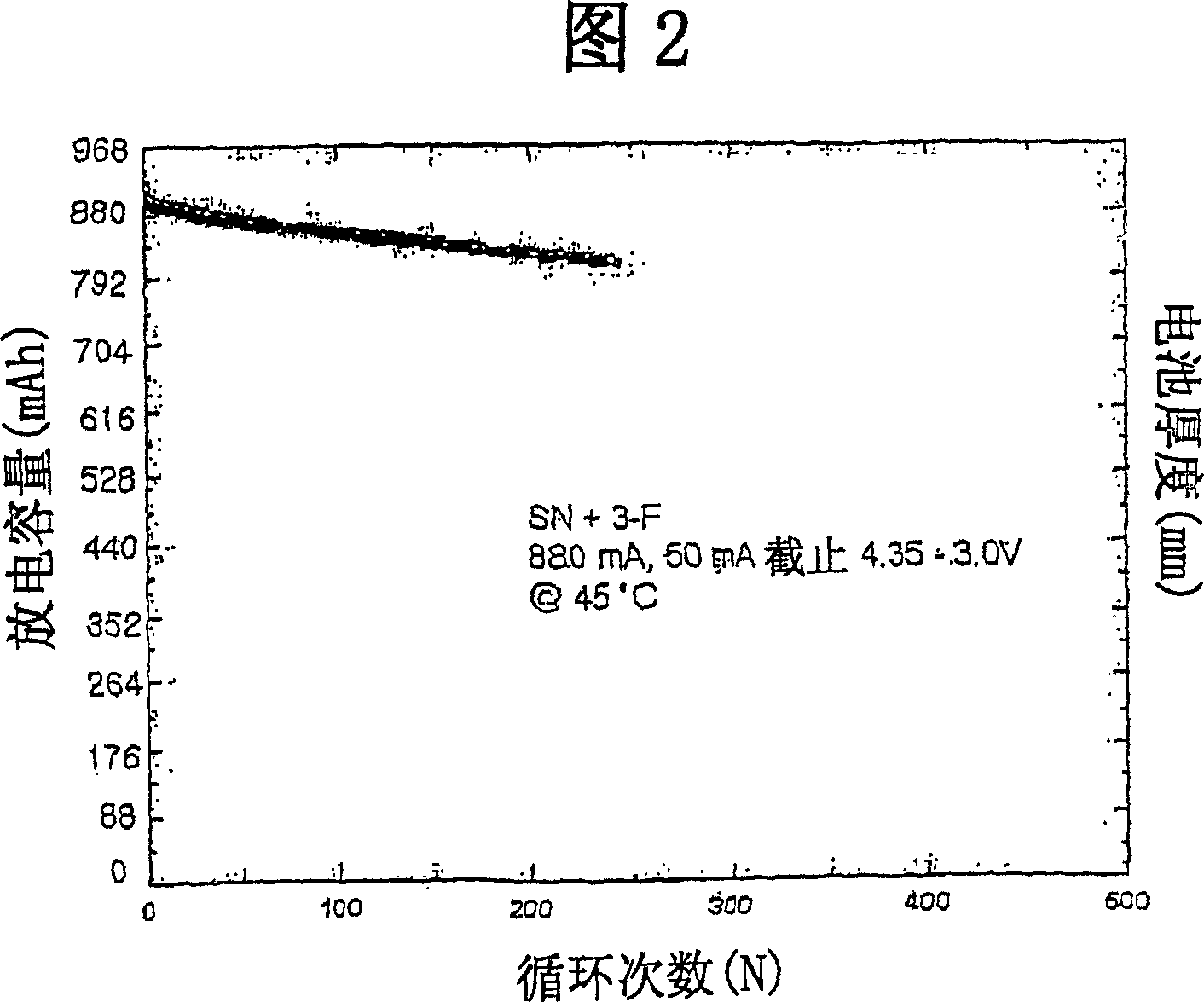
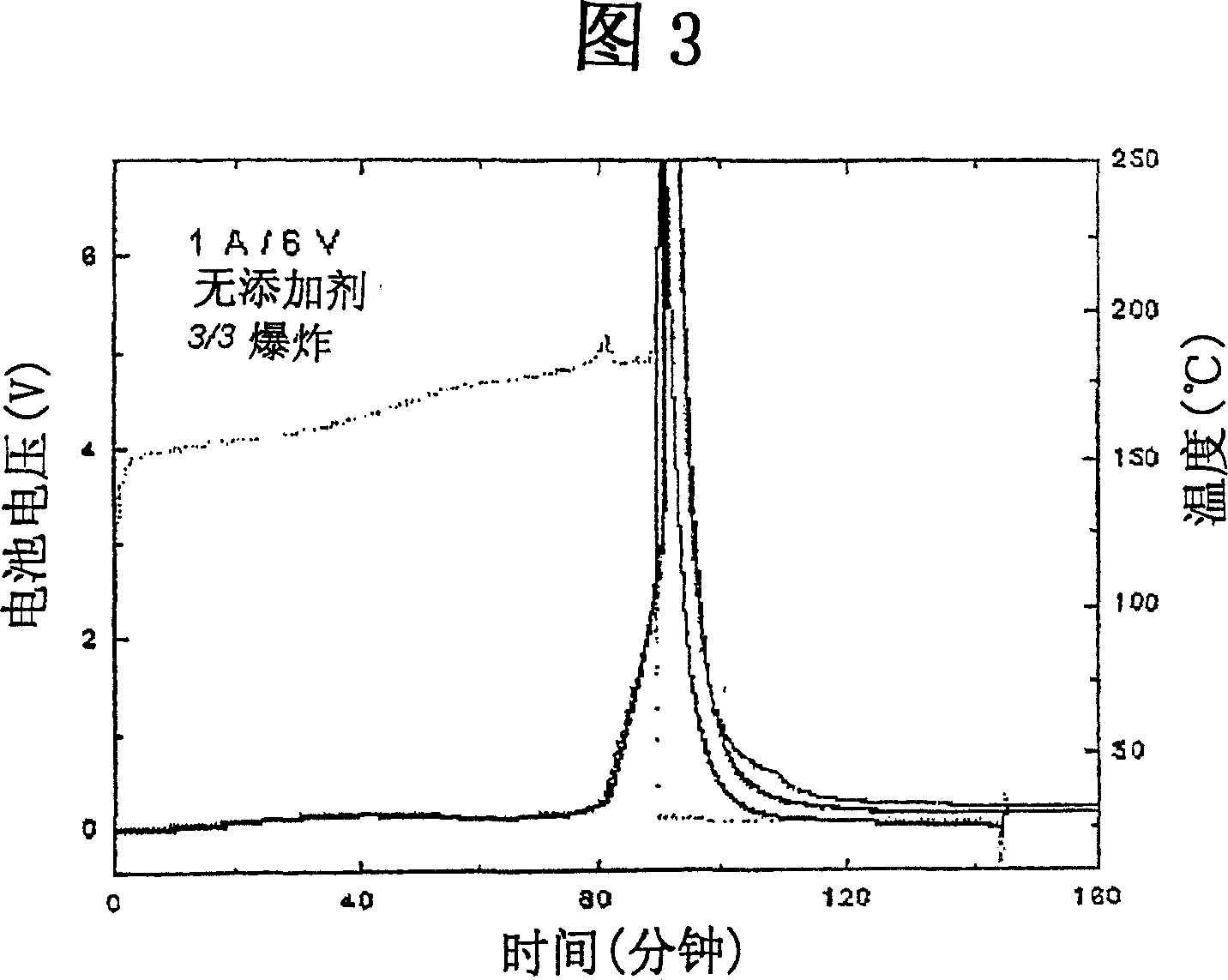
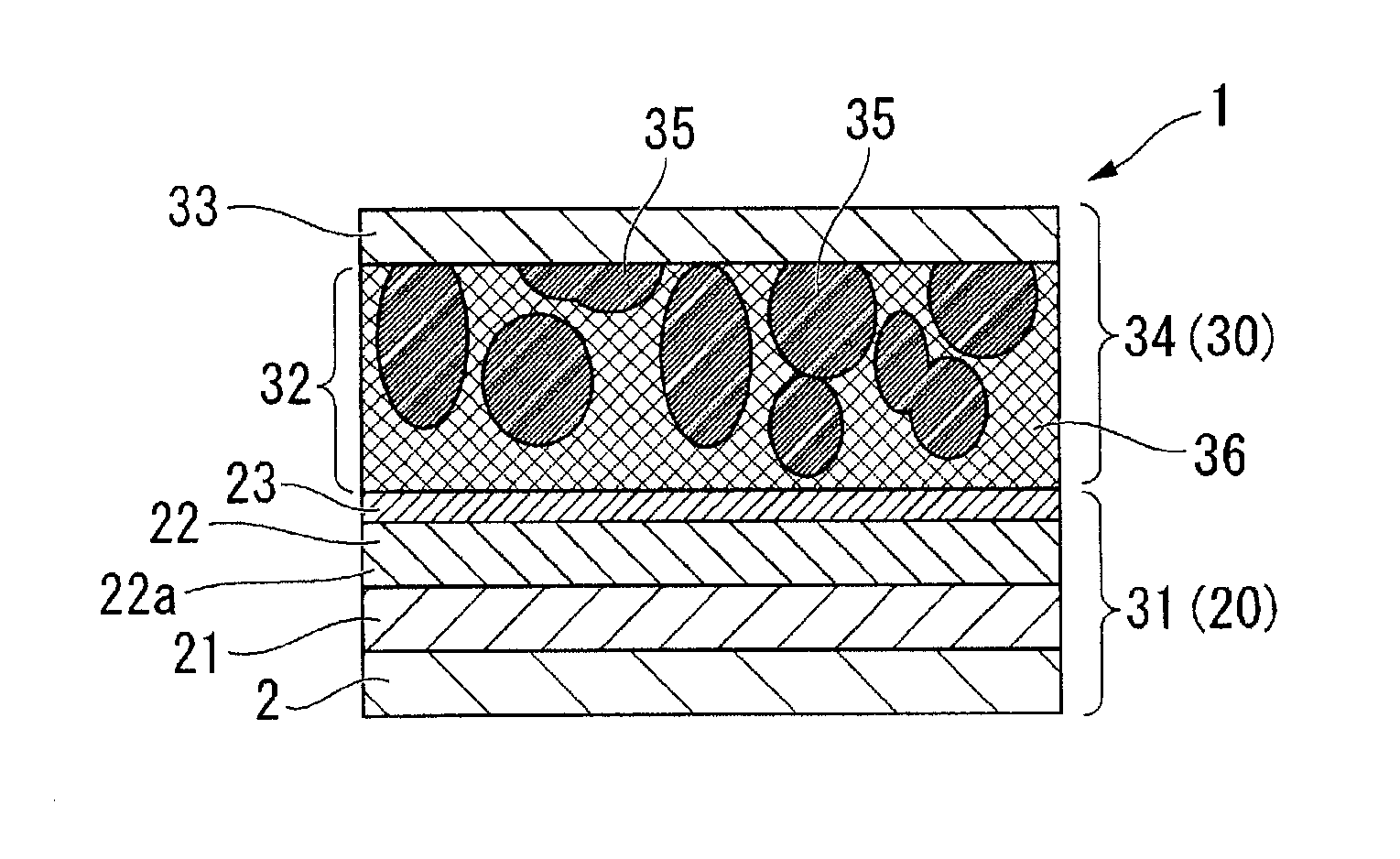
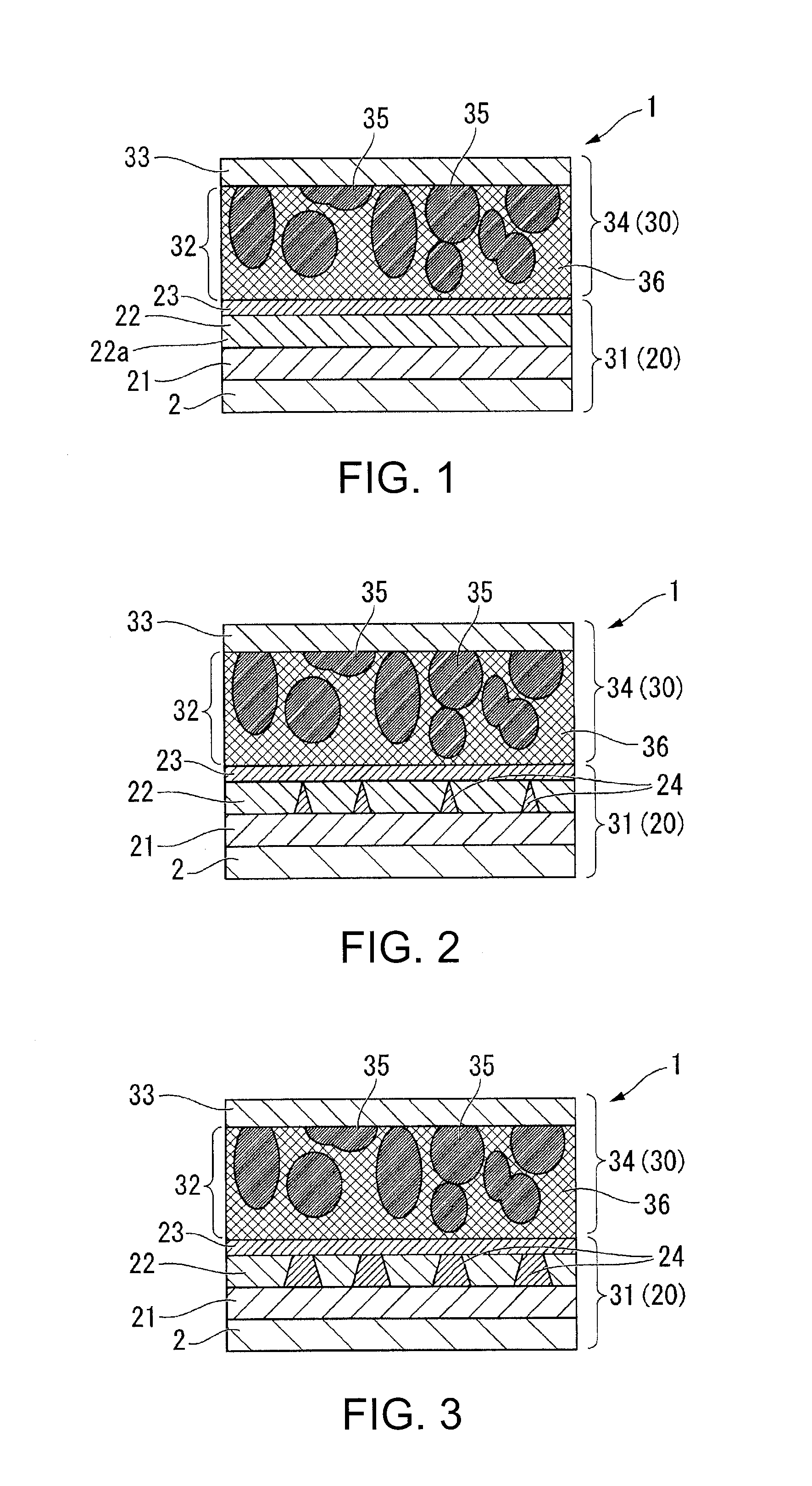
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106results about "Molten electrolytes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
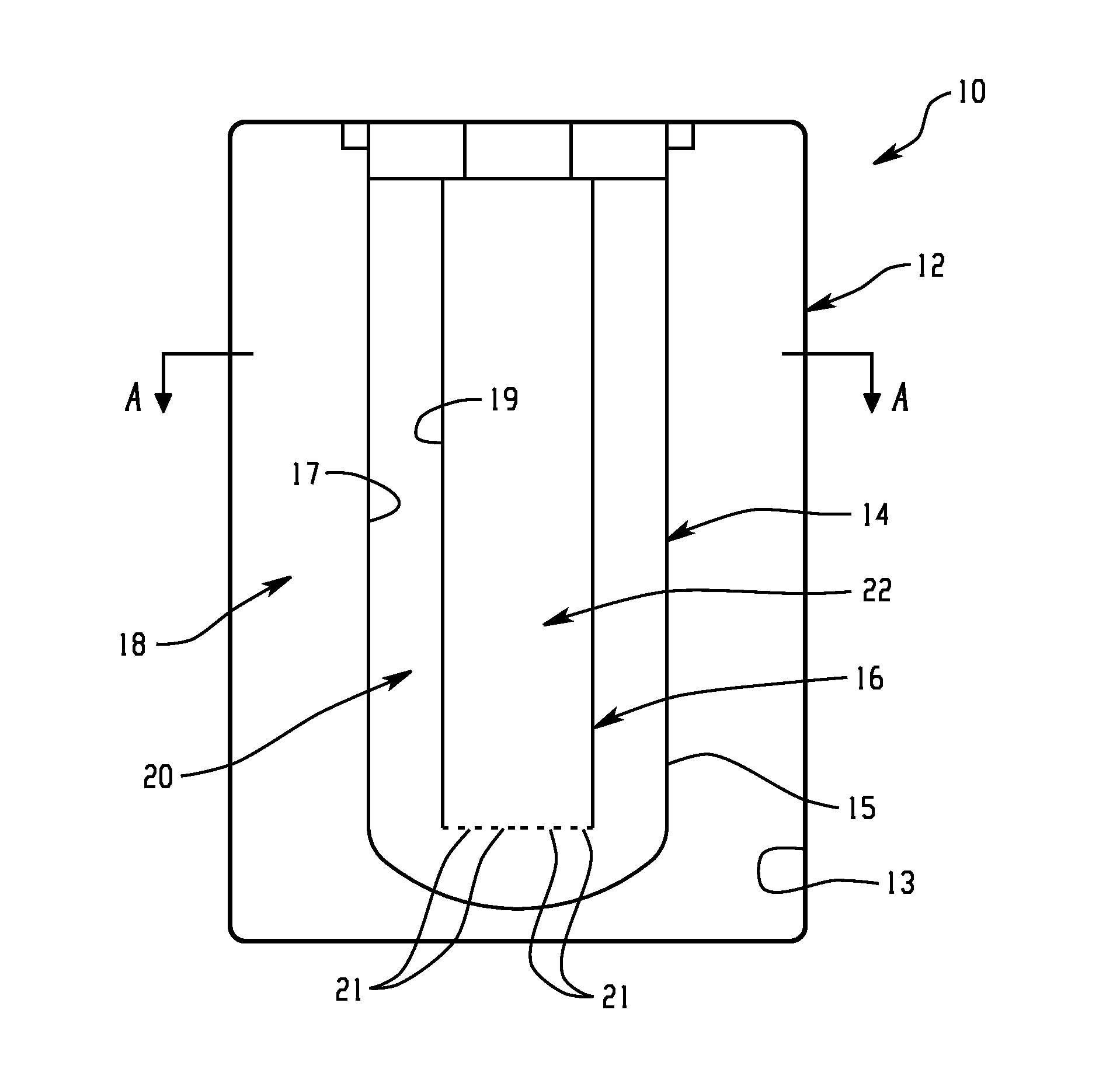
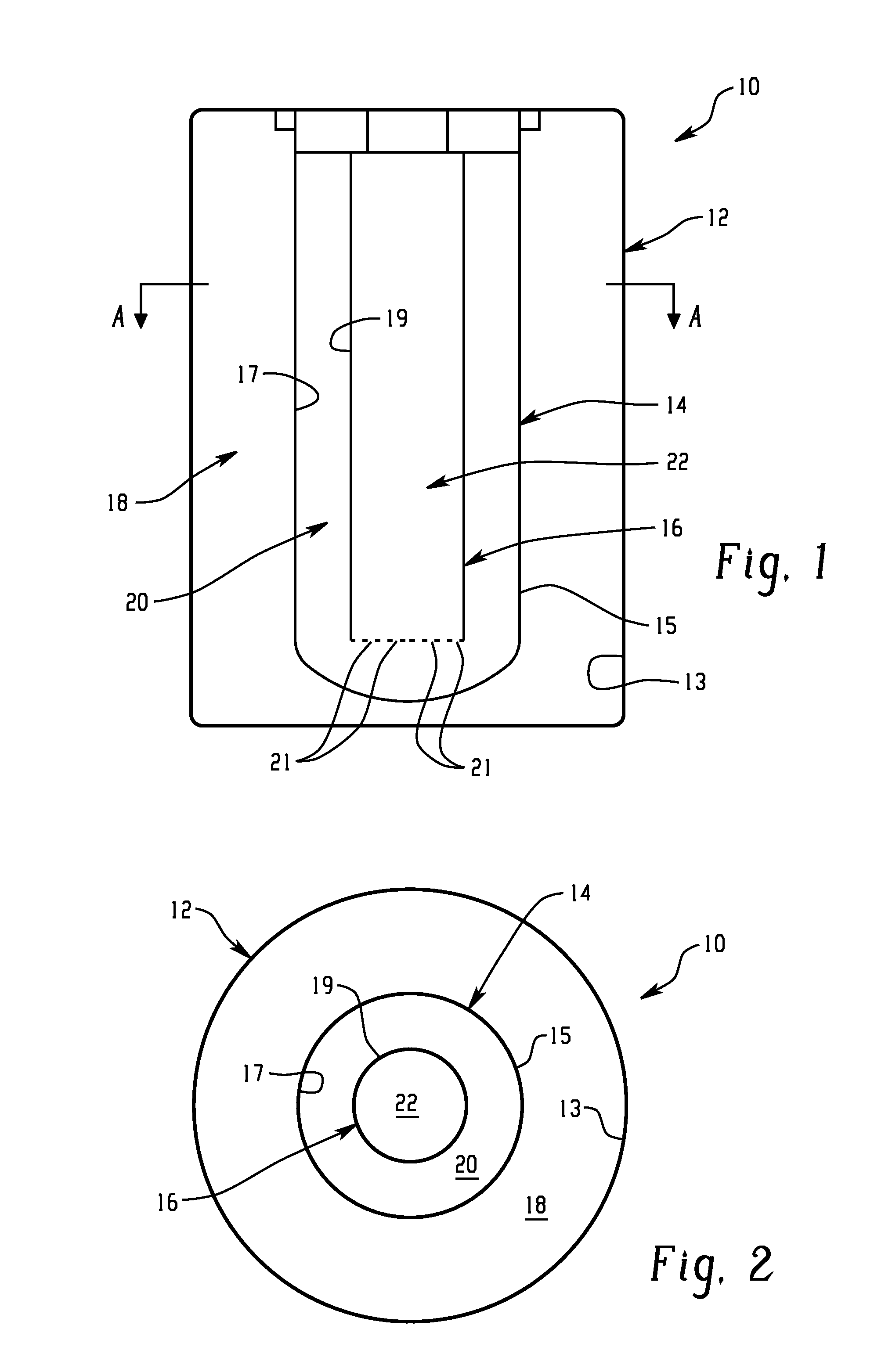
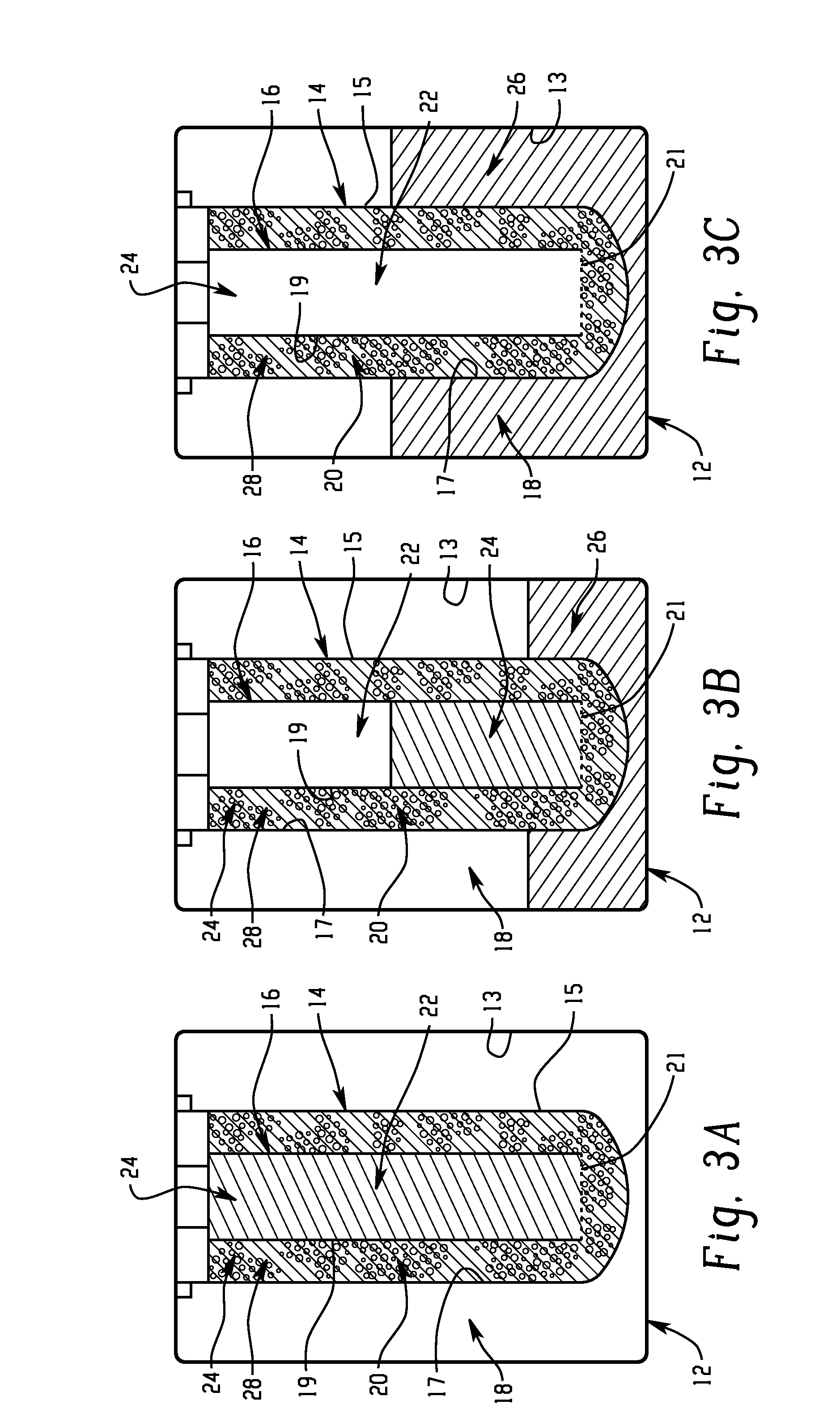
Battery with molten salt electrolyte and high voltage positive active material
InactiveUS20060088767A1High voltageActive material electrodesSecondary cellsMolten saltRechargeable cell
A lithium-based rechargeable battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a molten salt electrolyte that is electrically conductive lithium ions. The positive electrode includes a positive active material that has an electrochemical potential of at least approximately 4.0 volts relative to lithium, and more preferably at least approximately 4.5 V relative to lithium. The electrolyte may further include a source of lithium ions, such as a lithium compound. Other rechargeable batteries using other ionic species can be fabricated to an analogous design.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA +1
Additives for lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20060024584A1Improving high-temperature cycle characteristic and safety of batteryAvoid problemsAlkaline accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsLithiumElectrolyte
Disclosed is a lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode (C), an anode (A), a separator and an electrolyte, wherein the electrolyte comprises: (a) a nitrile group-containing compound and (b) a compound having a reaction potential of 4.7V or higher. The lithium secondary battery can prevent the problems caused by a nitrile group-containing compound added to the electrolyte for the purpose of improving high-temperature cycle characteristics and safety (such problems as a battery swelling phenomenon and a drop in recovery capacity under high-temperature (>80° C.) storage conditions), by adding a fluorotoluene compound.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
High temperature battery and electrolytes
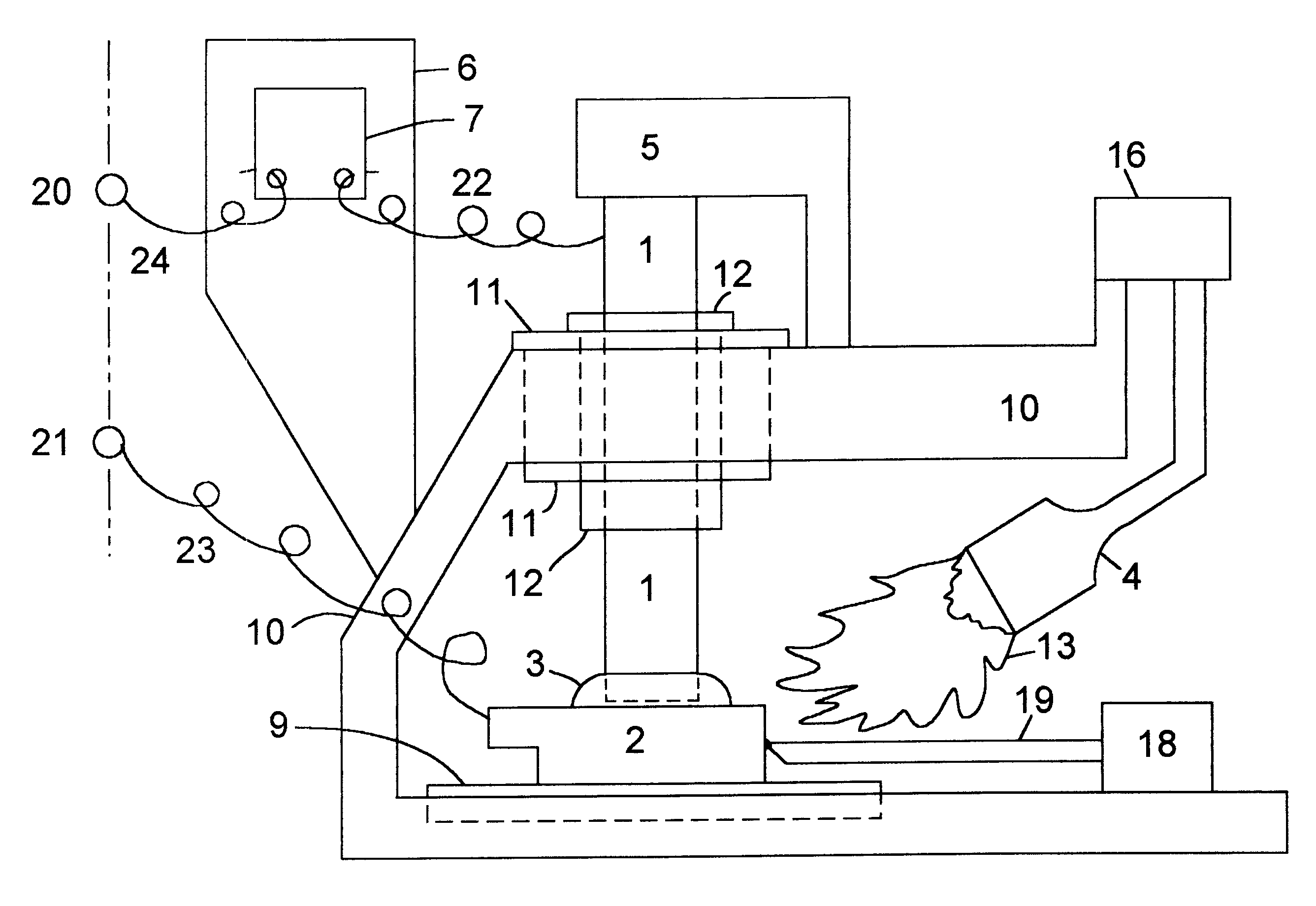
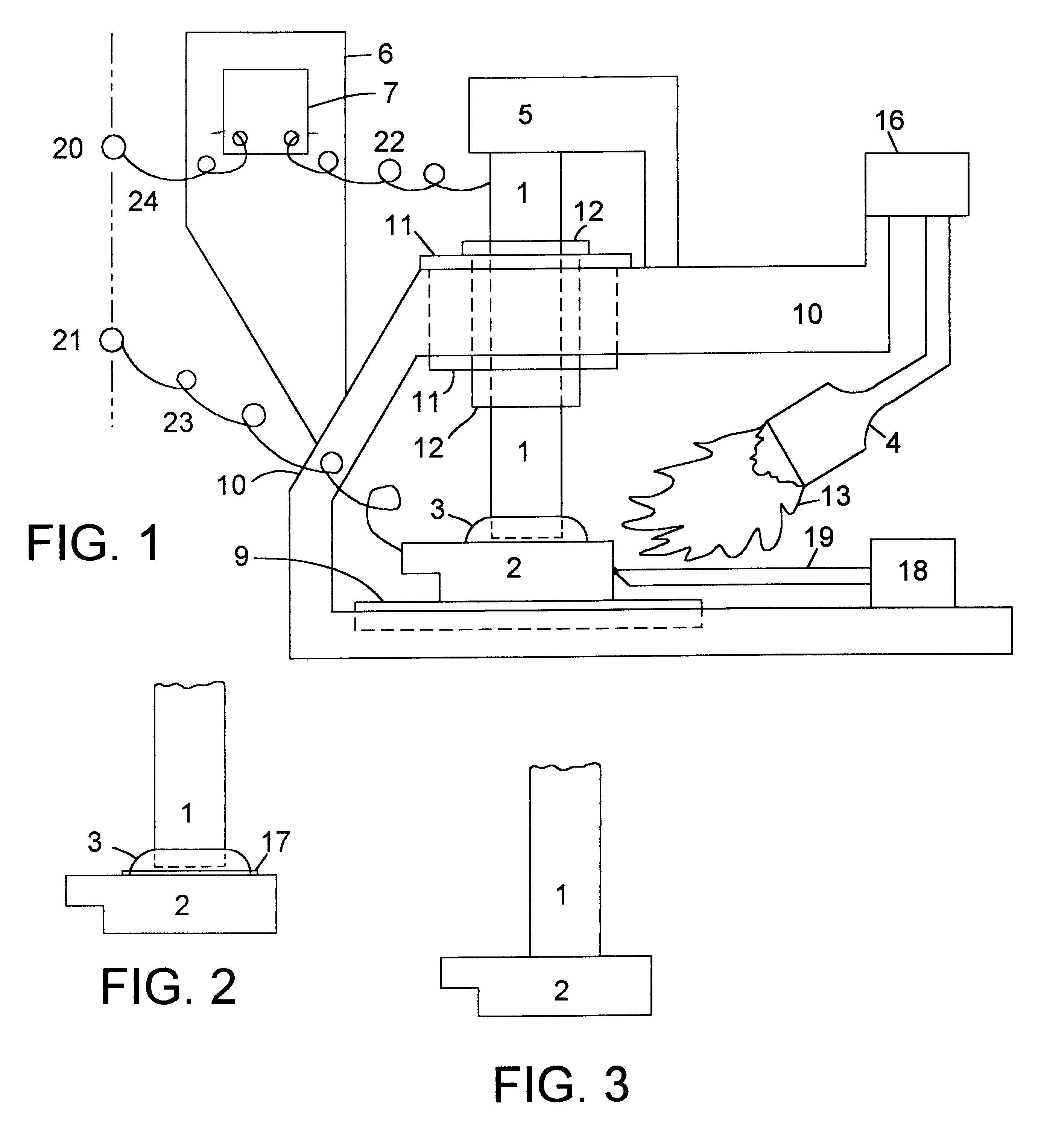
A high temperature battery of one or more cells is disclosed in which each cell is made by holding an anode electrode and a cathode electrode, of different metallic substances, together through a fused flux wetted to an electrode, which fused flux is an electrolyte, to make an anode-to-cathode contact, and the anode-to-cathode contact is heated, by a heat source, to a high temperature above a threshold temperature to generate voltaic voltage, in excess of any thermoelectric voltage; such batteries with electrodes of various configurations are disclosed. The heat-activated flux and electrolyte, such as borax, may have, vegetable-growth ashes or chemical constituents of ashes, such as lithium carbonate, added to the heat-activated flux and electrolyte to catalyze or improve the current-generating capability of the battery. The preferred anode substance is aluminum, and the preferred cathode substance is copper. With the preferred cathode and anode substances and a heat-activated flux and electrolyte of fused borax between the cathode and anode, the open circuit voltage generated per cell when heated increases from 0.05 volts at 304° C. to 1.3 volts at 651° C.; the threshold temperature in this case is 279° C. Also disclosed is means to move the anode metal with respect to the cathode metal, when the heat-activated flux and electrolyte is fluid, for changing the battery characteristics and for replacing depleted heat-activated flux and electrolyte.
Owner:WILSON JOHN T R
Secondary electrochemical cell
The invention provides an electrochemical cell having a first electrode having an electrode active material containing at least one electrode active material charge-carrier, a second electrode, and an electrolyte containing at least one electrolyte charge-carrier. In the electrochemical cell's nascent state, the at least one electrolyte charge carrier differs from the at least one electrode active material charge-carrier.
Owner:VALENCE TECH INC
Slurry for secondary battery electrode, electrode for secondary battery, process for production of electrode for secondary battery, and secondary battery
InactiveUS20100075222A1Satisfactory charge-discharge characteristicFinal product manufactureConductive materialMetal foilMolten salt
There is provided a slurry for a secondary battery electrode and an electrode for a secondary battery that produce satisfactory charge-discharge characteristics for secondary batteries, as well as a secondary battery that exhibits satisfactory charge-discharge characteristics.The invention provides a slurry for a secondary battery electrode comprising an electrode active material and an ambient temperature molten salt composed of a cation component and an anion component, an electrode for a secondary battery wherein an electrode active material layer is formed by coating the slurry for a secondary battery electrode onto a current collector, a process for production of an electrode for a secondary battery whereby the slurry for a secondary battery electrode is coated onto a current collector metal foil to form a coated film, and a secondary battery comprising a positive electrode and / or negative electrode fabricated using the electrode for a secondary battery, and an electrolyte.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Sodium Ion Batteries
InactiveUS20110052986A1High operation potentialHigh specific capacityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLi-accumulatorsPhosphateSodium-ion battery
Sodium ion batteries are based on sodium based active materials selected among compounds of the general formula AaMb(XY4)c wherein A comprises sodium, M comprises one or more metals, comprising at least one metal which is capable of undergoing oxidation to a higher valence state, and XY4 represents phosphate or a similar group. The anode of the battery includes a carbon material that is capable of inserting sodium ions. The carbon anode cycles reversibly at a specific capacity greater than 100 mAh / g.
Owner:VALENCE TECH INC
High temperature battery
InactiveUS6022637AIncrease current availableLower internal resistanceDeferred-action cellsCell electrodesMaterials scienceElectrolyte
A high temperature battery of one or more cells is disclosed in which each cell is made by holding an anode electrode and a cathode electrode, of different metallic substances, together through a fused flux wetted to an electrode, which fused flux is an electrolyte, to make an anode-to-cathode contact, and the anode-to-cathode contact is heated, by a heat source, to a high temperature range above a threshold temperature to generate voltaic voltage, in excess of any thermoelectric voltage; such batteries with electrodes of various mechanical configurations are disclosed. The flux, such as borax, may have powdered, vegetable-growth ashes or powdered chemical constituents of ashes, such as lithium carbonate, added to the flux or to the electrolyte to catalyze or improve the current-generating capability of the battery. The preferred anode substance is aluminum, and the preferred cathode substance is copper. With the preferred cathode and anode substances and a fused borax flux between the cathode and anode, the open circuit voltage generated per cell when heated increases from 0.05 volts at 304 DEG C. to 1.3 volts at 651 DEG C.; the threshold temperature in this case is 279 DEG C. Also disclosed is means to move the anode metal with respect to the cathode metal, when the electrolyte is fluid, for changing the battery characteristics.
Owner:WILSON JOHN T R
Method of making and using composition and energy storage device
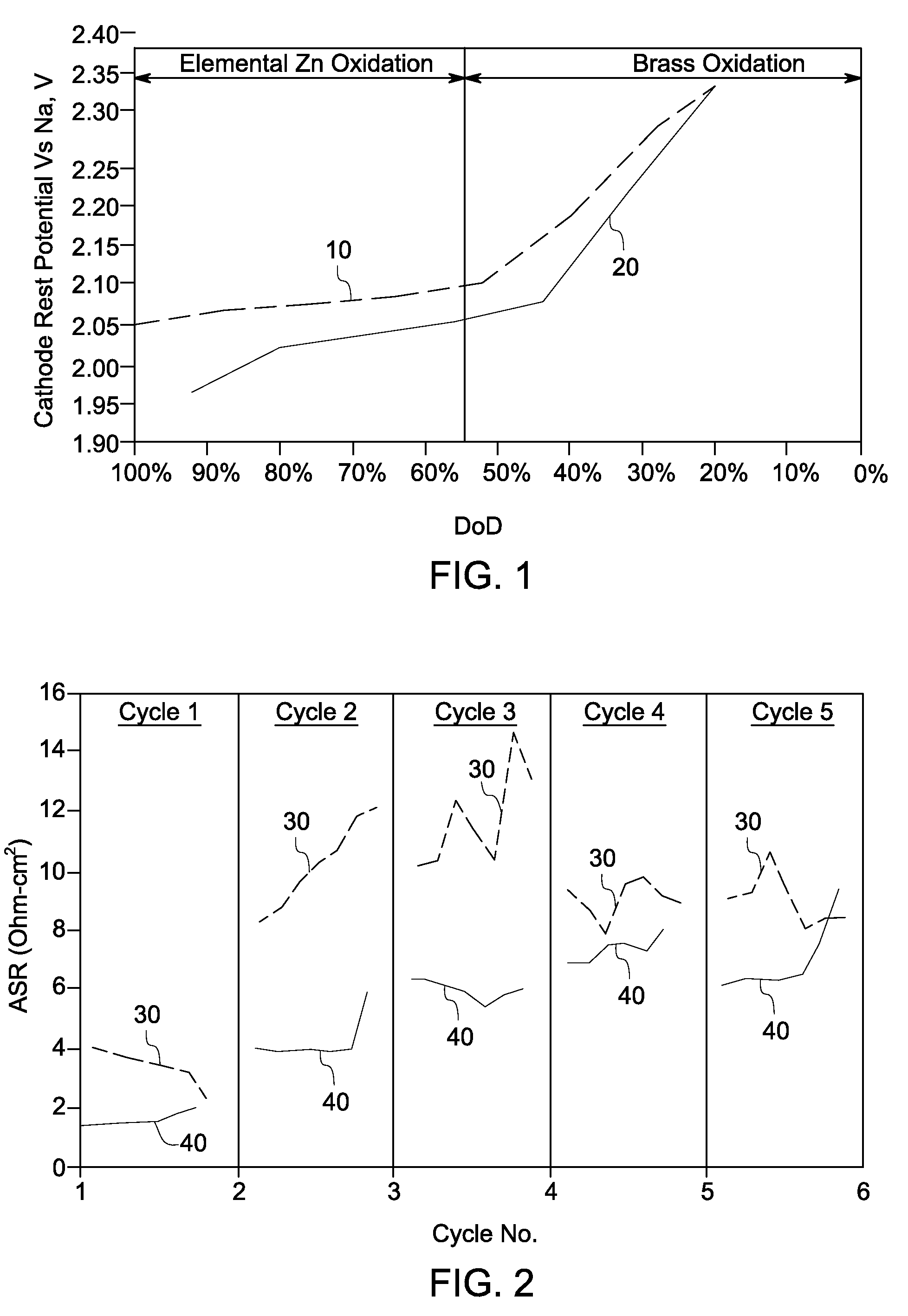
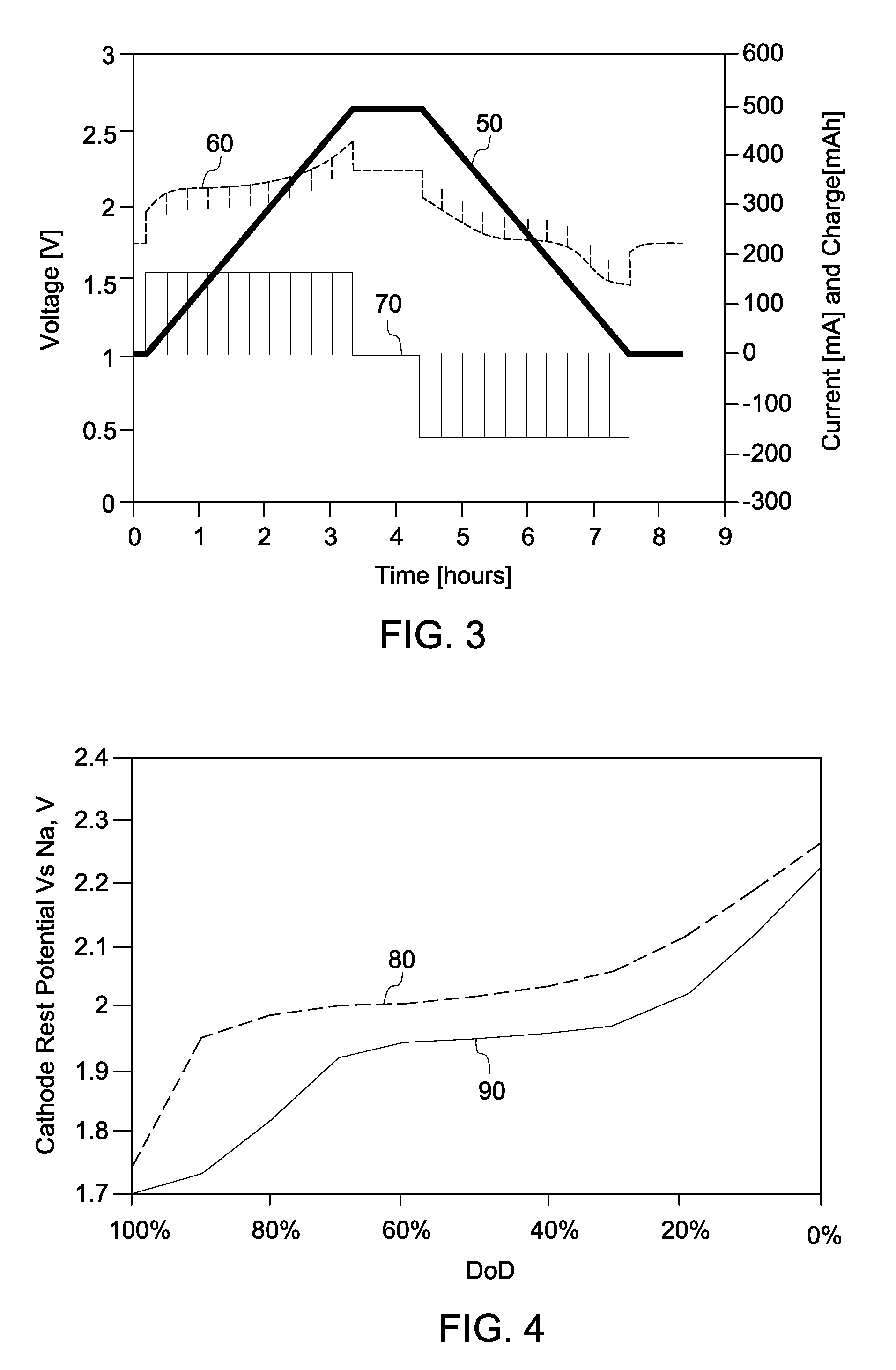
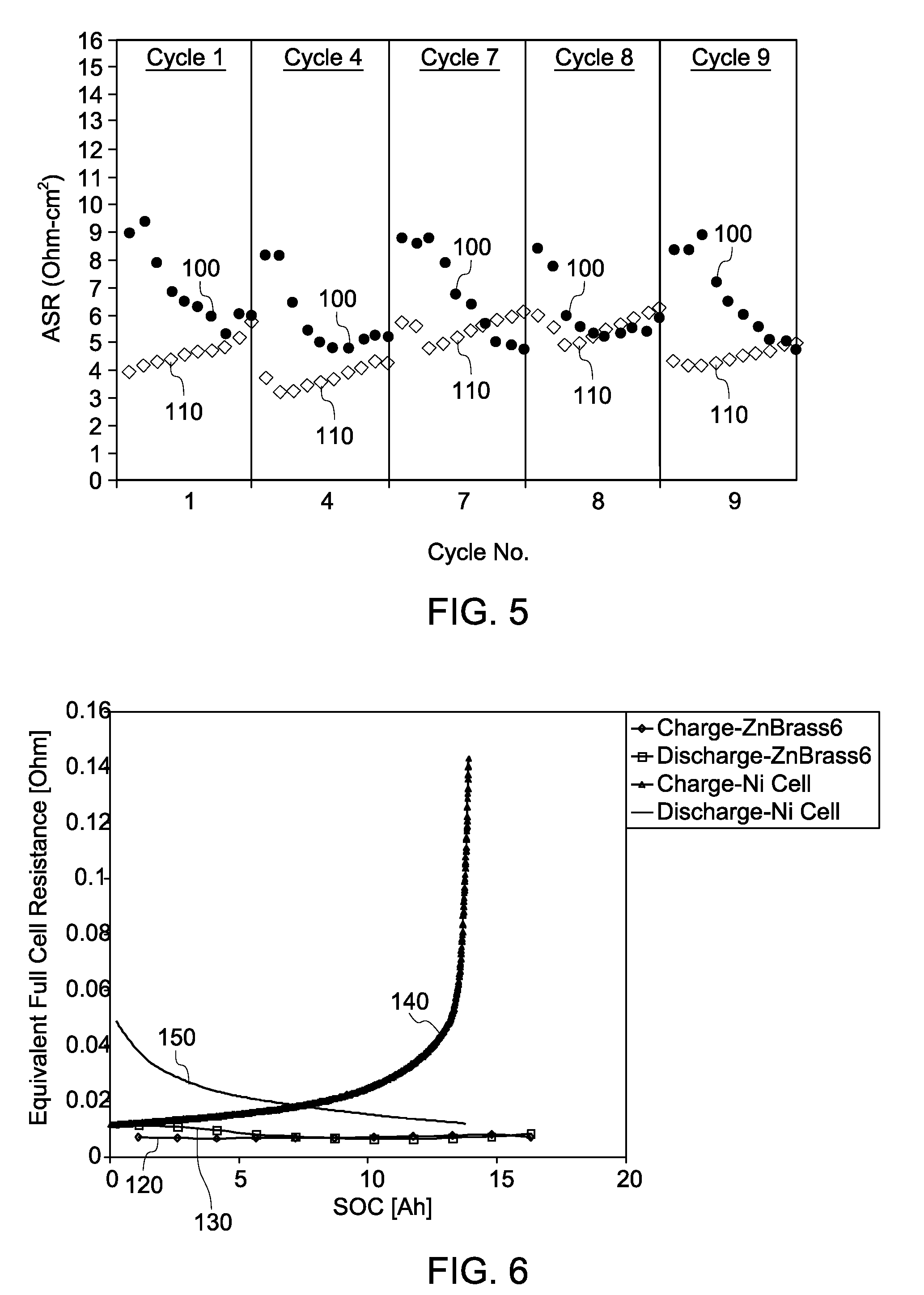
A method is provided that includes forming brass from zinc powder and copper powder in the presence of a sodium electrolyte. In one aspect, an electrochemical cell is loaded with copper and zinc, the electrochemical cell is heated, and at least one charge / discharge cycle of the electrochemical cell is performed. Alpha brass is converted to gamma brass in presence of zinc and sodium. Methods of producing and operating an energy storage device are also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nonaqueous solvent and power storage device
InactiveUS20120328960A1Excellent reduction resistanceLow freezing pointHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrolytic capacitorsQuaternary ammonium cationPhysical chemistry
A nonaqueous solvent having excellent reduction resistance, which can be applied to an electrolyte solution, is provided. Further, a nonaqueous solvent which can be used in a wide temperature range and applied to an electrolyte solution is provided. Furthermore, a high-performance power storage device is provided. A nonaqueous solvent containing at least an ionic liquid including an alicyclic quaternary ammonium cation having one or more substituents and a counter anion to the alicyclic quaternary ammonium cation, and a freezing-point depressant is provided. A power storage device including the nonaqueous solvent for an electrolyte solution is also provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Molten metal rechargeable electrochemical cell
ActiveUS20150010792A1Low costImprove usabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrical batteryElectrochemical cell
The present invention provides rechargeable electrochemical cells comprising a molten anode, a cathode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte salt, wherein the electrolyte salt is situated between the molten anode and the cathode during the operation of the electrochemical cell, and the molten anode comprises an aluminum material; also provided are batteries comprising a plurality of such rechargeable electrochemical cells and processes for manufacturing such rechargeable electrochemical cells.
Owner:EOS ENERGY TECH HLDG LLC
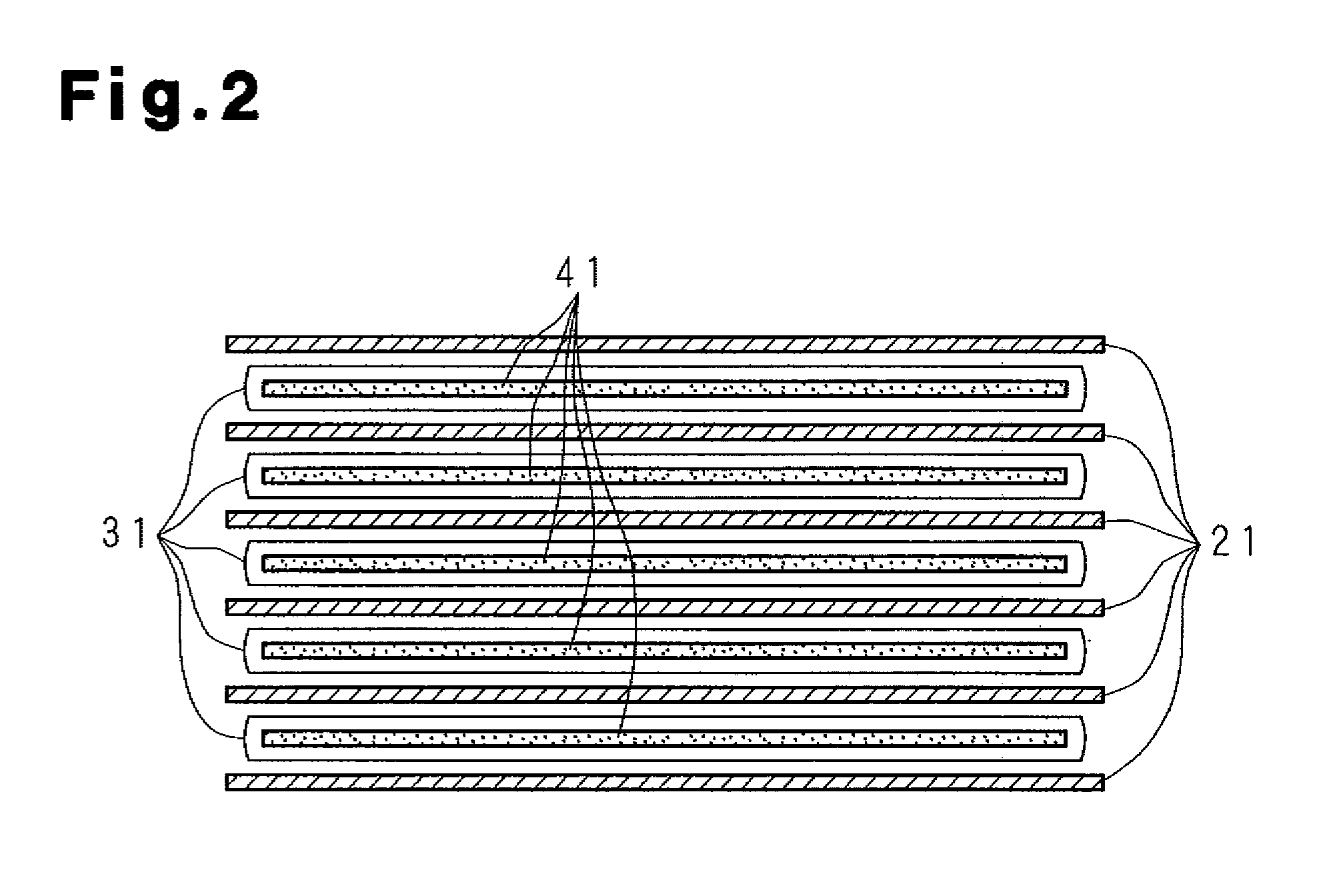
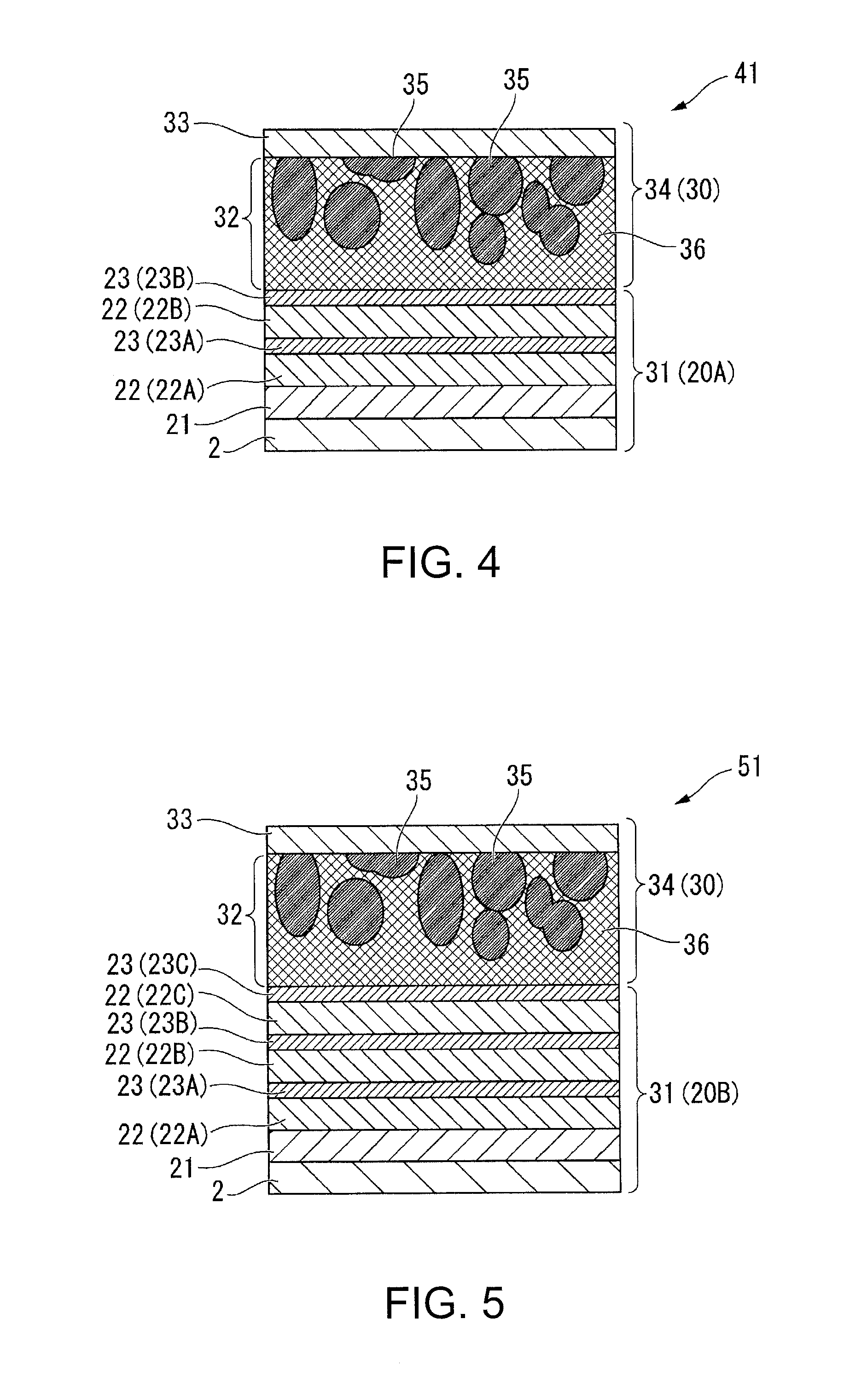
Molten salt battery
ActiveUS20130202942A1Increase surface areaHigh capacity densityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureMolten saltEngineering
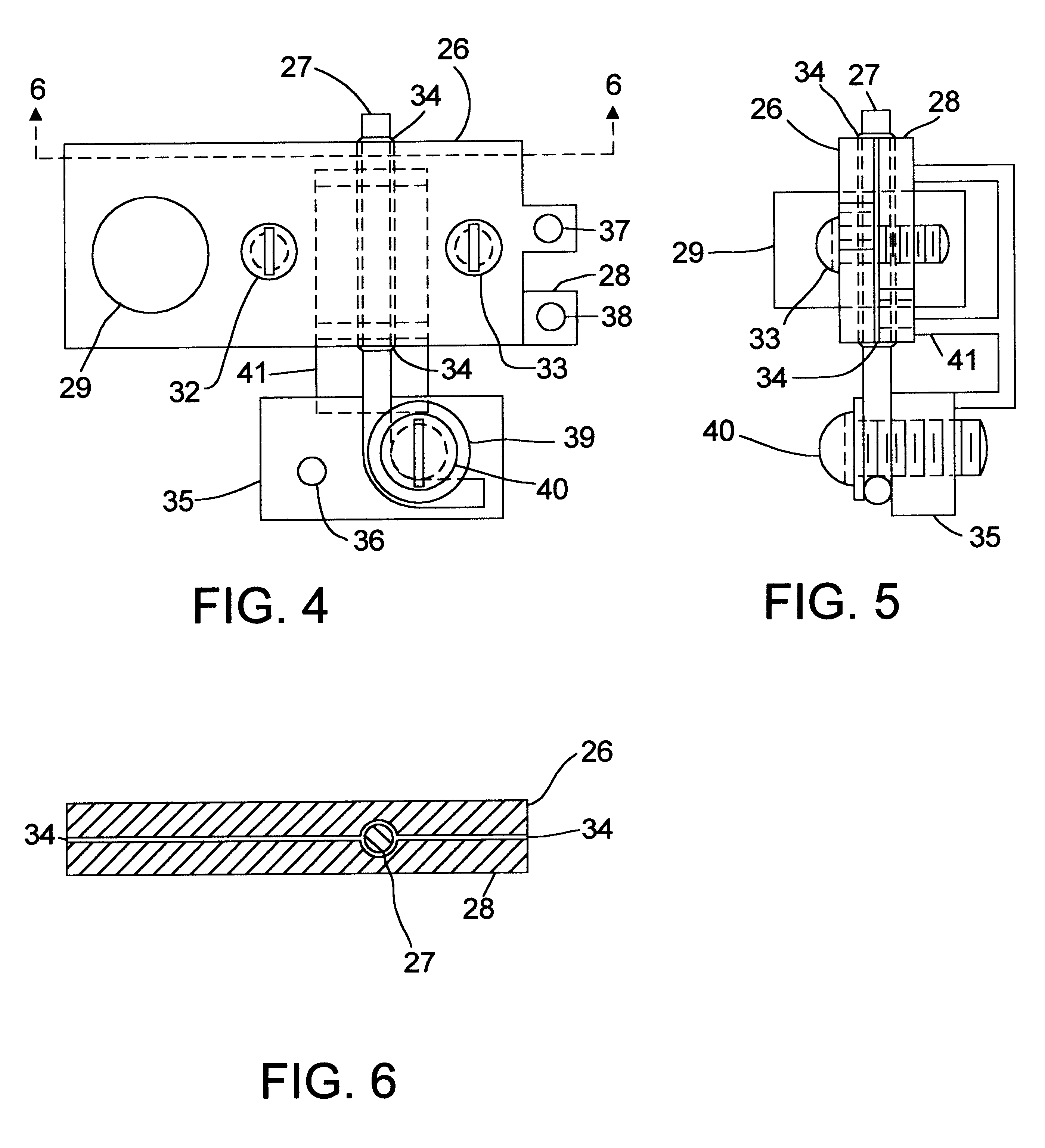
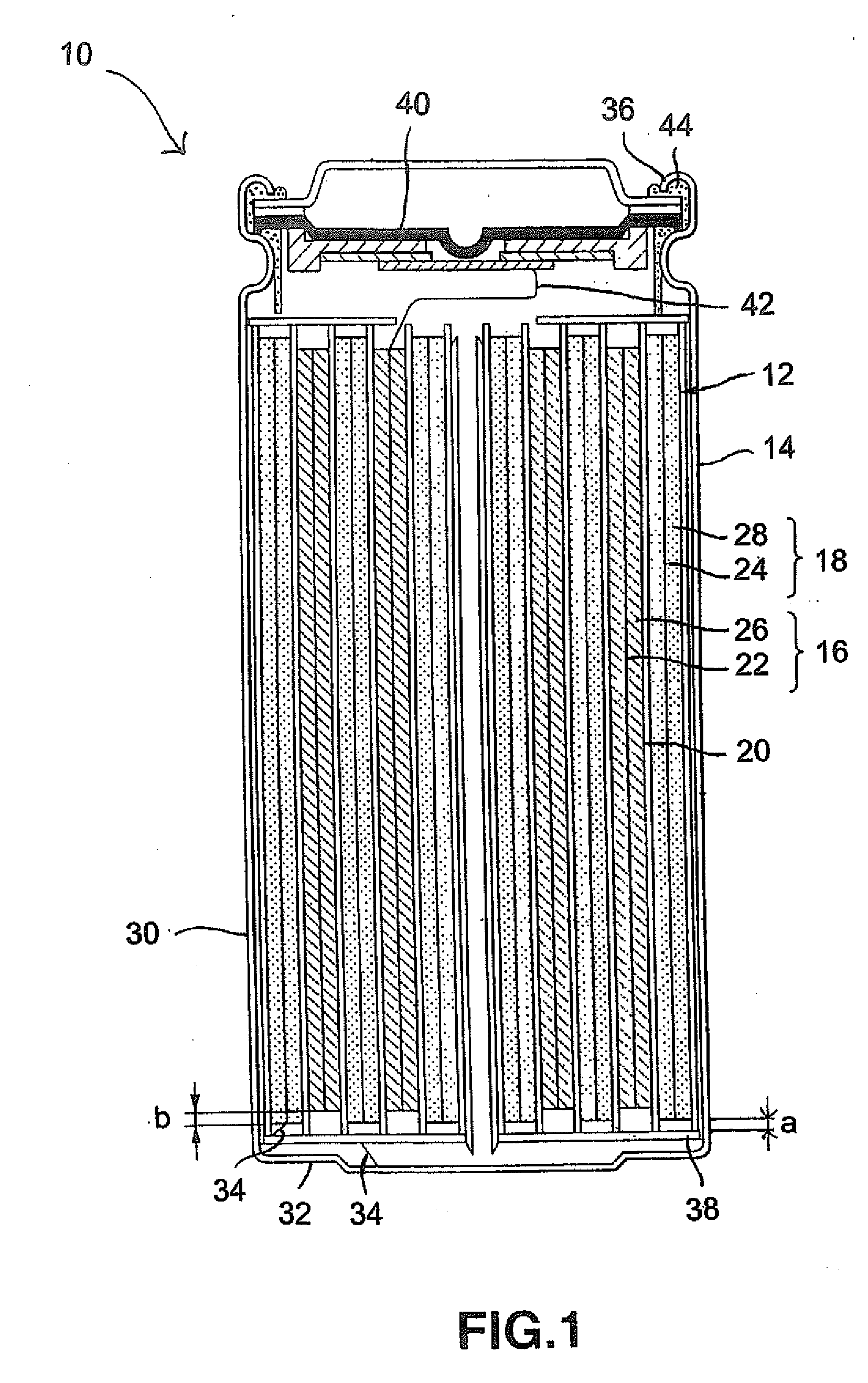
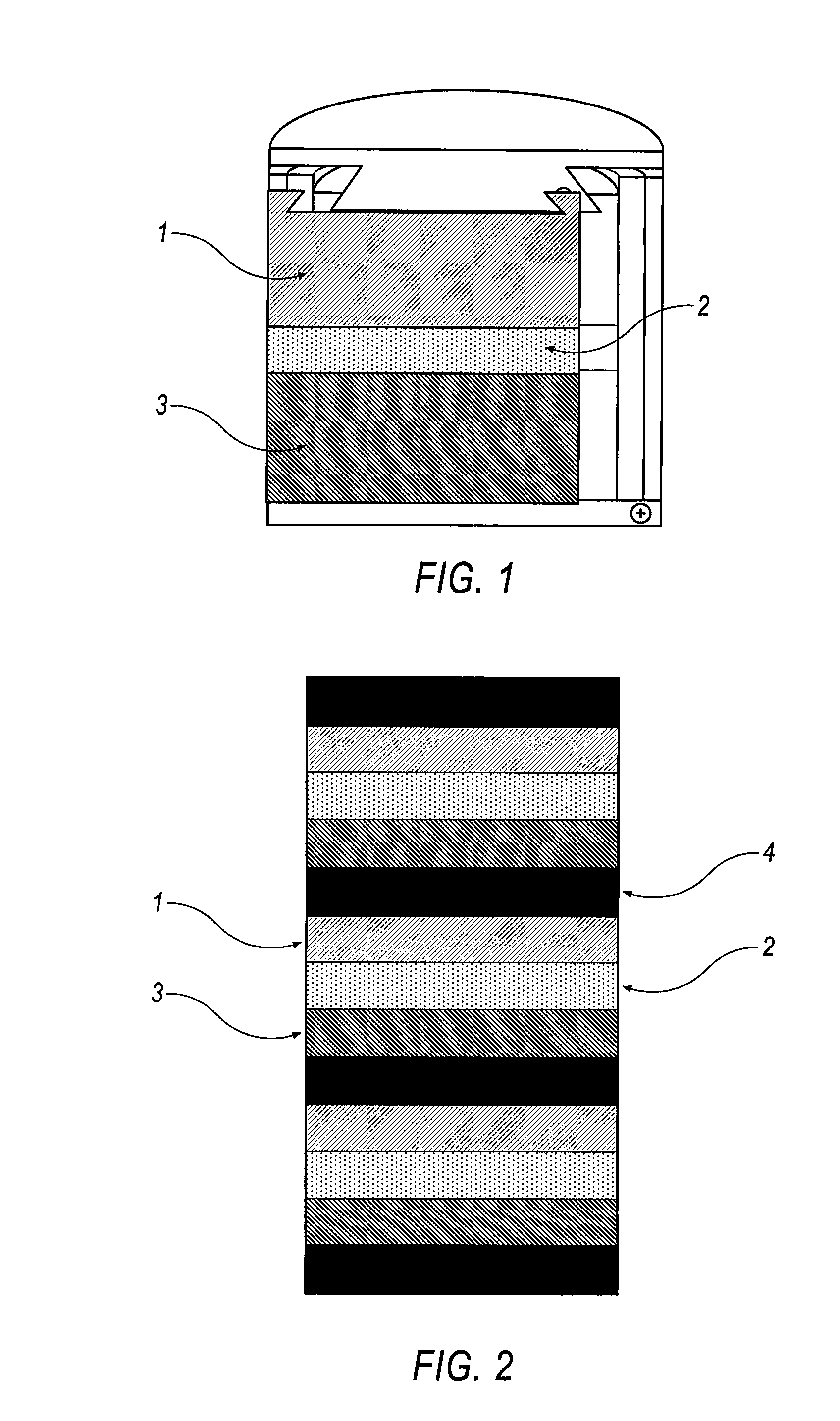
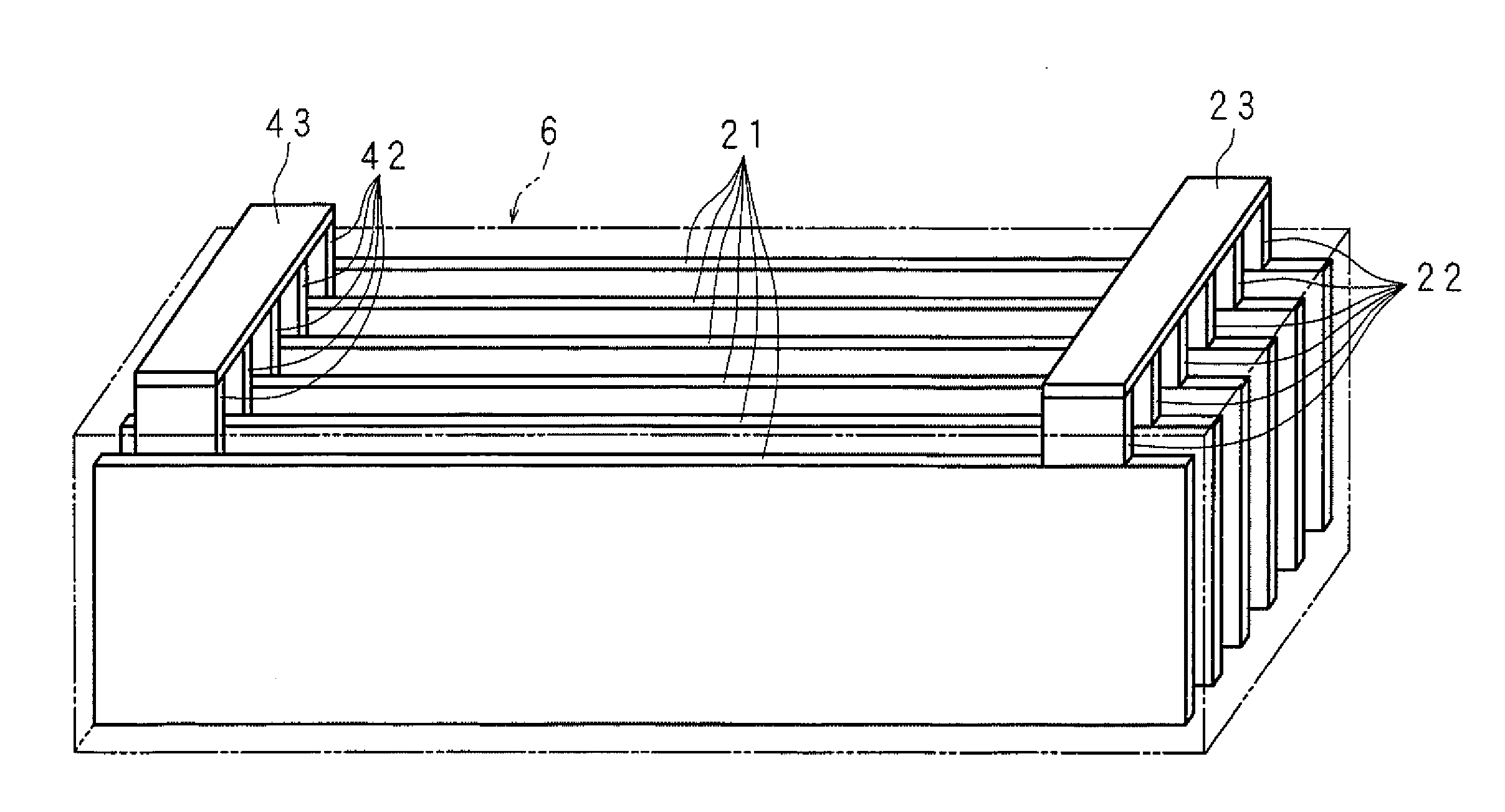
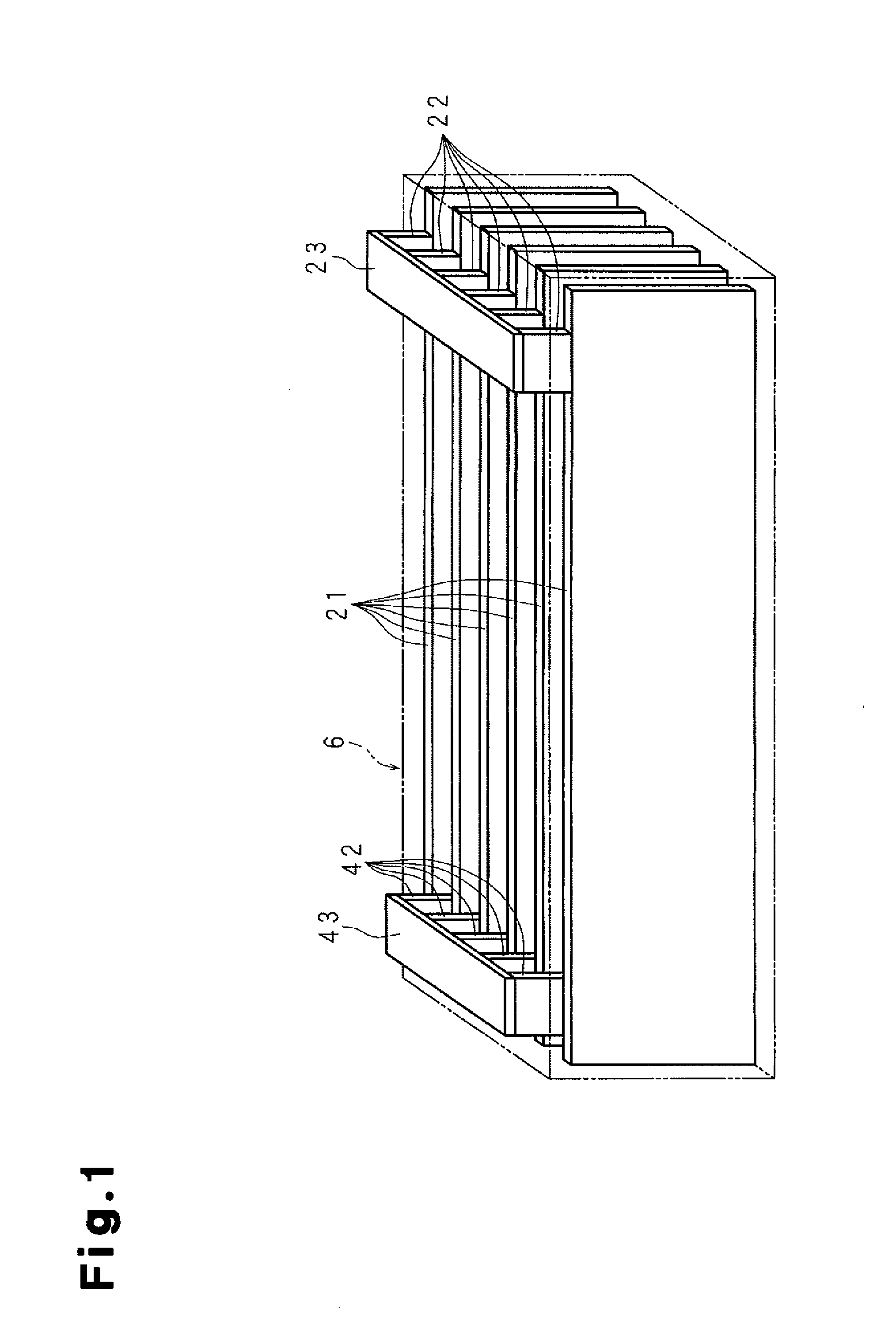
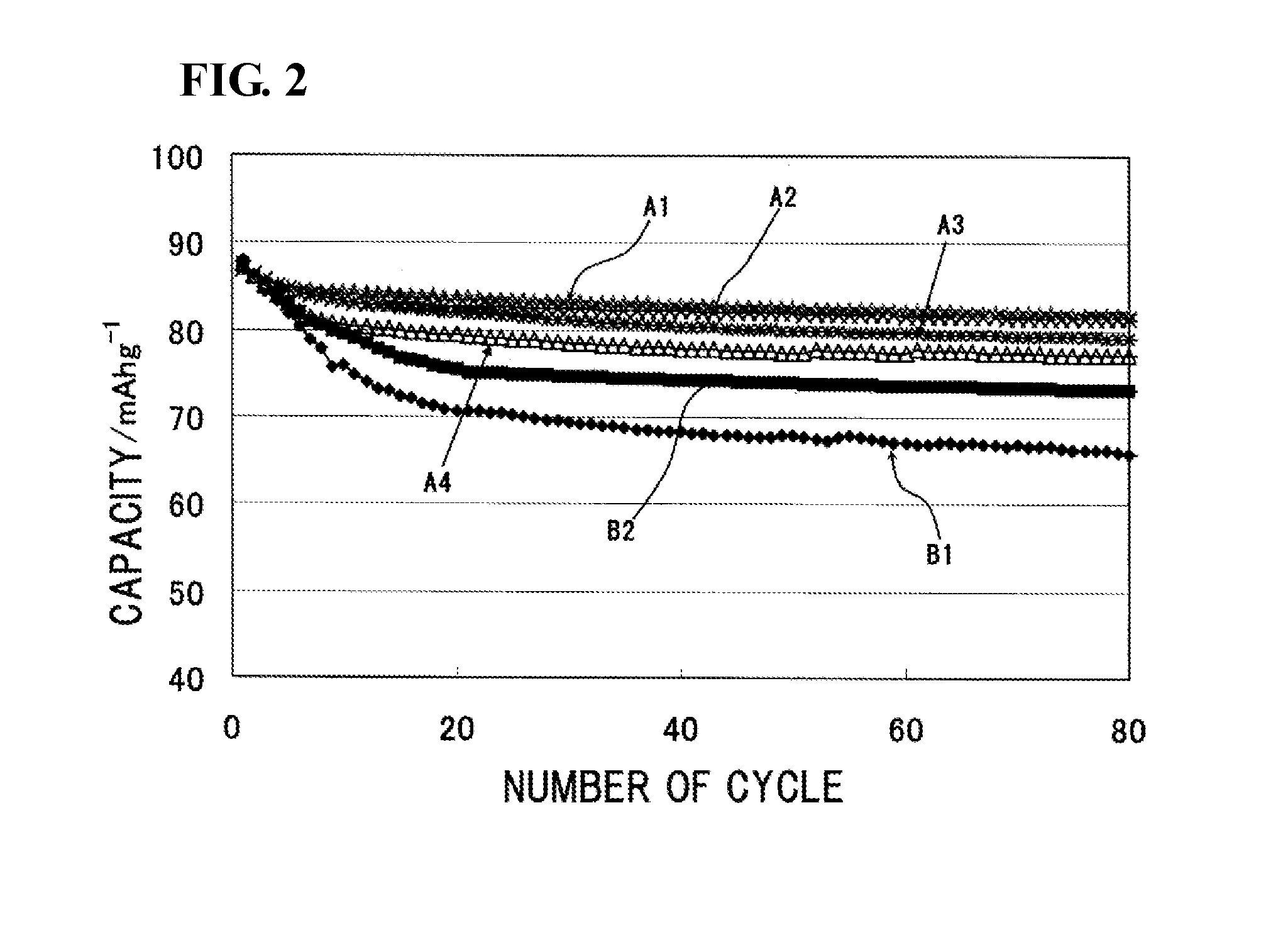
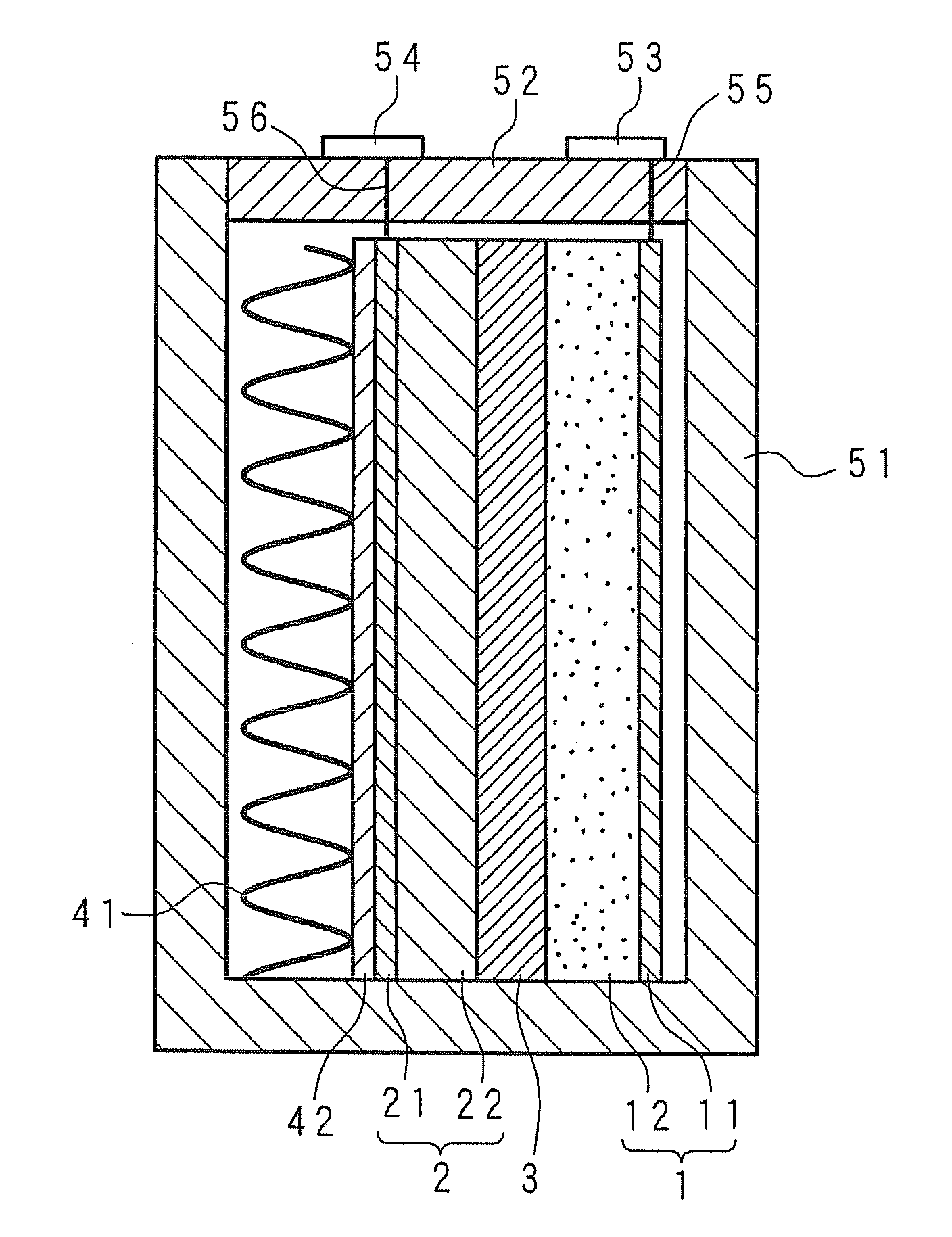
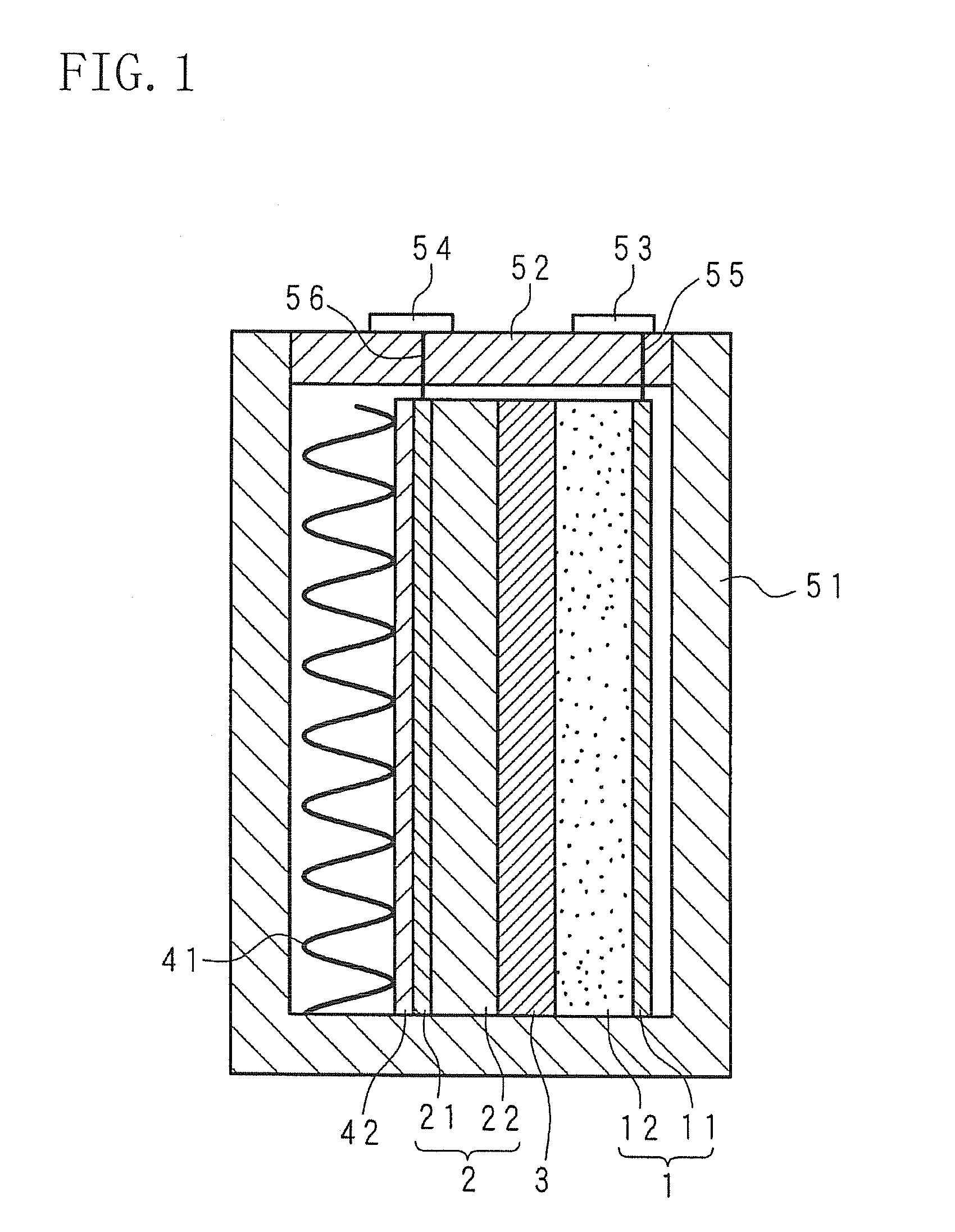
A molten-salt battery is provided with rectangular plate-like negative electrodes (21) and rectangular plate-like positive electrodes (41) each housed in a bag-shaped separator (31). The negative electrodes (21) and positive electrodes (41) are arranged laterally and alternately in a standing manner. A lower end of a rectangular tab (22) for collecting current is joined to an upper end of each negative electrode (21) close to a side wall (1A) of a container body (1). The upper ends of the tabs (22) are joined to the lower surface of a rectangular plate-like tab lead (23). A lower end of a rectangular tab (42) for collecting current is joined to an upper end of each positive electrode (41) close to a side wall (1B) of the container body (1). The upper ends of the tabs (42) are joined to the lower surface of a rectangular plate-like tab lead (43).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
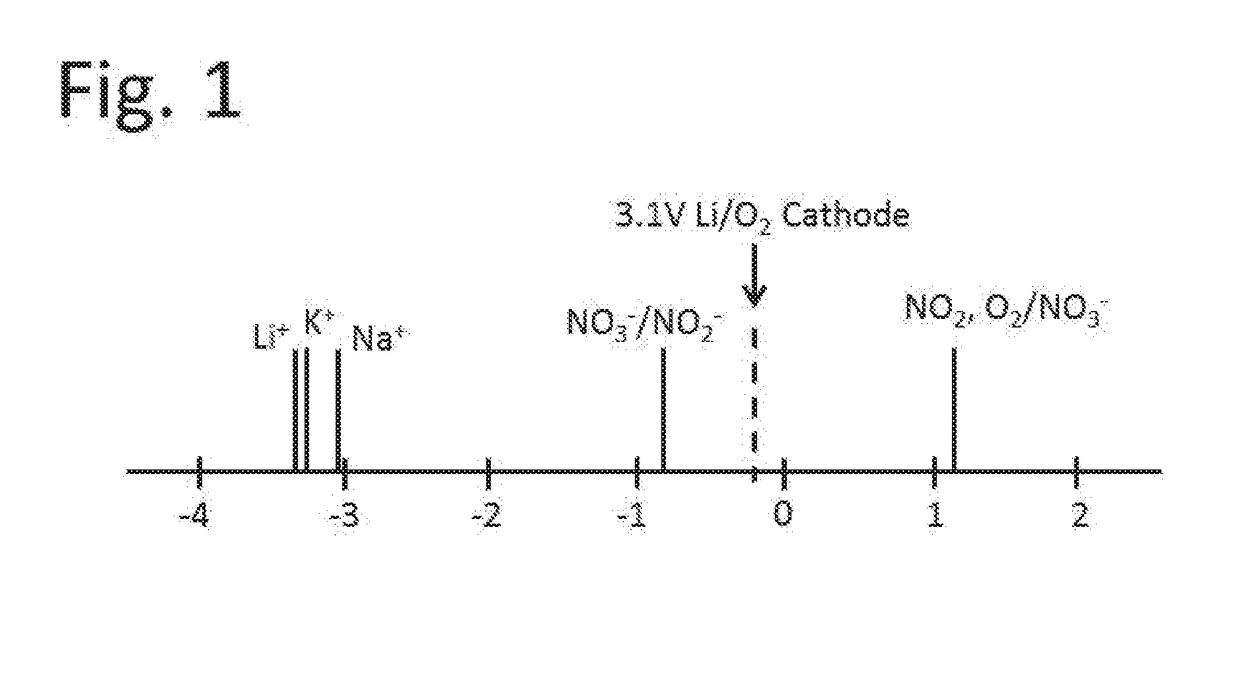
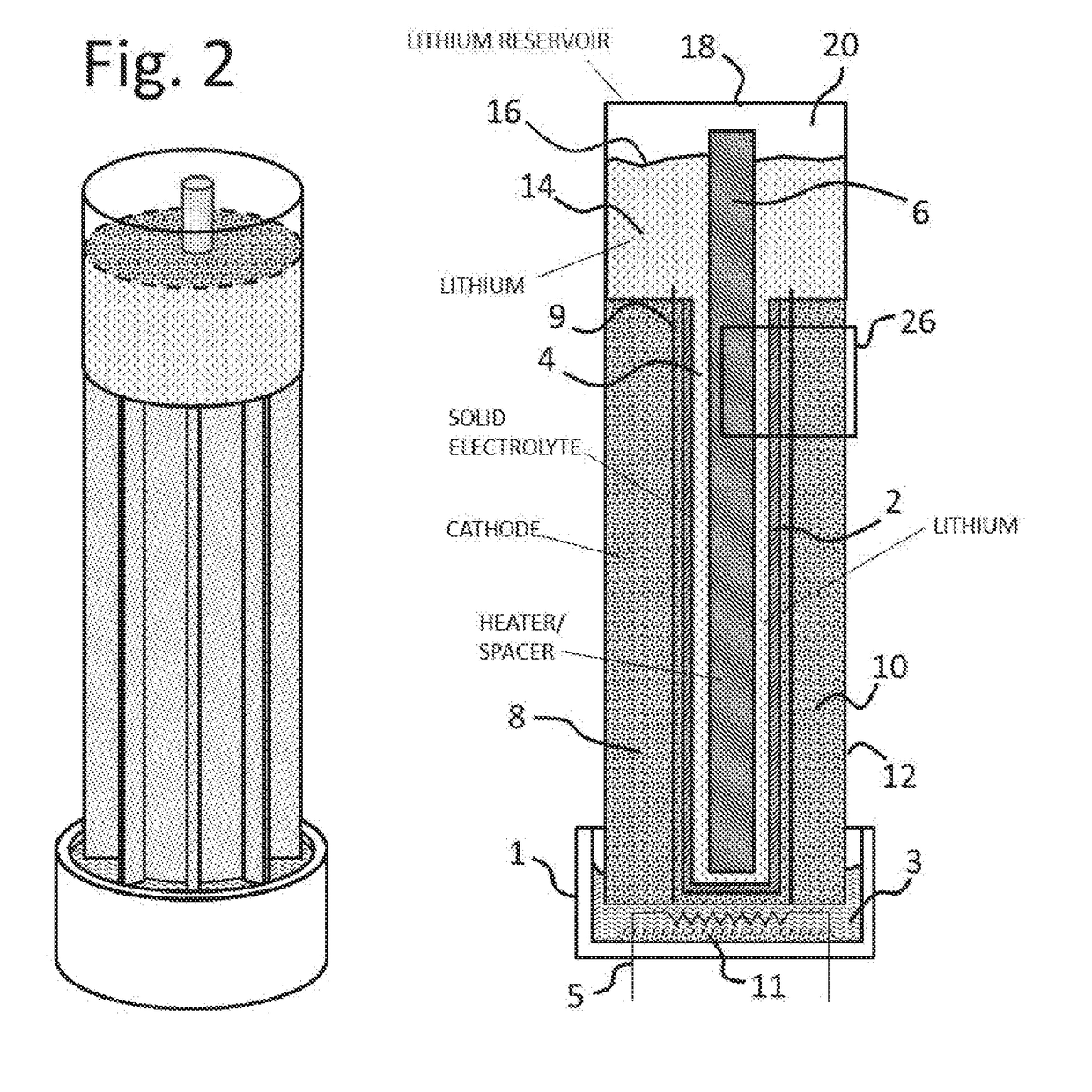
Lithium-air battery for electric vehicles and other applications using molten nitrate electrolytes
InactiveUS20160028133A1Minimization requirementsReduce oxygenFuel and secondary cellsHybrid cell detailsElectrical batteryLithium–air battery
Owner:MILES MELVIN H
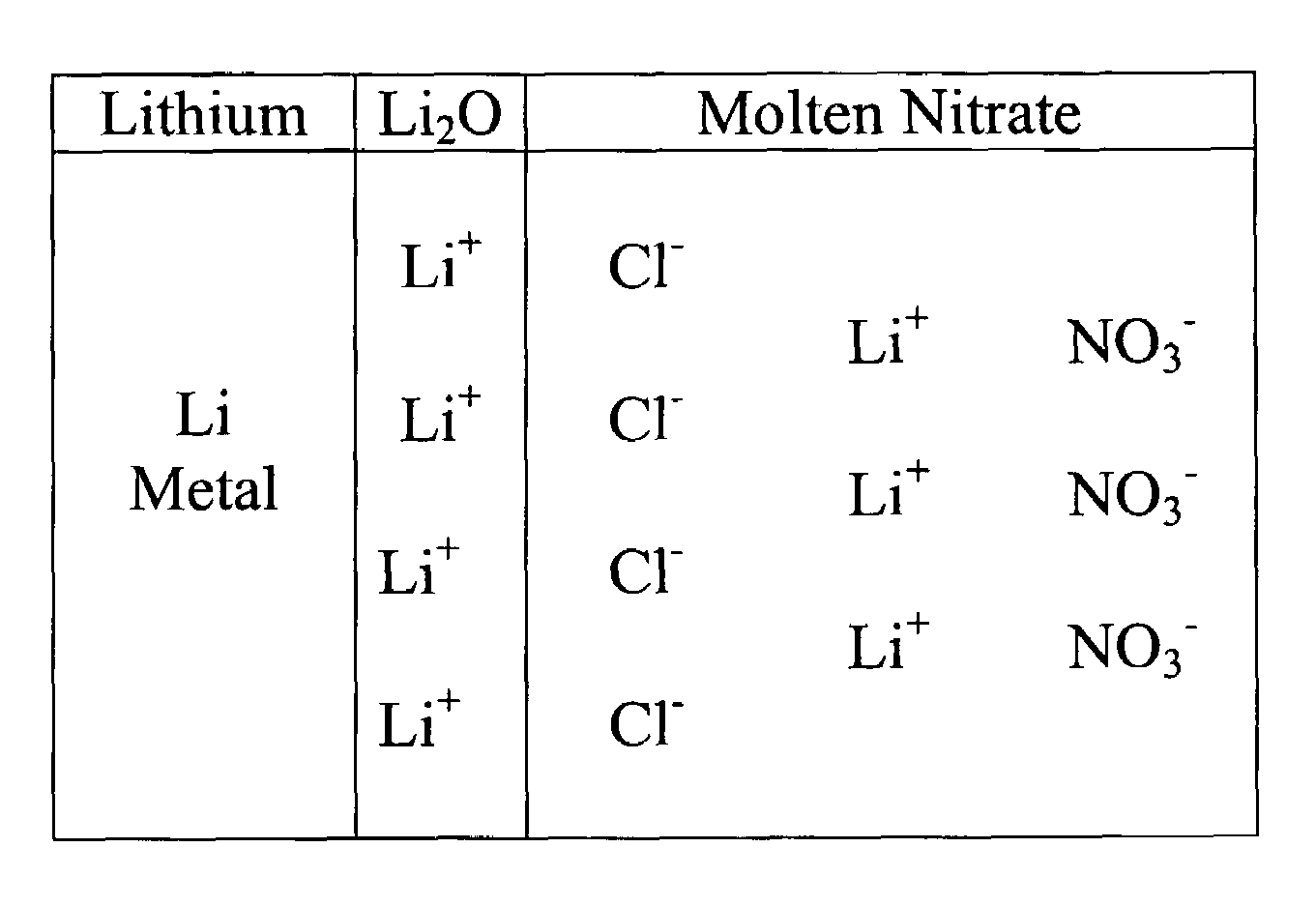
Rechargeable lithium-air and other lithium-based batteries using molten nitrates
ActiveUS8795868B1Reduce moisture contentMinimize amount of waterDeferred-action cellsCell electrodesLithium oxideMolten salt
A rechargeable molten salt electrolyte battery has an anode comprising lithium, a cathode electrode comprising a conductive metal that is compatible with the nitrate melt, an electrolyte comprising lithium nitrate or lithium nitrate mixtures with other nitrates which electrolyte is capable of becoming an ionic conductive liquid upon being heated above its melting point, wherein oxygen for reaction at the cathode or within the melt is provided from an external source to be delivered to the cathode through the electrolyte and provision is made to collect lithium oxide formed during discharge to be reconstituted as lithium ions and oxygen during recharge. At least a portion of the oxygen reduction reaction is provided by a nitrate ion pathway.
Owner:MILES MELVIN H
Additive for lithium secondary batteries
Disclosed is a lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode (C), an anode (A), a separator and an electrolyte, wherein the electrolyte comprises: (a) a nitrile group containing compound and (b) a compound having a reaction potential of 4.7V or higher. The lithium secondary battery can prevent the problems caused by a nitrile group-containing compound added to the electrolyte for the purpose of improving high-temperature cycle characteristics and safety (such problems as a battery swelling phenomenon and a drop in recovery capacity under high-temperature (>80 DEG C) storage conditions), by adding a fluorotoluene compound.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Electrode body for lithium battery, and lithium battery
InactiveUS20160072153A1Safely securedPrevent short-circuitingFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte cellsMolten saltAlloy
An electrode body for a lithium battery includes a collector electrode, a negative electrode active material layer which is provided to come into contact with one surface of the collector electrode and contains a Li metal or a Li alloy, a soggy sand electrolyte layer that is provided on a side of the negative electrode active material layer which is opposite to a collector electrode side, and an inorganic solid electrolyte layer that is provided on a side of the soggy sand electrolyte layer which is opposite to a negative electrode active material layer side. In the soggy sand electrolyte layer, a plurality of particles is impregnated with an ordinary temperature molten salt electrolyte.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
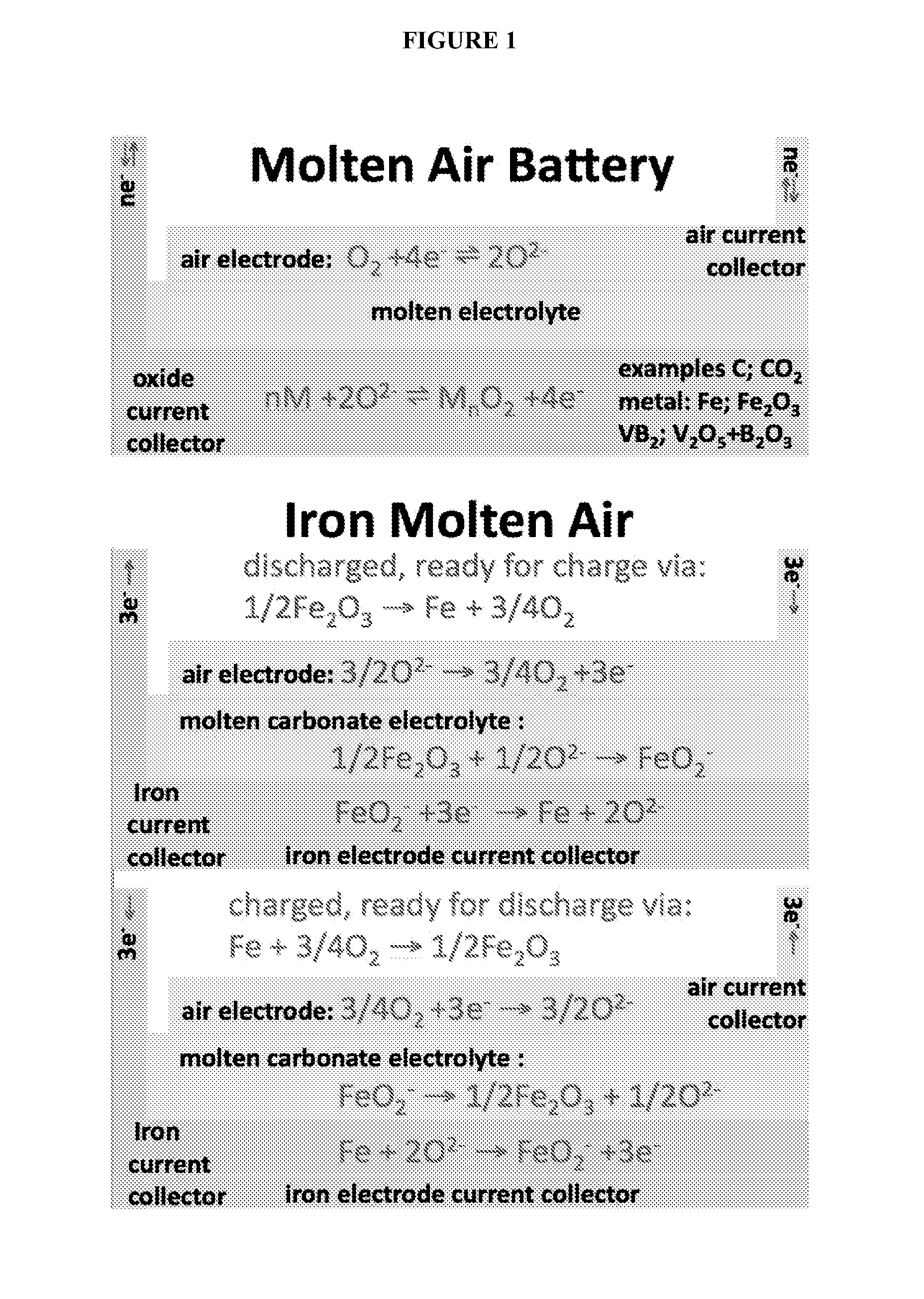
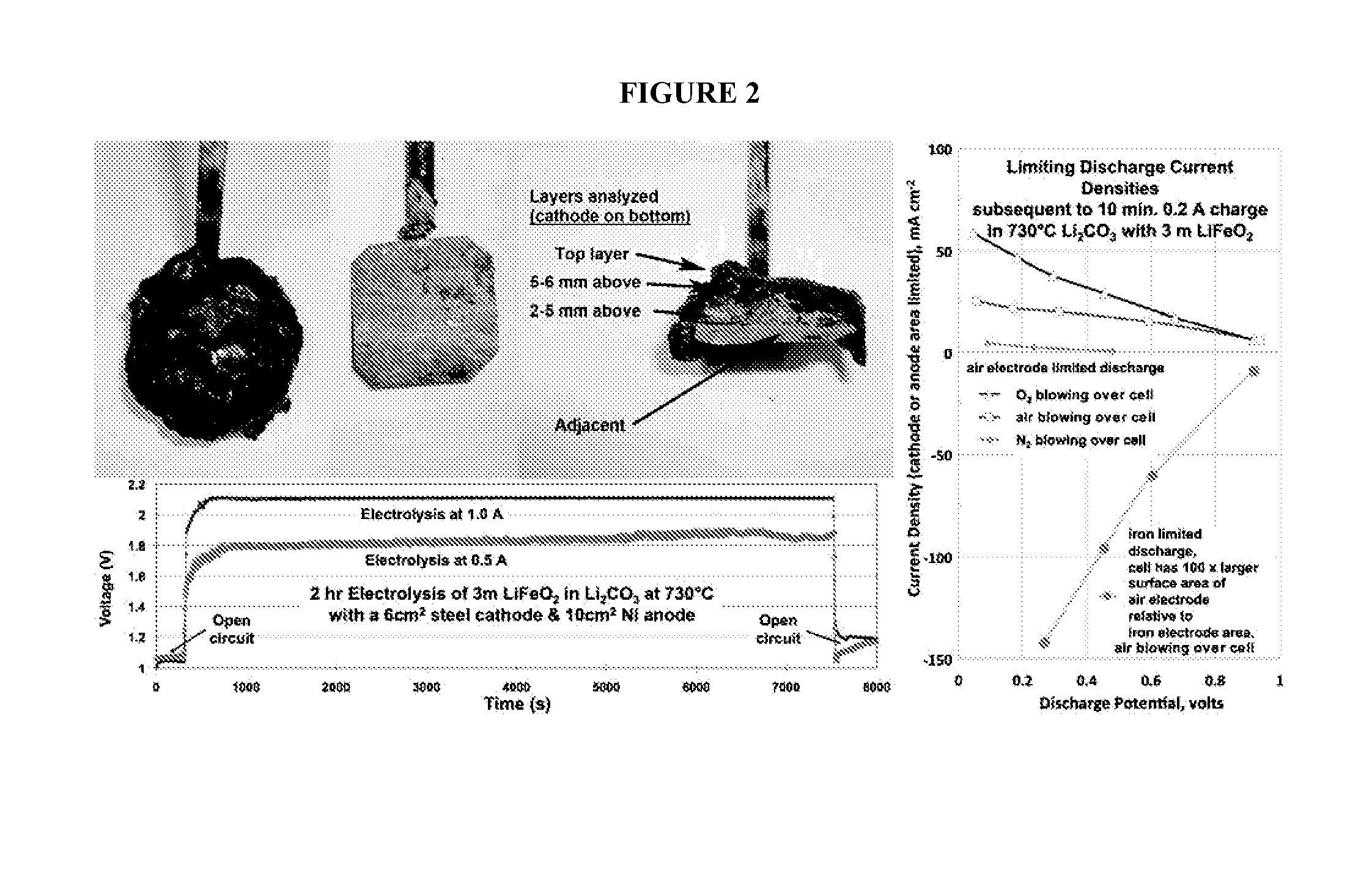
Molten air rechargeable batteries
ActiveUS20160006090A1Improve cycle lifeHigh intrinsic electric energy storage capacityFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesElectrical batteryAutomotive battery
The present disclosure relates to rechargeable electrochemical battery cells (molten air batteries). The cells use air and a molten electrolyte, are quasi-reversible (rechargeable) and have the capacity for multiple electrons stored per molecule and have high intrinsic electric energy storage capacities. The present disclosure also relates to the use of such in a range of electronic, transportation and power generation devices, such as greenhouse gas reduction applications, electric car batteries and increased capacity energy storage systems for the electric grid.
Owner:C2CNT LLC
Molten metal rechargeable electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20170149095A1Low costHigh commercial availabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrical batteryElectrochemical cell
The present invention provides rechargeable electrochemical cells comprising a molten anode, a cathode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte salt, wherein the electrolyte salt is situated between the molten anode and the cathode during the operation of the electrochemical cell, and the molten anode comprises an aluminum material; also provided are batteries comprising a plurality of such rechargeable electrochemical cells and processes for manufacturing such rechargeable electrochemical cells.
Owner:EOS ENERGY STORAGE
Chloride-free thermal batteries using molten nitrate electrolytes
ActiveUS20090047573A1Shorten activation timeReduce weightDeferred-action cellsCell electrodesHigh cellDecomposition
Thermal batteries using molten nitrate electrolytes offer significantly higher cell voltages and marked improvements in energy and power densities over present thermal batteries. However, a major problem is gas-evolution reactions involving the molten nitrate electrolytes. This gassing problem has blocked the advantages offered by thermal batteries using molten nitrates. The solution to this problem is the use of chloride-free molten nitrate electrolytes. Most important is the avoidance of potassium perchlorate (KClO4) or any other chlorine-containing substances that can decompose to produce chloride ions in any thermal battery component. The Fe+KClO4 pyrotechnic used to activate thermal batteries is a key example. The decomposition of such substances into chloride ions (Cl−) results in passivating-film breakdown and gas-producing reactions with the molten nitrate electrolyte. These reactions largely involve the lithium-component of the anode used in thermal batteries such as Li—Fe (LAN), Li—Si, and Li—Al. The introduction of chloride ions into the nitrate melt via the pyrotechnic materials produces a rapid breakdown of the protective oxide film on lithium-based anodes and leads to gas-producing reactions.
Owner:AXIENT LLC
Novel paste electrolyte used for high-temperature molten salt battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103825058AImprove conductivityReduce short circuitFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsFiberFilling materials
The invention discloses a paste electrolyte used for a high-temperature molten salt battery. The electrolyte material is prepared by adding a MgO filling material or an Al2O3 fiber filling material into a molten salt electrolyte, wherein the content of the MgO filling material is 20-50 wt%, and the content of the Al2O3 fiber filling material is 5-20% by volume. At the working temperature of the battery, the mixture of the molten salt and the filling materials exists in a form of paste with high viscosity, so that the paste electrolyte basically has characteristics of the high conductive rate, quick mass transfer, and the like of liquid electrolytes, and is capable of effectively reducing the risks of short circuit and open circuit of the battery and enhancing the stability and safety of the battery operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
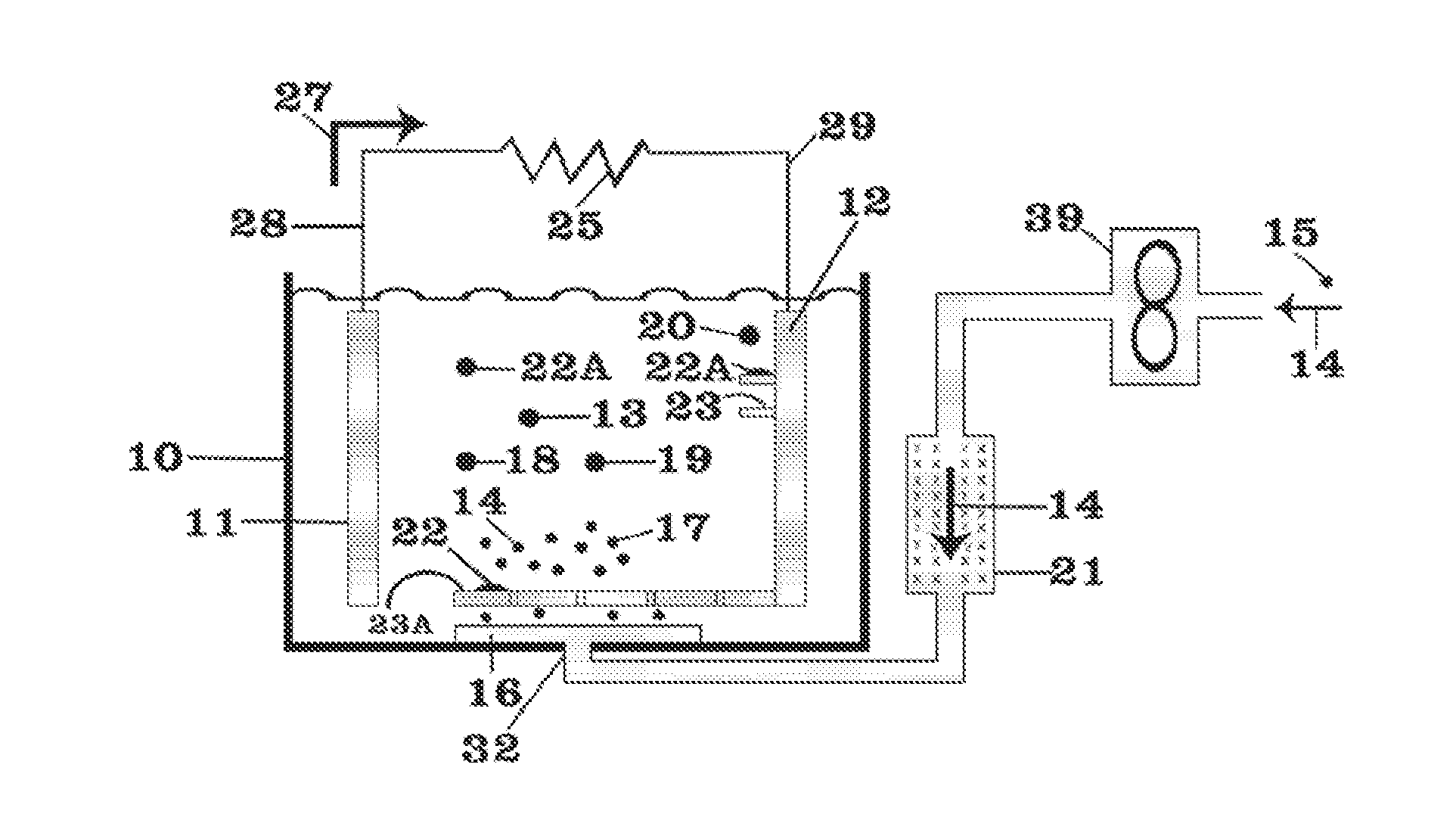
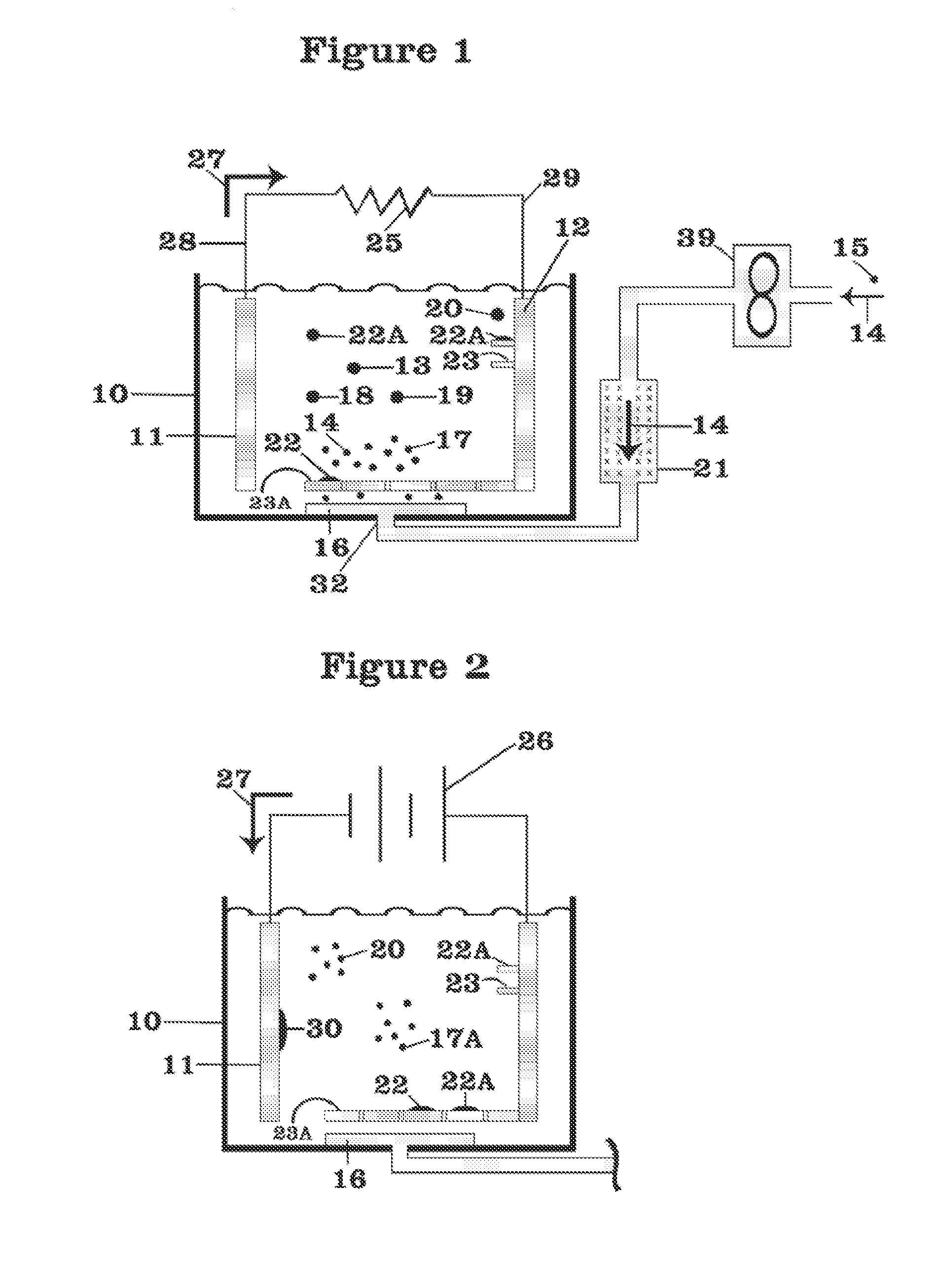
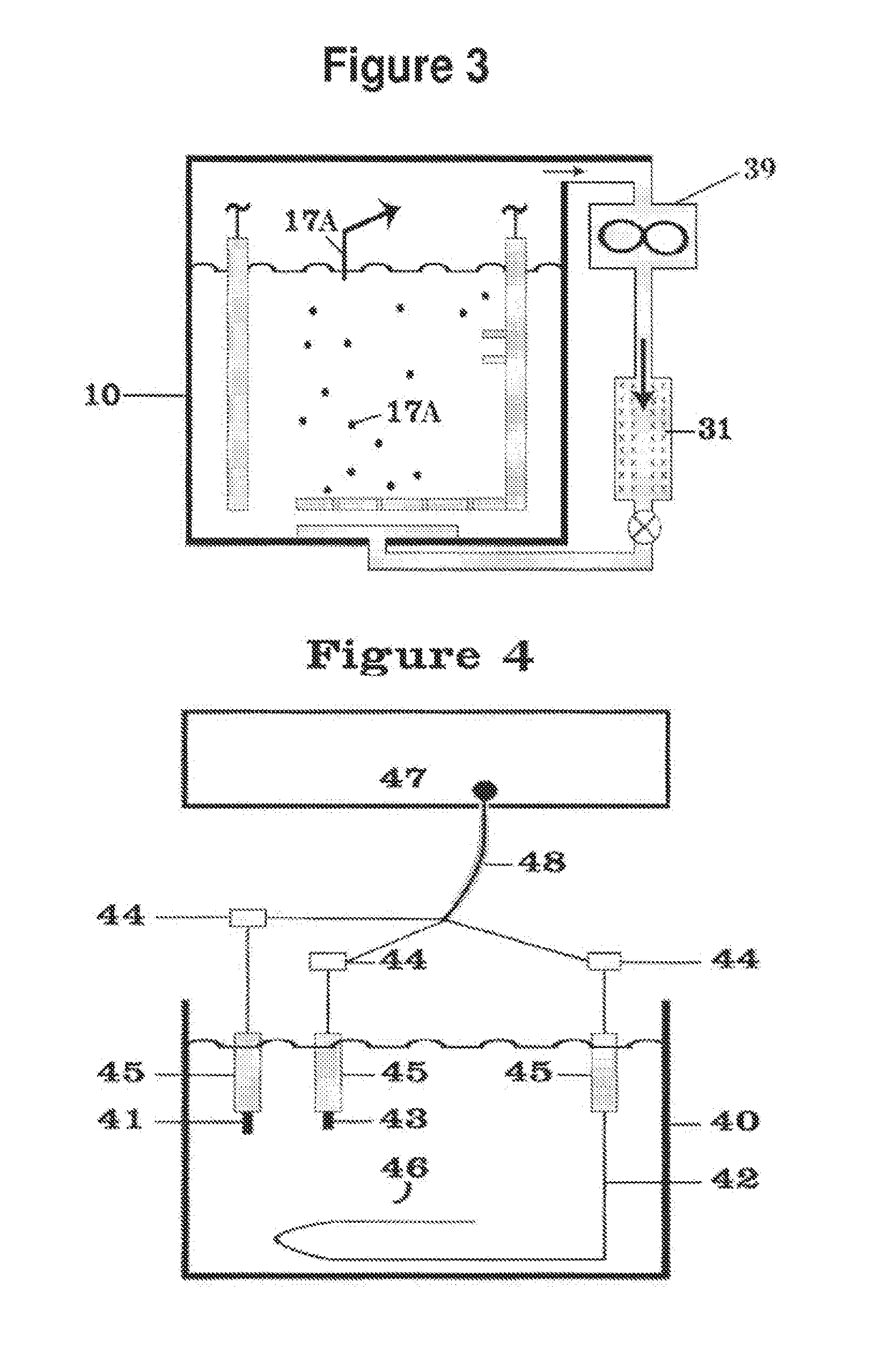
Current collector design to reduce granule bed disruption
ActiveUS20160344066A1Reduce disruptionElectrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cellsMetal halidesElectrochemical cell
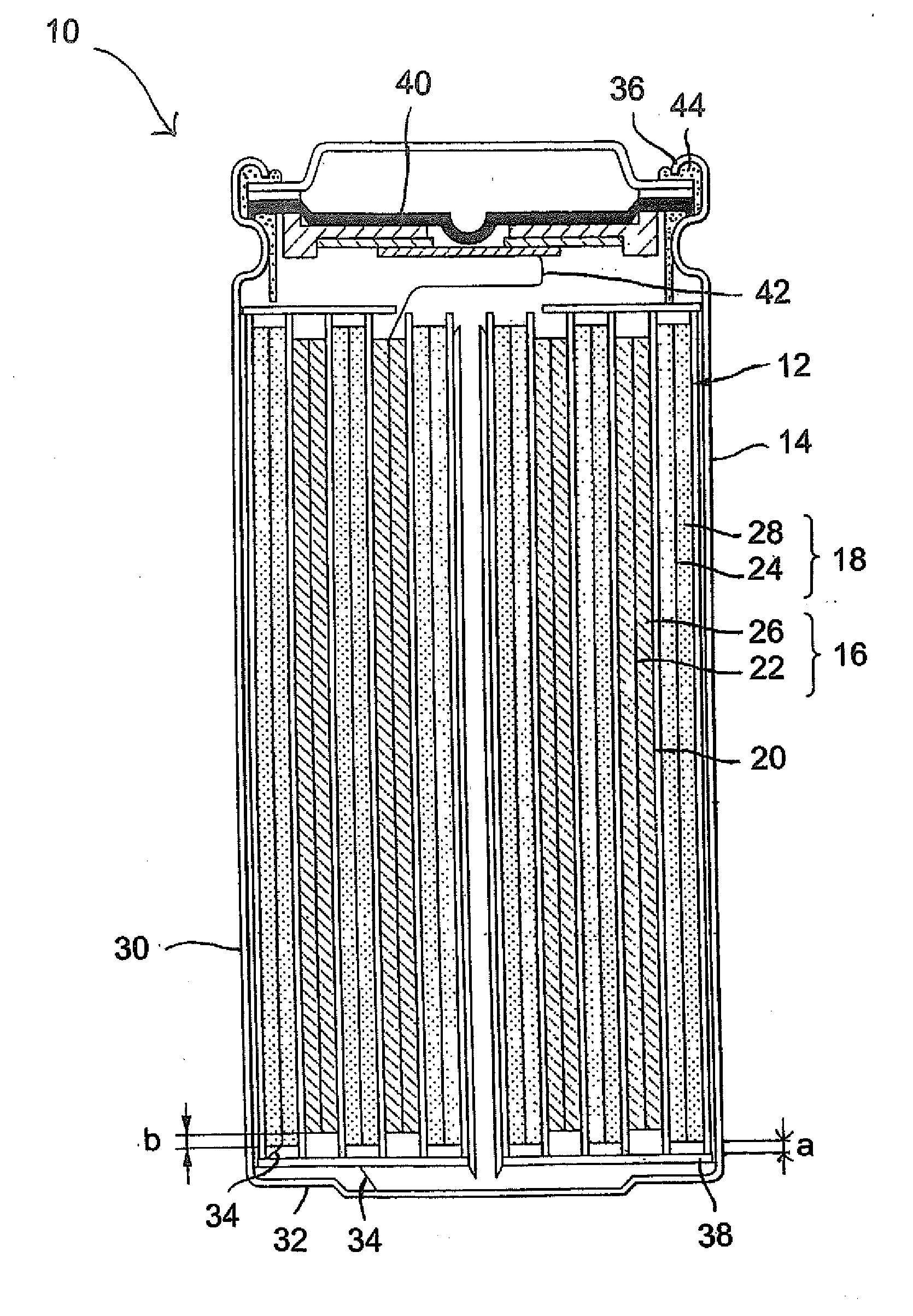
Apparatus and methods to reduce granule disruption during manufacture of electrochemical cells, such as a metal halide electrochemical cell, are provided. In one embodiment, a current collector can include a diffuser strip extending beneath an aperture configured to receive an injection stream of molten electrolyte. The diffuser strip can be configured to dissipate an injection stream of molten electrolyte when the molten electrolyte is injected into an electrochemical cell. In this way, disruption of a granule bed by the injection of the molten electrolyte during manufacture of the electrochemical cell can be reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
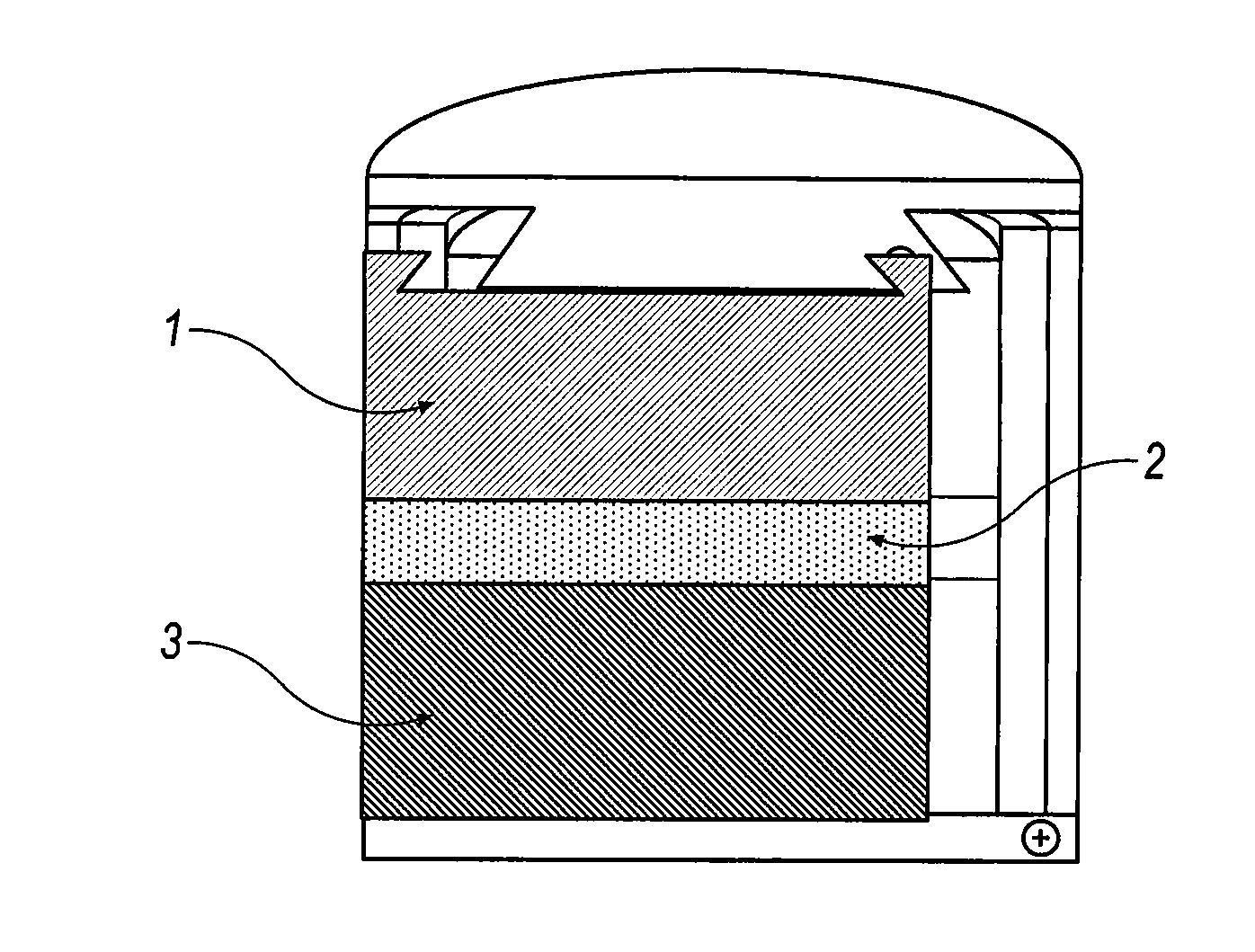
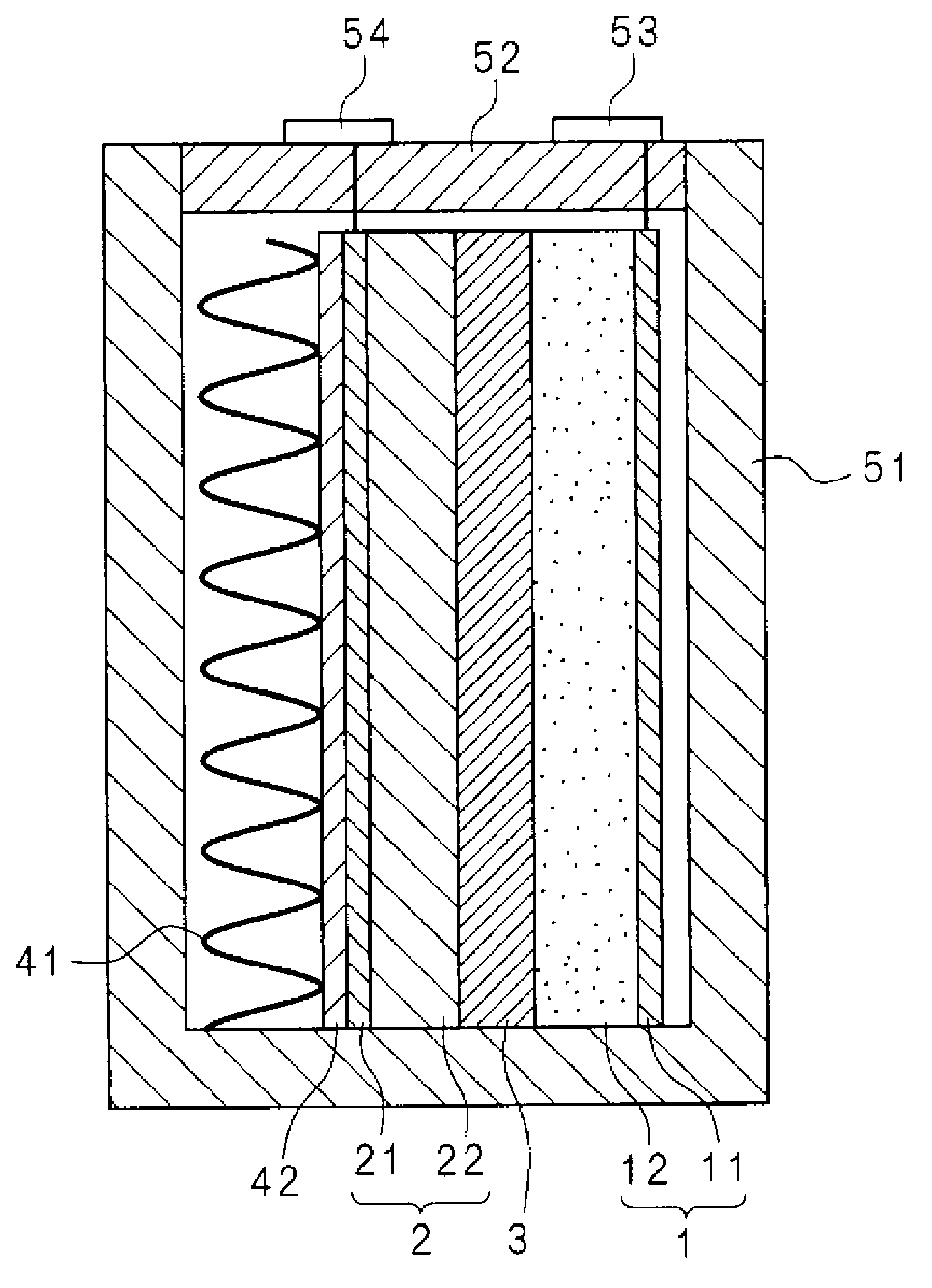
Energy storage device and method
InactiveUS20090291365A1Secondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesEngineeringElectrochemical energy conversion
An article of electrochemical energy conversion is provided that includes a separator. The separator has a first surface that defines at least a portion of a first chamber, and a second surface that defines a second chamber, and the first chamber is in ionic communication with the second chamber through the separator. The energy storage device further includes a plurality of cathodic materials. The plurality includes at least a first cathodic material and a second cathodic material. Both of the cathodic materials are in electrical communication with the separator and both are capable of forming a metal halide. A proviso is that if either of the first cathodic material or the second cathodic material is a transition metal, then the other cathodic material is not iron, arsenic, or antimony.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
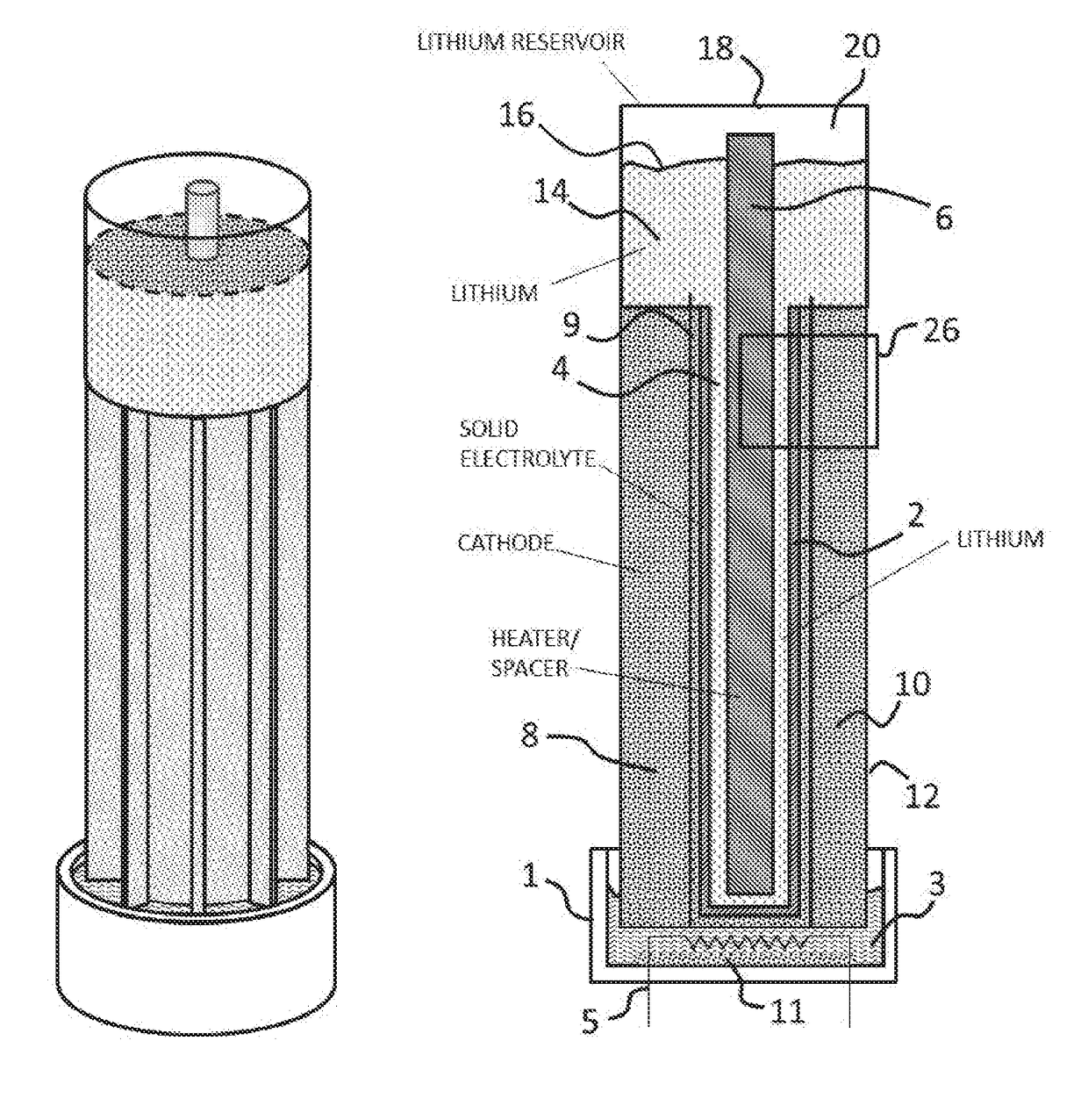
Johnson lithium oxygen electrochemical engine
A rechargeable lithium air battery is provided. The battery contains a ceramic separator forming an anode chamber, a molten lithium anode contained in the anode chamber, an air cathode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte. The cathode has a temperature gradient comprising a low temperature region and a high temperature region, and the temperature gradient provides a flow system for reaction product produced by the battery.
Owner:JOHNSON IP HLDG LLC
Chloride-free thermal batteries using molten nitrate electrolytes
ActiveUS7629075B2Shorten activation timeReduce weightDeferred-action cellsCell electrodesHigh cellDecomposition
Thermal batteries using molten nitrate electrolytes offer significantly higher cell voltages and marked improvements in energy and power densities over present thermal batteries. However, a major problem is gas-evolution reactions involving the molten nitrate electrolytes. This gassing problem has blocked the advantages offered by thermal batteries using molten nitrates. The solution to this gassing problem is to eliminate the chloride ion contaminates. The most important step in reducing chloride contamination is the avoidance of potassium perchlorate (KClO4) or any other chlorine-containing substances that can decompose to produce chloride ions in any thermal battery component. The Fe+KClO4 pyrotechnic used to activate thermal batteries is a key example. The decomposition of such substances into chloride ions (Cl—) results in passivating-film breakdown and gas-producing reactions with the molten nitrate electrolyte. These reactions largely involve the lithium-component of the anode used in thermal batteries such as Li—Fe (LAN), Li—Si, and Li—Al. The introduction of chloride ions into the nitrate melt via the pyrotechnic materials produces a rapid breakdown of the protective oxide film on lithium-based anodes and leads to gas-producing reactions.
Owner:AXIENT LLC
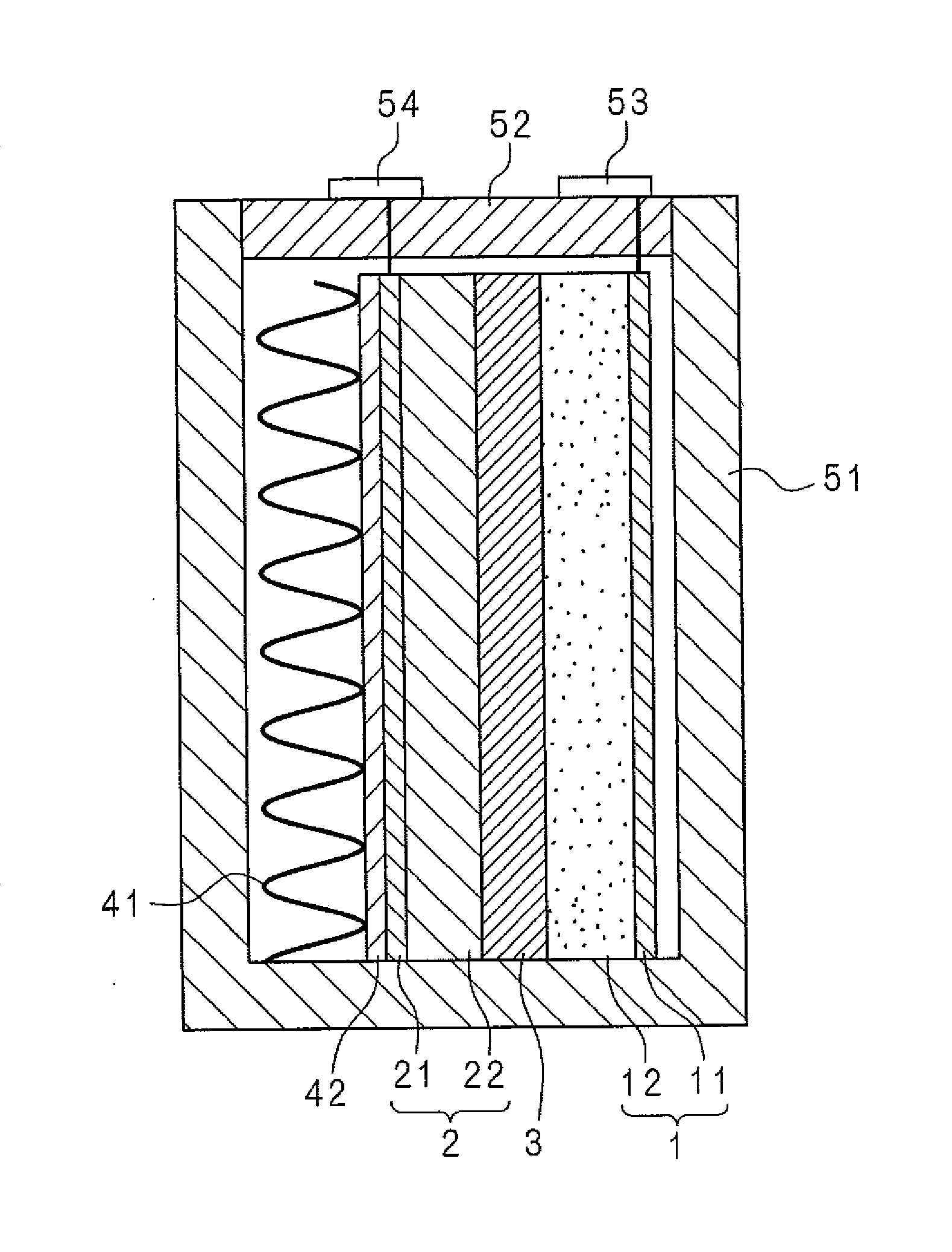
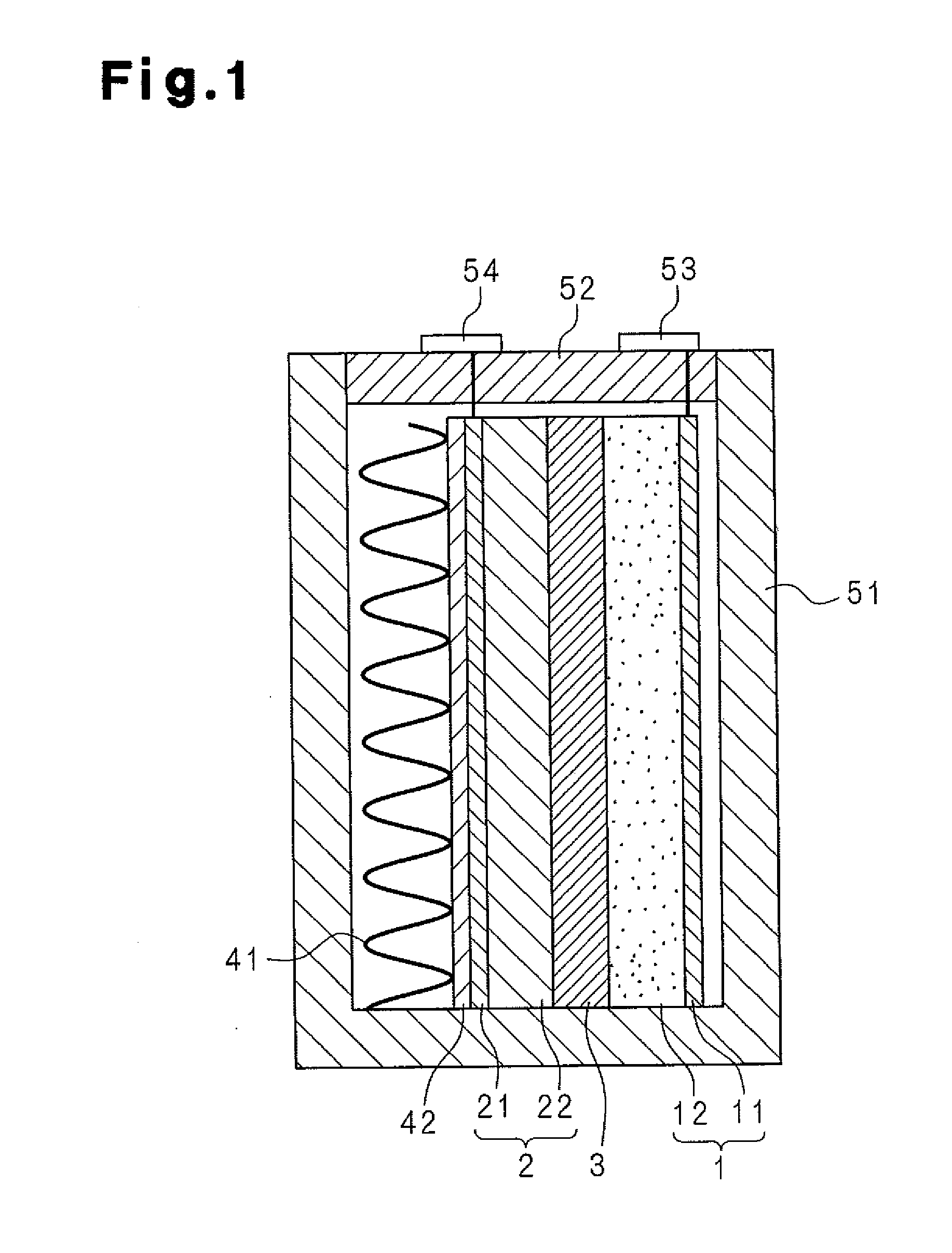
Molten salt battery
InactiveUS20140170458A1Lower operating temperatureCell electrodesSolid electrolyte cellsPyridiniumPhosphonium
A separator (3) of a molten salt battery is impregnated with a molten salt that serves as the electrolyte. The molten salt contains, as cations, at least one kind of ions selected from among quaternary ammonium ions, imidazolium ions, imidazolinium ions, pyridinium ions, pyrrolidinium ions, piperidinium ions, morpholinium ions, phosphonium ions, piperazinium ions and sulfonium ions in addition to sodium ions. These cations do not have adverse effects on a positive electrode (1). In addition, the melting point of the molten salt, which contains sodium ions and the above-mentioned cations, is significantly lower than the operating temperature of sodium-sulfur batteries, said operating temperature being 280-360 DEG C. Consequently, the molten salt battery is capable of operating at lower temperatures than sodium-sulfur batteries.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
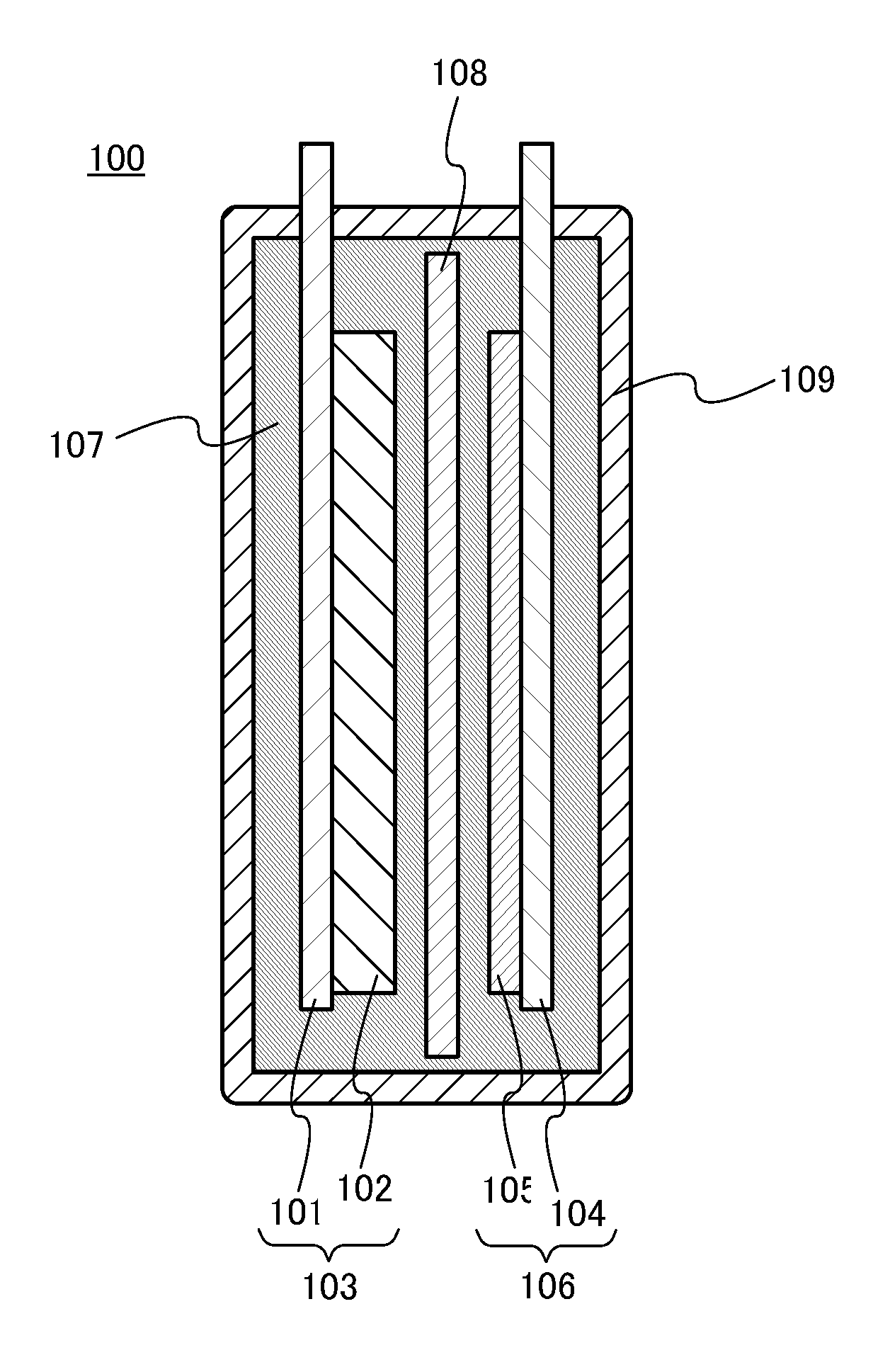
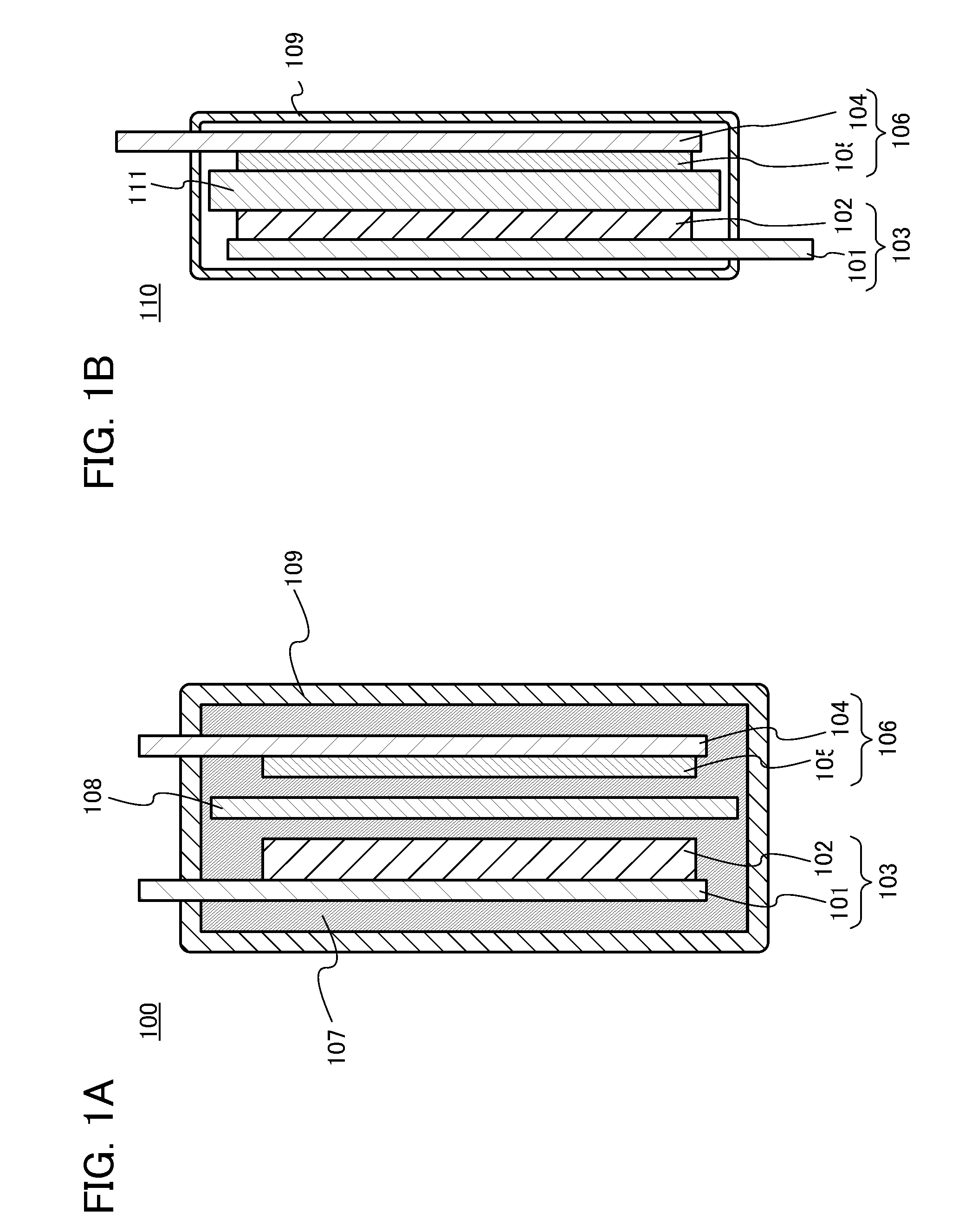
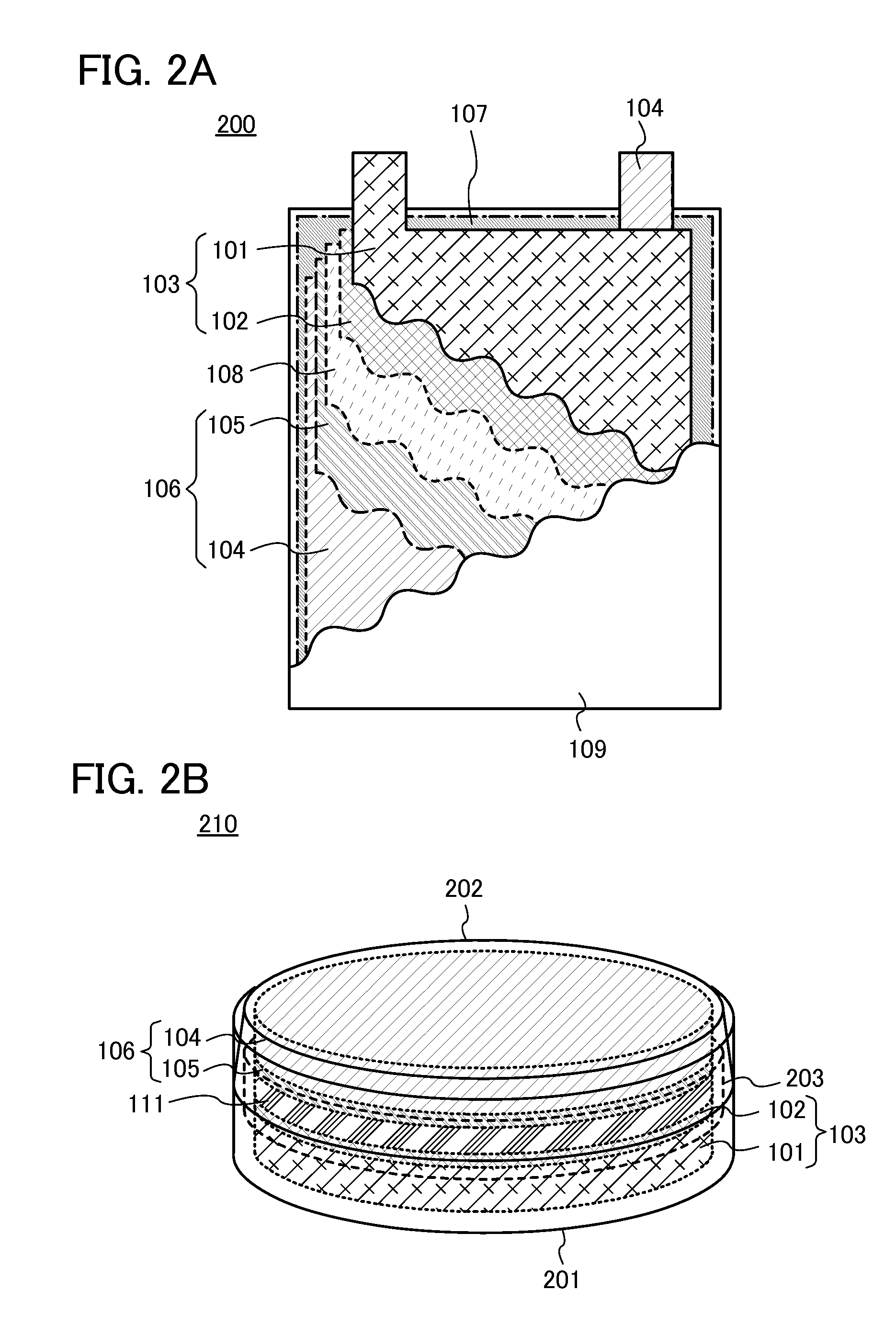
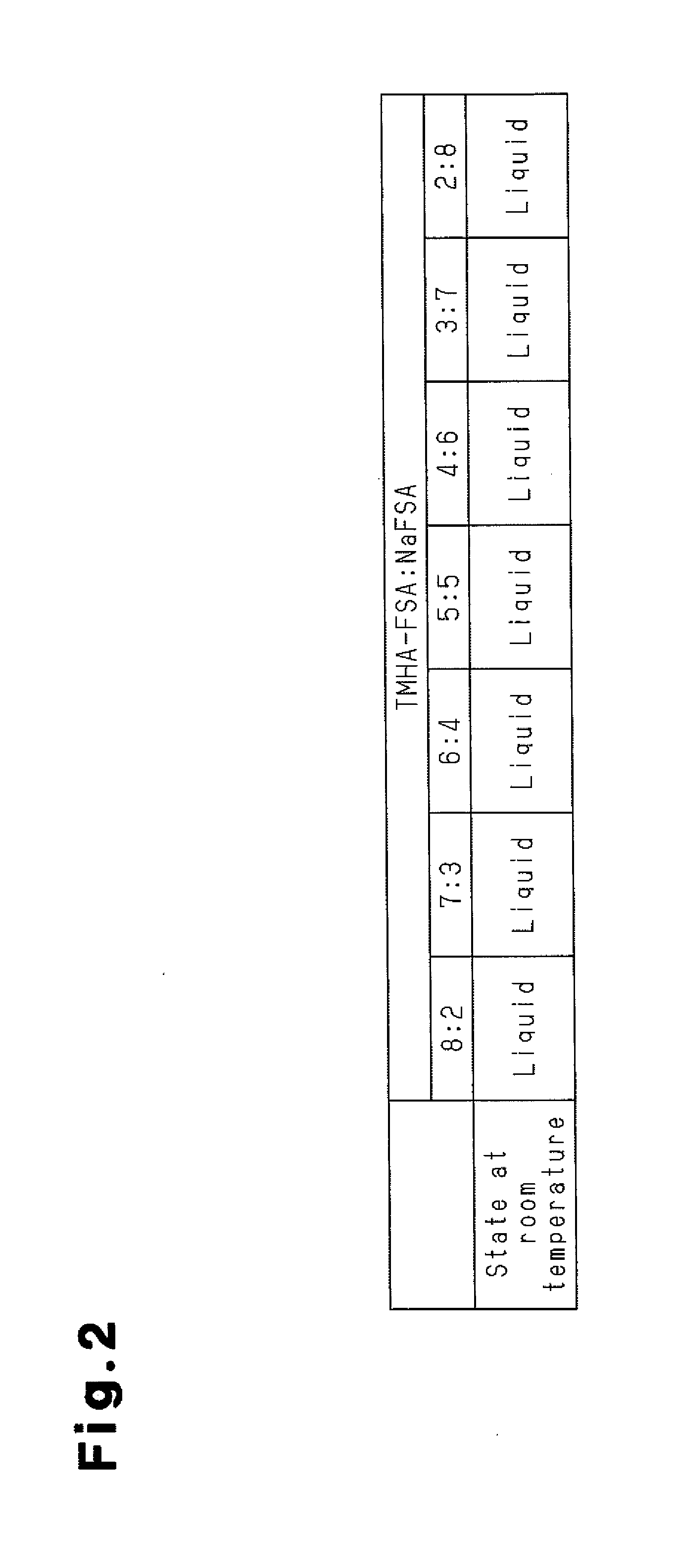
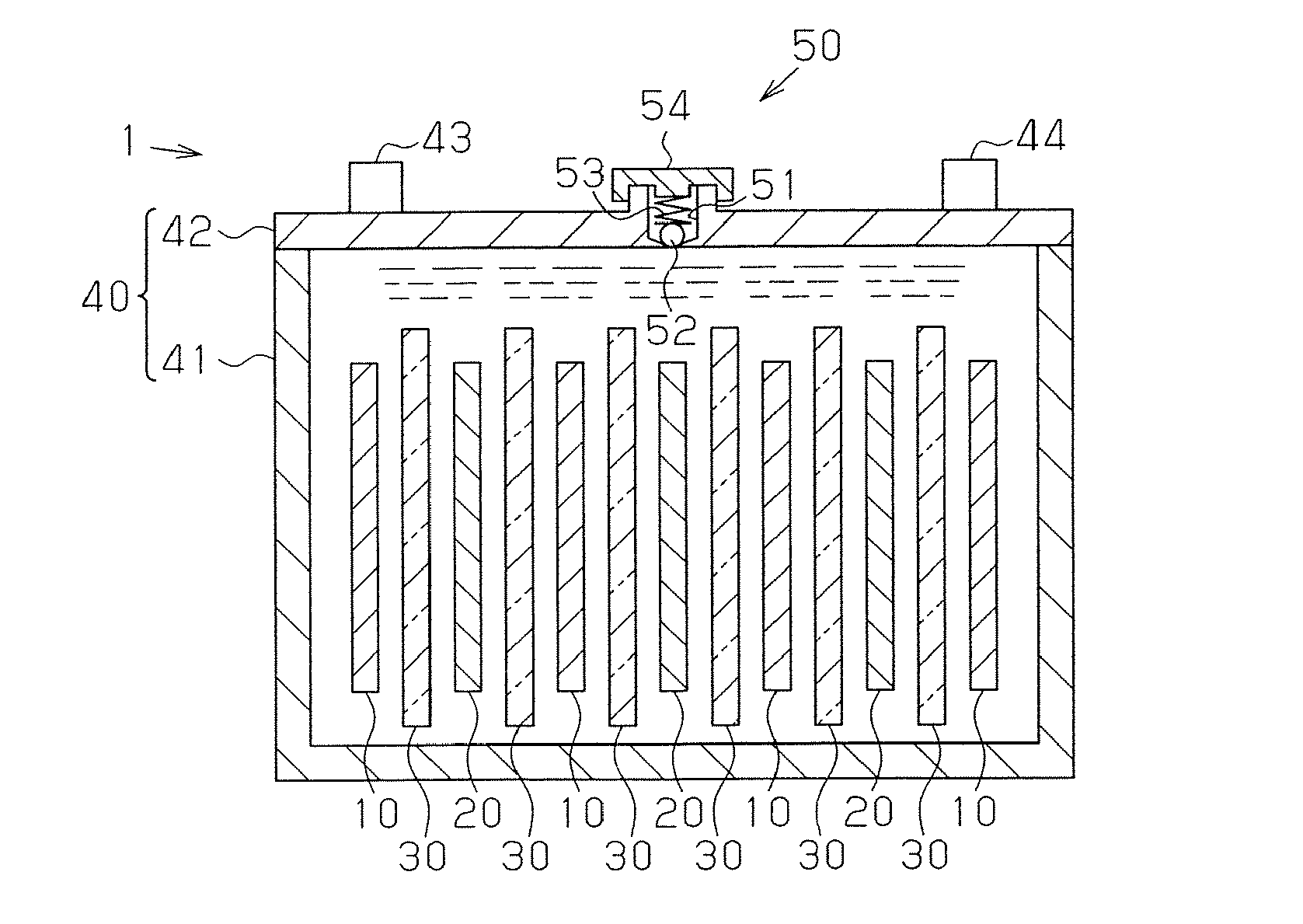
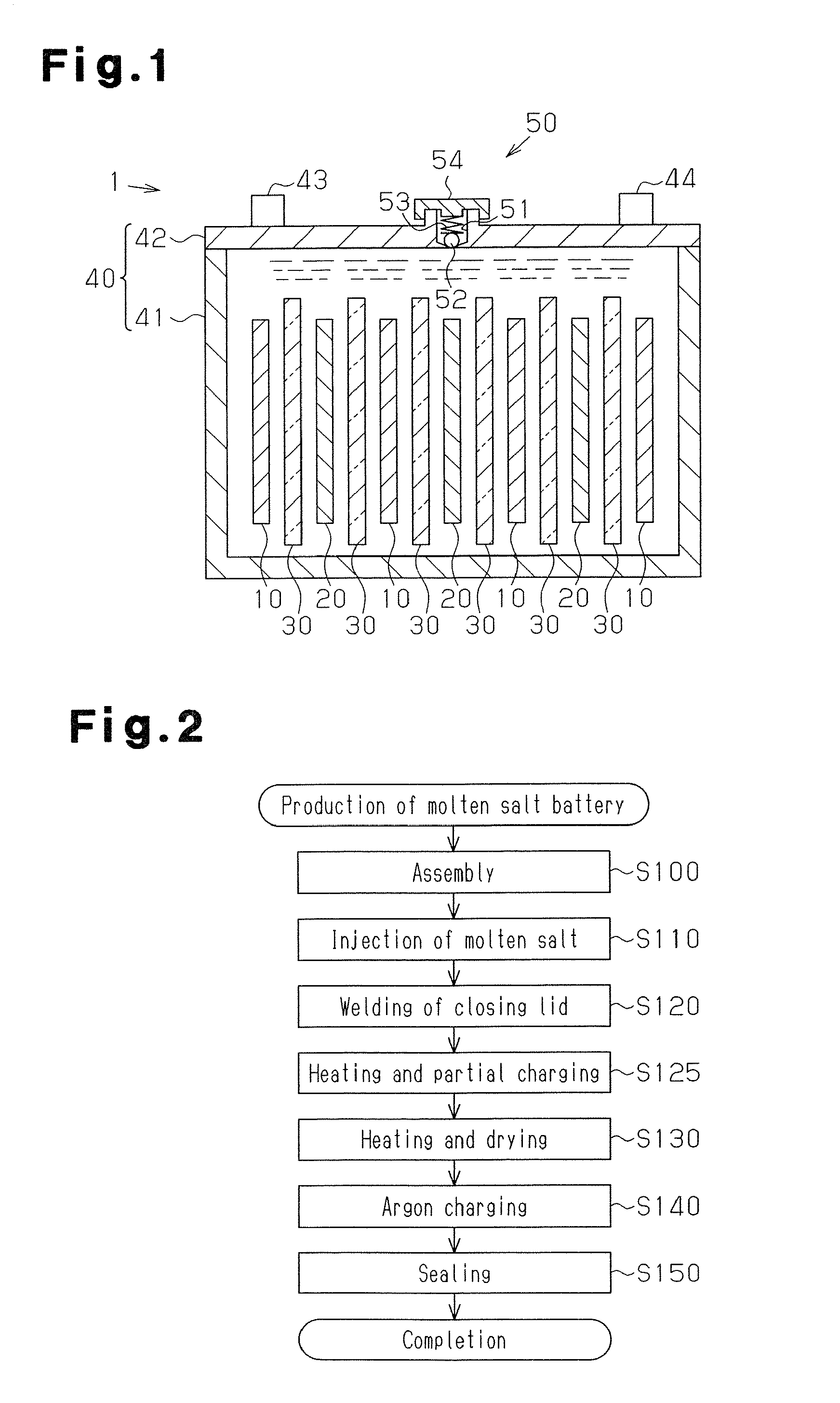
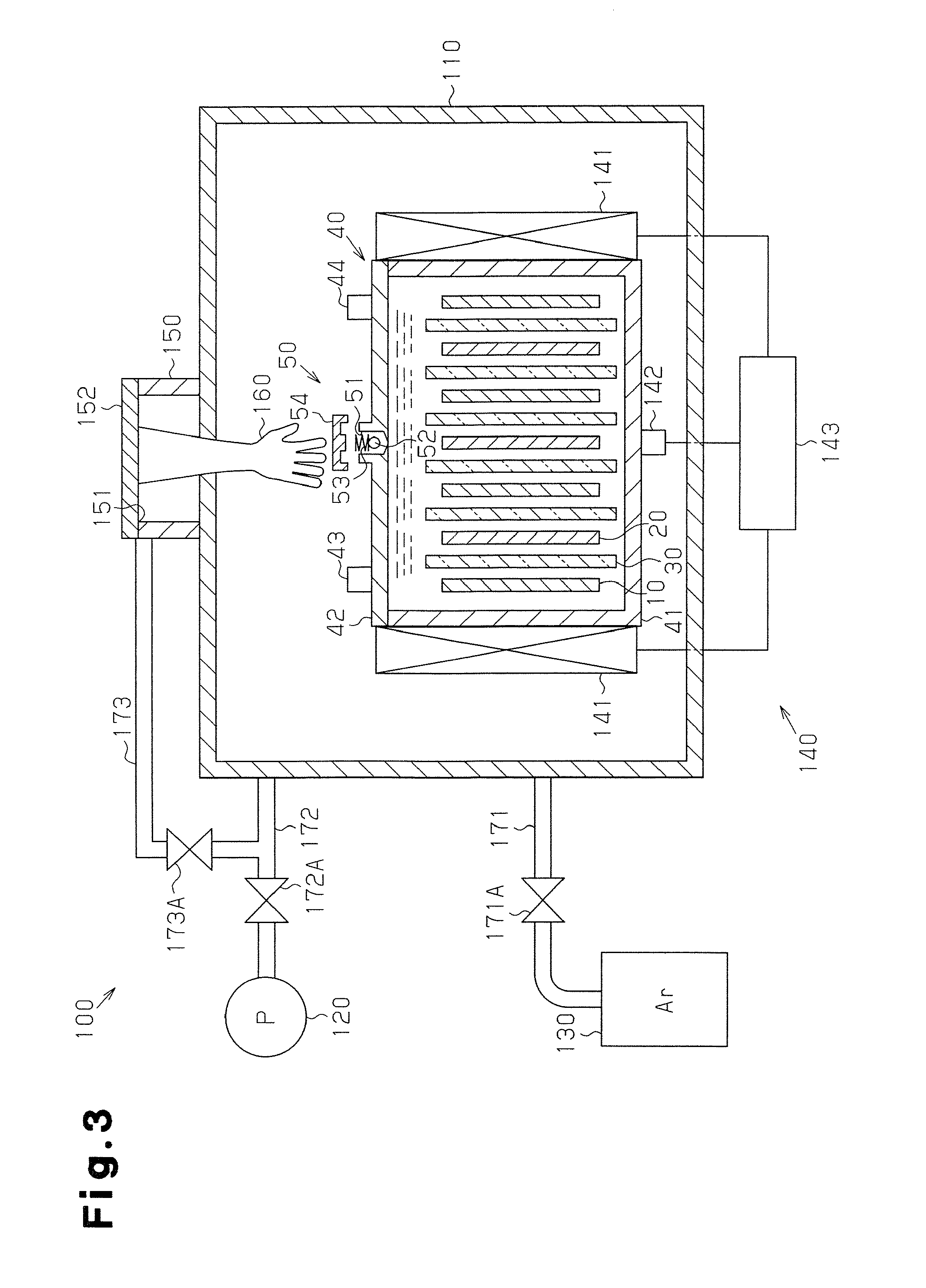
Manufacturing method for molten salt battery and molten salt battery
ActiveUS20140093757A1Reduce moistureReduce water contentLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesFinal product manufactureMolten saltCheck valve
Provided is a method for manufacturing a molten salt battery. The method includes a housing step (S100) for housing a positive electrode, a negative electrode and a separator in a battery container; an injecting step (S110) for injecting the molten salt into the battery container while heating the battery container; a closing step (S120) for closing the battery container with a closing lid; a heating and drying step (S130) for heating the battery container in a vacuum state with a check valve open; and a sealing step (S150) for closing the check valve. In summary, the positive electrode, negative electrode, separator and molten salt are heated and dried in a vacuum state.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Energy storage device and associated method
InactiveUS20130040171A1Avoid enteringCell electrodesFinal product manufactureEnergy storageCharge cycle
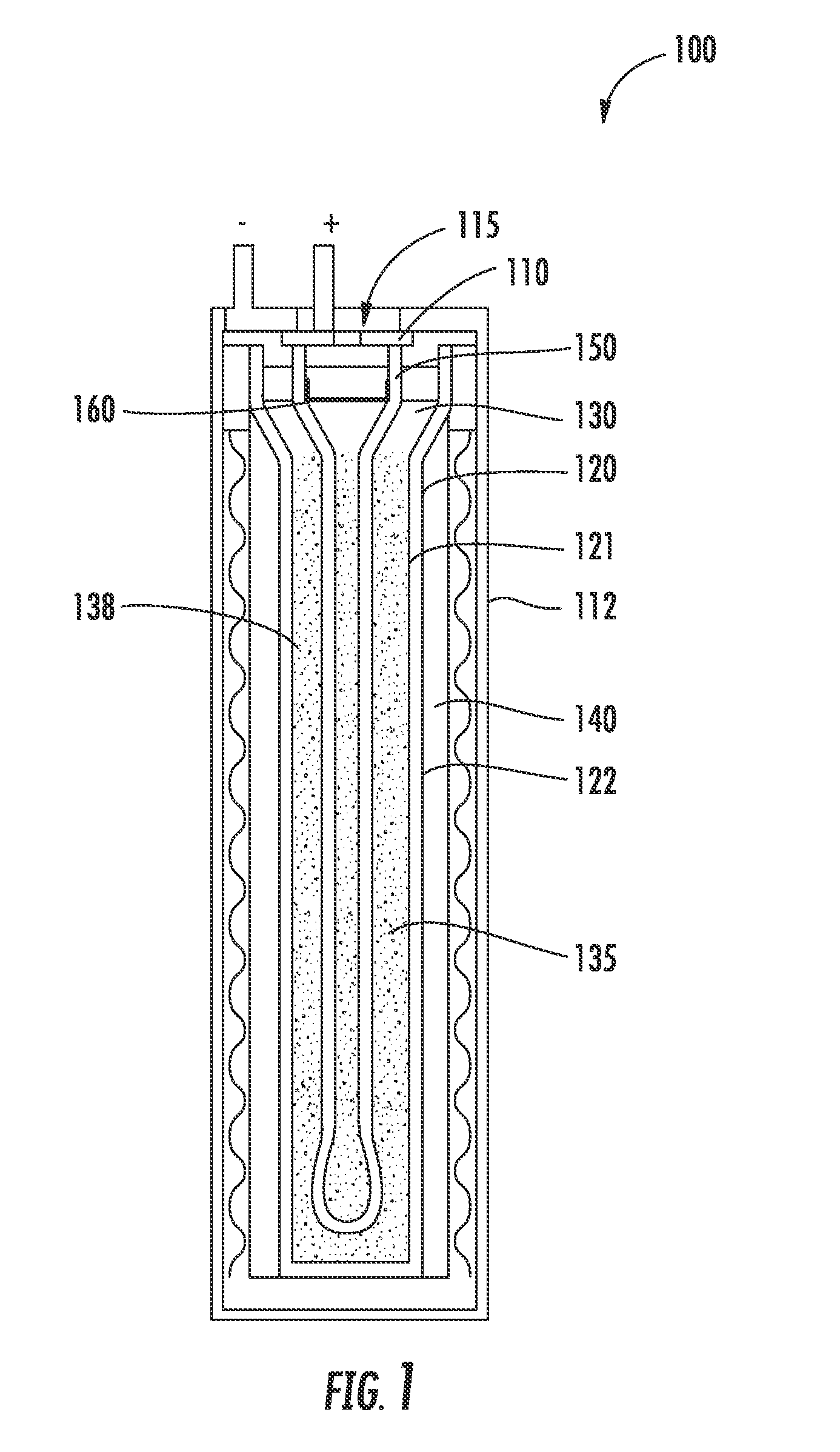
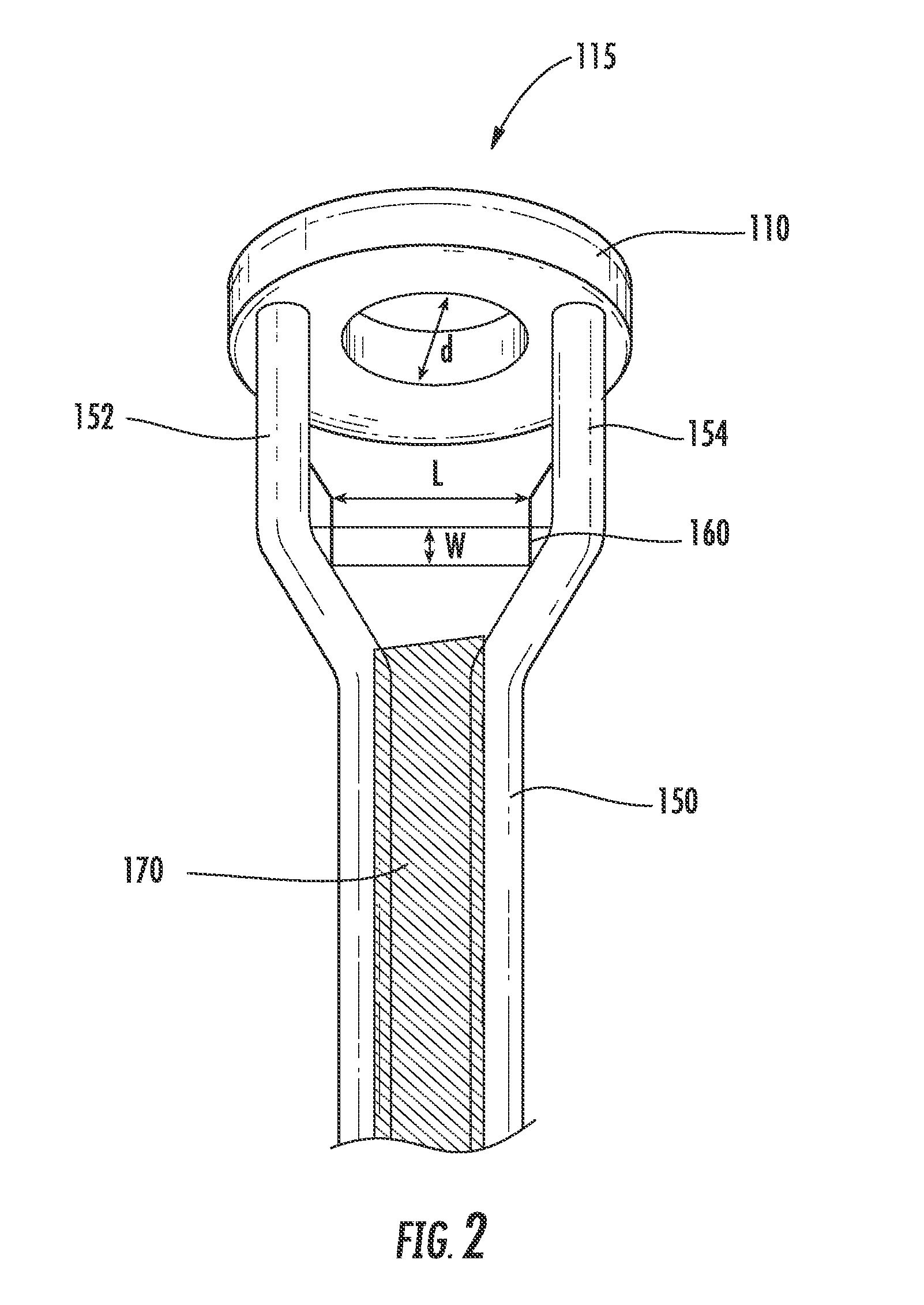
An energy storage device is provided that includes a reservoir in operative communication with a positive electrode such that the positive electrode remains fully flooded, even at the top of the charge cycle. The device more particularly includes a housing receiving therein, in a coaxial manner, an ion conducting member, and a current collector member received coaxially within the ion conducting member. In this device, a first region is provided in the space between the housing and the ion conducting member and a second region is provided in the space between the ion conducting member and the current collector member. The interior of the current collector member defines a reservoir having a certain volume at least equal to the volume of the void space created in the second region during charging of the device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Molten salt battery
A separator (3) of a molten salt battery is impregnated with a molten salt that serves as an electrolyte. The molten salt contains, as cations, at least one kind of ions selected from among quaternary ammonium ions, imidazolium ions, imidazolinium ions, pyridinium ions, pyrrolidinium ions, piperidinium ions, morpholinium ions, phosphonium ions, piperazinium ions and sulfonium ions in addition to sodium ions. These cations do not have adverse effects on a positive electrode (1). In addition, the melting point of the molten salt, which contains sodium ions and the above-mentioned cations, is significantly lower than the operating temperature of sodium-sulfur batteries, said operating temperature being 280-360 DEG C. Consequently, the molten salt battery is capable of operating at lower temperatures than sodium-sulfur batteries.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Sodium molten salt battery
InactiveUS20160156069A1Increase battery capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsDeferred-action cellsCell electrodesMolten saltMetal
The sodium molten salt battery includes a positive electrode containing a positive electrode active material, a negative electrode containing a negative electrode active material, a separator arranged between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and a molten salt electrolyte having sodium ion conductivity, in which the positive electrode active material contains a sodium-containing transition metal oxide, the negative electrode active material contains hard carbon, and the ratio of the reversible capacity Cn of the negative electrode to the reversible capacity Cp of the positive electrode, i.e., Cn / Cp, is 0.86 to 1.2.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for producing separator, method for producing molten salt battery, separator, and molten salt battery
ActiveUS20120208068A1Reduce riskLower internal resistancePrimary cell to battery groupingCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSurface layerMolten salt
A separator of a molten salt battery made of a porous resin sheet. The separator is improved in wettability to a molten salt by giving hydrophilicity to the resin sheet. In the case of a fluororesin sheet, the sheet is impregnated with water, and irradiated with ultraviolet rays so that C—F bonds in the fluororesin are cleaved and the resultant reacts with water to generate hydrophilic groups, such as OH groups, in each surface layer thereof. The separator gains hydrophilicity through the hydrophilic groups. The separator made of the resin can be made into a bag form. In a molten salt battery having the bag-form separator, the growth of a dendrite is prevented.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
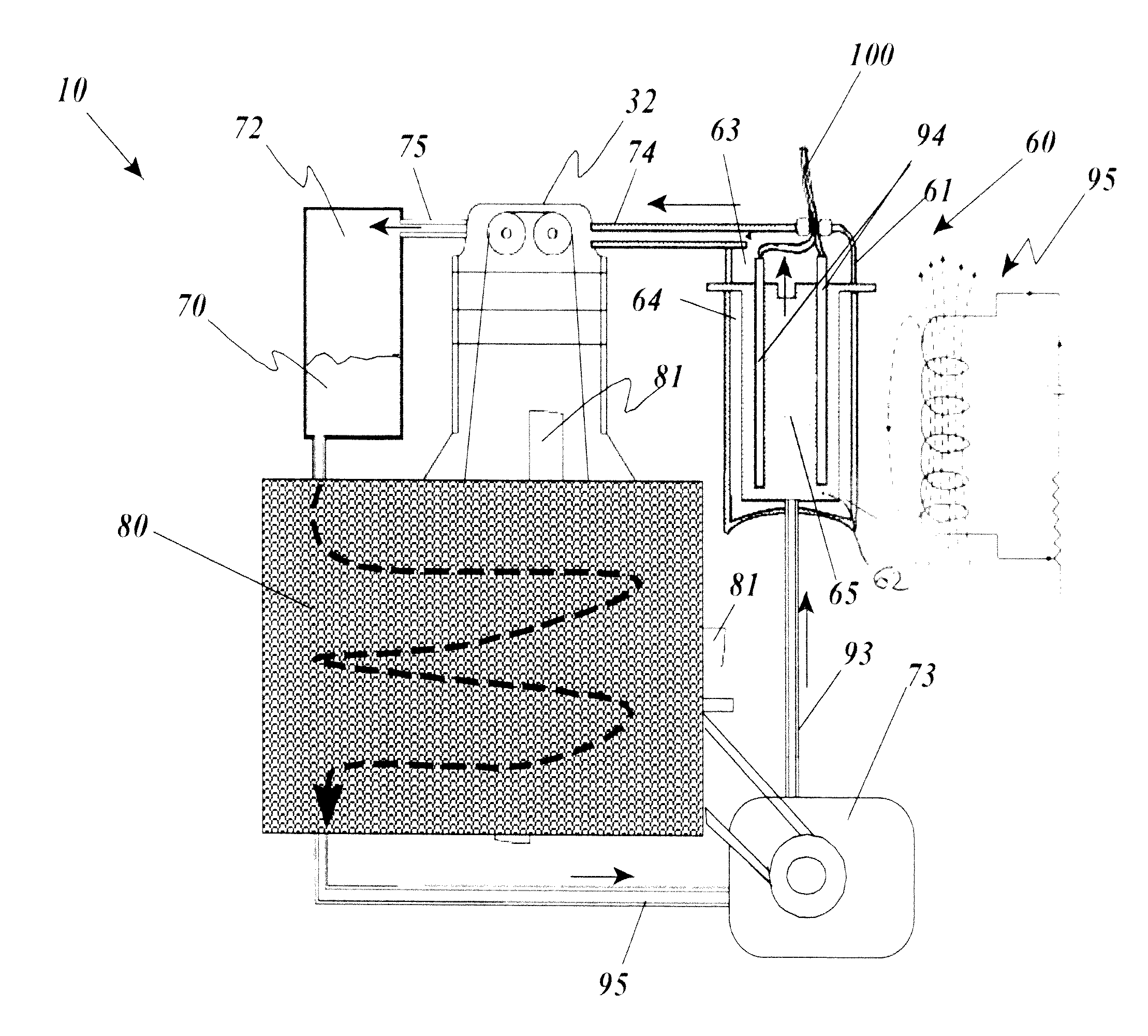
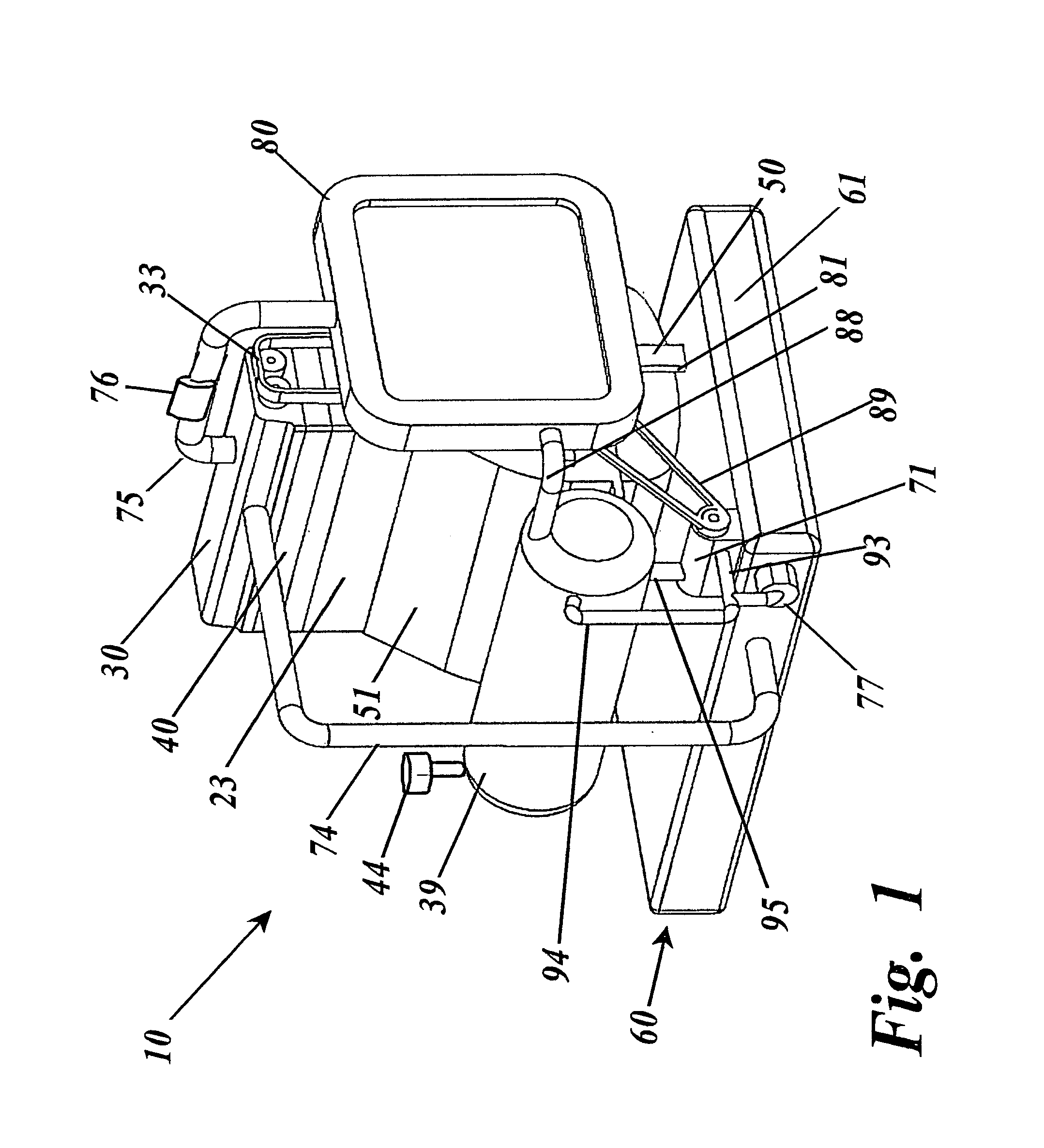
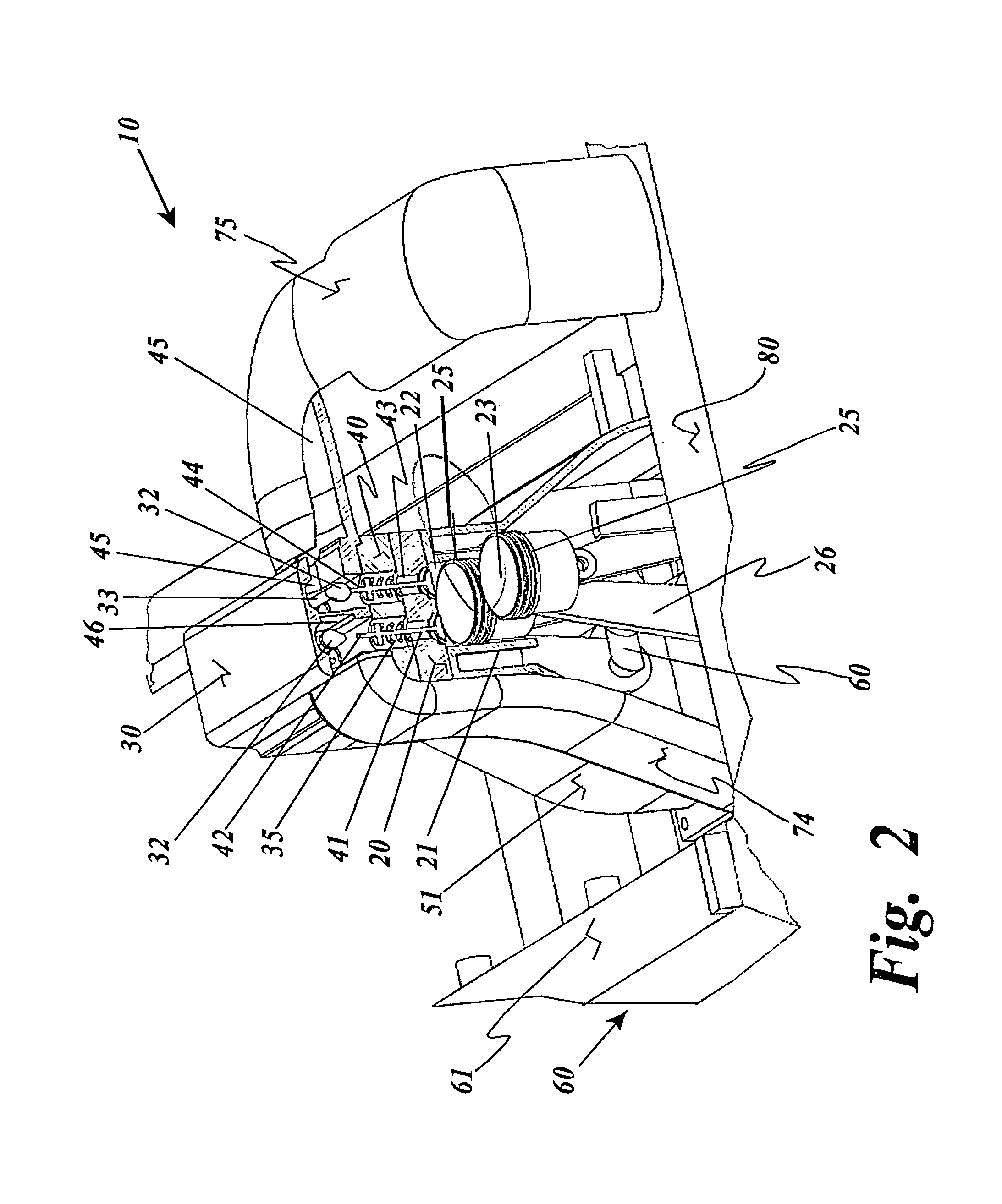
Thermal engine for operation with noncombustible fuels
ActiveUS9500158B1Minimal radiationLength minimizationInternal combustion piston enginesAir coolingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A thermal engine includes a cylinder and piston and an insulated thermal battery including at least a thermal mass such as the engine block itself for storing and retaining heat to enhance or cause fluid expansion within the cylinder and drive the piston, the thermal battery optionally including an electrolyte chamber containing a thermal electrolyte for functioning as an electric thermal battery. Heat is stored in the thermal battery such as by activating electric resistance heating elements in the thermal mass. The stored heat either causes expansion of a non-combustible expansion fluid such as water or enhances the expansion of a combustible expansion fluid such as gasoline. Where the thermal battery is an electric thermal battery containing an electrolyte, the storage of heat also stores electricity which can be used to power an electric motor.
Owner:ANTHONY MICHAEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com