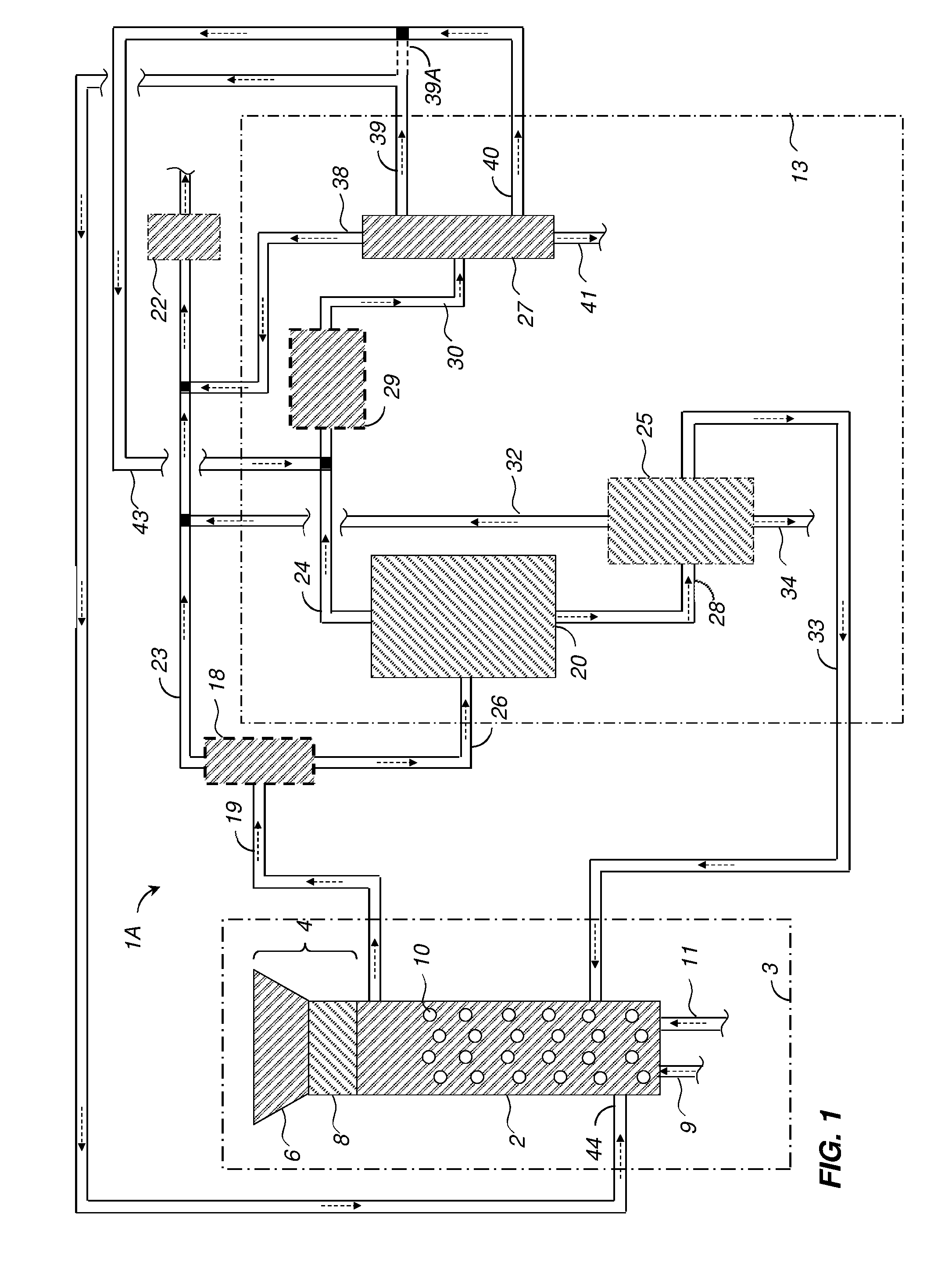
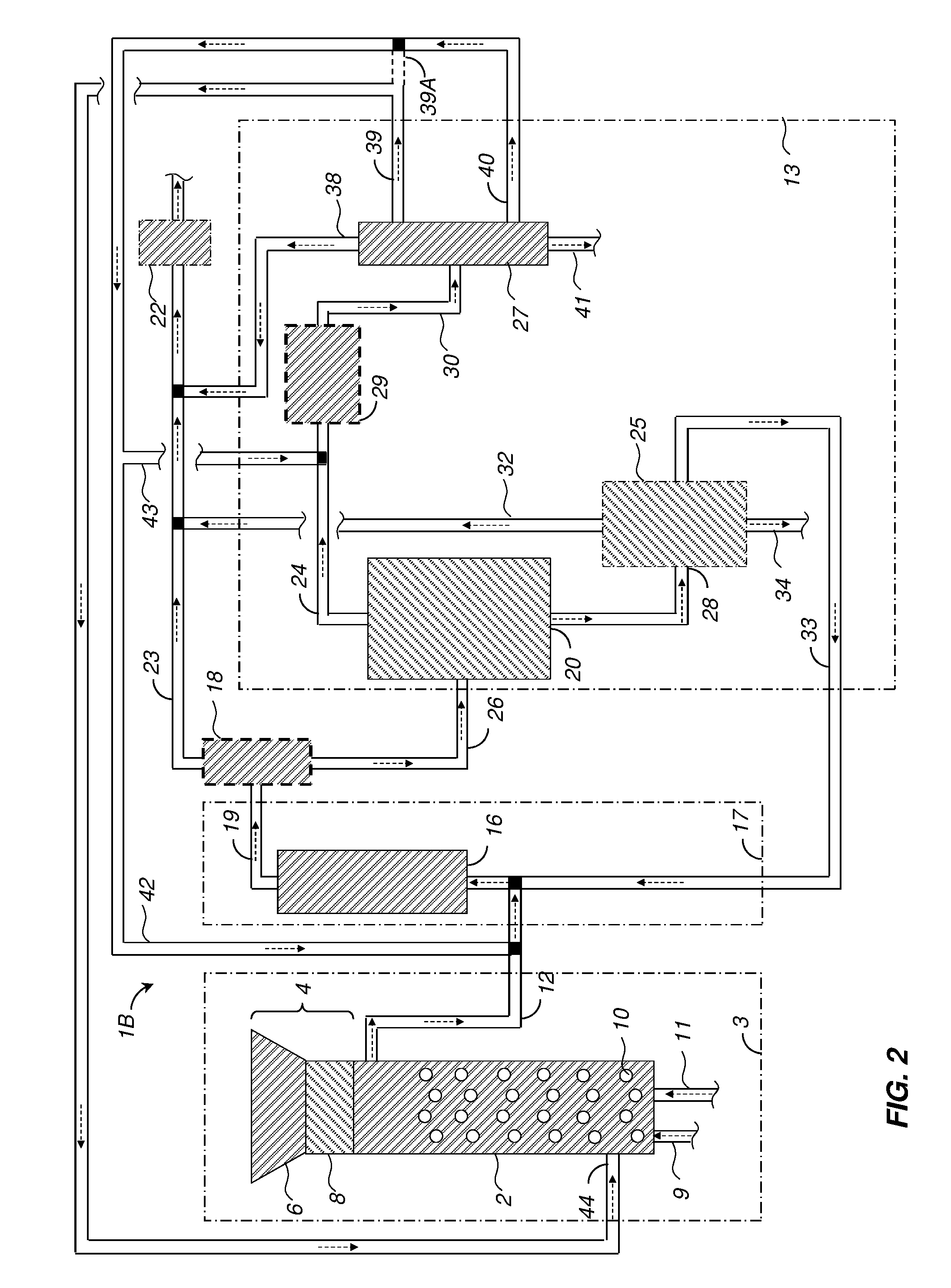
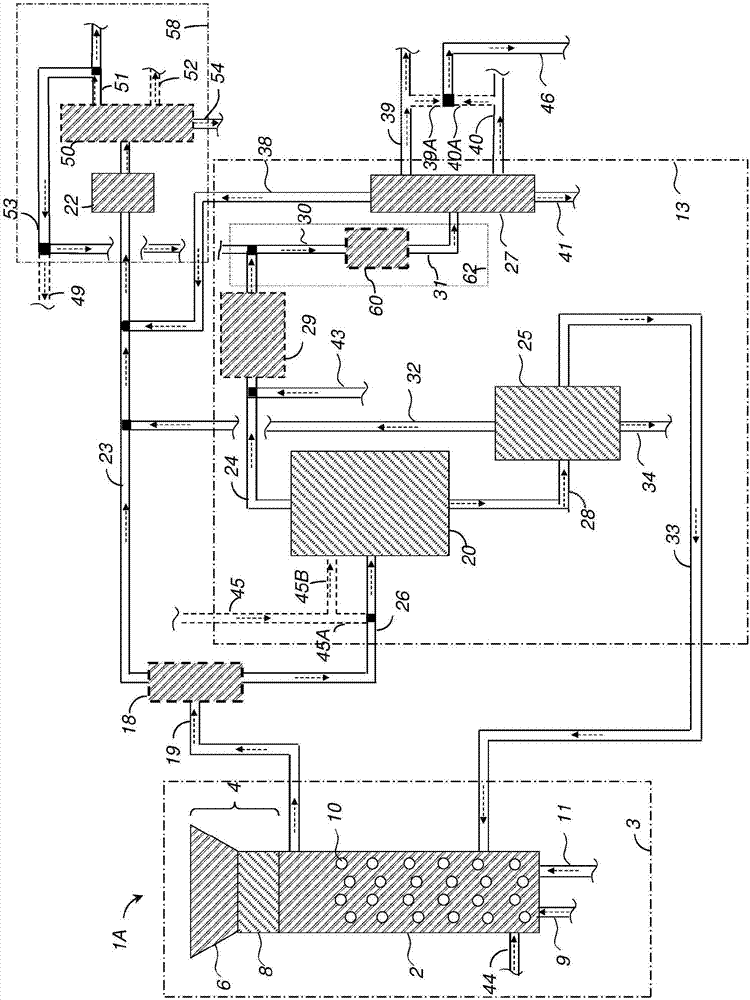
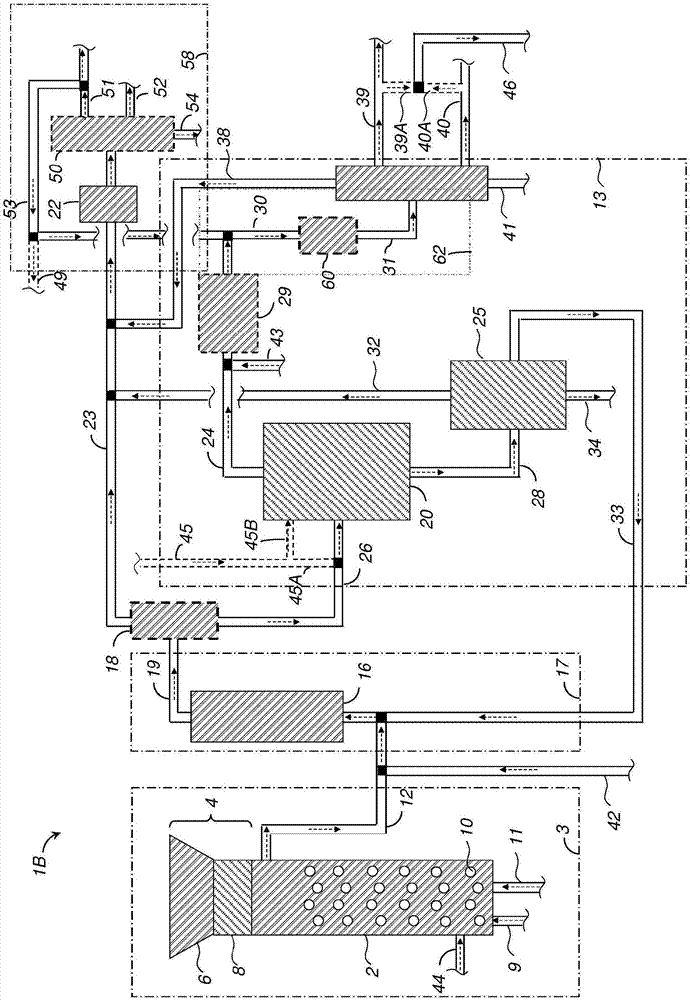
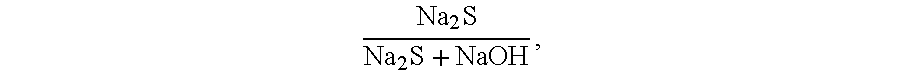Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75results about "Fractionation/concentration of spent liquors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
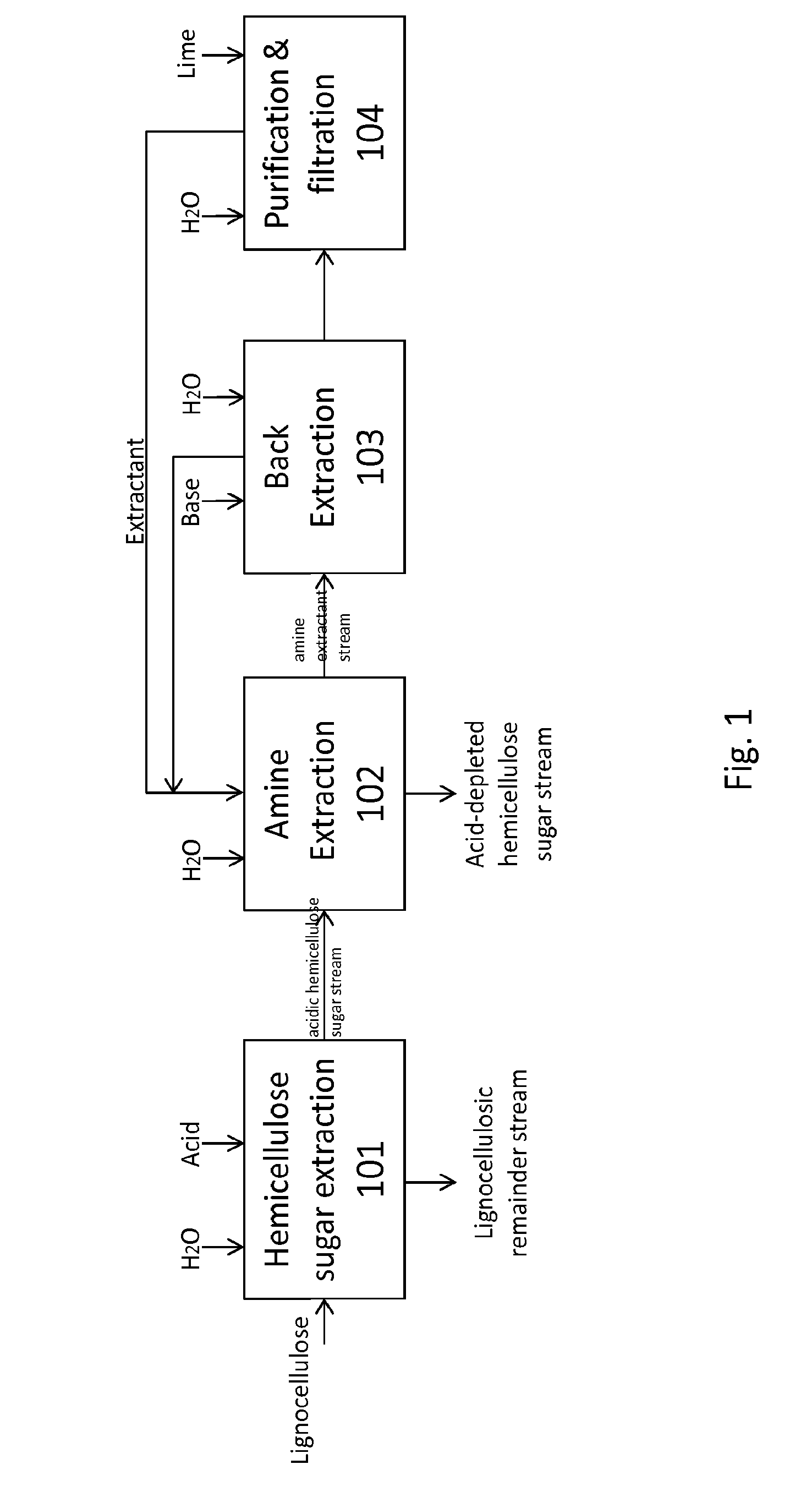
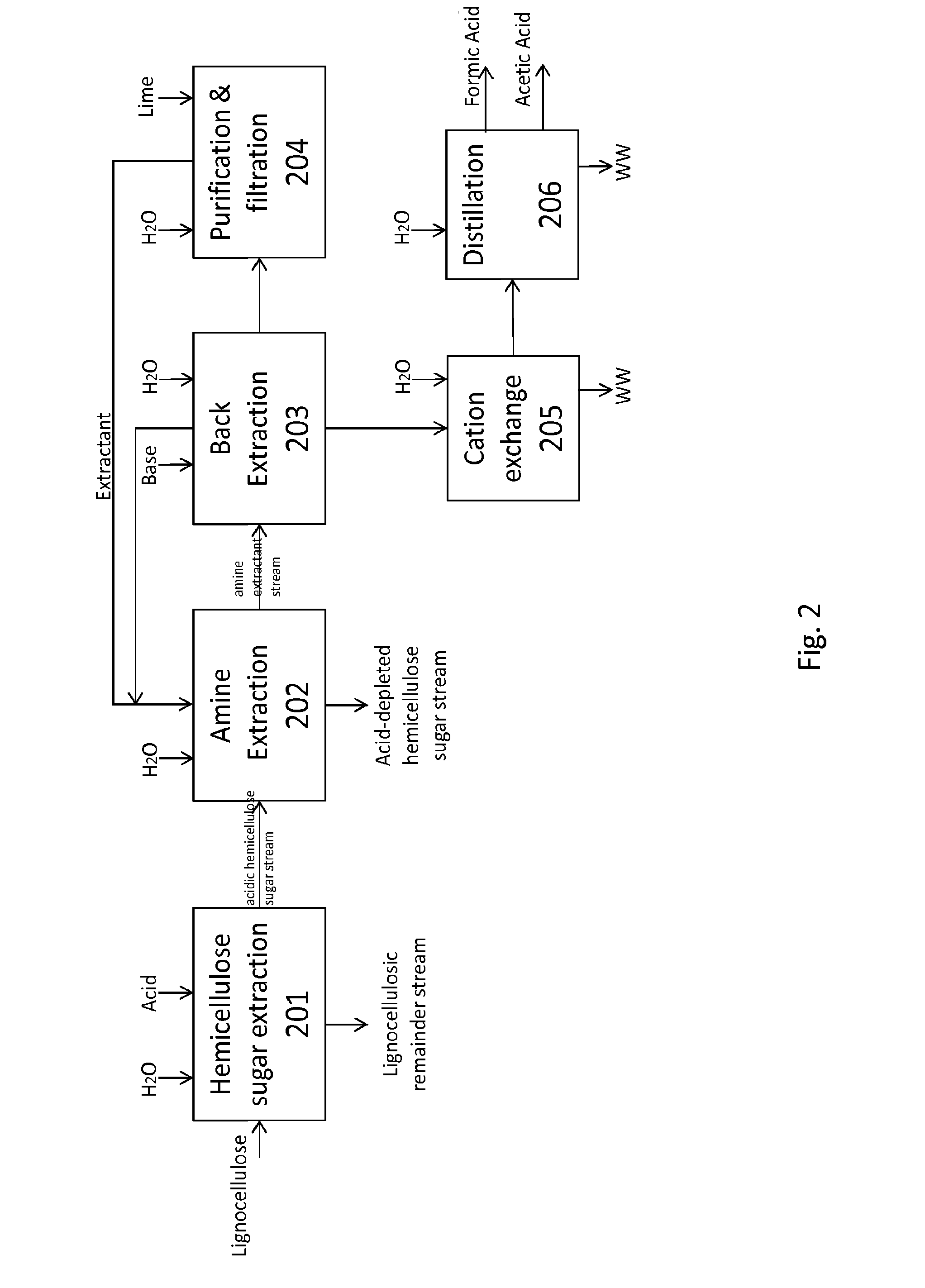
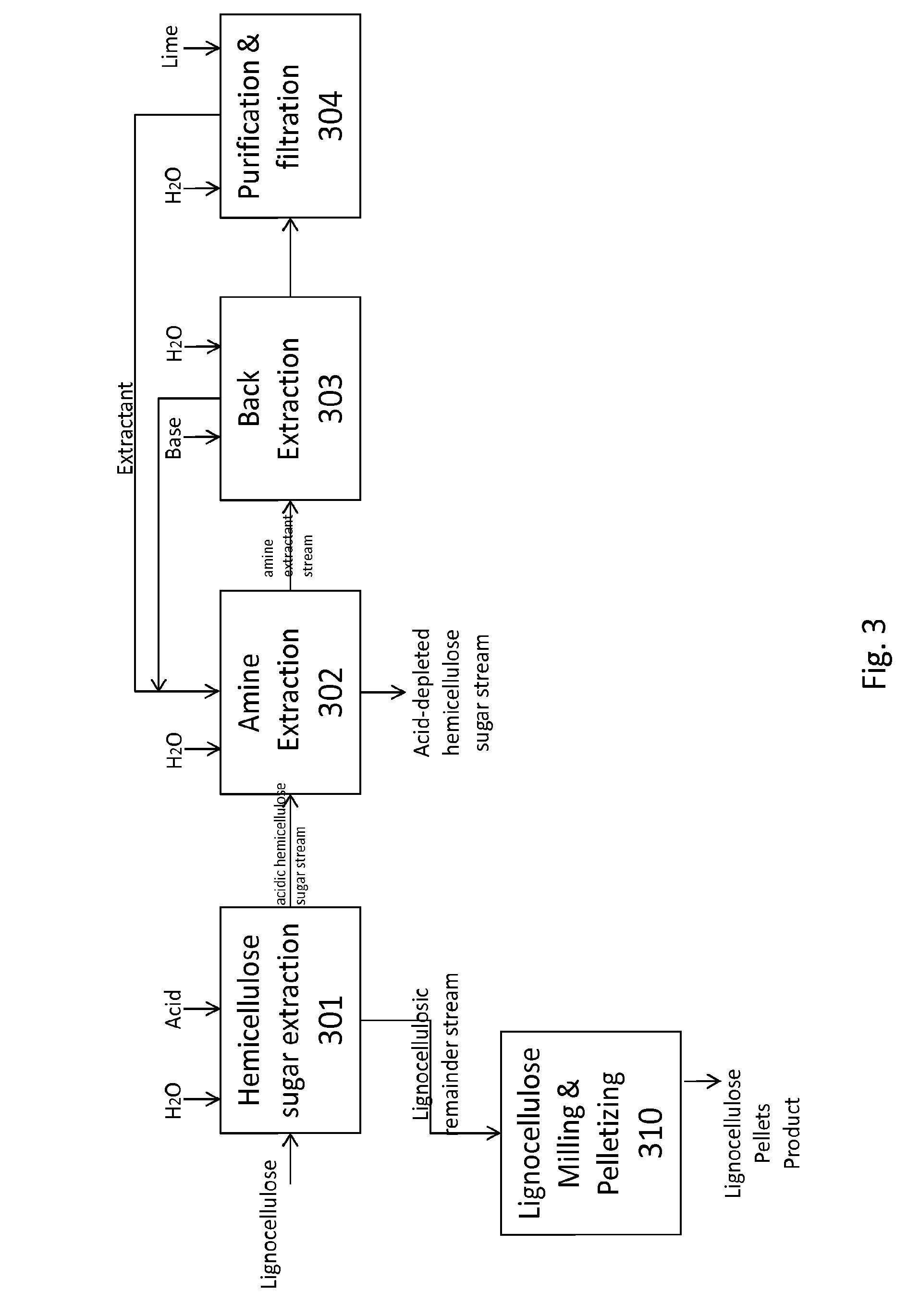
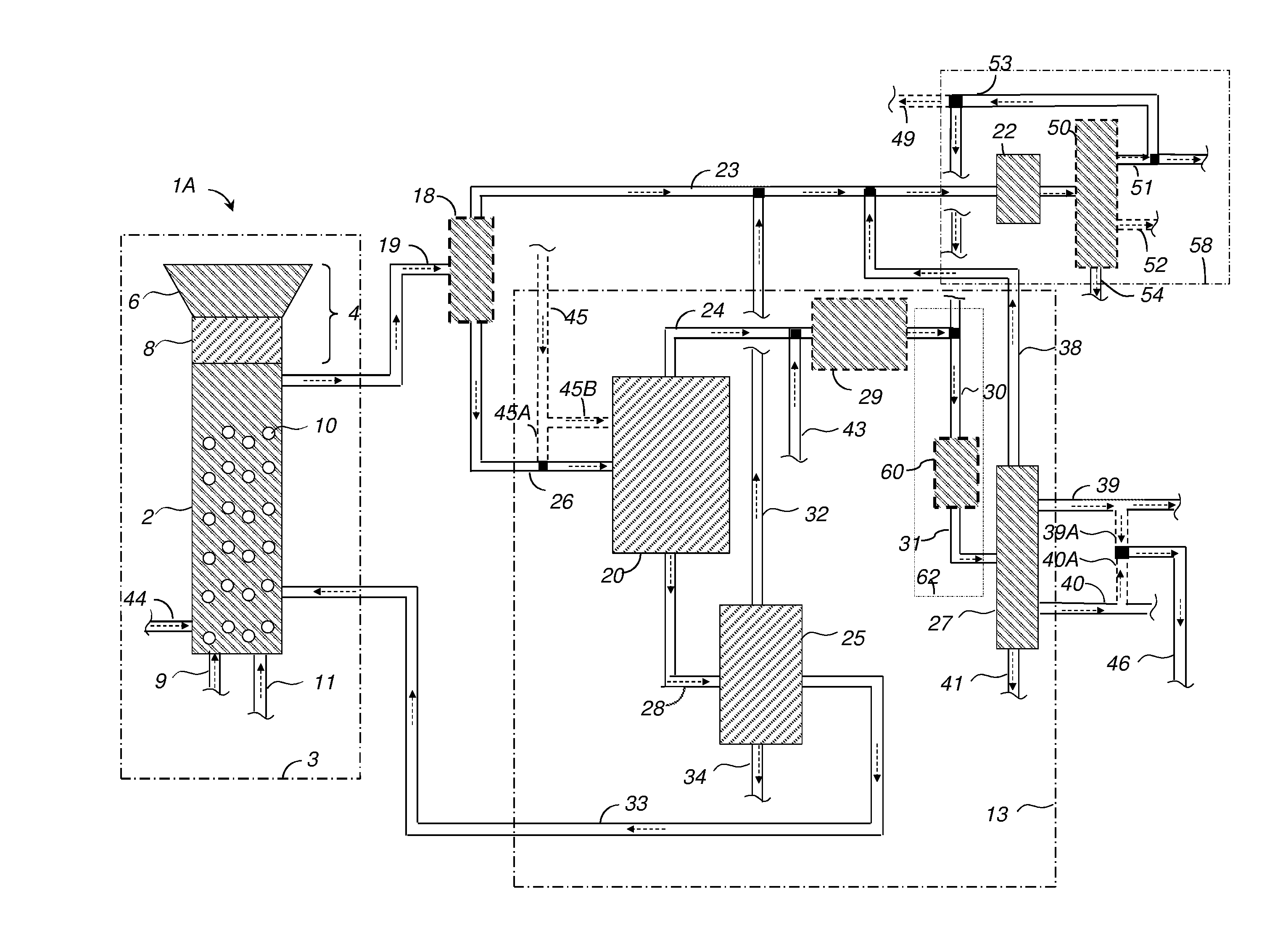
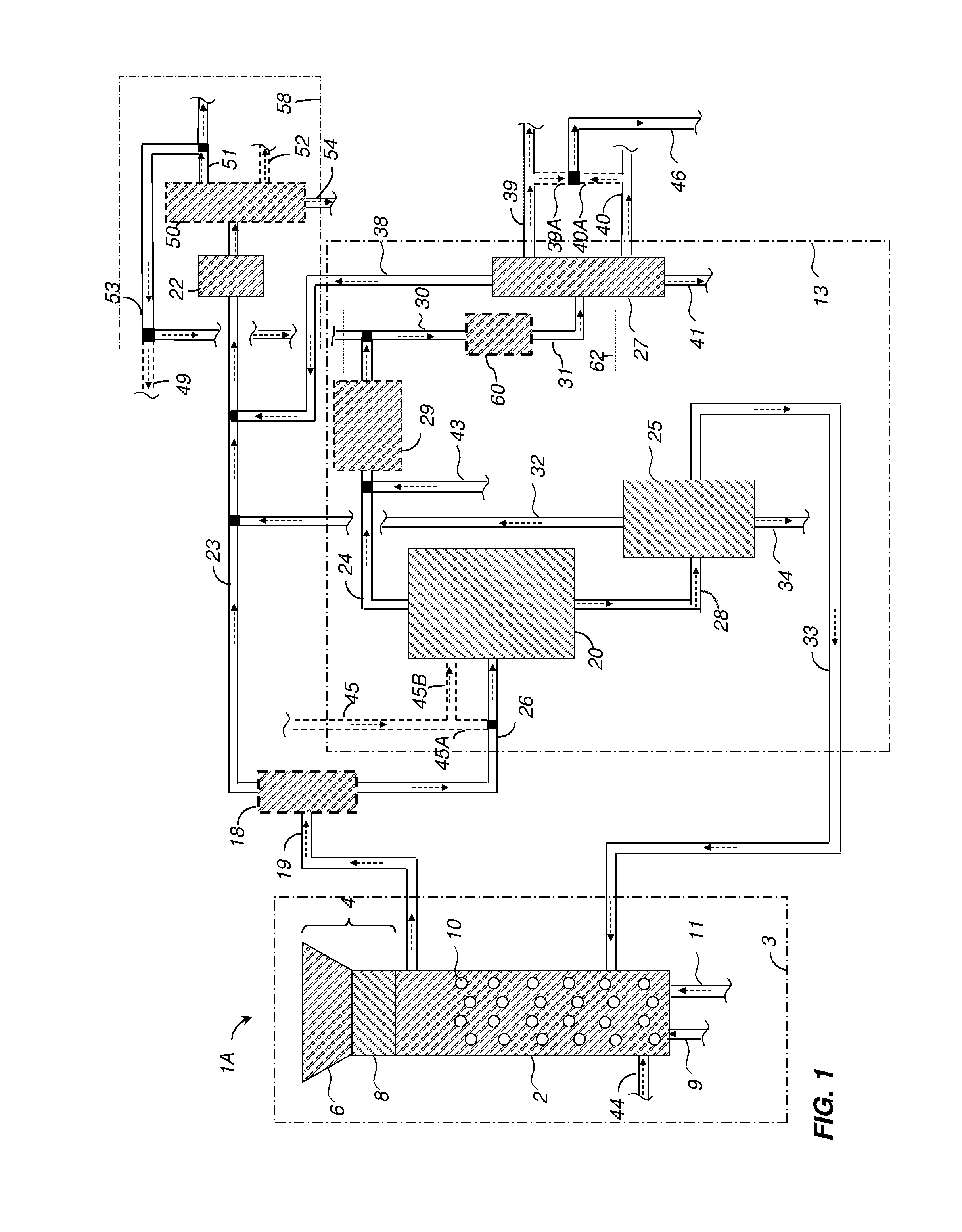
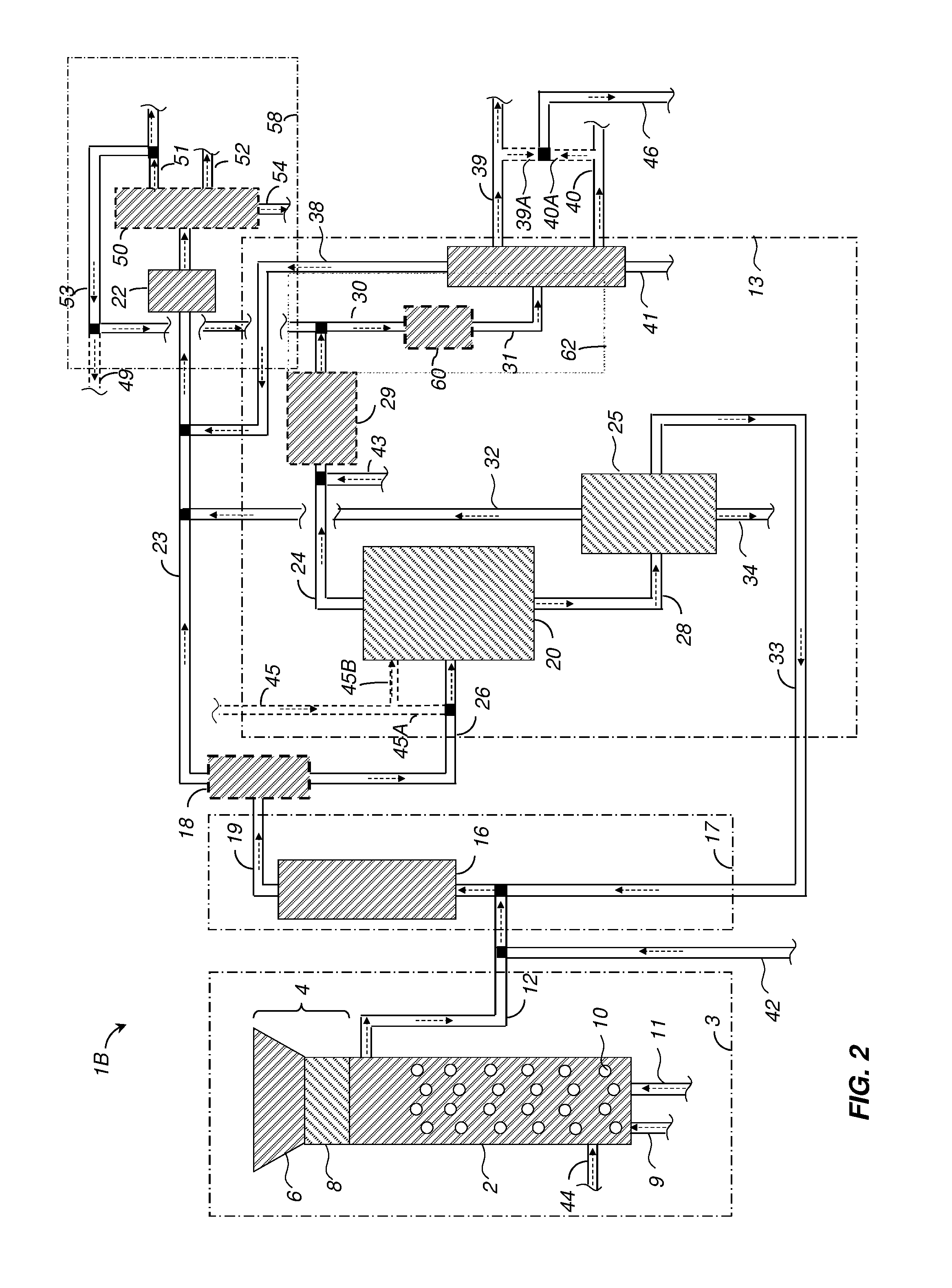
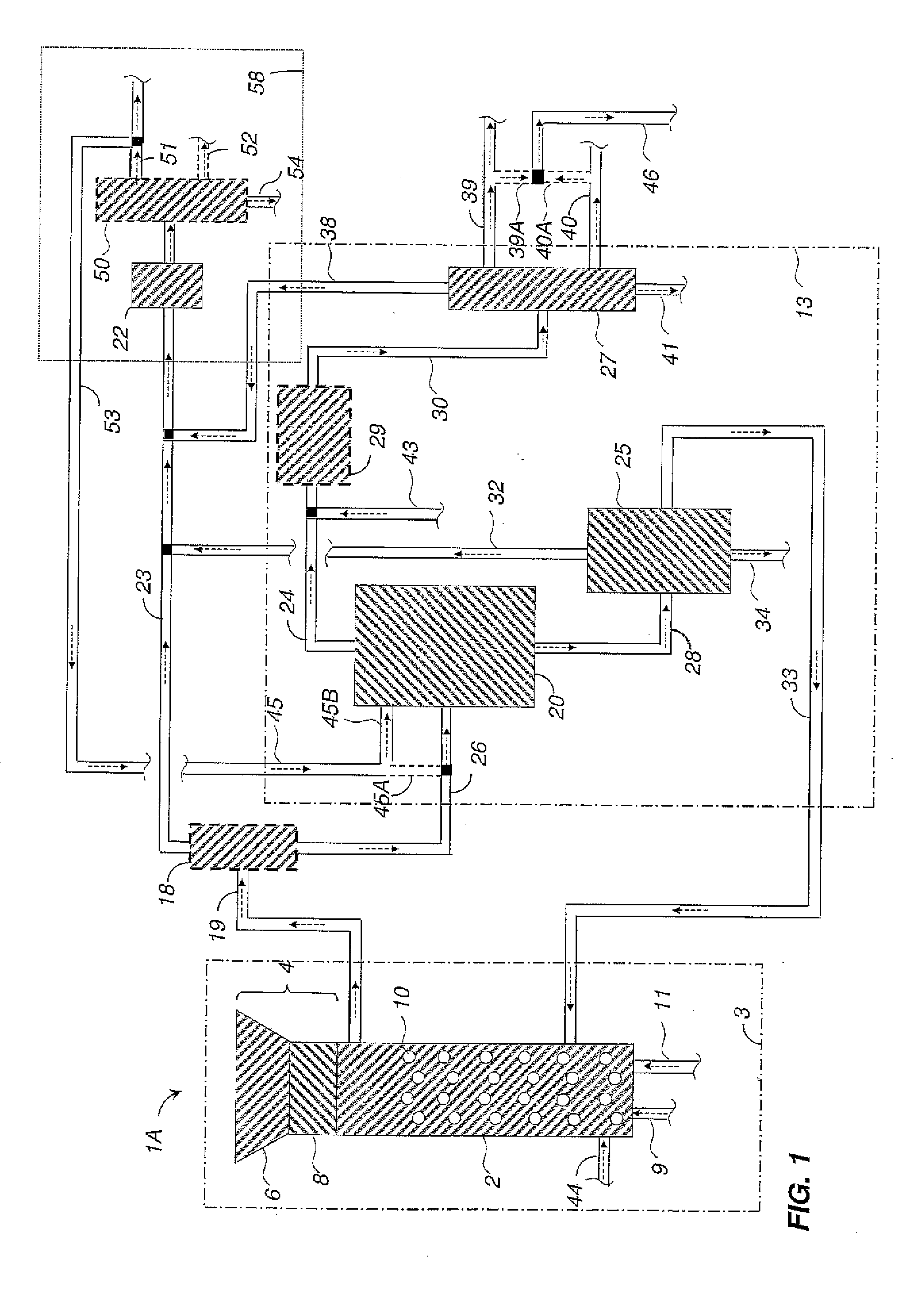
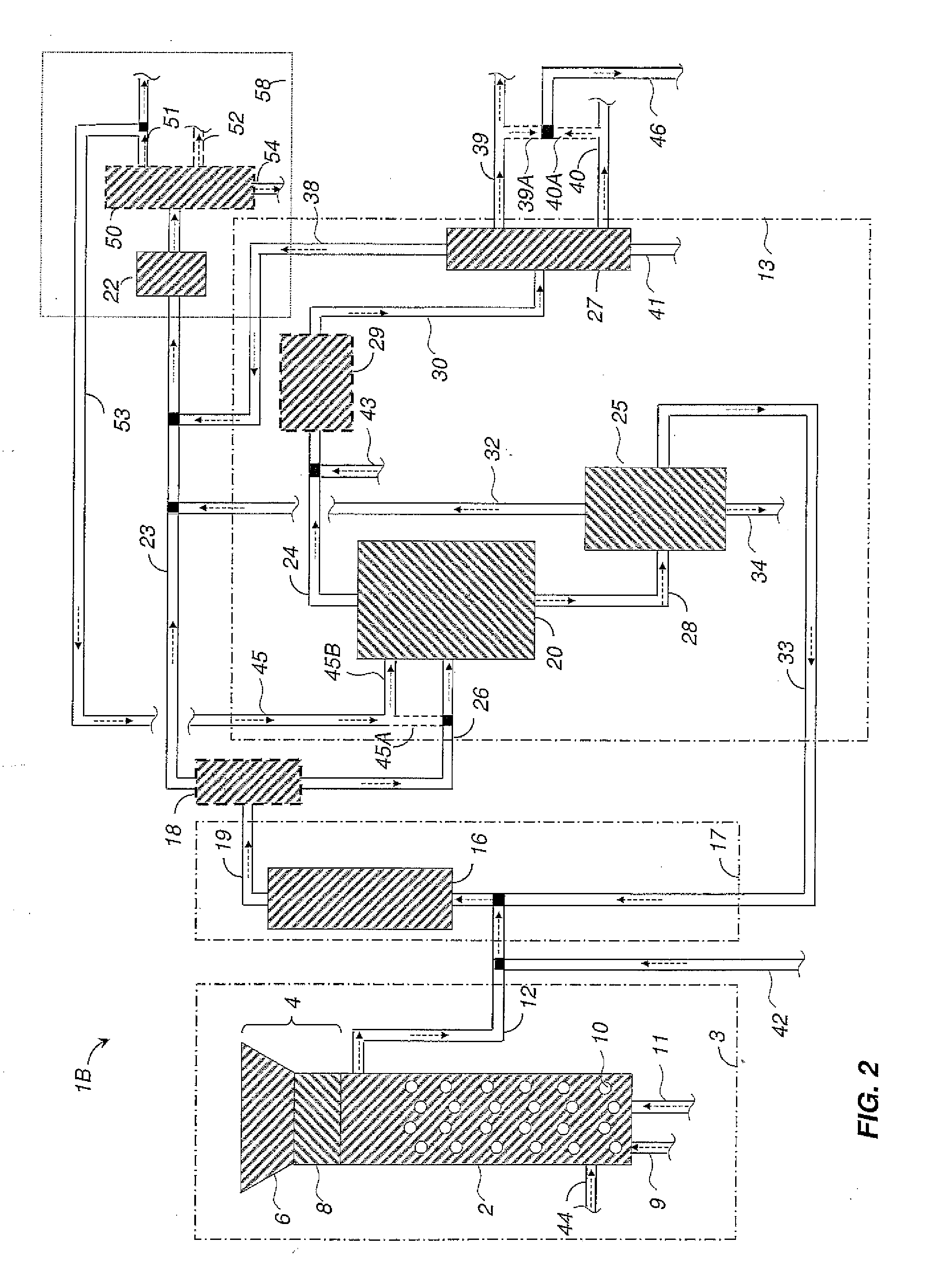
Detoxifying and Recylcing of Washing Solution Used In Pretreatment Of Lignocellulose-Containing Materials
ActiveUS20090056889A1Improve hydrolysis efficiencyImprove filtering effectWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsBiofuelsPre treatmentOrganic chemistry
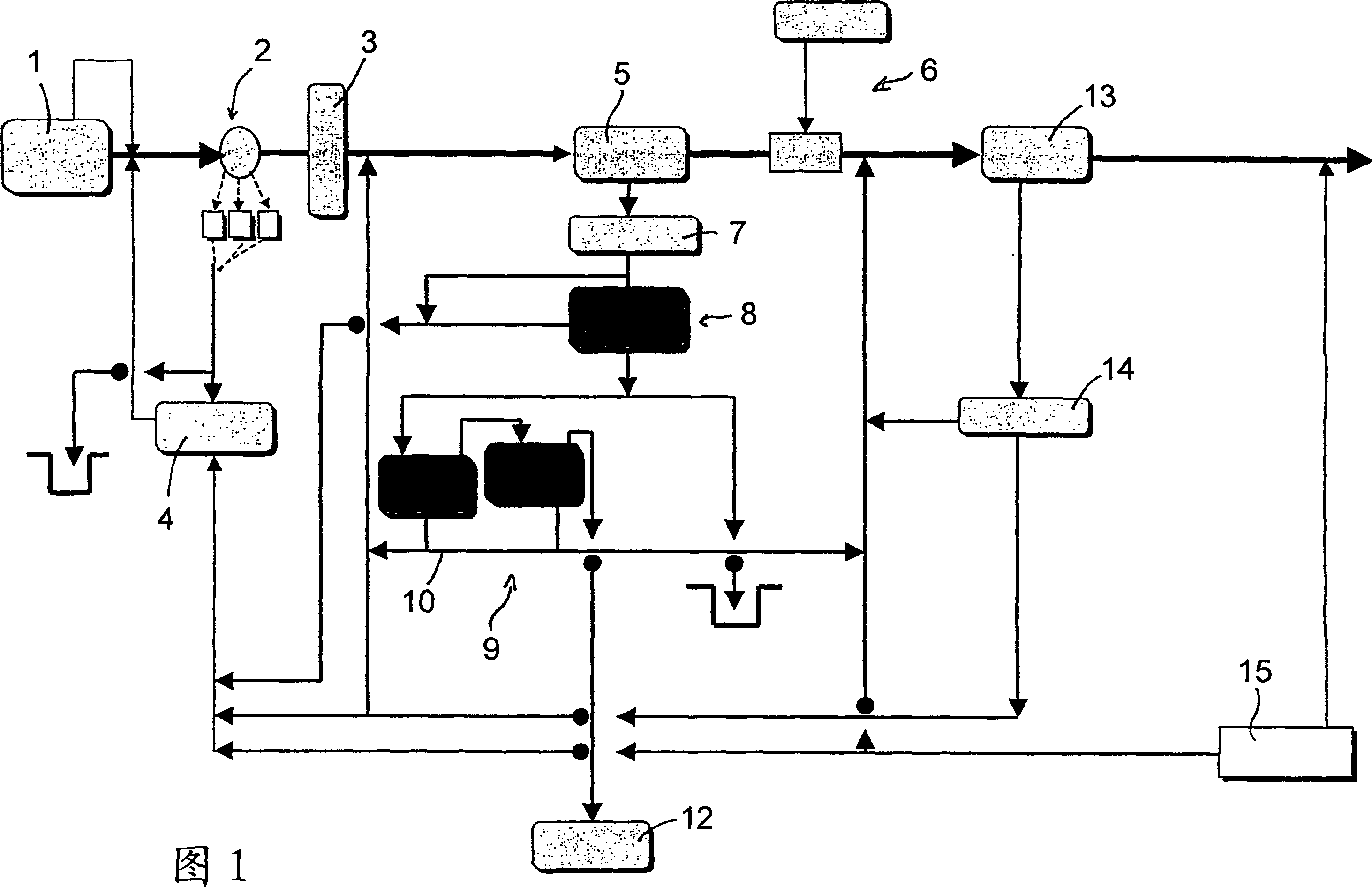
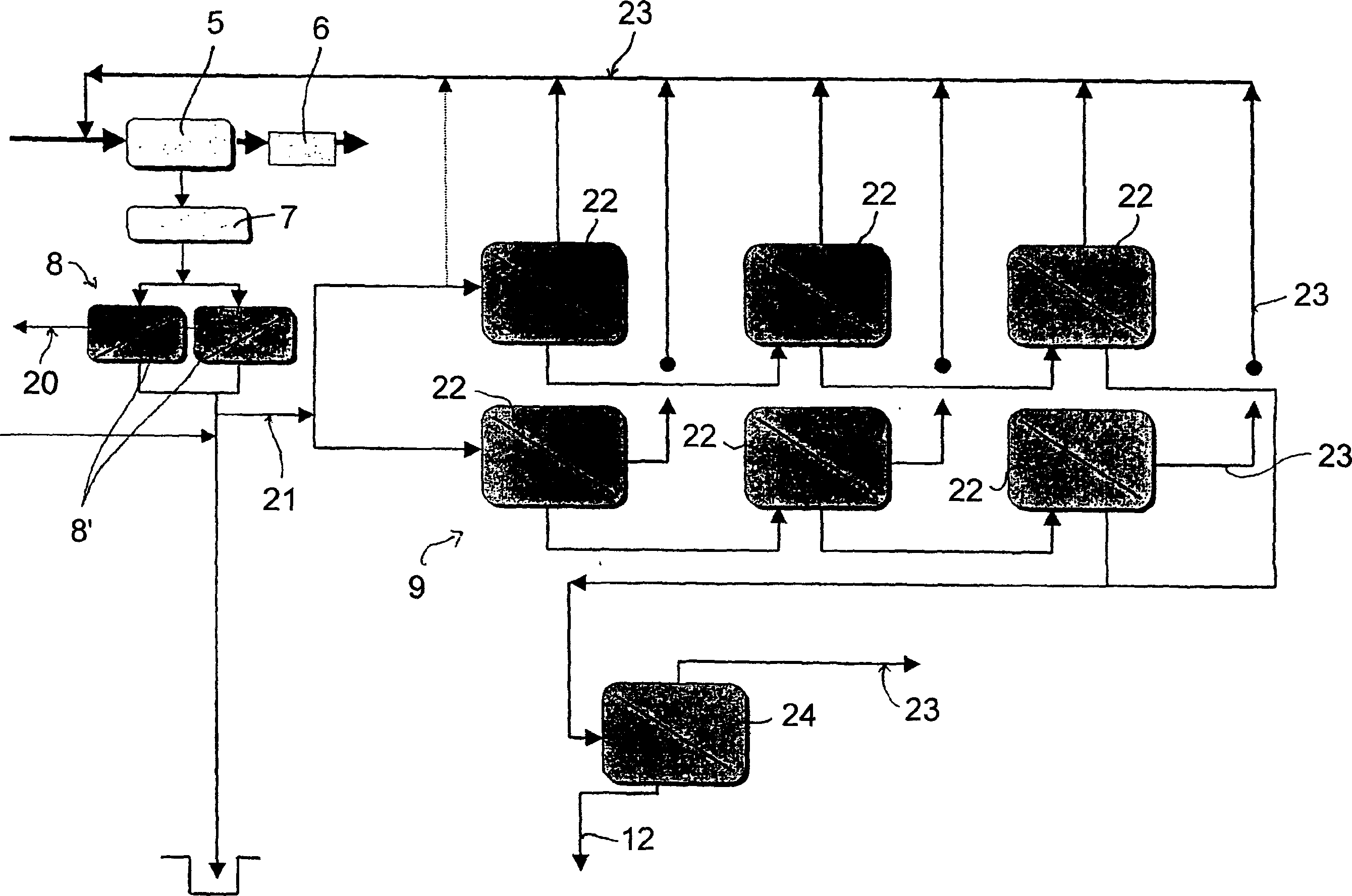
The invention relates to a process of detoxifying pretreated lignocellulose-containing material comprising washing the pretreated lignocellulose-containing material in a washing solution and treating the used washing solution to remove an enzyme inhibitor and / or an inhibitor of a fermenting organism before recycling the used washing solution.
Owner:COFCO GROUP
Process for producing xylooligosaccharide from lignocellulose pulp
InactiveUS6942754B2Improve efficiencyLow costFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulp bleachingCellulose pulpHemicellulose
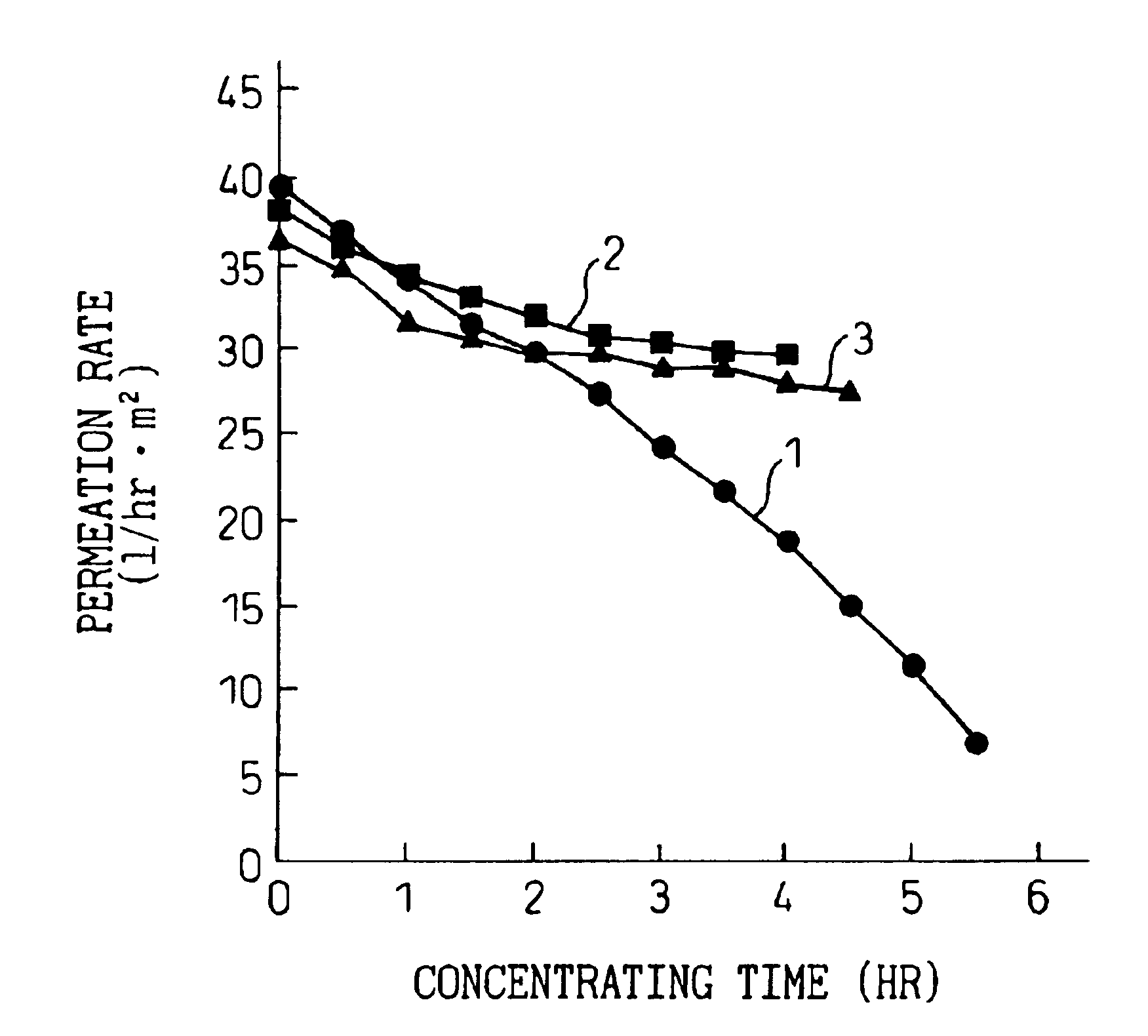
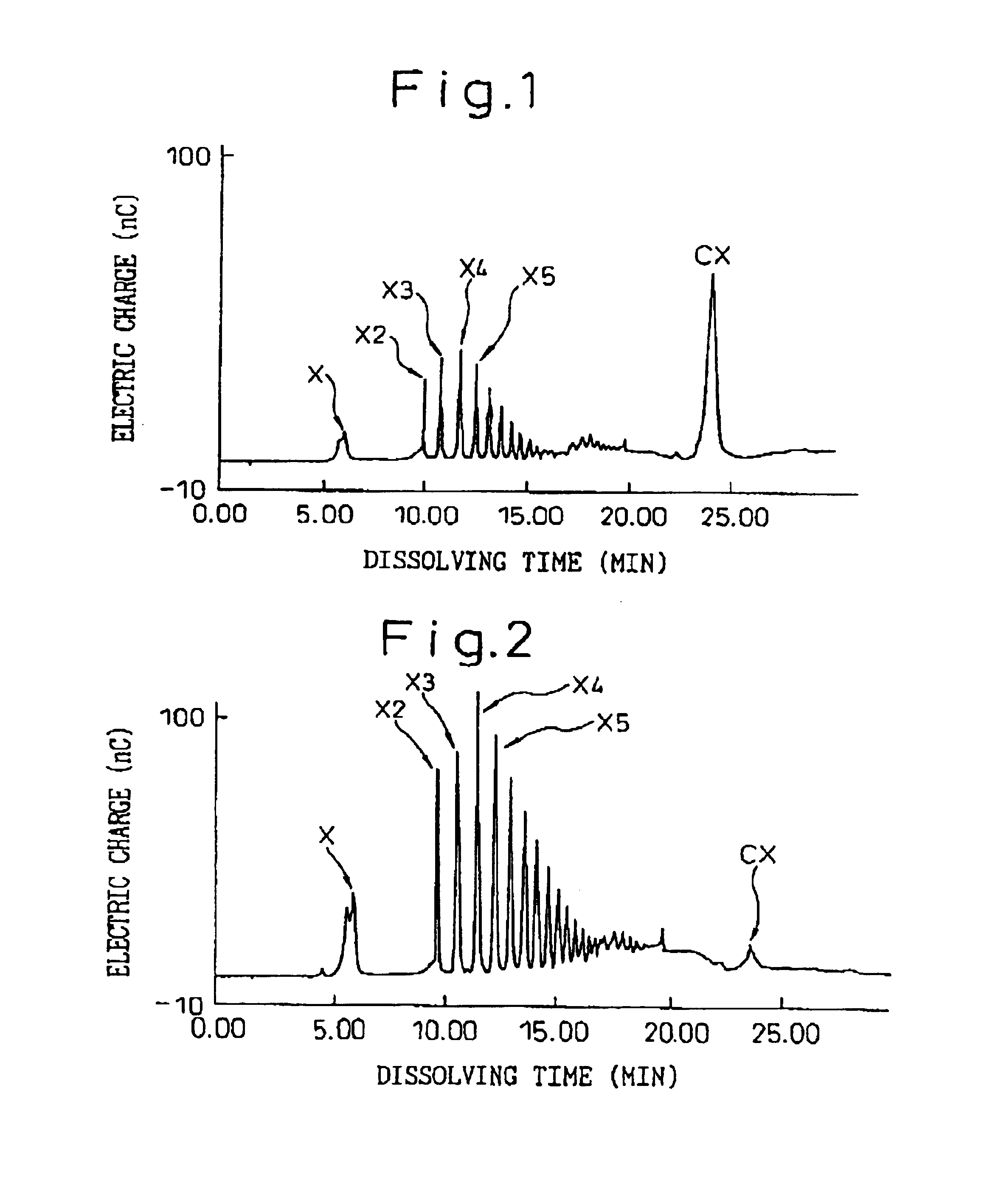
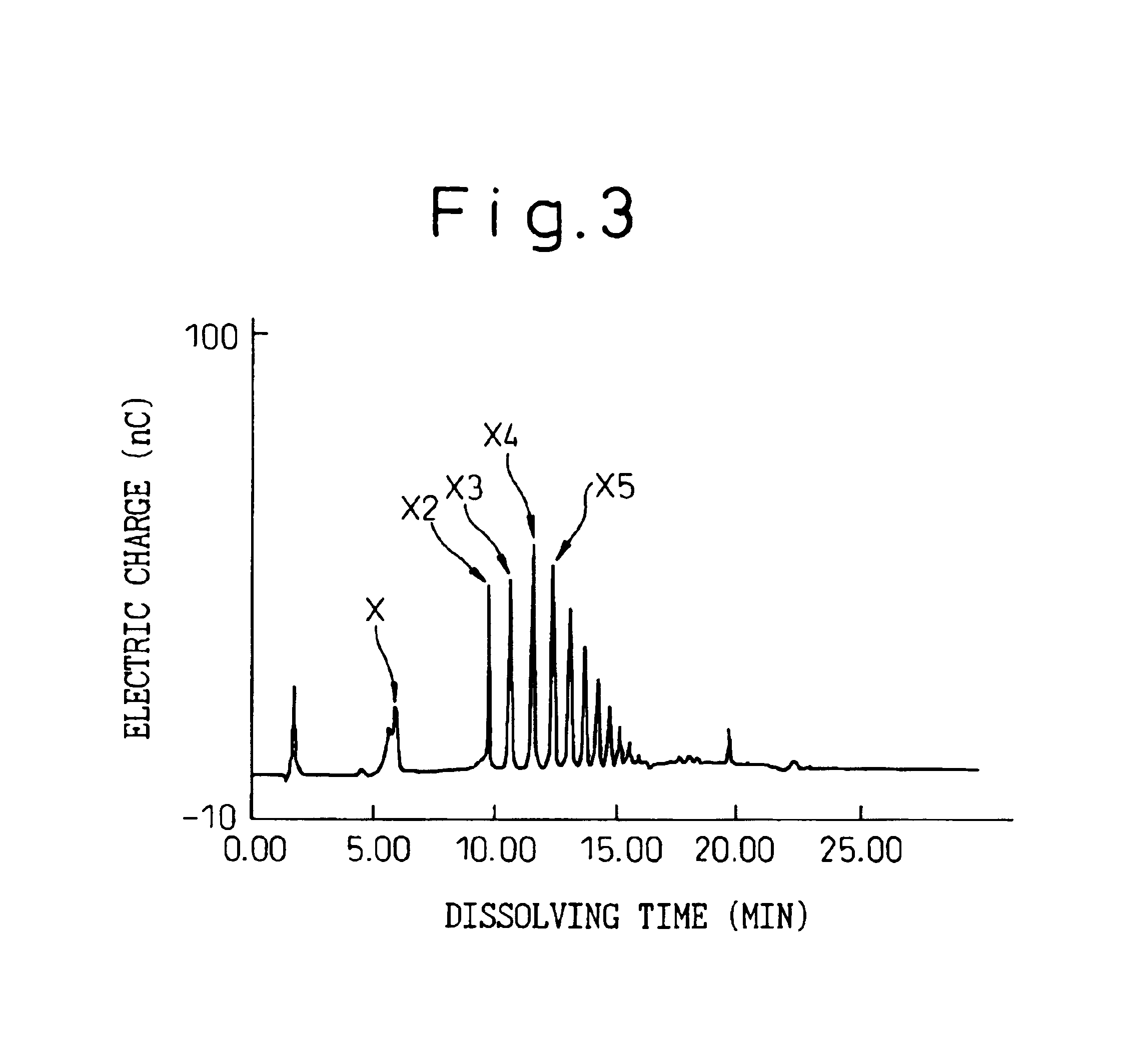
Xylooligosaccharide is produced from a lignocellulose pulp by enzyme-treating a lignocellulose pulp with hemicellulase, filtering the resultant reaction mixture to separate a liquid fraction from the enzyme-treated pulp, subjecting the separated liquid fraction to a permeation treatment through a separation membrane to separate a non-permeated fraction containing xylooligosaccharide-lignin complex with an increased concentration from a permeated fraction, collecting the non-permeated fraction, and separating and recovering xylooligosaccharide from the collected non-permeated fraction.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Hybrid biorefining and gasification of lignocellulosic feedstocks
InactiveUS20120202260A1Significant commercial valueProduce energyBiofuelsHydroxy compound preparationCelluloseSyngas
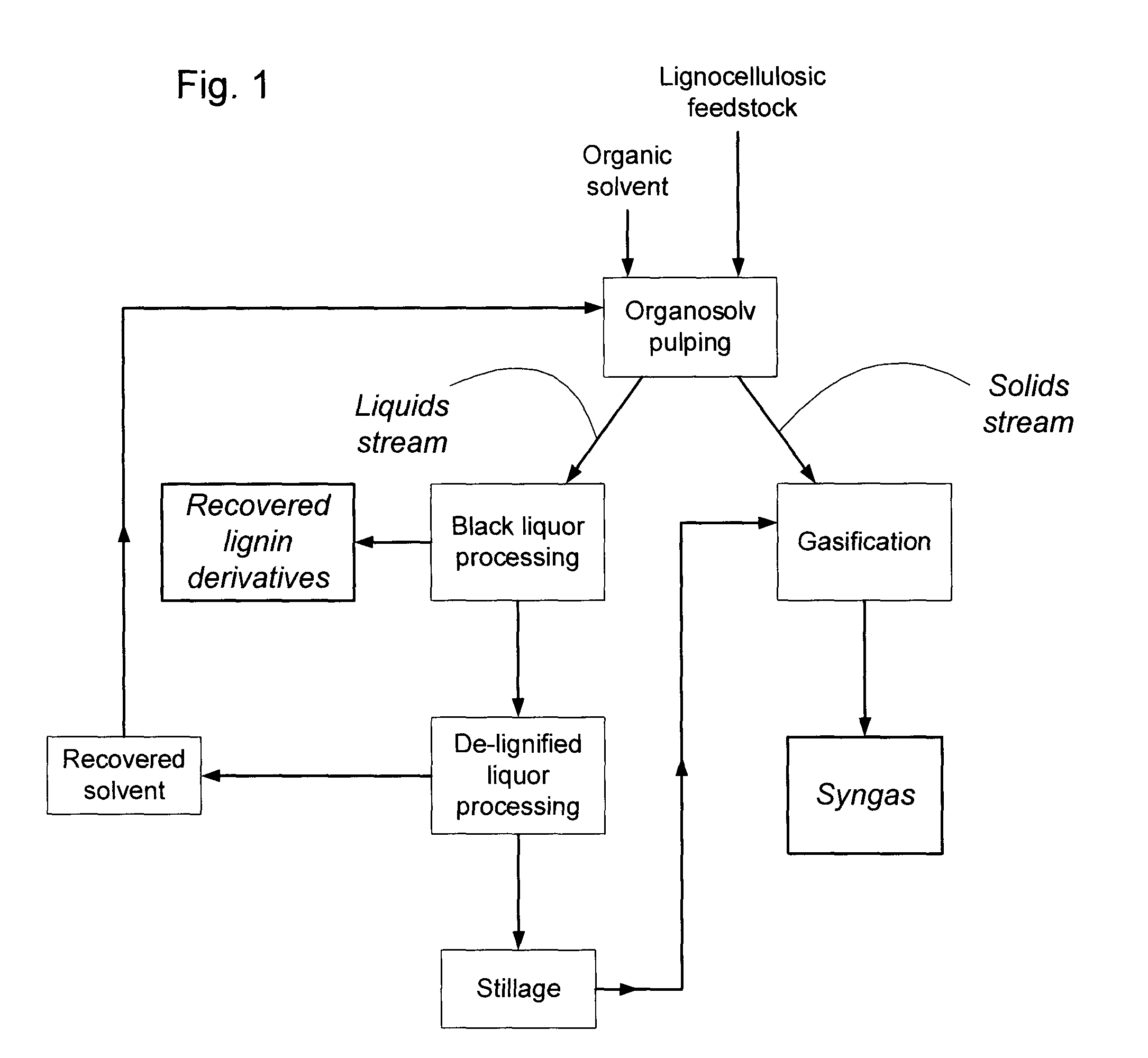
Processes and systems for concurrent recovery of lignin derivatives and syngas from a lignocellulosic feedstock. The processes and systems therefor generally comprise the steps of: (a) perfusing and cooking the lignocellulosic feedstock with a suitable organic solvent for a suitable period of time thereby producing a cellulosic solids output stream and a spent liquid solvent stream, said spent liquid solvent stream comprising solubilized lignin derivatives and other organic compounds; (b) separating said cellulosic solids output stream and said spent liquid solvent stream; (c) recovering lignin derivatives from the spent liquid solvent stream thereby producing at least a partially de-lignified spent liquid solvent stream; (d) recovering a portion of the organic solvent from the at least partially de-lignified spent liquid solvent stream thereby producing a stillage; and (e) gasifying the cellulosic solids output stream thereby producing a combustible syngas.
Owner:LIGNOL INNOVATIONS
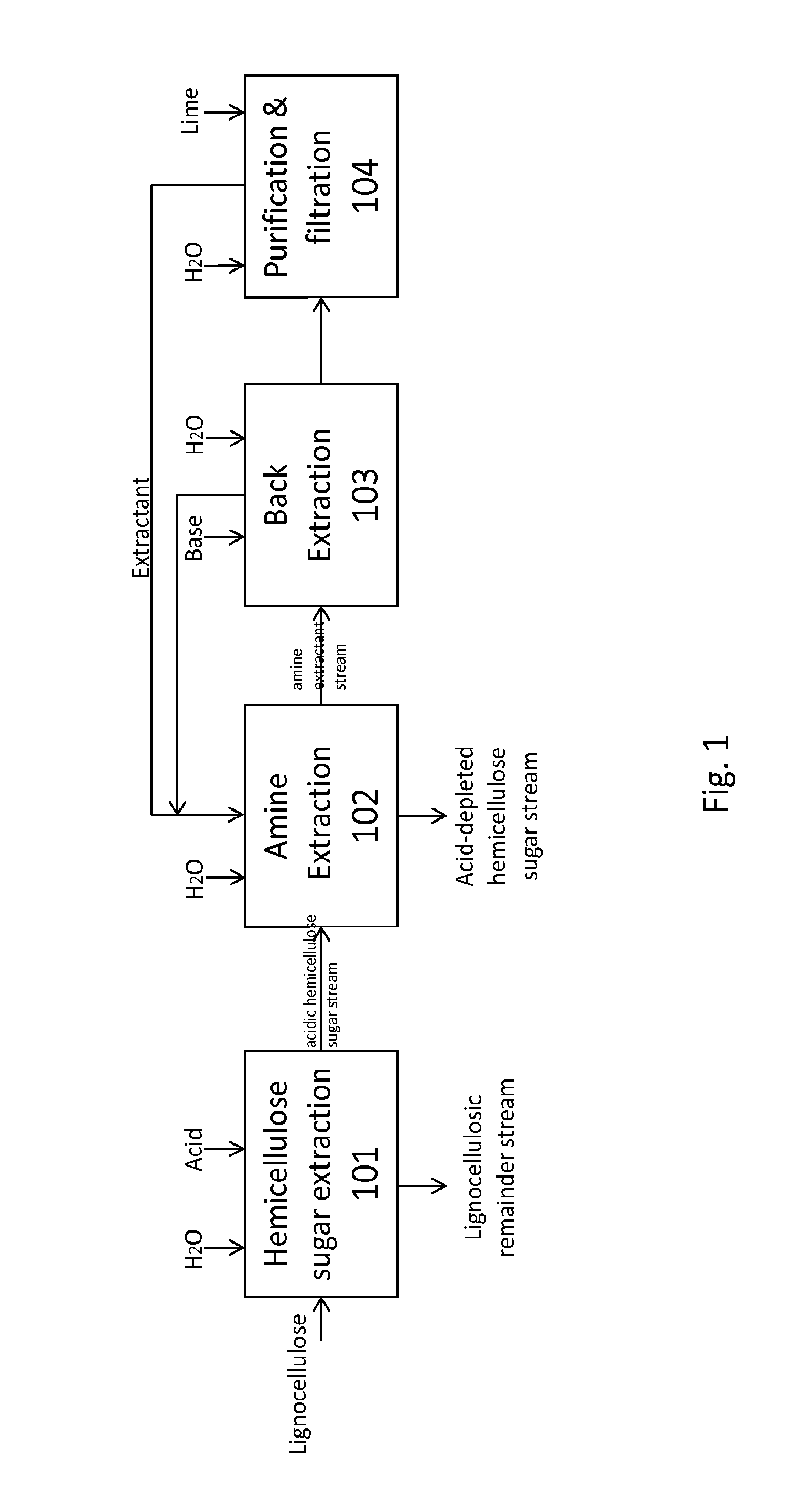
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
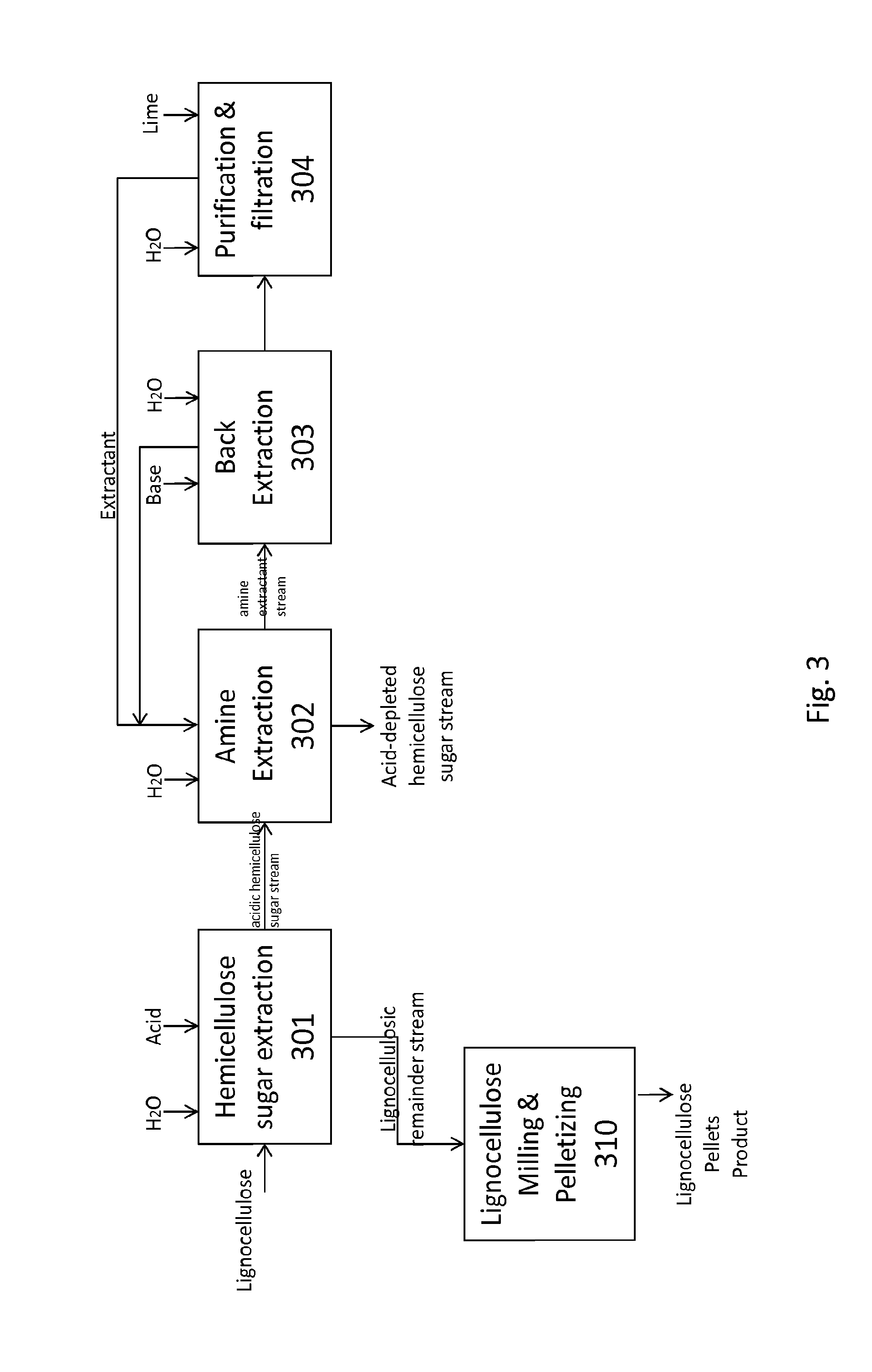
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products.
Owner:VIRDIA
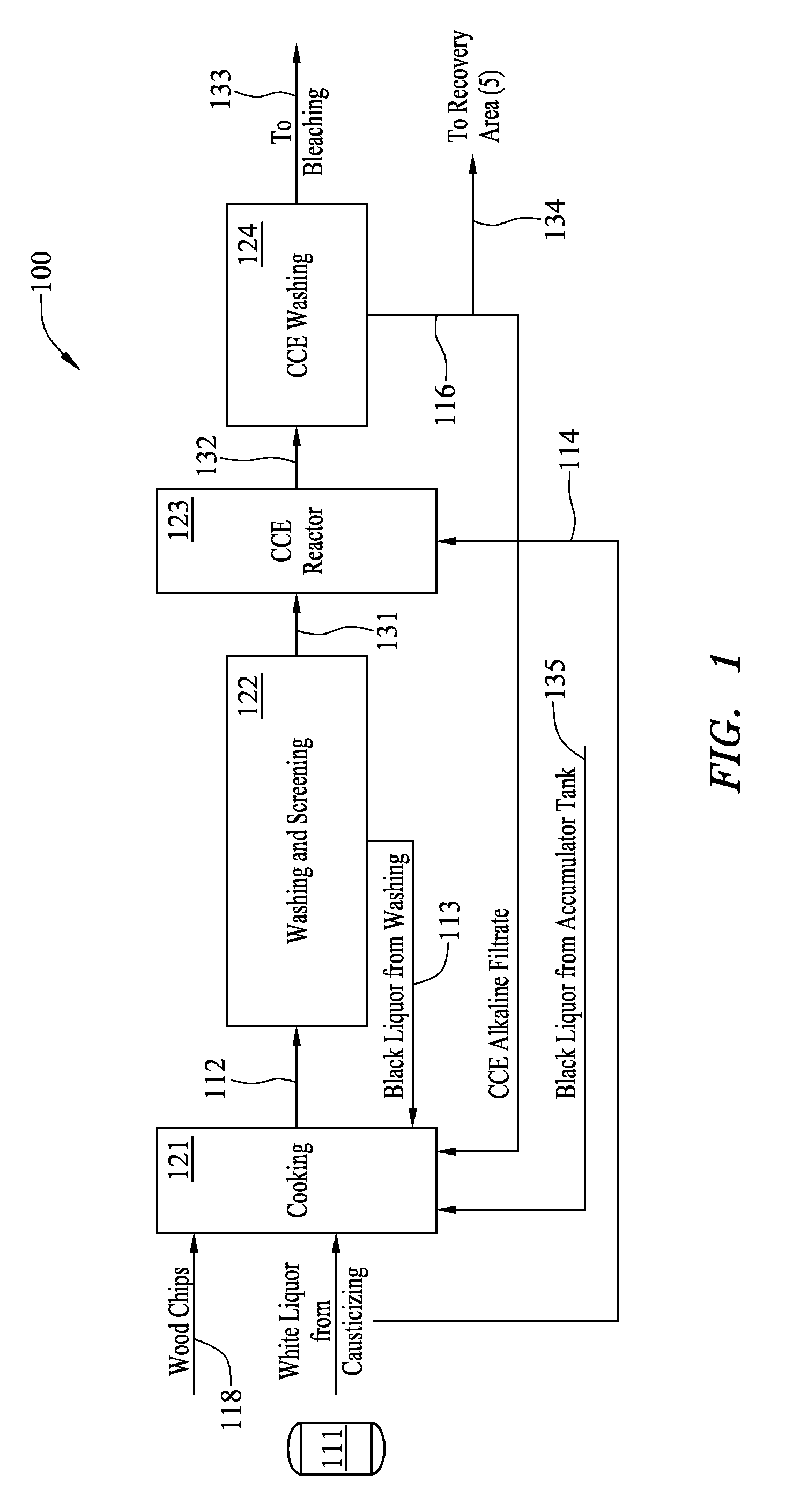
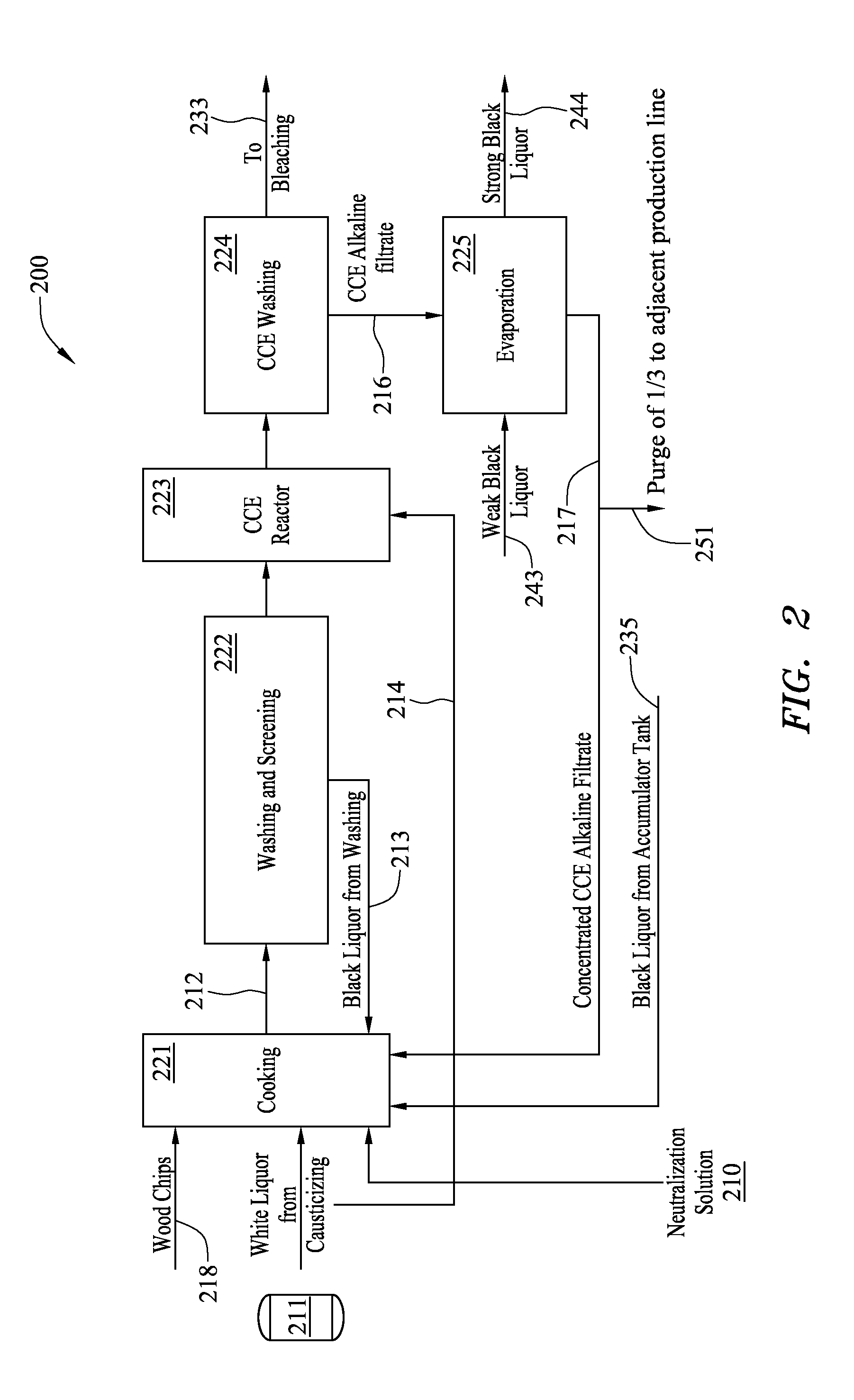
Method and system for pulp processing using cold caustic extraction with alkaline filtrate reuse
ActiveUS20110272109A1Improve efficiencyHigh purityPretreatment with water/steamNatural cellulose pulp/paperWood fibreEvaporation
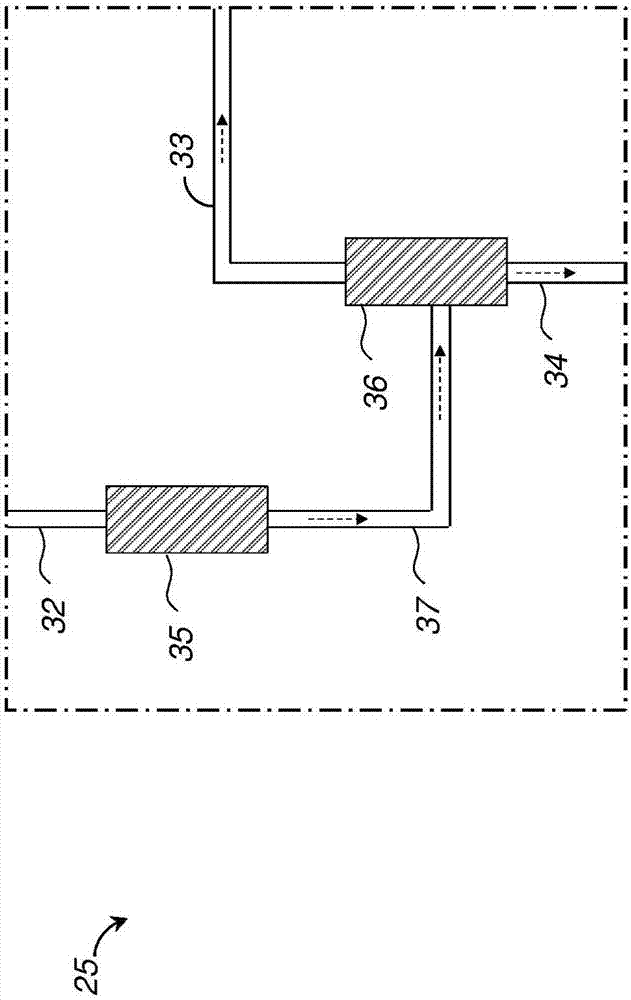
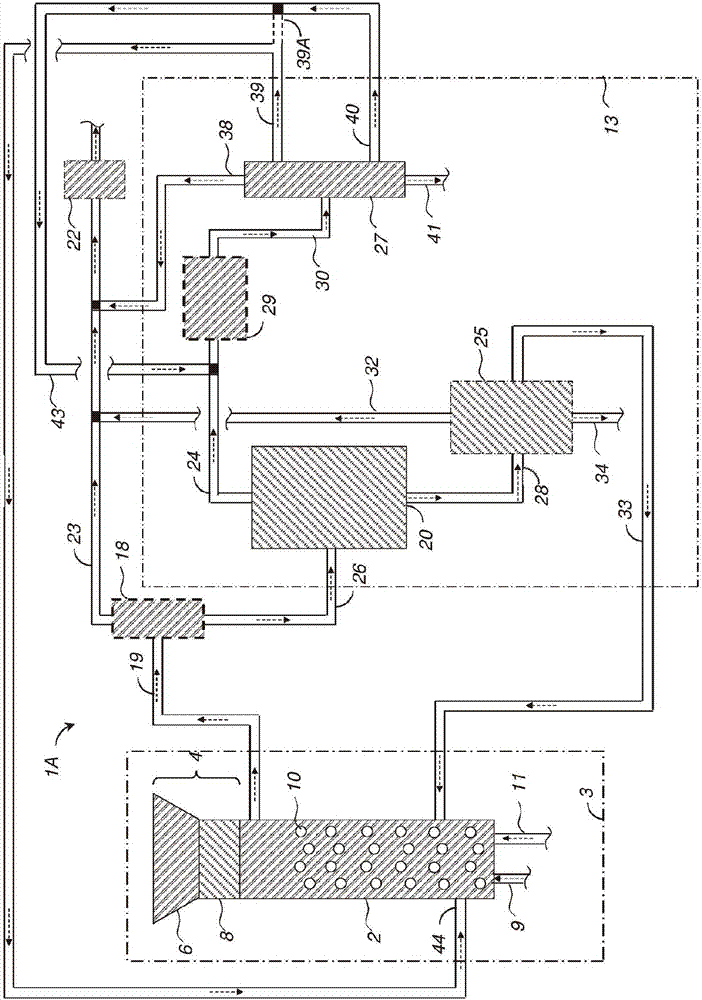
A method for pulp processing includes a cold caustic extraction stage in which the spent cold caustic solution and the spent liquid used to wash the extracted pulp are concentrated by an evaporation system. The concentrated liquid can be used as part of the neutralization and cooking liquor in the pulp process, leading to increased efficiency without significant reduction in pulp quality. Highly concentrated filtrate from the cold caustic extraction stage may help reduce hemicellulose deposition on wood fiber during the cooking step.
Owner:BAHIA SPECIALTY CELLULOSE
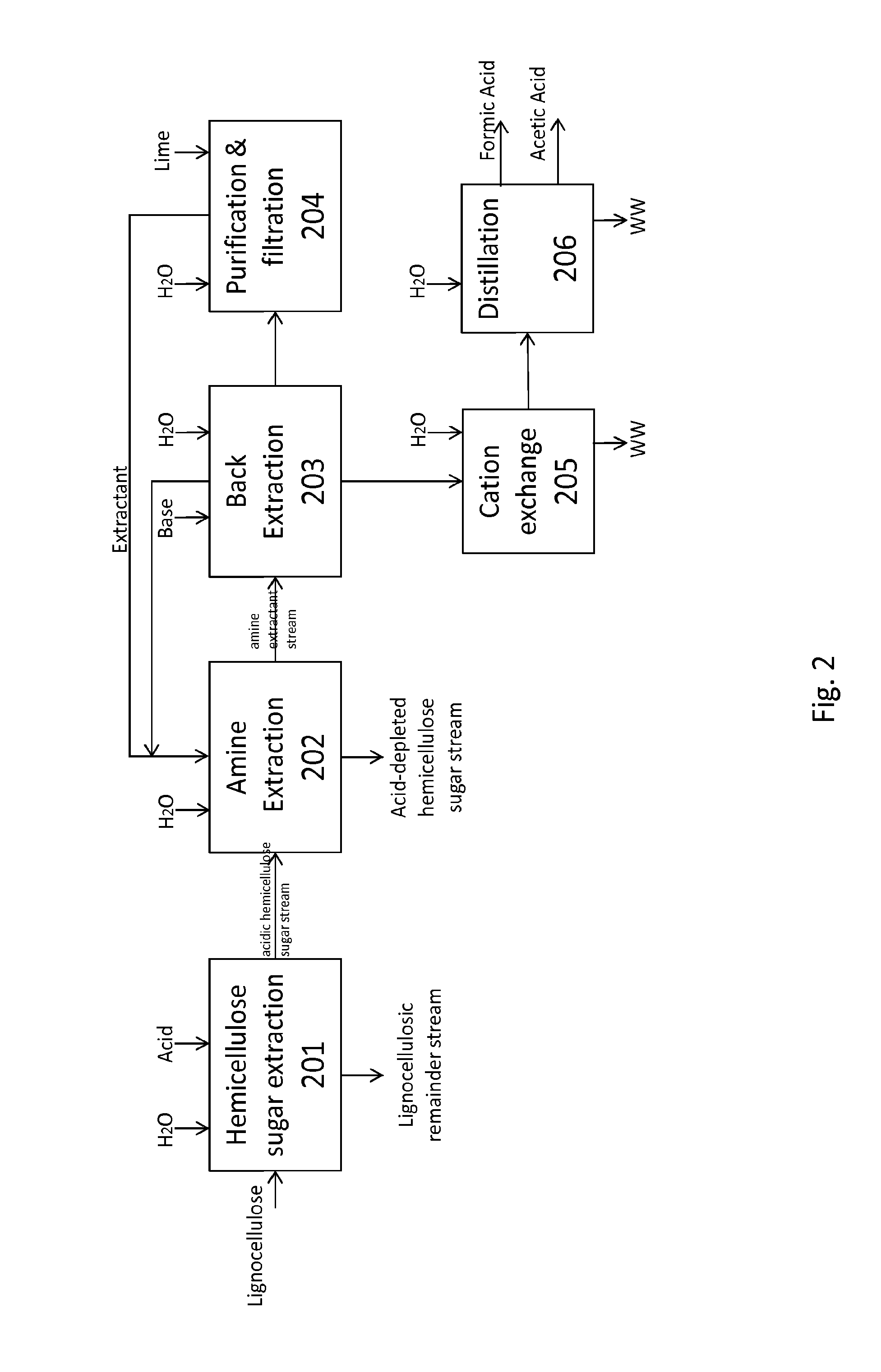
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
ActiveUS20150136121A1Increase acid concentrationChromatographic cation exchangersPurification using adsorption agentsSugarHemicellulose
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products.
Owner:VIRDIA
Method for producing high purity lignin
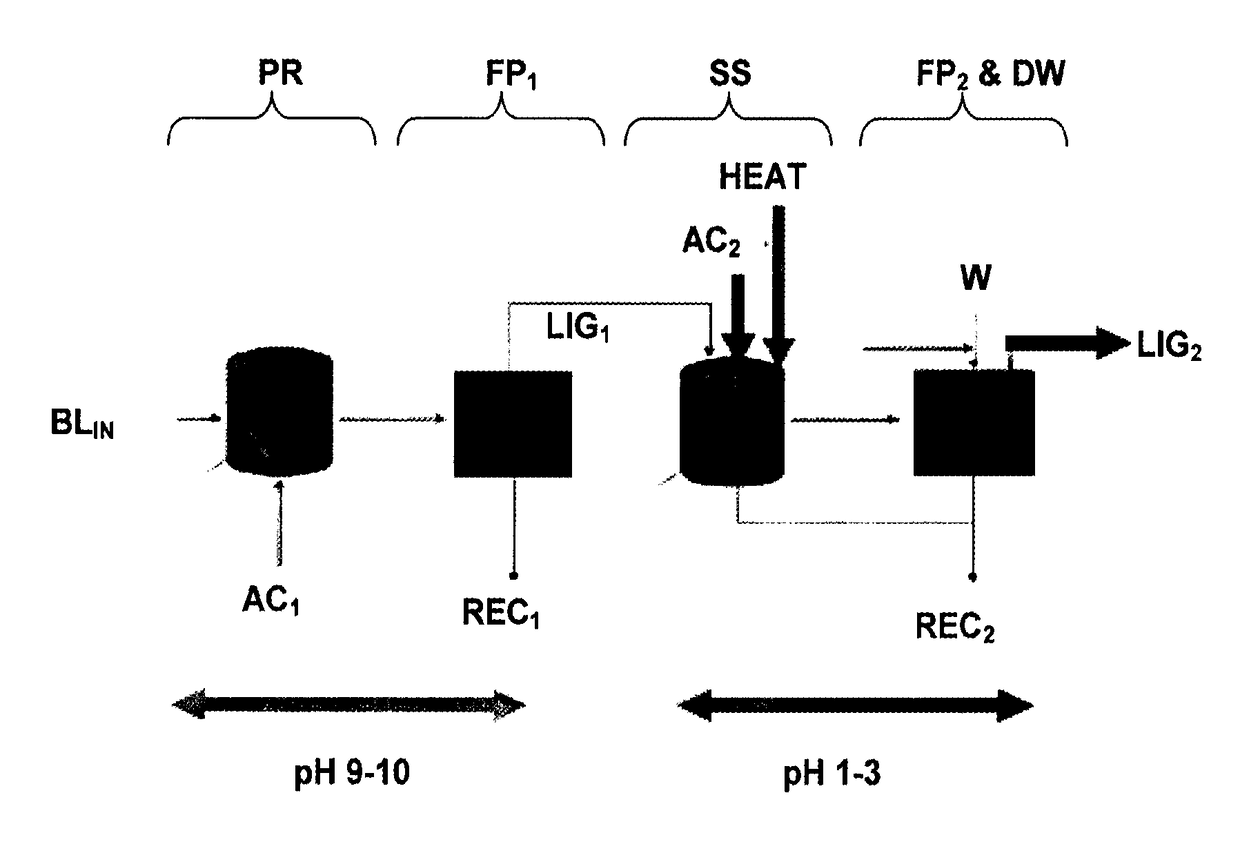
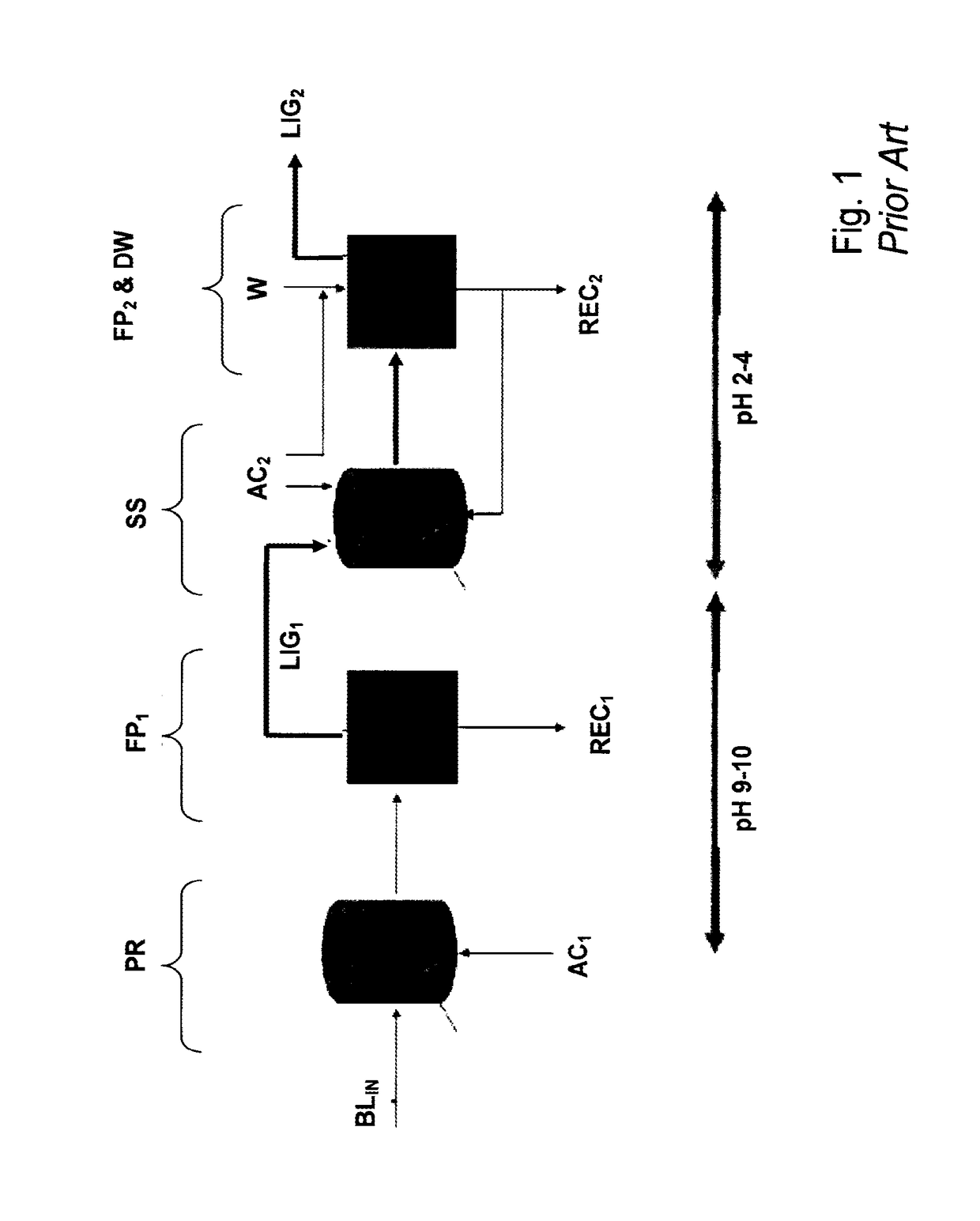
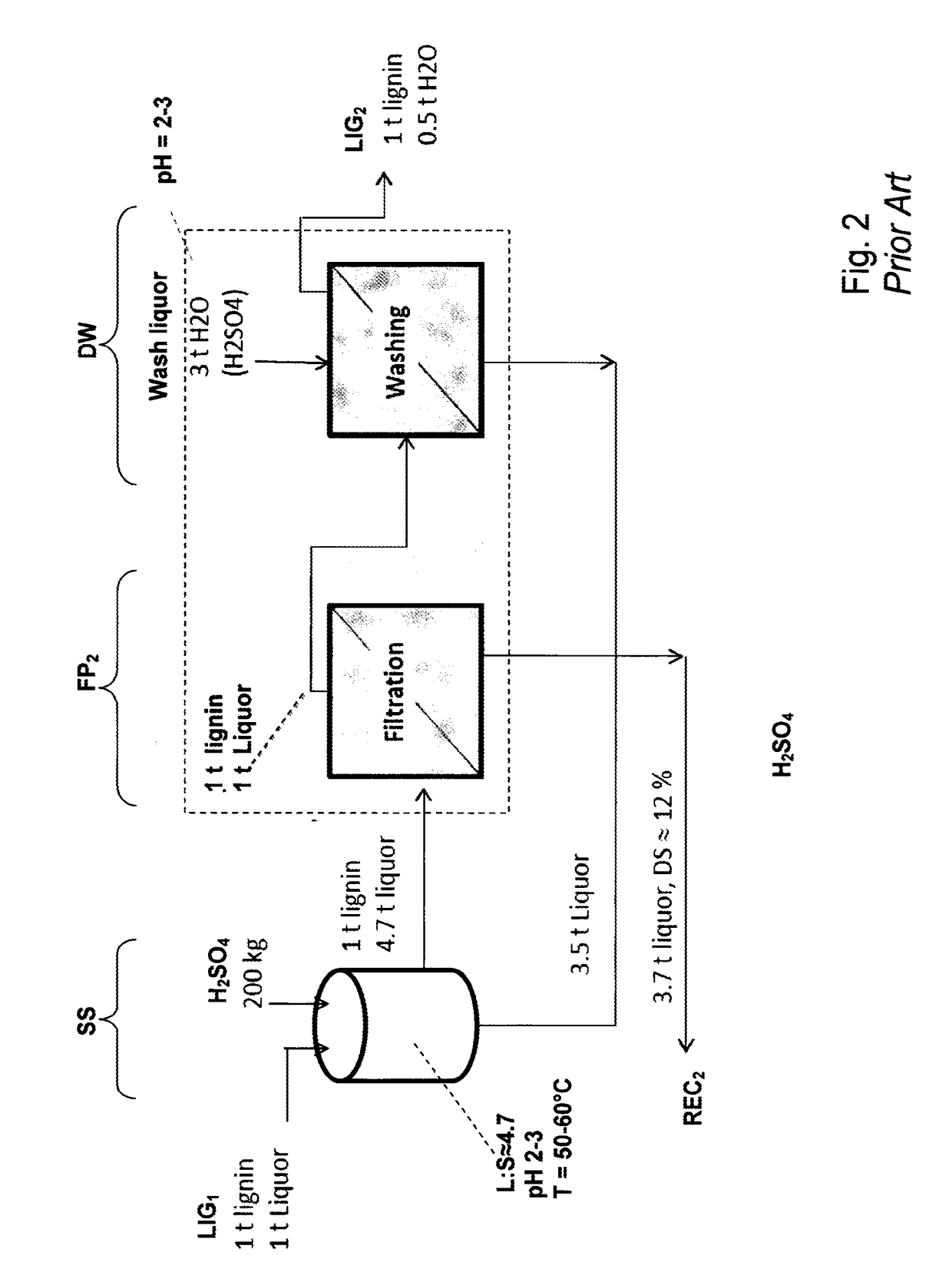
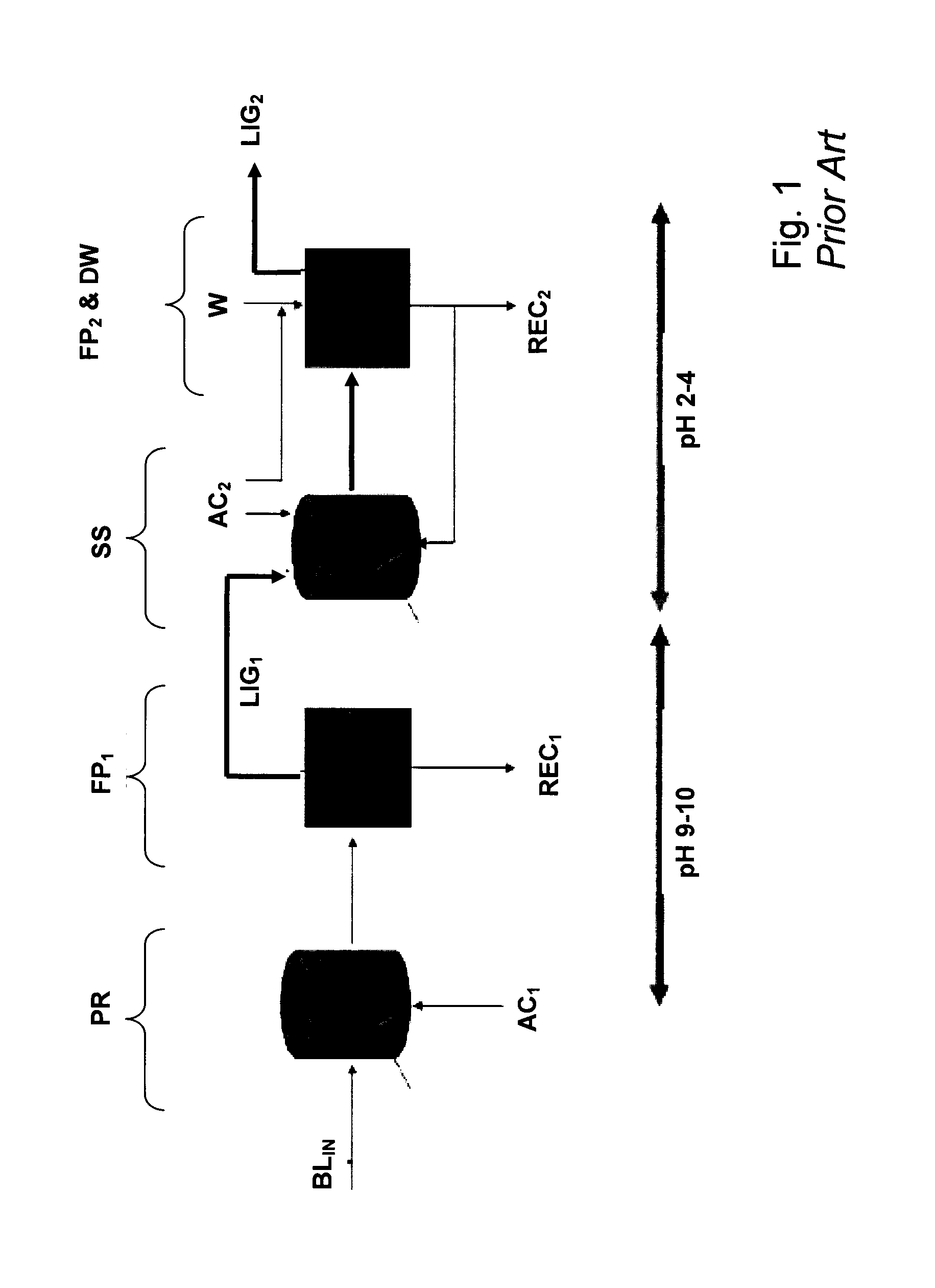
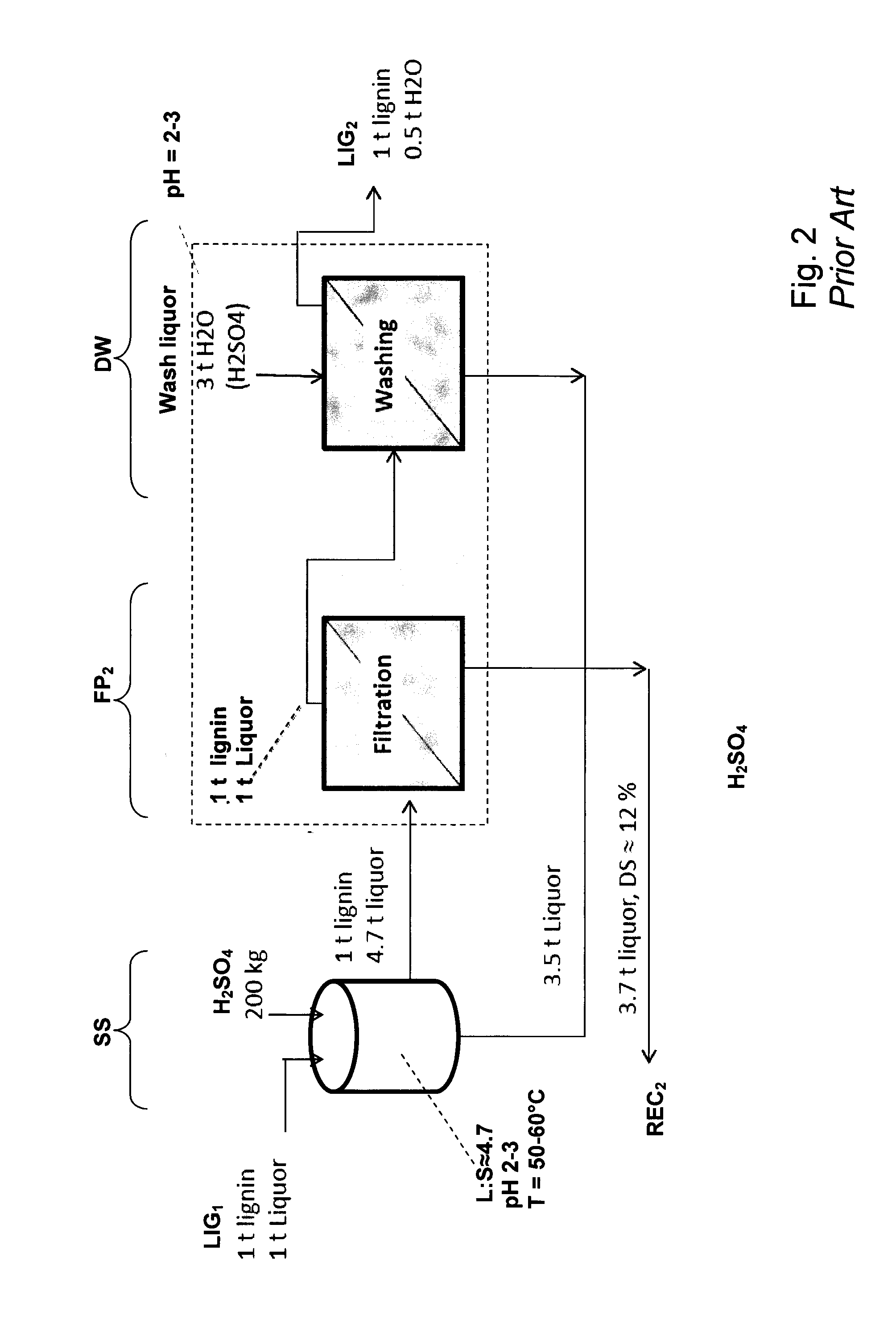
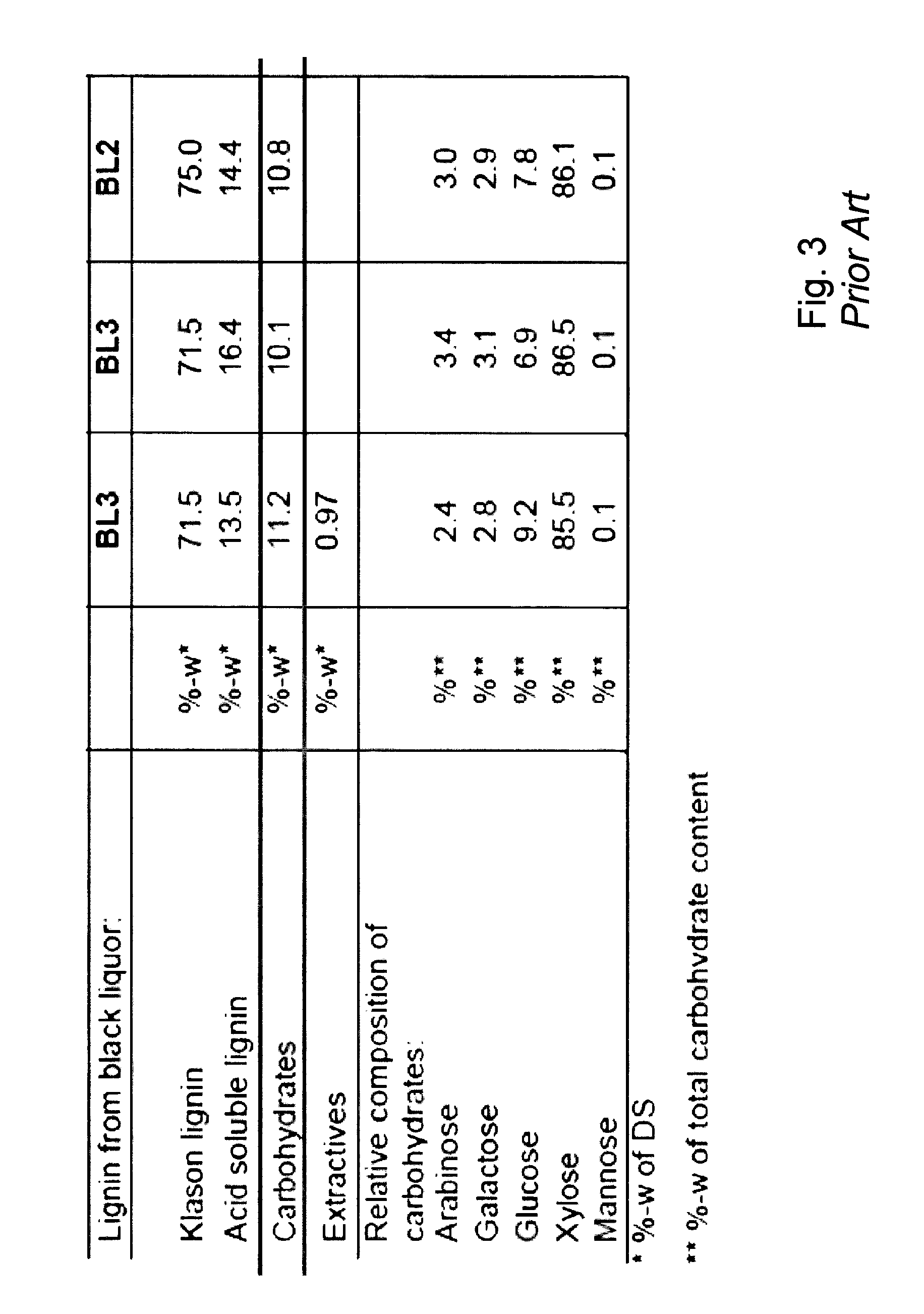
InactiveUS20170355723A1Low in carbsLoss is producedLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryBlack liquorStrong acids
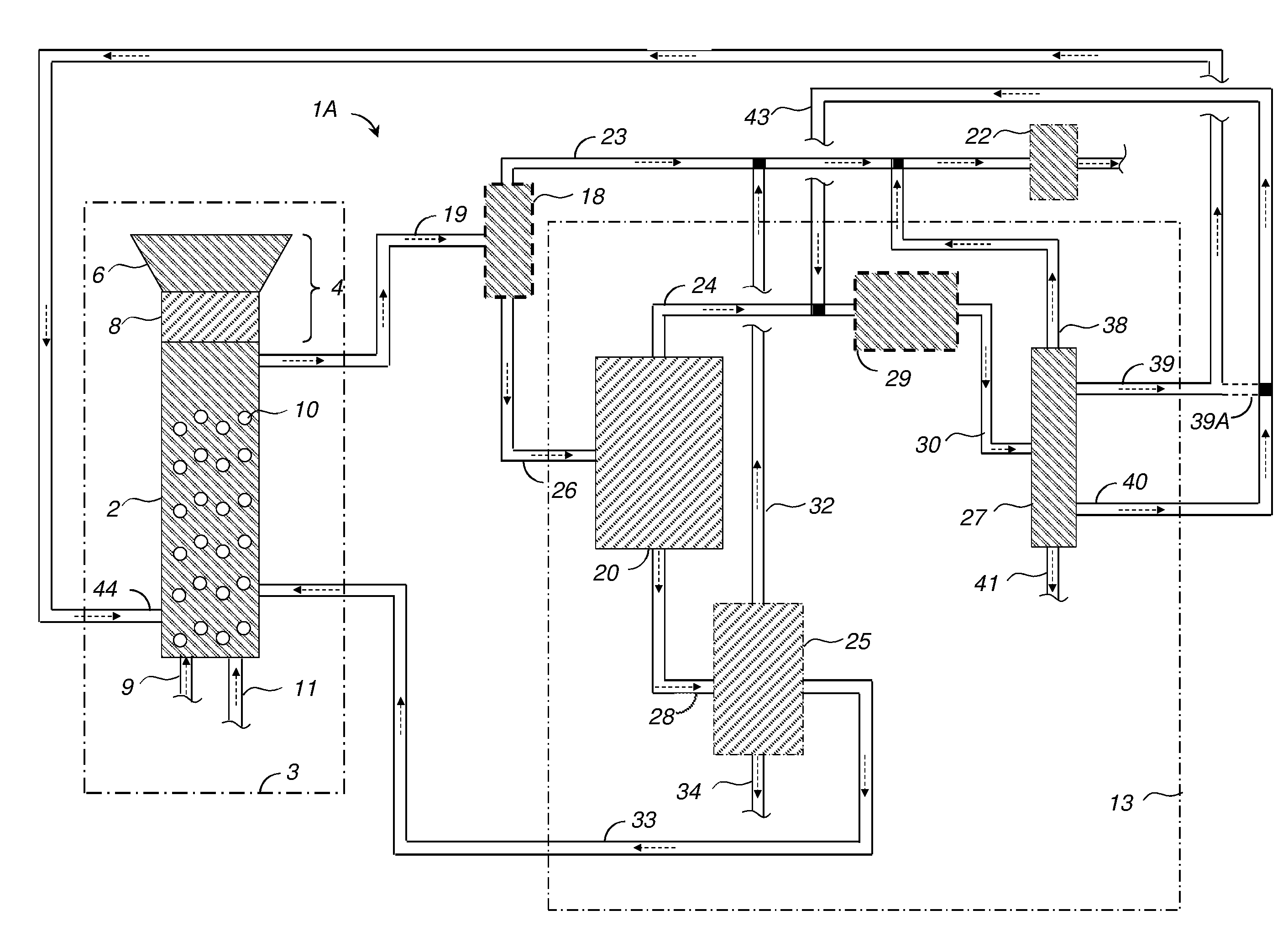
The method is for separation of lignin from original black liquor (BLIN) that has a first precipitation stage (PR) for precipitation of lignin by a first acidification using acidifier AC1, preferably using CO2, at alkaline conditions, then separating a lignin cake with subsequent suspension of the lignin cake in a strong acid in order to leach our metals from the lignin followed by dewatering and obtaining a clean lignin product LP. The process further is improved by intensified hydrolysis of lignin cake such that most of the carbohydrates are broken down to dissolvable monomers that could be separated from the lignin in the filtrate from a filtering stage subsequent to the hydrolysis. The improved hydrolysis could reduce as much as 90% of the carbohydrate content using a moderately increased temperature and increased charge of acidifier while avoiding any larger lignin yield losses.
Owner:VALMET AB
Method for extracting ammonium salt and methanol from a liquid obtained from foul condensates in a cellulose pulp mill
InactiveUS20100316553A1Avoid NOx emissionIncrease the number ofAmmonium nitratesNitrogen compoundsCellulose pulpAmmonia
Desirable chemicals are recovered from a raw material that is formed in substantial amounts during the production of cellulose pulp from renewable lingo-cellulose material. An ammonia / ammonium-containing methanol / water mixture is acidified with an acid that has the ability of forming ammonium salt with the ammonium. The mixture is circulated and passed through an apparatus that has an indirect heat exchanger combined with an storage volume fitted with a gas collection device.
Owner:METSO POWER AB +1
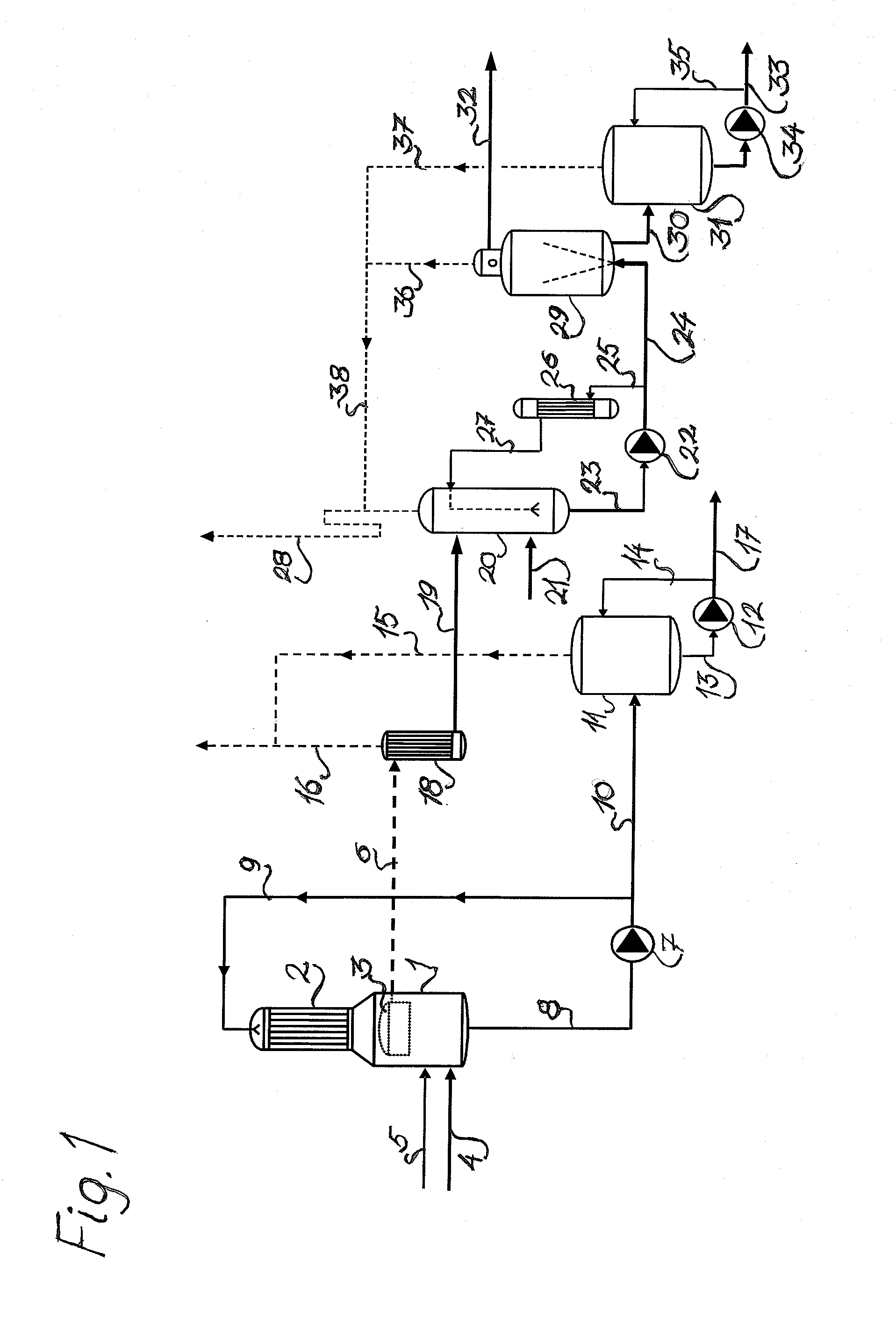
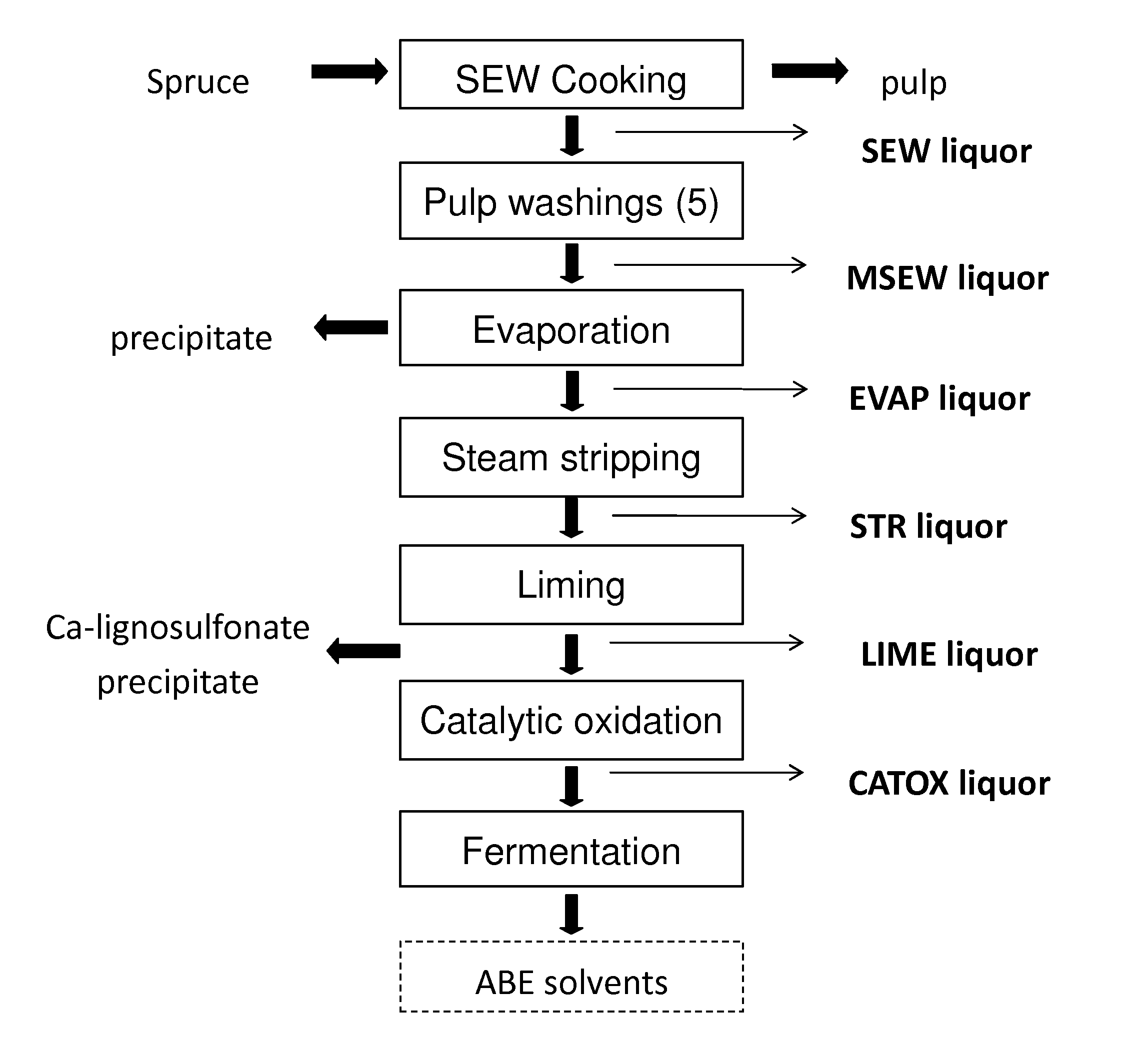
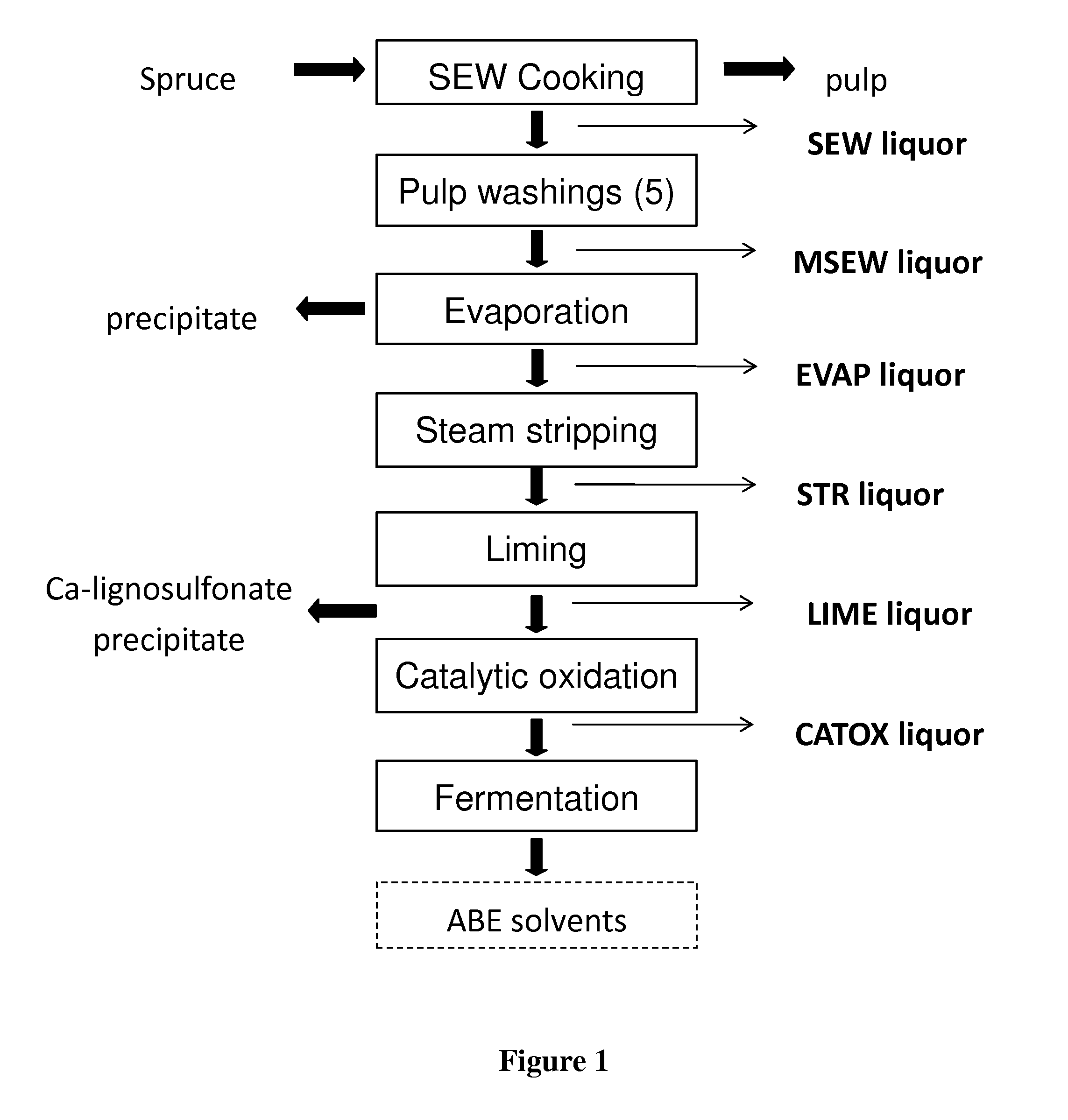
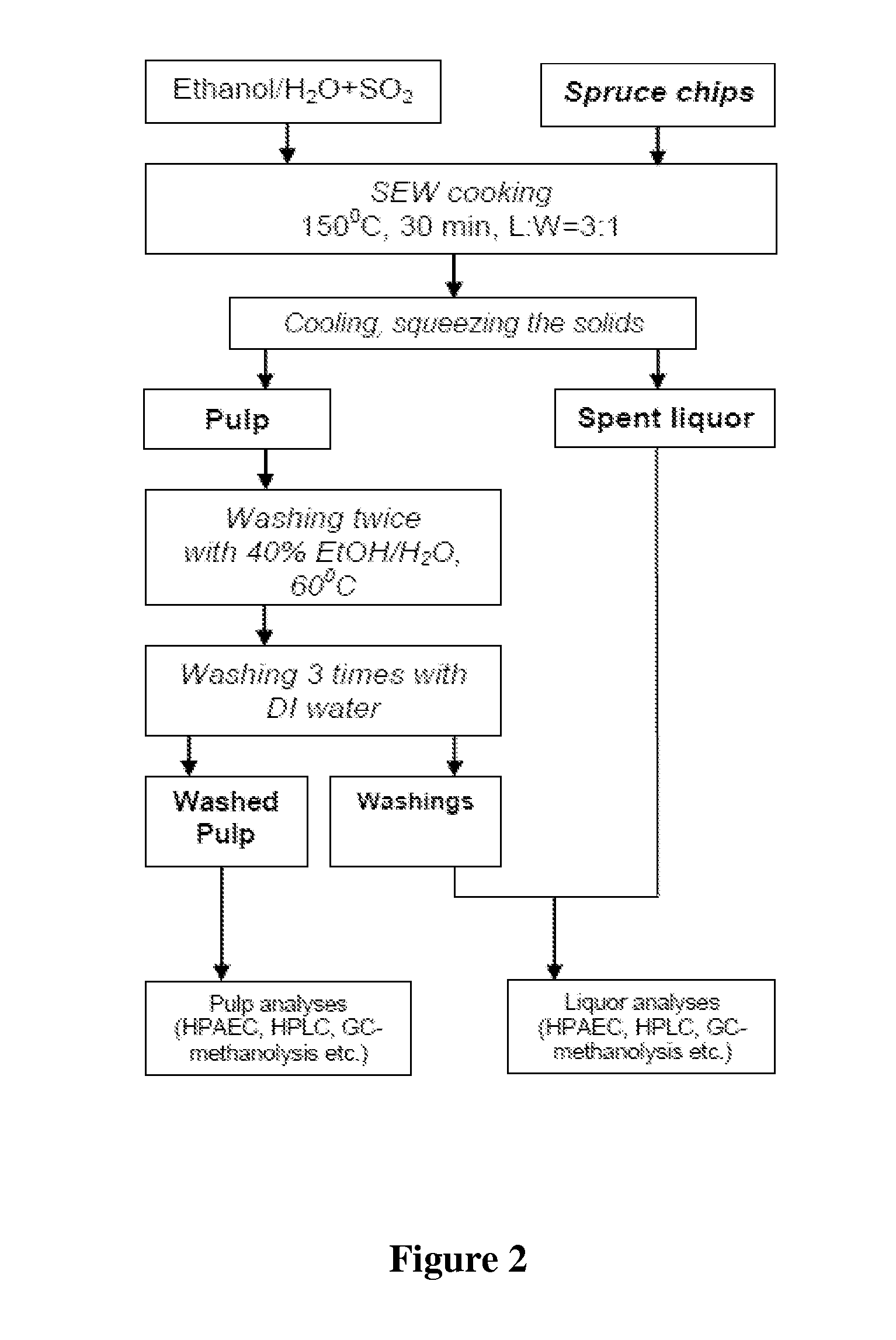
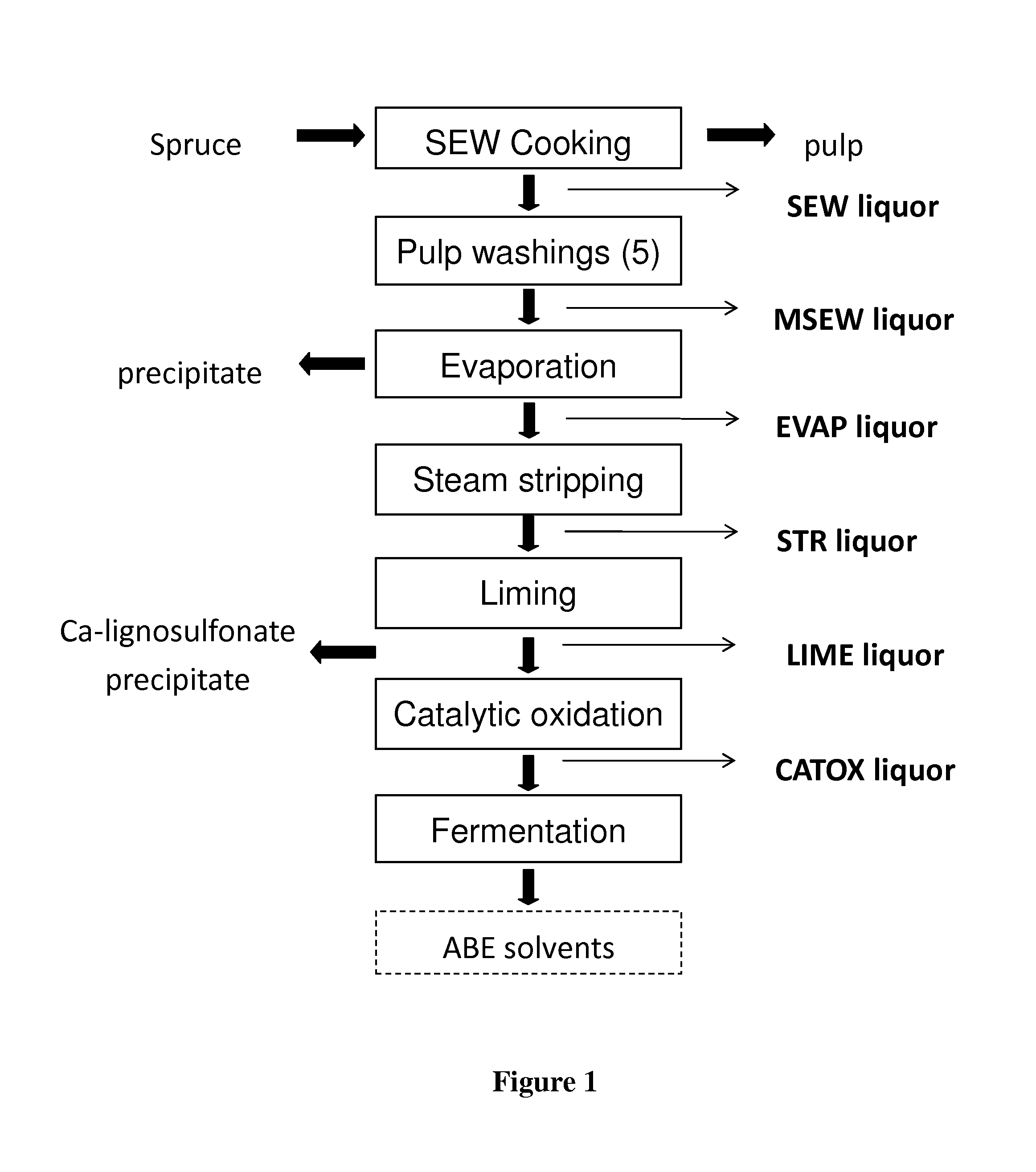
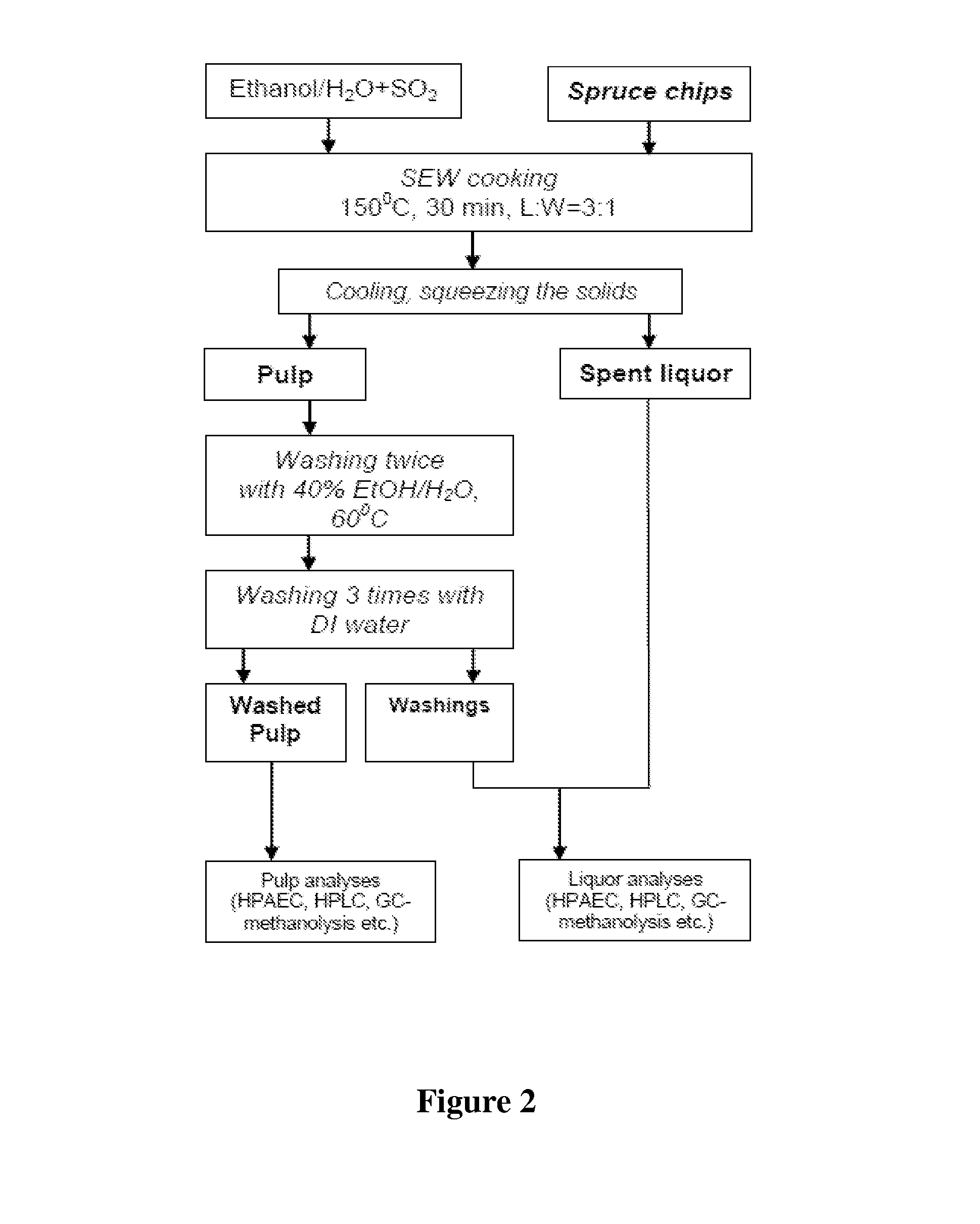
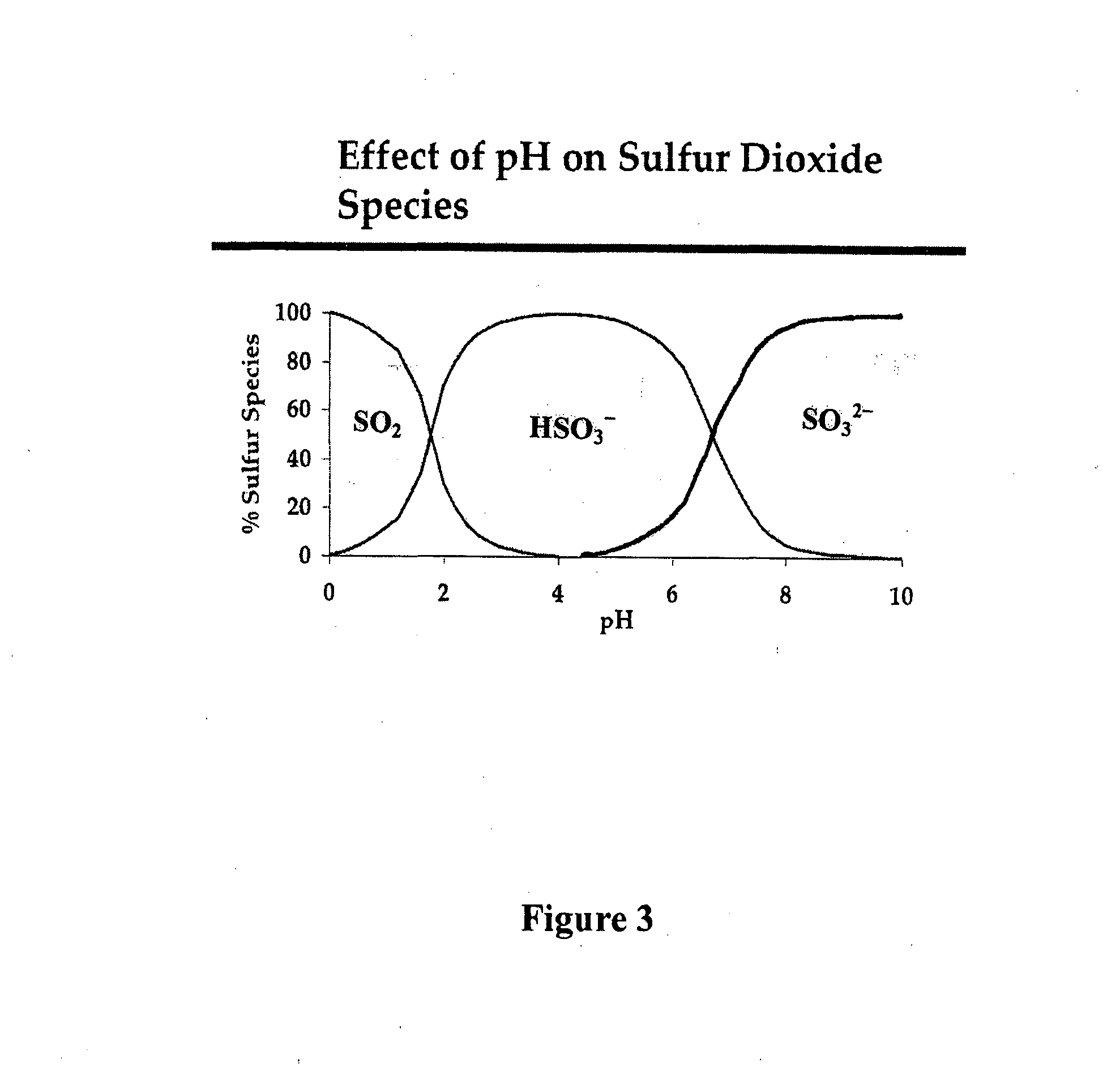
Conditioning of SO2-ethanol-water spent liquor for fermentation by clostridia
The present invention relates to producing chemicals and biofuels from wood material, e.g. mixed forest biomass. Specifically, the invention concerns a process for conditioning spent liquor produced by SO2-ethanol-water (SEW) fractionation of wood chips for fermentation to butanol, ethanol and acetone / isopropanol (so called ABE process) by Clostridia bacteria.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Process for the isolation of lignin from black liquor and modification of the lignin for plastic applications
A process for the isolation of lignin from black liquor and modification of lignin for use in many plastic applications is disclosed. The isolation of lignin consists of removing all of the non-lignin components from black liquor solution. The non-lignin components including but not limited to organic acids, sugars, and inorganic materials can be removed using either solvent extraction or ion-exchange resin or a combination of both methods. The isolated lignin is water soluble. The non-lignin components can be further isolated and sold or reused in the pulping or lignin isolation processes. The isolated lignin can be further modified in order to meet the needs of the desired plastic application.
Owner:ORGANIC CHEM
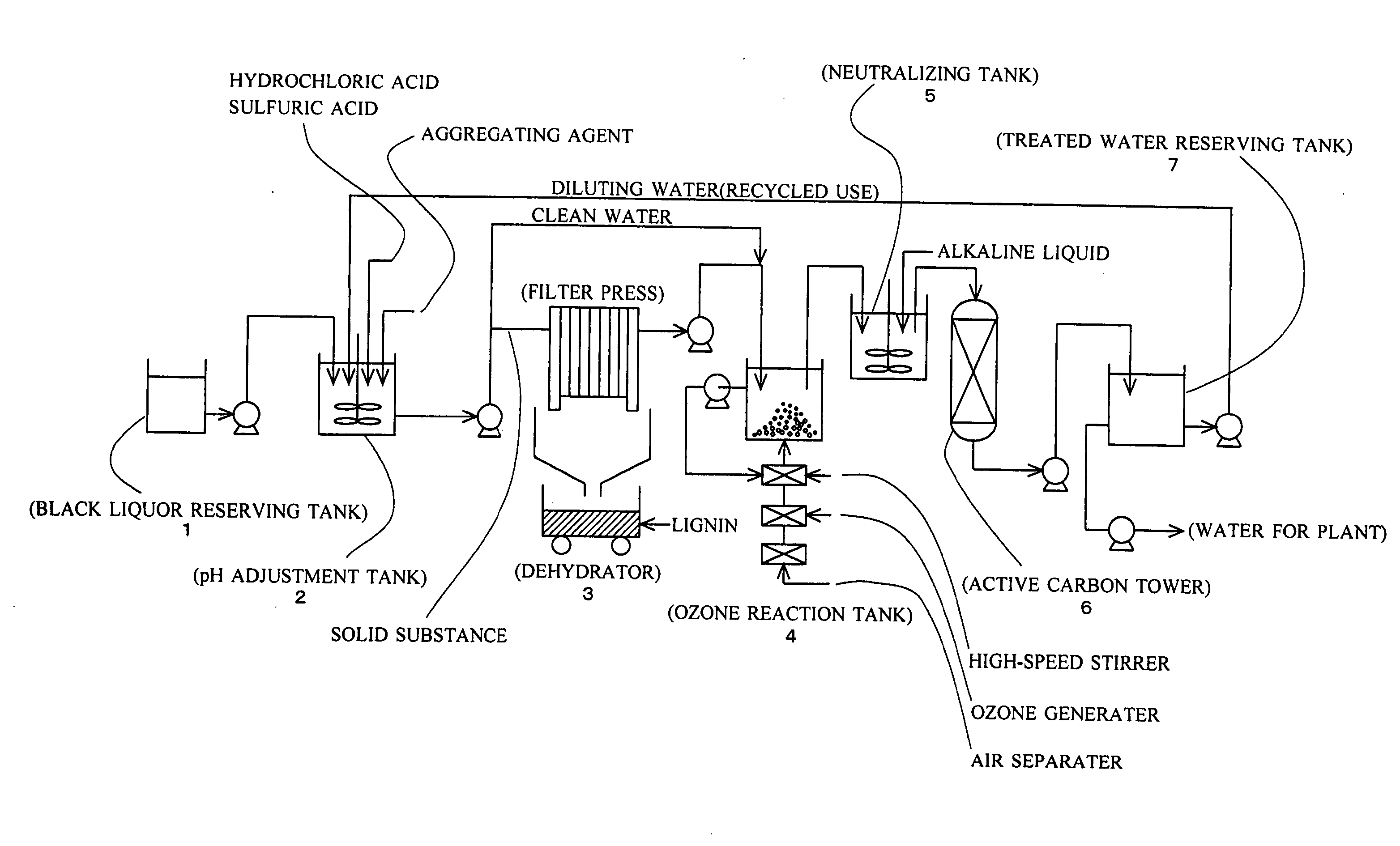
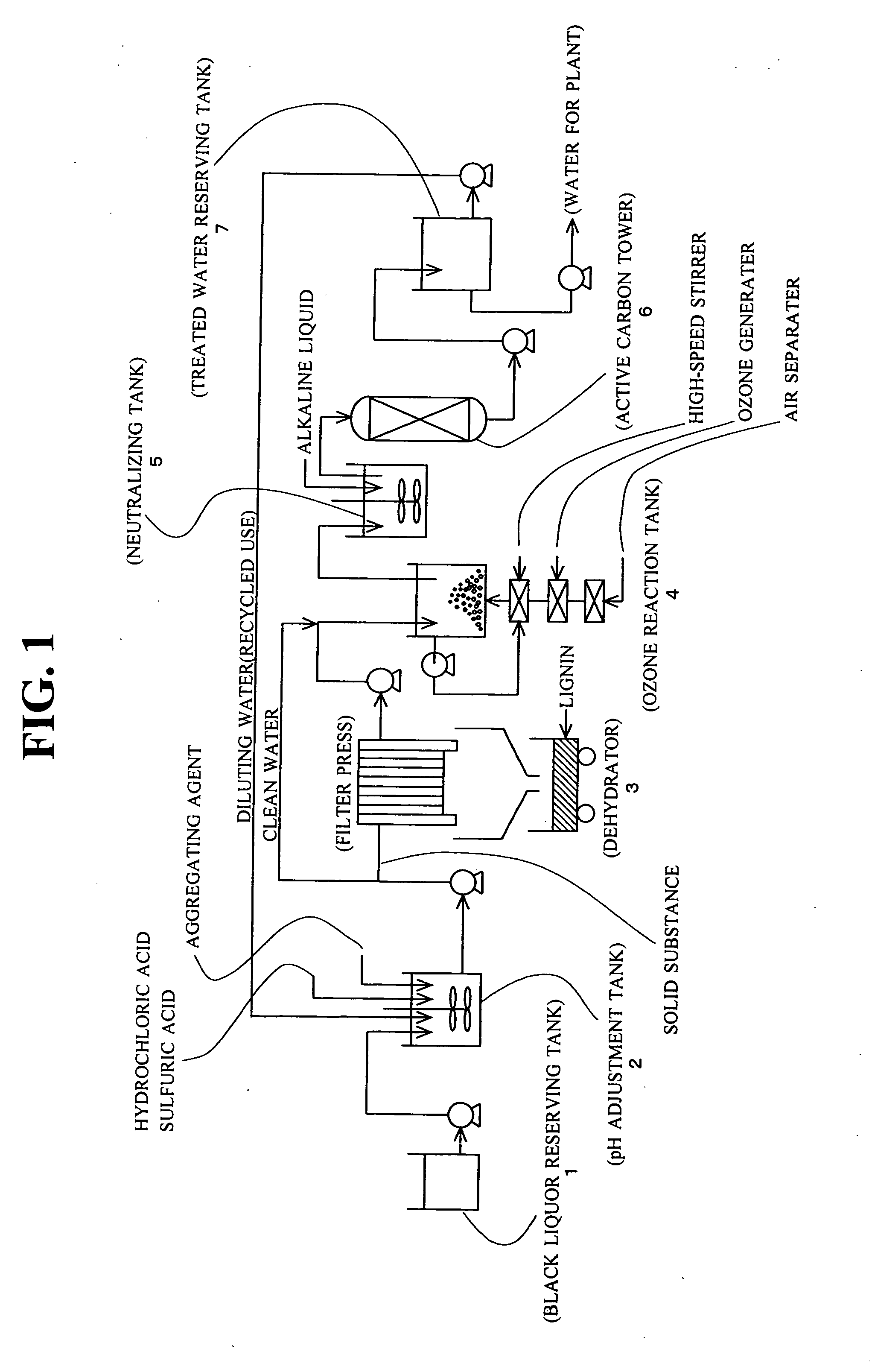
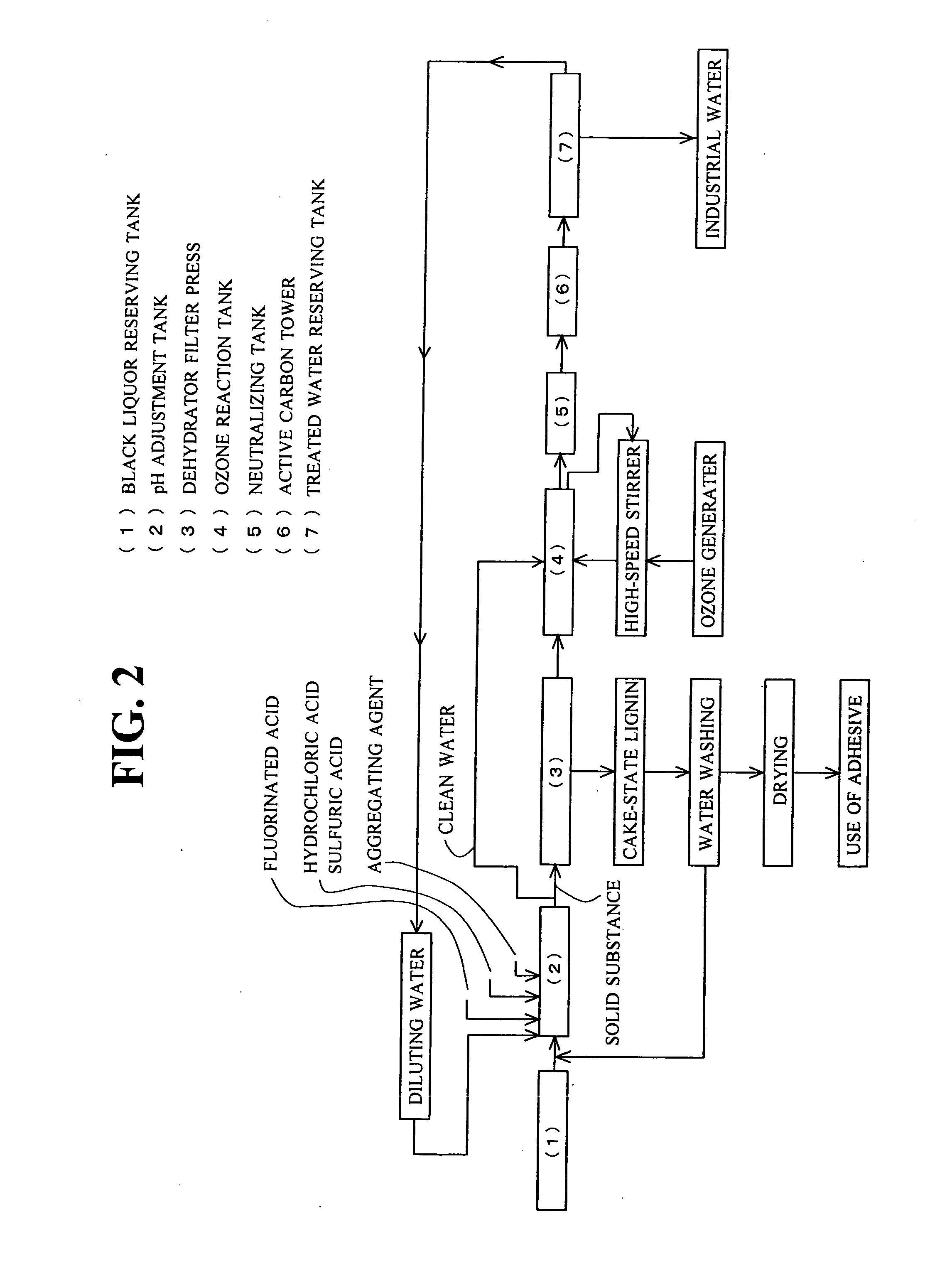
Black Liquor Treatment Method
InactiveUS20070227979A1Easy to disassembleDecomposing power is improvedPulp liquors combustionSolid sorbent liquid separationLignin degradationBlack liquor
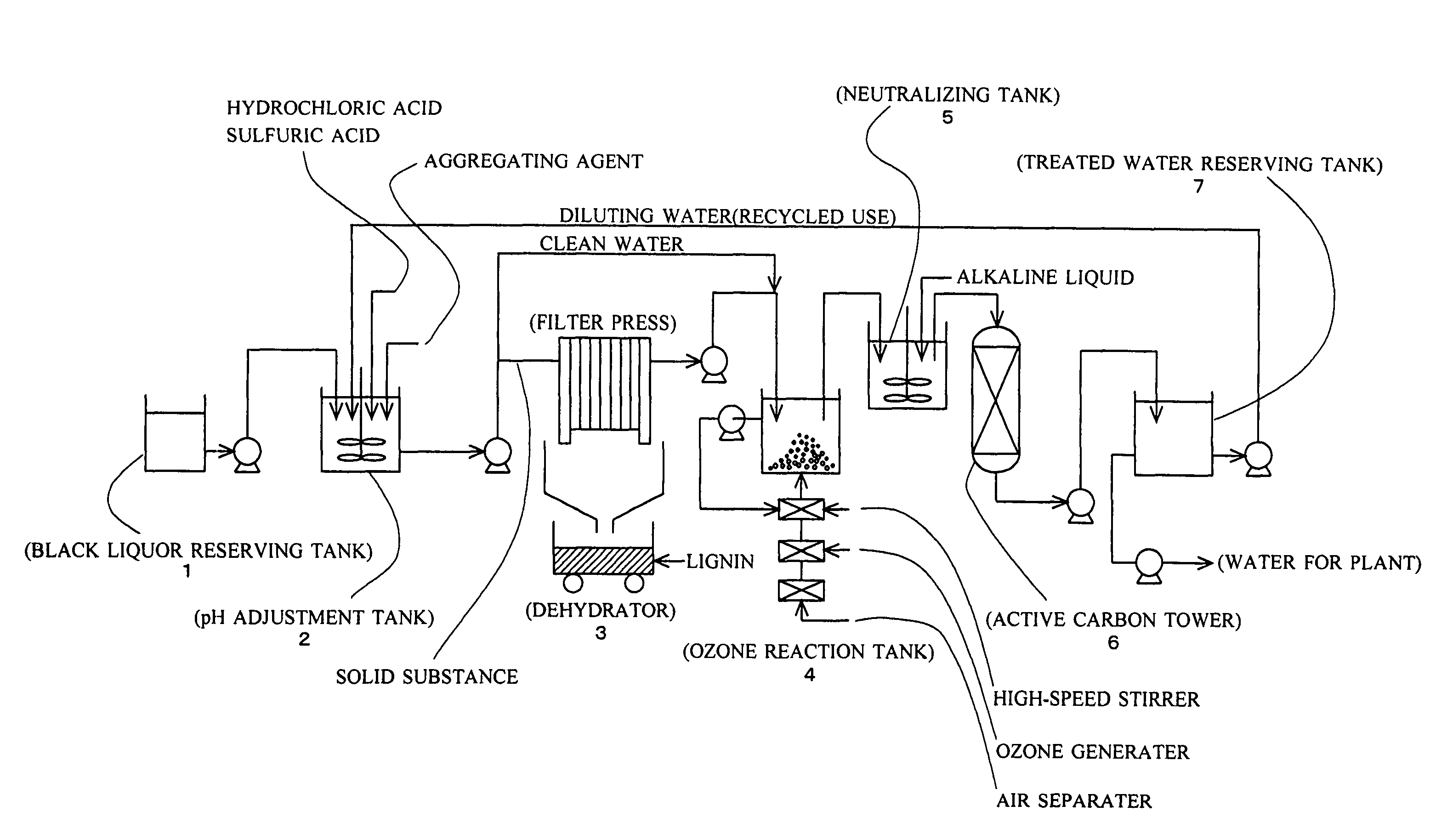
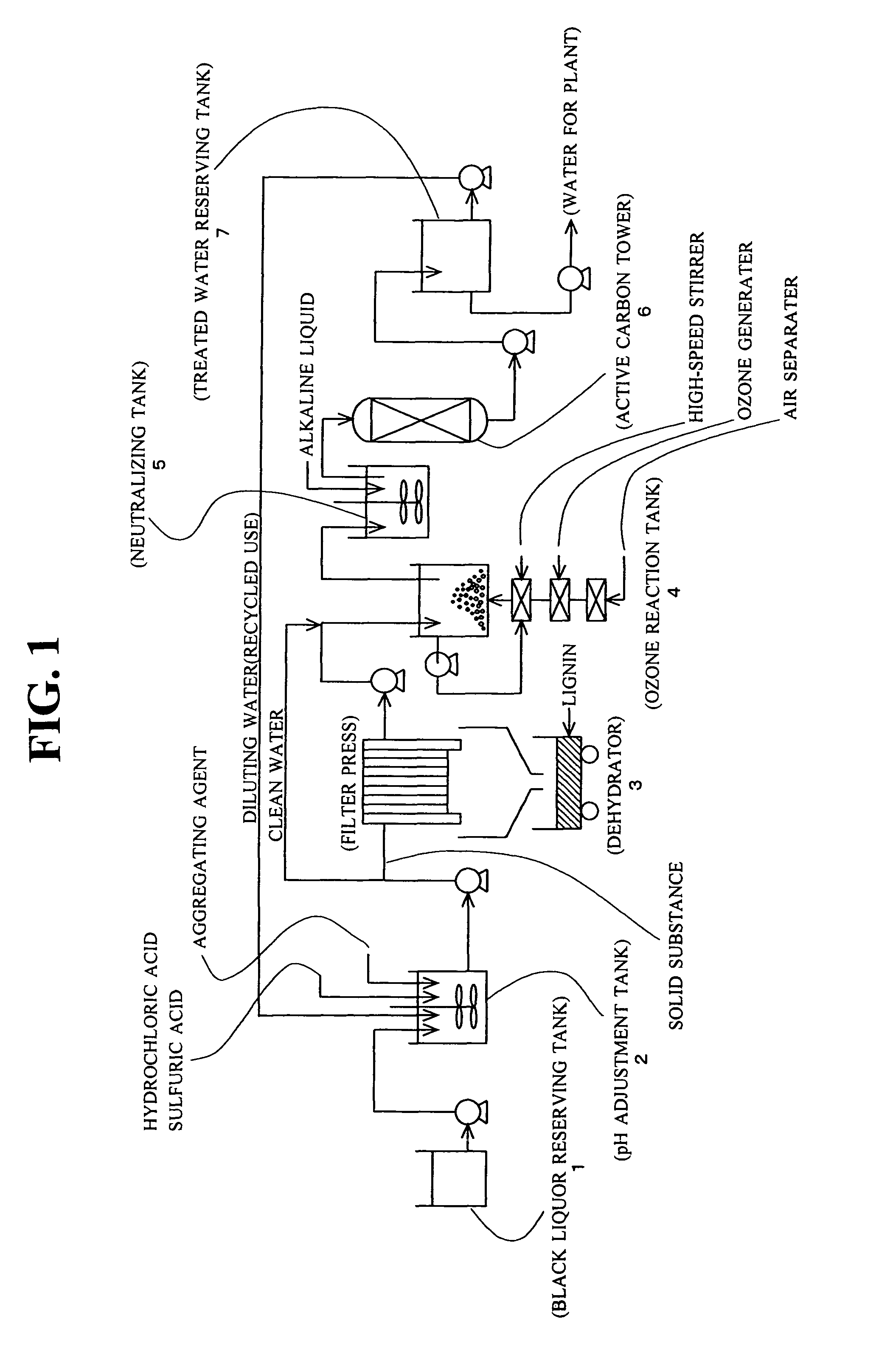
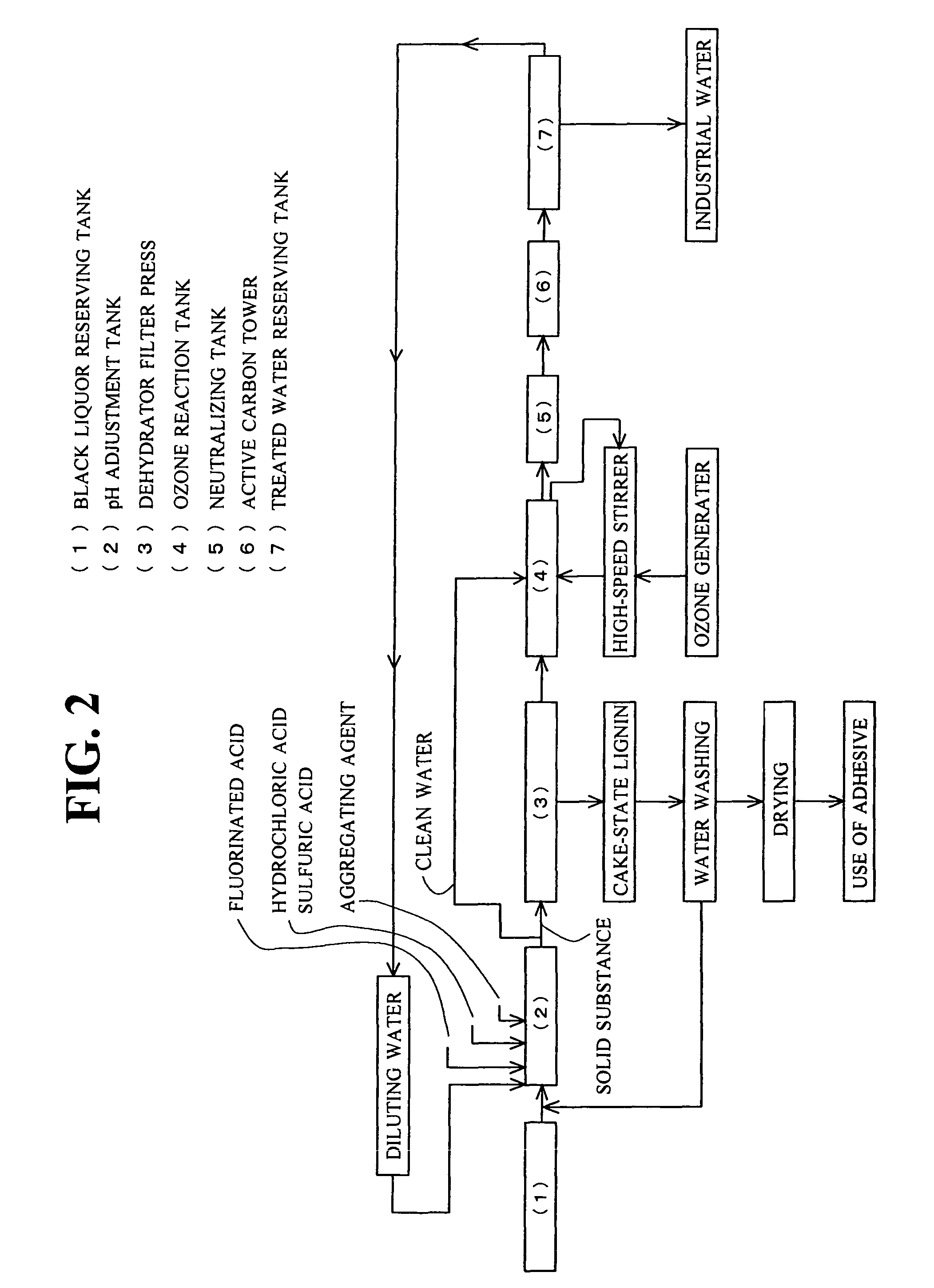
Lignin and alkali are efficiently sorted out of alkaline black liquor discharged from the paper manufacturing / pulp and paper manufacturing industries and the treated water is made as purified water. Acid is added to the black liquor and its pH is adjusted to 2.5 to 3.5. An aggregating agent is added to have lignin contained in the black liquor settled and the black liquor is separated into lignin and clean water. Ozone gas, preferably in the micro bubble state, is given to the clean water for contact reaction.
Owner:K I SYST
Process for treating black liquor
The present invention relates to a method of membrane-filtrating a lignin containing composition in order to obtain a lignin fraction more suitable for further treatments. In particular it relates to treating a liquid lignin composition to obtain a lignin fraction having a desired molecular weight distribution by a membrane filtration. It comprises subjecting the liquid lignin composition to a first membrane filtration with a first filter cut-off adapted to remove species having a first molecular weight thereby providing a permeate with a molecular weight distribution defined by said cut-off. Then, the permeate from the first membrane filtration is; subjected to at least one further filtration step with a second filter cut-off, different from said first filter cut-off to provide a retentate (concentrate) with a molecular weight distribution defined by both the cut-off in the first filter the cut-off in said second filter. A dilution is performed on a desired lignin containing fraction at some point downstream of the first filtration unit. A lignin containing retentate (concentrate) is collected from the further ultrafiltration for further processing.
Owner:REN FUEL K2B
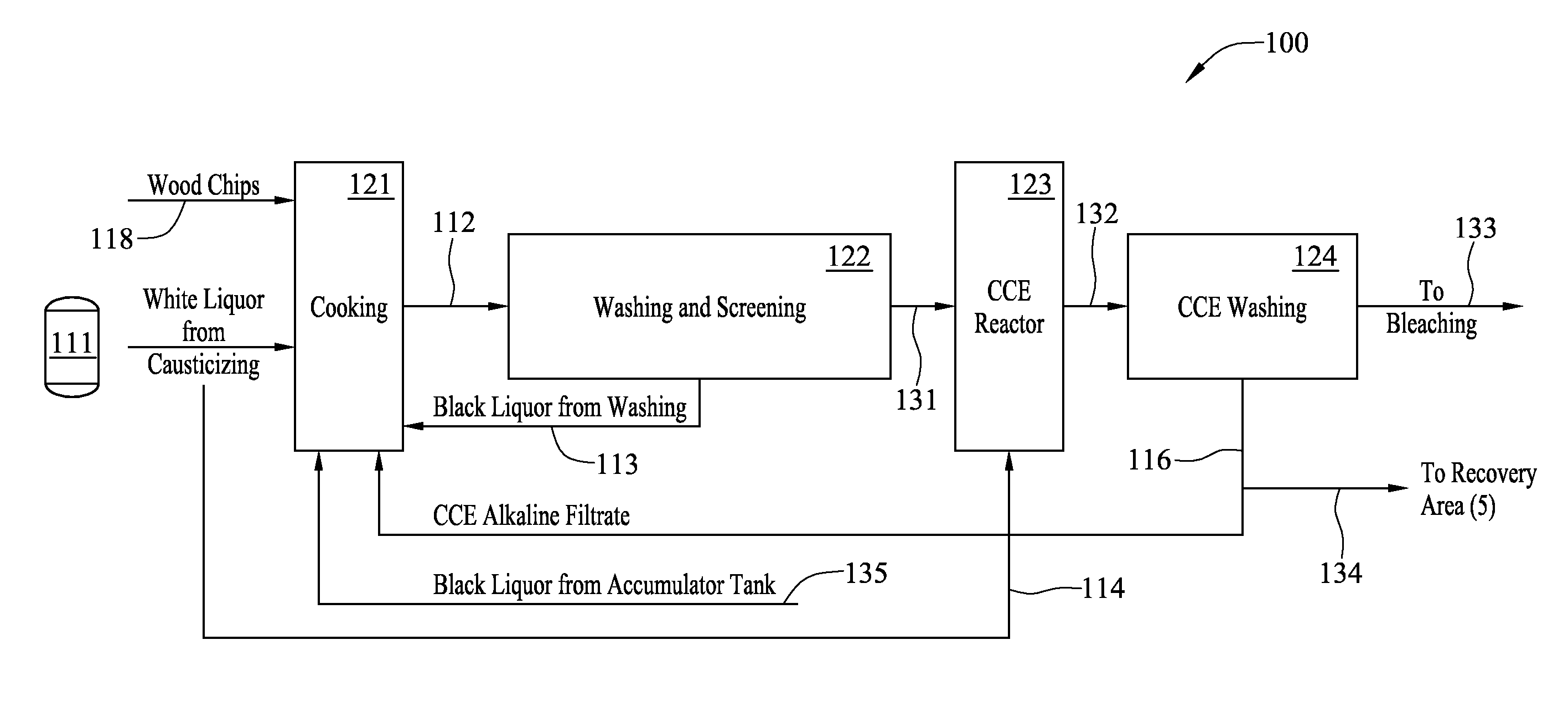
CRP Purge Treatment
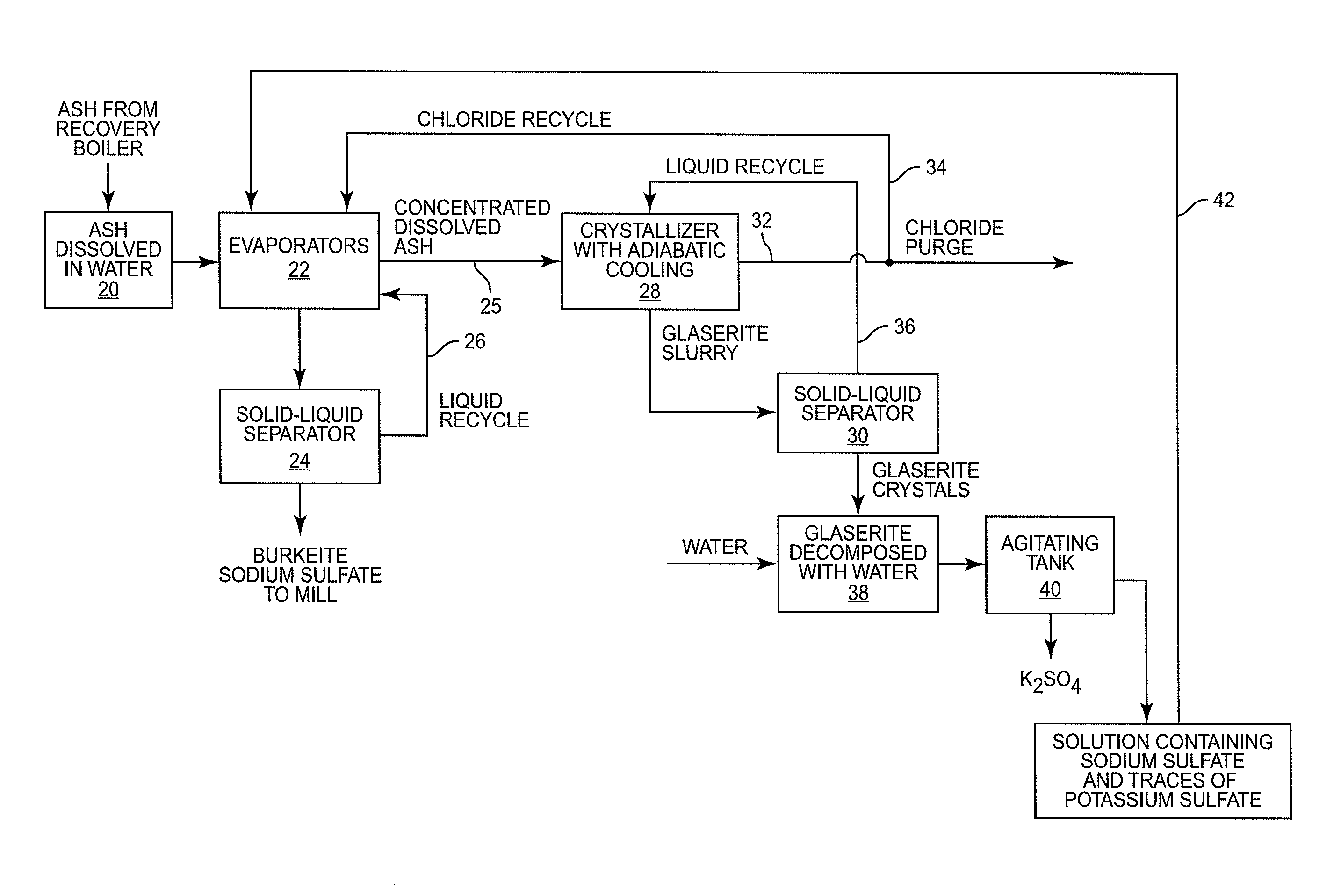
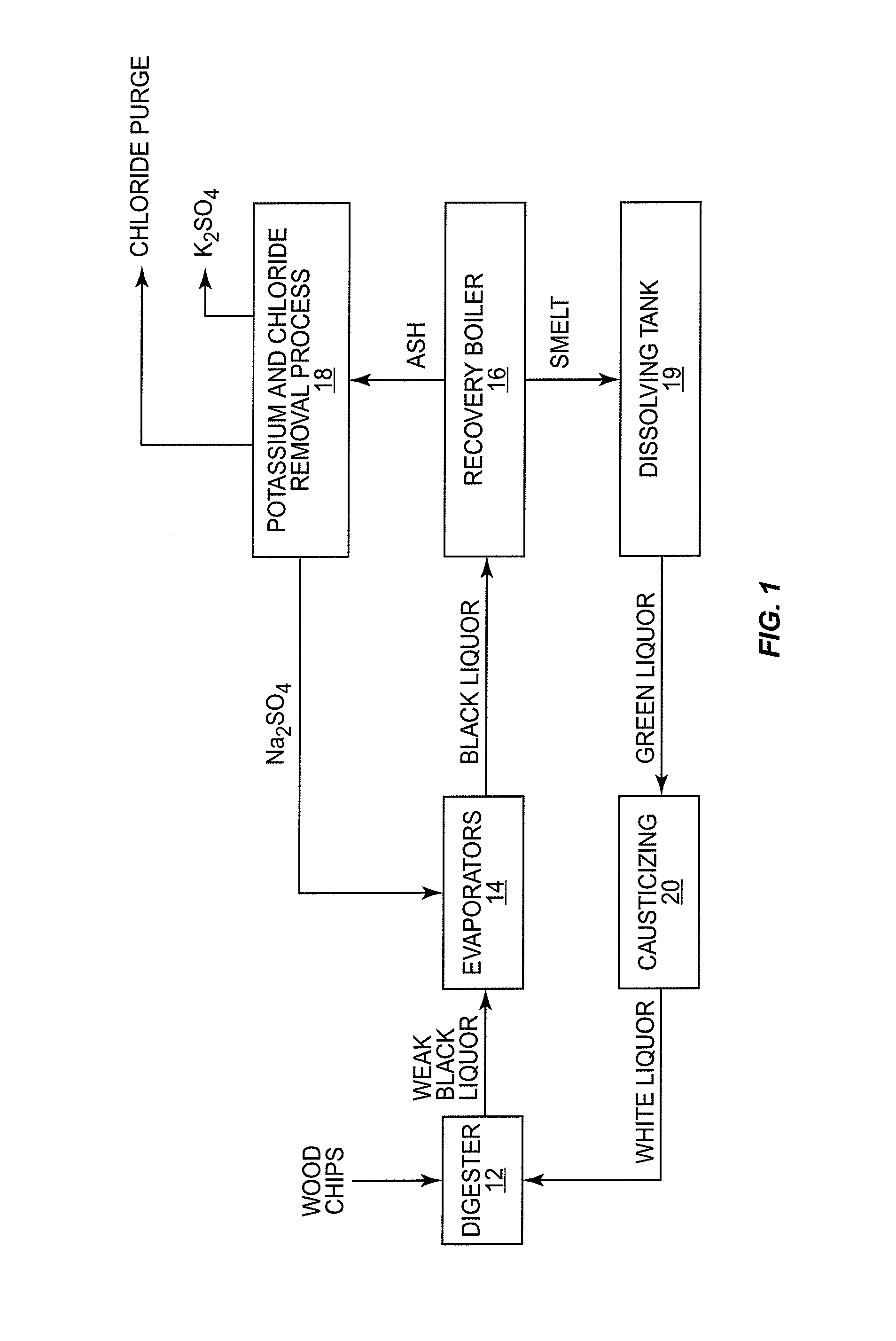
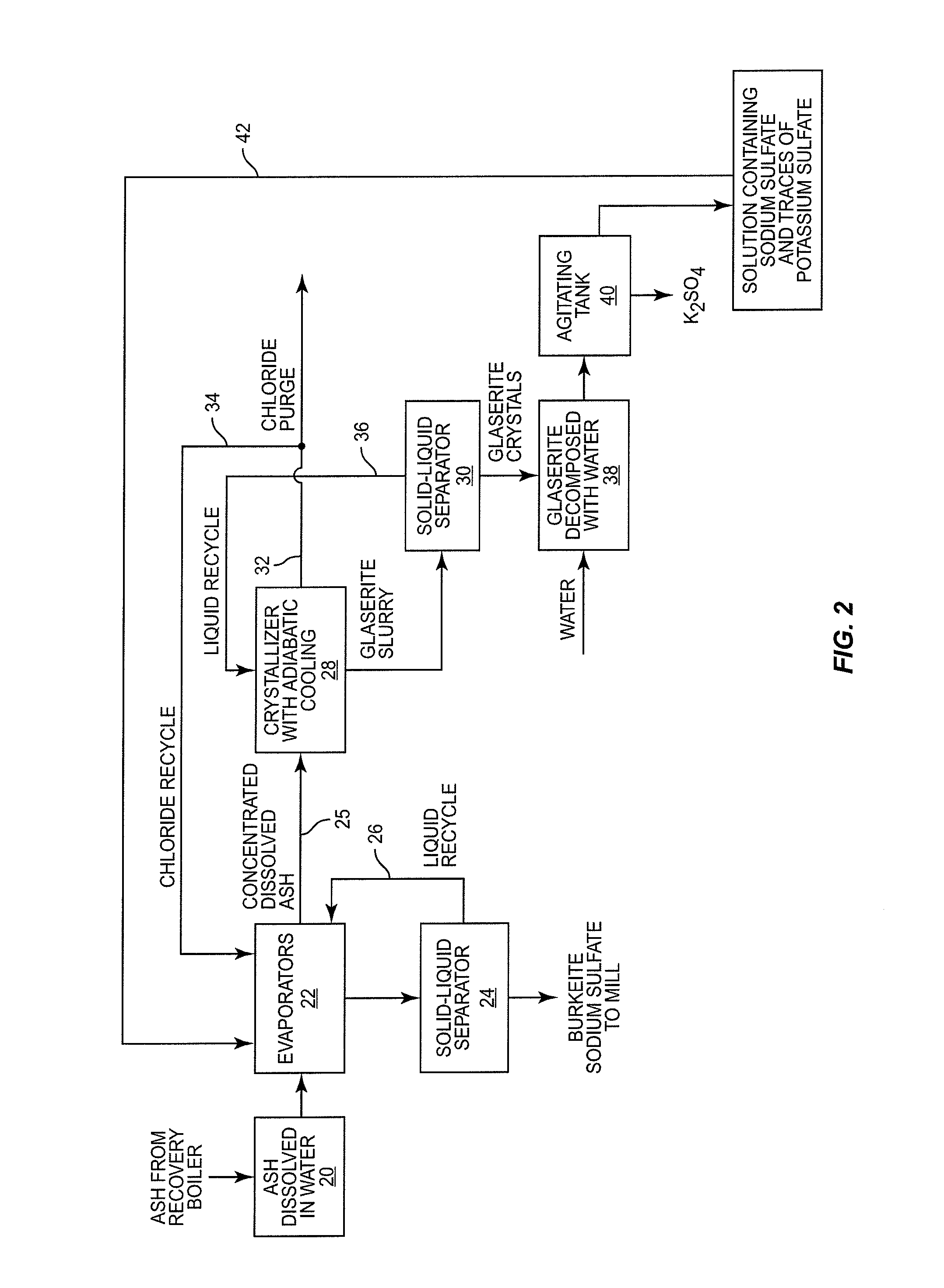
ActiveUS20140027076A1Pulp liquors combustionFractionation/concentration of spent liquorsBlack liquorWhite liquor
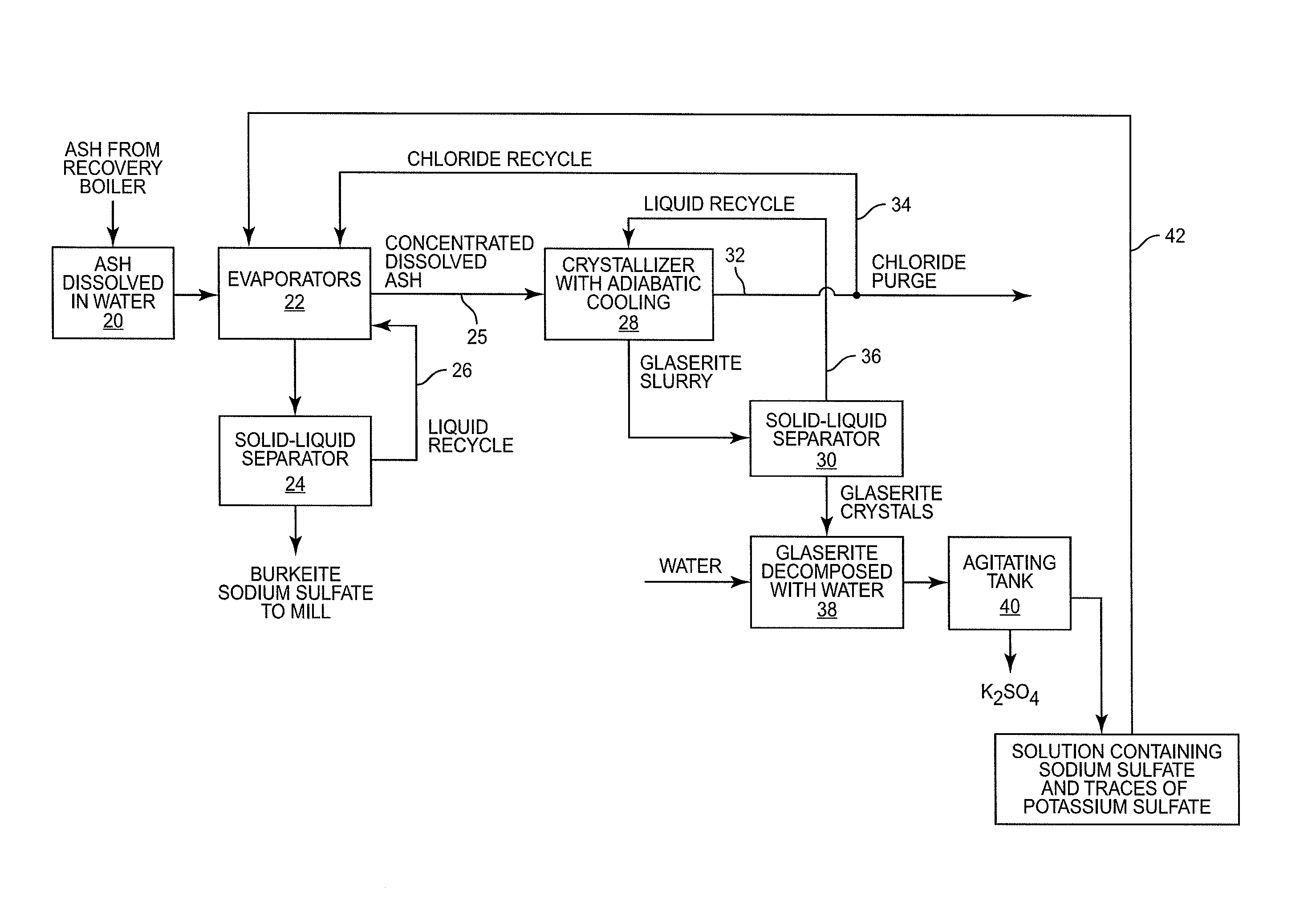
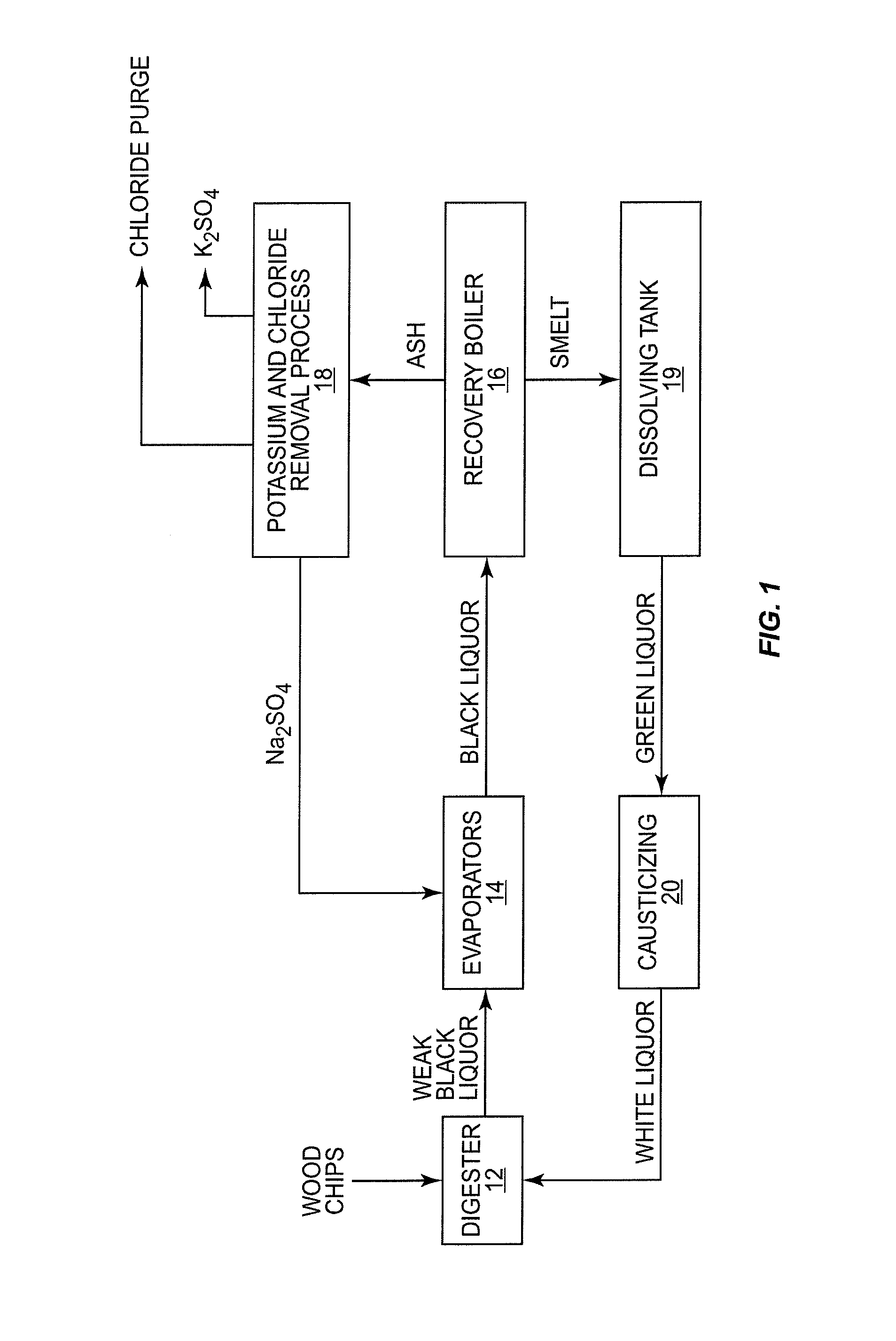
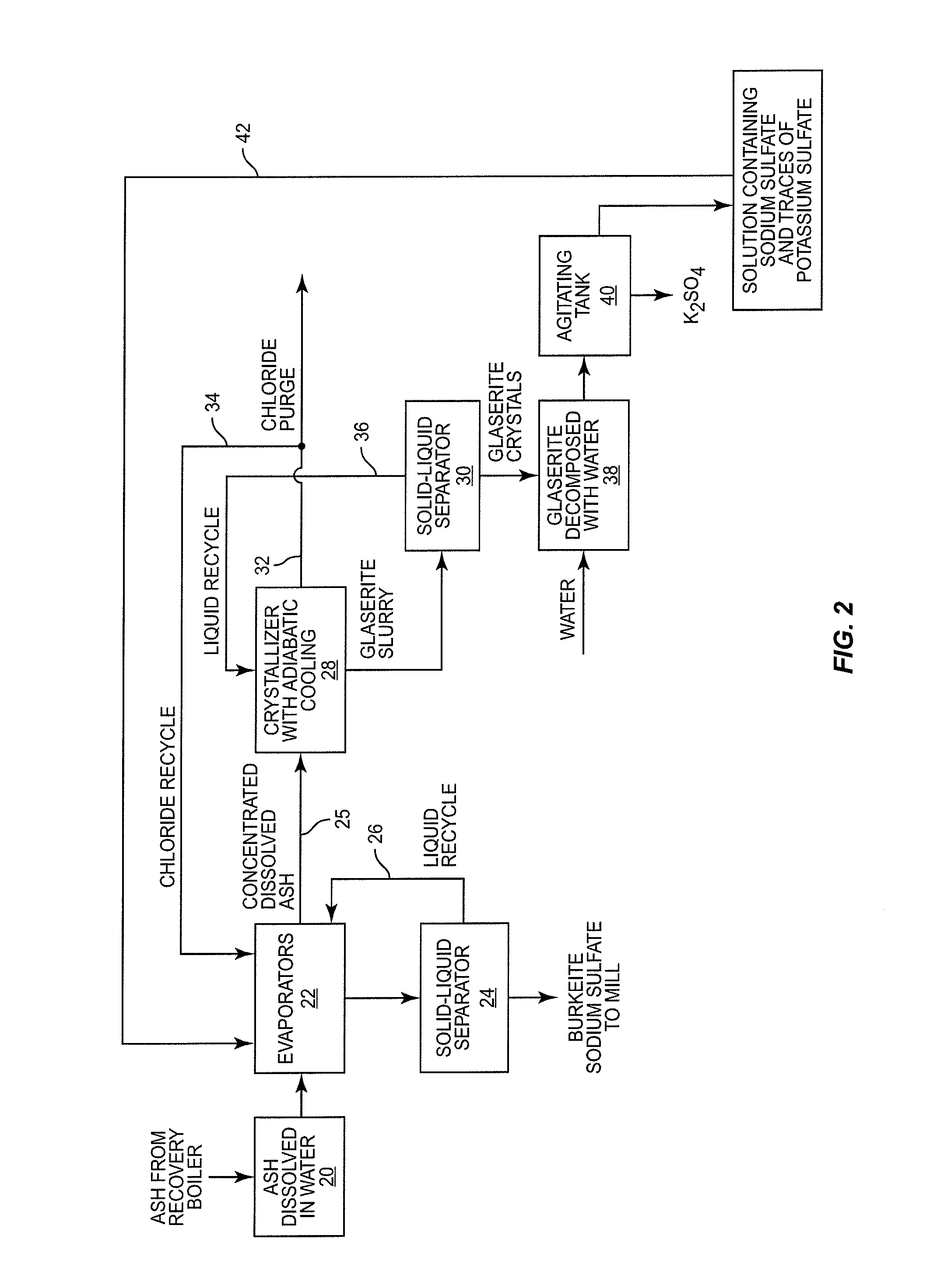
In a digester, wood chips and white liquor are combined and cooked under pressure to pulp the wood. This produces black liquor which is concentrated and burned in a recovery boiler. The recovery boiler produces ash that contains sodium, sulphur, potassium and chloride. The ash is dissolved and subjected to a process that recovers sodium sulfate and burkeite. The concentration of potassium and chloride is reduced, in part at least, by subjecting the ash to adiabatic cooling in a crystallizer which produces glaserite and a purge stream rich in chloride. By leaching the glaserite, sodium sulfate is removed from the glaserite, leaving potassium sulfate. The recovered sodium sulfate and burkeite can be recycled and used as pulping chemicals. The removed potassium and chloride can be further treated or appropriately discarded.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER TECH INC
Method for producing high purity lignin
InactiveUS20150322104A1Low in carbsLoss is producedLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryBlack liquorStrong acids
The method is for separation of lignin from original black liquor (BLIN) that has a first precipitation stage (PR) for precipitation of lignin by a first acidification using acidifier AC1, preferably using CO2, at alkaline conditions, then separating a lignin cake with subsequent suspension of the lignin cake in a strong acid in order to leach our metals from the lignin followed by dewatering and obtaining a clean lignin product LP. The process further is improved by intensified hydrolysis of lignin cake such that most of the carbohydrates are broken down to dissolvable monomers that could be separated from the lignin in the filtrate from a filtering stage subsequent to the hydrolysis. The improved hydrolysis could reduce as much as 90% of the carbohydrate content using a moderately increased temperature and increased charge of acidifier while avoiding any larger lignin yield losses.
Owner:VALMET AB
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20160186067A1Reduced steam stripping effectFacilitate product separationHydrocarbon distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, comprise providing the reaction product of a further processing (such as condensation reaction) to a non-aqueous stream to at least part precipitate the lignin and removing the precipitated lignin.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
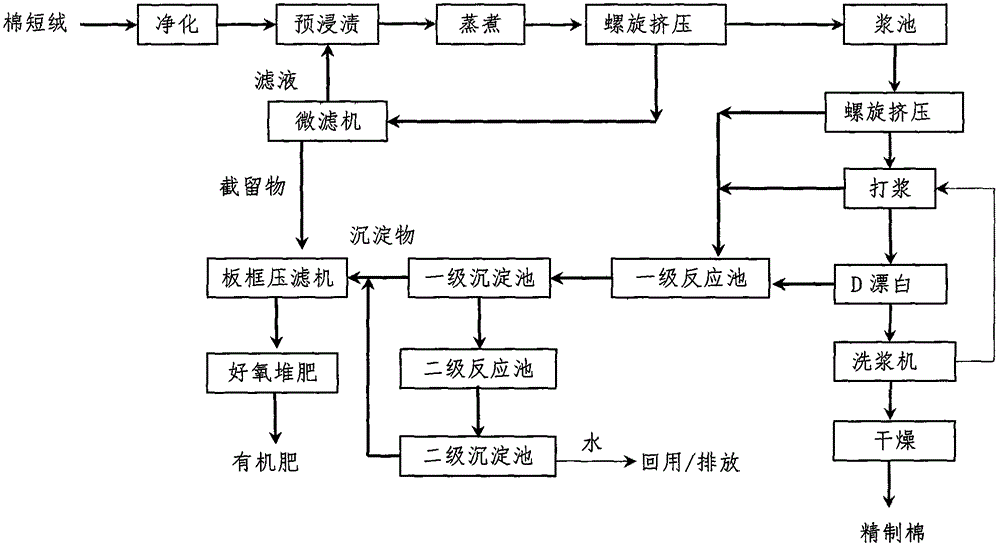
Refined cotton production and pollutant treatment method
ActiveCN104878636AReduce processingAchieve governanceClimate change adaptationPulp de-wateringSludgePapermaking
The invention relates to a refined cotton production and pollutant treatment method and belongs to the field of pulping and papermaking or spinning. The method specifically includes the following steps that cotton linter is subjected to deep purification, preimpregnation, cooking, pulping, bleaching and drying prior to obtaining refined cotton, waste liquid is lower than 100mg / L in COD concentration after secondary physicochemical treatment, and sludge generated in the waste liquid treatment process is produced into compound fertilizer via aerobic composting. The method has the advantages that consumption of fresh water in the refined cotton production process is low, waste liquid generation amount is small, the waste liquid treatment process is high in flexibility, and treated secondary pollutants are utilized comprehensively.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
Conditioning of so2-ethanol-water spent liquor for fermentation by clostridia
The present invention relates to producing chemicals and biofuels from wood material, e.g. mixed forest biomass. Specifically, the invention concerns a process for conditioning spent liquor produced by SO2-ethanol-water (SEW) fractionation of wood chips for fermentation to butanol, ethanol and acetone / isopropanol (so called ABE process) by Clostridia bacteria.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for recovering pulping chemicals and reducing the concentration of potassium and chloride therein
In a digester, wood chips and white liquor are combined and cooked under pressure to pulp the wood. This produces black liquor which is concentrated and burned in a recovery boiler. The recovery boiler produces ash that contains sodium, sulphur, potassium and chloride. The ash is dissolved and subjected to a process that recovers sodium sulfate and burkeite. The concentration of potassium and chloride is reduced, in part at least, by subjecting the ash to adiabatic cooling in a crystallizer which produces glaserite and a purge stream rich in chloride. By leaching the glaserite, sodium sulfate is removed from the glaserite, leaving potassium sulfate. The recovered sodium sulfate and burkeite can be recycled and used as pulping chemicals. The removed potassium and chloride can be further treated or appropriately discarded.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER TECH INC
Process for isolation of hemicelluloses from biomass pulping process waters or spent liquors
ActiveCN109642394AEfficient separationThermally isolated processing costs are lowBiofuelsPulp by-products recoveryXylanInorganic salts
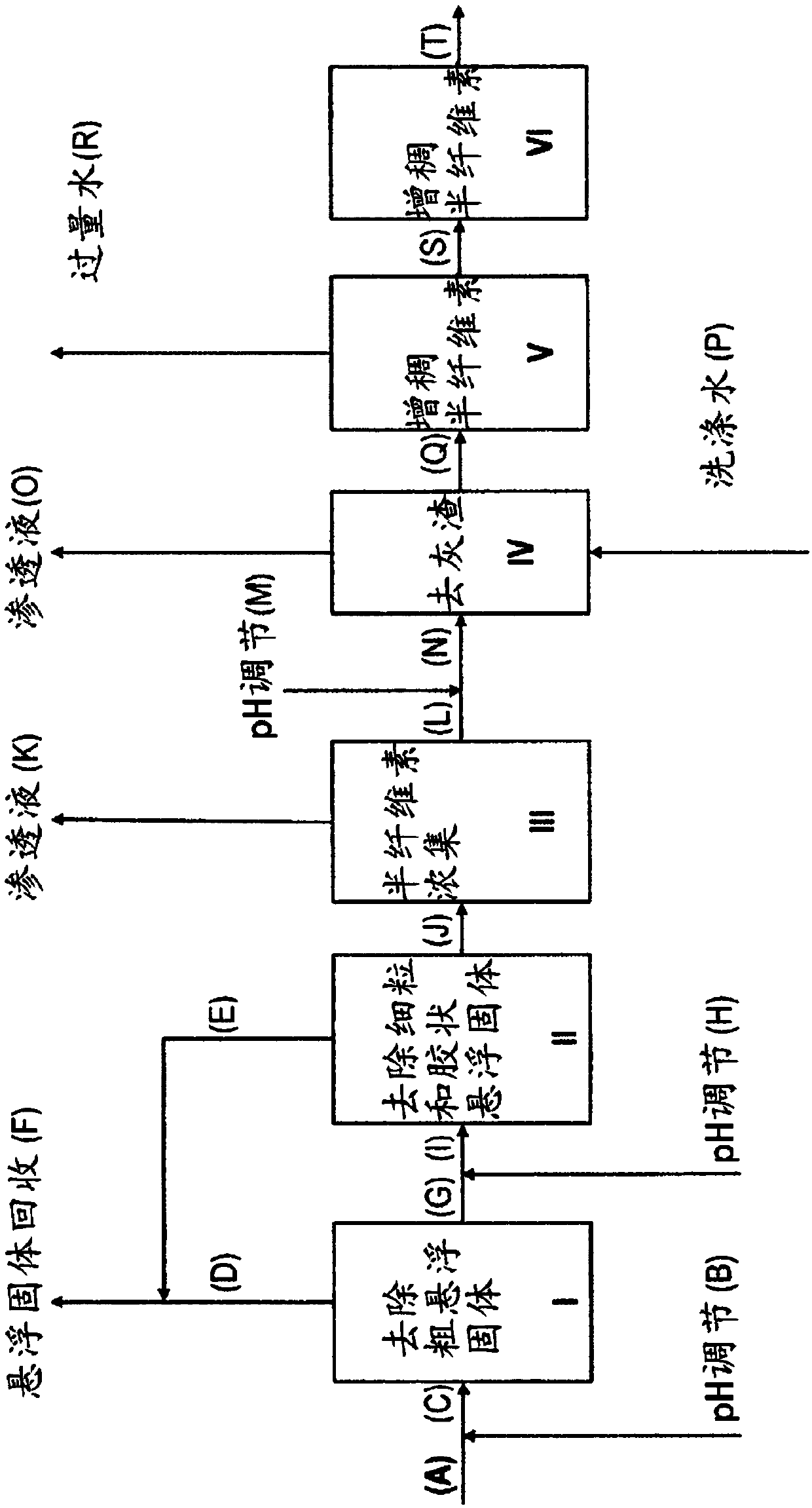
The invention relates to a process for isolation of hemicelluloses from biomass pulping process waters or spent liquors with removal of suspended solids, concentration of the product and purificationof the product by removal of inorganic salts and low molecular weight substances. It is characterized in that the hemicellulose isolation process conditions at several separation / purification stages are adjusted separately by e.g. pH adjustment. The invention further relates to a plant for carrying out the process. With such process and plant it is possible to recover most of the suspended solids,especially xylan and other hemicelluloses.
Owner:ANDRITZ AG
Method for recovery of molybdate in a molybdate-catalysed delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide
In a delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide catalysed with molybdate, molybdate can be recovered by bringing the aqueous solution containing molybdate into contact with a carrier material that comprises a layered silicate ion-exchanged with a quaternary ammonium salt at a pH value ranging between 2 and 7 and subsequent flotation, without the need to add a tenside for the flotation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Black liquor treatment method
InactiveUS7713422B2Easy to separateEasy to disassemblePulp liquors combustionSolid sorbent liquid separationBlack liquorPaper manufacturing
Lignin and alkali are efficiently sorted out of alkaline black liquor discharged from the paper manufacturing / pulp and paper manufacturing industries and the treated water is made as purified water.Acid is added to the black liquor and its pH is adjusted to 2.5 to 3.5. An aggregating agent is added to have lignin contained in the black liquor settled and the black liquor is separated into lignin and clean water. Ozone gas, preferably in the micro bubble state, is given to the clean water for contact reaction.
Owner:K I SYST
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20160184795A1Residue reductionMinimizing any vaporizationOther chemical processesLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseFluid phase
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, comprise providing the reaction product to a separation zone comprising a liquid-liquid phase separation unit. The liquid-liquid phase separation unit can provide an aqueous portion and a non-aqueous portion, where these portions can be separated into various fractions individually. For example, desirable compounds in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and optionally combined to be further processed into a fuels product. Heavier components in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and used in the process, such as phenolics that can be used as a digestion solvent.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveCN107109245AHydrocarbon distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, comprise providing the reaction product of a further processing (such as condensation reaction) to a non-aqueous stream to at least part precipitate the lignin and removing the precipitated lignin.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Method and arrangement in making of mechanical pulp
InactiveCN1714194ADoes not increase pHLess quantityFractionation/concentration of spent liquorsFiberFiltration
The object of the present invention is a method and arrangement in making of mechanical pulp to reduce the amount of organic dissolved and colloidal substances in the pulp making process water by treating a part of the process water. According to the method the treating is carried out by leading the process water filtrate, separated from the pulp by a press located before bleaching, to pre-treatment, where elongated fibres are fractionated from the process water to be treated. The filtrate that has passed the pre-treatment is led to membrane filtration, where at least part of the organic dissolved and colloidal substances included in the process water are separated from the rest of the process water. The membrane filtration concentrate i.e. the colloidal and dissolved substances separated from the process water, is led to further treatment and the permeate i.e. the process water that has passed the membrane filtration is led back to the pulp making process. An arrangement according to the present invention comprises means to carry out the method according to the invention.
Owner:METSO PAPER INC
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveCN107106924AReduce gasificationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionPulp by-products recoveryCelluloseDigestion
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, comprise providing the reaction product to a separation zone comprising a liquid-liquid phase separation unit. The liquid- liquid phase separation unit can provide an aqueous portion and a non-aqueous portion, where these portions can be separated into various fractions individually. For example, desirable compounds in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and optionally combined to be further processed into a fuels product. Heavier components in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and used in the process, such as phenolics that can be used as a digestion solvent.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20160186073A1Reduced steam stripping effectFacilitate product separationHydroxy compound preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseOrganic acid
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, and organic salts, comprise providing acid solution to the organic salt containing process stream to convert the organic acid salts to acids to for further processing.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
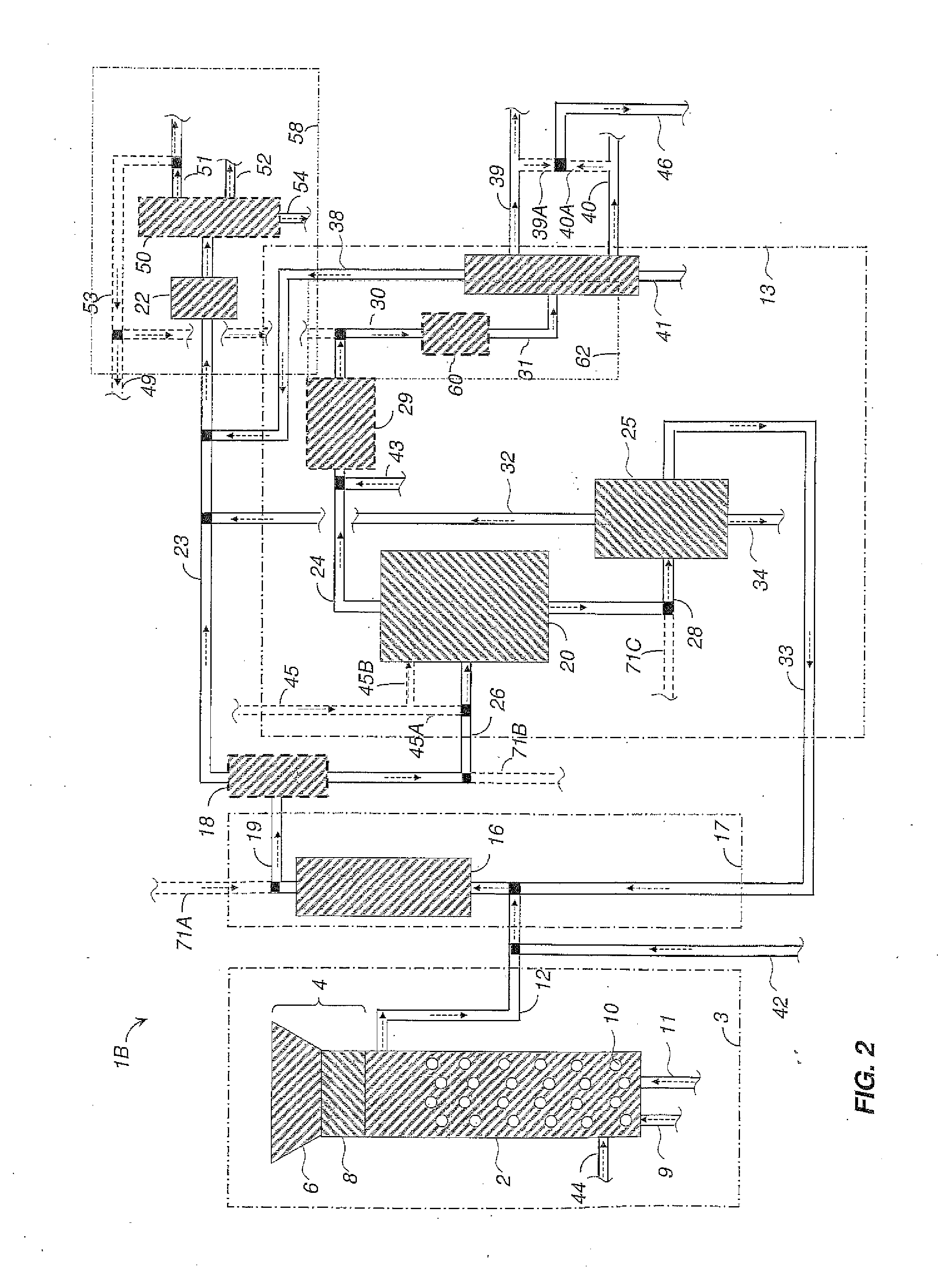
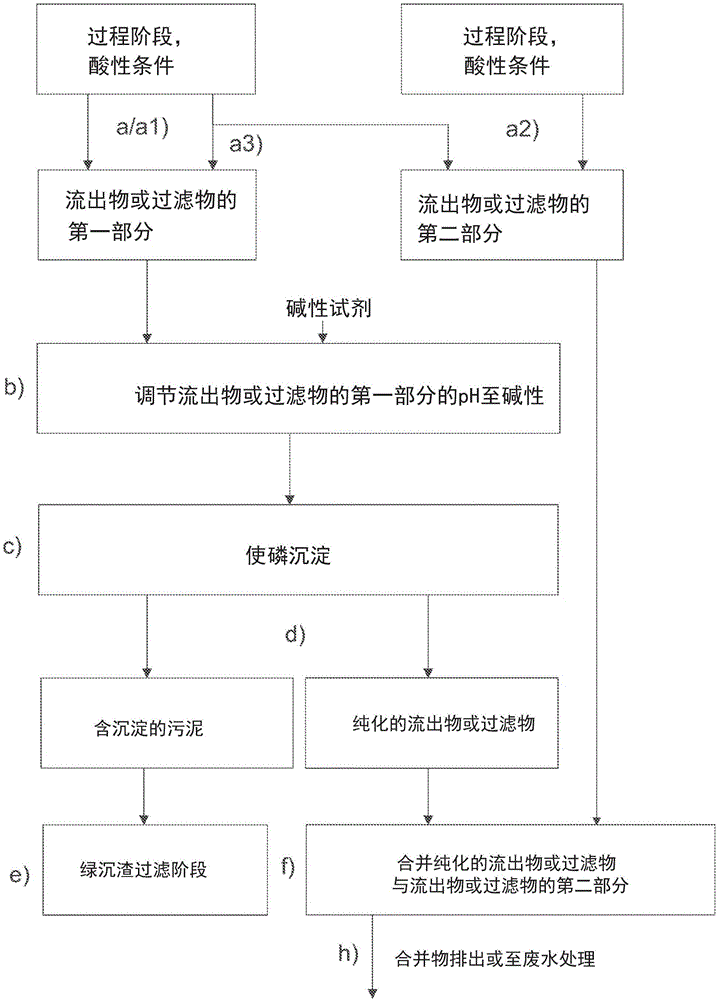
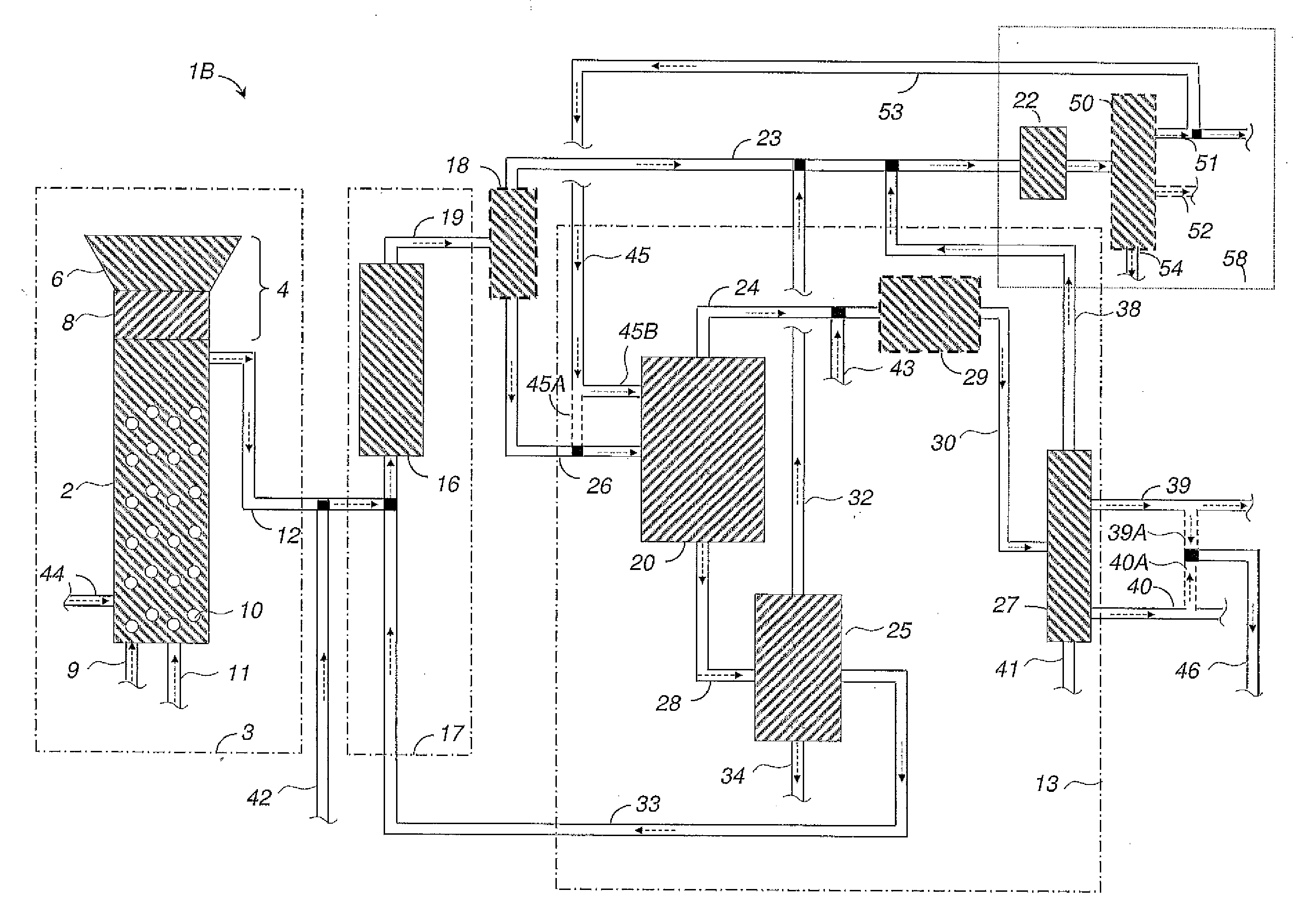
Method and system for reducing phosphorus in effluent or filtrate
ActiveCN106414347AReduce phosphorus contentTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationSludgePhosphate
The invention relates to a method for reducing phosphorus in effluent or filtrate from a process which comprises a stage in which green liquor dregs are filtered using a green liquor dregs filter and at least one stage in which conditions are acidic, wherein the method comprises the steps of: a) obtaining an effluent or filtrate from a stage in which conditions are acidic; b) adjusting pH of at least a portion of the effluent or filtrate to alkaline with an alkaline agent; c) allowing phosphorus to be precipitated in form of a phosphate salt; d) separating the precipitate to produce purified effluent or filtrate and a sludge comprising the precipitate; and e) filtering the sludge comprising the precipitate obtainable from step d) using the green liquor dregs filter.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20160186066A1Reduced steam stripping effectAdequate product separationDistillation purification/separationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Separation of a product of digestion of cellulosic biomass solids may be challenging due to the various components contained therein. Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass, particularly a reaction product of a hydrothermal reaction containing lignin-derived products, such as phenolics, comprise providing the reaction product of a further processing (such as condensation reaction) comprising a liquid-liquid extraction unit. The liquid-liquid extraction unit can provide an aqueous portion and a non-aqueous portion, where these portions can be separated into various fractions individually. For example, desirable compounds in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and optionally combined to be further processed into a fuels product. Heavier components in the aqueous portion and non-aqueous portion can be recovered from the portions individually and used in the process, such as phenolics that can be used as a digestion solvent.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
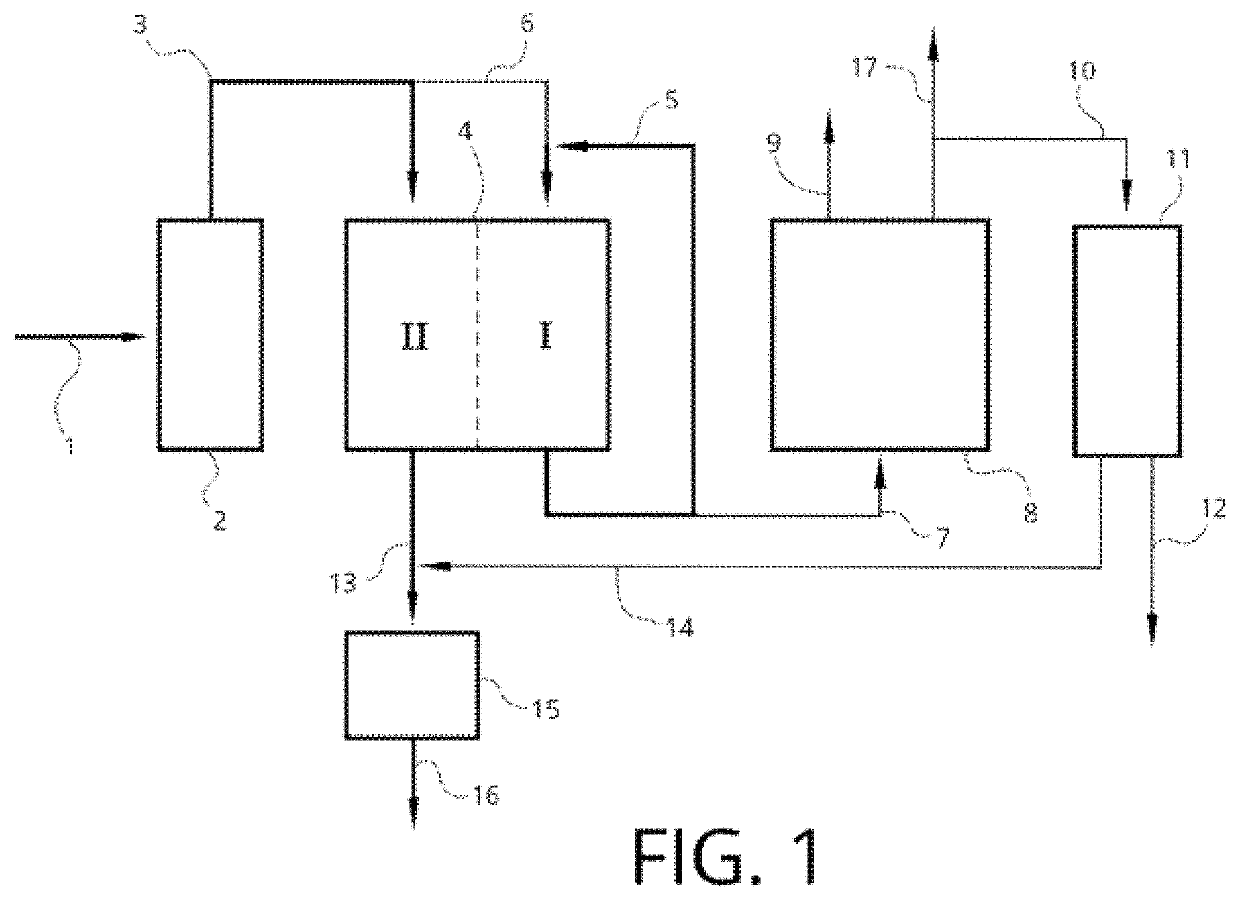
Method for recovering water and chemicals from plants for treating effluents from pulp and paper factories
PendingUS20220204377A1Production is limitedAvoid accumulationTreatment involving filtrationAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationChemical recoveryPaper production
Process for upgrading effluent treatment plants for pulp and paper production processes, where salts are removed from the effluent for water reuse and chemical recovery. The process comprises a first dialysis system for salt removal, a second treatment system for recovery or re-concentration, and optionally a post-treatment of the re-concentrate preventing liquid discharges to the environment. In the first system, a reversible electrodialysis or reversible pulsed step is carried out, separating the salts from the effluent, which are sent to the second treatment system to concentrate the salts (re-concentrate) or transform them into useful chemicals for the same process (recovery). Chemical recovery is achieved by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes or metathesis, to reduce the re-concentrate stream, which cannot be reused in the same plant. Lastly, this stream may be treated by spray drying, crystallization or evaporation.
Owner:INVESTIGACIONES FORESTALES BIOFOREST SA
A method of purifying lignin by subjecting a slurry comprising lignin to an electric field
ActiveCN106794425AEasy to purifyIncrease dry contentLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryFree sugarSlurry
The present invention relates to a process for purifying, such as salt / ion depletion, and / or ash reduction,and / or sulphur removal, and / or free sugar depletion,and / or VOC depletion or fractionating,preferably by using dewatering, of a slurry comprising a lignin or lignin derivative or a combination thereof. A lignin or lignin derivative obtainable from said process and uses thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Popular searches
Fermentation Cellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymes Finely-divided material pretreatment Pulp gases treatment Water/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysis Reverse osmosis Pulping with organic solvents Cellulose pulp after-treatment modification Hydrogen production Hydrogen/synthetic gas production
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com