Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86results about "Chemical to radiation conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-step system and method for curing a dielectric film
ActiveUS7622378B2Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltravioletMoisture
A multi-step system and method for curing a dielectric film in which the system includes a drying system configured to reduce the amount of contaminants, such as moisture, in the dielectric film. The system further includes a curing system coupled to the drying system, and configured to treat the dielectric film with ultraviolet (UV) radiation and infrared (IR) radiation in order to cure the dielectric film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
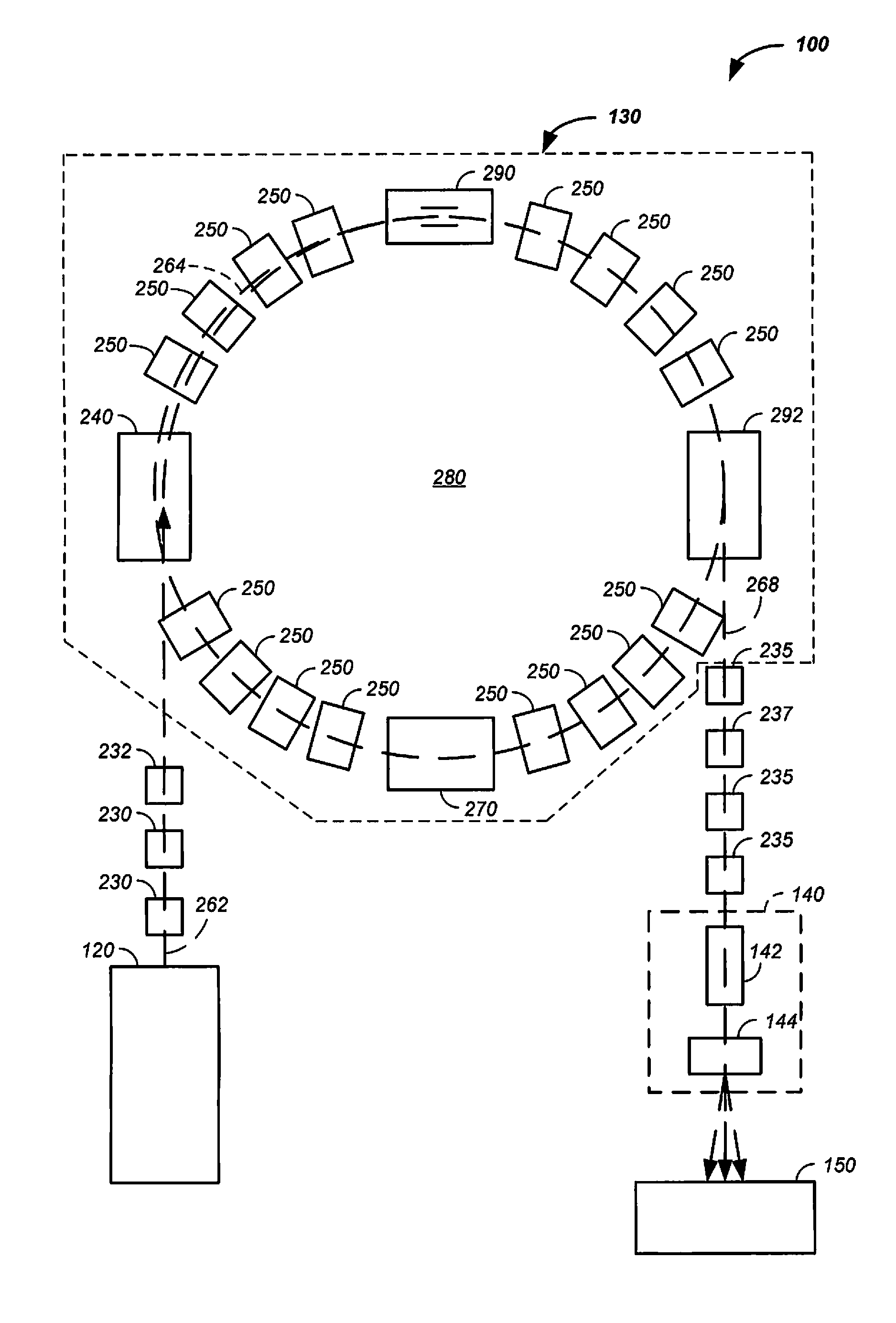
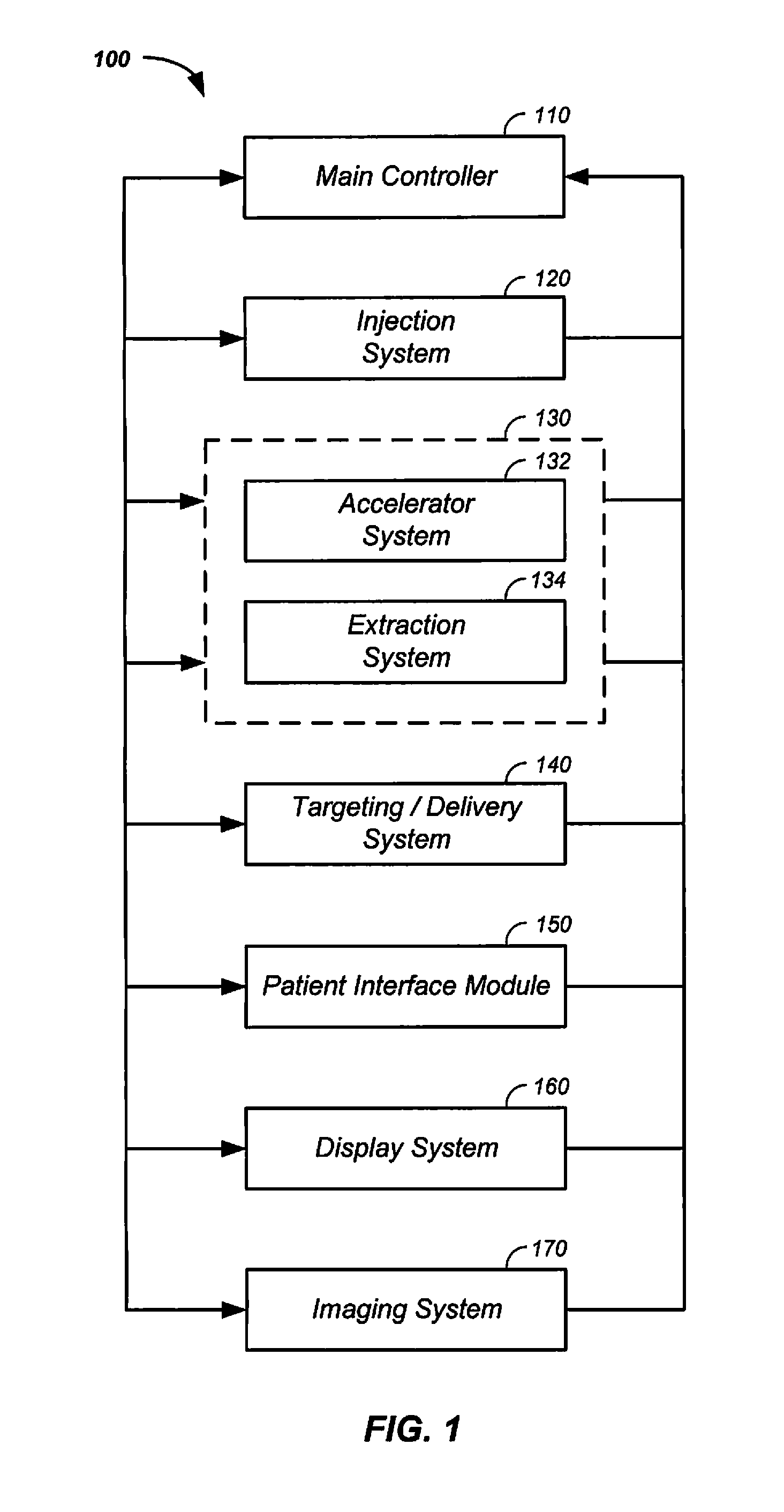
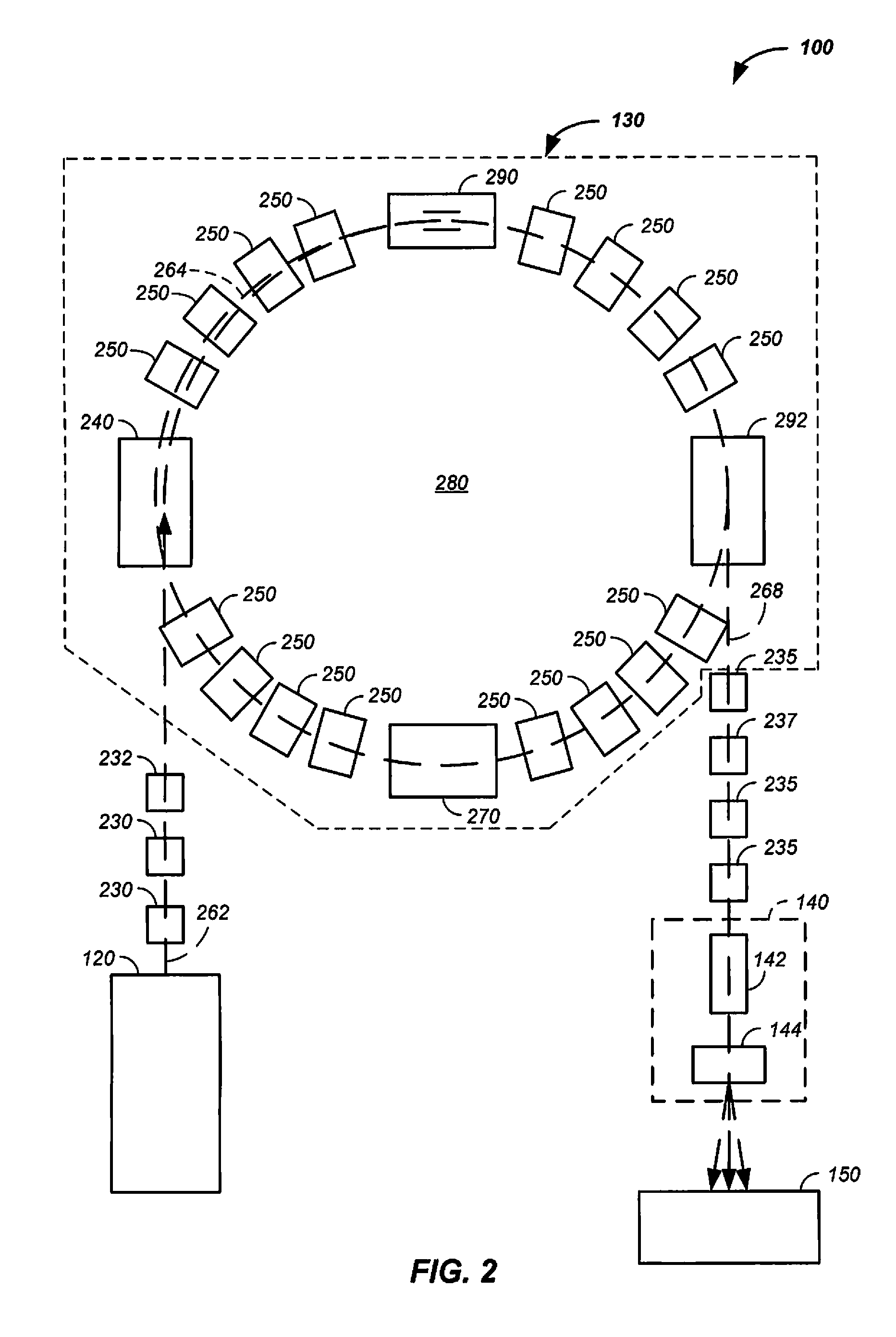
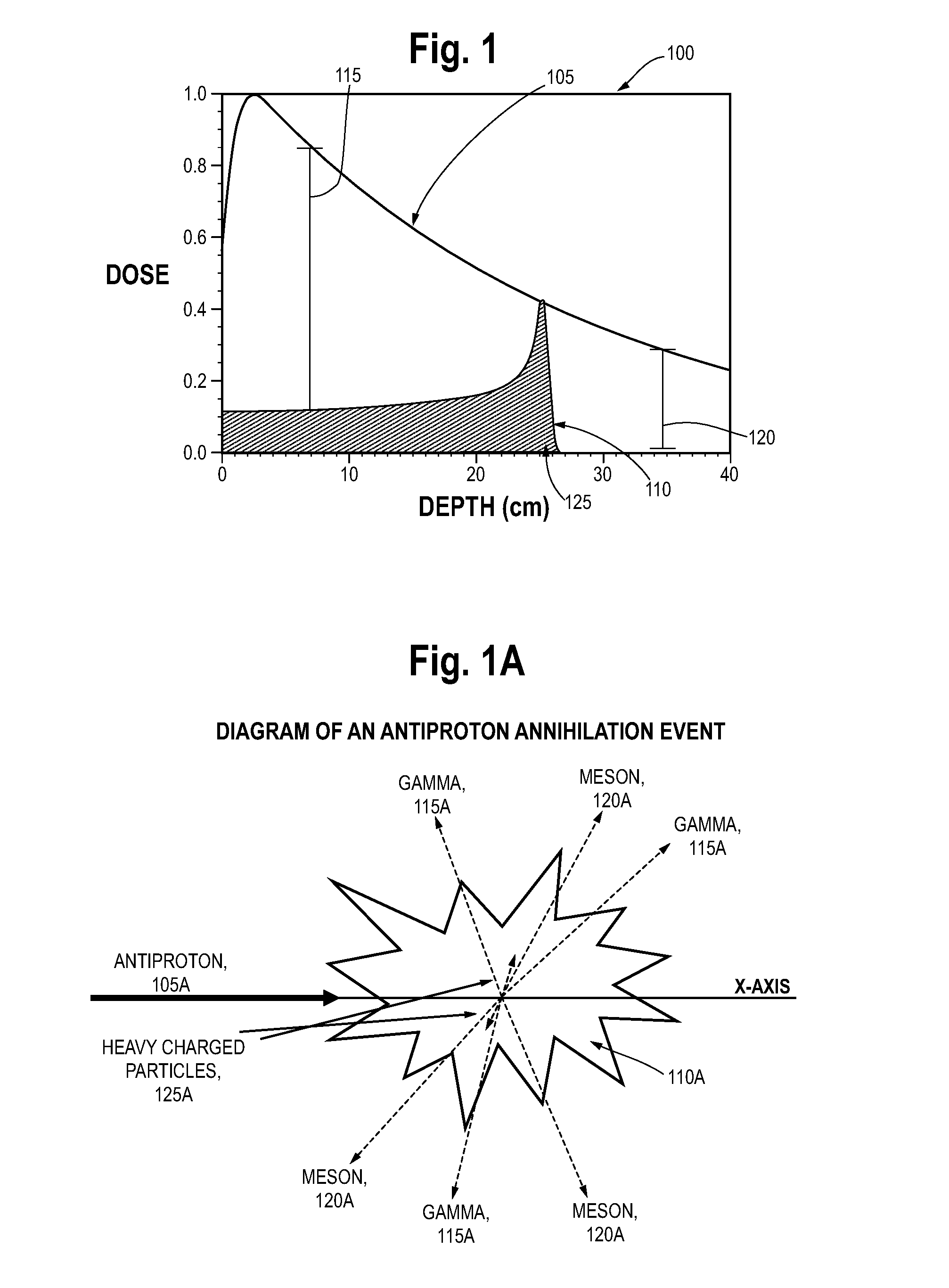
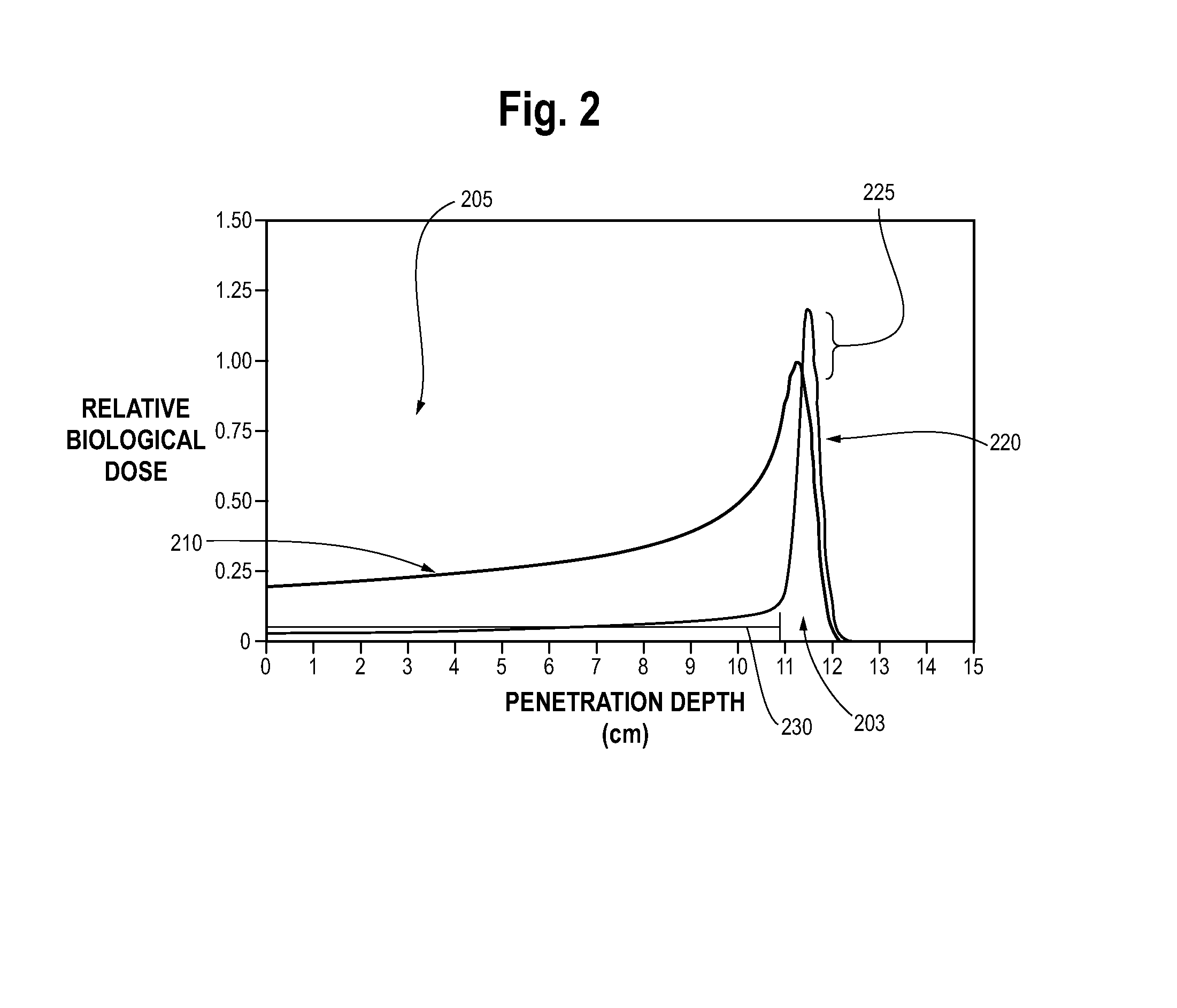
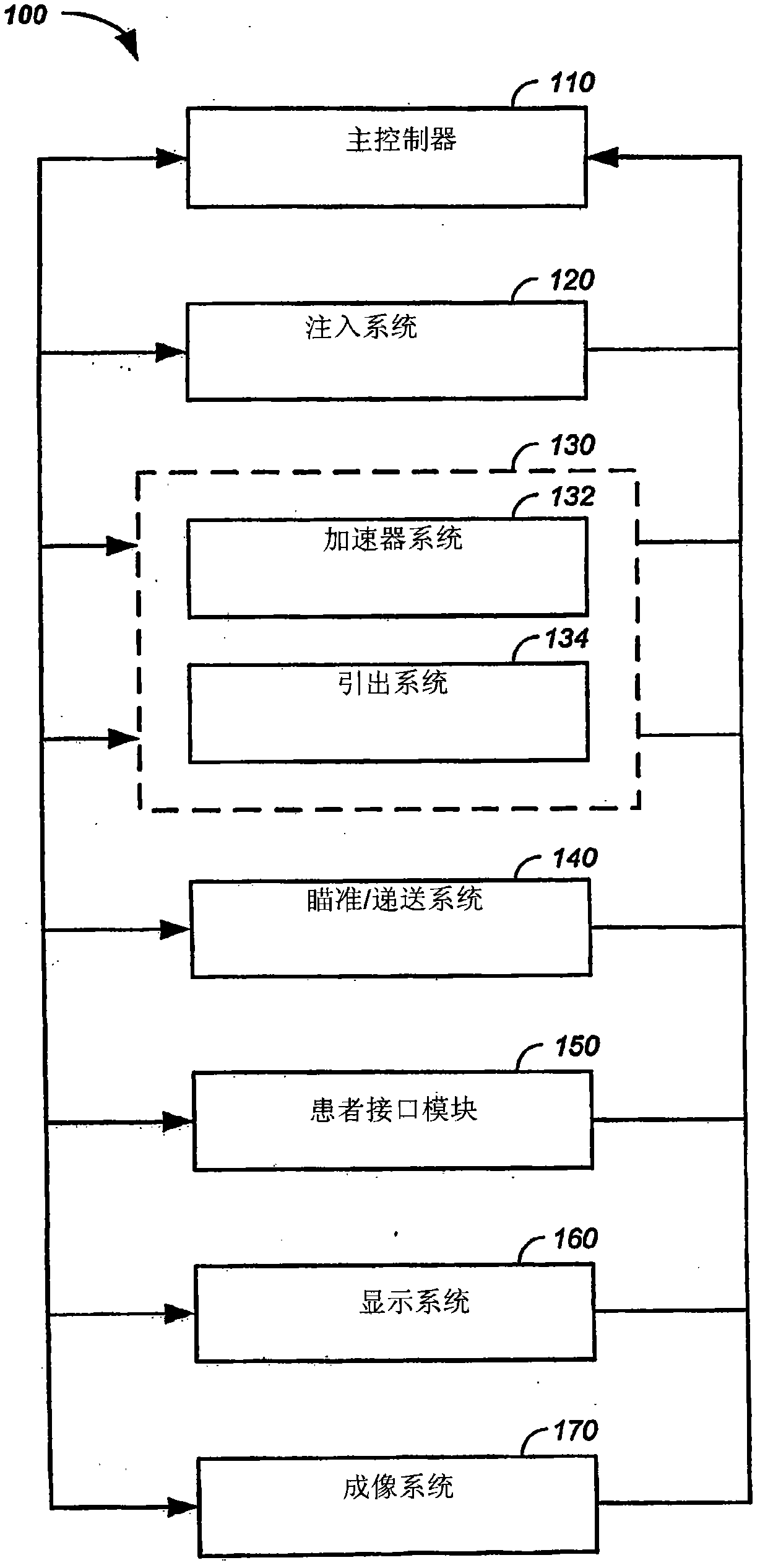
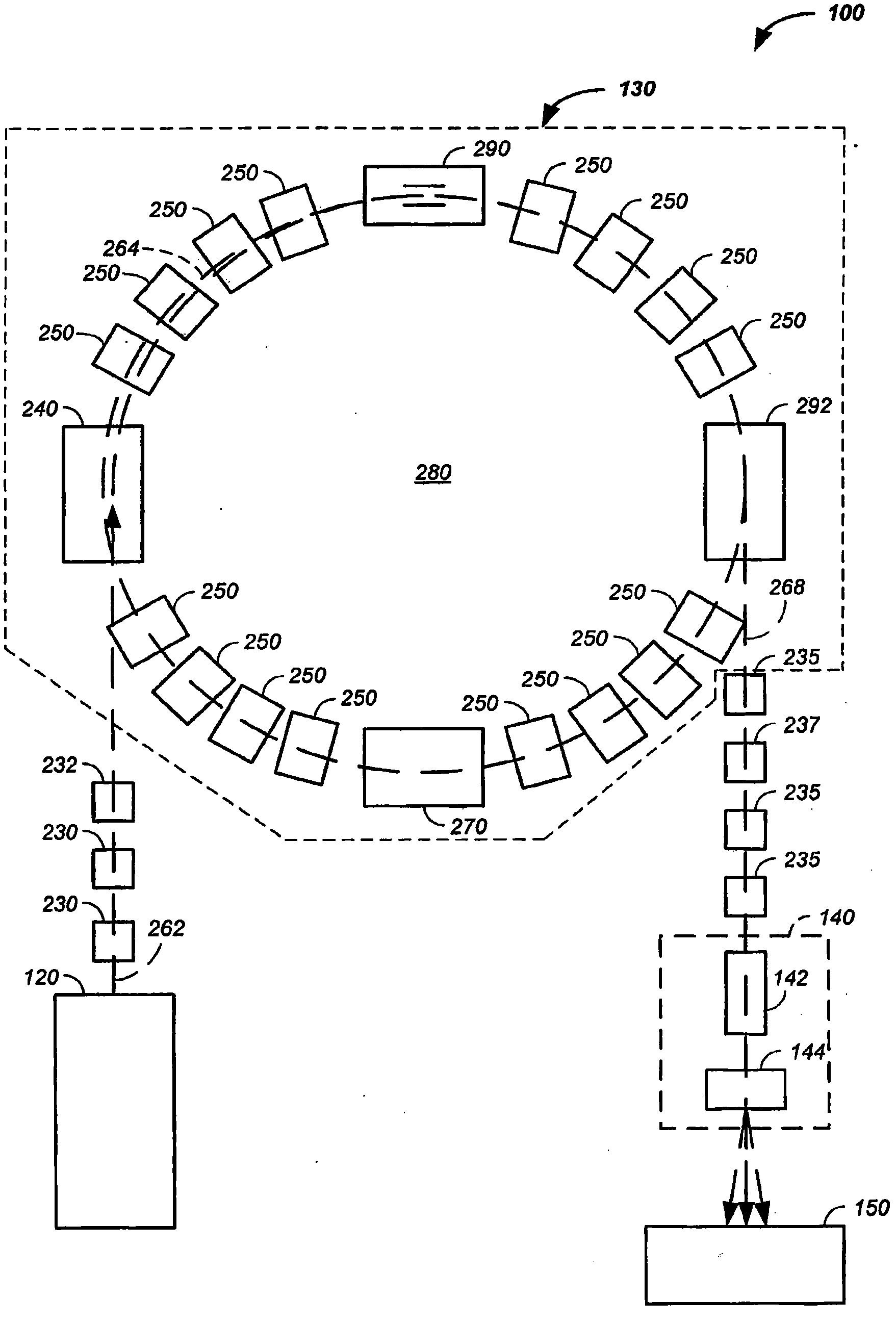
Multi-Field Charged Particle Cancer Therapy Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20110313232A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMulti fieldMedicine
The invention relates generally to treatment of solid cancers. More particularly, the invention relates to a multi-field charged particle cancer therapy method and apparatus coordinated with negative ion beam creation, ion beam focusing, charged particle acceleration, patient rotation, and / or patient respiration. Preferably, the charged particle therapy is performed on a patient in a partially immobilized and repositionable position. Proton delivery is preferably timed to patient respiration via control of charged particle beam injection, acceleration, and / or targeting methods and apparatus.
Owner:BALAKIN VLADIMIR EGOROVICH
Radioisotope generator
InactiveUS7091494B2Easy constructionRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsIsotopeCatheter
The invention relates to a device for producing a fluid containing a radioactive constituent, the device comprising: a shielded chamber (5) within which is located an isotope container (6) housing a radioactive isotope (7), the shielded chamber including first and second fluid connections (12,13) to opposing ends of the isotope container and a fluid conduit (14,15) extending from each of the first and second fluid connections to a fluid inlet (16) and a fluid outlet (17) respectively characterised in that the fluid inlet comprises a single spike (22) having a substantially circular cross-section, the spike being adapted to penetrate the rubber seal of a vial and the spike having two bores, the first bore extending from a first aperture adjacent the tip of the spike to a fluid connection with the fluid conduit and the second bore extending from a second, separate aperture in the spike to a filtering air inlet.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
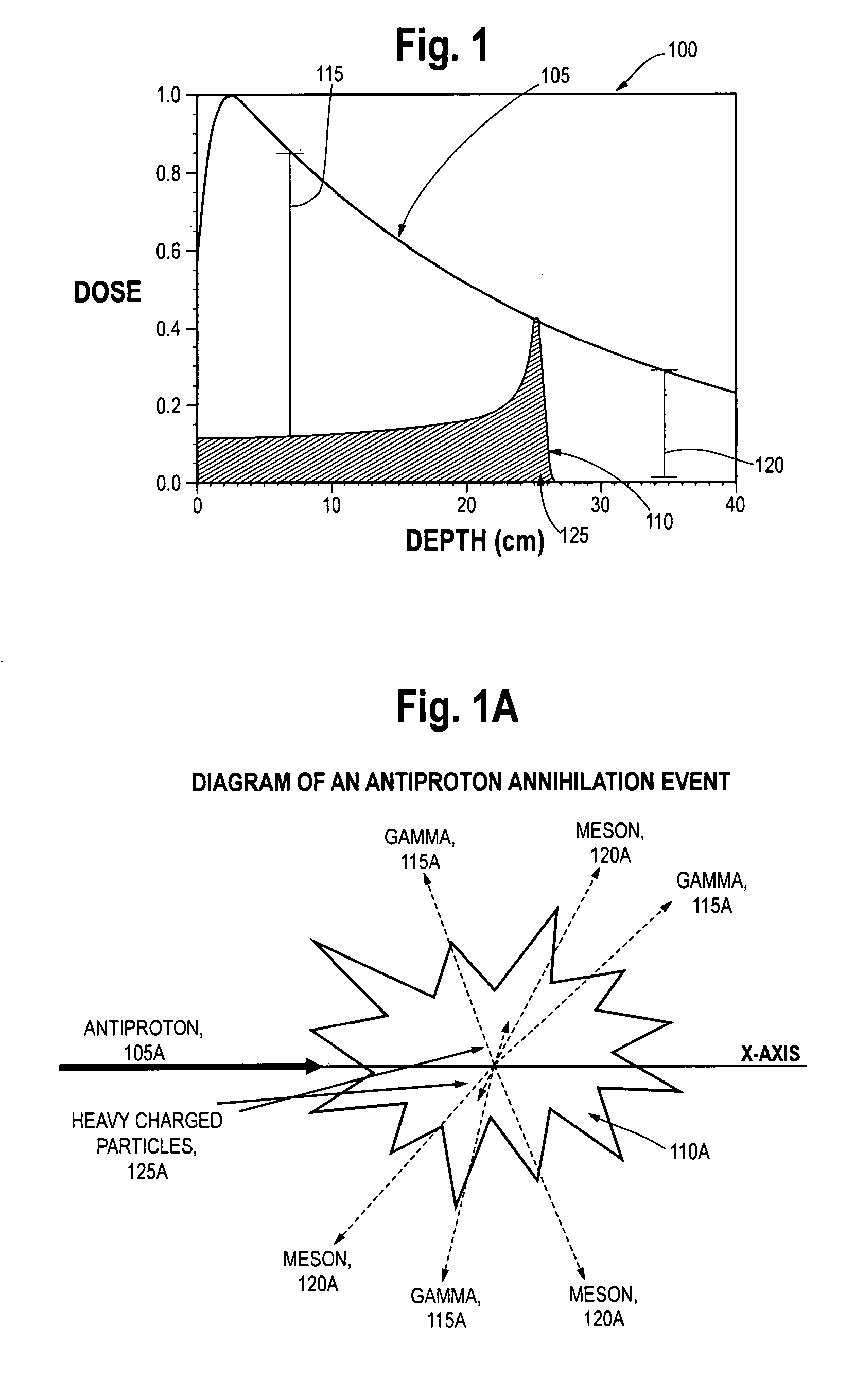
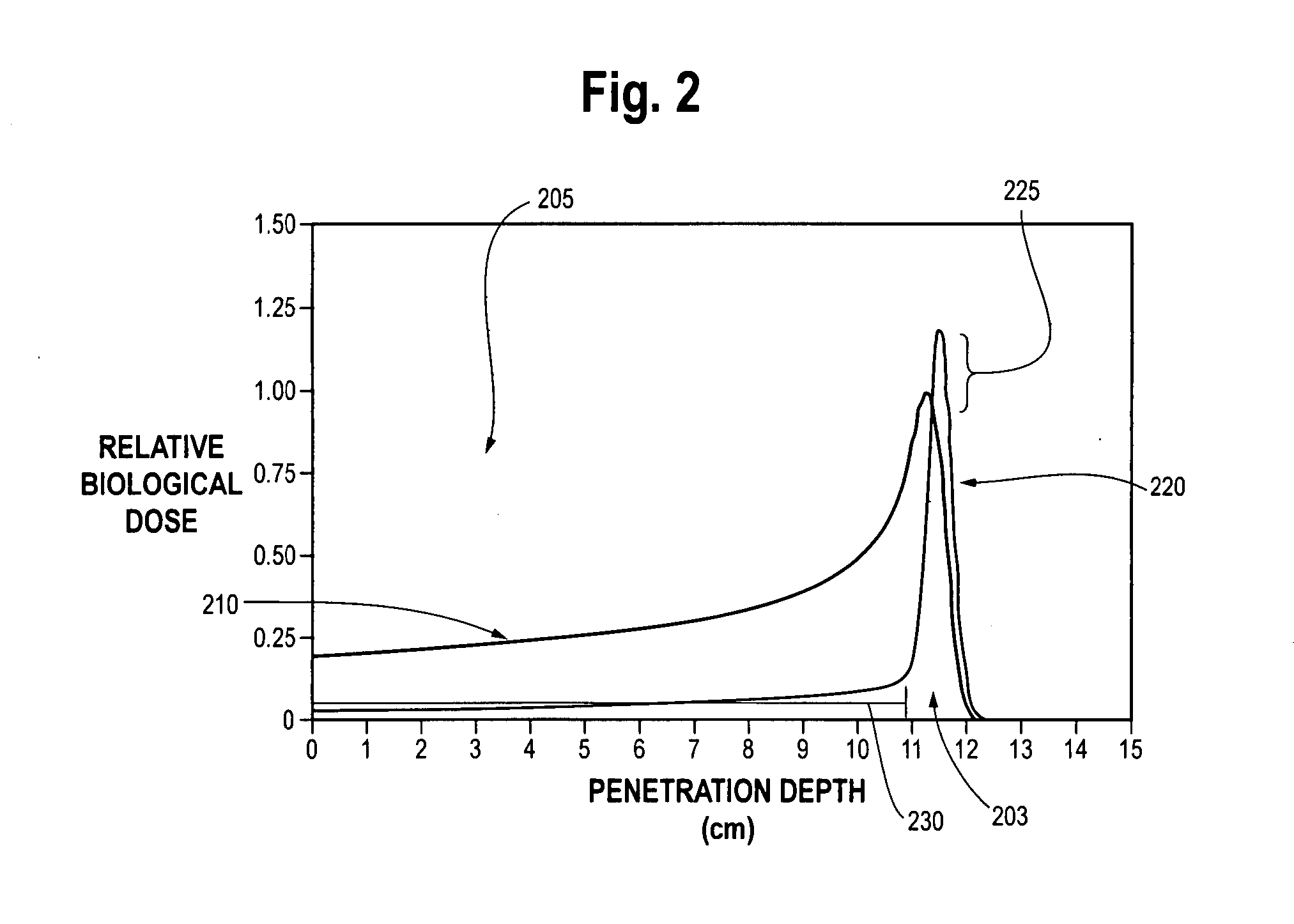
Antiproton production and delivery for imaging and termination of undersirable cells
ActiveUS20070225603A1Minimize the numberEliminating fractionation requirementRadiation/particle handlingMagnetic resonance acceleratorsAntiprotonDetector array
Systems and methods for using antiprotons for terminating unwanted or undesirable cells which can be used in the treatment of conditions caused by the existence and / or proliferation of such undesirable cells. Such conditions include cardiovascular ailments, Parkinson's disease, wet macular degeneration, endocrine disorders, dermatological ailments, and cancer. Because of the unique nature of antiprotons and their annihilation characteristics, the preferred antiproton delivery device (1010, 1015, 1030) embodiments further incorporate detector arrays (1050a), capable of detecting characteristic emissions in the course of treatment.
Owner:HBAR TECH
Electrochemical 18f extraction, concentration and reformulation method for raiolabeling
InactiveUS20100069600A1Avoid disadvantagesRaise the ratioCellsPolycrystalline material growthFluorideAqueous solution
A method to extract out of water, concentrate and reformulate [18F] fluorides includes passing a dilute aqueous [18F] fluoride solution entering by an inlet (1) in a cavity (6) embodying an electrochemical cell with at least two electrodes (3, 4, 5), flowing in the cavity (6) and coming out of the cavity (6) by an outlet (2), an external voltage being applied to the electrodes. One electrode (4) is used as an extraction electrode, another one (3) is used for polarizing the solution, and configured so that at least the extraction electrode (4), either used as a cathode or as an anode, is in contact with and polarizes a large specific surface area conducting material (7), contained in the cavity (6). The extracted ions are released from the surface of the large specific surface area conducting material (7) by turning off the applied external voltage. During its passage in the cavity (6), the dilute aqueous [18F] fluoride solution entirely crosses and internally soaks the large specific surface area conducting material (7).
Owner:TRASIS
High density storage of excited positronium using photonic bandgap traps
A device is provided that can capture and store electrically neutral excited species of antimatter or exotic matter (a mixture of antimatter and ordinary matter), in particular, excited positronium (Ps*). The antimatter trap comprises a three-dimensional or two-dimensional photonic bandgap (PBG) structure containing at least one cavity therein. The species are stored in the cavity or in an array of cavities. The PBG structure blocks premature annihilation of the excited species by preventing decays to the ground state and by blocking the pickoff process. A Bose-Einstein Condensate form of Ps* can be used to increase the storage density. The long lifetime and high storage density achievable in this device offer utility in several fields, including medicine, materials testing, rocket motors, high power / high energy density storage, gamma-ray lasers, and as an ignition device for initiating nuclear fusion reactions in power plant reactors or hybrid rocket propulsion systems.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Antiproton production and delivery for imaging and termination of undesirable cells
InactiveUS8109865B2Radiation/particle handlingMagnetic resonance acceleratorsAntiprotonDetector array
Systems and methods for using antiprotons for terminating unwanted or undesirable cells which can be used in the treatment of conditions caused by the existence and / or proliferation of such undesirable cells. Such conditions include cardiovascular ailments, Parkinson's disease, wet macular degeneration, endocrine disorders, dermatological ailments, and cancer. Because of the unique nature of antiprotons and their annihilation characteristics, the preferred antiproton delivery device (1010, 1015, 1030) embodiments further incorporate detector arrays (1050a), capable of detecting characteristic emissions in the course of treatment.
Owner:HBAR TECH
Multi-field charged particle cancer therapy method and apparatus
The invention relates generally to treatment of solid cancers. More particularly, the invention relates to a multi-field charged particle cancer therapy method and apparatus coordinated with negative ion beam creation, ion beam focusing, charged particle acceleration, patient rotation, and / or patient respiration. Preferably, the charged particle therapy is performed on a patient in a partially immobilized and repositionable position. Proton delivery is preferably timed to patient respiration via control of charged particle beam injection, acceleration, and / or targeting methods and apparatus.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKTSIONERNOE OBSHCHESTVO PROTOM
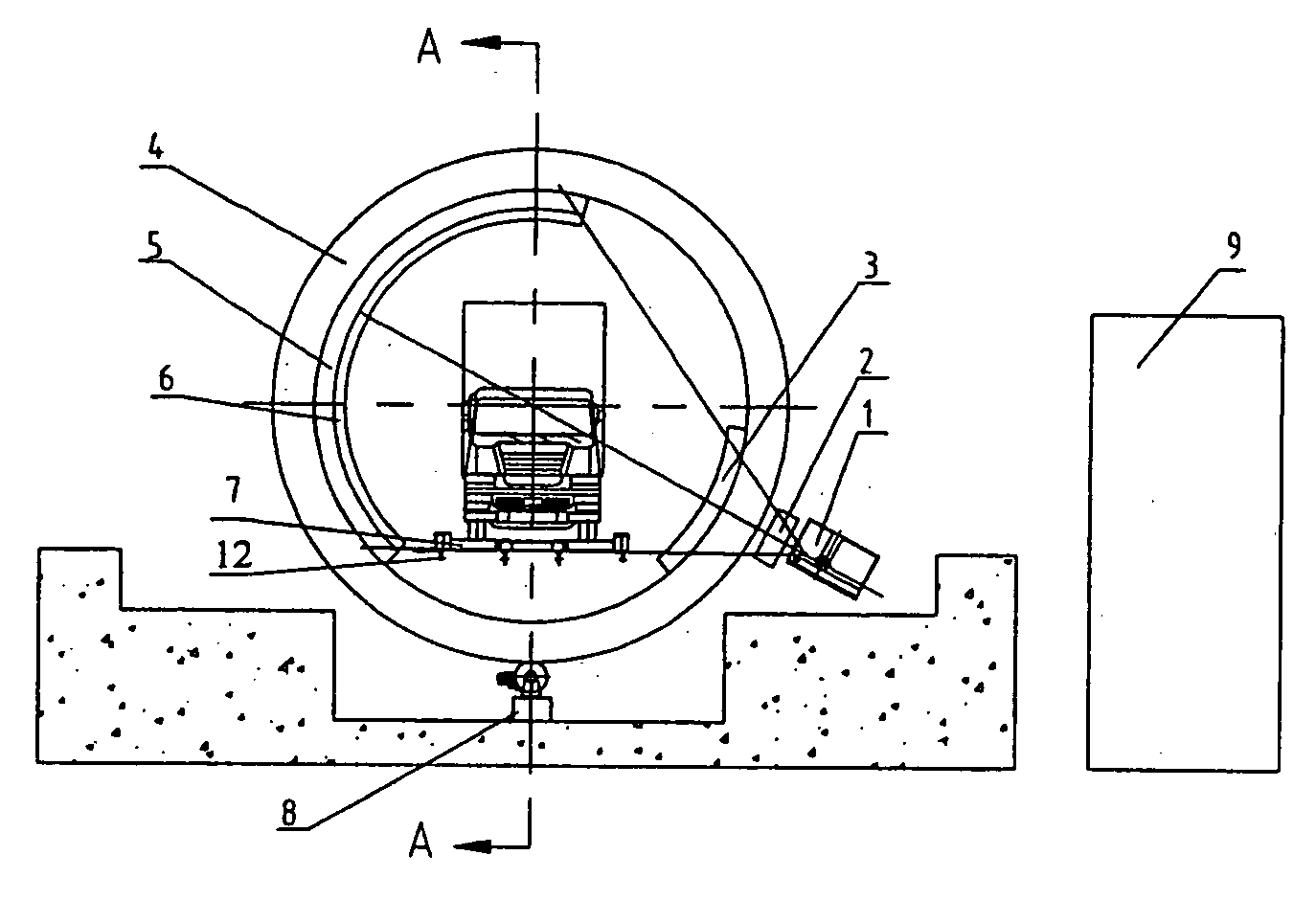
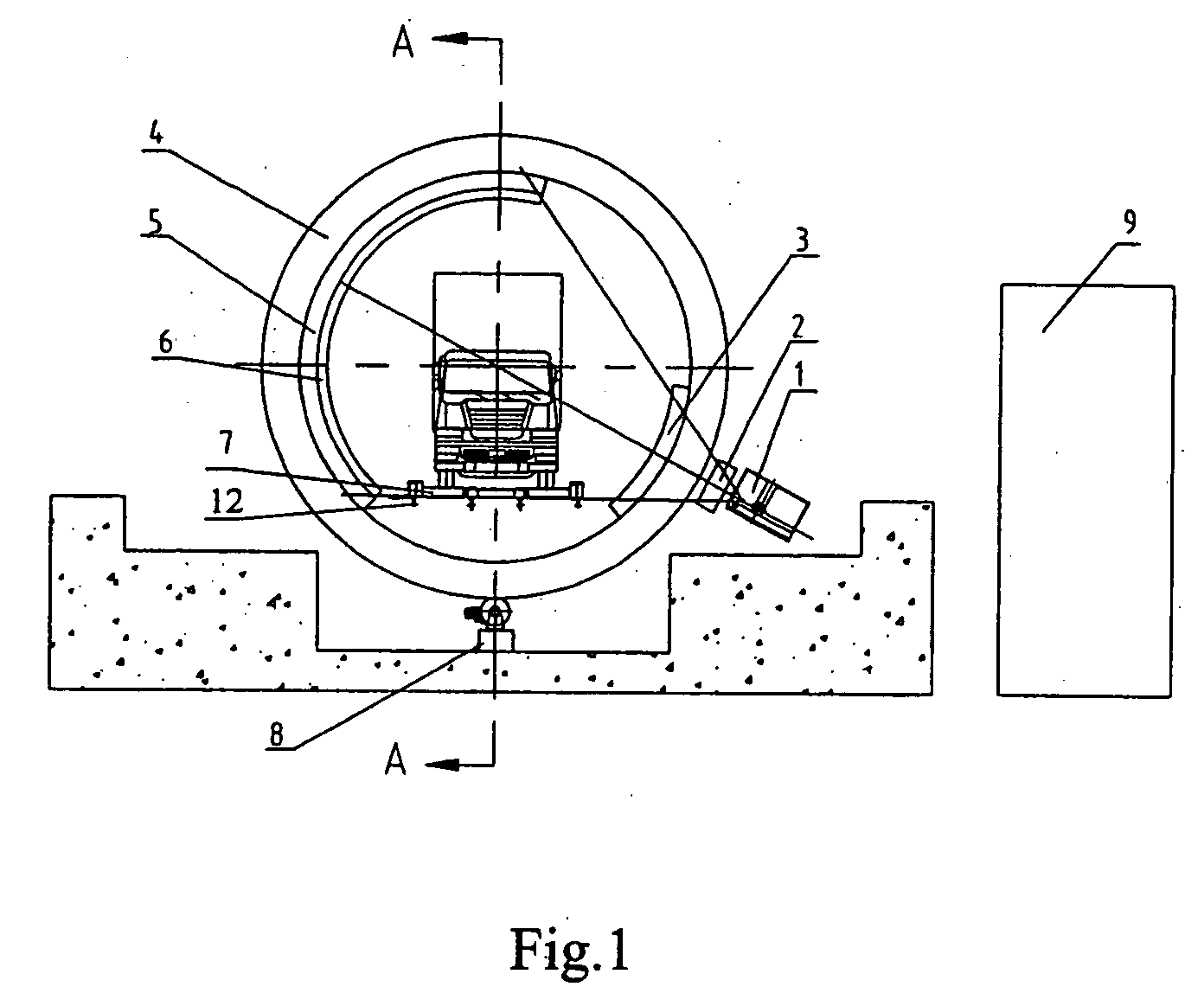
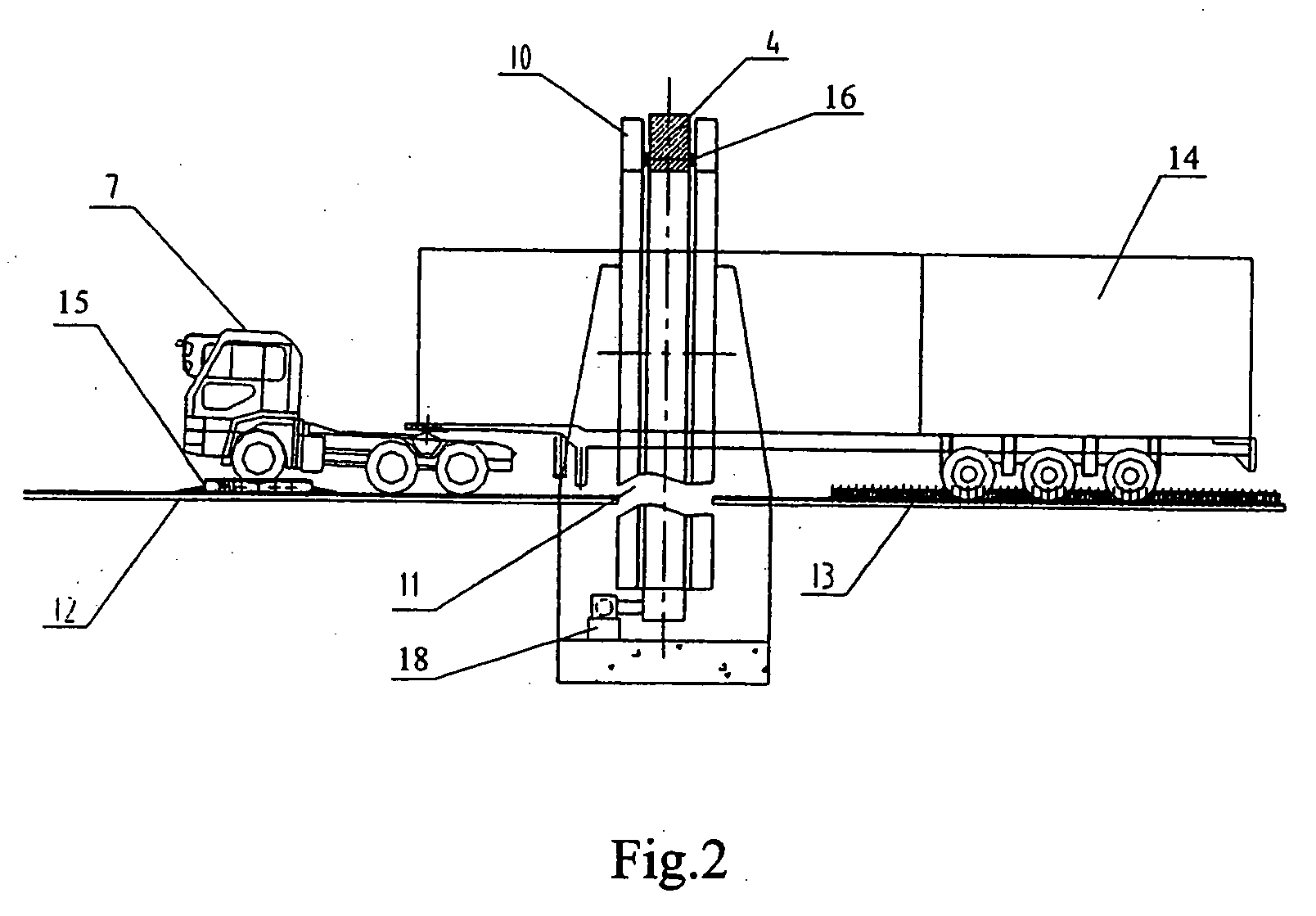
Container inspection system with CT tomographic scanning function
InactiveUS20060126772A1Easy to operateEasy maintenanceChemical to radiation conversionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAccuracy improvementVertical plane
A container inspection system with CT tomographic scanning function, which is related to a large container inspection system for Customs, is disclosed, comprising: a radiation source; an annular rotatable rack with the radiation source provided at the outside thereof and rotated with it; an annular rack body for supporting the annular rotatable rack in a vertical plane; a driving device for rotating the annular rotatable rack; a detector array provided in the inner side of said annular rotatable rack and opposed to a side where the radiation source is provided; a transmission device passing through the annular rotatable rack and annular rack body, and transmitting a container truck to be detected in linear movement; a remote control device for controlling the operations of the radiation source, the driving device and the transmission device, and receiving / displaying the image signal obtained by the detector array. Not only can general inspection of the objects to be detected be undertaken, but also does repeated tomographic inspection of suspicious locations within the inspected objects, thus achieves effective accuracy improvement of the contrabands detection.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
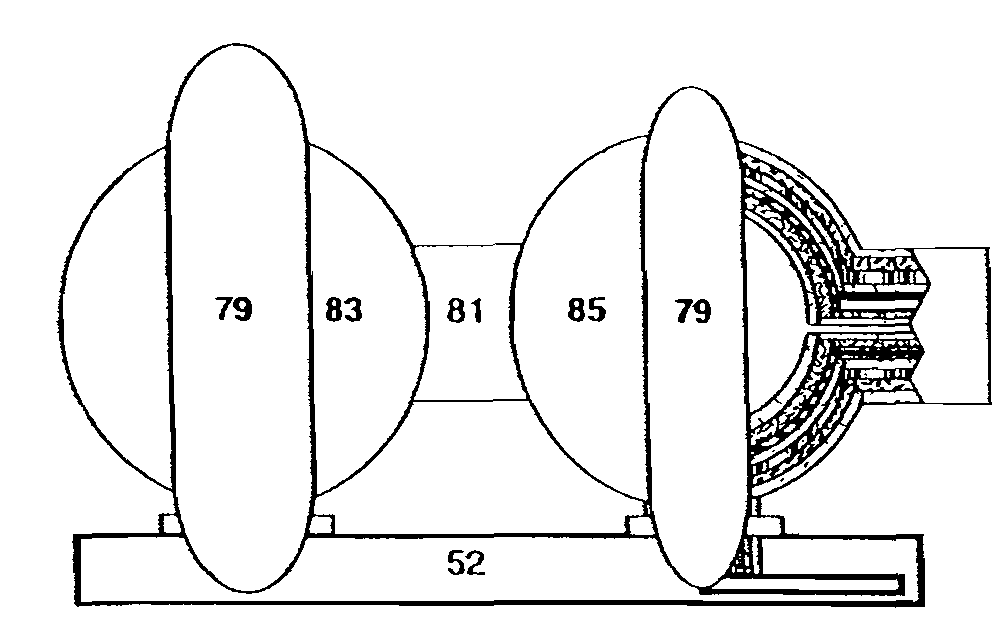
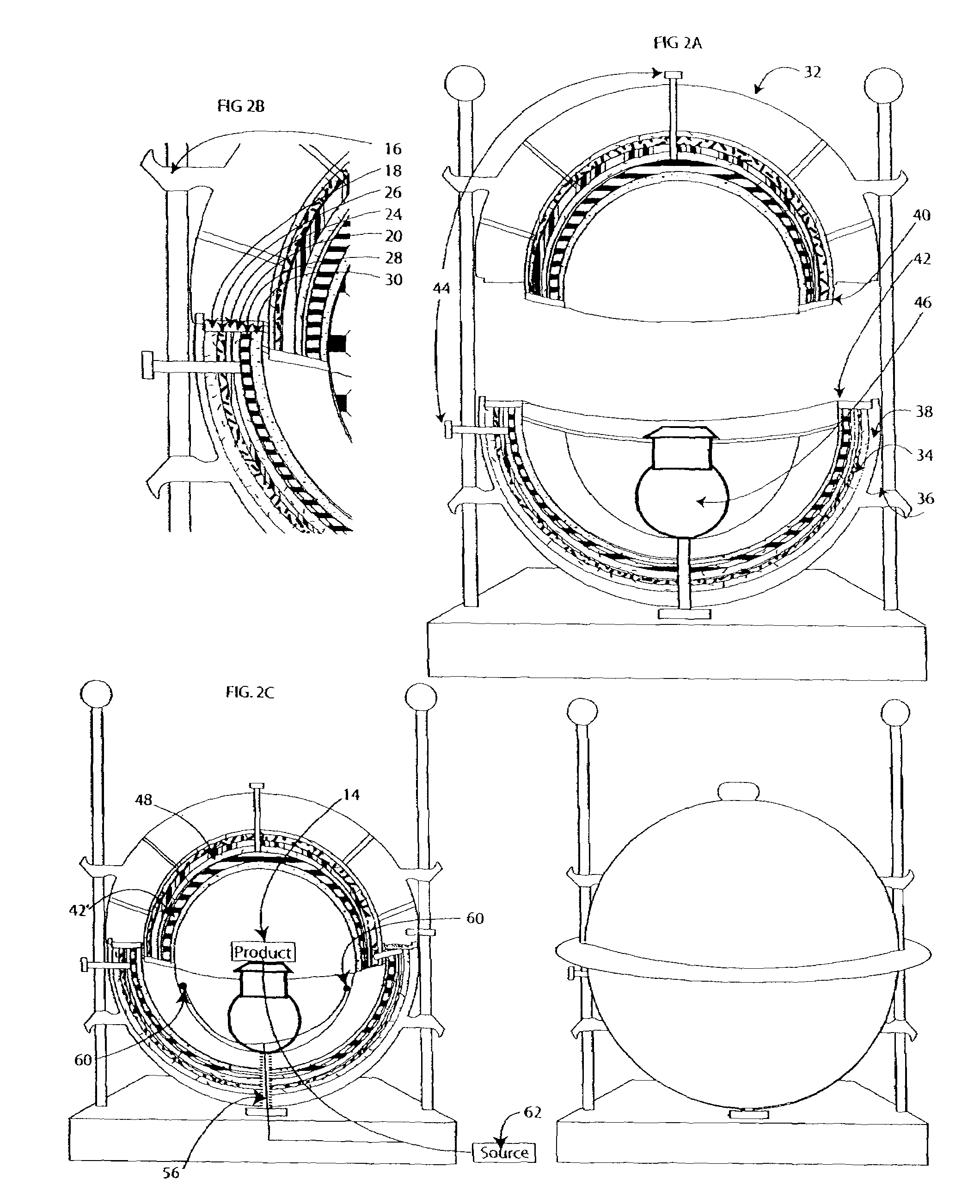
Spheric alignment mechanism
ActiveUS20050265508A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic/electric field screeningElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
A chamber for manipulating a work product is formed in layers as a series of nested shells. The shells have an outer structural casing and an electromagnetic shield that surrounds a superconducting shell. The superconducting shell is immersed in a cryogenic coolant contained in a reservoir. The work product is further manipulated using kinetic energy and electromagnetic energy.
Owner:KESSLER STEPHEN BURNS
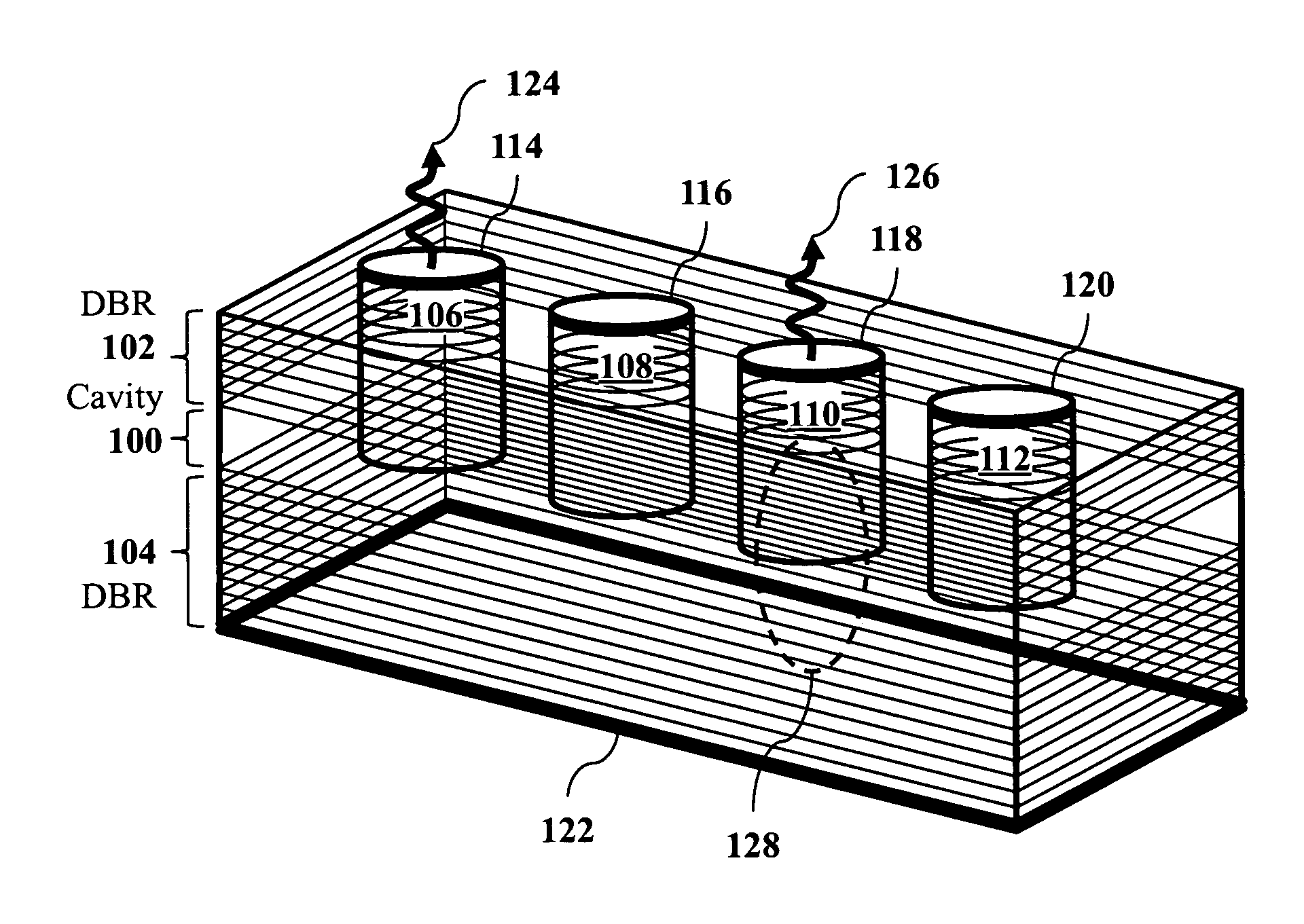
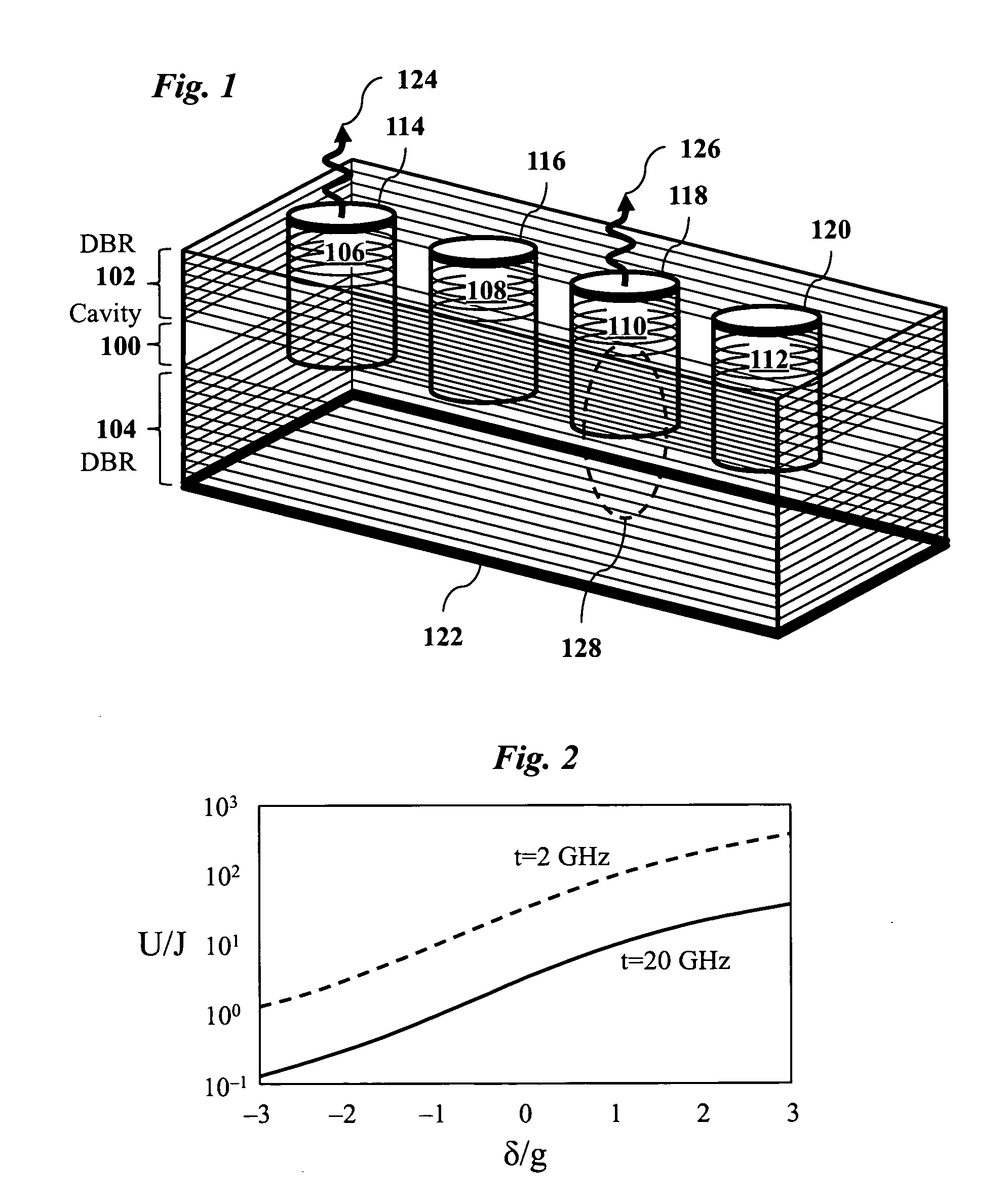
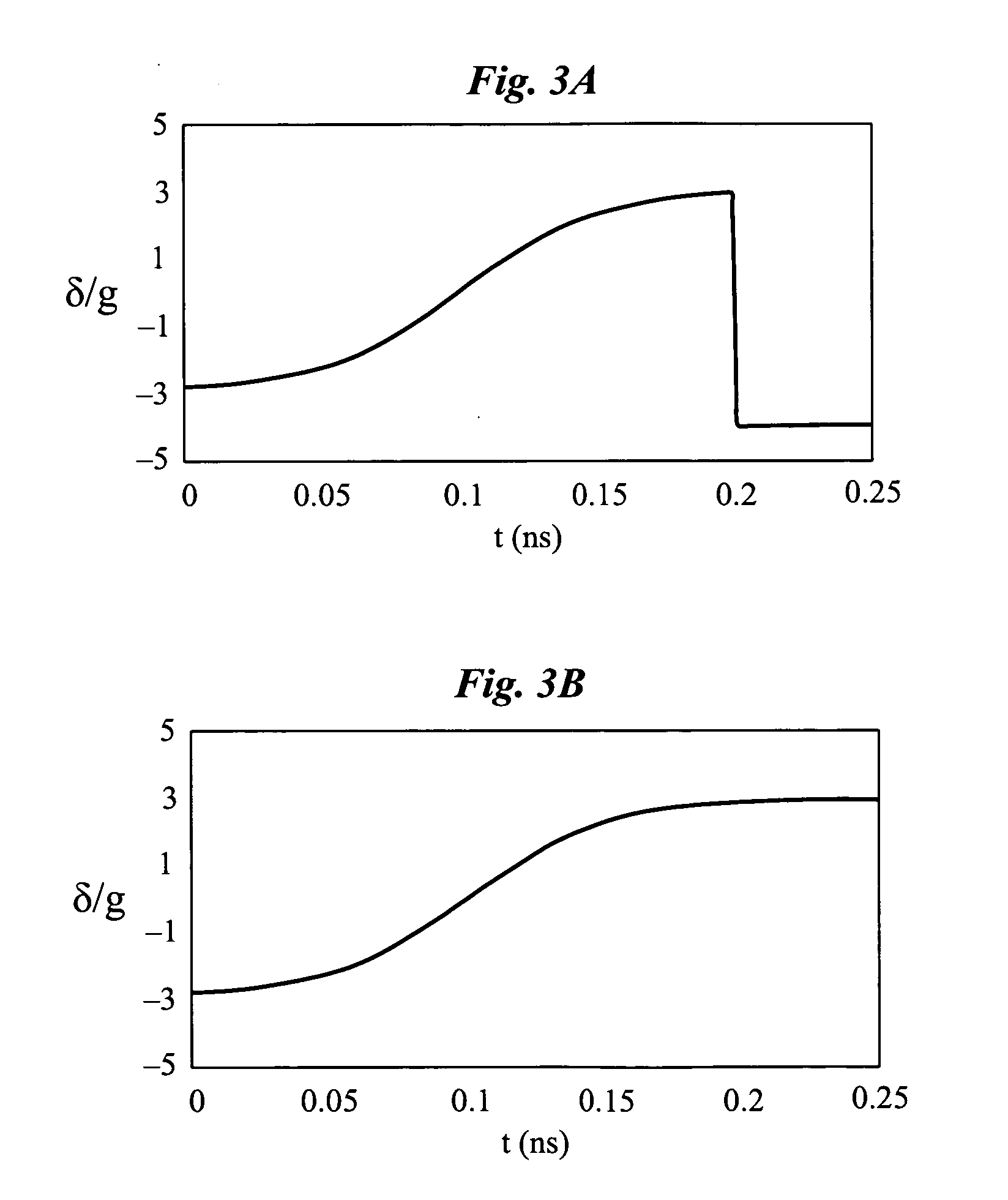
Massive parallel generation of nonclassical photons via polaritonic superfluid to mott- insulator quantum phase transition
InactiveUS20100258746A1Improve developmentQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPotential wellSuperfluid state
Deterministic generation of nonclassical photons by producing a dilute gas of exciton-polaritons in a solid-state microcavity that includes a periodic array of potential well traps. A photon-exciton frequency detuning is modulated in the microcavity to produce a polaritonic quantum phase transition from a superfluid state to a Mott-insulator state. The nonclassical photons are then generated simultaneously by radiative decay of exciton-polaritons in the microcavity. The nonclassical photons may be indistinguishable single photons, in which case the dilute gas of exciton-polaritons is produced such that on to average there is one polariton per potential well trap. Alternatively, the generated nonclassical photons may be polarization-entangled photon pairs, in which case the dilute gas of exciton-polaritons is produced such that on average there are two polaritons per potential well trap.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
UV devices, systems and methods for UV sterilization
Provided herein are ultraviolet (UV) devices, systems, and methods for UV disinfection and sterilization, more specifically, UV devices, systems, and methods for UV disinfection and sterilization of a container, room, space or defined environment. The systems, UV devices, and methods are particularly useful for the UV disinfection and sterilization of a container used in the food and dairy industry and for containers used in the process of fermentation for an alcoholic beverage. Provided are also UV devices, systems, and methods for inhibiting the growth of one or more species of microorganisms present in a container, room, space or defined environment, preferably for inhibiting the growth of one or more species of microorganisms present on an interior surface of a container, room, space or defined environment.
Owner:BLUEMORPH
Isotope generator
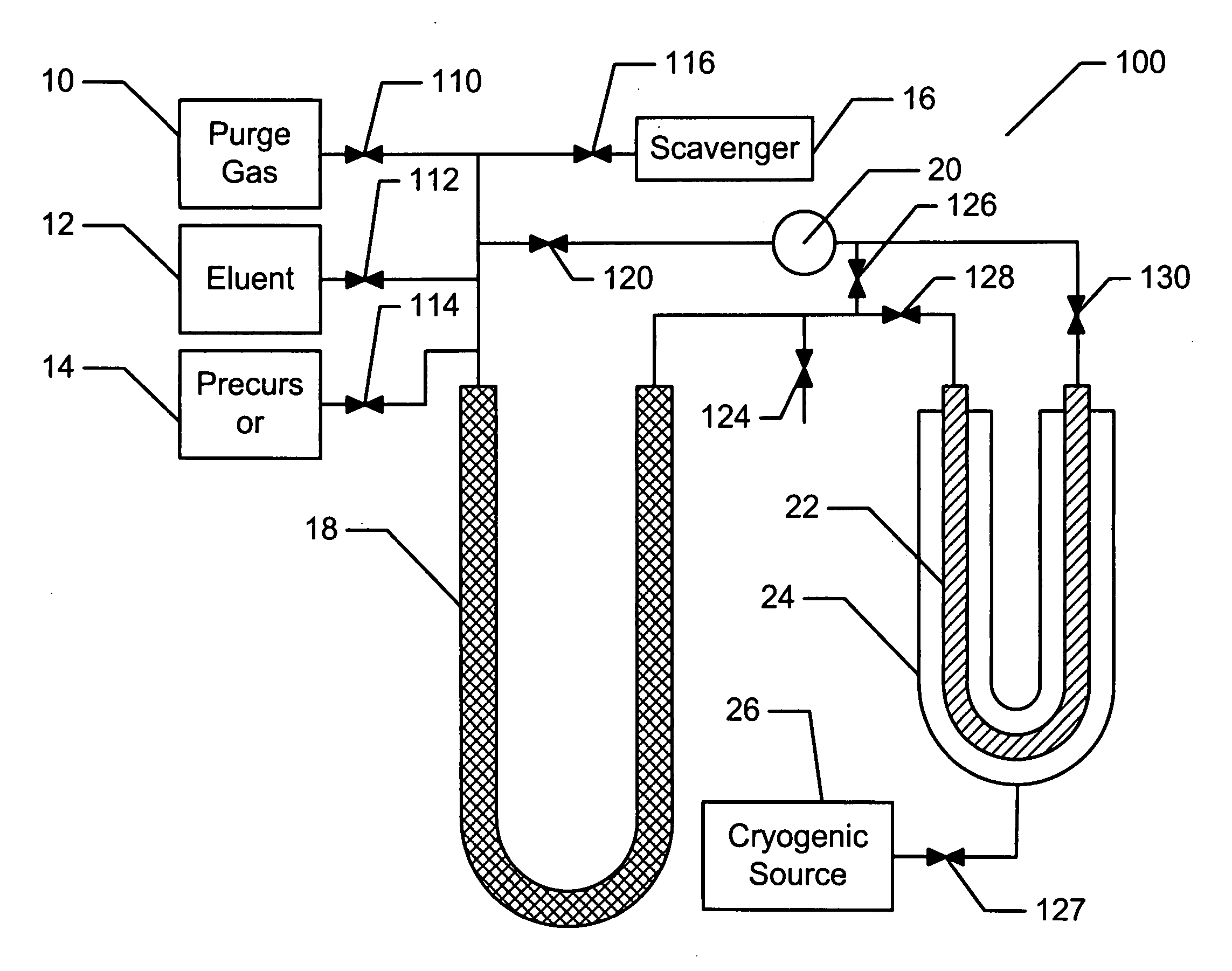
InactiveUS7023000B2Improve efficiencyLaser detailsScattering properties measurementsIsotopeRadiochemistry
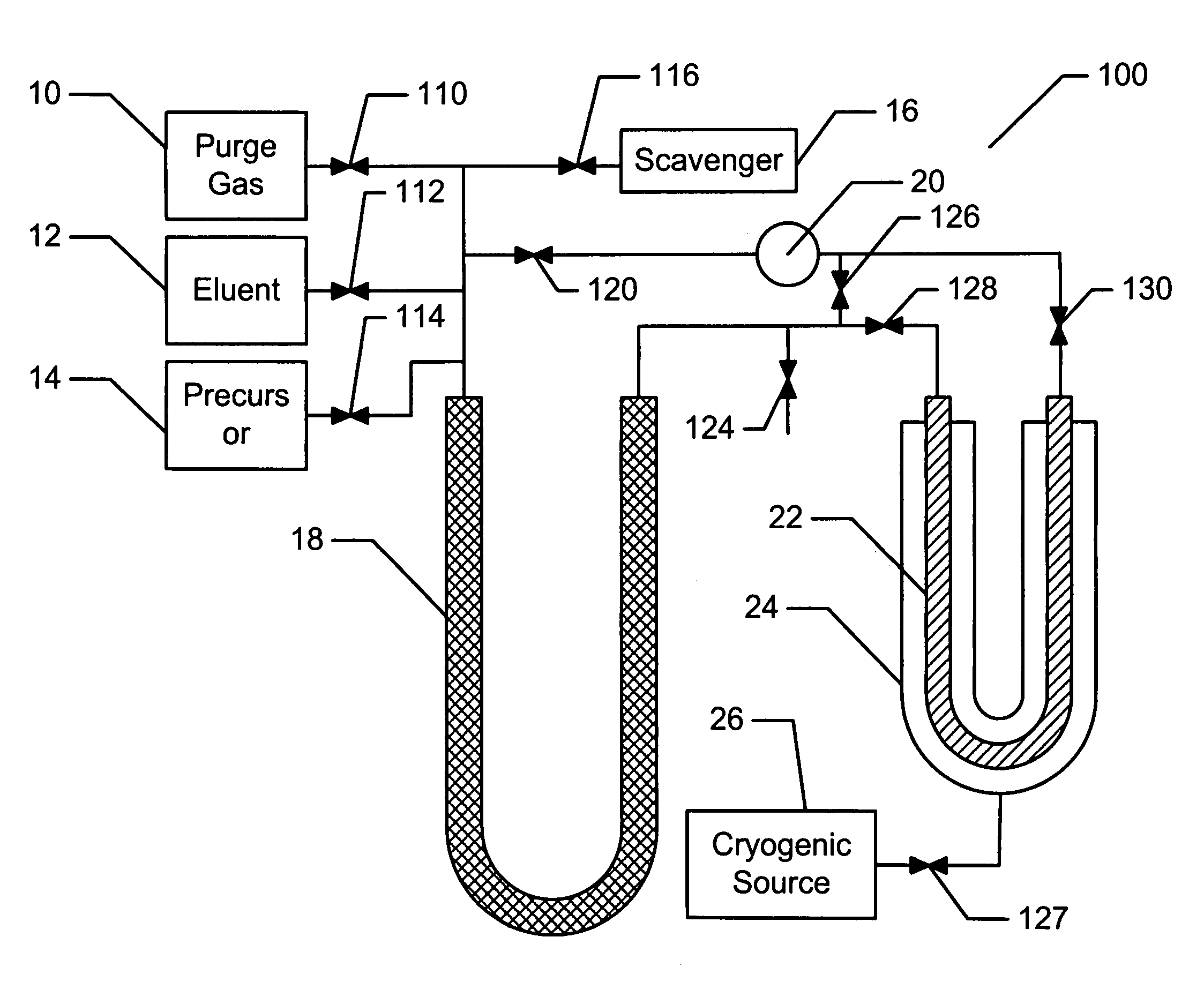
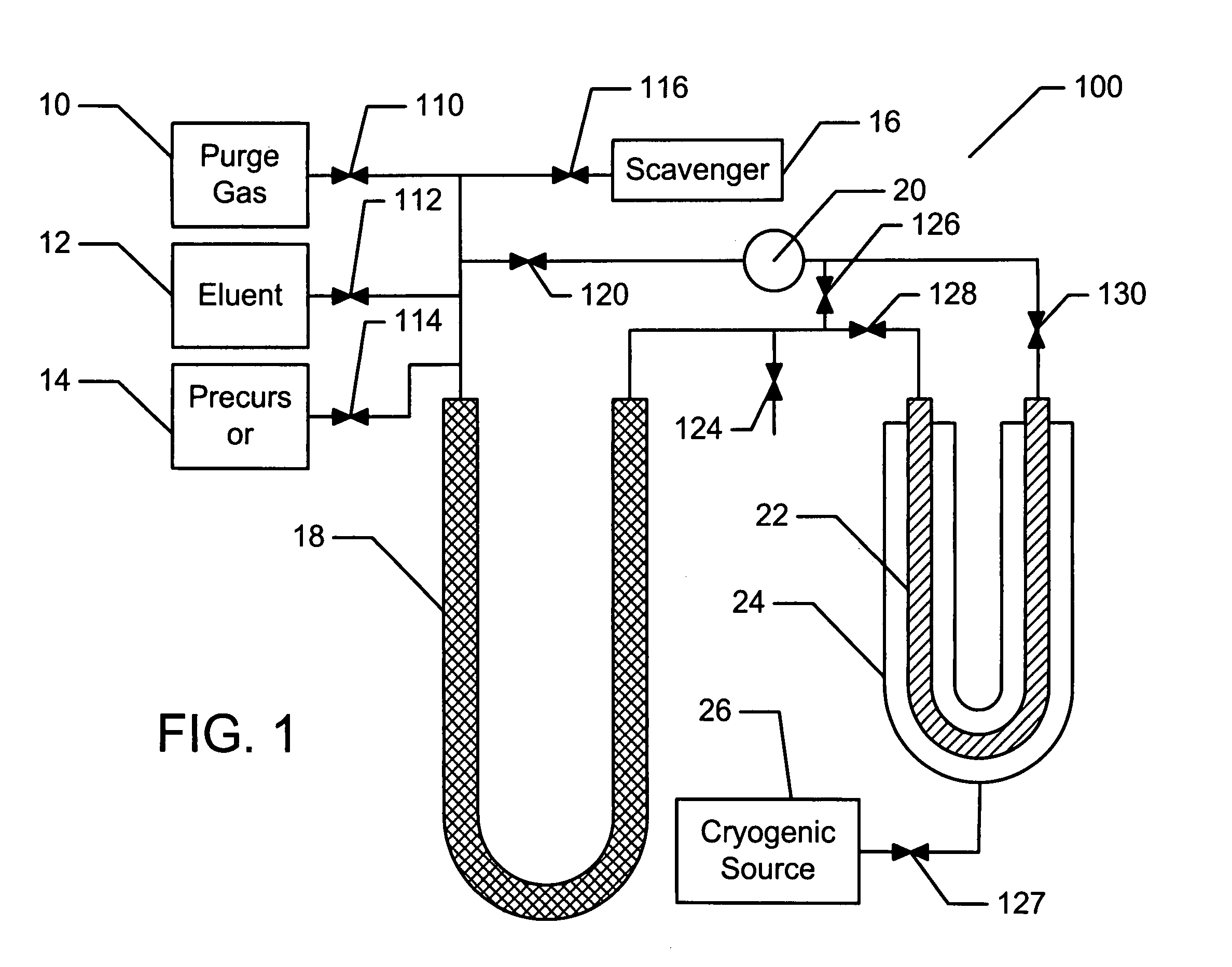
Disclosed are a method and an apparatus for generating and collecting a secondary compound that includes daughter isotope, such as 68Ga, resulting from the decay of a parent isotope, such as 68Ge, present in a precursor compound. The apparatus includes a generator system comprising a collector vessel, a cold trap and a pump, that are operatively connected to sources for introducing a precursor compound and an eluant solution, and optionally purging gases and oxygen scavengers, into the generator system. In a generation mode a substantial portion of the precursor compound is maintained in or flows through the collector vessel while in recovery mode substantially all of the precursor compound is confined in the cold trap while the collector vessel is flushed with an eluant to remove the collected secondary compound.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +4
Instrumented capsule for nuclear fuel irradiation tests in research reactors
ActiveUS20050105667A1Improve integrityImprove securityNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringIrradiationThermocouple
An instrumented capsule for nuclear fuel irradiation tests in research reactors. The capsule includes an outer shell; a rod tip assembly assembled to a lower end plate of the shell, thus absorbing impact; fuel rod assemblies supported in the shell by means of support tubes and housing therein sintered fuel bodies and in-capsule instruments, such as thermocouples and self-powered neutron detectors (SPND); a protective tube connected to the upper end plate and protecting instrument control cables; and a guide pipe connected to the inclined extension part of a junction tree and guiding the instrument control cables to a control unit provided outside the reactor. The capsule further includes upper and lower end caps provided around the upper and lower ends of the shell; and a lower stopper and an upper stopper fitted over the protective tube to be supported in the upper portion of the irradiation hole of the reactor and to be locked to the locking clamp provided at the upper portion of the chimney of the reactor, respectively. The capsule is used to measure in real time the properties of nuclear fuels irradiated in the reactor during a nuclear fuel irradiation test, thus providing nuclear fuel irradiation test data required for the design of nuclear fuels and the determination of in-pile performance and structural integrity of the nuclear fuels.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Mobile/transportable PET radioisotope system with omnidirectional self-shielding
InactiveUS20060017411A1Readily attainable and wide and economic distributionLinear acceleratorsChemical to radiation conversionLight beamPhysics
Owner:ACCSYS TECH
Capsule assembling apparatus for neutron re-irradiation experiments
InactiveUS20050286675A1Liquid surface applicatorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates generally to an apparatus of assembling a capsule for neutron-irradiation experiments. The capsule may contain test specimens to develop nuclear fuel, and may comprise a capsule main body and protection tube that may be assembled and disassembled using separate joining means. The present invention provides a capsule assembling apparatus that may enable safe and easy assembly / disassembly of the capsule placed at a given depth in a working pool through remote working. The capsule assembling apparatus may comprise a base structure loading the capsule main body, a guiding pipe of a given length extending from the base structure to provide a pathway through which the capsule main body is loaded on the base structure, a damper fixing the capsule main body to the guiding pipe, and a coupler coupling the capsule main body with the protection tube.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Binocular method and apparatus for stoichiometric analysis and imaging using subatomic particle activation
InactiveUS20050195931A1Detection speedHigh energyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationChemical to radiation conversionGamma rayBiological activation
An apparatus and method for detecting, locating, and analyzing chemical compounds located within a test subject using subatomic particle activation. In a first embodiment, an excitation source excites a target to simultaneously produce beams each consisting of certain subatomic species, for example fast neutrons and alpha particles. The test subject (and chemical compounds contained therein) is irradiated by the fast neutrons, thereby stimulating the emission of prompt gamma rays. Gamma and alpha detectors are positioned relative to the test subject and target(s) so as to detect the emitted prompt gamma rays and alpha particles in substantial coincidence, and the known physical relationship between the beams is used to spatially locate the activated chemical compound. Energy spectra derived from the gamma detectors are filtered to eliminate all non-relevant spectral artifacts, thereby 1) permitting the creation of a plurality of parallel coincidence channels; 2) reducing the subsequent signal processing required; and 3) increasing the overall accuracy and efficiency of the chemical compound identification and analysis processes. In a second embodiment, thermal neutron-induced gamma emissions are detected and analyzed in conjunction with the fast neutron-induced gammas to provide a warning signal of the possible presence of certain types of contraband. A multi-beam / multi-target embodiment is also disclosed for more accurate spatial location. A method for calibrating and evaluating the efficacy of the system under varying test parameters is further disclosed.
Owner:CALSEC +2
Isotope generator
Disclosed are a method and an apparatus for generating and collecting a secondary compound that includes daughter isotope, such as 68Ga, resulting from the decay of a parent isotope, such as 68Ge, present in a precursor compound. The apparatus includes a generator system comprising a collector vessel, a cold trap and a pump, that are operatively connected to sources for introducing a precursor compound and an eluant solution, and optionally purging gases and oxygen scavengers, into the generator system. In a generation mode a substantial portion of the precursor compound is maintained in or flows through the collector vessel while in recovery mode substantially all of the precursor compound is confined in the cold trap while the collector vessel is flushed with an eluant to remove the collected secondary compound.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +4
Formation of [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for [18F] fluorinations
The present invention claims a method for forming [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species. The present invention also provides for an apparatus for forming [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species. Kit claims for formation of [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
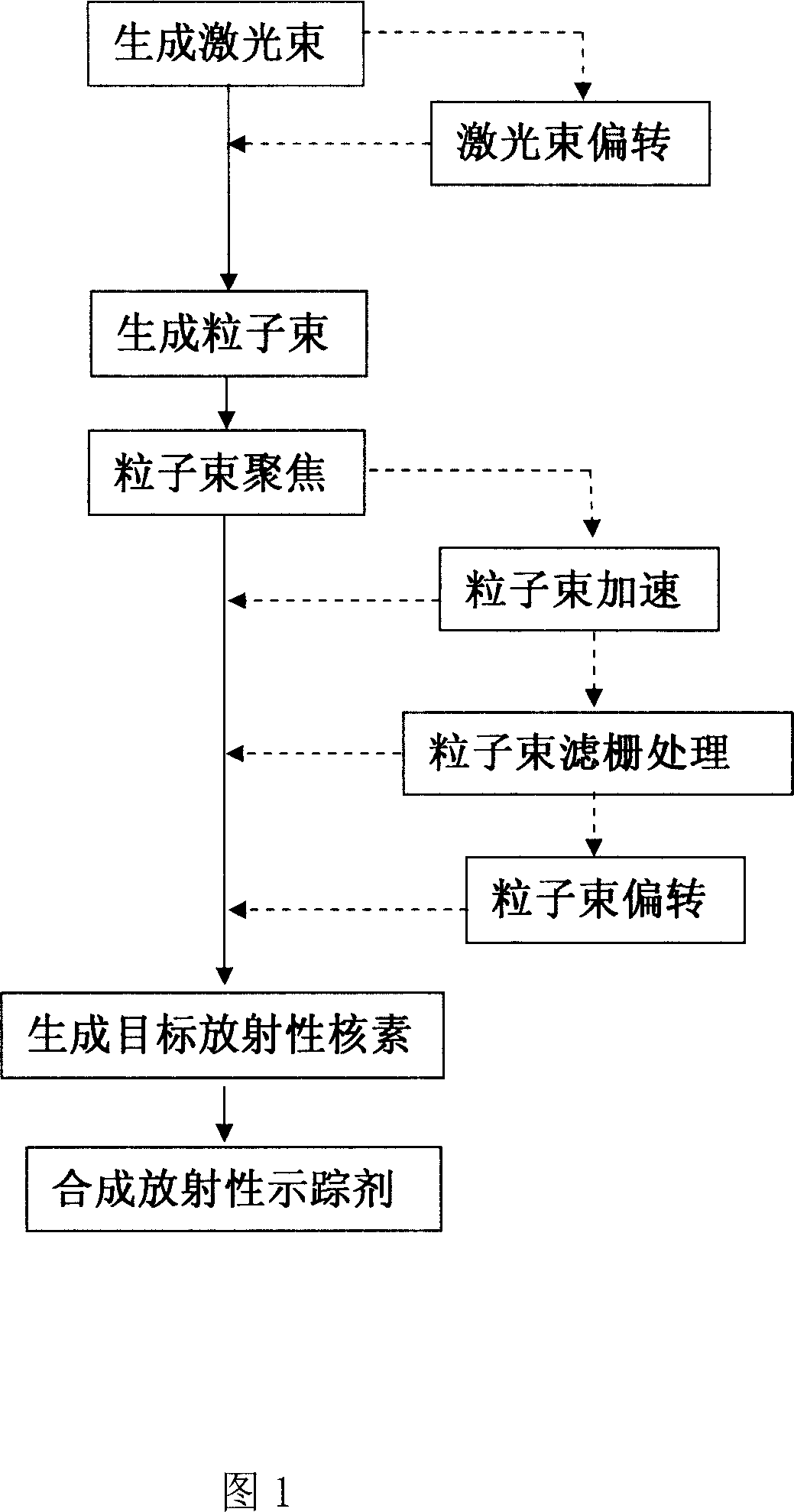
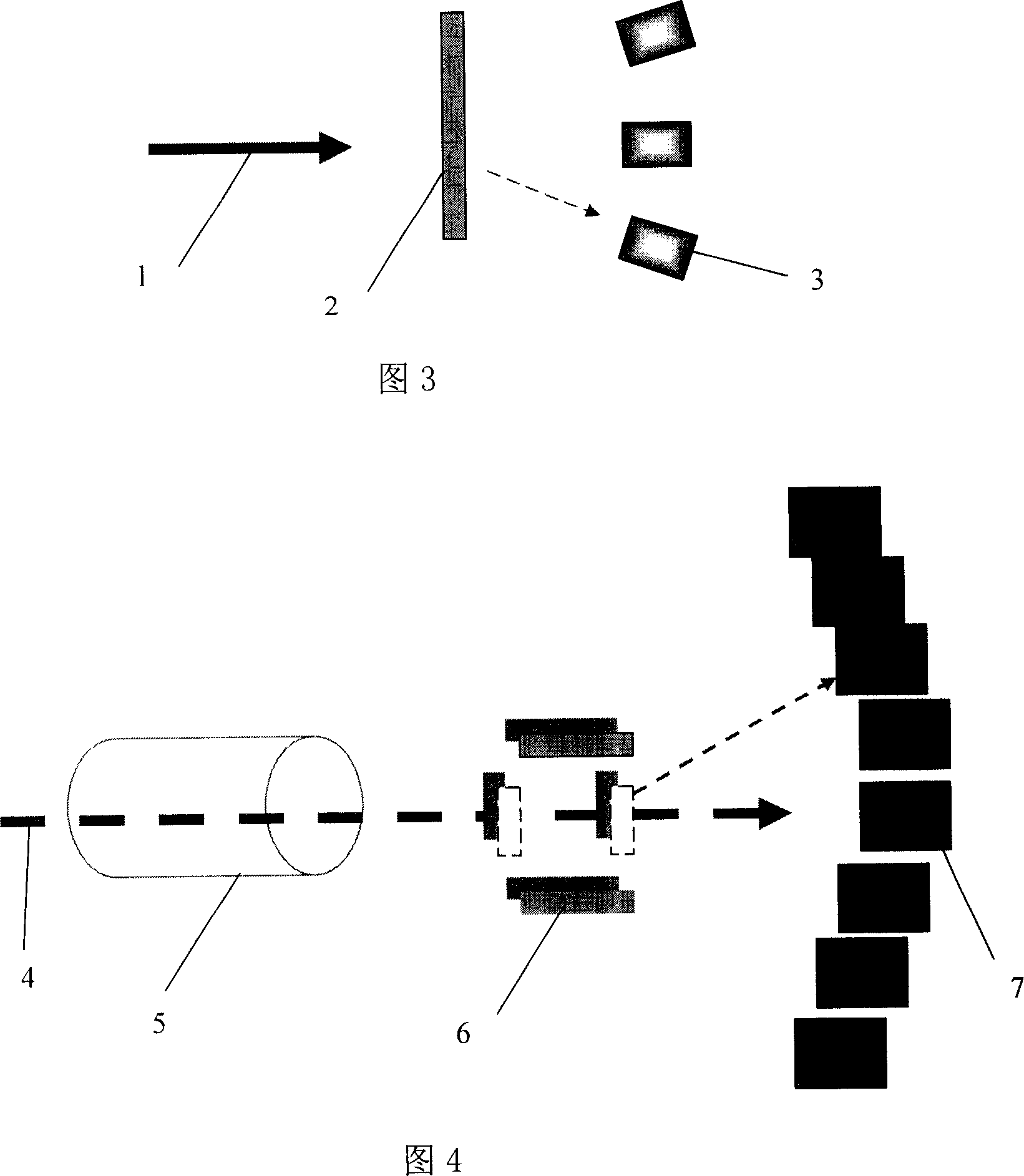
Method for producing radiotracer
InactiveCN101154476AHigh densityHigh strengthIn-vivo radioactive preparationsChemical to radiation conversionRadioactive tracerHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a production method of radioactive tracer and includes the following steps: a high power laser is adopted to match with a primary target to generate particle beam; the particle beam completes nuclear reaction with the matter on a radioactive tracer target after focusing and accelerating so as to generate target radioactive tracer; finally, the target radioactive tracer is transmitted to a radioactive tracer synthesis system to synthesize radioactive tracer which is used in human body visualization. The method overcomes the disadvantages of the prior radioactive tracer production method through adopting cyclotron such as low efficiency, incapability of on-line production, big equipment volume, complex design, incapability of repeated starting up for use in a short time, poor flexibility in use and high maintenance cost; meanwhile, the invention has the advantages of instant on-line production of radioactive tracer, realization of desktop radioactive tracer production system, low shielding requirements of equipment, overall performance improvement of radioactive tracer production system and reduction in production and operating costs.
Owner:王黎
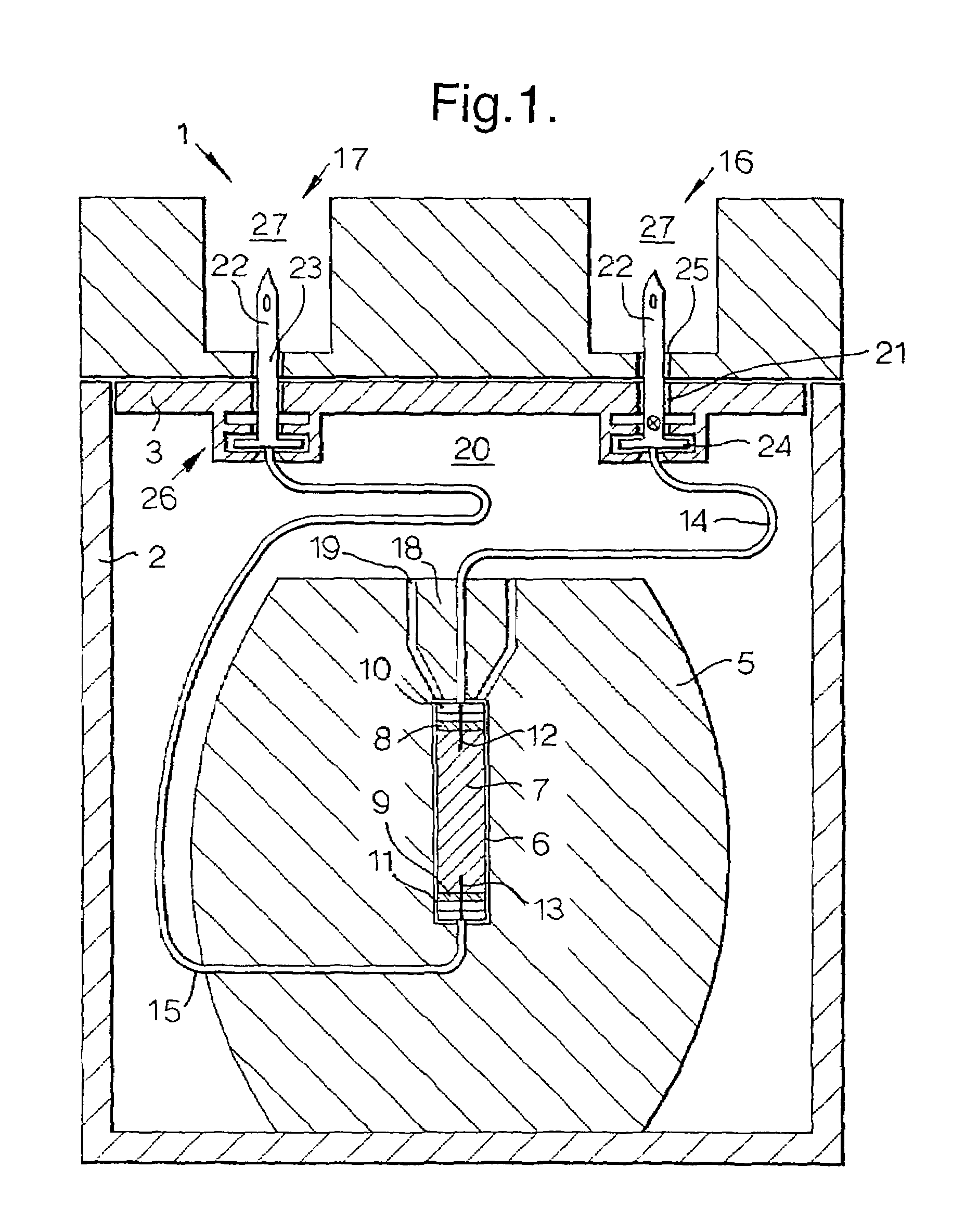
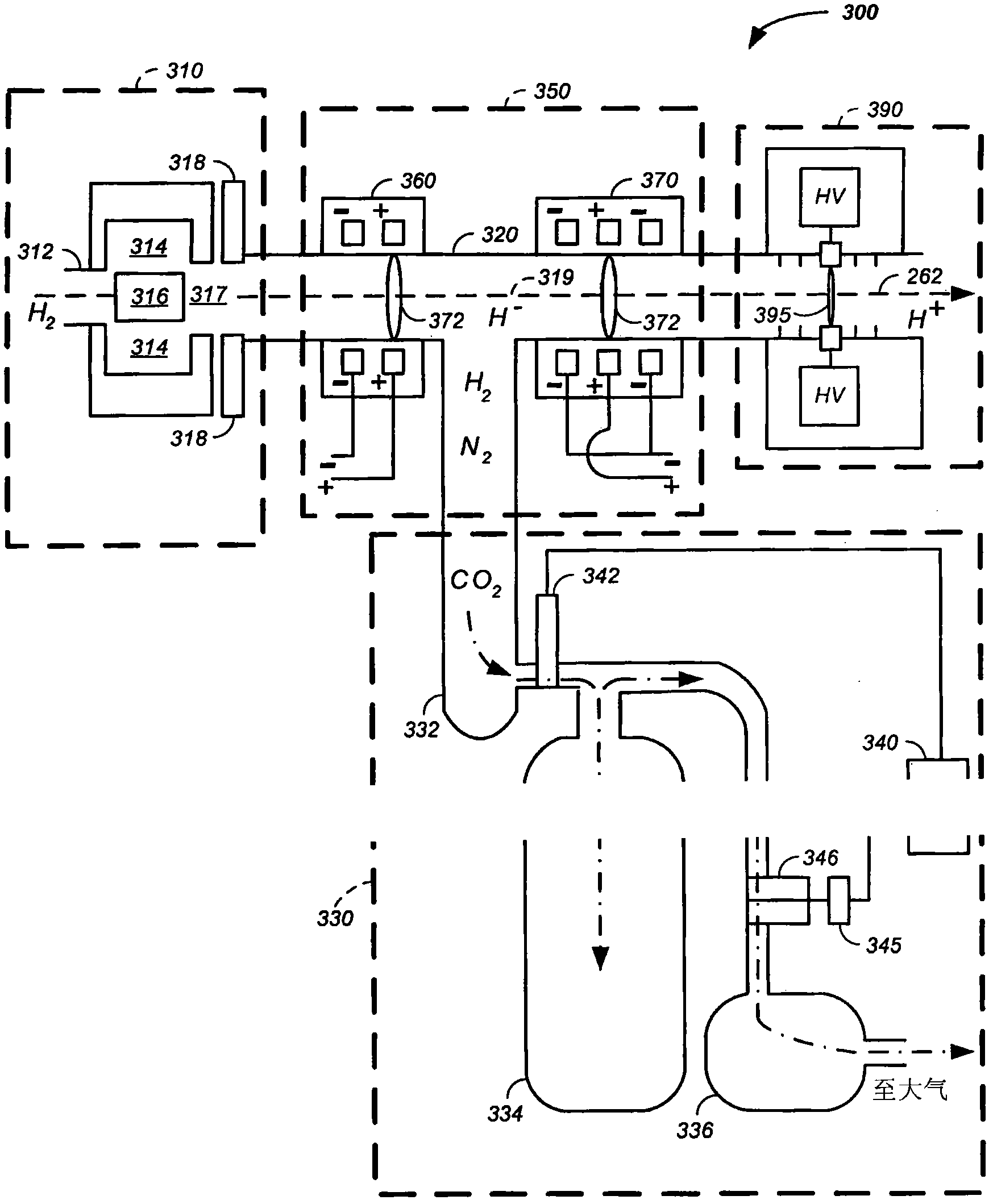
18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine
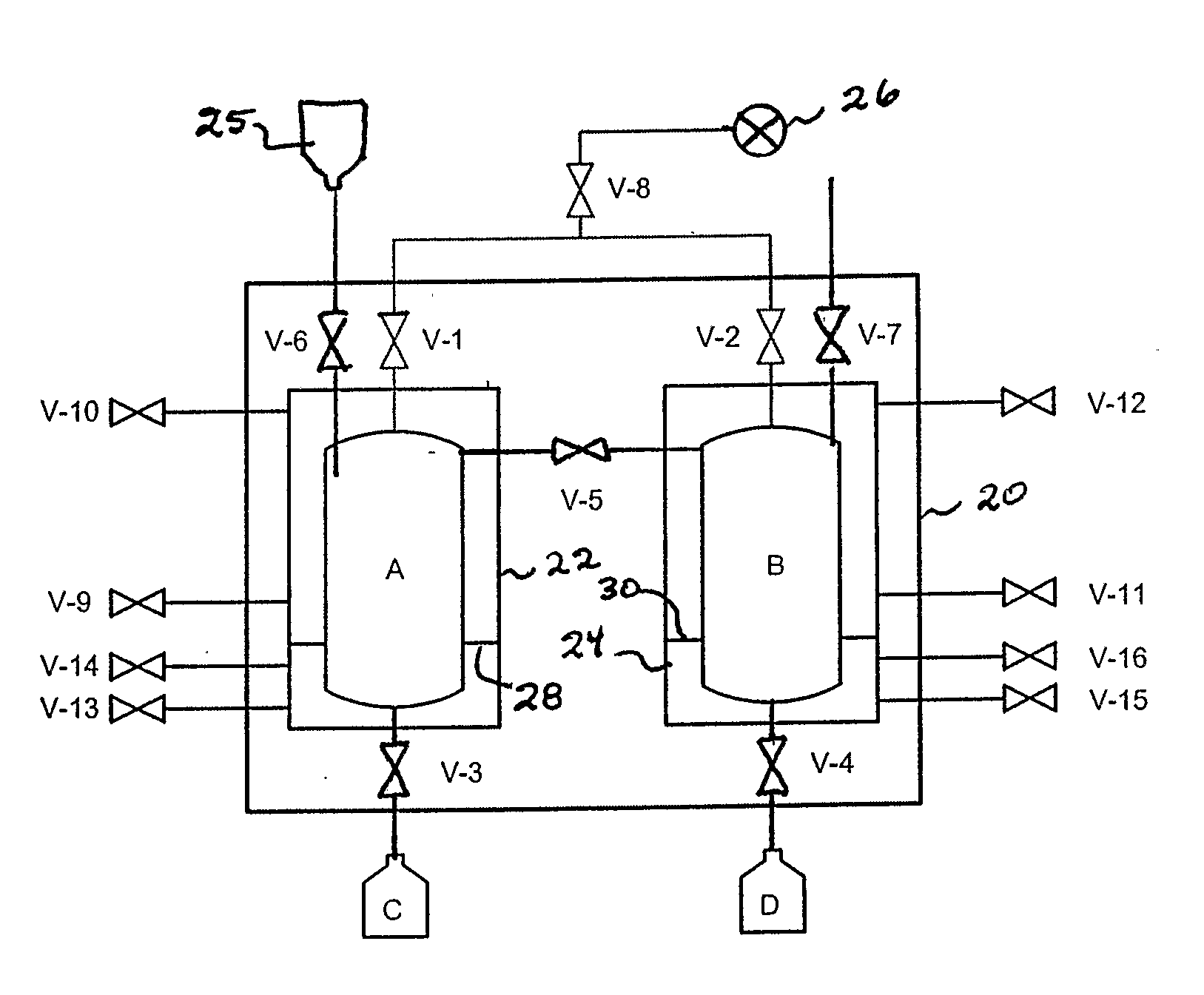
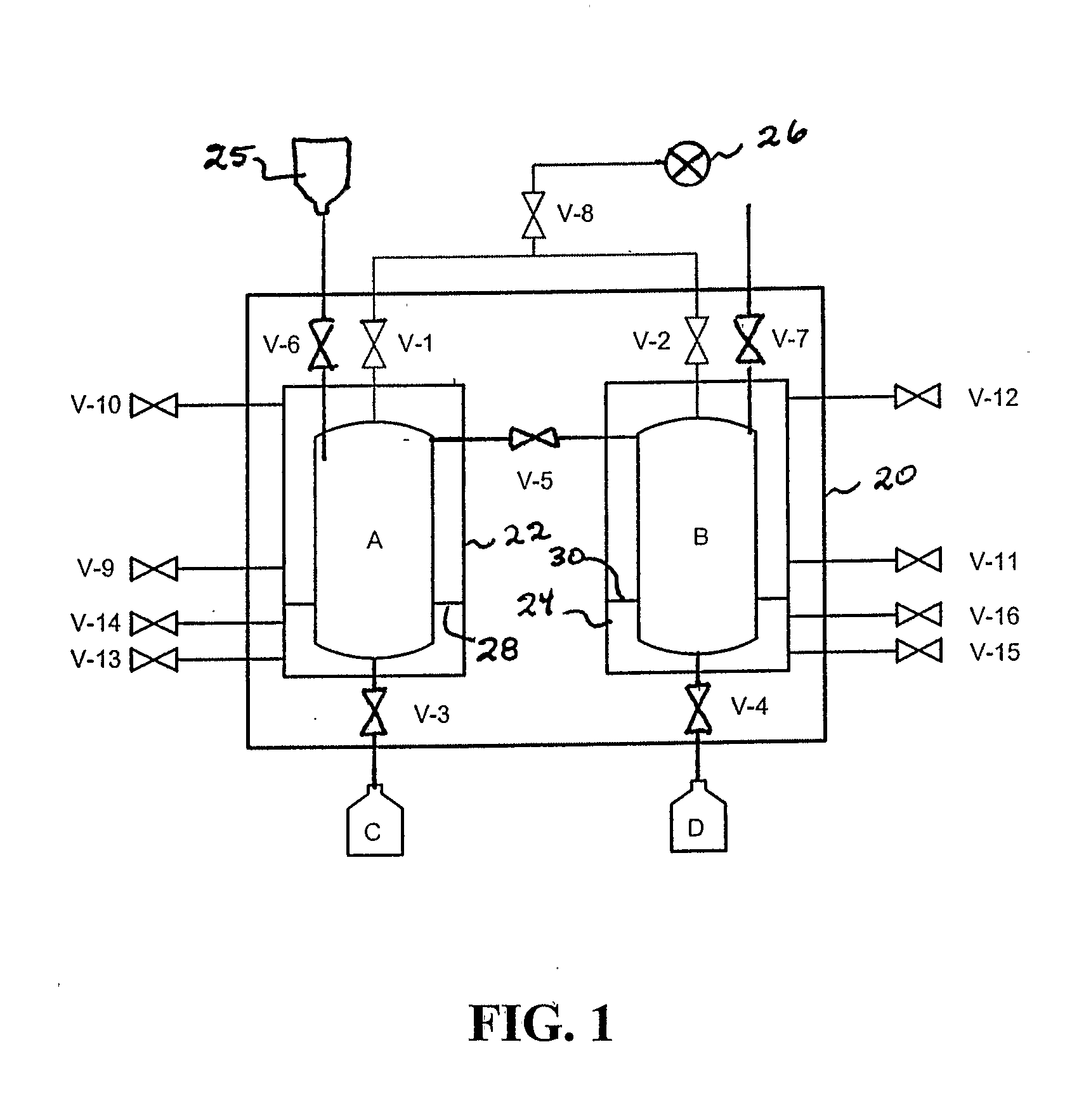
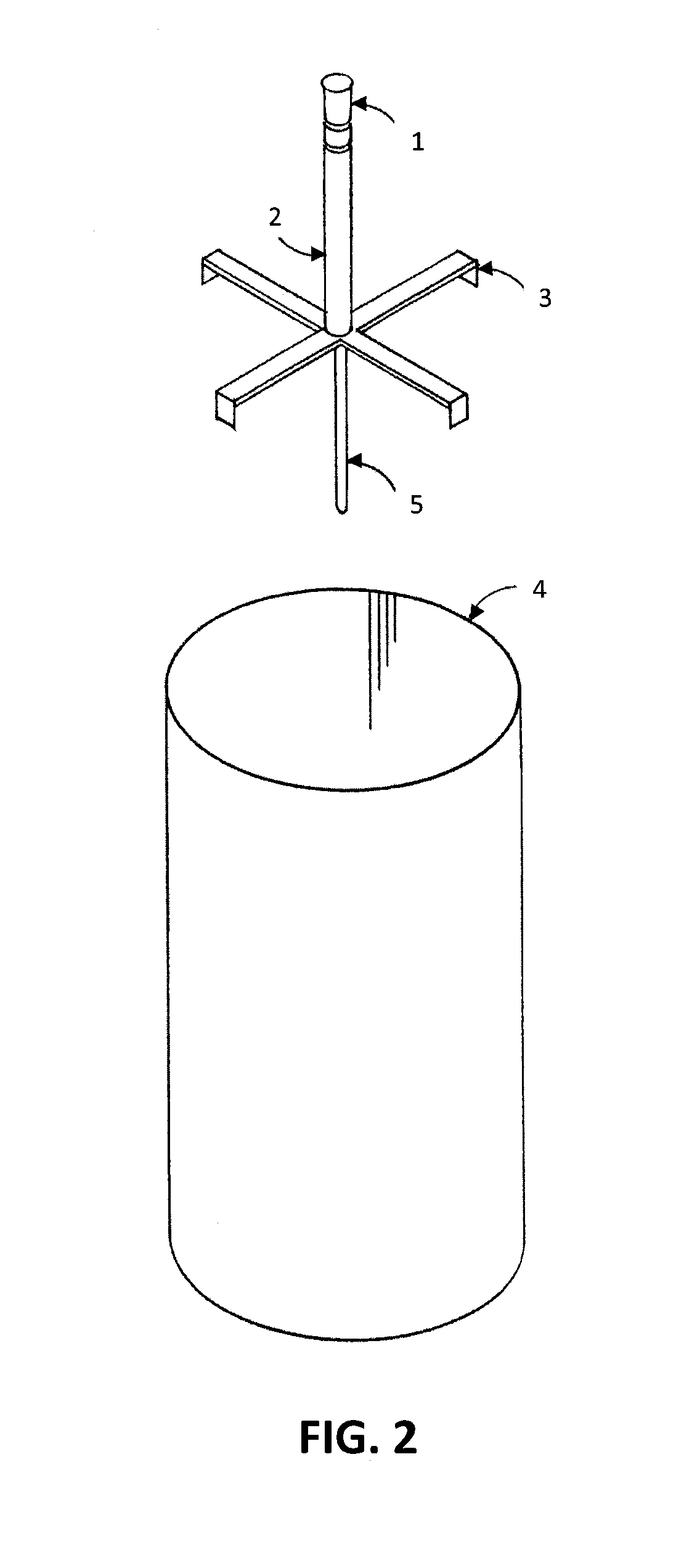
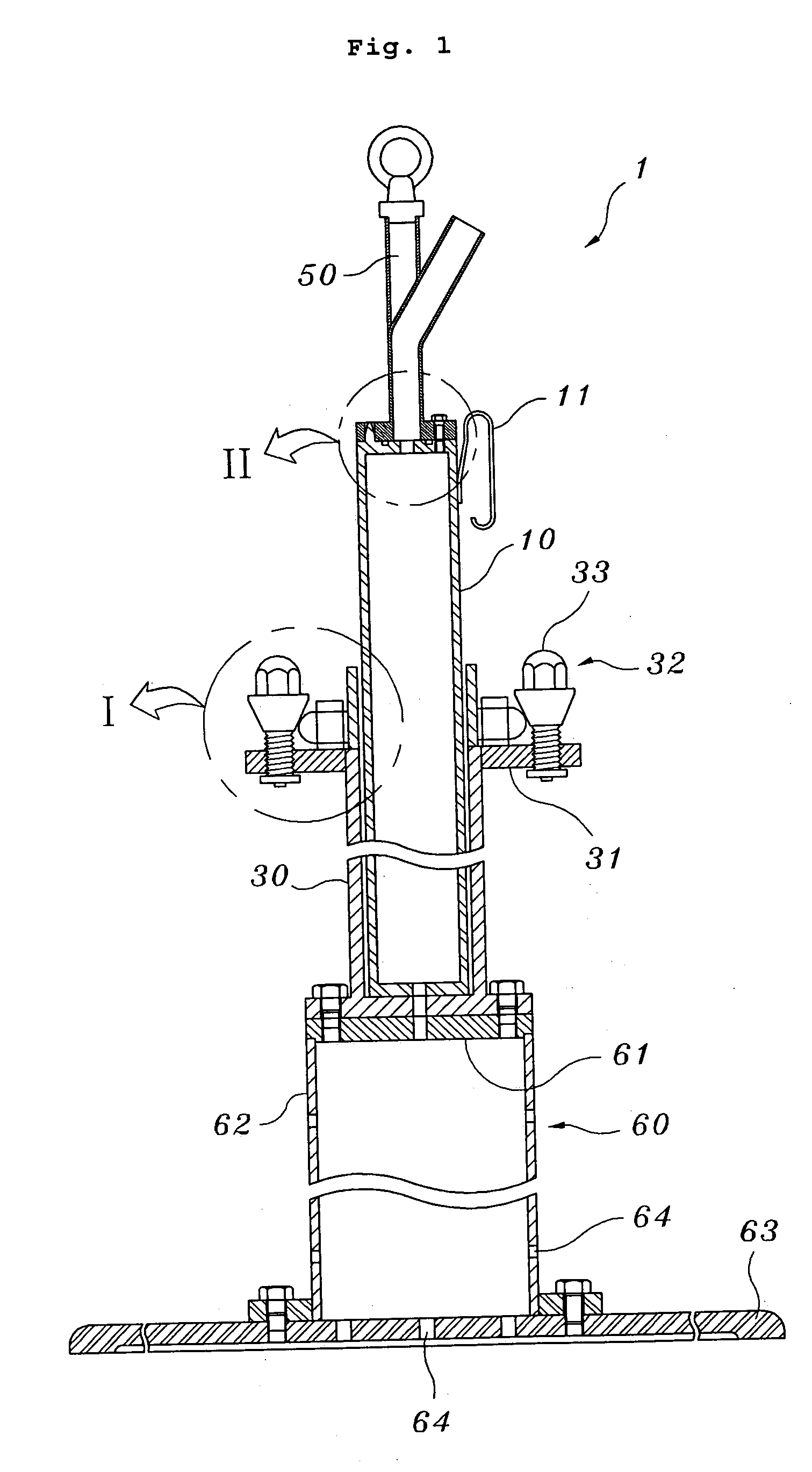
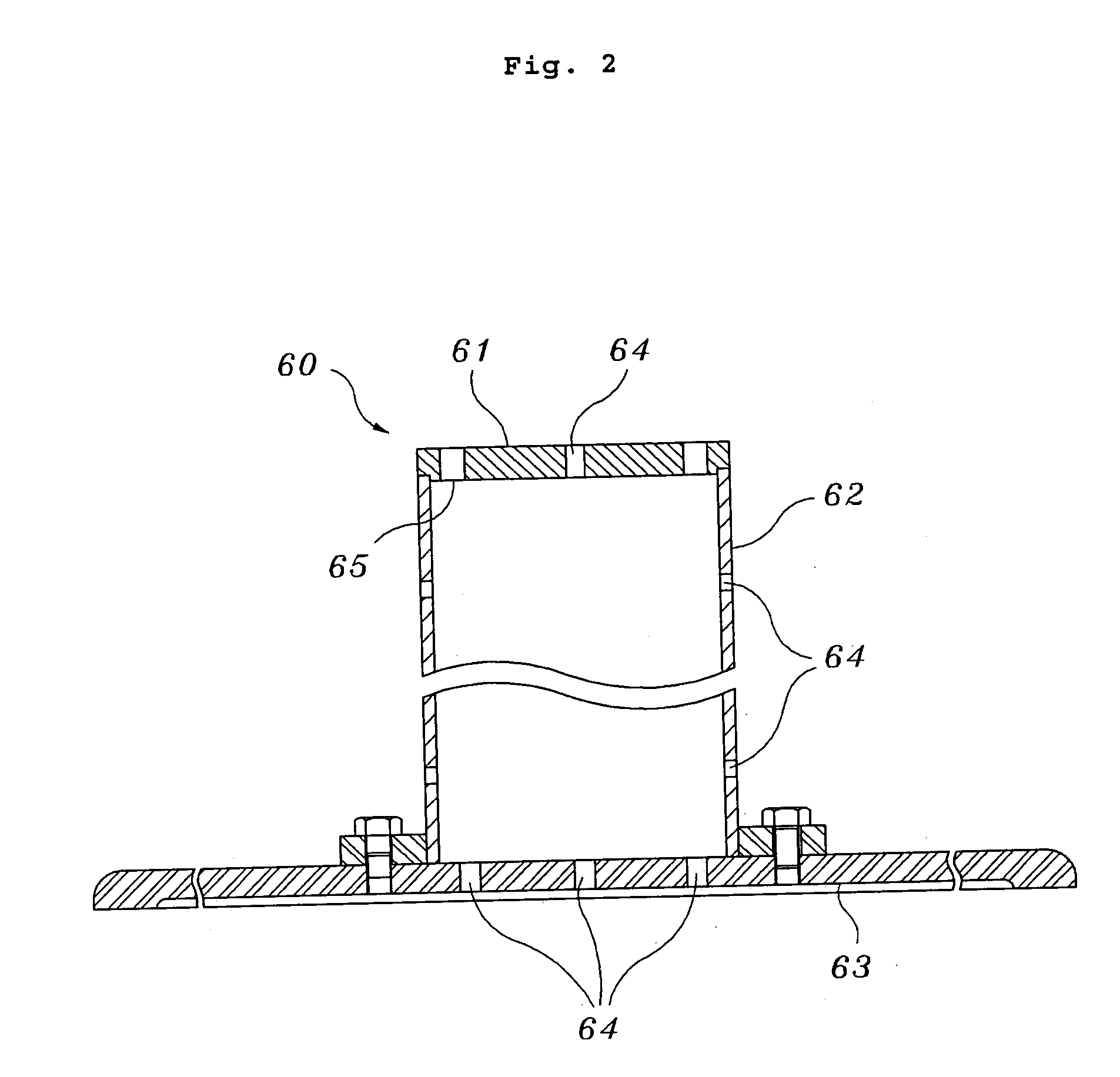
InactiveUS20050279130A1Reliable and safe techniqueHigh gas puritySolidificationLiquefactionProduct gasEngineering
The present invention is a controlled high-purity apparatus and method for transporting a well defined gas volume from a larger gas volume with high pressure into a smaller volume by cryogenic cooling. Particularly, a refilling apparatus includes a first fluid container, a second fluid container, and an interface for coupling the first and second fluid containers to a supply of gas. The first fluid container has a volume corresponding to a certain amount of liquid condensed from the gas, which upon phase transformation provides a desired gas pressure within the total volume of the first and second fluid containers. The first fluid container is preferably a coil of tubing for submersion into a bath of liquid nitrogen to cryogenically cool the first fluid container, thereby condensing the gas into liquid form. The invention is particularly well-suited for providing [18O]oxygen gas to a [18O]O2 / F2 target system producing [18F]fluorine gas. The desired pressure is ideally 40 to 50 bar in order to supply the [18O]O2 / F2 target system with an appropriate amount of [18O]oxygen gas for a commercially significant number of production runs between refills of the refilling apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Generator and Method for Production of Technetium-99m
InactiveUS20080187489A1Improve efficiencyHigh purityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDecay productNeutron irradiation
A generator that allows for a non-fission based method of producing and recovering 99mTc from neutron-irradiated molybdenum. This generator system is based on the isolation of 99mTc, as the decay product from a source of 99Mo labelled molybdenum carbonyl Mo(CO)6 through a distillation process. The 99mTc obtained from this distillation is produced with high efficiency and purity in a solvent-free form, which can then be dissolved in water or other solvents to produce a solution at the required specific activity and concentration, as reasonably determined by the operator.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
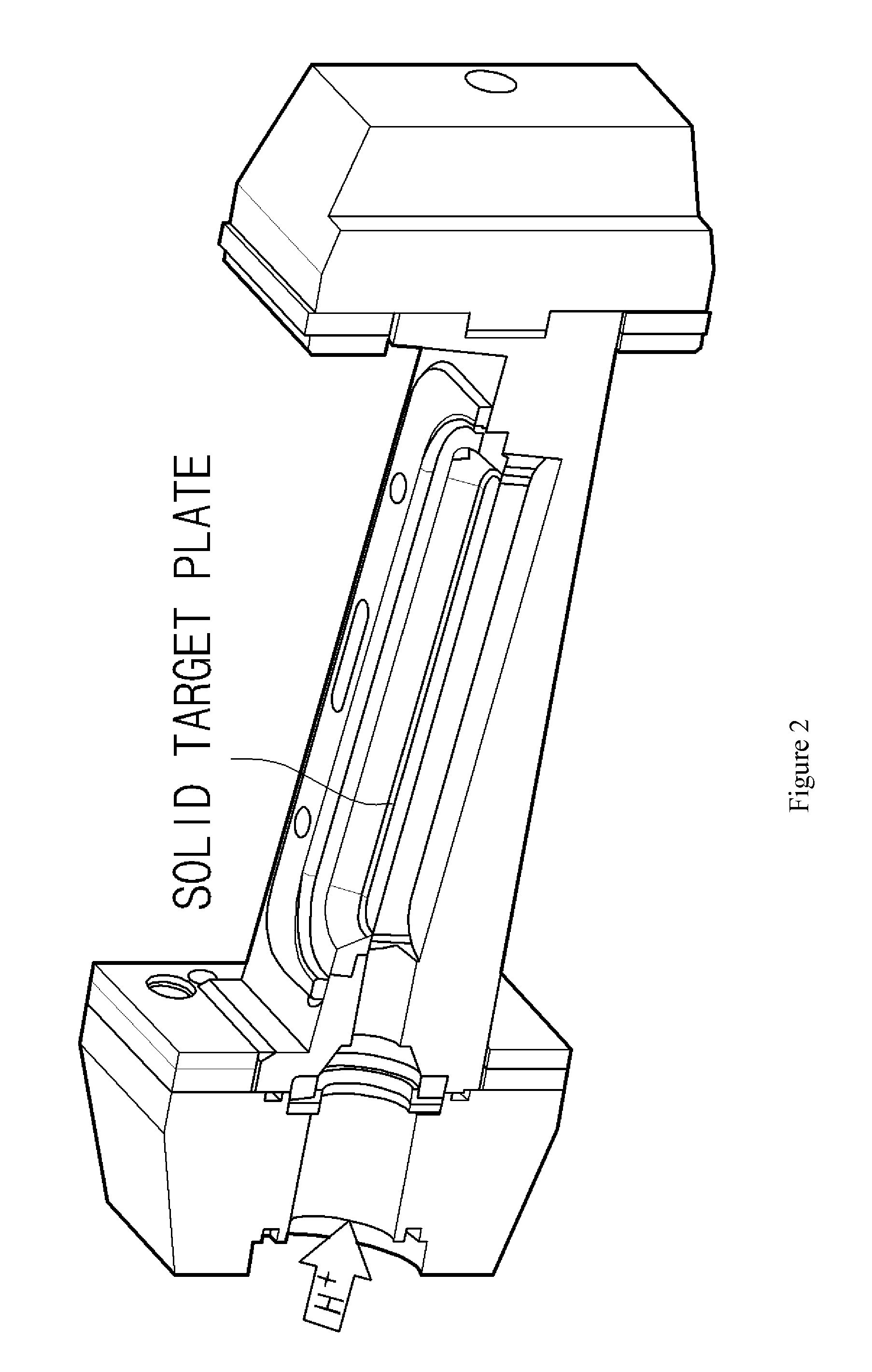
High current solid target for radioisotope production at cyclotron using metal foam
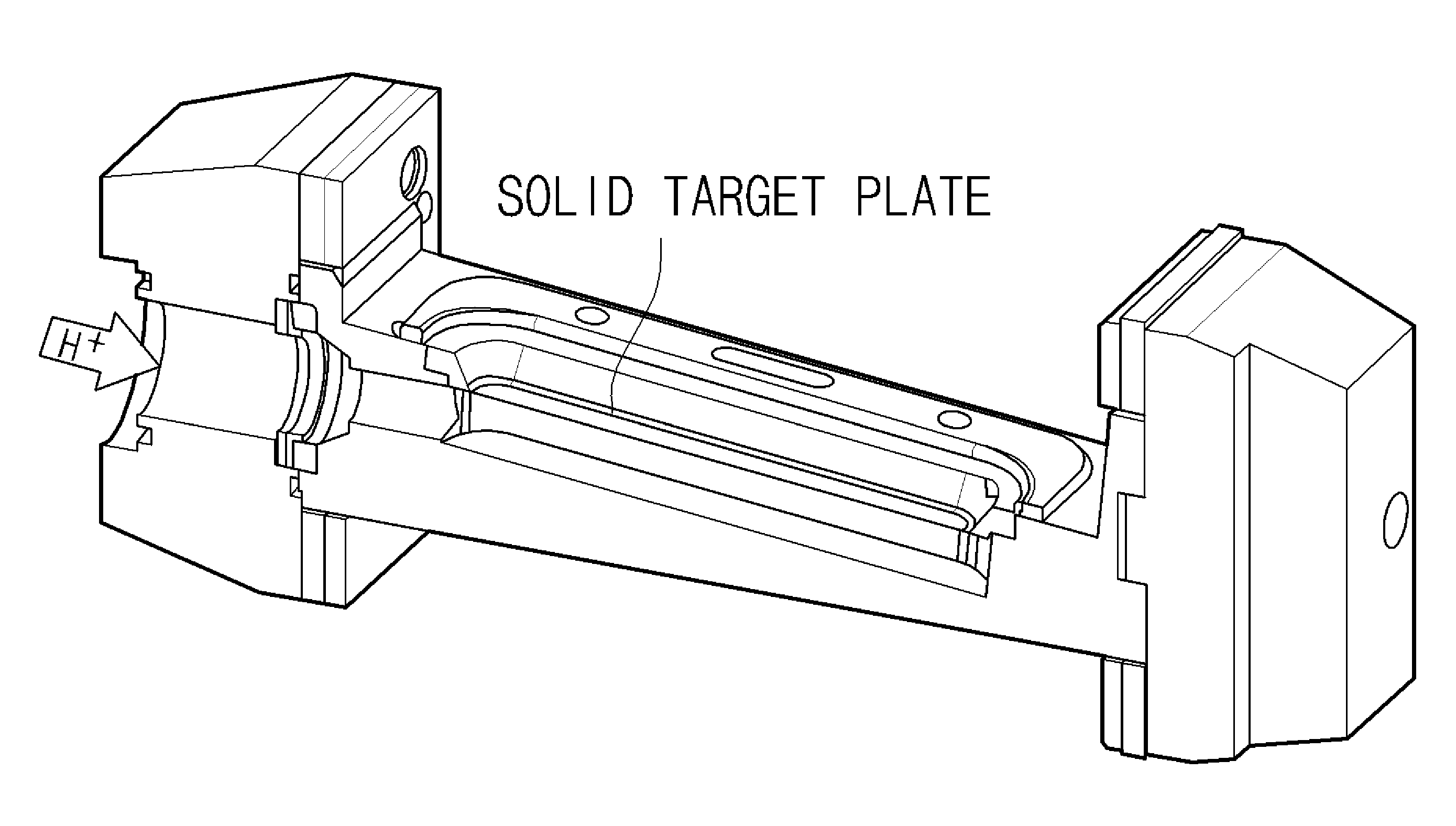
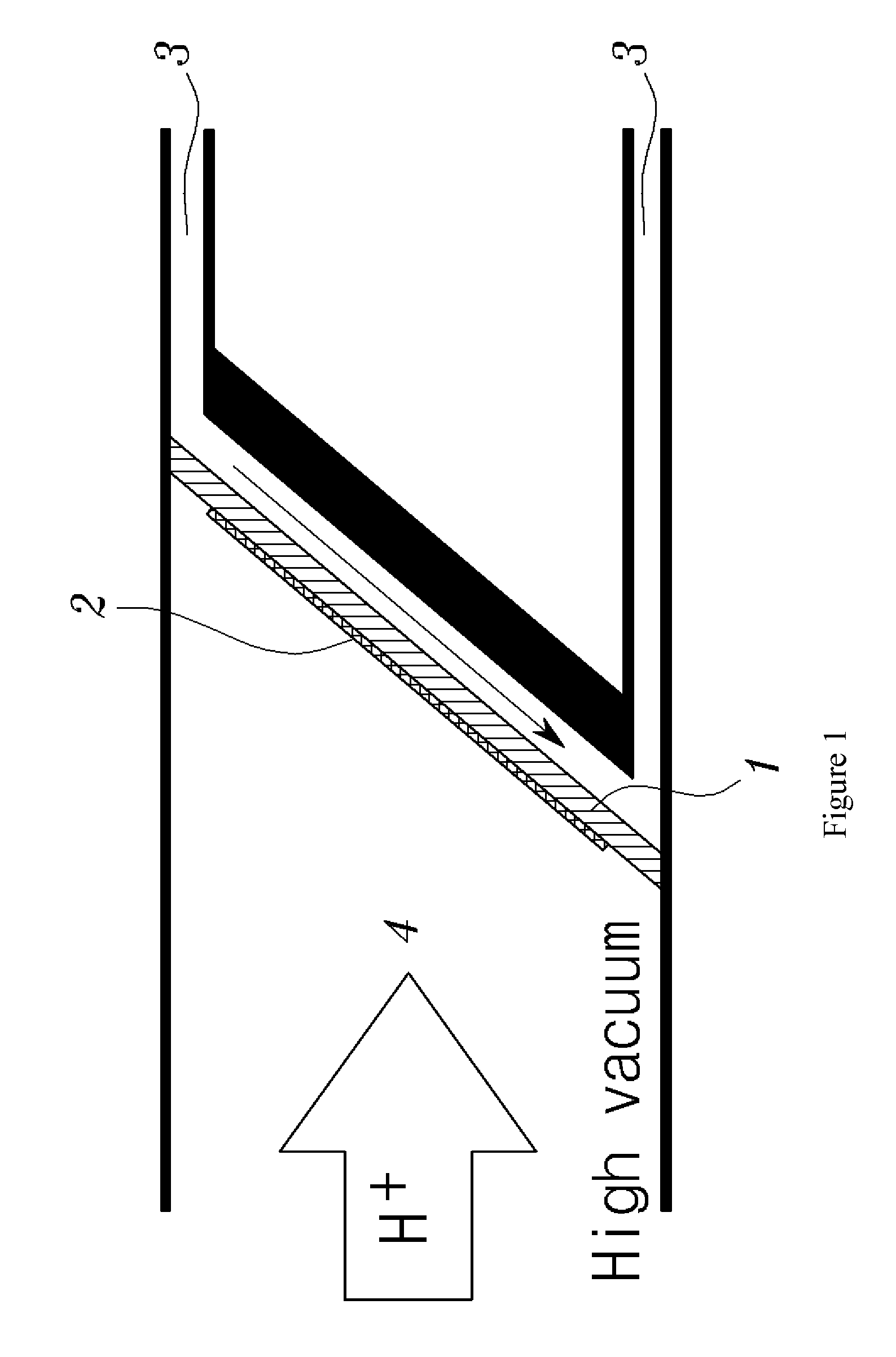
InactiveUS20110091001A1Improve cooling effectIncrease volumeDirect voltage acceleratorsNuclear targetsProtonIsotope
Disclosed herein is a high current solid target for radioisotope production at a cyclotron using a metal foam, and more specifically, a high current solid target for isotope production, which attaches a metal foam to the rear surface of the solid target plate. A high current solid target for isotope production including a metal foam according to the present invention may exhibit excellent cooling performances to increase the amount of proton beam current irradiated on the solid target compared to conventional planar-type solid targets. Because the irradiation of the increased proton beam current may increase the amount of an isotope produced per unit time and even an irradiation of proton beam in a short time may allow for production of a desired amount of an isotope, the solid target may be usefully used for production of medical cyclotron nuclides.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Magnitites Pycnonuclear Reactions within Electrochemical, Radioactive and Electromagnetic Medias
InactiveUS20140140461A1Facilitate cold nuclear conversionHeating fastNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorChemical reactionX-ray
The electrochemically active elements of the transition series include both the third, fourth and fifth d block elements, the lanthanides and the actinides. These transition elements have distinct electrochemistry for driving many chemical reactions, in particular the absorption of large volumes of hydrogen and the formation of various hydrides. In particular, Pd, Th, Ti, Ag, Au and La hydrides exhibit anomalous effects. The chemical reactions for forming, decomposing and rearranging the bonds of metal hydrides involve large energies. Furthermore these metal hydrides and mixtures are here demonstrated to exhibit greater strange cold nuclear reactions both cold fission and cold fusion. This invention provides magnetic, x-ray, laser irradiation, pressure, neutron beam, beta ray, alpha ray, gamma ray and catalytic technology for accommodating the special conditions for more controlled and accelerated cold nuclear reactions within the dense plasma (pycno) provided by the lattice of these metal hydrides. Under these conditions, the cold nuclear reactions are controllably enhanced to rates for practical energy sources but the very nonsynergistic nature of these pycnonuclear phenomena diminishes the possibility of runaway or explosive systems.
Owner:LITTLE REGINALD B
Formation of [18f] fluoride complexes suitable for [18f] fluorinations
InactiveUS20090242421A1Inhibit side effectsAvoid electrochemical reactionsCellsPhotography auxillary processesFluorideCoordination complex
The present invention claims a method for forming [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species. The present invention also provides for an apparatus for forming [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species. Kit claims for formation of [18F] fluoride complexes suitable for performing radio-labelling reactions to generate [18F] fluorinated species are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Device and method for producing neutrons
InactiveCN108140431AShort lifeTest for Radiation ResistanceNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsElectron donorProton
The invention relates to a method for producing and / or capturing neutrons, including the following steps: a) exposing nuclei selected among protons, deuterons and / or tritons to an electric field in order to extract said nuclei and to direct said nuclei thus extracted towards a target (20) containing free electrons; b) for example, exposing said nuclei to a spatial and / or temporal gradient of a first magnetic field so as to give a predefined orientation to the magnetic moments of the nuclei; c) either exposing the target to a second magnetic field so as to give a predefined orientation to the magnetic moments of the free electrons of the target; d) or using an electron-donor superparamagnetic material so that the electrons of the free layers of these materials are oriented in preferred directions generated by the orientation of the resulting magnetic moment of the superparamagnetic material; and e) for example, in the case of using a superparamagnetic material, not exposing the proton beam and / or the target to the external magnetic fields. A heating device and / or a device for generating magnetic fields may be required in order to activate the superparamagnetic properties of the material.
Owner:NEUSCA
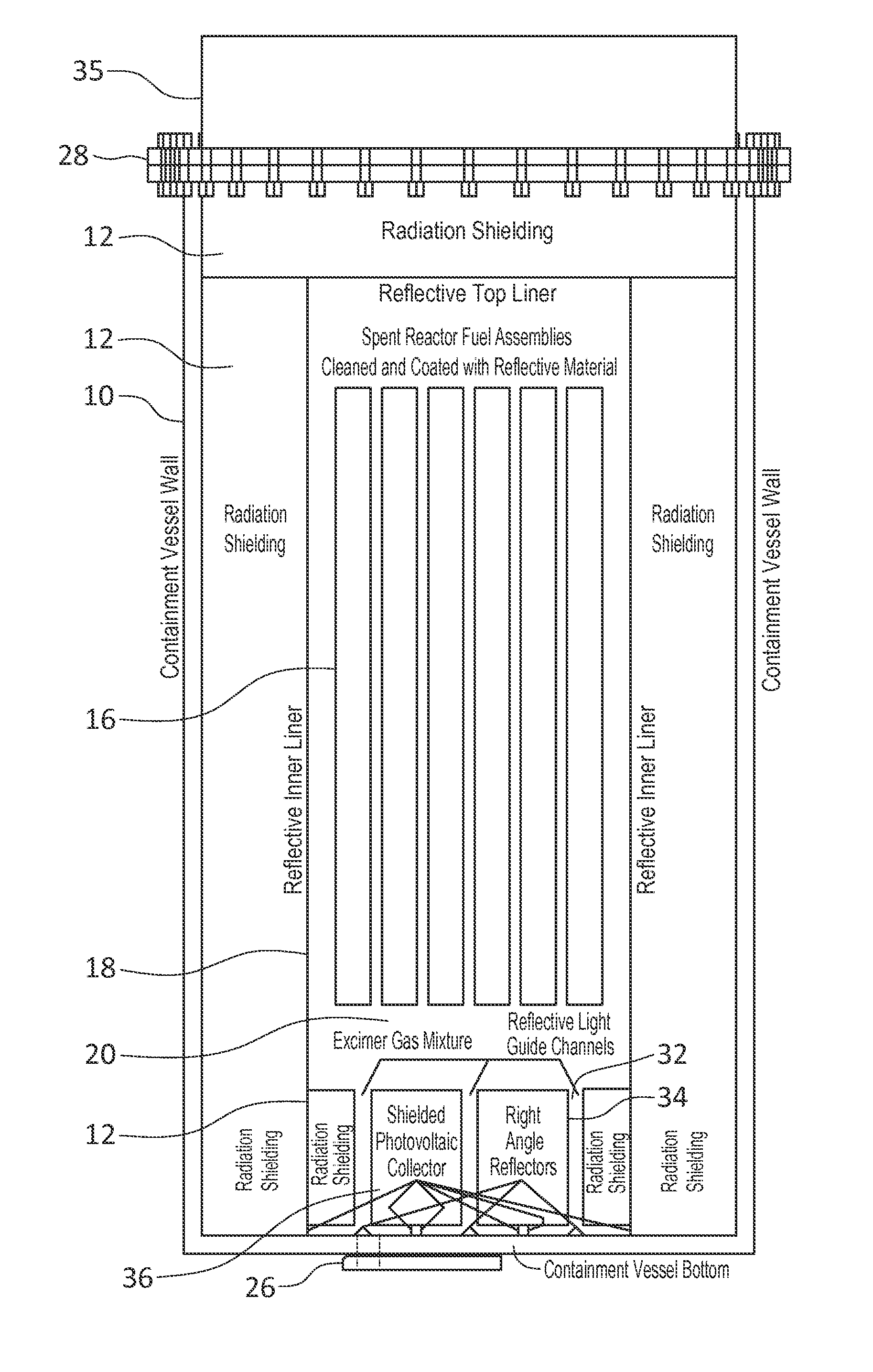
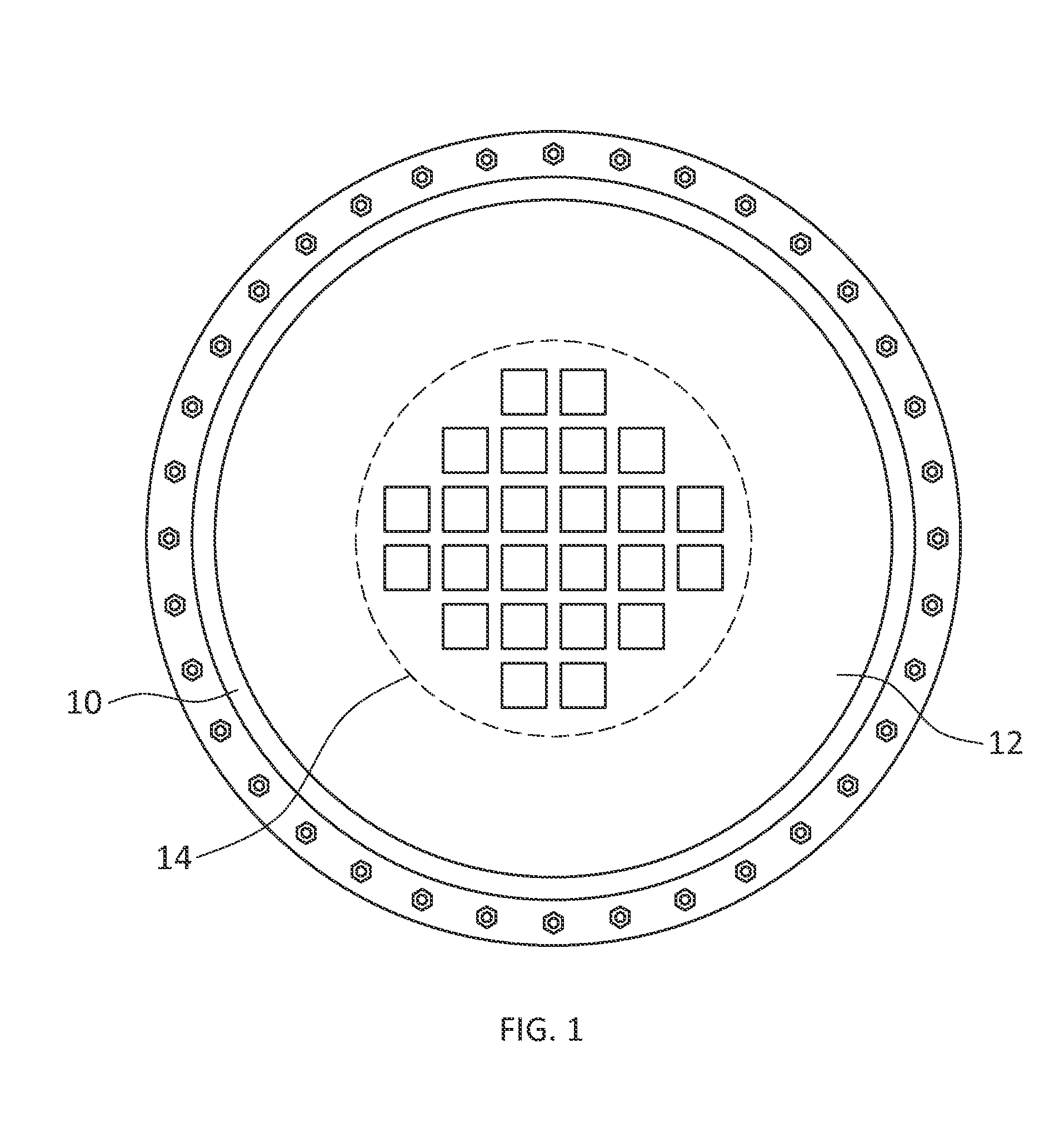
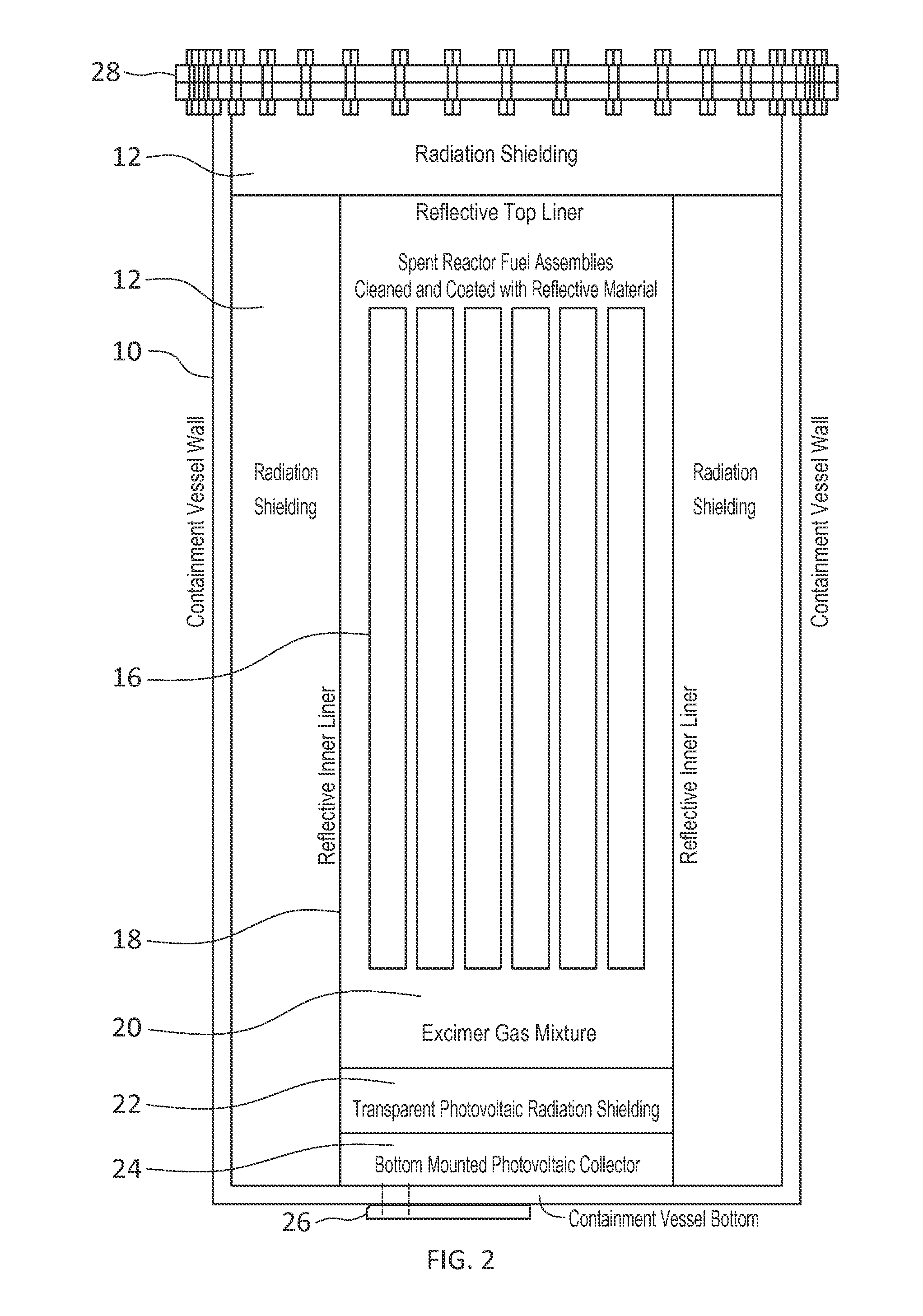
Isotope energy conversion and spent nuclear fuel storage systems
InactiveUS20160093411A1Portable shielded containersChemical to radiation conversionIsotopeEngineering
The invention provides methods, devices and systems for excimer fluorescence energy conversion from isotopes. Unprocessed spent nuclear fuel can be used as an isotope, and processed spent nuclear fuel can be used as an isotope. A method includes placing an excimer in the path of radiation decay from the isotope. The excimer is selected according to the isotope to absorb the radiation decay and emit photons in response. Surrounding environment is shielded from the radiation decay. Photons generated from the fluorescence of the excimer are received with photovoltaic material to generate electrical energy. The electrical energy is applied to a load. Systems of the invention can be based upon spent storage casks and handle unprocessed spent nuclear fuel, or can be greatly reduced in size and handle processed fuel, with single isotope isolation allowing consumer battery sized systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Spheric alignment mechanism entropic step down and propulsion system
InactiveUS7465886B1Shielding materialsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsAudio power amplifierRoom temperature
A chamber or series of chambers for manipulating a work product is formed in layers as a series of nested shells. The shells have an outer structural casing and an electromagnetic shield that surrounds a superconducting shell. The superconducting shell is either room temperature or immersed in a cryogenic coolant contained in a reservoir. The work product is further manipulated using kinetic energy to move it through electromagnetic field amplifiers to facilitate energy release for power generation or motive propulsion.
Owner:KESSLER STEPHEN BURNS
Solid target system for the handling of a Cu-64 target
InactiveUS20060285624A1Efficiently cost-effectively accommodateAcceleratorsChemical to radiation conversionEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a system and method for a system for accommodating a solid target in an accelerator. The system and method includes a target changer having at least one port for accommodating the solid target, an insert for receiving the solid target in the target changer, a piston for providing a vacuum and a cooling system for the solid target, a cylinder for displacing the piston in one of three positions; and a bracket for securing the insert, piston and cylinder to the target changer.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
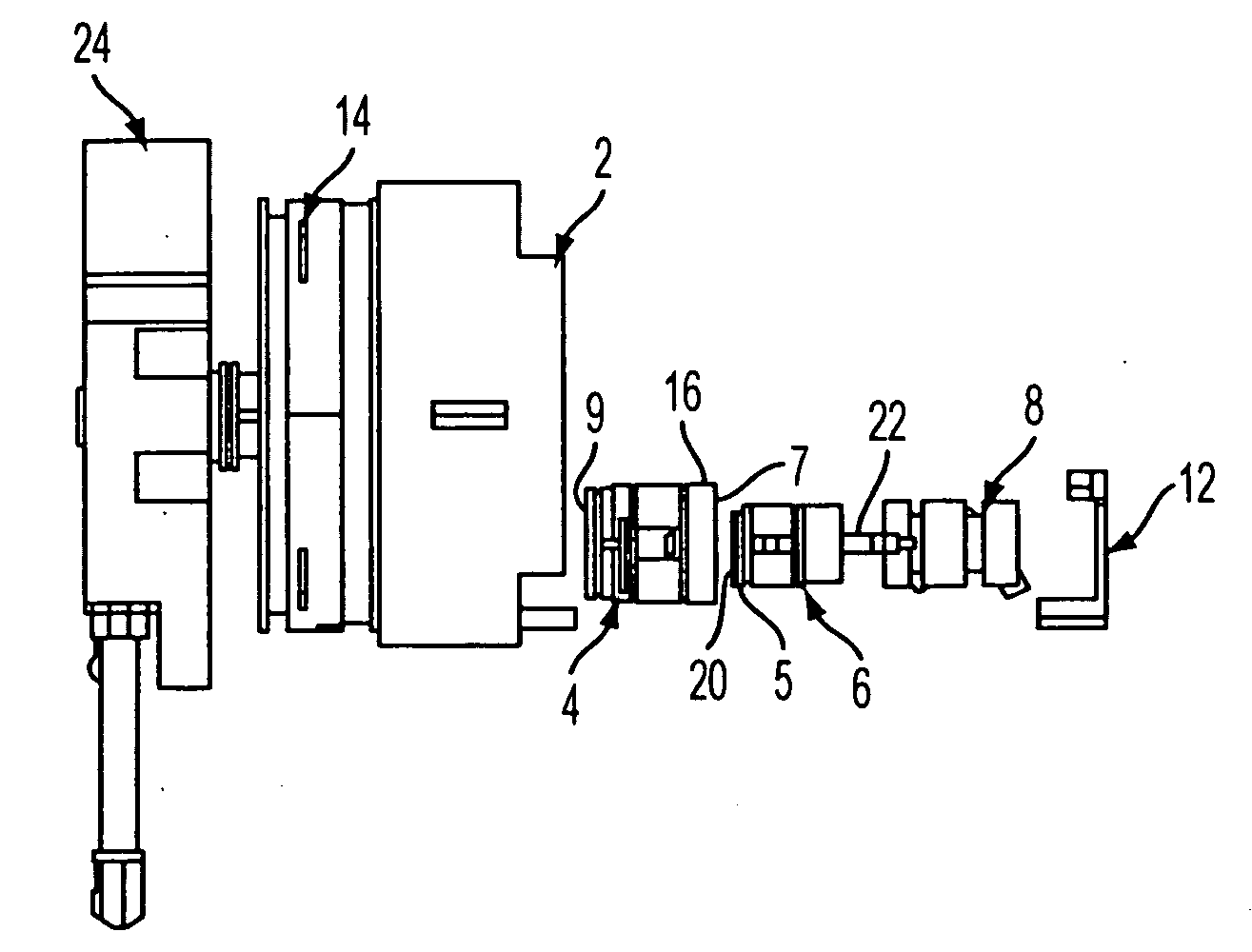
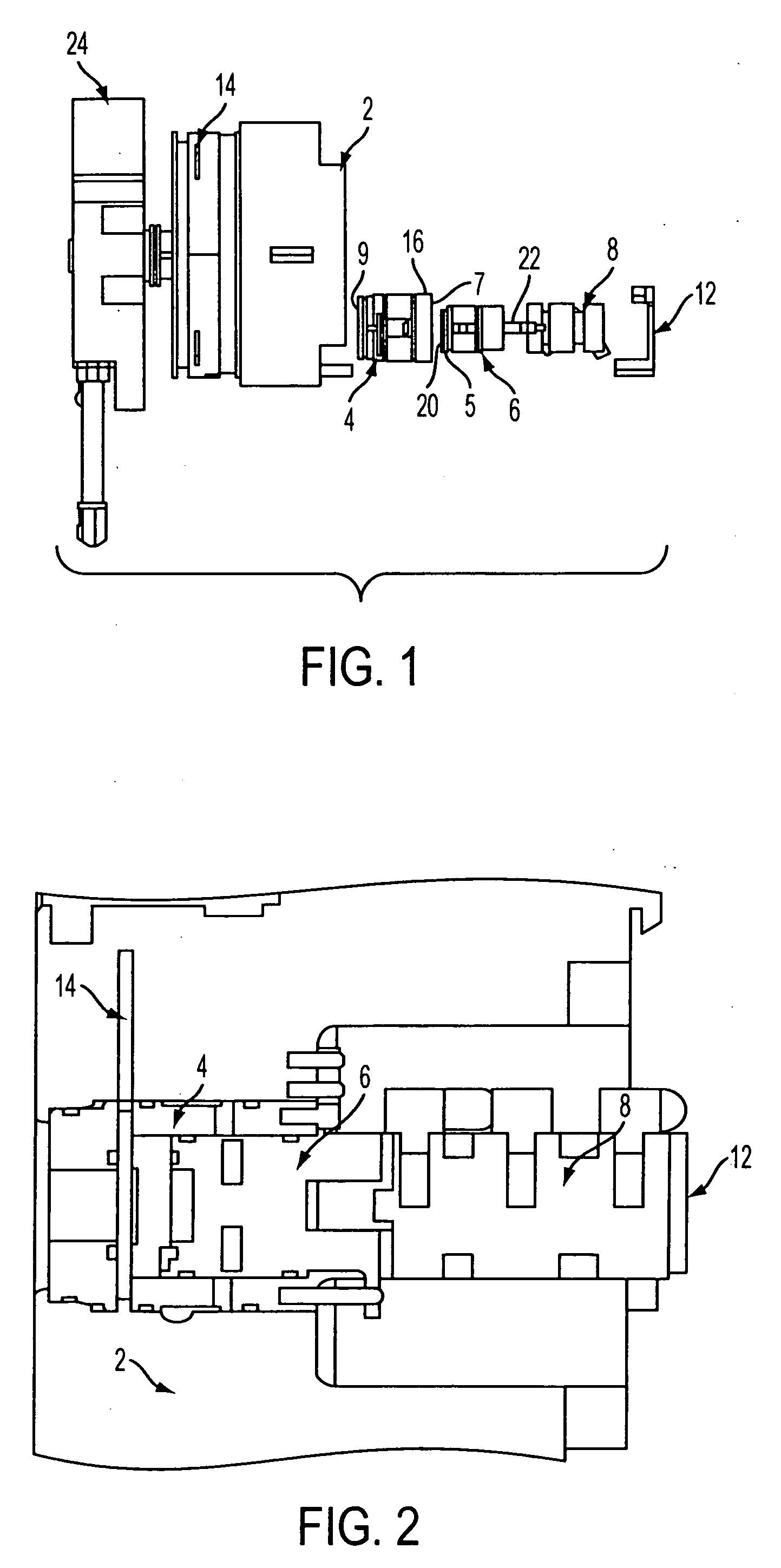
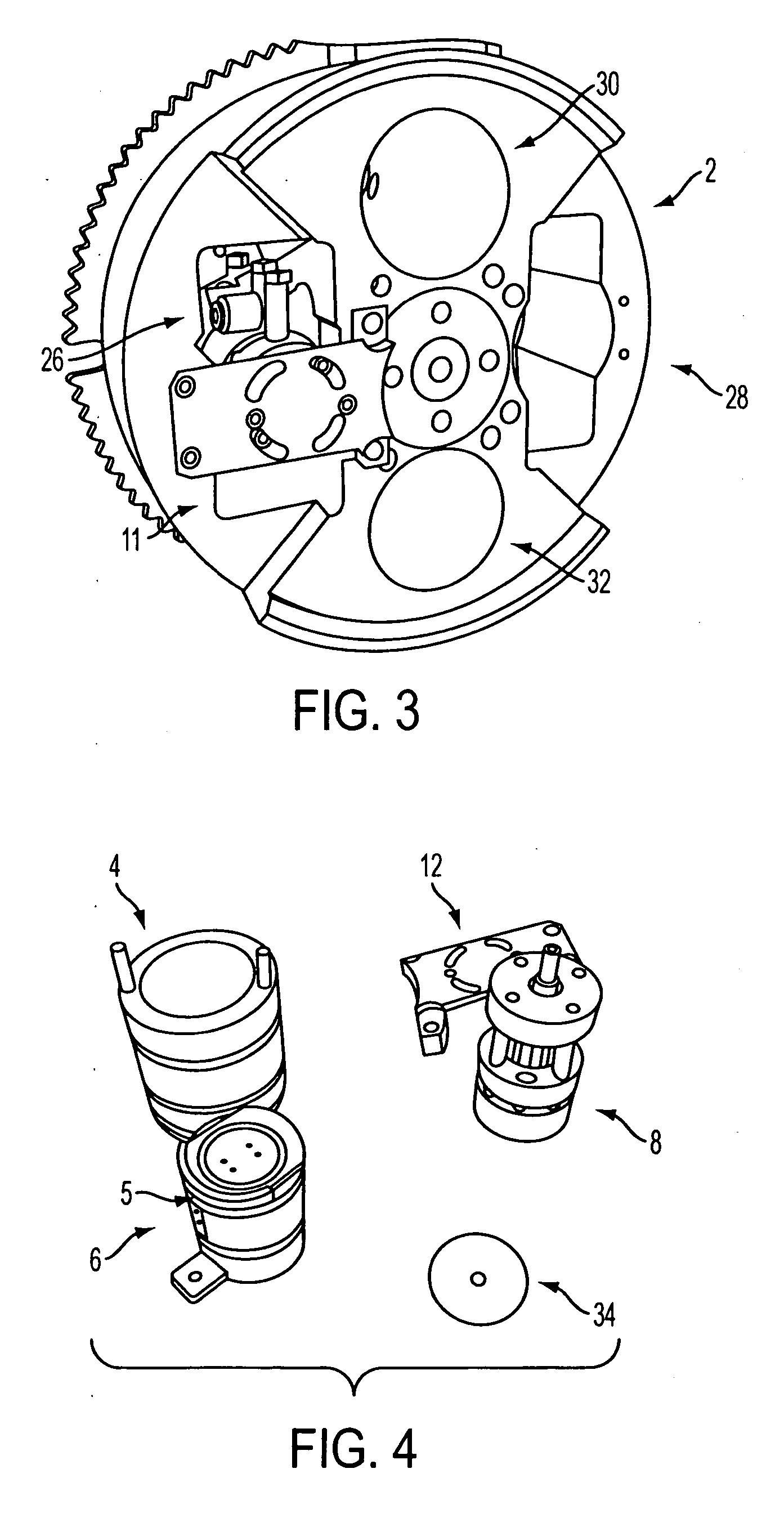
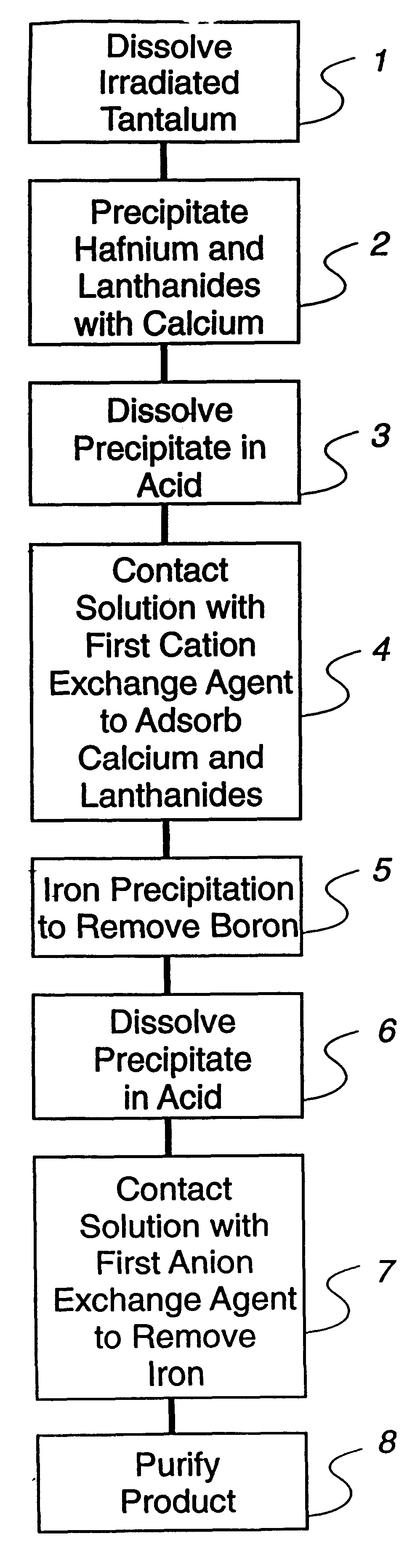
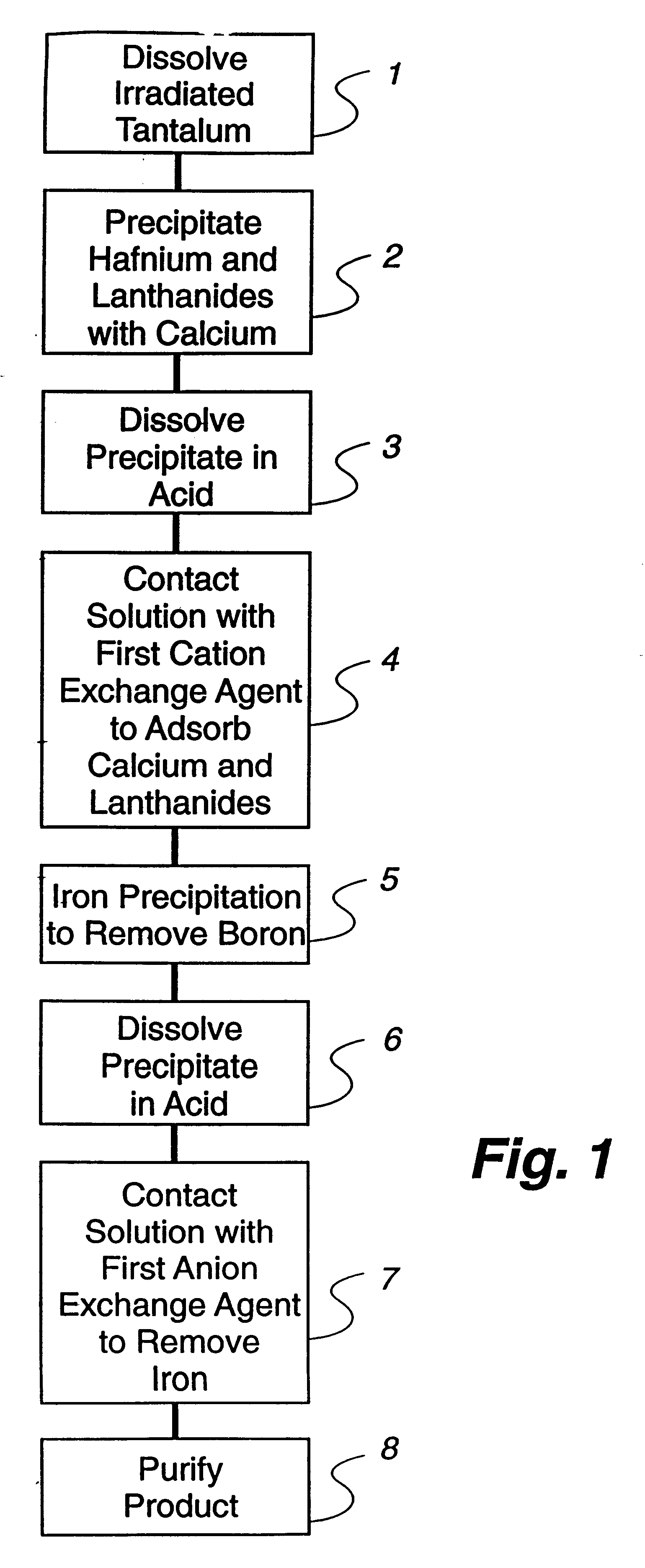
Hafnium radioisotope recovery from irradiated tantalum
Hafnium is recovered from irradiated tantalum by: (a) contacting the irradiated tantalum with at least one acid to obtain a solution of dissolved tantalum; (b) combining an aqueous solution of a calcium compound with the solution of dissolved tantalum to obtain a third combined solution; (c) precipitating hafnium, lanthanide, and insoluble calcium complexes from the third combined solution to obtain a first precipitate; (d) contacting the first precipitate of hafnium, lanthanide and calcium complexes with at least one fluoride ion complexing agent to form a fourth solution; (e) selectively adsorbing lanthanides and calcium from the fourth solution by cationic exchange; (f) separating fluoride ion complexing agent product from hafnium in the fourth solution by adding an aqueous solution of ferric chloride to obtain a second precipitate containing the hafnium and iron; (g) dissolving the second precipitate containing the hafnium and iron in acid to obtain an acid solution of hafnium and iron; (h) selectively adsorbing the iron from the acid solution of hafnium and iron by anionic exchange; (i) drying the ion exchanged hafnium solution to obtain hafnium isotopes. Additionally, if needed to remove residue remaining after the product is dried, dissolution in acid followed by cation exchange, then anion exchange, is performed.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY +1
Popular searches
Electrostatic spraying apparatus Chemical vapor deposition coating Beam/ray deflecting arrangements Material analysis by optical means Beam deviation/focusing by electric/magnetic means Light therapy Radioactive sources X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapy Isotope separation Discharge tube/lamp details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




















![18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine 18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7bc23d23-80a7-4177-adf7-7d610ee7e236/US20050279130A1-20051222-D00000.png)
![18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine 18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7bc23d23-80a7-4177-adf7-7d610ee7e236/US20050279130A1-20051222-D00001.png)
![18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine 18O[O2] oxygen refilling technique for the production of 18[F2] fluorine](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7bc23d23-80a7-4177-adf7-7d610ee7e236/US20050279130A1-20051222-D00002.png)