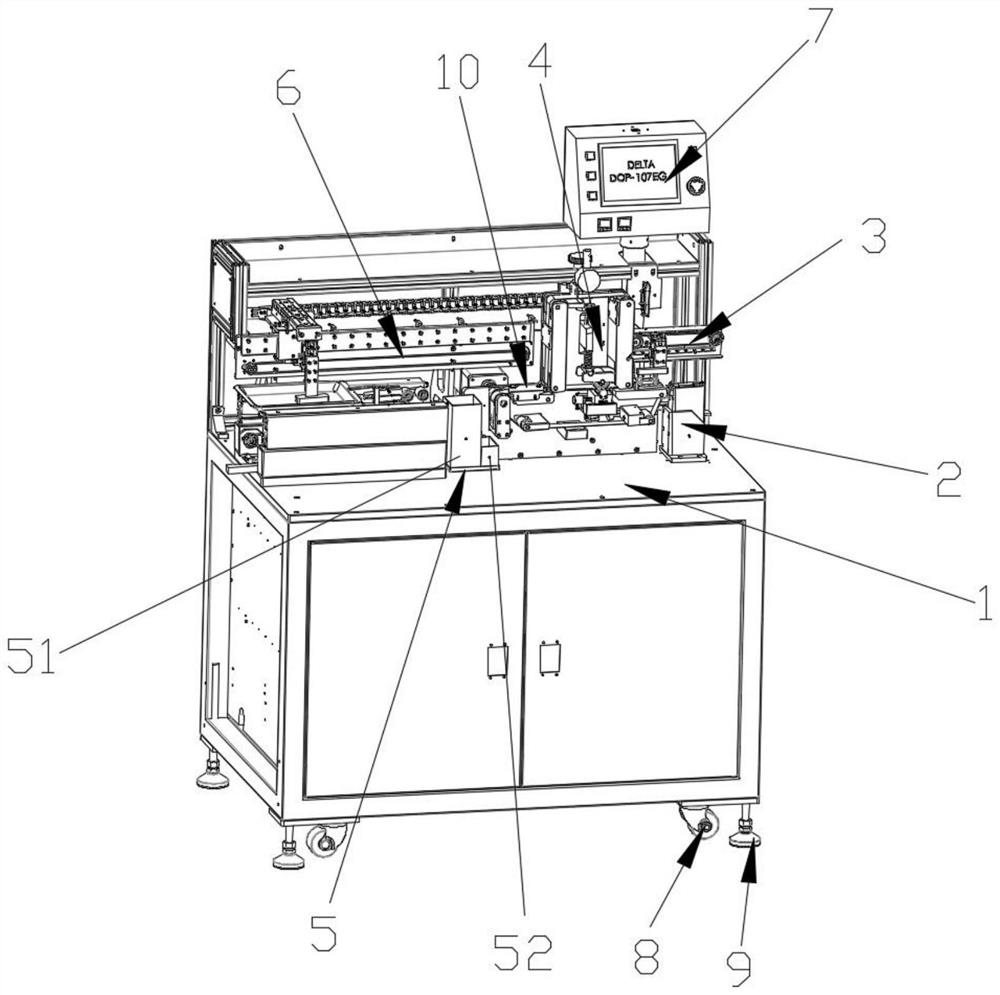
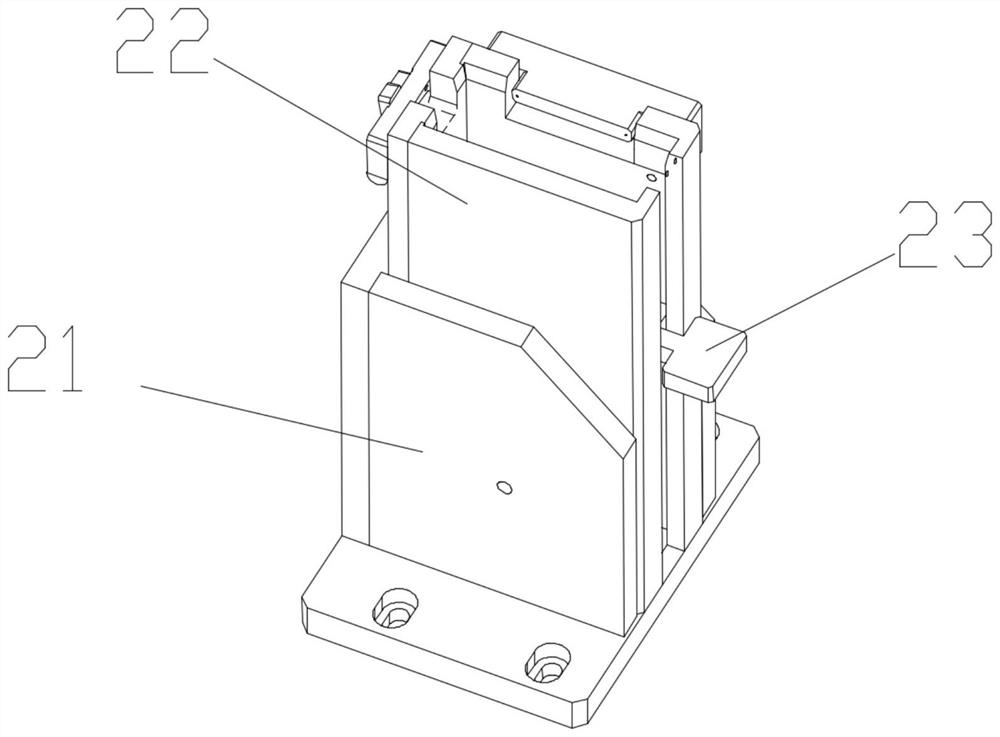
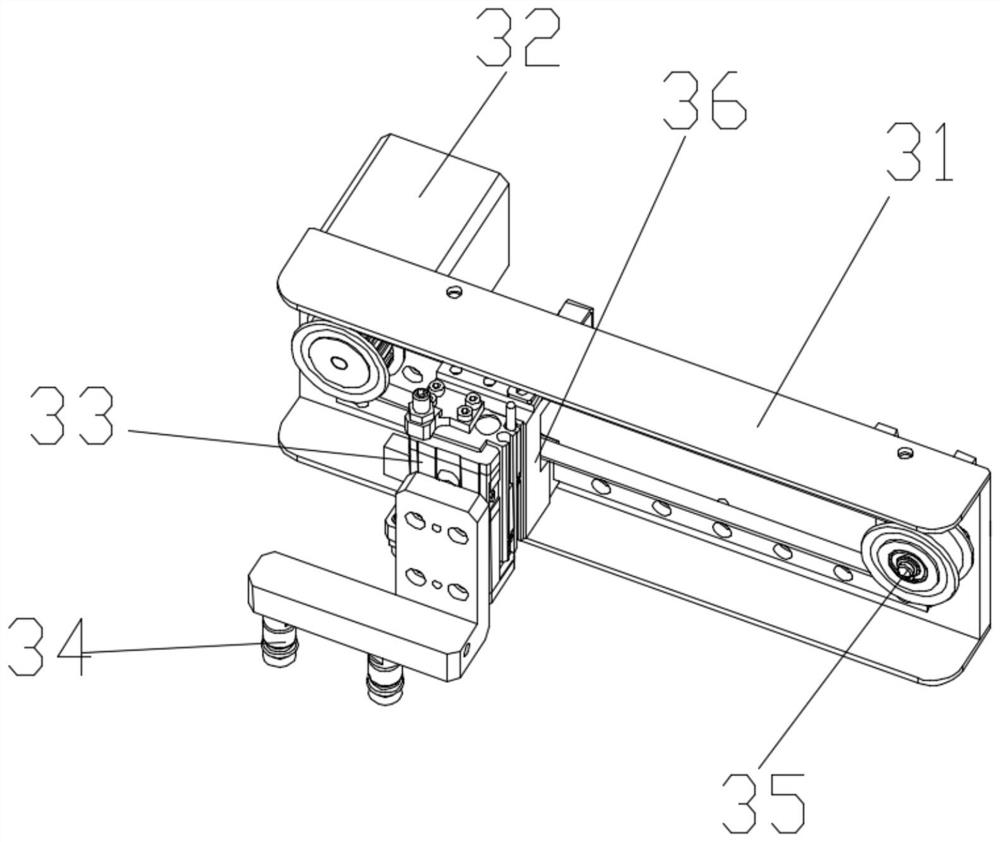
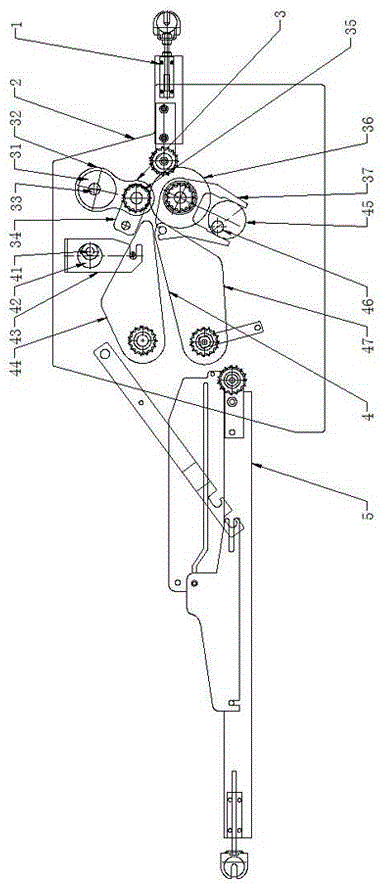
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Improve efficiency and yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
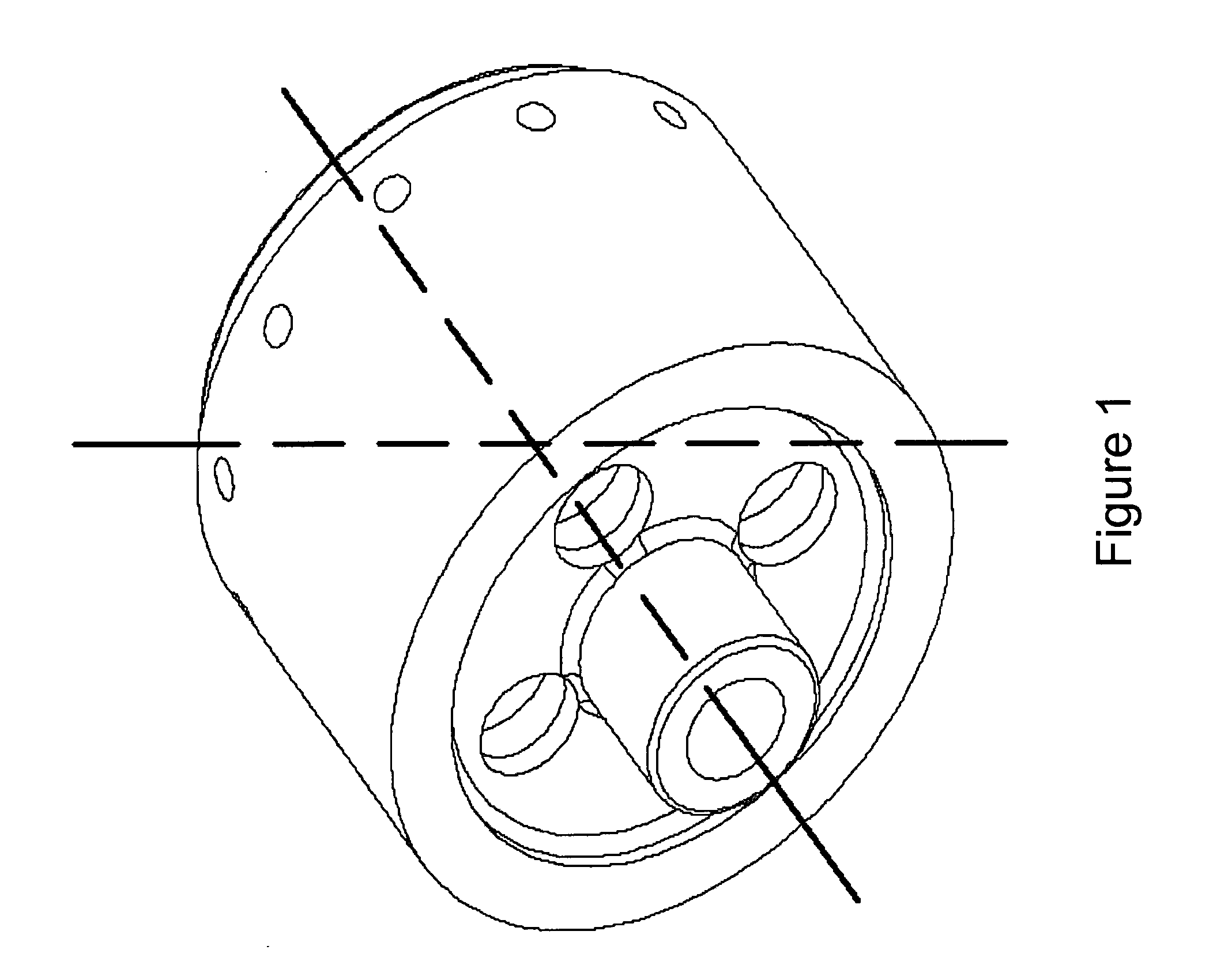
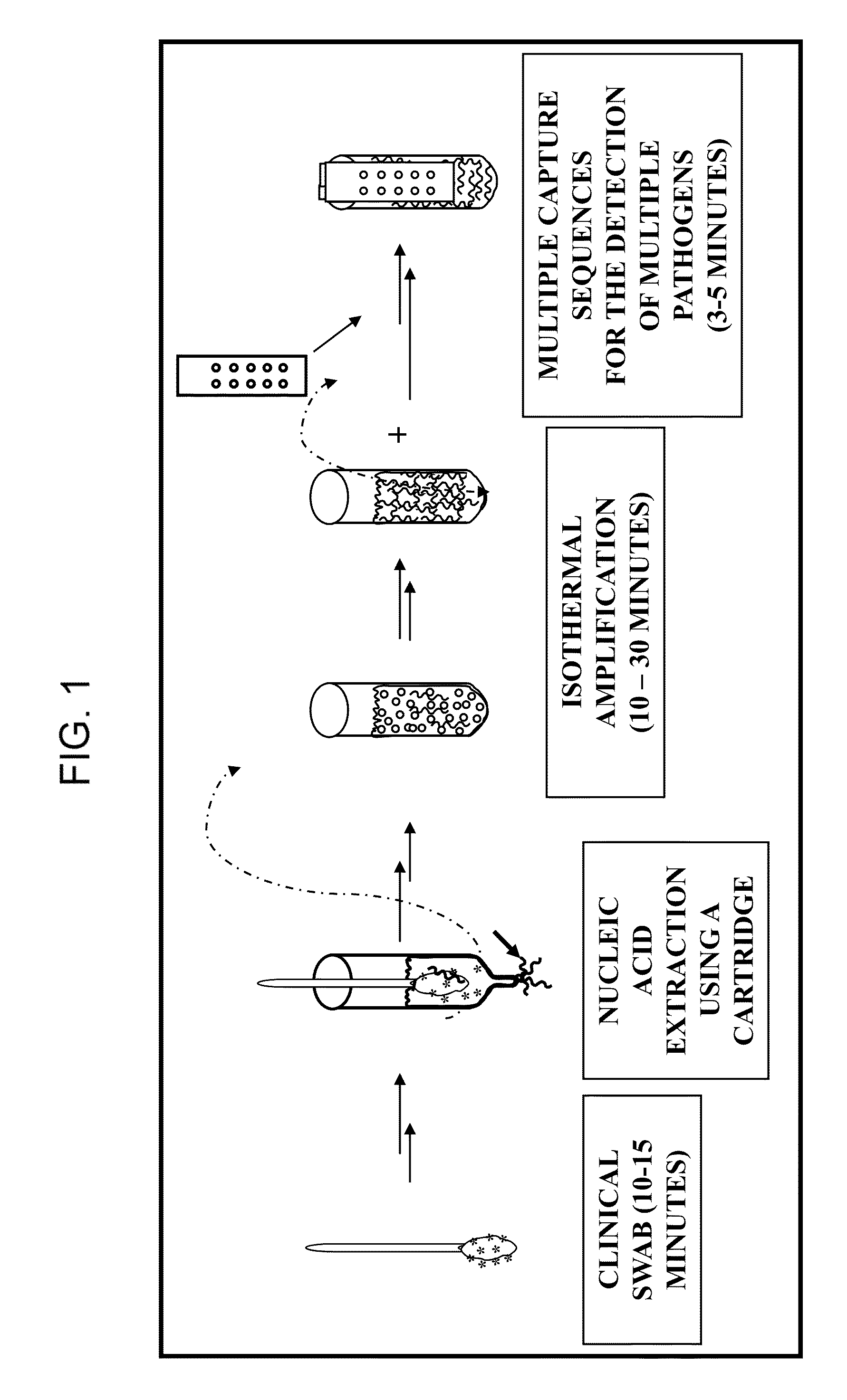
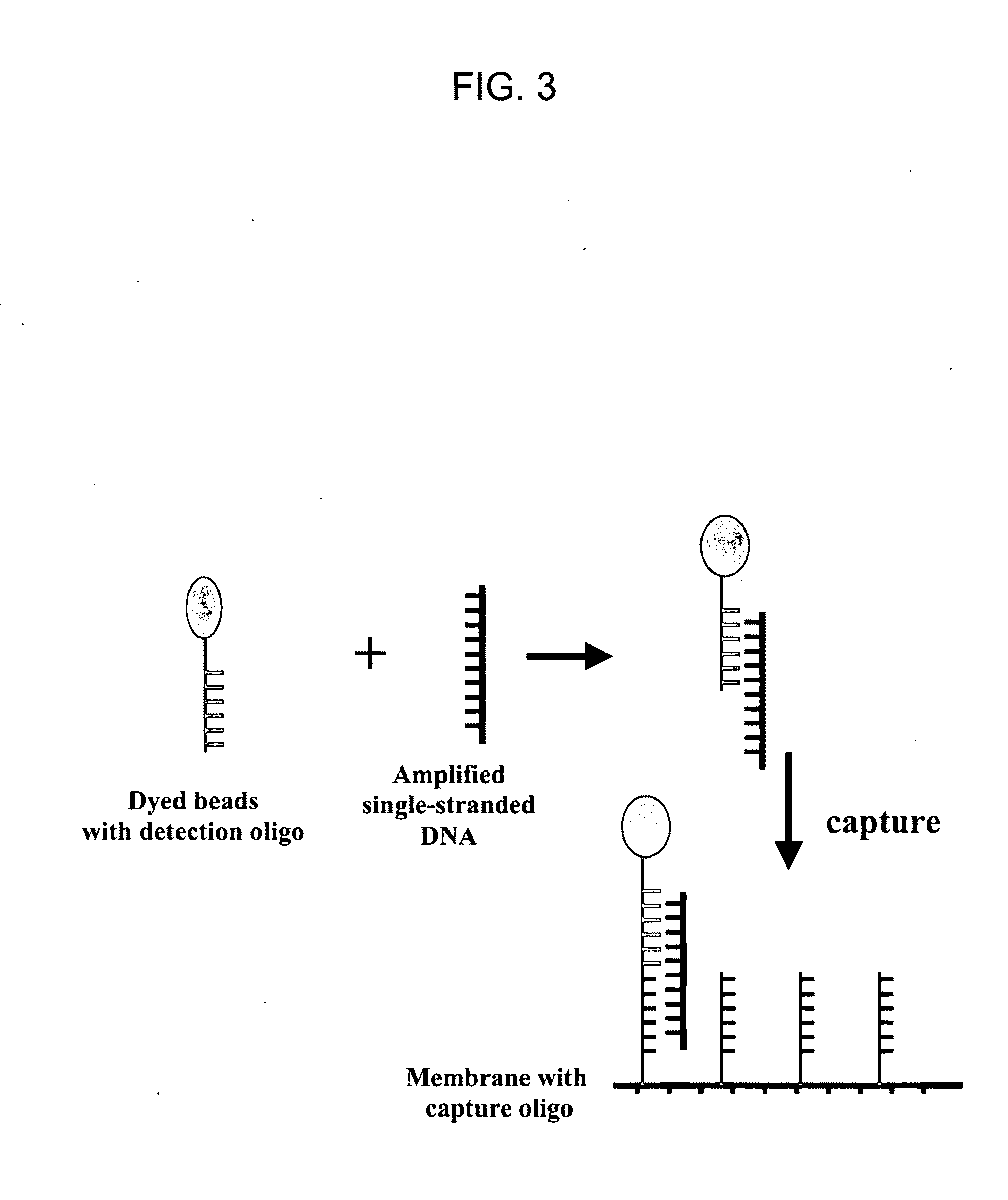
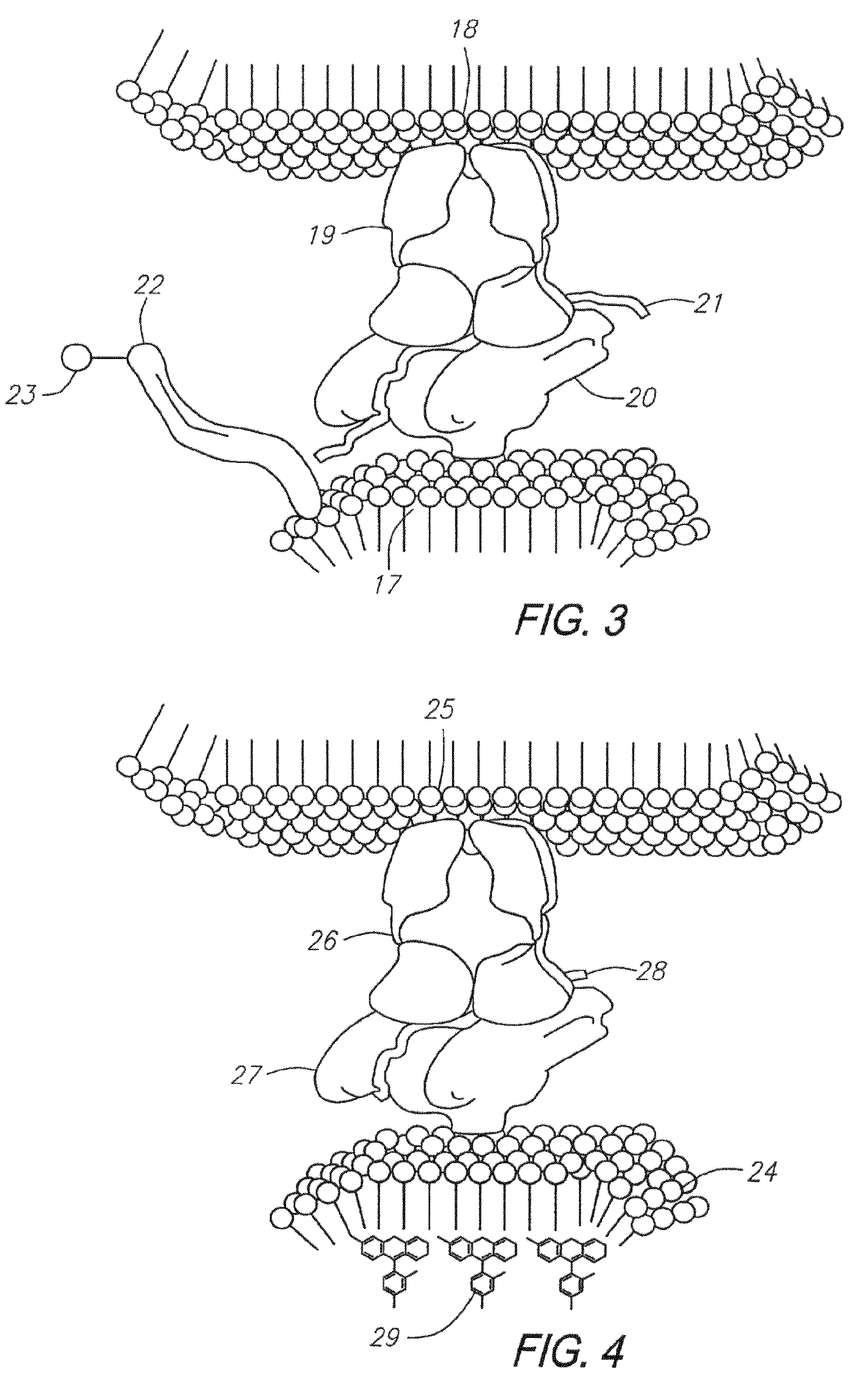
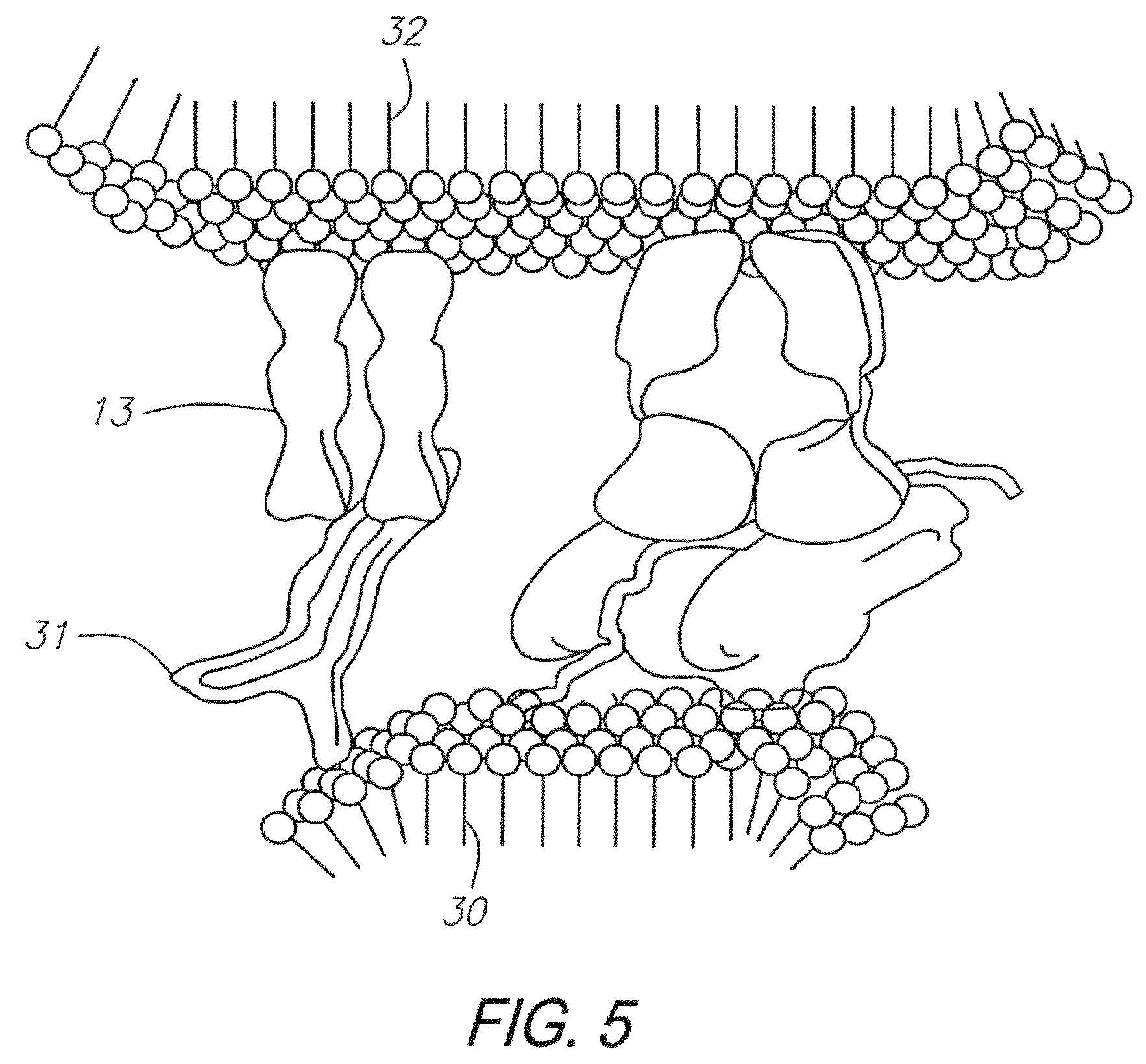
Nucleic acid detection system and method for detecting influenza
ActiveUS8980561B1Minimize extentUnprecedented assay speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationSingle strand dna
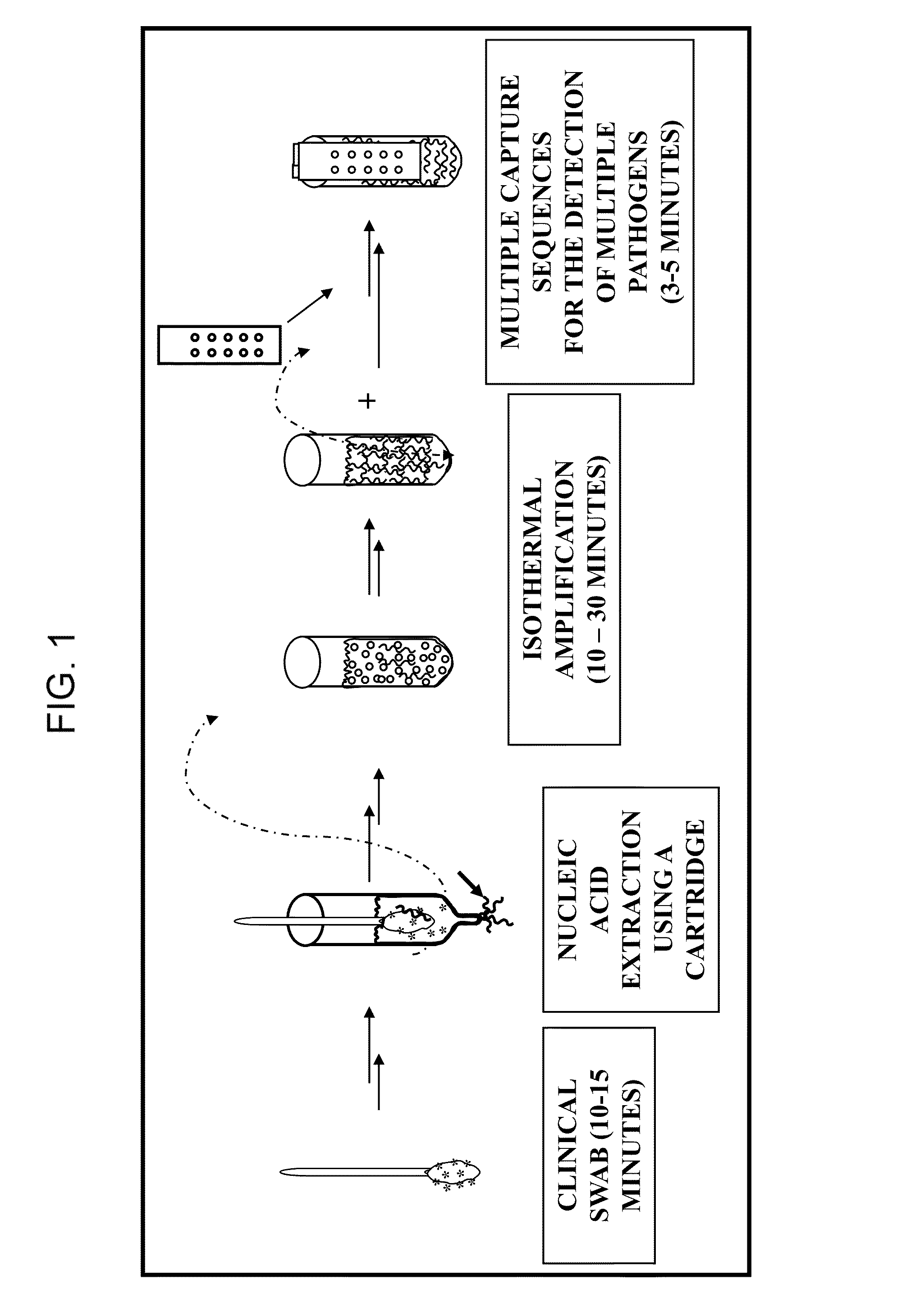
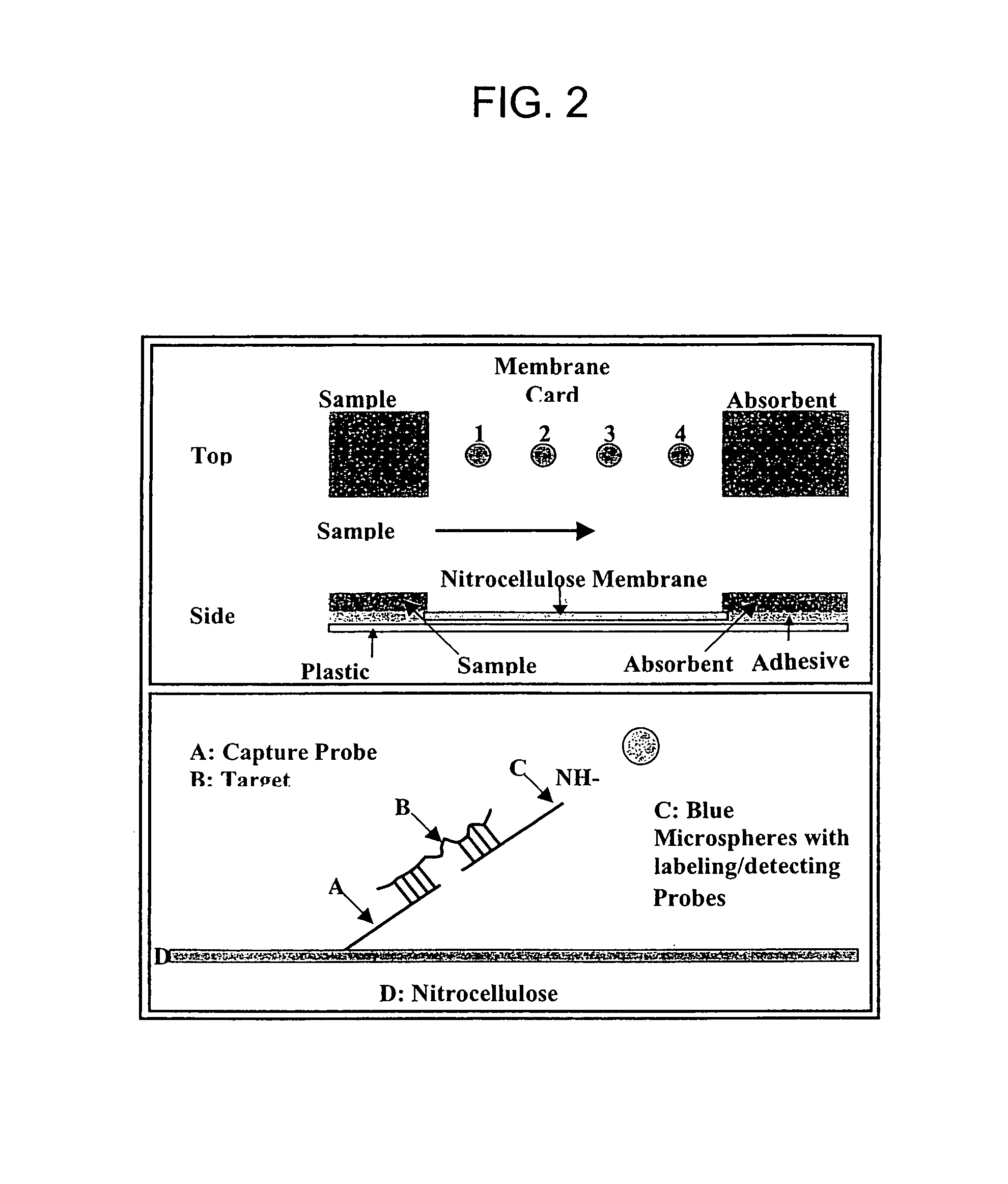
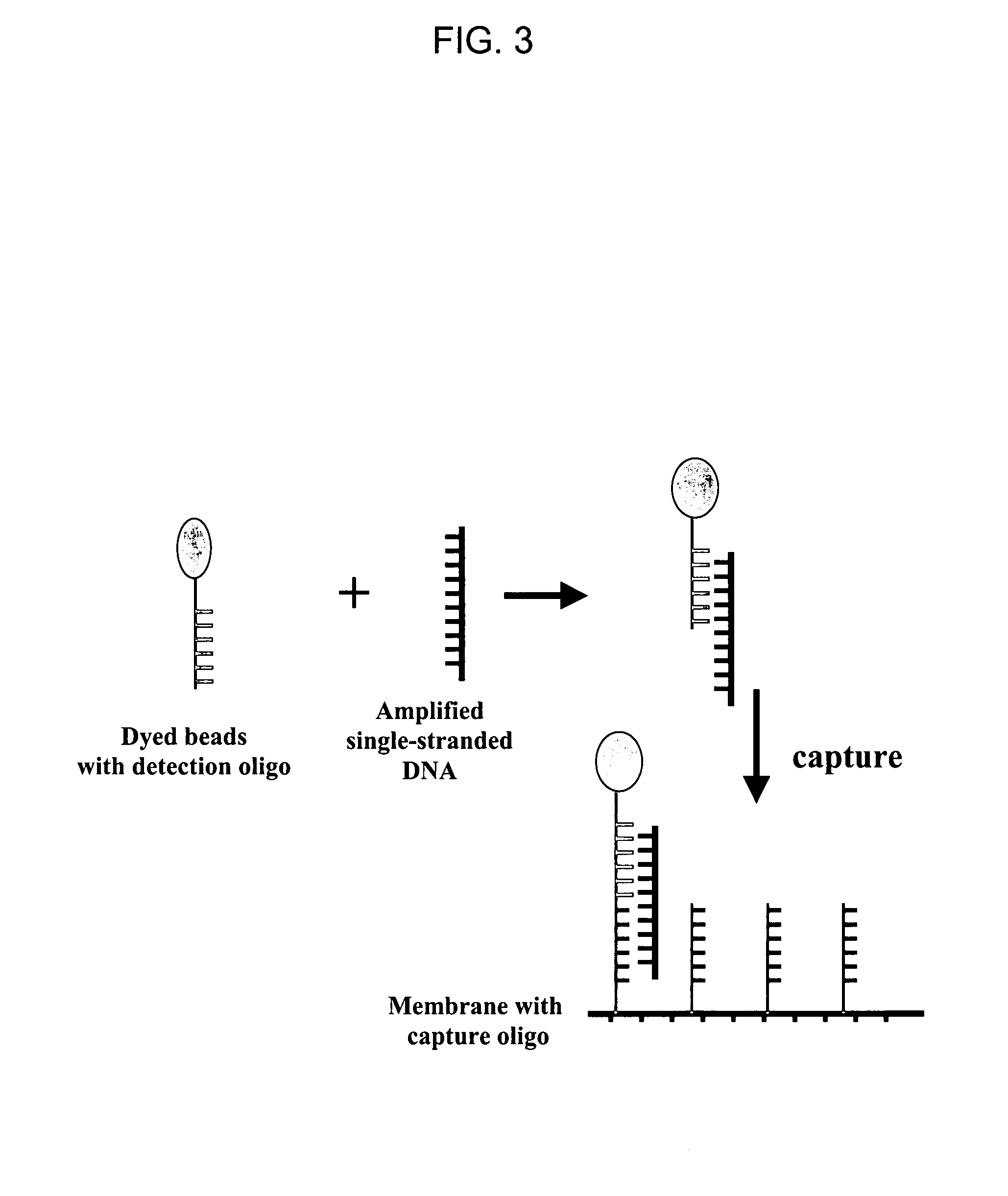
The invention provides a rapid, sensitive and specific nucleic acid detection system which utilizes isothermal nucleic acid amplification in combination with a lateral flow chromatographic device, or DNA dipstick, for DNA-hybridization detection. The system of the invention requires no complex instrumentation or electronic hardware, and provides a low cost nucleic acid detection system suitable for highly sensitive pathogen detection. Hybridization to single-stranded DNA amplification products using the system of the invention provides a sensitive and specific means by which assays can be multiplexed for the detection of multiple target sequences.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Device for providing improved combustion in a carbon black reactor
InactiveUS20060034748A1Improve efficiency and overall yieldImprove efficiency and yieldPigmenting treatmentAlkali metal halidesCarbon blackInternal cavity
An oxidant diffusion device for use in an axial flow tread carbon black reactor that is capable of providing improved uniformity in the physical and chemical profiles of the combustion gas produced in the combustion zone of a carbon black reactor. In one aspect, the oxidant diffusion device comprises a housing member having a distal end and a proximal end and further defining an internal cavity; an opening defined by the proximal housing end and in fluid communication with the internal cavity; a plurality of radial oxidant inlet apertures defined by the housing and in fluid communication with the internal cavity; and a plurality of axial oxidant inlet apertures defined by the distal housing end and in fluid communication with the internal cavity.
Owner:COLUMBIAN CHEM CO
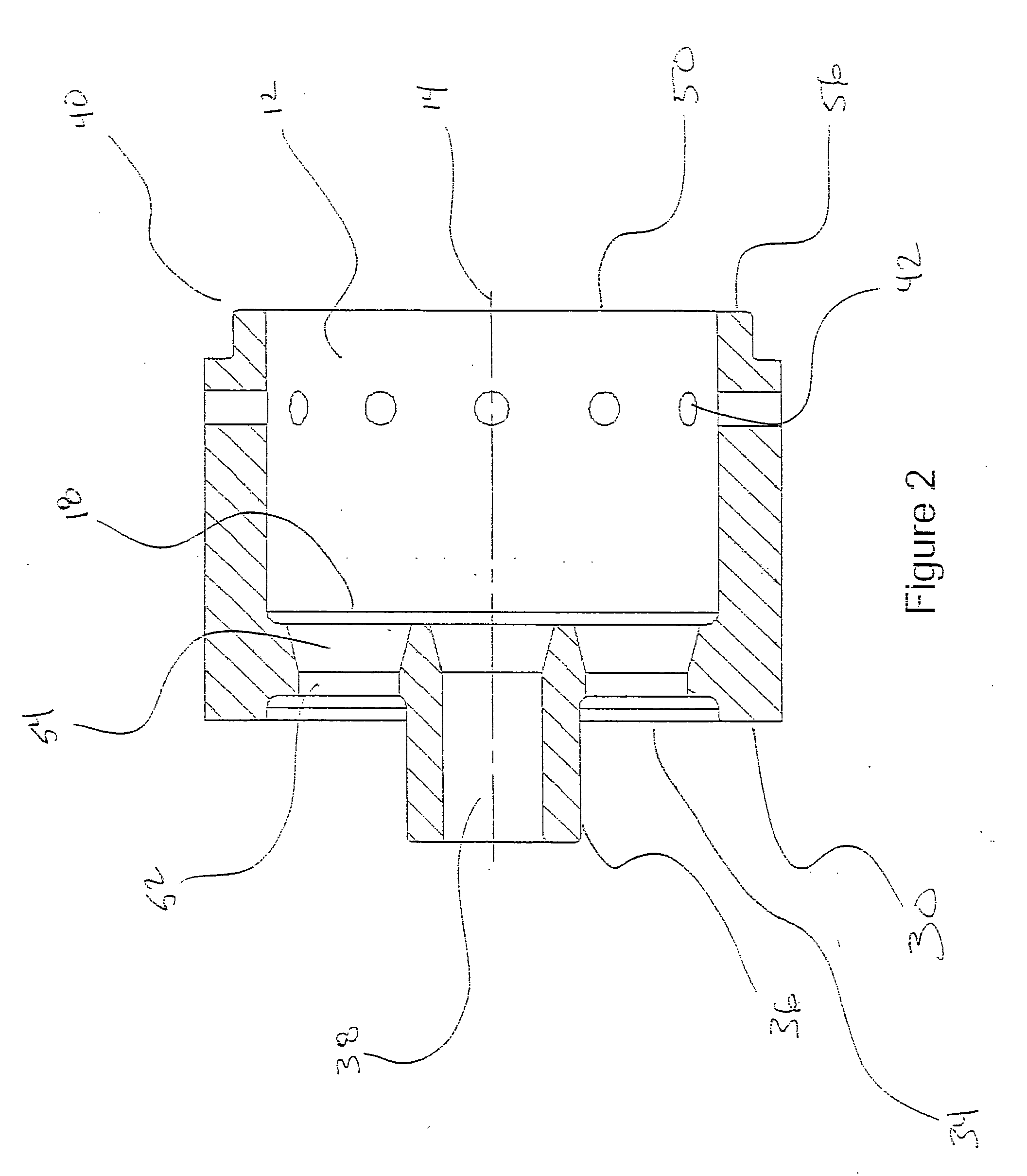
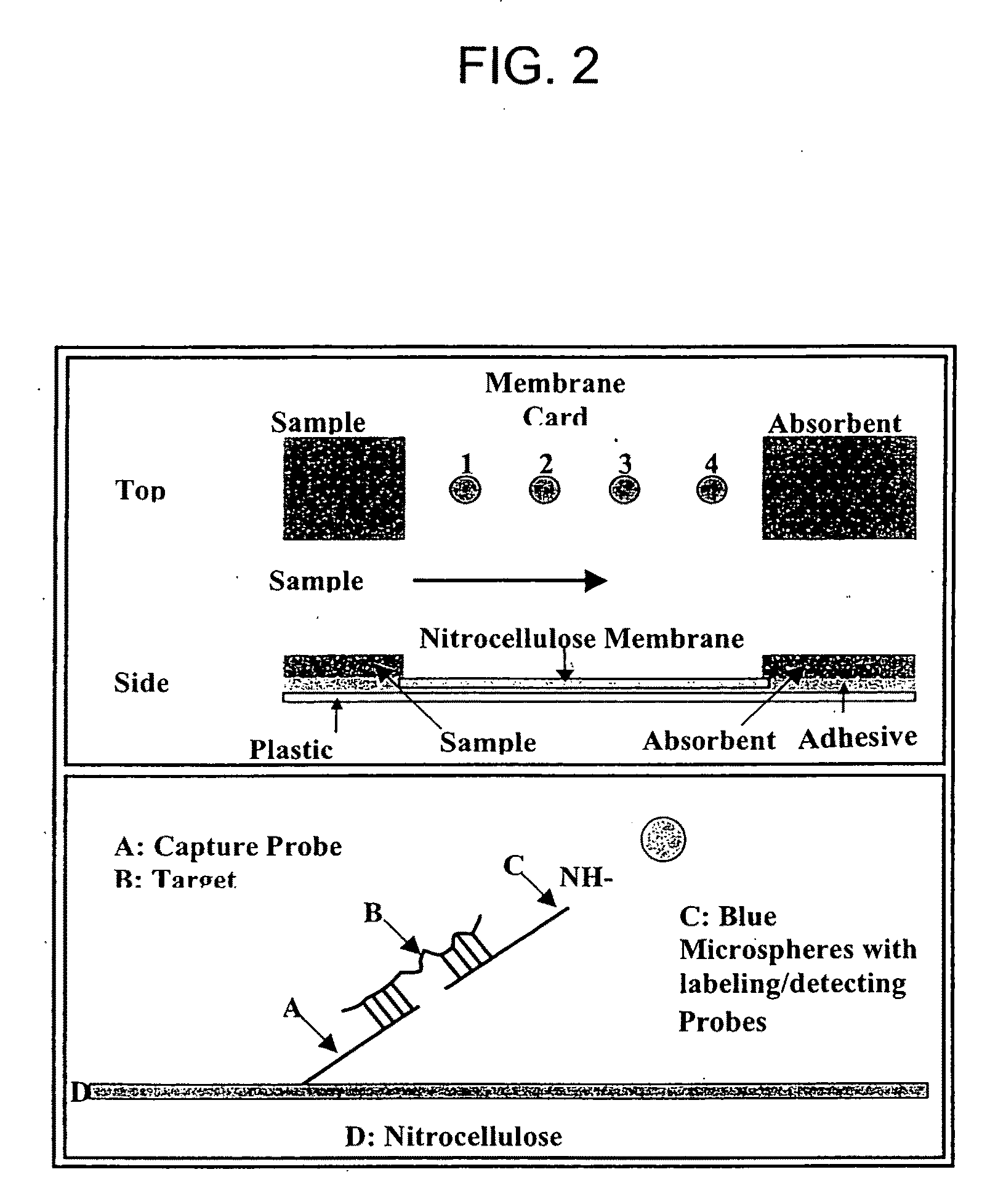
Nucleic Acid Detection System and Method for Detecting Influenza
InactiveUS20150184255A1Low costRapid, sensitive and specific nucleic acid detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleic acid detectionAssay
The invention provides a rapid, sensitive and specific nucleic acid detection system which utilizes isothermal nucleic acid amplification in combination with a lateral flow chromatographic device, or DNA dipstick, for DNA-hybridization detection. The system of the invention requires no complex instrumentation or electronic hardware, and provides a low cost nucleic acid detection system suitable for highly sensitive pathogen detection. Hybridization to single-stranded DNA amplification products using the system of the invention provides a sensitive and specific means by which assays can be multiplexed for the detection of multiple target sequences.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
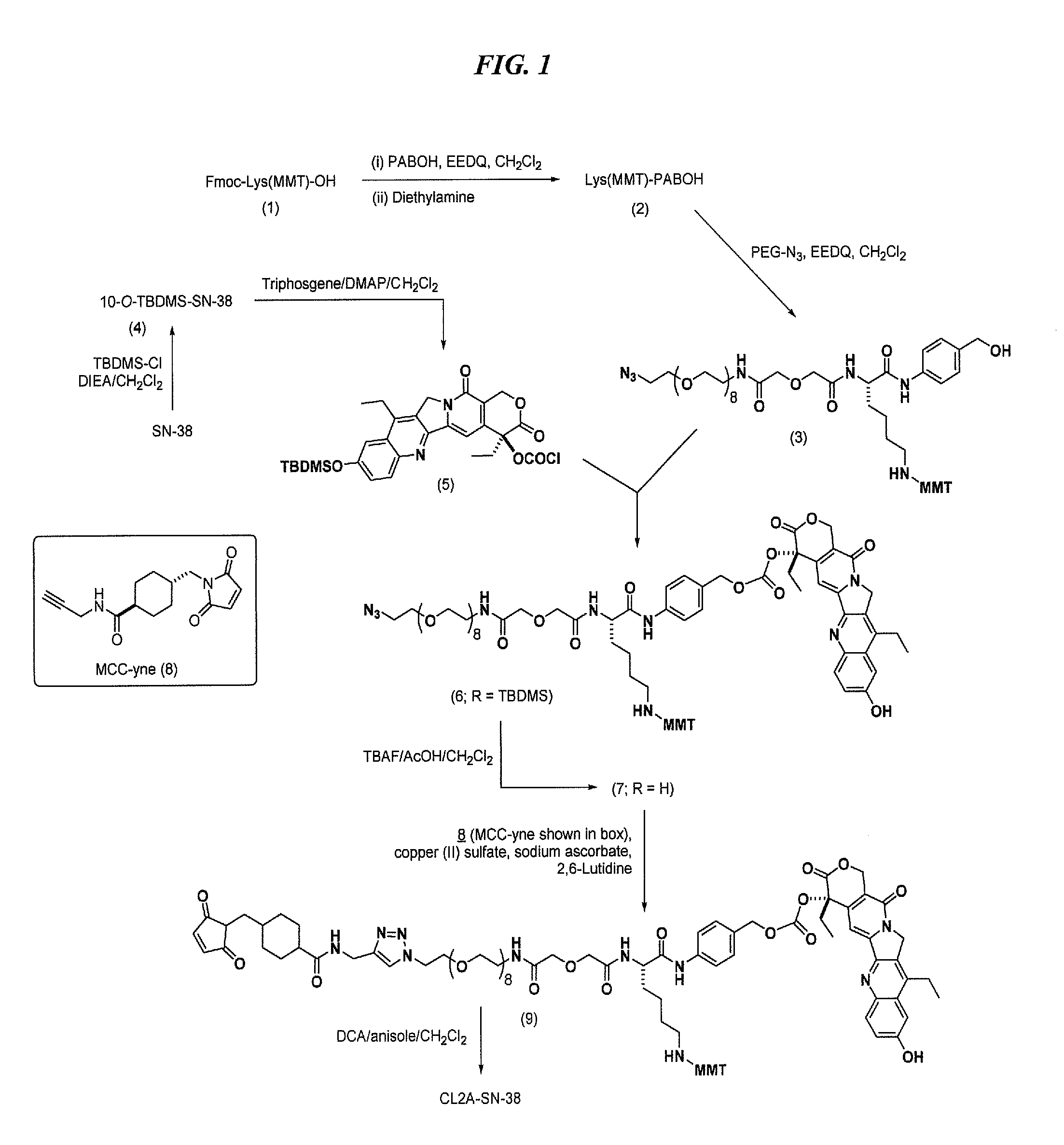
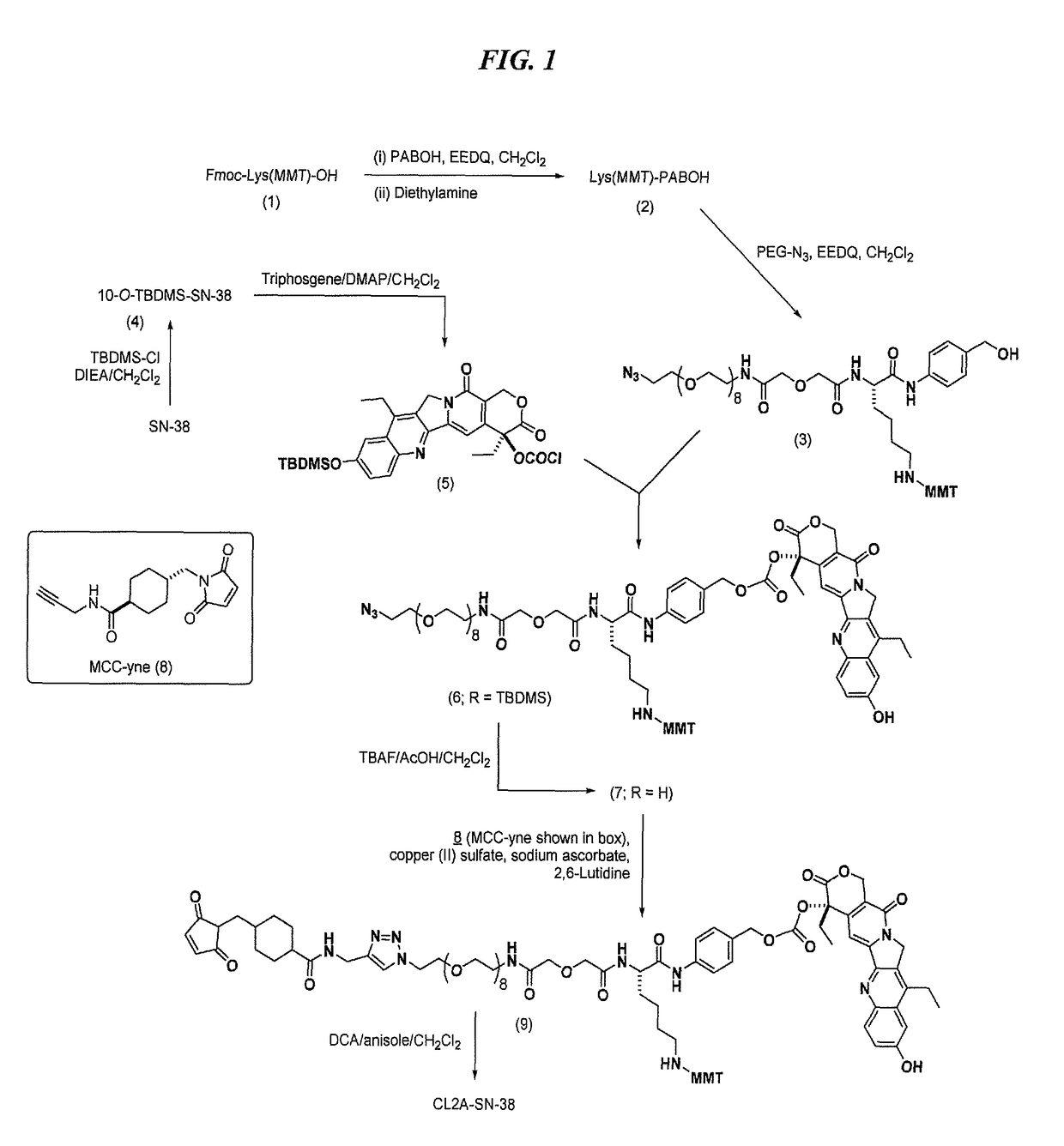
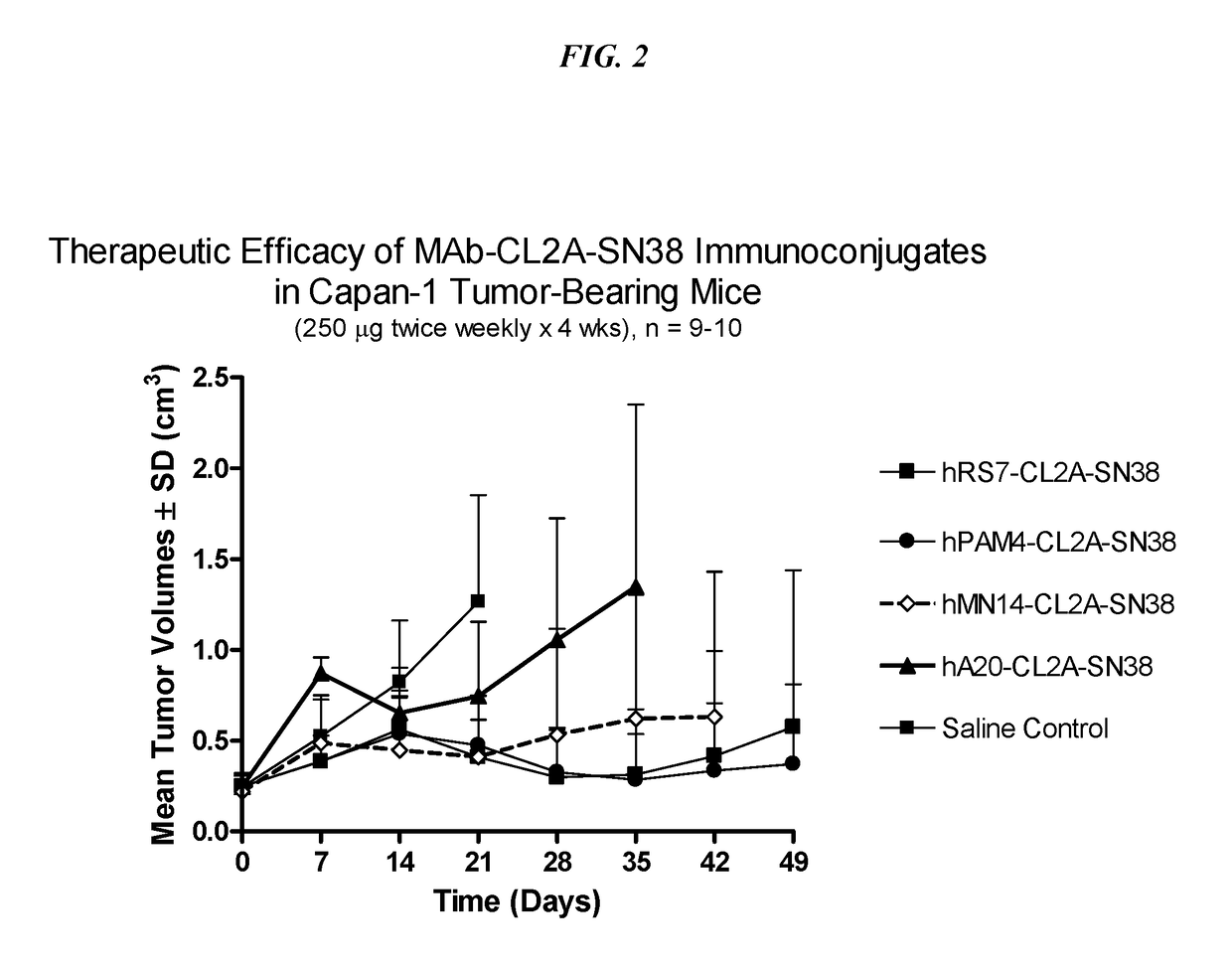
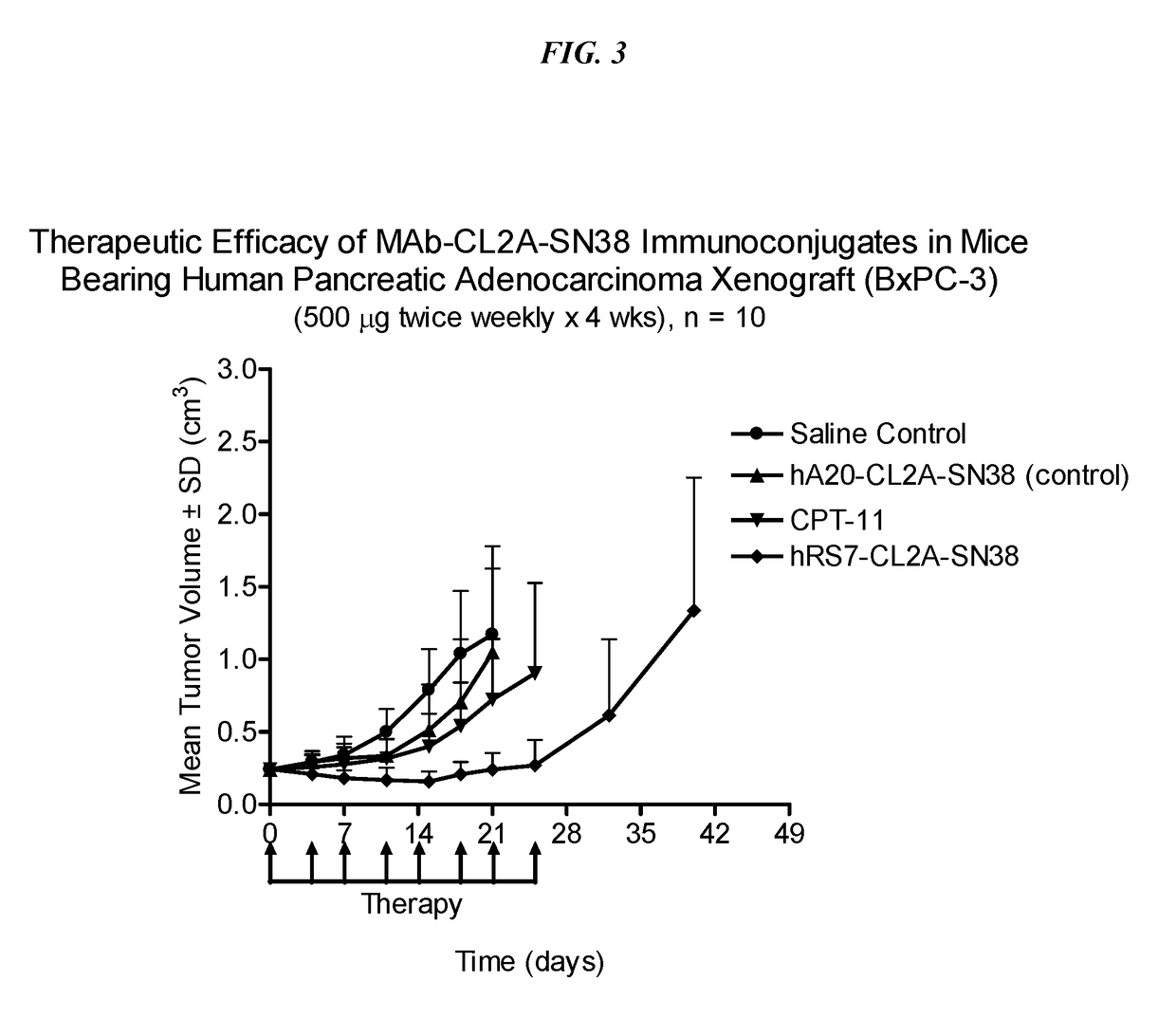
Antibody-sn-38 immunoconjugates with a cl2a linker
ActiveUS20160303253A1High protein recoveryImprove efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for preparing SN-38 conjugates of proteins or peptides, preferably immunoconjugates of antibodies or antigen-binding antibody fragments. More preferably, the SN-38 is attached to the antibody or antibody fragment using a CL2A linker, with 1-12, more preferably 6-8, alternatively 1-5 SN-38 moieties per antibody or antibody fragment. Most preferably, the immunoconjugate is prepared in large scale batches, with various modifications to the reaction scheme disclosed herein to optimize yield and recovery in large scale. Other embodiments concern optimized dosages and / or schedules of administration of immunoconjugate to maximize efficacy for disease treatment and minimize side effects of administration.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Gettering filter and associated method for removing oxygen from a gas
InactiveUS20050053535A1Improve efficiency and yieldReduce in quantityOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideDispersed particle separationOxygenMoisture
A method and apparatus are provided for removing oxygen and moisture from a gas such that wafers subsequently exposed to the gas develop less haze. The apparatus includes a process chamber for receiving a wafer. The apparatus also includes a gettering filter in fluid communication with the process chamber for removing oxygen from a gas that passes through the gettering filter in route to the process chamber. The gettering filter includes a vessel and a plurality of pieces of an oxidizable material disposed within the vessel. The oxidizable material is selected to oxidize upon exposure to oxygen in the gas such that the gas exiting the vessel has less oxygen than the gas entering the vessel. The oxidizable material may also be selected such that the resulting oxide layer is etchable upon exposure to an etchant, thereby permitting the gettering filter to be regenerated.
Owner:SEH AMERICA
Antibody-SN-38 immunoconjugates with a CL2A linker
ActiveUS9931417B2Improve efficiency and yieldDecrease in levelPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for preparing SN-38 conjugates of proteins or peptides, preferably immunoconjugates of antibodies or antigen-binding antibody fragments. More preferably, the SN-38 is attached to the antibody or antibody fragment using a CL2A linker, with 1-12, more preferably 6-8, alternatively 1-5 SN-38 moieties per antibody or antibody fragment. Most preferably, the immunoconjugate is prepared in large scale batches, with various modifications to the reaction scheme disclosed herein to optimize yield and recovery in large scale. Other embodiments concern optimized dosages and / or schedules of administration of immunoconjugate to maximize efficacy for disease treatment and minimize side effects of administration.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
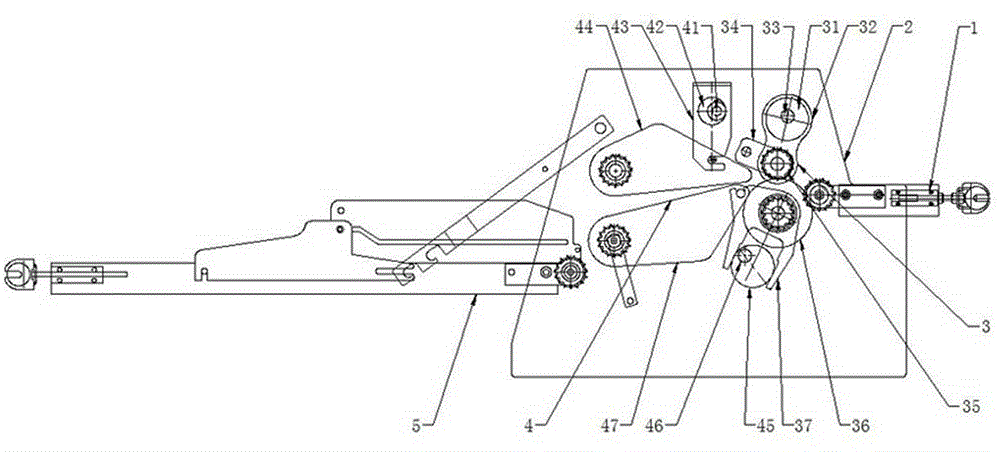
Automatic assembly tool for tool handle
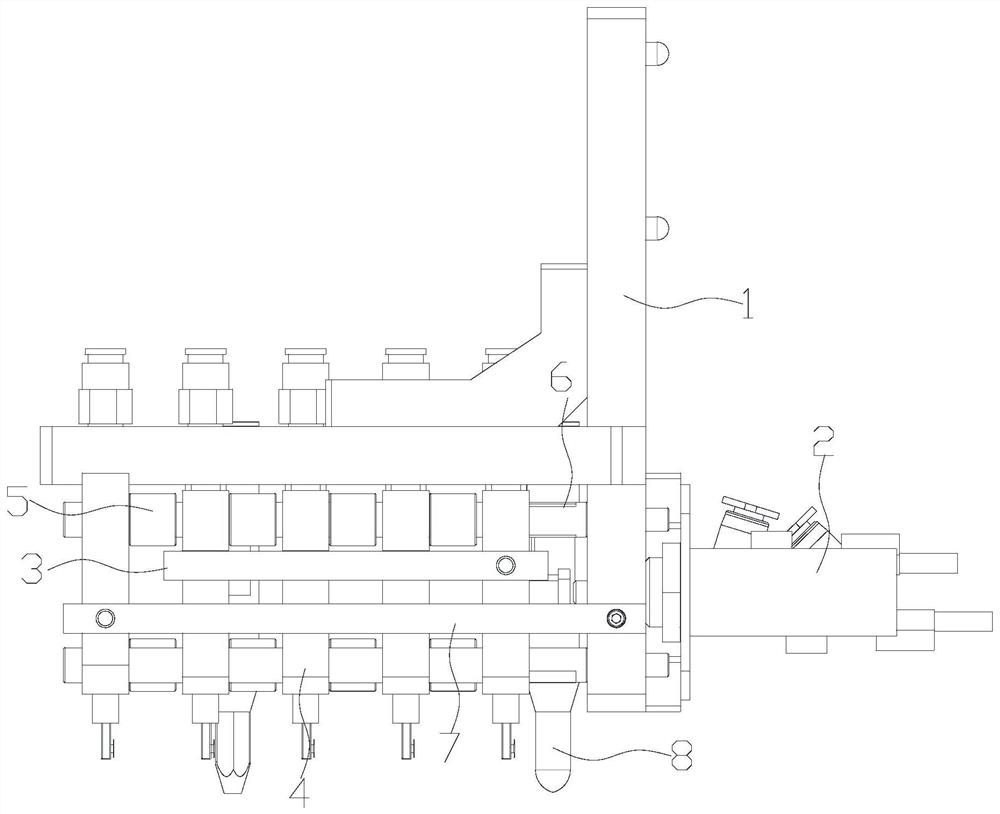
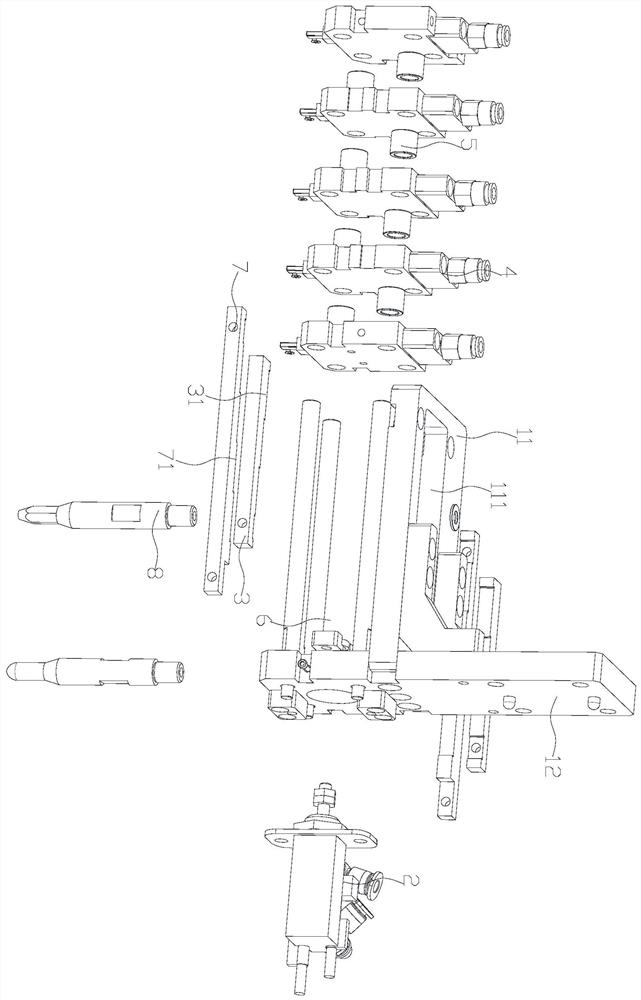
ActiveCN105382544AImprove efficiency and yieldSave labor costs and site costsOther manufacturing equipments/toolsMetal working apparatusOil pressureEngineering
The invention relates to an automatic assembly tool for a tool handle. The automatic assembly tool is characterized by comprising six clamps used for fixing a holding part and a connecting rod, six work stations distributed in the circumference direction, and a rotary disc rotating according to beats; a horizontal pressing mechanism and a reverse drilling rivet hole mechanism which are arranged on the second work station, a vertical drilling rivet hole mechanism arranged on the third work station, a rivet installing mechanism arranged on the fourth work station, a workpiece rotating mechanism arranged on the fifth work station, and an oil pressure rivet machine arranged on the sixth work station. According to the automatic assembly tool for the tool handle, a handle structural workpiece can be installed automatically, not only are the efficiency and the yield improved, but also the manpower cost and the site cost are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE TOOLS
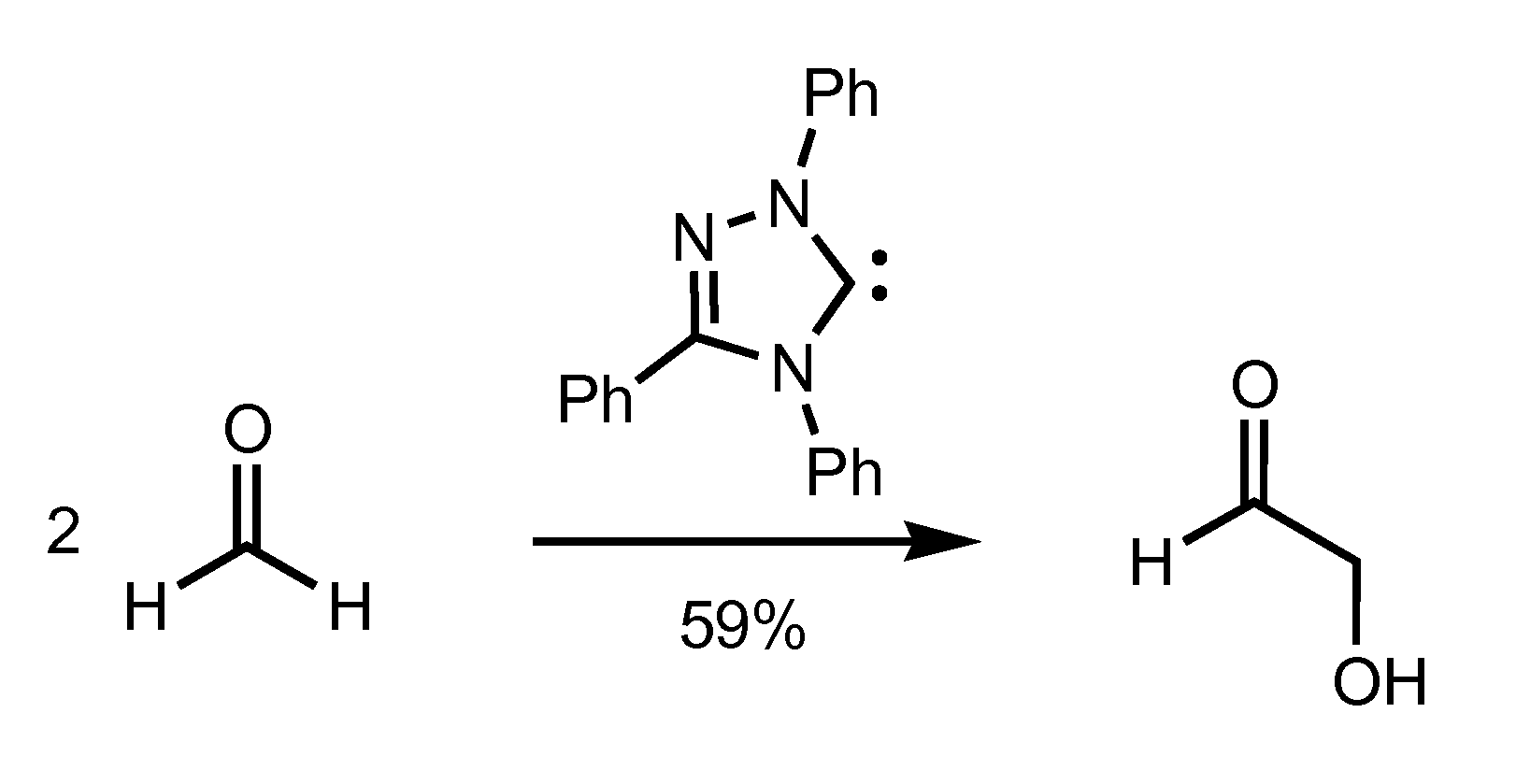
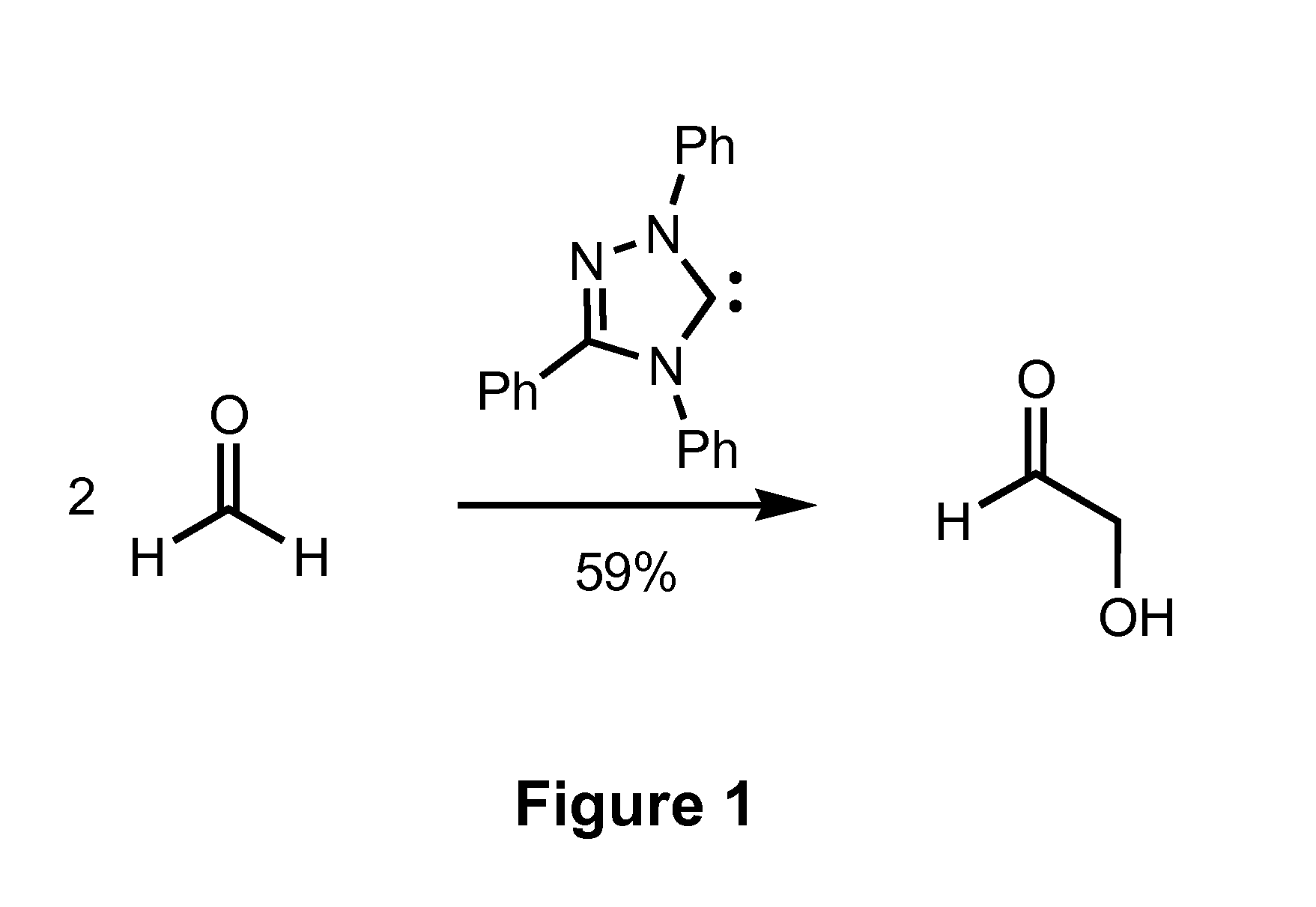
Combined Formose/Transfer Hydrogenation Process for Ethylene Glycol Synthesis
InactiveUS20100305368A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSelf-condensationCarbene
The present invention provides a process for the production of a glycol via tandem self condensation of formaldehyde via formoin condensation and transfer hydrogenation of the reaction products of the formoin condensation. In some aspects, synthetic processes of the present invention utilize a combination of a N-heterocyclic carbene catalyst and a transition metal hydrogen-transfer catalyst providing enhanced selectivity and increased yields for the production of ethylene glycol relative to conventional synthetic approaches based on formoin condensation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
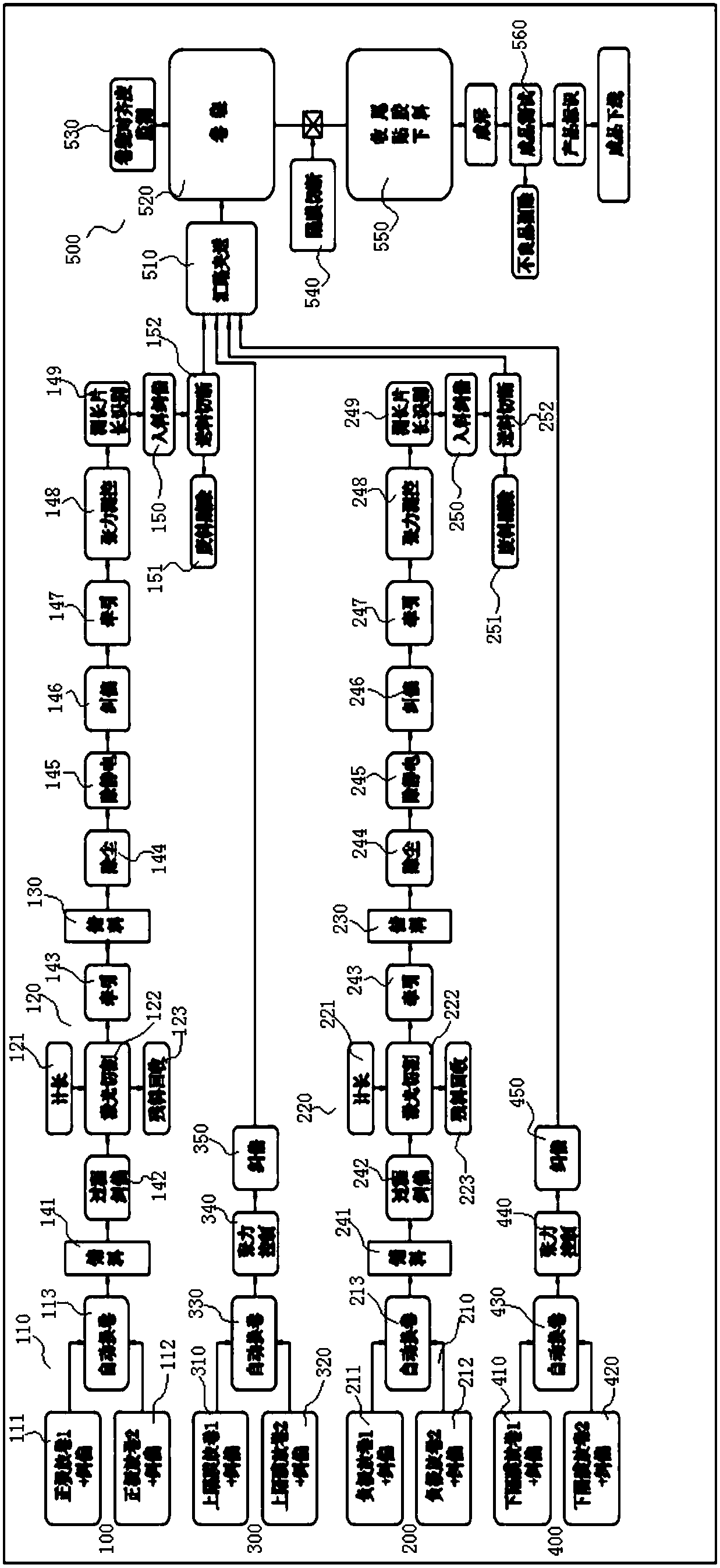
Power battery tab die-cutting and winding integrated machine
PendingCN108400369AImprove production efficiency and product performanceImprove efficiency and yieldAssembling battery machinesFinal product manufacturePower batteryEngineering
The invention discloses a power battery tab die-cutting and winding integrated machine. The power battery tab die-cutting and winding integrated machine comprises a positive electrode unwinding tab cutting unit, a negative electrode unwinding tab cutting unit, a separator unwinding unit and a winding and formation unit, wherein the positive electrode unwinding tab cutting unit is used for completing die-cutting of a positive electrode plate, the negative electrode unwinding tab cutting unit is used for completing die-cutting of a negative electrode plate, the separator unwinding unit is used for providing an upper separator, the winding and formation unit is used for completing winding and formation of a battery cell, the positive electrode unwinding tab cutting unit, the negative electrode unwinding tab cutting unit, an upper separator unwinding unit and a lower separator unwinding unit are matched and are matched with the winding and formation unit so that a positive electrode platefilm of which die-cutting is completed, separators and a negative electrode plate film of which die-cutting is completed are sequentially arranged at intervals and synchronously enter to the winding and formation unit, and the winding and formation unit is used for winding and formation. According to the scheme given by the invention, two important processes of a battery cell formation technologyare organically combined, the production efficiency of a product and the product performance are greatly improved, so that the winding efficiency and the finished rate of a battery cell are greatly improved.
Owner:上海乾得智能科技有限公司
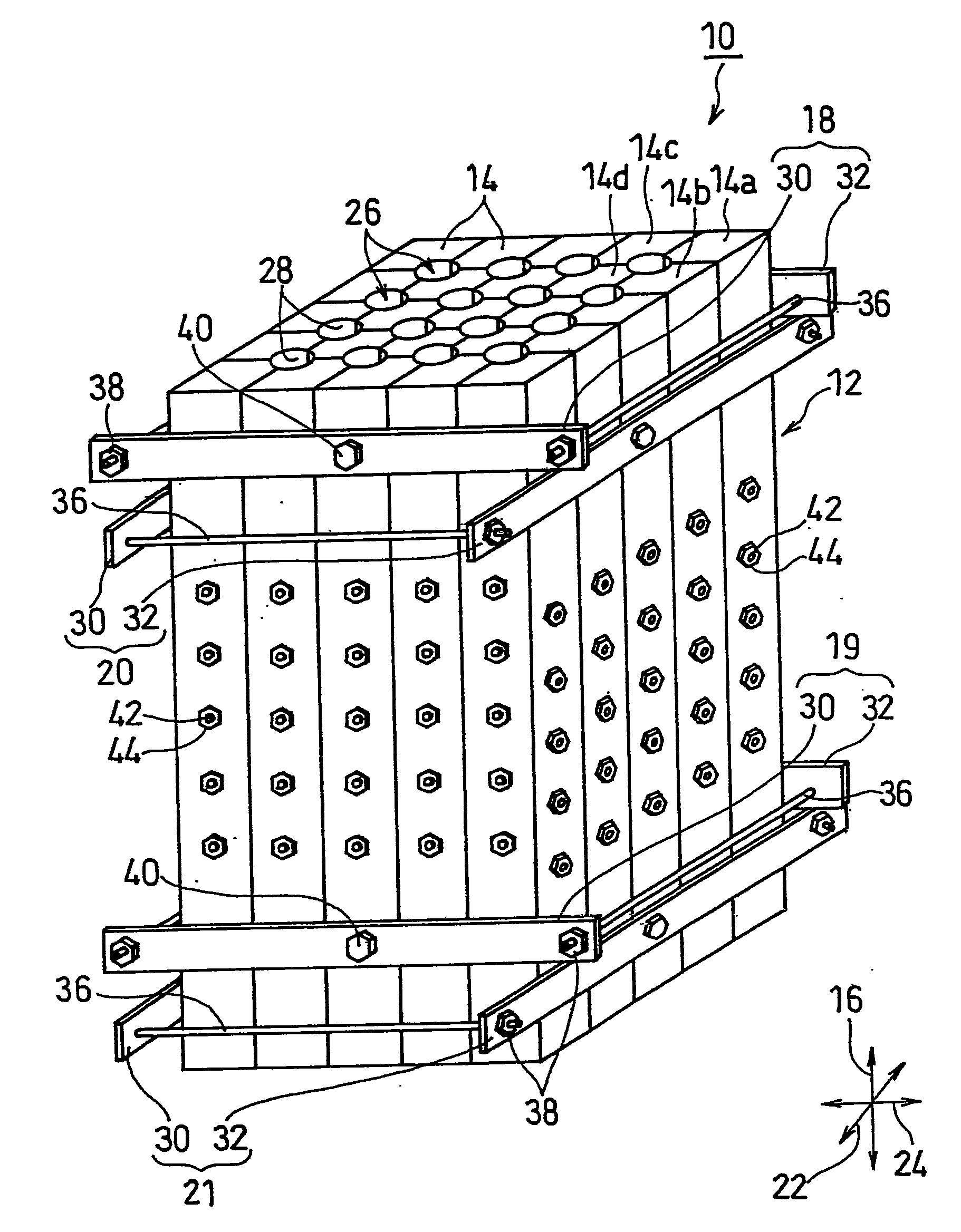
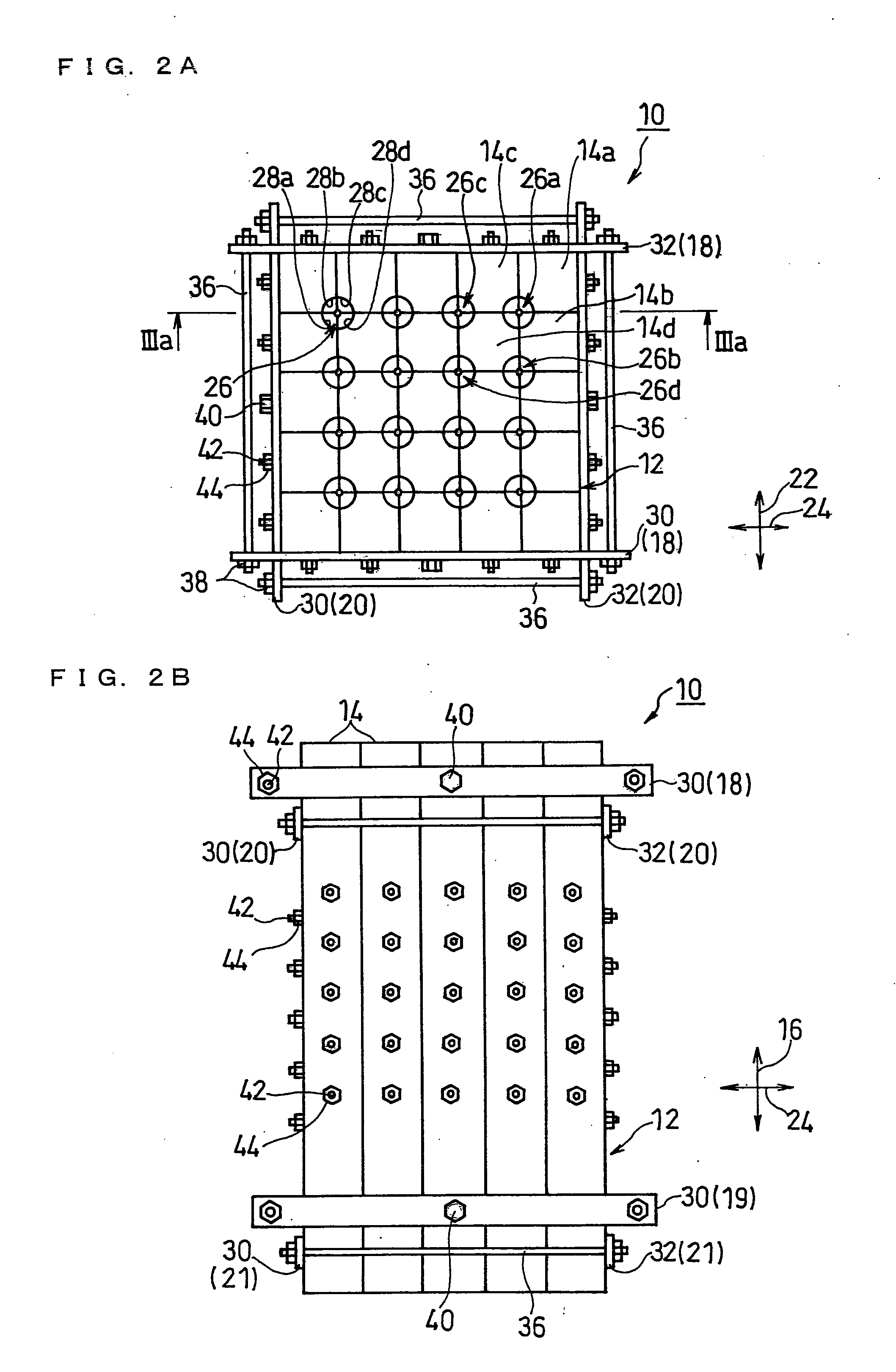
Mold for forming cast rods, casting apparatus, and production method of cast rods
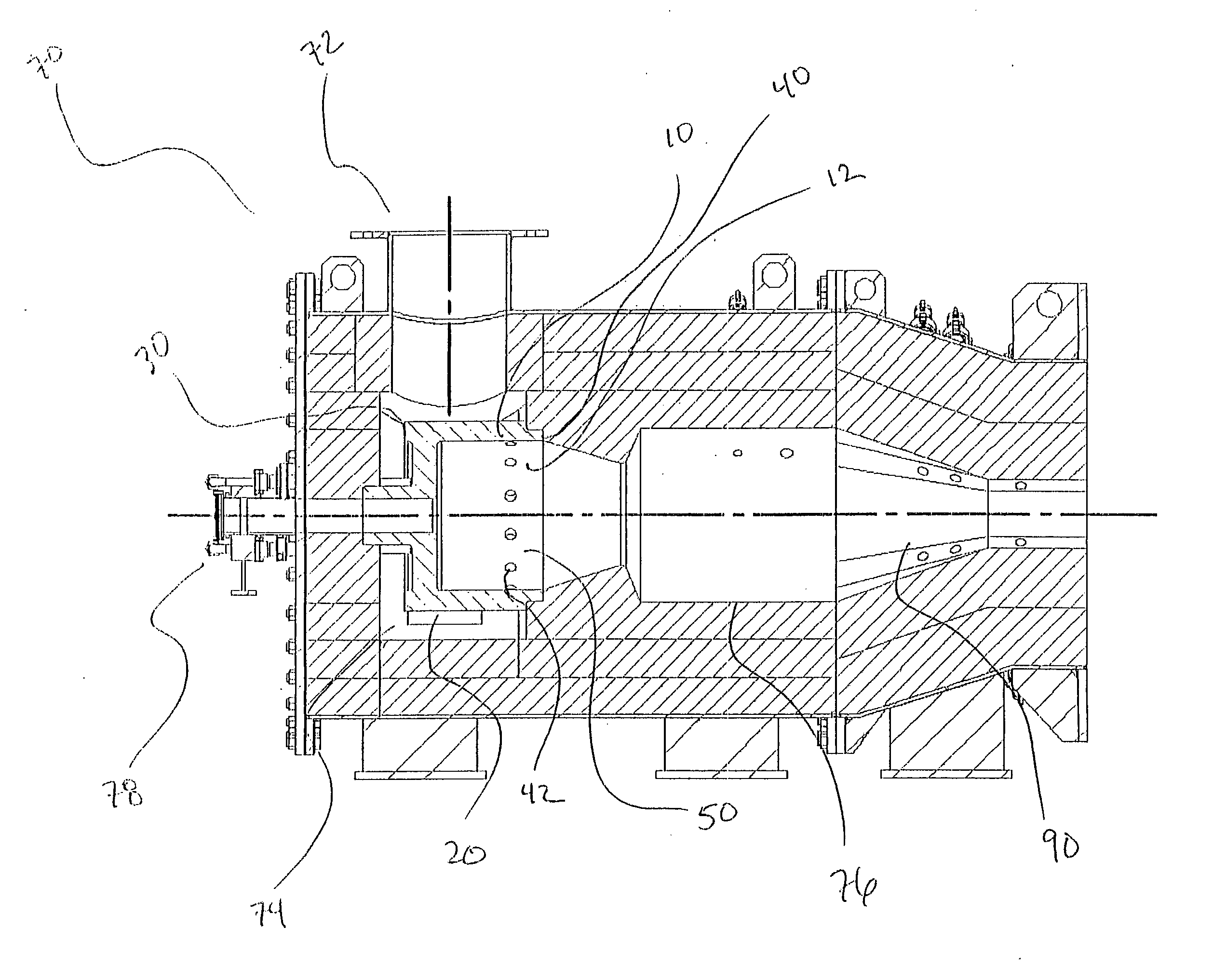
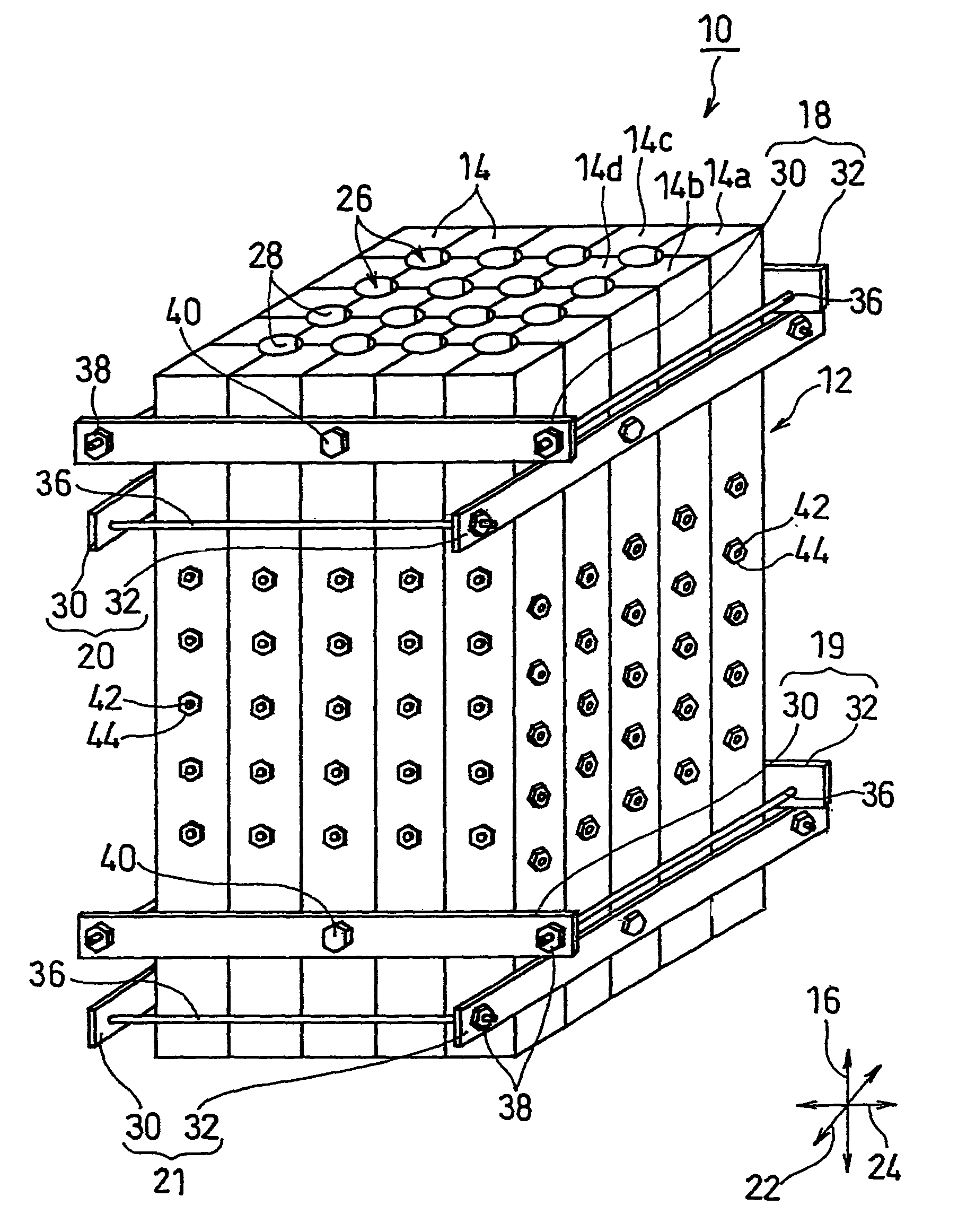
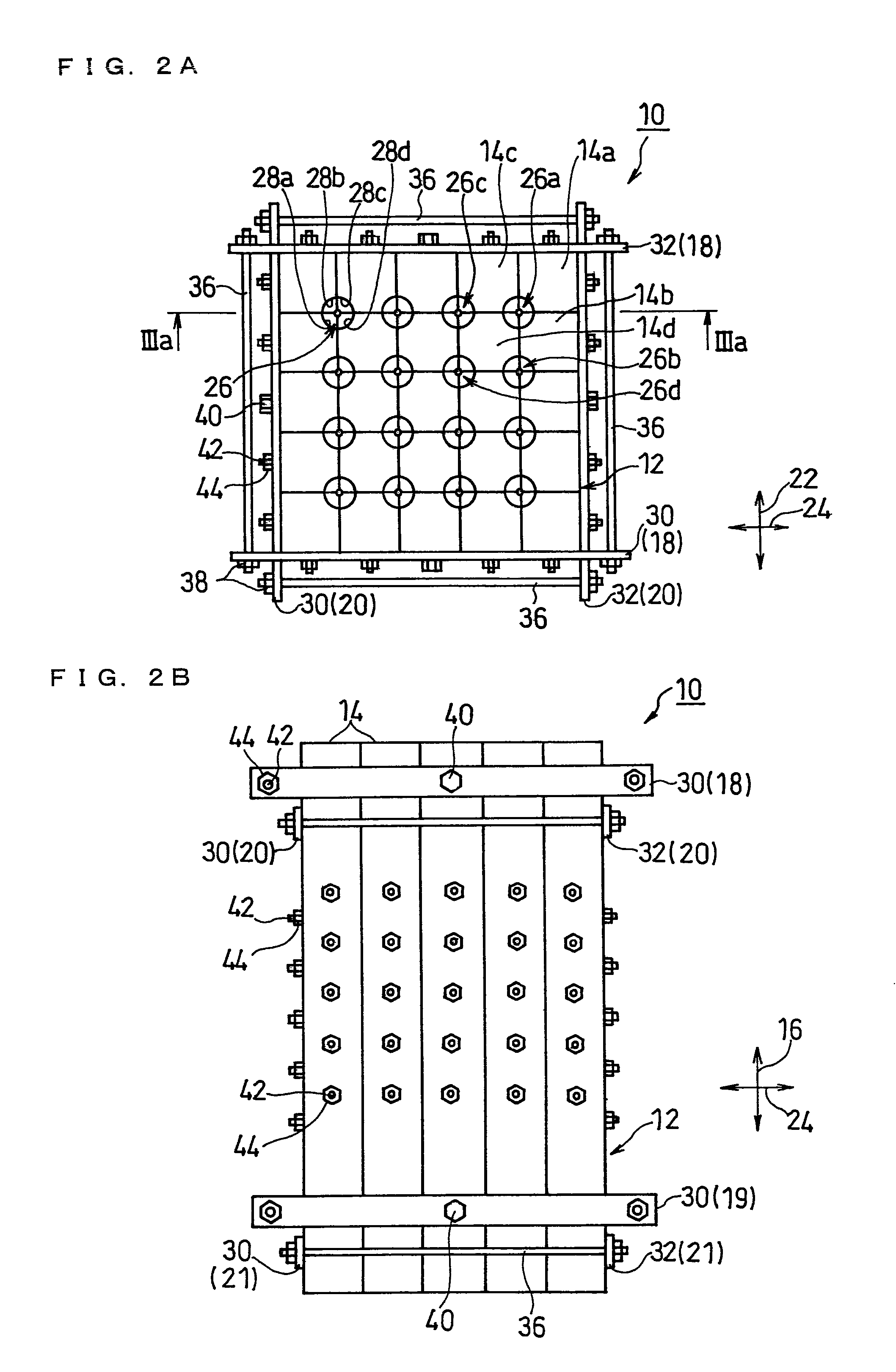
InactiveUS20100089544A1Improve efficiency and yieldEfficient productionMelt-holding vesselsMould separation apparatusMaterials scienceCast iron
Disclosed is a mold 10 for forming cast rods including: a segment assembly 12 including a plurality of segments 14 being placed side by side, and a plurality of cavities 26 extending along a longitudinal direction 16; and clamping means (18 to 21) for clamping the segment assembly 12 in directions orthogonal to the longitudinal direction 16. The mold 10 has one or more cavity-forming portions 28 each forming a part of one of the peripheral surfaces of the cavities 26. Each cavity 26 is formed by a combination of two or more segments 14, and at least one of the plurality of segments 14 has two or more cavity-forming portions 28.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Appetizing and summer heat relieving tangxin raw cider and high-efficiency deep processing technology thereof
PendingUS20210123002A1Large specific surface areaHigh porosityAlcoholic beverage preparationDrug compositionsFiberThermodynamics
The disclosure relates to an appetizing and summer heat relieving tangxin raw cider and a high-efficiency deep processing technology thereof. The high-efficiency deep processing technology comprises the following steps: (1) preparing raw pulp; (2) detoxifying patulin; (3) inoculating and precisely fermenting; (4) performing enzymolysis of residues; (5) clarifying and filtering; (6) ageing; and (7) canning after adsorbing and clarifying. According to the disclosure, aiming at a phenomenon that cider is muddy after being stored, it is solved by adsorption with a multi-stimuli responsive nano fiber modified resin. Exterior stimuli include change in environment temperature or acidity-basicity (pH value), light, electric field, magnetic field or specific molecules. In response to exterior stimuli, nano fiber may include physicochemical properties such as size, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, refractive index, transmittance, mechanical strength, color or conductivity.
Owner:SDIC ZHONGLU FRUIT JUICE +1
Ejecting and breaking packaging equipment
PendingCN112498823AHigh degree of automationRealize in-line productionPackagingProcess engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an ejecting and breaking packaging device which comprises a machine table, an ejecting and breaking device and a tray placing device, the ejecting and breaking device and the tray placing device being arranged on the machine table. The ejecting and breaking packaging device further comprises an automatic tray replacing device arranged on the machine table, wherein the ejecting and breaking device is configured to eject and break a material belt, and the tray placing device is configured to transport workpieces obtained after the ejecting and breaking device ejects and breaks the material belt and place the workpieces into trays. The automatic tray replacing device is configured to transport and replace trays; and the automatic tray changing device comprises a firsttray mechanism, a second tray mechanism and a tray conveying mechanism, wherein the first tray mechanism is configured to bear a first tray, the second tray mechanism is configured to bear a second tray, the first tray is an empty tray, the second tray is a full tray, and the tray conveying mechanism is configured to convey the first tray and / or the second tray. The packaging equipment is high inautomation degree, can achieve continuous production, saves the manpower, improves the efficiency and yield, improves the safety coefficient, and facilitates production management and control.
Owner:SUZHOU LINGYU ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
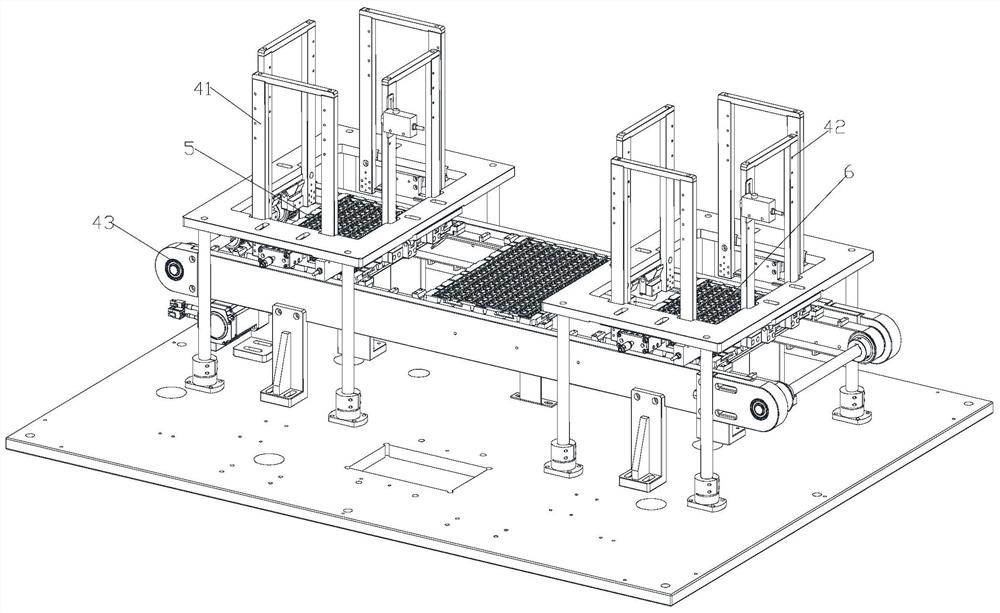
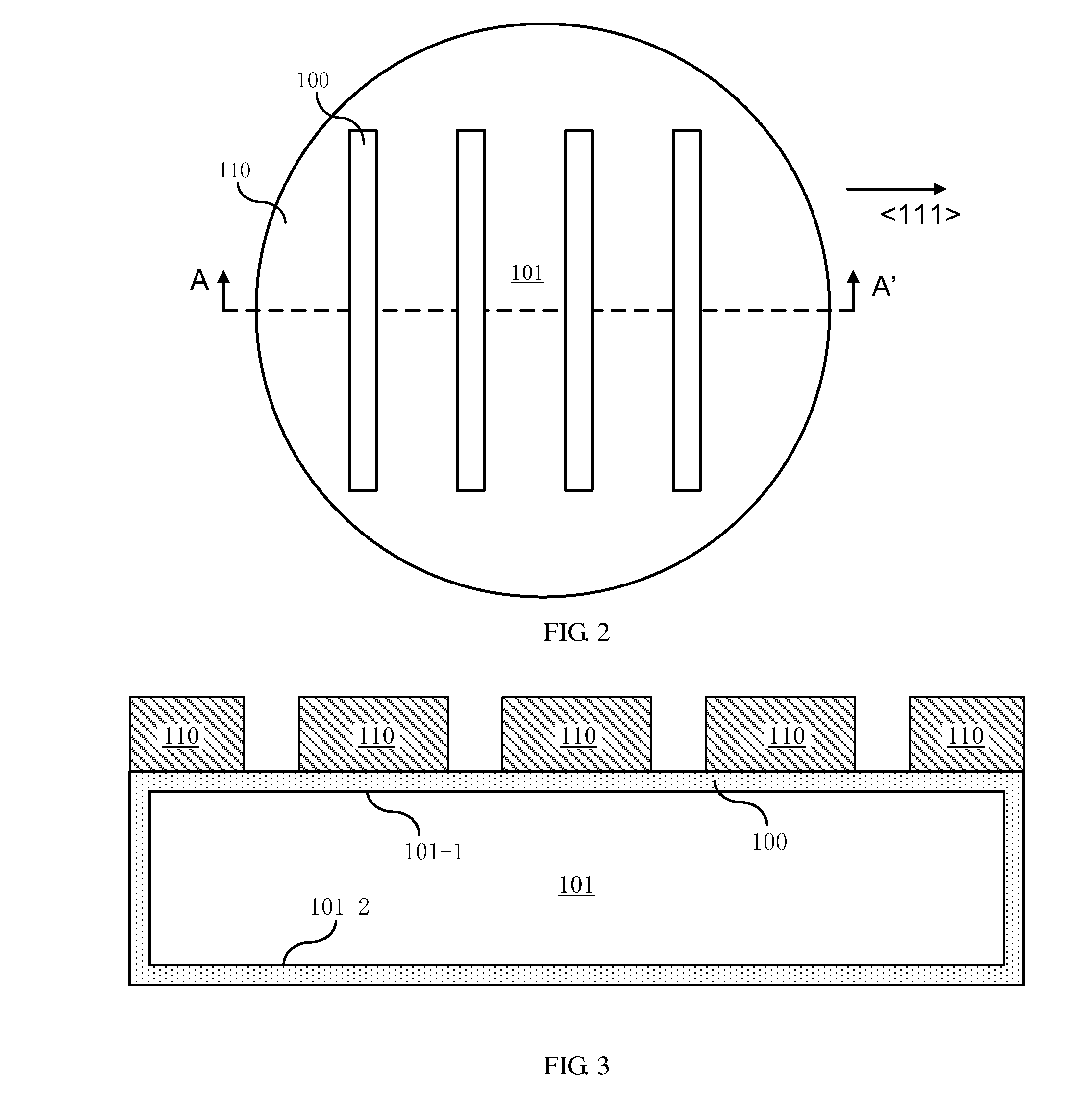
Substrate strip plate structure for semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS8754503B2Increase processable surface area and utilization rate of surface areaImprove efficiency and yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a strip plate structure and a method for manufacturing the same. The strip plate structure comprises a strip plate array, which comprises a plurality of strip plates arranged with spacing in a predetermined direction on a same plane, wherein each of the strip plates has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface and the strip plate array is arranged on a plane parallel to the first surface of the strip plates; a plurality of strip sheets which connect neighboring ones of the strip plates; flexible material layers, which are located on at least a portion of the surfaces of the strip sheets and / or on at least a portion of the surfaces of the strip plates.
Owner:SUNOVEL SUZHOU TECH
Adsorbent Product for the Removal of Hydrocarbon Pollutants, and Method for Removing Hydrocarbon Pollution, In Particular at the Surface of the Water, Using Said Product
InactiveUS20120048807A1Easy to manufactureImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPollutantHydrocarbon
The adsorption properties of the adsorbent product, based on a porous mineral such as particularly pumice stone, result from the carbon formed on the walls of the pores of the mineral by cracking of an organic product, such as sugar or treatment plant sludges, previously impregnated in the pores of the mineral, the carbon thus formed making the product hydrophobic. After absorption of pollutant hydrocarbons by the product, the impregnated mineral is heated in a heat treatment unit, in the absence of oxygen, to bring it to a sufficient temperature to evaporate the hydrocarbons and / or decompose by cracking the organic product or hydrocarbon molecules and form or regenerate the carbon deposit. Application to the manufacture and to the recycling of an adsorbent product for the depollution particularly of bodies of waters or rivers polluted by hydrocarbons.
Owner:ECOPOMEX M
Method of isolating antigen-specific T cells employing artificial antigen presenting cells
InactiveUS7807377B2Improve efficiency and yieldPromote maturityBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiseaseRegulatory T cell
The present invention concerns artificial antigen presenting cells (aAPCs) and methods of making and using the same, for example, to isolate, identify, and expand T cell populations specifically reactive against a disease-associated antigenic peptide, as well as to modulate responses of antigen-specific T cells both in vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro. Accordingly, the aAPCs of the invention can be used to treat conditions that would benefit from modulation of a T cell response, for example, autoimmune disorders, allergies, cancers, viral infections, and graft rejection. In certain preferred embodiments, the aAPCs are liposomes comprised of MHC:peptide complexes and accessory molecules. Other molecules, such as co-stimulatory molecules and adhesion molecules, can also be included in the compositions of the invention. In other embodiments, the aAPCs are comprised of a scaffold to which a plurality of MHC:peptide complexes and accessory molecules (as well as other molecules) can be attached at high density.
Owner:ALBANI SALVATORE
Bread maker
InactiveCN104920522AAccelerateImprove efficiency and yieldDough sheet coiling machinesDough-sheeters/rolling-machines/rolling-pinsEngineeringFast speed
The present invention discloses a bread maker which relates to the machinery field of food processing. The bread maker is characterized in that the bread maker consists of a flour patch inlet conveying rack, a wall panel, a compression roller assembly, a flour patch rubbing and rolling assembly and a finished product conveying rack. The flour patch inlet conveying rack is connected with the wall panel, the compression roller assembly and the flour patch rubbing and rolling assembly are arranged on the wall panel, and the wall panel is connected with the finished product conveying rack. The bread maker can rub and roll flour patches with various shapes and different thickness, and has fast speed and high successful rate.
Owner:合肥市开平食品贸易有限责任公司
Substrate strip plate structure for semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120187543A1Increase processable surface area and utilization rate of surface areaImprove efficiency and yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBand shapeDevice material
The present invention provides a strip plate structure and a method for manufacturing the same. The strip plate structure comprises a strip plate array, which comprises a plurality of strip plates arranged with spacing in a predetermined direction on a same plane, wherein each of the strip plates has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface and the strip plate array is arranged on a plane parallel to the first surface of the strip plates; a plurality of strip sheets which connect neighboring ones of the strip plates; flexible material layers, which are located on at least a portion of the surfaces of the strip sheets and / or on at least a portion of the surfaces of the strip plates.
Owner:SUNOVEL SUZHOU TECH
In-mold variable-pitch material moving module
The invention discloses an in-mold variable-pitch material moving module, comprising a mounting base, a driving member, a linkage rod, a plurality of material taking assemblies, a plurality of guide rods and a plurality of push rings. The plurality of material taking assemblies are arranged on the guide rods in a linear array manner; the material taking assembly located at the tail end is fixedlyarranged, and the other material taking assemblies are slidably arranged; the driving member is arranged at one end of the mounting base and in driving connection with the material taking assembly atthe head end; the plurality of push rings are slidably sleeved on the guide rods; the plurality of push rings are all located between every two adjacent material taking assemblies; and the plurality of driving assemblies are in one-way linkage through the linkage rod. The distance between workpieces can be controlled through the module; linkage pitch changing is performed by the push rings and thelinkage rod; when the driving member drives, the material taking assemblies are in linkage through the push rings to implement pitch changing; and when the driving member is reset, the material taking assemblies are linked and reset through the linkage rod. The material moving module can achieve the purposes of implementing on-line production, saving manpower, improving the efficiency and yield and improving the safety coefficient, and facilitates production management and control.
Owner:SUZHOU LINGYU ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
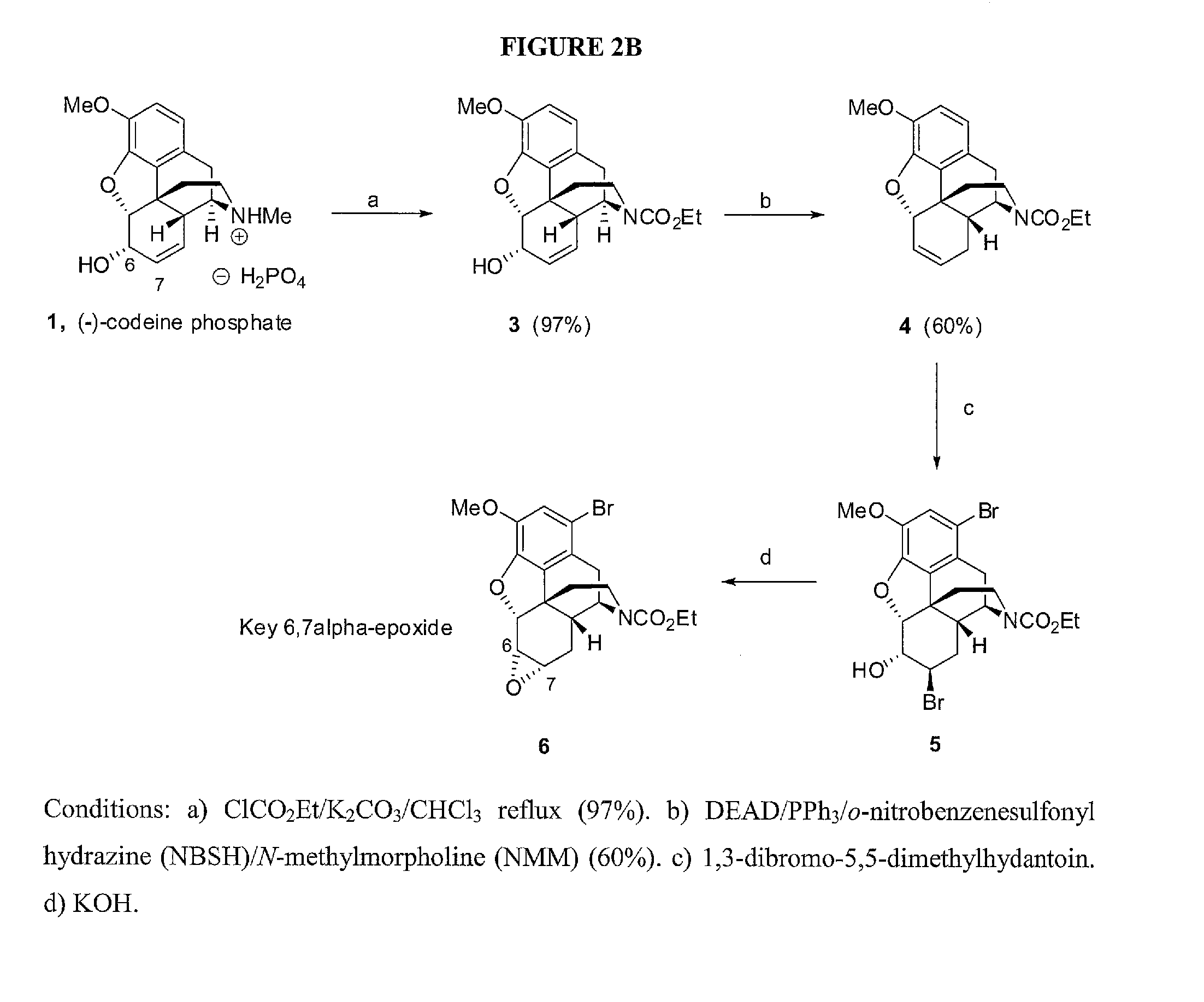
Chemical transformations of (-)-codeine to afford derivatives of codeine and morphine thereof
InactiveUS20150133664A1Improve efficiency and yieldImprove efficiencyNervous disorderOrganic chemistryMedicinal chemistryCodeine
The present invention relates to methods for the synthesis of morphine, codeine, intermediates, salts and derivatives thereof. In preferred embodiments, the invention relates to methods for improving the efficiency, steroselectivity, and overall yield of said codeine and morphine related derivatives and intermediates thereof. The present invention relates to new codeine and morphine related derivative compositions.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
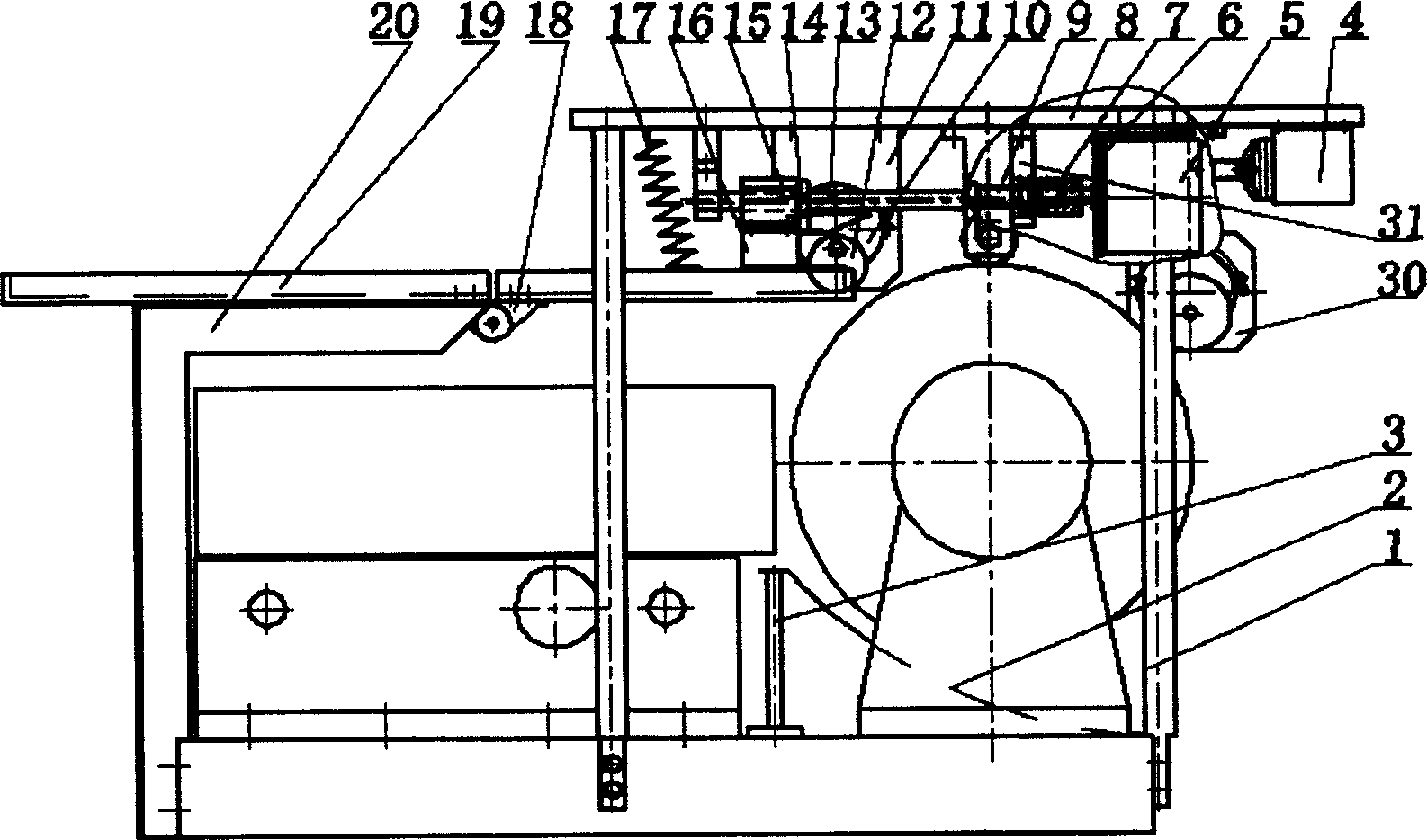
Negative pressure fully automatic upper/lower sheet device of laser plotter
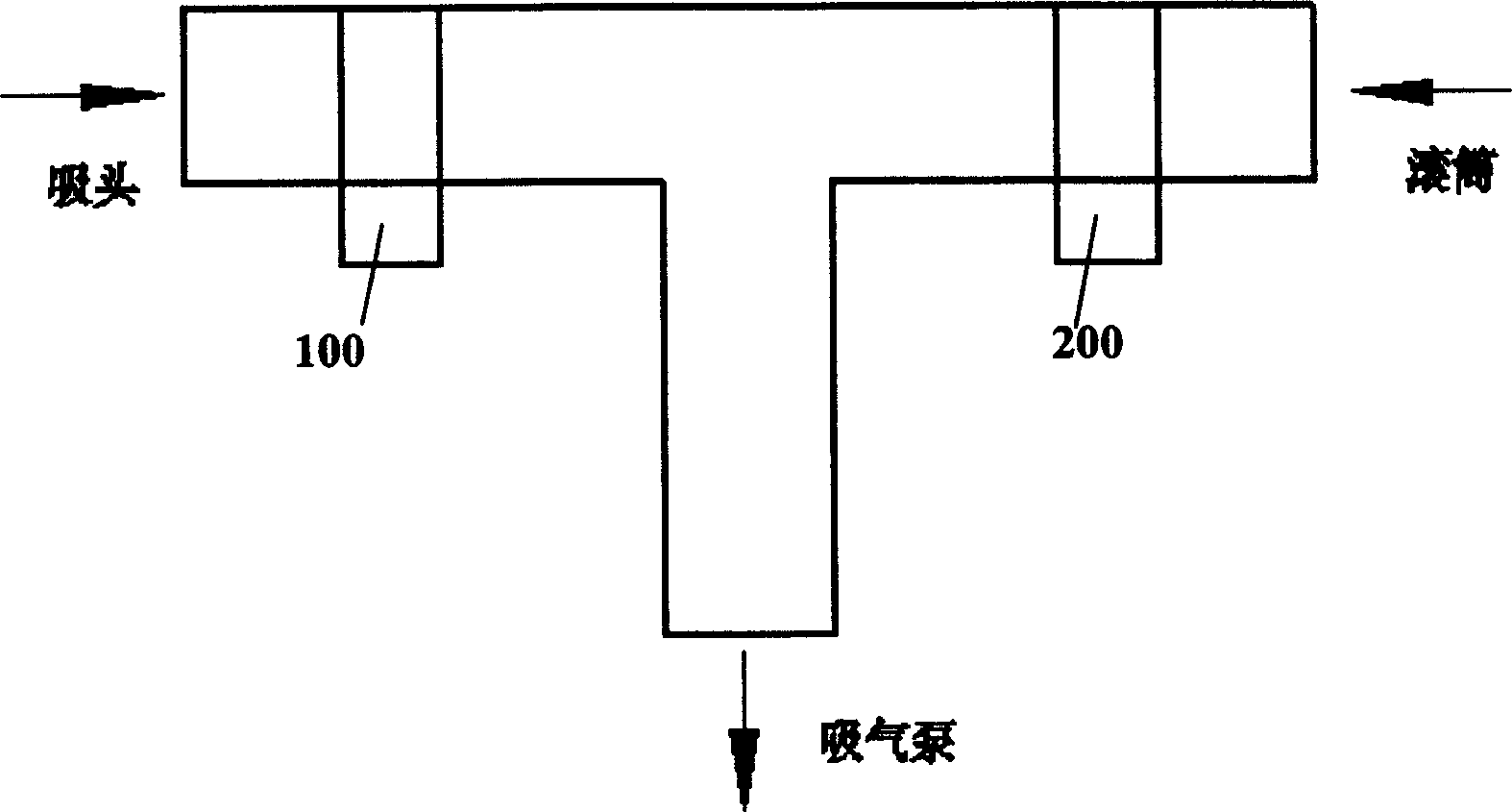
InactiveCN1564082AEliminate the effects ofImprove efficiency and yieldPhotomechanical apparatusLaser lightFully automatic
Through posts and angle bar rack, the equipment is fixed above platform of laser light plotter. A small platform is fixed on upper parts of posts. The equipment includes air flow control part, can part, film shift control part, part for pressing film, drum control part for spinning in slow speed, and guide plate for loading and unloading film. Advantages of the invention are: darkroom is net needed for loading or unloading film; even, operator can operate plotter through network, eliminating influence on film from artifacts, raising yield and efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Mold for forming cast rods, casting apparatus, and production method of cast rods
InactiveUS8122934B2Improve efficiency and yieldEfficient productionMelt-holding vesselsMould separation apparatusMaterials scienceCast iron
Disclosed is a mold 10 for forming cast rods including: a segment assembly 12 including a plurality of segments 14 being placed side by side, and a plurality of cavities 26 extending along a longitudinal direction 16; and clamping means (18 to 21) for clamping the segment assembly 12 in directions orthogonal to the longitudinal direction 16. The mold 10 has one or more cavity-forming portions 28 each forming a part of one of the peripheral surfaces of the cavities 26. Each cavity 26 is formed by a combination of two or more segments 14, and at least one of the plurality of segments 14 has two or more cavity-forming portions 28.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
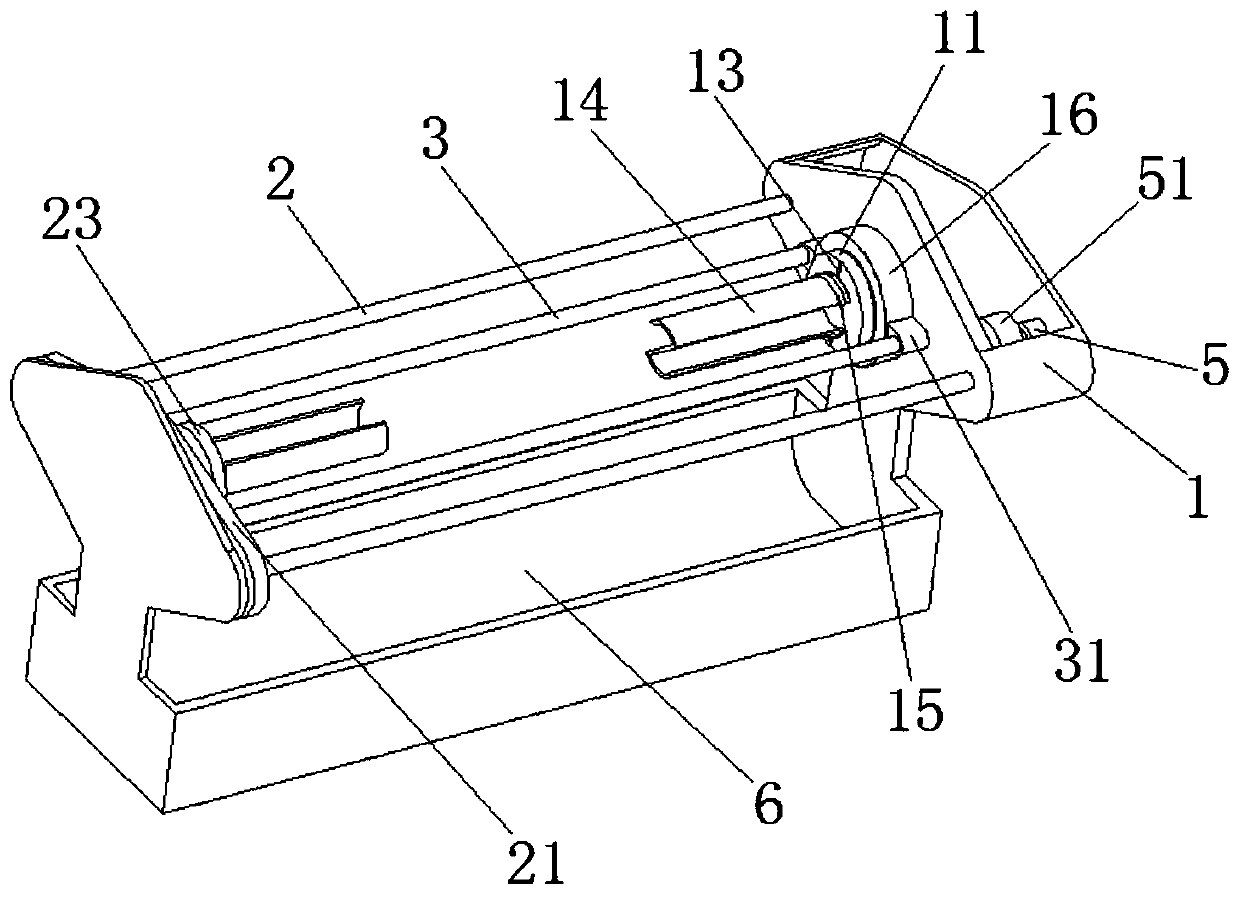
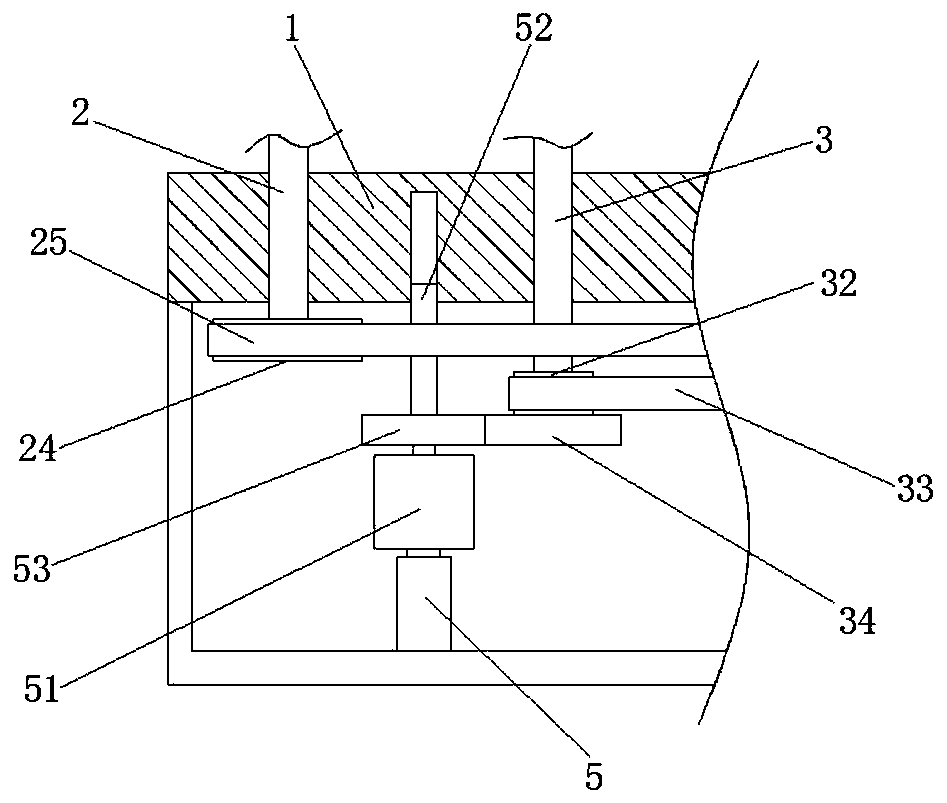
Heart rate module
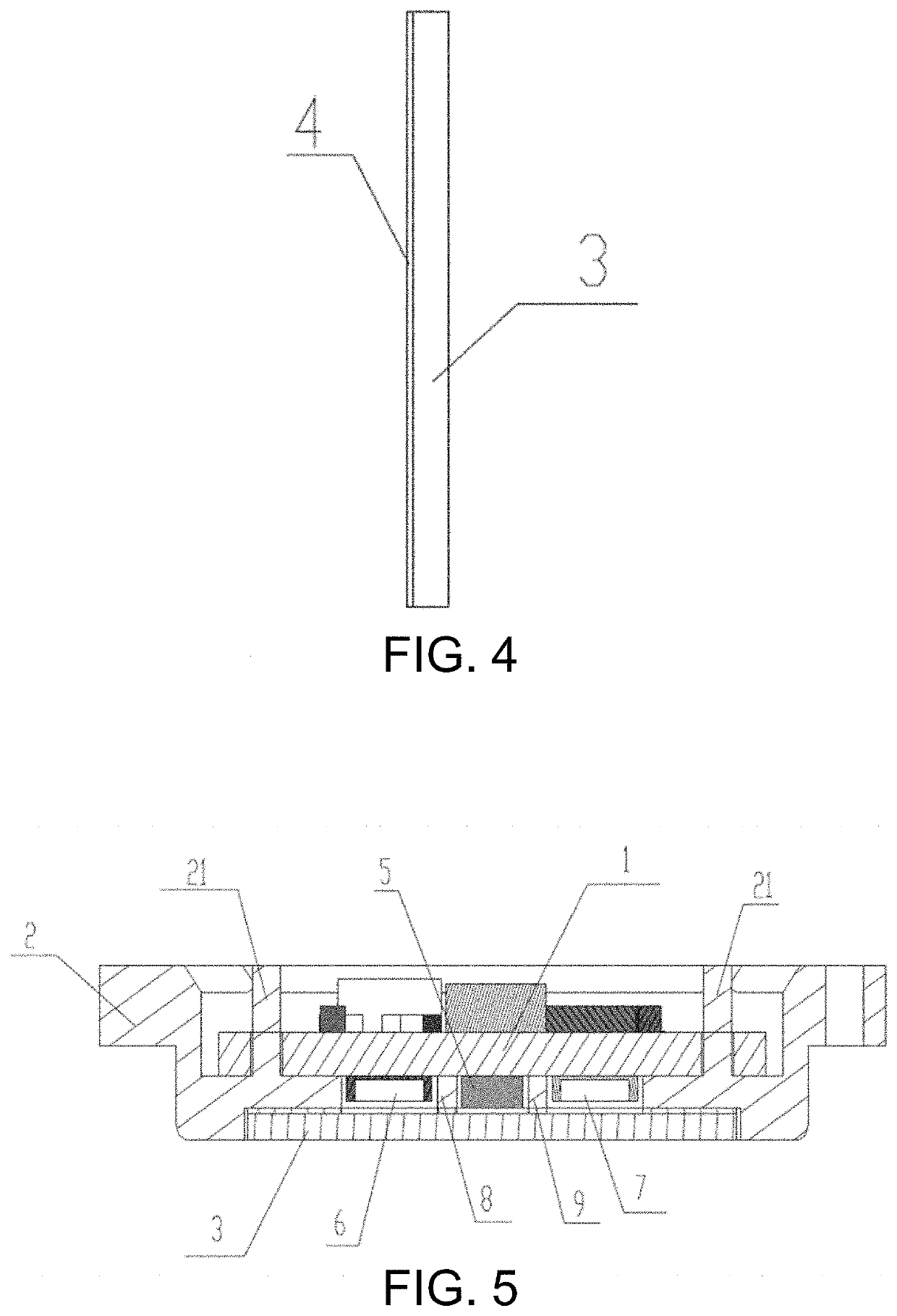
ActiveUS20200229721A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldOptical sensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateStructural engineeringHot melt
A heart rate module, comprising a housing structure composed of a rear housing (2) and a light-transmitting cover plate (3), the housing structure being internally provided with a PCB assembly (1); the PCB assembly (1) comprises a PCB, PDs (6, 7) and an LED (5), the PDs (6, 7) and the LED (5) being fixed on the PCB according to a preset distance; a hot melt positioning column (21) is provided on the rear housing (2), and the PCB assembly (1) is fixed, by means of the hot melt positioning column (21), on the rear housing (2). Use of the heart rate module can solve the problems of the assembly method of the available heart rate meter being complicated and the requirement for a terminal product being high.
Owner:WEIFANG GOERTEK MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ceramic resistor strip folding machine
PendingCN114843056AImprove efficiency and yieldReduce labor costsResistor chip manufactureReclaimerStructural engineering
The invention relates to a ceramic resistor strip folding machine which comprises a rack, a feeding mechanism, a material taking mechanism, a strip folding mechanism, a waste recycling mechanism, a conveying mechanism and a control mechanism. The feeding mechanism is arranged on one side of the table top of the rack. The material taking mechanism is arranged between the feeding mechanism and the strip folding mechanism. The strip folding mechanism is arranged between the feeding mechanism and the waste recycling mechanism. The conveying mechanism is arranged on the other side of the strip folding mechanism; the feeding mechanism supplies materials to be machined to the strip folding mechanism. The strip folding mechanism is used for splitting the material provided by the feeding mechanism; the conveying mechanism adsorbs and recycles the striped materials obtained through the strip folding mechanism and conveys redundant waste into the waste recycling mechanism at the same time. According to the invention, the problem that the resistor tiles are small and cannot be subjected to strip folding processing is solved, full-automatic production is realized, and the requirements of enterprises are met.
Owner:苏州沃乔电子科技有限公司
Bread making machine
The invention discloses a bread making machine and relates to the field of food processing machines. The bread making machine is characterized by comprising a flour-feeding conveying frame, a wall plate, a pre-pressing roller component, a flour-belt twisting and rolling component and a finished-product conveying frame, wherein the flour-feeding conveying frame is connected with the wall plate which is provided with the pre-pressing roller component and the flour-belt twisting and rolling component; and the wall plate is connected with the finished-product conveying frame. The bread making machine disclosed by the invention has the advantages that flour slices with various shapes and different thicknesses can be twisted and rolled, the speed is fast and the success rate is high.
Owner:安徽晟萌粮油食品有限公司
Methods And Materials For Producing Enhanced Sugar, Starch, Oil, And Cellulose Output Traits In Crop Plants
InactiveUS20170037419A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldHydrolasesClimate change adaptationCelluloseBiotechnology
Described are crop-related materials and methods for metabolic engineering. Certain aspects of the invention include applications in food production, carbon sequestration, and biofuel production. Described are methods of enhancing plant traits for increased production of sugar, starch, cellulose, and oil. Described methods include altering cytosolic asparagine to promote production of non-nitrogenous plant compounds.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Adeno-associated virus "x" oncogene
InactiveUS20160272687A1Promotes AAV replicationImprove efficiencySugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsOncogene ETSPHA granule
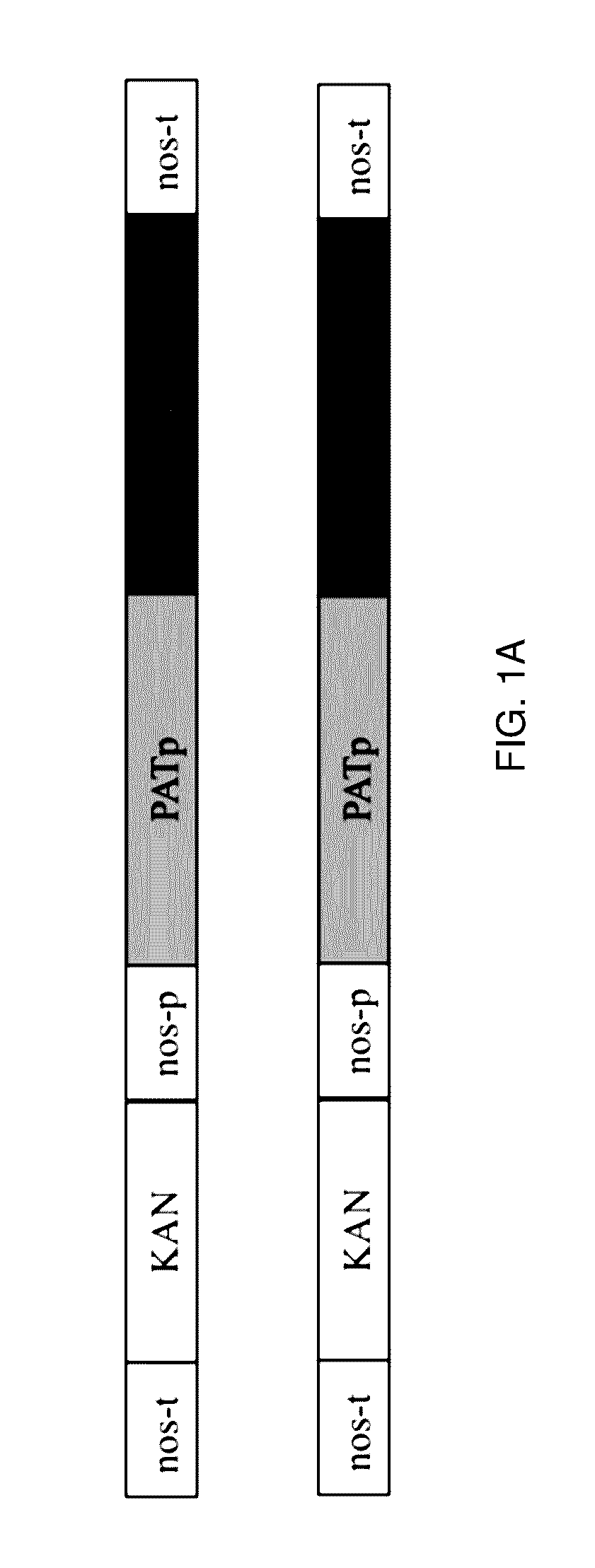
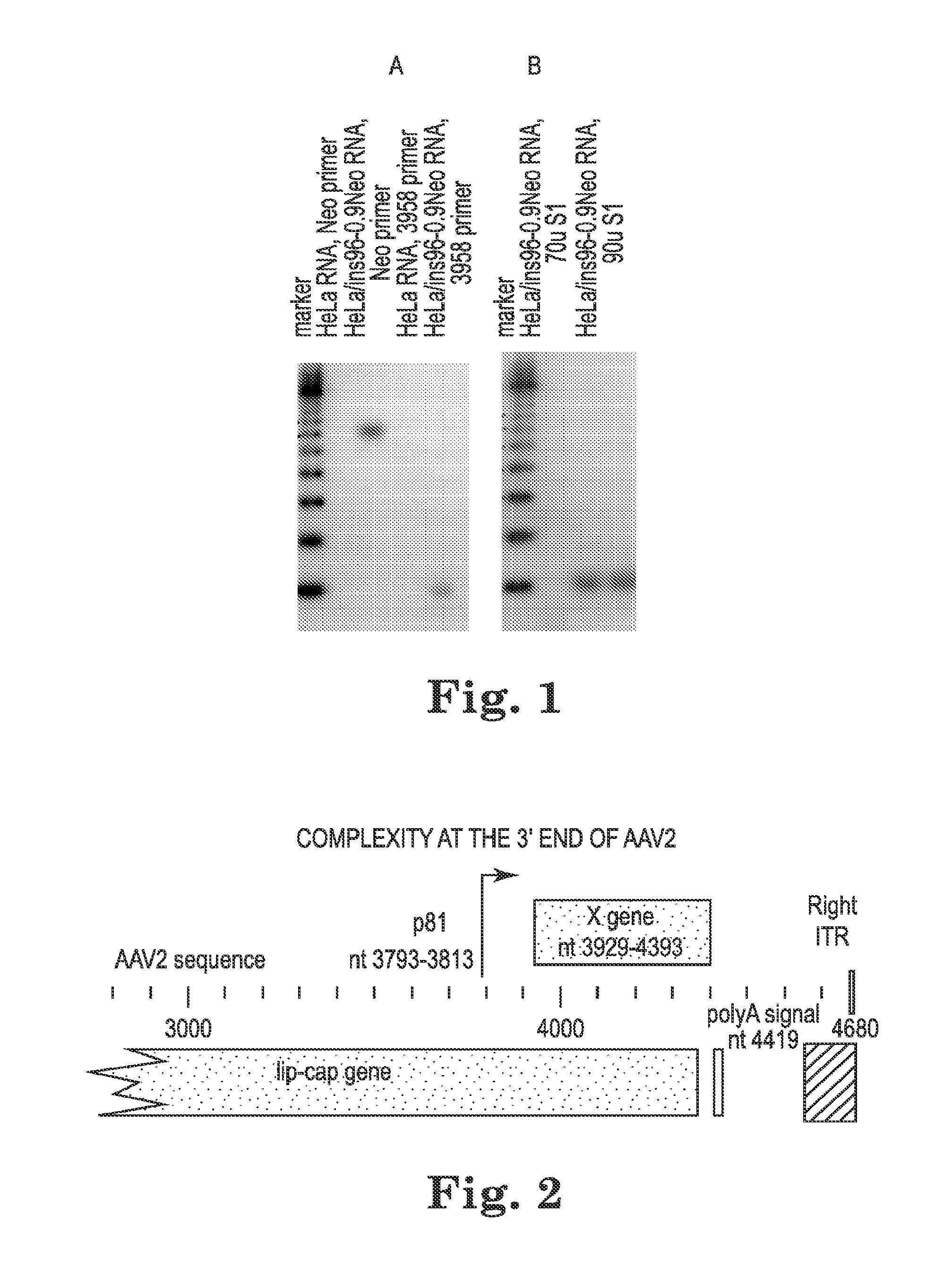
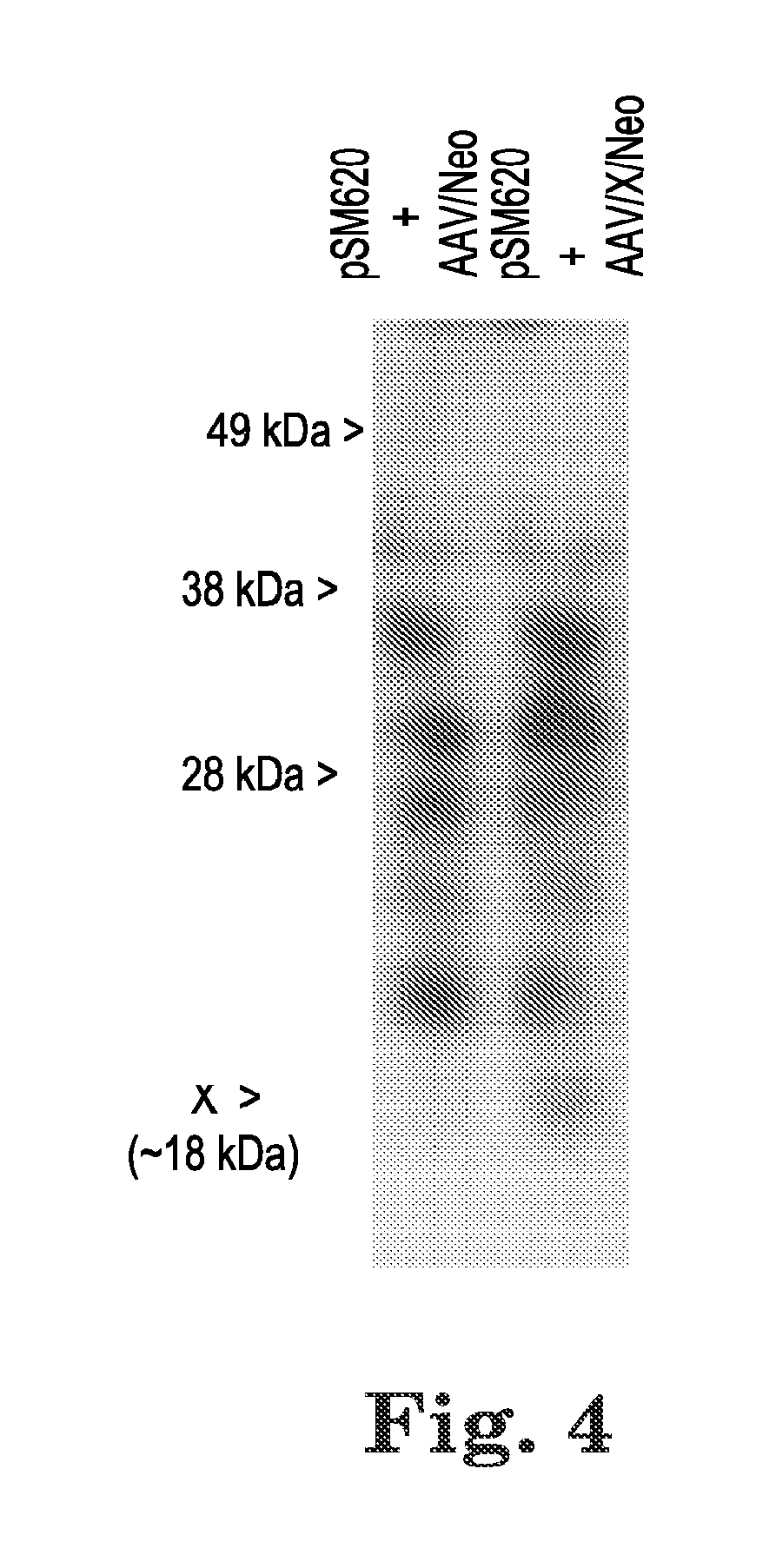
A novel gene “X” of adeno-associated virus is presented, which is found to be an oncogene and to promote efficient production of recombinant AAV virus particles that may be used for human gene therapy. Since the AAV X gene appears to be an oncogene, it is desirable that it not be included in active form in recombinant AAV virus particles. Therefore A therapeutic composition comprising: a plurality of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) virus particles comprising native AAV DNA and recombinant therapeutic DNA, wherein none of the AAV virus particles has an active AAV X gene is presented. Also provided are methods of expressing the X gene to improve production of recombinant AAV virus particles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Machine for machining pipeline compensating component
InactiveCN111545380AImprove efficiency and yieldImprove smudge effectSpraying apparatusEngineeringClassical mechanics
The invention relates to the field of pipe fitting machining, in particular to a machine for machining a pipeline compensating component. The machine comprises a base. A first clamp is inserted in thebase. A slot of an inclined structure is formed in one end of the first clamp. Slide grooves are formed in the first clamp symmetrically. Clamping plates are inserted in the slide grooves correspondingly. First hydraulic cylinders are fixedly connected into the first clamp symmetrically. Output ends of the first hydraulic cylinders are fixedly connected with one ends of the symmetrical clamping plates correspondingly. First lead screws and second lead screws are inserted in the base symmetrically. A movable plate is arranged on the first lead screws in an inserted mode and is in threaded connection with the first lead screws. The movable plate is symmetrically provided with through holes. The second lead screws penetrate through the symmetrical through holes correspondingly. One side of the movable plate is fixedly connected with a second clamp. The second clamp and the first clamp are symmetrically staggered. By means of the machine, metal corrugated pipes of different specificationscan be clamped, meanwhile the surfaces of the metal corrugated pipes are evenly smeared, and the yield of the metal corrugated pipes is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU YAOYAO PHOTOVOLTAIC TECH CO LTD
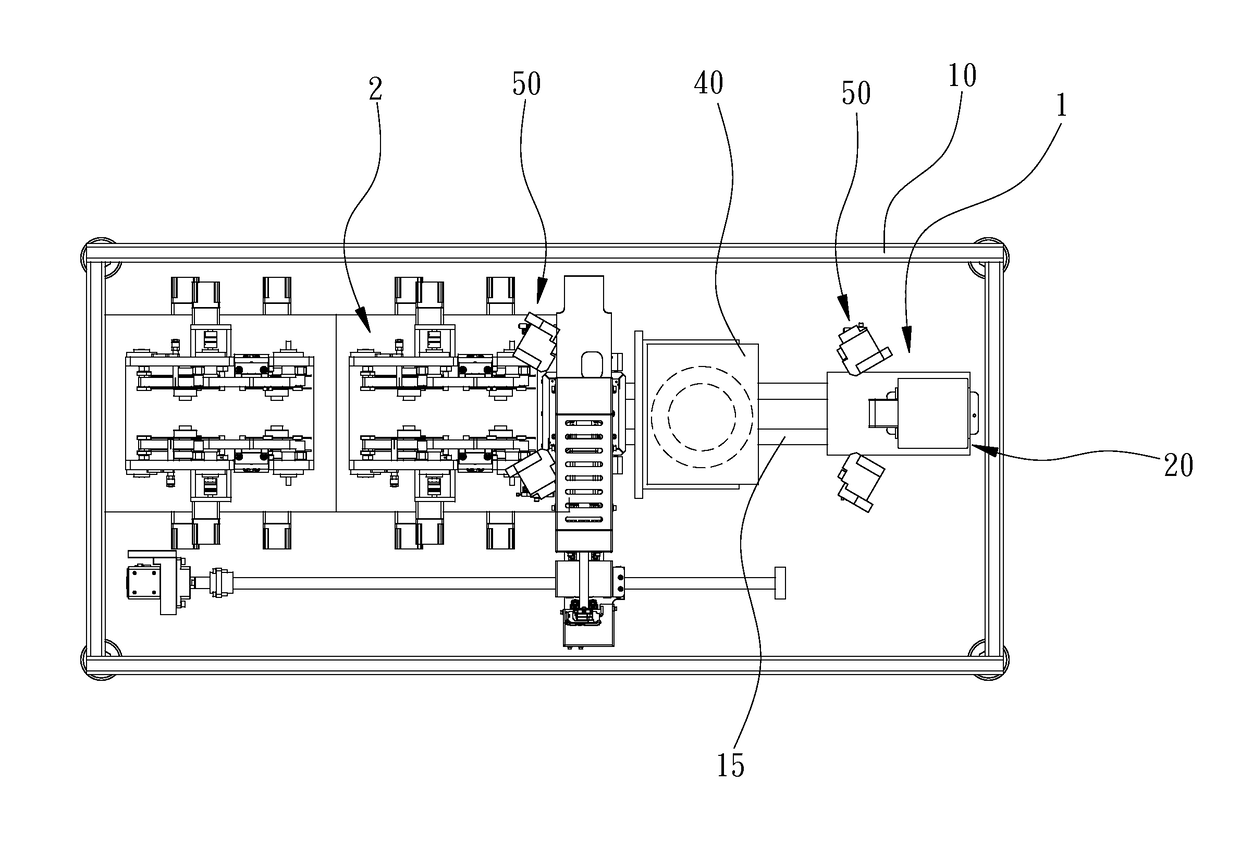
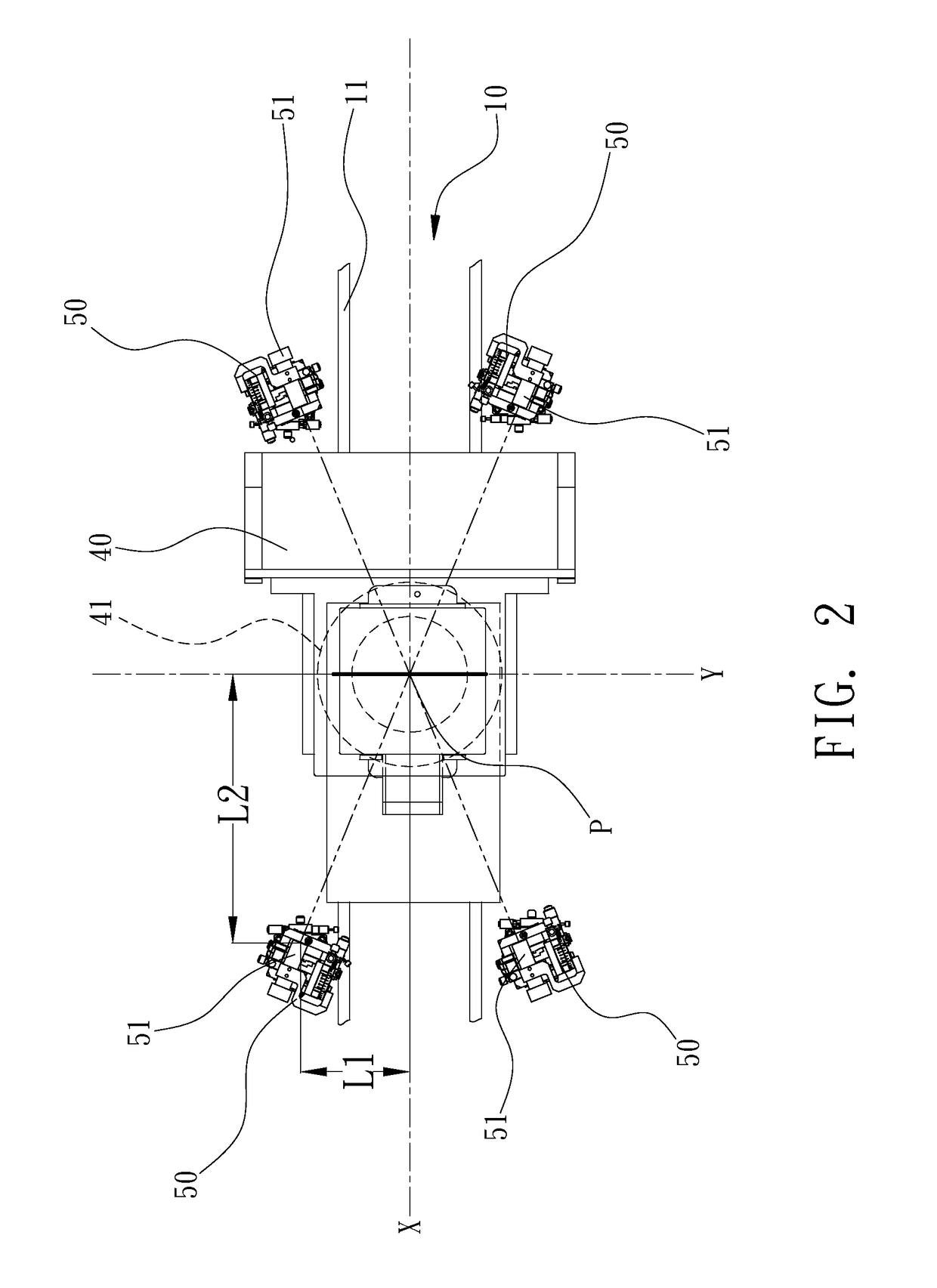
Machine for detecting tiny particles
InactiveUS20170160207A1Increase yield and efficiencyImprove efficiency and yieldOptically investigating flaws/contaminationEngineeringLaser transmitter
A machine for inspecting a face of a transparent plate includes a frame, a carrier module, an optical module and at least two illumination modules. The frame includes an X-axis. The carrier module is adapted for carrying a transparent plate in need of inspection on the frame along the X-axis. The optical module is located on the frame and movable relative to the carrier module and includes at least one detector adapted for rectilinear scanning along a Y-axis perpendicularly intersecting the X-axis of the carrier module at a crossing point. The illumination modules are located on two opposite sides of the X-axis of the frame. Each of the illumination modules includes a laser emitter. The laser emitters are located at a same distance from the crossing point and adapted for emitting rays on the transparent plate at a same angle of 0.5° to 6°.
Owner:CHEN MING SHENG
Process and catalyst-electrolyte combination for electrolysis
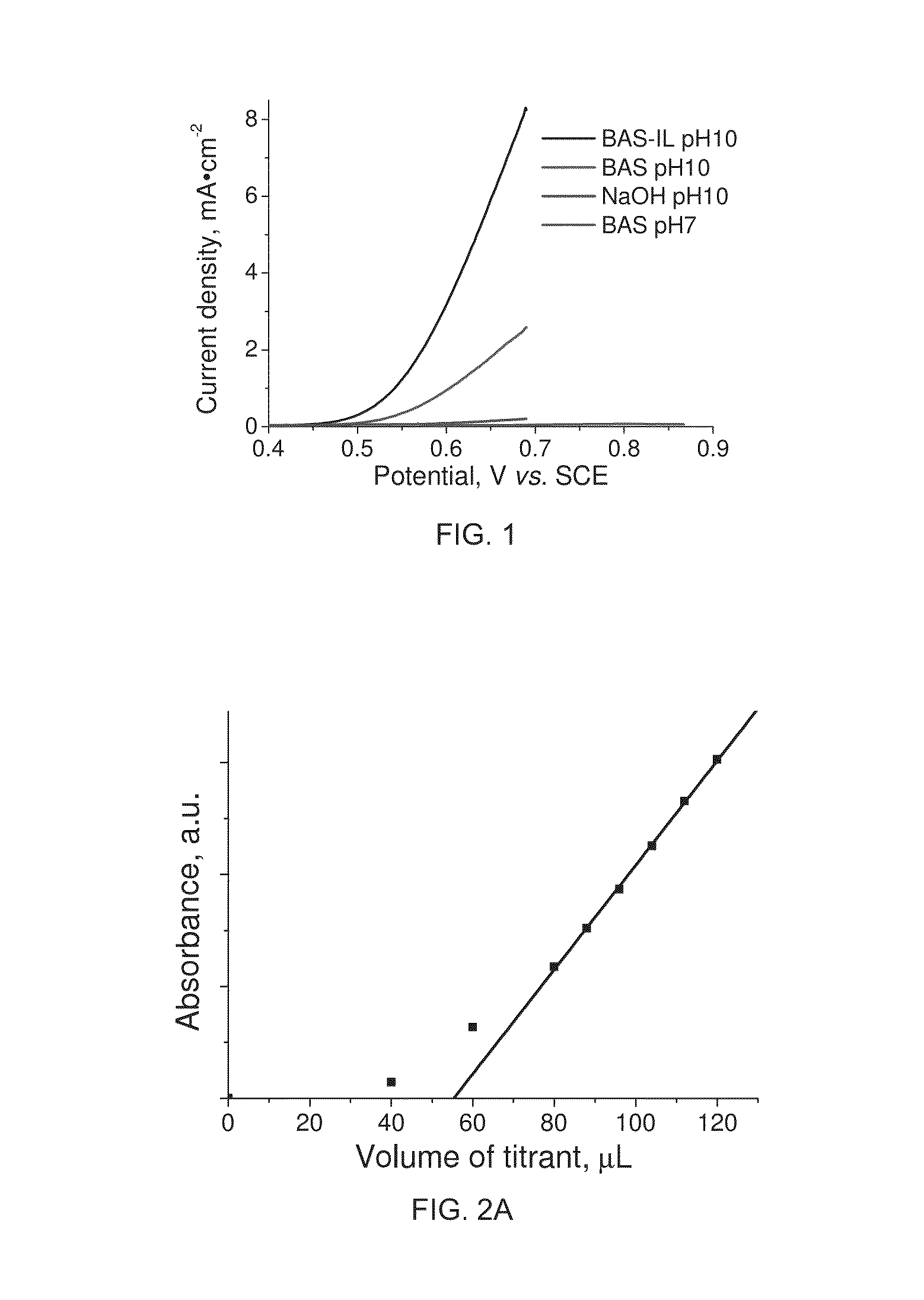
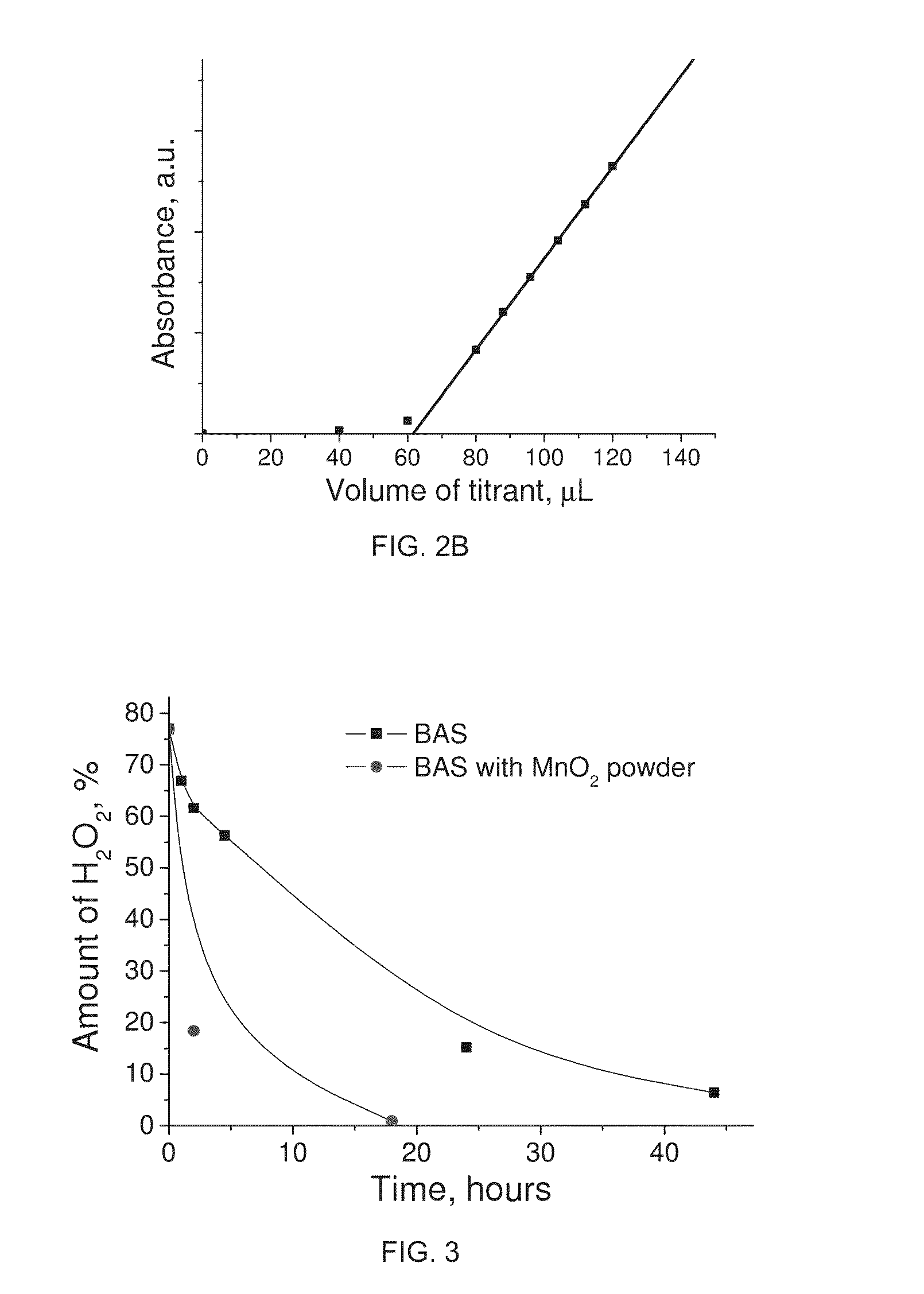
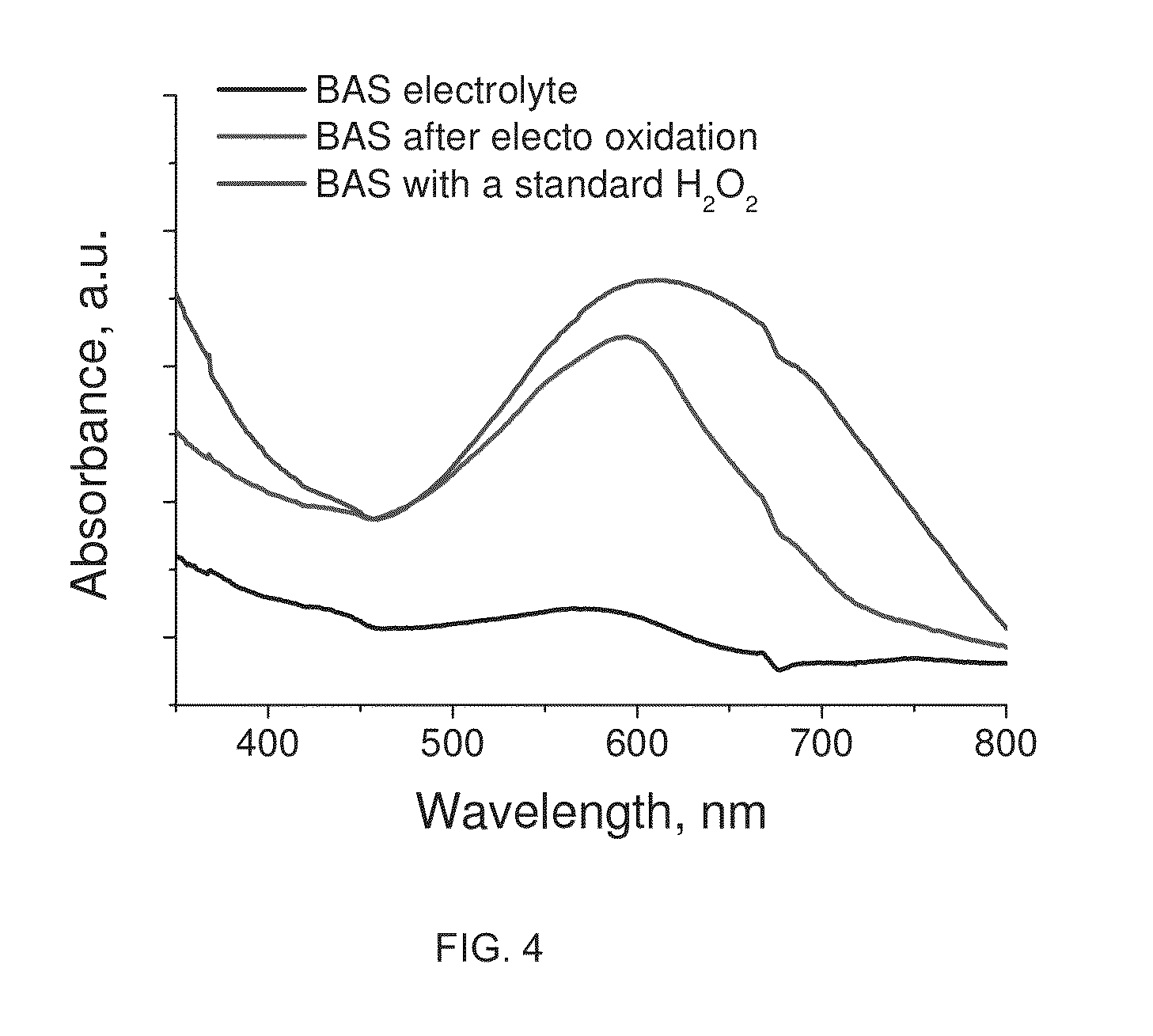
InactiveUS20150108006A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldElectrolysis componentsPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesAnodeSemiconductor
The invention relates to a process for electrolysis comprising a cathode and an anode comprising a catalyst, both the cathode and anode at least partly immersed in an electrolyte, the process characterised in that the electrolyte at least partly inhibits further oxidation of a product formed at the anode. Typically the catalyst comprises one or more metal-(Group VIb) semiconductors, and one or more metal-(GroupVIb))-phosphorous species.
Owner:AQUAHYDREX INC
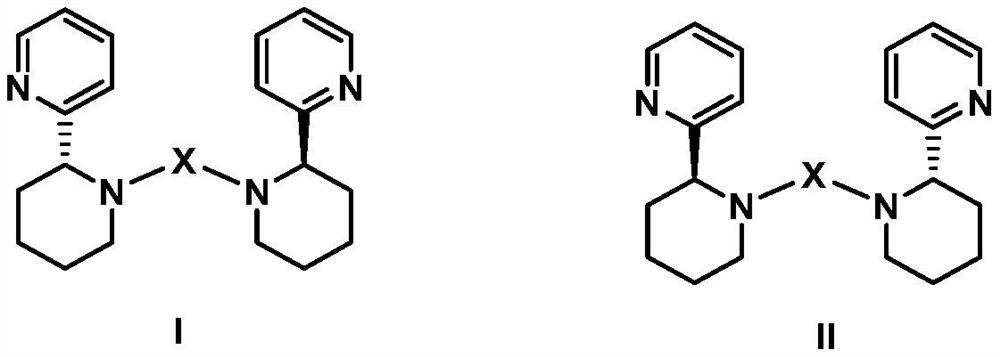
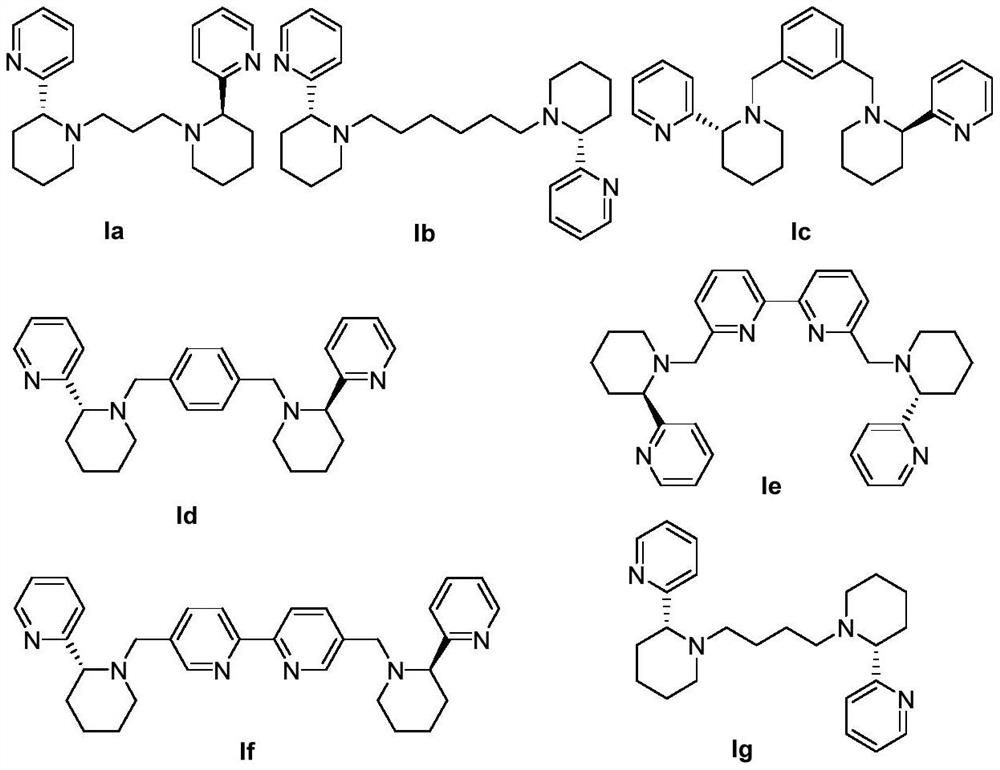
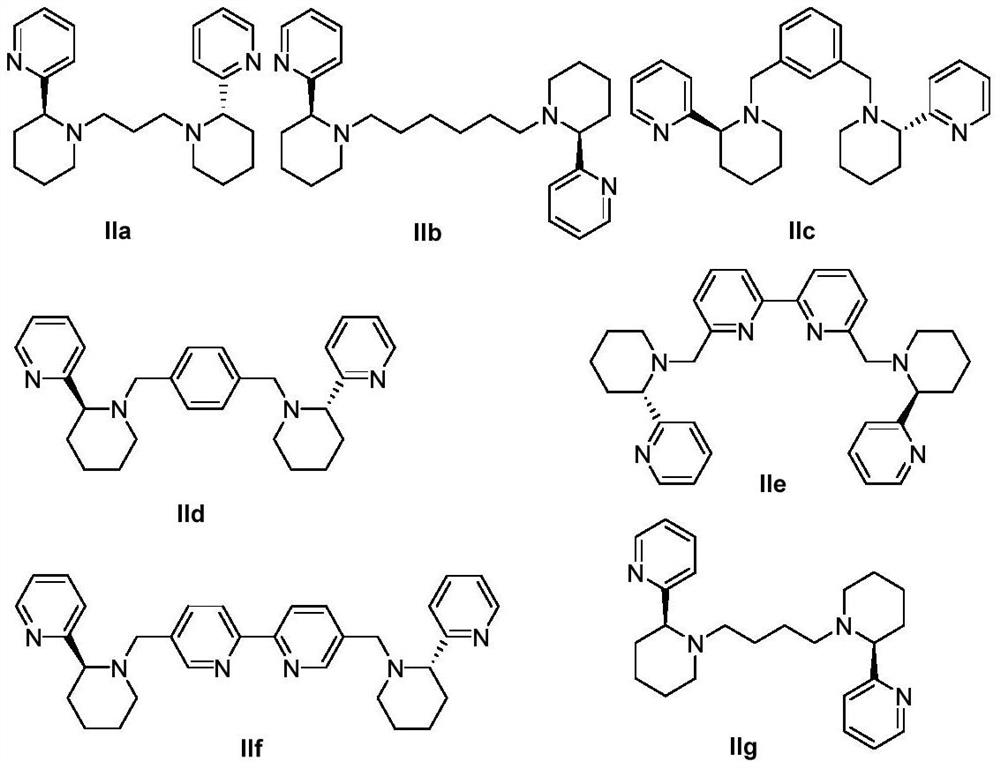
Novel chiral pyridine-containing polydentate nitrogen ligand and palladium complex as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113278009AImprove efficiency and yieldGood enantioselectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCombinatorial chemistrySubstitution reaction
The invention provides a novel chiral pyridine-containing polydentate nitrogen ligand, a palladium complex as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention relates to a novel chiral pyridine-containing polydentate nitrogen ligand, the novel chiral pyridine-containing polydentate nitrogen ligand is successfully prepared into a palladium complex, the palladium complex is applied to an asymmetric allylic substitution reaction, the reaction efficiency and yield are greatly improved, the minimum reaction time can reach 2 hours, the yield is as high as 98%, a reaction product can reach better enantiomer selectivity, the ee value is as high as 57%, and a new choice is provided for a novel efficient metal complex catalytic system constructed by carbon-carbon bonds.
Owner:中山大学新华学院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com