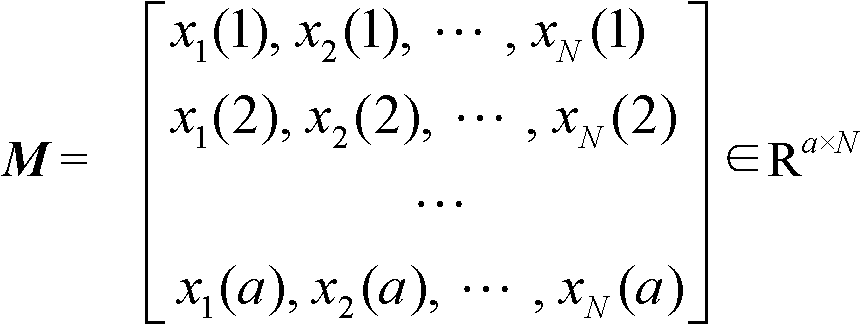Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Unit impulse response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
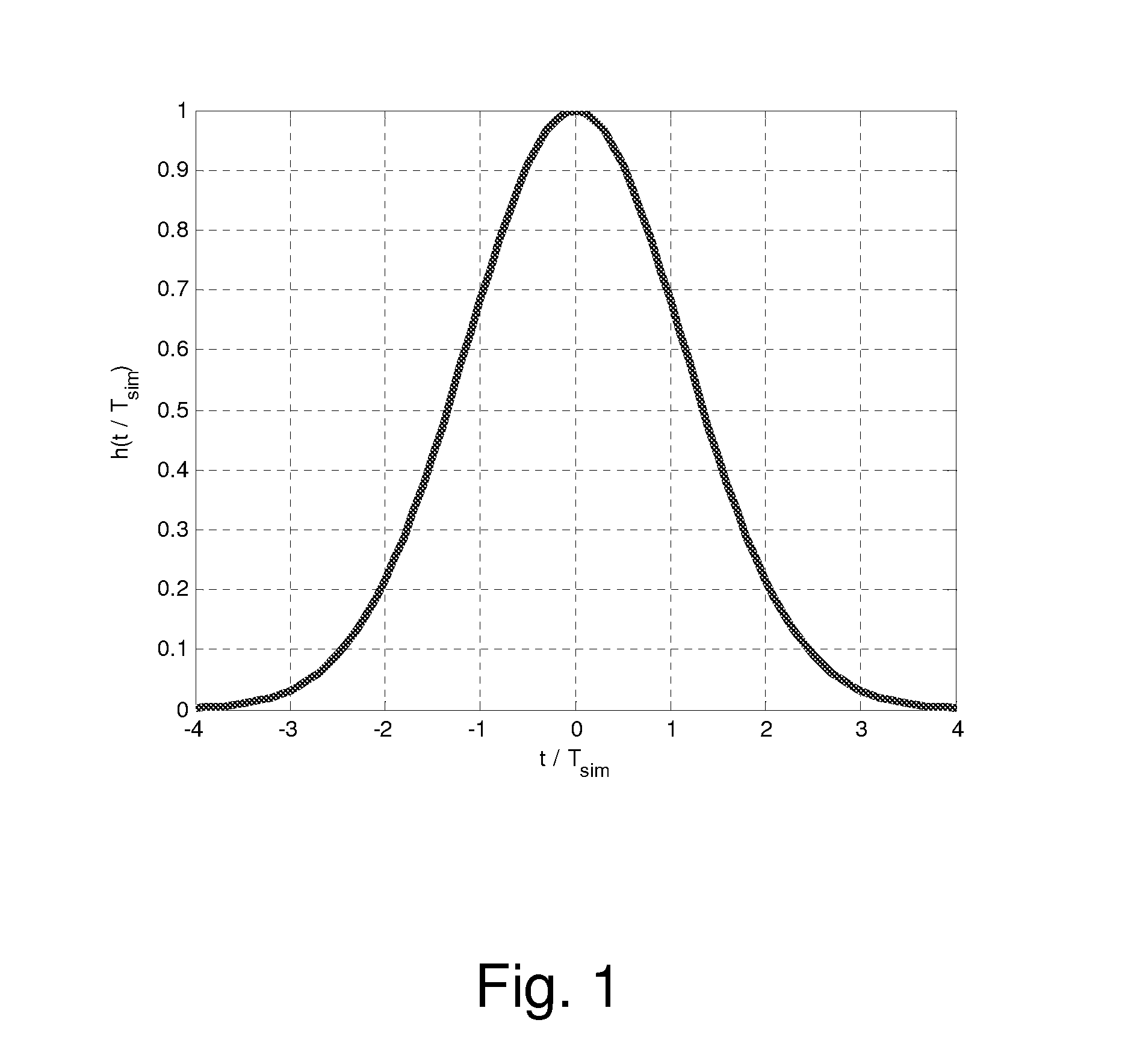
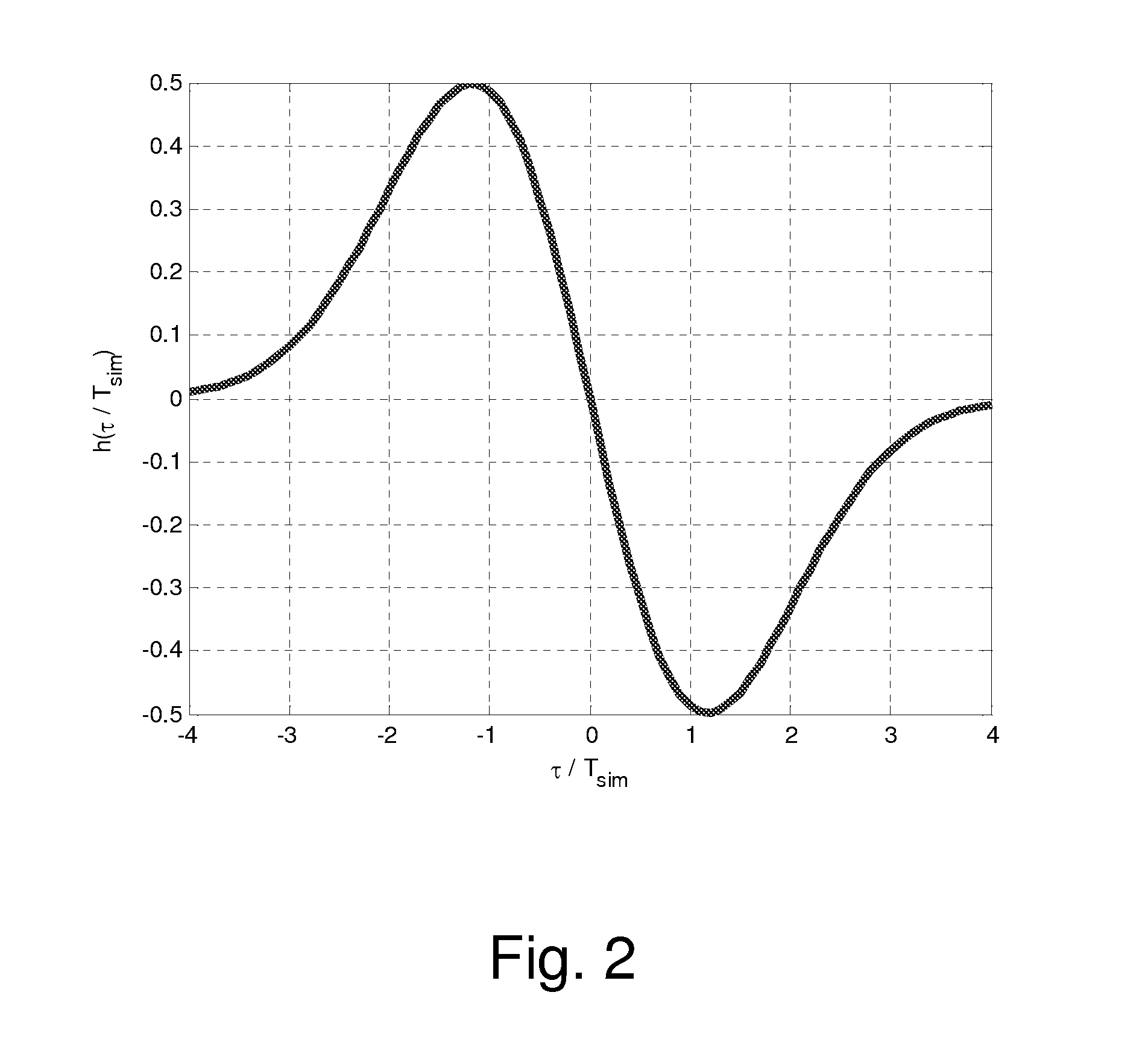
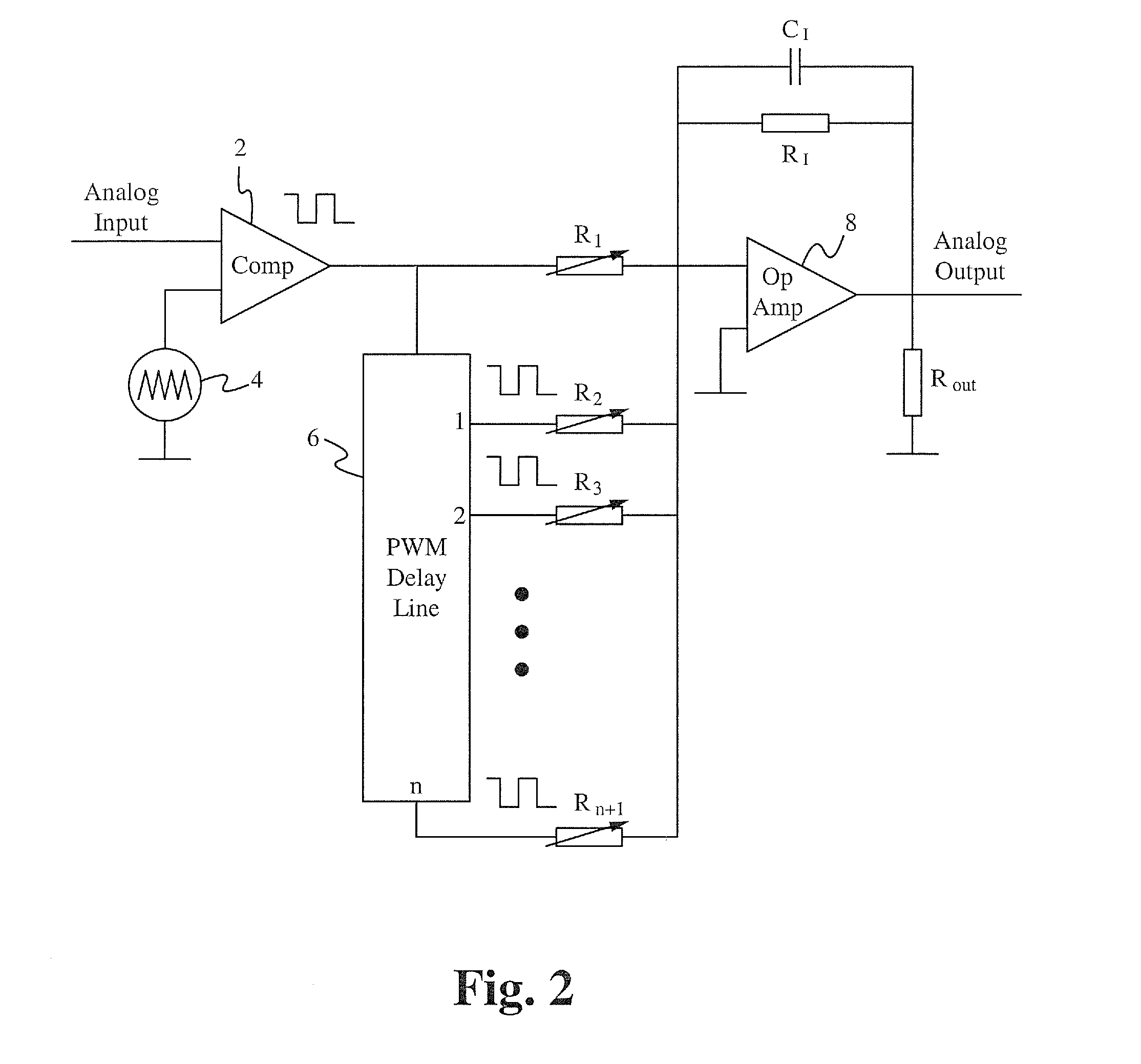
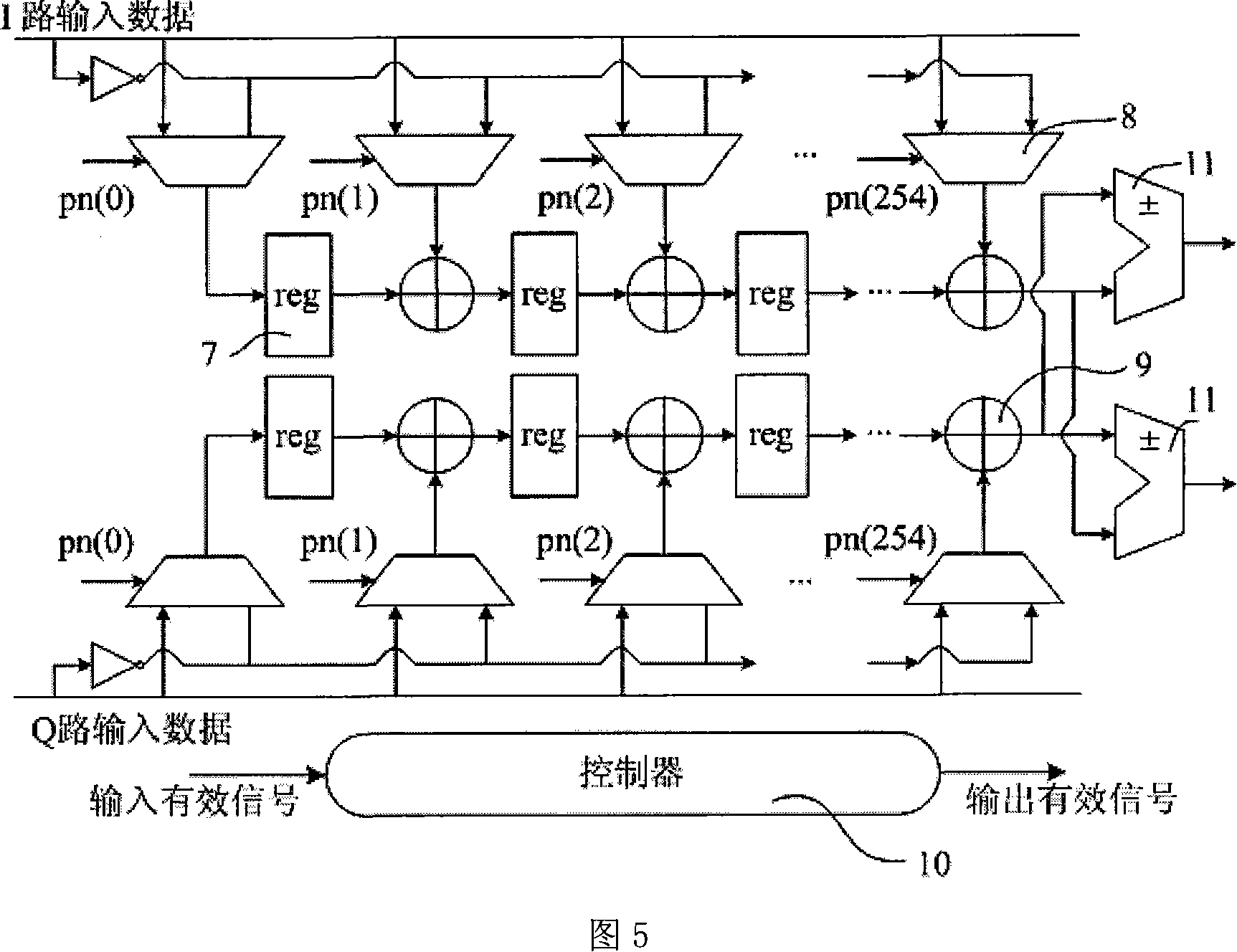
Impulse calculates the unit impulse response of a dynamic system model. For continuous-time dynamic systems, the impulse response is the response to a Dirac input δ(t). For discrete-time systems, the impulse response is the response to a unit area pulse of length Ts and height 1/Ts, where Ts is the sample time of the system.
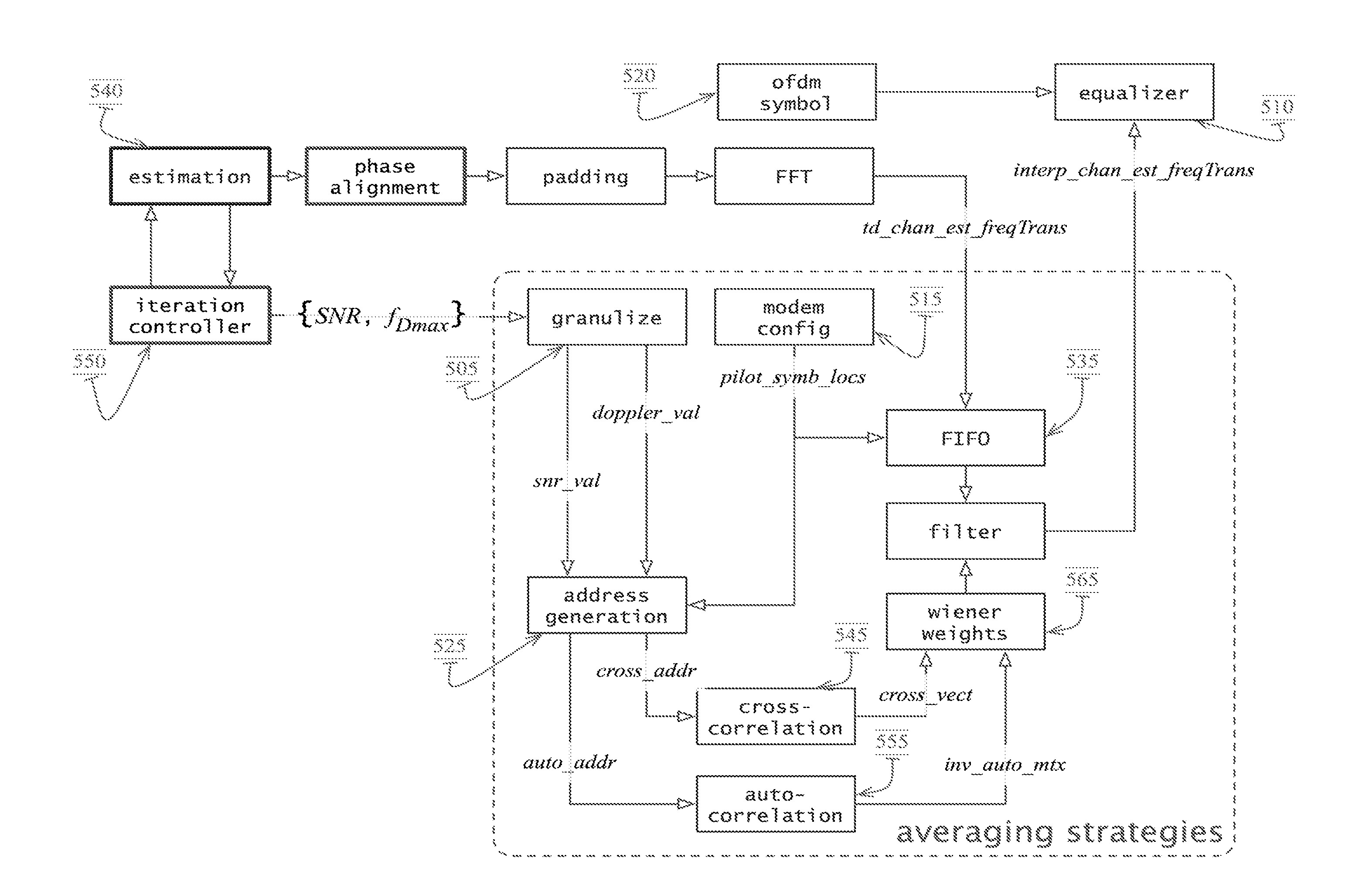
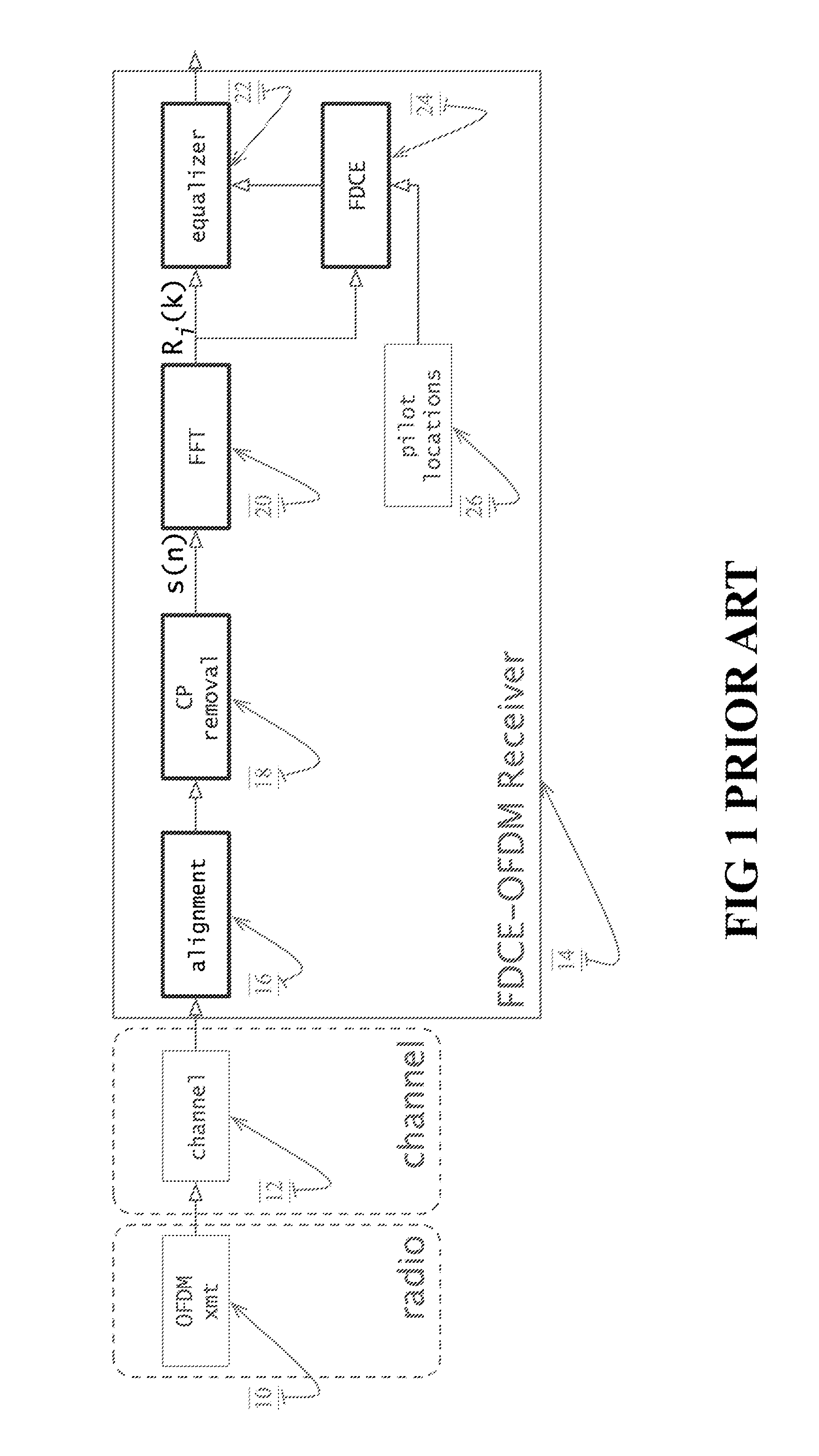
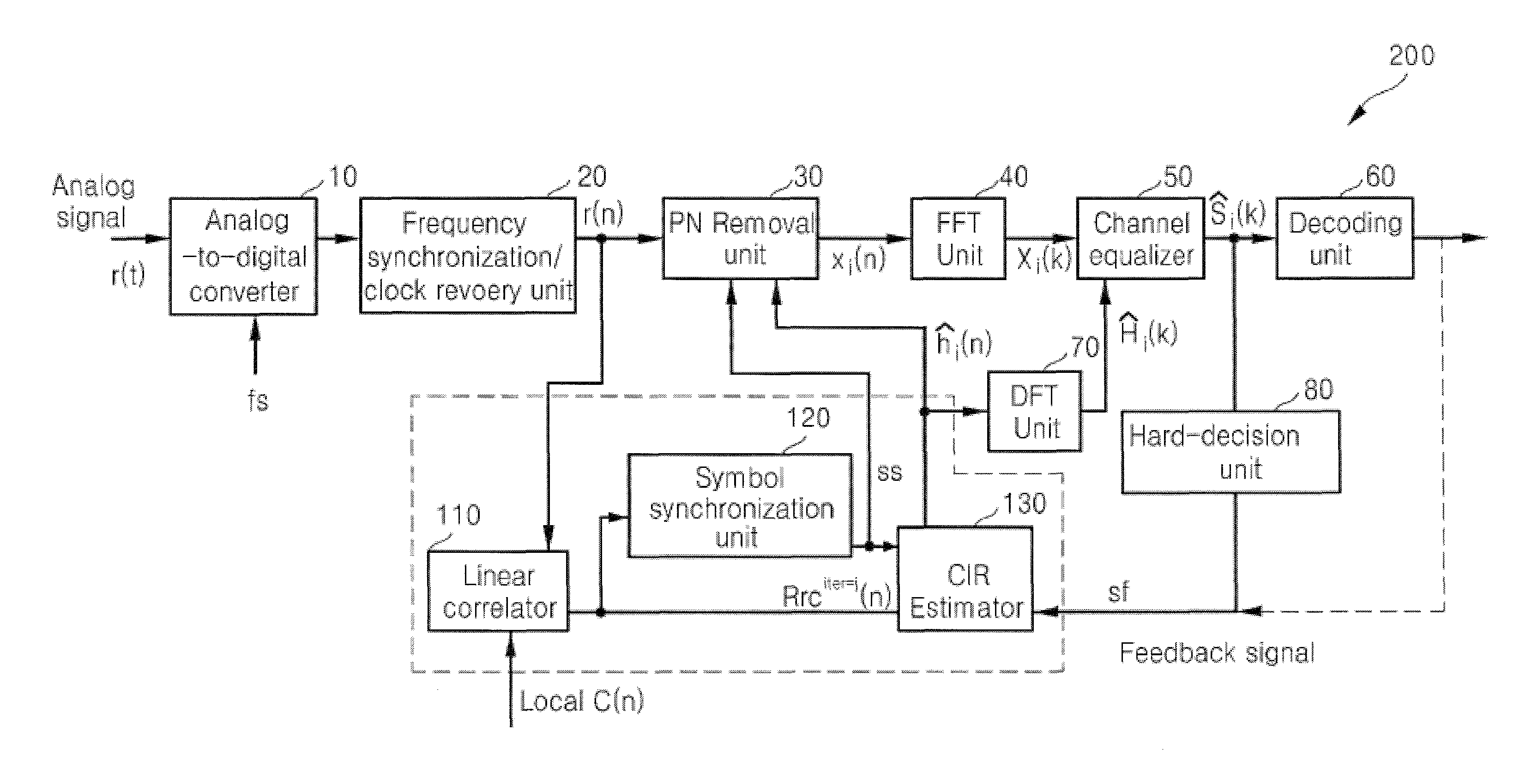
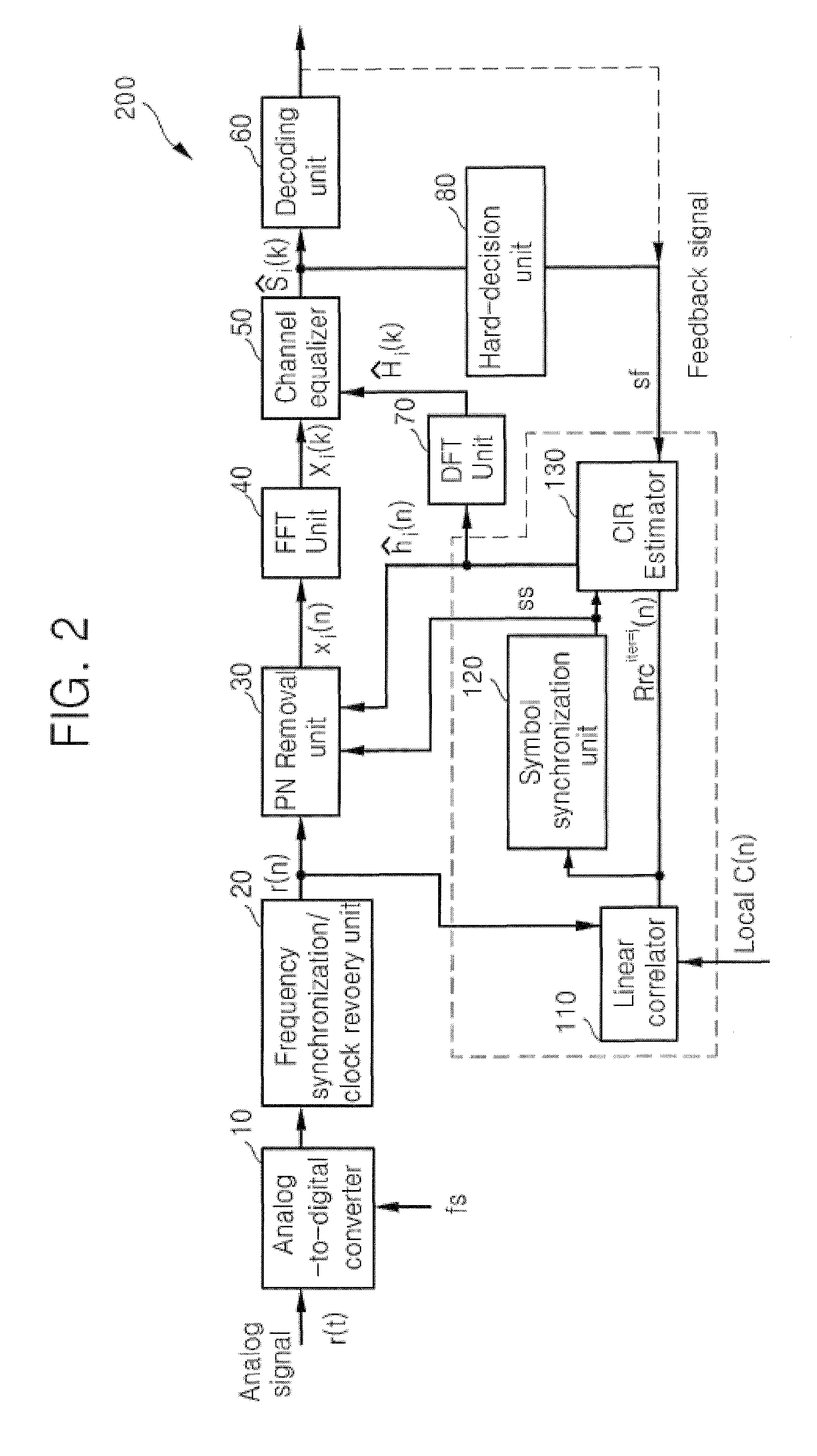
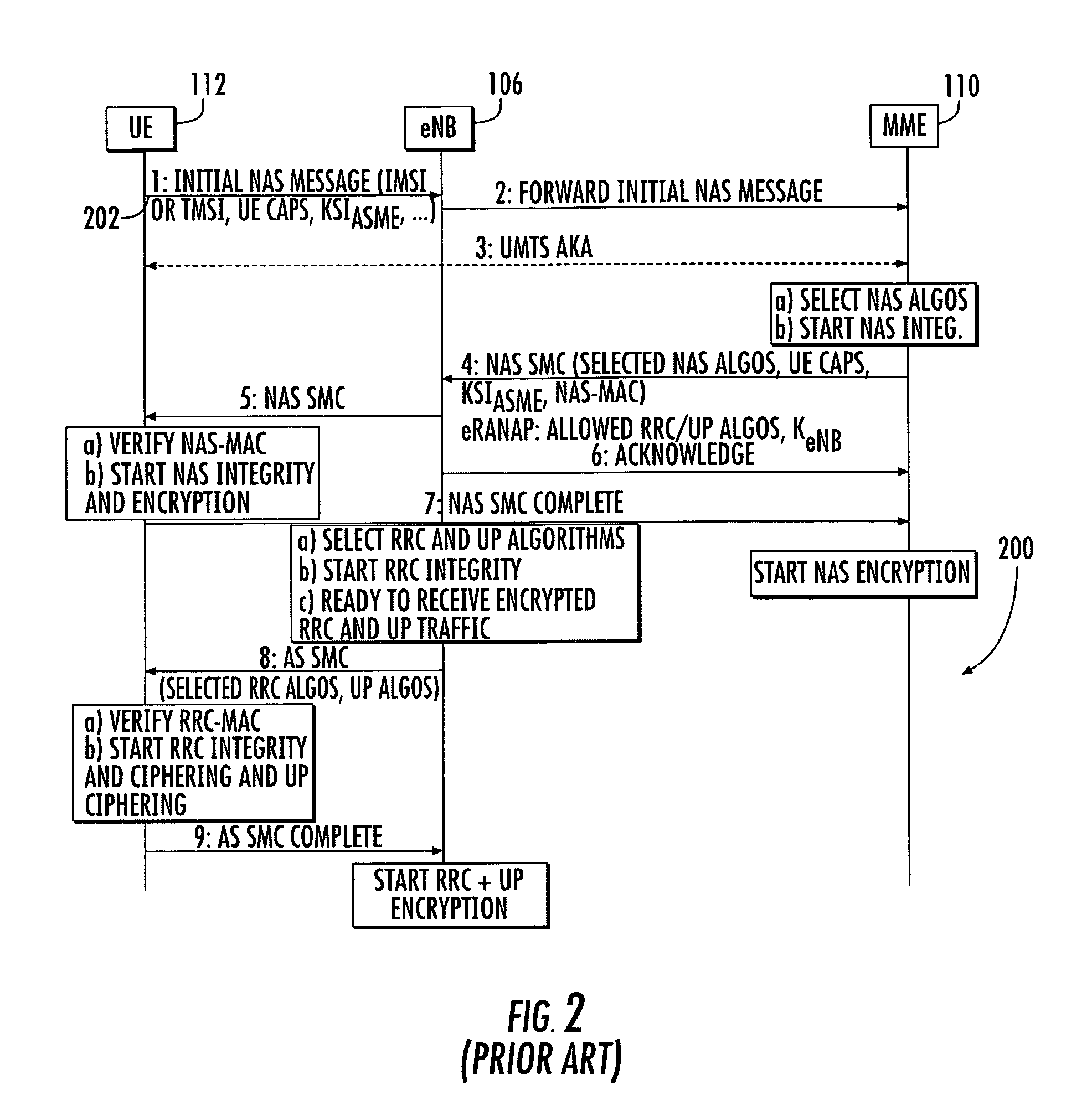
OFDM Receiver With Time Domain Channel Estimation
ActiveUS20130121392A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseTime domain
An OFDM communication system performs time domain channel estimation responsive to received symbols before the symbols are processed by a fast Fourier transform. The communication system generates virtual pilots from actual pilots to improve the stability and quality of channel estimation. The system generates a reference signal from the actual and virtual pilots and correlates the resulting reference signal with a signal responsive to the received symbol to generate an initial channel impulse response (CIR) and to determine statistics about the channel. In some circumstances, the resulting reference signal is correlated with a modified symbol in which the actual and virtual pilot locations are emphasized and the data locations are deemphasized. Time domain channel estimation iteratively improves on the initial CIR. The system determines channel estimates for data only symbols through averaging such as interpolation.
Owner:ACORN TECH INC
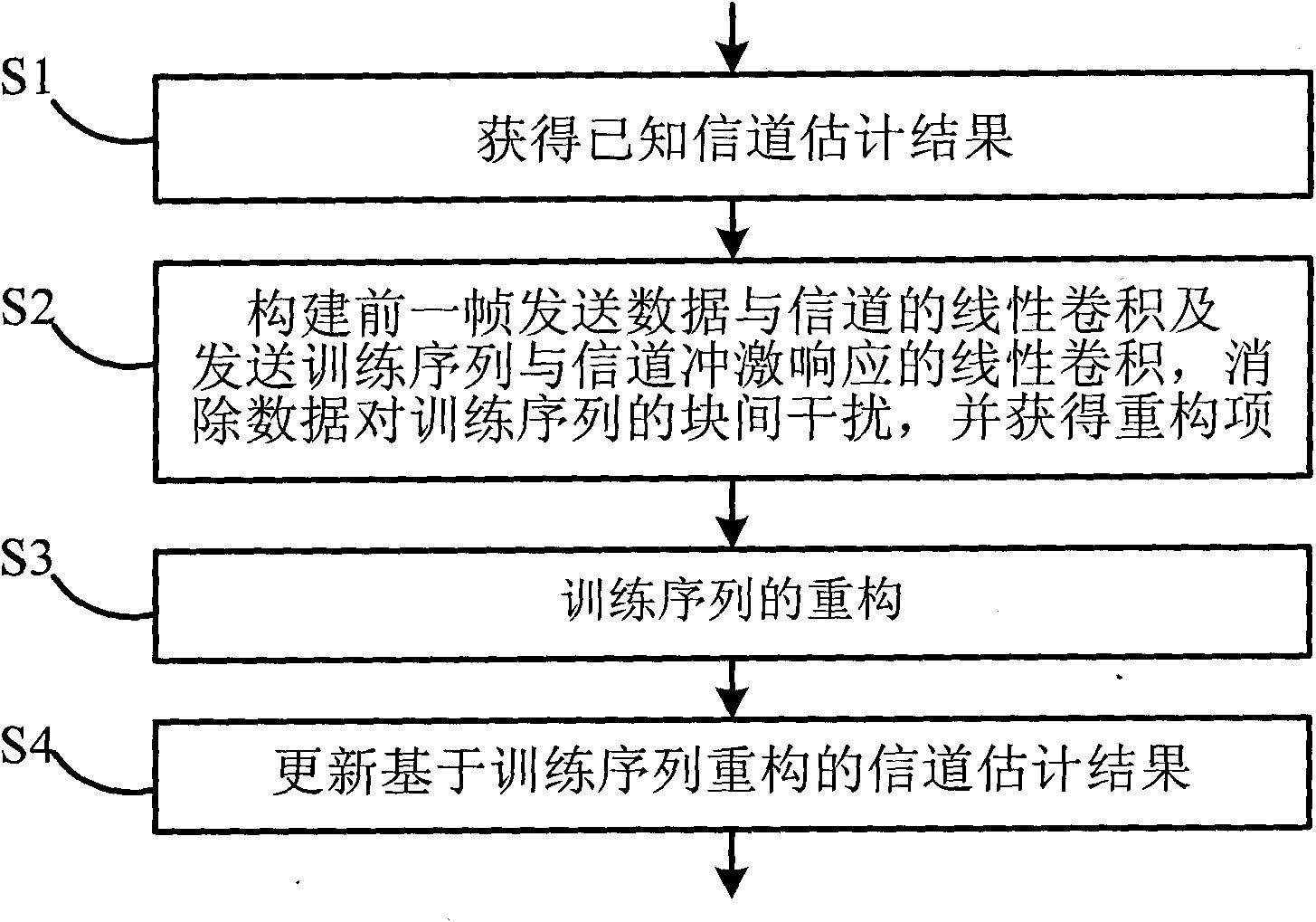
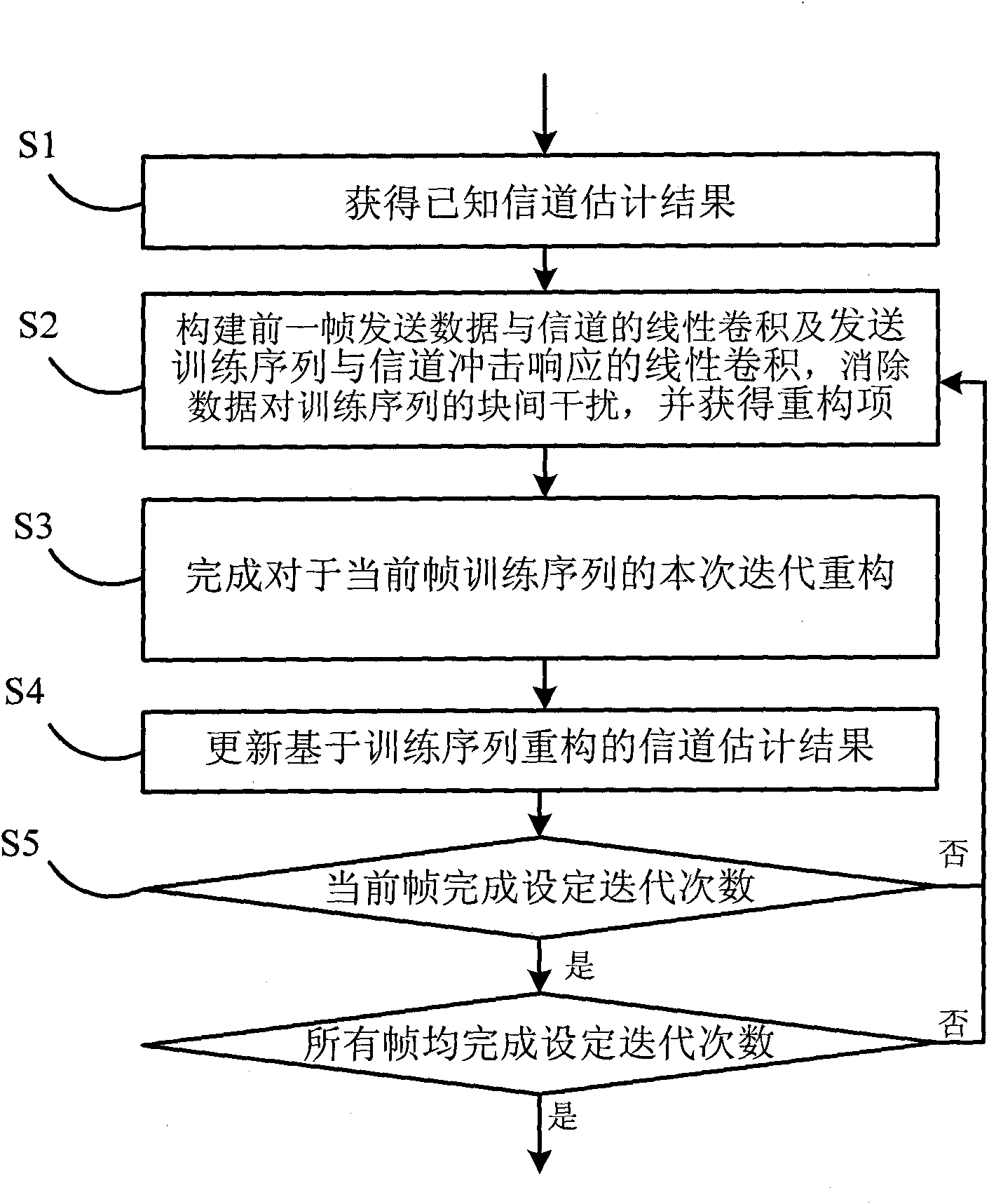
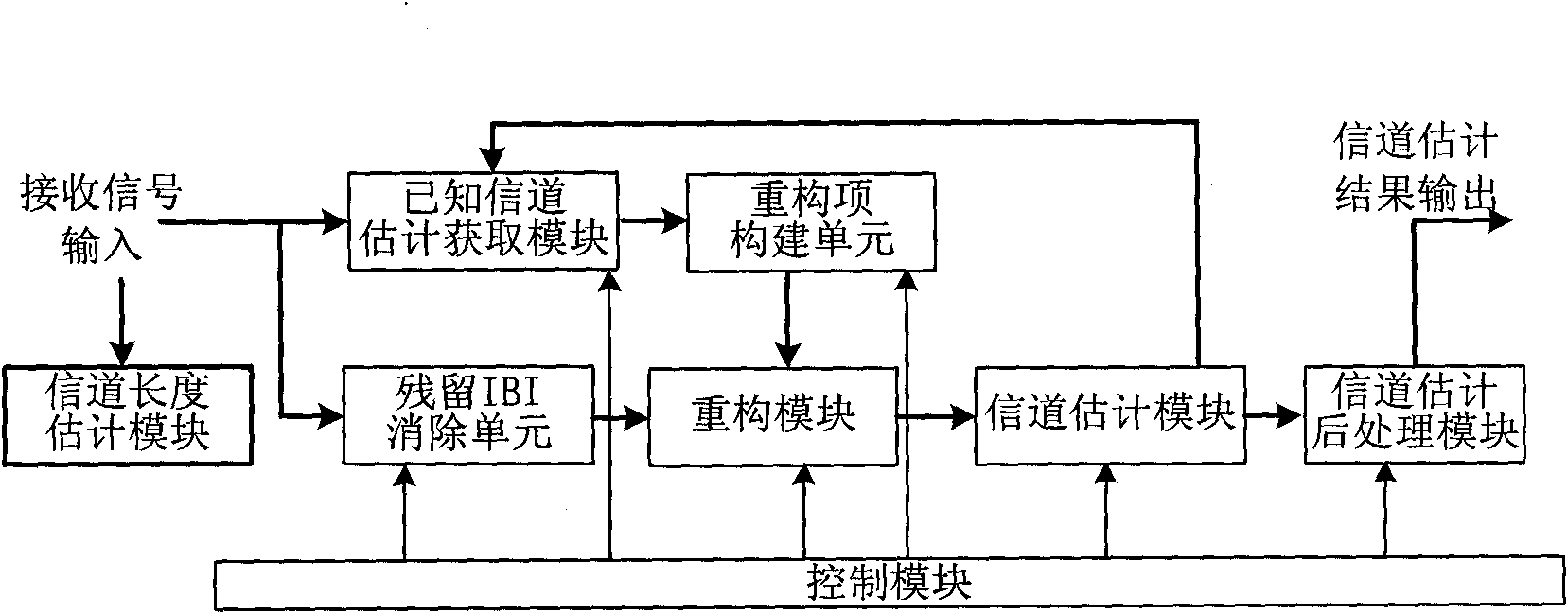
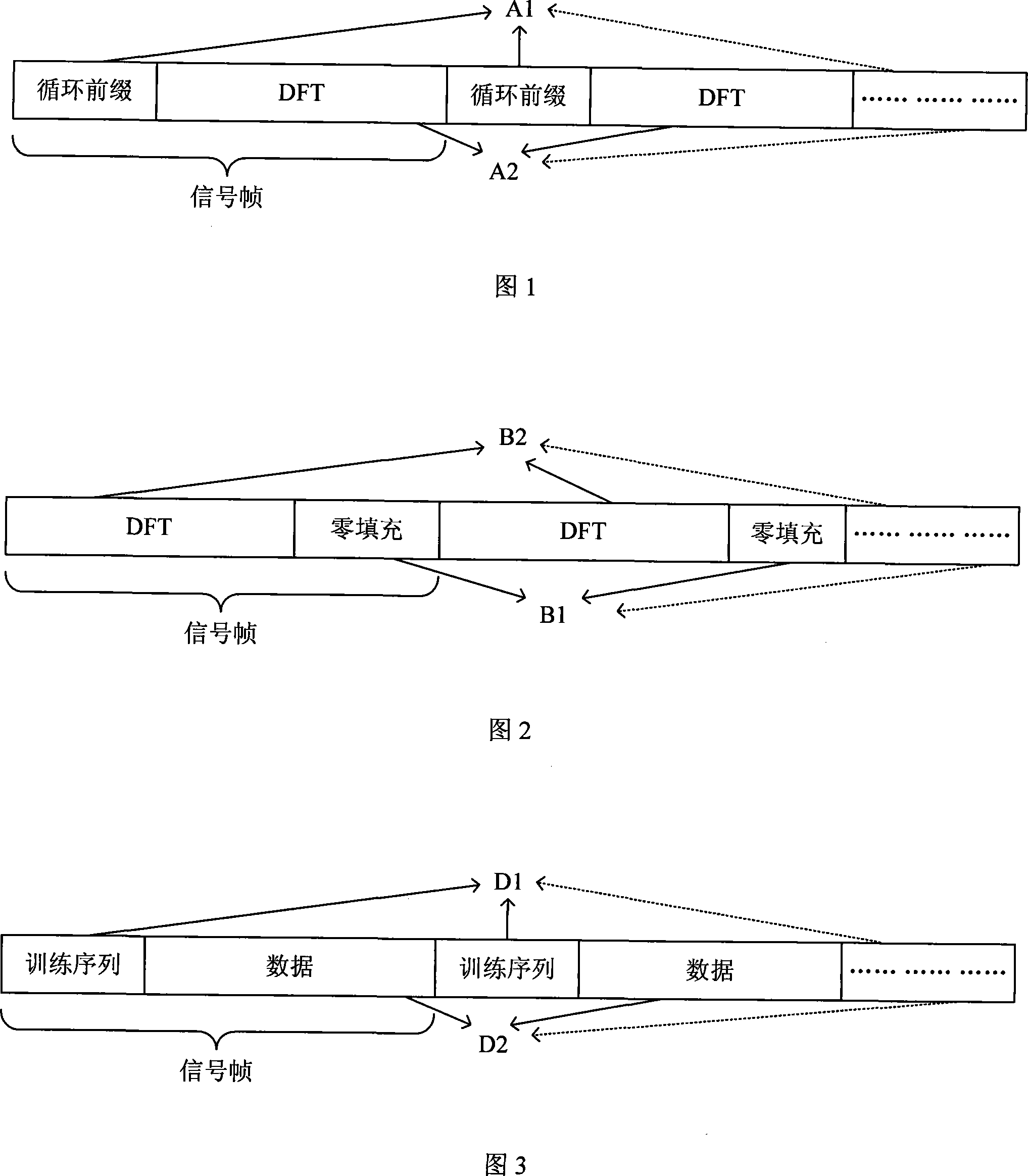
Training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation method and system
ActiveCN101808056AAccurate estimateImprove estimation accuracyMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSequence reconstructionDelay spread
The invention discloses a training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation method and a training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a known channel estimation result; according to the known channel estimation result, constructing linear convolution of former frame transmitted data and a channel and the linear convolution of a transmitted training sequence and a channel impulse response; eliminating inter-block interference of data on a training sequence; obtaining a cyclic convolution, of the training sequence and the channel impulse response, serving as a reconstruction item; according to the reconstruction item, reconstructing the training sequence; and performing channel estimation by utilizing the reconstructed training sequence, and updating a channel estimation result. The method and the system of the invention can ensure that a TDS-OFDM system can also obtain relatively accurate channel estimation when maximum delay extension of the channel exceeds the guard space length of the training sequence, simultaneously improves the accuracy of the channel estimation and improves the spectrum utilization ratio and the mobility performance of the system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Filter structure for driving an optical modulator
InactiveUS20150295650A1Radio-over-fibreElectromagnetic receiversFinite impulse responseDriver circuit
We disclose an opto-electronic circuit having an optical modulator and a driver circuit configured to generate a plurality of electrical drive signals for the optical modulator in a manner that causes the opto-electronic circuit to operate as a finite-impulse-response (FIR) filter. Different electrical drive signals generated by the driver circuit represent different taps of the FIR filter and are individually applied to different respective electrodes in the optical modulator without first being combined with one another prior to said individual application. The optical modulator represents an adder of the FIR filter and is configured to use the applied electrical drive signals to perform signal summation in the optical domain, thereby alleviating some of the limitations associated with the electrical RF circuitry used in the driver circuit. The opto-electronic circuit can be employed in optical transceivers and equalizers and be configured to implement signal pre-emphasis, feed-forward equalization, or decision-feedback equalization.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
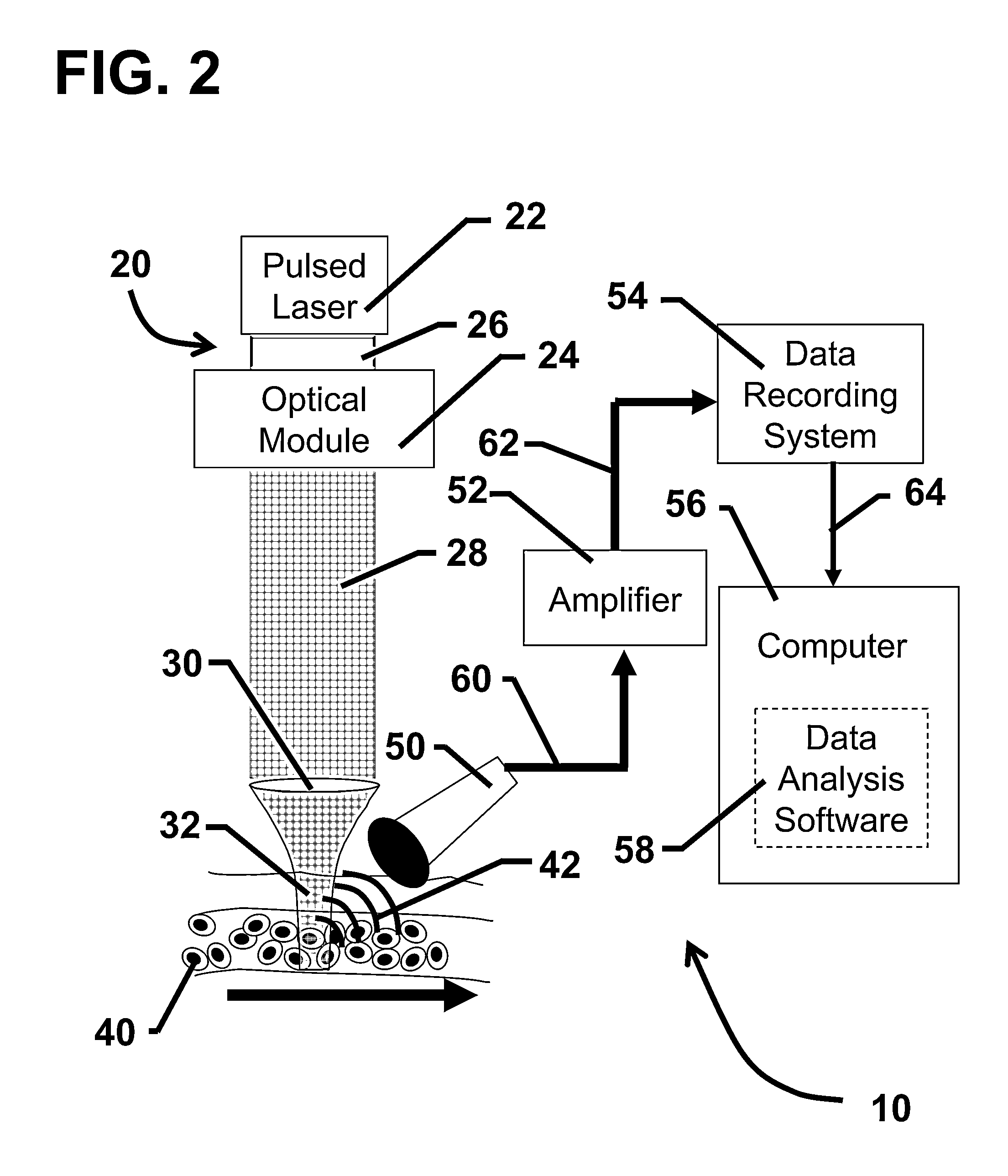
Device and method for in vivo flow cytometry using the detection of photoacoustic waves
ActiveUS20130060122A1Diagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionLymphatic vesselLaser light
A photoacoustic flow cytometry (PAFC) device for the in vivo detection of cells circulating in blood or lymphatic vessels is described. Ultrasound transducers attached to the skin of an organism detect the photoacoustic ultrasound waves emitted by target objects in response to their illumination by at least one pulse of laser energy delivered using at least one wavelength. The wavelengths of the laser light pulse may be varied to optimize the absorption of the laser energy by the target object. Target objects detected by the device may be unlabelled biological cells or cell products, contrast agents, or biological cells labeled with one or more contrast agents.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
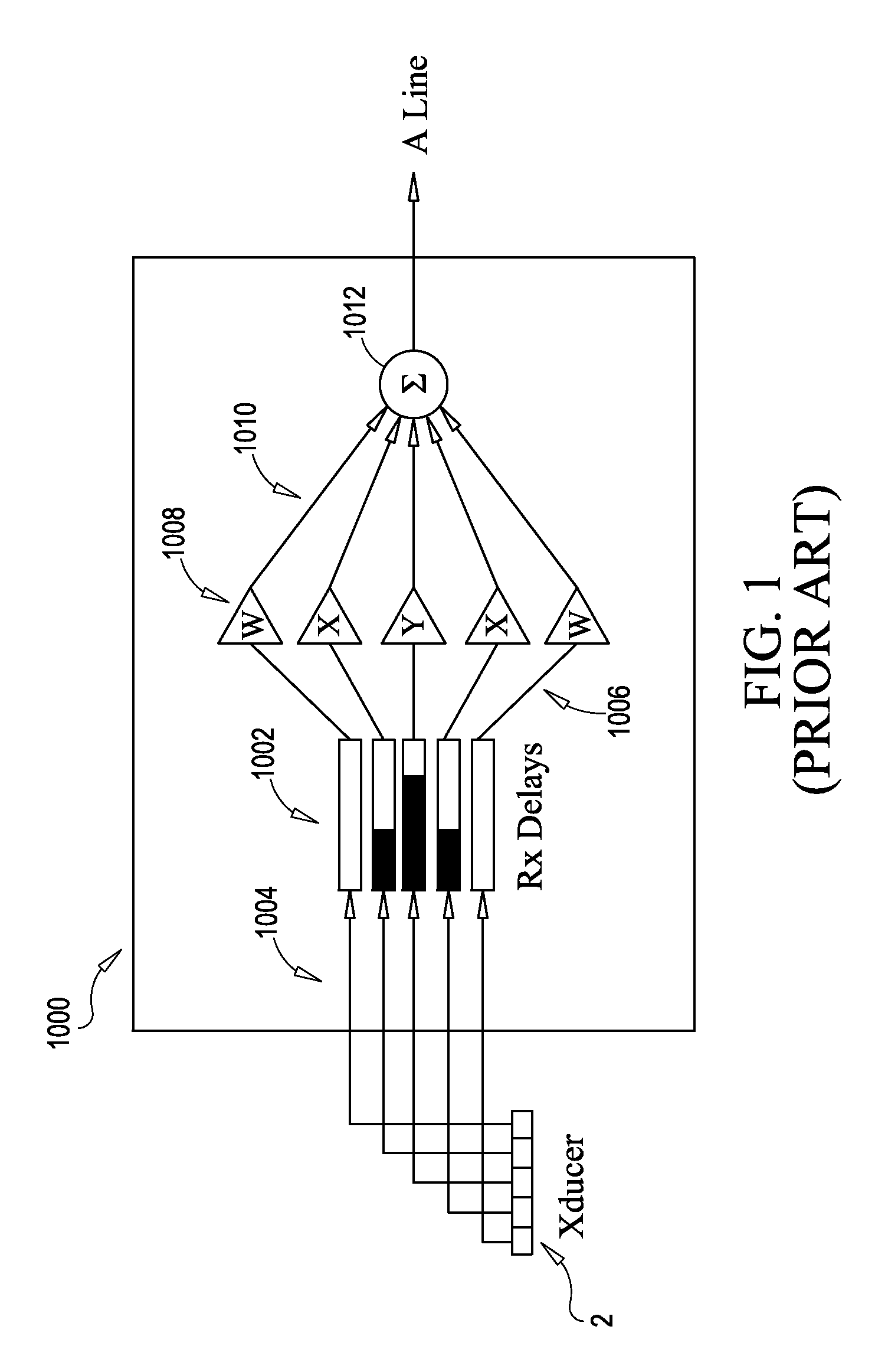
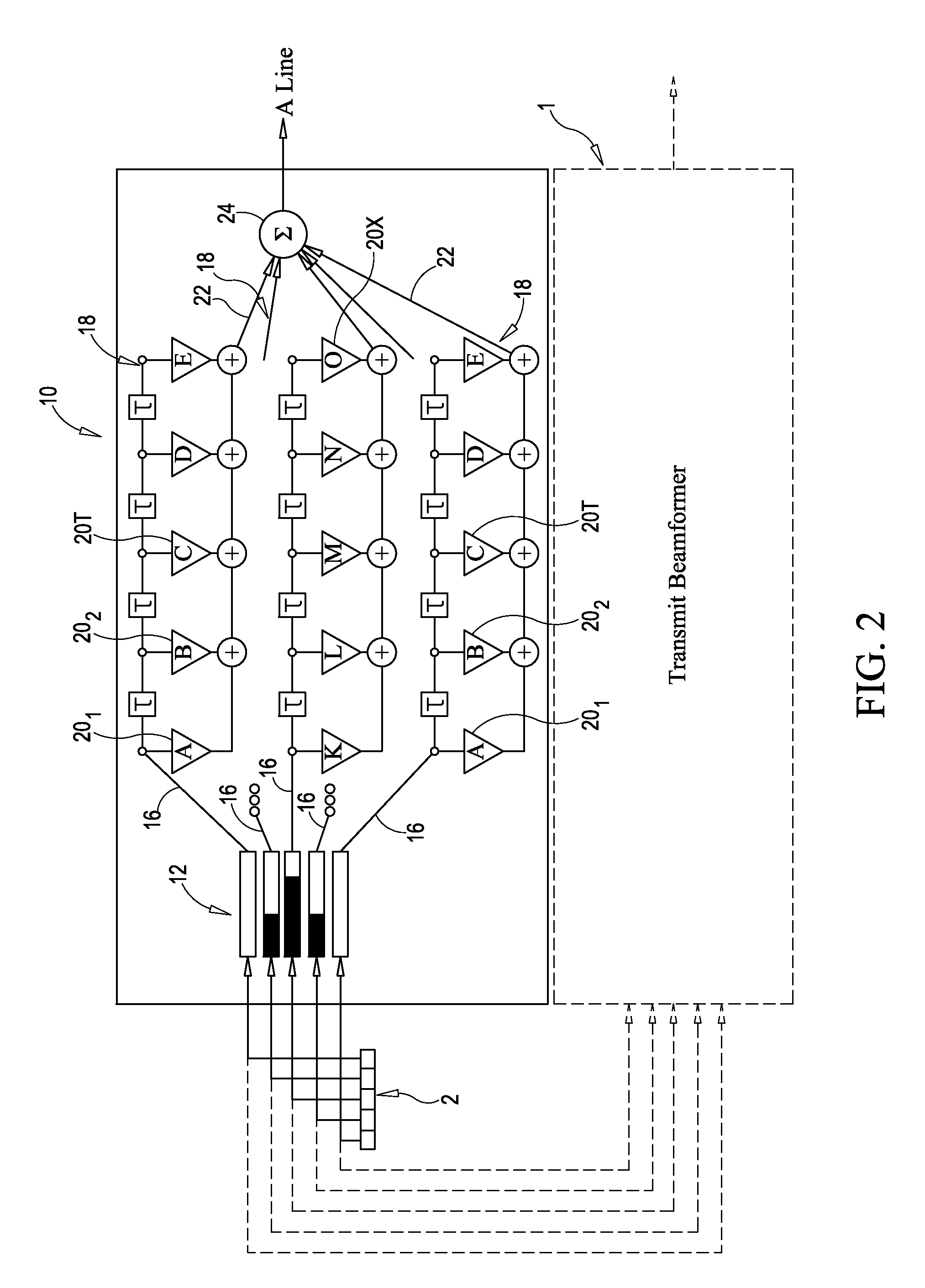
Imaging or communications system utilizing multisample apodization and method
ActiveUS8744155B2Minimizing ratioOptimization of contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFinite impulse responseContrast resolution
Methods, systems and system components for optimizing contrast resolution of an imaging or sensing system utilizing multiple channels of broadband data associated with an array of transducers. Channels or data are filtered by passing the channels of data through finite impulse response (FIR) filters on each channel. The filters each have multiple taps having tap weights pre-calculated as a function of distance of the array from an object that energy is being transmitted to or reflected from. The weights are pre-computed through a deterministic equation based on an a priori system model.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
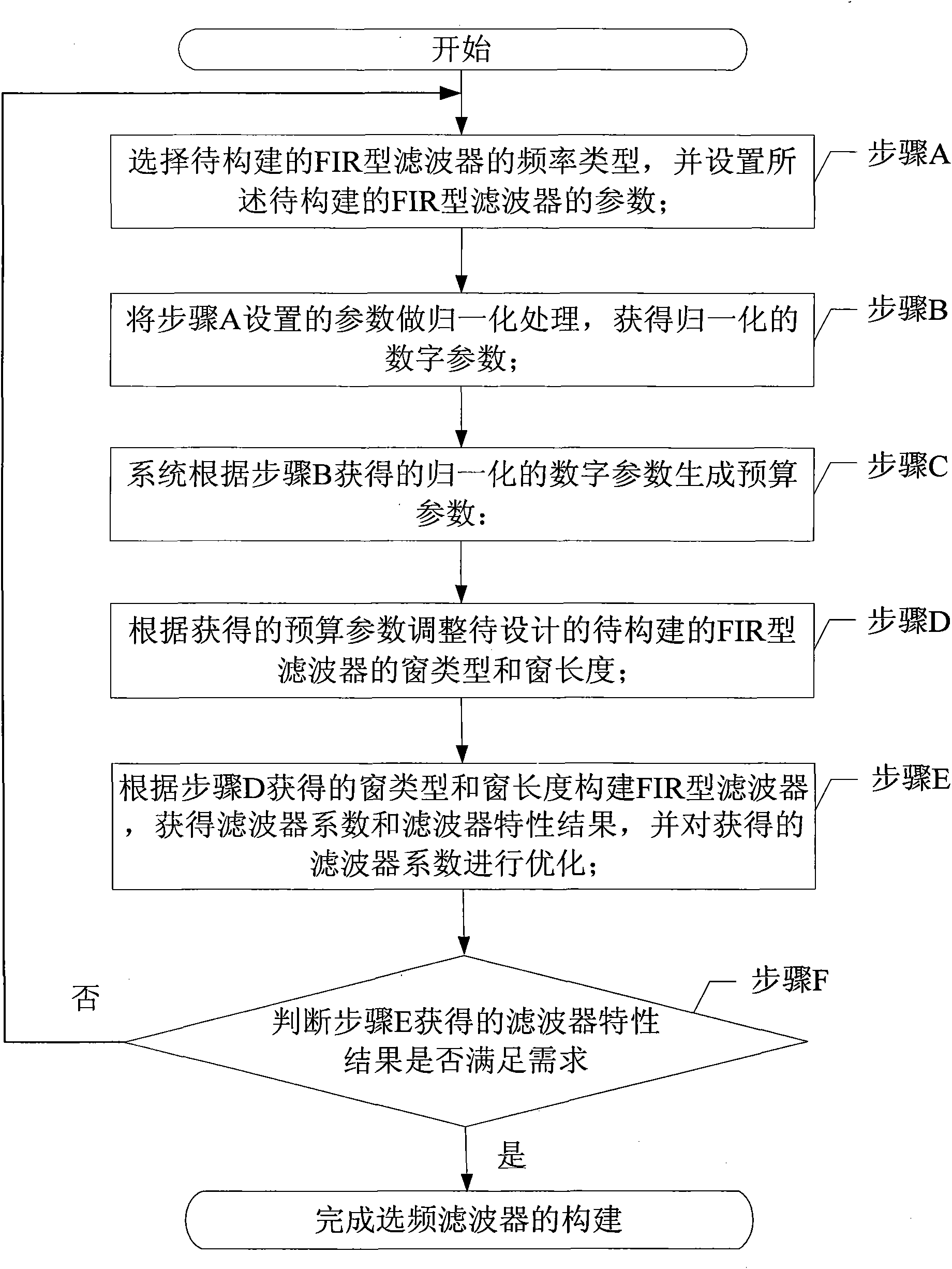
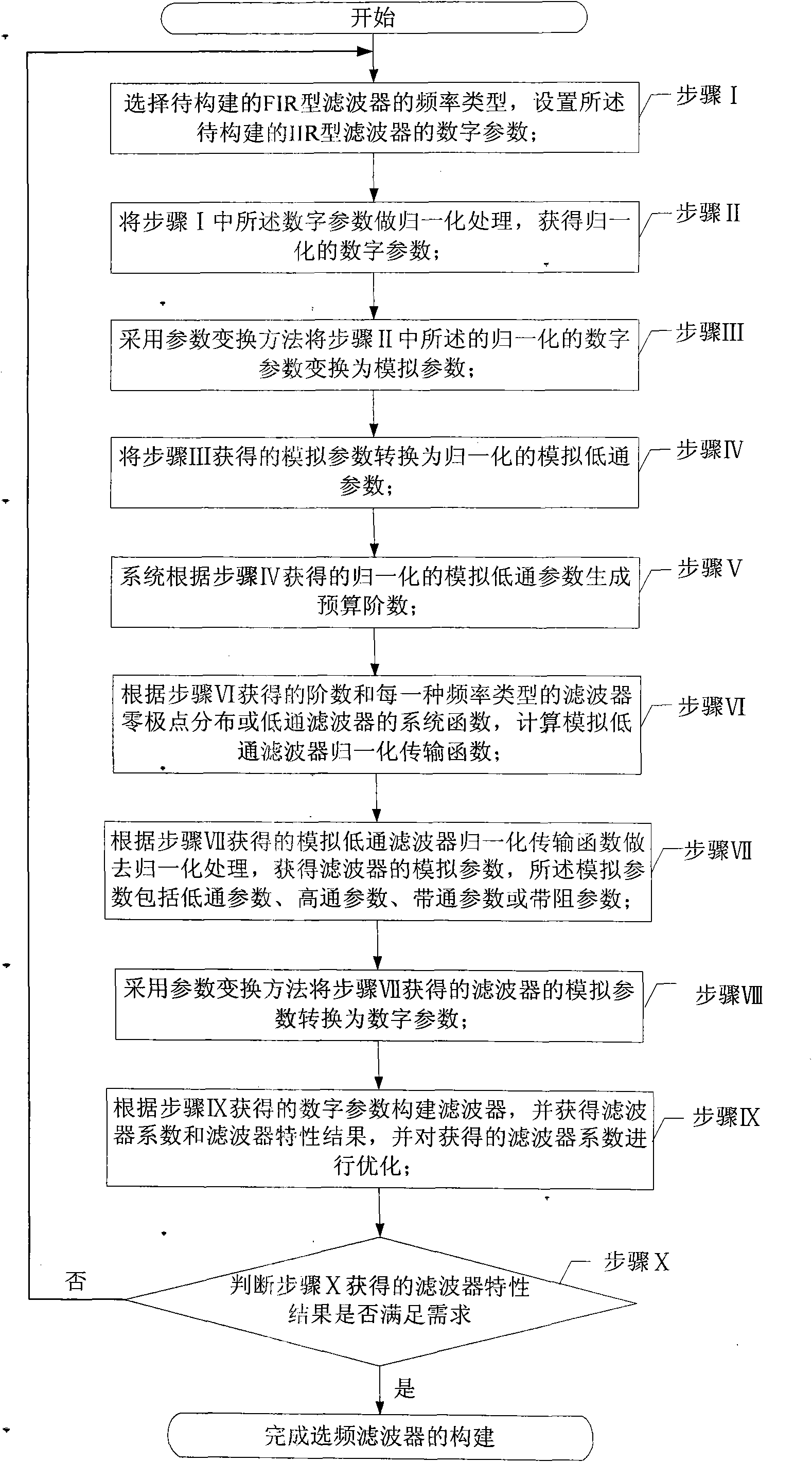
Construction method of frequency-selecting filter and construction method for realizing FIR-type and IIR-type filters by adopting same
InactiveCN101860344APromote generationEasy to storeDigital technique networkUnit impulse responseStep response
Owner:刘海成 +1
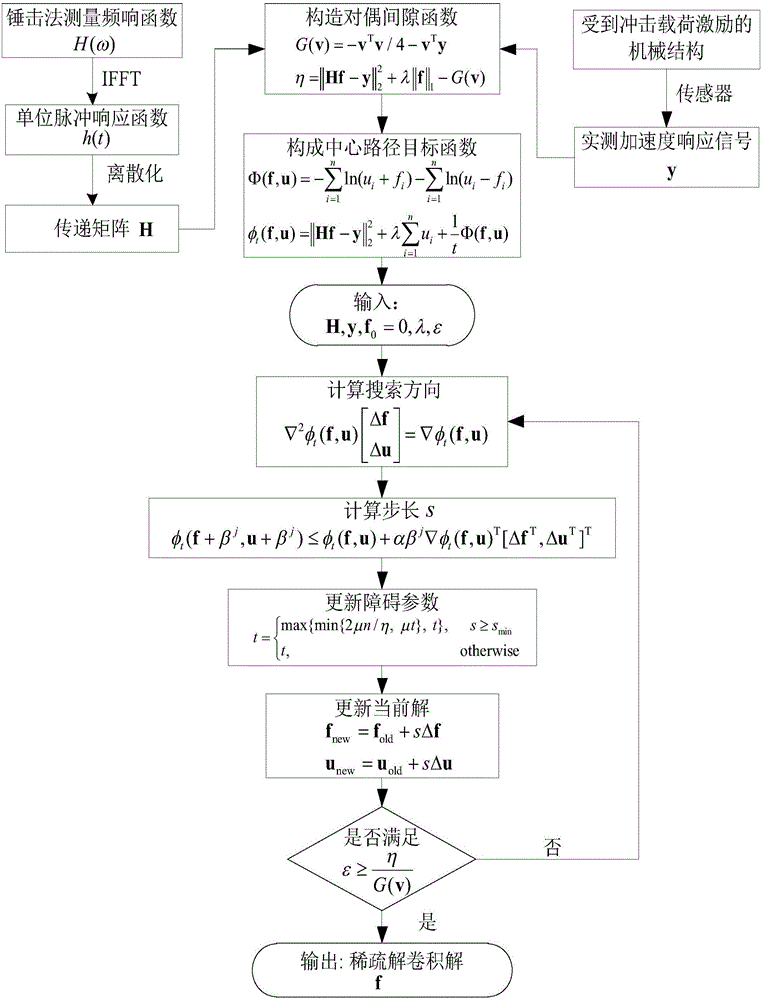
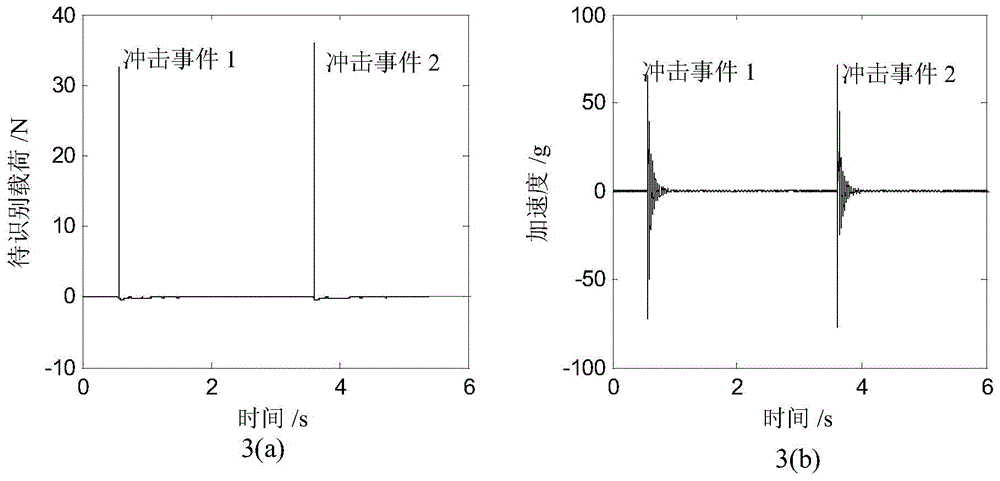
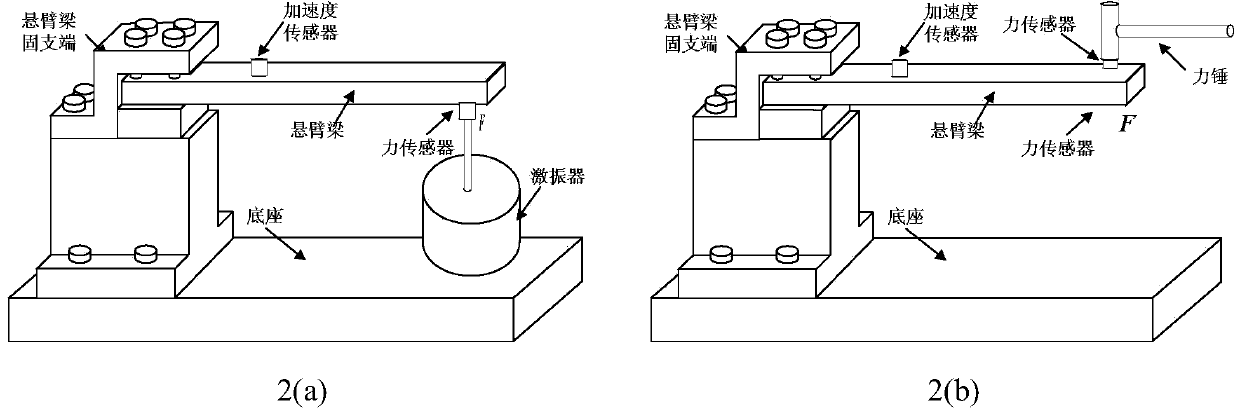
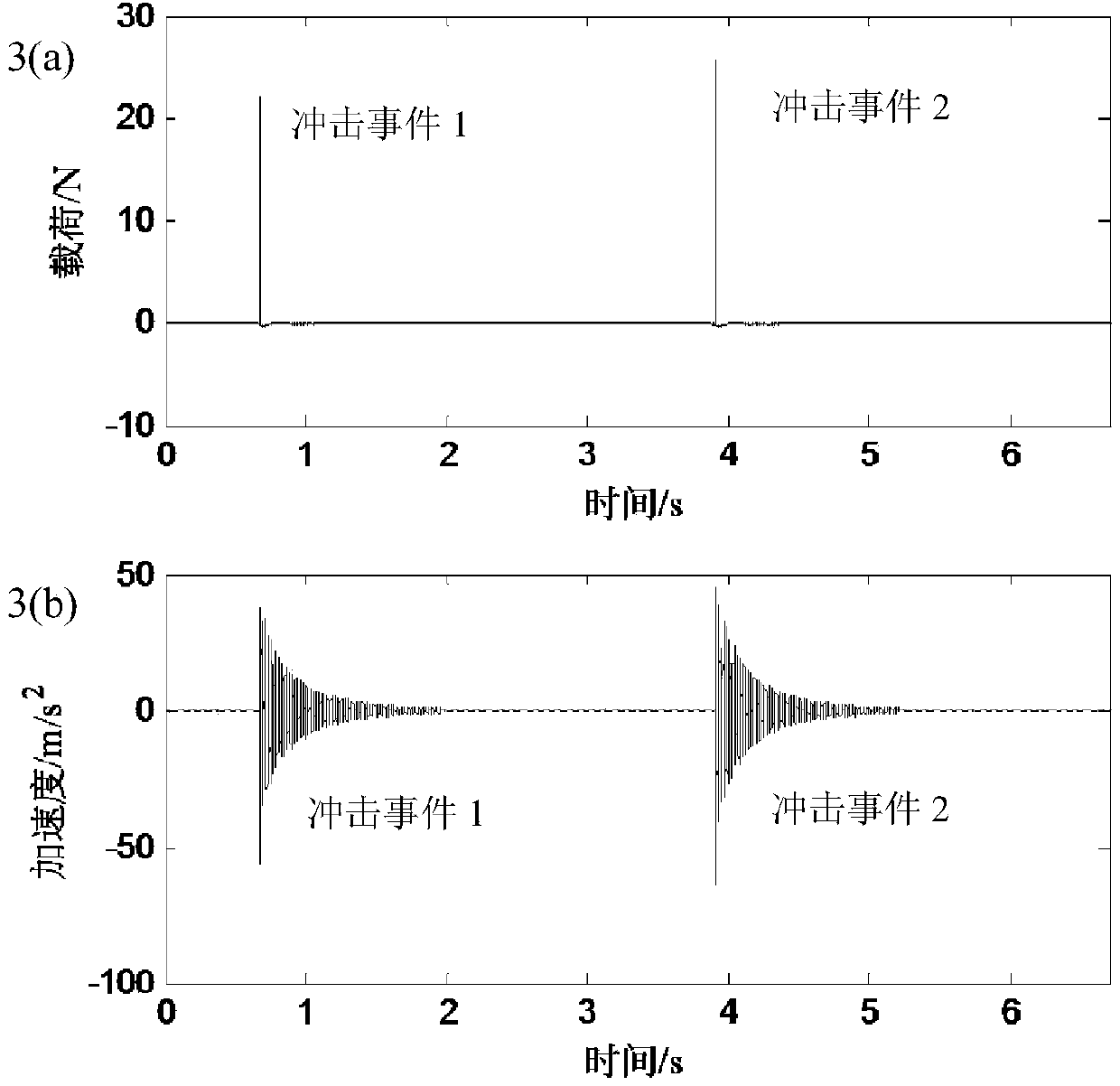
Sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of mechanical structure
ActiveCN105843780AGrowth inhibitionImprove recognition accuracyComplex mathematical operationsMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention relates to a sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of a mechanical structure. The method is used for solving the ill-posed nature of the impact load identification inverse problem and comprises steps as follows: 1) a frequency response function between an impact load acting point and a response measurement point of the mechanical structure is measured with a hammering method, a unit impulse response function is obtained through inverse fast fourier transform, discretization is further performed, and a transfer matrix is obtained; 2) an acceleration signal generated by impact load of the mechanical structure is measured with an acceleration sensor; 3) an L1-norm-based sparse deconvolution convex optimization model for impact load identification is established; 4) the sparse deconvolution optimization model is resolved with a primal-dual interior point method, and a sparse deconvolution solution, namely, a to-be-identified impact load, is obtained. The sparse deconvolution method is suitable for identifying the impact load acting on the mechanical structure. Compared with conventional Tikhonov regularization methods based on an L2 norm, the sparse deconvolution method has the advantages of high identification accuracy, high computation efficiency and high stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
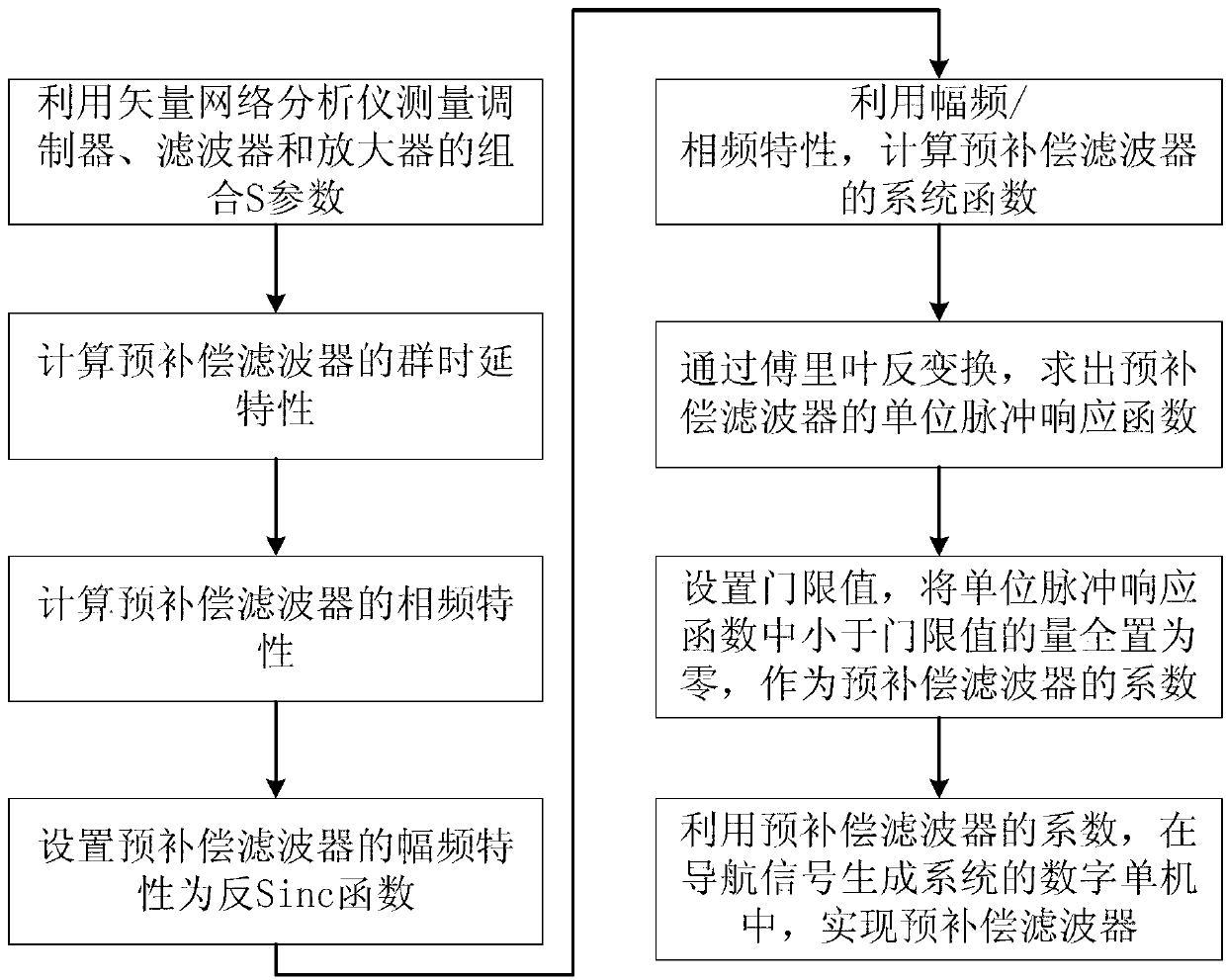
Precompensation method for in-band group delay fluctuation of satellite navigation signal generating system
ActiveCN103281268AFlexible modificationImprove correction accuracyTransmission monitoringTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAudio power amplifierUnit impulse response
The invention relates to a precompensation method for in-band group delay fluctuation of a satellite navigation signal generating system, which comprises the following steps: (1) measuring a combined S parameter of a modulator, a filter and an amplifier in the satellite navigation signal generating system, and determining amplitude-frequency and group delay characteristic of the combination of the three devices; (2) counting the group delay characteristic of a precompensation filter according to the combined group delay characteristic; (3) obtaining the phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter; (4) setting the phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter to be an inverse Sinc function; (5) obtaining a system function of the precompensation filter according to the amplitude-frequency characteristic and phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter; (6) obtaining a unit impulse response function of the precompensation filter; (7) setting a threshold value, and setting the quantity in the unit impulse response function, which is smaller than the threshold value, to be zero to be as a coefficient of the precompensation filter; and (8) realizing the precompensaiton filter in a digital standalone of the satellite navigation signal generating system by using the coefficient of the precompensation filter, so as to compensate the group delay fluctuation of the satellite navigation signal generating system.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
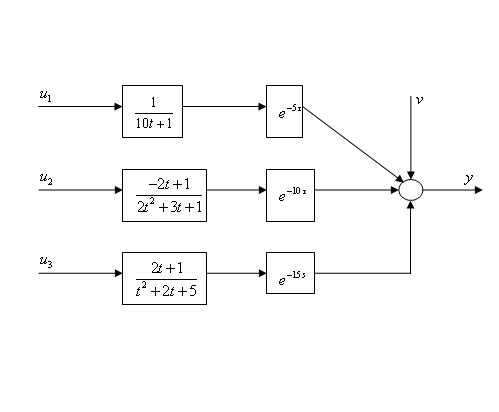
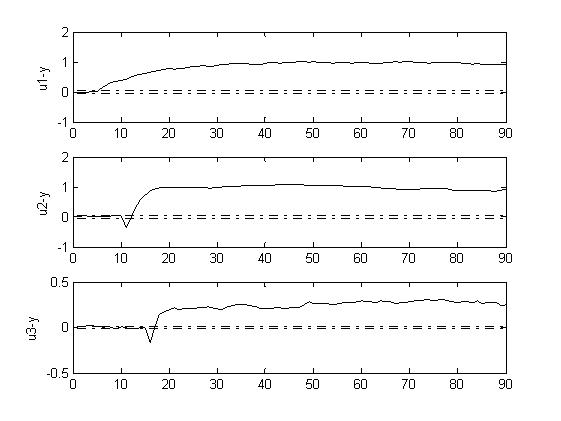
Multivariable time-lag parameter estimation method based on FIR (Finite Impulse Response) model identification
InactiveCN101924533AImprove applicabilityHigh precisionDigital technique networkEstimation methodsUnit impulse response
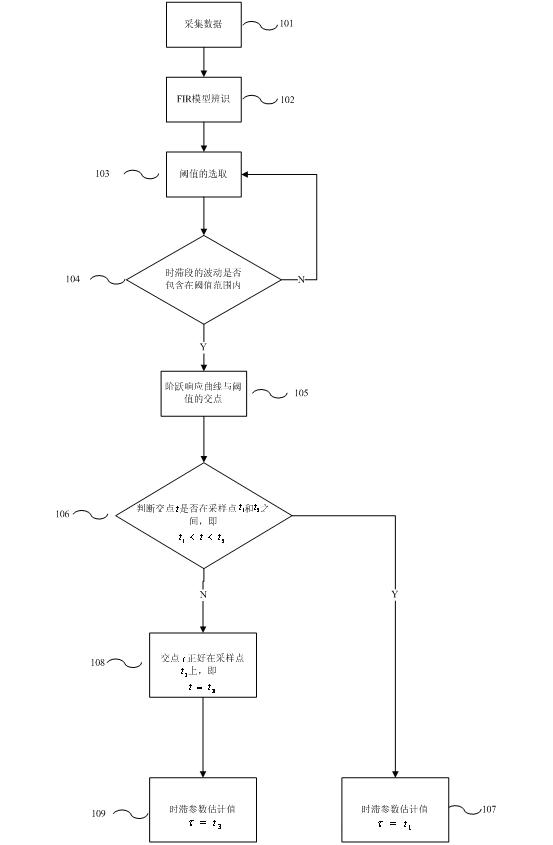
The invention discloses a multivariable time-lag parameter estimation method based on FIR (Finite Impulse Response) model identification, comprising the following steps of: step 101, collecting the input and output data of a system; step 102, carrying out the FIR model identification on the collected data to obtain a system step response coefficient and a step response curve; step 103, selecting threshold to be delta%(infinity); step 104, judging whether the fluctuation of a time-lag phase in the step response curve is in the threshold range or not; if the fluctuation does not exceed the threshold range, carrying out the step 105; otherwise, carrying out the step 103 to reselect a threshold; step 105, obtaining the first intersected point between the threshold and the step response curve; step 106, if t is judged to be larger than t1 and smaller than t2, carrying out a step 107 to obtain corresponding time-lag estimation value; otherwise, if the horizontal coordinator value t indicated by the intersected point is arranged on a sampling point t1 or t2, judging that the time-lag parameter estimation value zeta to be the sampling point t1 or t2; and step 107, obtaining the time-lag parameter estimation value zeta=t1. The invention has good applicability and high precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Digital self-interference residual cancellation
The present application a digital self-interference residual cancellation method that adjusts a magnitude of a sampled transmit signal based on compared magnitude and phases associated with tones. The digital self-interference residual cancellation method may follow an analog carrier cancellation stage where the digital self-interference residual cancellation is based on a determination of the channel circuit response used to control an infinite impulse response filter which can compensate using both poles and zeroes.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
Digital baud rate clock recovery of heavily ISI-induced signals
ActiveUS20150215138A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsChannel impulse responseClock recovery
System and method for digitally equalizing a data channel having wide channel impulse response for clock recovery of heavily ISI-induced received signals operating at one sample per symbol, according to which the received signal is pre-processed to provide a received signal with modified constellation, which is pre-processed for the decision process of signal with Inter-Symbol Interference by introducing controlled ISI to the received signal. The decision process is performed, based on a higher order vocabulary according to the introduced controlled ISI.
Owner:MULTIPHY
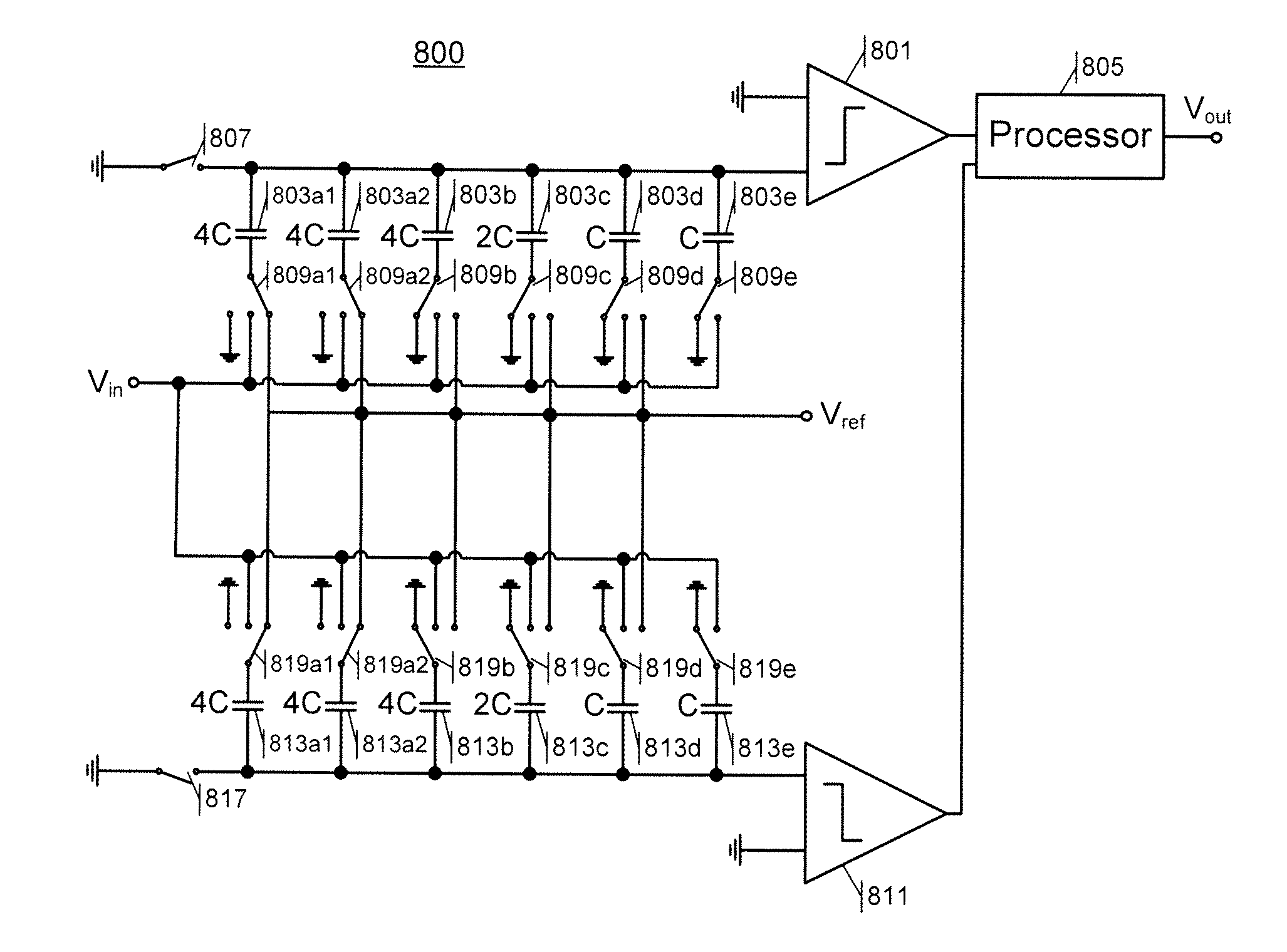
Anti-aliasing sampling circuits and analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS20140168000A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAnti-aliasingDigital down converter
A sampling circuit, such as the sampling circuit of a successive approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC), provides anti-aliasing filtering of a sampled input signal. The circuit samples the input signal using multiple capacitors, wherein each capacitor samples the input signal at a distinct time during a sampling time interval. The circuit combines the samples stored on different capacitors during a conversion time interval, and generates a digital output signal using the combined samples. In one example, a first bit of the output signal is generated using a sample stored on a first capacitor, and second bit of the output signal is generated using a sample stored on a second capacitor. In another example, the circuitry performs finite or infinite impulse response (FIR or IIR) filtering of the input signal, where a filter characteristic is determined by the relative sizes of the capacitors used for sampling.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
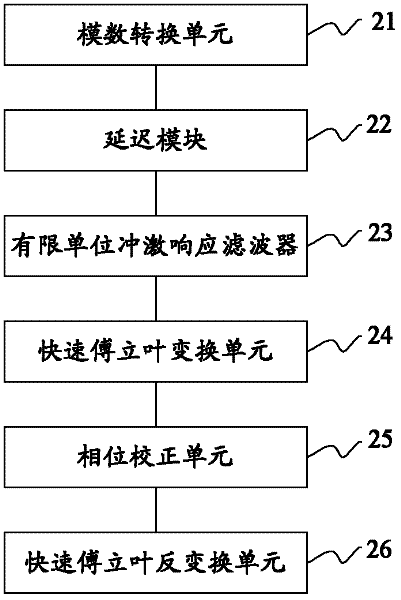
Method and device for obtaining noise-reducing NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) logging echo signal
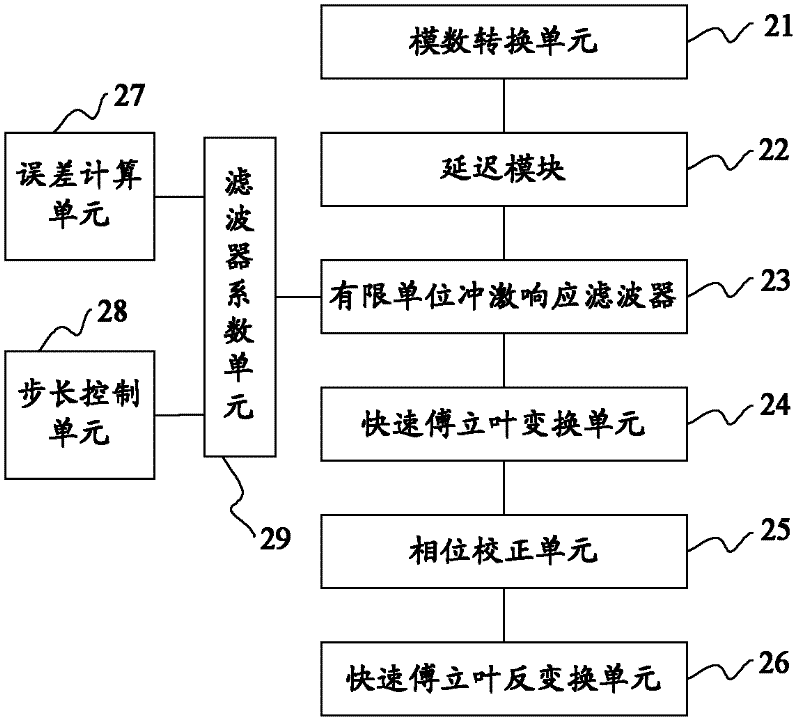
ActiveCN102565865AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceFinite impulse responsePhase correction
The invention provides a method and device for obtaining a noise-reducing NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) logging echo signal. The method comprises the following steps: a received NMR logging echo signal can be converted into a digital echo signal by an AD (Analog-to-Digital) converting unit; the digital echo signal is subjected to delay processing by a delay module, and thus a delayed digital echo signal can be obtained; the delayed digital echo signal is subjected to filter processing by an FIR (Finite Impulse Response) filter, and thus a filtered echo signal can be obtained; the filtered echo signal is subjected to FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) processing by an FFT unit, and thus a frequency domain filtered echo signal can be obtained; the frequency domain filtered echo signal is subjected to phase correction by a phase correction unit according to the digital echo signal obtained by a counter, and thus a phase correction filtered echo signal can be obtained; and the phase correction filtered echo signal is subjected to IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) processing by an IFFT unit, and thus the noise-reducing NMR logging echo signal can be obtained. According to the scheme, the problem of phase drift generated in a filtering process is removed.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
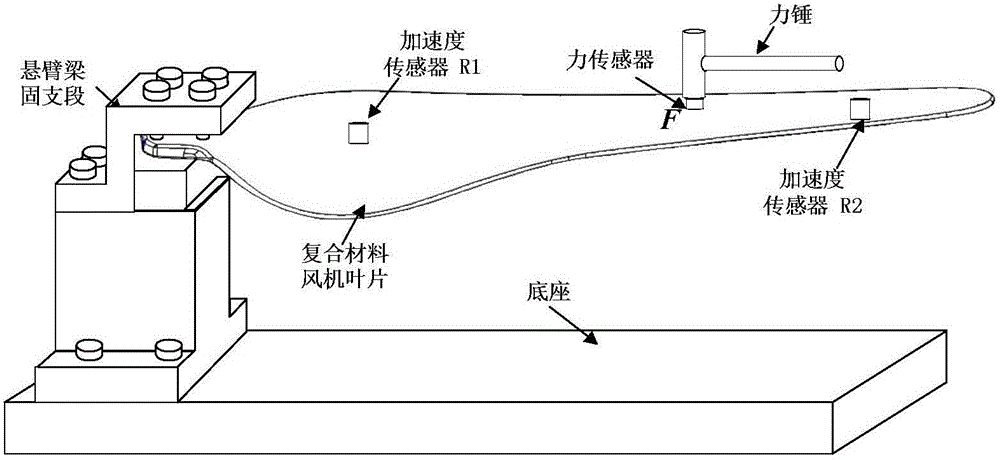
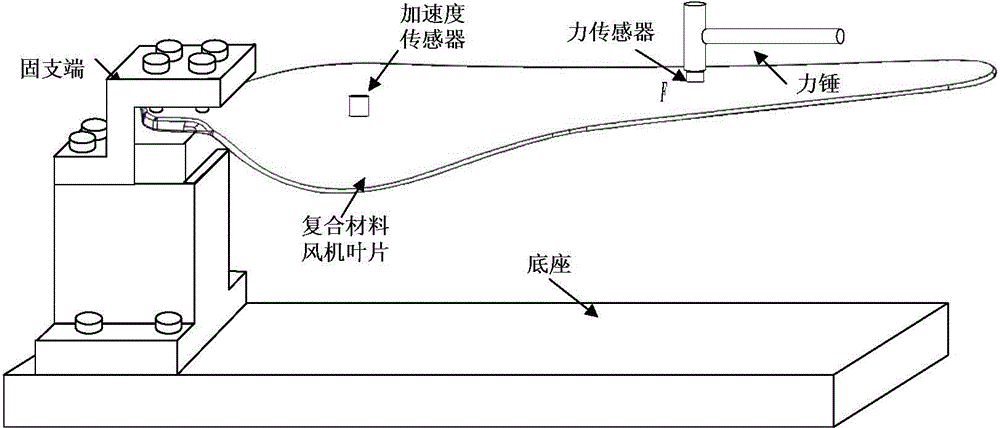
Fan blade impulse load recognition method
ActiveCN104537251AHigh precision reconstructionFast convergenceMachine part testingSpecial data processing applicationsTransfer matrixUnit impulse response
The invention relates to a fan blade impulse load recognition method. Based on the conjugate gradient least-squares iteration algorithm, the method comprises the following steps that (1), a hammering method is adopted for measuring the frequency-response function between a position point where an impulse load is exerted on a fan blade and a response measure point of the fan blade, inverse fast fourier transformation is used for obtaining a unit impulse response function, and therefore a transfer matrix is obtained through deconvolution; (2), an acceleration sensor is used for measuring acceleration response signals generated by the impulse load which acts on the fan blade; (3), the number of iterations, loads to be recognized, response residuals and iteration searching directions of the conjugate gradient least-squares iteration algorithm are initialized; (4), the number of iterations, loads to be recognized, response residuals, the conjugate gradient coefficients and the iteration searching directions under the current number of iterations are updated; (5) whether a heuristic type convergence termination criterion is met is judged; (6) regularized loads to be recognized are obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
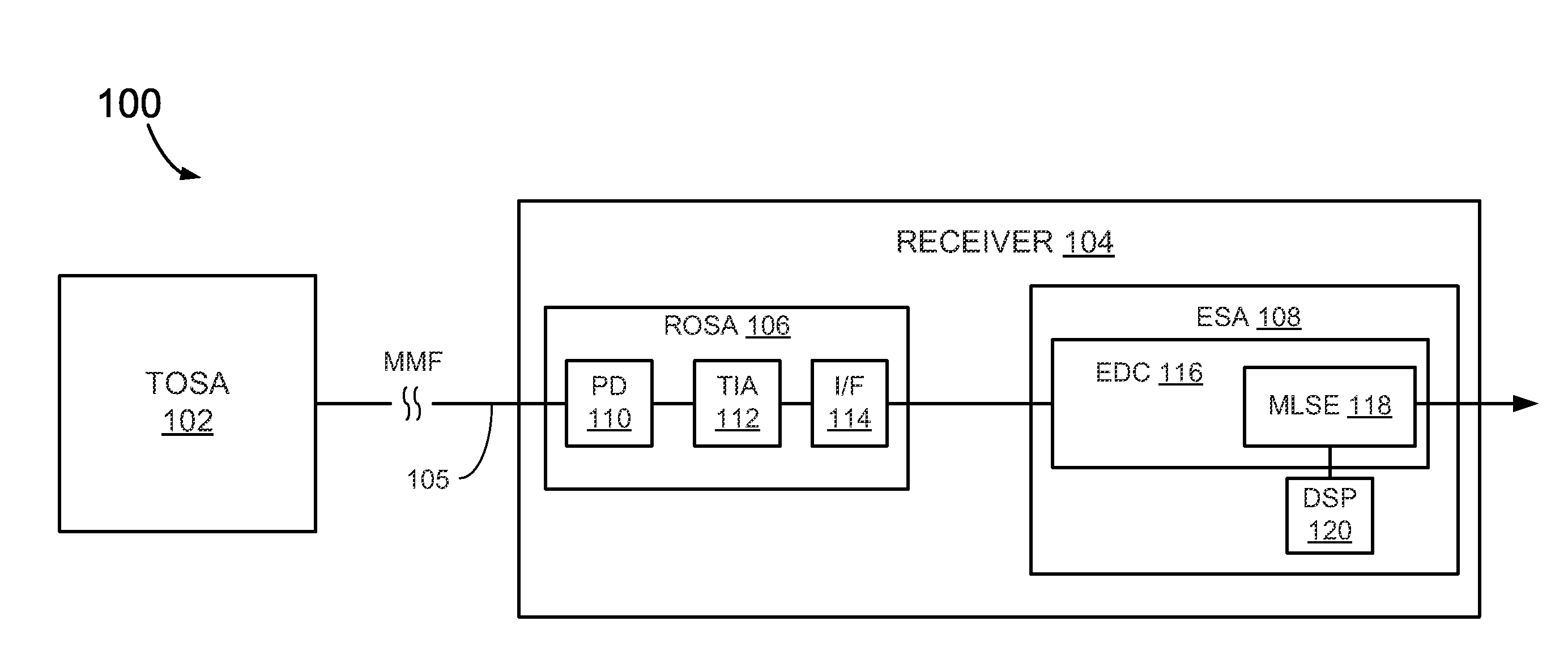
Apparatus and methods for estimating optical ethernet data sequences
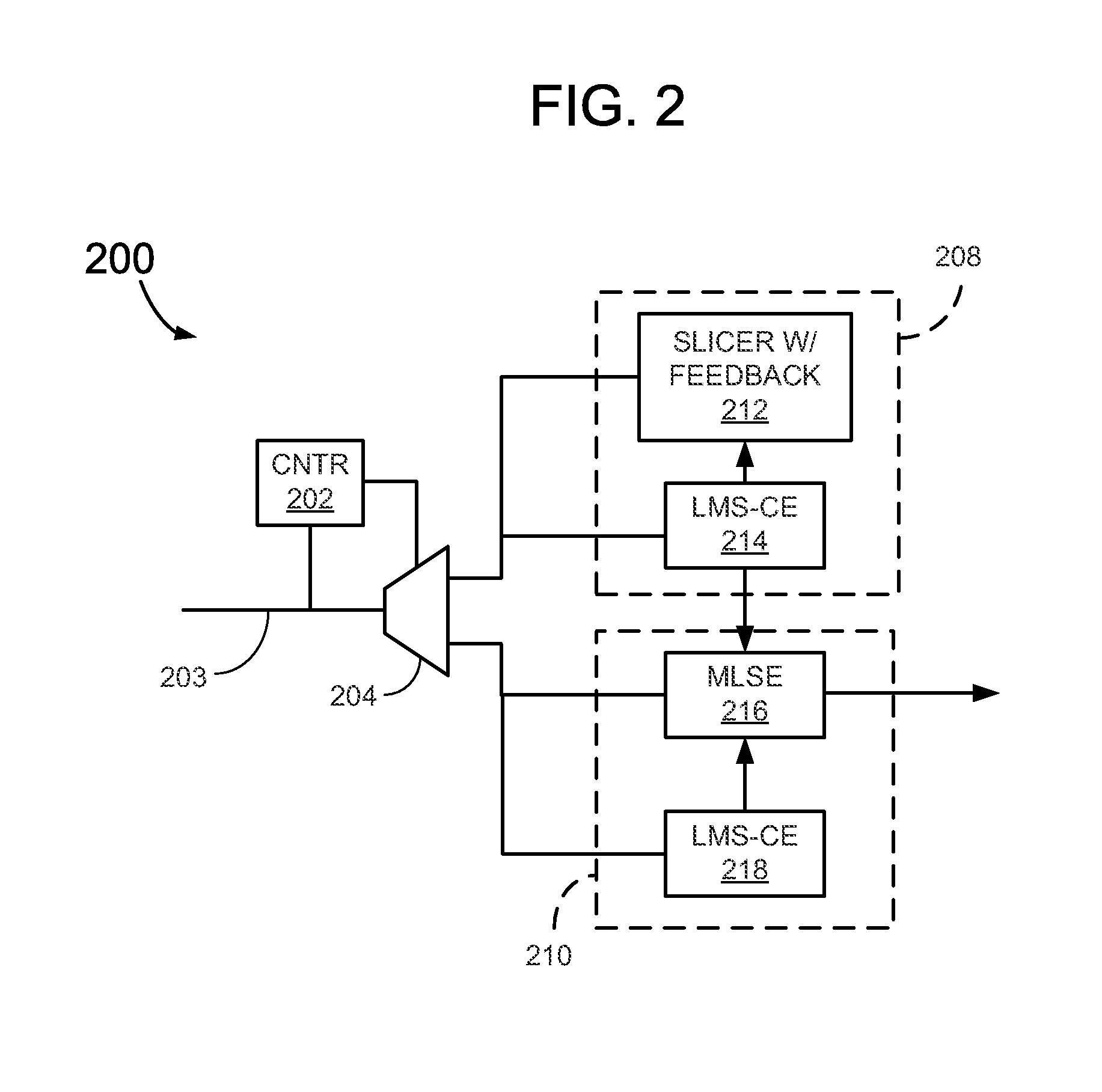
A receiver is disclosed that includes a slicer having an input to receive a sequence of symbols exhibiting inter-symbol-interference (ISI). The slicer determines a state associated with each symbol based on a threshold. A feedback equalization unit is coupled to the slicer to apply equalization to the symbol fed to the slicer input based on prior detected symbol states. A Least-Mean-Square (LMS) unit cooperates with the slicer and feedback equalization unit to estimate a channel impulse response based on the equalized symbols. The LMS unit feeds the estimated channel impulse response to a Maximum-Likelihood-Sequence-Estimation (MLSE) unit to generate an estimated sequence of bits based on the estimated channel impulse response.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wireless multipath fading channel simulating method and channel simulator
ActiveCN104683051AActual complianceReliable resultsTransmission monitoringSimulationModel parameters
The invention discloses a wireless multipath fading channel simulating method and a channel simulator. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a channel between a transmitting antenna and a receiving antenna in actual environment, and measuring the frequency response of an actual measurement channel through frequency sweep; performing fourier inverse transform on the frequency response of the actual measurement channel so as to obtain the unit impulse response of the actual measurement channel; separating parameters in the unit impulse response of the actual measurement channel, and performing modeling so as to obtain a parameter model; storing the parameters of the model into a database; reading the parameters of the model, and generating the unit impulse response of a simulating channel; calculating a bit error ratio by utilizing Monte-Carlo simulation so as to complete channel simulation under the actual environment. The simulator comprises a channel measuring module, a module for extracting the unit impulse response of the actual measurement channel, a model building module, a model parameter extracting module and a simulating channel generating and verifying module. According to the wireless multipath fading channel simulating method and the channel simulator, disclosed by the invention, data can be measured in an actual manner, the model can be established, the bit error properties in different communication processes can be analyzed, and the channel obtained through simulation more conforms to the actual environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Using multi-level pulse width modulated signal for real time noise cancellation
InactiveUS20120114033A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsFinite impulse responseSignal processing circuits
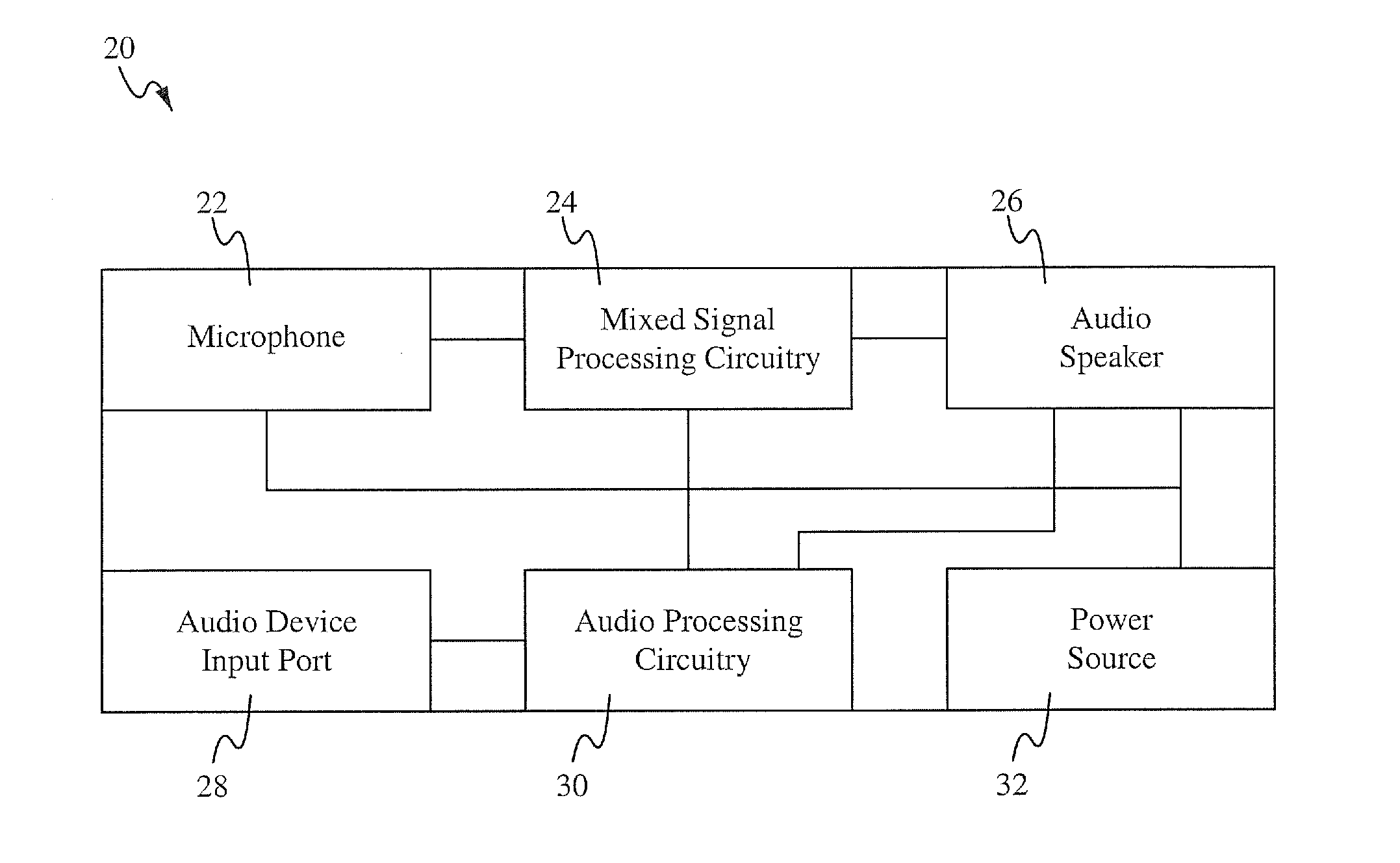
A mixed signal processing circuit includes an analog to PWM converting circuit and a finite impulse response (FIR) filter having a multiple output tapped delay line and a summing and integration circuit. The mixed signal processing circuit converts an input analog signal to a PWM signal, forms a multi-level PWM signal from the PWM signal and one or more delayed versions of the PWM signal, and converts the multi-level PWM signal to an output analog signal. The analog to PWM converting circuit is implemented using a triangle waveform generator and a comparator. The FIR filter is implement using a resistive network to apply scaling coefficients of the FIR filter. The mixed signal processing circuit can be implemented within a noise cancellation headphone to generate a noise cancelling signal or generally in applications that would be benefitted from the combination of analog input / output and digital filter techniques.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Method for estimating channel impulse response
InactiveCN101351012AThe effect of suppressing estimatesImprove the performance of balanced demodulationEnergy efficient ICTBaseband system detailsChannel impulse responseEstimation methods
The invention provides an estimation method for channel impulse response, which is used in mobile communication system and including the following steps: (a) the channel impulse response is estimated initially h(i), i is equal to 0...N-1, (b) the energy of the N paths of the channel impulse response is calculated. The energy maximum is En Max and energy threshold value is En Max / T. T is more than 1. If the path energy in the channel impulse response is less than the energy threshold value, the path is set as a noise path and the channel impulse response value corresponding to the path is cleared, (c) channel impulse response estimation value h(i){i is equal to 0, ...L-1} is gotten to estimate noise variance according to different channel impulse response orders L. L ranges from Lstart to N. Lstart is an integer less than or equal to N, (d) the L value corresponding to the smallest noise variance is taken as the dispersion length M of the channel. The channel impulse response value from path M+1 to path N is cleared. Compared with the traditional method, the invention can inhibit the influence of noise on channel impulse response estimation and consequently improve balanced demodulation performance.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
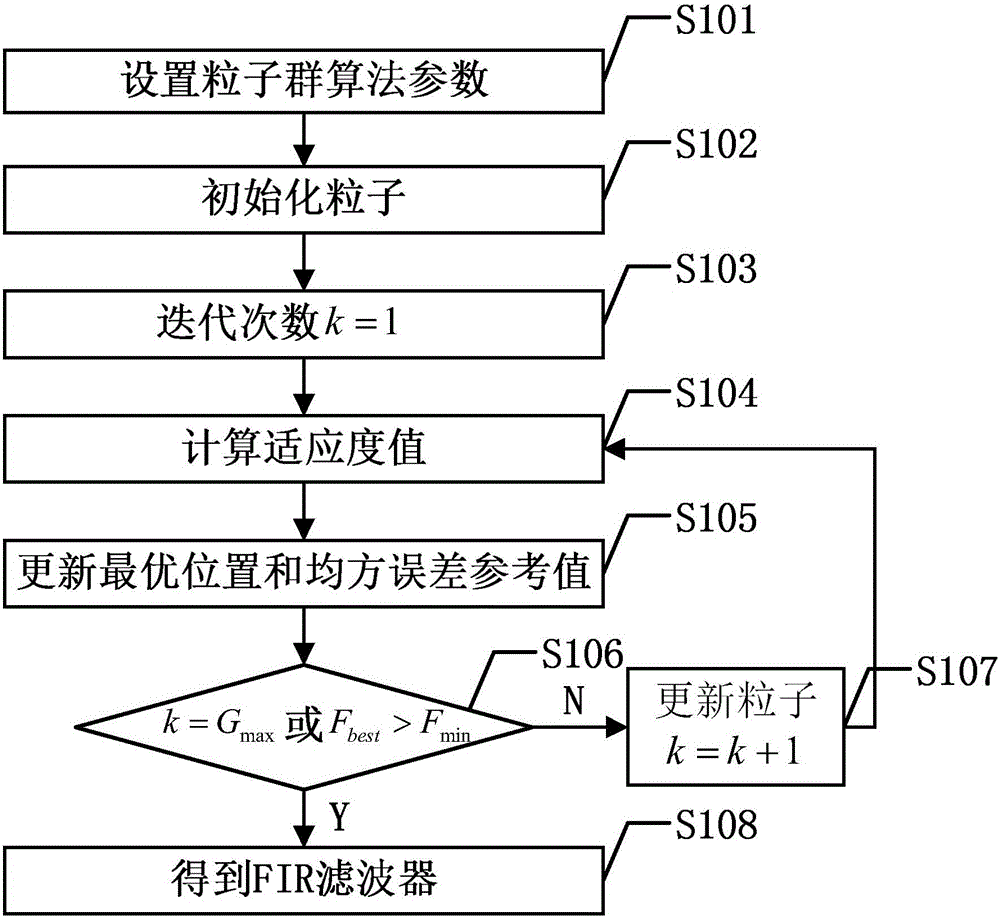
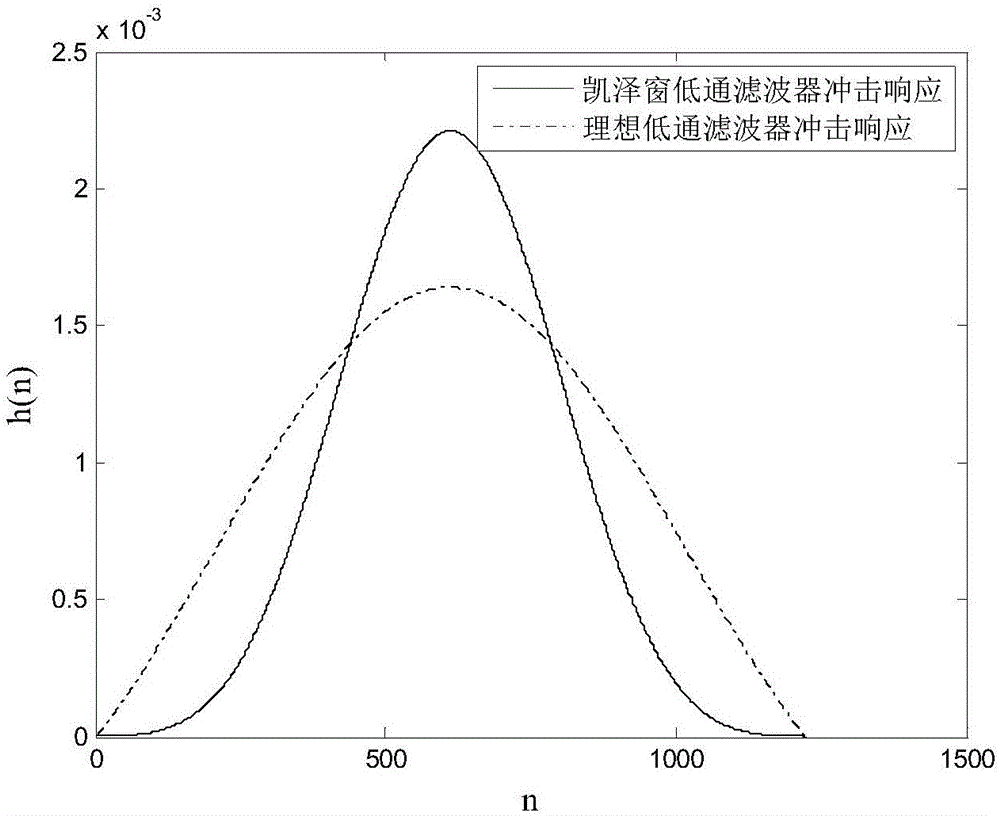
FIR filter design method based on particle swarm optimization
InactiveCN106067783AGuaranteed SNRAdapt to external disturbancesDigital technique networkFir filter designMean square
The invention discloses a FIR filter design method based on particle swarm optimization. The method is characterized by using the unit impulse response of a FIR filter as the particle position vector of the particle swarm optimization; designing the fitness function of the particle swarm optimization on the basis of a signal-to-noise ratio of a signal filtered by the FIR filter and the mean square error of the FIR filter and obtaining the FIR filter by iteration. The method designs the fitness function of the particle swarm optimization based on minimized signal-to-noise ratio and mean square error, and designs the FIR filter based on particle swarm optimization so as to achieve the FIR filter taking account of signal-to-noise ratio performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
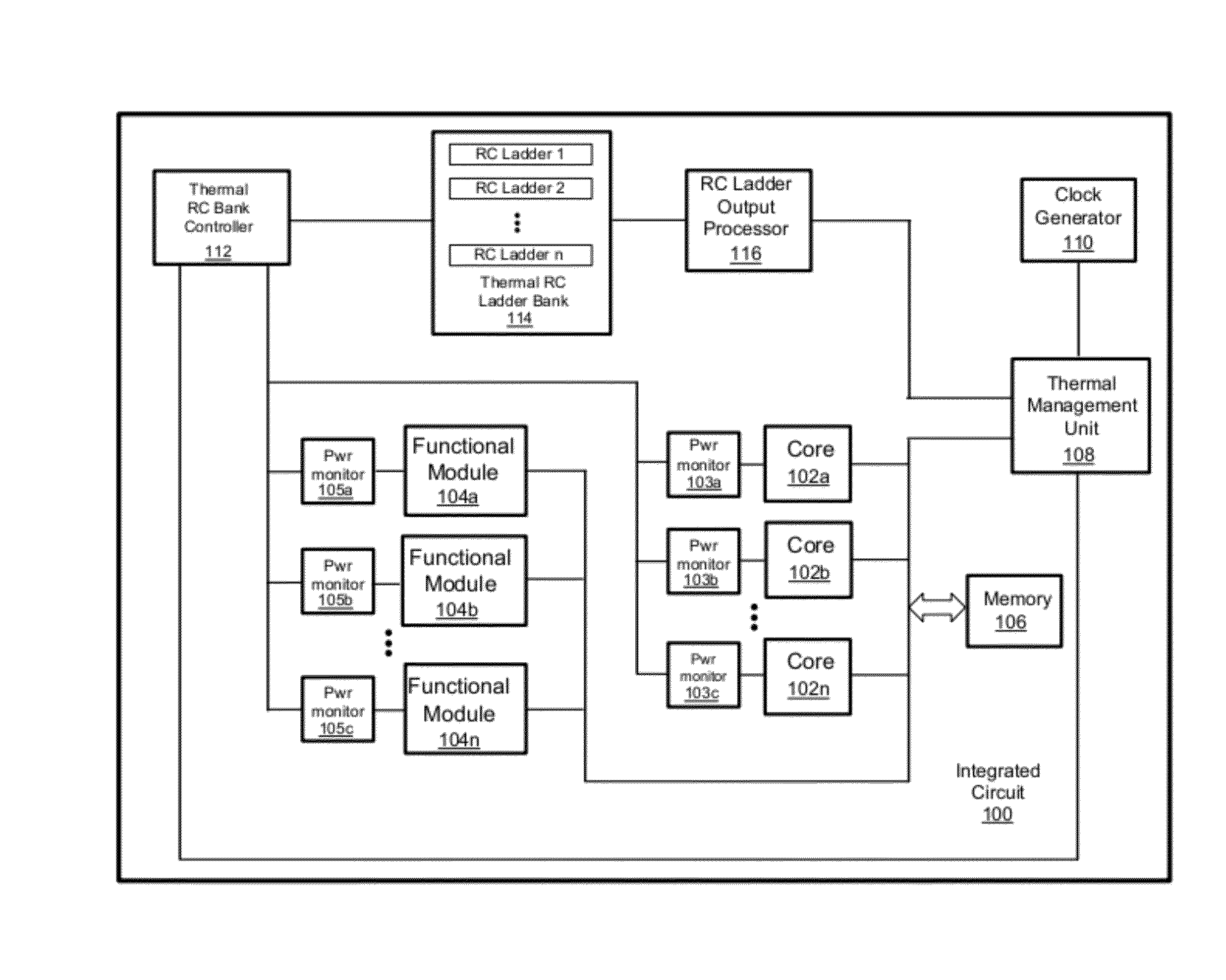
Transient Thermal Modeling of Multisource Power Devices
ActiveUS20120278029A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionTemperature responseEngineering
Embodiments of systems and methods for improved measurement of transient thermal responses in electronic systems are described herein. Embodiments of the disclosure use the known thermal transfer function of an electronic system to generate an equivalent resistor-capacitor (RC) network having a dynamic response that is identical to a given power excitation as the actual electronic system would have to that power excitation. Using the analogy between thermal and electrical systems, a Foster RC network is constructed, comprising a plurality of RC stages in which resistors and capacitors are connected in parallel. Subsequently, the analog thermal RC network is converted into an infinite impulse response (IIR) digital filter, whose coefficients can be obtained the Z-transform of the analog thermal RC network. This IIR digital filter establishes the recursive relationship between temperature output at the current time step and measured power input at the previous time step. Using this IIR digital filter, temperature response subject to arbitrary time-dependent power can be calculated in very small amount of time compared with prior art methods.
Owner:ATI TECH INC +1
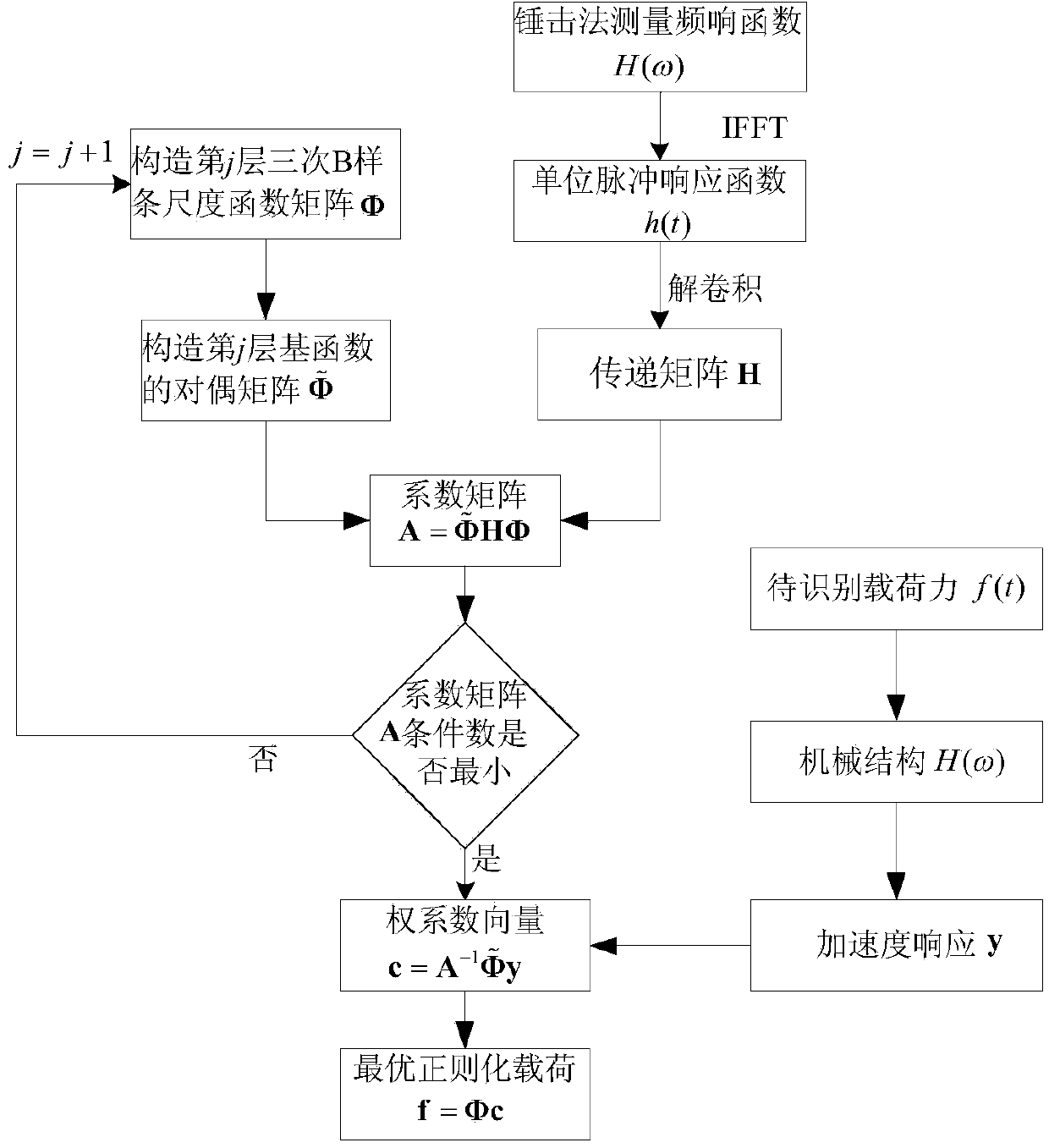
Mechanical structure dynamic load identification method based on cubic b-spline scaling function
InactiveCN104462862AImprove applicabilityHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsWeight coefficientMeasurement point
The invention relates to a mechanical structure dynamic load identification method based on a cubic b-spline scaling function. The method comprises the steps of (1) measuring a frequency-response function between a mechanical structure position point bearing a dynamic load and a mechanical structure response measurement point with the hammering method, obtaining a unit impulse response function through rapid Fourier inversion, and then obtaining a transfer matrix through deconvolution; (2) measuring an acceleration signal of the response point generated by the structure dynamic load through an accelerator sensor; (3) establishing scaling function matrixes, dual matrixes and coefficient matrixes of the cubic b-spline scaling function under different layer numbers, and selecting a coefficient matrix with the minimum conditional number; (4) calculating the weight coefficient of the cubic b-spline scaling function under the regularized layer number by means of an acceleration response and coefficient matrix; (5) obtaining a regularized mechanical structure dynamic load to be identified by multiplying the weight coefficient by the corresponding scaling function matrix.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Channel estimation method and system using linear correlation based interference cancellation (LCIC) combined with decision-feedback-equalization (DFE)
InactiveUS7933366B2Reduce complexityInterference cancellationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsLinear correlationChannel impulse response
A channel estimation method and system using linear correlation based interference cancellation combined with decision-feedback-equalization (LCIC-DFE) are provided. The channel estimation method includes generating a first correlation sequence by calculating a linear correlation between a baseband sampled complex signal and a locally stored pseudo-noise signal and obtaining a second correlation sequence by iteratively removing inter-path interference from the first correlation sequence and generating a first channel impulse response (CIR) sequence based on the second correlation sequence. And, obtaining a third correlation sequence by removing random-data interference from the second correlation sequence based on the first CIR sequence and a feedback signal and generating a second CIR sequence based on the third correlation sequence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
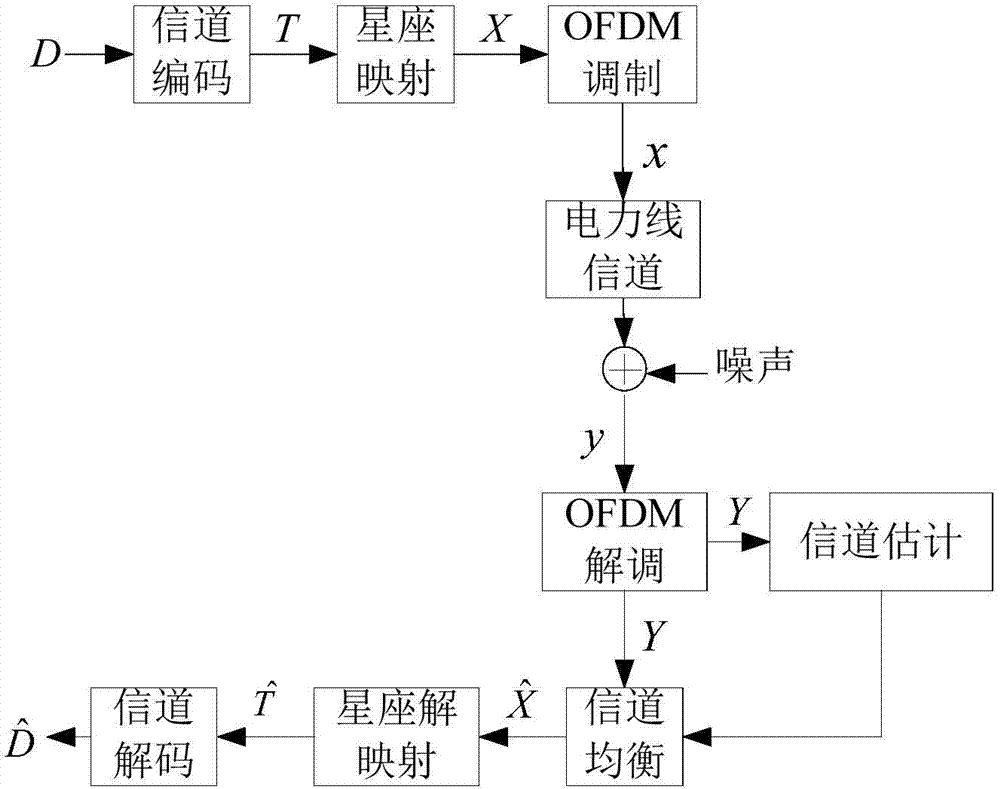
Power line communication channel estimation method
InactiveCN104506465AReduce computational complexityReduce the number of pilotsBaseband system detailsPower distribution line transmissionComputation complexityEngineering
The invention discloses a power line communication channel estimation method. The power line communication channel estimation method comprises the steps of receiving signal conversion; selecting pilot frequency; conducting estimation by using a compressed sensing signal recovery algorithm. Aiming at the disadvantages that the channel estimation performance of the traditional estimation algorithm based on a least square method and a minimum mean square error is reduced with pilot frequency number, the estimation accuracy is reduced, the calculation complexity is high and the like, power line channel estimation is conducted by using the feature that power line channels have sparsity and by adopting a compressed sensing method, unit impulse responses of the channels are obtained through the known pilot frequency information by using a matching tracking algorithm, the pilot frequency number is reduced, the calculation complexity is decreased and the transmission efficiency and communication quality are improved. By adopting irregular pilot frequency distribution and designing pilot frequency distribution according to channel and noise conditions, a typical strategy is to interpose pilot frequency reference information at frequency points with small channel attenuation or larger signal-to-noise ratio to improve the accuracy of channel estimation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
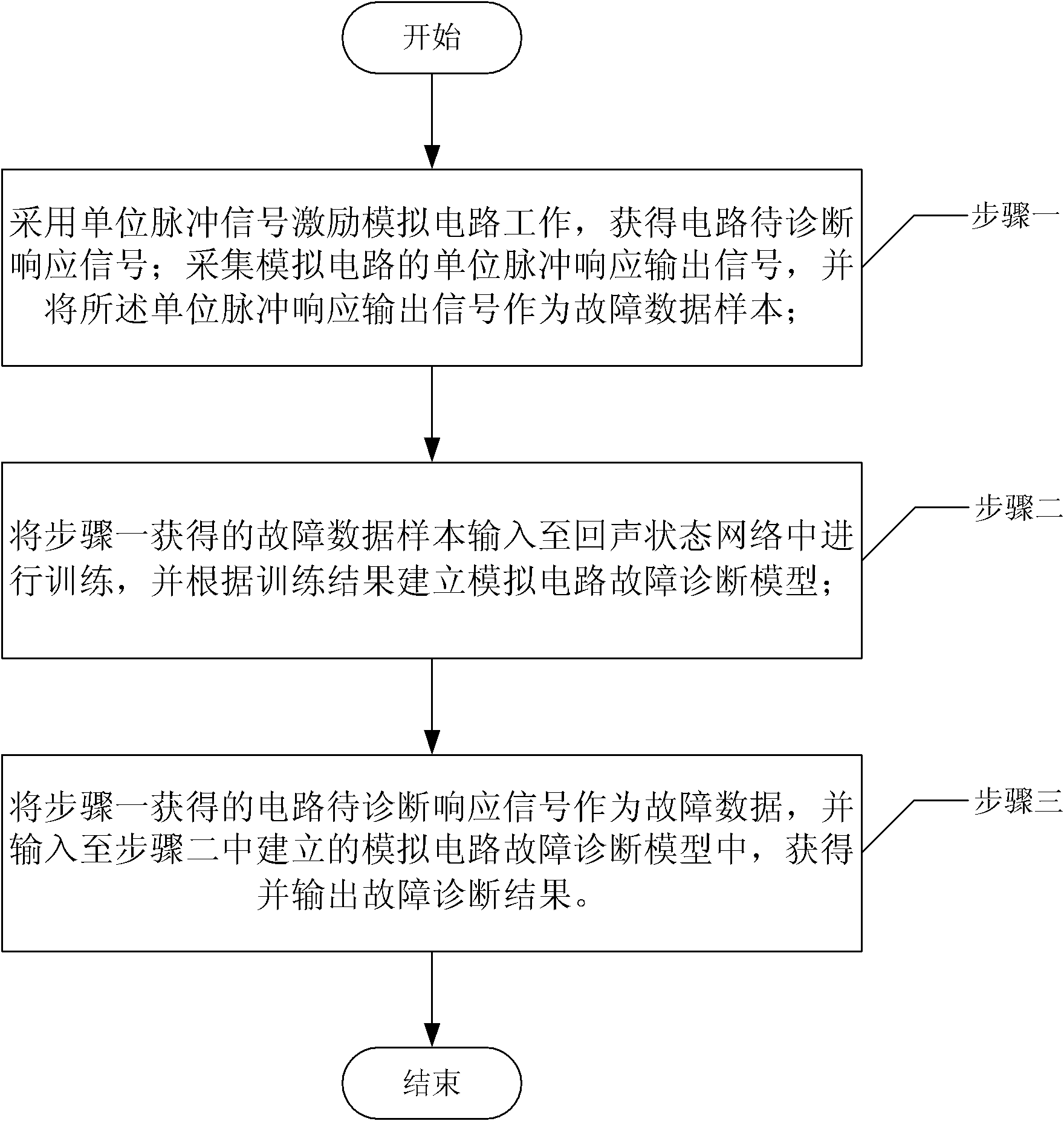
Fault Diagnosis Method for Analog Circuits Based on Echo State Network Dynamic Classification
An analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on echo state network dynamic classification relates to an analog circuit fault diagnosis method. It solves the problem of low diagnostic accuracy of analog circuit fault diagnosis using traditional neural network. Its method: use the unit pulse signal to excite the analog circuit to work, obtain the response signal of the circuit to be diagnosed; collect the unit pulse response output signal of the analog circuit, and use the unit pulse response output signal as the fault data sample; input the fault data sample to the echo Training is carried out in the state network, and an analog circuit fault diagnosis model is established according to the training results; the obtained circuit to-be-diagnosed response signal is used as fault data, and input into the analog circuit fault diagnosis model, and the fault diagnosis result is obtained and output. The invention is suitable for analog circuit fault diagnosis.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Channel estimator for ground digital multimedia broadcast system based on time domain relevancy
InactiveCN101106421AProcessing speedReduce usageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFourier transform on finite groupsUnit impulse response
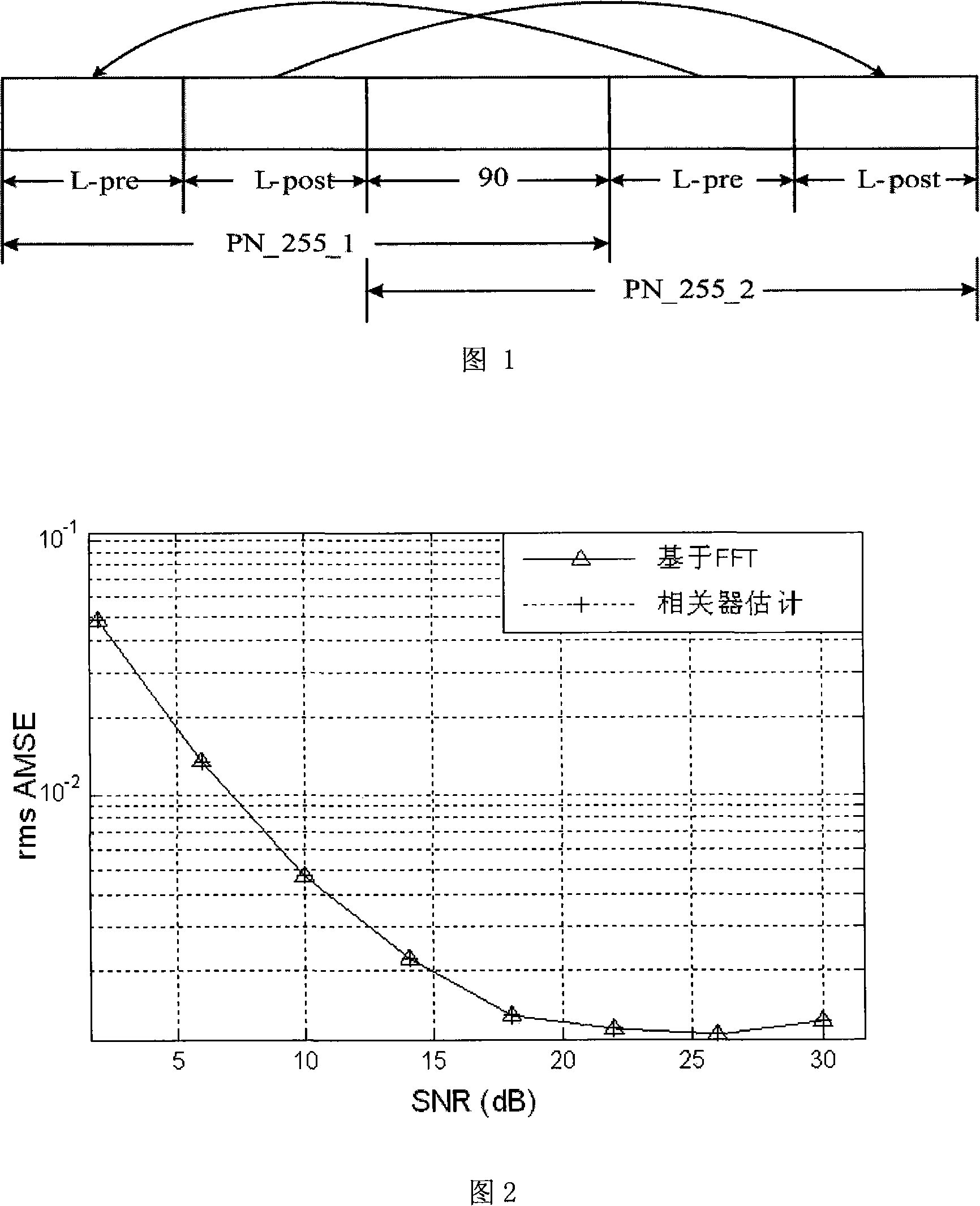
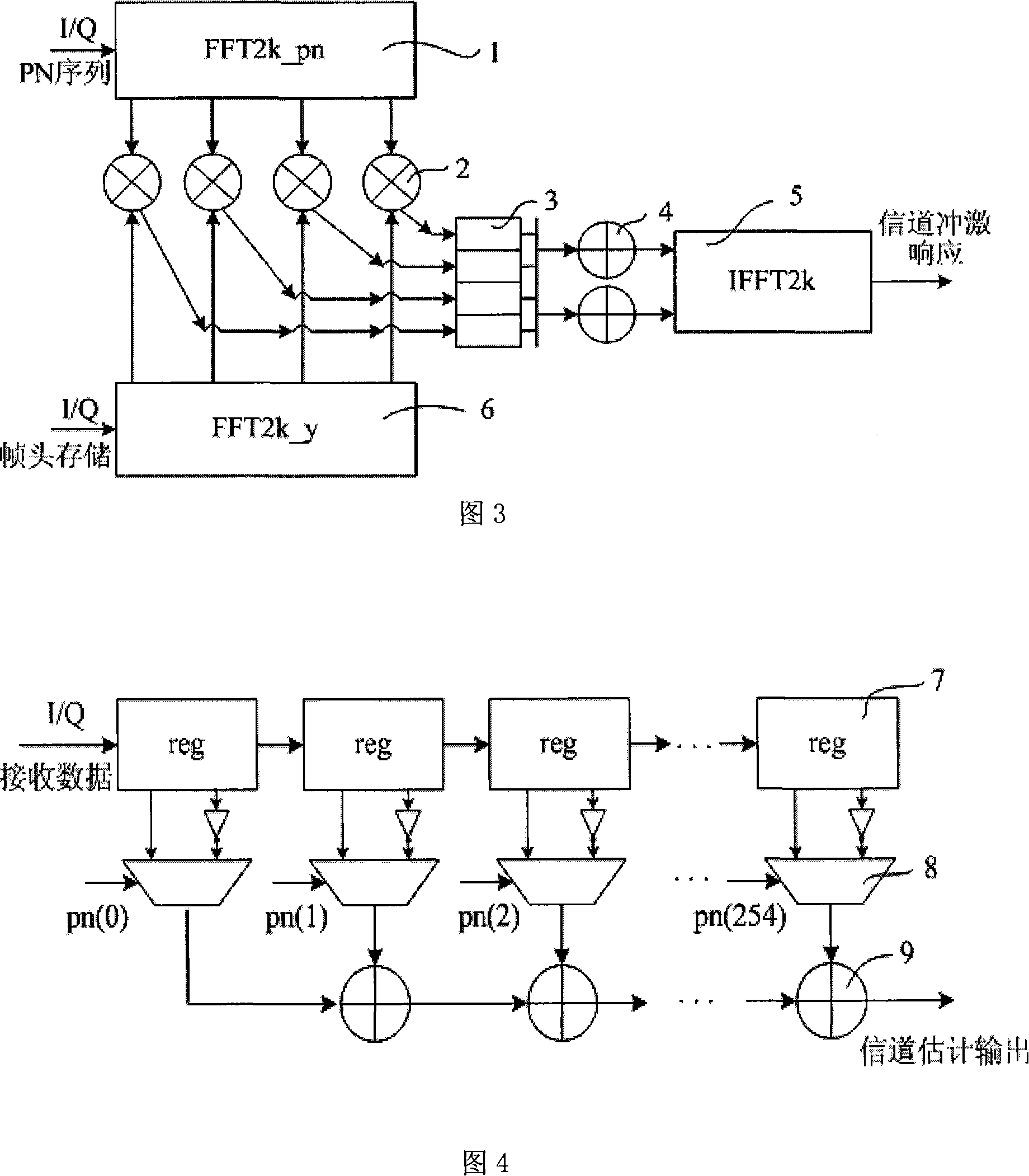
The invention belongs to the field of wireless digital communication technology, specifically relating to a ground digital television media broadcasting (DTMB) system channel estimator based on time domain correlation. The method of circular correlation is applied, and by using the quasi-cyclic PN (pseudo random) protection serial in the DTMB system frame structure, a channel impulse responses is obtained. Based on the CMOS technique in the standard of SMIC 0.18 micron, the channel estimator provided in the invention can work stably under the frequency of 60MHz, and the area is no more than 152k equivalent gates. Compared with the channel estimator based on fast fourier transform (FFT), the implementation scheme of channel estimation proposed in the invention reduces the design complexity by 50% on the premise of ensuring no performance loss, and the operation period reduces greatly.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
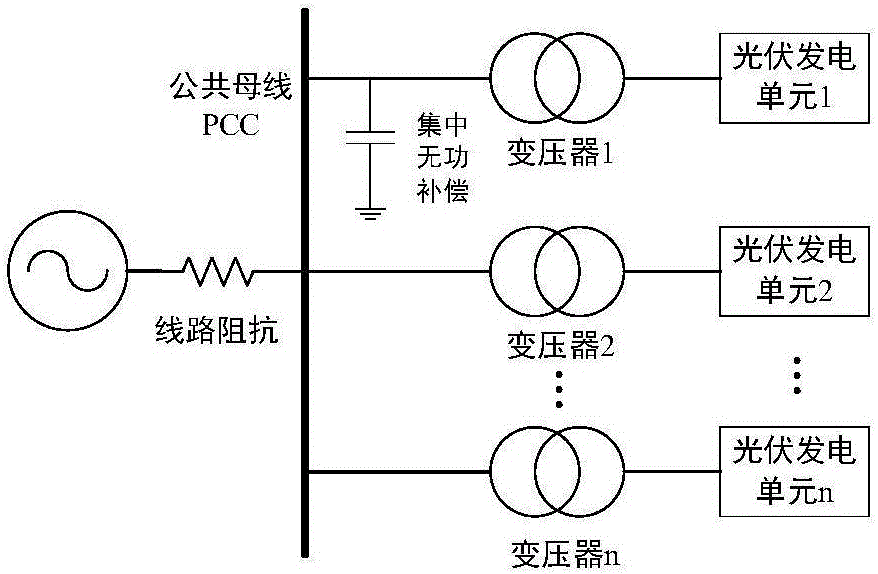
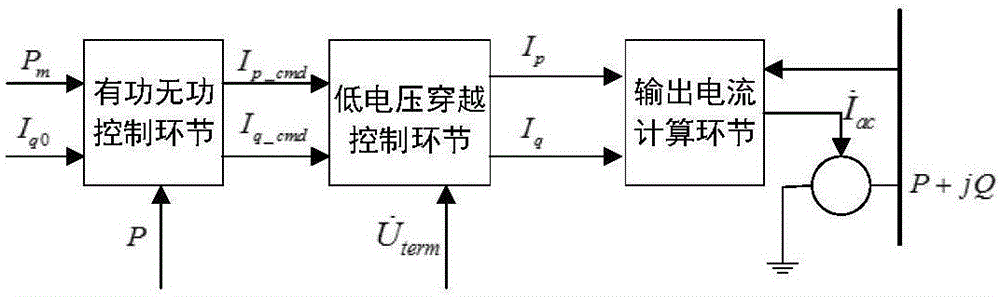
Online clustering equivalent modeling method of photovoltaic power plant
ActiveCN106451418ASmall amount of calculationPromote engineering applicationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationLow voltageEngineering
The invention discloses an online clustering equivalent modeling method of photovoltaic power plant. The method comprises the following steps: building photovoltaic power generation unit models with active and reactive power control links and low voltage crossing control links, and then building a photovoltaic power plant model with multiple photovoltaic units; according to the various types of photovoltaic power generation unit models of the photovoltaic power plant model, inferring and calculating the unit impulse curves corresponding to the model; using the distances among the unit impulse responding curves as clustering indexes; and utilizing the K-means algorithm to conduct online clustering to the photovoltaic power plant model so as to obtain the clustering result of the active and reactive power control links of an inverter; according to the actual output of each photovoltaic unit in the photovoltaic power plant model, calculating the equivalent parameters of each equalizer; and establishing an online clustering equivalent model of a photovoltaic power plant. In the invention, the clustering result bears no relationship with the output of the photovoltaic units and is solely determined by the control parameters of the inverter. Therefore, it is not necessary to establish a parameter sensitivity database offline, which greatly reduces the computational complexity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and apparatus for dynamic identification (ID) assignment in wireless networks
ActiveUS8711751B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsChannel impulse responseTransmission channel
Owner:APPLE INC
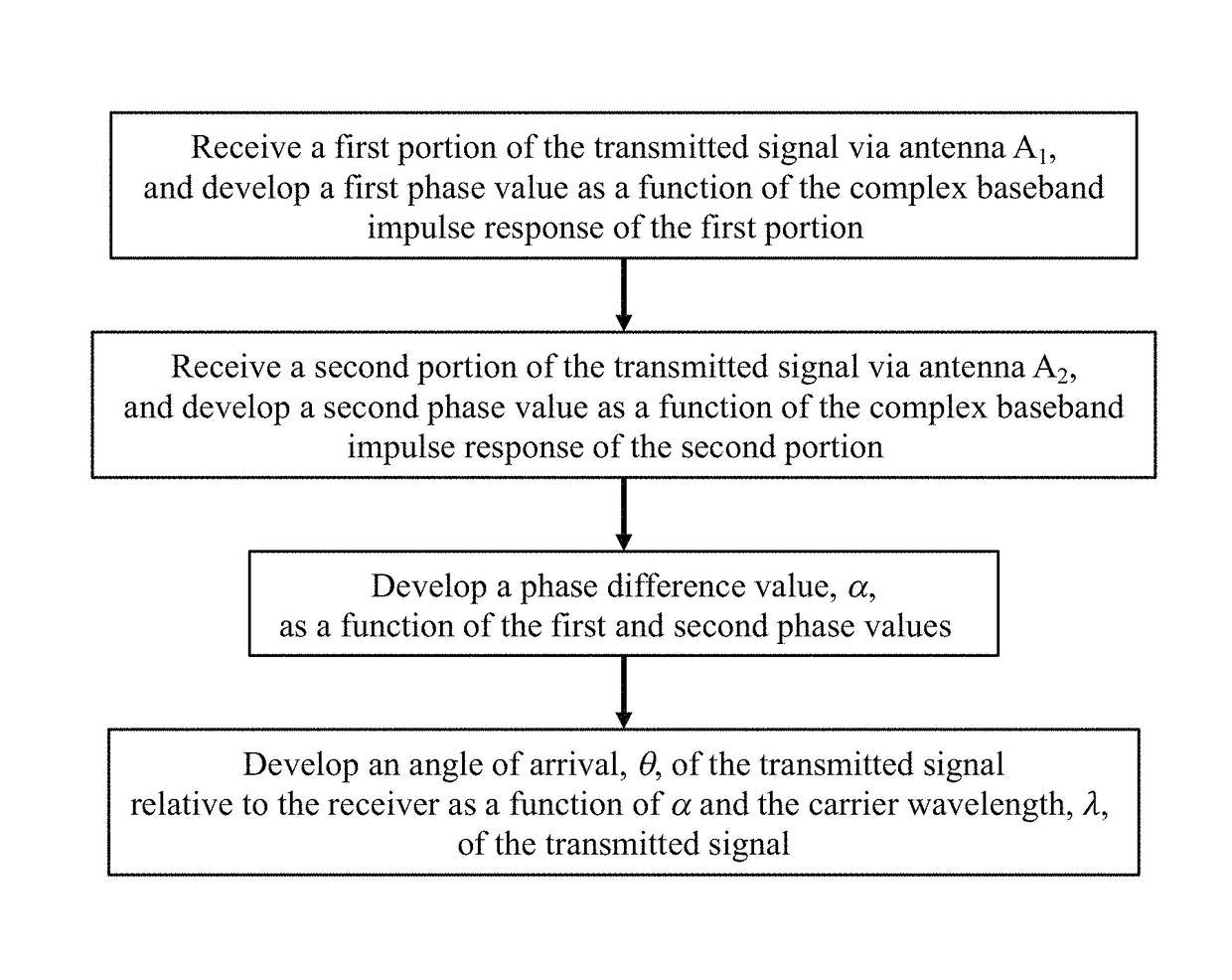
Angle of arrival using reduced number of receivers
In an ultra-wideband (“UWB”) receiver, a received UWB signal is periodically digitized as a series of ternary samples. During a carrier acquisition mode of operation, the samples are continuously correlated with a predetermined preamble sequence to develop a correlation value. When the value exceeds a predetermined threshold, indicating that the preamble sequence is being received, estimates of the channel impulse response (“CIR”) are developed. When a start-of-frame delimiter (“SFD”) is detected, the best CIR estimate is provided to a channel matched filter (“CMF”). During a data recovery mode of operation, the CMF filters channel-injected noise from the sample stream. Both carrier phase errors and data timing errors are continuously detected and corrected during both the carrier acquisition and data recovery modes of operation. The phase of the carrier can be determined by accumulating the correlator output before it is rotated by the carrier correction. By comparing the carrier phases of two receivers separated by a known distance, d, the angle of incidence, θ, of the signal can be determined. One or more receivers may be adapted to use multiple antennae, thus reducing the total number of receivers relative to the total number of antennae.
Owner:DECAWAVE
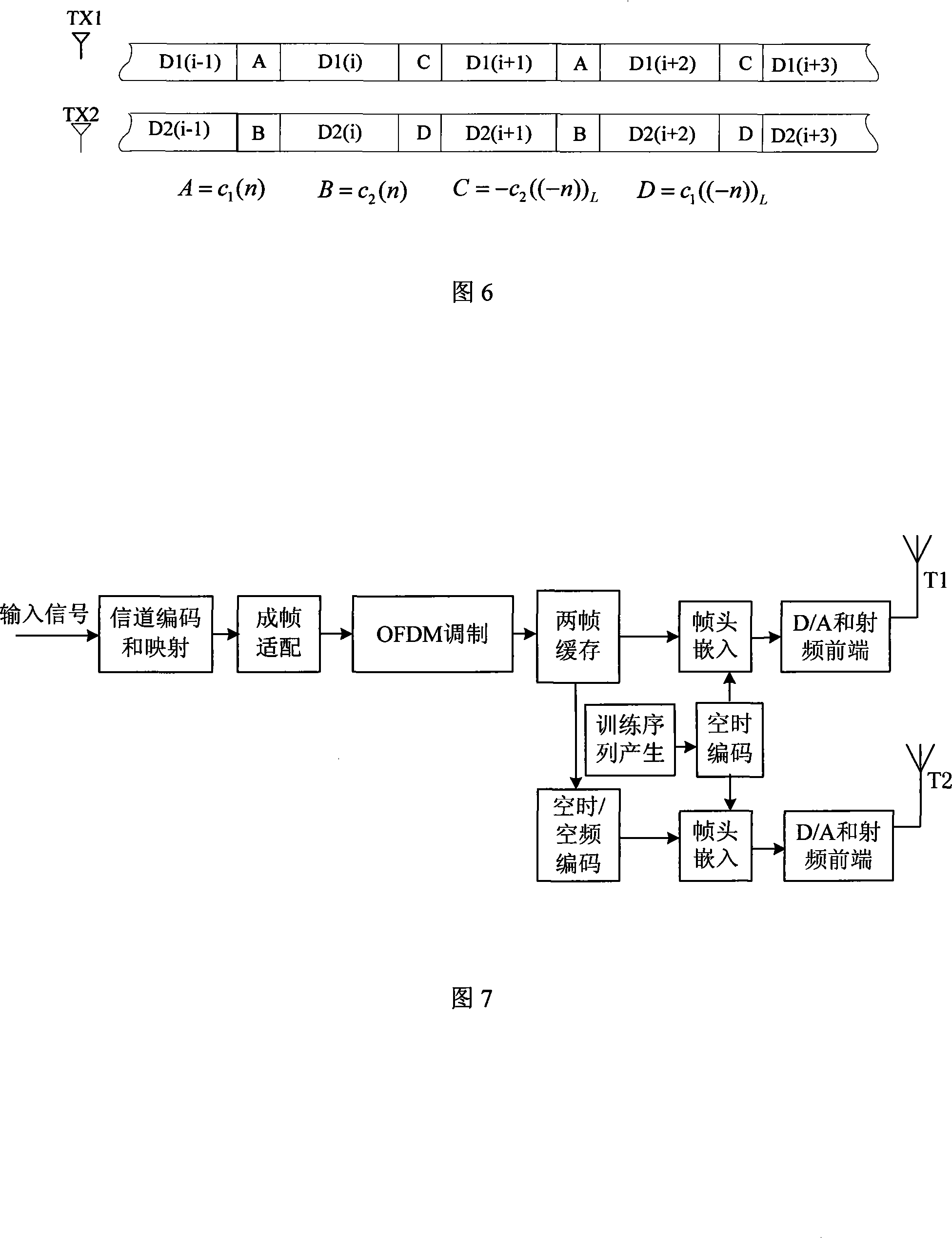
A channel estimation method for transmit diversity system
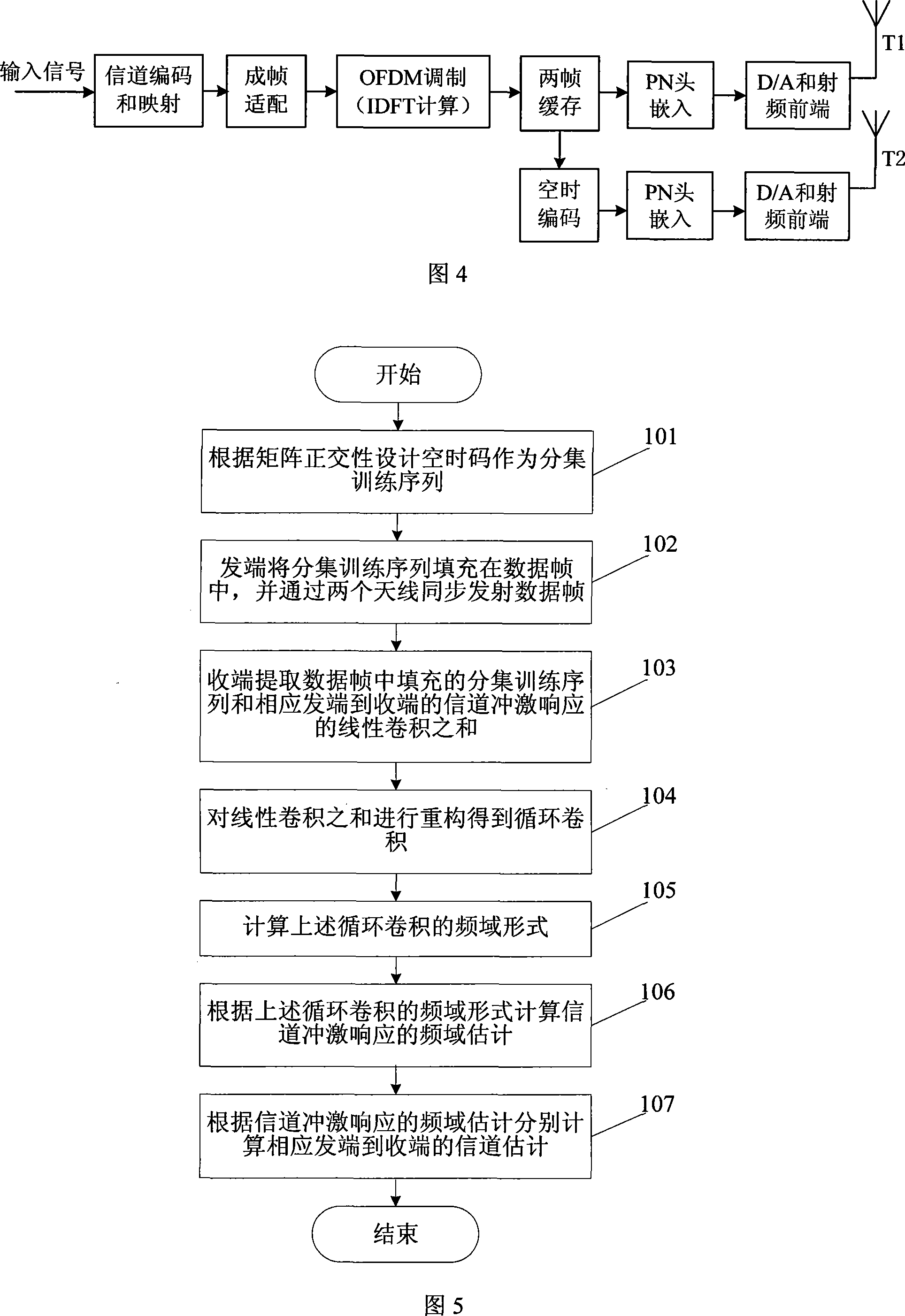
InactiveCN101217300AEliminate mutual interferenceReduce complexityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDesign spaceUnit impulse response
The invention discloses a signal channel estimation method of a transmission diversity system and belongs to the technical field of digital information transmission. The method comprises the following steps: a space time code designed according to the matrix orthogonality is taken as a diversity training sequence; a sender fills the diversity training sequence in a data frame and sends the data frame out; a receiver extracts the training sequence filled in the data frame and the linear convolutions of channel impulse response from the corresponding sender to the receiver; the sum of the linear convolutions is reconstructed for acquiring a circular convolution; the frequency domain form of the circular convolution is computed; the frequency domain estimation of the channel impulse response is computed according to the frequency domain form; the channel estimation from the sender to the receiver is computed according to the frequency domain estimation of the channel impulse response. The invention uses the designed space time code as the diversity training sequences, and selects the diversity training sequences with constant modulus in the frequency domains or the sum of frequency domains, thus effectively eliminating interference among the diversity training sequences and simplifying the channel estimation of the transmission diversity system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
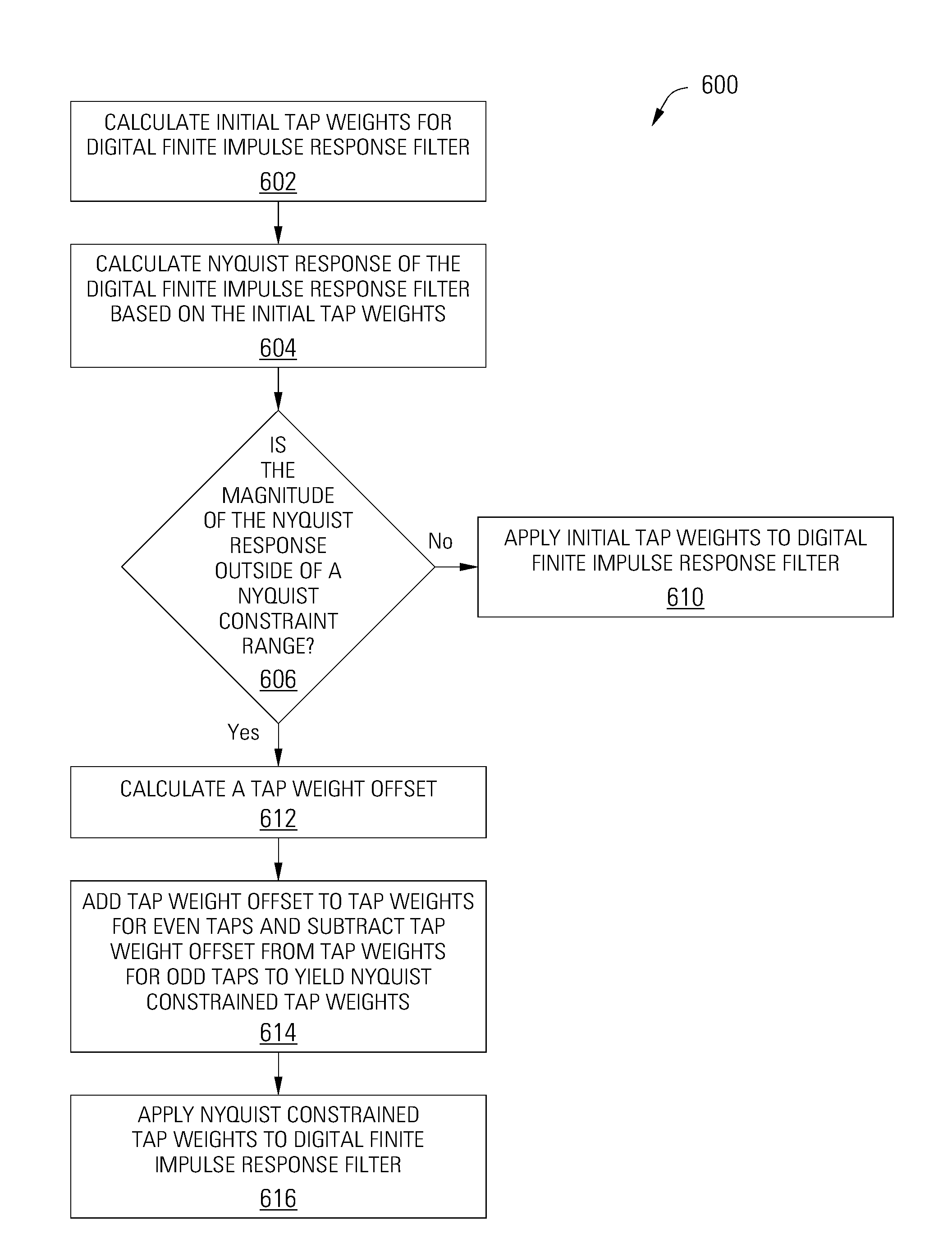
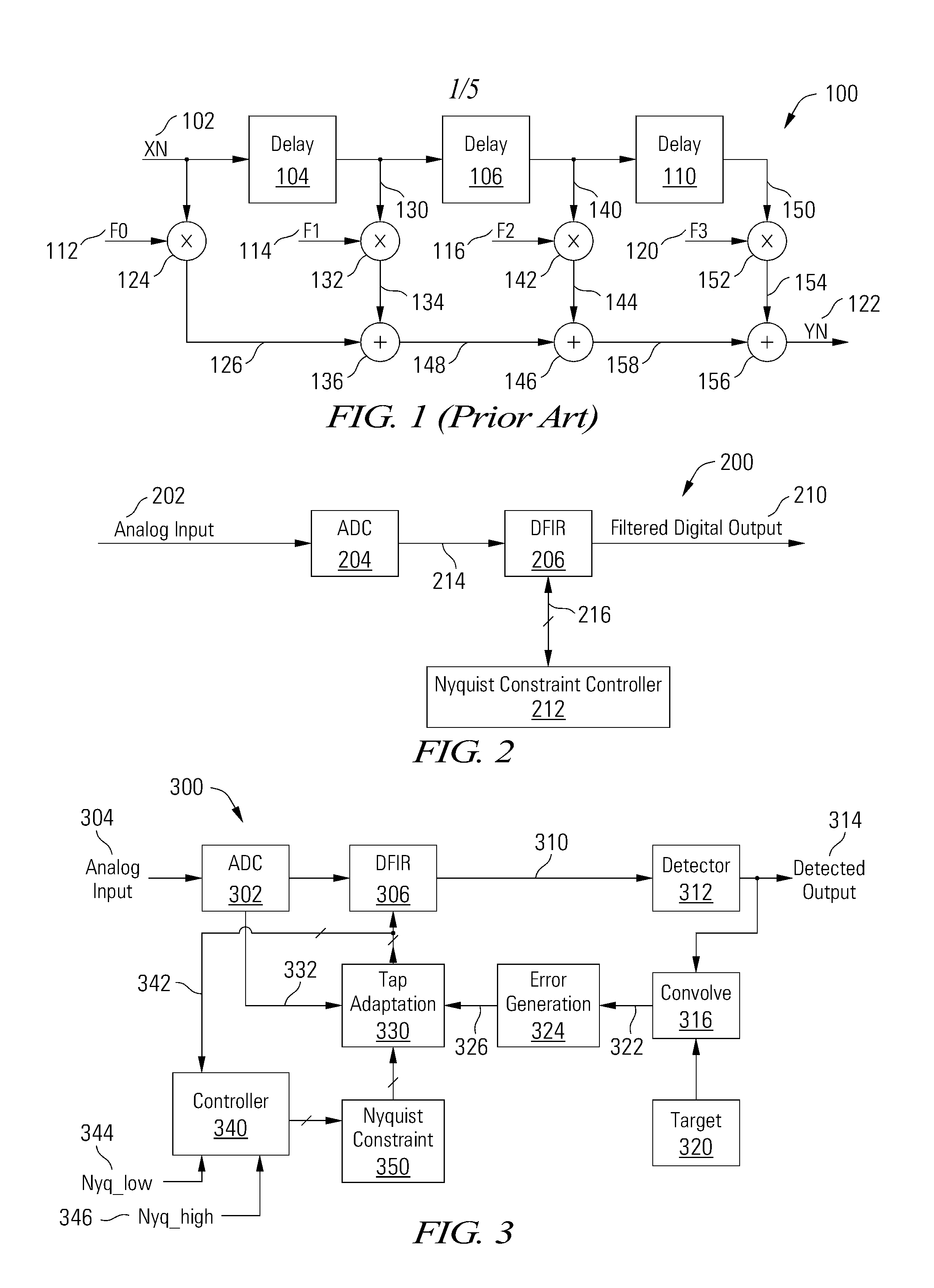
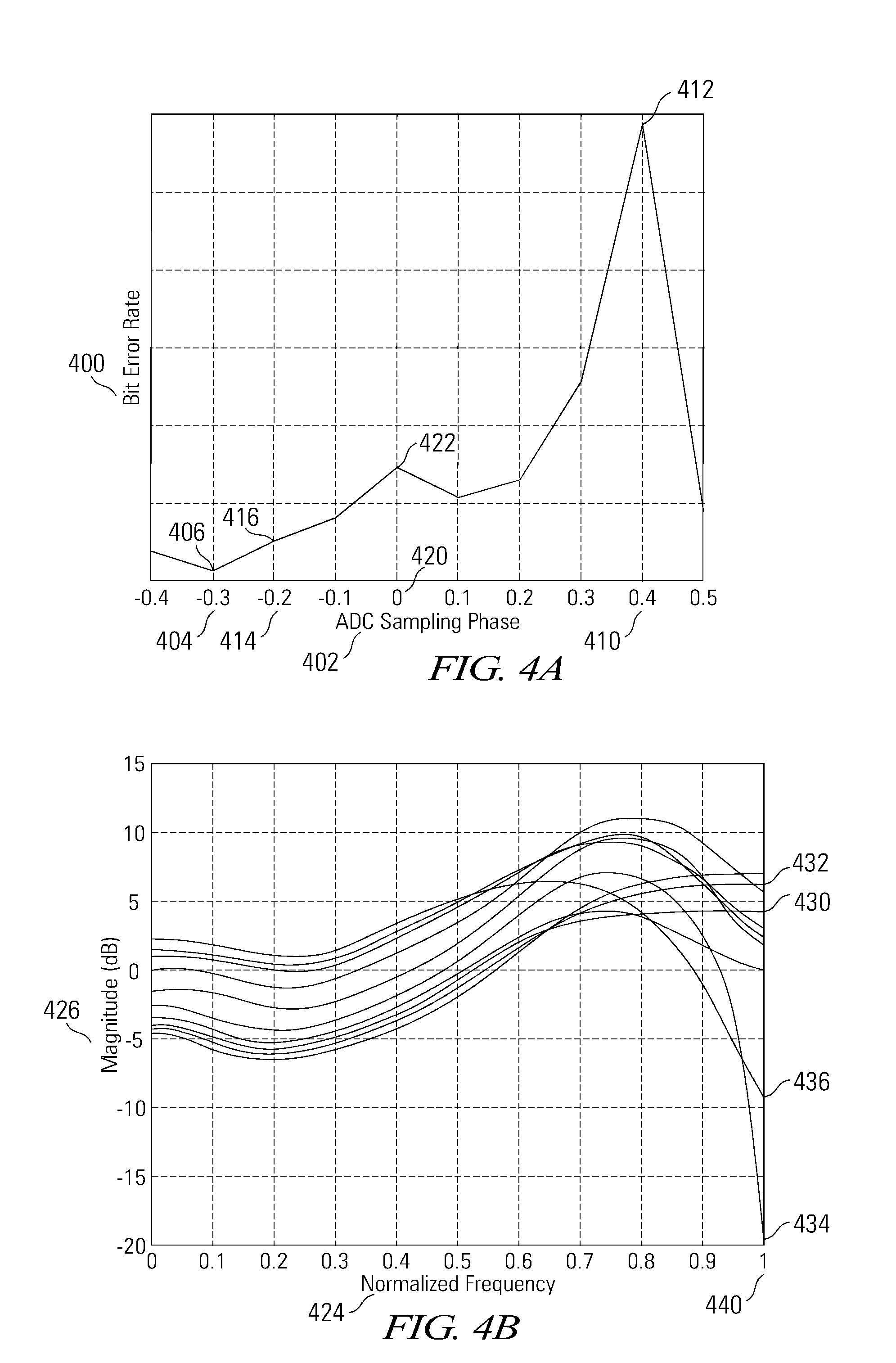
Nyquist Constrained Digital Finite Impulse Response Filter
InactiveUS20130097213A1Lower response sensitivityReduce sensitivityDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseDigital data
Various embodiments of the present invention provide apparatuses and methods for filtering a digital signal with a Nyquist constrained digital finite impulse response filter. For example, an apparatus for filtering digital data is disclosed that includes a digital finite impulse response filter having a plurality of taps. The apparatus also includes a tap weight controller connected to the digital finite impulse response filter, operable to adjust a tap weight for each of a subset of the taps such that a magnitude of a Nyquist response of the digital finite impulse response filter remains within a constraint range.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com