Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
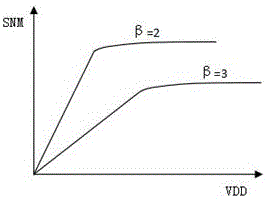
50results about How to "Improve static noise margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
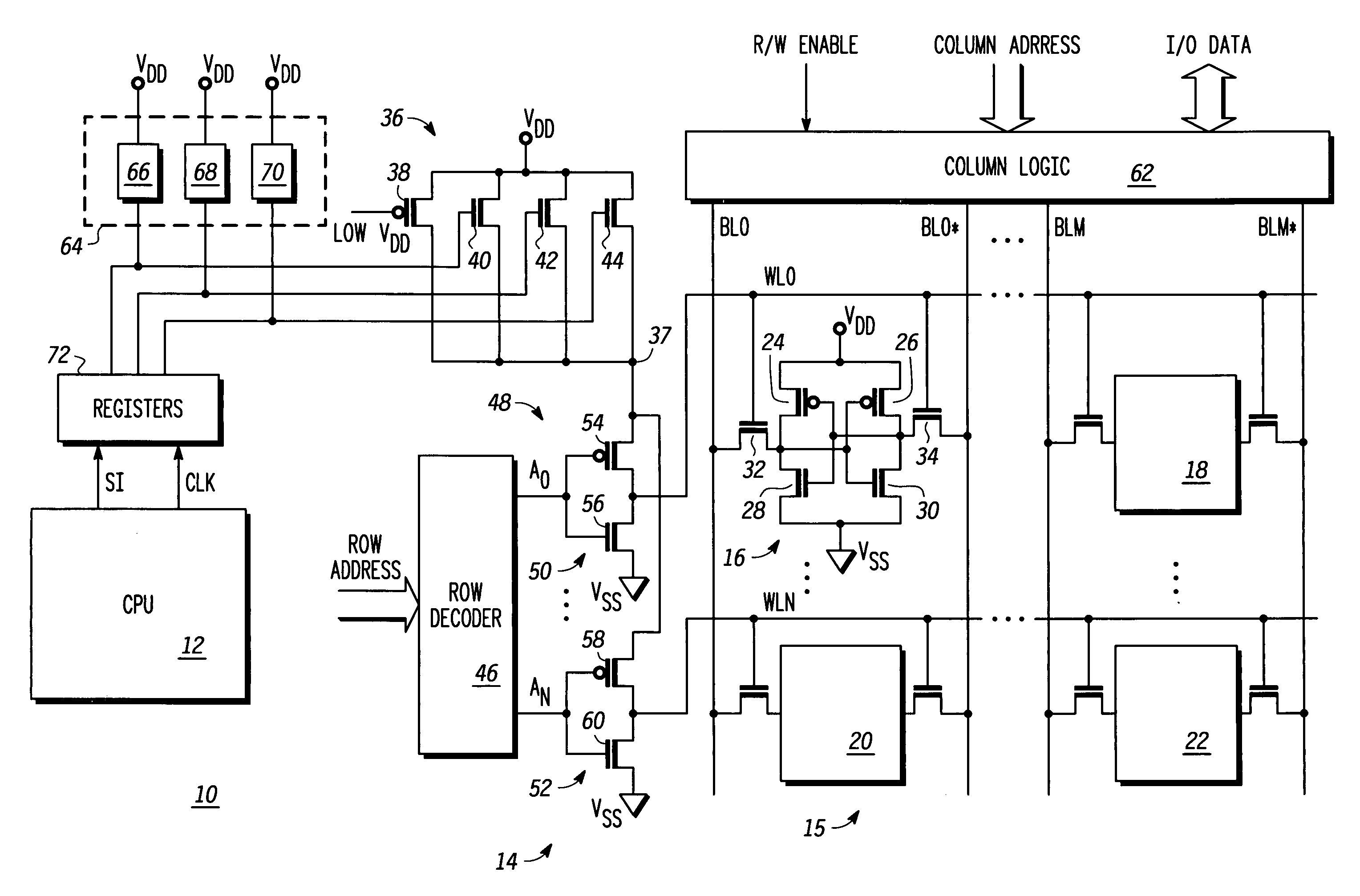
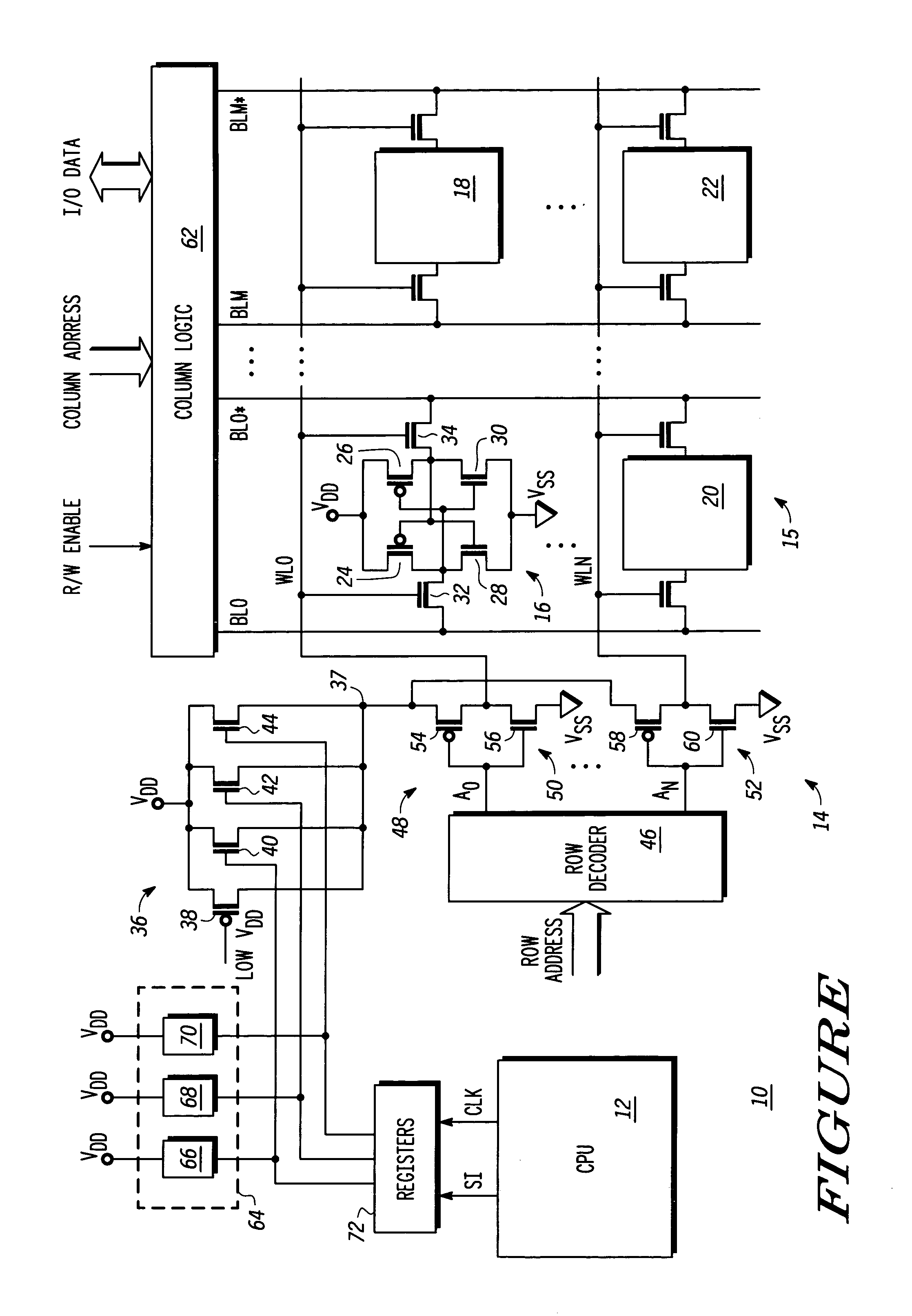
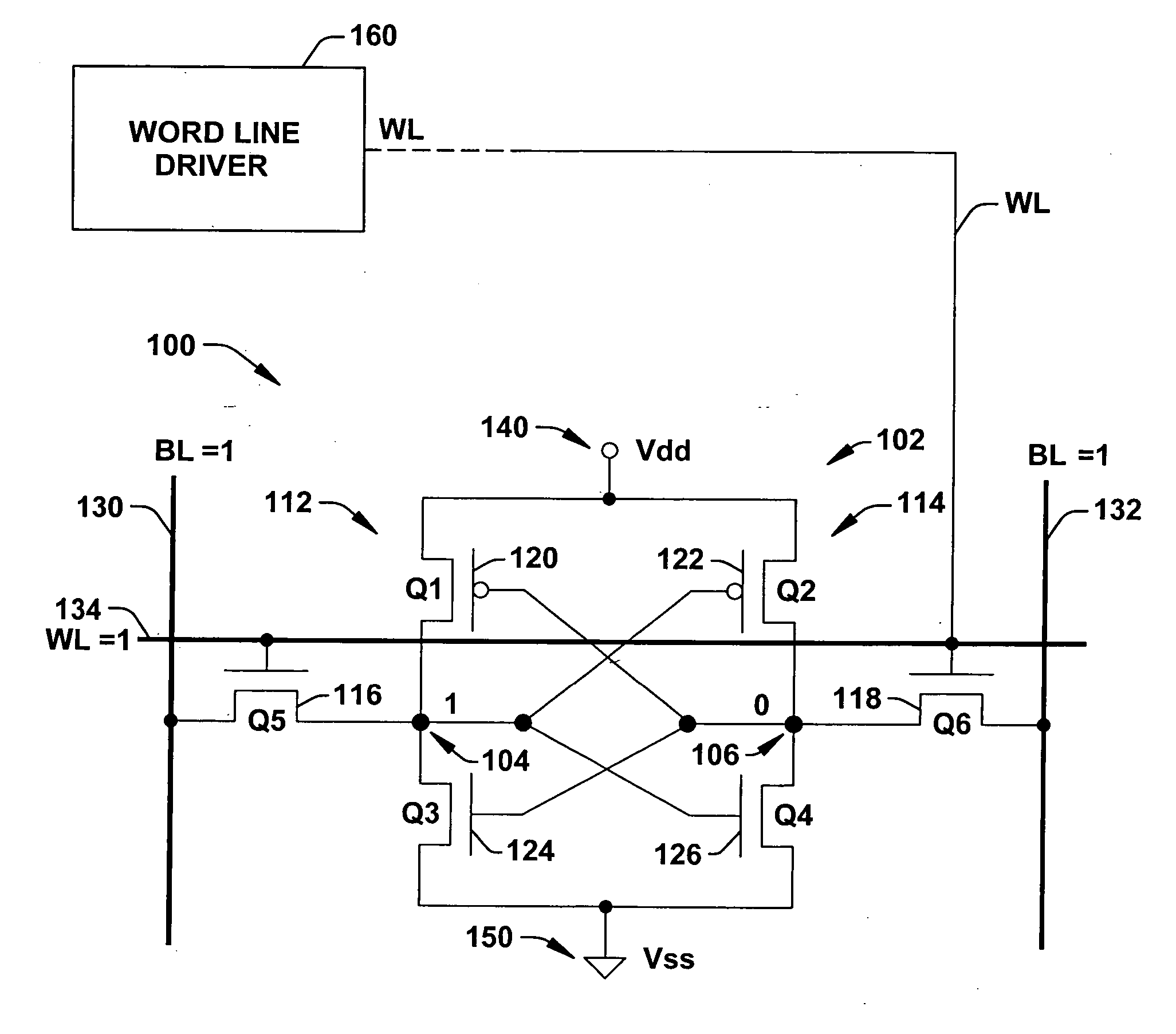
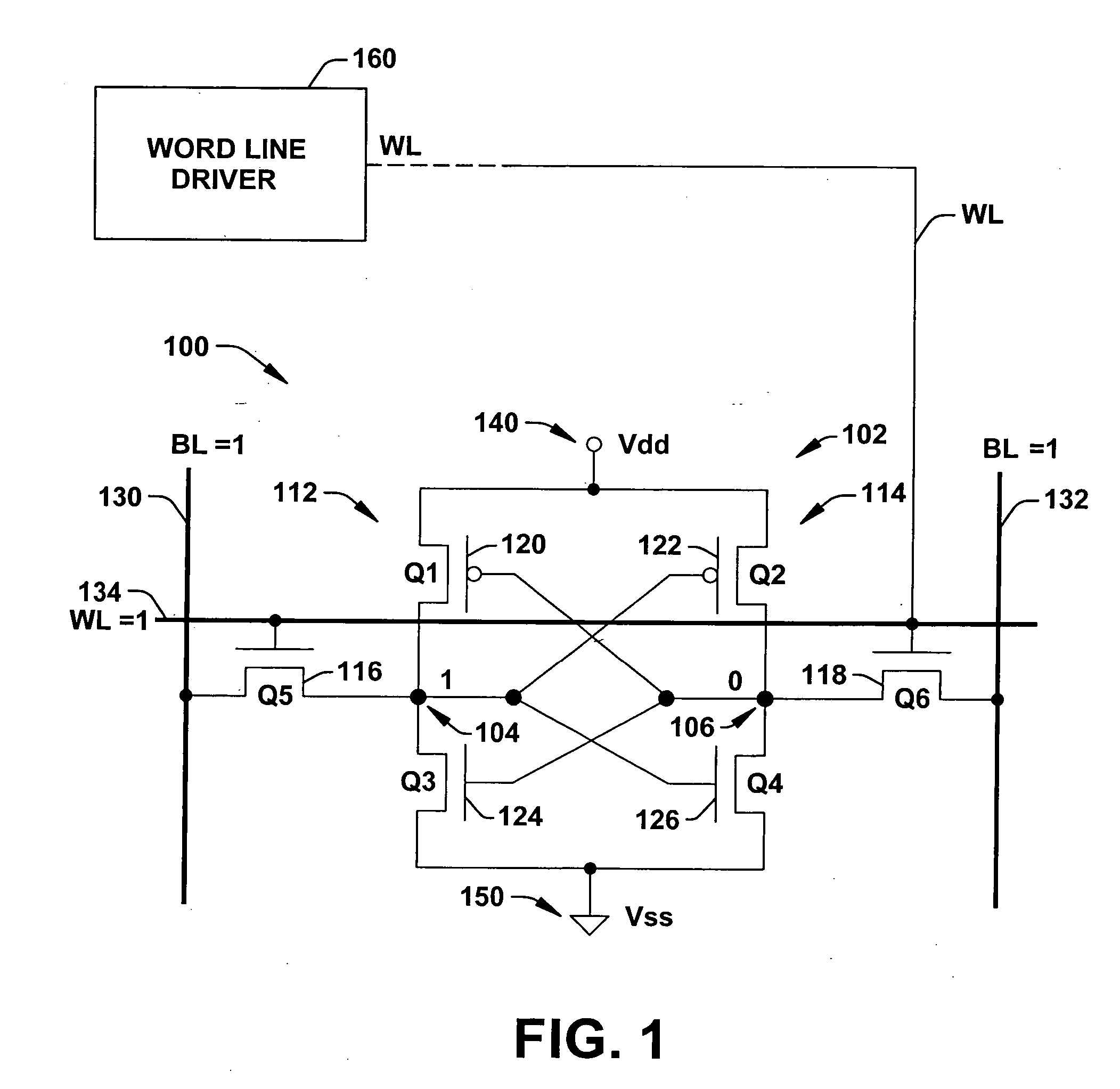
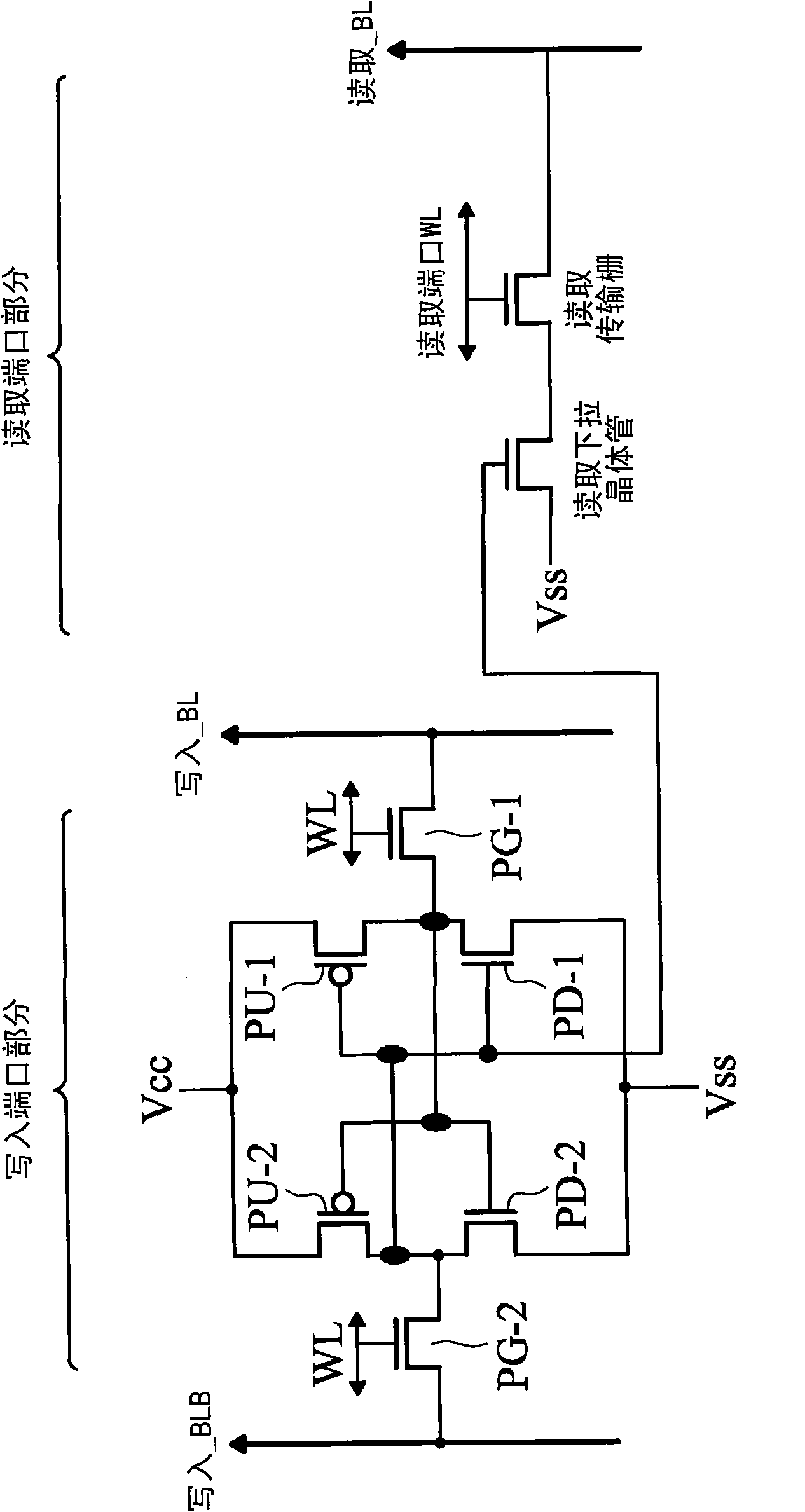
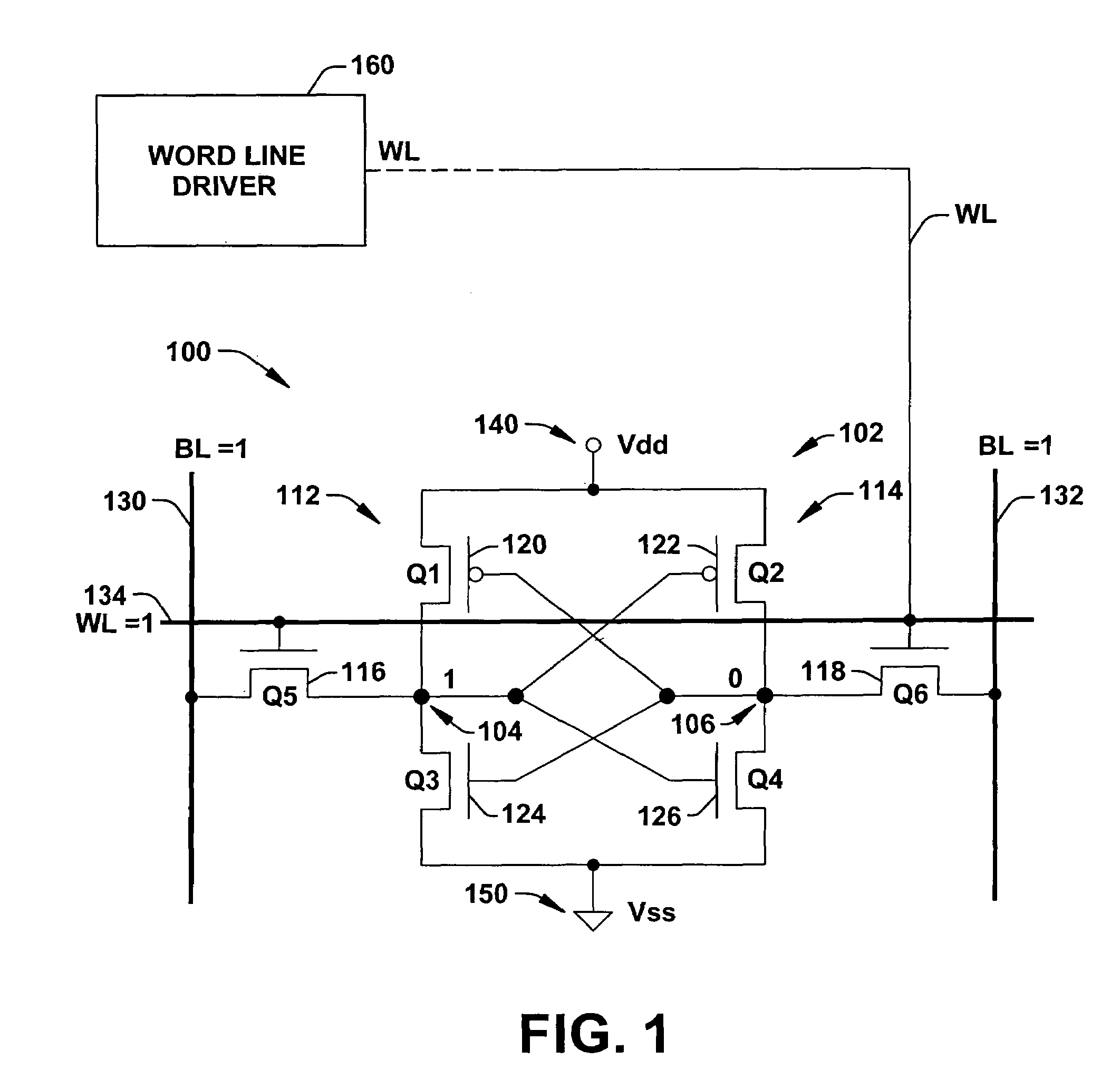
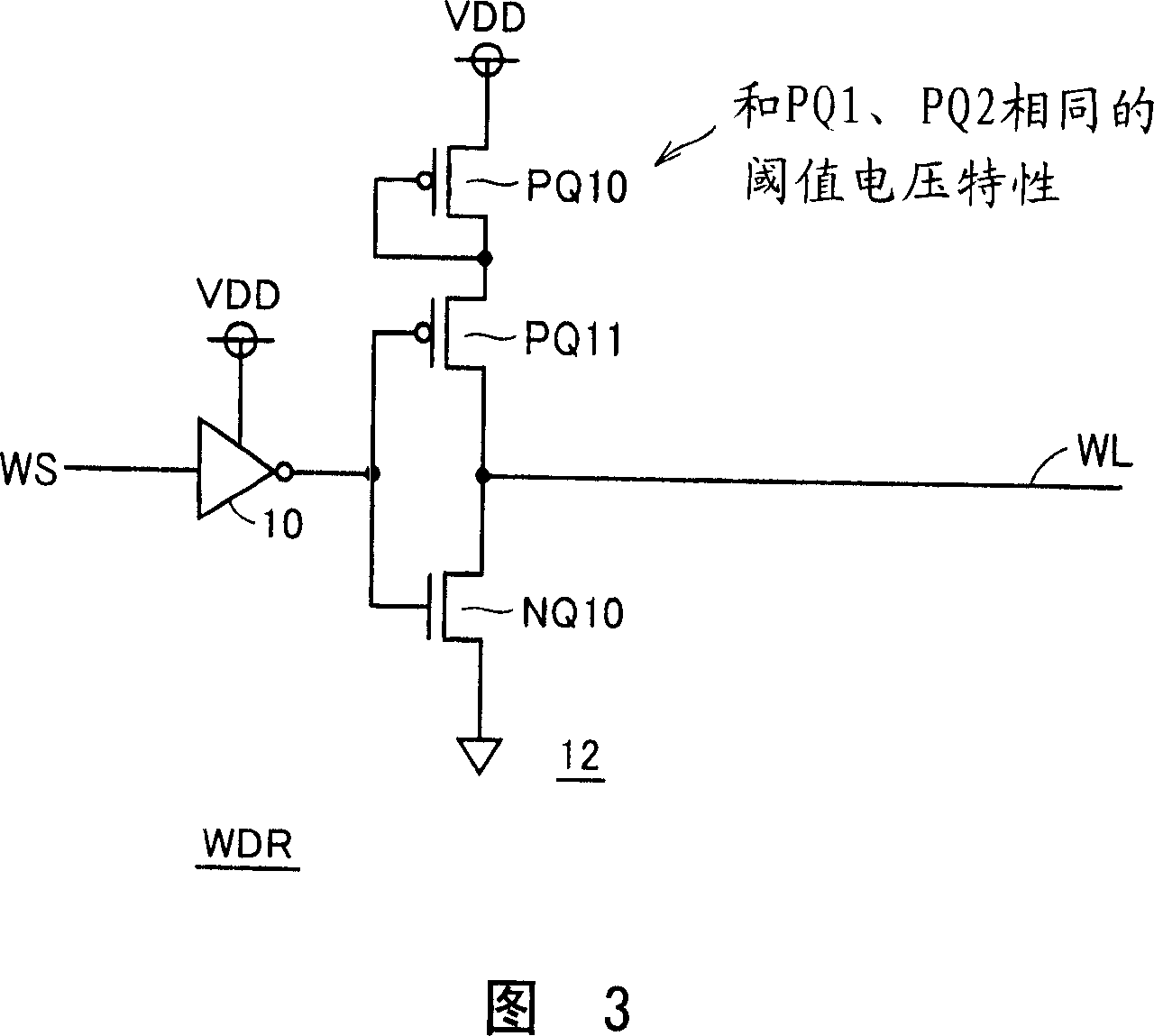
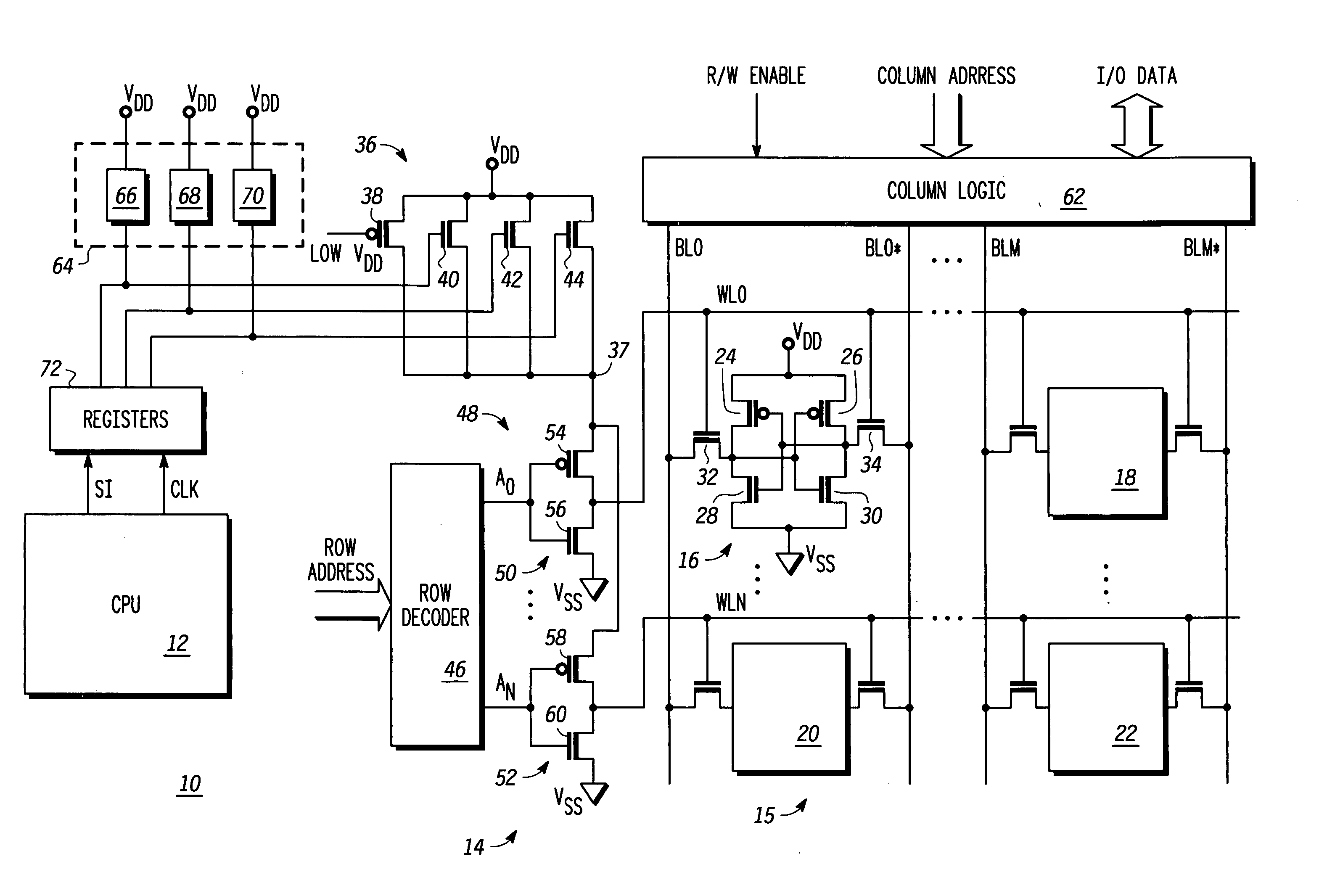
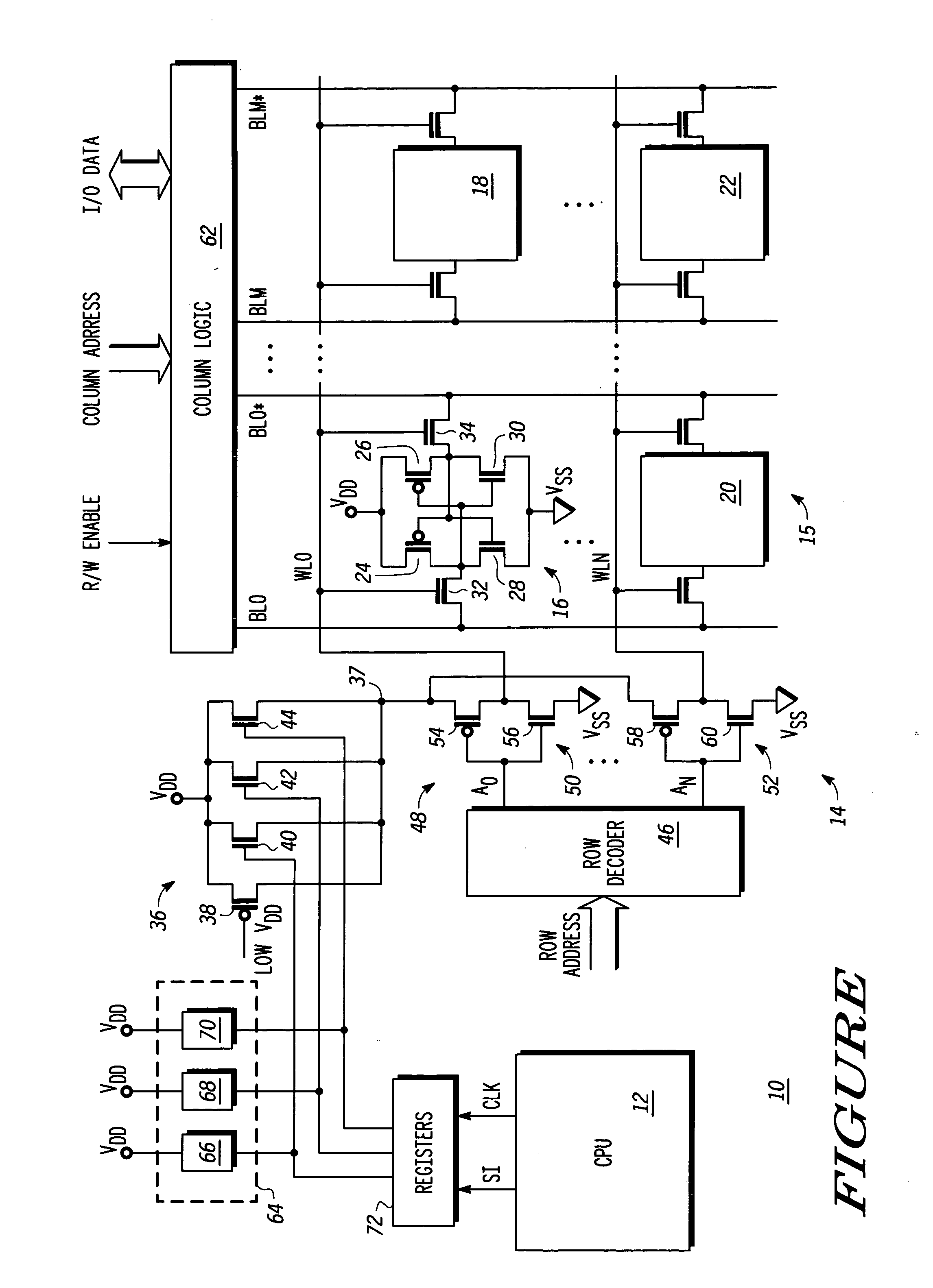
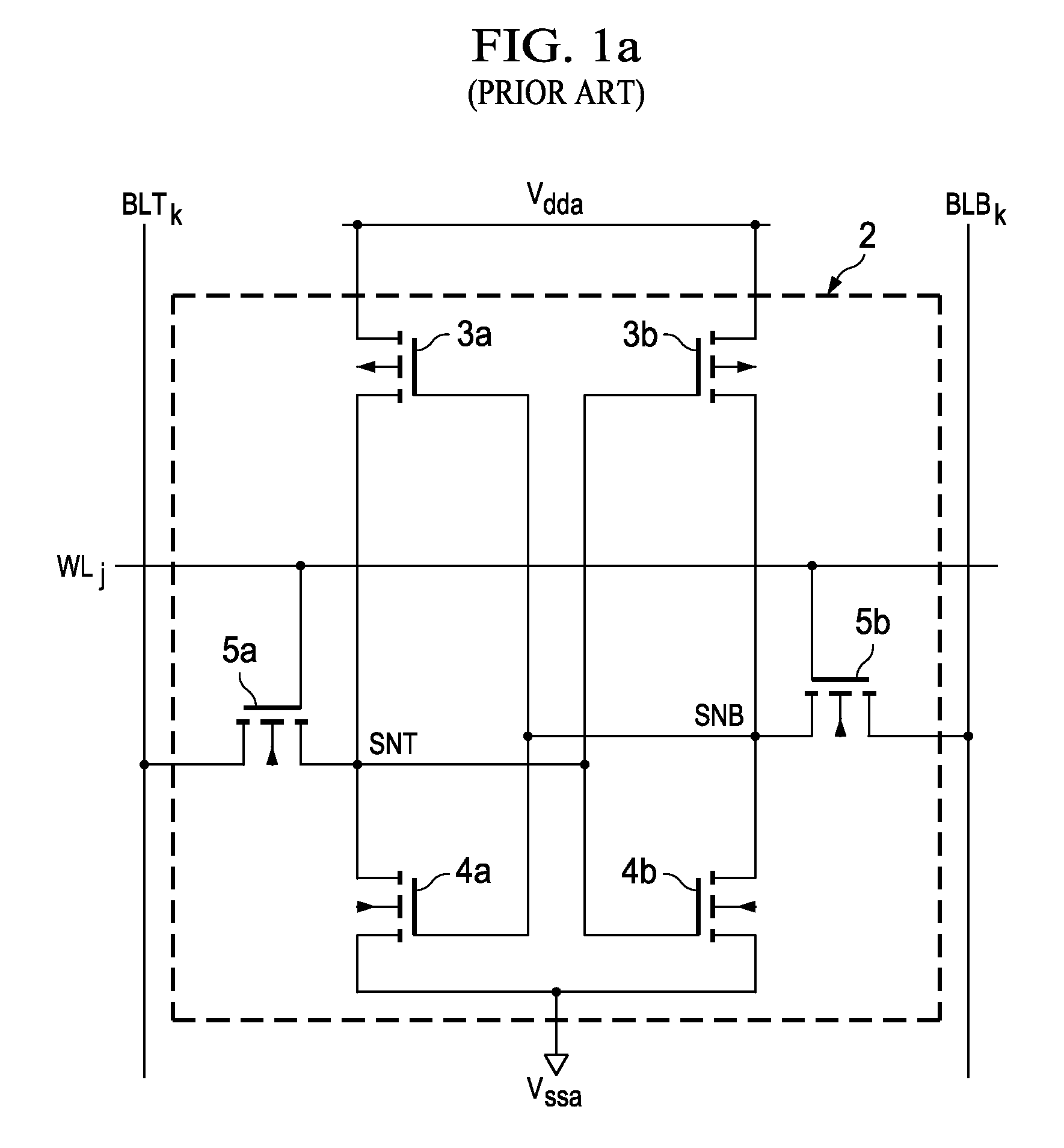
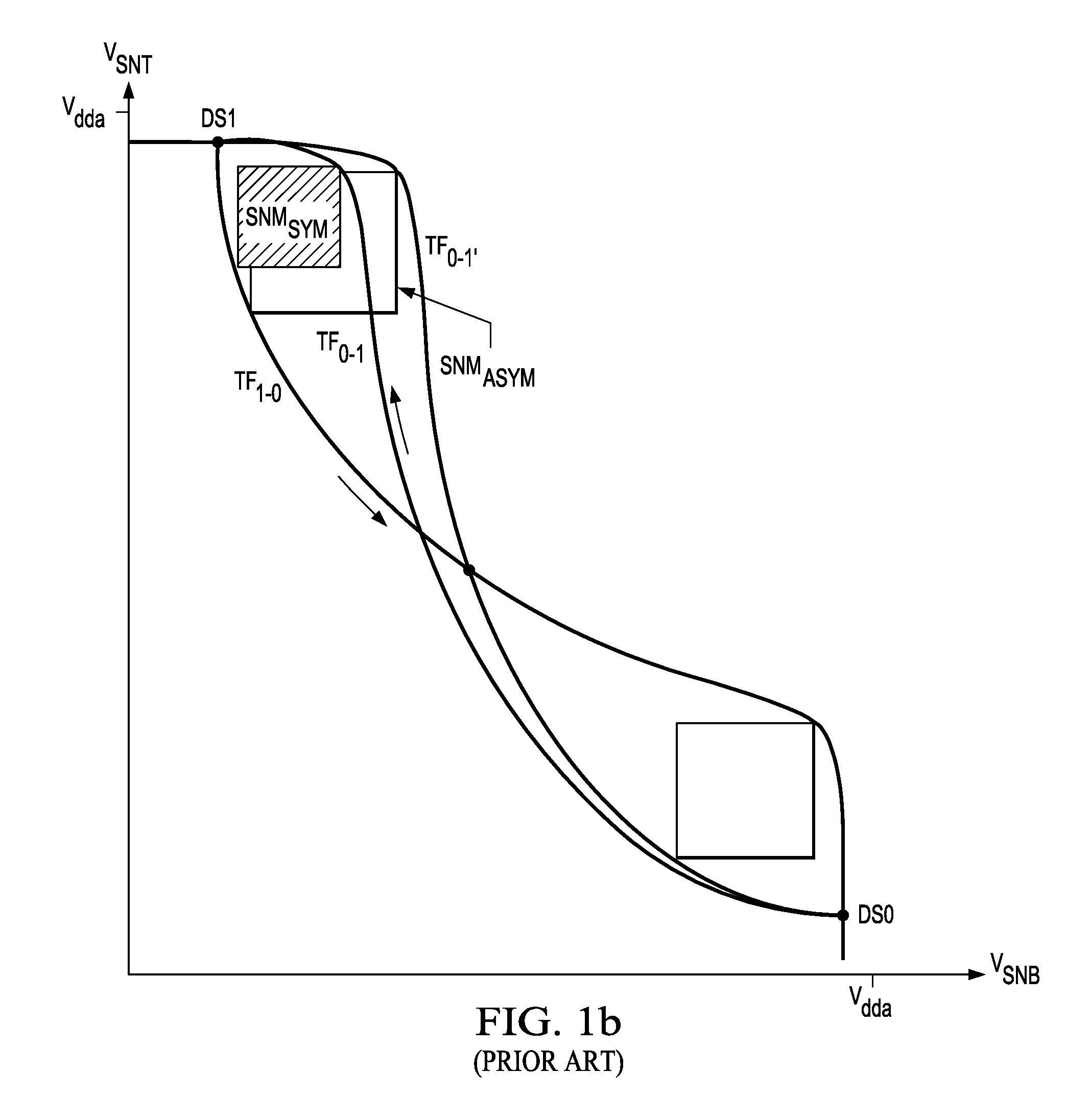
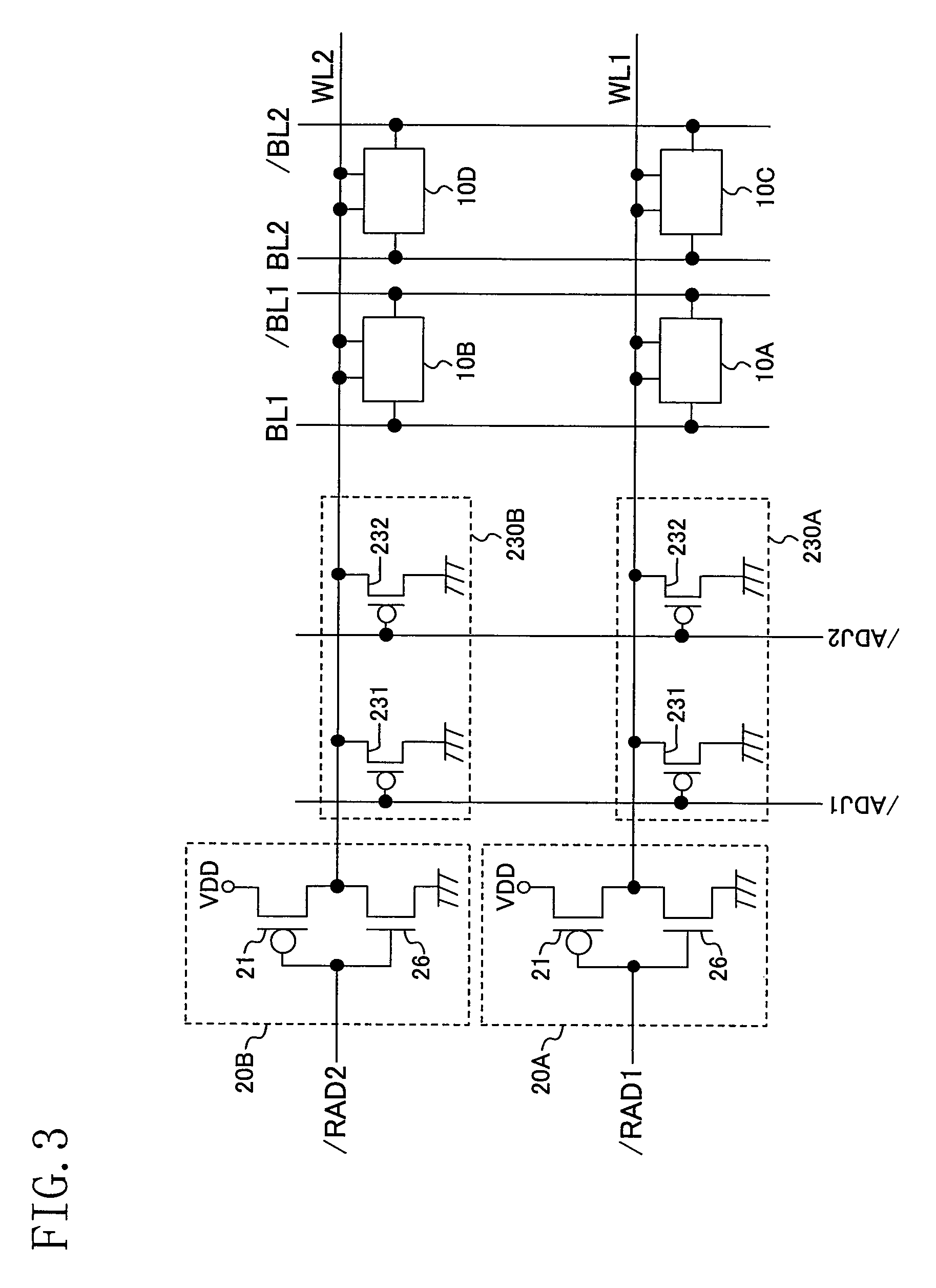
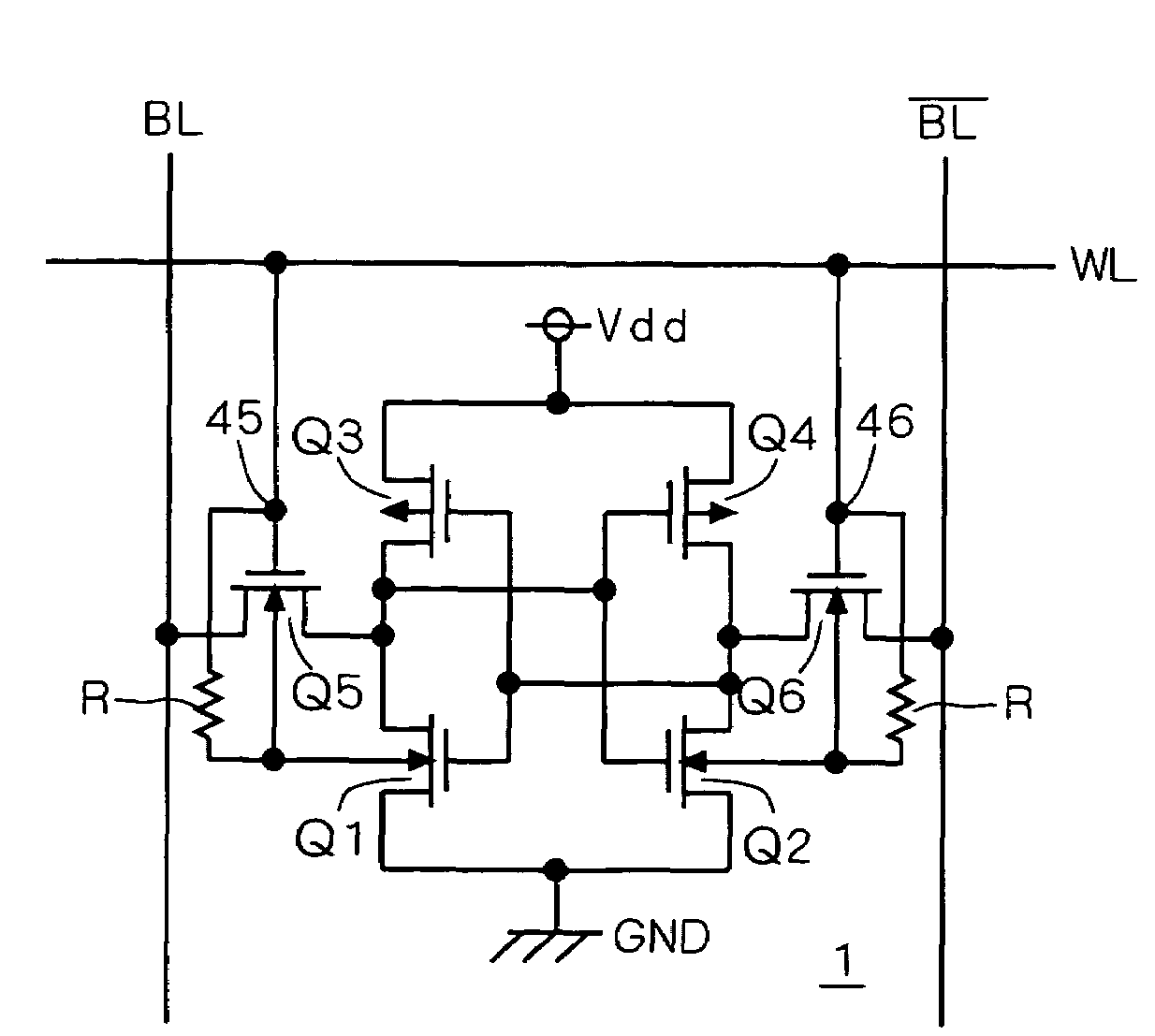
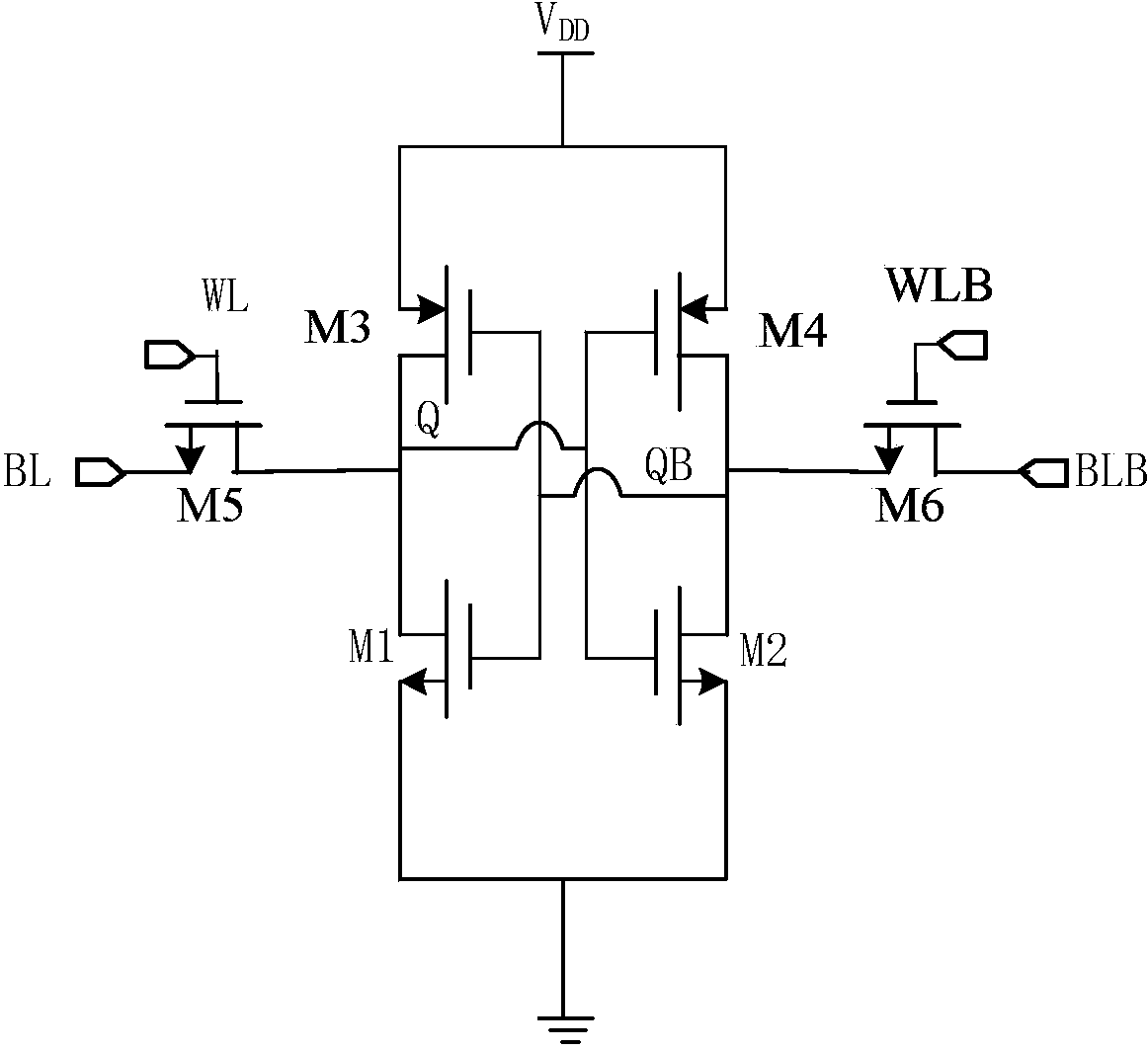
Word line driver circuit for a static random access memory and method therefor
ActiveUS7085175B2Improve static noise marginReduce decreaseRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
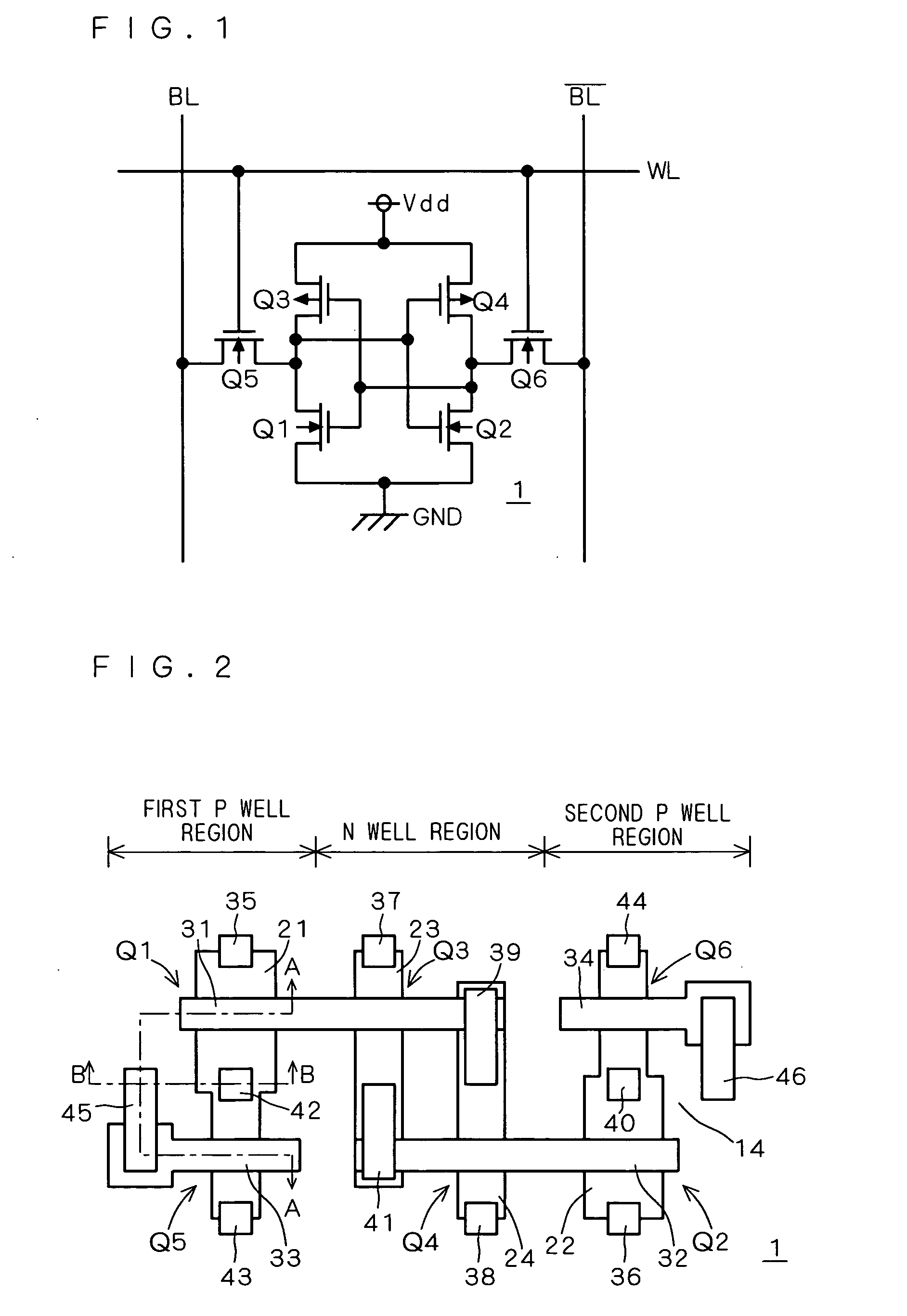
A static random access memory (14) has a normal mode of operation and a low voltage mode of operation. A memory array (15) includes memory cells (16) coupled to a first power supply node (VDD) for receiving a power supply voltage. A plurality of word line drivers is coupled to word lines of the memory array (15) and to a second power supply node (37). A word line driver voltage reduction circuit (36) has an input coupled to the first power supply node (VDD) and an output coupled to the second power supply node (37) for reducing a voltage on the output in relation to a voltage on the input in response to a low power supply voltage signal, and thus improving a static noise margin of the memory cells (16).
Owner:NXP USA INC
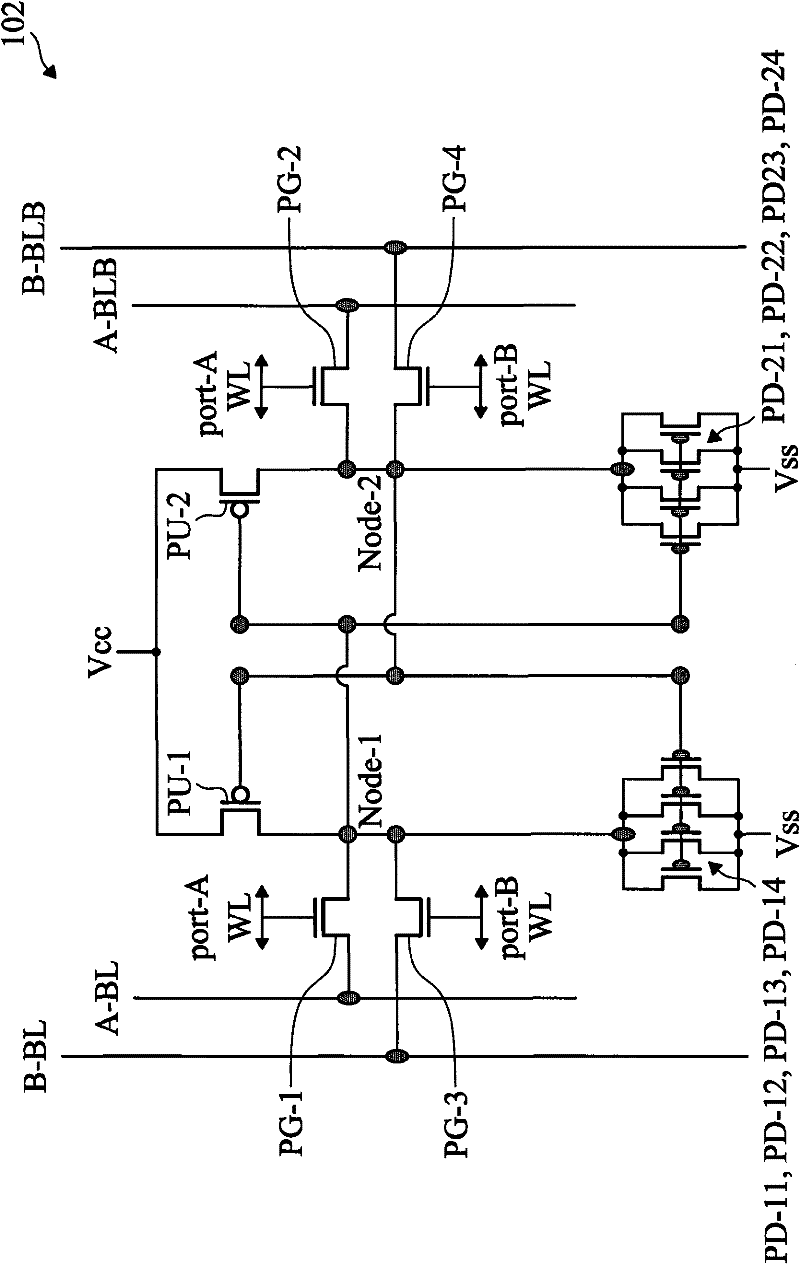
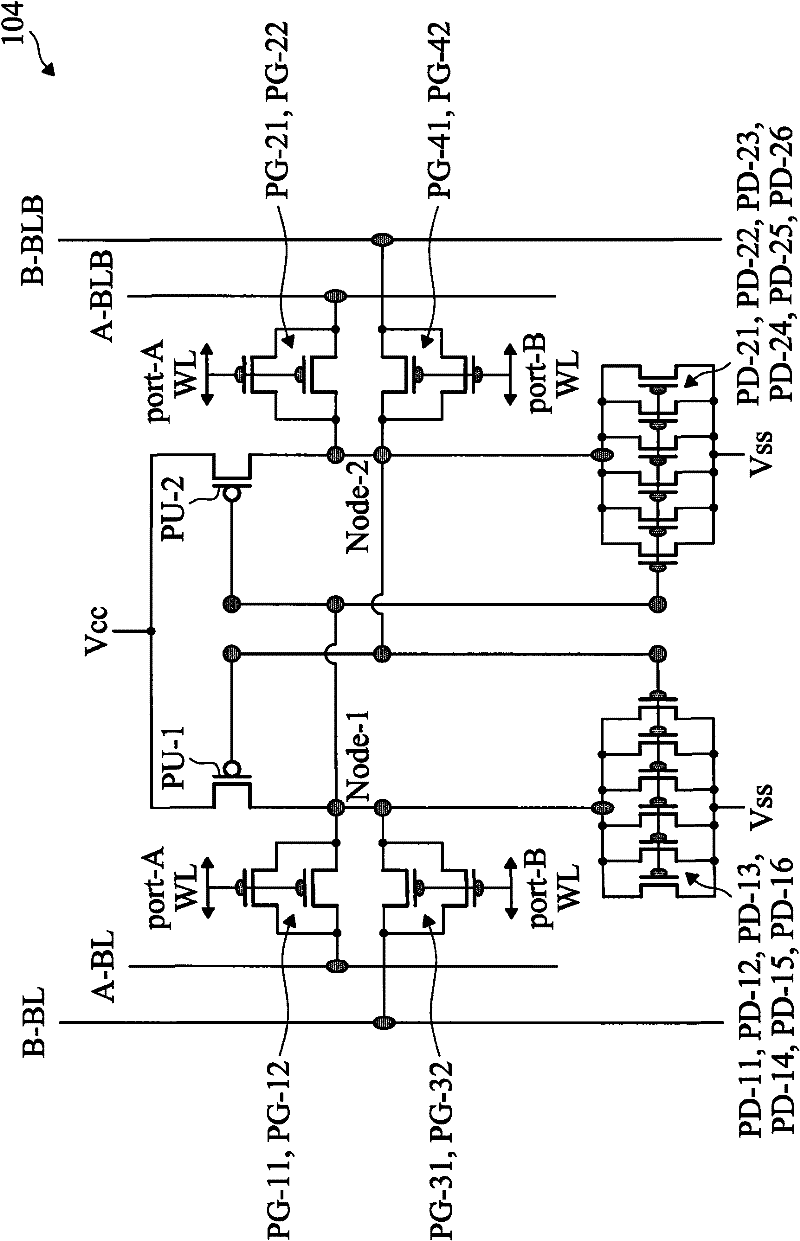
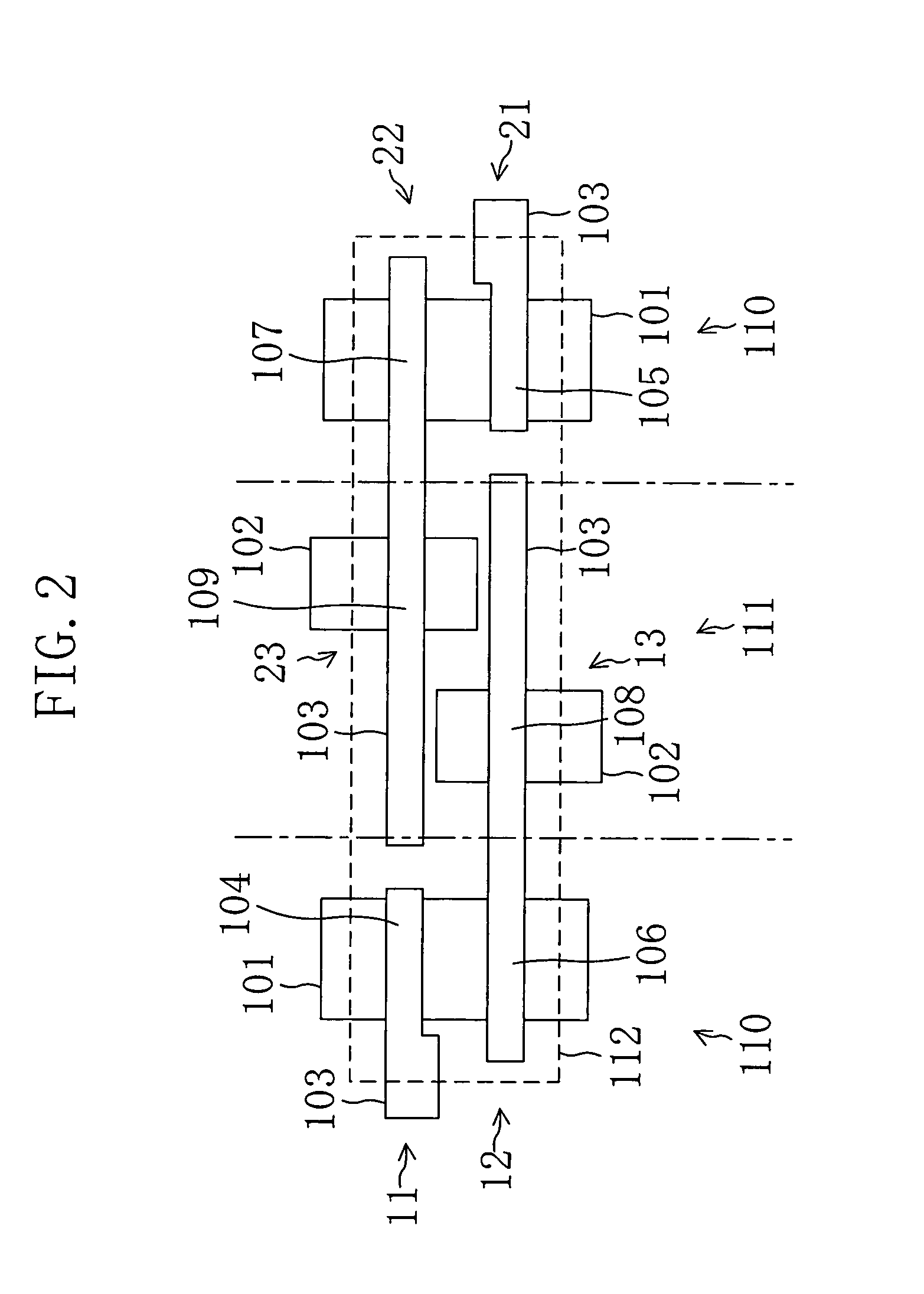
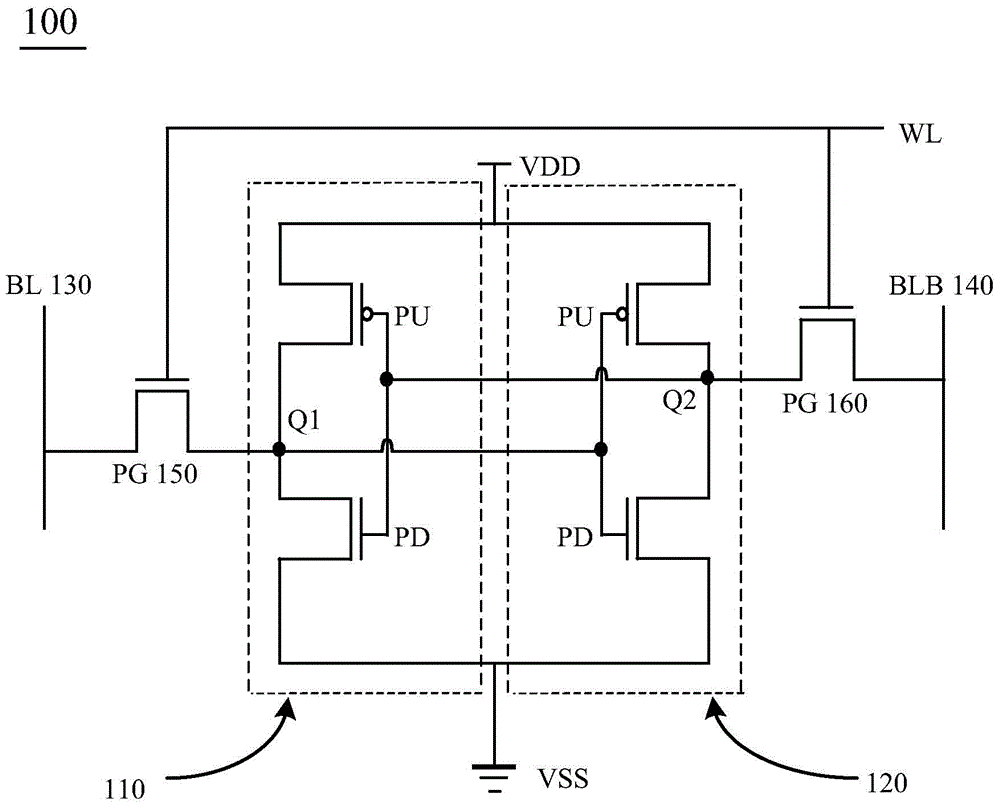
Cell Structure of Dual Port Static Random Access Memory
InactiveCN102298963ASolving Current Clustering ProblemsDevice Track/Match OKTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
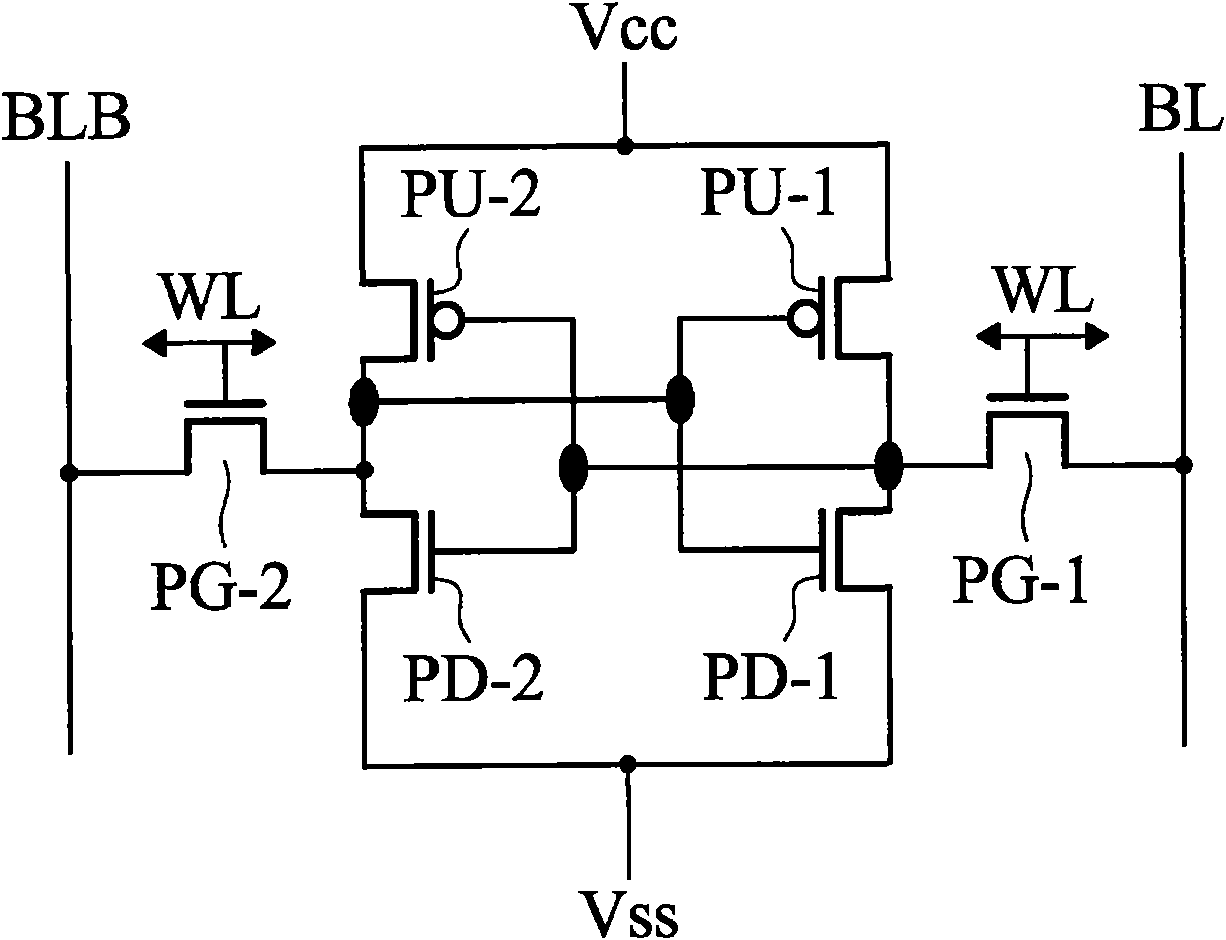
The present disclosure provides a dual port static random access memory (SRAM) cell. The dual-port SRAM cell includes a first and second inverters cross-coupled for data storage, each inverter includes a pull-up device (PU) and a plurality of pull-down devices (PDs); a plurality of pass gate devices configured with the two cross-coupled inverters; and at least two ports coupled with the plurality of pass gate devices (PGs) for reading and writing, wherein each of PU, PDs and PGs includes a fin field-effect transistor (FinFET), a ratio between a number of PDs in the SRAM cell and a number of PGs in the SRAM cell is greater than 1, and a number of FinFETs in the SRAM cell is equal to or greater than 12.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
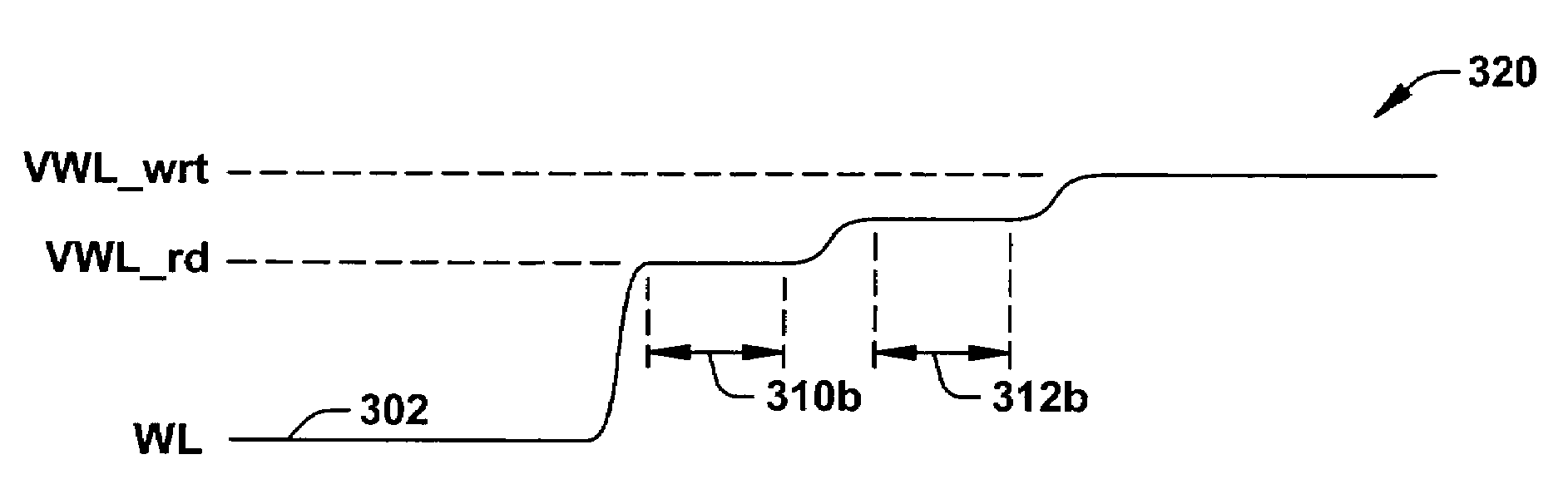
Memory array with a delayed wordline boost
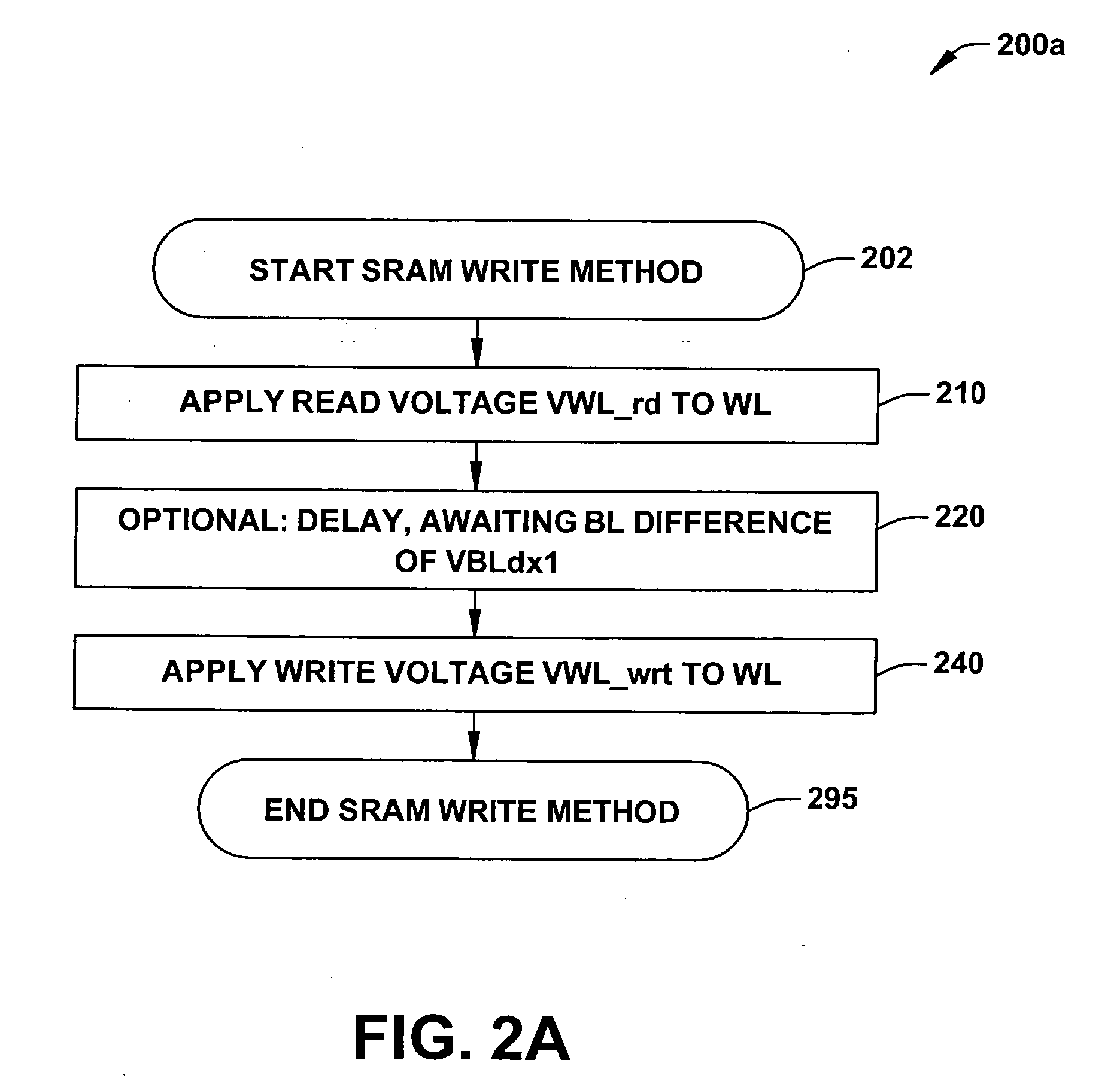
ActiveUS20070025169A1Least riskImprove static noise marginDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
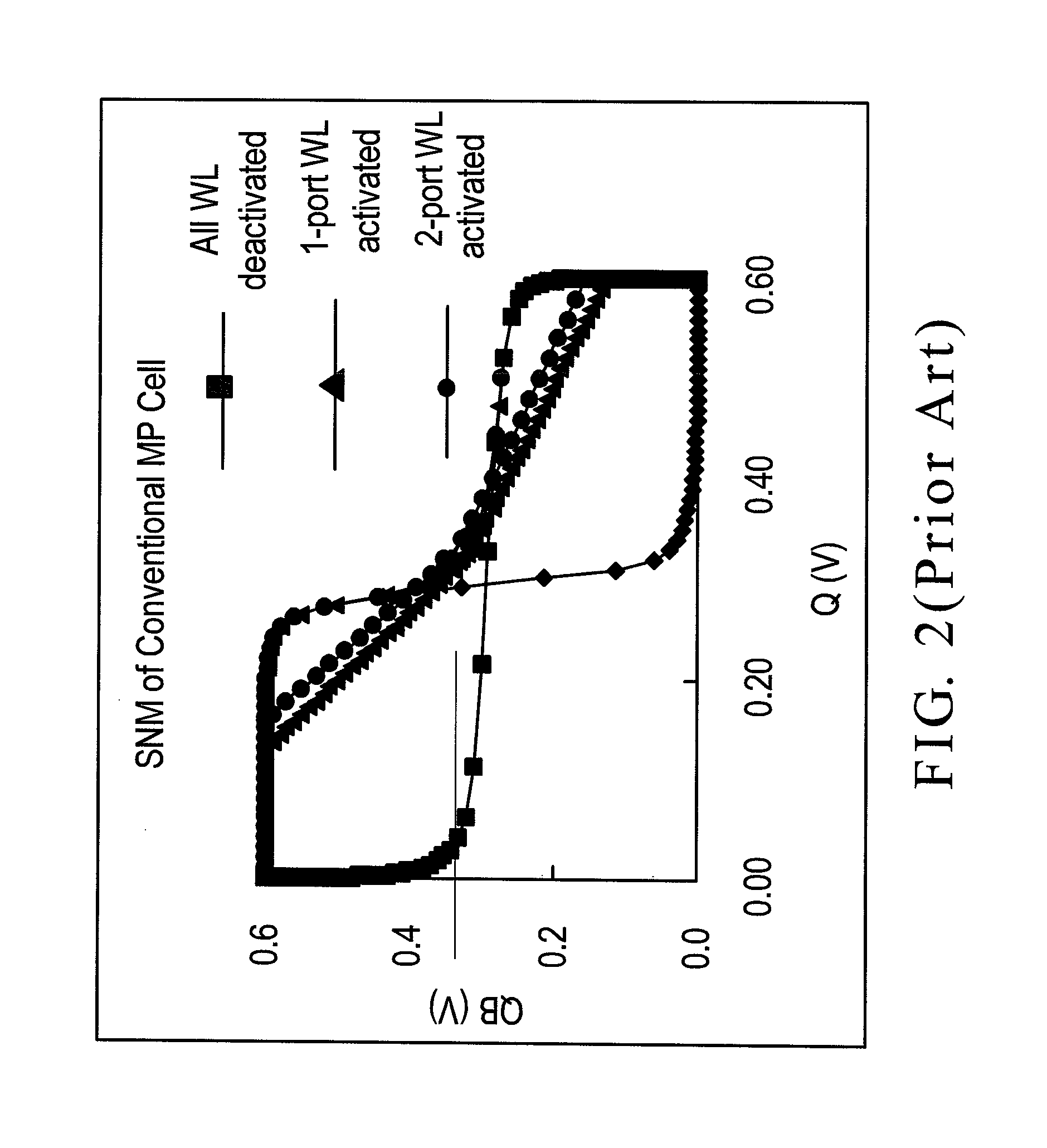
Methods and a circuit for writing to an SRAM memory cell of an array are discussed that provide improved static noise margin, and minimal risk of data upsets during write operations. The write method first rapidly raises the wordline to a lower read voltage level for access, then after a time delay that allows the cells in the selected row to establish a stabilizing differential voltage on the associated bitlines, raises the wordline voltage to a boosted or higher write voltage level. An SRAM bitline enhancement circuit may also be utilized in association with the SRAM memory array and writing method, for enhancing the differential voltage produced by an SRAM memory cell of the array on associated first and second bitlines of the array of conventional SRAM cells (e.g., a conventional 6T differential cell). In one implementation, the SRAM bitline enhancement circuit comprises a half-latch or a sense amplifier connected to associated bitline pairs of the array for amplifying the differential voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050078546A1Improve reliabilityIncrease the areaTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringBody region
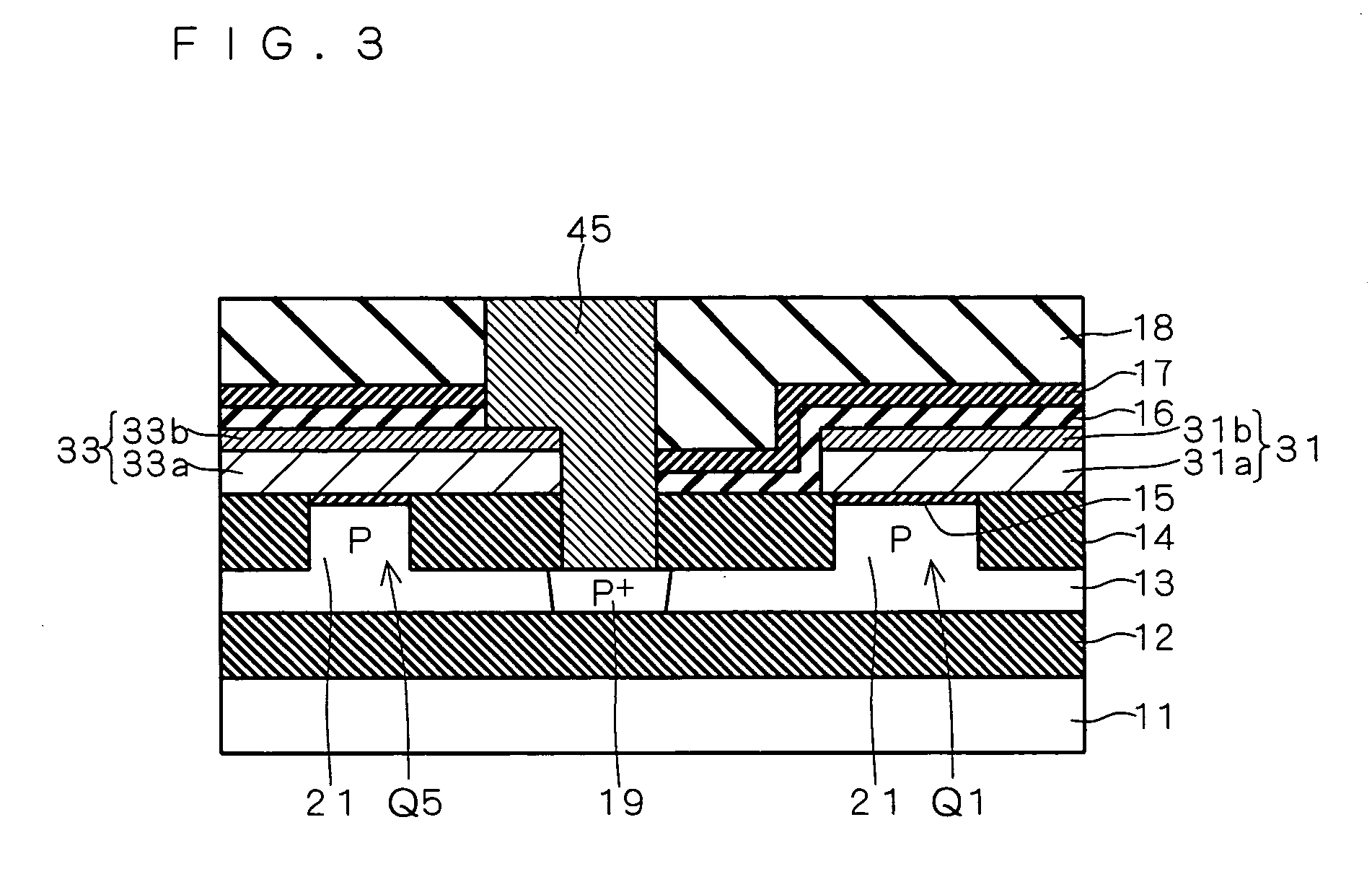
A contact connected to a word line is formed on a gate electrode of an access transistor of an SRAM cell. The contact passes through an element isolation insulating film to reach an SOI layer. A body region of a driver transistor and that of the access transistor are electrically connected with each other through the SOI layer located under the element isolation insulating film. Therefore, the access transistor is in a DTMOS structure having the gate electrode connected with the body region through the contact, which in turn is also electrically connected to the body region of the driver transistor. Thus, operations can be stabilized while suppressing increase of an area for forming the SRAM cell.
Multi-port SRAM with shared write bit-line architecture and selective read path for low power operation
InactiveUS9142285B2Low power operationImprove static noise marginDigital storageComputer architecturePre-charge
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Embedded sram structure and chip
ActiveCN102034825AImprove reliabilityGood compatibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryComputer architecture
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
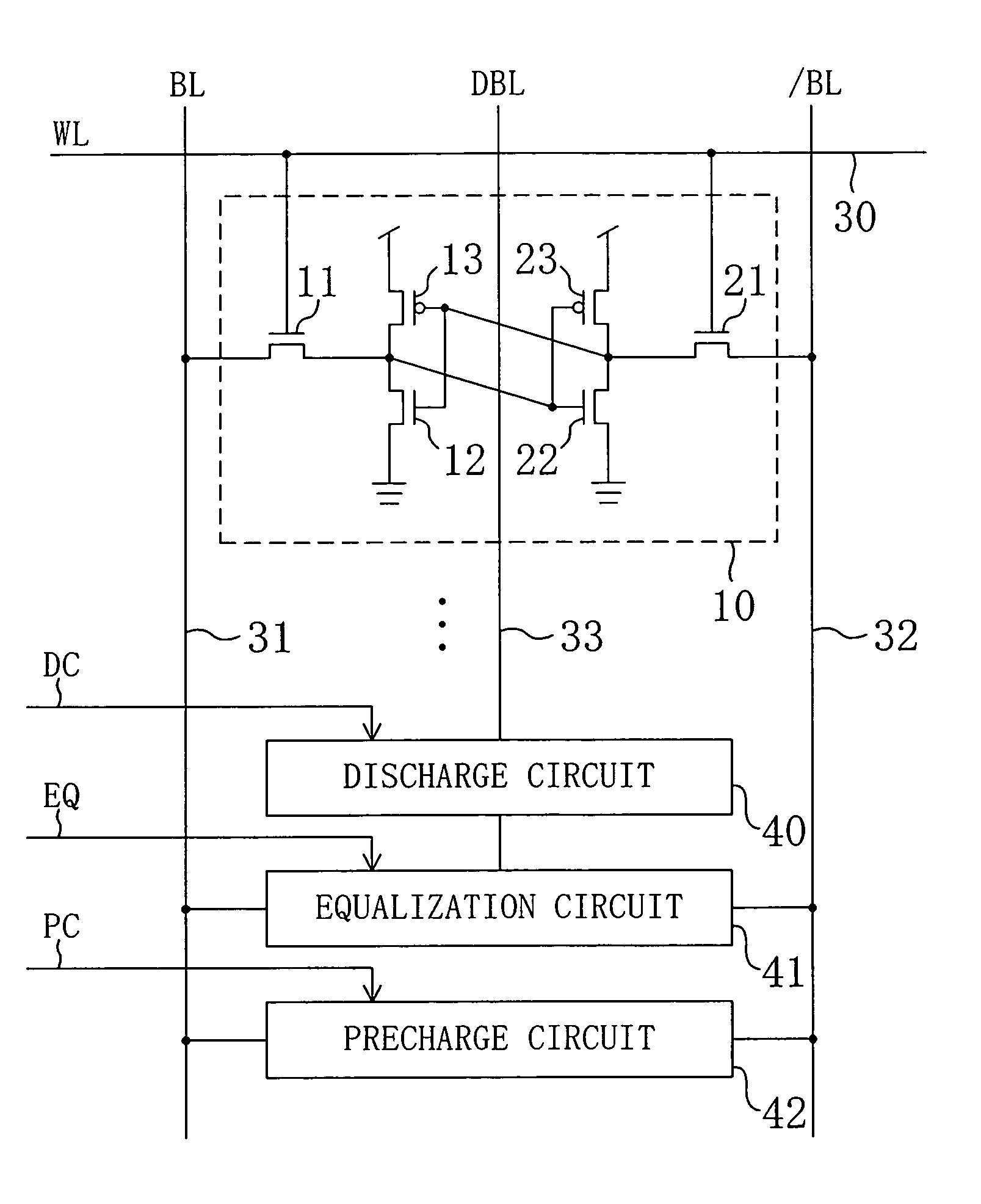
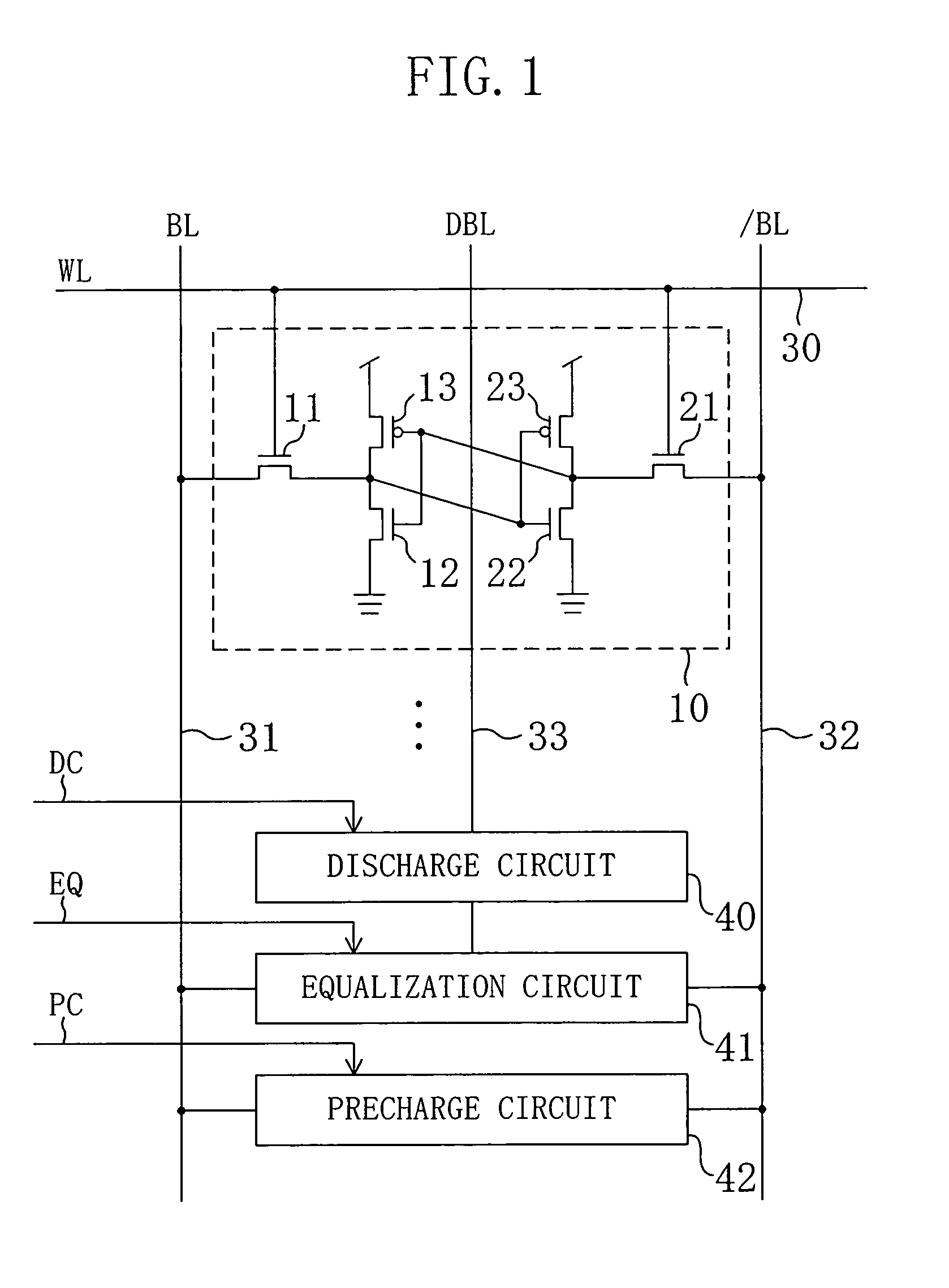
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS6982899B2Reduce voltageAvoid failureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStatic noise margin
A dummy bit line is provided between a pair of bit lines. The pair of bit lines is set at a power supply voltage and the dummy bit line is set at a ground voltage, and then the pair of bit lines and the dummy bit line are equalized. When a word line is activated in subsequent read operation, the pair of bit lines is at an intermediate potential lower than the power supply voltage, so that an apparent current drive capability of an access transistor decreases, and the static noise margin of a memory cell increases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Memory array with a delayed wordline boost
Methods and a circuit for writing to an SRAM memory cell of an array are discussed that provide improved static noise margin, and minimal risk of data upsets during write operations. The write method first rapidly raises the wordline to a lower read voltage level for access, then after a time delay that allows the cells in the selected row to establish a stabilizing differential voltage on the associated bitlines, raises the wordline voltage to a boosted or higher write voltage level. An SRAM bitline enhancement circuit may also be utilized in association with the SRAM memory array and writing method, for enhancing the differential voltage produced by an SRAM memory cell of the array on associated first and second bitlines of the array of conventional SRAM cells (e.g., a conventional 6T differential cell). In one implementation, the SRAM bitline enhancement circuit comprises a half-latch or a sense amplifier connected to associated bitline pairs of the array for amplifying the differential voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveCN1956098ASimple structureIncrease layout areaDigital storageSemiconductor storage devicesSemiconductor
A level shift element adjusting a voltage level at the time of selection of a word line according to fluctuations in threshold voltage of a memory cell transistor is arranged for each word line. This level shift element lowers a driver power supply voltage, and transmits the level-shifted voltage onto a selected word line. The level shift element can be replaced with a pull-down element for pulling down the word line voltage according to the threshold voltage level of the memory cell transistor. In either case, the selected word line voltage level can be adjusted according to the fluctuations in threshold voltage of the memory cell transistor without using another power supply system. Thus, the power supply circuitry is not complicated, and it is possible to achieve a semiconductor memory device that can stably read and write data even with a low power supply voltage.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Word line driver circuit for a static random access memory and method therefor
ActiveUS20060104107A1Improve static noise marginReduce decreaseRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A static random access memory (14) has a normal mode of operation and a low voltage mode of operation. A memory array (15) includes memory cells (16) coupled to a first power supply node (VDD) for receiving a power supply voltage. A plurality of word line drivers is coupled to word lines of the memory array (15) and to a second power supply node (37). A word line driver voltage reduction circuit (36) has an input coupled to the first power supply node (VDD) and an output coupled to the second power supply node (37) for reducing a voltage on the output in relation to a voltage on the input in response to a low power supply voltage signal, and thus improving a static noise margin of the memory cells (16).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Asymmetric static random access memory cell with dual stress liner
ActiveUS8467233B2Increase the areaImprove static noise marginTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryEngineering
A solid-state memory in which each memory cell is constructed of complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) inverters implemented with dual stress liner (DSL) technology. Asymmetry is incorporated into each memory cell by constructing one of the inverter transistors or the pass-gate transistor using the stress liner with opposite stress characteristics from its opposing counterpart. For example, both of the p-channel load transistors and one of the n-channel driver transistors in each memory cell may be constructed with a compressive nitride liner layer while the other driver transistor is constructed with a tensile nitride liner layer. In another implementation, one of the n-channel pass-gate transistors is constructed with a compressive nitride liner layer while the other pass-gate transistor is constructed with a tensile nitride liner layer. Improved cell stability due to the resulting asymmetric behavior is implemented in a cost-free manner.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit
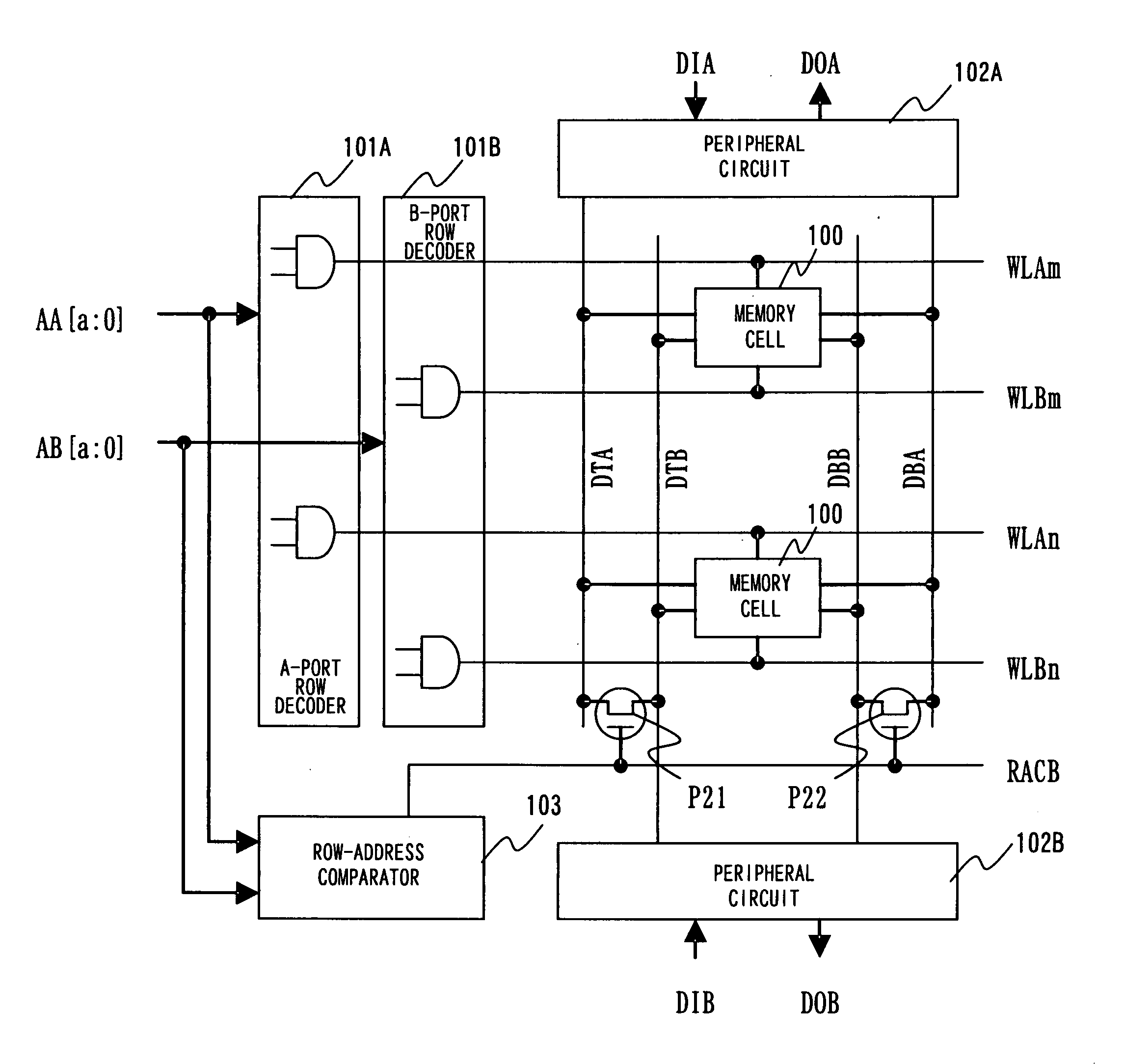
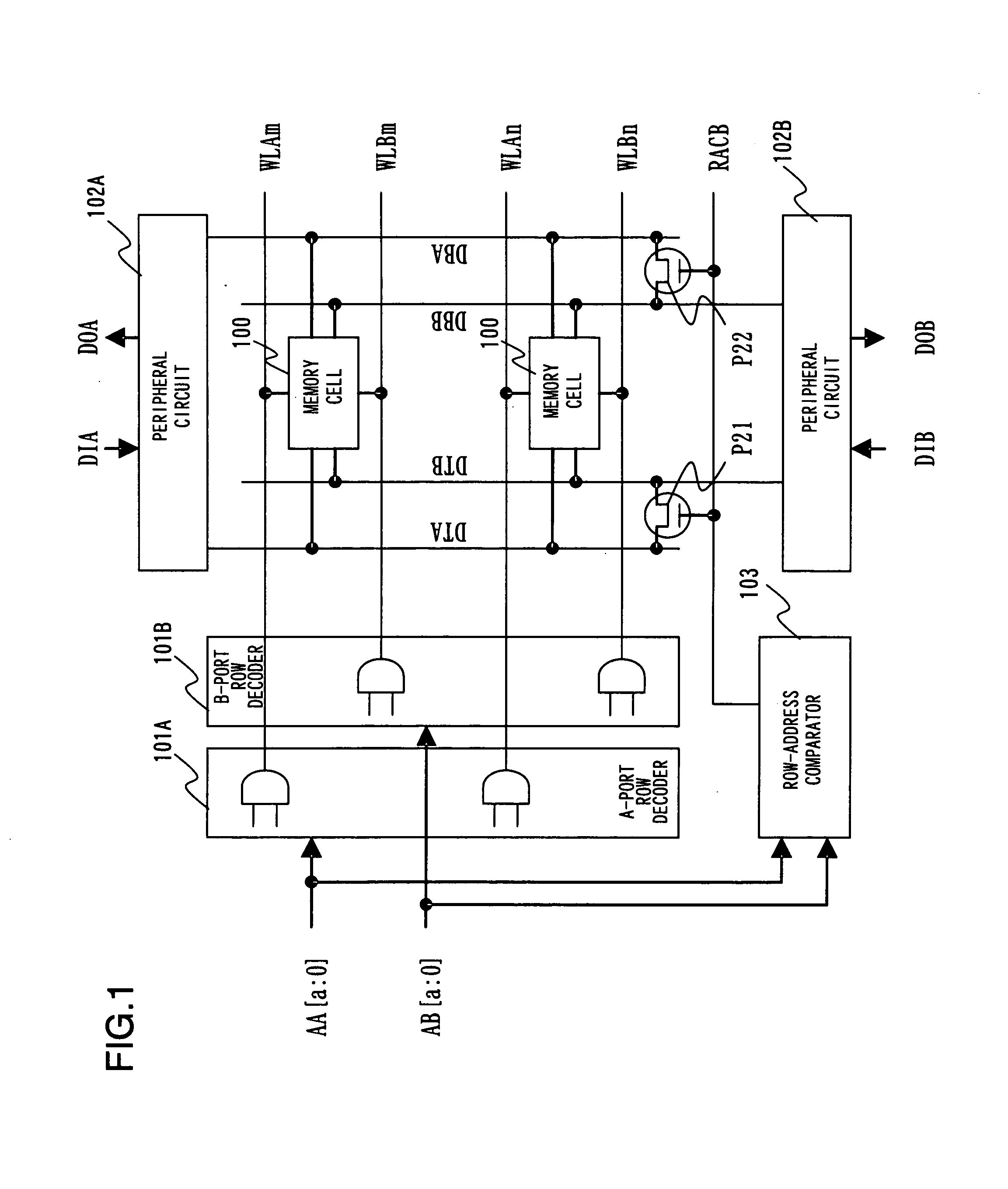
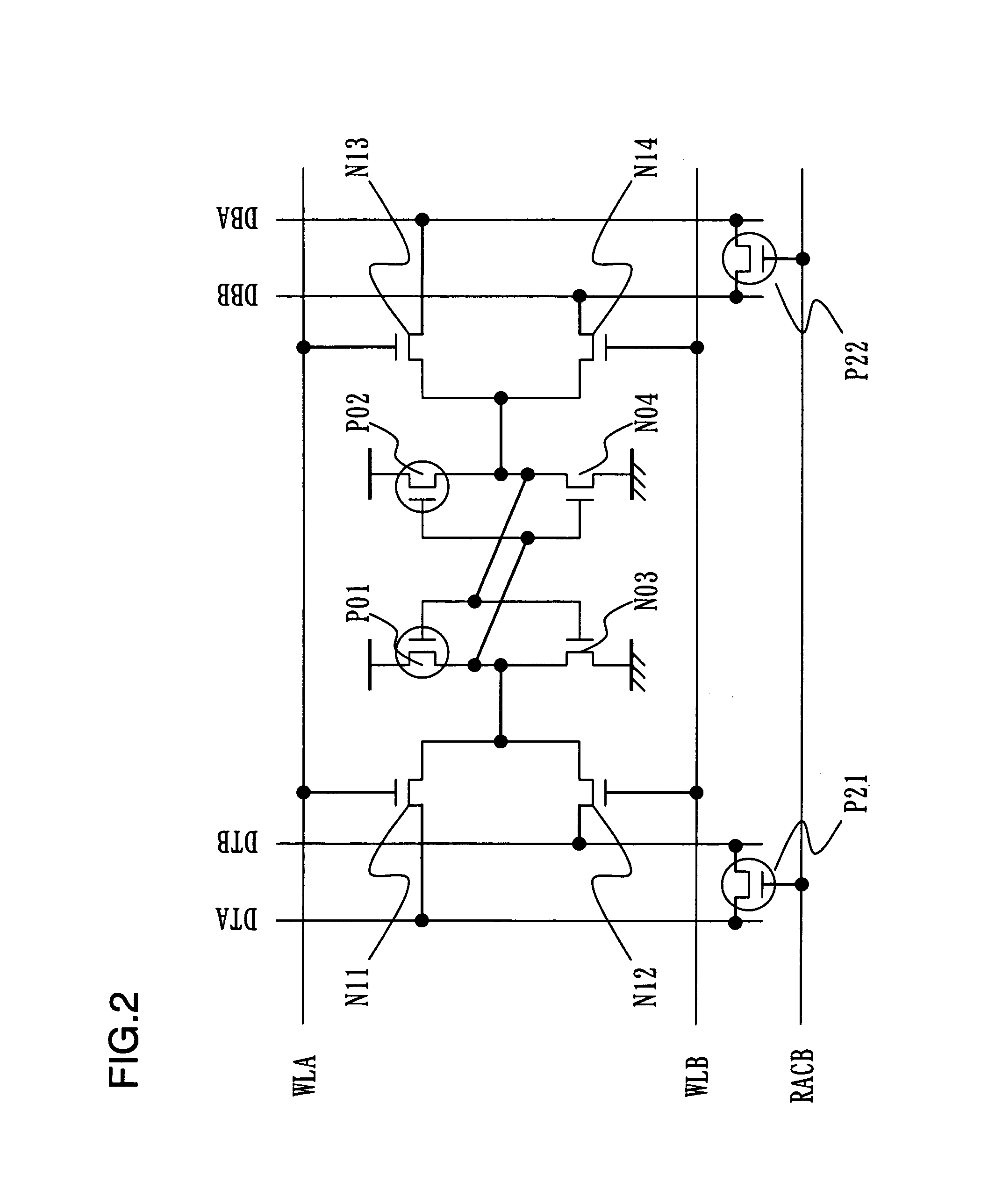
ActiveUS20080253172A1Improve static noise marginStable characteristicDigital storageIntegrated circuitStorage cell
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes a plurality of memory cells arranged in a matrix, a plurality of word lines corresponding to respective rows of the plurality of memory cells, a plurality of word line drivers for driving the plurality of word lines, respectively, and a plurality of pull-down circuits connected to the plurality of word lines, respectively, for causing voltages of the respective connected word lines to be lower than or equal to a power supply voltage when the respective word lines are in an active state. The word line drivers each have a transistor for causing the corresponding word line to go into the active state. The pull-down circuits each have a pull-down transistor for pulling down the corresponding word line, the pull-down transistor being a transistor having the same conductivity type as that of the transistor included the word line driver for driving the corresponding word line.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Semiconductor memory device
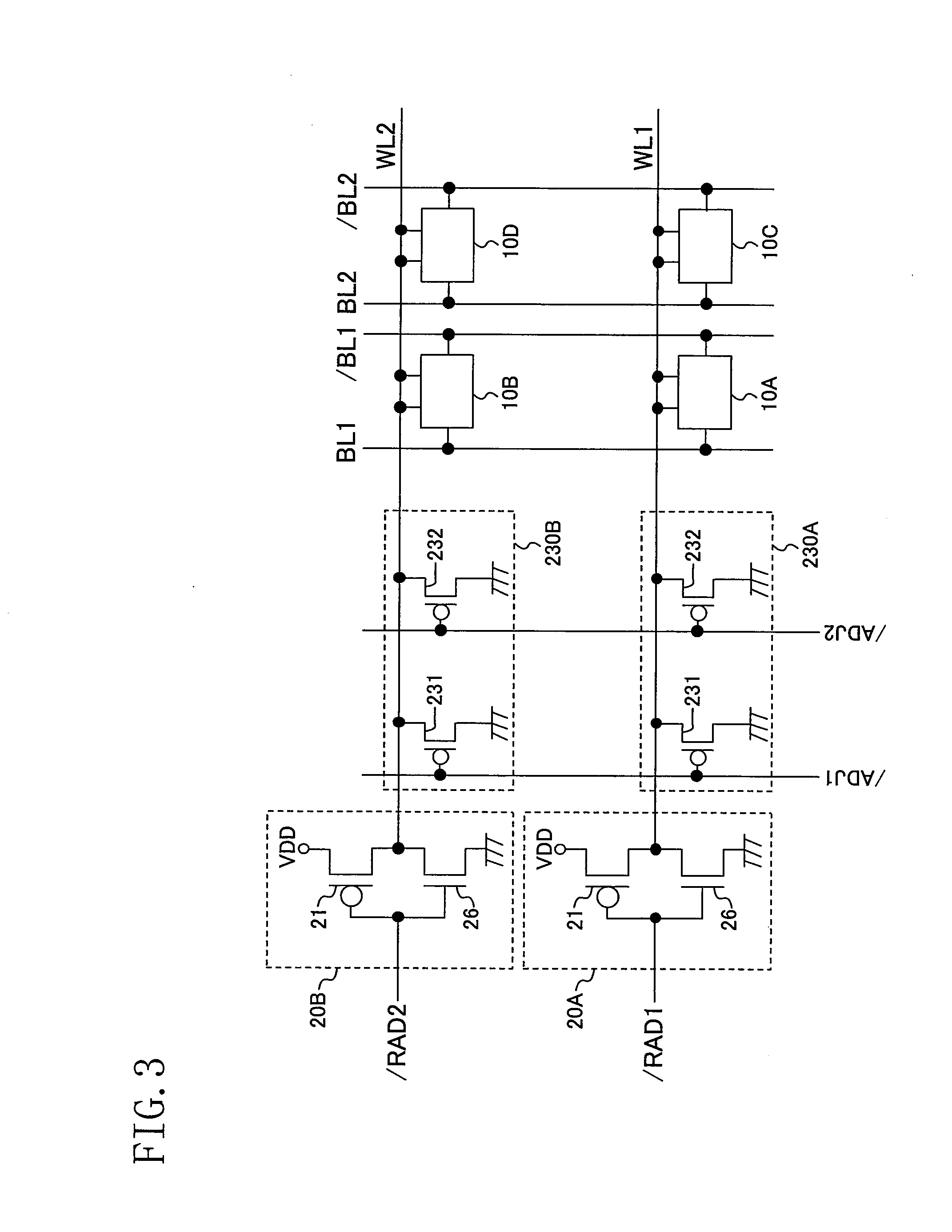
InactiveUS20080316851A1Improve data reading speedDecrease in malfunctionDigital storageBit lineComputer science
Disclosed is a semiconductor memory device including a plurality of memory cells, each of which is connected to word lines of first and second ports and to bit lines of the first and second ports, and first and second inter-port switches for electrically connecting first bit lines of the first port and second bit lines of the second port when row addresses of the first and second ports match each other.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes a plurality of memory cells arranged in a matrix, a plurality of word lines corresponding to respective rows of the plurality of memory cells, a plurality of word line drivers for driving the plurality of word lines, respectively, and a plurality of pull-down circuits connected to the plurality of word lines, respectively, for causing voltages of the respective connected word lines to be lower than or equal to a power supply voltage when the respective word lines are in an active state. The word line drivers each have a transistor for causing the corresponding word line to go into the active state. The pull-down circuits each have a pull-down transistor for pulling down the corresponding word line, the pull-down transistor being a transistor having the same conductivity type as that of the transistor included the word line driver for driving the corresponding word line.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
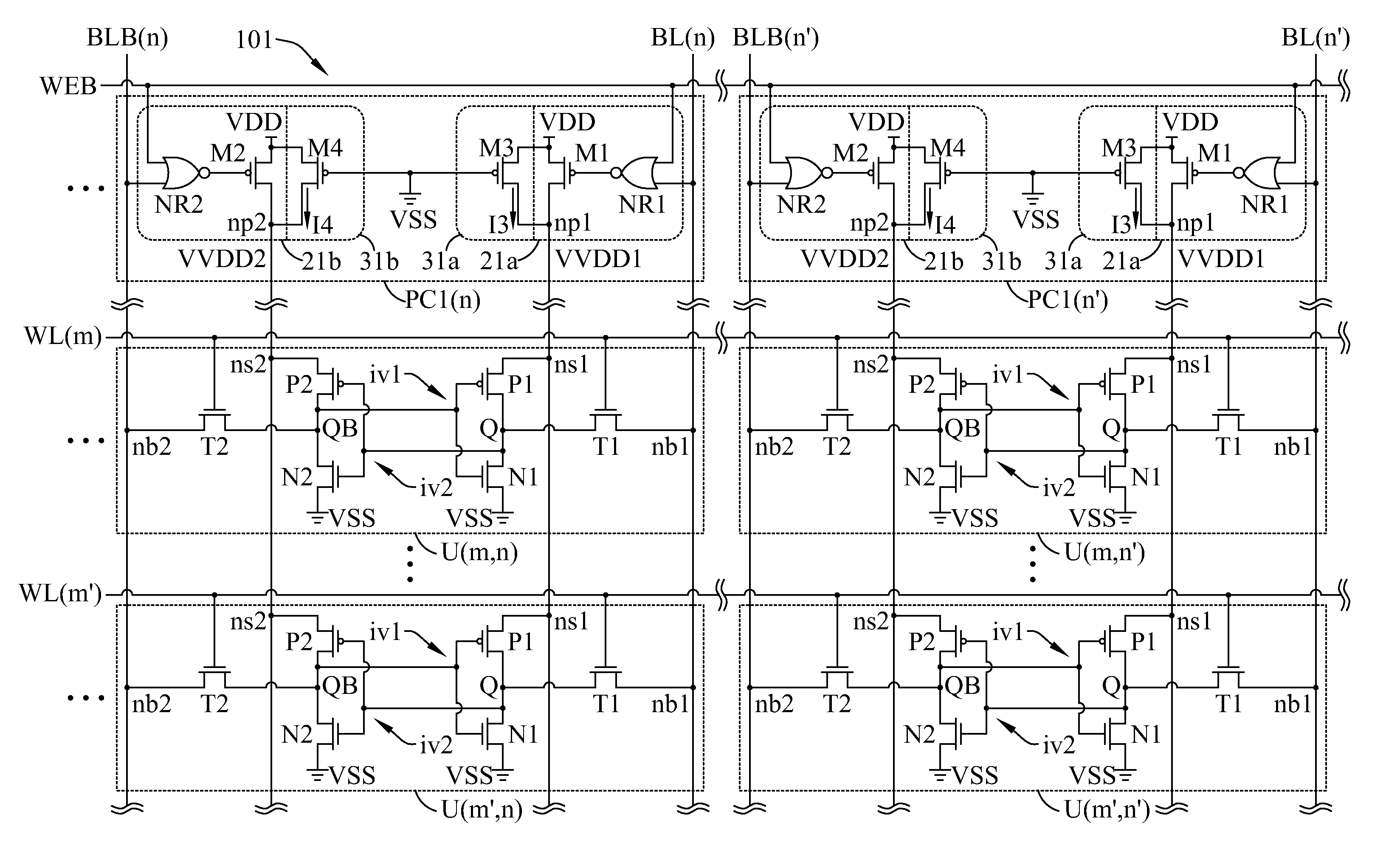
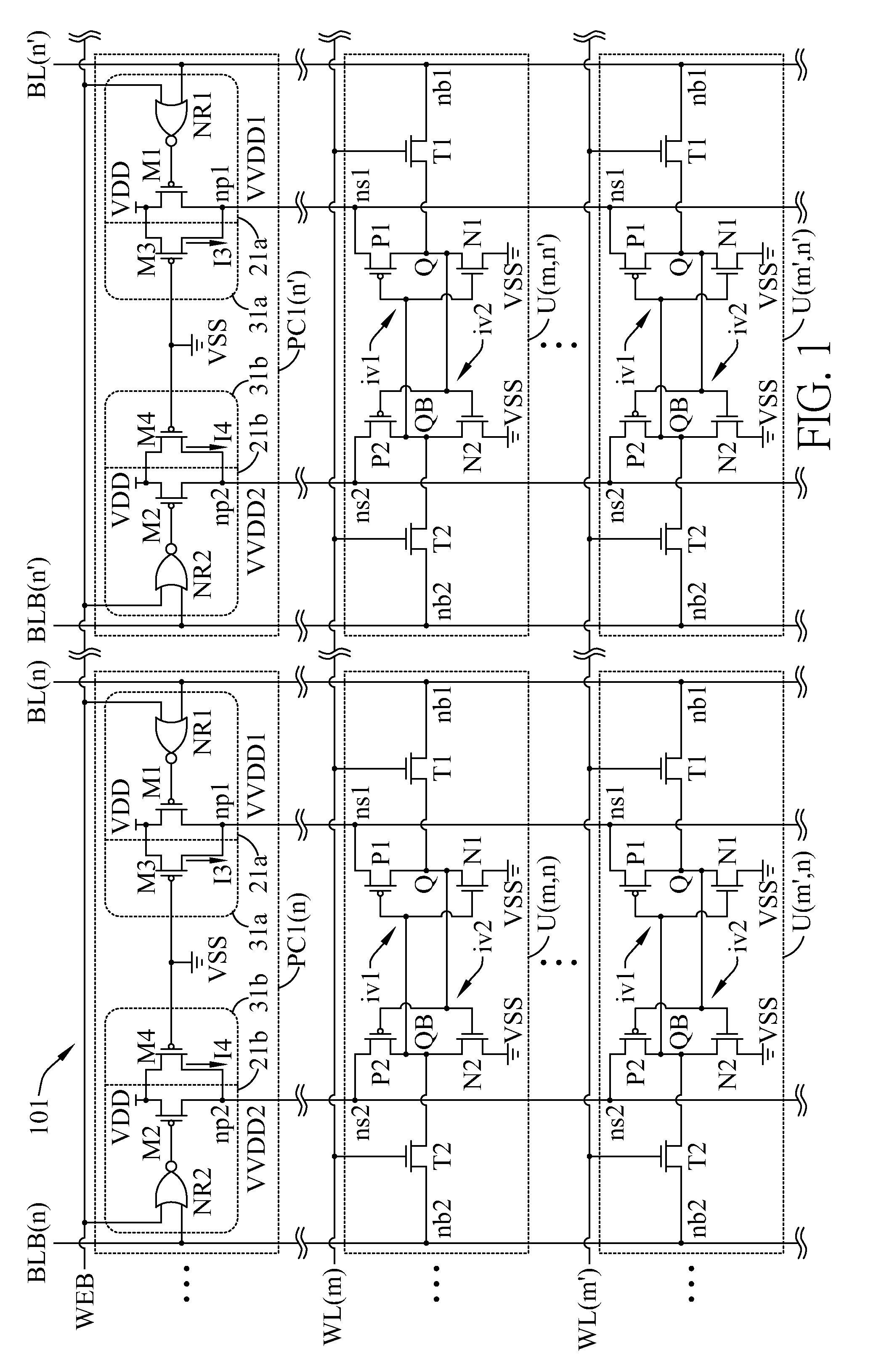
Data-aware dynamic supply random access memory
ActiveUS8345504B2Increase data storageReduce electrical conductivityDigital storageBit linePower inverter
A Random Access Memory (RAM) with a plurality of cells is provided. In an embodiment, the cells of a same column are coupled to a same pair of bit-lines and are associated to a same power controller. Each cell has two inverters; the power controller has two power-switches. For the cells of the same column, the two power-switches respectively perform independent supply voltage controls for the two inverters in each cell according to data-in voltages of the bit-lines during Write operation.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP +1
Eight-tube storage unit capable of automatically adjusting strength of transmission tube and strength of pull-down tube
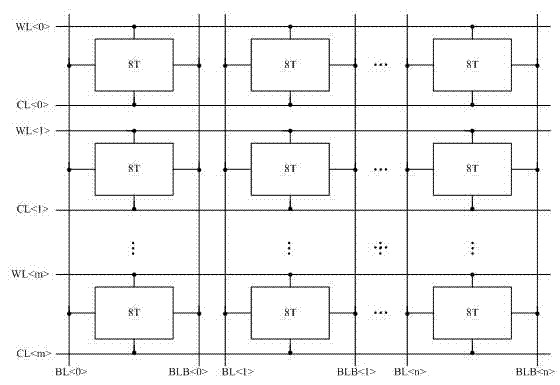
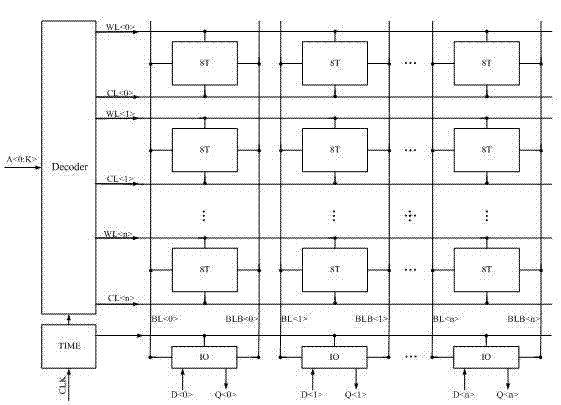
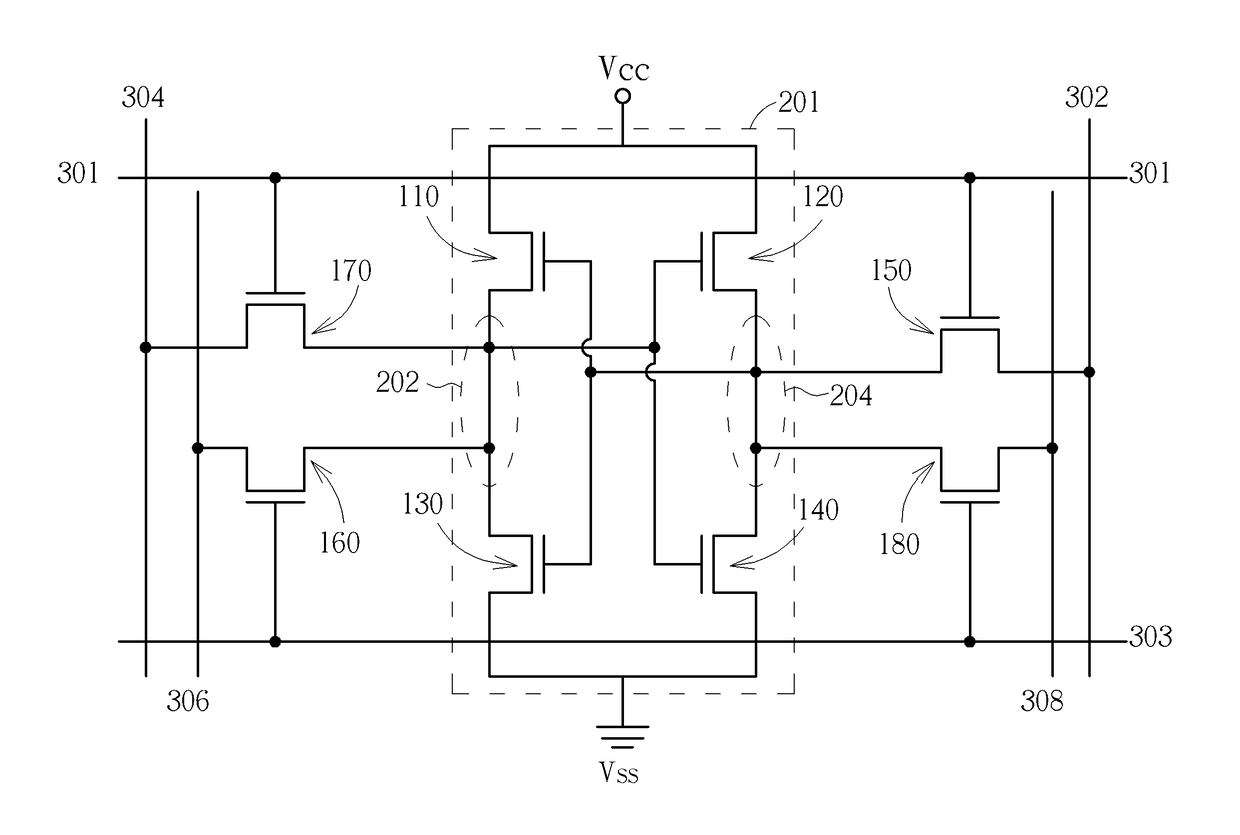
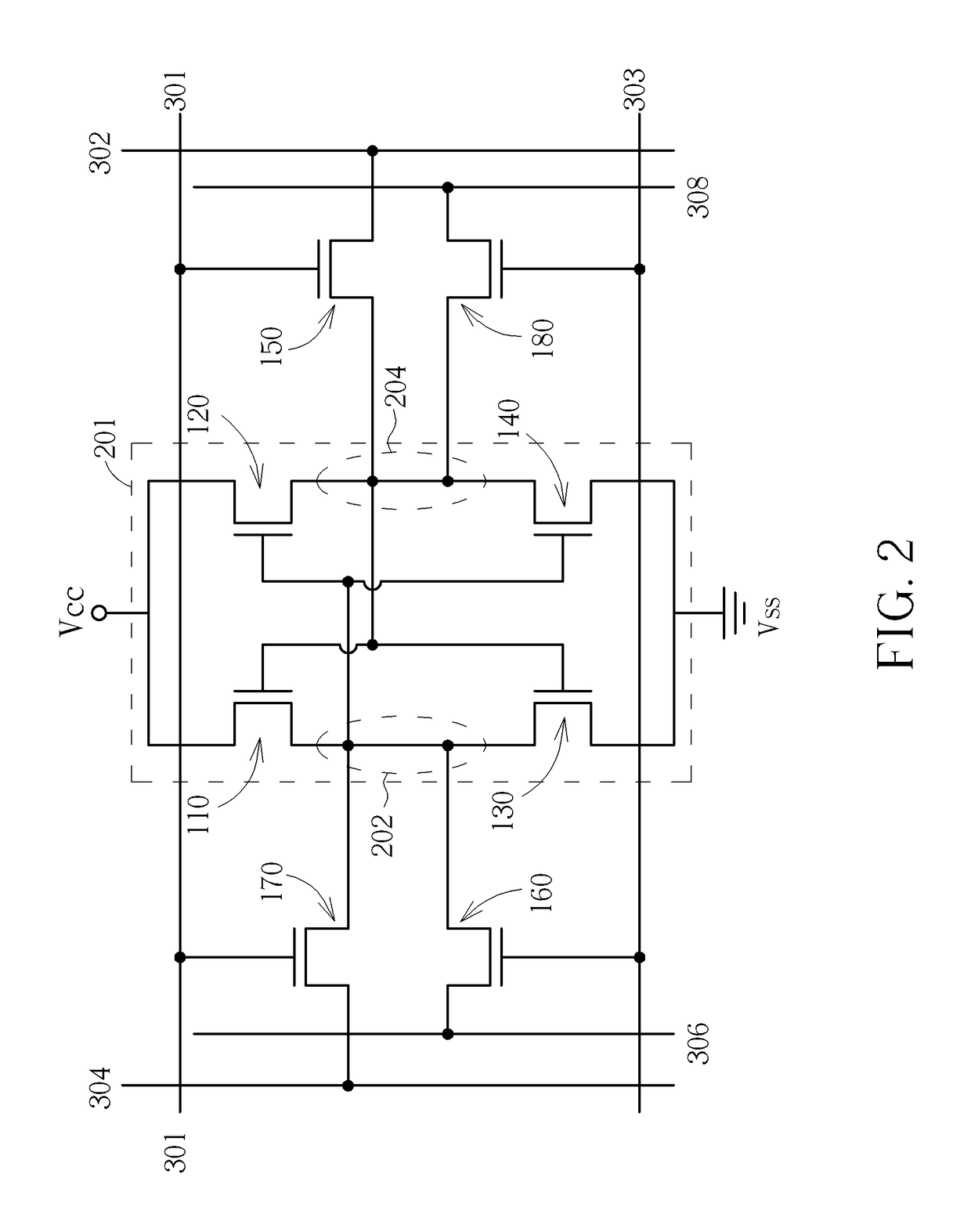
InactiveCN102360567AImprove static noise marginImprove stabilityDigital storageNoise marginStatic noise margin
The invention discloses an eight-tube storage unit capable of automatically adjusting the strength of a transmission tube and the strength of a pull-down tube. Two NMOS (non-channel metal oxide semiconductor) tubes capable of adjusting the strength of the transmission tube and the strength of the pull-down tube are added on the basis of a standard six-tube storage unit so as to realize the eight-tube storage unit which is capable of automatically adjusting the strength of the transmission tube and the strength of the pull-down tube according to types of reading and writing operation. When the storage unit is used for writing operation, the strength of the transmission tube is strengthened, writing noise margin of the storage unit is increased, and the speed of writing operation is increased. When the storage unit is used for reading operation, the strength of the pull-down tube is strengthened, reading noise margin of the storage unit is increased, and simultaneously, the speed of data reading operation is increased. The eight-tube storage unit has the advantages of high static noise margin, fine stability, fast reading and writing speeds and the like.
Owner:HUNAN LUGU FEITENG MICROELECTRONICS
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS10134744B1Preferable quality and elemental performanceImprove static noise marginTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringChannel width
A semiconductor memory device includes a first inverter, a second inverter, a first and second inner access transistors, and a first and second outer access transistors. The first inverter includes a first pull-up transistor and a first pull-down transistor, the second inverter includes a second pull-up transistor (PL2) and a second pull-down transistor, and the first inverter and the second inverter forms a latch circuit. The first and second inner access transistors and the first and second outer access transistors are electrically connected to the latch circuit, and channel widths of the second inner access transistor and the second outer access transistor are different from each other.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7271454B2Improve reliabilityIncrease in inhibition areaTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringBody region
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
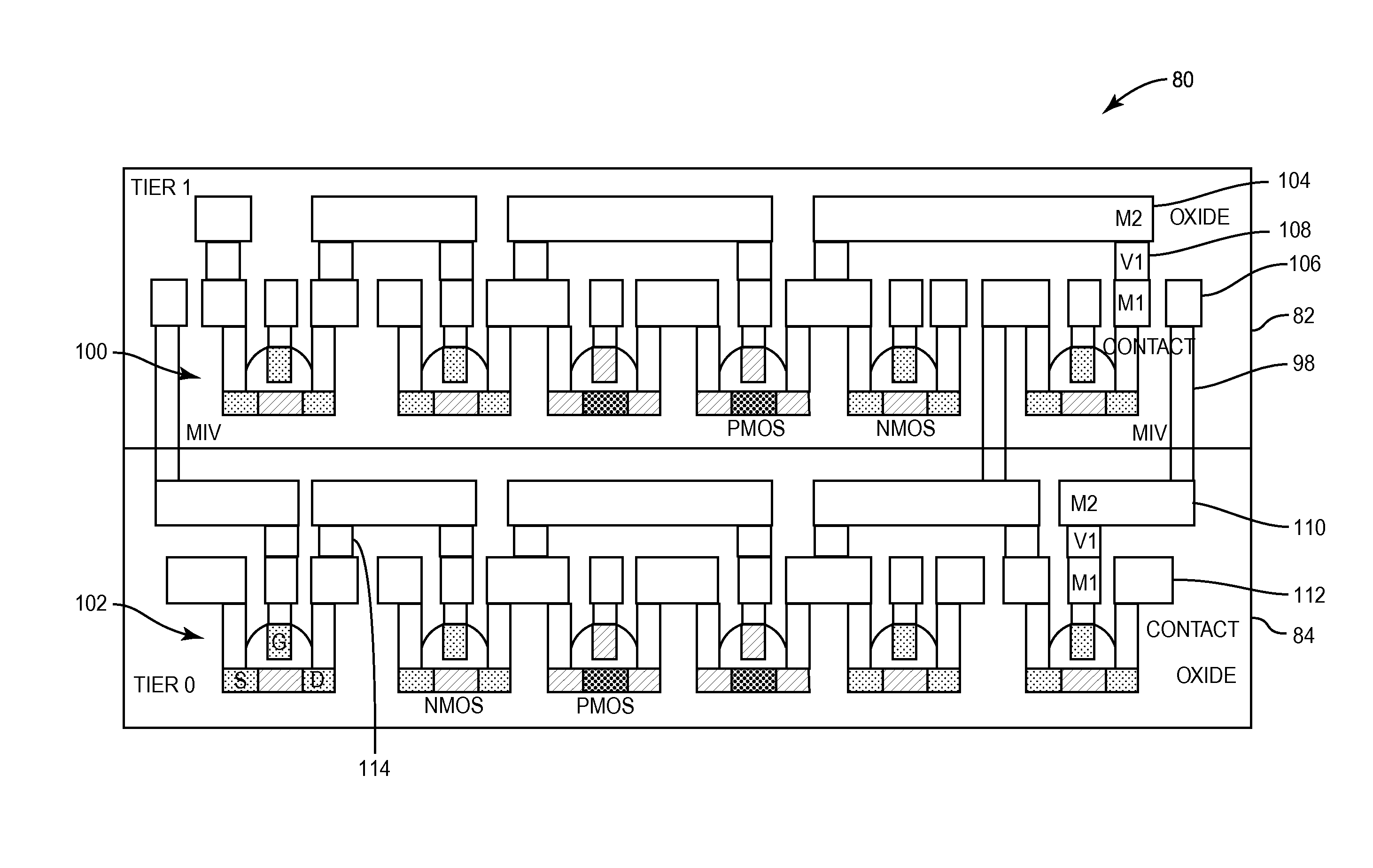
THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) MEMORY CELL SEPARATION AMONG 3D INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (IC) TIERS, AND RELATED 3D INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (3DICs), 3DIC PROCESSOR CORES, AND METHODS
ActiveUS20150302919A1Reduce power supply voltageHigh bulk densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device details3d integrated circuitComputer architecture
A three-dimensional (3D) memory cell separation among 3D integrated circuit (IC) (3DIC) tiers is disclosed. Related 3DICs, 3DIC processor cores, and methods are also disclosed. In embodiments disclosed herein, memory read access ports of a memory block are separated from a memory cell in different tiers of a 3DIC. 3DICs achieve higher device packing density, lower interconnect delays, and lower costs. In this manner, different supply voltages can be provided for the read access ports and the memory cell to be able to lower supply voltage for the read access ports. Static noise margins and read / write noise margins in the memory cell may be provided as a result. Providing multiple power supply rails inside a non-separated memory block that increases area can also be avoided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
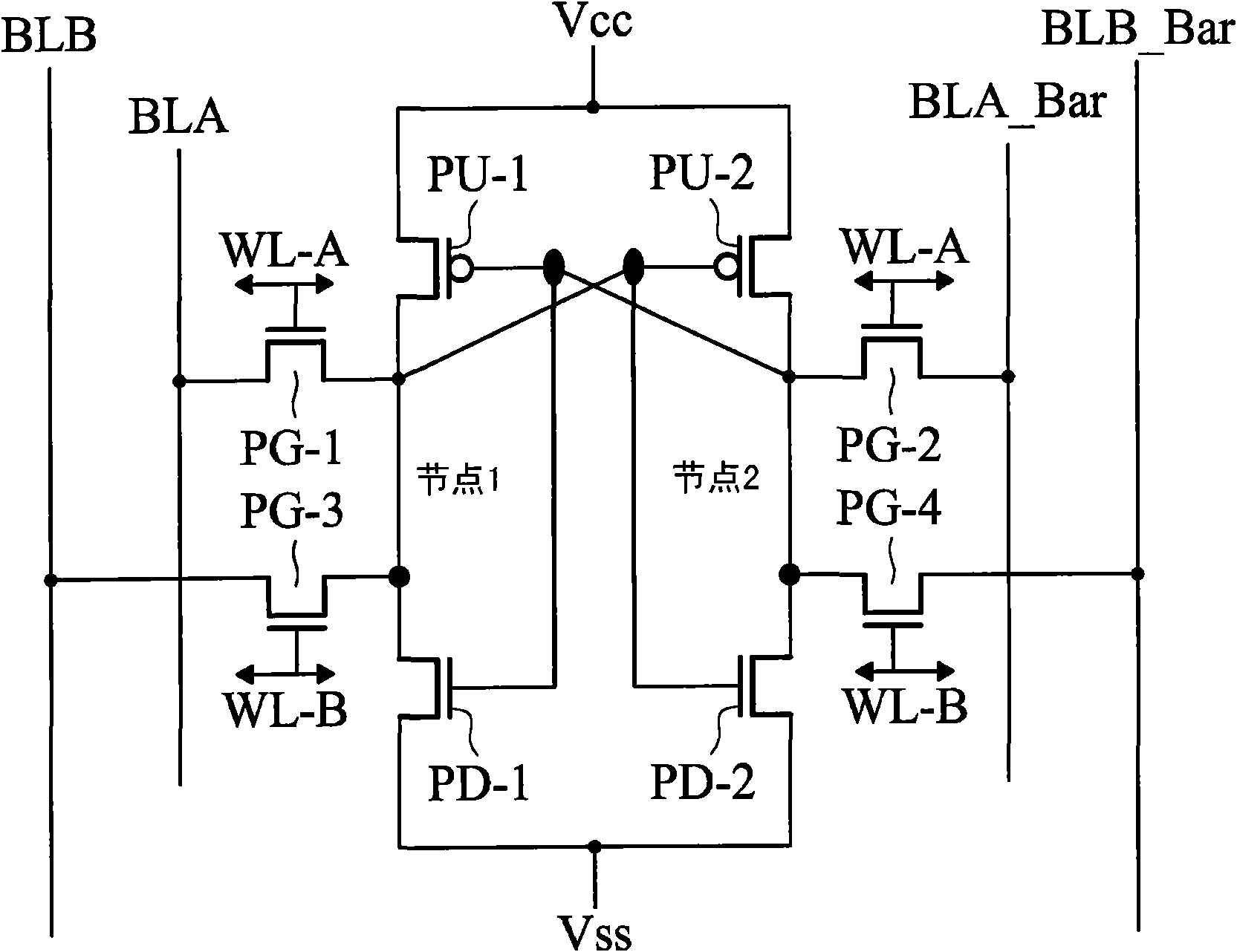
Ten-transistor dual-port SRAM with shared bit-line architecture
InactiveUS20140198562A1Improve static noise marginReduce digitsDigital storageComputer architectureTransistor
A 10-transistor dual-port SRAM with shared bit-line architecture includes a first memory cell and a second memory cell. The first memory cell has a first storage unit, a first switch set, and a second switch set. The second memory cell has a second storage unit, a third switch set, and a fourth switch set. The second switch set is coupled to a complement first A-port bit line and a complement first B-port bit line, and connected to the first storage unit. The third switch set is connected to a complement second A-port bit line, a complement second B-port bit line, and the second storage unit. Thus, the second memory cell can make use of the third switch set to share the complement first A-port bit line and the complement first B-port bit line with the first memory cell.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Ten-transistor dual-port SRAM with shared bit-line architecture
InactiveUS8891289B2Cancel read/write disturbImprove static noise marginDigital storageBit lineComputer architecture
A 10-transistor dual-port SRAM with shared bit-line architecture includes a first memory cell and a second memory cell. The first memory cell has a first storage unit, a first switch set, and a second switch set. The second memory cell has a second storage unit, a third switch set, and a fourth switch set. The second switch set is coupled to a complement first A-port bit line and a complement first B-port bit line, and connected to the first storage unit. The third switch set is connected to a complement second A-port bit line, a complement second B-port bit line, and the second storage unit. Thus, the second memory cell can make use of the third switch set to share the complement first A-port bit line and the complement first B-port bit line with the first memory cell.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
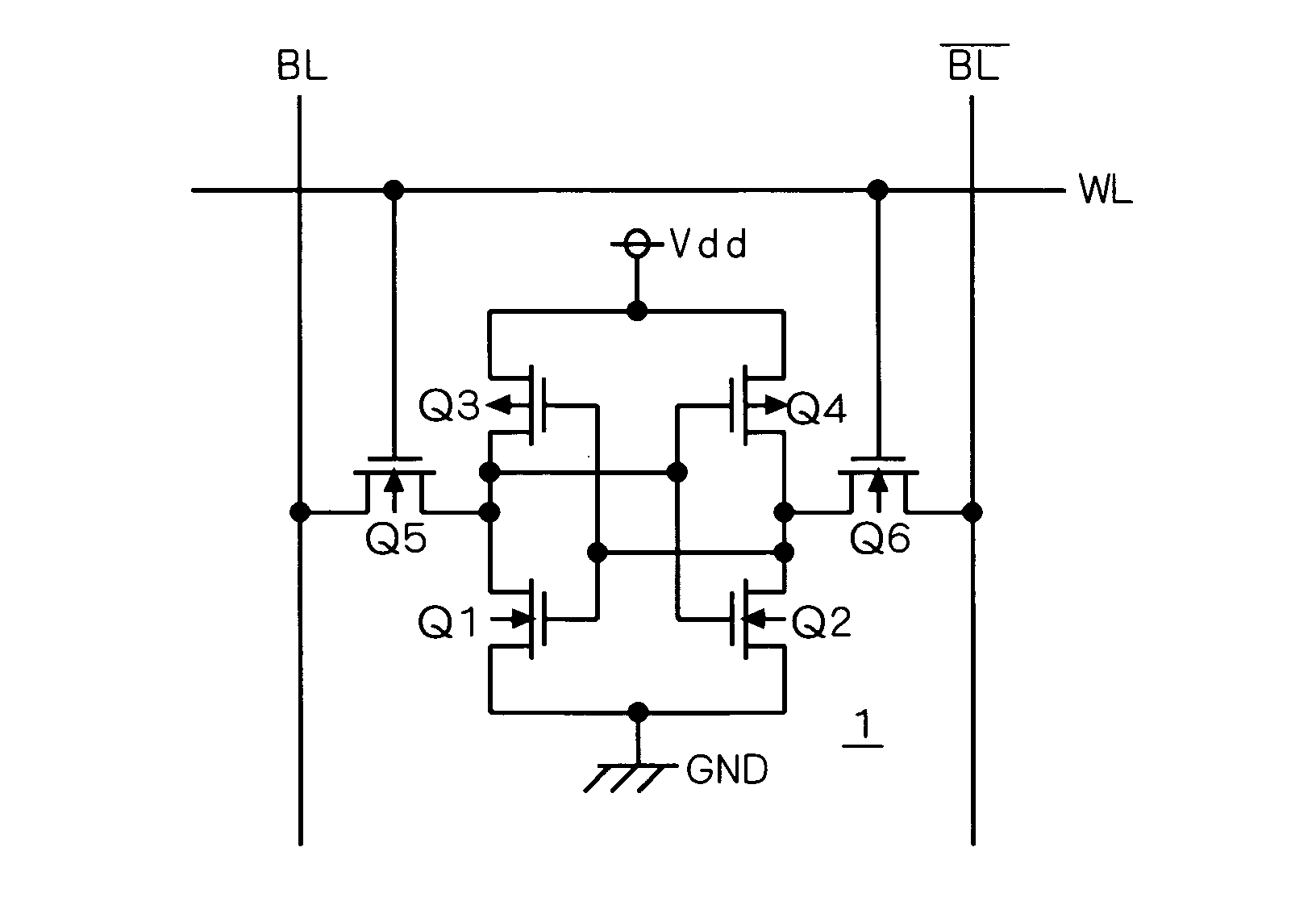
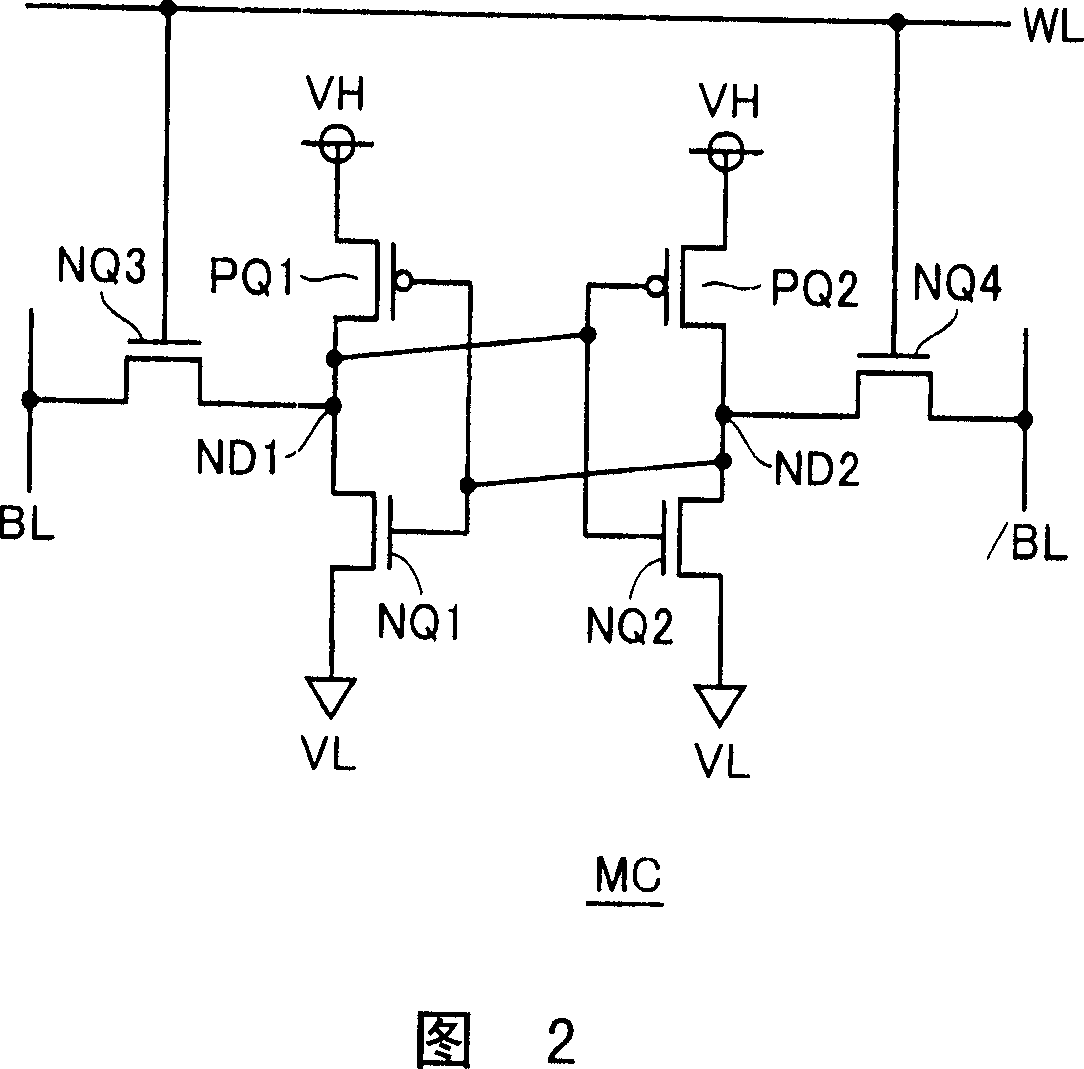
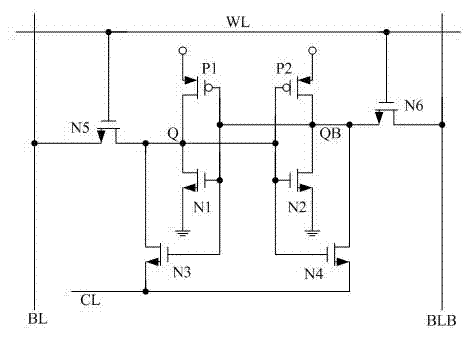
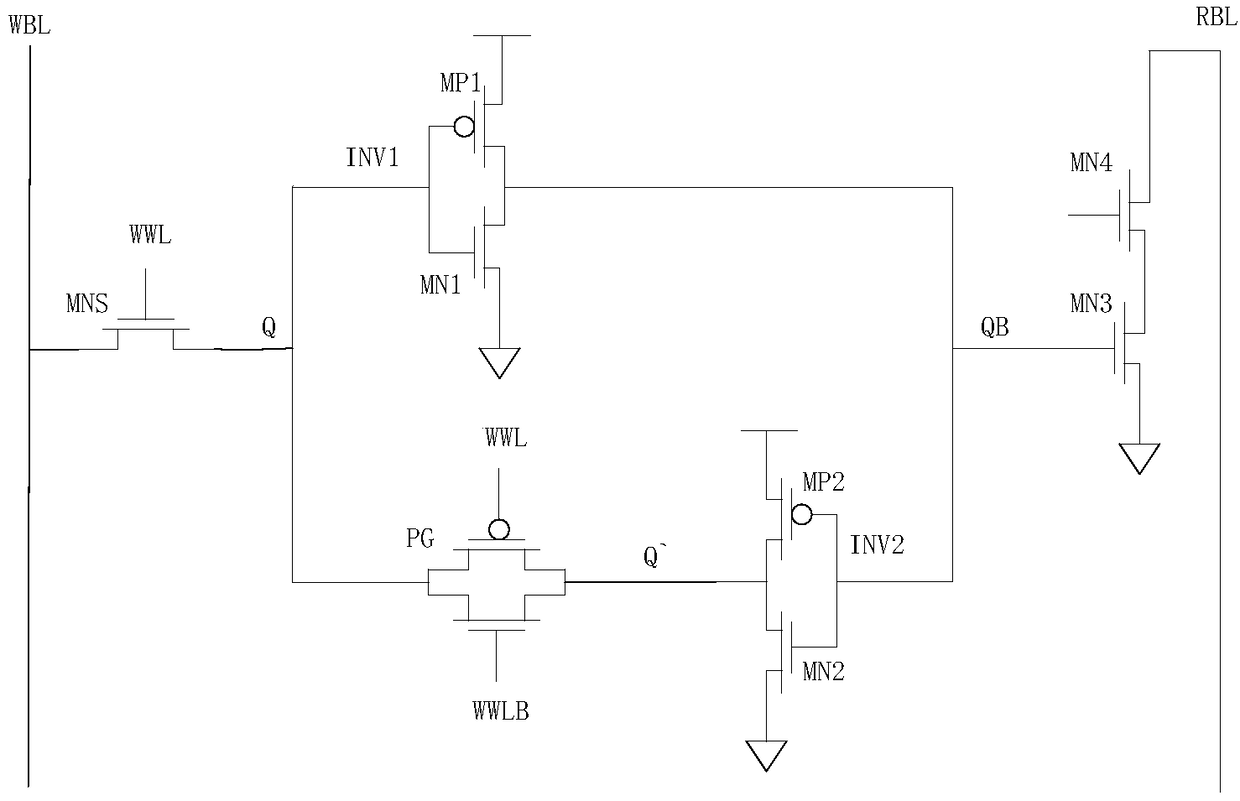
SRAM storage unit capable of stably working under low voltage
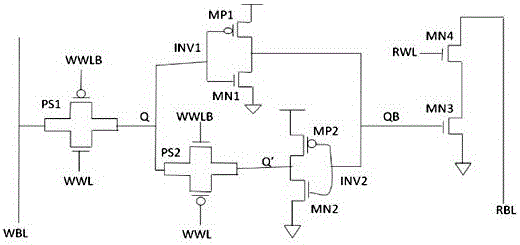
The invention discloses an SRAM storage unit capable of stably working under low voltage. The SRAM storage unit comprises two transmission gates, two phase inverters and two NMOS tubes, wherein the two NMOS tubes are connected with each other in series; the two phase inverters and a second transmission gate form a latch; a first storage end of the latch is connected to a data-writing bit line via the first transmission gate; a second storage end of the latch is connected to a grid of a first NMOS tube; a grid of a second NMOS tube is connected to a data-reading word line; a drain of the second NMOS tube is connected to a data-reading bit line. A circuit structure used in the SRAM storage unit is characterized in that data reading and writing word lines are separated and data reading and writing bit lines are separated; a transmission gate is inserted between the output end of a second phase inverter and the input end of a first phase inverter and is used for controlling data writing action; the accurate data writing can be achieved under the condition with low power voltage; the interference on stored data during reading the data can be reduced; the static noise margin of the storage unit can be improved.
Owner:SUZHOU WULI INFORMATION TECH
Static random access memory unit
ActiveCN104318953AImprove static noise marginReduce areaDigital storageCapacitanceStatic random-access memory
The invention discloses a static random access memory unit, which comprises a first inverter which includes a first N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistor and a first P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor, wherein a first self-stabilizing capacitor is arranged between the first NMOS transistor and the first PMOS transistor, a second inverter which includes a second NMOS transistor and a second PMOS transistor, wherein a second self-stabilizing capacitor is arranged between the second NMOS transistor and the second PMOS transistor, and a first reading and writing control unit and a second reading and writing control unit which are connected to one end of the first self-stabilizing capacitor and one end of the second self-stabilizing capacitor respectively, wherein the first self-stabilizing capacitor and the second self-stabilizing capacitor, together with one end of the first reading and writing control unit and one end of the second reading and writing control unit, are connected to different MOS transistors respectively. The static random access memory unit disclosed by the invention can effectively resist radiated interference, effectively reduce circuit area and save manufacturing cost.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
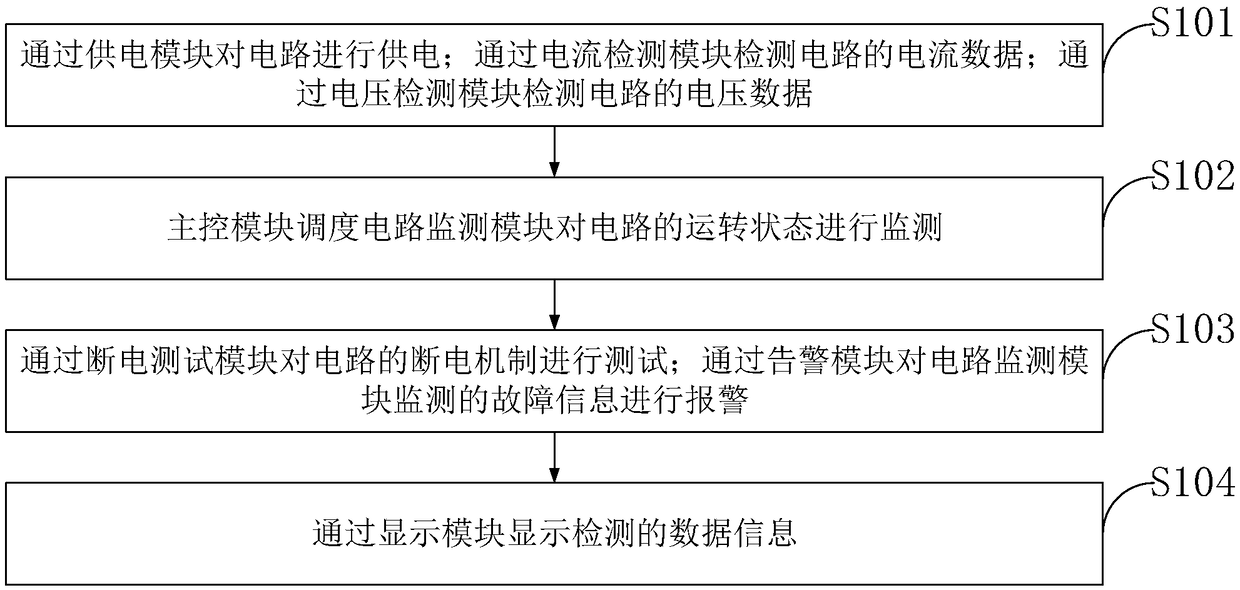
Intelligent circuit and method for controlling power-off
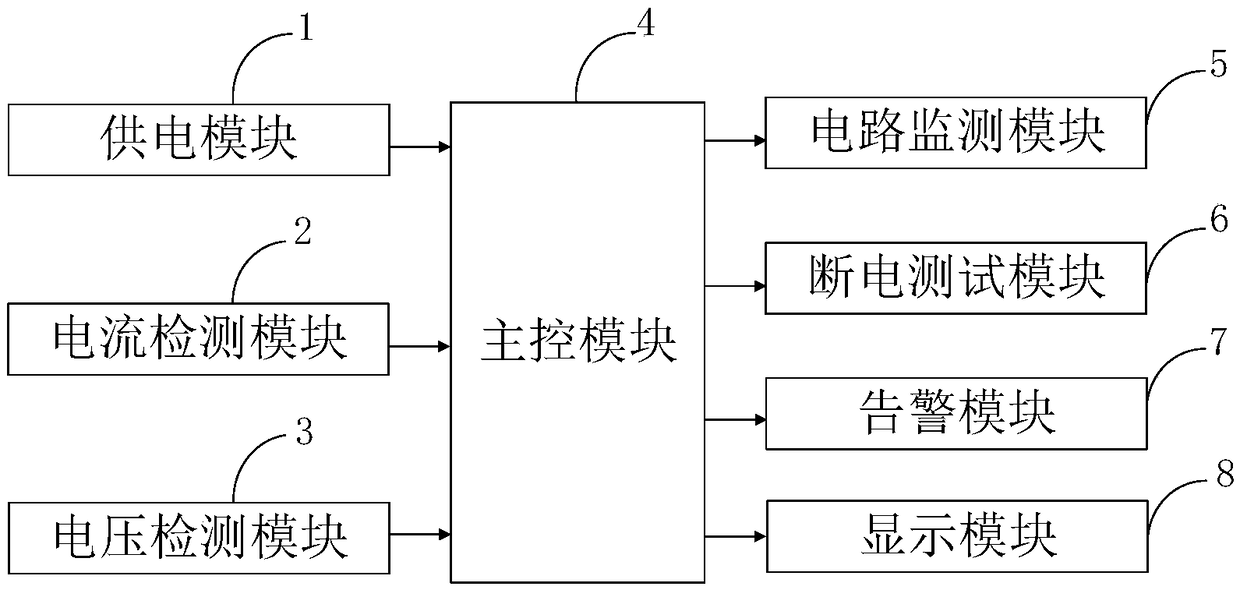
InactiveCN109032845AComprehensive test coverageSolve the problem of whether the power-off protection mechanism is correctHardware monitoringFault response safety measuresControl powerProtection mechanism
The invention belongs to the technical field of circuit power-off, and discloses an intelligent circuit and a method for controlling power-off. The intelligent circuit for controlling power-off comprises a power supply module, a current detection module, a voltage detection module, a main control module, a circuit monitoring module, a power-off test module, an alarm module and a display module. The circuit comprises a power supply module, a current detection module, a voltage detection module, a main control module, a circuit monitoring module, a power-off test module and a display module. Theinvention solves the problem that the existing single instruction power-off test can not detect whether the power-off protection mechanism is correct when the card executes data recovery or not through the power-off test in the execution process of writing data instructions to the smart card by the power-off test module and the power-off test in the execution process of the data recovery instructions. At the same time, through the circuit monitoring module, the alarm module can detect circuit faults in time, and send out a warning sound to remind the staff to do a good job of protective measures.
Owner:马晨光
SRAM cell
InactiveUS20180277197A1Increase costIncreased retention noise marginTransistorSolid-state devicesSram cellElectrical and Electronics engineering
A SRAM cell, including, in a stack of layers, transistors including at least first and second access transistors connected to a word line, the first access transistor coupling a first bit line and a first storage node and the second access transistor coupling a second bit line and a second storage node, and a flip-flop including a first conduction transistor coupling the first storage node to a source of a first reference potential and having its gate coupled to the second storage node and a second conduction transistor coupling the second storage node to the source of the first reference potential and having its gate coupled to the first storage node.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112038295ALower threshold voltageIncrease working currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialPhotoresist
The invention provides a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of providing a substrate which at least comprises a first active region, a second active region and a third active region, wherein the width of the first active region is equal to the width of the second active region, forming a shielding oxide layer on the substrate, wherein the shielding oxide layer covers the first active region, the second active region and the third active region, forming a patterned photoresist layer on the shielding oxide layer, wherein the patterned photoresist layer exposes the shielding oxide layer on the first active region and the second active region, and taking the exposed shielding oxide layer as a mask, carrying out ion doping on the first activeregion and the second active region so as to form a first channel in the first active region and the second active region, and removing the patterned photoresist layer. According to the manufacturingmethod of the semiconductor device, the performance of the semiconductor device can be improved.
Owner:晶芯成(北京)科技有限公司
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112038296AImprove performanceImprove matchTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialGate oxide
The invention provides a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of providing a substrate which at least comprises a pull-down region and a channel region, wherein the width of the pull-down region is equal to the width of the channel region, forming a gate oxide layer on the substrate, wherein the gate oxide layer covers the pull-down region and thechannel region, forming a polycrystalline silicon layer on the gate oxide layer, forming a patterned photoresist layer on the polycrystalline silicon layer, wherein the patterned photoresist layer exposes the polycrystalline silicon layer on the pull-down region, carrying out ion doping on the exposed polycrystalline silicon layer, and removing the patterned photoresist layer, and etching the polycrystalline silicon layer and the gate oxide layer so as to form a pull-down gate structure on the pull-down region and form a channel gate structure on the channel region. According to the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device, the performance of the semiconductor device can be improved.
Owner:晶芯成(北京)科技有限公司
Read and match circuit for low-voltage content addressable memory
InactiveUS8000120B2Improve stabilityImprove static noise marginDigital storageLow voltageHemt circuits
A read, write, and match circuit for a low-voltage content addressable memory. A write circuit inputs signals for storing data in the memory cells, a read circuit retrieves the stored data from the memory cells, and a match circuit compares the data stored in the memory cell with the data searched by the match circuit. The circuits for writing, reading and matching are separated from each other and exempt from mutual interference.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
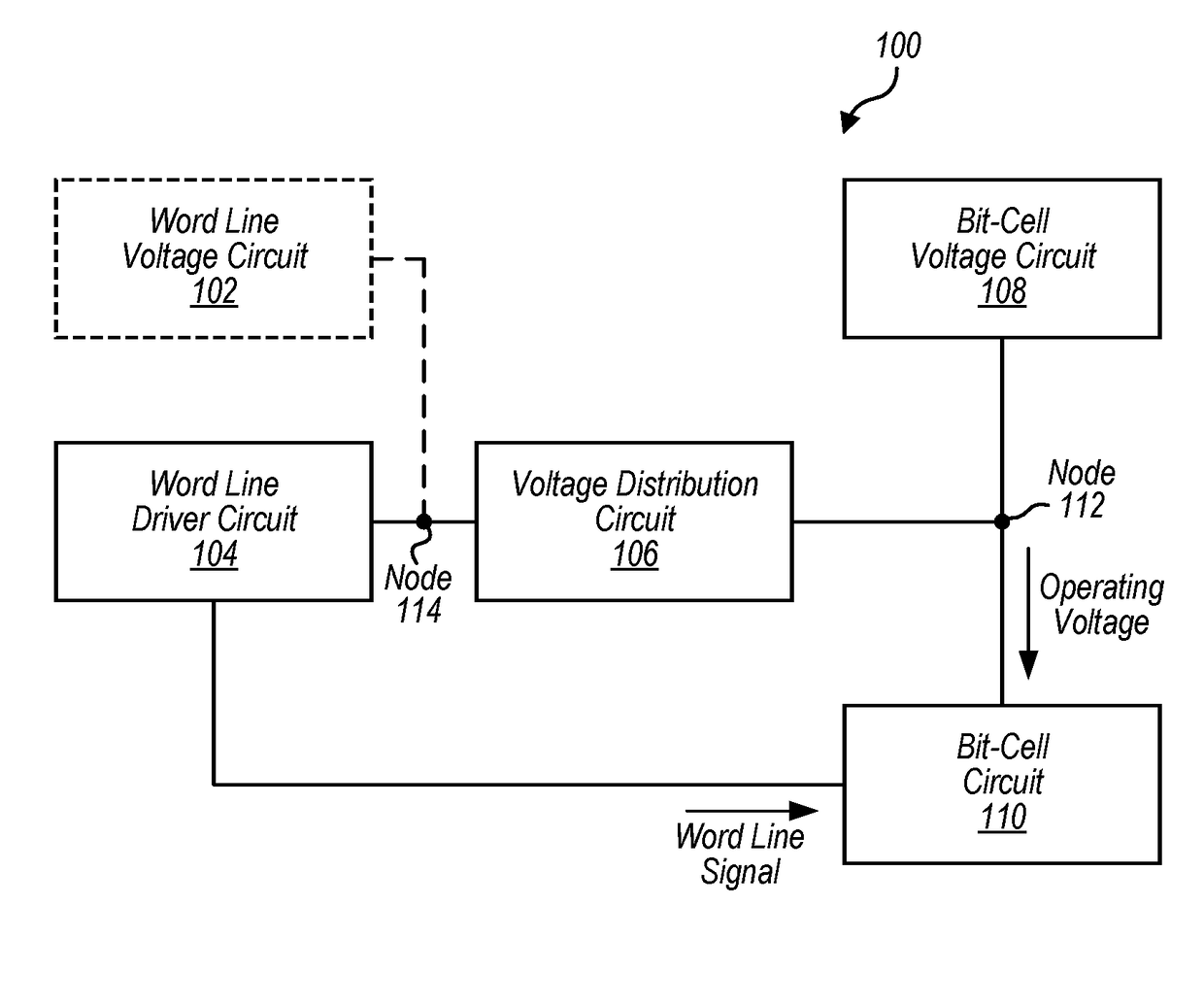
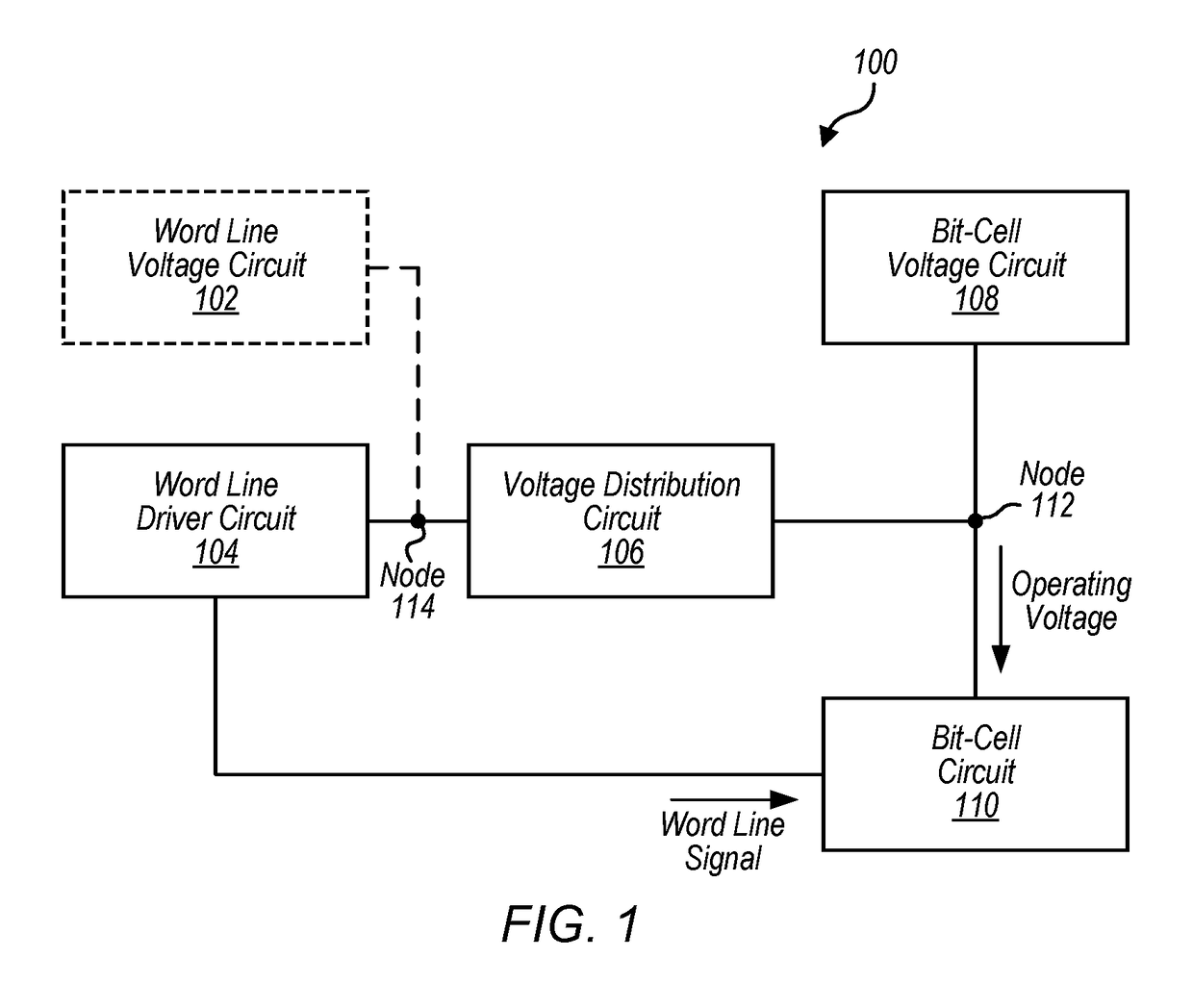
Bit-cell voltage distribution system
ActiveUS20170236577A1Improve static noise marginDigital storageDistribution systemStatic noise margin
In some embodiments, a method includes receiving, at a voltage distribution circuit, a power enable signal. In response to the power enable signal, the voltage distribution circuit may connect a word line driver circuit to a bit-cell voltage circuit such that an operating voltage is received at a bit-cell circuit before a word line signal form the word line driver circuit is received at the bit-cell circuit, where the operating voltage is provided by the bit-cell voltage circuit. The method may further include the bit-cell circuit providing the operating voltage along a bit line based on a data stored at the bit-cell circuit and based on the word line signal. In some embodiments, a static noise margin of one or more portions of the bit-cell circuit may be improved. Additionally, in some cases, a wakeup time of the bit-cell circuit may be ignored, resulting in a faster read operation.
Owner:APPLE INC
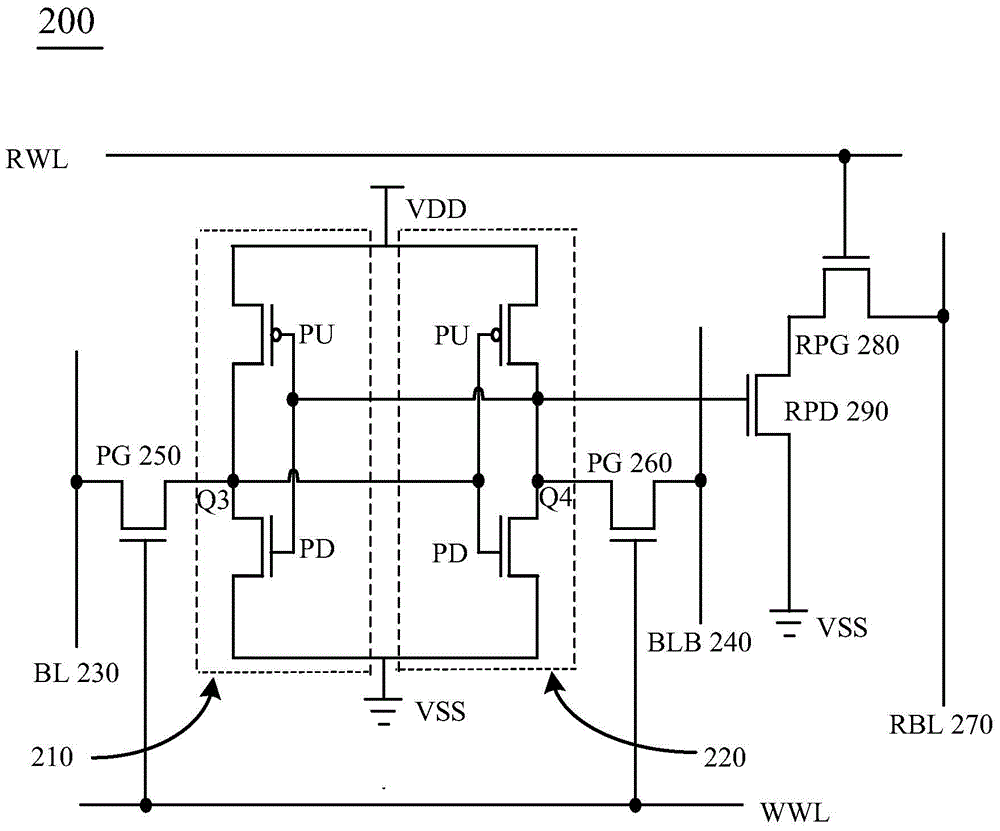
SRAM memory cell array, SRAM memory and control method thereof
The invention provides an SRAM storage unit array, an SRAM memory, and a control method thereof. The SRAM storage unit array comprises a plurality of word line pair arranged along the row direction, wherein each word line pair comprises a write word line and a read word line; a bit line pair arranged along the row direction, wherein the bit line pair comprises a first bit line and a second bit line; a plurality of storage units arranged between the word line pairs and the bit line pair, wherein each storage unit is connected to the corresponding work line pair and bit line pair and comprises a read terminal; and a read unit, wherein the read unit comprises a read transistor and a read bit line, and the read bit line is connected to the read terminals of the plurality of storage units through the read transistor. The provided SRAM storage unit array reduces the transistor number and the stability is improved at the same time.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com