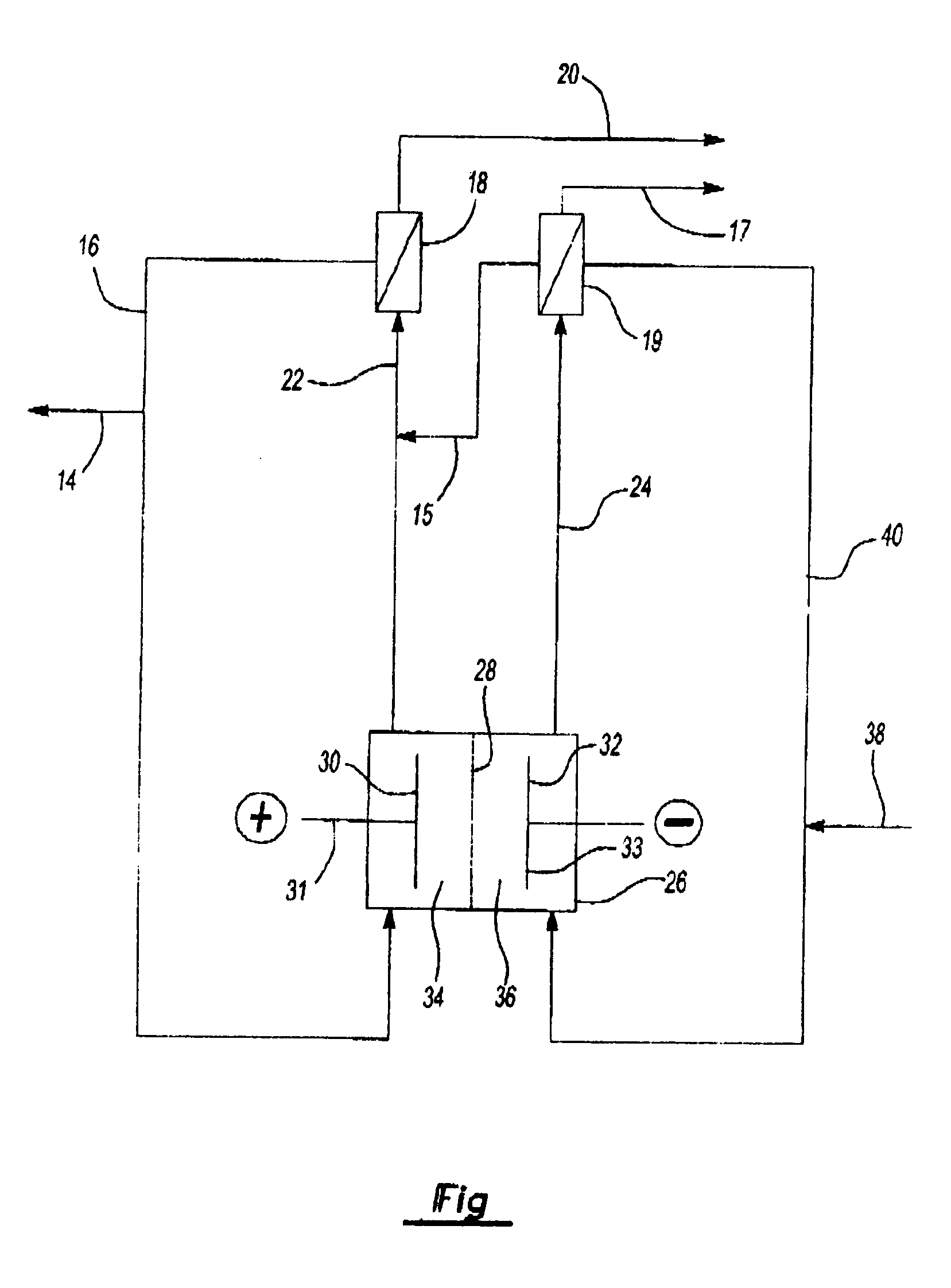
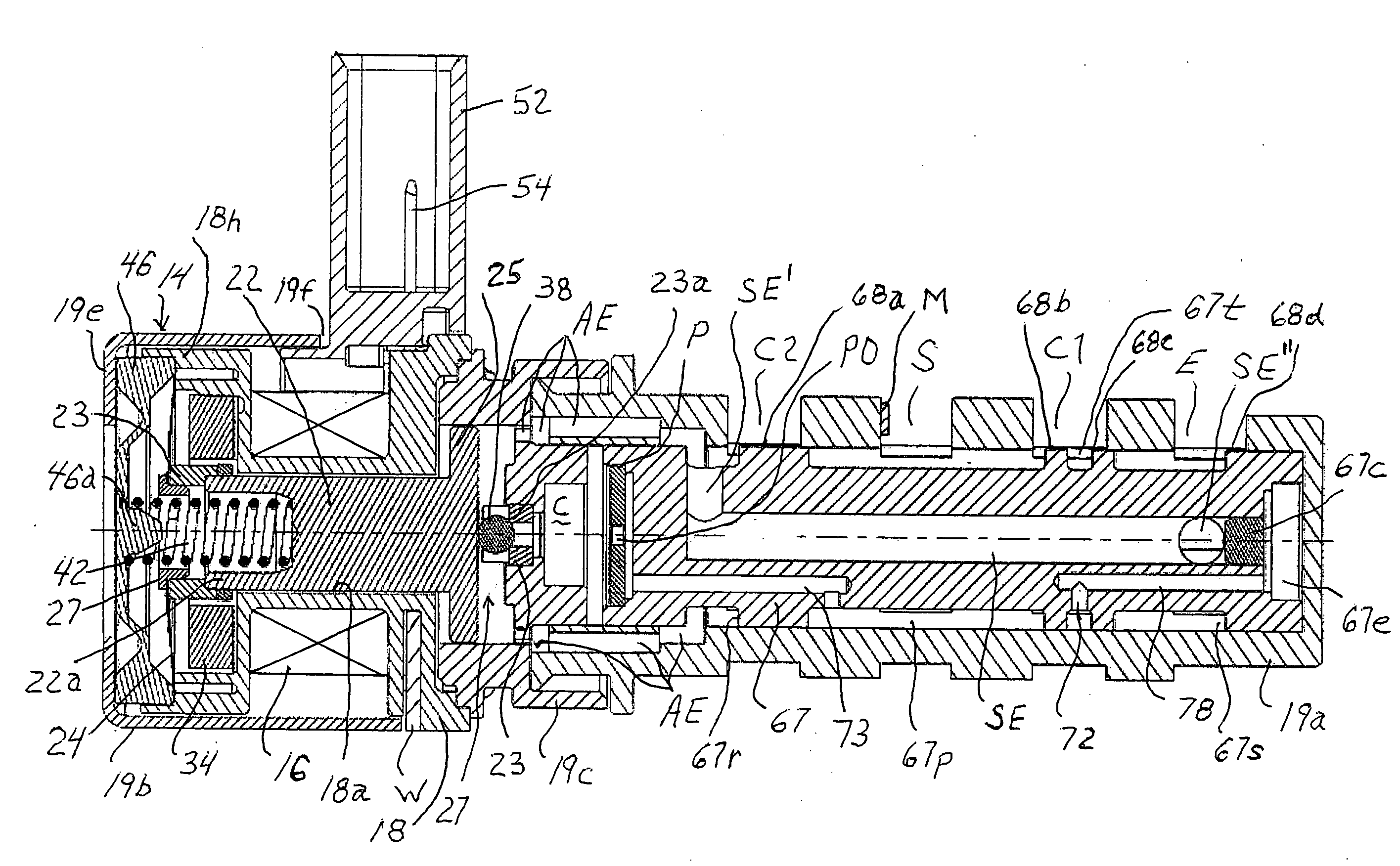
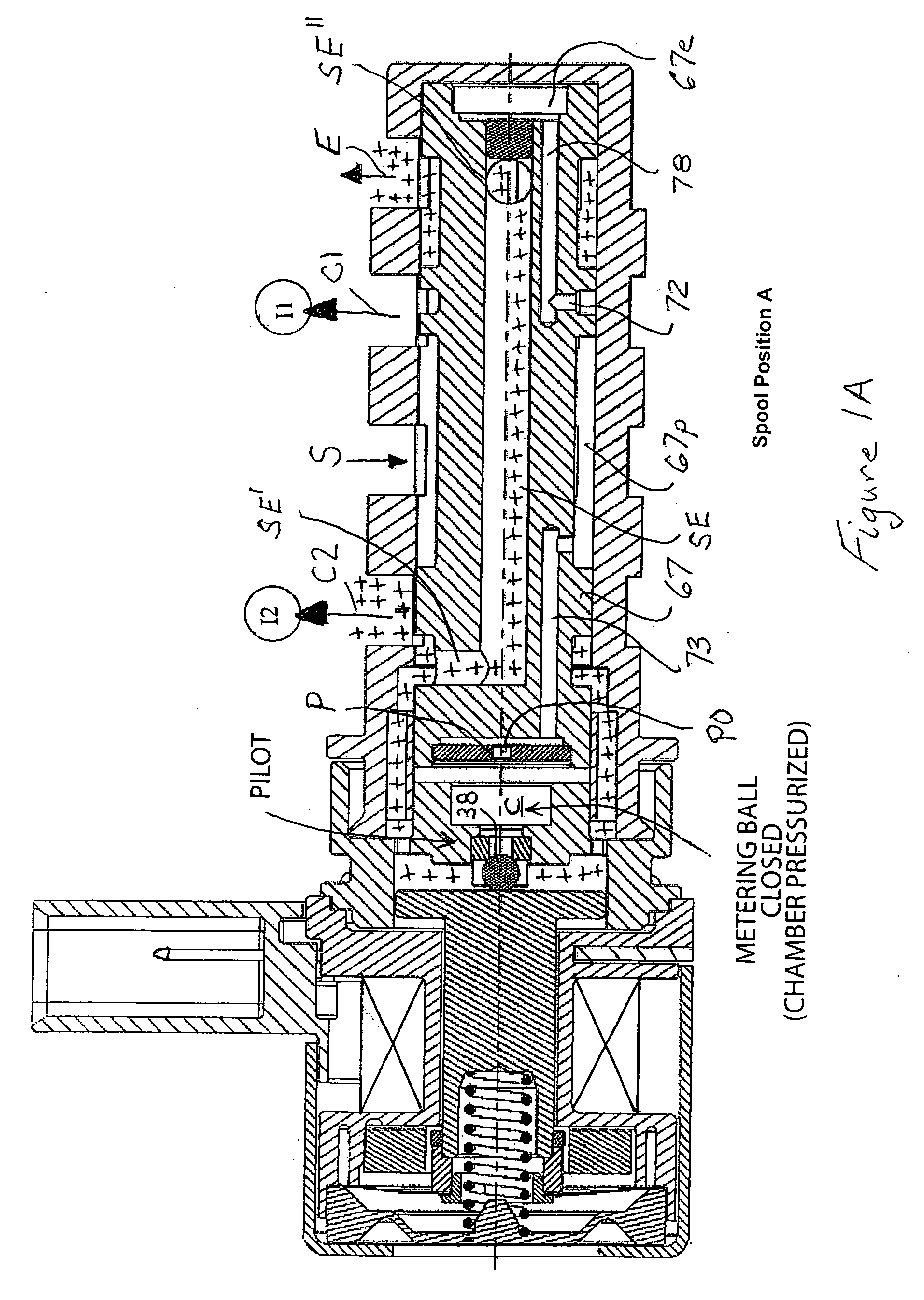
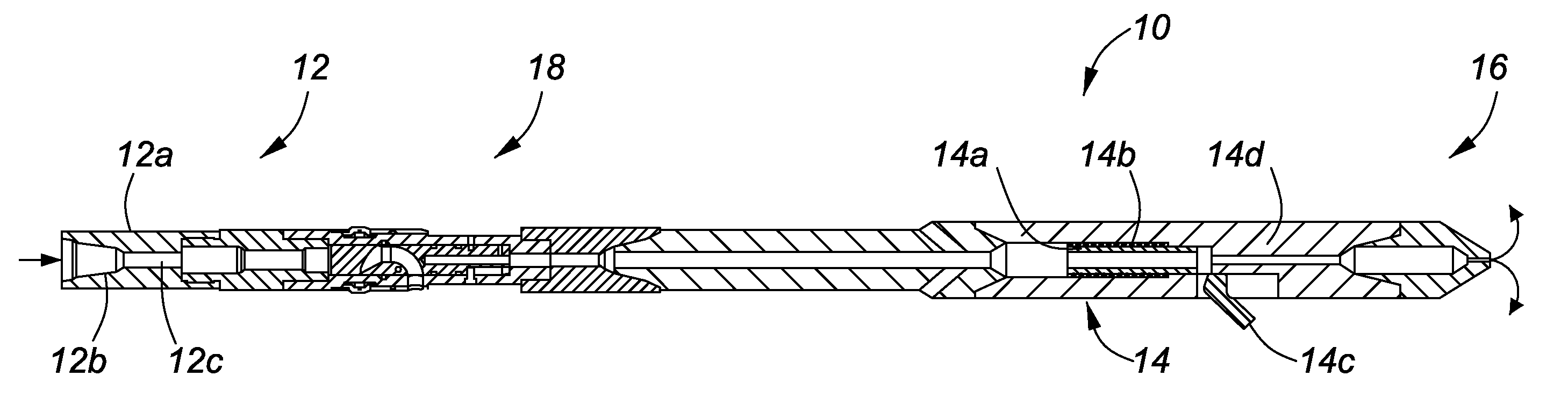
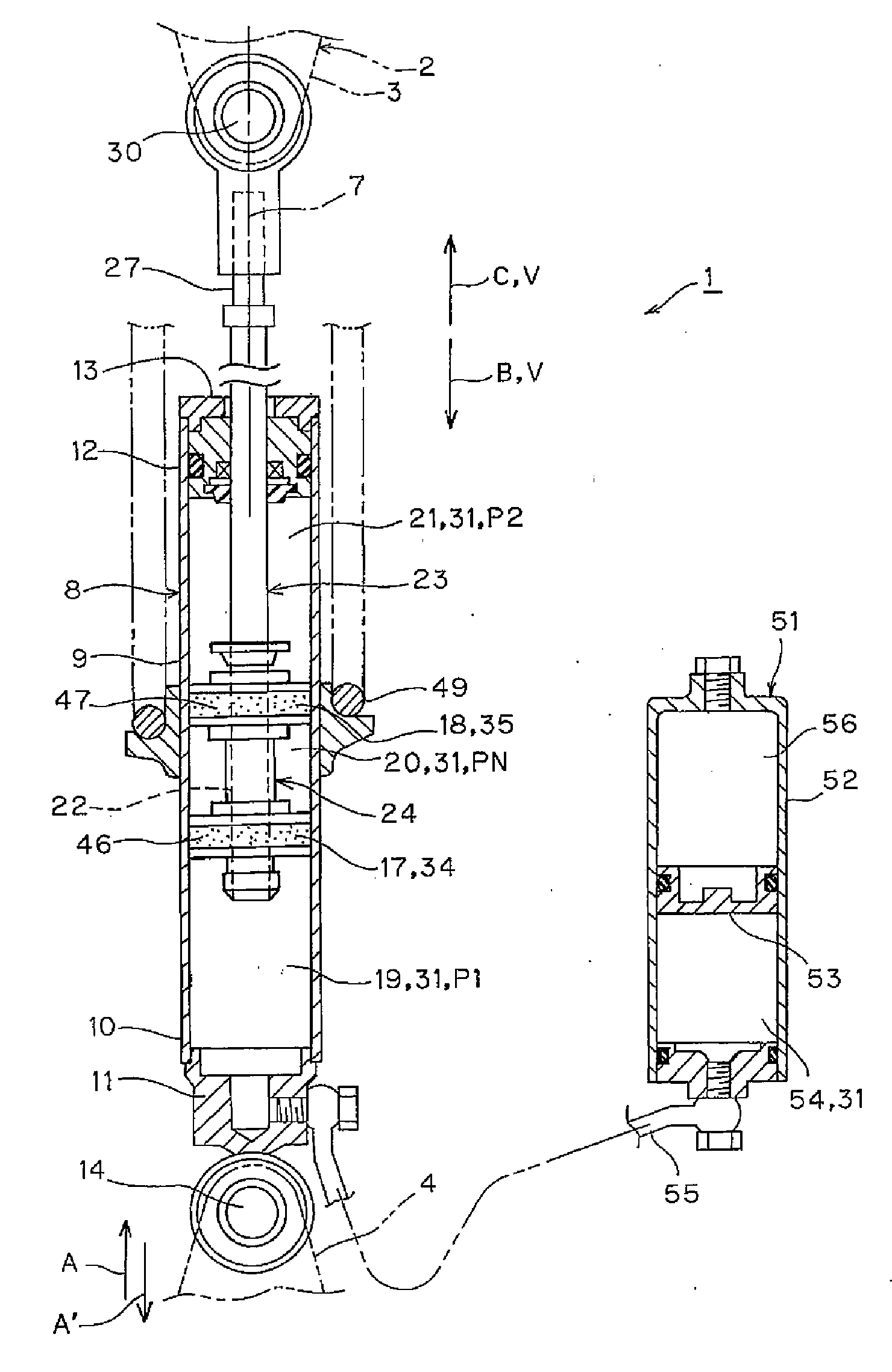
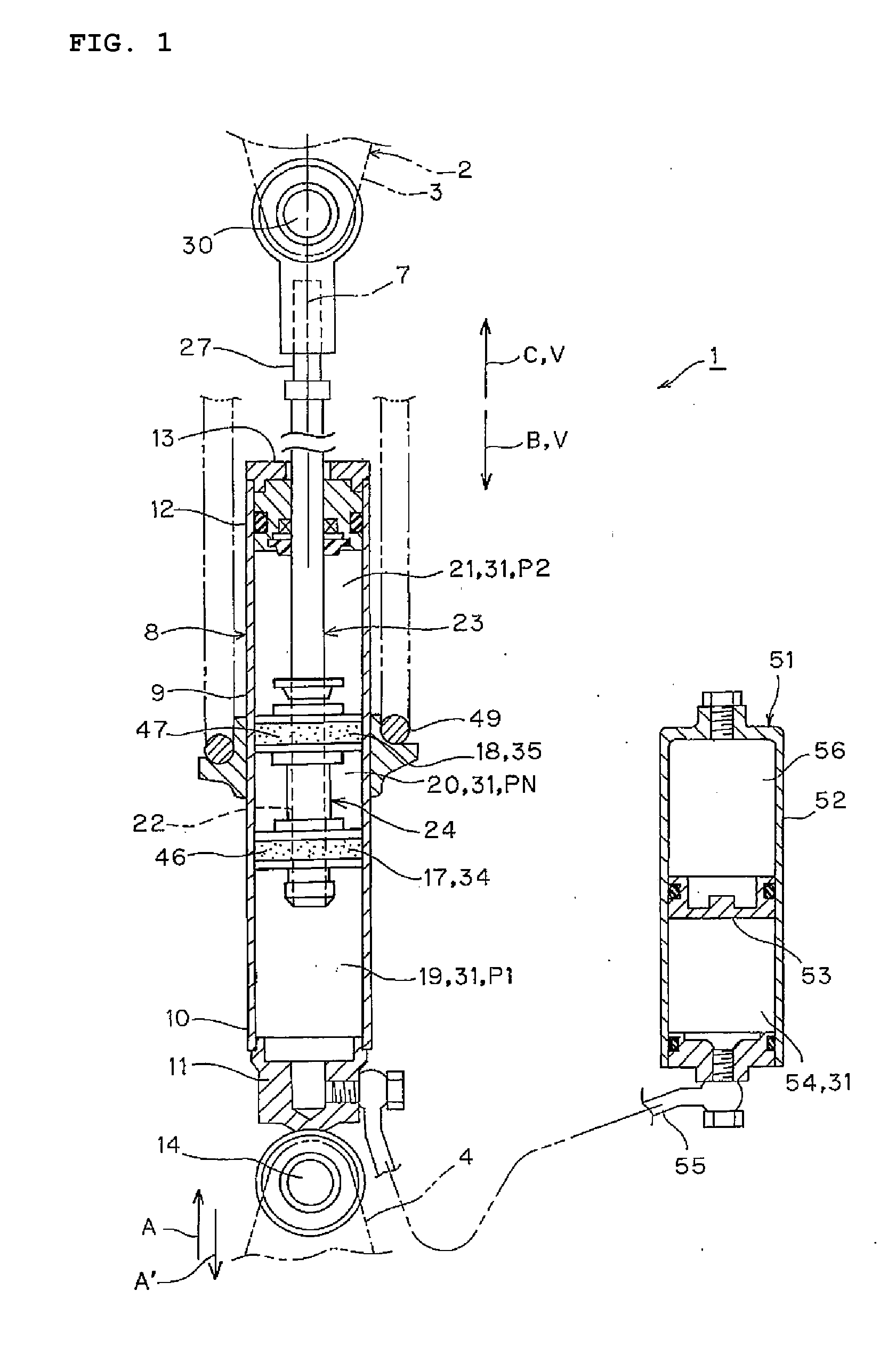
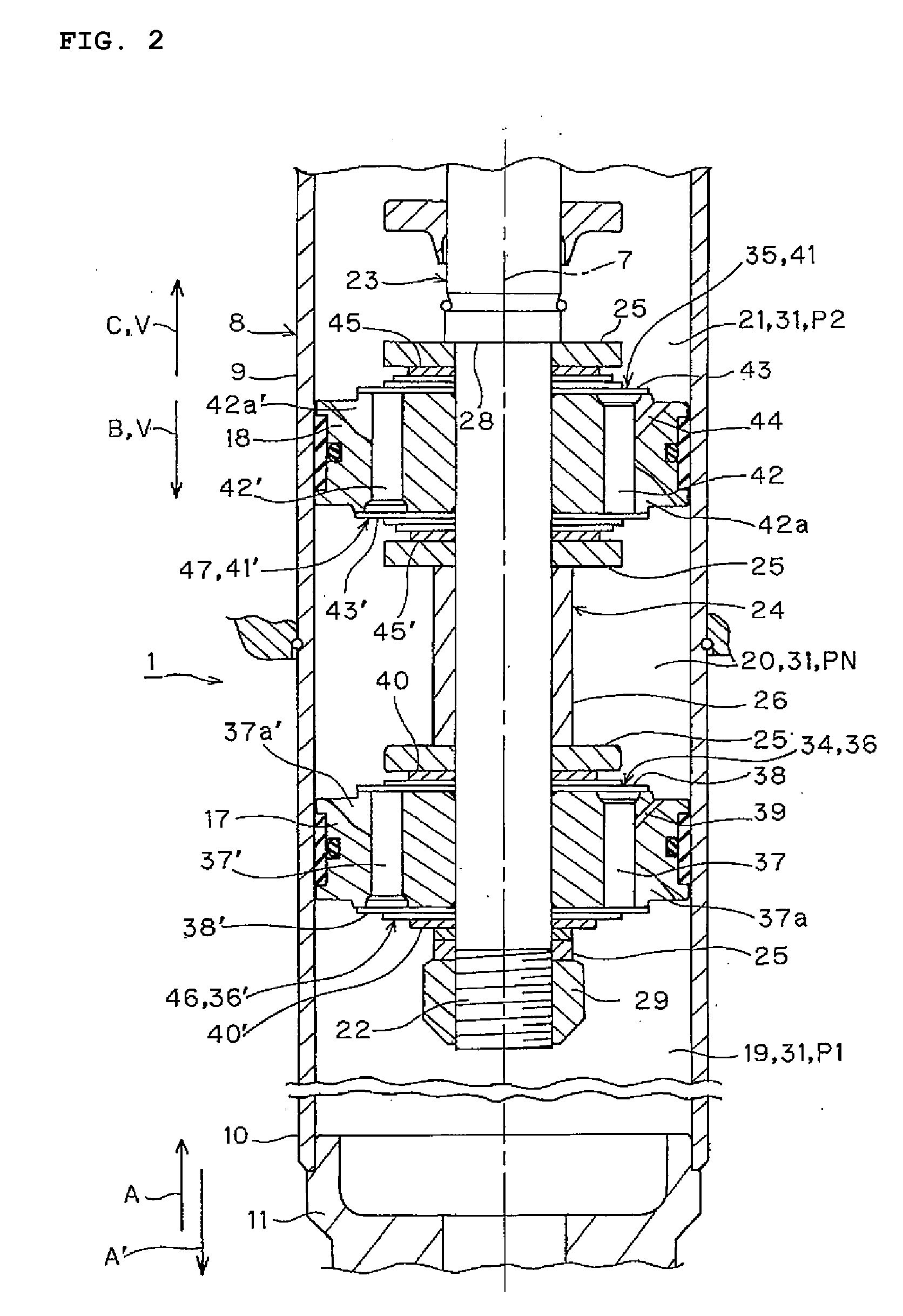
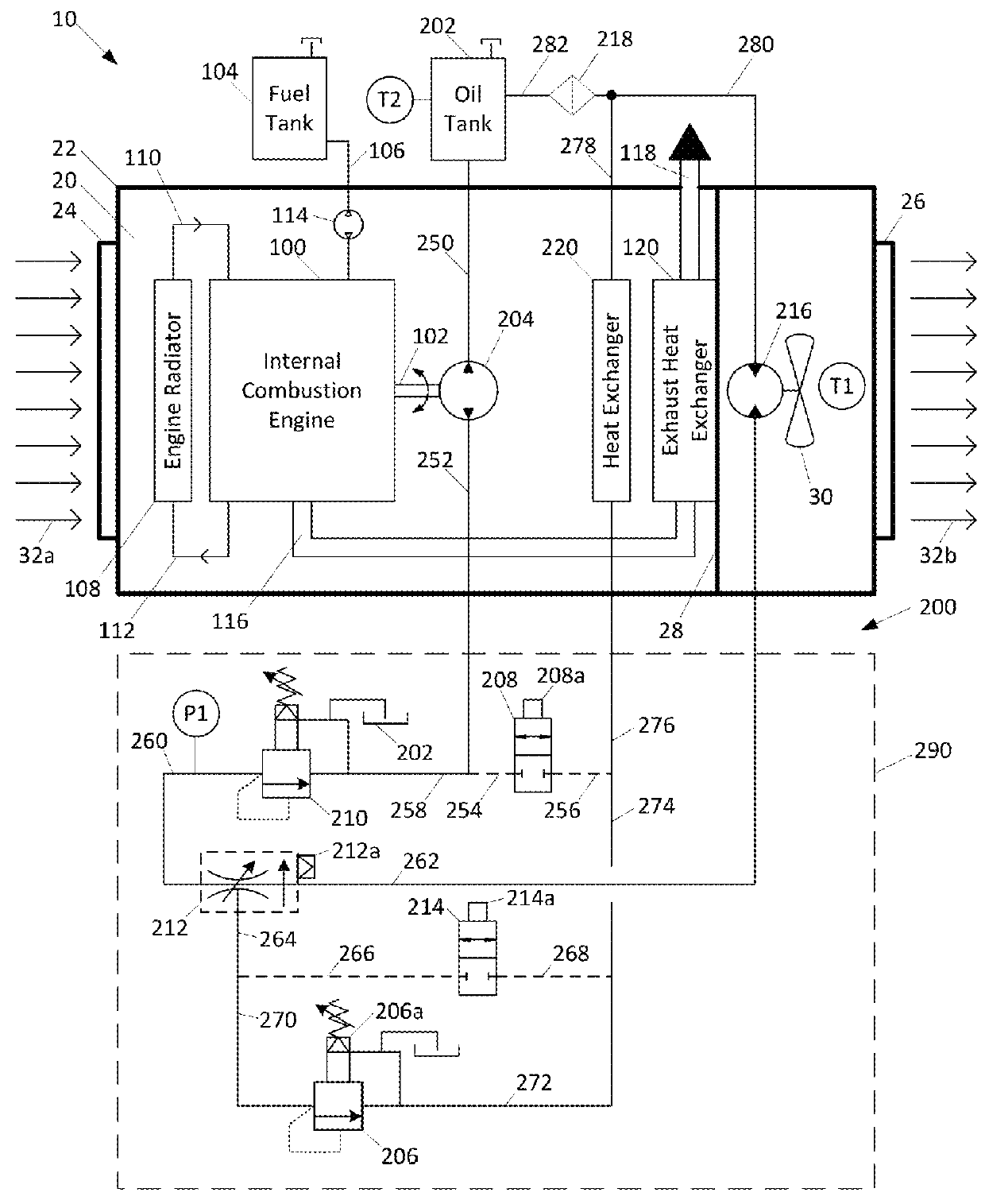
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223results about How to "Increase hydraulic pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
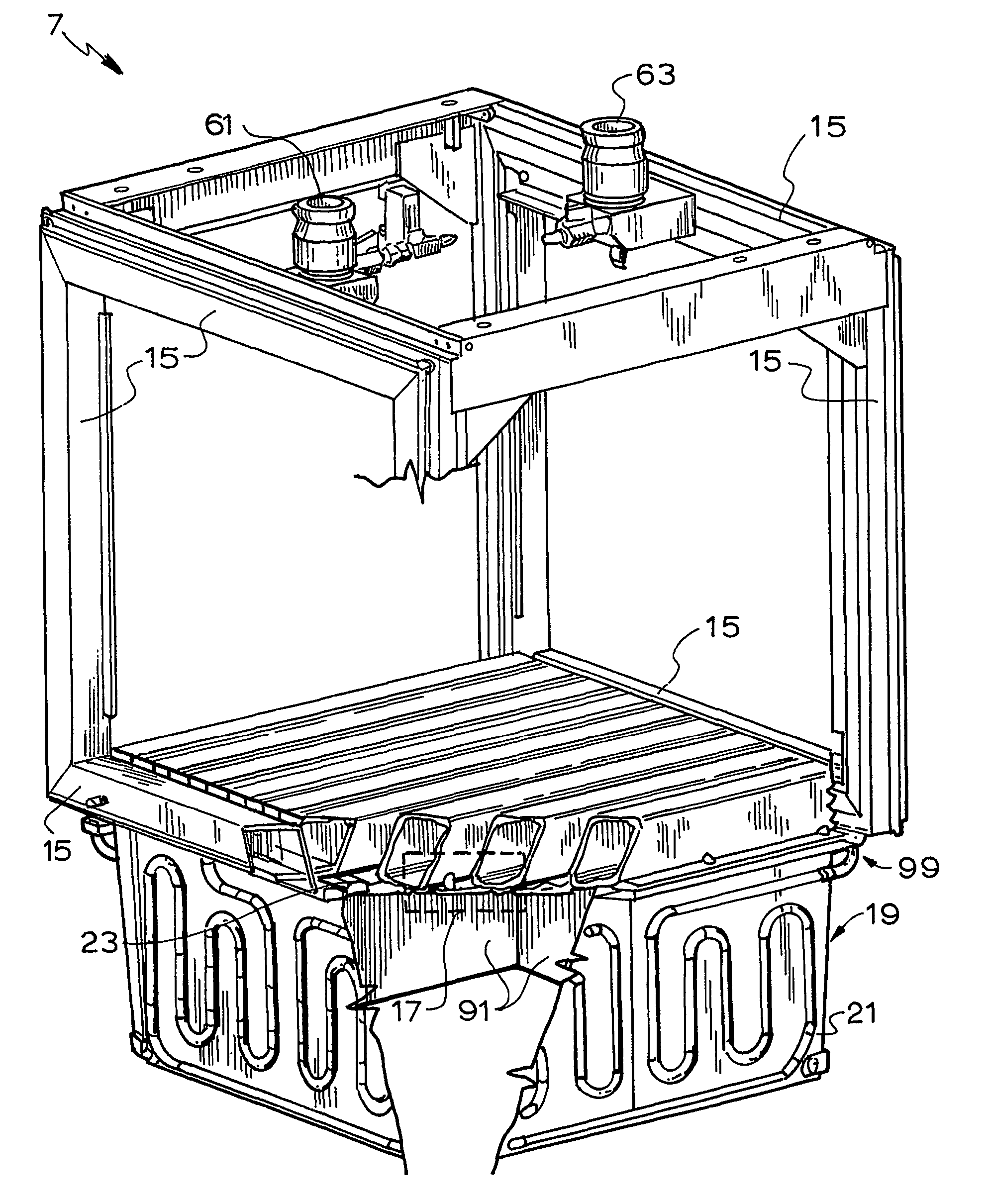
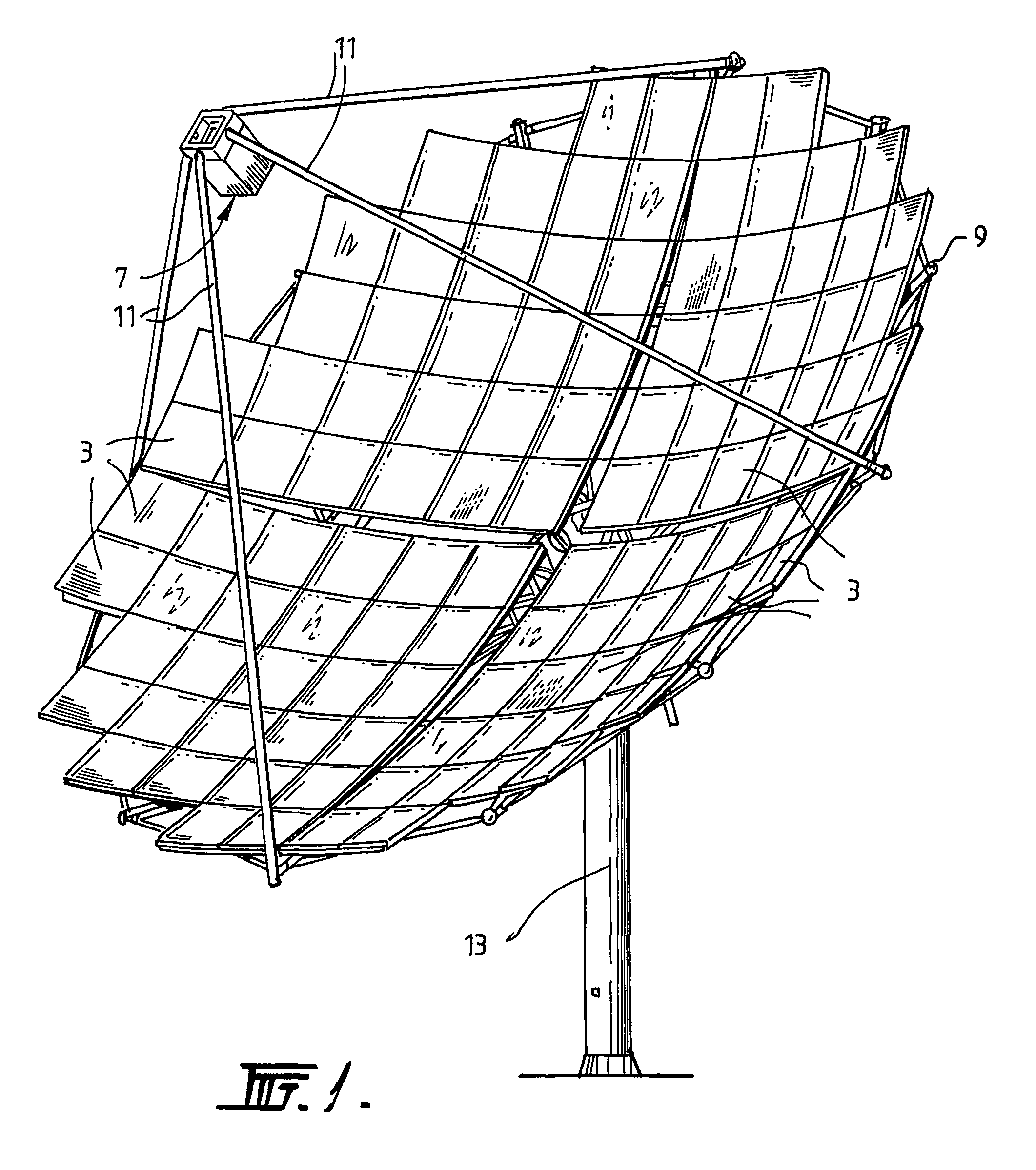
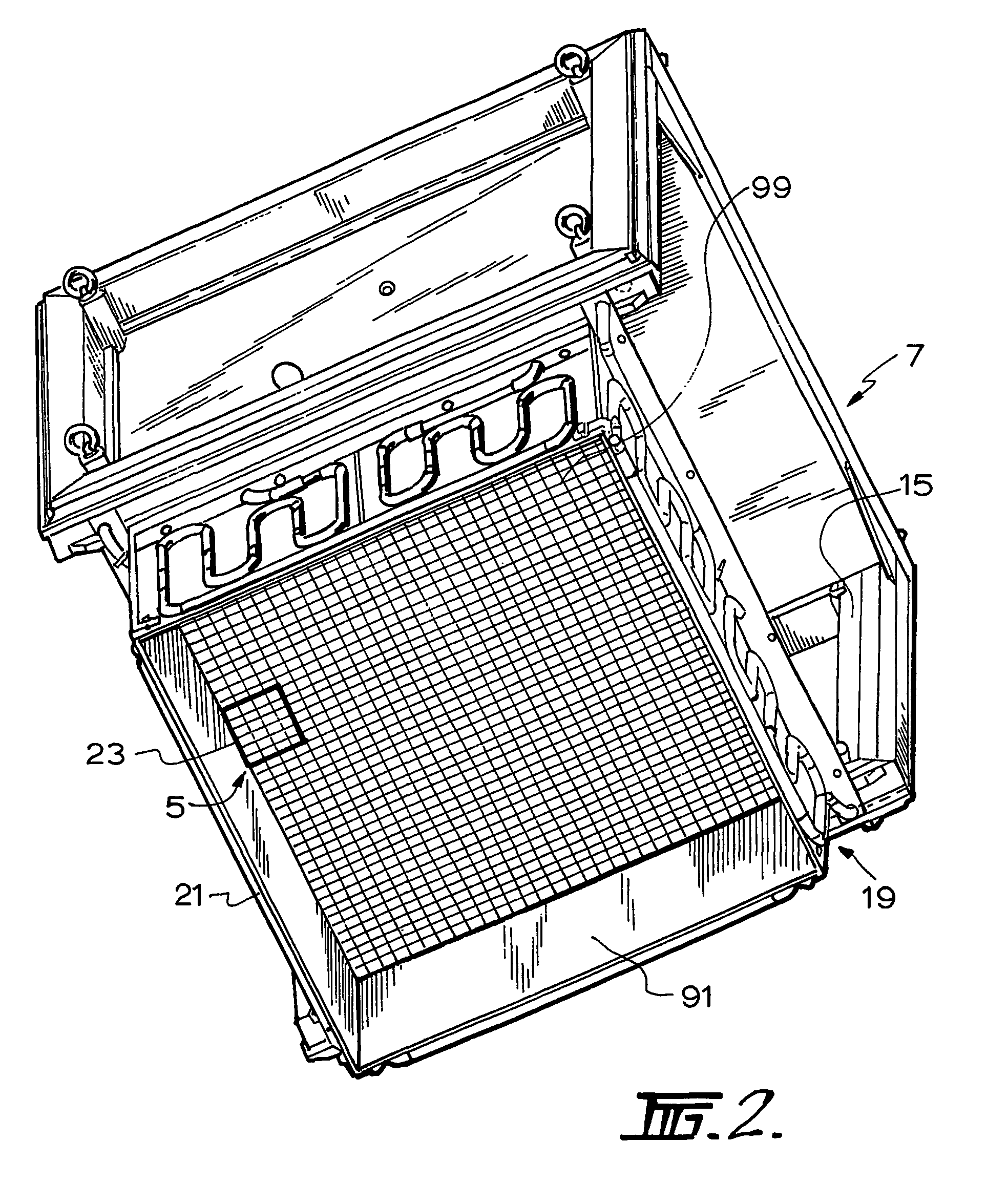
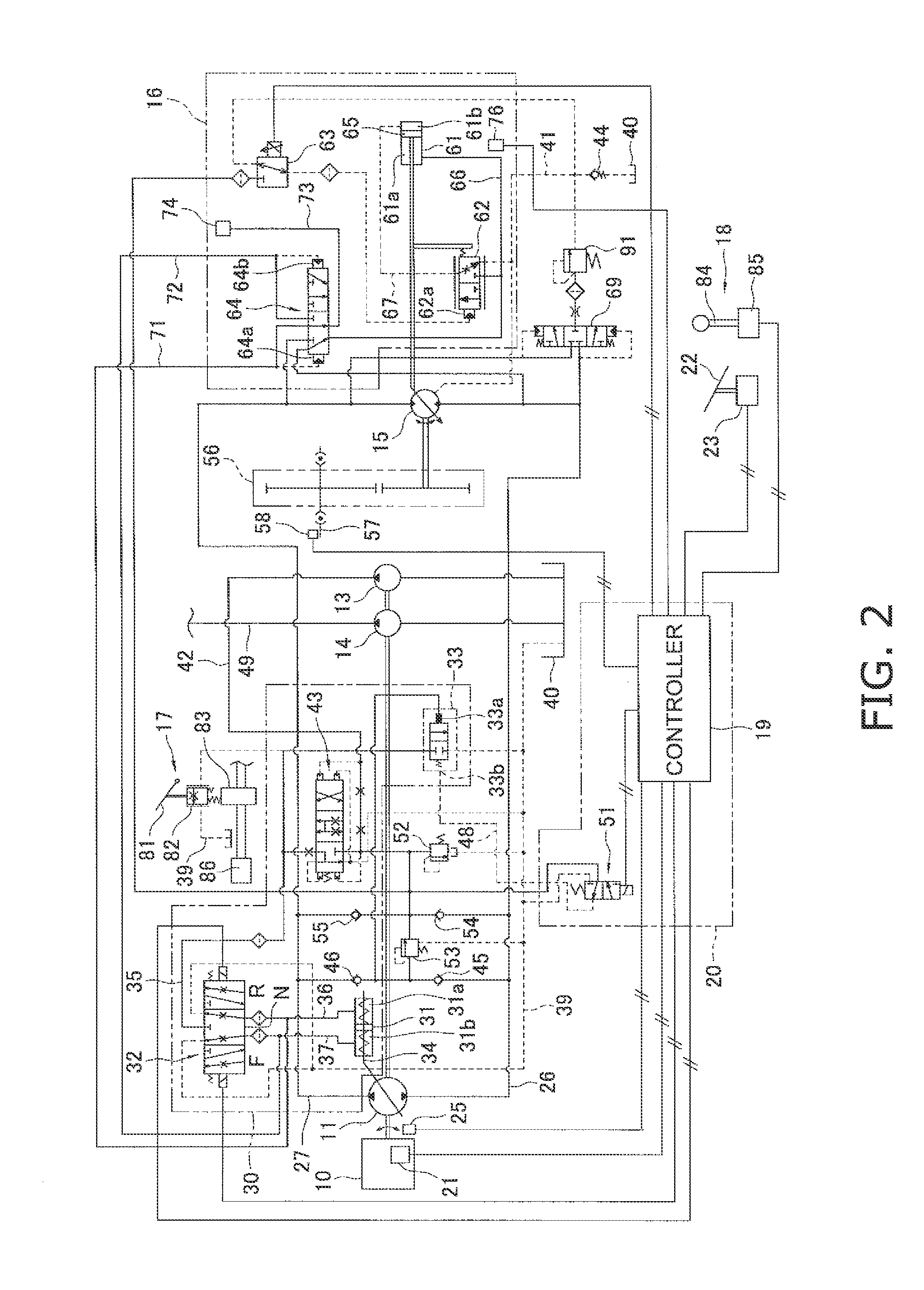
Cooling circuit for receiver of solar radiation
InactiveUS7076965B2Increasing available contact surface areaImprove heat transfer performancePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectrical batteryCoolant flow
A receiver for a system for generating electrical power from solar radiation is disclosed. The systems includes the receiver and a means (3) for concentrating solar radiation onto the receiver. The receiver includes a plurality of photovoltaic cell modules. Each module includes a plurality of photovoltaic cells (5), and includes an electrical connection that forms part of the receiver electrical circuit. The receiver includes a coolant circuit for cooling the photovoltaic cells with a coolant. The coolant circuit includes a coolant flow path in each module that is in thermal contact with the photovoltaic cells so that in use coolant flowing through the flow path extracts heat from the photovoltaic cells and thereby cools the cells.
Owner:SOLAR SYST PTY LTD
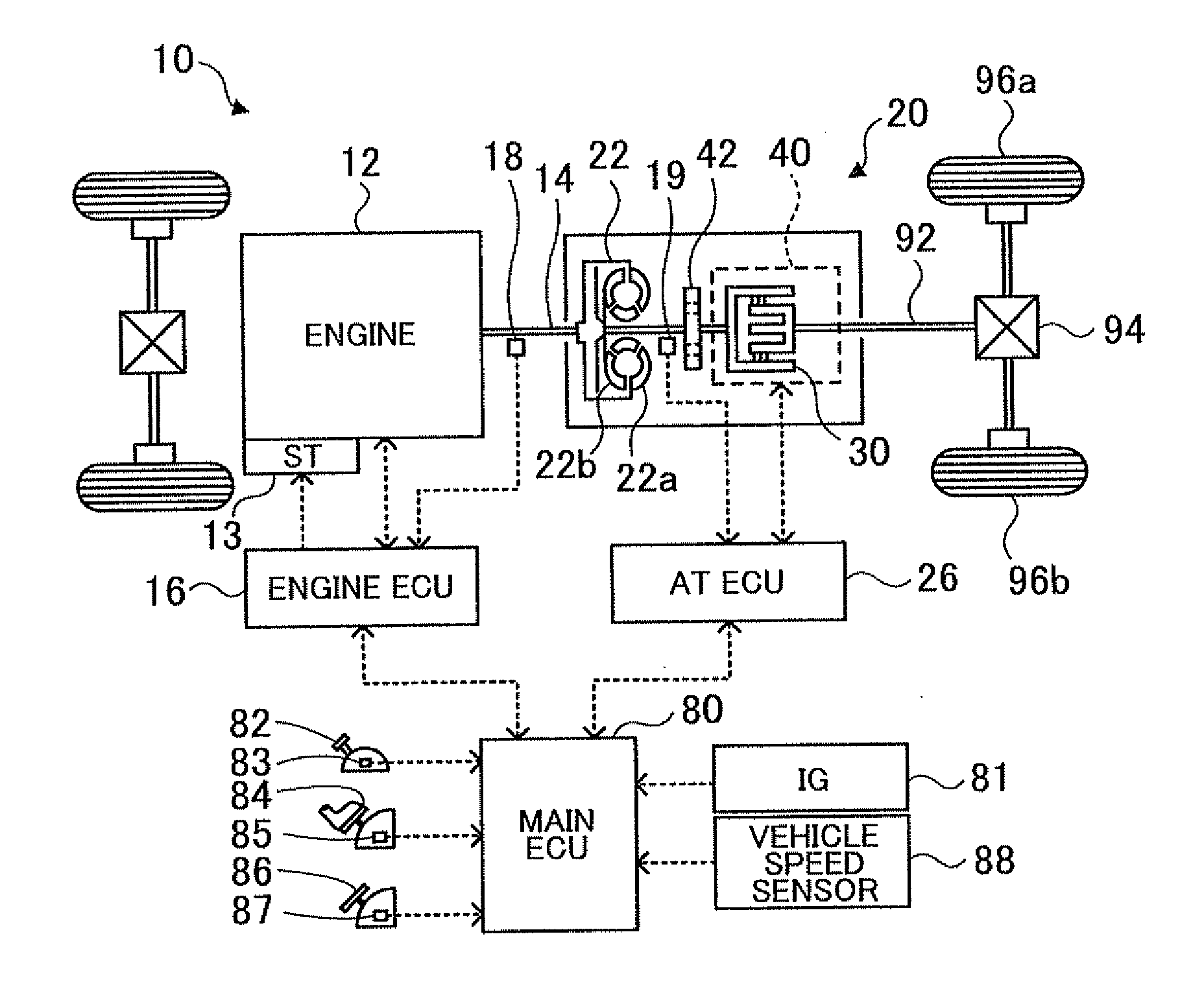
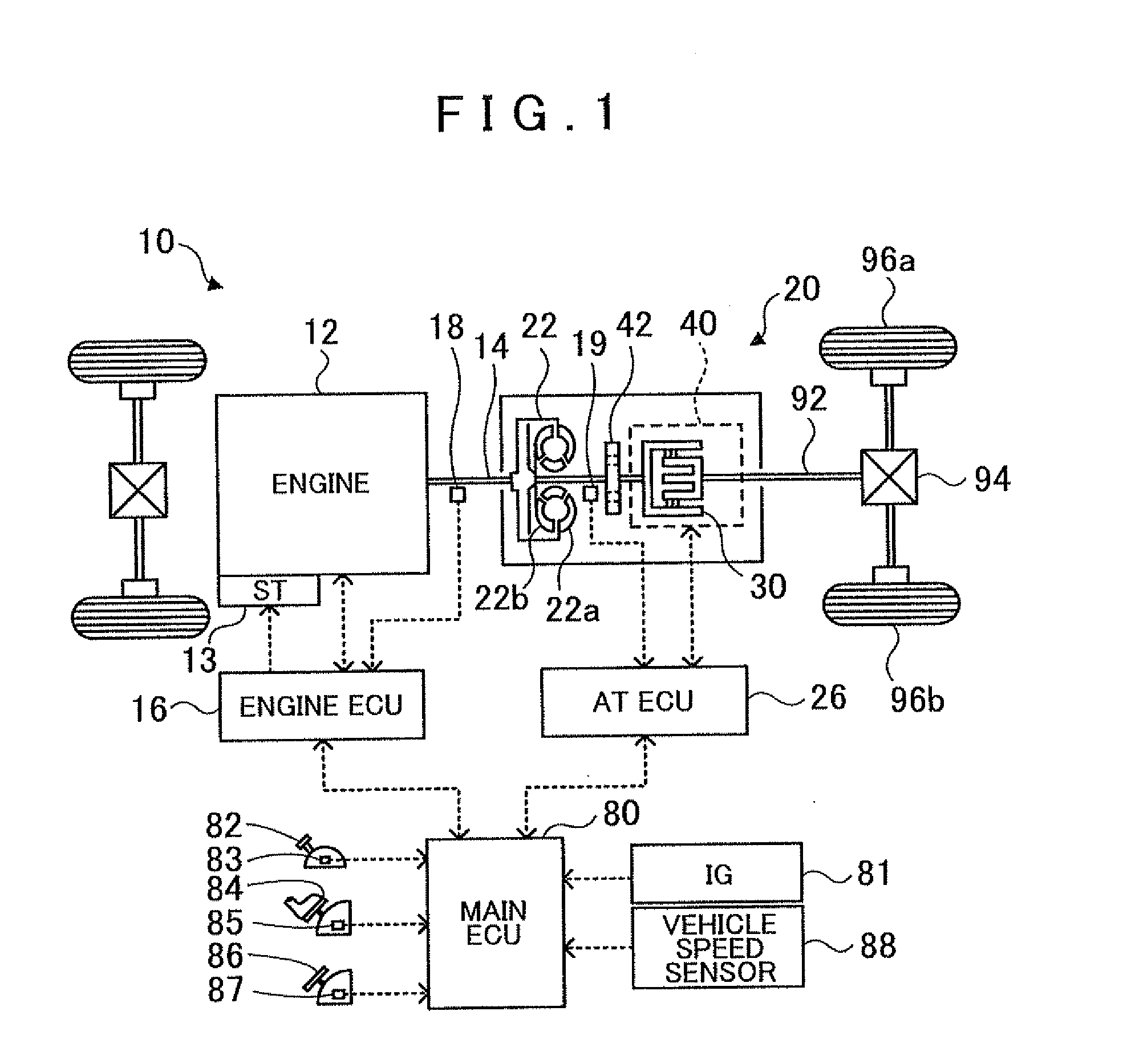
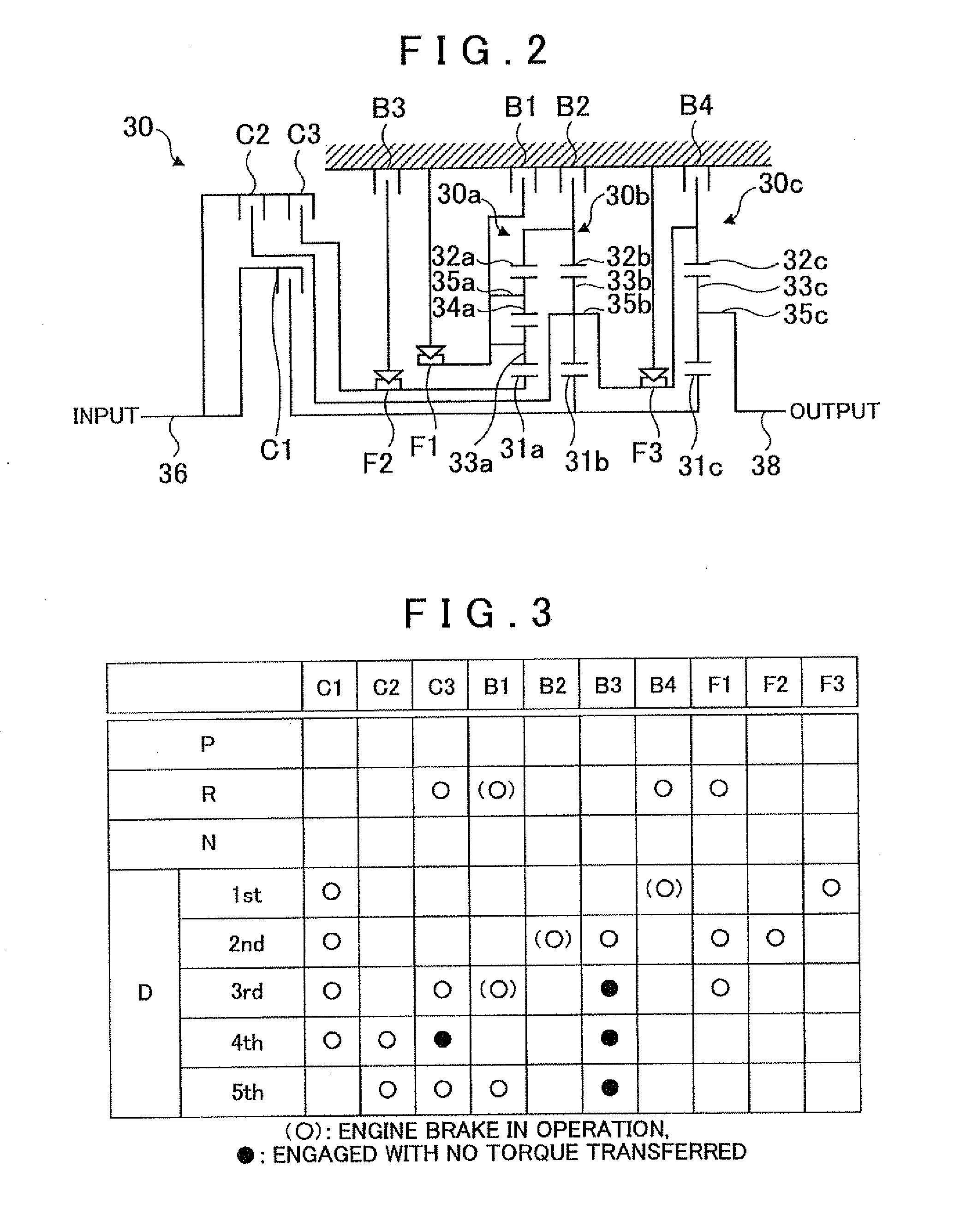
Power transmission mechanism
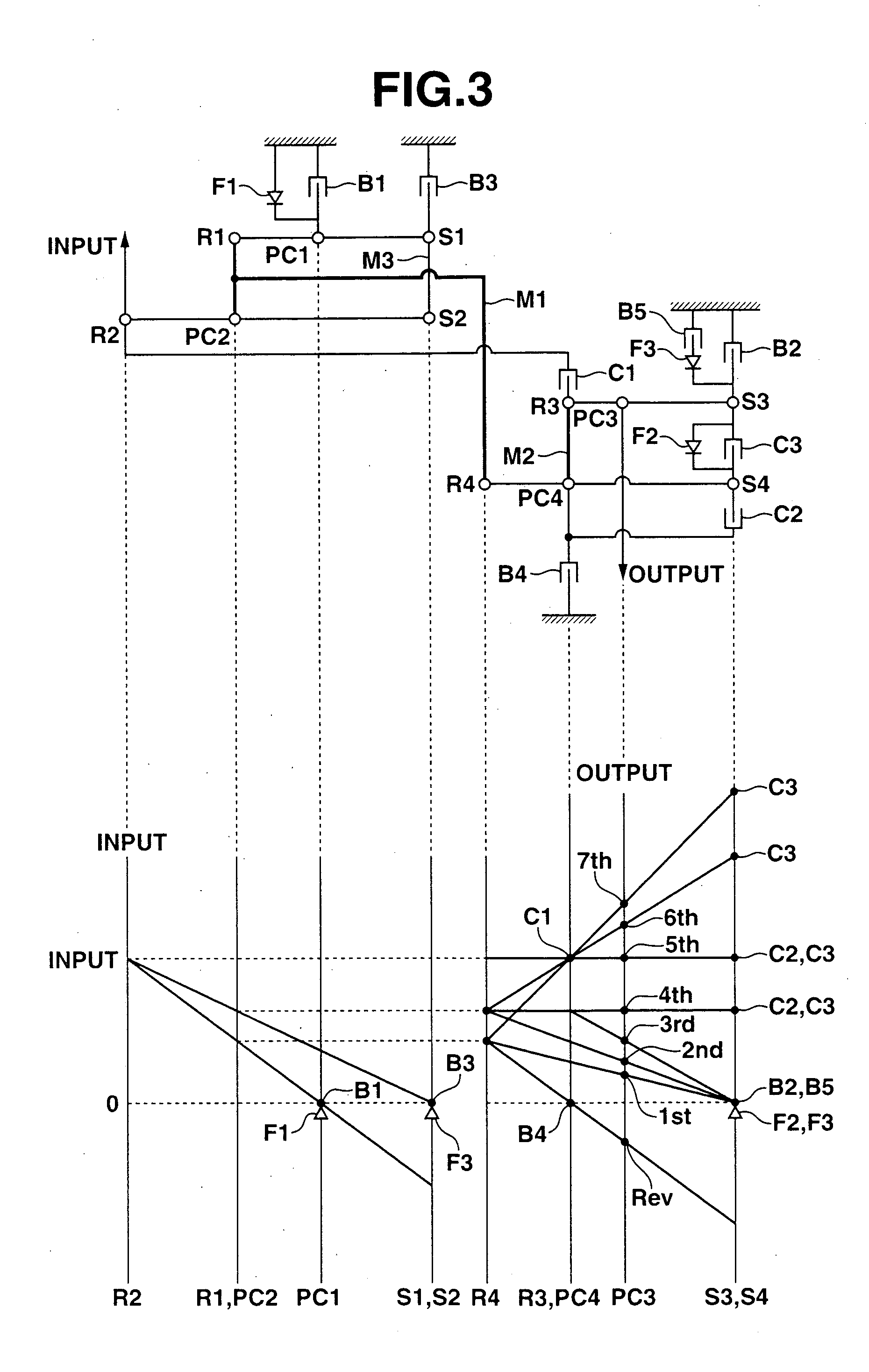
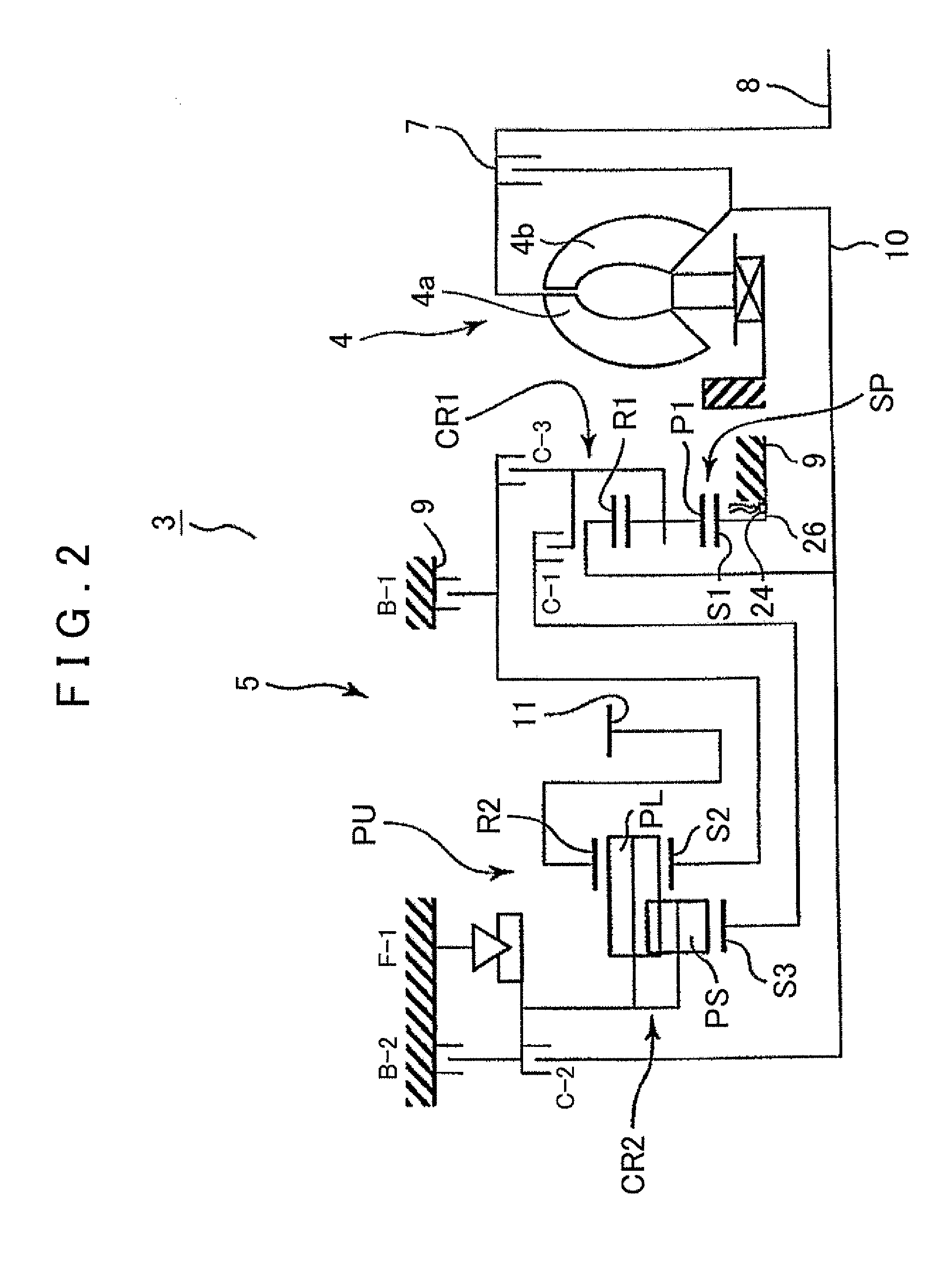
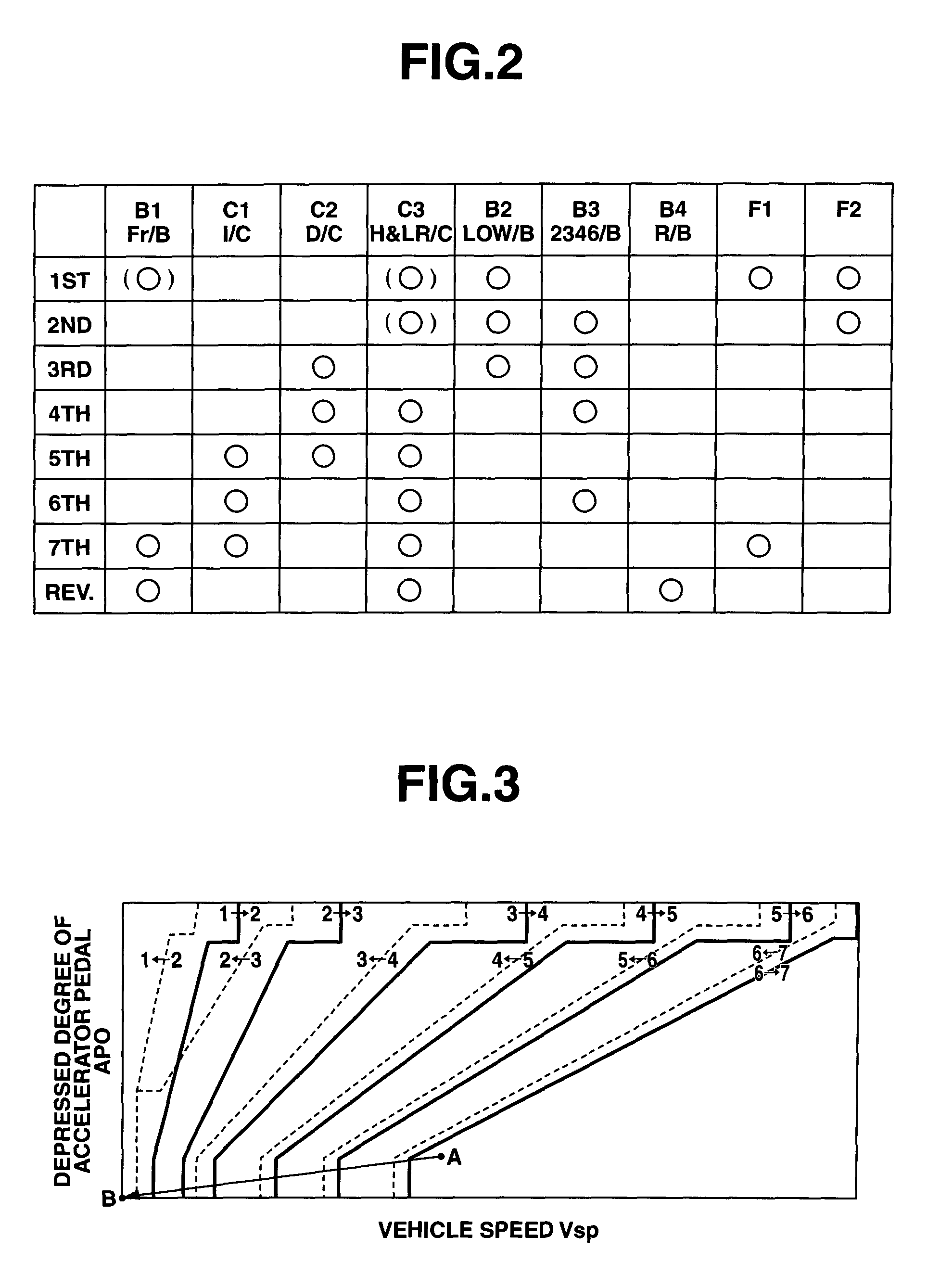
ActiveUS20050113205A1Difficult to processIncrease manufacturing costToothed gearingsTransmission elementsAutomatic transmissionEngineering
A power transmission mechanism for an automatic transmission, configured to establish seven or more forward speeds and one reverse speed. The power transmission mechanism includes four simple planetary gears, three connection members interconnecting two of the rotating members of the planetary gears, three clutches selectively connectable between two of the rotating members, and four brakes each operable to hold selectively against rotation one of the rotating members.
Owner:JATCO LTD
Brake apparatus
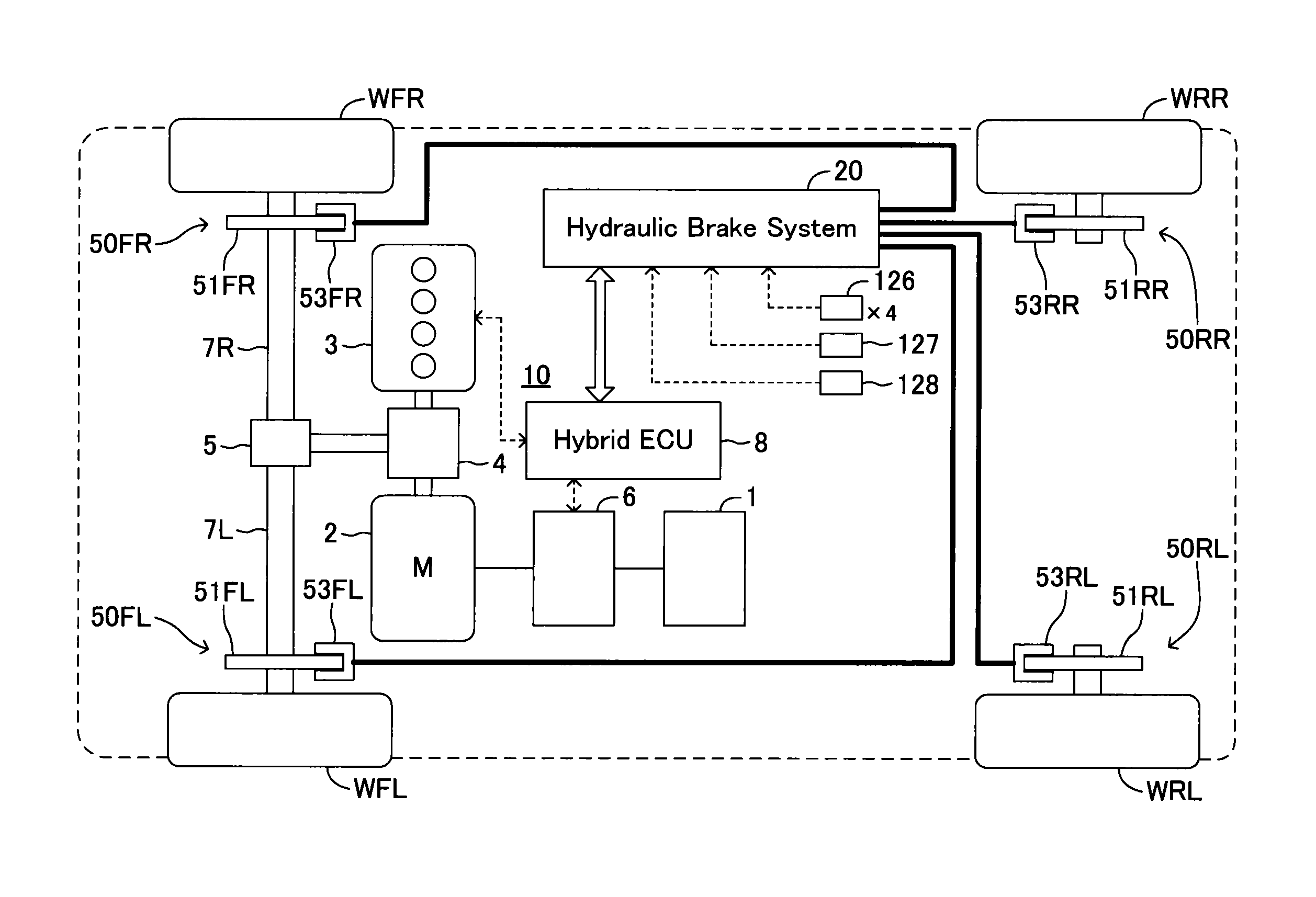
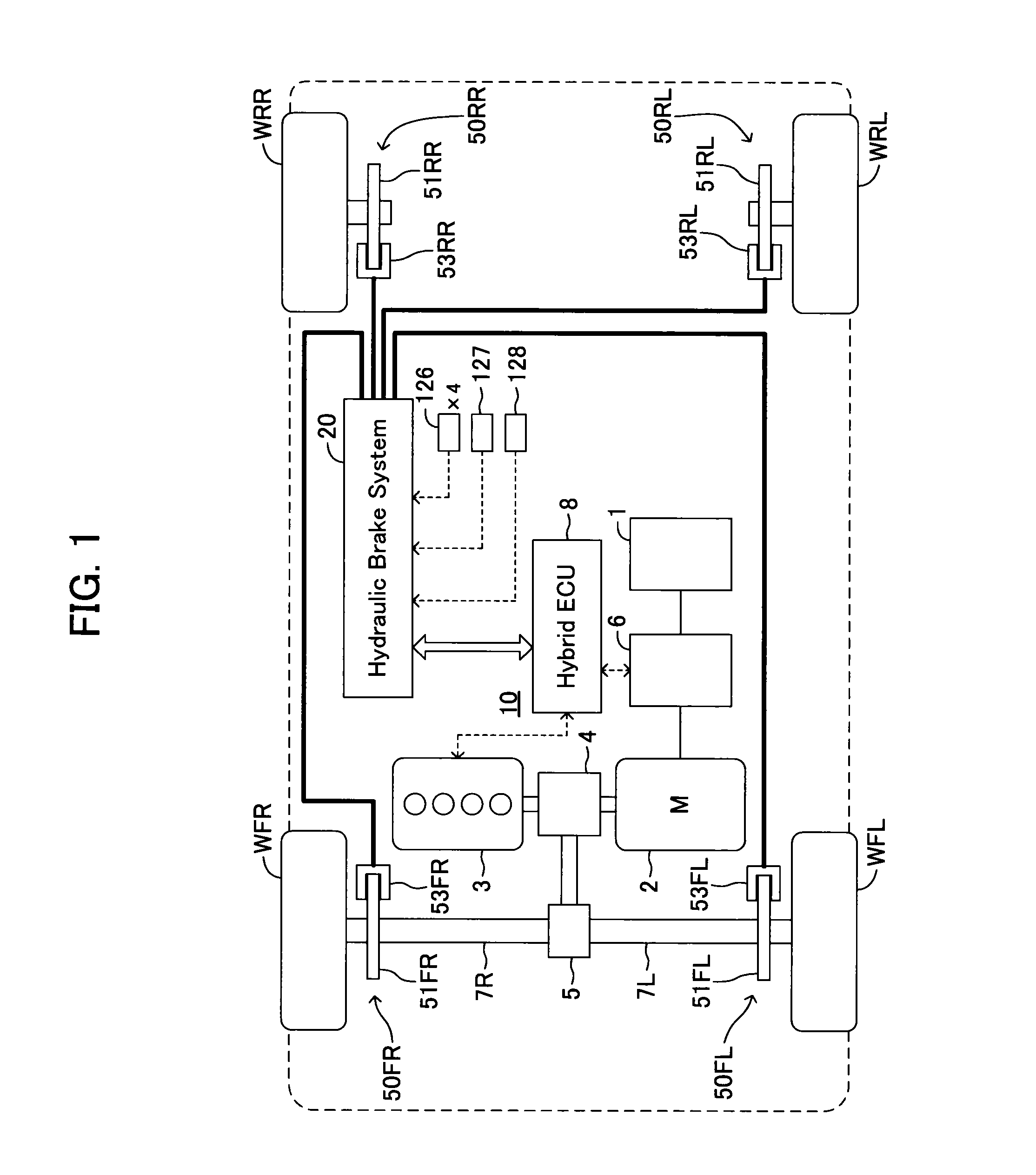
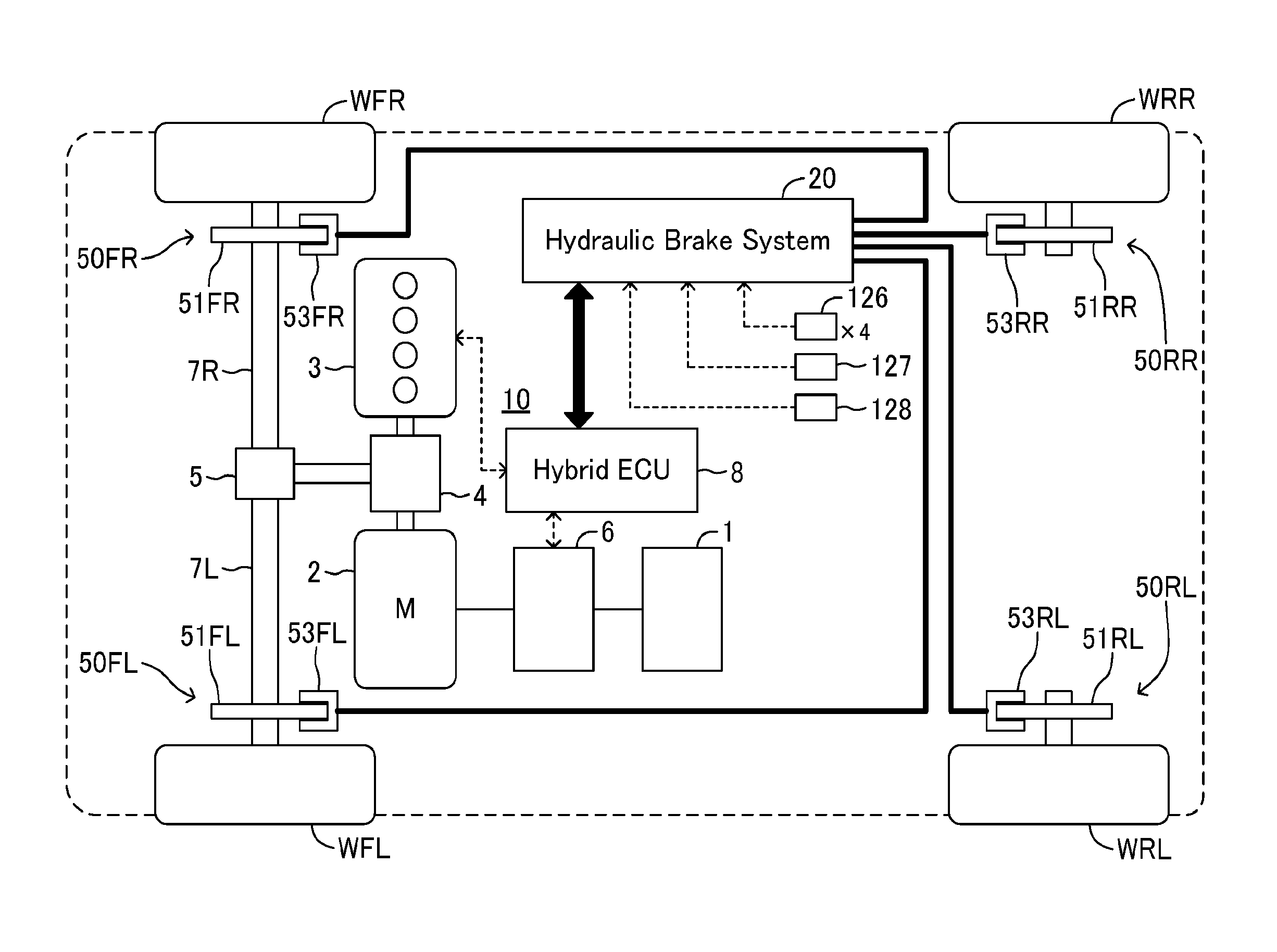
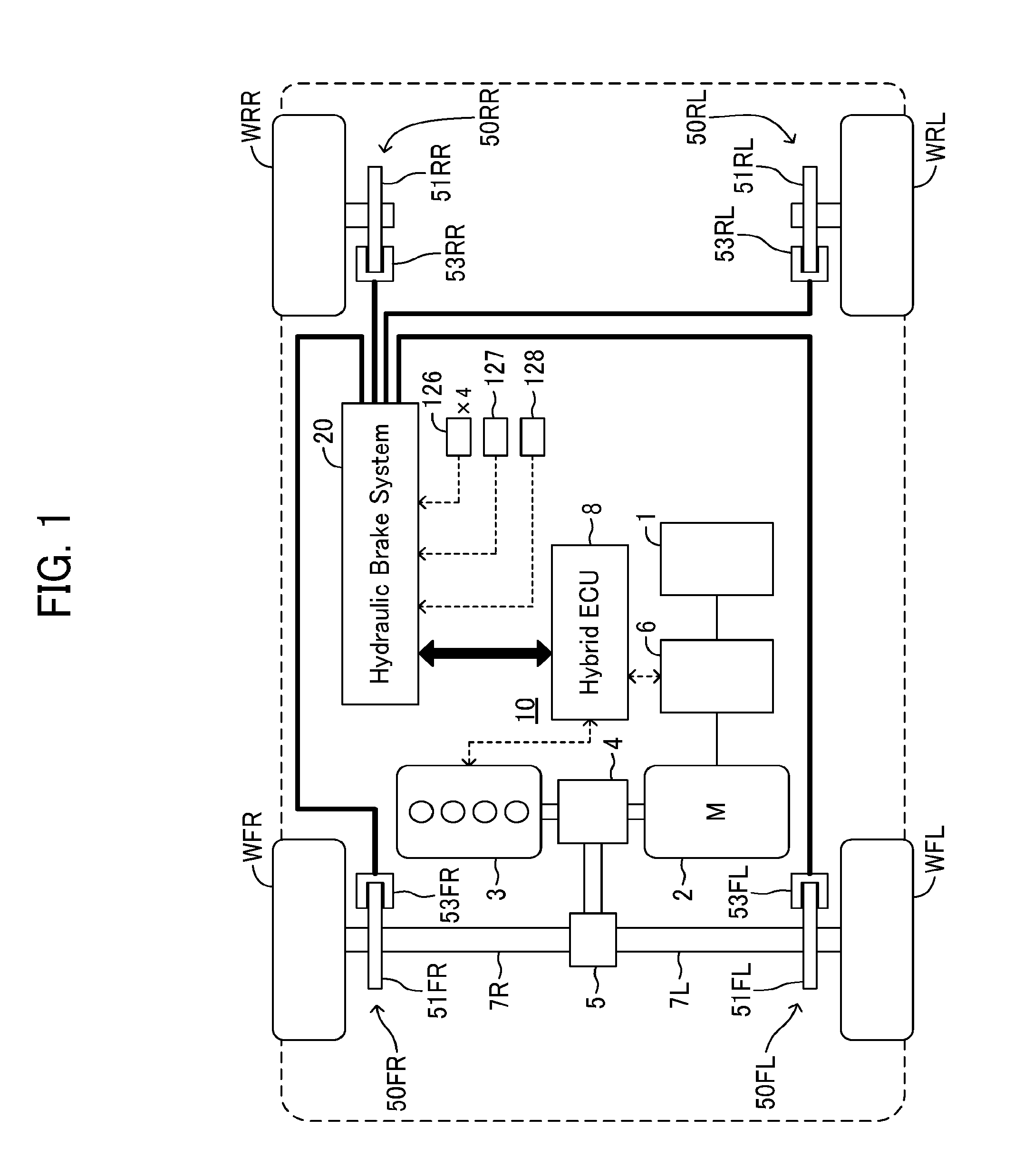
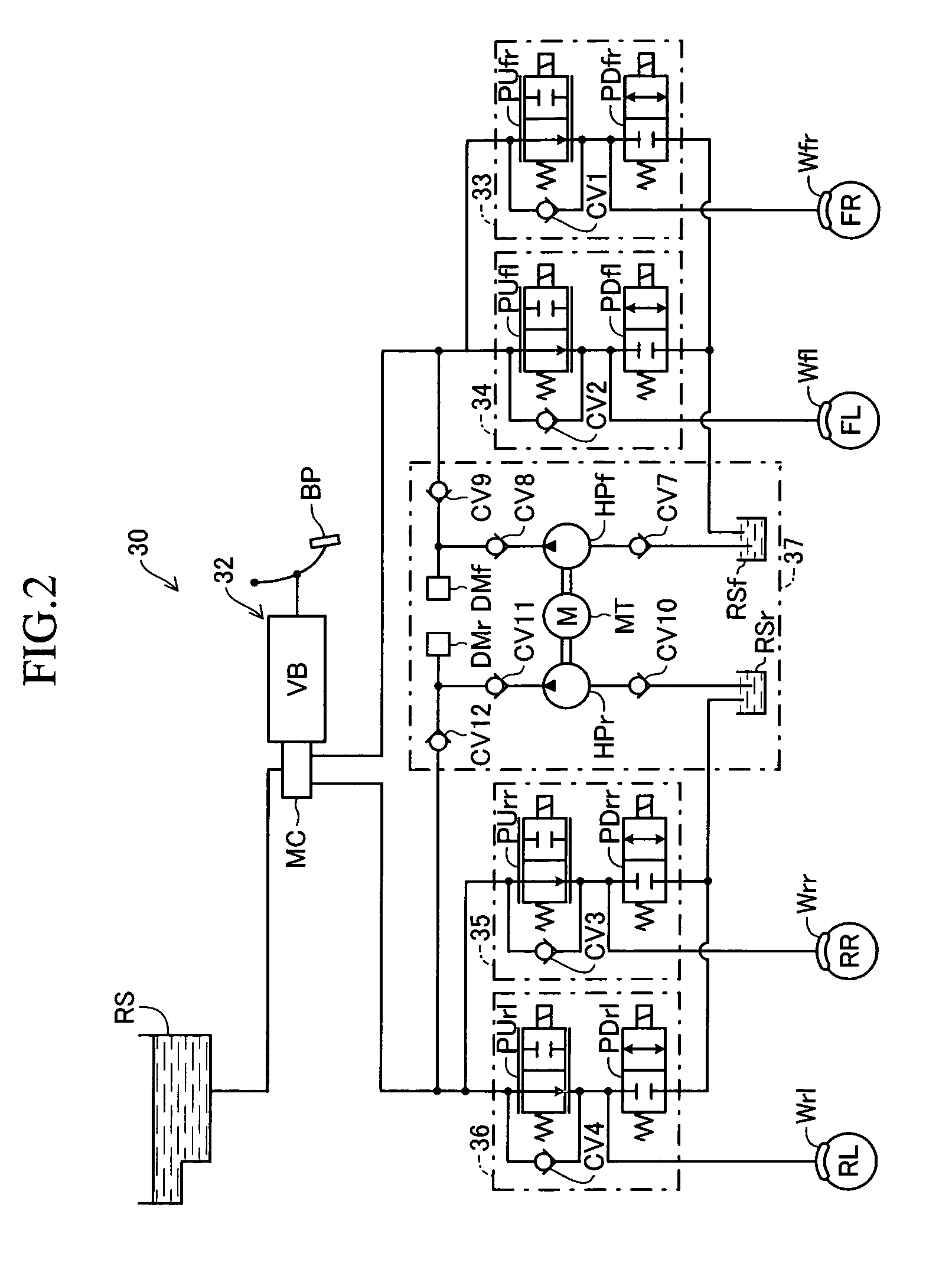
InactiveUS20160082937A1Assist brakingReduction of braking function can be suppressedBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsWheel cylinderActuator
A hydraulic brake system includes a first actuator for a regeneration coordination brake control and a second actuator for maintaining the stability of a vehicle in a hydraulic pressure passage between a master cylinder and a wheel cylinder. The first actuator is controlled by a first ECU, and the second actuator is controlled by a second ECU. When a failure occurs in the first actuator or the first ECU, the second ECU operates the second actuator according to the amount of a brake operation, and assists braking of a wheel.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
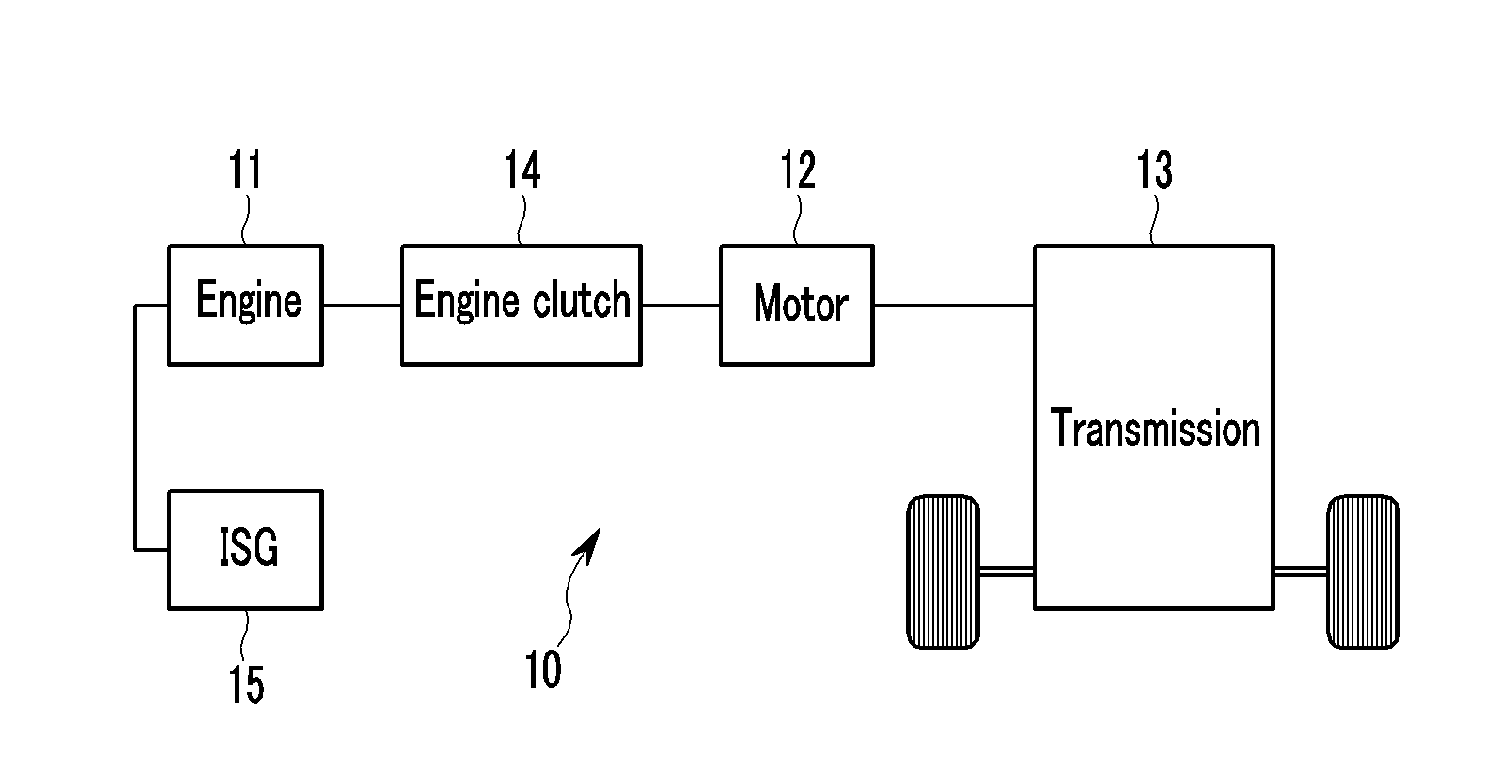
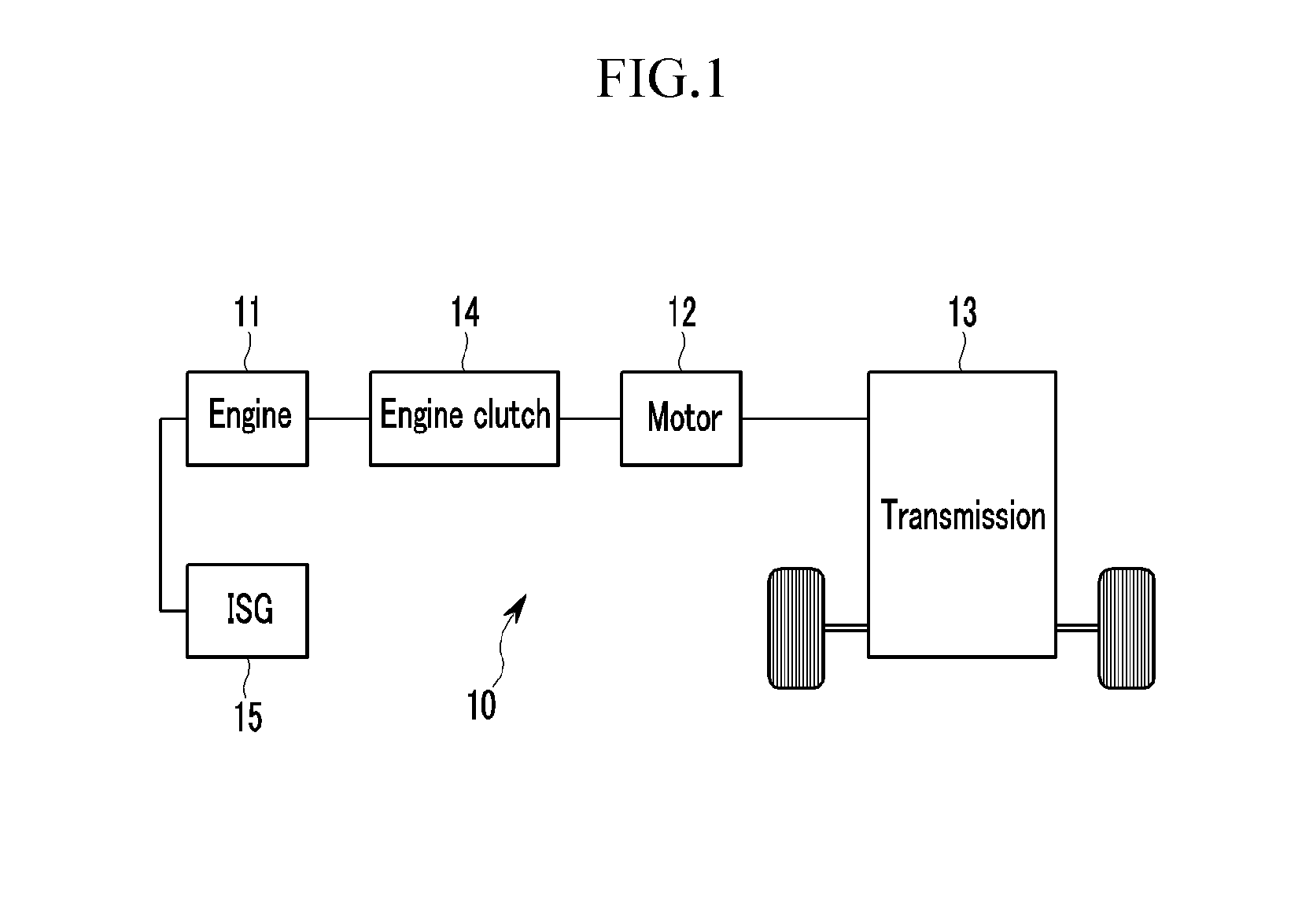
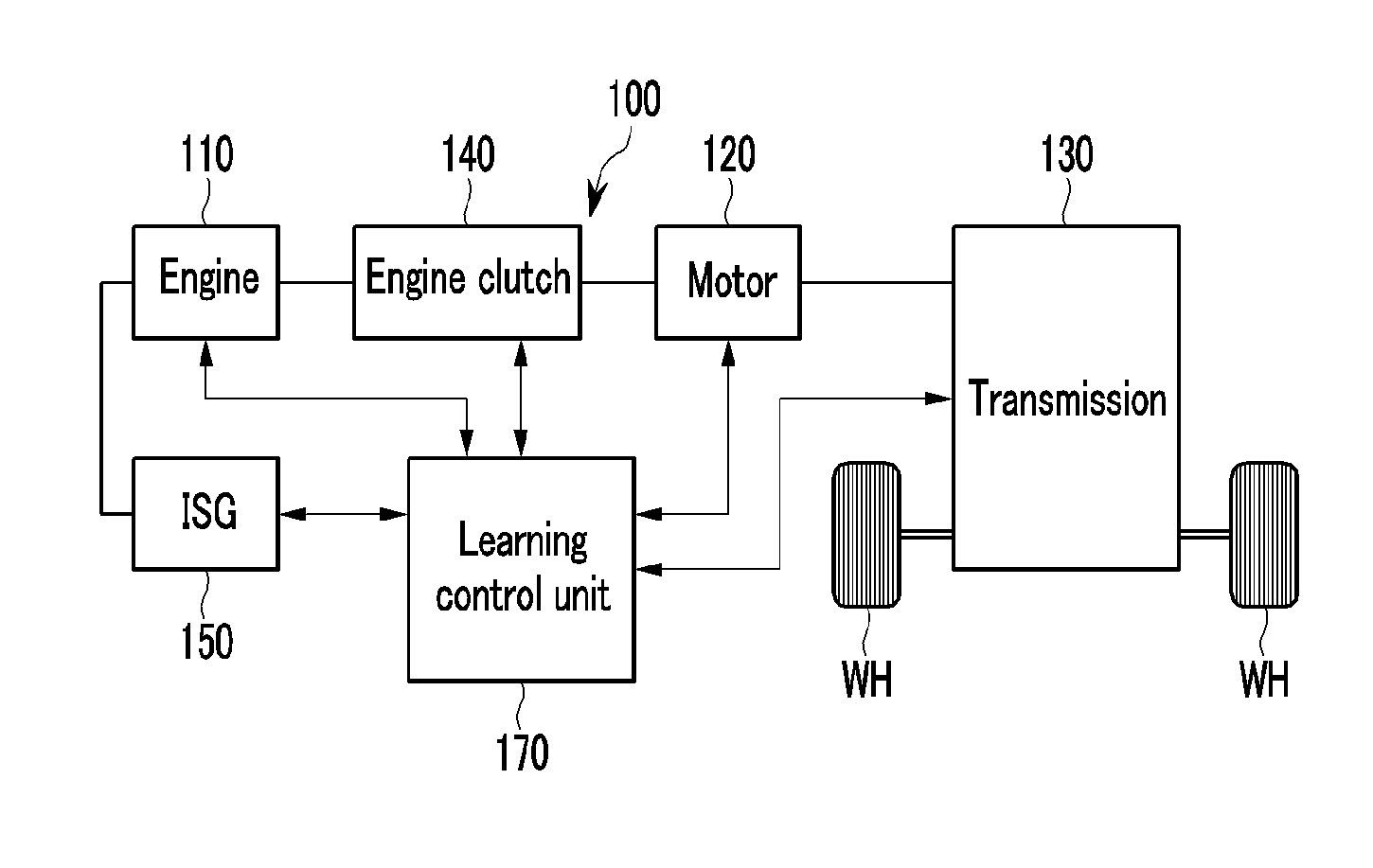
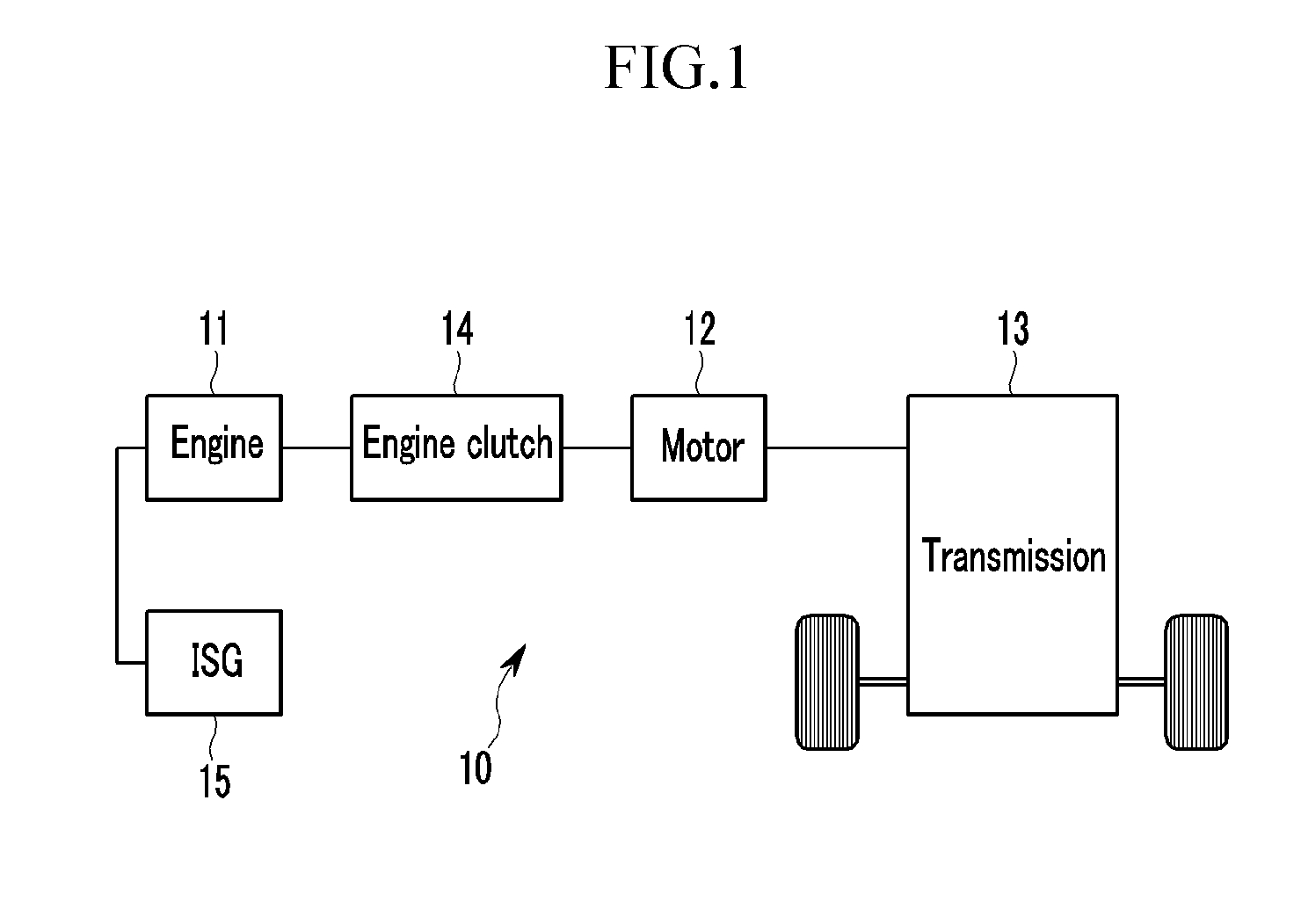
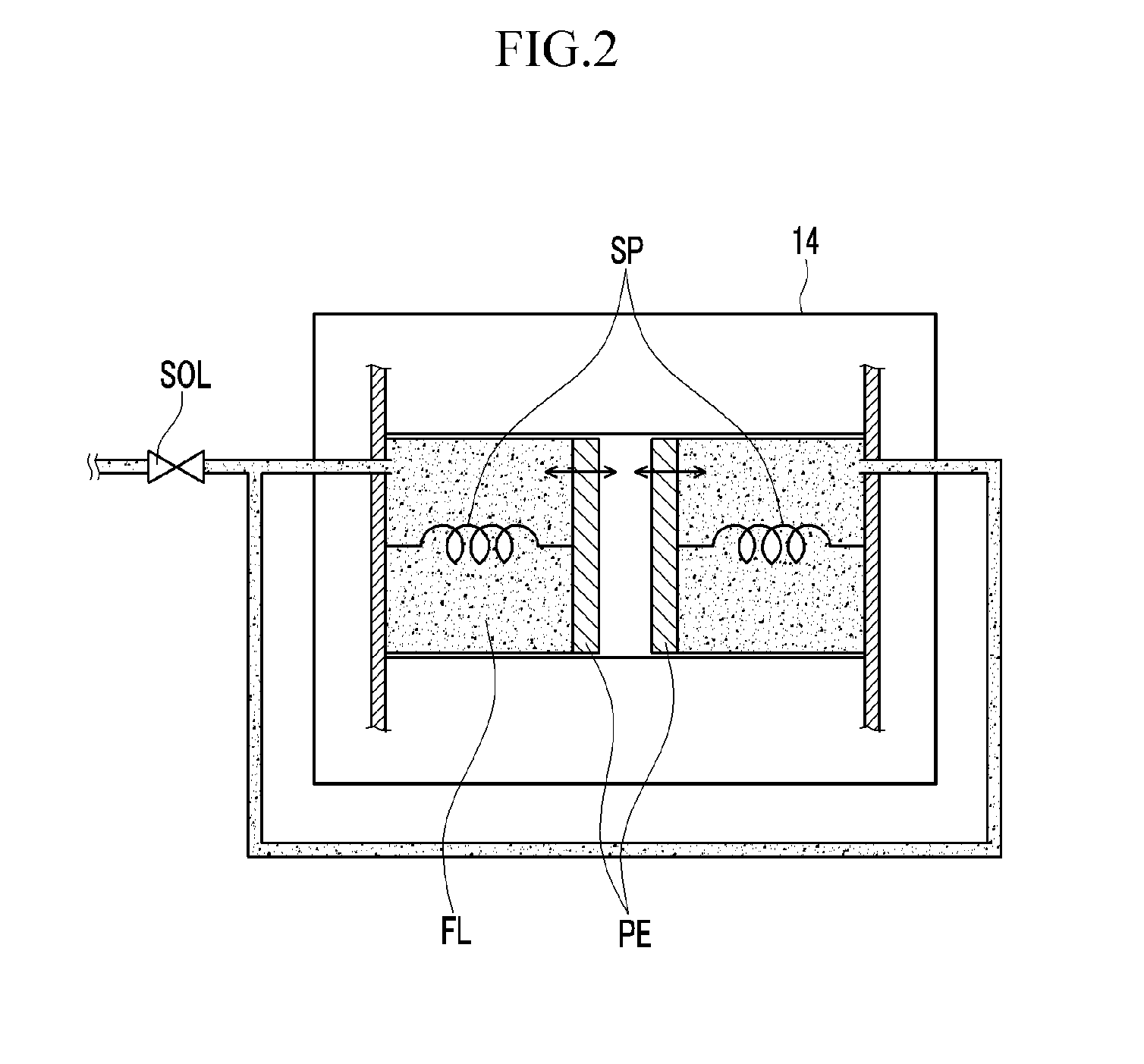
Method and system for learning and controlling torque transmission kiss point of engine clutch for hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20140067174A1Increase hydraulic pressureLearn accuratelyHybrid vehiclesClutchesState variationTorque transmission
Disclosed a system and method of learning and controlling a torque transmission kiss point of an engine clutch. In particular, a determination is made as to whether power transference to a transmission transmitting an output from the engine and the motor has been interrupted, and whether the engine is being driven. The motor is then controlled so that a speed of the motor is maintained at a set speed different from a speed of revolutions of the engine when the power transference to the transmission has been interrupted and the engine is being driven. A state change of the motor is then detected while increasing hydraulic pressure applied to the engine clutch at a set ratio and a torque transmission kiss point of the engine clutch is calculated based on the state change of the motor.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
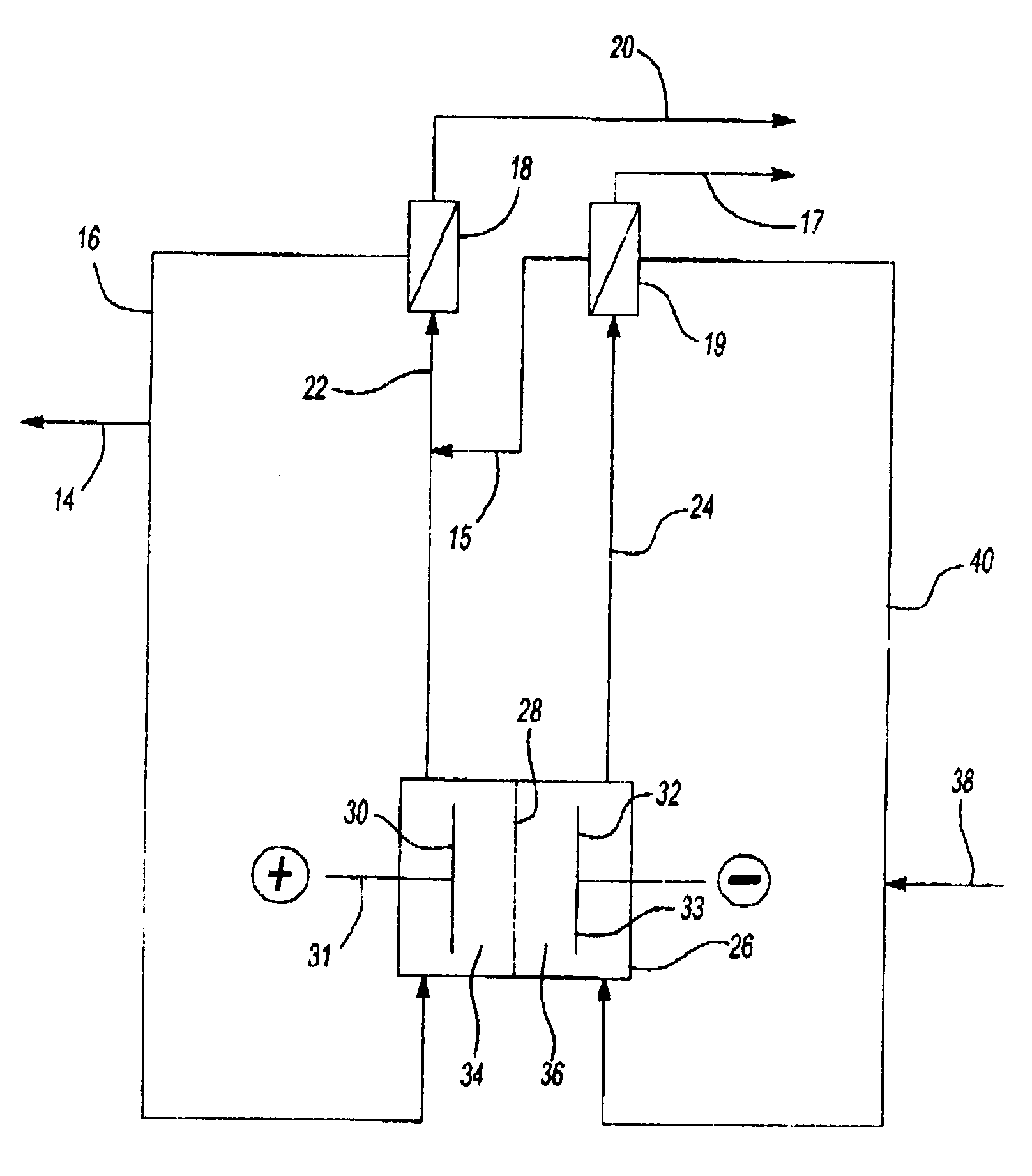
Low energy chlorate electrolytic cell and process
InactiveUS20050011753A1Electrical efficiency is optimalHigh hydraulic pressureCellsOrganic diaphragmsIonChemistry
Alkali metal chlorates are produced by electrolyzing an anolyte contained in an anode compartment of an electrolytic cell, the anode and cathode compartments separated by means of a permselective membrane having low alkali metal ion transport efficiency. The final chlorate product can be directly crystallized from the electrolyzed anolyte or fed directly to a chlorine dioxide generator. Alternatively, a microporous, hydrophilic diaphragm can be substituted for the permselective membrane provided that the catholyte compartment is maintained at a higher hydraulic pressure than the hydraulic pressure in the anolyte compartment.
Owner:JACKSON JOHN R +1
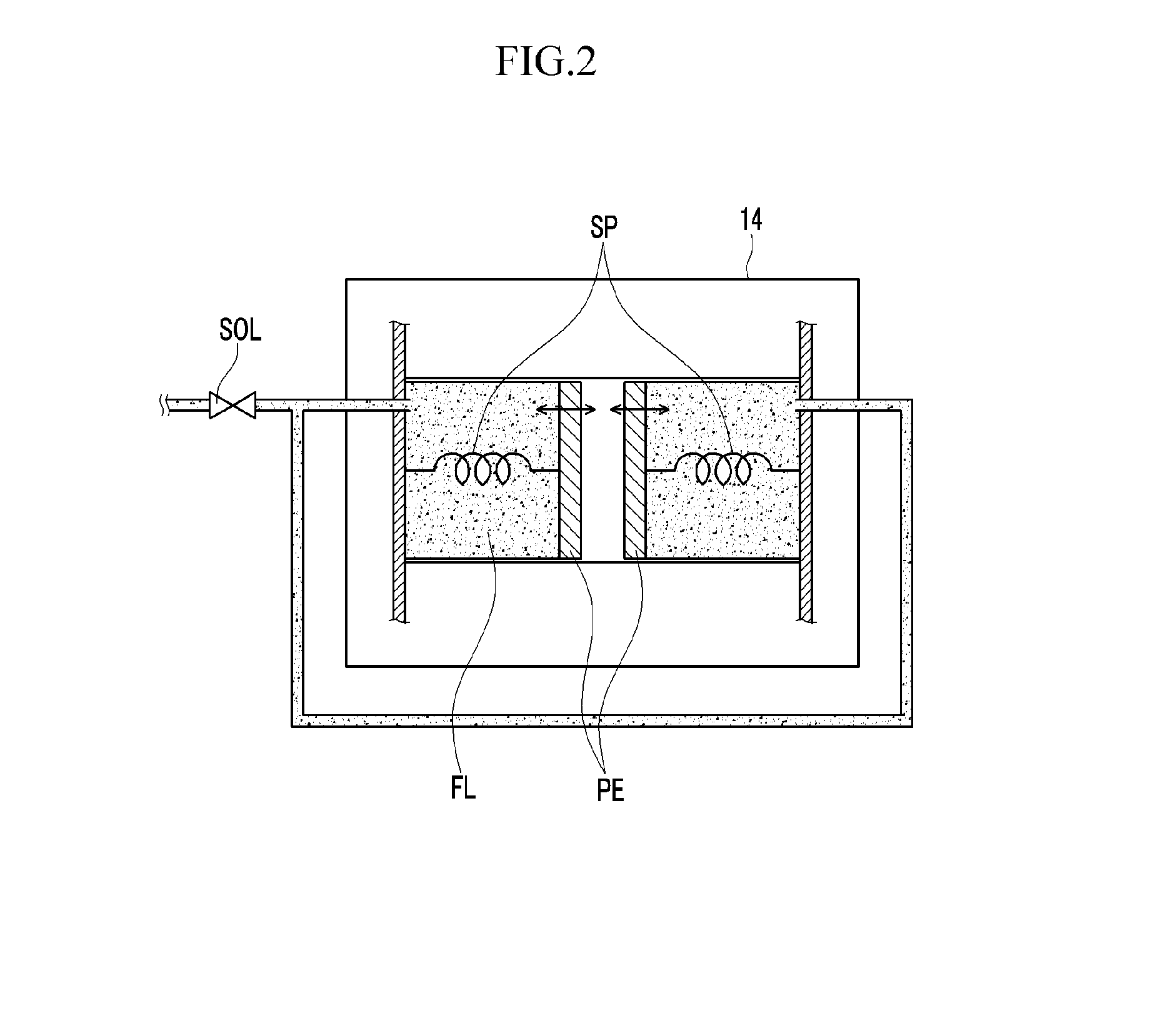
Solenoid operated fluid control valve
ActiveUS20080258090A1Improve liquidityIncrease control pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsSpool valveFluid control
Solenoid operated fluid control valve for a cam phasing mechanism of an internal combustion engine includes first and second control ports, a 2-stage hydraulically pilot-actuated, pressure balanced spool having an integral control feedback passage and a linear force solenoid actuator operably coupled to a pilot valve of a pilot stage. The spool valve includes an exhaust path common to pilot and spool exhaust passages.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AUTOMOTIVE USA
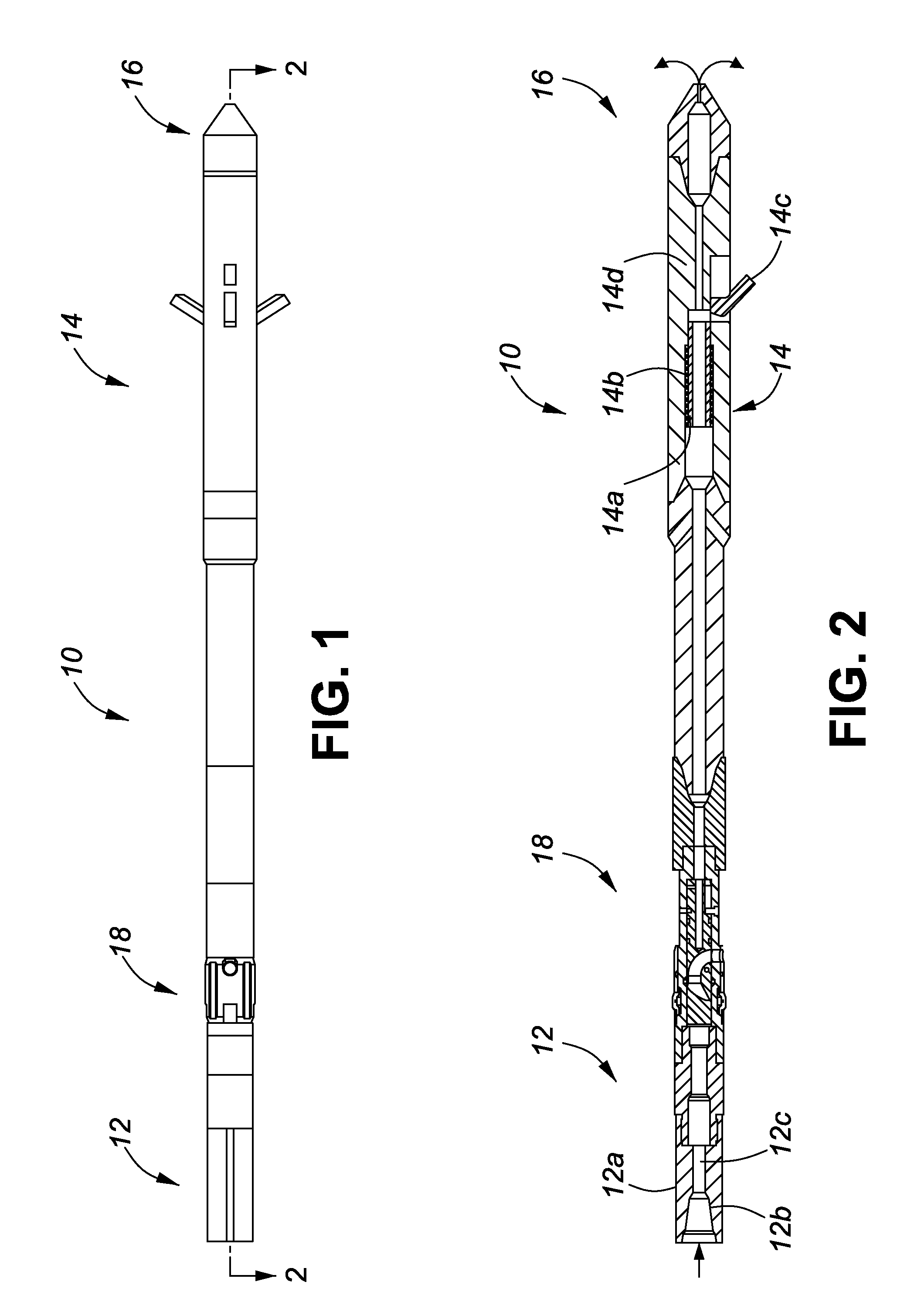
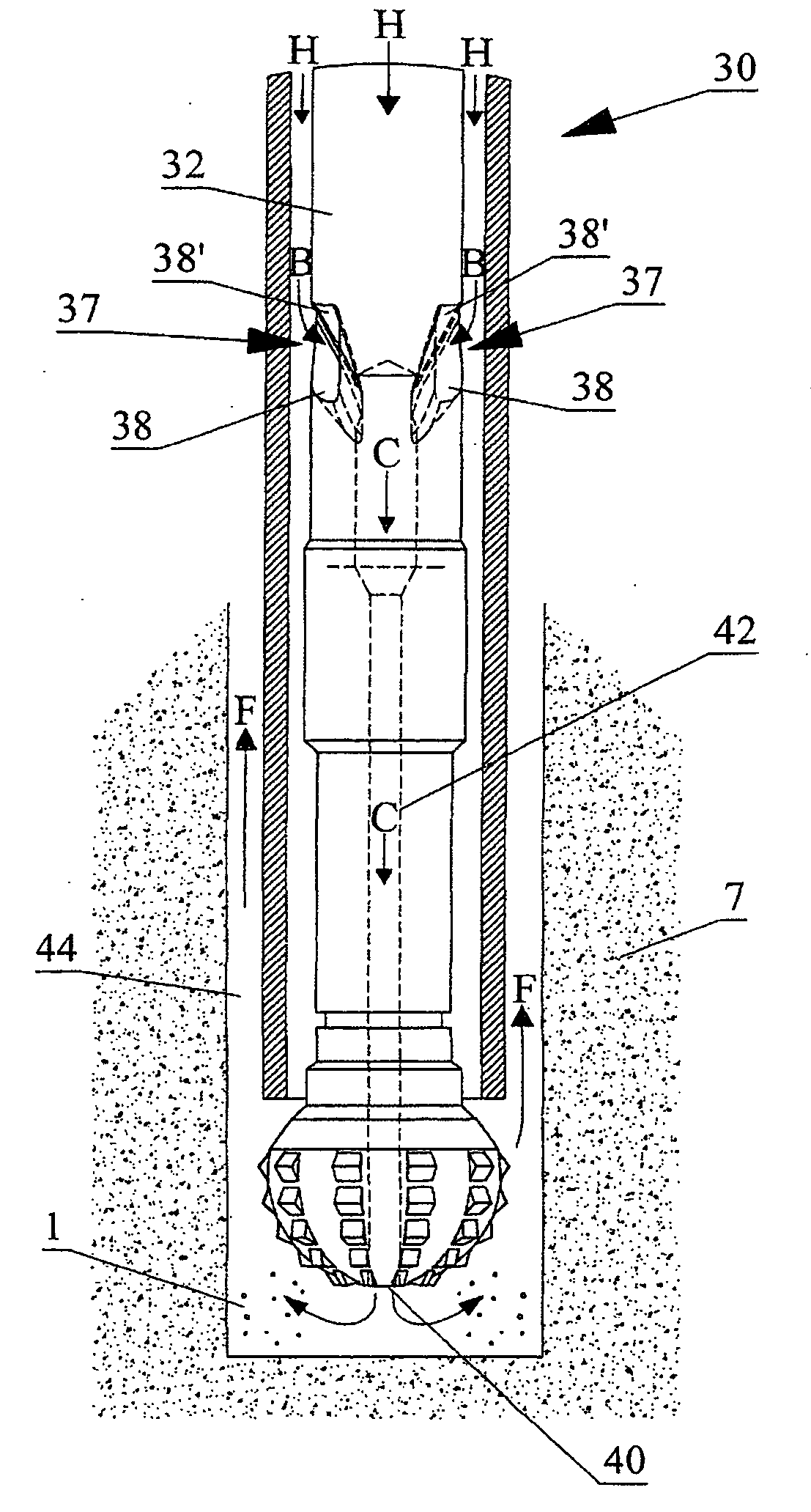
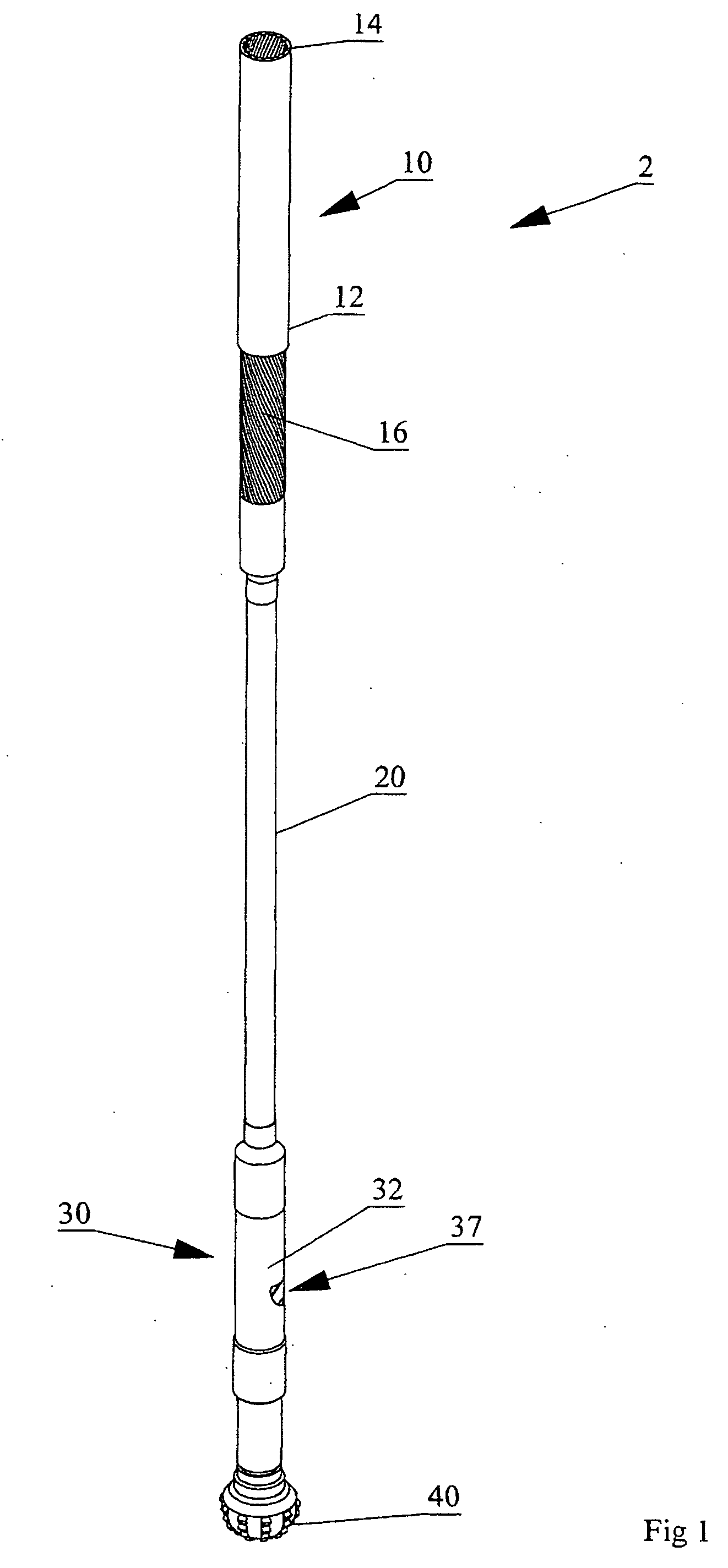
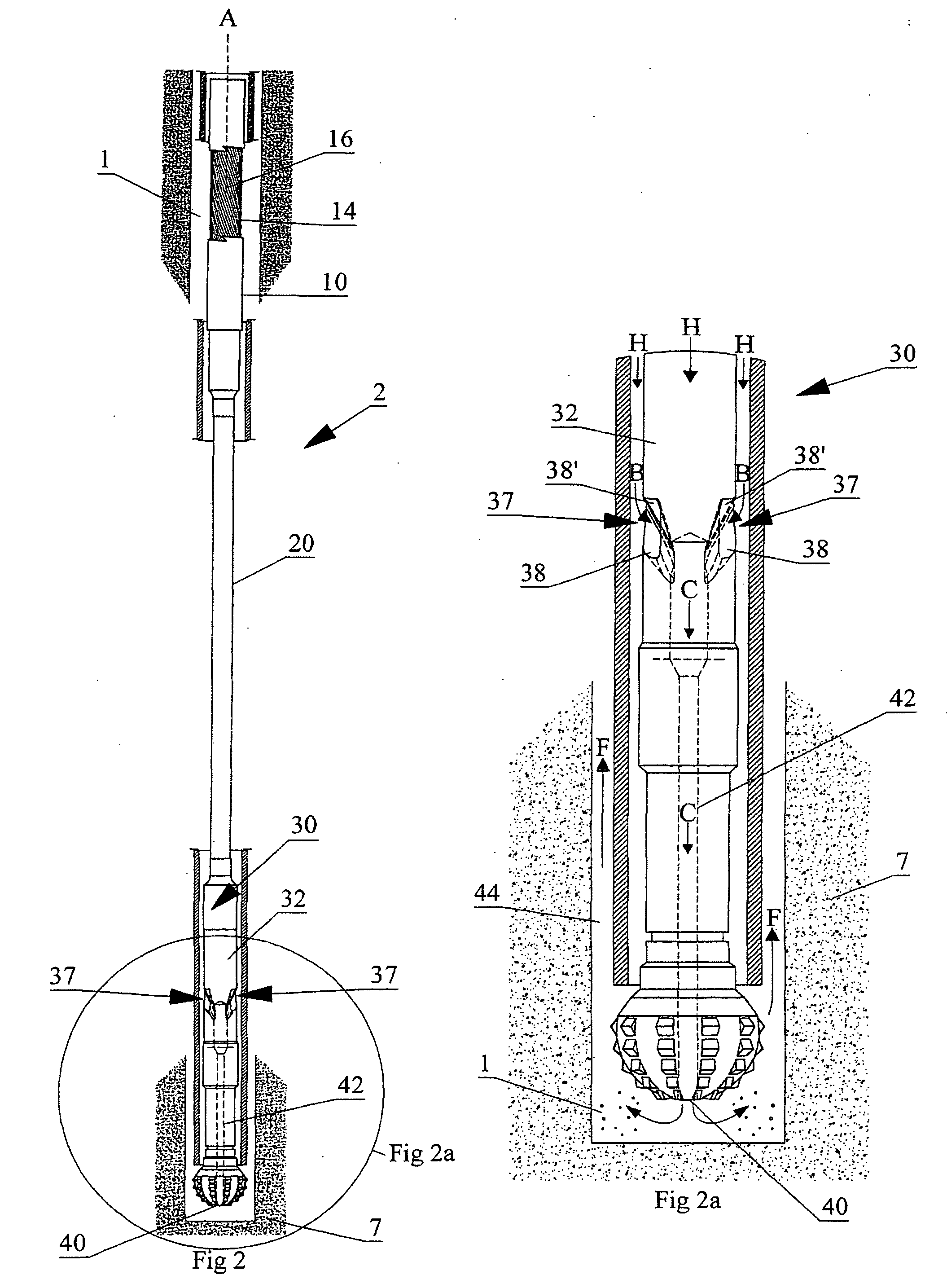
System and method for longitudinal and lateral jetting in a wellbore
InactiveUS20100243266A1Increase hydraulic pressureDrill bitsLiquid/gas jet drillingReamerMaterial Perforation
A system and method for enabling longitudinal and radial drilling in a wellbore is described. The system and method enable an operator to perforate the casing of a wellbore with an under-reamer at the end of a drill string and, without removing the drill string from the wellbore, initiate and complete lateral jetting of the wellbore into the surrounding formation. The system utilizes a perforation tool having a ball seat, which upon seating a drop ball in the ball seat enables the perforation tool to move from a closed position to an open position thereby allowing access to the formation using a jetting tool. Prior to seating the drop ball, an under-reaming operation may be performed using a hydraulic pressure activated under-reaming tool.
Owner:AXS TECH
Fluid driven drilling motor and system
InactiveUS20060283636A1Increase hydraulic pressureIncrease torqueDrilling rodsBorehole drivesElectric machineEngineering
A fluid driven drilling motor and system includes a flex shaft between the rotor and a cylindrical flow collar. The end of the flow collar opposite from the flex shaft has a bore in fluid communication with a drill bit. Ramped apertures are formed in the side wall of the flow collar. The ramped apertures are in fluid communication with the bore. Drilling fluid flowing under pressure down past the flex shaft is directed and drawn into the ramped apertures along a fluid flow path which spirals downwardly and radially inwardly of the flow collar so as to then flow into the bore. The pressure loss associated with drawing the drilling fluid down to the drill bit is thereby minimized.
Owner:BOW RIVER TOOLS & SERVICES
Brake apparatus
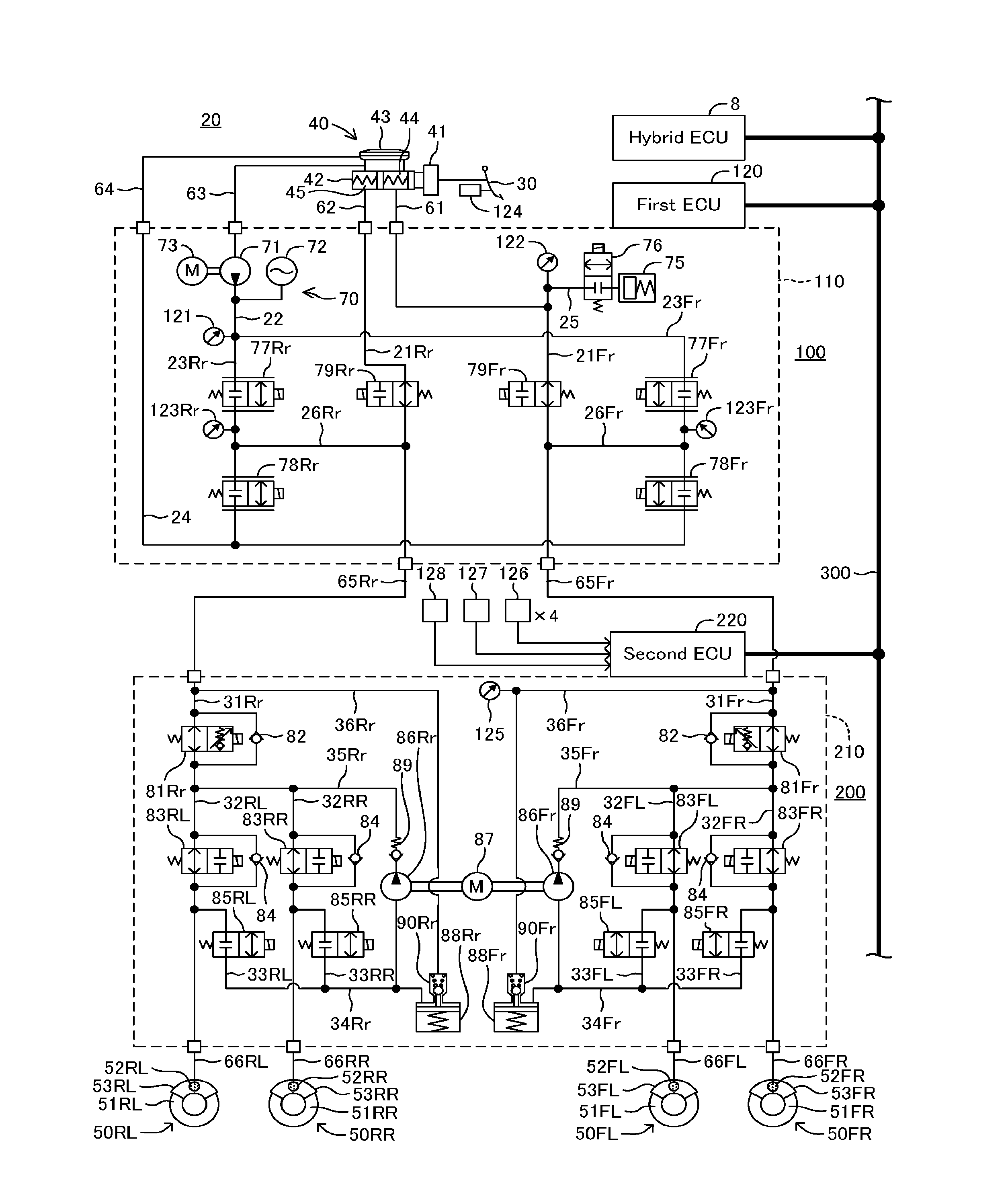
ActiveUS20160096434A1Reduce running noiseIncreased durabilityHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsLinear controlOperation mode
A first ECU estimates whether the operation of a second actuator has been started, based on the variation of the hydraulic pressure with respect to the flow rate of hydraulic fluid outputted from a first actuator. Even in a case where the operation information of the second actuator is not received, the first ECU sets the control mode to a simultaneous operation mode, when it is estimated that the operation of the second actuator has been started. In the simultaneous operation mode, a controlled parameter of linear control valves on assumption that the second actuator is operating is set up, and a stop instruction of regenerative braking is transmitted to a hybrid ECU.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Work vehicle
ActiveUS20120152641A1Easy to controlIncrease hydraulic pressureFluid couplingsGas pressure propulsion mountingAutomotive engineering
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Graphene-iron oxide complex and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20120168383A1Efficient and selective separationImprove adsorption capacityMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteIron nanoparticleCvd graphene
A graphene-iron oxide complex consists of graphene and needle-like iron oxide nanoparticles grown on a surface of the graphene, and a fabricating method thereof includes (A) preparing a reduced graphene dispersed solution, (B) mixing the dispersed solution with a solution containing iron oxide precursors to prepare a mixture, (C) stirring the mixture to prepare a graphene-iron oxide dispersed solution containing the graphene-iron oxide complex that needle-like iron oxide nanoparticles are grown on the surface of the graphene, and (D) separating the graphene-iron oxide complex from the graphene-iron oxide complex dispersed solution.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
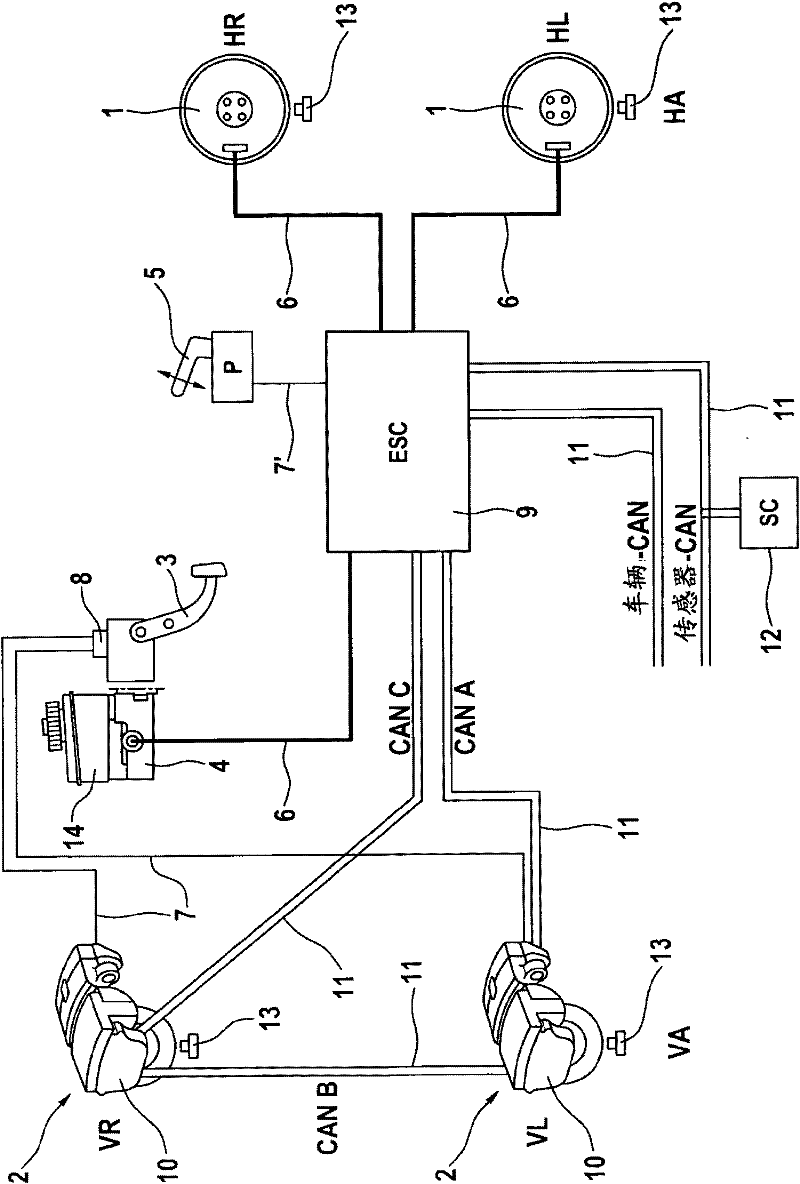
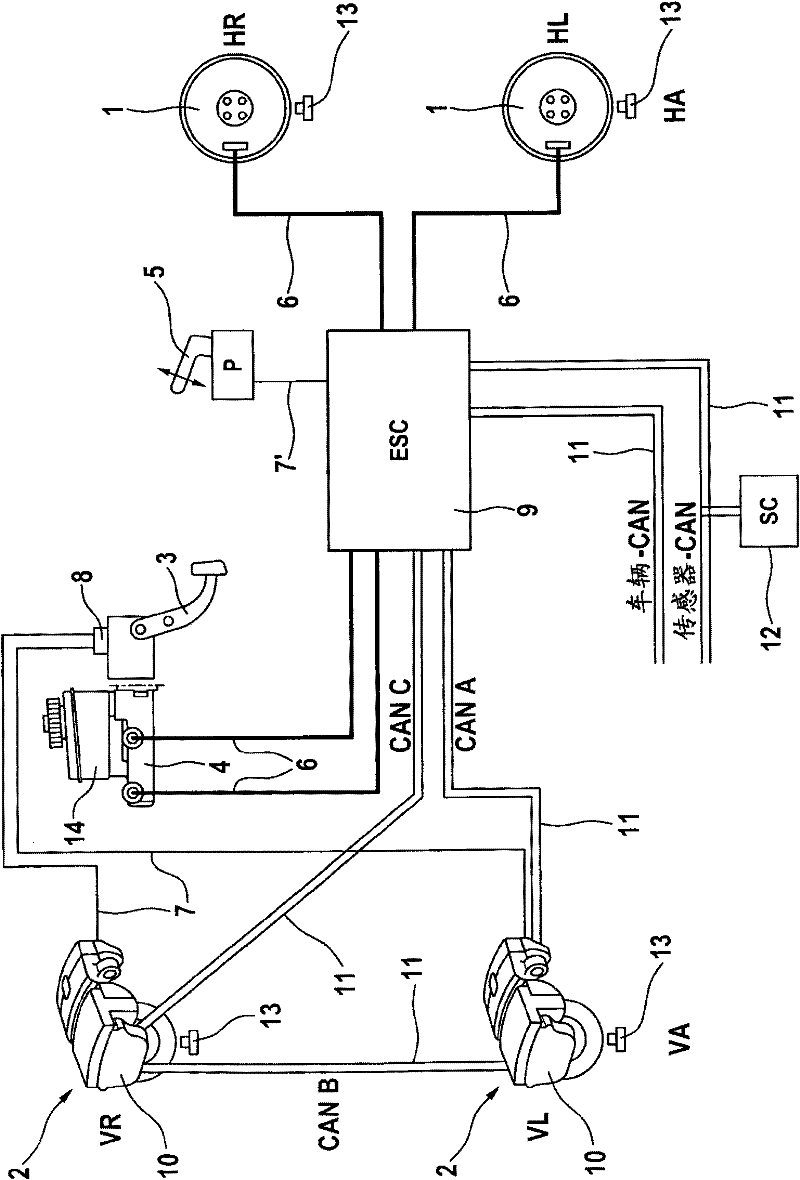
Combined vehicle brake system with hydraulically and electromechanically actuatable wheel brakes
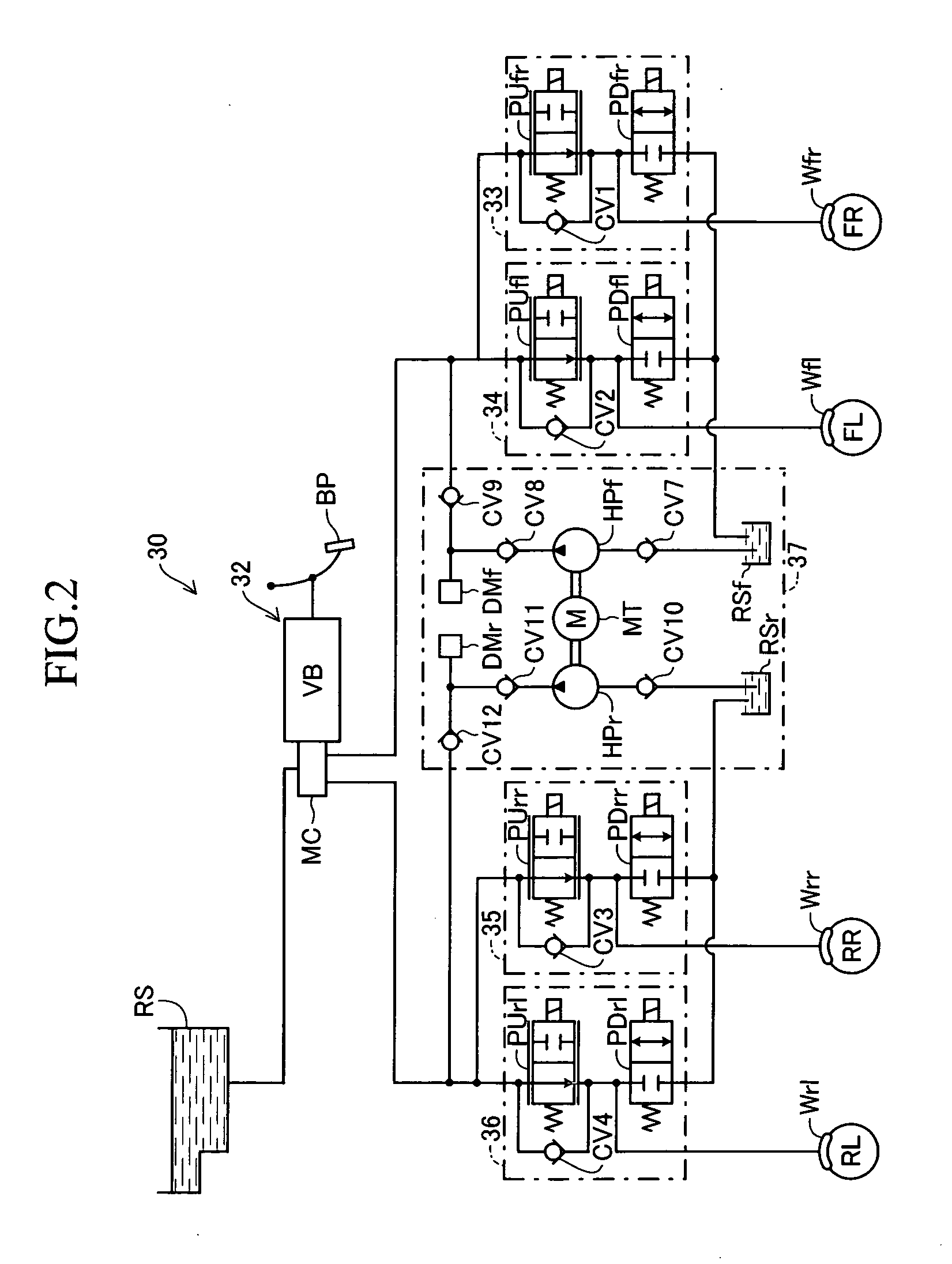
ActiveCN102164792ALow costSufficient braking powerBraking action transmissionHydraulic brakeBraking system
Combined vehicle braking system, in particular for motor vehicles, comprising an electromechanical service brake system for a first axle of the vehicle, said electromechanical brake system comprising at least one electromechanically actuatable wheel brake (2), and comprising a hydraulic service brake system for a second axle of the vehicle, said hydraulic brake system comprising a main brake cylinder (4) and at least one hydraulically actuatable wheel brake (1), wherein the first axle is a front axle (FA) and the second axle is a rear axle (RA).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
Multi function torque converter with lever spring and method for controlling hydraulic pressure and flow
InactiveUS20080149441A1Increase hydraulic pressureMechanical actuated clutchesRotary clutchesPistonTraffic volume
A torque converter including an impeller clutch with a first portion connected to a cover for the torque converter and a second portion connected to an impeller; and a lever element in contact with the clutch and displaceable to multiply a first force applied to the lever element for operation of the clutch. In some aspects, the converter includes an impeller piston plate engaged with the lever element and displaceable to apply the force to the lever element. In some aspects, the torque converter includes a torus and a charge chamber for the impeller clutch, a second force is associated with a hydraulic pressure to prevent cavitation in the torus, a third force is required to operate the impeller clutch to transmit a desired torque across the impeller clutch, and the multiplied force is at least equal to a sum of the second force and a third forces.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
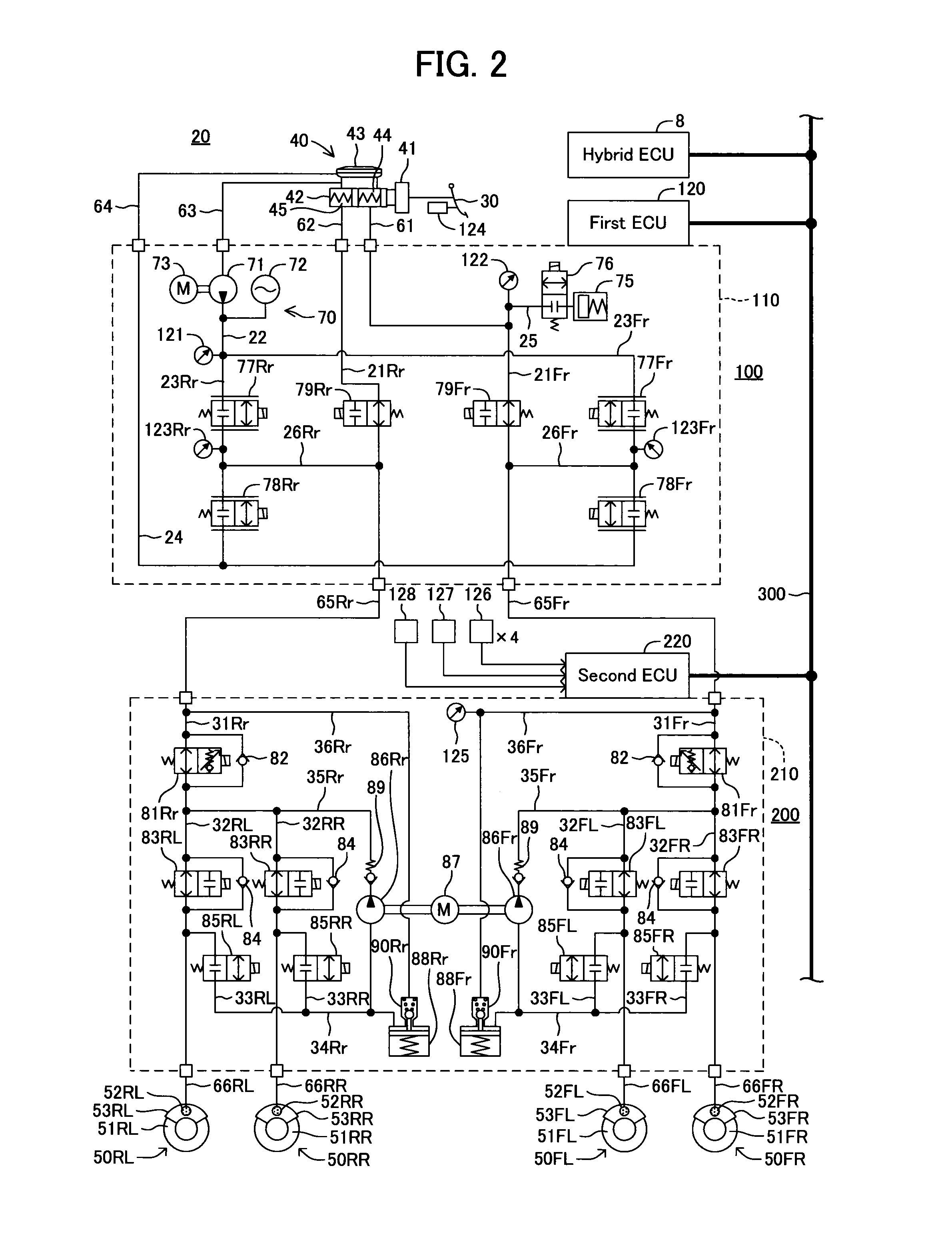
Hydraulic brake system
ActiveUS20120235469A1Avoid it happening againImprove operationBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsEngineeringHydraulic brake
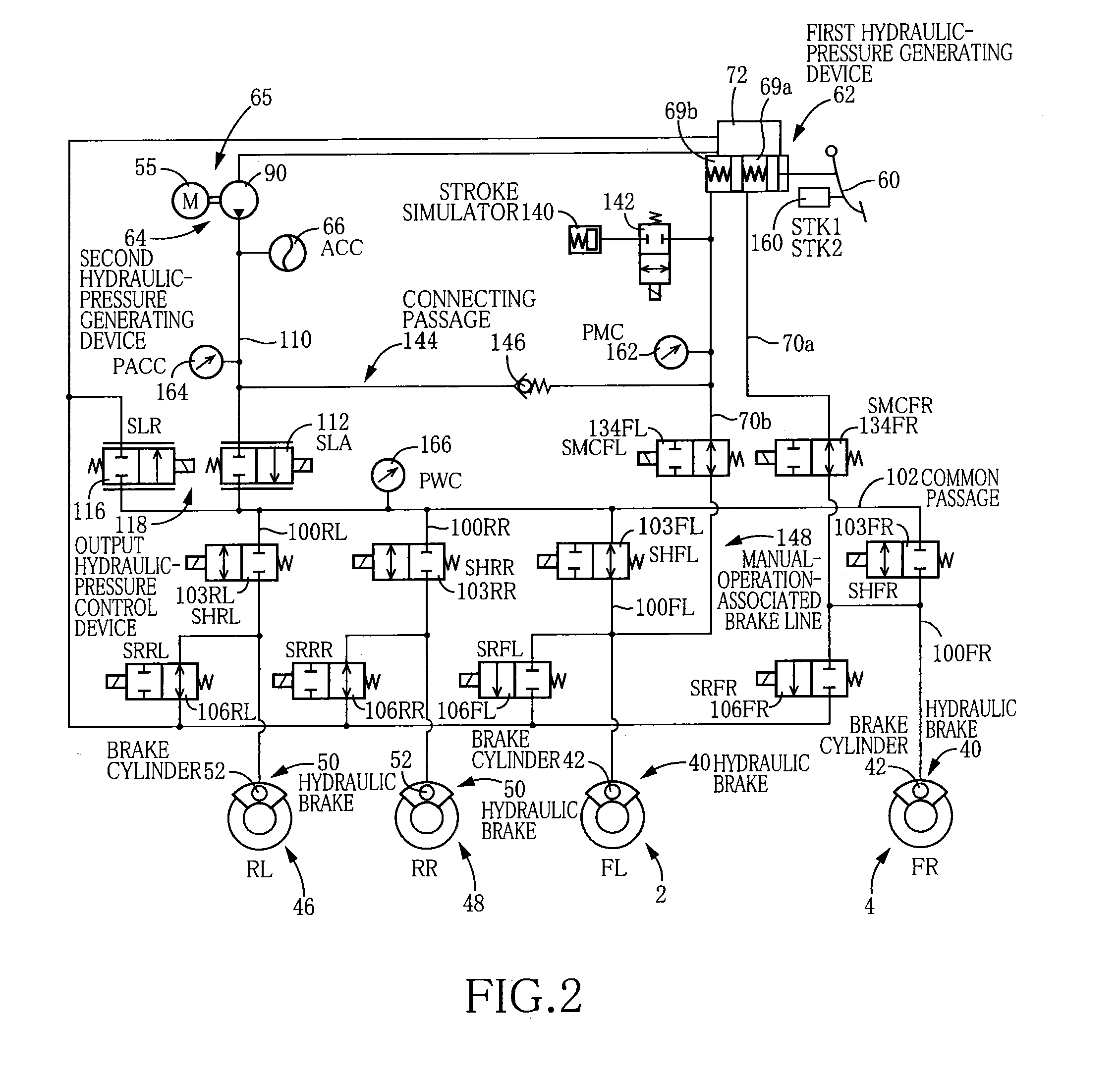
A hydraulic brake system including: (a) a first hydraulic-pressure generating device including a manual hydraulic pressure source; (b) a second hydraulic-pressure generating device including a power hydraulic pressure source; (c) a manual-operation-associated brake line including a communicating device that is to be brought into communication with the manual hydraulic pressure source and brake cylinder or cylinders of the plurality of hydraulic brakes; (d) an output hydraulic-pressure control device and a flow restraining device disposed in parallel with each other between the manual-operation-associated brake line and the second hydraulic-pressure generating device; and (e) a power hydraulic pressure source control device for activating the power hydraulic pressure source such that the hydraulic pressure is supplied to the manual-operation-associated brake line via the flow restraining device, when the output hydraulic-pressure control device cannot control the hydraulic pressure outputted by the second hydraulic-pressure generating device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hydraulic damping force control unit, hydraulic shock absorber, front fork for vehicle, and hydraulic rotary damper
InactiveUS7448479B2Increase hydraulic pressureSuitable damping forceSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringControl valves
A damping force is generated by keeping a damping force control valve closed when a piston of a hydraulic shock absorber starts to move from compression side dead center or expansion side dead center. A damping force control valve including a poppet valve for opening and closing a first fluid path is provided. A pilot pressure chamber defined from the fluid path by a valve element of the damping force control valve is provided. A linear solenoid and a pilot valve for increasing and reducing the hydraulic pressure in the pilot pressure chamber are provided. A check valve disposed in parallel with the damping force control valve is provided in a piston. A communication path for communication between the first fluid path downstream of the damping force control valve and the pilot pressure chamber is provided.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
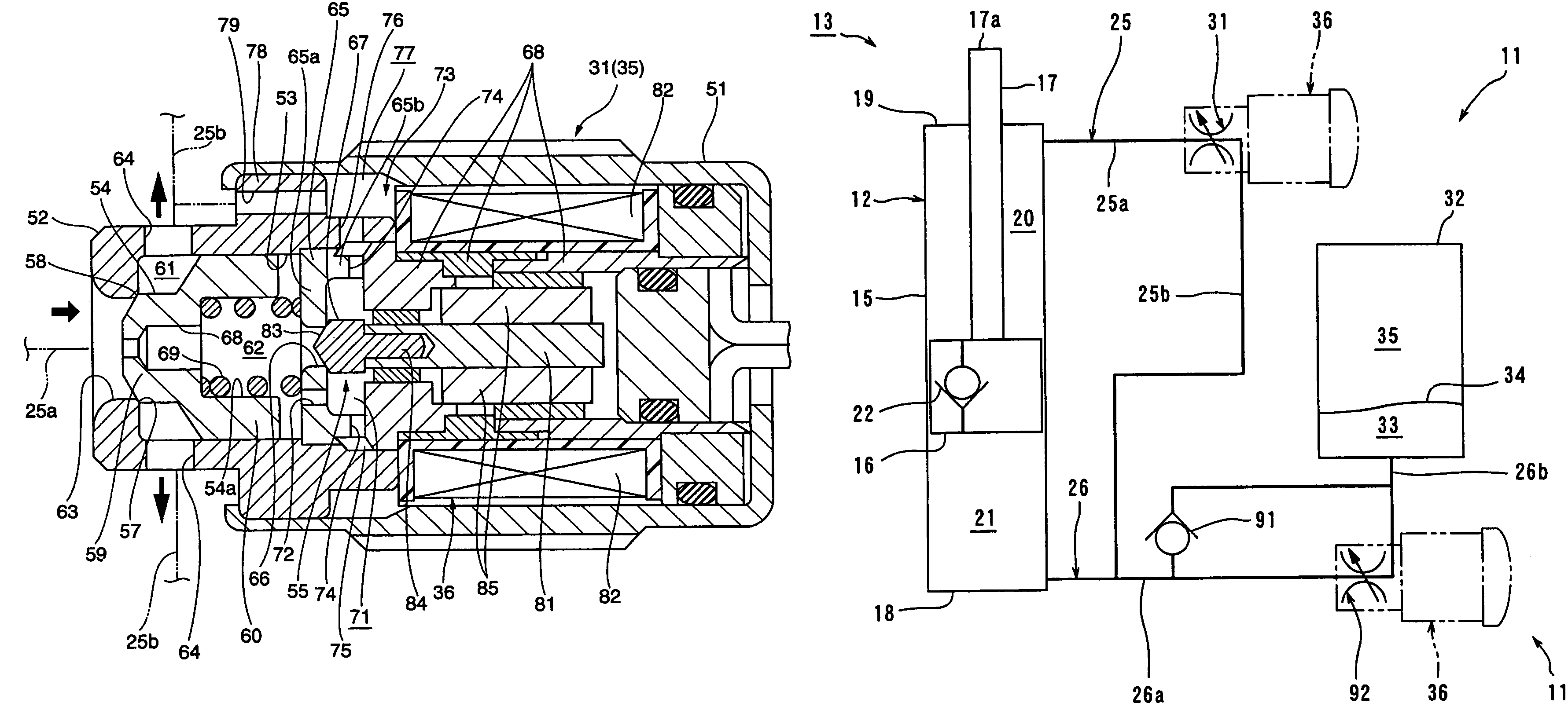
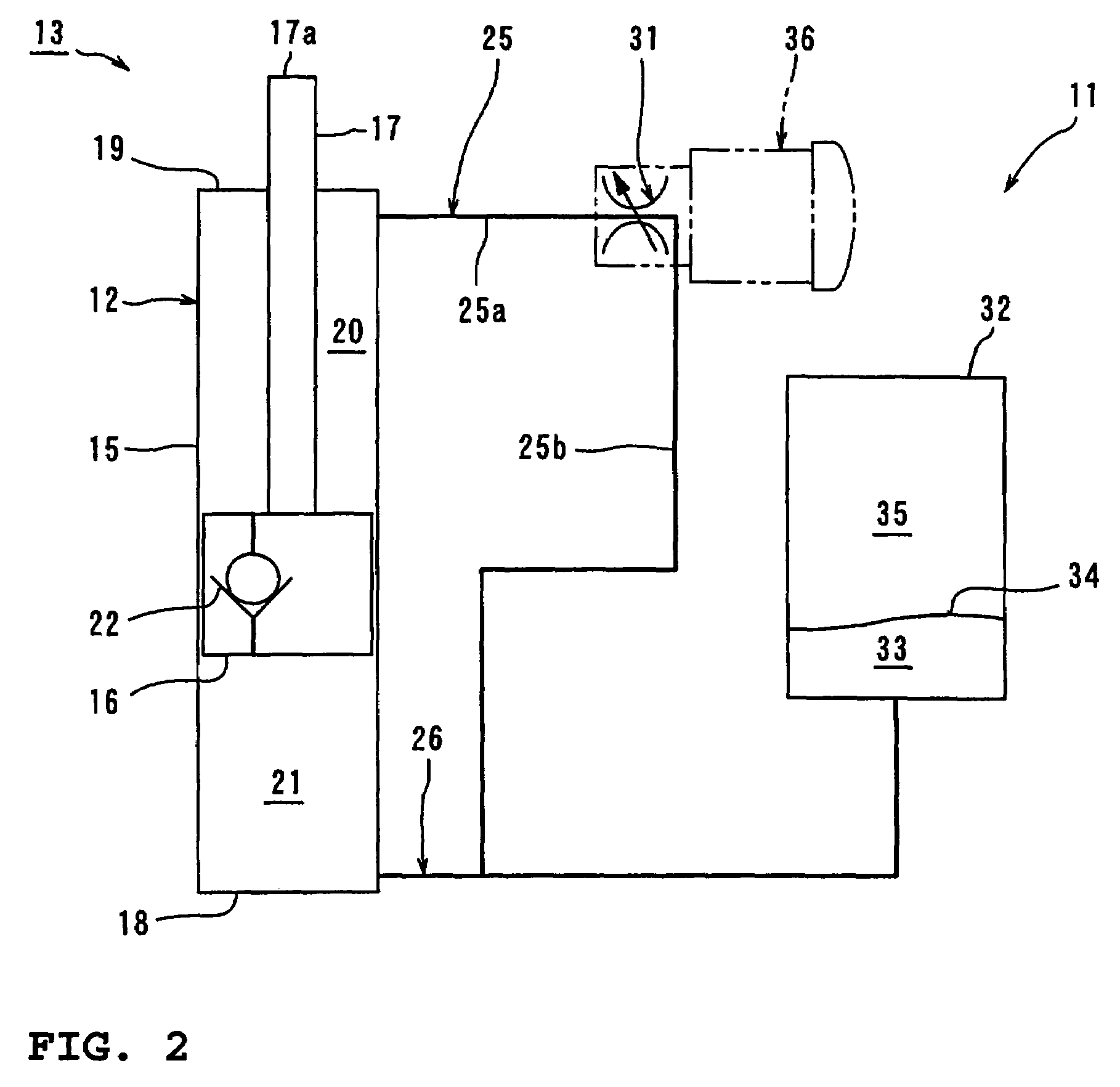
Brake Device and Controller for The Same
ActiveUS20080116740A1Satisfactory pedaling feelingSatisfactory pedalBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesTransmitted powerMaster cylinder
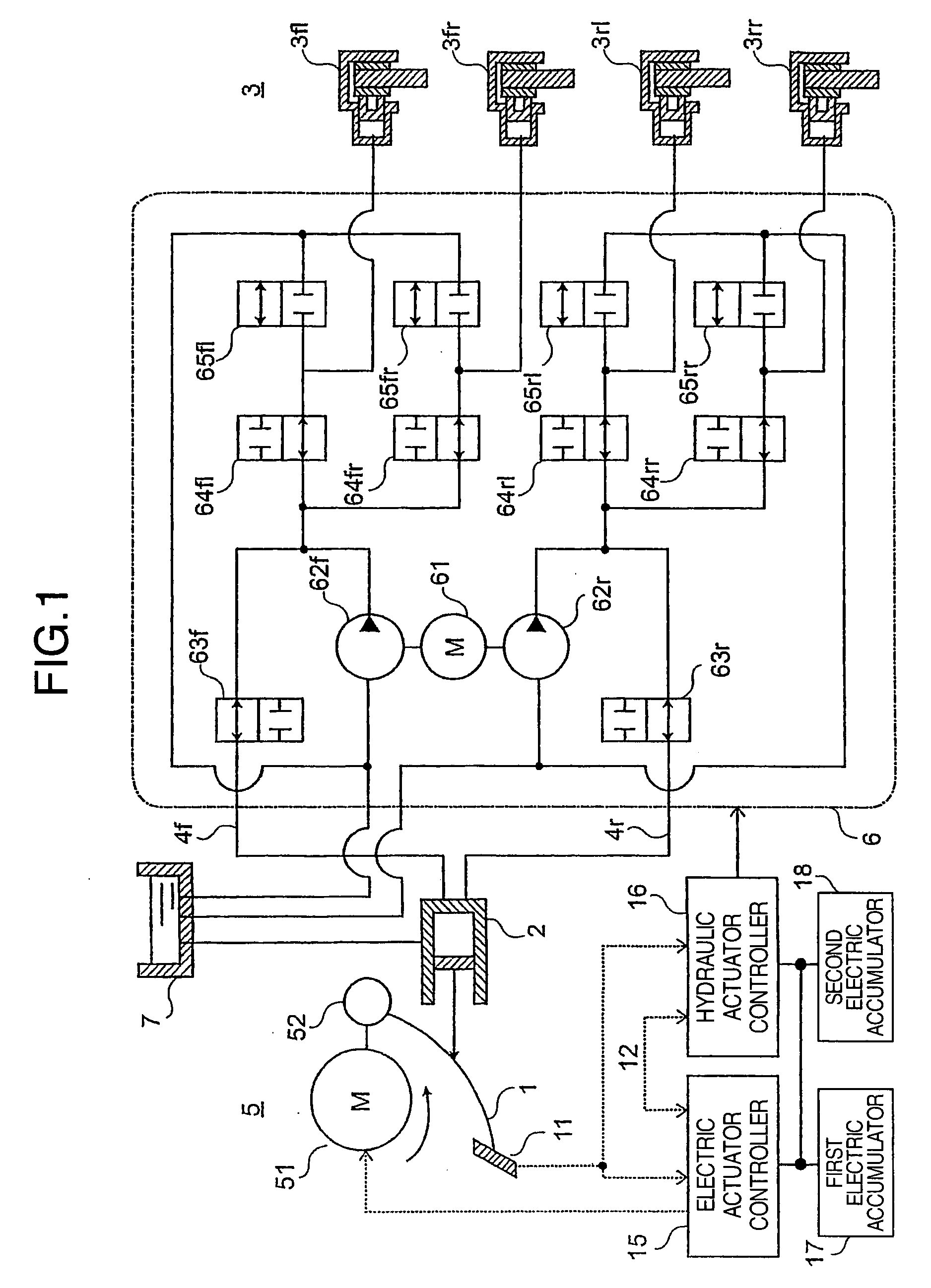
A brake system that provides a good pedal feel, that assists stepping force of a driver by a small motor, and that can control braking force of wheels individually. The brake system comprises a first actuator (5) for increasing a liquid pressure in a master cylinder (2) by driving torque of a motor (51), and a second actuator (6) capable of driving a brake generating mechanism (3) without transmitting power to the master cylinder (2), wherein the actuators (5, 6) to be driven are switched depending on the operation of a brake pedal (1). The first and second actuators (5, 6) are connected to hydraulic piping (4f, 4r), and a pressurized oil is supplied to the brake generating mechanism (3) through hydraulic valve means (63f, 63r, . . . 65rr).
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
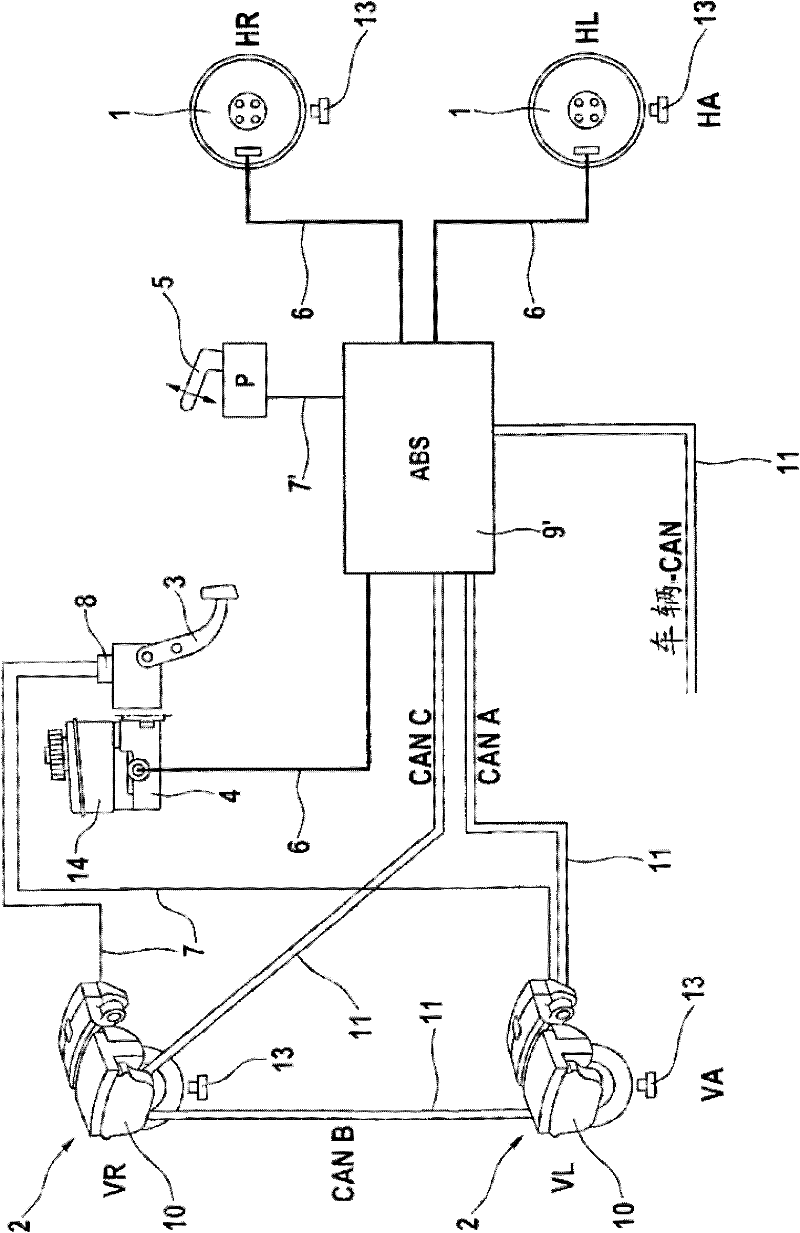
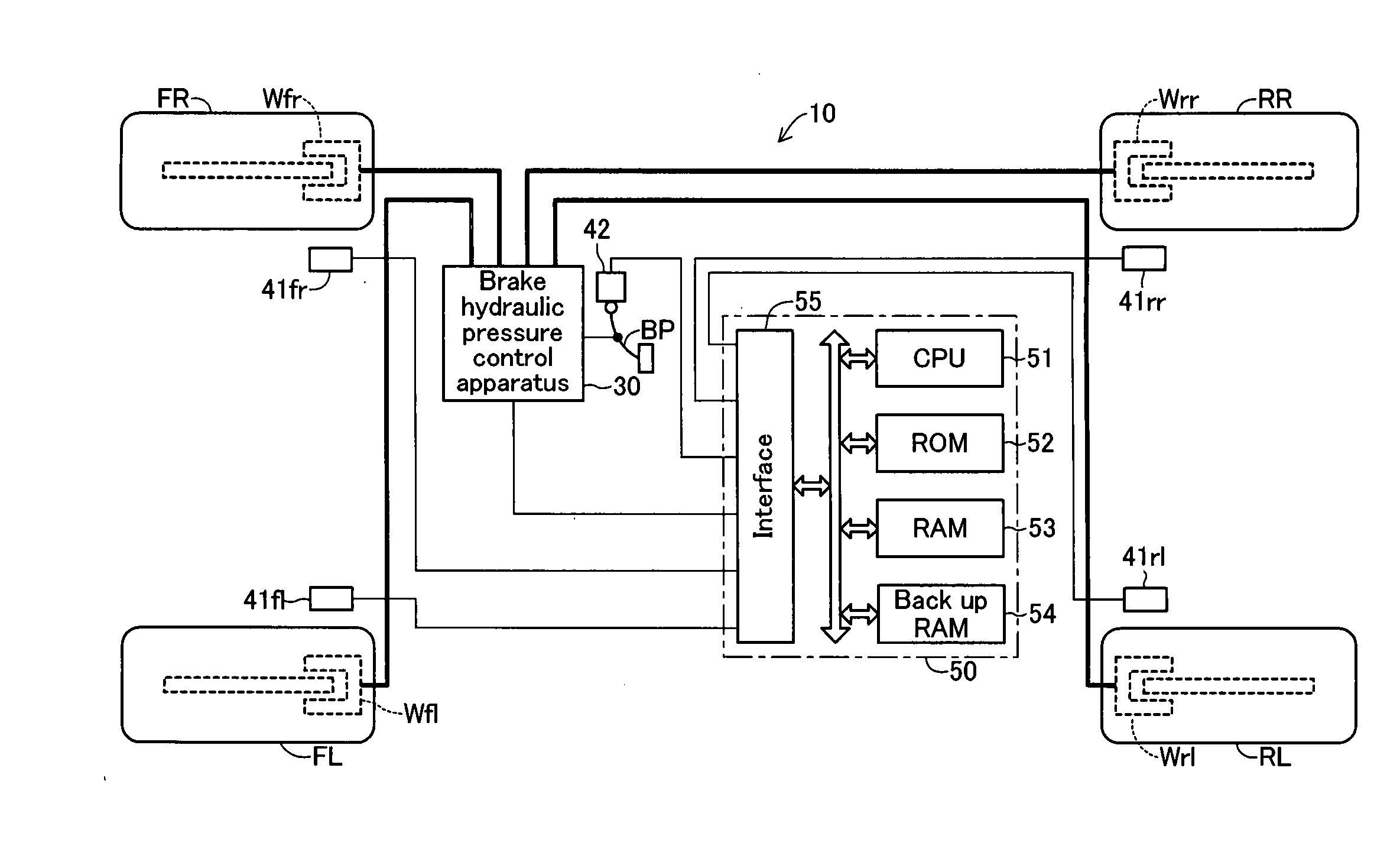
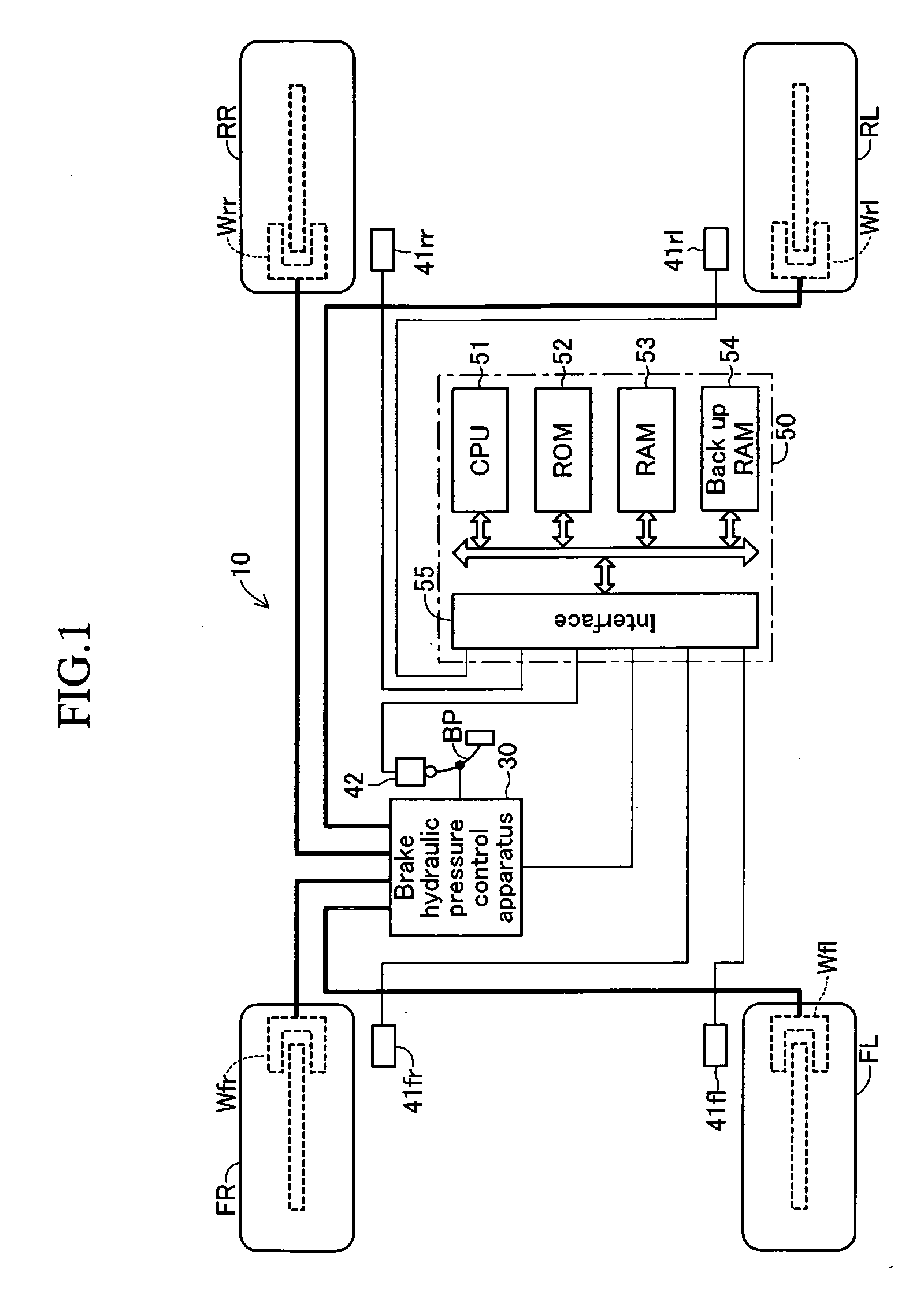
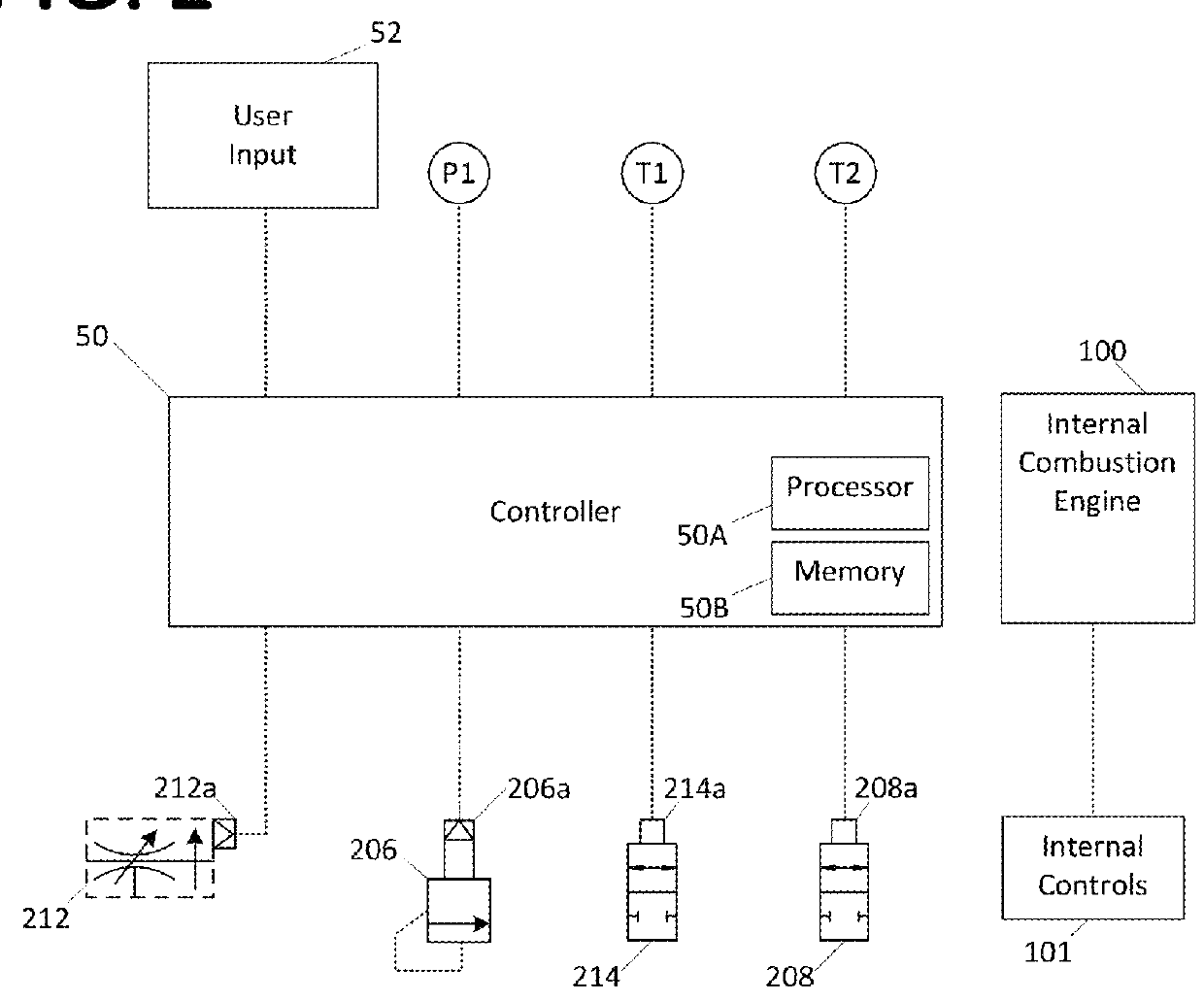
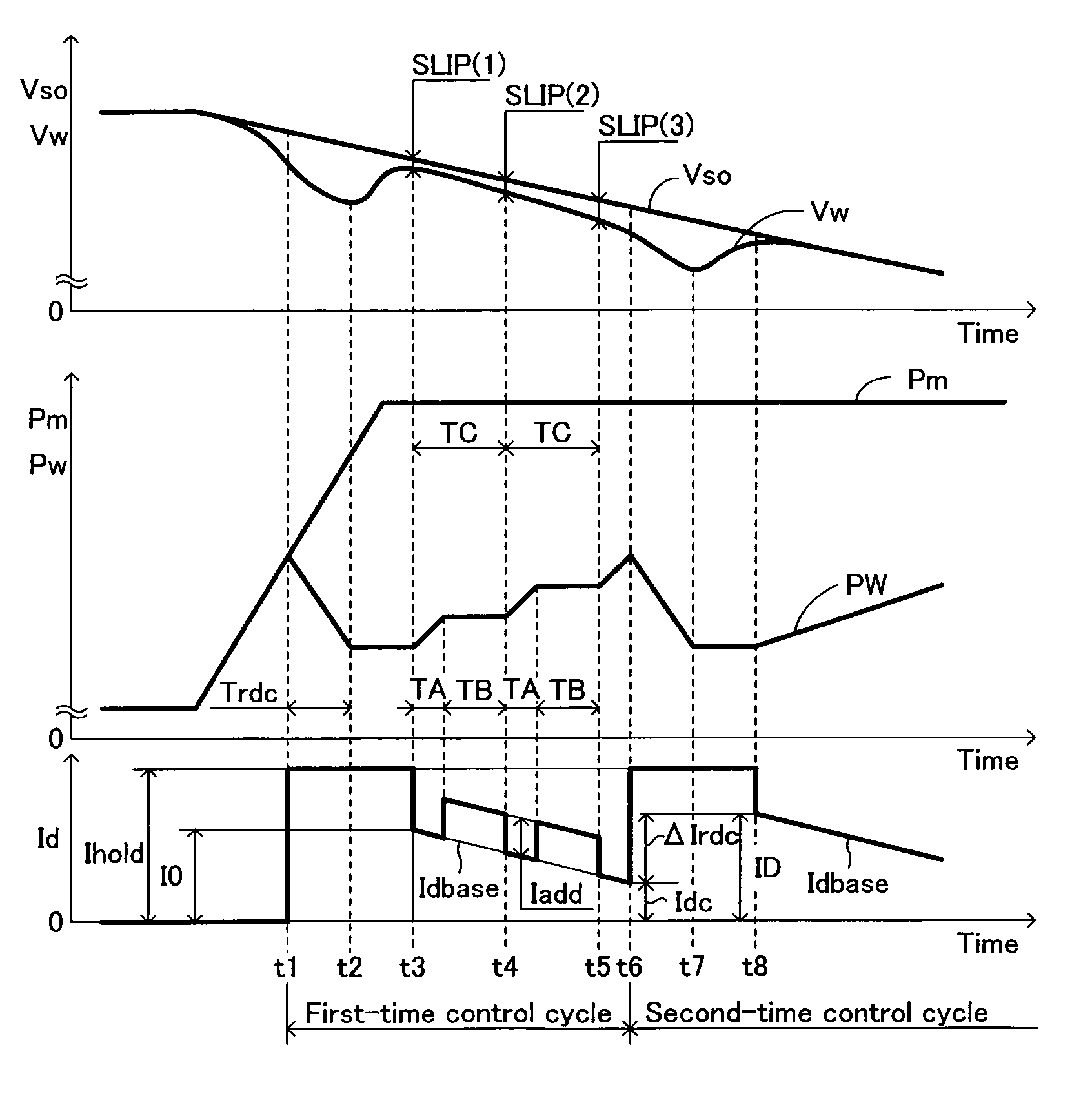
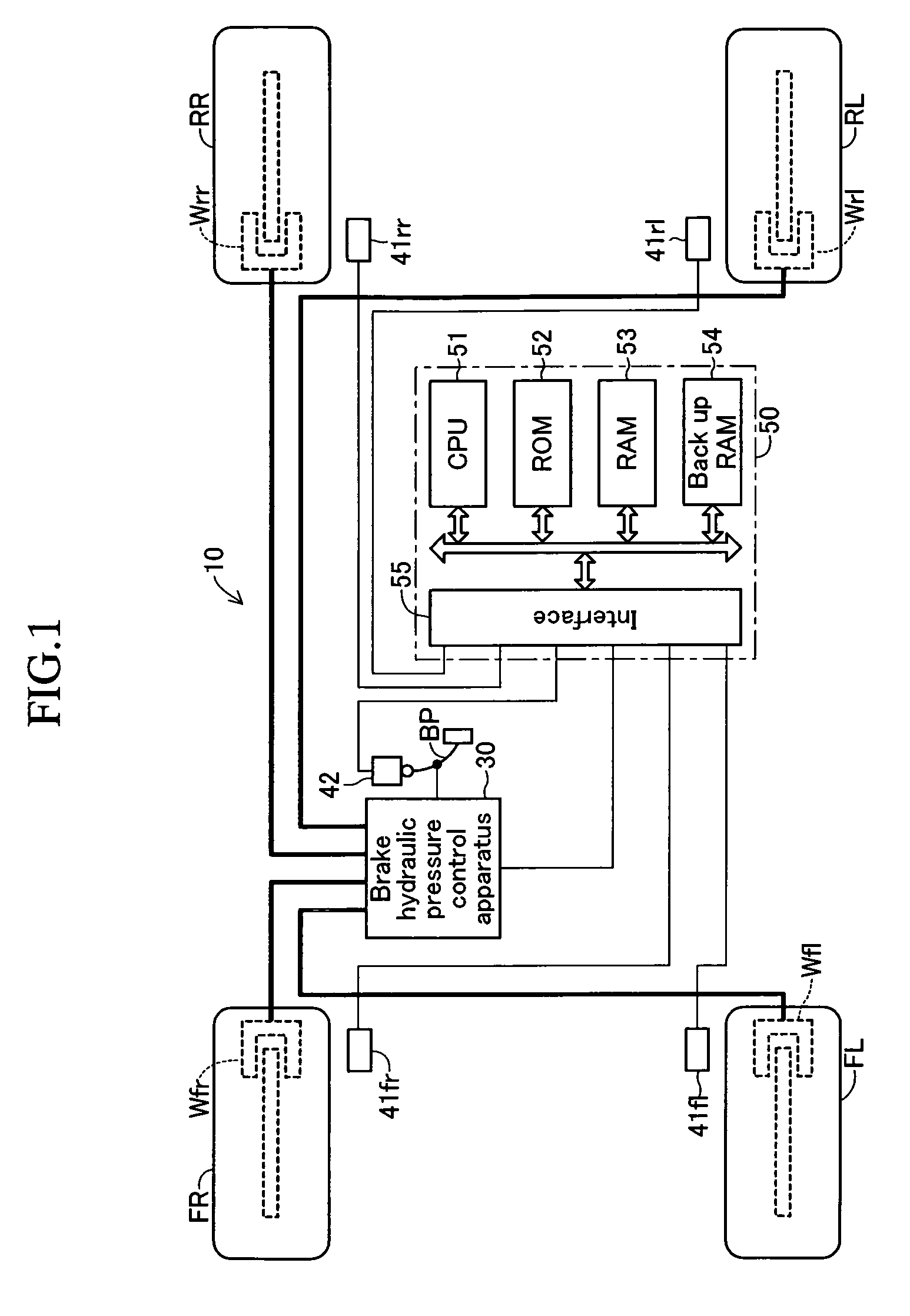
Vehicle brake hydraulic pressure control apparatus
InactiveUS20060255659A1Slow braking” is applied can be preventedIncrease hydraulic pressureBraking systemsDifferential pressureSolenoid valve
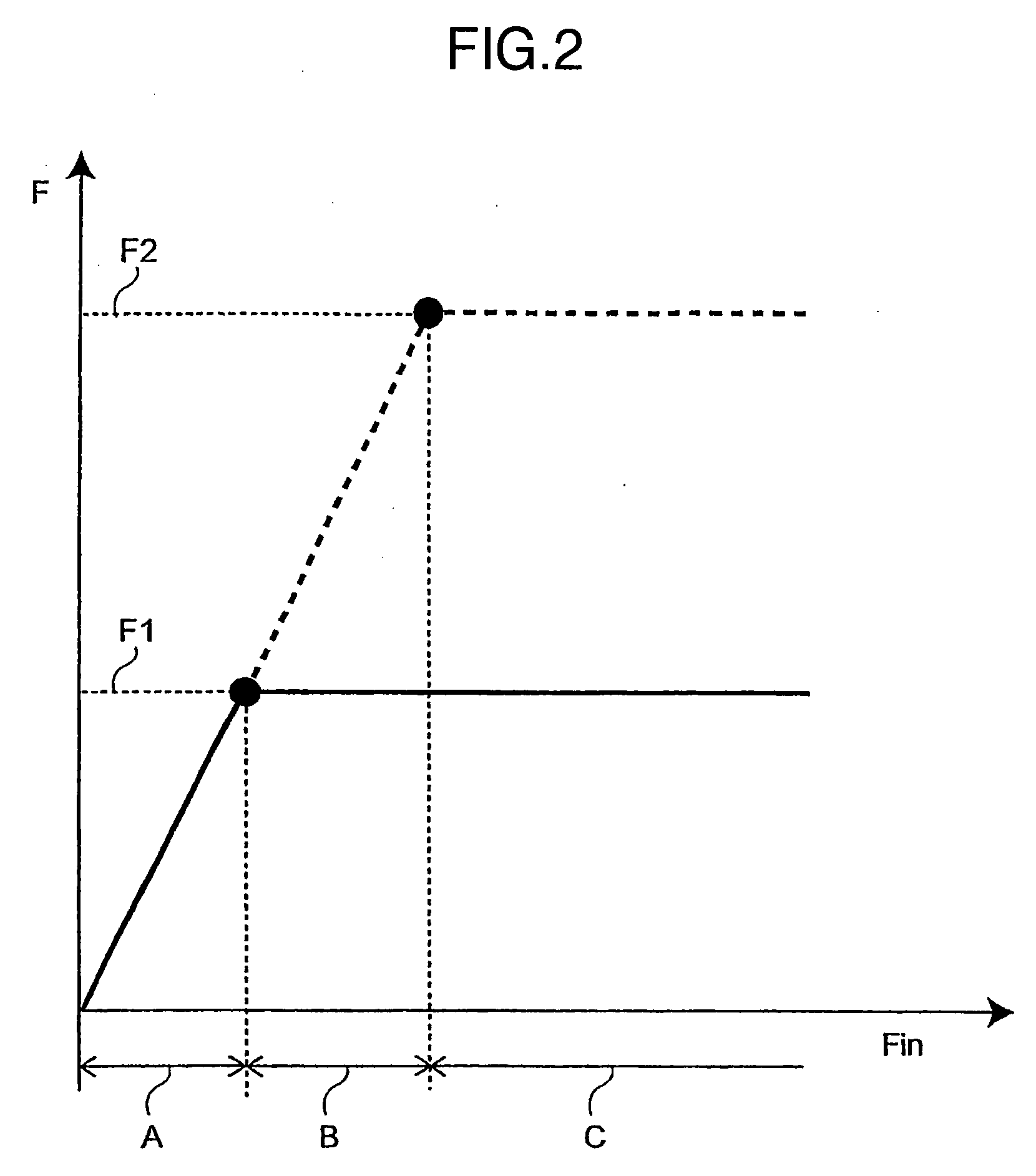
The brake hydraulic pressure control apparatus employs, as a pressure-increasing valve, a normally-open linear solenoid valve that can linearly adjust an actual differential pressure (a difference between a master cylinder hydraulic pressure Pm and a wheel cylinder hydraulic pressure Pw). This apparatus repeatedly executes, in principle, a control cycle in which a pressure-reducing control, holding control and linear pressure-increasing control make one set, while a “linear pressure-increasing control with holding period” is executed instead of the linear pressure-increasing control only in the first-time control cycle that is started in a state where a current-value-corresponding-to-actual-differential-pressure cannot correctly be obtained (the period from time t3 to time t6). The command current value Id (=I0) to the pressure-increasing valve at the point of starting the “linear pressure-increasing control with holding period” is set to a “current-value-corresponding-to-reduced-pressure” that is always smaller than the current-value-corresponding-to-actual-differential-pressure at the same point.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
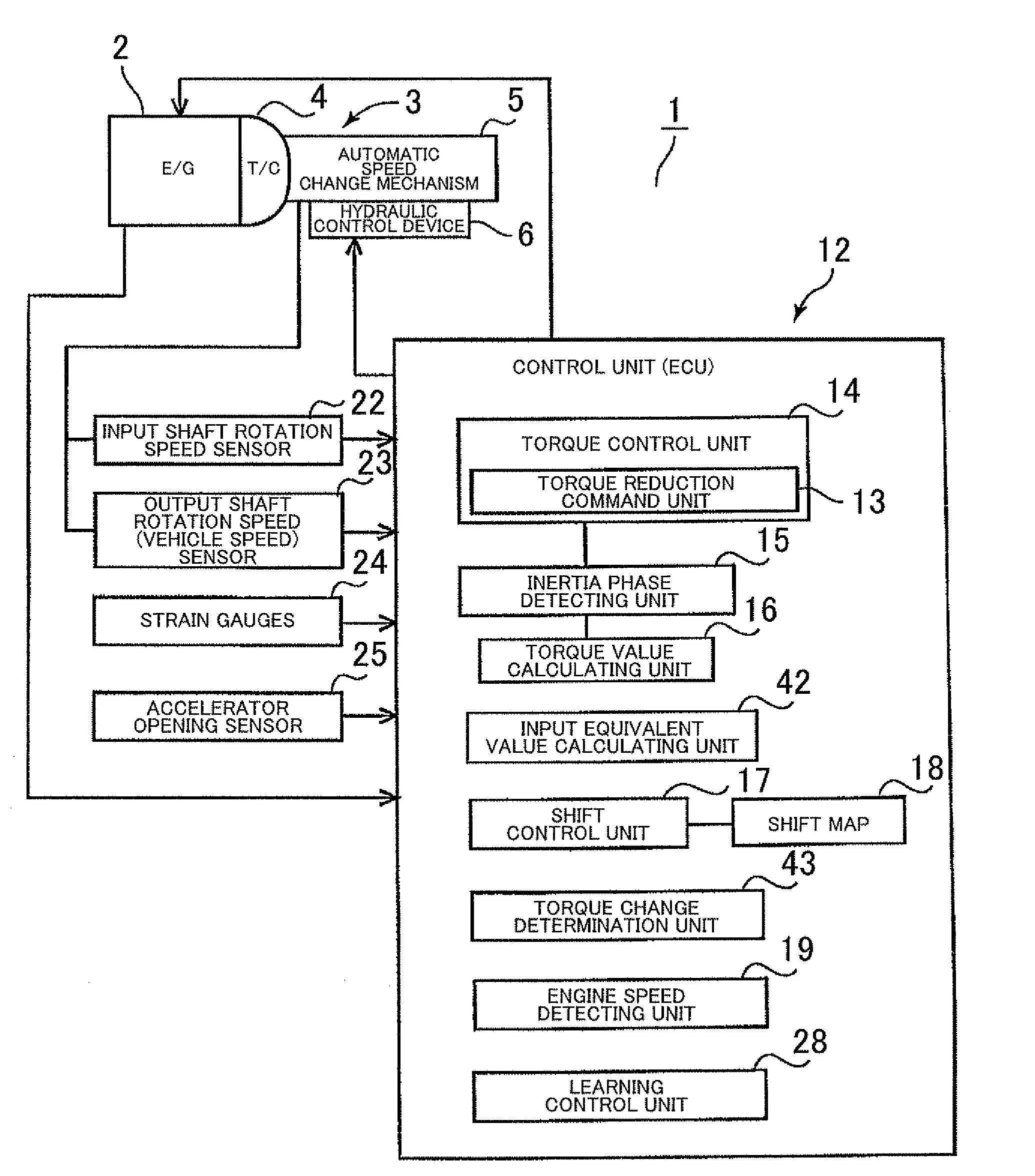
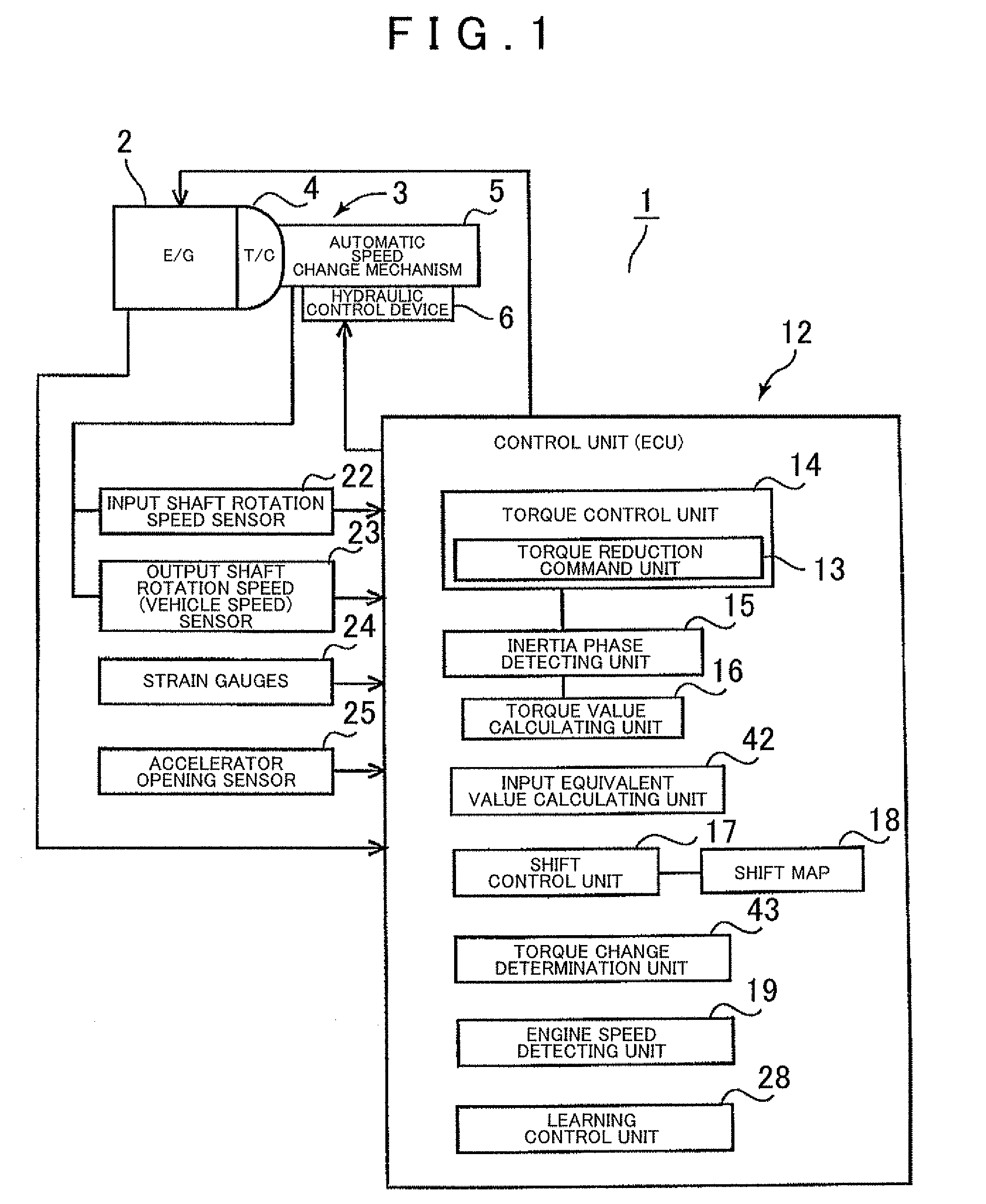
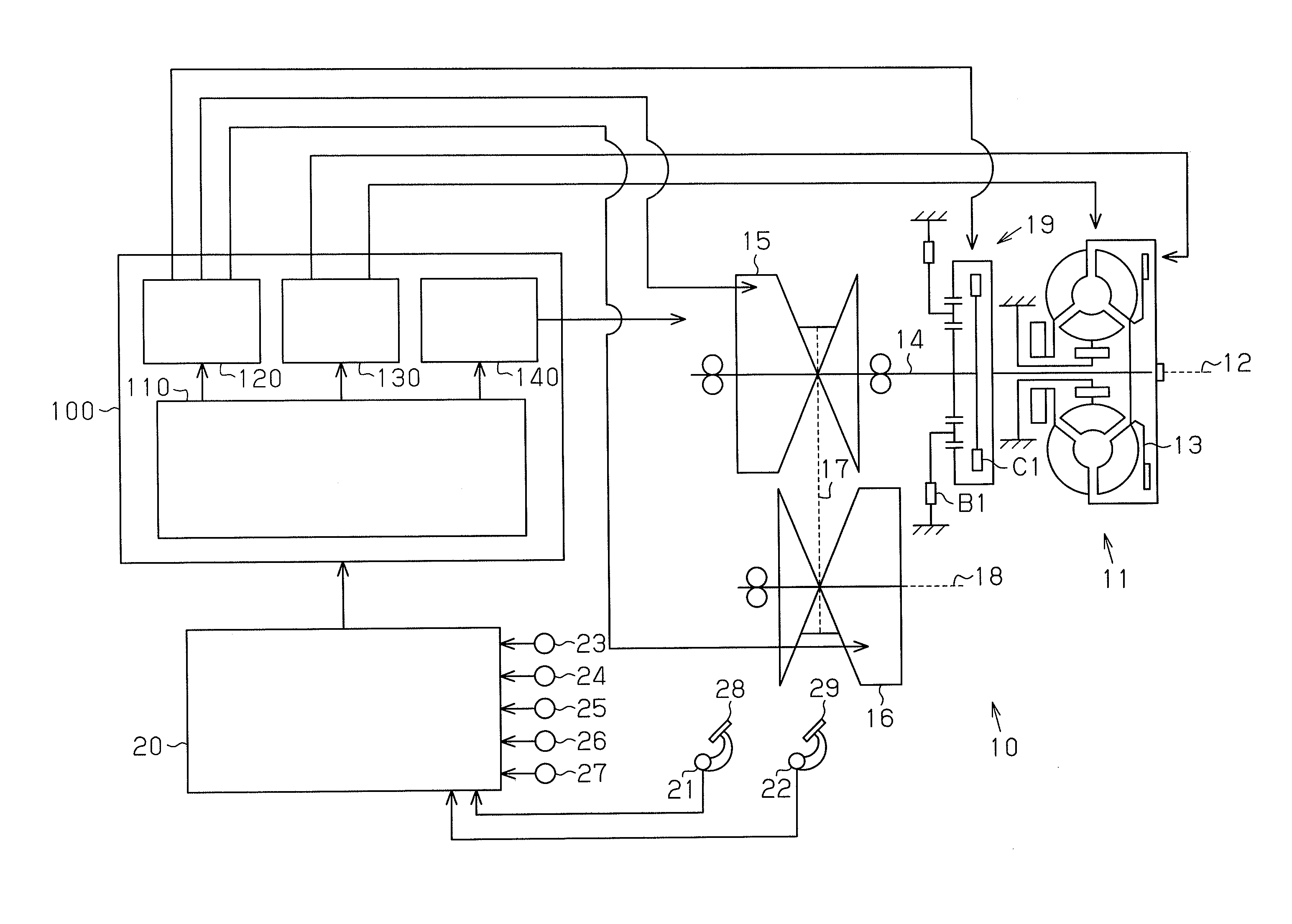
Shift control apparatus for automatic transmission
InactiveUS20090248263A1Simple structureLow costDigital data processing detailsVehicle sub-unit featuresAutomatic transmissionControl theory
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Liquid supply mechanism and liquid cooling system
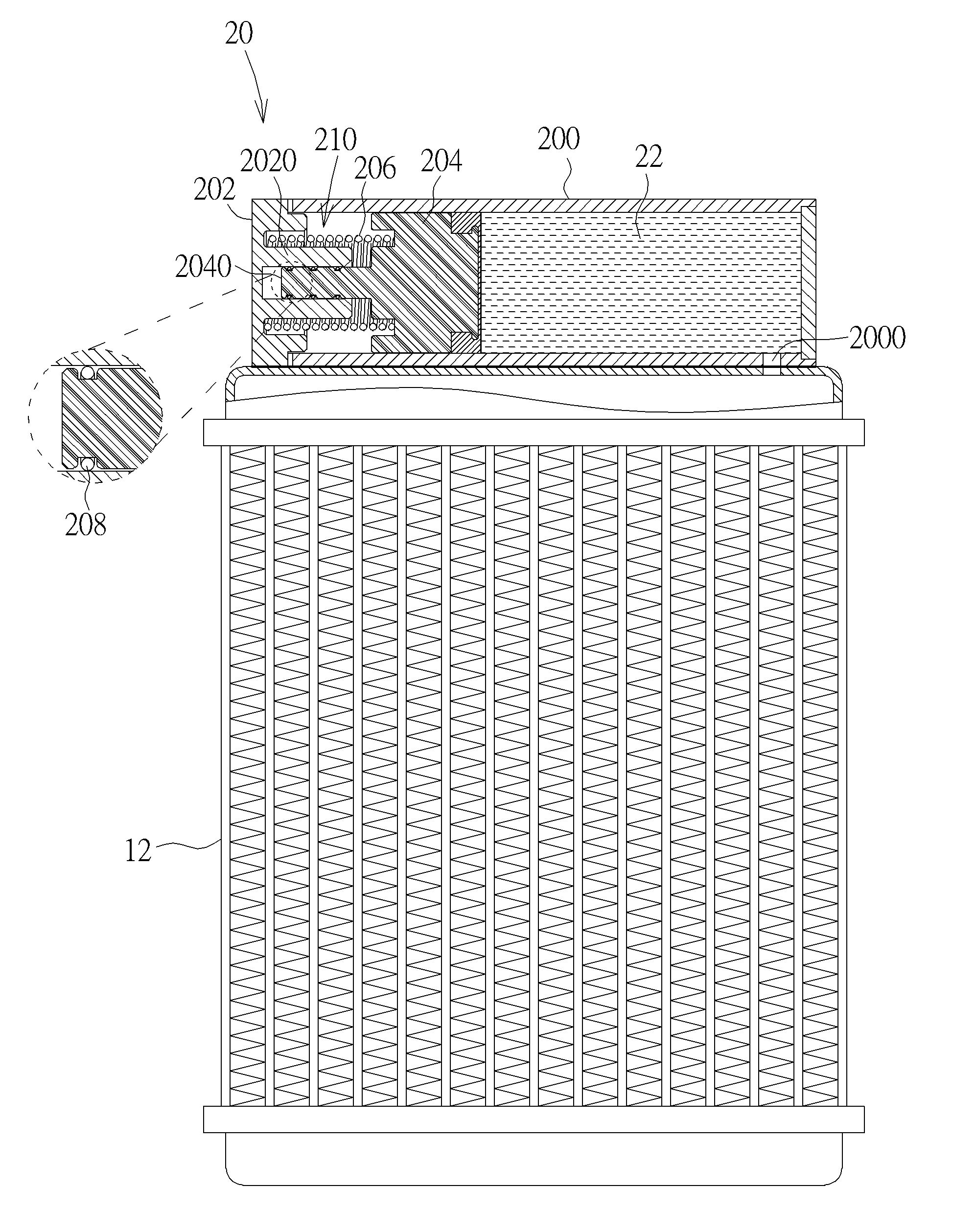
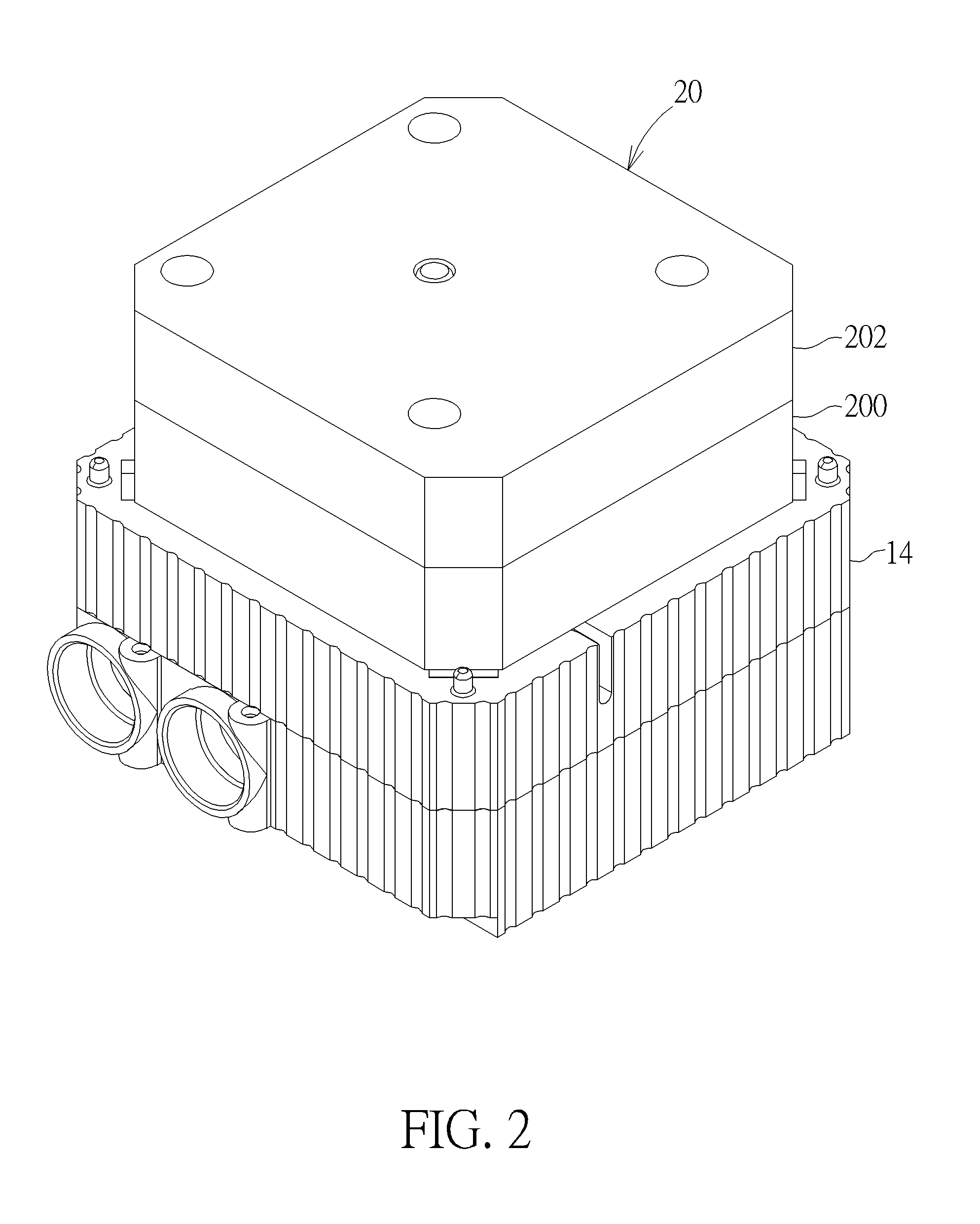
ActiveUS20160366788A1Increase hydraulic pressureReduce thrustSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid transferring devicesLiquid cooling systemEngineering
A liquid supply mechanism includes a lower cover, an upper cover, a plunger, at least one resilient member and at least one damping member. The lower cover has a liquid outlet and the upper cover is connected to the lower cover. A chamber is formed between the lower cover and the upper cover. The chamber communicates with the liquid outlet and contains a cooling liquid. The upper cover has an axial hole. The plunger is movably disposed in the chamber. The plunger has an axial rod and the axial rod is inserted into the axial hole. The resilient member is disposed in the chamber. Opposite ends of the resilient member abut against the upper cover and the plunger. The damping member is disposed on the axial rod and abuts against an inner wall of the axial hole.
Owner:COOLER MASTER CO LTD
Hydraulic control apparatus and hydraulic control method
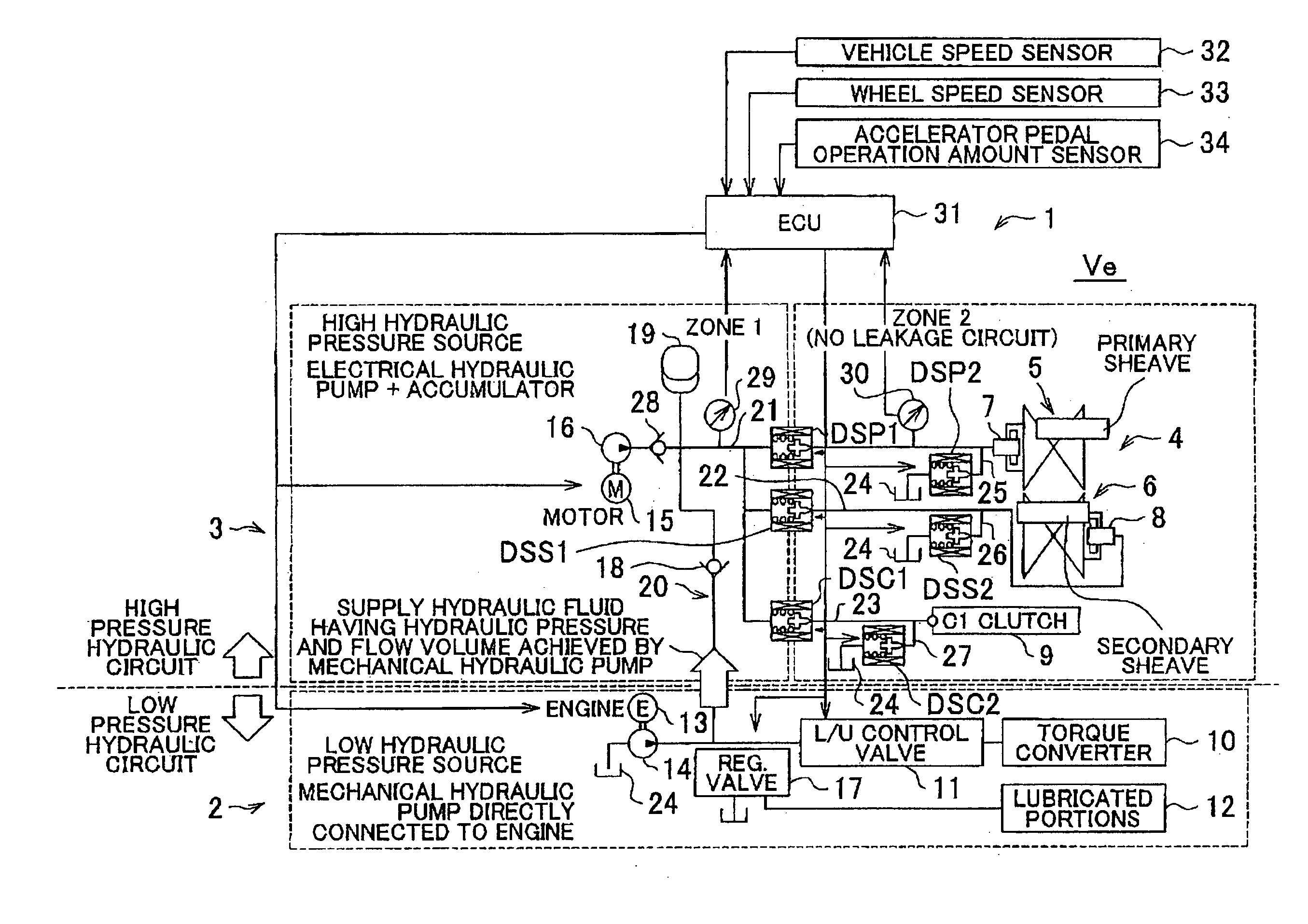
InactiveUS20110269583A1Sure easyEnhanced hydraulic volumeGearing controlEngine controllersControl engineeringHydraulic pump
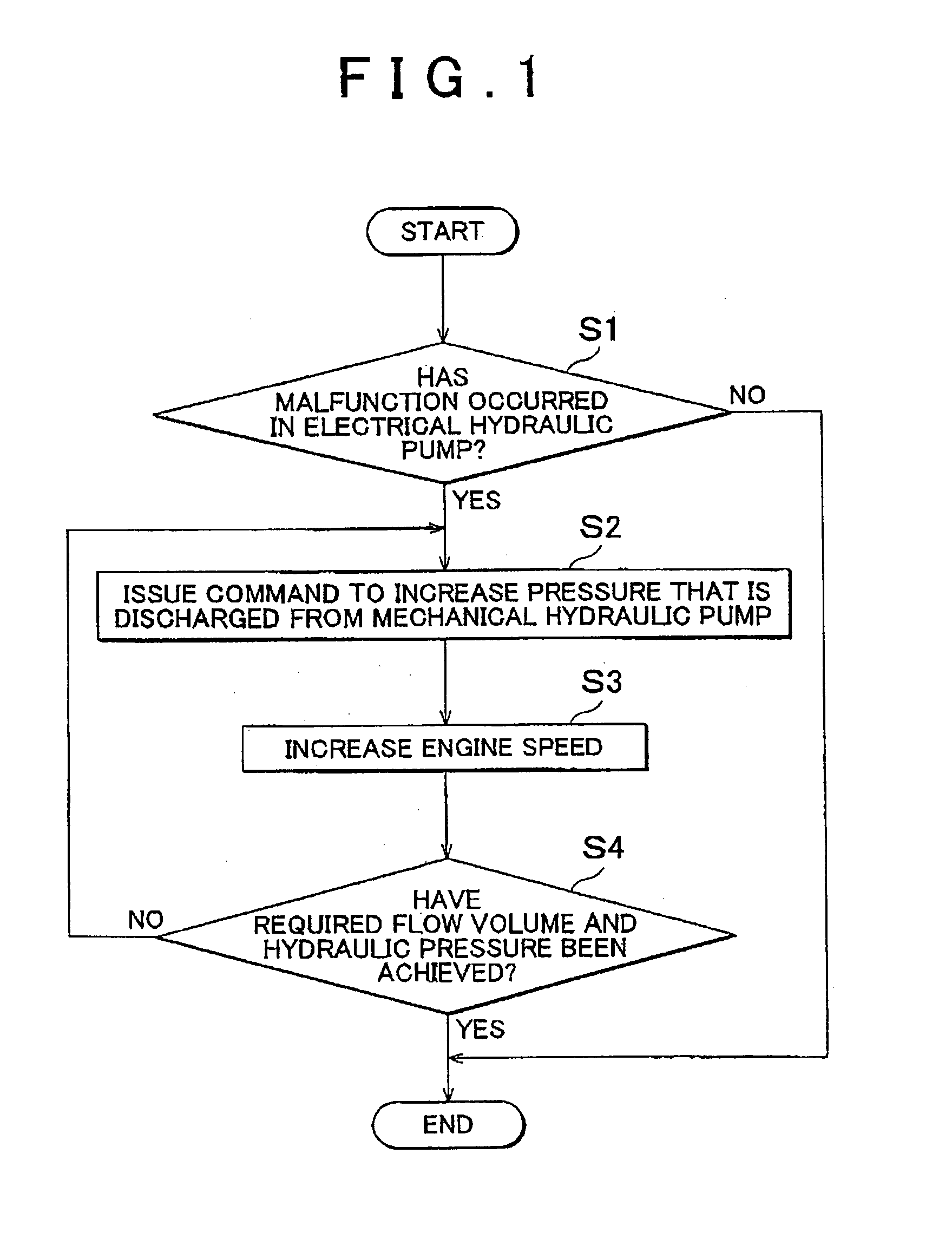
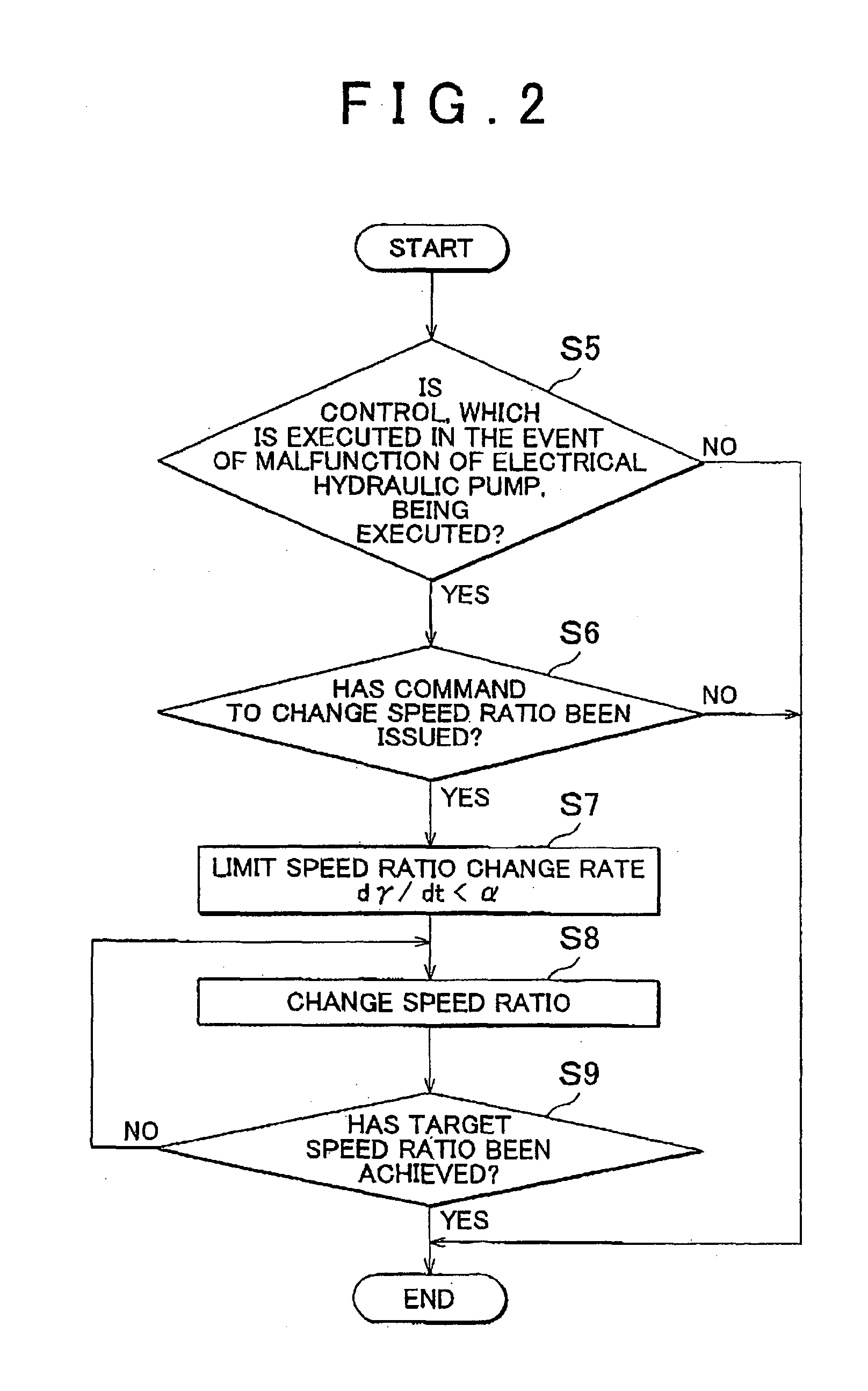
If it is determined that a malfunction has occurred in an electrical hydraulic pump and the hydraulic fluid is not supplied to a high hydraulic pressure supplied portion from the electrical hydraulic pump, the hydraulic fluid is supplied to the high hydraulic pressure supplied portion from a mechanical hydraulic pump that usually supplies the hydraulic fluid to a low hydraulic pressure supplied portion. In this case, the hydraulic pressure that is generated by the mechanical hydraulic pump is increased by increasing the output from the engine that drives the mechanical hydraulic pump.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Speed change control system of automatic transmission
ActiveUS8131436B2Increase hydraulic pressureReduce hydraulic pressureClutchesDigital data processing detailsAutomatic transmissionControl system
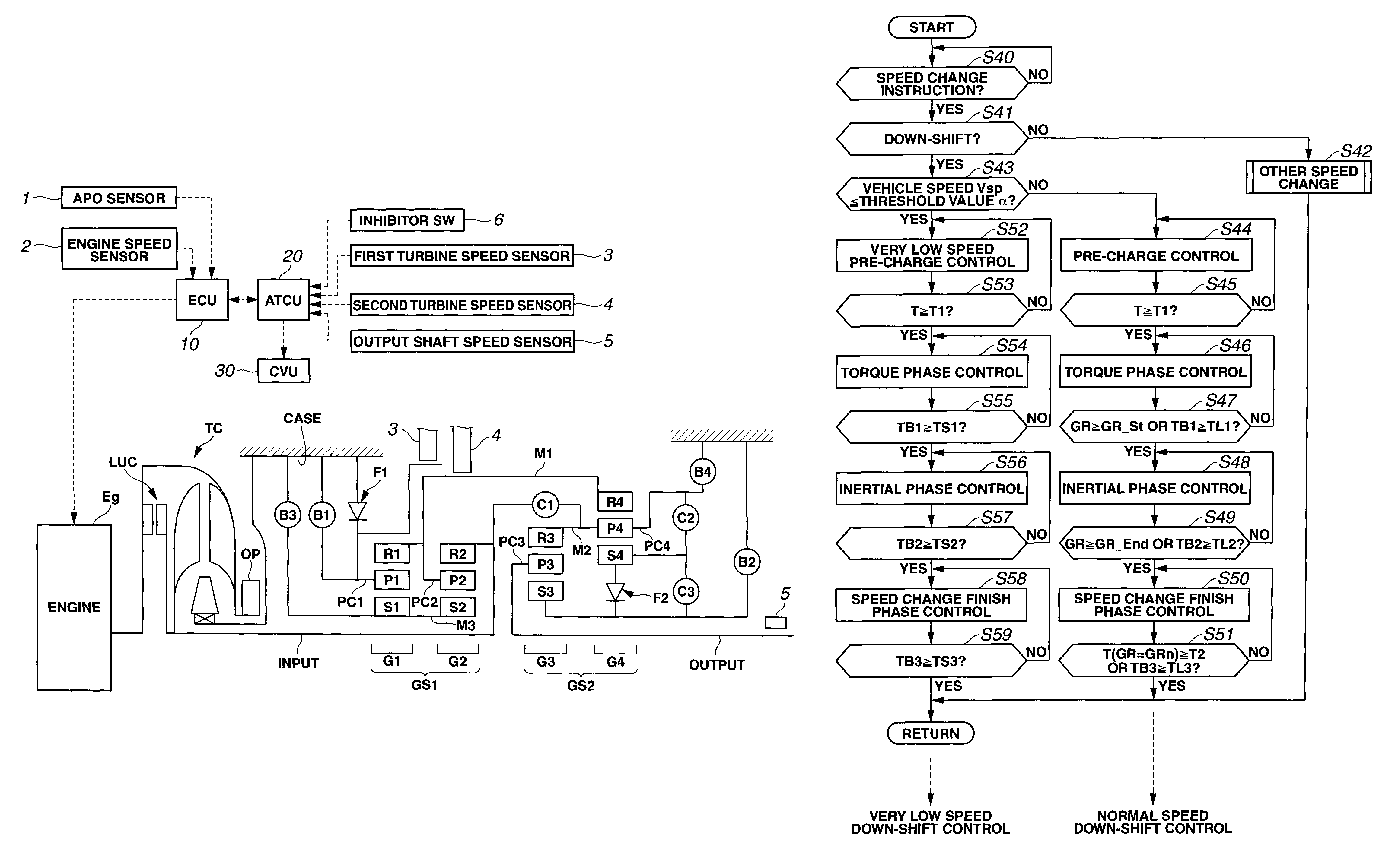
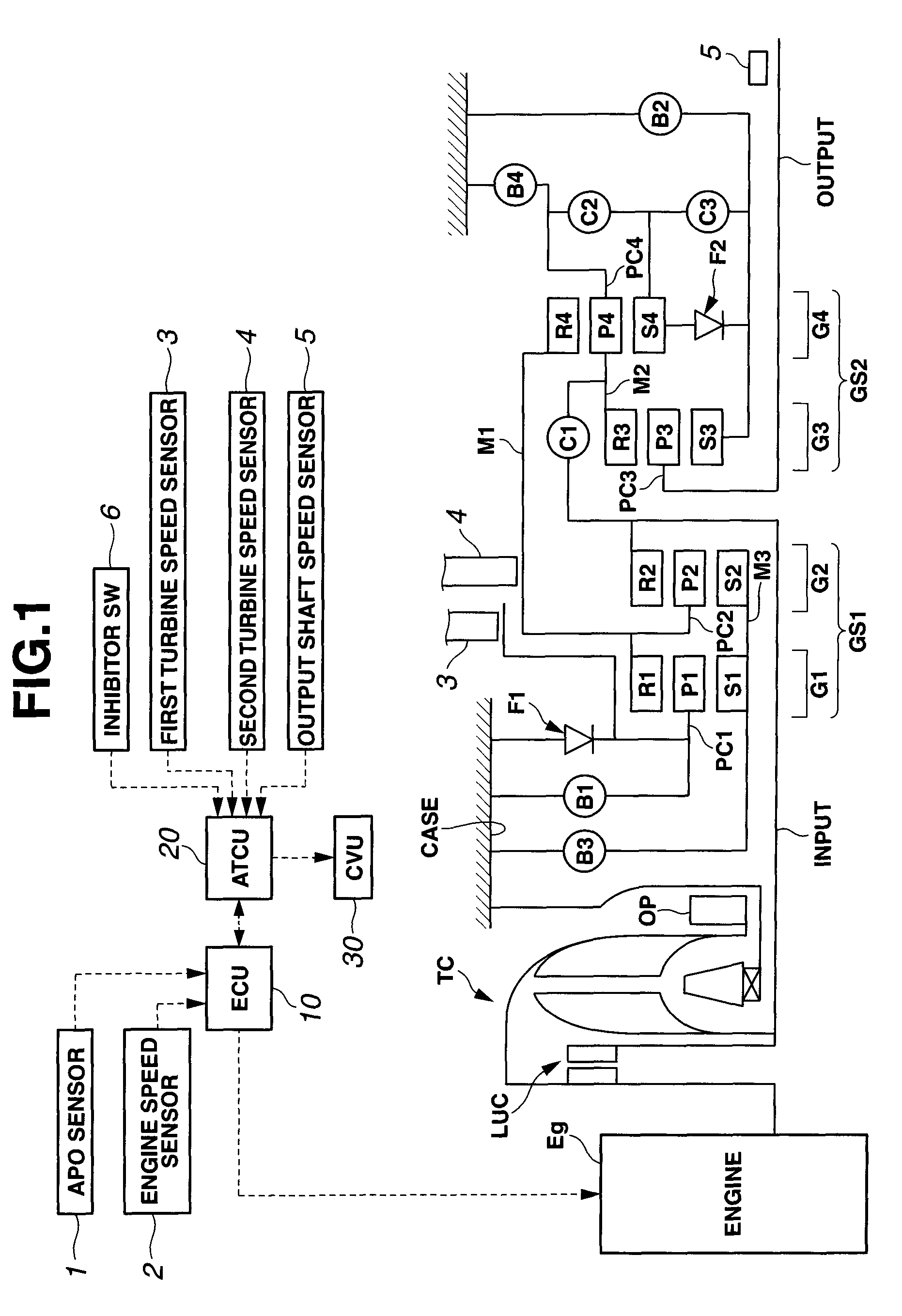
When it is judged that a vehicle speed detected by a vehicle speed sensor is equal to or lower than a predetermined very low value, that is, for example, 5 km / h, the hydraulic pressure applied to an engaging-side frictional element is sharply increased, sharply reduced and then held higher than a given value capable of effecting a piston stroke of a corresponding piston unit until a time when the piston stroke is completed. Upon completion of the piston stroke, the hydraulic pressure is increased to a maximum value in a time that is smaller or shorter than that set when the detected vehicle speed is higher than the predetermined very low value.
Owner:JATCO LTD +1
Vehicle drive system
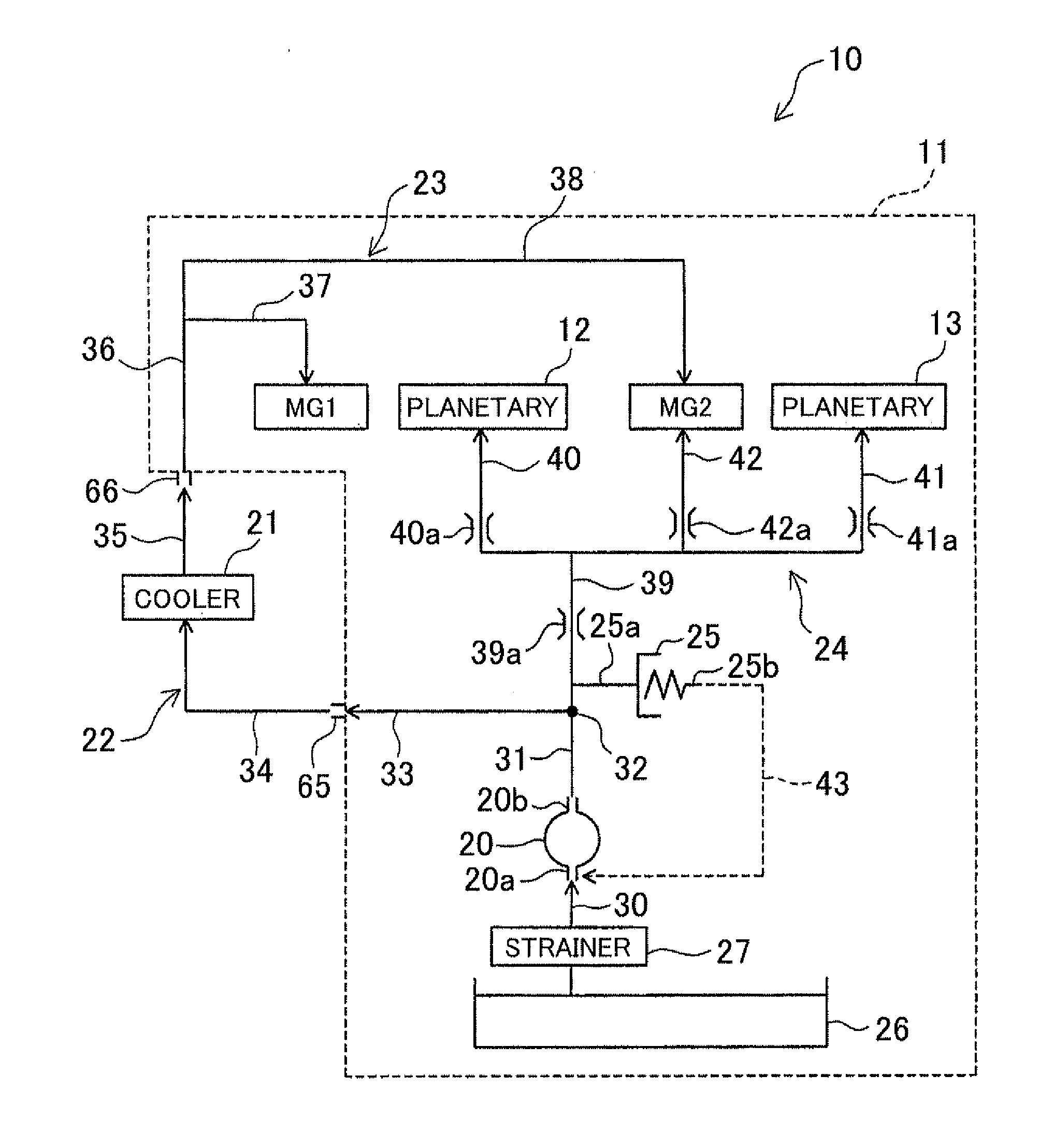
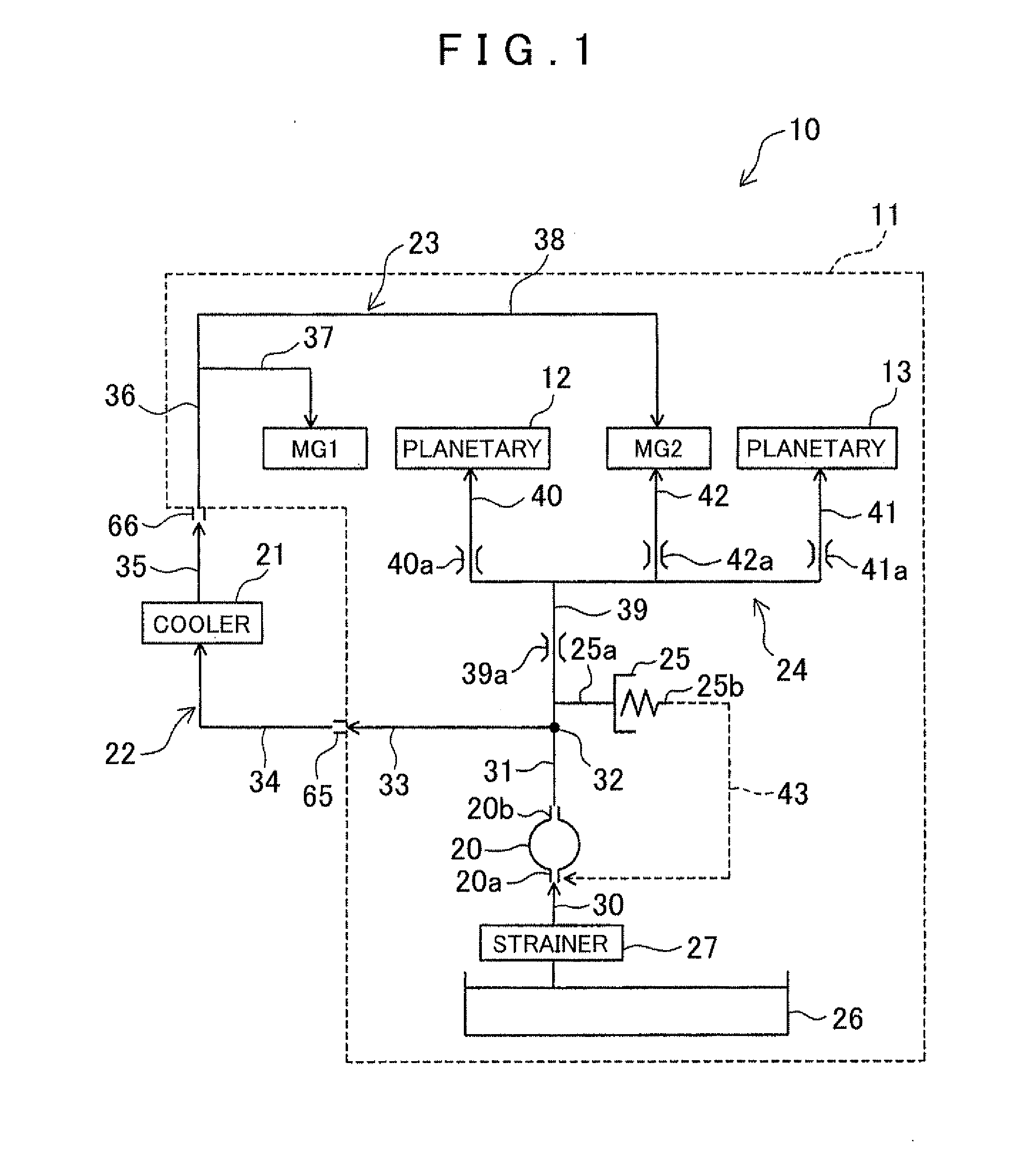
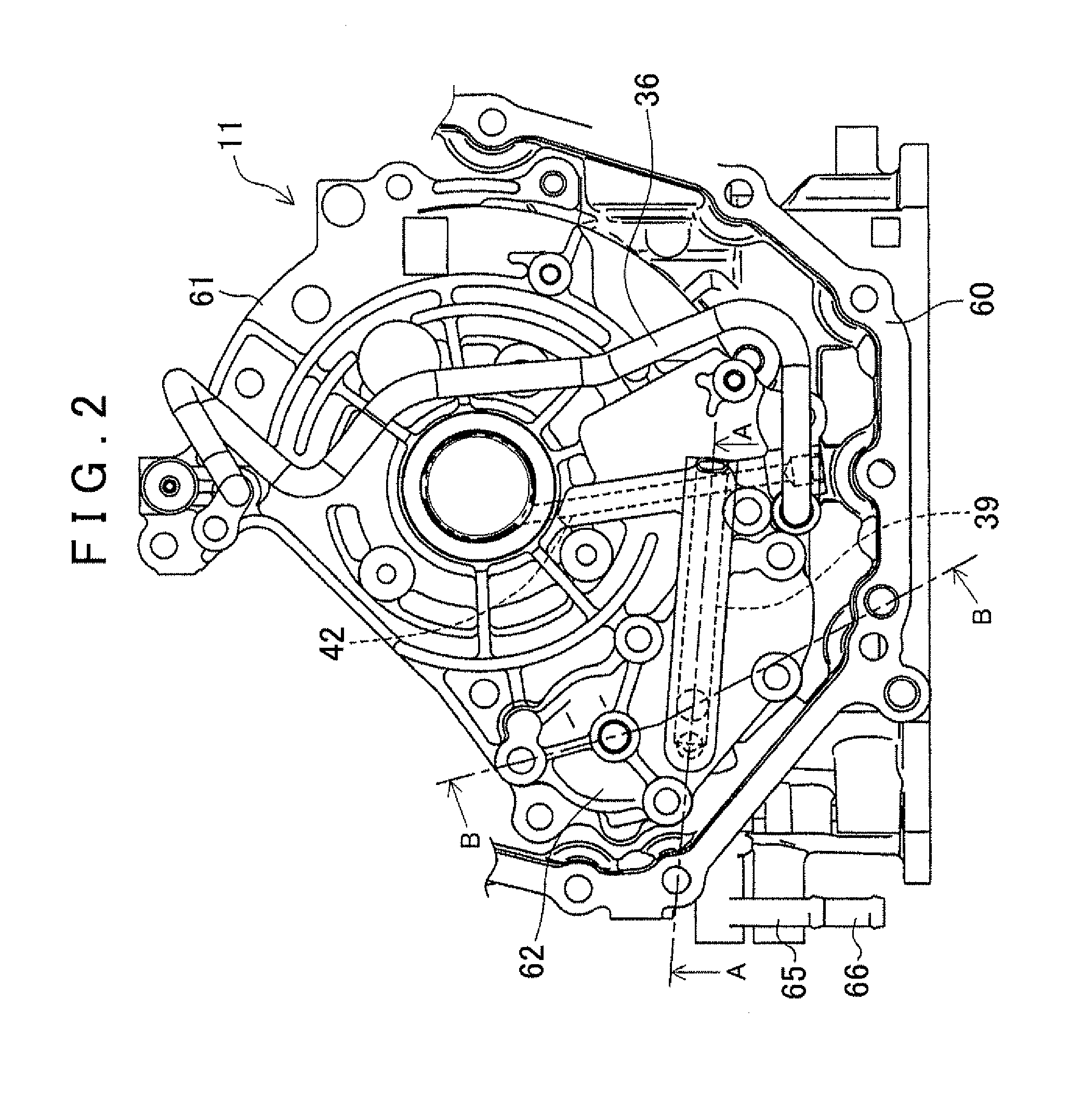
ActiveUS20110232786A1Efficiently returnedImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesGear lubrication/coolingMotor–generatorElectric motor
A vehicle drive system, including a motor generator; a gear group having a plurality of gears; and a motor cooling circuit for cooling the motor generator. The system further includes a lubricating circuit for lubricating the gear group; a cooler circuit in which an oil cooler is provided; and an oil pump that supplies oil to each circuit. The motor cooling circuit is arranged in series with and downstream of the cooler circuit, and the lubricating circuit is arranged parallel to the cooler circuit with respect to the oil pump.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
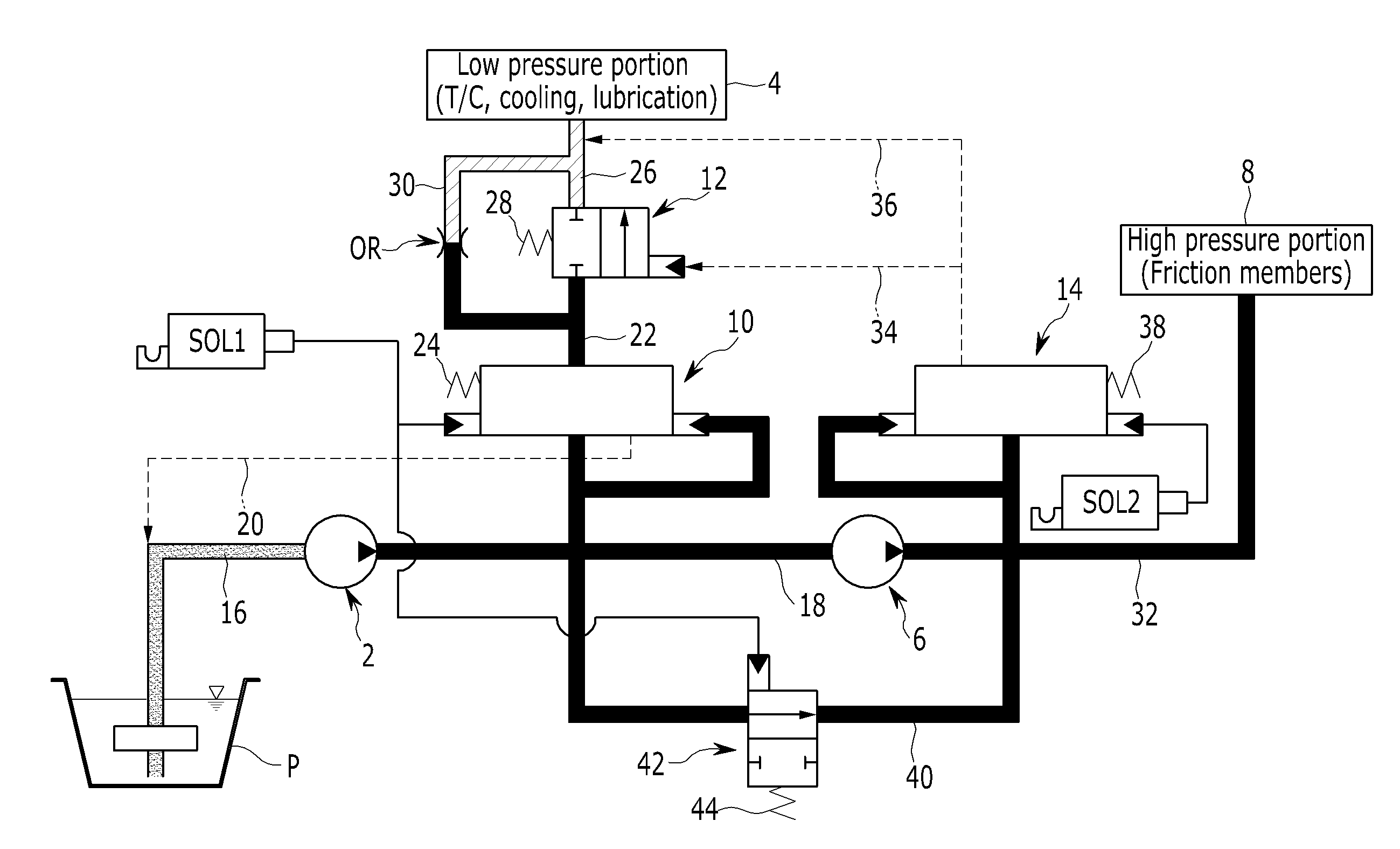
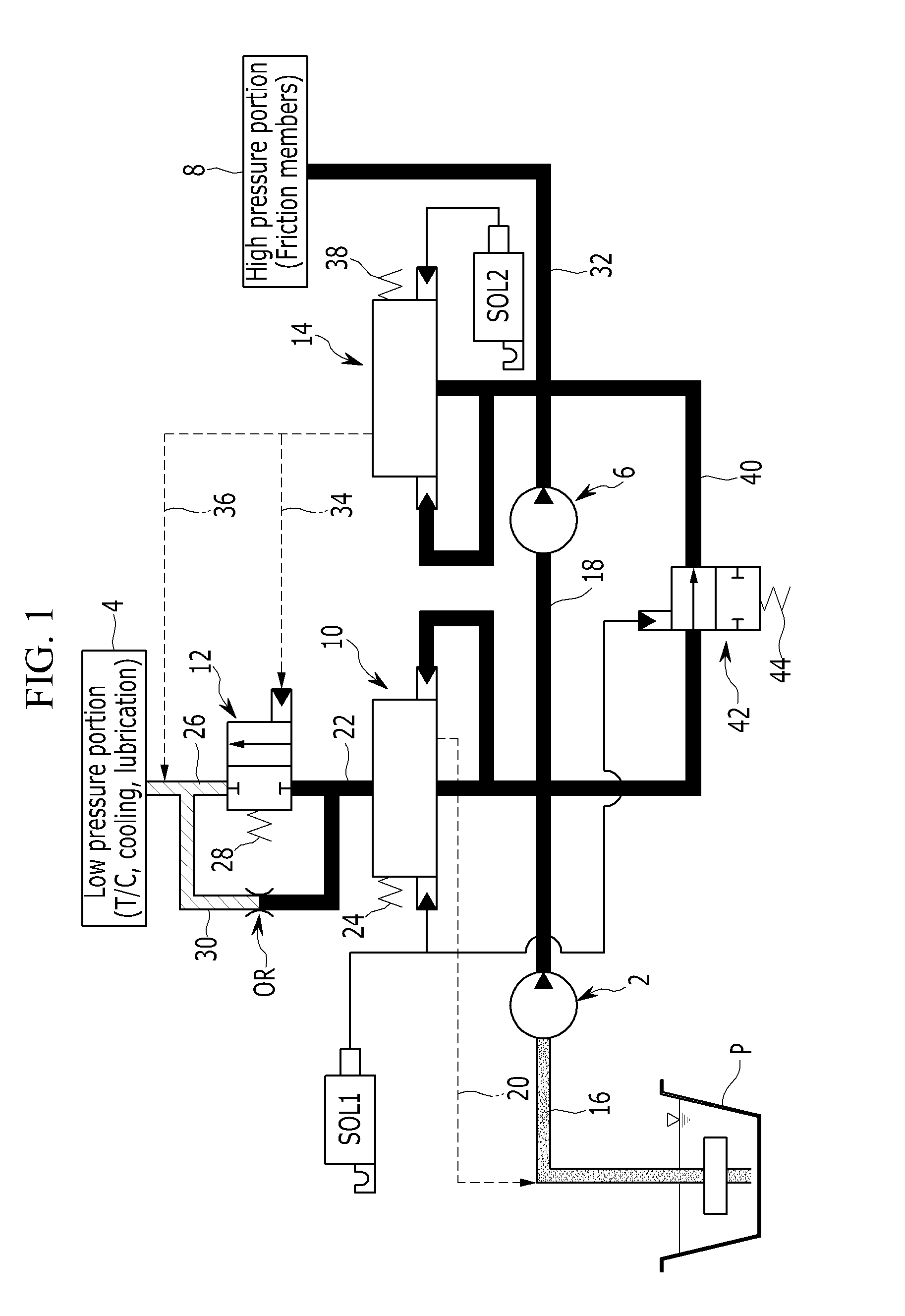
Hydraulic pressure supply system of automatic transmission for vehicle
ActiveUS20150027570A1Improve responsivenessImprove stabilityServomotorsGear lubrication/coolingAutomatic transmissionHydraulic pump
A hydraulic pressure supply system may supply low hydraulic pressure generated at a low-pressure hydraulic pump to a low pressure portion through a low-pressure regulator valve, may supply a portion of the low hydraulic pressure to a high-pressure hydraulic pump, and may supply high hydraulic pressure generated at the high-pressure hydraulic pump to a high pressure portion through a high-pressure regulator valve.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
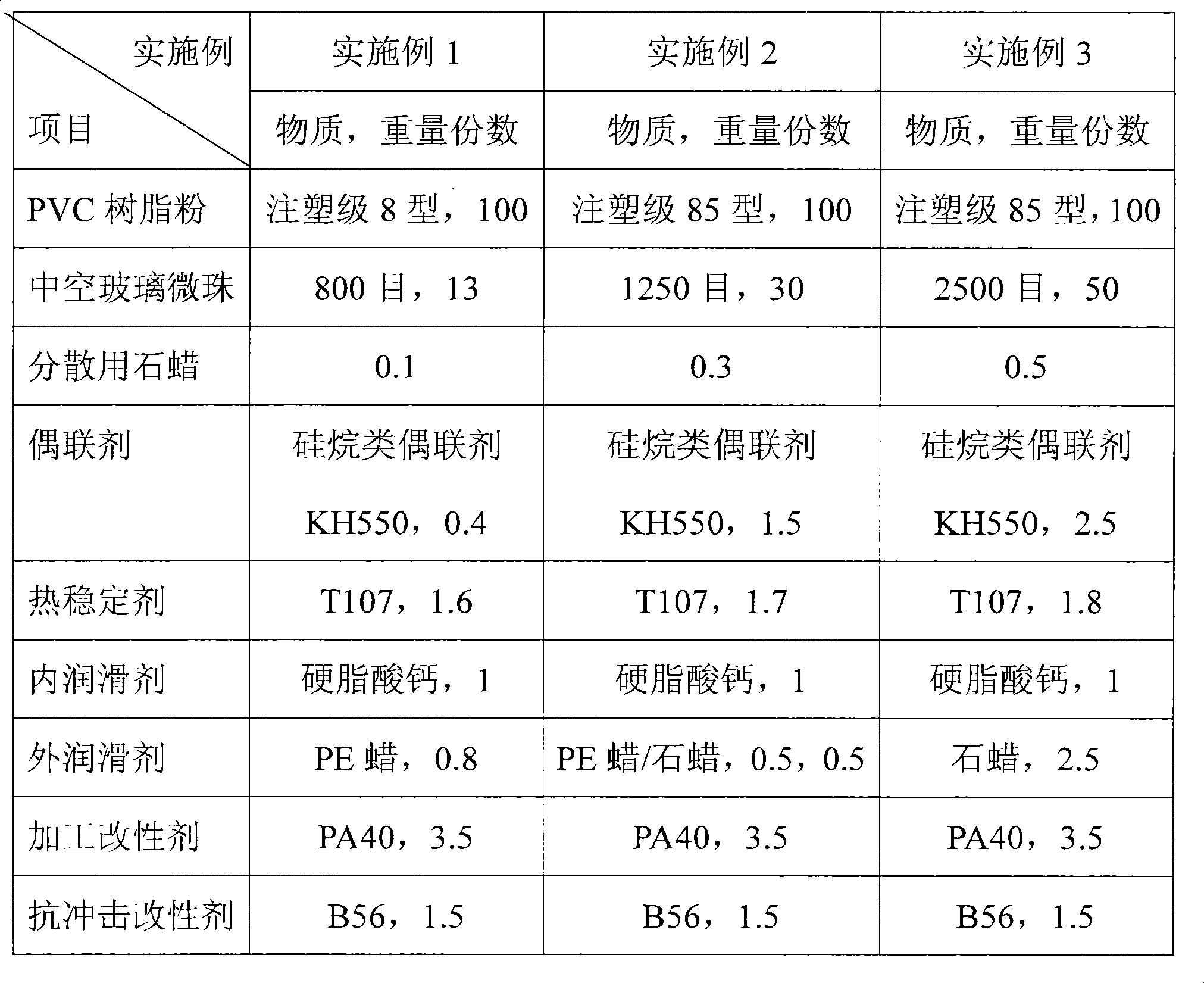
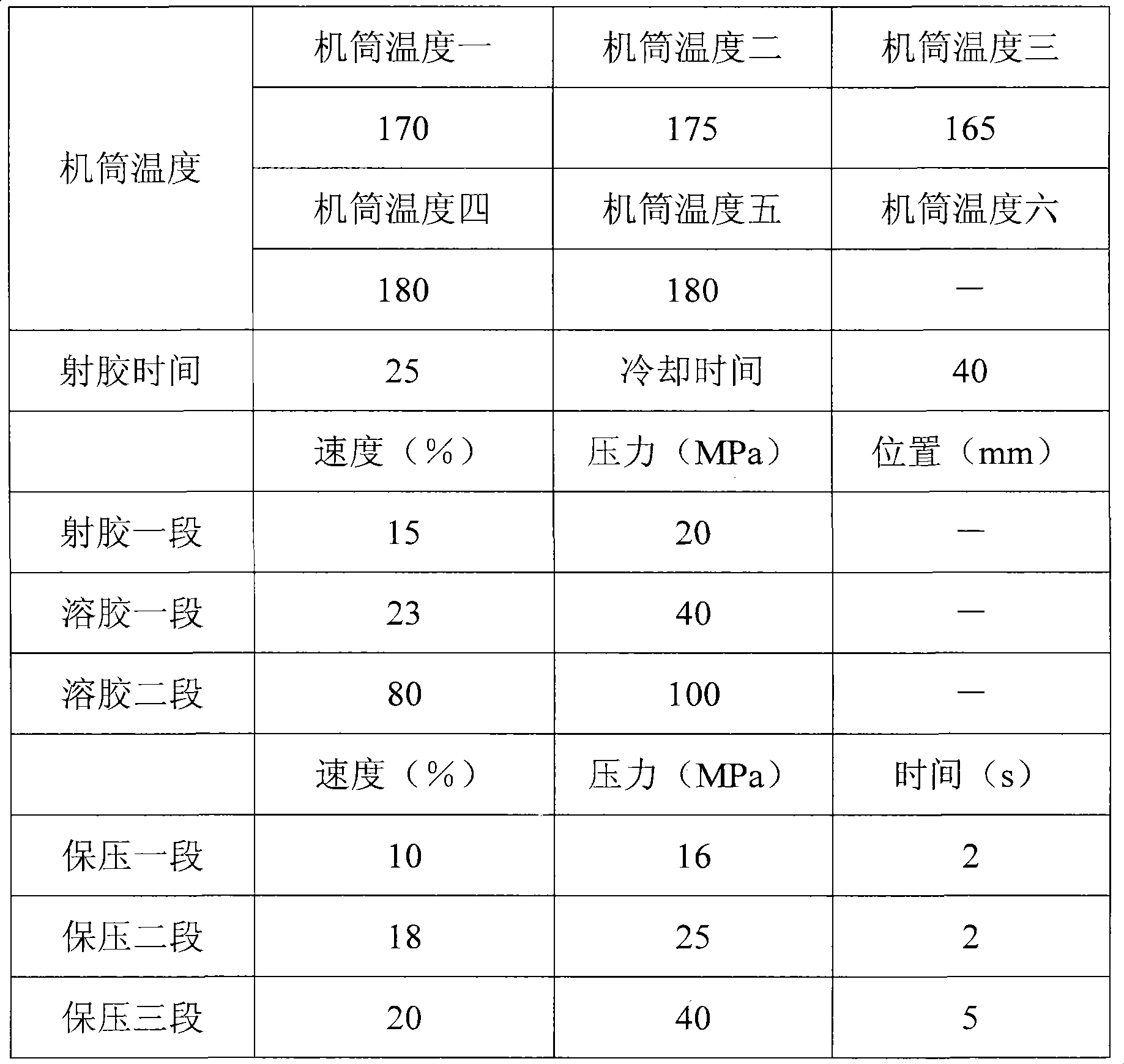
Hollow glass micro bead reinforcement rigid polyvinyl chloride material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a rigid polyvinyl chloride material reinforced by hollow glass microballoons and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises the following components in weight portion: 100 portions of polyvinyl chloride resin powder, 1 to 50 portions of the hollow glass microballoons, 0.1 to 10.0 portions of coupling agent, 0.5 to 3.0 portions of heat stabilizer, 0.2 to 5.0 portions of lubricant, 0.1 to 5.0 portions of processing modifier, and 0.1 to 10.0 portions of impact modifier. Through coupling compatibility and a distribution technology, the preparation method comprises the steps of compounding and directly injecting the hollow glass microballoons and the resin, and then processing the mixture to prepare the hollow glass microballoon reinforced rigid polyvinyl chloride material which has the advantages of higher impact resistance strength, hydraulic pressure resistance and explosion strength, higher size stability, and the like. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation method uses simple and practicable processes to deal with compatibility problem, accords with design requirements of industrialized production processes at the same time of meeting requirements on product properties, can achieve large-scale continuous production, and has relatively low production cost and stronger industrialized popularization.
Owner:湖南联塑科技实业有限公司
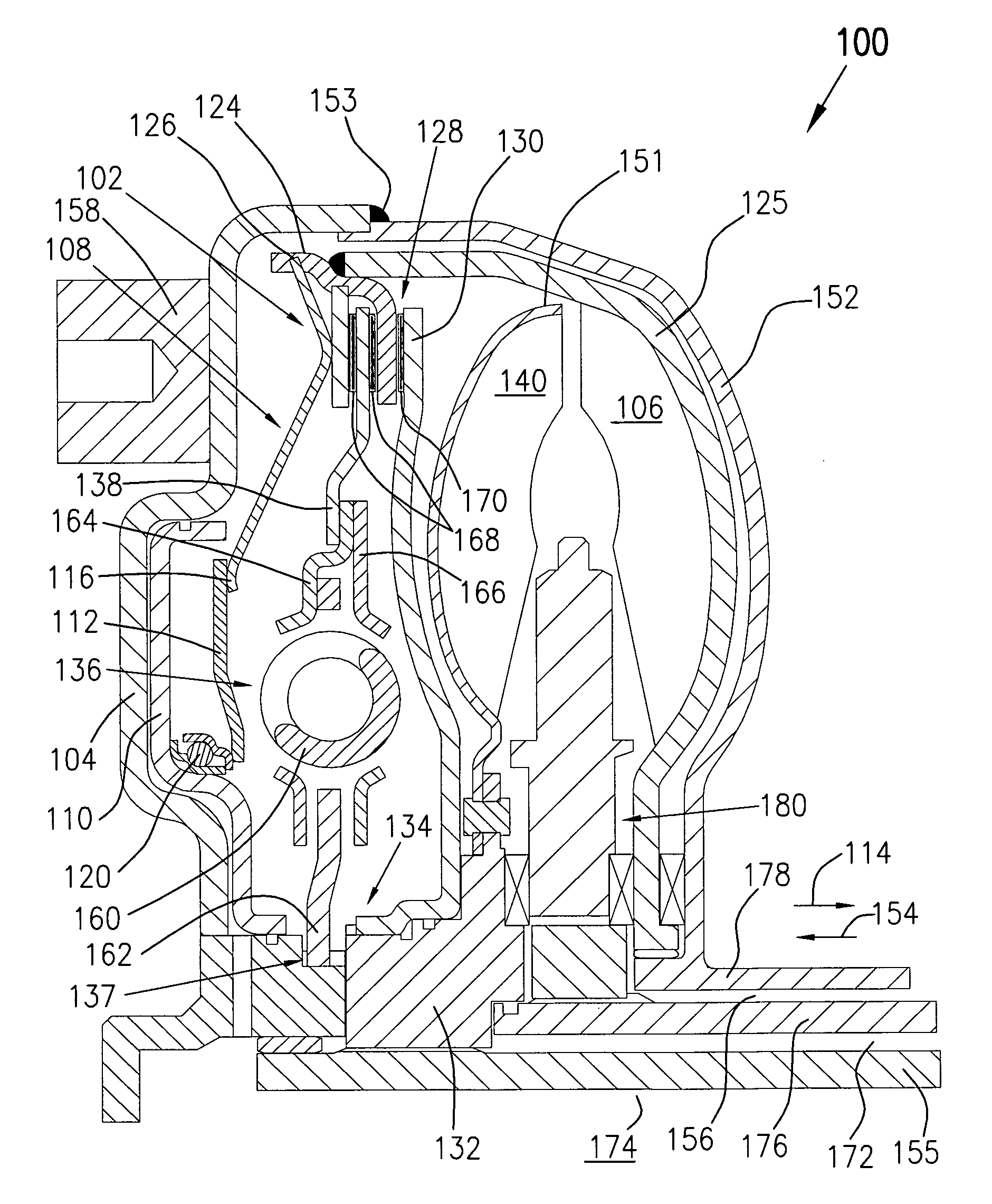
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS20090101459A1Increase hydraulic pressureHigh responseSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsMoving speedEngineering
In a shock absorber of a vehicle, when a moving speed of a piston rod in relation to a cylinder tube is slow and first and second input forces are externally applied to the shock absorber, damping forces of pressure side and extension side first damping force generating devices are larger than that of pressure side and extension side second damping force generating devices. On the other hand, when the moving speed is fast, the damping forces of the pressure side and the extension side second damping force generating devices are larger than that of the pressure side and the extension side first damping force generating devices. A gas enclosure chamber filled with gas is connected to a first chamber through a free piston.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Flameless heating system
ActiveUS9228760B2Increase hydraulic pressureAir-treating devicesOther heat production devicesHydraulic motorExternal combustion engine
A mobile heating system is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes an enclosure defining a plenum that houses a fan and an internal combustion engine. The heating system also includes a hydraulic circuit including a hydraulic pump operably coupled to the internal combustion engine and a first heat exchanger located in the plenum and in fluid communication with the hydraulic pump. The hydraulic circuit also includes a hydraulic motor operably coupled to the fan wherein the hydraulic motor is in fluid communication with and driven by the hydraulic pump. A first valve is disposed between the hydraulic pump and the heat exchanger and is configured to restrict fluid flow and to increase a fluid pumping pressure of the hydraulic pump. A second valve is located upstream of the first valve and is configured to selectively direct hydraulic fluid between the first valve and the hydraulic motor.
Owner:GENERAC POWER SYSTEMS
Vehicle brake hydraulic pressure control apparatus
InactiveUS7530648B2Slow braking” is applied can be preventedIncrease hydraulic pressureBraking systemsSolenoid valveDifferential pressure
The brake hydraulic pressure control apparatus employs, as a pressure-increasing valve, a normally-open linear solenoid valve that can linearly adjust an actual differential pressure (difference between master cylinder hydraulic pressure and a wheel cylinder hydraulic pressure). This apparatus repeatedly executes, in principle, a control cycle in which a pressure-reducing control, holding control and linear pressure-increasing control make one set, while a “linear pressure-increasing control with holding period” is executed instead of the linear pressure-increasing control only in the first-time control cycle that is started in a state where a current-value-corresponding-to-actual-differential-pressure cannot correctly be obtained. The command current value Id (=I0) to the pressure-increasing valve at the point of starting the “linear pressure-increasing control with holding period” is set to a “current-value-corresponding-to-reduced-pressure” that is always smaller than the current-value-corresponding-to-actual-differential-pressure at the same point.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Method and system for learning and controlling torque transmission kiss point of engine clutch for hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS9233684B2Increase hydraulic pressureLearn accuratelyHybrid vehiclesClutchesTorque transmissionEngineering
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Power transfer mechanism control device and power transfer device
InactiveUS20110237394A1Suppress transfer of torqueImprove vehicle performanceGearing controlEngine controllersCombustionExternal combustion engine
A power transfer mechanism control device controlling a power transfer mechanism mounted on a vehicle which transfers power from an internal combustion engine to an axle side via a friction engagement element actuated by a fluid pressure from either of a first fluid pressure actuator driven by the power from the internal combustion engine and a second fluid pressure actuator driven by a fluid pressure source different from a fluid pressure source for the first fluid pressure actuator. When the internal combustion engine is to be automatically started, the second fluid pressure actuator is controlled such that, before complete combustion occurs in the internal combustion engine, the friction engagement element stands by in a low-pressure state, and the first fluid pressure actuator is controlled such that the friction engagement element transfers the torque at predetermined timing after the complete combustion occurs in the internal combustion engine.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
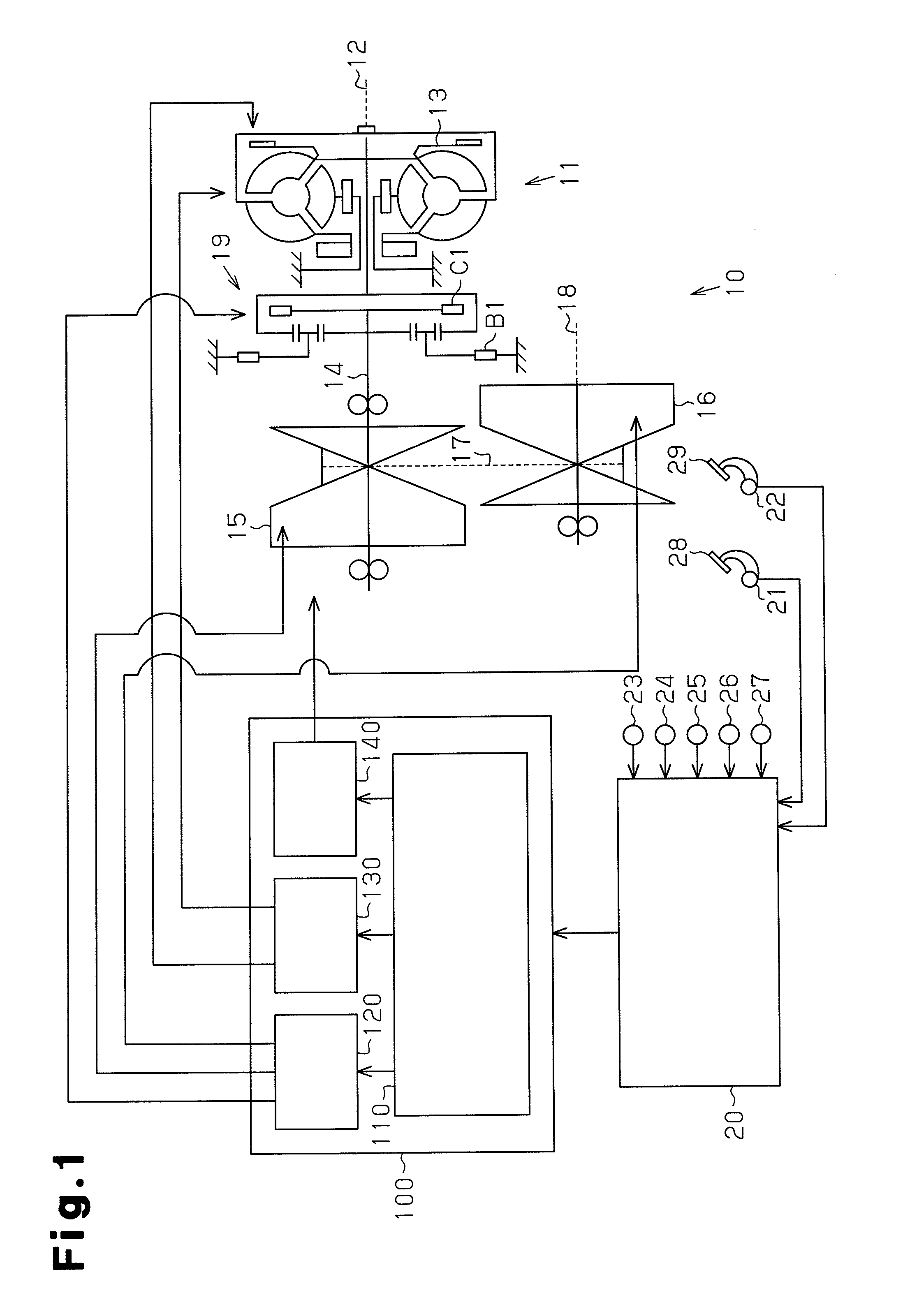
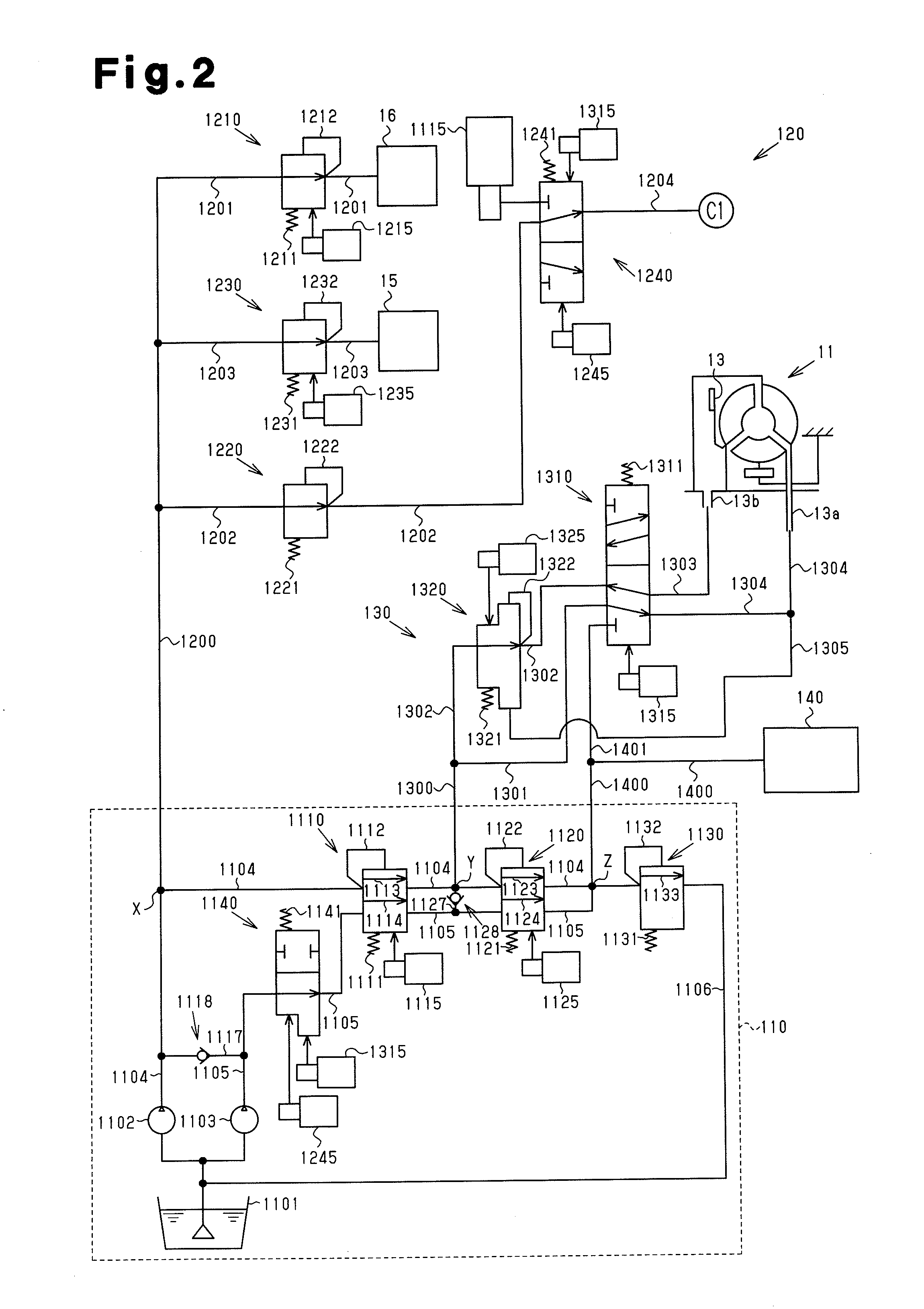
Hydraulic device for stepless transmission
InactiveUS20120011841A1Increase hydraulic pressure of hydraulic oilIncrease hydraulic pressureFluid couplingsGearing controlCheck valveEngineering
A hydraulic device includes a switch-over valve 1140 provided at a section of a sub-passage 1105 located downstream of a location where a first bypass passage 1117 is connected and located upstream of a primary regulator 1110. The switch-over valve 1140 is switched between a blocked state, where supply of hydraulic oil to a section of the sub-passage 1105 located downstream of the switch-over valve 1140 is blocked, and a communication state, where supply of hydraulic oil to the section of the sub-passage 1105 located downstream of the switch-over valve 1140 is permitted. In the hydraulic device, when the switch-over valve 1140 is switched to the communication state, as a discharge performance of a main pump 1102 increases, a first check valve 1118 closes. Supply paths for hydraulic oil discharged from the sub-pump 1103 are automatically switched in accordance with the discharge performance of the main pump 1102. When the switch-over valve 1140 is switched to the blocked state, the first check valve 1118 opens and hydraulic oil discharged from the sub-pump 1103 is introduced into a main passage 1104.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com