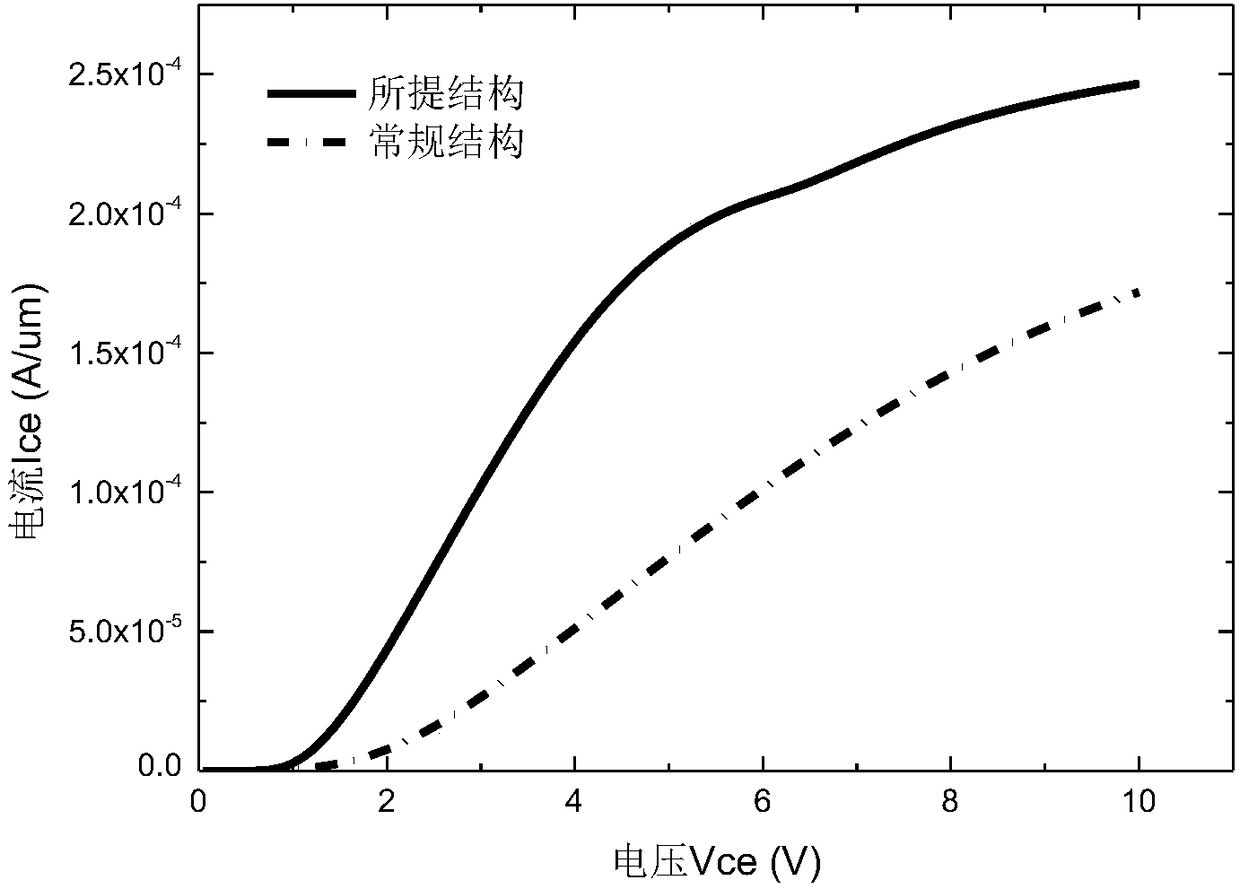
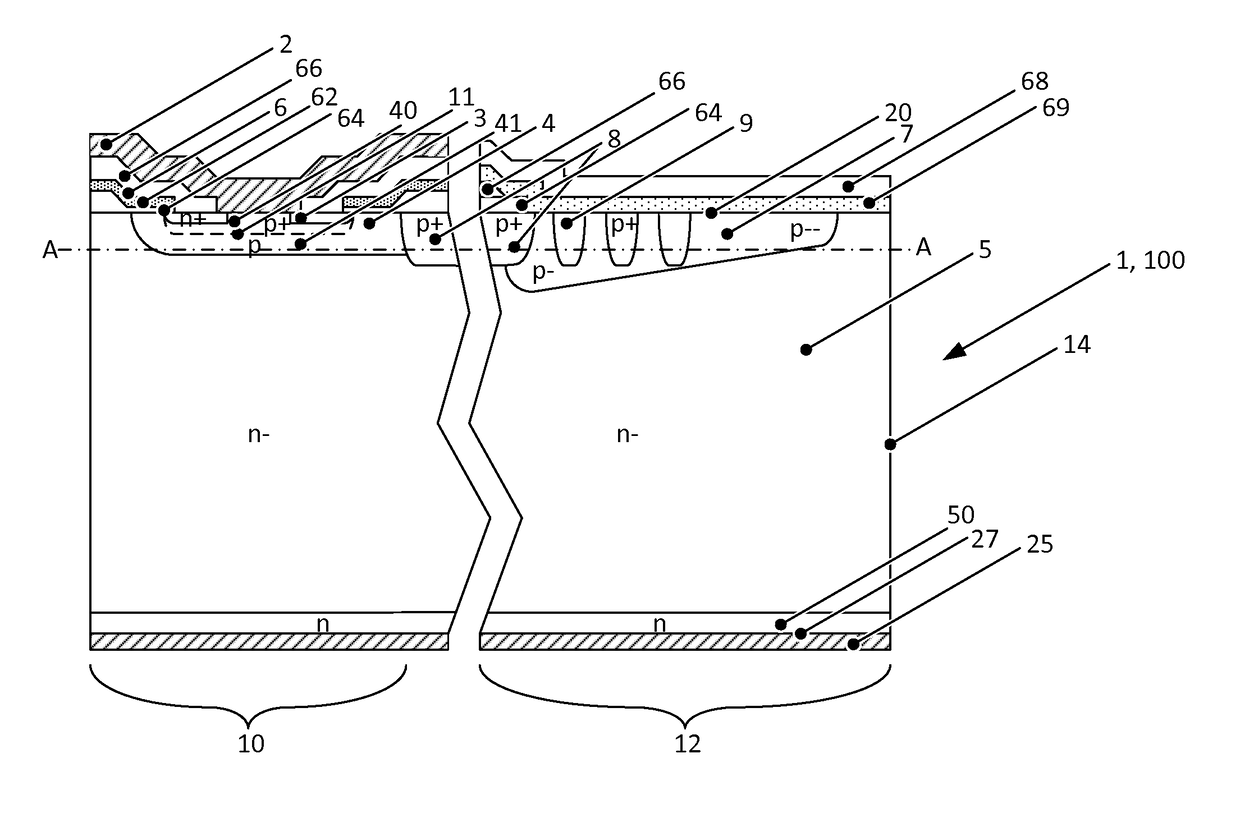
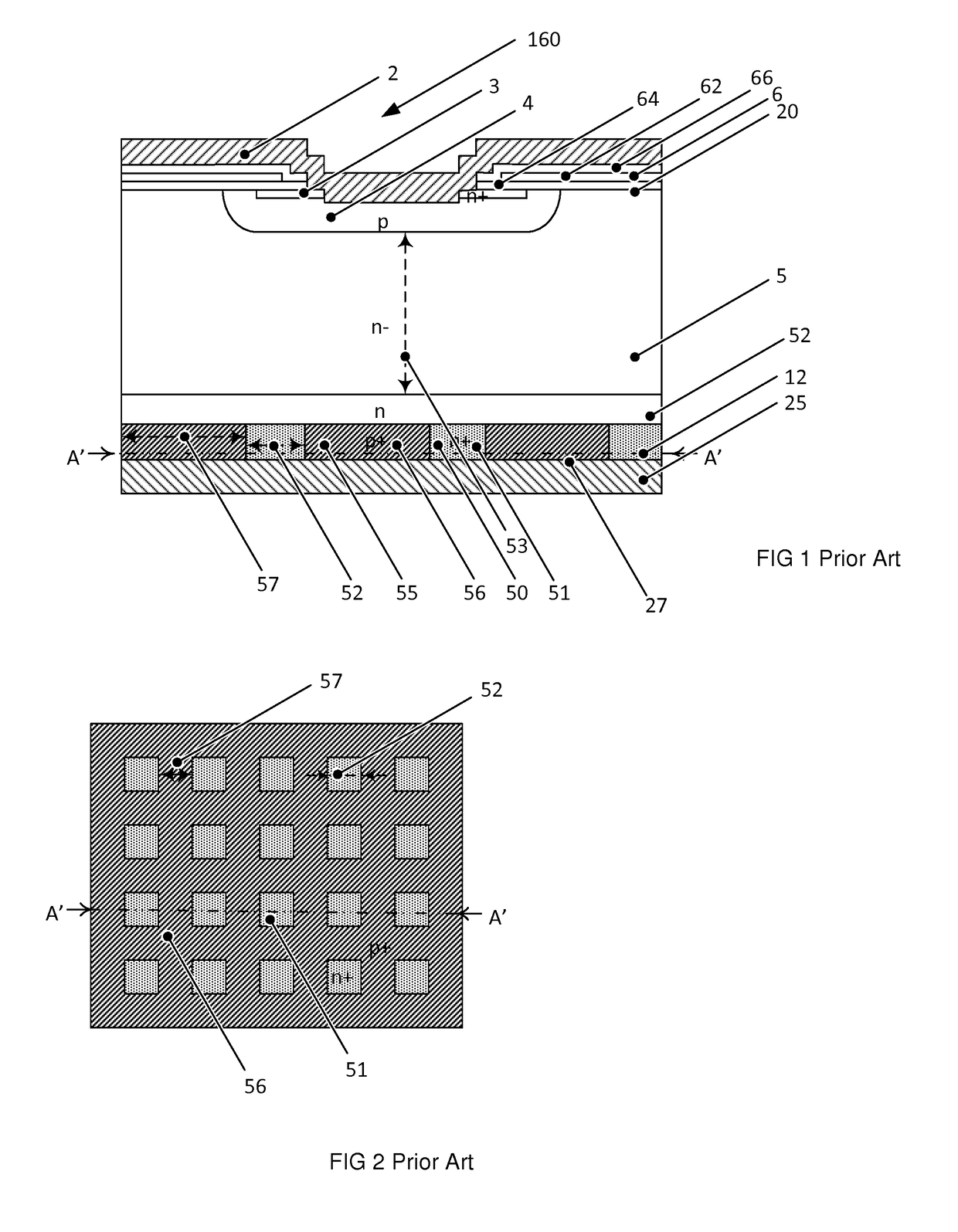
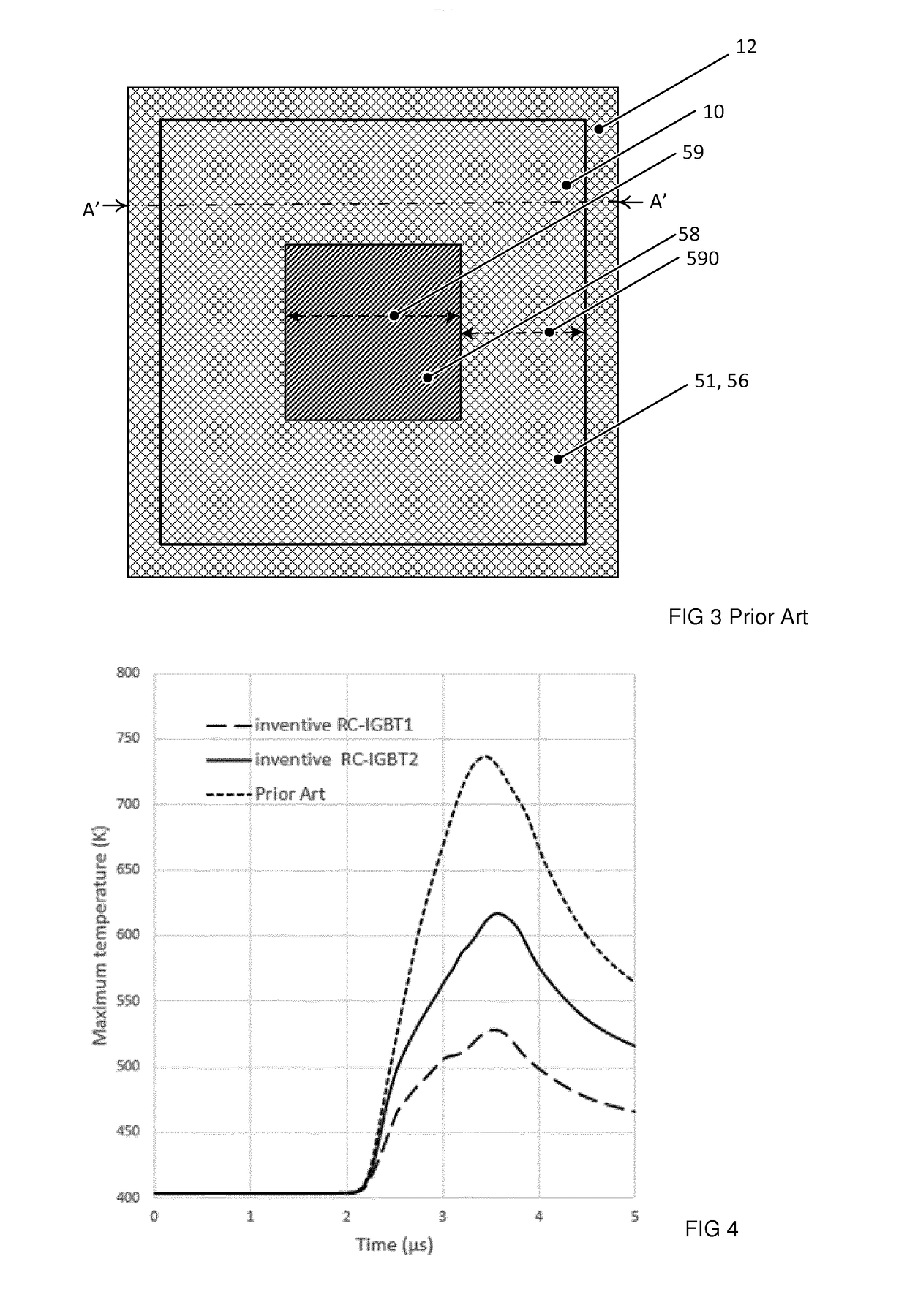
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "Improve shutdown capability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
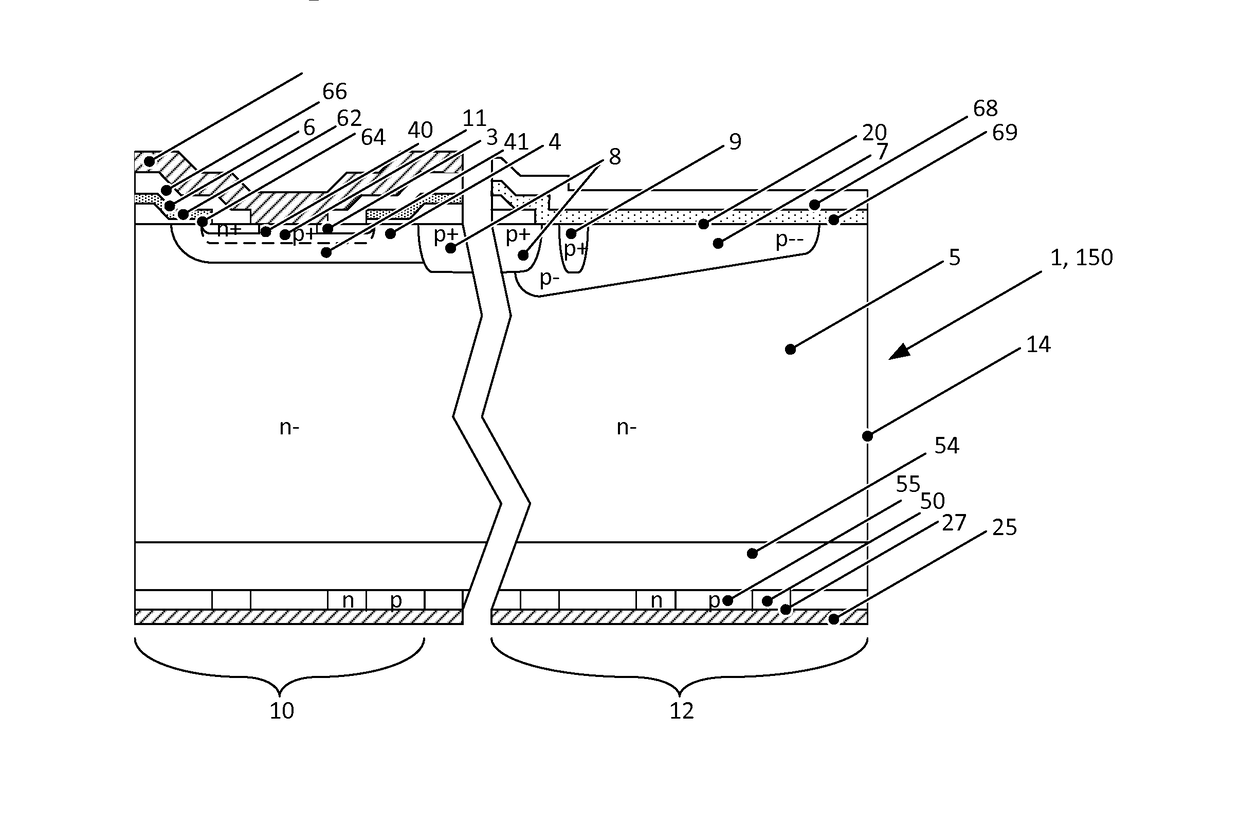
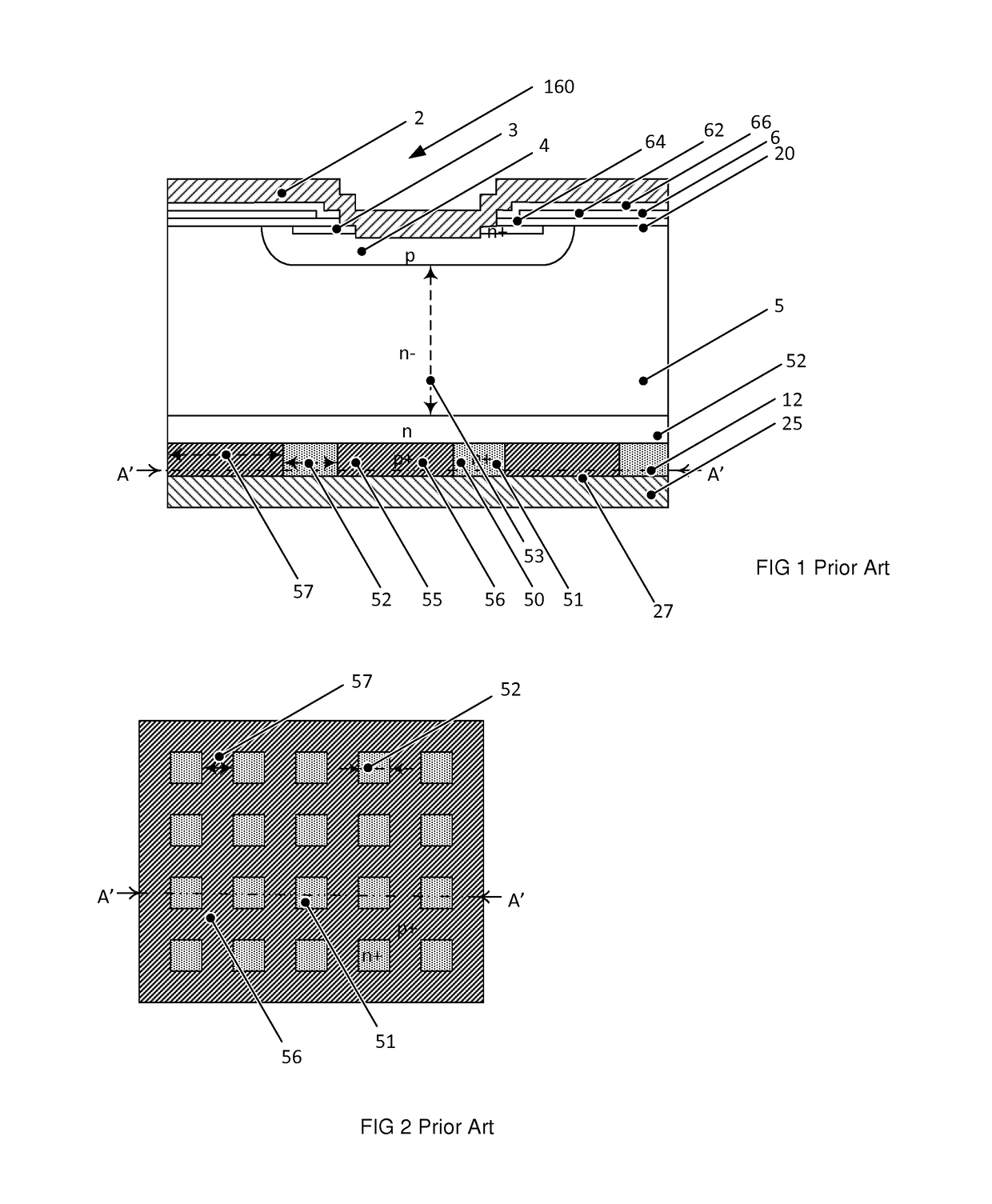
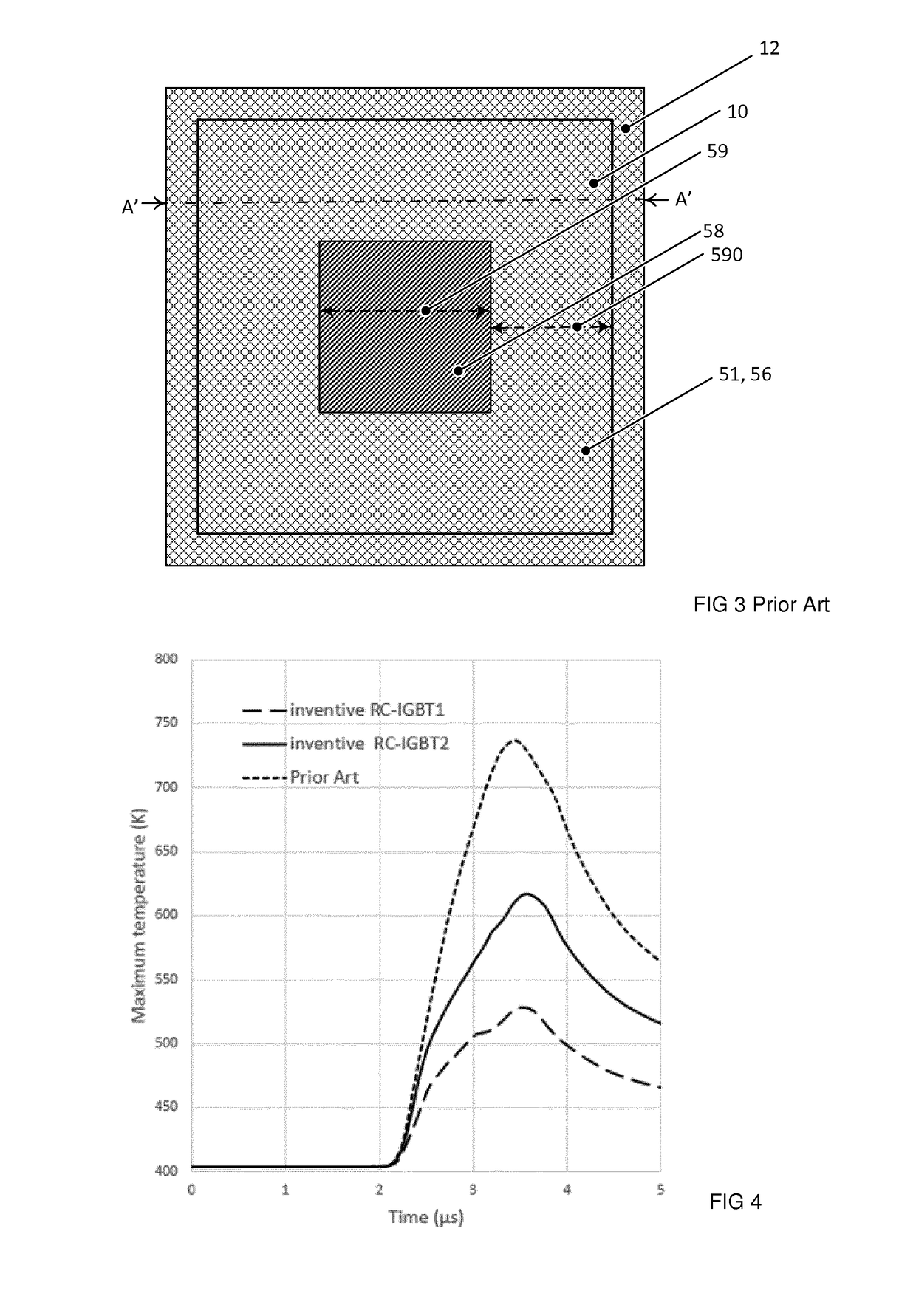
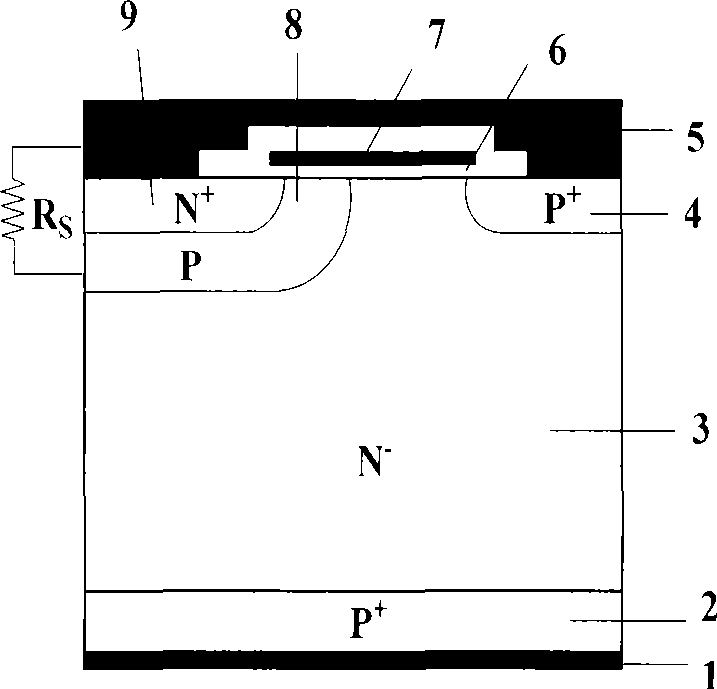
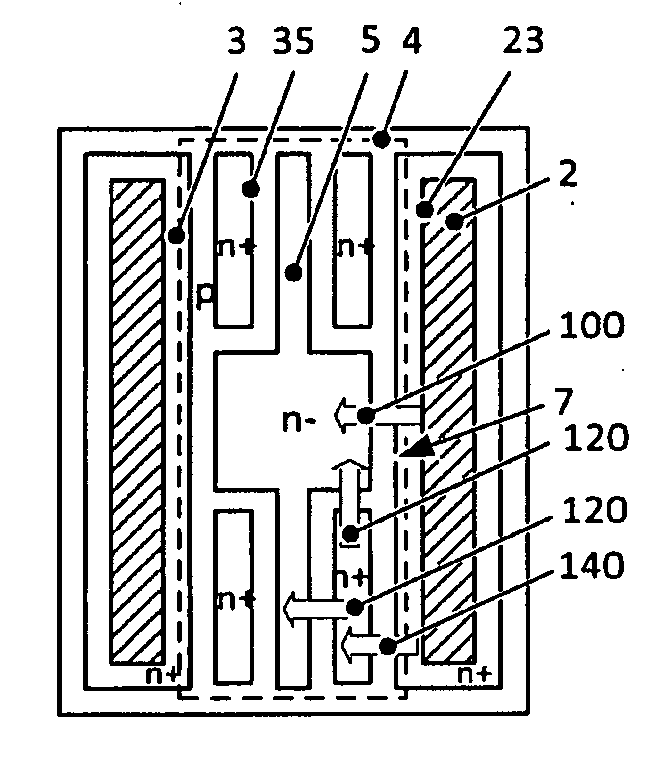
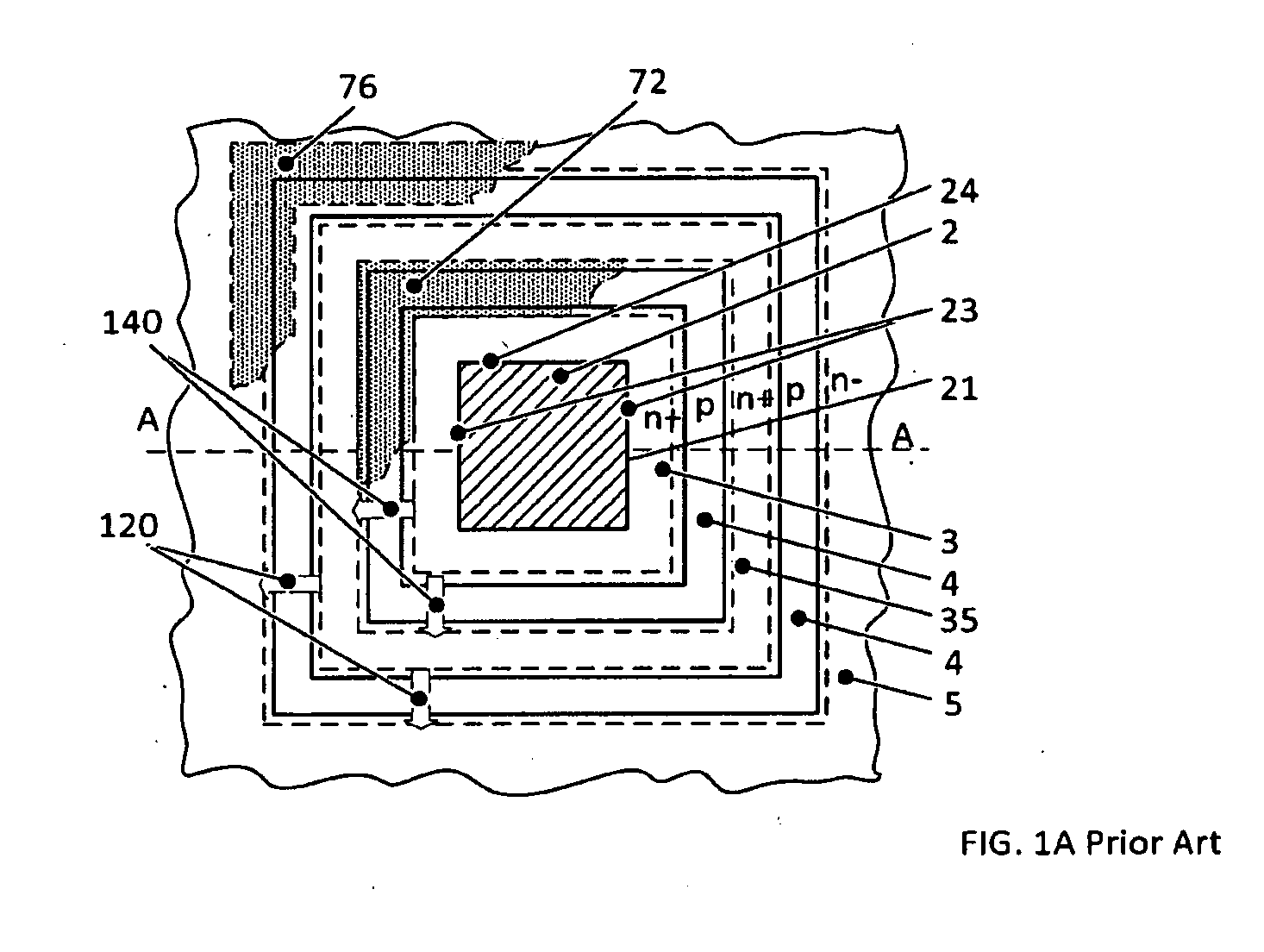
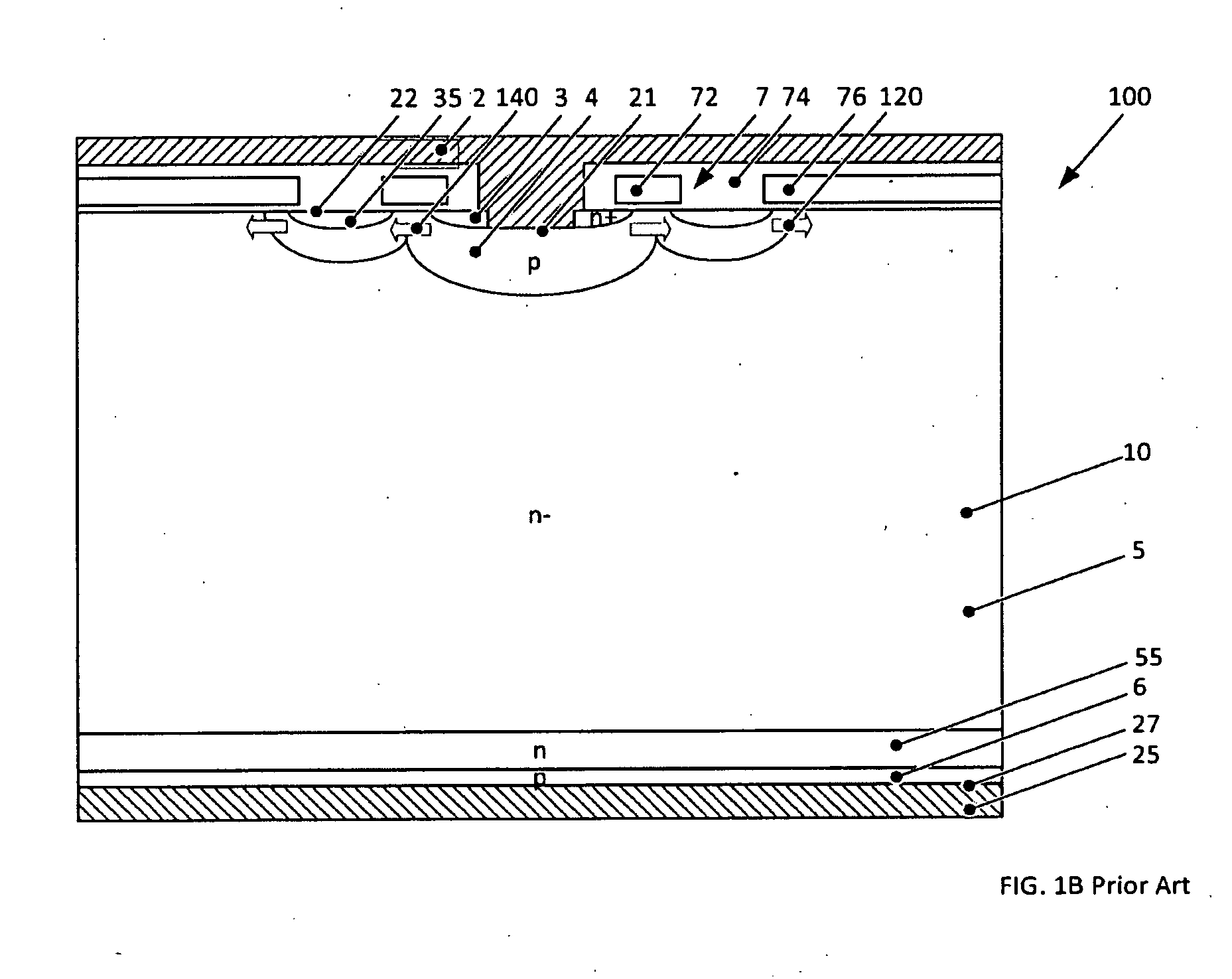
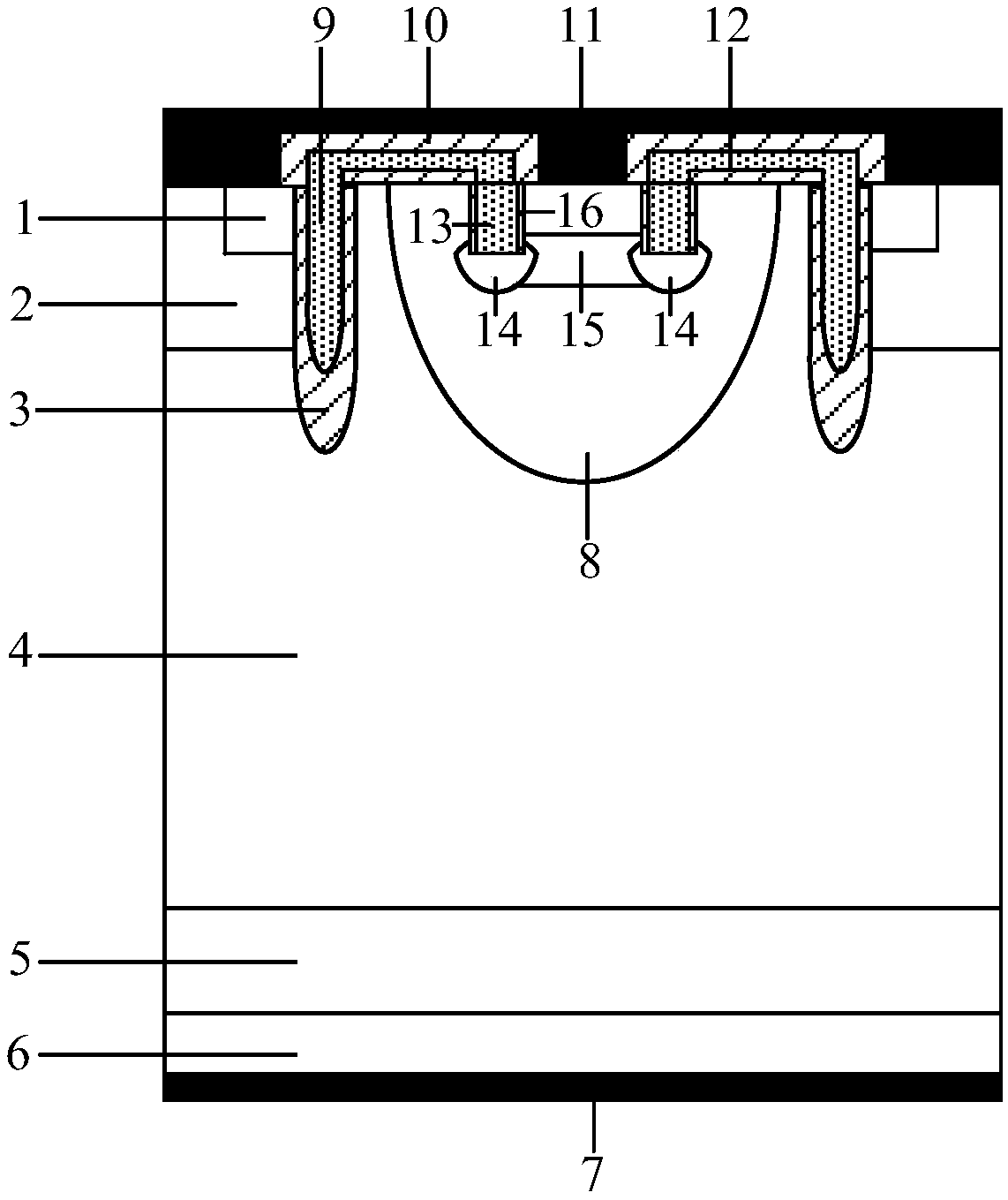
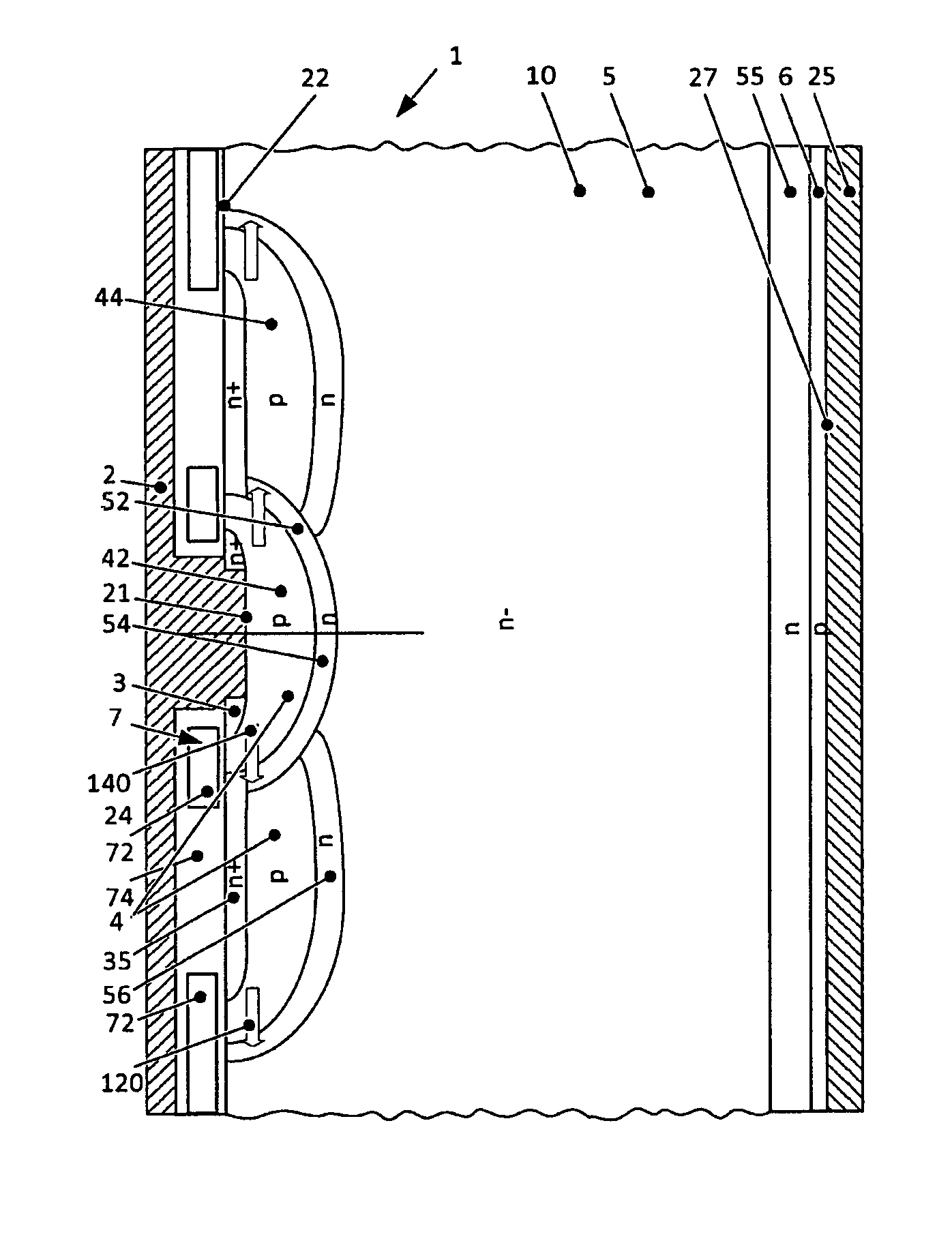
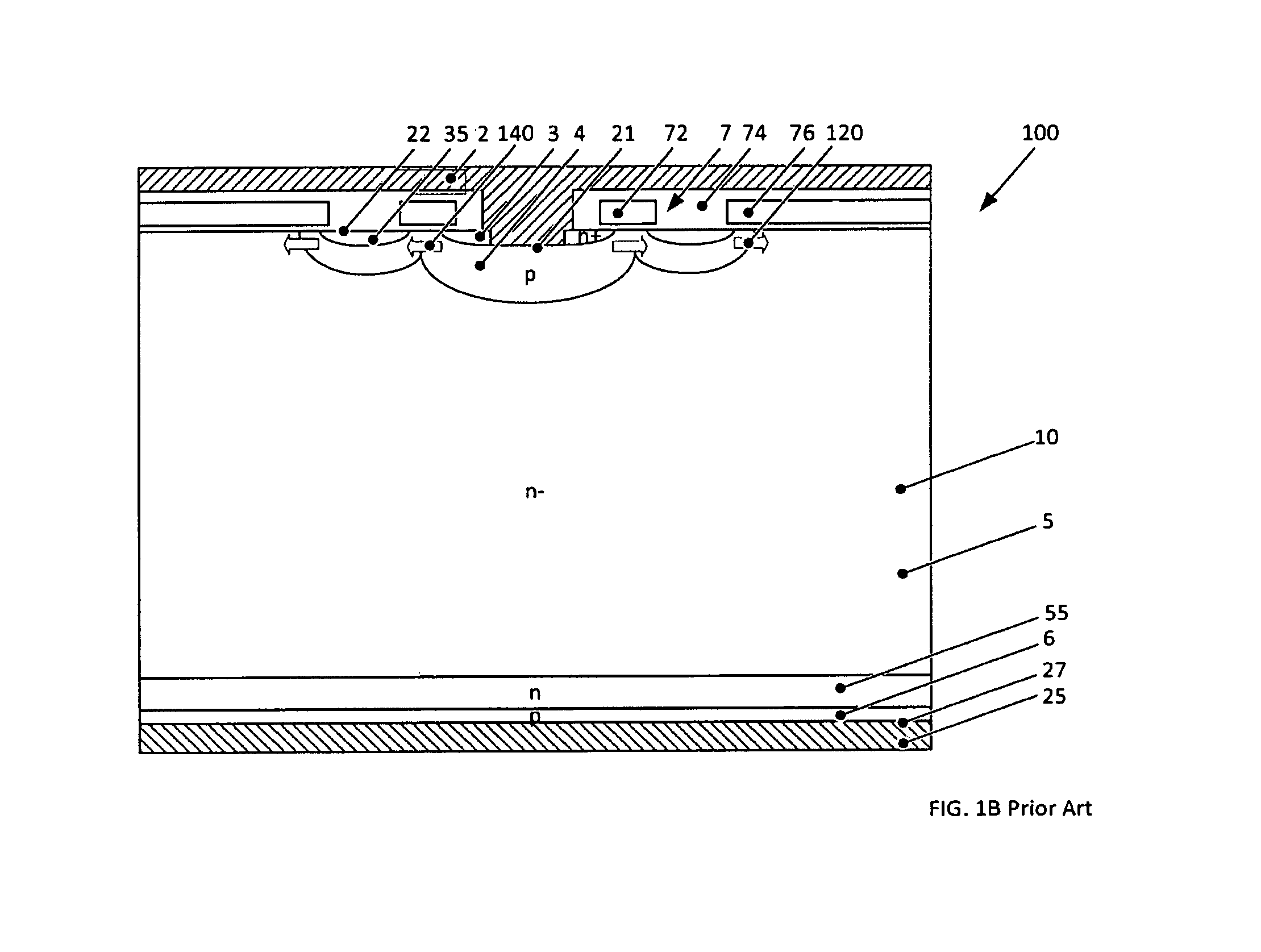
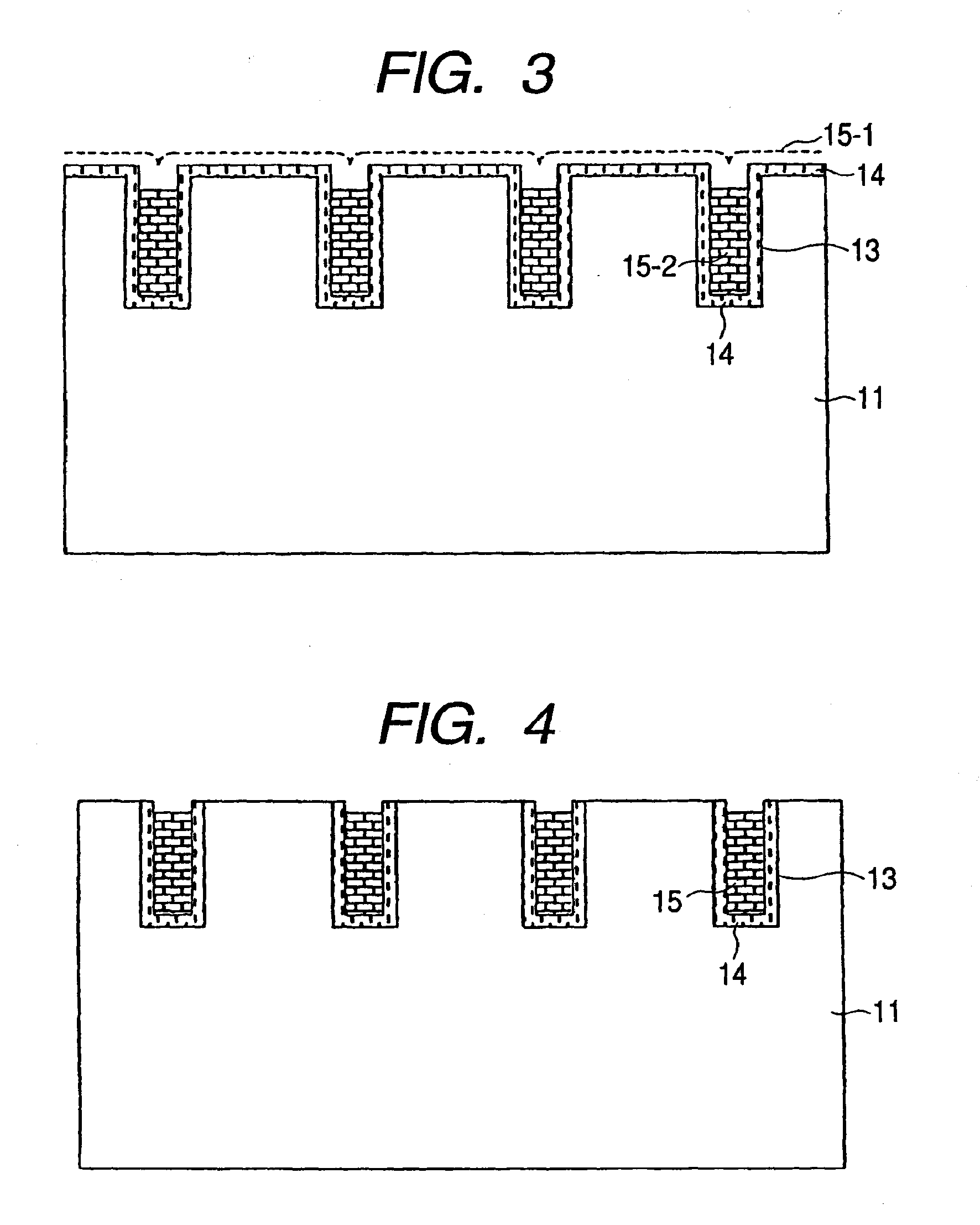
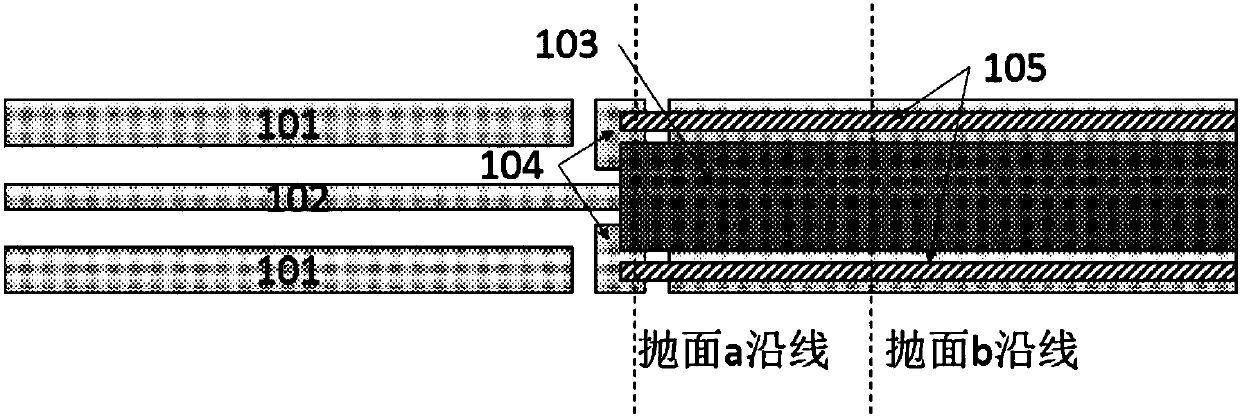
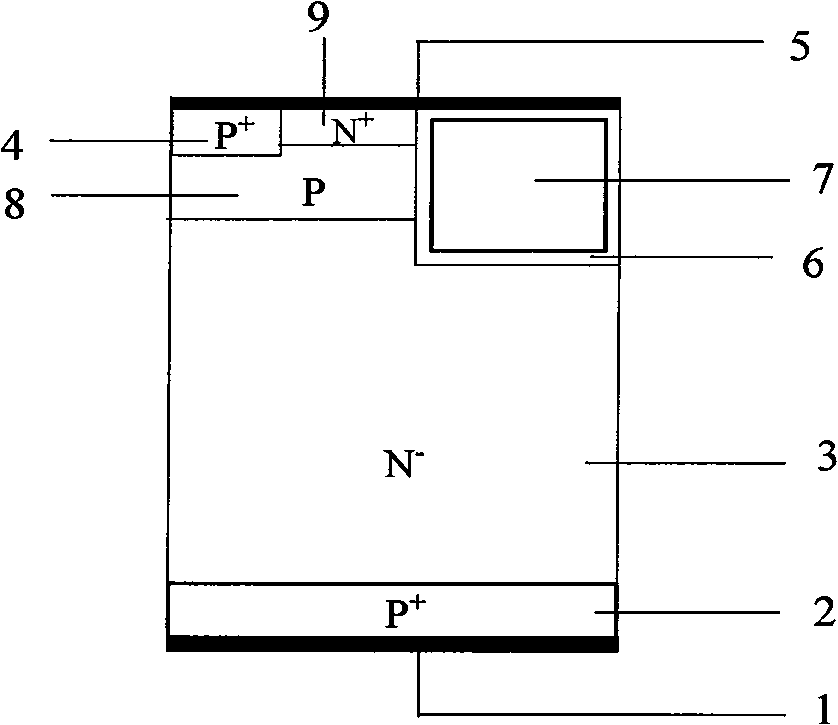
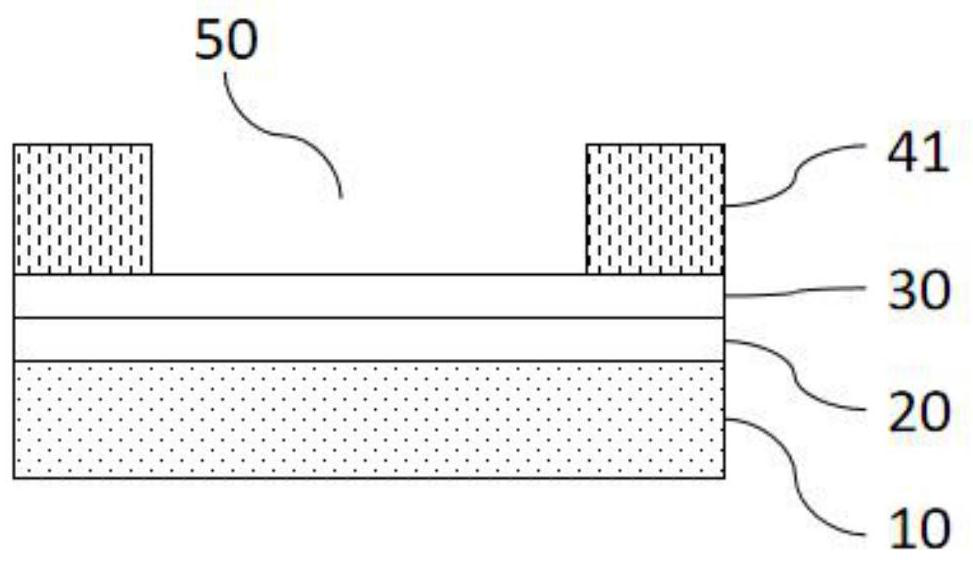
Reverse-conducting semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170294526A1Improve device performanceImprove shutdown capabilityDiodePower semiconductor deviceActive cell
A reverse-conducting MOS device is provided having an active cell region and a termination region. Between a first and second main side. The active cell region comprises a plurality of MOS cells with a base layer of a second conductivity type. On the first main side a bar of the second conductivity type, which has a higher maximum doping concentration than the base layer, is arranged between the active cell region and the termination region, wherein the bar is electrically connected to the first main electrode. On the first main side in the termination region a variable-lateral-doping layer of the second conductivity type is arranged. A protection layer of the second conductivity type is arranged in the variable-lateral-doping layer, which protection layer has a higher maximum doping concentration than the maximum doping concentration of the variable-lateral-doping layer in a region attached to the protection layer.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Multiple frequency one-way overlapped output standard continuous green light laser inside full solid multi-cavity combination cavity
InactiveCN101267083AReduce the risk of injuryIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFundamental frequencyAcousto-optics
The present invention provides a laser, especially a frequency doubling single direction overlapping output quasi-cw green laser in a full-solid multi-cavity combined cavity, composed of three or more F-P, each F-P adopts flat-concave cavity structure, F-P adopts side pumped Nd:YAG crystal of the semiconductor laser pumped component having same model, each F-P is optimized design by computer simulation, a stably rotatable 1064nm fundamental frequency laser is formed in the F-P, each F-P obtains 532nm quasi-cw green laser by the audio-optical Q switching and frequency doubling technology, overlapping in the several frequency doubling crystals, reflecting by the harmonic reflector, obtaining secondary frequency doubling and output together. The laser does not need any thermal lens and thermal double refraction compensation element, having high output power, better beam quality, high doubling efficiency, better stability, widely used for fields of laser material process, optical storage, laser full color display, laser medicine, scientific research, communication, defense and amusement.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Rapid cutoff system of photovoltaic module and restarting method after cutoff
ActiveCN109787269AWith automatic shutdown capabilityAvoid irreversible damageSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringBattery pack
The invention mainly relates to a rapid cutoff system of photovoltaic module and a restarting method after cutoff. The rapid cutoff system comprises a cutoff control module, a plurality of cutoff devices and a plurality of photovoltaic modules, wherein a plurality of photovoltaic modules are connected in series to form a battery pack, respective output voltages are superposed to obtain a DC bus voltage, and each cutoff device is used for removing the corresponding photovoltaic module from the battery pack so as to cut off or restoring from a cutoff state to a series connection state. When a cutoff command is received by the cutoff control module, a first instruction is send out to the plurality of cutoff devices so as to inform the plurality of cutoff devices to cut off the corresponding photovoltaic modules, or when a starting command is received by the cutoff control module, a second instruction is sent out to the plurality of cutoff devices so as to inform the plurality of cutoff devices to restore the corresponding photovoltaic modules from the cutoff states to the series connection states.
Owner:FONRICH NEW ENERGY TECH LTD
Contact of vacuum arc extinguishing chamber
InactiveCN104064398ALow costStrong breaking abilityHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesEngineeringField strength
The invention provides a contact of a vacuum arc extinguishing chamber. The contact comprises a first contact and a second contact. The first contact is connected with a first conducting rod, and the second contact is connected with a second conducting rod. An arc ignition contact is arranged on and protrudes out of an end surface of the first contact. The arc ignition contact is connected inside the first conducting rod by a spring. An auxiliary contact is arranged on an end surface of the second contact and is used to cooperate with the arc ignition contact to generate an arc. The invention provides the contact reducing the breakdown field strength, controlling the arcing point, improving the interrupting capability of the vacuum arc extinguishing chamber, and having a low cost.
Owner:王永法
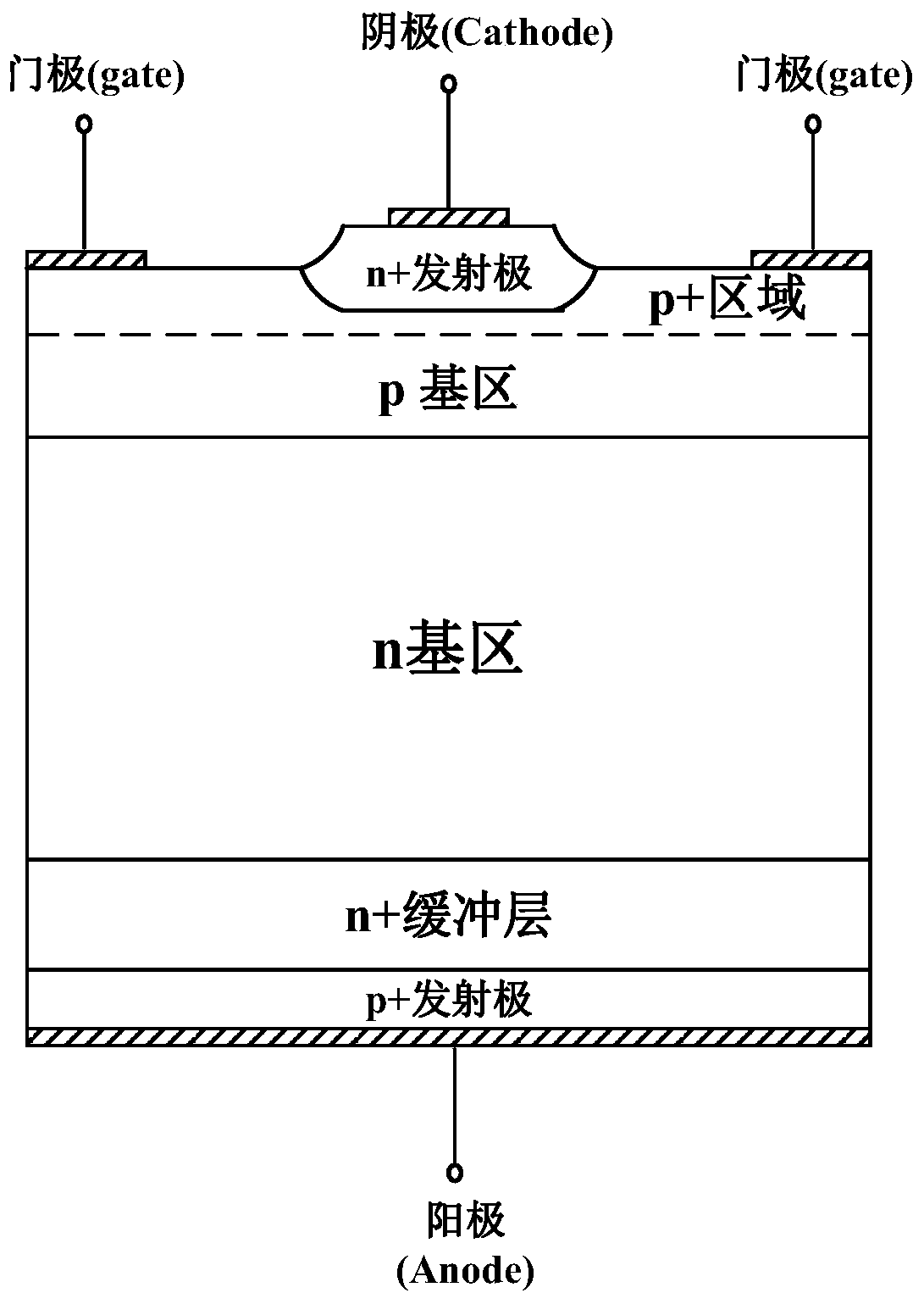
Thyristor controlled by accumulation layer
An accumulation layer controlled thyristor, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor power devices, is characterized in that the on / off of the thyristor can be controlled by stopping electron circulation through an electron barrier of an internal electric field formed in a P bypass region and an N depletion region. When a positive voltage is applied on a gate, an accumulation layer is formed at the interface between the N depletion region (33) and a gate oxide layer (6); an electron inversion channel is formed in a P-type base region (8); and electrons pass through an N active region (9), the accumulation layer, an N layer (200), and the electron inversion channel to the an N base region (3), thereby controlling the normal operation of the device. The accumulation layer controlled thyristor as the substitute of the conventional gate controlled thyristors, such as MOS controlled thyristors, has the advantages of lower conduction voltage drop, larger saturation current density, no parasitic effect, and greatly improved safety operation area, and can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional gate-controlled thyristors, such as the deficiency of current saturation characteristic and poor turn-off capability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
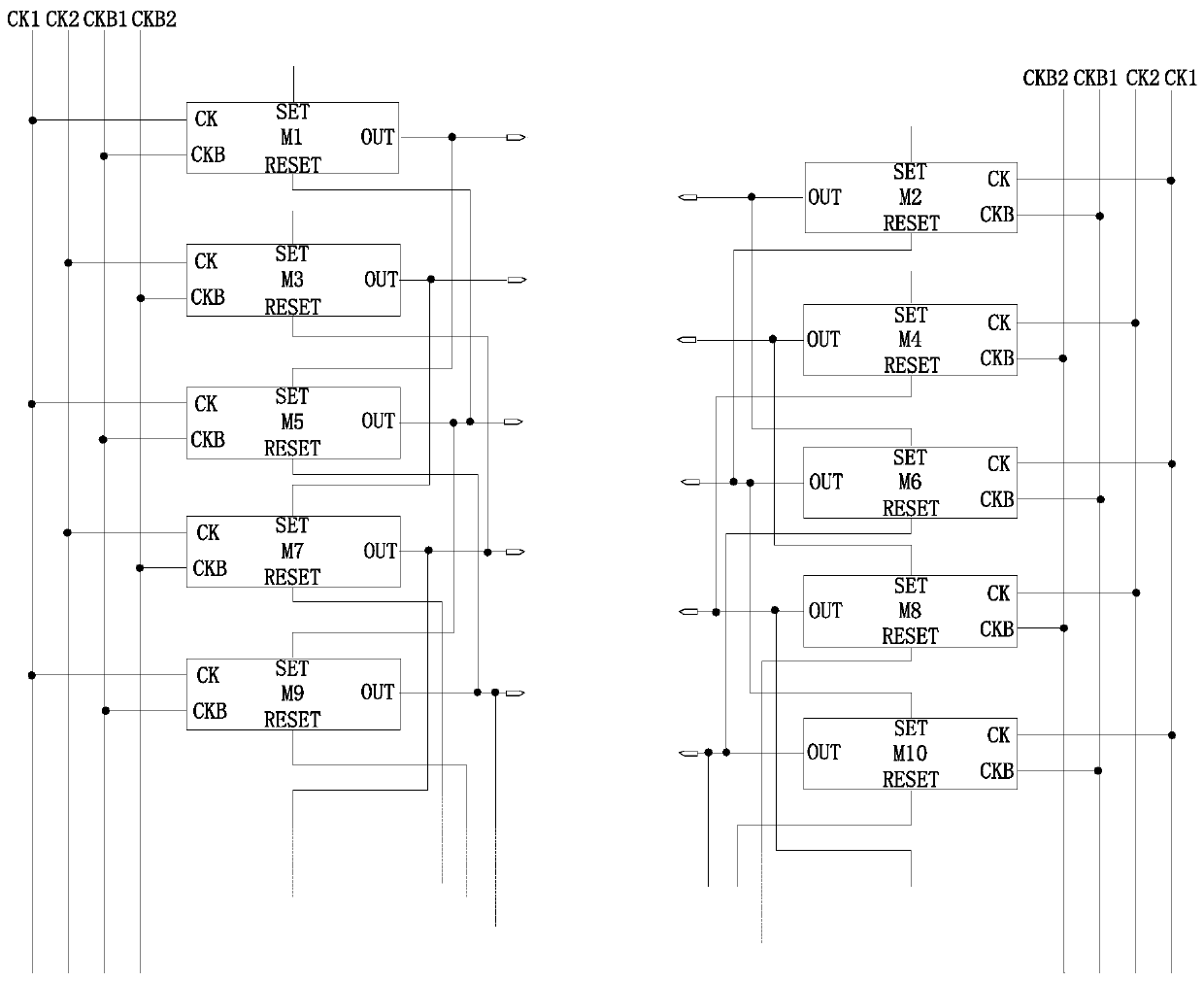
Gate drive circuit, array substrate and display device
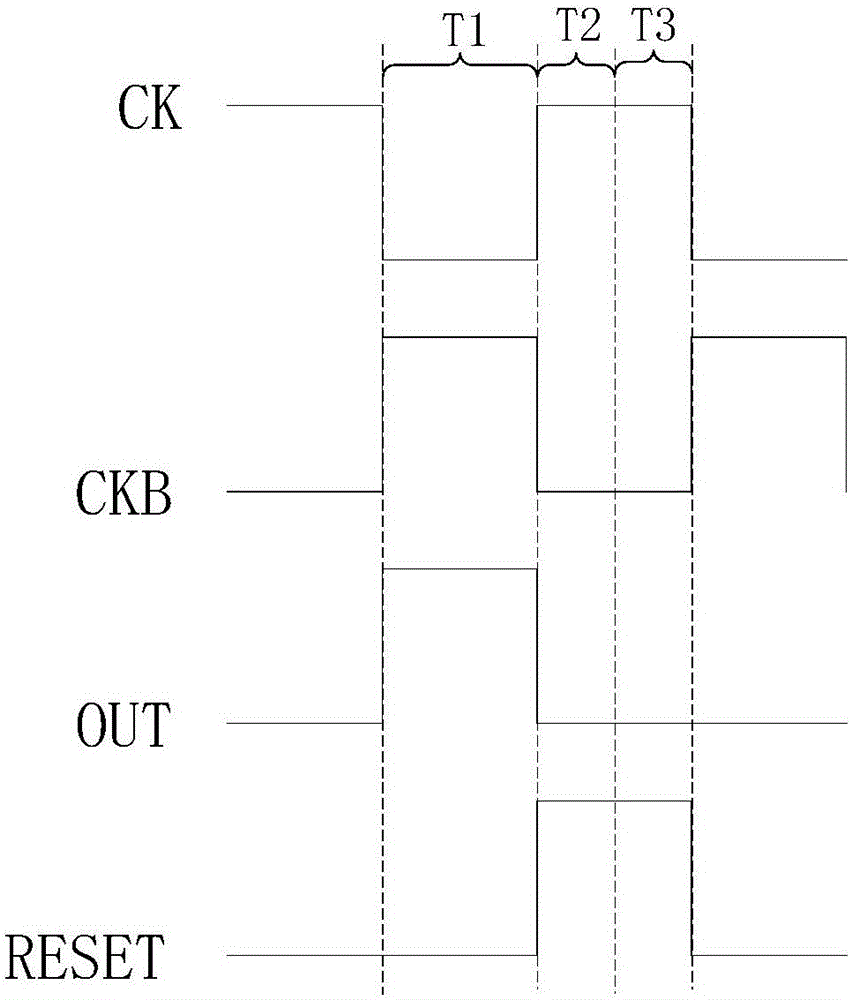
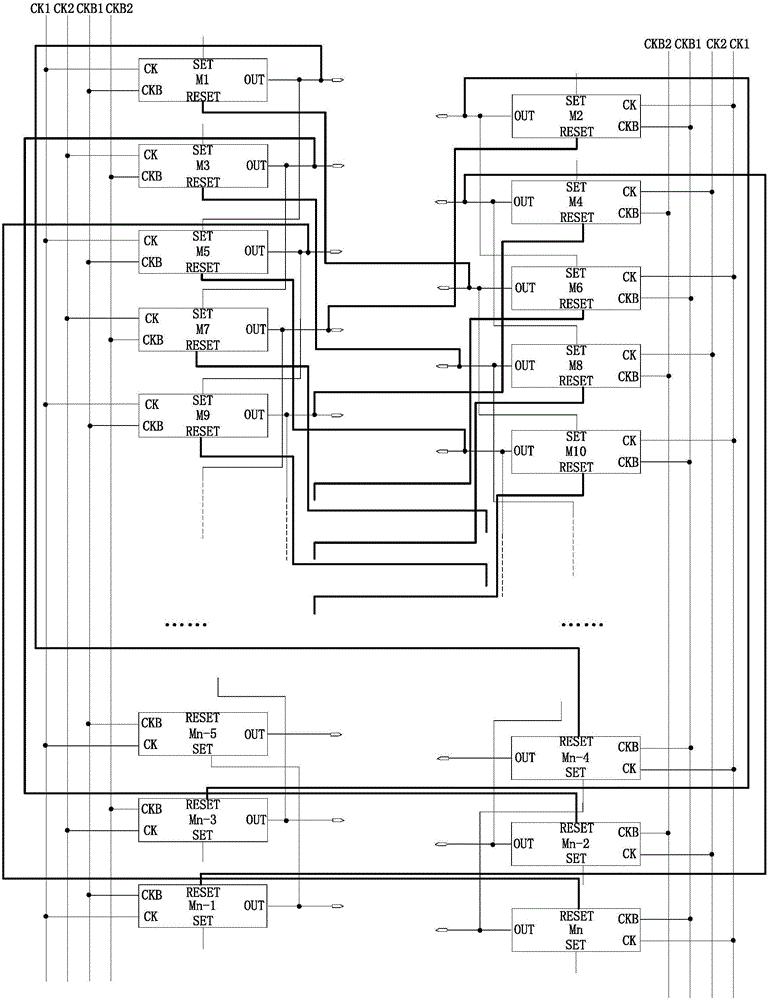
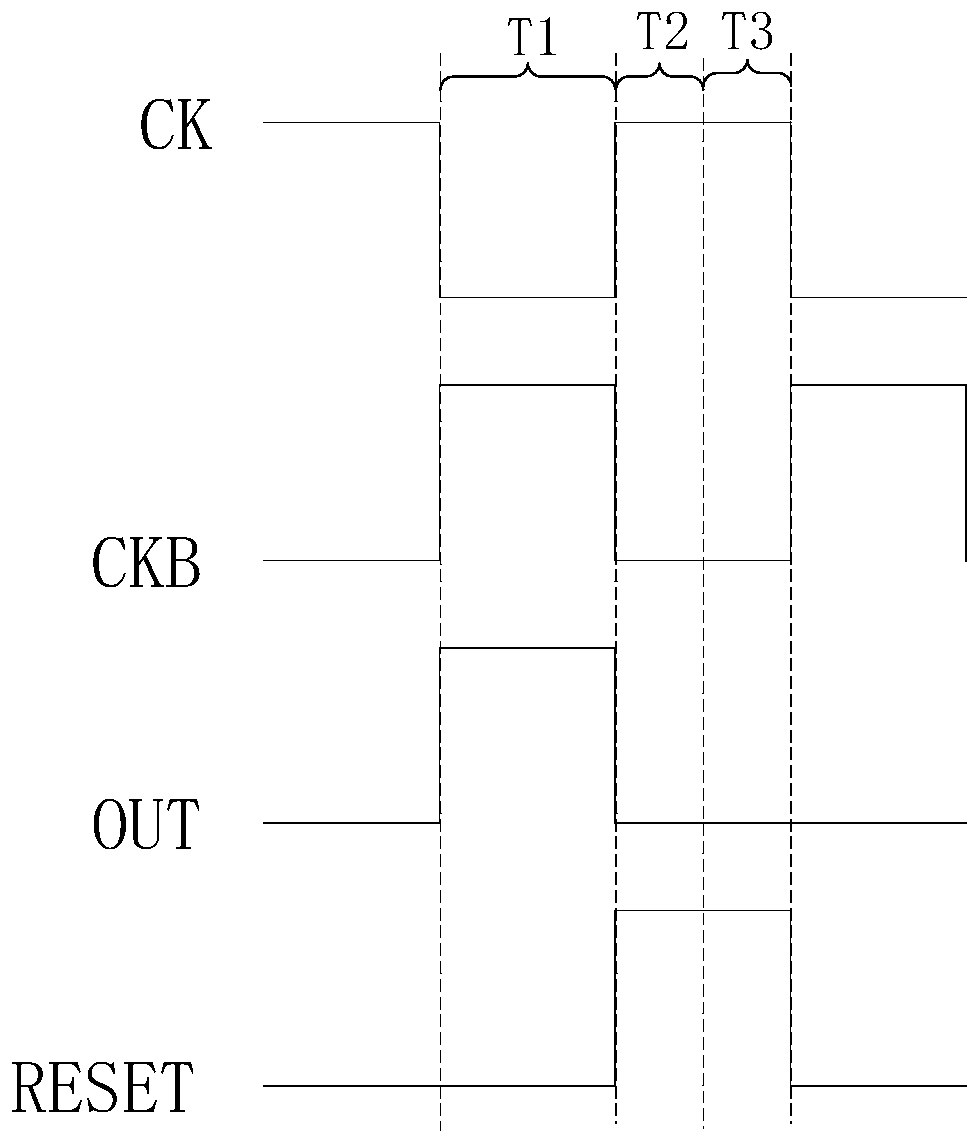
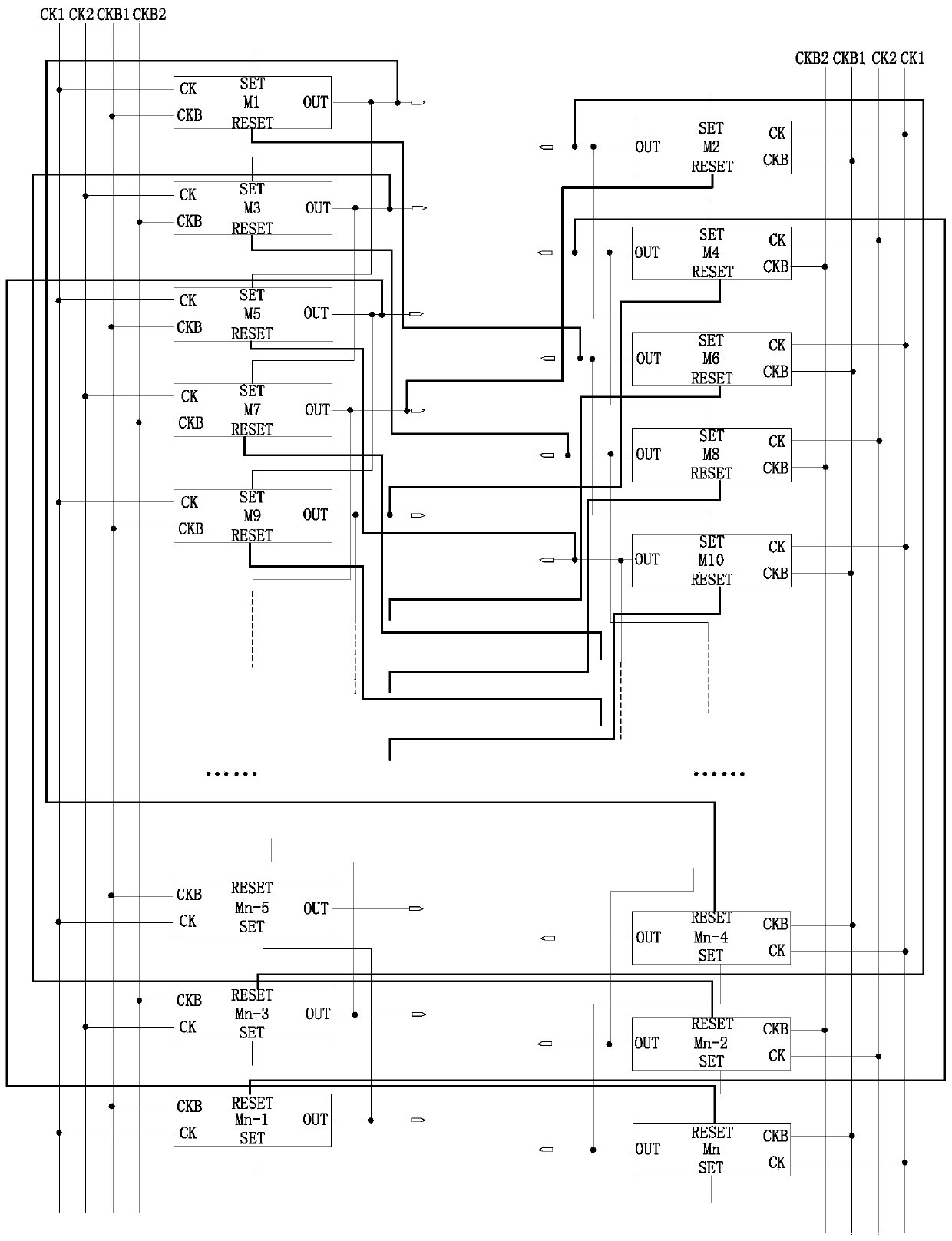
ActiveCN106409211ADrop down fastImprove shutdown capabilityStatic indicating devicesShift registerProcessor register
The invention provides a gate drive circuit, an array substrate and a display device. Under the control of a signal inputted by an input terminal, a shift register transmits a clock signal of a first electrical level inputted by a second clock signal terminal to an output terminal in the first period of time, and transmits a clock signal of a second electrical level inputted by the second clock signal terminal to the output terminal in the second period of time. Under the control of a signal inputted by a first clock signal terminal, the shift register transmits a pull-down signal of the second electrical level to the output terminal in the second and third periods of time. Under the control of a signal inputted by a first reset terminal, the shift register stops transmitting the clock signal inputted by the second clock signal terminal to the output terminal in the third period of time. On this basis, the electric potential of a gate line can be pulled down together by the clock signal of the second electrical level and the pull-down signal of the second electrical level in the second period of time. Therefore, fast pulldown of the gate line is guaranteed and the power-off capability of a thin film transistor of a pixel unit and the charging capability of the pixel unit are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Multiple frequency one-way overlapped output standard continuous green light laser inside full solid T double-cavity combination cavity
InactiveCN101267084AReduce the risk of injuryIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFundamental frequencyAcousto-optics
The present invention provides a laser, especially a frequency doubling single direction overlapping output quasi-cw green laser in a full-solid T type double-cavity combined cavity, composed of two F-P, each F-P adopts flat-concave cavity structure, F-P adopts side pumped Nd:YAG crystal of the semiconductor laser pumped component having same model, each F-P is optimized design by computer simulation, a stably rotatable 1064nm fundamental frequency laser is formed in the F-P, each F-P obtains 532nm quasi-cw green laser by the audio-optical Q switching and frequency doubling technology, overlapping in the several frequency doubling crystals, reflecting by the harmonic reflector, obtaining secondary frequency doubling and output together. The whole system finally obtains 532nm green laser which power achieves 202W. The laser does not need any thermal len and thermal double refraction compensation element, having high output power, better beam quality, high doubling efficiency, better stability, widely applied in medical, industry.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
IGBT apparatus provided with internal JFET structure
ActiveCN108493241AAvoid Short Circuit FailuresImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceHigh voltage igbt
The invention relates to an IGBT apparatus provided with an internal JFET structure and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor apparatuses. According to the IGBT apparatus structure, byintroducing a JEFT region in a body region of a conventional grate IGBT, the JFET region is equivalent to a variable resistor, a hole is stored when the apparatus is conducted forward and a quick releasing circuit is provided for the hole in forward blockage, so that the saturated conducting pressure drop and cut-off loss of the apparatus are reduced, the short-circuit failure phenomenon after the apparatus is cut off is avoided, and the cut-off ability of the apparatus is improved; moreover, a connecting bridge connecting the grate structure and the JFET region plays a field plate role whenthe apparatus is blocked forwardly, so that the electric field peak on the surface of the lower region of the connecting bridge is reduced effectively, and the voltage-resistant and operational reliability of the apparatus is improved. The IGBT apparatus provided with the internal JFET structure is compatible to an existing high voltage IGBT apparatus manufacturing process, so that industrialization is achieved favorably.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reverse-conducting semiconductor device
A reverse-conducting MOS device is provided having an active cell region and a termination region. Between a first and second main side. The active cell region comprises a plurality of MOS cells with a base layer of a second conductivity type. On the first main side a bar of the second conductivity type, which has a higher maximum doping concentration than the base layer, is arranged between the active cell region and the termination region, wherein the bar is electrically connected to the first main electrode. On the first main side in the termination region a variable-lateral-doping layer of the second conductivity type is arranged. A protection layer of the second conductivity type is arranged in the variable-lateral-doping layer, which protection layer has a higher maximum doping concentration than the maximum doping concentration of the variable-lateral-doping layer in a region attached to the protection layer.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY LTD
Power Semiconductor Device And Corresponding Module
InactiveUS20150380534A1Good mo controllabilityHigh safe operate areaTransistorThyristorPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
Power semiconductor device having a wafer, including emitter and collector electrodes arranged on opposite sides, wherein a gate electrode arranged on the emitter side has a conductive gate layer and an insulating layer arranged in the following order between the collector and emitter side: a p doped collector layer, an (n−) doped drift layer, an n doped enhancement layer, a p based base layer having a first and second base region, and an (n+) doped first and second emitter layer, wherein the emitter electrode contacts the first emitter layer and the first base region at an emitter contact area, wherein the second emitter layer is insulated from a direct contact to the emitter electrode by the insulating layer and wherein the second emitter layer is separated from the first emitter layer by the base layer.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
IGBT device with a groove gate type JFET structure
ActiveCN108766998AAvoid Short Circuit FailuresImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPeak valueJFET
The invention relates to an IGBT device with a groove gate type JFET structure, belonging to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. A JFET region equivalent to a JFET variable resistanceis introduced into a neutral region other than a depletion region generated in a forward block body region of the device, The holes are stored when the device is turned on forward, and a quick discharging loop is provided for the holes when the device is blocked forward, so that the saturation conduction voltage drop and the shutdown loss of the device are reduced, the short-circuit failure phenomenon after the device is turned off is avoided, and the shutdown ability of the device is improved. Moreover, the connection bridge between the gate structure and the JFET region can act as a field plate when the device is blocked in the forward direction, so that the surface electric field peak value under the connection bridge can be effectively reduced, and the withstand voltage and the workingreliability of the device can be improved. The manufacturing method of the IGBT device with a groove gate type JFET structure is compatible with that of the prior art. A JFET region is fabricated bya shallow groove etching and ion implantation process, which is conducive to reducing the gate resistance of the JFET region and enhancing the gate control ability of the JFET structure; it is helpfulto reduce the size of the JFET structure, increase cell density and realize industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Vertical and trench type insulated gate MOS semiconductor device
ActiveUS7737490B2Provides adequateLower on-resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A vertical and trench type insulated gate MOS semiconductor device is provided in which the surfaces of p-type channel regions and the surfaces of portions of an n-type semiconductor substrate alternate in the longitudinal direction of the trench between the trenches arranged in parallel, and an n+-type emitter region selectively formed on the surface of the p-type channel region is wide by the side of the trench and becomes narrow toward the center point between the trenches. This enables the device to achieve low on-resistance and enhanced turn-off capability.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
MOSFET isolation drive circuit
PendingCN108429435AAccelerated shutdownReliable shutdownEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsMOSFETCapacitance
The invention discloses an MOSFET isolation drive circuit. The MOSFET isolation drive circuit comprises a transformer winding, a triode Q1, a field-effect tube Q3, a triode Q2 and a capacitor C, wherein the triode Q1 is used for inputting a PWM control signal, the field-effect tube Q3 is connected with a secondary winding in the transformer winding, the triode Q2 is connected with a grid electrodeof the field-effect tube Q3, and the capacitor C is used for storing electricity during the breakover of the field-effect tube; two ends of a primary winding of the transformer winding are respectively connected with a collecting electrode and emitting electrode of the triode Q1; the primary winding of the transformer winding is also connected with a power supply; an emitting electrode of the triode Q1 is also connected with the ground; a G electrode and S electrode of the field-effect tube Q3 are respectively connected with two ends of the secondary winding in the transformer winding; a collecting electrode of the triode Q2 is connected with the G electrode of the field-effect tube Q3, a base electrode of the triode Q2 is connected with the other end of the secondary winding in the transformer winding; the capacitor C is respectively connected between the S electrode of the field-effect tube Q3 and an emitting electrode of the triode Q2.
Owner:FOSHAN POLYTECHNIC
Thin-film transistor, display device, and preparation method of thin-film transistor
PendingCN109742156AHigh conductivityImproved shutdown performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIonActive agent
The invention discloses a thin-film transistor; an active layer of the thin-film transistor is an indium-gallium-zinc oxide film, and a photosensitive active agent is doped into the indium-gallium-zinc oxide film. By adopting the photosensitive active agent, the turn-off performance of the thin-film transistor is improved, an off-state current (Ioff) of the thin-film transistor is reduced, and a specific value of an on-state current and the off-state current of the thin-film transistor is increased (Ion / Ioff), and the driving performance of the thin-film transistor is improved. The invention discloses a preparation method of the thin-film transistor, the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the active layer, dissolving the photosensitive active agent in a first preparation solution to form a precursor solution, distributing the precursor solution on a base and curing to form the indium-gallium-zinc oxide film containing the photosensitive active agent. Through the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the use of the photoresist can be avoided, the preparation process of the active layer is simplified, and the damage of the active layer caused by stripping the photoresist can be avoided.
Owner:YUNGU GUAN TECH CO LTD
Power semiconductor device and corresponding module
InactiveUS9455340B2LossBetter carrier enhancement at the emitterTransistorThyristorPower semiconductor deviceComputer module
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
High-voltage fast recovery diode structure
ActiveCN107342330AImproved reverse recovery softnessImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor devicesReverse recoveryHigh pressure
The invention provides a high-voltage fast recovery diode structure, and particularly relates to a double-sided terminal diode provided with a local p+ doping region negative electrode structure. The high-voltage fast recovery diode structure comprises an n- drift region, a positive electrode region, a local p+ doping negative electrode region and a double-sided terminal region, wherein the double-sided terminal structure comprises a front-surface terminal region and a back-surface terminal region, the front-surface terminal region and the back-surface terminal region are respectively encircled around the positive electrode region and the negative electrode region, so that the area efficiency of the terminal structure can be improved. The local p+ doping region is arranged on a surface of a back-surface negative electrode region or in the back-surface negative electrode region, different doping dosages, widths, depths and arrangement periods can be employed according to different application demands, holes can be injected in a reverse recovery tail period, electric field peak and current silkening at a negative electrode side can be prevented, and thus, the problem that a high punch-through effect brought by a double-sided terminal is not beneficial for improving the firmness of the high-voltage fast recovery diode structure and improving flexibility is solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Gate-commutated thyristor with double p-base gate-cathode structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105590959BImprove reverse breakdown voltageHigh voltageThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMetal electrodes
The invention relates to a gate commutated thyristor having a dual-p-base-region gate cathode structure and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits. The gate commutated thyristor comprises more than one chip cell. Each chip cell is composed of a p+ emitter electrode, an n' buffer region, an n- buffer region, a p base region 1, a p base region 2, a p+ short base region, an n+ emitter electrode, an anode metal electrode, a gate metal electrode and a cathode metal electrode. The p+ emitter electrode, the n' buffer region, the n- buffer region, the p base region 1, the p base region 2, the p+ short base region and the n+ emitter electrode are arranged in turn. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the gate metal electrode and the cathode metal electrode are ensured to be in the same plane with the surface of a silicon chip based on the conventional trenching process or the channeling abandonment process on the surface of the n+ emitter electrode and the gate electrode. The gate commutated thyristor is provided with an extra layer of p base region, so that the reverse breakdown voltage of a J3 junction is ensured to be larger. Furthermore, the voltage of an external reverse power supply is increased, so that the commutation speed is improved. The turn-off ability of GCT chips is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Parallel IGBT driving method of power electronic equipment
InactiveCN110890833ASuppress static and dynamic uneven flowImproved turn-on and turn-off capabilitiesPower conversion systemsGate voltageHigh current
The invention discloses a parallel IGBT driving method of power electronic equipment. The parallel IGBT driving method comprises the steps of configuring the driving number of parallel IGBTs, selecting a driving connection mode of the parallel IGBTs, setting IGBT gate voltage and driving resistance, and determining a graded turn-off mode of the IGBTs. According to the driving scheme, optical device isolation is not needed, non-delay synchronous driving of the parallel IGBT devices is guaranteed, and static and dynamic non-uniform currents are restrained; the single IGBT drive greatly improvesthe conduction and turn-off current capability of a single IGBT through gate voltage enhancement, drive resistor setting, hierarchical turn-off control and the like, reduces di / dt and overvoltage in the IGBT turn-off process, and guarantees the reliable operation of the IGBT. The IGBT drive circuit is simple in driving, flexible in control and quick in action, the IGBT parallel number can be flexibly configured according to a current target value, the capacity utilization rate of a single IGBT is high, and the IGBT drive circuit is suitable for large-current on-off valve group occasions of different voltage levels.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +3
Vertical and trench type insulated gate mos semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100207162A1Provides adequateLower on-resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
A vertical and trench type insulated gate MOS semiconductor device is provided in which the surfaces of p-type channel regions and the surfaces of portions of an n-type semiconductor substrate alternate in the longitudinal direction of the trench between the trenches arranged in parallel, and an n+-type emitter region selectively formed on the surface of the p-type channel region is wide by the side of the trench and becomes narrow toward the center point between the trenches. This enables the device to achieve low on-resistance and enhanced turn-off capability.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC DEVICE TECH CO
Integrated trans-MOS insulated gate bipolar transistor structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108022973ADoes not affect conduction characteristicsImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringDielectric layer
The invention provides an integrated trans-MOS insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) structure and a manufacturing method thereof. The structure comprises a substrate, a cellular doping region arranged on the upper surface of the substrate, an integrated trans-MOS doping region, a dielectric layer of an isolated gate electrode, an electrode metal matched with the cellular structure, and a gatestructure. According to the integrated trans-MOS IGBT high in turn-off ability, the minority carrier extraction capability of a device active region during the turn-off process is improved on the premise that other characteristics are not affected at all. Therefore, the turn-off ability of a chip is improved.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD
IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) device and method for manufacturing same
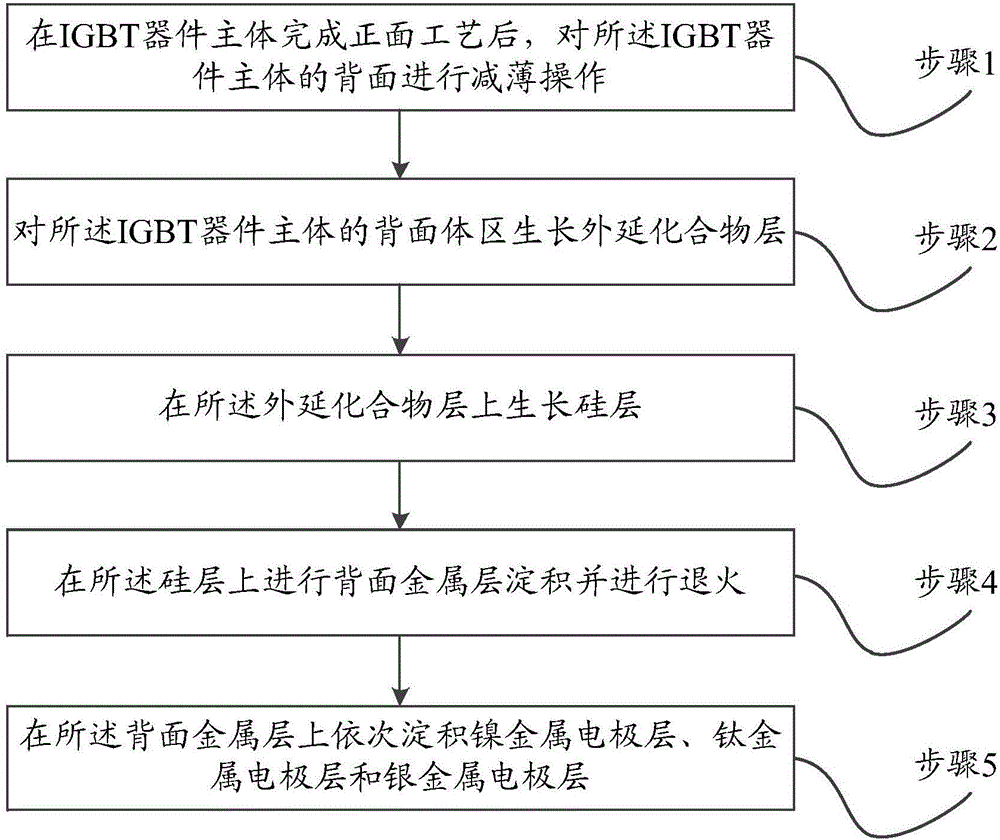
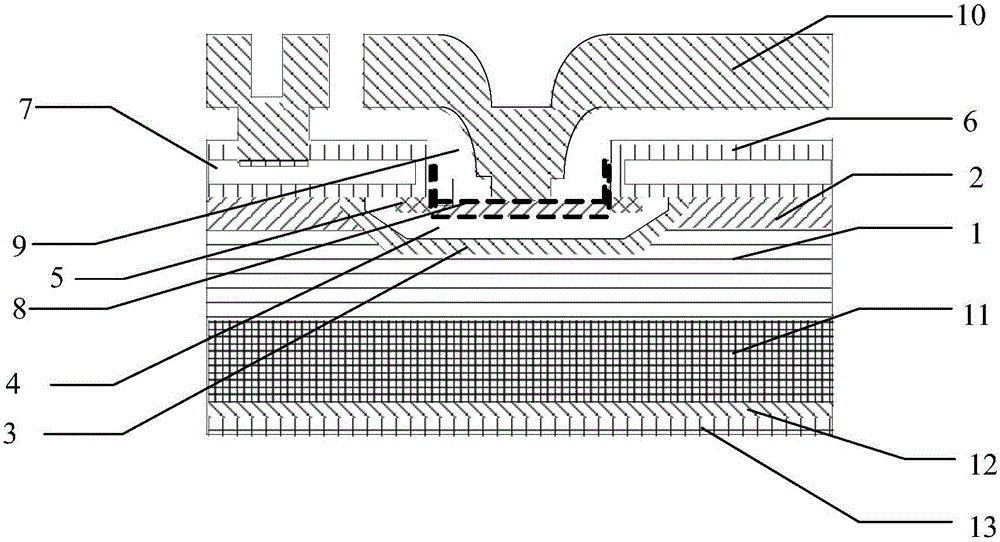
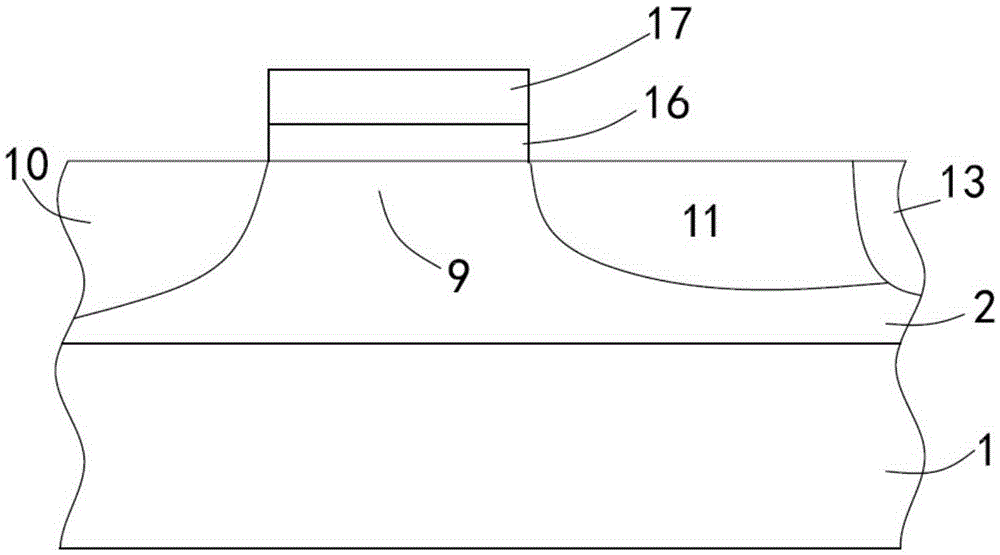
InactiveCN106783609AReduce tail currentFacilitate conductionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical compoundMetal electrodes
The invention discloses an IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) device and a method for manufacturing the same. The method includes steps of 1, completely carrying out front surface processes on an IGBT device body and carrying out thinning operation on the back surface of the IGBT device body; 2, growing an epitaxial chemical compound layer on a back-surface bulk area of the IGBT device body; 3, growing silicon layers on the epitaxial chemical compound layer; 4, depositing a back-surface metal layer on the corresponding silicon layer and carrying out annealing; 5, sequentially depositing a nickel metal electrode layer, a titanium metal electrode layer and a silver metal electrode layer on the back-surface metal layer. The IGBT device and the method have the advantages that the epitaxial chemical compound layer grows on the back-surface bulk area of the IGBT device body to form heterogenous junctions, accordingly, withstand voltages of IGBT chips can be increased, and the thicknesses of the chips can be reduced; excess current carriers can be quickly combined with one another in turn-off procedures, and accordingly the turn-on and turn-off performance of the IGBT device can be improved.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
MOS transistor device
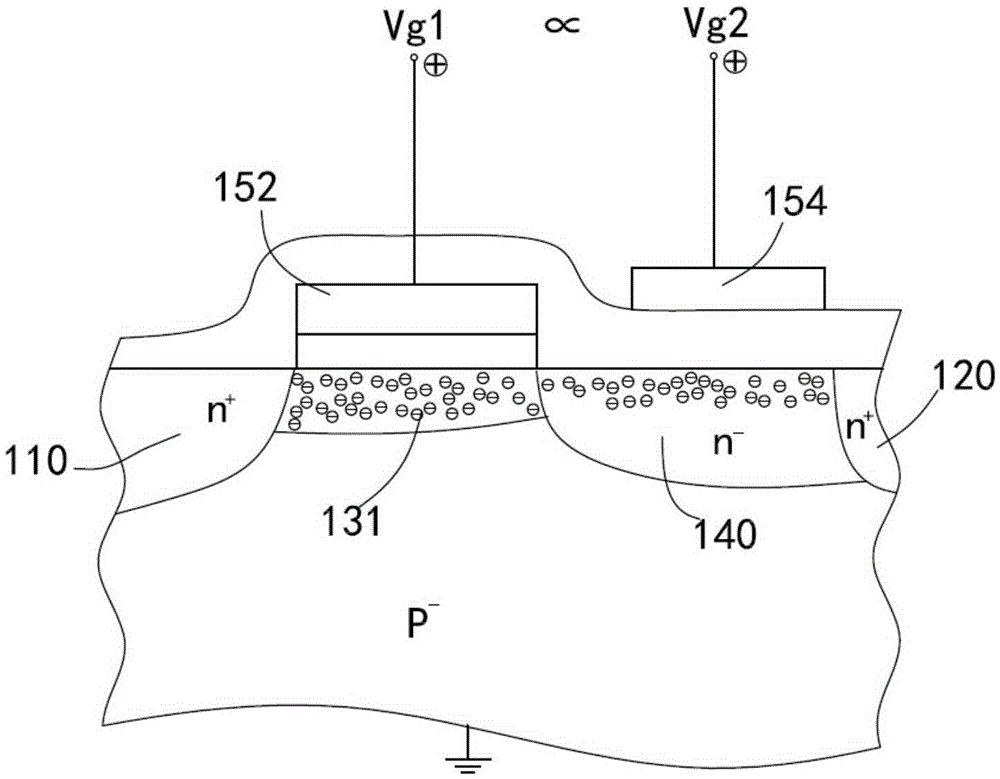
InactiveCN106611786AReduce work lossImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The invention discloses an MOS transistor device. The MOS transistor device is provided with two gates, the first gate is a common gate arranged above a channel for controlling on and off of the device, and the second gate is a newly-added gate arranged above an LDD area for controlling drain-source on resistance Rdson. Through regulation by the second gate, on one hand, when the device is in a working state, the drain-source on resistance Rdson can be reduced, thereby reducing the working loss of the device and improving the on-off efficiency, and on the other hand, when the device is in an off state, drain-source capacitance Cds is reduced, the impedance between the drain and the source and the breakdown voltage BVdss are improved, and the separation ability when the device is off and the voltage swing blocking ability are thus improved.
Owner:INNOGRATION SUZHOU
Thyristor controlled by accumulation layer
InactiveCN101478002BStrong shutdown capabilityReduce forward voltage dropThyristorElectronElectric field
An accumulation layer controlled thyristor, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor power devices, is characterized in that the on / off of the thyristor can be controlled by stopping electron circulation through an electron barrier of an internal electric field formed in a P<+> bypass region and an N<-> depletion region. When a positive voltage is applied on a gate, an accumulation layer is formed at the interface between the N<-> depletion region (33) and a gate oxide layer (6); an electron inversion channel is formed in a P-type base region (8); and electrons pass through an N<+> active region (9), the accumulation layer, an N<+> layer (200), and the electron inversion channel to the an N<-> base region (3), thereby controlling the normal operation of the device. The accumulation layer controlled thyristor as the substitute of the conventional gate controlled thyristors, such as MOS controlled thyristors, has the advantages of lower conduction voltage drop, larger saturation current density, no parasitic effect, and greatly improved safety operation area, and can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional gate-controlled thyristors, such as the deficiency of current saturation characteristic and poor turn-off capability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A High Voltage Fast Recovery Diode Structure
ActiveCN107342330BImproved reverse recovery softnessImprove shutdown capabilitySemiconductor devicesDopantReverse recovery
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fully-controlled semiconductor device packaging structure based on integrated commutation
The invention discloses a fully-controlled semiconductor device packaging structure based on integrated commutation. The fully-controlled semiconductor device packaging structure comprises a fully-controlled semiconductor device and a tube shell used for packaging the full-control type semiconductor device, the fully-controlled semiconductor device comprises a first chip assembly, a second chip assembly, a third chip assembly, a first transition layer, a second transition layer, a third transition layer and a fourth transition layer, the cathode terminal of the first chip assembly is connectedto the anode of the fully-controlled semiconductor device through the first transition layer; the anode terminal of the first chip assembly is connected to the cathode terminal of the second chip assembly through the second transition layer; the anode terminal of the second chip assembly is connected to the anode terminal of the third chip assembly through the third transition layer; the cathodeterminal of the third chip assembly is connected to the cathode of the fully-controlled semiconductor device through the fourth transition layer; and the first transition layer is connected with the third transition layer through a conductive plate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Vertical power device and barrier modulation method thereof
InactiveCN111129115AImprove shutdown capabilityReduce processing difficultySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectronegativityGallium nitride
Disclosed is an III-V group nitride power device. The III-V group nitride power device comprises an anode, a cathode and a substrate, and the III-V group nitride power device comprises an N-type gallium nitride drift region located above the substrate, and P-type-like regions and space charge windows are alternately arranged. The P-type-like regions are formed in the N-type gallium nitride drift region and located under the anode, electronegative ions are introduced into the P-type-like regions, the space charge windows are located between every two adjacent P-type-like regions, and a currentpath is provided between the anode and the cathode, wherein the P-like region and the space charge window are located in the N-type gallium nitride drift region or located on the surface of the III-Vgroup nitride power device. According to the structure, the forward conduction performance, the reverse breakdown performance and the reverse leakage current performance of the device can be considered at the same time, the feasibility of the technology for achieving the structure is high under the conditions of laboratories and industrial production, and the method is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A detection method for electrical reliability of circuit breaker contacts
ActiveCN105137344BFind and eliminate potential safety hazards in timeImprove shutdown capabilityCircuit interrupters testingDirect currentCircuit breaker
The invention discloses method for detecting the electrical reliability of a circuit breaker contact, and the method comprises the steps: 1, measuring a movement distance S1 before and after the switching of a circuit breaker operating mechanism; 2, continuously applying direct current to two ends of a circuit breaker single-phase arc-extinguishing chamber, and measuring a voltage Ui across two ends of the circuit breaker single-phase arc-extinguishing chamber and a current Ii flowing through the circuit breaker single-phase arc-extinguishing chamber in real time; 3, plotting changing curves of the voltage Ui and current Ii along with time t from the operation starting moment of the driving mechanism, wherein the changing curves specifically comprise a voltage (Ui)-time (t) curve and a current (Ii)-time (t) curve; 4, finding time T1 corresponding to a first peak, and calculating actual opening travels S2 of movable and static contacts; 5, judging the ablation degree of an arc-extinguishing chamber contact. The method solves a problem that the detection of the electrical reliability of the circuit breaker contact is not convenient.
Owner:YANCHENG POWER SUPPLY CO STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +4
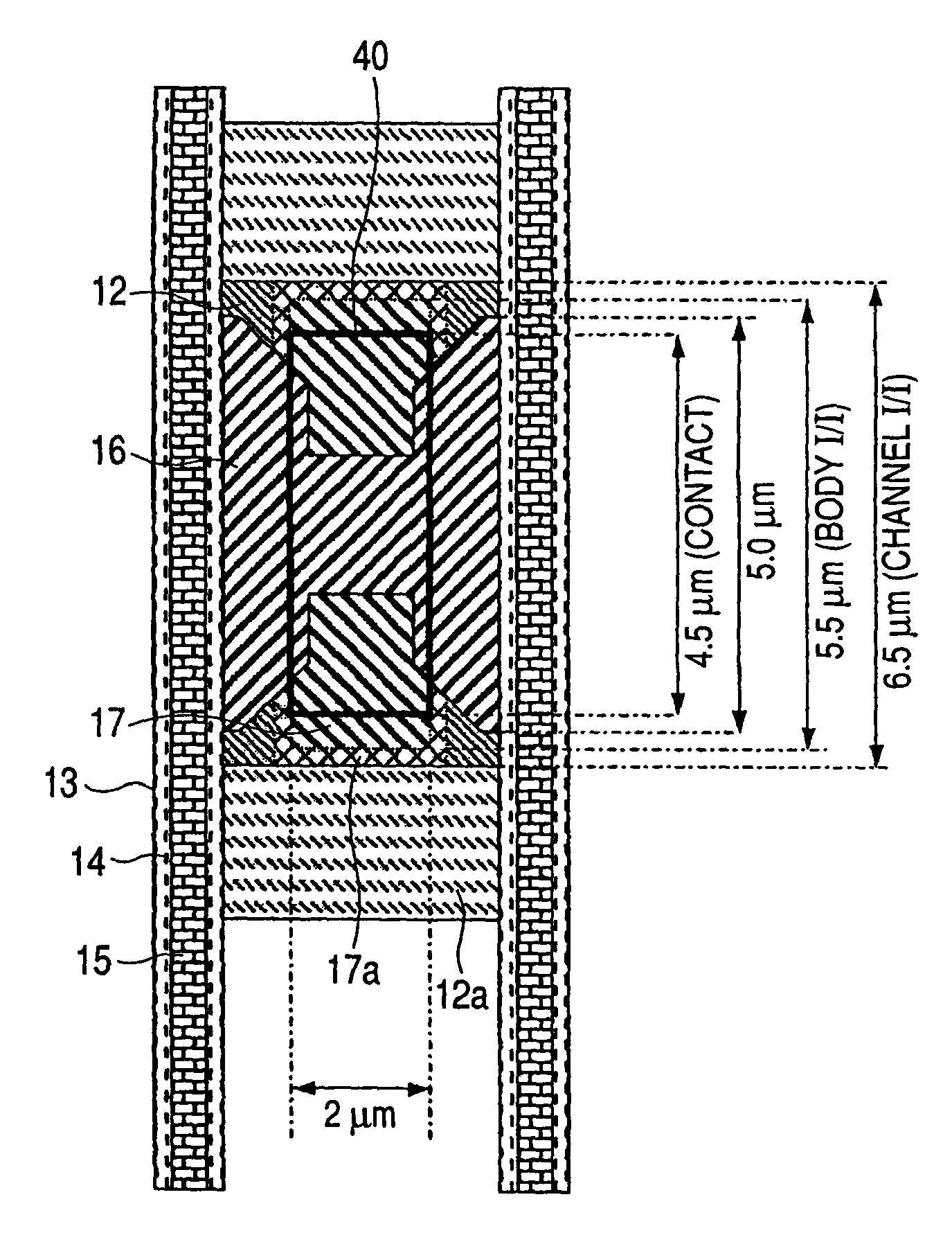
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
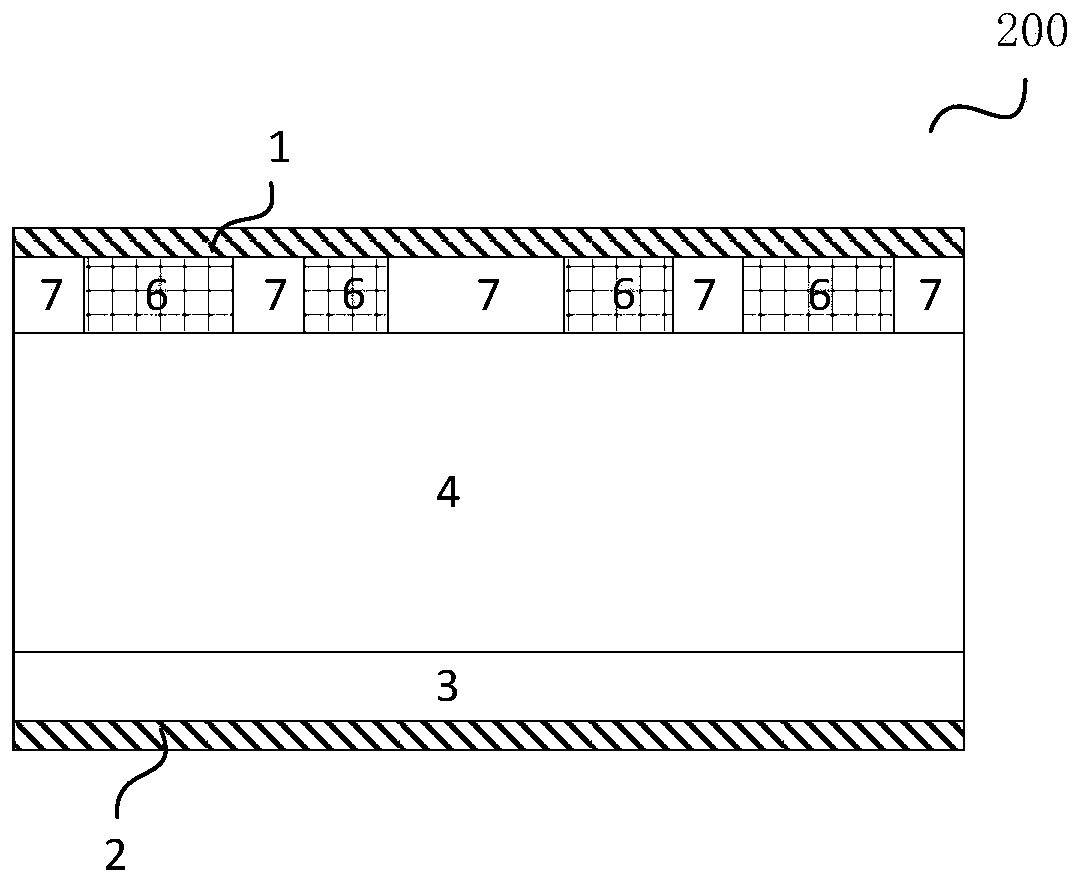
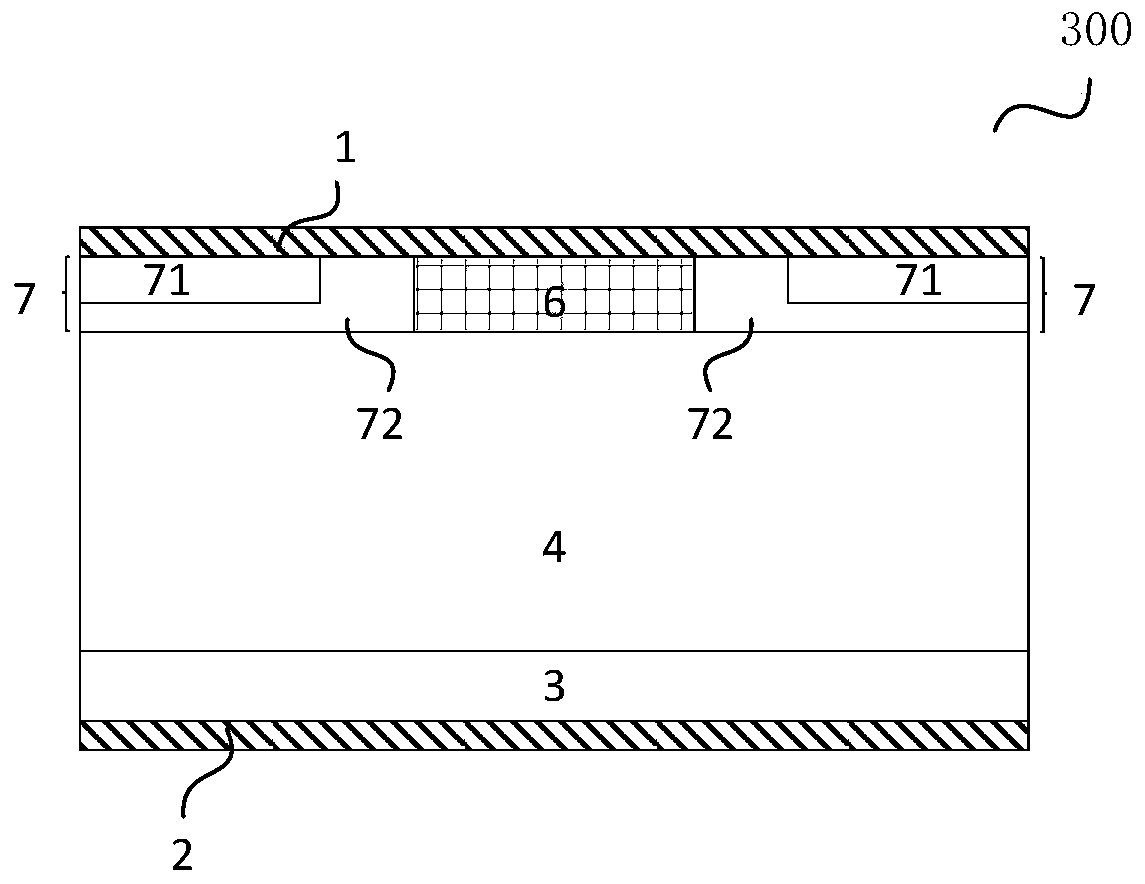
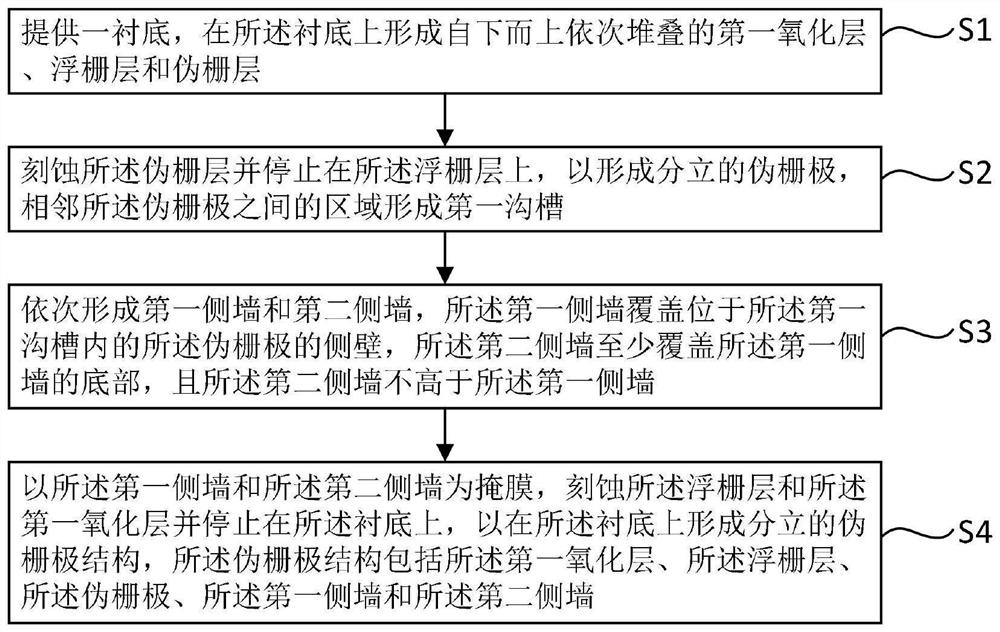
InactiveCN111799163AIncreasing the thicknessImprove shutdown capabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDevice materialMaterials science
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device. The manufacturing method comprises the steps: forming a first oxide layer, a floating gate layer and a pseudo gate layer whichare stacked in sequence from bottom to top on a substrate; etching the pseudo gate layer to form a pseudo gate; forming a first side wall and a second side wall sequentially, covering the side wall ofa pseudo gate by the first side wall, at least covering the bottom of the first side wall by the second side wall, and enabling the second side wall not to be higher than the first side wall; and etching the floating gate layer and the first oxide layer by taking the first side wall and the second side wall as masks and stopping on the substrate. The first side wall is formed; the second side wall is formed at the bottom of the first side wall, the thickness of the side wall is increased; the floating gate layer is etched by taking the first side wall and the second side wall as masks; due tothe fact that the thickness of the side wall is increased and the long floating gate layer is reserved, the turn-off capacity of a channel is enhanced, and the problem that the split-gate flash memory is prone to fail in the programming process due to the fact that the length of a floating gate of the split-gate flash memory is shortened because the thickness of the side wall is small is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Multiple frequency one-way overlapped output standard continuous green light laser inside full solid T double-cavity combination cavity
InactiveCN101267084BReduce the risk of injuryIncrease output powerActive medium materialFundamental frequencyAcousto-optics
The present invention provides a laser, especially a frequency doubling single direction overlapping output quasi-cw green laser in a full-solid T type double-cavity combined cavity, composed of two F-P, each F-P adopts flat-concave cavity structure, F-P adopts side pumped Nd:YAG crystal of the semiconductor laser pumped component having same model, each F-P is optimized design by computer simulation, a stably rotatable 1064nm fundamental frequency laser is formed in the F-P, each F-P obtains 532nm quasi-cw green laser by the audio-optical Q switching and frequency doubling technology, overlapping in the several frequency doubling crystals, reflecting by the harmonic reflector, obtaining secondary frequency doubling and output together. The whole system finally obtains 532nm green laser which power achieves 202W. The laser does not need any thermal len and thermal double refraction compensation element, having high output power, better beam quality, high doubling efficiency, better stability, widely applied in medical, industry.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
A gate drive circuit, array substrate and display device
ActiveCN106409211BDrop down fastImprove shutdown capabilityStatic indicating devicesShift registerProcessor register
The invention provides a gate drive circuit, an array substrate and a display device. Under the control of a signal inputted by an input terminal, a shift register transmits a clock signal of a first electrical level inputted by a second clock signal terminal to an output terminal in the first period of time, and transmits a clock signal of a second electrical level inputted by the second clock signal terminal to the output terminal in the second period of time. Under the control of a signal inputted by a first clock signal terminal, the shift register transmits a pull-down signal of the second electrical level to the output terminal in the second and third periods of time. Under the control of a signal inputted by a first reset terminal, the shift register stops transmitting the clock signal inputted by the second clock signal terminal to the output terminal in the third period of time. On this basis, the electric potential of a gate line can be pulled down together by the clock signal of the second electrical level and the pull-down signal of the second electrical level in the second period of time. Therefore, fast pulldown of the gate line is guaranteed and the power-off capability of a thin film transistor of a pixel unit and the charging capability of the pixel unit are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com