is unidirectionally connected to the central right-brain module BCR; the central left-brain module BCL is bidirectionally connected with the central right-brain module BCR.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
A method and system for anatomy structure segmentation and modeling in an image
A method is proposed for segmenting one or more ventricles in a three-dimensional brain scan image (e.g. MR or CT). The image is registered against a brain model, which comprises one or more respective ventricle models of each of the one or more ventricles. Respective regions of interest are defined based on the ventricle models. Object regions are first obtained by applying region growing procedure in the regions of interest, and then trimmed based on anatomical knowledge. A 3D surface model of one or more objects is constructed within a 3D space from the segmented structure. A 3D surface is edited and refined by a user selecting amendment points in the 3D space which are indicative of missing detail features. A region of the 3D surface near the selected points is then warped towards the amendment points smoothly, and the modified patch is combined with the rest of the 3D surface yields the accurate anatomy structure model.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
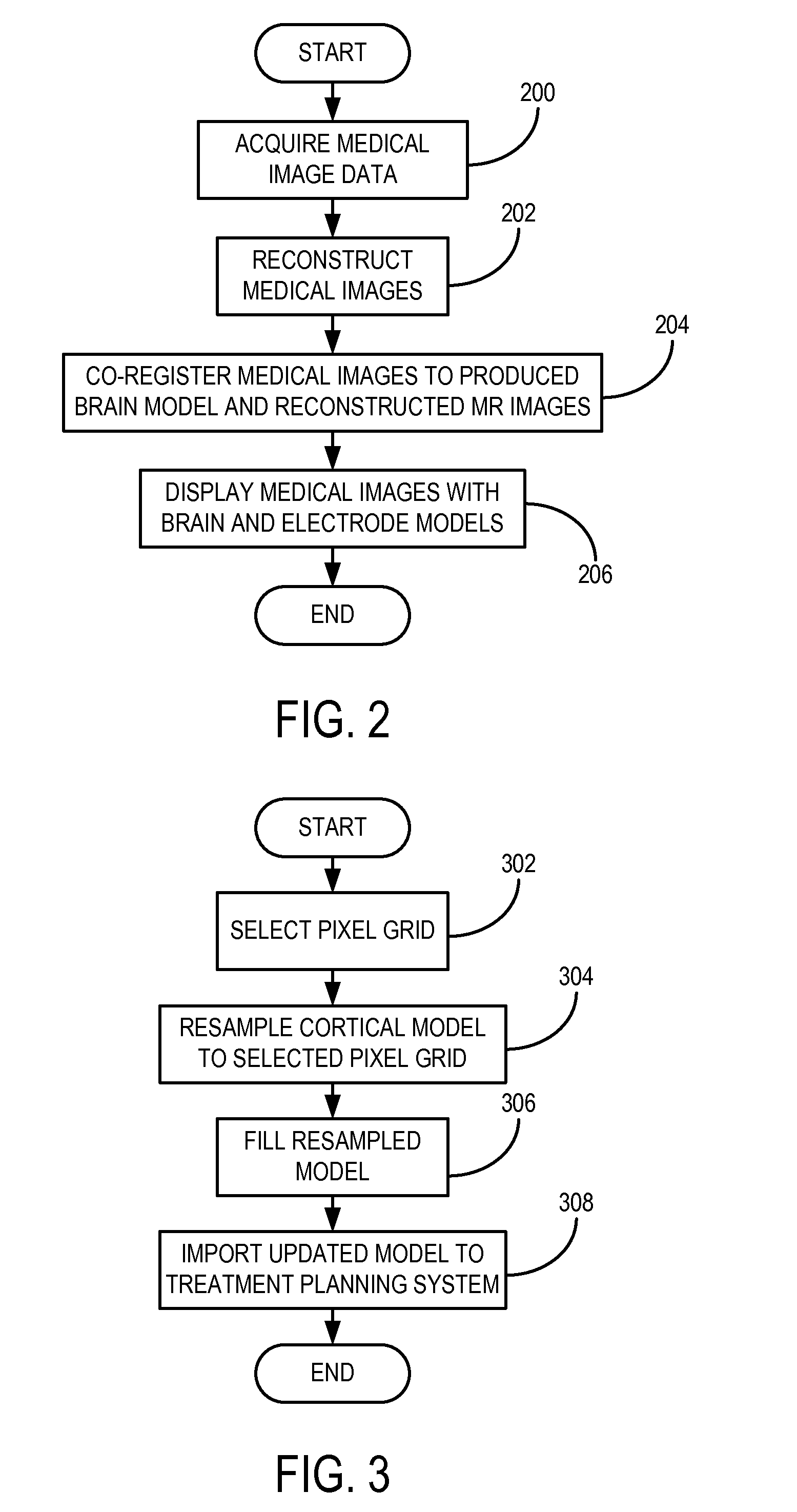
Image analysis of brain image data
InactiveUS20100260394A1Extract information very effectivelyEfficient processingMedical simulationImage enhancementImaging analysisBrain imag
The present invention relates to analysis of image data, e.g. brain image data, where regions of interest are identified in patient specific image data based on non-image data. The brain image data is analyzed by correlating non-image data (20) in the form of data indicative of a neurological deficit and an object model (21) to identify one or more regions of interest (22) in the brain model, mapping the brain model to patient specific brain image data to obtain target image data (24), and identifying the one or more regions of interest in the target image data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Intracerebral current simulation method and device thereof, and transcranial magnetic stimulation system including intracerebral current simulation device
InactiveUS20170049387A1Simple calculationEfficiently conductedMedical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesMedicineEddy current
An intracerebral current simulation method including a first step of providing head image data; a second step of forming a three-dimensional brain model including micro-polyhedron units; a third step of providing first information which includes conditions under which a coil is placed on a patient's head, an electric current is applied to the coil, and the patient's reaction to the magnetic stimulation is observed, the conditions including a position and orientation of the coil, an electric current applied to the coil, and a structure relating to a generated magnetic field of the coil; and a fourth step of calculating an eddy current or electric field induced inside each of the micro-polyhedron units on the basis of the first information provided in the third step and second information which includes conductivity assigned to each micro-polyhedron unit. Also disclosed is a transcranial magnetic stimulation device and system.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Brain model capable of being connected with liquid circulation power system
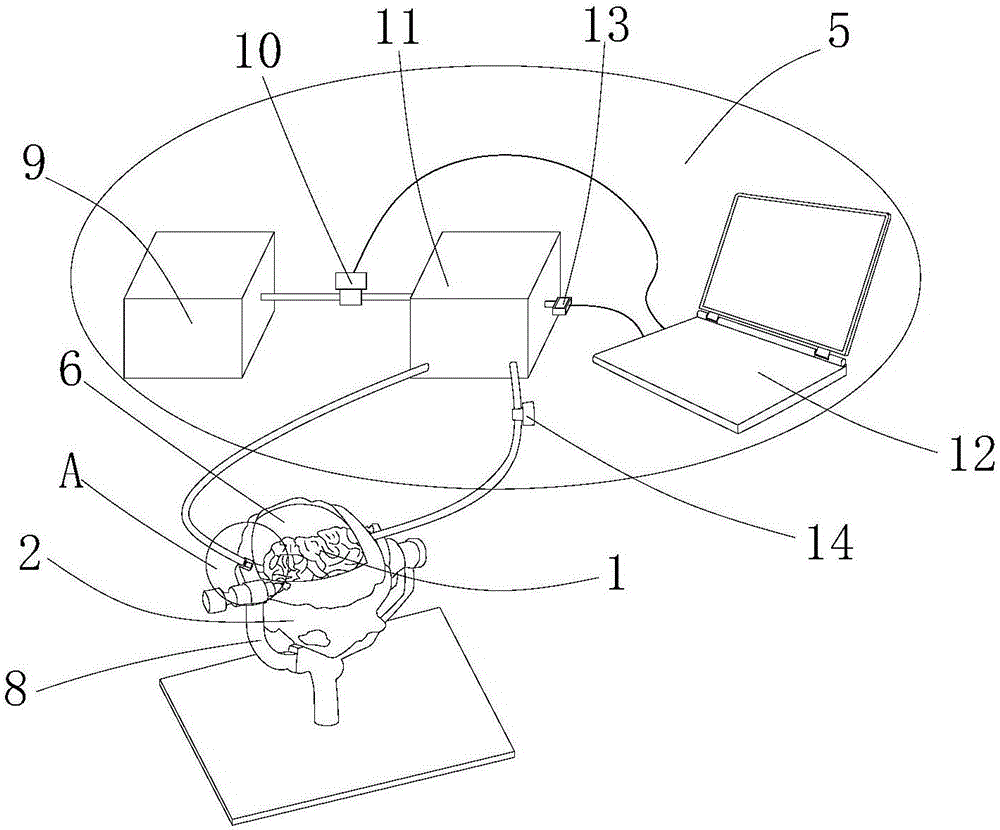
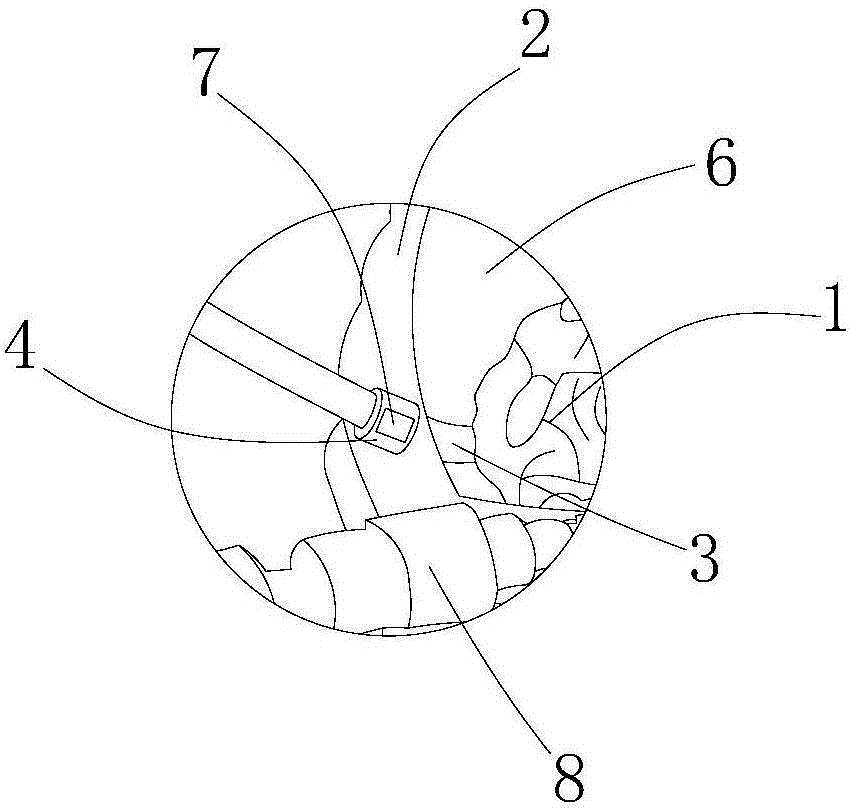
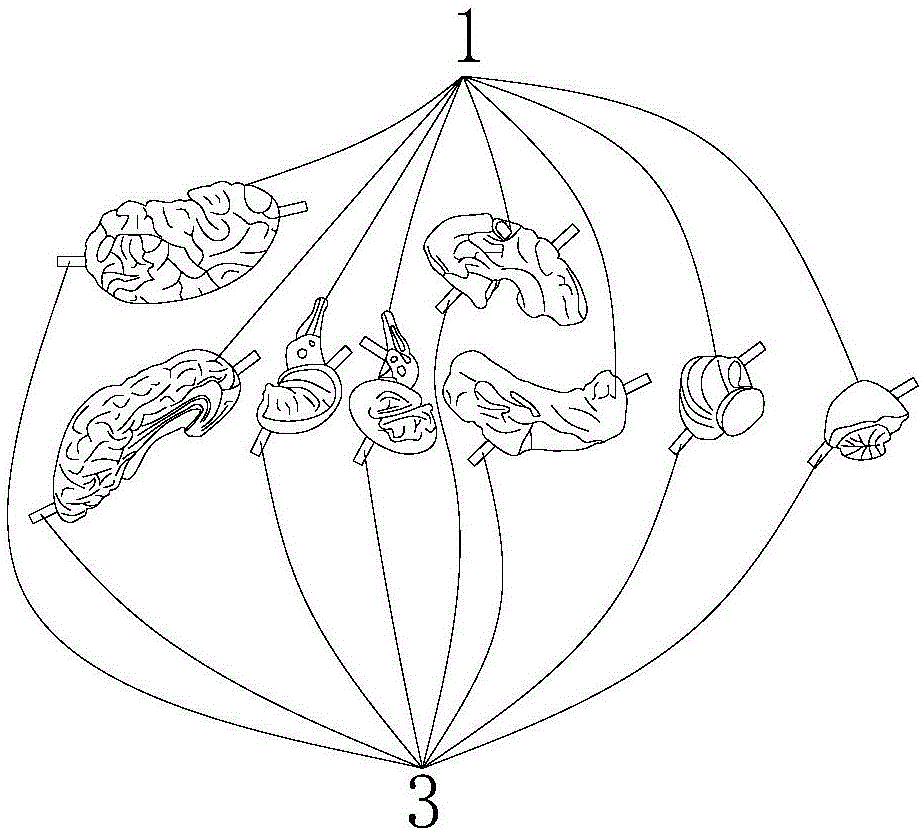
InactiveCN106205327AEasy to operateCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsLiving bodyLiquid circulation
The invention discloses a brain model capable of being connected with a liquid circulation power system. The brain model comprises a plurality of detachable simulation modules for simulating the elasticity of brain tissue of a living body and a detachable airtight skull. Blood vessel circulation systems with the cerebral artery as the basis are embedded in the simulation modules through 3D printing, all the simulation modules are arranged in the skull, connectors provided with liquid outlets and liquid inlets are installed on the blood vessel circulation systems in the simulation modules, and adapters are arranged on the skull. The brain model further comprises the liquid circulation power system provided with a power input port and a power output port. The liquid outlet ends of the connectors are communicated with the power input port of the liquid circulation power system through the corresponding adapters, and the liquid inlet ends of the connectors are communicated with the power output port of the liquid circulation power system through the corresponding adapters. The brain model has the advantages that the brain model is connected with the liquid circulation power system, the simulation modules can pulsate, and meanwhile the simulation module with lesions can be separated out for surgery.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Colloid brain parenchyma preparing method and physical brain model
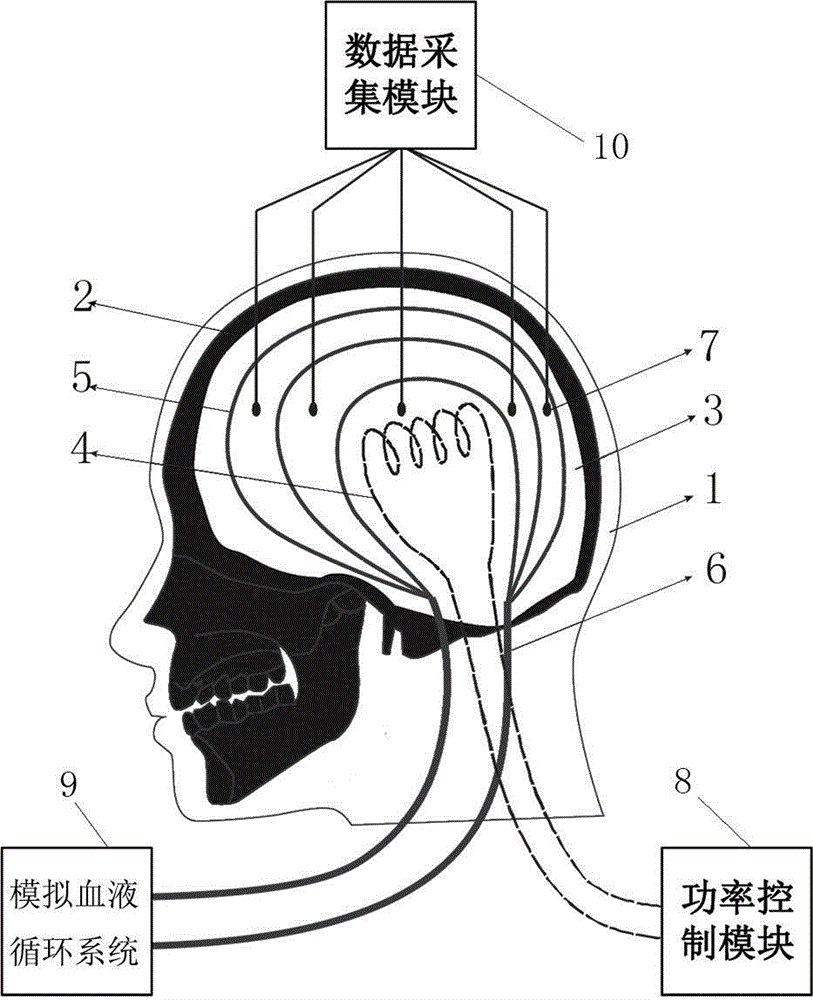
The invention discloses a colloid brain parenchyma preparing method and a physical brain model. The physical brain model comprises a scalp part, a skull part, colloid brain parenchyma, a power control module, a data collecting module and a blood circulation simulating module. The scalp part is attached to the outer surface of the skull part. The interior of the skull part is poured with the colloid brain parenchyma. A heating nickel wire, a plurality of temperature sensors and a plurality of capillary copper tubes are distributed in the colloid brain parenchyma. The heating nickel wire is electrically connected with the power control module. The temperature sensors are electrically connected with the data collecting module. The capillary copper tubes are intersected with two thick copper tubes. The thick copper tubes penetrate through a foramen magnum to be connected to the blood circulation simulating system. The blood circulation simulating system cyclically inputs liquid with the temperature the same as that of blood into the capillary copper tubes. The heating nickel wire emits heat under the control of the power control module. The temperature sensors detect the temperature of all the portions of the brain and transmit the temperature to the data collecting module. The scheme is suitable for researching and testing changes of the temperature in the brain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for constructing three-dimensional brain model
InactiveCN102609981AImprove visibilityImprove teaching efficiency3D modellingSource materialRadiology
The invention discloses a method for constructing a three-dimensional brain model, comprising the steps of using a magnetic resonance skull sagittal thin layer to image; obtaining data with a T1DICOM format as a source material; transforming the source material into an image with a bmp format; separating a target image from the image with the bmp format; introducing the obtained target image to a three-dimensional reconstruction software; setting space position in an empty manner, producing a mask and constructing a crude three-dimensional model; converting the crude three-dimensional model into a low surface target model by means of surface lowering processing; finally, connecting the low surface target model and the original data with the T1DICOM format to obtain the three-dimensional brain model. When the three-dimensional brain model constructed by the invention and the original skull magnetic resonance target picture are verified, the contour line of the three-dimensional brain model is nicely consistent with the edge of the original image with the T1DICOM format.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Image analysis of brain image data
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
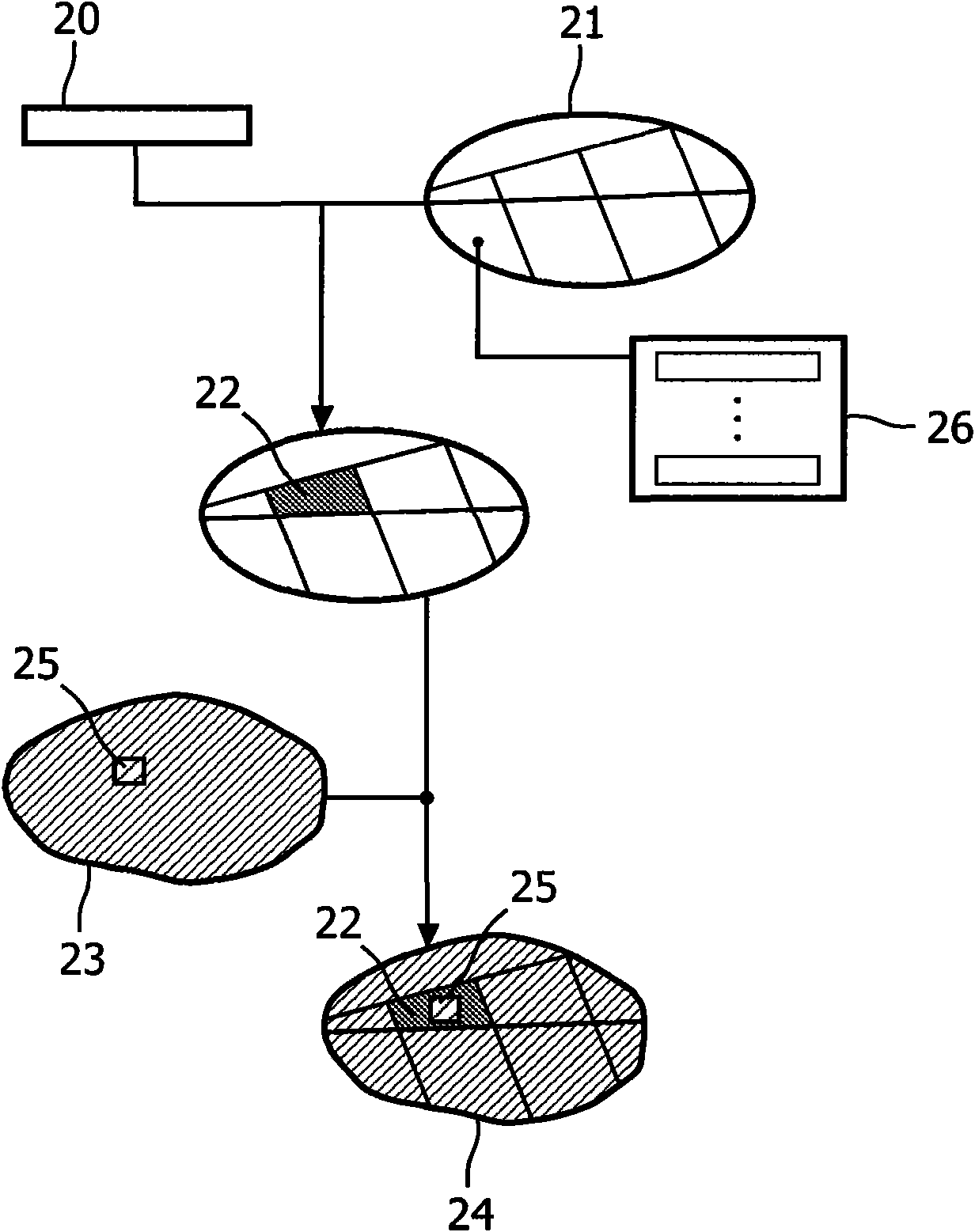
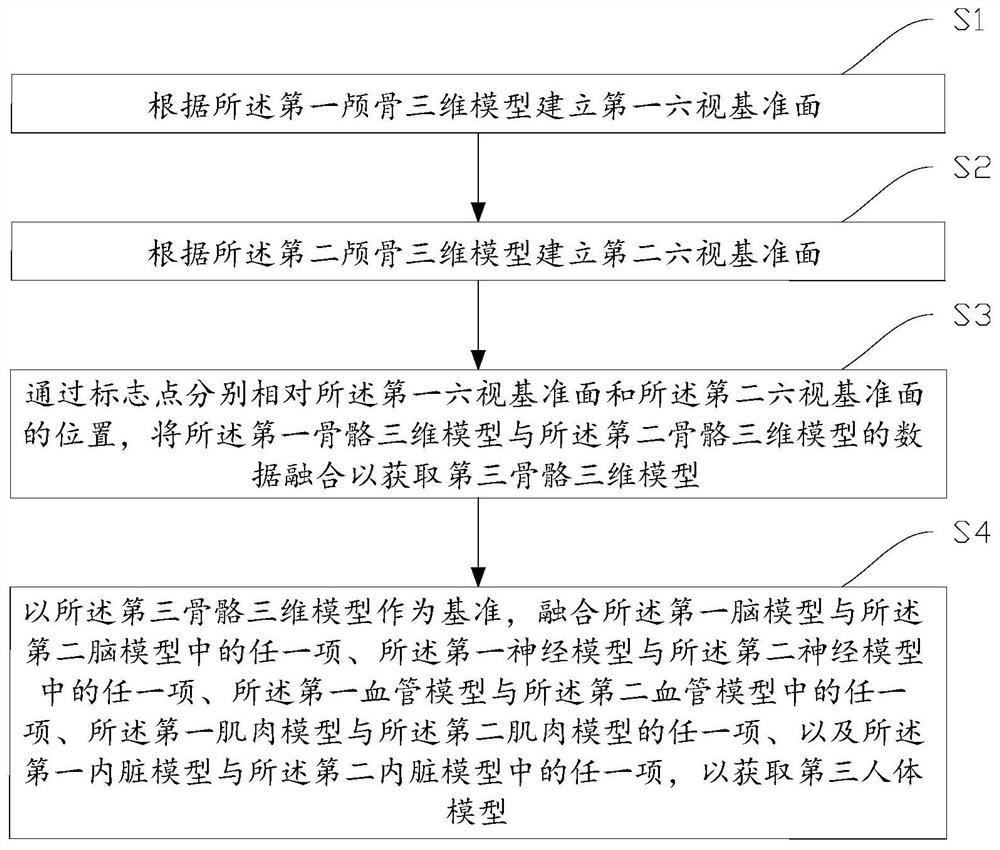
Human body model modeling method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
The invention provides a human body model modeling method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining model data of the same human body in different modes, and enabling the model data to comprise a skeleton three-dimensional model, a brain model neural model, a blood vessel model, a muscle model and an internal organ model, using a skull three-dimensional model in a skull three-dimensional model as a common point of two human body models, comparing and analyzing the two skull three-dimensional models under the same coordinate system by utilizing common mark points (anatomical mark points such as a nose base point and a nose root point) and the position of a six-view datum plane corresponding to the skull three-dimensional model, andfusing different data to obtain a more accurate skull three-dimensional model and even a skeleton three-dimensional model.
Owner:李艳 +2
Dynamical brain model for use in data processing applications
ActiveUS7398256B2Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsAdaptive learningDynamic models
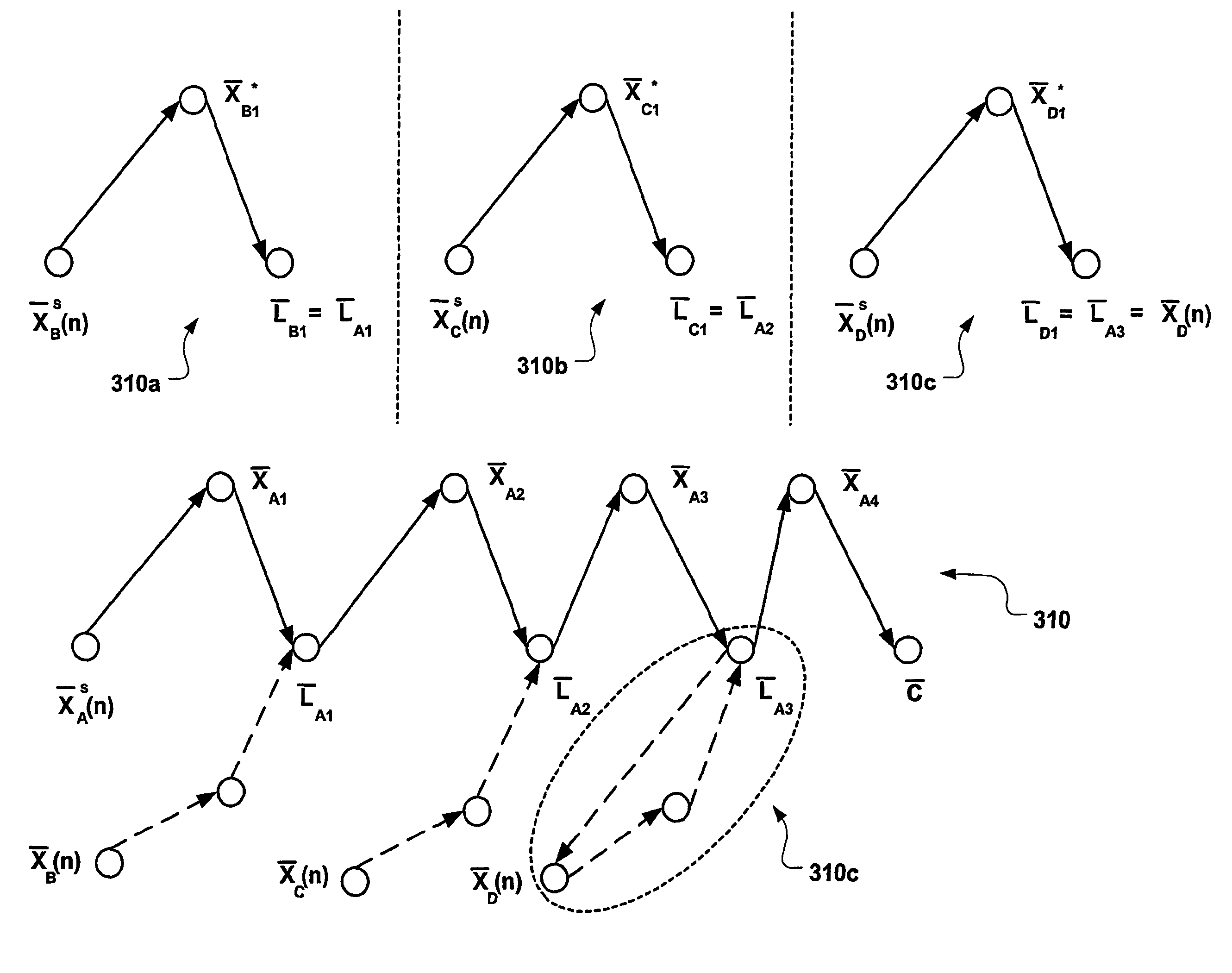
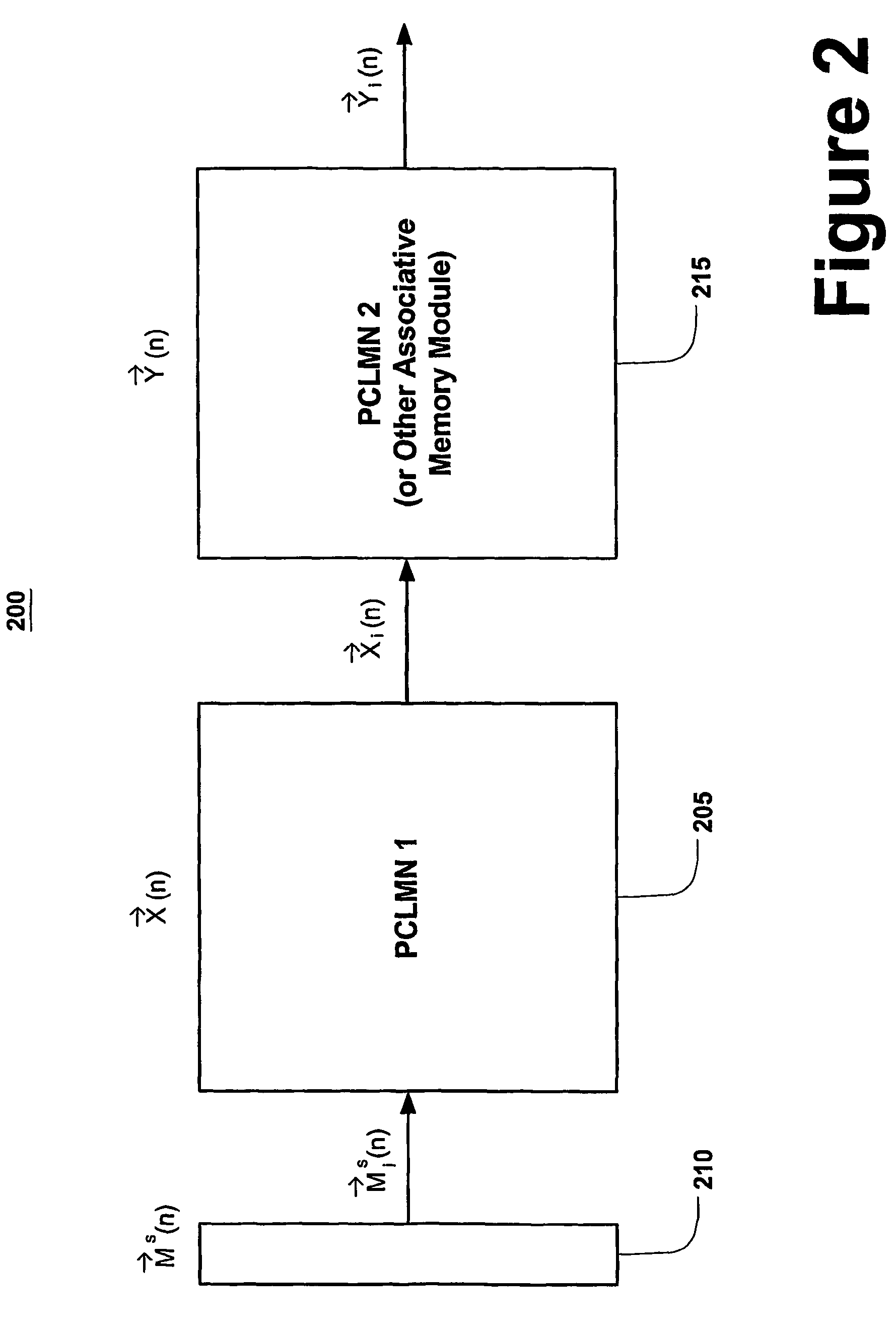
A system and methods offering a dynamical model of cortical behavior is provided. In an illustrative implementation, the present invention offers a corticonic network comprising at least one parametrically coupled logistic map network (PCLMN)(205). The PCLMN offers a non-linear iterative map of cortical modules (or netlets) that when executed exhibit substantial cortical behaviors. The PCLMN accepts dynamic and / or static spatio-temporal input (210) and determines a fixed point attractor in state-space for that input. The PCLM (205) operates such that if the same or similar dynamic and / or static spatio-temporal input is offered over several iterations, the PCLMN converges to the same fixed point attractor is provided rendering adaptive learning. Further, the present invention contemplates the memorization or association of inputs using the corticonic network in a configuration where the PCLMN cooperates with another cortical module model (e.g. another PCLMN, associative memory module, etc.)(215).
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF
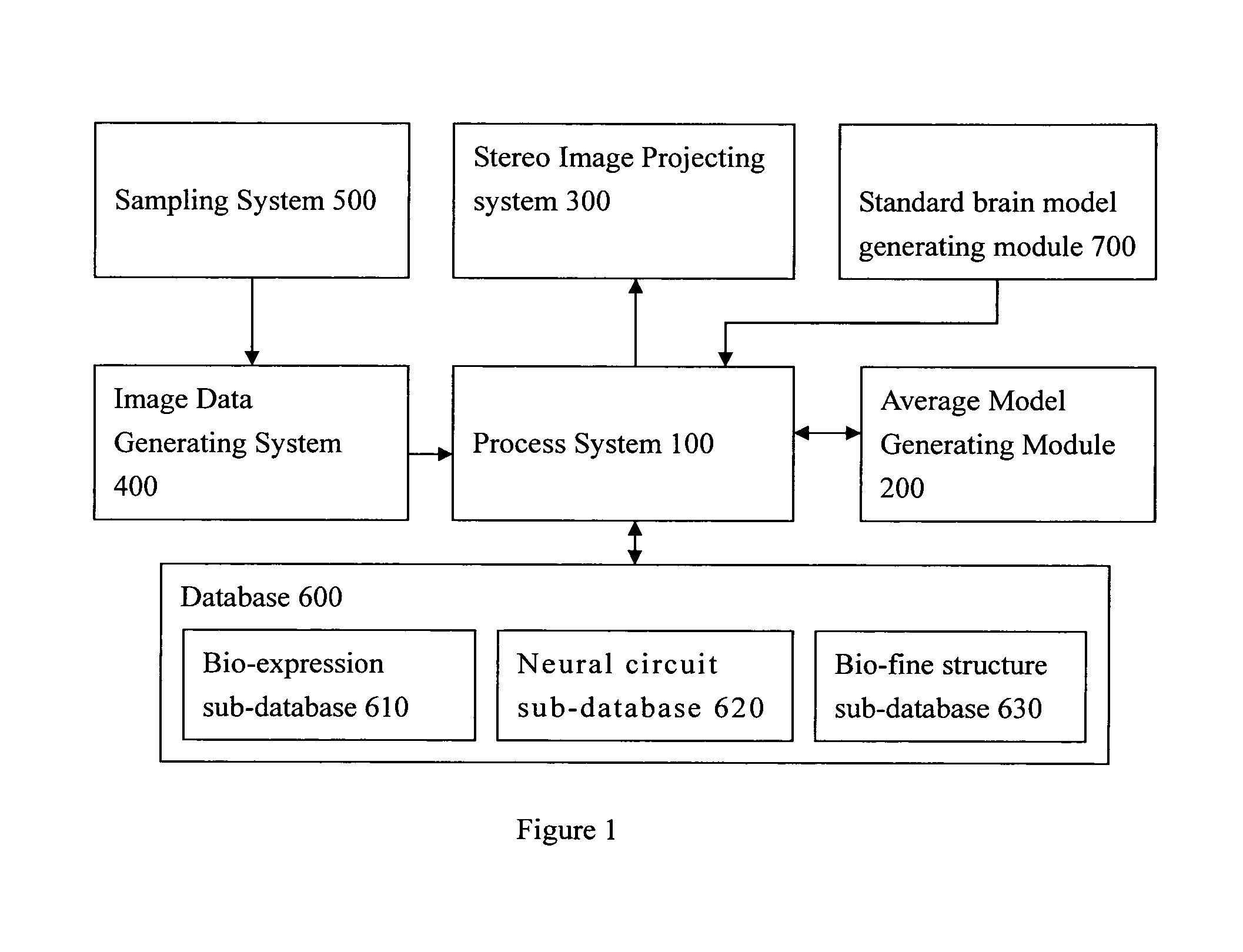
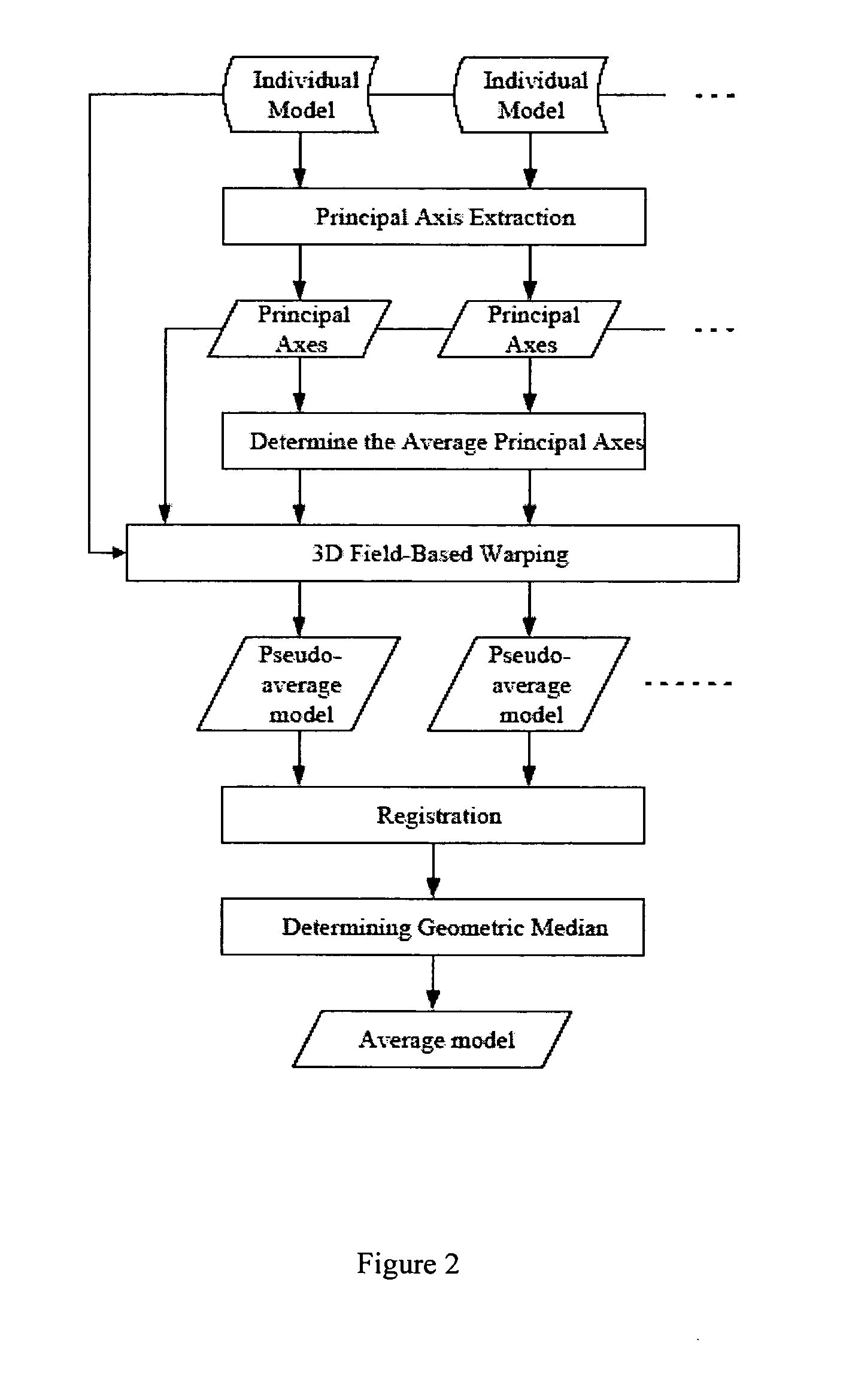
Bio-expression system with module for creating the standard drosophila brain model and its coordinate system
ActiveUS20090063119A1Digital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementComputer graphics (images)Transformation parameter
A method of generating standard brain model from a bio-expression system includes performing steps of registration to input standard surface and individual surface into affine registration; recording a transformation parameters from the affine registration; performing steps of inputting a individual neuropil and transform parameters into an affine transformation; applying the data of the affine transformation to transform individual neuropil to achieve transformed individual neuropil; and performing a step of affine registration to register a standard neuropil to the transformed individual neuropil to achieve a resulting transformation, wherein the resulting transformation can be output as a position and orientation of standard neuropil within the standard surface.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
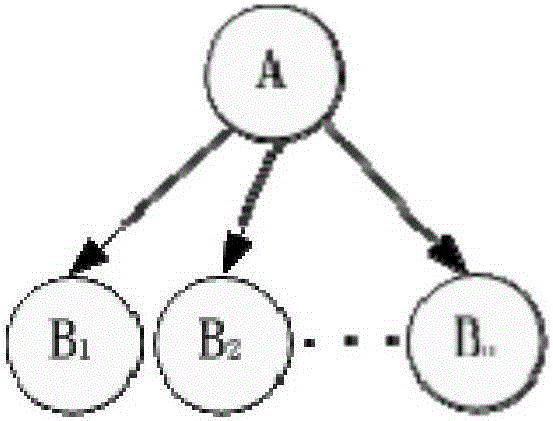
Reasoning algorithm based on importance sampling and neural circuit
ActiveCN105205538AImprove universalityBiological neural network modelsInference methodsPattern recognitionNODAL
The invention provides a reasoning algorithm based on importance sampling and a neural circuit. The algorithm comprises the following steps that a Bayesian network corresponding to a Bayesian brain model to be reasoned is decomposed into a tree-like Bayesian network, wherein the tree-like Bayesian network comprises a highest layer father node and a plurality of son nodes; probabilistic reasoning is performed on the multiple son nodes of the tree-like Bayesian network sequentially from bottom to top, and a plurality of obtained reasoning results are uploaded layer by layer; according to the multiple reasoning results, the posterior probability of the highest layer father node is obtained, and a reasoning result of the Bayesian brain model to be reasoned is obtained according to the posterior probability of the highest layer father node. According to the reasoning algorithm, any Bayesian brain model can be reasoned, and the good universality is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com