Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60results about How to "Improve spatial uniformity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
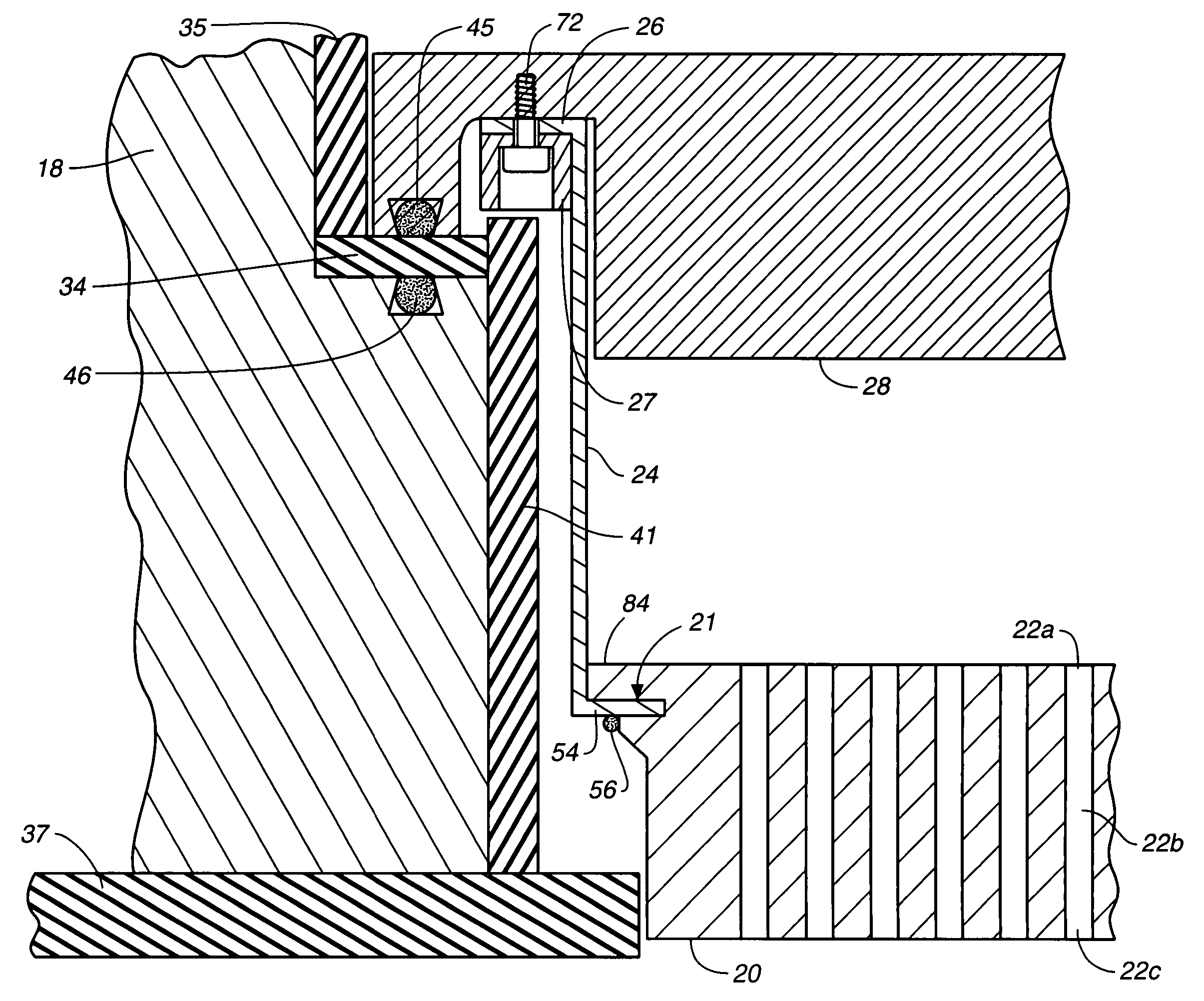
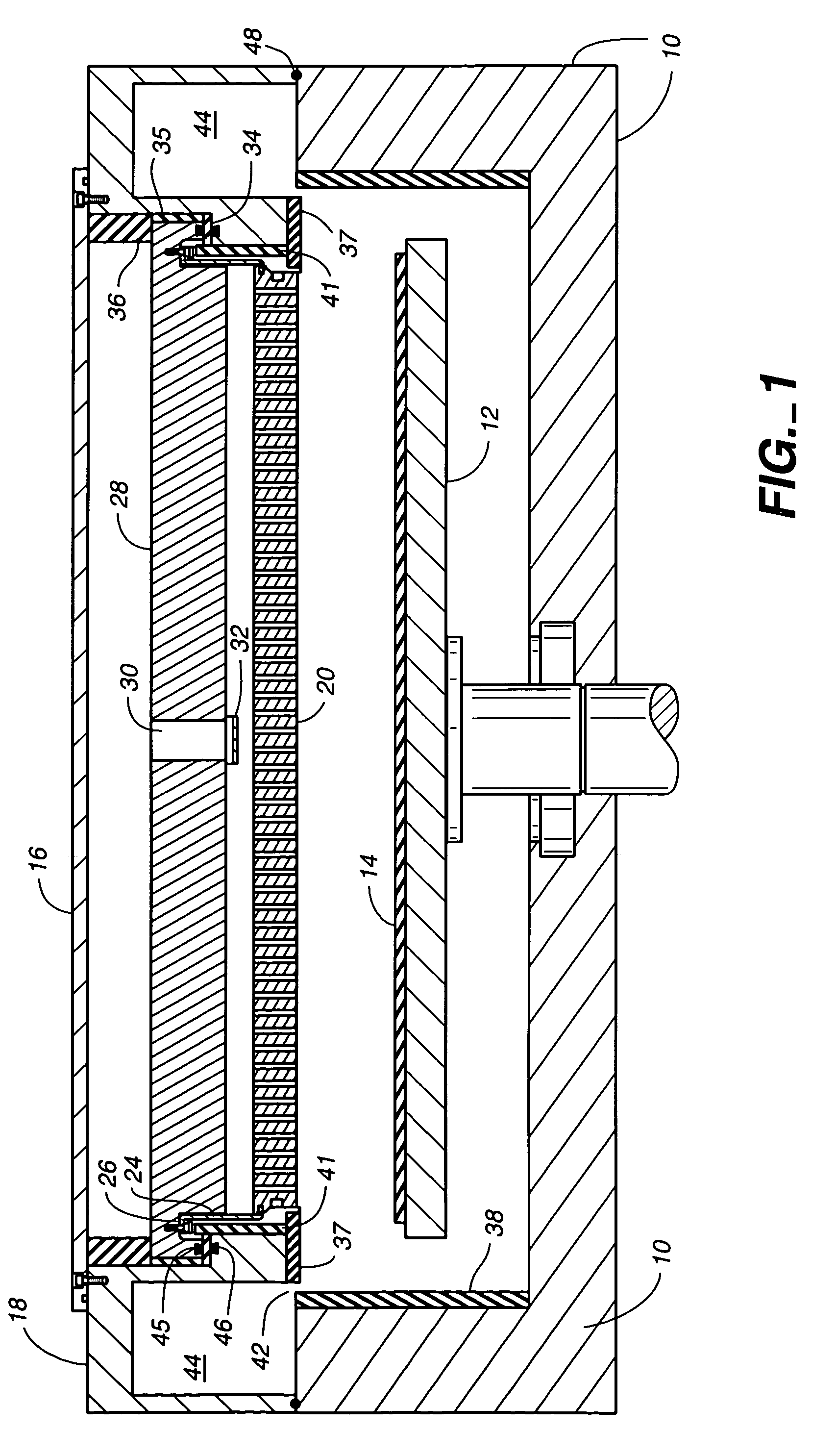
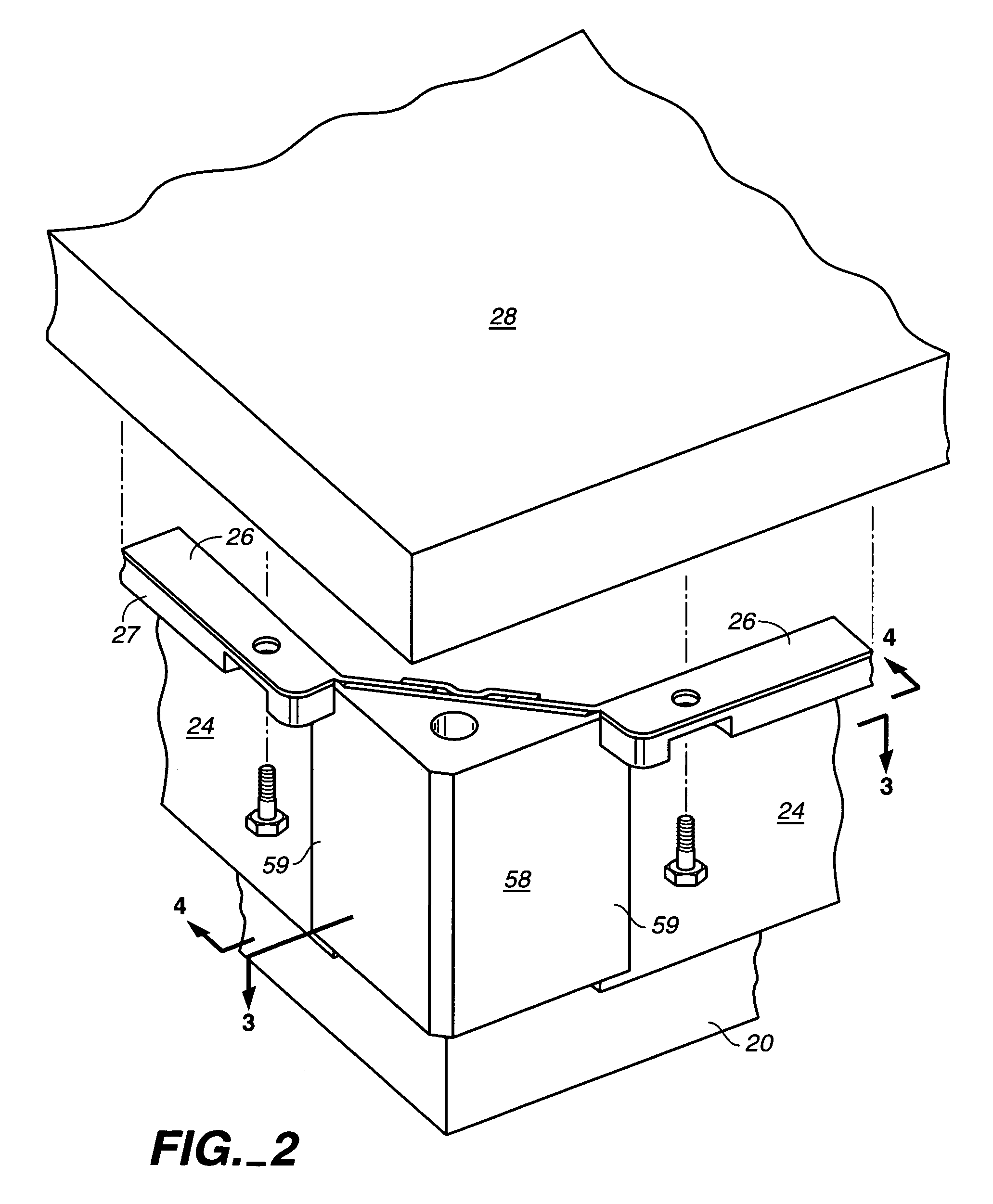
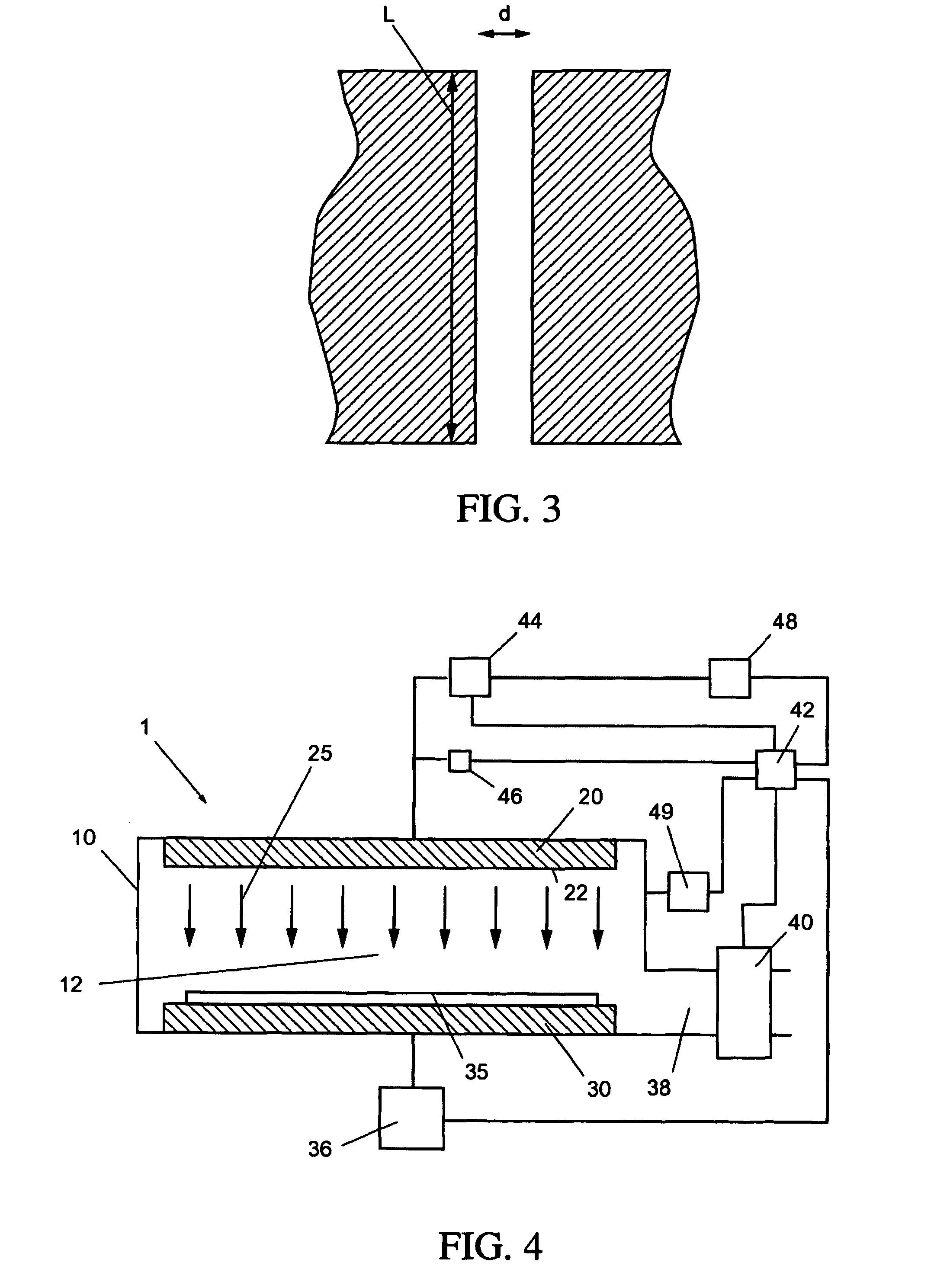
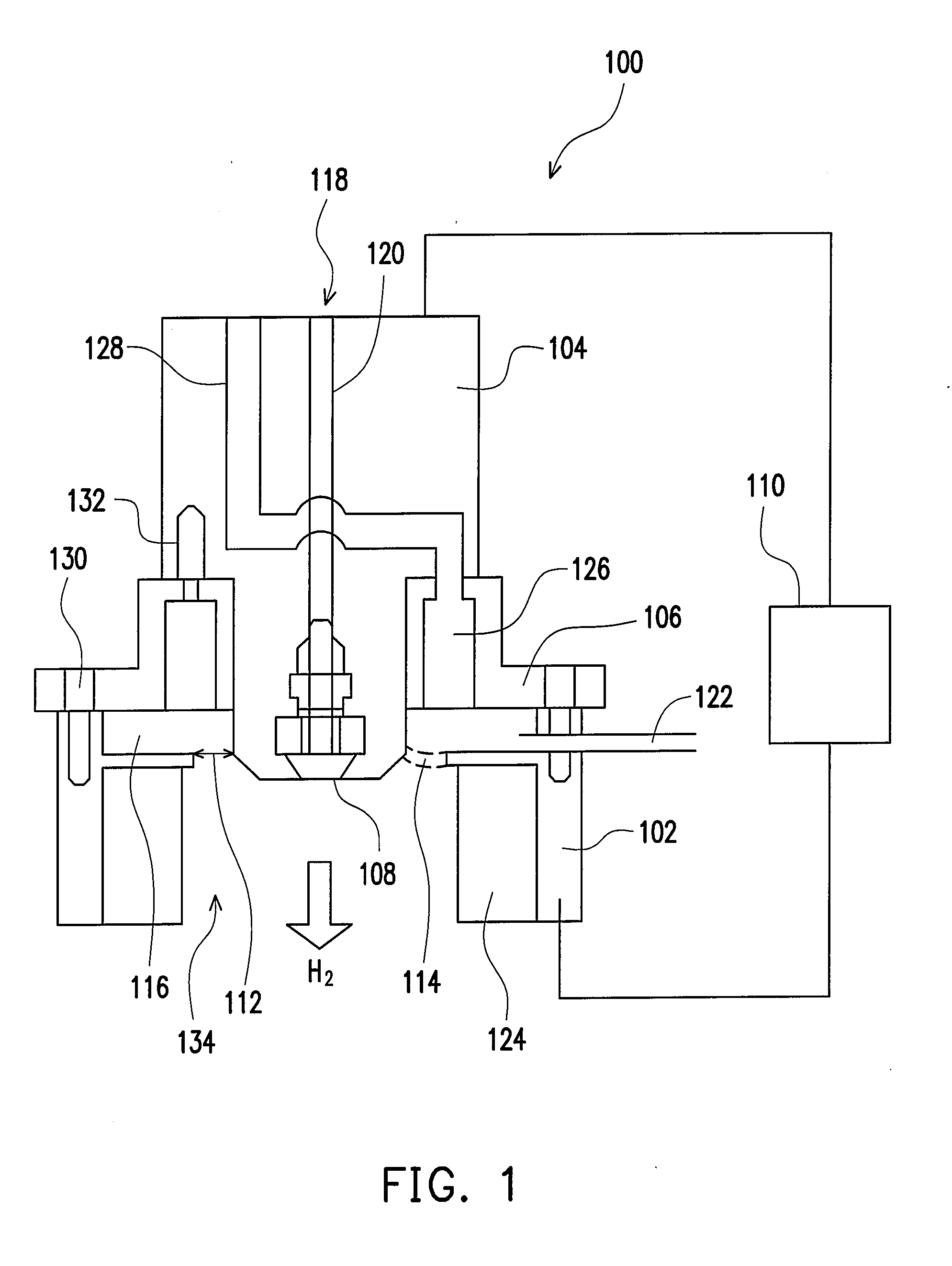
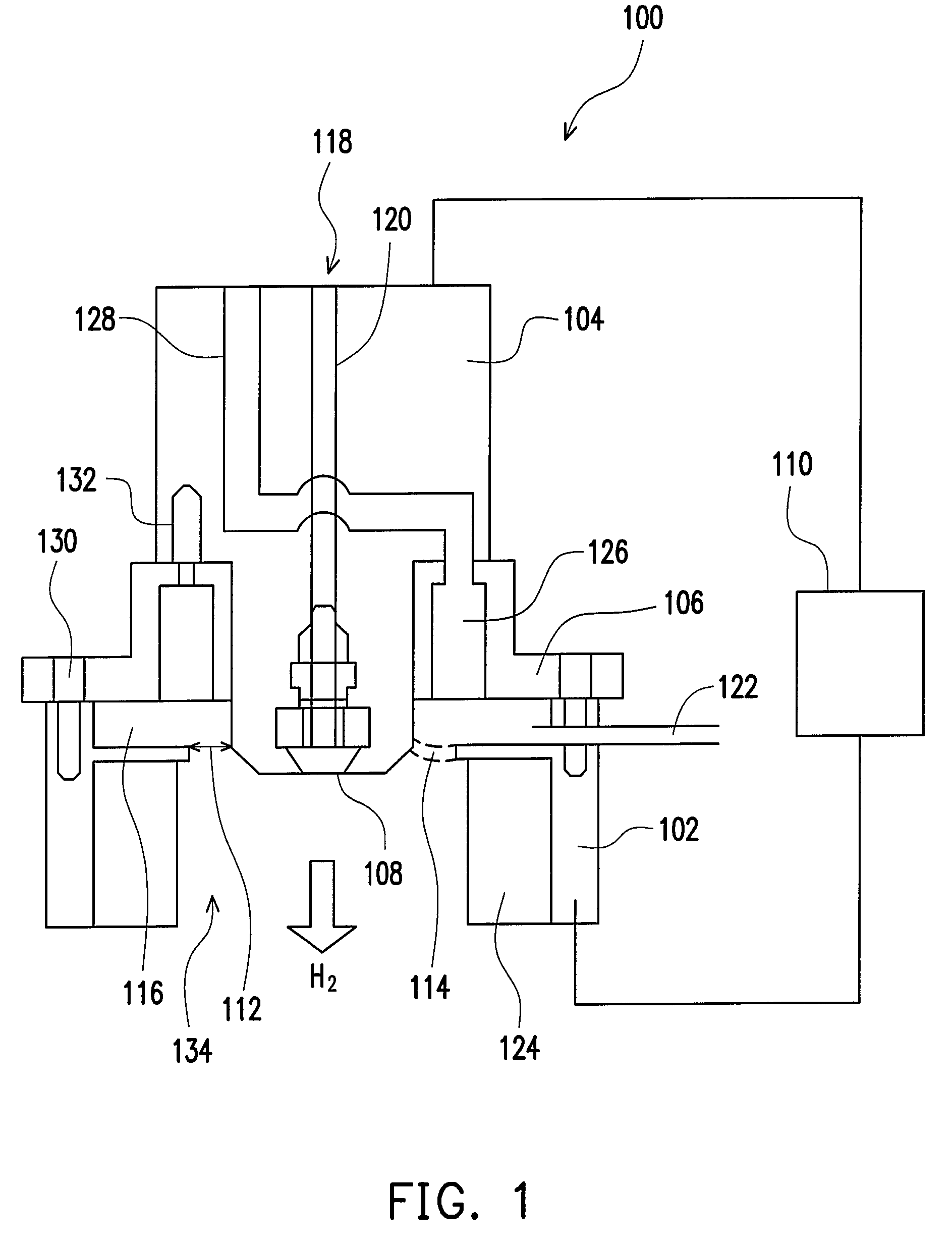
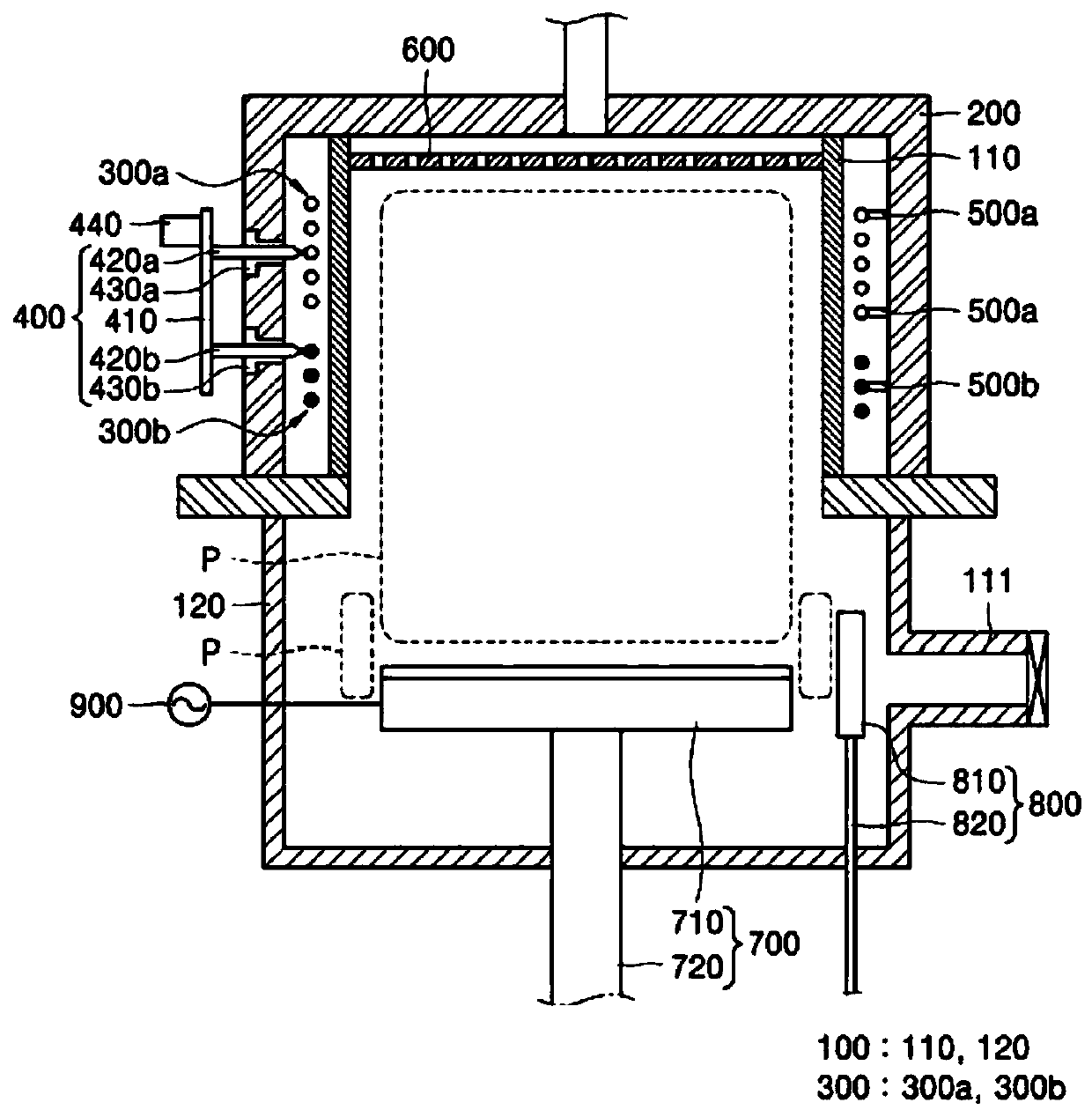
Suspended gas distribution manifold for plasma chamber
InactiveUS7484473B2Avoiding distortion and crackingImprove spatial uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal isolationProduct gas
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
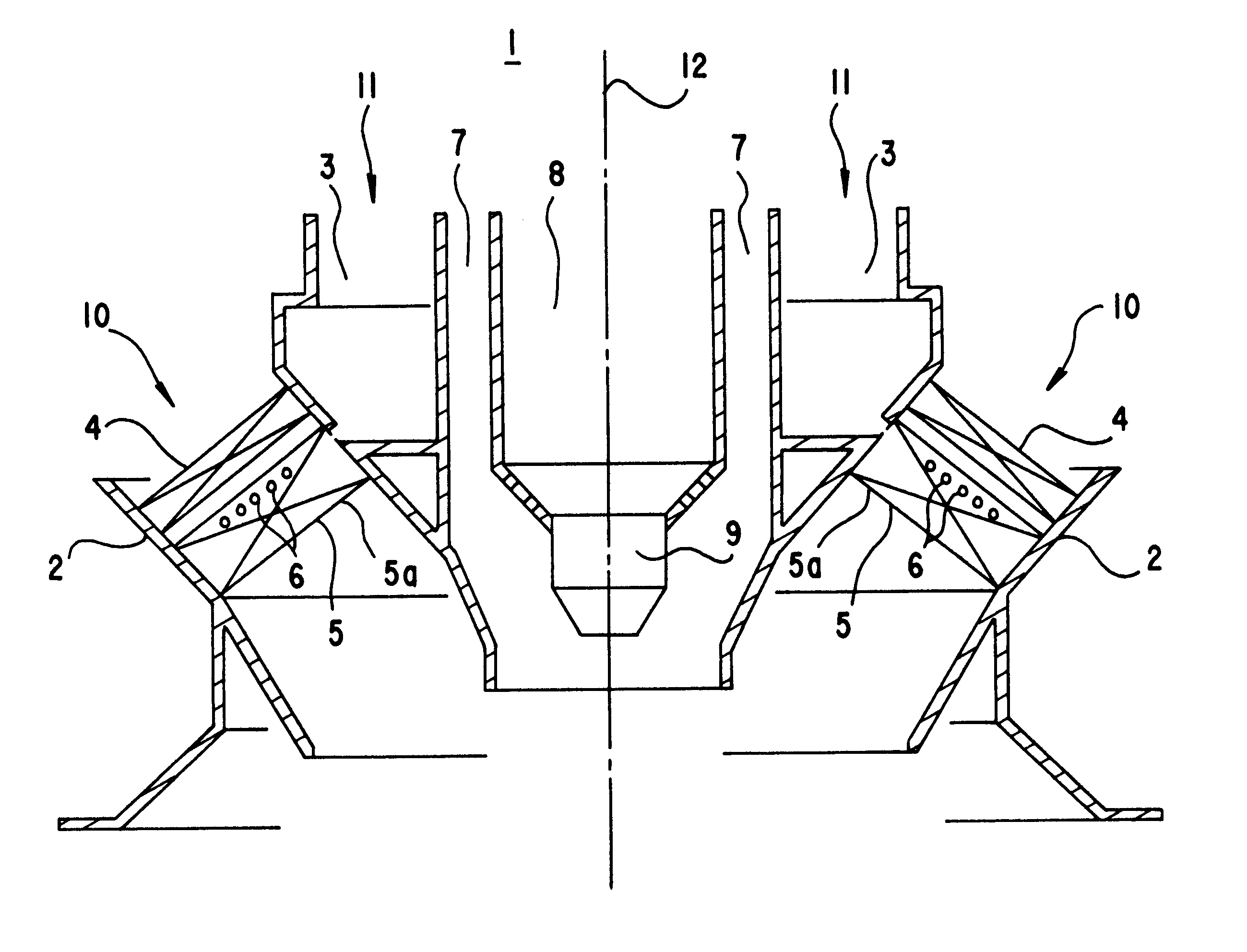
Burner for fluidic fuels having multiple groups of vortex generating elements
InactiveUS6189320B1Efficient mixingImprove spatial uniformityContinuous combustion chamberFlow mixersCombustorEngineering
A burner, in particular for a gas turbine, in which combustion air is subjected to a vorticity by a vortex element, admits fuel to the vortical combustion air. At the same time, a pressure loss produced by the vortex element is small. A low NO.sub.x emission at virtually the same efficiency is achieved.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
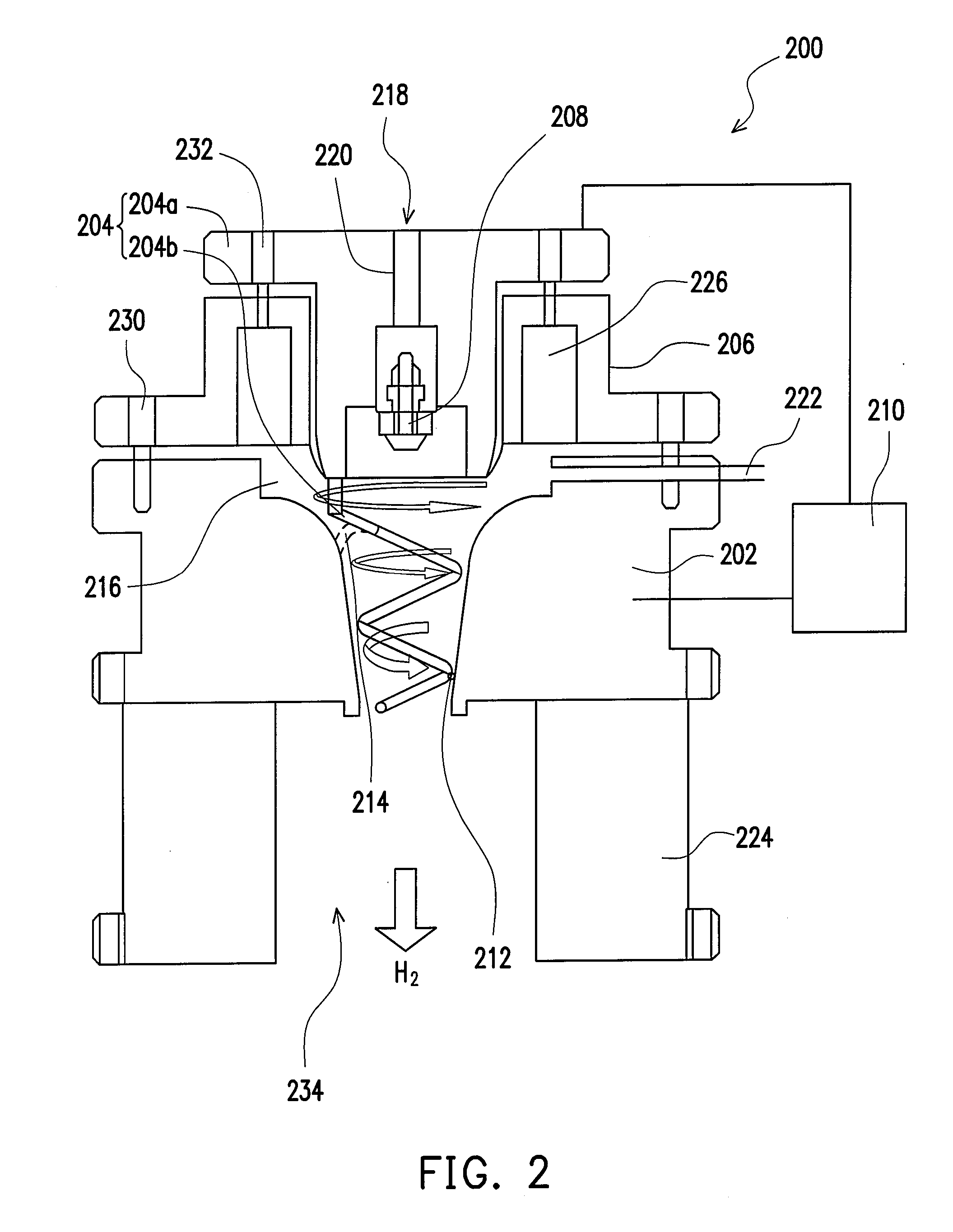
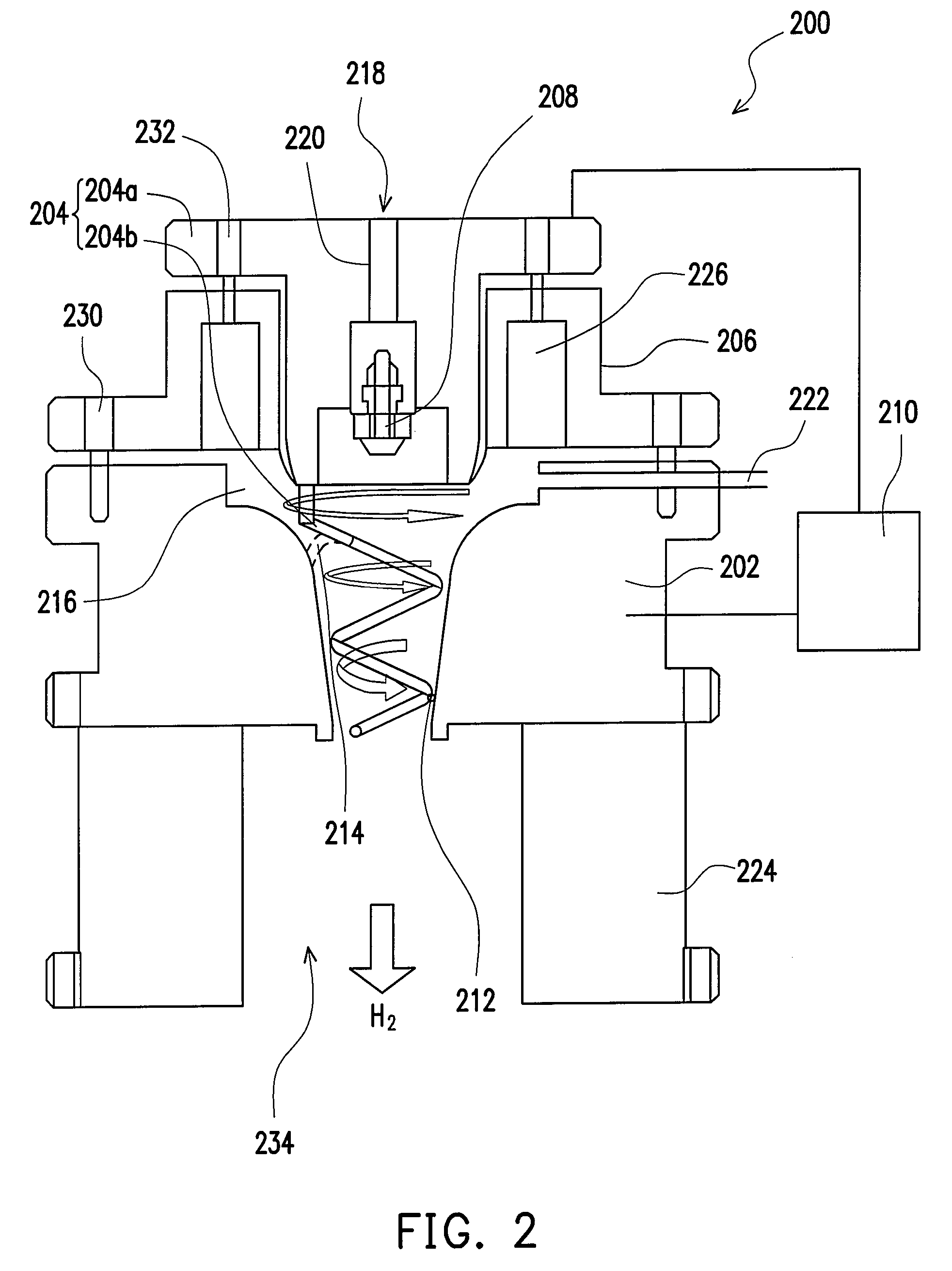
Directed gas injection apparatus for semiconductor processing
InactiveUS7103443B2Improve spatial uniformityExtended service lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesEngineeringHandling system
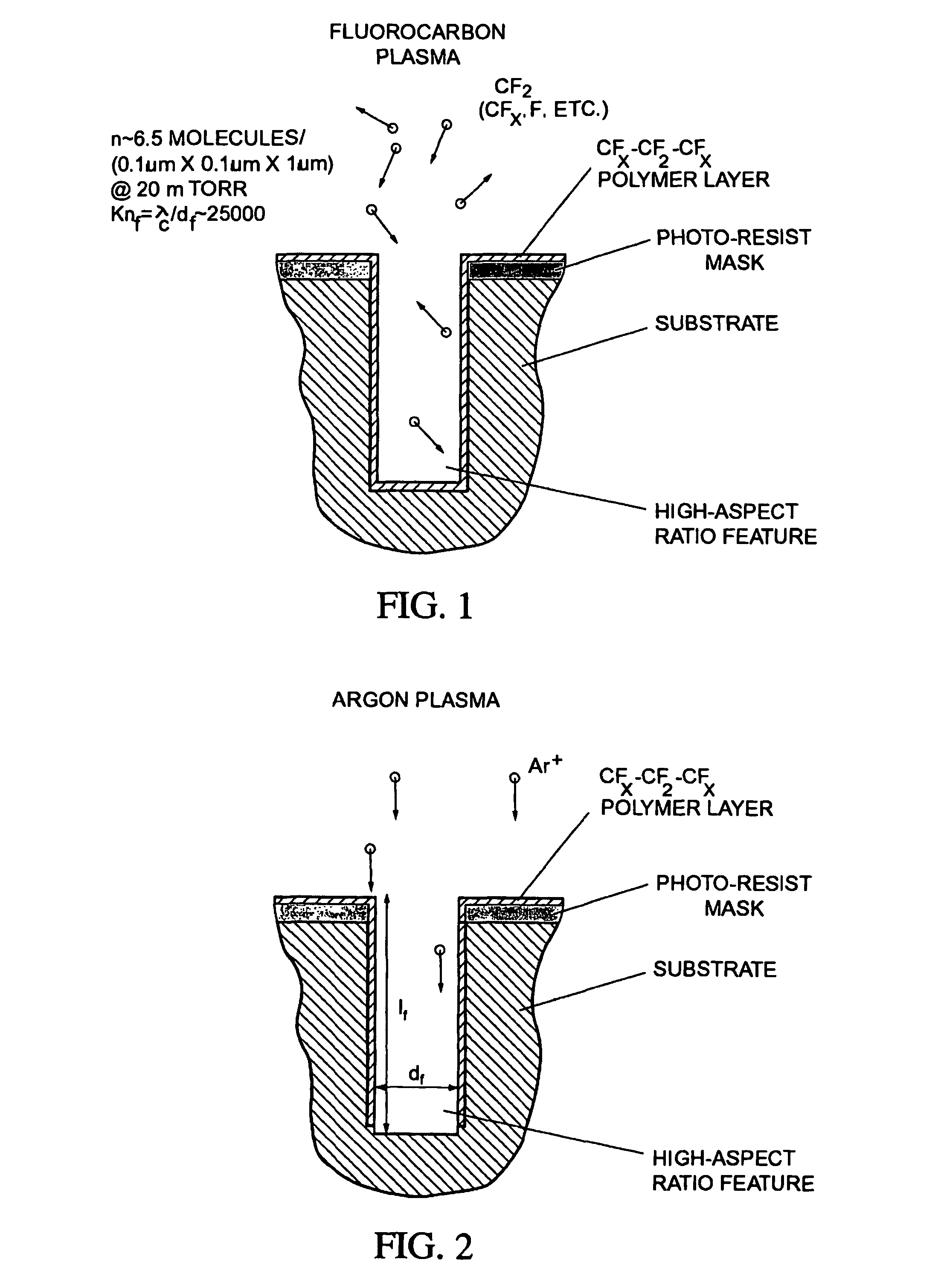
A method and system for utilizing a gas injection plate comprising a number of shaped orifices (e.g., sonic and simple orifices, and divergent nozzles) in the gas inject system as part of a plasma processing system. By utilizing the shaped orifices, directionality of gas flow can be improved. This improvement is especially beneficial in high aspect ratio processing.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
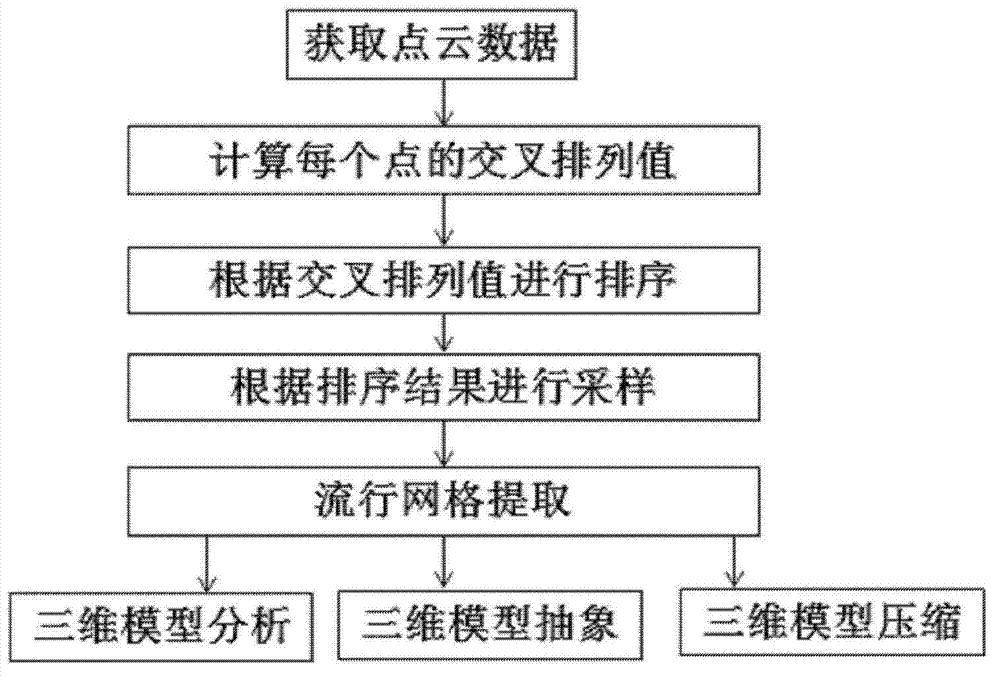
Processing method for three-dimensional model of external memory
The invention discloses a processing method for a three-dimensional model of an external memory. The method can be used for point resampling of the three-dimensional model of the external memory, the gridding reconstruction of point cloud of the external memory and compression of the three-dimensional model for model analysis on the external memory on the basis of space curve sequencing. According to the method, point cloud data can be sampled in a large scale, a sampling result has high spatial uniformity, the constraints of original data are also utilized during reconstruction, and a triangular manifold grid consistent with the topology structure of original point cloud data can be generated.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
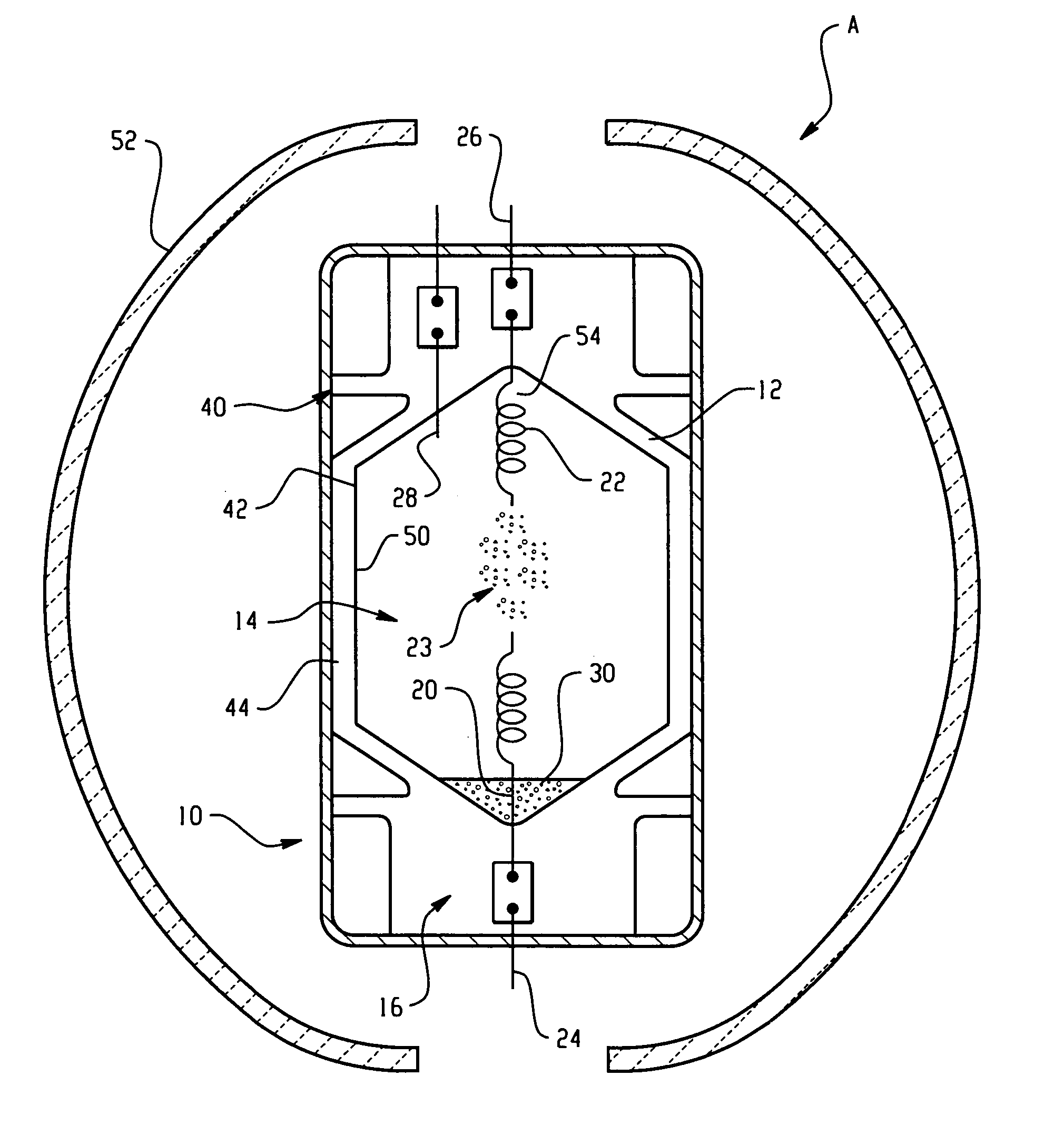
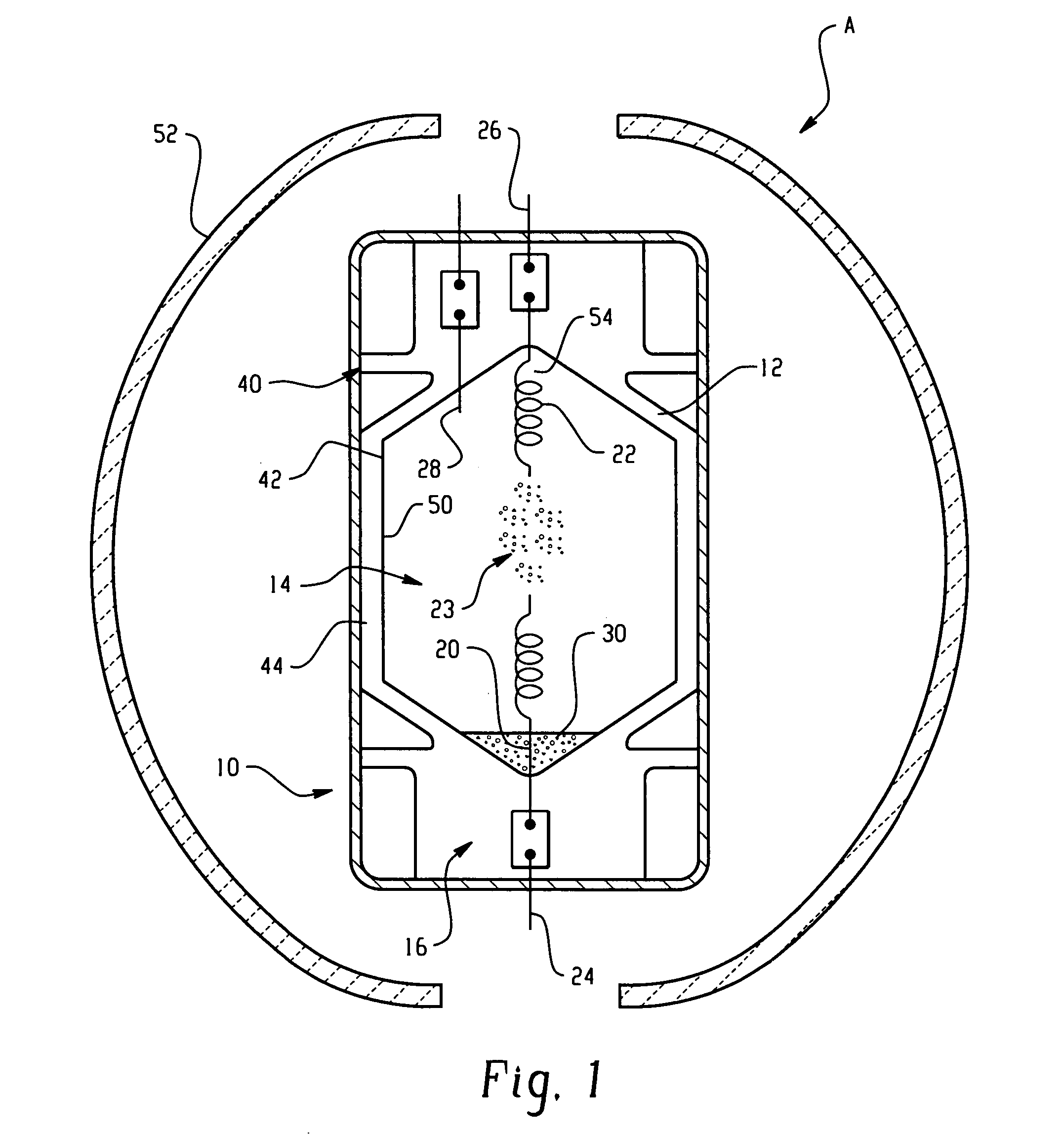
Optimized ultraviolet reflecting multi-layer coating for energy efficient lamps
InactiveUS20050127840A1RelieveImprove spatial uniformityTube/lamp screens manufactureIncadescent screens/filtersTransmittanceAngle of incidence
A metal halide lamp (10) includes a light-transmissive envelope (12) which encloses a metal halide pool (30) for generating a discharge when spaced apart electrodes (20, 22) within the envelope are supplied with an electric current. A multi-layer coating (40) is deposited on a surface (42) of the envelope. The coating includes several layers of at least two materials of different refractive index, which, in combination, reflect radiation in the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Rather than optimizing the coating for a normal (i.e., 0°) angle of incidence on the coating, the multi-layer coating is optimized at an angle which is selected to be within 10° of the mean angle (α) of incidence of the UV radiation on the arctube surface, thereby increasing the amount of UV radiation which is returned to the metal halide pool. The coating is preferably optimized for high reflectivity in the UV-region of the spectrum and high transmission in the visible region of the spectrum to maximize useful light output while reflecting UV light back to the metal halide pool for improved heating of the pool.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20200124834A1Improve spatial uniformityImprove efficiencyStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesLuminous intensityLight equipment
An illumination apparatus comprises an array of micro-LEDs, an aligned plurality of directional catadioptric optical elements, light redirecting micro-optics and a reflective polariser. The directional illumination apparatus is arranged to provide a uniform spatial distribution across its output area by recirculating reflected high luminous intensity regions into low luminous intensity regions of the catadioptric optical element. A thin and efficient illumination apparatus with high spatial uniformity may be provided for illumination in environmental lighting, display backlighting or direct display.
Owner:OPTOVATE
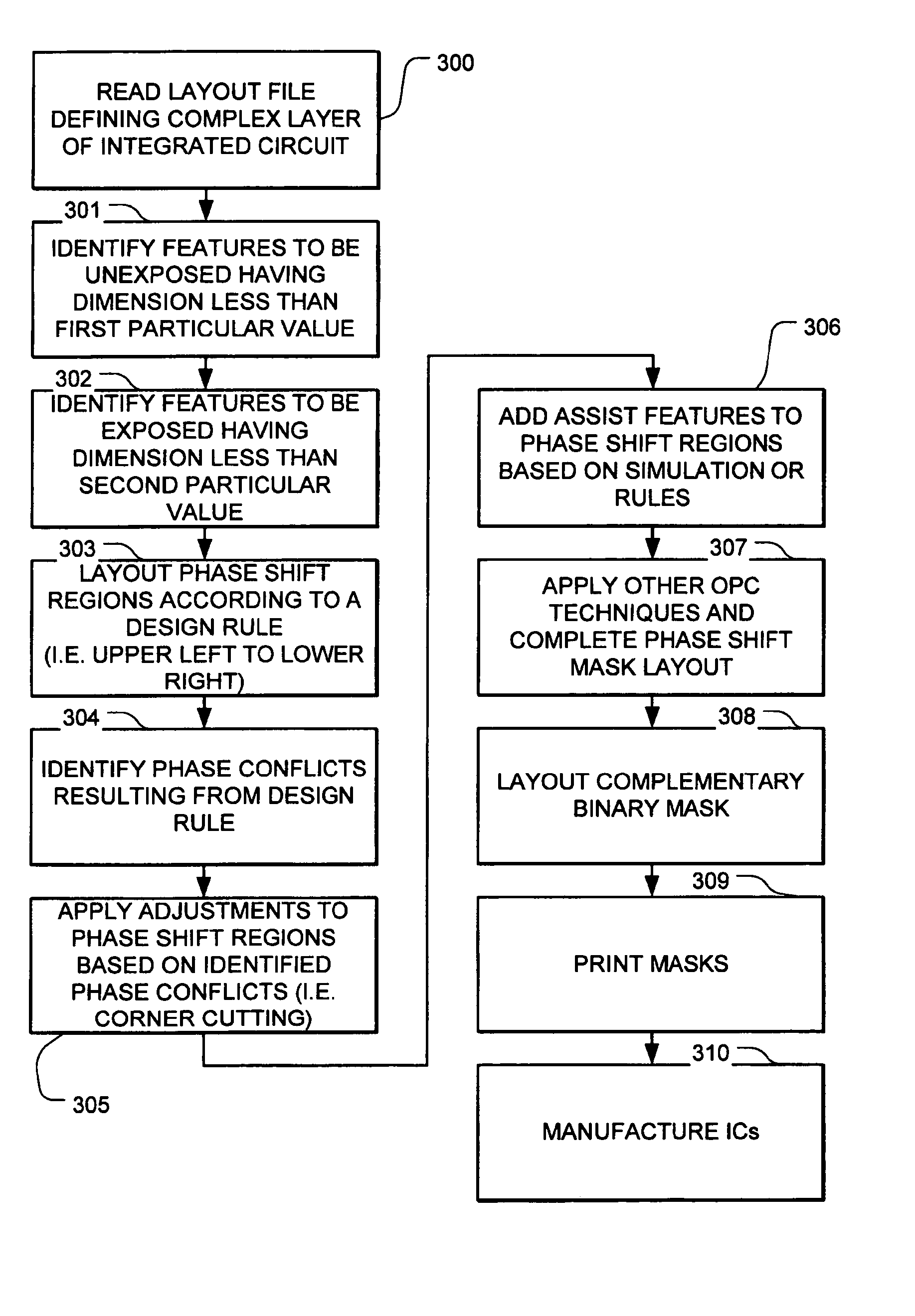
Phase shift mask including sub-resolution assist features for isolated spaces
InactiveUS20050042527A1Prevent and minimize phase conflictImproved small dimension structureOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsPhase shiftedEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Plasma reformer and internal combustion engine system having the same
ActiveUS20080149050A1Reduce decreaseExtended service lifeInternal combustion piston enginesEngine operationsInternal combustion engineElectrical and Electronics engineering
A plasma reformer includes a first electrode, a second electrode, an insulating member, an atomizing device and a power supply. A discharge gap is defined between the first electrode and the second electrode. The insulating member is arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode to insulating the first electrode and the second electrode, and a vortex gas flow route is formed between the insulating member and the first electrode, the second electrode. The second electrode penetrates the insulating member. The atomizing device is arranged on the first electrode and / or the second electrode. The power supply is connected with the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
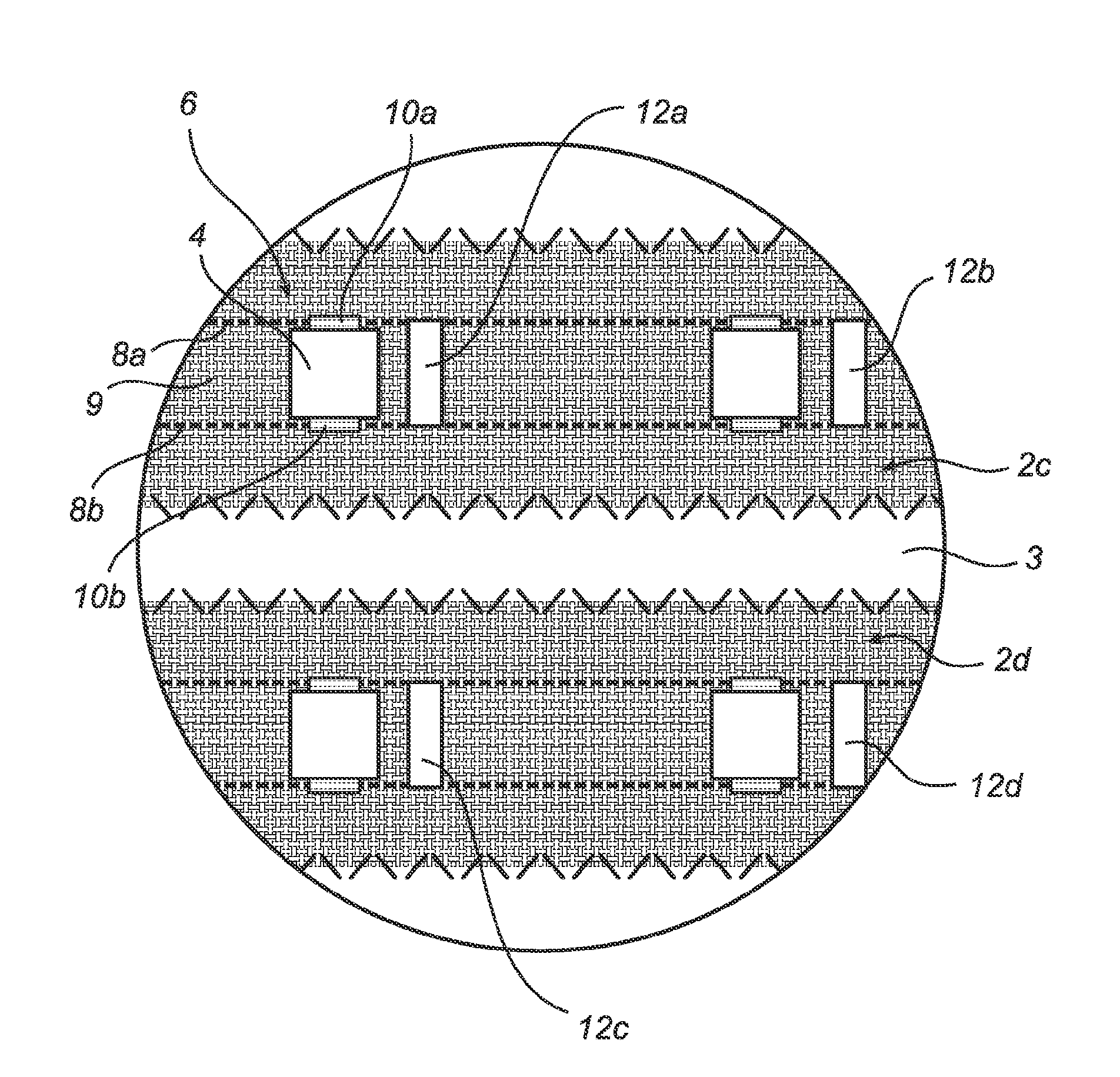
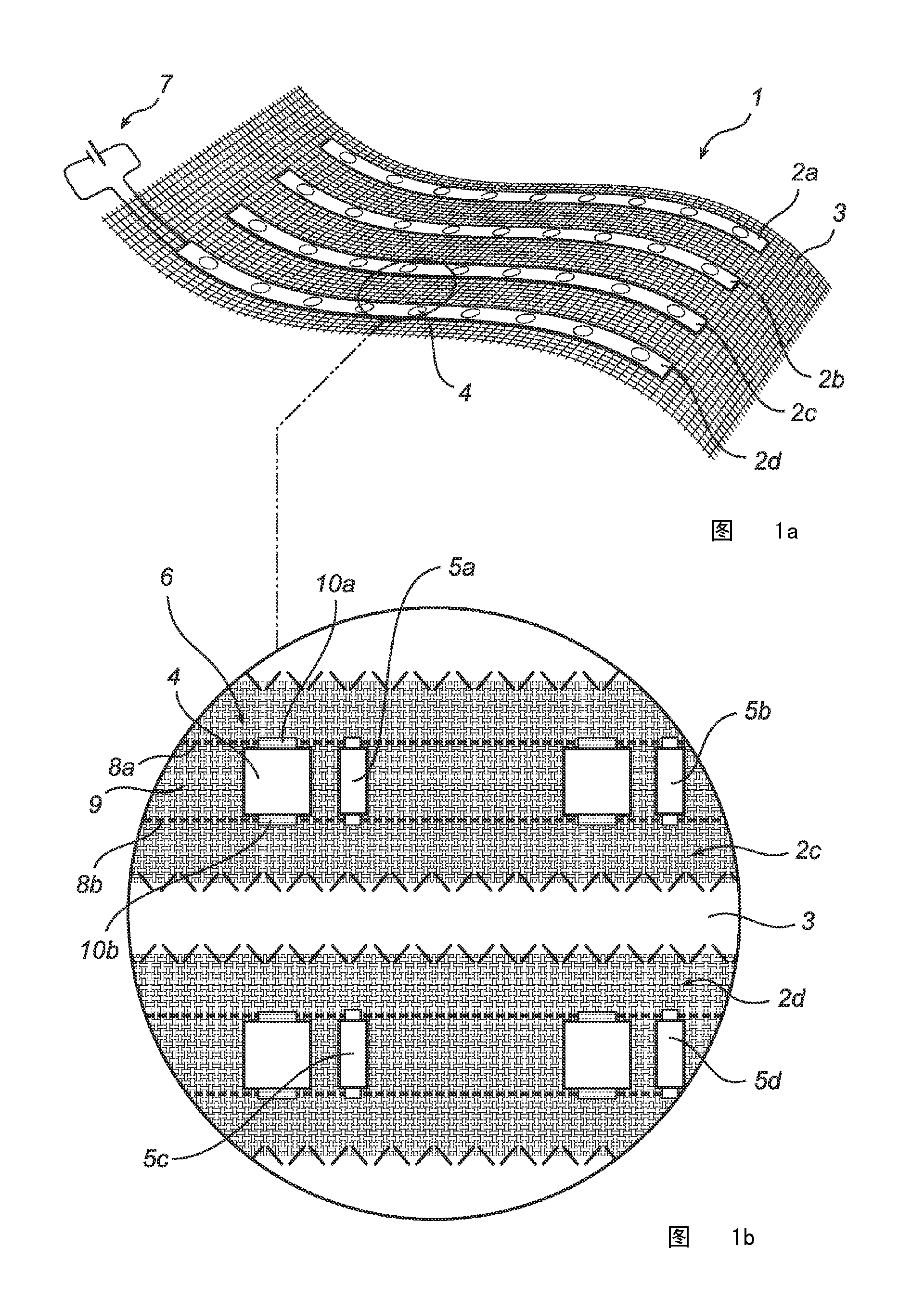
Electronic textile with local energy supply devices
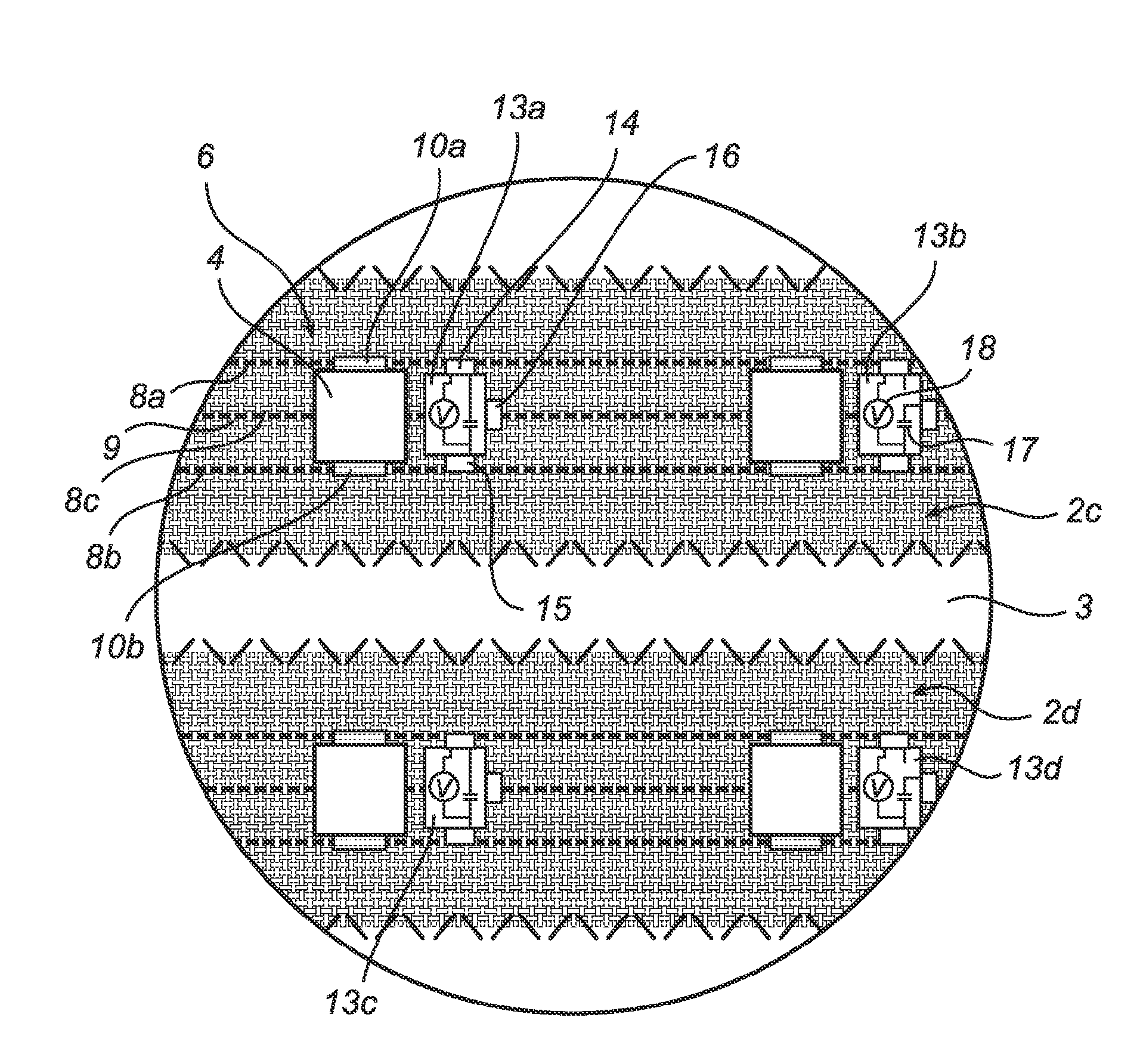
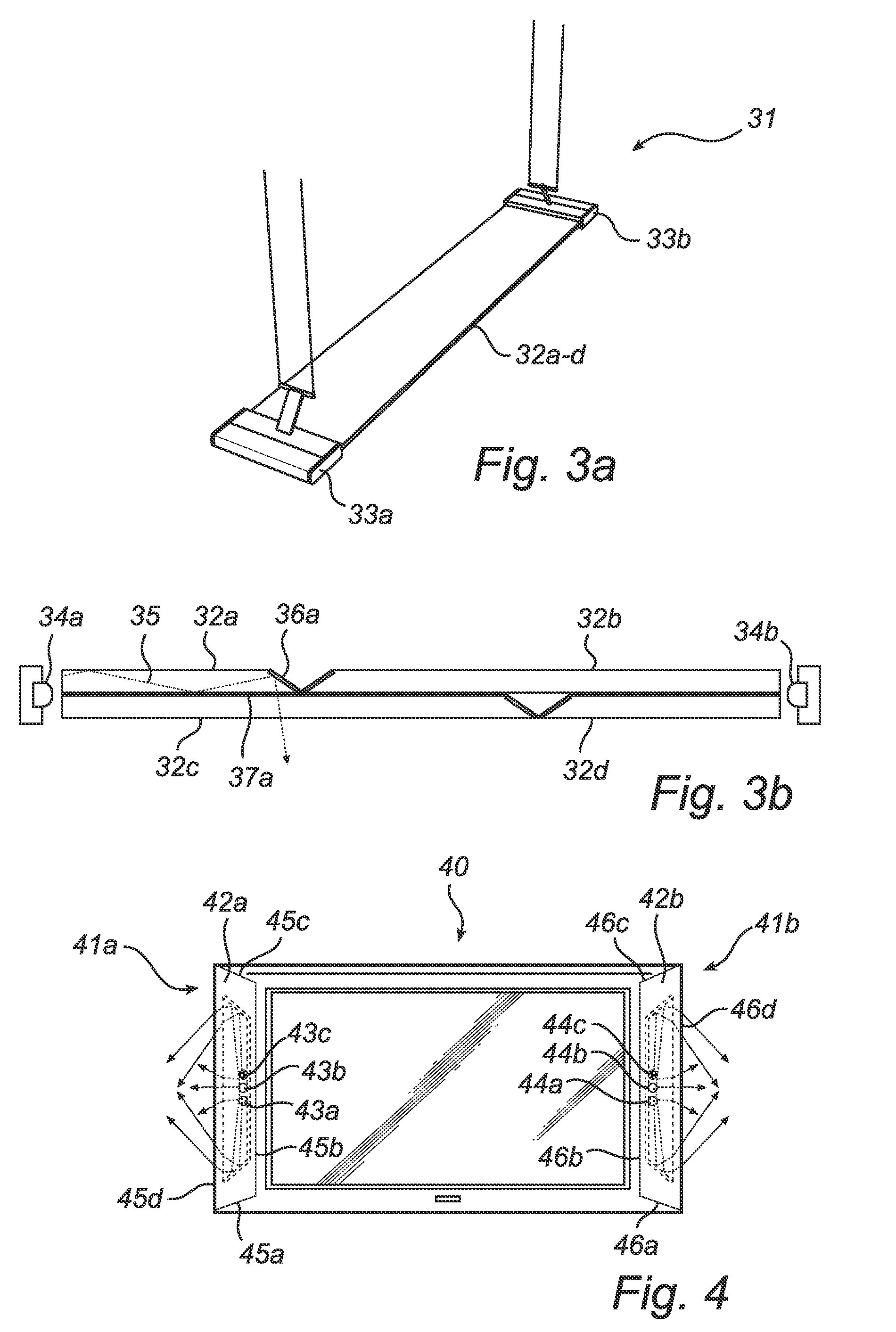
InactiveCN102511203AImprove spatial uniformitySpatial Uniformity AchievedLighting elementsPrinted circuit aspectsElectricityElectrical conductor
An electronic textile (1) comprising: a textile substrate (3) comprising at least one textile substrate conductor (8a-b),and a plurality of electronic energy consuming devices (4) arranged on the textile substrate (3), each of the electronic energy consuming devices (4) being electrically connected to the at least one textile substrate conductor (8a-b) for supply of electrical power to the electronic energy consuming devices (4) from a main power supply (7). The electronic textile (1) further comprises a plurality of local energy supply devices (5a-d,12a-d,13a-d) arranged on the textile substrate (3), each of the local energy supply devices (5a-d,12a-d,13a-d) being arranged to supply electrical power to at least one of the electronic energy consuming devices (4) being associated with the local energy supply device (5a-d,12a-d,13a-d), in addition to electrical power supplied by the main power supply (7).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Burner for combustion of a low-calorific fuel gas and method for operating a burner
InactiveCN101040149AImprove spatial uniformityAvoid installationBurnersContinuous combustion chamberLow nitrogenProcess engineering
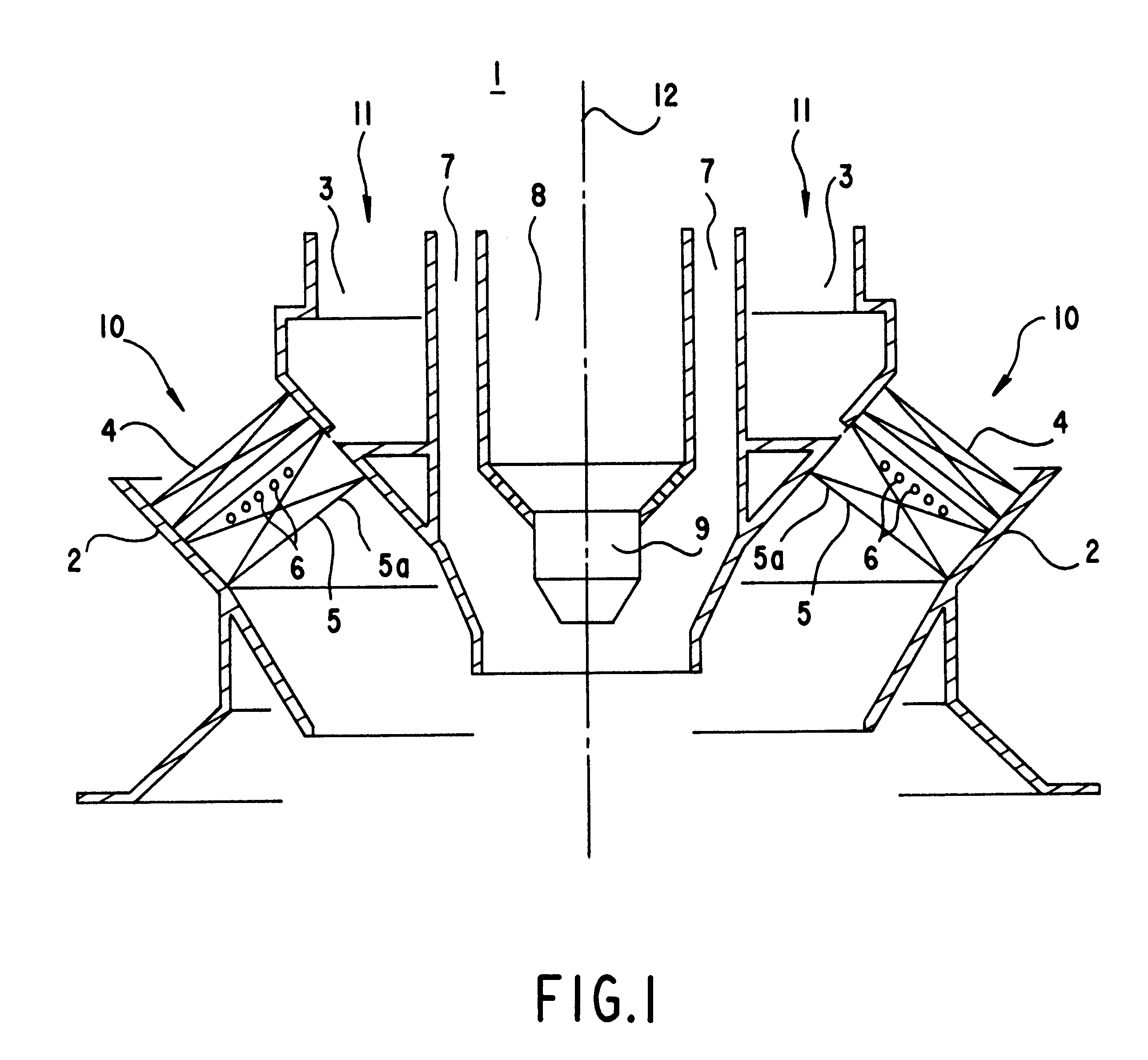
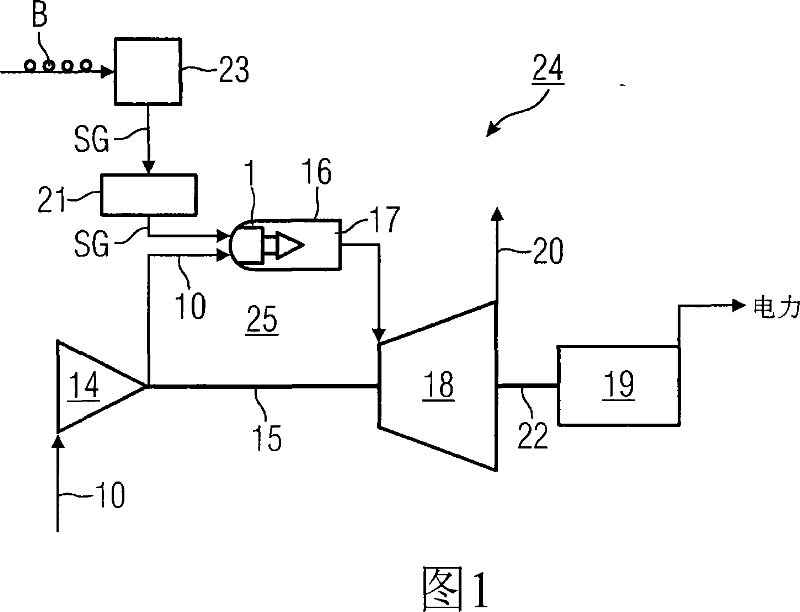
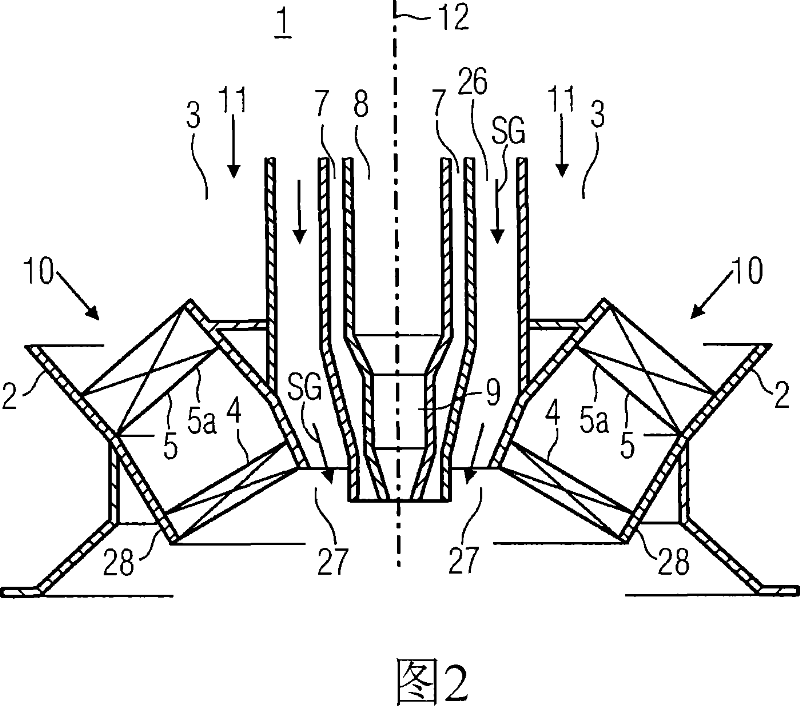
The invention relates to a burner (1), for the combustion of a low-calorific fuel gas (SG), with an air channel (2), running along a burner axis (12), for the introduction of combustion air (10) and a fuel gas channel (26), embodied for a high volumetric flow of low-calorific fuel gas (SG), whereby the fuel gas channel (26) and the air channel (2) open out into a mixing region (27). According to the invention, a low-nitrogen oxide synthesis gas operation of the burner (1) may be achieved, whereby a swirl element (4) is arranged in the air channel (2) for the generation of turbulent combustion air (10). The swirling element is provided in an opening region (28) directly adjacent to the flow of the mixing region (27). The invention further relates to a method of operation of a synthesis gas burner (1), whereby, directly before the mixing of the synthesis gas (SG) with the combustion air (10), the level of turbulence of the mass air flow is significantly increased on the microscopic level and a temporally and spatially homogenous mixing of the synthesis gas / air mixture is achieved.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Chip-grade LED (Light Emitting Diode) packaging device with controllable light emitting angle and packaging process
InactiveCN106784250AAvoid short circuitReduced diffusion areaSemiconductor devicesFluorescenceLed packaging
The invention discloses a chip-grade LED (Light Emitting Diode) packaging device with a controllable light emitting angle and a packaging process. According to the LED packaging device, first white wall adhesive layers are arranged on side faces of an LED chip, a diffusion layer and a fluorescent adhesive layer and are used as reflection surfaces; the reflection surfaces with different shapes can be designed aiming at requirements on different light emitting angles, so that the LED packaging device with the controllable light emitting angle is obtained; furthermore, the diffusion layer is arranged between the LED chip and the fluorescent adhesive layer, and the diffusion layer has a refractive index higher than that of a fluorescent adhesive; the difference between the refractive indexes of the LED chip and the fluorescent adhesive layer is reduced; the refractive indexes of the LED chip, the diffusion layer and the fluorescent adhesive layer have a certain gradient and the light emitting efficiency of the LED chip is improved, so that the luminous flux of the device is improved; the refractive indexes of diffusion powder and a packaging adhesive in the diffusion layer are different, and the condition that light emission of blue light of the LED chip is not uniform can be improved, so that the space color uniformity of the device is improved; and the design of a concave groove and white wall structure is adopted, so that the reliability problem of a product is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHU JUFEI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
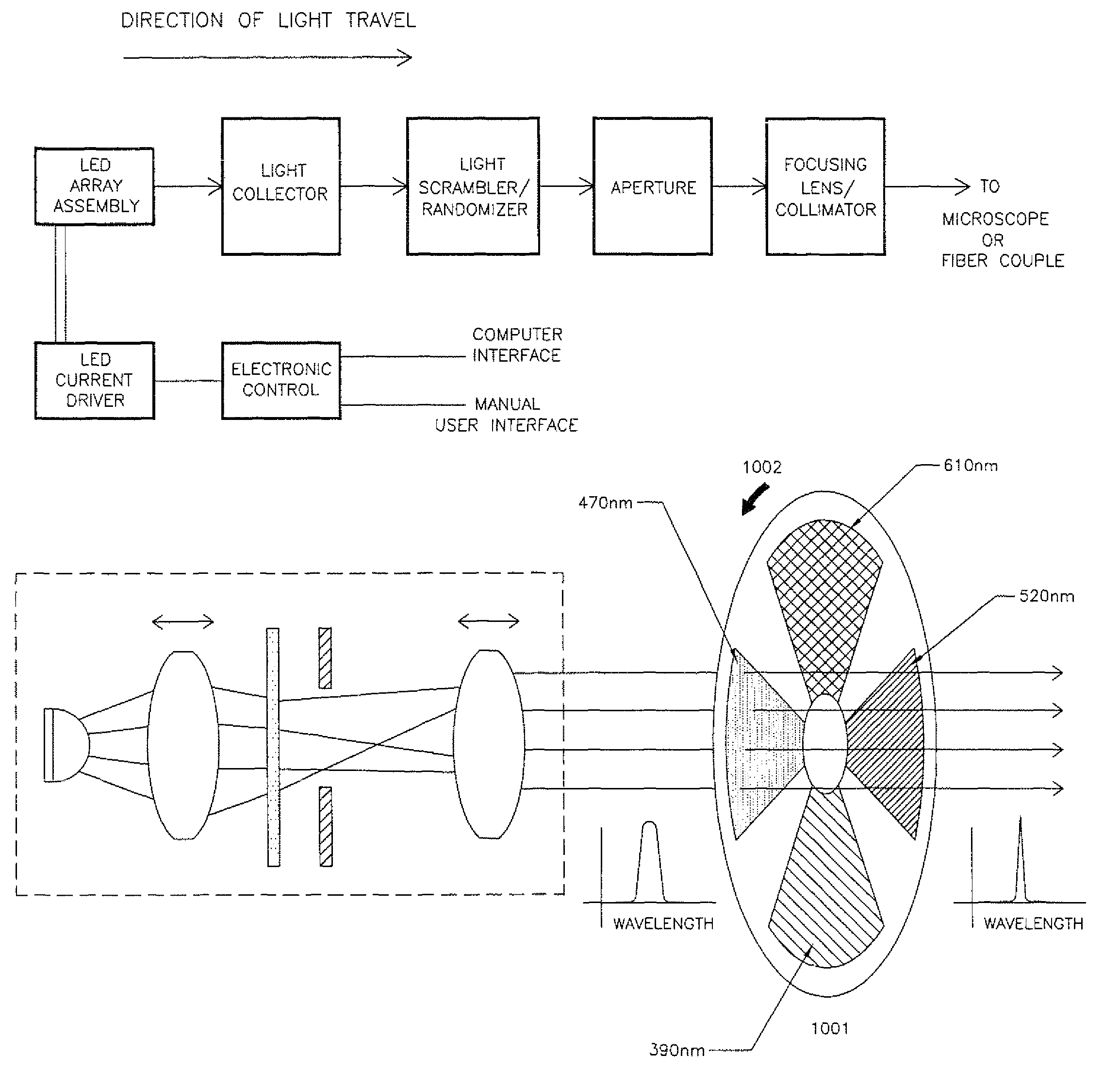
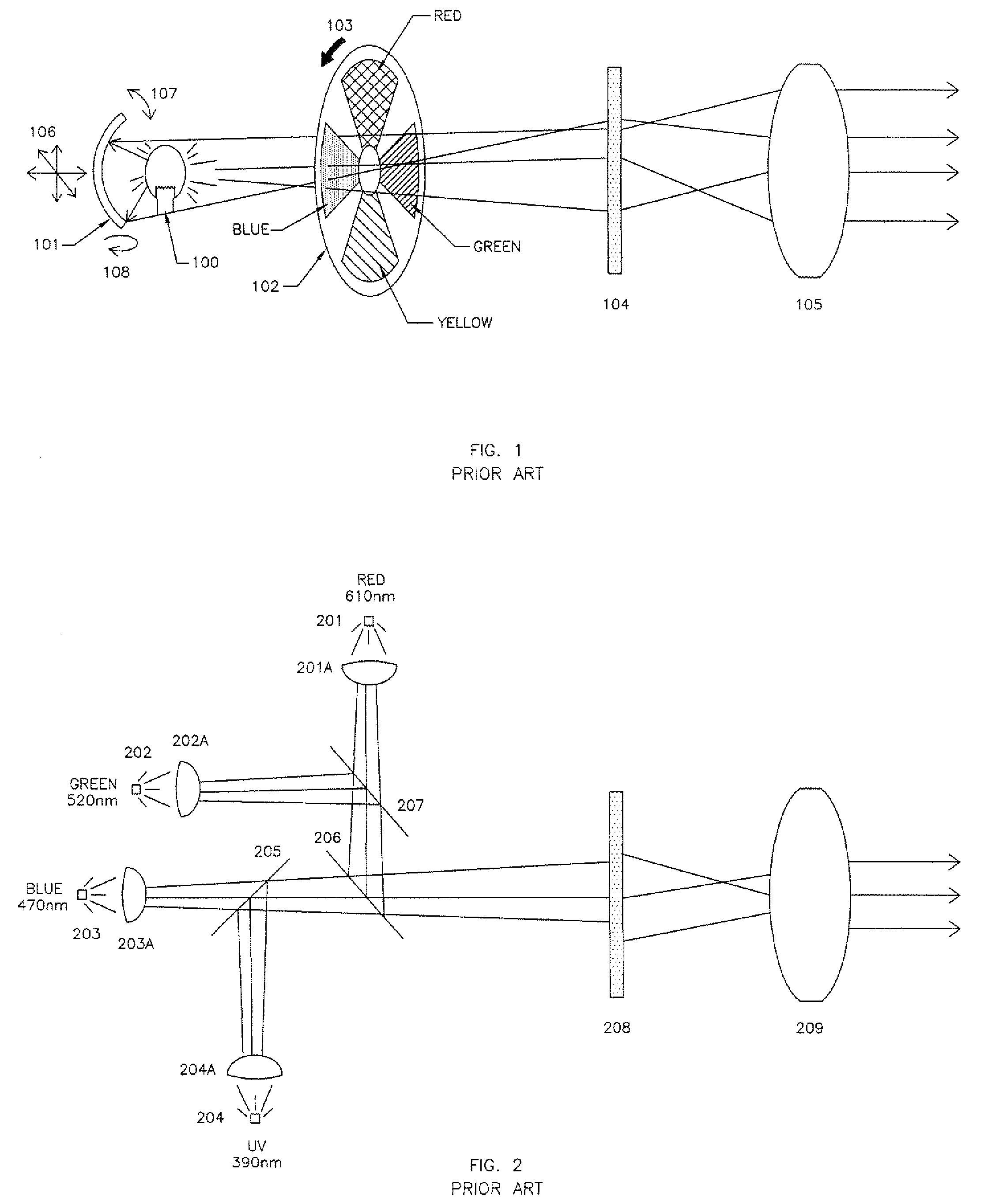
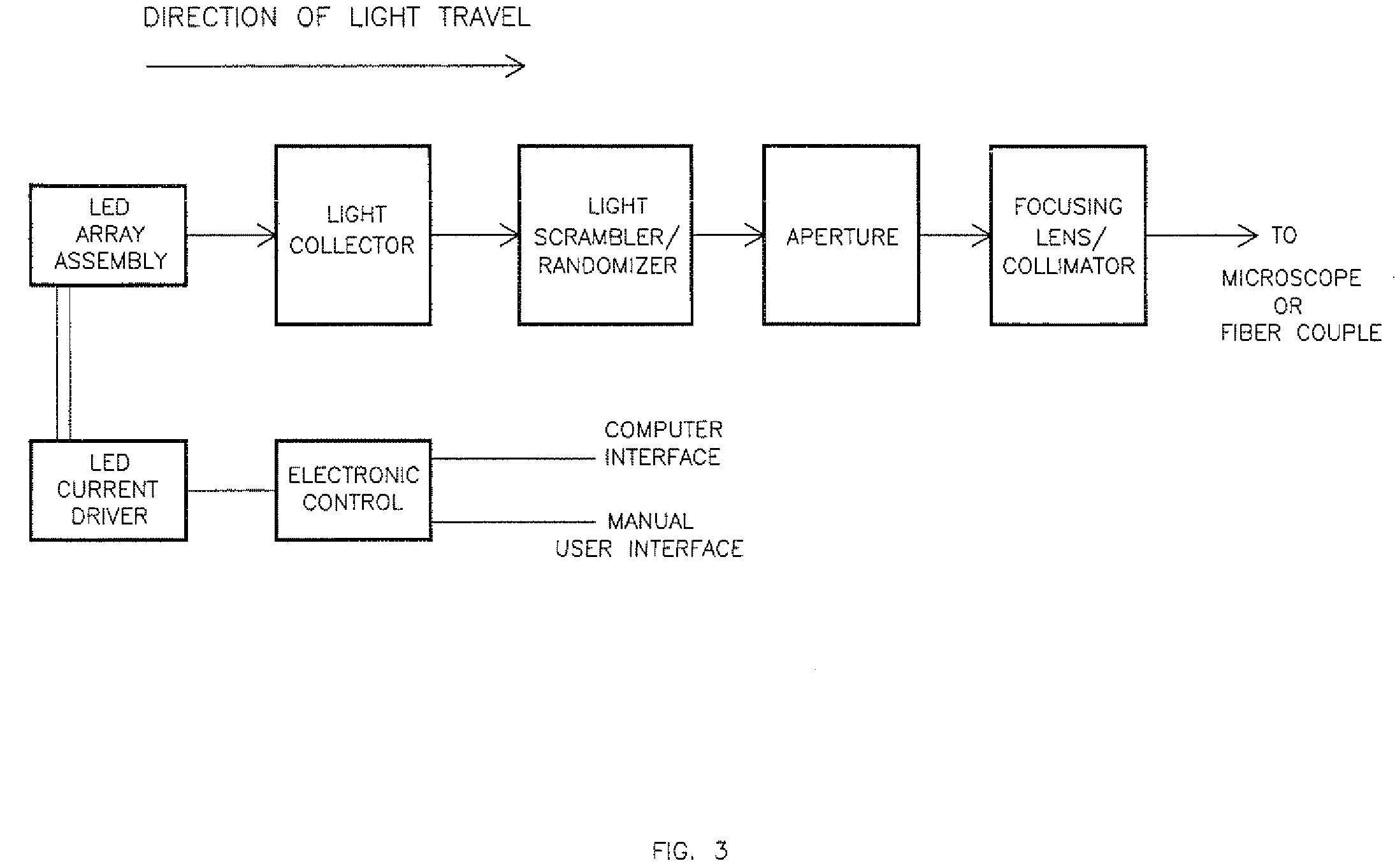
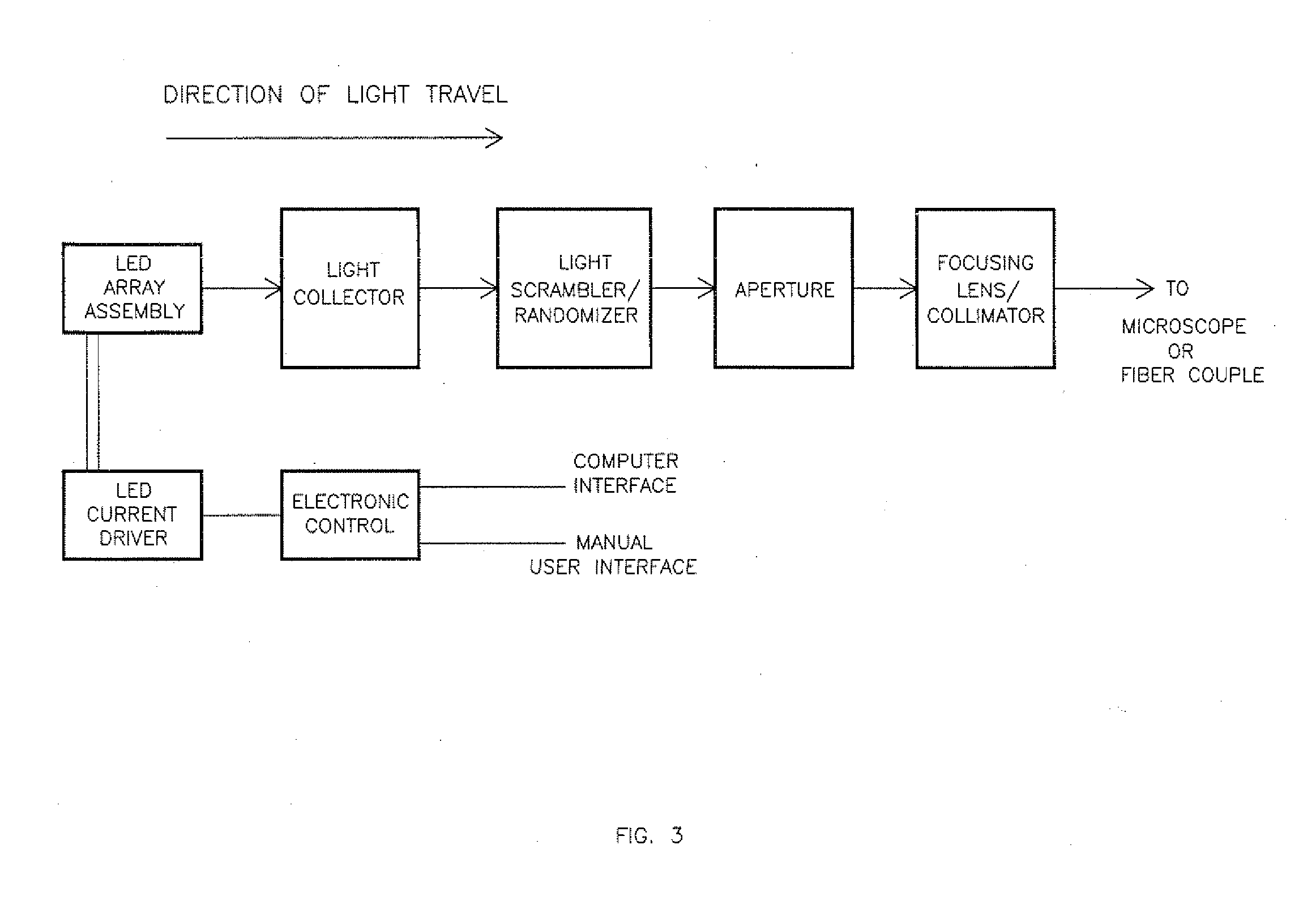
Multiple wavelength LED array illuminator for fluorescence microscopy
ActiveUS8596815B2Improve spatial uniformityIncrease the number ofElectrical apparatusLighting support devicesPower flowLed array
One embodiment provides light along an optical axis. It comprises a substrate and at least one array of multiple LED chips without individual packaging supported by the substrate. The LED chips emit light within different wavelength ranges and are distributed laterally with respect to the axis over an area, the LED chips having light emitting surfaces for emitting light in directions transverse to the area. An optical element adjacent to the light emitting surfaces of the LED chips in the at least one array collects and directs light emitted by the LED chips of the at least one array along the axis towards a target. Another embodiment is directed to a method for providing multiple wavelength light for fluorescent microscopy using the above system. Electric current is supplied to the multiple LED chips, causing them to emit light of multiple wavelengths. The currents supplied to the multiple LED chips are controlled so as to control the exposure of fluorescent dyes with different excitation wavelengths wherein the light emitted by the multiple LED chips include wavelength components at such different excitation wavelengths without having to move the multiple LED chips.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Plasma reformer and internal combustion engine system having the same
ActiveUS7591242B2Extended service lifeReforming effectInternal combustion piston enginesEngine operationsInternal combustion engineElectrical and Electronics engineering
A plasma reformer includes a first electrode, a second electrode, an insulating member, an atomizing device and a power supply. A discharge gap is defined between the first electrode and the second electrode. The insulating member is arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode to insulating the first electrode and the second electrode, and a vortex gas flow route is formed between the insulating member and the first electrode, the second electrode. The second electrode penetrates the insulating member. The atomizing device is arranged on the first electrode and / or the second electrode. The power supply is connected with the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
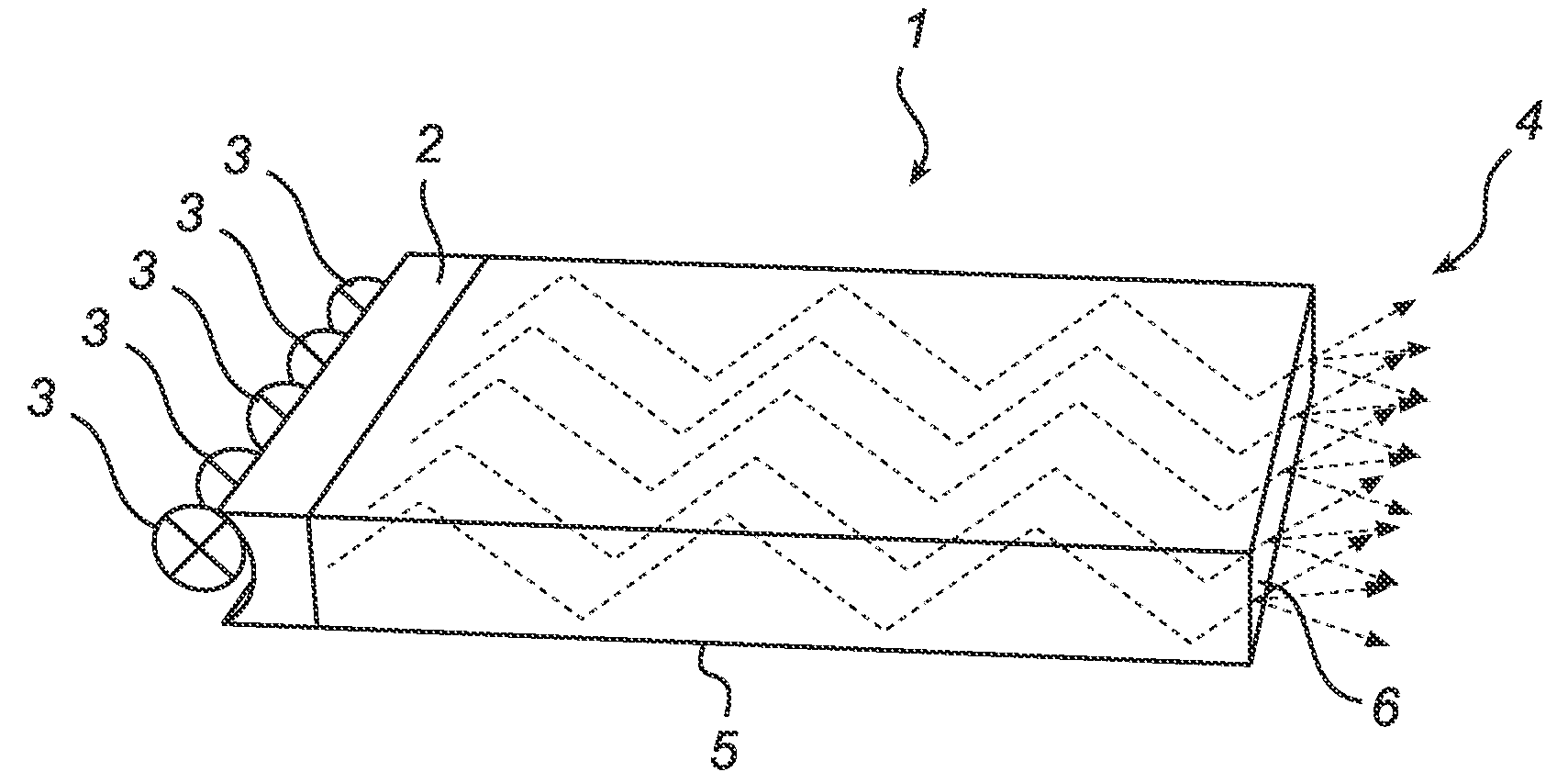
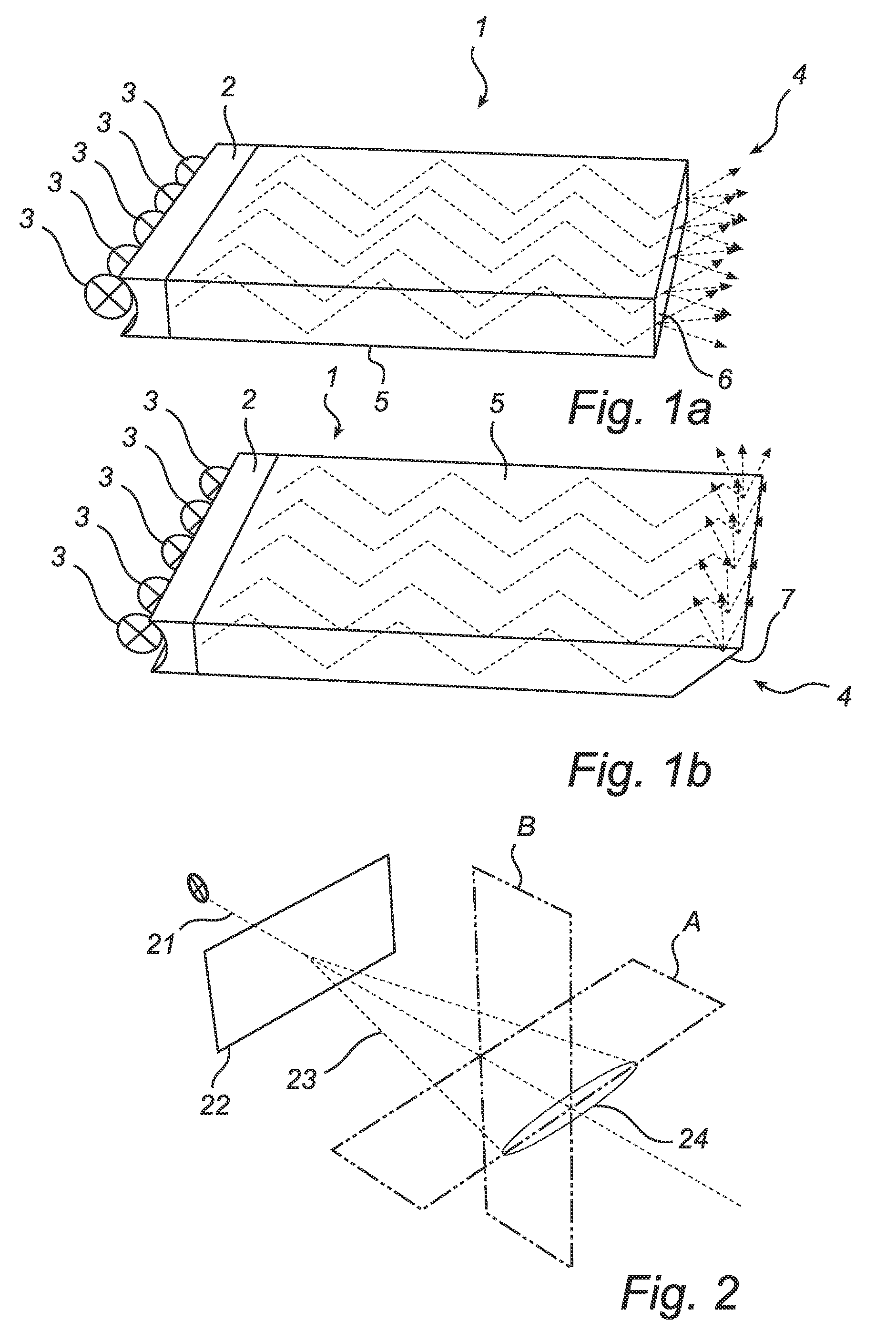
Waveguide with asymmetric outcoupling
InactiveUS20090257712A1Improve spatial uniformityImprove color mixingPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesUltimate tensile strengthWaveguide
A waveguide (1), arranged to guide light from at least one light source (3), comprising an outcoupling structure (4) adapted to enable outcoupling of said light from said waveguide in a general outcoupling direction, and at least one guiding edge (5) adapted to contain said light in said waveguide by reflecting said light on its way towards said outcoupling structure, wherein the outcoupling structure comprises an asymmetrically diffusing layer (6; 7). Such asymmetric diffusion improves the color mixing, and removes or limits the occurrence of color bands or intensity bands, while limiting the divergence in the direction where no color mixing or intensity variation problems exist.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Polycrystalline silicon production device and method
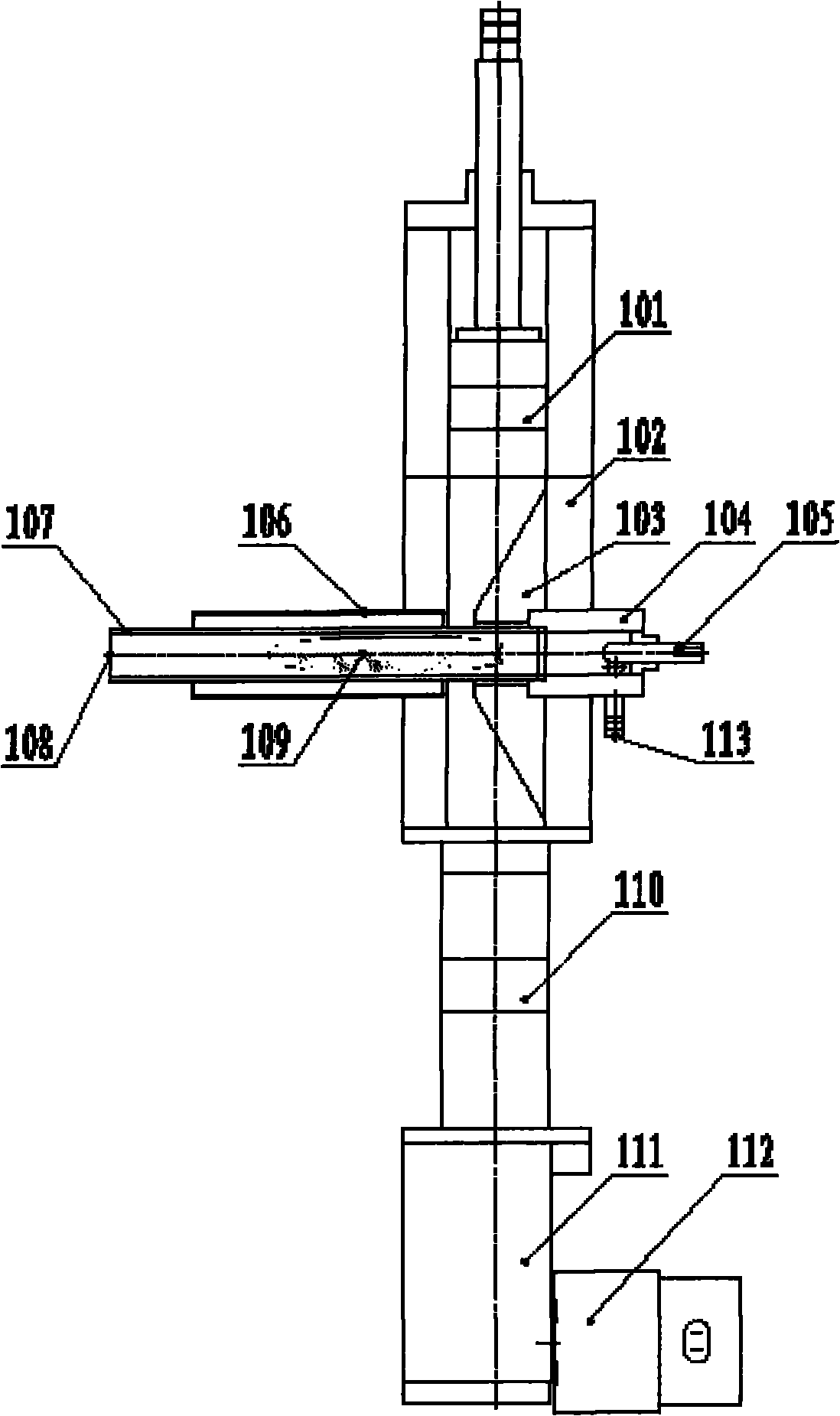
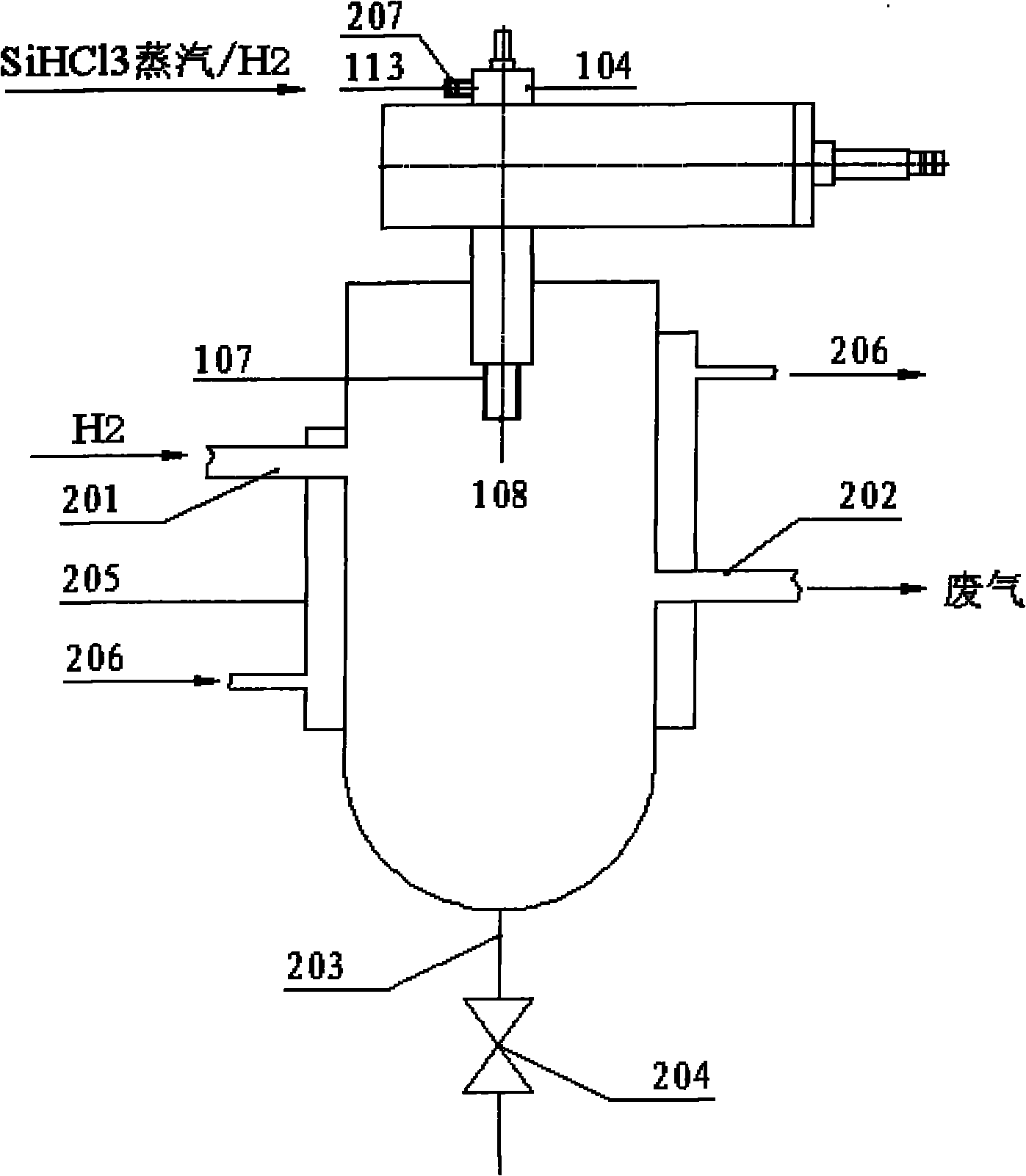
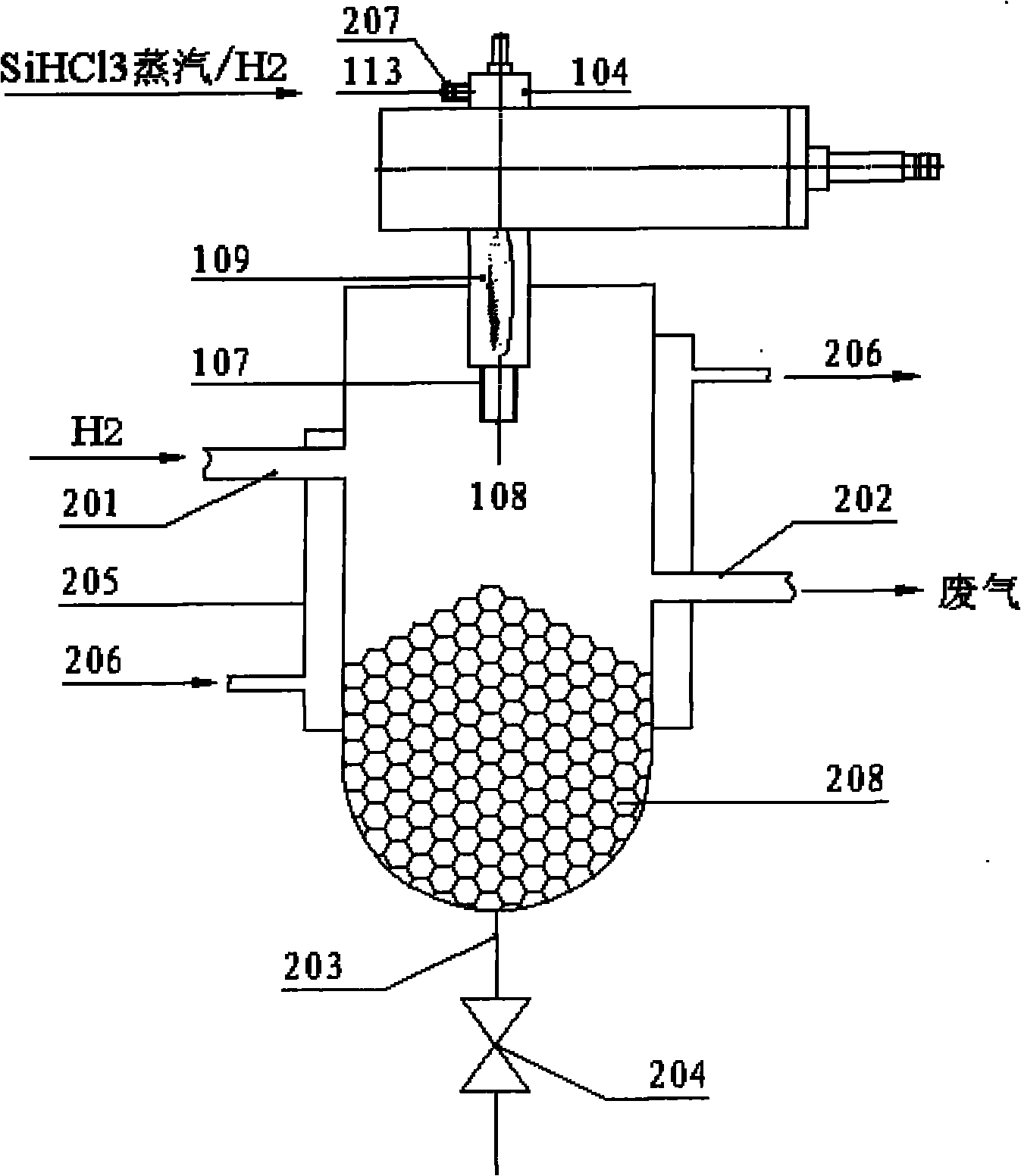
The invention discloses a polycrystalline silicon production device which comprises a polycrystalline silicon curing and receiving container and a microwave surface wave plasma torch, wherein the polycrystalline silicon curing and receiving container is used for receiving polycrystalline silicon produced by the microwave surface wave plasma torch. The invention also discloses a polycrystalline silicon production method which comprises the following steps of: with SiHC13 steam and H2 gas as raw material reactants, discharging electricity to the raw material reactants through the microwave surface wave plasma torch so as to heat the raw material reactants in a dielectric tube, and cooling and curing produced silicon in the polycrystalline silicon curing and receiving container to obtain polycrystalline silicon.
Owner:HEFEI FEIFAN PLASMA TECH
Large single crystal diamonds
ActiveCN101657253AImprove spatial uniformityUltra-high pressure processesFrom chemically reactive gasesPhysicsAspect ratio
The present invention relates to an HPHT method for synthesizing single crystal diamond, wherein a single crystal diamond seed having an aspect ratio of at least 1.5 is utilized. Single crystal diamond seeds having an aspect ration of at least 1.5 and synthetic single crystal diamond which may be obtained by the method recited are also described, wherein the longest dimension of the growth surface substantially aligned along a <100> or <110> direction in the plane of the growth surface.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Inorganic metallic oxide thin-film with composite crystal form and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107946365AQuality improvementImprove featuresTransistorVacuum evaporation coatingCharge carrier mobilityEvaporation
The invention discloses an inorganic metallic oxide thin film with a composite crystal form and a manufacturing method thereof. The inorganic metallic oxide thin film comprises a composite crystal form structure, wherein the composite crystal form structure is composed of crystal grains and an amorphous structure, the crystal grains are surrounded by the amorphous structure, and the grain size ofthe crystal grains ranges from 0.5 to 10 nm; and the inorganic metallic oxide thin film is manufactured by depositing a raw material on a substrate by adopting a magnetron sputtering method or an evaporation method. According to the manufacturing method, the raw material is deposited on the substrate by adopting a simple method, so as to form the inorganic metallic oxide thin-film having the crystal grains and the amorphous structure, the presence of the crystal grains makes the atom arrangement of the inorganic metallic oxide thin-film more orderly, and a current carrier mobility of the thinfilm is increased; meanwhile, due to the simultaneous presence of the crystal grains and the amorphous frame, the thin film maintains good spatial uniformity, so that a corresponding small-sized device maintains good and uniform device performance in large-sized application. The inorganic metallic oxide thin-film and the manufacturing method thereof can be widely applied to the semiconductor field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
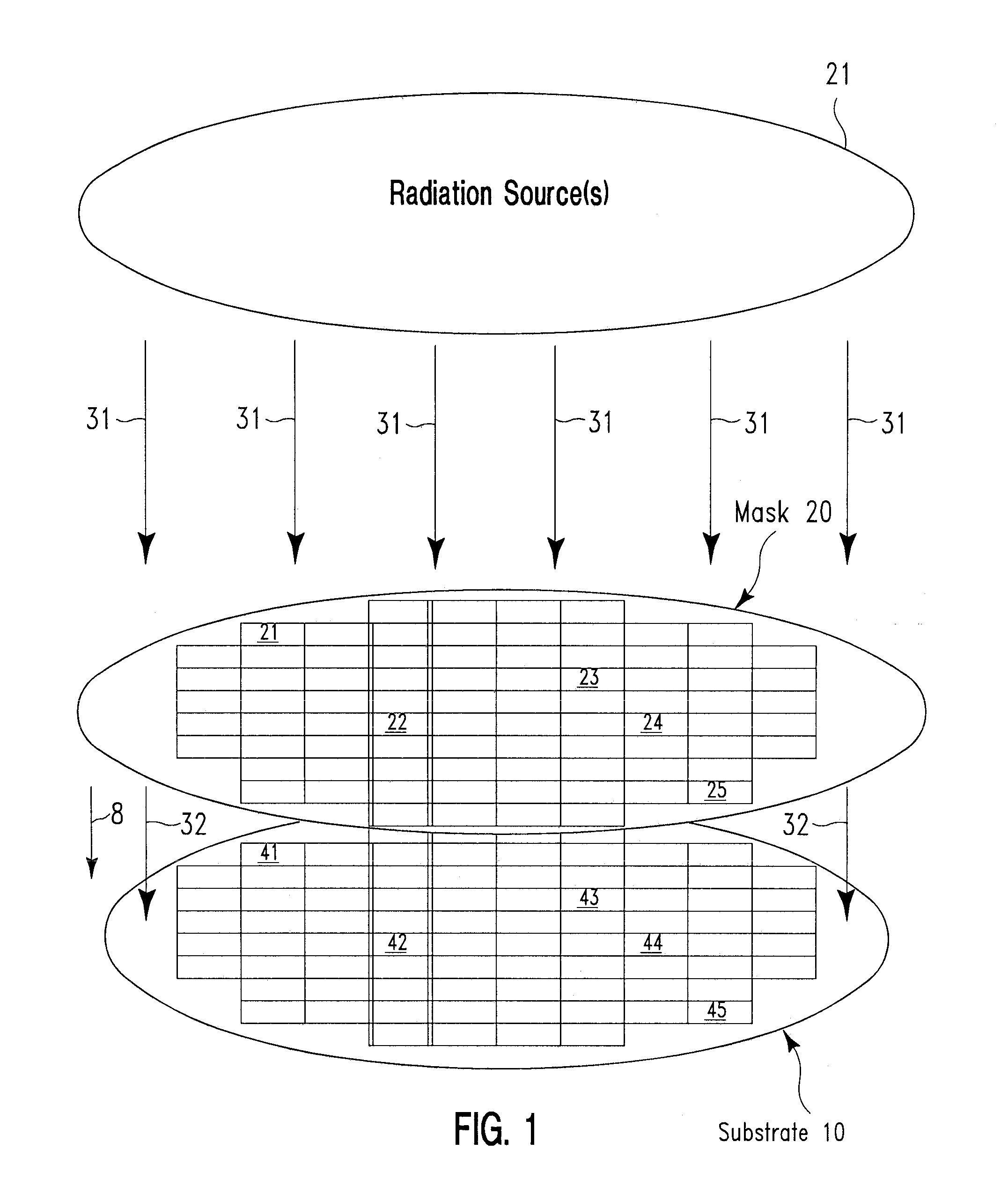
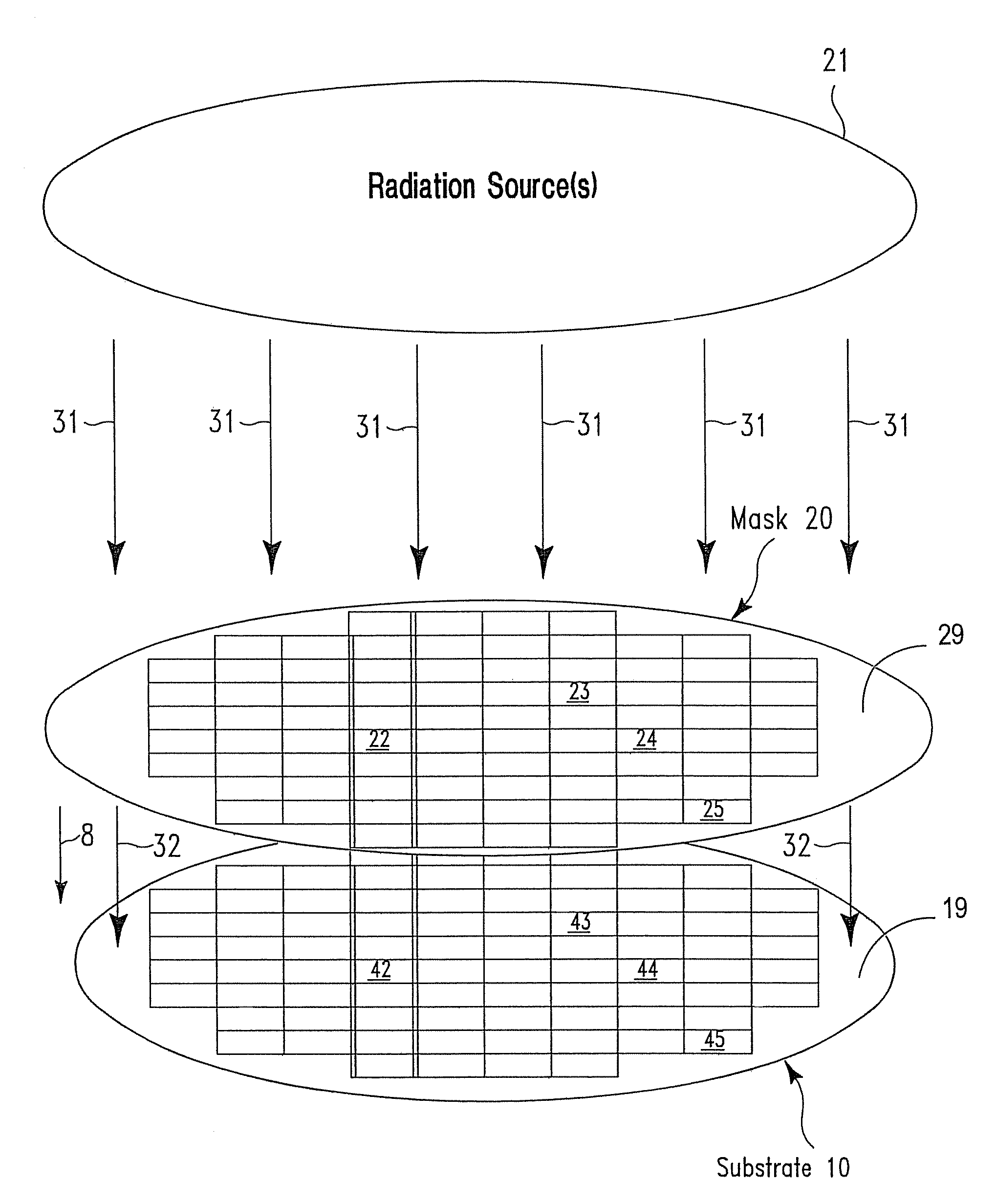
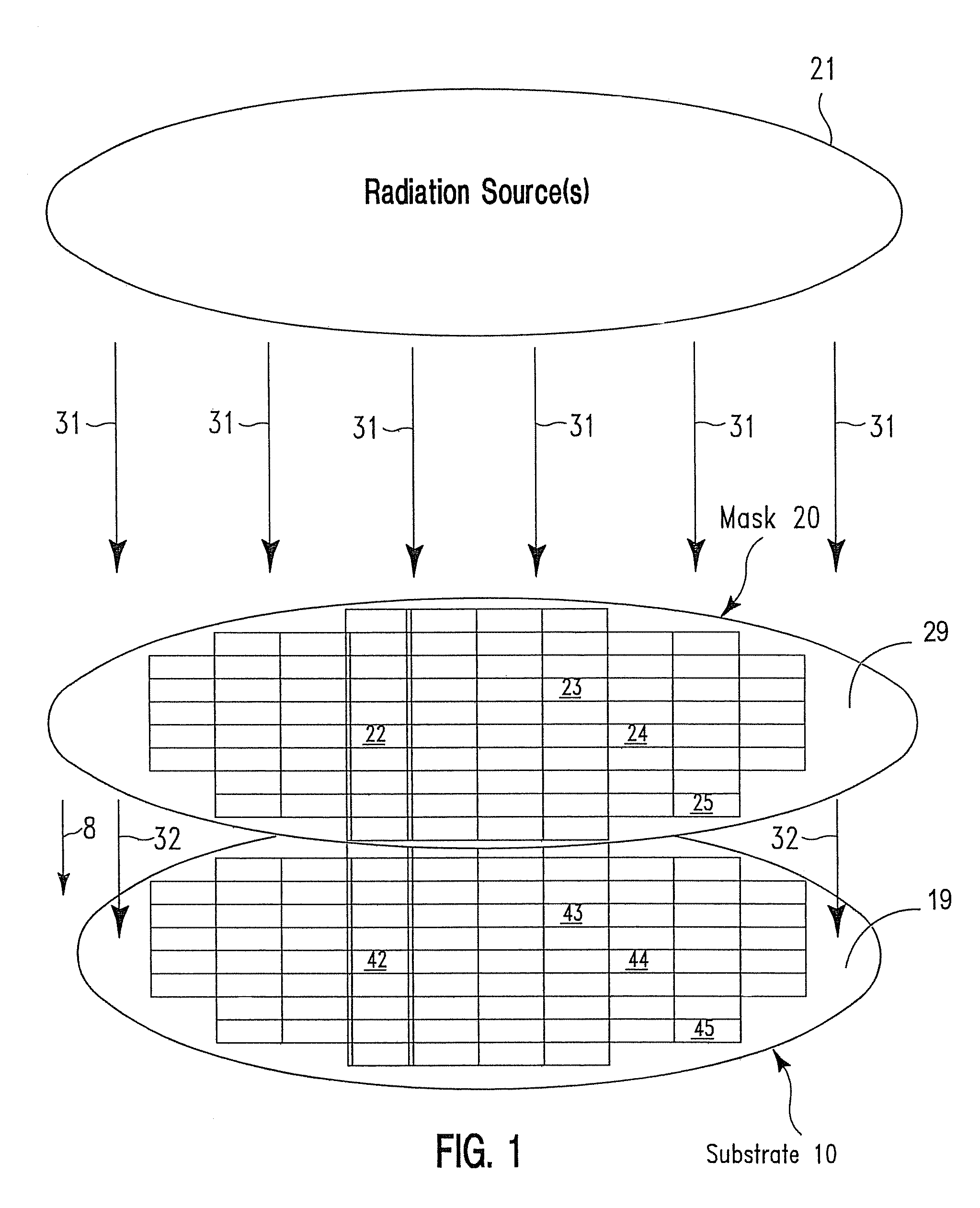
Serial irradiation of a substrate by multiple radiation sources
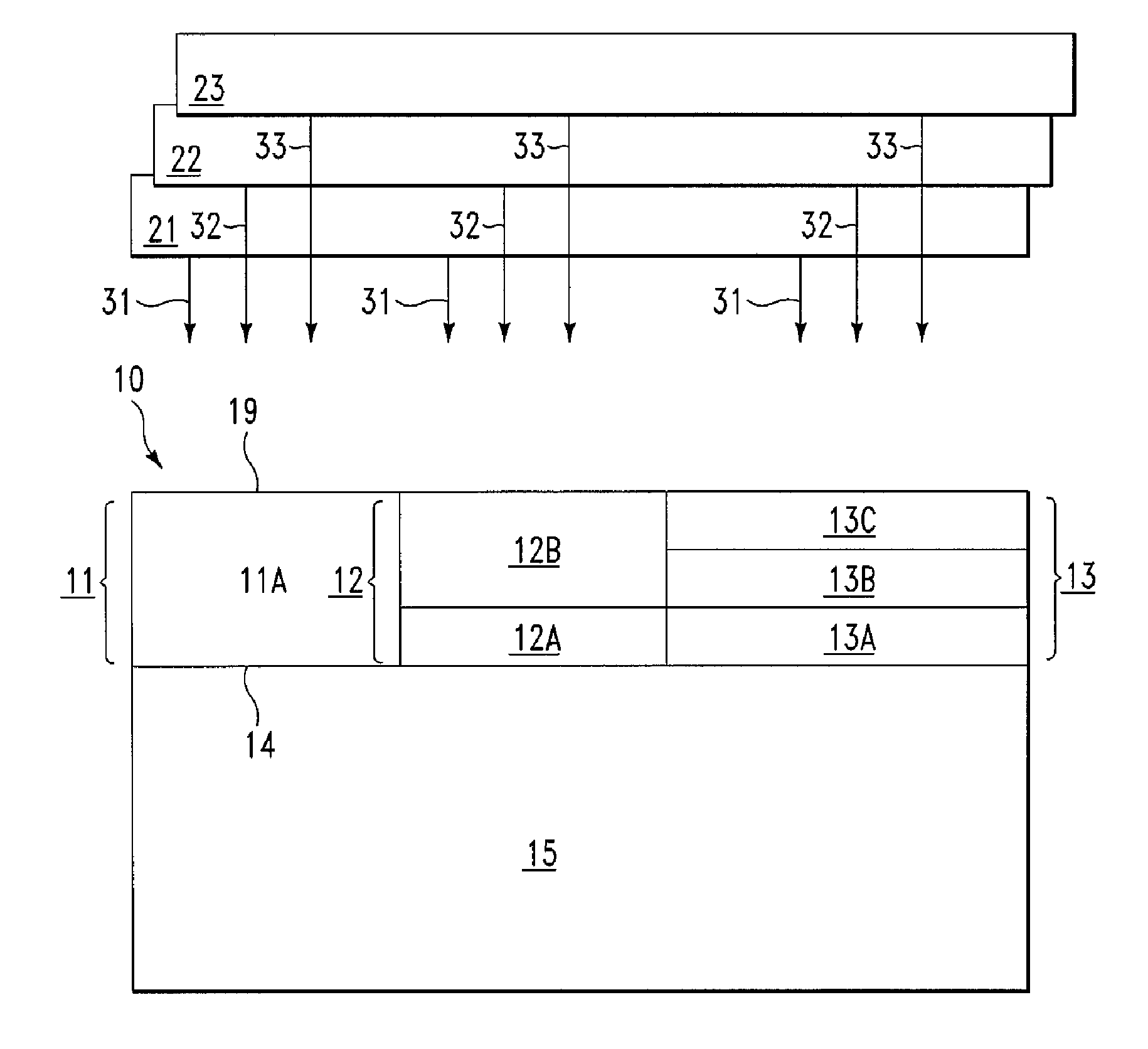
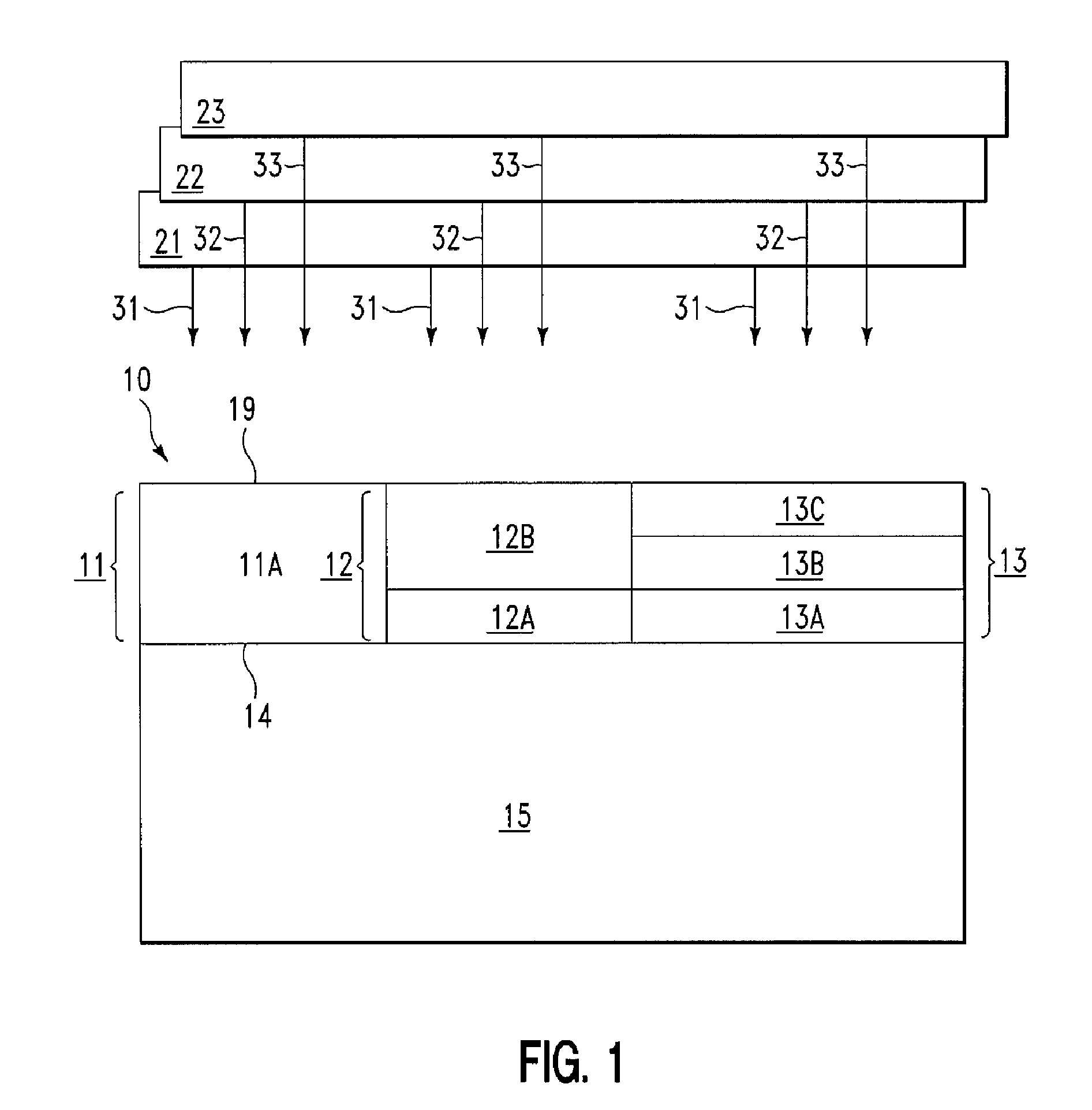
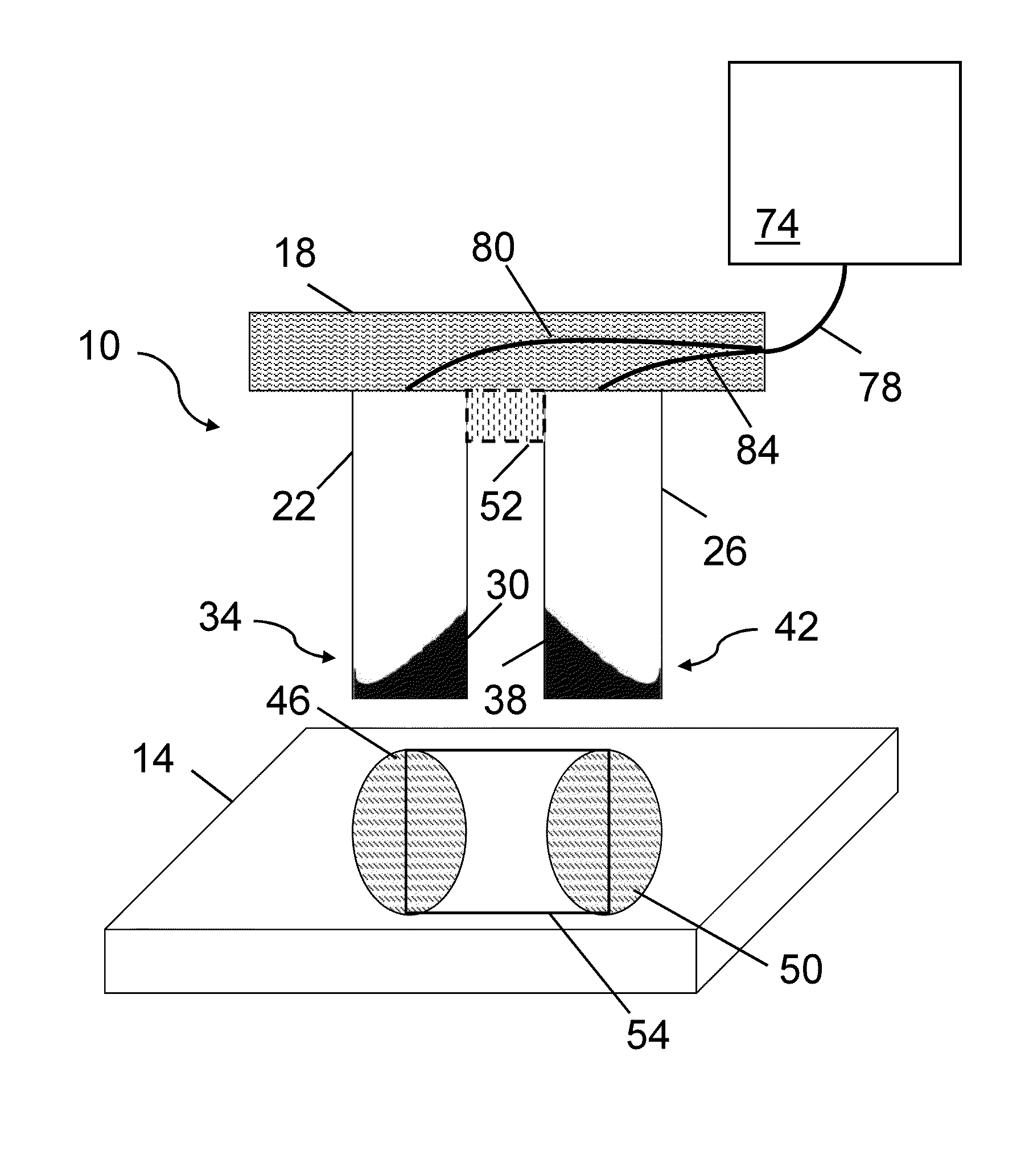
InactiveUS20080070422A1Improve spatial uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusIncident energyEnergy flux
A method for configuring J electromagnetic radiation sources (J≧2) to serially irradiate a substrate. Each source has a different function of wavelength and angular distribution of emitted radiation. The substrate includes a base layer and I stacks (I≧2; J≦I) thereon. Pj denotes a same source-specific normally incident energy flux on each stack from source j. In each of I independent exposure steps, the I stacks are concurrently exposed to radiation from the J sources. Vi and Si respectively denote an actual and target energy flux transmitted into the substrate via stack i in exposure step i (i=1, . . . , I). t(i) and Pt(i) are computed such that: Vi is maximal through deployment of source t(i) as compared with deployment of any other source for i=1, . . . , I; and an error E being a function of |V1−S1|, |V2−S2|, . . . , |VI−SI| is about minimized with respect to Pi (i=1, . . . , I).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Serial irradiation of a substrate by multiple radiation sources
InactiveUS7635656B2Improve spatial uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusIncident energyEnergy flux
A method for configuring J electromagnetic radiation sources (J≧2) to serially irradiate a substrate. Each source has a different function of wavelength and angular distribution of emitted radiation. The substrate includes a base layer and I stacks (I≧2; J≦I) thereon. Pj denotes a same source-specific normally incident energy flux on each stack from source j. in each of I independent exposure steps, the I stacks are concurrently exposed to radiation from the J sources, Vi and Si respectively denote an actual and target energy flux transmitted into the substrate via stack i in exposure step i (i=1, . . . , I). t(i) and Pt(i) are computed such that: Vi is maximal through deployment of source t(i) as compared with deployment of any other source for i=1, . . . , I; and an error E being a function of |V1−S1|, |V2−S2|, . . . , |Vi−Si| is about minimized with respect to Pi (i=1, . . . , I).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Simultaneous irradiation of a substrate by multiple radiation sources
InactiveUS7790636B2Improve spatial uniformityFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthIncident energyElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
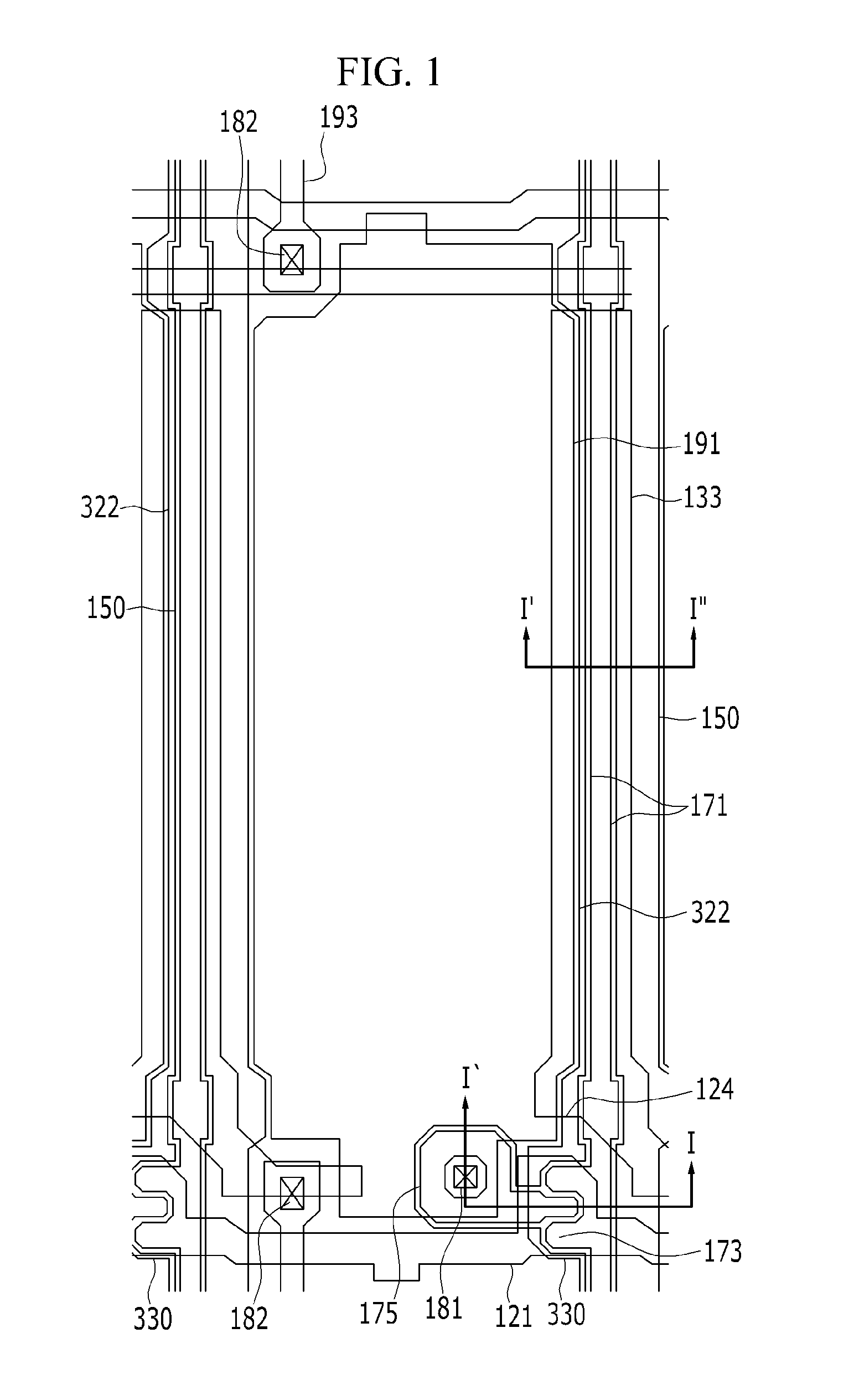
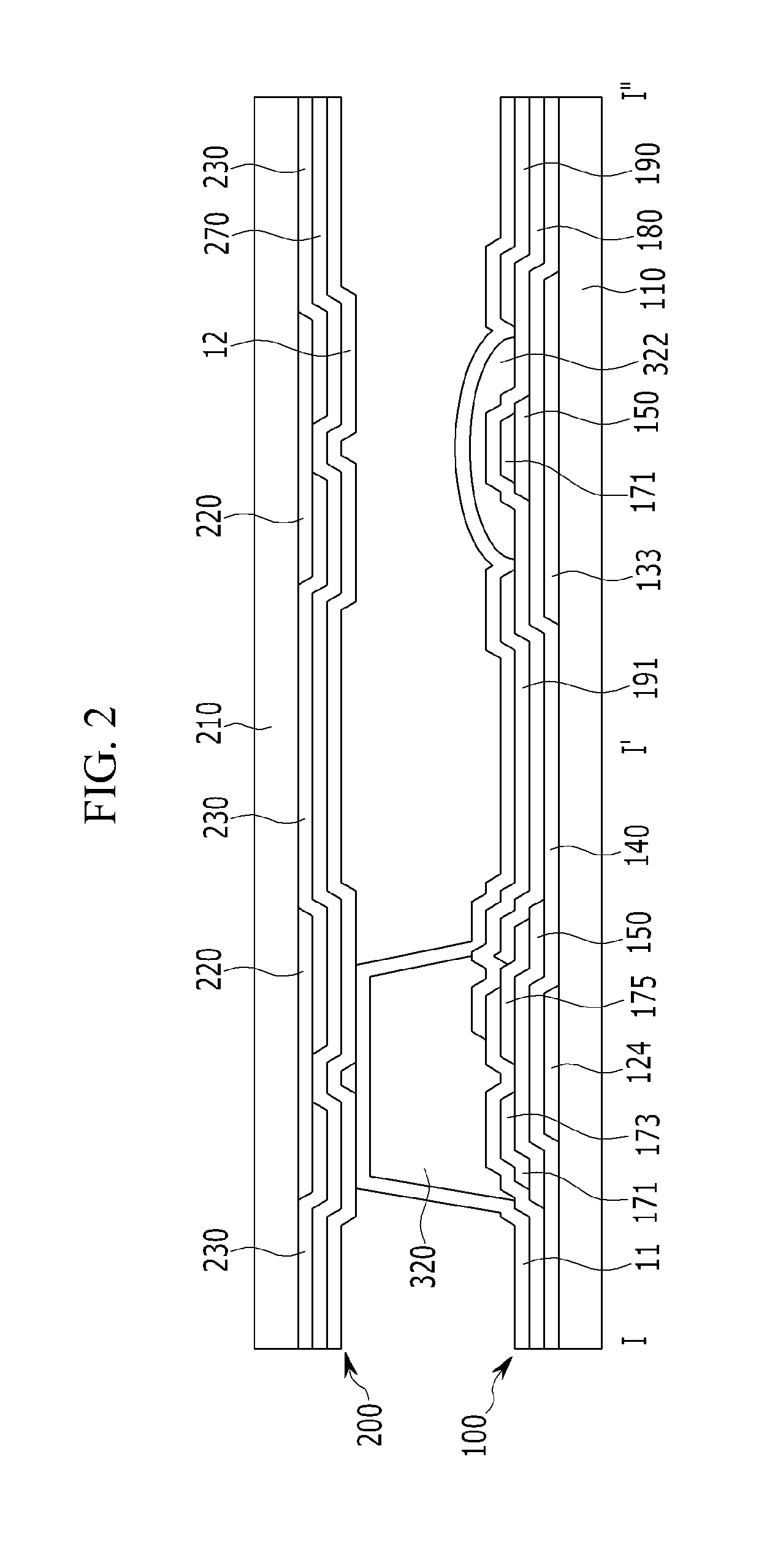
Thin film transistor array panel, liquid crystal display, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS8665413B2Eliminating and reducing step differenceIncrease the effective area ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayArea ratio
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
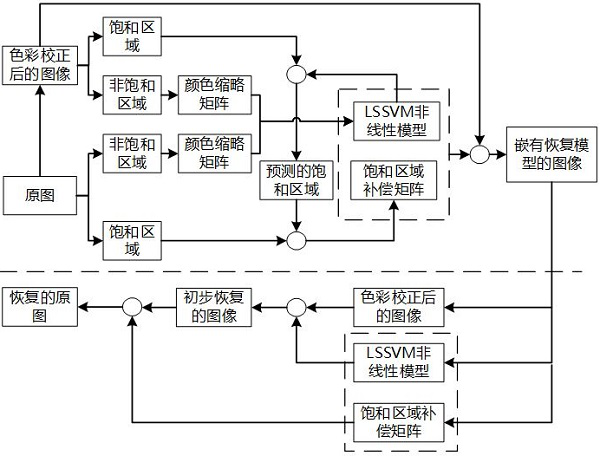
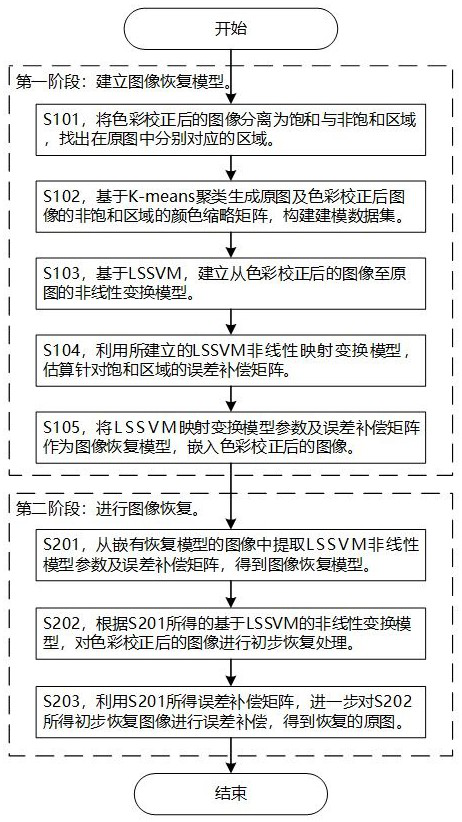
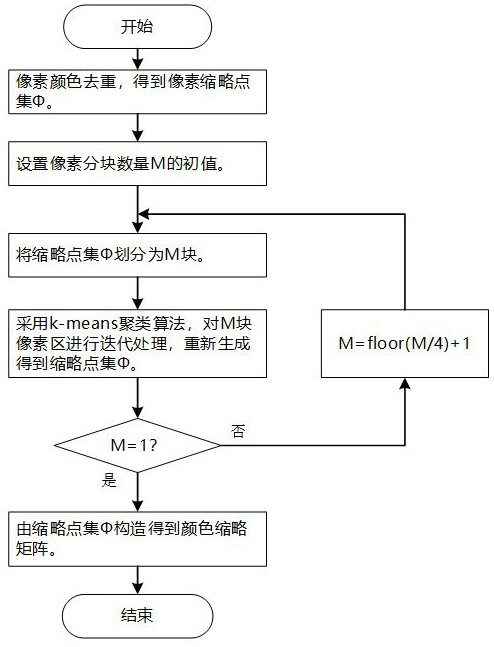
Method for accurately recovering original image of digital image after color correction
ActiveCN112669238AImprove generalization abilityImprove spatial uniformityImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionNonlinear model
The invention discloses a method for accurately recovering an original image of a digital image after color correction, and the method comprises the steps: generating a color thumbnail matrix based on K-means clustering according to the original image and the image after color correction, training a nonlinear model of a least square support vector machine, and estimating an error compensation matrix for an image saturation region; obtaining an image recovery model and embedding the image recovery model into the image; and when the original image needs to be restored, extracting model parameters from the image embedded with the restoration model to perform transformation processing, and accurately restoring to obtain the original image. According to the method provided by the invention, after the digital image is subjected to color correction or some nonlinear processing, even if partial pixel color component values exceed a gray scale range to cause truncation and saturation, the original image color can still be effectively and accurately recovered. The method provided by the invention is beneficial to good color traceability of the digital image in the transmission and copying process, and can be effectively applied to accurate readjustment of image color display and reediting after image color correction in the printing and copying process.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Compact wavelength selective switching and/or routing system
InactiveUS20050111076A1Improve spatial uniformityOvercomes shortcomingProjectorsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength selective switchingEngineering
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
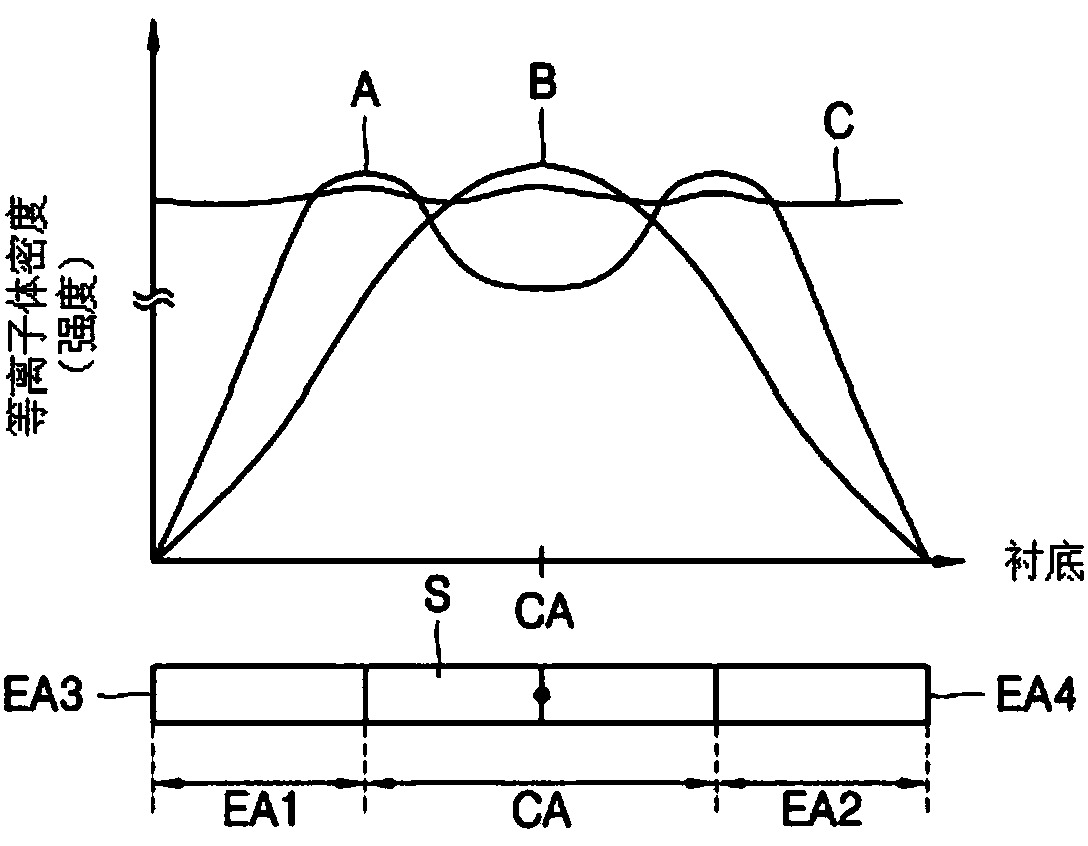
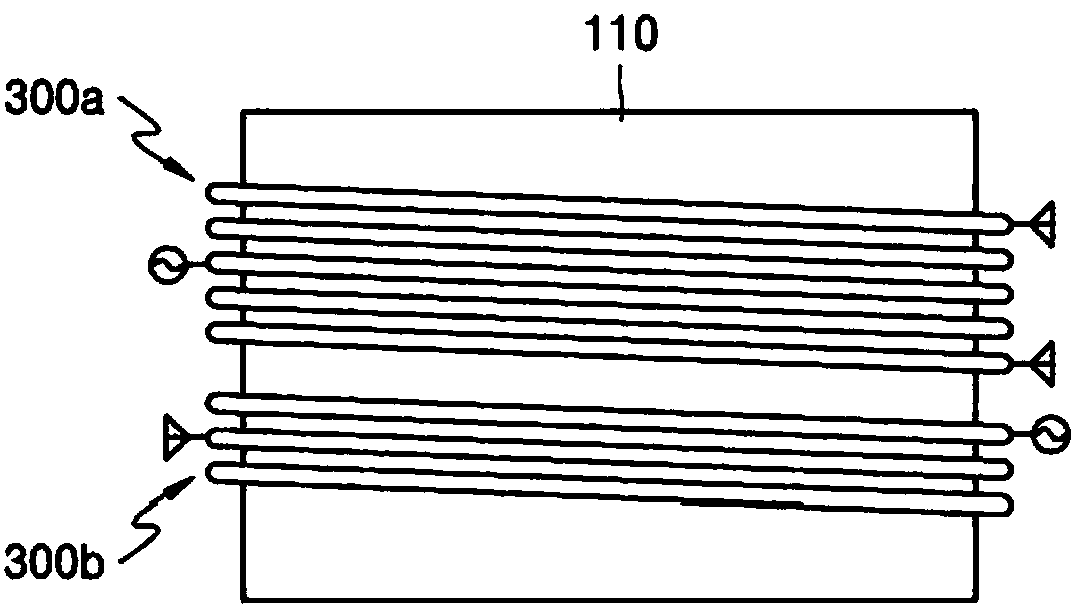
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveCN107946162AImprove spatial uniformityHigh densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma densityProcess region
A substrate processing apparatus includes a cavity having a substrate processing space and a coil portion having a plurality of inductance coils each of which has a shape winding the outer circumference of the cavity and is arranged at the extending direction of the cavity. The plurality of inductance coils include margin type inductance coils forming plasma in the cavity, with the density of theplasma in a zone corresponding to a margin zone of the substrate being higher than the density of the plasma in a zone corresponding to the central zone of the substrate; and central type inductance coils forming plasma in the cavity, with the density of the plasma in the zone corresponding to a central zone of the substrate being higher than the density of the plasma in a zone corresponding to the margin zone of the substrate. Effects of increasing plasma spatial uniformity and increasing substrate processing uniformity are achieved in embodiments. Through stacking and mounting the pluralityof inductance coils at the vertical direction, a capacity of plasma formed corresponding to a substrate processing surface is increased, and the plasma density changing along with processing zones isincreased.
Owner:AP SYST INC
Multiple Wavelength LED Array Illuminator for Fluorescence Microscopy
ActiveUS20120262782A1Improve spatial uniformityIncrease the number ofElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementPower flowLed array
One embodiment provides light along an optical axis. It comprises a substrate and at least one array of multiple LED chips without individual packaging supported by the substrate. The LED chips emit light within different wavelength ranges and are distributed laterally with respect to the axis over an area, the LED chips having light emitting surfaces for emitting light in directions transverse to the area. An optical element adjacent to the light emitting surfaces of the LED chips in the at least one array collects and directs light emitted by the LED chips of the at least one array along the axis towards a target. Another embodiment is directed to a method for providing multiple wavelength light for fluorescent microscopy using the above system. Electric current is supplied to the multiple LED chips, causing them to emit light of multiple wavelengths. The currents supplied to the multiple LED chips are controlled so as to control the exposure of fluorescent dyes with different excitation wavelengths wherein the light emitted by the multiple LED chips include wavelength components at such different excitation wavelengths without having to move the multiple LED chips.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Radiation mask with spatially variable transmissivity
InactiveUS20080085456A1Improve spatial uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentTransmittanceReflectivity
A mask, a method for creating a mask, and a method for irradiating a substrate through use of the mask. Creating the mask establishes the mask by designing the mask, forming the mask, or both designing and forming the mask. Creating the mask includes receiving a specified target transmittance (TS) of the substrate with respect to radiation propagated from a radiation source and transmitted through the mask with spatial selectivity in accordance with a spatially varying transmissivity (TM) of the mask with respect to the radiation. The mask is disposed between the radiation source and the substrate. The mask includes transparent portions and reflective portions distributed within the transparent portions. The first radiation after having passed through the mask is transmitted into the substrate in accordance with a spatially varying reflectance (R) of the substrate such that TM*(1−R) is about equal to TS.
Owner:IBM CORP
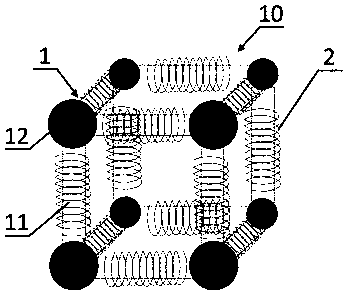
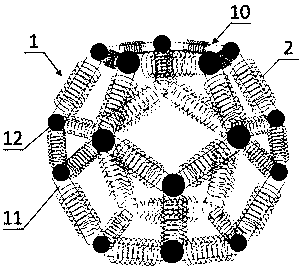
Radio energy transmission multi-directional transmitting three-dimensional coil and radio energy transmission system
PendingCN108987079ASymmetricalMaintain stabilityTransformersCircuit arrangementsDegrees of freedomElectromagnetic shielding
The invention provides a radio energy transmission multi-directional transmitting three-dimensional coil and a radio energy transmission system. The transmitting three-dimensional coil comprises: a three-dimensional skeleton, wherein three-dimensional skeleton is a three-dimensional structure with iron cores as the edges and the non-magnetic conductive material as the vertex and is used as a bearing mechanism of the transmitting three-dimensional coil. A transmitting coil is wound around each edge of the three-dimensional skeleton for converting electrical energy into electromagnetic energy for radio energy transmission. The 3D stereoscopic structure is adopt, so that the need for multiple loads at different locations to be powered simultaneously when a single power supply is used can be met, and the requirement of high degree of freedom movement of a receiving device is satisfied. Further, the degree of freedom and flexibility of the radio energy transmission system are improved, thespatial uniformity of the magnetic field of the transmission system is improved, the dependence of the receiving system on the transmitting system is reduced, and the stable electric energy transmission of the single-source and multi-load system and the receiving device at any spatial position is realized, so that the transmission efficiency and the transmission stability of the radio energy transmission are improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Accommodating device for accommodation and mounting of a wafer
InactiveCN104718608AImprove performanceFast heating rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingEngineering
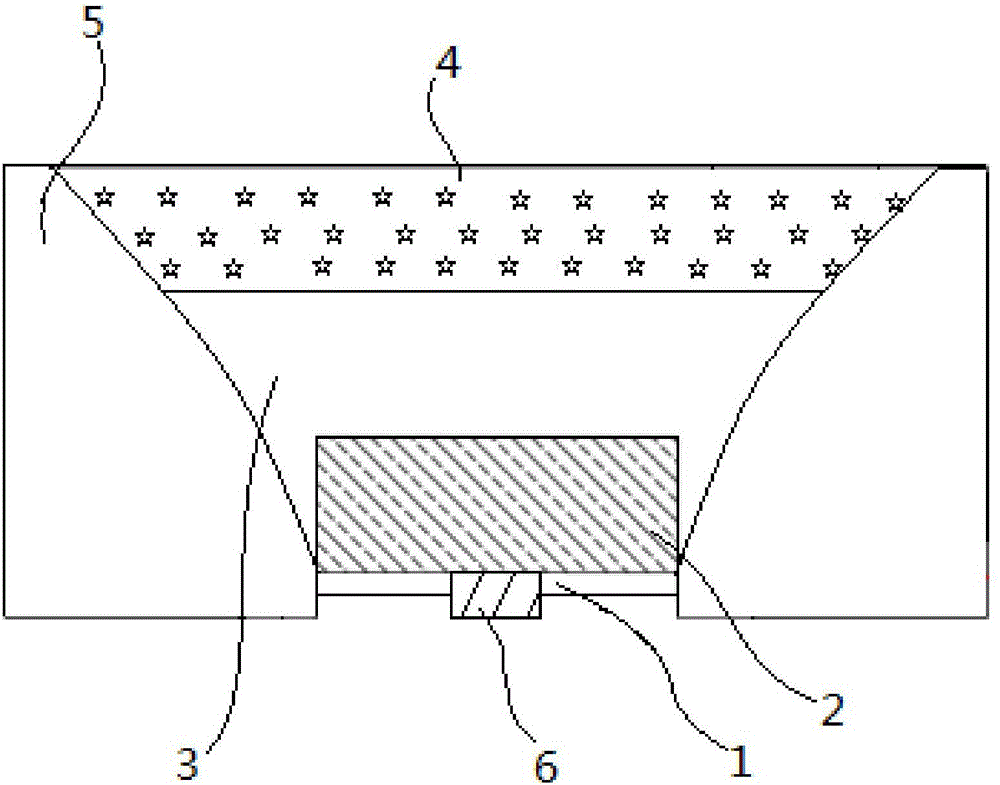
The present invention relates to an accommodating device for accommodation and mounting of a wafer (3 ) for application of a fluid (9) to a top (3o) of the wafer (3) with the following features: a revolving ring section (4) with:d) a revolving upper edge (5), e) a revolving recess (6) and f) a circumferential wall (7) running from the upper edge (5) to the recess (6), a contact plane (A) arranged within the ring section (4) for the accommodation of the wafer (3) on a contact surface (3a) of the wafer (3), wherein the ring section (4) by means of accommodation of the wafer (3) forms with said wafer an accommodating space (8) for accommodation of the fluid (9).
Owner:イーヴィーグループインコーポレイテッド
Radiation mask with spatially variable transmissivity
InactiveUS7685557B2Improve spatial uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentTransmittanceEngineering
A mask, a method for creating a mask, and a method for irradiating a substrate through use of the mask. Creating the mask establishes the mask by designing the mask, forming the mask, or both designing and forming the mask. Creating the mask includes receiving a specified target transmittance (TS) of the substrate with respect to radiation propagated from a radiation source and transmitted through the mask with spatial selectivity in accordance with a spatially varying transmissivity (TM) of the mask with respect to the radiation. The mask is disposed between the radiation source and the substrate. The mask includes transparent portions and reflective portions distributed within the transparent portions. The first radiation after having passed through the mask is transmitted into the substrate in accordance with a spatially varying reflectance (R) of the substrate such that TM*(1−R) is about equal to TS.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Reduction of RF Electrode Edge Effect
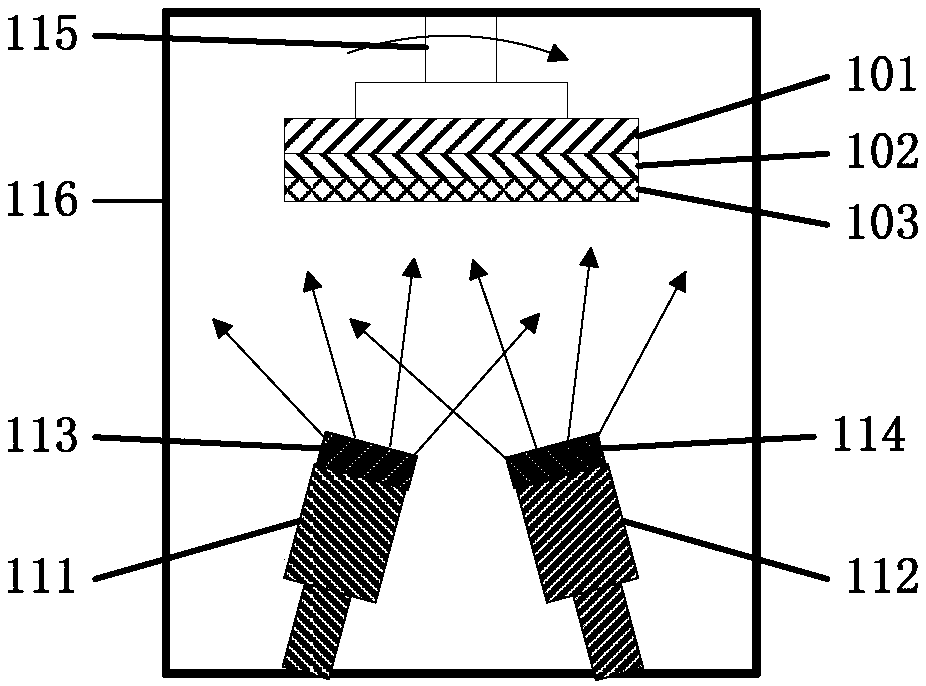
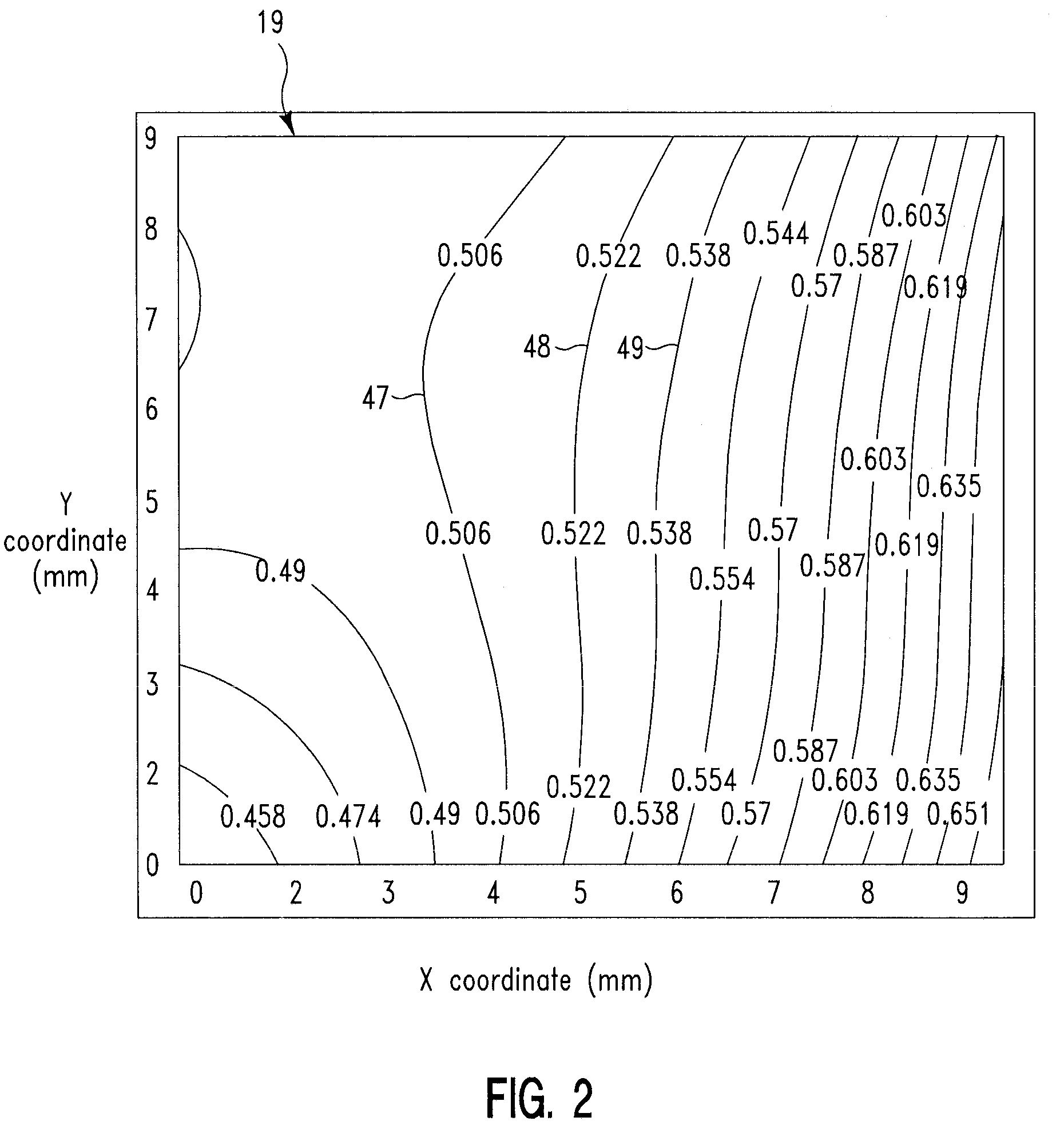
ActiveUS20130218242A1Reduce deliveryImprove spatial uniformityElectrotherapyRadiation therapySkin contactSkin surface
A skin surface is treated with bipolar RF energy. A first semiconductive cap disposed on a first distal end of a first electrode and a second semiconductive cap disposed on a second distal end of a second electrode are applied to the skin surface. RF energy is delivered from the first electrode and the second electrode through the first semiconductive cap and the second semiconductive cap, respectively, through the skin surface. A thickness of each semiconductive cap between a blunt skin contacting surface and a curved surface affixed to a respective electrode is thicker at an inner portion and thinner at a center portion to homogenize the electrical field at the skin surface.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com