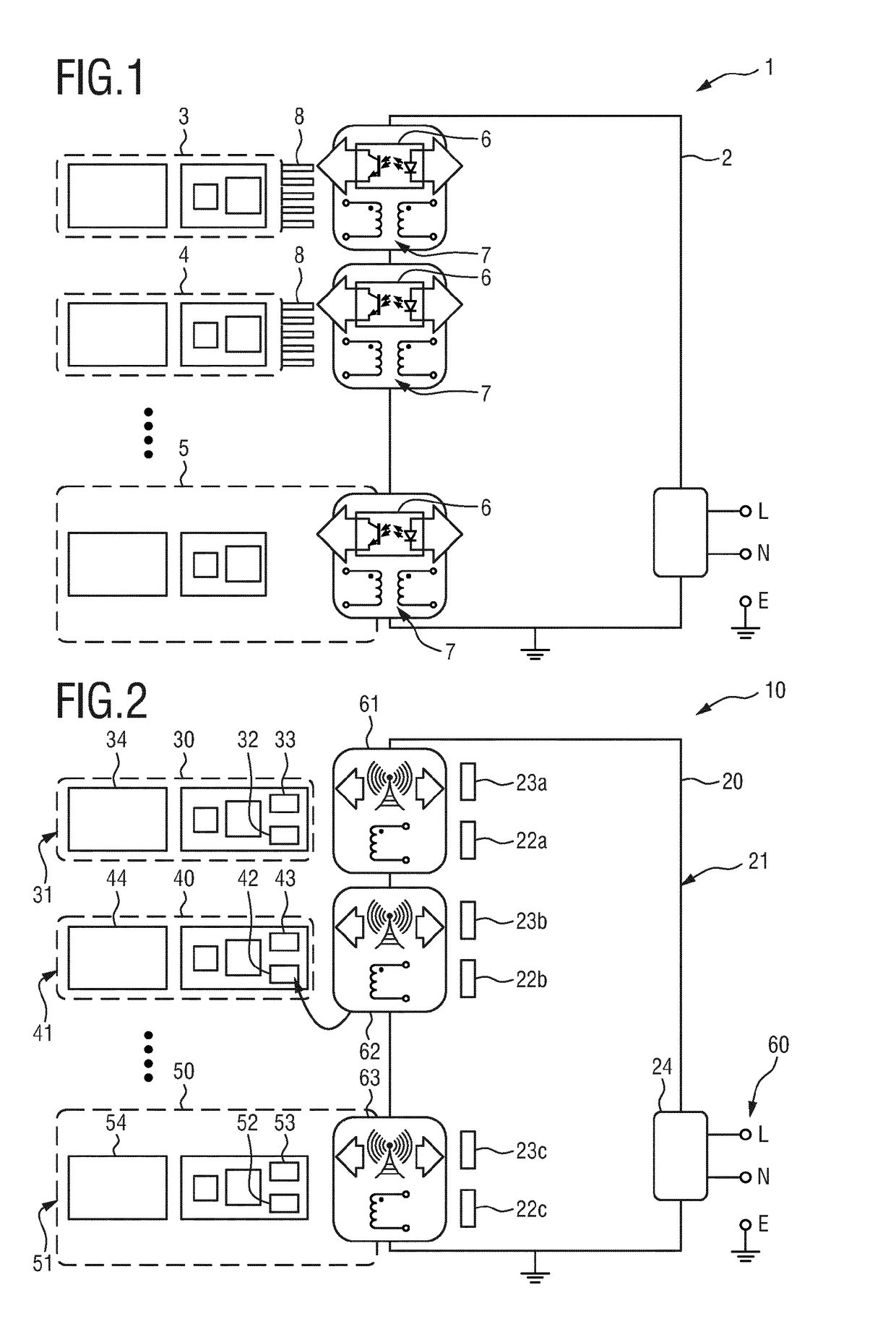
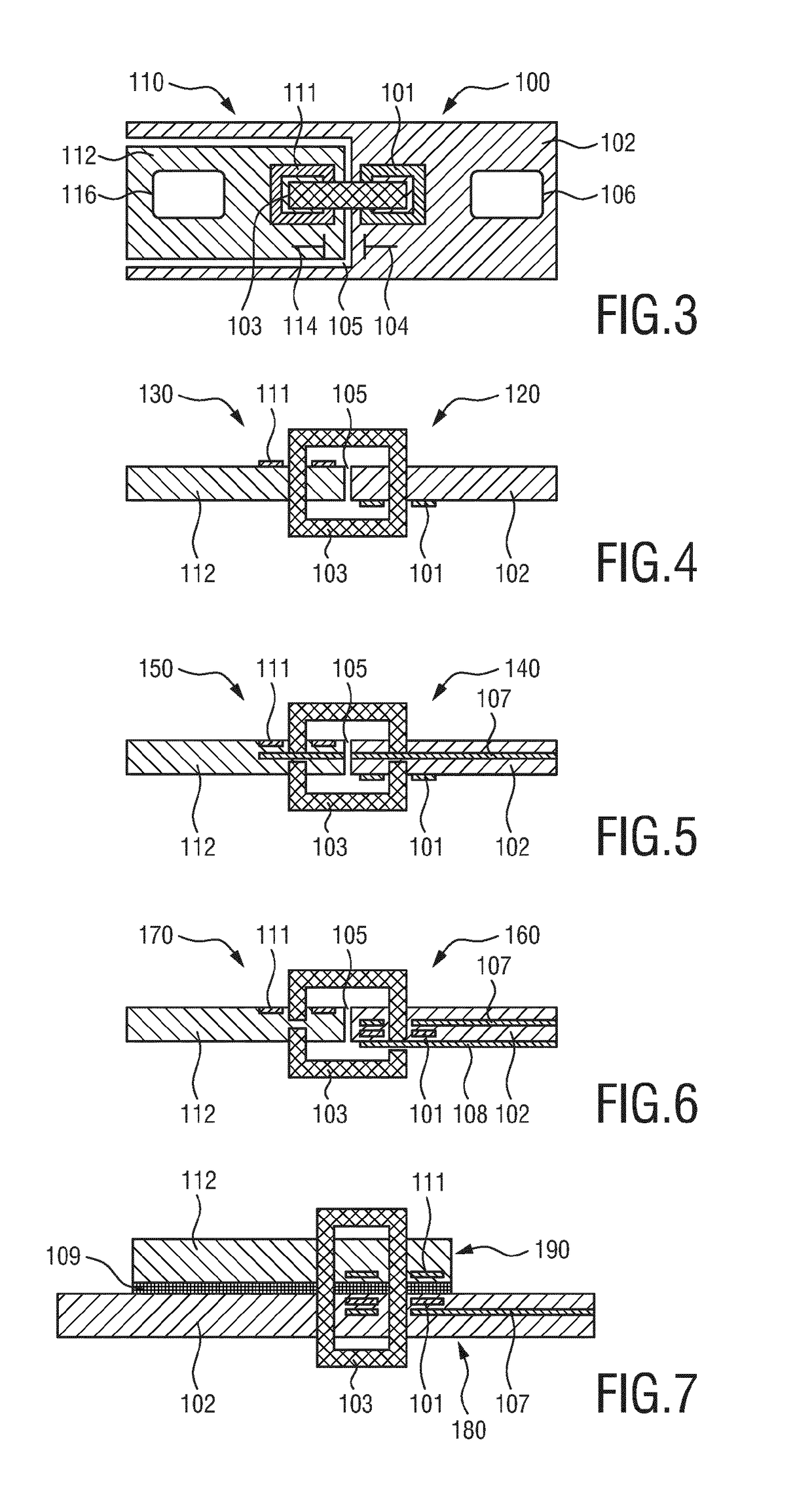
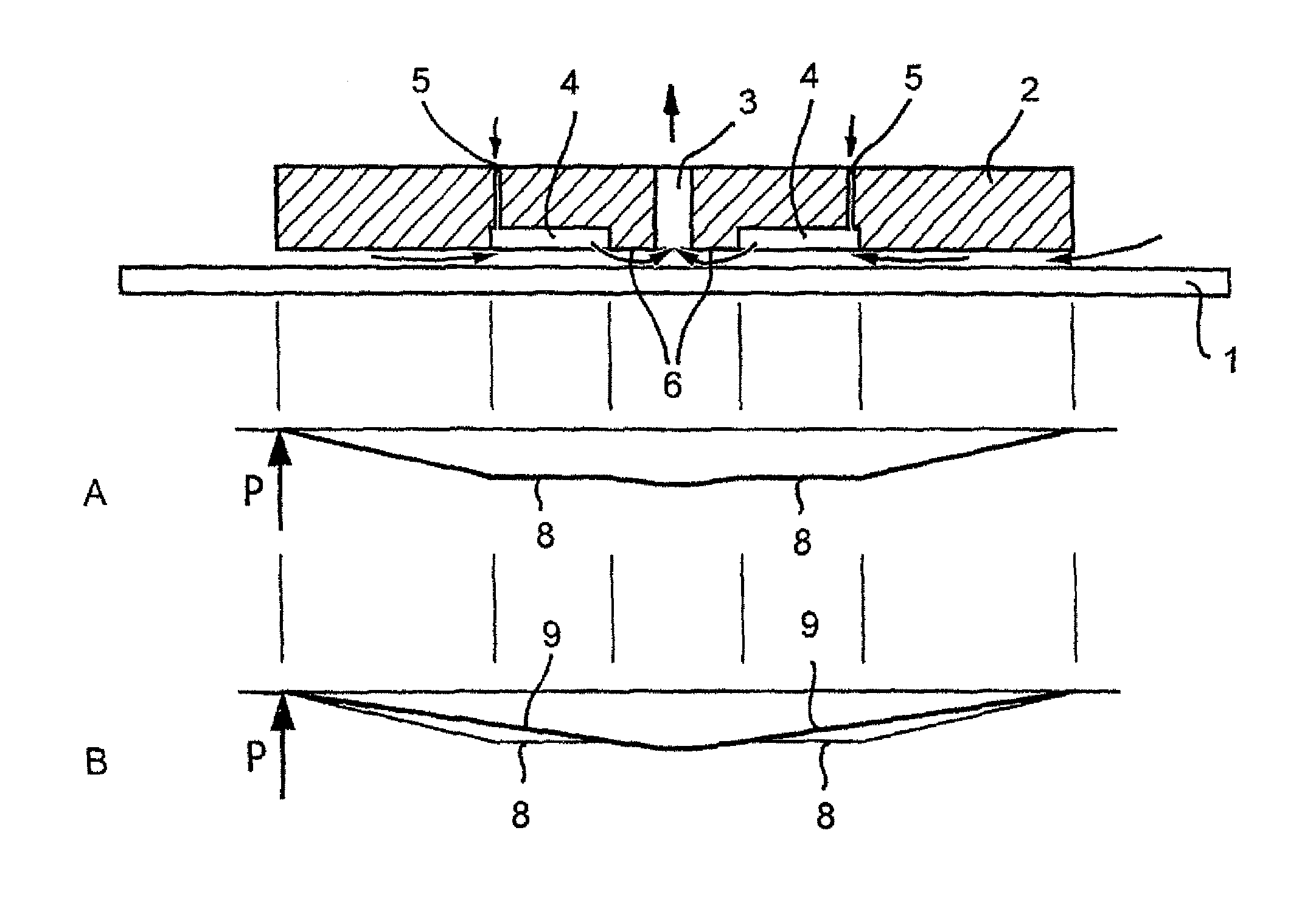
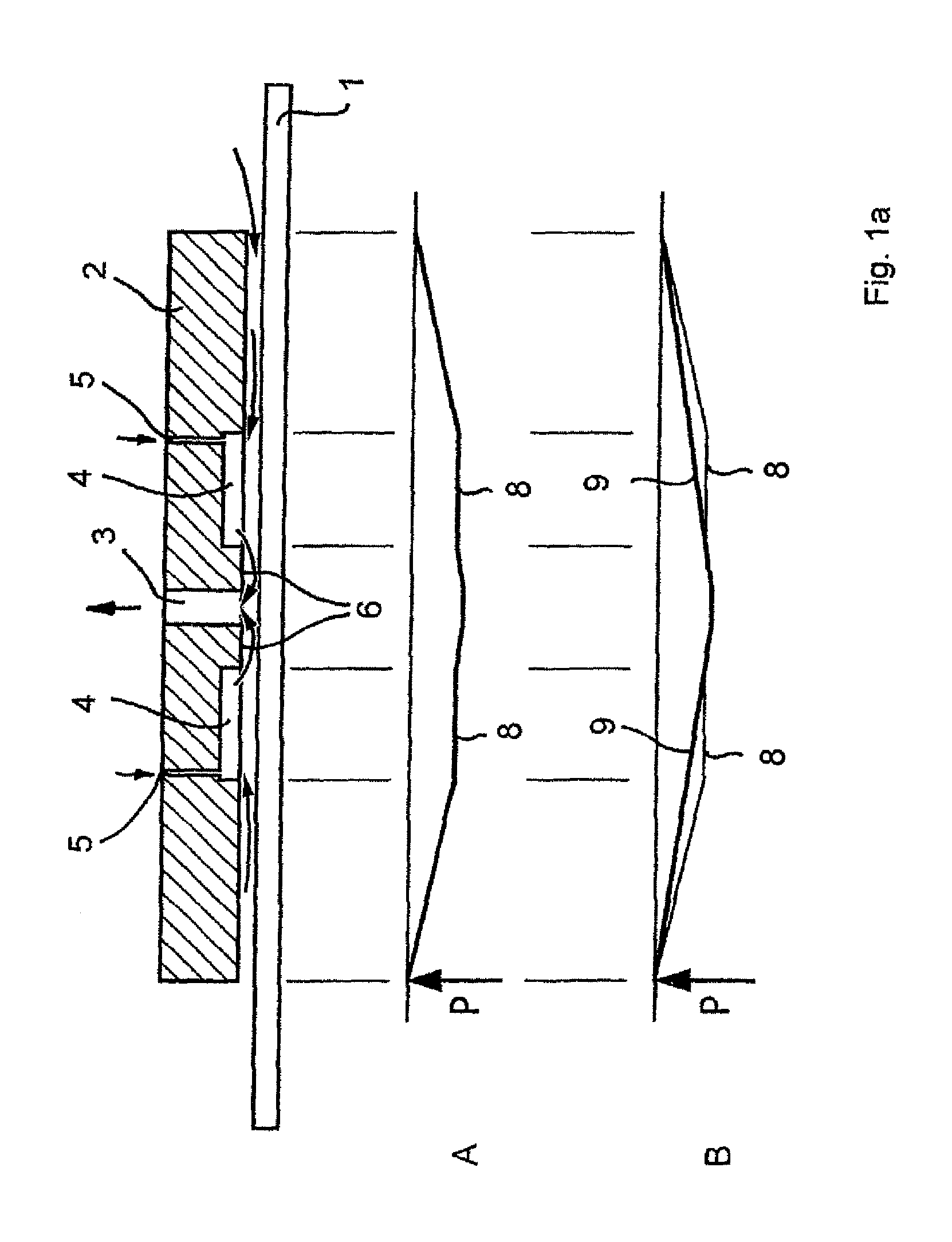
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Reliable and low cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
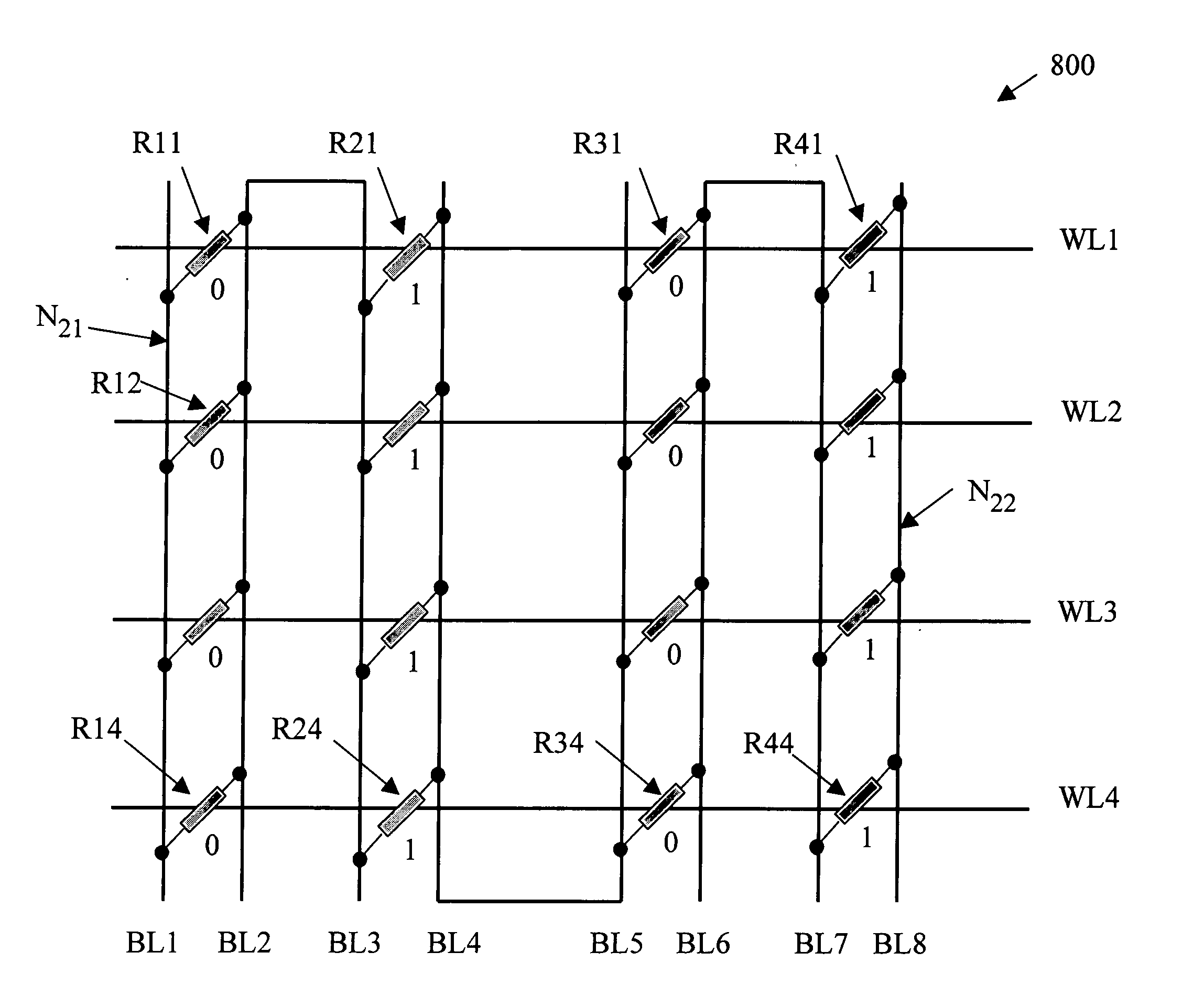
Reference current source for current sense amplifier and programmable resistor configured with magnetic tunnel junction cells
InactiveUS20060092689A1Improve reliabilityWithout compromising device design marginDigital storageAudio power amplifierReference current
A reference current source for a magnetic memory device is preferably configured with magnetic tunnel junction cells and includes more than four reference magnetic memory cells to improve reliability of the magnetic memory device and to reduce sensitivity at a device level to individual cell failures. The reference current source includes a large number of magnetic memory cells coupled in an array, and a current source provides a reference current dependent on the array resistance. In another embodiment a large number of magnetic memory cells are coupled to current sources that are summed and scaled to produce a reference current source. A current comparator senses the unknown state of a magnetic memory cell. In a further embodiment, an array of magnetic memory cells is configured to provide a non-volatile, adjustable resistance. In a further embodiment, the array of magnetic memory cells is configured with a tap to provide a non-volatile, adjustable potentiometer.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
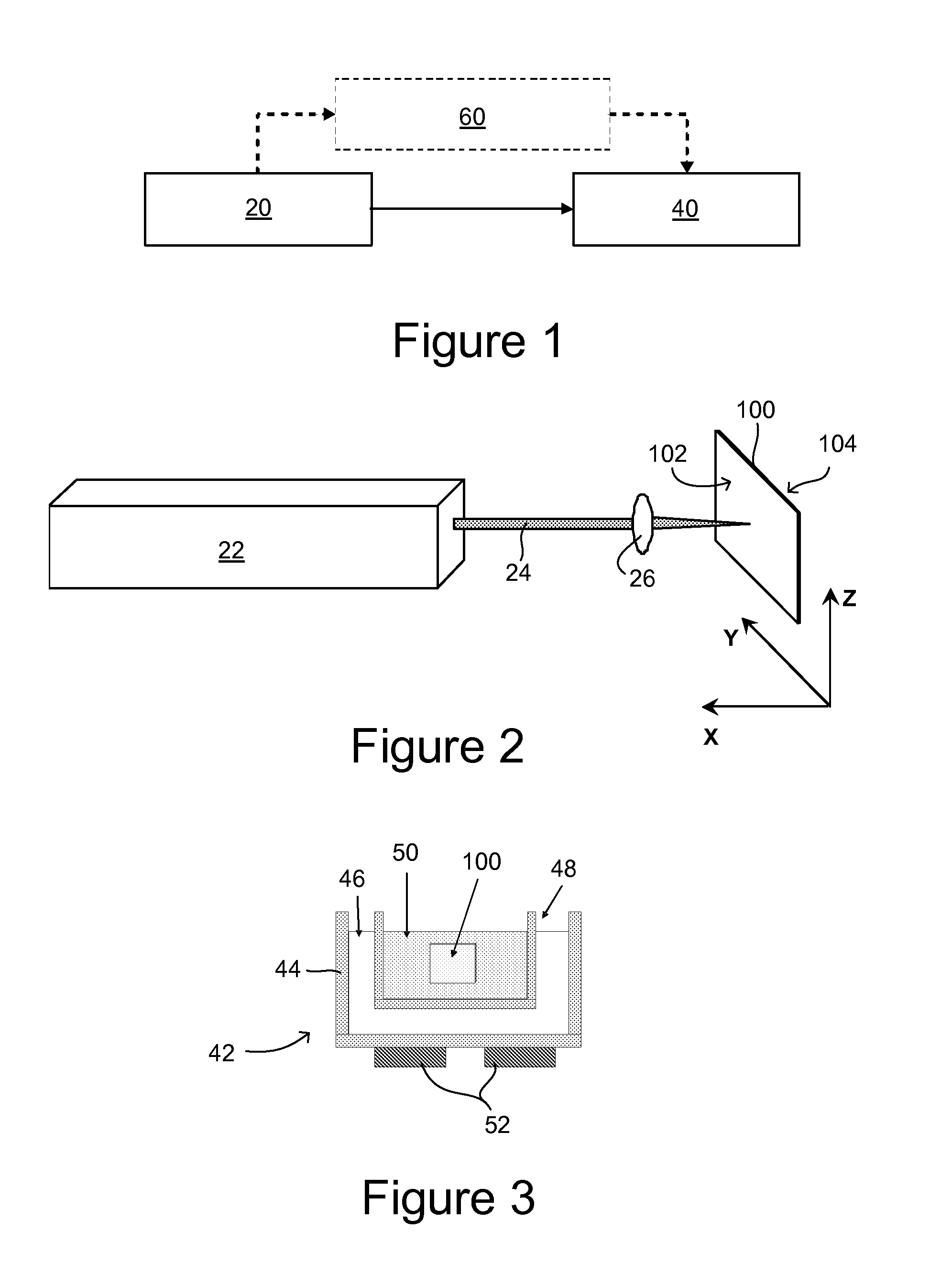
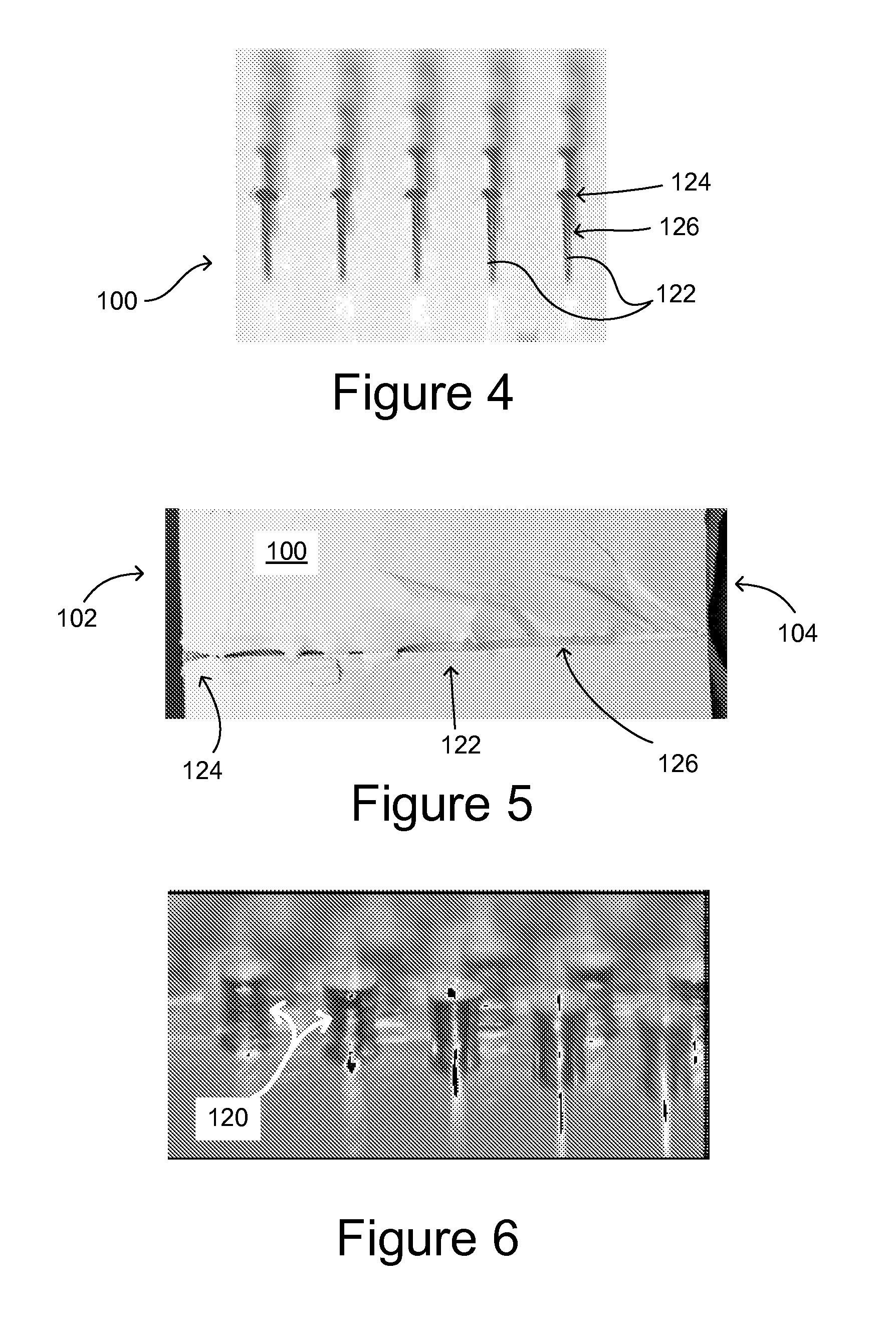
Methods of forming high-density arrays of holes in glass
ActiveUS20130247615A1High positioning accuracyReliable and low-costGlass furnace apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsUv laserEtching
A method of fabricating a high-density array of holes in glass is provided, comprising providing a glass piece having a front surface, then irradiating the front surface of the glass piece with a UV laser beam focused to a focal point within + / −100 μm of the front surface of the glass piece most desirably within + / −50 μm of the front surface. The lens focusing the laser has a numerical aperture desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.4, more desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.15 for glass thickness between 0.3 mm and 0.63 mm, even more desirably in the range of from 0.12 to 0.13, so as to produce open holes extending into the glass piece 100 from the front surface 102 of the glass piece, the holes having an diameter the in range of from 5 to 15 μm, and an aspect ratio of at least 20:1. For thinner glass, in the range of from 0.1-0.3 mm, the numerical aperture is desirably from 0.25 to 0.4, more desirably from 0.25 to 0.3, and the beam is preferably focused to within + / −30 μm of the front surface of the glass. The laser is desirable operated at a repetition rate of about 15 kHz or below. An array of holes thus produced may then be enlarged by etching. The front surface may be polished prior to etching, if desired.
Owner:CORNING INC
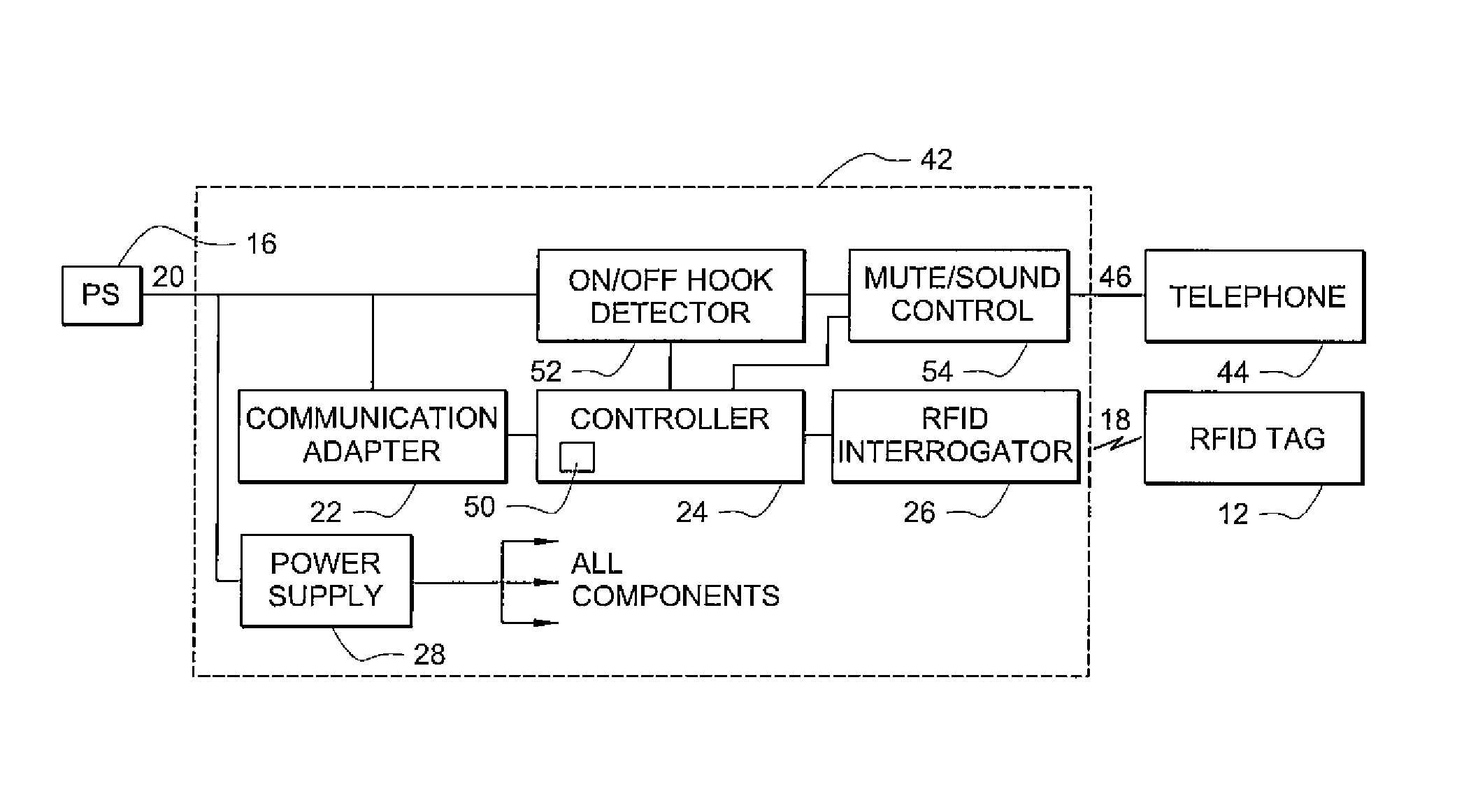
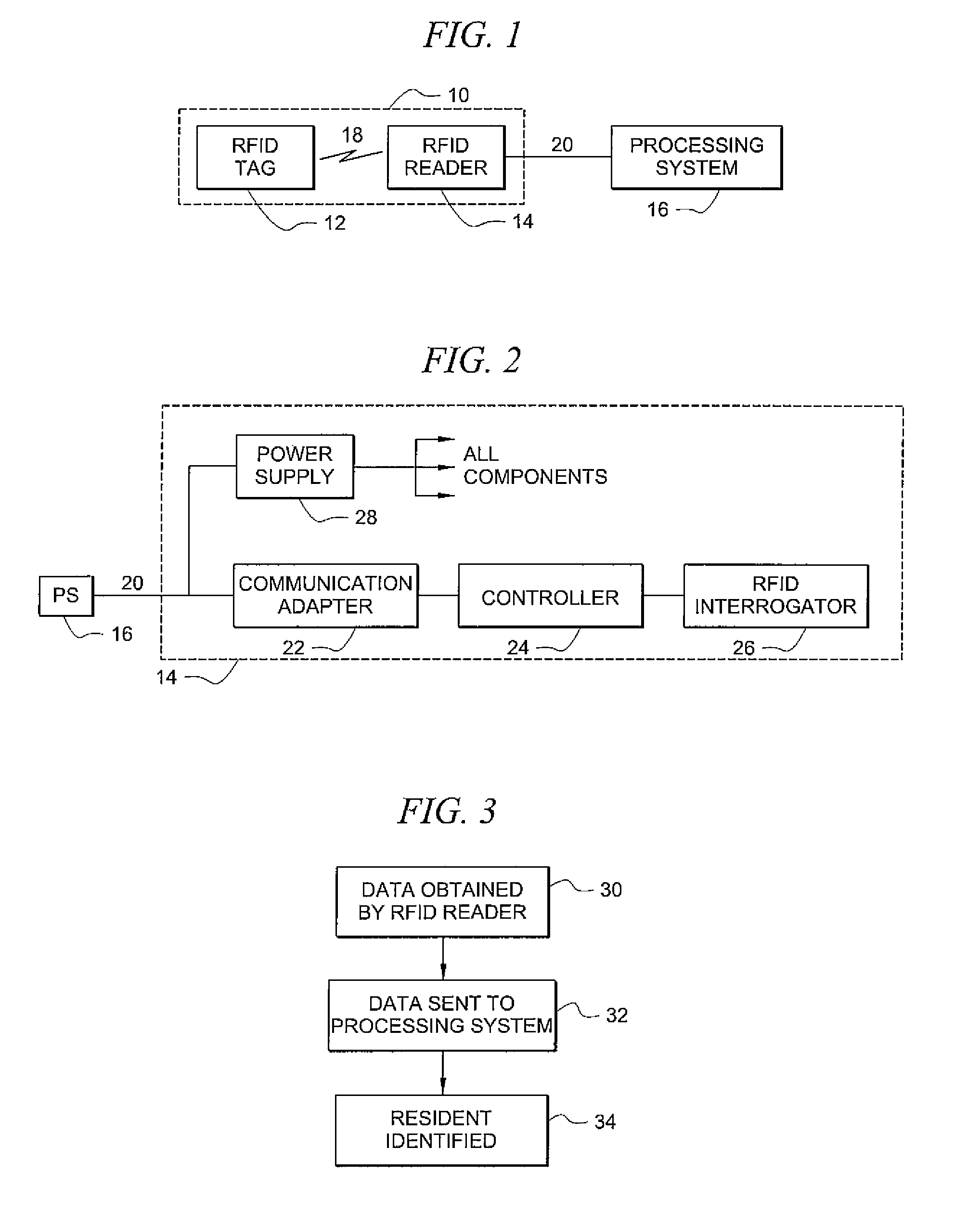
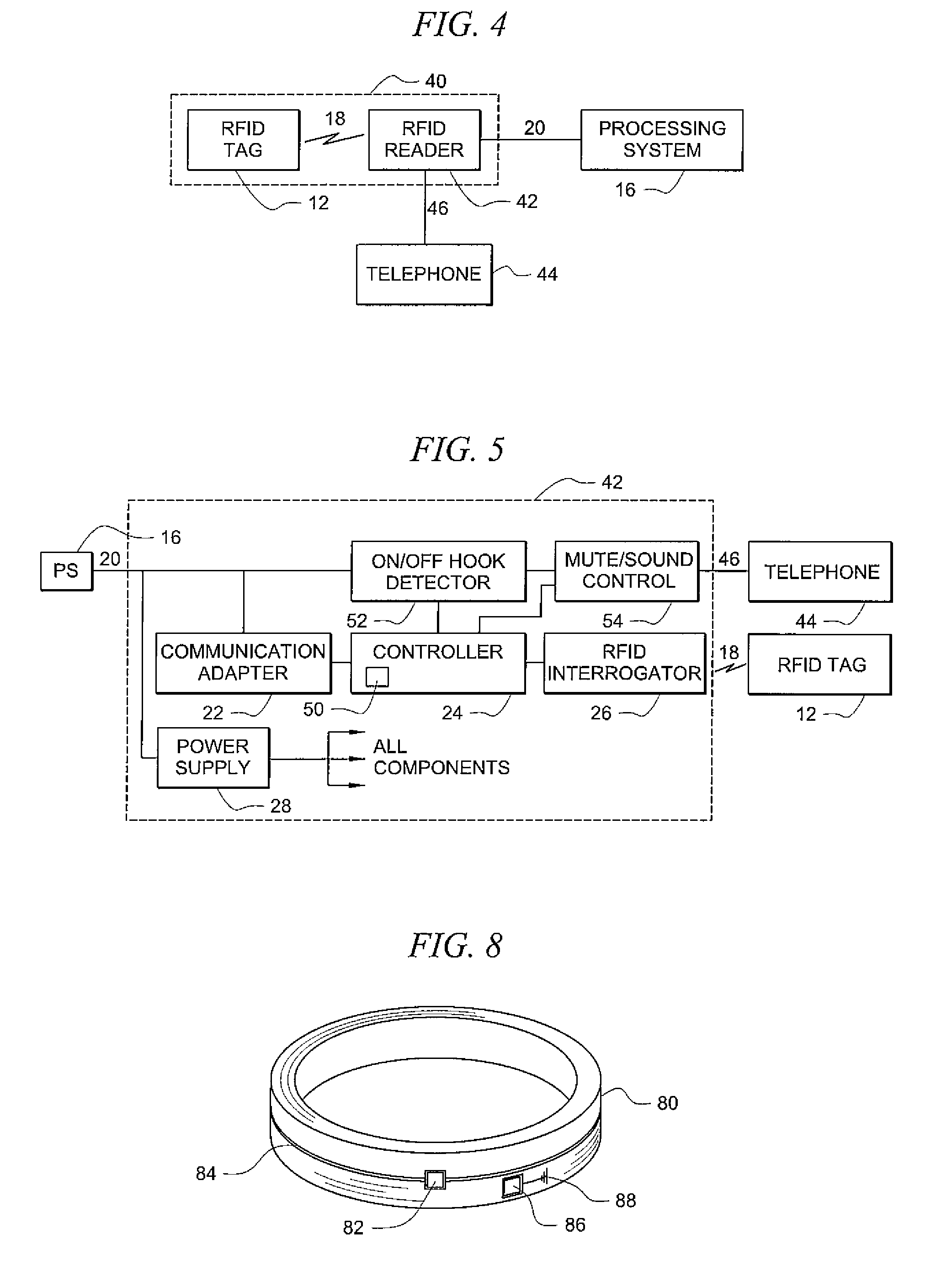
Systems and methods for radio frequency identification
ActiveUS8031052B2Enhanced investigatory toolExpanding investigatory potentialProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsTelecommunications linkTransducer
Systems and methods providing radio frequency identification (RFID) of individuals, as may be implemented with respect to a controlled environment facility, using RFID transducer technology deployed in association with a user terminal, such as telephone or multimedia kiosk, are shown. Embodiments operate to identify residents of a controlled environment facility and control one or more transactions associated with the residents and / or actions of the residents using a RFID system in which a user presents a RFID transponder in proximity to a RFID transducer for identification. RFID tags of embodiments comprise data which identifies an individual, data which may be used to identify an individual, or a combination of both. RFID systems of embodiments are adapted to utilize existing communication links for identification of individuals using RFID and / or for controlling transactions, such as calls, using RFID.
Owner:SECURUS TECH LLC
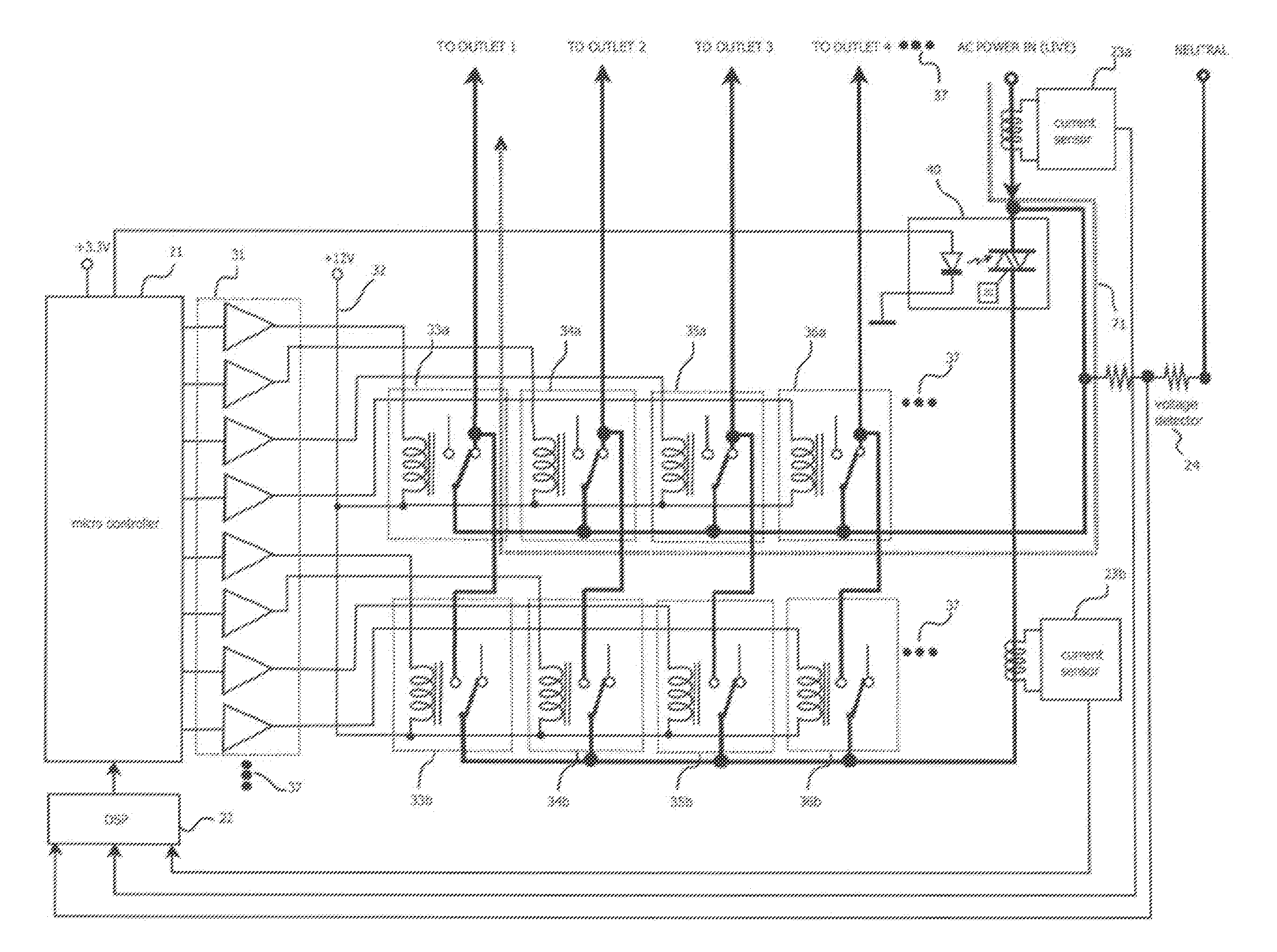
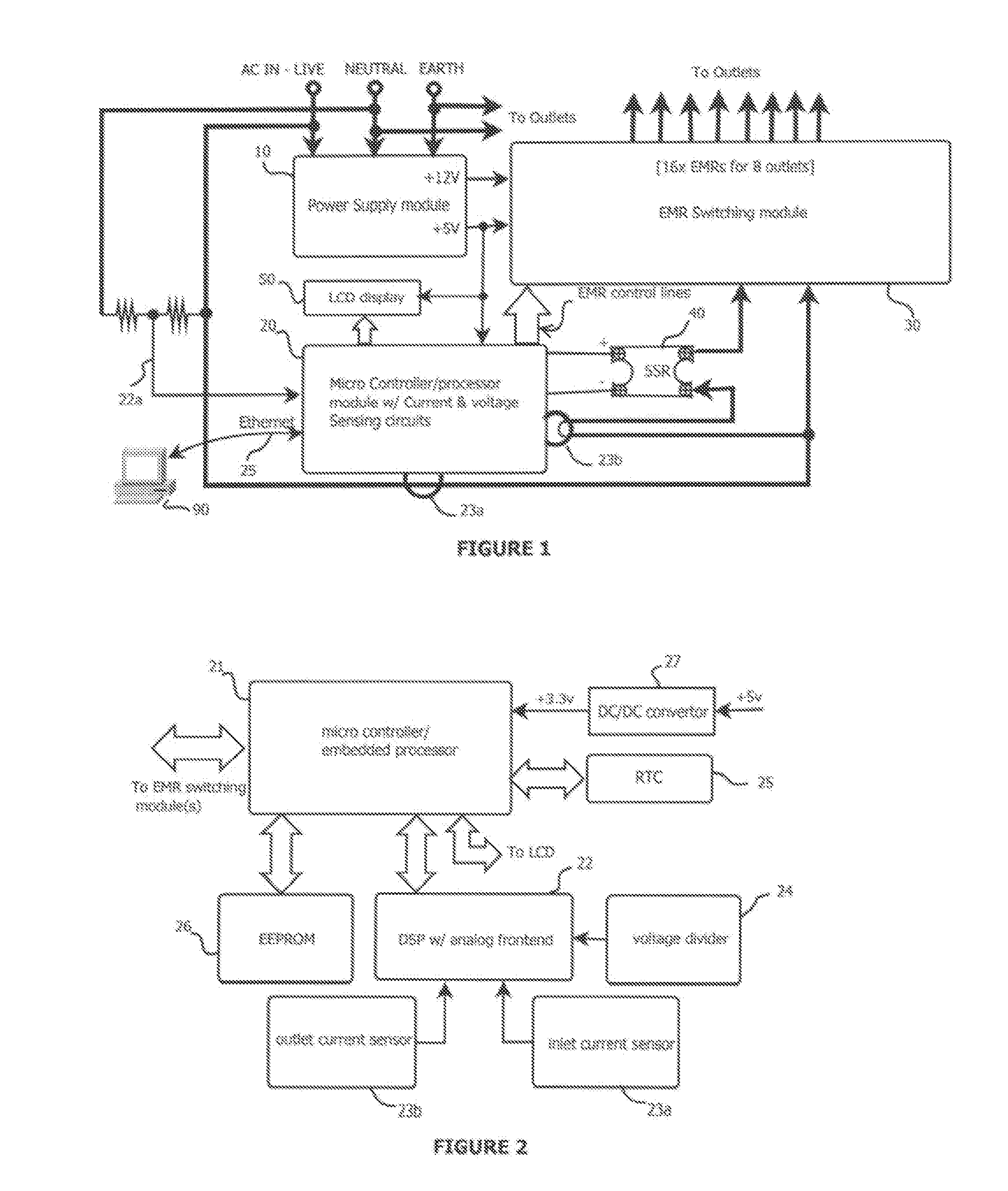
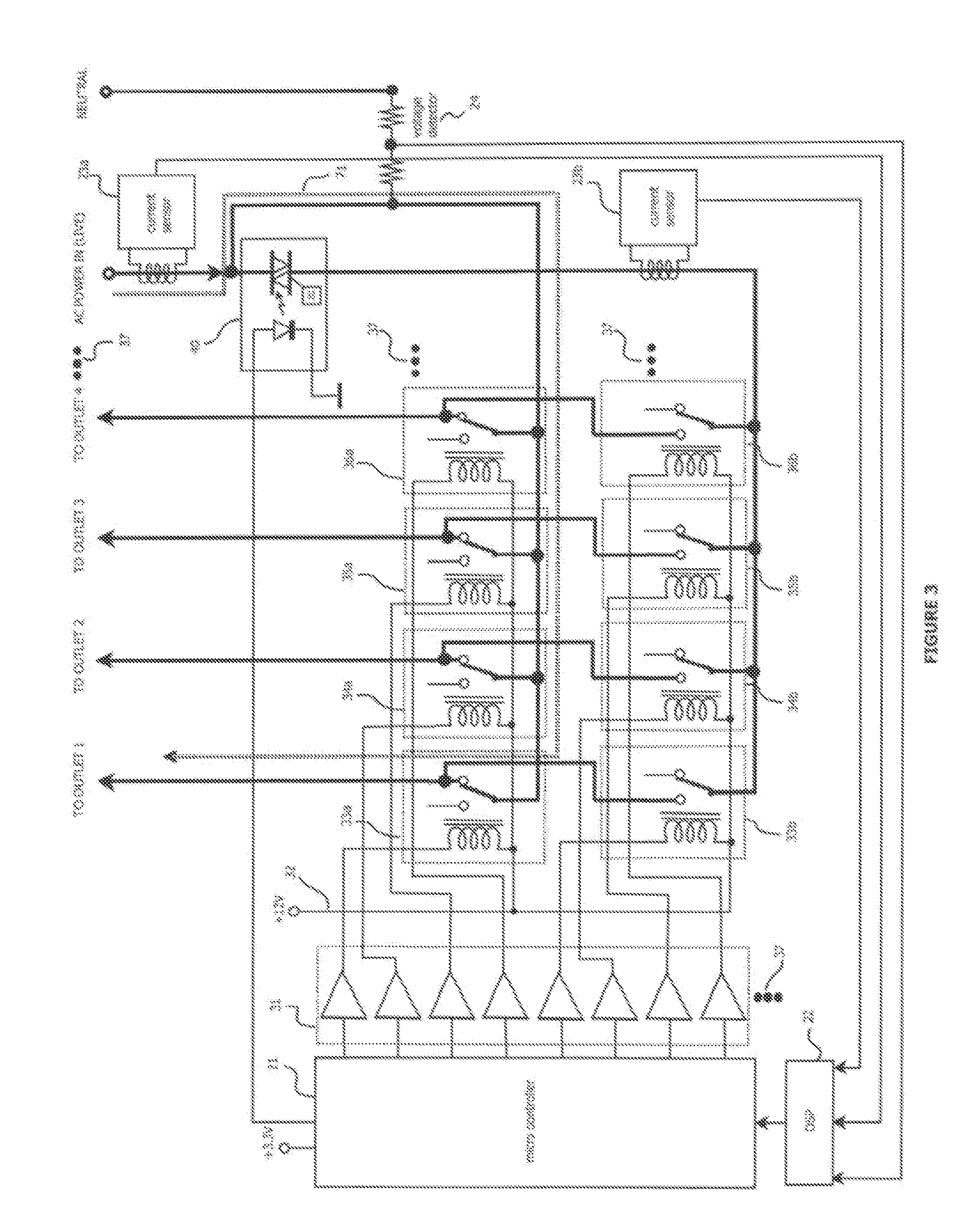
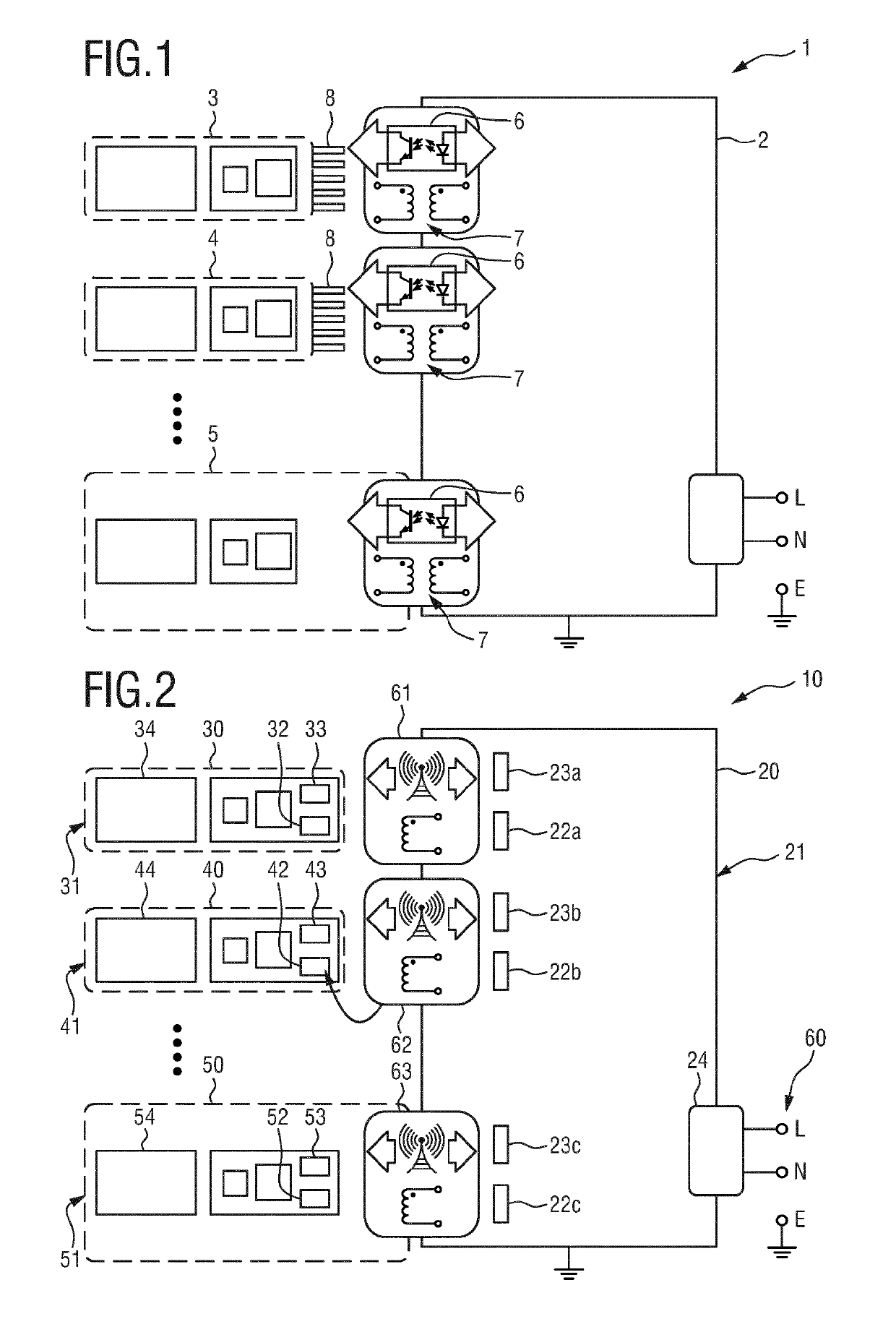
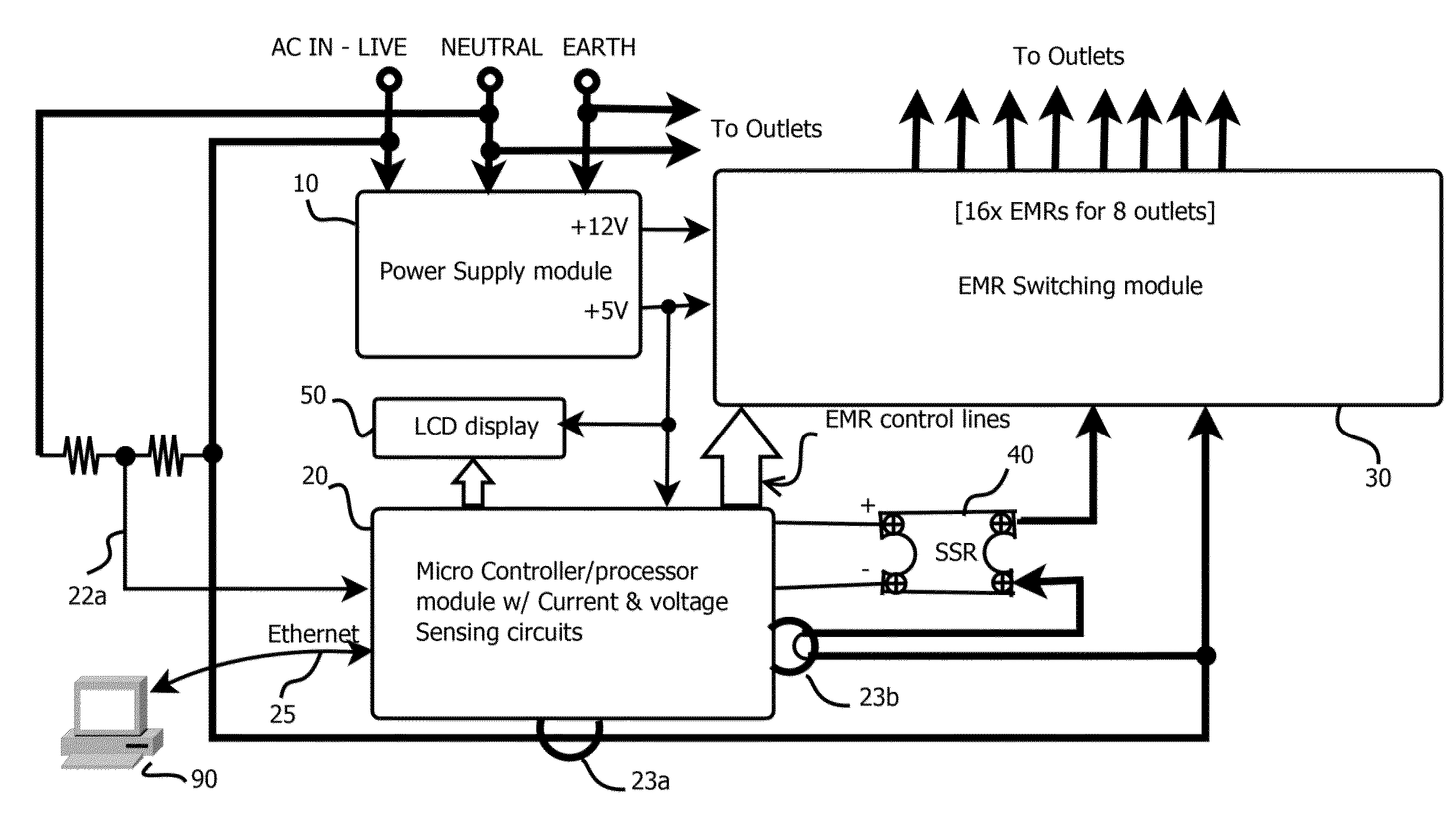
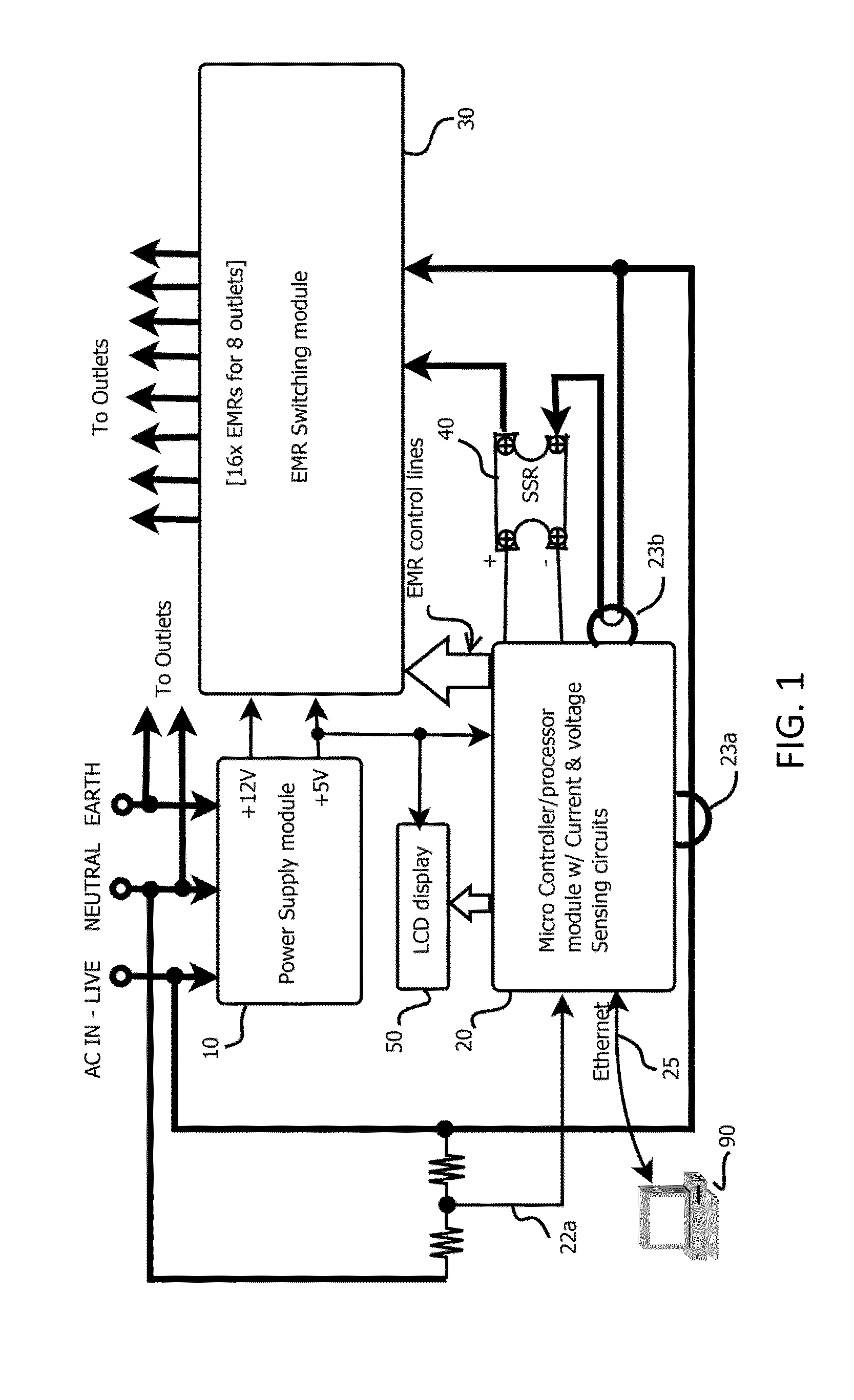
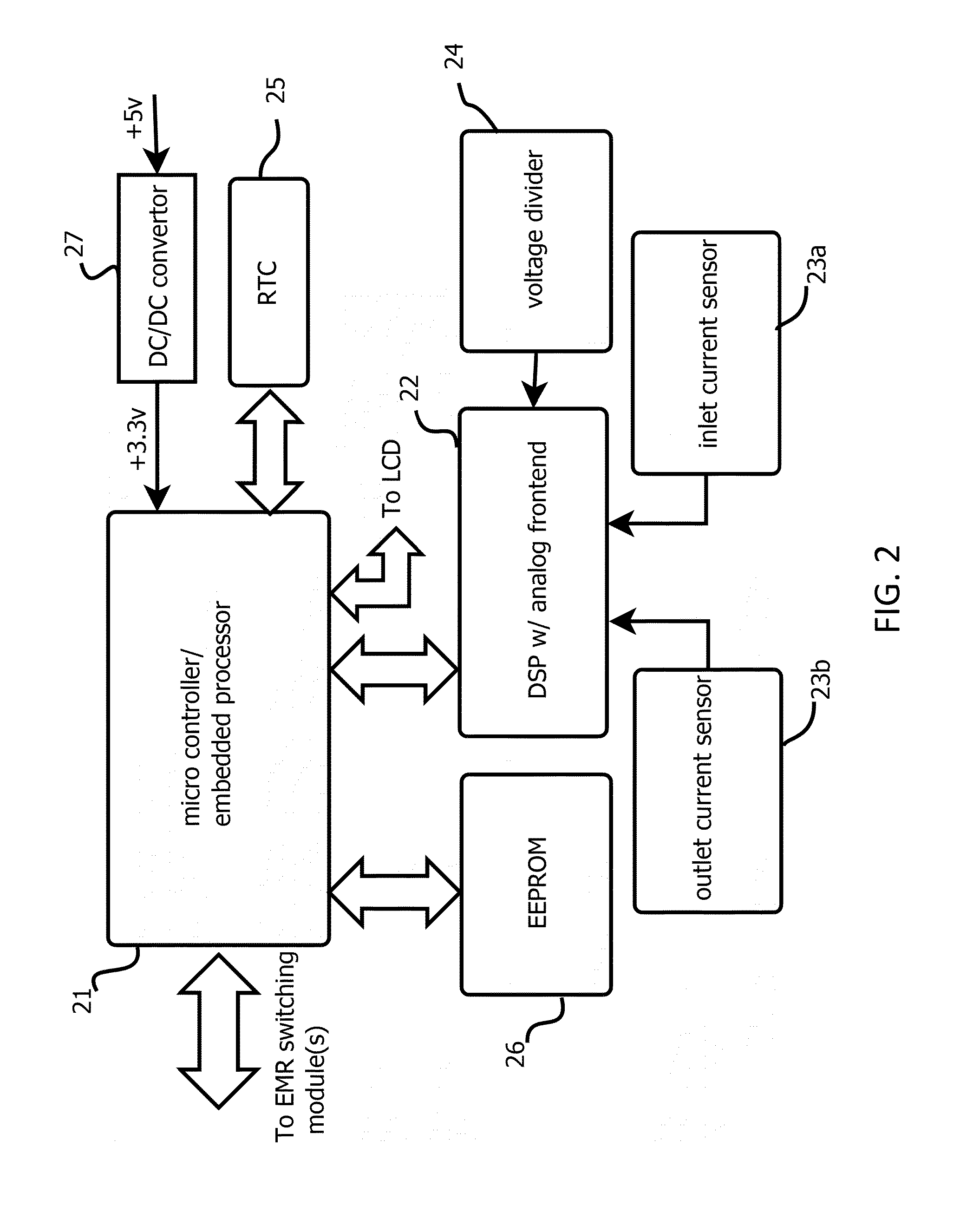
Reliable low-cost hybrid switch module for switched power distribution systems
ActiveUS20120092060A1Reliable and low costLittle powerThyristorElectronic switchingInternet serversDistribution power system
Disclosed are method and apparatus for implementing power distribution unit with a hybrid switching module. The apparatus comprises multiple outlets coupled to a hybrid switching module that switches on or off the plurality of outlets. The apparatus further comprises a single SSR for the hybrid switching module and two EMRs for an outlet and a controller that communicates with the hybrid switching module via digital line(s) to control power distribution. The apparatus comprises a display for displaying information related to the power outlets, two current detection circuitries for monitoring the total input current and an individual outlet, and a voltage detection circuitry for sensing voltages. The number of outlets may be scaled by using one or more hybrid switching module that share the single SSR. The apparatus further comprises an Internet server running thereon to interface with remote users to process the user's requests for the apparatus.
Owner:ECHOLA SYST
Ceramic Crack Inspection
InactiveUS20120235693A1Reliable and low-costLow operationResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial resistanceCeramicMaterials science
A method and apparatus for non-destructive inspection including detection, quantification, and location of a surface or subsurface crack in a body made of advanced technical ceramics. The method and apparatus can detect all cracks in a ceramic body, including microscopic cracks, with a high sensitivity, accuracy and reliability, by measuring changes in electrical resistances through a plurality pairs of electrodes affixed on surfaces of the ceramic body. The extent of the cracks can be quantified and expressed as numerical data, and the location of the cracks can be identified. An automated inspection process enables a convenient, real-time, cost-effective crack inspection.
Owner:FENG HONG
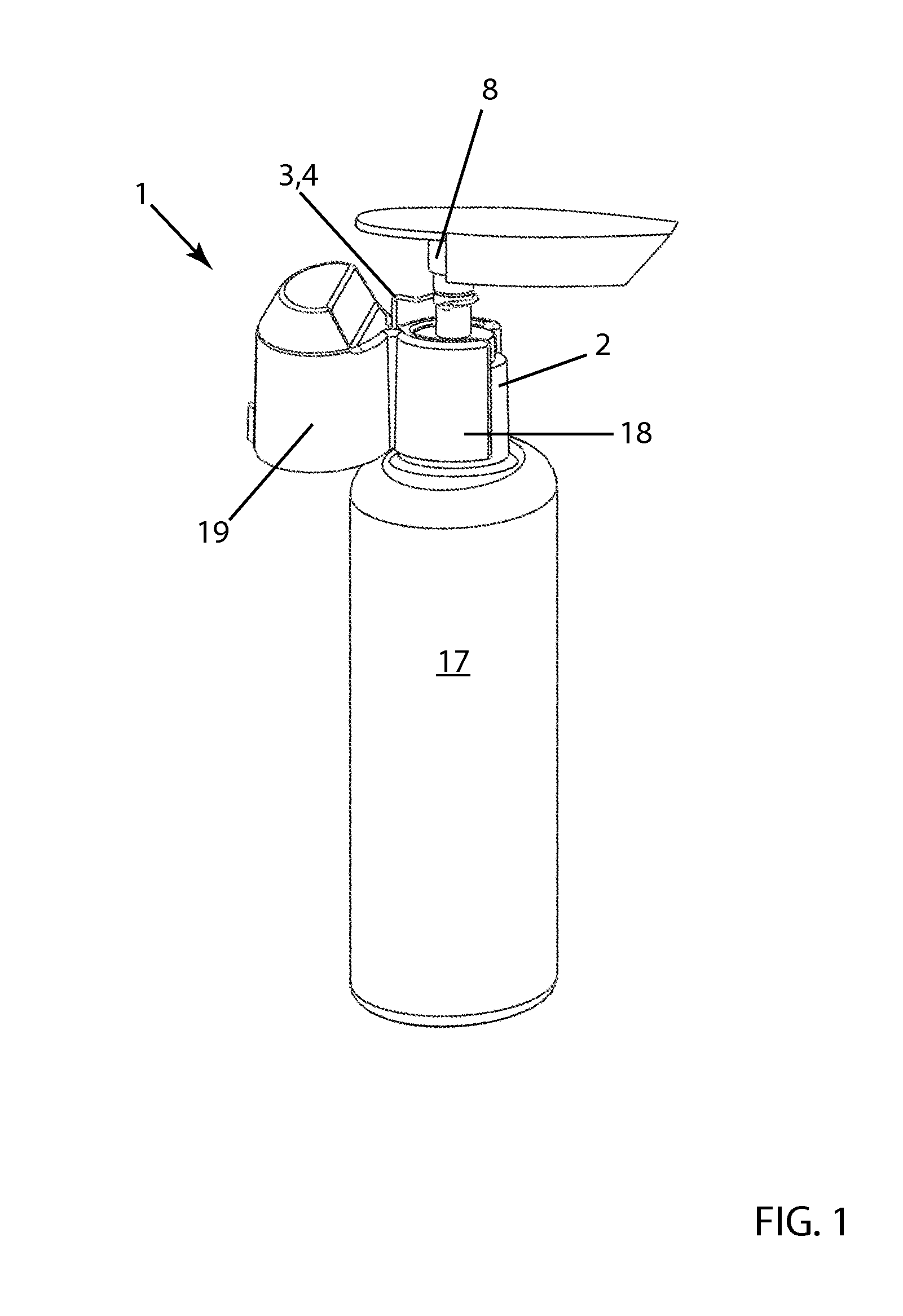
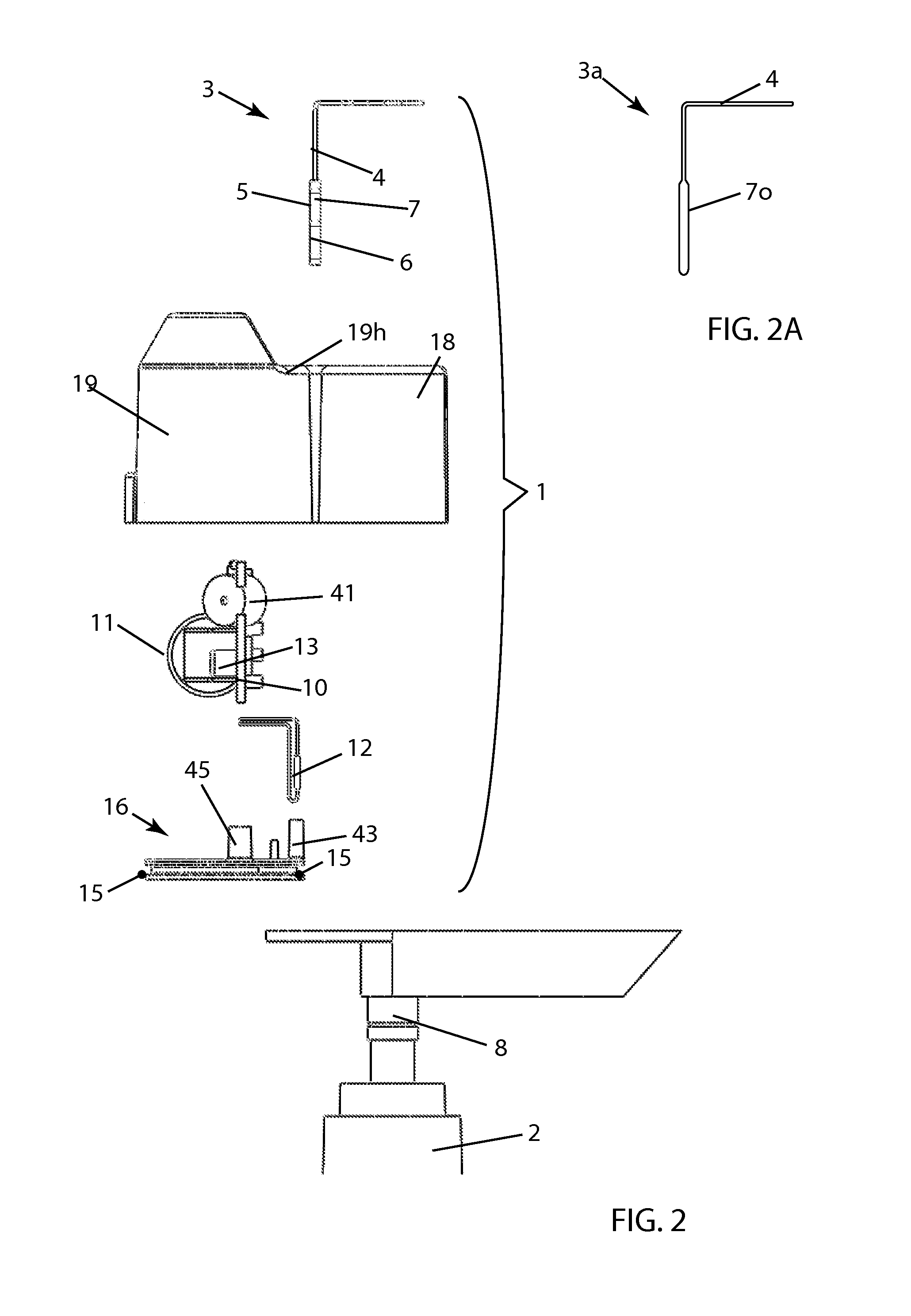
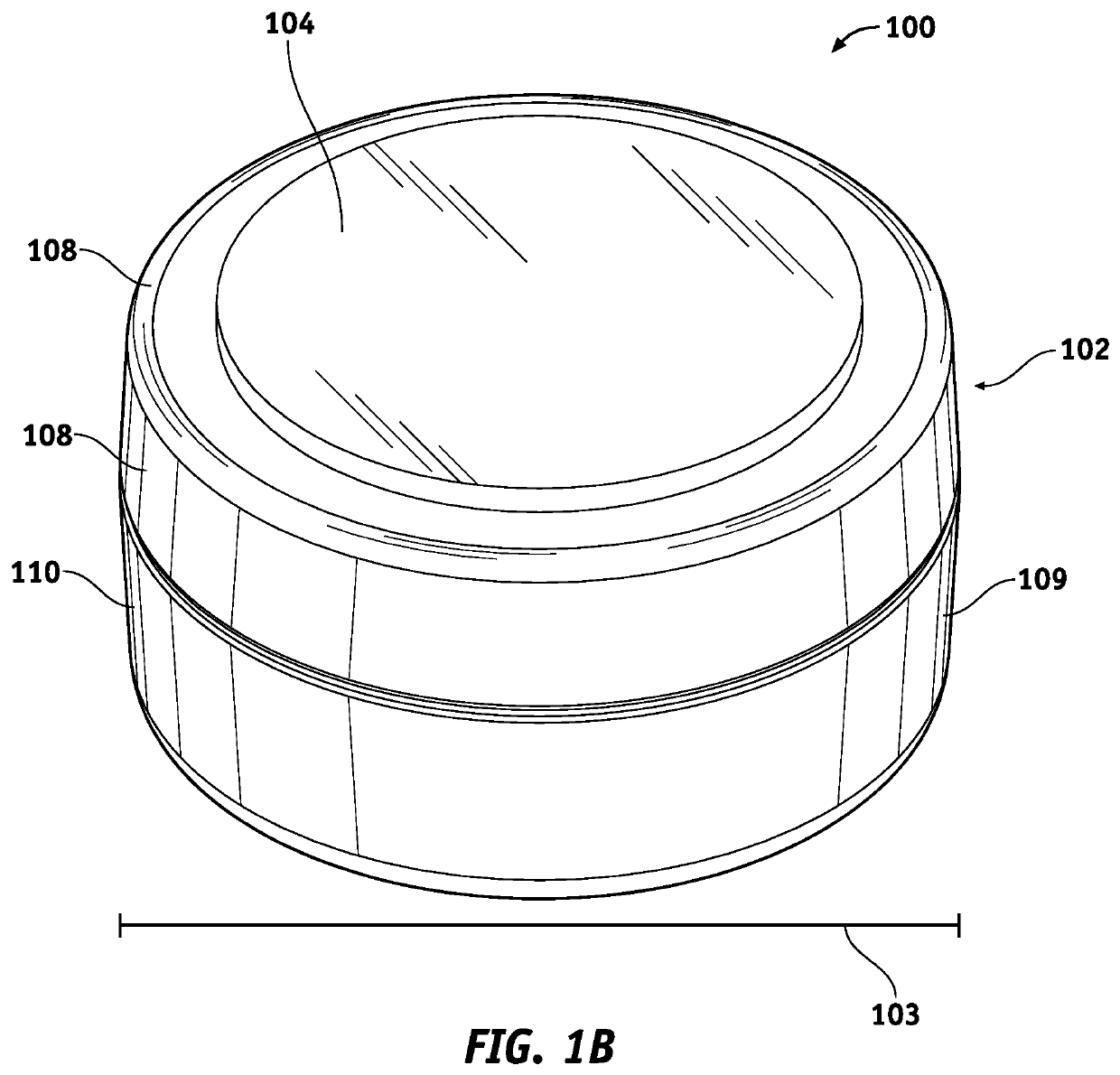
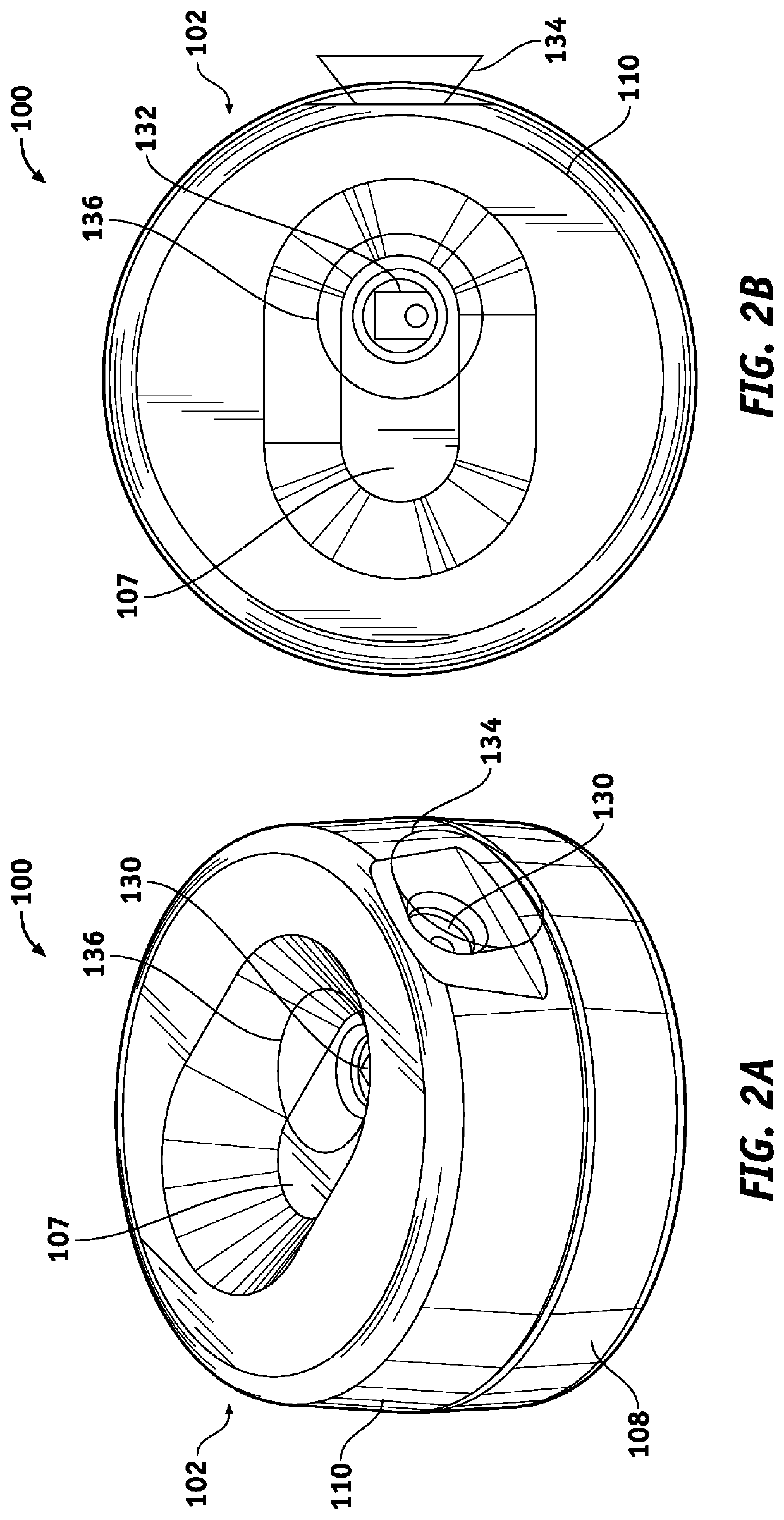
Actuator Sensor Apparatus for a Dispenser Bottle for Wireless Automatic Reporting of Dispenser Usage
InactiveUS20130099900A1Reliable and low-costGood adhesionSensing detailsHolders and dispensersEngineeringActuator
Actuation sensor apparatus configured to removably attach to a liquid dispenser, the apparatus comprising (a) an electronic circuit including a dispense sensor and a wireless transmitter and (b) a power supply for the electronic circuit, whereby, when dispenser actuation occurs, an identification code unique to the apparatus is wirelessly transmitted to a receiver. In a preferred embodiment, the dispense sensor is a magnetic sensor and the apparatus further includes an actuator arm having a magnet, and the actuator arm is configured to move with respect to the magnetic sensor during actuation.
Owner:MATRIX PROD DEV
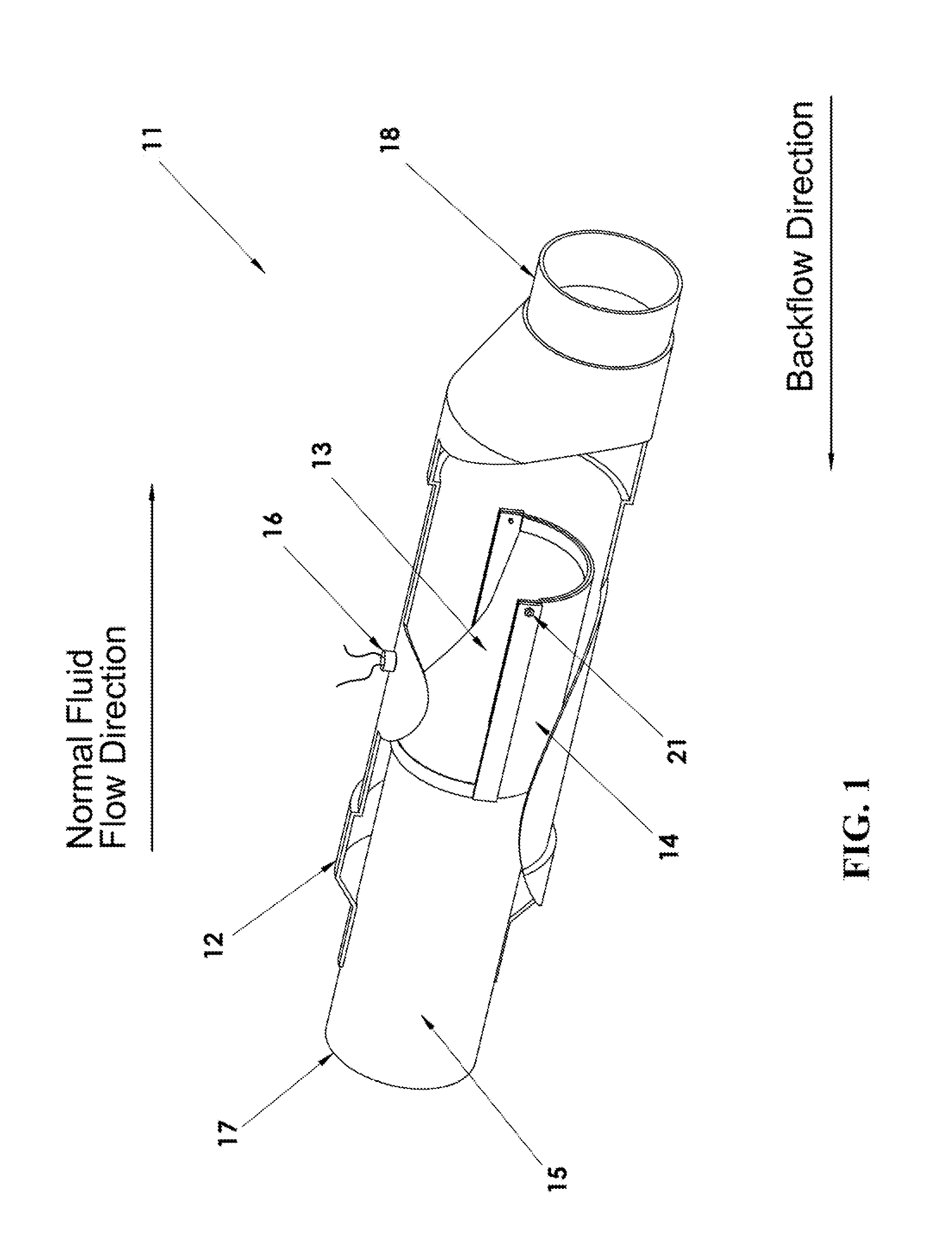
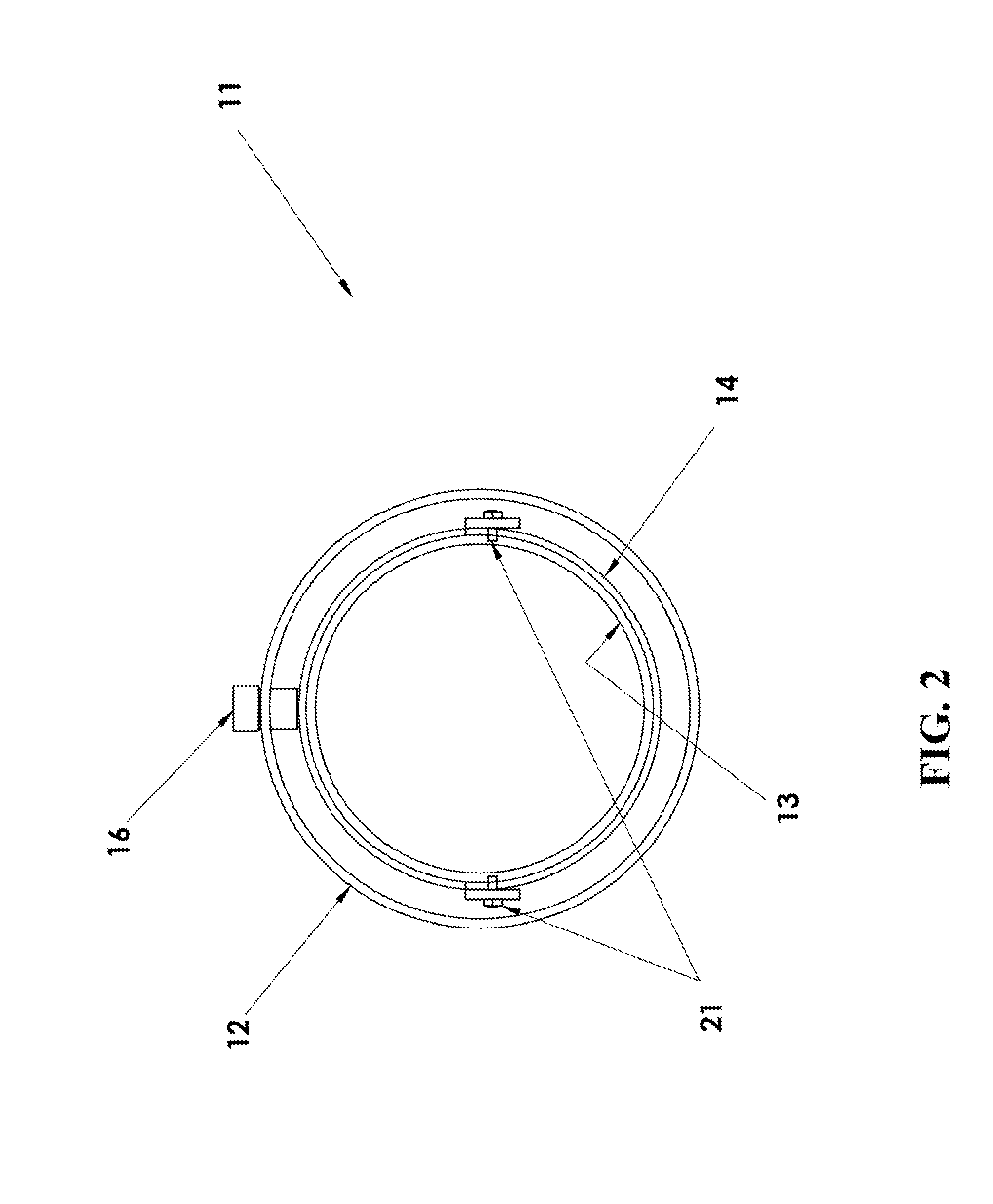
Back Flow Prevention System
InactiveUS20110132474A1Easy to cleanReliable and low-costOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheck valvesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system that prevents the backflow of fluid is disclosed. The system comprises a housing, two rubber flaps that are attached in such a way to create a one-way valve, and a water sensor. The flaps are anchored to the inside of the housing and open due to the force of fluid flowing in one direction. Fluid flowing in the opposite direction presses the ends of the flaps against each other, thus closing the valve and preventing water from backflowing through the system. A water sensor, mounted within the housing, is activated when a backflow fills the housing, thus providing an alarm to indicate a backflow event has occurred.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Infrared Detection and Imaging Device With No Moving Parts
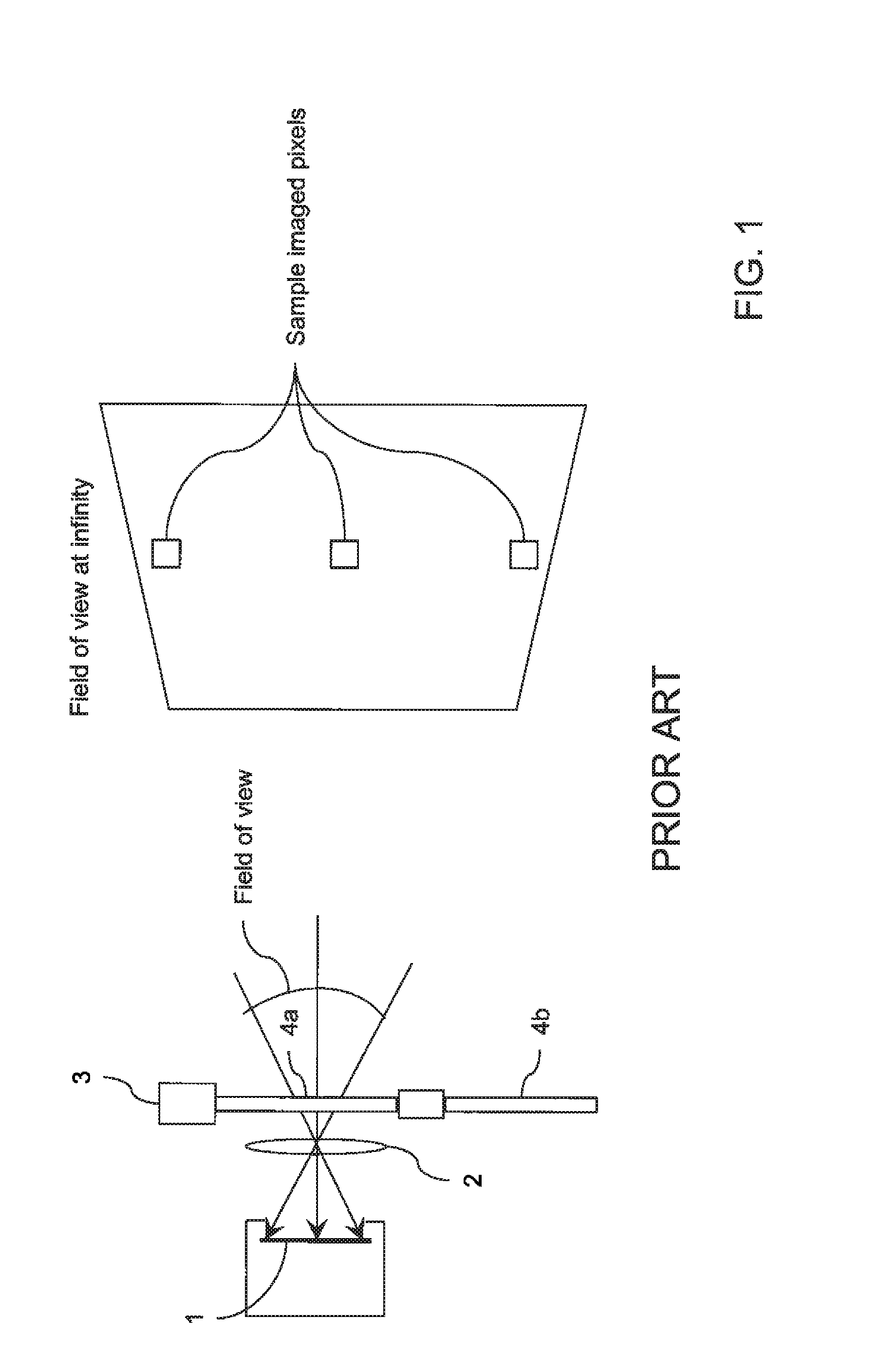
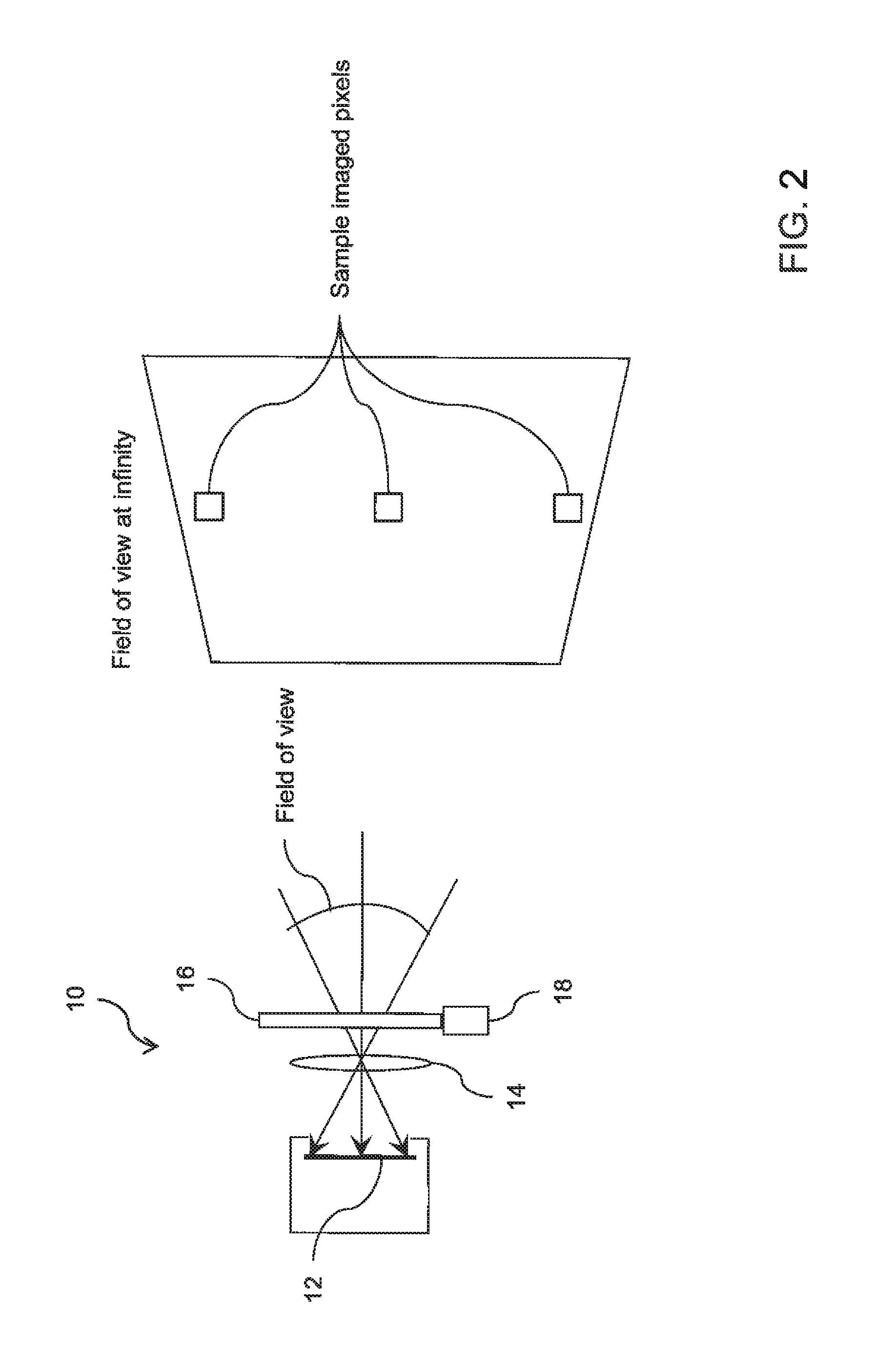
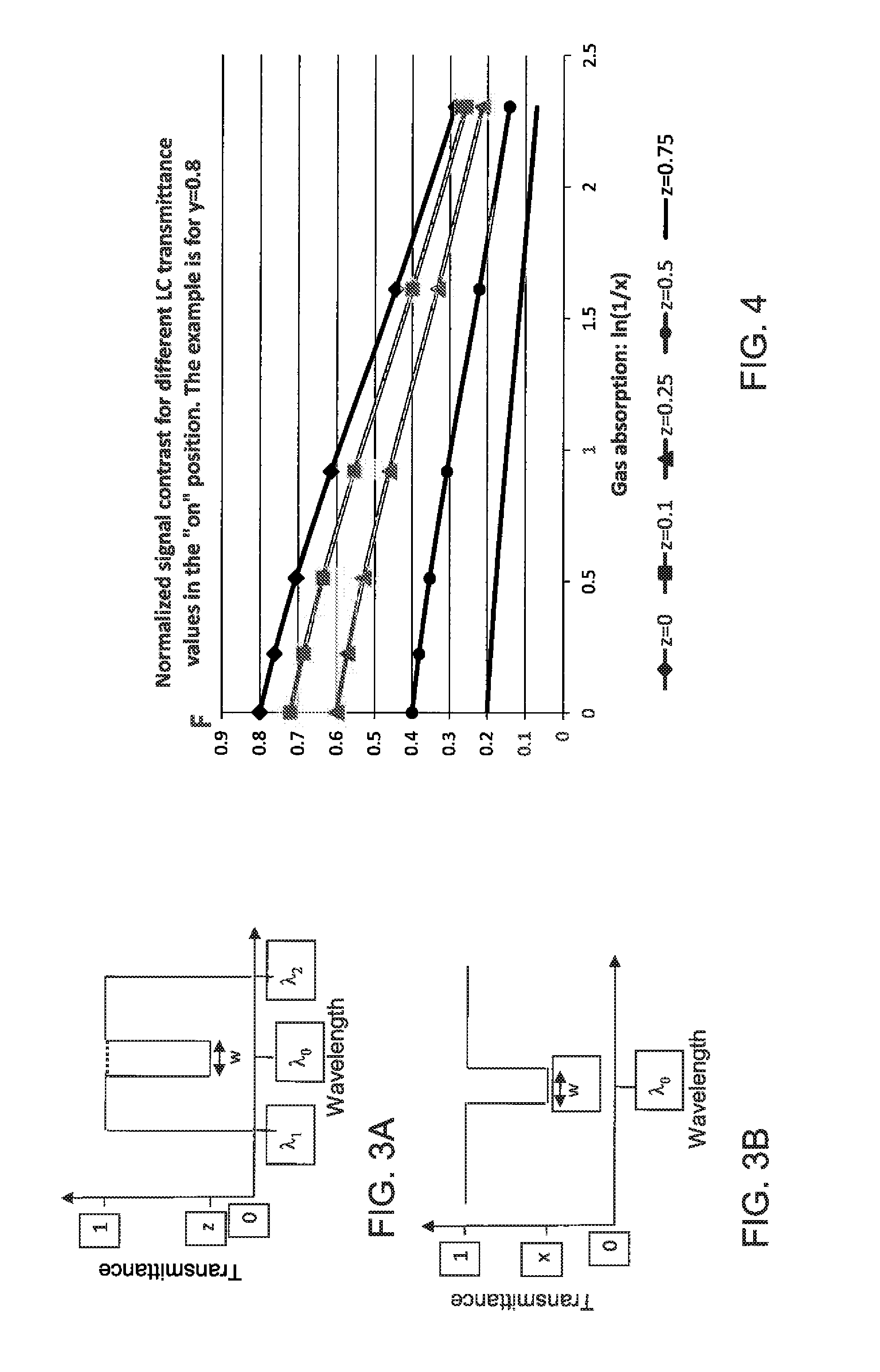
ActiveUS20160131576A1Reliable and low costTelevision system detailsColor/spectral properties measurementsMoving partsControl unit
A device images radiation from a scene. A detector is sensitive to the radiation in a first wavelength band. A lens forms an image of the scene on the detector. A filtering arrangement includes two sets of radiation absorbing molecules. A control unit switches the filtering arrangement between two states. In the first state, all of the radiation in the first wavelength band is transmitted to the detector. In the second state, the radiation in a second wavelength band within the first wavelength band is absorbed by the radiation absorbing molecules. The control unit synchronizes the switching of the filtering arrangement with the detector. Each pixel of the image formed on the detector includes two signals. The first signal includes information from the scene radiation in the first wavelength band. The second signal excludes information from the scene radiation absorbed by the filtering arrangement in the second wavelength band.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Circuit board and semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS20050258550A1Eliminate possibility in deformation and denaturation and breakdownReliable and low costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHigh frequency powerThermal expansion
There is provided a thinner high frequency power module structure having reduced the mounting area. An insulated board is provided with a composite metal board in which the Cu2O powder particles are dispersed into a matrix metal (Cu) (amount of addition of Cu2O: 20 vol %; thermal expansion coefficient: 10.0 ppm / ° C.; thermal conductivity: 280 W / m•K; thickness: 1 mm; size: 42.4×85 mm), a silicon nitride board (thermal expansion coefficient: 3.4 ppm / ° C.; thermal conductivity: 90 W / m•K; thickness: 0.3 mm; size: 30×50 mm) deposited with Ag-system bonding metal layer to one principal surface of the composite metal board, and a wiring metal board formed of copper or copper alloy provided to the other principal surface of the ceramics insulated board. For example, the bonding metal layer is adjusted in the thickness to 50 μm, while the wiring metal board is also adjusted in the thickness to 0.4 mm. In the integrated board of the wiring and heat radiating boards, the Ni plating layer (thickness: 6 μm, not illustrated) is formed with the non-electrolyte wet plating process to the surface metal layer of the wiring metal board and composite metal board. This Ni plating layer is formed to the wiring metal boards in order to attain the solder bondability to mount the semiconductor base material with the brazing method and to enhance the wire bondability of the wiring metal board. Moreover, this Ni plating layer effectively prevents denaturation of the internal side by shutting off from the external atmosphere.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Flexible metal stacked body
InactiveUS20050104214A1Improve thermal stabilityReliable and low-costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMaterials scienceMetal
A flexible metal stacked body includes: a metal layer; and a resin stacked body formed on the metal layer, in which the resin stacked body includes at least one thermosetting resin layer and at least one thermoplastic resin layer, one of the at least one thermosetting resin layer is provided adjacent to the metal layer, and the at least one thermosetting resin layer and the at least one thermoplastic resin layer are stacked alternately.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
Polishing slurry and chemical mechanical planarization method using the same
ActiveUS20130178064A1Reliable and low costLow costOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical-mechanical planarizationMaterials science
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Connector and device for wireless transmission of data and power
ActiveUS20180262236A1Reliable and low-costMinimal crosstalkCircuit authenticationNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsPower modeWireless transmission
The present invention relates to a connector for wireless transmission of data and / or power between separate devices comprising such a connector of a system, in particular of a patient monitoring system, said separate devices comprising such a connector. The connector comprises a data transmission unit (271) arranged for transmitting data to and / or receiving data from another device of the system having a counterpart connector, a magnetic coupling unit (272) for transmitting power to and / or receiving power from another device of the system having a counterpart connector by use of inductive coupling, a detection unit (273) for detecting the strength of magnetic coupling between the magnetic coupling unit and a magnetic coupling unit of a counterpart connector, and a control unit (274) for switching the data transmission unit into a low-power mode and / or for enabling the magnetic coupling unit, if the detected magnetic coupling is above a first threshold and / or its increase is above a second threshold, and for switching the data transmission unit into a high-power mode and / or for disabling the magnetic coupling unit, if the detected magnetic coupling is below a third threshold and / or its decrease is above a fourth threshold.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Vacuum gripper
Owner:ZIMMERMANN & SCHILP HANDHABUNGSTECHN
Switch mechanism
InactiveUS20050016962A1Effective dampingMaintain positionSpringsContact vibration/shock dampingControl theoryVertical orientation
The aim of the invention is to be able to arrange a switch mechanism comprising a hydraulic damping element (7) in two different assembly positions on a switch. To this end, the hydraulic damping element (7) must demonstrate a full functional capacity in both assembly positions. In order to ensure the same functional capacity in a first, for example, vertical assembly position and in a second, for example, horizontal assembly position, the damping element (7) is arranged in a position which deviates by 45° from the vertical.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Connector and device for wireless transmission of data and power
ActiveUS10511349B2Reliable and low-costMinimal crosstalkCircuit authenticationNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsPower modeWireless transmission
The present invention relates to a connector for wireless transmission of data and / or power between separate devices comprising such a connector of a system, in particular of a patient monitoring system, said separate devices comprising such a connector. The connector comprises a data transmission unit (271) arranged for transmitting data to and / or receiving data from another device of the system having a counterpart connector, a magnetic coupling unit (272) for transmitting power to and / or receiving power from another device of the system having a counterpart connector by use of inductive coupling, a detection unit (273) for detecting the strength of magnetic coupling between the magnetic coupling unit and a magnetic coupling unit of a counterpart connector, and a control unit (274) for switching the data transmission unit into a low-power mode and / or for enabling the magnetic coupling unit, if the detected magnetic coupling is above a first threshold and / or its increase is above a second threshold, and for switching the data transmission unit into a high-power mode and / or for disabling the magnetic coupling unit, if the detected magnetic coupling is below a third threshold and / or its decrease is above a fourth threshold.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
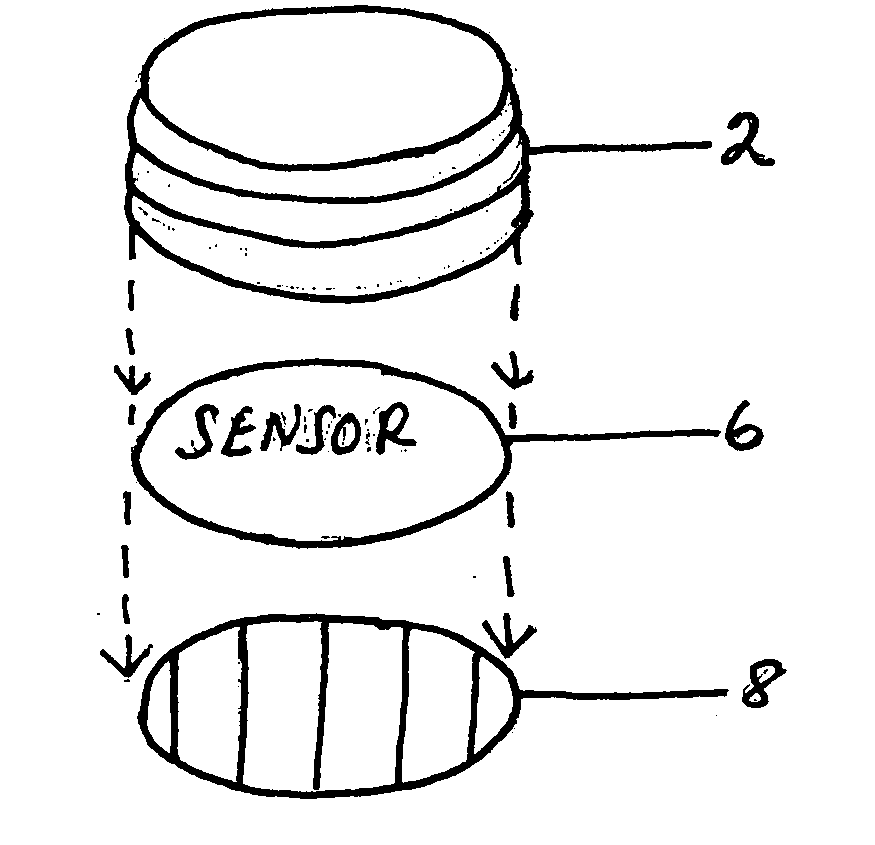
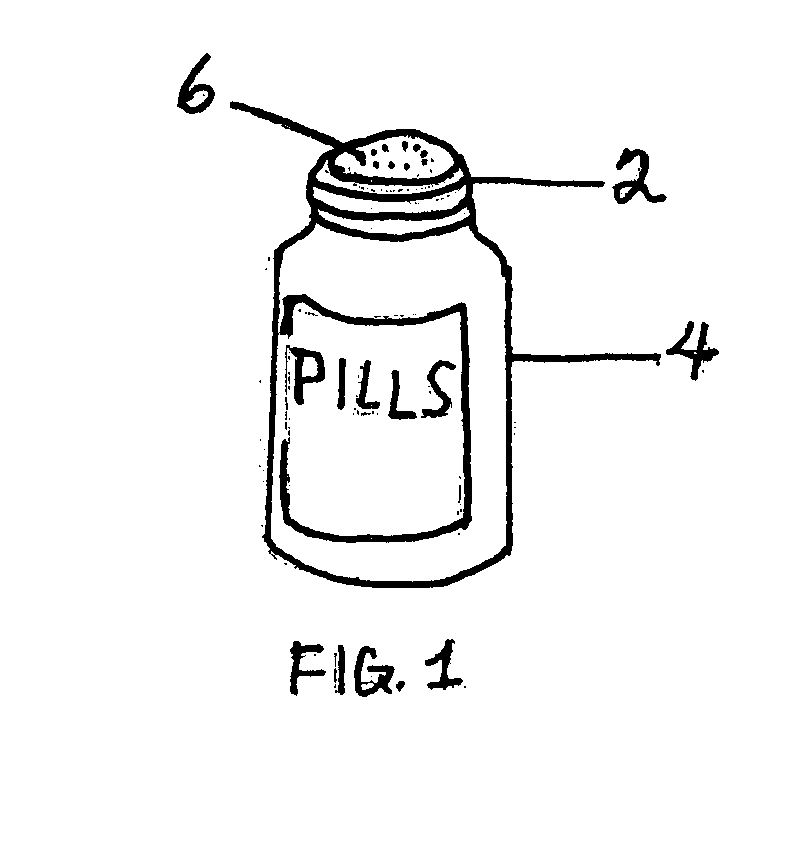
Device for tracking medication adherence
ActiveUS10957436B1Reliable and low-costDrug and medicationsPharmaceutical containersData packMedication adherence
A medication adherence tracking device is configured for being attached to a cap of a conventional medication container. The tracking device includes an adhesive layer for attaching the device to the cap. The device also includes an infrared proximity sensor for detecting an amount of light that is reflected by a wall surface and / or a bottom surface of the medication container. A transmitter of the tracking device transmits adherence data to an external computing device, wherein the adherence data comprises a timestamp identifying when the cap was removed from the container. Reflected light data obtained by the sensor is sent to a processor, and the processor uses the data to determine whether the cap has been removed from the container. When the cap is removed from the container, the processor generates the timestamp.
Owner:PATCHTEK
Container cap for assuring quality
InactiveUS20080184927A1Low costReliable and low costThermometer detailsThermometers using mean/integrated valuesBiomedical engineering
A cap for a container that holds pharmaceutical material, the cap comprising a means of detecting heat and humidity.
Owner:PHAM PAUL PHONG ANH +1
Vehicle automatic transmission axle assembly
ActiveUS20160200193A1Improve vehicle performanceLow costElectric propulsion mountingToothed gearingsAutomatic transmissionGear train
An automobile automatic transmission axle assembly: A power input shaft extends into a transmission compartment; the power input shaft in the transmission compartment is provided with a transmission mechanism; the transmission mechanism comprises a transmission sliding sleeve assembly, modified isolators, gear-position sun gears, planet gears, a planet carrier and gear rings; the gear-position sun gears, planet gears and gear rings constitute a mechanism having a fixed transmission ratio; the transmission sliding sleeve assembly fits the modified isolators. The automobile automatic transmission axle assembly realizes an integrated automatic transmission axle for electric vehicle.
Owner:LIU PEISHENG
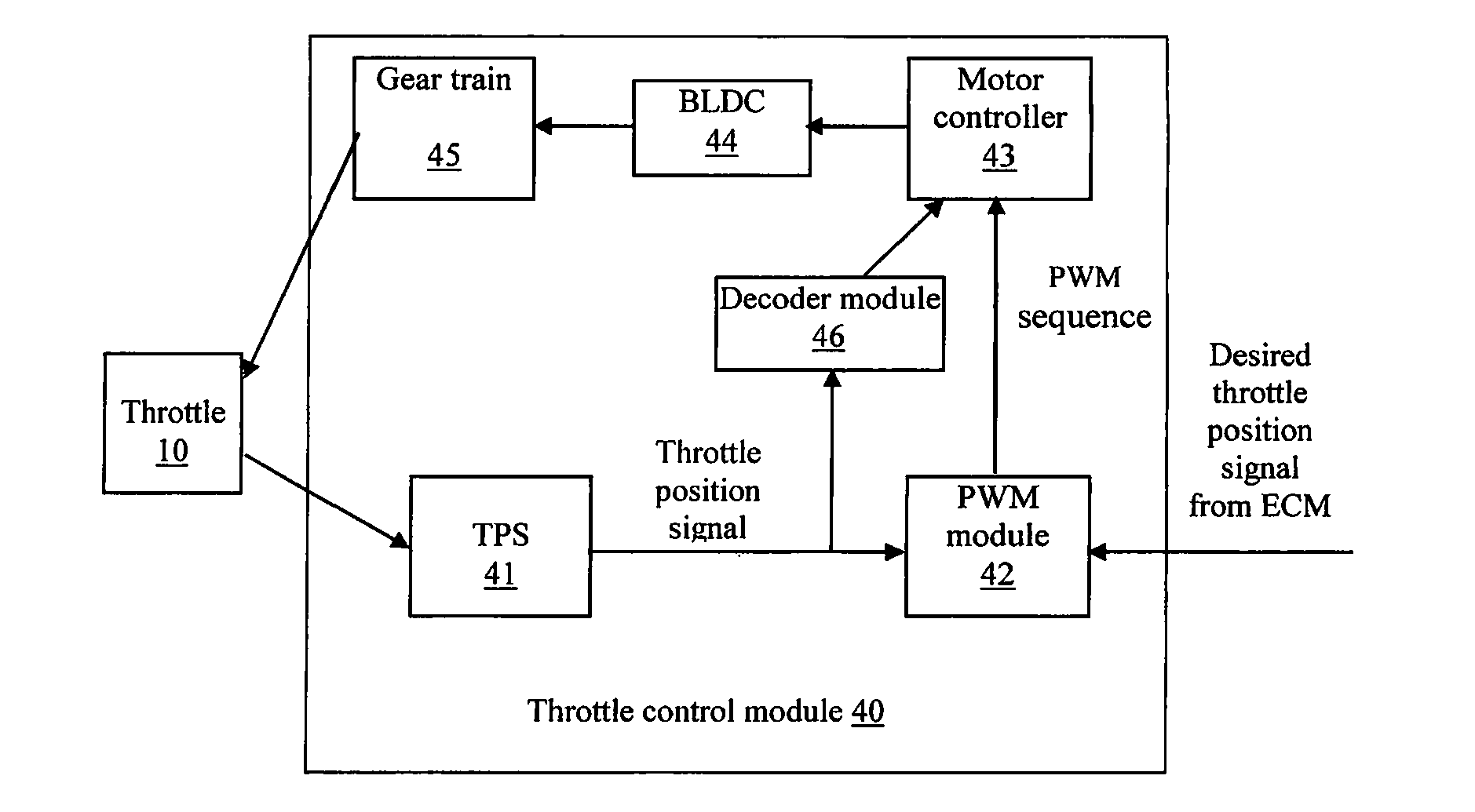
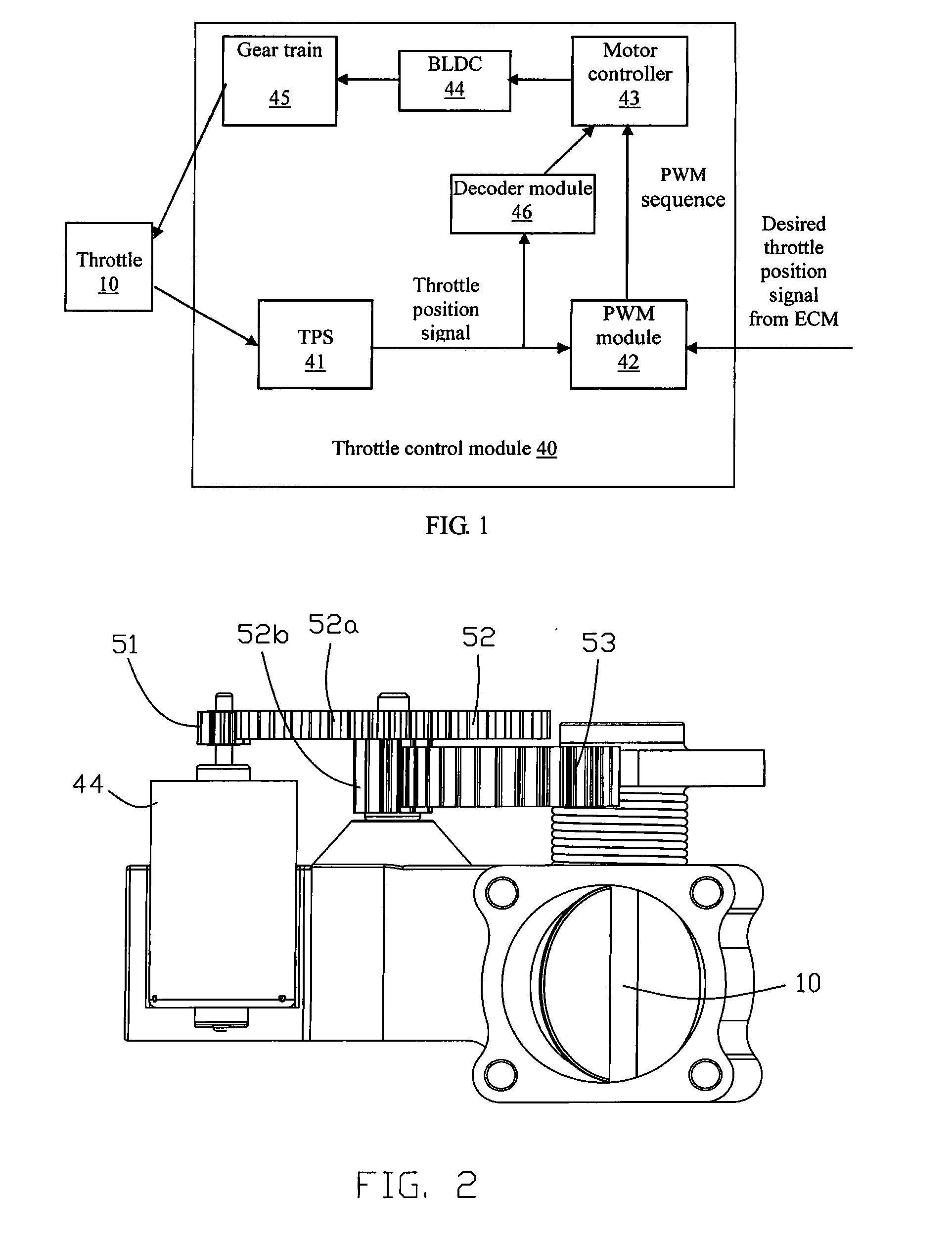
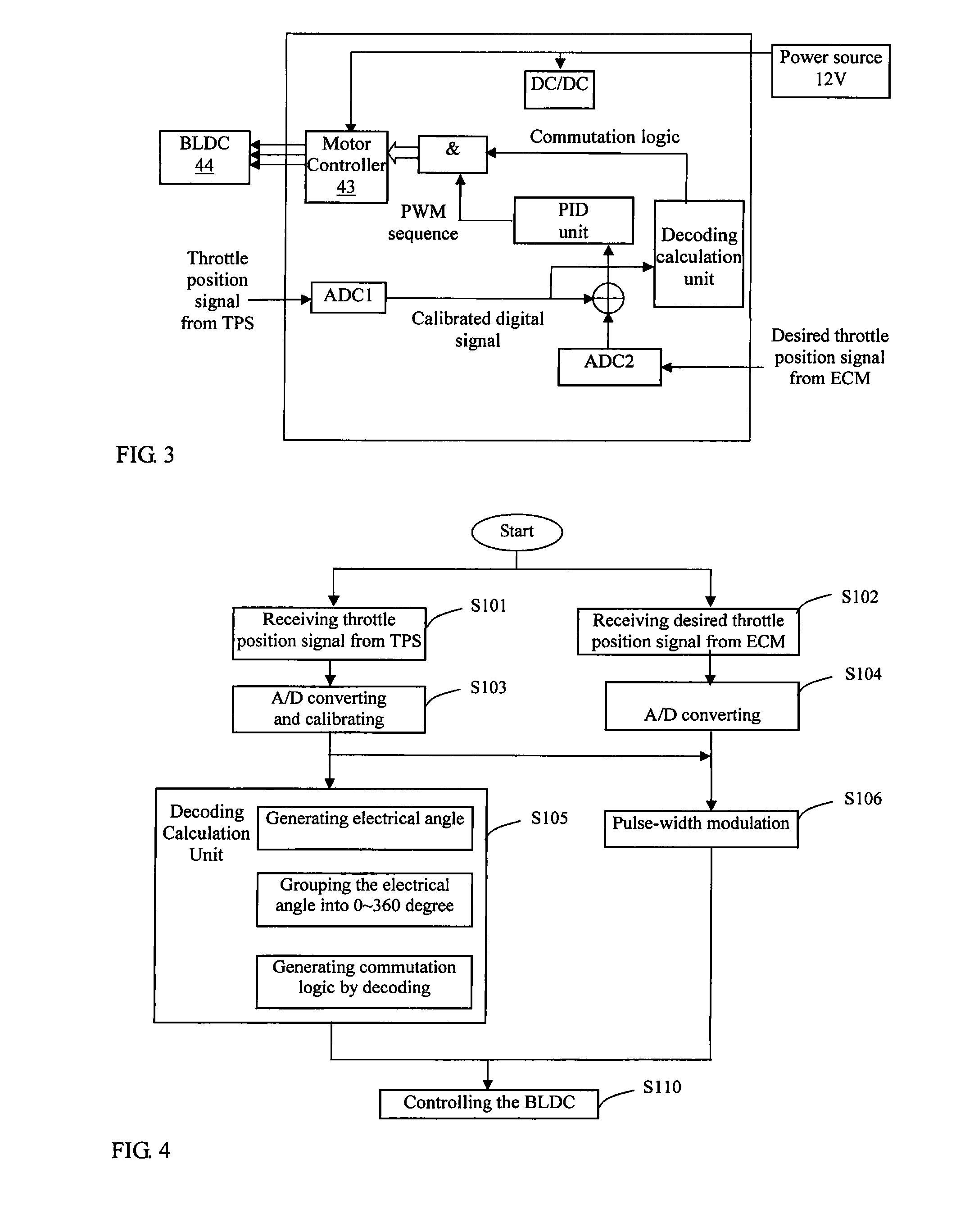
Throttle control module
ActiveUS20100212628A1Reliable and low-costReliable and reliableAnalogue computers for vehiclesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesThrottle controlMotor controller
A throttle control module for controlling a throttle, comprises: a BLDC motor; a gear train connecting the motor to the throttle; and a throttle position sensor. A PWM module is connected to the throttle position sensor and generates a pulse-width modulation sequence according to the signal from the throttle position sensor and a desired throttle position signal. A decoder module generates commutation logic for the motor based on the signal from the throttle position sensor. A motor controller controls commutation of the motor according to the pulse-width modulation sequence and the commutation logic.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
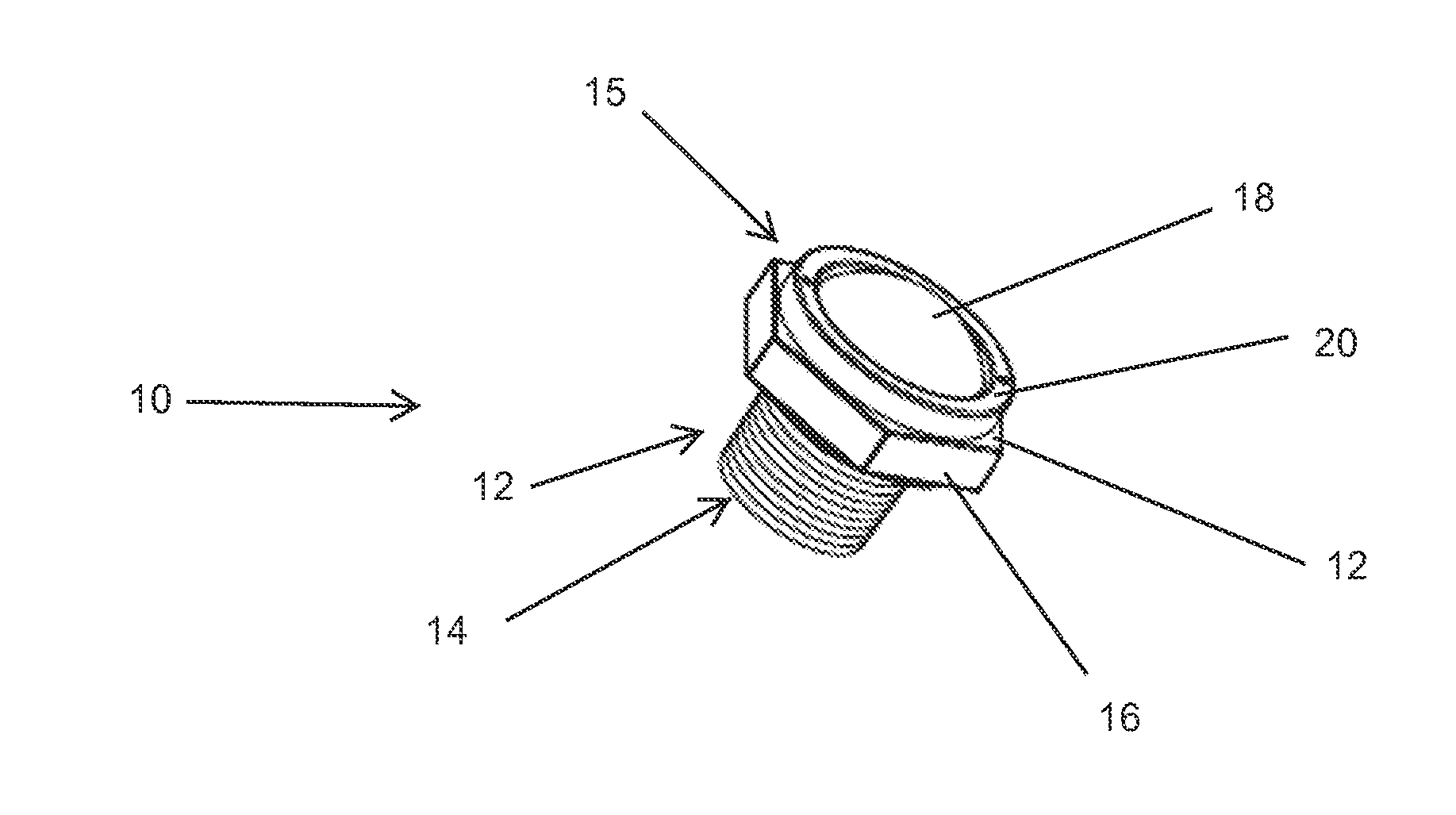
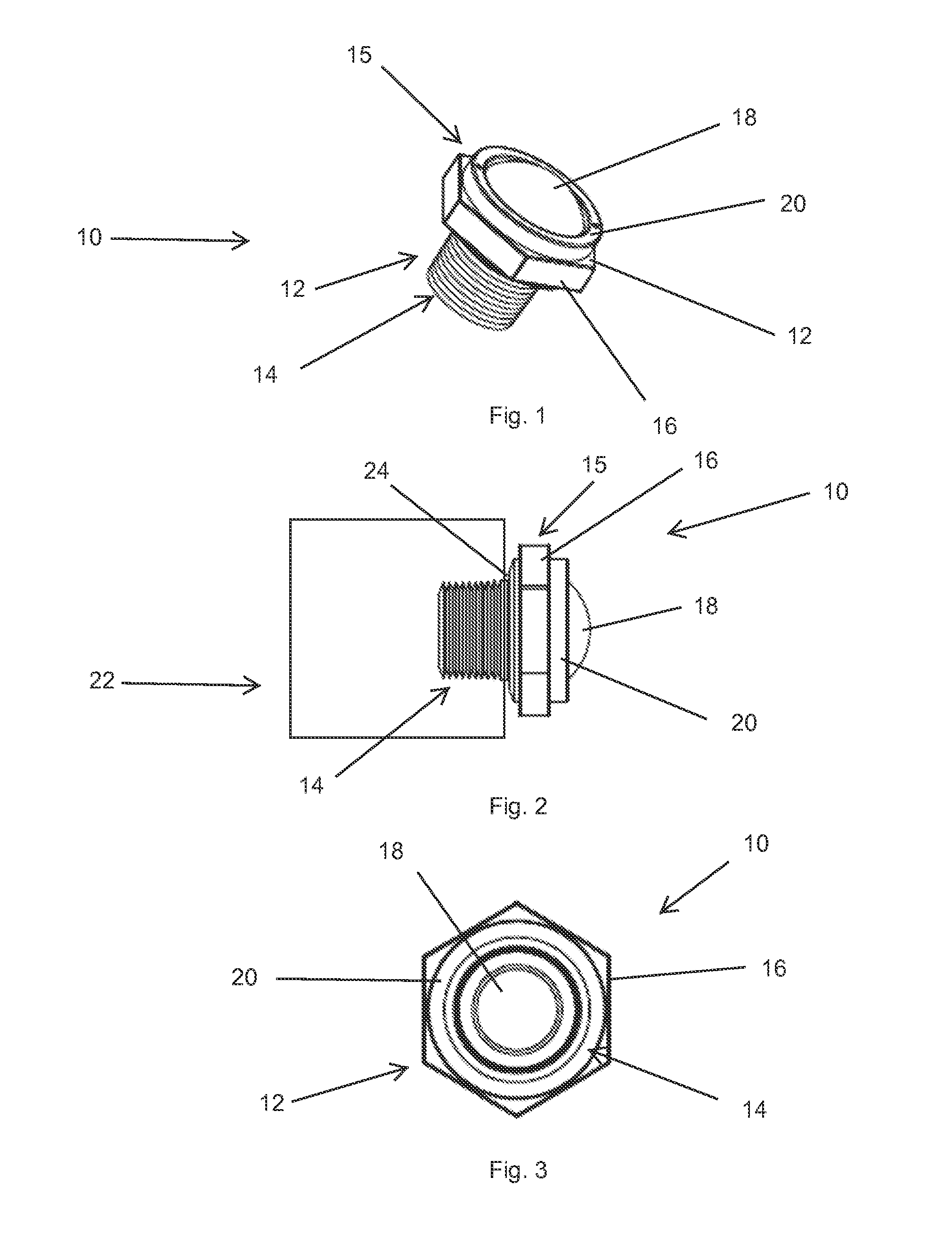
Transformer hydrogen indicator
ActiveUS8999723B2Quick testReliable and low costAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationHydrogenTransformer
A reliable, low cost device for determining when dangerous levels of hydrogen gas have been generated in a transformer is disclosed. The hydrogen indicator is defined by a module assembly that threads into either the headspace or into the oil-filled body of a transformer. The module has an open interior that contains a film that incorporates a hydrogen-sensitive chemochromic indicator. The indicator film is visible through a lens. When the film has been exposed to hydrogen, chemical changes in the chemochromic indicator cause the film to change color—the color change is immediately visible through the lens.
Owner:SERVERON CORP
Vacuum gripper
Owner:ZIMMERMANN & SCHILP HANDHABUNGSTECHN
Infrared detection and imaging device with no moving parts
ActiveUS9581543B2Reliable and low costTelevision system detailsColor/spectral properties measurementsCamera lensWavelength
A device images radiation from a scene. A detector is sensitive to the radiation in a first wavelength band. A lens forms an image of the scene on the detector. A filtering arrangement includes two sets of radiation absorbing molecules. A control unit switches the filtering arrangement between two states. In the first state, all of the radiation in the first wavelength band is transmitted to the detector. In the second state, the radiation in a second wavelength band within the first wavelength band is absorbed by the radiation absorbing molecules. The control unit synchronizes the switching of the filtering arrangement with the detector. Each pixel of the image formed on the detector includes two signals. The first signal includes information from the scene radiation in the first wavelength band. The second signal excludes information from the scene radiation absorbed by the filtering arrangement in the second wavelength band.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Reliable low-cost hybrid switch module for switched power distribution systems
ActiveUS8928184B2Reliable and low costLittle powerThyristorBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsControl powerDisplay device
Disclosed are method and apparatus for implementing power distribution unit with a hybrid switching module. The apparatus comprises multiple outlets coupled to a hybrid switching module that switches on or off the plurality of outlets. The apparatus further comprises a single SSR for the hybrid switching module and two EMRs for an outlet and a controller that communicates with the hybrid switching module via digital line(s) to control power distribution. The apparatus comprises a display for displaying information related to the power outlets, two current detection circuitries for monitoring the total input current and an individual outlet, and a voltage detection circuitry for sensing voltages. The number of outlets may be scaled by using one or more hybrid switching module that share the single SSR. The apparatus further comprises a web server running thereon to interface with remote users to process the user's requests for the apparatus.
Owner:ECHOLA SYST
Sliding contact assembly
InactiveUS20110297429A1Reliable and low costIncrease contact surfaceElectrically conductive connectionsPrinted circuit manufactureContact padContact element
A sliding contact assembly includes a printed circuit board having a substrate on which is arranged at least one contact pad. The at least one contact pad is made of several layers including a thin external layer essentially made of gold. The gold layer is deposited on the at least one contact pad through a gold flash type process. The assembly also includes a movable contact element including a support member. The support member has a contact surface provided with a protective coating and the contact surface is biased against the said contact pad when the movable contact element is moved in relation to the contact pad. The protective coating includes a palladium alloy layer. Methods to manufacture a sliding contact assembly are also presented.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
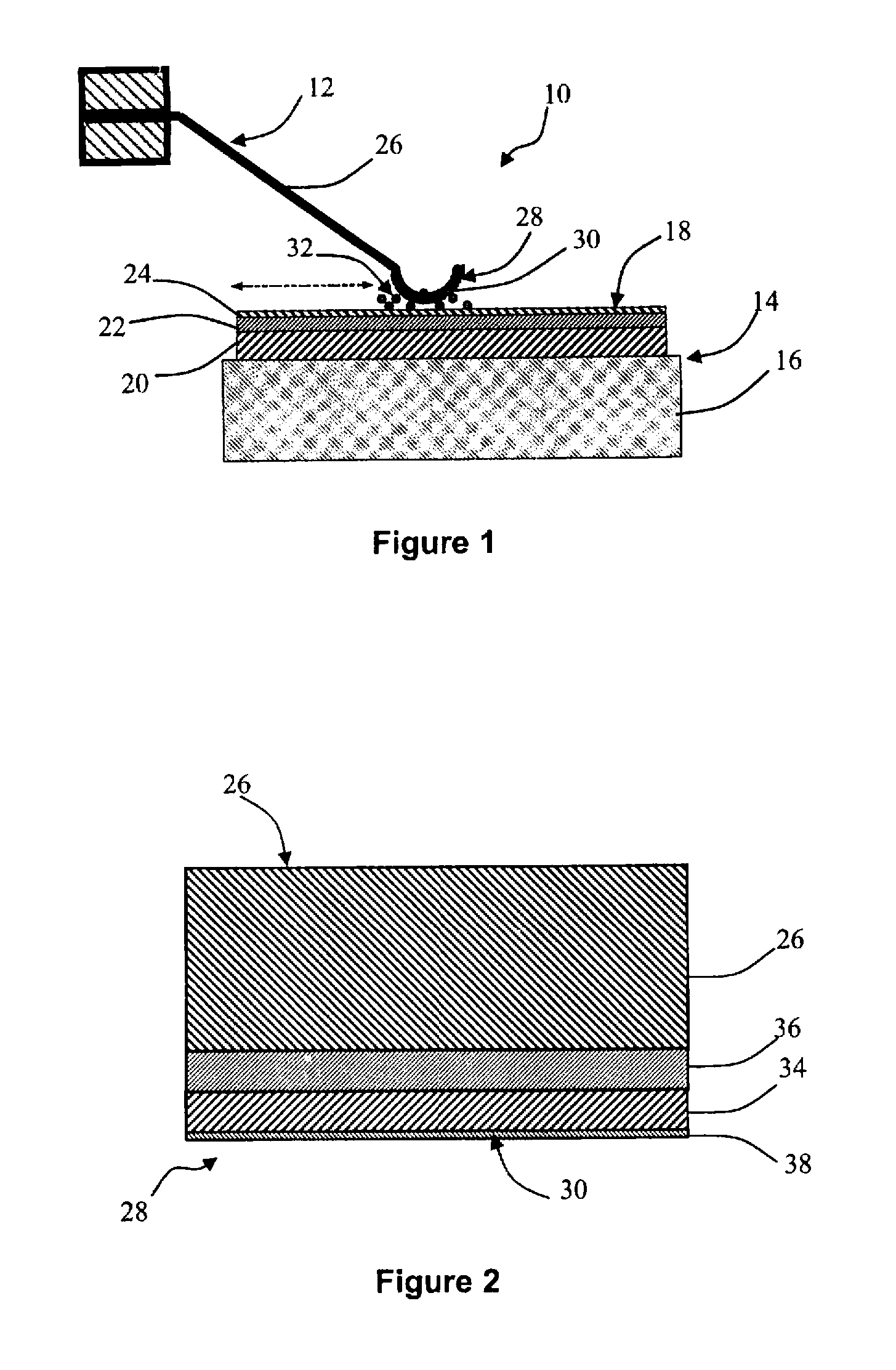
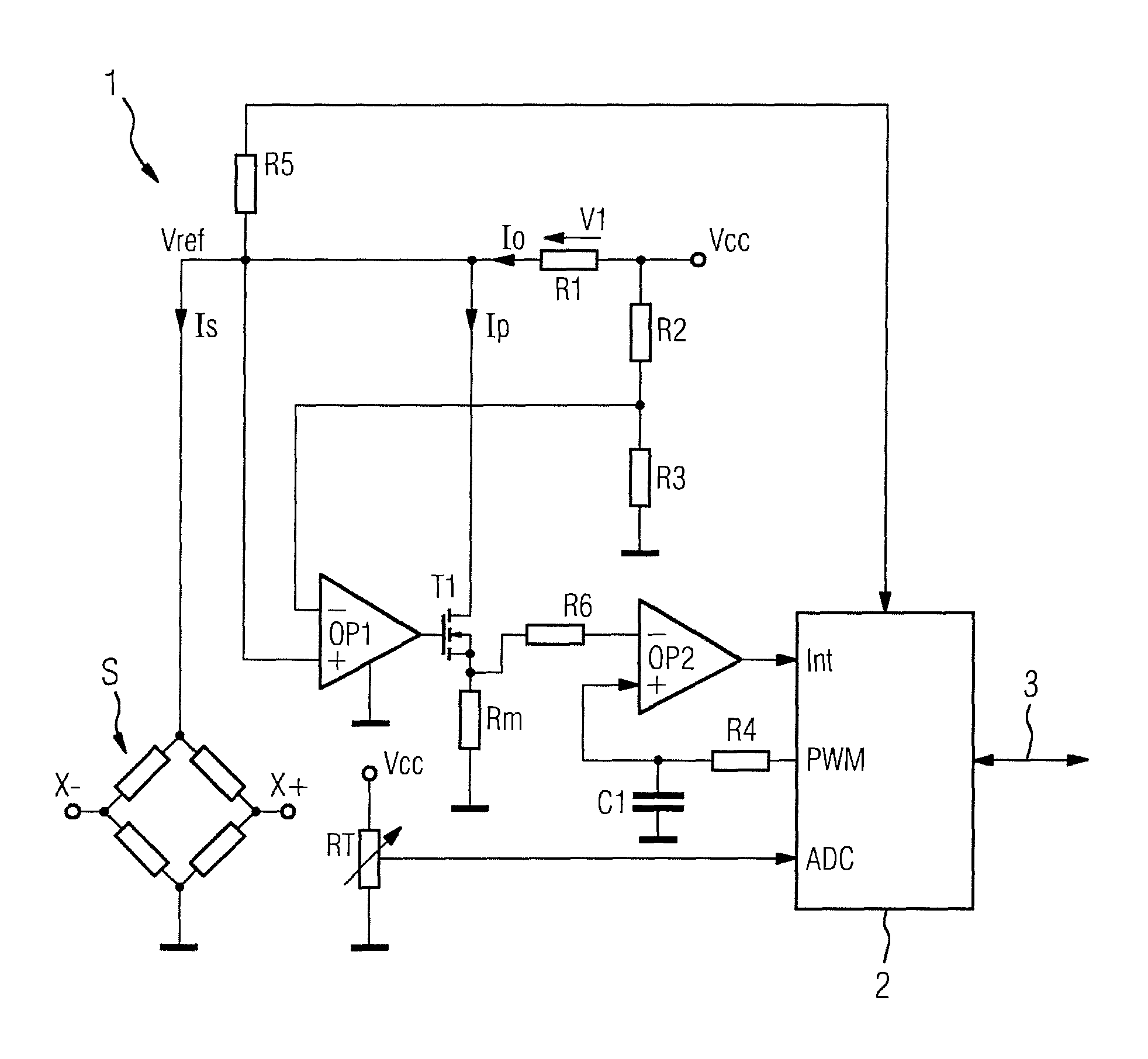
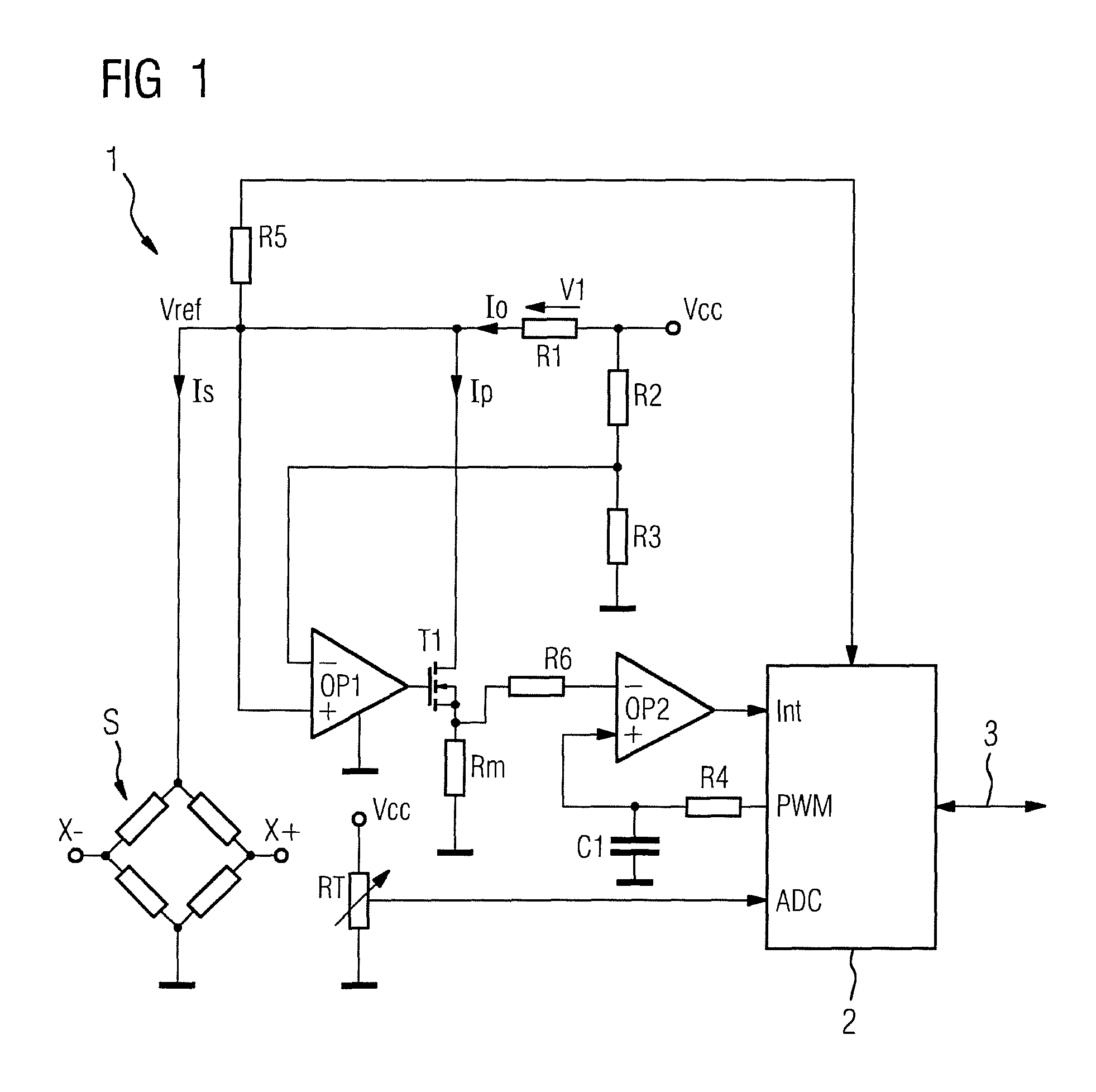
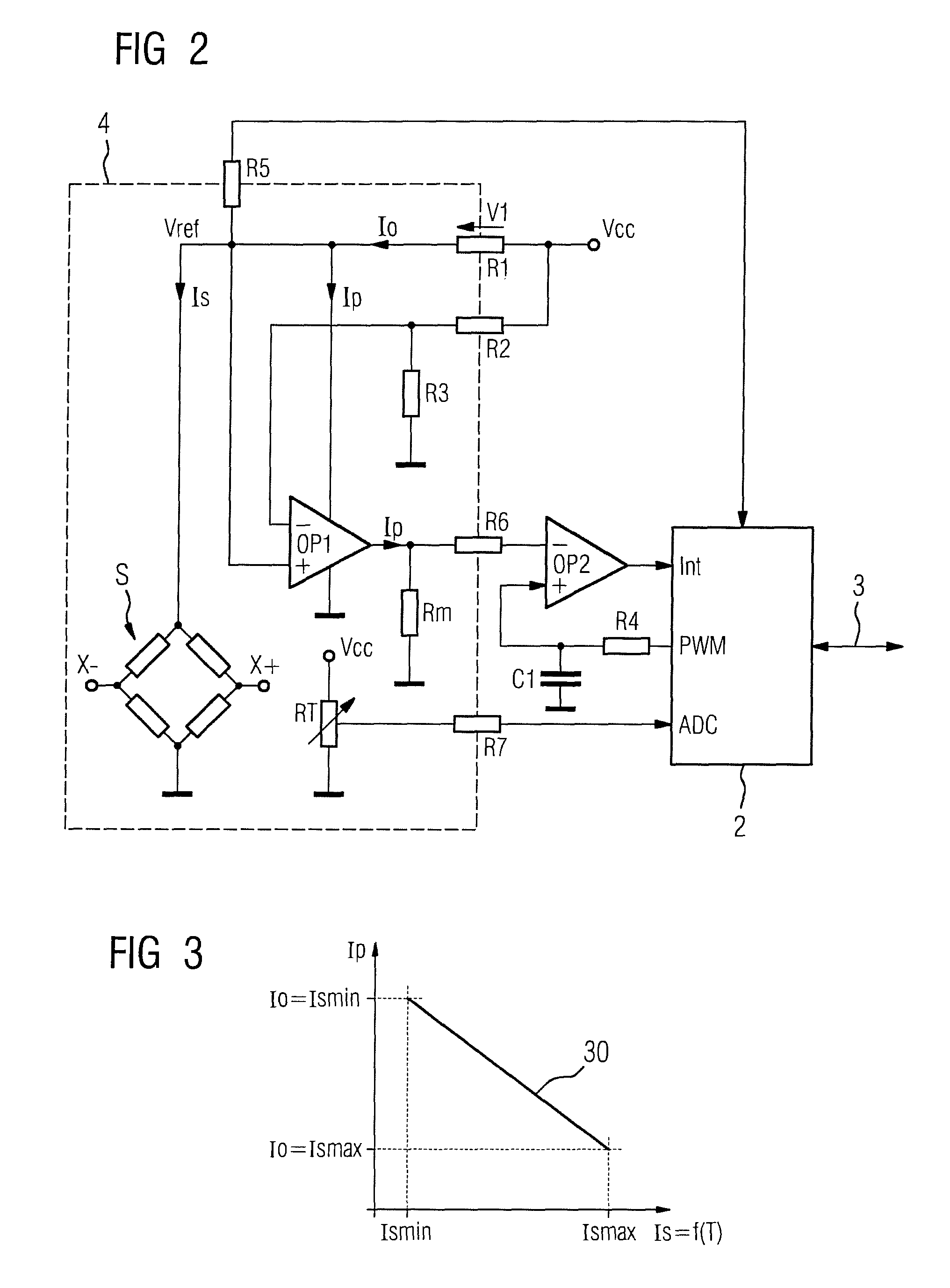
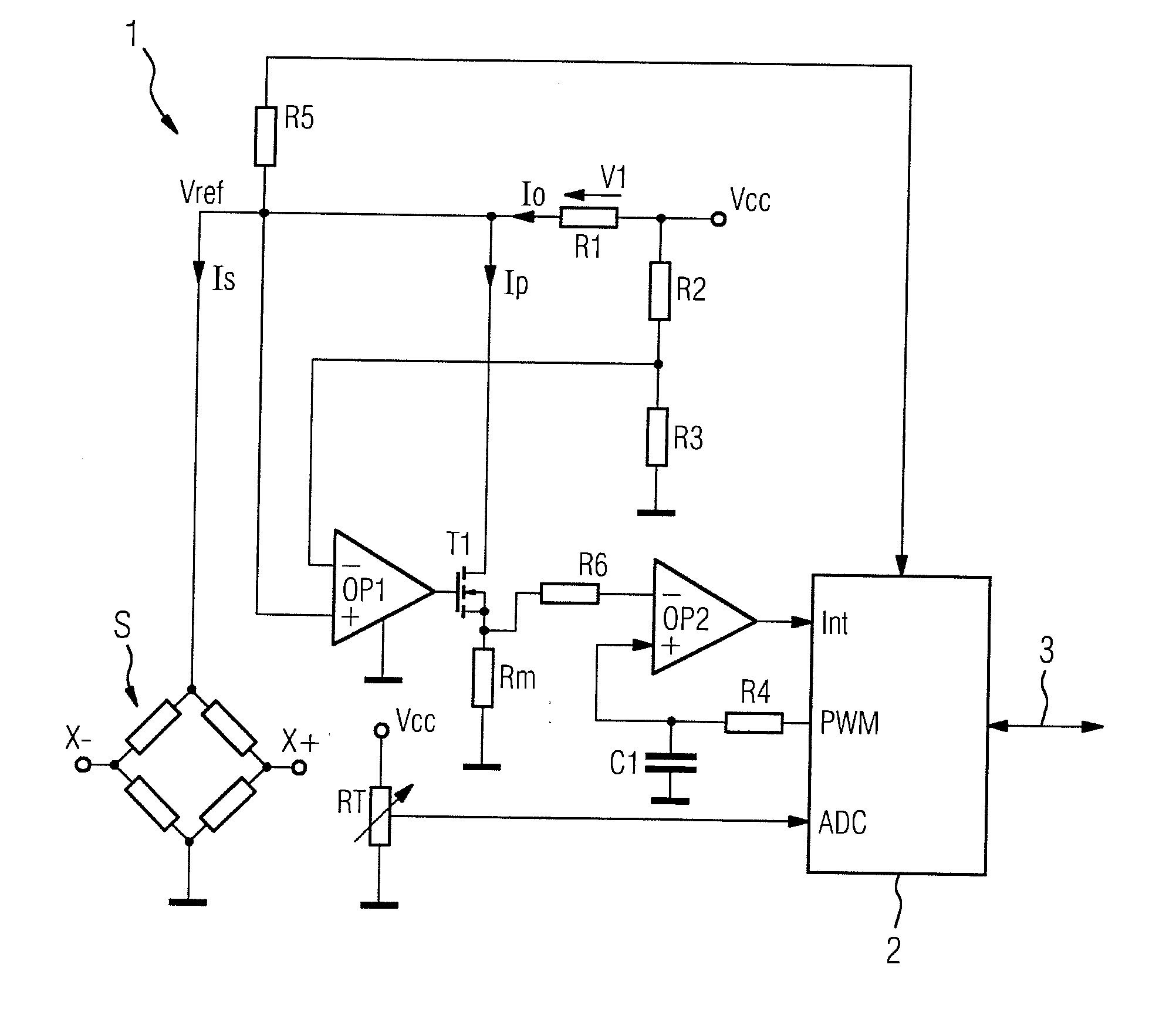
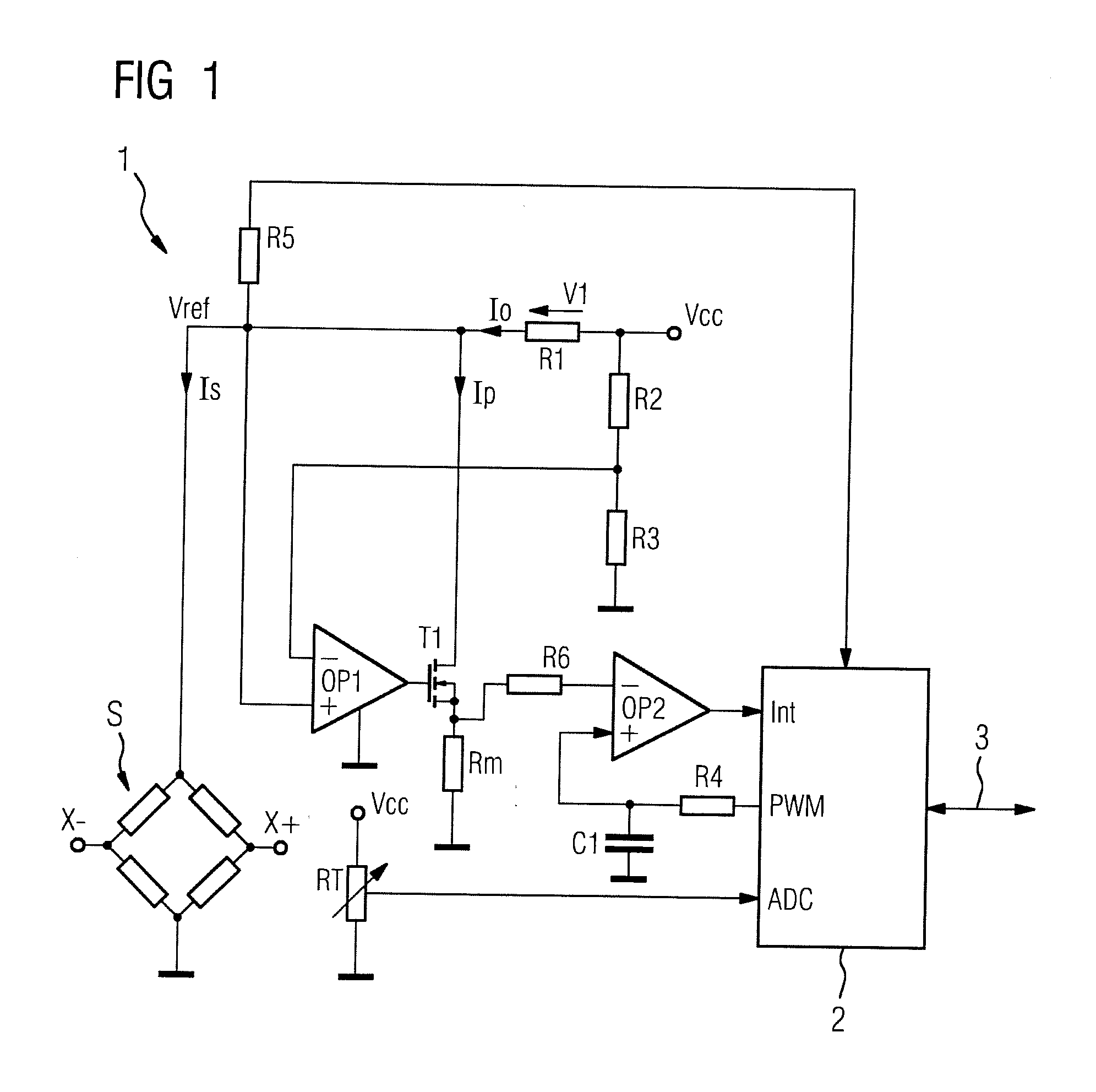
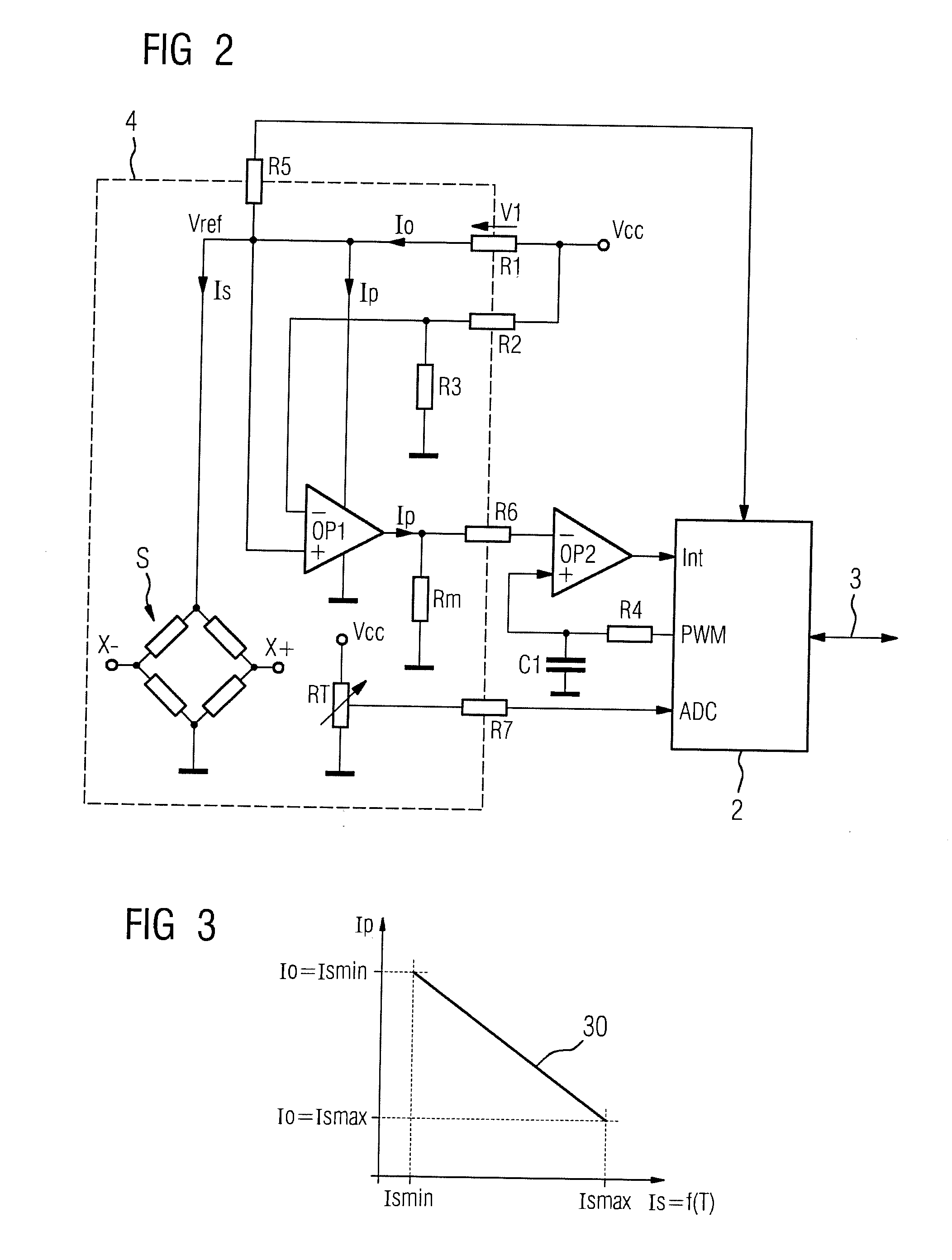
Measurement transducer for process instrumentation, and method for monitoring the state of its sensor
A measurement transducer for process instrumentation includes a sensor for detecting a physical or chemical quantity, where a supply voltage to the sensor is regulated by a cross regulator to a constant value, and the current intensity of the current adjusted by the cross regulator and flowing parallel to the sensor is determined and monitored to maintain a specified criterion in order to detect a sensor error such that error conditions of the sensor can be determined in a particularly simple and effective way.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Transformer Hydrogen Indicator
ActiveUS20140329328A1Reliable and low costFast inspectionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionHydrogenTransformer
A reliable, low cost device for determining when dangerous levels of hydrogen gas have been generated in a transformer is disclosed. The hydrogen indicator is defined by a module assembly that threads into either the headspace or into the oil-filled body of a transformer. The module has an open interior that contains a film that incorporates a hydrogen-sensitive chemochromic indicator. The indicator film is visible through a lens. When the film has been exposed to hydrogen, chemical changes in the chemochromic indicator cause the film to change color—the color change is immediately visible through the lens.
Owner:SERVERON CORP
Method of fabricating a semiconductor device having a photo-sensitive polyimide layer and a device fabricated in accordance with the method
InactiveUS20050029631A1Avoid developmentCracking of the PSPL layer is mitigated or eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
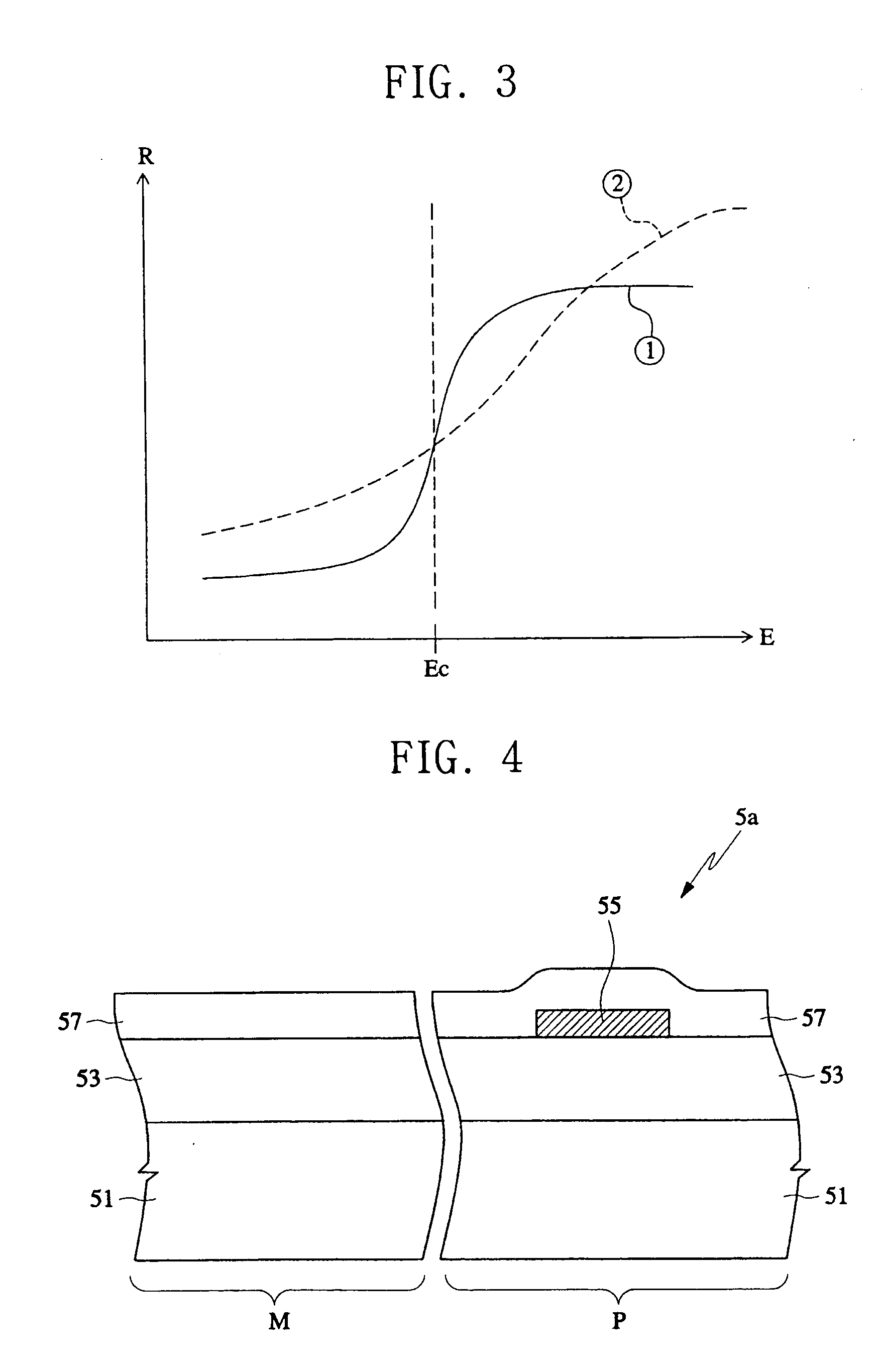
In a semiconductor device fabrication method and in a product formed according to the method, a photosensitive polyimide layer (PSPL) layer is applied to a semiconductor device in a manner which overcomes the limitations of the conventional approaches. The beneficial qualities of an added photoresist layer are utilized to avoid unwanted development of the underlying PSPL layer. In this manner, cracking of the PSPL layer is mitigated or eliminated, reducing the device soft error rate (SER) and increasing device yield. This is accomplished in a reliable and low-cost approach that employs standard device fabrication techniques.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Deeply Rechargeable Battery Systems and Methods
PendingUS20220255068A1Reliable and low-costImprove performanceFuel and primary cellsNegative electrodesChemical physicsRechargeable cell
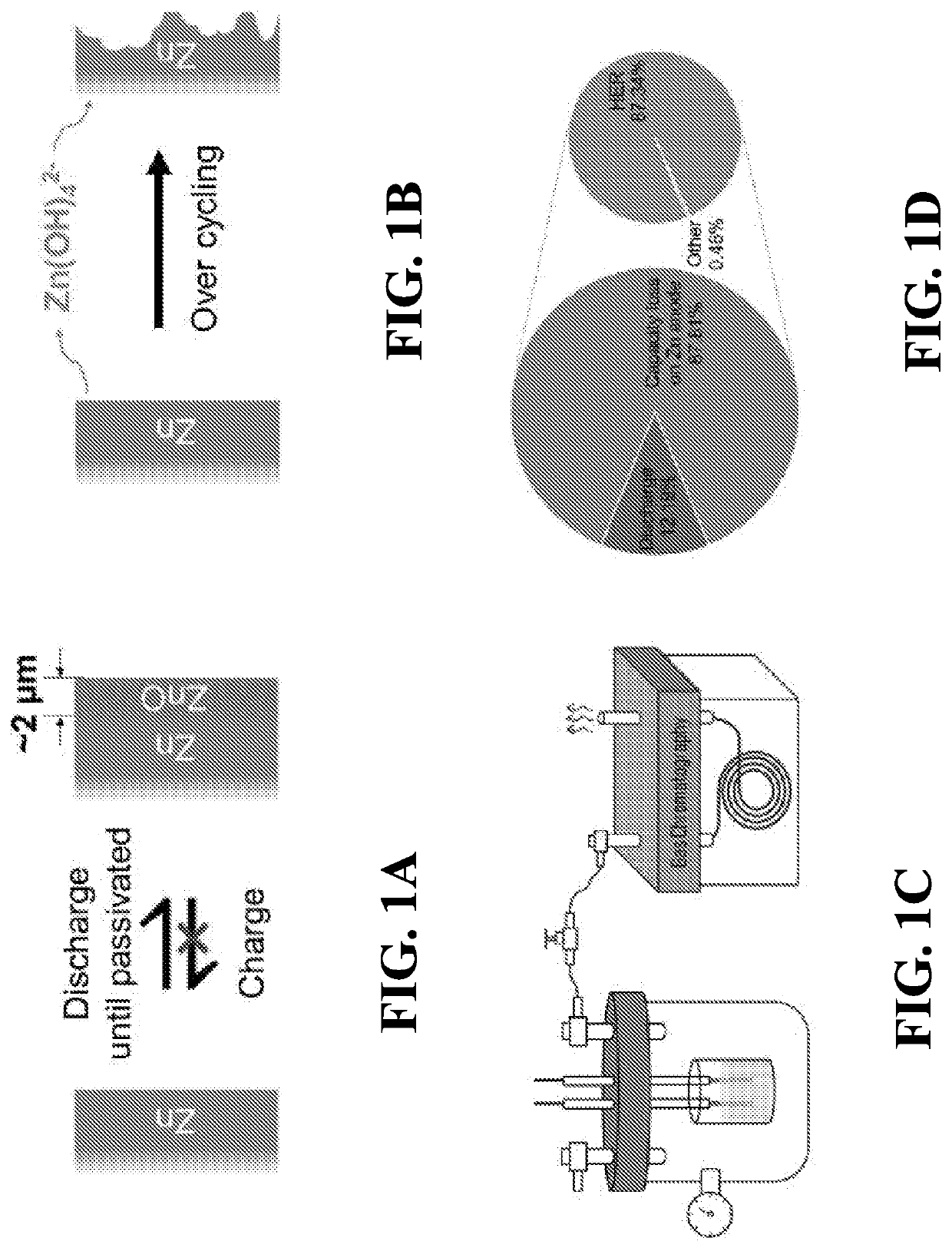
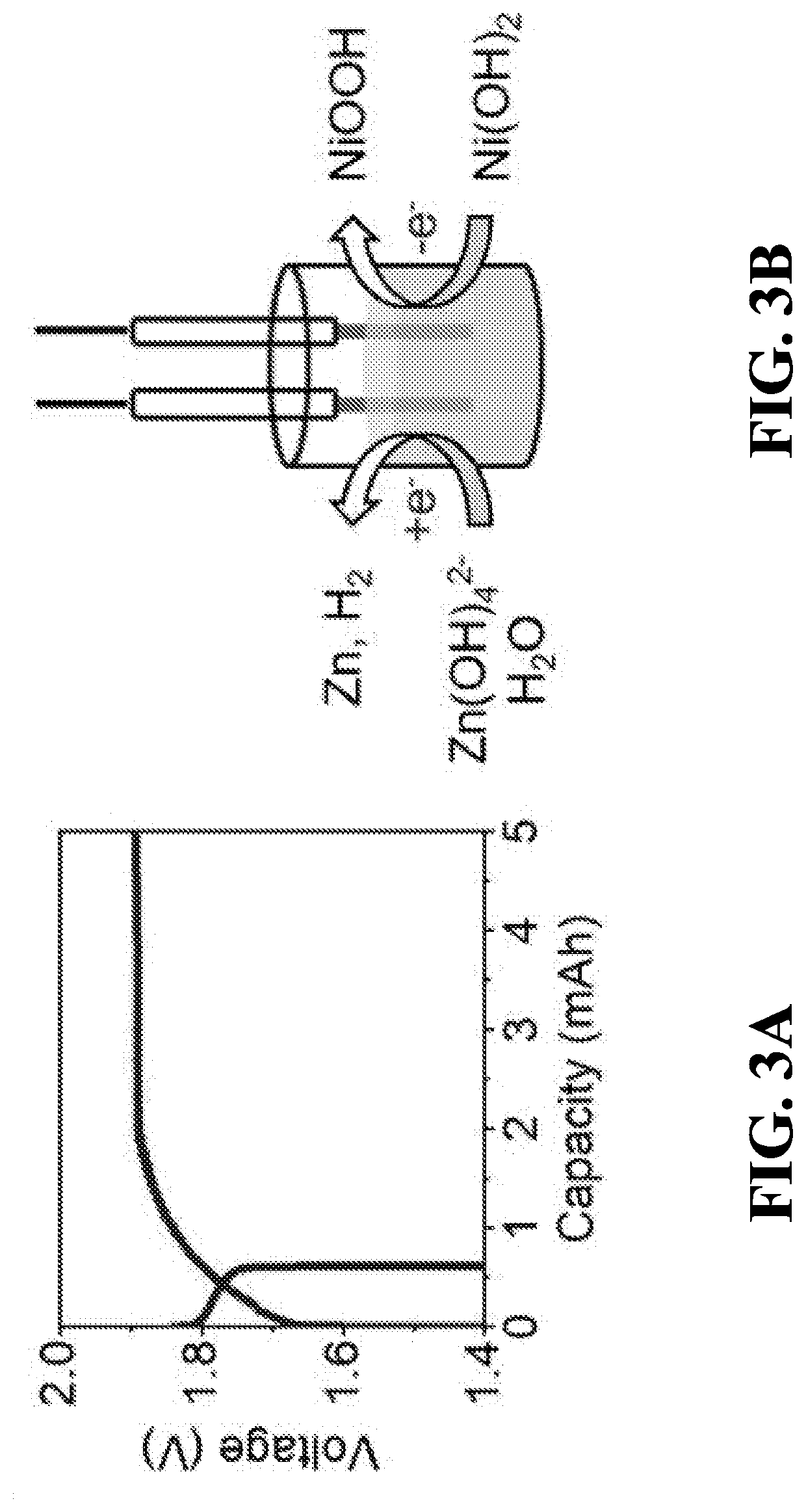
Deeply rechargeable battery systems and methods, where a core / shell nanoscale structure provides deeply rechargeable anodes that overcome intrinsic limitations of conventional battery materials that involve soluble intermediates or insulating discharge products. The deeply rechargeable battery systems and methods simultaneously overcome the dilemmas of passivation and dissolution. An ion-sieving concept is applied to a Zn anode that confines larger zincate ions and allows smaller hydroxide ions to permeate, can limit / prevent ZnO dissolution and electrode shape change.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Measurement transducer for process instrumentation, and method for monitoring the state of its sensor
ActiveUS20160025528A1Reliable and low mannerReliable and low costWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusPower flowTransducer
A measurement transducer for process instrumentation includes a sensor for detecting a physical or chemical quantity, where a supply voltage to the sensor is regulated by a cross regulator to a constant value, and the current intensity of the current adjusted by the cross regulator and flowing parallel to the sensor is determined and monitored to maintain a specified criterion in order to detect a sensor error such that error conditions of the sensor can be determined in a particularly simple and effective way.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
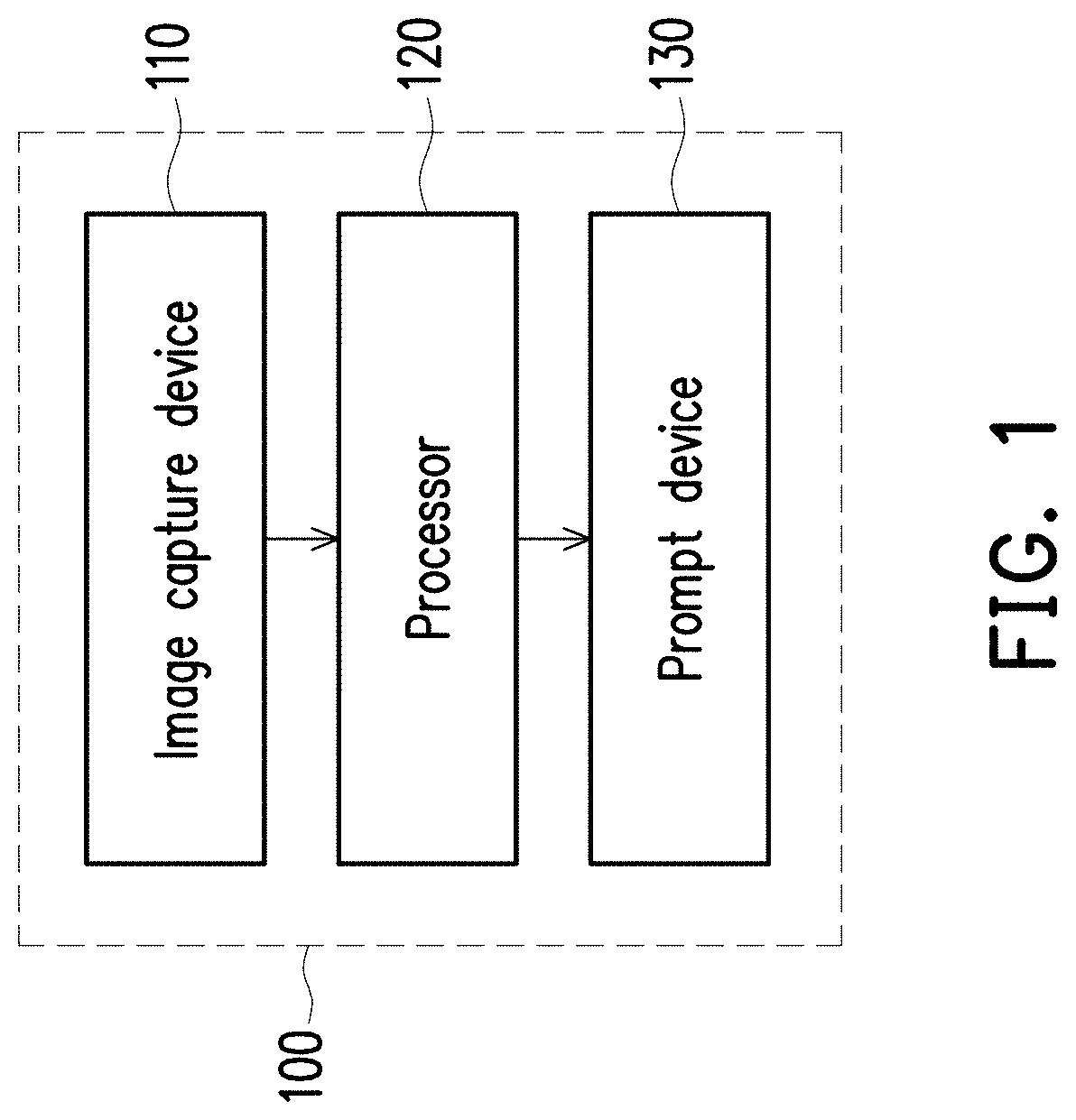
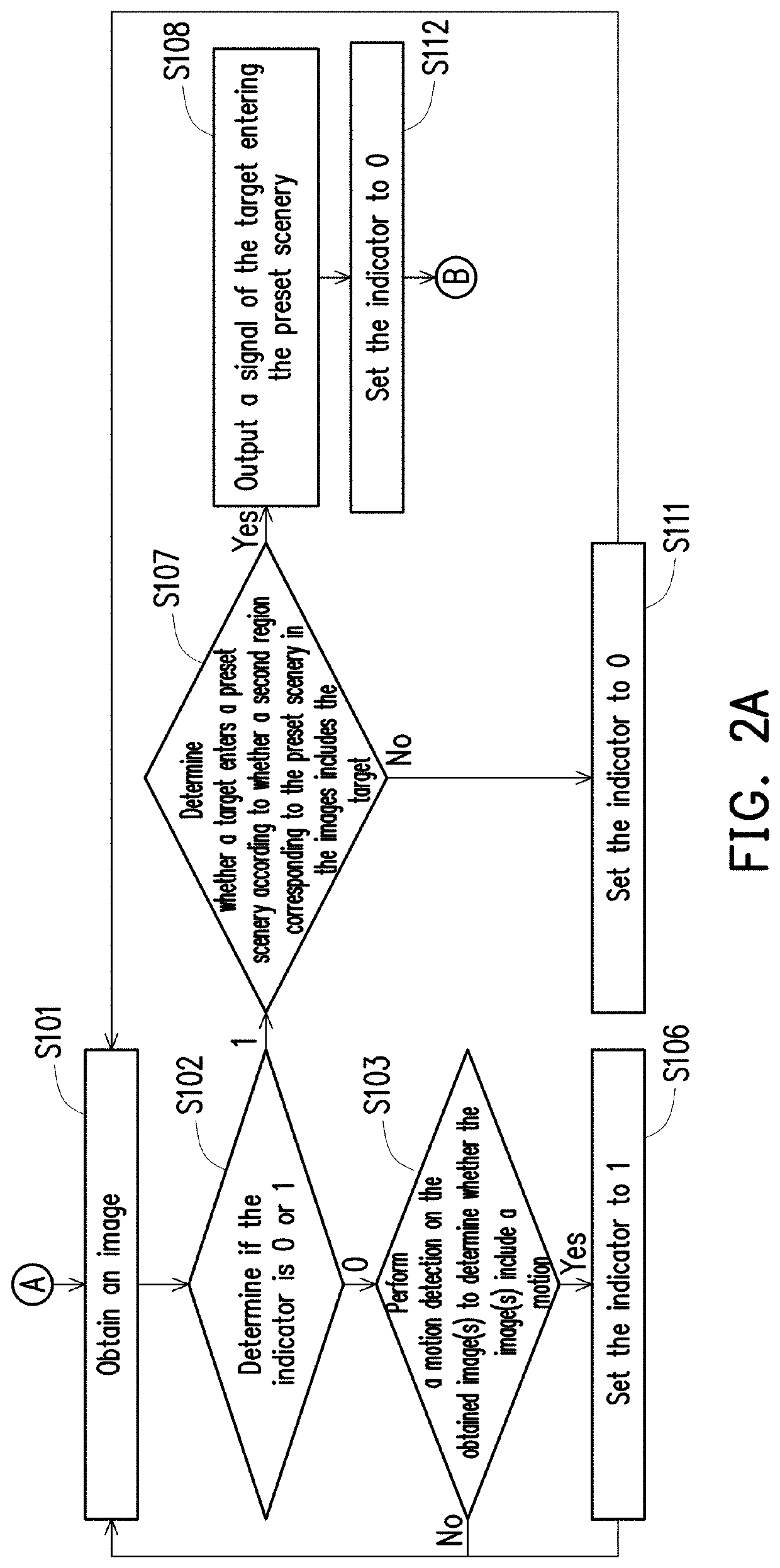
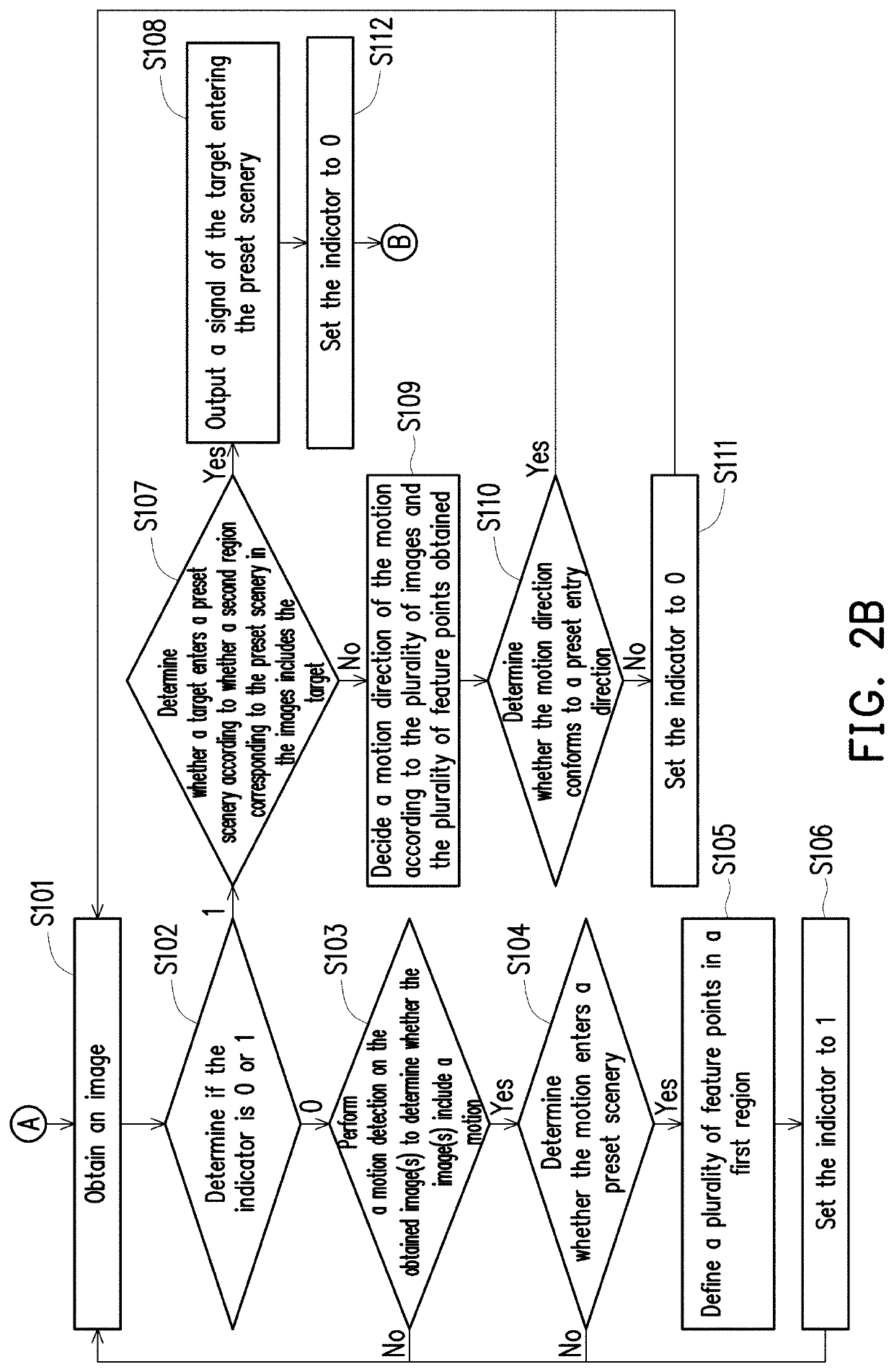
Image analysis method, electronic system, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS20190385314A1Reliable and low-costAvoid excessive computationImage enhancementImage analysisElectronic systemsImaging analysis
An image analysis method applicable to an electronic system is provided. The electronic system includes an image capture device. The image analysis method includes: obtaining a plurality of images captured by the image capture device; performing a motion detection on the plurality of images to determine whether the images include a motion; and determining whether a target enters the preset scenery or leaves the preset scenery in response to a determination that the plurality of images include the motion according to the motion detection.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com