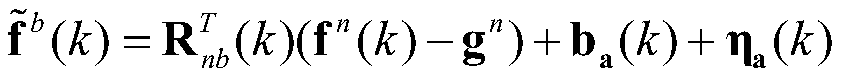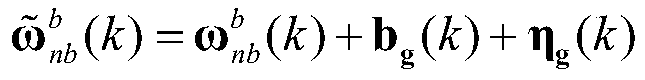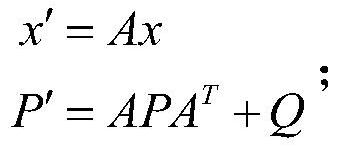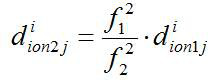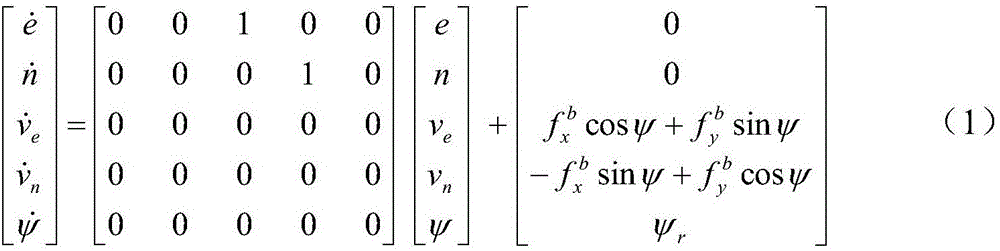Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78results about How to "Correct position error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kinect-based robot self-positioning method
ActiveCN105045263ARealize self-positioningIndependent positioning and stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsPoint cloudRgb image
The invention discloses a Kinect-based robot self-positioning method. The method includes the following steps that: the RGB image and depth image of an environment are acquired through the Kinect, and the relative motion of a robot is estimated through the information of visual fusion and a physical speedometer, and pose tracking can be realized according to the pose of the robot at a last time point; depth information is converted into three-dimensional point cloud, and a ground surface is extracted from the point cloud, and the height and pitch angle of the Kinect relative to the ground surface are automatically calibrated according to the ground surface, so that the three-dimensional point cloud can be projected to the ground surface, and therefore, two-dimensional point cloud similar to laser data can be obtained, and the two-dimensional point cloud is matched with pre-constructed environment raster map, and thus, accumulated errors in a robot tracking process can be corrected, and the pose of the robot can be estimated accurately. According to the Kinect-based robot self-positioning method of the invention, the Kinect is adopted to replace laser to perform positioning, and therefore, cost is low; image and depth information is fused, so that the method can have high precision; and the method is compatible with a laser map, and the mounting height and pose of the Kinect are not required to be calibrated in advance, and therefore, the method is convenient to use, and requirements for autonomous positioning and navigation of the robot can be satisfied.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIAZHI TECH CO LTD
Three-dimensional (3D) rapid forming printing system and method
The invention relates to the field of rapid prototyping and discloses a three-dimensional (3D) rapid forming printing system. The system comprises a personal computer (PC) end with a control unit, an extruder, a printing base plate with a heating function, a servo motor which controls motion of the printing base plate, and a motion control unit, wherein the extruder is positioned above the printing base plate on the top of a body operating area; the servo motor and the printing base plate are positioned below the extruder at the bottom of the body operating area; the motion control unit is an embedded chip group; each chip comprises a task module for executing a control task; the motion control unit is positioned in a chip group slot below the body operating area; the extruder, the servo motor and the printing base plate are respectively and electrically connected with the motion control unit; the motion control unit is electrically connected with the PC end. By virtue of an incremental manufacturing method, namely models are established on the printing base plate layer by layer, rapid manufacturing is realized, processing of any model can be finished, and the system has certain application value and application prospects and can be applied to household and industrial production.
Owner:林岚 +1
Underwater navigation and positioning method capable of combining terrain and environment characteristics
ActiveCN104075715AGood navigationGood autonomyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOcean bottomTerrain
The invention discloses an underwater navigation and positioning method capable of combining terrain and environment characteristics. The method comprises the steps of judging whether all sub-areas in a planned track of an underwater vehicle are matched or not according to terrain information; if so, positioning by a terrain-aided inertial navigation system; and if not, positioning by a simultaneous localization and composition algorithm auxiliary master inertial navigation system. The method can be used for calculating the terrain information of a navigation area, and the underwater terrain is divided into a matched terrain area and an unmatchable terrain area. Different navigation algorithms are adopted aiming at the different areas, so that the position error of a master inertial navigation system can be corrected, and the method is relatively high in autonomy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and system for positioning
ActiveCN103379619ALow costHigh precisionTransmission monitoringLocation information based serviceUser devicePositioning system
The invention provides a method for positioning, which includes: carrying out positioning based on an access point of a wireless local network, and obtaining an estimated initial position of a user device; obtaining course angle and speed information of the user device; and correcting the estimated initial position according to the course angle and speed information, and obtaining final position information. The invention also provides a system for positioning. With the method and the system for positioning, positioning error caused by strength floating of received information and accumulative error caused by sensor noise are corrected, so that a combined positioning system with low cost and high precision is obtained.
Owner:ZTE CORP +1
Mobile robot image visual positioning method in dynamic environment
ActiveCN108460779AReduce hardware costsOvercoming complexityImage analysisNavigation instrumentsMobile robotTransformation matrix
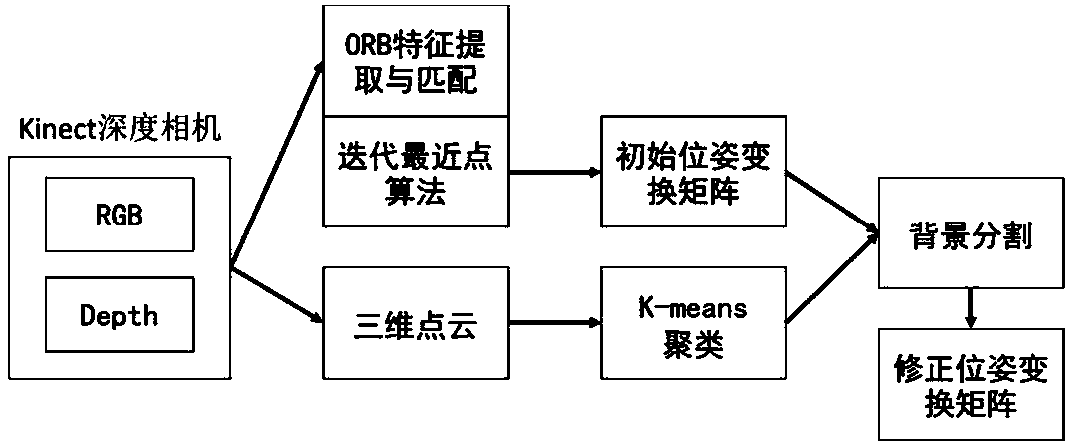
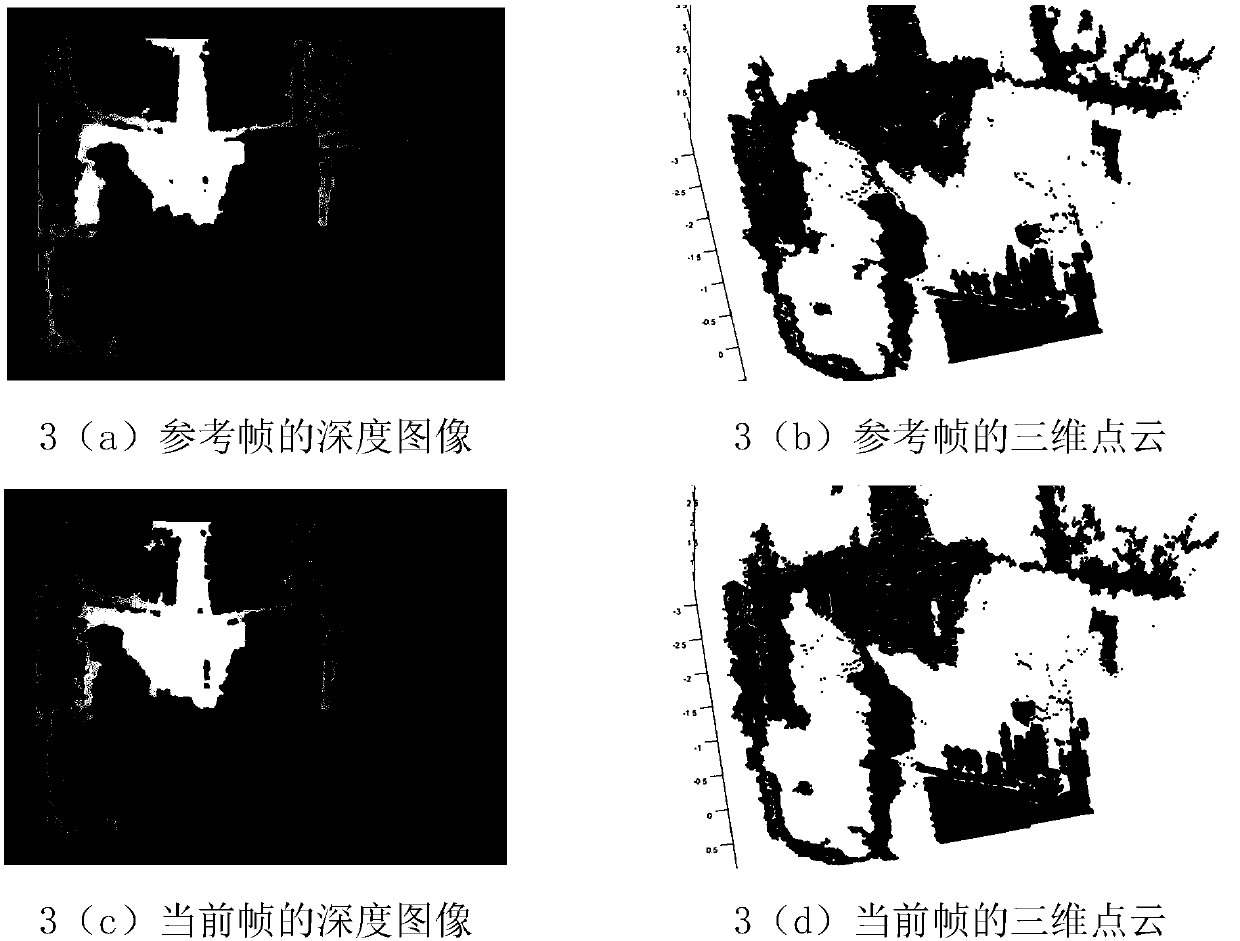
The invention discloses a mobile robot image visual positioning method in a dynamic environment. A Kinect depth camera is fixed to a mobile robot, and for the two adjacent frames of images, the three-dimensional point cloud of the depth image is obtained and a matching point pair of the RGB color image is obtained; an initial pose transformation matrix between the two adjacent frames of images isobtained through an iterative nearest point algorithm; the three-dimensional point cloud clustering transformation is carried out, and the residual difference between the three-dimensional point cloudclusters of the two adjacent frames of images is calculated; the matching point pair and the three-dimensional point cloud in a static background repeatedly processed to obtain a more accurate pose transformation matrix, the pose transformation matrix between every two adjacent frames of images is calculated, and the image visual positioning of the mobile robot is realized. According to the invention, the hardware cost is reduced, the complexity of recovering the pixel depth value is overcome, the positioning error of the robot is corrected, and the moving track of the moving robot in the room is estimated more accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for navigating and positioning motion carrier
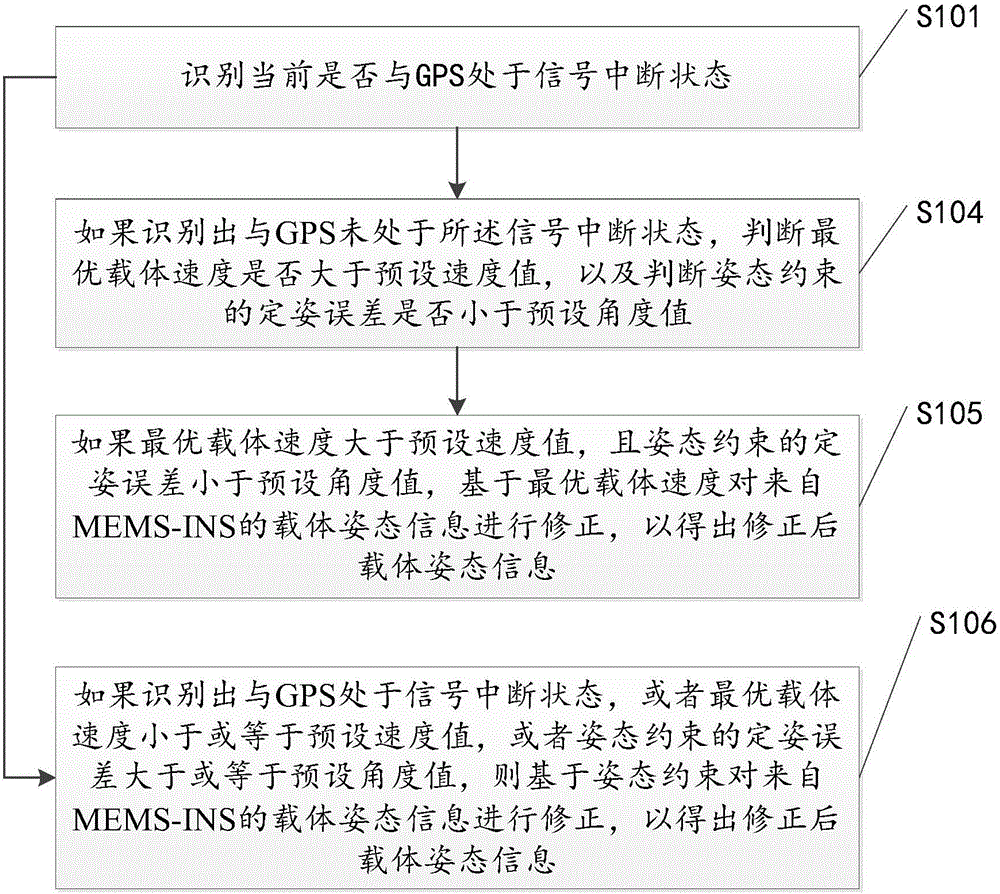
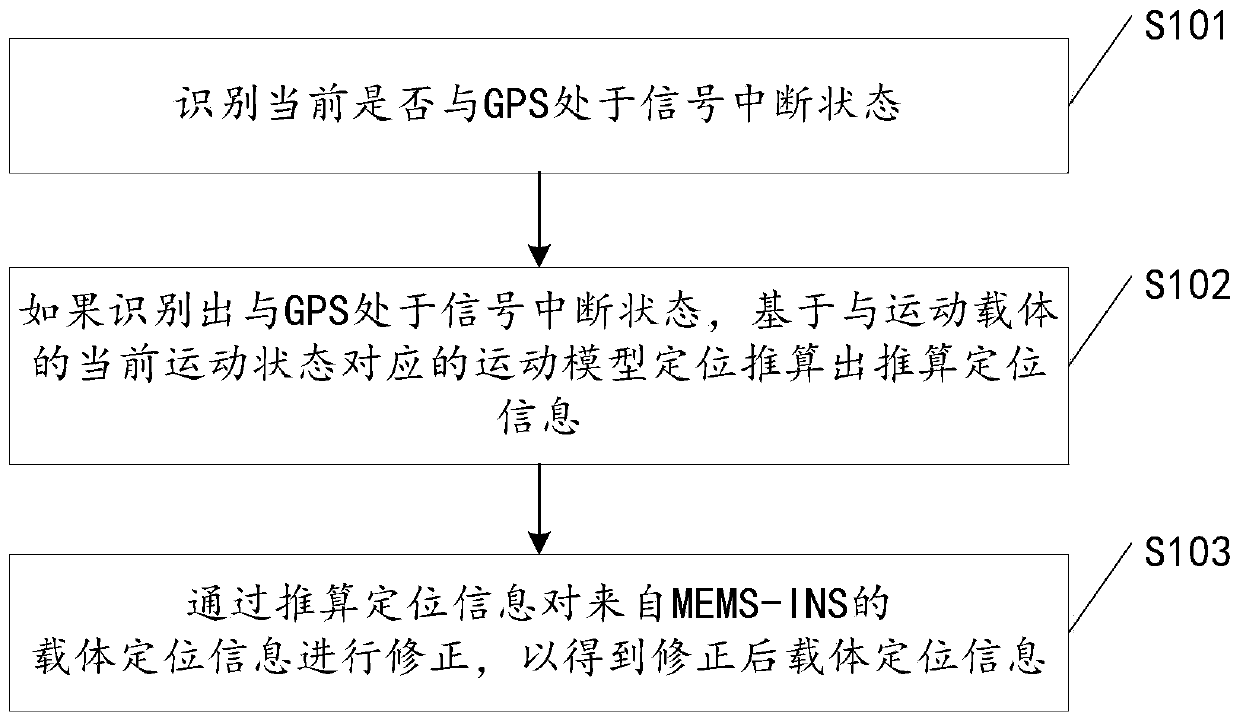
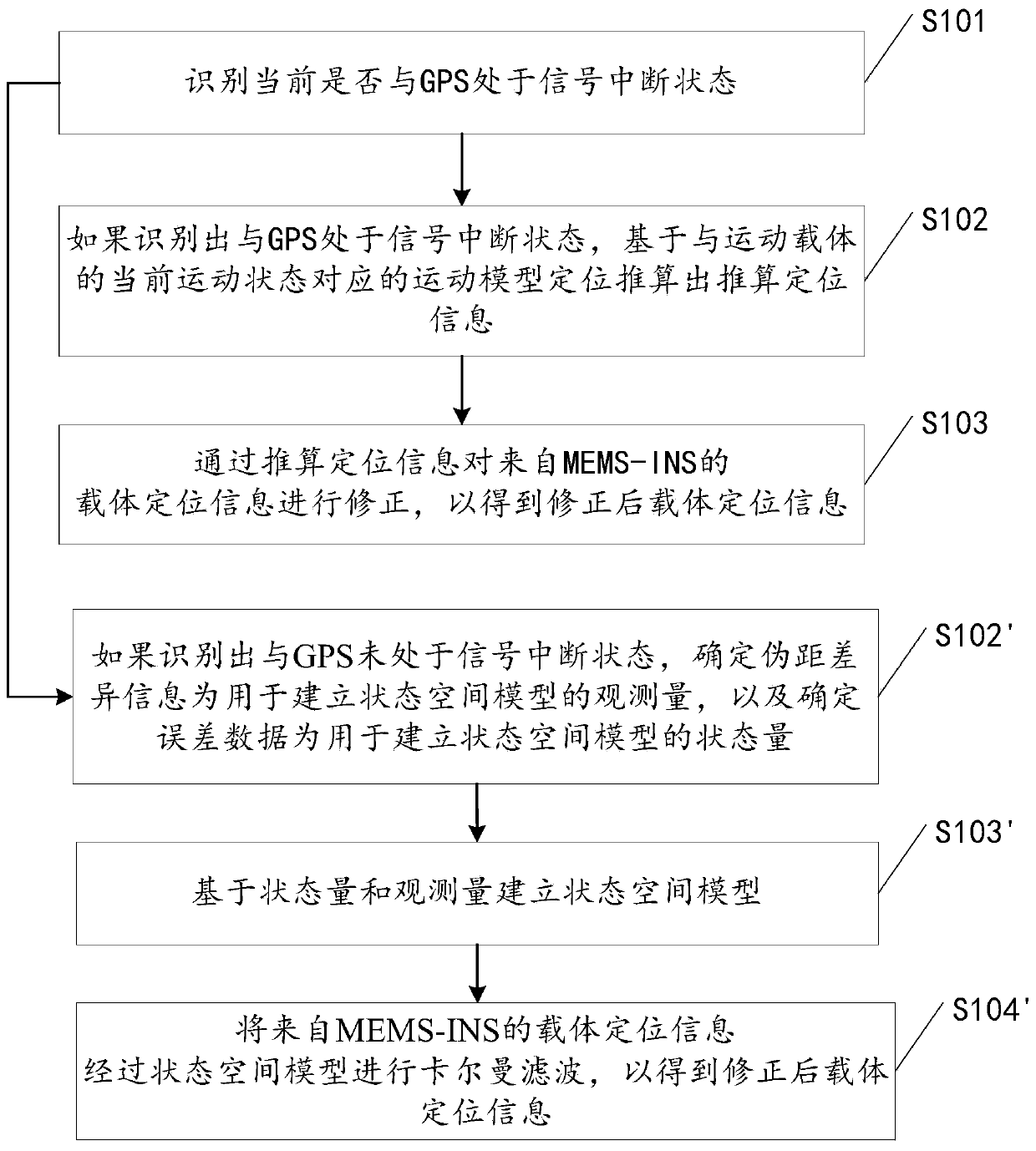
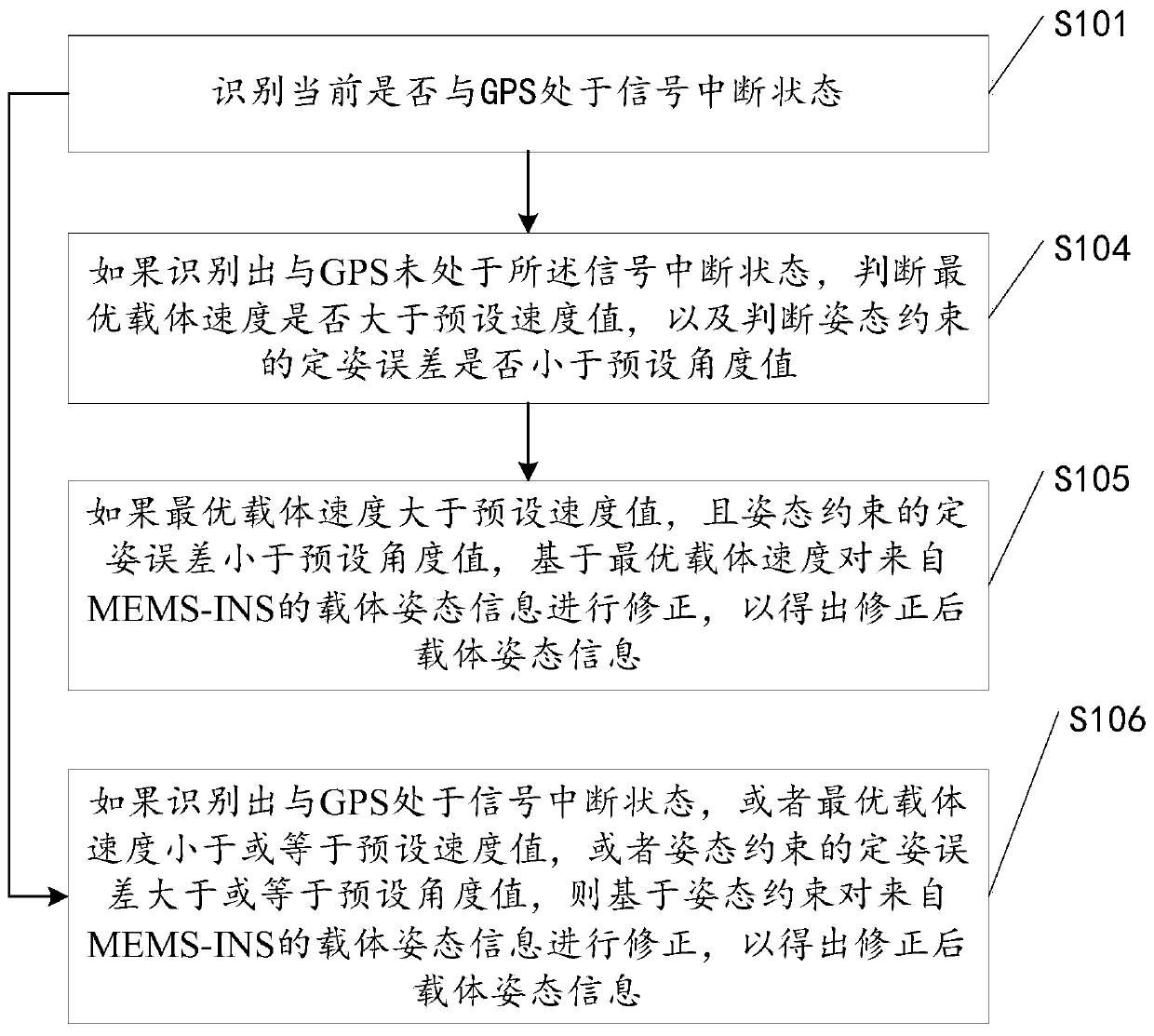
ActiveCN106679657ACorrect position errorAvoid accumulationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingComputer visionArtificial intelligence
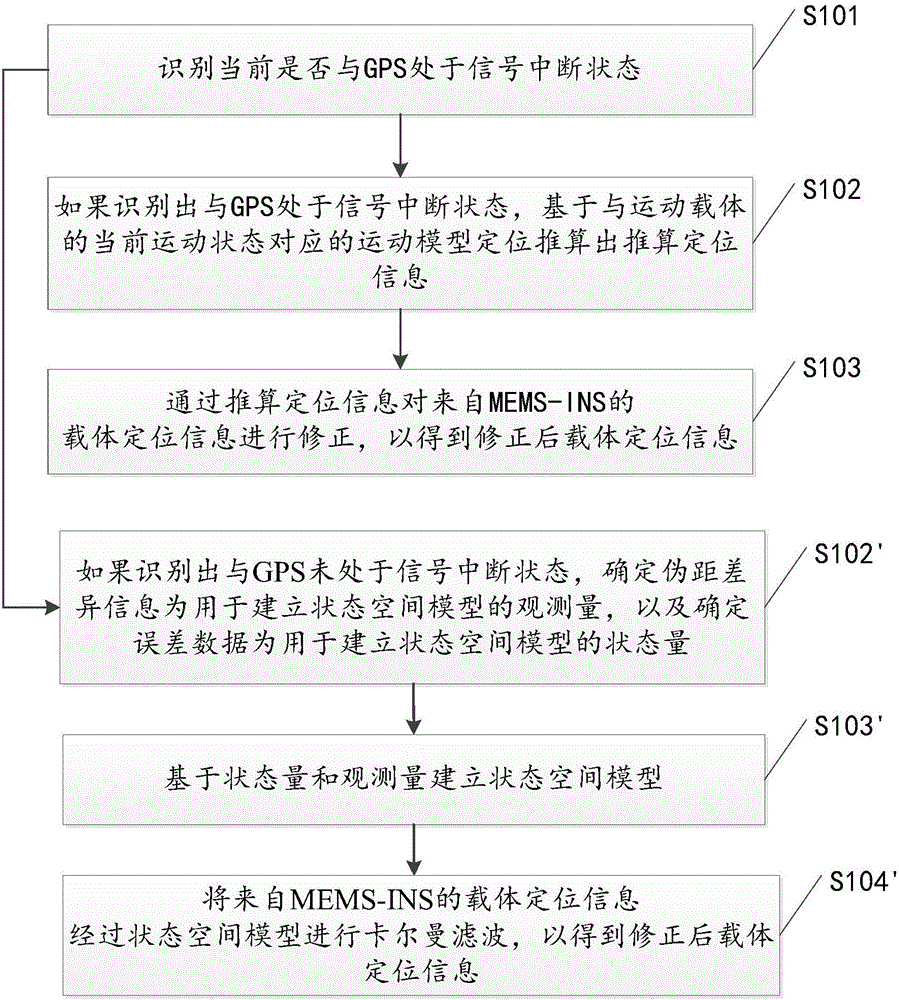
The invention discloses a method and a device for navigating and positioning a motion carrier. The method comprises the following steps: identifying whether a global positioning system (GPS) is in a signal interruption state or not; if the GPS is identified to be in the signal interruption state, positioning based on a motion model corresponding to the current motion state of the motion carrier, and calculating calculation positioning information; and amending carrier positioning information from MEMS-INS through the calculation positioning information so as to obtain amended carrier positioning information. When GPS signals are interrupted, positioning errors for the motion carrier can be more efficiently, more simply and more conveniently amended in comparison with a complex non-linear model, so that the accumulation of positioning errors is avoided, and the positioning errors during GPS signal interruption are reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS)/ultra short base line (USBL) phase difference tightly integrated navigation locating method based on double transponders
ActiveCN109737956AEliminate clock errorsReduce mistakesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationDouble differenceHydrophone
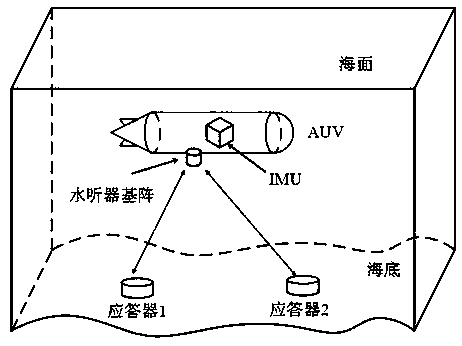
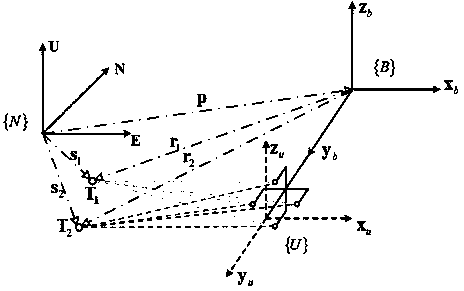
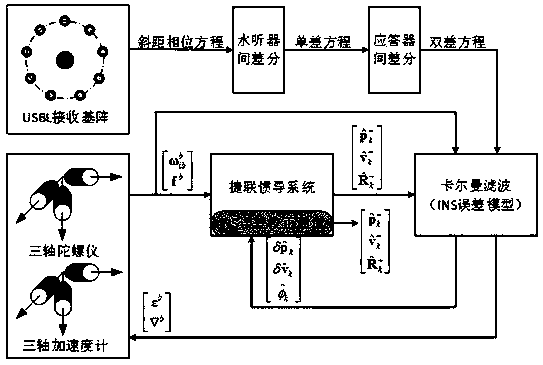
The invention provides a strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) / ultra short base line (USBL) phase difference tightly integrated navigation locating method based on double transponders. The SINS / USBL phase difference tightly integrated navigation locating method refers to a SINS and an USBL locating system which are mounted on an AUV; a hydrophone of the USBL system receives calibration of errors existing in fixed connection and mounting of a base array and the INS, the two transponders are laid on the seabed, and a slope distance phase observation model between the hydrophone of the USBLsystem and the transponders is built; the USBL locating system with the structure of the double transponders conducts differential processing on a slope distance phase equation on the hydrophone layer surface and the transponder layer surface; and then the slope distance phase difference equation subjected to double-layer differential processing is refined into an integrated navigation system observation equation to be filtered. The similarity errors in the USBL locating system can be effectively counteracted through a double-difference processing method, the USBL phase difference is adoptedas the observation quantity to be tightly integrated, the coordinate transformation error and the base array offset error which are caused by direct position computing of a USBL are avoided, and the precision of the AUV integrated navigation locating system can be effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Permanent magnet brushless motor sensorless starting method
InactiveCN104378030ASwitch as soon as possibleFast startupElectric motor controlStarter arrangementsBrushless motorsClosed loop
The invention discloses a permanent magnet brushless motor sensorless starting method. The permanent magnet brushless motor sensorless starting method comprises the steps that firstly, a rotor is positioned at a specific position through a rotor prepositioning device, single-step acceleration is carried out according to the given single-step acceleration current and single-step acceleration time obtained by calculation, single-step acceleration is directly switched to closed loop acceleration after being carried out, rotor position signals in a three-phase suspended state are detected every fixed period, the power-on phase sequence is determined according to the rotor position signals, whether counter potential signals are stable or not is judged through a signal comparison method while closed loop acceleration is carried out, and when stable counter potential signals can be detected within one phase conversion period, a normal counter potential method is switched to for operation, wherein the single-step acceleration and the signal comparison method can ensure that a motor is started at the highest speed, and the closed loop acceleration process can ensure that the motor supplies power accurately in the acceleration start process and step-out is avoided. By means of the method, an efficient permanent magnet brushless motor can be started accurately, rapidly and efficiently, the optimization process is simple, universality is high, the success rate of starting can be improved greatly, no sensitivity to load changes exists, and the start program does not need to be changed when loads and the working station change within a certain range.
Owner:张前
Navigational positioning and calibration method for deep-sea underwater autonomous vehicle
PendingCN109782323ACorrect position errorGood effectNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingHydroacousticsMarine navigation
The invention discloses a navigational positioning and calibration method for a deep-sea underwater autonomous vehicle. A working mother ship acquires accurate position information of the underwater autonomous vehicle through a hydroacoustic positioning system mounted on the underwater autonomous vehicle, generates active calibration information of the underwater autonomous vehicle based on the information, and sends the active calibration information to the underwater autonomous vehicle for calibration of the navigation information, thereby solving the problem that the satellite navigation data cannot be calibrated by floating to the surface during the operation of the deep-sea underwater autonomous vehicle.
Owner:CSIC NO 710 RES & DEV INST
External measured speed information-based horizontal attitude error correction method for SINS (serial inertial navigation system)
InactiveCN103674059ACorrect position errorTime overheadNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDesign controlCelestial navigation
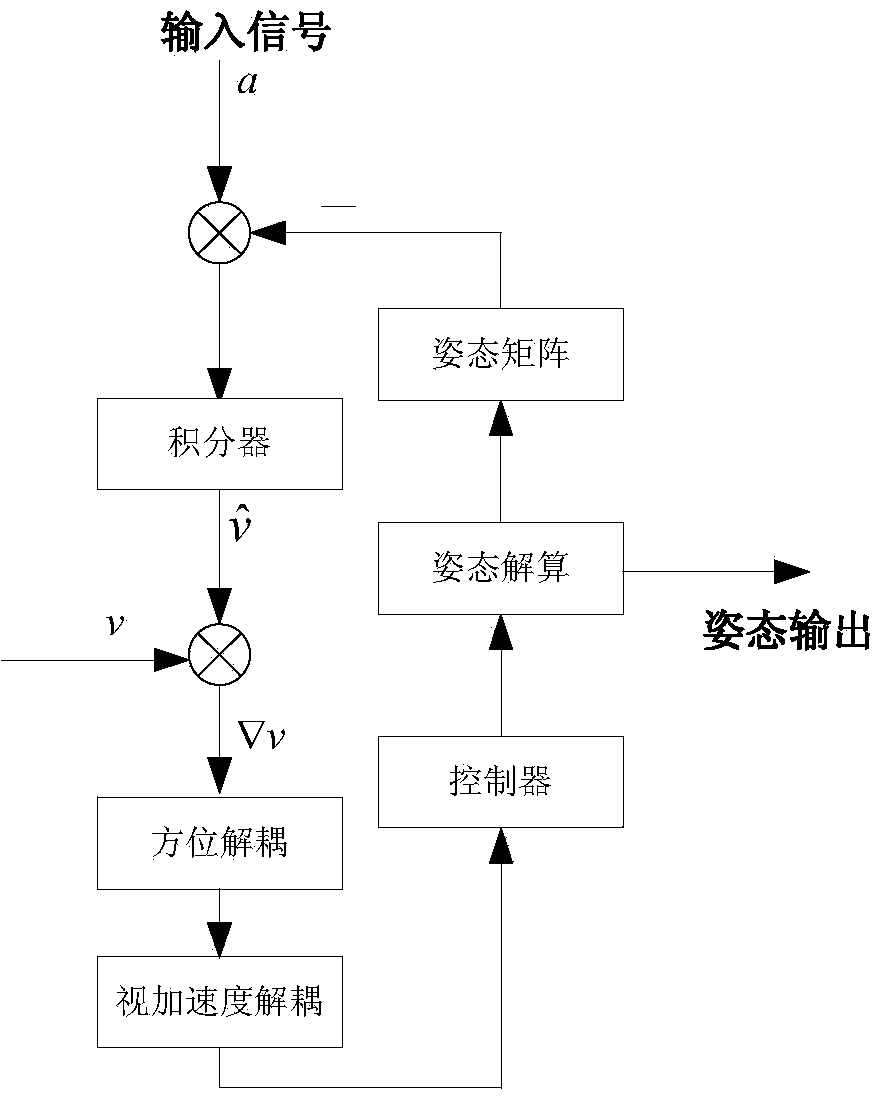
The invention discloses an external measured speed information-based horizontal attitude error correction method for a SINS (serial inertial navigation system). A speed error signal is sequentially subjected to azimuth decoupling and apparent acceleration decoupling, and a controlled variable is formed by the controller to correct the horizontal attitude to realize the correction of an inertial navigation system error. Compared with other combined navigation methods, the method has the advantages that the inertial navigation position and the horizontal attitude are corrected, and meanwhile, the designed controller is used for filtering signal noise, so that not only is the robustness of a combined navigation system improved, but also the navigation system of the combined navigation system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Three-dimensional cooperative positioning method for unmanned aerial vehicle group
ActiveCN111123341AEnable co-locationPrecise positioningSatellite radio beaconingDisaster monitoringUncrewed vehicle
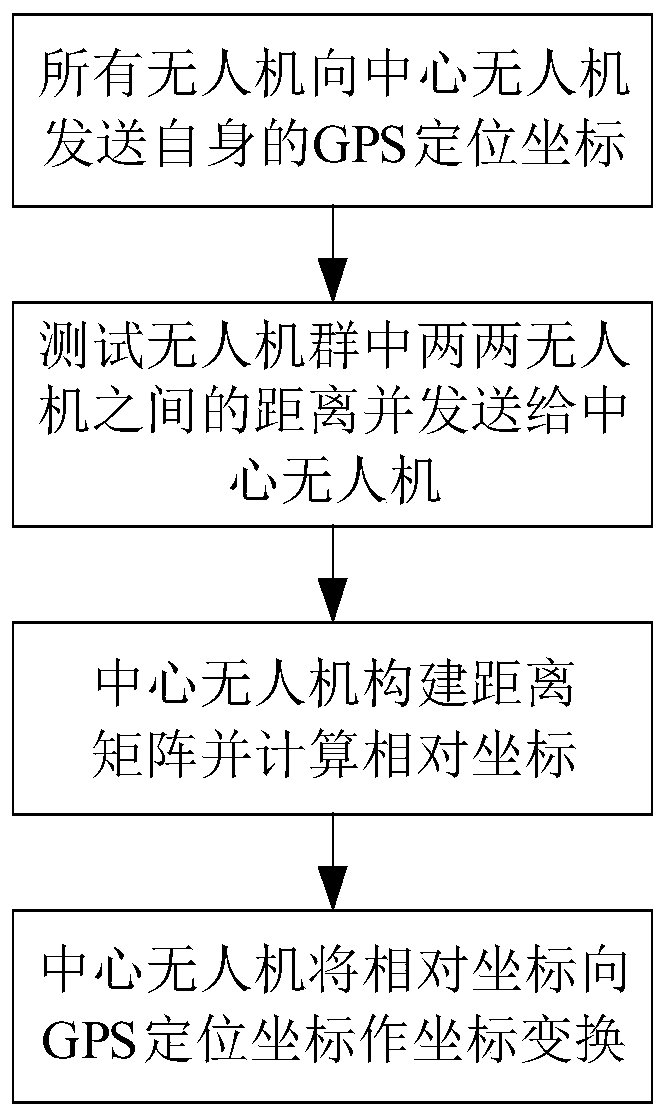
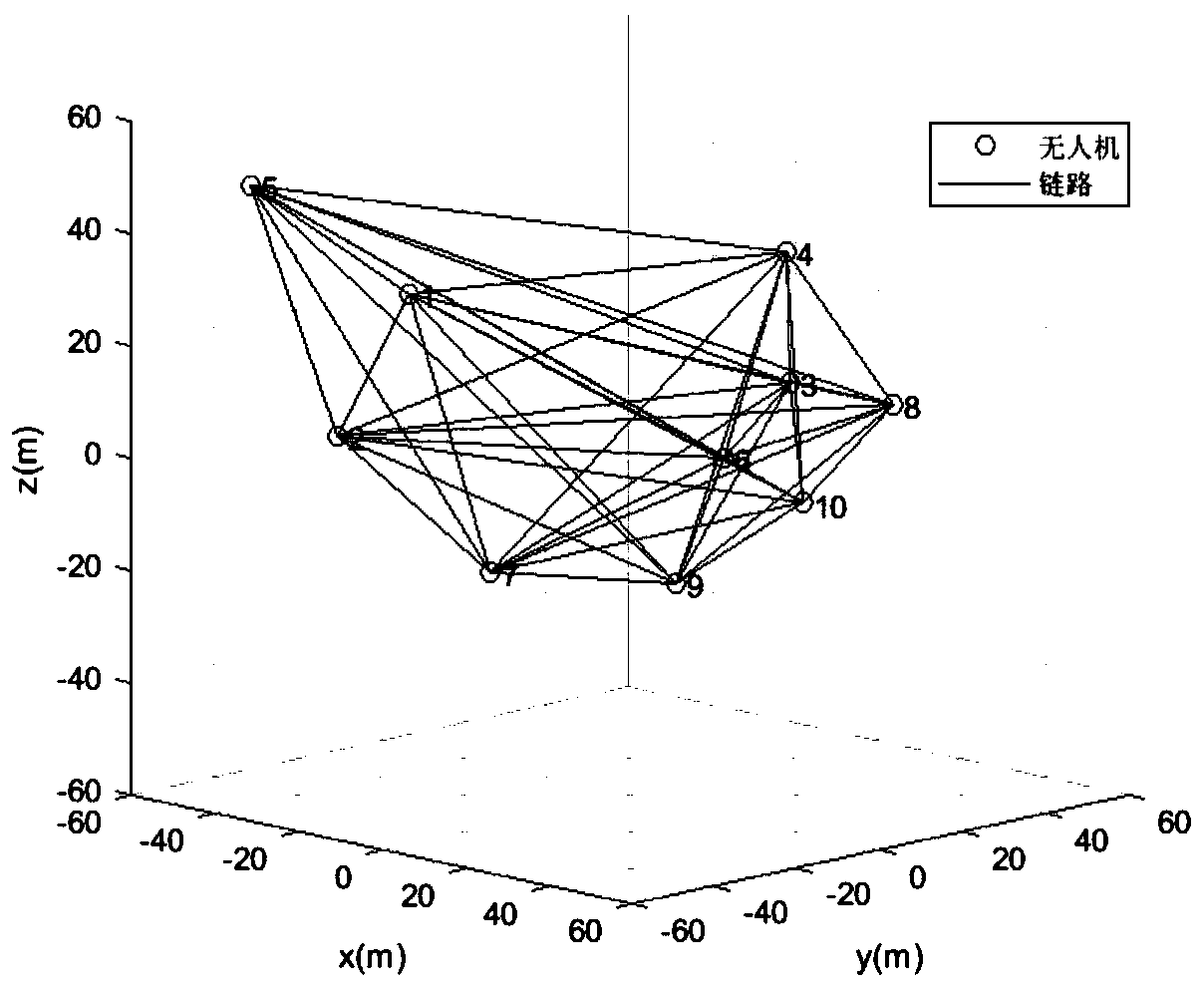
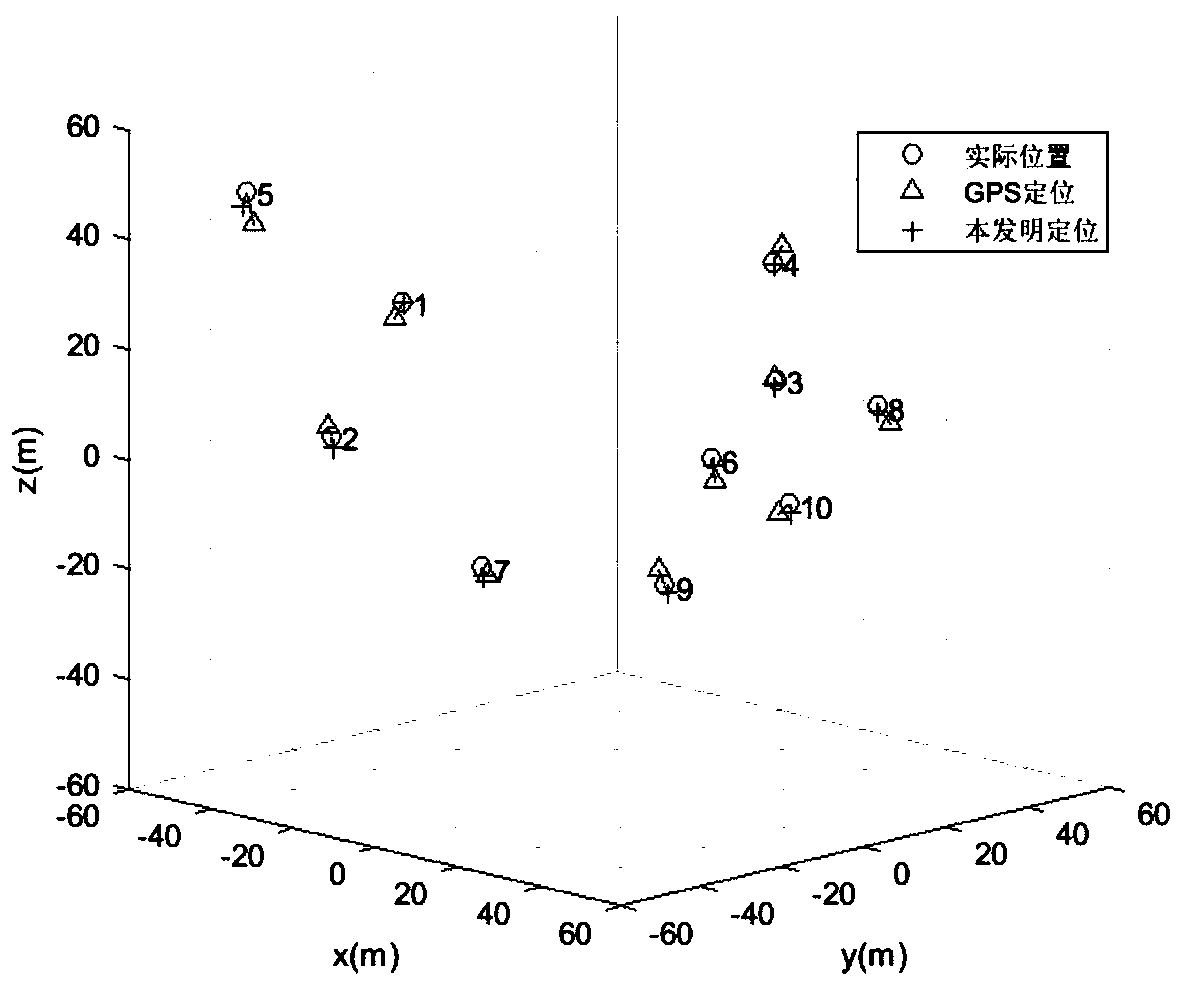
The invention discloses a three-dimensional cooperative positioning method for an unmanned aerial vehicle group, and mainly solves the problems that an existing method only adopts a GPS to position the unmanned aerial vehicle group, and the positioning error is large. According to the scheme, the method comprises the steps of: allowing all unmanned aerial vehicles in an unmanned aerial vehicle group to send GPS positioning coordinates of the unmanned aerial vehicles to a central unmanned aerial vehicle undertaking a calculation task; testing the distance between every two unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle group, and sending the measured distance information to the central unmanned aerial vehicle; allowing the central unmanned aerial vehicle to construct the received distance information into a distance matrix, and obtaining the relative coordinates of all the unmanned aerial vehicles in the unmanned aerial vehicle group by adopting a multi-dimensional scale analysis algorithm according to the distance matrix; and allowing the central unmanned aerial vehicle to convert the relative coordinates into GPS positioning coordinates by adopting a least square principle, calculate the absolute coordinates of the unmanned aerial vehicles, and send the absolute coordinates to the whole unmanned aerial vehicle group. The method can reduce the GPS positioning error, accurately estimates the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and can be used for the unmanned aerial vehicle group to cooperatively complete the path planning of express transportation, disaster monitoring, agricultural production, formation performance and combat tasks.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
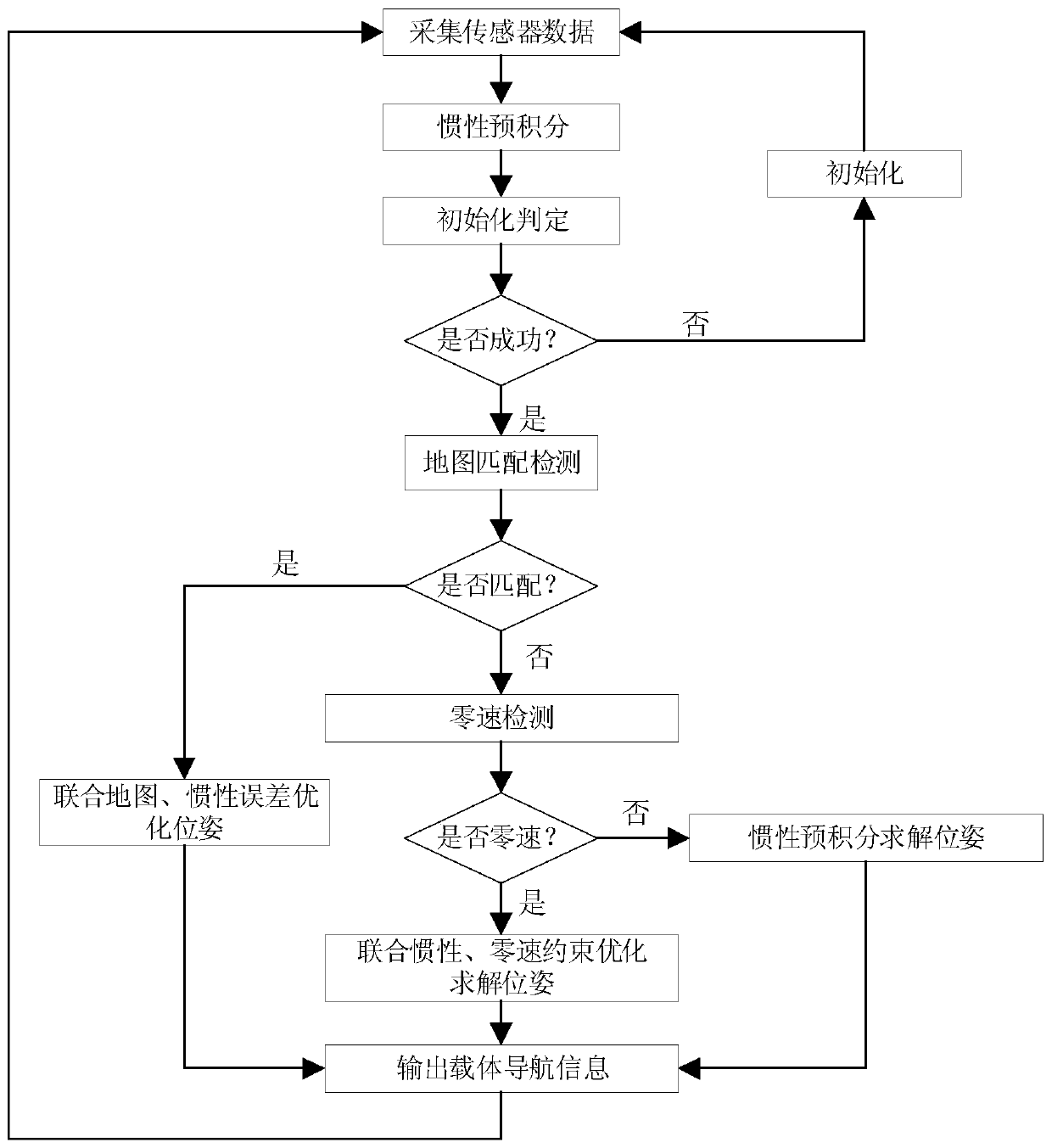
Map-assisted inertial pre-integral pedestrian navigation method
ActiveCN110207692AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometer dataGyroscope
The present invention discloses a map-assisted inertial pre-integral pedestrian navigation method. Data of an accelerometer and data of a gyroscope at moment k are collected periodically. Navigation information of a carrier at moment k is predicted using the obtained data pre-integral measured by an inertial sensor. It is determined whether an navigation system has been initialized. If yes, the map matching detection is performed. If the matching succeeds, overall optimization of poses is performed on a unity map and an inertial error and navigation information of the carrier is output. If thematching fails, zero-speed detection is performed. If a zero-speed does not exist, an inertial pre-integral solution pose is performed. If the zero-speed exists, the inertial error and the zero-speedconstrained optimization solution pose are united to output the navigation information of the carrier. The present invention, using the value measured by the inertial sensor, performs the pre-integral optimization solution to output the pedestrian navigation information and carries out the zero-speed constrained correction and optimization. Moreover, map information is imported for optimizing overall traces and removing cumulative errors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
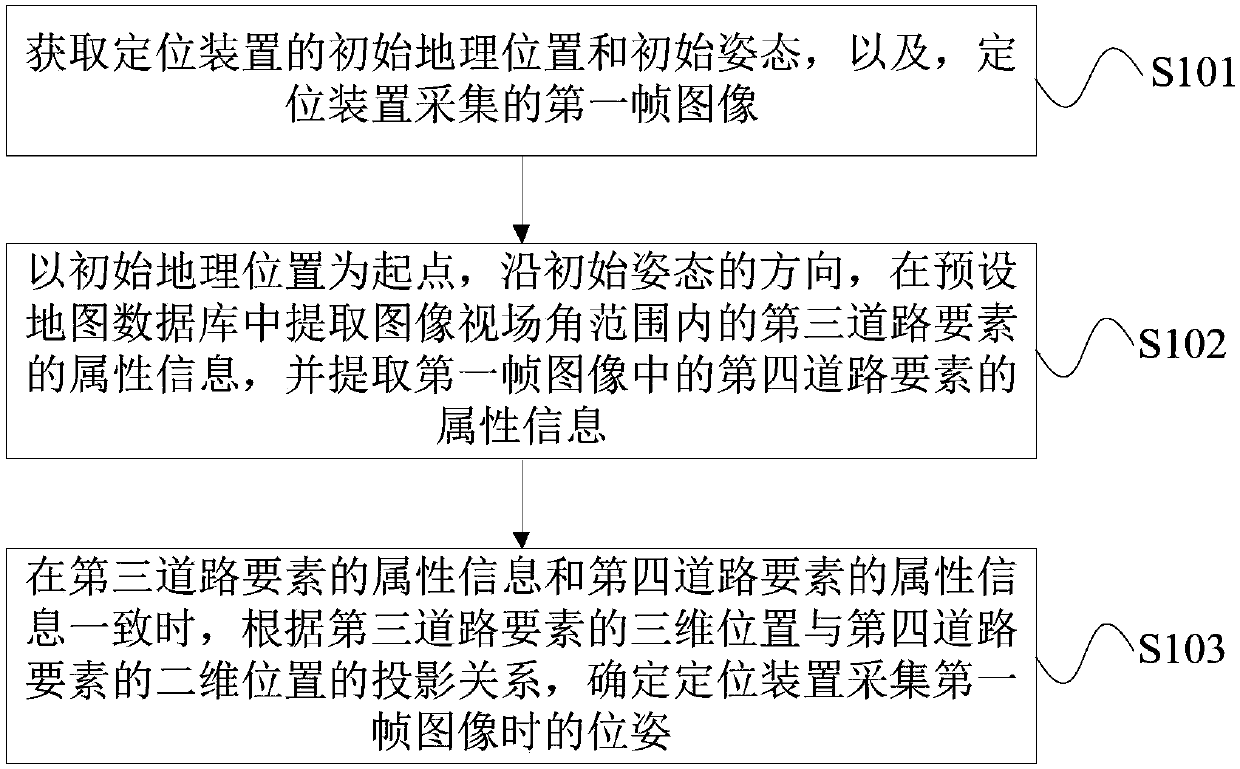
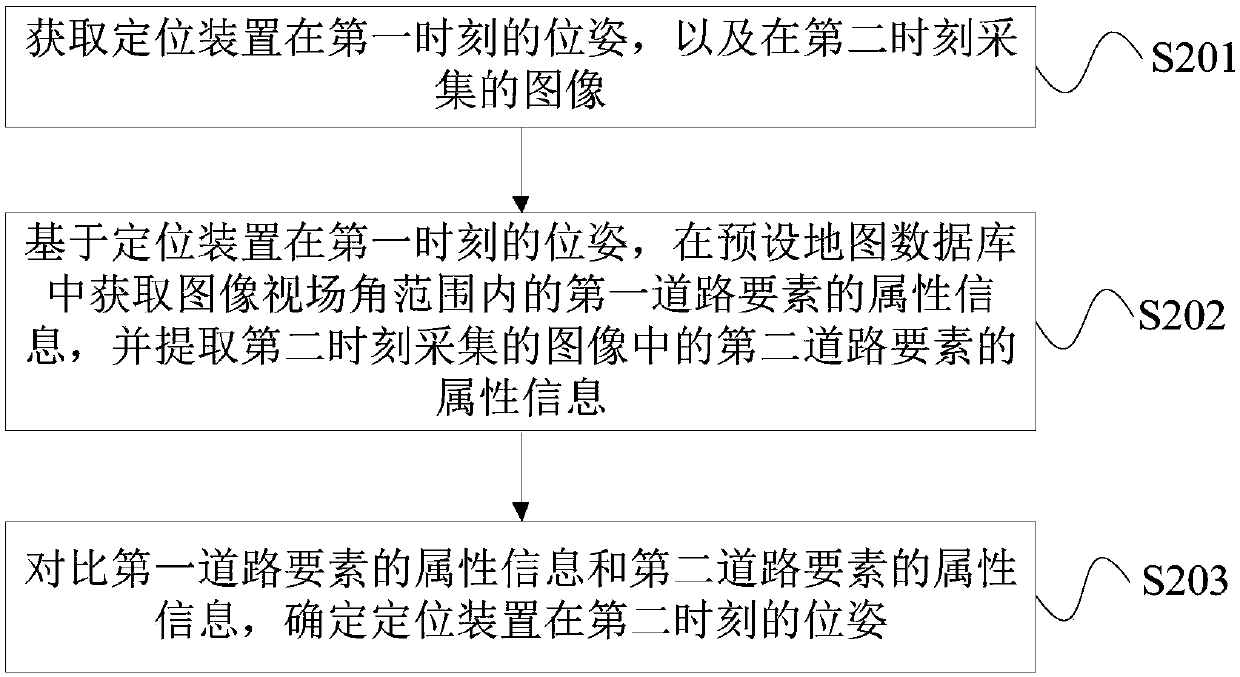
Positioning method, positioning device and storage medium
ActiveCN110617821AImprove robustnessLow costImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationComputer graphics (images)Image field
The invention provides a positioning method, a positioning device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the pose of the positioning device at a first moment and animage collected at a second moment; obtaining attribute information of a first road element in an image field angle range in a preset map database according to the pose of the positioning device at the first moment, and extracting attribute information of a second road element in the image collected at the second moment; and comparing the attribute information of the first road element with the attribute information of the second road element, and determining the pose of the positioning device at the second moment. Low-cost and high-precision positioning can be realized through the positioningmethod, the positioning device and the storage medium.
Owner:BEIJING DIDI INFINITY TECH & DEV
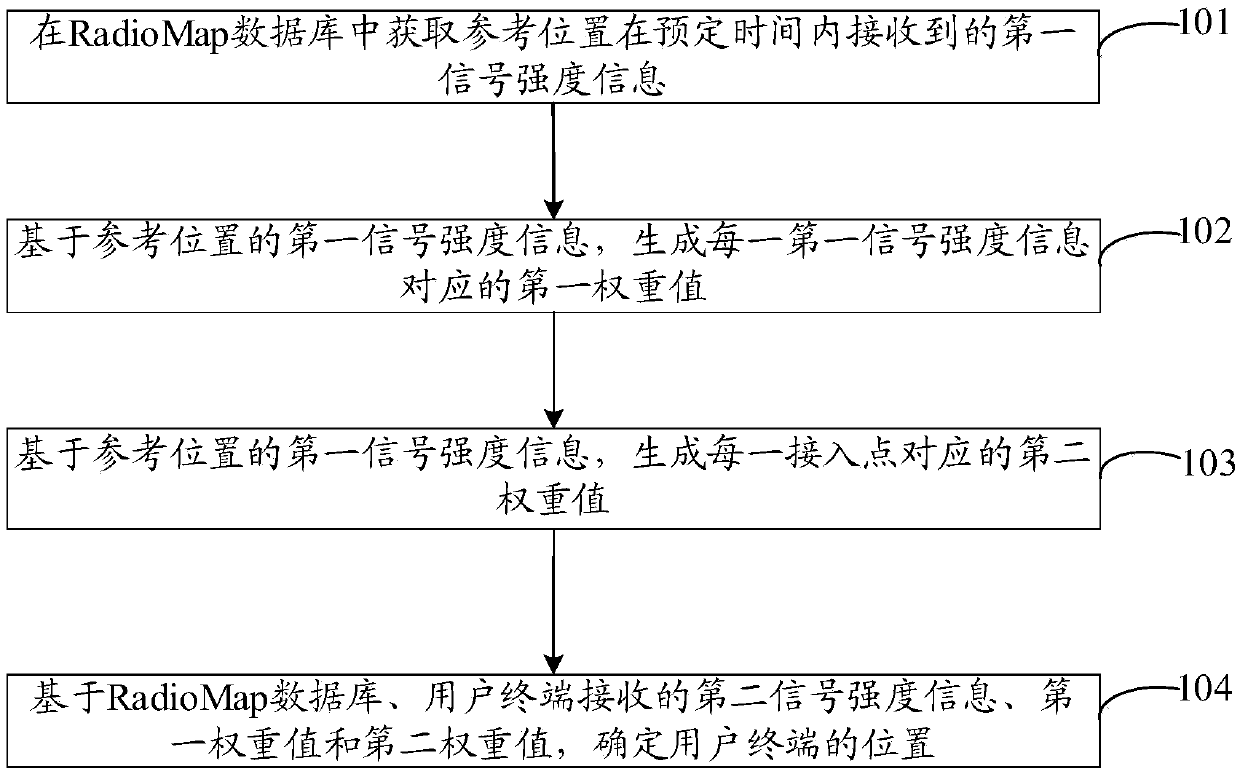
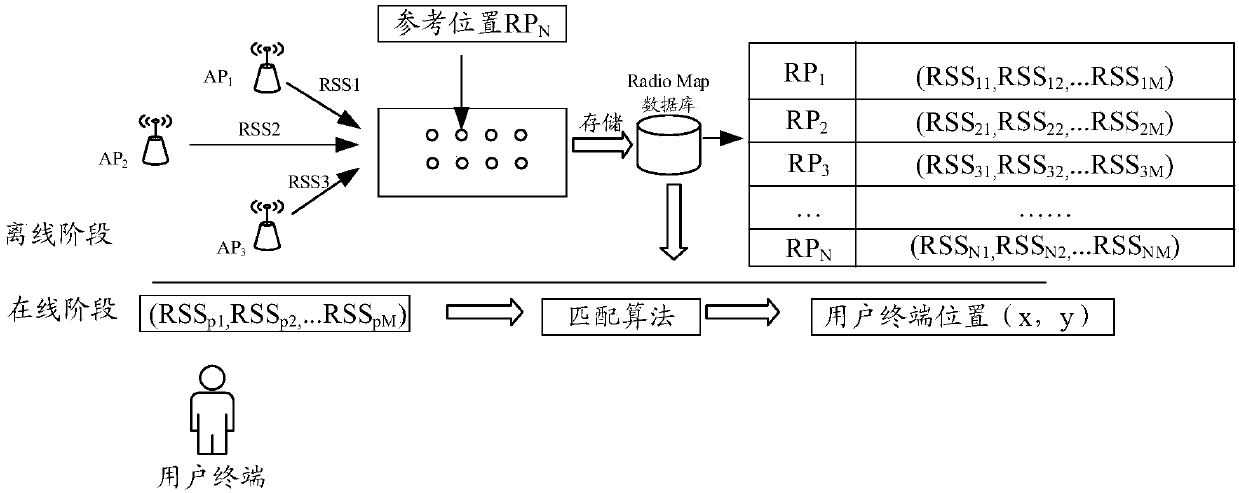
Positioning method, terminal and computer readable storage medium
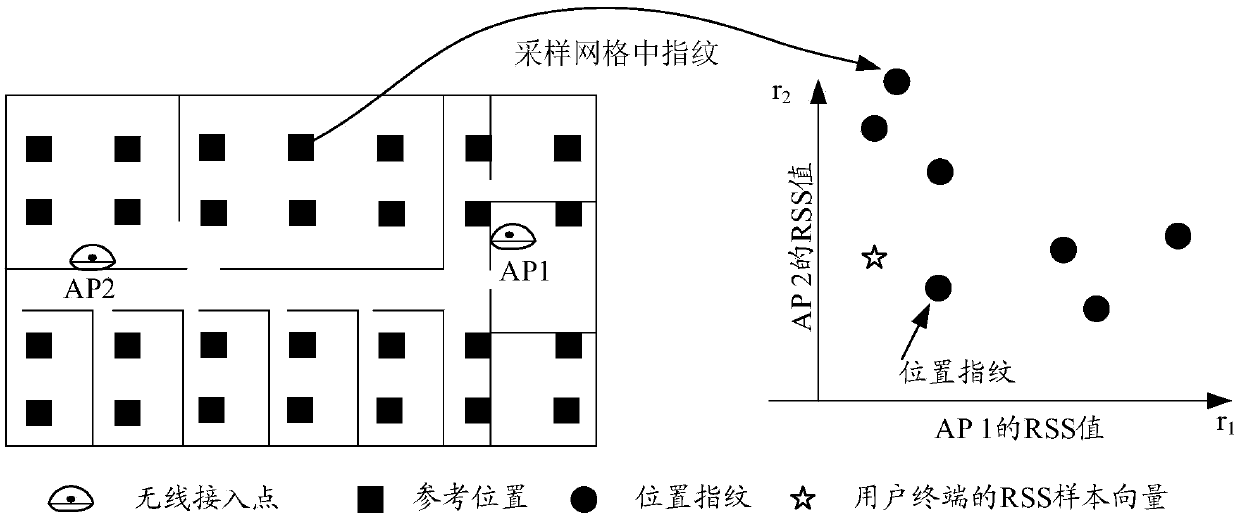
ActiveCN111225334ACorrect position errorNo longer affects positioning accuracyParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesEngineeringRadio map
The invention discloses a positioning method which comprises the following steps: in a Radio Map database, obtaining first signal strength information received by a reference position within a presettime, wherein the first signal strength information is the signal strength of a signal which is received by the reference position at different time points and is transmitted for an access point; based on the first signal intensity information of the reference position, generating a first weight value corresponding to each piece of first signal intensity information and a second weight value corresponding to each access point; determining the position of the user terminal based on the Radio Map database, second signal strength information received by the user terminal, the first weight value and the second weight value. The invention further discloses a terminal and a computer readable storage medium.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD +2
Method for correcting measurement errors of inertial navigation system based on global positioning system (GPS) information
ActiveCN103471593ACorrect position errorTime overheadNavigational calculation instrumentsWorkloadTime cost
The invention discloses a method for correcting measurement errors of an inertial navigation system based on global positioning system (GPS) information. A series control method is adopted; the external GPS position information and speed information are introduced to correct an inertial navigation error; by virtue of an appropriate controller, input signal noise can be filtered, system input can be tracked by system output, and speed and position errors of the inertial navigation system can be corrected. The method does not depend on the accuracy of a system error model and is high in operation speed and low in time cost; when the external measurement data frequency is high, the speed and position measurement errors of the inertial navigation system can be corrected; the system error model can be re-built by correcting the parameters of the controller; the workload is small.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
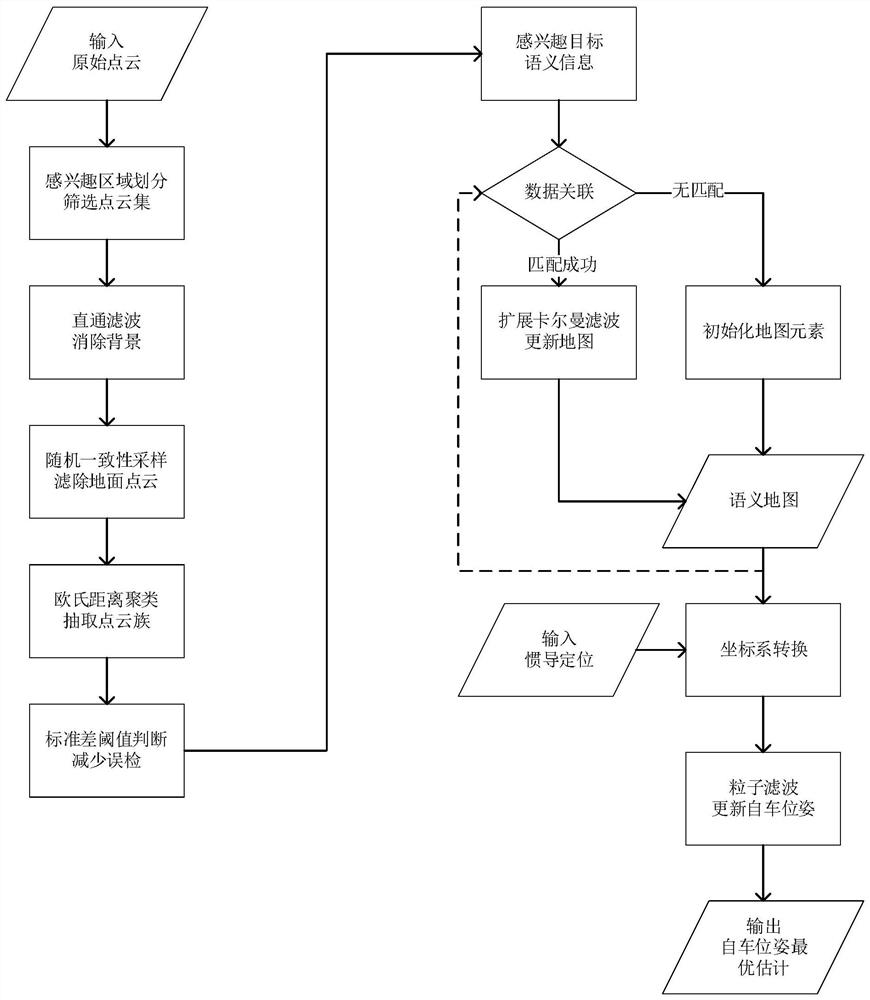
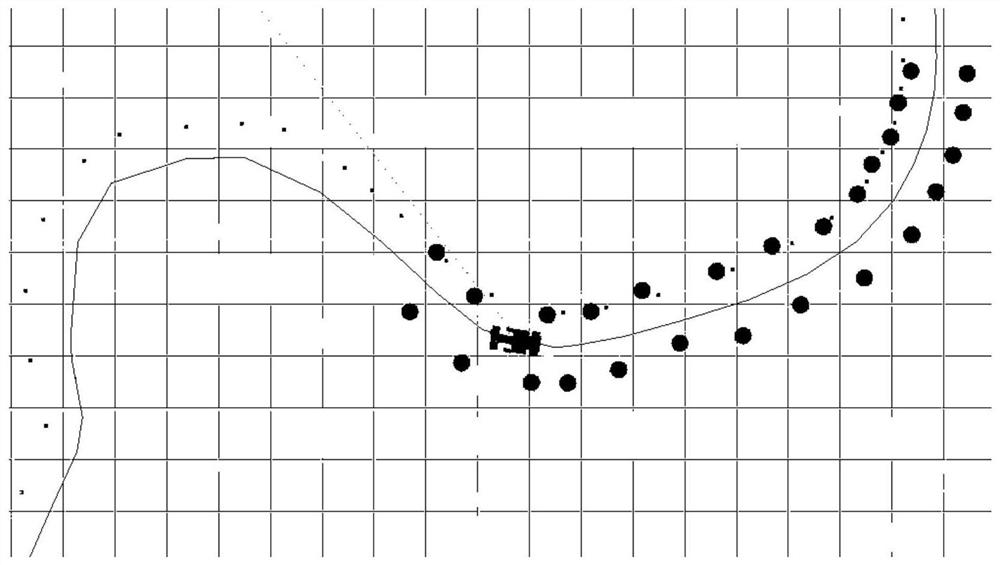
Target-level semantic positioning method based on vehicle-mounted laser radar
PendingCN113238251ASustainable and stable outputStrong real-timeNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingTransverse Mercator projectionGps positioning
The invention discloses a target-level semantic positioning method based on a vehicle-mounted laser radar. The method comprises the following steps: scanning a surrounding environment by using a vehicle-mounted laser radar, collecting point cloud data, and performing preprocessing; processing the point cloud by using random consistency sampling and Euclidean clustering, and detecting the central position of a static interested target; solving the world pose of the interested target through horizontal axis Mercator projection by using vehicle-mounted laser radar installation parameters and a GPS positioning result; constructing a semantic map or updating semantic information of an interested target in the semantic map by using an extended Kalman filtering algorithm; and correcting the positioning drift of the vehicle in real time by taking the relative pose of the interested target and the vehicle as an observed quantity by using a particle filtering algorithm. According to the invention, the positioning error of the inertial navigation unit in high-rise and tunnel scenes can be effectively corrected, the problem of positioning drift of the vehicle in a static state is solved, and compared with a positioning module only using inertial navigation, the application range is wider.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
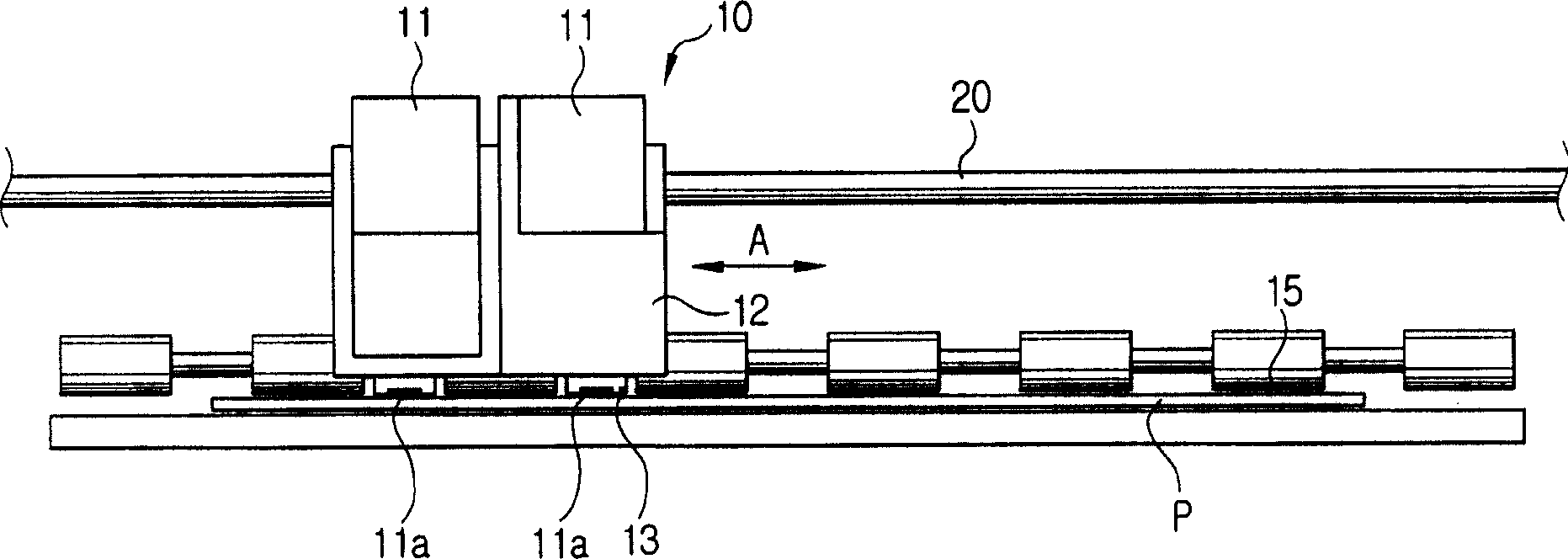
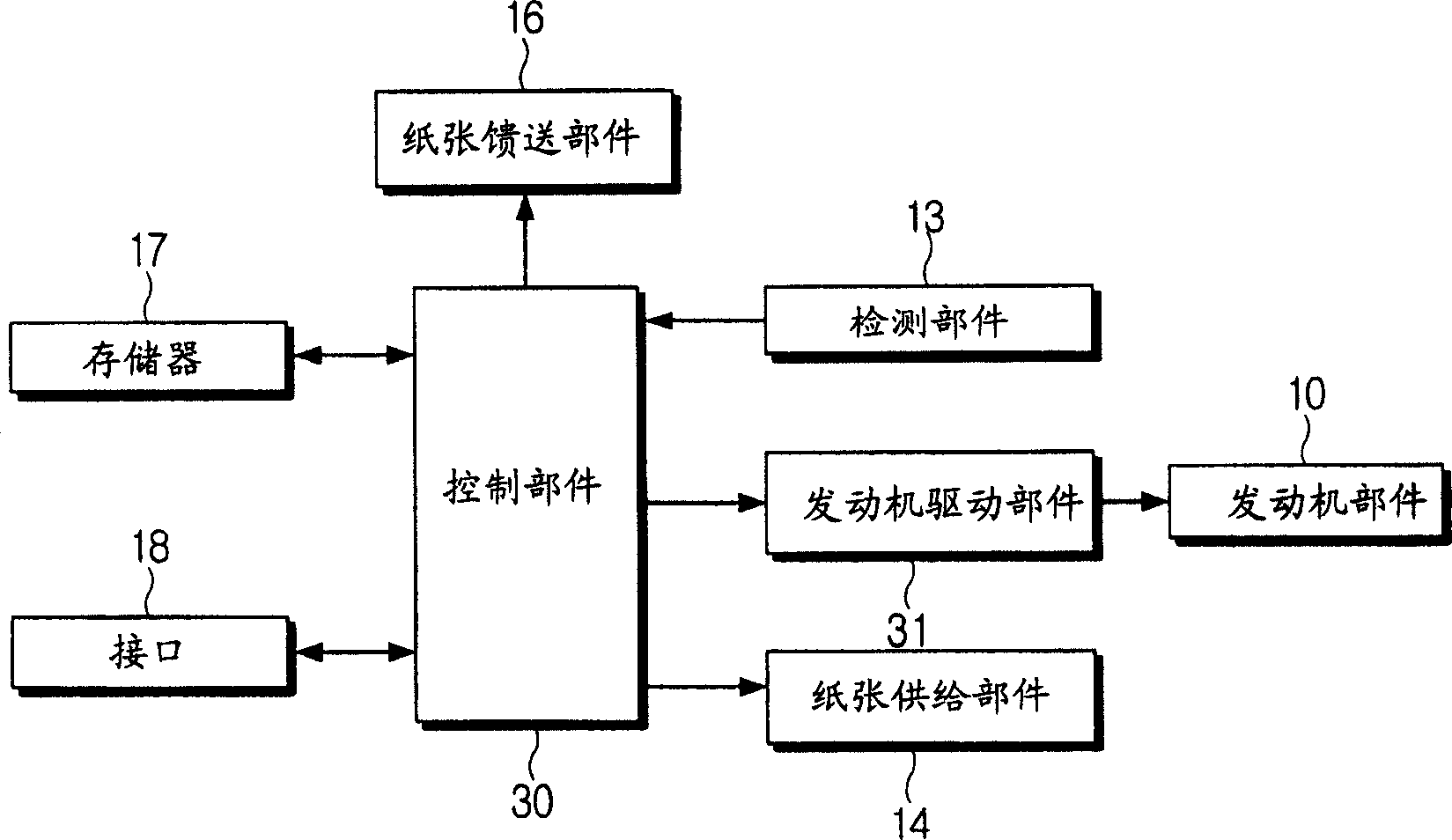
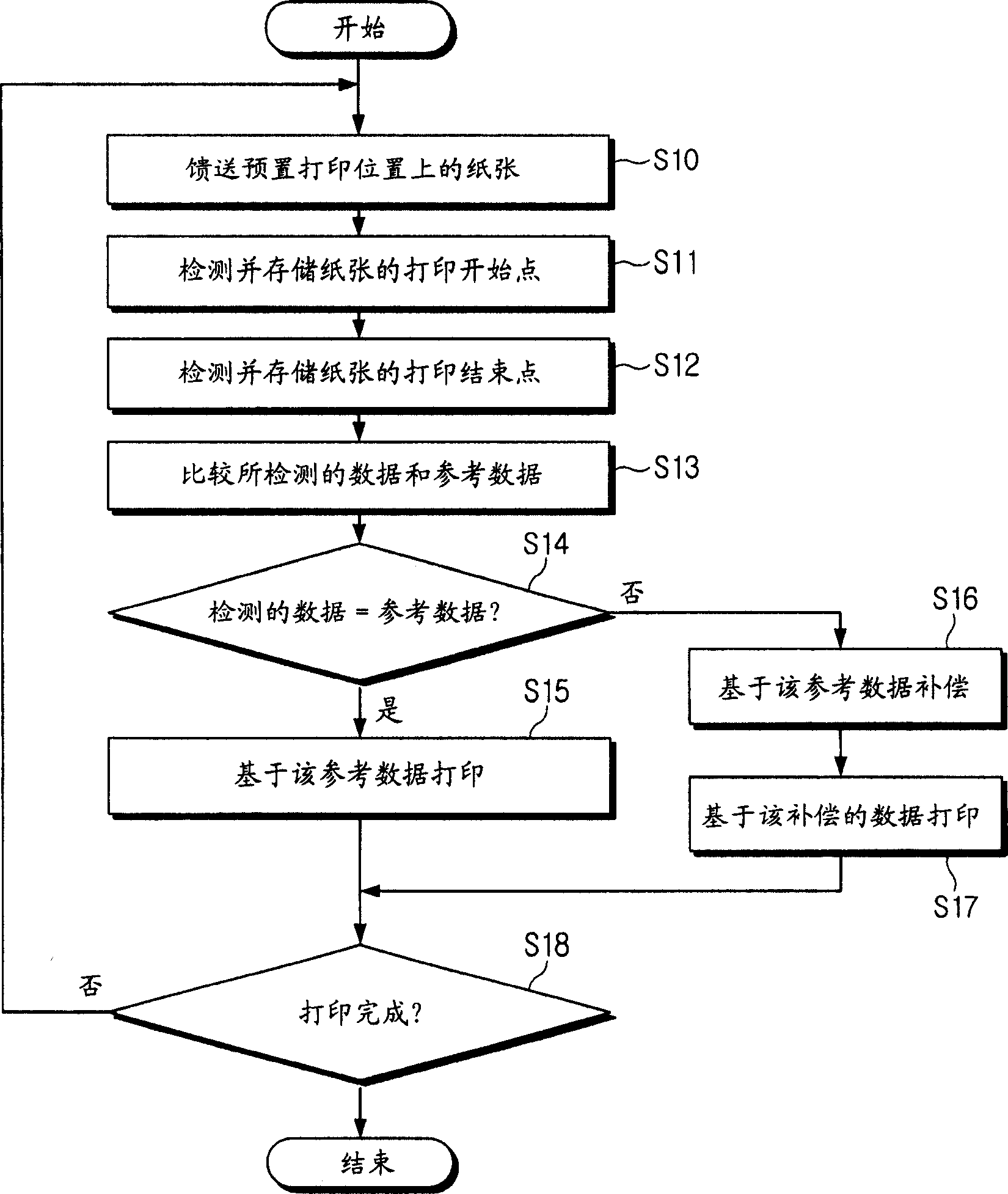
Printing method and image forming apparatus for performing the same
InactiveCN1647921ACorrect position errorPower drive mechanismsEducational modelsPaper basedEngineering
In an image forming apparatus using an engine part which is capable of moving in the width direction of paper fed in the print direction, a printing method has the steps of measuring a position in the width direction of paper fed in the print position, comparing measured position value with a preset reference position value, compensating a position to be printed based on the compared difference, and printing on the paper based on the compensated position data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
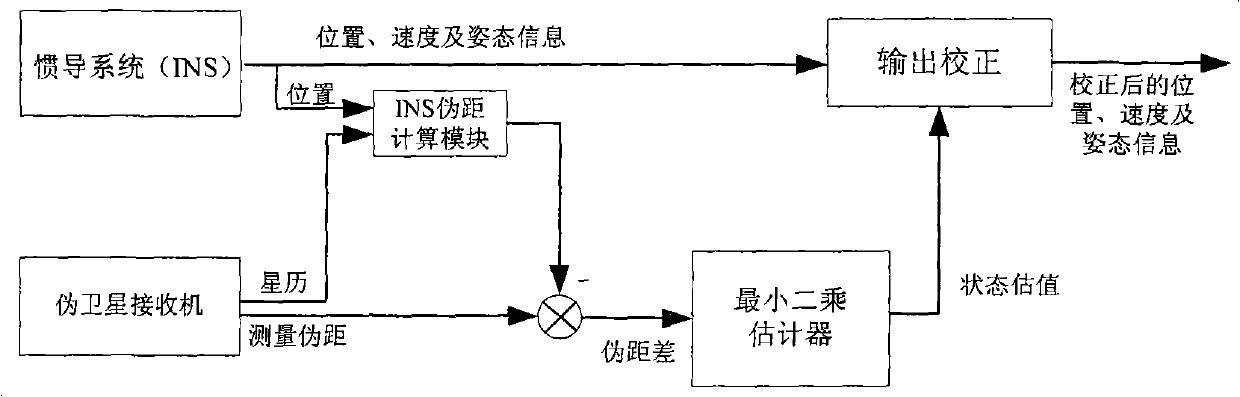
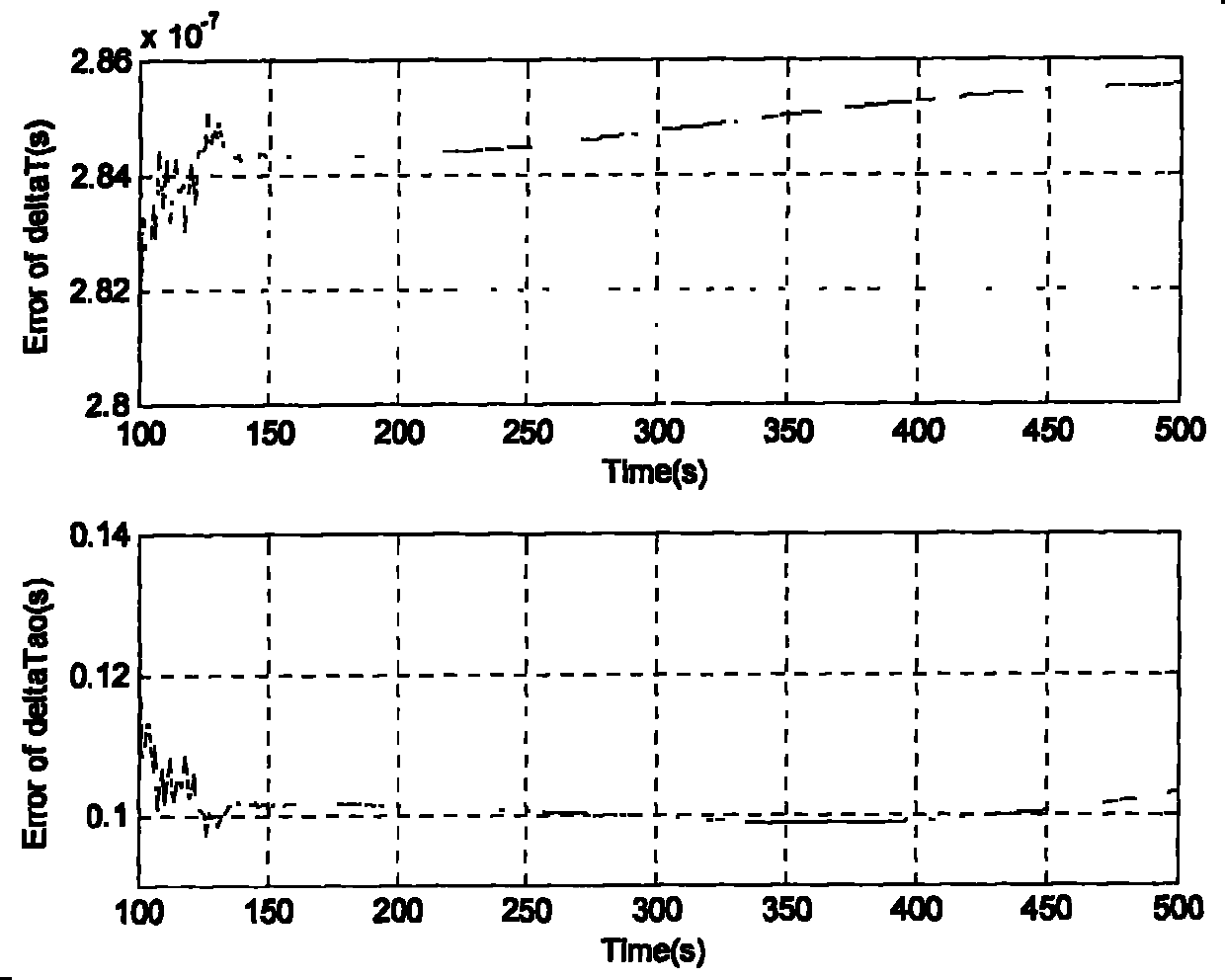
Double pseudo satellite aided position calibration method of inertial navigation system
ActiveCN101793529ACorrect position errorHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingMathematical modelAid positions
The invention relates to a method for calibrating the position error of an inertial navigation system aided by double pseudo satellites, which comprises the following steps: taking the position errors of the inertial navigation system, i.e. delta x and delta y, the out-of-sync time between the inertial navigation system and the pseudo satellites, i.e. delta tau, and the clock error of a pseudo satellite receiver, i.e. delta T0, as variables to be calculated; subtracting a calculated pseudo range from the measured pseudo range output by the pseudo satellite receiver to calculate the clock error of the pseudo satellite receiver, wherein the calculated pseudo range is the inertial navigation system-pseudo satellite distance calculated based on the output of inertial navigation system when the carrier starts to receive the signals of the two pseudo satellites; establishing a mathematical model between the difference between the measured pseudo range of the pseudo satellite receiver and the calculated pseudo range and the variables to be calculated, and using the least square method to estimate the variables to be calculated; and using the estimated state vector to calibrating the position information of the inertial navigation system, and then outputting. The invention calibrates the position errors of the inertial navigation system by using the information of the two pseudo satellites, and improves the navigation accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
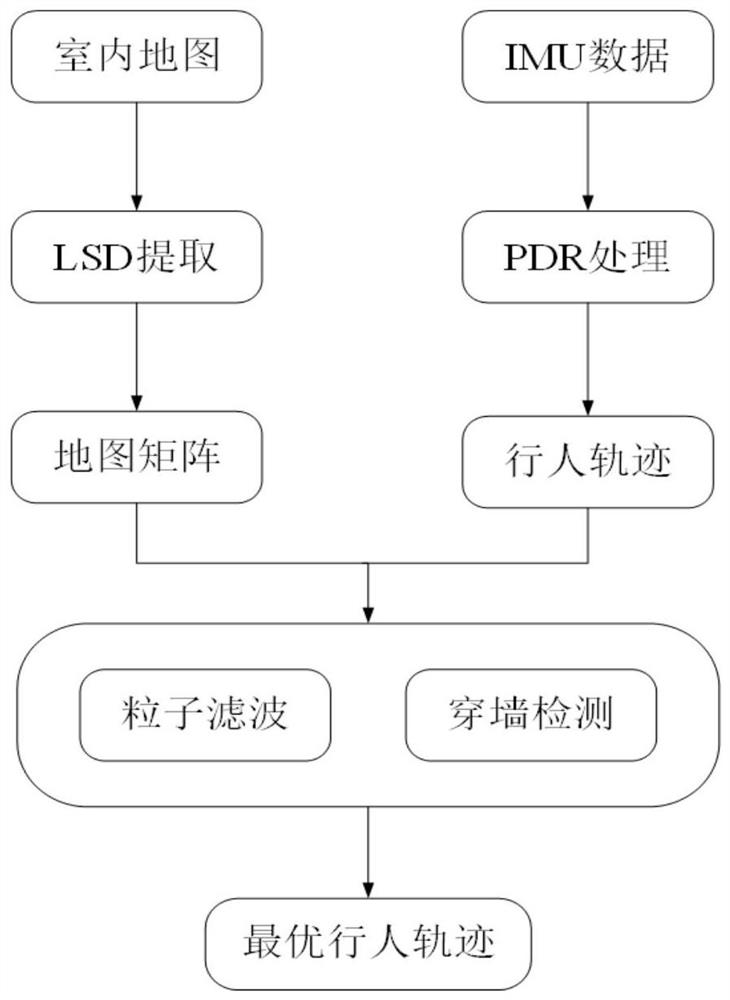
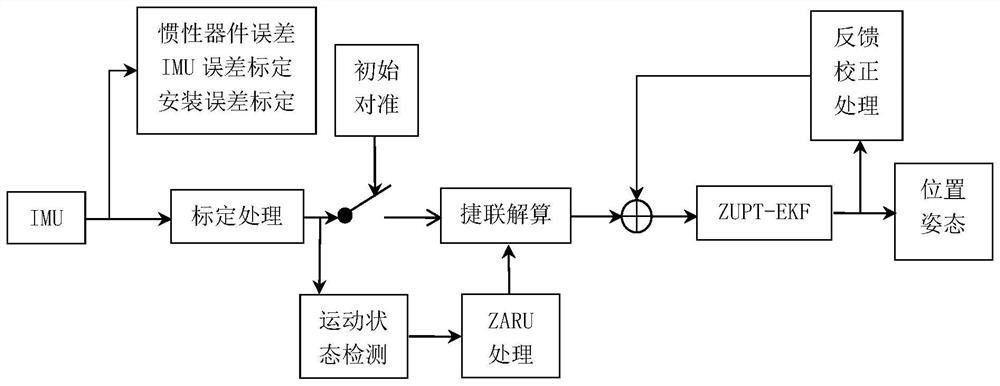
Pedestrian indoor positioning method fusing PDR and priori map
PendingCN112562077ACorrect position errorHigh positioning accuracyImage analysisNavigational calculation instrumentsFeature extractionParticle filtering algorithm
The invention discloses a pedestrian indoor positioning method fusing a PDR and a prior map. The method comprises the steps: firstly respectively obtaining IMU data of an indoor map and a pedestrian,performing the LSD feature extraction of the obtained indoor map, and converting map information into a matrix with wall information; carrying out PDR processing on the obtained pedestrian IMU data toobtain an original pedestrian indoor track, and aligning the original pedestrian indoor track with a map after being processed; judging a'through-wall 'phenomenon by utilizing map information and theprocessed track information to obtain through-wall points and coordinates of the through-wall points; and finally, obtaining an optimal trajectory coordinate by adopting a particle filter algorithm,and updating a positioning result to obtain an optimal pedestrian indoor trajectory. According to the method, the positioning error caused by PDR integral characteristics is corrected, the positioningprecision is improved, and a better positioning effect is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
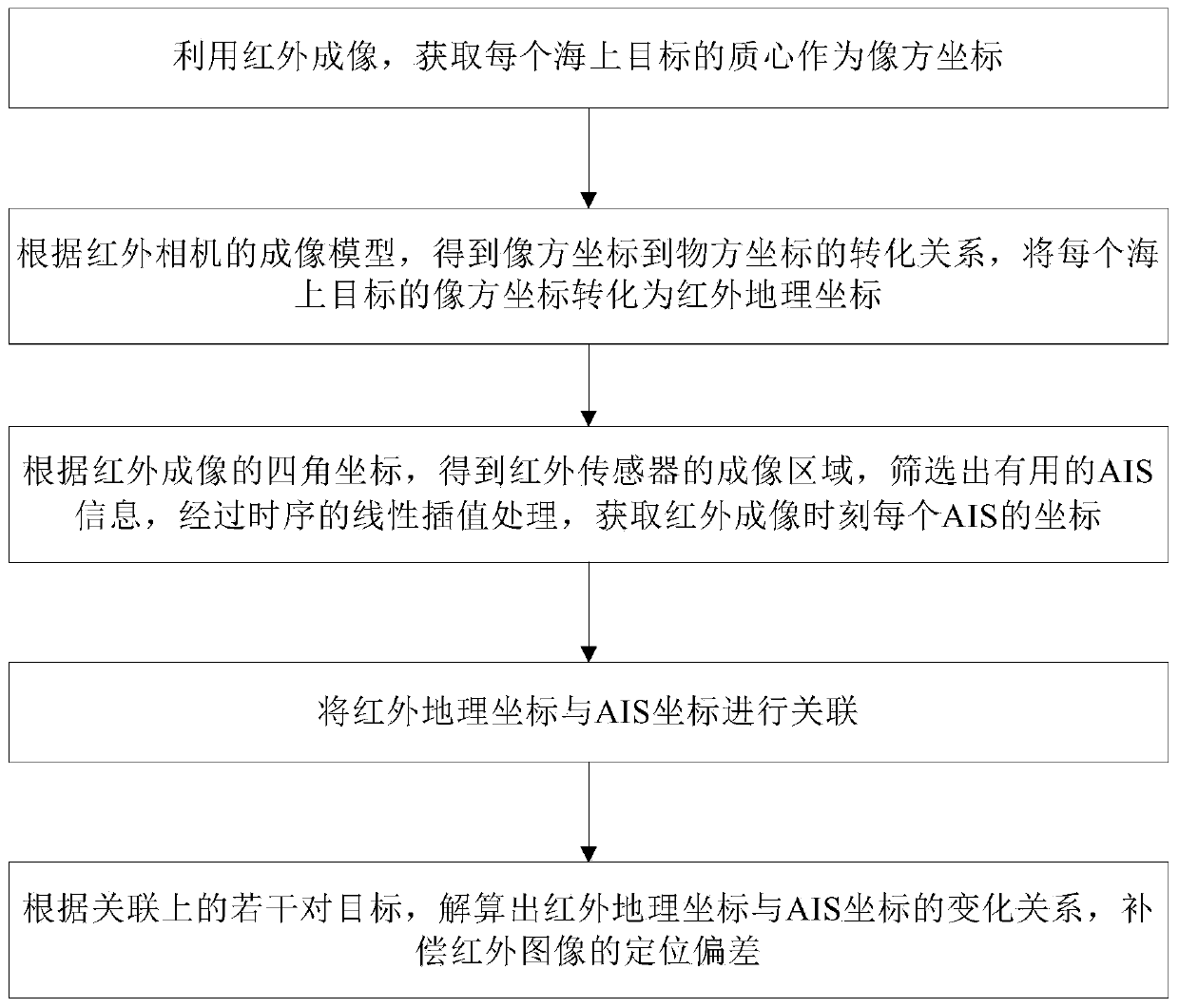
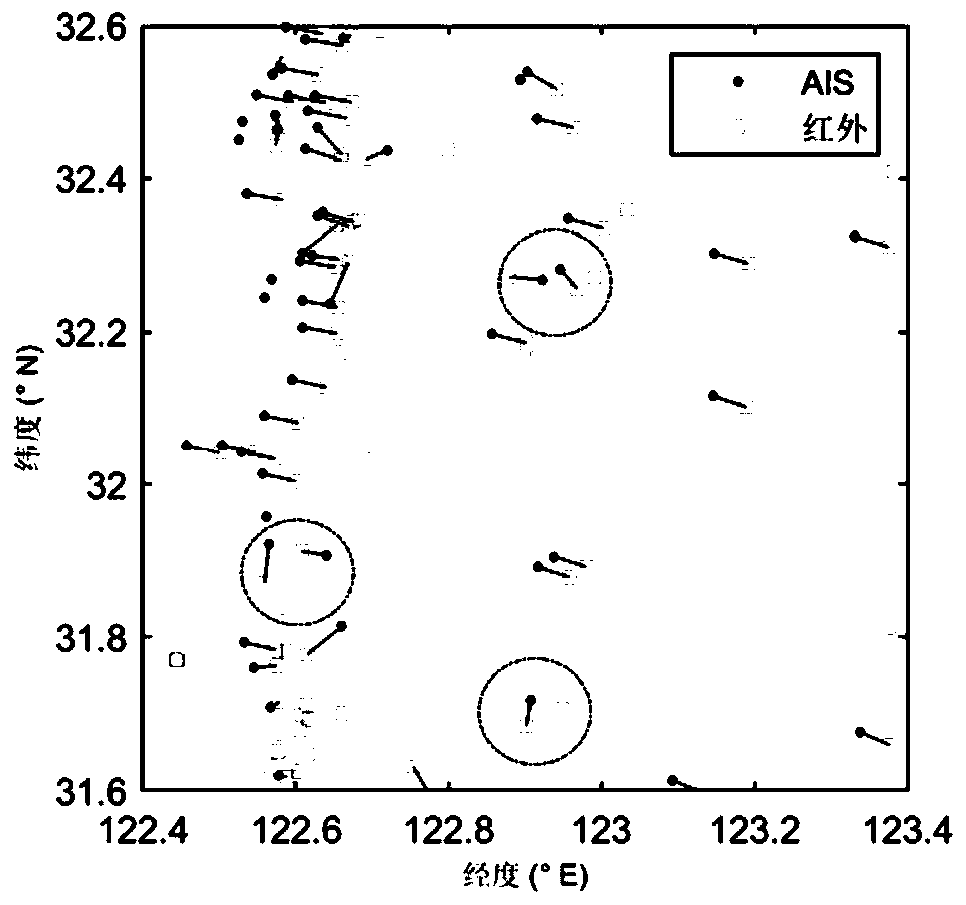
Co-location method for marine targets based on satellite-borne AISs and infrared camera
ActiveCN110780327ACorrect position errorHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingComputer visionRemote sensing
The invention discloses a co-location method for marine targets based on satellite-borne AISs and an infrared camera. The method comprises: S1, using infrared imaging to obtain a centroid of each seatarget as an image space coordinate; S2, according to an imaging model of the infrared camera, acquiring the conversion relationship from the image space coordinates to object space coordinates, and converting the image space coordinate of each marine target into an infrared geographic coordinate; S3, according to four-corner coordinates of the infrared imaging, obtaining an imaging area of an infrared sensor, screening out useful AIS information, and performing sequential linear interpolation processing to obtain a coordinate of each AIS at an infrared imaging moment; S4, associating the infrared geographic coordinates with the AIS coordinates; and S5, according to the plurality of pairs of associated targets, calculating the change relationship between the infrared geographic coordinatesand the AIS coordinates to compensate the positioning deviation of an infrared image. The co-location method for the marine targets based on the satellite-borne AISs and the infrared camera can correct a location error of the infrared image and improve the location accuracy of non-cooperative targets.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
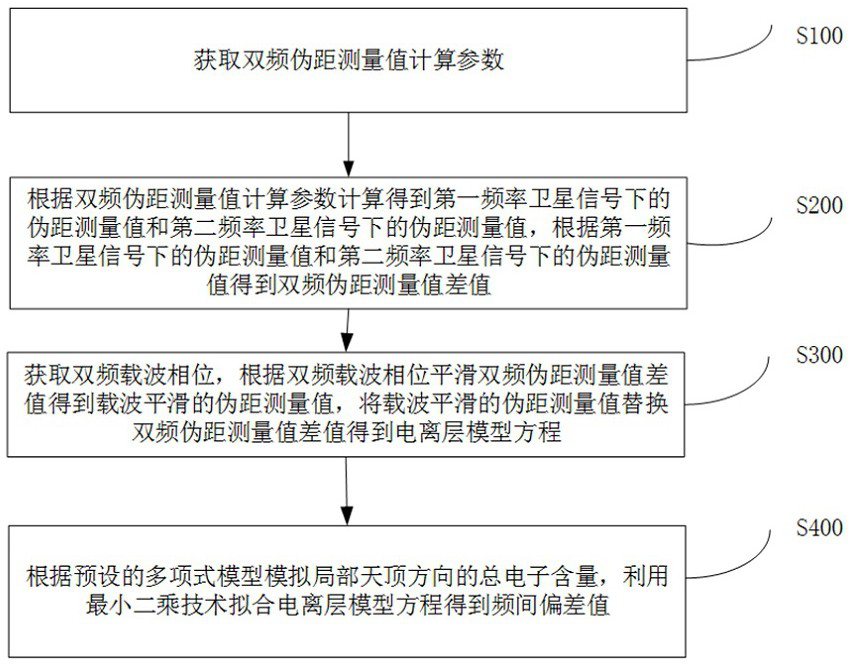
Satellite navigation positioning error correction method and device considering hardware inter-frequency difference
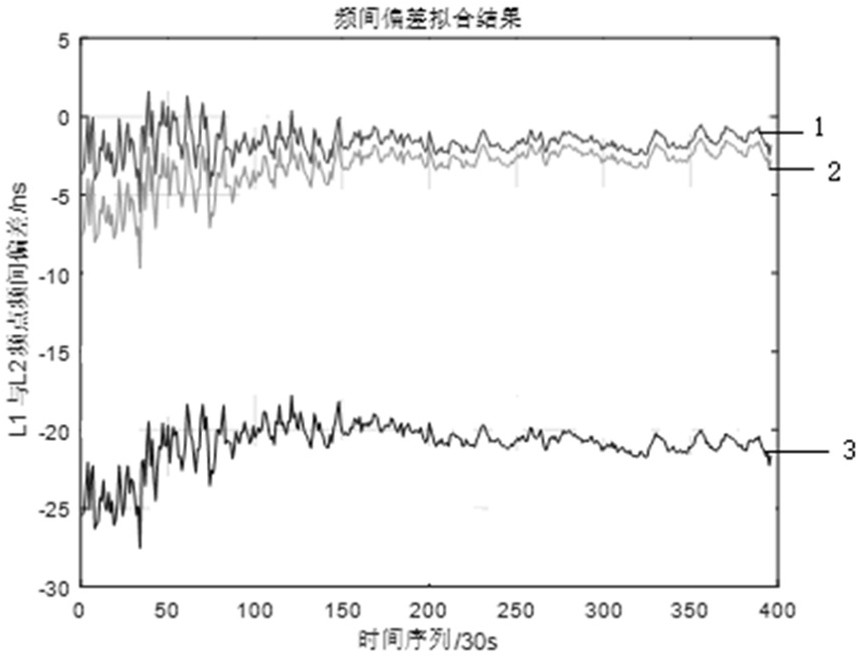
InactiveCN113568020ACorrect position errorImprove fitting accuracySatellite radio beaconingTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
The invention discloses a satellite navigation positioning error correction method and device taking hardware inter-frequency difference into account. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a double-frequency pseudo-range measurement value calculation parameter; according to the dual-frequency pseudo-range measurement value calculation parameter, calculating pseudo-range measurement values under the first frequency satellite signal and the second frequency satellite signal, and according to the pseudo-range measurement values under the first frequency satellite signal and the second frequency satellite signal, acquiring a dual-frequency pseudo-range measurement value difference value; obtaining a dual-frequency carrier phase, obtaining a carrier-smoothed pseudo-range measurement value according to the dual-frequency carrier phase smoothed dual-frequency pseudo-range measurement value difference value, and replacing the dual-frequency pseudo-range measurement value difference value with the carrier-smoothed pseudo-range measurement value to obtain an ionosphere model equation; simulating the total electron content in the local zenith direction according to a preset polynomial model, and fitting the ionosphere model equation by using a least square technology to obtain an inter-frequency deviation value. And the difference value of the double-frequency pseudo-range measurement values is smoothed by the high-precision double-frequency carrier phase measurement value, so the positioning error is effectively corrected, and the positioning precision is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
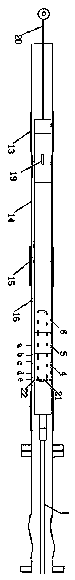
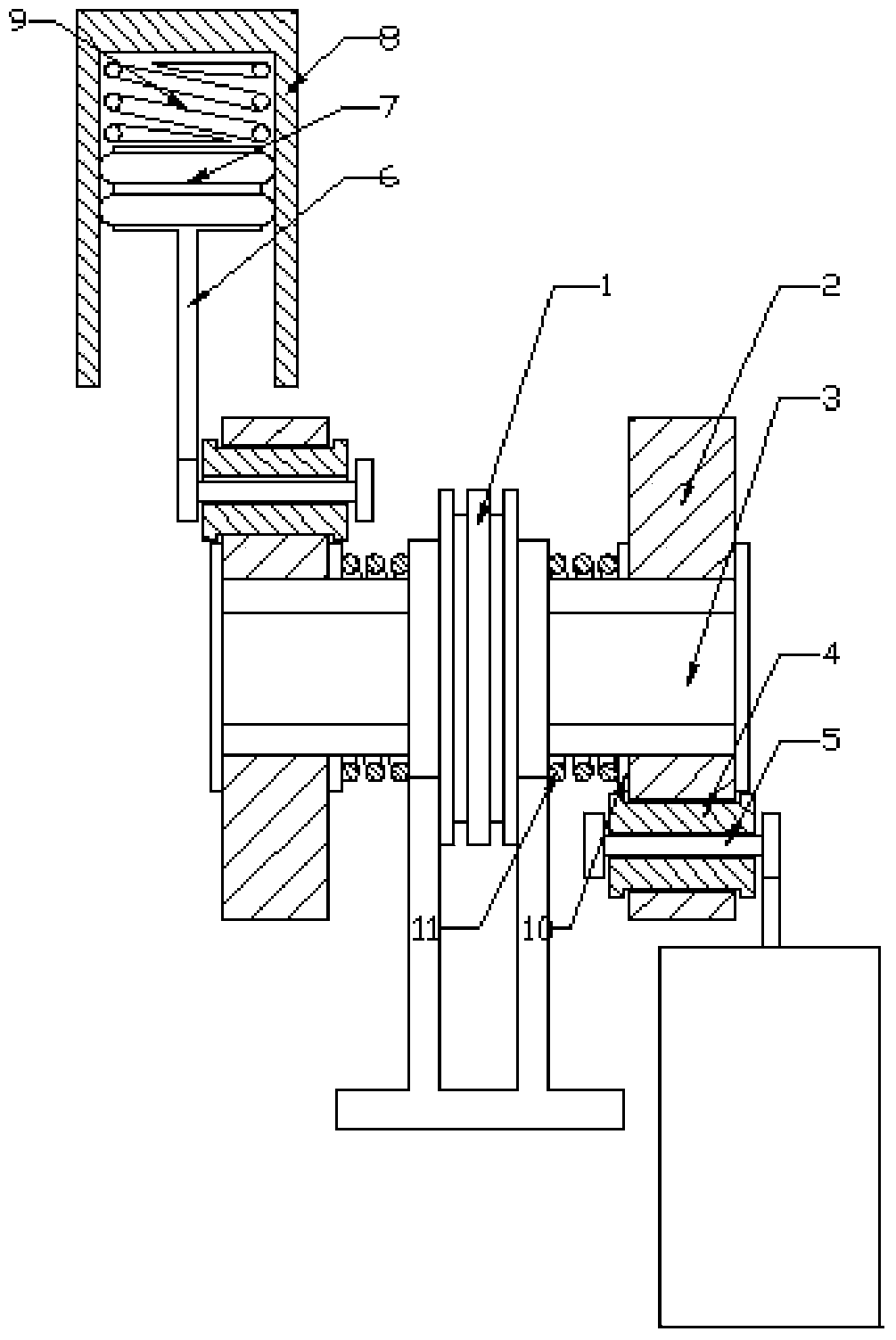
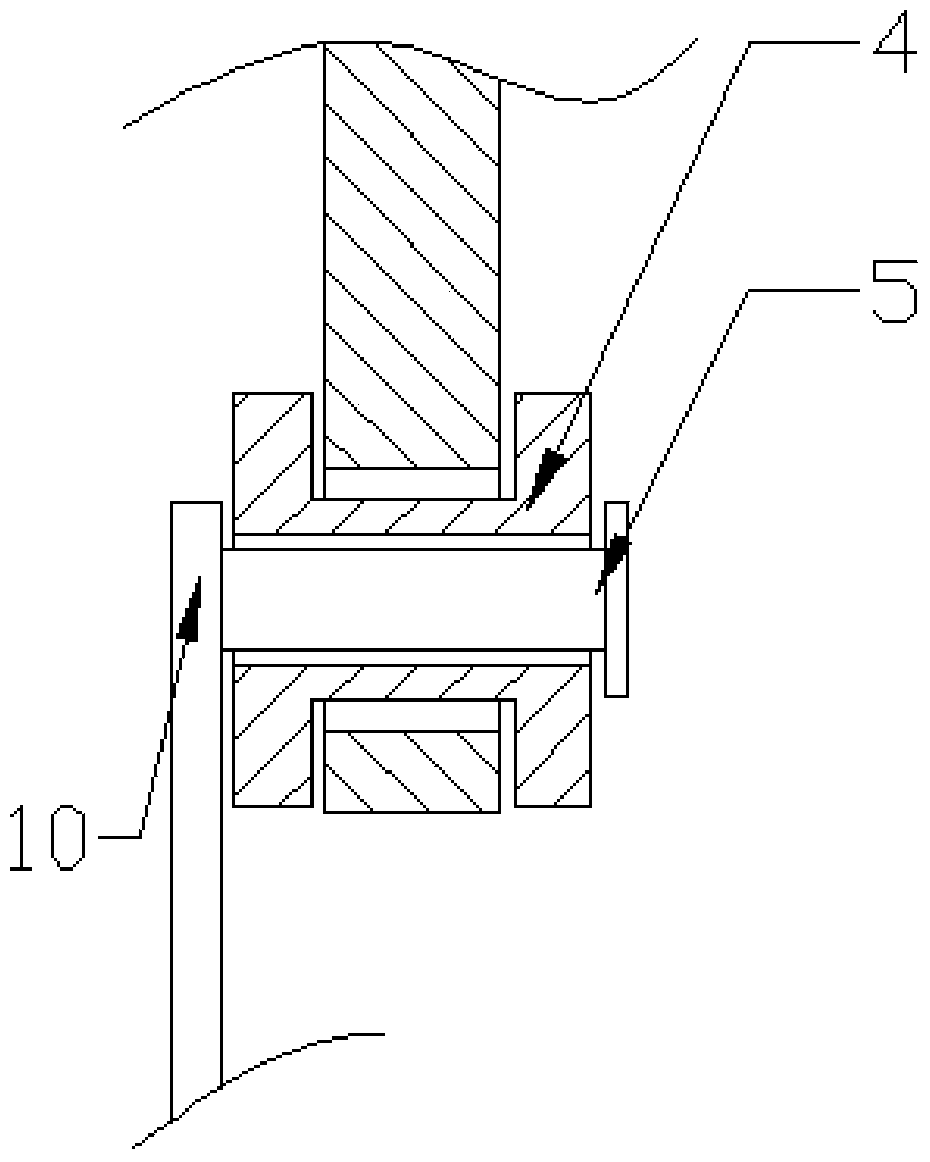
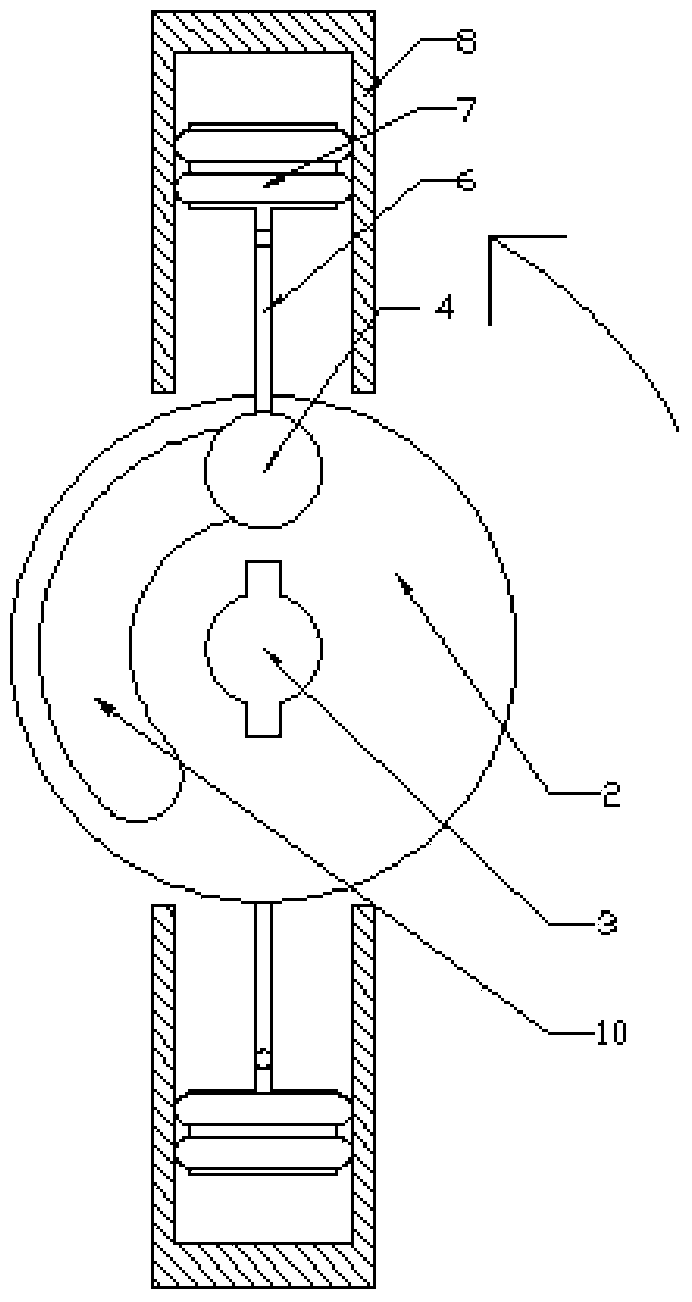
Experimental coiled tubing fracturing tool positioning error measurement system and method
The invention provides an experimental coiled tubing fracturing tool positioning error measurement system and method. The system comprises a coiled tubing, a connector, a fracturing tool, a first short casing, a second short casing, an open window experiment casing, a third casing coupling, a horizontal shaft and a soft measuring tape. One end of the open window experiment casing is connected withthe horizontal shaft while the other end is connected with the second short casing, and the other end of the second short casing is connected with the first short casing. One end of the fracturing tool is connected with the coiled tubing through the connector, and the other end of the fracturing tool is connected with the soft measuring tape. The coiled tubing is positioned in the open window experiment casing, the fracturing tool is positioned in the second short casing and the first short casing, and the open window experiment casing is provided with an open window portion. Aiming at an opening condition that a sensing block of a positioner is right in a hoop of the second short casing, measured positioning errors are corrected according to an up-flow quantity measuring value in an up-lifting process of the fracturing tool, references are provided, perforation positioning accuracy is improved, and project complexity caused by positioning errors are reduced.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Air conditioner compressor
ActiveCN104047827ACorrect position errorReduce sliding frictionPositive displacement pump componentsMulti-stage pumpsEngineeringCylinder block
The invention relates to an air conditioner compressor, comprising a rack, a driving shaft, two driving discs, a driving wheel and an air cylinder array formed by two compression air cylinders, wherein the driving shaft is rotationally connected with the rack, the driving discs are fixed on the two ends of the driving shaft, the driving wheel is fixed between the two driving discs, an arc-shaped bent groove with the radian being 180 degrees is arranged on each driving disc, the arc-shaped bent grooves in the driving discs are in mirroring arrangement with the axis of the driving shaft, the compression axes of the two compression air cylinders are mutually parallel and are vertical to the axis of the driving shaft, each compression air cylinder comprises a cylinder body, a piston, a piston rod and a contracting spring, each cylinder body is fixed on the rack, each contracting spring is arranged between the closed end of the corresponding cylinder body and the corresponding piston, the piston rods are connected with the pistons, and two sliding heads of the compression air cylinders can freely slide along the arc-shaped bent grooves in the two driving discs. Thus, the technical problem that the vibration of equipment is too strong due to large starting energy consumption during working in the prior art is solved.
Owner:江苏昊科汽车空调有限公司
Radio-based integrated navigation method
ActiveCN111189446AHigh positioning accuracyCorrect position errorNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemPosition error
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial measurement, and relates to suppression of inertial navigation position error divergence by using radio direction finding and ranging information and barometric altimeter information. According to the scheme, radio and barometric altimeter error models are established, radio direction finding errors and barometric altimeter errors are estimated through Kalman filtering, and navigation system position and attitude errors are corrected so as to improve the elevation precision of a positioning and orientation system.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Double-satellite integrated positioning method based on inertial sensor
InactiveCN106595655AImprove applicabilityLow costNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterIntegrated design
The invention provides a double-satellite integrated positioning method based on an inertial sensor. The double-satellite integrated positioning method based on the inertial sensor has the advantages that the micro-machined inertial sensor and a satellite navigation system are in integrated design, and accordingly the size and the material cost of a satellite integrated navigation system are reduced; in a double-satellite environment, the satellite navigation system is used for obtaining the observed quantity to provide real-time pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate observation information for a Kalman filter, so that positioning error of micro-machined inertial navigation is corrected; the method is simple, feasible, highly practical and capable of improving applicability of the satellite navigation system in a few satellite environment.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
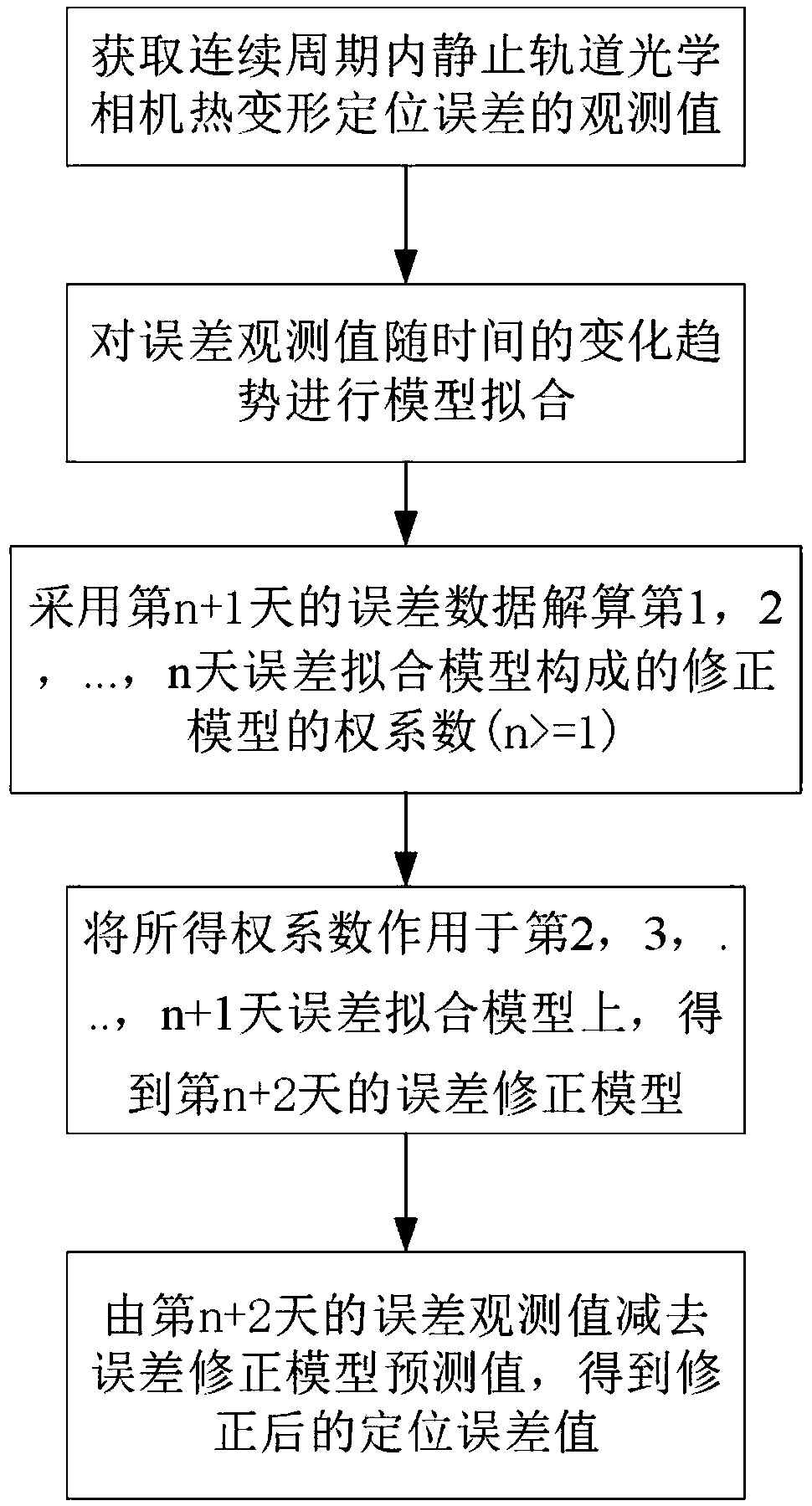
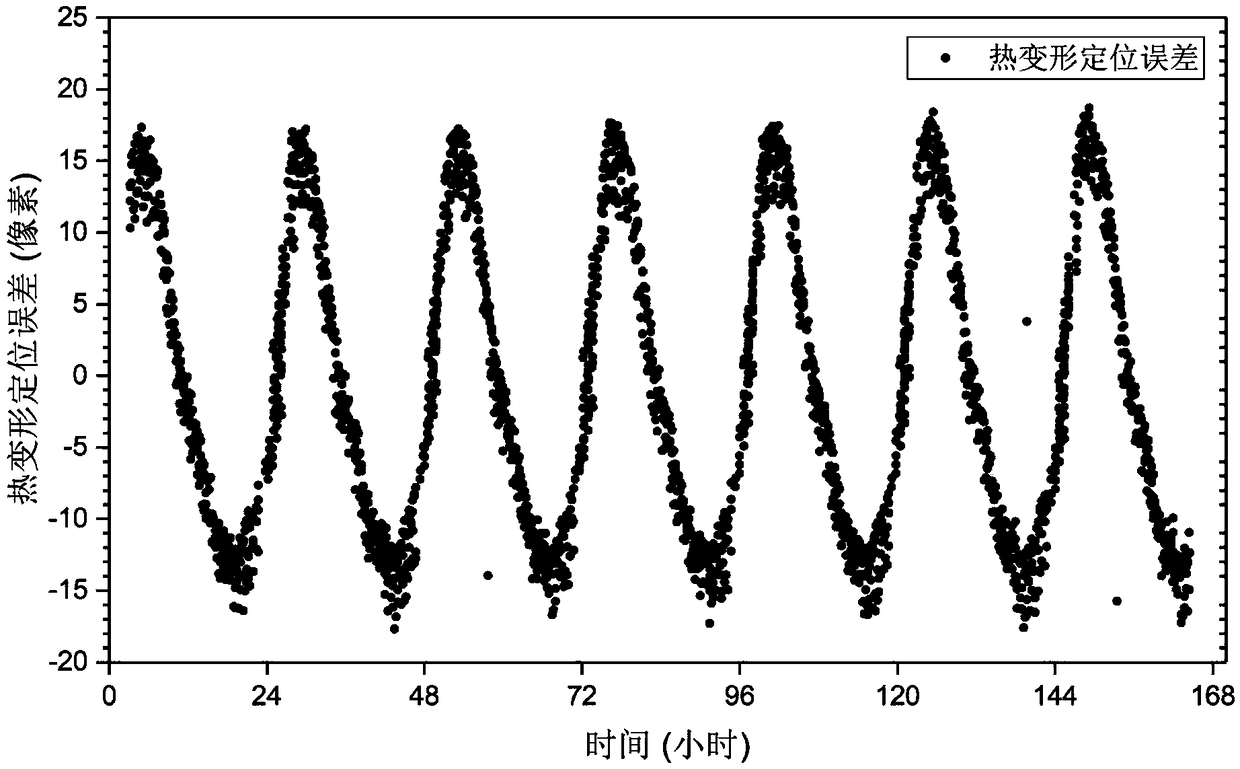
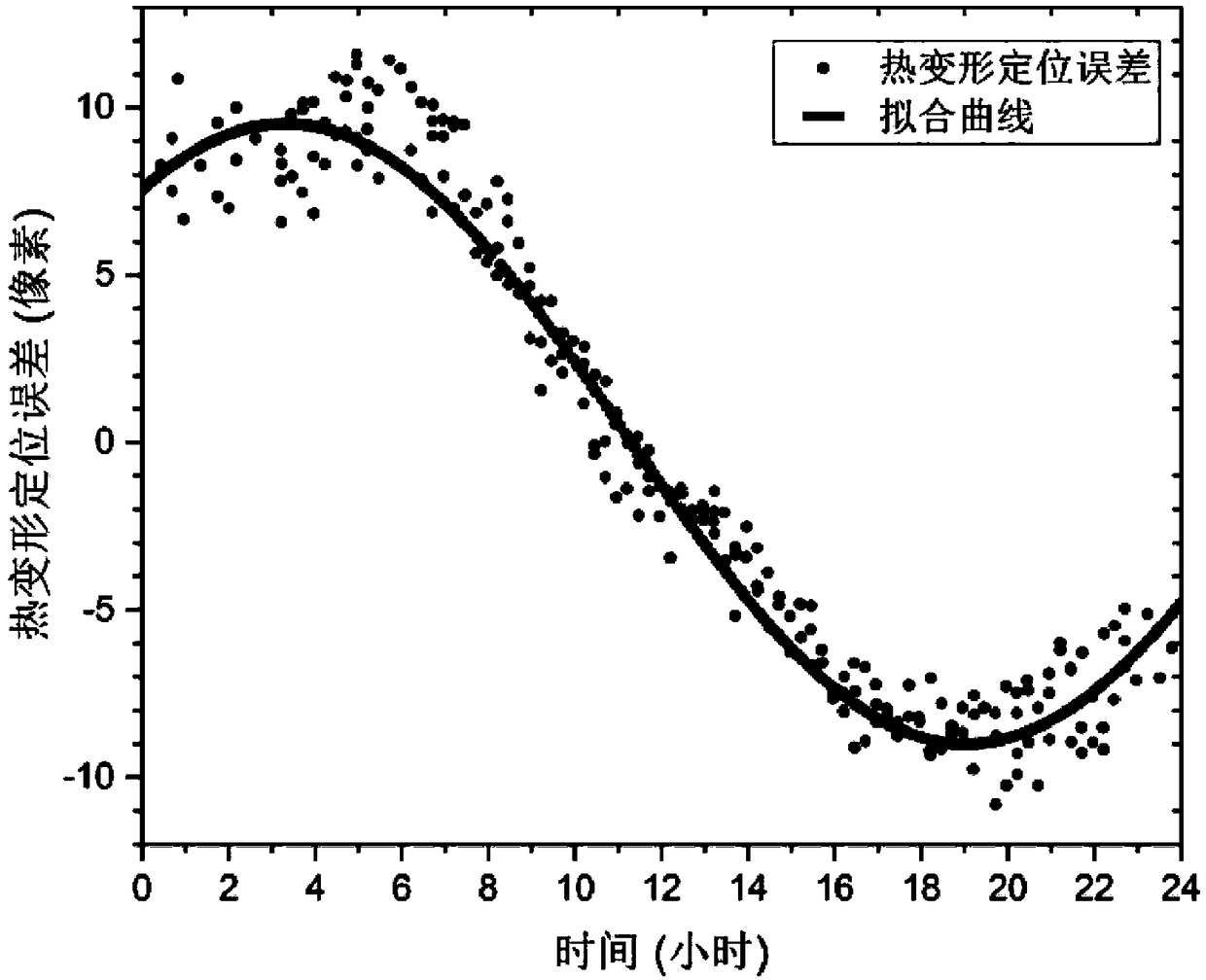
Method of correcting thermal deformation errors of geostationary orbit optical camera
ActiveCN109443380AImprove on-orbit positioning accuracyShorten evasion timeMeasurement devicesTime changesGeostationary orbit
The invention discloses a method of correcting thermal deformation errors of a geostationary orbit optical camera. The method includes the steps of (1) acquiring an observation value of a thermal deformation positioning error of the geostationary orbit optical camera; (2) using a mathematical model to fit over-time change law of the observation value of the error; (3) using error data of day n+1 to resolve weight coefficient of a correction model composed of error fitting models of days 1, 2 to n; (4) applying the weight coefficient of step (3) to the error fitting models of days 2, 3 to n+1 so as to obtain an error correction model of day n+2; (5) subtracting a prediction value of the error correction model by the observed value of the error of day n+2 so as to obtain the corrected positioning error value. The method herein is suitable for effectively correcting geostationary orbit optical camera positioning errors due to thermal deformation, has the advantages of reasonable design, high precision, low cost, good convenience of use and the like, and is applicable and popularizable in the field of high-precision remote sensing satellite geometric locating.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
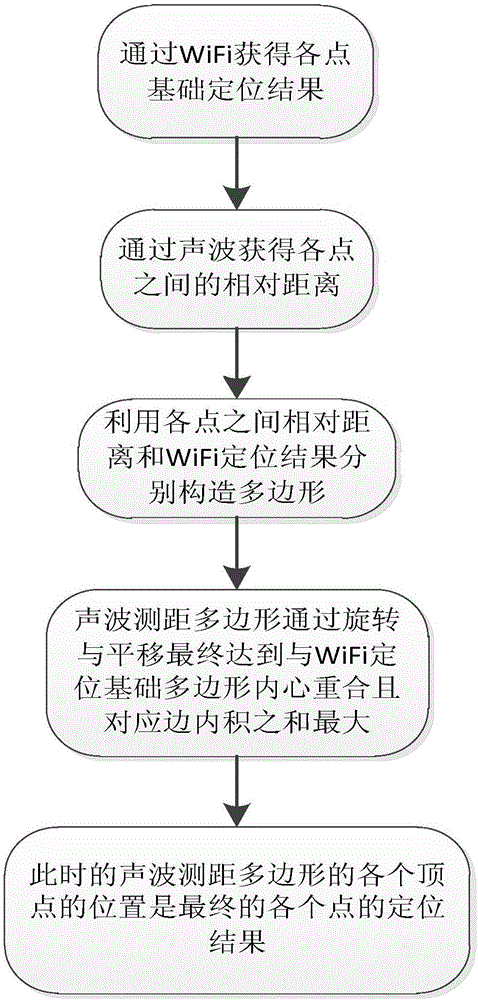
Multipoint topology approximation indoor positioning method based on WiFi and acoustic wave
InactiveCN106230518AHigh positioning accuracyThe positioning result is accurateSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionWireless commuication servicesAcoustic waveComputer science
The invention discloses a multipoint topology approximation indoor positioning method based on WiFi and acoustic wave. A positioning method for acquiring a more precise user coordinate via the topology approximation by use of the base WiFi positioning and acoustic wave ranging is proposed. The method comprises the following steps: each user under the WiFi environment acquiring the positioning through a WiFi fingerprint database; using each point WiFi positioning coordinate as the vertex on a map to form a WiFi polygon G; each user acquiring the mutually opposite distance as the side length by use of of the acoustic wave, thereby forming an acoustic wave polygon G'; rotated and translated acoustic wave polygon G' topologically approximating the WiFi polygon G, thereby obtaining a determined position; using the coordinate of each vertex of the topologically approximated acoustic wave polygon G' as the final positioning result of each user to finish the user positioning. Through the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the positioning is precise, and the multiuser positioning precision is higher. The method is mainly applied to indoor positioning, the positioning in the large building cannot be performed through a satellite, the position information with high precision can be acquired through the adoption of the method, thereby providing a new method for indoor position information acquisition and navigation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
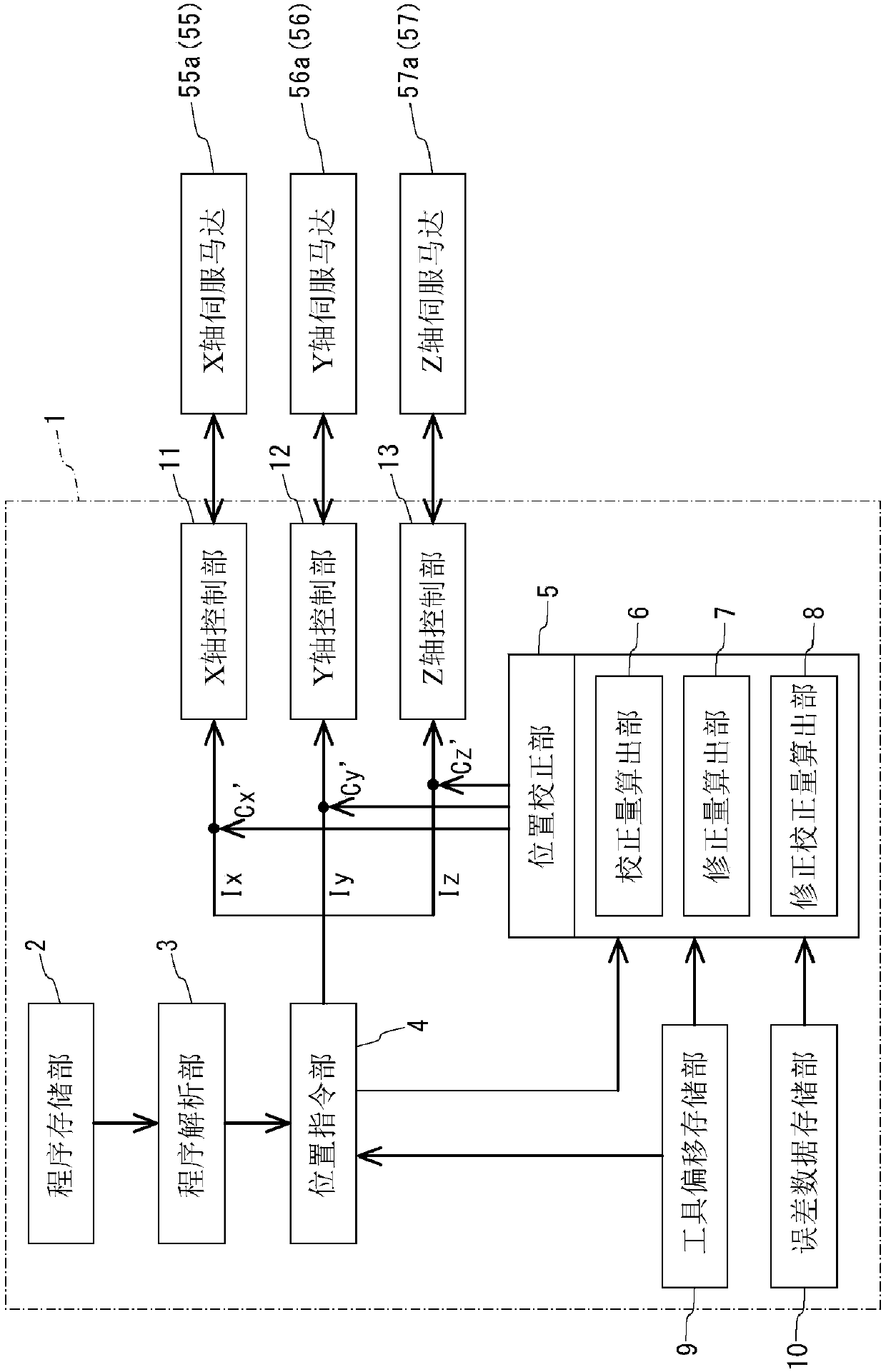
Numerical control device
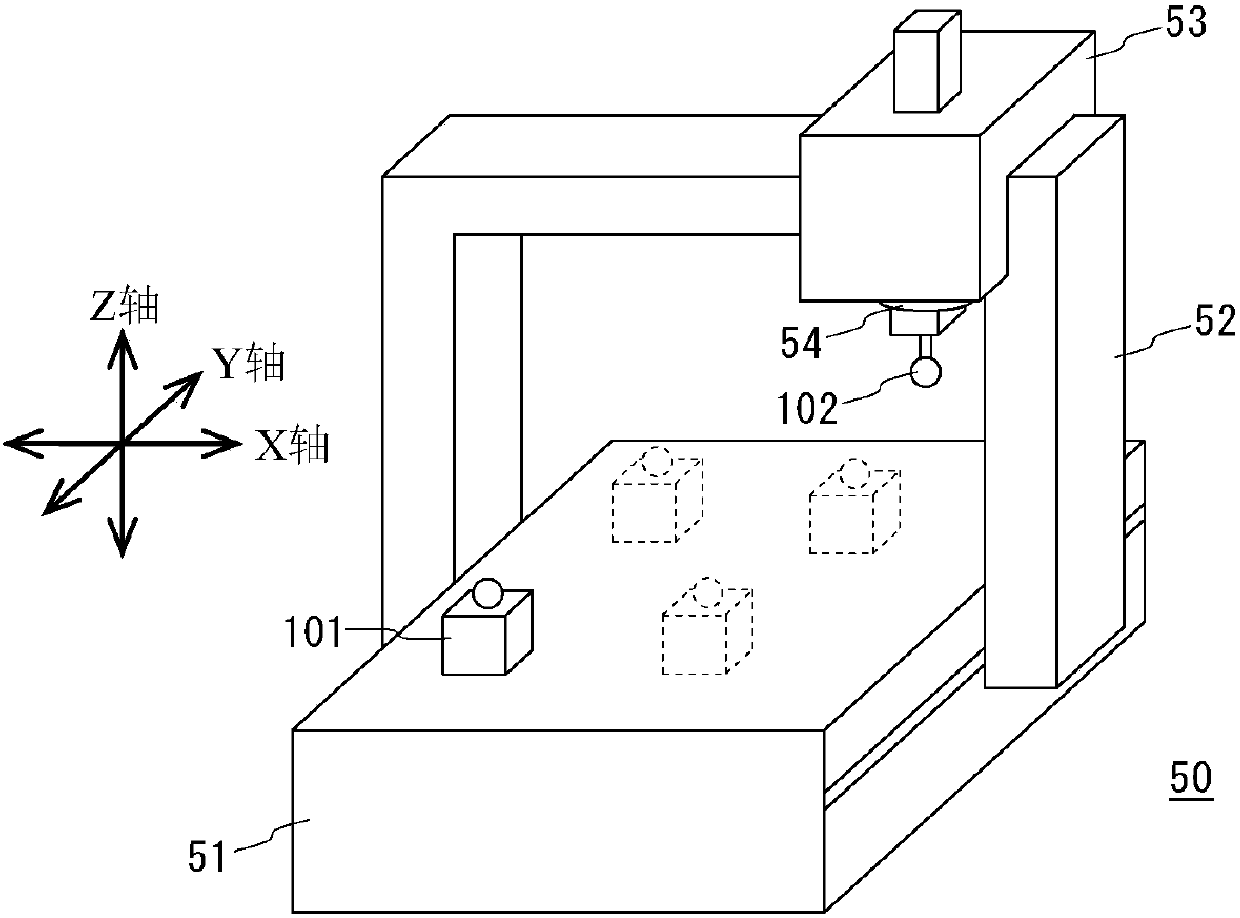
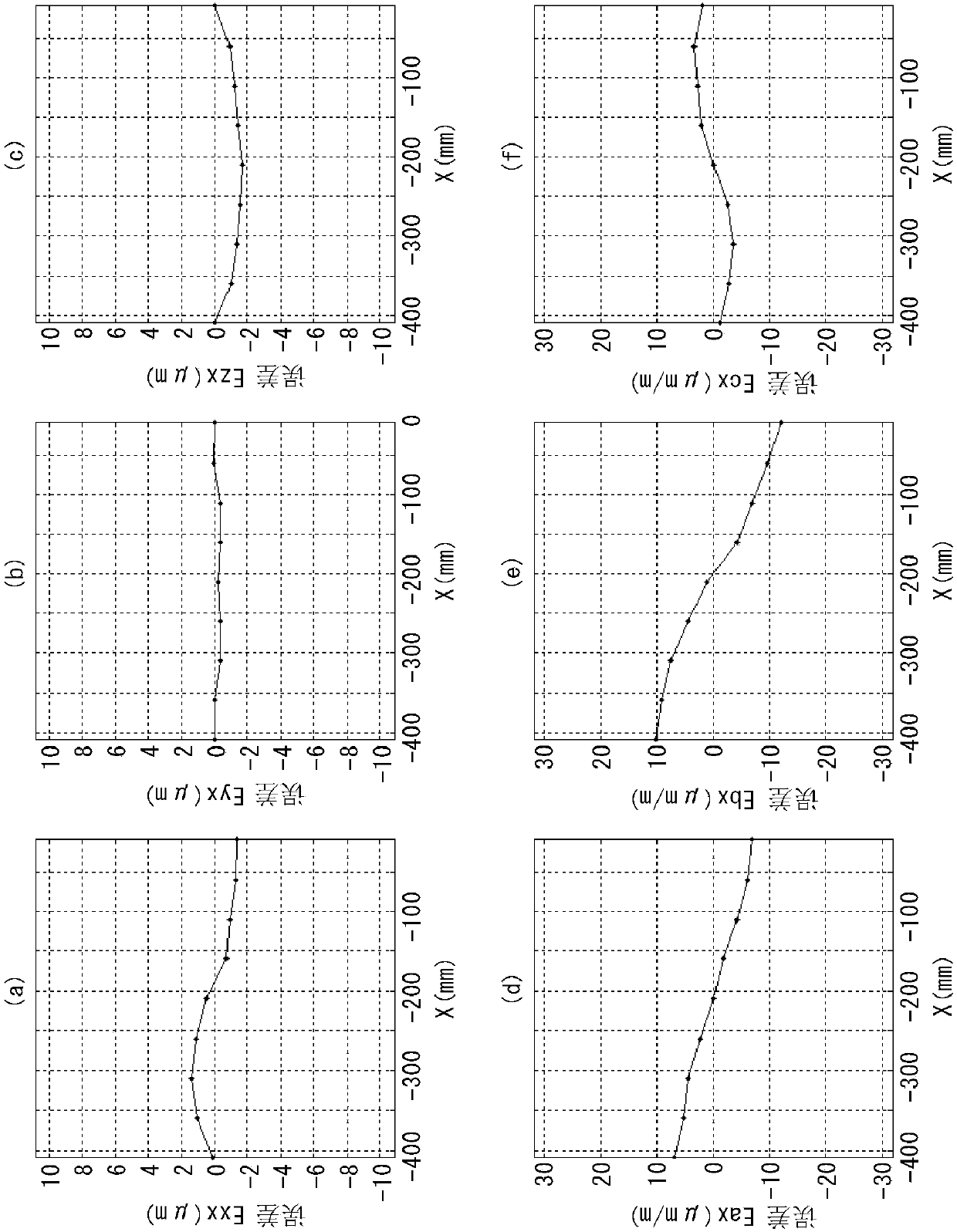
InactiveCN108027601ACompensate for motion errorsCorrect movement errorProgramme controlAutomatic control devicesNumerical controlThree-dimensional space
Provided is a numerical control device with which the tip position of a tool can be positioned with high precision in a three-dimensional space. This numerical control device (1) is equipped with a position correction unit (5) and an error data storage unit (10). The error data storage unit (10) stores error data for the X-, Y-, and Z-axes, that is, data pertaining to the angular error (Eax, Eay,Eaz) around the X-axis, the angular error (Ebx, Eby, Ebz) around the Y-axis, and the angular error (Ecx, Ecy, Ecz) around the Z-axis. The position correction unit (5) calculates a revision amount (Mx,My, Mz) in accordance with the tool length, on the basis of a command position (Ix, Iy, Iz), the error data, and tool length data for the tool being used, revises a correction amount (Cx, Cy, Cz) forthe command position (Ix, Iy, Iz), and uses the revised correction amount to correct the command position (Ix, Iy, Iz).
Owner:DMG MORI CO LTD
Navigation and positioning method and device for a moving carrier
ActiveCN106679657BCorrect position errorAvoid accumulationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingGlobal Positioning SystemMarine navigation
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
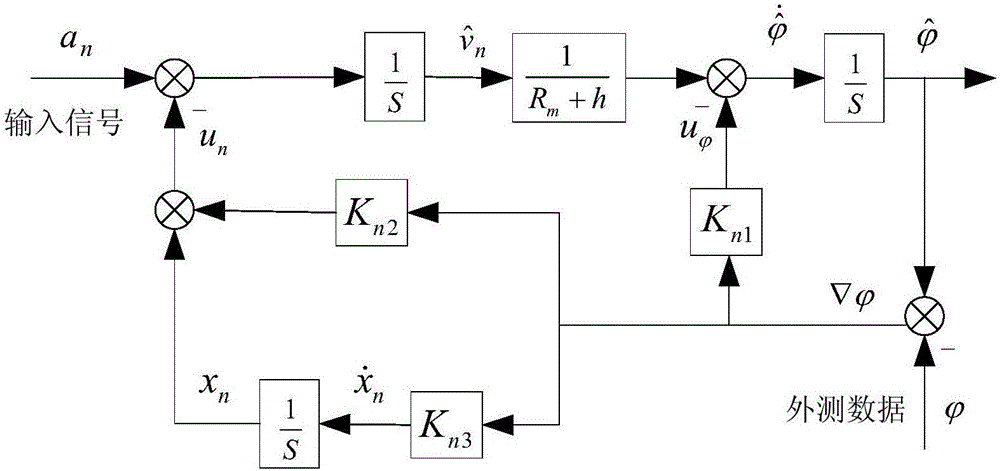
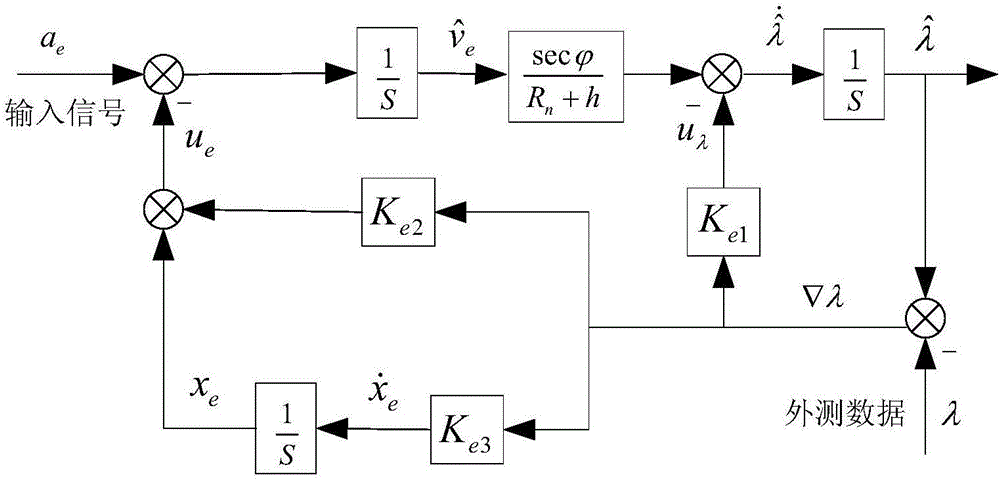
Inertial navigation system measuring error correction method based on external measuring information
ActiveCN106595709ACorrect measurement errorImprove robustnessMeasurement devicesData informationLongitude
The invention discloses an inertial navigation system measuring error correction method based on external measuring information. The method comprises the steps that external measuring data information is acquired, wherein the external measuring data information comprises at least one of the external measuring latitude phi, the external measuring longitude lambda and the external measuring height h; an inertial navigation system measuring error is corrected according to the external measuring data information and input information input into the input end, and correction results are obtained, wherein the input information comprises at least one of the north accelerated speed a<n>, the east accelerated speed a<e> and the uranic accelerated speed a which are determined according to an inertial navigation system; the correction results are output, wherein the correction results comprise a north channel position error correction result, an east channel position error correction result and a uranic channel position error correction result. According to the method, correction on the speed and the position of the inertial navigation system is achieved, and the robustness and the navigation precision of a combined navigation system are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com