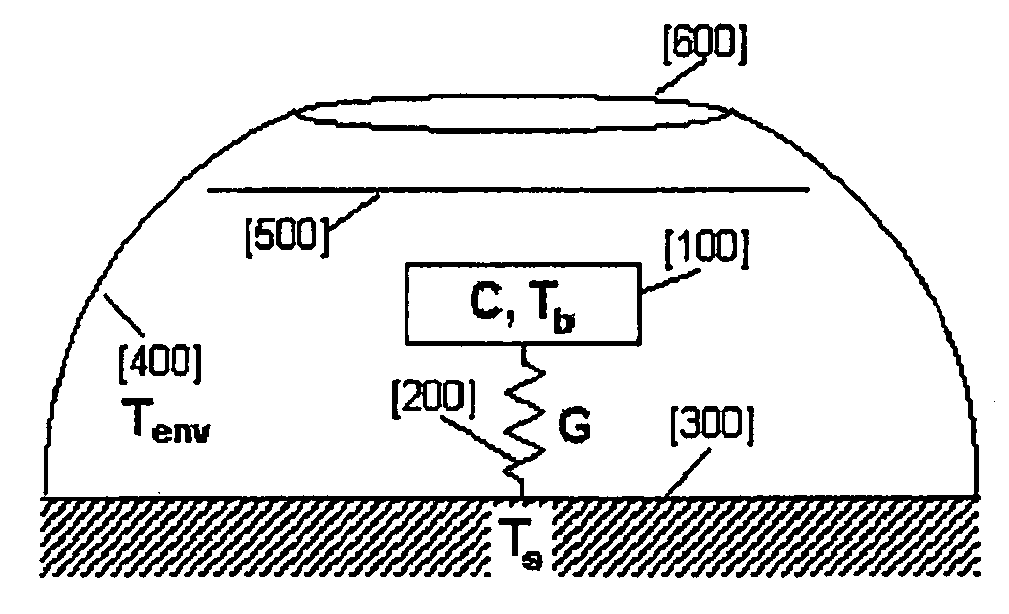
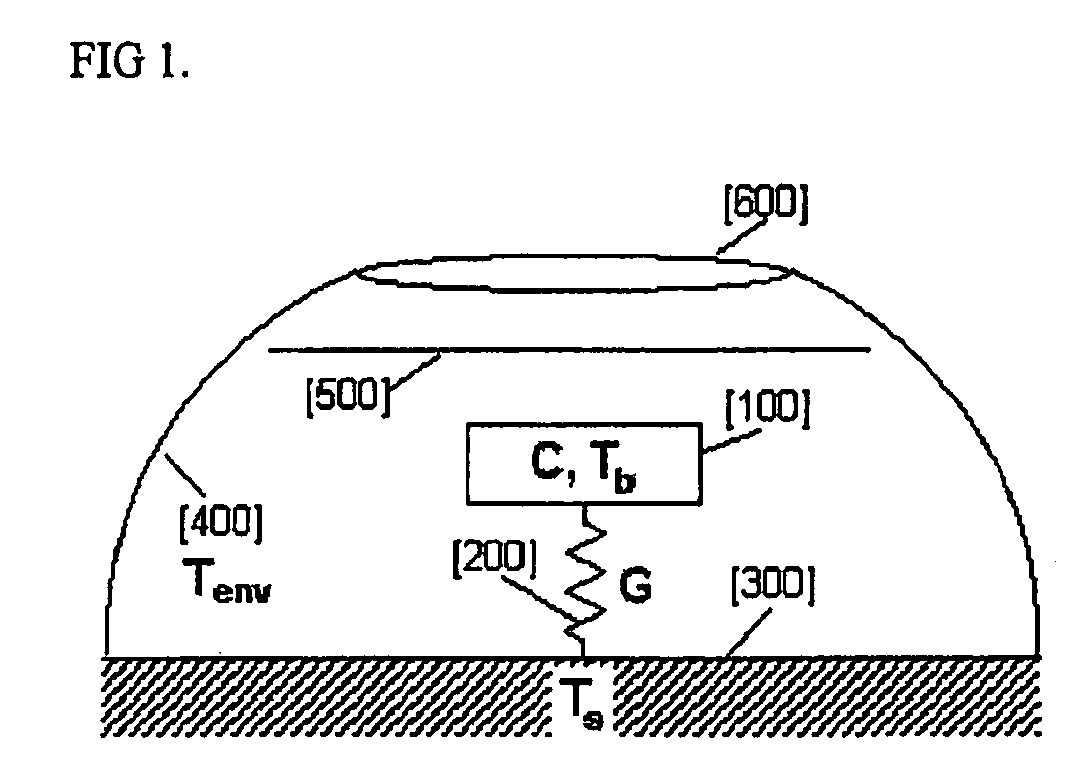
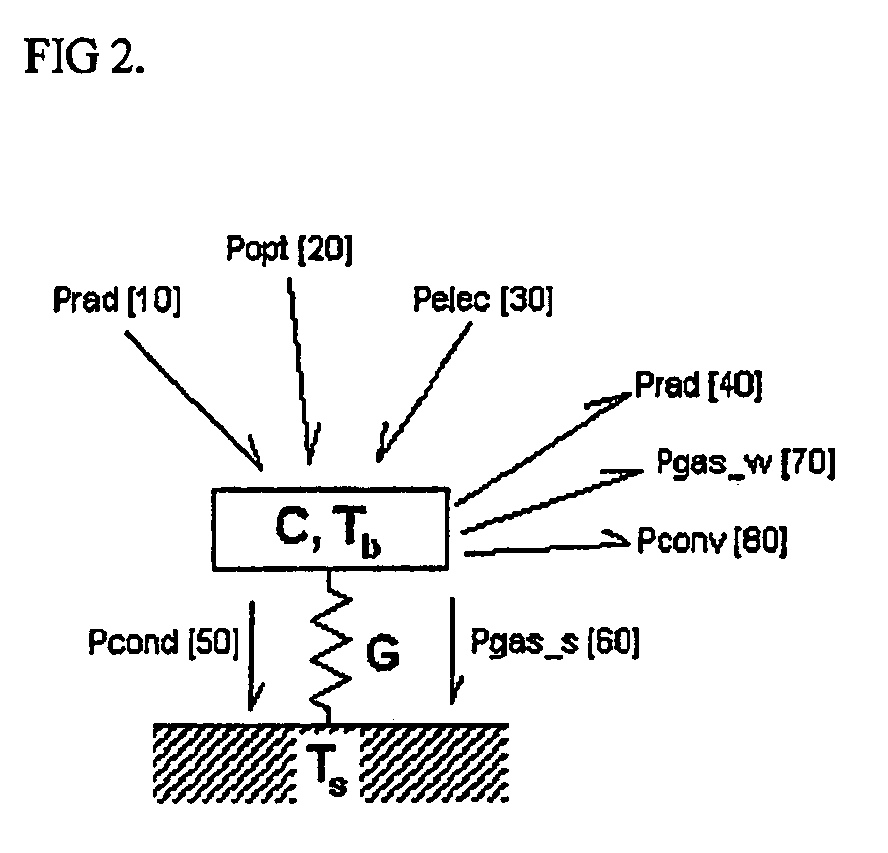
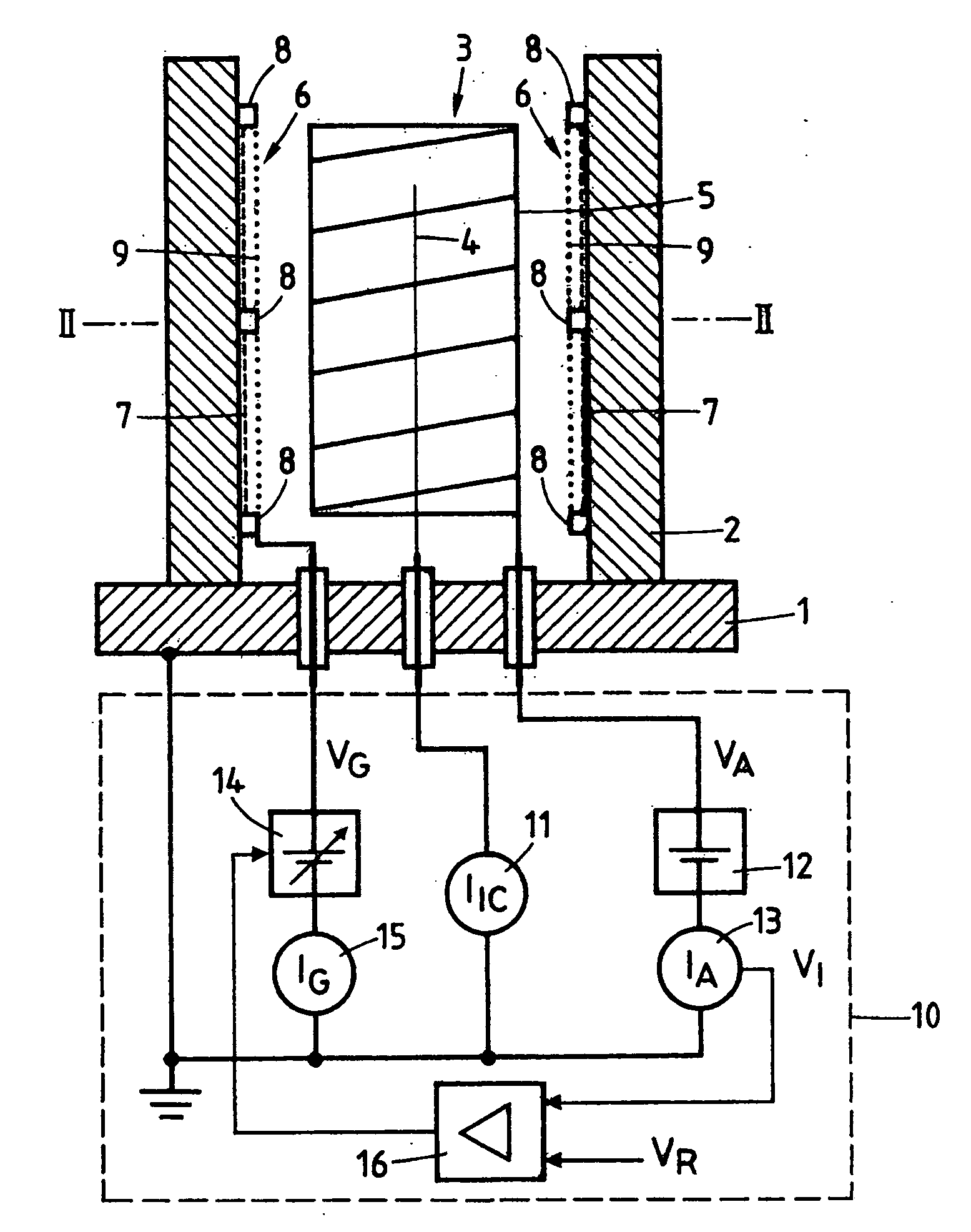
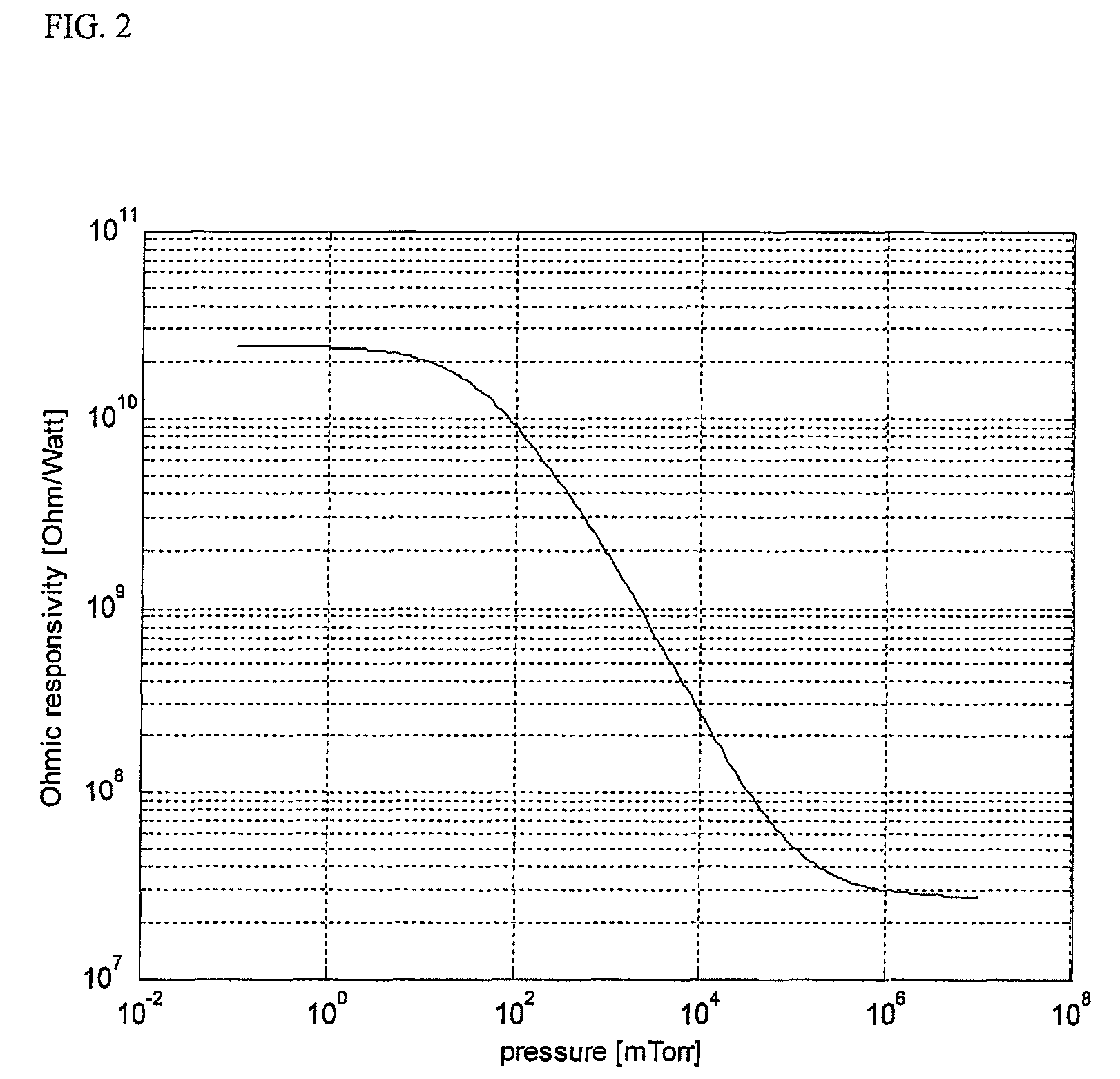
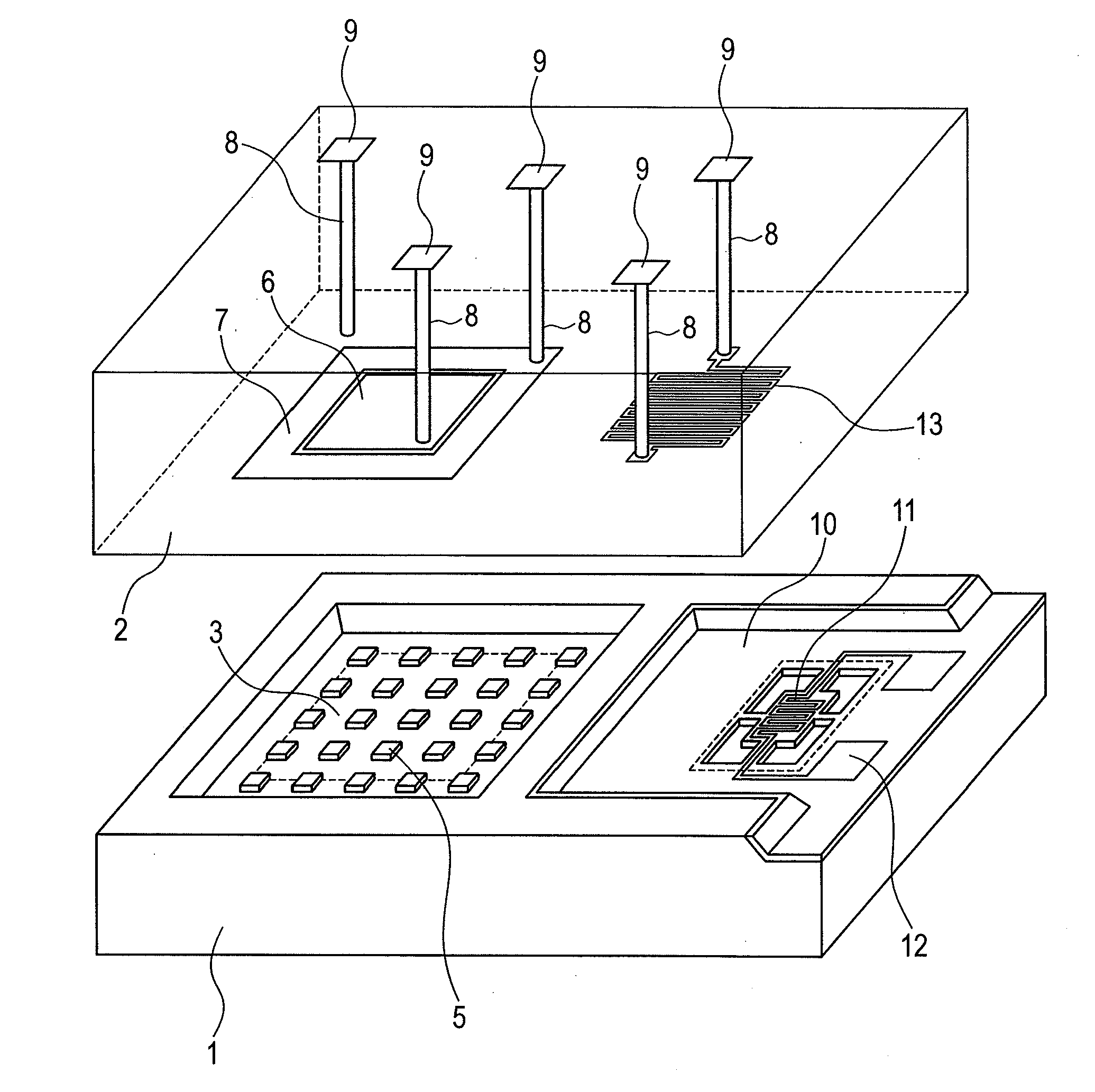
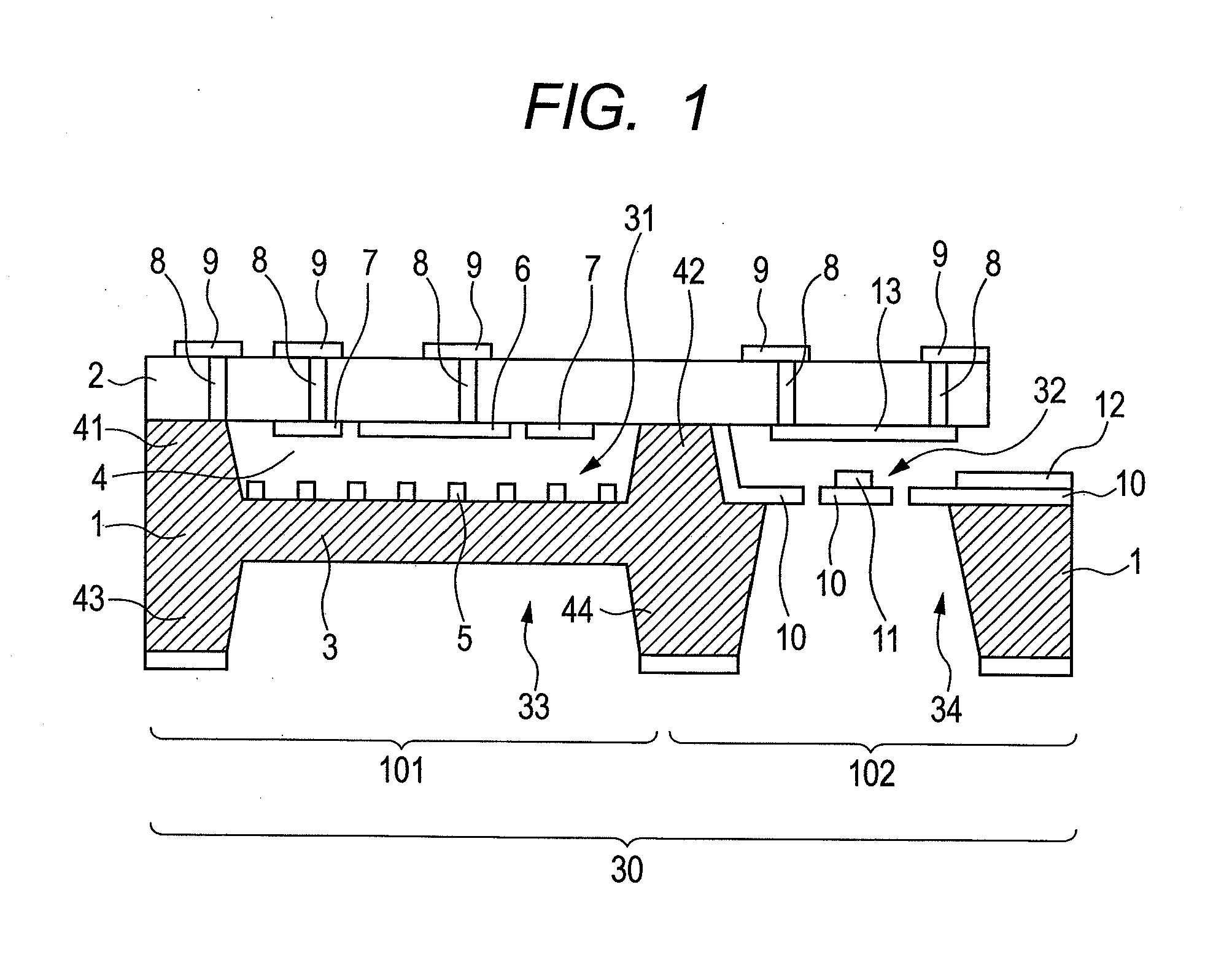
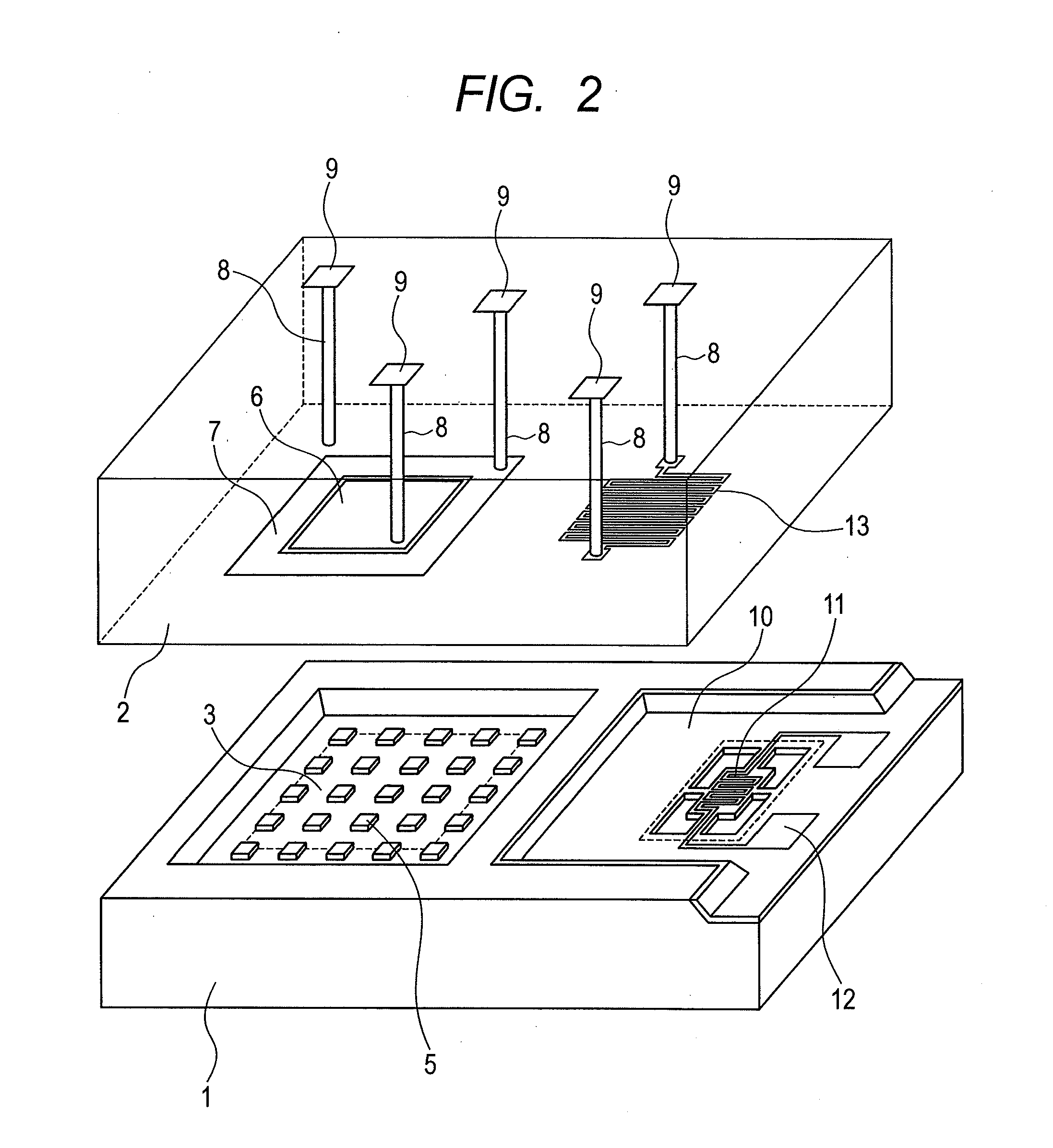
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148results about "Vacuum gauge using heat conductivity variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
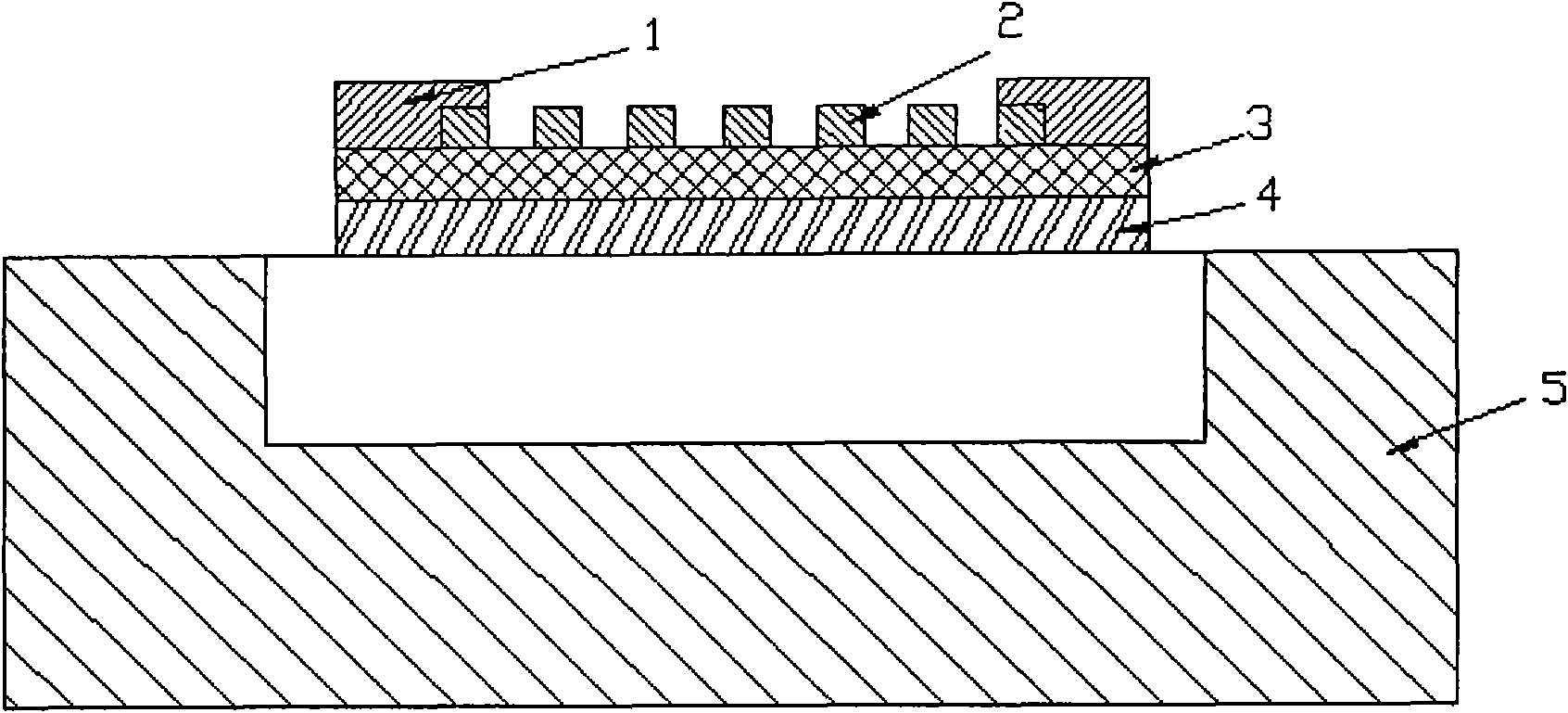
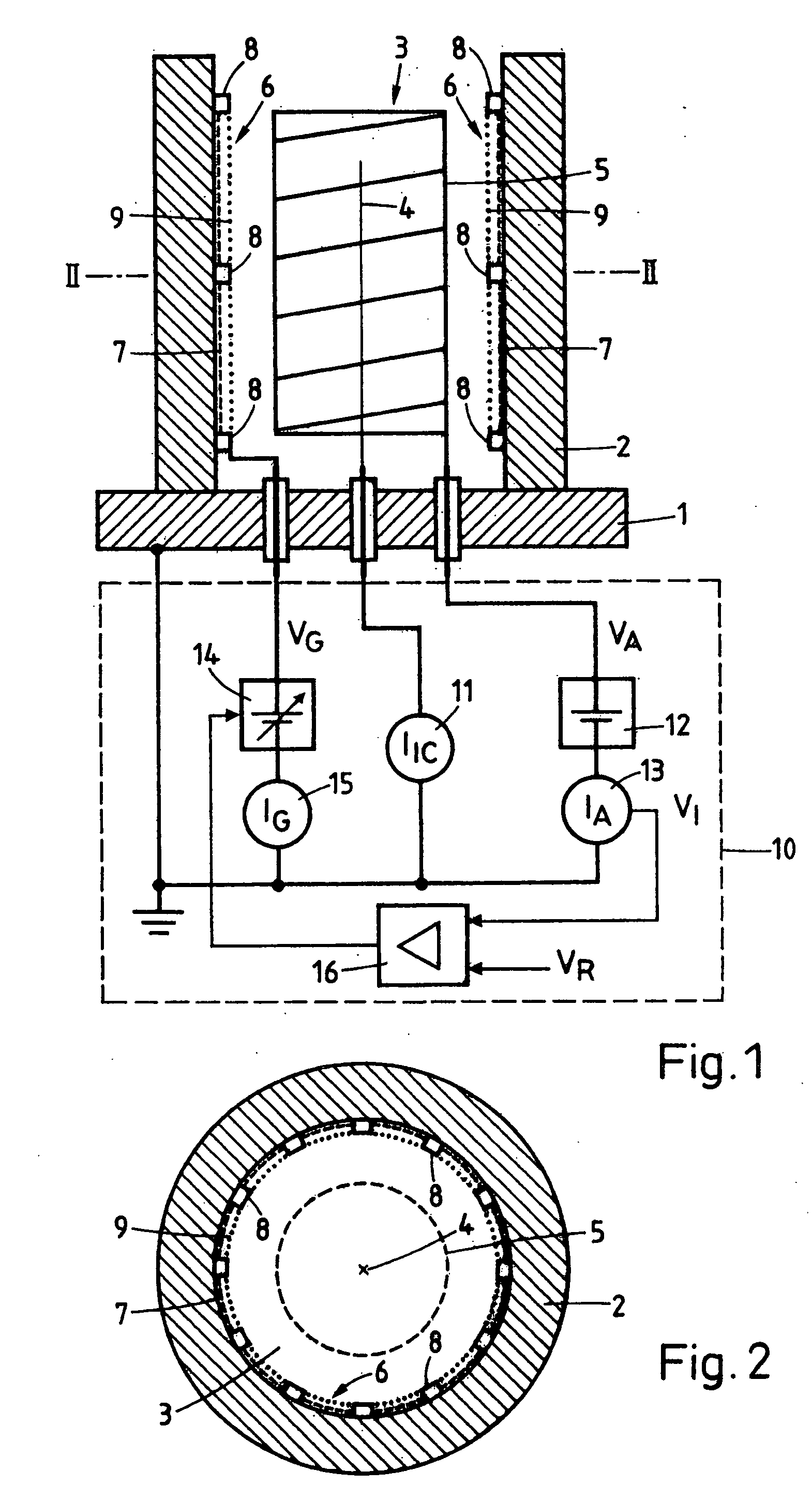
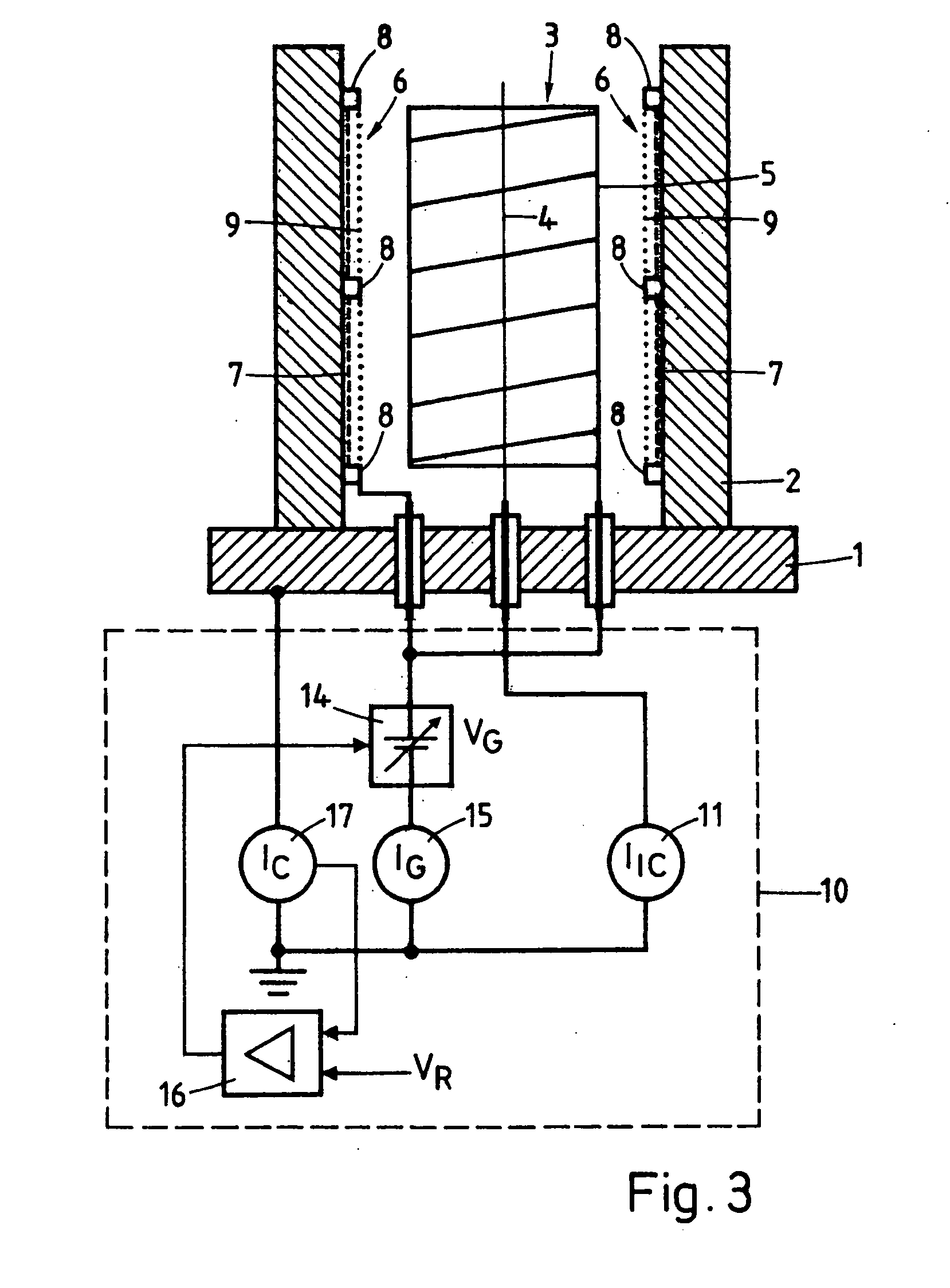
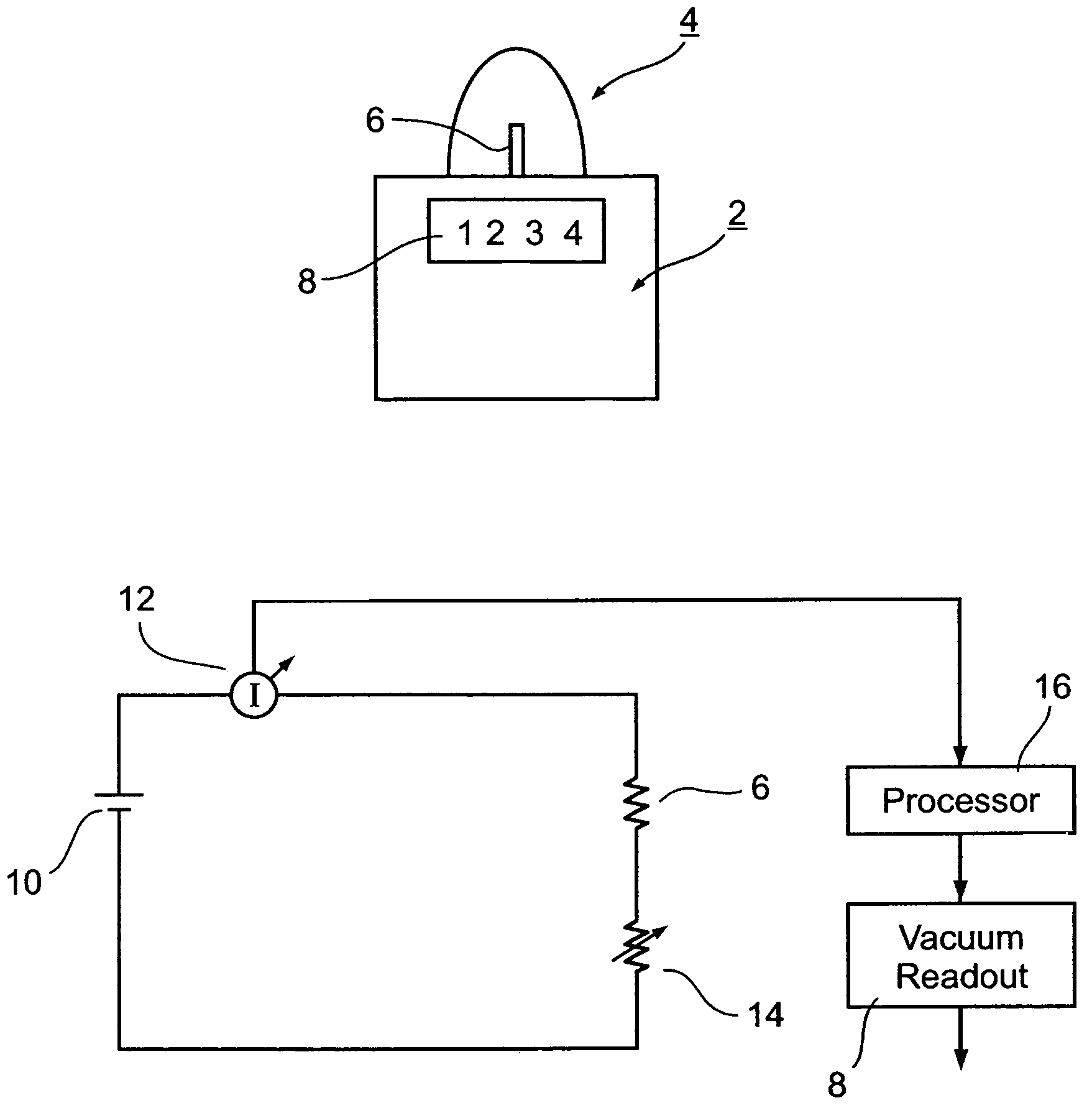
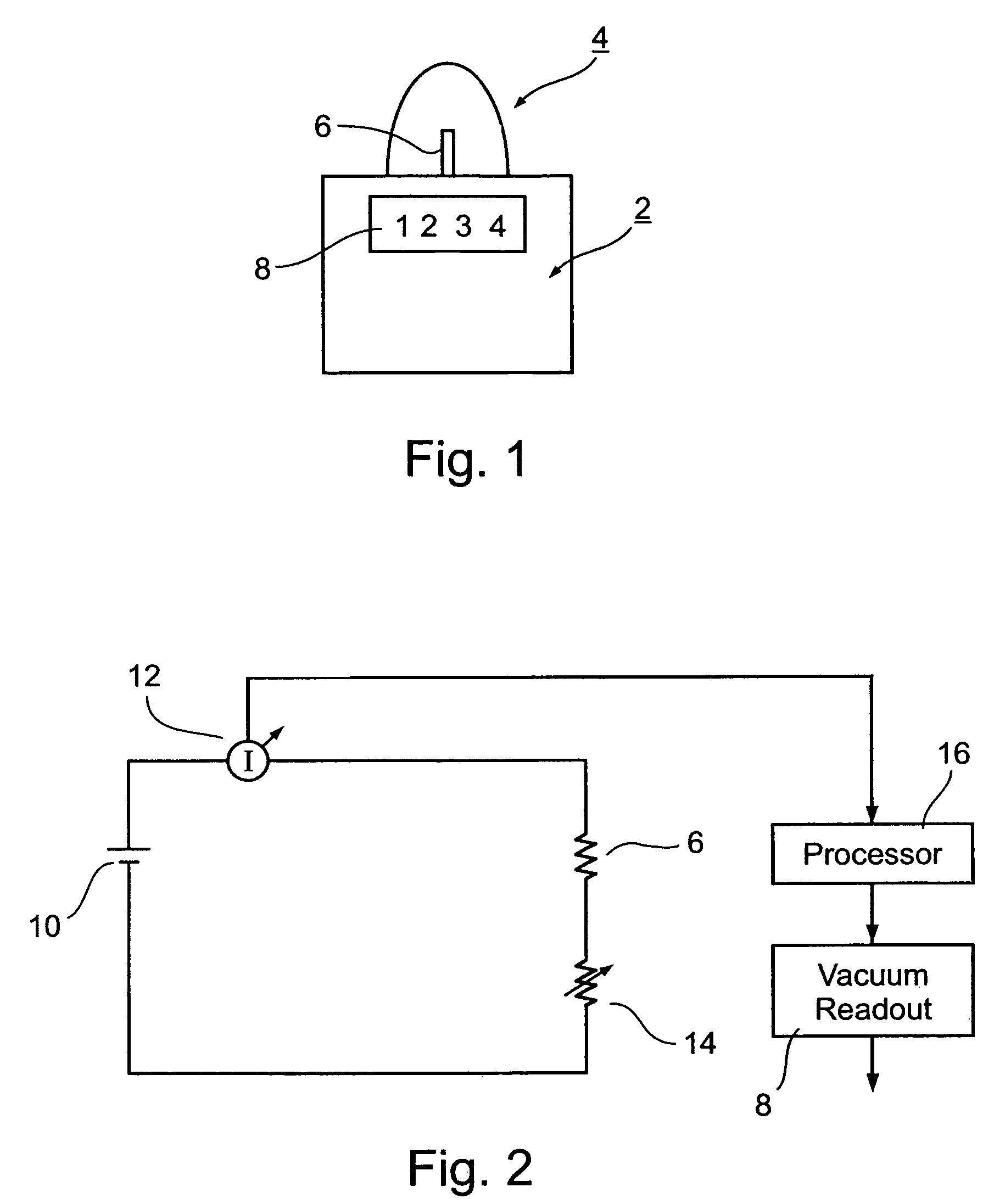
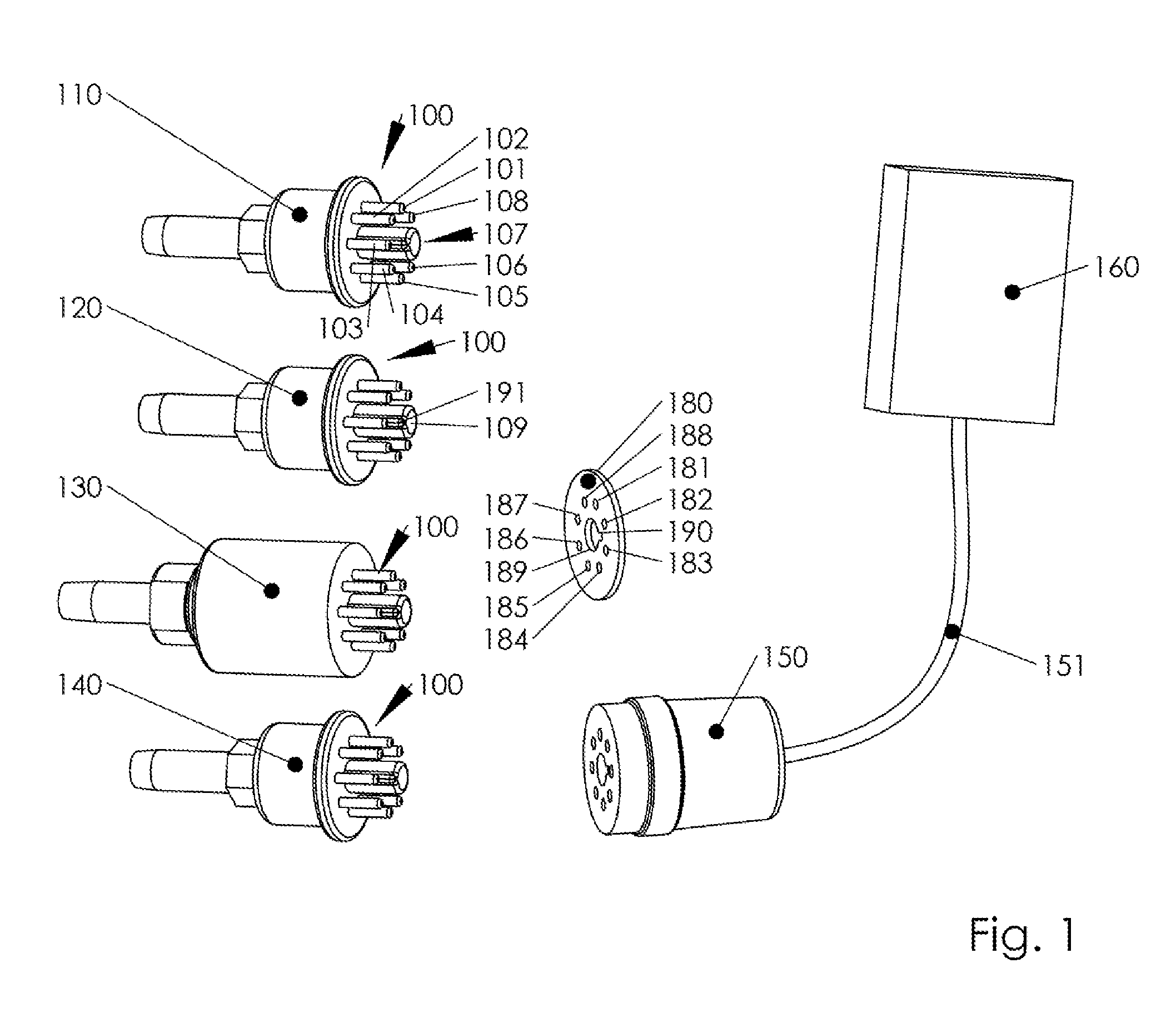
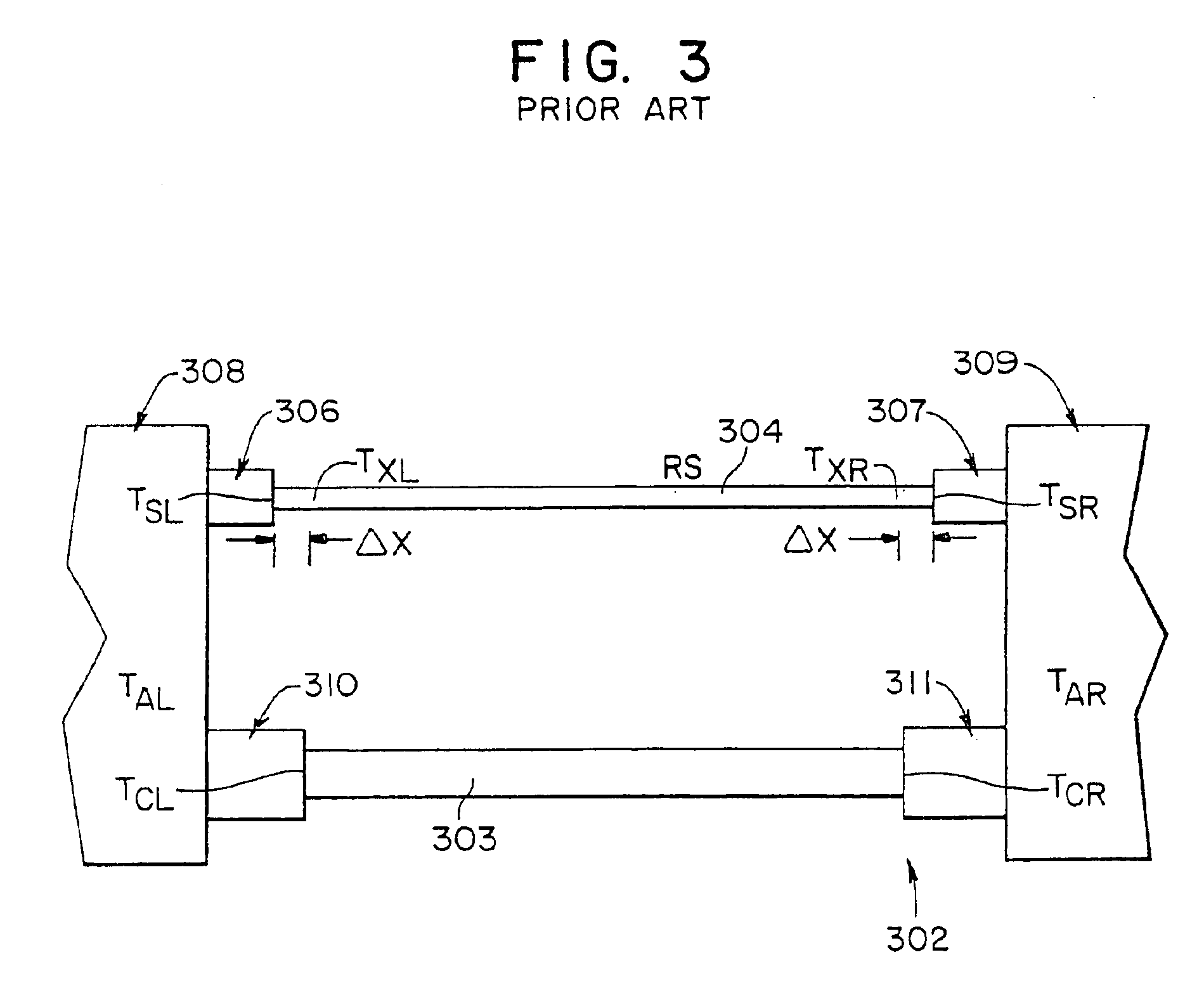
Thermocouple vacuum gauge
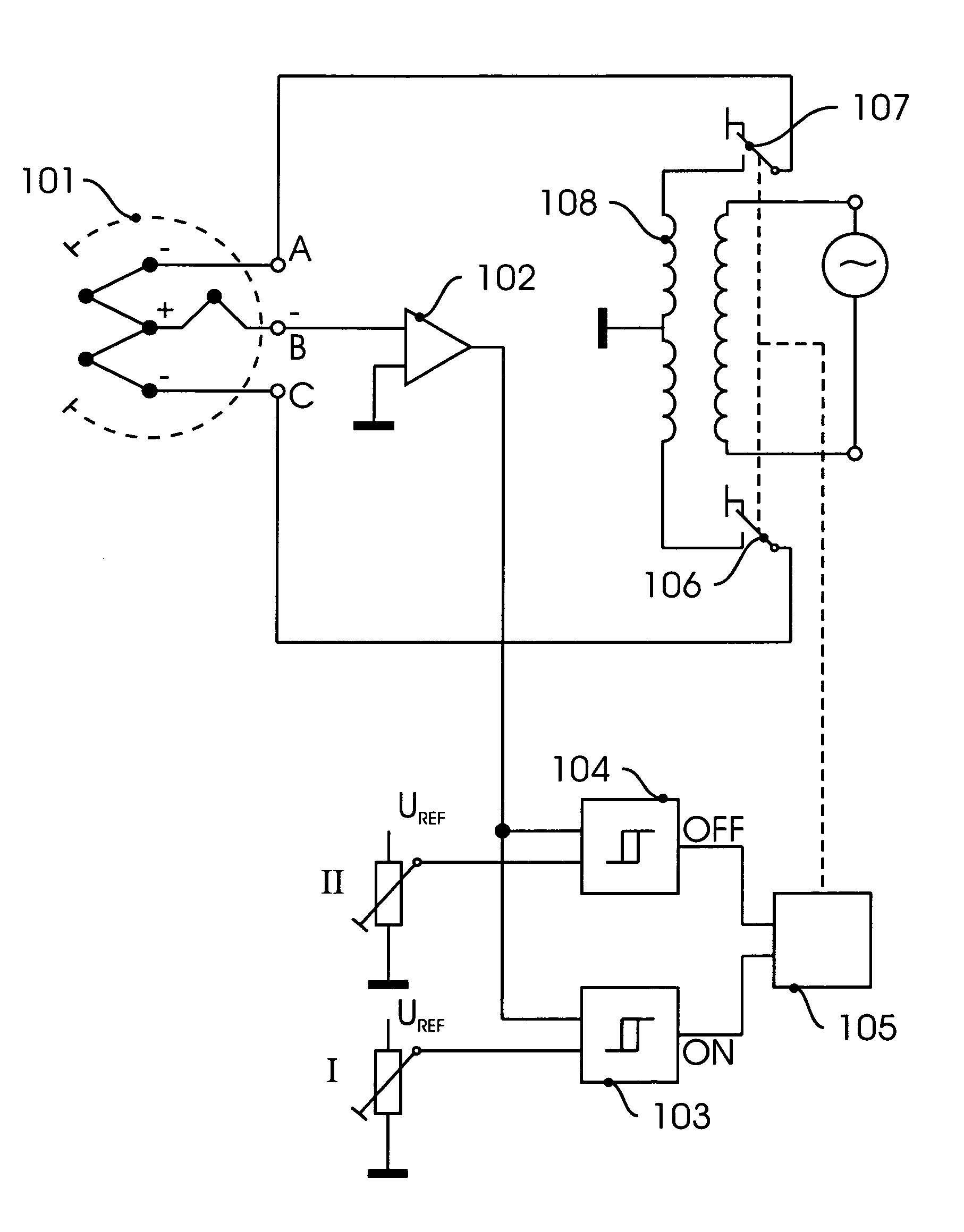
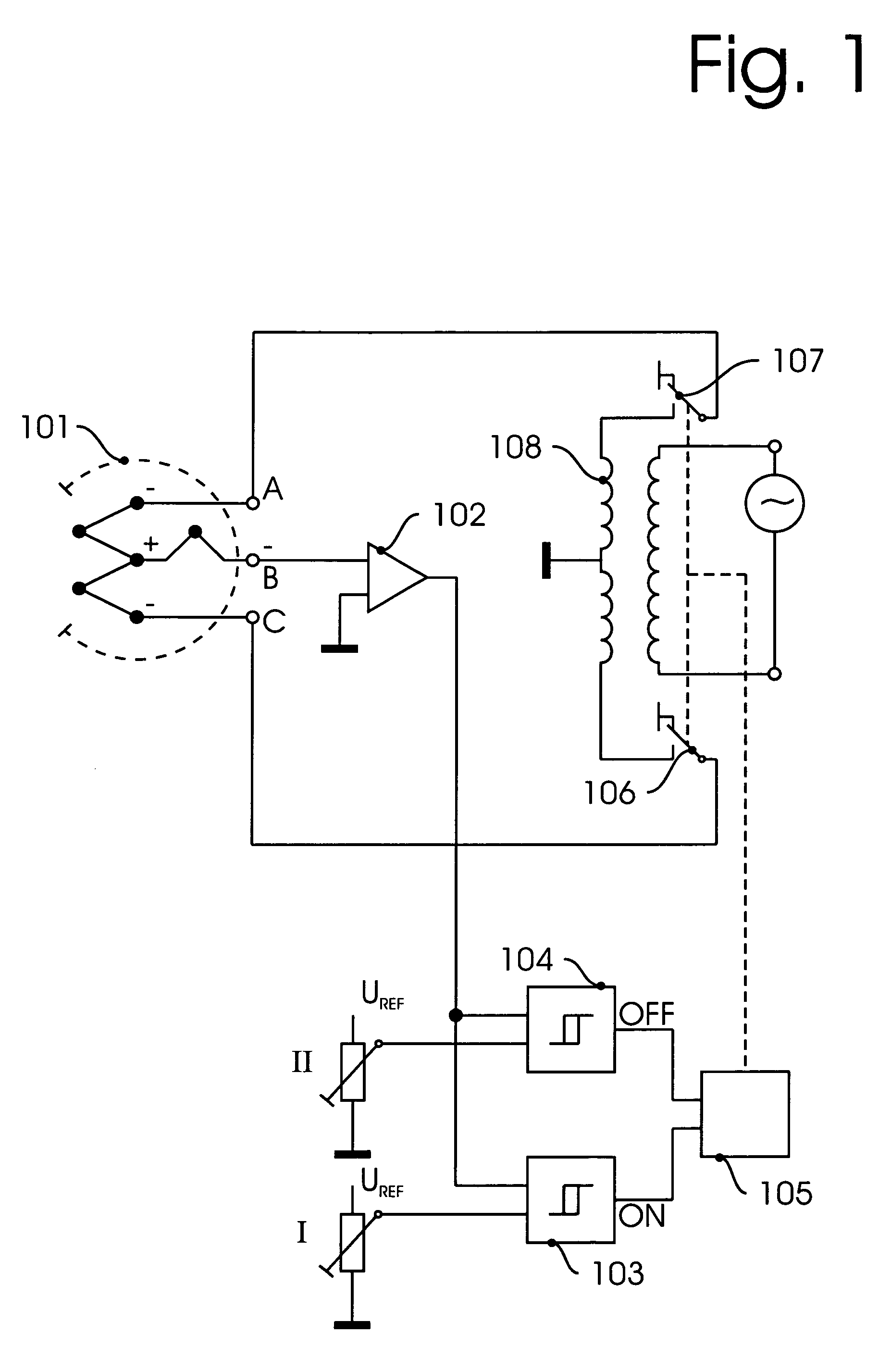
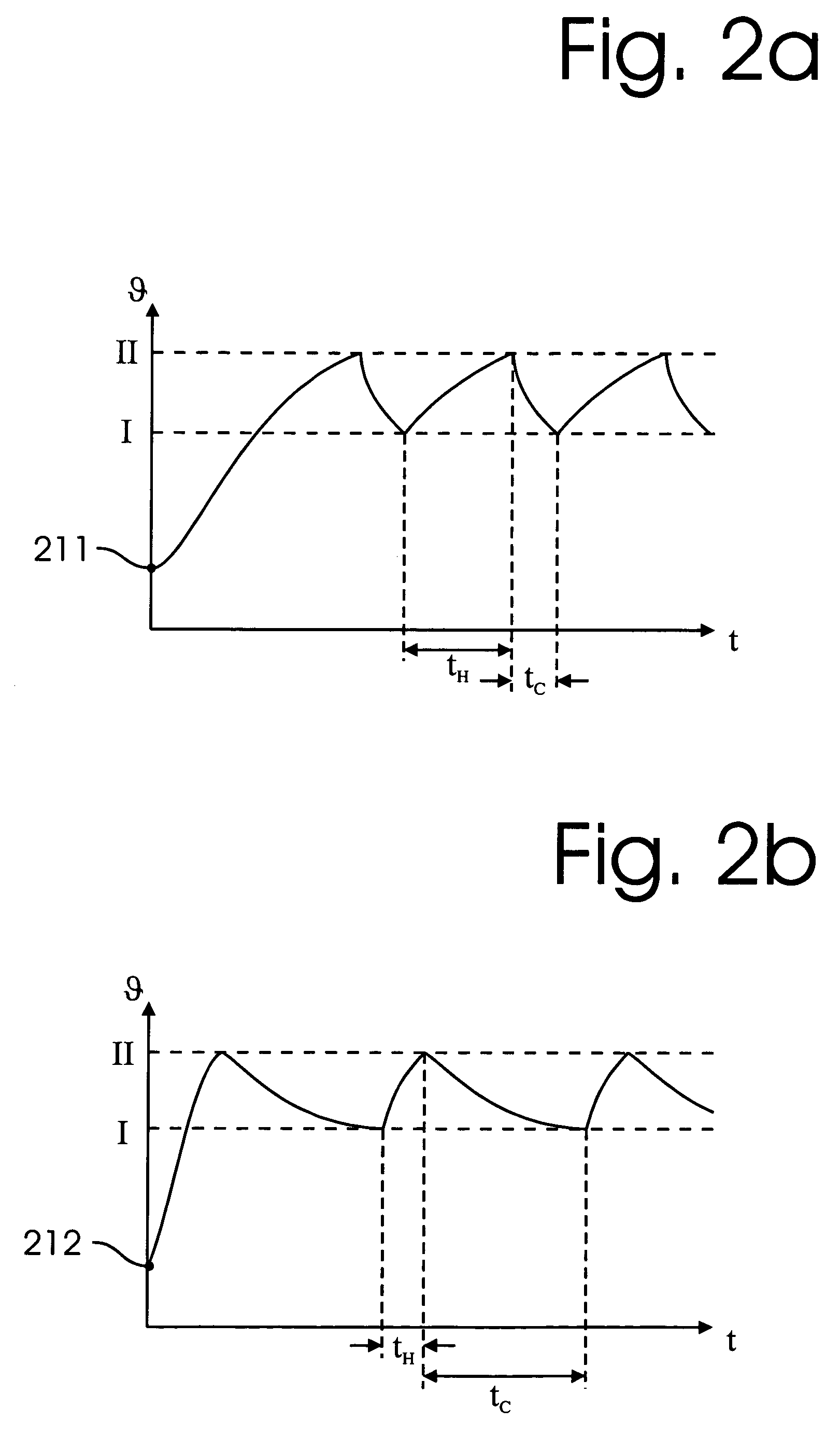
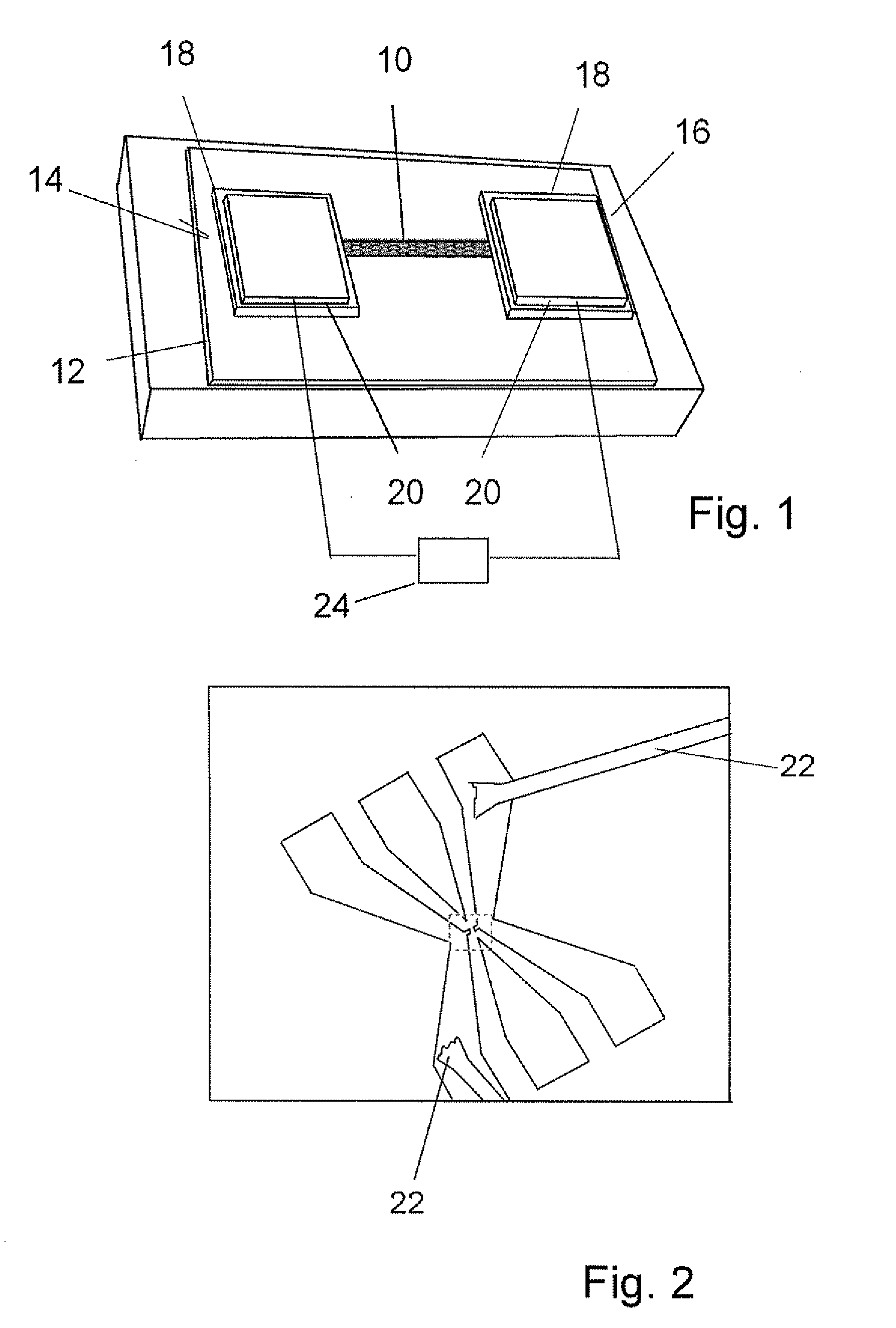
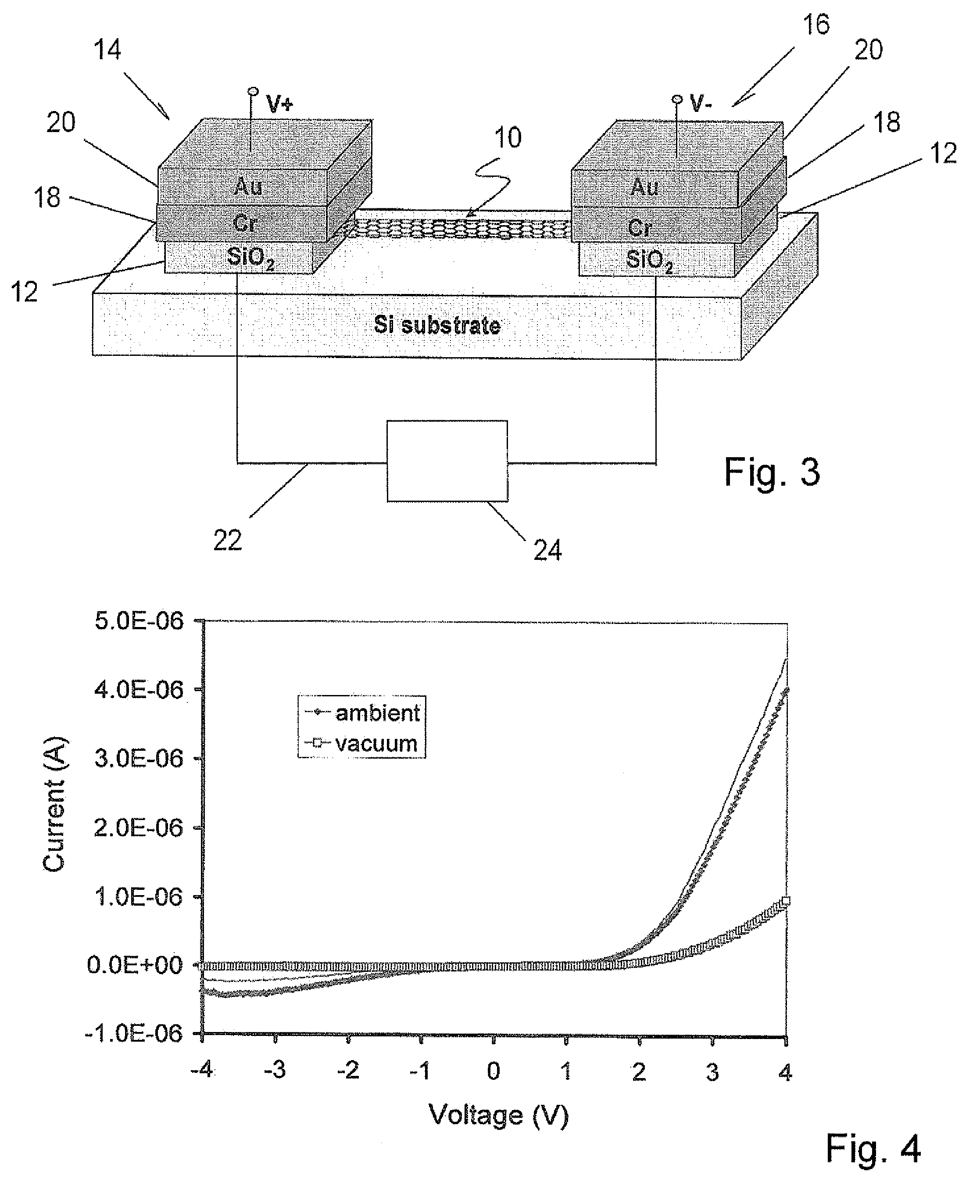
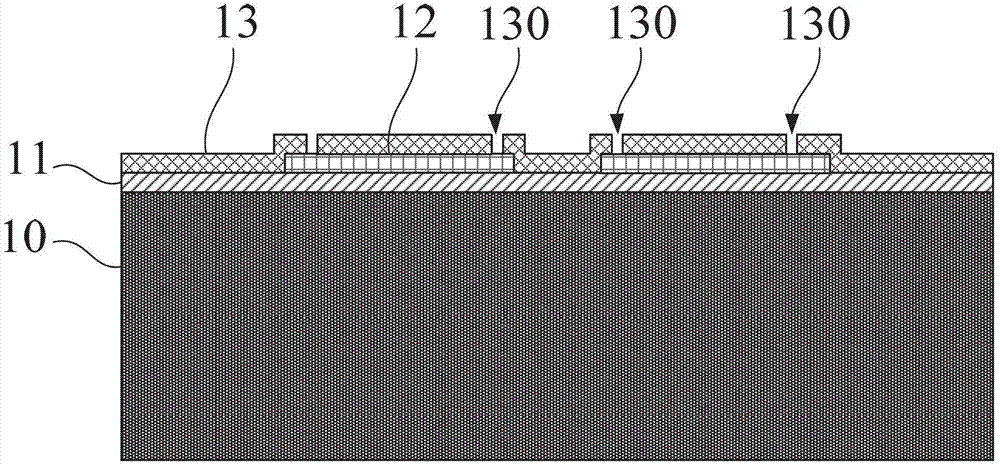
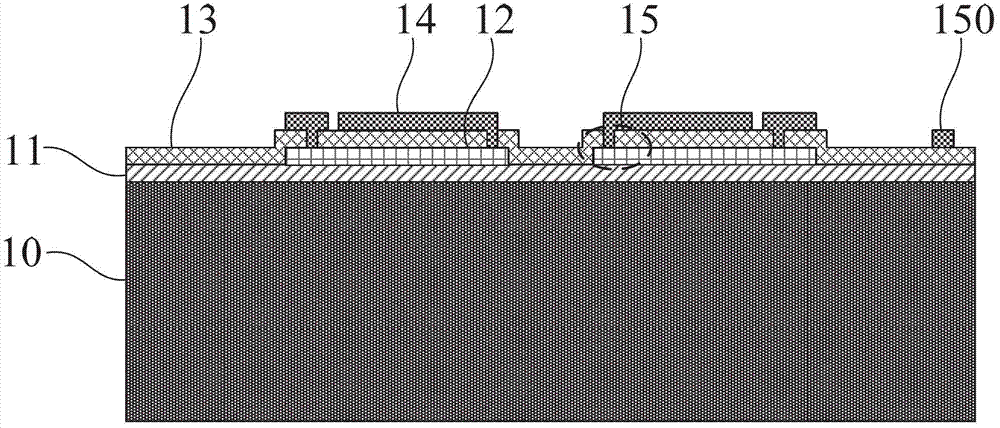
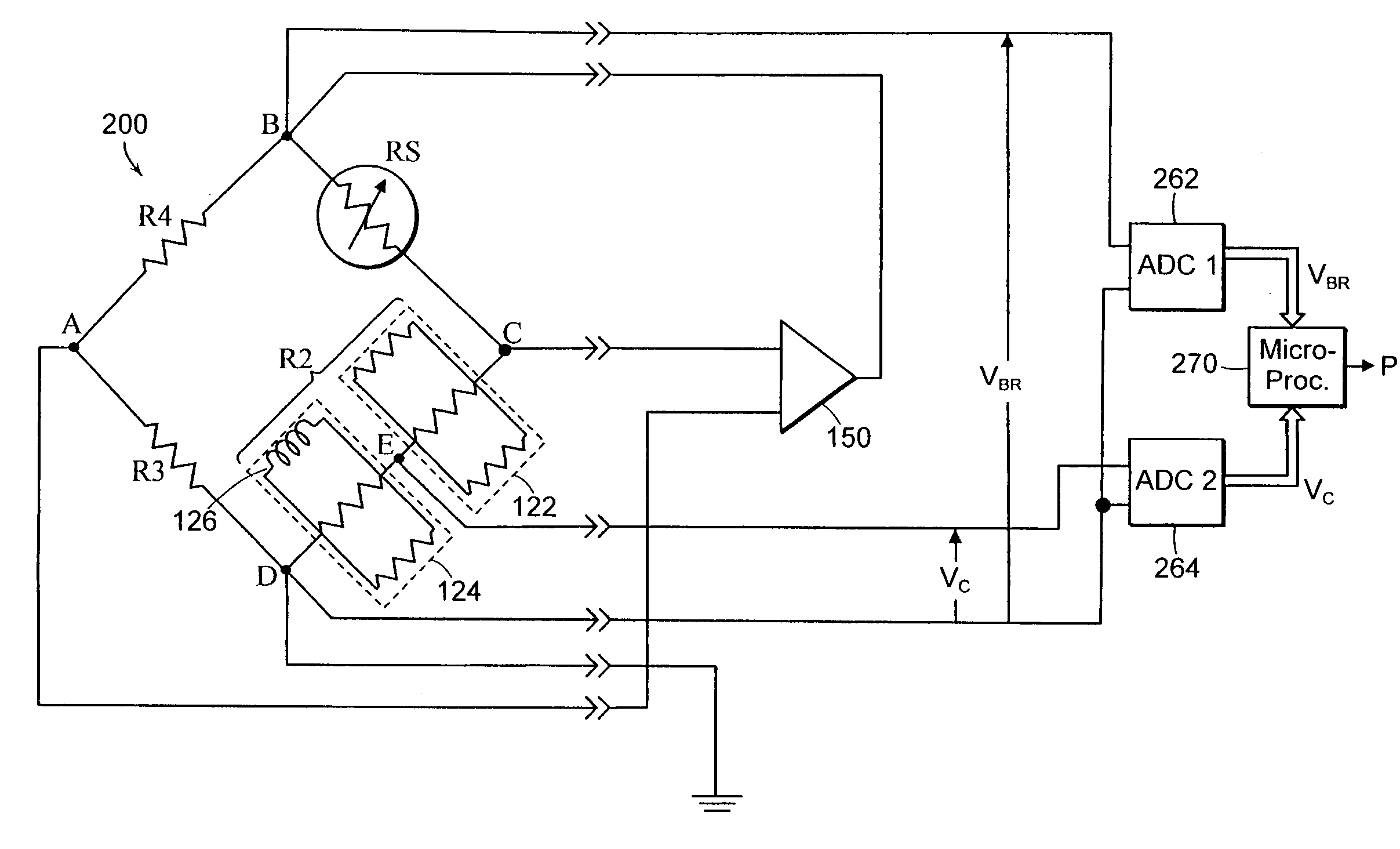
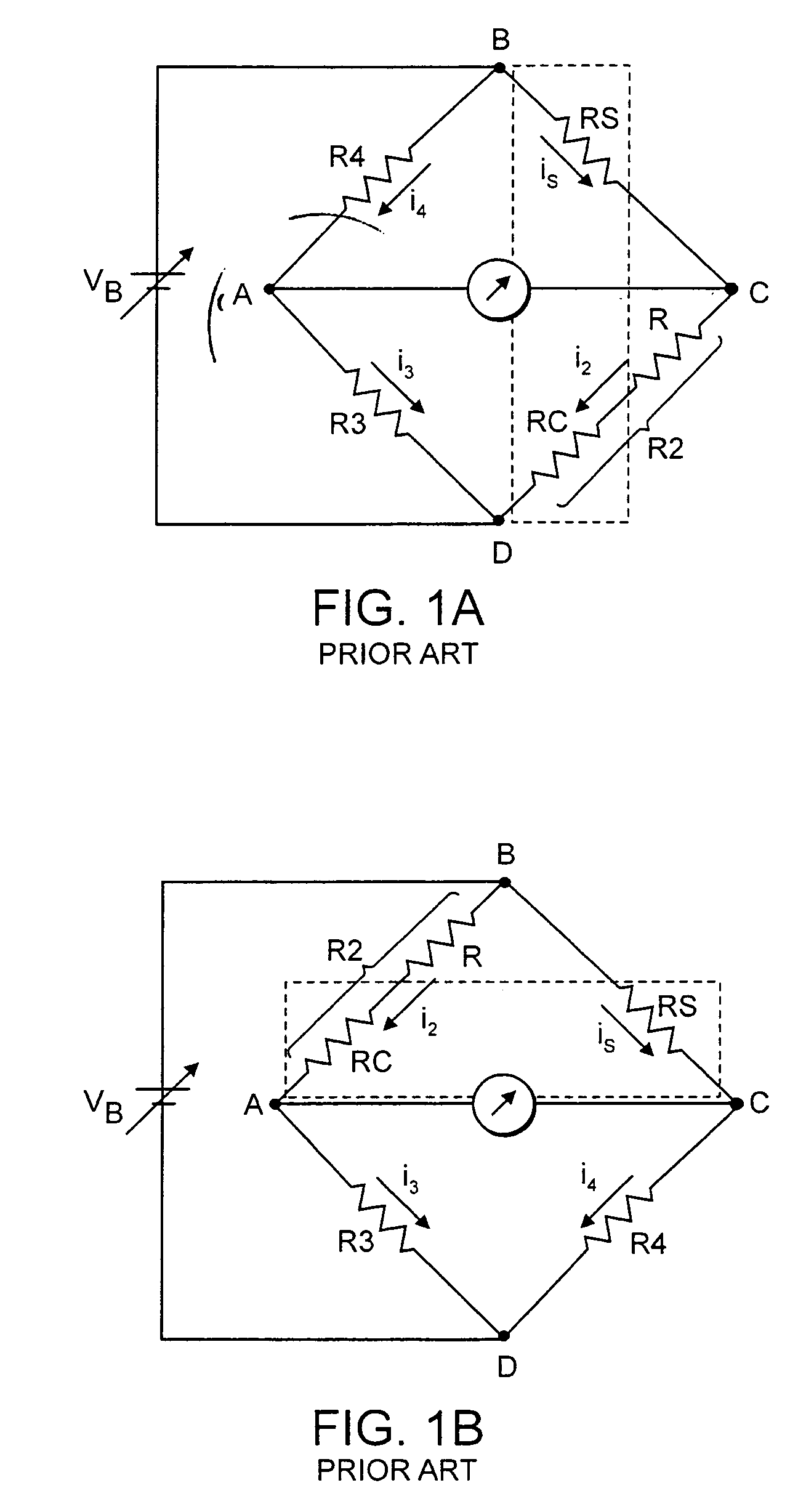
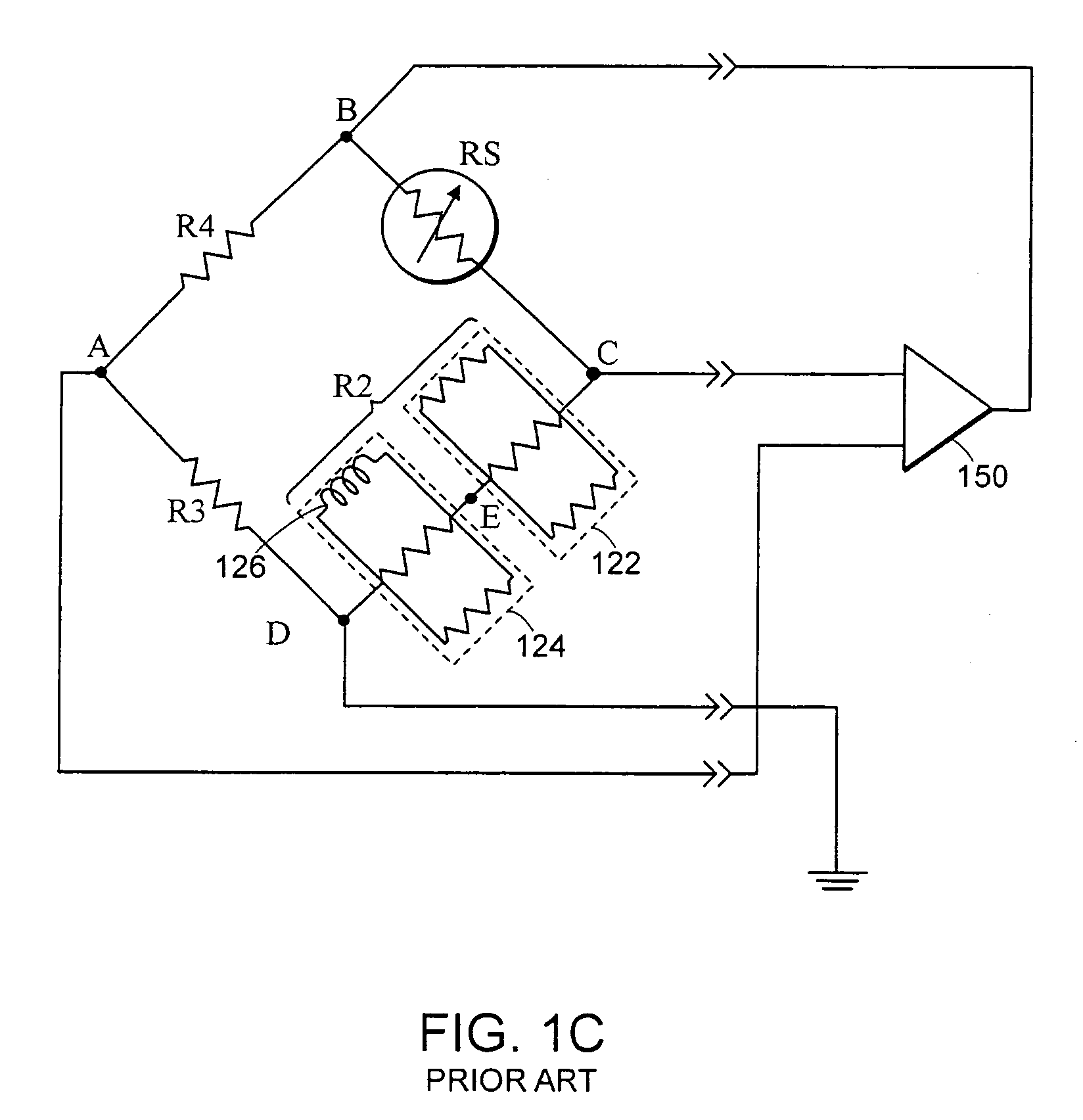
InactiveUS8047711B2Reduce heatLow thermal conductivityThermometer detailsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationHeating timeEngineering
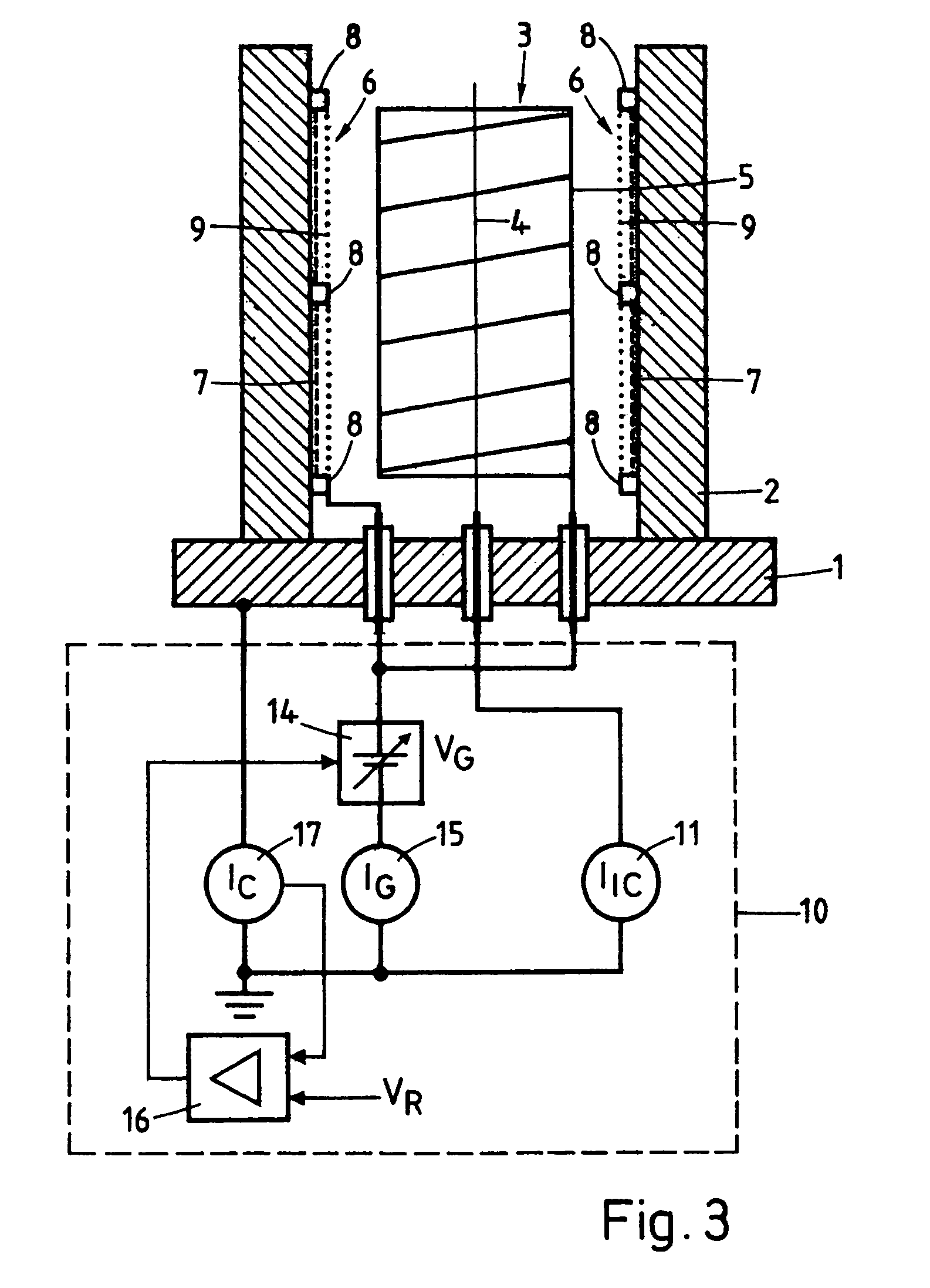
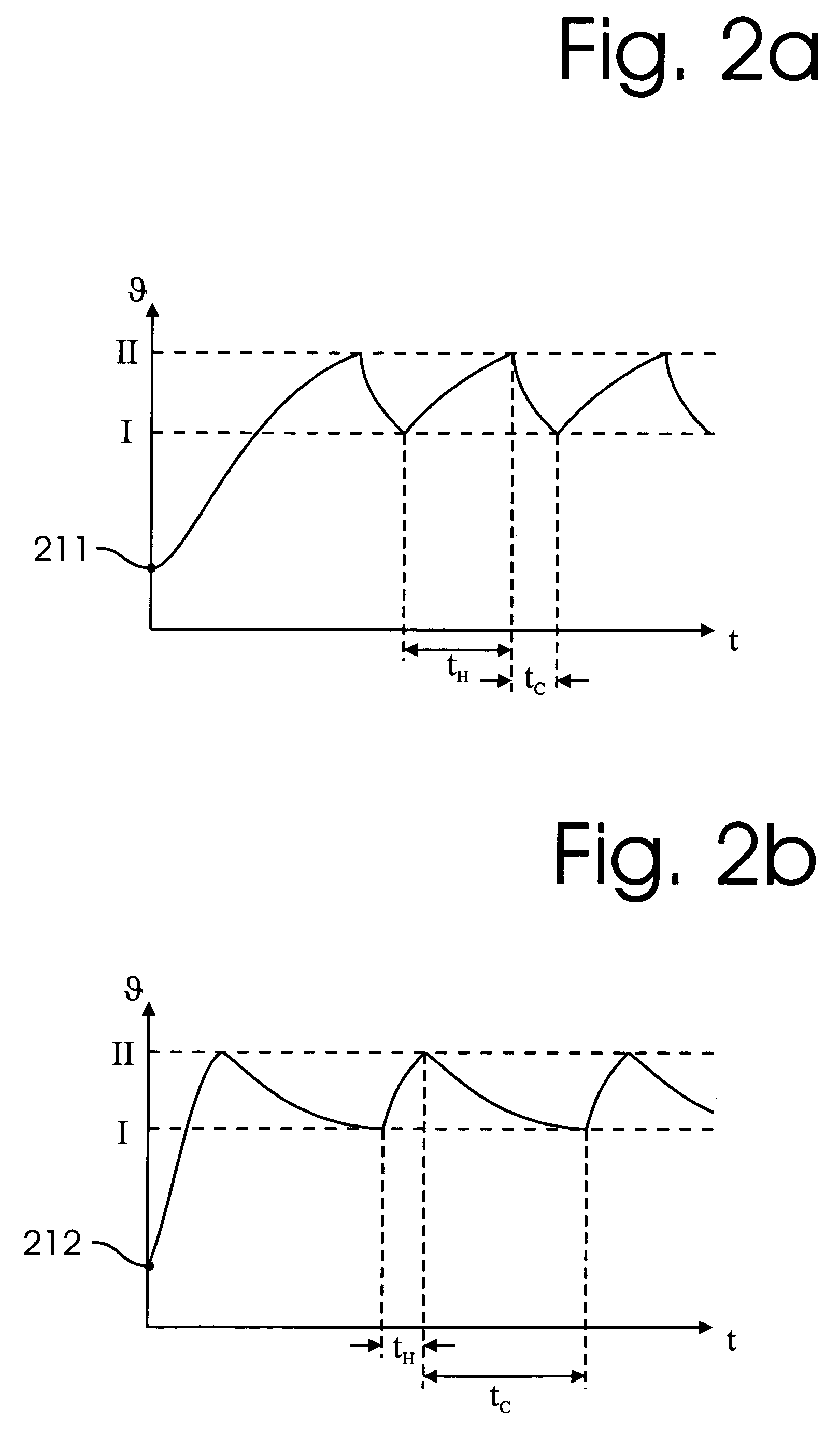
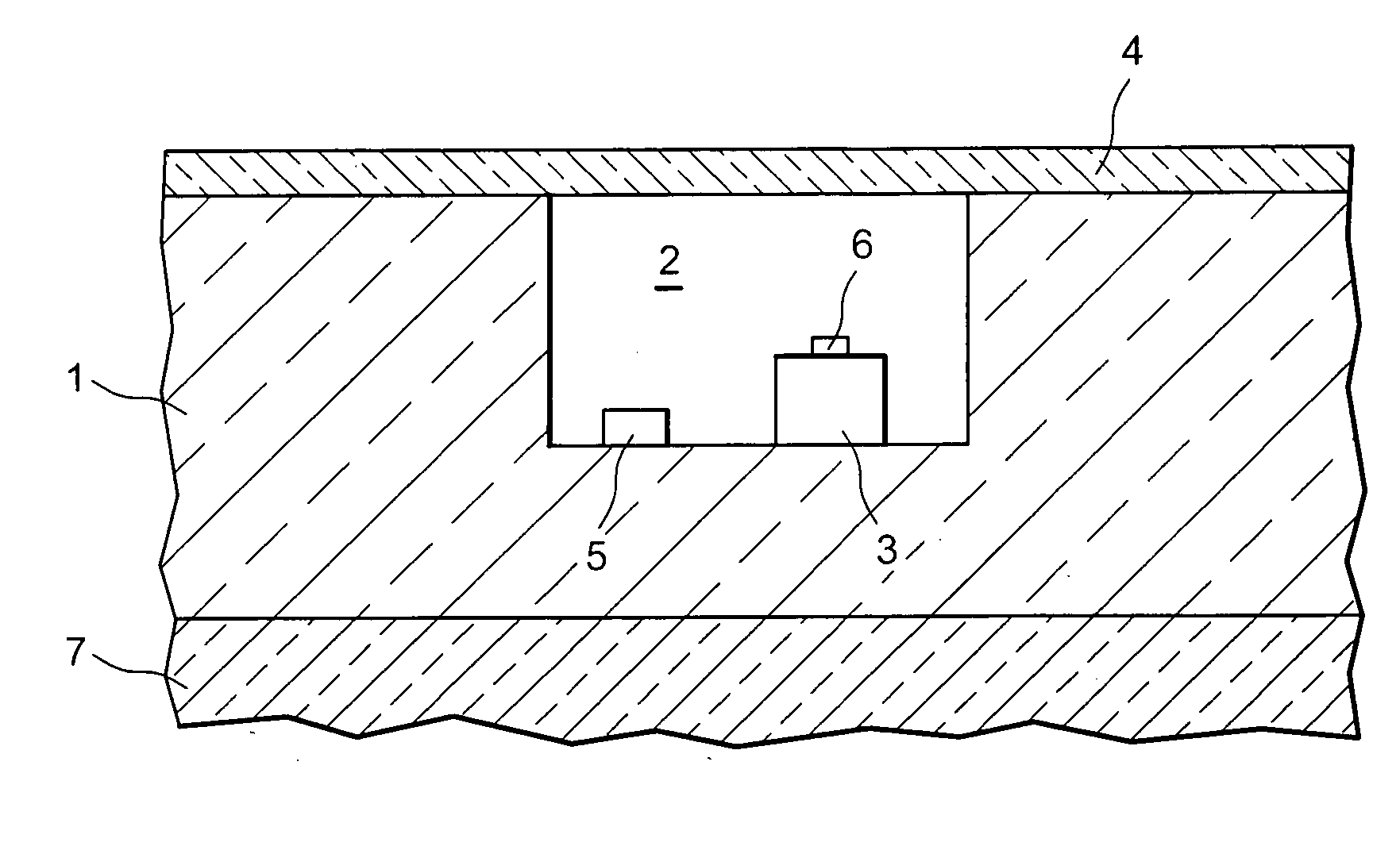
A thermocouple vacuum sensor is provided, the thermocouple being surrounded by a gas or mixture of gases the pressure of which is to be measured. Cyclically the thermocouple is heated until its temperature reaches an upper temperature threshold. The thermocouple is subsequently cooled until its temperature reaches a lower temperature threshold. The heating time required to heat the thermocouple from the lower to the upper temperature threshold is measured. The cooling time required to cool the thermocouple from the upper temperature threshold to the lower temperature threshold may also be measured. The pressure surrounding the thermocouple may then be determined as a function of either the heating time, or the cooling time, or both.
Owner:HEINZ PLOECHINGER
Mems capacitive pressure sensor
ActiveCN103308239AFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesForce measurementInternal pressureCapacitive pressure sensor
A pressure sensor measures pressure by measuring the deflection of a MEMS membrane using a capacitive read-out method. There are two ways to implement the invention. One involves the use of an integrated Pirani sensor and the other involves the use of an integrated resonator, to function as a reference pressure sensor, for measuring an internal cavity pressure.
Owner:希奥检测有限公司
Pressure gauge for organic materials
ActiveUS7322248B1Reduce riskEffective sensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationElectrical resistance and conductanceHeat losses
A vacuum gauge of the Pirani type for measuring the pressure of vaporized organic or inorganic material used in forming a layer of a device, comprising: an extended filament having a thickness of 5 microns or less and having a temperature coefficient of resistance greater than 0.0035 / ° C., the filament being subject to the vaporized organic or inorganic material; means for applying a current to the filament so that the temperature of the filament is less than 650° C. so as not to degrade the molecular structure of the organic material; and a structure responsive to a change in resistance or a change in current to determine heat loss from the filament, which is a function of the pressure of the vaporized organic or inorganic material.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
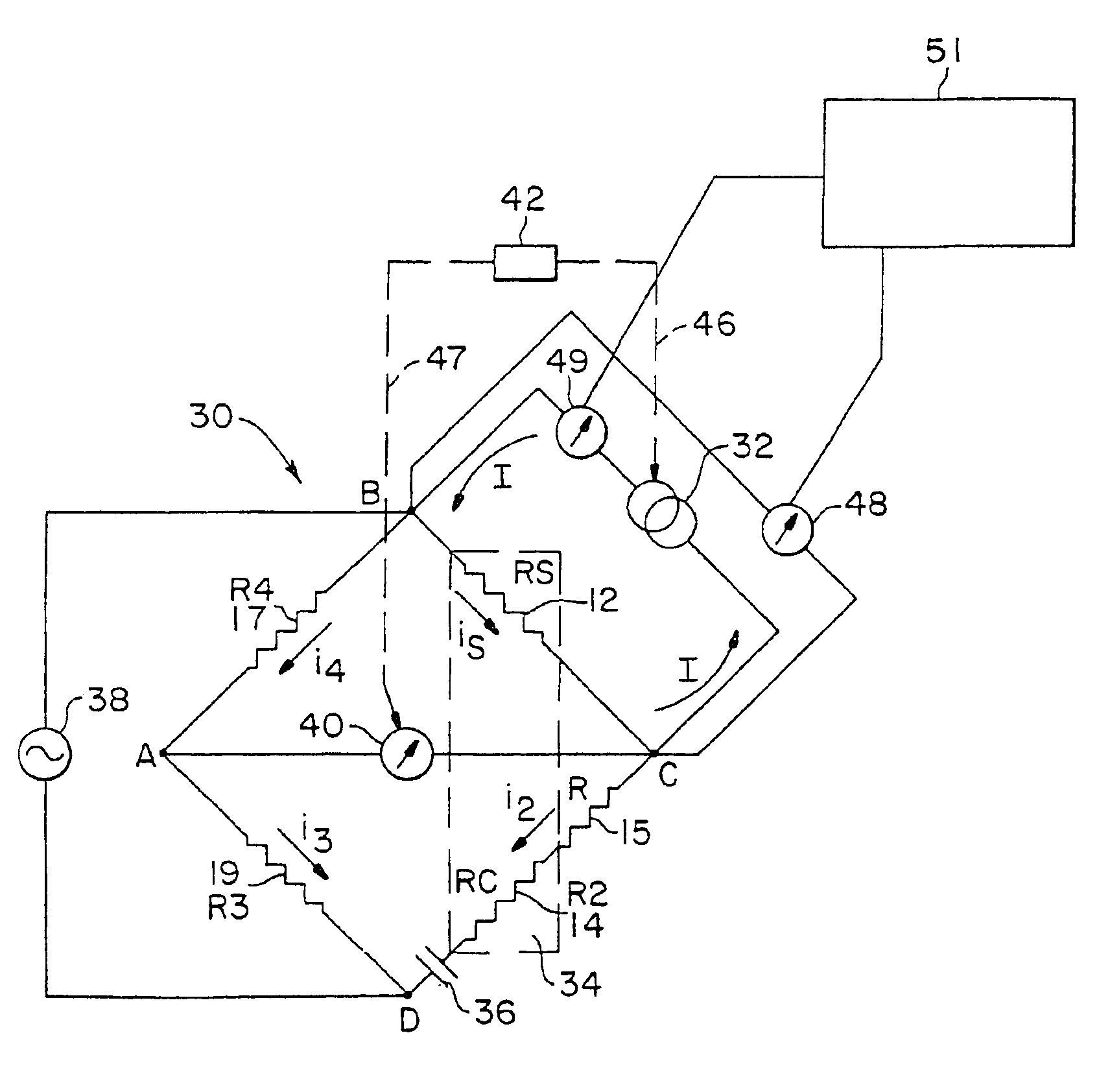
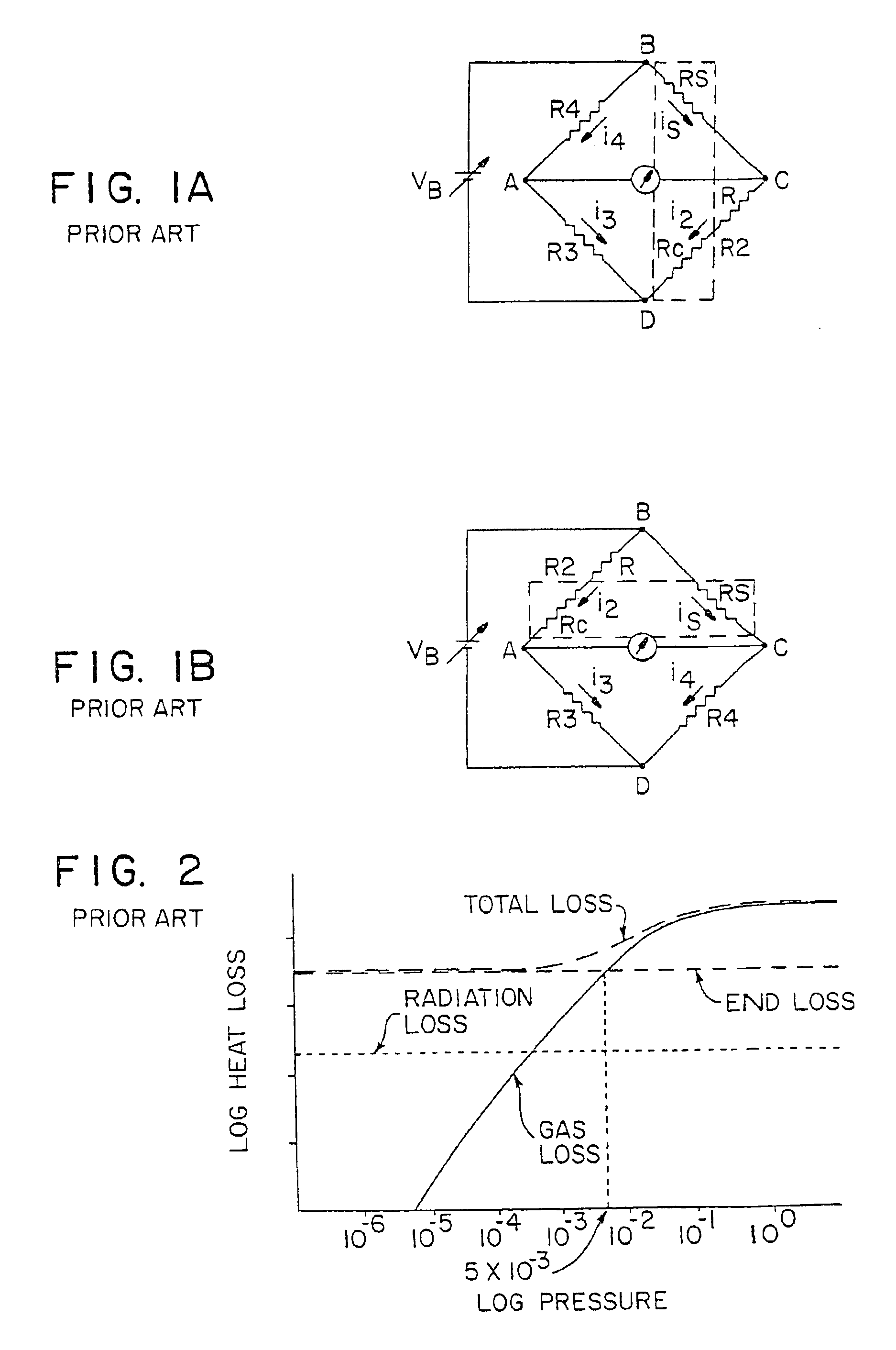
Apparatus and methods for heat loss pressure measurement
InactiveUS6865952B2Improve pressure measurement accuracyIncrease rangeFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A heat loss gauge for measuring gas pressure in an environment includes a resistive sensing element and a resistive compensating element. The resistive compensating element is in circuit with the sensing element and is exposed to a substantially matching environment. An electrical source is connected to the sensing element and the compensating element for applying current through the elements. The current through the sensing element is substantially greater than the current through the compensating element. Measuring circuitry is connected to the sensing element and the compensating element for determining gas pressure in the environment to which the sensing element and compensating element are exposed based on electrical response of the sensing element and the compensating element.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Wide-range combination vacuum gauge
InactiveUS7207224B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDifferential pressureUltra-high vacuum
A combination vacuum gauge provides simultaneous absolute and differential pressure measurements over a wide range of pressures ranging from atmospheric pressures to ultrahigh vacuum by processing the readings from an absolute high vacuum gauge (e.g., an ionization gauge and / or a heat-loss sensor), a differential low vacuum gauge providing a differential relative to ambient pressure (e.g., a diaphragm sensor), and a barometric absolute pressure sensor exposed to the ambient atmosphere outside the measurement region. The barometric absolute pressure sensor reading is used to convert the differential vacuum gauge reading from uncalibrated differential pressure to calibrated absolute pressure.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Wide-range combination vacuum gauge
InactiveUS20060278004A1Accurate differential pressureAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDifferential pressureUltra-high vacuum
A combination vacuum gauge provides simultaneous absolute and differential pressure measurements over a wide range of pressures ranging from atmospheric pressures to ultrahigh vacuum by processing the readings from an absolute high vacuum gauge (e.g., an ionization gauge and / or a heat-loss sensor), a differential low vacuum gauge providing a differential relative to ambient pressure (e.g., a diaphragm sensor), and a barometric absolute pressure sensor exposed to the ambient atmosphere outside the measurement region. The barometric absolute pressure sensor reading is used to convert the differential vacuum gauge reading from uncalibrated differential pressure to calibrated absolute pressure.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
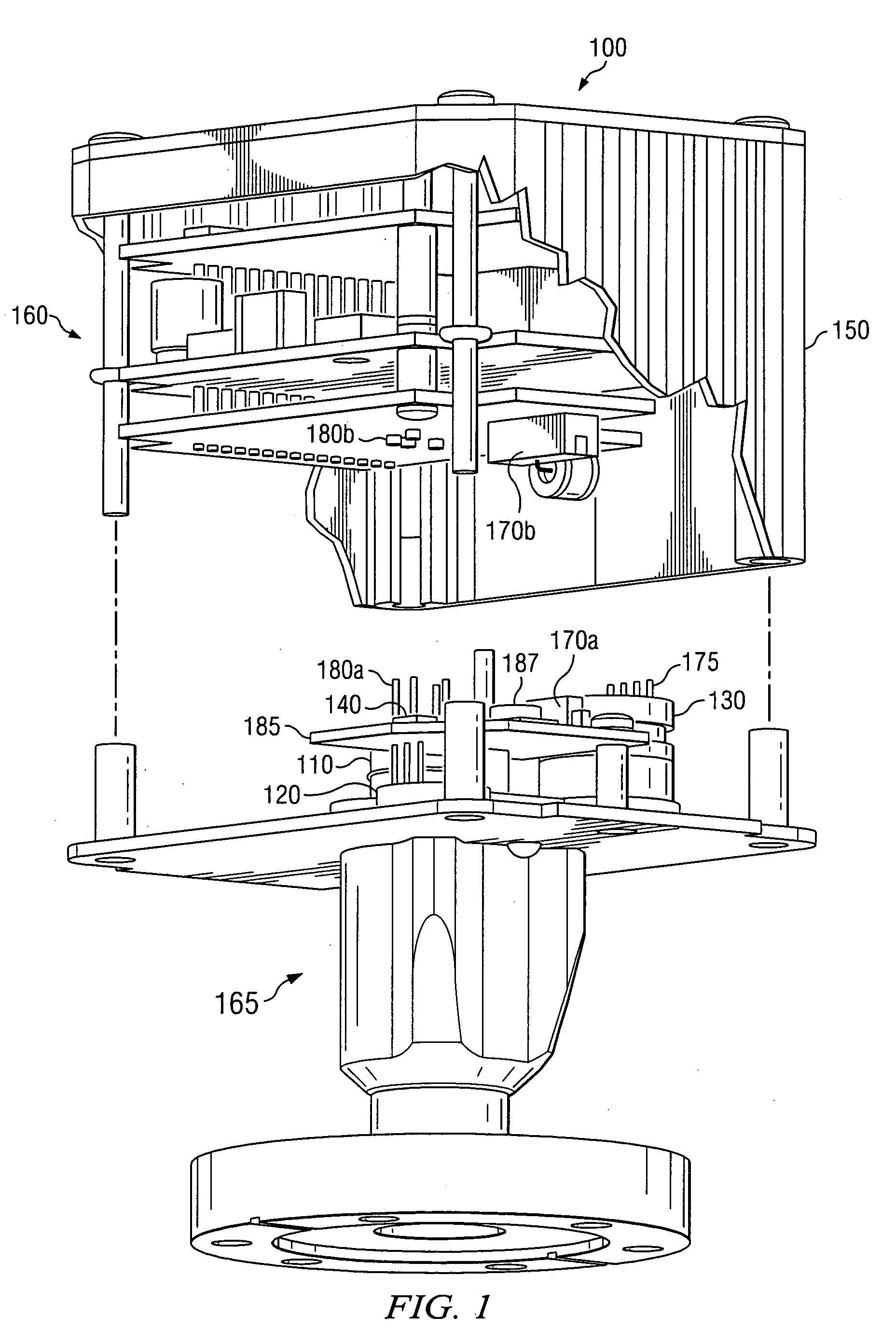
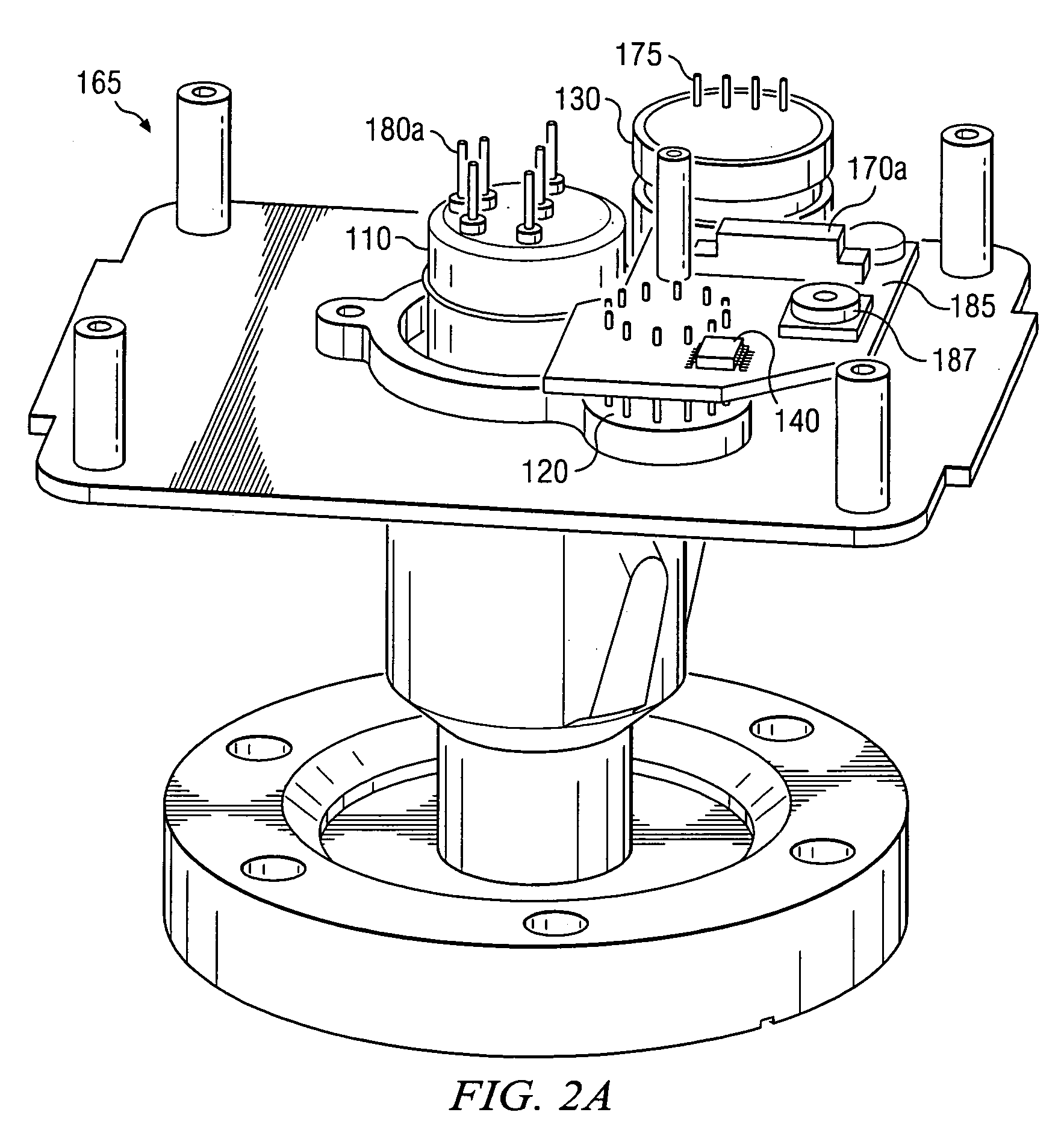
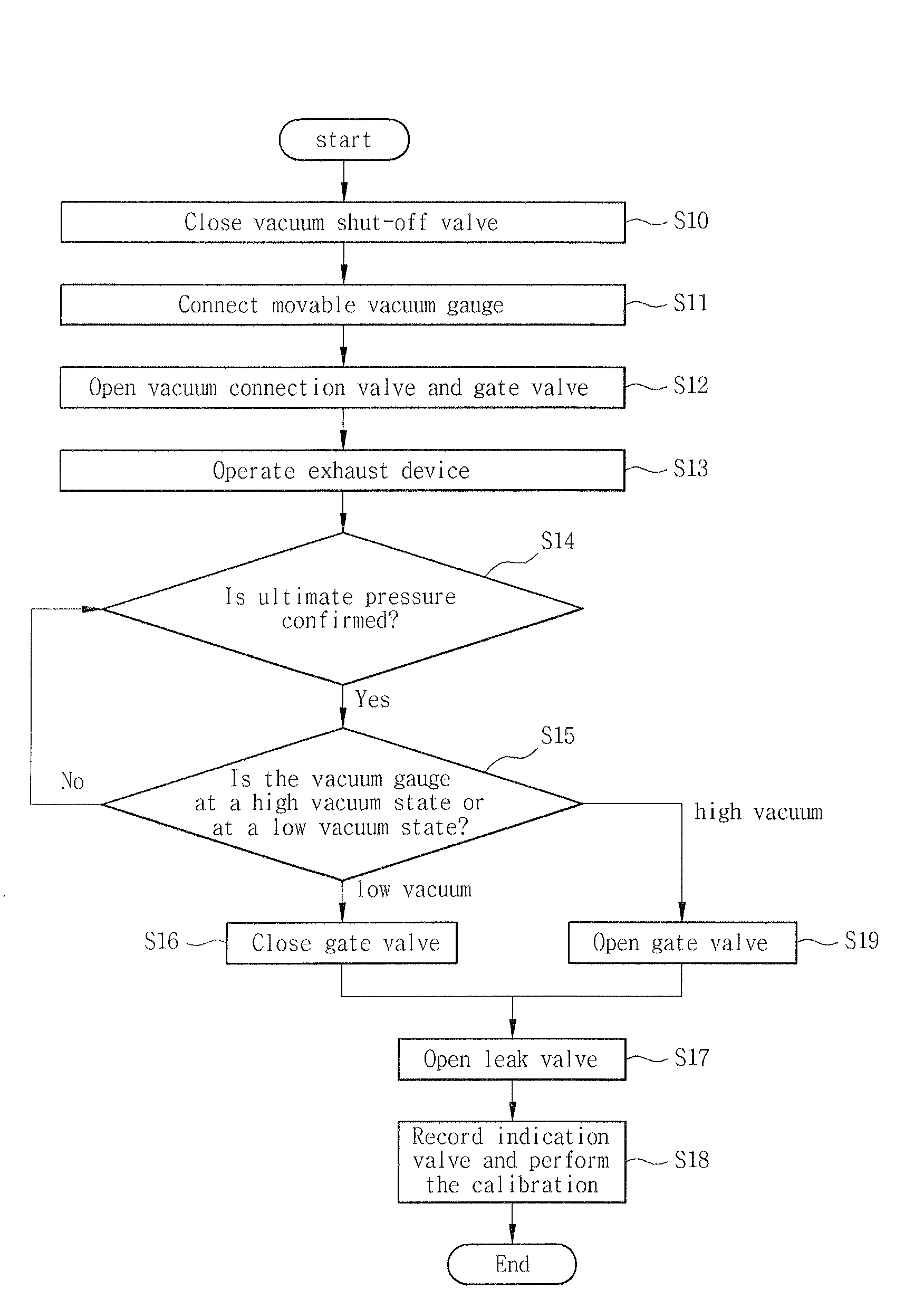
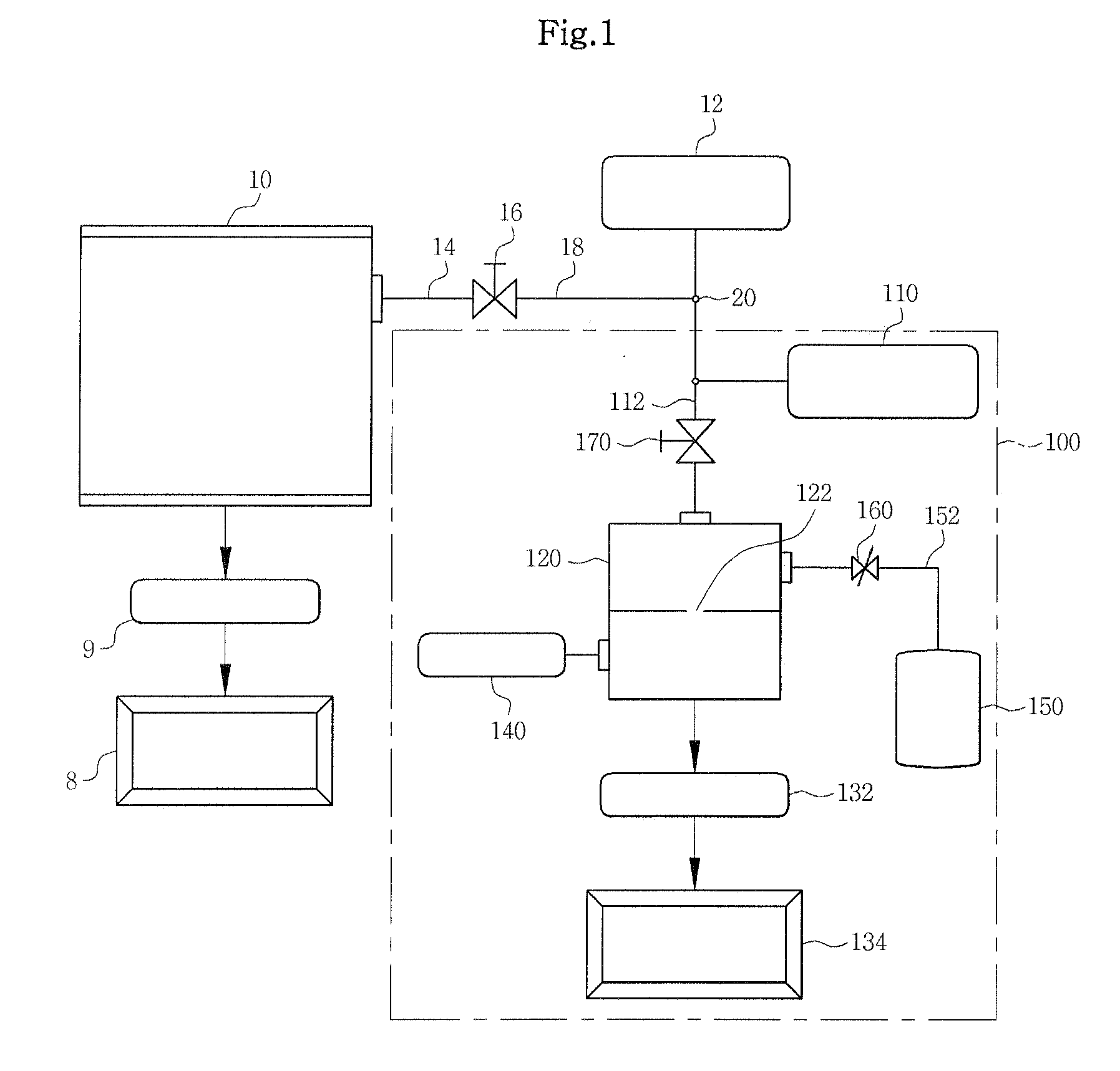
Vacuum gauge calibration apparatus capable of calibrating and testing without displacement and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20090064756A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationVacuum pressureVacuum chamber
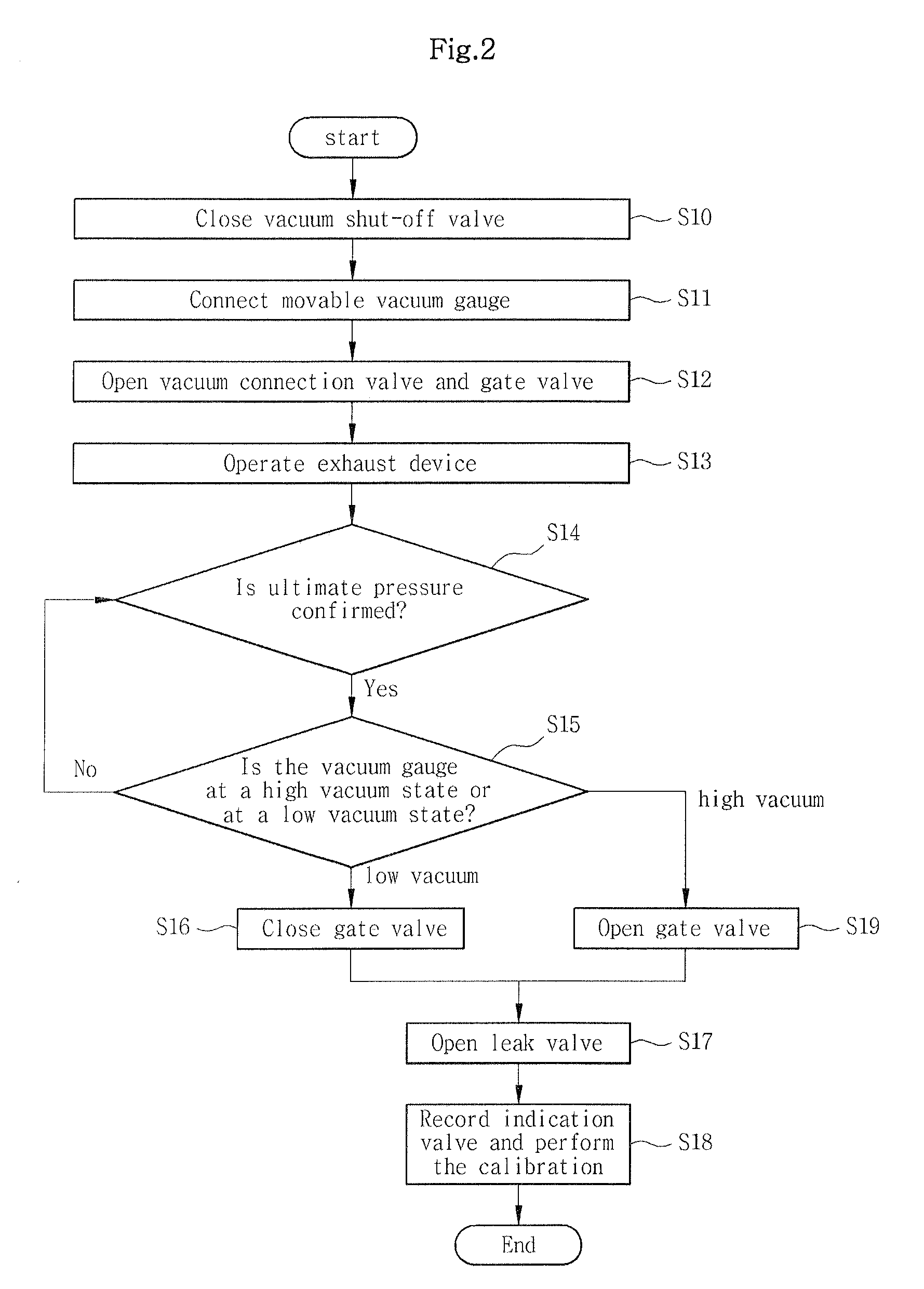
The present invention provides a vacuum gauge calibration apparatus capable of calibrating and testing a vacuum gauge without displacement or separation of the vacuum gauge, the vacuum gauge being attached to a vacuum device under operation together with developing a movable vacuum gauge calibration device, and an operating method thereof. According to the present invention, there is provided an apparatus for calibrating and testing a vacuum gauge to be calibrated without displacement, the vacuum gauge being connected to a vacuum device, the apparatus comprising: a vacuum shut-off valve for opening and closing a piping for connecting the vacuum device to the to-be-calibrated vacuum gauge; and a movable vacuum gauge calibration device connected to the to-be-calibrated vacuum gauge, wherein the movable vacuum gauge calibration device includes: a reference vacuum gauge, a vacuum connection valve, a vacuum chamber, a gate valve, and an exhaust device which are connected to the to-be-calibrated vacuum gauge side in series; a gas supply source connected to the vacuum chamber for generating pressure in the vacuum chamber; a leak valve for controlling gas flow in the gas supply source and supplying the gas the vacuum chamber; and a vacuum gauge for the vacuum chamber for measuring vacuum pressure in the vacuum chamber.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Microbolometer IR Focal Plane Array (FPA) with In-Situ Micro Vacuum Sensor and Method of Fabrication
ActiveUS20070069133A1Poor heat transferSubstantial temperature increaseVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A microbolometer IR FPA is provided with in-situ vacuum sensing capability by realizing that the IR sensor microbolometer pixel element itself may be used as a vacuum sensor. The application of an electrical signal to the resistive element heats the bolometer material thereby producing a variable resistance related to vacuum level. The degree of variability for a given material depends on the efficiency of heat transfer from the material to the surrounding environment. In a good vacuum, heat transfer is poor, and thus heat will be retained in the material to produce a relatively large temperature increase and the resistance variability will be large. In a poor vacuum, heat is readily transferred to the environment and the temperature rise will be relatively small and thus resistance variability will be small. Consequently, the variable resistance magnitude can be readout to determine the vacuum level.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Method and apparatus for storing vacuum gauge calibration parameters and measurement data on a vacuum gauge structure
ActiveUS20060123915A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationEngineeringHeat sensitive
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Micro Pirani gage
ActiveCN101608962AReduce volumeReduce weightTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A micro Pirani gage belongs to vacuum degree measuring element of micro electro mechanical system, aiming at overcoming the problems of large volume and not high enough sensibility of the existing micro Pirani gage. In the invention, a groove is arranged on a silicon substrate, a thermal isolation layer is arranged on the surface of the groove, an insulating layer is covered on the surface of the thermal isolation layer, a heating body is sputtered on the insulating layer, and the two ends of the heating body are sputtered with a metal electrode; wherein the heating body is made by platinum or nickel metal in bend shape; the insulating layer material is silicon nitride or silicon oxide; and the thermal isolation layer material is one or two of silicon oxide and silicon nitride. The invention has small volume, light weight and stable performance, the heating body adopts platinum metal, and the platinum metal has good linearity, stable performance, high sensibility and favourable chemical stability; and the invention has simple manufacturing technology, low cost, high yield and high reliability. The invention is applicable to vacuum degree real time detection in various vacuum encapsulation and micro cavities.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Vacuum measuring gauge
InactiveUS7352187B2Lower requirementWide choiceVacuum tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsSemiconductor materialsDiamond-like carbon
An electron-emitting cathode consists of an electrically conducting emitter layer attached to a side wall which consists of stainless steel and a gate which is fixed at a mall distance inside a concave emitter surface of the emitter layer. The cathode surrounds a reaction area containing a cylindrical grid-like anode and a central ion collector which consists of a straight axial filament. An ion collector current reflecting the density of the gas in the reaction region is measured by a current meter while a gate voltage is kept between the ground voltage of the emitter layer and a higher anode voltage and is regulated in such a way that an anode current is kept constant. The emitter layer may consists of carbon nanotubes, diamond-like carbon, a metal or a mixture of metals or a semiconductor material, e.g., silicon which may be coated, e.g., with carbide or molybdenum. The emitter surface can, however, also be a portion of the inside surface of the side wall roughened by, e.g., chemical etching. The gate may be a grid or it may be made up of patches of metal film covering spacers distributed over the emitter area or a metal film covering an electron permeable layer placed on the emitter surface.
Owner:INFICON GMBH
Pressure sensor
InactiveUS7197939B2Effective limitAccurate pressure detectionFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationEngineeringSemiconductor
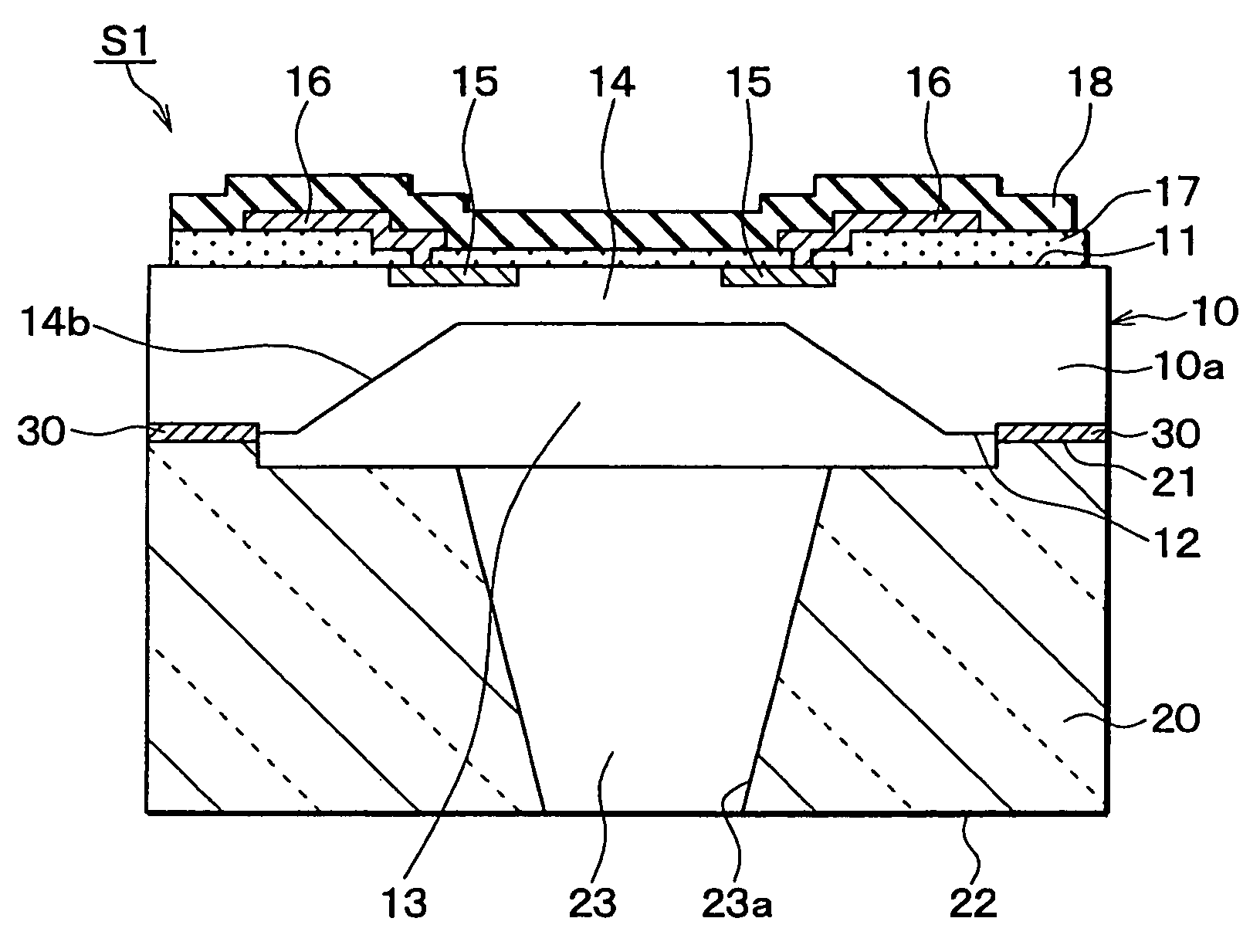
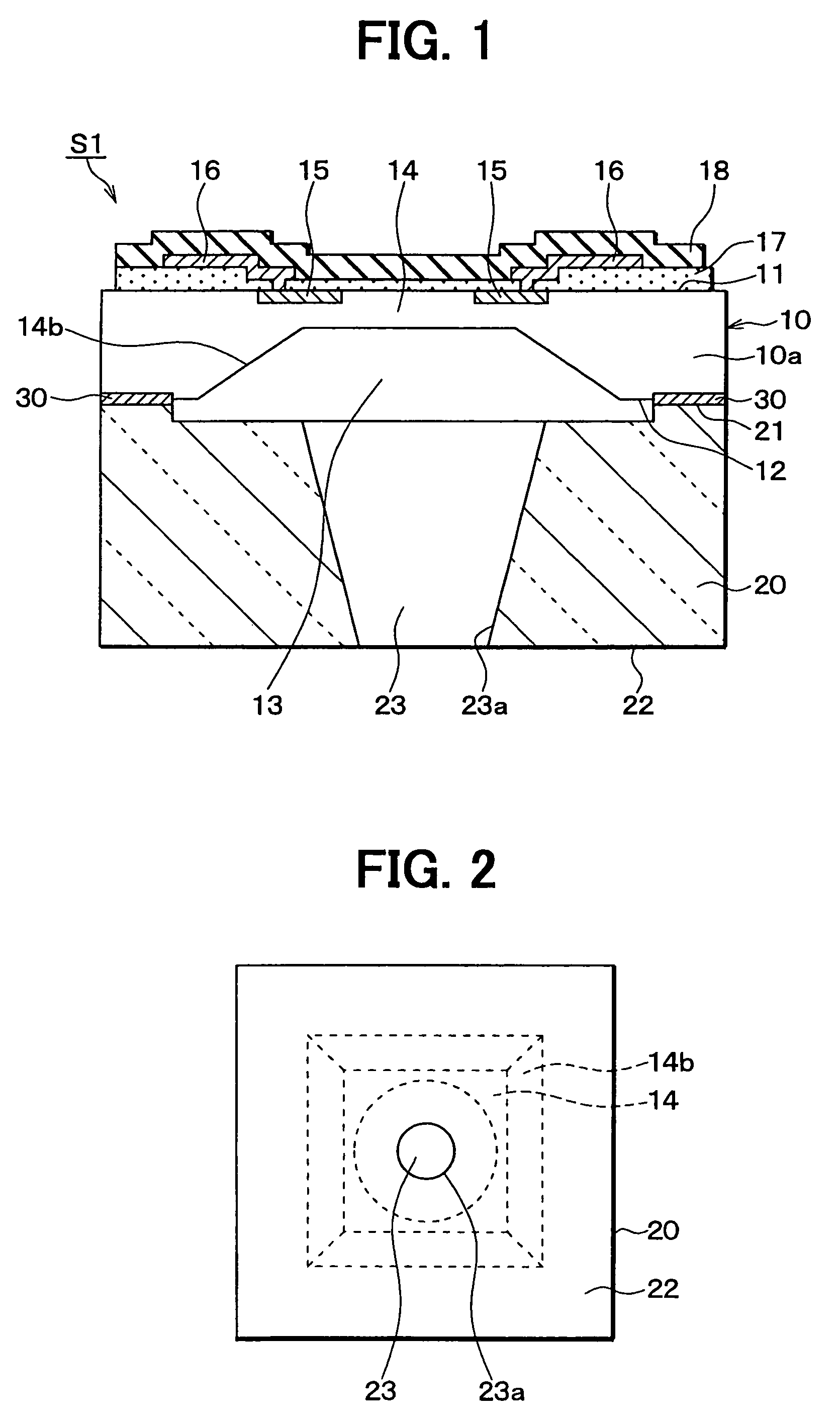
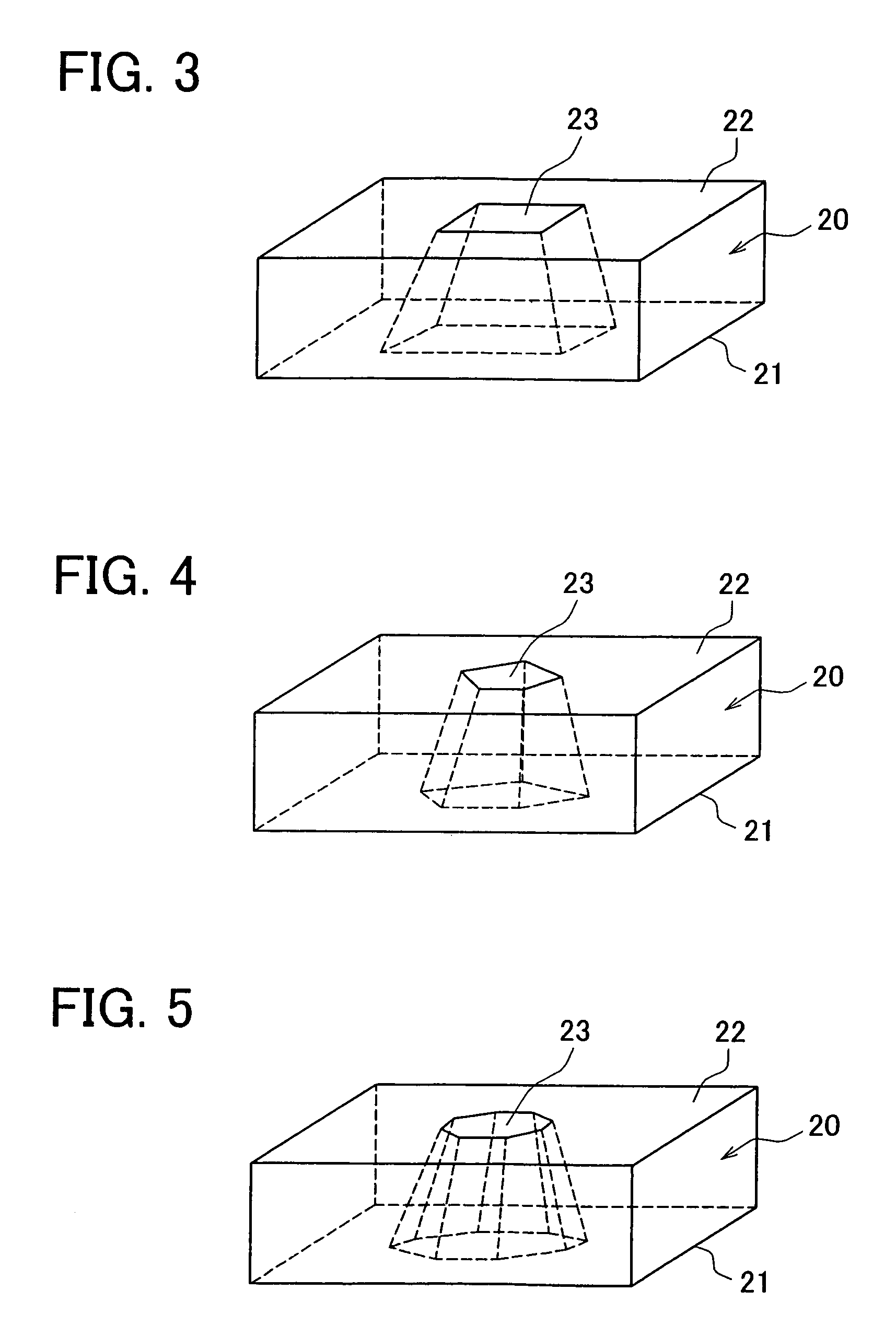
A pressure sensor includes a semiconductor substrate and a pedestal member such as a glass pedestal. The semiconductor substrate has a diaphragm for detecting a pressure and a thick portion positioned around the diaphragm. The pedestal member has one surface bonded to the thick portion of the semiconductor substrate and the other surface opposite to the one surface. In the pressure sensor, the pedestal member has a through hole through which pressure is introduced to the diaphragm. The through hole penetrates through the pedestal member from an opening of the other surface to the one surface of the pedestal member, and the through hole has a hole diameter that becomes smaller from the one surface toward the other surface of the pedestal member. Accordingly, it can effectively restrict foreign materials such as dusts from being introduced into the through hole of the pressure sensor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for sensing gas composition and pressure
ActiveUS20100154510A1Material thermal conductivityVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationGas compositionThermal constant
A method for sensing gas composition and gas pressure, based on the thermal constants of a variable electrical resistor, is presented. The method for sensing gas composition and pressure includes monitoring a variable electrical resistor whose dynamic thermal response is determined by the thermal conductivity and thermal capacity of the surrounding gas of a given atmospheric environment. In the thermal domain, the sensor has a low-pass characteristic, whose phase delay is determined by the thermodynamic characteristics of the surrounding gas such as composition and pressure. The method can be used for sensing gas composition and can also be used for sensing gas pressure.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Vacuum measuring gauge
InactiveUS20060202701A1Increase the areaLower requirementVacuum tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsSemiconductor materialsDiamond-like carbon
An electron-emitting cathode consists of an electrically conducting emitter layer attached to a side wall which consists of stainless steel and a gate which is fixed at a mall distance inside a concave emitter surface of the emitter layer. The cathode surrounds a reaction area containing a cylindrical grid-like anode and a central ion collector which consists of a straight axial filament. An ion collector current reflecting the density of the gas in the reaction region is measured by a current meter while a gate voltage is kept between the ground voltage of the emitter layer and a higher anode voltage and is regulated in such a way that an anode current is kept constant. The emitter layer may consists of carbon nanotubes, diamond-like carbon, a metal or a mixture of metals or a semiconductor material, e.g., silicon which may be coated, e.g., with carbide or molybdenum. The emitter surface can, however, also be a portion of the inside surface of the side wall roughened by, e.g., chemical etching. The gate may be a grid or it may be made up of patches of metal film covering spacers distributed over the emitter area or a metal film covering an electron permeable layer placed on the emitter surface.
Owner:INFICON GMBH
Microbolometer IR focal plane array (FPA) with in-situ mirco vacuum sensor and method of fabrication
ActiveUS7385199B2Poor heat transferSubstantial temperature increaseVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A microbolometer IR FPA is provided with in-situ vacuum sensing capability by realizing that the IR sensor microbolometer pixel element itself may be used as a vacuum sensor. The application of an electrical signal to the resistive element heats the bolometer material thereby producing a variable resistance related to vacuum level. The degree of variability for a given material depends on the efficiency of heat transfer from the material to the surrounding environment. In a good vacuum, heat transfer is poor, and thus heat will be retained in the material to produce a relatively large temperature increase and the resistance variability will be large. In a poor vacuum, heat is readily transferred to the environment and the temperature rise will be relatively small and thus resistance variability will be small. Consequently, the variable resistance magnitude can be readout to determine the vacuum level.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Three-dimensional vacuum sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102923644AMiniaturizationIncrease the upper limit of pressure measurementDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesHeat conductingEngineering
The invention provides a three-dimensional vacuum sensor and a manufacturing method of the three-dimensional vacuum sensor. A thermo-electric pile and a heater manufactured by adopting the method are located on different planes, and the thermo-electric pile is arranged on the heater, thus the miniaturization of the thermo-electric vacuum sensor can be further implemented. The shorter vertical distance between the micro heater to a substrate can be obtained by adopting a dry etching release structure through controlling the etching opening and the etching time, the pressure measurement upper limit of a heat conducting vacuum gauge can be improved, the problem of adhesion of a structural layer and the substrate can be avoided, and the rate of finished production of the devices can be improved. Due to the additional arrangement of a silicon cover plate, the thermal conductivity of the gas can be enhanced, and the sensitivity of the heat conducting vacuum gauge on the higher gas pressure end can be improved. In addition, the materials of the semiconductor substrate, the thermo-electric pile and the micro-heater and the preparation technology adopted in the invention are commonly used in the semiconductor process and can be easily compatible with the existing CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vacuum degree on-line detecting system
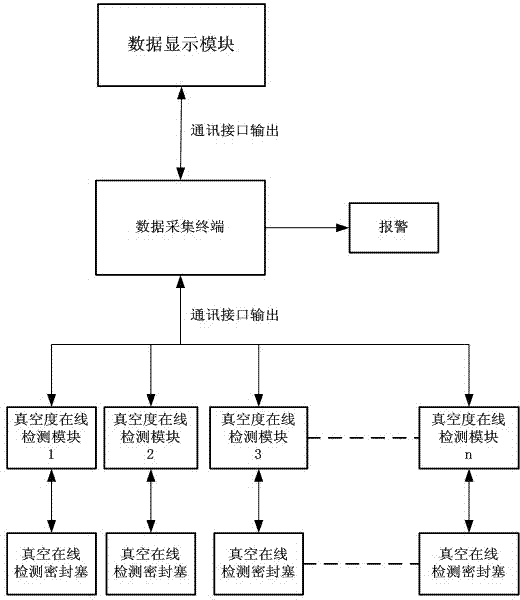
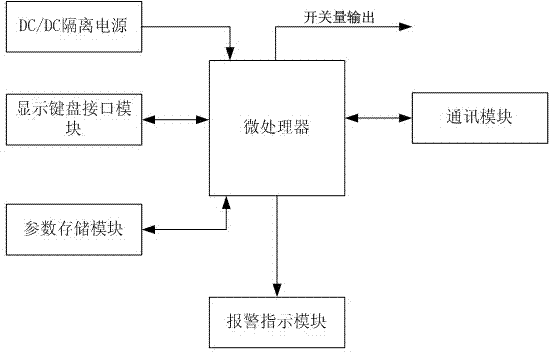
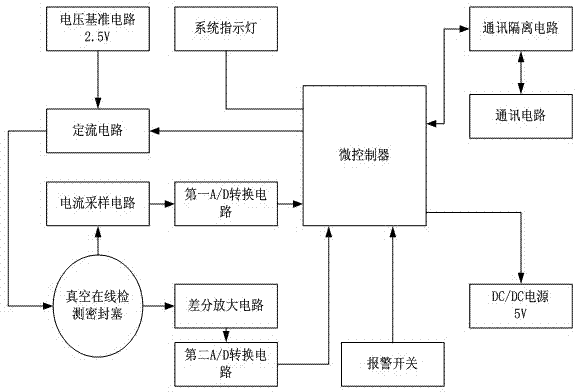
InactiveCN103196628APlay a role in preventing potential safety hazardsReduced chance of vacuum leaksVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationData displayData acquisition
The invention discloses a vacuum degree on-line detecting system which comprises a display module, a data collection terminal, a vacuum degree on-line detecting module and a vacuum on-line detecting sealing plug, wherein the vacuum on-line detecting sealing plug is used for obtaining vacuum data of vacuum equipment, the vacuum degree on-line detecting module is used for processing the vacuum data obtained by the vacuum on-line detecting sealing plug so that the vacuum degree of a vacuum layer of the vacuum equipment is obtained, and the data collecting terminal is used for obtaining vacuum degree data which is sent by at least one vacuum degree on-line detecting module and conducting alarm notification and / or outputting a signal which can control the vacuum equipment to be shut down according to a comparing result of the vacuum degree data and the preset vacuum degree parameter. The vacuum degree on-line detecting system has the advantages of achieving on-line detection of the vacuum degree of the vacuum equipment, detecting a plurality of targets, effectively playing a role in preventing safety hazard, reducing the rate of vacuum leaking and accidents of the equipment, and guaranteeing the using safety.
Owner:成都倍特科技有限责任公司
Carbon nanotube vacuum gauges with wide-dynamic range and processes thereof
InactiveUS20110174079A1Reduce dimensionalitySubstantial pressure sensitivityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationElectricityCurrent meter
A miniature thermal conductivity gauge employs a carbon single-walled-nanotube. The gauge operates on the principle of thermal exchange between the voltage-biased nanotube and the surrounding gas at low levels of power and low temperatures to measure vacuum across a wide dynamic range. The gauge includes two terminals, a source of constant voltage to the terminals, a single-walled carbon nanotube between the terminals, a calibration of measured conductance of the nanotube to magnitudes of surrounding vacuum and a current meter in electrical communication with the source of constant voltage. Employment of the nanotube for measuring vacuum includes calibrating the electrical conductance of the nanotube to magnitudes of vacuum, exposing the nanotube to a vacuum, applying a constant voltage across the nanotube, measuring the electrical conductance of the nanotube in the vacuum with the constant voltage applied and converting the measured electrical conductance to the corresponding calibrated magnitude of vacuum using the calibration. The nanotube may be suspended to minimize heat dissipation through the substrate, increasing sensitivity at even tower pressures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Micro-thermistor gas pressure sensor
ActiveUS8171801B2Fluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Combined type pressure gauge, and manufacturing method of combined type pressure gauge
ActiveUS20110209554A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizeLamination ancillary operationsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationManufacturing cost reductionMiniaturization
The present invention allows manufacturing of a capacitive diaphragm pressure gauge and a Pirani pressure gauge on a single silicon substrate, which makes it possible to reduce the manufacturing cost by the miniaturization of products and mass production. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the manufacturing method of a combined type pressure gauge is a manufacturing method of a combined type pressure gauge including a capacitive diaphragm pressure gauge and a Pirani pressure gauge, the method including a groove-forming step of forming a first groove portion and a second groove portion on a first surface side of a silicon substrate by etching, and a bonding step to bond a glass substrate to the silicon substrate so as to cover the first groove portion and the second groove portion on the first surface side of the silicon substrate.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring pressure of a fluid medium and applications thereof
InactiveUS6973834B1Large lifetime improvementSimple and inexpensive and efficientFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Method and apparatus for measuring the pressure of a fluid medium, by immersing within the fluid medium an electrical resistor having a resistance varying with temperature; applying electrical current through the electrical resistor to heat it to a predetermined temperature above that of the fluid medium; and measuring the rate of change in resistance of the electrical resistor to produce a measurement of the rate of thermal heat dissipation, varying with the density of the fluid medium in which the electrical resistor is immersed, and thereby a measurement of the pressure of the fluid medium. The electrical resistor is a positive temperature coefficient thermistor driven by a constant voltage source and having a resistance which increases sharply at the predetermined temperature, such that the thermistor is automatically self-controlled to substantially maintain the predetermined temperature, whereby the electrical current drawn by the thermistor is a measurement of the thermal load on the thermistor resulting from the thermal heat dissipation therefrom, and thereby a measurement of the pressure of the fluid medium. Many applications of such method and apparatus are described, including a vacuum gauge, a pressure gauge, a barometer, a Pitot tube type speedometer, and a helicopter blade leak detector.
Owner:A T C T ADVANCED THERMAL CHIP TECH
Three-dimensional vacuum sensor and preparation method of three-dimensional vacuum sensor
ActiveCN102928153AMiniaturizationAvoid stickingDecorative surface effectsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationCMOSThermopile
The invention provides a three-dimensional vacuum sensor and a preparation method of the three-dimensional vacuum sensor, wherein a thermopile and a heater prepared by the method are located on different planes; the thermopile is located below the heater to further implement miniaturization of a thermoelectric vacuum sensor; a dry etching release structure is utilized to avoid a problem that a structural layer is adhered with a substrate in a wet etching release process, and the yield of devices is improved; a silicon cover board is additionally arranged, that is, gas heat conduction between the cover board and the heater is increased so as to be beneficial to improving sensitivity of a thermal radiation vacuum gauge on an end with higher pressure intensity. In additional, the materials and the preparation process of the semiconductor substrate, the thermopile and the micro heater are all frequently used in the semiconductor process, so the three-dimensional vacuum sensor is easily compatible with an existing CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermocouple vacuum gauge
InactiveUS20100034236A1Reduce heatLow thermal conductivityThermometer detailsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationEngineeringThermocouple device
A thermocouple vacuum sensor is provided, the thermocouple being surrounded by a gas or mixture of gases the pressure of which is to be measured. Cyclically the thermocouple is heated until its temperature reaches an upper temperature threshold. The thermocouple is subsequently cooled until its temperature reaches a lower temperature threshold. The heating time required to heat the thermocouple from the lower to the upper temperature threshold is measured. The cooling time required to cool the thermocouple from the upper temperature threshold to the lower temperature threshold may also be measured. The pressure surrounding the thermocouple may then be determined as a function of either the heating time, or the cooling time, or both.
Owner:HEINZ PLOECHINGER
Capped microsensor
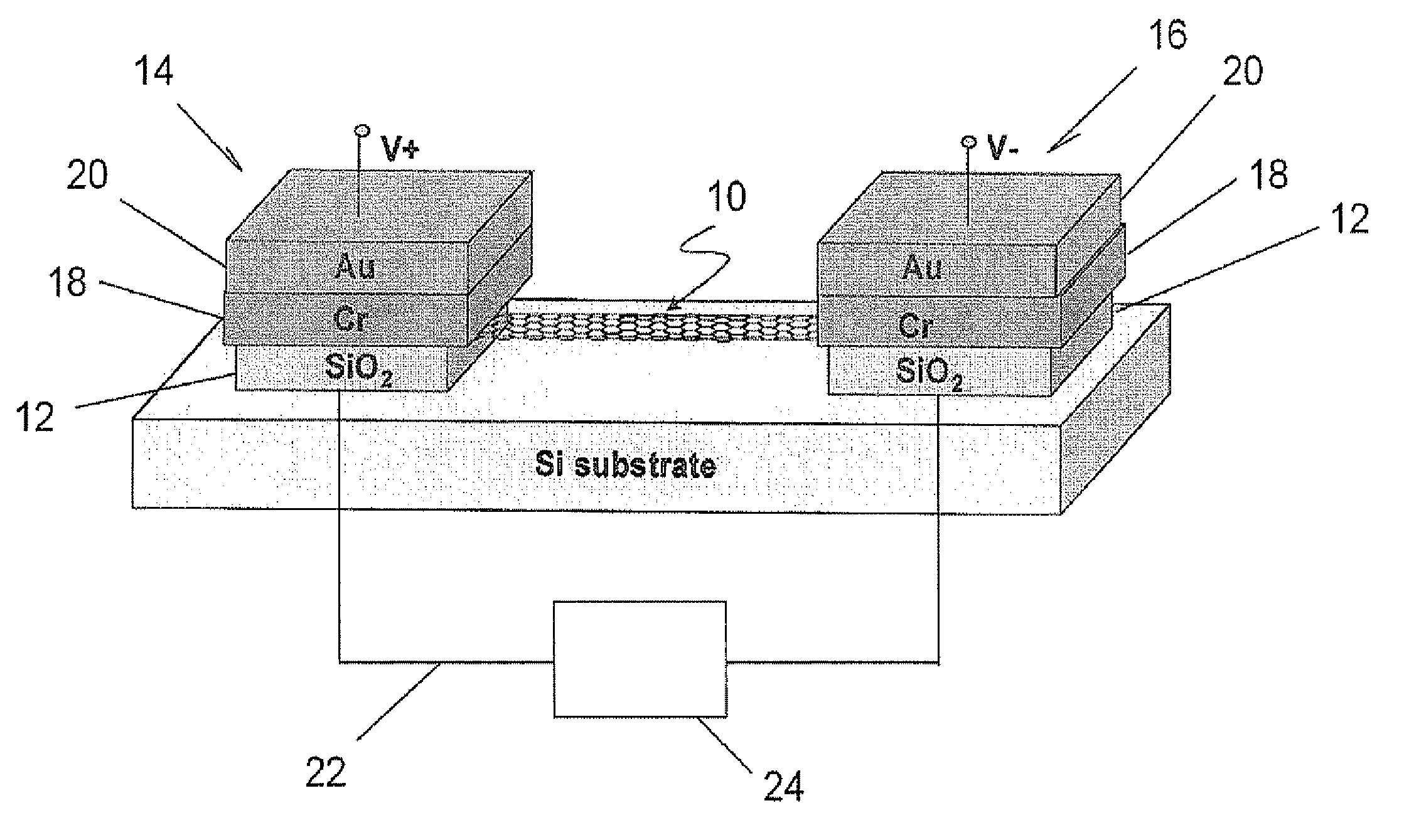
InactiveUS20050028582A1Easy to manufactureCost-effective manufacturingDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateElectrical conductorEngineering
A capped microsensor is described. It is suggested that a current conductor, positioned in the cavity and having at least two voltage taps, be provided, this configuration being used for seal testing, e.g., during quality control, by detecting at least one thermodynamic variable of a gaseous medium present inside the cavity via this configuration.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
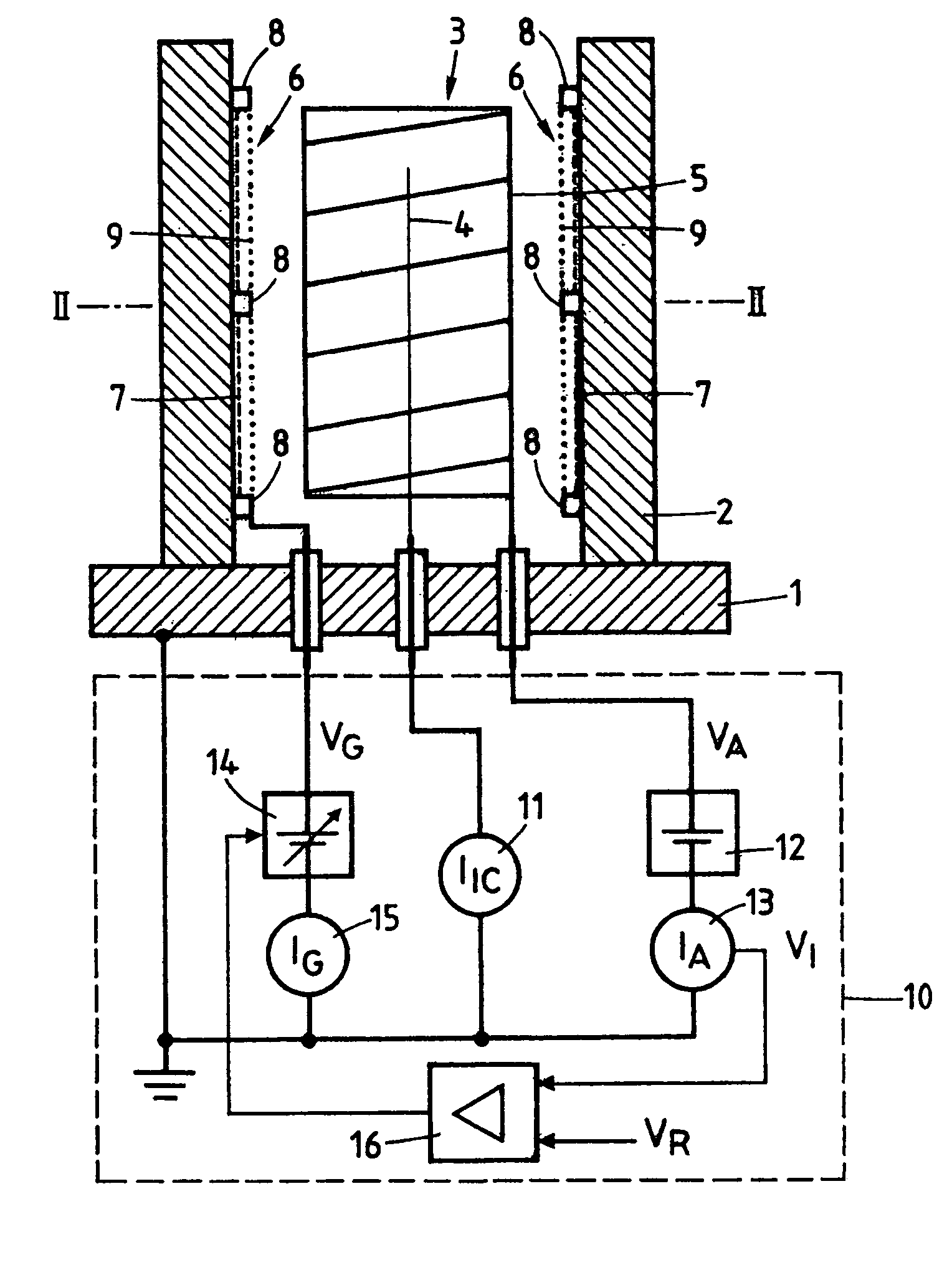
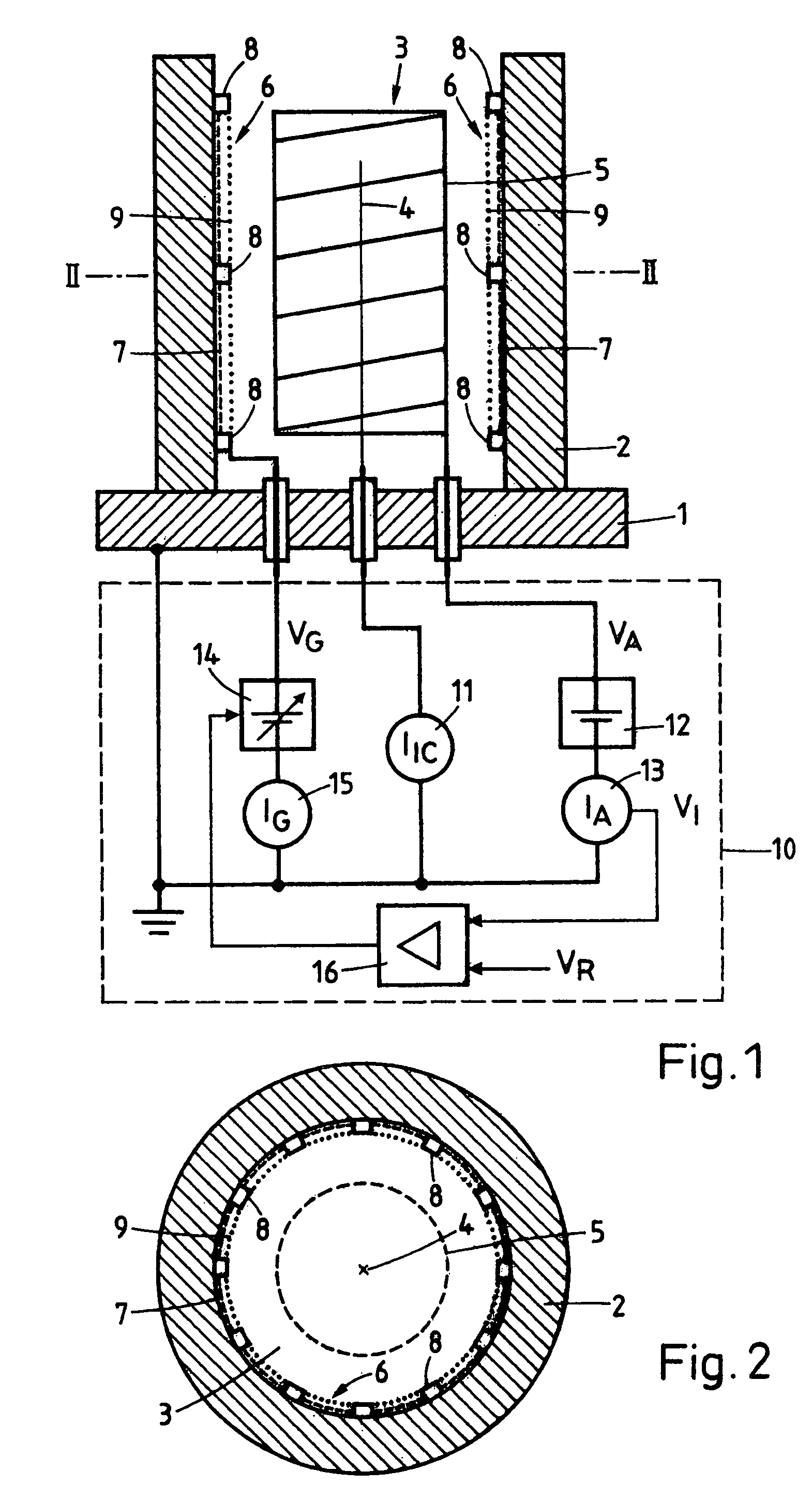
Technique for improving Pirani gauge temperature compensation over its full pressure range
InactiveUS7331237B2Vacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationElectrical resistance and conductanceCurve fitting
A method and apparatus are provided for achieving nearly perfect temperature compensation of a heat-loss vacuum gauge over its full pressure range. A voltage is measured across a sensor leg, a sensor leg and a temperature compensating leg connected together in series, or a sensor leg and a fixed resistive leg coupled together in series. A voltage is also measured across a subleg of the temperature compensating leg. The temperature compensating leg may include a temperature sensitive subleg and a temperature stable subleg connected together in series. The sublegs may include one or more temperature sensitive and / or temperature stable elements. The measured voltages are combined to produce temperature independent pressure indications over a pressure range. Three-dimensional curve-fitting or similar techniques may be used to combine the measured voltages.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Vacuum measuring device with interchangeable sensors
InactiveUS20110167919A1Simple taskSensing detailsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
An interoperable vacuum measuring device is presented, which automatically adjusts to one of two or more vacuum sensors having different electrical characteristics. The interoperable vacuum measuring device in a first step detects which type of vacuum sensor it is connected to. In a second step it controls and evaluates the vacuum sensor, using control parameters determined in response to the detection of the first step.Detection of a vacuum sensor type is achieved by measuring the electrical resistance between any two pins of a vacuum sensor's connector and comparing the measured resistance values with stored resistance values of known vacuum sensors.Further, a vacuum measuring device is presented, which automatically identifies a vacuum sensor, and associates a vacuum pressure measurement with a vacuum sensor. The identification of a vacuum sensor is facilitated by an identification disk, which is placed onto and operatively connected to the male terminals of a vacuum sensor's connector.
Owner:PLOECHINGER PATENT
Apparatus and methods for heat loss pressure measurement
InactiveUS6945119B2Improve pressure measurement accuracyIncrease rangeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A heat loss gauge for measuring gas pressure in an environment includes a resistive sensing element and a resistive compensating element. The resistive compensating element is in circuit with the sensing element and is exposed to a substantially matching environment. An electrical source is connected to the sensing element and the compensating element for applying current through the elements. The current through the sensing element is substantially greater than the current through the compensating element. Measuring circuitry is connected to the sensing element and the compensating element for determining gas pressure in the environment to which the sensing element and compensating element are exposed based on electrical response of the sensing element and the compensating element.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Heat conduction-type barometric sensor utilizing thermal excitation
InactiveUS20120118060A1Improve accuracySimple structureFluid pressure measurement using pressure-sensitive liquidThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermal expansionIntermittent heating
A heat conduction type barometric sensor has high sensitivity and high accuracy that has simple structure and circuit configuration and can measure a barometric pressure in the range of a very low barometric pressure to ≧1 atm using one sensor chip. The sensor includes a cantilever-shaped thin film provided with a thin-film temperature sensor, a heating element, and an excitation element. The excitation element utilizes warpage and bending based on a difference in thermal expansion between two main layers constituting the thin film during intermittent heating by a thin-film heater as the heating element. The two main layers are a silicon layer and a thermally oxidized film of silicon which are significantly different from each other in the coefficient of thermal expansion. A circuit in which the sensitivity is enhanced by the integration of a seebeck current for a predetermined period of time can be also provided.
Owner:KIMURA GIKEN KK
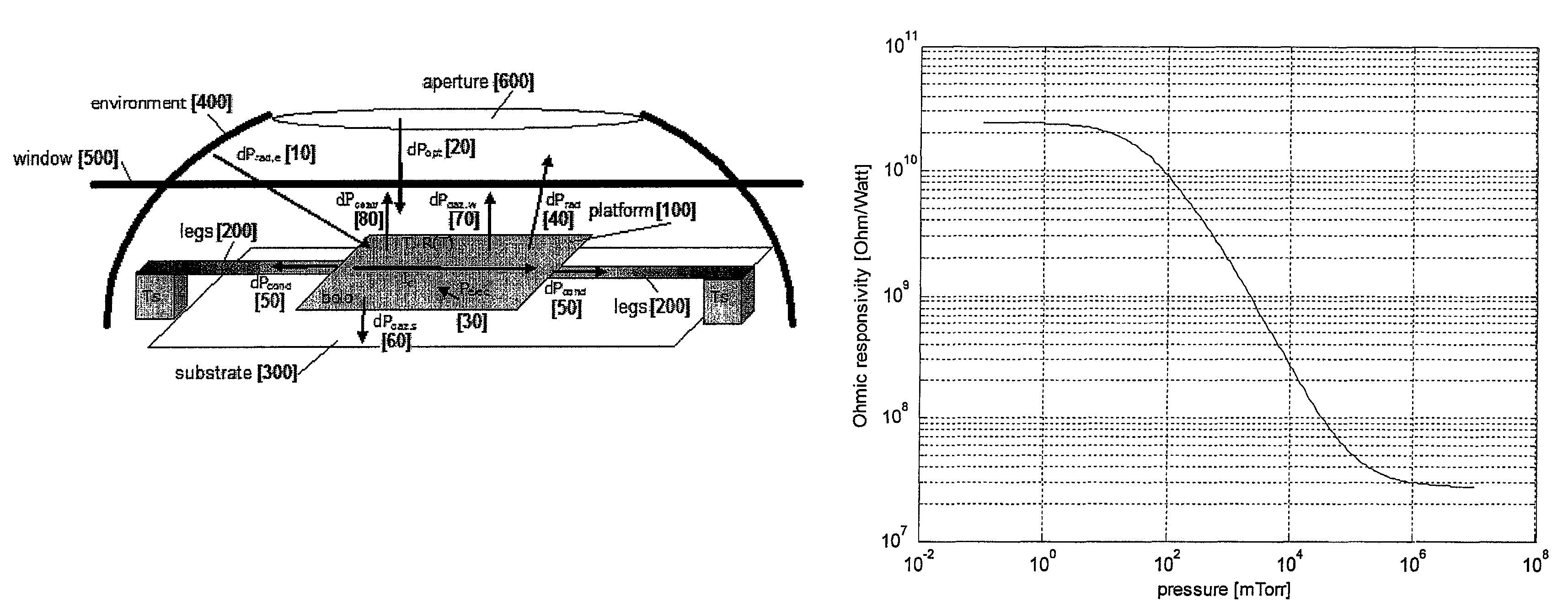
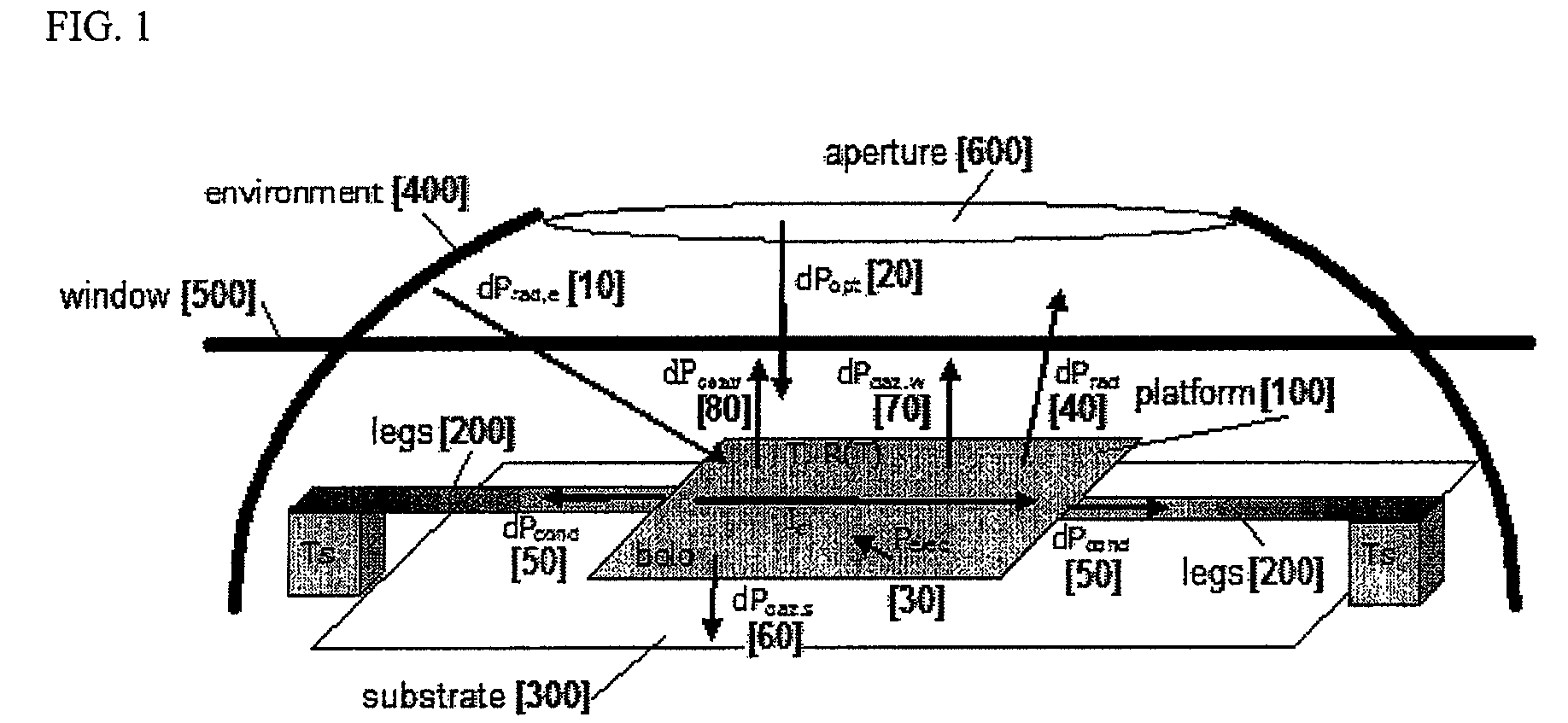
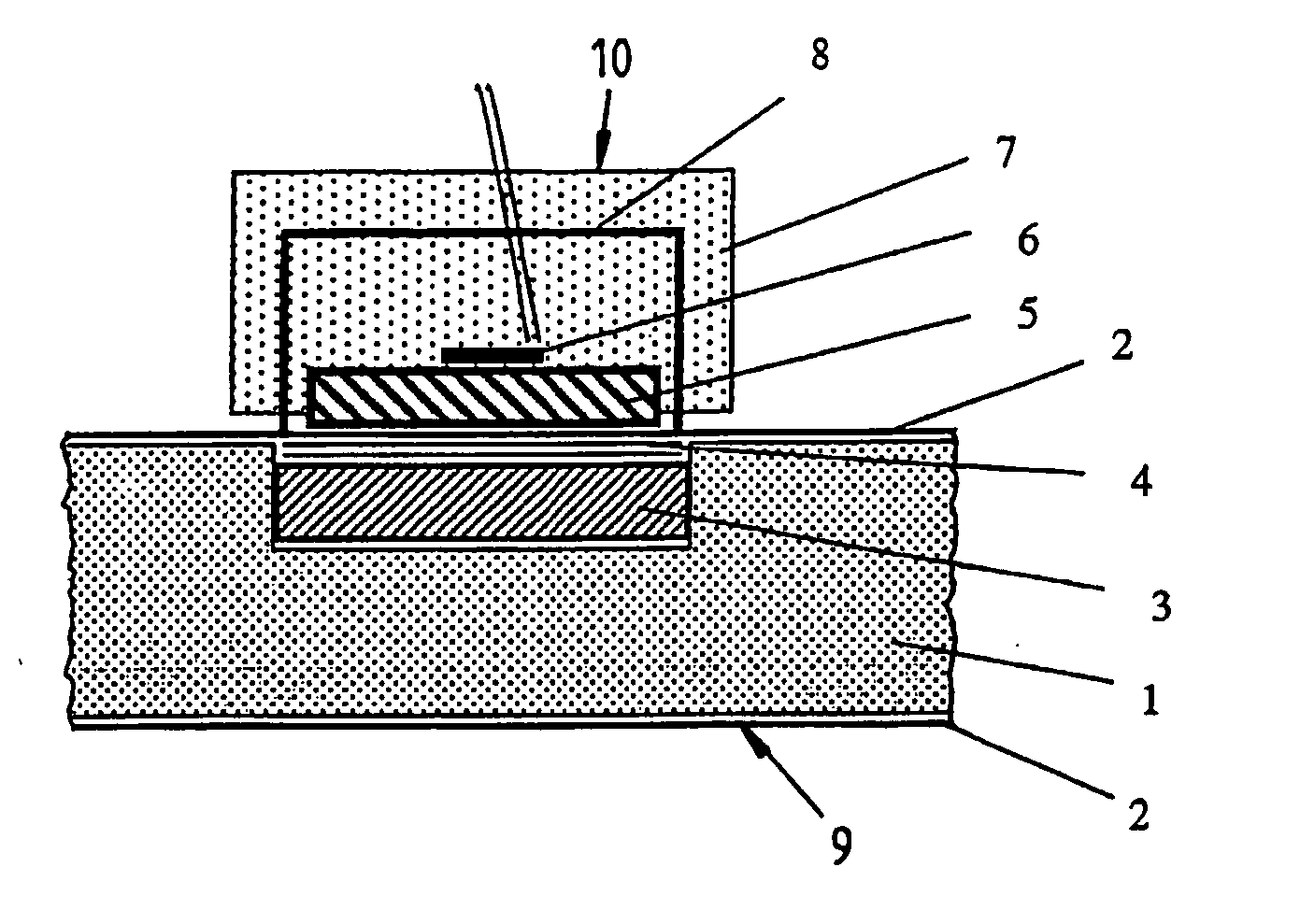
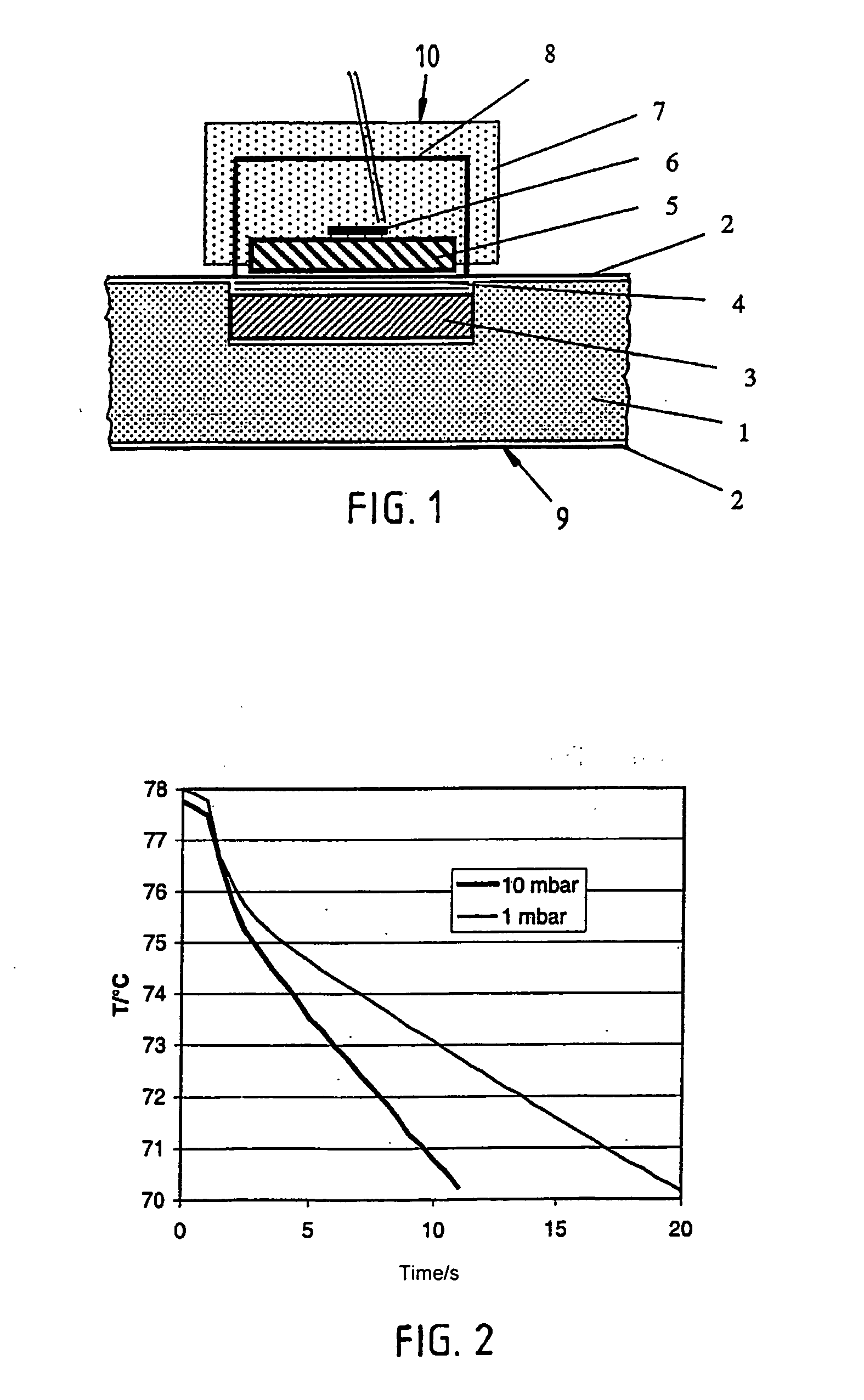
Determination of the gas pressure in an evacuated thermal insulating board (vacuum panel) by using a heat sink and test layer that are intergrated therein
ActiveUS20050199067A1Heat suppressionMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateMaterial thermal conductivityGlass fiberHeat flux
The invention relates to the determination of the gas pressure in an evacuated thermal insulating board (9) having an insulating core (1) covered by a film (2). The inventive device comprises an assembly, which is integrated between the insulating core and the covering film of the thermal insulating board and which has a body that acts as a heat sink (3) (Al, Co, Fe, ceramic), and the body's thermal conductivity and thermal capacity relative to volume are greater than those of the insulating core. Said assembly also comprises a test layer (4) (0.3 mm nonwoven fabric made of plastic and glass fibers), which is arranged between the heat sink and the covering film and has a defined thermal conductivity that changes according to the gas pressure inside the evacuated thermal insulating board. From the exterior, a sensor device is applied to or pressed against the test device, which is placed inside the evacuated thermal insulating board and which is covered by the covering film. Said sensor device comprises a body (5) (coppered steel 78° C., thermoelement (6)) having a distinctly different temperature than that of the test device (heat sink) whereby creating a heat flux, which is influenced by the thermal conductivity of the test layer, said thermal conductivity varying according to the gas pressure inside the thermal insulating board, and the magnitude of this heat flux is metrologically determined. The heat sink (3) can be provided in the form of a bottom part of a container for a getter material.
Owner:VA Q TEC AG
Tightness Test for Mems or for Small Encapsulated Components
InactiveUS20070234782A1Easily deducedThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityVolumetric Mass DensityMechanical engineering
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Popular searches
Material thermal analysis Thermometer applications Vacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variation Pressure difference measurement between multiple valves Multiple fluid pressure valves simultaneous measurement Fluid pressure measurement using capacitance variation Photovoltaics Using electrical means Semiconductor devices Material analysis by electric/magnetic means
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com