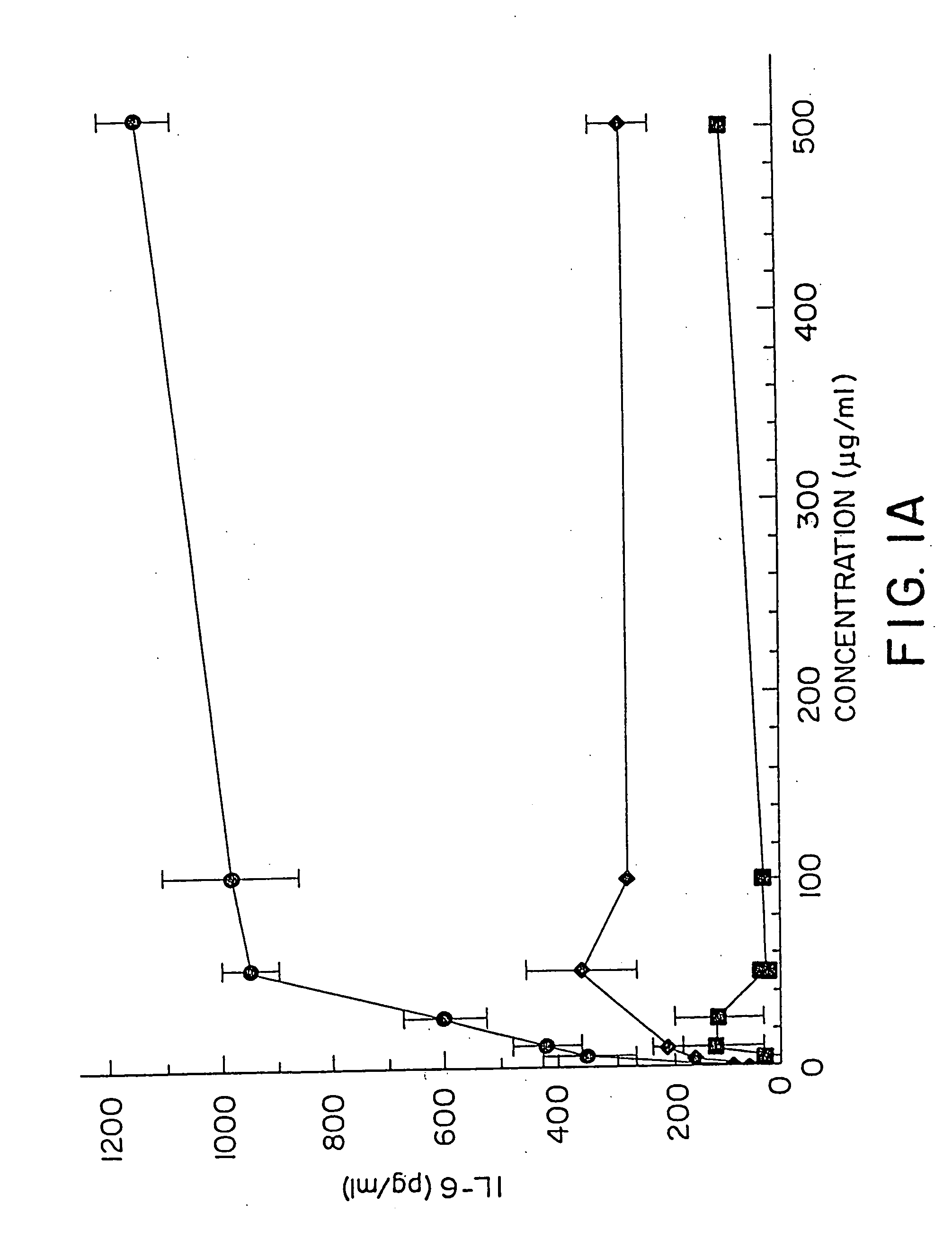
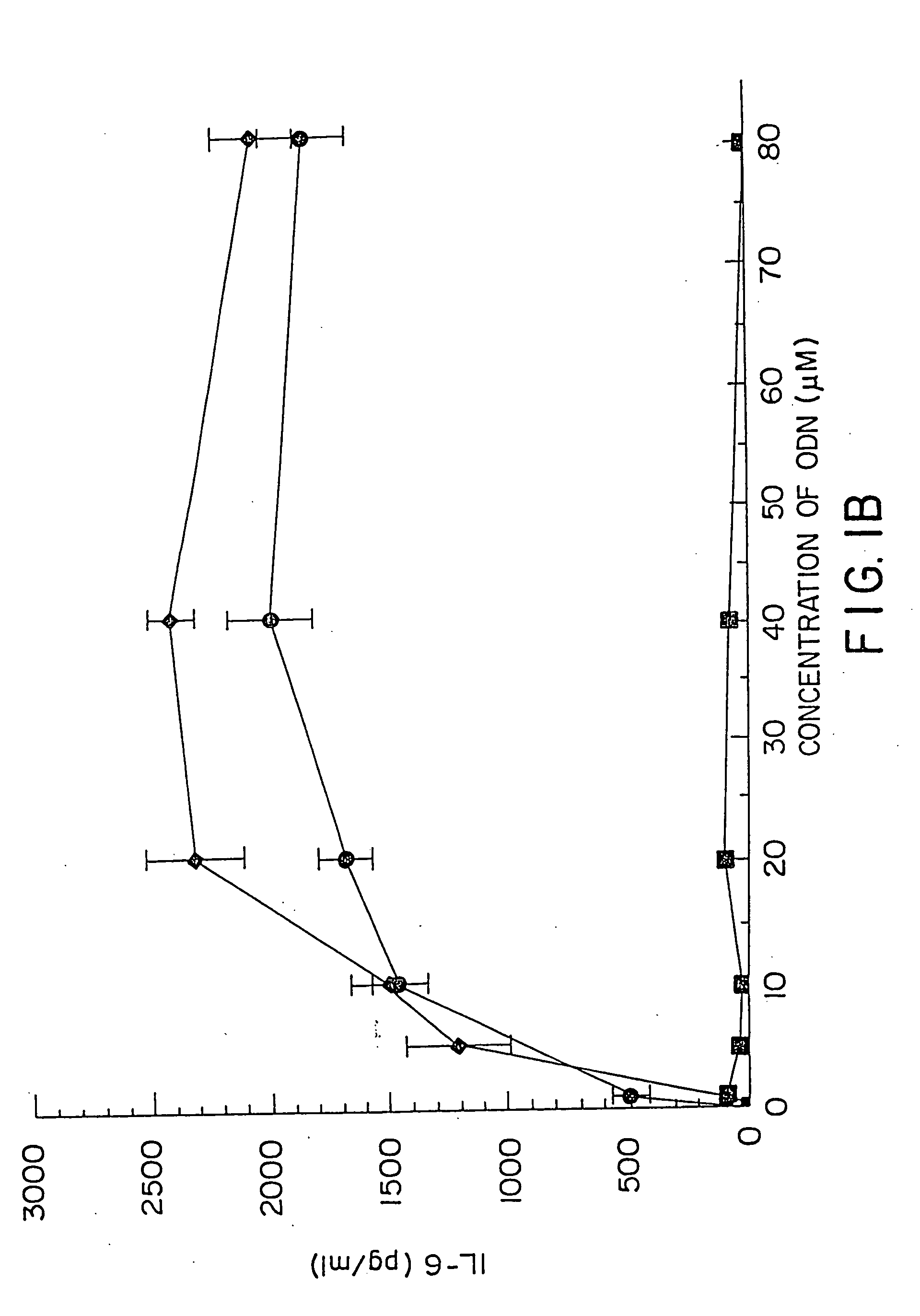
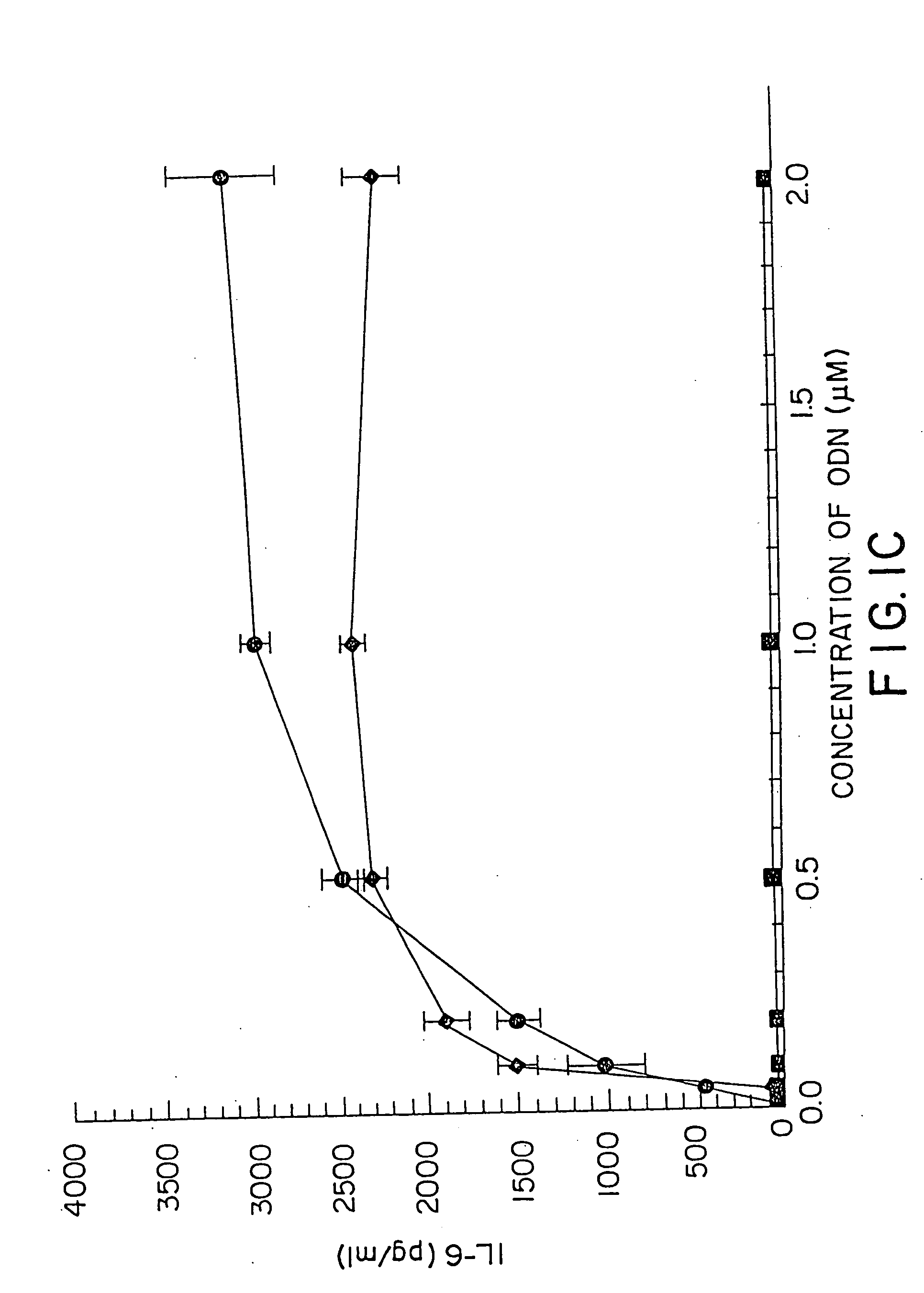
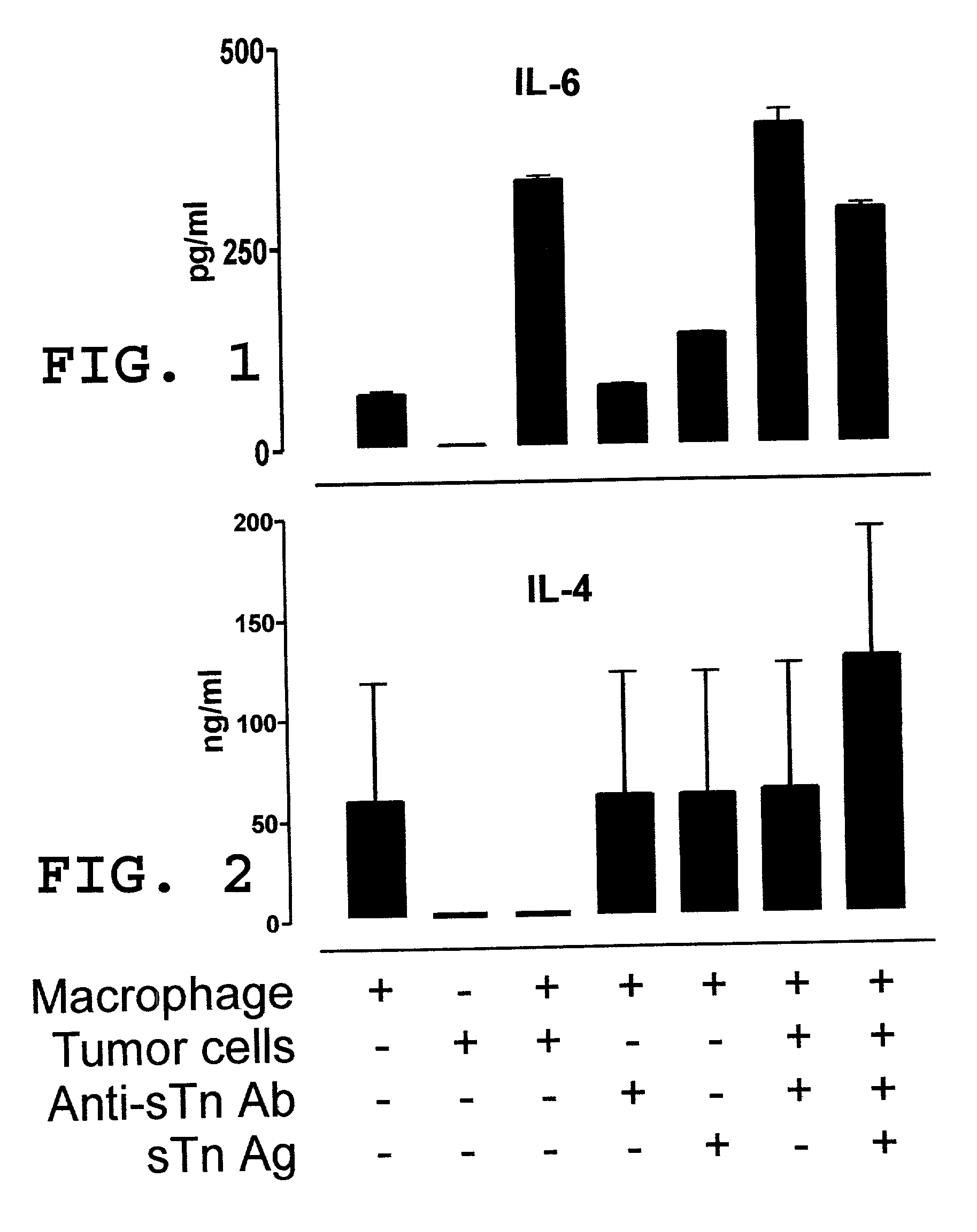
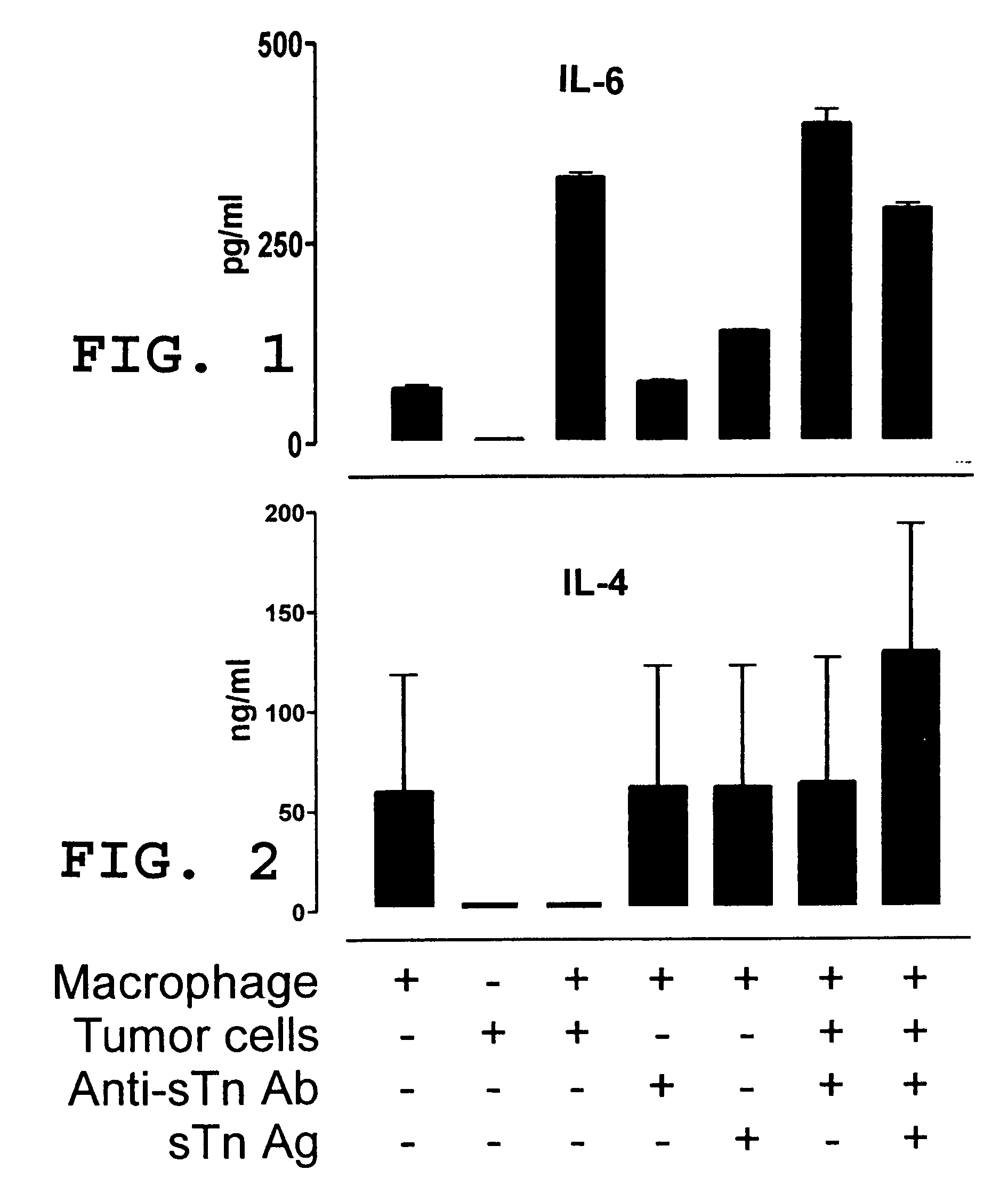
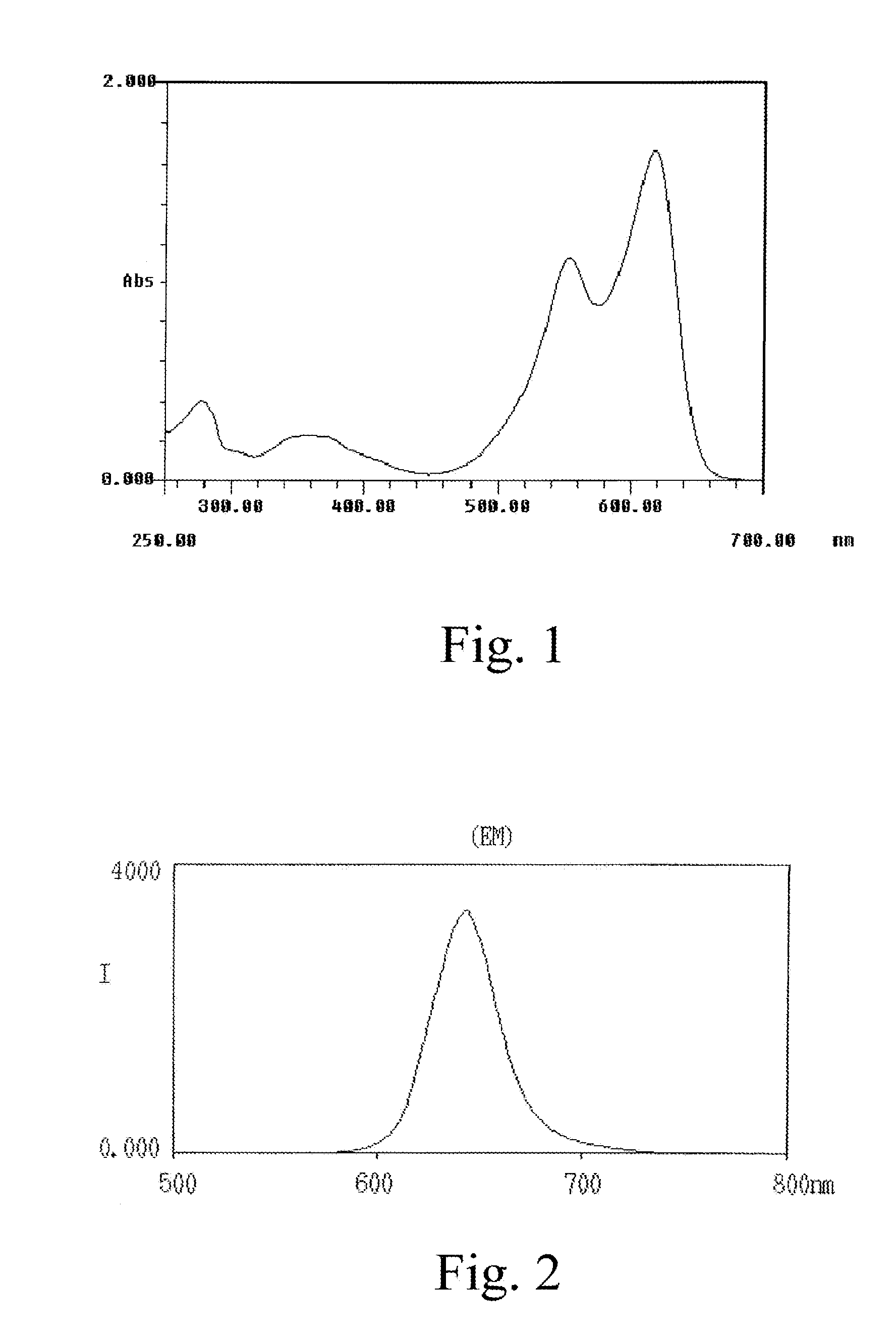
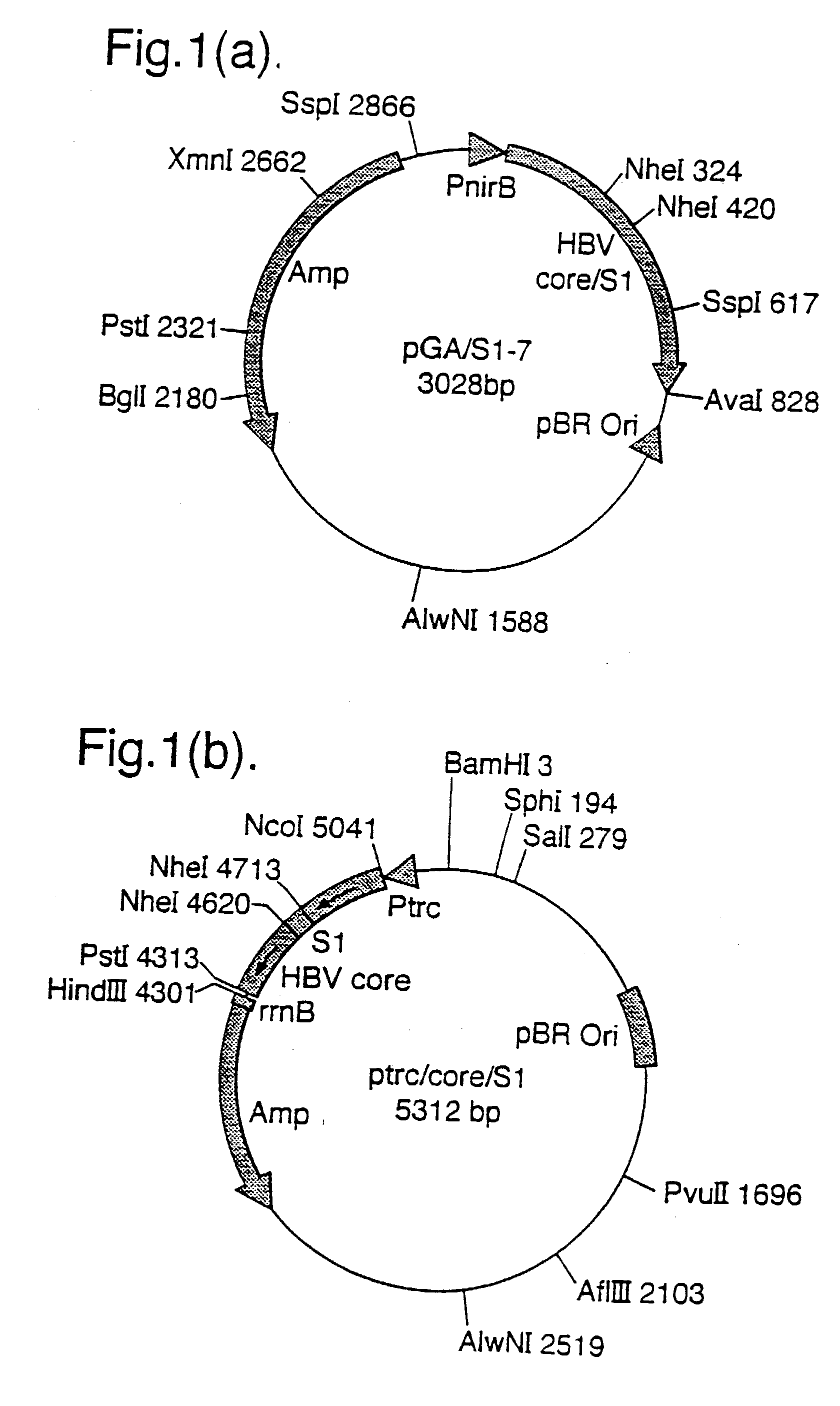
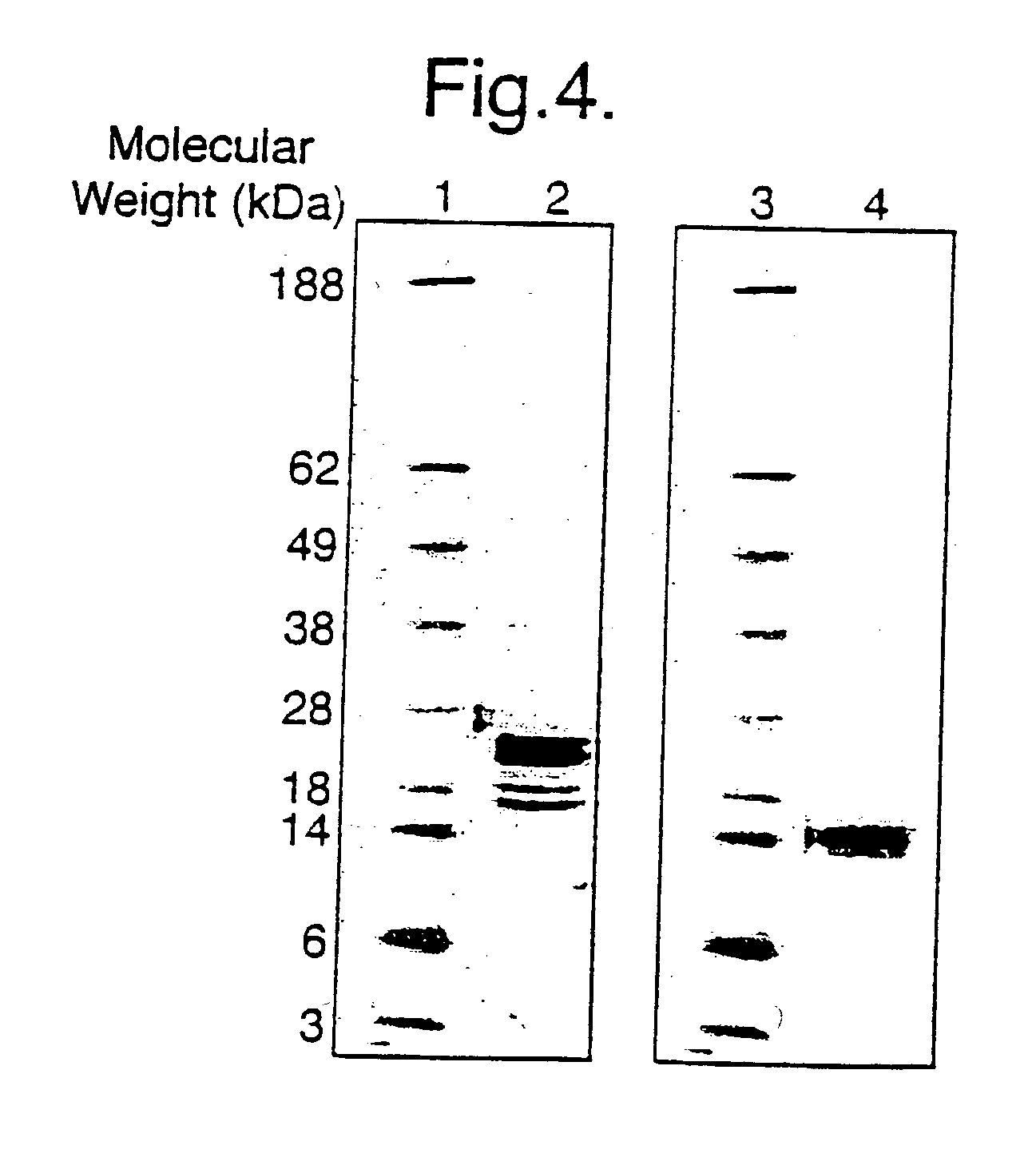
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Th1 response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
TH1 immune response is the immune response generated by the TH1 cells. It occurs through the production of cytokines, including interferon-gamma. Moreover, it is a type of proinflammatory response, which leads to cell-mediated immunity.
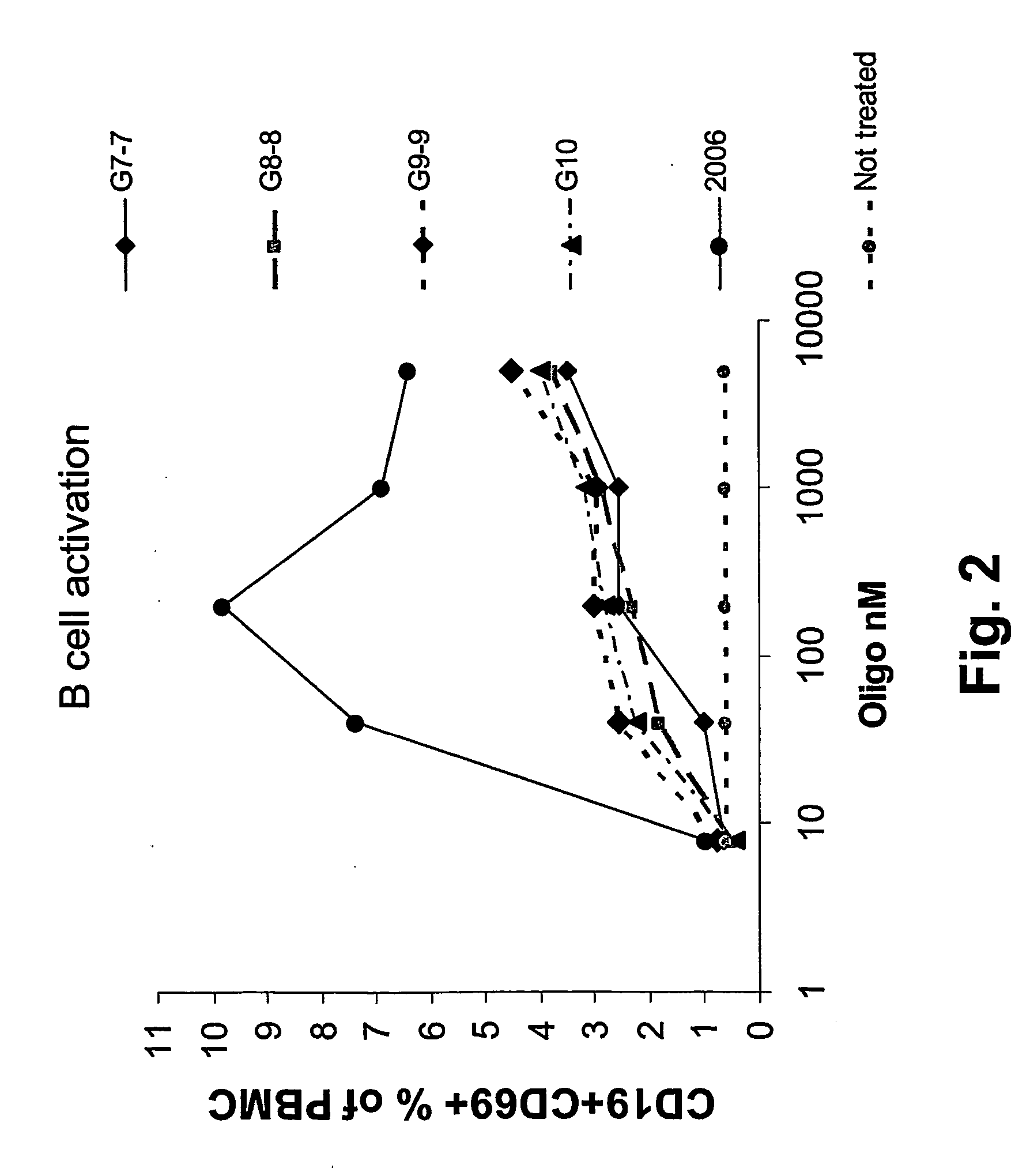
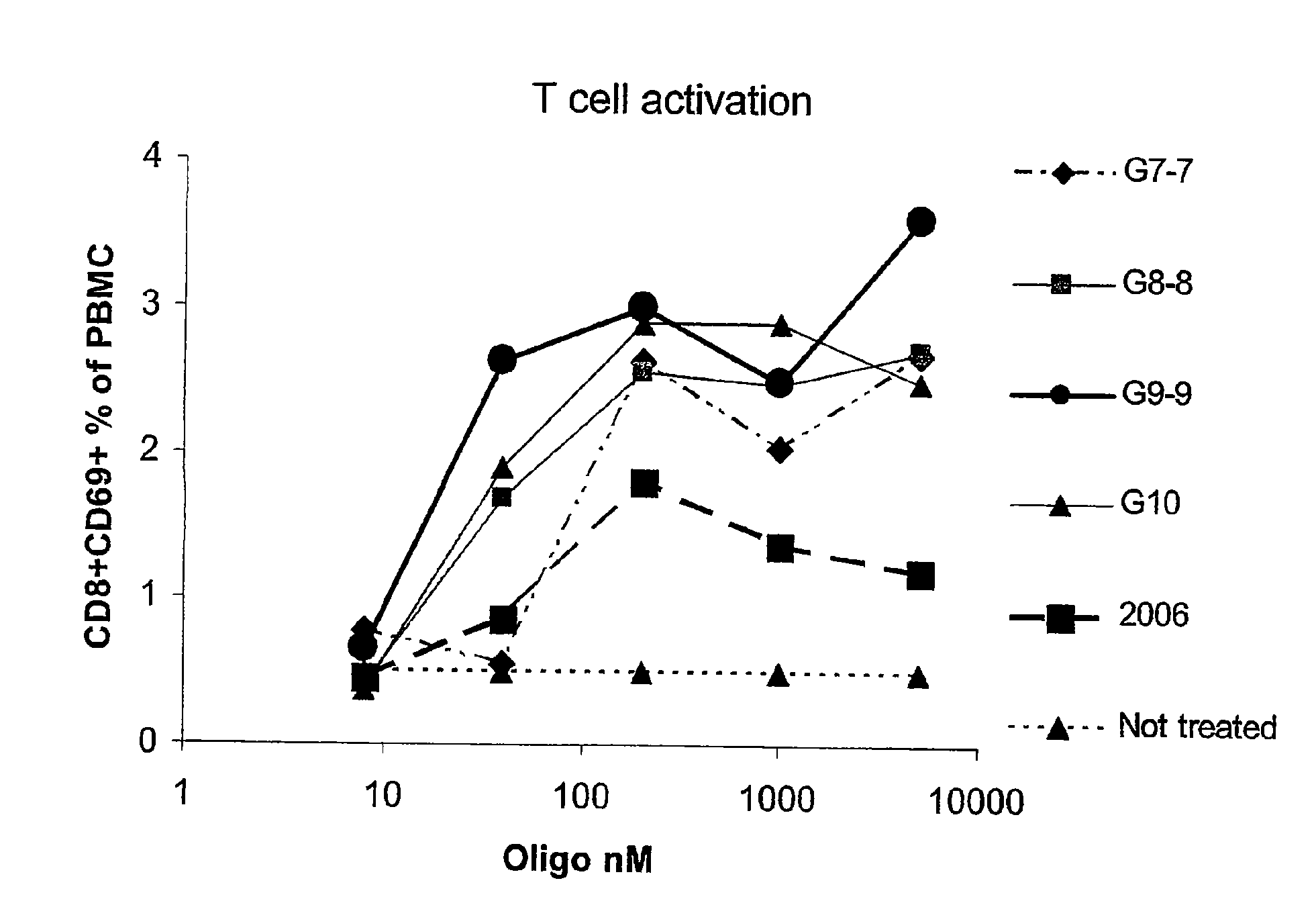
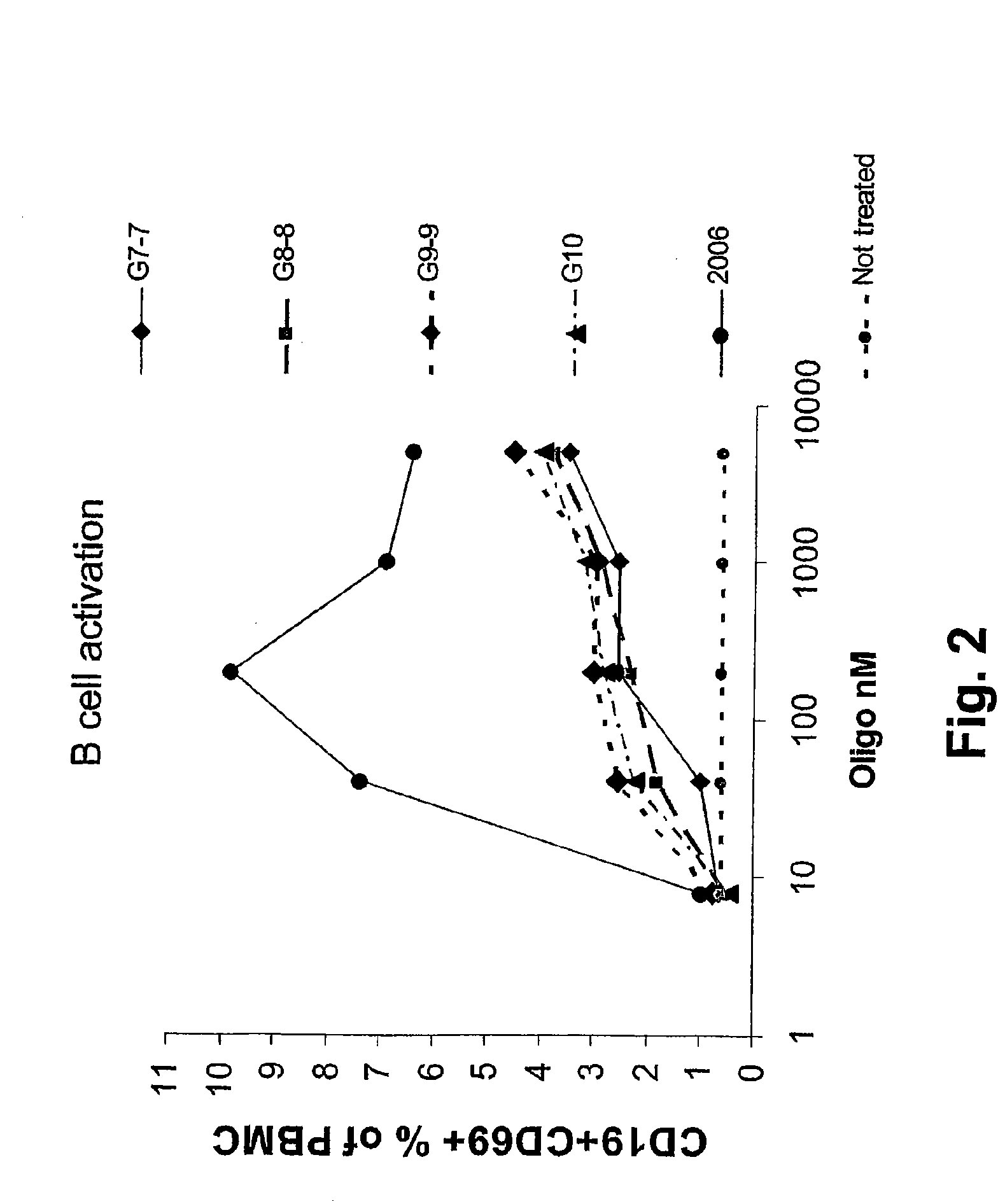
Immunostimulatory nucleic acid molecules
Nucleic acids containing unmethylated CpG dinucleotides and therapeutic utilities based on their ability to stimulate an immune response and to redirect a Th2 response to a Th1 response in a subject are disclosed. Methods for treating atopic diseases, including atopic dermatitis, are disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +2
Methods of modulating an immune response using immunostimulatory sequences and compositions for use therein
The invention provides methods of modulating an immune response to a second antigen which entail administration of a first antigen and an immunostimulatory polynucleotide. Modulation of the immune response is generally manifested as stimulation of a Th1 response.
Owner:DYNAVAX TECH CORP
Preparation and composition of peptides useful for treatment of autoimmune and transplant related graft versus host conditions
InactiveUS6995237B1Effectively eliminate subsetDecrease and eliminate adverse effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCardiac myosinDisease
Peptide constructs including a first peptide segment which includes an amino acid sequence associated with autoimmune disease, asthma, allergy or xeno- or allograft transplantation rejections bonded directly or via a linker or spacer to a second peptide which binds to T cells and which will redirect the immune response from a harmful Th1 response to a less harmful Th2 response, or which will bind to T cells to initiate, but not complete, an immune response causing the T cells to which the first peptide binds, to undergo anergy and apoptosis, are useful in treating autoimmune conditions. For instance, the peptide construct NGQEEKAGVVSTGLIGGGDSAFDVLSFTAEEKAGVYK (SEQ ID NO:14) wherein Th2 stimulating Peptide G (SEQ ID NO:15) is covalently linked, via spacer GGG, to cardiac myosin molecule My1 (SEQ ID NO:16), can be used for treatment or prevention of myocarditis.
Owner:CEL SCI CORP
Vaccine and immunotherapy for solid nonlymphoid tumor and related immune dysregulation
InactiveUS20010033839A1Inhibitory responseInduceSnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthTh2 response
Provided are vaccines, methods of making the vaccines and methods for administering the vaccines for immunotherapy of an individual bearing, or at risk for developing, solid nonlymphoid tumor. The vaccine comprises an immunotherapeutic composition and tumor-associated antigen, and may further comprise one or more of an immunomodulator or a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A method of immunotherapy of an individual comprises administering to the individual an amount of the vaccine effective to suppress a TH2 response, and to induce a TH1 response against solid nonlymphoid tumor, in an individual having a TH2 / TH1 imbalance.
Owner:BIOCRYSTAL LTD
Influenza vaccines including combinations of particulate adjuvants and immunopotentiators
InactiveUS20090304739A1Eliminate needAvoid the needSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsParticulatesTh2 response
Influenza vaccines containing insoluble particulate adjuvants have been found to elicit an IgG response that is primarily a TH2 response (IgG1). This response can be shifted towards a TH1 response (IgG2a) by including immunopotentiators in the compositions. Thus the invention provides an immunogenic composition comprising: (i) an influenza virus antigen; (ii) an insoluble particulate adjuvant; and (iii) a immunopotentiator.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Use of Parasitic Biological Agents for Diseases Prevention and Control
InactiveUS20100303721A1Reduce excessive immune responsePrevent excessive immune responseProtozoa antigen ingredientsAntipyreticManagement of ulcerative colitisAutoimmune responses
The invention relates to a method of treating an excessive immune response including an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response by administering a helminthic parasite preparation in an amount sufficient to reduce the excessive immune response in an individual. This invention is generally directed to autoimmune diseases which involve an excessive immune response or an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response. More specifically, the present invention is directed to the treatment of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, both known as IBD. While the present invention discloses specific information about the treatment of IBD, the disclosure is in no way limiting. Additionally, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosis, sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune thyroiditis, allergic rhinitis, colon polyps / colon cancer and asthma can be treated by the methods and compositions disclosed therein.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Chimeric molecule for the treatment of th2-like cytokine mediated disorders
InactiveUS20050142105A1Relieve symptomsInhibit expressionBacterial antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseTh2 response
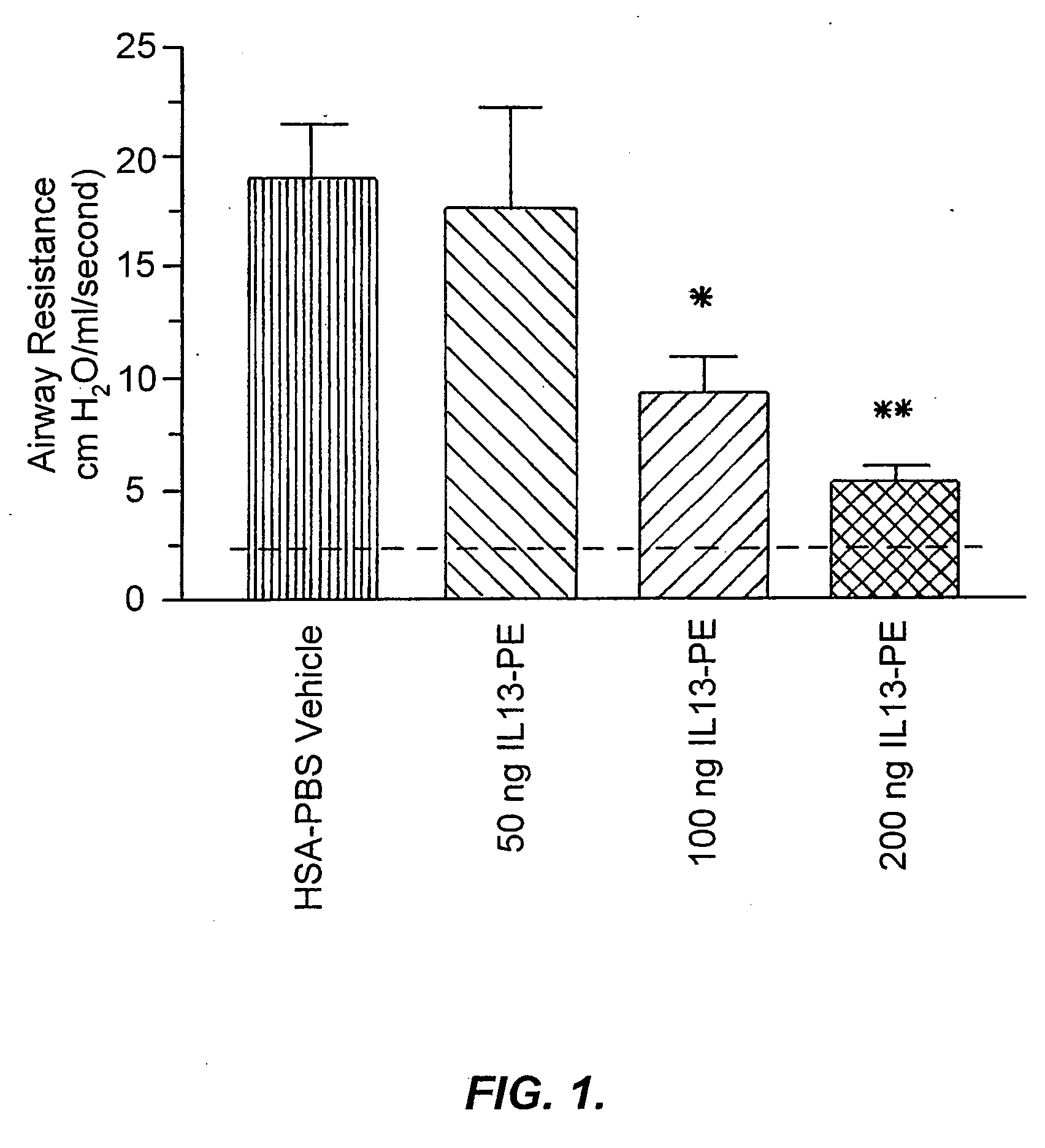
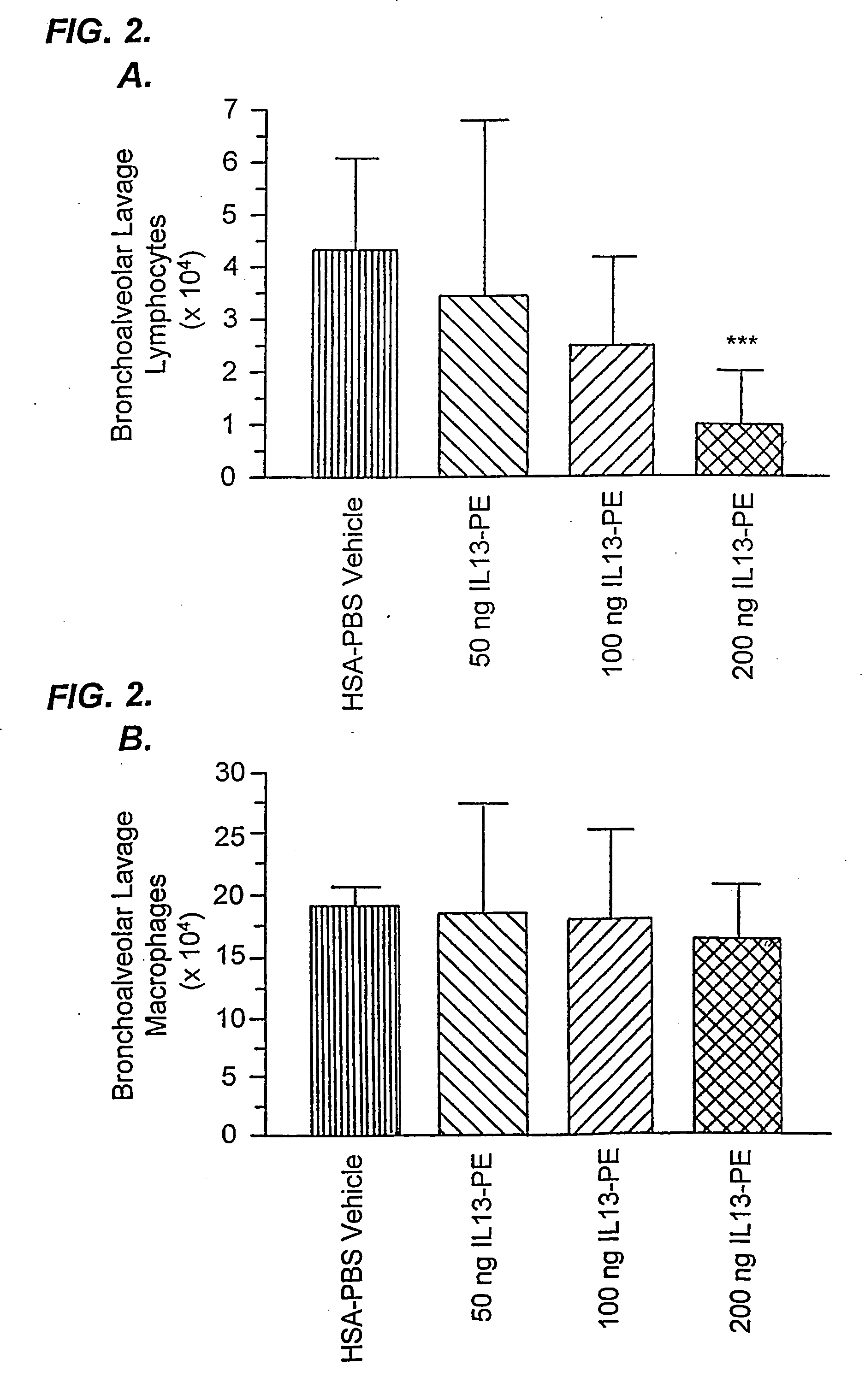
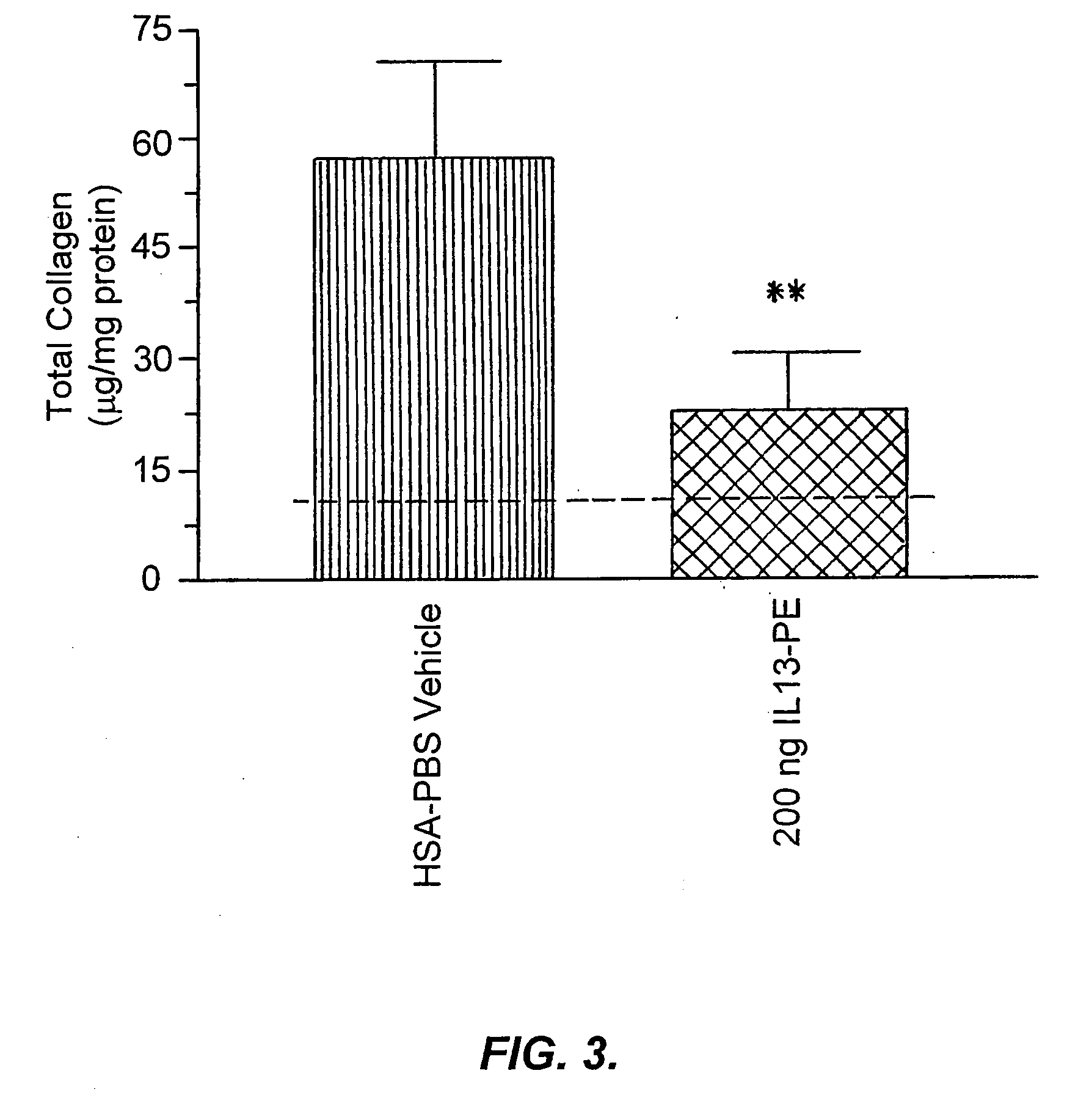
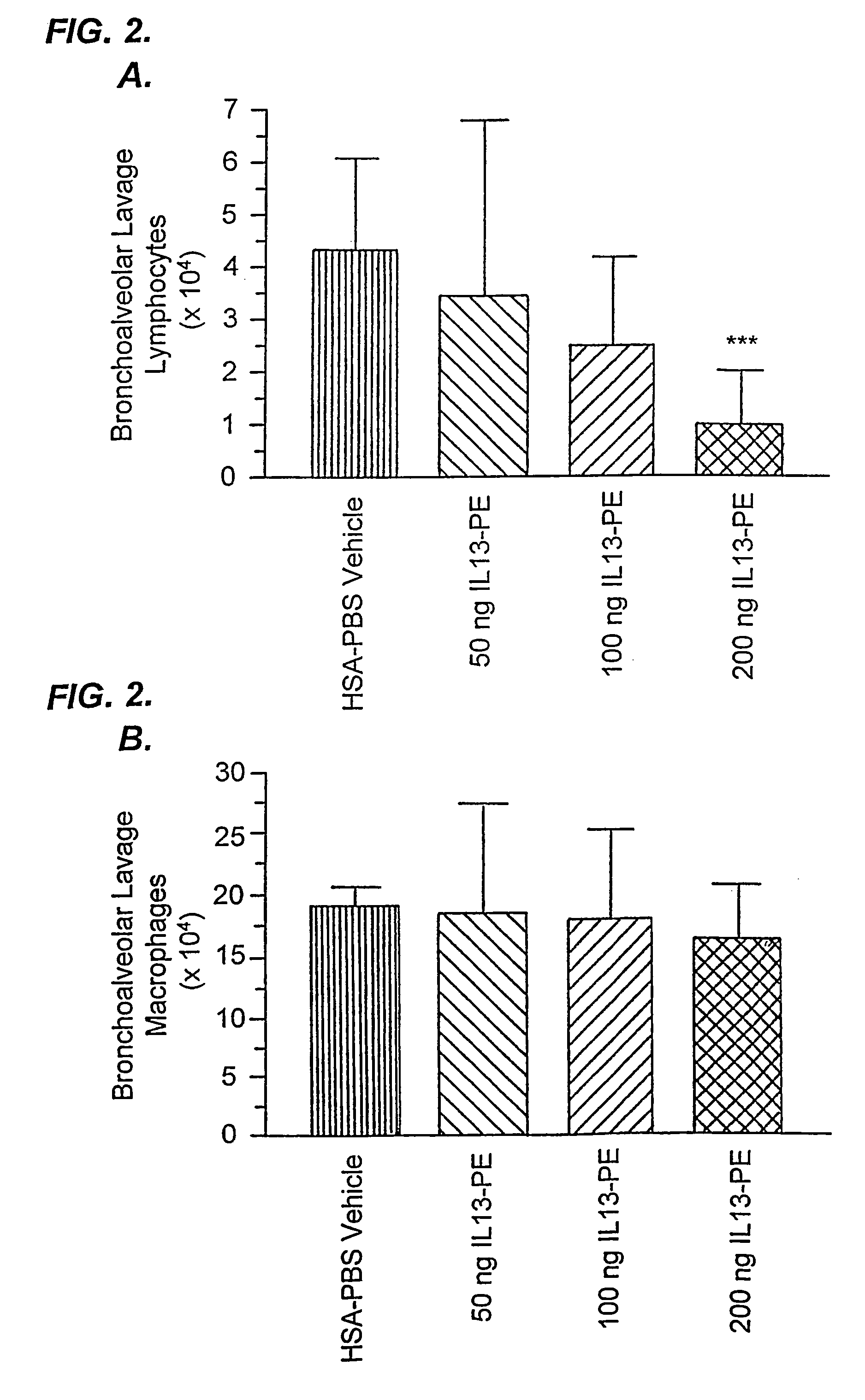
The invention provides uses and methods for alleviating respiratory tract symptoms of allergy, asthma, and of viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections by shifting inappropriate TH2 responses to TH1 responses by administering IL-13 receptor-targeted immunotoxins to the respiratory tract.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Cpg-packaged liposomes
InactiveUS20060182793A1Good curative effectImprove the level ofGenetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersIn vivoLiposome
Liposomes are known to enhance the activity of K- (B-) type CpGs which trigger the production of IL-12. In the present invention, the surprising finding was made that liposomes also enhance the activity of D- (A-) type CpGs, leading to the production of IFNα in vivo. These findings are relevant for the humans situation, since IFNα rather than IL-12 is the key cytokine for the induction of Th1 responses and anti-viral protection in humans.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Cpg-packaged liposomes
InactiveUS20090074851A1Good curative effectImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoLiposome
Liposomes are known to enhance the activity of K- (B-) type CpGs which trigger the production of IL-12. In the present invention, the surprising finding was made that liposomes also enhance the activity of D- (A-) type CpGs, leading to the production of IFNα in vivo. These findings are relevant for the humans situation, since IFNα rather than IL-12 is the key cytokine for the induction of Th1 responses and anti-viral protection in humans.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
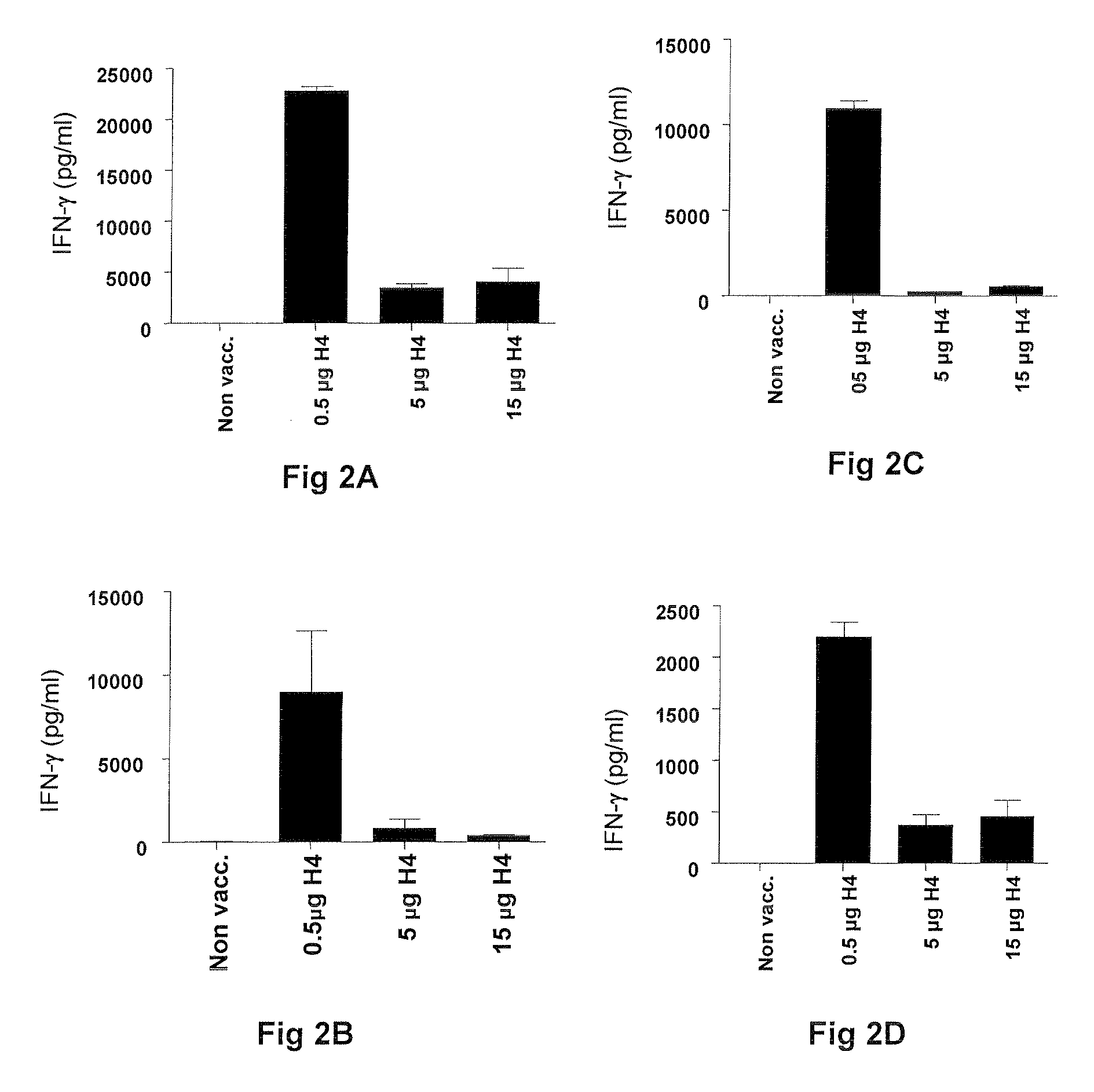
Vaccines comprising tb 10.4
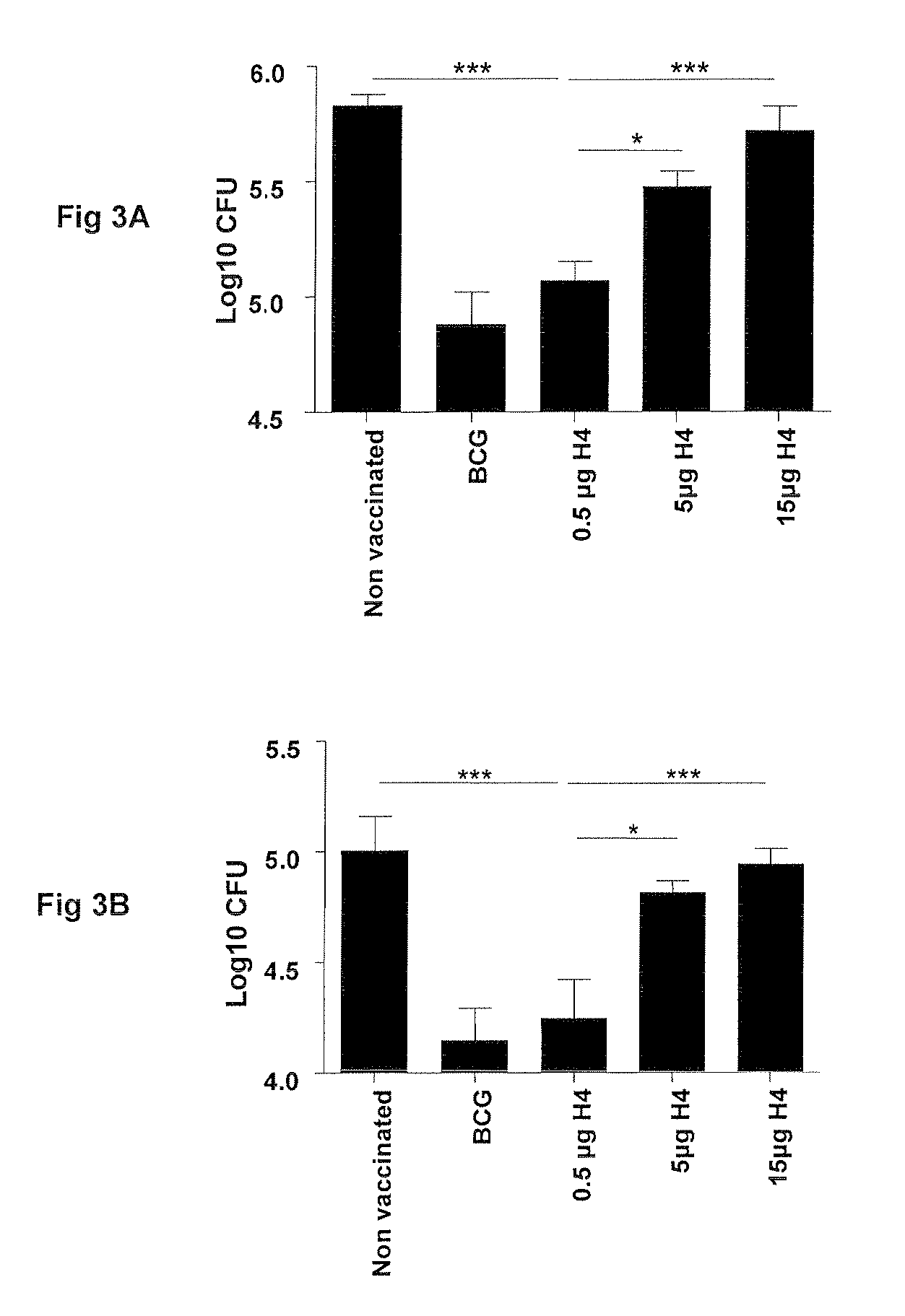
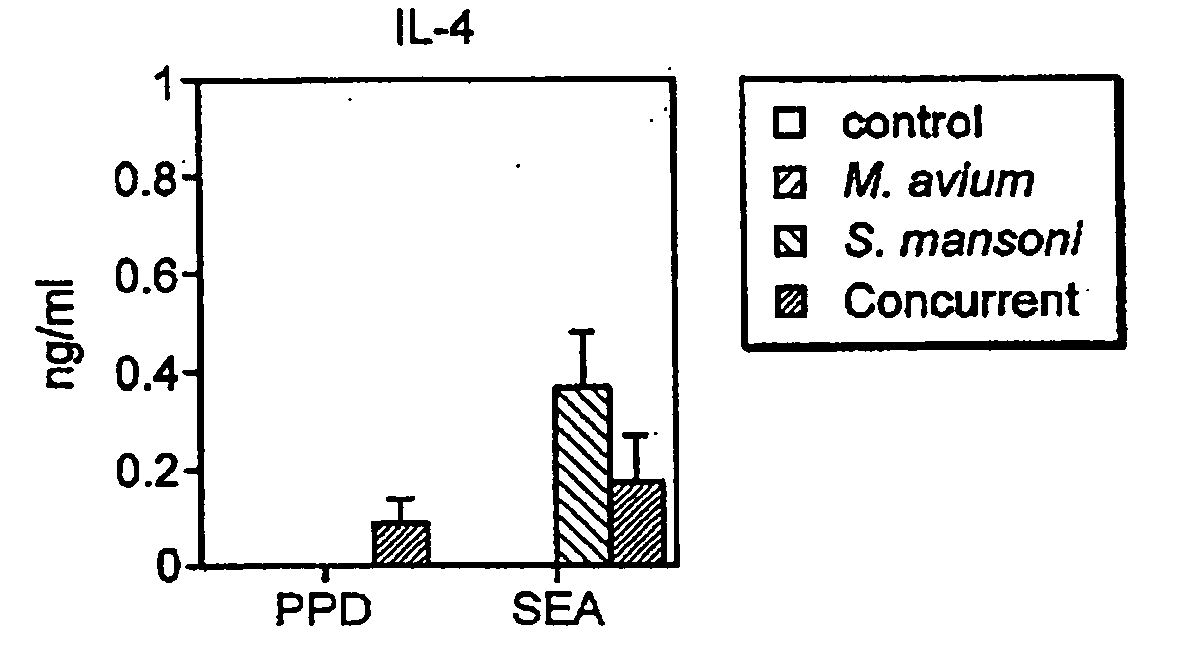
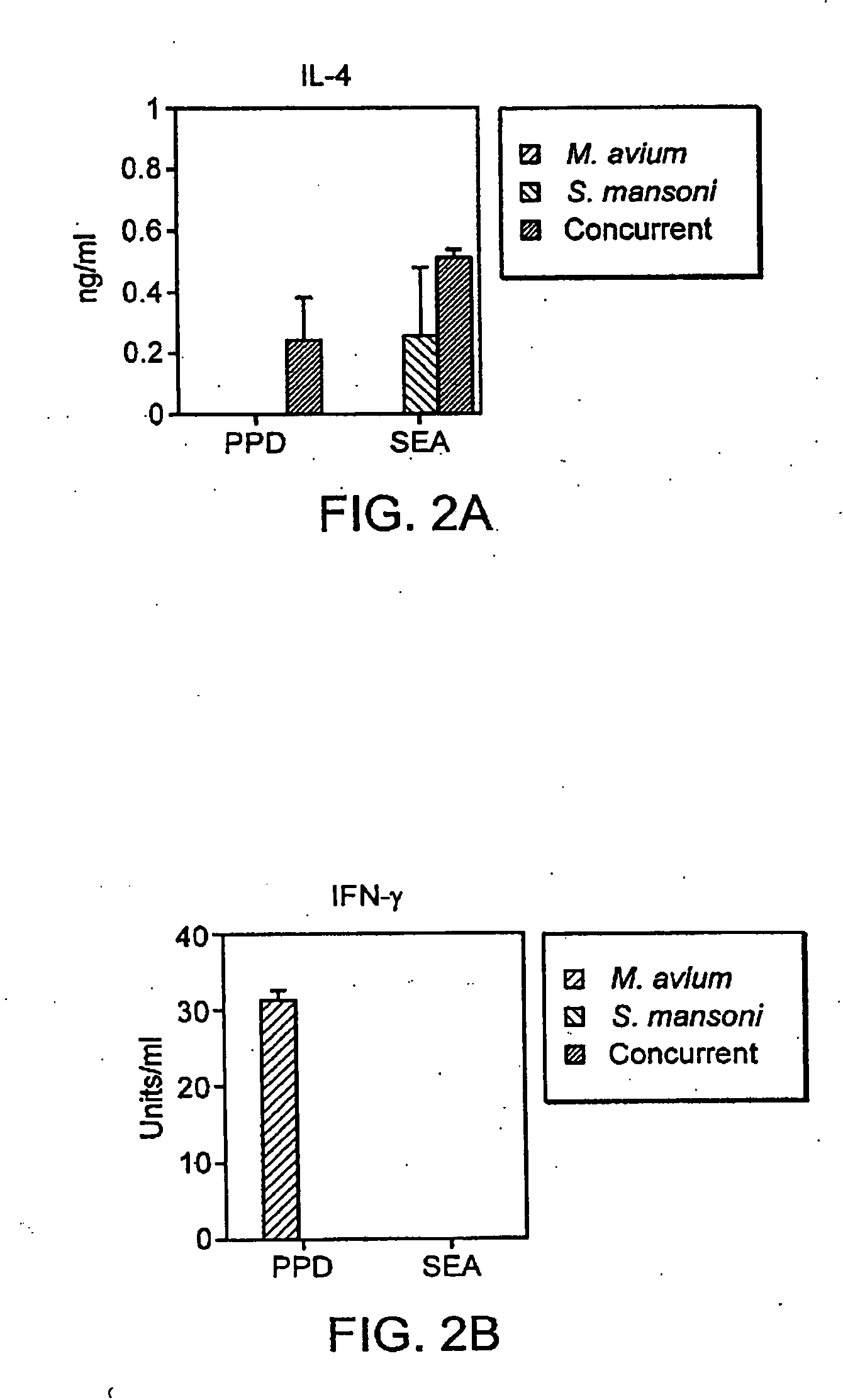
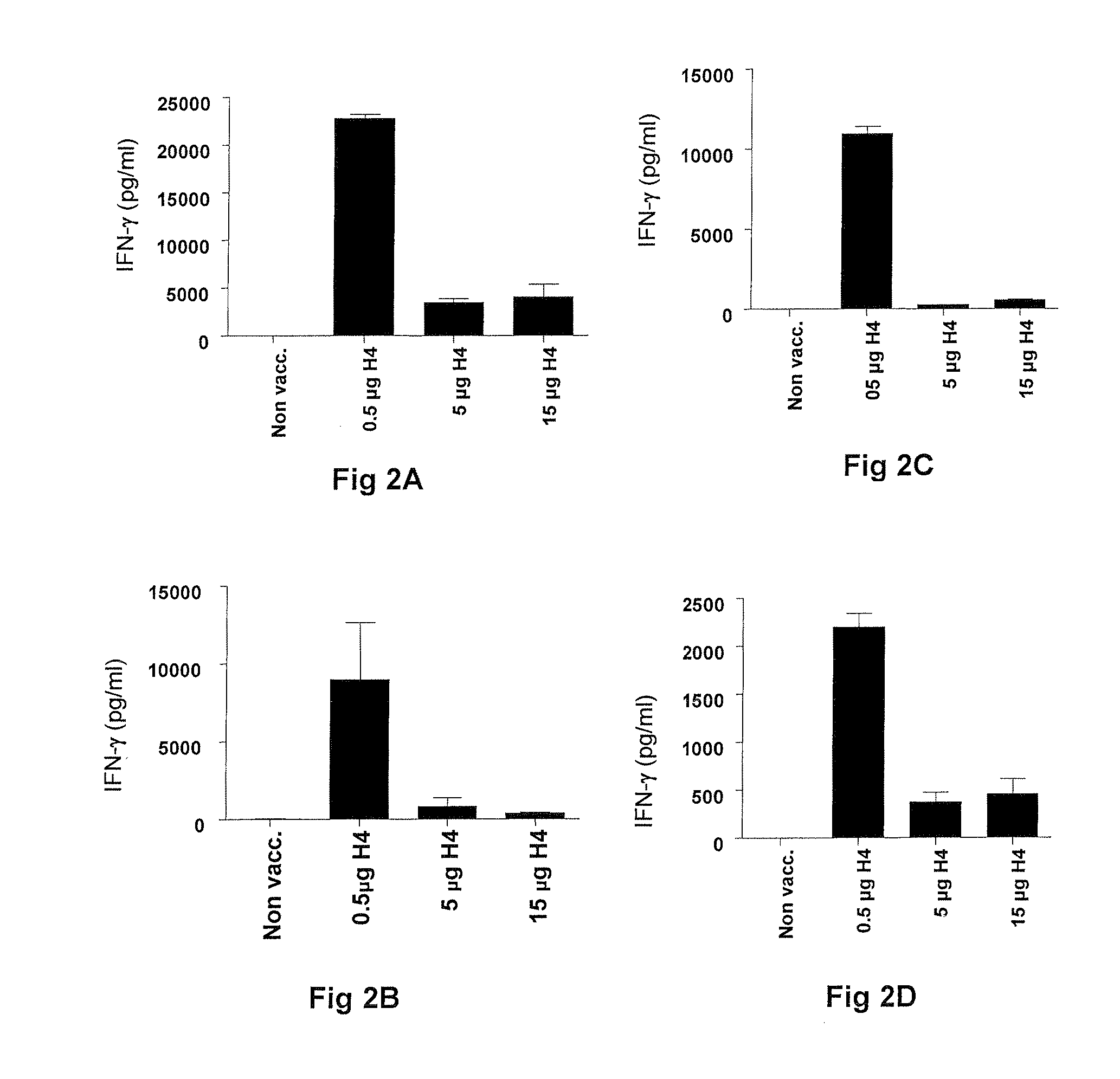
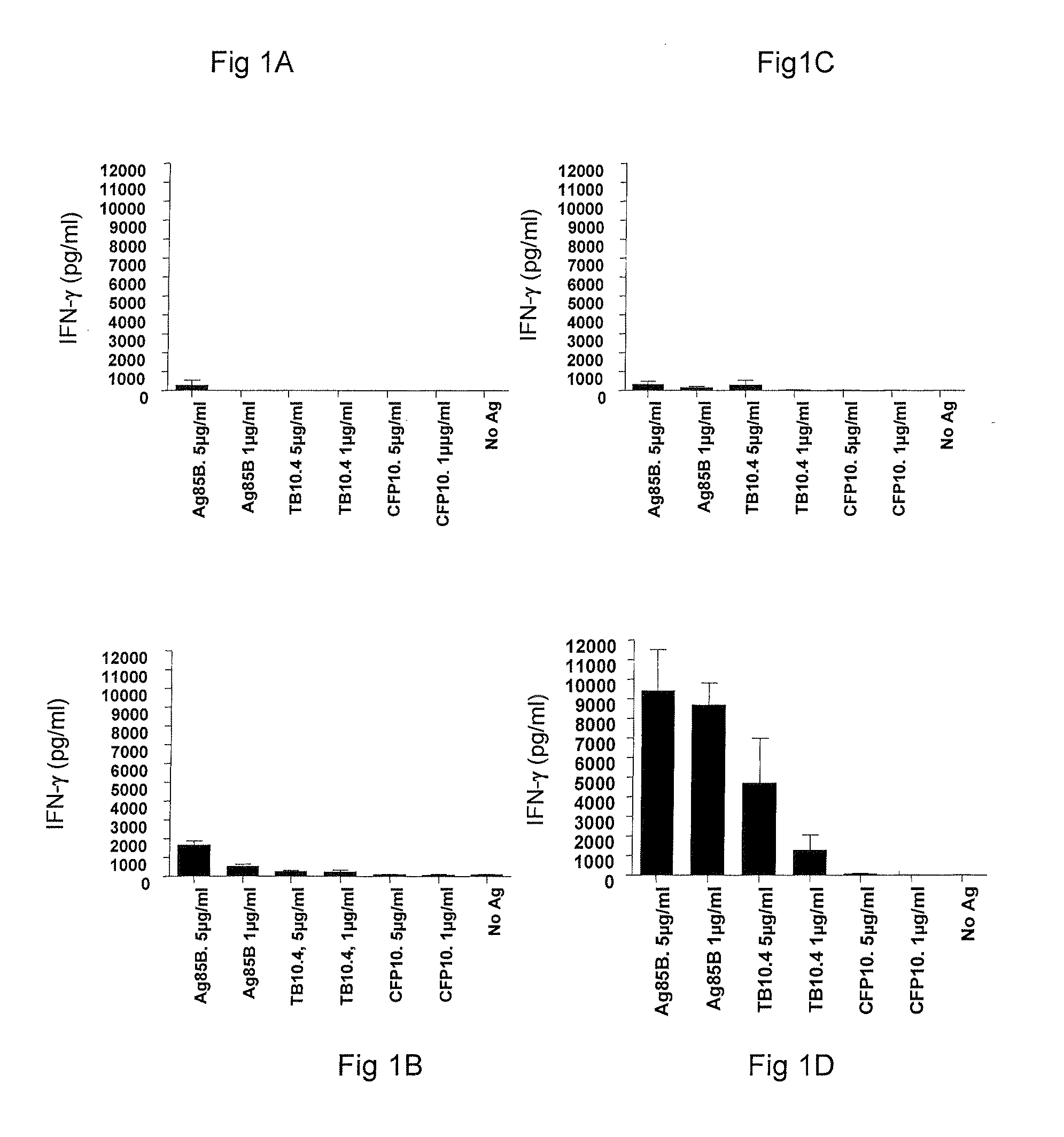
Vaccination with the combination of Ag85B-TB10.4 and IC31® adjuvant generated a high amount of polyfunctional CD4+T cells expressing high levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2. This in turn led to significant protection against infection with M. tuberculosis in the mouse aerosol challenge model of tuberculosis. Both the immunogenicity of the vaccine and its ability to protect against TB infection was highly dependent on the antigen dose. Thus, whereas the standard antigen dose of 5 μg, as well as 15 μg, did not induce significant protection against M. tuberculosis, reducing the dose to 0.5 μg increased both the immunogenicity of the vaccine as well as its protective efficacy to a level comparable to that observed in BCG vaccinated mice. Thus, the IC31® adjuvant, with the specified antigen dose, can induce a strong protective Th1 response against M. tuberculosis.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
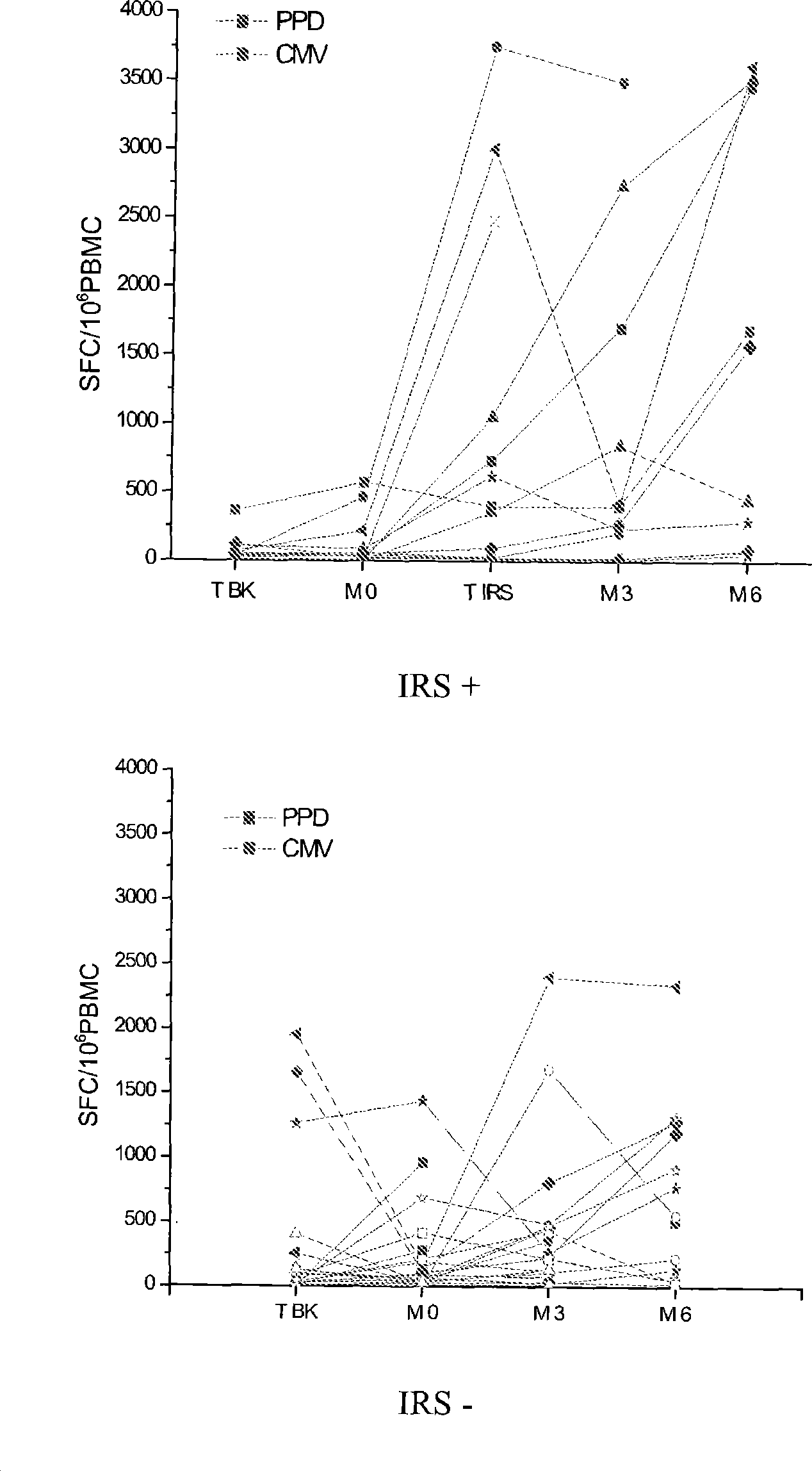
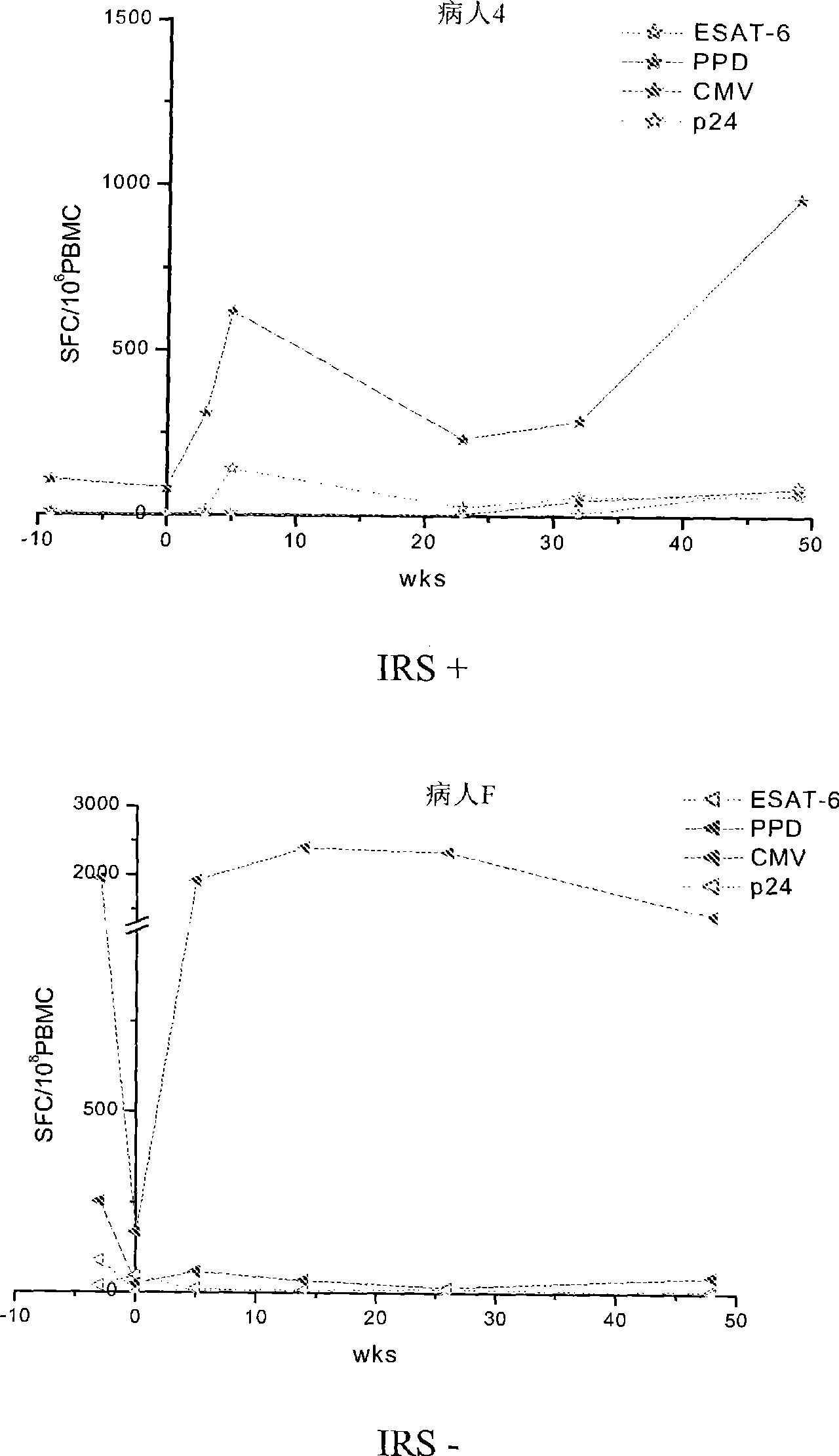
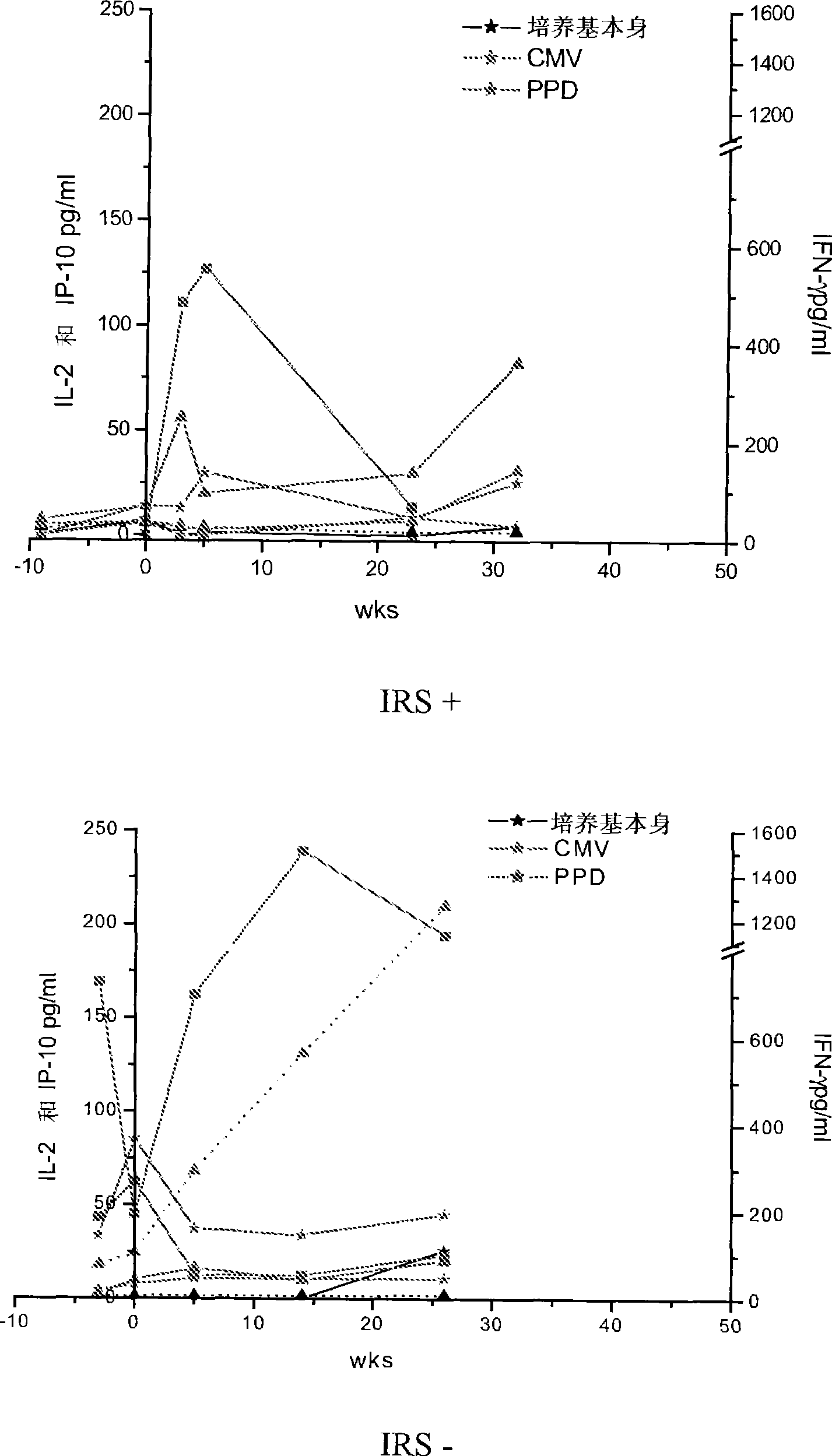
Method of diagnosis of tuberculosis related immune restoration syndrome (IRS)
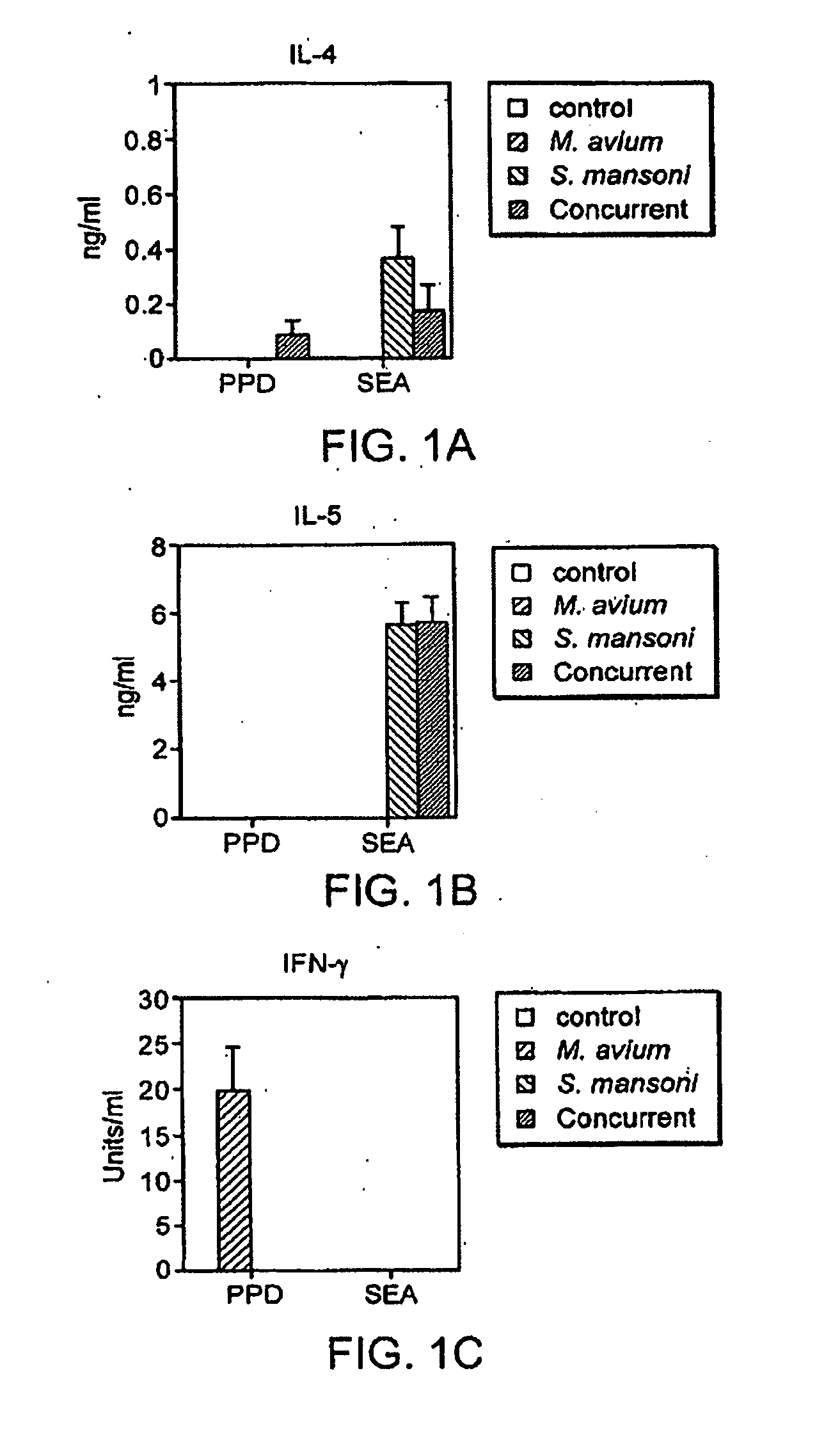
The present invention relates to a method and kit of diagnosis of Immune Restoration Syndrome associated with tuberculosis (TB-IRS) in patients infected with tuberculosis (TB) as well as in HIV co-infected patients comprising detecting an acute increase in Th1 response following exposure to mycobacterial extract, referred as tuberculin or PPD (Purified Protein Derivative) as well as to the 16kDa protein, but not to ESAT-6 or CFP-10, two antigens from mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Vaccine and immunotherapy for solid nonlymphoid tumor and related immune dysregulation
InactiveUS20050191313A1Good curative effectInhibitory responseImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthTh2 response
Provided are vaccines, methods of making the vaccines and methods for administering the vaccines for immunotherapy of an individual bearing, or at risk for developing, solid nonlymphoid tumor. The vaccine comprises an immunotherapeutic composition and tumor-associated antigen, and may further comprise one or more of an immunomodulator or a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A method of immunotherapy of an individual comprises administering to the individual an amount of the vaccine effective to suppress a TH2 response, and to induce a TH1 response against solid nonlymphoid tumor, in an individual having a TH2 / TH1 imbalance.
Owner:BIOCRYSTAL LTD
Methods for Treating Allergic Disease
InactiveUS20110038882A1Safe to drinkSafe to eatPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticT cellDisease cause
A method for treating or alleviating allergic disease in a mammal in need thereof having administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition having phycocyanin is provided. A method for modulating balance between Th1 and Th2 immune response in a mammal in need thereof, having administering to the mammal an effective amount of phycocyanin, wherein immune response of the mammal is skewed toward the Th1 immune response is also provided. Phycocyanin from Bangia atropupurea (Ba-PC) is identified to regulate mammalian immunological response indicating that Ba-PC can direct skewed immune response toward Th1 response through modulating DC function, increase proliferative activity of antigen-specific T cells and alleviate airway inflammation, confirming that phycobiliproteins are effective in treating allergic disease.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Designing immunogens
InactiveUS20040106174A1Dramatic effect on the Th subclass responseStabilise particlePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseChronic hepatitis
The invention provides a method for designing protein immunogen, which comprises (a) modifying the amino acid sequence of the immunogen, and (b) determining whether the T-helper (Th) cell response to the modified immunogen is of the Th1 type or the Th2 type. The method is useful in identifying immunogens for use in immunotherapy of diseases. For example, chronic hepatitis is believed to be associated with a Th2-dominated response which fails to clear the virus, and switching the Th response to a Th1 response by administration of an immunogen that induces a Th1 response may help in clearing the virus.
Owner:CELLTECH PHARMA EURO
Methods of preparation and composition of peptide constructs useful for treatment of autoimmune and transplant related host versus graft conditions
InactiveUS7256254B2Effectively eliminate set and subsetTreating or preventing inappropriate autoimmune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesCardiac myosinImmunologic disorders
Peptide constructs including a first peptide segment which includes an amino acid sequence associated with autoimmune disease, asthma, allergy or xeno- or allograft transplantation rejections bonded directly or via a linker or spacer to a second peptide which binds to T cells and which will redirect the immune response from a harmful Th1 response to a less harmful Th2 response, or which will bind to T cells to initiate, but not complete, an immune response causing the T cells to which the first peptide binds, to undergo anergy and apoptosis, are useful in treating autoimmune conditions. For instance, the peptide construct NGQEEKAGVVSTGLIGGGDSAFDVLSFTAEEKAGVYK (SEQ ID NO:14) wherein Th2 stimulating Peptide G (SEQ ID NO:15) is covalently linked, via spacer GGG, to cardiac myosin molecule My1 (SEQ ID NO:16), can be used for treatment or prevention of myocarditis.
Owner:CEL SCI CORP
Chimeric molecule for the treatment of th2-like cytokine mediated disorders
The invention provides uses and methods for alleviating respiratory tract symptoms of allergy, asthma, and of viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections by shifting inappropriate TH2 responses to TH1 responses by administering IL-13 receptor-targeted immunotoxins to the respiratory tract.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Immunologic activity measures for t helper on-associated conditions
InactiveUS20060216716A1Accurately reflectAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesWhite blood cellStimulant
A method of providing a reproducible and clinically relevant disease activity measurement for a group of immunologic disorders that share features of a T “helper” 1 (Th1) immune activation phenotype is disclosed. Th1 responses are characterized by the release of a set of pro-inflammatory substances by white blood cells (WBC) By evaluating the ex vivo activation response of whole blood in terms of the extent of release of Th1 produced pro-inflammatory substances in blood (i.e., WBC activity) following activation with a Th1-associated stimulant, the level of, e.g., disease activity or immunosuppression in a specific individual can be determined. The method of the invention provides a disease activity marker for a wide variety of Th1 inflammatory responses, including Crohn's Disease, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis and solid organ transplant rejection.
Owner:SAUBERMANN LAWRENCE J +2
Novel lactic acid bacterium strains and application thereof to adjustment of immune reaction
ActiveCN102604854AHas immunomodulatory effectsSuppress immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacteriaTh2 responseTh1 response
The invention relates to novel lactic acid bacterium strains MP137 and MP108 and the application thereof to the adjustment of immune reaction. Specifically, the lactic acid bacterium strains can promote Th1 reaction and inhibit Th2 reaction.
Owner:CHING BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Mucosal adjuvant and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN102688488ASafe and non-toxicReduce releaseAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsNasal cavityVaccination
The invention provides a mucosal adjuvant. The mucosal adjuvant is prepared by copolymerization crosslinking compounding of oligo-chitosan and lymphotactin encoding plasmids. The invention also discloses a preparation method and a use of the mucosal adjuvant. When the mucosal adjuvant and a gene vaccine composed of chitosan or oligo-chitosan are synchronously dropped into a nasal cavity for immunization, coxsackievirus specific serum antibody and systemic (spleen and lymph glands) Th1-type immune responses are induced and especially, intestinal mucosa partially-reinforced specific-secretion-type sIgA and IFNgama+Th1 responses are induced, and thus a gene vaccine used with the mucosal adjuvant is obviously superior to an exposed gene vaccine and effectively prevents coxsackievirus-caused myocarditis. The mucosal adjuvant can be used as a novel mucosal vaccination adjuvant.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods of modulating an immune response using immunostimulatory sequences and compositions for use therein
InactiveUS20090148479A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenImmune Stimulation
The invention provides methods of modulating an immune response to a second antigen which entail administration of a first antigen and an immunostimulatory polynucleotide. Modulation of the immune response is generally manifested as stimulation of a Th1 response.
Owner:DYNAVAX TECH CORP
Streptococcus-suis-disease-resistant fusion protein with autoimmune activity and preparing and application thereof
The invention discloses a streptococcus-suis-disease-resistant fusion protein with the autoimmune activity and preparing and application thereof. The fusion protein is composed of Omp16<26-168> peptide located at the amino terminal and Sao<28-138> peptide located at the carboxyl terminal. The Sao<28-138> peptide is an amino acid fragment which is exposed out of a streptococcus suis cell in a Sao protein molecule, has the immunogenicity, and is highly conservative between different strains and subtypes, and the Omp16<26-168> peptide is an amino acid fragment is exposed out of a Brucella cell in a Omp16 molecule, has the TLR4 activating activity, and is free of Lipobox (the Lipobox is lowly toxic or completely nontoxic). Mice are subjected to an immunity virus attacking test through the Omp16<26-168> / Sao<28-138> fusion protein, it is shown that the Omp16<26-168> / Sao<28-138> fusion protein has the good immune protection effect, a quite-high cellular immune response and a quite-high humoral immune response can be induced, but a Th1 response is the main response, and the fusion protein has the self-adjuvant effect, is an ideal vaccine antigen of streptococcus, and has the important value in development and application aspects of novel vaccine.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Use of parasitic biological agents for prevention and control of autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS7250173B2Reduce excessive immune responsePrevent excessive immune responseNervous disorderAntipyreticManagement of ulcerative colitisImmunologic disorders
The invention relates to a method of treating an excessive immune response including an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response by administering a helminthic parasite preparation in an amount sufficient to reduce the excessive immune response in an individual. This invention is generally directed to autoimmune diseases which involve an excessive immune response or an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response. More specifically, the present invention is directed to the treatment of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, both known as IBD. While the present invention discloses specific information about the treatment of IBD, the disclosure is in no way limiting. Additionally, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosis, sarcoidosis and multiple sclerosis can be treated by the methods and compositions disclosed therein.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Use of parasitic biological agents for prevention and control of autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20070298011A1Reduced responseInhibitory responseBiocideNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionUlcerative colitis
The invention relates to a method of treating an excessive immune response including an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response by administering a helminthic parasite preparation in an amount sufficient to reduce the excessive immune response in an individual. This invention is generally directed to autoimmune diseases which involve an excessive immune response or an aberrant / enhanced Th1 response. More specifically, the present invention is directed to the treatment of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, both known as IBD. While the present invention discloses specific information about the treatment of IBD, the disclosure is in no way limiting. Additionally, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosis, sarcoidosis and multiple sclerosis can be treated by the methods and compositions disclosed therein.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Influenza vaccines including combinations of particulate adjuvants and immunopotentiators
InactiveUS8697087B2Reduce in quantityFacilitate matterSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesParticulatesTh2 response
Influenza vaccines containing insoluble particulate adjuvants have been found to elicit an IgG response that is primarily a TH2 response (IgG1). This response can be shifted towards a TH1 response (IgG2a) by including immunopotentiators in the compositions. Thus the invention provides an immunogenic composition comprising: (i) an influenza virus antigen; (ii) an insoluble particulate adjuvant; and (iii) a immunopotentiator.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Vaccines comprising tb10.4
Vaccination with the combination of Ag85B-TB10.4 and IC31® adjuvant generated a high amount of polyfunctional CD4+T cells expressing high levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2. This in turn led to significant protection against infection with M. tuberculosis in the mouse aerosol challenge model of tuberculosis. Both the immunogenicity of the vaccine and its ability to protect against TB infection was highly dependent on the antigen dose. Thus, whereas the standard antigen dose of 5 μg, as well as 15 μg, did not induce significant protection against M. tuberculosis, reducing the dose to 0.5 μg increased both the immunogenicity of the vaccine as well as its protective efficacy to a level comparable to that observed in BCG vaccinated mice. Thus, the IC31® adjuvant, with the specified antigen dose, can induce a strong protective Th1 response against M. tuberculosis.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Vaccines comprising TB10.4
Vaccination with the combination of Ag85B-TB10.4 and IC31® adjuvant generated a high amount of polyfunctional CD4+T cells expressing high levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2. This in turn led to significant protection against infection with M. tuberculosis in the mouse aerosol challenge model of tuberculosis. Both the immunogenicity of the vaccine and its ability to protect against TB infection was highly dependent on the antigen dose. Thus, whereas the standard antigen dose of 5 μg, as well as 15 μg, did not induce significant protection against M. tuberculosis, reducing the dose to 0.5 μg increased both the immunogenicity of the vaccine as well as its protective efficacy to a level comparable to that observed in BCG vaccinated mice. Thus, the IC31® adjuvant, with the specified antigen dose, can induce a strong protective Th1 response against M. tuberculosis.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Methods for treating autoimmune disorders
InactiveUS20090280082A1Reduce T-lymphocyte proliferationReduction in T-lymphocyte proliferationCompound screeningSenses disorderImmunologic disordersDisease
The present invention relates to methods for treating autoimmune disorders. In an embodiment, the invention is directed to a method for treating an autoimmune disorder comprising administering a TCCR agonist. In an embodiment, the autoimmune disorder is at least partially mediated by a Th1 response. In an embodiment, the autoimmune disorder is at least partially mediated by CD8+ T-cell proliferation.
Owner:GHILARDI NICO +1
The E type DNA vaccine of Chlamydi trachomatis and its preparation methods and applications
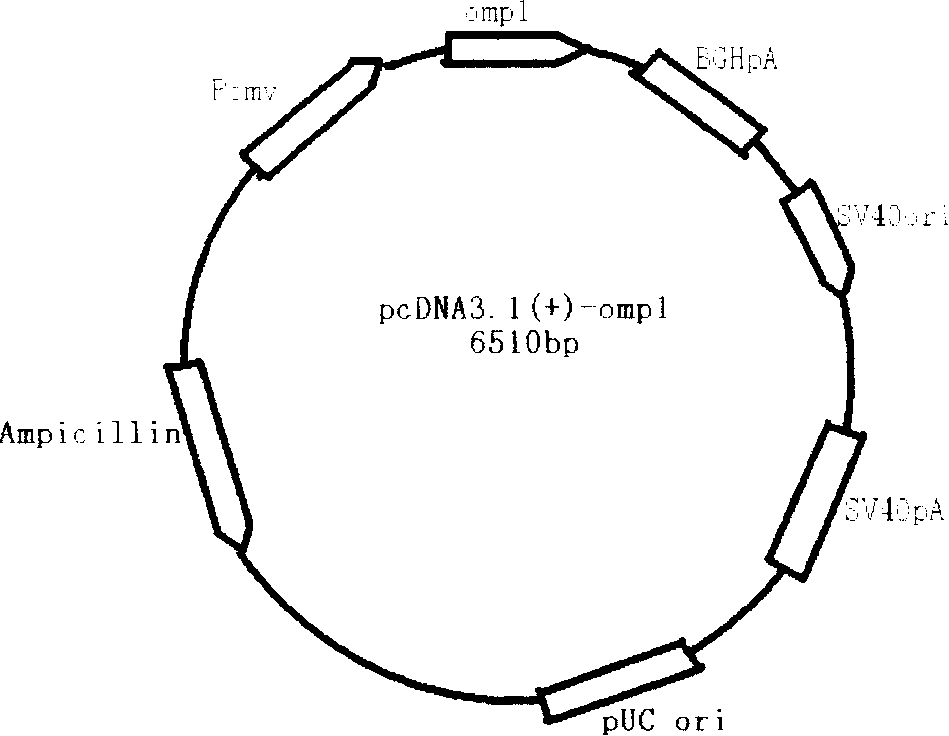
InactiveCN100391544CProtectiveImmunization process is simpleGenetic material ingredientsAntiinfectivesGenetic engineeringPcr cloning
The invention provides preparation method and use of E-DNA vaccines of chlamydia trachoma. By means of molecular cloning and other genetic engineering technology, the invention clones the major outer membrane protein gene (CR genes) from E-chromosome gene of Chlamydia trachoma using PCR technology then directional connected with eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3.1 (+) to construct the DNA vaccine. Confirmed through animal experiments, the constructed E-DNA vaccine of chlamydia trachoma induces mice to produce certain cell and humoral immunity specific to chlamydia trachoma. Cellular immunity is even more markedly, predominated with the Th1 reaction, and acts as a protection to the attacks of chlamydia trachoma to E-genital tract. The vaccine is expected to improve the high incidence of chlamydia trachoma infections in genitourinary tract, difficult to cure, easy to relapse and costly conditions.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Methods for monitoring CD4+ t-helper type 1 response in cancer and immune restoration
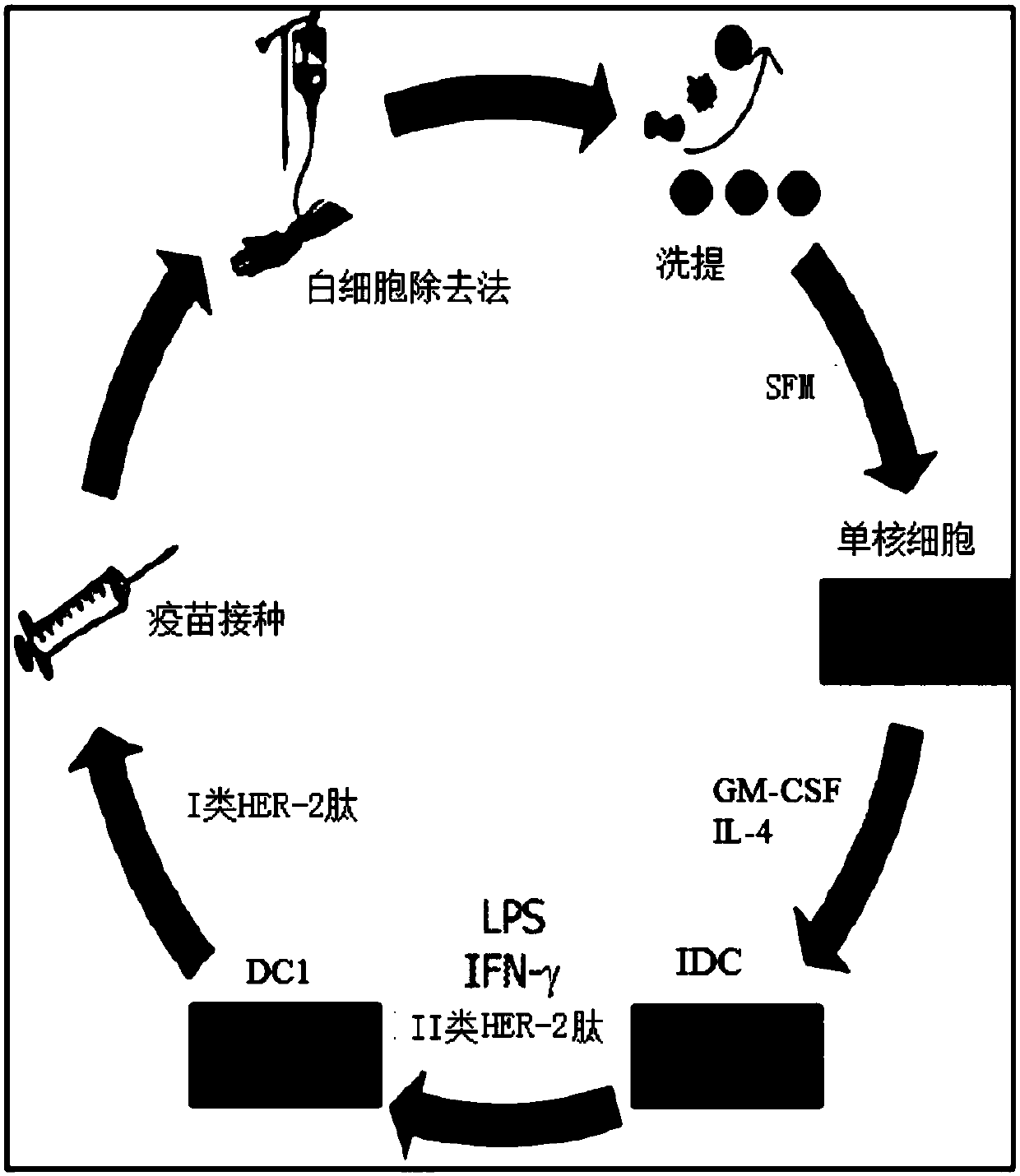
InactiveCN107073038APeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsDc vaccinationBinding peptide
A method for diagnosing or treating a mammalian subject having, or at risk of developing cancer, comprises: generating a circulating anti-cancer CD4+ Th1response from antigen presenting cells or their precursors and CD4+ T-cells from a sample of said subject's blood which causes secretion of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma); and detecting said anti-cancer CD4+ Th1 response to determine if said response is depressed. A method for restoring HER2-specific CD4+ Th1immune response in a HER2 -positive breast cancer patient in need thereof, comprises: administering to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of a dendritic cell (DC) vaccine comprising autologous DCs pulsed with HER2 -derived MHC class II binding peptides (DC vaccination) to elevate said patient's anti-HER2 CD4+ Th1 response; and measuring said anti-HER2 Th1 response of said patient pre- and post-DC vaccination to determine the amount of increase in said response.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Immunization with rabies virus vector expressing foreign protein antigen
An immune response in a subject is elicited by a regiment comprising immunization with an attenuated recombinant rabies virus encoding at least one foreign protein antigen, and booster immunization with the at least one foreign protein antigen in a vehicle that does not contain adjuvant. The foreign protein antigen may comprise a prion protein antigen, a cancer-associated antigens, a viral antigen, a bacterial antigens, or a protozoal antigen. The prime / boost regimen produces predominantly IgG 2A / C and IgG 2B antibodies against the foreign protein antigen, indicating a TH1 response. Rabies virus attenuation may be provided, for example, by one or more mutations in the rabies glycoprotein gene which confers attenuation of pathogenicity.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com