Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about How to "Inexpensive cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
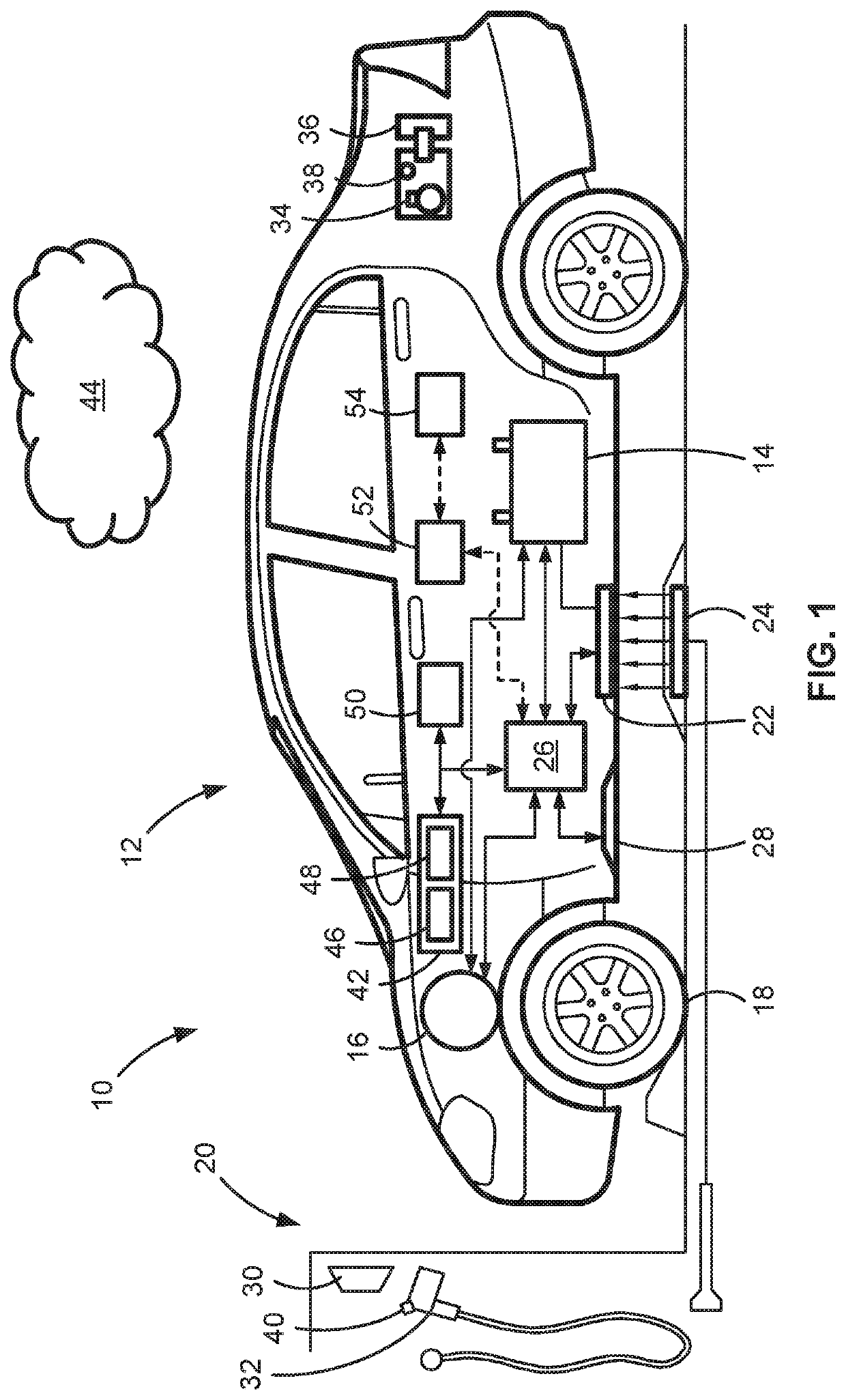
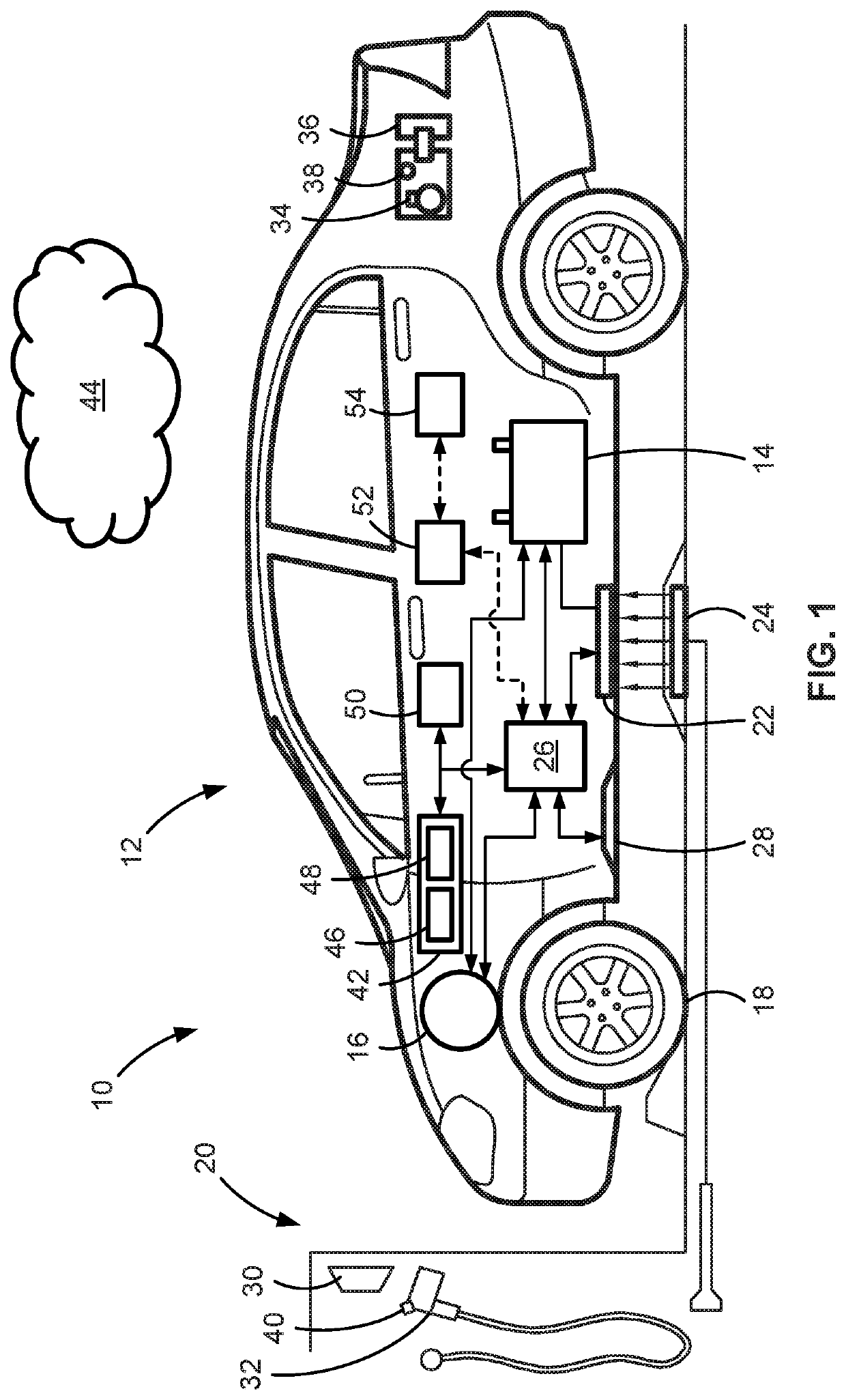
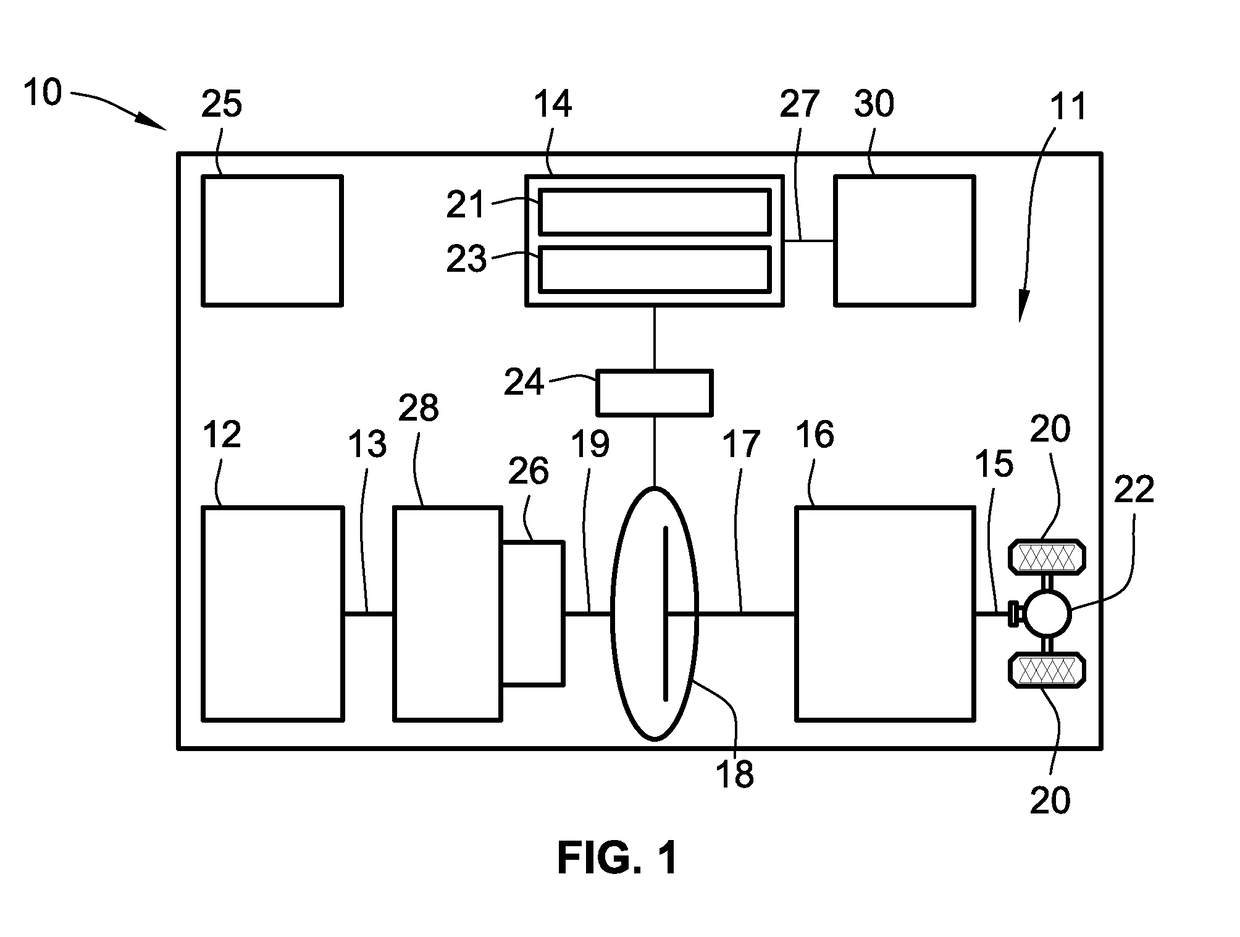
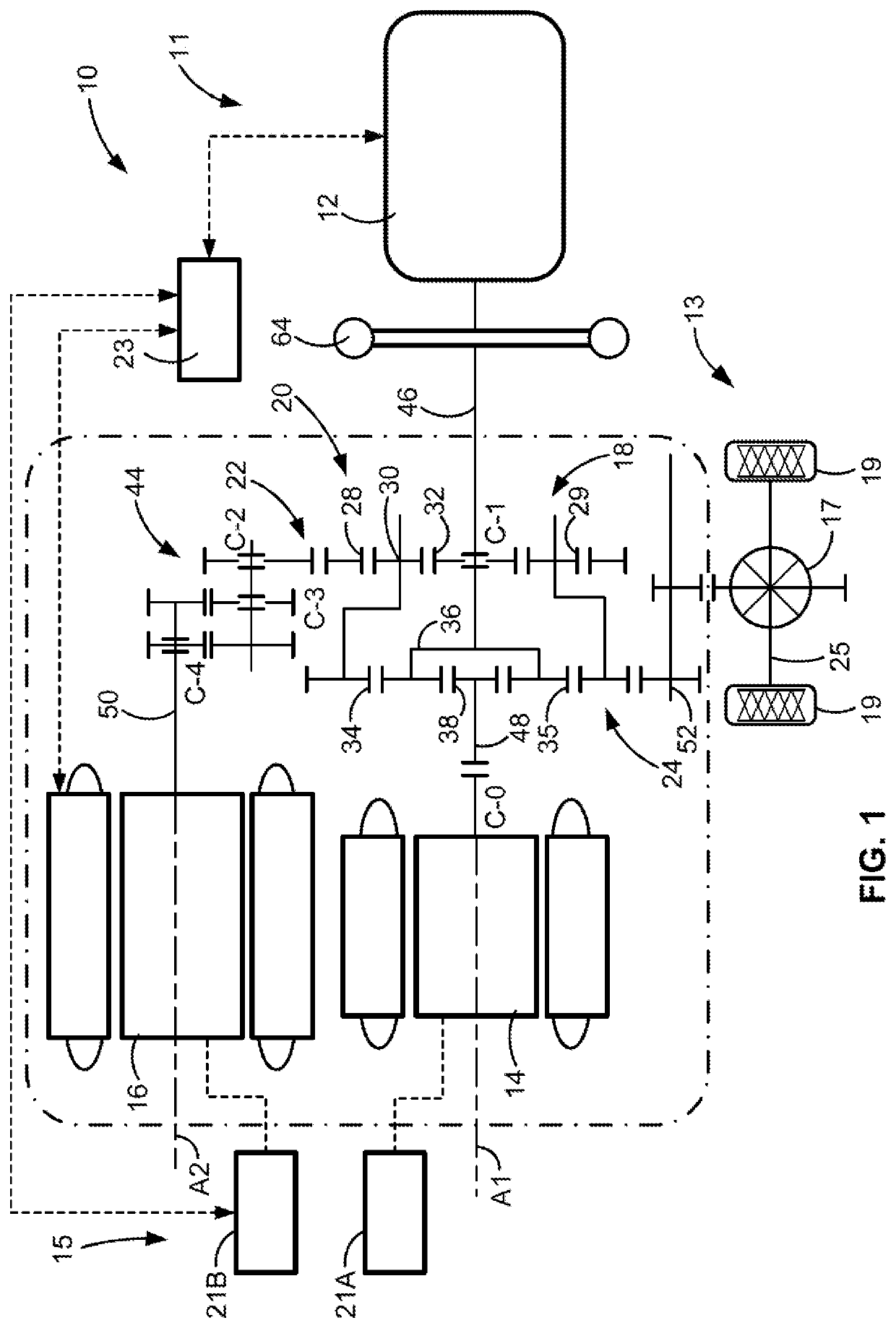
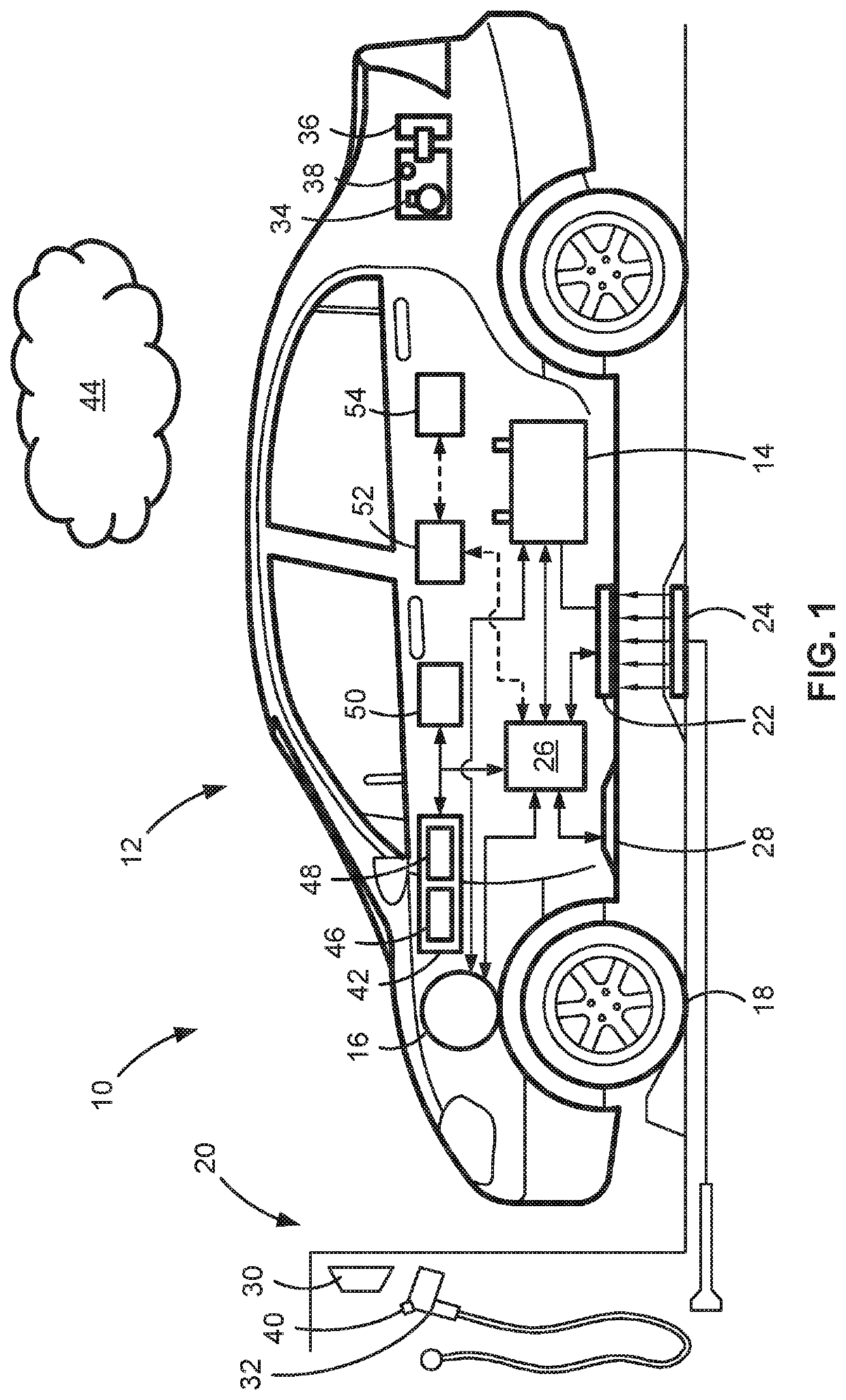
Electric-drive motor vehicles, systems, and control logic for predictive charge planning and powertrain control
ActiveUS20200070679A1Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costHybrid vehiclesCharging stationsDriver/operatorElectric cars
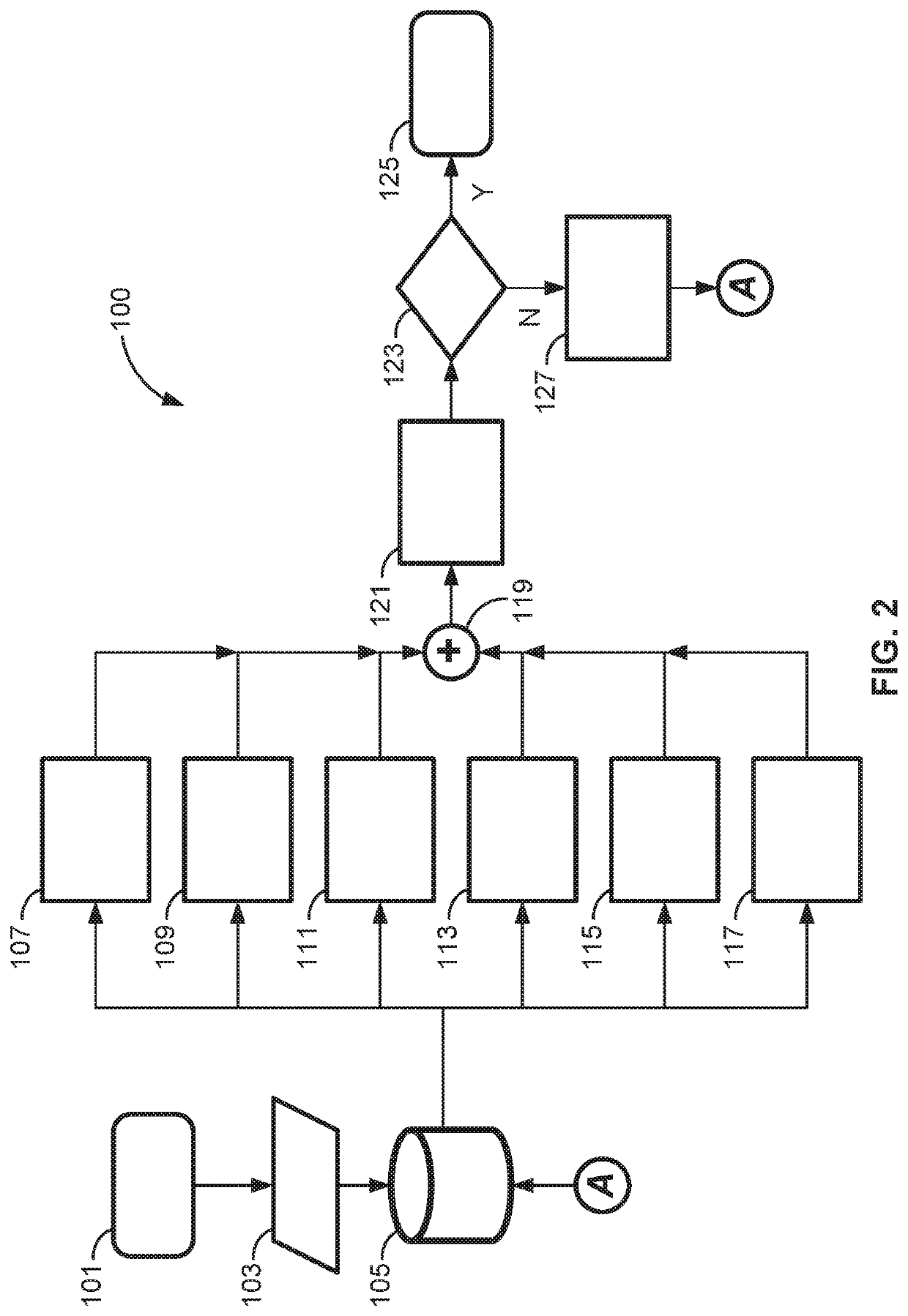
Presented are intelligent vehicle systems and control logic for predictive charge planning and powertrain control of electric-drive vehicles, methods for manufacturing / operating such systems, and electric-drive vehicles with smart charge planning and powertrain control capabilities. Systems and methods of AI-based predictive charge planning for smart electric vehicles use machine-learning (ML) driver models that draws on available traffic, location, and roadway map information to estimate vehicle speed and propulsion torque requirements to derive a total energy consumption for a given trip. Systems and methods of AI-based predictive powertrain control for smart hybrid vehicles use ML driver models with deep learning techniques to derive a drive cycle profile defined by a preview route with available traffic, geopositional, geospatial, and map data. ML-generated driver models are developed with collected data to replicate driver behavior and predict the drive cycle profile, including predicted vehicle speed, propulsion torque, and accelerator / brake pedal positions for a preview route.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Intelligent motor vehicles, charging systems, and control logic for governing vehicle grid integration operations
ActiveUS20200353839A1Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costCharging stationsElectric devicesElectric power transmissionElectrical battery
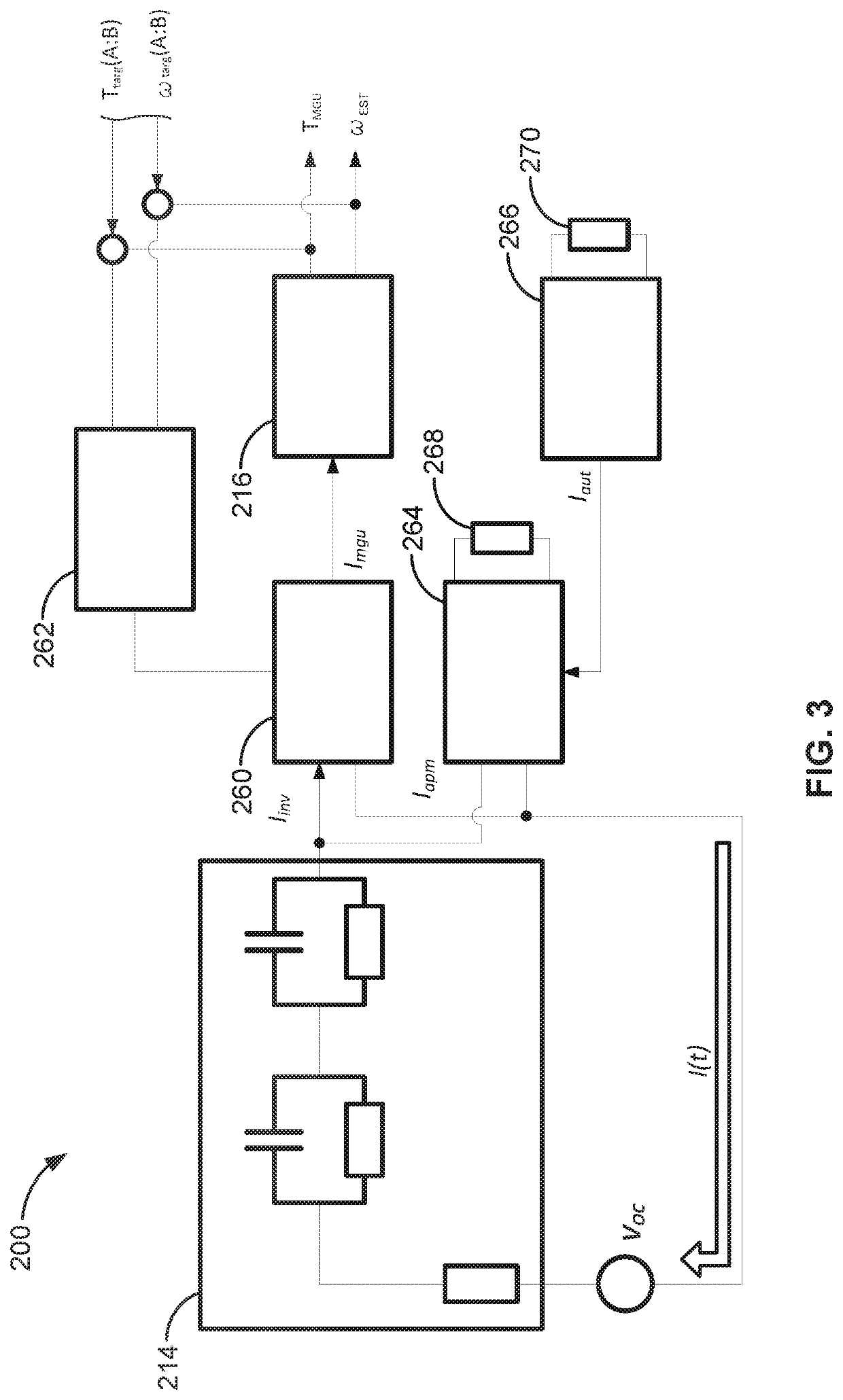
Presented are vehicle charging systems and control logic for provisioning vehicle grid integration (VGI) activities, methods for making / using such charging systems, and electric-drive vehicles with intelligent vehicle charging and VGI capabilities. A method of controlling charging operations of electric-drive vehicles includes a vehicle controller detecting if a vehicle is coupled to an electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), and determining if the vehicle's current mileage exceeds a calibrated mileage threshold. Responsive to the vehicle being connected to the EVSE and the vehicle's current mileage exceeding the calibrated mileage threshold, the controller determines the current remaining life of the vehicle's traction battery pack and the current time in service of the vehicle. The vehicle controller determines if the current remaining battery life exceeds a predicted remaining battery life corresponding to the current time in service. If so, the vehicle controller enables the traction battery pack to transmit electrical power to the EVSE.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
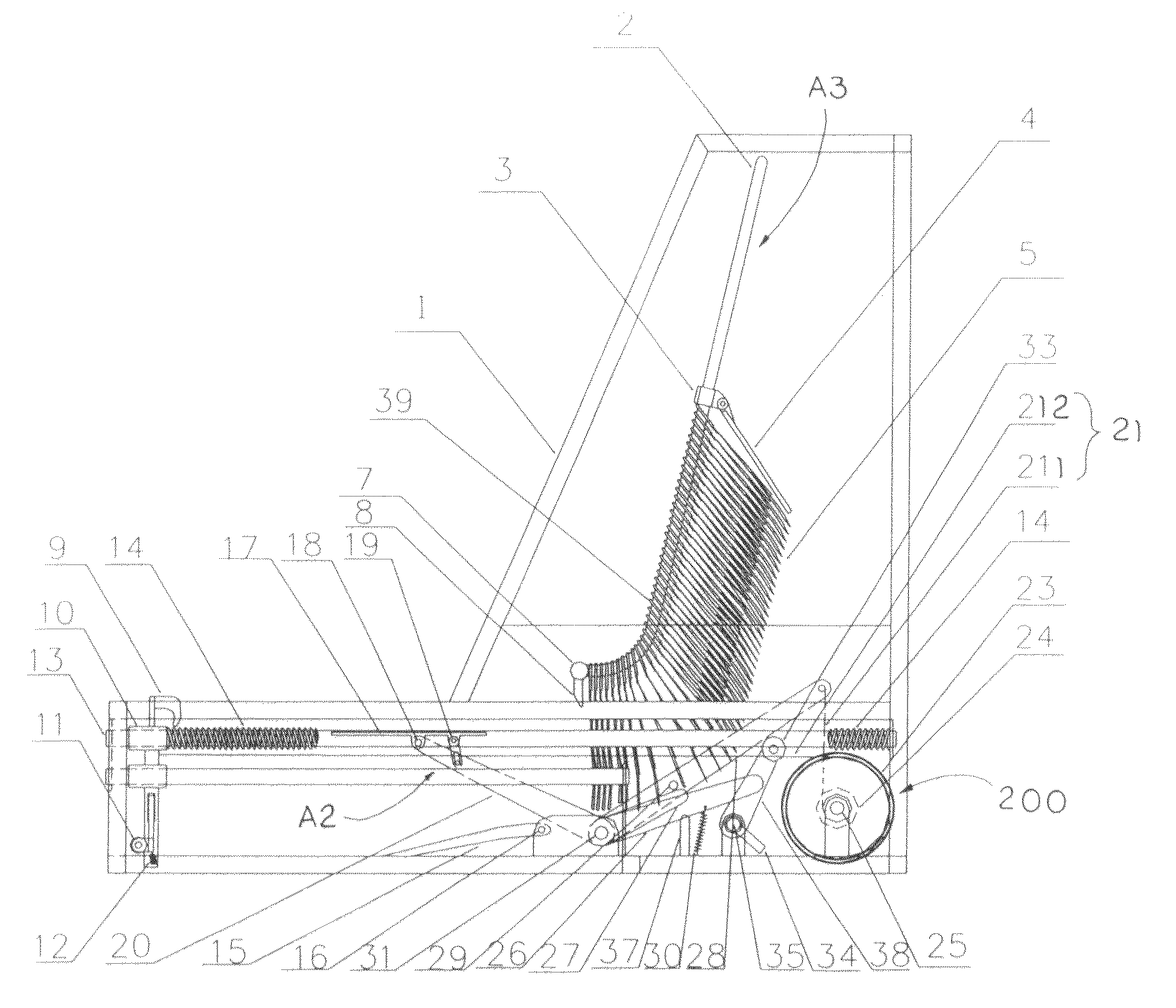
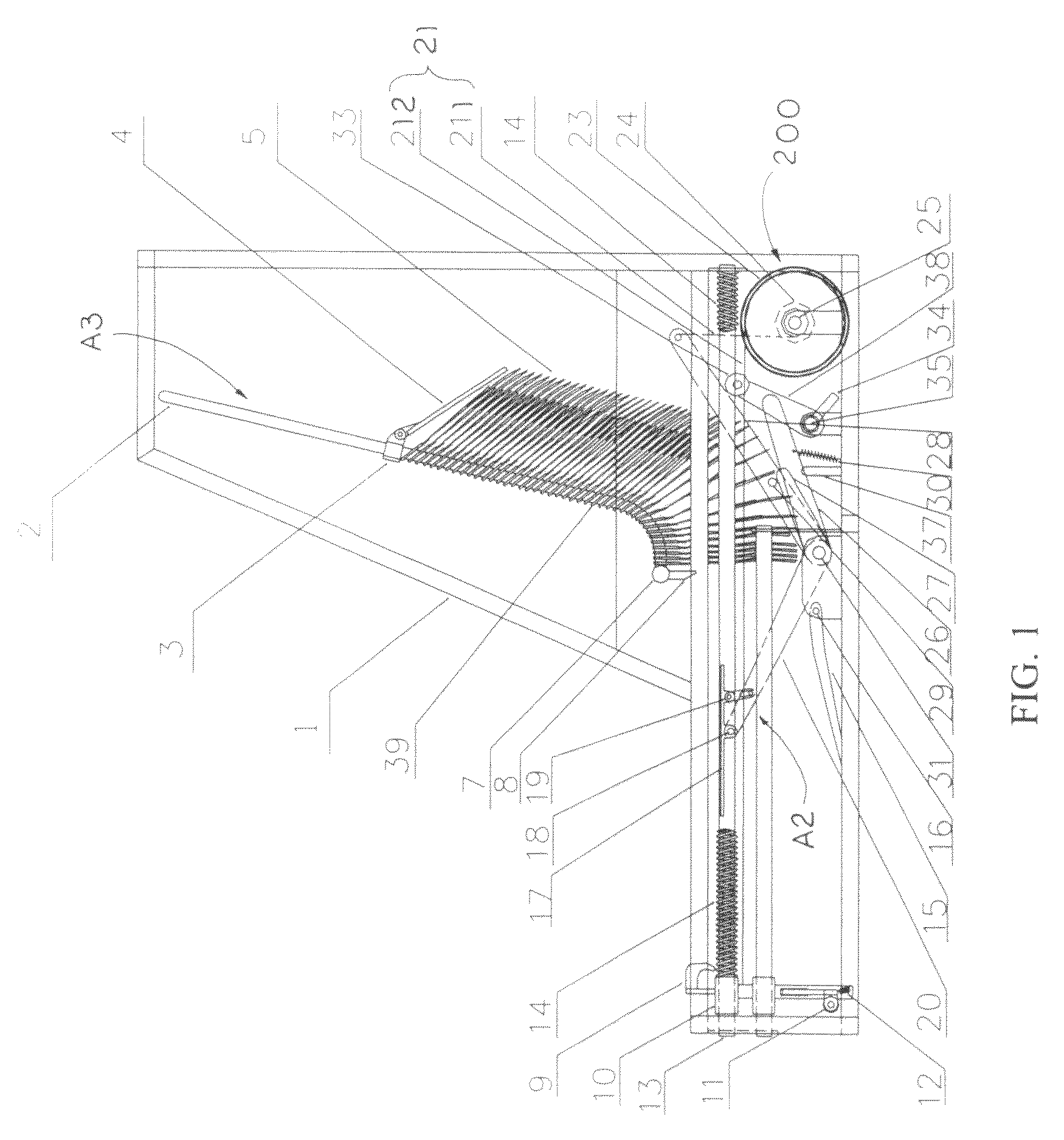
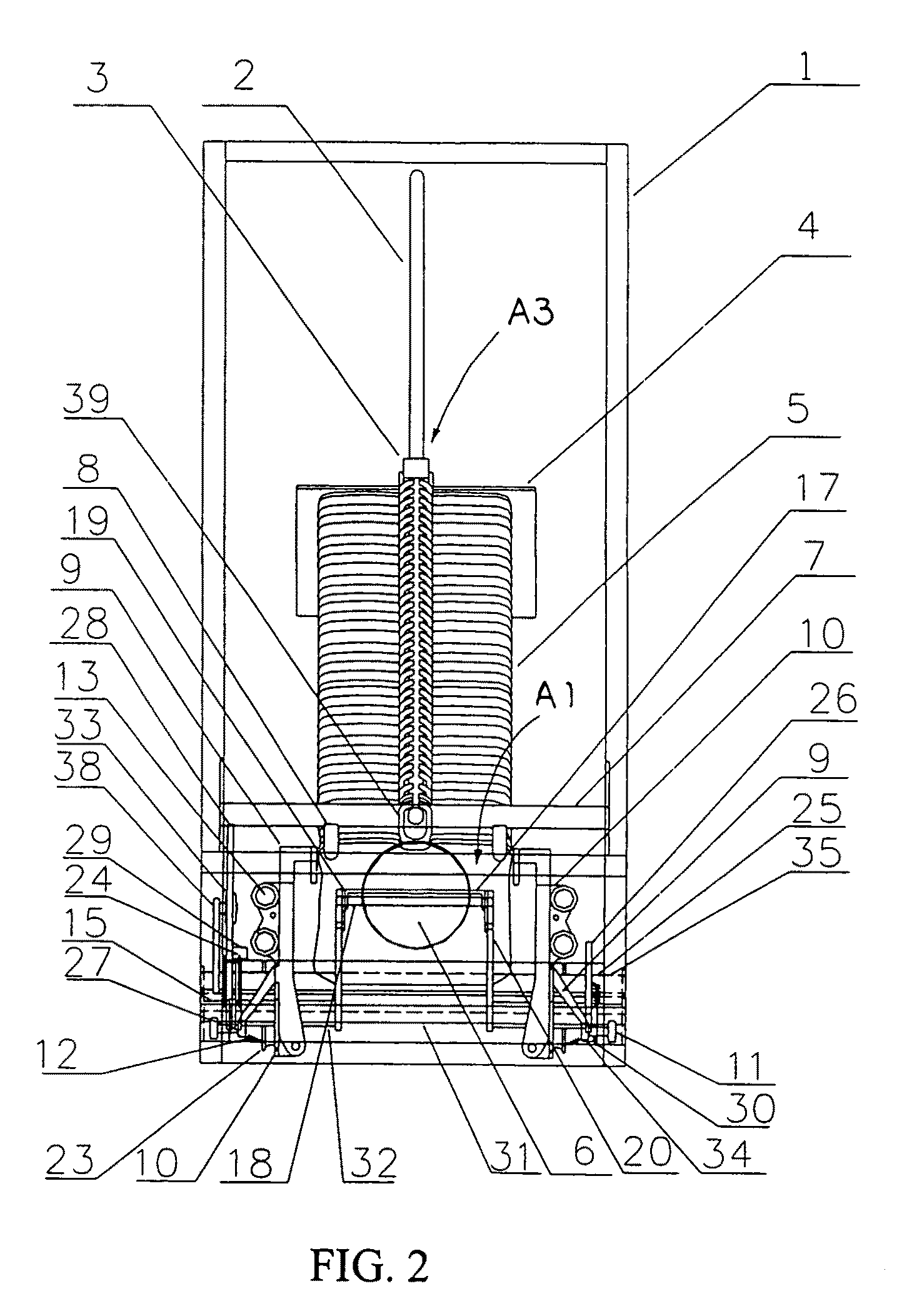
Automatic shoe cover dispenser
ActiveUS20100288800A1Increase manufacturing costSimple structureApparel holdersRegistering devicesEngineering
Owner:OTO IND SHANGHAI
Intelligent motor vehicles, systems, and control logic for real-time eco-routing and adaptive driving control
InactiveUS20200089241A1Significant computational savingReducing in-vehicle processing loadInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processControl engineeringMotorized vehicle
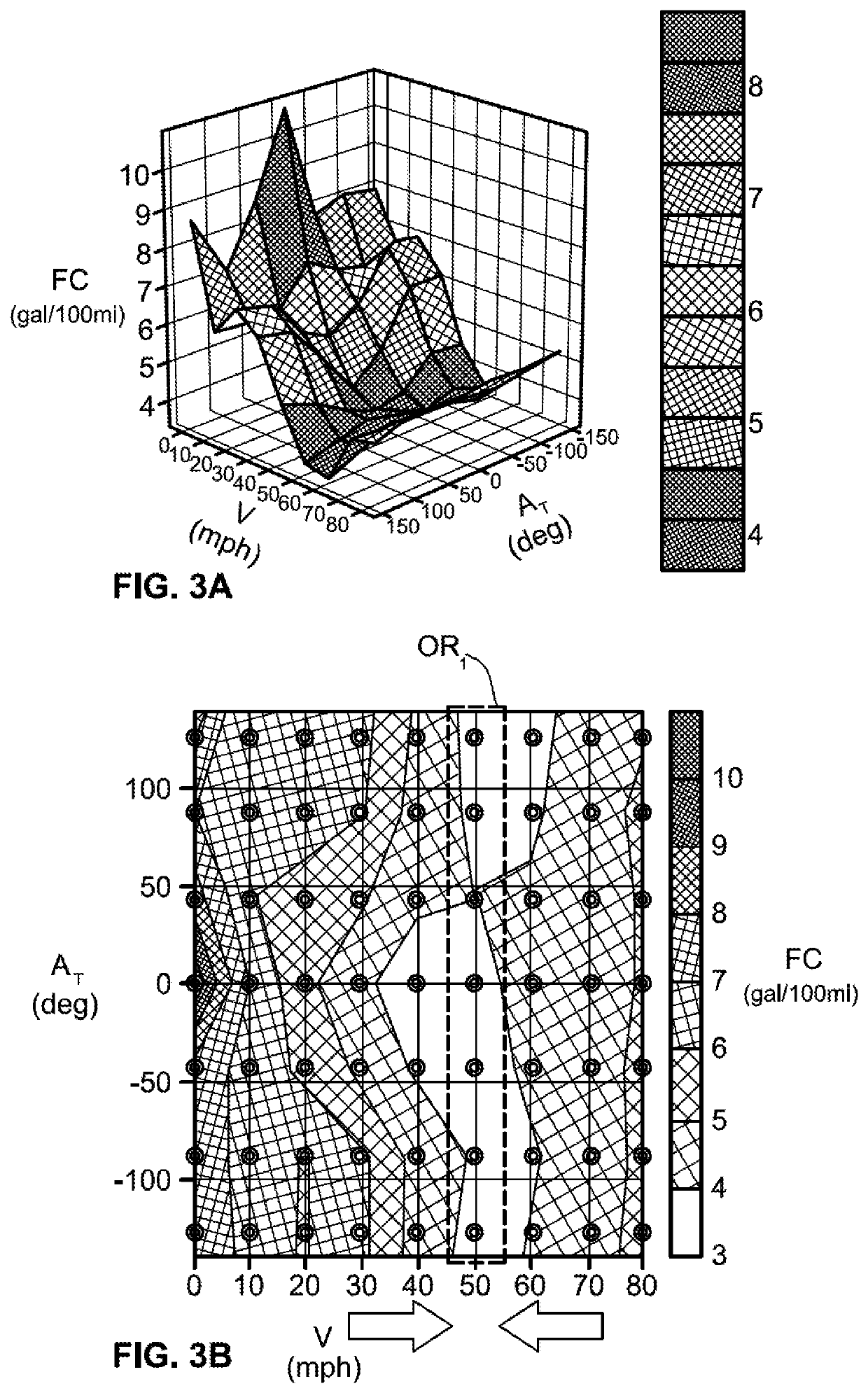
Presented are intelligent vehicle systems and control logic for predictive route planning and adaptive control, methods for manufacturing / operating such systems, and motor vehicles with real-time eco-routing and automated driving capabilities. A method for controlling operation of a vehicle includes determining vehicle origin and destination information, and identifying candidate routes for traversing from the origin to the destination. Road-level data, including speed and topology data, is received for each candidate route. Total energy uses are estimated for propelling the vehicle from the origin to the destination across each of the candidate routes. This estimating includes evaluating respective road-level data of each candidate route against a memory-stored table that correlates energy consumption to speed, turn angle, and / or gradient. A resident vehicle controller commands a resident vehicle subsystem to execute a control operation based on one or more of the estimated total energy uses corresponding to one or more of the candidate routes.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Intelligent motor vehicles, systems, and control logic for driver behavior coaching and on-demand mobile charging
ActiveUS20200117204A1Extend eDriving rangeImprove vehicle fuel economyHybrid vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationDriver/operatorVehicle miles of travel
Presented are intelligent vehicle systems and control logic for driver coaching and on-demand vehicle charging, methods for making / using such systems, and motor vehicles with real-time eco-routing and automated driving capabilities. A method for controlling operation of a vehicle includes: determining an origin and destination for the vehicle; conducting a geospatial query to identify a candidate route for traversing from the origin to the destination; determining, based on current electrical characteristics of the vehicle's battery pack, an estimated driving range for the vehicle; responsive to the estimated driving range being less than the candidate route's distance, evaluating energy characteristics of the candidate route to derive an estimated energy expenditure to reach the destination; using the estimated energy expenditure, generating an action plan with vehicle maneuvering and / or accessory usage actions that extend the estimated driving range; and commanding a resident vehicle subsystem to execute a control operation based on the action plan.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
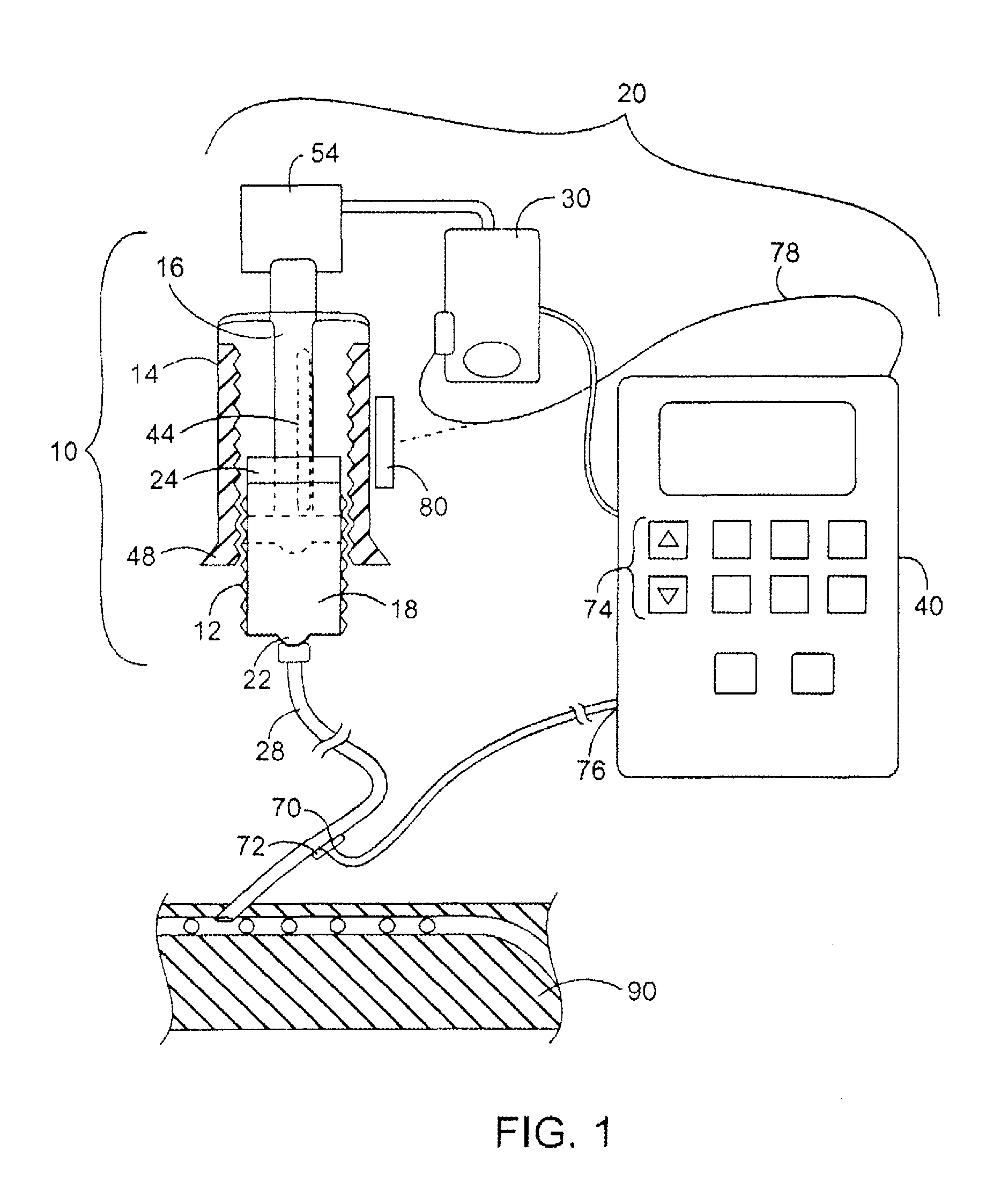
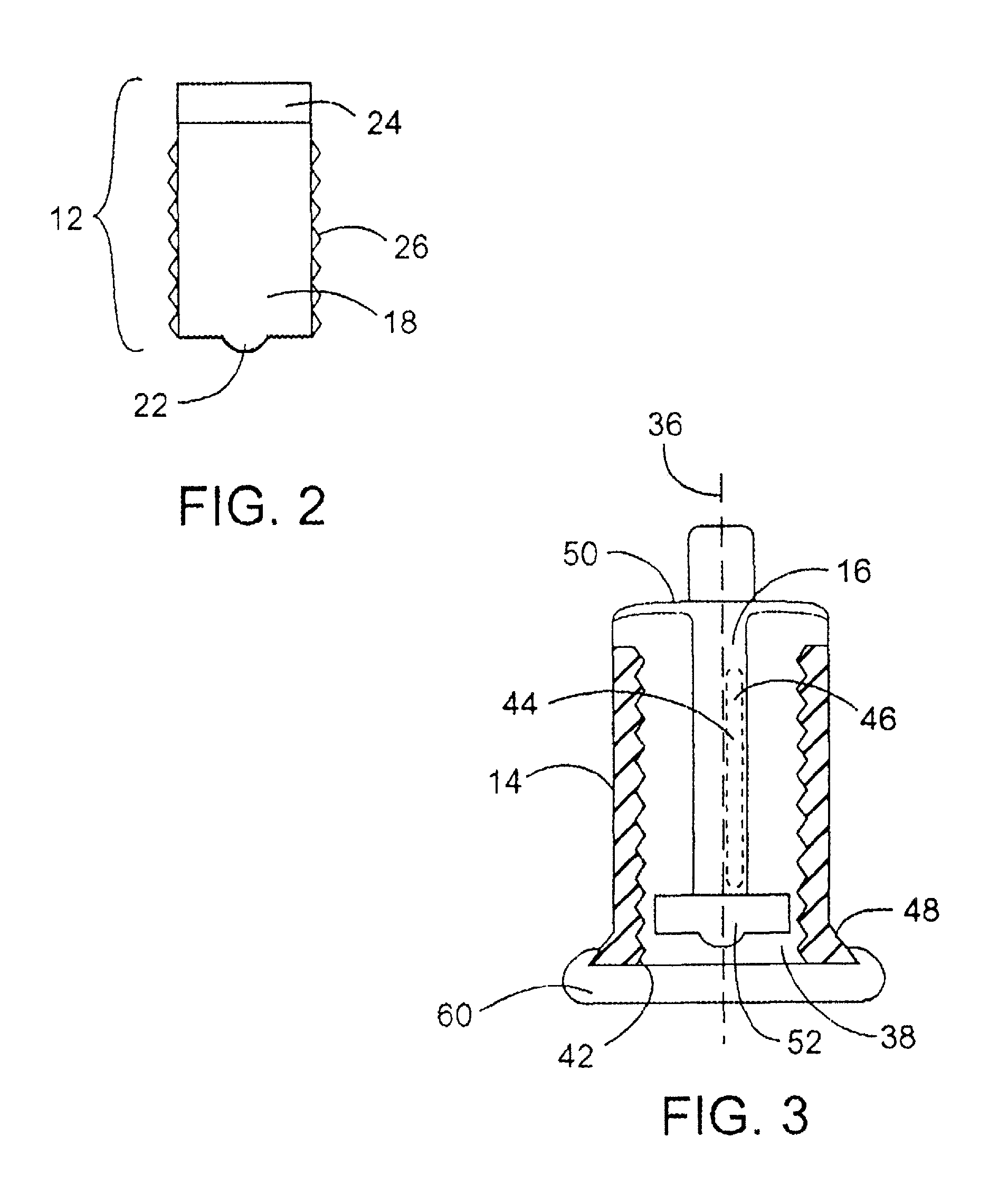
Medical infusion device producing adenosine triphosphate from carbohydrates
InactiveUS20130172808A1Increase flow rateOvercomes forceMedical devicesIntravenous devicesLine sensorGlycemic
A medical infusion system which increases adenosine triphosphate from carbohydrates by a pump delivering precisely timed and calculated boluses of hormones such as insulin resulting in oscillations of hormones in whole blood sufficient to cover a carbohydrate load equal to no less than forty percent (40%) of the minimum daily allowance for carbohydrates where the blood glucose is from 60 mg / dl to 300 mg / dl. The system comprises a pump and optimally a cassette or cartridge where the plunger rotates as it advances in reference to the cartridge to provide additional accuracy and overcome the forces of inertia and slip-stick as well as eliminate backlash. The system can also use an encoded area and an opening for connection to an infusion tube with an in-line sensor area where sampling probes can be located to optimized adenosine triphosphate production from the mitochondria in the cells.
Owner:GILBERT G FORD
Automatic shoe cover dispenser
ActiveUS20080237277A1The process is stable and efficientEfficient and stable processingApparel holdersRegistering devicesEngineeringFootplate
Owner:XU LIANG JIE
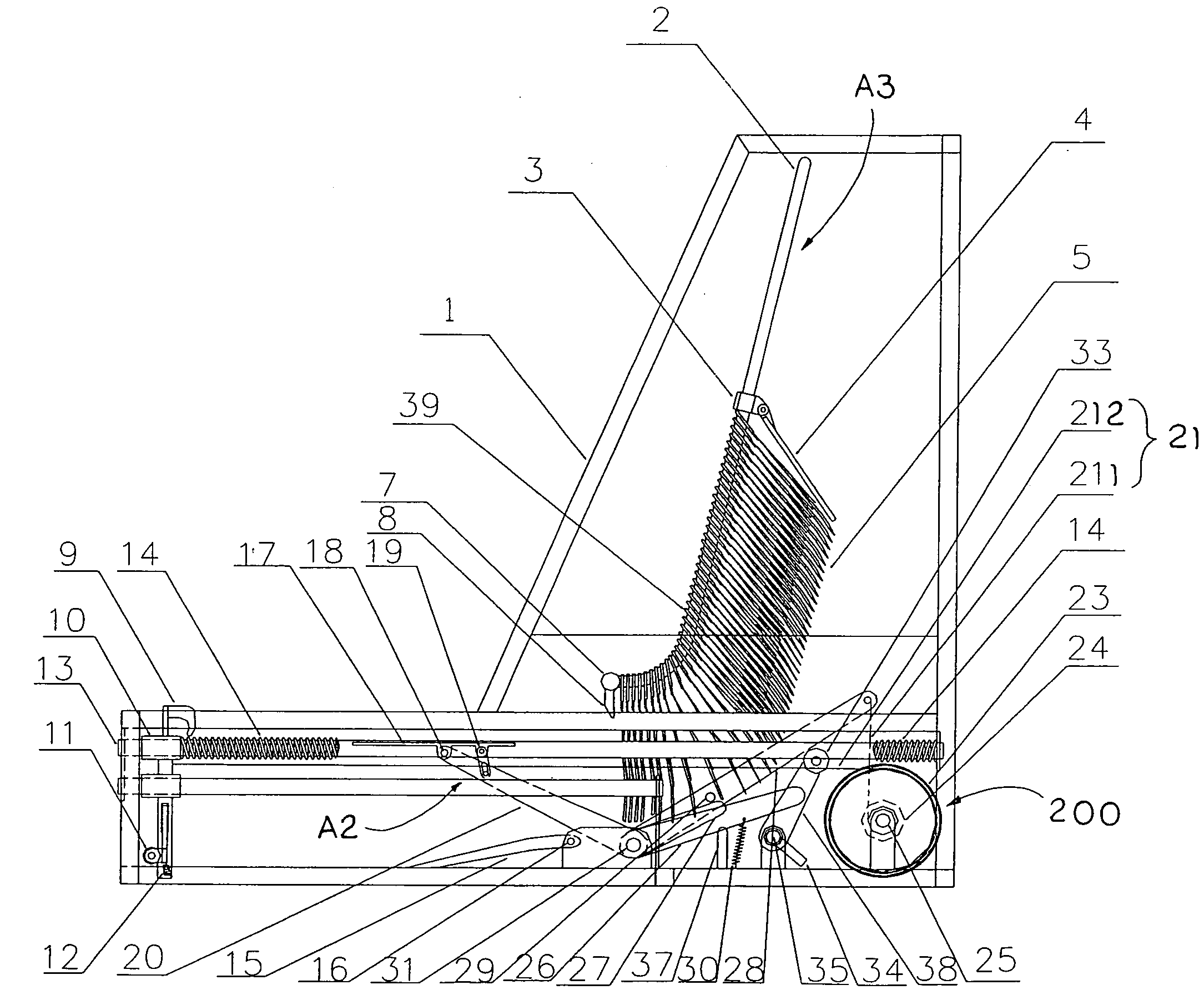
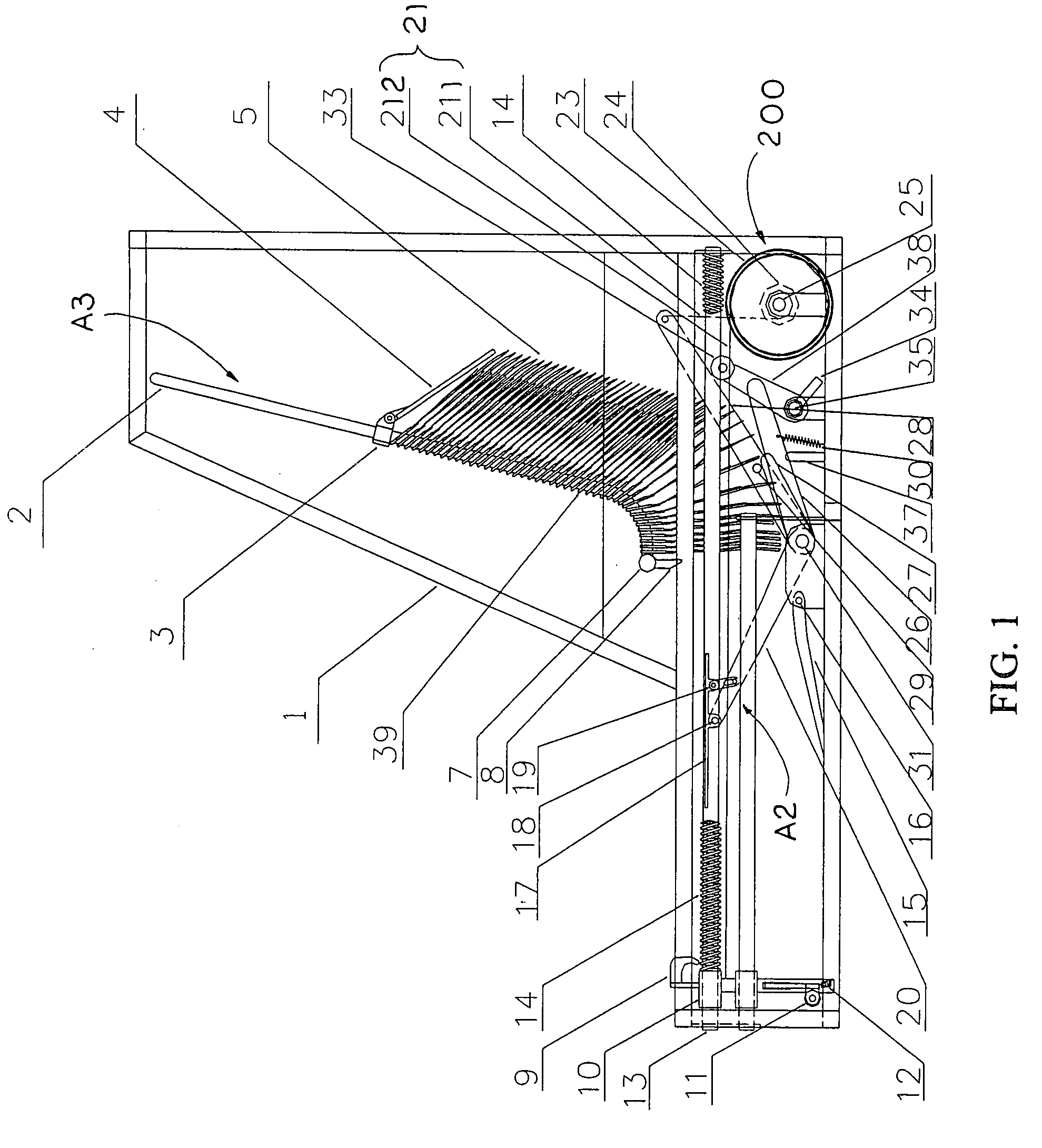
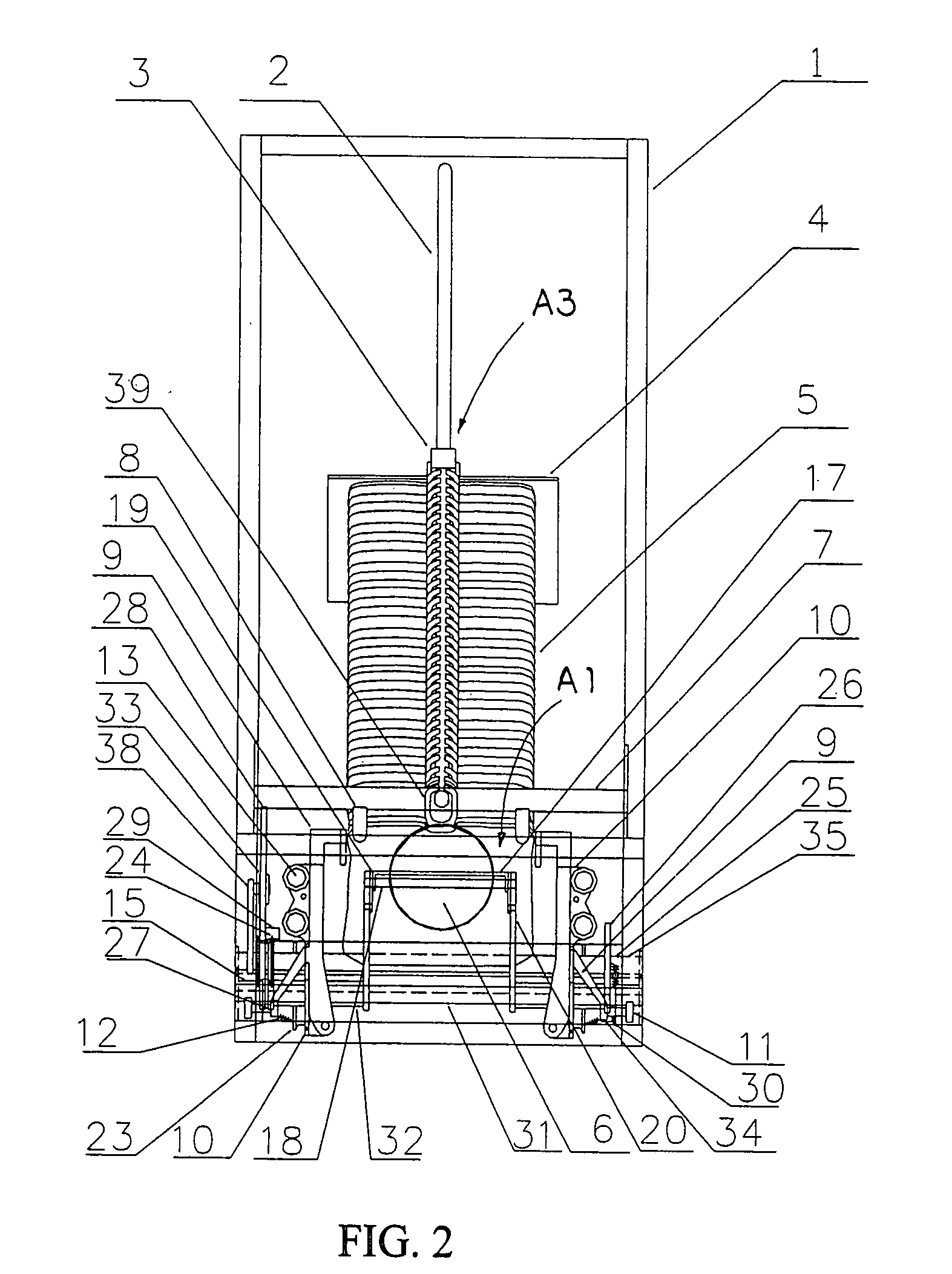
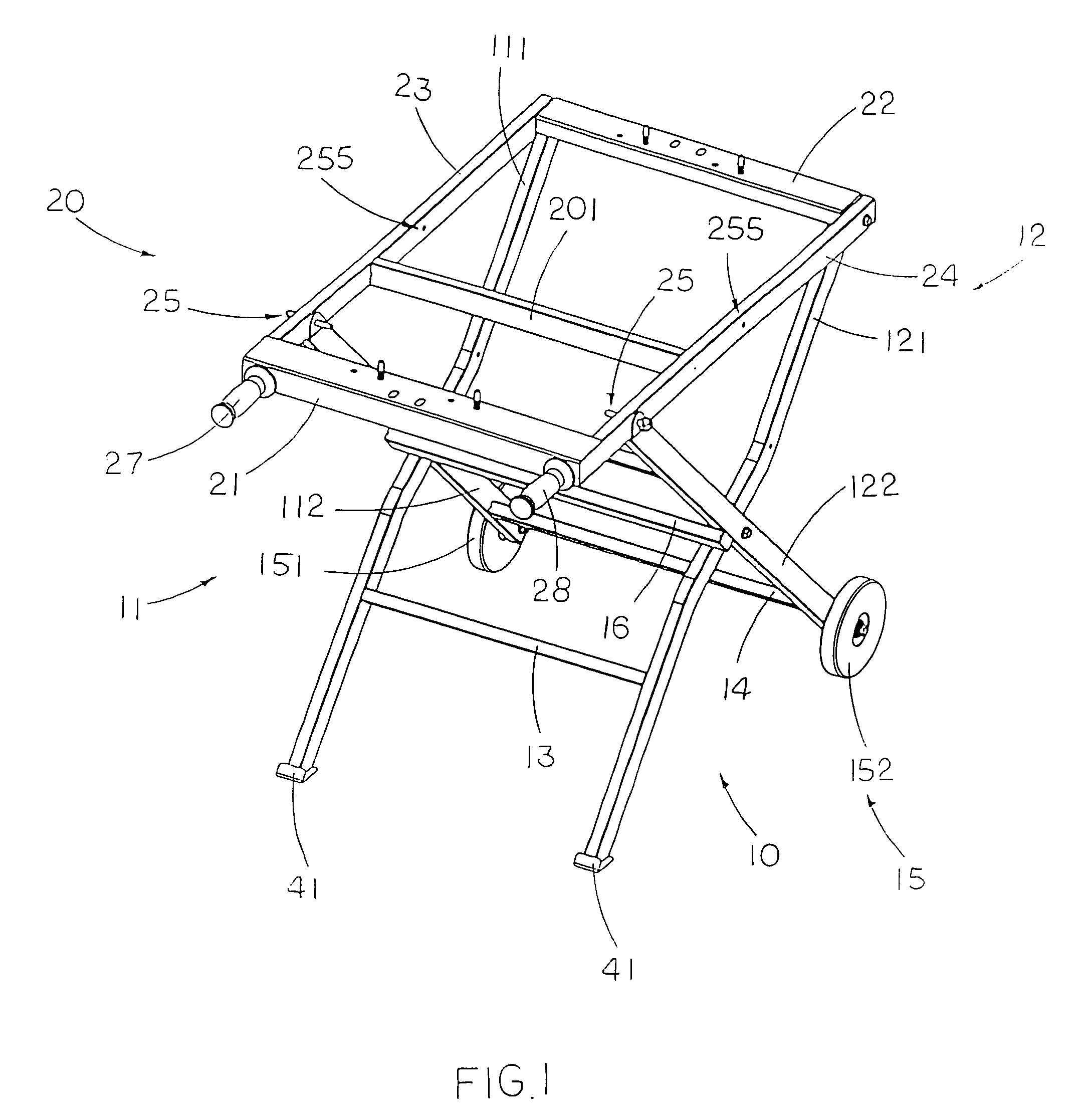
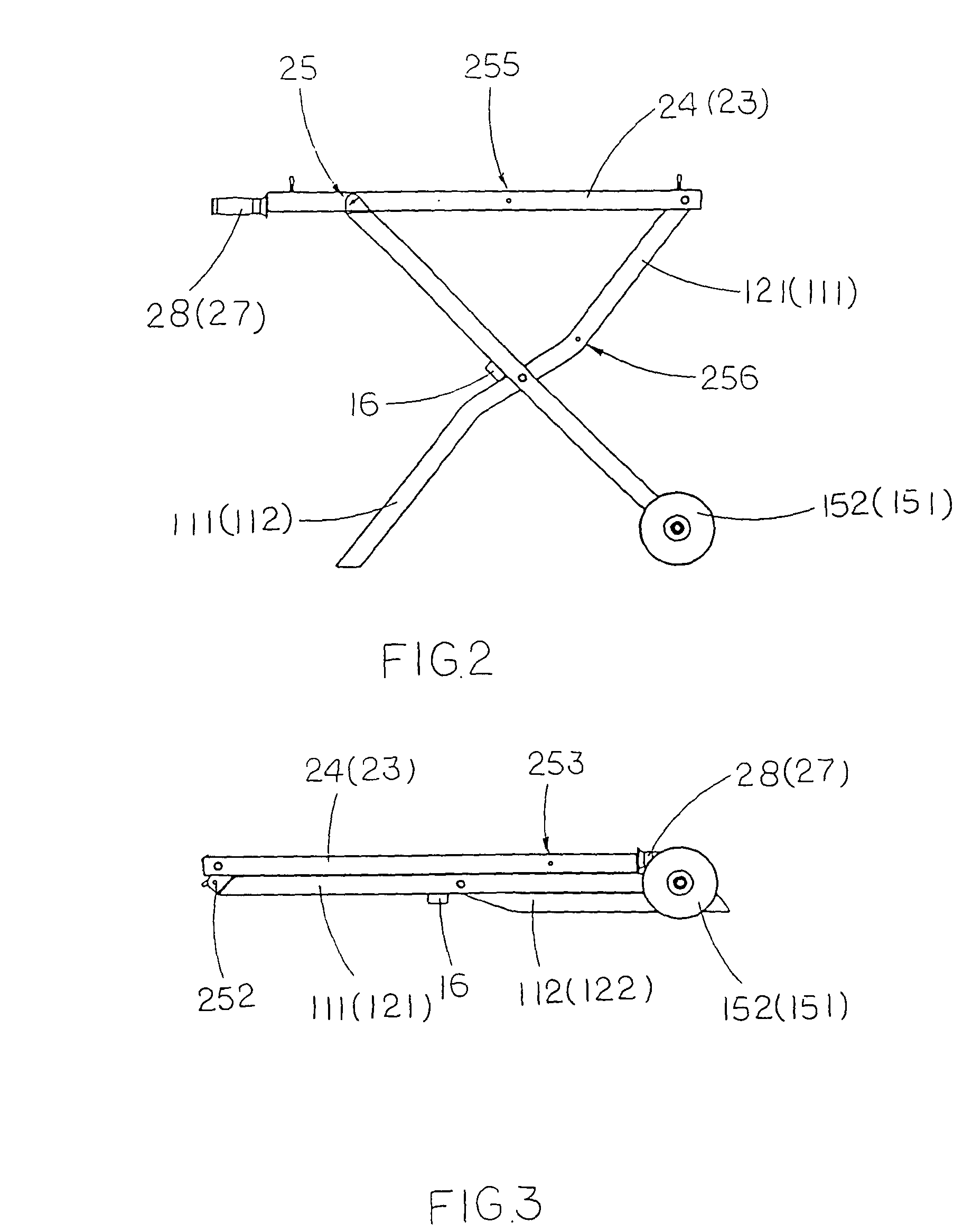
Portable supporting frame for cutting machine
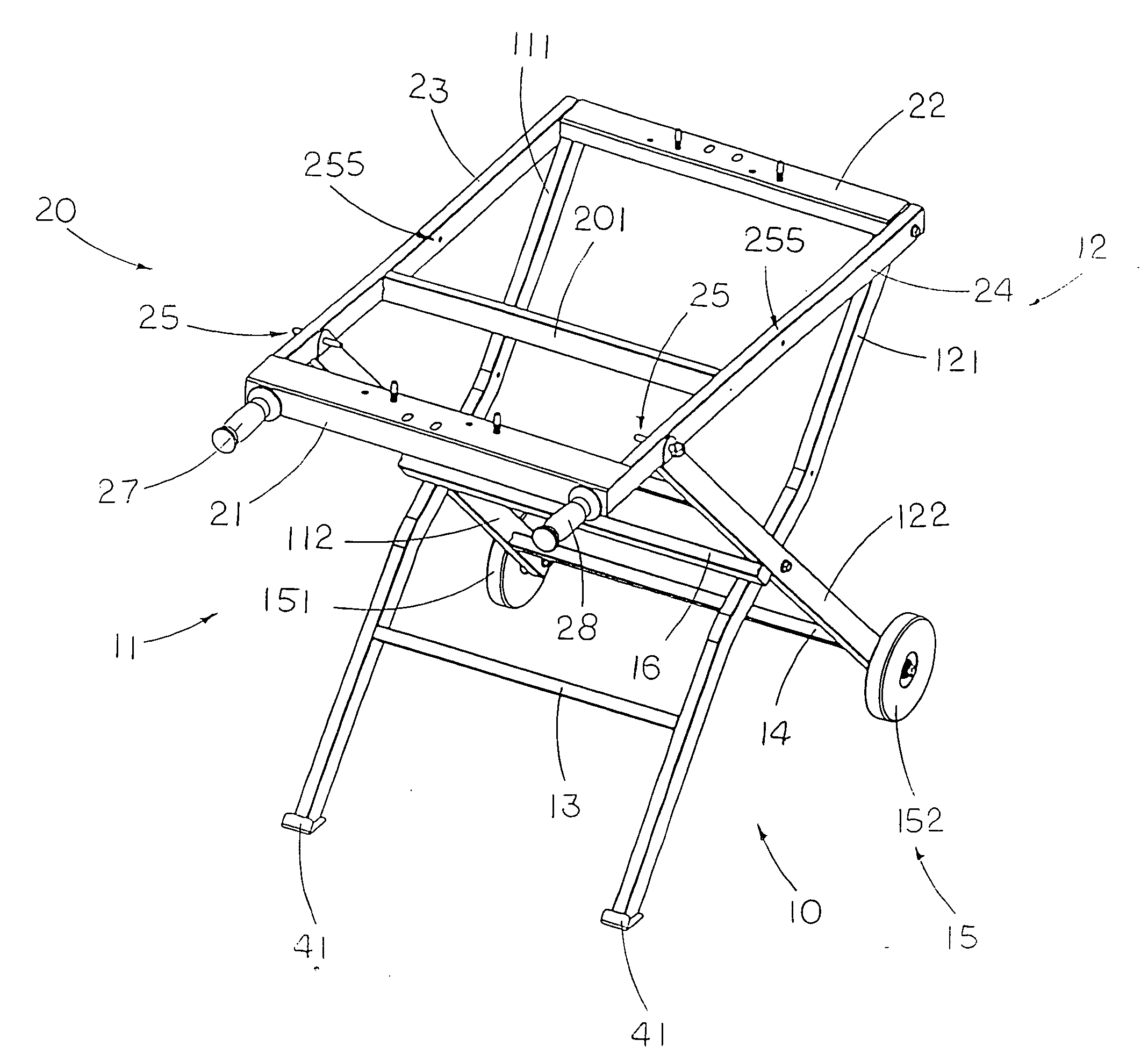
InactiveUS7882870B2Easy to foldSimple structureUnderstructuresFoldable cyclesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A portable supporting frame for a cutting machine includes a leg frame, a tabletop frame, and a frame locker. The leg frame includes two opposing pairs of first and second supporting legs. The tabletop frame includes two table arms pivotally connected to the first crossed legs respectively. The frame locker is used for locking the top ends of the second crossed legs to the table arms respectively to retain the portable supporting frame at a set up position. When the frame locker is released, the tabletop frame is adapted to pivotally fold at 180° to overlap on the folded leg frame at a folded position.
Owner:LEE WY PERON
Automatic shoe cover dispenser
ActiveUS7775396B2The process is stable and efficientEfficient and stable processingApparel holdersRegistering devicesEngineeringFootplate
Owner:XU LIANG JIE
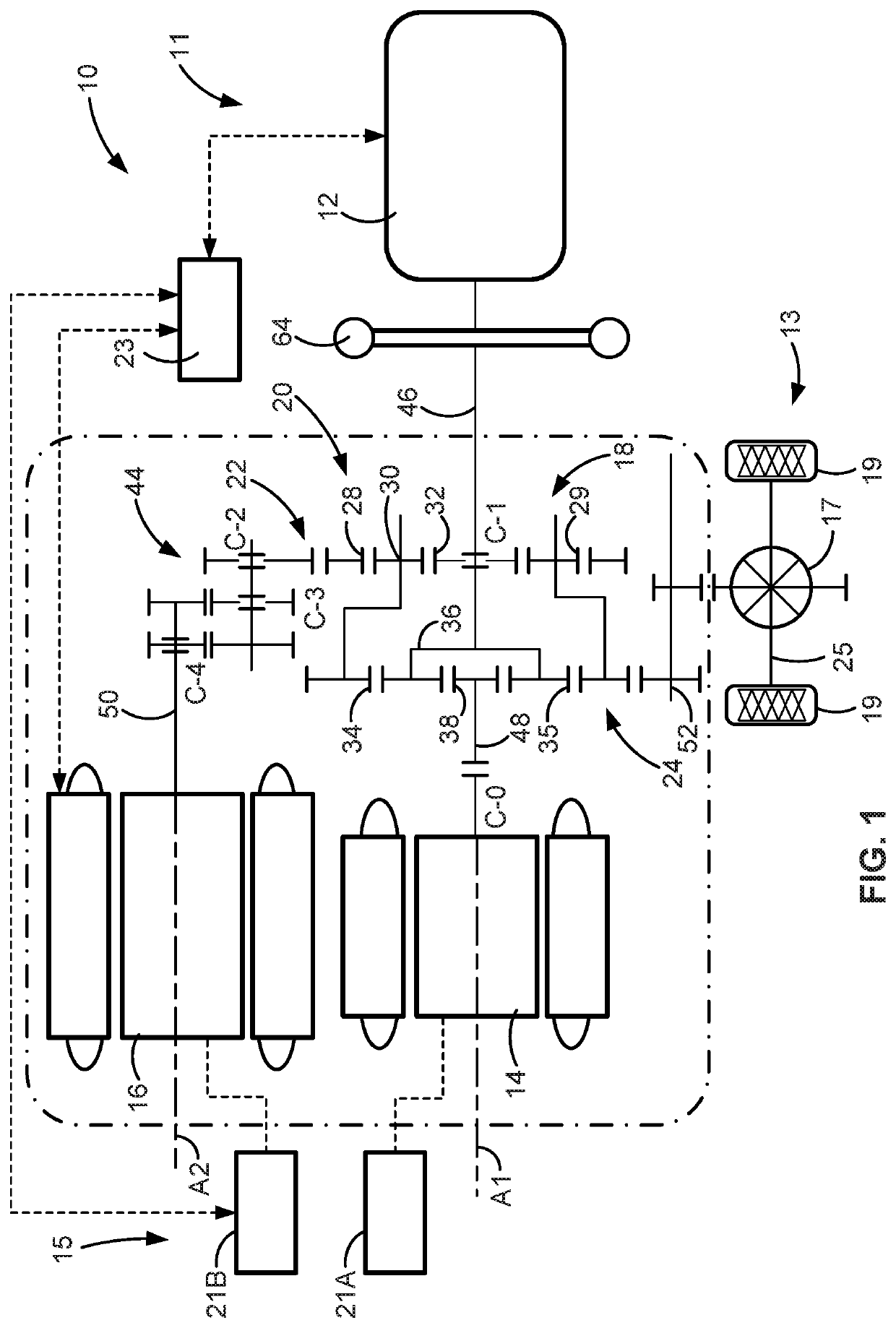
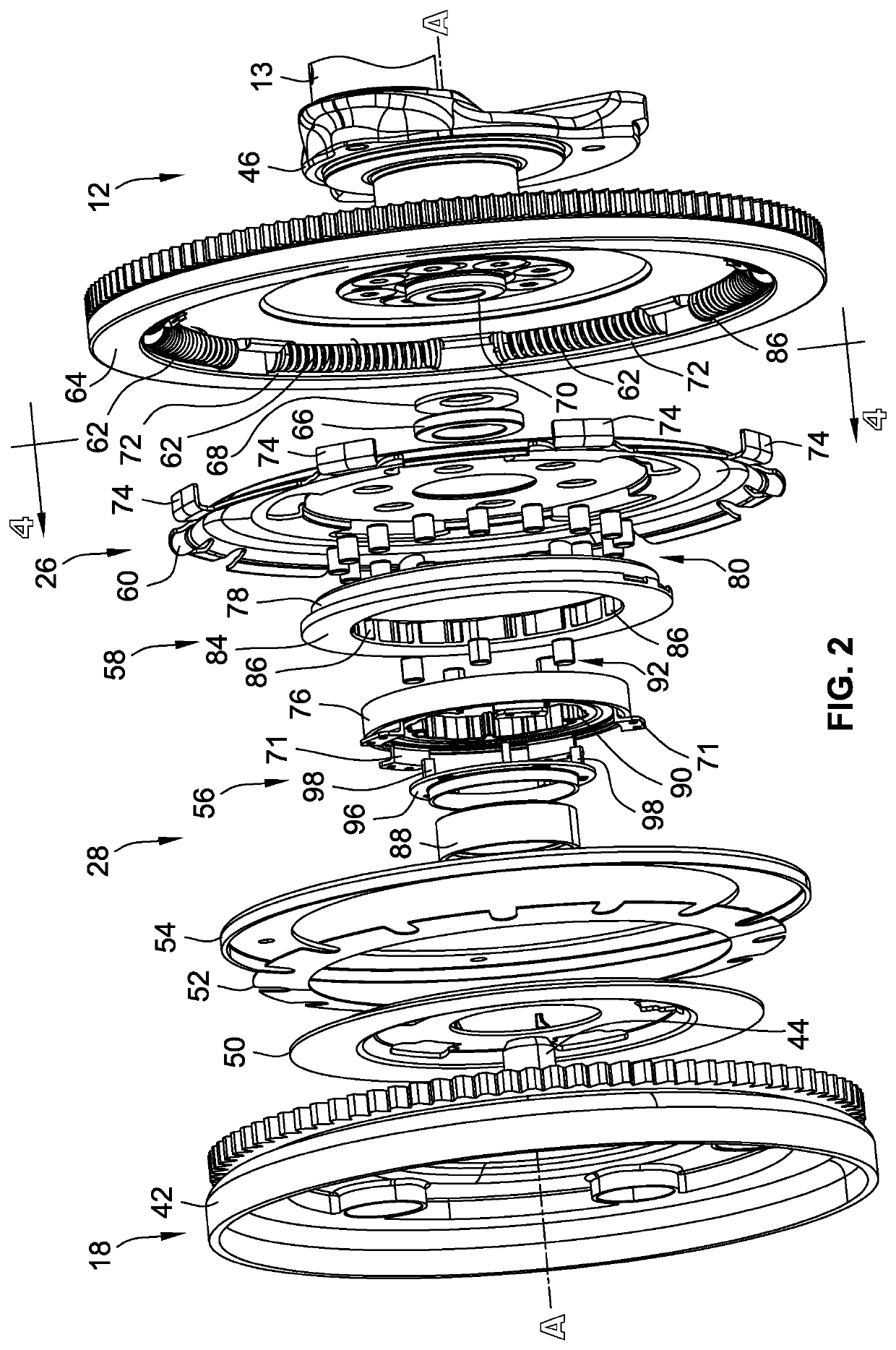
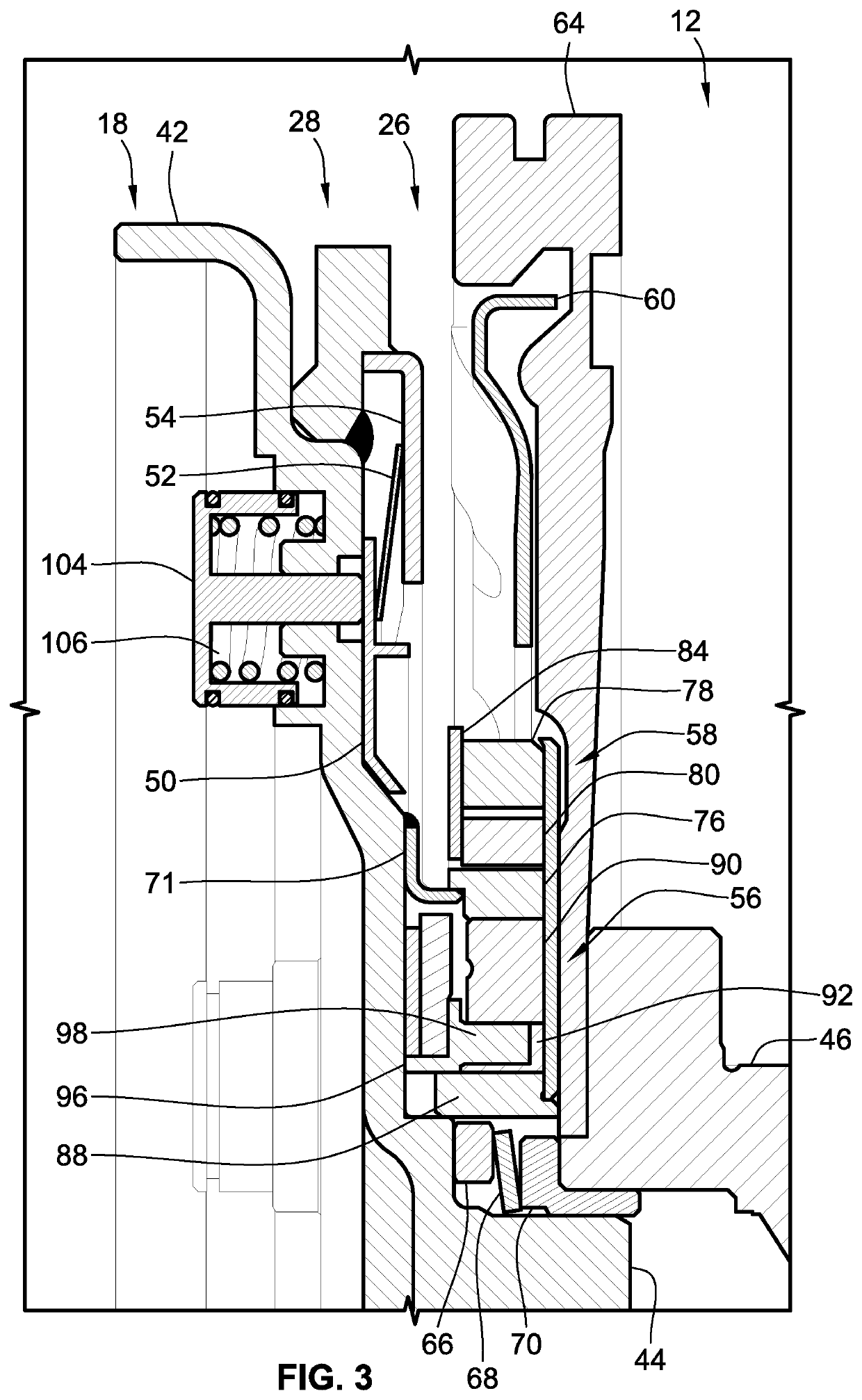
Engine disconnect clutches having torque converter feed-through activation for vehicle powertrains
ActiveUS10293674B1Minimize powertrain system complexityLow costHybrid vehiclesRotary clutchesImpellerBiological activation
Presented are engine disconnect clutches, methods for making / using such clutch devices, and vehicles with an engine that is coupled to / decoupled from a transmission and motor via a disconnect clutch. A vehicle includes a transmission with an input shaft connected with a transmission gearing arrangement, and an output shaft connecting the gearing arrangement with the vehicle's wheels. A torque converter pump housing drivingly connects to the vehicle's traction motor. A turbine is mounted inside the pump housing in fluid communication with an impeller. A turbine shaft connects the turbine to the transmission's input shaft. A clutch hub of a disconnect clutch drivingly connects to the vehicle's engine and selectively attaches to the pump housing. The disconnect clutch selectively connects the engine to the motor and transmission by drawing oil from the transmission's oil sump, through a turbine shaft channel and a pump housing port, and into a clutch hub cavity.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
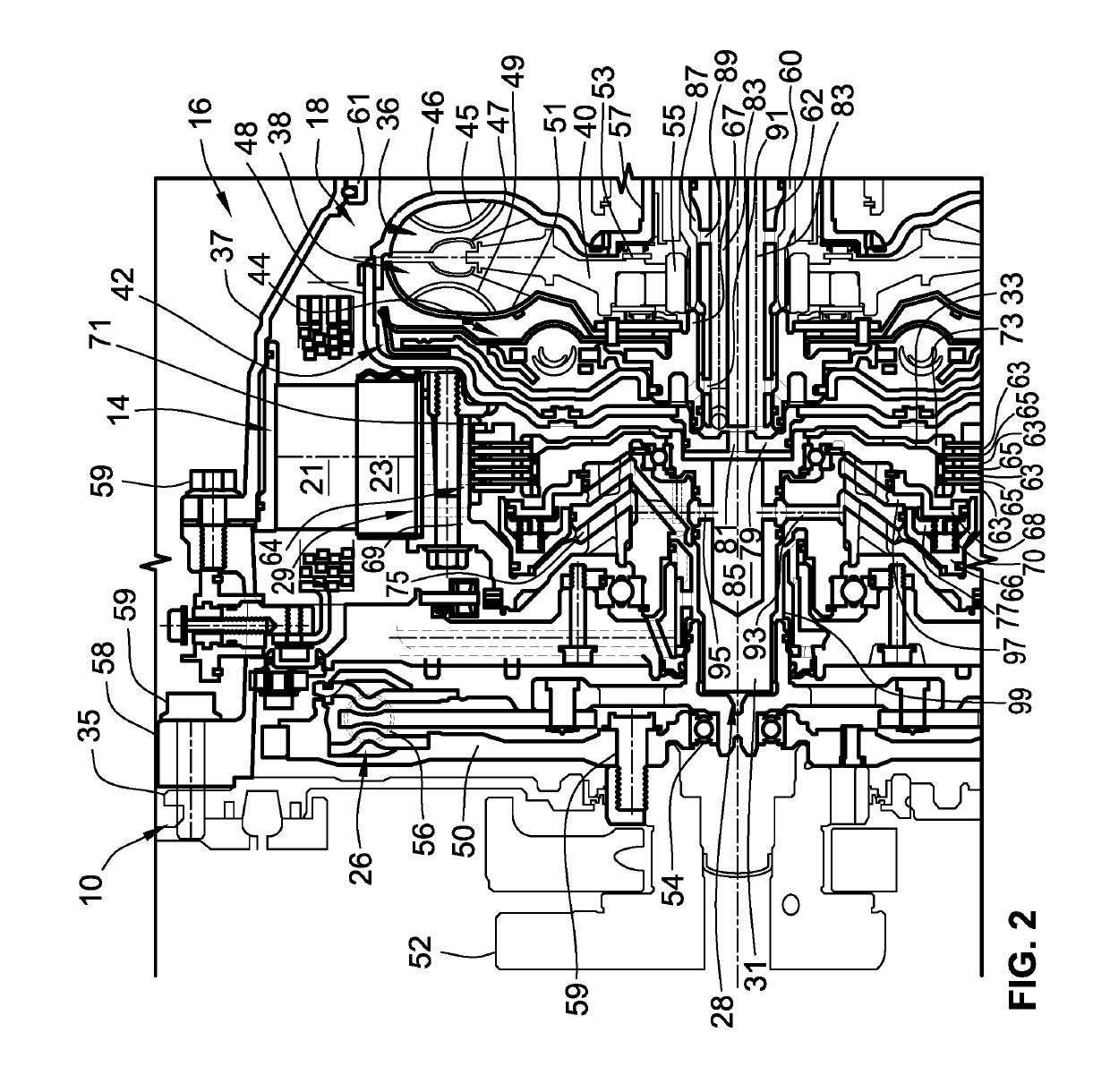
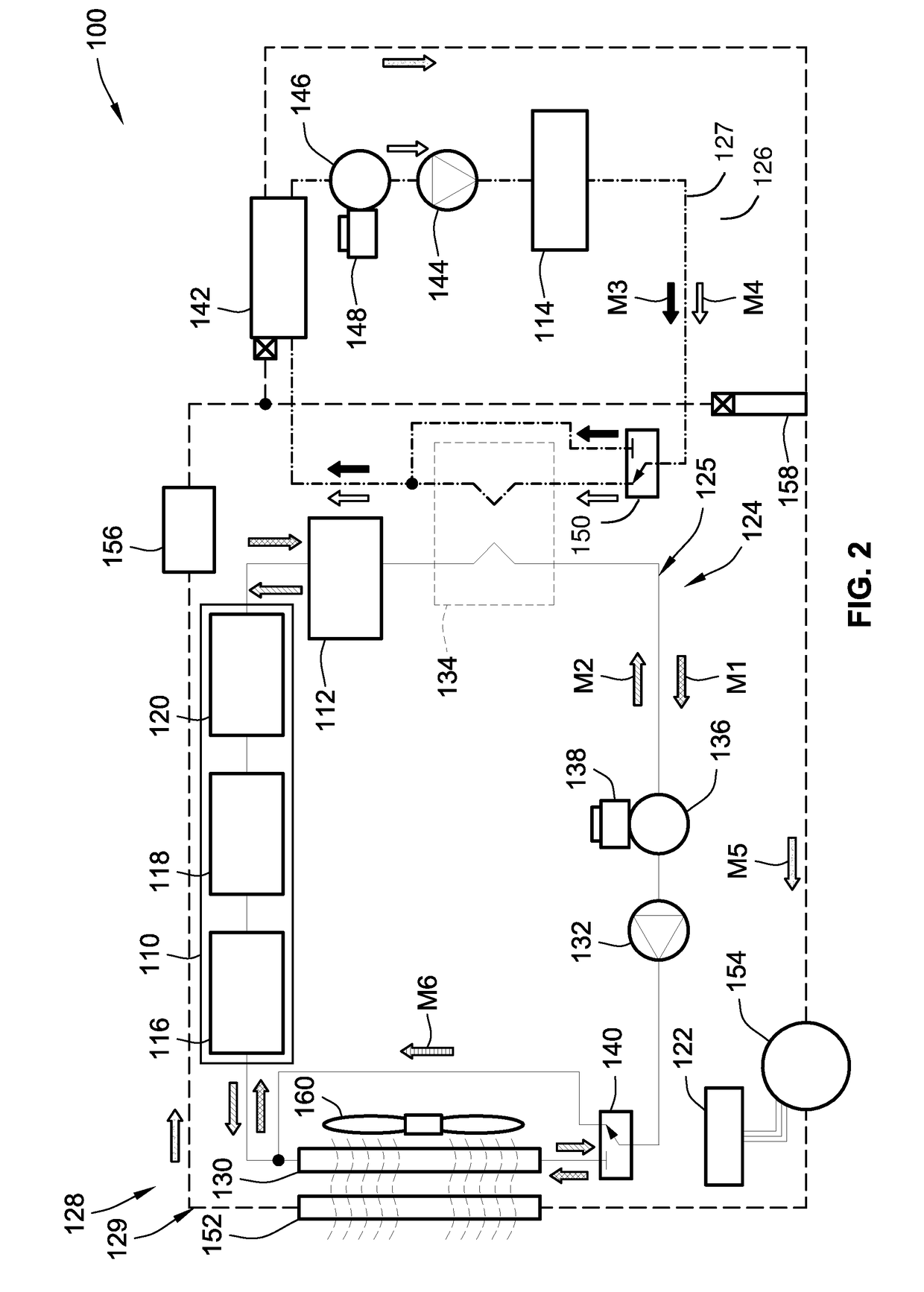
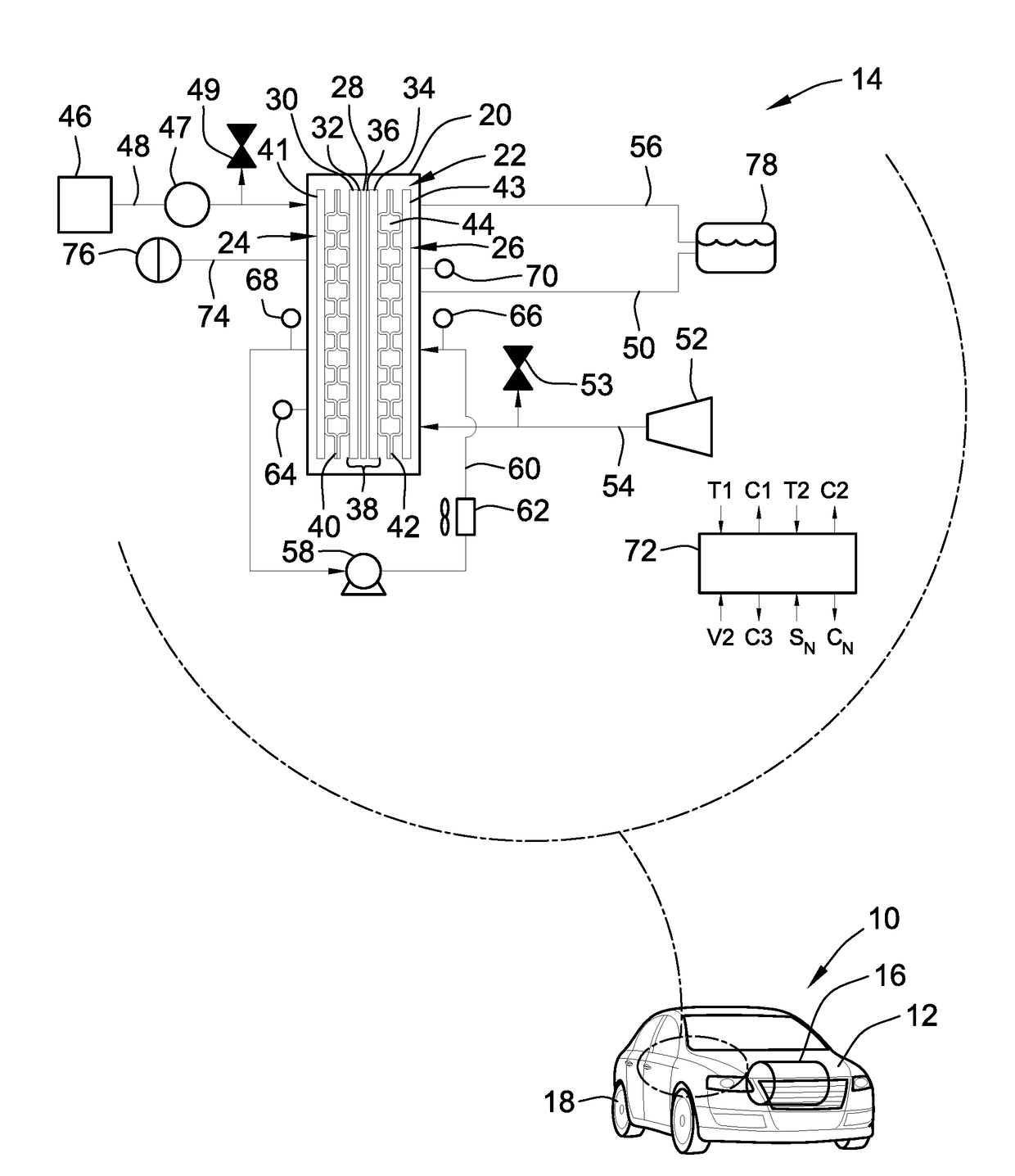
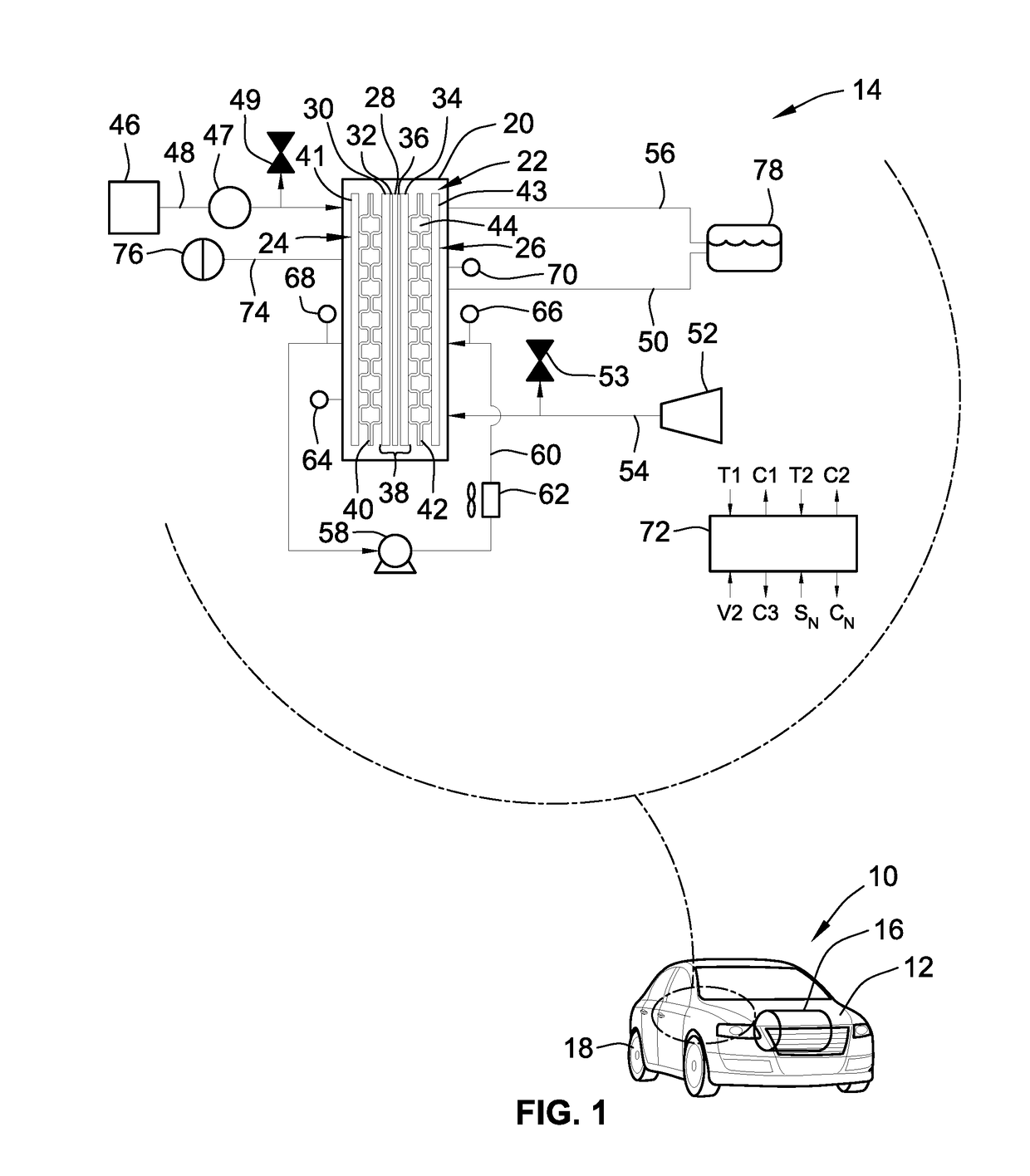
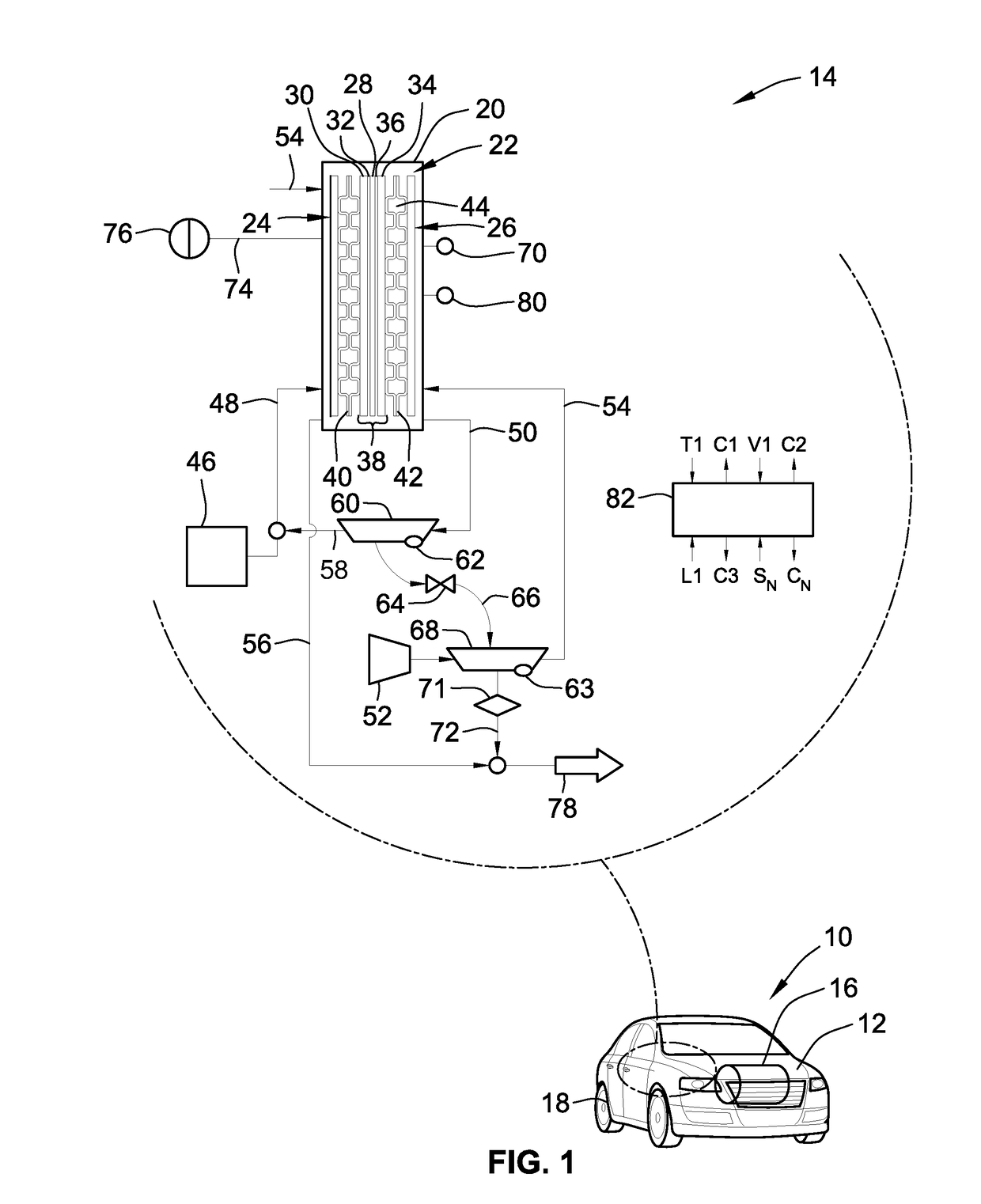
Joint active thermal management system and control logic for hybrid and electric vehicles
InactiveUS20190039434A1Inexpensive costInexpensive efficiencyHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresThermal management systemEngineering
Disclosed are joint active thermal management (ATM) systems for electric-drive vehicles, control logic for operating such ATM systems, and electric-drive vehicles equipped with a joint ATM system for heating / cooling the powertrain's drive unit (DU) section, power electronics (PE) section, and rechargeable energy storage system (RESS) section. A disclosed active thermal management system includes a first coolant loop with fluid conduits fluidly connecting a first electronic heat exchanger and a first pump with the DU and PE sections. The ATM system also includes a second coolant loop with fluid conduits fluidly connecting a second electronic heat exchanger and a second pump with the RESS section. A coolant-to-coolant heat exchanger, which is fluidly connected to the first and second coolant loops, is operable to selectively transfer heat between the coolant fluid circulating in the first set of fluid conduits and the coolant fluid circulating in the second set of fluid conduits.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Battery state estimation control logic and architectures for electric storage systems
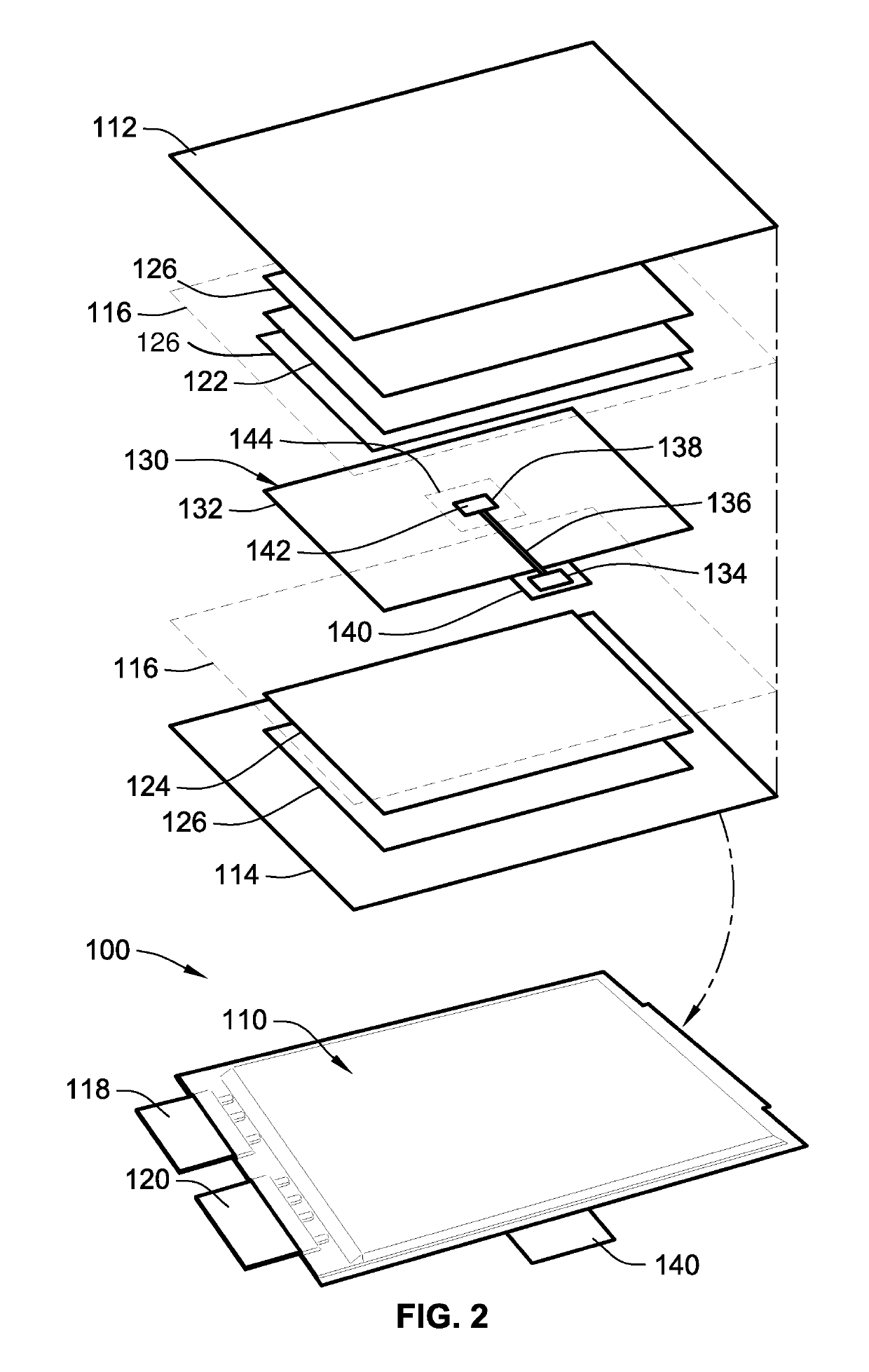
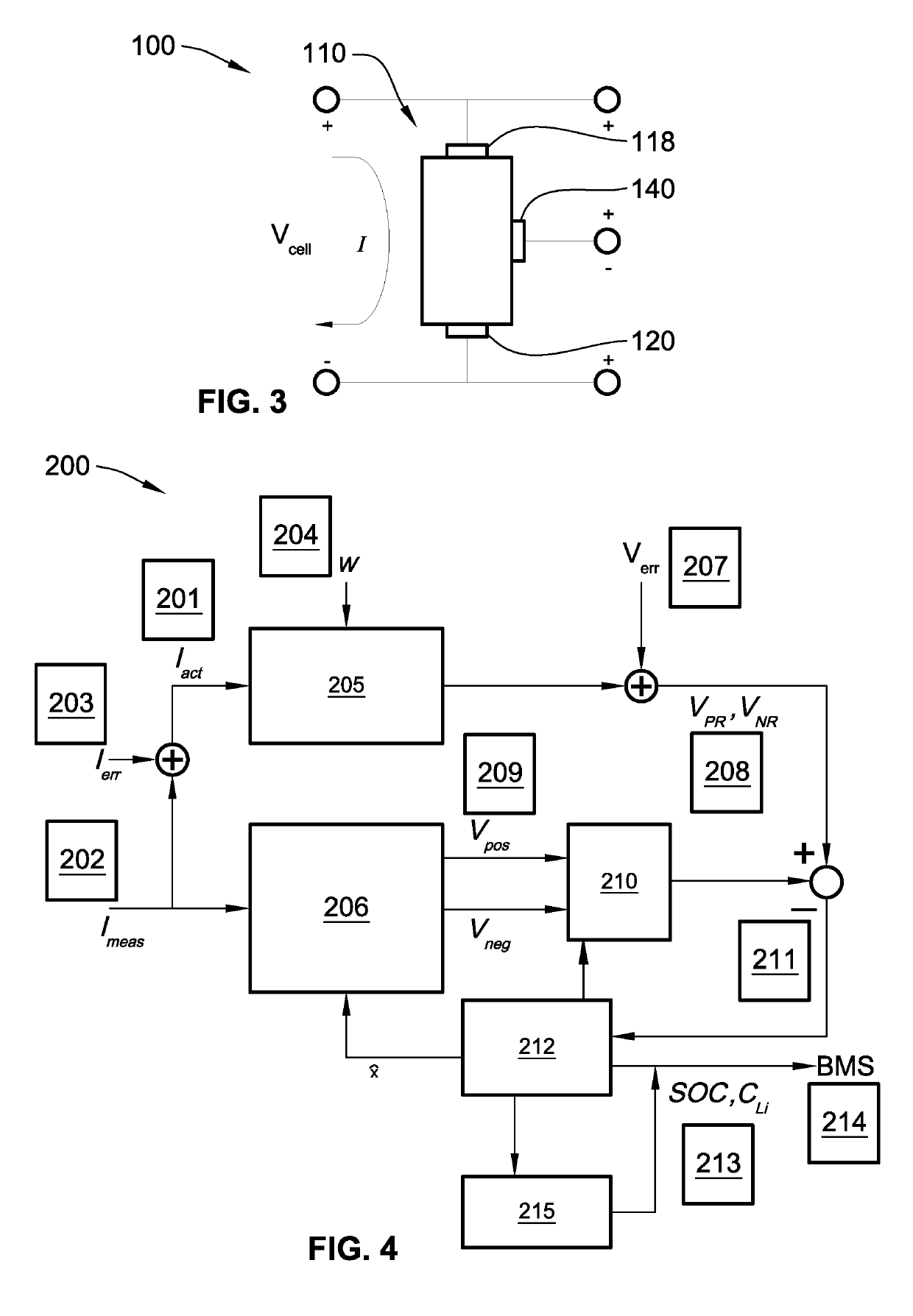
ActiveUS20190126770A1Eliminate uncertaintyLarge uncertaintyBatteries circuit arrangementsFinal product manufactureIonElectric drive
Disclosed are battery management systems with control logic for battery state estimation (BSE), methods for making / using / assembling a battery cell with a reference electrode, and electric drive vehicles equipped with a traction battery pack and BSE capabilities. In an example, a battery cell assembly includes a battery housing with an electrolyte composition stored within the battery housing. The electrolyte composition transports ions between working electrodes. A first working (anode) electrode is attached to the battery housing in electrochemical contact with the electrolyte composition. Likewise, a second working (cathode) electrode is attached to the battery housing in electrochemical contact with the electrolyte composition. A reference electrode is interposed between the first and second working electrodes, placed in electrochemical contact with the electrolyte composition. The reference electrode and one or both working electrodes cooperate to output a half-cell voltage signal that is indicative of a battery state of the battery cell assembly.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Multi-mode engine-disconnect clutch assemblies and control logic for hybrid electric vehicles
ActiveUS20190168731A1Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerTorque transmissionEngineering
Presented are engine-disconnect clutches with attendant control logic, methods for making / operating such disconnect clutches, and hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) equipped with an engine that is coupled to / decoupled from a transmission and electric motor via a disconnect clutch. A representative method for controlling an HEV powertrain includes receiving an HEV powertrain operation command, then determining a clutch mode of a multi-mode clutch device to execute the HEV powertrain operation. This multi-mode clutch device is operable in: a lock-lock mode, in which the clutch device transmits torque to and from the engine; a free-free mode, in which the clutch device disconnects the engine's output member from the transmission's input member, preventing torque transmission to and from the engine; a lock-free mode, in which the clutch device transmits torque from but not to the engine; and, a free-lock mode, in which the clutch device transmits torque to but not from the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Portable supporting frame for cutting machine
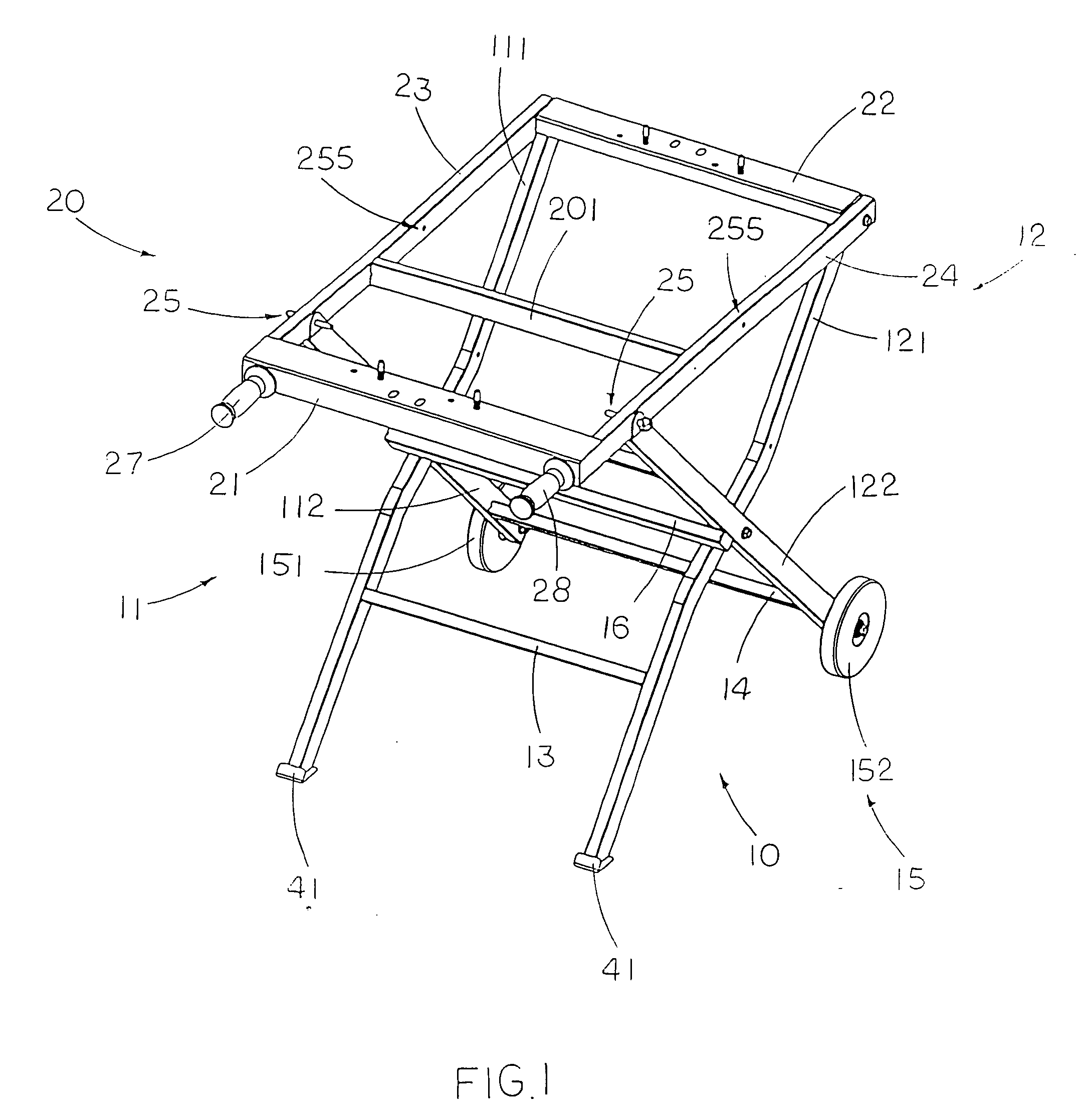
InactiveUS20090133780A1Easy to foldSimple structureUnderstructuresFoldable cyclesBraced frameEngineering
A portable supporting frame for a cutting machine includes a leg frame, a tabletop frame, and a frame locker. The leg frame includes two opposing pairs of first and second supporting legs. The tabletop frame includes two table arms pivotally connected to the first crossed legs respectively. The frame locker is used for locking the top ends of the second crossed legs to the table arms respectively to retain the portable supporting frame at a set up position. When the frame locker is released, the tabletop frame is adapted to pivotally fold at 180° to overlap on the folded leg frame at a folded position.
Owner:LEE WY PERON
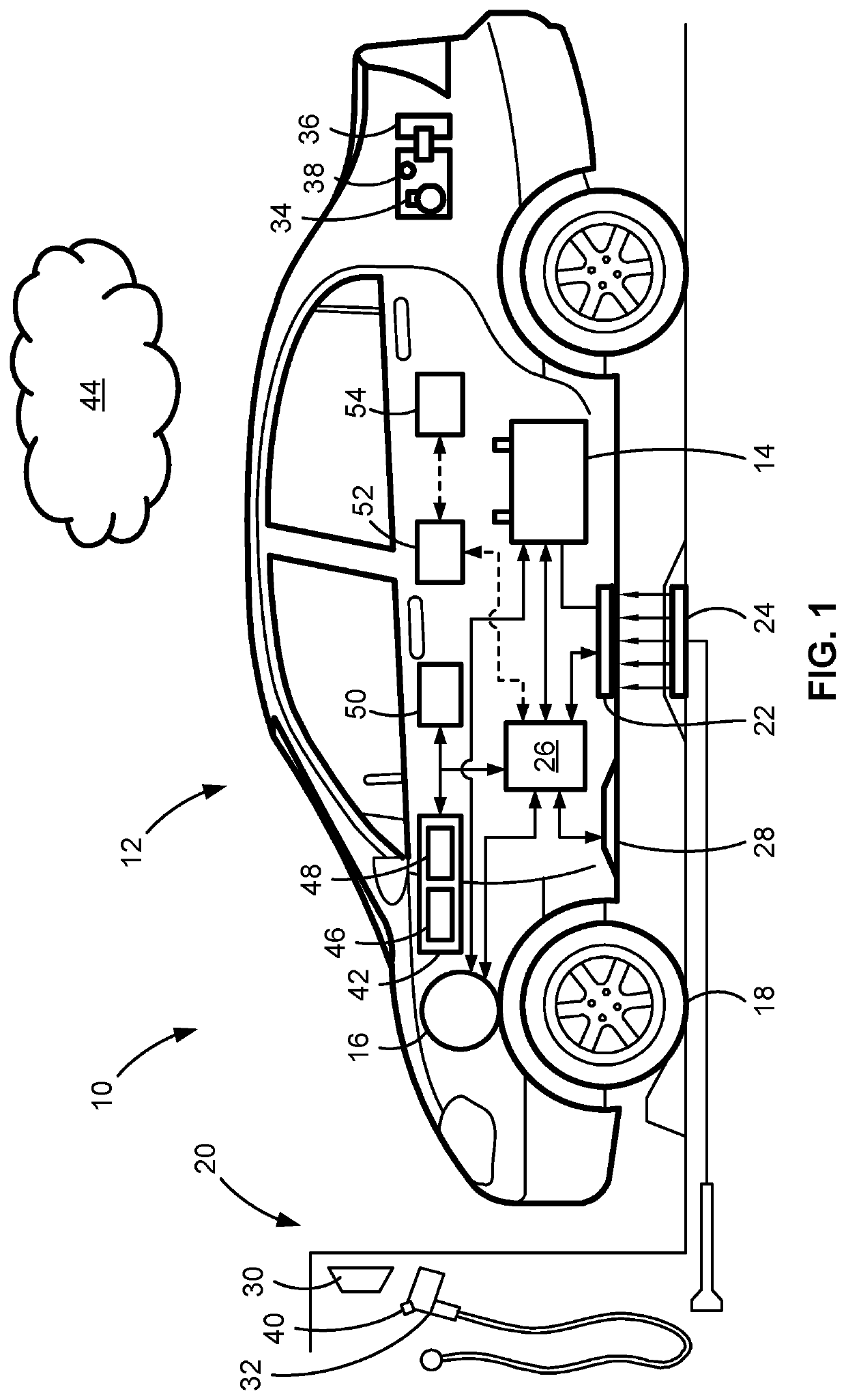
Intelligent vehicles with advanced vehicle camera systems for underbody hazard and foreign object detection
ActiveUS20210237594A1Improve charging efficiencyMaintaining high level of overall system robustnessRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCircuit arrangementsForeign matterDriver/operator
A method for operating an advanced driver assistance (ADAS) system of a motor vehicle includes a vehicle controller receiving, from side and end cameras mounted to the vehicle, camera signals indicative of real-time images of outboard-facing side and end views of the vehicle. The controller determines a region of interest (ROI) inset within each end / side view within which is expected foreign objects and / or hazards. These ROIs are analyzed to detect if a foreign object / hazard is present in the vehicle's end and / or side views. Responsive to detecting the foreign object / hazard, movement of the foreign object / hazard is tracked to determine if the foreign object / hazard moves towards or away from the vehicle's underbody region. If the foreign object / hazard moves to the underbody region, control signals are transmitted to the vehicle's propulsion and / or steering system to automate preventative action that prevents collision of the vehicle with and / or removes the foreign object / hazard from the underbody.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Electronic Apparatus And Controlling Component And Controlling Method For The Electronic Apparatus
InactiveUS20110136543A1Cost reductionInexpensive costDigital data processing detailsSubstation equipmentElectric equipmentTouchscreen
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
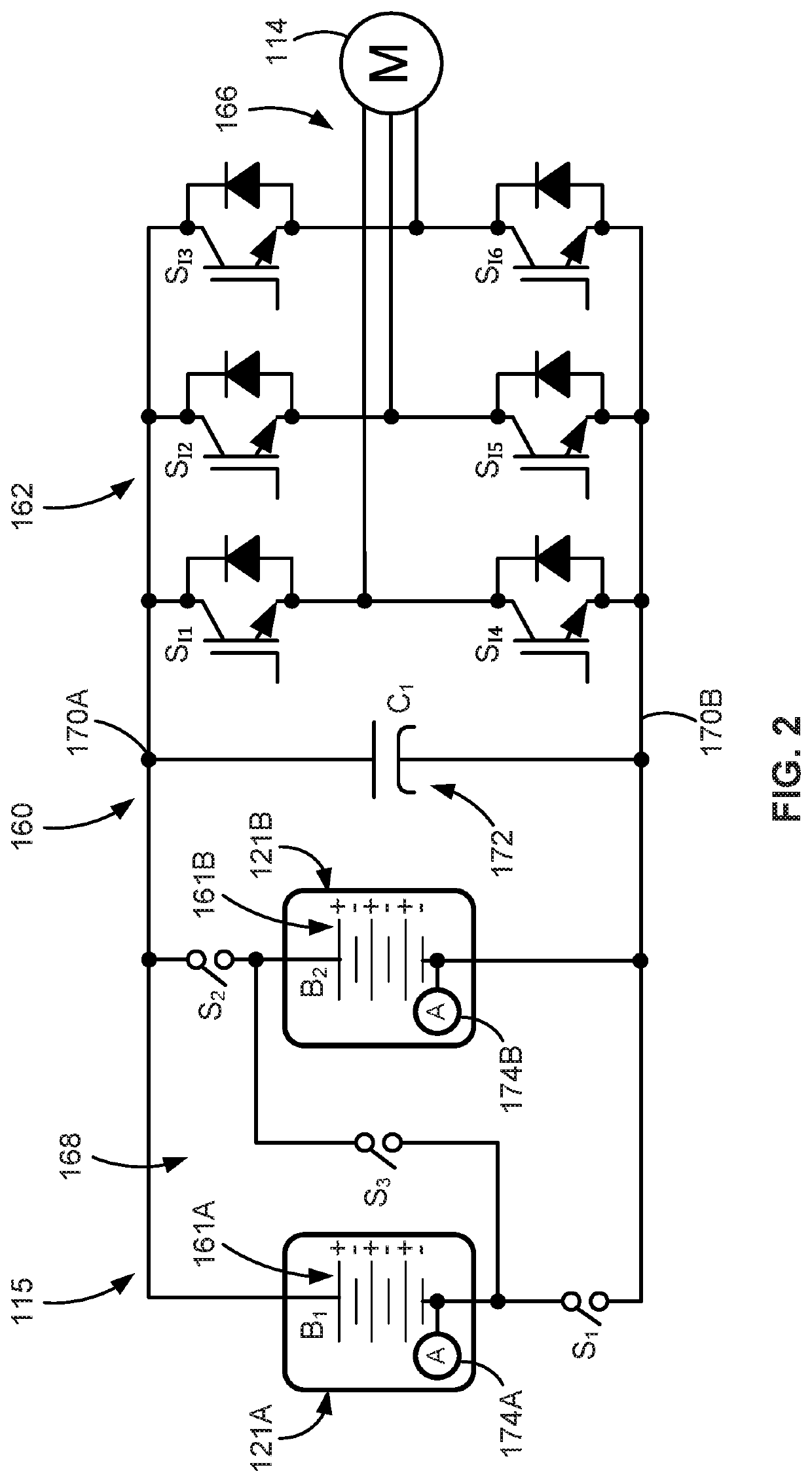
Battery pack voltage-switching systems and control logic for multi-pack electric-drive motor vehicles
ActiveUS20200235440A1Improve motor efficiencyIncrease propulsion powerElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical batteryDrive motor
Presented are battery pack voltage-switching (“V-switch”) systems, methods for making / operating such systems, and multi-pack, electric-drive motor vehicles with battery pack V-switch capabilities. A method for controlling operation of a vehicle includes a vehicle controller receiving a voltage switch signal to change a voltage output of the vehicle's battery system. The vehicle controller determines if a speed of a traction motor is less than a calibrated base speed; if so, the controller transmits a pack isolation signal to a power inverter to electrically disconnect the traction battery packs from the traction motor. The vehicle controller determines if a bus current of a DC bus is less than a calibrated bus current threshold; if so, the controller transmits an open signal to open one or more pack contactor switches and a close signal to close one or more pack contactor switches thereby causing the vehicle battery system to output the second voltage.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
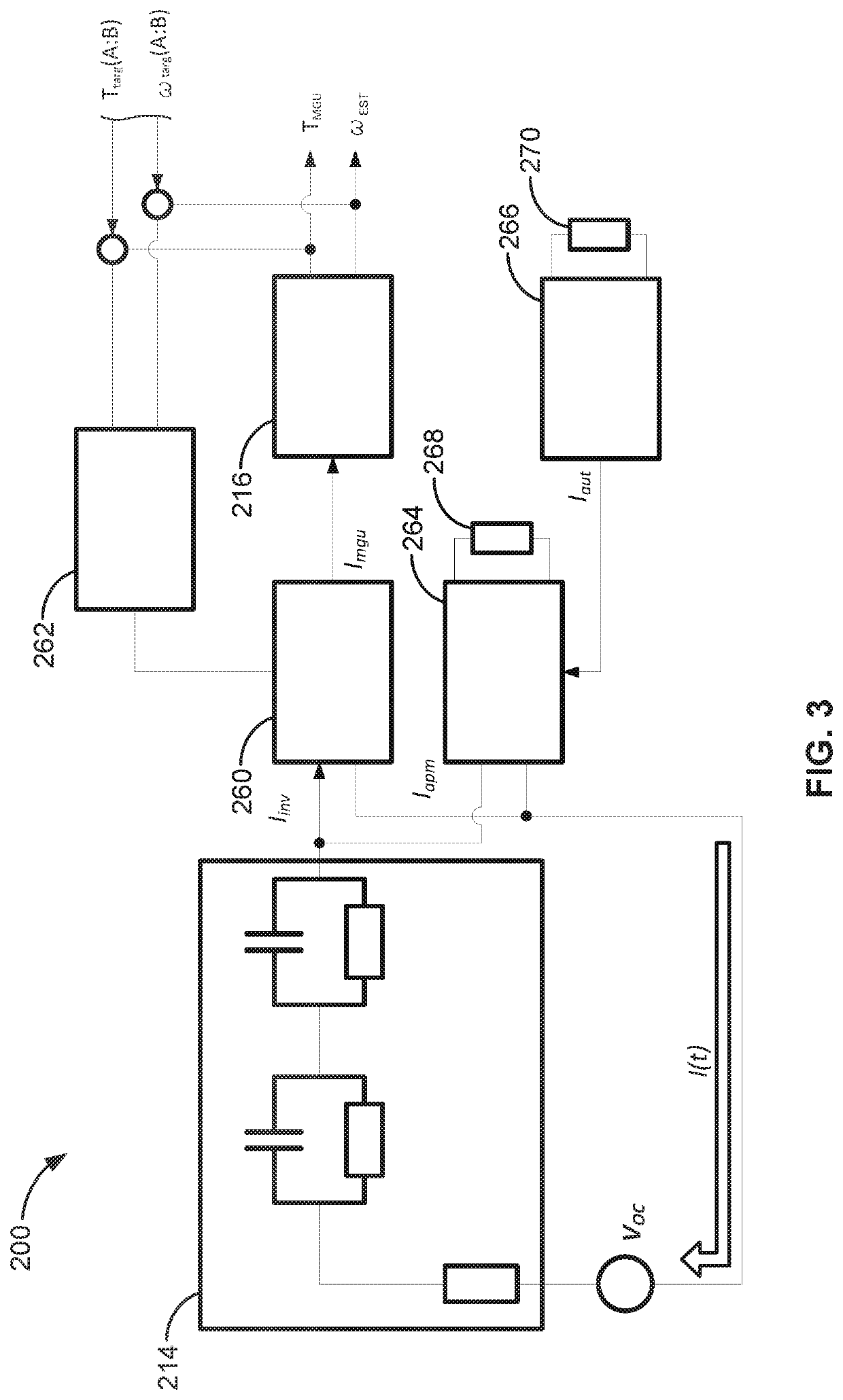
Coordinated torque and speed control systems and logic for hybrid electric vehicles
ActiveUS20190232941A1Improve fuel economyIncreased disturbance rejectionHybrid vehiclesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingSpeed control systemControl system
Presented are model-based control systems for operating parallel hybrid powertrains, methods for making / using such systems, and motor vehicles with parallel hybrid powertrains and model-based torque and speed control capabilities. A method for controlling operation of a hybrid powertrain includes receiving a command signal for a hybrid powertrain operation associated with a driver input and a current operating mode of the powertrain. A desired output torque for executing the powertrain operation is then determined. The method determines if a speed differential between an engine speed of an engine and a torque converter output speed of a torque converter is less than a calibrated threshold; if so, the method responsively engages a clutch device to operatively connect the engine's output member to the transmission's input member. Engine torque is then coordinated with motor torque such that the sum of the engine and motor torques is approximately equal to the desired output torque.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Battery pack balancing systems and control logic for multi-pack electric-drive motor vehicles
ActiveUS20200223422A1Guaranteed safe operationImprove battery system efficiencyHybrid vehiclesCharge equalisation circuitDrive motorControl theory
Presented are traction battery pack balancing systems, methods for making / operating such systems, and multi-pack, electric-drive motor vehicles with battery pack balancing capabilities. A method for controlling operation of a motor vehicle includes a vehicle controller: receiving a key-off command signal to power off the motor vehicle; determining if a difference between corresponding electrical characteristics of first and second traction battery packs is greater than a calibrated characteristic differential threshold; determining if a difference between corresponding battery pack capacities of the first and second traction battery packs is greater than a calibrated capacity differential threshold; and, responsive to the characteristic difference not being greater than the calibrated characteristic differential threshold and the capacity difference being greater than the calibrated capacity differential threshold, transmitting a key-on command signal to power on the motor vehicle, and a pack balancing command signal to reduce the capacity difference to below the calibrated capacity differential threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
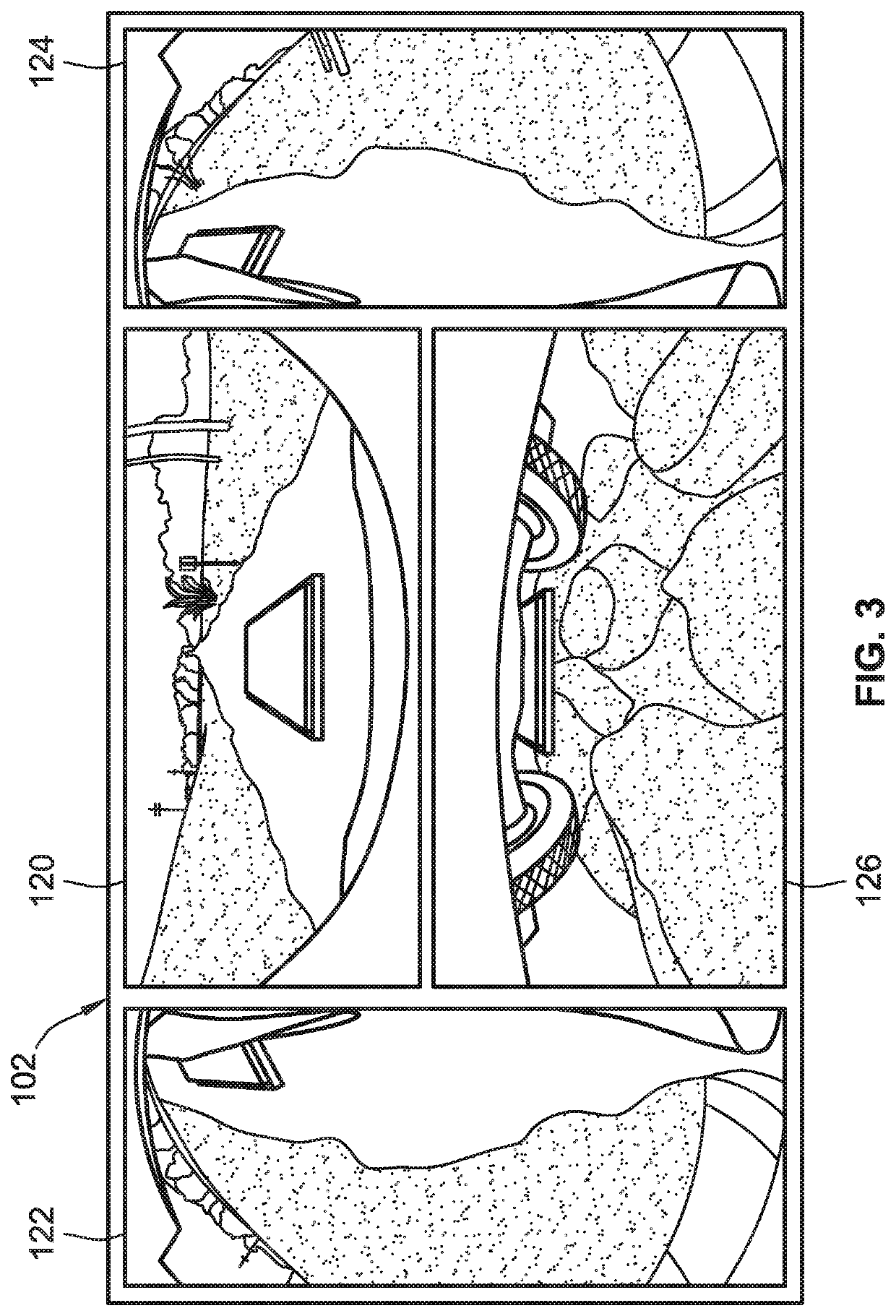
Intelligent vehicles, control logic, and advanced park assist systems with camera-based automated vehicle alignment
InactiveUS20210237716A1Improve charging efficiencyImprove the level ofTelevision system detailsCharging stationsControl signalControl engineering
A method for operating an advanced park assist system of a vehicle includes a vehicle controller receiving, from front and side cameras mounted proximate front and side sections of the vehicle, real-time images of the vehicle's forward-facing and side-facing views. These images are analyzed to detect target elements present in the vehicle's forward-facing and / or side-facing views. Responsive to detecting a target element, heading control signals are transmitted to the vehicle's steering system to reposition the vehicle and thereby locate the target element at the center of the forward-facing view and at the top of the side-facing view. Speed control signals are transmitted to the vehicle's propulsion system to propel the vehicle such that the target element disappears from the side-facing view and moves to a calibrated distance from the vehicle body's front end. The control signals are modulated to align the vehicle with a target marker of the target element.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Automatic shoe cover dispenser
ActiveUS8490842B2Stable and efficient procedureEffectively prevents the conventional shortcomingsSolesDispensing apparatusEngineering
Owner:OTO IND SHANGHAI
Electric-drive motor vehicles, systems, and control logic for predictive charge planning and powertrain control
ActiveUS10759298B2Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costHybrid vehiclesCharging stationsDriver/operatorGeolocation
Presented are intelligent vehicle systems and control logic for predictive charge planning and powertrain control of electric-drive vehicles, methods for manufacturing / operating such systems, and electric-drive vehicles with smart charge planning and powertrain control capabilities. Systems and methods of AI-based predictive charge planning for smart electric vehicles use machine-learning (ML) driver models that draws on available traffic, location, and roadway map information to estimate vehicle speed and propulsion torque requirements to derive a total energy consumption for a given trip. Systems and methods of AI-based predictive powertrain control for smart hybrid vehicles use ML driver models with deep learning techniques to derive a drive cycle profile defined by a preview route with available traffic, geopositional, geospatial, and map data. ML-generated driver models are developed with collected data to replicate driver behavior and predict the drive cycle profile, including predicted vehicle speed, propulsion torque, and accelerator / brake pedal positions for a preview route.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Intelligent motor vehicles, charging systems, and control logic for governing vehicle grid integration operations
ActiveUS11091055B2Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectric power transmissionElectrical battery
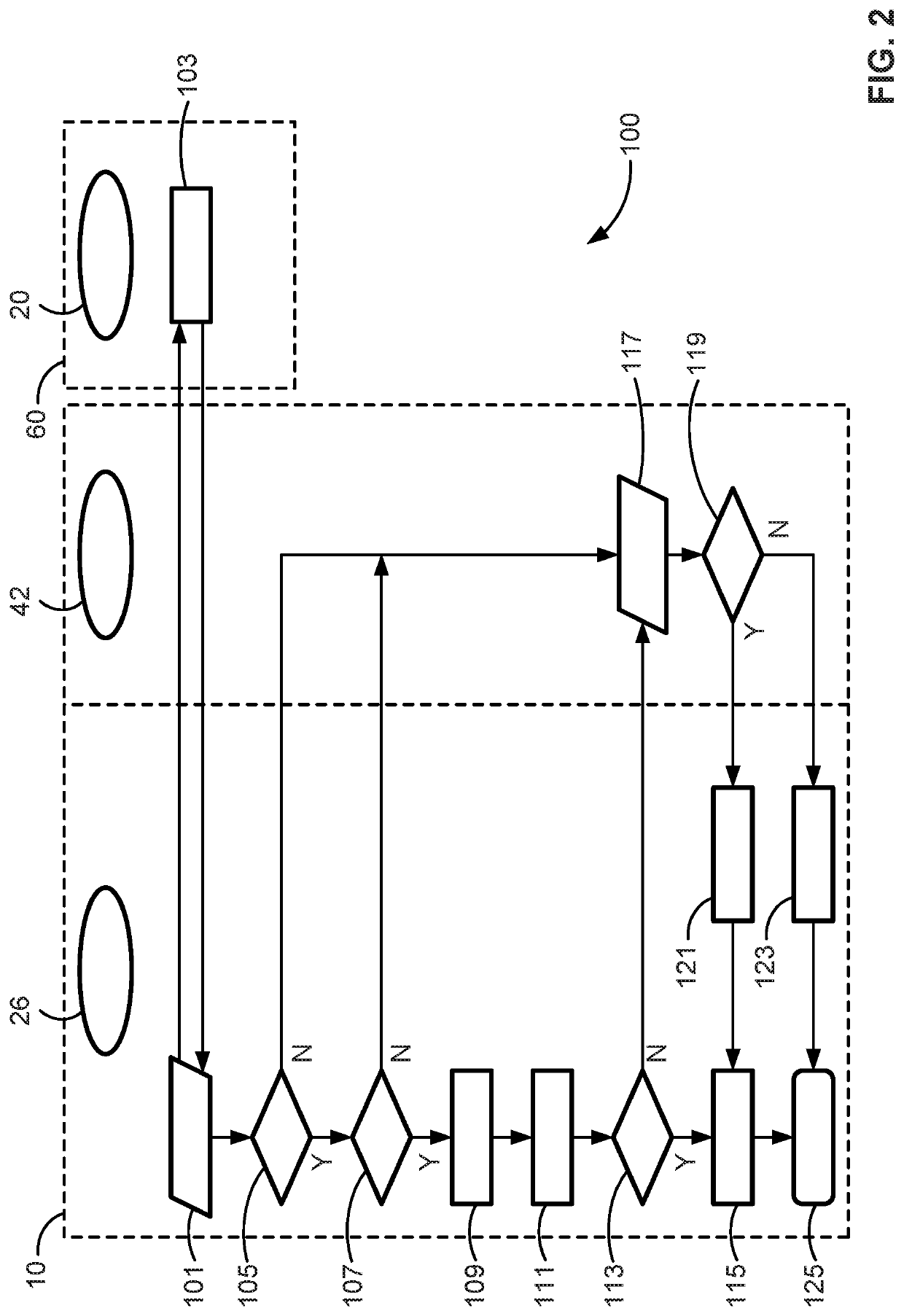
Presented are vehicle charging systems and control logic for provisioning vehicle grid integration (VGI) activities, methods for making / using such charging systems, and electric-drive vehicles with intelligent vehicle charging and VGI capabilities. A method of controlling charging operations of electric-drive vehicles includes a vehicle controller detecting if a vehicle is coupled to an electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), and determining if the vehicle's current mileage exceeds a calibrated mileage threshold. Responsive to the vehicle being connected to the EVSE and the vehicle's current mileage exceeding the calibrated mileage threshold, the controller determines the current remaining life of the vehicle's traction battery pack and the current time in service of the vehicle. The vehicle controller determines if the current remaining battery life exceeds a predicted remaining battery life corresponding to the current time in service. If so, the vehicle controller enables the traction battery pack to transmit electrical power to the EVSE.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
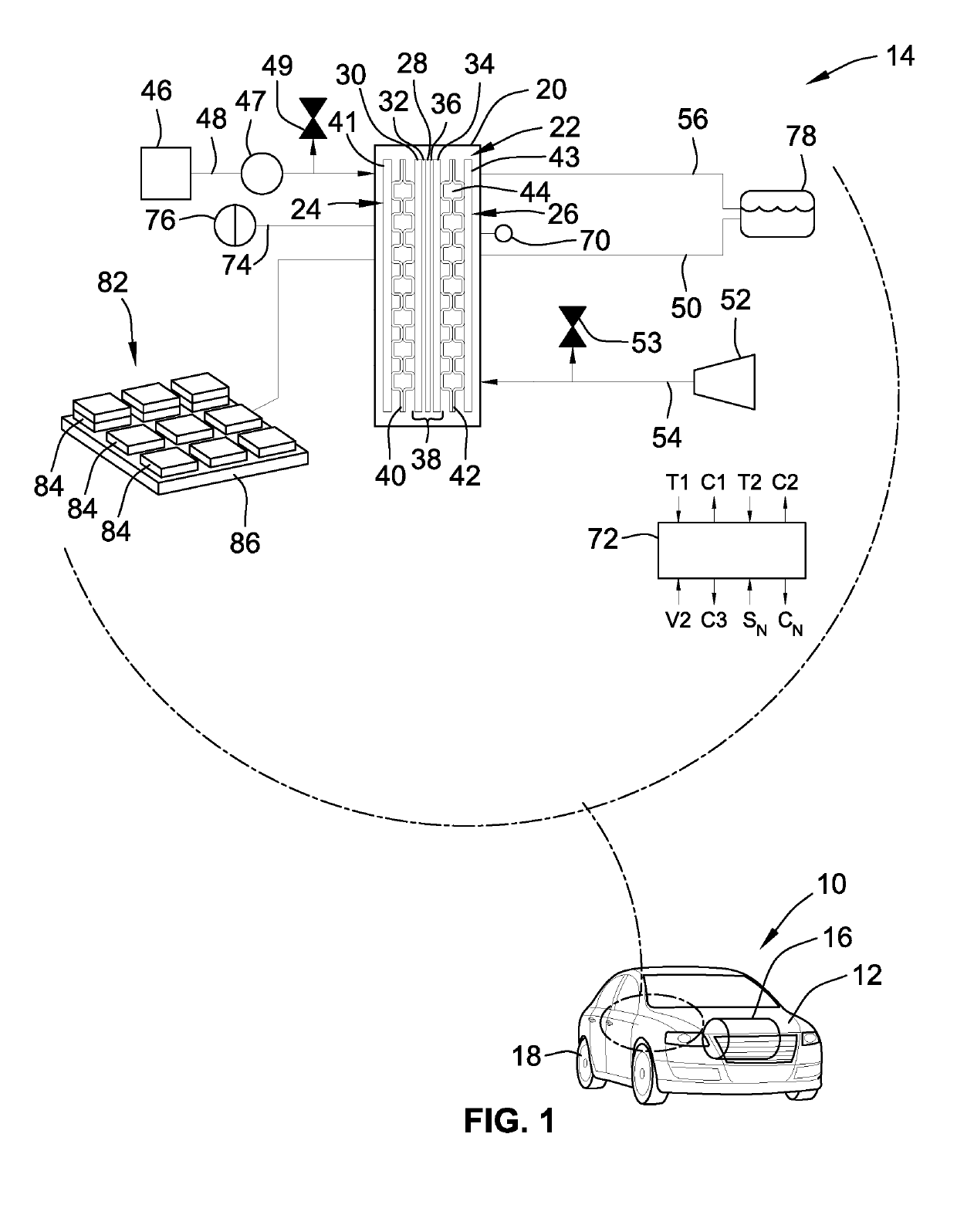
Fuel cell architectures, thermal systems, and control logic for efficient heating of fuel cell stacks
ActiveUS20180323453A1Improved fuel cell system reliabilityIncreased system heating efficiencyFuel cell heat exchangeElectric devicesFuel cellsFluid control
Disclosed are fuel cell architectures, thermal sub-systems, and control logic for regulating fuel cell stack temperature. A method is disclosed for regulating the temperature of a fuel cell stack. The method includes determining a pre-start temperature of the fuel cell stack, and determining, for this pre-start temperature, a target heating rate to heat the stack to a calibrated minimum operating temperature. The method then determines a hydrogen bleed percentage for the target heating rate, and executes a stack heating operation including activating the fuel cell stack and commanding a fluid control device to direct hydrogen to the cathode side at the hydrogen bleed percentage to generate waste heat. After a calibrated period of time, the method determines if an operating temperature of the stack exceeds the calibrated minimum stack operating temperature. Responsive to the operating temperature being at or above the minimum operating temperature, the stack heating operation is terminated.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
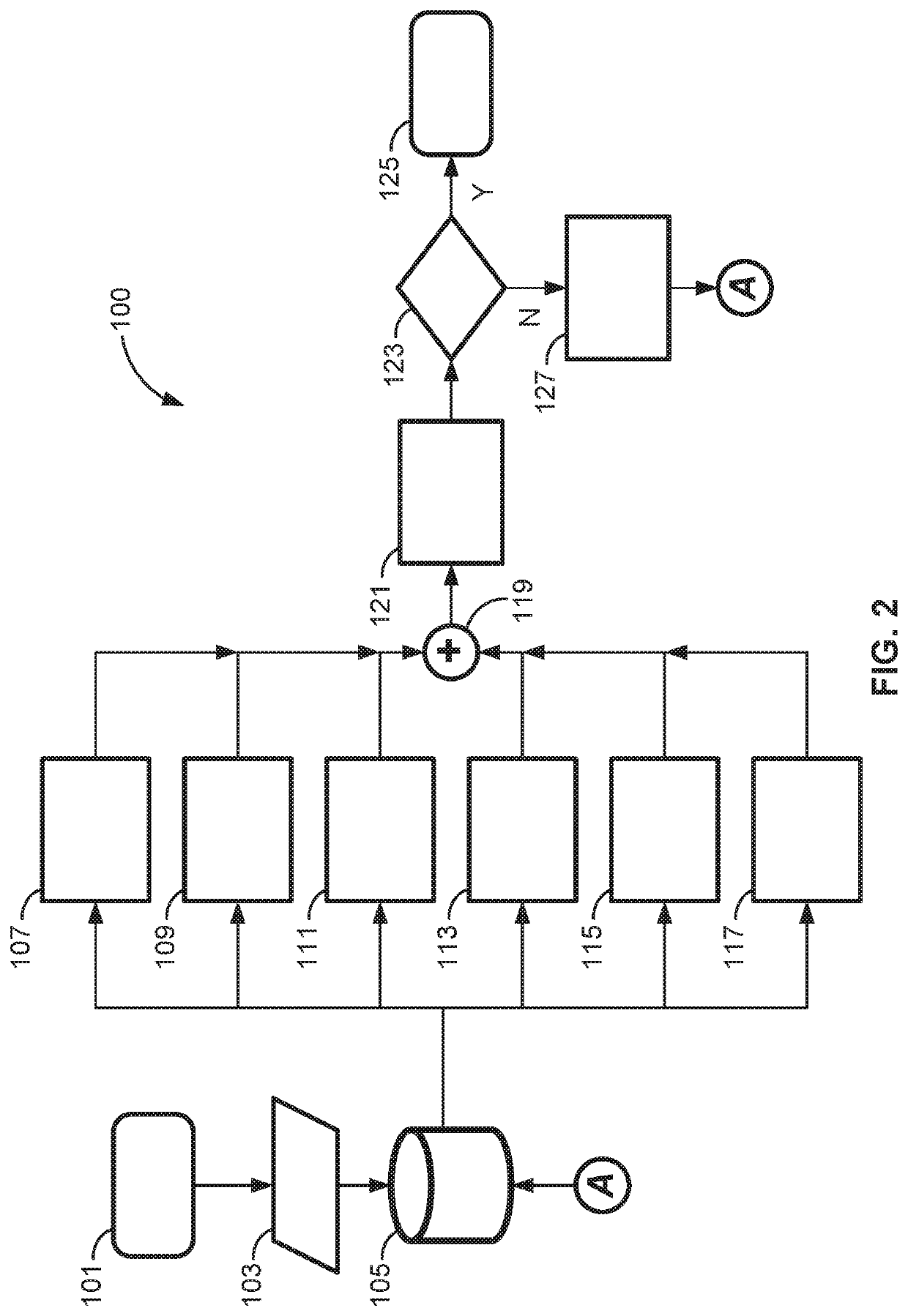
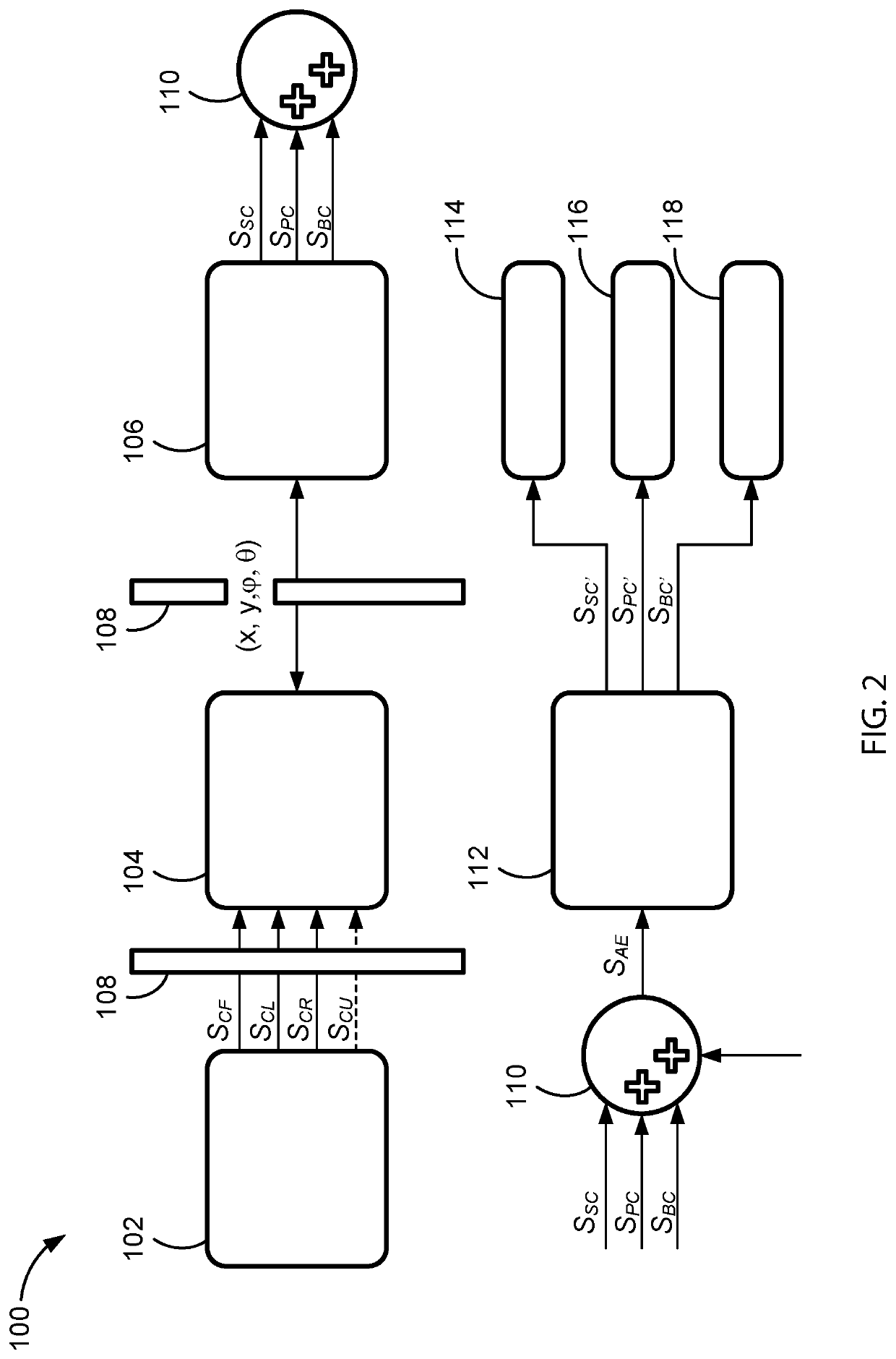
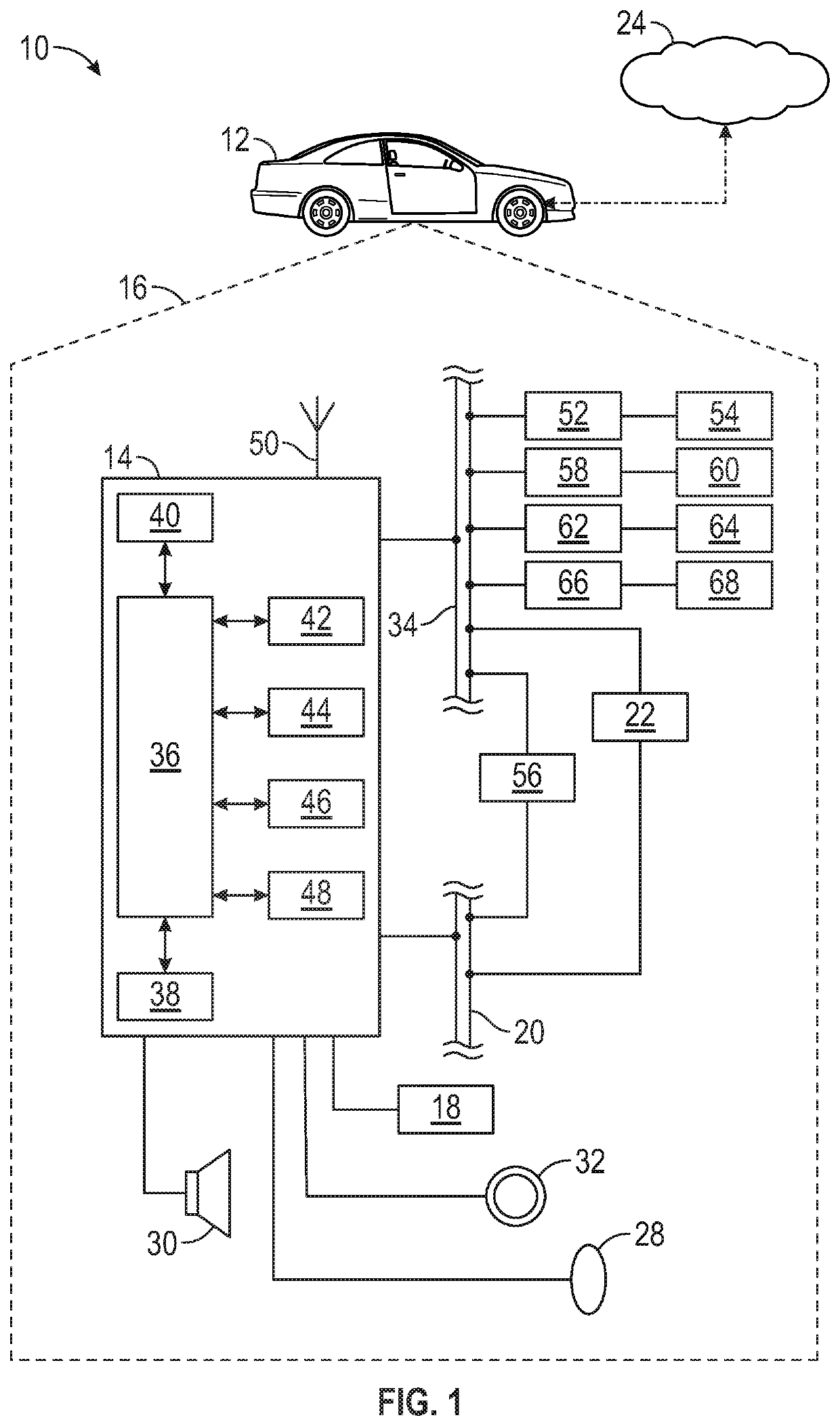
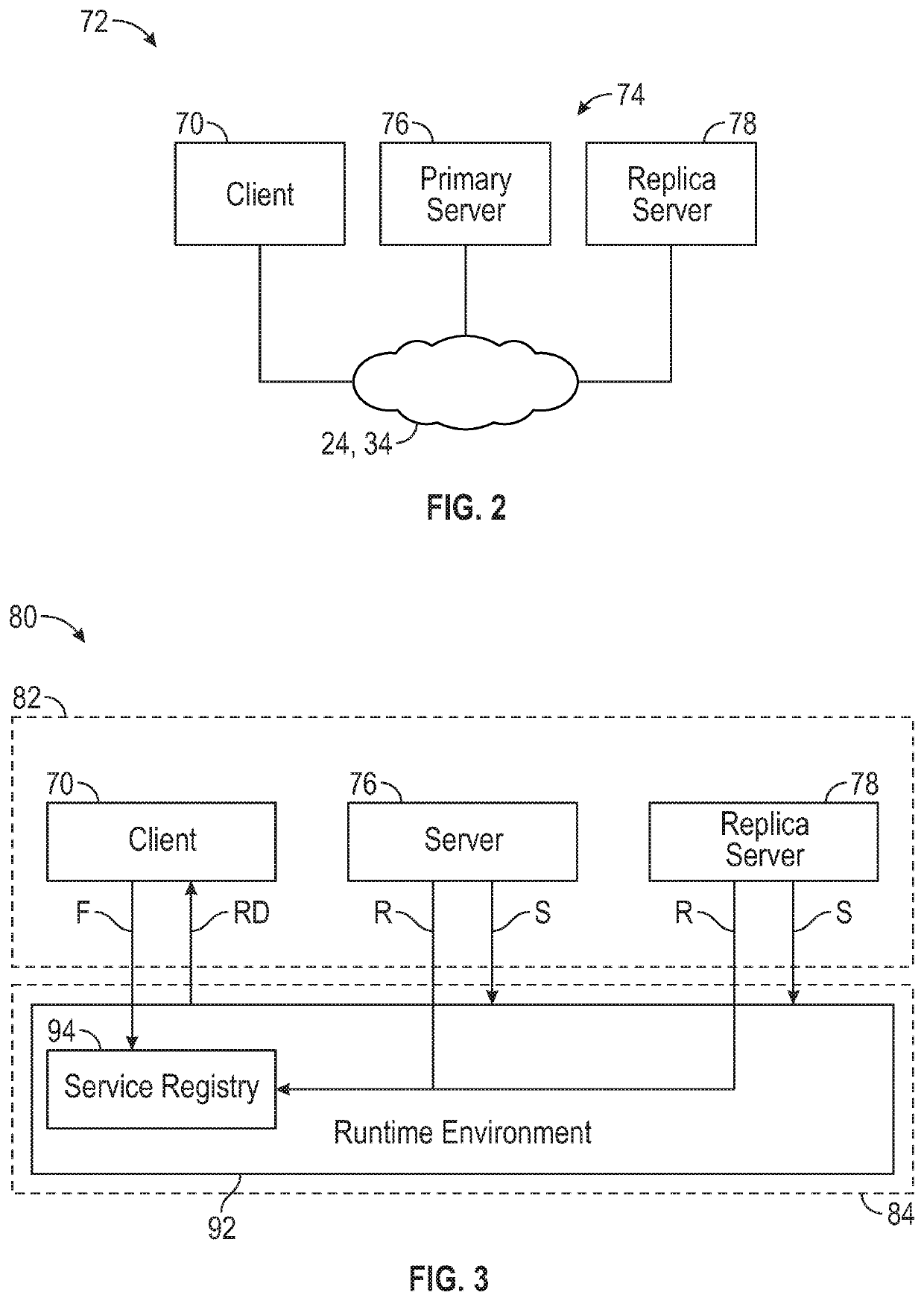
Middleware support for fault-tolerant execution in an adaptive platform for a vehicle
InactiveUS20200133267A1Cost-effective replicationGuaranteed maintenanceError detection/correctionRoad vehicles traffic controlSelf adaptiveMiddleware
A method for controlling a vehicle includes: establishing, by a vehicle controller, a connection between a client and a plurality of servers, the plurality of servers includes a primary server and at least one replica server, the at least one replica server is a replica of the primary server; making, by the vehicle controller, a data request about a given service to the plurality of servers; in response to the data request, receiving reply data from the plurality of servers to the data request via a middleware; fusing, by the middleware, the reply data from the plurality of servers to generate a resulting data; receiving, by the vehicle controller, the resulting data; and controlling, by the client, the vehicle based on the resulting data.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Fuel cell architectures, monitoring systems, and control logic for characterizing fluid flow in fuel cell stacks
ActiveUS20180316029A1Improve system reliabilityIncrease stack efficiencyElectric devicesOperating modesVoltage amplitudeAutomotive engineering
Disclosed are fuel cell architectures, fuel cell stack monitoring systems, and control logic for detecting fluid property changes in a fuel cell stack. A method is disclosed for detecting a flow property change of a fluid in a fuel cell system. This method includes determining, e.g., through system analysis or accessing a look-up table, a correlation between voltage change of the fuel cell system and flow property of the fluid, and determining, from the voltage-property correlation, a calibrated voltage drop corresponding to the property change of the fluid. The method monitors system voltage (e.g., moving average voltage of the fuel cell stack operating at steady state), and detecting a voltage magnitude change in the system voltage, e.g., when an anode exhaust valve is opened. Responsive to the voltage magnitude change being greater than the calibrated voltage drop, a signal is generated indicating detection of the flow property change.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Battery pack voltage-switching systems and control logic for multi-pack electric-drive motor vehicles
ActiveUS10854933B2Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesElectrical batteryDrive motor
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Automatic Shoe Cover Dispenser with Shoe Cover Cartridge
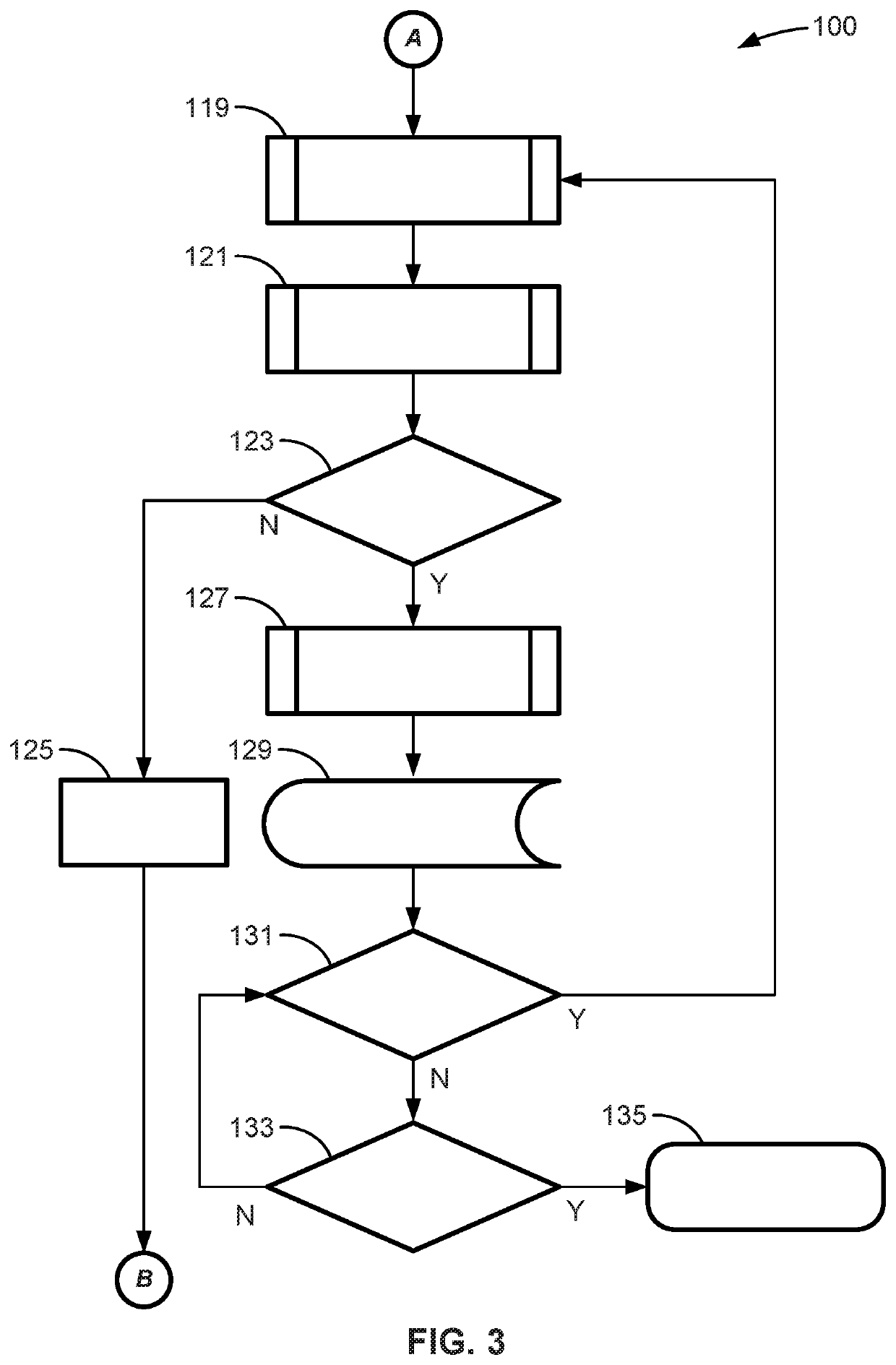
ActiveUS20170088339A1Simplify the installation processSimple structureFlat article dispensingFootwearEngineeringMechanical engineering
A shoe cover cartridge includes two guiding arms and a plurality of shoe covers overlapped in a sequential manner to define a standby shoe cover and a subsequent shoe cover. Front and rear interlocking units are provided at front and rear sides of each of the shoe cover respectively and are slidably engaged with the guiding arms at a position that the front interlocking unit at the subsequent shoe cover is located in front of the rear interlocking unit at the standby shoe cover along the guiding arms. Therefore, when the standby shoe cover is pulled for dispensing, the subsequent shoe cover is pulled by the standby shoe to dispense the shoe covers in a sequential order.
Owner:OTO IND WUHAN CO LTD
Vascular cooling system for electrical conductors
ActiveUS20210267097A1Improve conductor coolingReduce the total massVehicle connectorsCharging stationsElectrical conductorElectric devices
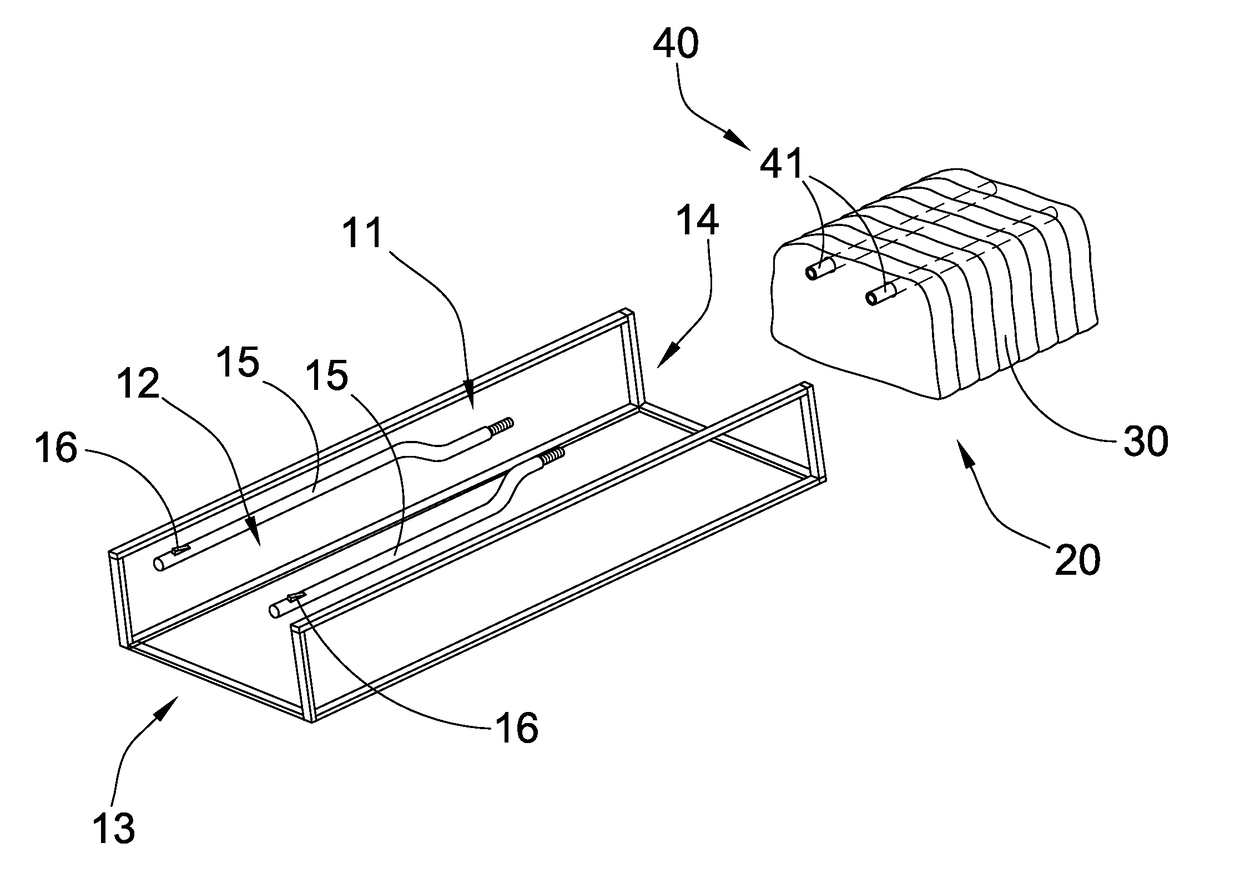
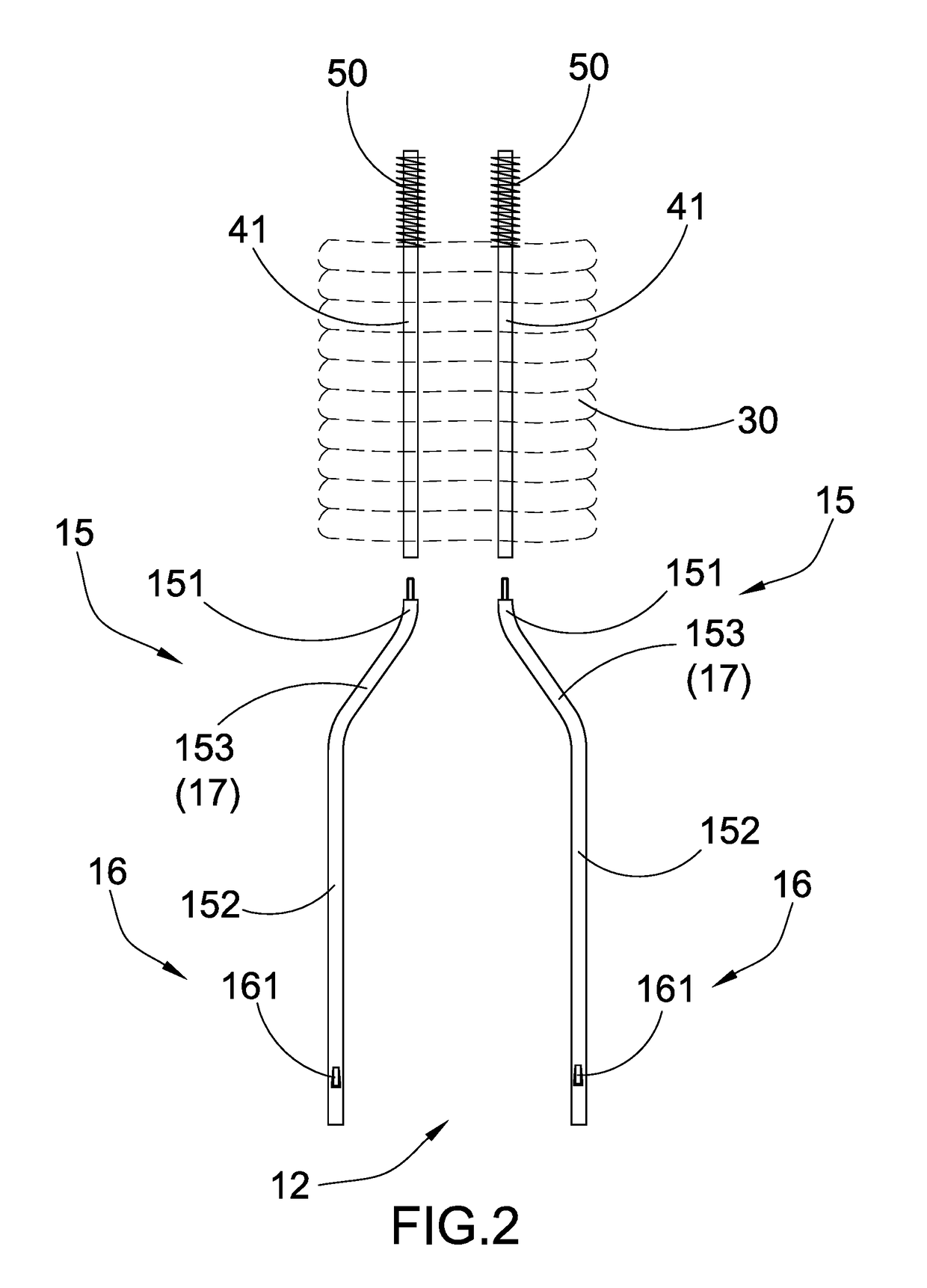
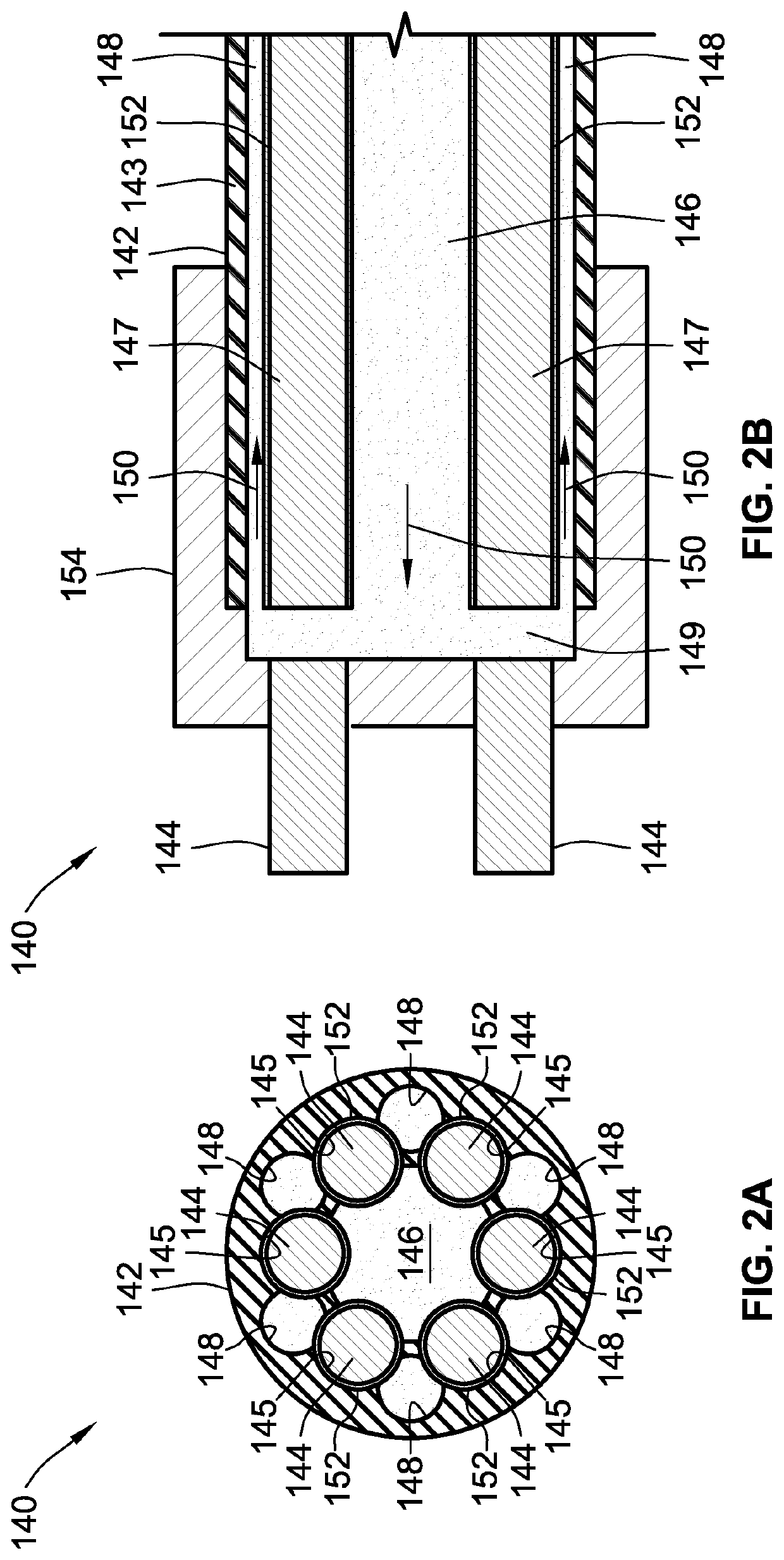
Presented are electrical conductor assemblies with vascular cooling systems, methods for making / using such assemblies, and vehicles equipped with such assemblies for transmitting power and coolant between electric devices. An electrical conductor assembly includes an outer sheath, an electrical conductor extending through the sheath, a coolant channel defined through the sheath, and an optional cable jacket encasing the electrical conductor. The outer sheath has a tubular body formed from an electrically insulating material. The electrical conductor has a solid cable body located within a conductor duct extending through the sheath. The coolant channel, which is coaxial with and thermally connected to the cable body, passes therethrough coolant fluid that cools the electrical conductor. The cable jacket may be formed from an electrically insulating material having a thermal conductivity and melting point higher than that of the sheath. The conductor assembly may include multiple electrical conductors circumferentially spaced around the coolant channel.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Back-to-back selectable one-way clutches for engine disconnect devices of motor vehicle powertrains
ActiveUS10864813B2Minimize and eliminate relianceInexpensive costHybrid vehiclesFluid couplingsControl theoryMotorized vehicle
Presented are dual-clutch engine disconnect devices, methods for making / using such disconnect devices, and motor vehicles equipped with such disconnect devices. An engine disconnect device for a vehicle includes a first one-way clutch (OWC) with concentric inner and outer races and torque elements interposed between and transferring torque across these races in a first direction. The first outer race rigidly attaches to a damper plate for common rotation therewith, and the first inner race rigidly attaches to a pump cover of a torque converter for common rotation therewith. A second OWC, which concentrically aligns within the first OWC, includes concentric inner and outer races with torque elements interposed between and transferring torque across these races in a second direction. The second outer race is splined to the first inner race for common rotation with the pump cover. The second inner race rigidly attaches to the damper plate for common rotation therewith.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com