Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
430results about "Capacitor with voltage varied dielectric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
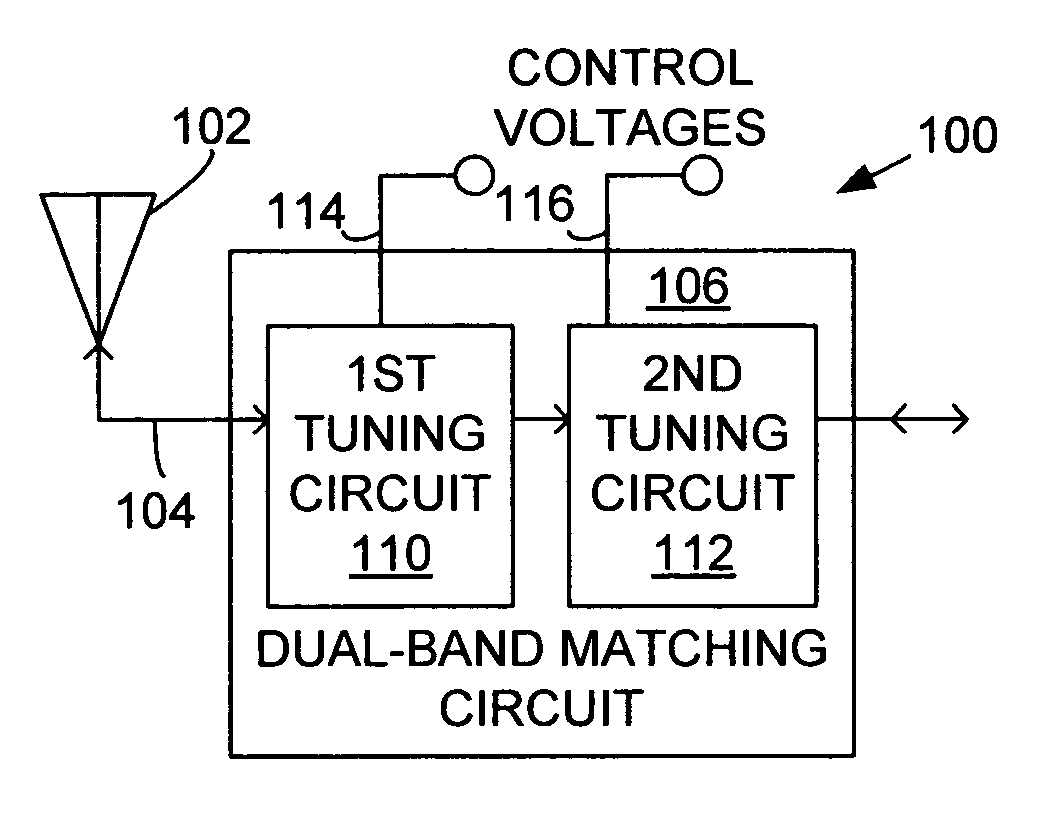
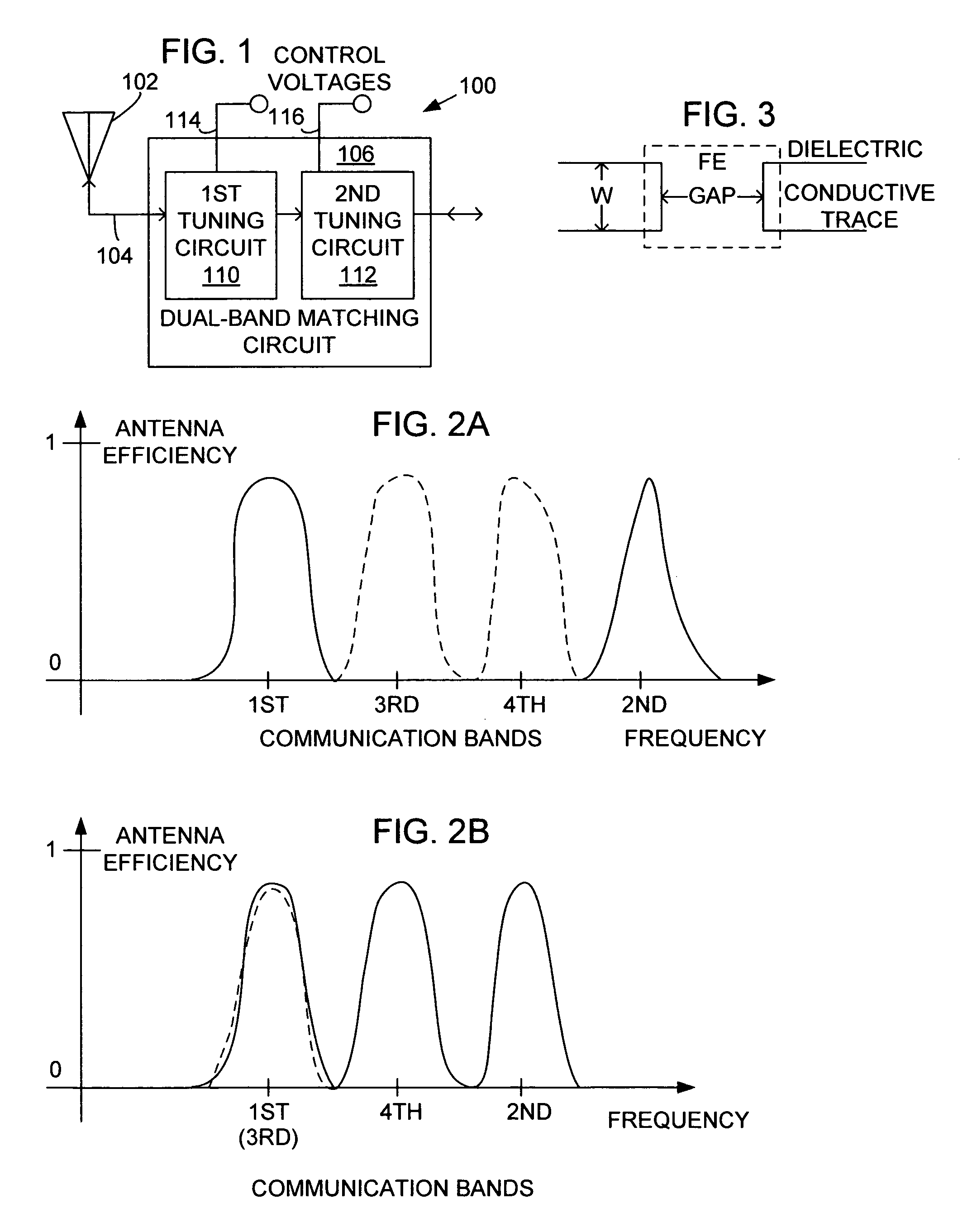
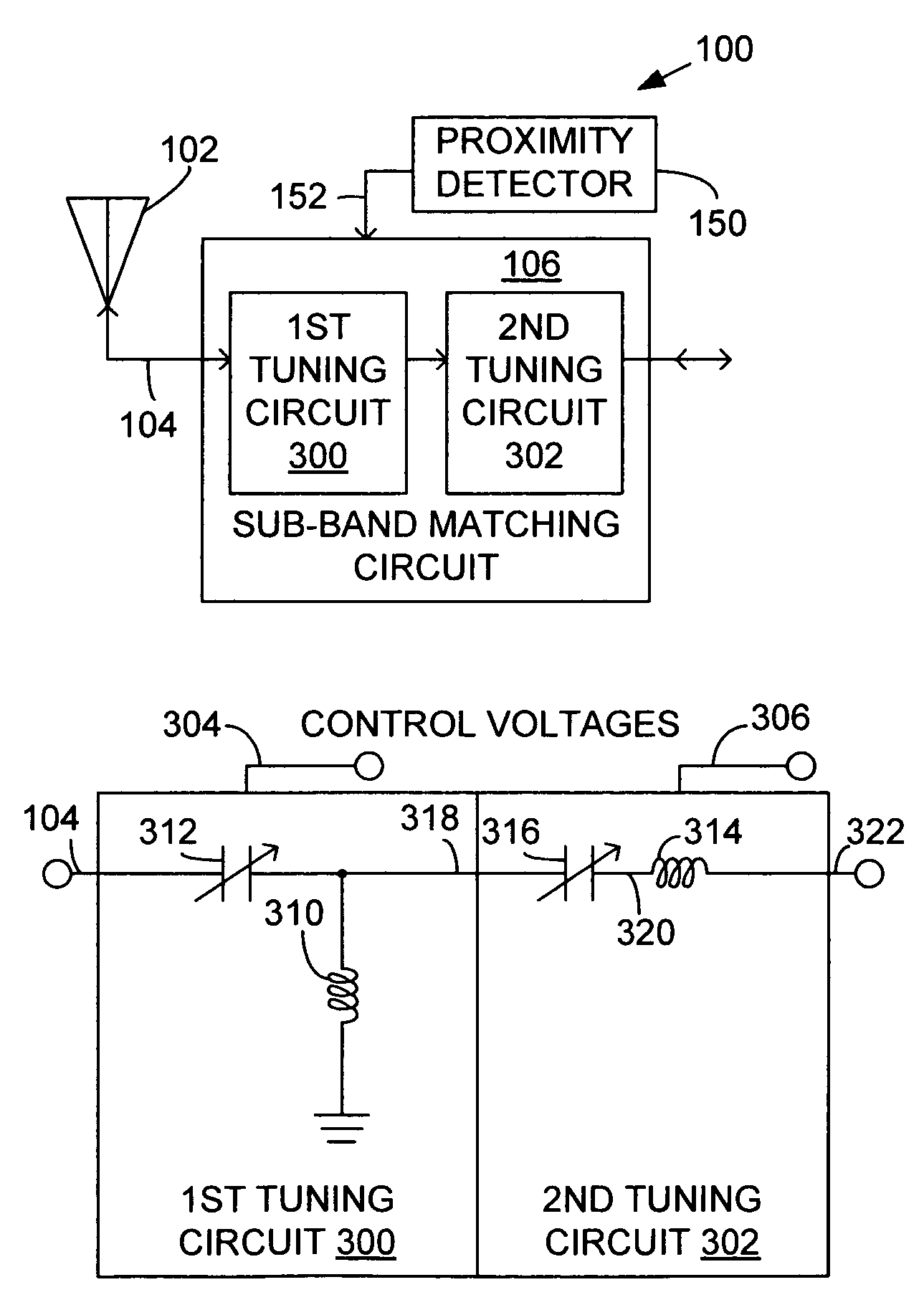
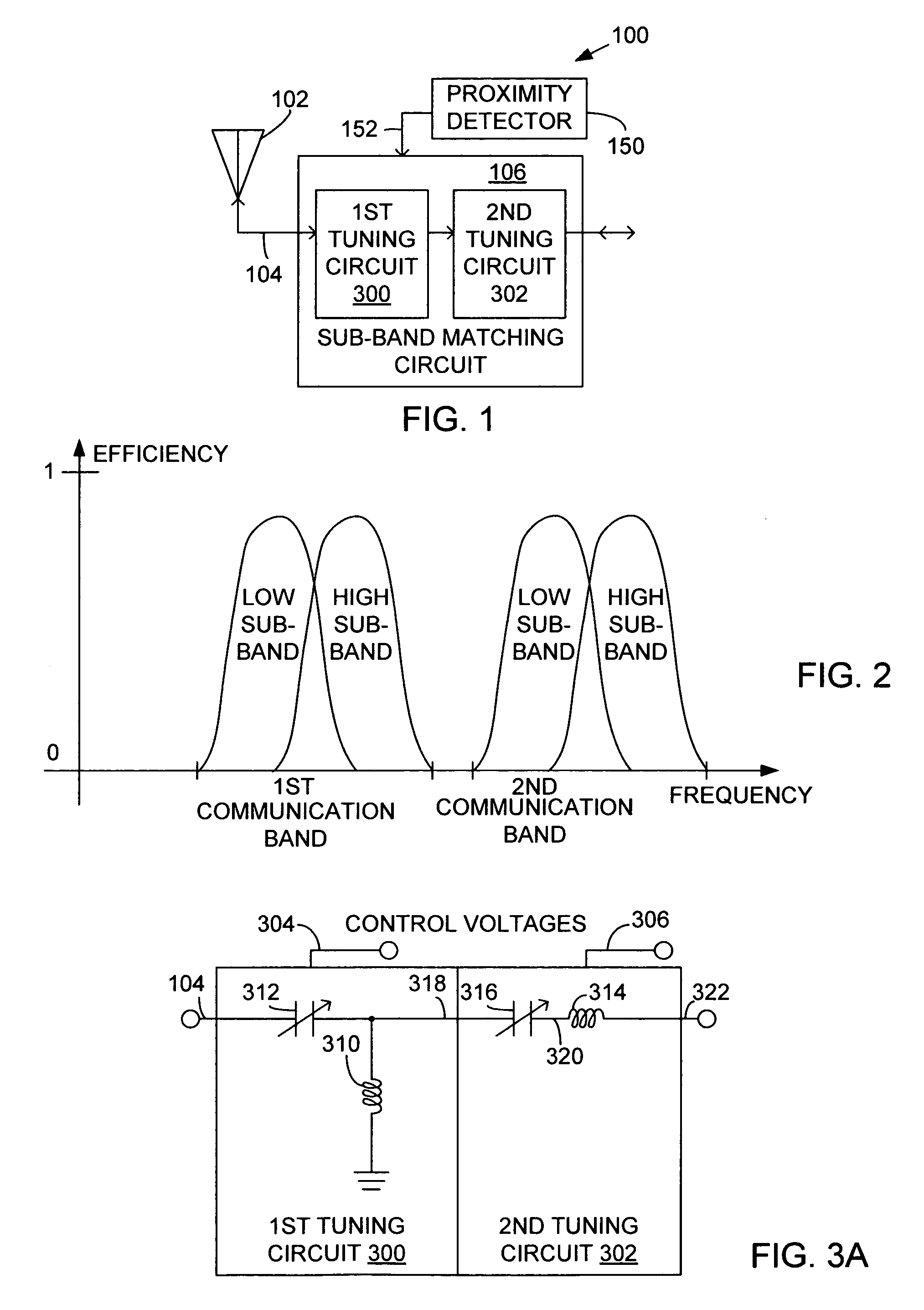
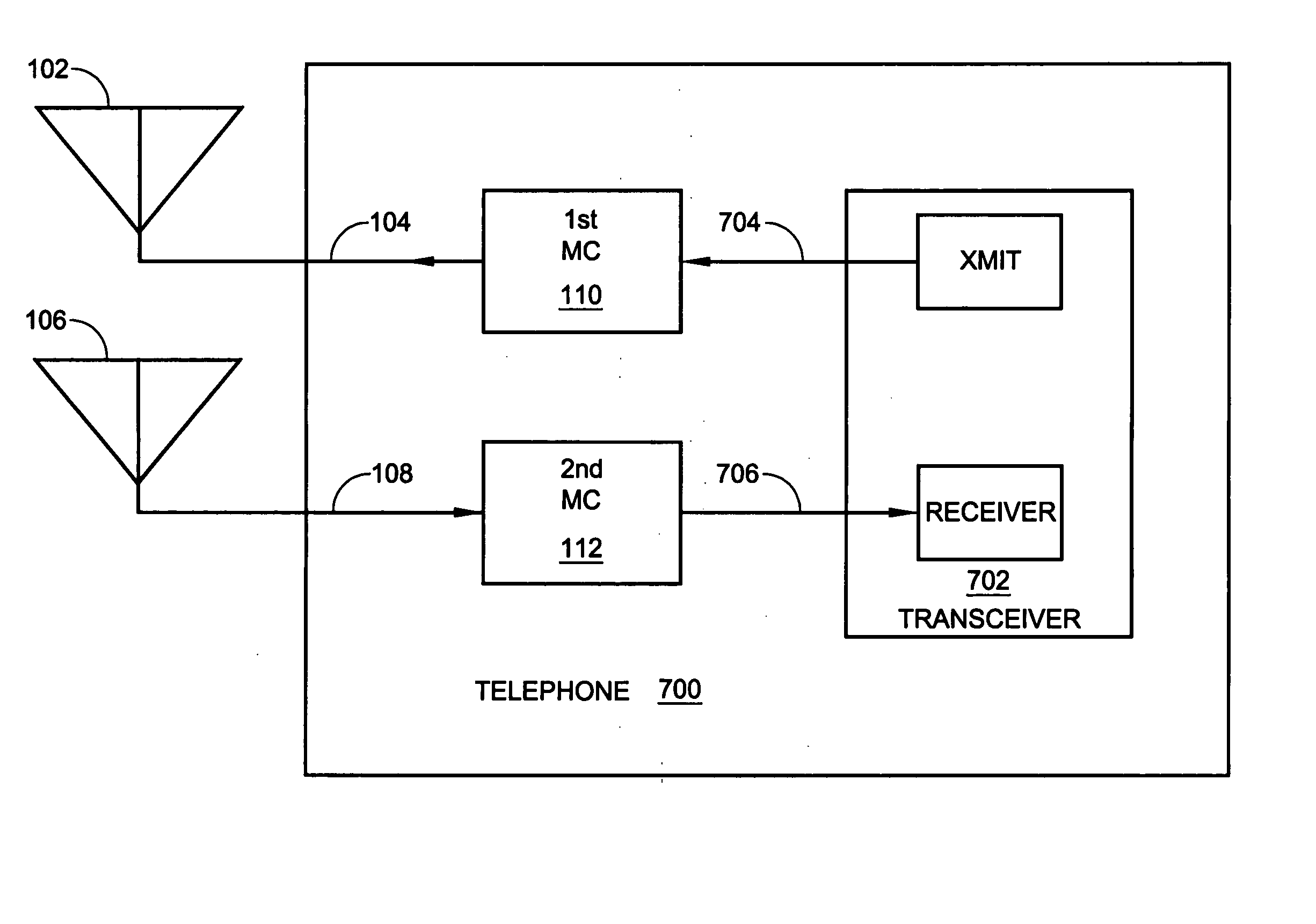
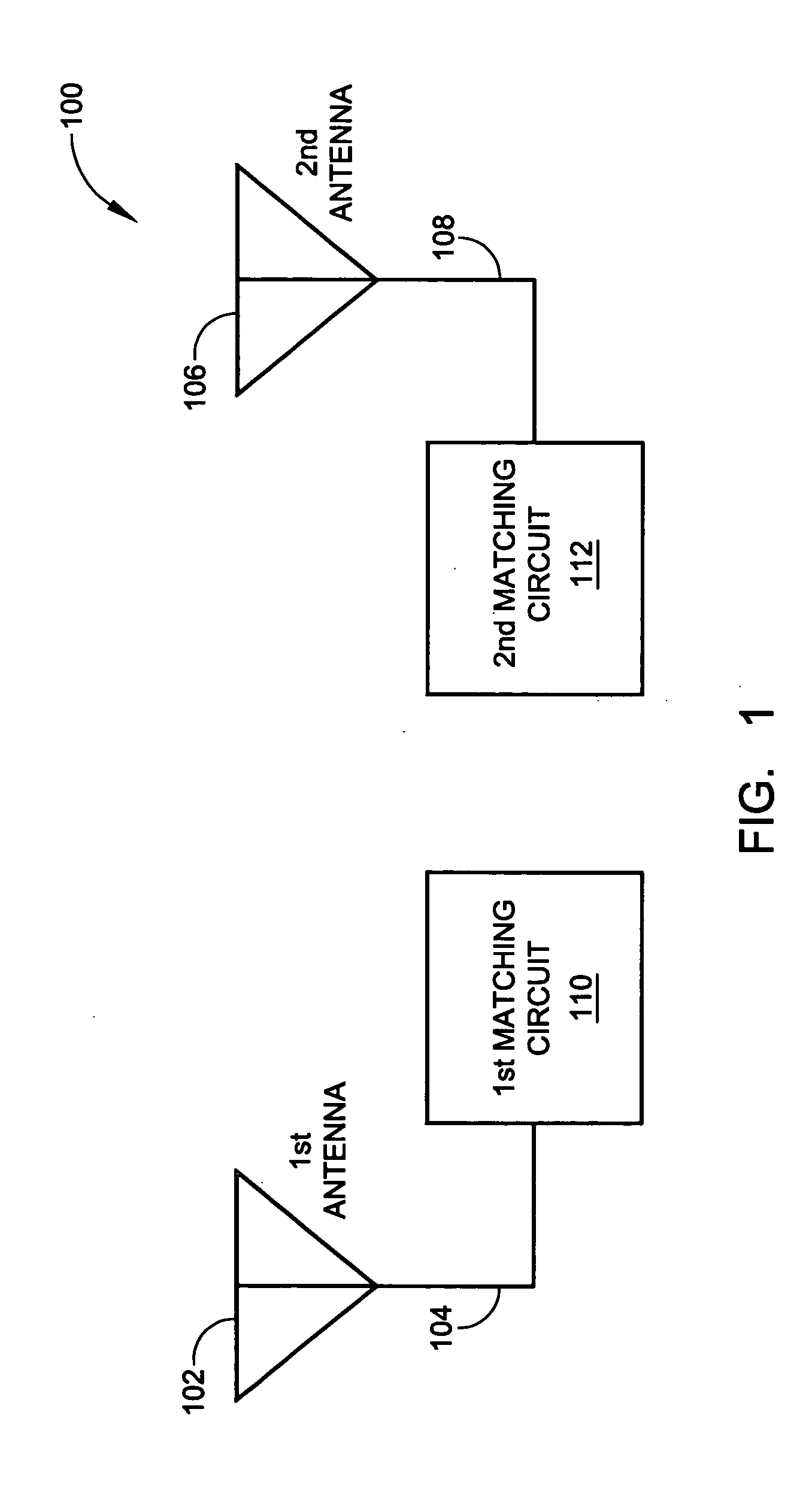
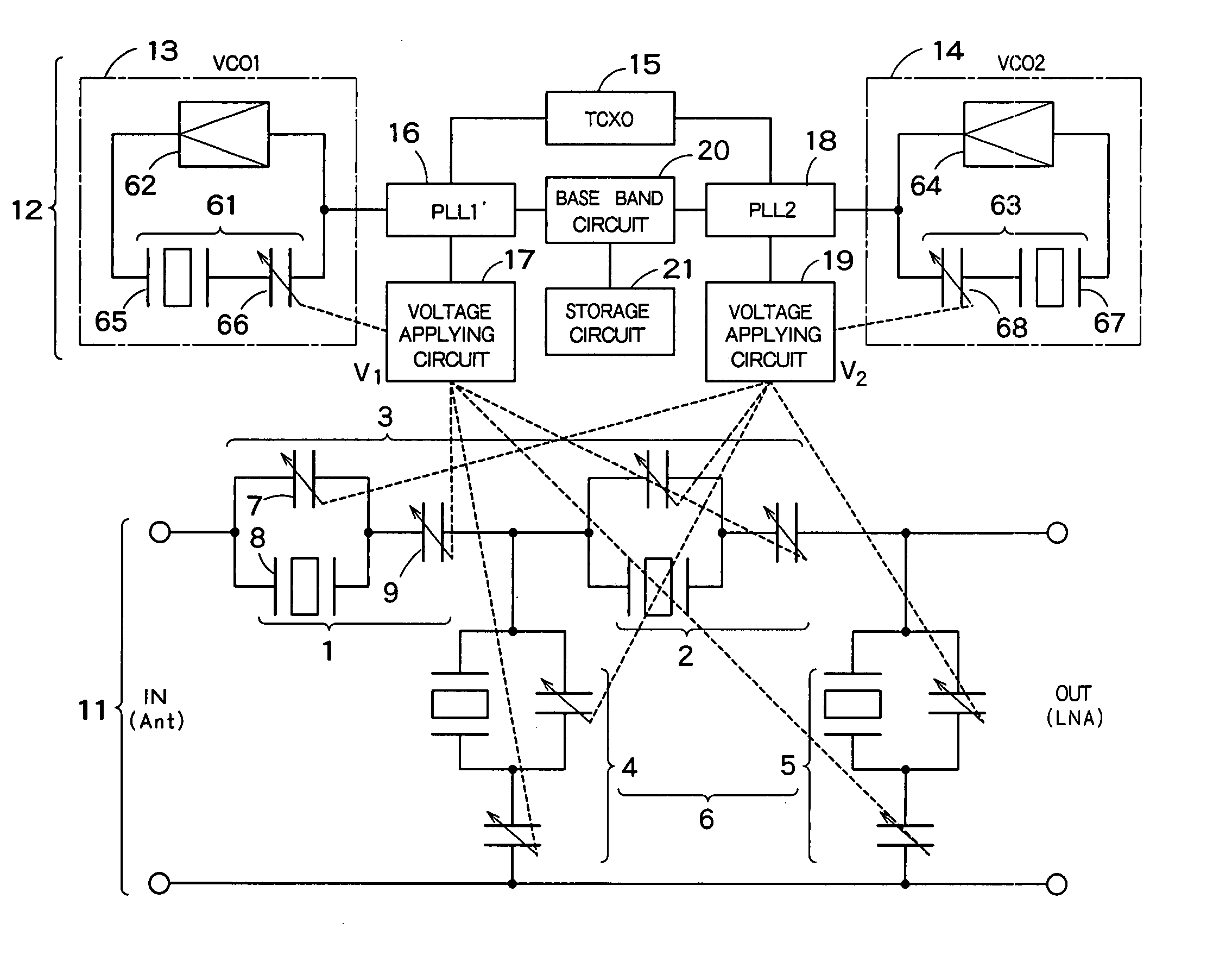
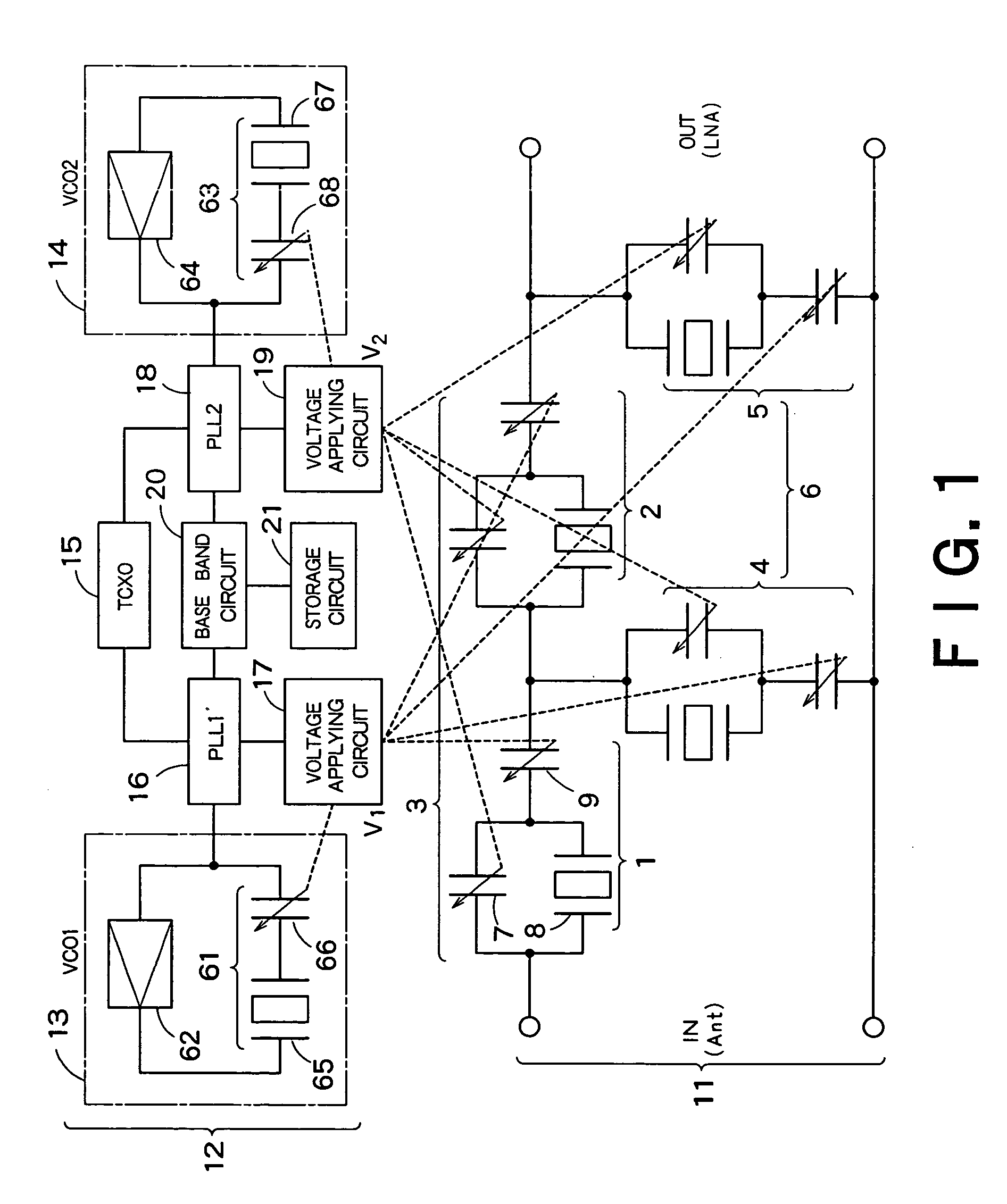
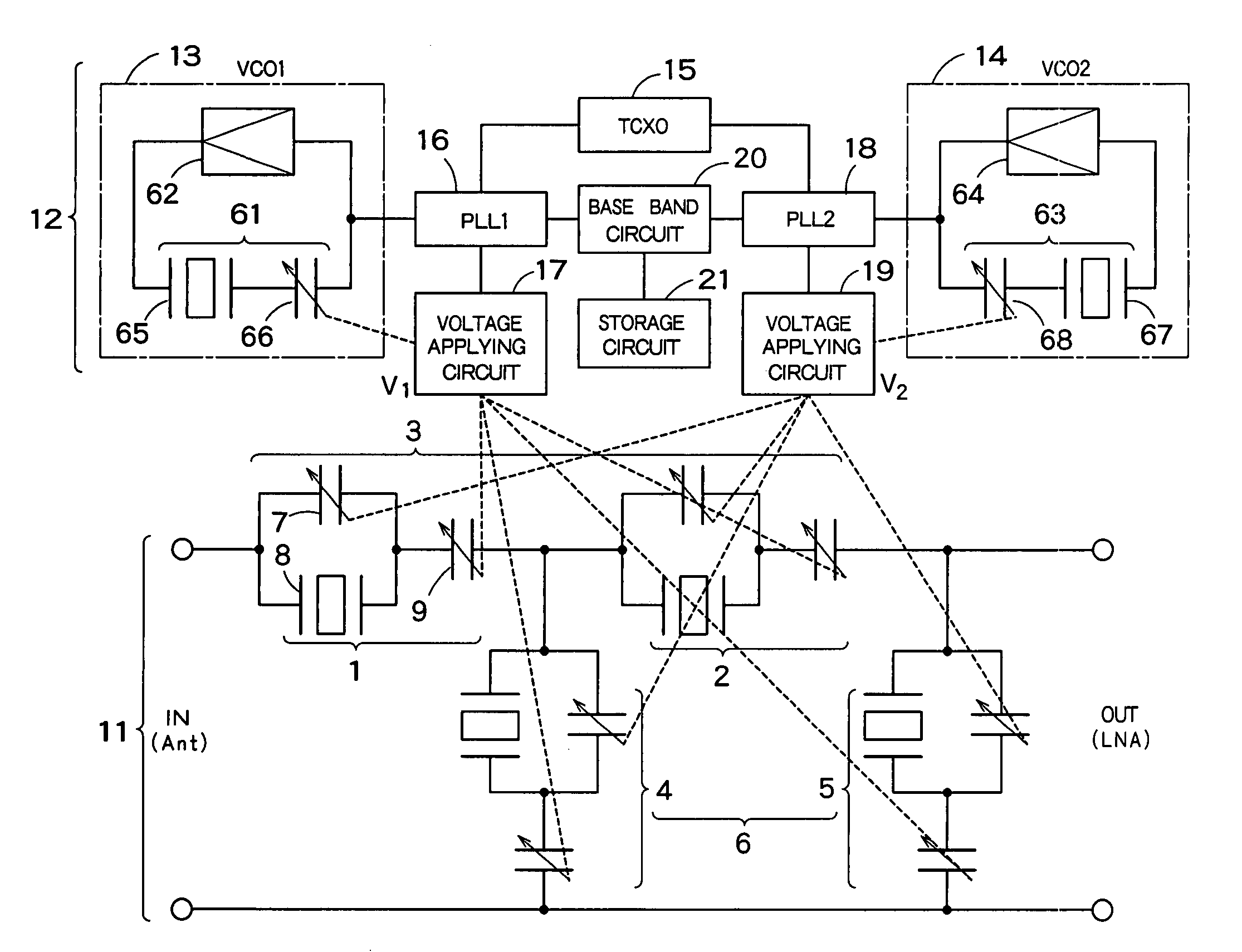
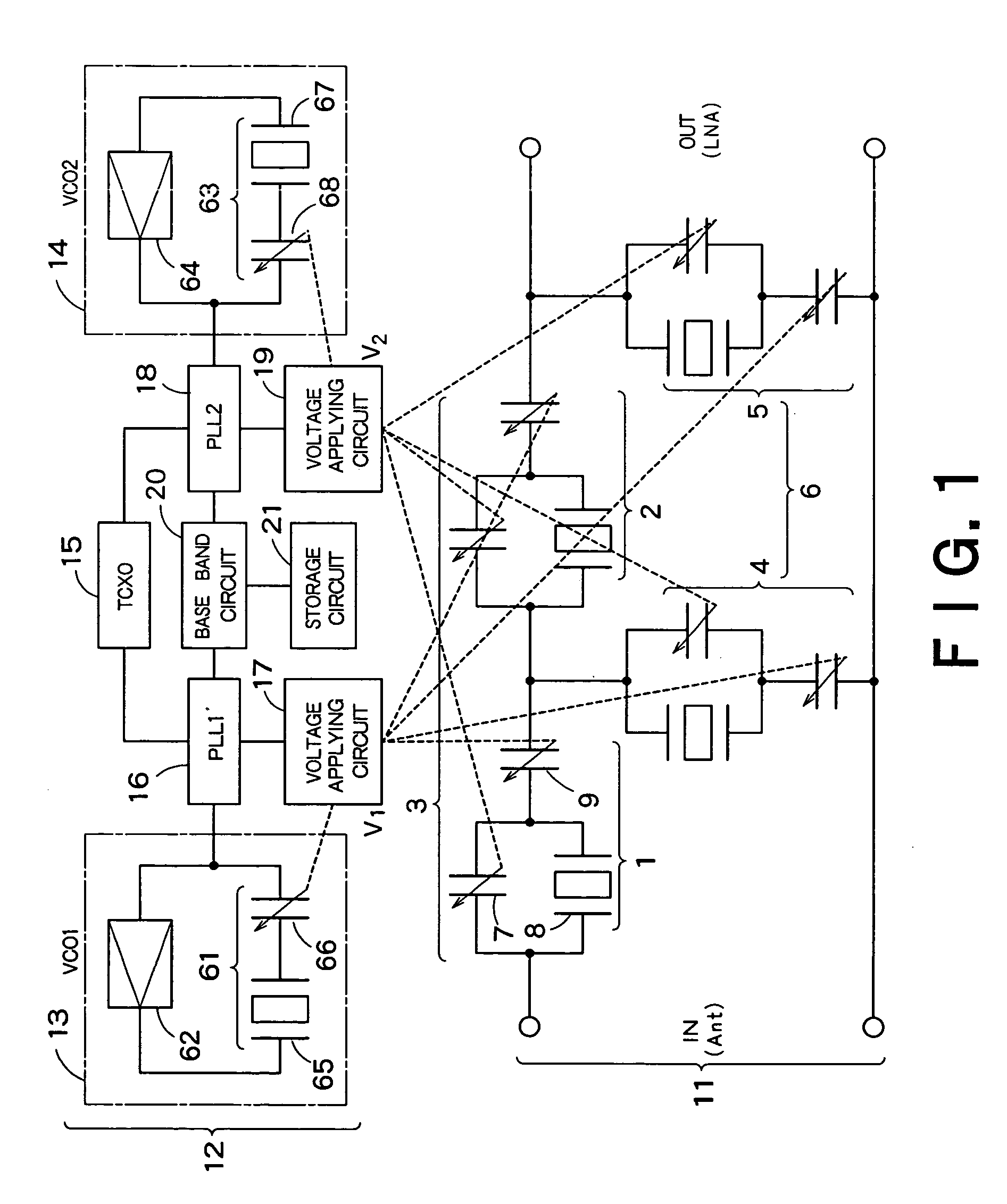
System and method for dual-band antenna matching
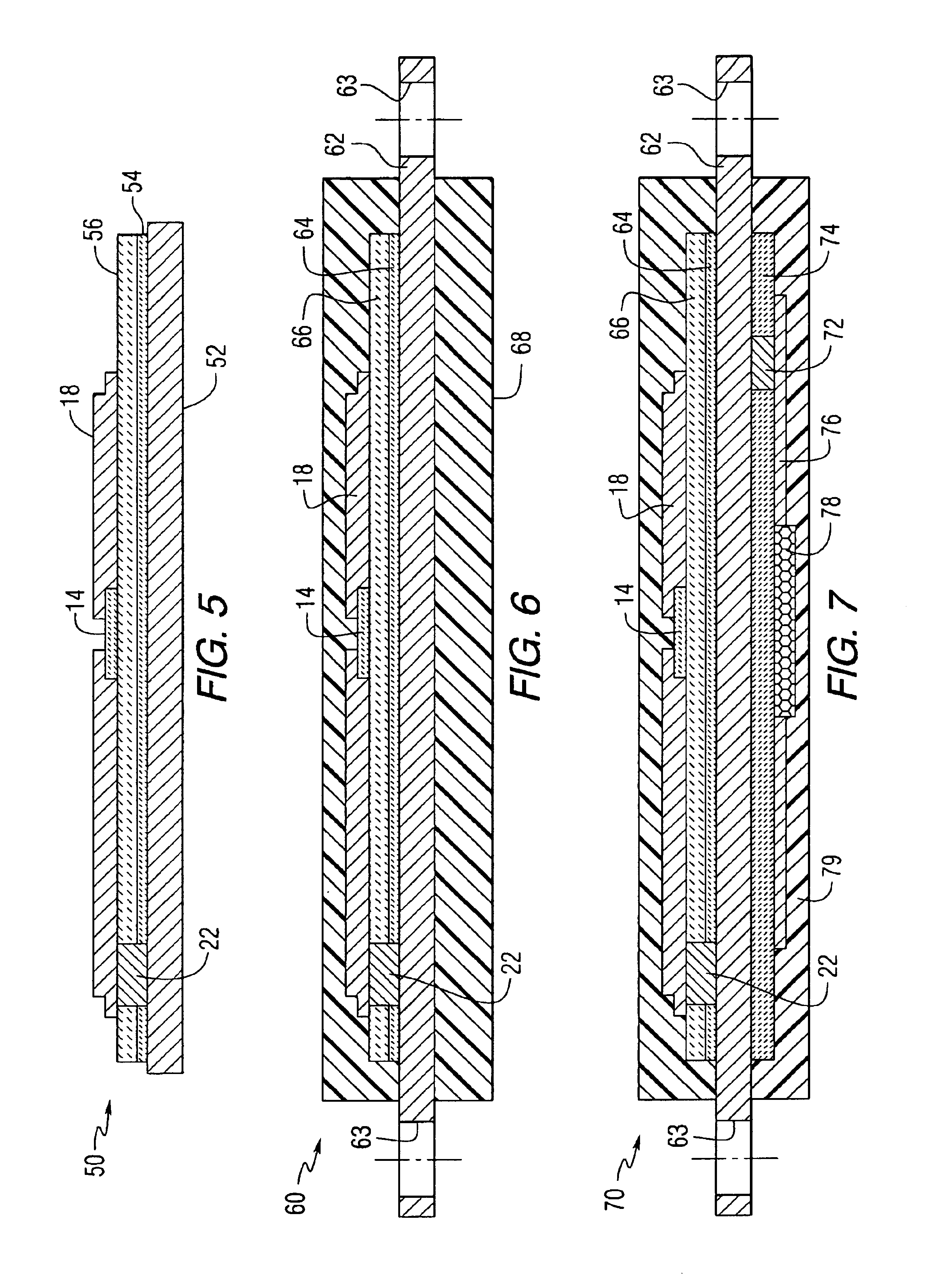
A dual-band antenna matching system and a method for dual-band impedance matching are provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at either a first and a second communication band, or a third and a fourth communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; and, simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency. In response, a conjugate match is supplied to the antenna in the first communication band in response to the first frequency. Simultaneously, the antenna is matched in the second communication band in response to the second frequency. When the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency, and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency, then conjugate matches are supplied for the third and fourth communication bands, responsive to the third and fourth frequencies, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
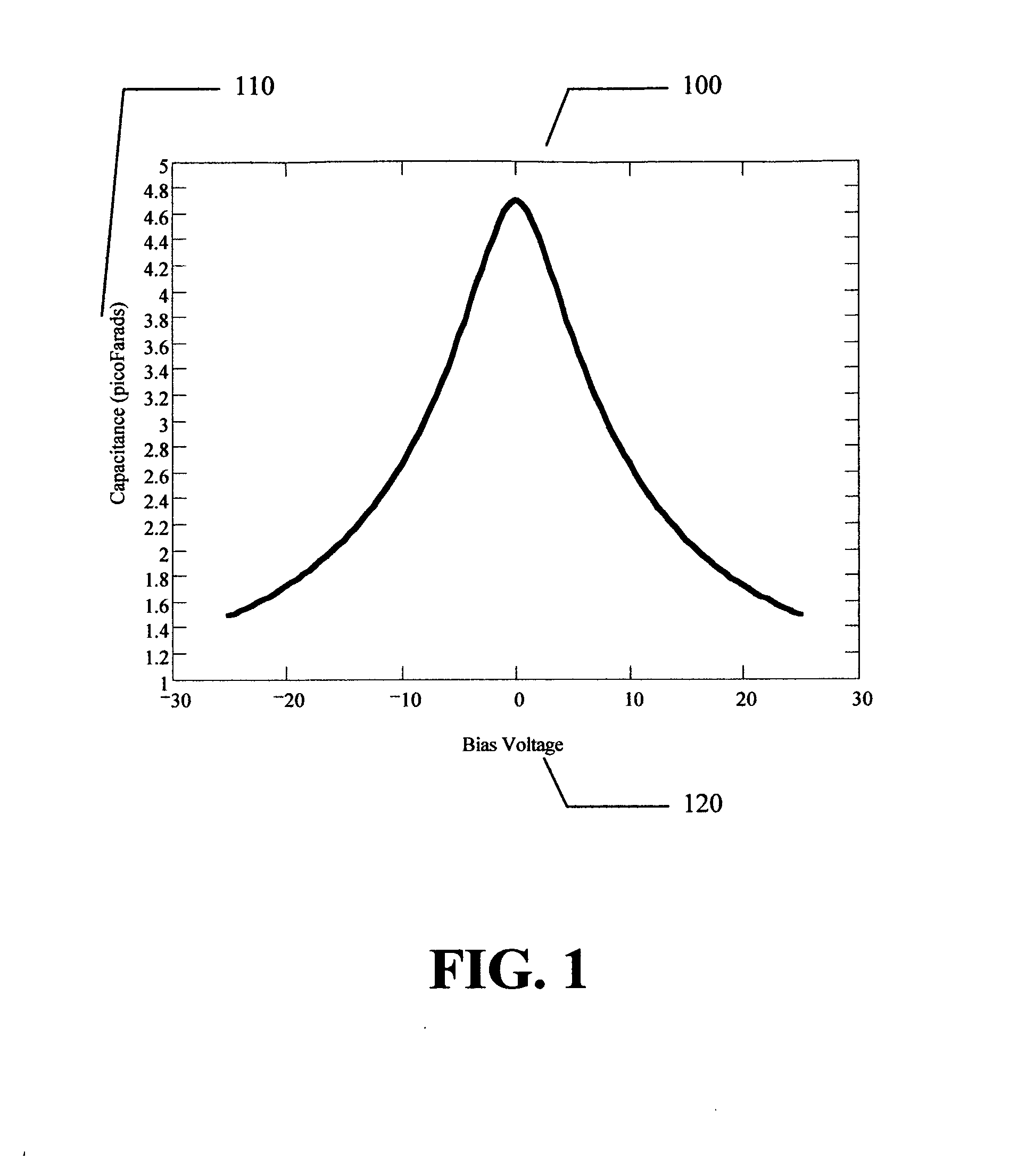
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
InactiveUS6905989B2Lower sintering temperatureIncrease varietyFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic layered productsBreakdown strengthStrontium titanate
Tunable dielectric materials including an electronically tunable dielectric ceramic and a low loss glass additive are disclosed. The tunable dielectric may comprise a ferroelectric perskovite material such as barium strontium titanate. The glass additive may comprise boron, barium, calcium, lithium, manganese, silicon, zinc and / or aluminum-containing glasses having dielectric losses of less than 0.003 at 2 GHz. The materials may further include other additives such as non-tunable metal oxides and silicates. The low loss glass additive enables the materials to be sintered at relatively low temperatures while providing improved properties such as low microwave losses and high breakdown strengths.
Owner:NXP USA INC
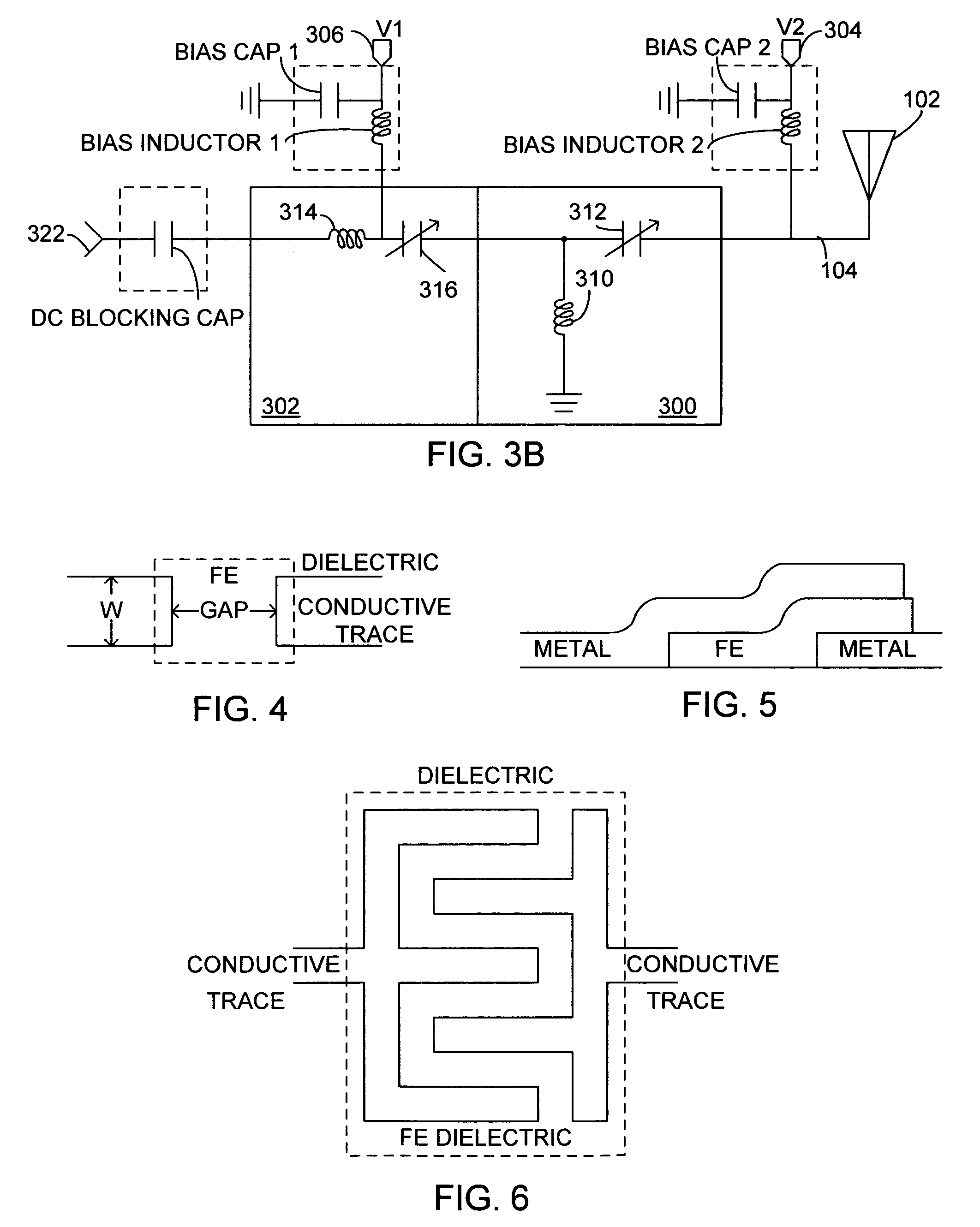
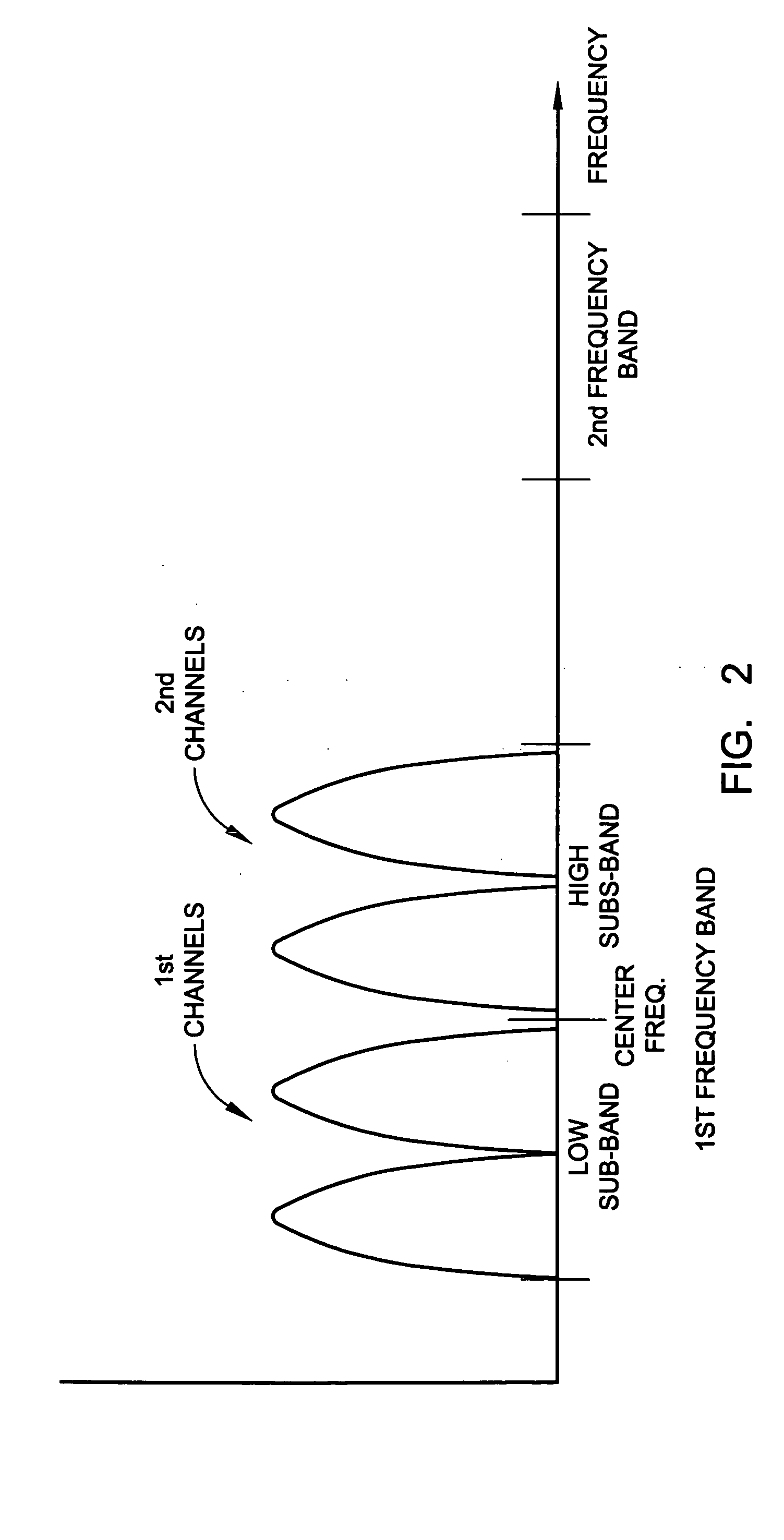
System and method for impedance matching an antenna to sub-bands in a communication band
InactiveUS7176845B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMultiple-port networksAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna impedanceMethod selection
A sub-band antenna matching method and an antenna matching system for selectively matching a communication bandwidth segment impedance have been provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a first communication band. In some aspects, the method selectively supplies a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a second communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency to match the antenna at a low end of the first communication band. Likewise, the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency to match the antenna at a high end of the first communication band in response to the third and fourth frequencies.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Full-duplex antenna system and method
A system and method is provided for full-duplex antenna impedance matching. The method comprises: effectively resonating a first antenna at a frequency selectable first channel in a first frequency band; generating a first antenna impedance at the first channel frequency; effectively resonating a second antenna at a frequency selectable second channel in the first frequency band; generating a second antenna impedance at the second channel frequency; supplying a first conjugate impedance match at the first channel frequency; and, supplying a second conjugate impedance match at the second channel frequency. For example, the first antenna may be used for transmission, while the second antenna is used for received communications. The antennas effectively resonant in response to: supplying frequency selectable conjugate impedance matches to the antennas; generating frequency selectable antenna impedances; and / or selecting the frequency of antenna resonance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
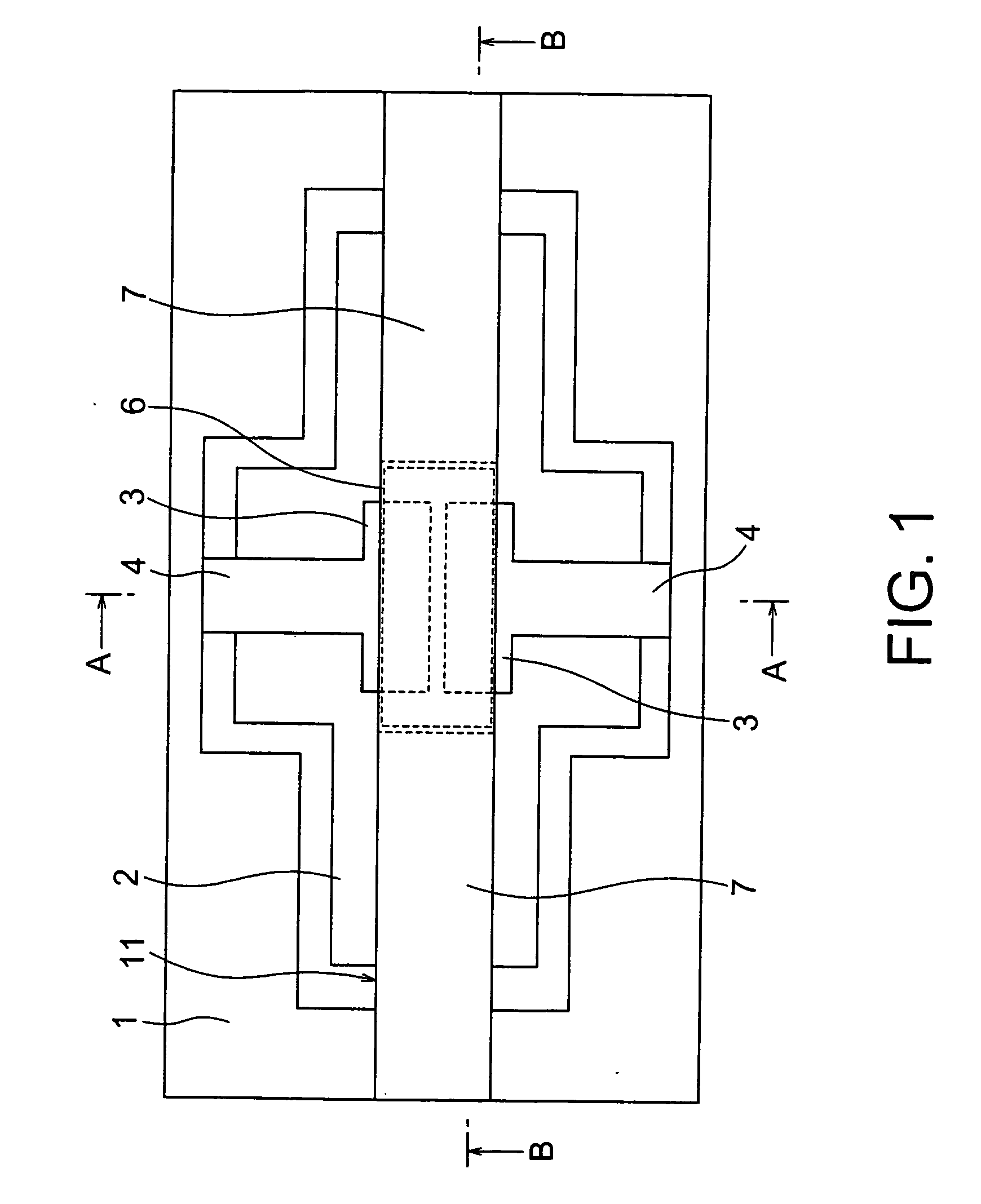
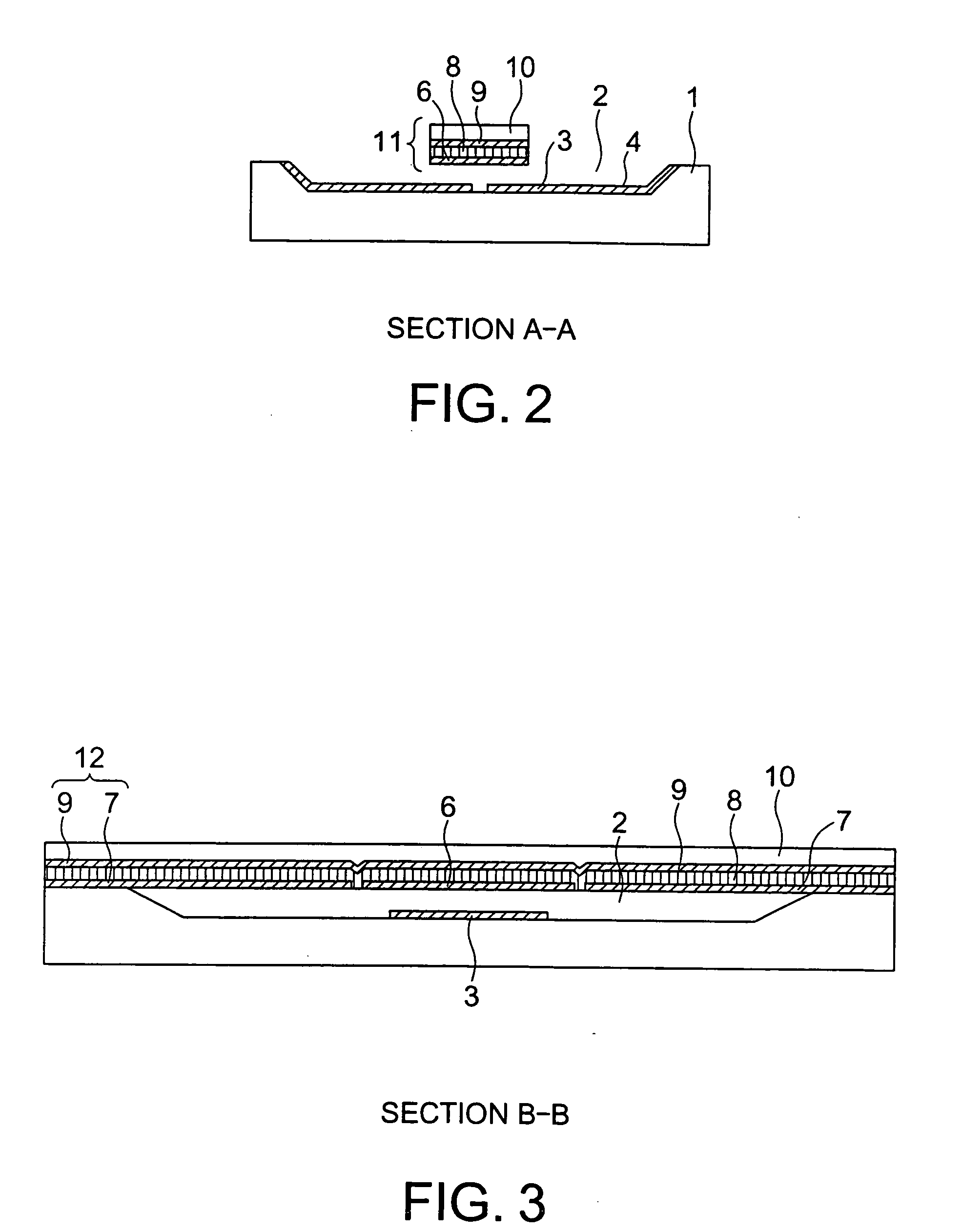
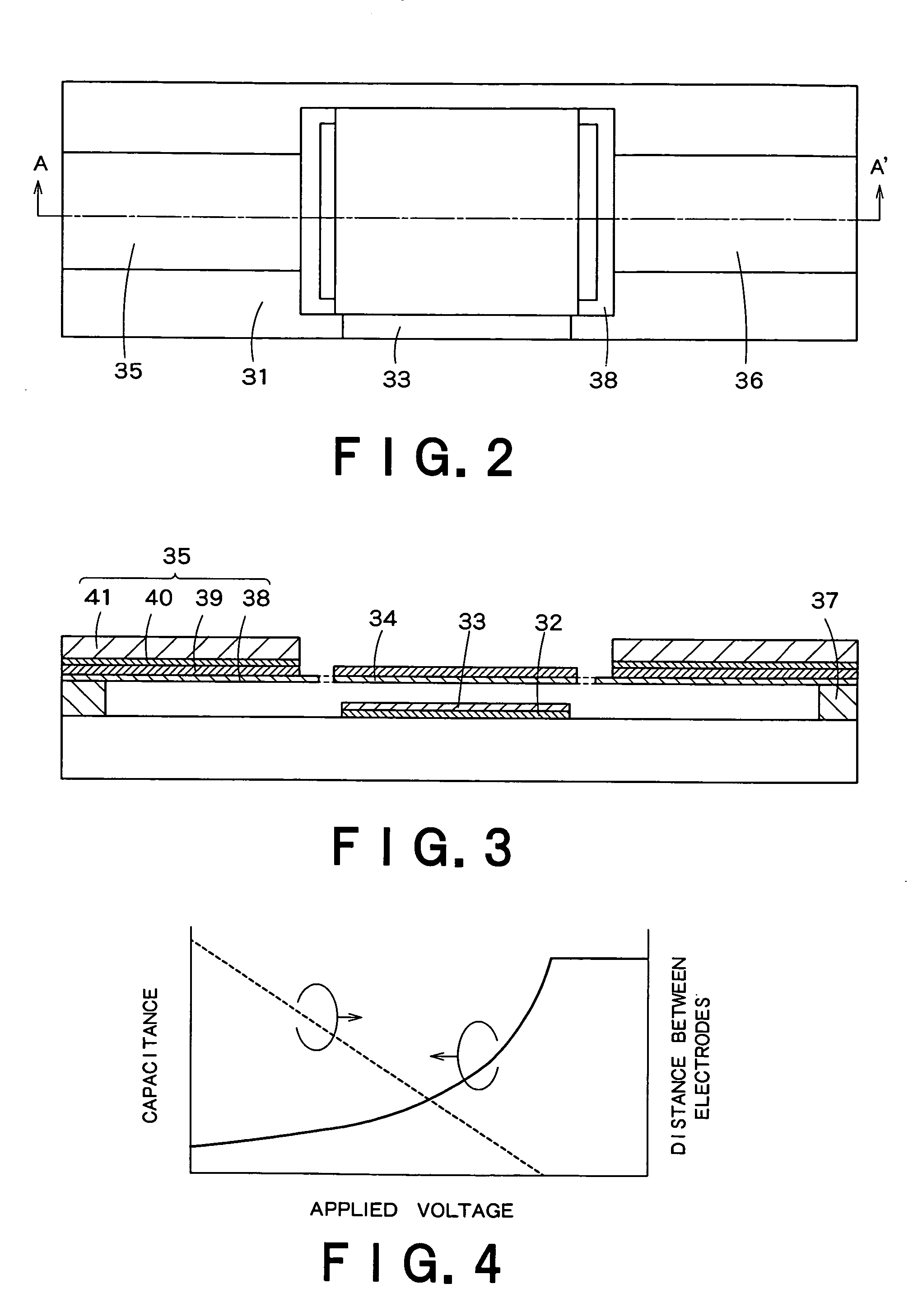
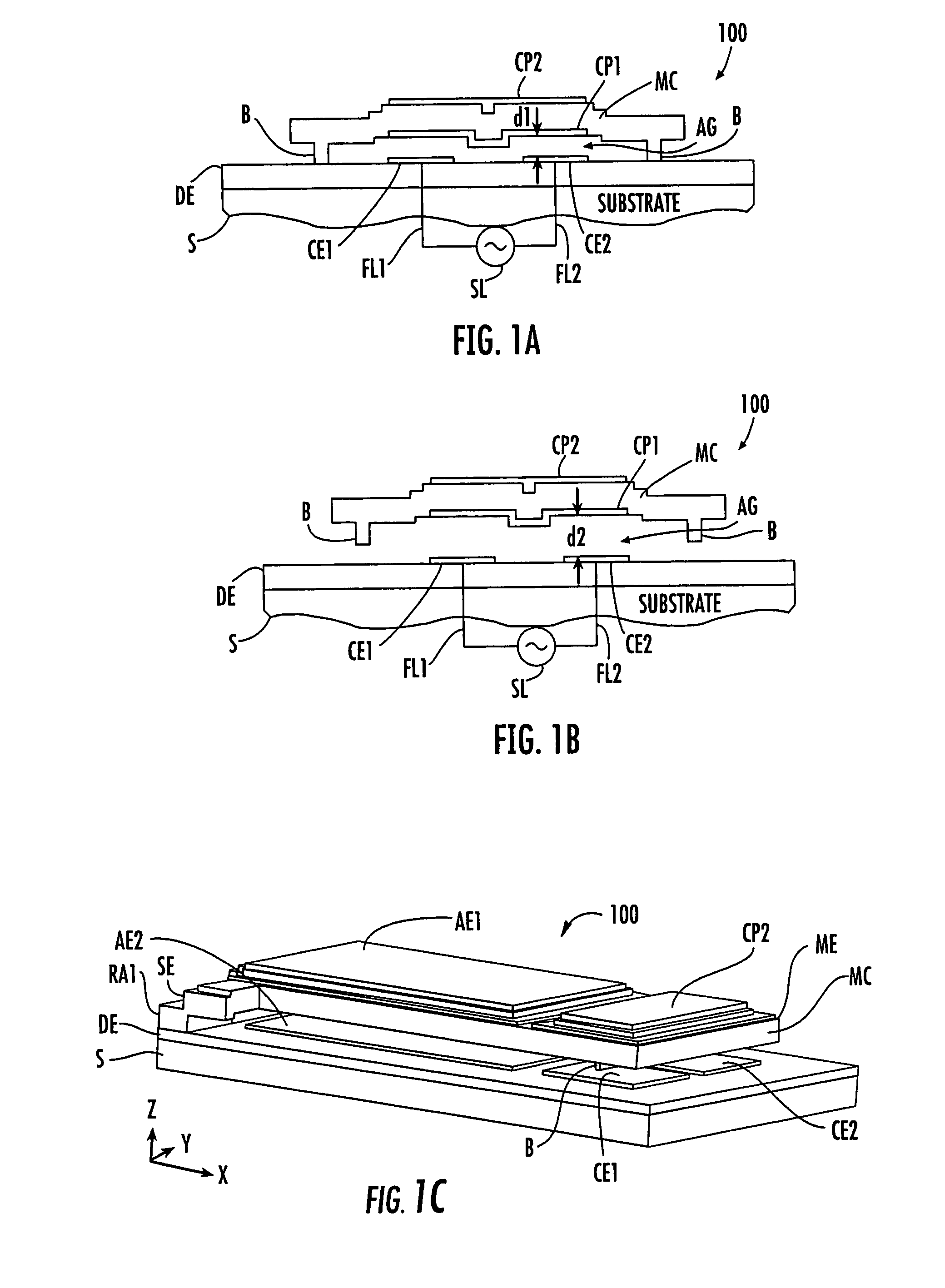
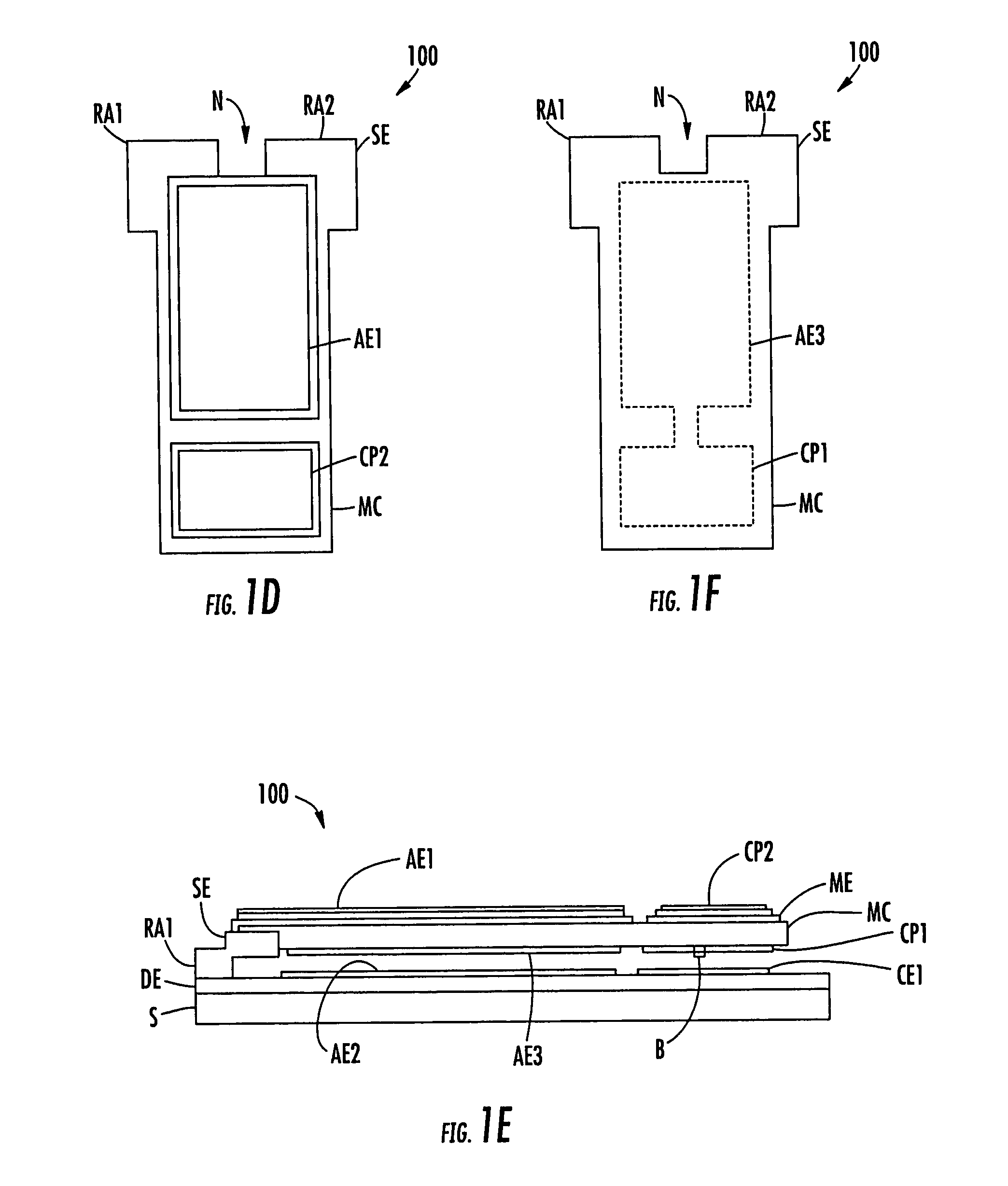
Piezoelectric-driven MEMS device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050242687A1Fabricated reliably and consistentlyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin membraneEngineering
A piezoelectric-driven MEMS device can be fabricated reliably and consistently. The piezoelectric-driven MEMS device includes: a movable flat beam having a piezoelectric film disposed above a substrate with a recessed portion such that the piezoelectric film is bridged over the recessed portion, piezoelectric drive mechanisms disposed at both ends of the piezoelectric film and configured to drive the piezoelectric film, and a first electrode disposed at the center of the substrate-side of the piezoelectric film, and a second electrode disposed on a flat part of the recessed portion of the substrate and facing the first electrode of the movable flat beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Tunable filter and portable telephone
InactiveUS20050212612A1Low insertion lossImprove reliabilityMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceEngineering
A tunable filter has a plurality of variable capacitors and a plurality of inductor elements, each being formed on a common substrate, a filter circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a monitor circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a detecting circuit which detects a prescribed circuit constant of the monitor circuit, a storage which stores information relating to a reference circuit constant of the monitor circuit, and a capacitance control circuit which controls capacitance of the variable capacitors in the monitor circuit and capacitance of the variable capacitors in the filter circuit, based on a result detected by the detecting circuit and information stored in the storage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Thin film piezoelectric actuator
InactiveUS20050194867A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric actuatorsElectrical and Electronics engineering
A thin film piezoelectric actuator comprises a driving part at least one end of which is supported by an anchor portion. The driving part includes: a piezoelectric film, a first lower electrode provided under a first region of the piezoelectric film, a second lower electrode provided under a second region different from the first region of the piezoelectric film, a first upper electrode provided opposite to the first lower electrode on the piezoelectric film, a second upper electrode provided opposite to the second lower electrode on the piezoelectric film, a first connection part that electrically connects the first lower electrode and the second upper electrode via a first via hole formed in the piezoelectric film, and a second connection part that electrically connects the second lower electrode and the first upper electrode via a second via hole formed in the piezoelectric film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
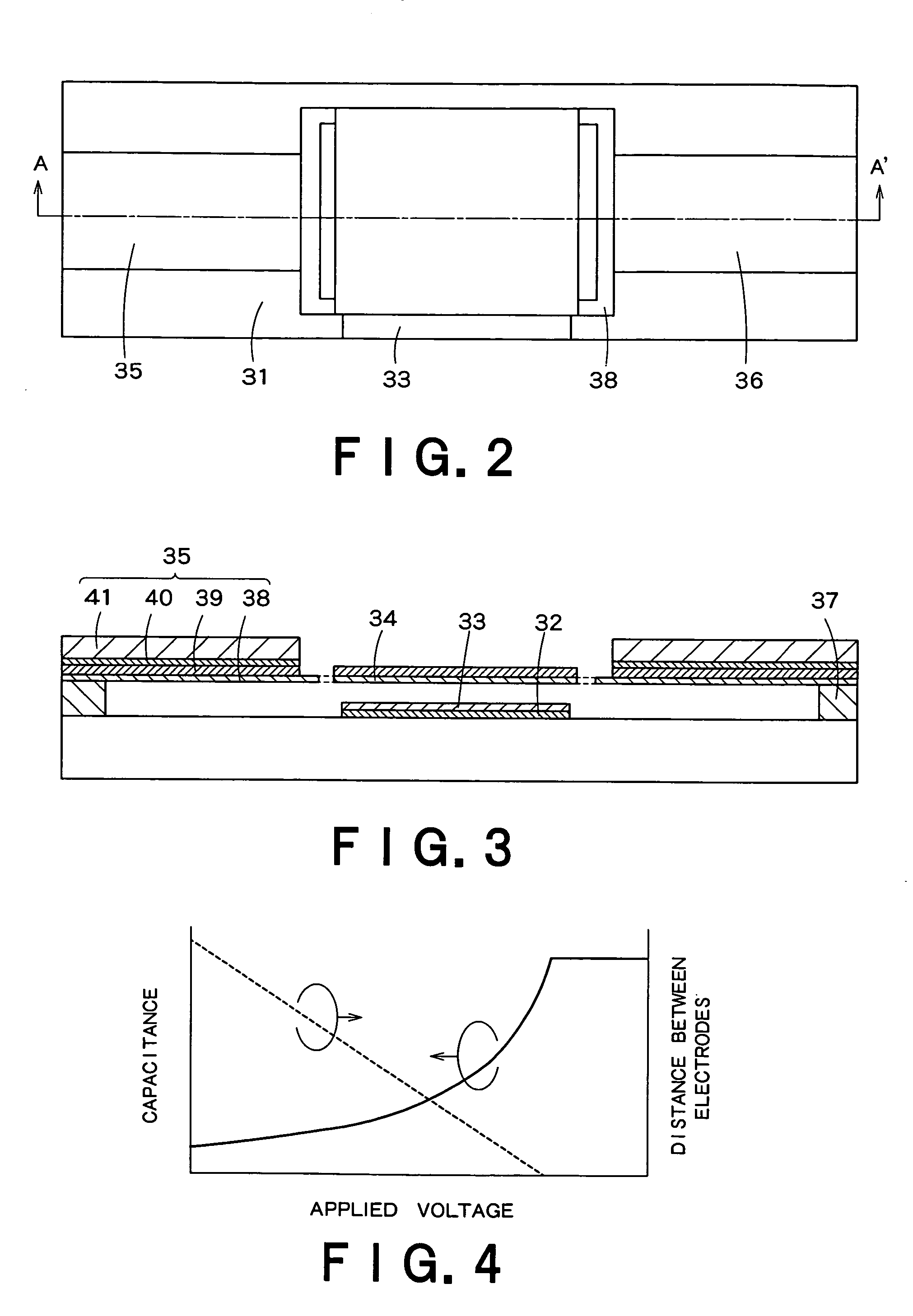
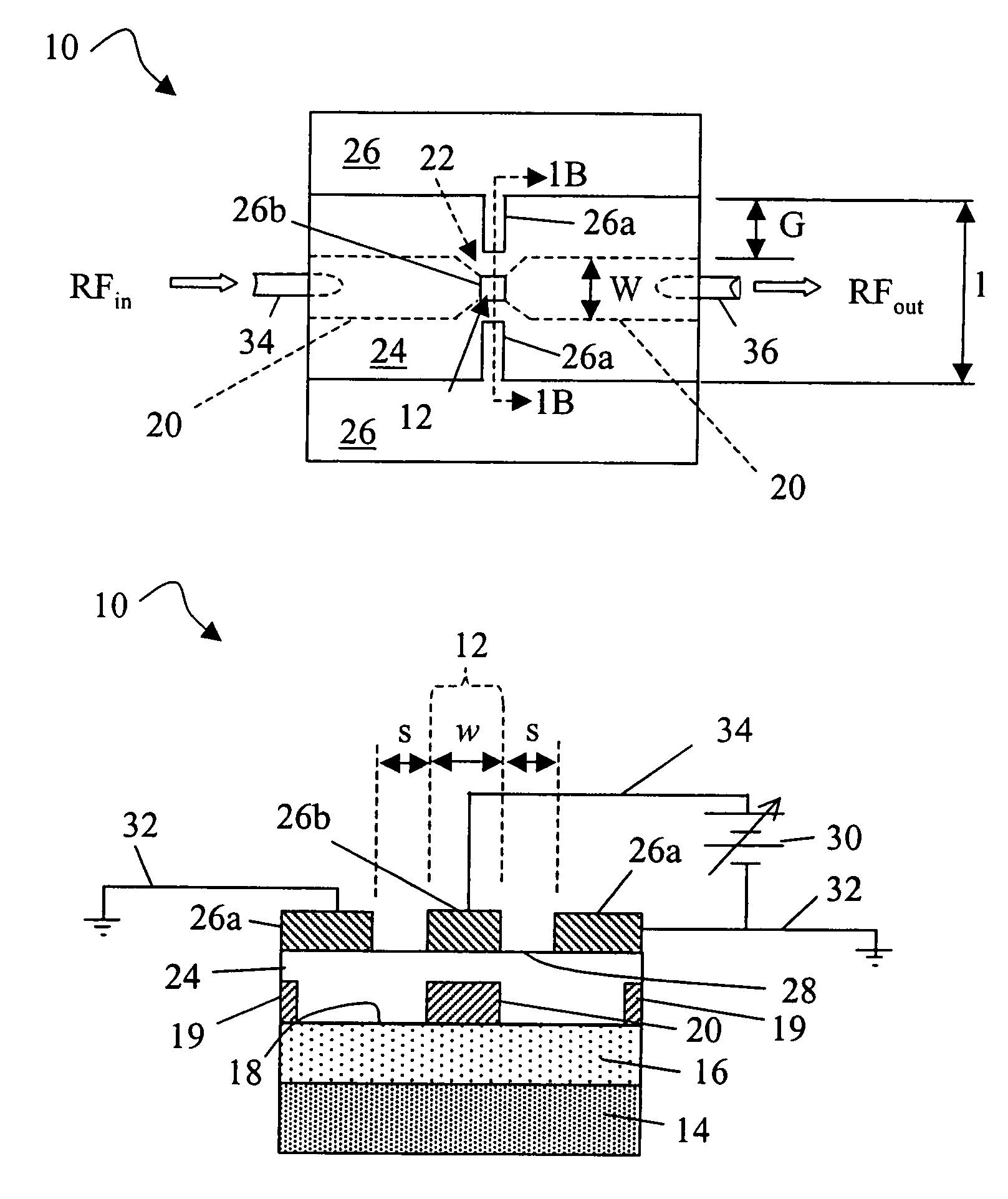
MEMS-based variable capacitor
ActiveUS6909589B2Low loss tangentSimple processMechanically variable capacitor detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceClosed loop
A variable capacitor device using MEMS or micromachining techniques wherein thin-films of materials are deposited, patterned and etched to form movable micromechanical elements on the surface of a substrate composed of either semiconductor, glass, metal, or ceramic material. In one embodiment of the present invention to achieve higher frequency performance as well as other benefits, the substrate is comprised of Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramics (LTCC). The variable capacitor is an electrostatically actuated micromechanical device and if fabricated on a LTCC multi-layered substrate material has continuous electrical connections through the layers. The same LTCC substrate material can also be used to enclose the device by selectively removing a portion of the upper substrate so as to form a cavity. The two substrates are then bonded together to enclose and protect the variable capacitor. An integrated circuit can be incorporation onto the multi-level substrate structure to enable a electronic closed-loop controlled variable capacitor module. The integrated circuit is flip-chip bonded at the bottom of the substrate structure with appropriate electrical connections between the integrated circuit and the MEMS variable capacitor device. A variation of the present invention utilizes a zipper actuation method wherein the tuning ratio of the variable capacitor is increased to very high levels. Yet another variation of the present invention utilizes a differential gap between the top and bottom electrodes such that the actuation electrodes do not physically contact one another. Yet another implementation of the present invention uses an extra set of electrodes or mechanical mechanism so as to lock the value of the capacitor indefinitely. Yet another implementation uses shaped actuation electrodes so as to linearize the relationship between the applied actuation voltage and the resultant capacitance of the device.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
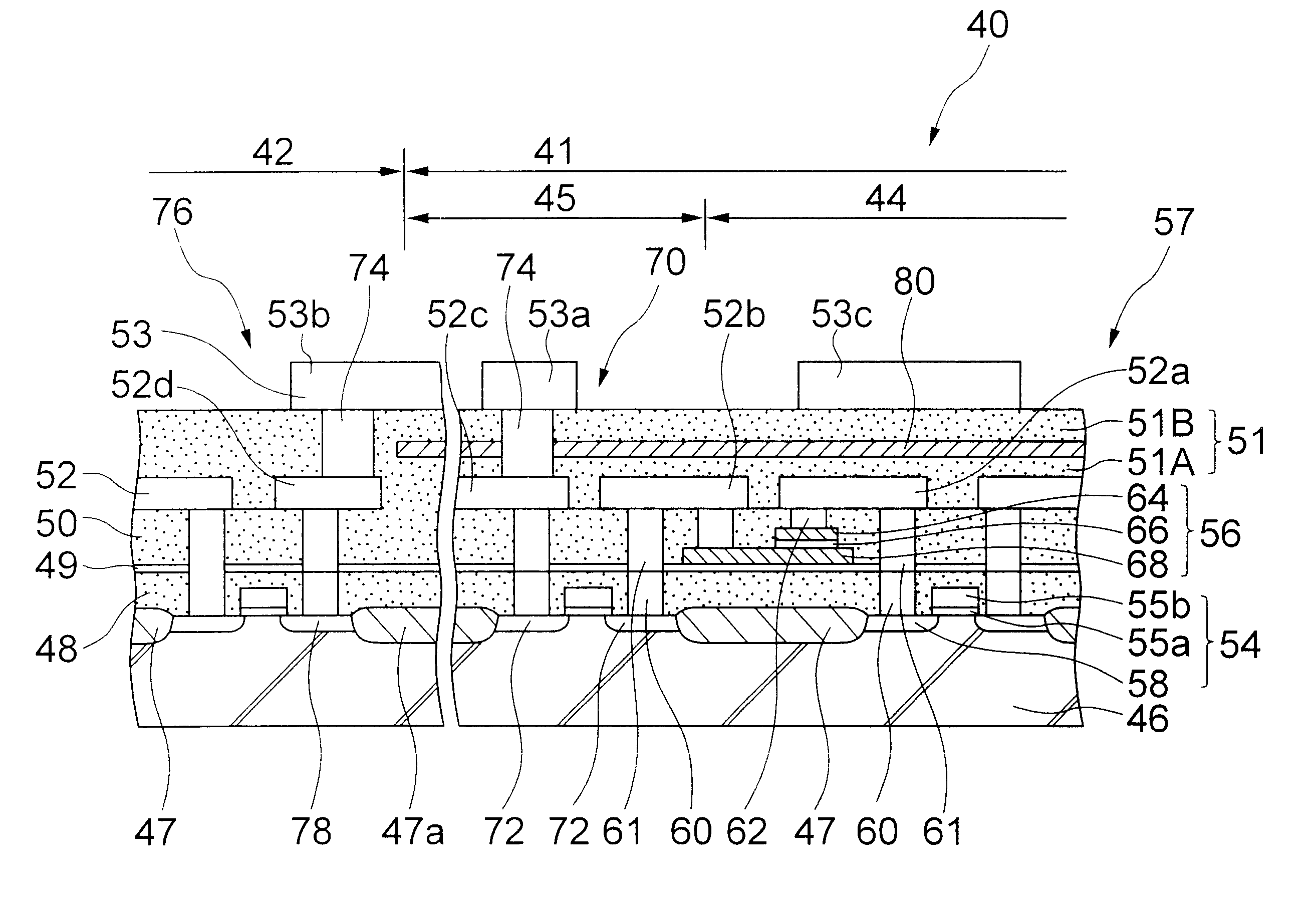
Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitors and actuation components and related methods
Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitors and actuation components and related methods are provided. A MEMS variable capacitor can include first and second feed lines extending substantially parallel to one another. Further, MEMS variable capacitors can include first and second capacitive plates being spaced apart from the first and second feed lines. The first and second capacitive plates can be separately movable with respect to at least one of the first and second feed lines for varying the capacitance between the first and second feed lines over a predetermined capacitance range.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
Capacitive micro-electro-mechanical sensors with single crystal silicon electrodes
ActiveUS7539003B2Mechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitor with electrode area variationIn planeAccelerometer
The devices presented herein are capacitive sensors with single crystal silicon on all key stress points. Isolating trenches are formed by trench and refill forming dielectrically isolated conductive silicon electrodes for drive, sense and guards. For pressure sensing devices according to the invention, the pressure port is opposed to the electrical wire bond pads for ease of packaging. Dual-axis accelerometers measuring in plane acceleration and out of plane acceleration are also described. A third axis in plane is easy to achieve by duplicating and rotating the accelerometer 90 degrees about its out of plane axis Creating resonant structures, angular rate sensors, bolometers, and many other structures are possible with this process technology. Key advantages are hermeticity, vertical vias, vertical and horizontal gap capability, single crystal materials, wafer level packaging, small size, high performance and low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
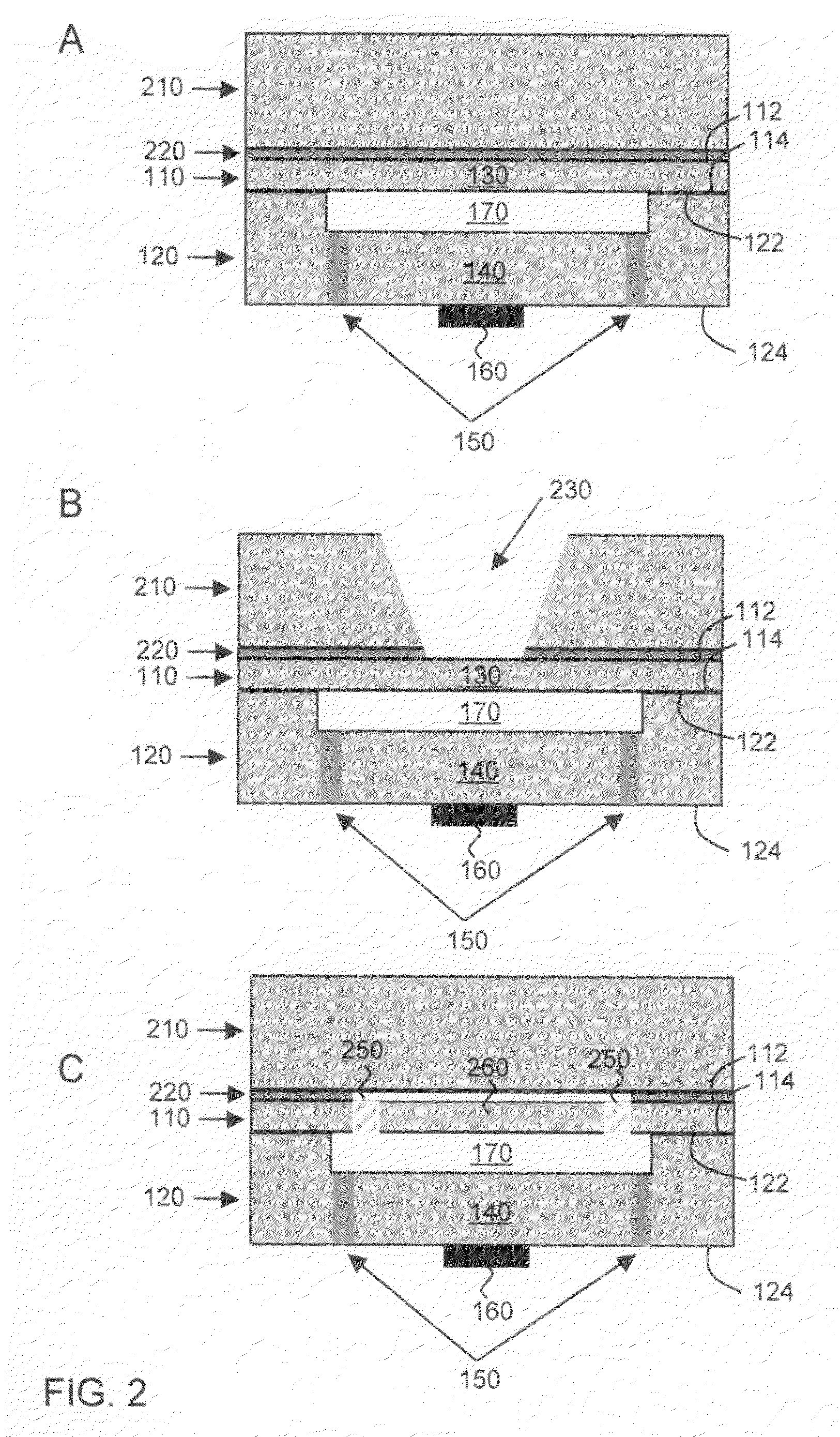
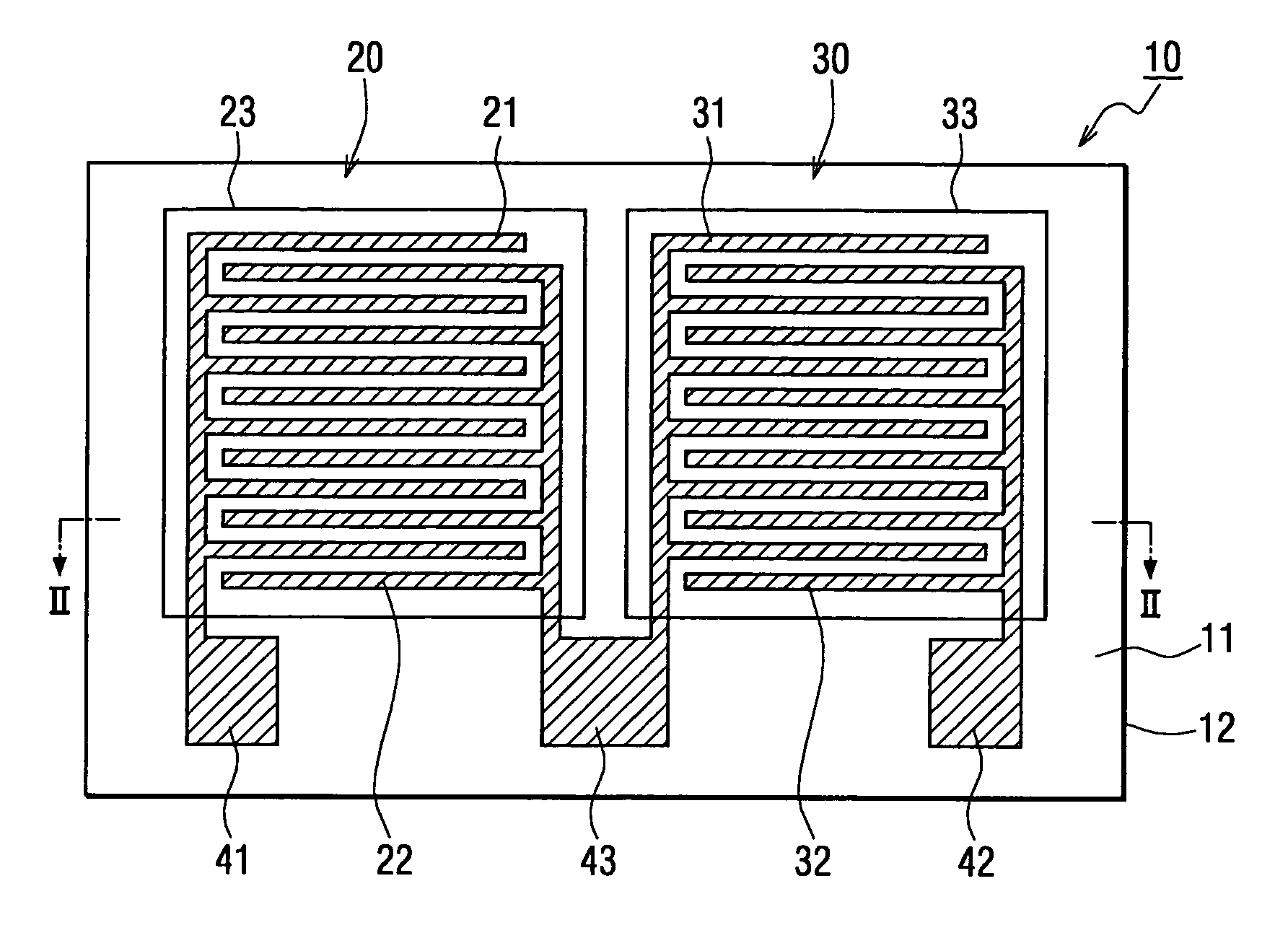
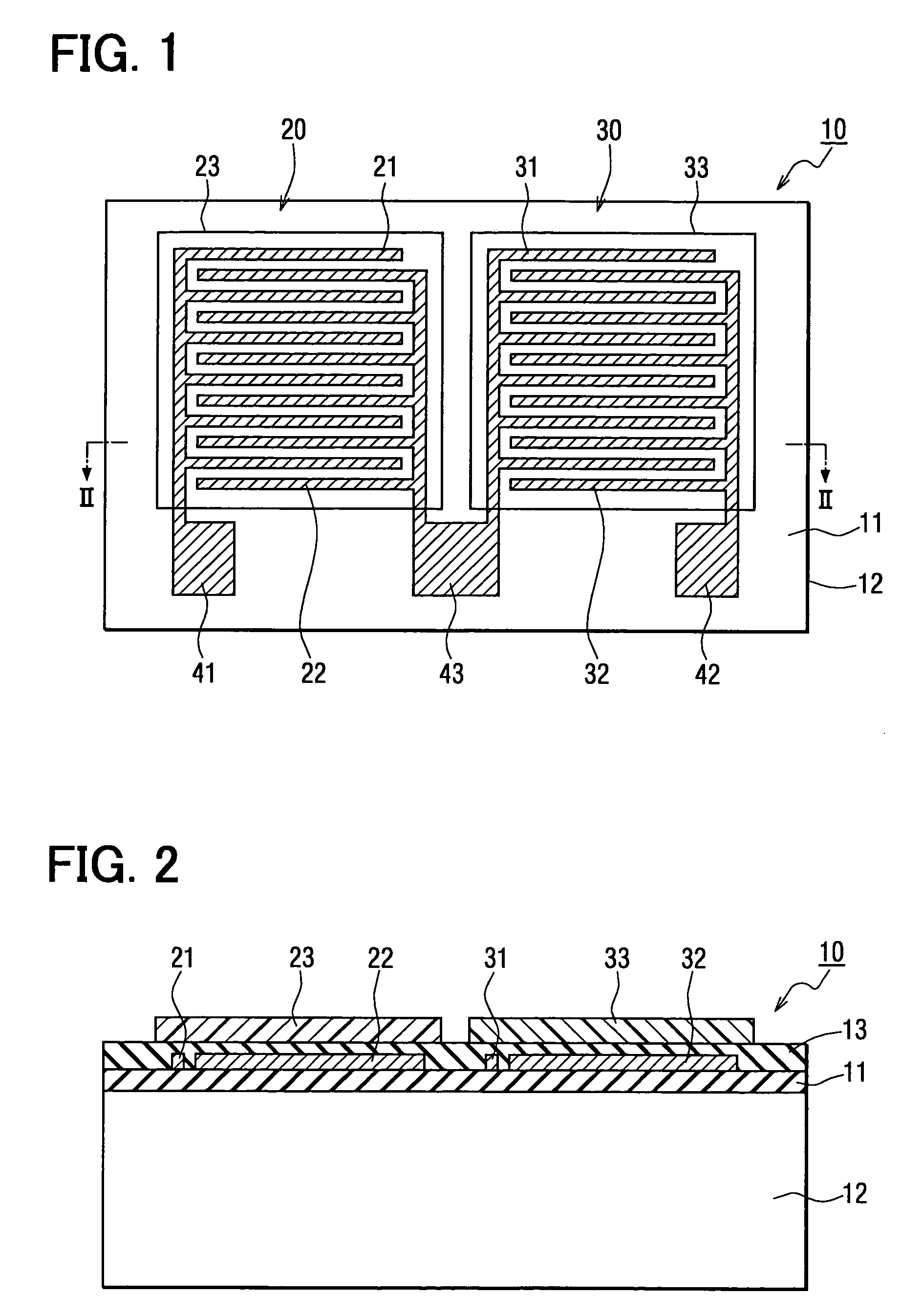
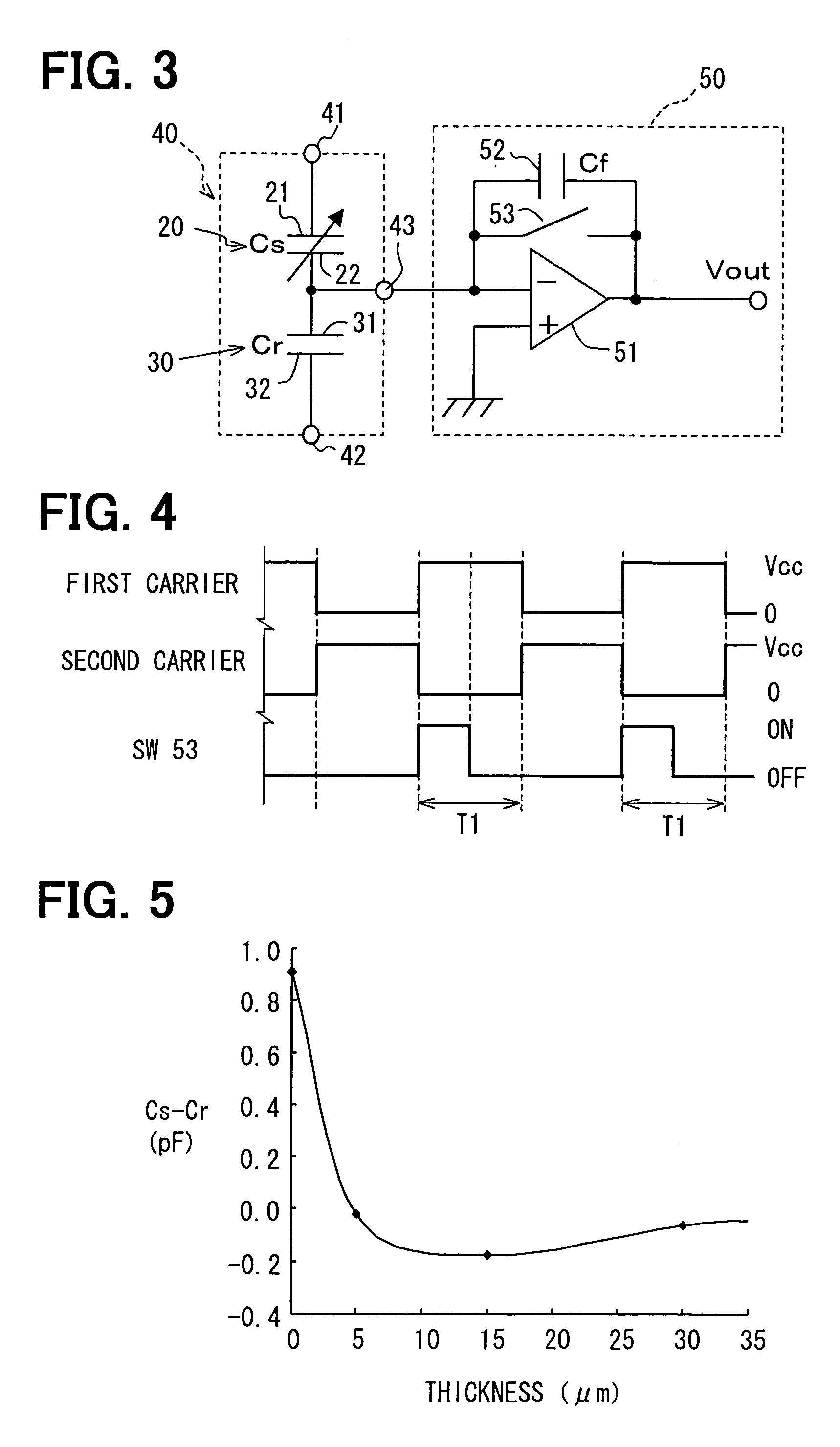
Capacitive humidity sensor
InactiveUS7032448B2Lower Offset VoltageSmall sizeResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing mechanical meansMoisture permeationMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes a detection portion and a reference portion. The detection portion includes detection electrodes and a moisture sensitive film. The reference portion includes reference electrodes and a moisture permeation film as a capacitance adjusting film. The capacitive humidity sensor detects humidity by converting a capacitance difference between a capacitance of the detection electrodes and a capacitance of the reference electrodes to an electric signal by using a capacitance-voltage conversion circuit. The moisture permeation film reduces offset voltage of the capacitive humidity sensor. Thus, an offset compensation circuit or the like is not required.
Owner:DENSO CORP
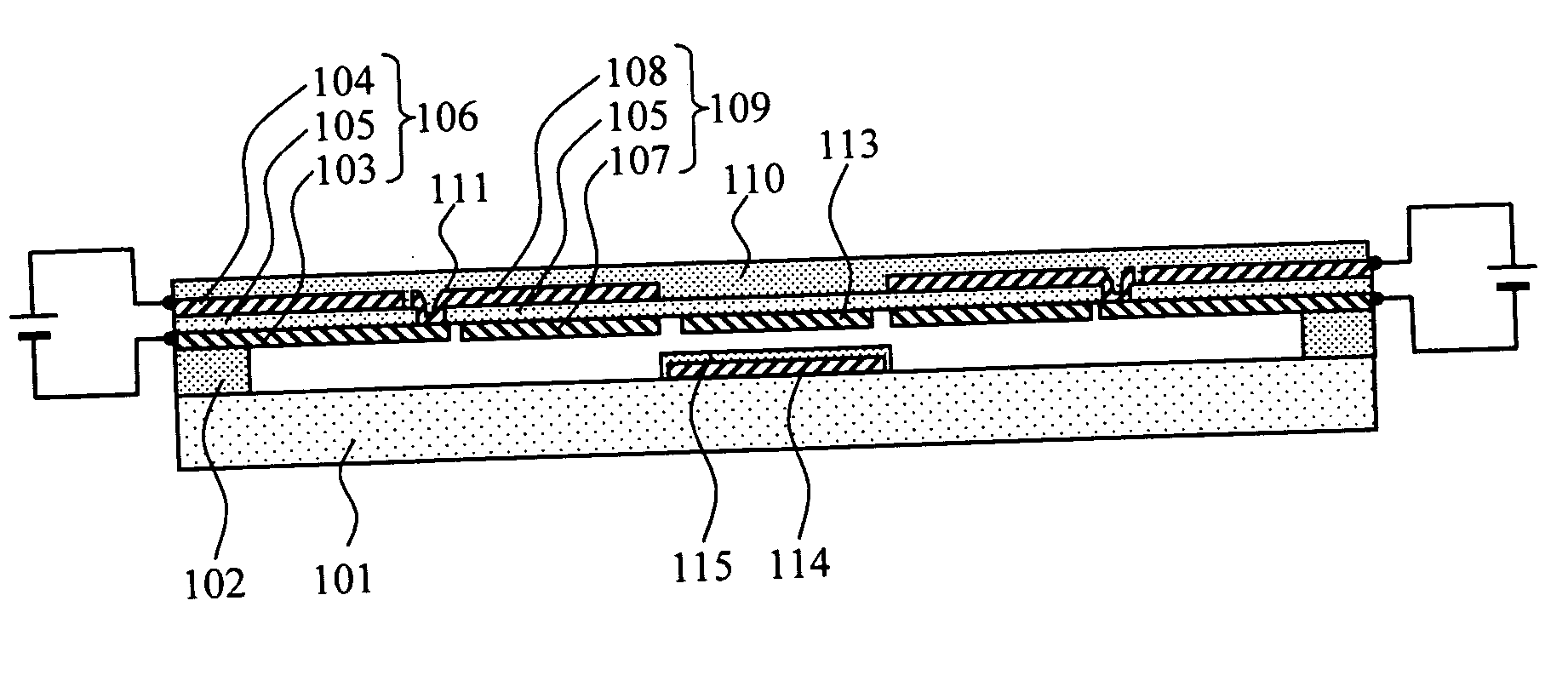
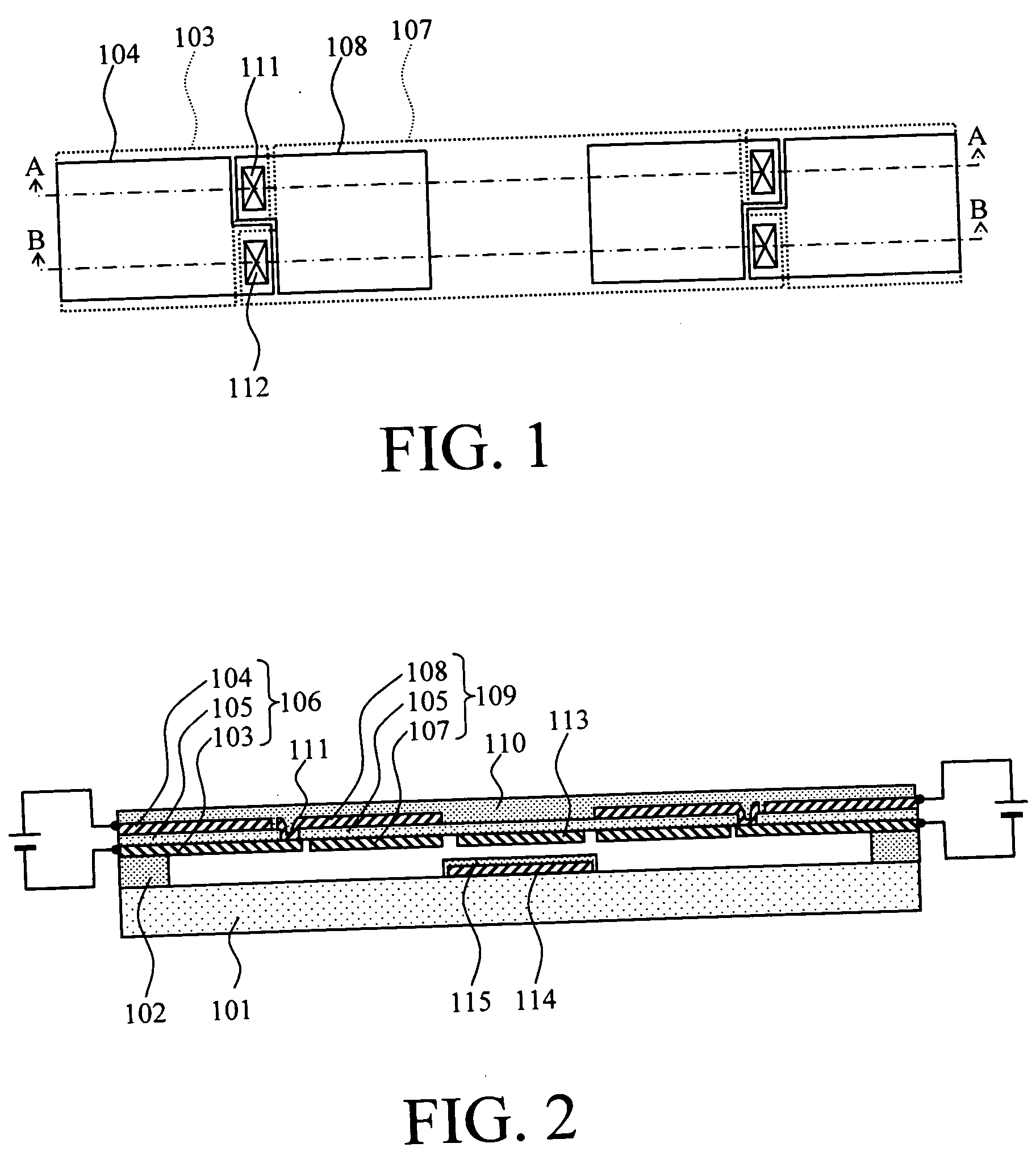
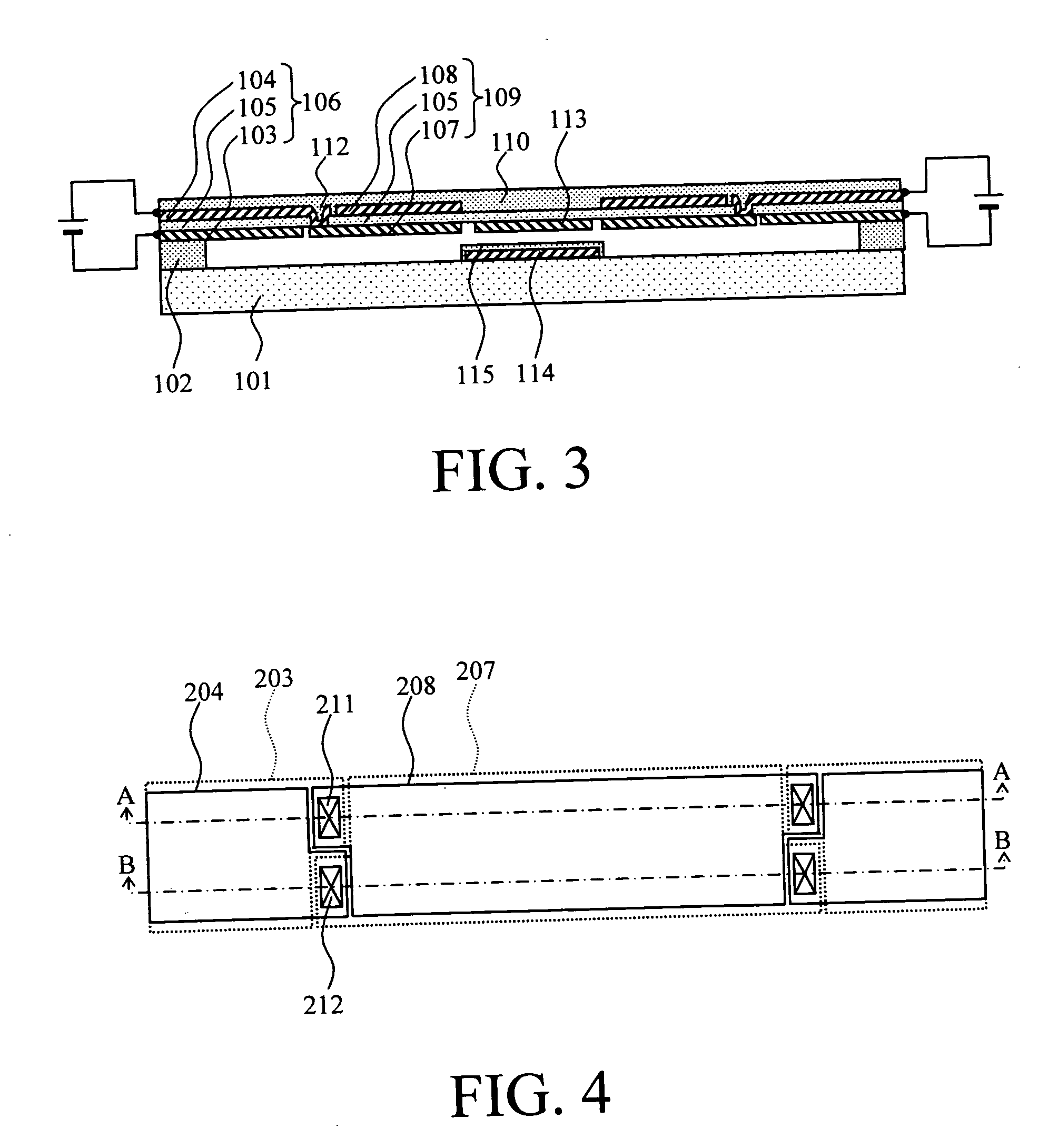
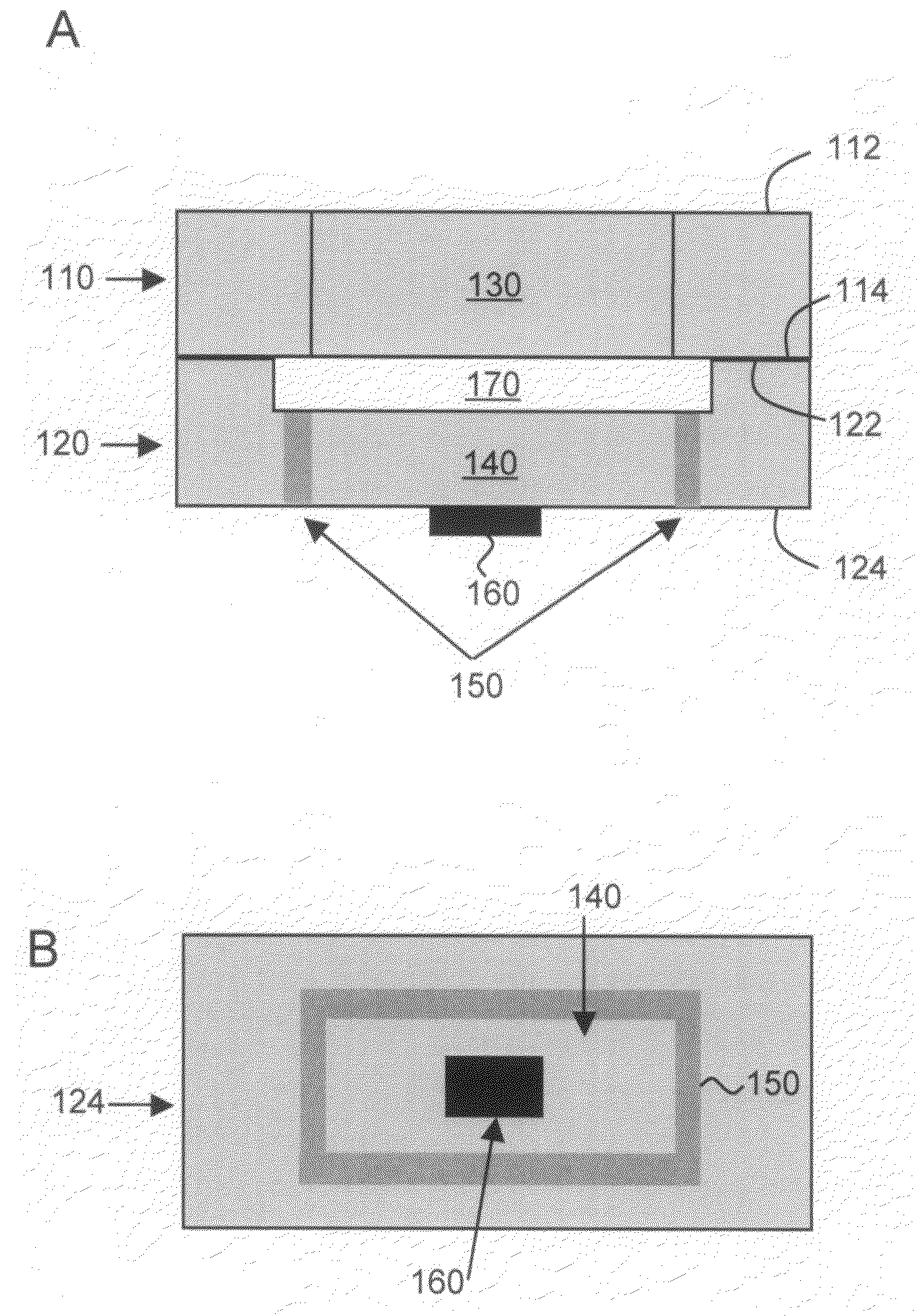
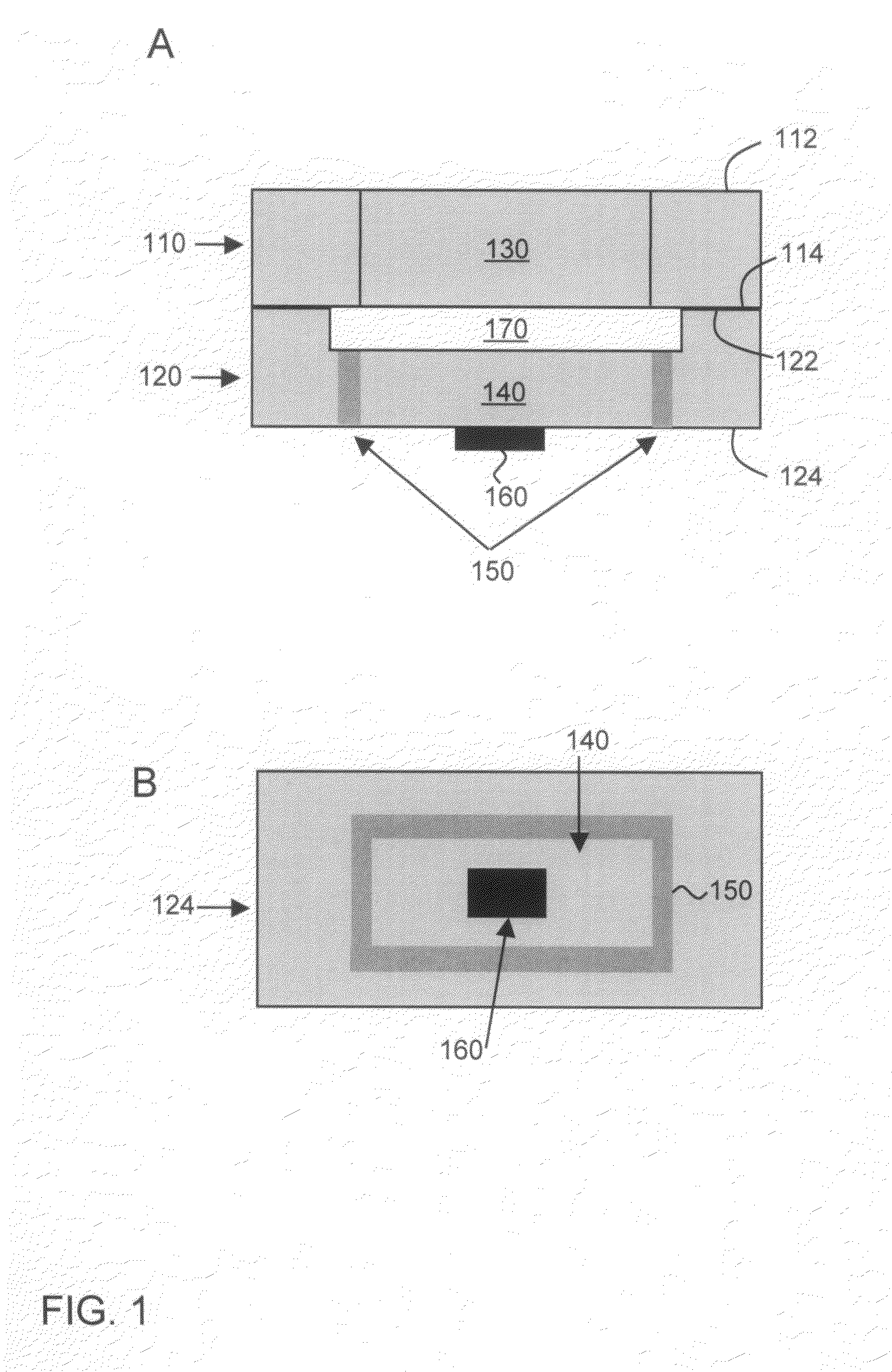
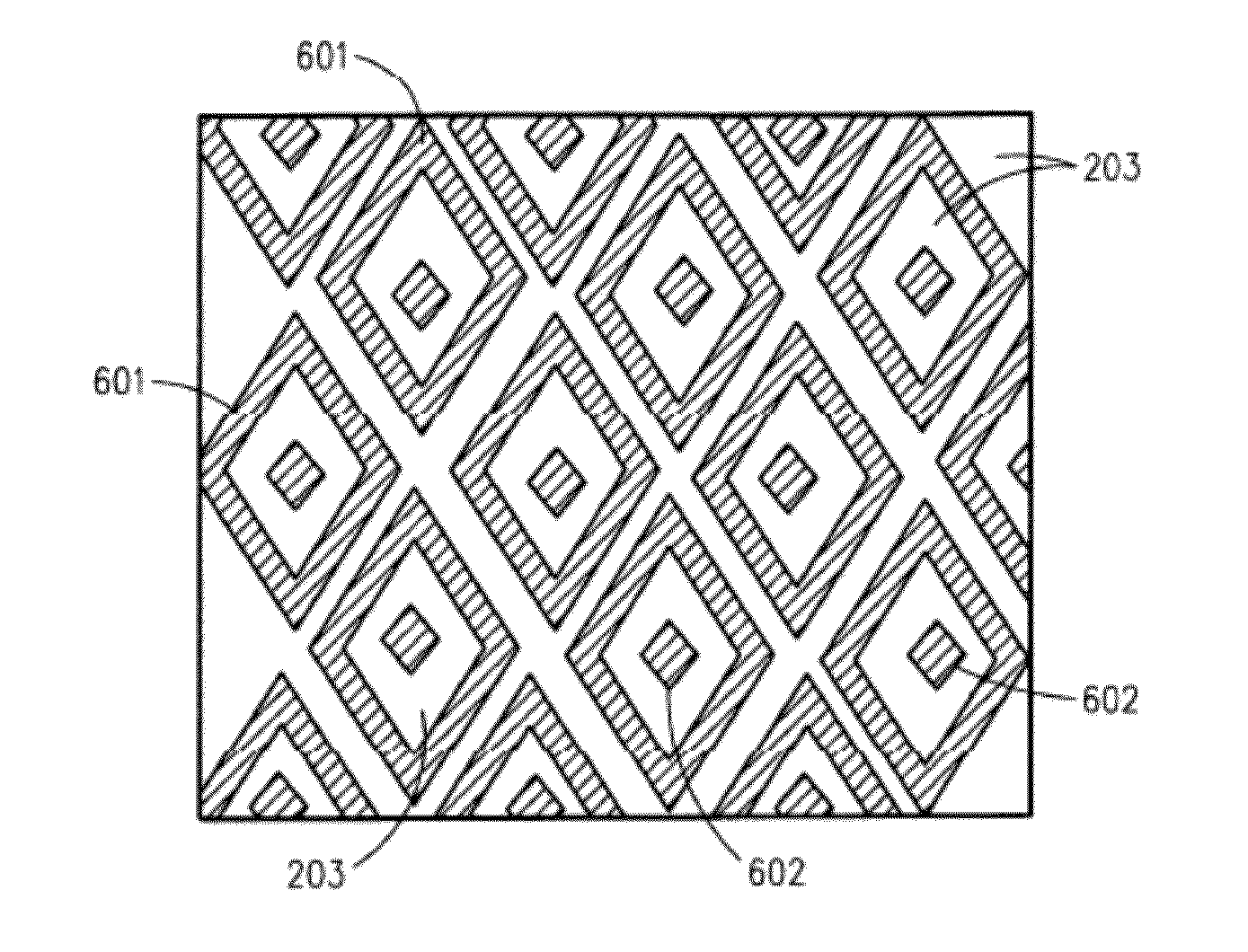
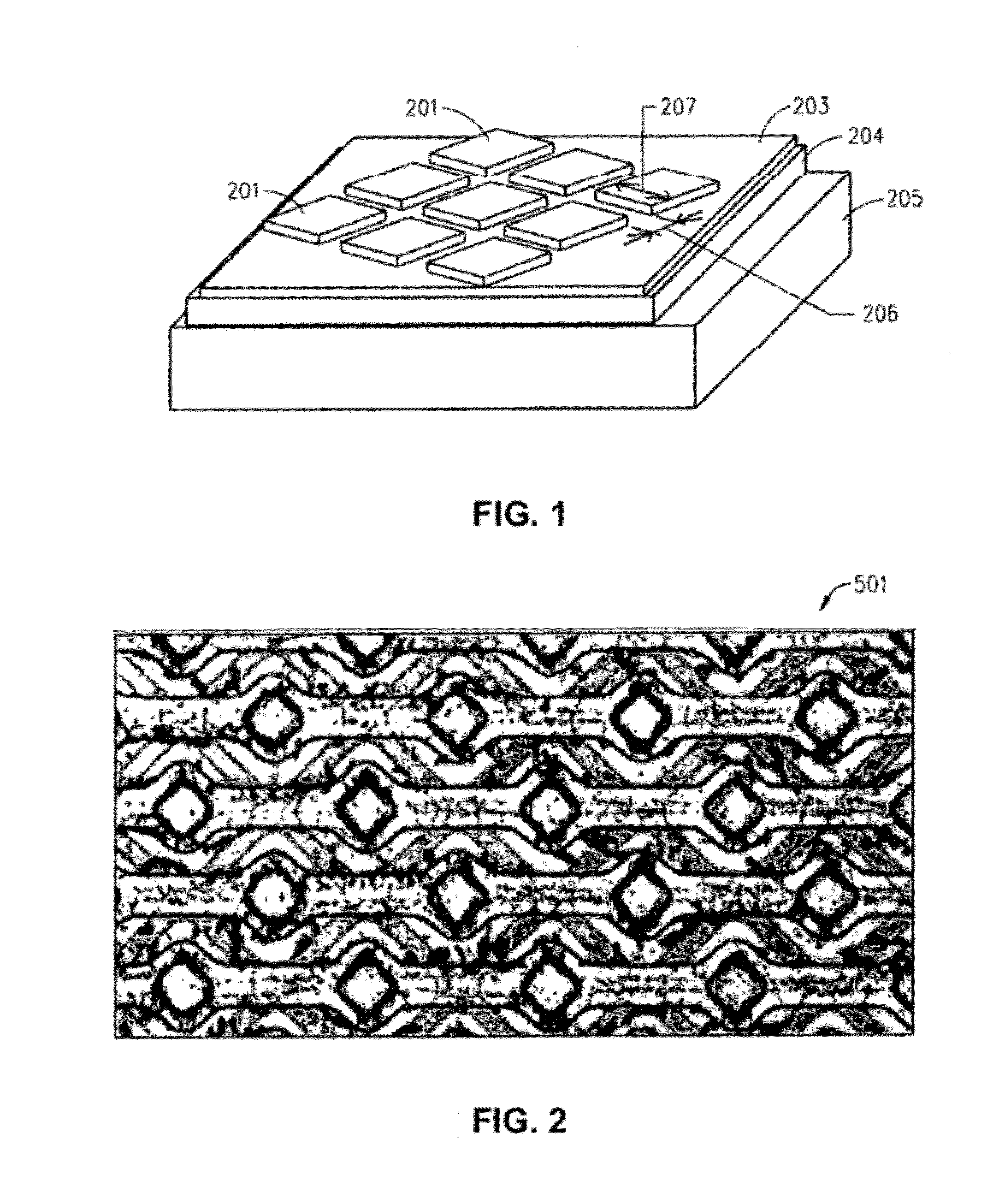
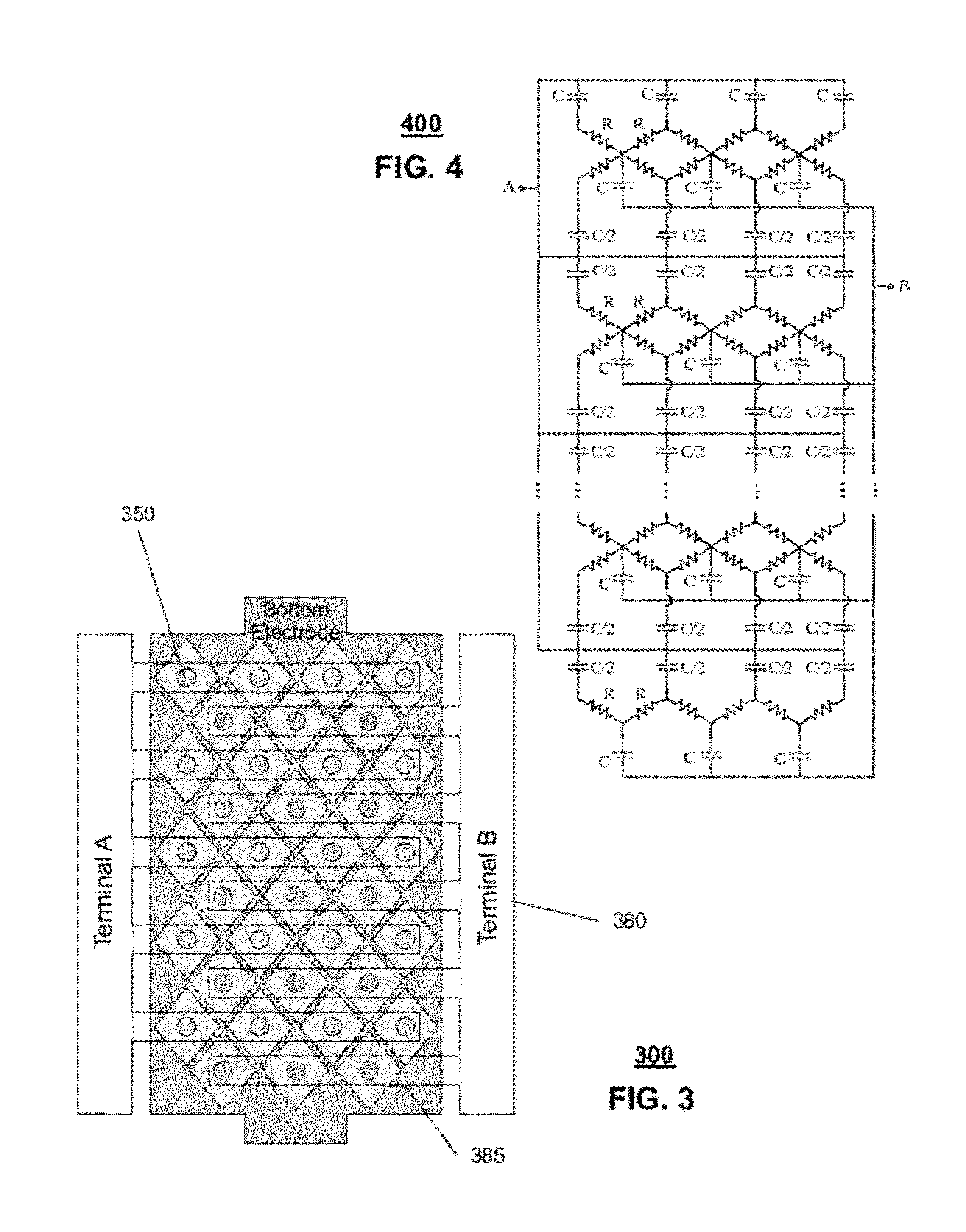
Thin film capacitors
A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a first solid electrode, a second electrode separated into subsections, and a dielectric medium separating the subsections from the first solid electrode, where the subsections of the second electrode include a first group of subsections and a second group of subsections, where the first group of subsections are connectable with a first terminal for receiving an input signal, and where the second group of subsections is connectable with a second terminal for providing an output signal. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Tunable filter and portable telephone
InactiveUS7135940B2Good reproducibility and reliabilityLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceInductor
A tunable filter has a plurality of variable capacitors and a plurality of inductor elements, each being formed on a common substrate, a filter circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a monitor circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a detecting circuit which detects a prescribed circuit constant of the monitor circuit, a storage which stores information relating to a reference circuit constant of the monitor circuit, and a capacitance control circuit which controls capacitance of the variable capacitors in the monitor circuit and capacitance of the variable capacitors in the filter circuit, based on a result detected by the detecting circuit and information stored in the storage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
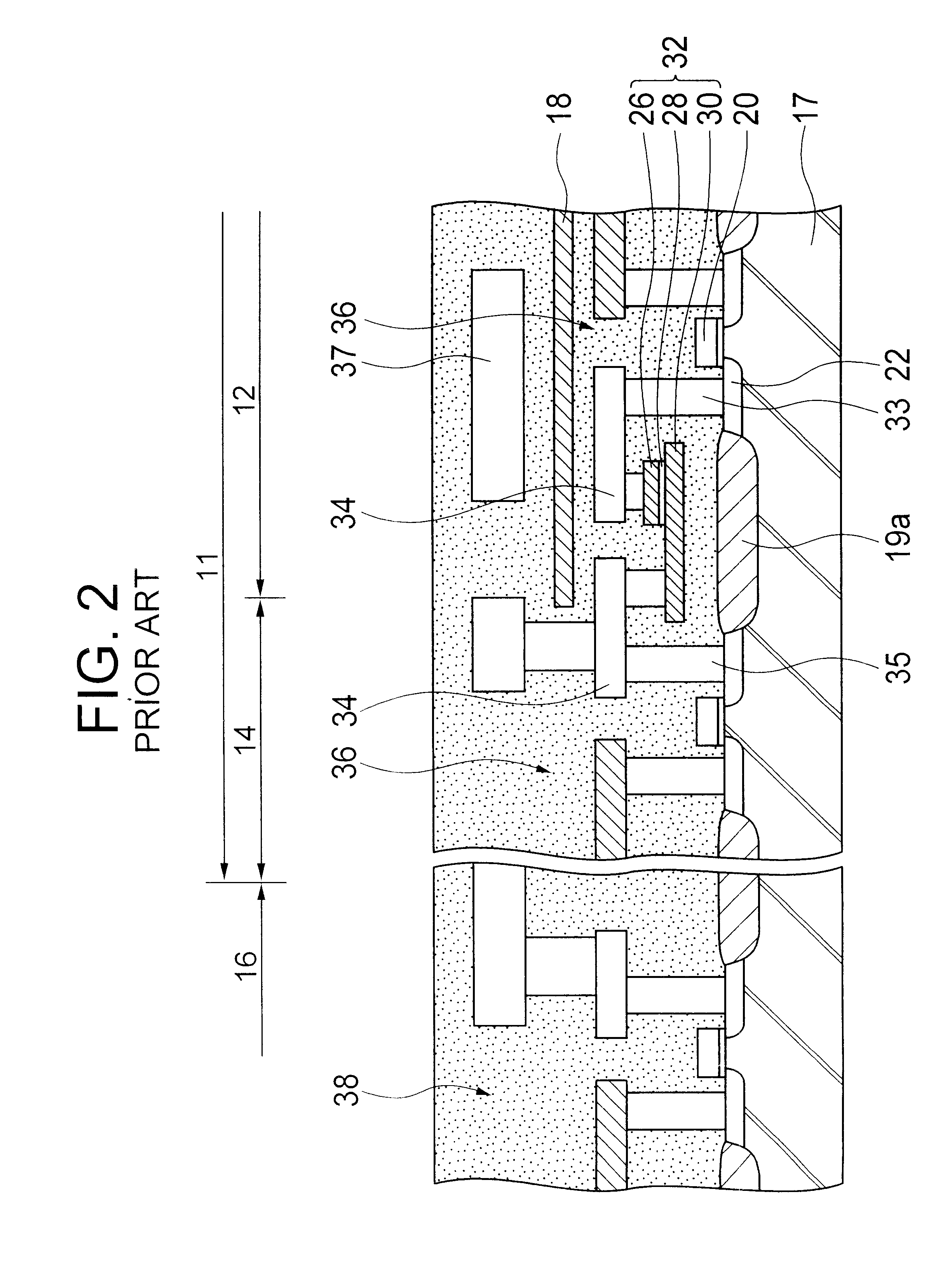
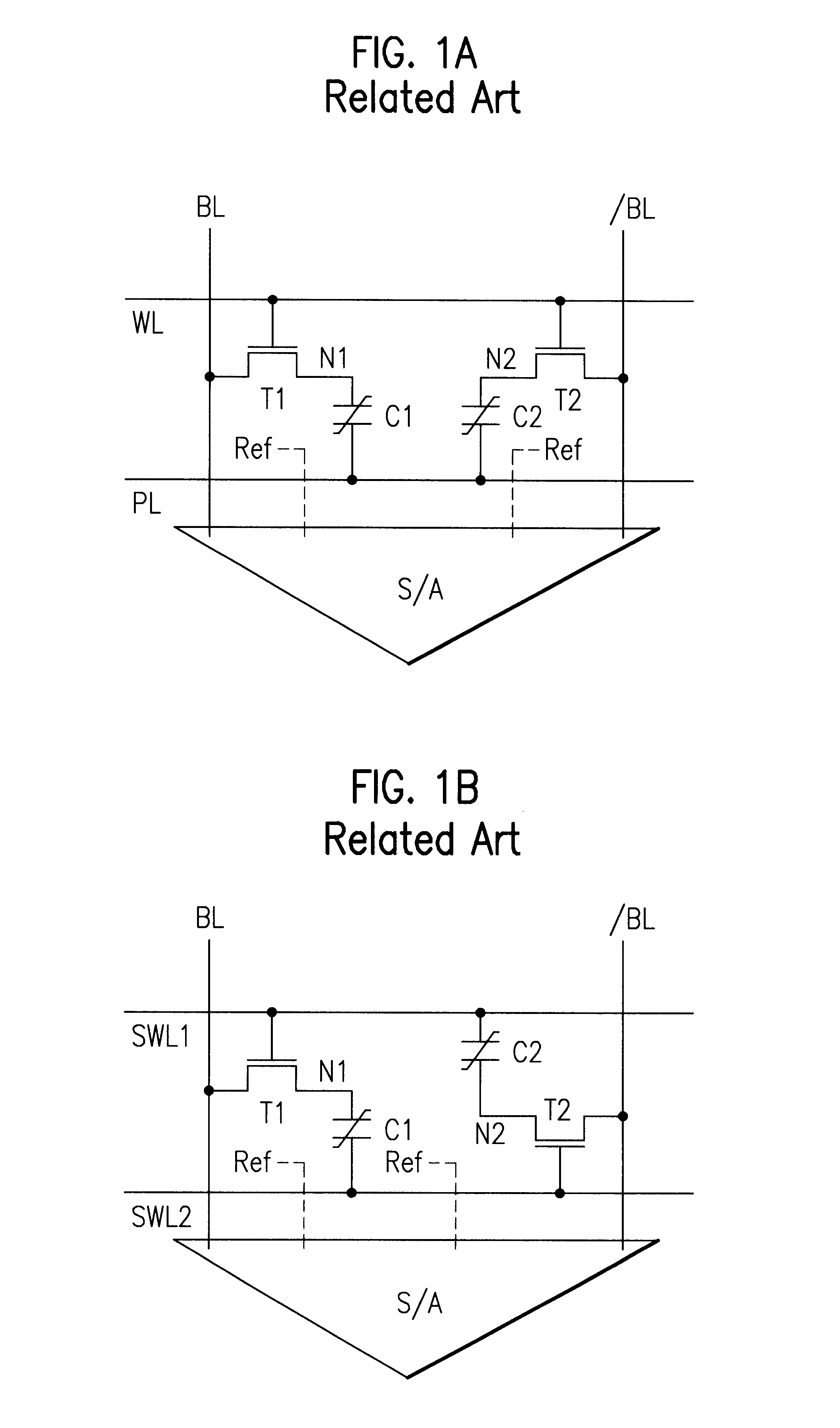
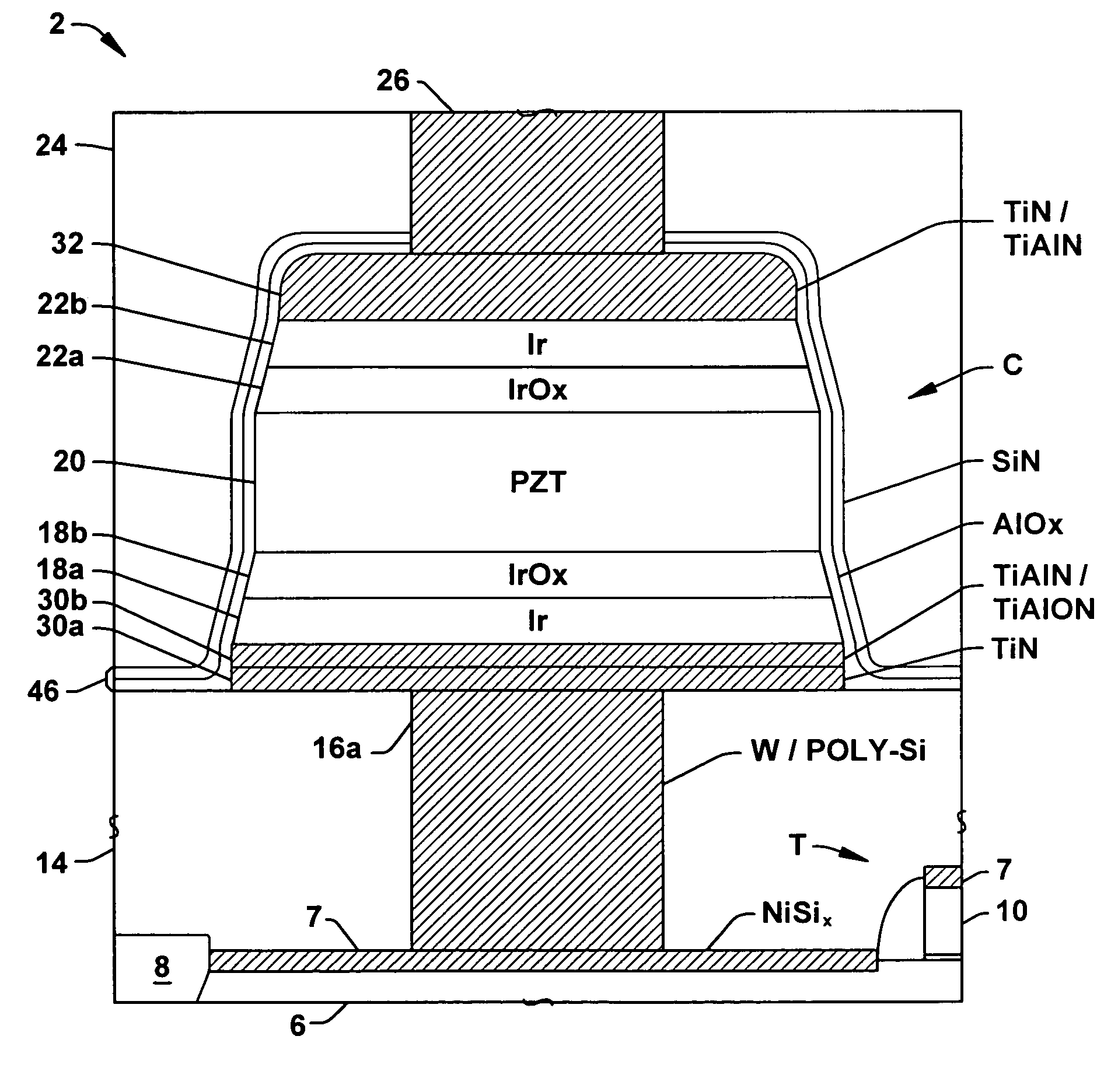
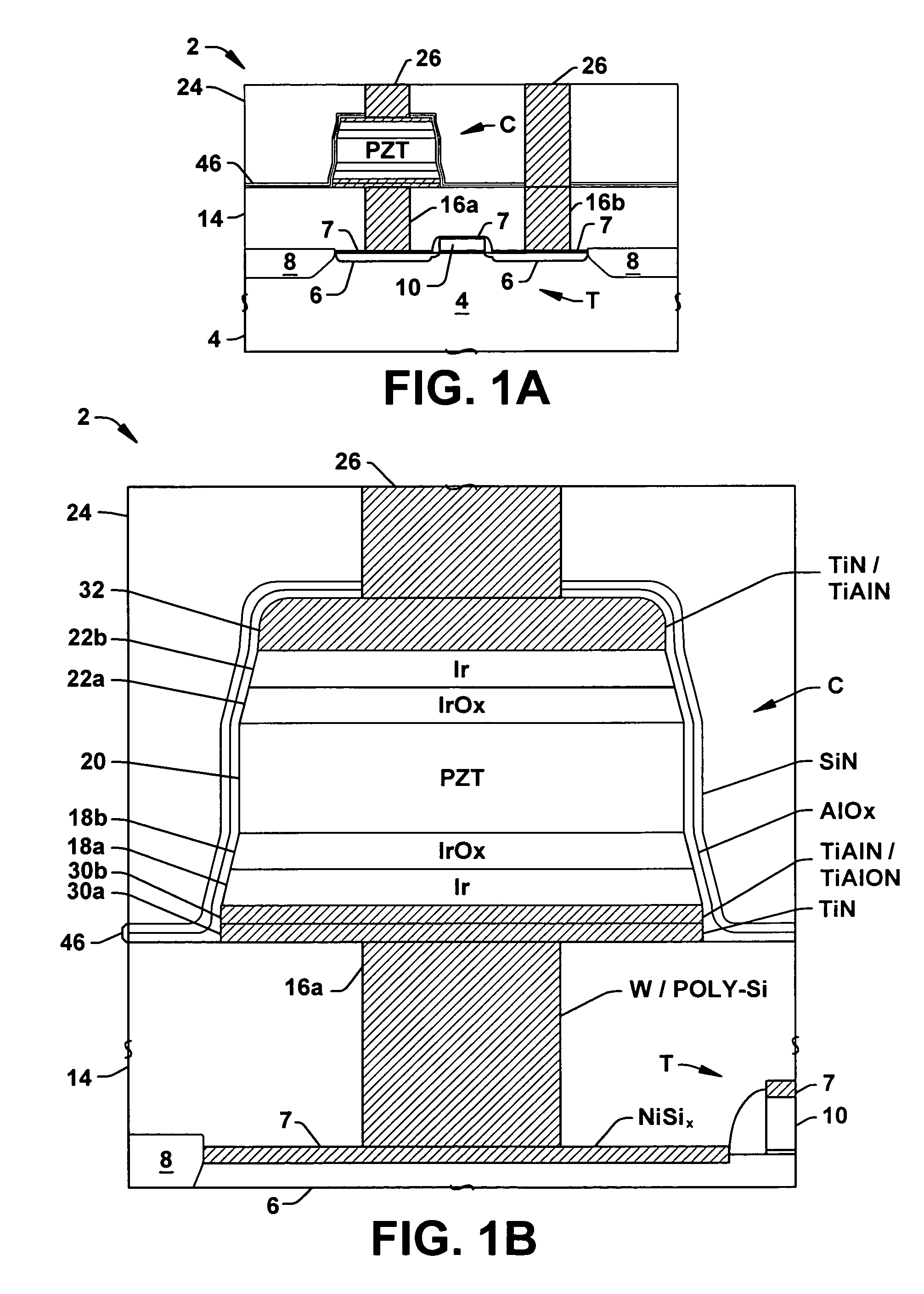
Embedded LSI having a FeRAM section and a logic circuit section
InactiveUS6218197B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen annealingLogic circuitry
An embedded LSI includes a FeRAM macro block and an associated logic circuit section. A hydrogen barrier layer covers the FeRAM macro block as a whole and exposes the logic circuit section. The edge of the hydrogen barrier layer overlies the peripheral circuit of the FeRAM macro block and the boundary separating the FeRAM macro block from the logic circuit section. The ferroelectric capacitor is protected by the hydrogen barrier layer against hydrogen during a hydrogen-annealing process.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
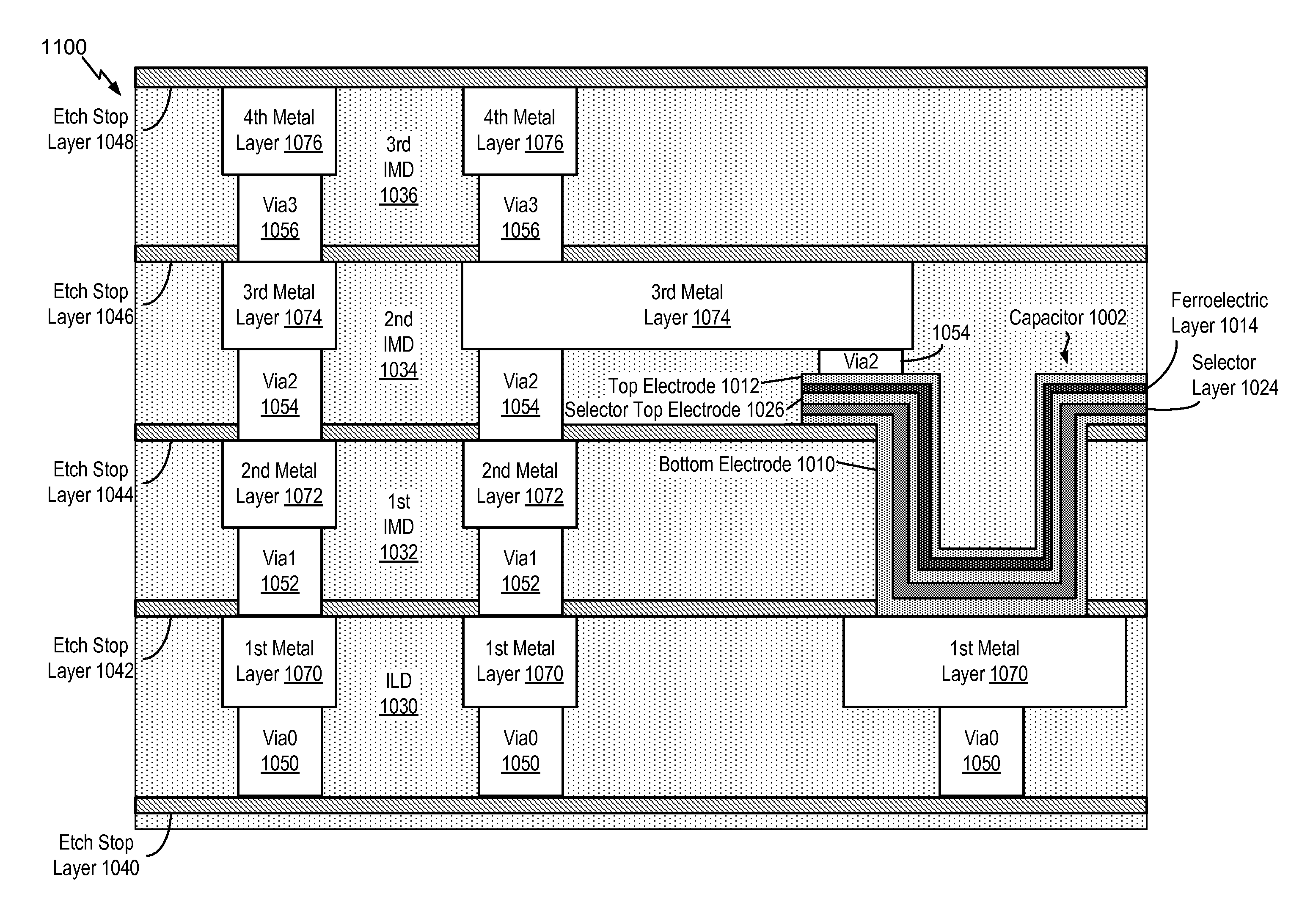
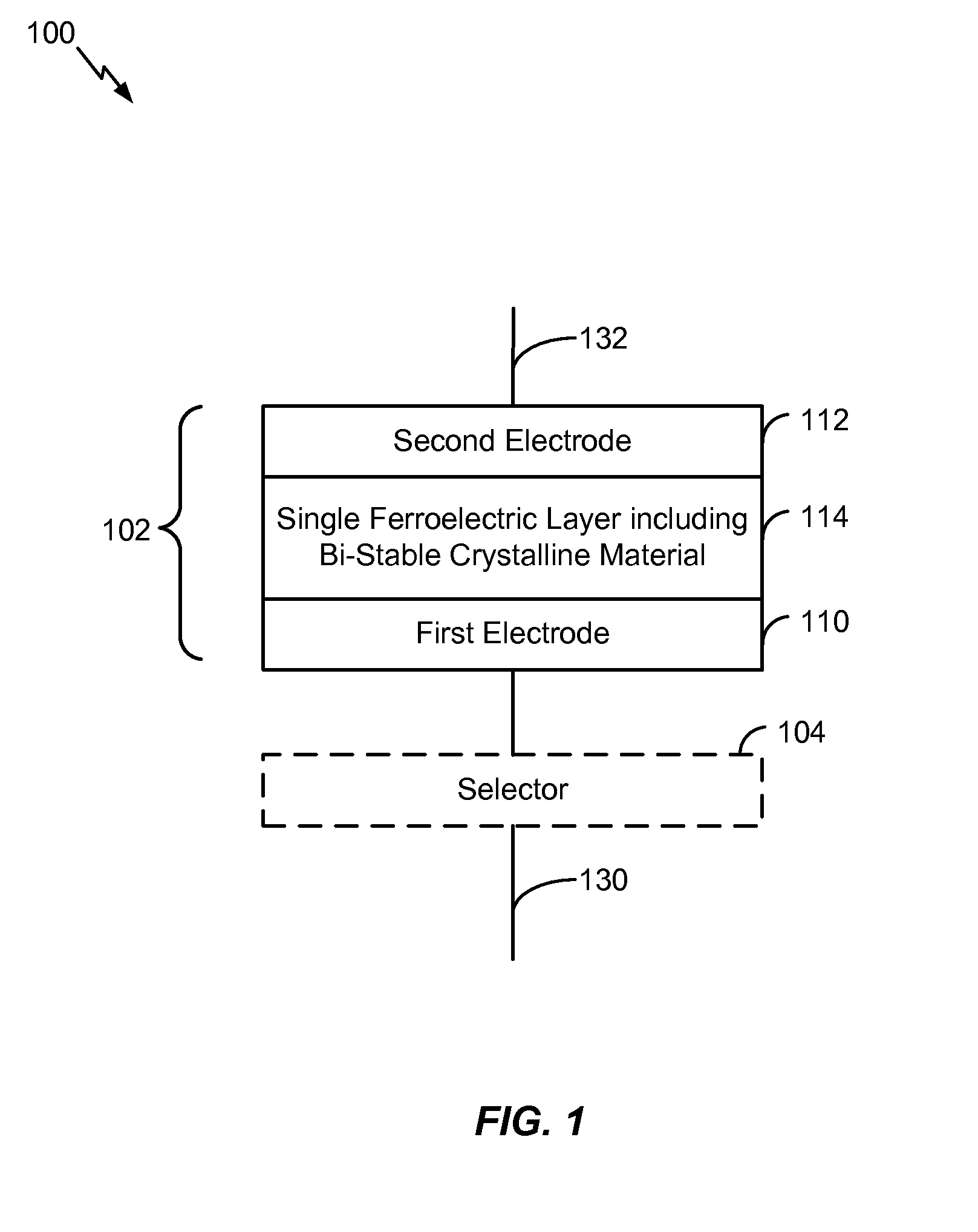
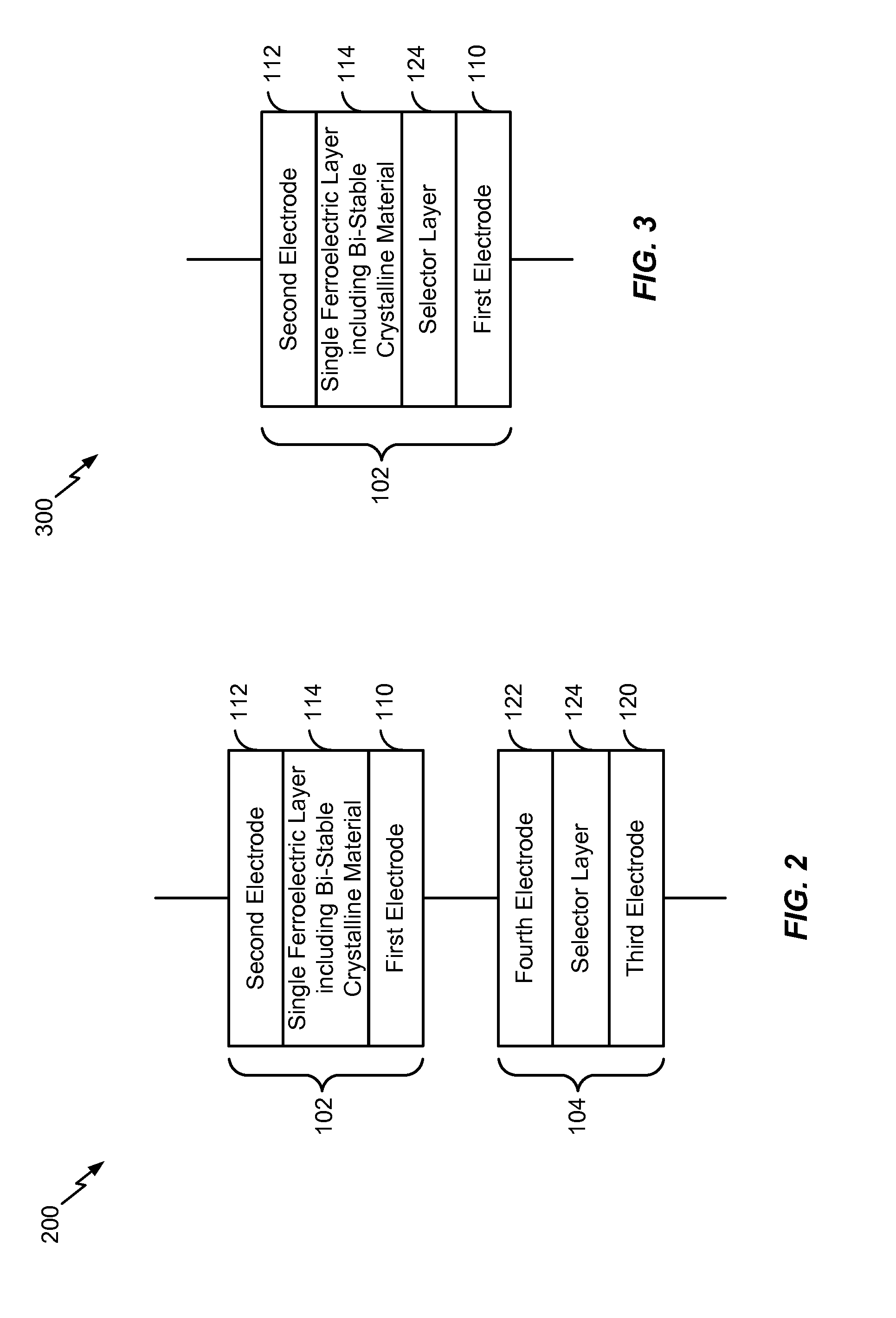
Dynamic random access memory cell including a ferroelectric capacitor
InactiveUS20160064391A1Small sizeExtended retention timeTransistorSolid-state devicesCrystalline materialsMetal
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Phase shift device
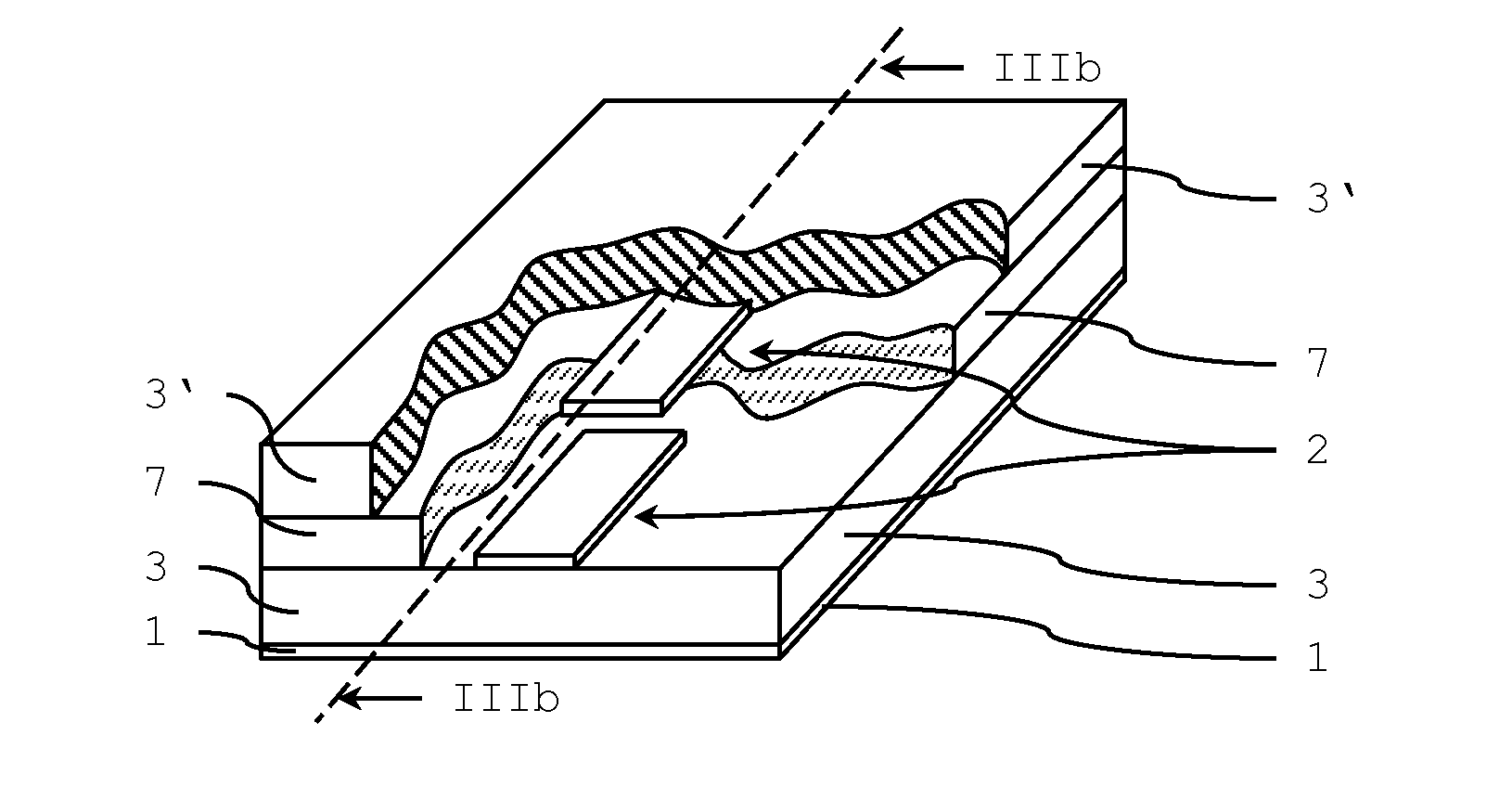
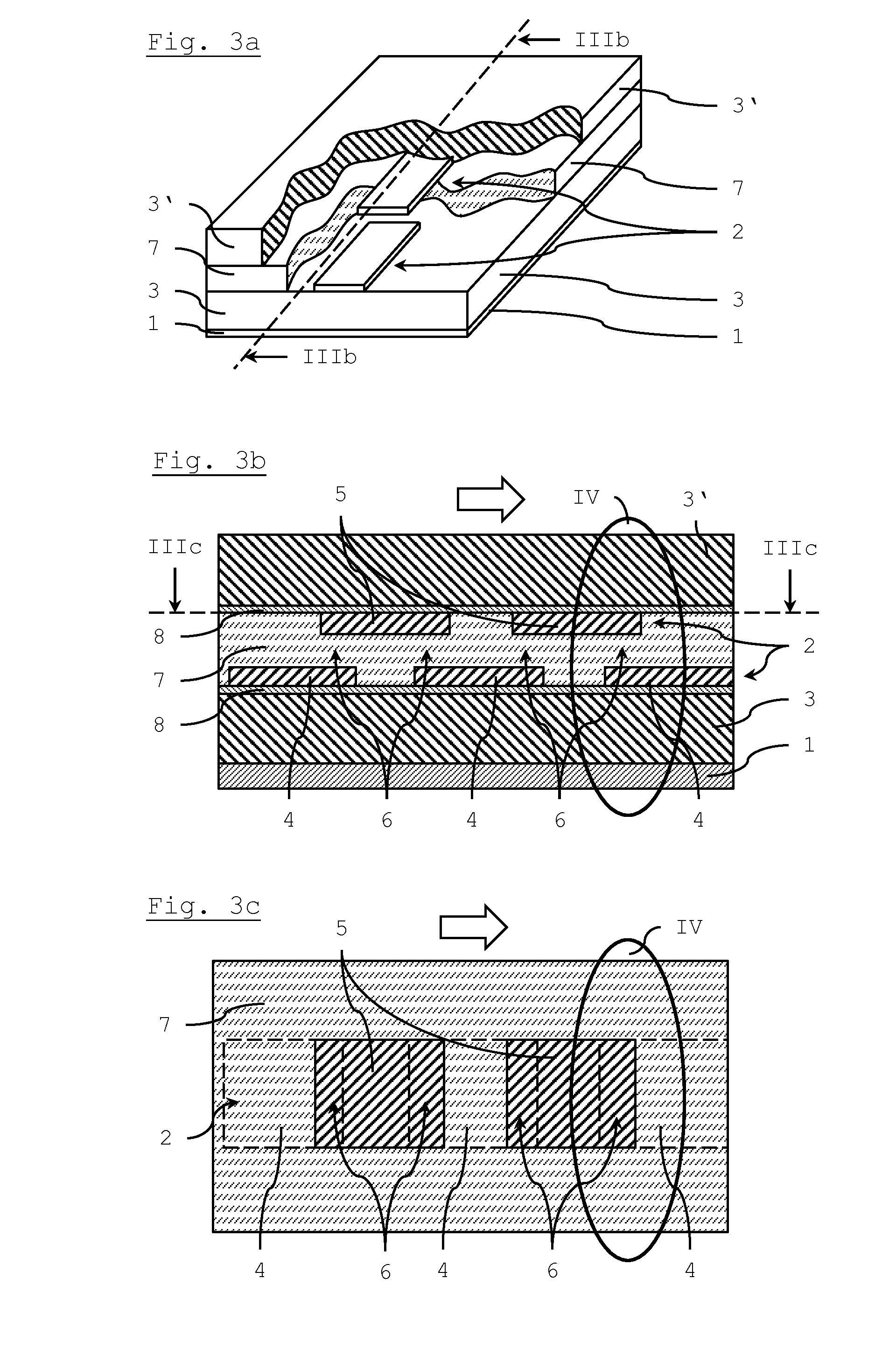
ActiveUS20150380789A1Easy and cost-saving fabricationFast and cheap fabricationCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricDelay linesMetal-insulator-metalElectricity
A phase shift device includes a planar transmission line that is formed by a signal electrode and a ground electrode which are separated by a dielectric substance, whereby the signal electrode of the planar transmission line is divided into several pieces and includes overlapping areas of adjacent pieces that are filled with a tunable liquid crystal material, thereby forming a dielectric tunable component (varactor) with a metal-insulator-metal type capacitor. The several pieces of the signal electrode are arranged at two or more different distance levels with respect to the ground electrode. The tunable liquid crystal material is arranged as a continuous layer between several pieces of the signal electrode that are arranged at two different distance levels.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
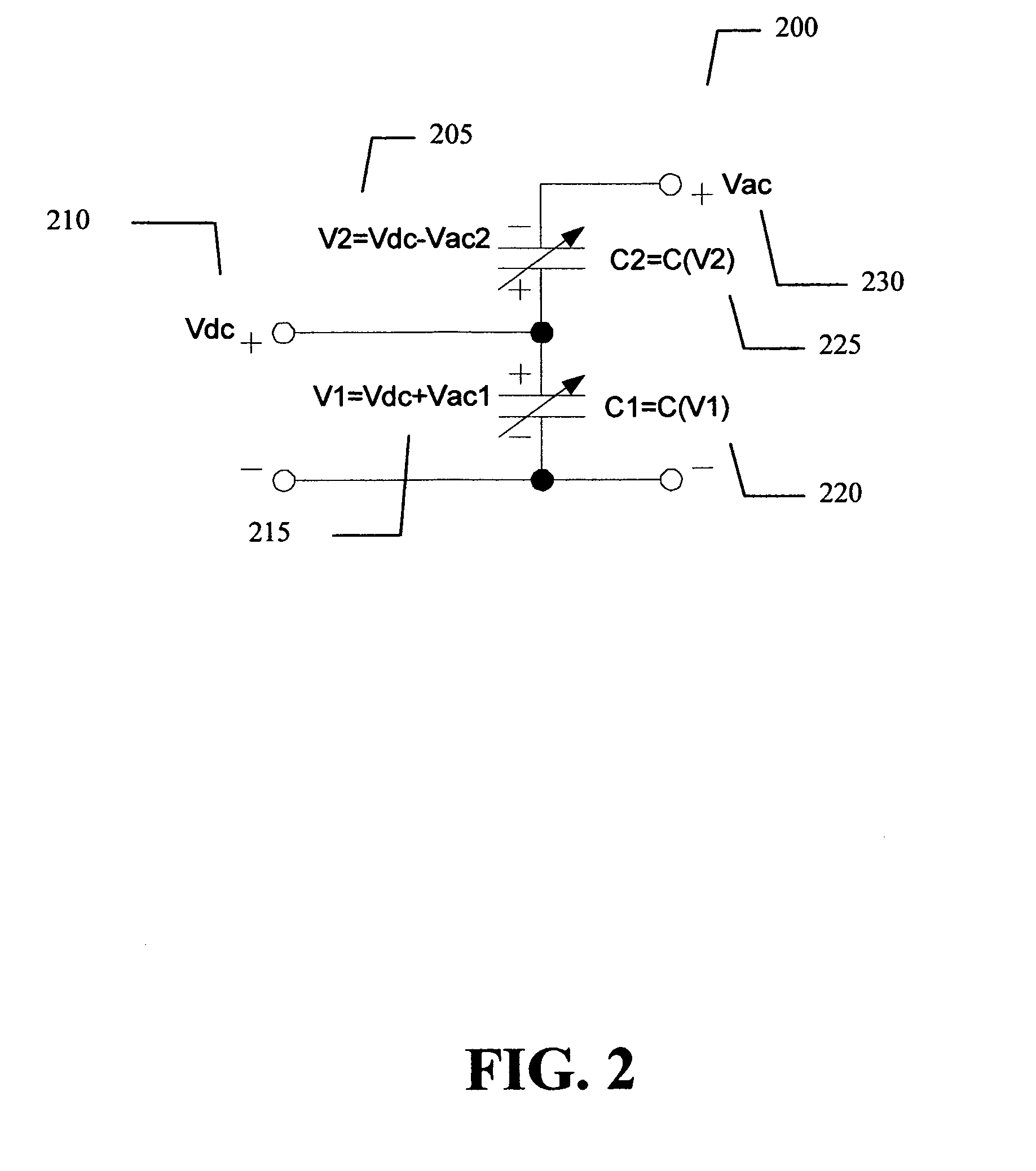
Multiple Control Transcap Variable Capacitor
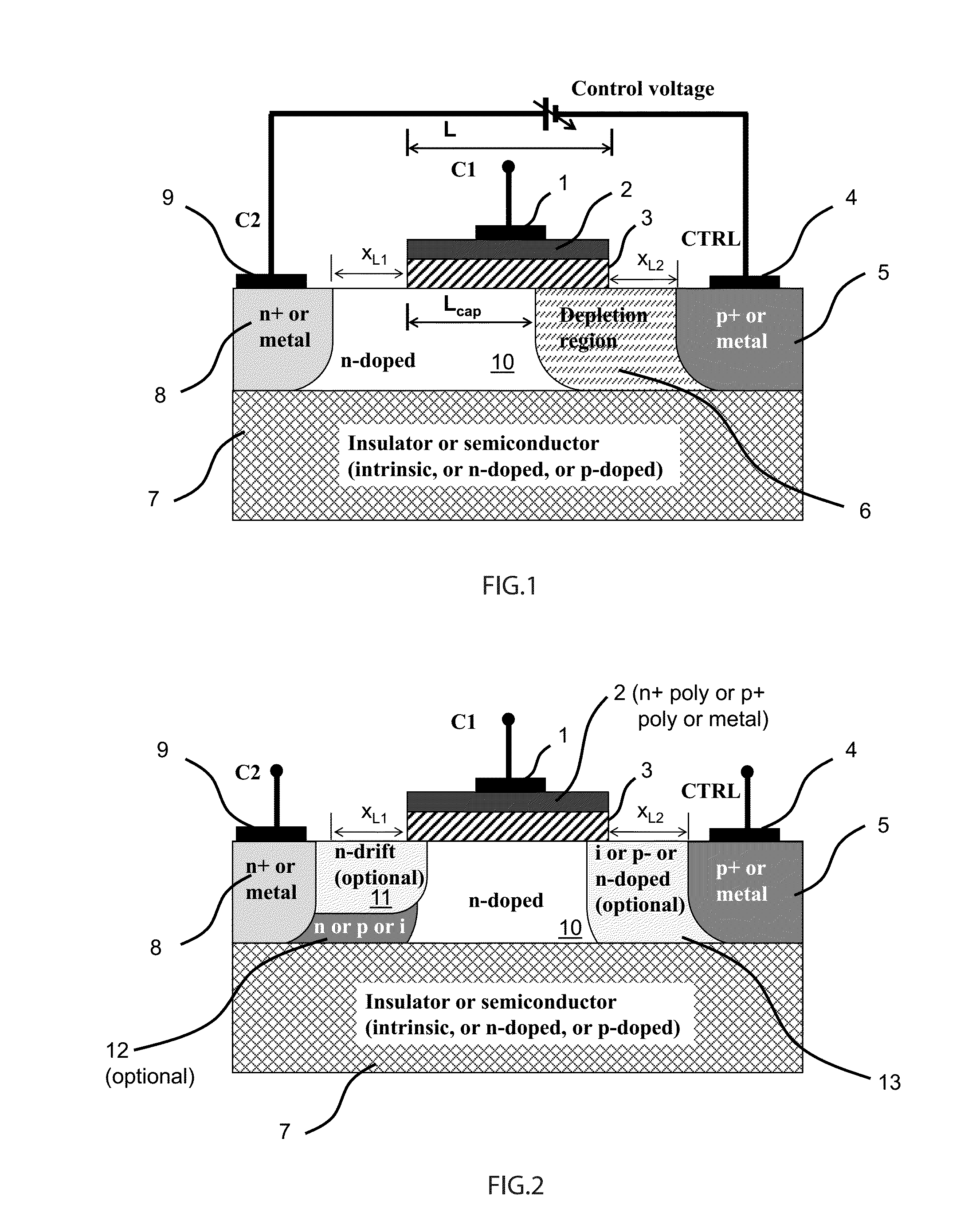
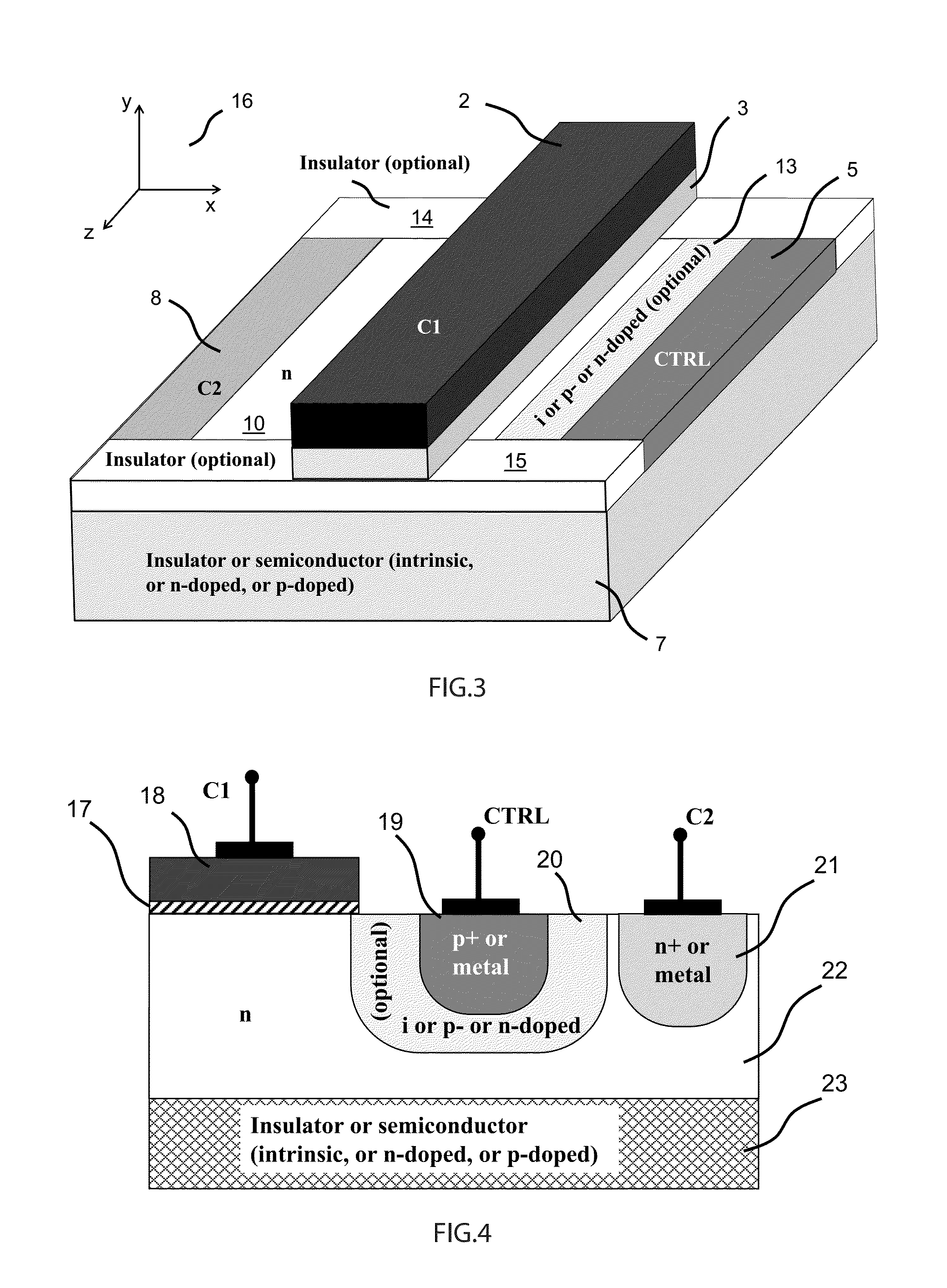
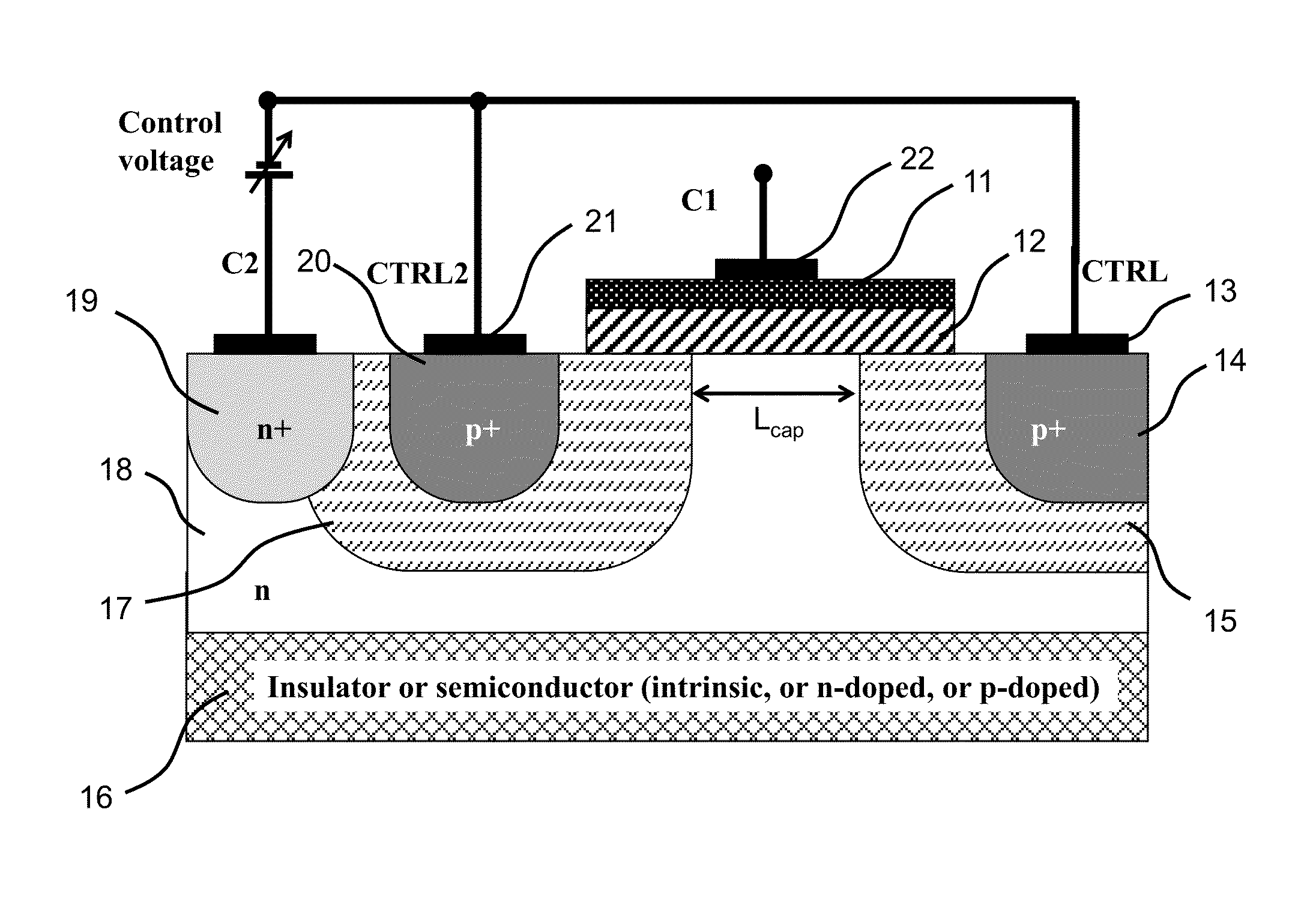
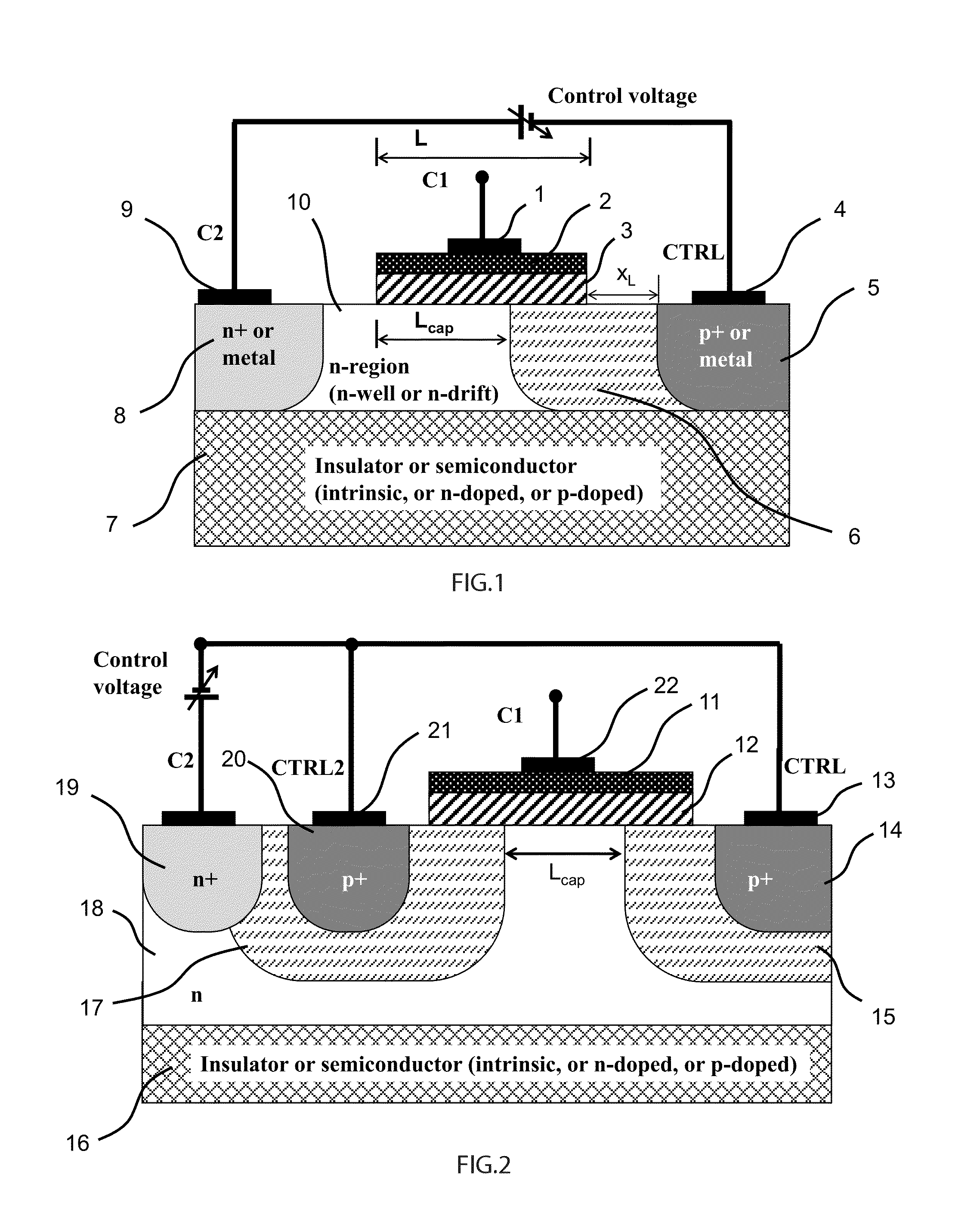
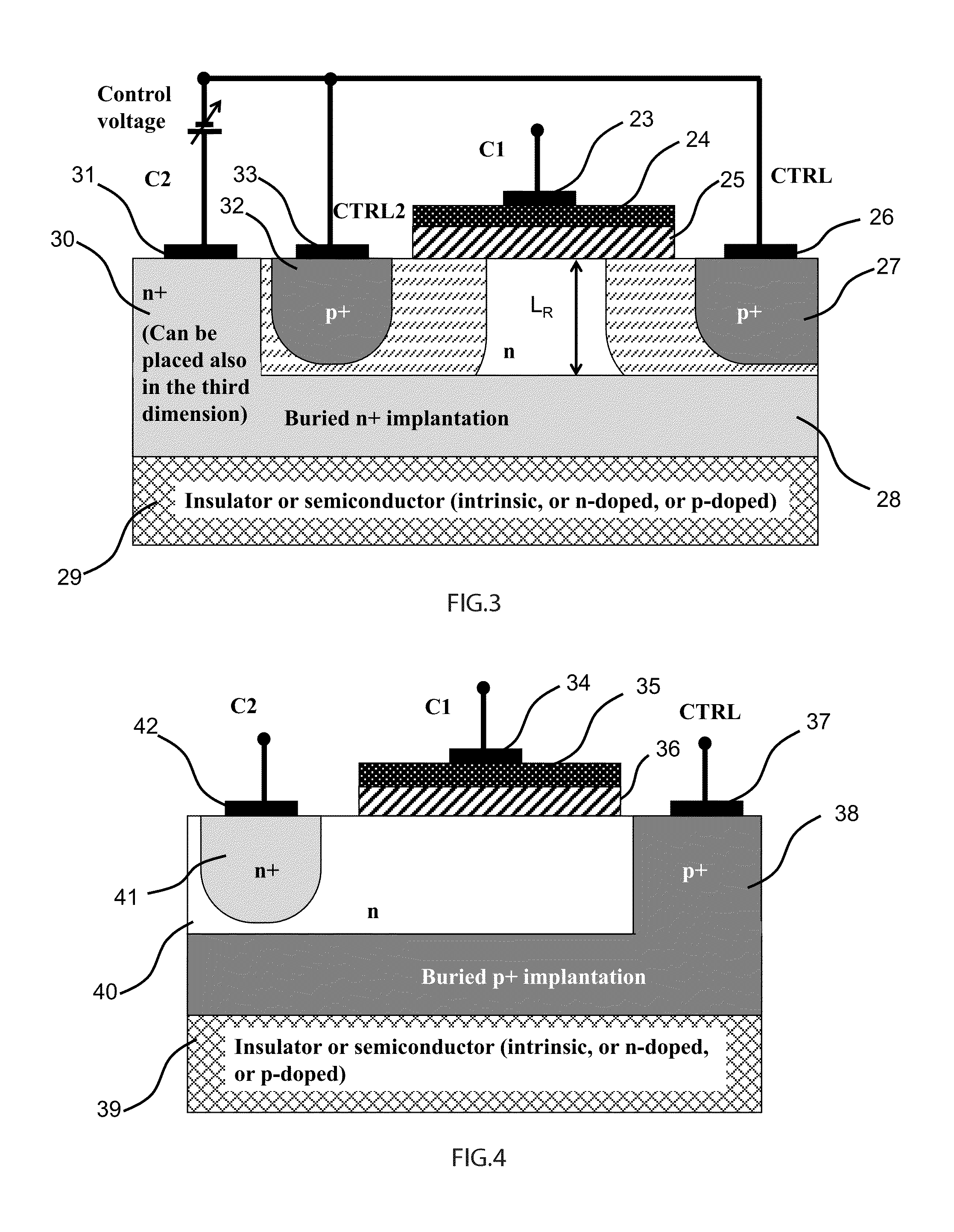
ActiveUS20150194538A1Improve device performanceAvoid distortionSolid-state devicesCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricCapacitanceManufacturing technology
A novel semiconductor variable capacitor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a semiconductor variable MOS capacitor structure suitable for integrated circuits, which has at least three terminals, one of which is used to modulate the equivalent capacitor area of the MOS structure by increasing or decreasing its DC voltage with respect to another terminal of the device, in order to change the capacitance over a wide ranges of values. Furthermore, the present invention decouples the AC signal and the DC control voltage minimizing the distortion and increasing the performance of the device, such as its control characteristic. The present invention is simple and only slightly dependent on the variations due to the fabrication process. It exhibits a high value of capacitance density and, if opportunely implemented, shows a quasi linear dependence of the capacitance value with respect to the voltage of its control terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
InactiveUS20030073565A1Fixed capacitor dielectricCeramic layered productsStrontium titanateBreakdown strength
Tunable dielectric materials including an electronically tunable dielectric ceramic and a low loss glass additive are disclosed. The tunable dielectric may comprise a ferroelectric perskovite material such as barium strontium titanate. The glass additive may comprise boron, barium, calcium, lithium, manganese, silicon, zinc and / or aluminum-containing glasses having dielectric losses of less than 0.003 at 2 GHz. The materials may further include other additives such as non-tunable metal oxides and silicates. The low loss glass additive enables the materials to be sintered at relatively low temperatures while providing improved properties such as low microwave losses and high breakdown strengths.
Owner:NXP USA INC
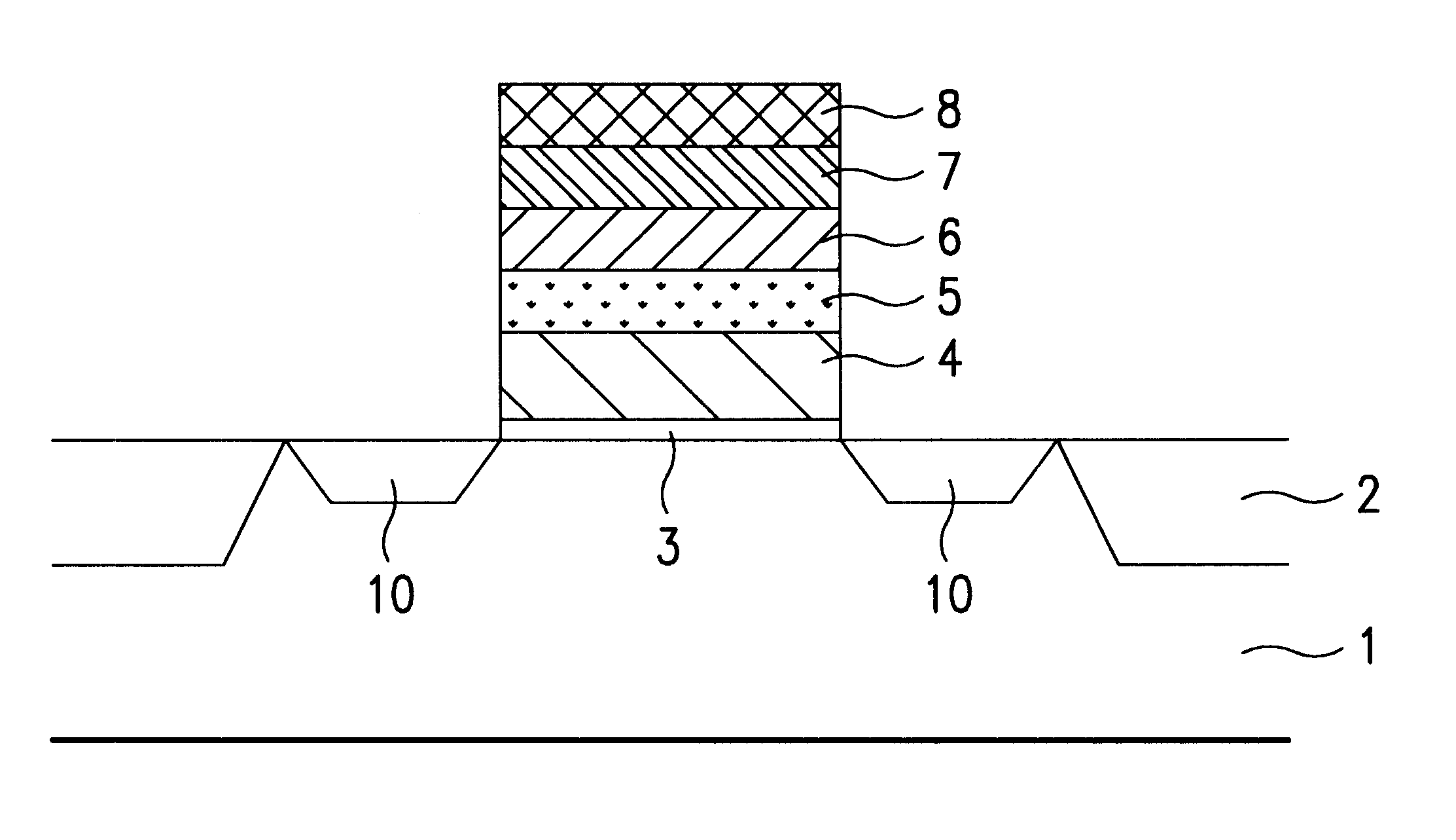
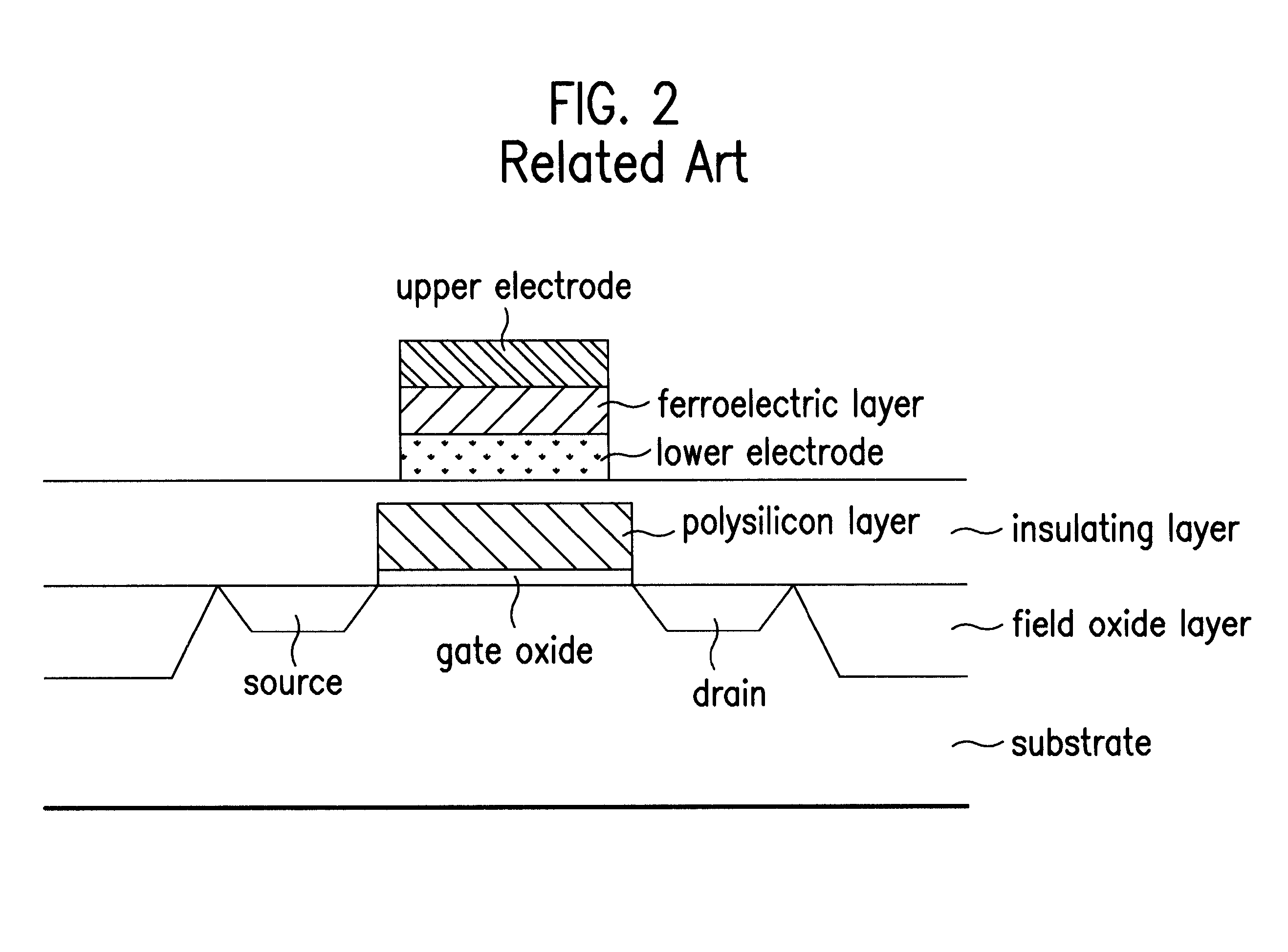
Method for fabricating ferroelectric memory
Method for fabricating a nonvolatile ferroelectric memory, including the steps of (1) forming an insulating layer, a semiconductor layer, an etch stop layer, a lower electrode, a ferroelectric layer, and an upper electrode on a substrate in succession, (2) forming an etch mask pattern of a required form on the upper electrode, (3) using the etch mask pattern as a mask in subjecting the upper electrode, the ferroelectric layer, the lower electrode, the etch stop layer, the semiconductor layer, and the insulating layer to en bloc etching, to expose the substrate, and (4) removing the etch mask pattern, and forming source / drain regions in the exposed substrate, whereby providing a simple fabrication process and permitting to minimize an alignment allowance.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Tuneable electromagnetic bandgap structures based on high resistivity silicon substrates
ActiveUS7030463B1Small sizeSmall size and tunableCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitor with temperature varied dielectricFerroelectric thin filmsHigh resistivity silicon
Electrically tunable electromagnetic bandgap (“TEBG”) structures using a ferroelectric thin film on a semiconductor substrate, tunable devices that include such a TEBG structure, such as a monolithic microwave integrated circuit (“MMIC”), and a method producing such a TEBG structure are disclosed. The present invention provides a semiconductive substrate having an oxide layer, a first conductive layer positioned on the oxide layer, a ferroelectric layer covering the first conductive layer, and a second conductive layer positioned on a surface of the tunable ferroelectric layer. The use of the ferroelectric layer, which have a DC electric field dependent permittivity, enables a small size, tunable EBG structure.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
Electrically tunable filters with dielectric varactors
InactiveUS7145415B2Increase powerReduce distortion problemsMultiple-port networksActive element networkEngineeringBand-stop filter
Owner:NXP USA INC
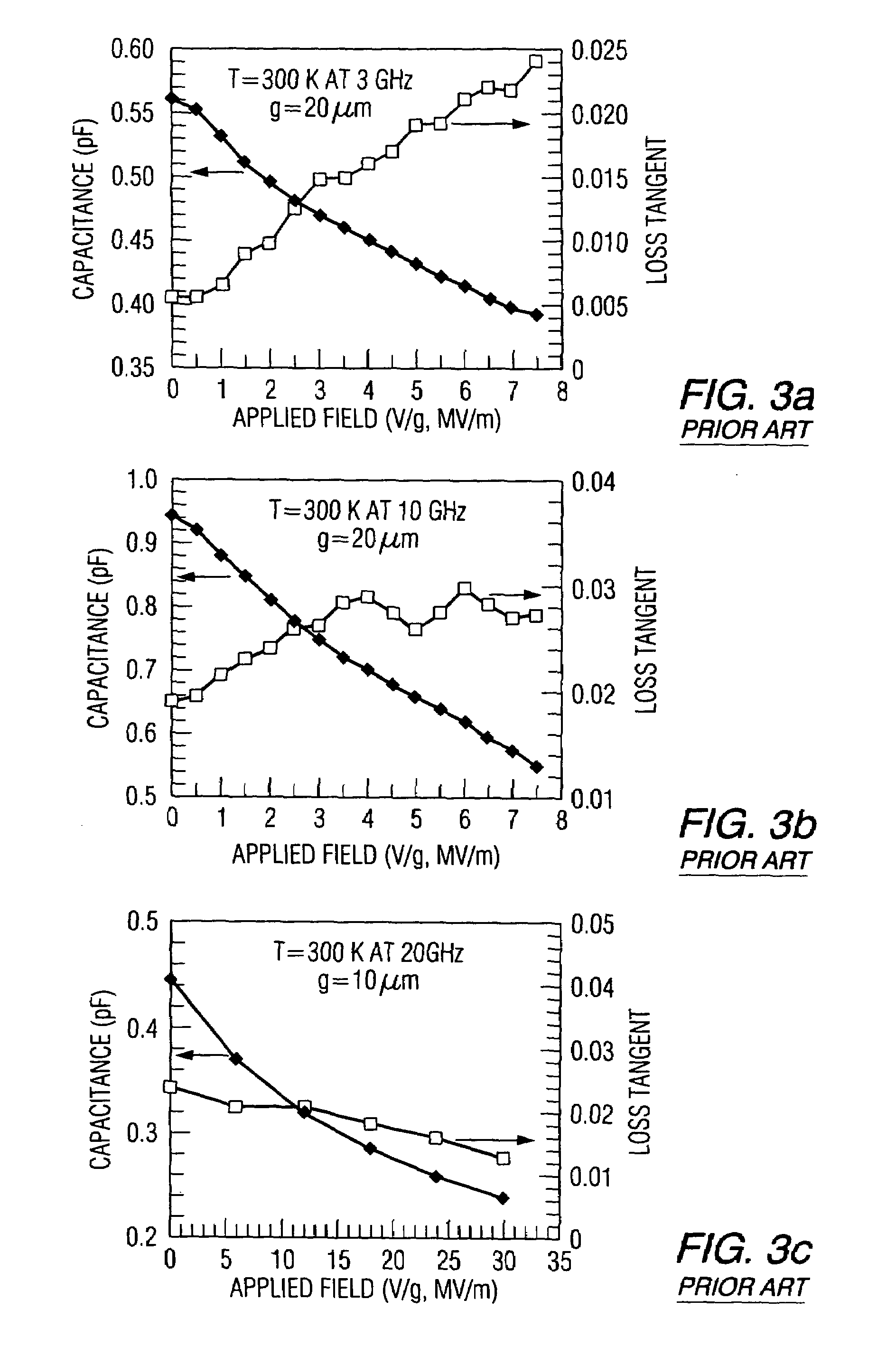
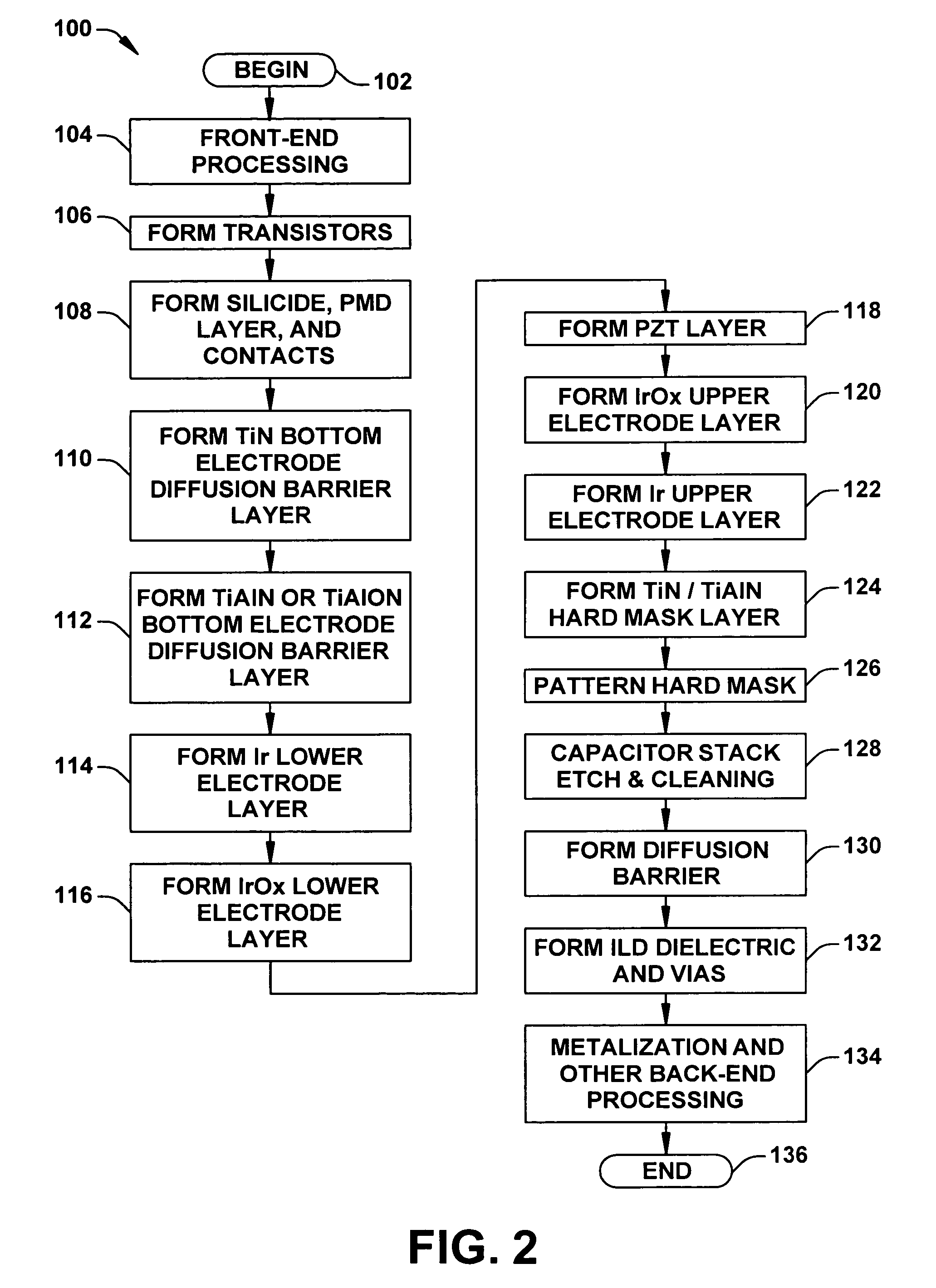
Ferroelectric capacitor stack etch cleaning methods
ActiveUS7220600B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricEtchingCleaning methods
Methods (100) are provided for fabricating a ferroelectric capacitor structure including methods (128) for etching and cleaning patterned ferroelectric capacitor structures in a semiconductor device. The methods comprise etching (140, 200) portions of an upper electrode, etching (141, 201) ferroelectric material, and etching (142, 202) a lower electrode to define a patterned ferroelectric capacitor structure, and etching (143, 206) a portion of a lower electrode diffusion barrier structure. The methods further comprise ashing (144, 203) the patterned ferroelectric capacitor structure using a first ashing process, performing (145, 204) a wet clean process after the first ashing process, and ashing (146, 205) the patterned ferroelectric capacitor structure using a second ashing process directly after the wet clean process at a high temperature in an oxidizing ambient.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Analog transcap device
ActiveUS8803288B1Improve device performanceAvoid distortionSolid-state devicesCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricCapacitanceSemiconductor structure
A novel semiconductor variable capacitor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a semiconductor variable MOS capacitor structure suitable for integrated circuits, which has at least three terminals, one of which is used to modulate the equivalent capacitor area of the MOS structure by increasing or decreasing its DC voltage with respect to another terminal of the device, in order to change the capacitance over a wide ranges of values. Furthermore, the present invention decouples the AC signal and the DC control voltage avoiding distortion and increasing the performance of the device, such as its control characteristic. The present invention is simple and only slightly dependent on the variations due to the fabrication process. It exhibits a high value of capacitance density and, if opportunely implemented, shows a quasi linear dependence of the capacitance value with respect to the voltage of its control terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multi-Sacrificial Layer and Method
ActiveUS20100240215A1Reduction and elimination of variationReduce eliminateElectrolytic capacitorsPretreated surfacesCapacitorElectrical and Electronics engineering
MEMS devices and methods for utilizing sacrificial layers are provided. An embodiment comprises forming a first sacrificial layer and a second sacrificial layer over a substrate, wherein the second sacrificial layer acts as an adhesion layer. Once formed, the first sacrificial layer and the second sacrificial layer are patterned such that the second sacrificial layer is undercut to form a step between the first sacrificial layer and the second sacrificial layer. A top capacitor electrode is formed over the second sacrificial layer, and the first sacrificial layer and the second sacrificial layer are removed in order to free the top capacitor electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Capacitors adapted for acoustic resonance cancellation
ActiveUS20080232023A1Reduce lossesImproving QMechanically variable capacitor detailsFixed capacitor electrodesAcousticsDielectric permittivity
An embodiment of the present invention provides a device, comprising a multilayered tunable dielectric capacitor, wherein said multilayers of tunable dielectric are adapted to be DC biased to reduce the dielectric constant; and wherein the DC bias is arranged so that the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased positively is equal to the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased negatively.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Capacitive humidity sensor
InactiveUS20040182153A1Reduce the differenceReduce capacitance differenceUsing mechanical meansCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricMoisture permeationMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes a detection portion and a reference portion. The detection portion includes detection electrodes and a moisture sensitive film. The reference portion includes reference electrodes and a moisture permeation film as a capacitance adjusting film. The capacitive humidity sensor detects humidity by converting a capacitance difference between a capacitance of the detection electrodes and a capacitance of the reference electrodes to an electric signal by using a capacitance-voltage conversion circuit. The moisture permeation film reduces offset voltage of the capacitive humidity sensor. Thus, an offset compensation circuit or the like is not required.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Quantum energy storage or retrieval device
InactiveUS6501093B1Small leakageEliminate air pollutionSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaicsHigh energyBusbar
A solid state Quantum high Energy density Storage Or Retrieval device known as a quensor, and the trademark ENSOR(TM), having an energy density of about 1-15 kwhr / kg, comparable to gasoline, or more, is described. A fundamentally new principle is employed: A quensor film comprises oriented molecules with donor and acceptor groups and with metal layers on its surfaces. A dipole electric field may be established in the gap between a donor and an acceptor. Electric energy is stored in or retrieved from dipole electric fields throughout the volume of the quensor film. Electric energy is stored in the quensor film by charging the dipole electric fields from an electric energy source. Electric energy is retrieved from a quensor film by discharging the dipole electric fields and supplying the energy to a load. Electric breakdown in the film is avoided because positive and negative electric charges in the film are balanced everywhere. Busbars attached to the metal layers are connected to terminals for charging or discharging the device. The manufacture of a quensor film is described. A composite photovoltaic and quensor panel for the storage or retrieval of solar-electric energy day or night on demand is also described.
Owner:MARKS ALVIN M
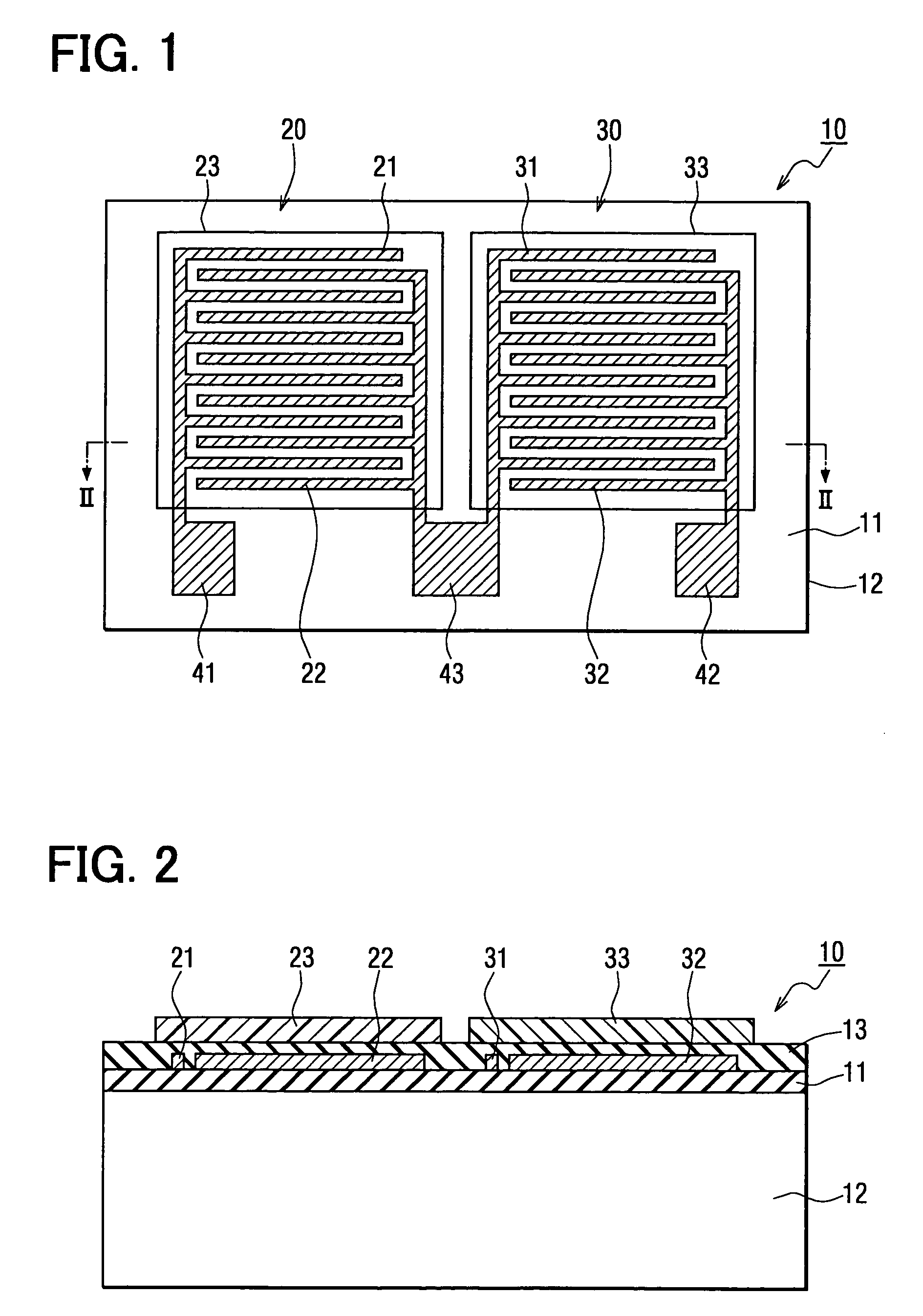
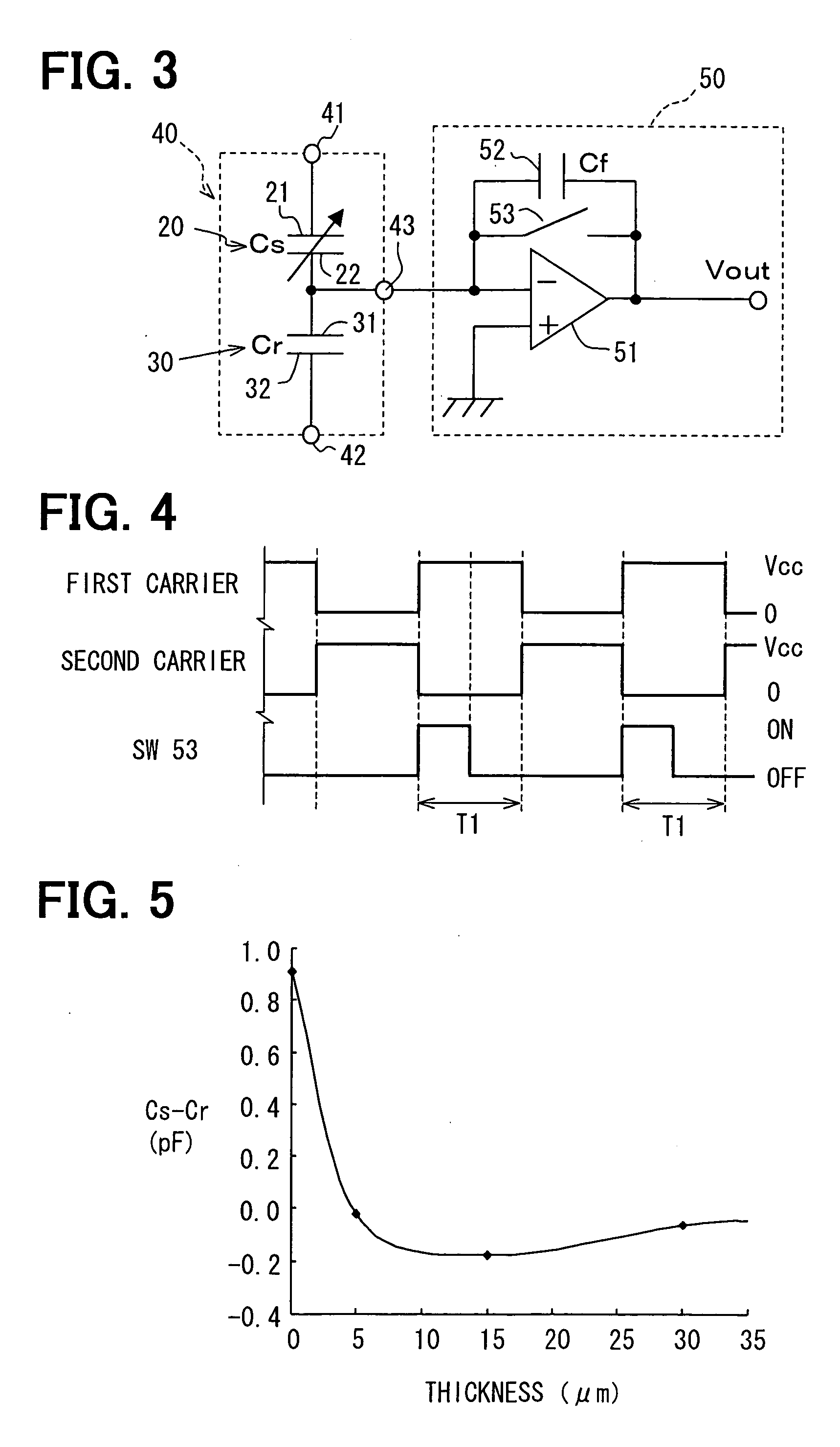
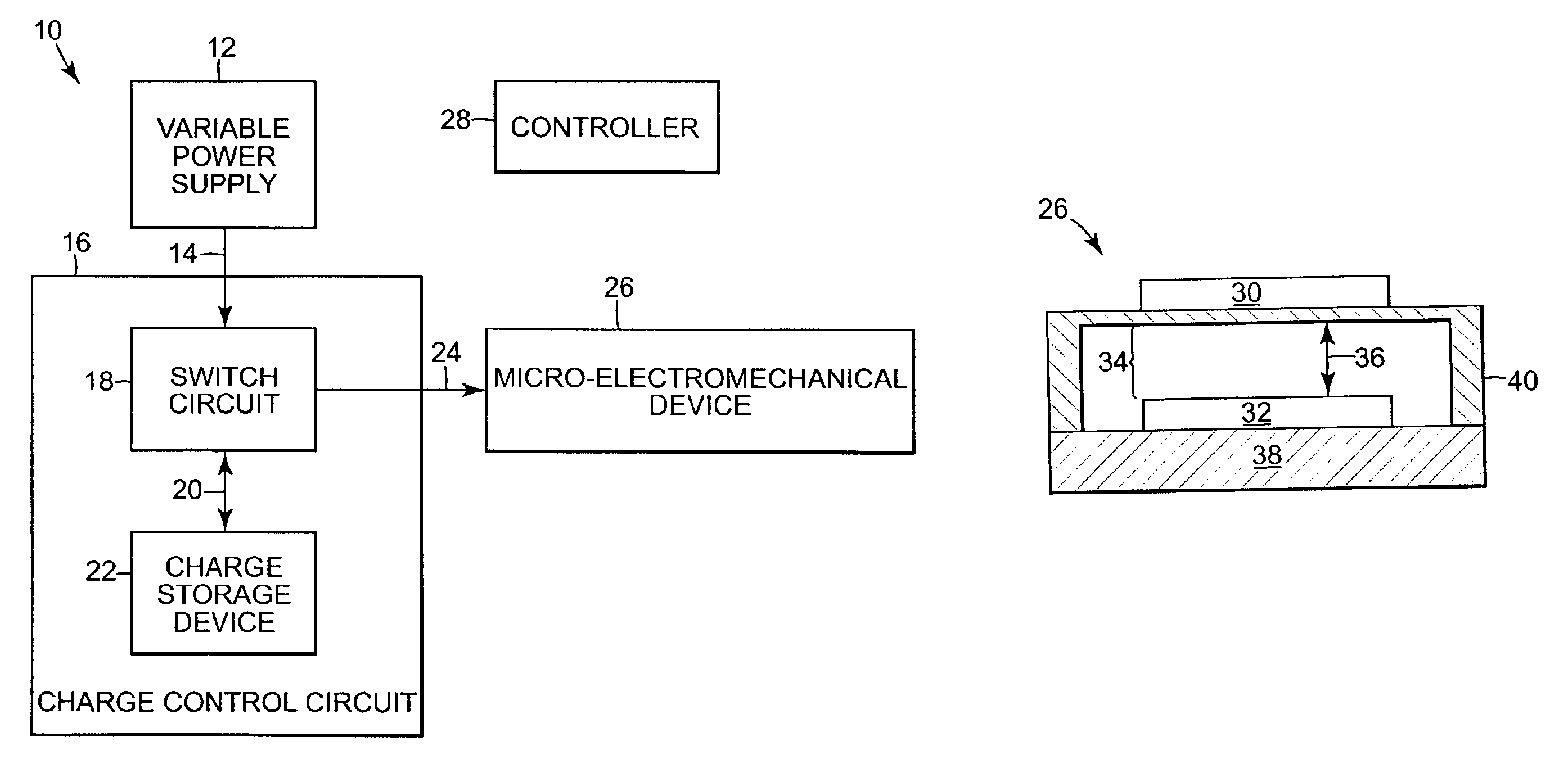
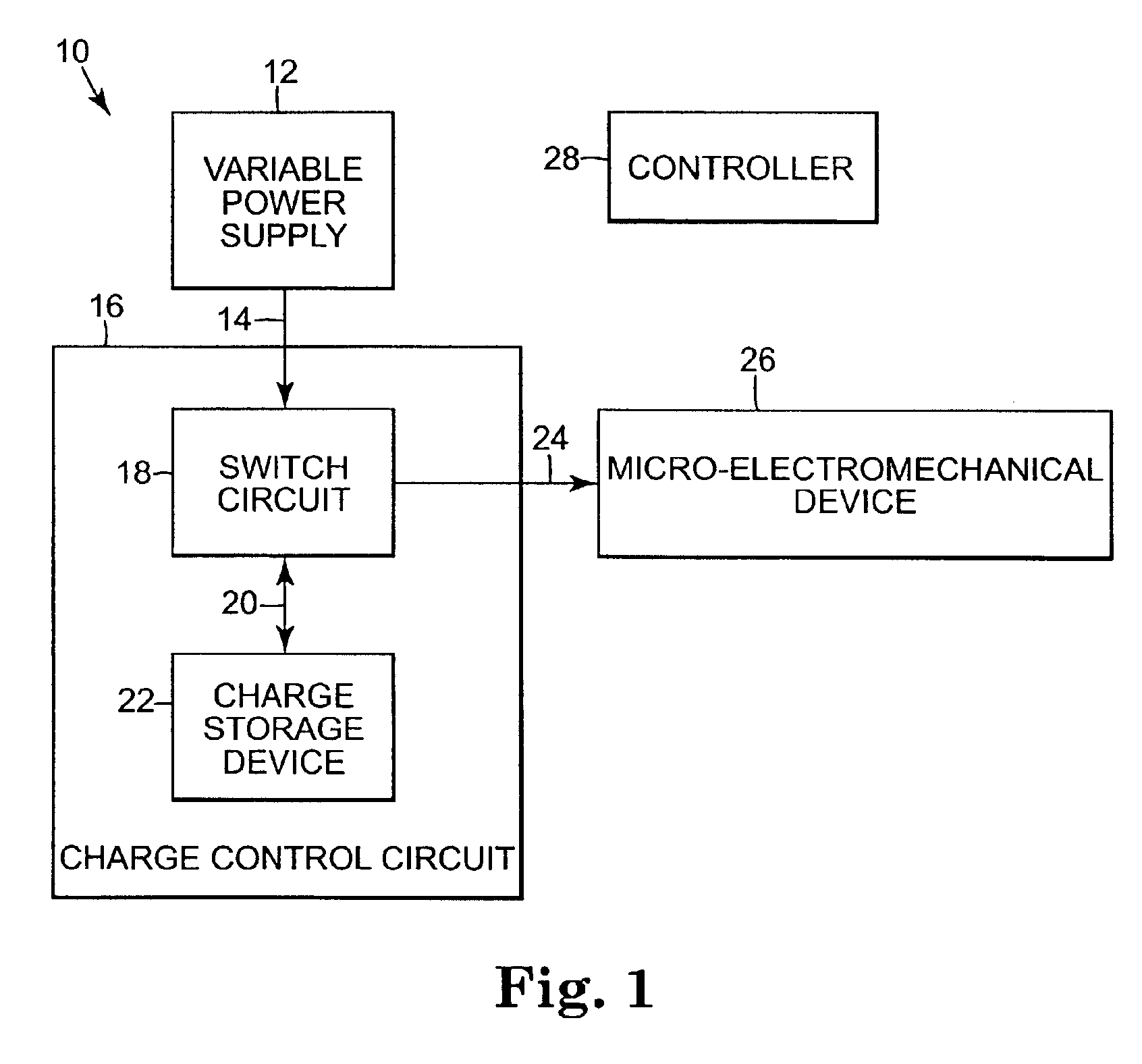
Charge control circuit for a micro-electromechanical device
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
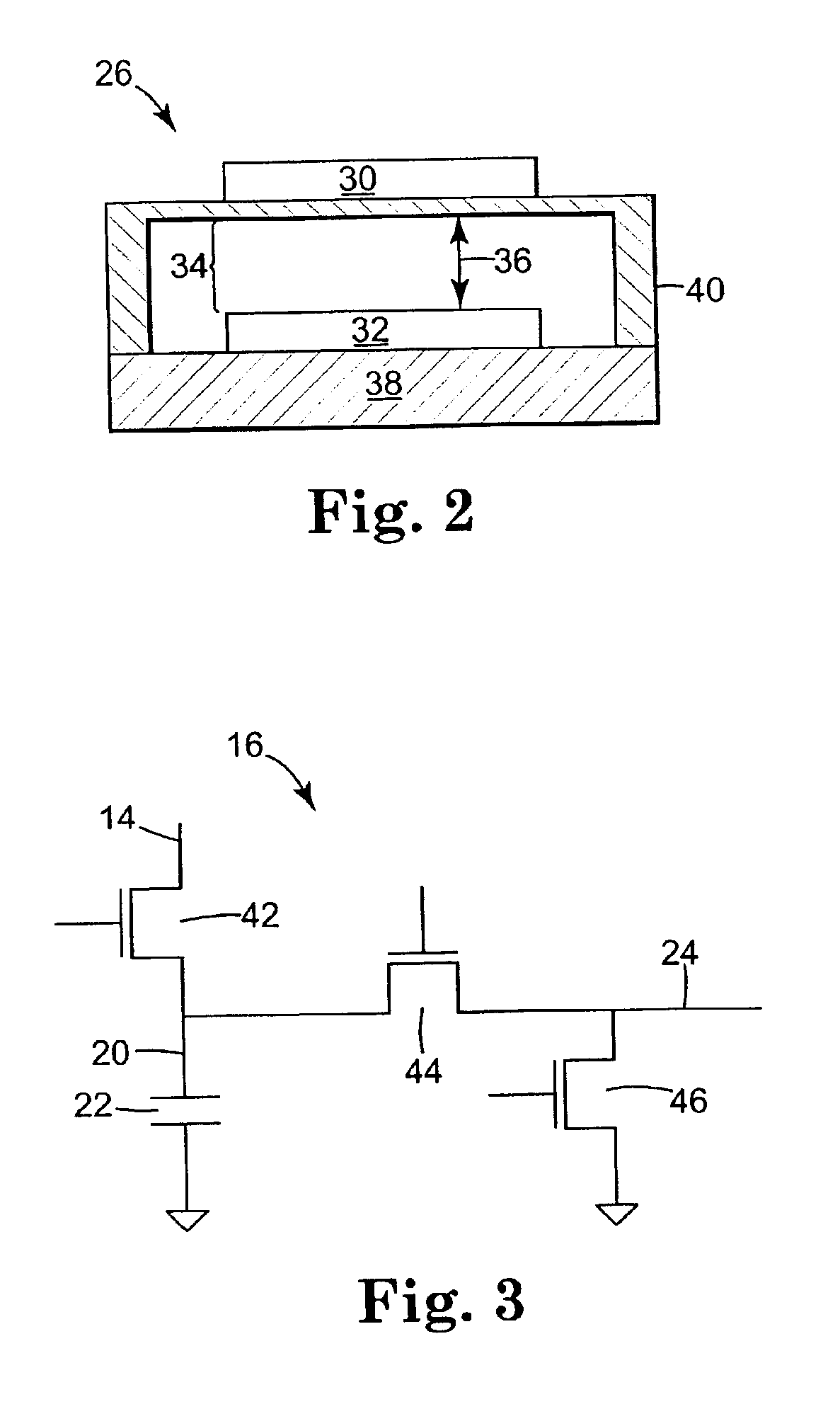
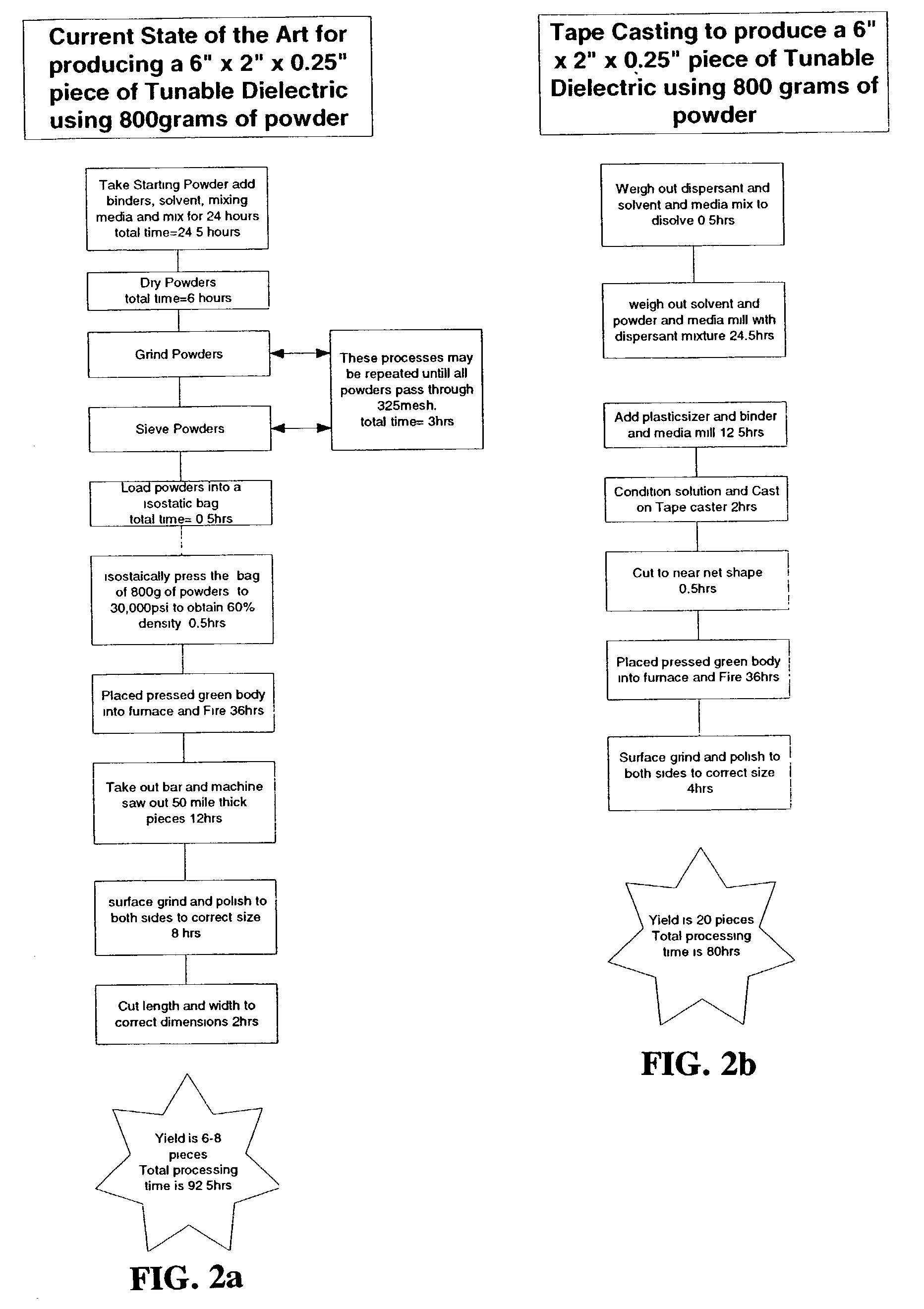
Method for producing low-loss tunable ceramic composites with improved breakdown strengths
InactiveUS20030119656A1Improved propertyLow cost productionLayered productsFixed capacitor dielectricBreakdown strengthMicrowave
The production of low-loss, tunable composite ceramic materials with improved breakdown strengths is disclosed. The composite materials comprise ferroelectric perovskites such as barium strontium titanate or other ferroelectric perovskites combined with other phases such as low-loss silicate materials and / or other low-loss oxides. The composite materials are produced in sheet or tape form by methods such as tape casting. The composite tapes exhibit favorable tunability, low loss and tailorable dielectric properties, and can be used in various microwave devices.
Owner:NXP USA INC
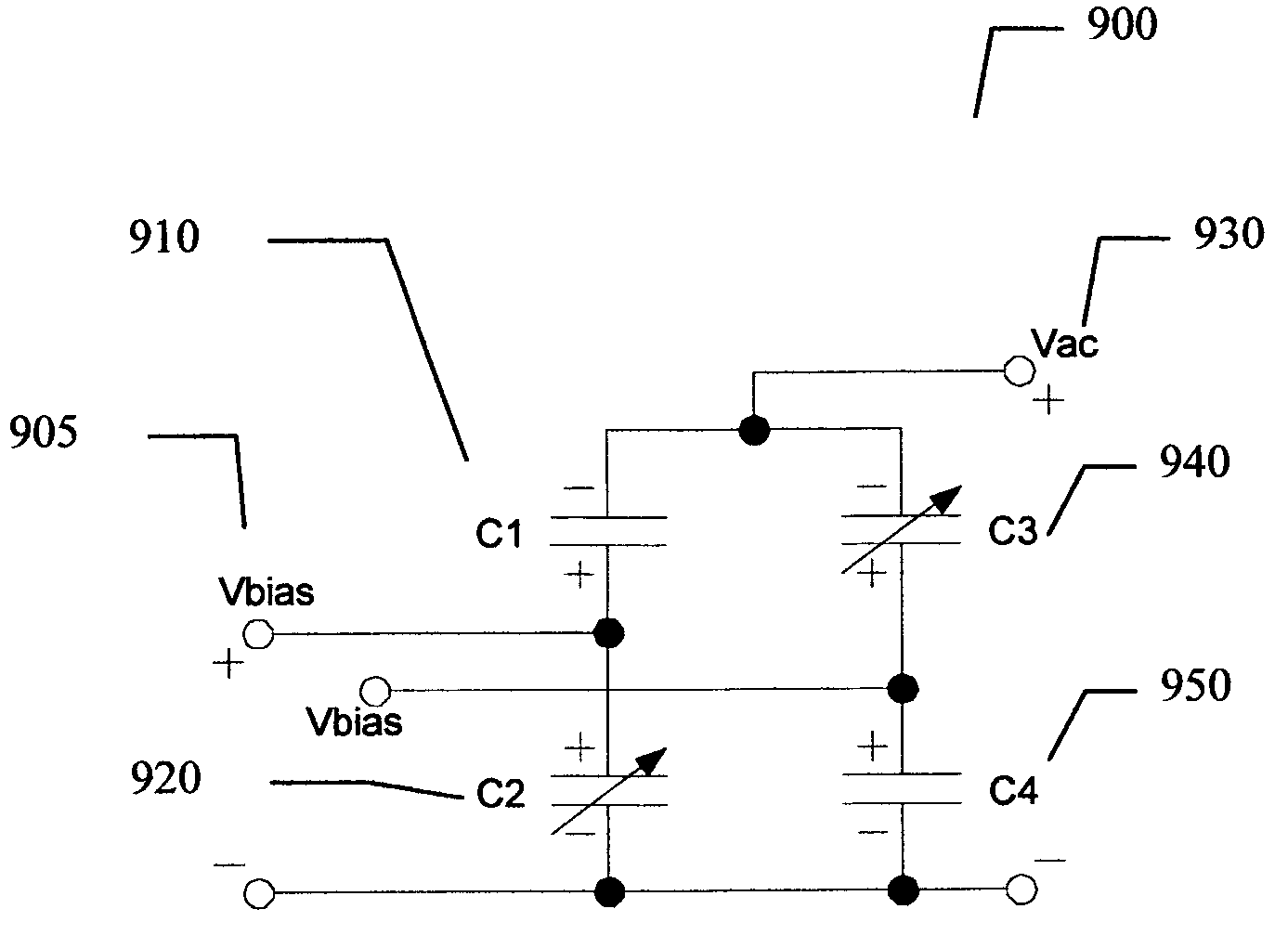
Apparatus, system and methods for enabling linearity improvement in voltage controlled variable capacitors
ActiveUS20090160263A1Multiple fixed capacitorsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceEngineering
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising at least one anti-parallel pair VVC network comprised of two parallel VVCs with one biased in the opposite polarity of the other and at least one anti-series VVC network comprised of two VVCs configured in series, one biased in the opposite polarity of the other such that the resulting AC capacitive variations produce a desired capacitance variation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com