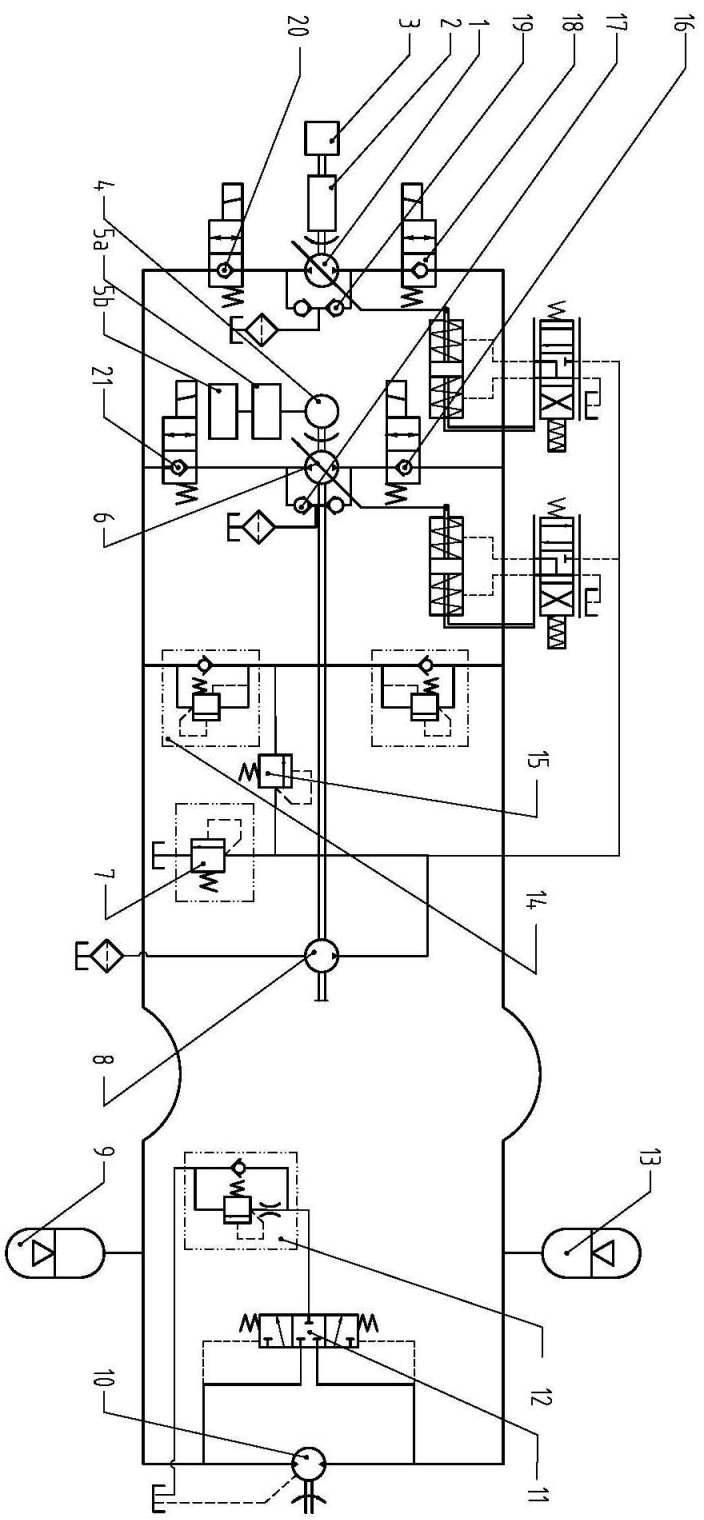
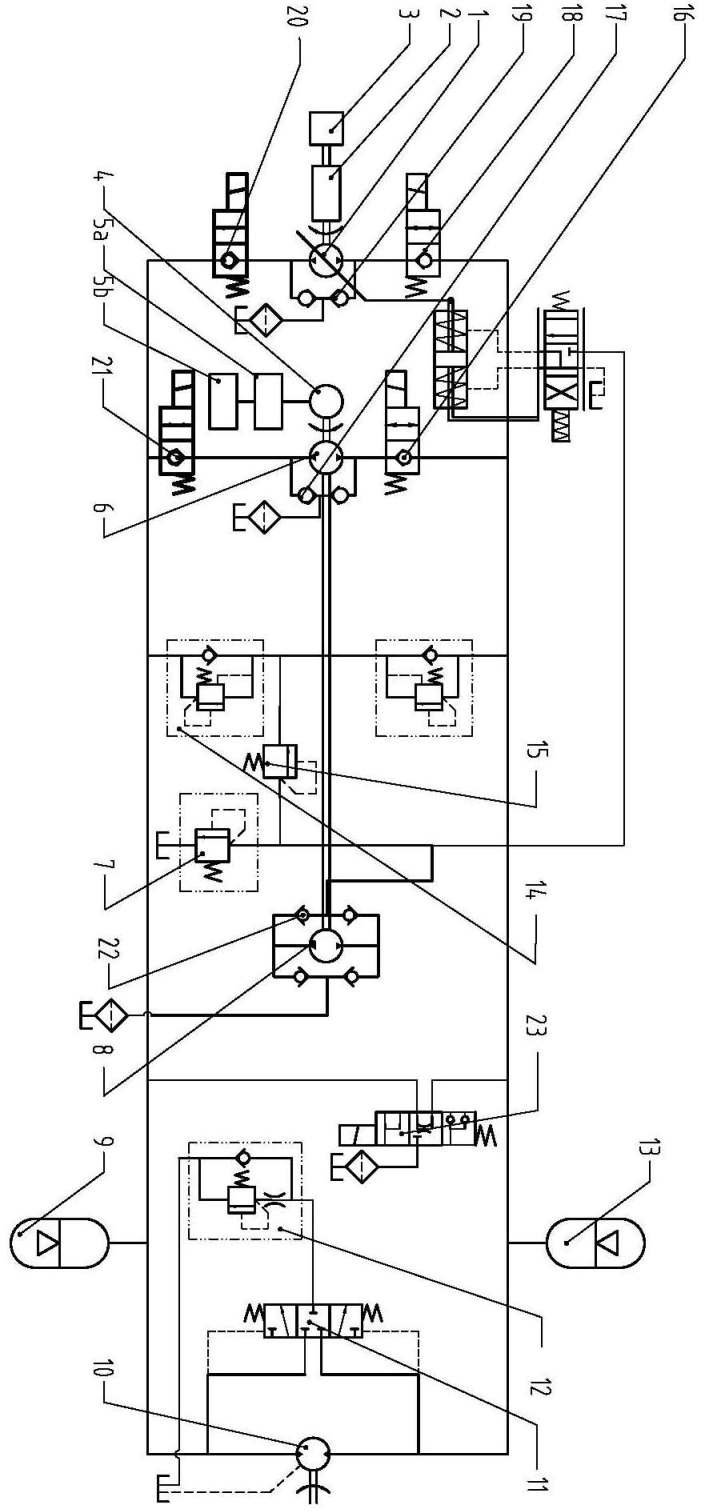
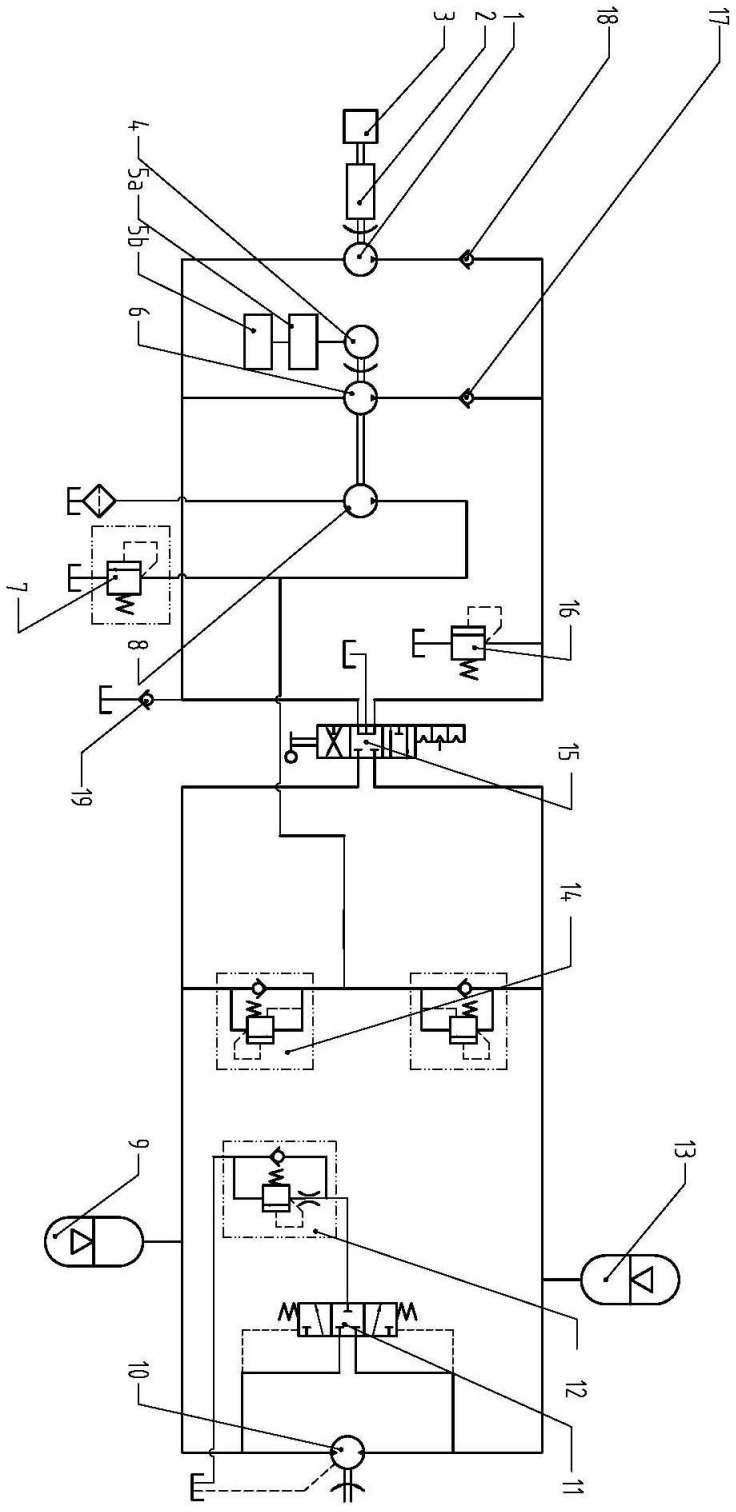
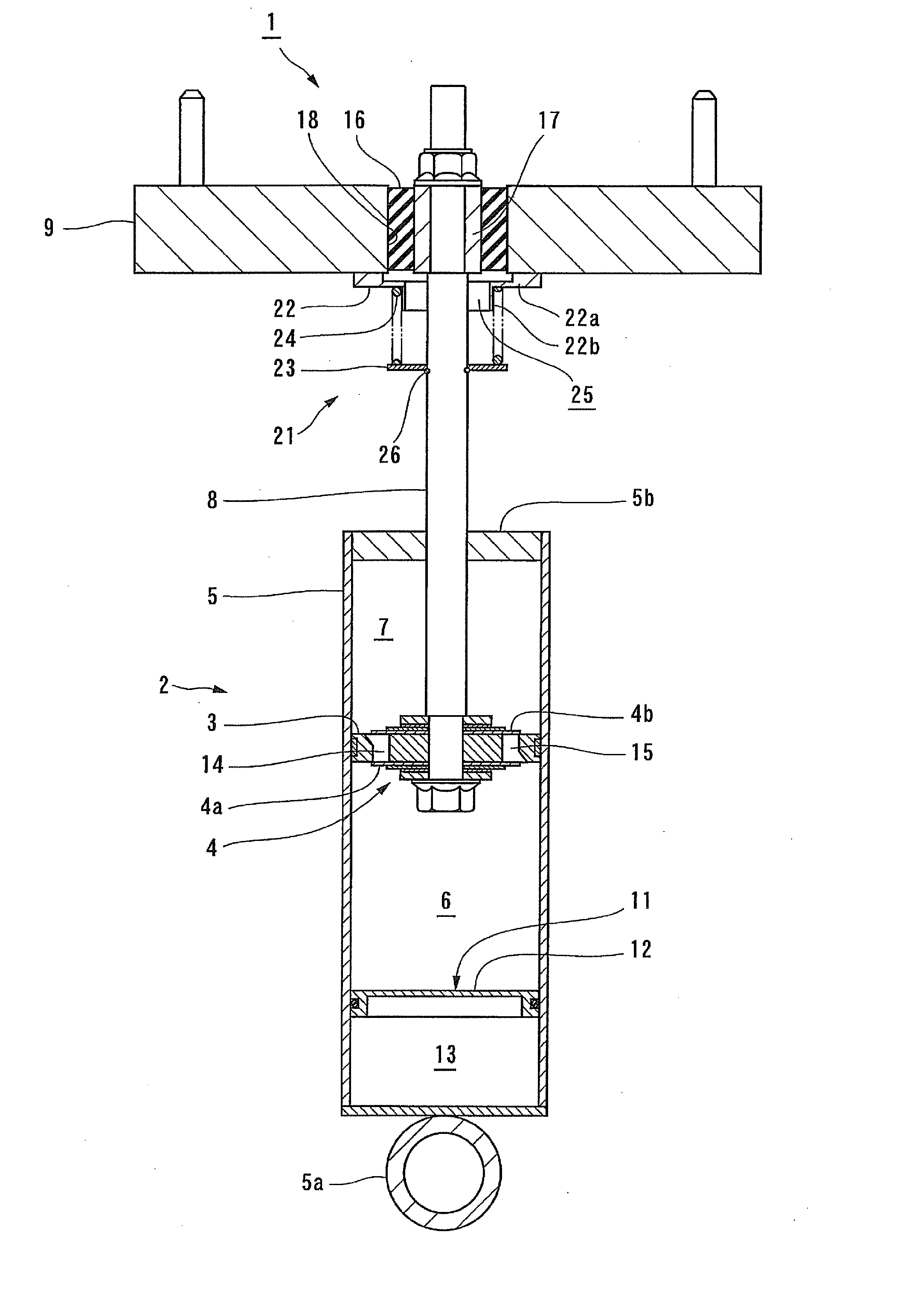
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1016 results about "Hydraulic shock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
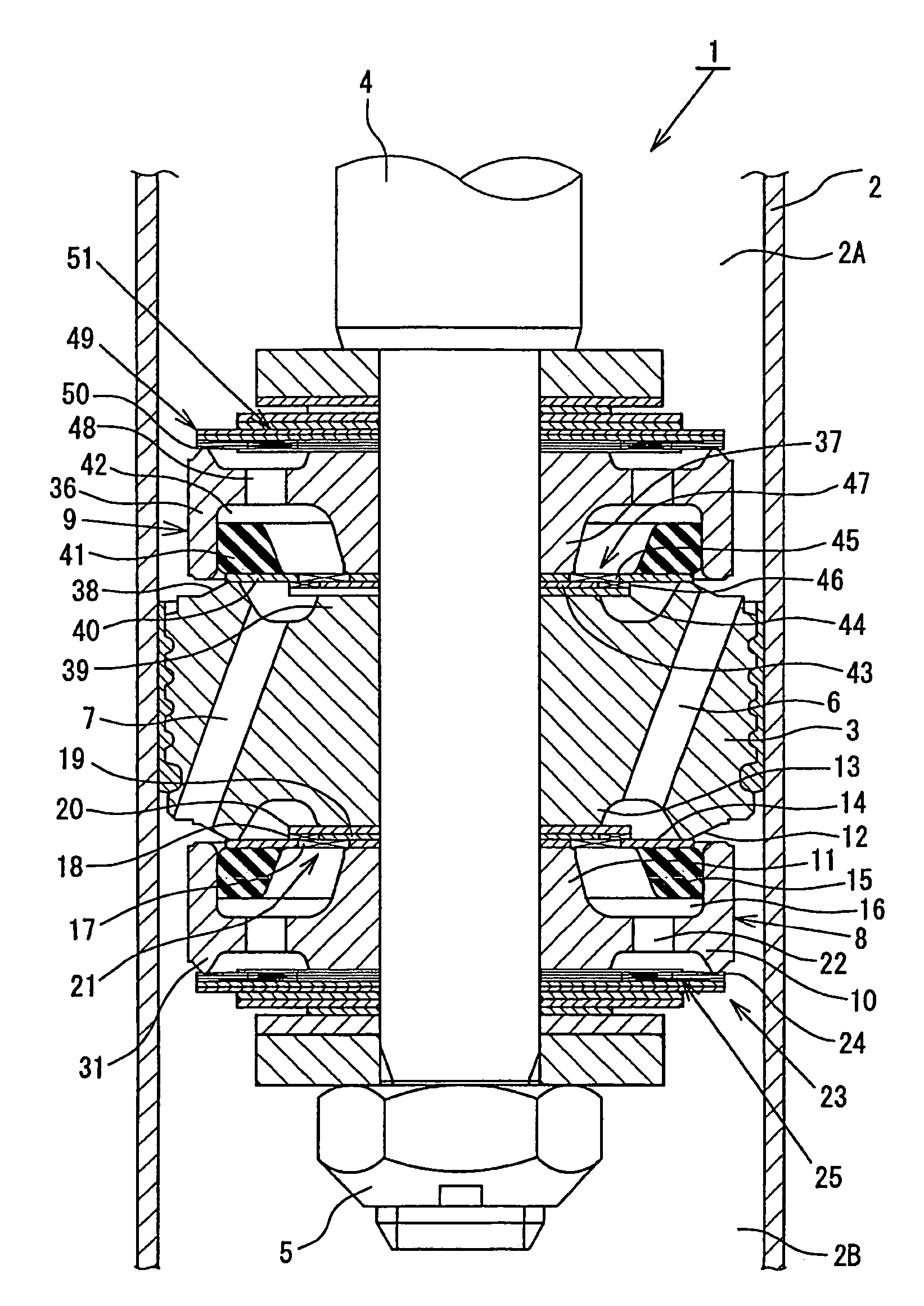
Hydraulic shock occurs when oil rapidly starts or stops flowing in a hydraulic system. The oil flow rate in the pressure line of systems below 3,000 psi is usually 15-20 feet per second. In systems above 3,000 psi, the flow rate can be as high as 30 feet per second. Shock can also occur when an external force acts on a hydraulic cylinder or motor.
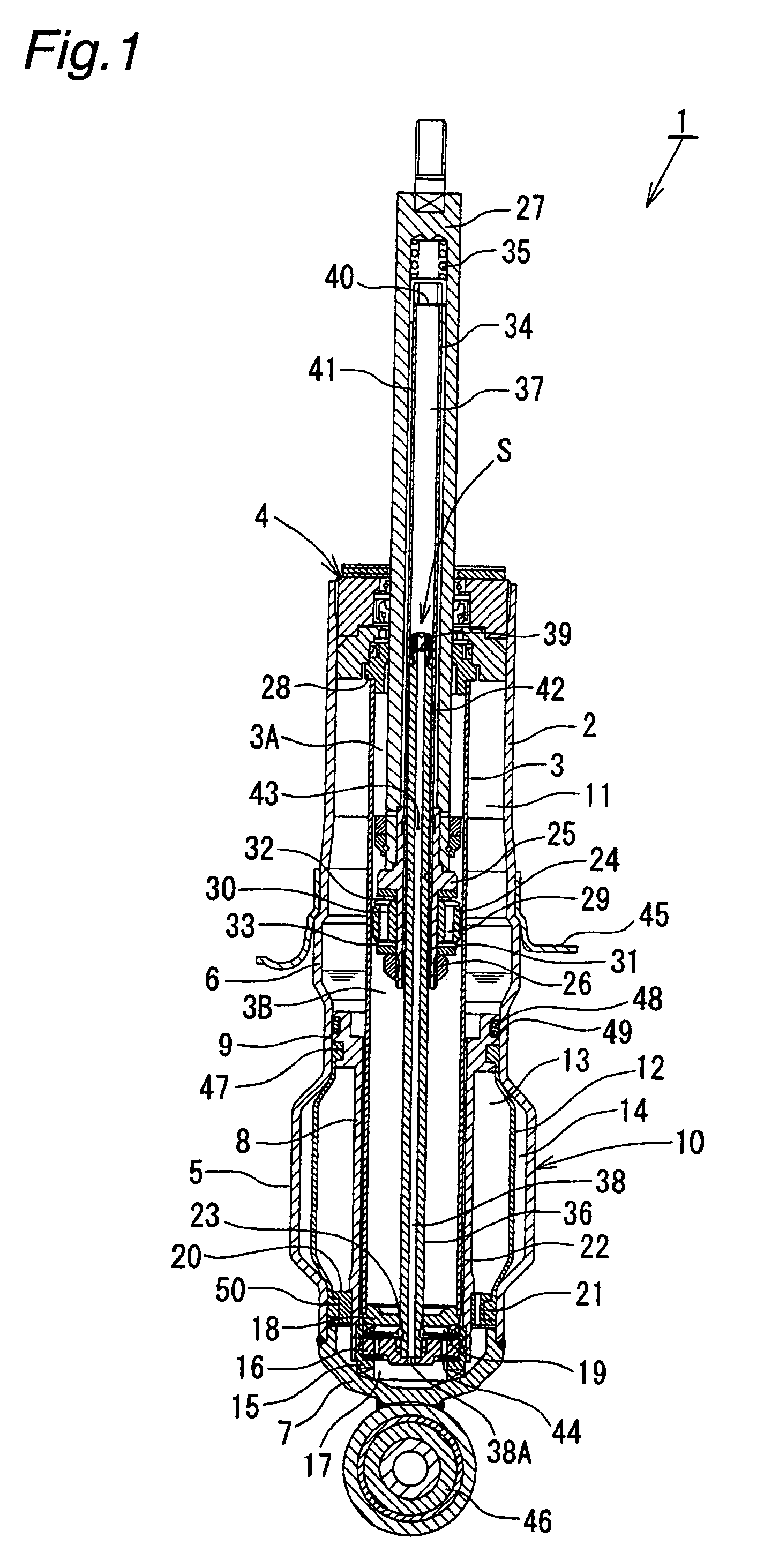
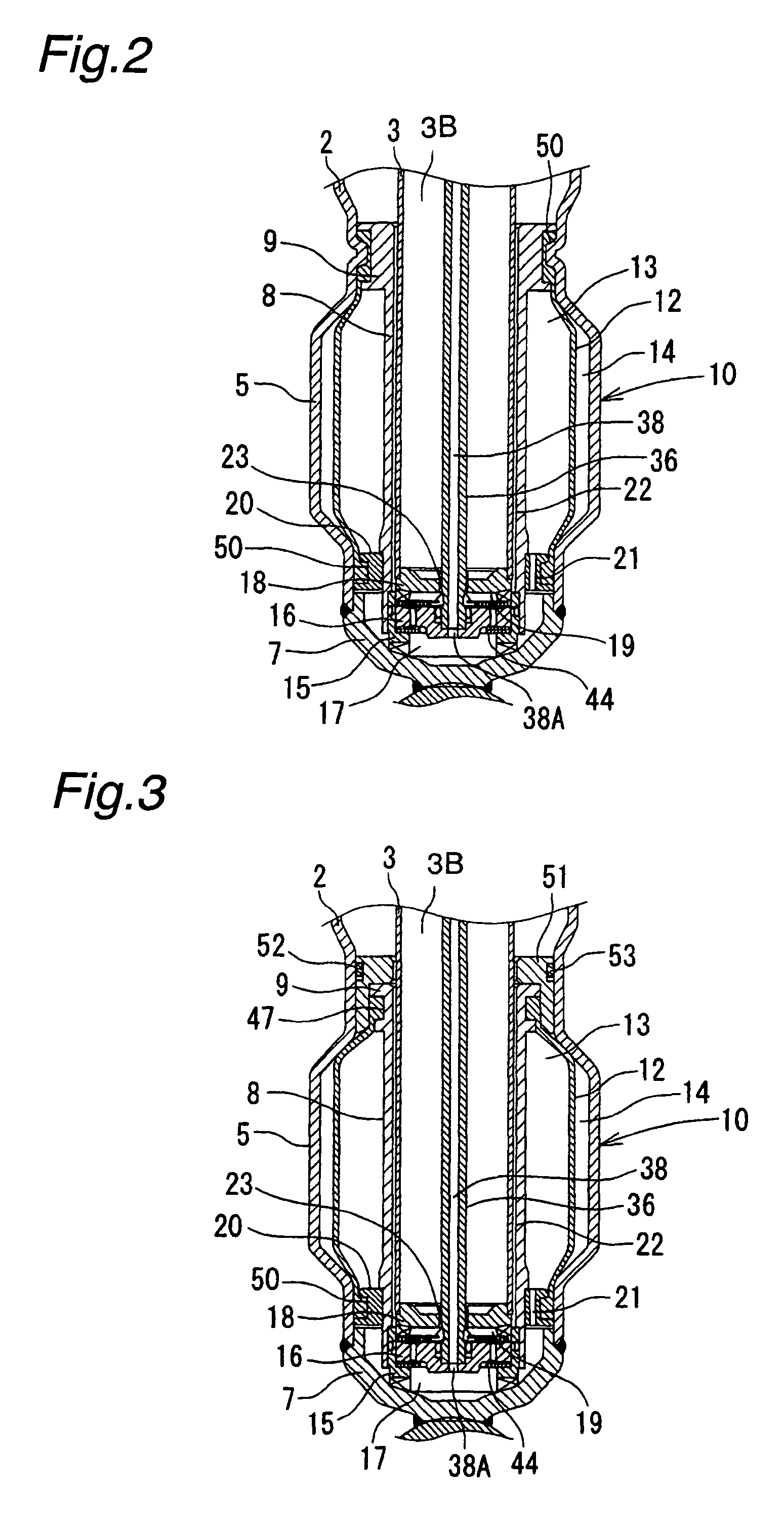
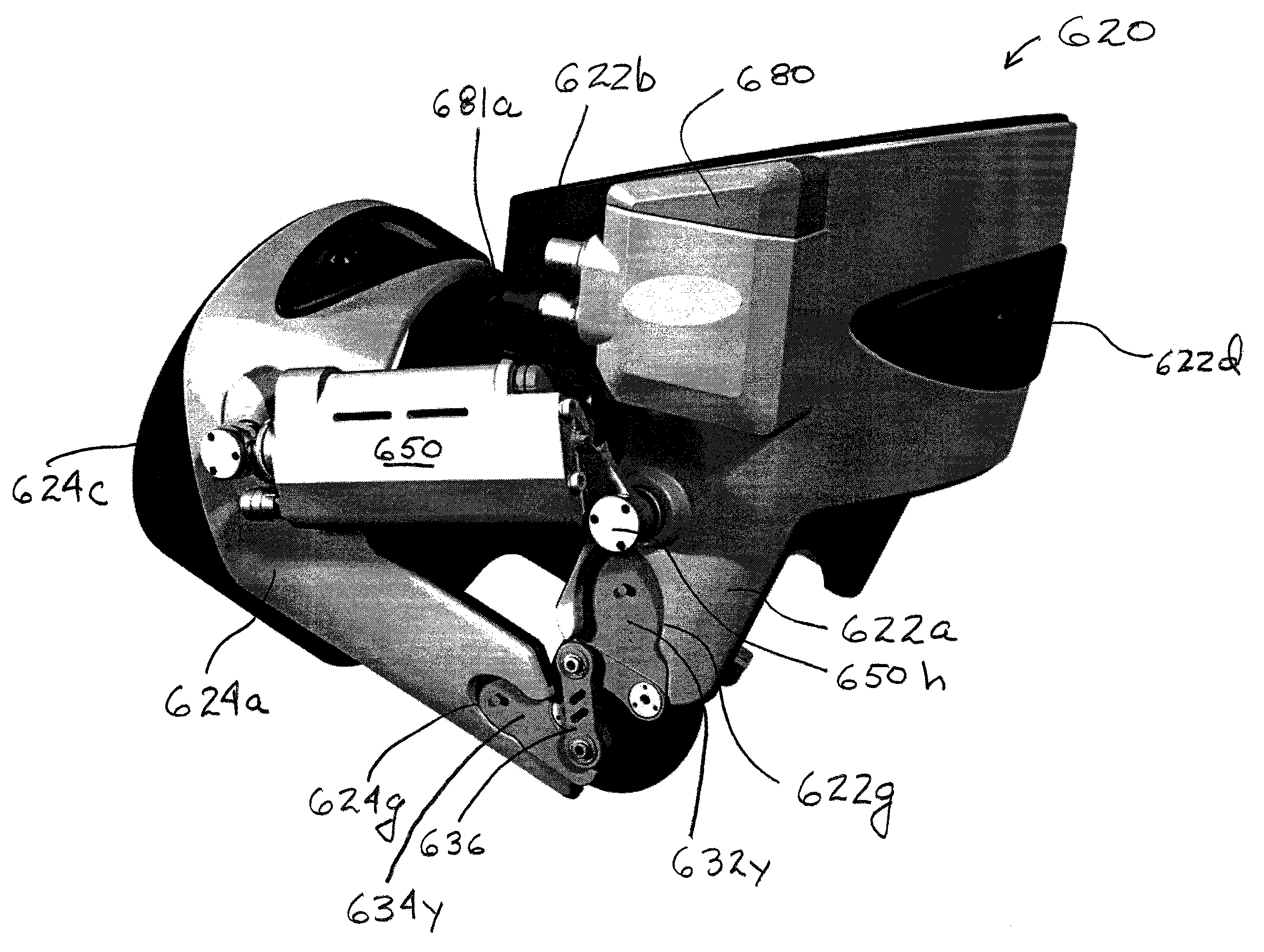
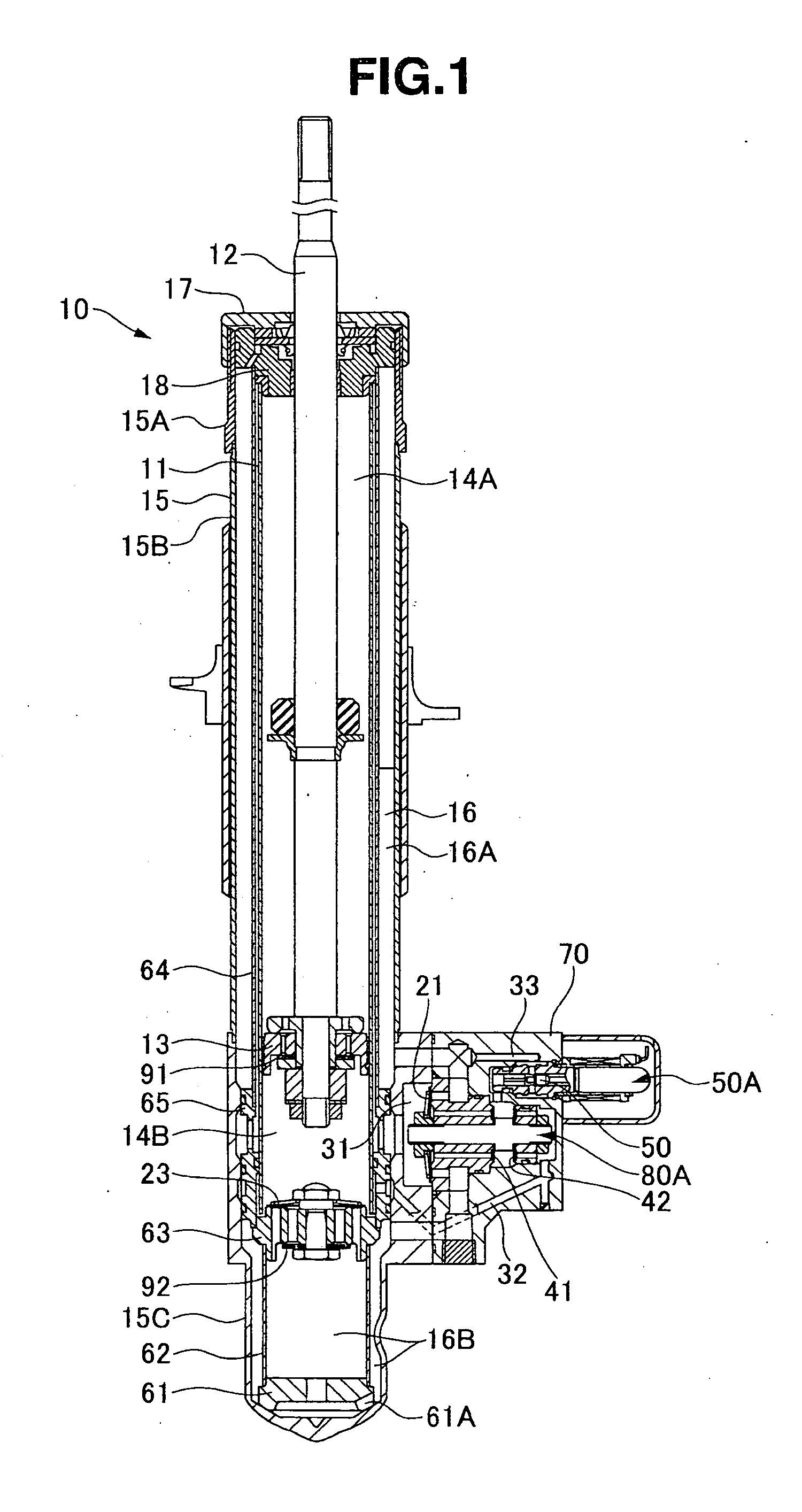
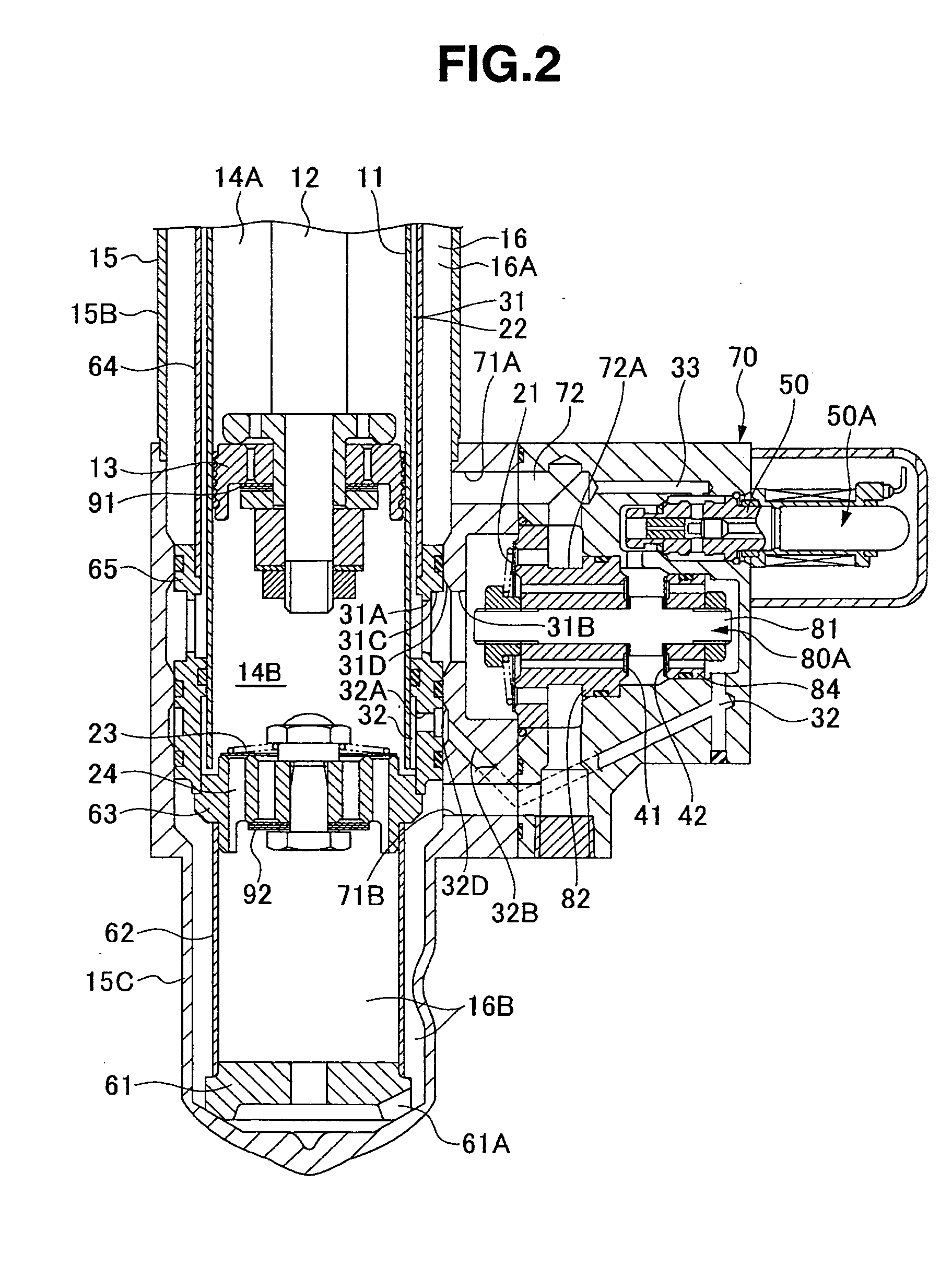
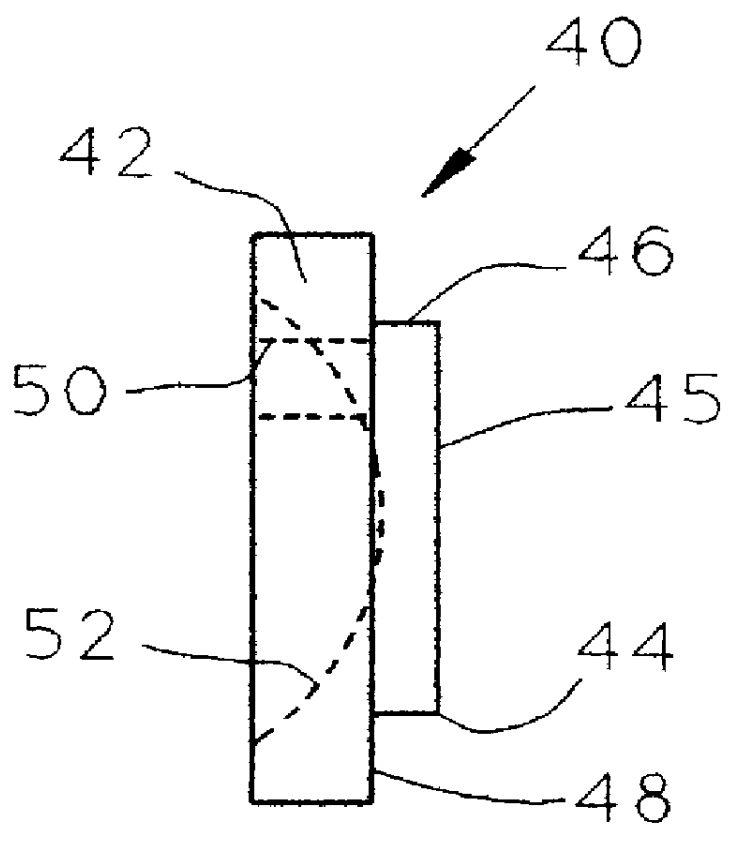
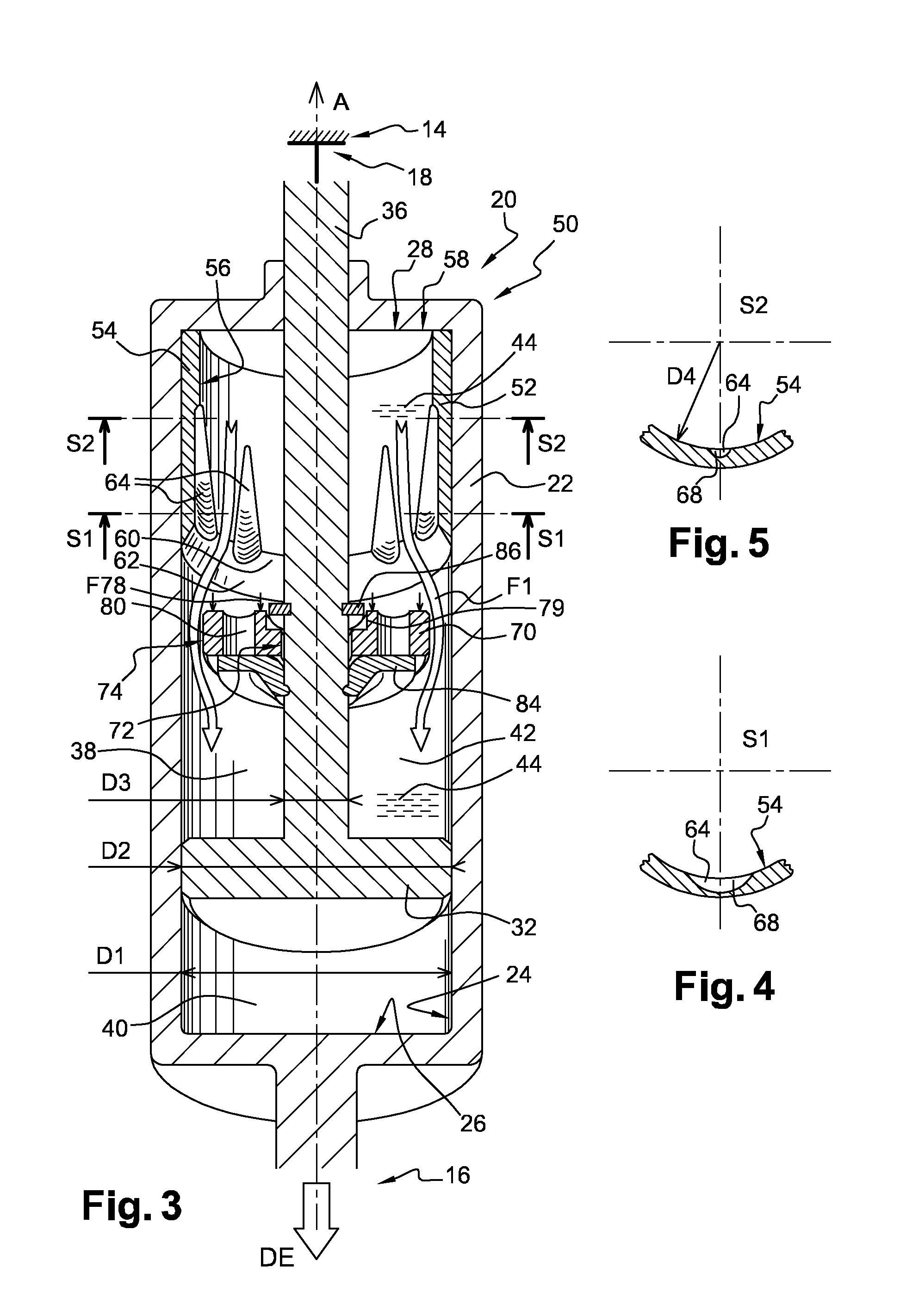
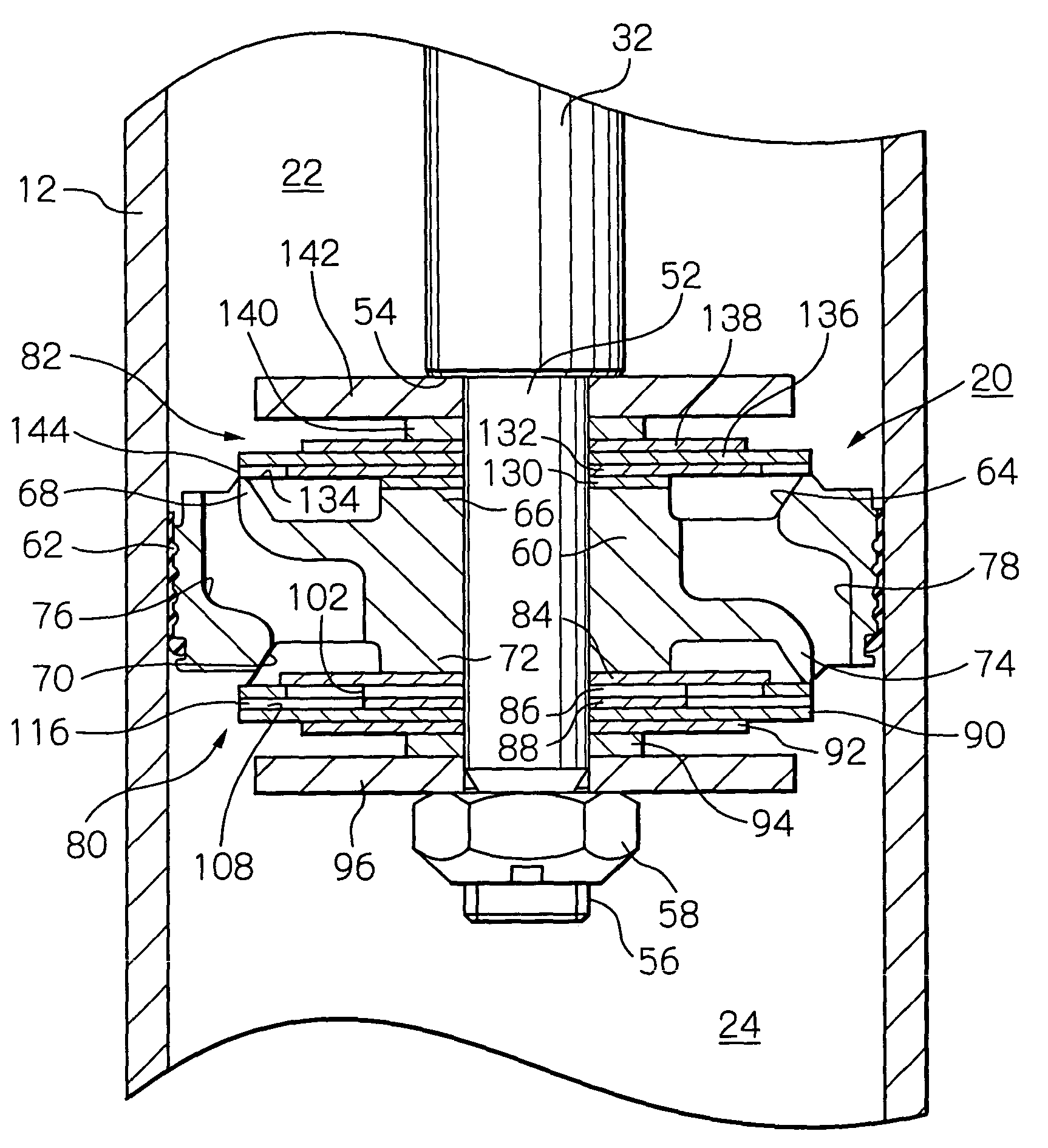
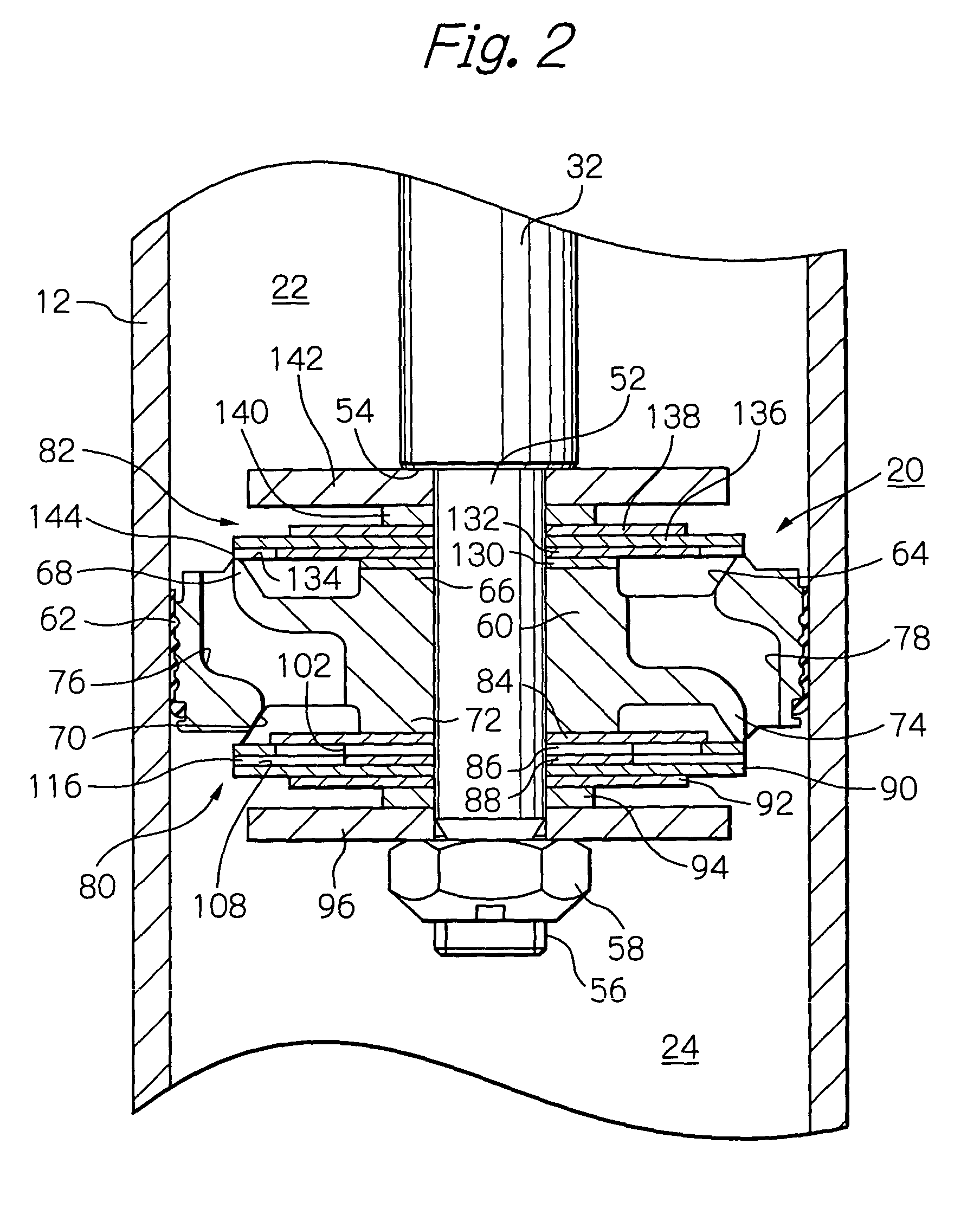
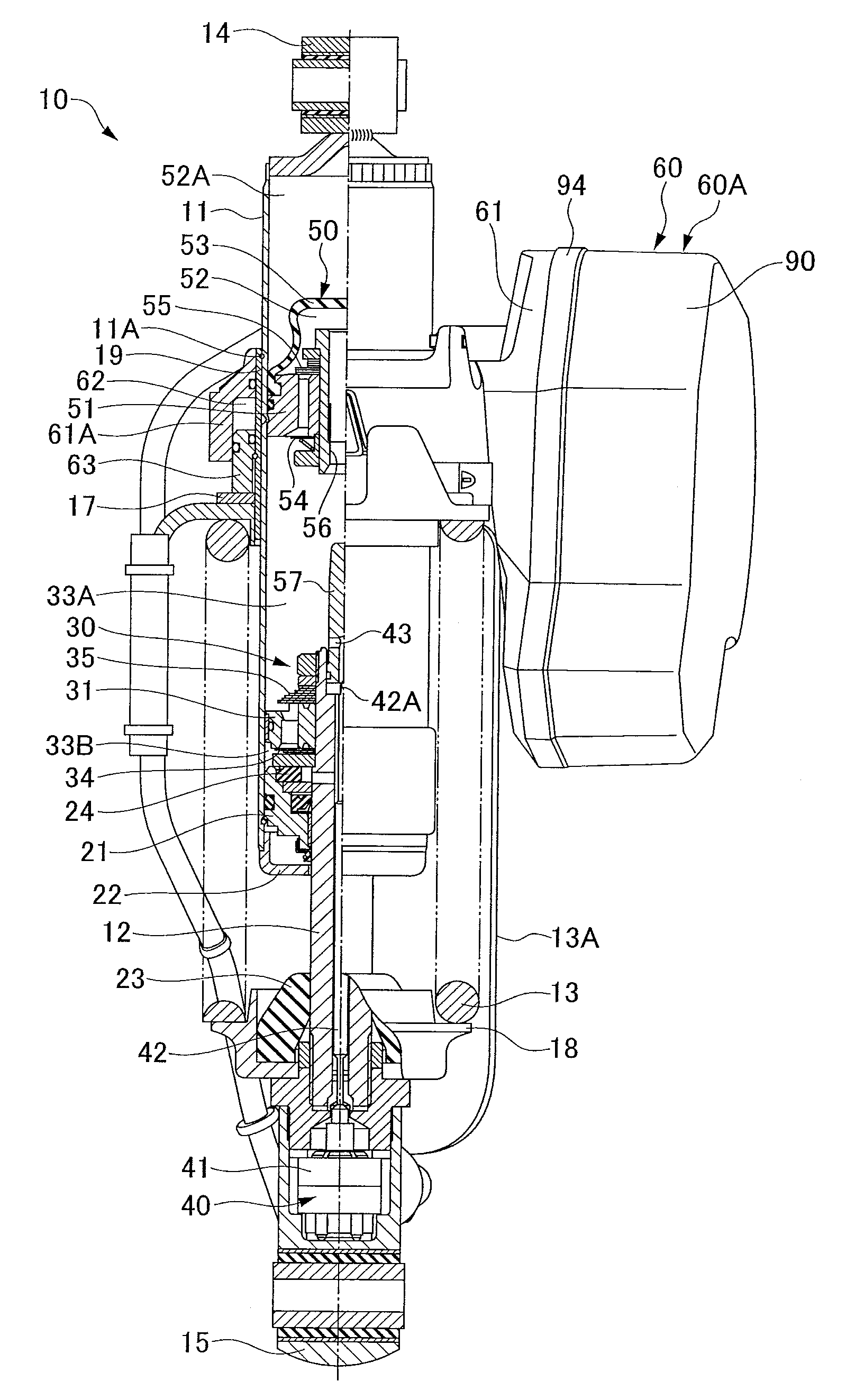
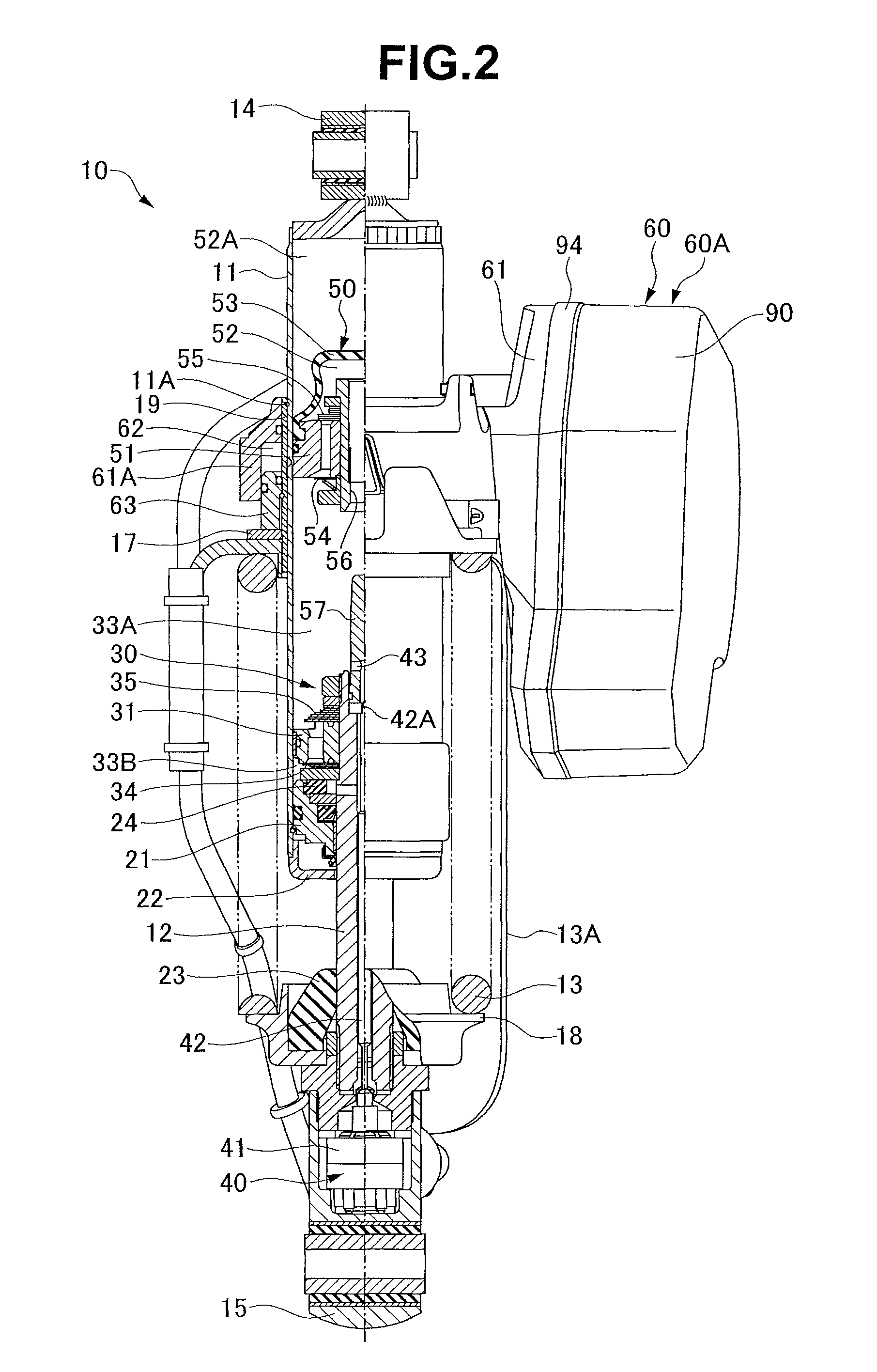
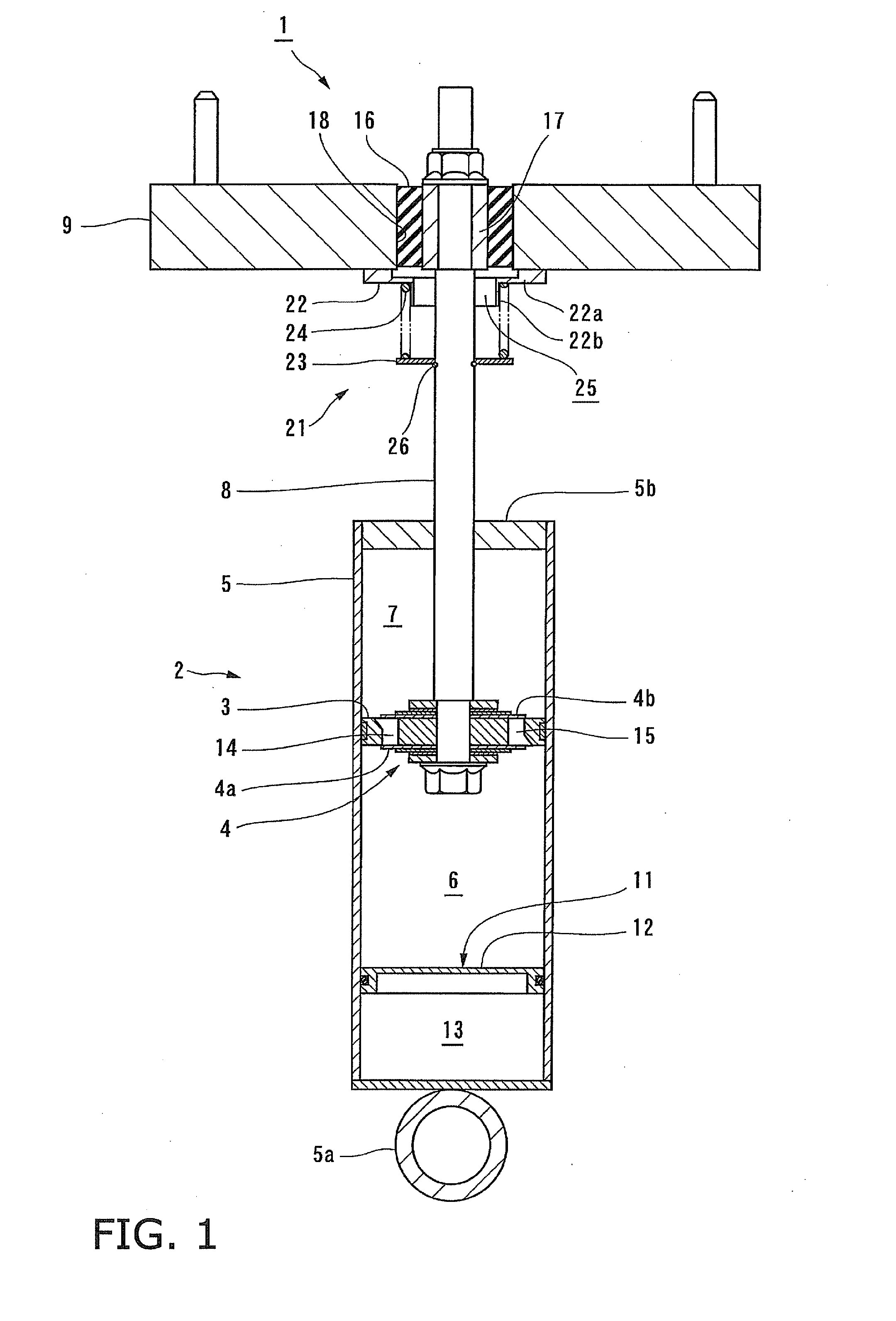
Controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber
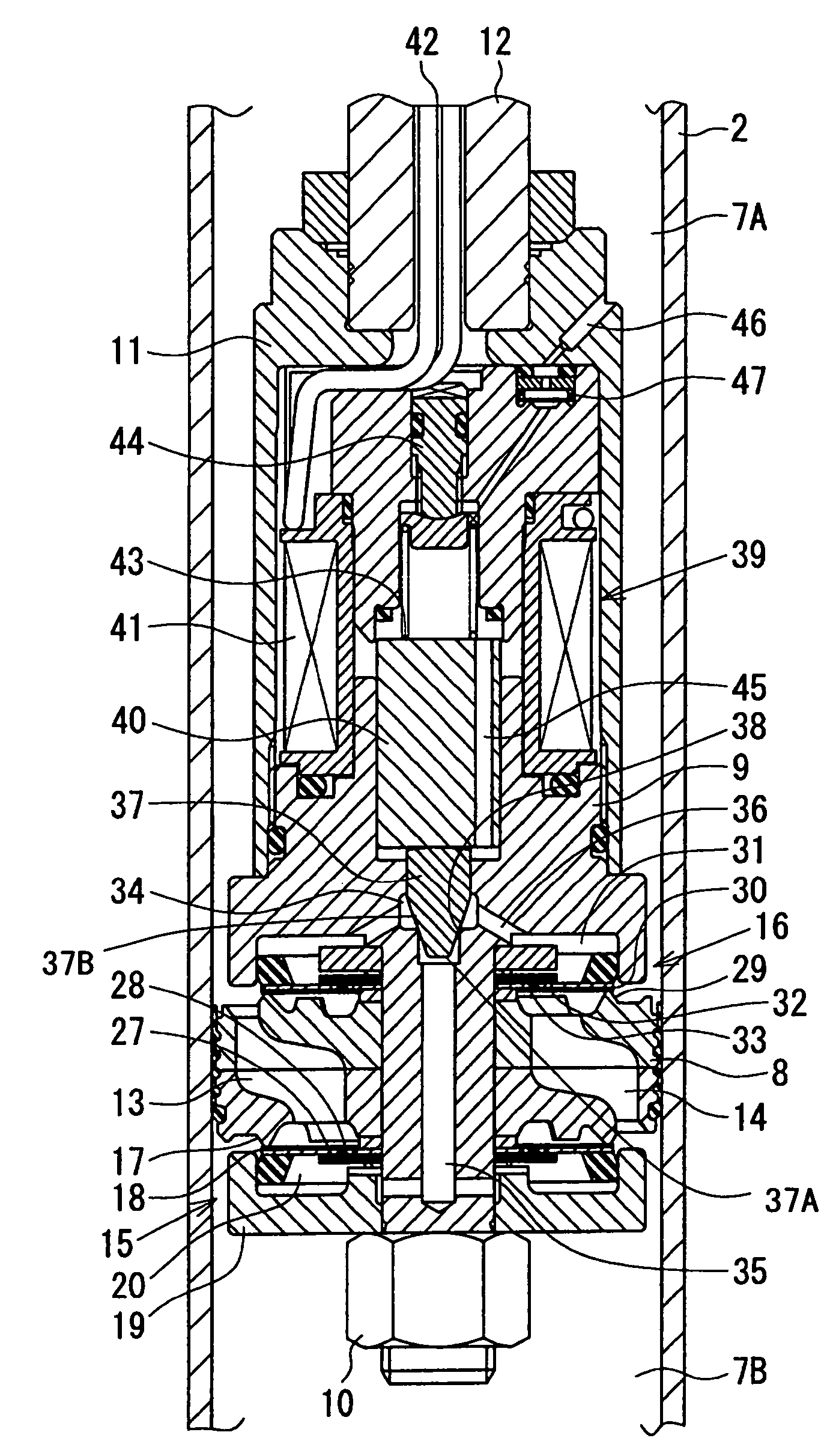
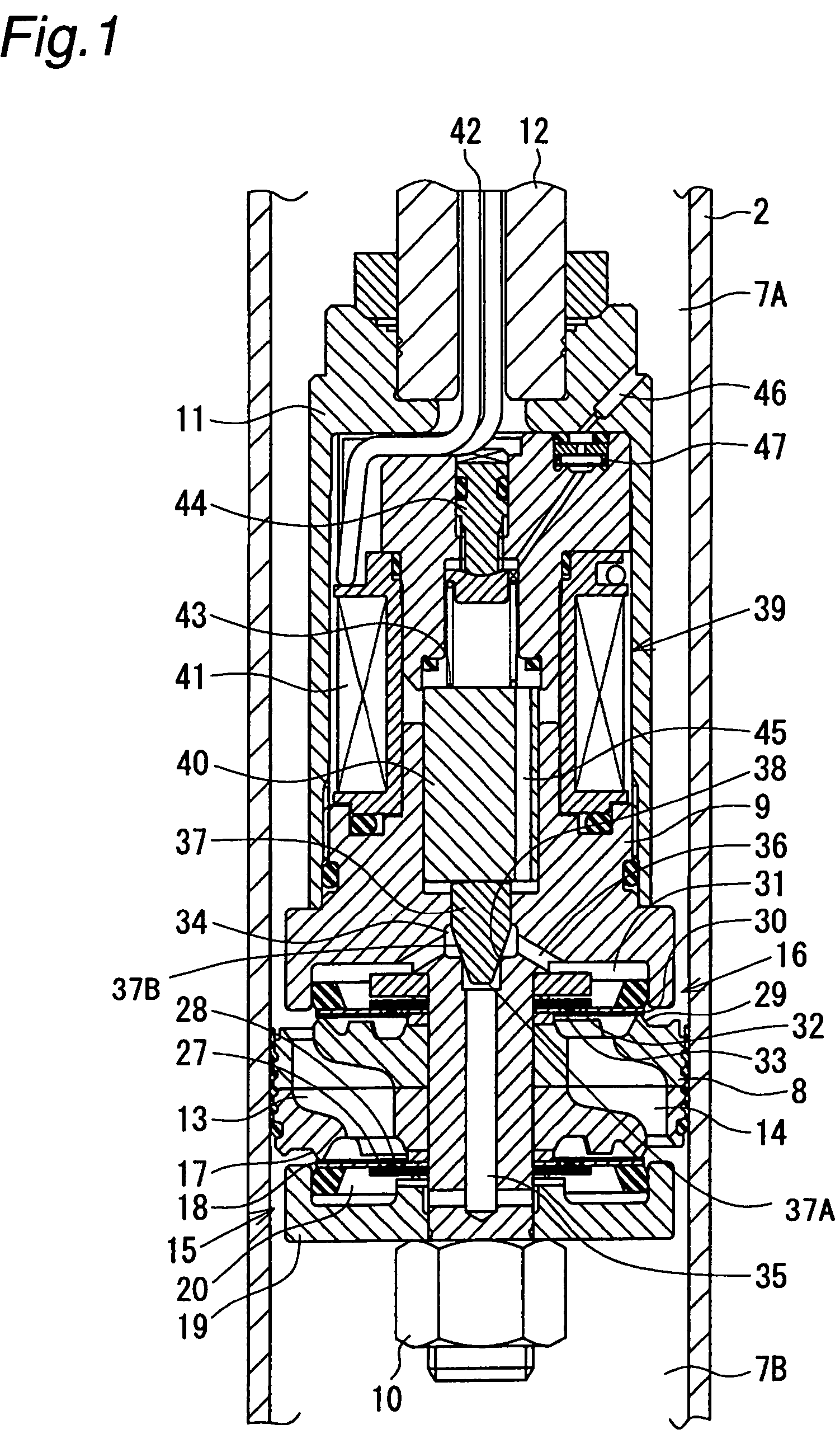
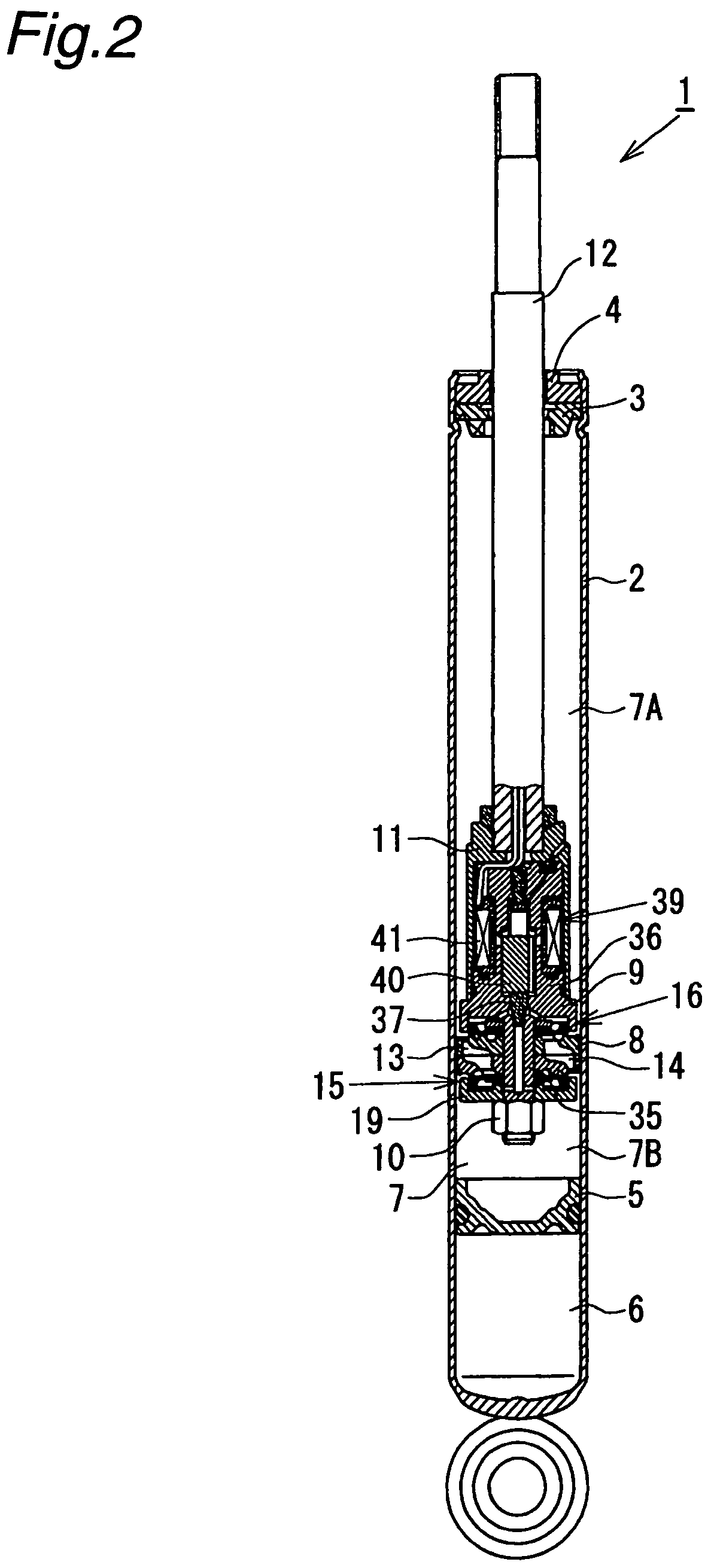
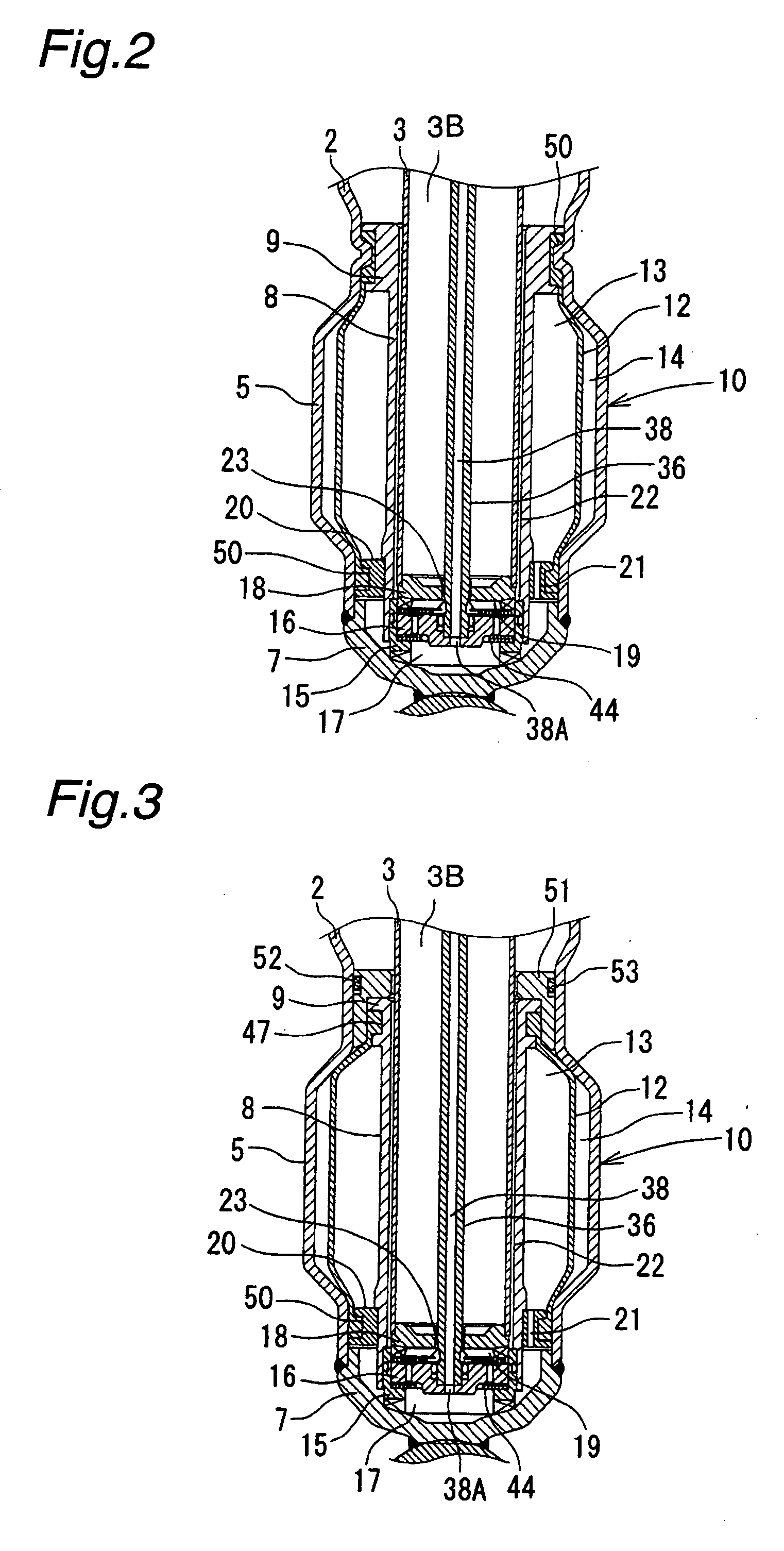
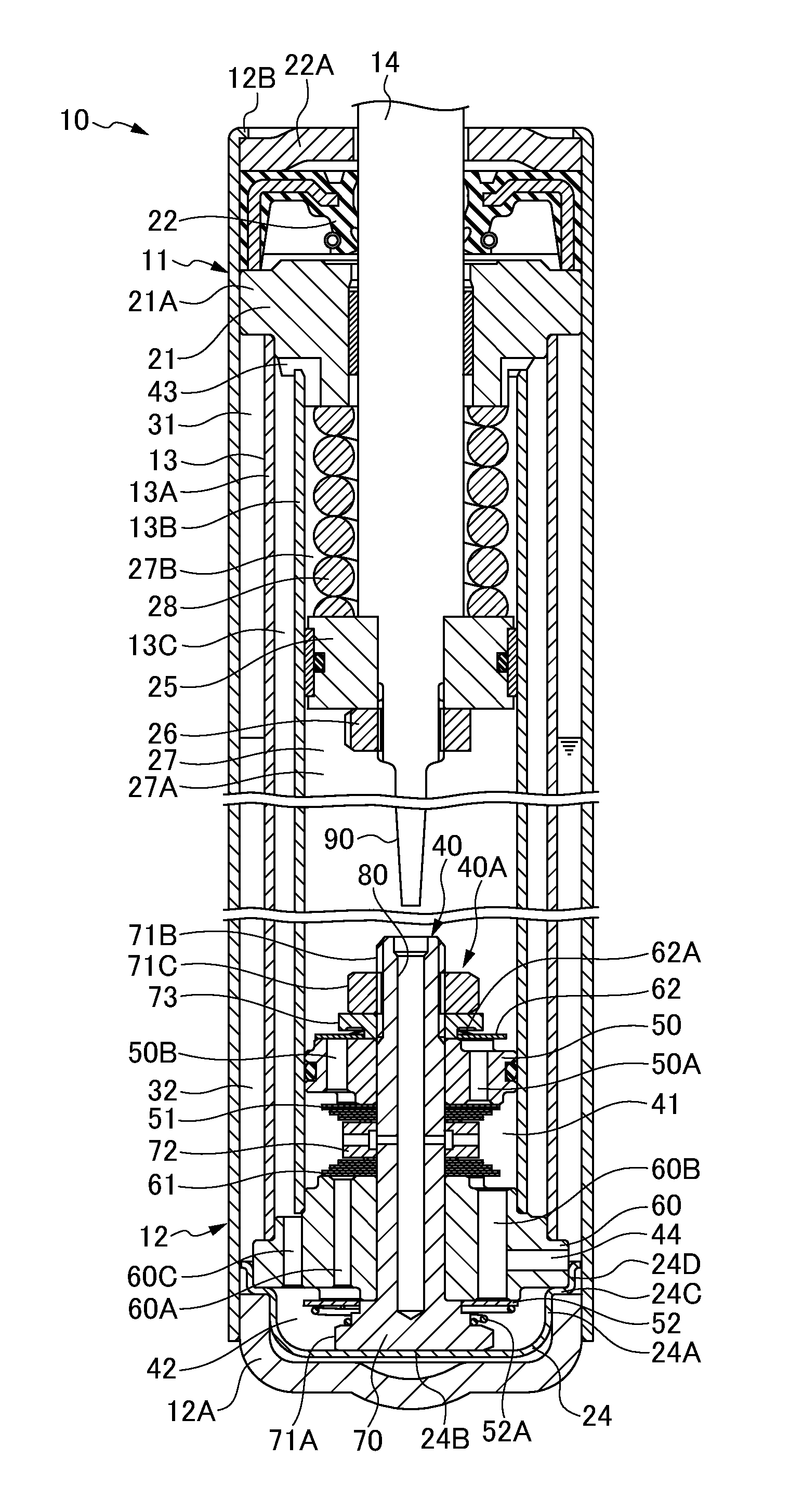
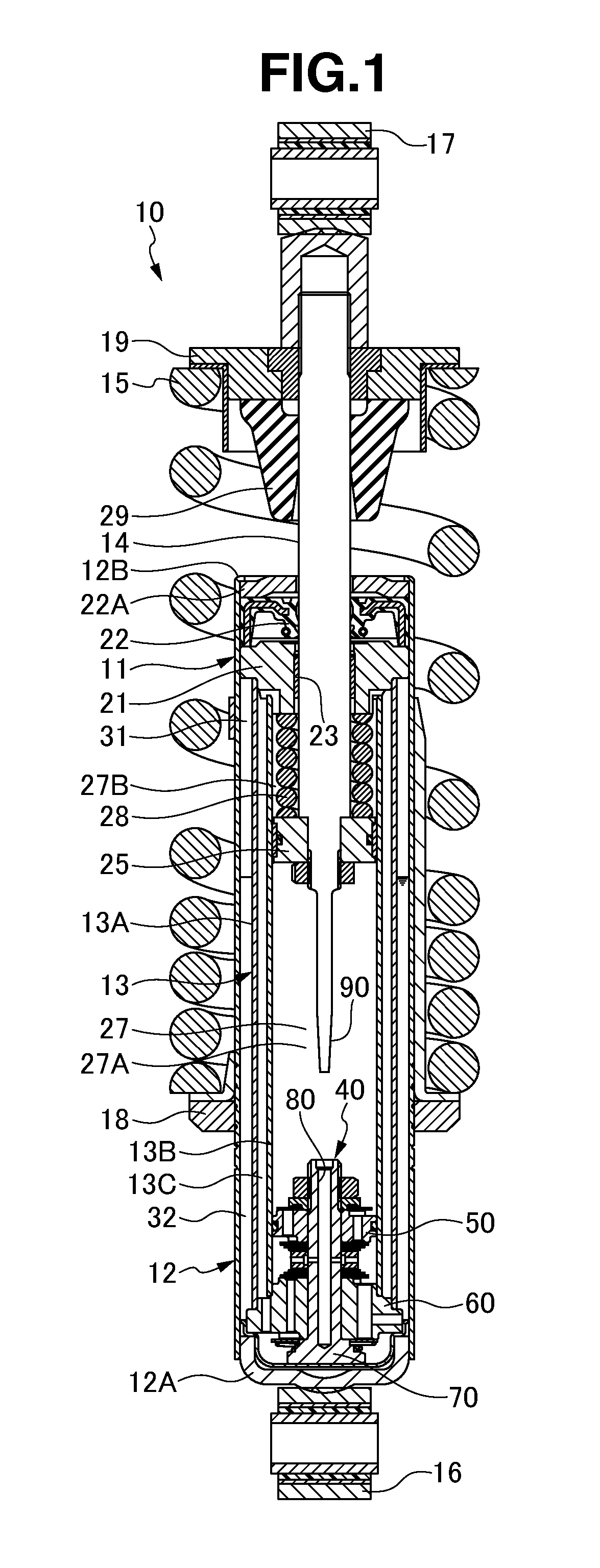
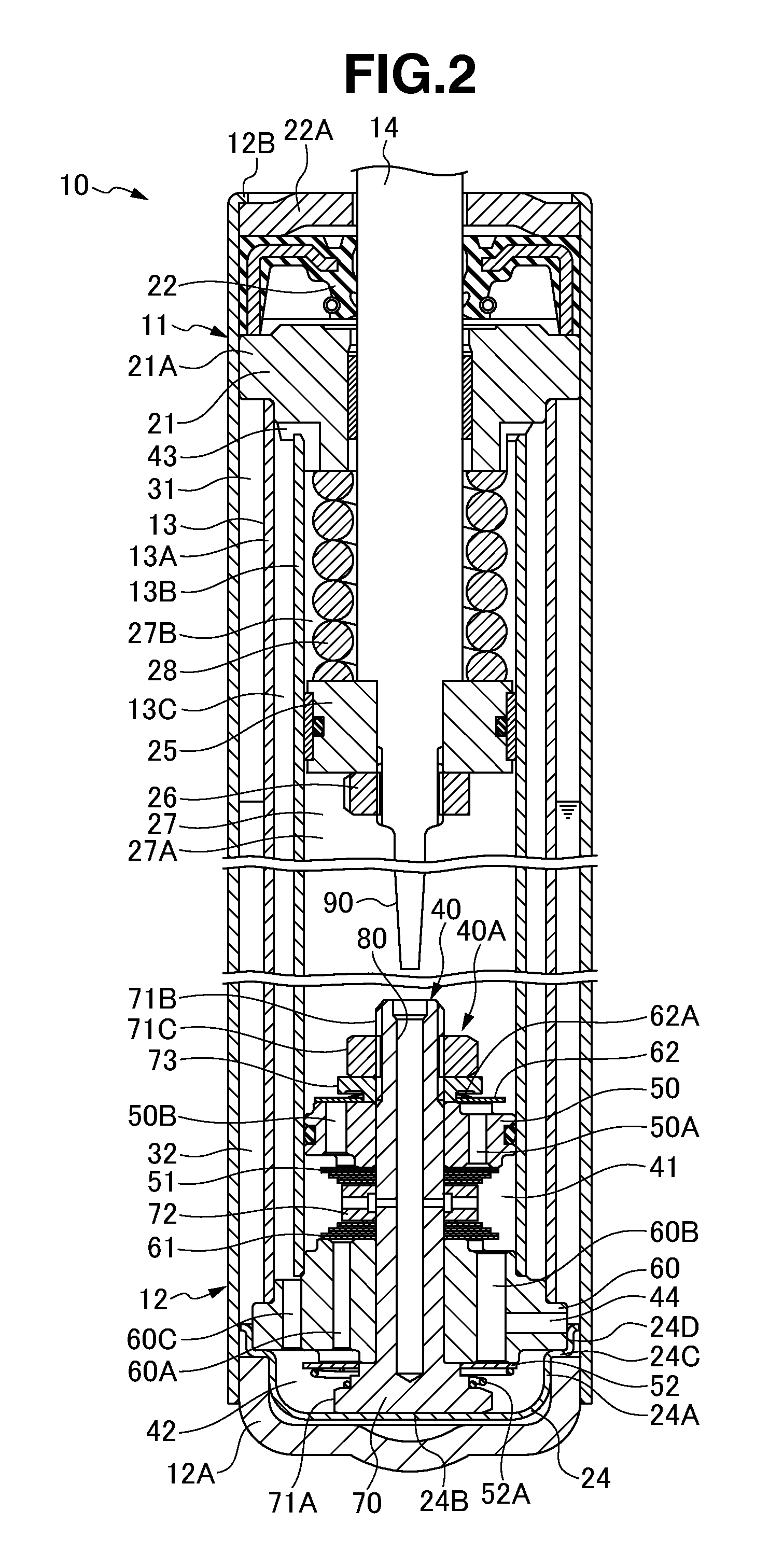
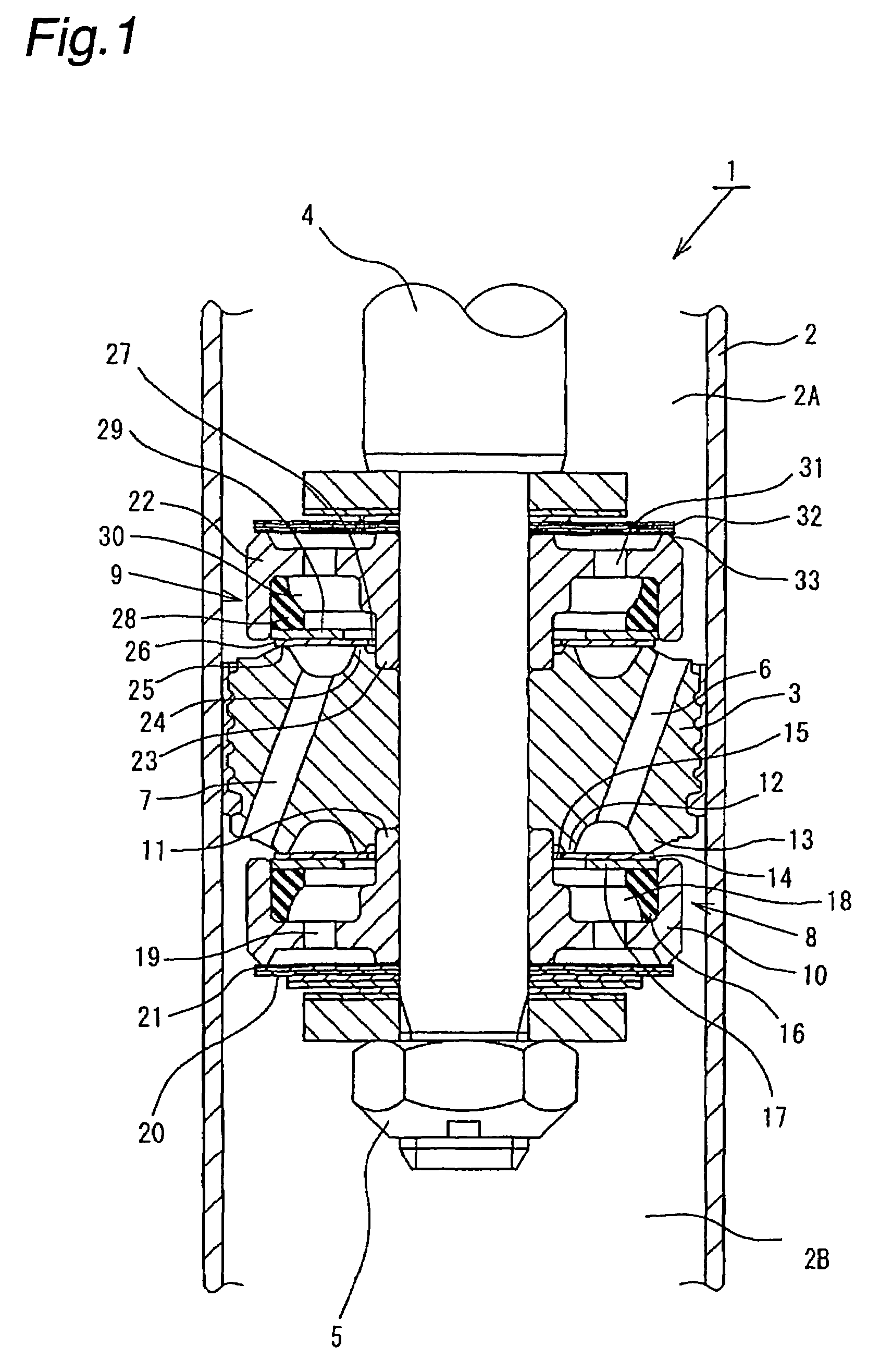
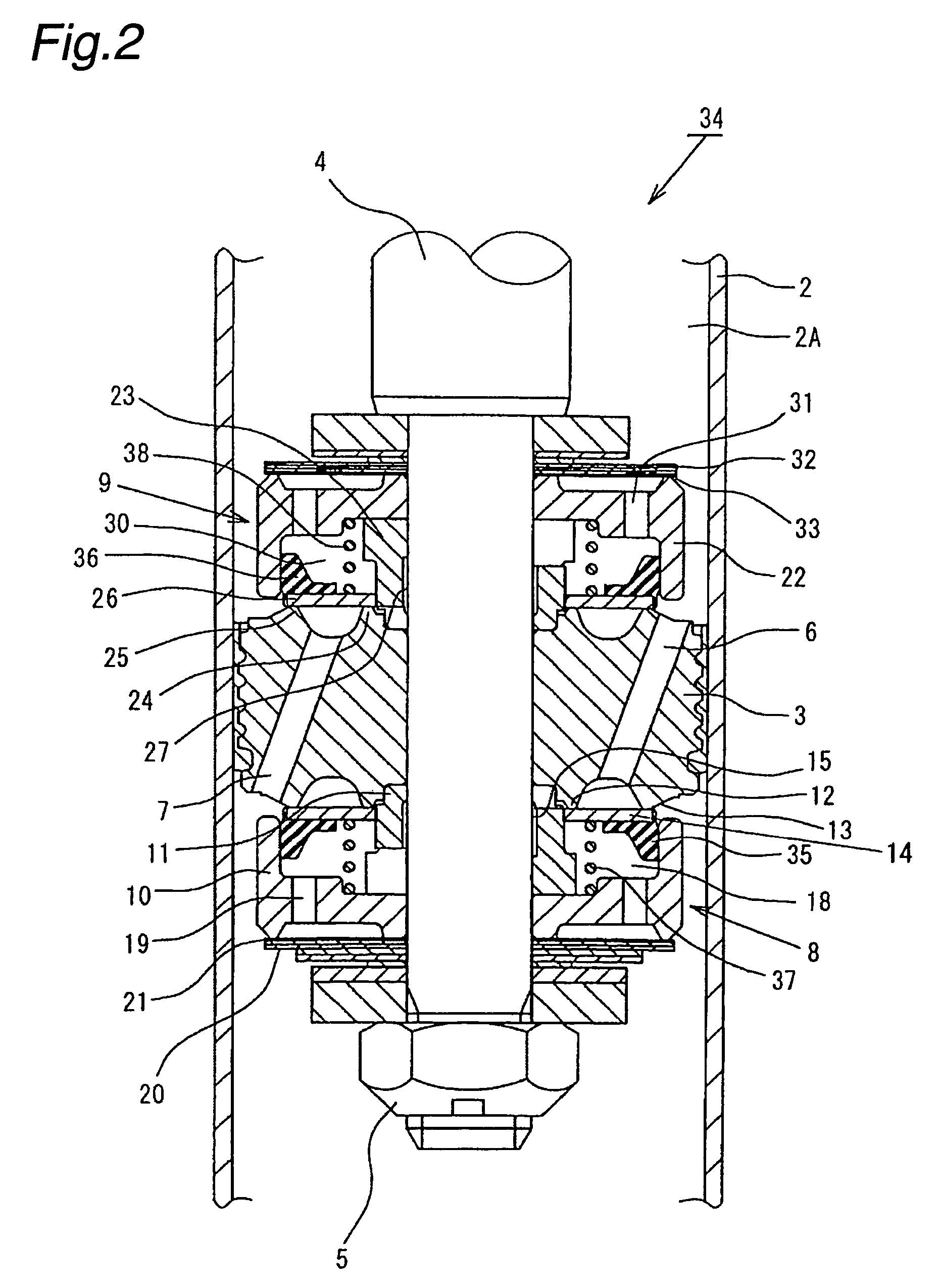
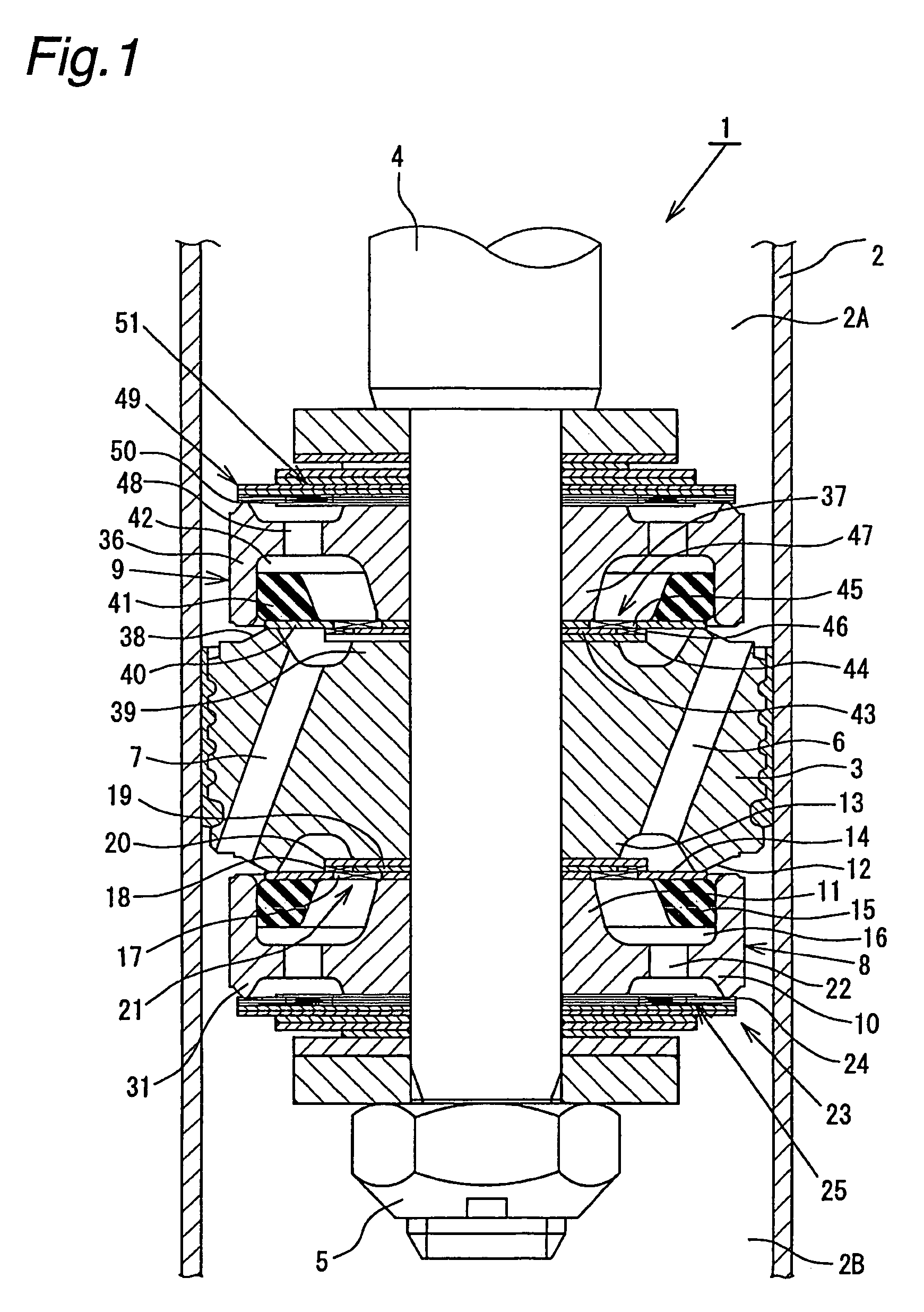
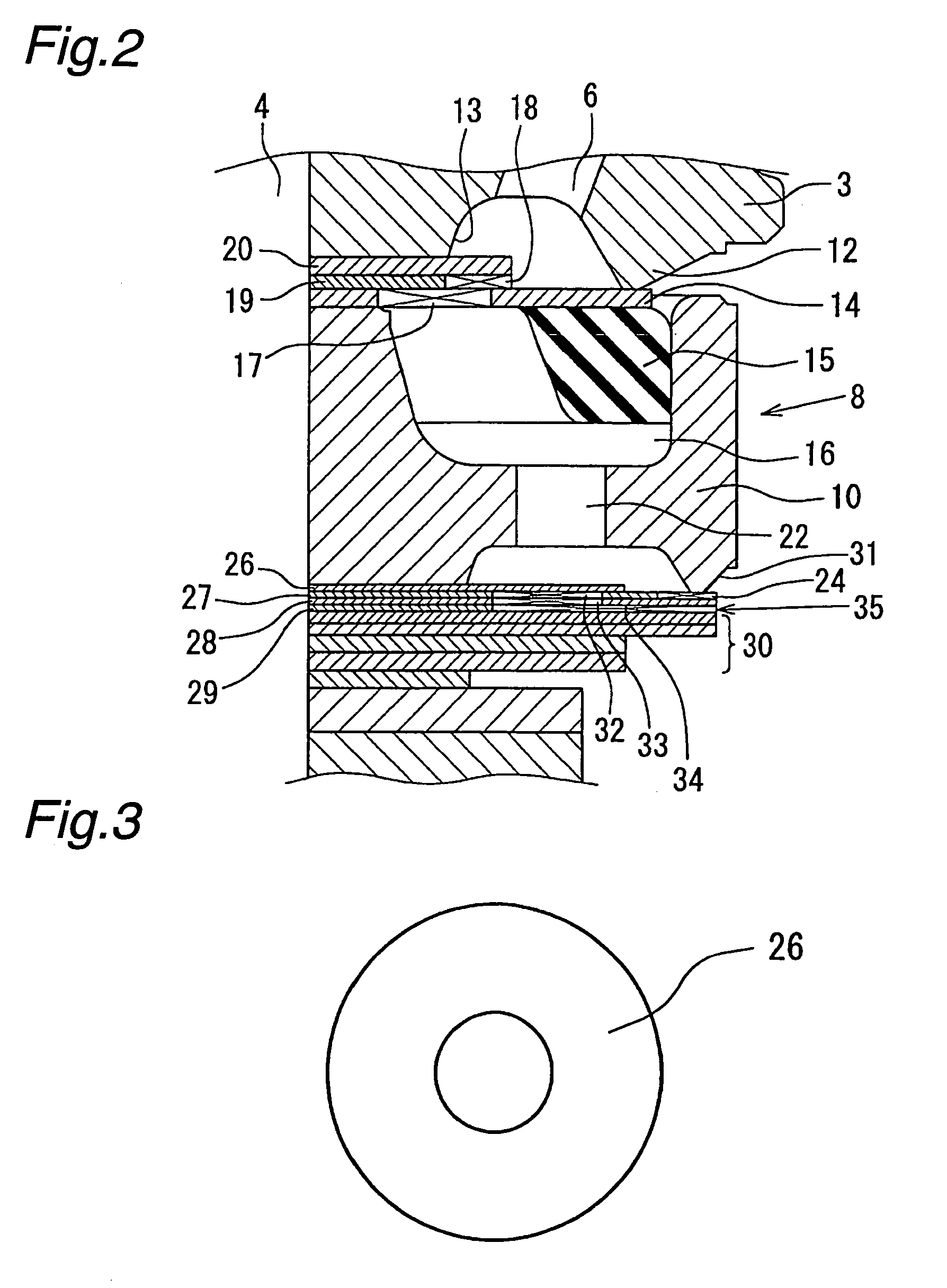
A controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber including a pilot type damping valve having a back-pressure chamber for each of an extension stroke and a compression stroke. A piston connected to a piston rod is fitted into a sealed cylinder in which a hydraulic fluid is contained. During an extension stroke of the piston rod, the hydraulic fluid in an upper cylinder chamber flows to a lower cylinder chamber through an extension-side hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side orifice hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side back-pressure chamber, an axial hydraulic fluid passage, a radial hydraulic fluid passage, a compression-side back-pressure chamber, an extension-side check valve and a compression-side hydraulic fluid passage. During a compression stroke, the hydraulic fluid in the lower cylinder chamber flows to the upper cylinder chamber through the compression-side hydraulic fluid passage, the compression-side orifice passage, the compression-side back-pressure chamber, the radial hydraulic fluid passage, the axial hydraulic fluid passage, the extension-side back-pressure chamber, the compression-side check valve and the extension-side hydraulic passage. The hydraulic fluid passage for an extension stroke and the hydraulic fluid passage for a compression stroke have some elements in common, thus simplifying the structure of the controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Liquid piston internal combustion power system
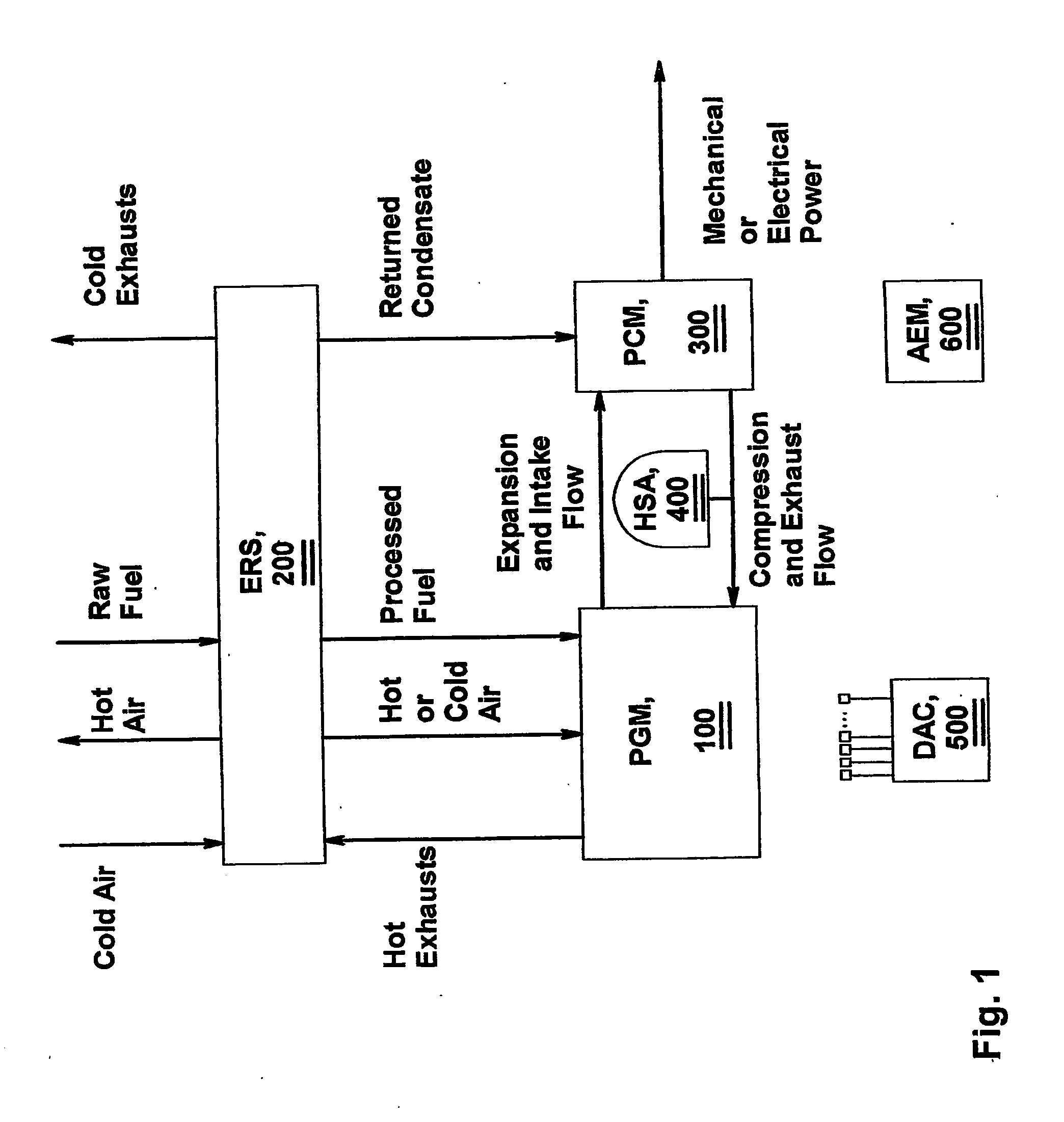
InactiveUS20050166869A1Reduce pollutionRotary slide valveSteam engine plantsLiquid pistonEnergy recovery
Methods, devices and systems for power generation through liquid piston internal combustion engine. The liquid piston internal combustion engine of the invention, utilizes a novel, synergetic combination of internal combustion and steam piston engines within the framework of one and the same system. The engine may comprise or a plurality of cylinders, each having a liquid piston. The ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) system comprises six modules viz PGM (Power Generating Module) (100), ERS (Energy Recovery System) (200), PCM (Power Conversion Module) (300), HAS (Hydraulic Shock Absorbers Module) (400), DAC (Data Acquisition & Control Module) (500) and AEM (Auxiliary Equipment Module) (600).
Owner:LIQUIDPISTON INC
Shock dampening biocompatible valve
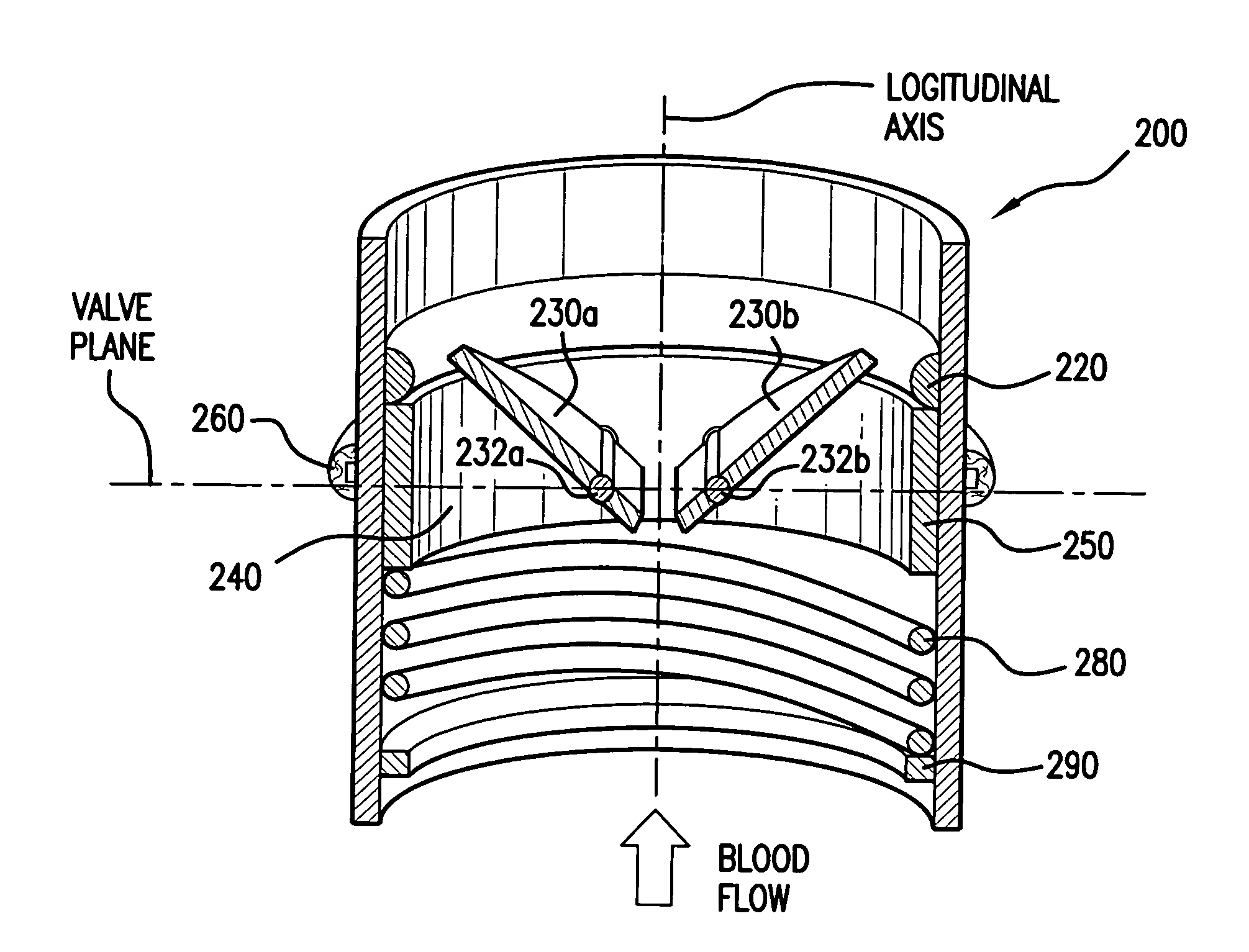
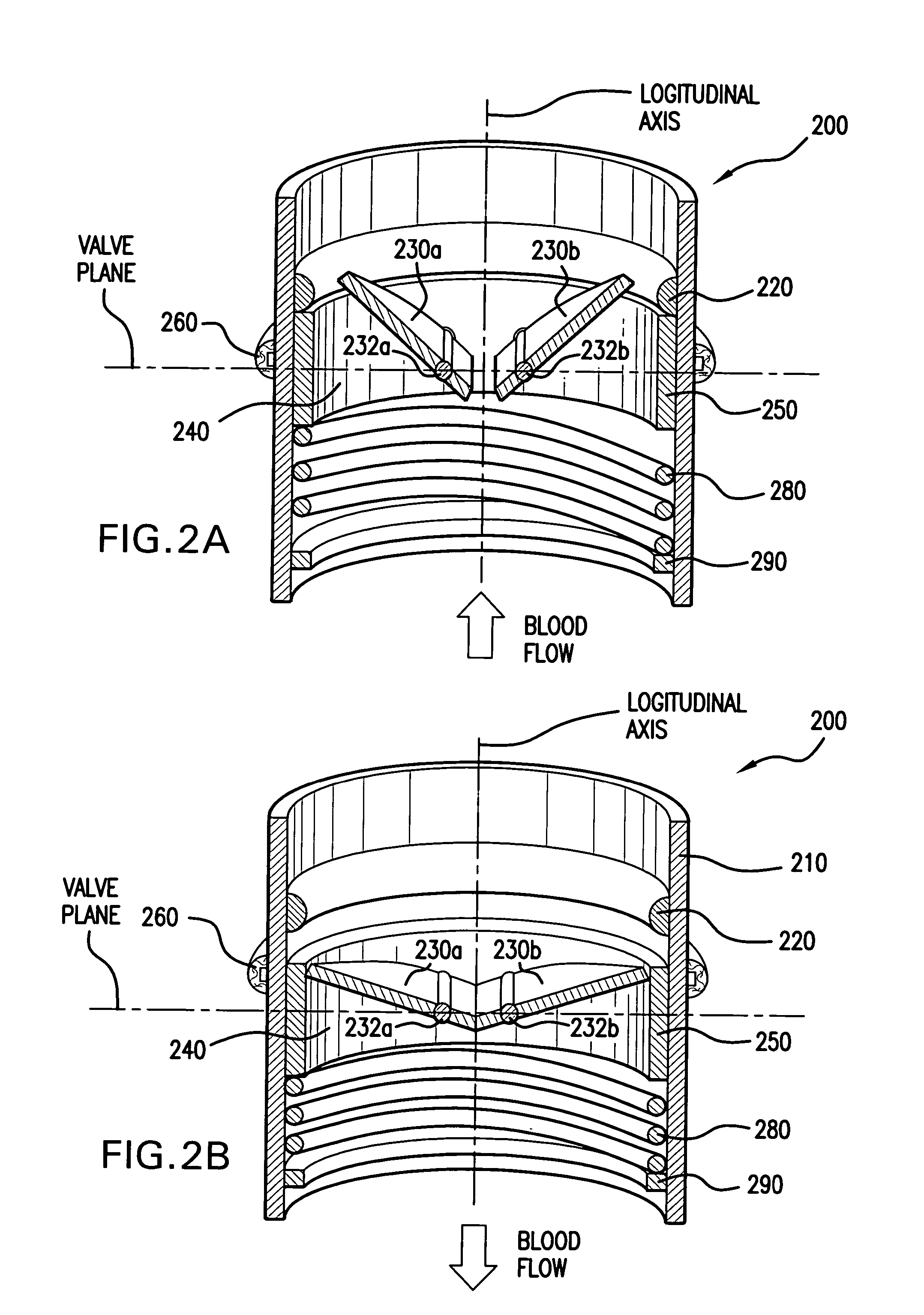
A biocompatible valve (200) includes a valve mechanism (250, 230a, 230b), which is mounted and is longitudinally displaceable within a valve mount (210) affixed to a recipient patient. A valve annulus (250) defines an orifice (240) in which a closing mechanism (230a, 230b) is received. Upon a transition from an open position to a closed position of the closing mechanism (230a, 230b), hydraulic shock is introduced into the fluid passing through the valve. The present invention provides a dampening mechanism (280) to mitigate the shock and to dissipate its energy. Various embodiments allow for high order frequency response through relationships between dampening mechanism components.
Owner:SIERACKI JEFFREY M
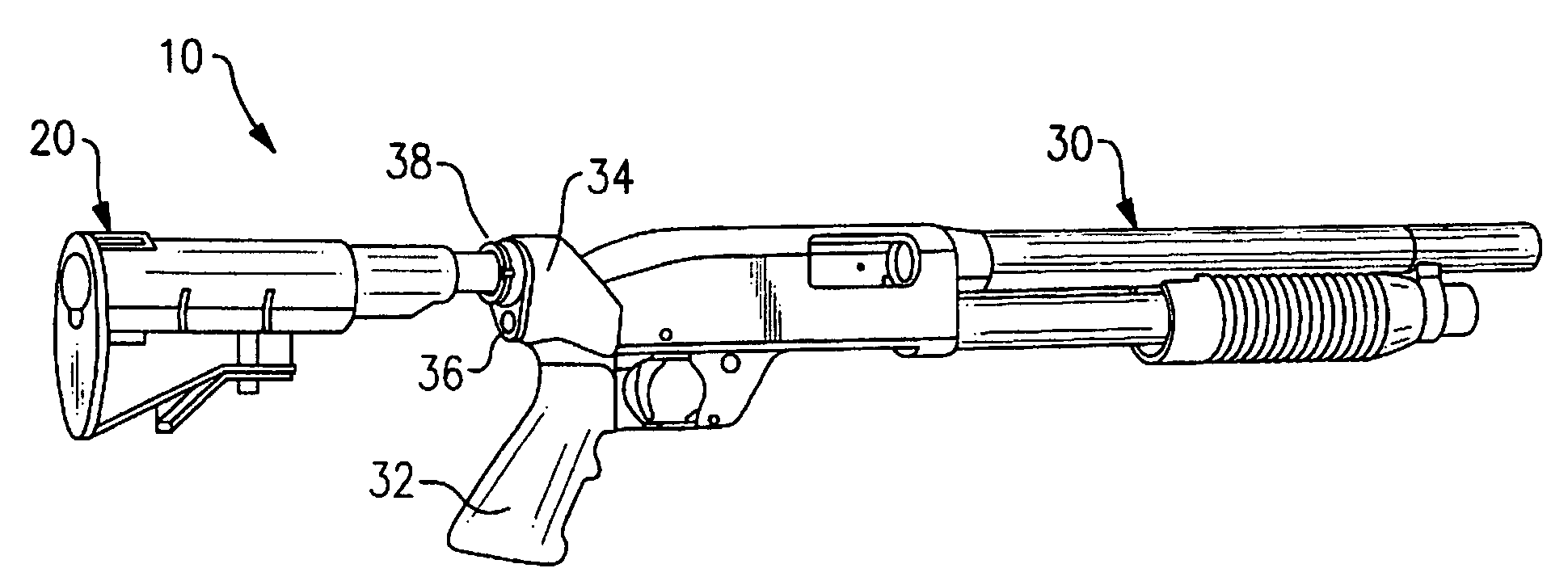
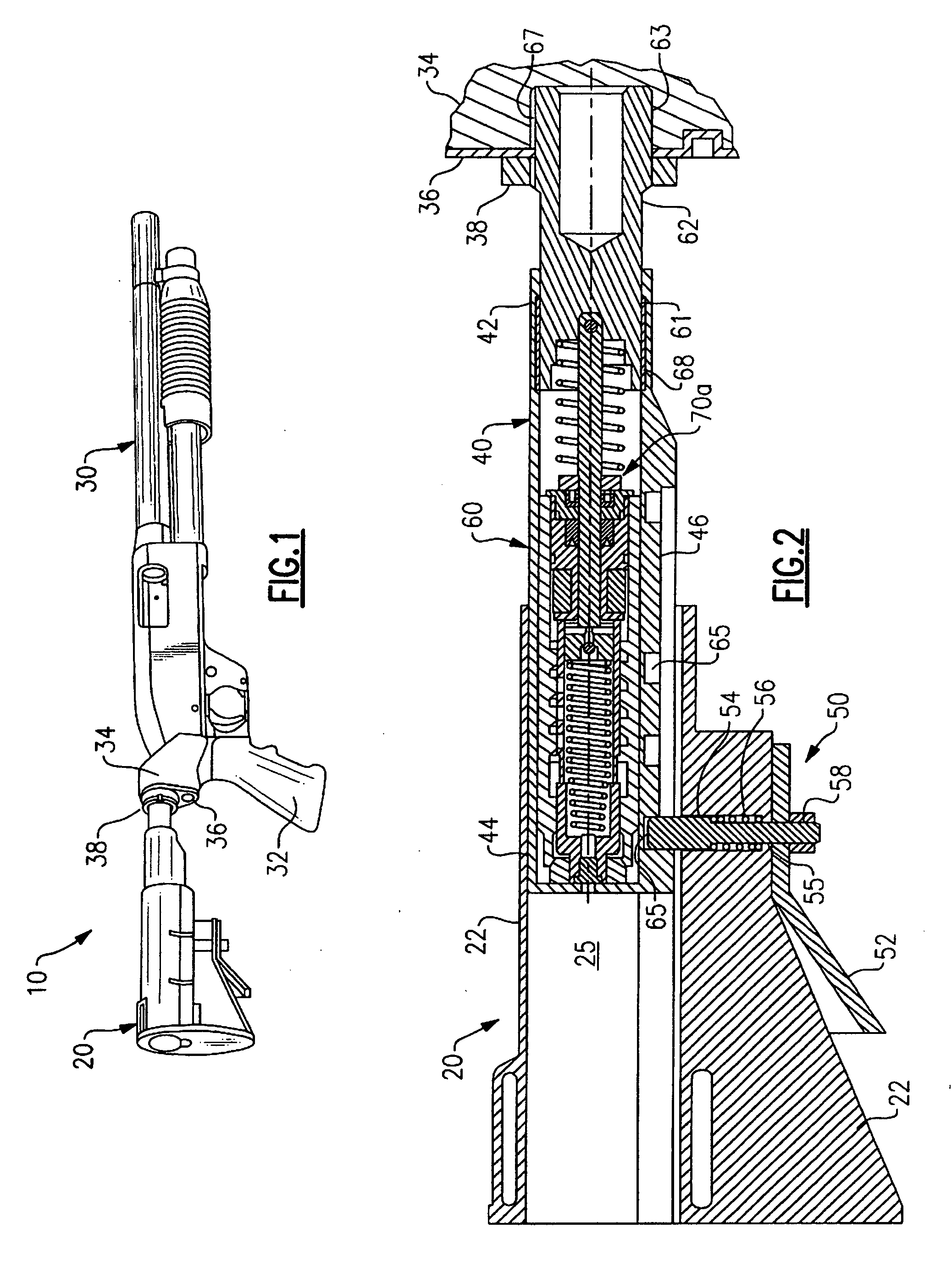
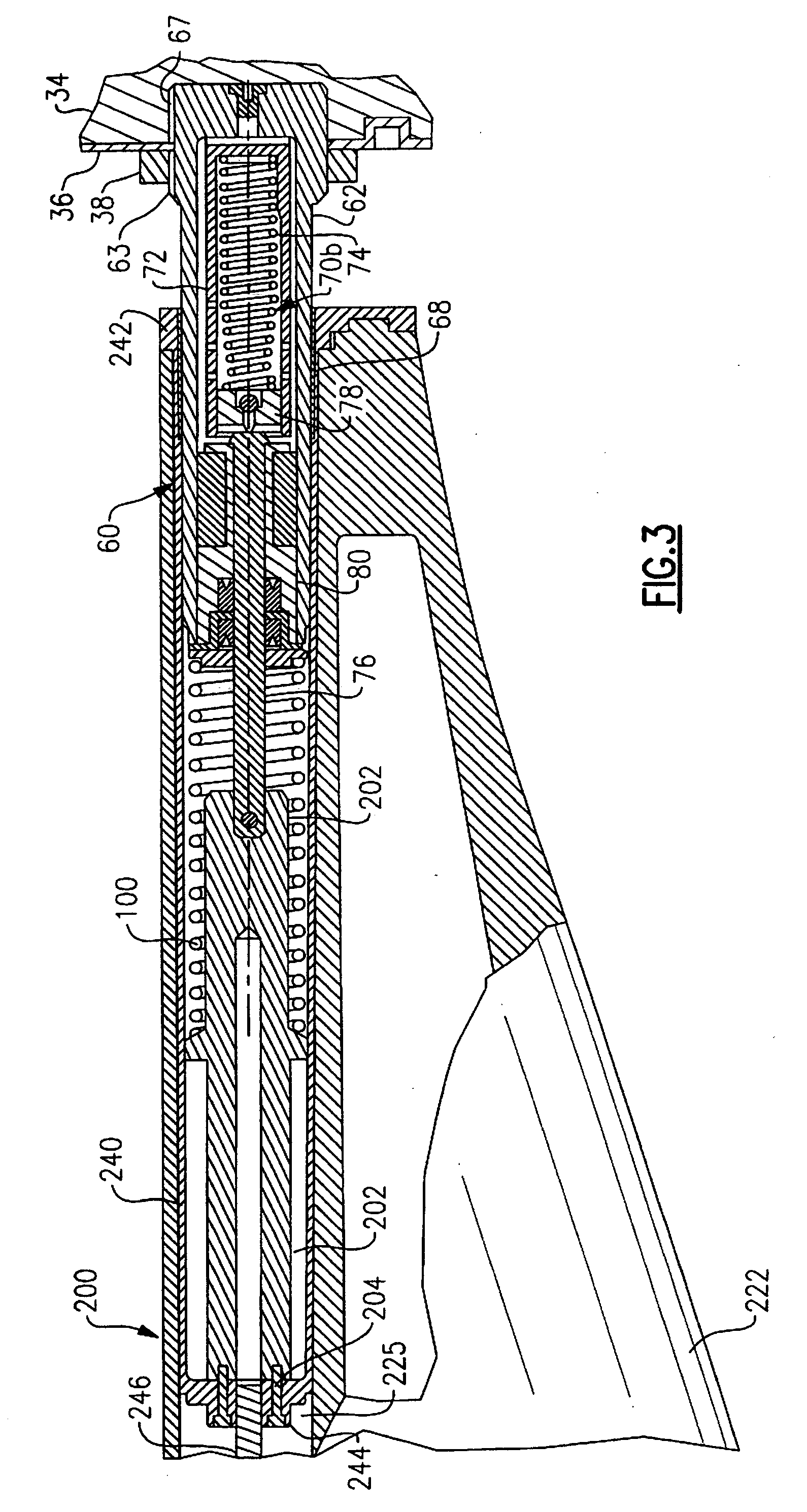
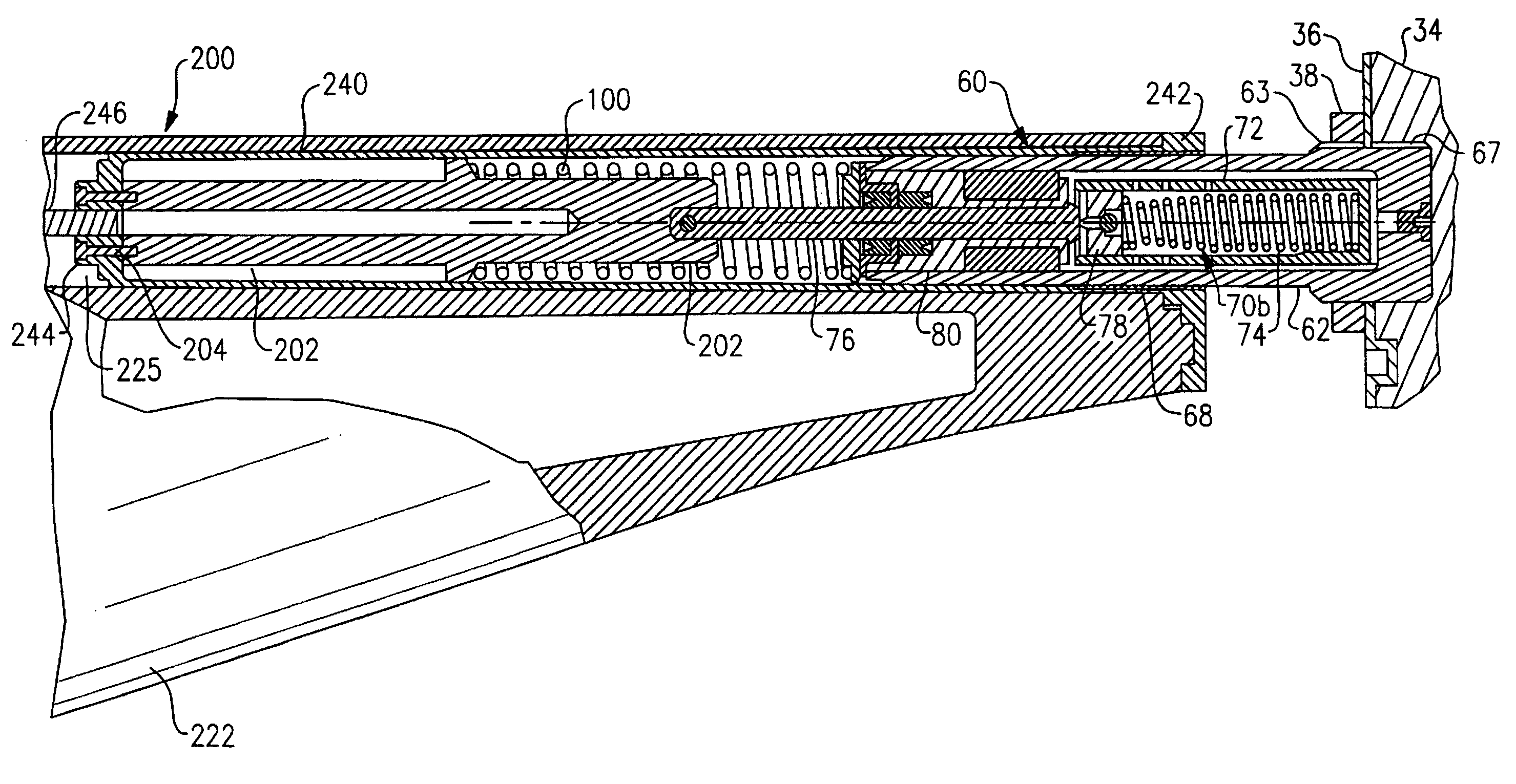
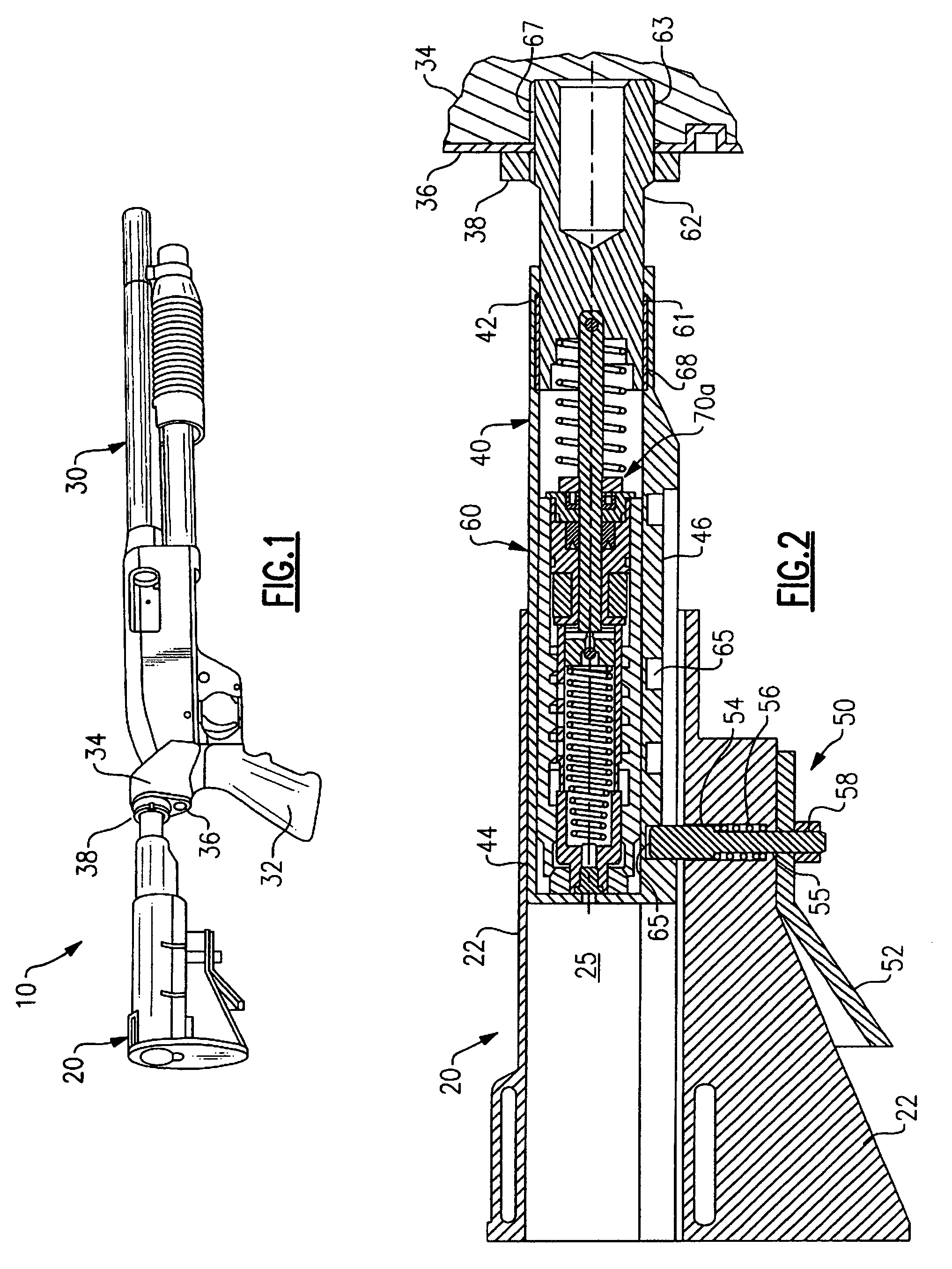
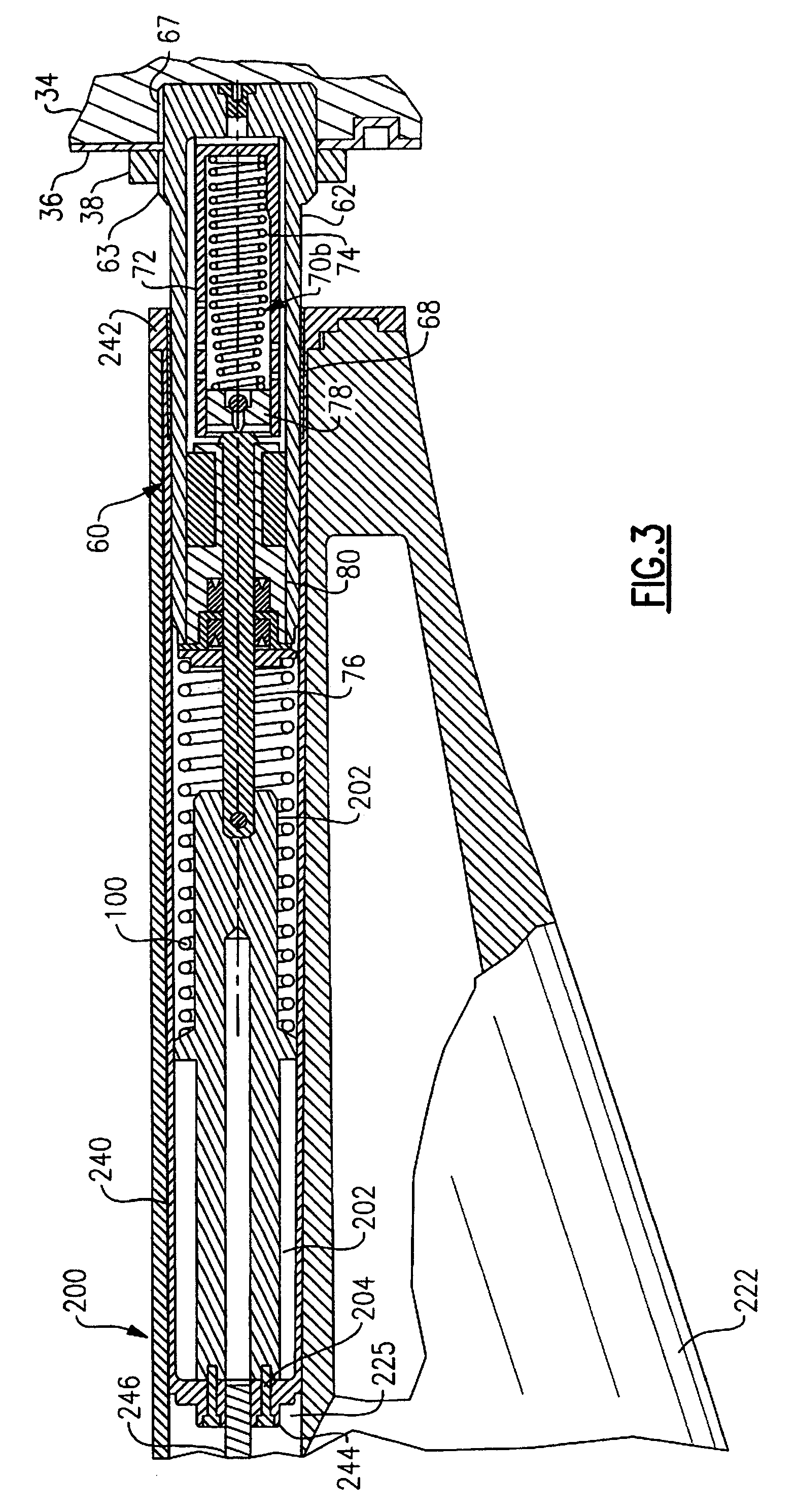
Hydraulic recoil buffer assembly
A hydraulic recoil buffer assembly for a firearm having a receiver and a fixed or collapsible stock assembly including an end cylinder adapted to be secured to the pistol grip or receiver of the firearm and slidably translatable with respect to the extension tube, and a hydraulic shock absorption assembly operative to produce a hydraulic resistance to a rearward movement of the end cylinder during recoil of the firearm. The hydraulic shock absorption assembly has an orifice restricted fluid flow passage and a piston head that compresses a return spring as the end cylinder moves rearward against a recoil coil spring. The recoil buffer assembly stores a portion of the recoil energy through compression of the recoil spring and the return spring, and dissipates a portion of the recoil energy through the resistance provided by fluid flow through the orifice restricted flow passage.
Owner:ENIDINE
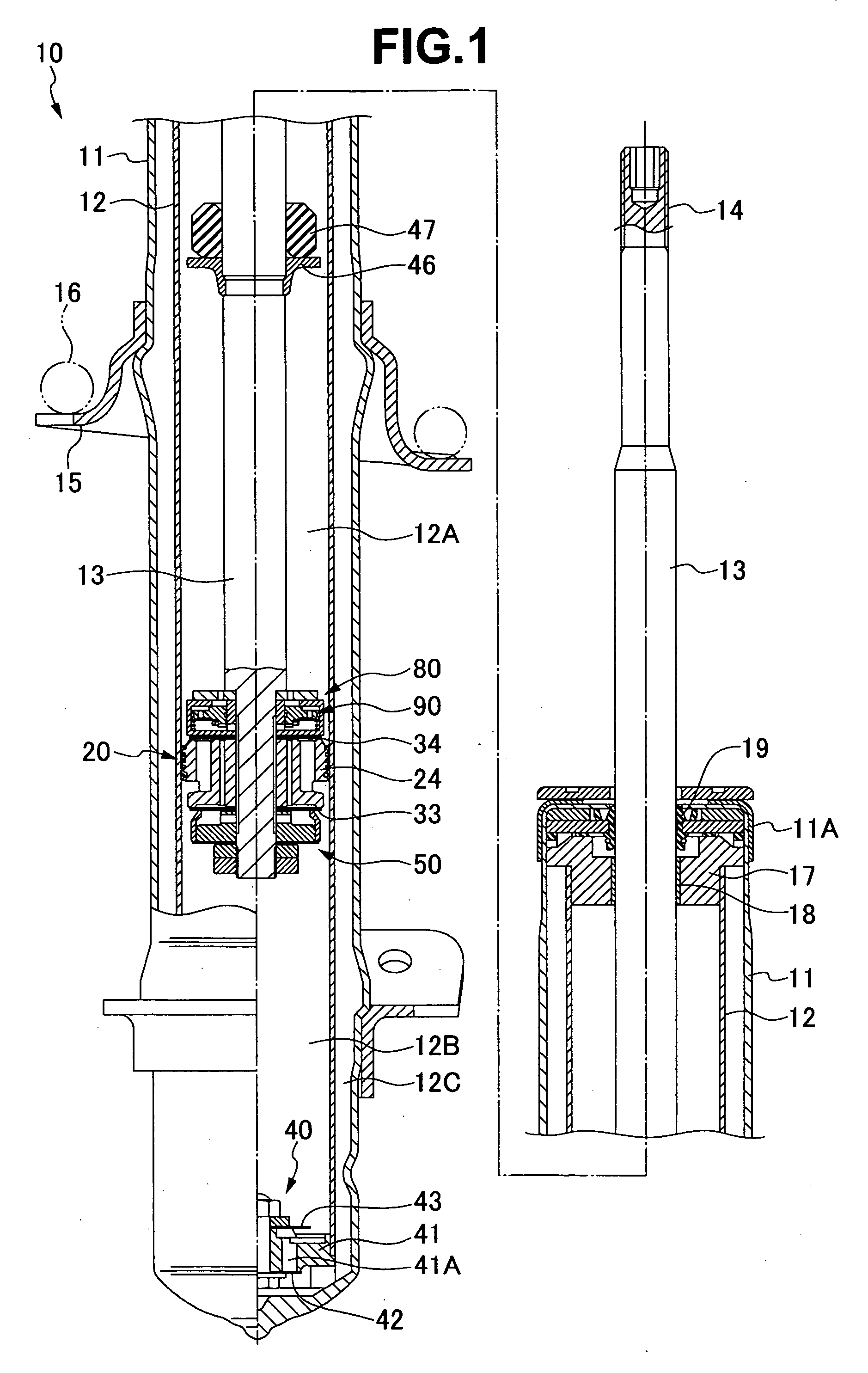
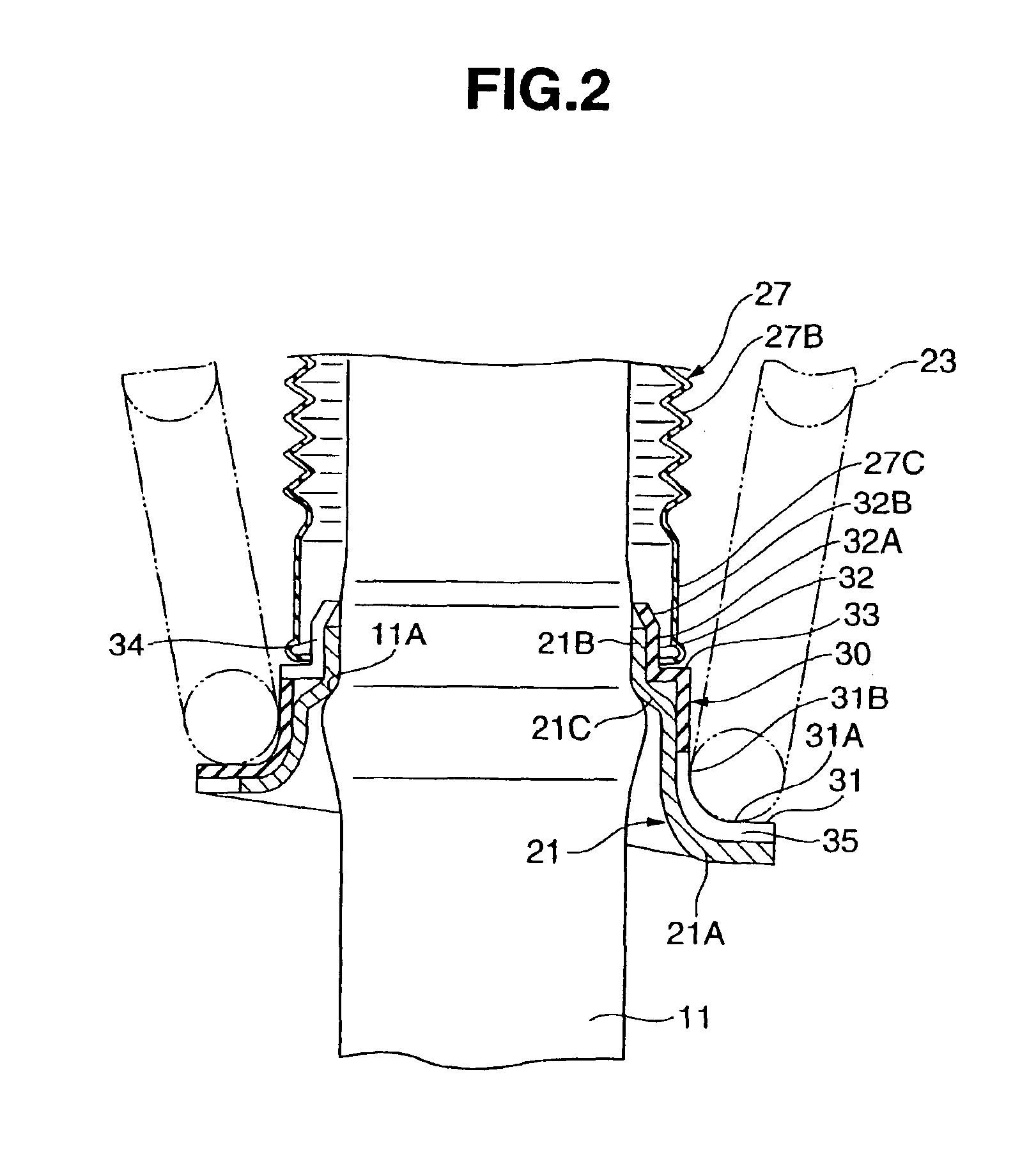
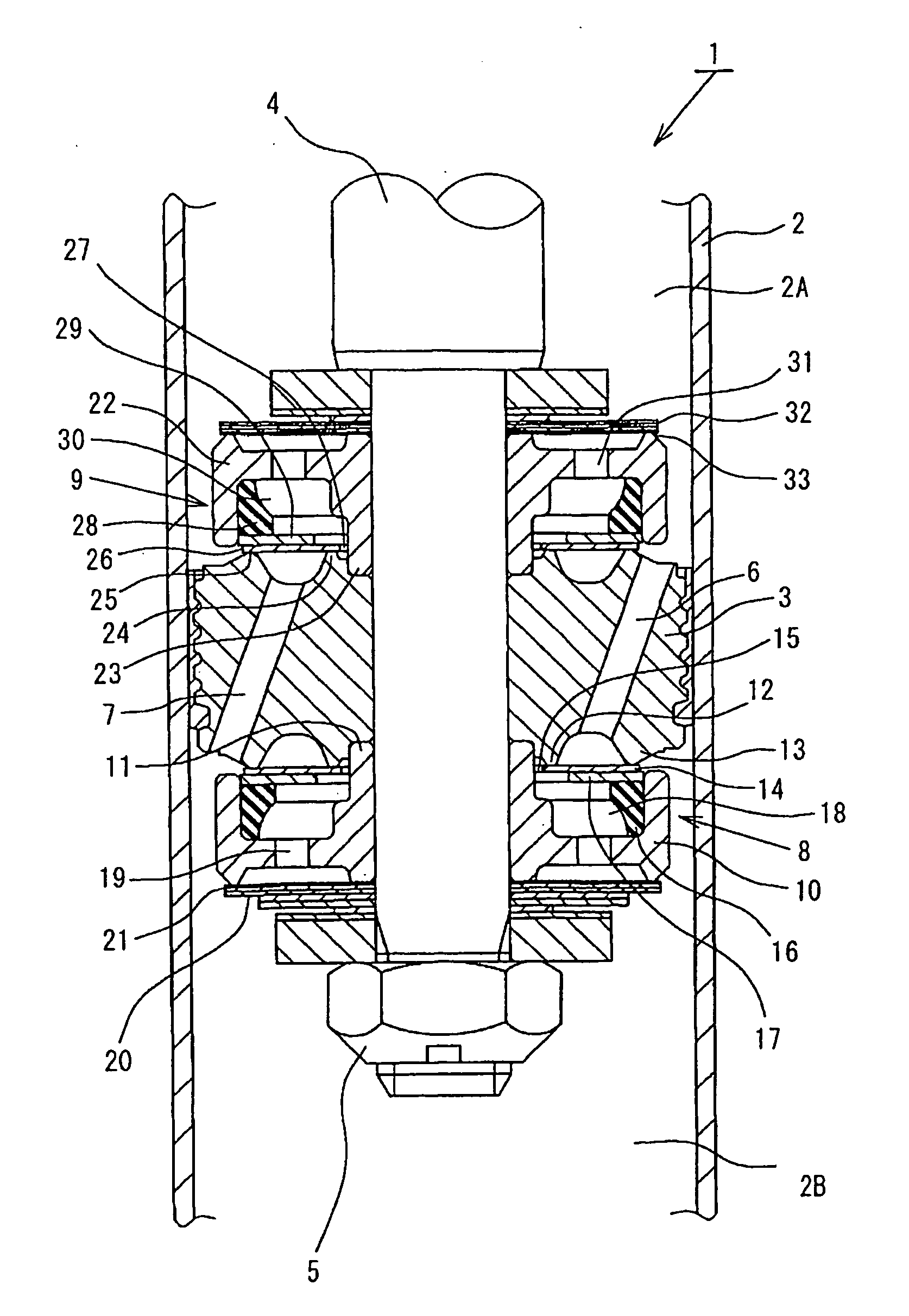
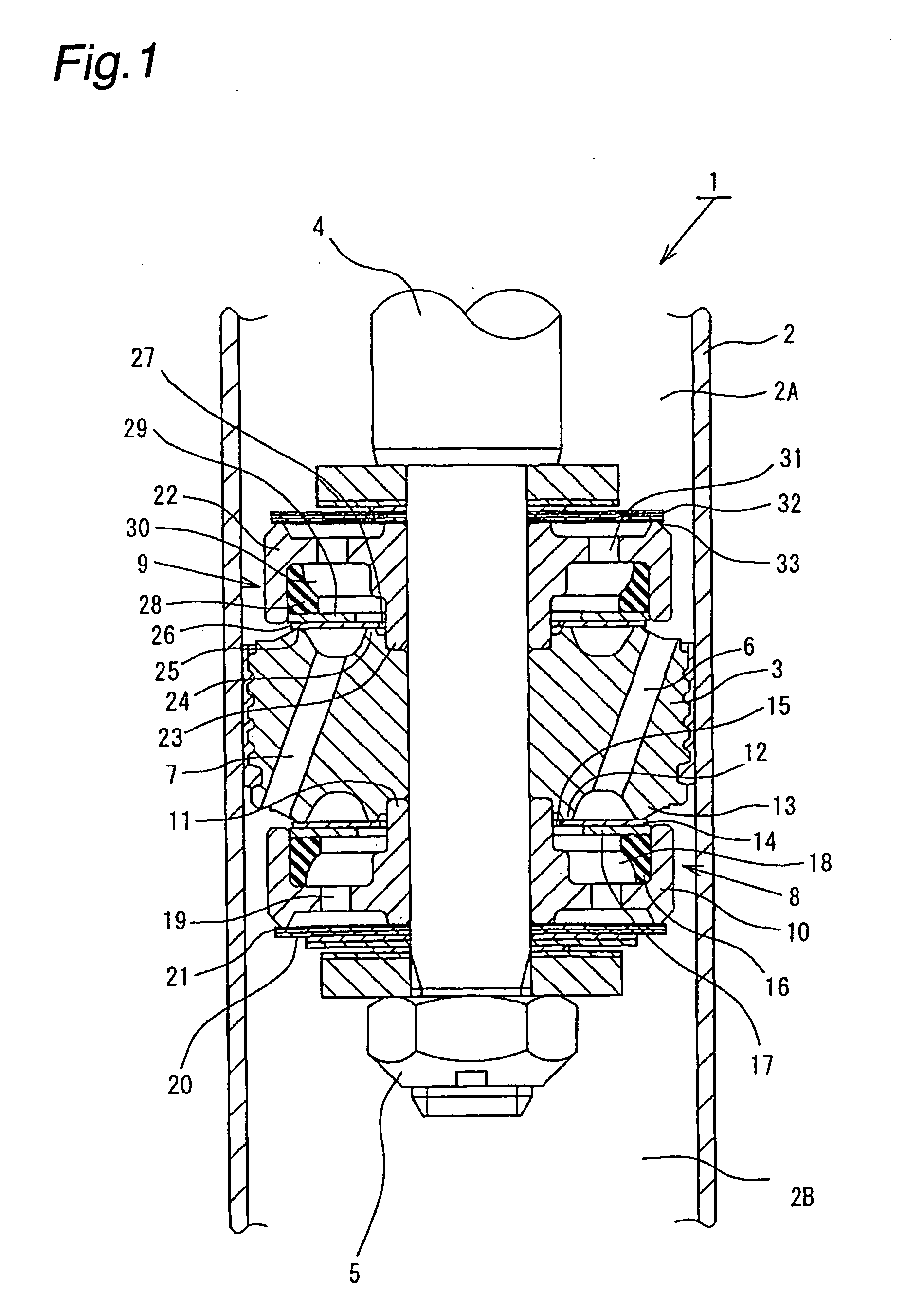
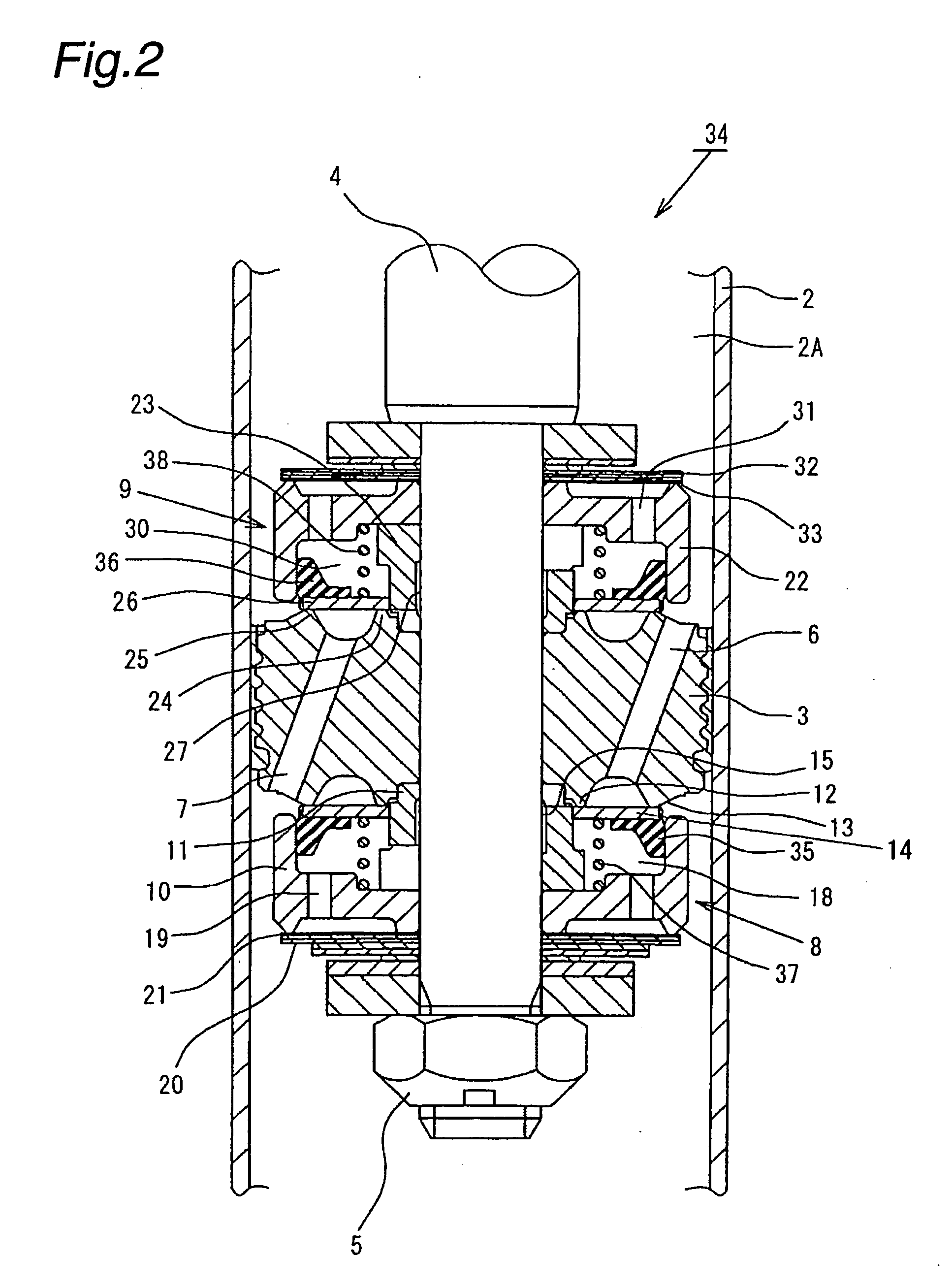
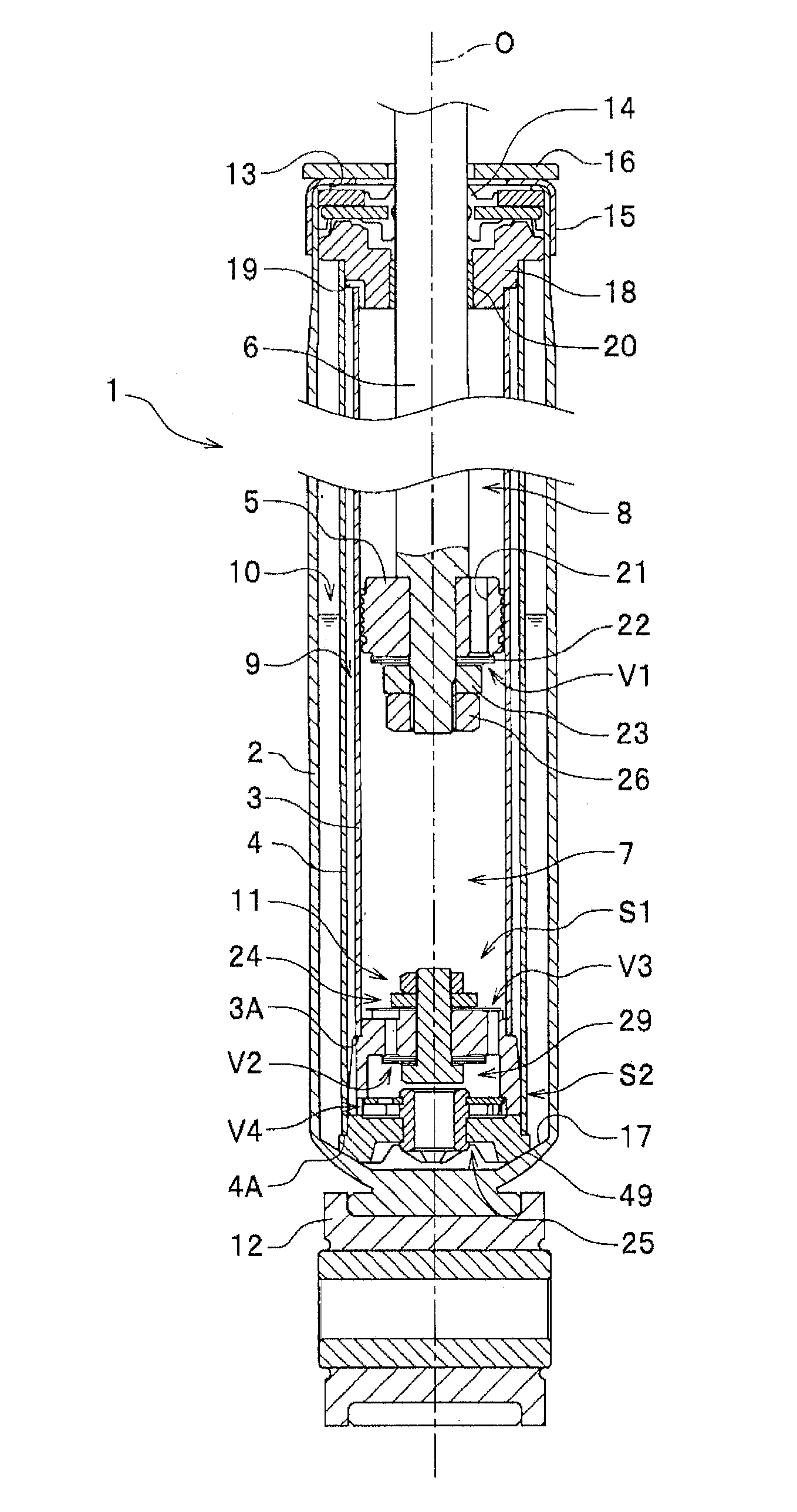
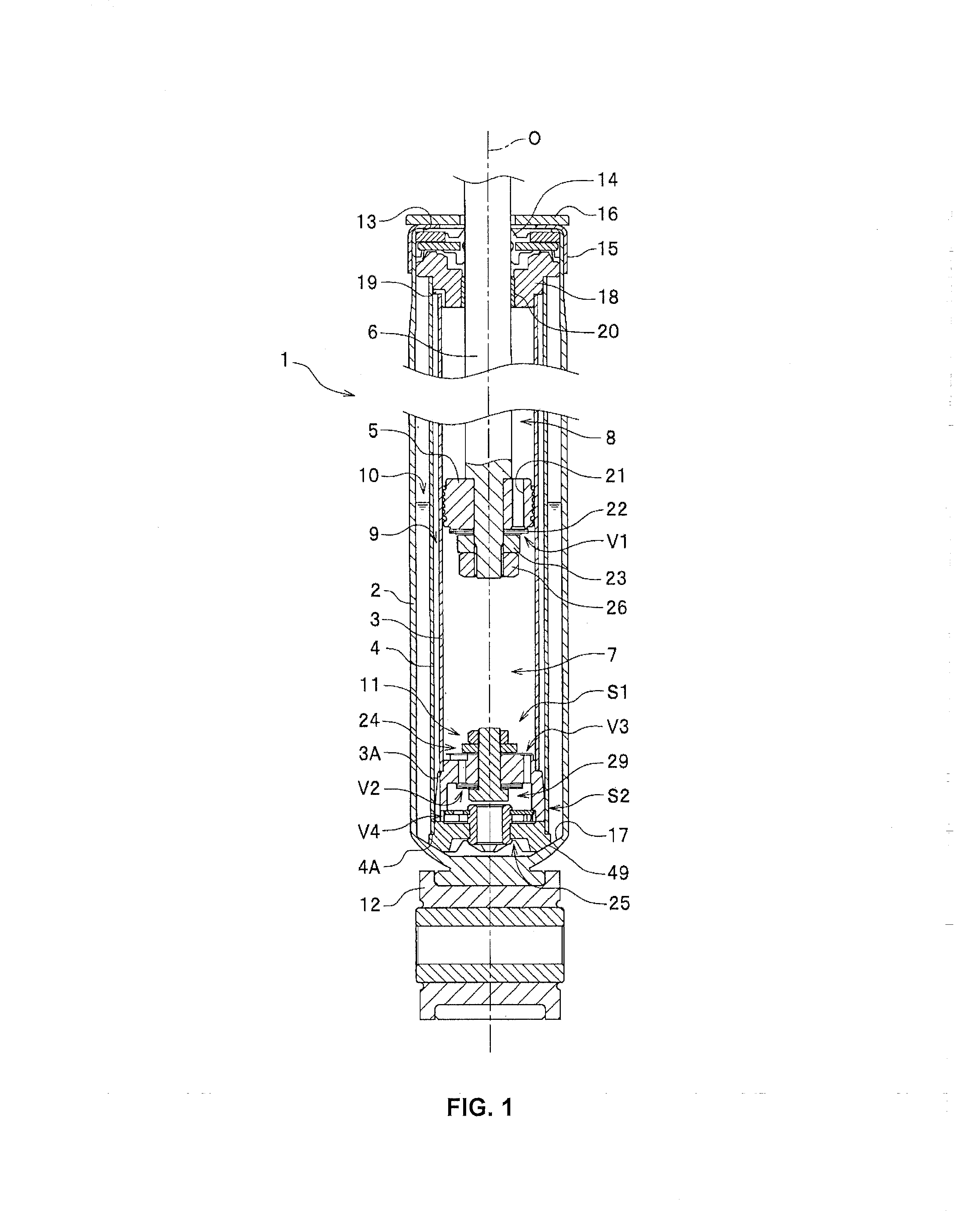
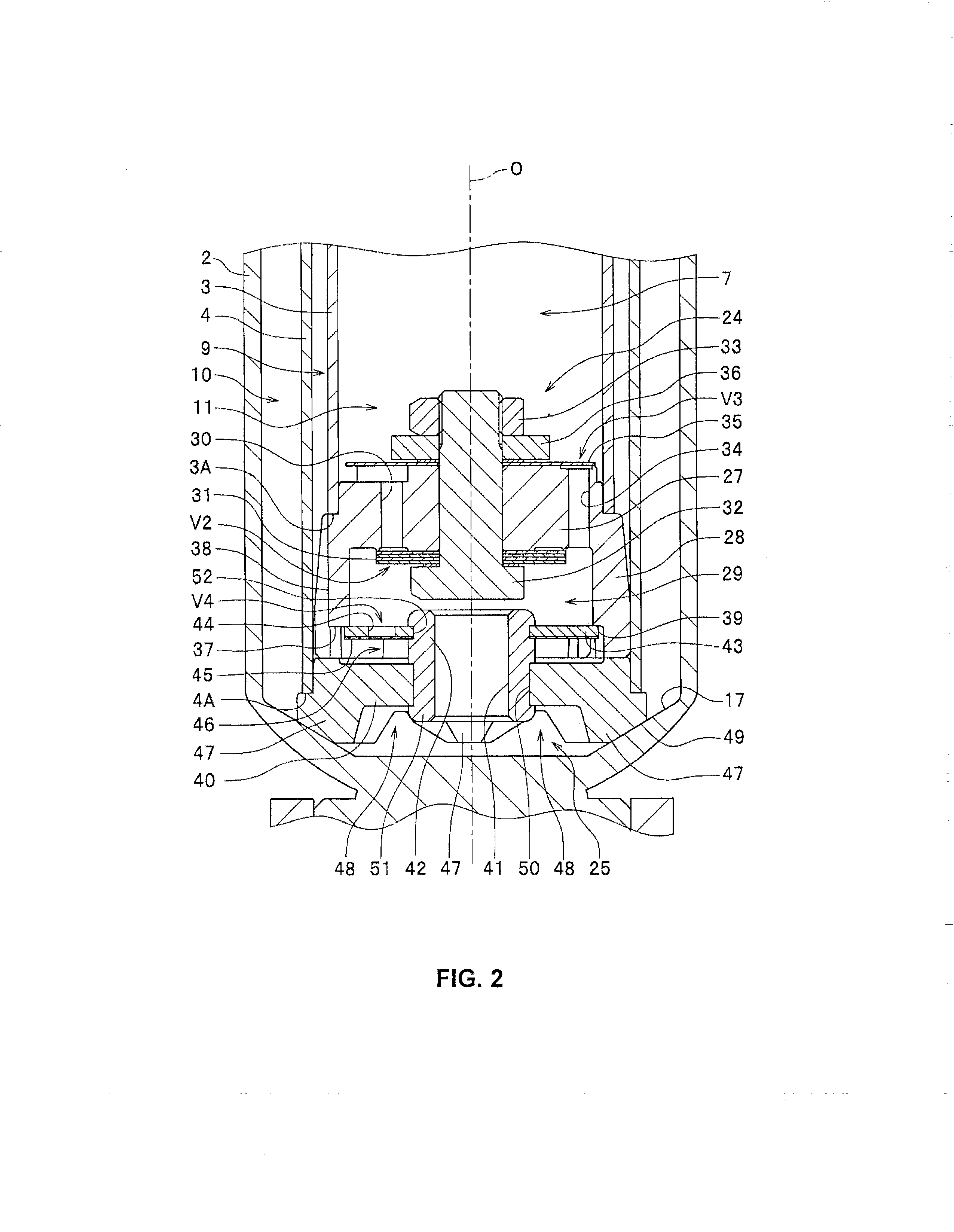
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS20080185244A1Improve space efficiencyReduce in quantitySpringsLiquid based dampersThermal deformationFuel tank
A piston connected with a piston rod is fitted in a cylinder having a hydraulic fluid sealed therein. A damping force is generated through extension and compression disk valves and an orifice. Vehicle height adjustment is performed with a self-leveling mechanism by transferring the hydraulic fluid between the cylinder and a hydraulic fluid tank. A bladder of the hydraulic fluid tank is clamped between an outer flange portion of a partition member and a casing. Because the hydraulic fluid tank is formed without welding, it is possible to avoid contamination of the hydraulic fluid by welding sputter and thermal deformation. Provision of an O-ring on the outer flange portion can reduce the pressure acting from a reservoir on the clamped portion of the bladder and hence prevent dislodging of the bladder.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
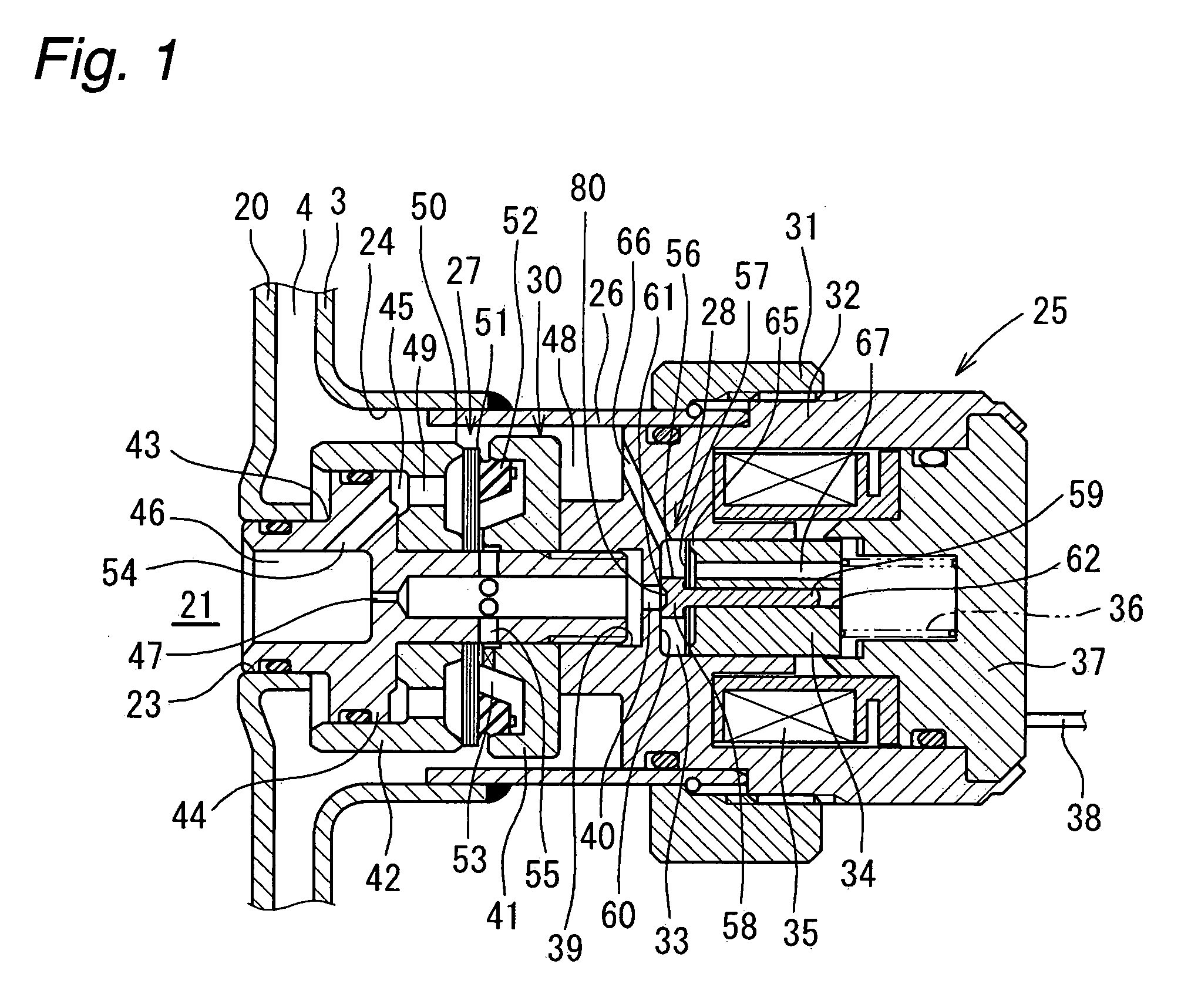
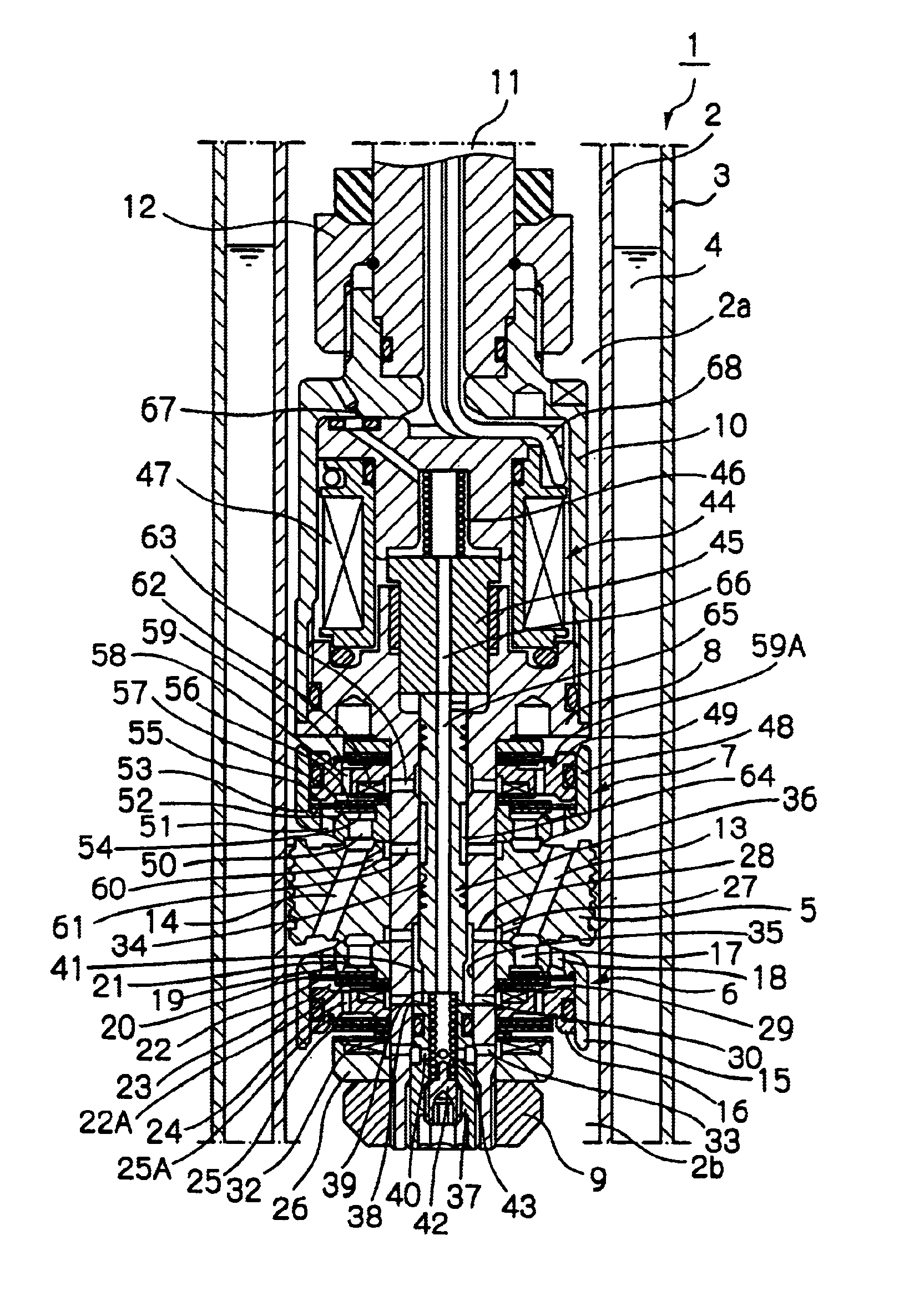
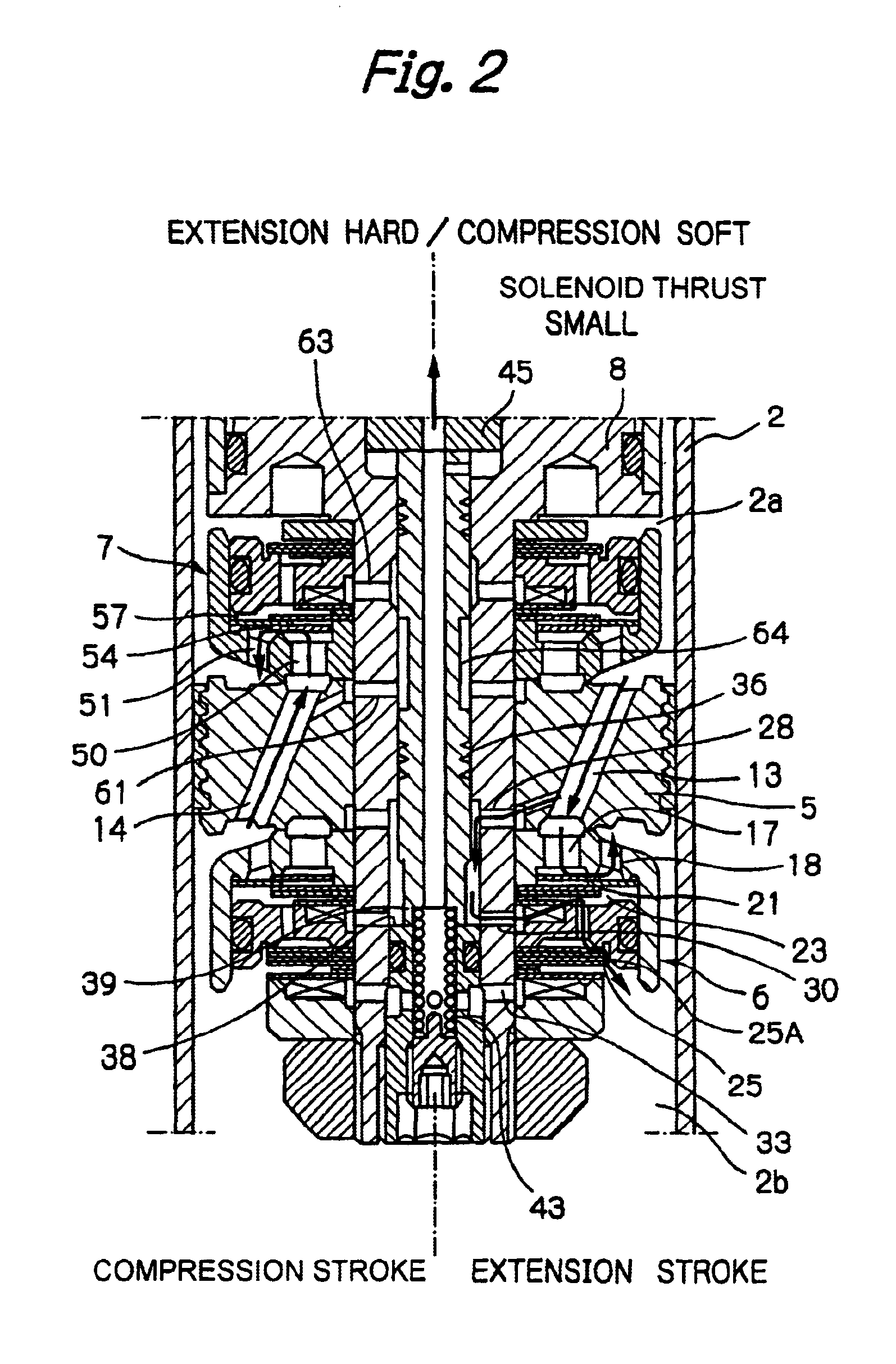
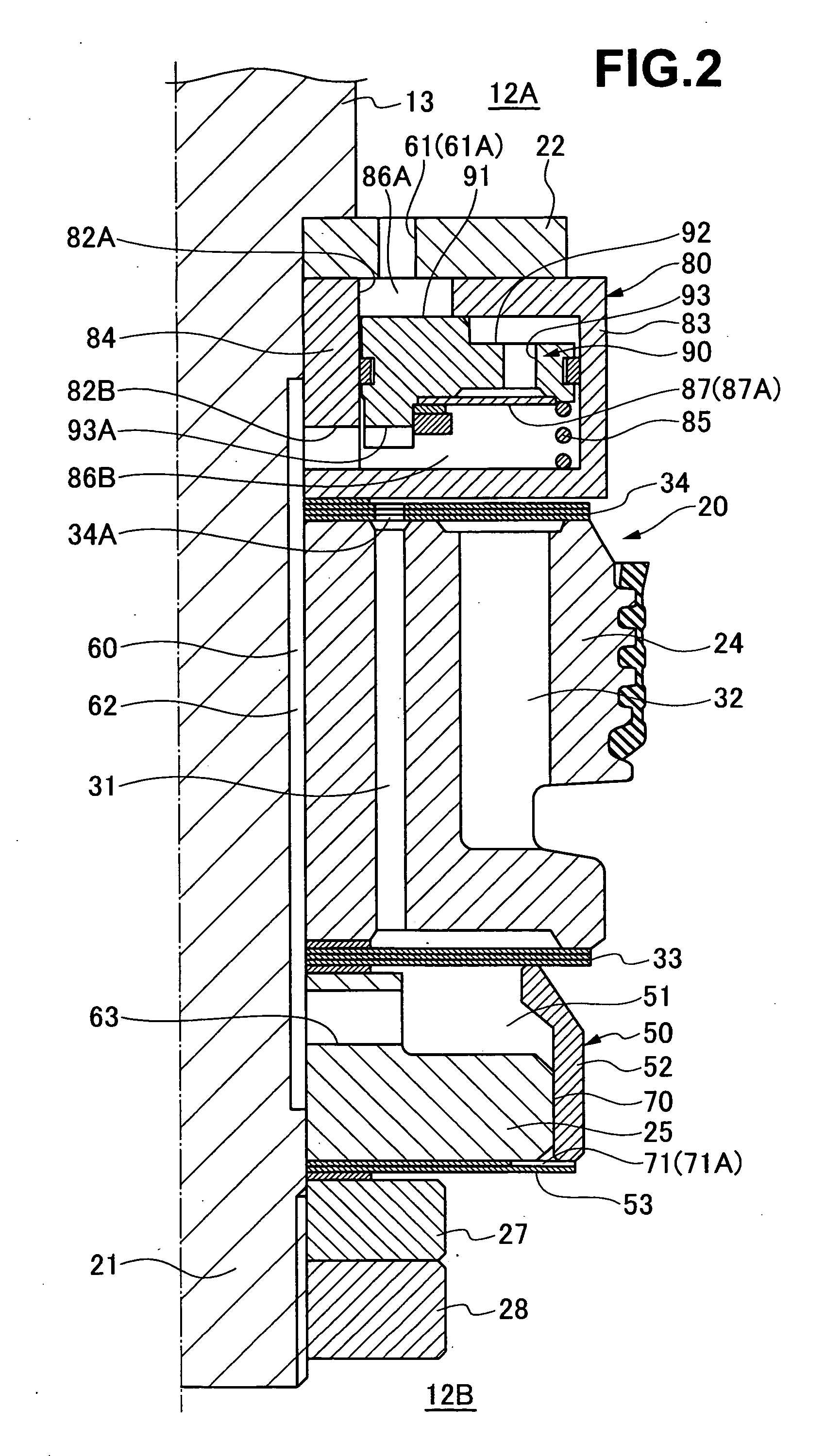
Damping force adjustable shock absorber
ActiveUS20090242339A1Avoid response delaysImprove responsivenessSpringsShock absorbersInternal pressureSelf excited
An object of the present invention is to provide a damping force adjustable hydraulic shock absorber, in which response delay of a pressure control valve and self-excited vibration of a valve body can be prevented. A damping force is generated by controlling an oil flow between an annular oil passage 21 and a reservoir 4 generated by a sliding movement of a piston in a cylinder with use of a back-pressure type main valve 27 and a pressure control valve 28. The damping force is directly generated by the pressure control valve 28, and a valve-opening pressure of the main valve 27 is adjusted by adjusting an inner pressure of a back-pressure chamber 53. In the pressure control valve 28, a valve spring 57 is disposed between a valve body 56 and a plunger 34. A mass of the valve body 56 is sufficiently less than that of a plunger 34, and a spring stiffness of the valve spring 57 is higher than that of a plunger spring 36. As a result, it is possible to improve the responsiveness of the valve body 56 to prevent response delay in a damping force control. In addition, since the natural frequency of the valve body 56 is high, it is possible to prevent self-excited vibration of the valve body 56.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
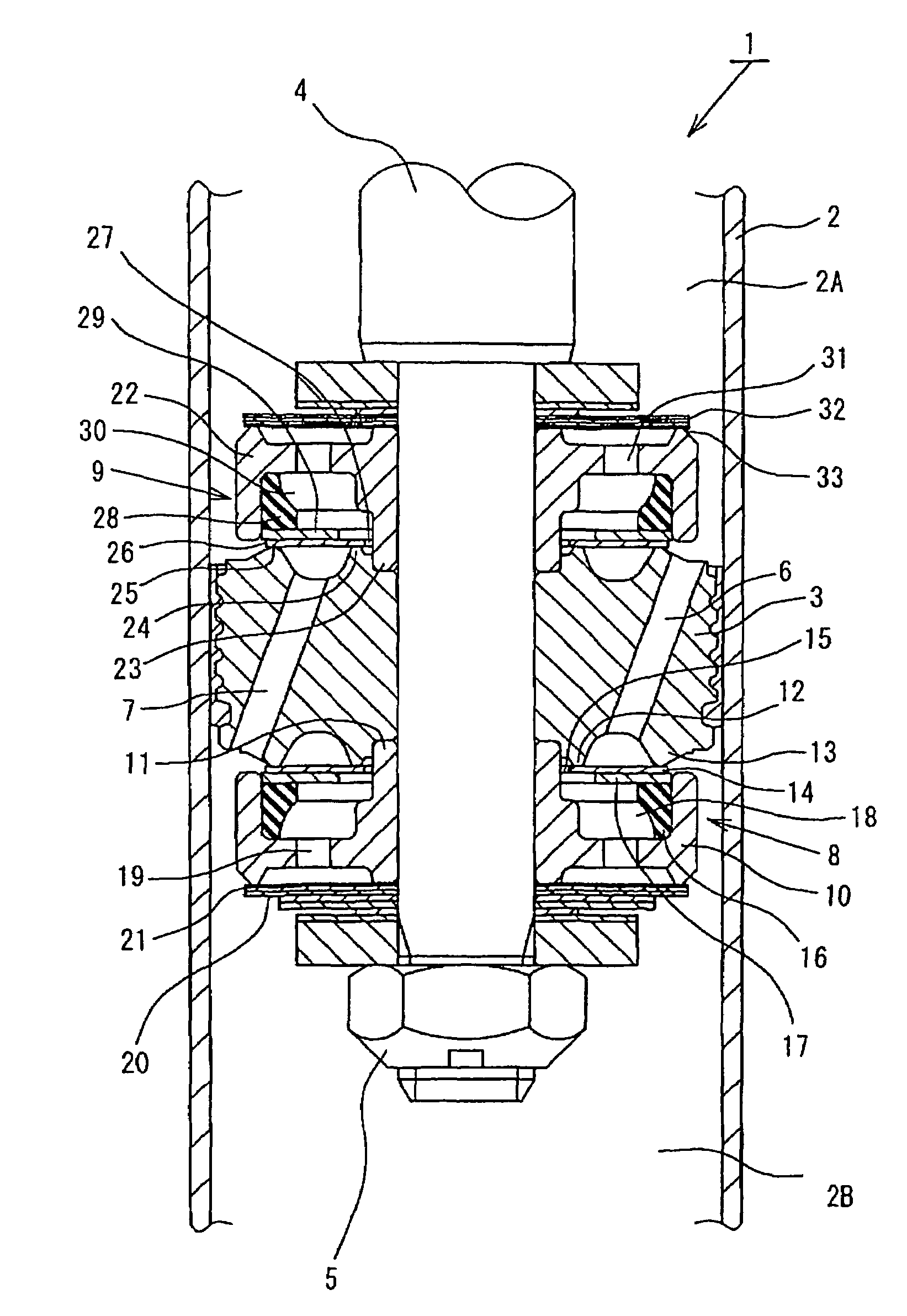
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS8991571B2Increase damping forceIncrease changeSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS8556048B2Reduce in quantityAvoid pollutionSpringsLiquid based dampersThermal deformationFuel tank
A piston connected with a piston rod is fitted in a cylinder having a hydraulic fluid sealed therein. A damping force is generated through extension and compression disk valves and an orifice. Vehicle height adjustment is performed with a self-leveling mechanism by transferring the hydraulic fluid between the cylinder and a hydraulic fluid tank. A bladder of the hydraulic fluid tank is clamped between an outer flange portion of a partition member and a casing. Because the hydraulic fluid tank is formed without welding, it is possible to avoid contamination of the hydraulic fluid by welding sputter and thermal deformation. Provision of an O-ring on the outer flange portion can reduce the pressure acting from a reservoir on the clamped portion of the bladder and hence prevent dislodging of the bladder.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing fluid cavitation
A method and apparatus for producing fluid cavitation is provided. For a given channel cross-section of a pressure line, the flow is accelerated so as to reach a speed at which Re>Recr, where Re is the Reynolds number and Recr is the critical Reynolds number; the flow is then interrupted for a time less than half of the phase of the hydraulic shock. The device for cavitation of fluid flow is mounted in the channel of a pressure line and includes a cavitator which has the form of a working body placed in the casing and can move radially inside the line and, to a limited extent, along the axis of the line. The maximum cross-section surface of the working body in a plane perpendicular co the axis of the line is more than 0.8 of the passage of the line but not equal to it.
Owner:BIP TECH
Orthotic brace
Owner:JRI SHOCKS LLC
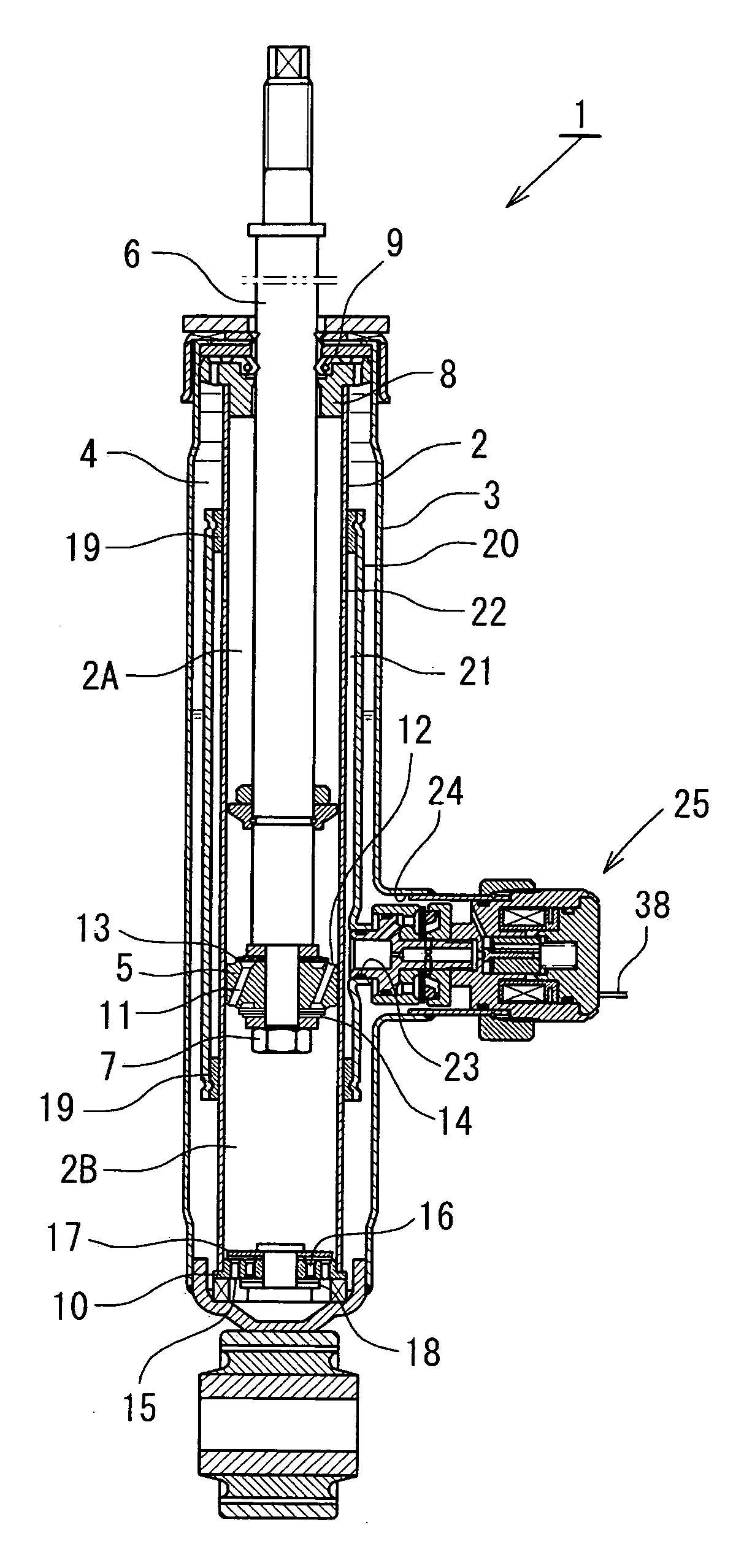
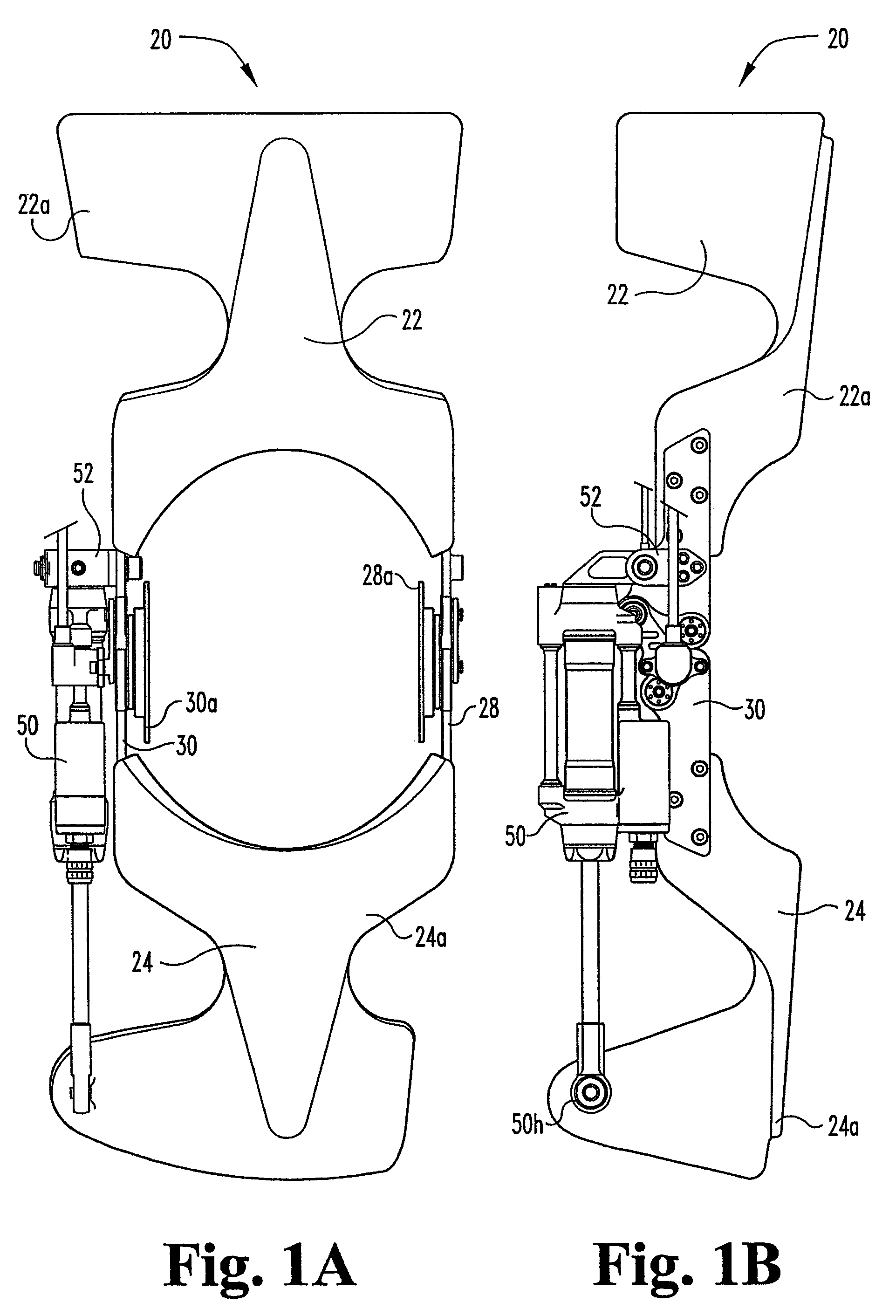
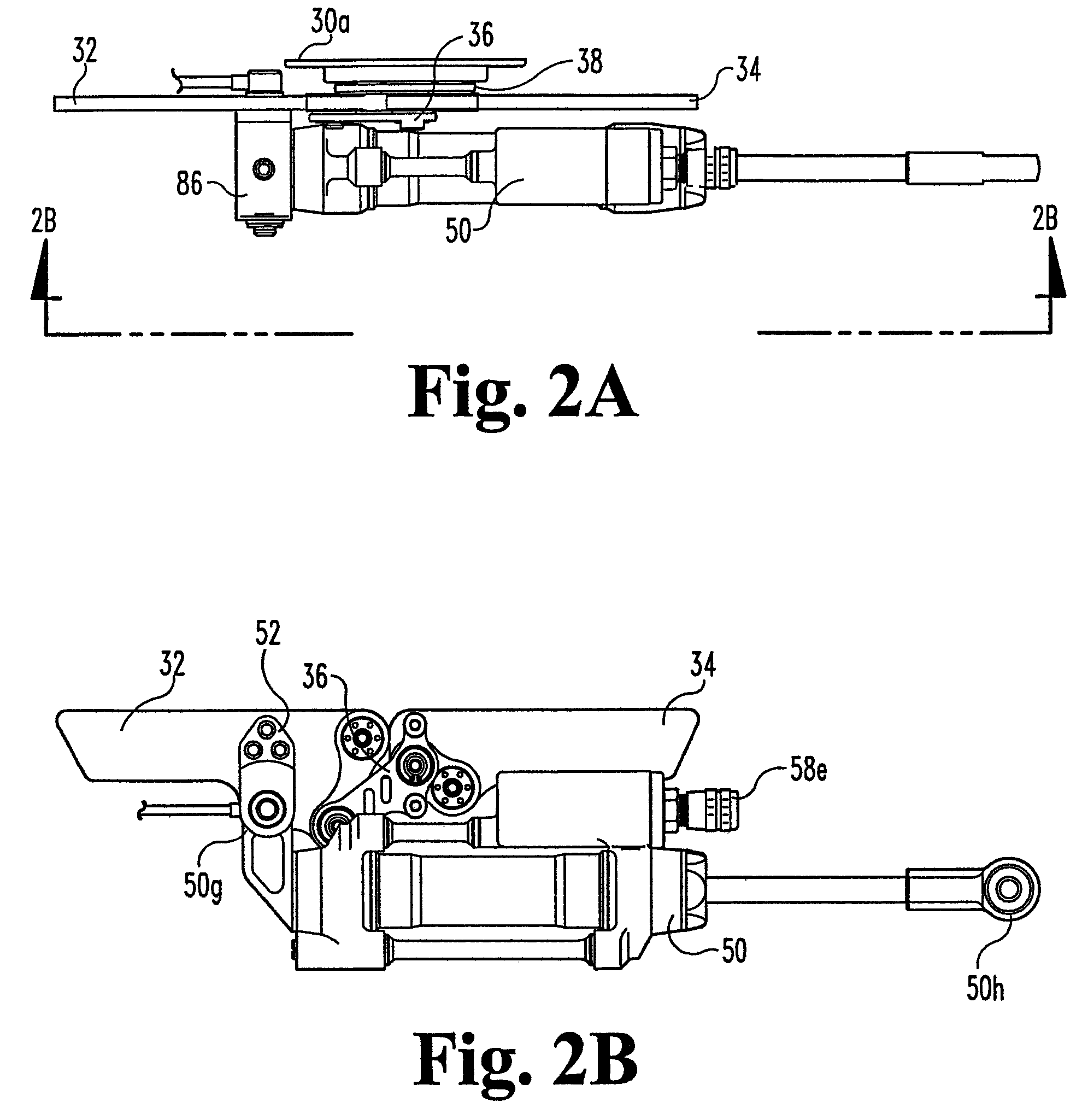
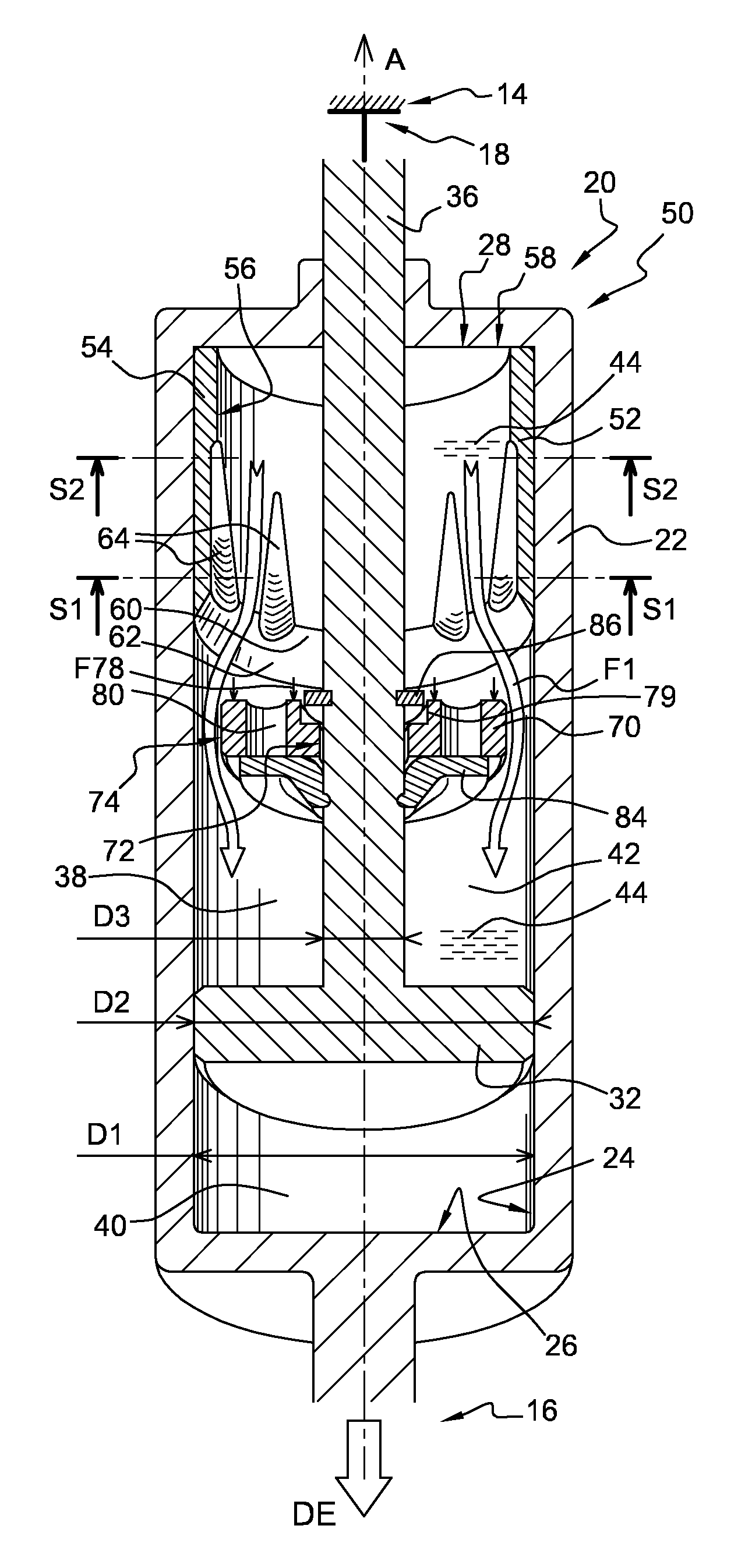
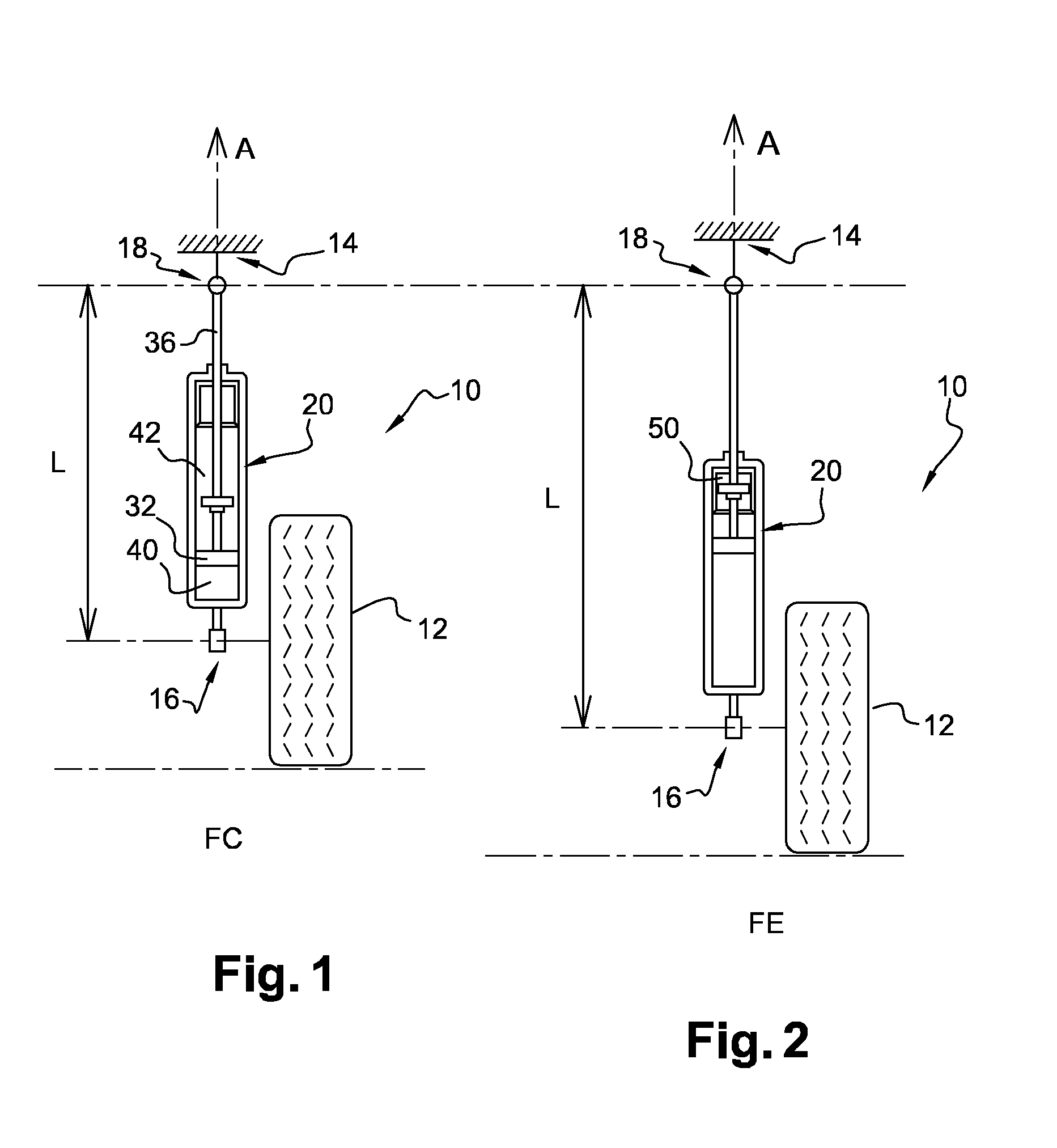
Adjustable damping force hydraulic shock absorber
A damping force adjustable hydraulic shock absorber is provided with a first passage connected to a rod side chamber, a second passage connected to a piston side chamber, a main passage combining the first passage and the second passage so as to communicate with a reservoir, a first check valve allowing only an oil flow to the main passage from the rod side chamber via the first passage, and a second check valve allowing only an oil flow to the main passage from the piston side chamber via the second passage, and a proportional solenoid type relief valve provided in the main passage, and adjusting a damping force by controlling a relief pressure of the oil flow to the reservoir from the rod side chamber or a relief pressure of the oil flow to the reservoir from the piston side chamber.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
Controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber
A piston having a piston rod connected thereto is slidably fitted in a cylinder in which a hydraulic fluid is sealably contained. Extension-stroke and compression-stroke pilot type damping force control mechanisms are provided in the piston. Check valves are provided at inlet openings of back-pressure chambers (pilot chambers). Relief valves provided in the pilot chambers include orifice passages. When the direction of stroke of the piston rod is reversed, the pressures in the back-pressure chambers are maintained due to the check valves, and the back-pressure chambers are pressurized to a satisfactory level through the orifice passages.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Hydraulic recoil buffer assembly
Owner:ENIDINE
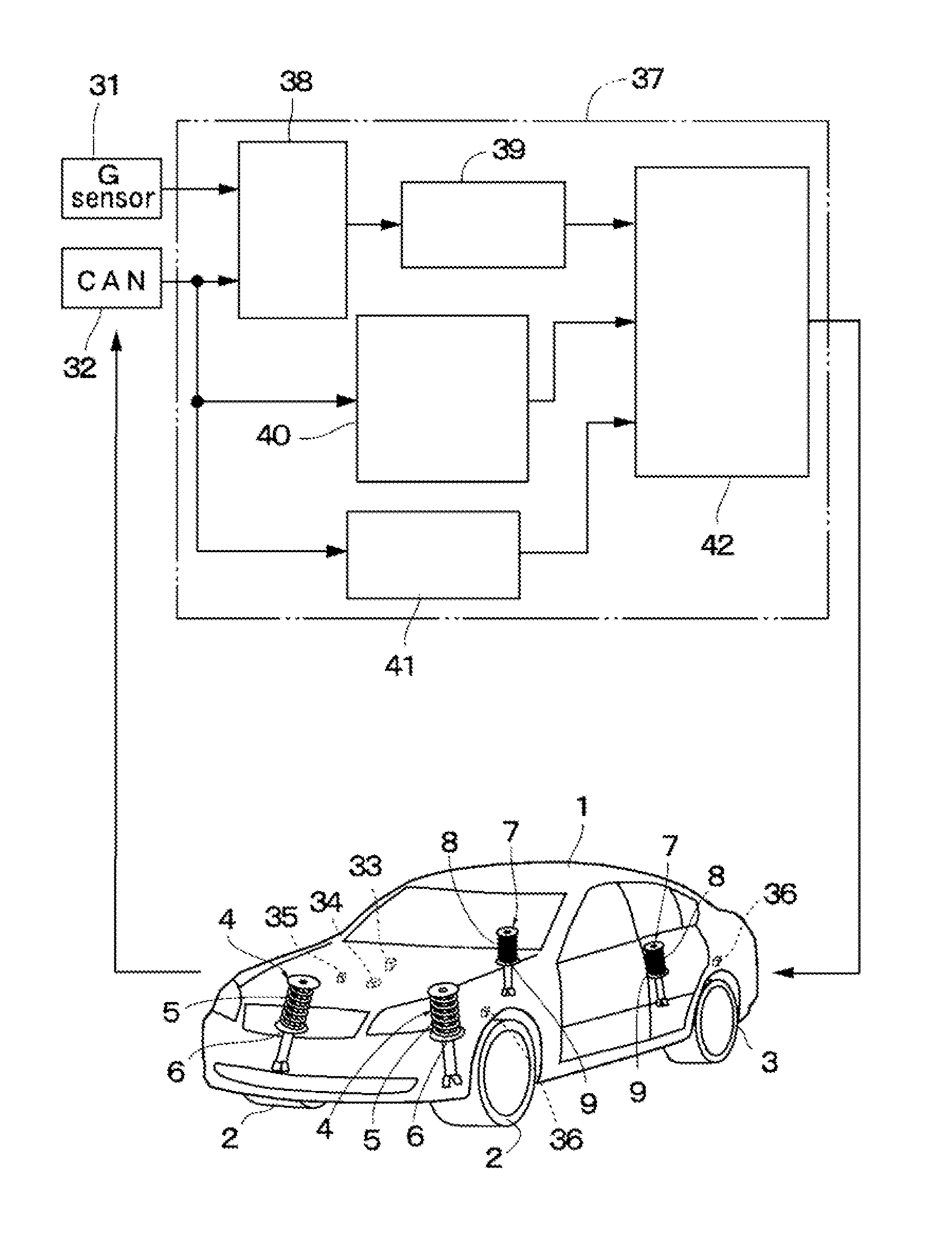
Suspension apparatus
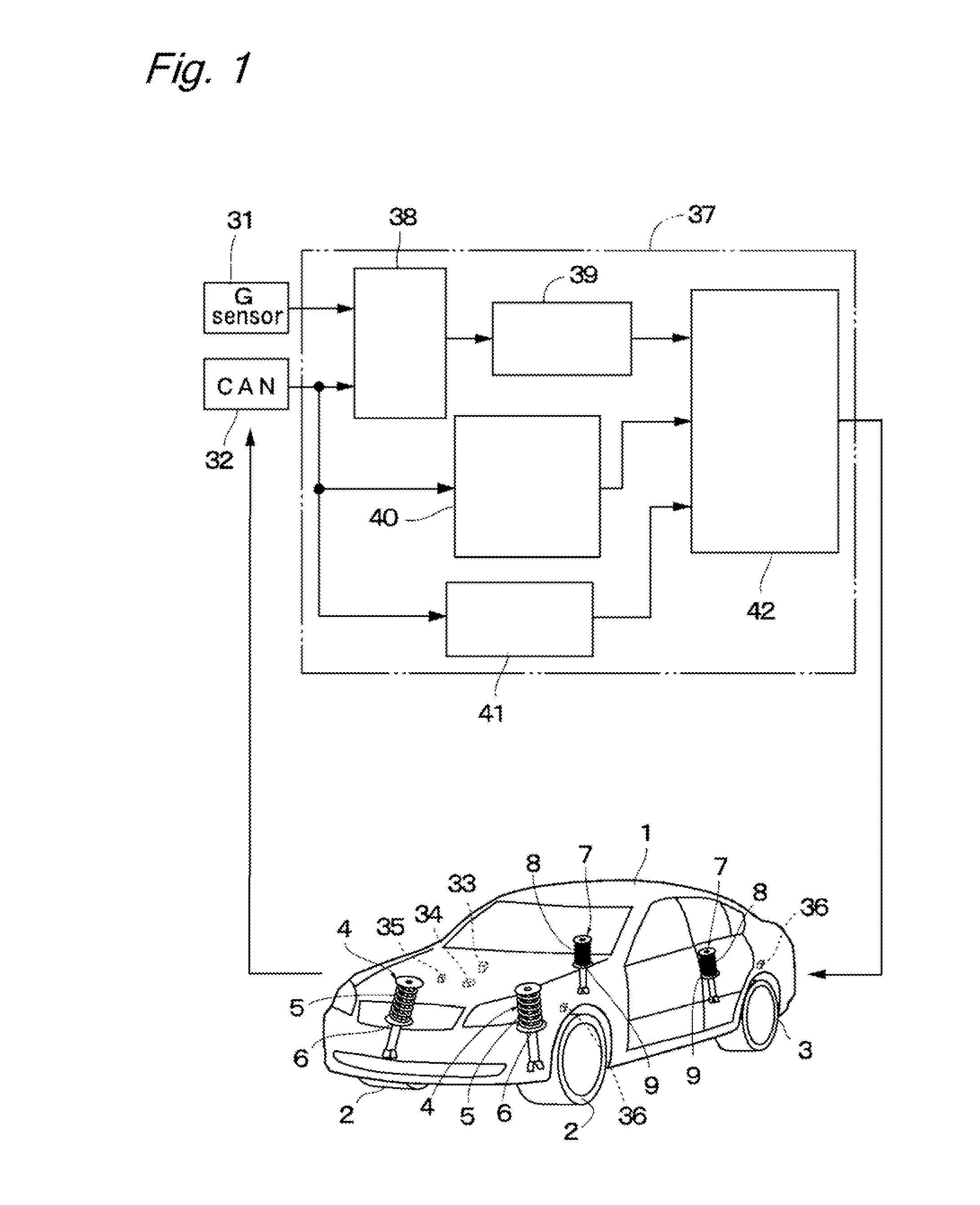
ActiveUS20120247888A1Scarifies ride comfortScarifies steering stabilitySpringsDigital data processing detailsVertical vibrationActuator
Shock absorbers of left and right front wheel suspensions and shock absorbers of left and right rear wheel suspensions each are constituted by a damping force adjustable hydraulic shock absorber provided with a frequency response unit. An actuator of a damping force variable mechanism provided to the shock absorber is driven and controlled by a controller. The controller variably adjusts the damping force between the soft side and the hard side by the damping force variable mechanism according to a vertical vibration when a vehicle body vertically vibrates at a low frequency. The controller does not adjust the damping force when the vehicle body vibrates at a higher frequency than the low frequency.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Wide range proportional flow control valve
InactiveUS6109591AStable controlAvoid it happening againPlug valvesLift valveControl systemClosed loop
A continuous flow type proportional flow control valve having a very wide controllable flow range and having a valve seat port design permitting a continuous, stable closed loop control to be achieved. The flow port design cooperates with a simple cylindrical flow passage of a movable valve element and provides the valve with a very wide flow control range and the ability to smoothly control the opening, modulation, and closing of the valve to eliminate undesirable hydraulic shock which is an undesirable characteristic of pulse operated flow control systems. The flow controlling seat has a flow controlling port therein that cooperates with the flow port of the closure to define an effective valve opening that is proportionally variable over a wide range of closure movement. The seat port is provided with an extremely narrow elongate slot section less than +E,fra 1 / 50+EE th of the maximum width of the aperture. The seat opening also defines a large final, generally circular orifice section having a radius comparable to the radius of the bore in the ball. Further, the seat opening is defined by a transition between the elongate narrow slot and final circular orifice section in the form of two diverging curves offering an exponential flow characteristic of the form K=Nx.
Owner:TUTTLE JAMES D +1
Damping force adjusting structure of hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS20090084647A1Increase damping forceIncrease back pressureSpringsLiquid based dampersEngineeringValve opening
In a damping force adjusting structure of a hydraulic shock absorber, a blow valve blowing an oil liquid in a rod side chamber to a back pressure chamber is provided in a back pressure introduction path introducing the oil liquid in the rod side chamber to the back pressure chamber, and a blow valve has a first pressure receiving portion capable of receiving the pressure of the rod side chamber before and after the valve opening, and a second pressure receiving portion capable of receiving the pressure of the rod side chamber after the valve opening.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
Hydraulic shock absorber
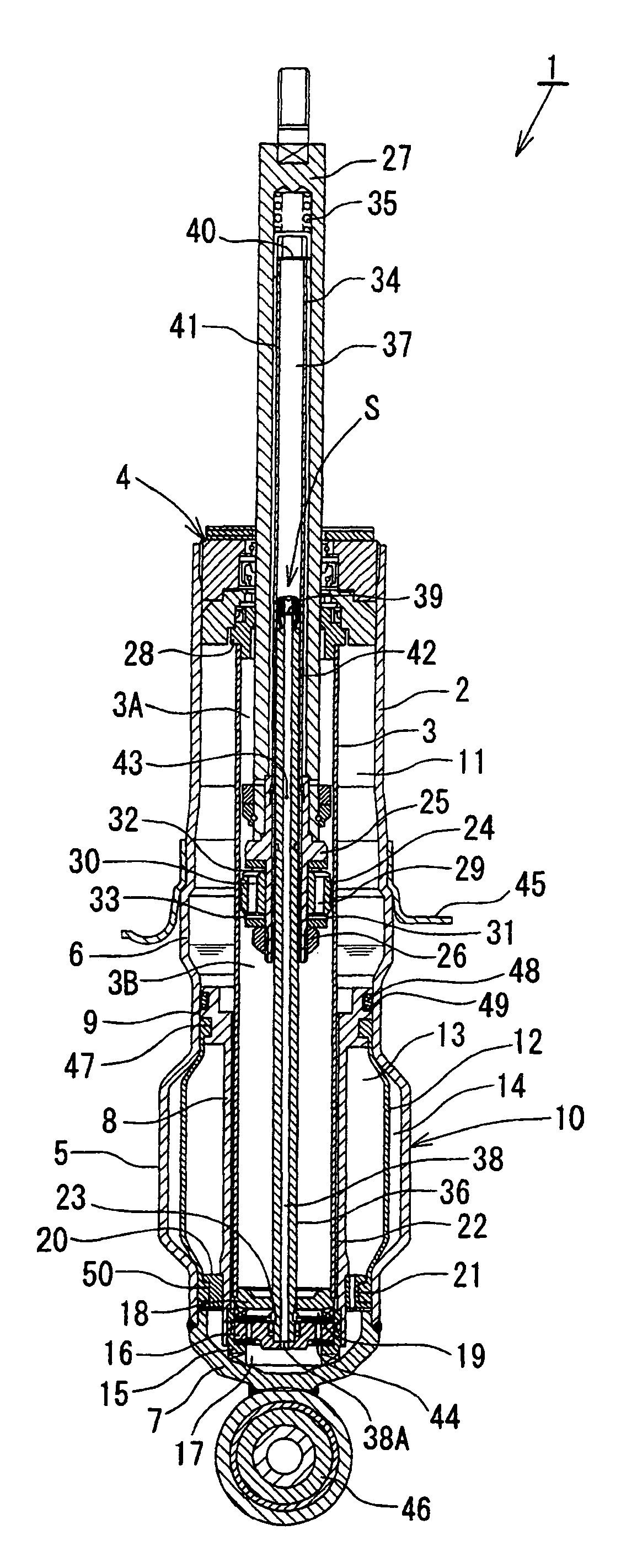
A hydraulic shock absorber in which the flow of hydraulic fluid induced in each of extension and compression hydraulic fluid passages, by sliding movement of a piston, is controlled by a main disk valve to generate damping force. The valve opening pressure of the main disk valve is adjusted by the pressure in a back-pressure chamber. In a low piston speed region, the main disk valve closes a back-pressure chamber inlet passage. Therefore, the pressure in the backpressure chamber will not rise, and sufficiently small damping force is obtained. When the main disk valve opens, the backpressure chamber inlet passage opens simultaneously. Consequently, the pressure in the backpressure chamber rises, and the damping force increases.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Dust cover receiving structure of hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS6883651B2DownsizingDownsizing of a spring seatLiquid springsResilient suspensionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A dust cover receiving structure of a hydraulic shock absorber in which a seat rubber is interposed between a suspension spring and a spring seat. The seat rubber has a spring receiving portion which is arranged between the suspension spring and the spring seat, a centering portion which is fitted to a damper tube and guides an end portion of a dust cover in such a manner as to align the dust cover with an axial center of the damper tube, and a cover receiving portion which is provided between the spring receiving portion and the centering portion, and which receives an end surface of the dust cover.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
Hydraulic shock absorber
In the disclosed hydraulic shock absorber, the flow of hydraulic fluid induced in each of extension and compression hydraulic fluid passages by sliding movement of a piston is controlled by a main disk valve to generate damping force. The valve opening pressure of the main disk valve is adjusted by the pressure in a back-pressure chamber. In a low piston speed region, the main disk valve closes a back-pressure chamber inlet passage. Therefore, the pressure in the back-pressure chamber will not rise, and sufficiently small damping force is obtained. When the main disk valve opens, the back-pressure chamber inlet passage opens simultaneously. Consequently, the pressure in the back-pressure chamber rises, and the damping force increases.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Electromechanical coupling vibration test device for maglev train
ActiveCN101995322ASimple structureLight weightMechanical vibrations separationVibration testingLevitationControl system design
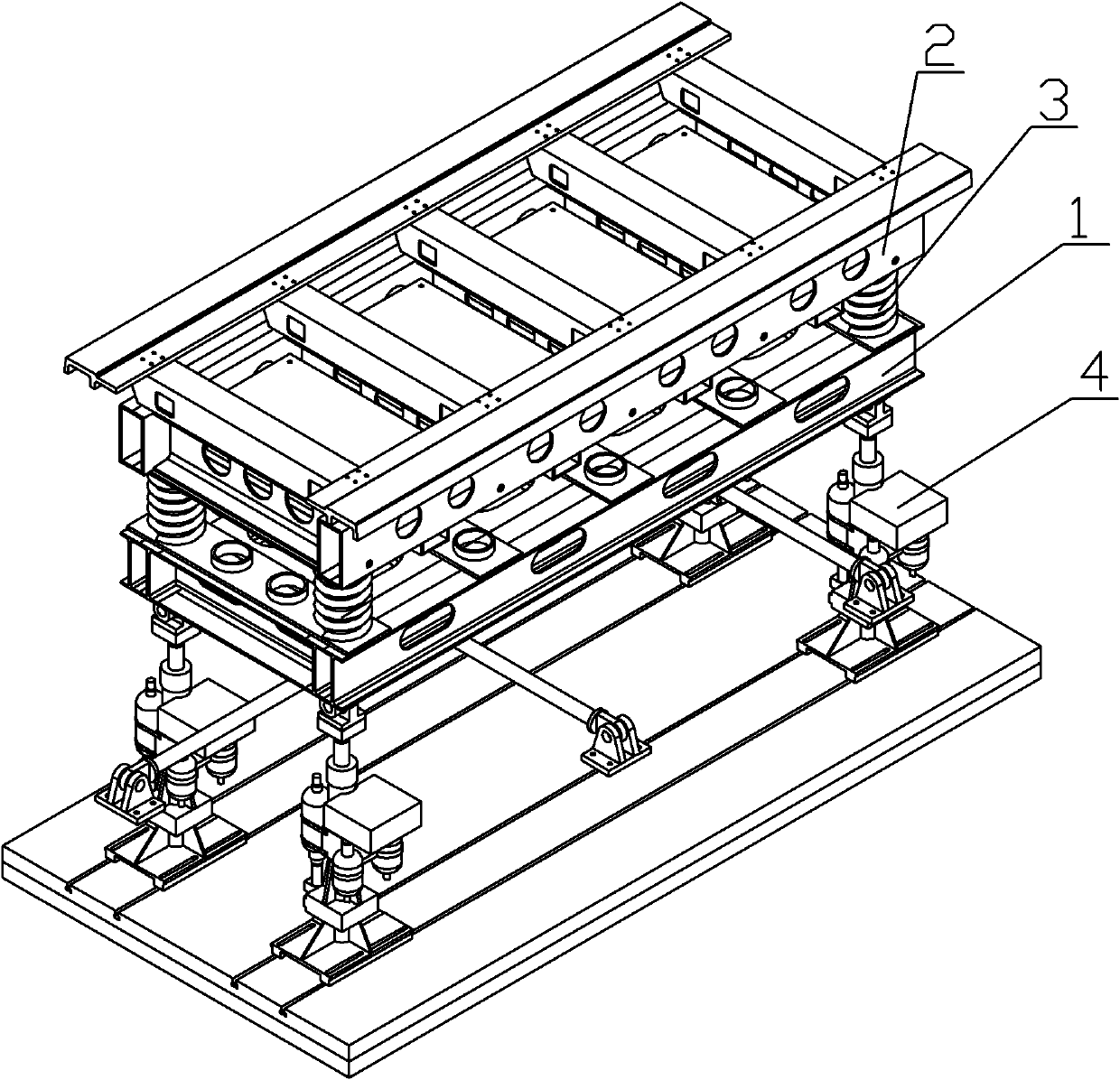
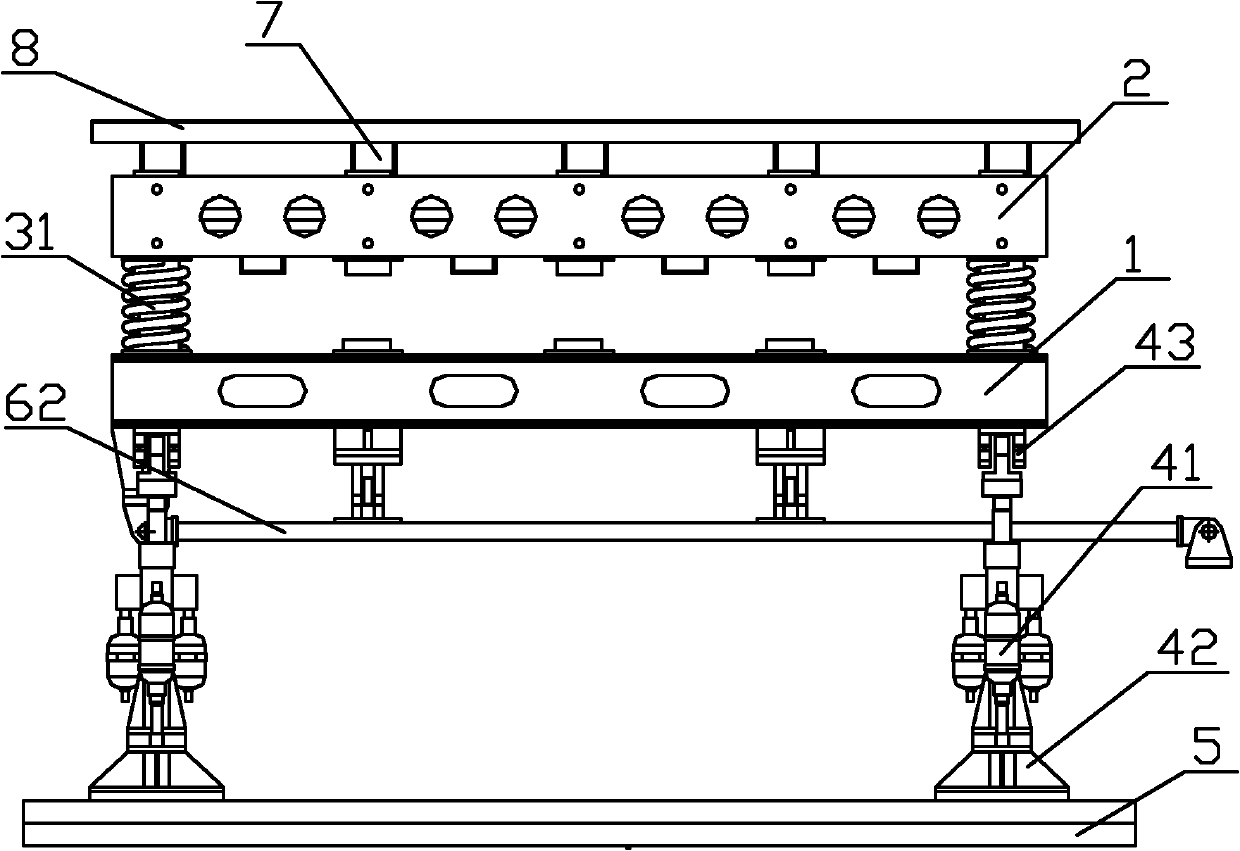
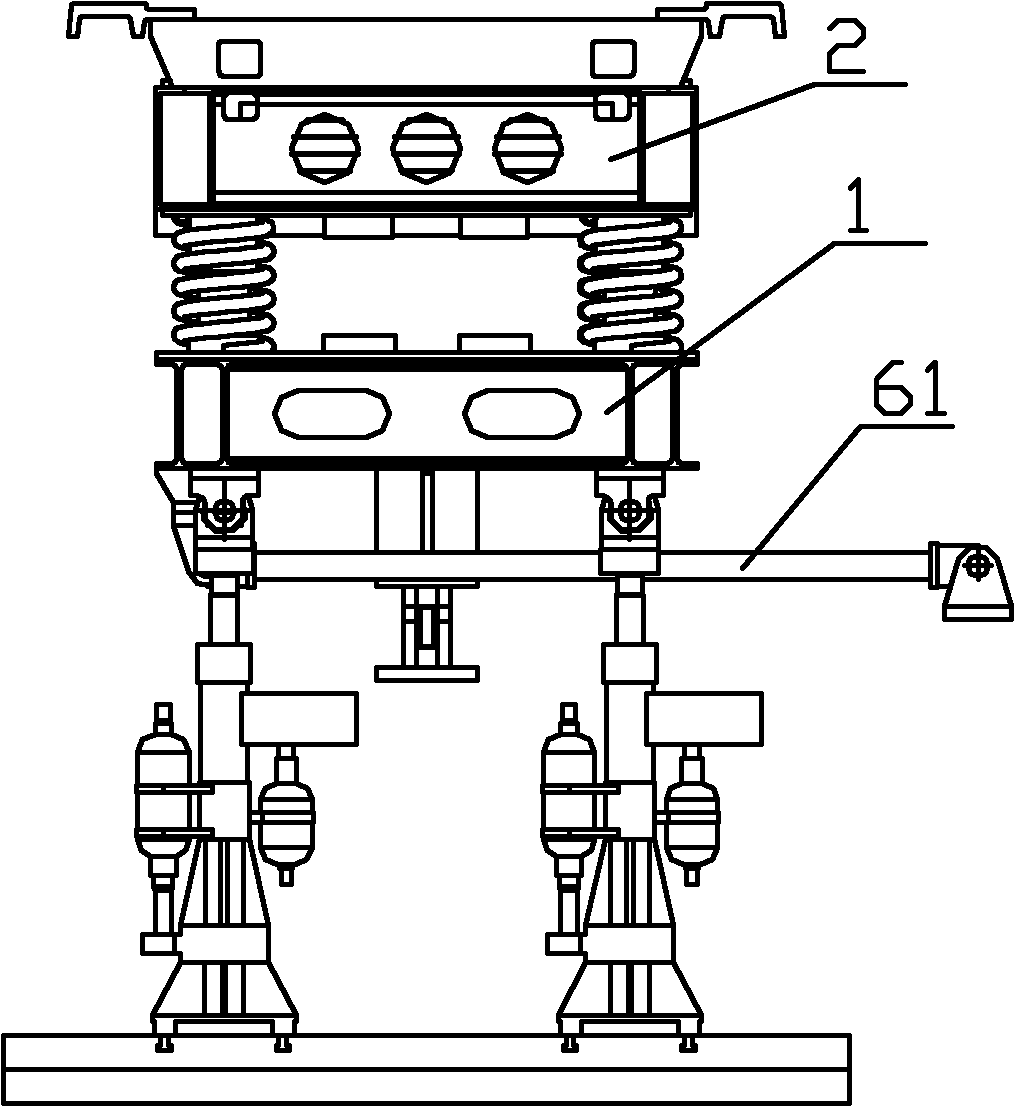
The invention relates to the technical field of single levitation chassis testing for a maglev train, in particular to an electromechanical coupling vibration test device for the maglev train. The device comprises a primary platform for simulating ground support, a secondary platform which is positioned above the primary platform and simulates a track beam, and a track beam rigidity adjusting system for connecting the primary platform and the secondary platform, wherein the track beam rigidity adjusting system and the secondary platform supported by the track beam rigidity adjusting system form simulated maglev train track beam characteristics; and a hydraulic shock excitation system which applies excitation to the primary platform so as to simulate geometrical irregularity of track ground is fixed under the primary platform. The defects of the simplified single-point test or complete-vehicle debugging test for the conventional maglev train are overcome, the complex laboratory simulation of levitation control, elastic beam and coupling vibration environment of a levitation chassis mechanism for the maglev train is realized, the gap in research of key technology for domestic and overseas maglev trains is filled, and a scientific test means is provided for design of a levitation control system of the maglev train, the track beam characteristics and design of the mechanical structure of the levitation chassis.
Owner:常州西南交通大学轨道交通研究院 +1
Hydraulic shock absorber
A piston connected to a piston rod is fitted into a cylinder in which a hydraulic fluid is sealably contained. A flow of the hydraulic fluid is generated in an extension-side fluid passage and a compression-side fluid passage according to a sliding motion of the piston, and this flow of the hydraulic fluid is controlled by a main disk valve, to thereby generate a damping force. A valve-opening pressure of the main disk valve is controlled by an internal pressure of a back-pressure chamber generated due to a difference in flow path area between a back-pressure chamber inlet fluid passage and a downstream-side orifice. During a reverse stroke, a check valve is opened, to thereby introduce a pressure in a downstream-side cylinder chamber into the back-pressure chamber, so that the main disk valve can be maintained in a closed position and a stable damping force can be generated.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Shock absorber
InactiveUS20120090931A1Easy to manufactureLarge sectionSpringsResilient suspensionsAxial displacementAbutment
A hydraulic shock absorber comprising a main tube divided, by a piston-rod extending through the extension chamber. The shock absorber is further provided with a hydraulic rebound stop, called HRS fixed in the extension chamber and comprising a HRS-tube restricting the main tube, bottom and an 10 entry. The HRS also has HRS-piston freely slidably mounted on the rod and having a diameter adjusted to the HRS-tube and being provided with at least one fluid-passage substantially axially oriented. The axial displacements of the HRS-piston are limited between a Rebound-stop and a HRS-ring, both fixed to the rod. The fluid-passage is open to a flow of fluid when in abutment against the HRS-ring and being sealed when in abutment against the Rebound-stop. The HRS is further provided with at least one fluid-passage connecting the HRS-chamber to the extension chamber and providing to the fluid a way-out for an exiting flow generating a HRS-damping which is tunable and varies as the HRS-piston penetrates the HRS-tube, their relative position determining the size of the way-out.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS20130313057A1Simplify the assembly processEasy to assembleSpringsLiquid based dampersRefluxEngineering
A hydraulic shock absorber includes: a cylinder which demarcates a piston oil chamber and a rod oil chamber; an outer cylinder body which demarcates between the cylinder and the outer cylinder body a reflux path that connects the piston oil chamber and the rod oil chamber with each other and which demarcates between a damper case and the outer cylinder body a reservoir chamber; and a valve structure mounted to the cylinder and the outer cylinder body. The valve structure has a valve for controlling an oil flow between the piston oil chamber and the reflux path and between the piston oil chamber and the reservoir chamber. The valve structure comprises a first valve structure mounted to an open end of the cylinder and a second valve structure mounted to an open end of the outer cylinder body. A cylinder assembly and an outer cylinder assembly are independently arranged.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS7040468B2Prevent undue flexingExtended service lifeSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A hydraulic shock absorber includes a cylindrical housing within which a piston assembly is slidably received. The piston assembly includes a piston element connected to a piston rod and adapted to divide an interior of the housing into compression and rebound chambers. The piston element has compression and rebound passages to provide fluid communication between the compression and rebound chambers. A valve assembly includes a first valve disc positioned on a lower side of the piston element, and a second valve disc retained on the first valve disc. The second valve disc includes apertures arranged in a circumferentially spaced relationship and are selectively openable and closeable by the first valve disc. A third valve disc is retained on the second valve disc and has notches arranged in a circumferentially spaced relationship. The notches cooperate with the apertures to collectively form ports. The ports are communicated with the compression chamber. A fourth valve disc cooperates with the second valve disc to sandwich the third valve disc so that restrictive orifices are defined in an outer end of the notches. Each of the ports has a cross sectional area greater than that of the restrictive orifices regardless of a relative angular position between the second and third valve discs.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS20120247890A1Increase damping forceIncrease changeSpringsLiquid based dampersEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a hydraulic shock absorber, a damping force generating device provided between a piston side oil chamber of a cylinder and a rod side oil chamber is provided with a through-hole which communicates the piston side oil chamber of the cylinder with the rod side oil chamber of the cylinder via an outer flow path of the cylinder. A leading end portion of a piston rod is provided with a needle which can come in and out of the through-hole of the damping force generating device, and an opening degree of the through-hole can be varied by the needle according to a forward and backward position of the piston rod with respect to the oil chamber of the cylinder.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
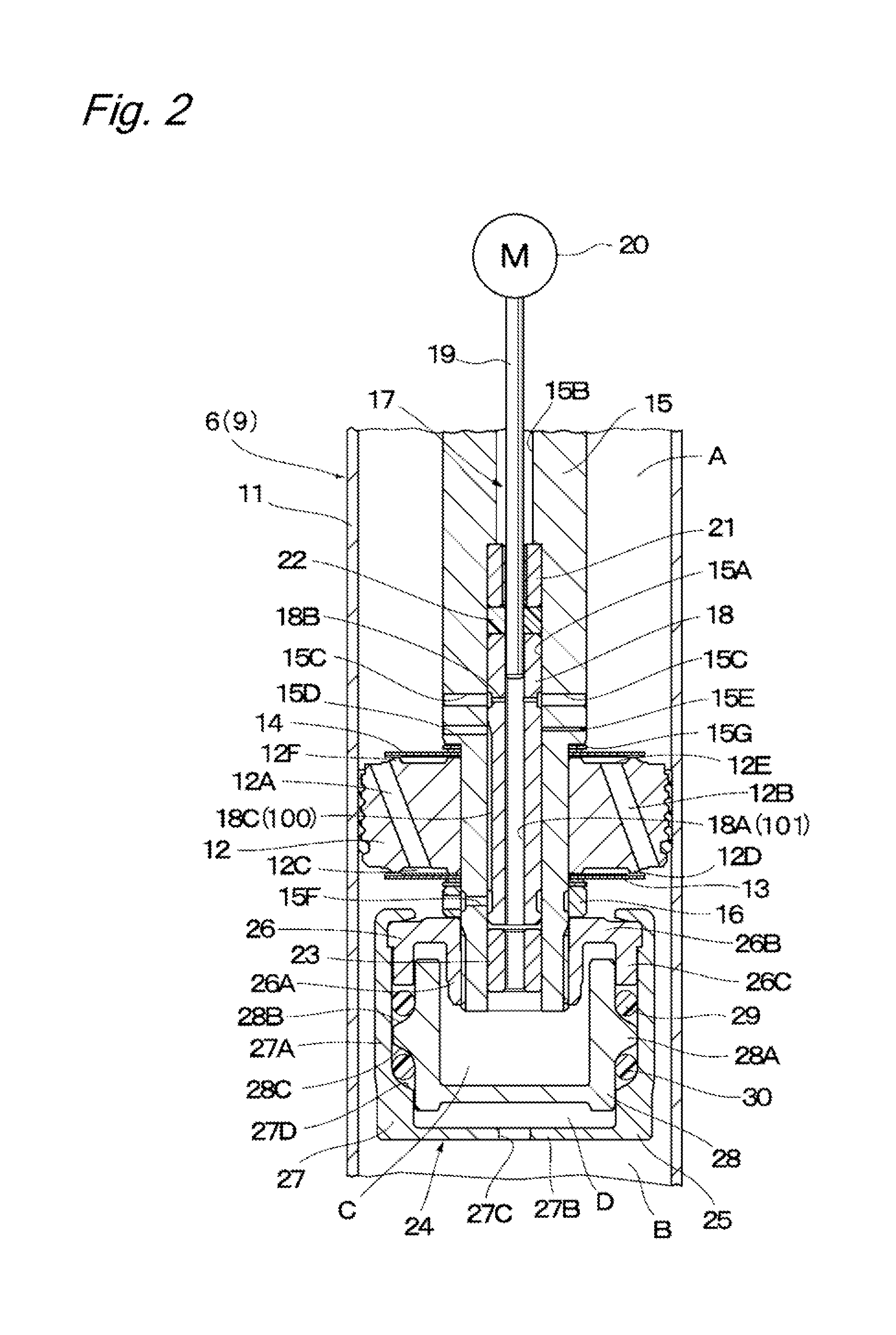
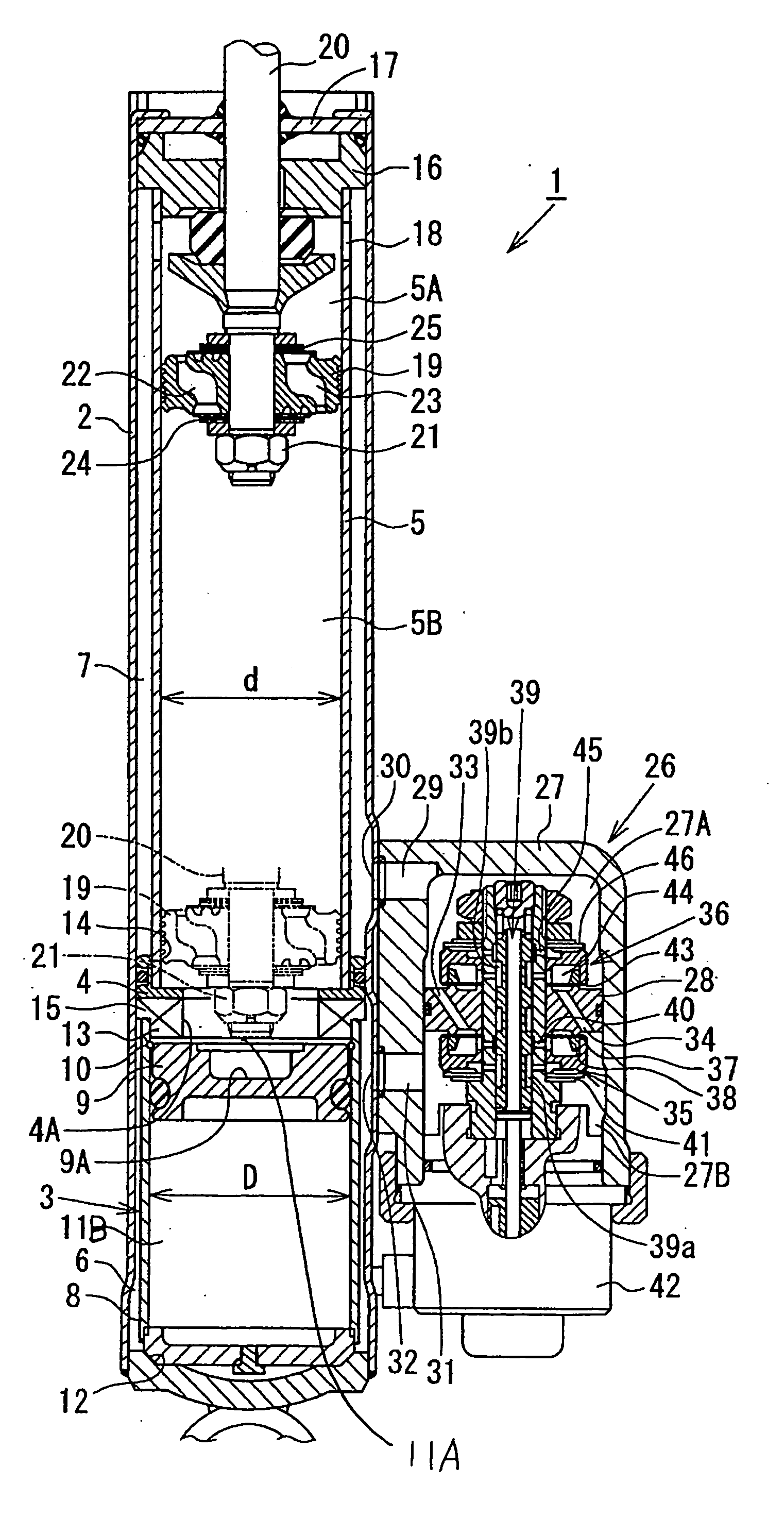
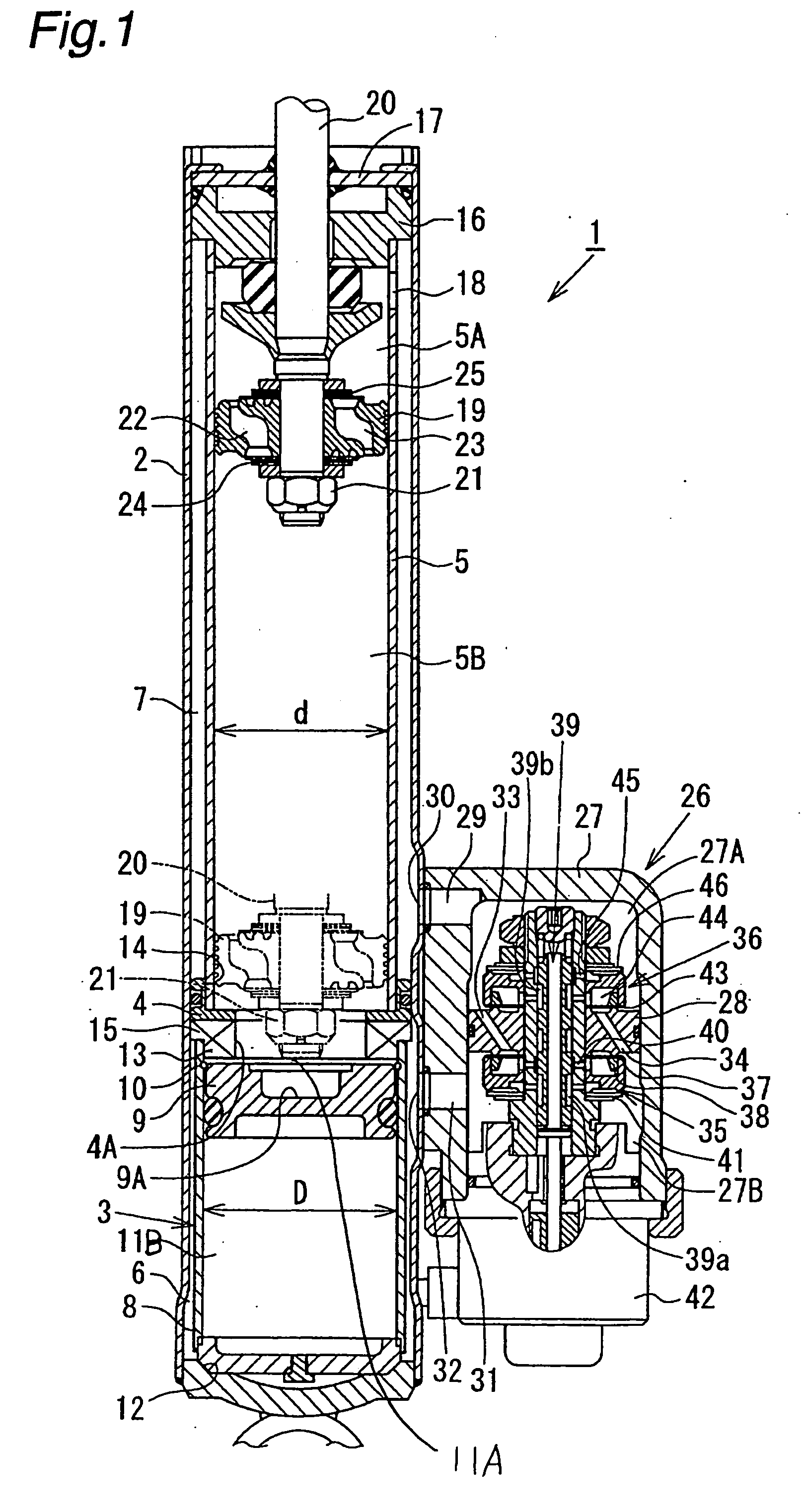
Suspension spring adjusting apparatus of hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS7967117B2Reduced strengthVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentEngineeringMotor shaft
In a suspension spring adjusting apparatus of a hydraulic shock absorber, a mounting structure of a motor to a spring adjusting case is constituted by a three-point support structure in a plan view including a motor shaft of the motor.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
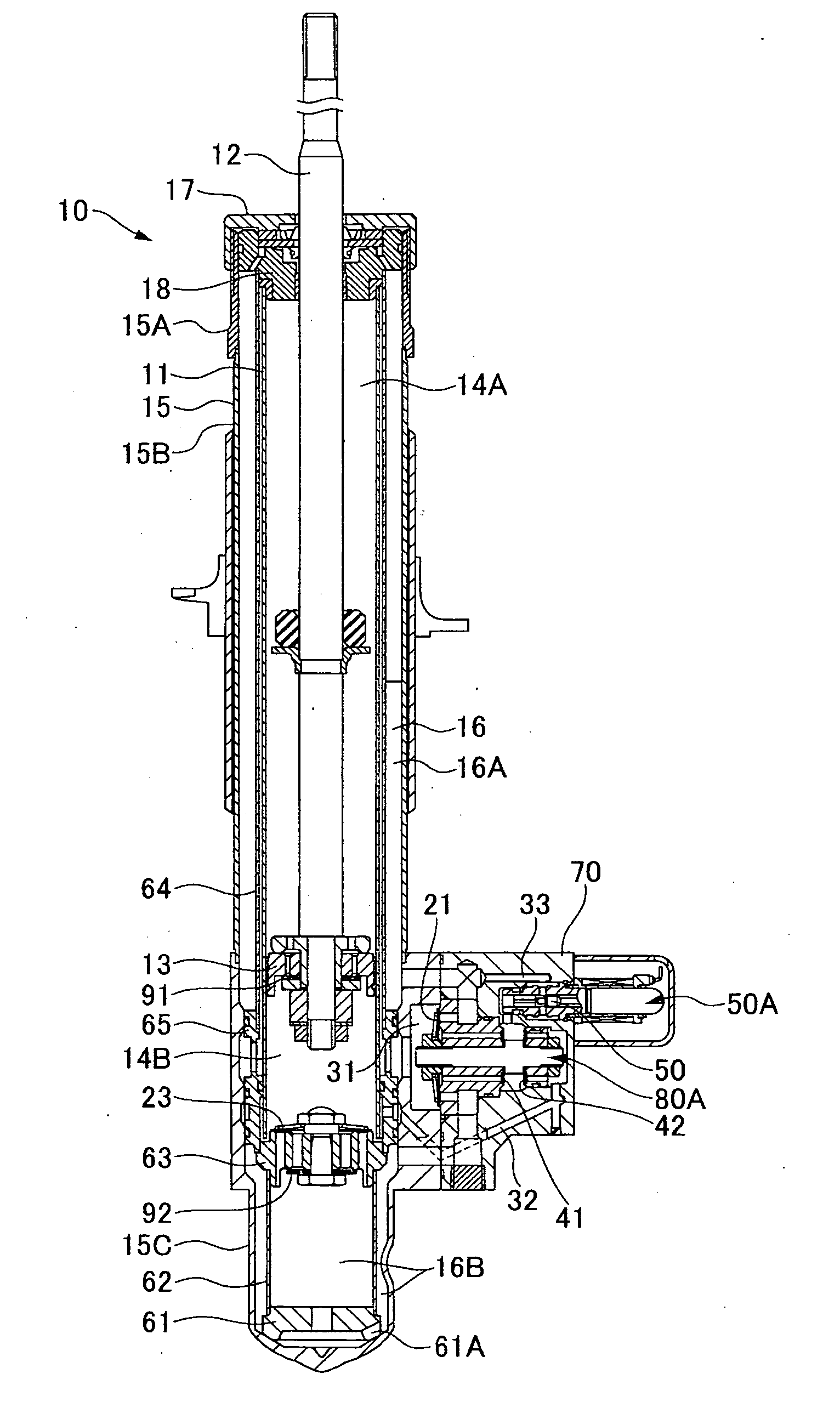
Hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS20060054435A1Easy to assembleDamping forceSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringHydraulic fluid
A hydraulic shock absorber has a subassembled reservoir cartridge including a gas chamber and a free piston. The reservoir cartridge, a separator and a cylinder are inserted into a base shell, and an oil seal is secured to the base shell under application of a predetermined axial load, thereby fixing together these members in the axial direction. An annular hydraulic fluid passage is formed between the base shell and the reservoir cartridge, and another annular hydraulic fluid passage is formed between the base shell and the cylinder. A damping force generating mechanism is attached to a side of the base shell. Damping force is generated by supplying a hydraulic fluid sealed in the cylinder to the damping force generating mechanism through the annular hydraulic fluid passages. Stable damping force is obtained through pressurization by the gas chamber and through gas-liquid separation by the free piston.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
A new type of rotating drive system for mixing drum of concrete mixer truck
InactiveCN102275223AReduced power ratingImprove work efficiencyCement mixing apparatusPrime moverHydraulic motor
The invention relates to a novel rotation driving system for a mixing drum of a concrete mixing transport vehicle. In the system, two prime movers, two hydraulic main pumps, an oil supply pump and a hydraulic motor form a hydraulic closed loop together with a hydraulic valve block with the functions of relatively completing oil supply, cooling and safe buffering; the delivery volumes of the two hydraulic main pumps are different; and the low-delivery volume hydraulic main pump is used for separately realizing slow and constant mixing action of the mixing drum, and the high-delivery volume hydraulic main pump is used for rotating the mixing drum along positive and negative directions at a high speed during feeding and discharging when separately operated or combined with the low-delivery volume hydraulic main pump. The system aims to solve the problems of the influence on the concrete uniformity and the influence on the driving dynamic performance and driving safety performance which are caused by driving a roller to rotate by separately using a chassis engine under different working conditions and different road conditions in the mixing drum, fuel waste caused by the long-term operation of the high-power chassis engine at low-efficiency points and the hydraulic shock generated during the switching of the mixing drum under different working conditions.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
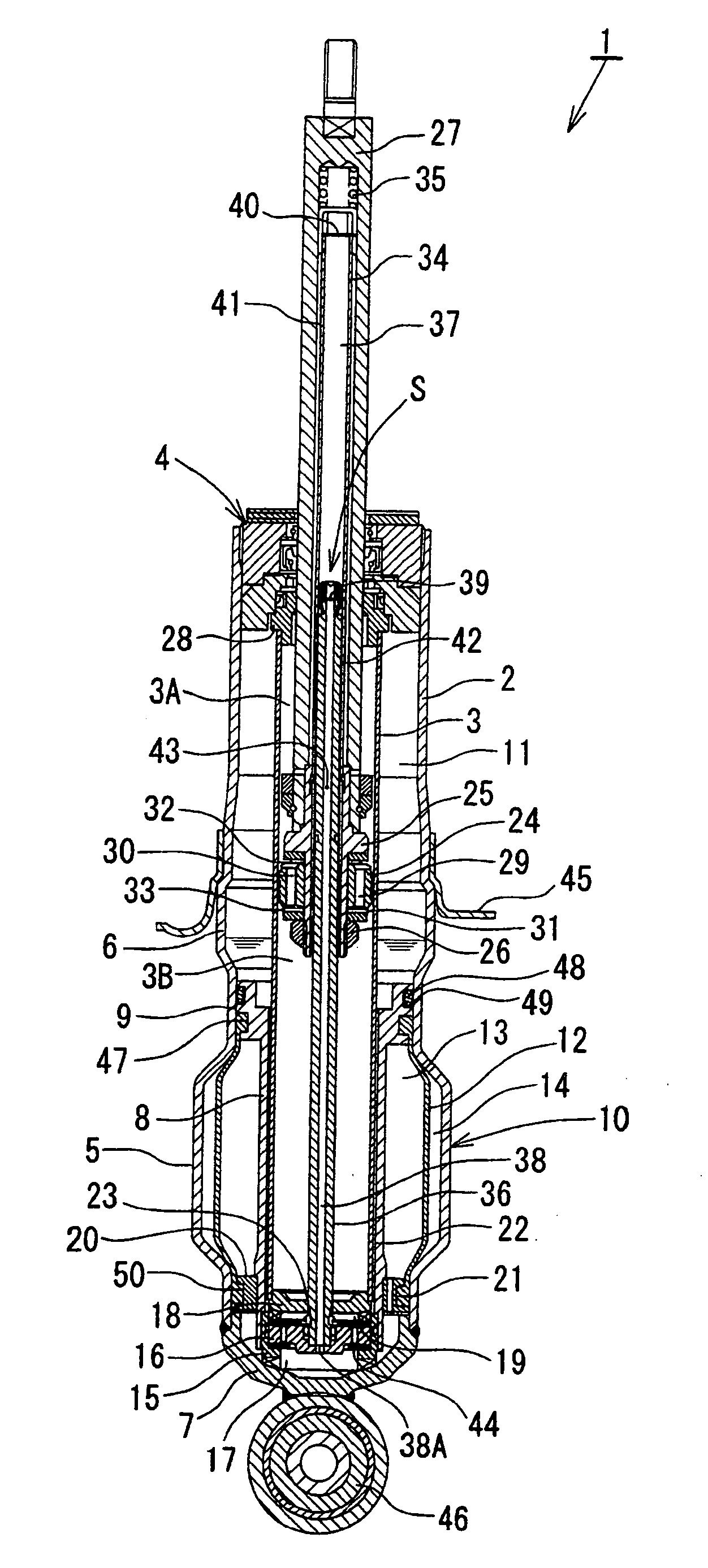
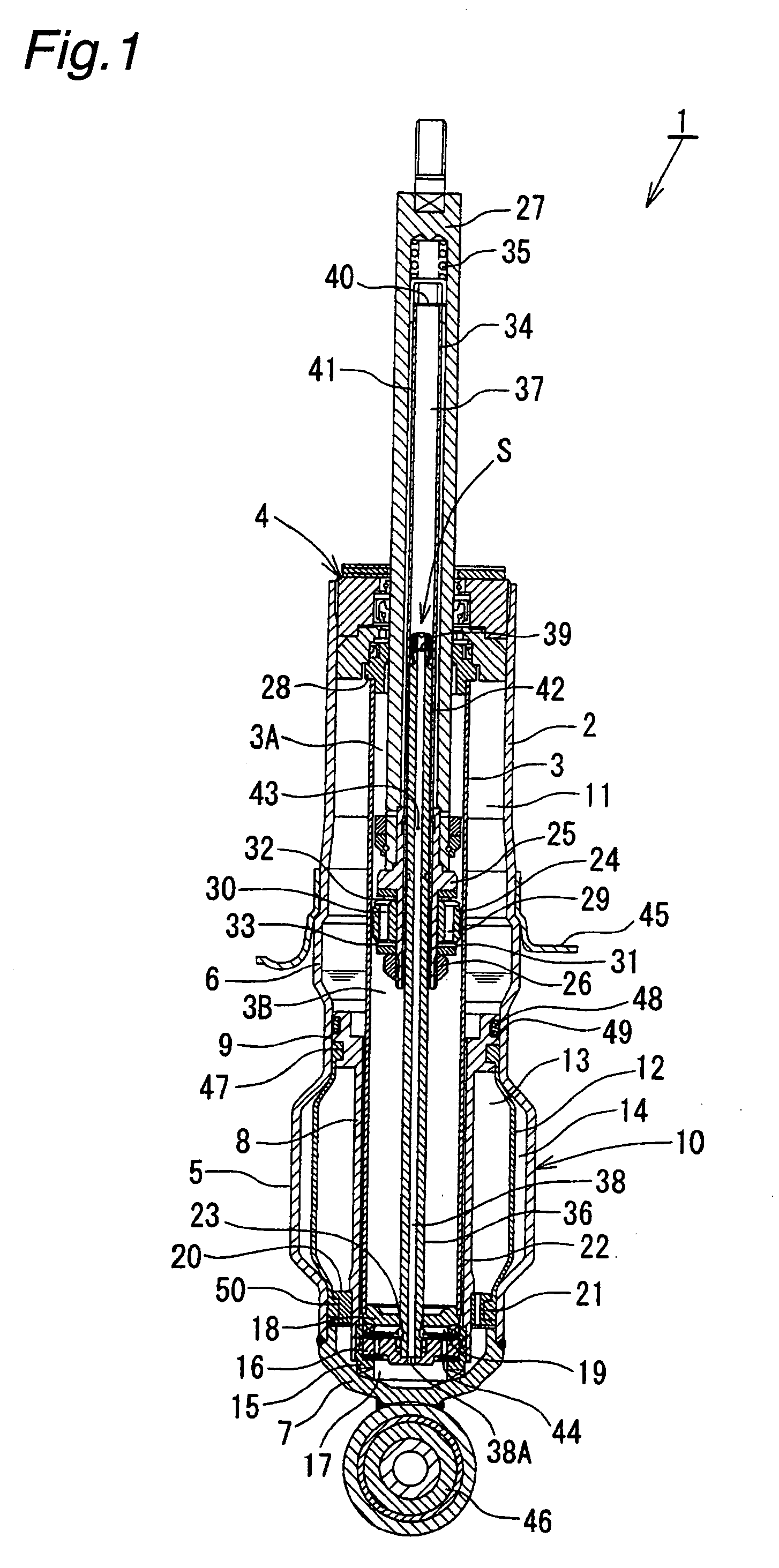
Automobile hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS20110120822A1Small overall lengthLight weightResilient suspensionsGas and liquid based dampersCylinder blockPiston rod
An automobile hydraulic shock absorber includes a cylinder body, a piston, an upper support, a piston rod, a volume adjustment mechanism, first and second communicating passages, and a pressure-applying mechanism. The piston rod is attached to the upper support via a rubber cushion. The volume adjustment mechanism includes a free piston. The first and second communicating passages communicate the first oil chamber and second oil chamber with each other in the cylinder body via a diaphragm. The pressure-applying mechanism is disposed outside the cylinder body, movement thereof is restricted by the upper support, and the pressure-applying mechanism pushes the piston rod downward.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
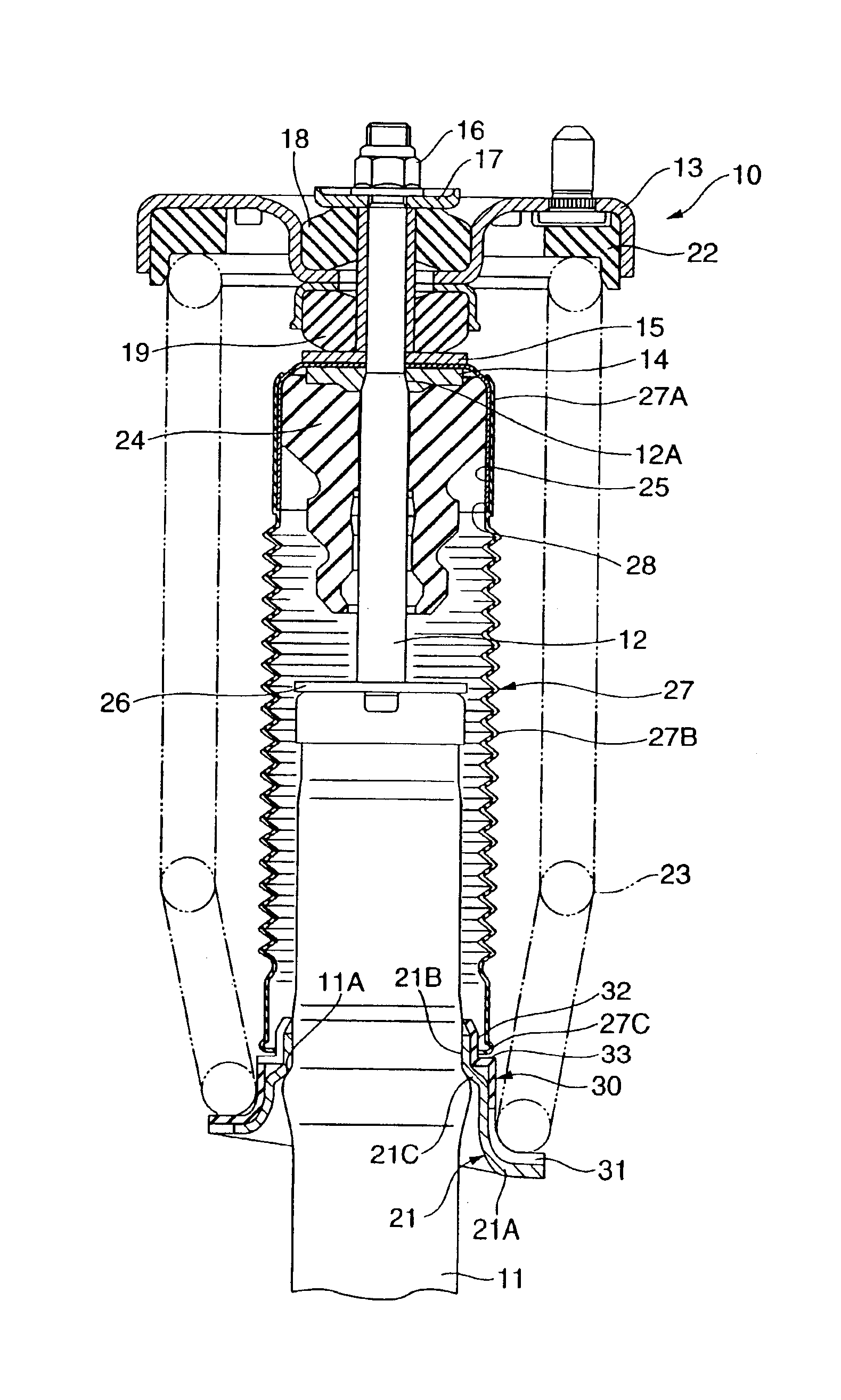
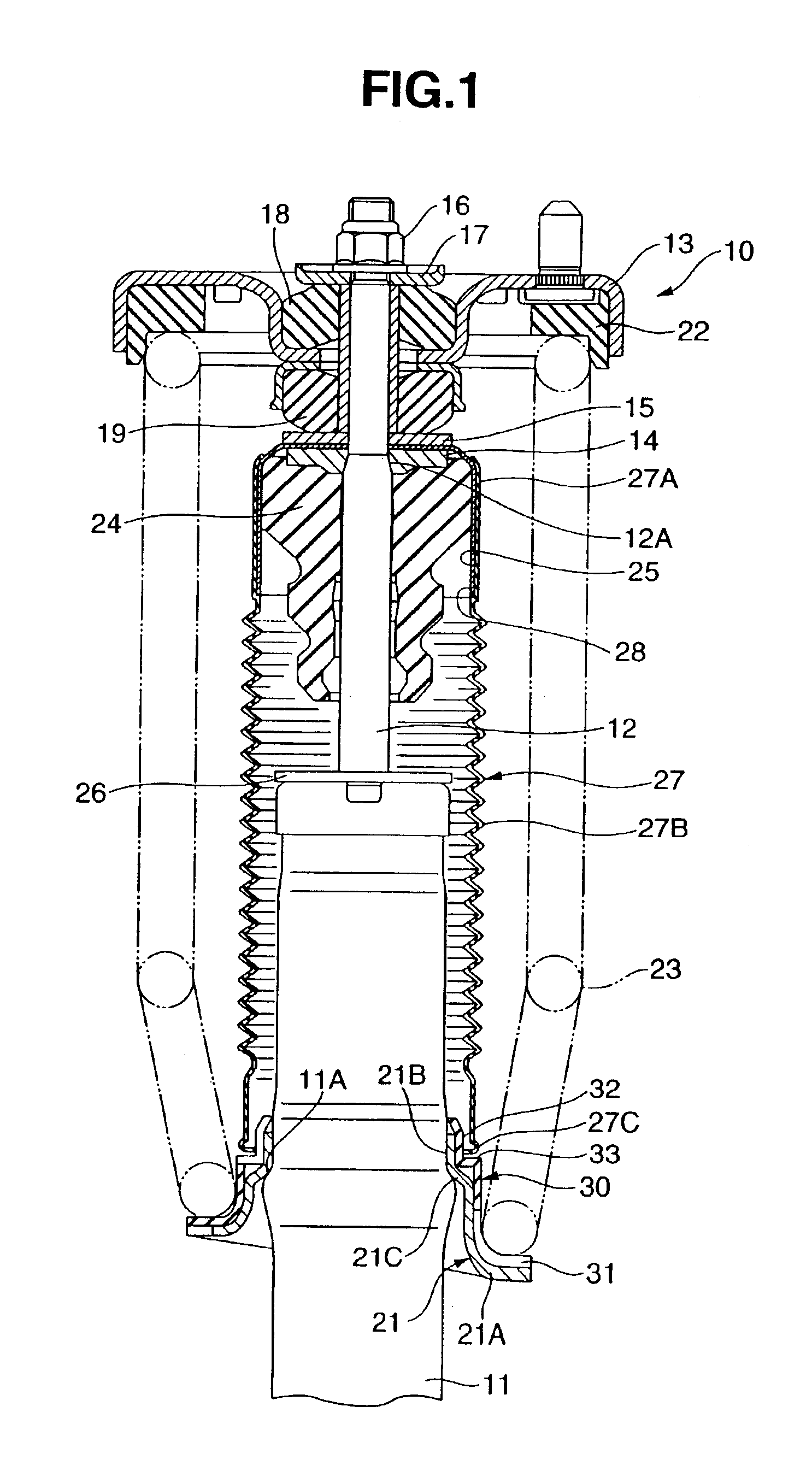
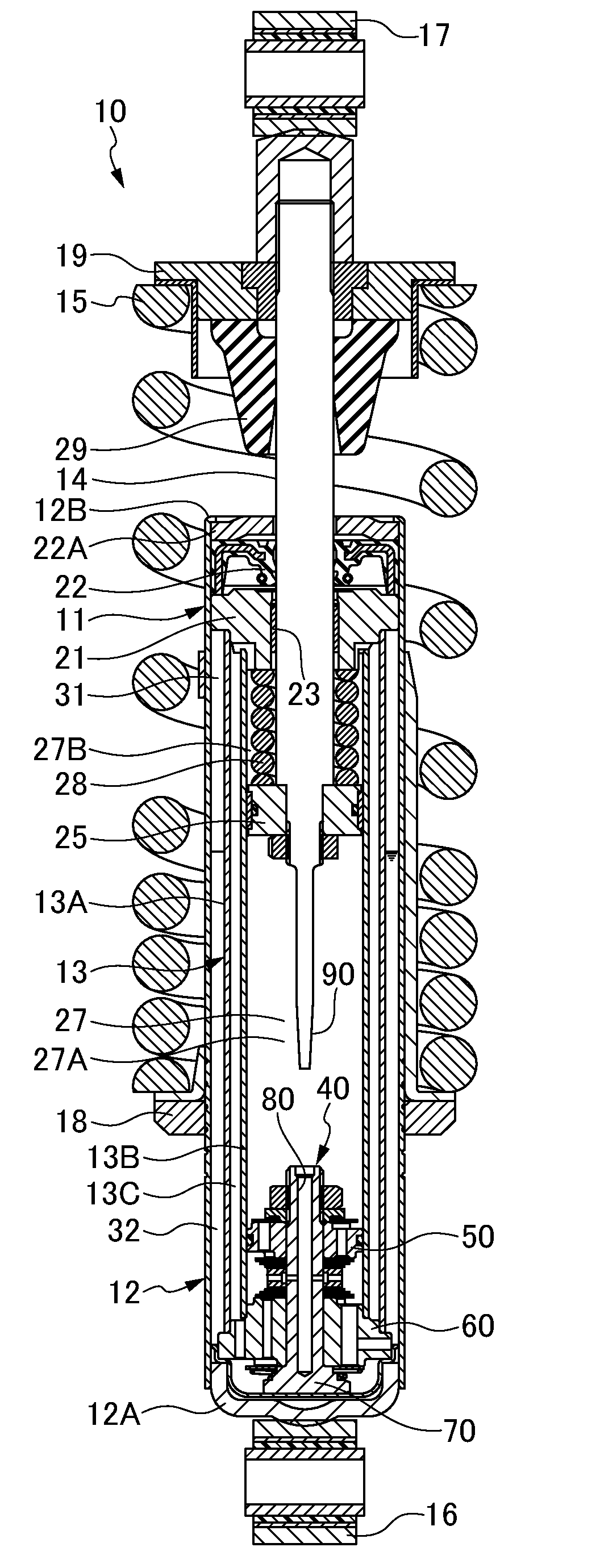
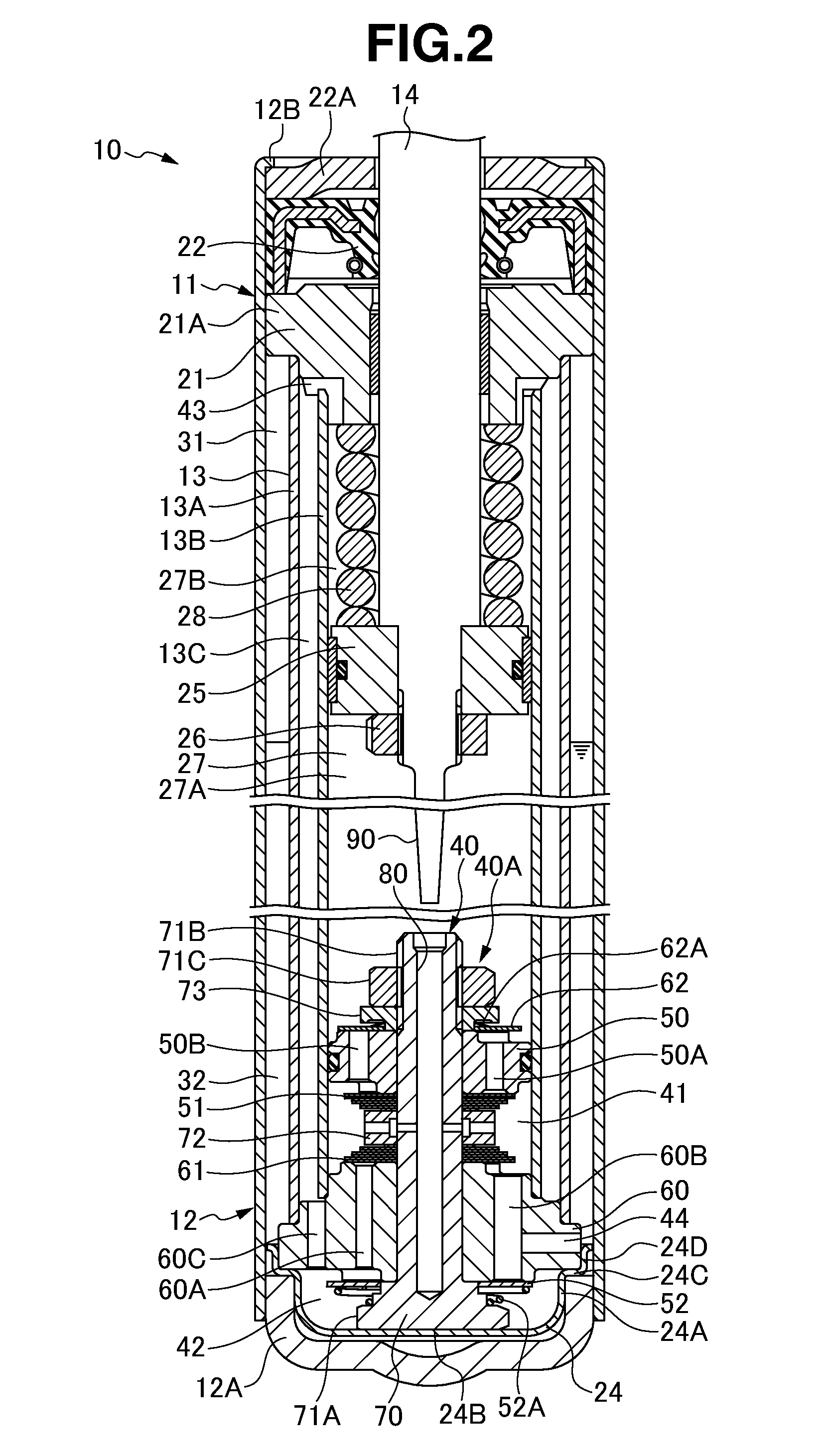
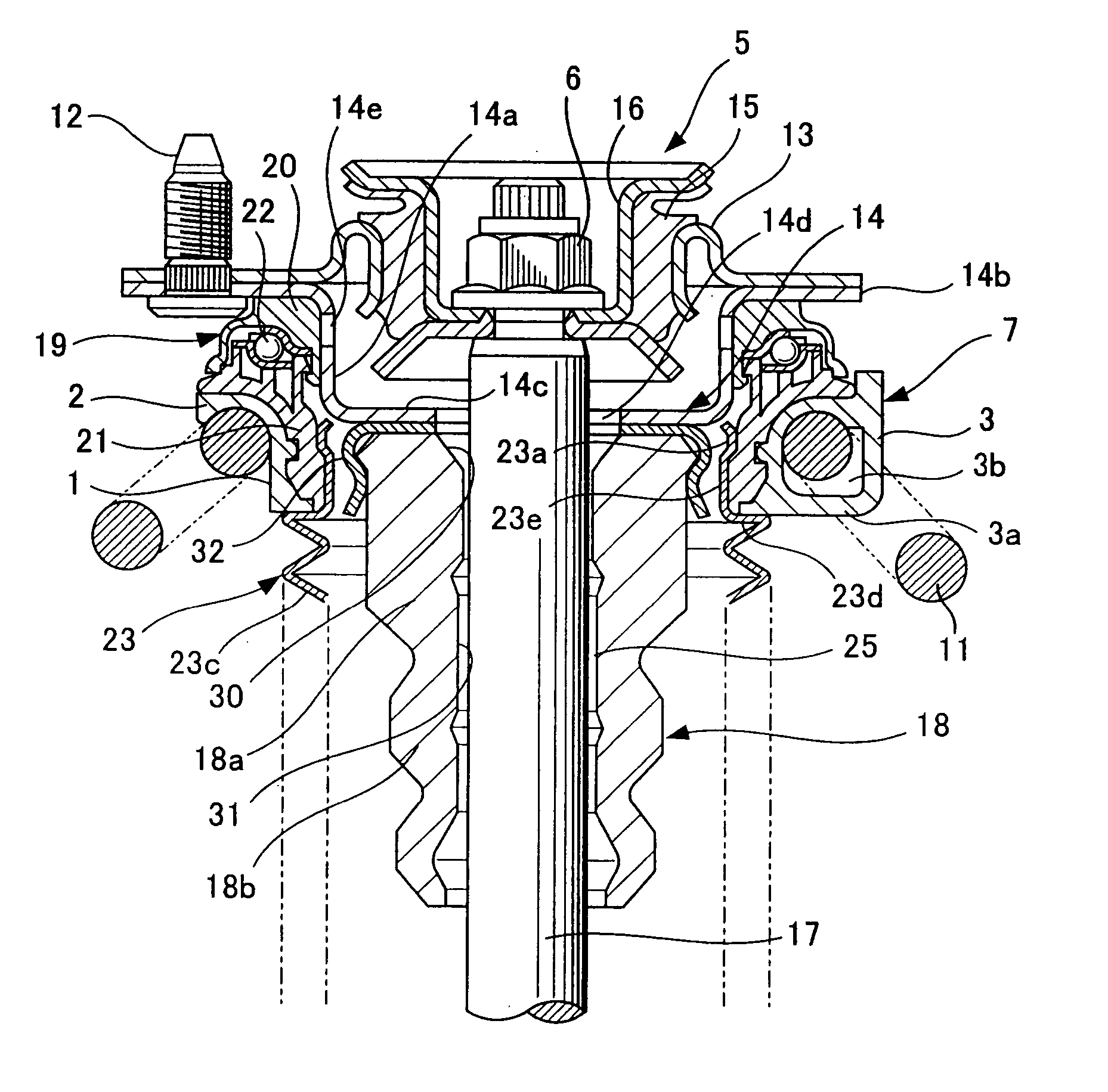
Hydraulic shock absorber
InactiveUS20050247531A1Prevent degradationIncreased durabilitySpringsRigid suspensionsEngineeringHydraulic shock
A bump cushion (18) is inserted and fixed in an outer periphery of an upper portion of a piston rod (17) connected to a vehicle body mount (5), and the bumping of the upper portion of a cylinder (8) on the bump cushion (18) at the time of the compression operation absorbs the jolts. A circular clearance (25) is all the time formed between an inner periphery of the bump cushion (18) and an outer periphery of the piston rod (17) and the clearance (25) is communicated with an outside.
Owner:KYB CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com