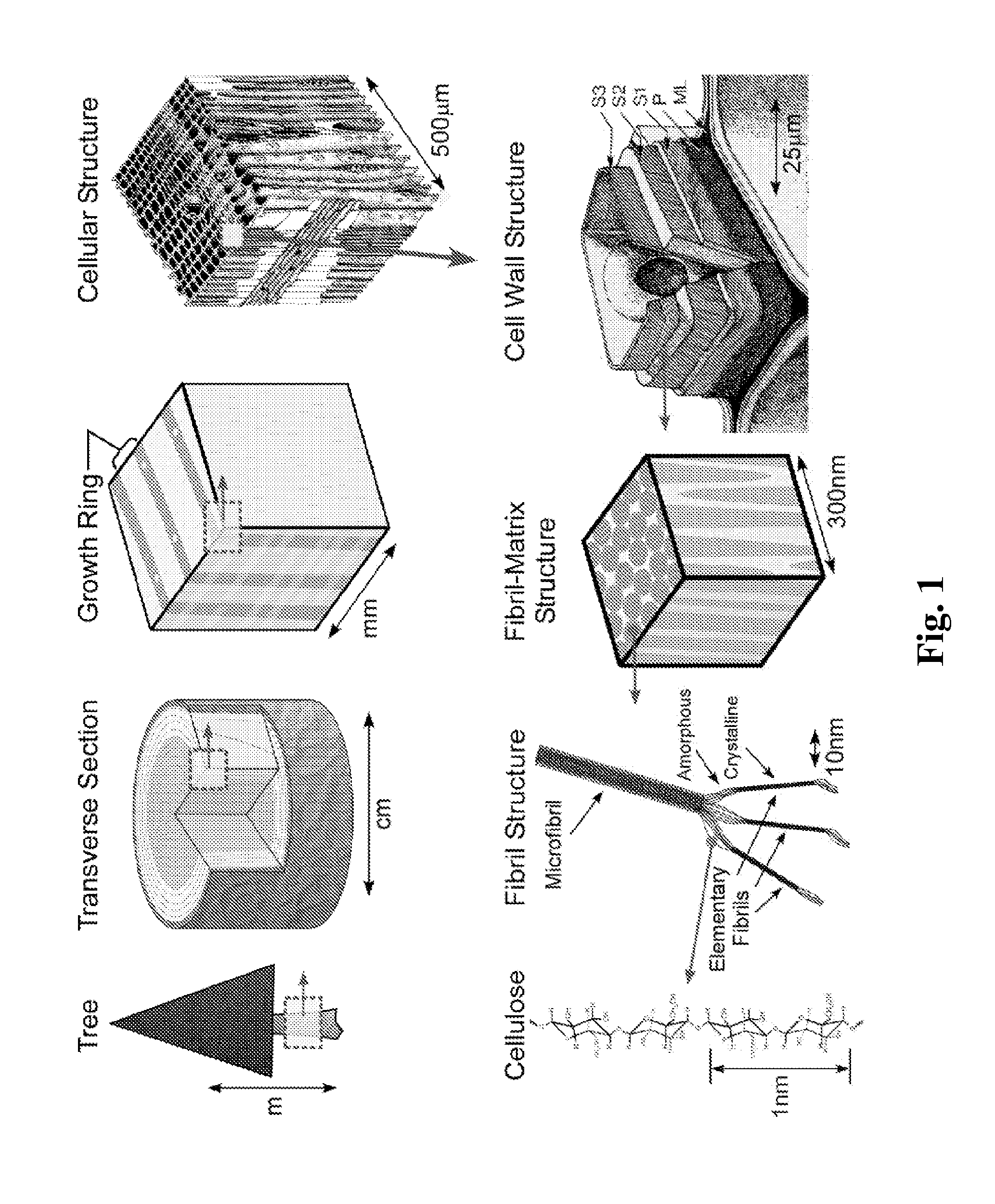
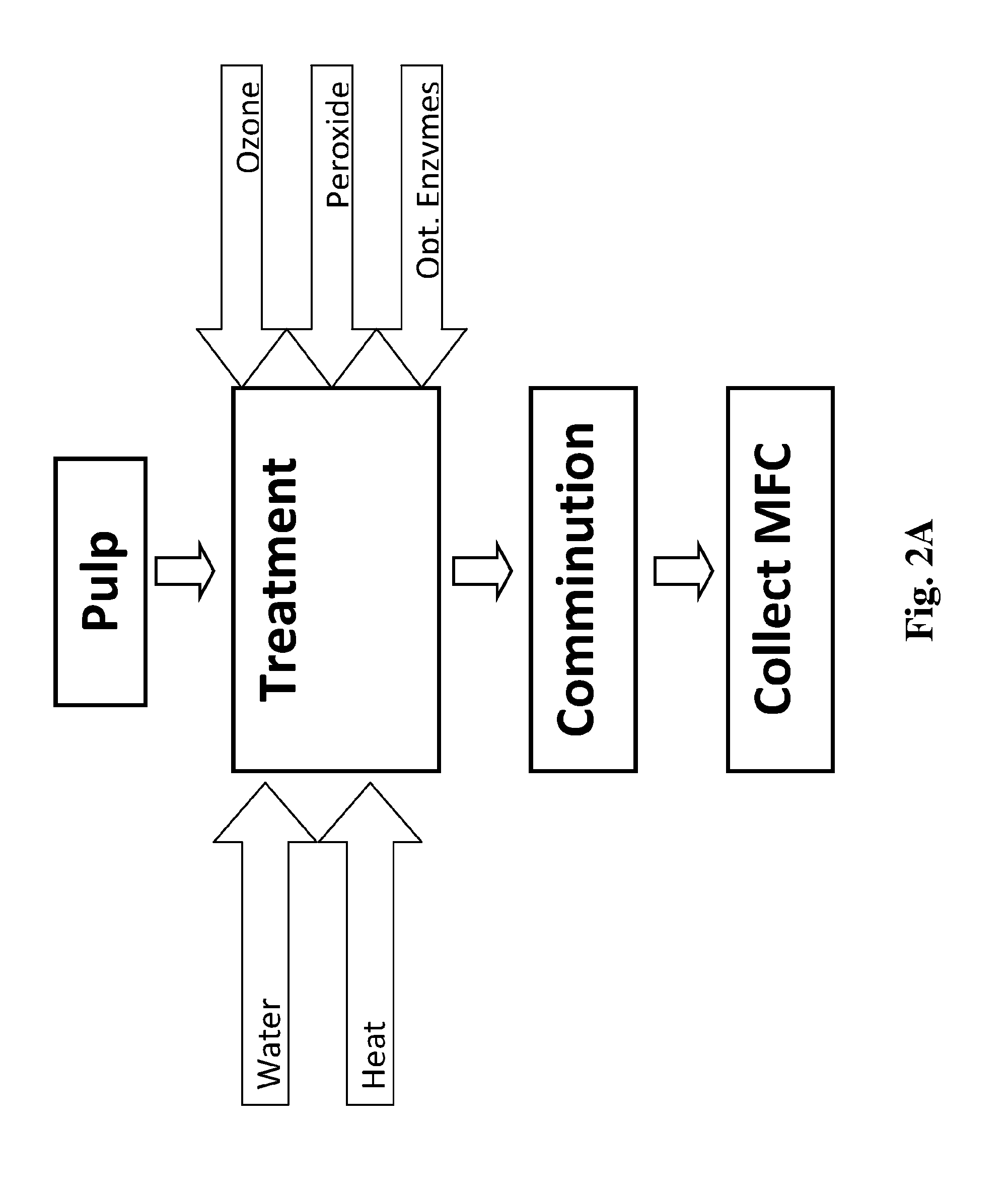
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246results about "Microorganism/enzyme addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
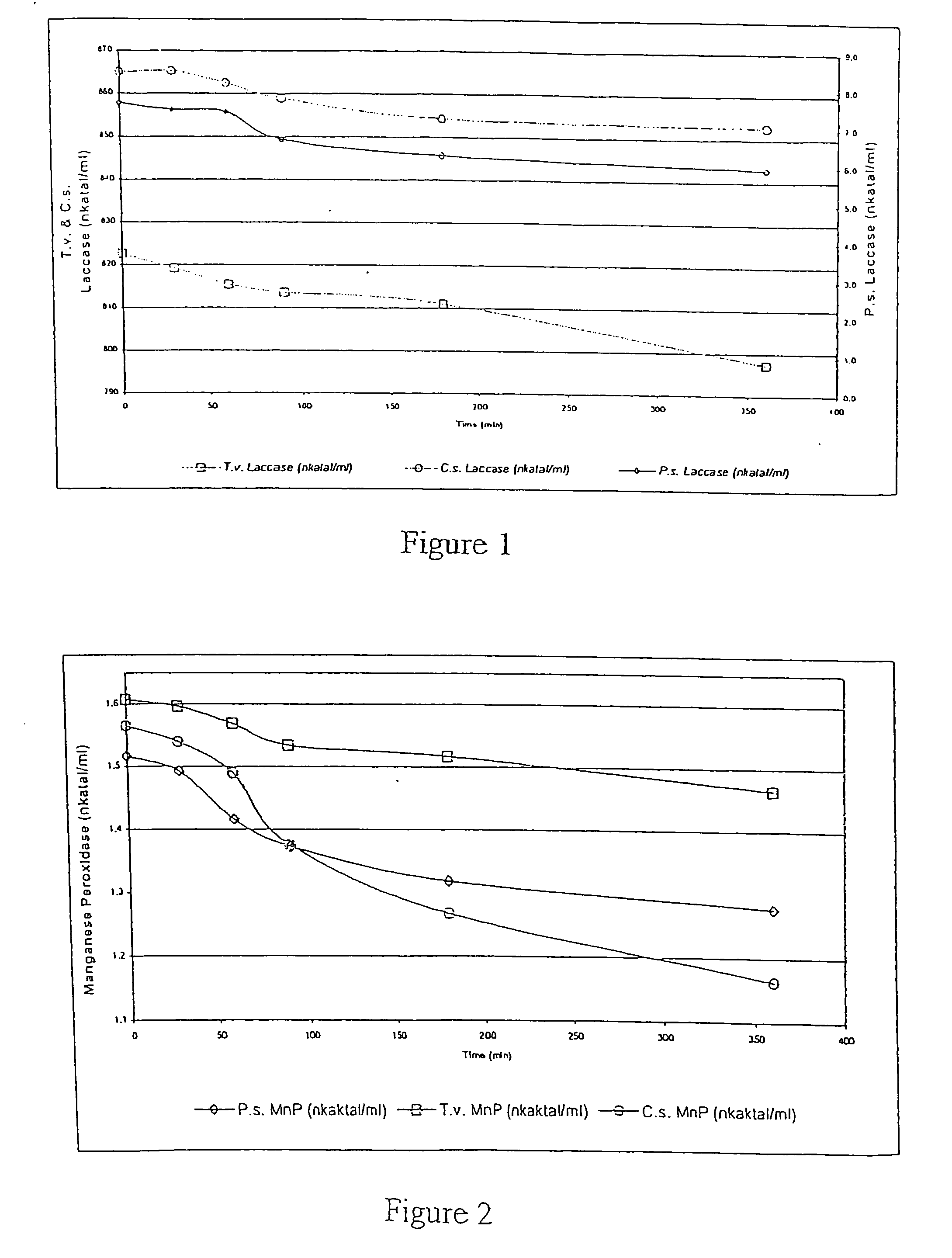
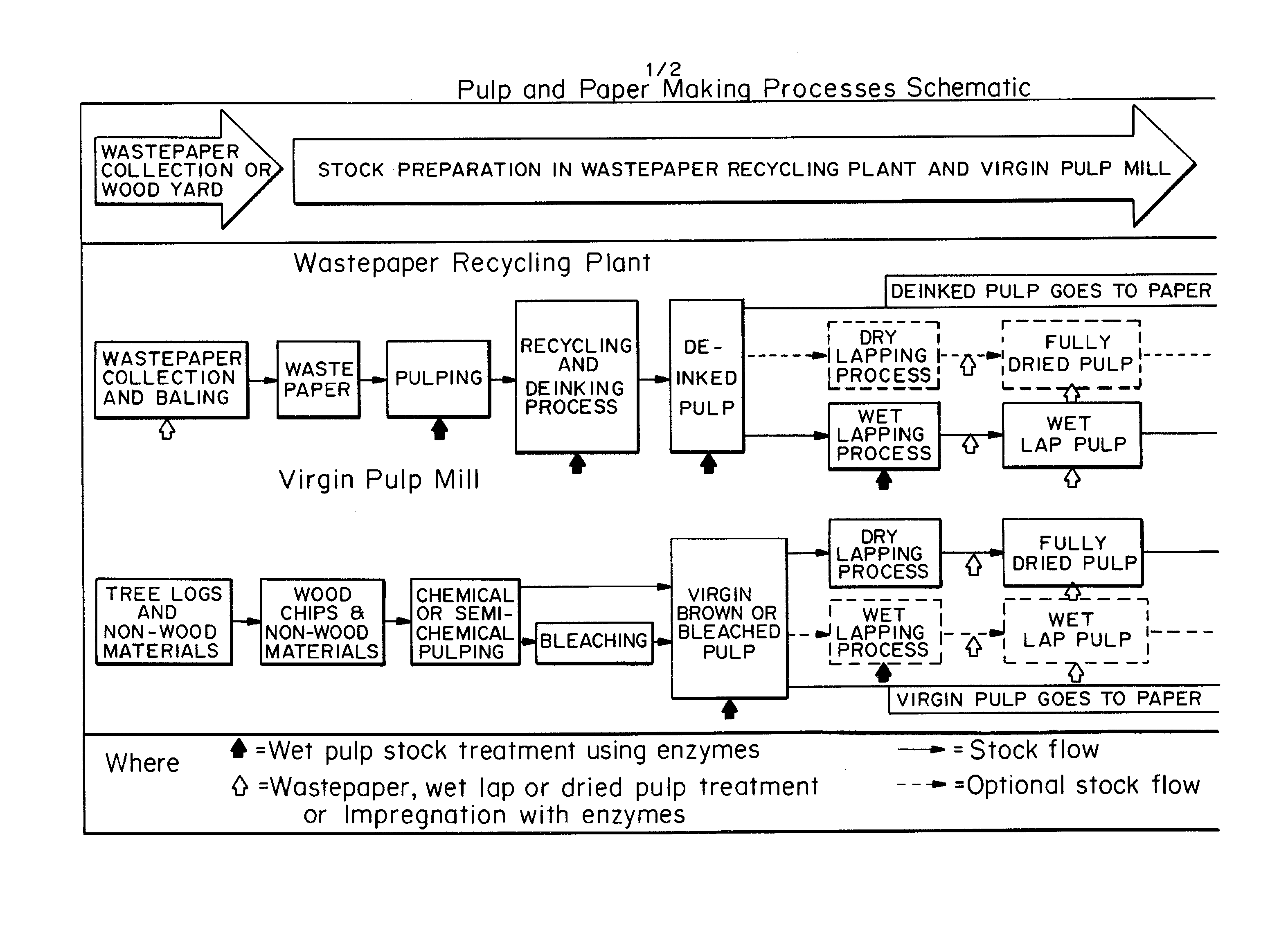
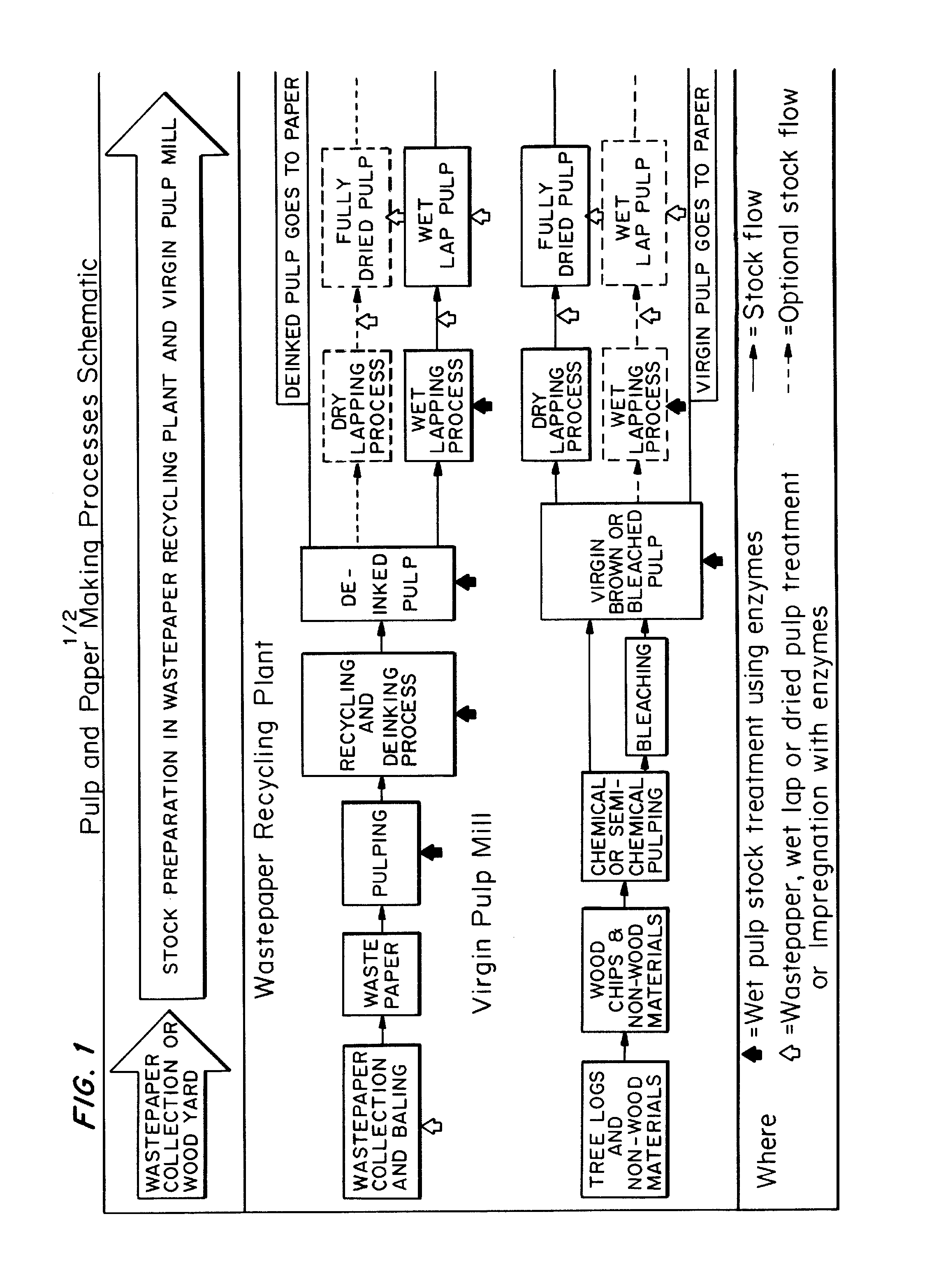
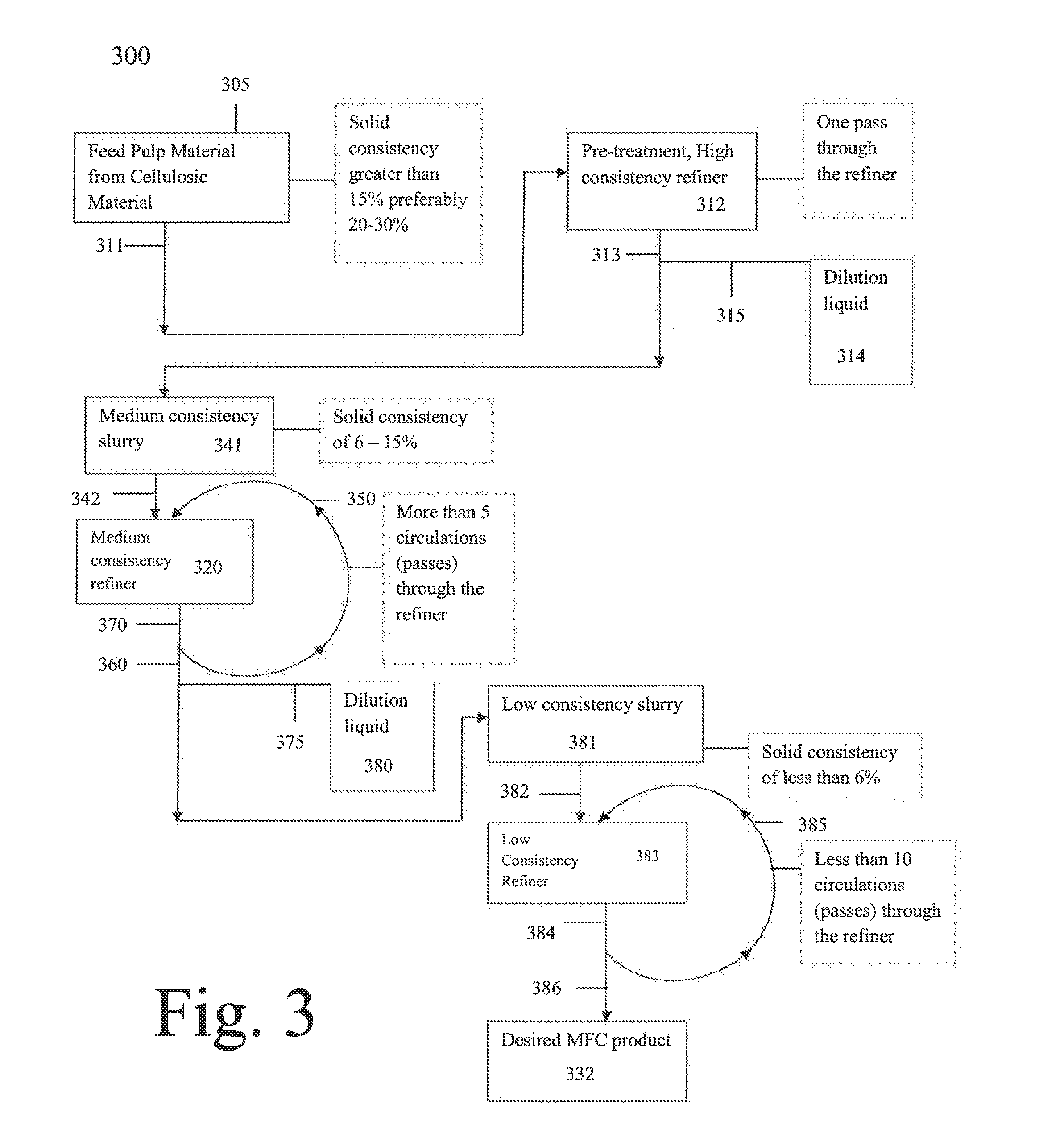
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
ActiveUS20070079944A1Easy to optimizePretreatment with water/steamPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp and paper industrySugar
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Energy Efficient Process for Preparing Nanocellulose Fibers
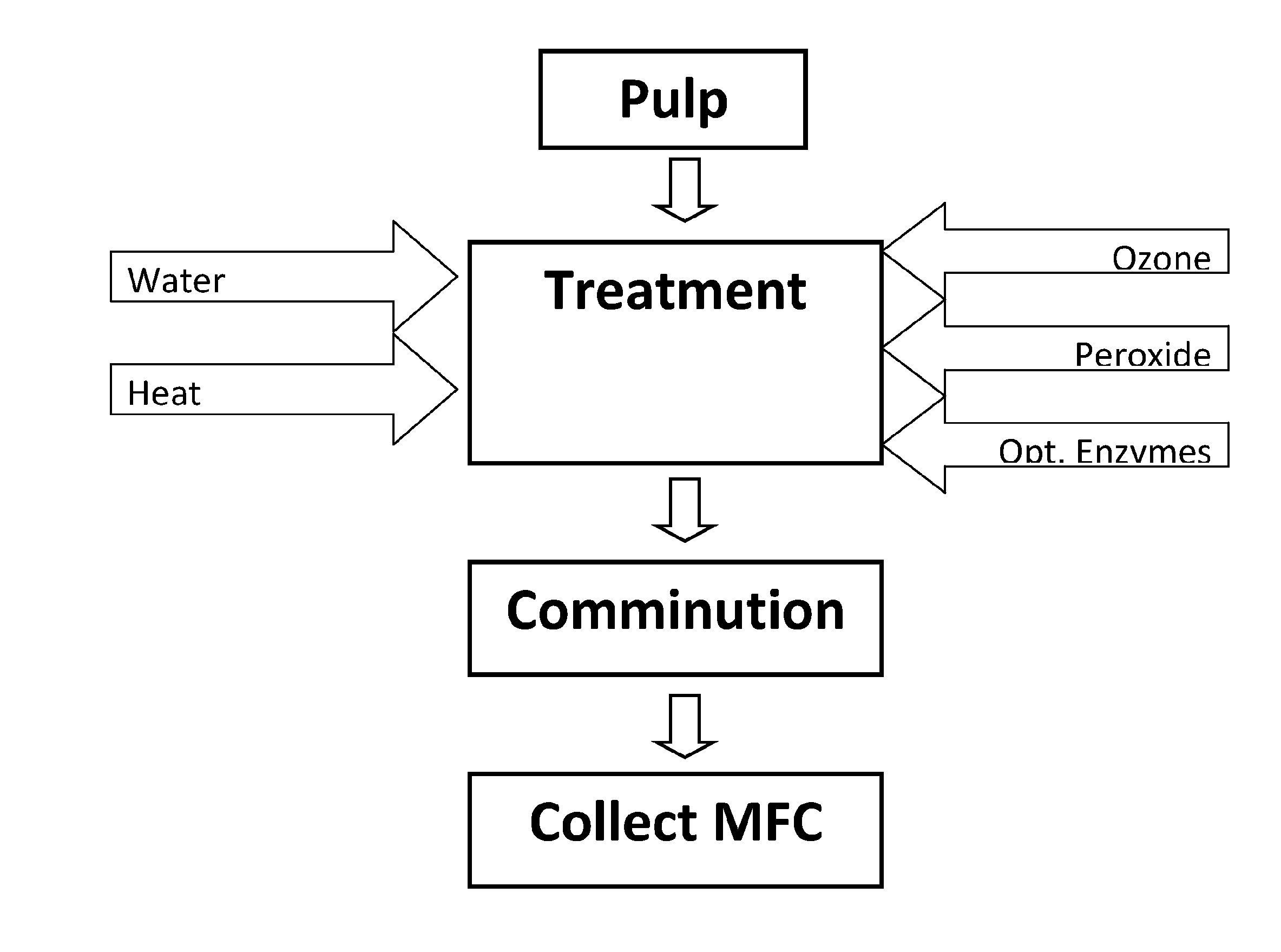
ActiveUS20150167243A1Improve efficiencyWeaken energySpecial paperPaper after-treatmentDepolymerizationNanofiber
A scalable, energy efficient process for preparing cellulose nanofibers is disclosed. The process employs a depolymerizing treatment with one or both of: (a) a relatively high charge of ozone under conditions that promote the formation of free radicals to chemically depolymerize the cellulose fiber cell wall and interfiber bonds; or (b) a cellulase enzyme. Depolymerization may be estimated by pulp viscosity changes. The depolymerizing treatment is followed by or concurrent with mechanical comminution of the treated fibers, the comminution being done in any of several mechanical comminuting devices, the amount of energy savings varying depending on the type of comminuting system and the treatment conditions. Comminution may be carried out to any of several endpoint measures such as fiber length, % fines or slurry viscosity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE
Xylanases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20060003433A1Low viscosityIncrease profitBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsXylanase YIncrease ph
The invention relates to xylanases and to polynucleotides encoding the xylanases. In addition, methods of designing new xylanases and methods of use thereof are also provided. The xylanases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Material for odor control
The present invention is directed to materials containing an enzyme inhibitor, including treated fibers, nonwovens, functional particles and processes for making these materials. These materials are useful in reducing or delaying onset of odor generation from various waste materials including human and animal elimination products.
Owner:BUCKEYE TECH INC
Enzymatic pre-treatment of market pulp to improve fiber drainage and physical properties
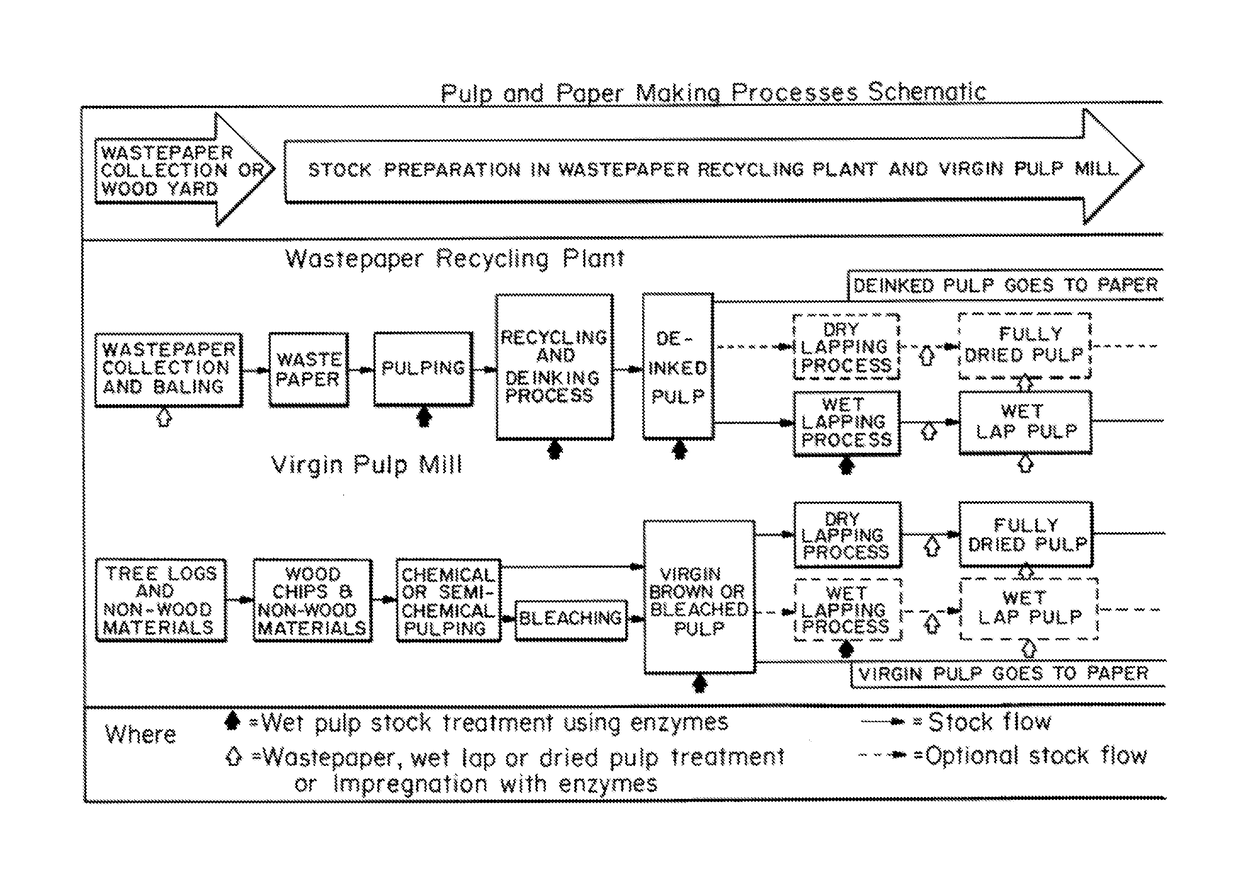
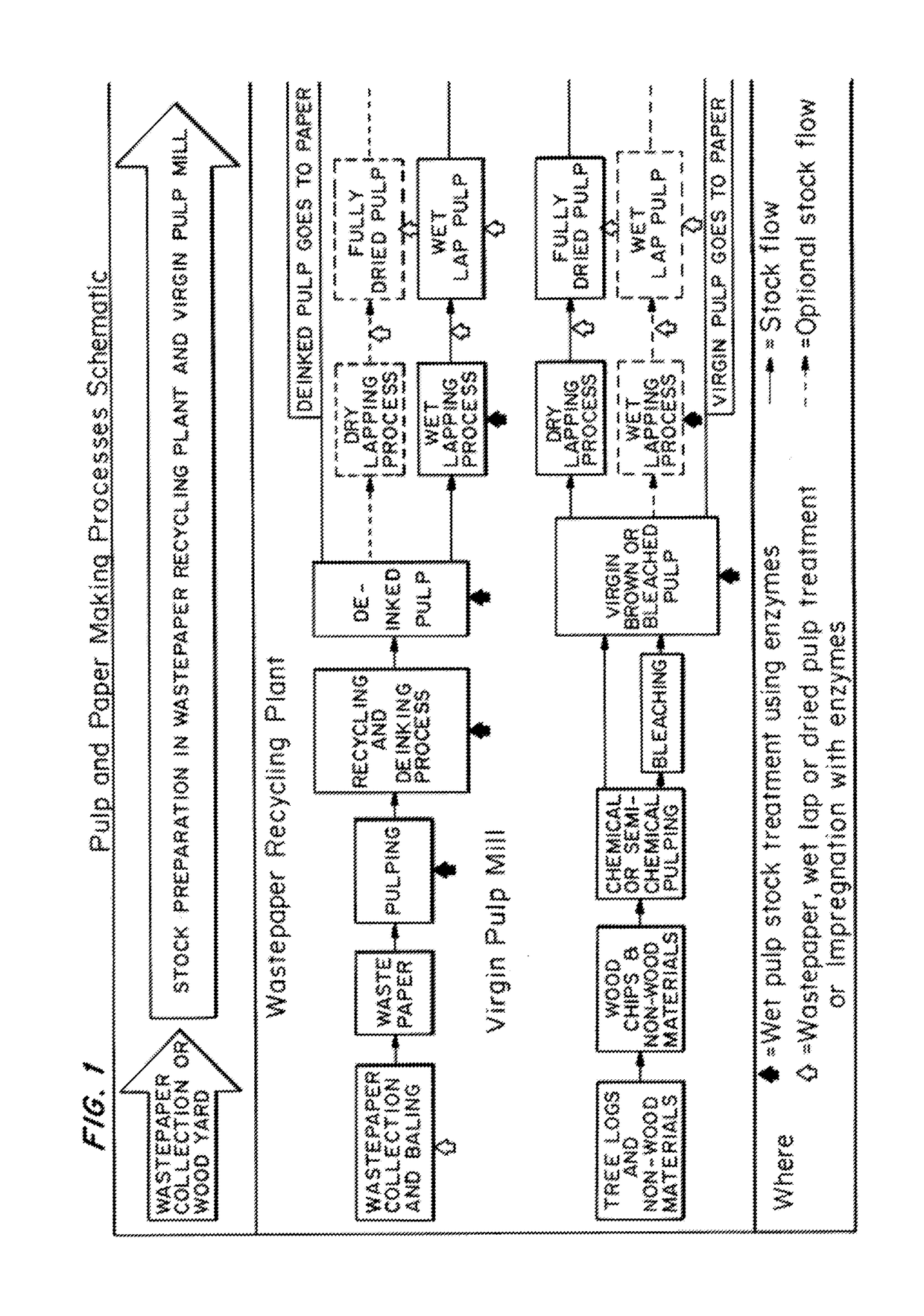
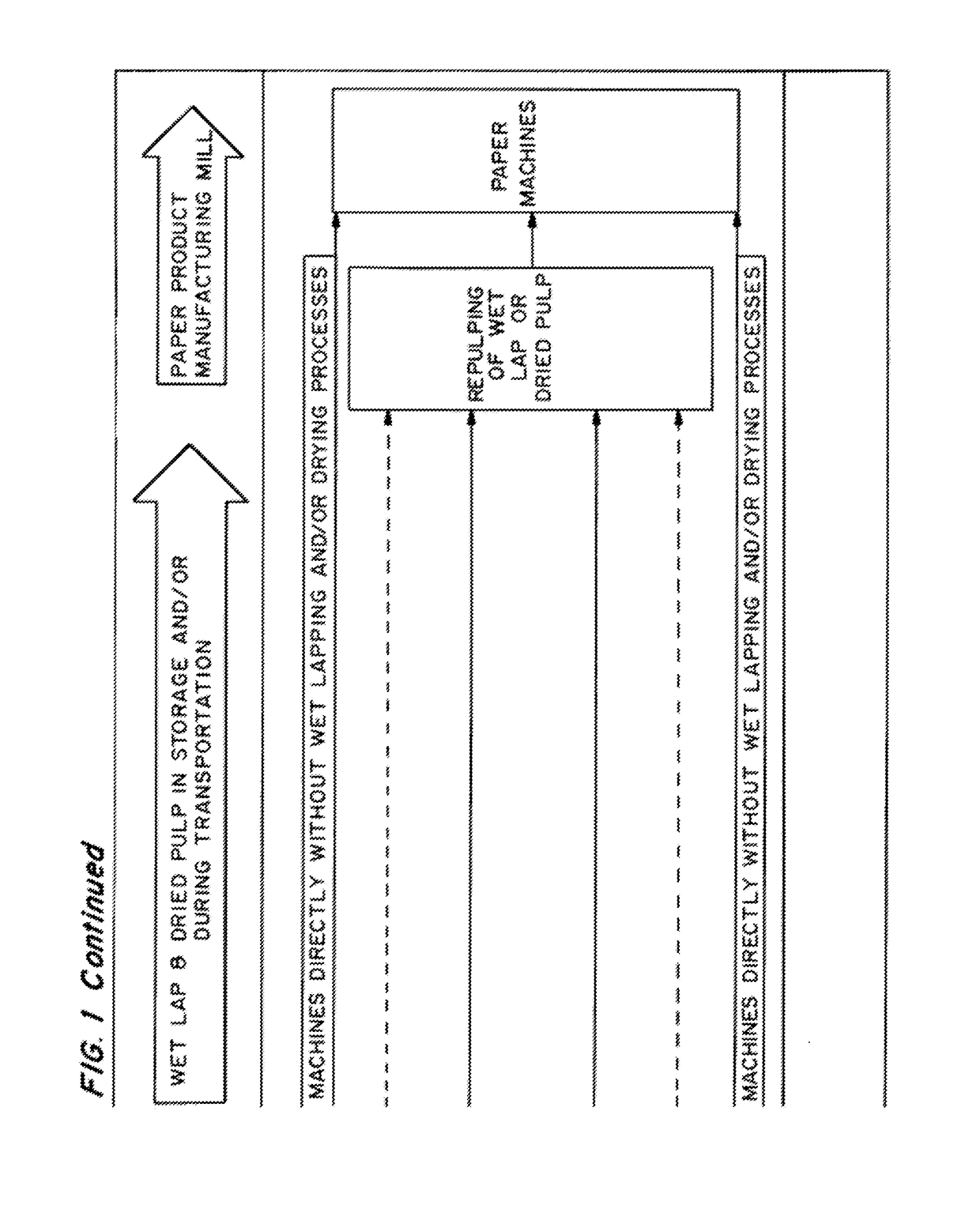
ActiveUS20170328006A1Increasing pulp drainage and strength propertyQuality improvementMicroorganism/enzyme additionPaper recyclingFiberPulp and paper industry
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Composition comprising microfibrillated cellulose and a process for the production of a composition
ActiveUS20130047893A1Easy to moveIncrease dry contentPigmenting treatmentCoatings with pigmentsCellulose fiberViscosity
The present invention relates to a composition comprising microfibrillated cellulose, mono-, di- or oligo-saccharides and a pigment in order to achieve a composition with improved rheological properties such as a low viscosity even at high dry content. The present invention further relates to process for the production of said composition. The microfibrillated cellulose is produced by at least partly enzymatic treatment of cellulosic fibers such that even mono-, di- or oligo-saccharide is formed.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
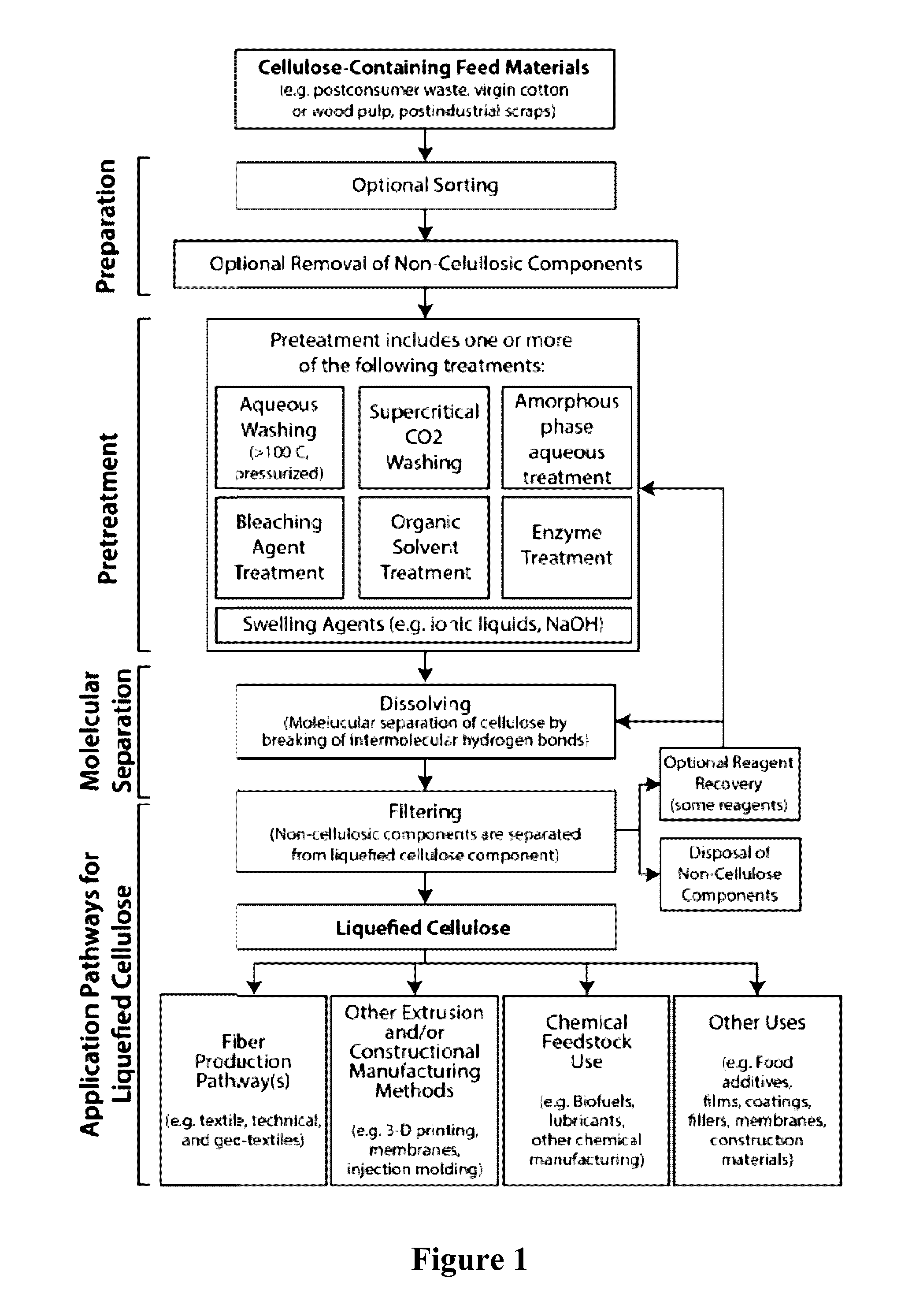
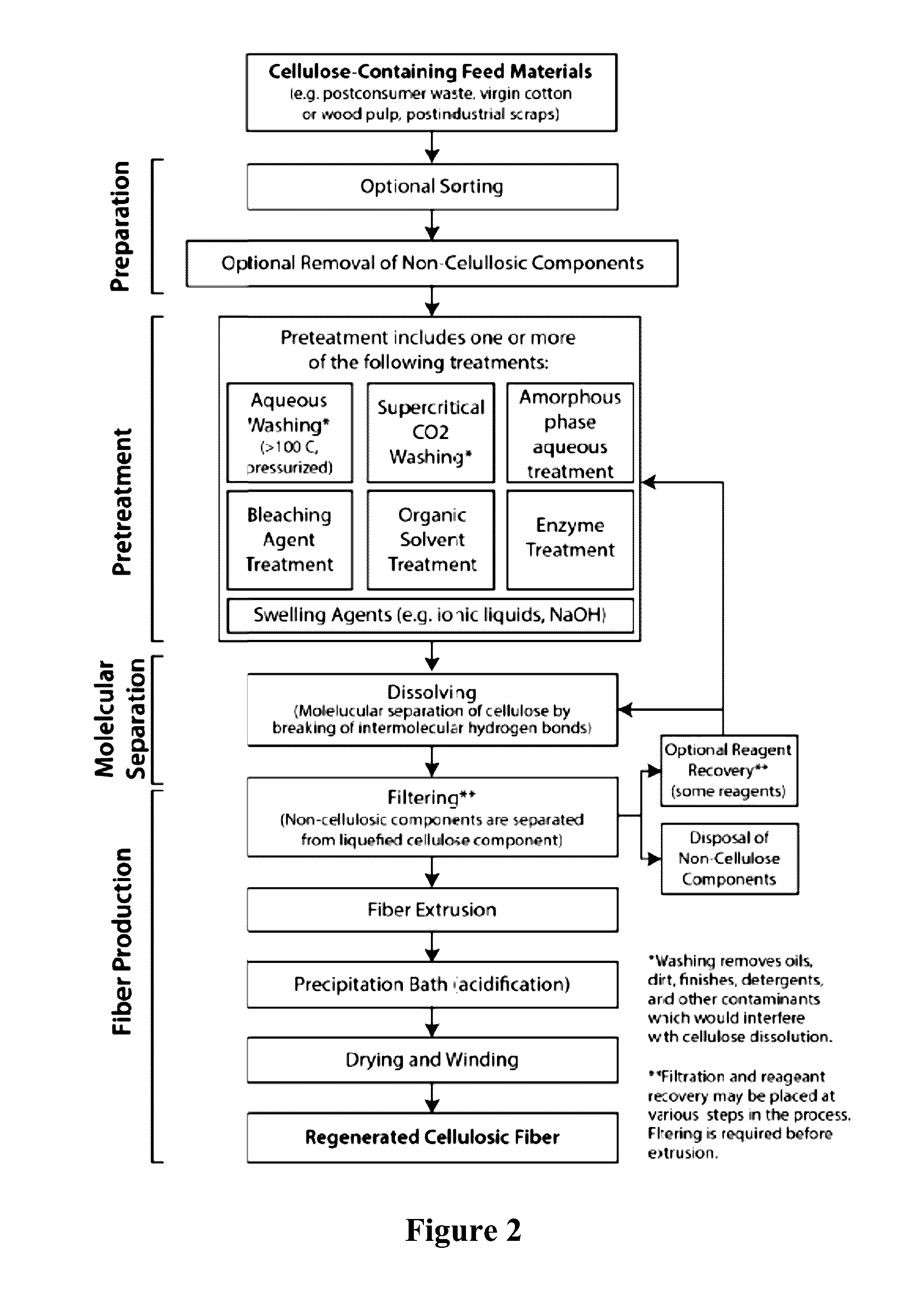
Methods and systems for processing cellulose-containing materials and isolating cellulose molecules; methods for regenerating cellulosic fibers
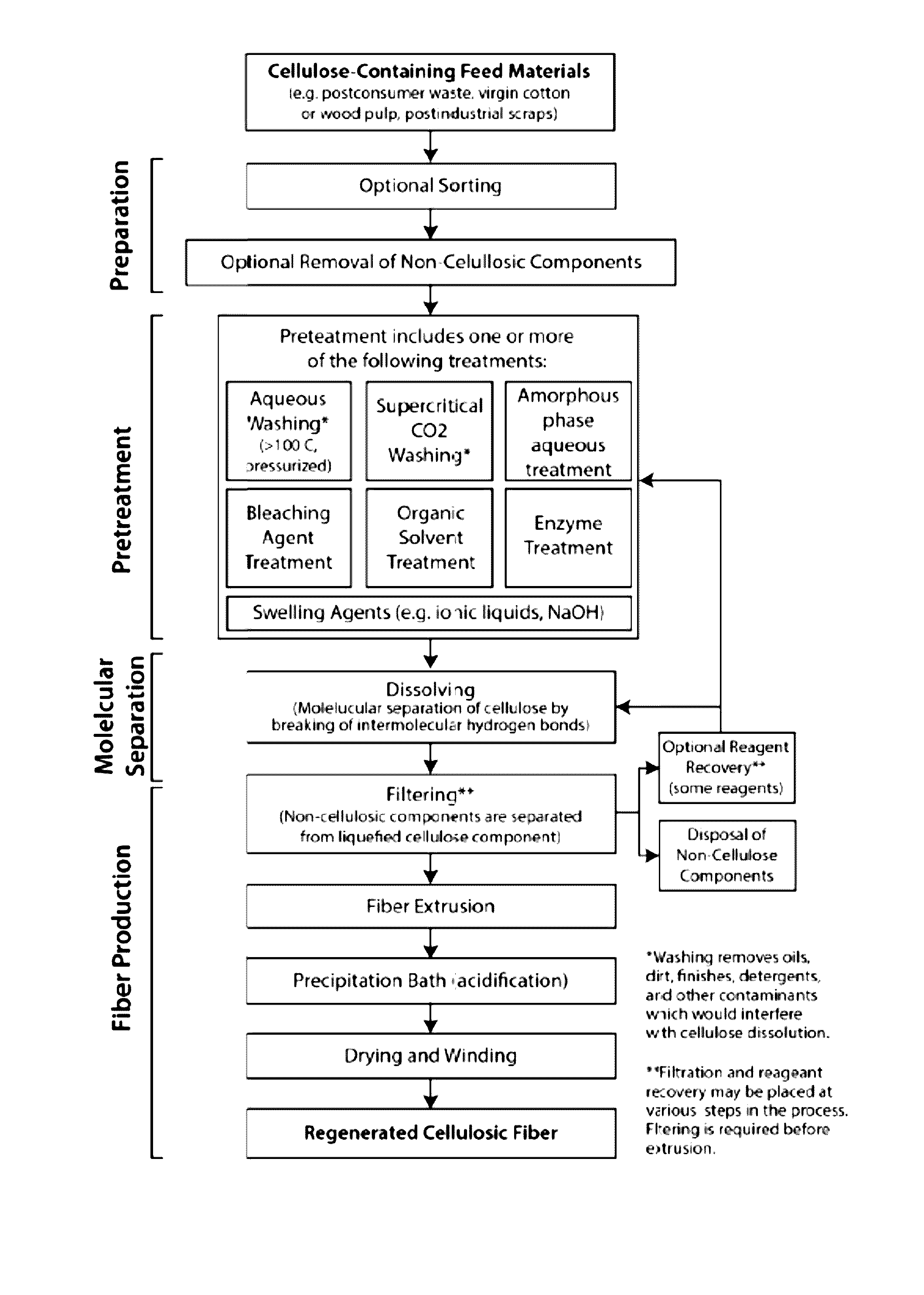
InactiveUS20160369456A1Reduce environmental impactPretreatment with water/steamPulp properties modificationPost-consumer wastePre treatment
Methods and systems of the present invention use cellulose-containing materials, which may include post-consumer waste garments, scrap fabric and / or various biomass materials as a raw feed material to produce isolated cellulose molecules having desirable properties that can be used in the textile and apparel industries, and in other industries. A multi-stage process is provided, in which cellulose-containing feed material is subjected to one or more pretreatment stages, followed by a pulping treatment, to isolate cellulose molecules. The isolated cellulose molecules may be used in a variety of downstream applications. In one application, isolated cellulose molecules are extruded to provide regenerated cellulose fibers having desirable (and selectable) properties that are usable in various industrial applications, including textile production.
Owner:EVRNU SPC
Enzymatic pre-treatment of market pulp to improve fiber drainage and physical properties
ActiveUS20130146239A1Increasing pulp drainageImprove strength propertiesMicroorganism/enzyme additionPaper recyclingFiberPulp and paper industry
Methods for reducing the effects of wetlapping, drying, and hornification of pulp fibers and consequently increasing the pulp drainage and strength properties in the final product (i.e., paper) are provided. The method which has been developed creates a “value-added” product by the wastepaper supplier or at the pulp and / or deinking (recycled paper) mill—a wastepaper load / bale, wet pulp stock or wet lap, or dried pulp treated with or impregnated with enzymes that enhance the quality of the pulp or paper product when it is repulped and processed at the paper mill.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Novel laccase enzyme and use thereof
ActiveUS20060063246A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce usageCosmetic preparationsBacteriaNucleic acid sequencingGenus
The present invention relates to a novel laccase enzyme obtainable from the strains of genus Thielavia. The invention relates also to the nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme, a recombinant host into which the nucleic acid sequence has been introduced and a method for the production of the enzyme in a recombinant host. The enzyme of the invention is suitable for several applications, in particular for increasing the lightness of denim.
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
Pitch and stickies control in pulp and papermaking processes
ActiveCN101548045AFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMicroorganism/enzyme additionProcess equipmentPapermaking
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Treatment of Pulp Stocks Using Oxidative Enzymes to Reduce Pitch Deposition
InactiveUS20070261806A1Lower energy requirementsImprove paper strengthPulp liquors combustionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpTime rangeResin acid
Methods of treating pulp stocks with an enzyme formulation containing one or more oxidative enzymes, to reduce pitch deposition, control pitch related problems, modify the physical and / or chemical properties of tri, di-, and mono-glycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, esters of fatty acids and resin acids, and metal soaps of fatty acids and resin acids, or change the concentration of triglycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, and esters of fatty acids and resin acids, have been developed. The pulp stock is treated with an enzyme formulation containing laccases, peroxidases, esterases, and / or combinations thereof. The enzyme formulations may also contain a laccase mediator and / or a dispersant. The enzyme formulation can be applied at any of several locations during the pulping and / or papermaking process. The enzyme formulation is typically applied as a solution to the pulp stock. The enzyme treatment is effective at a temperature of between about 30° C. to about 95° C., more preferably from about 50° C. to about 80° C. The pH of the pulp stock is from about 4.0 to about 7.0, more preferably from about 4.5 to 5.5. The stock can be treated for a period of time ranging from about 5 minutes to about 10 hours.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Process for increasing the charge on a lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS6187136B1Avoid reactionIncrease surface charge densityFungiPaper/cardboardCatalytic oxidationCellulose fiber
A process for production of a lignocellulosic material modified by conjugation thereto of a phenolic substance comprising a substituent which, in the conjugated form of the phenolic substance, is, or may become, negatively or positively charged, respectively, comprises: reacting a lignocellulosic fibre material and the phenolic substance with an oxidizing agent in the presence of an enzyme capable of catalyzing the oxidation of phenolic groups by the oxidizing agent; and reacting together the products of the reactions; with the proviso that the phenolic substance is not a phenolic polysaccharide. A strengthened lignocellulose-based product (e.g. a paper product) may be prepared by a procedure wherein a product produced in accordance with the latter process is treated with a strengthening agent having an ionic charge of sign opposite to that which is conferred on the modified lignocellulosic material by the charge-conferring substituent.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Energy-saving enhanced defibrination method for composite pretreatment and production of viscous paper pulp
ActiveCN104452398AImprove the physical properties of paperSave paper physical propertiesMicroorganism/enzyme additionPaper/cardboardPre treatmentPulp fibre
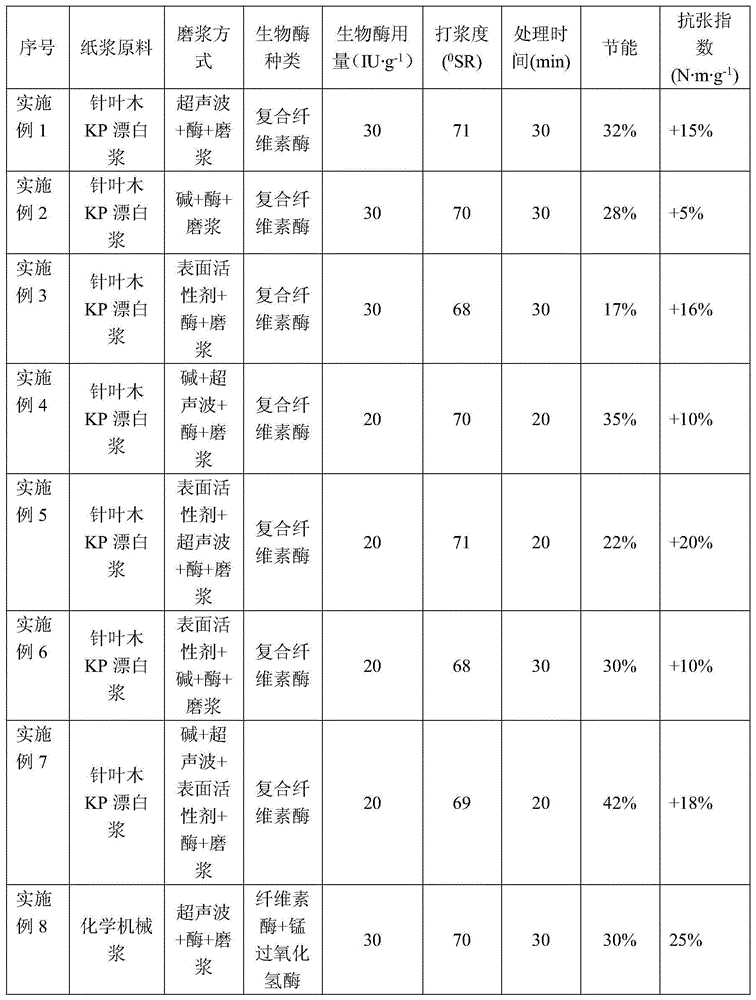
The invention discloses an energy-saving enhanced defibrination method for composite pretreatment and production of viscous paper pulp. The method comprises the following steps that (1) paper pulp fibers are dissolved in water, even defibering is carried out, and then pretreatment is carried out; (2) biological enzymes are added to the treated paper pulp for treatment, the dosage of the biological enzymes ranges from 10 IU / g to 60 IU / g, the temperature ranges from 40 degrees to 60 degrees, the pH value ranges from 6 to 9, the concentration of the paper pulp ranges from 3 wt% to 8 wt%, and treatment is carried out for 10 min to 30 min; (3) continuous millstone milling and beating are carried out on the pulp of the step (2), and the pulp is stored for standby application. The method remarkably improves the efficiency of subsequent biological enzyme treatment, and overcomes the defects that enzyme treatment time is too long in biological enzyme assistant defibrination production and energy conservation in defibrination and the physical strength of finished paper formed by fibers cannot be achieved at the same time, the defibrination energy consumption and the defibrination time for producing the viscous paper pulp are saved, the defibrination energy consumption of chemical bleached needle wood pulp and chemithermomechanical pulp of needle wood is reduced by 15%-45%, and the physical properties of finished paper formed by pulp fibers can be improved.
Owner:五洲特种纸业(龙游)有限公司
Method for production of micro fibrillated cellulose
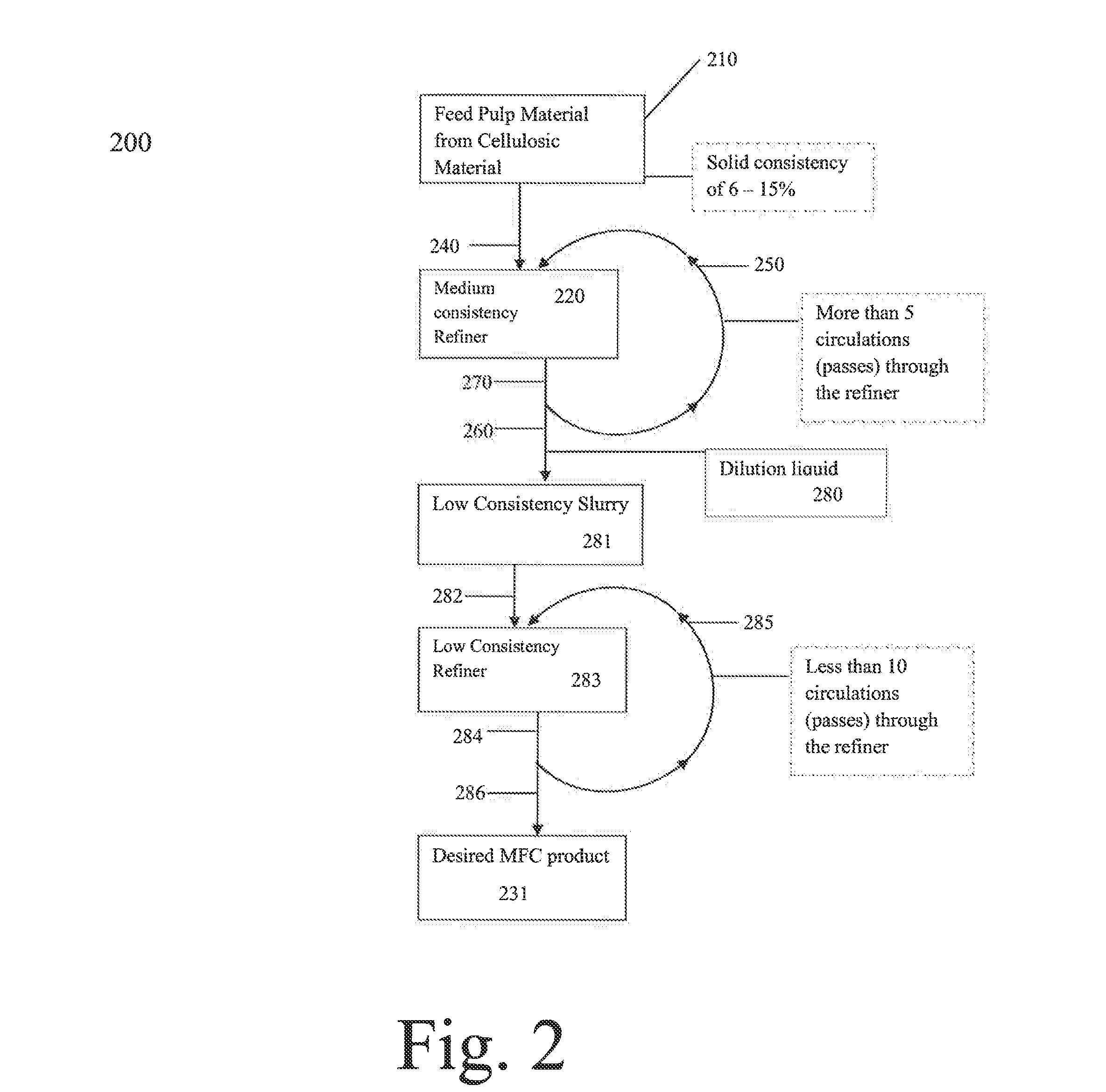
ActiveUS20140124150A1Reduce energy consumptionIncrease temperaturePulp properties modificationMicroorganism/enzyme additionCelluloseEngineering
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Method for producing lignin degradation product
ActiveUS20150041083A1Microorganism/enzyme additionNon-macromolecular organic additionSolventSolubility
The present invention relates to [1] a process for producing a lignin degradation product, including the following steps (1) to (3), and [2] a lignin degradation product produced by the process as described in the above [1]: Step (1): subjecting a lignocellulose raw material to enzymatic saccharification treatment to obtain a saccharification residue; Step (2): subjecting the saccharification residue obtained in the step (1) to heat treatment in a mixed solvent containing water and an organic solvent having a solubility in 20° C. water of not less than 90 g / L to obtain a heat treatment solution containing the lignin degradation product; and Step (3): subjecting the heat treatment solution obtained in the step (2) to solid-liquid separation to remove insoluble components from the heat treatment solution, thereby obtaining the lignin degradation product. The present invention provides a process for producing a novel lignin degradation product having a low degree of denaturation, a high solubility in solvents and a high versatility with a high yield.
Owner:KAO CORP
Process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose and produced microfibrillated cellulose
InactiveUS20120136146A1Improve accessibilityHigh activityPulp properties modificationMicroorganism/enzyme additionFiberCellulose
A process for producing microfibrillated cellulose comprises providing a slurry comprising cellulosic fibers, treating the slurry with an enzyme, mechanically treating the slurry so that the fibers are disintegrated wherein the mechanical treatment and the treatment with the enzyme is performed simultaneously in a single treatment step. In this way it is possible to produce microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) in an improved and energy efficient way. A microfibrillated cellulose is produced according to the process.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
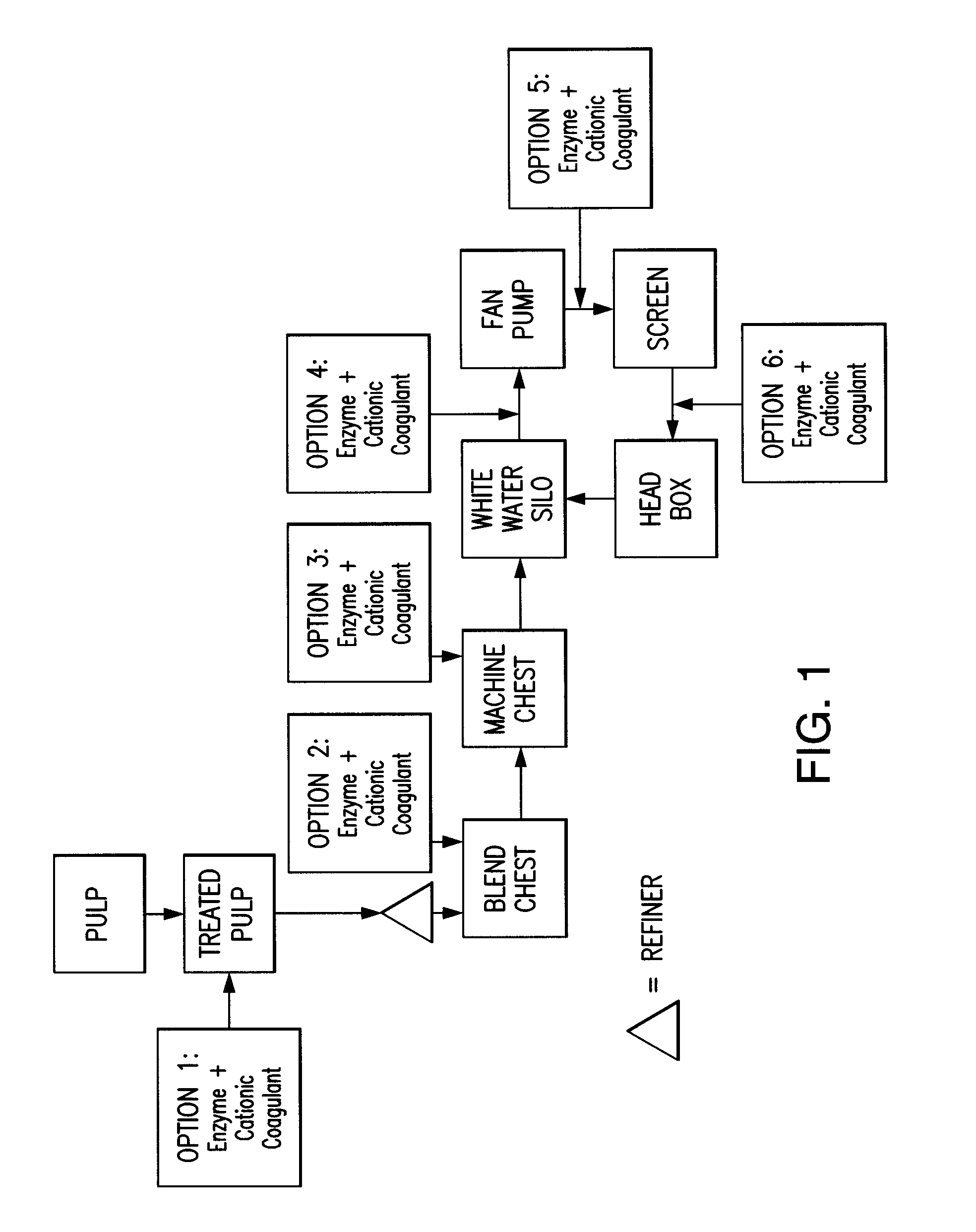
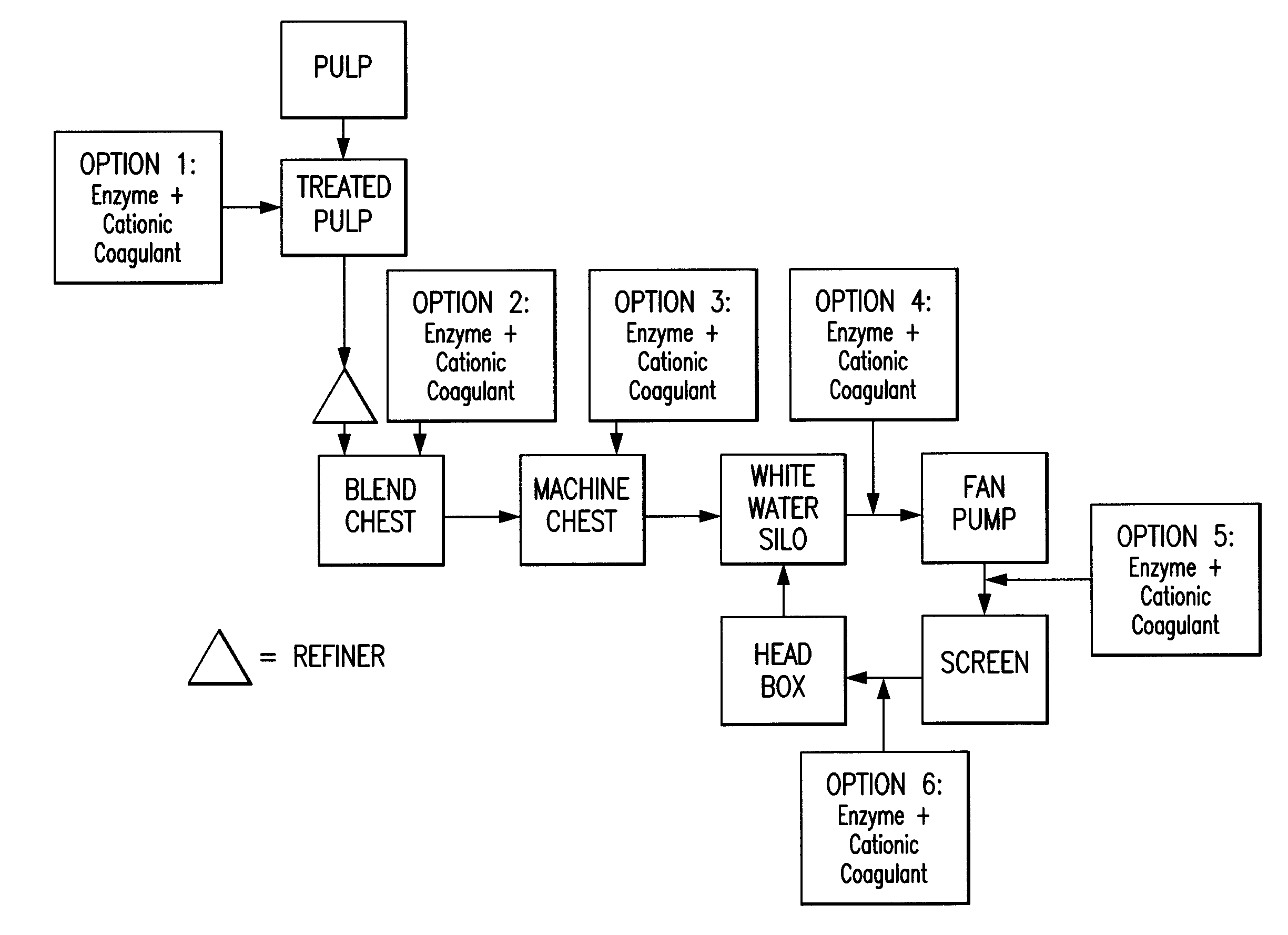
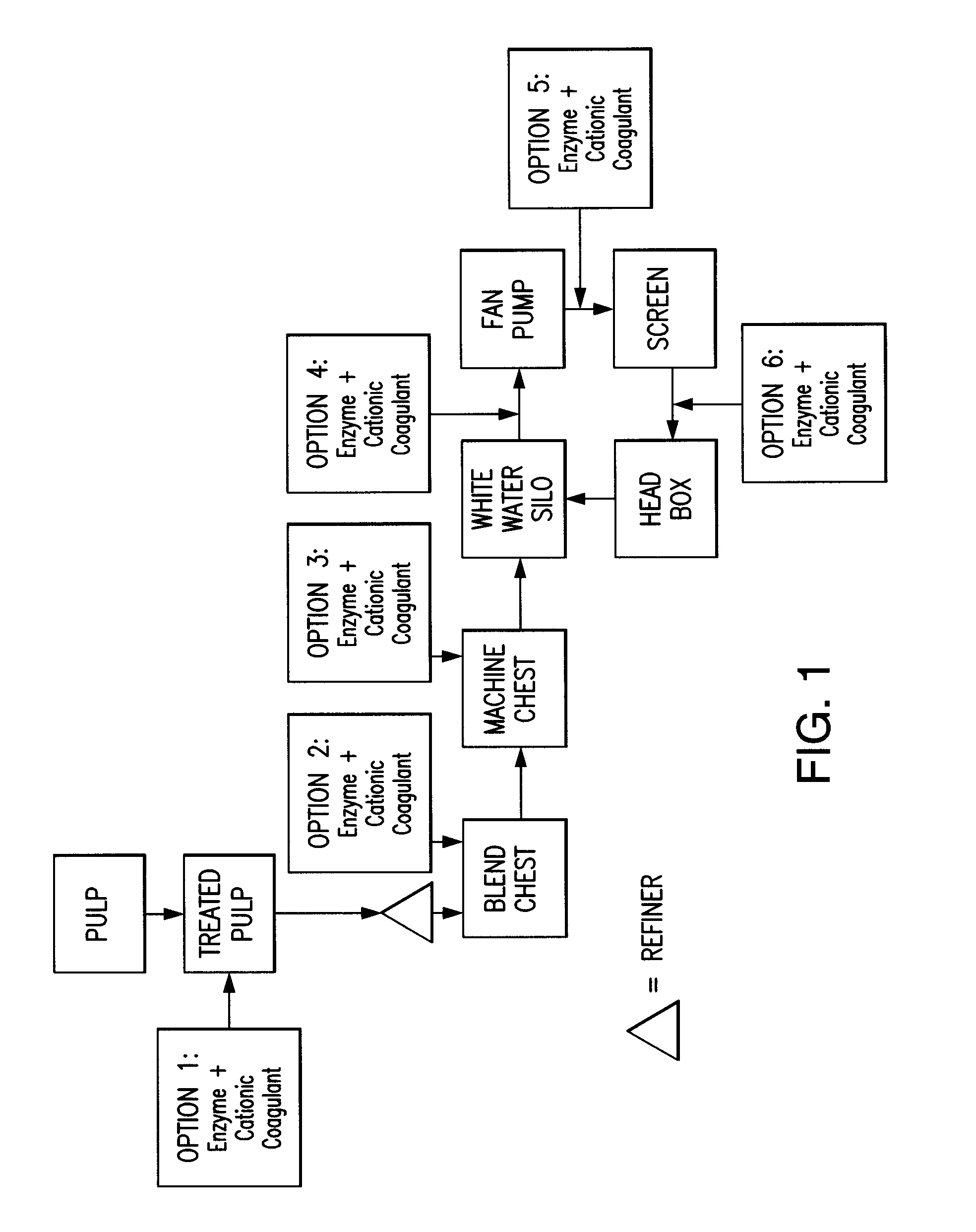
Paper making processes and system using enzyme and cationic coagulant combination
ActiveUS8454798B2Improved cellulosic pulp drainage and retentionHigh retention rateNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPaperboardPulp and paper industry
A method is described for making paper or paper board by applying a composition containing enzyme and cationic coagulant to papermaking pulp prior to paper forming to preferably improve drainage, retention, or both. Sheets of pulp from which paper or paperboard products are made with the method can exhibit excellent drainage, excellent retention of pulp fines, or both. The method also can be applied to other pulp treatments, such as waste water treatments. A system for making such treatments of paper furnish is also provided.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
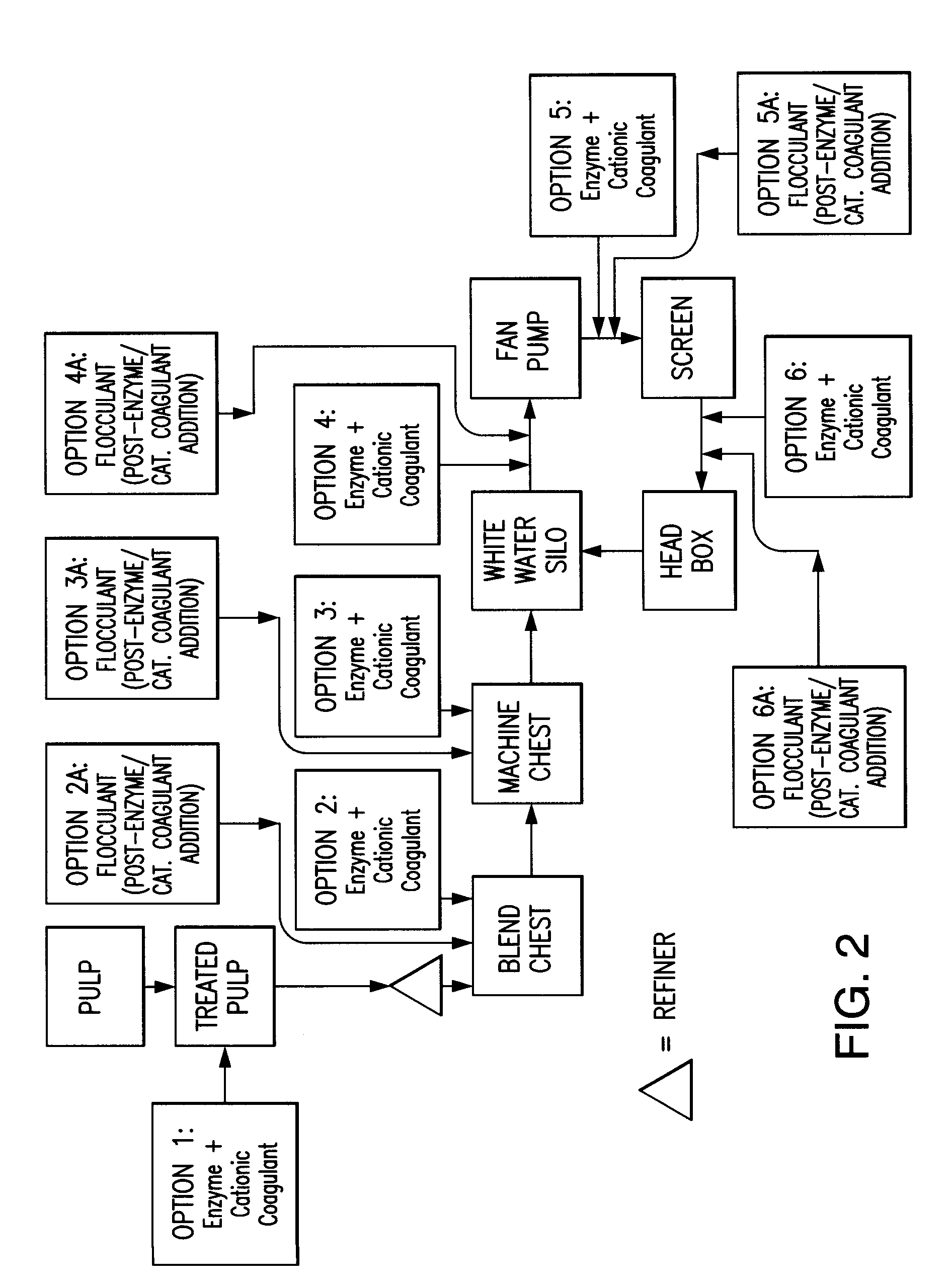
Paper Making Processes and System Using Enzyme and Cationic Coagulant Combination
ActiveUS20110253333A1Improved cellulosic pulp drainageImprove retentionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperWastewaterPaperboard
A method is described for making paper or paper board by applying a composition containing enzyme and cationic coagulant to papermaking pulp prior to paper forming to preferably improve drainage, retention, or both. Sheets of pulp from which paper or paperboard products are made with the method can exhibit excellent drainage, excellent retention of pulp fines, or both. The method also can be applied to other pulp treatments, such as waste water treatments. A system for making such treatments of paper furnish is also provided.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Pitch and stickies control in pulp and papermaking processes
InactiveUS20080169073A1Avoid depositionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentMicroorganism/enzyme additionProcess equipmentPapermaking
Methods for inhibiting the depositions of organic contaminants from pulp in pulp and papermaking systems are disclosed. A combination of an enzyme and a nonionic polymeric detackifier are added to the pulp or applied to deposition-prone process equipment surfaces of a pulp and papermaking system.
Owner:HERCULES INC
Nano cellulose composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109971014AImprove hydrophobicityGood thermal expansion resistancePulp properties modificationMicroorganism/enzyme additionVegetable oilAcrylic resin
The invention provides a nano cellulose composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method uses nanocellulose as a raw material, nanocellulose is oxidized by using a TEMPO / NaClO / NaBr oxidation system, amidation modification of oxidized nanocellulose is carried out with hexadecylamine as a monomer, after natural vegetable oil is added, a film is prepared bya tape casting method, and under a negative pressure condition, the film is compounded with polyurethane acrylic resin through impregnation, so that the nano cellulose composite material is obtained and has the biodegradability and recyclability of cellulose, and at the same time is endowed with good hydrophobicity, resistance to thermal expansion, flexibility and light transmission, is an ideal flexible screen matrix material, and has broad application prospects in the field of flexible screen matrix materials.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method of producing microfibrillated cellulose
ActiveUS20150337493A1High aspect ratio MFCImprove mechanical propertiesSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentFiberCellulose
The invention relates to methods of producing microfibrillated cellulose (MFC). According to the invention a fibrous pulp suspension is fibrillated mechanically at a consistency of less than 12.5%, dewatered to raise the consistency of the fibrillated suspension to at least 12.5%, and then subjected in the dewatered condition to further fibrillation. Alternatively an initially fibrillated fibrous pulp suspension may be dewatered and fibrillated in the dewatered condition, after which these dewatering and fibrillating steps are repeated one or more times so that pulp consistency is increased for each fibrillation step. The goals of raising the consistency between subsequent fibrillations are energy saving and an increased aspect ratio in MFC. The invention even comprises uses of the MFC product, e.g. as an additive for papermaking furnish or injection molded plastic composites.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Production method of oil-proof food wrap paper
The invention discloses a production method of oil-proof food wrap paper. The production method includes the steps of subjecting polylactic acid fibers to modified treatment; preparing modified polylactic acid fibers into an aqueous solution, heating and regulating a pH value; adding sodium alginate and microcrystalline cellulose for ultrasonic treatment prior to stirring so as to obtain a polylactic acid fiber solution; adding xylanase into pulp and beating so as to obtain mixed pulp; conducting papermaking, namely diluting the polylactic acid fiber solution obtained from modified treatment of the polylactic acid fibers, adding the diluted polylactic acid fiber solution into the diluted mixed pulp with mixing evenly, adding chitosan, microfibrillated cellulose and silica sol and conducting dewatering pressing so as to obtain a wet paper web; preparing a carboxymethyl chitosan solution and a cationic guar gum solution, mixing the two solutions, and subjecting the wet paper web to surface sizing in the papermaking step so as to obtain the oil-proof food wrap paper. The oil-proof food wrap paper produced from a natural polymer assistant is simple in production method, safe and nonhazardous, and has excellent oil-proof performance and high surface strength.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High quality and long natural cellulose fibers from rice straw and method of producing rice straw fibers
InactiveUS20060180285A1Increase valueBenefitMicroorganism/enzyme additionBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsCellulose fiberXylanase
A method and kit for rice fiber extraction is provided. In an exemplary embodiment, the method may include treating rice straw with an alkali solution such as a sodium hydroxide solution. Further, the method may include extracting coarse rice fibers from the rice straw and treating the extracted coarse rice fibers with an enzyme solution. For instance, the enzyme solution may include cellulase and a xylanase preparation. Implementation of the method results in high quality natural cellulose rice fibers which may be suitable for all textile applications that use natural cellulose fibers (e.g., cotton and linen). In addition, extracted rice fibers that are at least ten (10) millimeters in length, no more than 0.5 millimeters in width and include a generally smooth surface are disclosed. For example, textile or composite products may be produced with such rice fibers.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
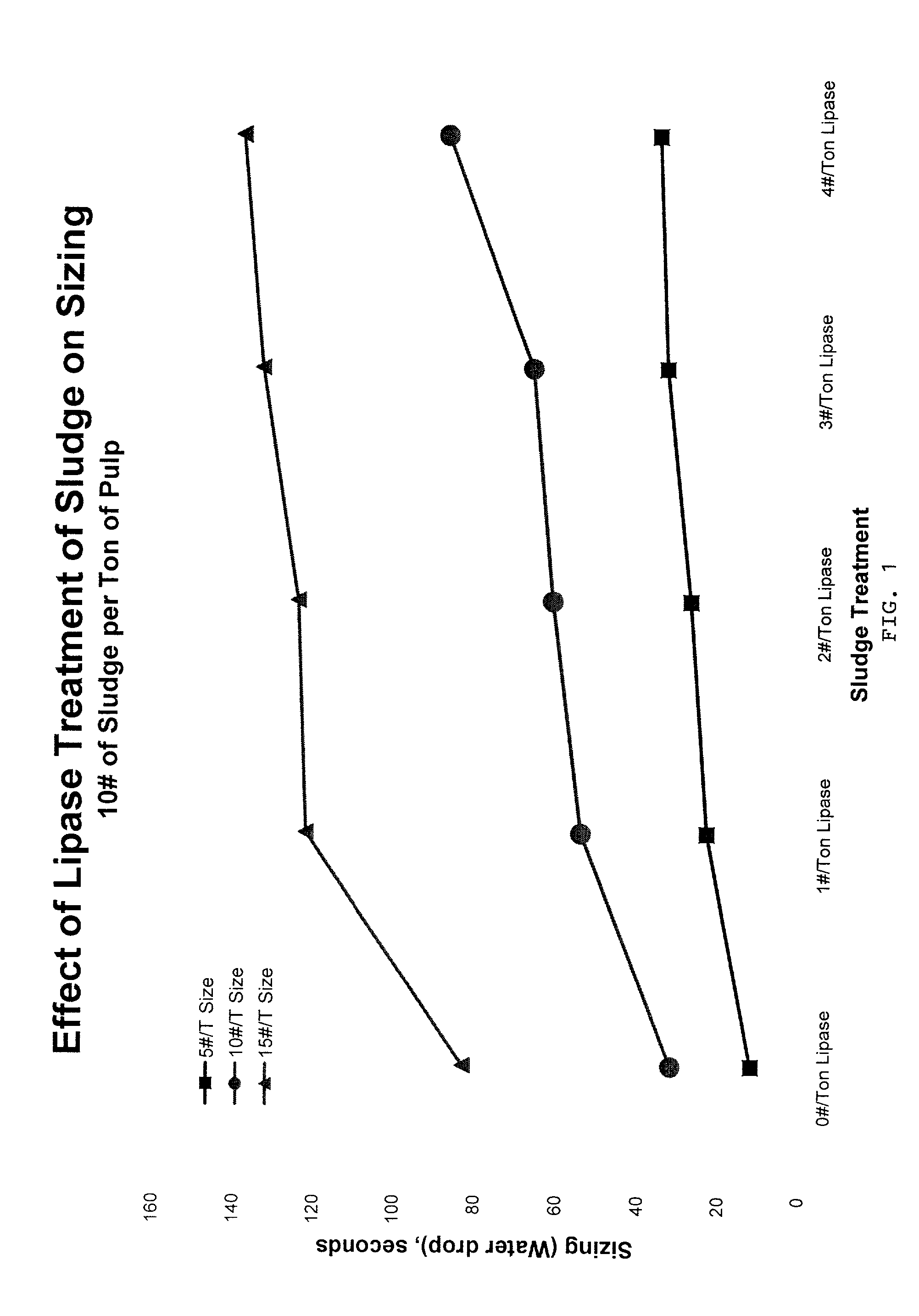
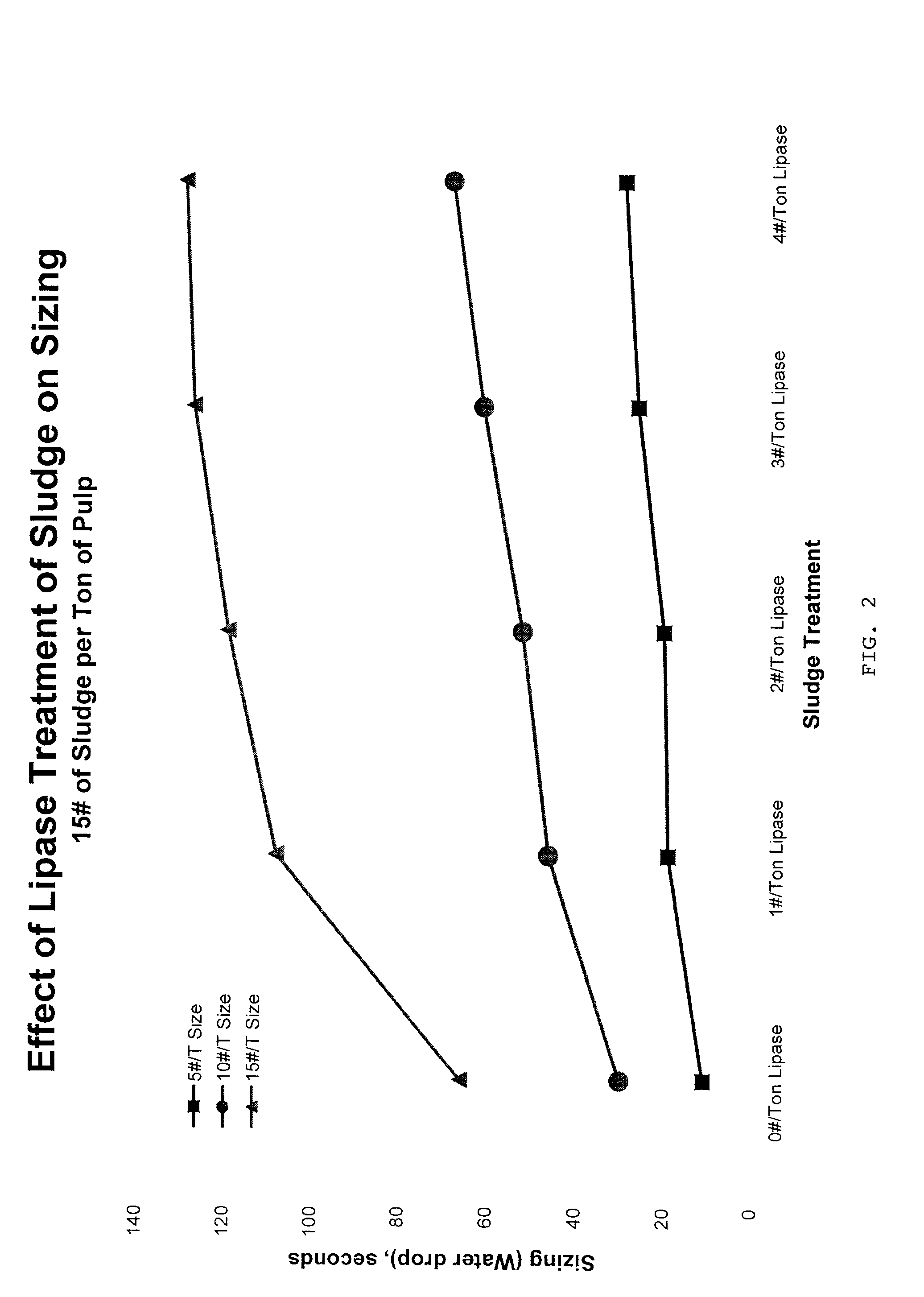
Papermaking process using enzyme-treated sludge, and products
InactiveUS7125471B2Increase in sizeRetention resistanceSpecial paperWater-repelling agents additionSludgePapermaking
Enzyme-treated papermaking sludges are provided, as are methods of making the enzyme-treated sludge. Papermaking processes that incorporate the enzyme-treated papermaking sludges into papermaking pulp are also provided as are paper and paperboard products made from the resultant pulp.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Cellulase composition containing cellulase and papermaking polymers for paper dry strength application
Disclosed herein are cellulase compositions useful as papermaking performance additives for improving paper dry strength of a paper product and reducing refining energy in papermaking processes, and improving paper production. These cellulase compositions are formulated using cellulase, papermaking contaminant control polymers, protein stabilizers and cellulase enhancers. These cellulase compositions measure higher in endo-cellulase activity with better stability than conventional cellulase, and have shown differentiating performance in improving paper dry strength properties versus cellulase alone.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Mediator-Enzyme System for Controlling Pitch Deposits in Pulp and Paper Production
InactiveUS20080210393A1Reduce decreaseQuality improvementFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMicroorganism/enzyme additionEnzyme systemFatty alcohol
The invention relates to the use of mediator-enzyme system, which is characterised in that the enzyme comprises a laccase-type enzyme and the mediator comprises a chemical compound which acts as a redox intermediate in the enzymatic oxidation, for the elimination of lipophilic compounds (including, among others, sterols that are free and conjugated in the form of esters and glycosides, triglycerides, fatty alcohols and resin acids) which cause deposits in the product, the machinery and the circuits during the production of pulp and paper (both from hardwood and softwood and non-woody plants). The treatment eliminates up to 100% of the aforementioned lipophilic compounds, depending on the material treated, and, in this way, improves the quality of the pulp obtained, the operation of the industrial installations and the characteristics of the end product.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
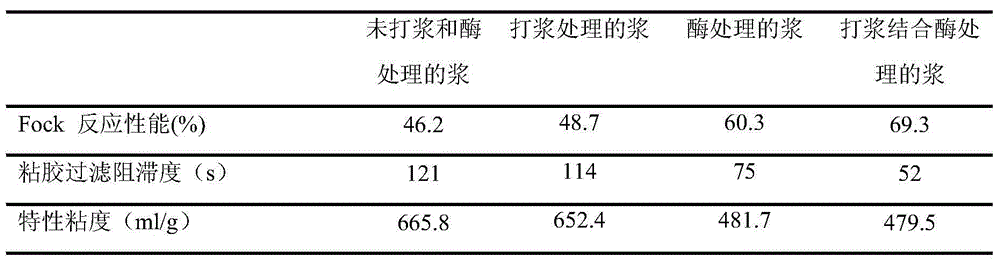
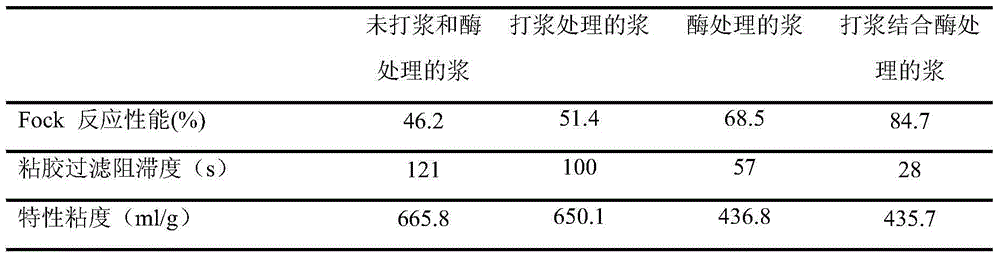
Method for improving reactive performance of prehydrolysis sulfate dissolving pulp
InactiveCN104452397AImprove responseGuaranteed viscosityMicroorganism/enzyme additionPulp beating methodsWater bathsSulfate
The invention discloses a method for improving the reactive performance of prehydrolysis sulfate dissolving pulp. The prehydrolysis sulfate dissolving pulp of needle leaf wood or broad leaf wood with the concentration of 30 percent is adopted, 18 L of water are firstly added to a pulp tank of a pulping machine, the pulp is added slowly, water is supplemented, so that the concentration of the pulp reaches 1.57 percent, pulping is carried out for 10-90 minutes, the pulp is concentrated to the concentration of 20 percent, then the pulp is taken and transferred into a polyethylene plastic bag with a sealing opening, distilled water and cellulase liquid are added to dilute the pulp to the concentration of four percent, enzyme / bone dry pulp is 3.0 u / g-4.0 u / g, the pH value is adjusted to be three to six, and the pulp is placed in a water bath kettle to be treated. Suction filtration is carried out on the treated pulp, water of 90 DEG C is added to the pulp until the concentration of the pulp is four percent, heating is carried out for 30 minutes, and the pulp is air-dried to the concentration of 95 percent under the condition of constant temperature and constant humidity. The method has the advantages that the reactive performance of the dissolving pulp is improved by combining mechanical treatment and enzyme treatment, and the reactive performance of the prehydrolysis sulfate dissolving pulp can be improved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Enzymatic opacifying composition for paper, pulp or paperboard, processes using same and pulp, paper or paperboard produced therefrom
InactiveUS20070029059A1High opacityHigh strengthMicroorganism/enzyme additionVegetable material additionPorosityPaperboard
An organic agent for enhancing opacity in paper, paperboard or pulp comprises a hydrolase or an oxido-reductase; this enzymatic opacifying agent overcomes drawbacks associated with traditional organic and inorganic opacifying agents but also serves to provide increased strength and reduced porosity in paper and paperboard.
Owner:TRI TEX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com