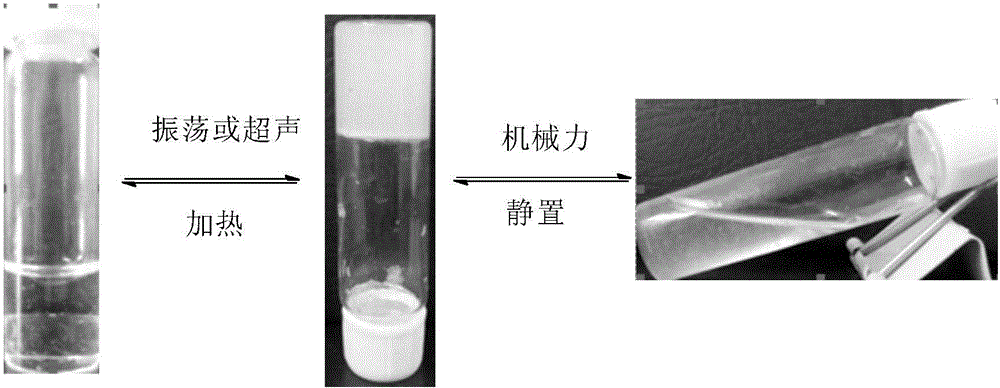
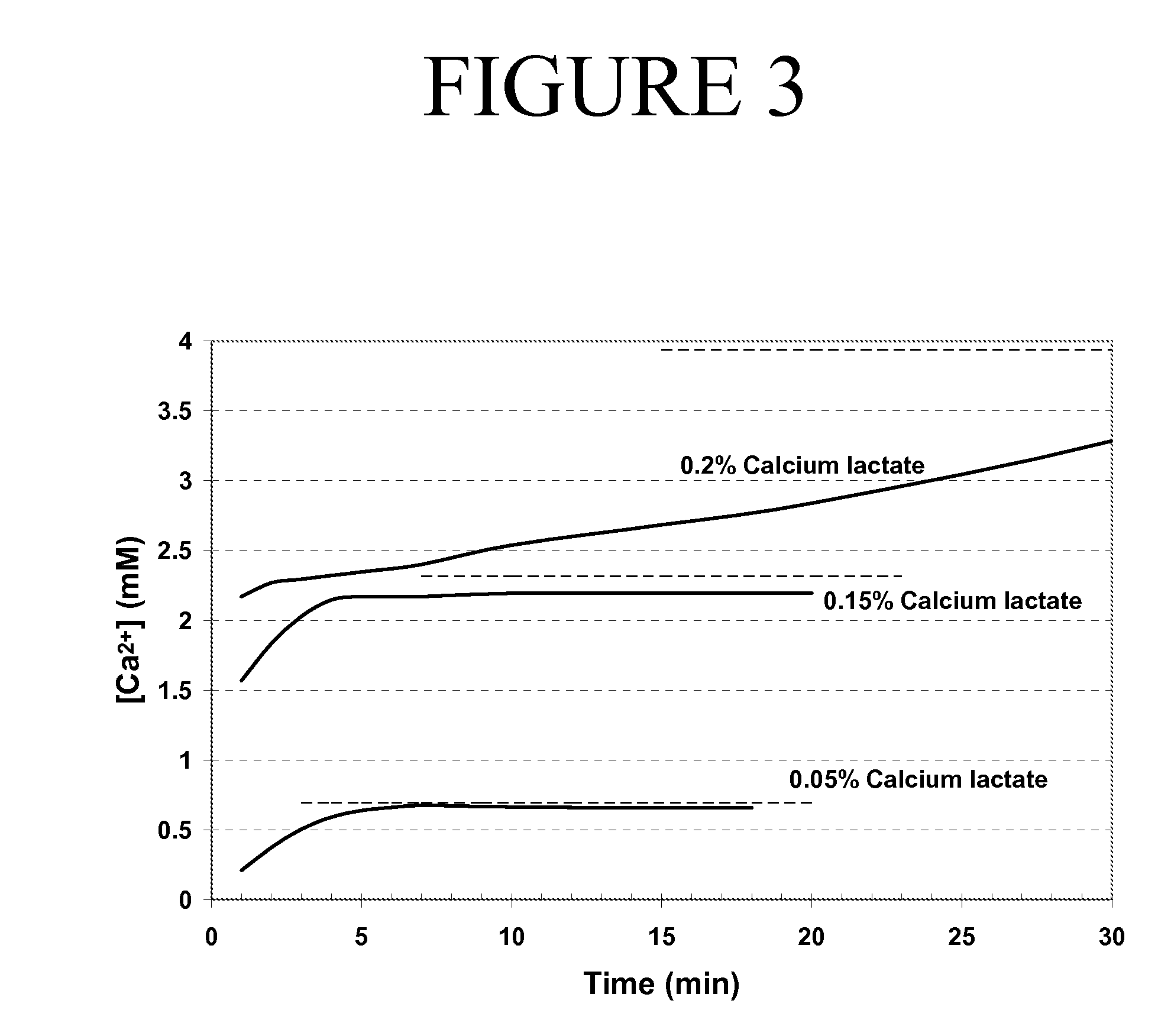
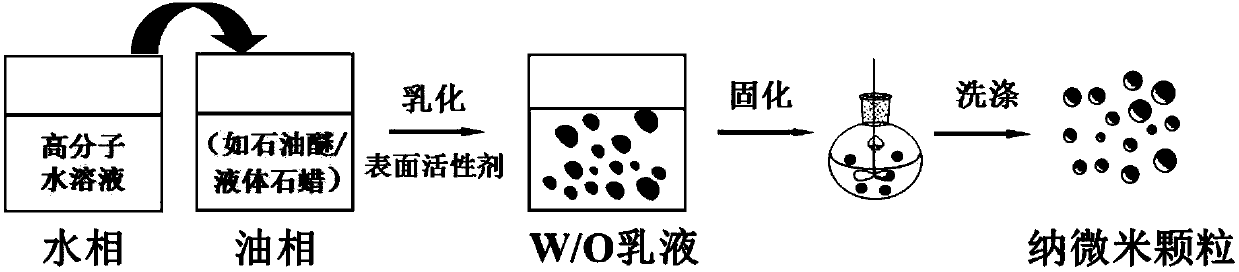
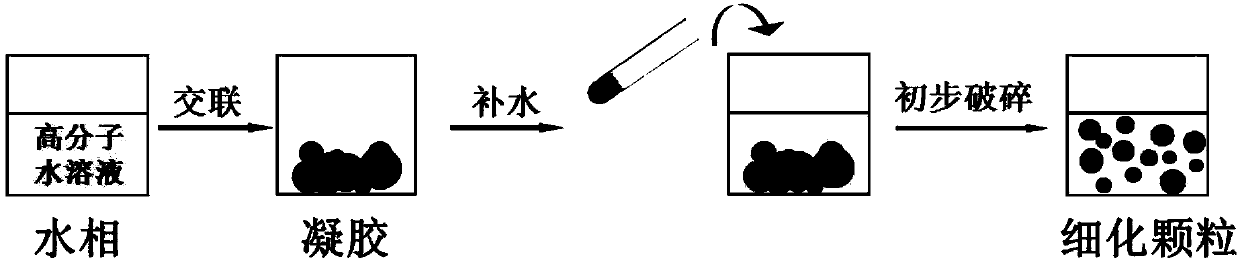
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
870results about "Gel preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
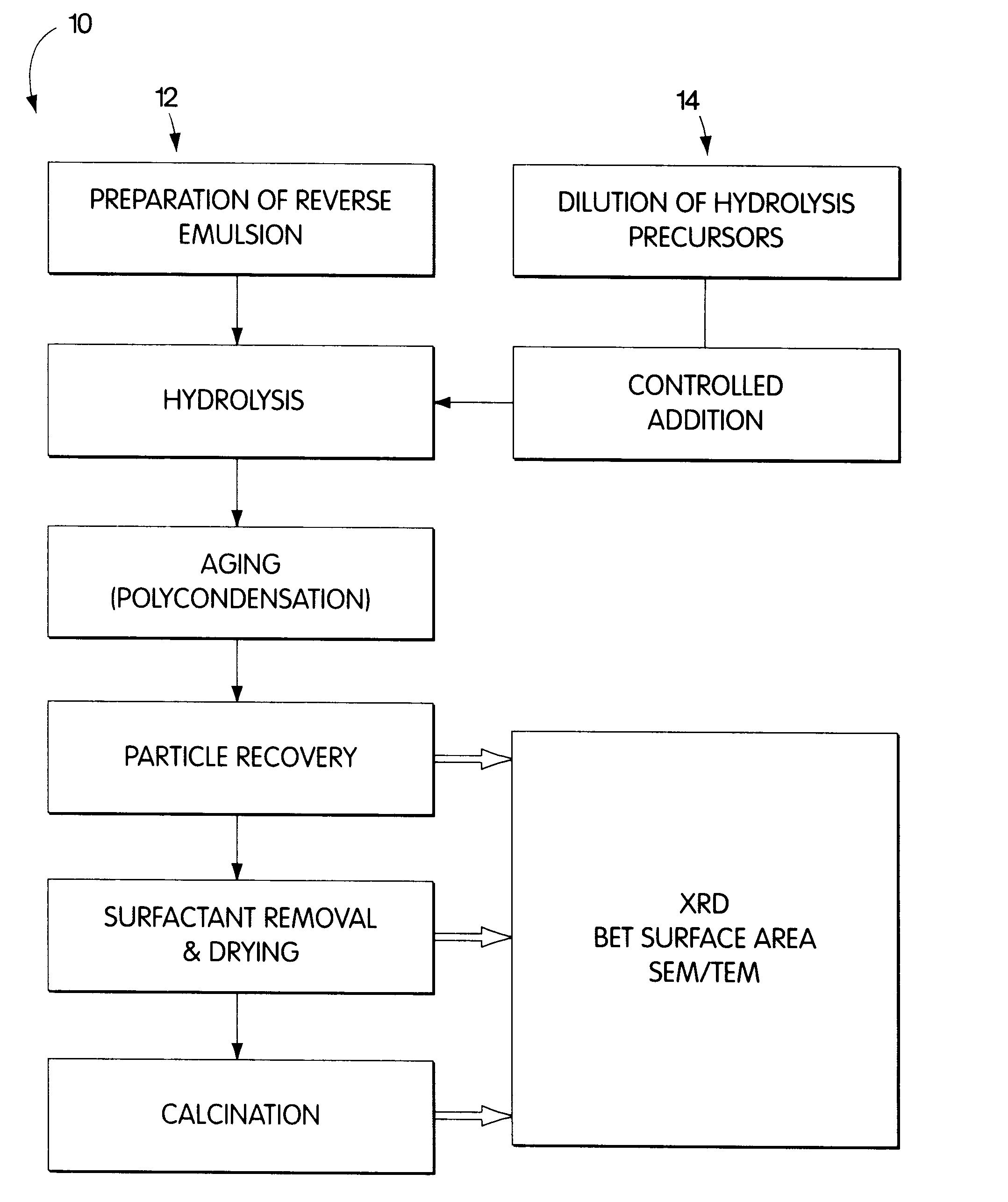
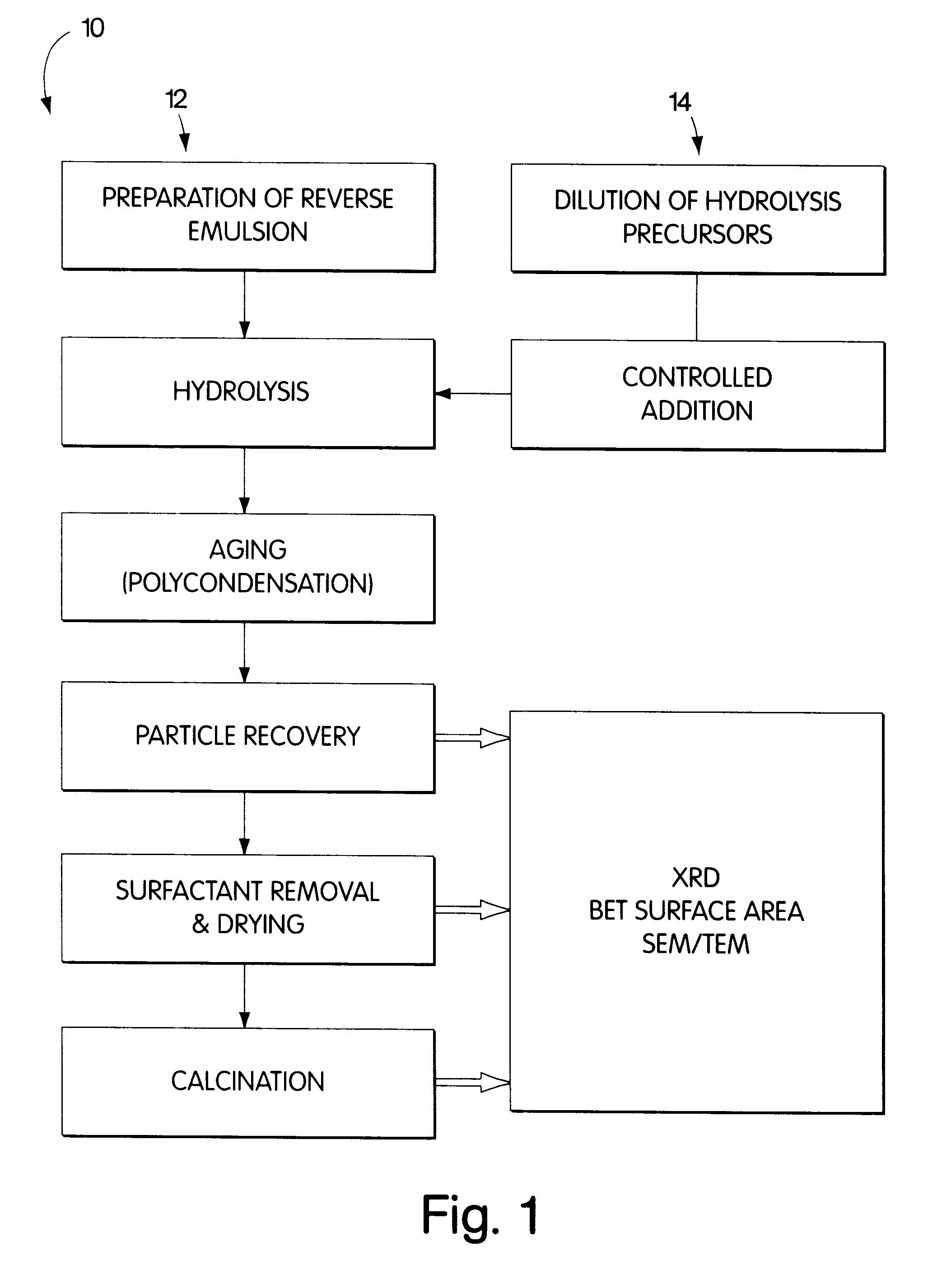
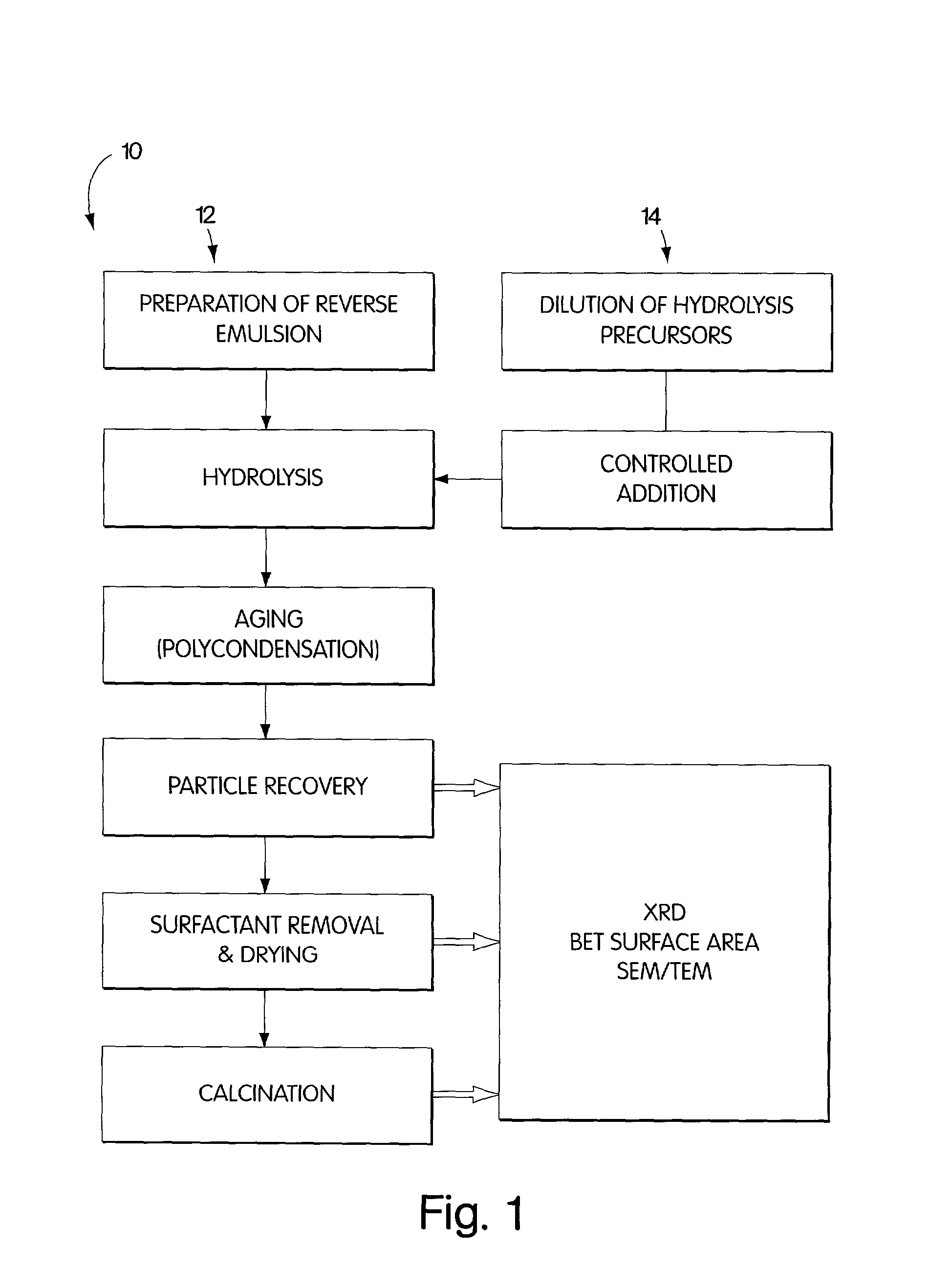
Synthesis of nanometer-sized particles by reverse micelle mediated techniques
The present invention relates to a method of producing particles having a particle size of less than 100 nm and surface areas of at least 20 m2 / g where the particles are free from agglomeration. The method involves synthesizing the particles within an emulsion having a 1-40% water content to form reverse micelles. In particular, the particles formed are metal oxide particles. The particles can be used to oxidize hydrocarbons, particularly methane.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation of polysaccharide beads
The present invention relates a method of preparing agarose beads, which method results in a population of beads which are of relatively uniform particle size. In an advantageous embodiment, the beads are of a particle size less than 10 μm, and the coefficient of variation C.V. of the population is less than 15%. The beads according to the invention are advantageously used in biological separation methods, such as in the production of chromatographic packing materials; drug carriers; or in any method of biological engineering.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
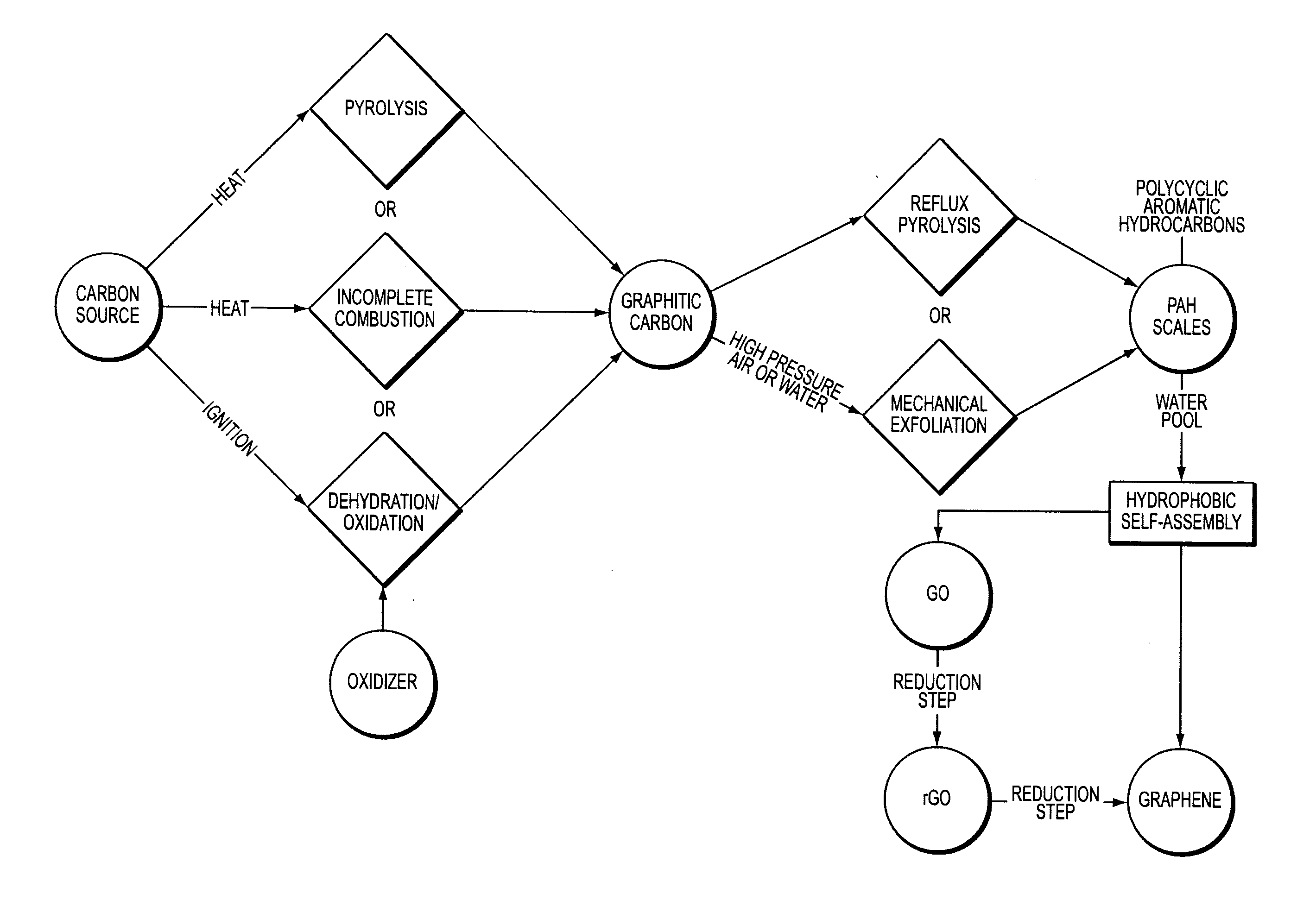
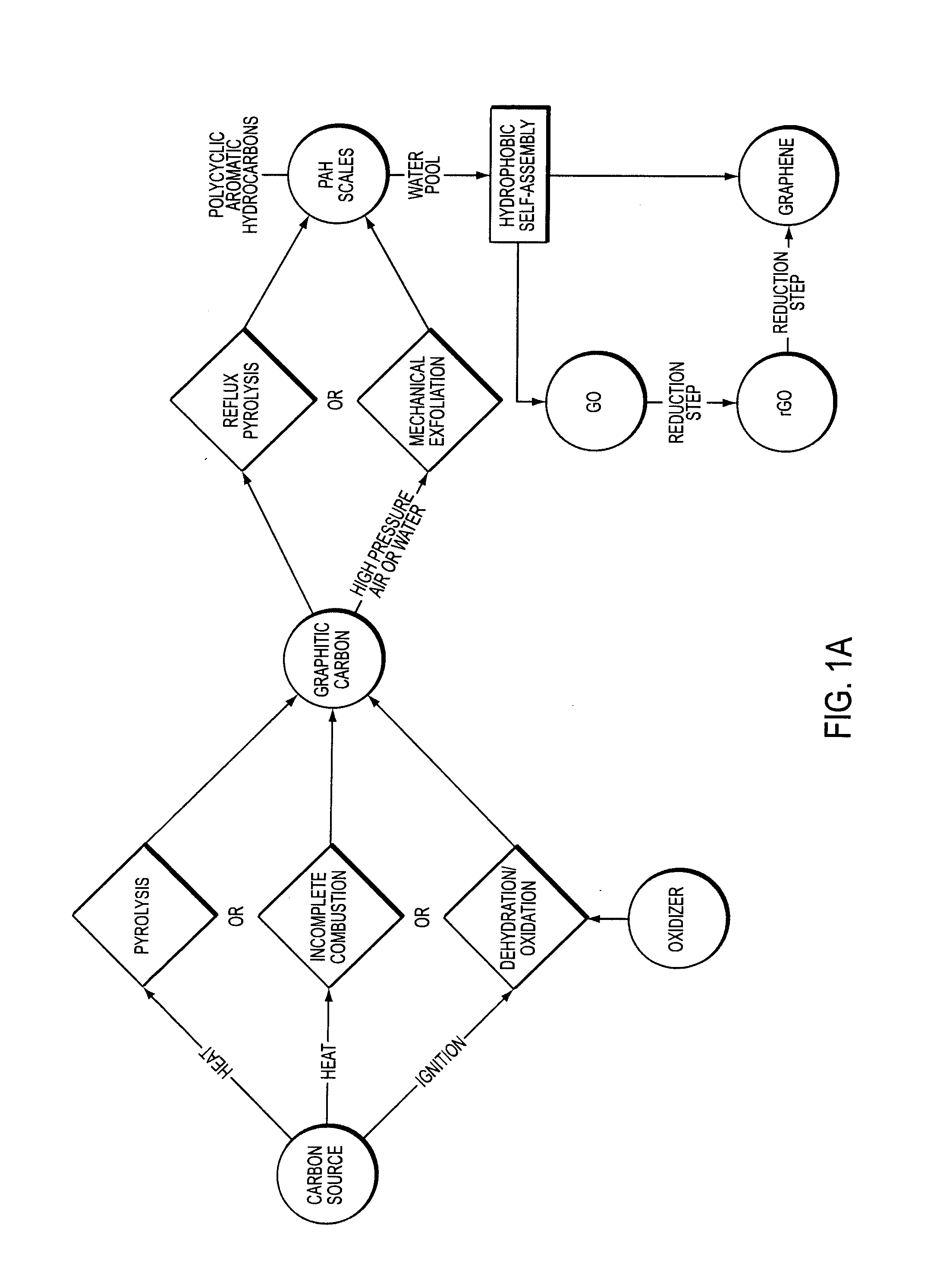
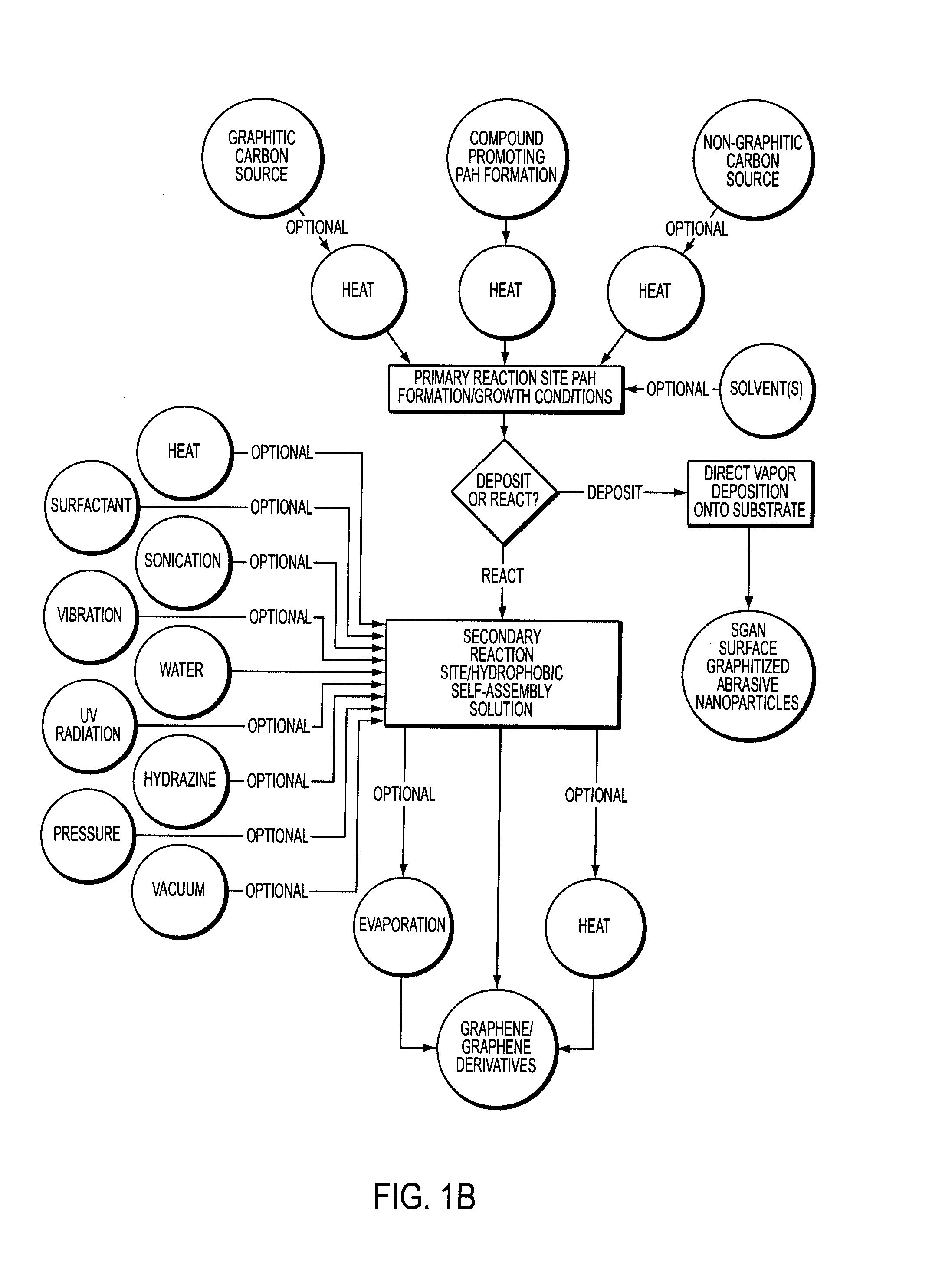
Facile synthesis of graphene, graphene derivatives and abrasive nanoparticles and their various uses, including as tribologically-beneficial lubricant additives
ActiveUS20140134092A1Reduce frictionImprove smoothnessMaterial nanotechnologyCosmetic preparationsNanoparticleGraphene derivatives
Owner:PEERLESS WORLDWIDE
Synthesis of nanometer-sized particles by reverse micelle mediated techniques
InactiveUS20020110519A1Reduce rateMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideEmulsionNanometre
The present invention relates to a method of producing particles having a particle size of less than 100 nm and surface areas of at least 20 m2 / g where the particles are free from agglomeration. The method involves synthesizing the particles within an emulsion having a 1-40% water content to form reverse micelles. In particular, the particles formed are metal oxide particles. The particles can be used to oxidize hydrocarbons, particularly methane.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hydrogels and hydrogel particles
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Material and applications therefor
ActiveUS20130180912A1Increase temperatureLarge inter-sheet spacingMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsPolymer scienceDispersed media
A gel film or an isolated gel film comprising sheets of graphene or chemically converted graphene at least partially separated by a dispersion medium, such as water, and arranged in a substantially planar manner to form an electrically conductive matrix.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Cosmetic and/or pharmaceutical emulsions
A cosmetic and / or pharmaceutical composition containing: (a) an oil component; (b) a viscosity modifier selected from the group consisting of a C6-22 hydroxyfatty acid, a salt of a C6-22 hydroxyfatty acid, and mixtures thereof; and (c) water.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
Microfluidic technology for one-step continuous preparation of calcium alginate microgel
ActiveCN107930542AFast shippingMaintain biological activityLaboratory glasswaresGel preparationOil phaseWater in oil emulsion
The invention relates to a microflow droplet technology-based method for one-step continuous preparation of multi-chamber calcium alginate microgel for immobilization of bioactive substances. The method realizes high-throughput continuous production of a microgel material. The method comprises forming a parallel and stable flow field through different hydrogel prepolymer solutions in a microfluidic channel, pouring the hydrogel prepolymer solutions for forming different chambers of the microgel into a microfluidic chip to form water phase solutions of multiple phase parallel fluids, mixing thewater phase solutions and an immiscible fluid (oil phase) through a T-shaped channel or a fluid focusing design to obtain water-in-oil emulsion drops and then alginic acid in the drops is linked immediately so that multi-chamber microgel is prepared, and cleaning the emulsion drops on the microfluidic chip so that the microgel is fast conveyed into a water phase. The method realizes one-step preparation of the calcium alginate microgel immobilized with bioactive substances and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUA NOVA BIOTECH LTD
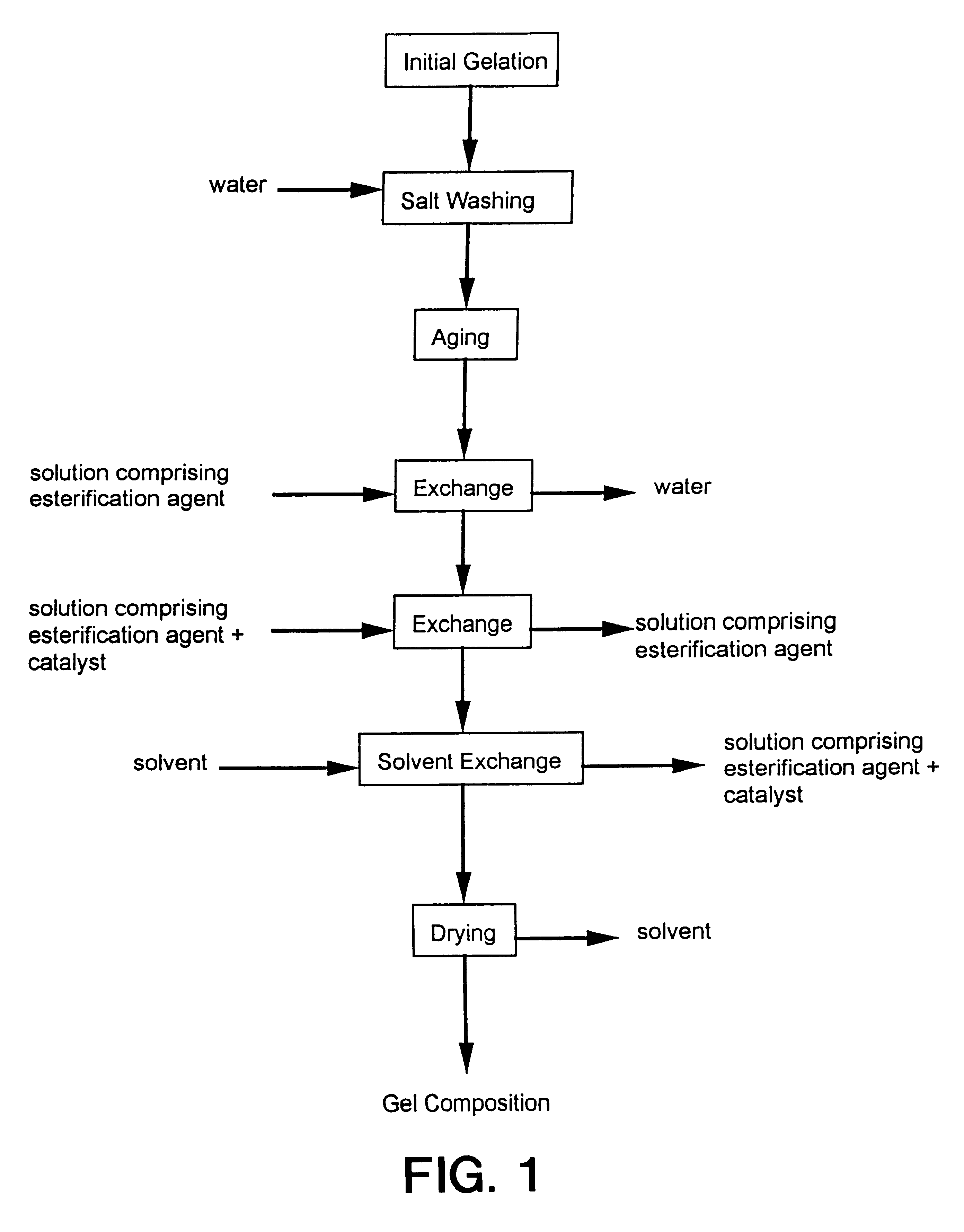
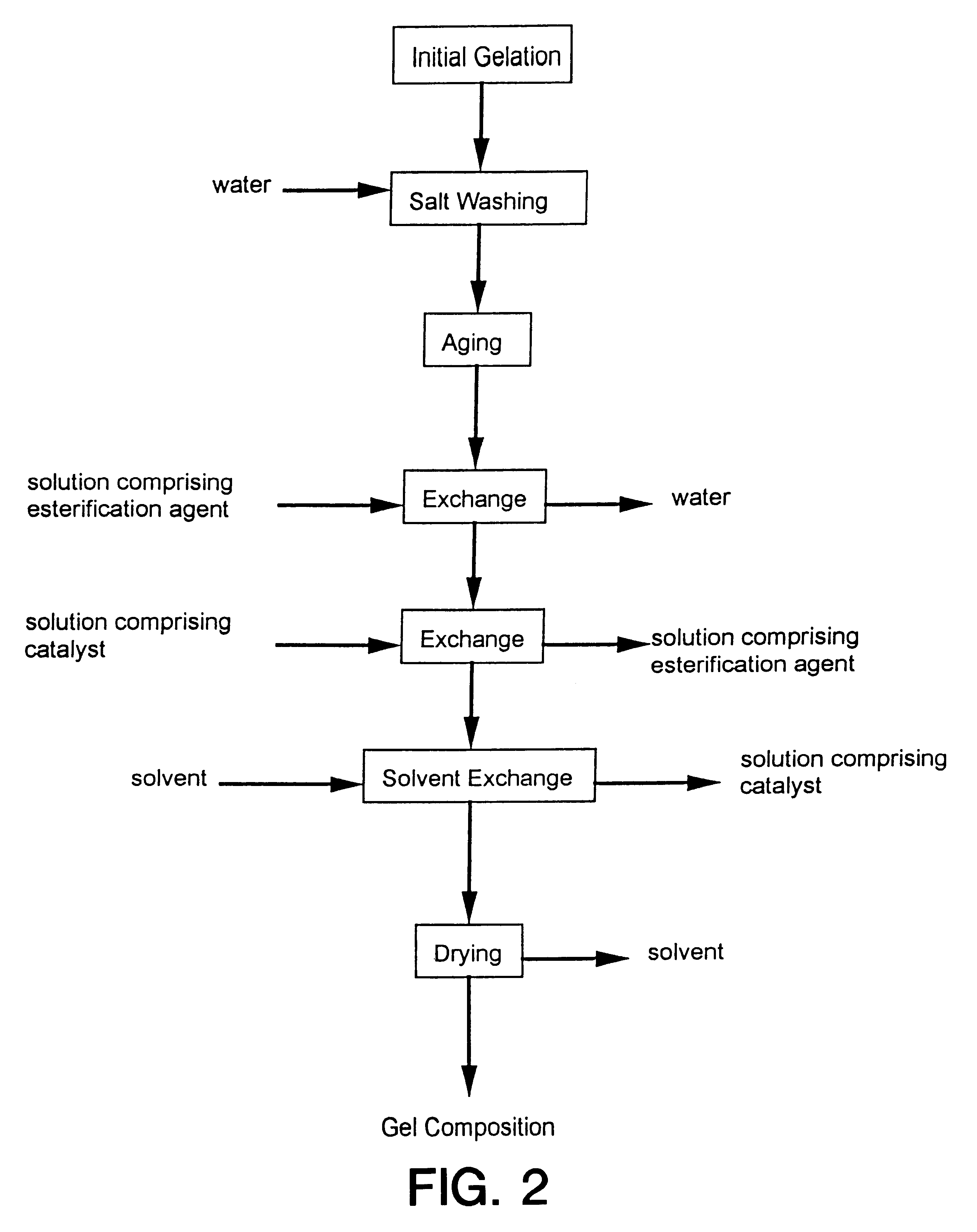
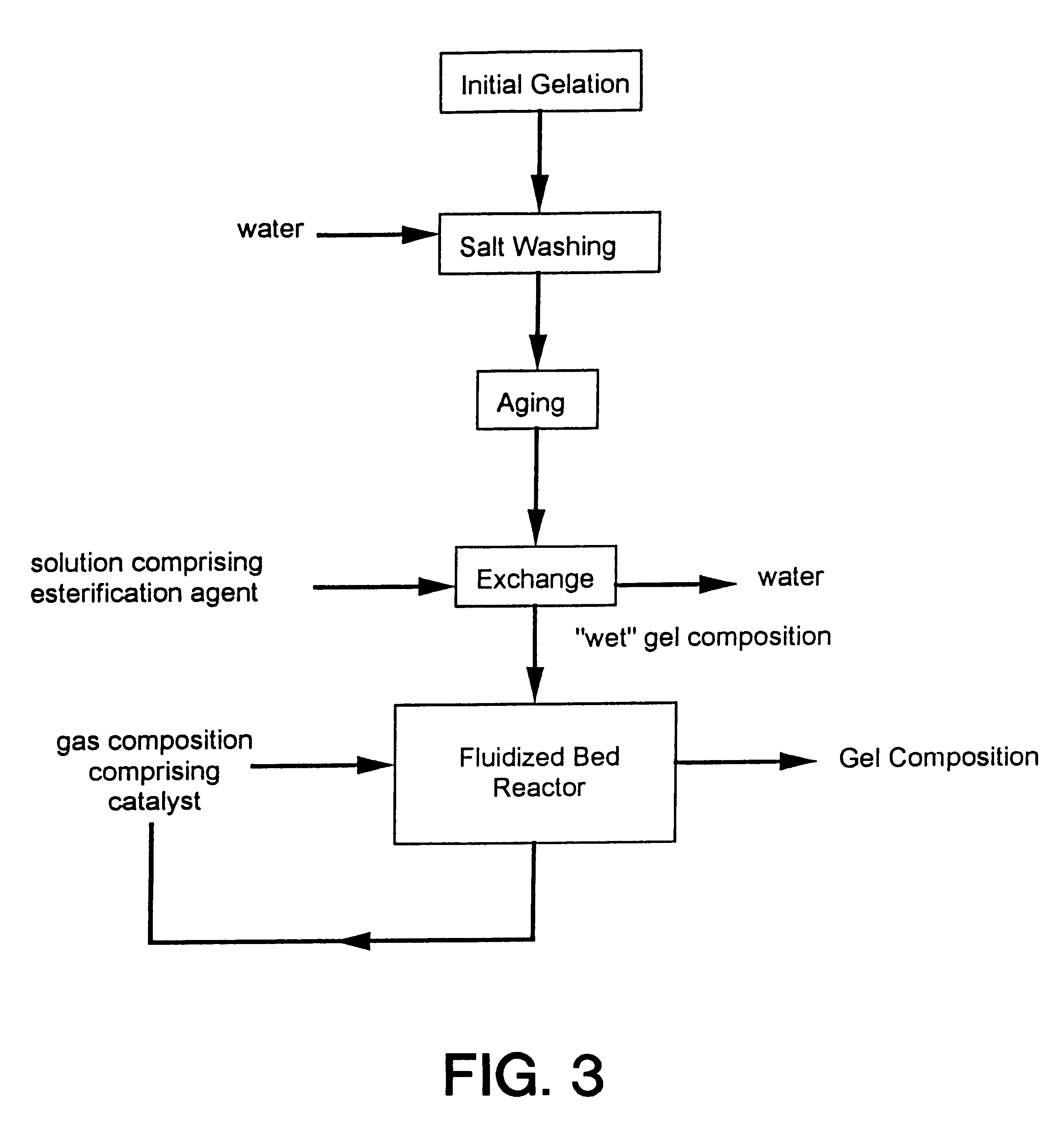
Process for producing low density gel compositions
InactiveUS6172120B1Data processing applicationsOxide/hydroxide preparationSupercritical dryingComposition process
Processes for producing gel compositions comprising: esterifying a portion of the surface of a gel composition sufficient to produce a gel composition having a rod density of less than or equal to 0.15 g / cc, and / or a tap density of less than or equal to 0.2 g / cc through contact with at least one esterification agent and at least one catalyst. The processes may be utilized to produce low density gel compositions without the need for a supercritical drying step or thermal treatment.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Intelligent polymerized crystalline colloidal array carbohydrate sensors
InactiveUS7105352B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
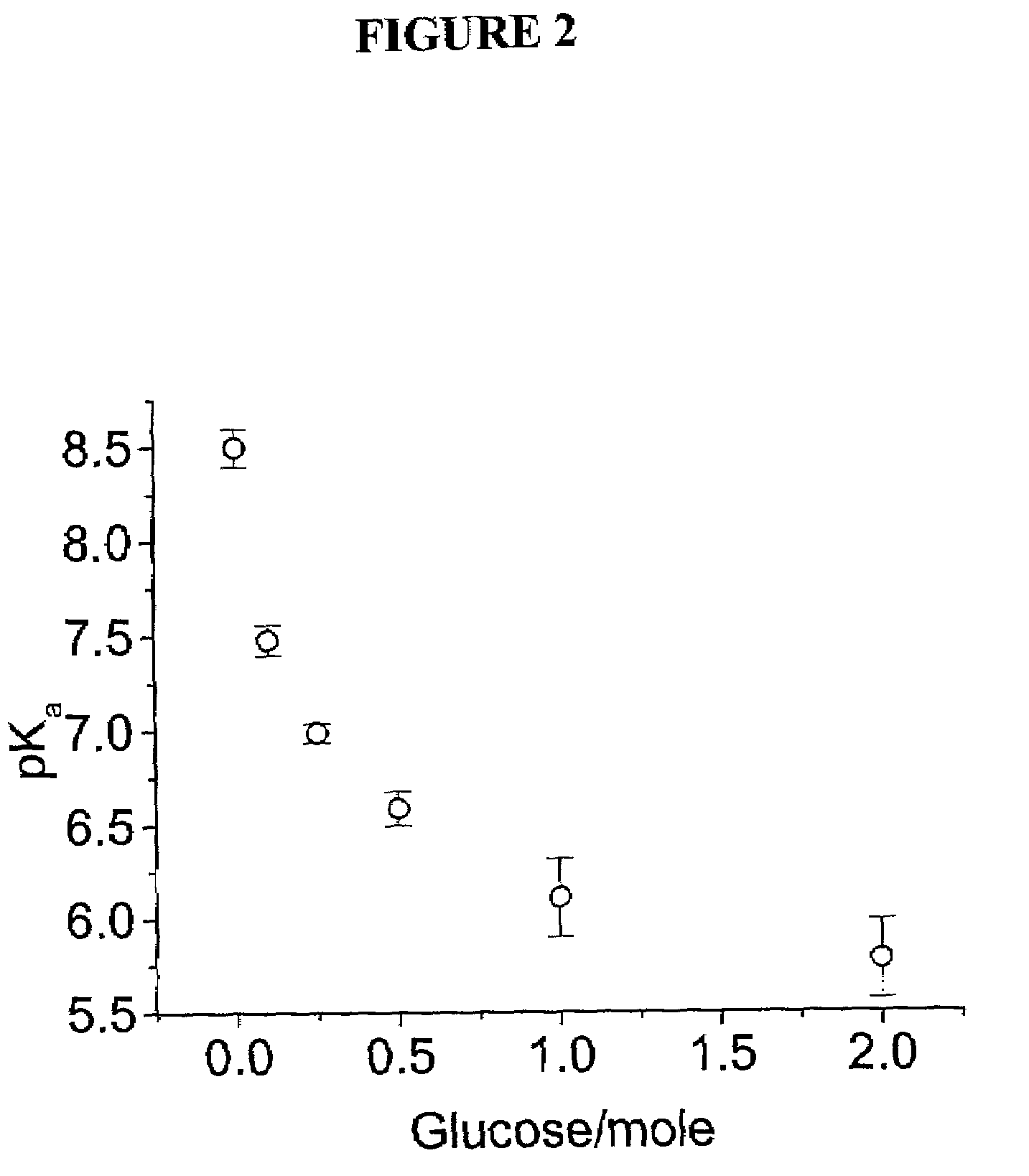
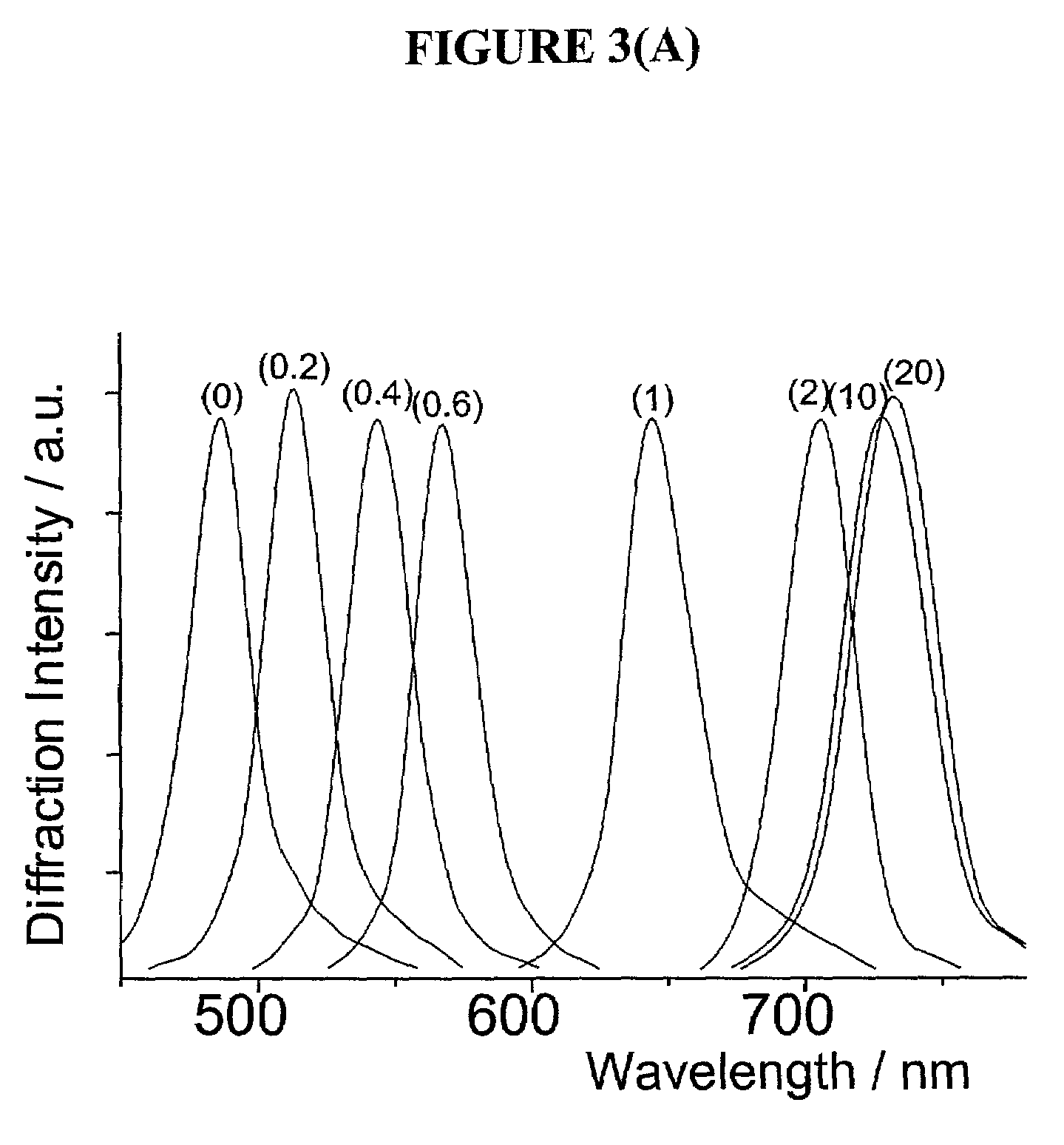
The present invention is related to glucose sensors that are capable of detecting the concentration or level of glucose in a solution or fluid having either low or high ionic strength. The glucose sensors of the present invention comprise a polymerized crystalline colloidal array (PCCA) and a molecular recognition component capable of responding to glucose. The molecular recognition component may be a boronic acid, such as a phenylboronic acid, glucose oxidase, a combination of phenylboronic acid and poly(ethylene)glycol or crown ether, or another component capable of detecting glucose in various fluids and solutions. The glucose sensors of the present invention may be useful in the development of noninvasive or minimally invasive in vivo glucose sensors for patients having diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Clear, polymeric gel composition and method for producing the same
Disclosed is a clear, crosslinked, polymeric gel composition that is the reaction product of a microemulsion containing (a) from 1-70 wt. %, preferably from 1-40 wt. %, and more preferably from 10-25 wt. % of an anhydride functionalized polymer, (b) from 0.1-40 wt. %, preferably from 0.1-20 wt. %, and most preferably from 0.5-5 wt. % of a cross-linking agent, (c) from 0.01-50 wt. %, preferably from 0.1-20 wt. %, and more preferably from 0.5-10 wt. % surfactant, (d) from 0.01-30 wt. %, preferably from 0.1-10 wt. %, and more preferably from 0.1-5 wt. % water, and (e) from 10.0-95.0 wt. % of a hydrophobic liquid, based on the total weight of the polymeric gel composition. The gel composition is prepared by combining the anhydride functionalized polymer, the cross-linking agent, the surfactant, the water, and the hydrophobic liquid-form a microemulsion and then gelling the microemulsion.
Owner:INT FRAGRANCE & TECH
Polytetrahydrofuran-Based Coating for Capillary Microextraction
InactiveUS20060013981A1Avoid breakingLayered productsPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteGas phase
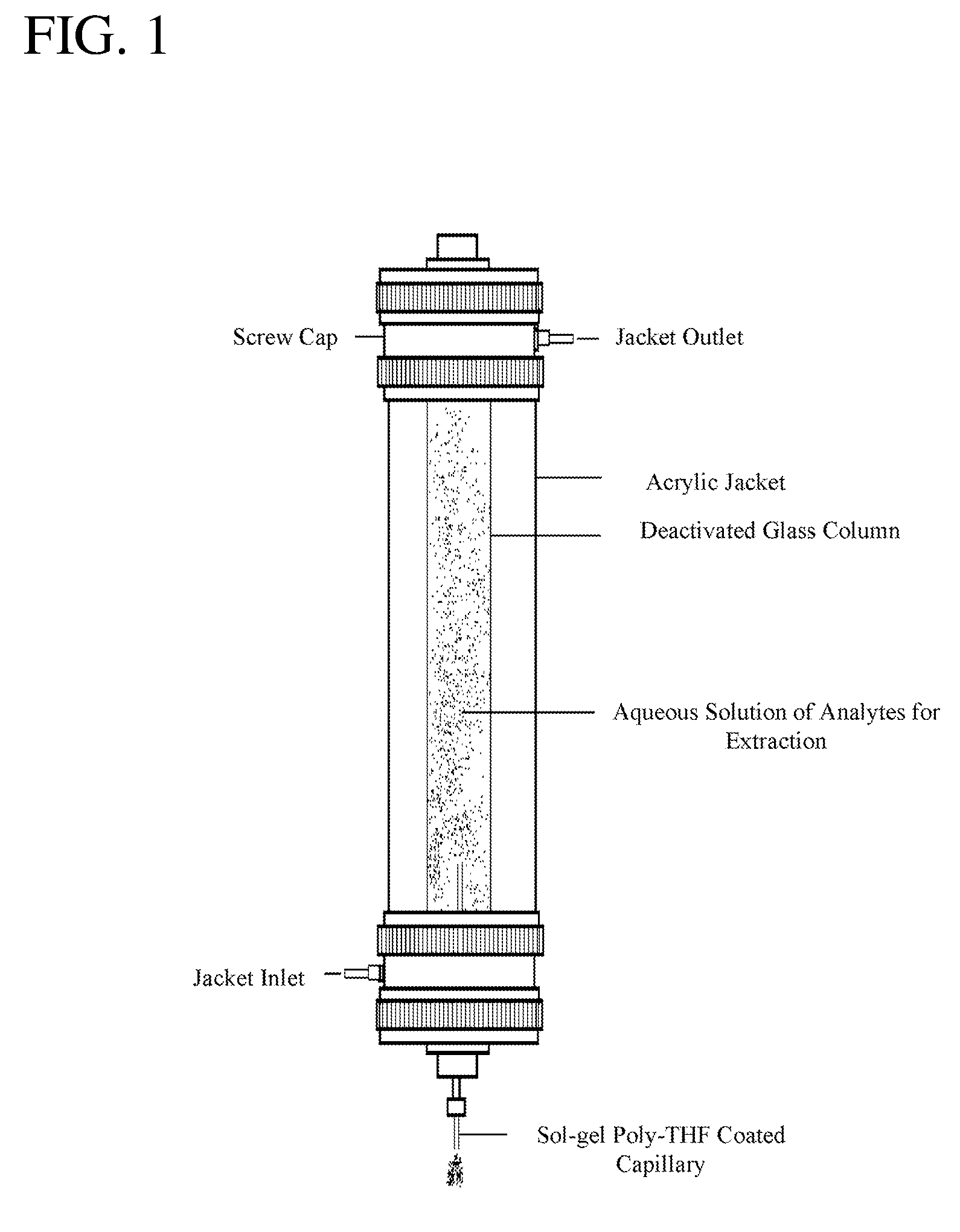
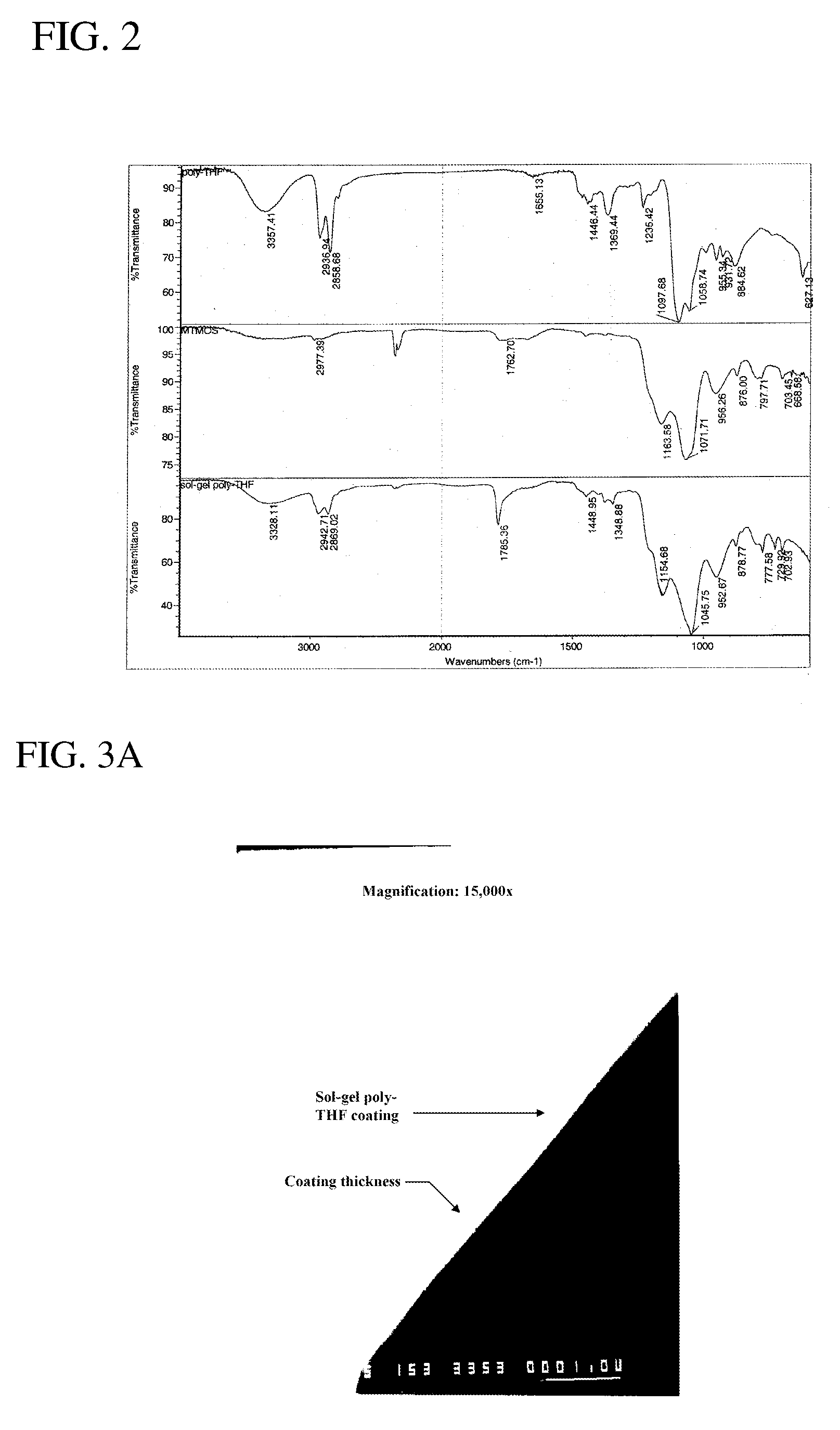
A sol-gel poly-THF coating was developed for high-performance capillary microextraction to facilitate ultra-trace analysis of polar and nonpolar organic compounds. Parts per quadrillion level detection limits were achieved using Poly-THF coated microextraction capillaries in conjunction with GC-FID. Sol-gel Poly-THF coatings showed extraordinarily high sorption efficiency for both polar and nonpolar compounds, and proved to be highly effective in providing simultaneous extraction of nonpolar, moderately polar, and highly polar analytes from aqueous media. Sol-gel poly-THF coated microextraction capillaries showed excellent thermal and solvent stability, making them very suitable for hyphenation with both gas-phase and liquid-phase separation techniques, including GC, HPLC, and CEC. In CME-HPLC and CME-CEC hyphenations, sol-gel poly-THF coated microextraction capillaries have the potential to provide new levels of detection sensitivity in liquid-phase trace analysis, and to extend the analytical scope of CME to thermally labile-, high molecular weight-, and other types of compounds that are not amenable to GC.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Multifunctional Supramolecular Hydrogels as Biomaterials
The present invention provides supramolecular hydrogels having a three-dimensional, self-assembling, elastic, network structure comprising non-polymeric, functional molecules and a liquid medium, whereby the functional molecules are noncovalently crosslinked. The functional molecules may be, for instance, anti-inflammatory molecules, antibiotics, metal chelators, anticancer agents, small peptides, surface-modified nanoparticles, or a combination thereof. Applications of the present invention include use of the supramolecular hydrogel, for instance, as a biomaterial for wound healing, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and drug / inhibitor screening.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stabilizer composition of co-attrited microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose, method for making, and uses
Methods of making a high gel strength, water-dispersible, stabilizing colloidal microcrystalline cellulose composition are disclosed. This stabilizer composition is useful in many food and non-food applications.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION USA INC
Hydrogel materials with crystalline colloidal array of watervoids for detection and macromolecule separations
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Organogel particles
InactiveUS6858666B2Plastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsParticulatesAdditive ingredient
A method forms self-sustaining particles that comprise a hydrophobic (oleophilic) phase in particulate form, with no need for a rigid shell to encapsulate the phase, and usually with no shell present. The oleophilic phase contains a gelation agent, and preferably an organogelation agent. The particles may be stored alone or in a minor amount (e.g., less than 40% by volume) of water to assist their stability and act as a barrier against their coalescence. These water-separated compositions are not necessarily dispersions or suspensions, but may be merely particles in an aqueous storage environment. The particles have prolonged stability and can be readily, simply, and inexpensively formed. A simple method of manufacture comprises forming a solution of the ingredients (e.g., at least the oleophilic material and gelation agent) at a temperature above their gelation temperature, forming droplets or molten, or liquid or flowable particles of the solutions, and cooling the droplets to form the particulates. Cooling may be effected by exposure to ambient conditions (e.g., room temperature) when the ingredients are properly selected, or an actual cooling environment may be needed.
Owner:AVEKA INC
Ashless Controlled Release Gels
The present invention relates to a control release gel for delivery of additives free of producing ash to substantially free of producing ash into a lubricant. Further, the invention provides for a method of controlled release of additive(s) into the lubricant.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Flexible boron nitride nano-belt aerogel and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN109704296AImprove flexibilityIncrease elasticityMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsNitrogenBoron nitride
The invention discloses flexible boron nitride nano-belt aerogel and a preparation method therefor. The flexible boron nitride nano-belt aerogel has a communicating three-dimensional porous network structure, wherein the three-dimensional porous network structure is formed through interwinding and lapping boron nitride nano-belts and is made of macropores with a pore size greater than 50nm, mesopores with a pore size of 2nm to 50nm and micropores with a pore size smaller than 2nm. The preparation method comprises the steps of subjecting boric acid and a nitrogen-containing precursor to high-temperature digestion so as to form a transparent precursor solution, then, preparing precursor aquagel, and then, carrying out drying and high-temperature pyrolysis, thereby obtaining the flexible boron nitride nano-belt aerogel. The boron nitride nano-belt aerogel disclosed by the invention has excellent flexibility and elasticity restorability, can bear outside loads of different forms in a widetemperature range and is restorable in elasticity; and the preparation process is mild in reaction conditions, easy in operation and low in cost, is concise, environmentally friendly and pollution-free and can achieve continuous production.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
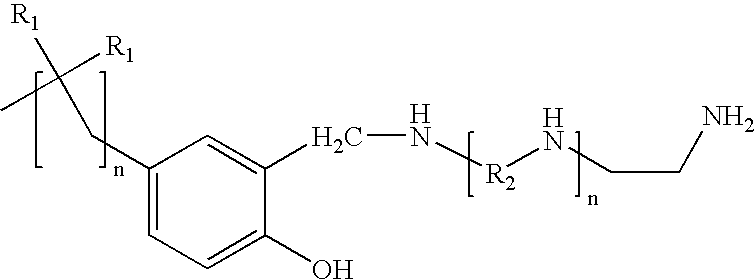
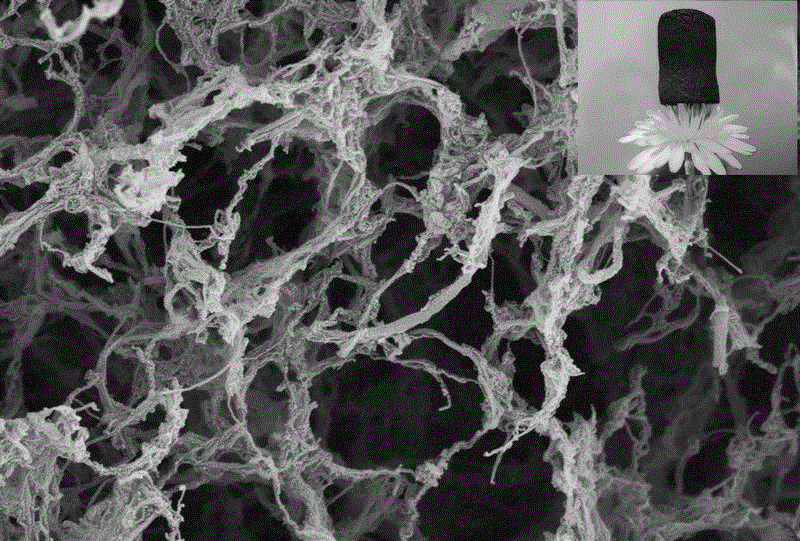
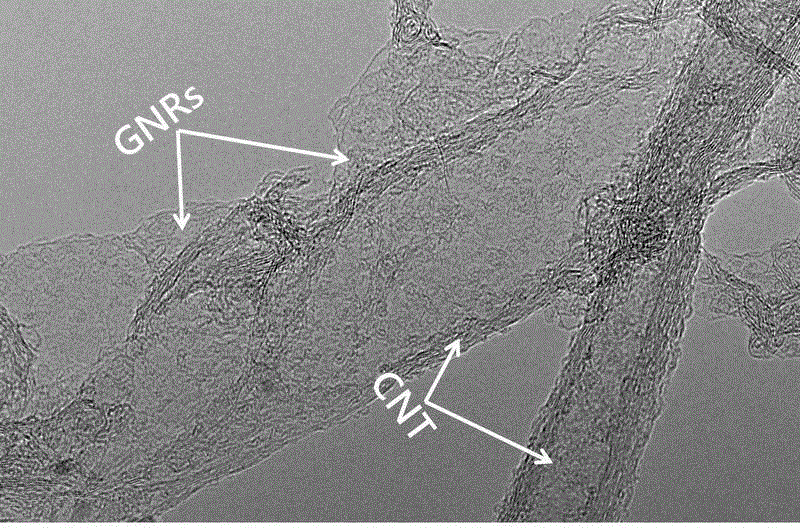
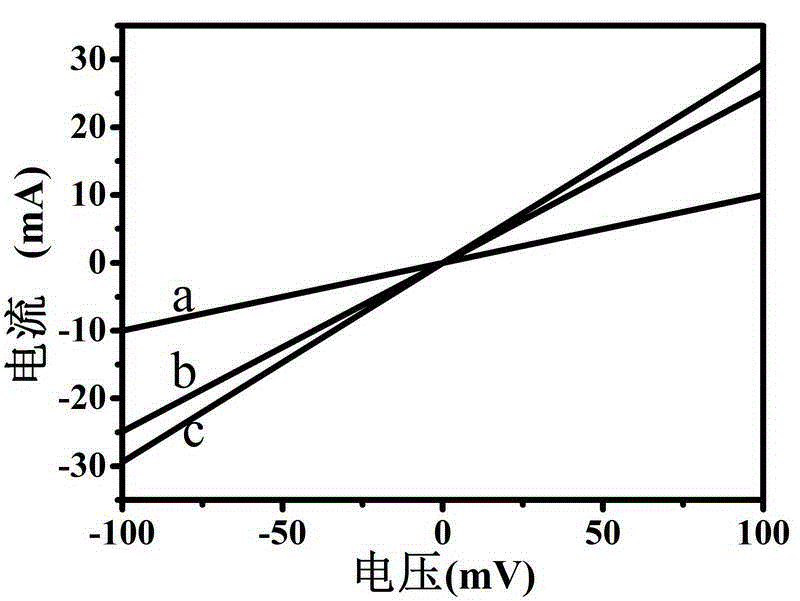
Heteroatom doped leaf-shaped carbon nanometer aerogel material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104437278AIncrease the areaUndamagedCell electrodesGel preparationCarbon nanotubeStructural unit
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials and particularly relates to a heteroatom doped leaf-shaped carbon nanometer aerogel material and a preparation method and an application of the heteroatom doped leaf-shaped carbon nanometer aerogel material. The carbon nanometer leaf is a biomimetic concept, a carbon nanometer tube is used for simulating the leaf vein of the leaf, a graphene nanoribbon is used for simulating the leaf, and the carbon nanometer leaf is a seamless bridged hybrid structure of the carbon nanometer tube and the grapheme nanoribbon. The aerogel is assembled by adopting the carbon nanometer leaves as basic structural units, and then a heteroatom doped three-dimensional net structure is realized. The preparation method of the aerogel comprises the following steps: preparing a carbon nanometer leaf solution, adding moderate amount of soluble dopants to the solution, and then carrying out hydrothermal to obtain uniform hydrogel, and then drying and charring to obtain the heteroatom doped carbon nanometer leaf aerogel. The aerogel can be used as a cathode catalyst of the fuel cell, and has a catalytic performance better than that of the commercial Pt / C and the potential application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
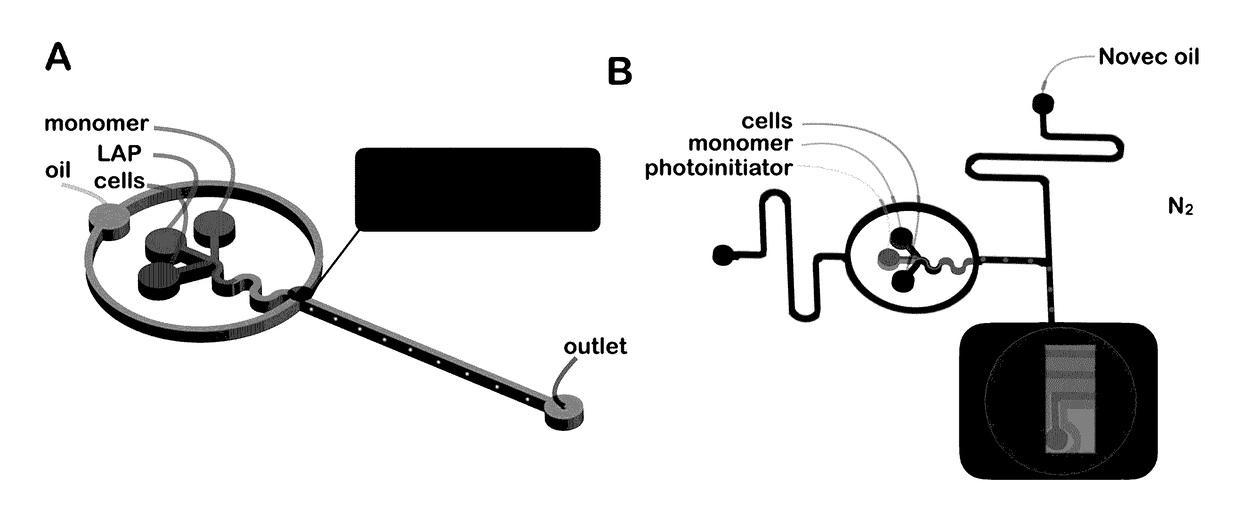
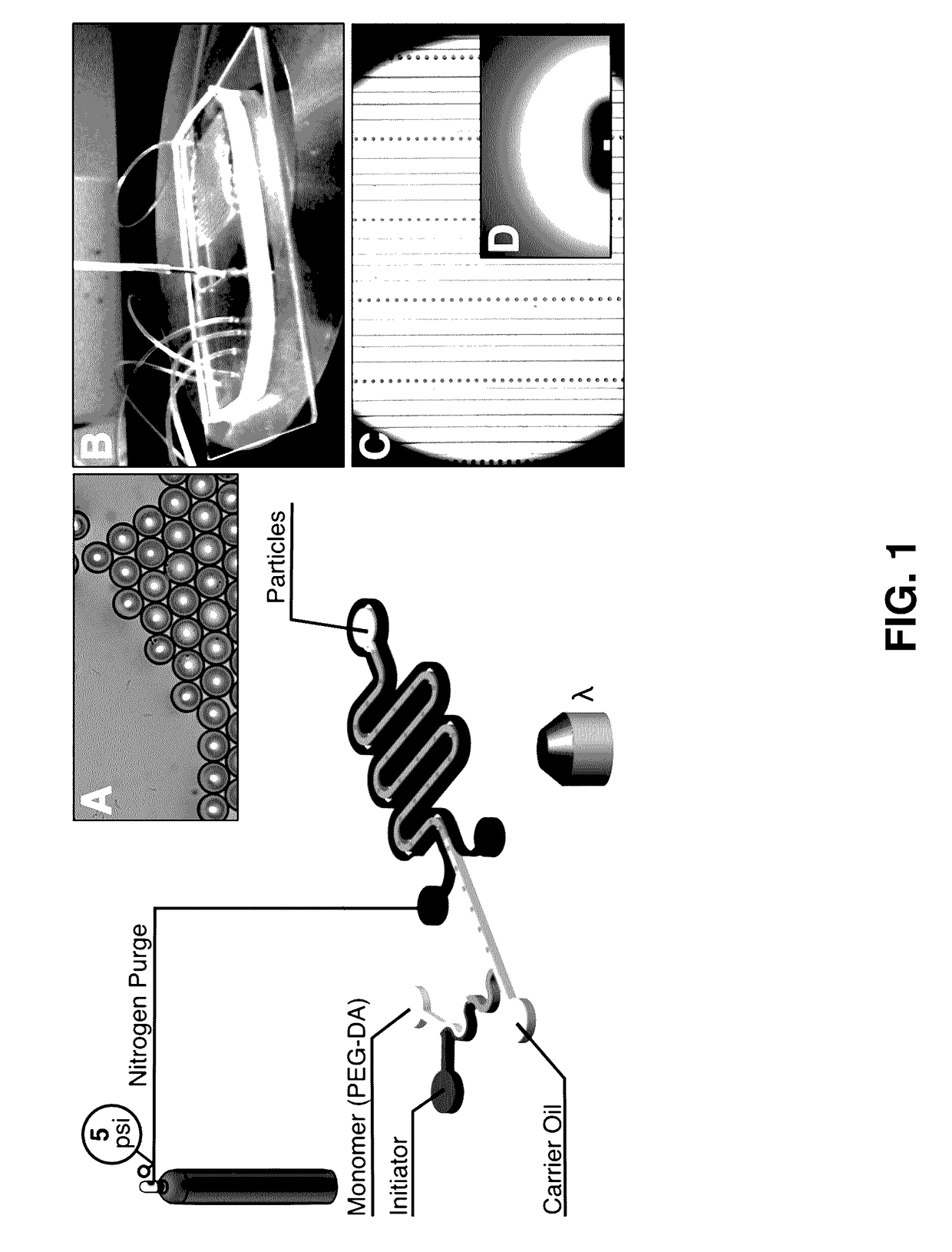
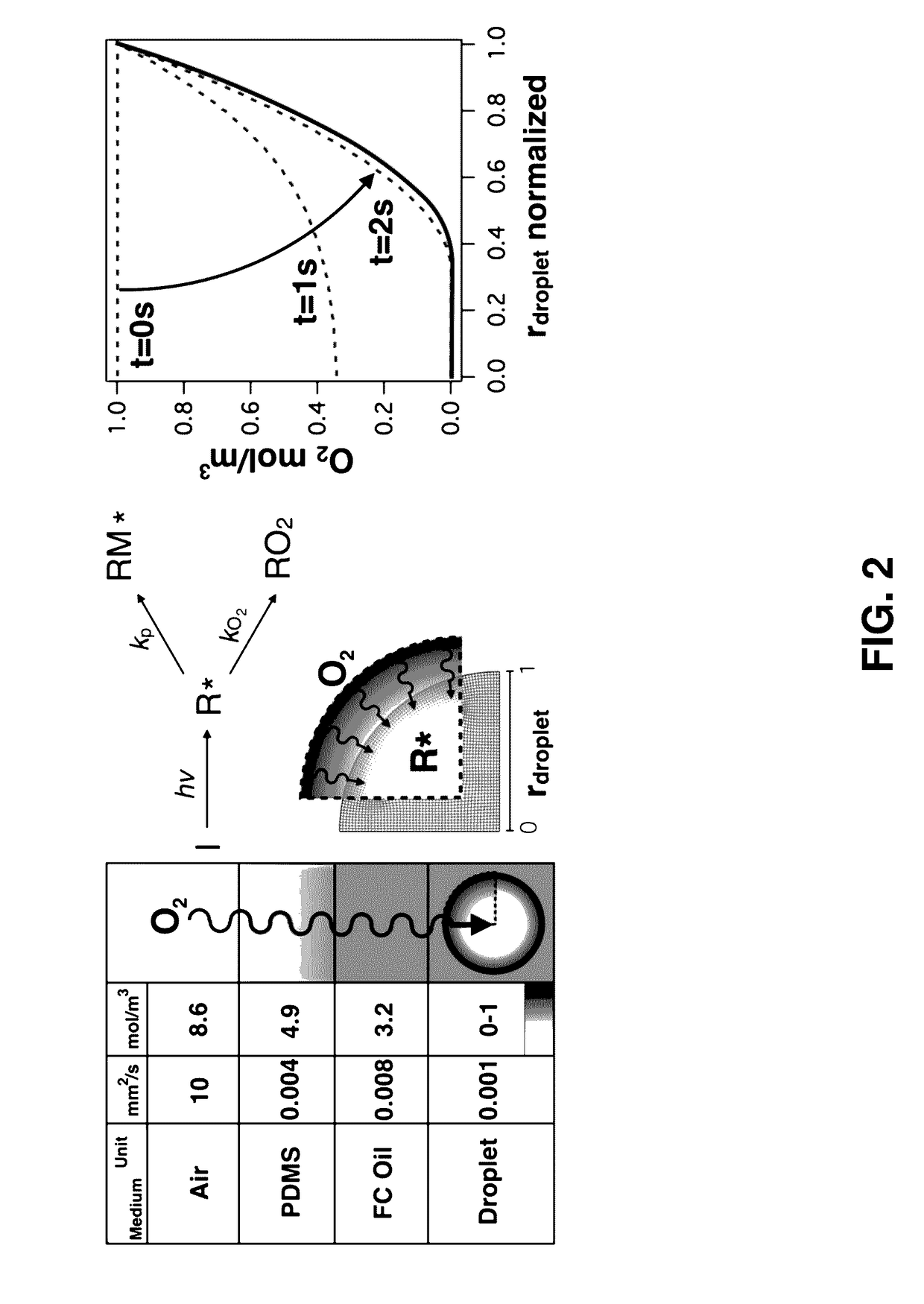
Methods of Generating Microparticles and Porous Hydrogels Using Microfluidics
PendingUS20170145169A1Ability to control the amount of oxygen presentInhibition of polymerizationFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMicrofluidicsAqueous droplet
Provided herein are methods utilizing microfluidics for the oxygen-controlled generation of microparticles and hydrogels having controlled microparticle sizes and size distributions and products from provided methods. The included methods provide the generation of microparticles by polymerizing an aqueous solution dispersed in a non-aqueous continuous phase in an oxygen-controlled environment. The process allows for control of size of the size of the aqueous droplets and, thus, control of the size of the generated microparticles which may be used in biological applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel
The invention discloses gelators PC5 based on naphthalimide functionalized pillar[5]arene. Organic supramolecular gel PC5G with yellow aggregate state induced fluorescence can be formed by the gelators in a cyclohexanol solution under the external-wall pi-pi action. When Fe<3+> is added to PC5G, Fe<3+> can produce cation-pi action with naphthalimide, and the external-wall pi-pi action between thegelators is damaged, as a result, fluorescence of PC5G is quenched; when H2PO4<-> is added to metallogel PC5-FeG after fluorescence quenching, H2PO4<-> and Fe<3+> are complexed, the external-wall pi-pi action of PC5G is restored again, and aggregate state induced fluorescence appears again, so that continuous reversible supersensitive detection for Fe<3+> and H2PO4<-> is realized. Besides, the organic supramolecular gel PC5G can remove Fe<3+> from an aqueous solution very well, and removal rate is up to 99.42%.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Acetal-substituted glucosamide, preparation method and method for preparing supramolecular gel
InactiveCN104478847AThixotropicHigh response rateOrganic chemistryFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesDyeing wastewaterSupramolecular assembly
The invention discloses acetal-substituted glucosamide, a preparation method and a method for preparing a supramolecular gel. The acetal-substituted glucosamide is as shown in formula I (as shown in Specification), wherein n is selected from 1-10, 12, 14, 16 or 18. The supramolecular gel formed from the acetal-substituted glucosamide disclosed by the invention in a solution is thixotropic, high in recovery rate and controllable. The gel factors are capable of achieving oil and water separation, dye wastewater purification and the like. The supramolecular gel can be used for preparing coatings, ink and lubricants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Isothermal preparation of heat-resistant gellan gels with reduced syneresis
InactiveUS20090104141A1Other chemical processesSedimentation separationGellan gumSphingomonas elodea
A gel comprising a deacylated gellan gum, an effective amount of a sequestrant, an effective amount of a syneresis control agent, and a gelation inducer is described. Also methods for making the gel are disclosed including a method for forming heat-resistant gels comprising mixing deacylated gellan gum and xyloglucan; hydrating the blend; resting the hydrated blend until a gel forms. The gels can be used in a variety of applications such as air freshener gels.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
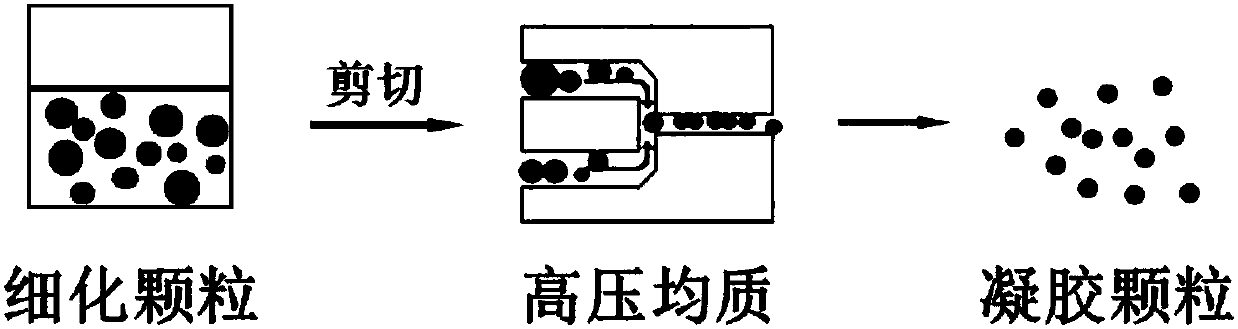
Polymer gel particles, preparation method thereof, composite gel particles containing polymer gel particles and application of composite gel particles
ActiveCN107855080AImprove hydrophilicityGood bioadhesionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention provides polymer gel particles, a preparation method thereof, composite gel particles containing the polymer gel particles and an application of the composite gel particles. The Young modulus of the polymer gel particles is 5-5000Pa, the average particle size is 100nm-100[mu]m, the polydispersity index is less than 0.5, and an organic solvent is not contained. The polymer gel particles are obtained by the following steps: performing cross-linking on a polymer aqueous solution to form a hydrogel with a Young modulus of 5-5000Pa, then performing preliminary crushing and refining onthe hydrogel, and using a fluid shearing method to prepare the polymer gel particles. The composite gel particles include the above polymer gel particles, and a functional substance supported on thepolymer gel particles. According to the method provided by the invention, organic solvents or surfactants are not used in the process of preparing the polymer gel particles, the obtained polymer gel particles are safe and reliable, the particle size is controllable in the range from the nanometer to the micrometer, the particle sizes are uniform, and the prepared composite gel particles can be used in the fields of biomedicines and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composition in gel form comprising carbon nanotube and ionic liquid and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20050156144A1Improve workabilityEasy to processMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsCarbon nanotubeSolvent
Disclosed is a novel technology, by which carbon nanotubes can be easily worked without degrading the characteristic properties thereof A gel composition comprising a carbon nanotube and an ionic liquid is produced by pulverizing, in the presence of the ionic liquid, the carbon nanotube by applying a shearing force thereto, and then, if needed, subjecting the product of the pulverization to centrifugal separation. The gel composition exhibits an excellent workability and can be worked simply by forming a desired shape by subjecting the composition in a fluidized state to application of an external force by such an operation as a printing, coating, extrusion or injection operation, and then removing the ionic liquid with a solvent or an absorbent.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
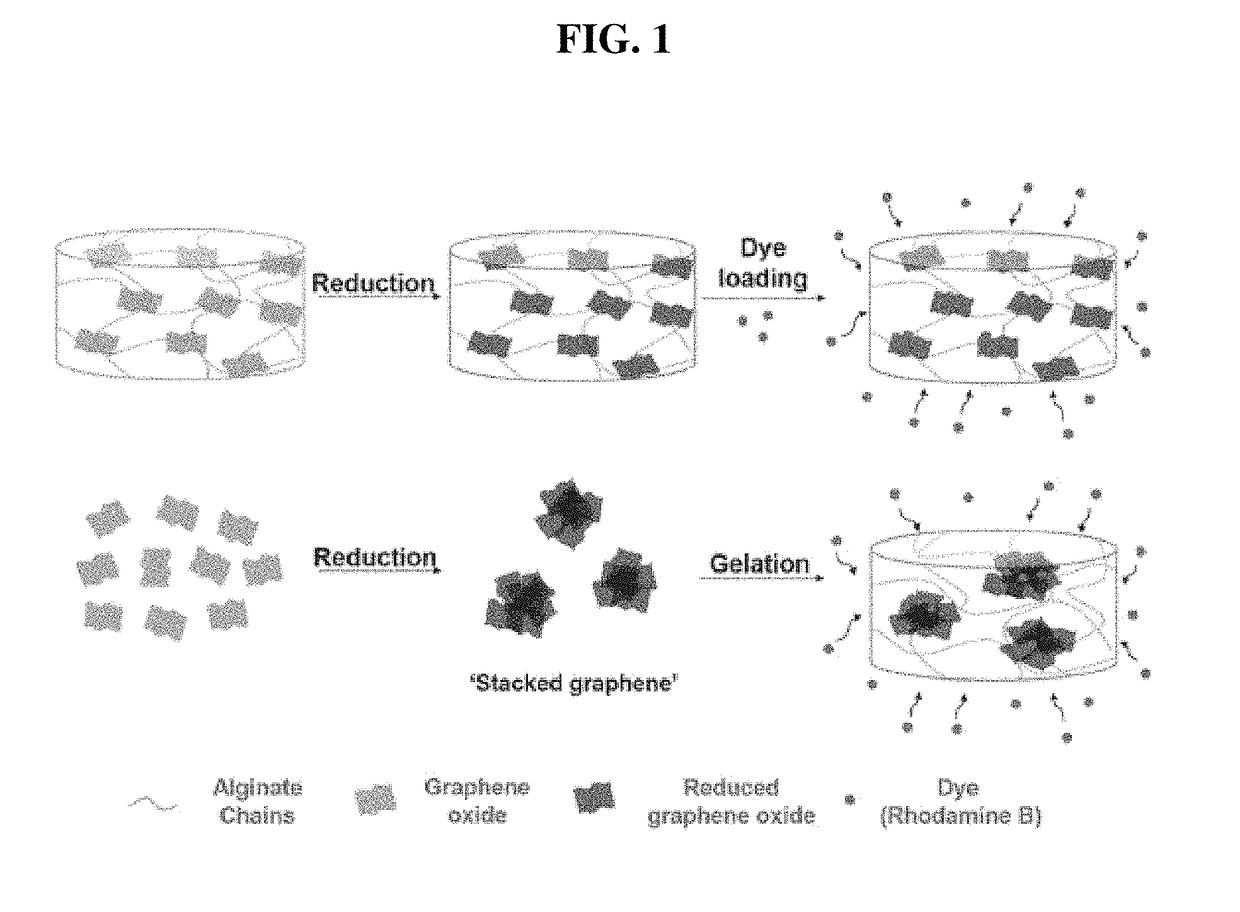
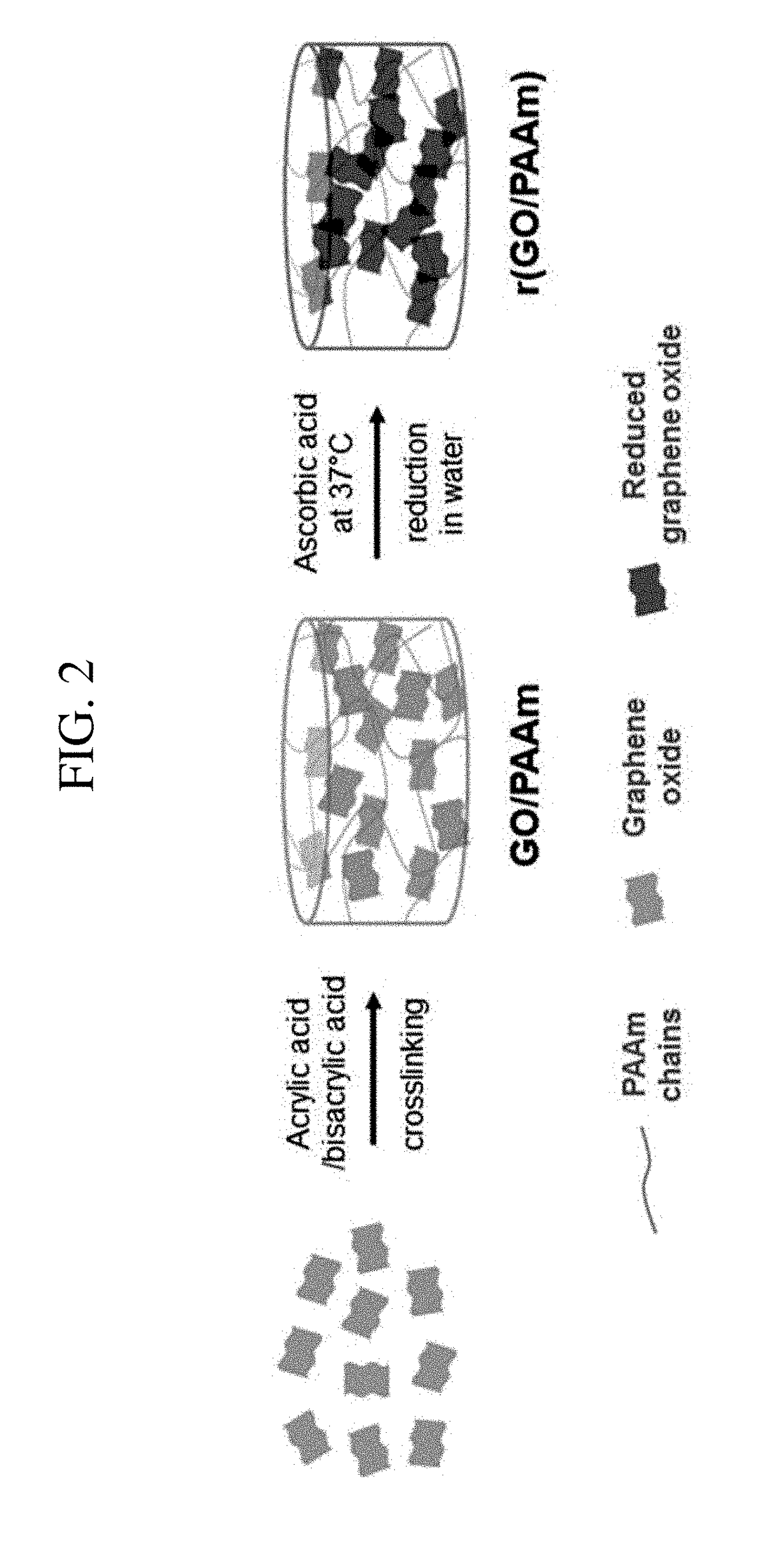
Method for preparing hydrogel containing reduced graphene oxide
InactiveUS20180193261A1Excellent dye adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityWater treatment compoundsAerosol deliveryGraphene derivativesPolyacrylamide Hydrogel
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a natural or synthetic polymer hydrogel loading graphene oxide or graphene, and to the selective and high-capacity adsorption and loading of the hydrogel with respect to a low-molecular weight material or a high-molecular weight material. More specifically, an alginate or polyacrylamide hydrogel loading graphene and a graphene derivative is prepared, wherein the hydrogel can be controlled to enable selective absorption according to the characteristics of an adsorbate by adjusting the reduction degree of graphene oxide, exhibits high adsorption capacity, and is easy to handle as a hydrate. These characteristics can significantly improve the adsorption efficiency with respect to a material in water or an organic phase material, compared with existing hydrogels.
Owner:AKROCELL BIOSCIENCES INC
Hydrogel containing protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108130321AIncrease enzyme activityAvoid mass transfer obstructionHydrolasesAlcoholic beverage preparationHydrophilic polymersProteinase activity
The invention discloses a hydrogel type enzyme catalytic material which contains protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower and is prepared through secondary immobilization synthesis, and a preparation method and applications thereof. According to the preparation method, protease is taken as an organic component, and is subjected to self-assembling with inorganic metal ions so as to obtain the protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower; the protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower is embedded with a gel carrier system which is excellent in biocompatibility and contains at least two hydrophilic polymers, repeat freezing-unfreezing method is adopted to obtain the hydrogel containing protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower. The unique tridimensional network of the hydrogel containing protease-inorganic hybrid nanoflower is capable of realizing stable existing of enzymes in a catalytic system, and secondary immobilization is achieved. According to the preparation method, secondary immobilization is adopted,so that protease is protected from external environment influences, enzyme stability is improved, enzyme reusability is improved. Separation of the catalytic material with reactants is not necessary,so that a step of separation of enzymes with substrates is avoided, and the application prospect in the field of enzyme immobilization is promising.
Owner:山东同益光刻胶材料科技有限公司
Method of preparing carbon aerogel precursor, carbon aerogel precursor prepared thereby, and carbon aerogel
ActiveUS20200330947A1Improve conductivityImprove machinabilityGraphiteCarbon nanotubesOrganic chemistryMaterials science
The present invention relates to a carbon aerogel precursor, a preparation method thereof and a carbon aerogel prepared thereby and, more particularly, to a carbon aerogel precursor which can be converted into a carbon aerogel that exhibits excellent specific surface area and physical properties by using a binder that has a low carbonization ratio and is capable of performing phase conversion while using a carbon material having physical properties such as diameter, length and the like that are not adjusted, a preparation method thereof, and a carbon aerogel prepared thereby.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MATERIALS SCI
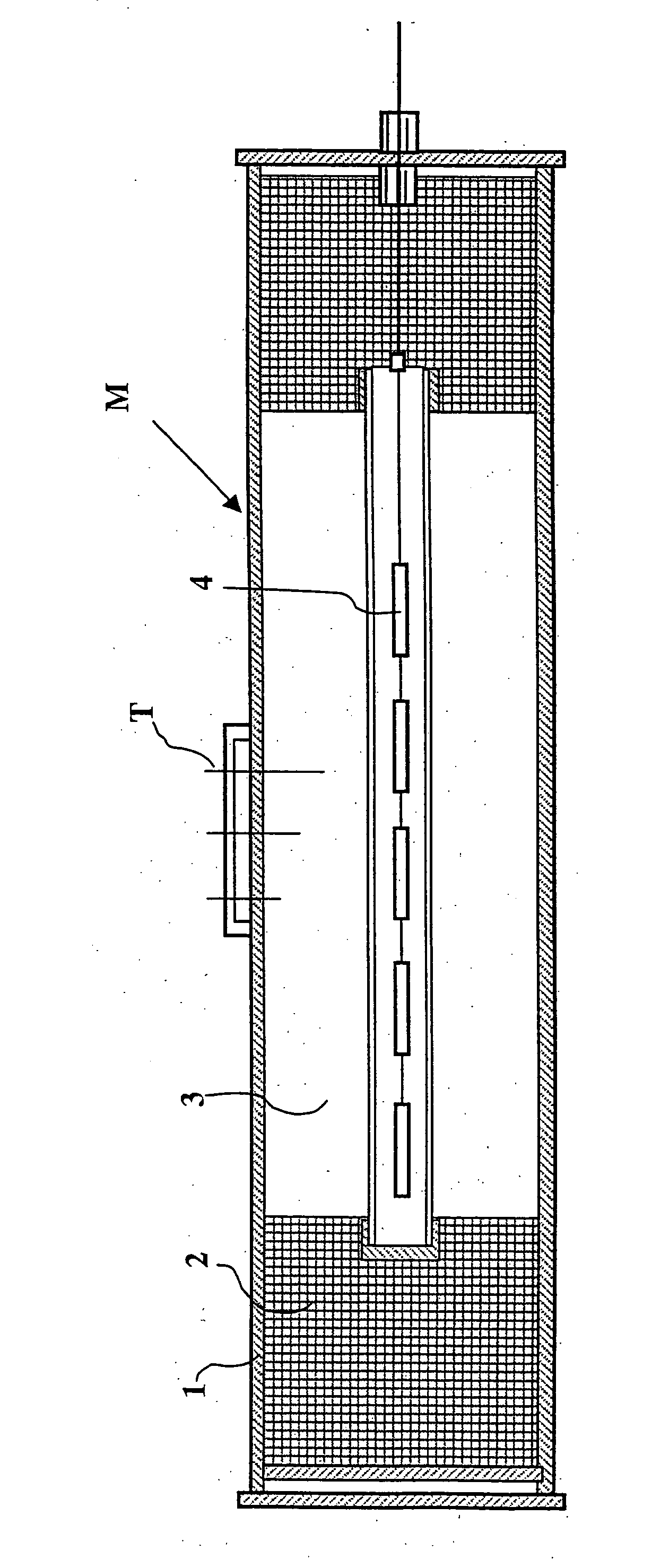
Thermal insulation gel with controlled crosslinking for petroleum hydrocarbon transmission lines
The present invention relates to and uses, in order to prevent crude oil from “congealing” in a transportation line, a controlled-crosslinking thermal insulation gel, i.e. relatively fluid at the start and developing in-situ gelation in lines only under certain conditions, temperature conditions among other things. In order to obtain controlled crosslinking, it is possible to carry out 1) Physical crosslinkings, i.e. physical bonds between polymers—completely reversible bonds by thermal effect and / or mechanical shear—and 2) Chemical crosslinkings: monomers or polymers having functions allowing chemical bonds to be established between polymers.
Owner:SAIPEM SA +2
Composition and process for production thereof
InactiveUS20120128749A1Good effectReduce compositionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMedicineWater soluble drug
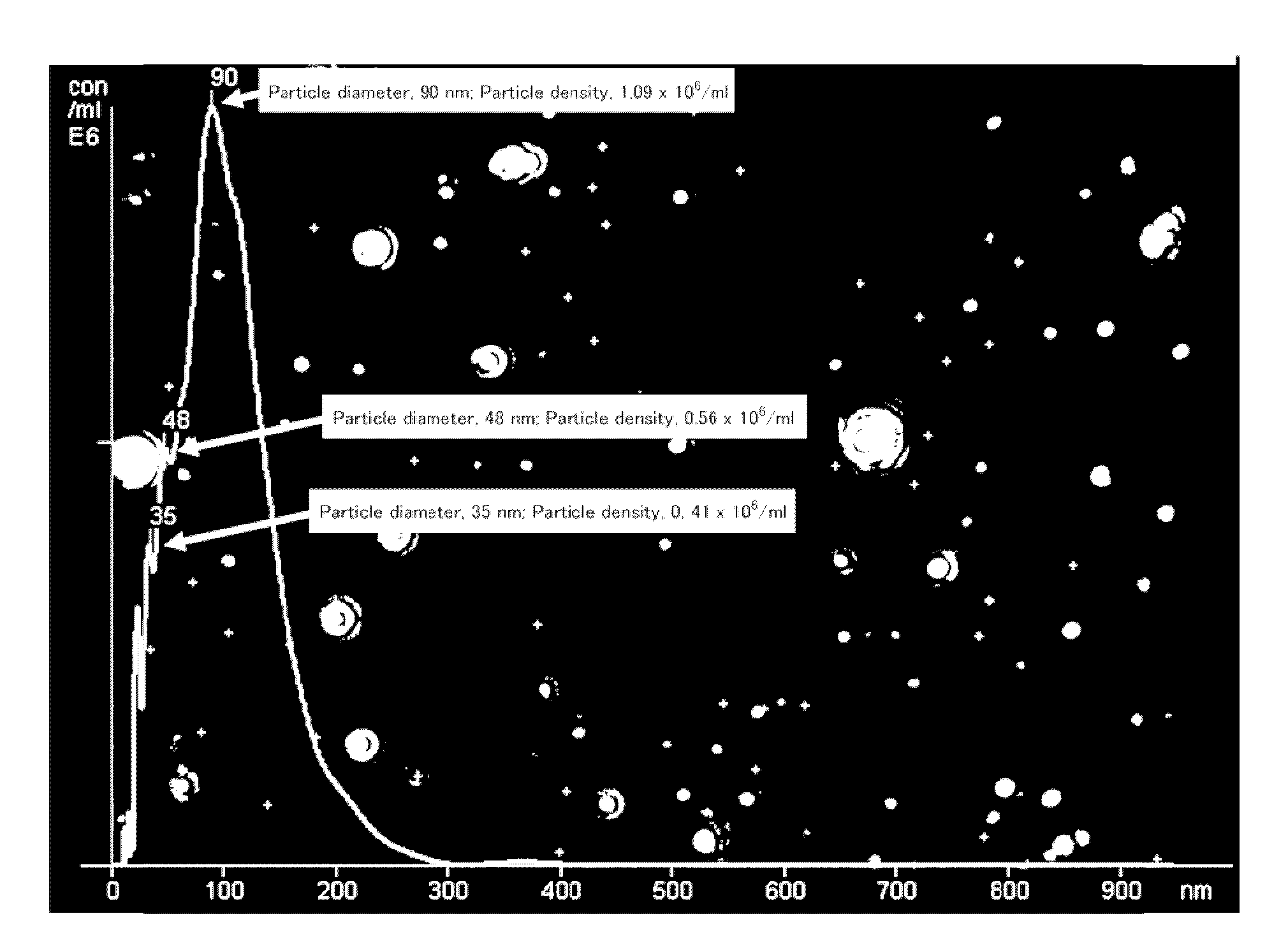
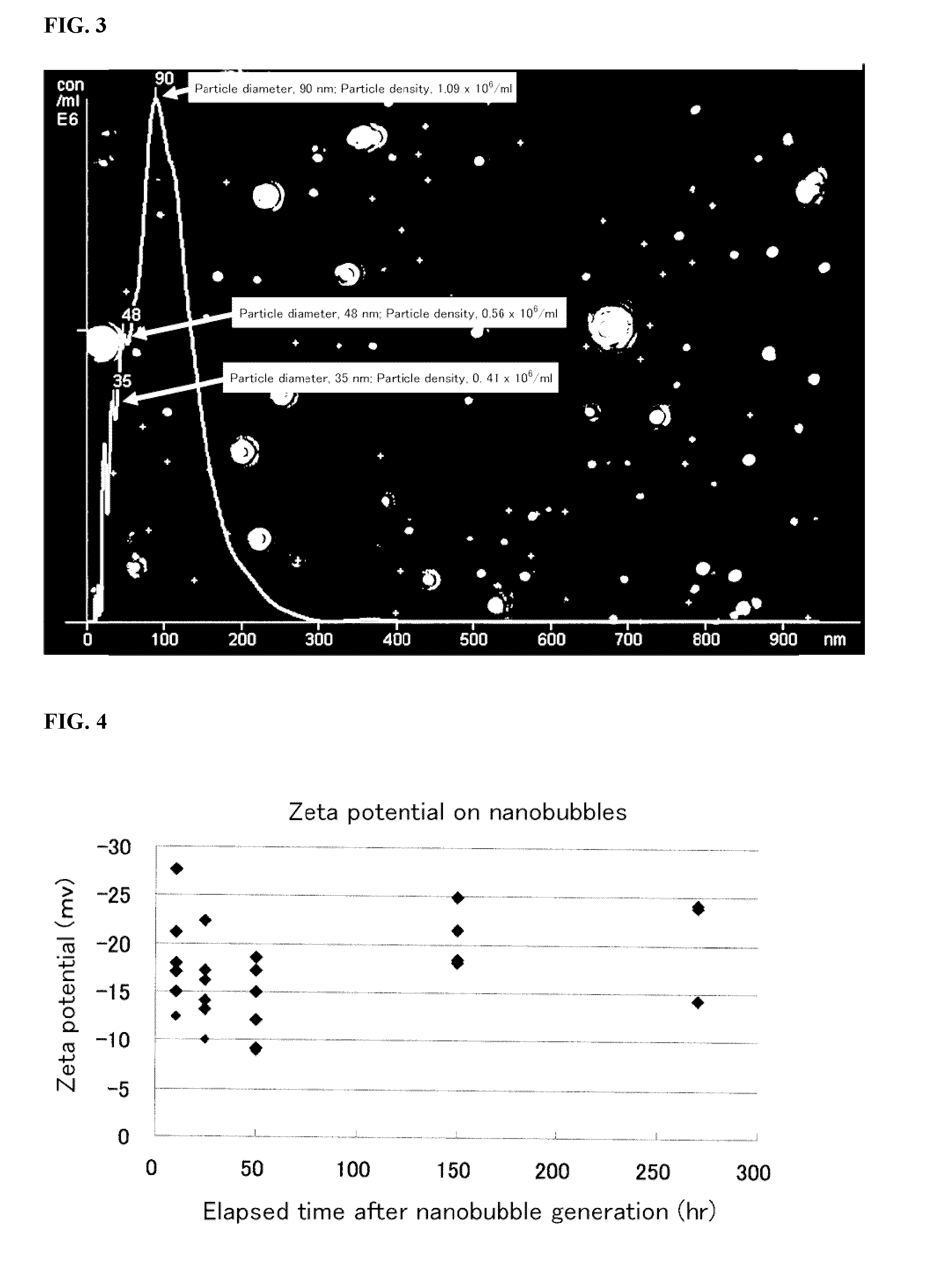
Disclosed are: a composition which enables the more effective development of the efficacy of a water-soluble drug in a solution containing the drug; and a dispersion in which a hydrophobic drug can be dispersed stably without requiring the use of any surfactant. Specifically disclosed are: a composition comprising ultra-fine bubbles having a mode particle size of 500 nm or less, a drug and water; and a process for producing a composition comprising ultra-fine bubbles having a mode particle size of 500 nm or less, a drug and water, which utilizes an ultra-fine bubble generation apparatus.
Owner:SUNSTAR GIKEN KK +1
Popular searches
Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts Mixing methods Catalyst activation/preparation Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Colloidal chemistry details Wood layered products Natural mineral layered products Thin material handling Metal layered products Selective adsorption
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com











![Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7c4e2fc2-469b-4732-bf52-ae3c8dc01732/171120154139.png)
![Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7c4e2fc2-469b-4732-bf52-ae3c8dc01732/171120154143.png)
![Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel Pillar[5]arene based gelators and application of organogel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7c4e2fc2-469b-4732-bf52-ae3c8dc01732/171120154148.png)