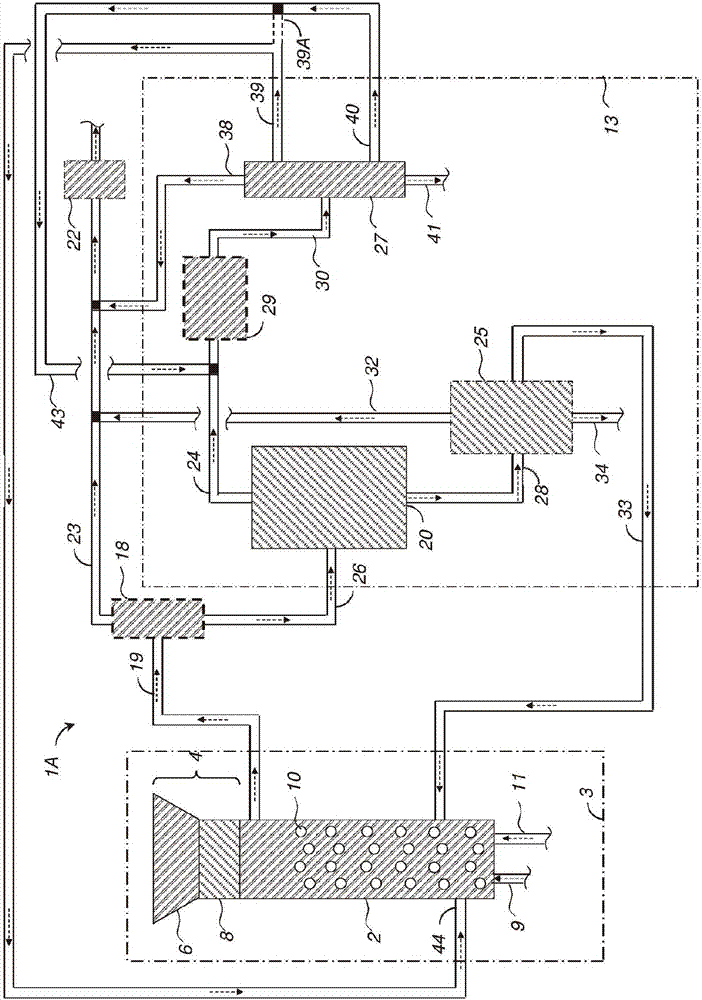
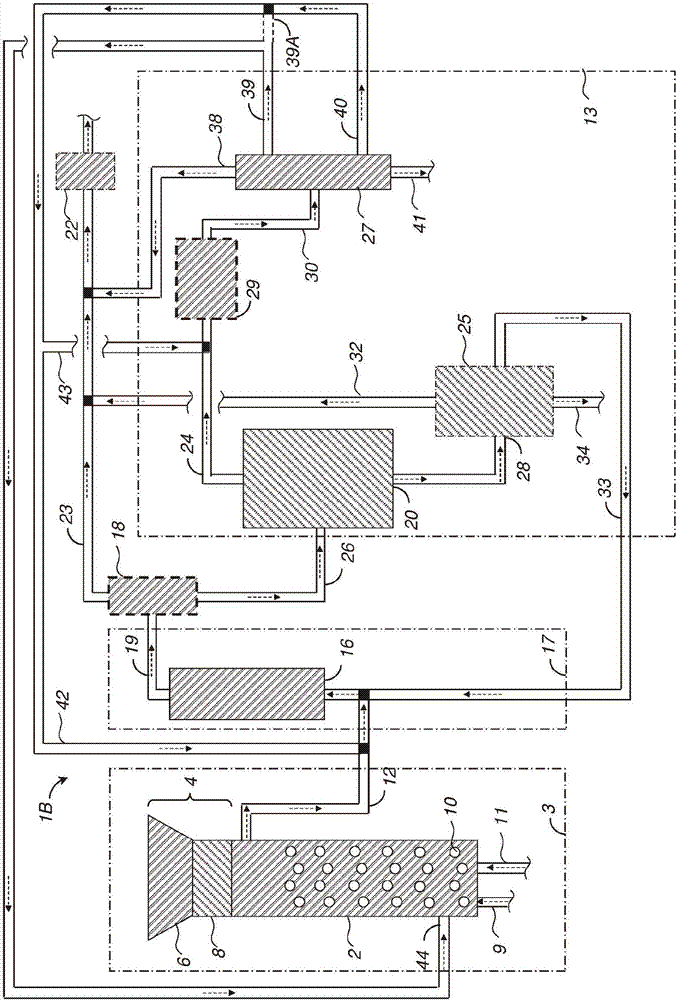
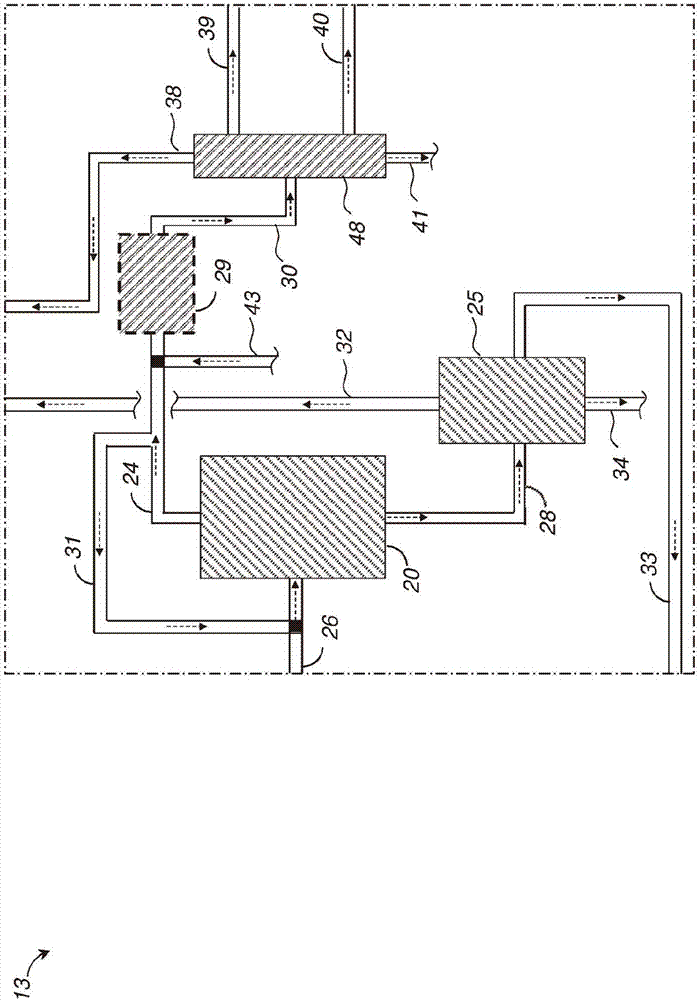
Methods and systems for processing cellulosic biomass
A technology of biomass and logistics, applied in pulping of cellulose raw materials, separation methods, biological raw materials, etc., can solve problems such as system downtime, scaling of processing equipment, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0138] Example 1: Phase Separation of Phenolic Solvents from MIBC-Rich Organics-Water Solvents
[0139] A solvent mixture was prepared from 57.02 grams of methyl isobutyl carbinol and 3.01 grams of deionized water. A 100 ml Parr 4590 series reactor was fed with solvent mixture along with 0.19 g of potassium carbonate buffer and 1.8 g of nickel oxide promoted cobalt molybdate catalyst (DC-2534, containing 1-10% cobalt oxide and trioxide on alumina Molybdenum (up to 30 wt%) and less than 2% nickel). The catalyst was obtained from Criterion Catalyst & Technologies L.P. and sulfided by the method described in Example 5 of US Application Publication No. 2010 / 0236988. The reactor was then fed with 6 grams of small southern pine chips (50% moisture) with a size of about 3 x 5 x 5 mm, then pressurized with 52 bar hydrogen and heated to 190° C. with stirring for 1 hour, followed by Heat to 250°C for 4 hours.
[0140] After 6 cycles of wood addition, a mixed sample was taken via a ...
example 2
[0143] Example 2: Larger scale synthesis of a phase rich in phenolic compounds
[0144] Using a 450 ml Parr reactor, Example 1 was repeated using 212.2 grams of MIBC and 5.01 grams of deionized water as solvent, 0.8556 grams of potassium carbonate buffer, 8.104 grams of cobalt sulfide molybdate catalyst. 27 grams of southern pine wood at nominal 50% moisture was added, and the reaction cycle was performed, again, at 52 bar H 2 , heated to 190°C for 1 hour, followed by heating to 240°C for 4 hours.
[0145] The process was continued for 17 cycles of wood addition. For cycles 1-7, at the end of the reaction, the mixed hot sample was removed via a filter dip tube to provide wood material to be added in the next cycle, thus maintaining a constant mass inventory in the reactor. After seven cycles, the sintered metal dip tube plugged so product samples were removed for cycles 8-18 after depressurization and opening of the reactor to remove primarily from the aqueous interlayer a...
example 3
[0147] Example 3: Distillation of Separated Phases
[0148] Approximately 25 gram aliquots of the MIBC-rich phase of the final upper layer and the aqueous phase of the middle layer from the 17th cycle of Example 2 were separated in a 100 ml distillation flask equipped with a 4-stage Vigreux column distilled. Distillation of the aqueous fraction yields an overhead fraction containing light monooxygenates (alcohols less than C4), water and, when increasing the bottoms temperature, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. No detectable phenolic compounds were observed in the overhead fraction from the aqueous distillation.
[0149] The upper layer distillation gives some light monooxygen compounds smaller than C4 early in the distillation, followed by C5 and C6 ketones and alcohols and contains cyclopentanol, cyclopentanone, methylcyclopentanone, hexanone.
[0150] Upon applying vacuum (100 Torr absolute) and increasing the bottoms temperature to more than 250°C but less than 31...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com