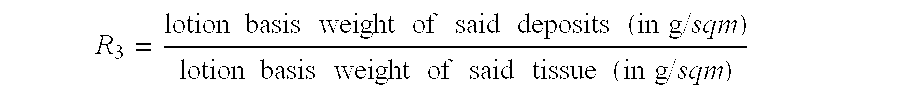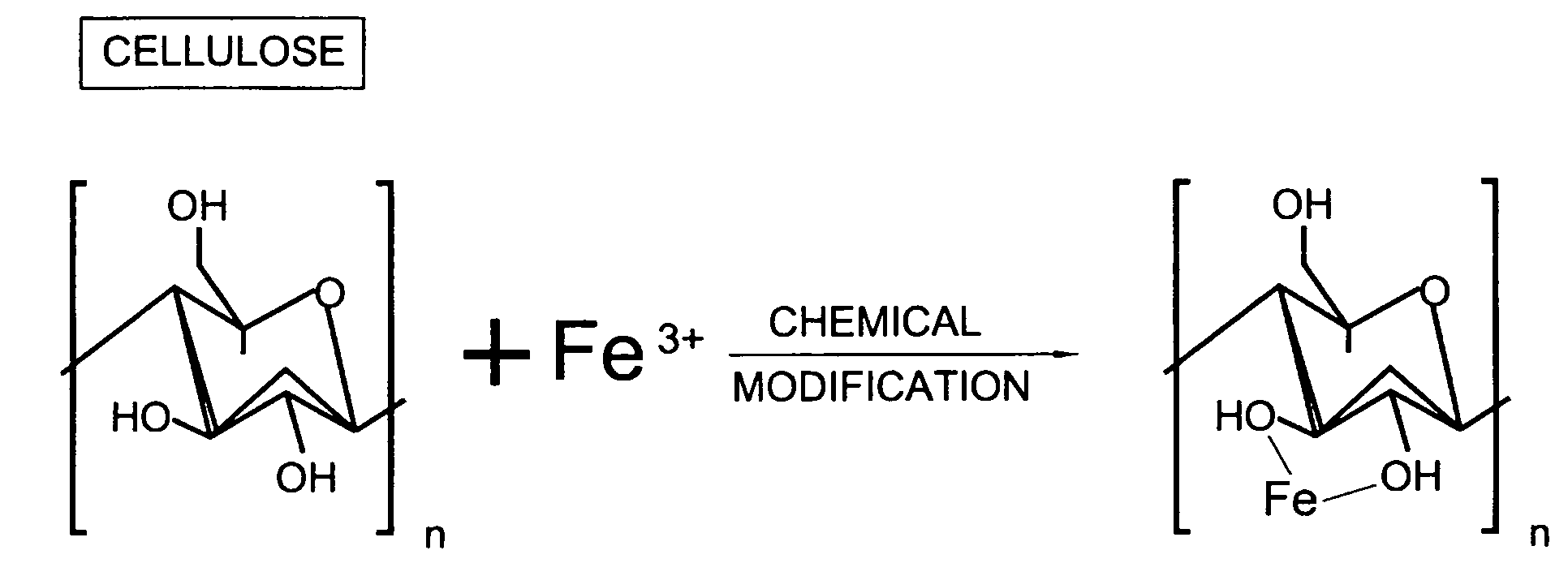Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170results about "Chemical/biochemical paper treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
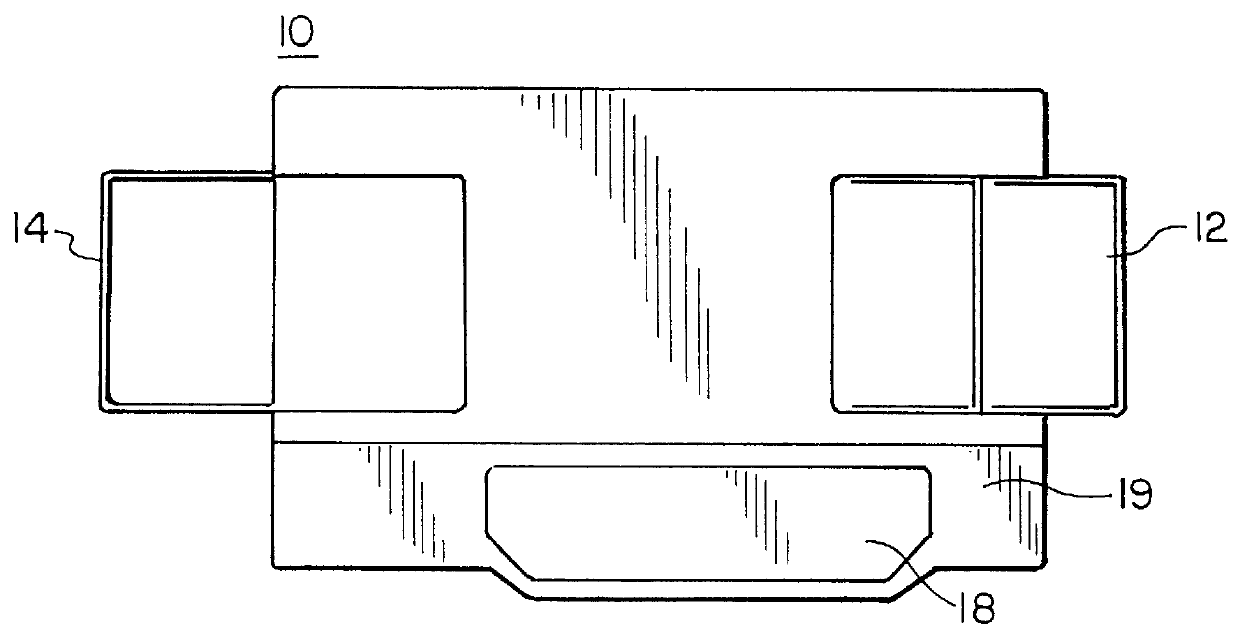
Hydrophilic polymer treatment of an activated polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS6830782B2Simple materialImprove nucleationRadiation applicationsFibre typesFiberMicroorganism
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof. The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
Machine and treatment process via chromatogenous grafting of a hydroxylated substrate
ActiveUS20130236647A1DissipationWater-repelling agents additionNon-macromolecular organic additionGraft reactionPulp and paper industry
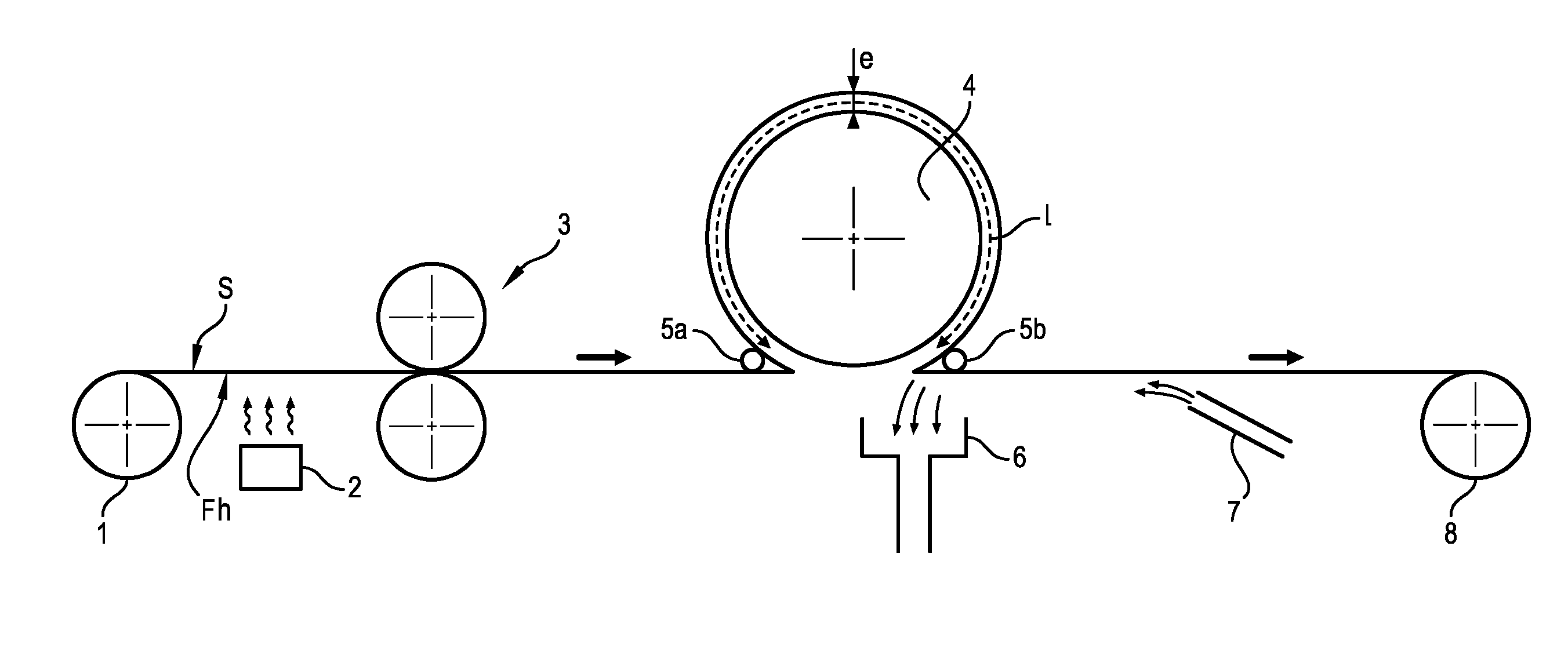
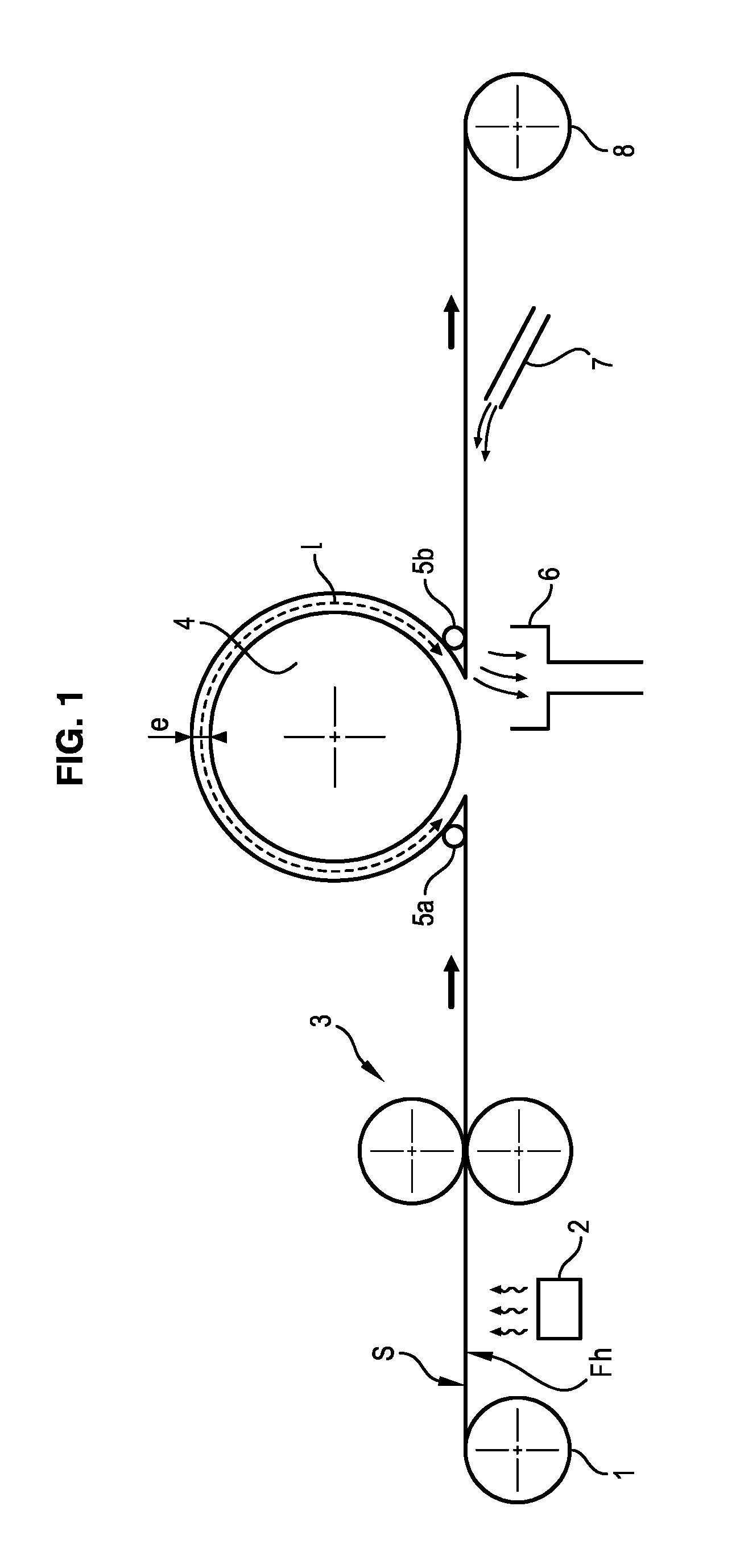
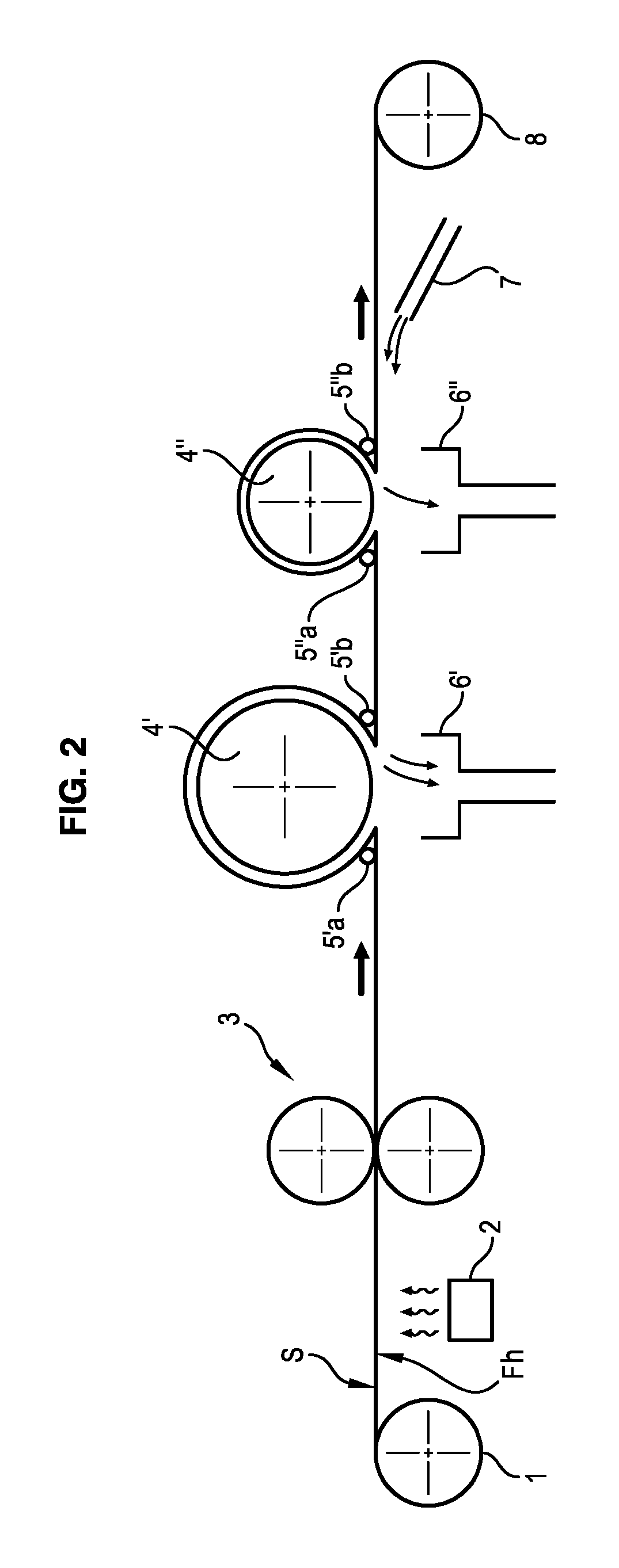
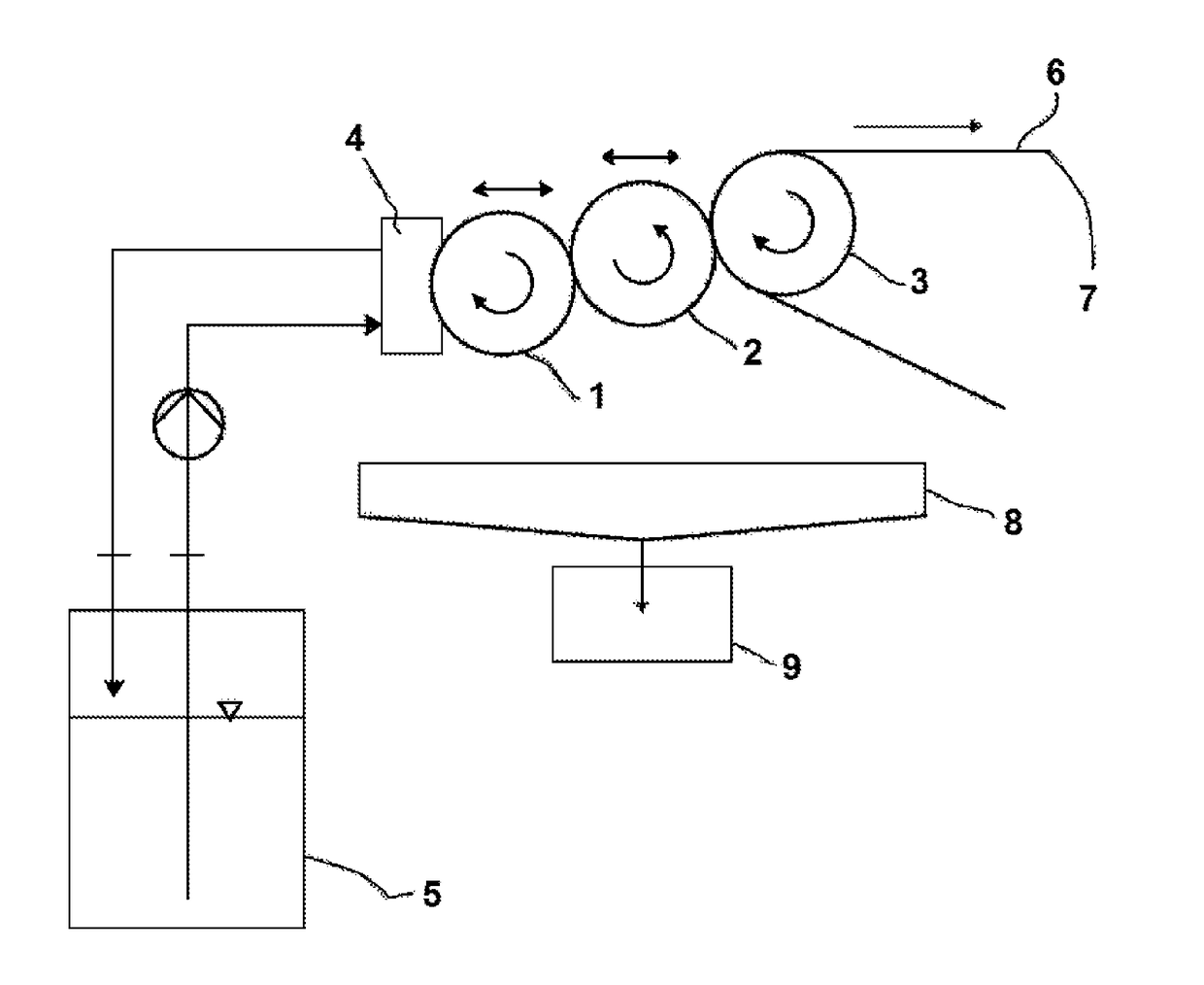
The invention relates to a machine for chromatogenous grafting treatment of a scrolling substrate (S) having a hydroxylated face (Fh), comprising:an application device (3) of a grafting reagent on the hydroxylated face (Fh) of the substrate,a heating roller (4) for the development of the grafting reaction on the hydroxylated face (Fh) of the substrate, said roller (4) being provided with a bar-end system (5a, 5b) for applying a face of the substrate (S) against said heating roller (4),an extraction device (6) of the hydrochloric acid produced during the grafting reaction,an application device (7) of an air knife on the treated face of the substrate for eliminating the residual grafting reagent.The invention also relates to a chromatogenous grafting process used in said machine.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Method of modifying polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS20030087982A1Improve hydrophilicityImprove adhesionAlkaline accumulatorsFibre typesFiberPolyolefin
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
Multifunctional nano compound treating fluid for protecting paper cultural relics and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103276627ALittle side effectsImprove efficiencyChemical/biochemical paper treatmentOld paper after-treatmentSolventUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses multifunctional nano compound treating fluid for protecting paper cultural relics. The multifunctional nano compound treating fluid takes deionized water as a solvent, and comprises nano magnesium hydroxide, nano titanium dioxide and hydroxyethyl cellulose, wherein nano magnesium hydroxide accounts for 0.2-1.0% of the weight of deionized water, nano titanium dioxide accounts for 0.1-0.8% of the weight of deionized water, and hydroxyethyl cellulose accounts for 0.2-0.8% of the weight of deionized water. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the multifunctional nano compound treating fluid. The multifunctional nano compound treating fluid can be used for large-area treatment of the paper cultural relics, and can be used for providing protection for deacidification, solidification, light-resistant degradation and mould proofing of the paper cultural relics during a large-area treatment of the paper cultural relics. The pH value of the paper cultural relics treated by the multifunctional nano compound treating fluid can reach an alkalescence degree, and the paper cultural relics have a certain alkali residue, can resist external acid, can be greatly improved in tensile strength, and have a certain antibacterial property.
Owner:NANJING MUSEUM
Battery separator
InactiveUS20020090876A1High modulusReduce unevennessDead plant preservationArtificial flowers and garlandsMetallurgyFiber diameter
Disclosed is a battery separator consisting essentially of a nonwoven fabric having a substantially unilayered structure, wherein an apparent total surface area of fibers per a surface density of the nonwoven fabric is 20 m2 / m2 or more, a thickness of the nonwoven fabric is 0.1 mm or less, a uniformity index of the nonwoven fabric is 0.15 or less, and the nonwoven fabric contains fine fibers having a fiber diameter of 4 mum or less.
Owner:NIPPON BAIRIIN
Compositions comprising (poly) alpha olefins
ActiveUS8071667B2Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationAlpha-olefinSURFACTANT BLEND
A release aid comprising one or more (poly)C5-C20 alpha olefins and one or more surfactants for use in releasing a paper web from the fabric in through air drying processes and / or from the Yankee dryer, compositions comprising the release aid and methods of using the release aid.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC +1
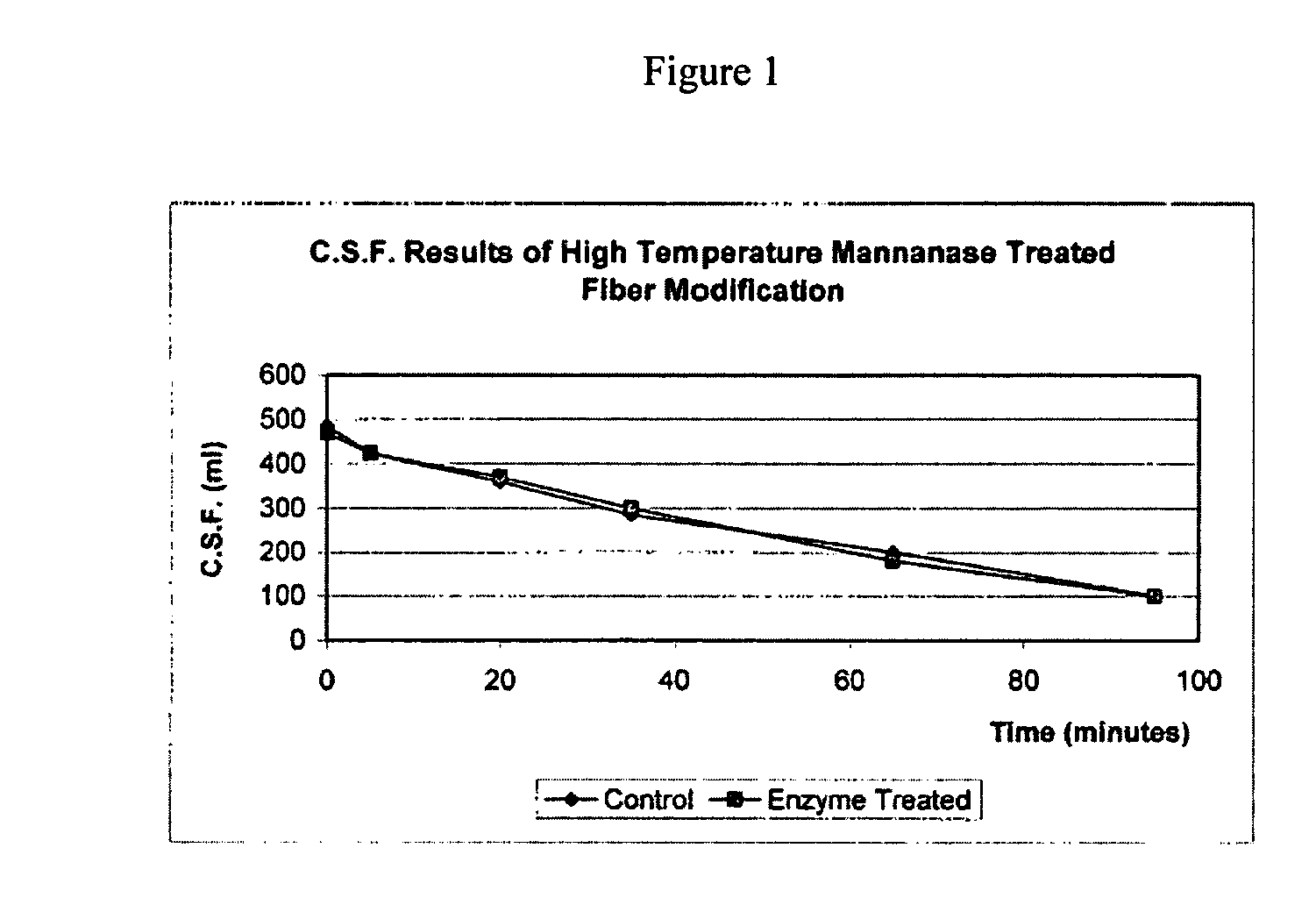
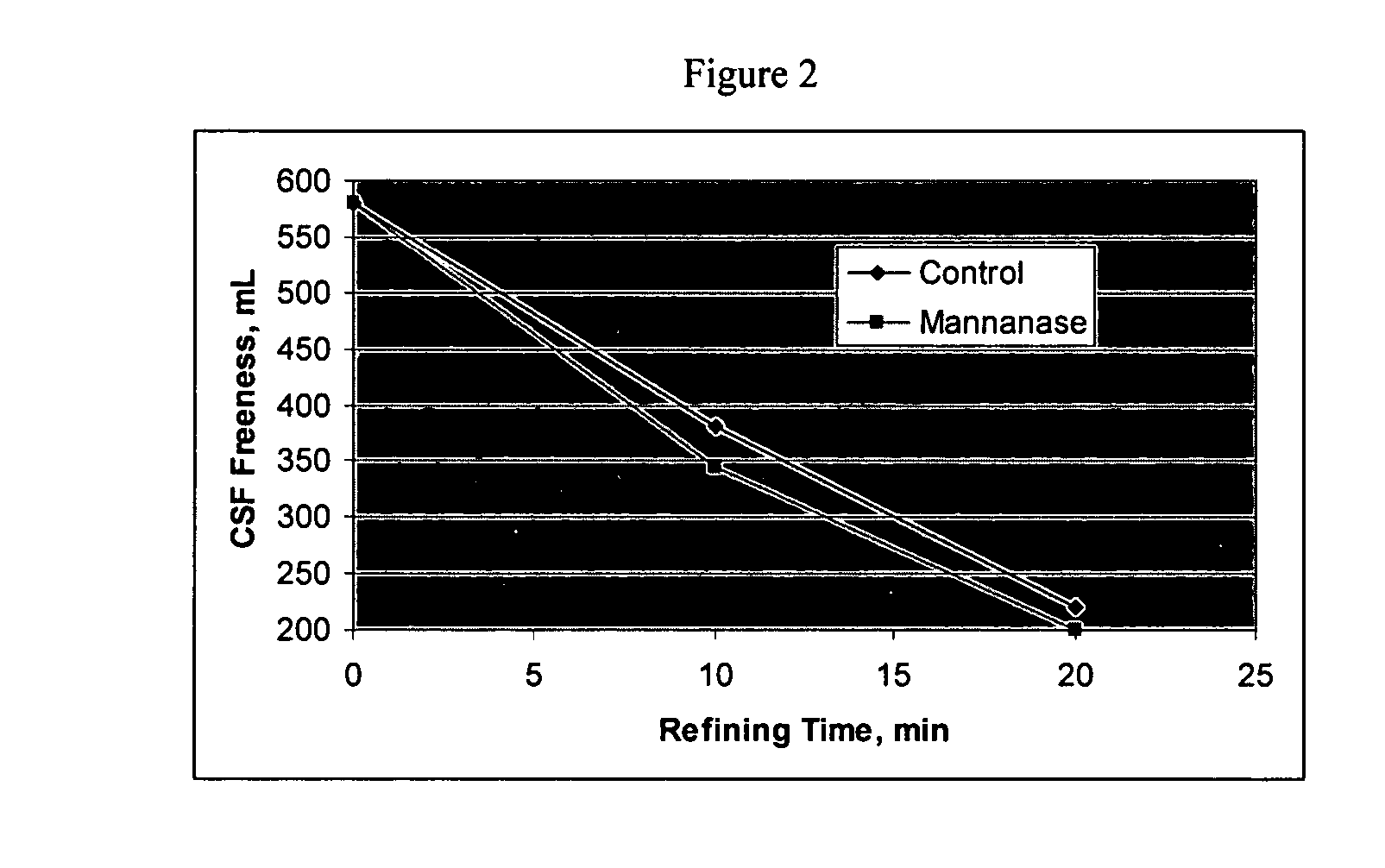
Use of hemicellulase composition in mechanical pulp production
InactiveUS20050000666A1High strengthLess energyFibrous raw materialsPulp beating/refining methodsPulp and paper industryHemicellulose
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
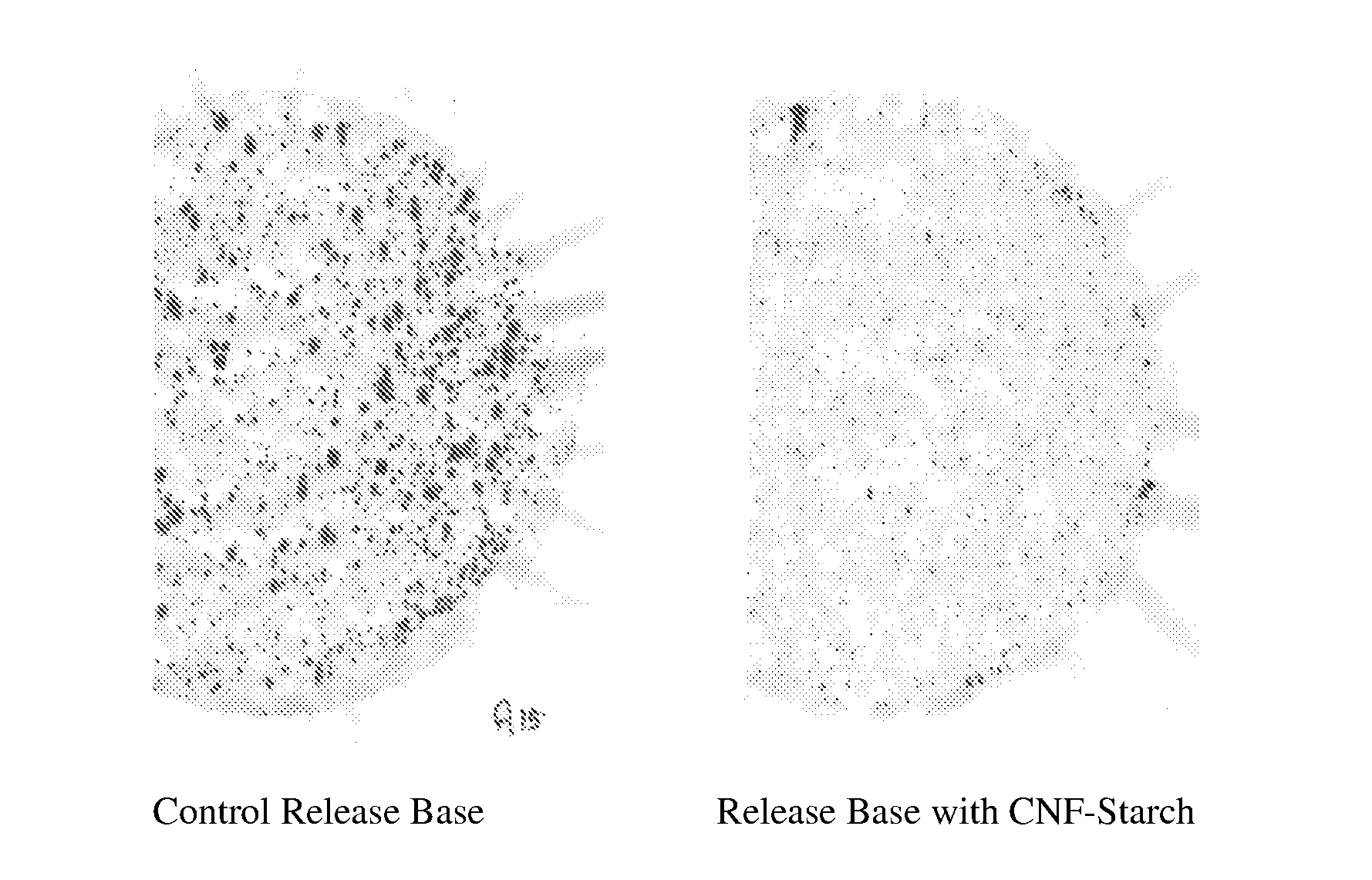
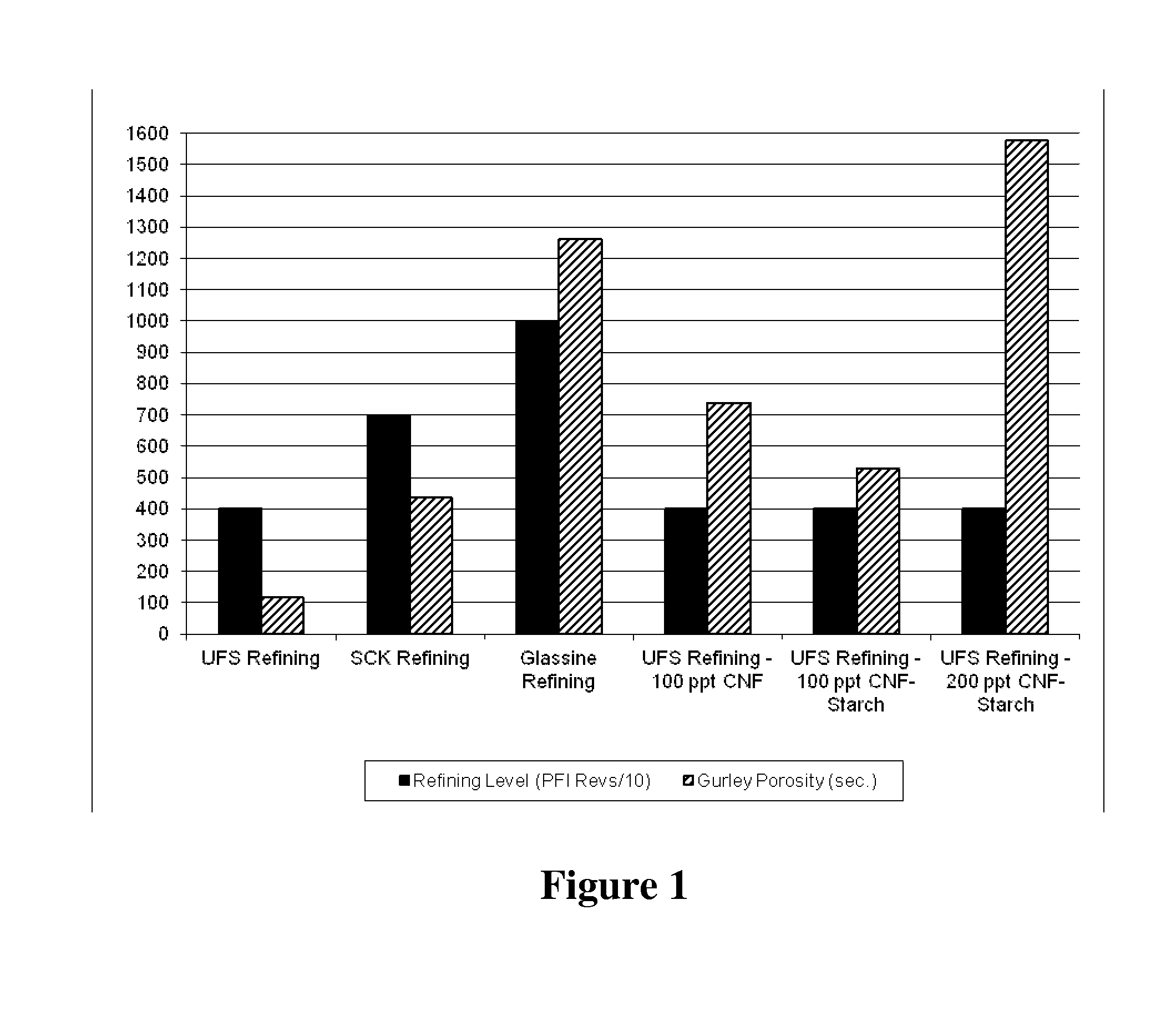
Release Paper and Method of Manufacture
ActiveUS20150125658A1Increase speedLower requirementNon-fibrous pulp additionRecord information storageCellulosePolymer science
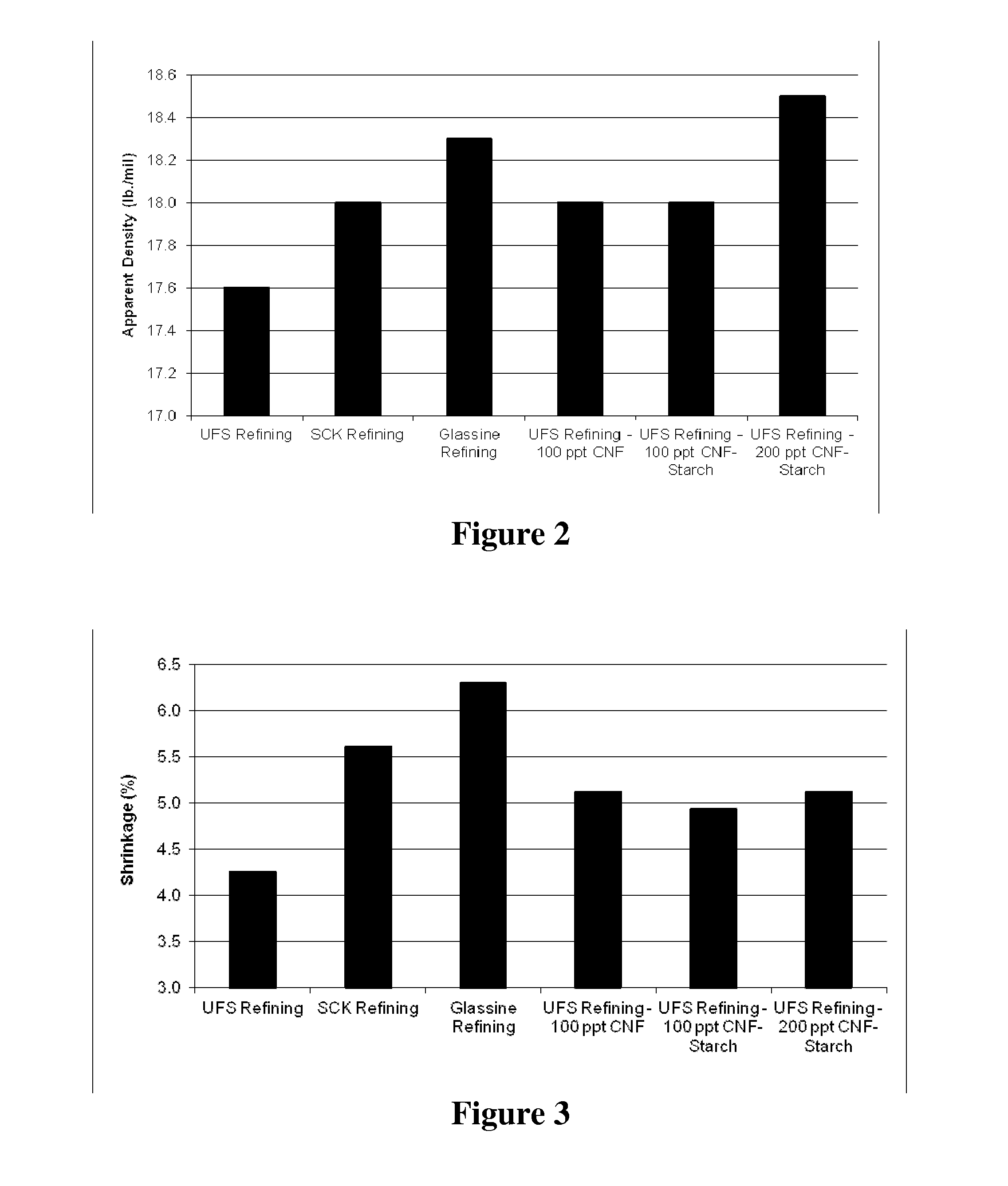
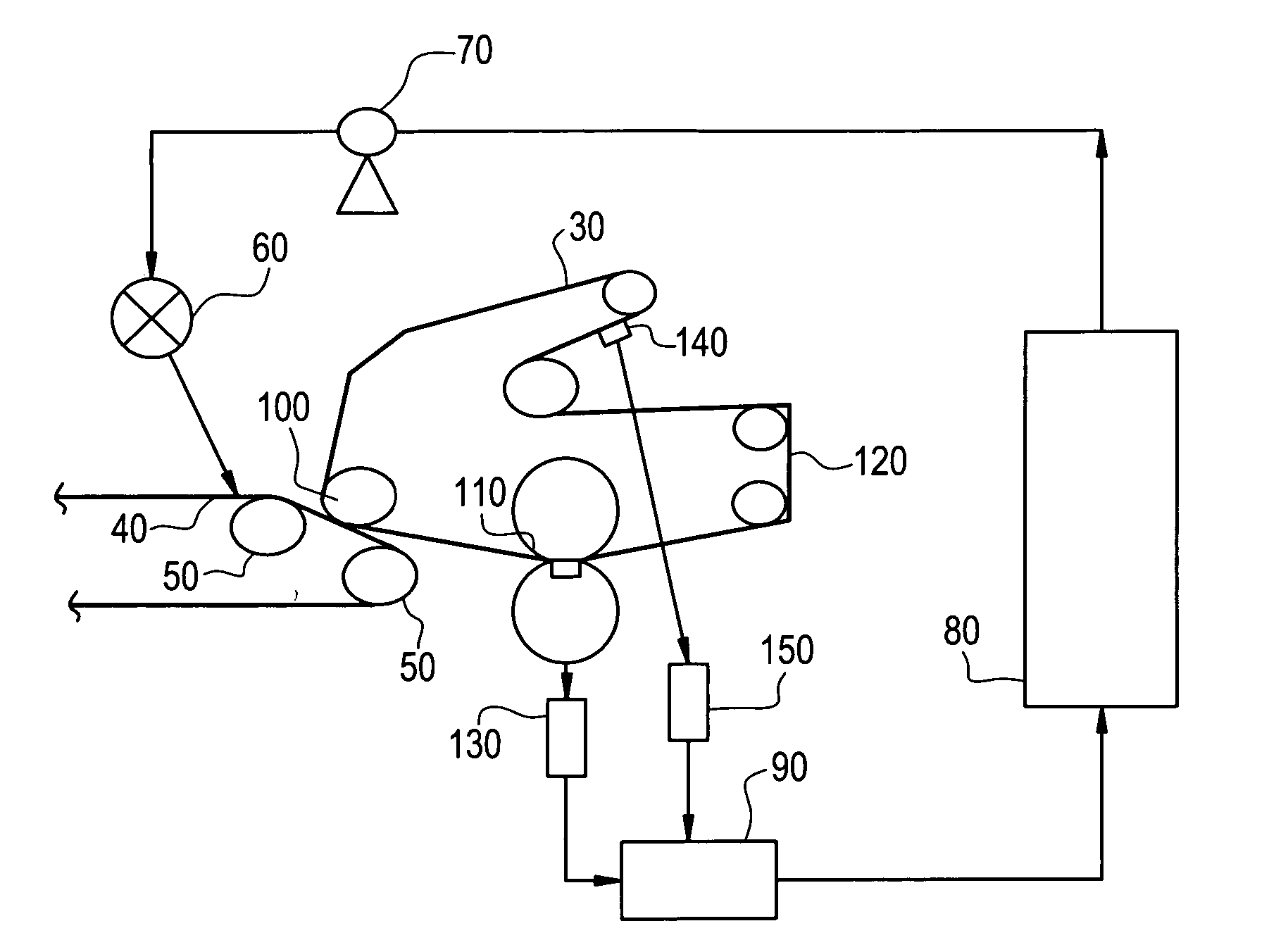
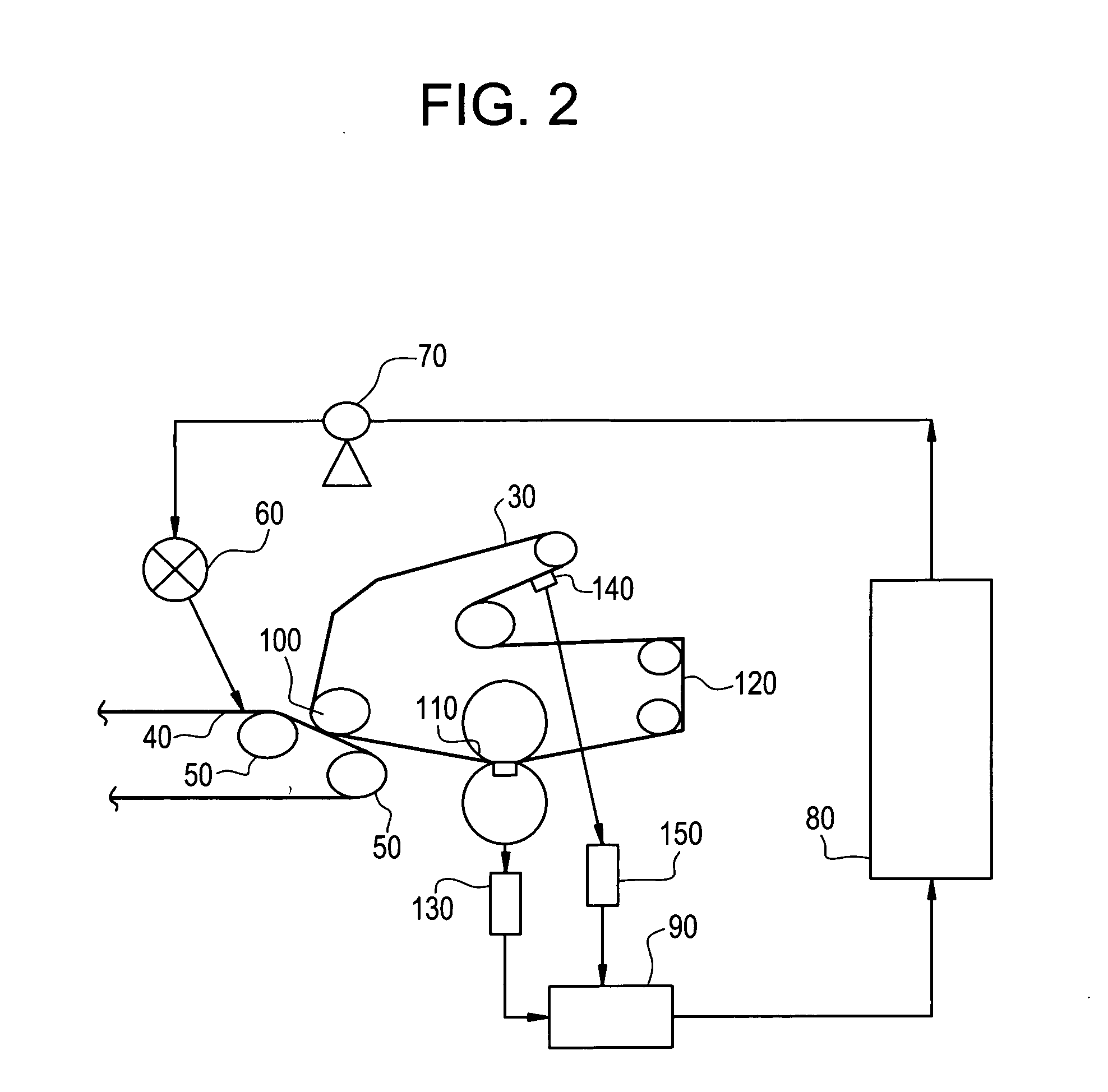
Release base papers with improved surface properties and more efficient manufacturing potential are made using cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) along with high freeness, less refined pulp. Release papers serve as the backing for common adhesive labels, for industrial film coatings, and also for certain food processing uses. The CNF may be added to the furnish and processed to paper, or the CNF may be added as a coating onto a partially dried web of paper. The CNF may optionally be combined with a starch and a starch crosslinker.
Owner:STIRLING CONSULTING +1
Fibre-Reinforced Film, Process for Producing the Same, and Use for Food Packaging
InactiveUS20100227164A1Excellently suitableSynthetic resin layered productsNon-macromolecular organic additionFiberPolyol
The present invention is directed to a fibre-reinforced film comprising a paper-reinforced alginate film containing polyhydric alcohol. Further, the invention is directed to a process for producing the fibre-reinforced film, and the use thereof for packaging food products, particularly meat products to be cooked and smoked.
Owner:VISKOTEEPAK BELGIUM NV
Process for increasing the charge on a lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS6187136B1Avoid reactionIncrease surface charge densityFungiPaper/cardboardCatalytic oxidationCellulose fiber
A process for production of a lignocellulosic material modified by conjugation thereto of a phenolic substance comprising a substituent which, in the conjugated form of the phenolic substance, is, or may become, negatively or positively charged, respectively, comprises: reacting a lignocellulosic fibre material and the phenolic substance with an oxidizing agent in the presence of an enzyme capable of catalyzing the oxidation of phenolic groups by the oxidizing agent; and reacting together the products of the reactions; with the proviso that the phenolic substance is not a phenolic polysaccharide. A strengthened lignocellulose-based product (e.g. a paper product) may be prepared by a procedure wherein a product produced in accordance with the latter process is treated with a strengthening agent having an ionic charge of sign opposite to that which is conferred on the modified lignocellulosic material by the charge-conferring substituent.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
System and method to control press section dewatering on paper and pulp drying machines using chemical dewatering agents
InactiveUS20060162887A1Automatic controlEnhanced advantageChemical/biochemical paper treatmentDigital differential analysersAutomatic controlControl system
The present invention provides an automatic control system, method and paper manufacturing machine using such control system for automatically controlling the amount of press section dewatering via the metered application of chemical dewatering agents applied to a paper web in a paper manufacturing process. The control system includes a feedback controller for controlling the amount of chemical dewatering agent applied to a paper web, and a monitoring device for obtaining a measurement of the moisture of the paper web exiting the press section.
Owner:NALCO CO
Method for the Continuous Coating of a Cellulose-Based Fibrous Substrate Web with Fatty Acid Chloride
InactiveUS20170241080A1Low viscosityMassive lossWrappersWater-repelling agents additionCelluloseBoiling point
The present invention concerns a process for continuously coating a cellulose-based fibrous substrate web with fatty acid chloride, comprising the steps of a) pre-drying a cellulose-based fibrous substrate web to an EN ISO 638:2008 dry matter content of less than 10%; b) coating the cellulose-based fibrous substrate web pre-dried in step a) with a liquid fatty acid chloride composition at a DIN EN 20187 relative humidity of less than 20 rH and a temperature below the boiling temperature of the liquid fatty acid chloride composition; c) thermally treating the coated cellulose-based fibrous substrate web obtained from step b).
Owner:DELFORTGROUP
Process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose and produced microfibrillated cellulose
InactiveUS20120136146A1Improve accessibilityHigh activityPulp properties modificationMicroorganism/enzyme additionFiberCellulose
A process for producing microfibrillated cellulose comprises providing a slurry comprising cellulosic fibers, treating the slurry with an enzyme, mechanically treating the slurry so that the fibers are disintegrated wherein the mechanical treatment and the treatment with the enzyme is performed simultaneously in a single treatment step. In this way it is possible to produce microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) in an improved and energy efficient way. A microfibrillated cellulose is produced according to the process.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Process for manufacturing flat vulcanized fibre
The invention discloses a process for manufacturing flat vulcanized fibre. The process comprises the following steps of: performing gelling treatment on base paper by using solution of zinc chloride according to the preset temperature condition; cramming a plurality of gelled raw vulcanized fibre flat plates into grids to perform ageing treatment; performing desalination on the aged raw vulcanized fibre by using the solution of zinc chloride with degressive relative concentration; and cleaning, drying and shaping the desalted raw vulcanized fibre flat plates sequentially. The manufacturing process can overcome the defects of non-uniform shrinkage, easy deformation, easy cracking, low safety and the like in the prior art so as to realize the advantages of uniform shrinkage, no deformation, no cracking and high safety.
Owner:新疆源一科创有限公司
Special anti-counterfeiting rice paper for postage stamp, postage stamp and production method thereof
ActiveCN101748642ARaise the gradeRich market needsStampsDefoamers additionBleachPulp and paper industry
The invention provides a production method of special anti-counterfeiting rice paper for a postage stamp, which comprises the following steps: adopting wingceltis barks and straws from sand fields as raw materials, preparing pulp through soaking, beating and bleaching with calcium hypochlorite bleach solution; purifying the prepared pulp, fetching paper, drying, and cutting to manufacture raw rice paper; performing the alum dragging treatment of the raw rice paper in alum solution, and naturally drying the rice paper to obtain non-absorbent rice paper; and applying glue on the back of the non-absorbent rice paper, and drying and flattening to manufacture the special anti-counterfeiting rice paper for the postage stamp. Since the production method in the invention is an improvement based on the conventional production process, the produced rice paper not only preserves the properties of the conventional rice paper, but also has excellent printing applicability. Therefore, the rice paper can be used as the special anti-counterfeiting rice paper for stamps, stamped postcards and other postage stamps.
Owner:北京邮票厂有限公司 +3
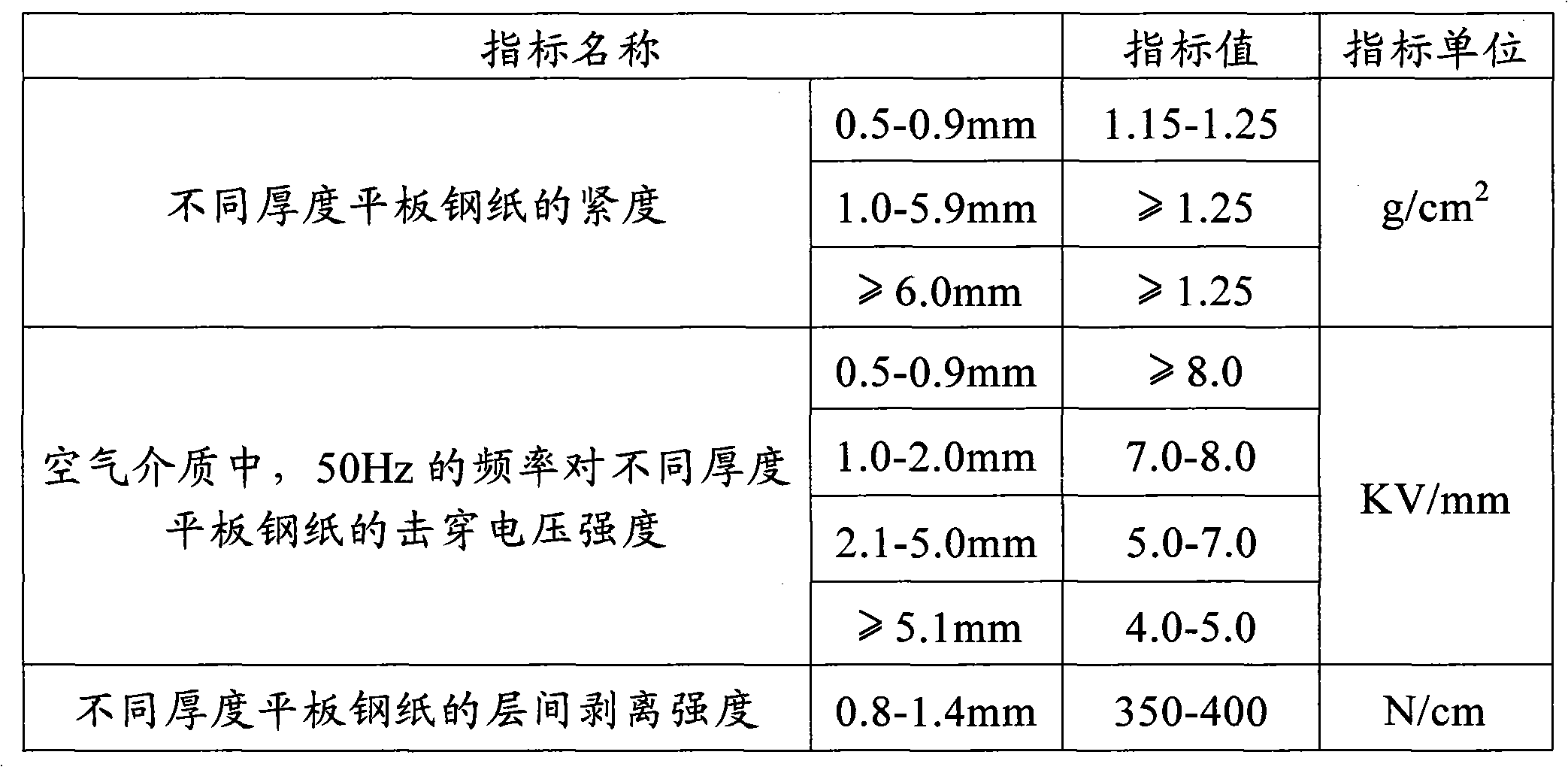
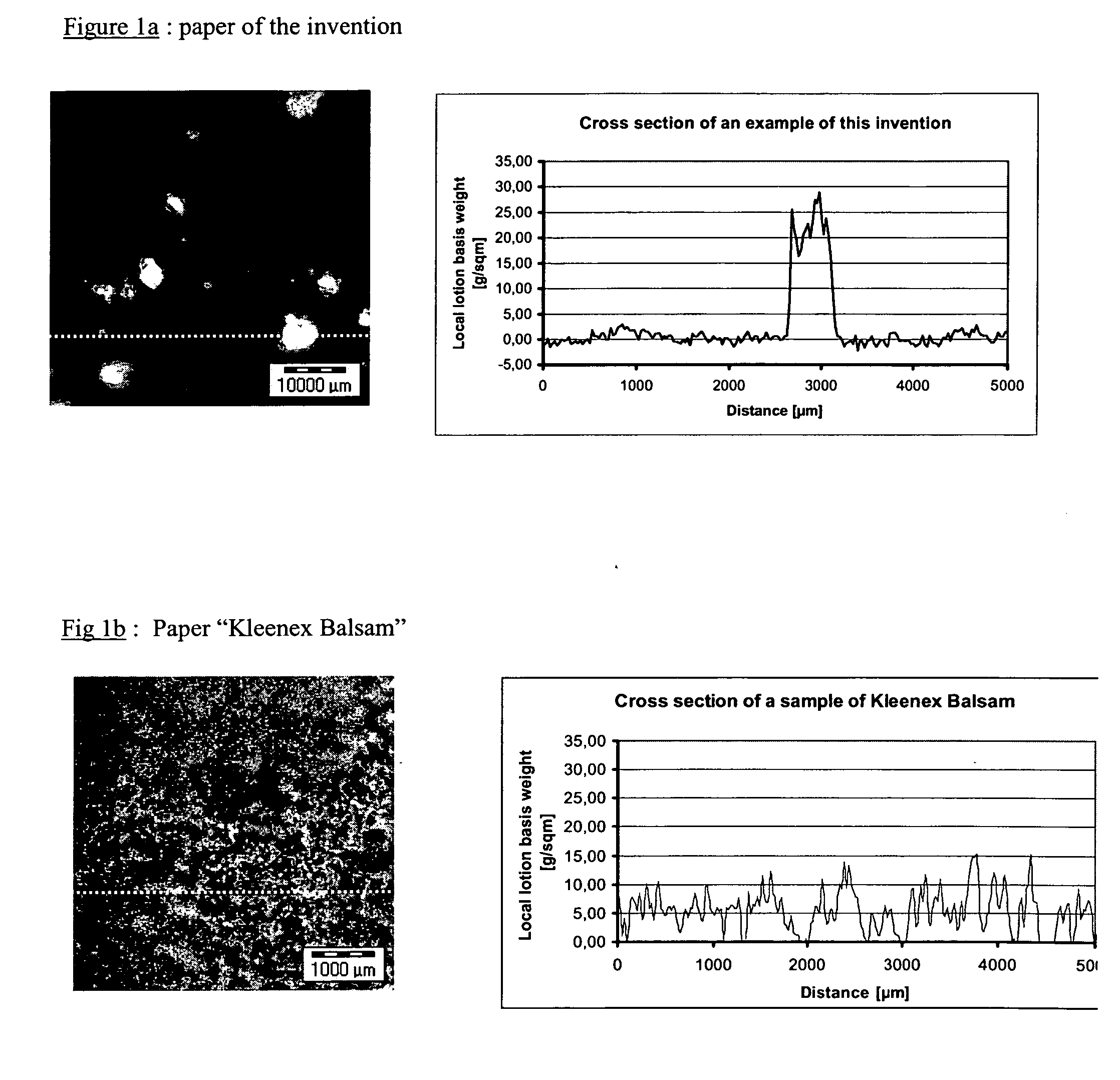
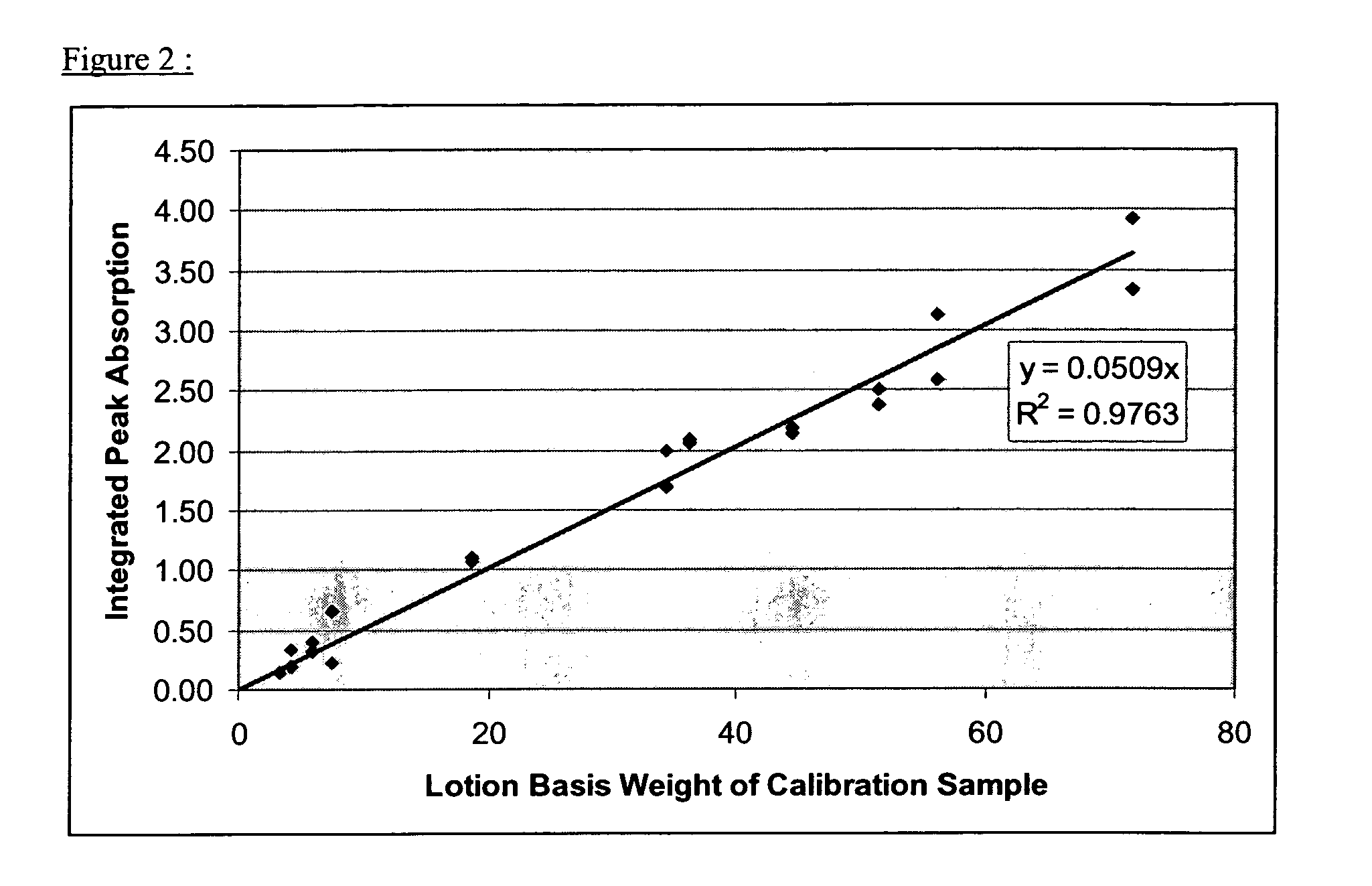
Paper tissue with high lotion transferability
A paper tissue and products made from paper tissue, such as paper handkerchiefs, facial tissues, bath and cosmetic tissues, paper tissue wipes of any kinds and the like. The invention describes both the process for making a smooth and absorbent lotioned paper tissue, with high transferability of the lotion. The process steps comprises the steps of (a) providing a paper tissue web continuously moving next to a lotion application unit comprising at least one rotating surface, (b) transferring said lotion onto one rotating surface,’(c) expulsing said lotion from the said rotating surface into a stream of lotion droplets, by primarily the centrifugal force of the rotation of said rotating surface, (d) intercepting said paper tissue with said stream of lotion droplets. The invention also describes a paper tissue comprising a lotion distributed as discrete deposits on its surface. The deposits have a high local concentration of lotion and cover a relatively small area of the tissue.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation of carbon nano tube/acrylic carbon fiber composite carbon fiber paper and use
InactiveCN1986961AImprove conductivityGood flexibilityChemical/biochemical paper treatmentSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperFiberAdhesive
A process for making the composite carbon nanotube-acrylonitrile based carbon fiber paper includes such steps as immersing the acrylonitrile based carbon fibers and carbon nanotubes in the solution of activating agent for 1-3 hr, water washing until they become neutral, proportioning, pulping, adding disperser solution and adhesive, and conventionally making paper by wet method. The resultant paper can be used as antistatic packing material, planar heating material, novel energy source material, electrochemical material, electromagnetic shielding material, high-fidelity sounding material, etc.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
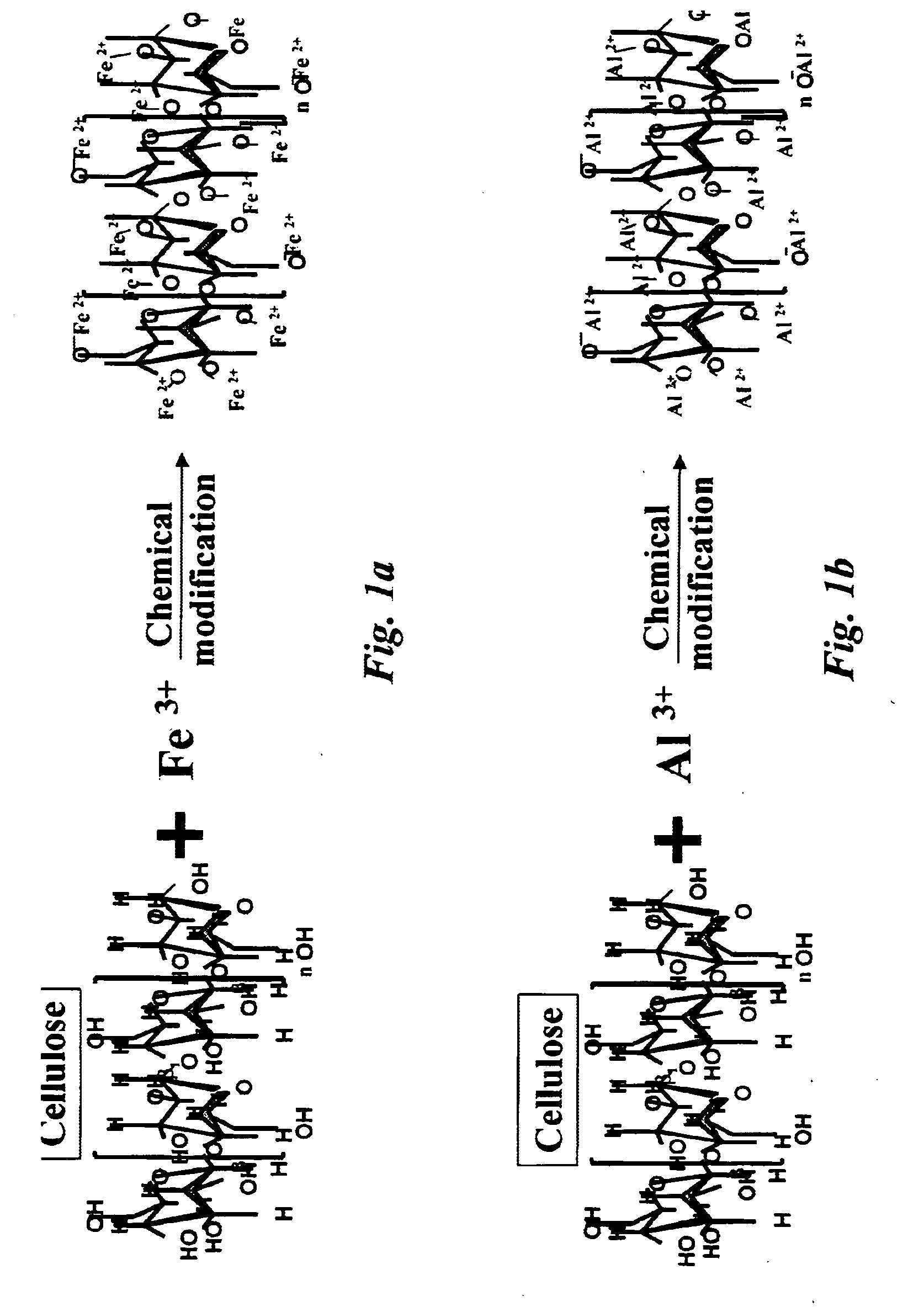
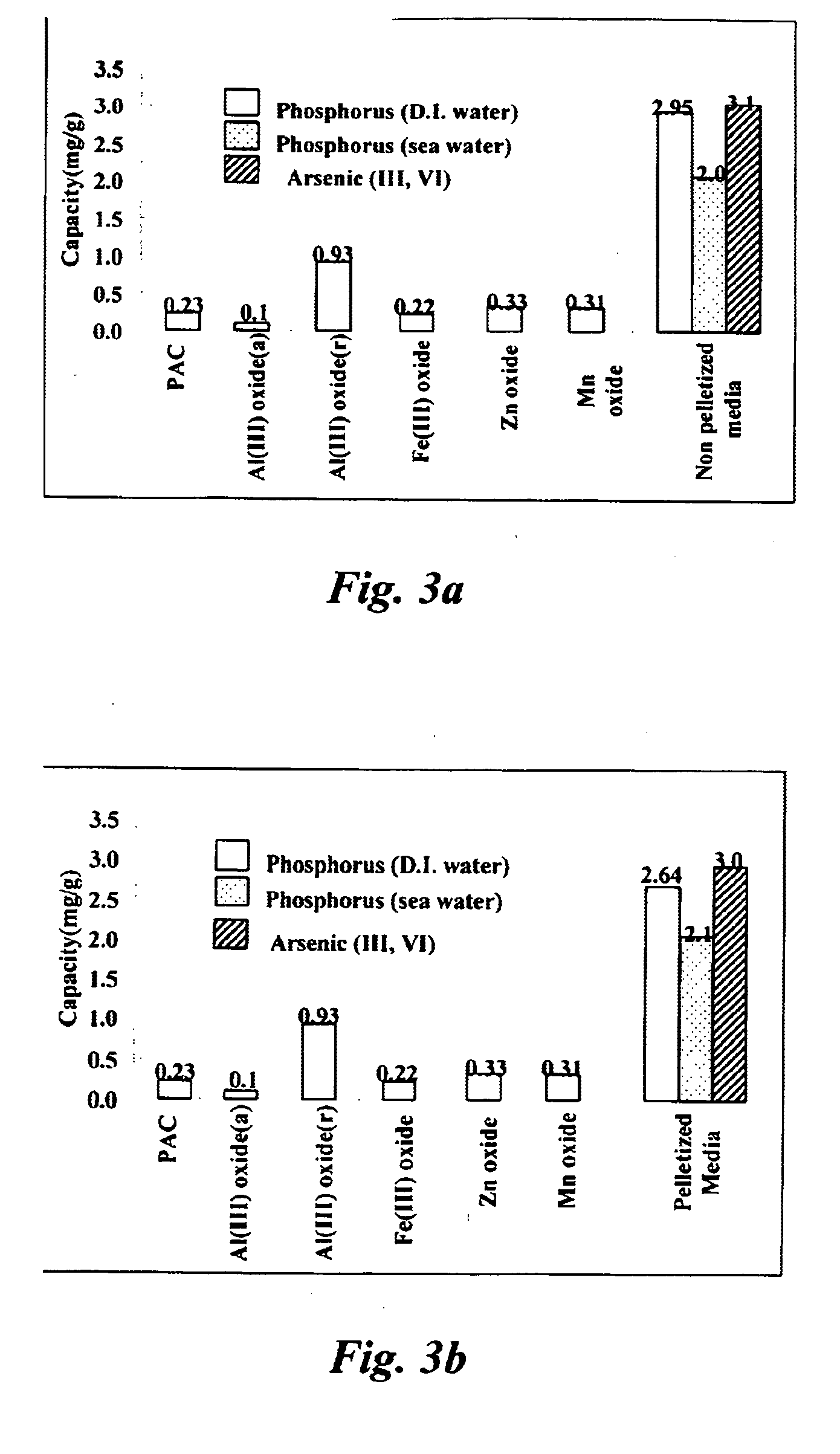
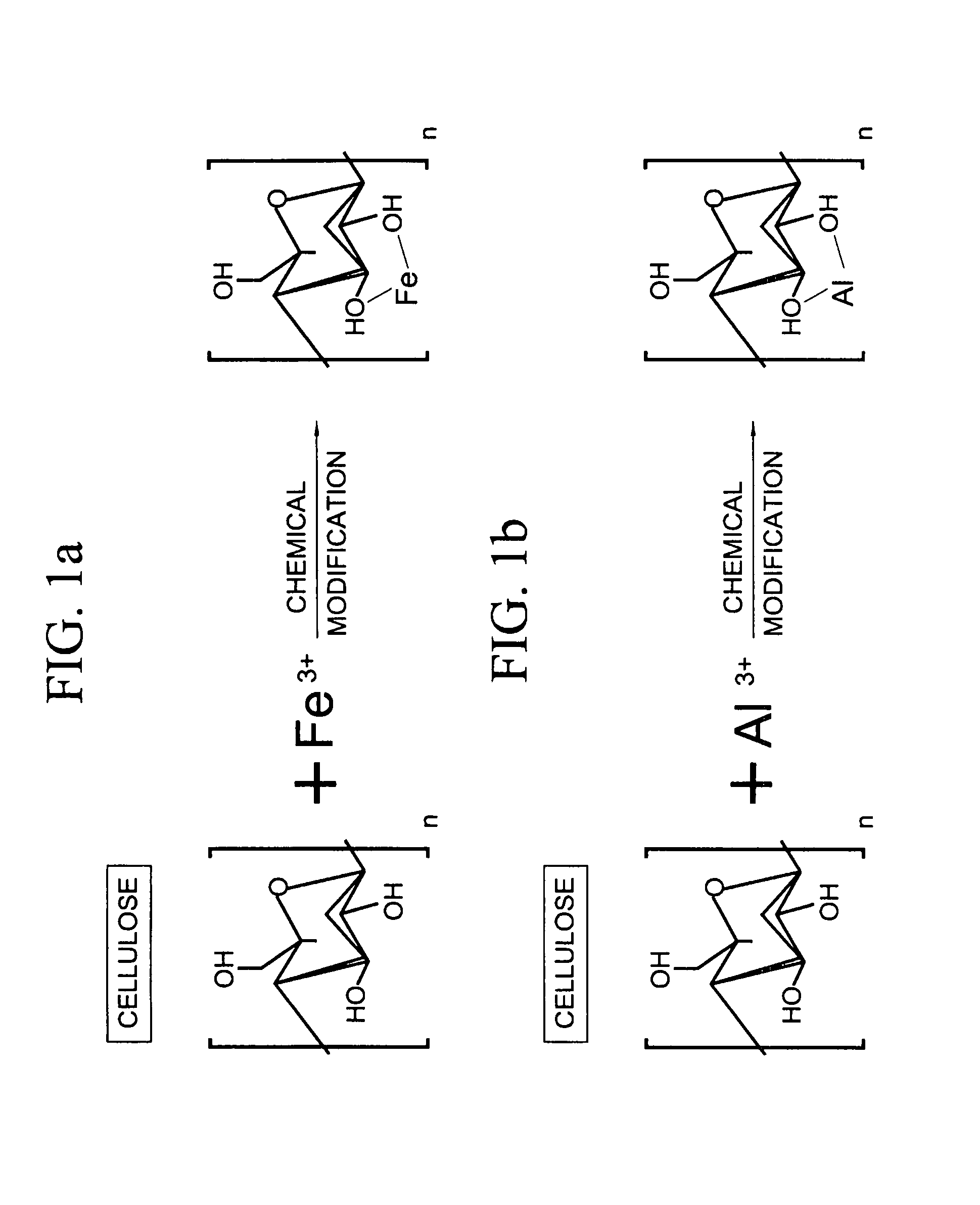
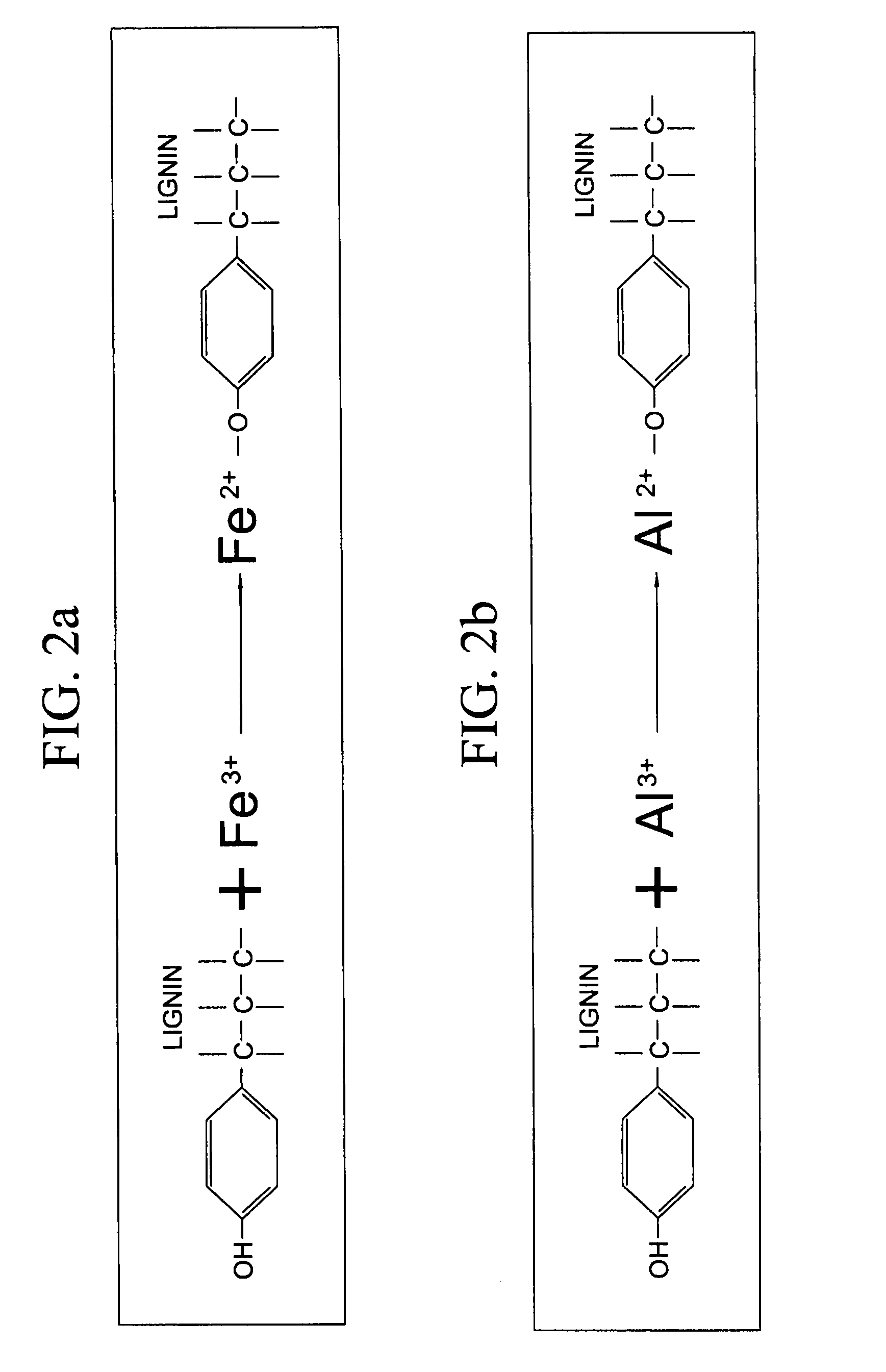
Lignocellulose-based anion-adsorbing medium (LAM) and process for making and using same for the selective removal of phosphate and arsenic anionic contaminants from aqueous solutions.
InactiveUS20050098503A1Waste water treatment from quariesPulp properties modificationCelluloseHydrogen
A lignocellulose-based anion-adsorbing medium (LAM) and process for making and using same for selectively removing phosphates and arsenic contaminants from aqueous solutions is disclosed. Making the LAM comprises (a) dissociating cations such as Fe and Al, from their counterions by adding a chemical compound containing said cations to water and acidifying; (b) pelletizing a lignocellulose; (c) adsorbing the cations to the lignocellulose by bringing the lignocellulose into contact with the solution of step (a) and incubating; and, (d) exposing the lignocellulose of step (c) to an alkaline fixing agent to replace hydrogens (H) of the hydroxyl groups of the lignocellulose with the adsorbed cations to produce the LAM with a positive charge. The LAM may be used to selectively and cost-effectively remove phosphate and arsenic contaminants from aqueous solutions by retaining them at the Fe or Al on the LAM.
Owner:BIOTECH
Method for deinking paper
InactiveUS6022423AQuality improvementLess expensiveLighting and heating apparatusChemical/biochemical paper treatmentPulp and paper industrySURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:DECOPIER TECH
Diaphragm paper, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20160049627A1Small apertureImprove isolationNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperEngineeringElectrolyte
Diaphragm paper, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The diaphragm paper comprises a first layer, a second layer, and a third layer, wherein the second layer is located between the first layer and the third layer; the first layer and the third layer are loose layers, of which the average aperture is larger than 10 μm and the basis weight is 5 to 30 g / m2; and the second layer is a compact layer, of which the average aperture is smaller than 5 μm and the basis weight is 2 to 15 g / m2. The compact layer has small aperture and good insulating performance, and is capable of effectively insulating a positive electrode and a negative electrode. The loose layers have good liquid permeability and electrolyte absorptivity, and can guarantee the discharge performance of a battery. The material is further advantageous in having good dimensional stability and being thin, so that a battery can achieve high capacity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and enzymatic preparation for treatment of cellulose pulps
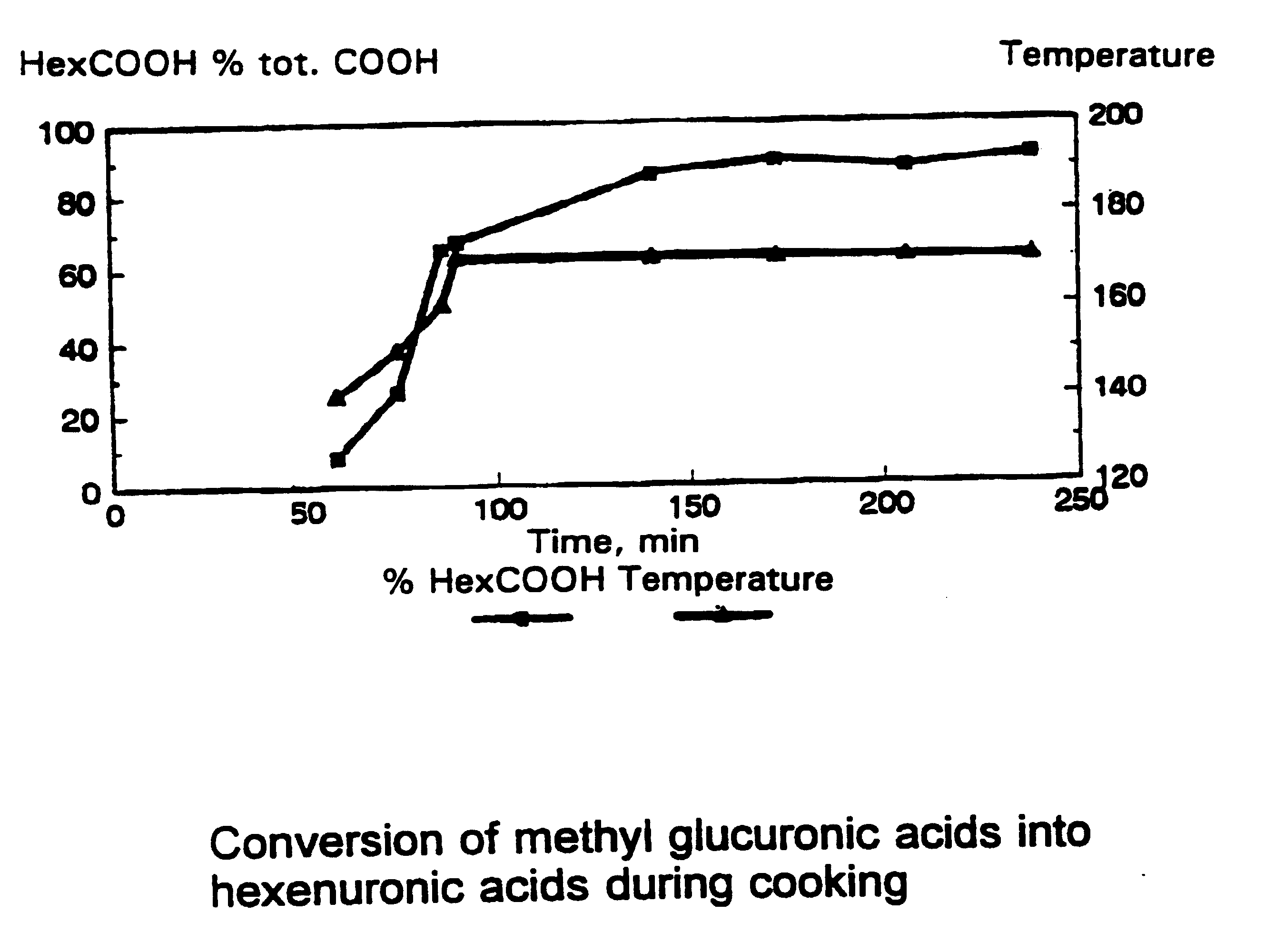
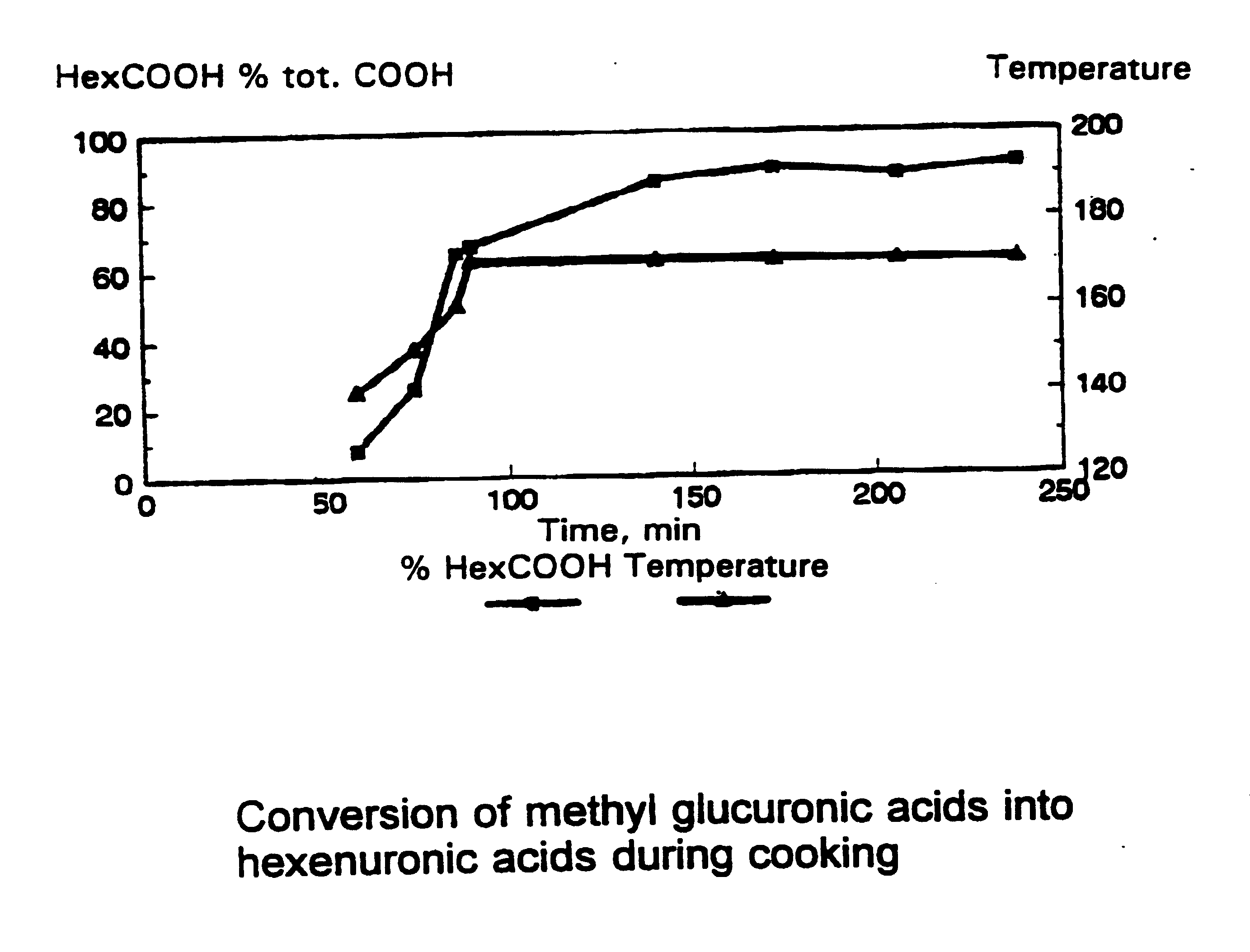
InactiveUS20040069426A1Improve low-chlorineImprove chlorine-free bleaching methodChemical/biochemical paper treatmentPulping with organic solventsXylanCellulose
The present invention concerns a method for enzymatic treatment of lignocellulosic materials which contain xylan-polymers, such as cellulose kraft pulps. According to a method of the present kind, at least a part of the hexenuronic acid groups present in the material is selectively removed in order to remove metal ions from the pulp, to change the surface charge thereof, to improve the brightness stability of the pulp and to render the material more suitable for enzymatic treatment.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Preparation method of three-dimensional paper-based metal organic framework
InactiveCN105924478ALow reaction temperatureShort reaction timeChemical/biochemical paper treatmentPlatinum organic compoundsPaper basedMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a preparation method of a three-dimensional paper-based metal organic framework, and belongs to the field of preparation of organic nano materials. The method comprises the following steps of selection of a paper base, design of paper-based hydrophobic wax batch printing patterns, electrode printing and paper-based metal organic framework growing. The preparation method of the three-dimensional paper-based metal organic framework has the advantages that due to the fact that paper is selected as the base material, reserves are rich, and the advantages of being easy to fold, convenient to carry and the like are achieved. The preparation technology is simple, the paper-based metal organic framework can achieve on-site instant visual detection easily, and meanwhile a very good foundation is laid for preparation of multifunctional paper-based electronic devices.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Superhydrophobic paper and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107653744ALarge specific surface areaIncrease roughnessWater-repelling agents additionChemical/biochemical paper treatmentPulp and paper industryPre treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of functional paper, in particular to superhydrophobic paper and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of 1), subjectingthe paper to hydroxylation modification; 2), etching the paper with a plasma etching method; 3), subjecting the paper to plasma pretreatment with Ar as an air source; 4), deposing a superhydrophobic membrane on the surface of the paper with a plasma chemical vapor deposition method. A micro-structure can be prepared on the surface of the paper by adopting the plasma etching method to have the paper etched, specific surface area of the paper is increased, roughness of the paper is increased, the surface of the paper is enabled to be difficult to infiltrate, contact angle is favorably increased,the fluorine-containing superhydrophobic membrane is deposed on the surface of the paper with a plasma chemical vapor deposition method through fluorine modification, the superhydrophobic membrane has the advantages of high strength and scratch resistance, and hydrophobicity has a long lasting effect.
Owner:邱禹
Lignocellulose-based anion-adsorbing medium (LAM) and process for making and using same for the selective removal of phosphate and arsenic anionic contaminants from aqueous solutions
A lignocellulose-based anion-adsorbing medium (LAM) and process for making and using same for selectively removing phosphates and arsenic contaminants from aqueous solutions is disclosed. Making the LAM comprises (a) dissociating cations such as Fe and Al, from their counterions by adding a chemical compound containing said cations to water and acidifying; (b) pelletizing a lignocellulose; (c) adsorbing the cations to the lignocellulose by bringing the lignocellulose into contact with the solution of step (a) and incubating; and, (d) exposing the lignocellulose of step (c) to an alkaline fixing agent to replace hydrogens (H) of the hydroxyl groups of the lignocellulose with the adsorbed cations to produce the LAM with a positive charge. The LAM may be used to selectively and cost-effectively remove phosphate and arsenic contaminants from aqueous solutions by retaining them at the Fe or Al on the LAM.
Owner:BIOTECH
Process for producing microfibrillated cellulose
ActiveUS20120160433A1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease heightPulp properties modificationMicroorganism/enzyme additionCellulose fiberEnzyme
A process for treating cellulosic fibres comprises mechanically pre-treating the fibres followed by treating the fibres with an enzyme and thereafter mixing the fibres with a solution comprising an alkali metal hydroxide followed by mechanically treating the fibres to form microfibrillated cellulose. In this way it is possible to produce microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) in an improved and energy efficient way.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Soft durable tissue
InactiveUS7377995B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove smoothnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberBiomedical engineering
Single-ply throughdried tissue sheets, particularly suitable as bath tissue, are produced with at least three layers. One or both of the outer layers suitably contain predominantly softwood fibers and a chemical bonding agent. One or more of the inner layers suitably contains a chemical debonder. The resulting tissues have a high level of durability and softness.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Mehtod for the modification of polymeric carbohydrate materials
InactiveUS20040091977A1Chemical/biochemical paper treatmentBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsCompound (substance)Chemical groups
The invention makes available a method to introduce specific chemical groups onto the surface of any polymeric carbohydrate material to alter the physico-chemical properties of said material. In particular, the method comprises the controlled introduction of chemically-modified oligosaccharides into a carbohydrate polymer using a transglycosylating enzyme.
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
Soft tissue hydrophilic tissue products containing polysiloxane and having unique absorbent properties
ActiveUS7186318B2Reduce hydrophobicityReduce molecular weightNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperMedicinePulp fibre
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell and preparation method of gas diffusion layer
ActiveCN113555563ASolve the problem of low carbon residual rateSolve for uniformityCell electrodesChemical/biochemical paper treatmentFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a gas diffusion layer for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell and a preparation method thereof, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out papermaking and drying on a carbon fiber suspension mainly composed of a fibrous adhesive, water, a dispersant and carbon fibers with different length-diameter ratios to obtain carbon fiber raw paper, carrying out carbonization and graphitization treatment under the protection of nitrogen or inert gas to obtain the gas diffusion layer for the proton exchange membrane fuel cell; the fibrous adhesive being a composite fiber or a blend fiber composed of phenolic resin and other resin; the finally prepared gas diffusion layer for the proton exchange membrane fuel cell having pore gradient, and the layer with the minimum pore diameter being an intrinsic microporous layer. According to the method, the step of impregnating the base paper with the resin is omitted, integrated forming of the carbon paper and the microporous layer can be achieved, subsequent coating preparation of the microporous layer is omitted, the process is simple, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Battery separator
InactiveUS7402539B2High modulusHigh strengthLayered productsChemical/biochemical paper treatmentMetallurgyFiber diameter
Disclosed is a battery separator consisting essentially of a nonwoven fabric having a substantially unilayered structure, wherein an apparent total surface area of fibers per a surface density of the nonwoven fabric is 20 m2 or more, a thickness of the nonwoven fabric is 0.1 mm or less, a uniformity index of the nonwoven fabric is 0.15 or less, and the nonwoven fabric contains fine fibers having a fiber diameter of 4 μm or less.
Owner:JAPAN VILENE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com