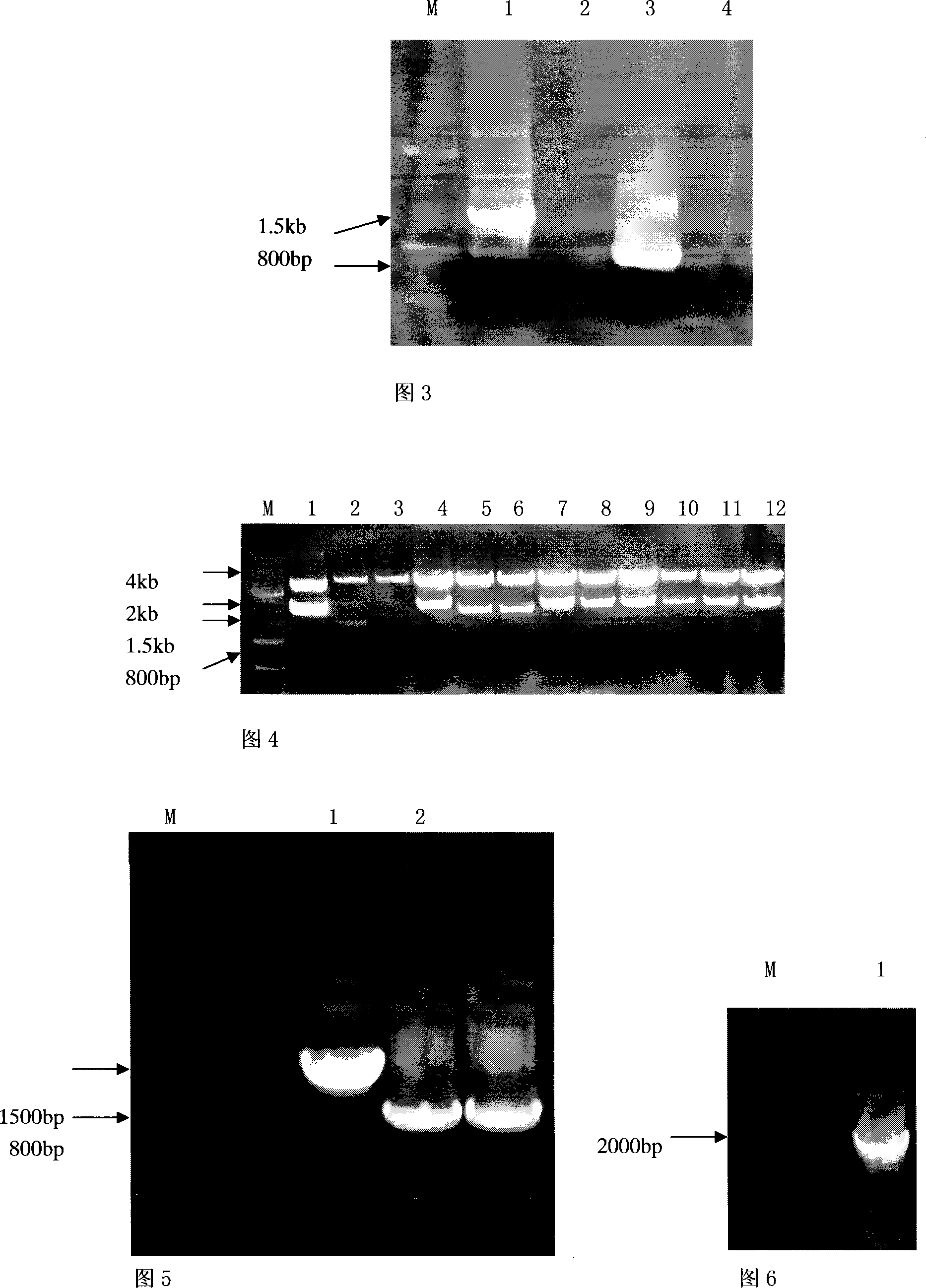
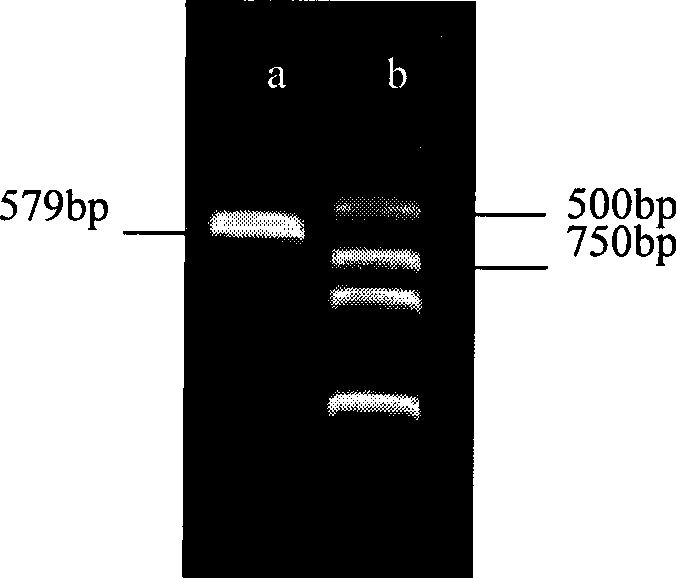
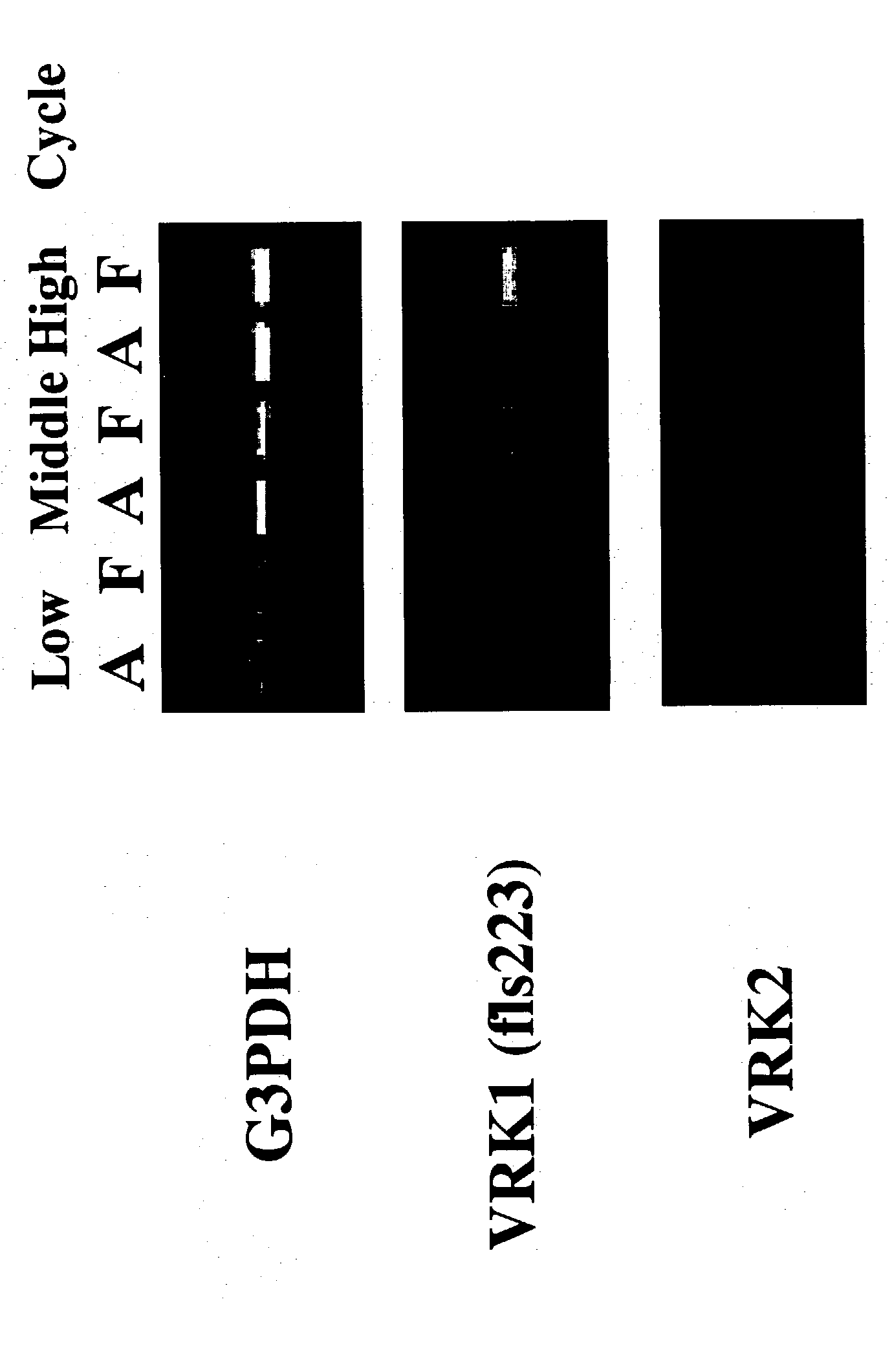
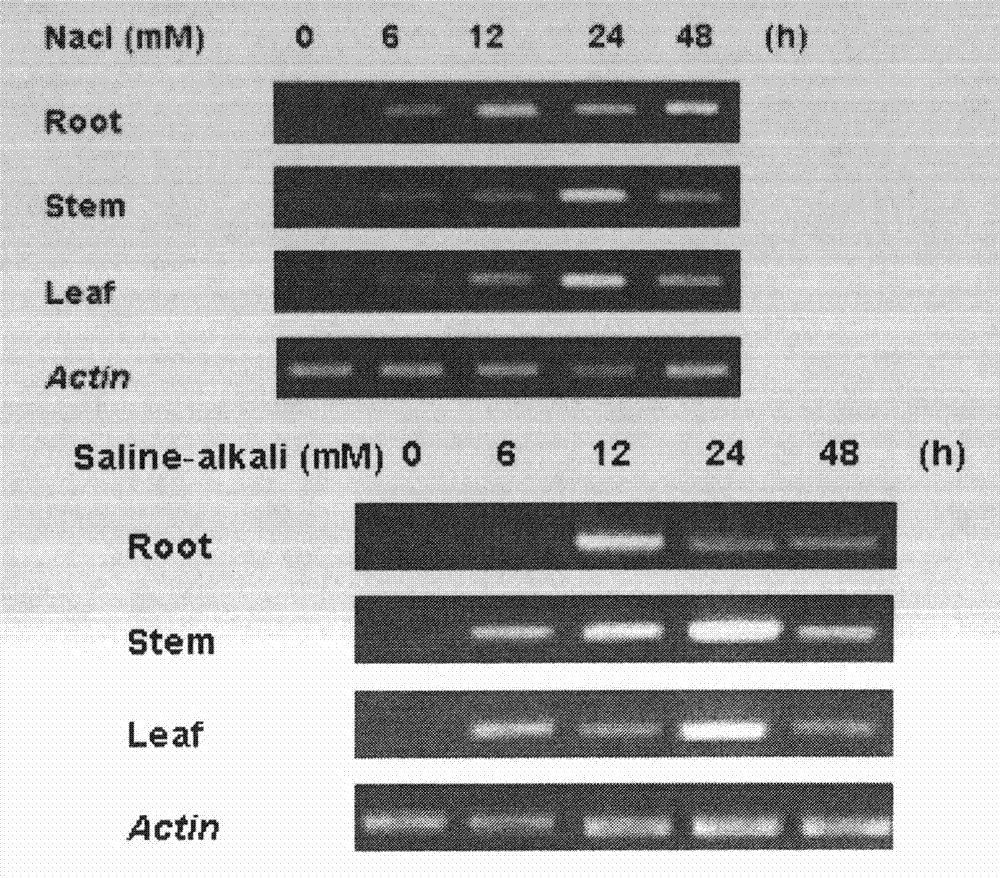
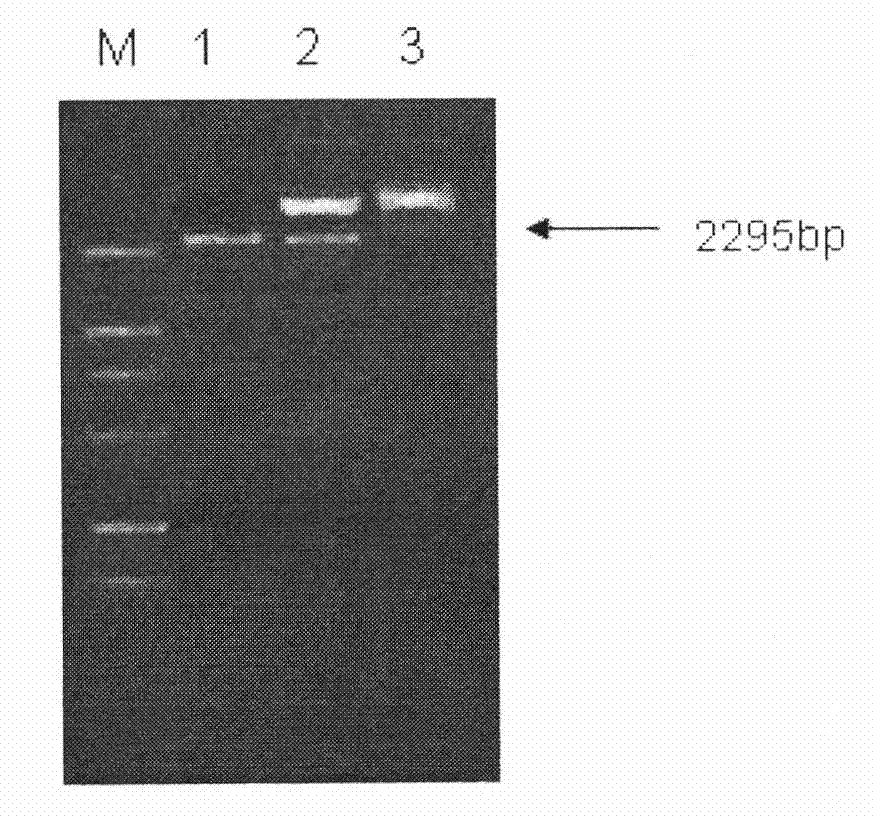
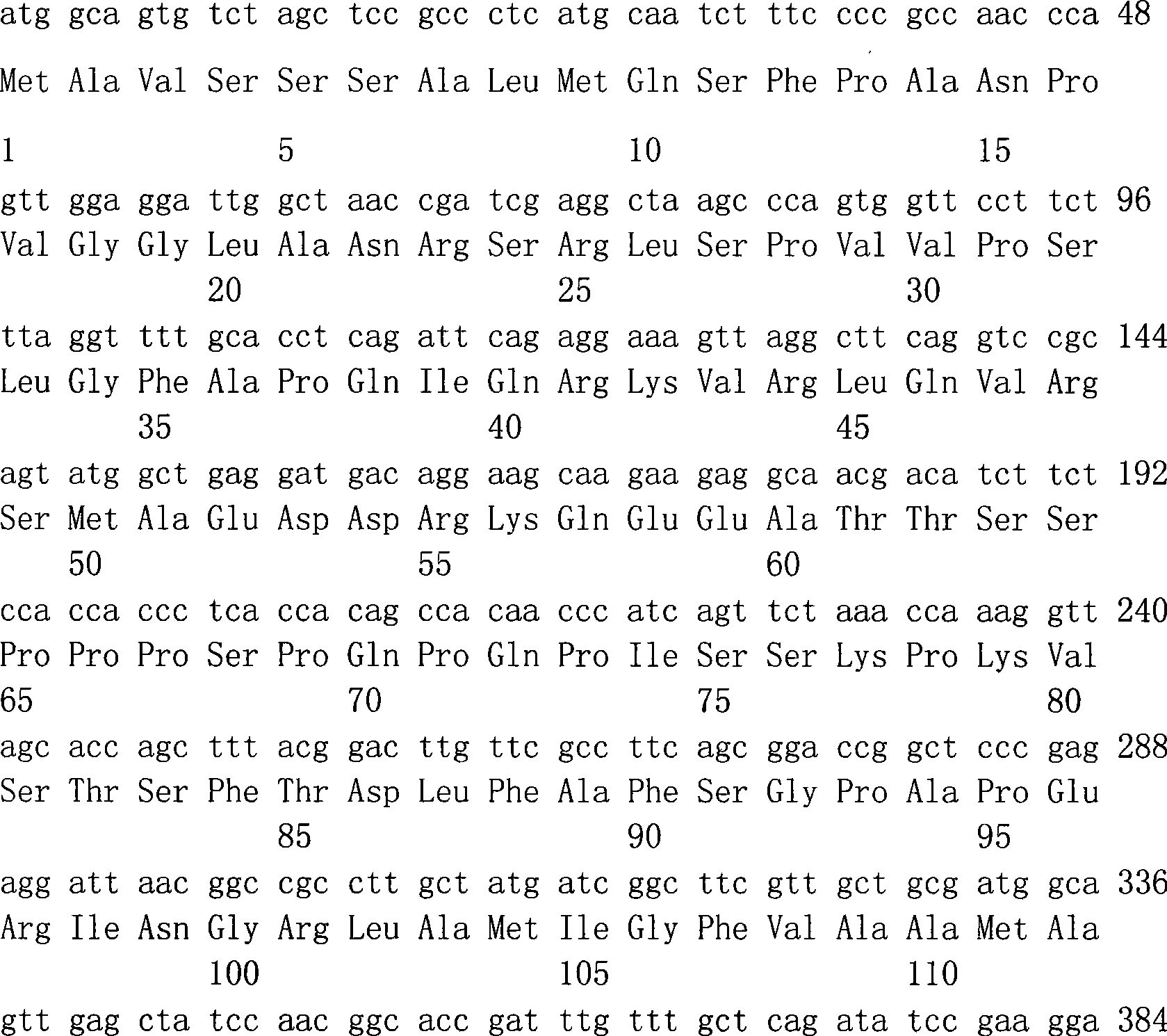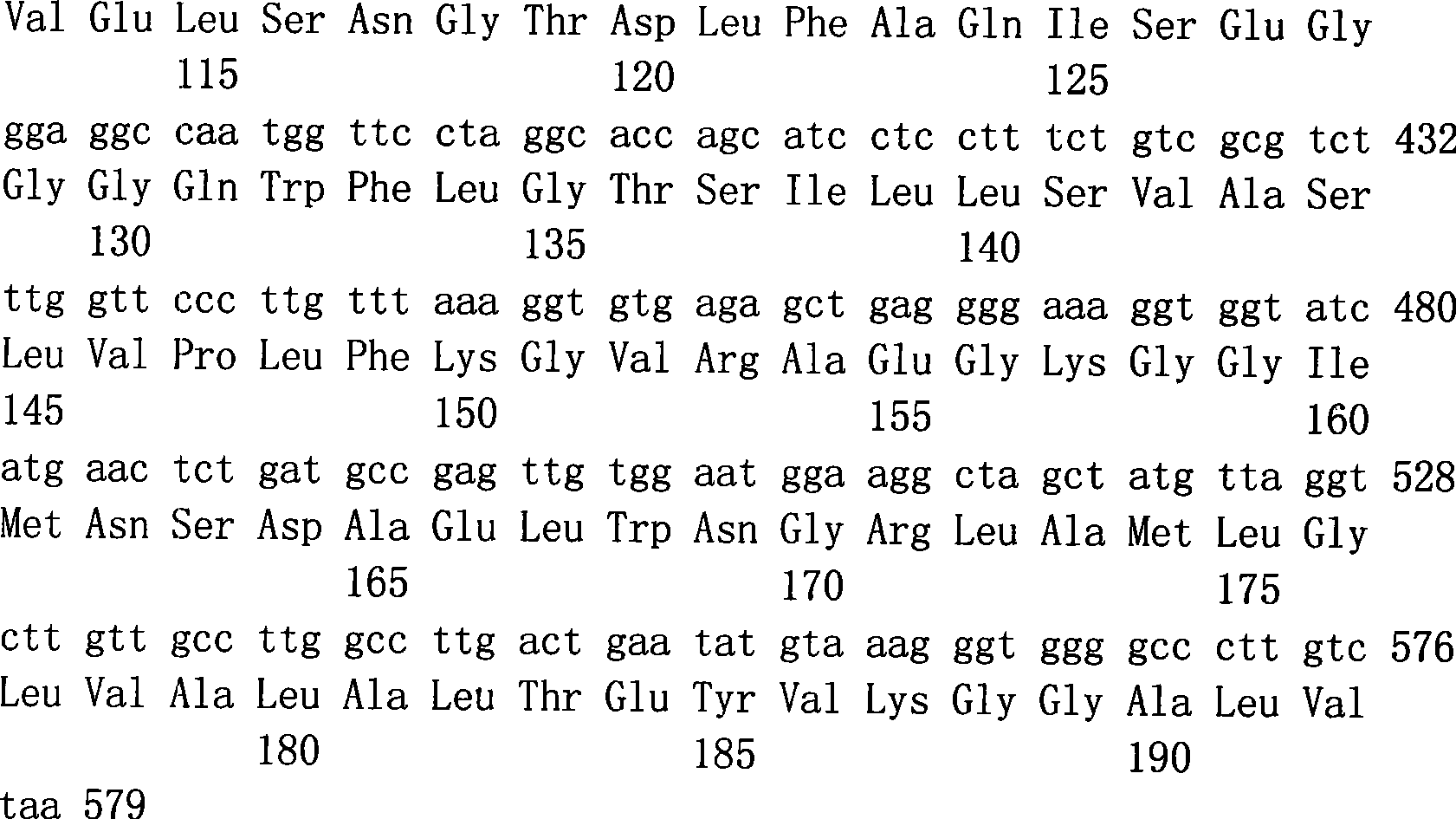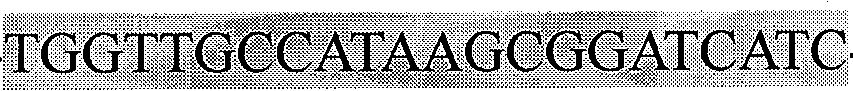Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Suppression subtractive hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
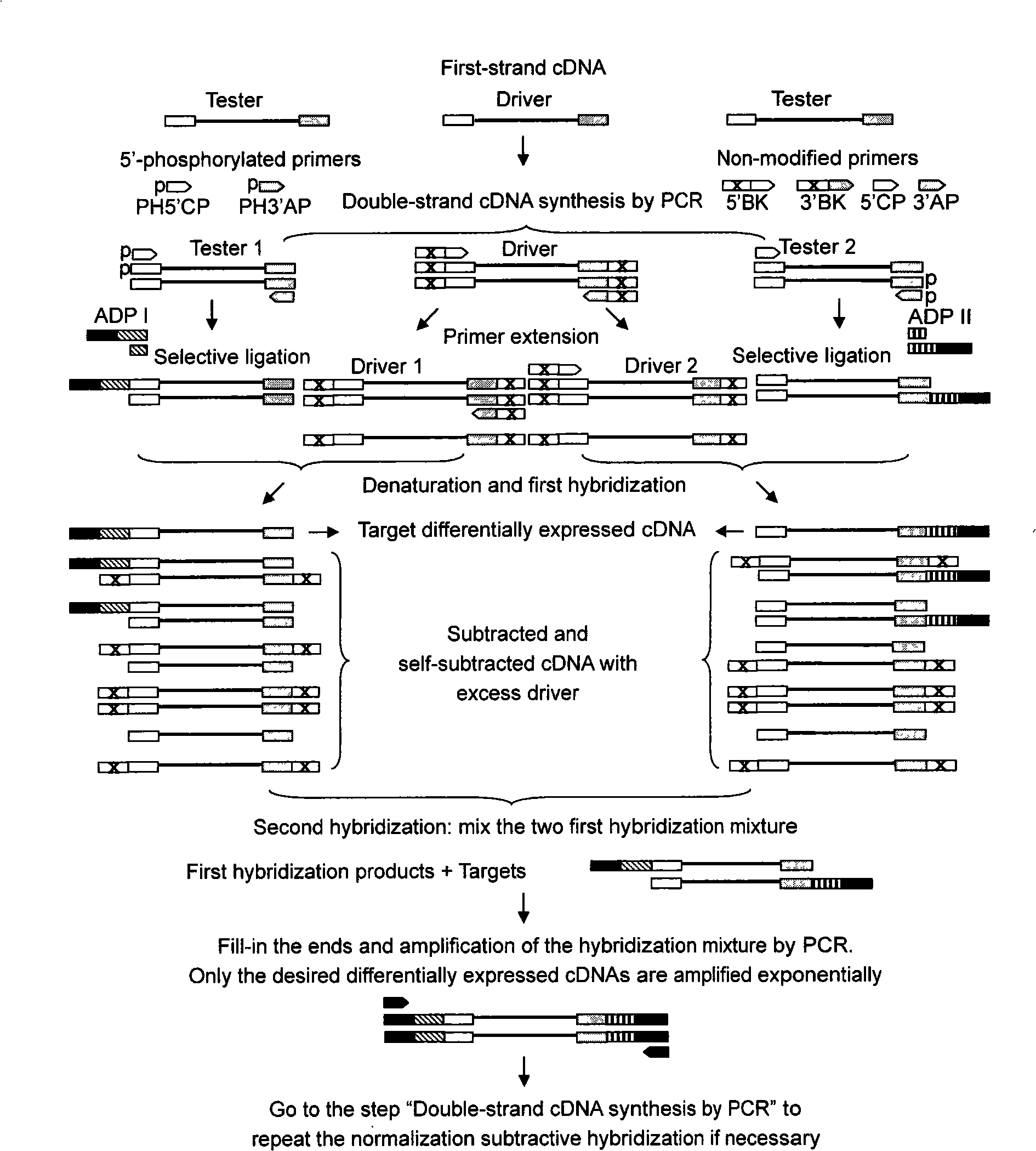
Subtractive hybridization is a technology that allows for PCR-based amplification of only cDNA fragments that differ between a control (driver) and experimental transcriptome. cDNA is produced from mRNA. Differences in relative abundance of transcripts are highlighted, as are genetic differences between species. The technique relies on the removal of dsDNA formed by hybridization between a control and test sample, thus eliminating cDNAs or gDNAs of similar abundance, and retaining differentially expressed, or variable in sequence, transcripts or genomic sequences.
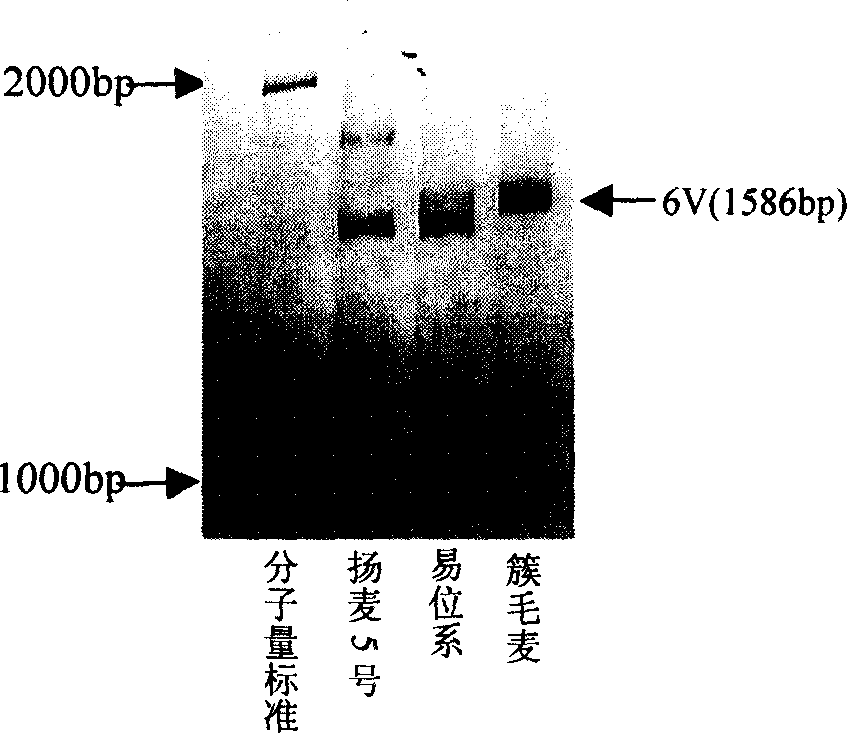
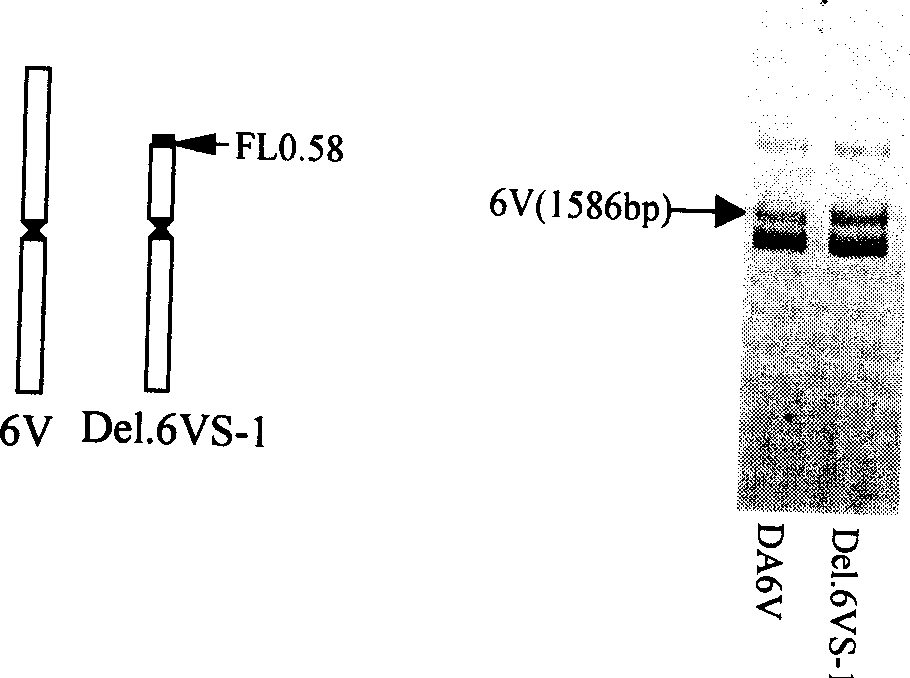
Wheat anti-powdery mildew gene Pm21 linked codorminant PCR marker and its usage
InactiveCN1737151AClosely linkedHigh degree of genetic linkageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence designAgricultural science
The invention discloses a wheat anti-powdery mildew gene Pm21 linked codorminant PCR marker and its use, wherein disease-resistant gene analogues Ta-LRR2 sequence design primers NAU / XiBao 16F and NAU / XiBao 16R are obtained through suppression subtractive hybridization between Yangmai No.5 and translocation lines, a series of material tests have shown that, the label NAU / XiBao16 is interlocked with translocation lines 6VS / 6AL powdery mildew resistant gene Pm21, and one PCR experiment can amplify two specific belts from common wheat 6AS and Haynaldia Vollosa 6VS chromosomes simultaneously, the label NAU / XiBao16 can be used for the molecular label auxiliary selection in wheat powdery mildew disease resistant breeding, and for the purity identification of common wheat seeds.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
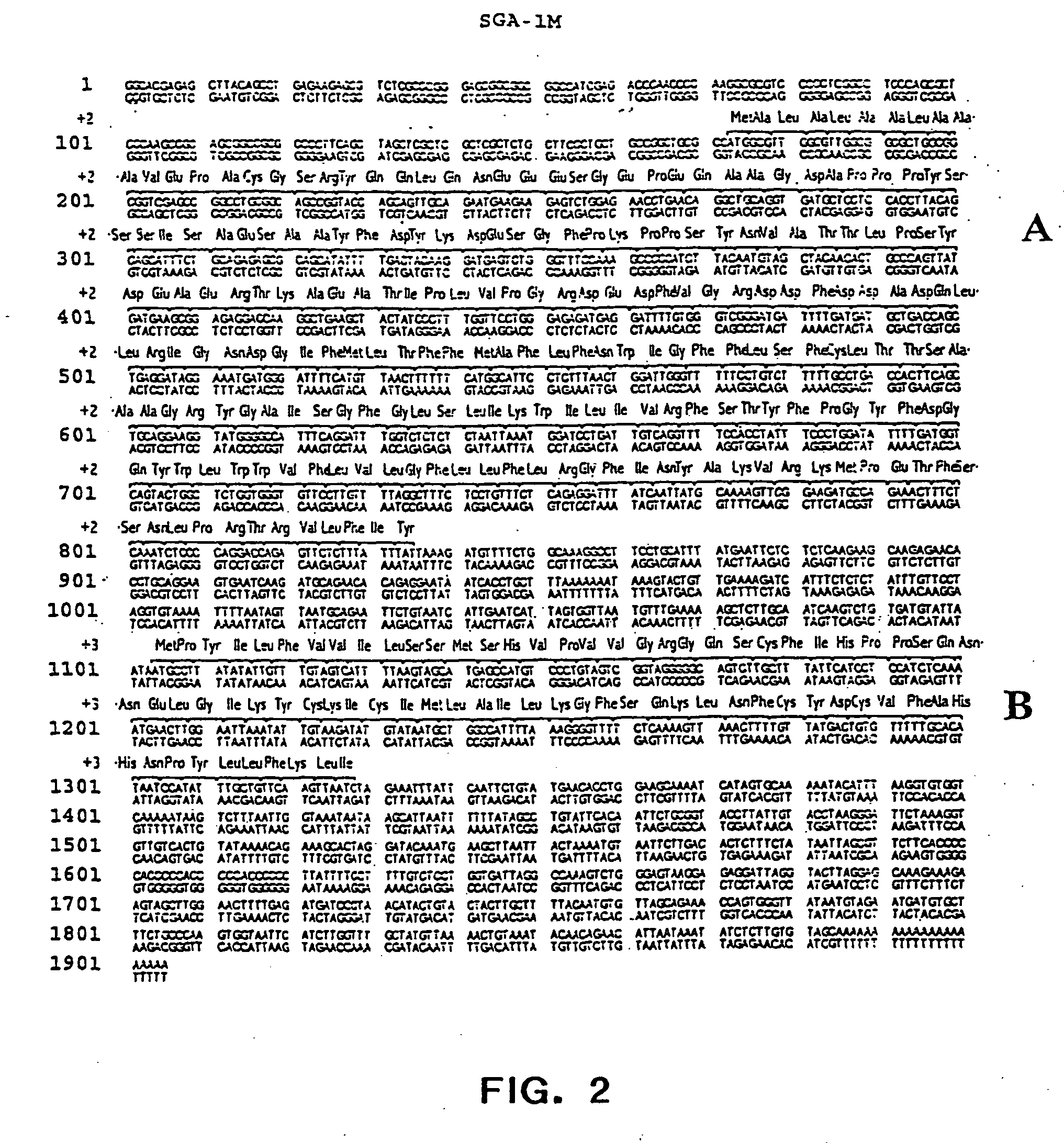
Sga-1m, a cancer associated antigen, and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a gene and gene product, SGA-1M that is differentially expressed in cancer tissues and cell lines. Suppression Subtractive Hybridization and microarray screening were used to screen for differential expression of SGA-1M in cancer tissues and cell lines. Expression analysis has demonstrated overexpression of SGA-1M in breast cancer tissue and breast cancer derived cell lines, in ovarian cancer, skin cancer, a cancer of the lymphoid system, thyroid cancer, pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer. The gene is expressed as a 1.95 kb mRNA. The full length cDNA comprises two open reading frames encoding polypeptides of 221 and 75 amino acids, respectively. Monitoring expression levels of SGA-1M is useful for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer as well as for evaluating the risk of developing certain types of cancers and the risk of metastasis of cancer. Reagents that target SGA-1M are useful for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Method for identifying nucleic acid molecules associated with angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060246452A1Improve expression efficiencyImprove efficiencySenses disorderAntipyreticTotal rnaModel system
A method for the identification of a nucleic acid molecule differentially expressed in an in vitro model of a biological system, comprising the steps of: (1) harvesting cells from the model system at predetermined time points; (2) obtaining total RNA from the cells harvested at each time point; (3) preparing cDNA from the total RNA from each time point to provide a plurality of pools of cDNA; (4) performing a suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) on the cDNA pools from each time point sequentially so as to progressively amplify cDNAs derived from nucleic acid molecules differentially expressed from one time period to the next.
Owner:BONOMICS LTD +1
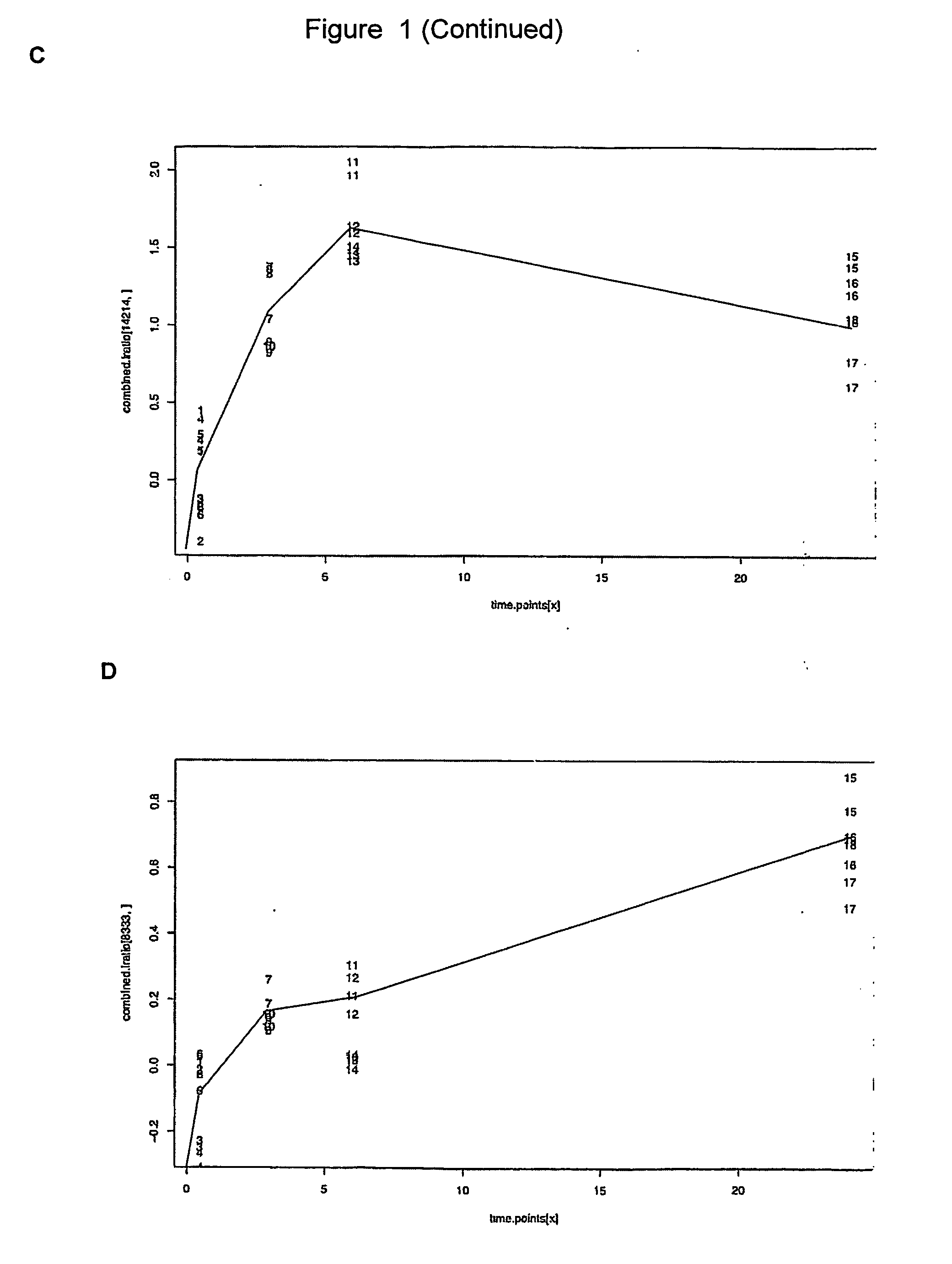
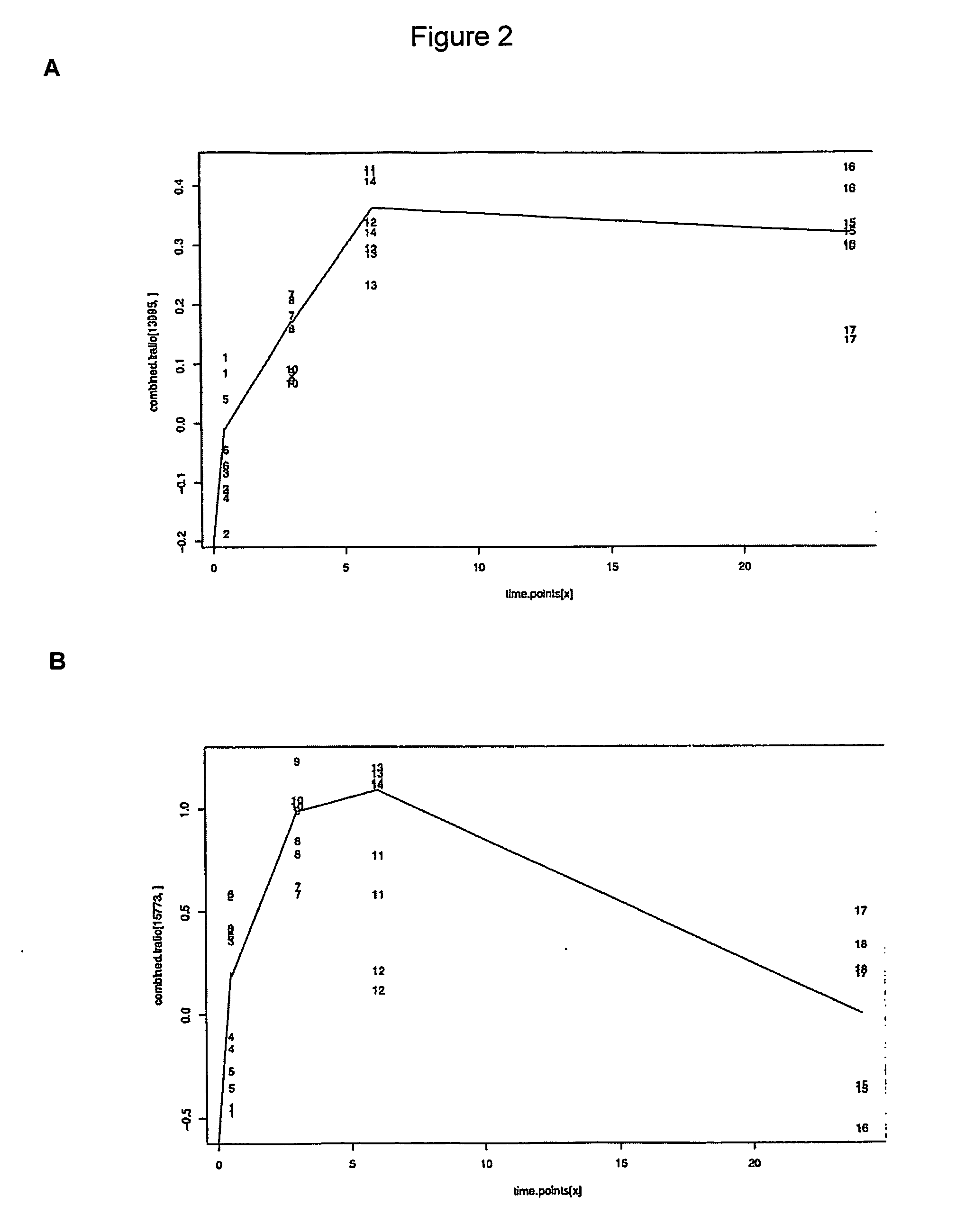
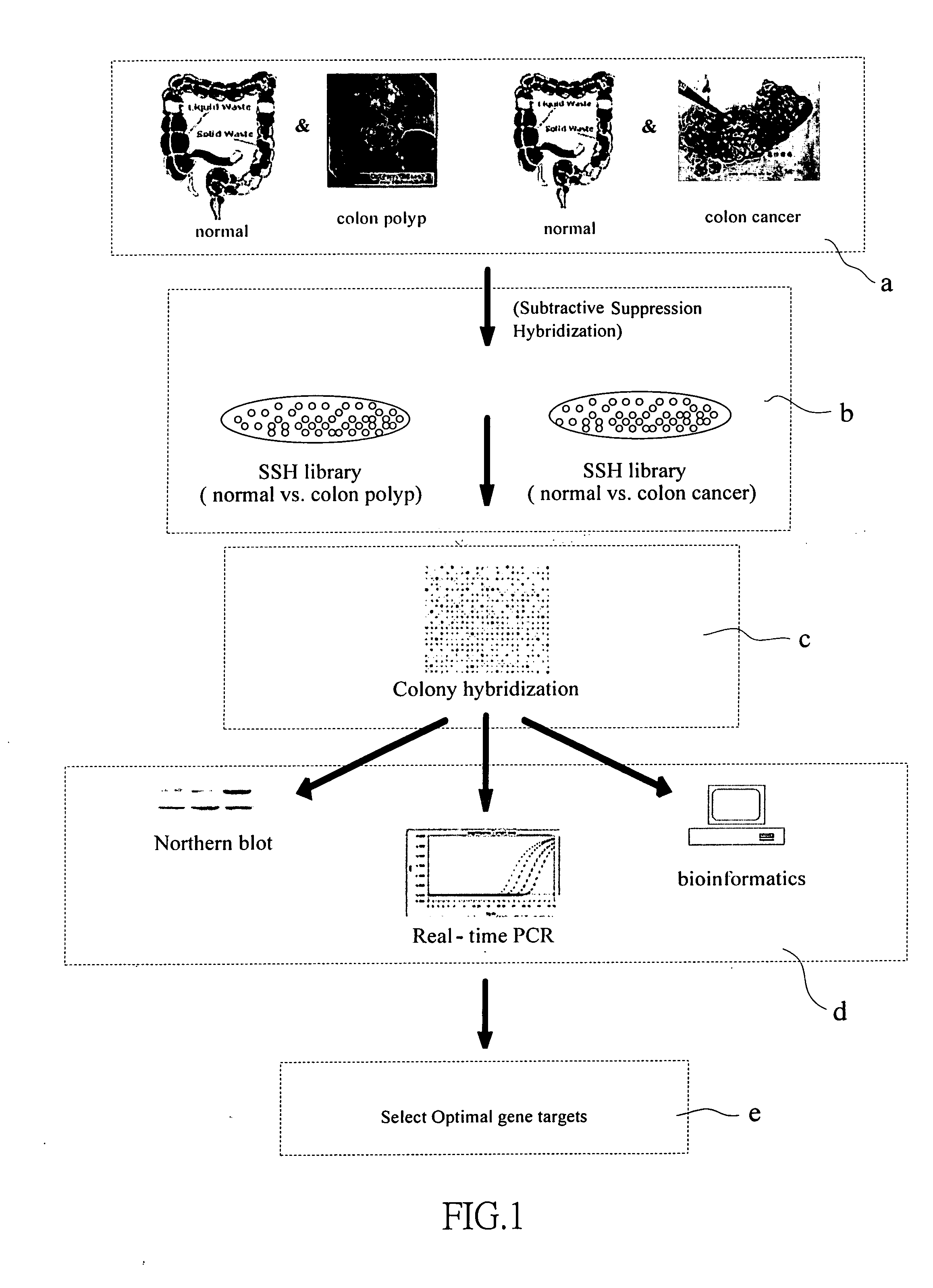
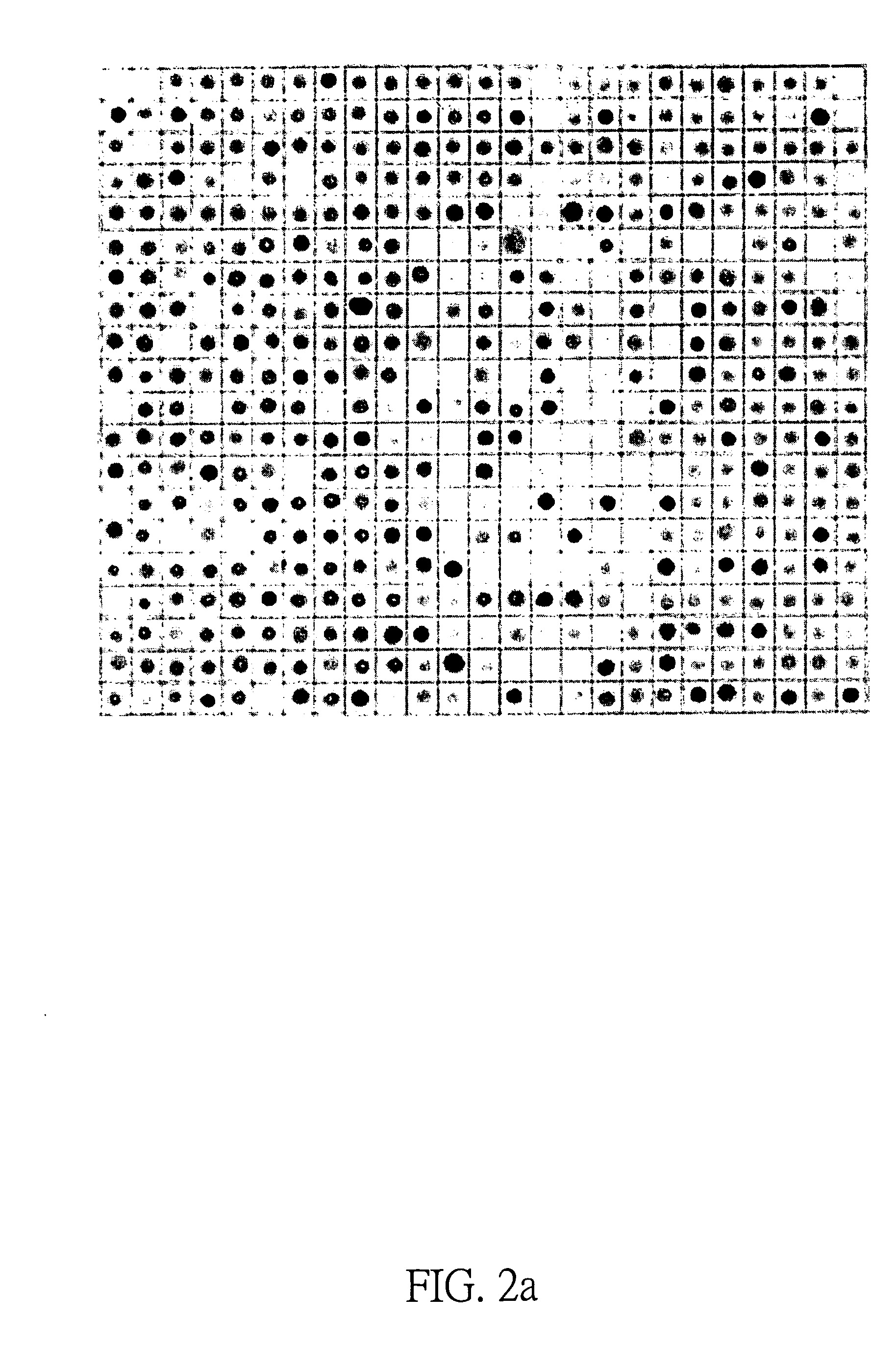
Genes for diagnosing colorectal cancer
InactiveUS20050191634A1High sensitivityImprove securitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitheliumIntestinal structure
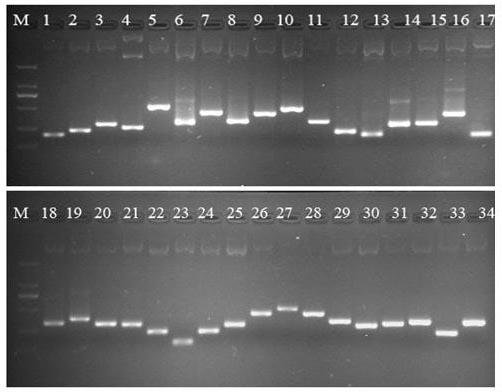
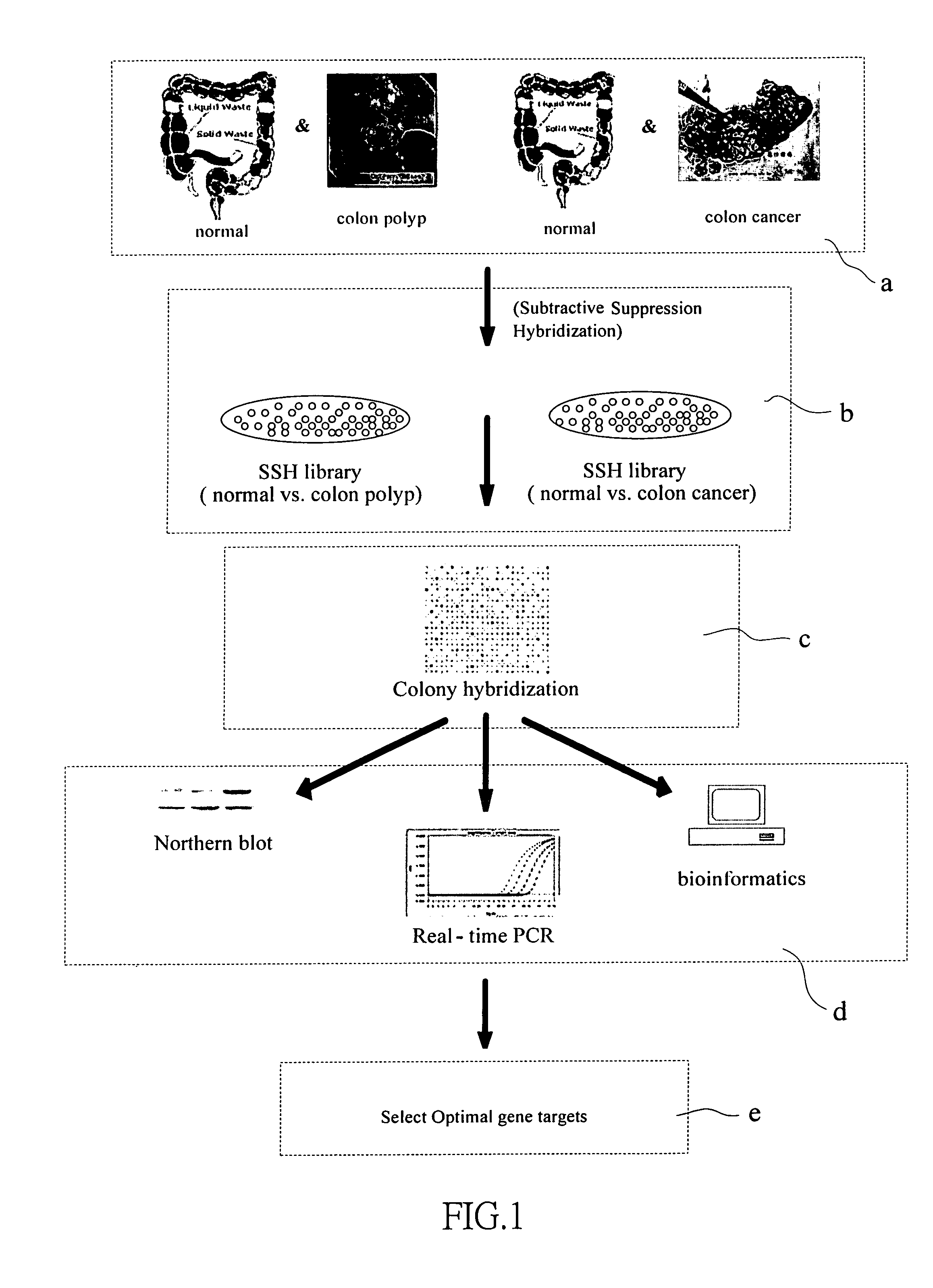
This invention relates to provide the genes for diagnosing colorectal cancer, the gene sequences searching comprise the steps of: (1) deriving epithelium cells from normal intestines, polypus of intestines and colorectal cancer tissue; (2) collecting genes with highly differential gene expression by Suppression Subtractive Hybridization (SSH), and building library; (3) deriving colonies with relatively high signal intensities from cancer tissue; (4) collecting more clinically cancer tissues by Northern Hybridization, real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) combined with analysis of bioinformation to affirm variation between differential gene expression; and (5) selecting the most suitable genes from said library, and using the gene sequence as reagent provides the effects of early diagnosis, specificity, highly sensitivity and safety.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs
InactiveCN102660777AHigh sensitivitySuppression Subtraction Libraries GoodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTotal rnaPolarization mode dispersion
The invention discloses a method for constructing a suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs. The method includes steps of: sample processing, total ribonucleic acid (RNA) extraction, mRNA purification, suppression subtractive hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of testing parts and driven elements, PCR products and polarization mode dispersion 18-T (pMD18-T) carrier connection restraining, connection product conversion, monoclonal storing and the like. The SSH library of oryza rufipogon threatened by bacterial blight germs constructed by the method is high in sensitivity, even length of insertion elements of the library is 450bp, a large number of difference expressed sequence tags (ESTs) of the oryza rufipogon threatened by the bacterial blight germs can be obtained fast in one step, partial sequence information is provided for separating overall-length cDNA sequence of clone bacterial blight resisting related genes, simultaneously important theoretical basis for improvement of biology is provided and new bacterial blight resisting related genes can be obtained.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
Genes for diagnosing colorectal cancer
InactiveUS7575928B2High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIntestinal structureEpithelium
This invention relates to provide the genes for diagnosing colorectal cancer, the gene sequences searching comprise the steps of: (1) deriving epithelium cells from normal intestines, polypus of intestines and colorectal cancer tissue; (2) collecting genes with highly differential gene expression by Suppression Subtractive Hybridization (SSH), and building library; (3) deriving colonies with relatively high signal intensities from cancer tissue; (4) collecting more clinically cancer tissues by Northern Hybridization, real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) combined with analysis of bioinformation to affirm variation between differential gene expression; and (5) selecting the most suitable genes from said library, and using the gene sequence as reagent provides the effects of early diagnosis, specificity, highly sensitivity and safety.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
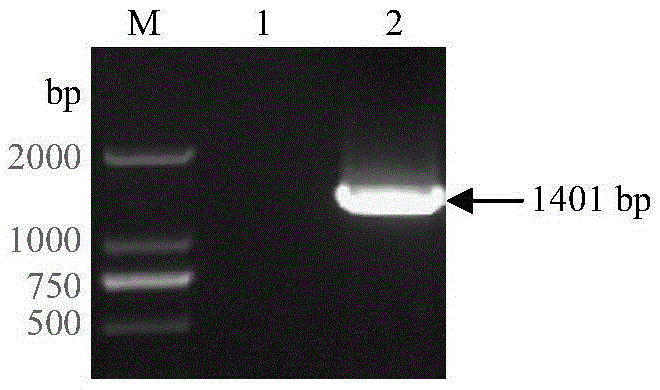
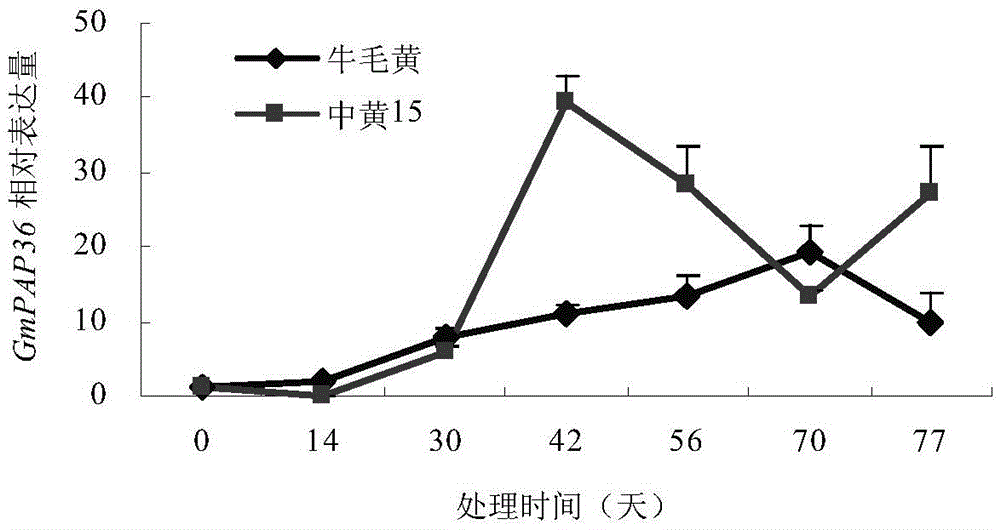
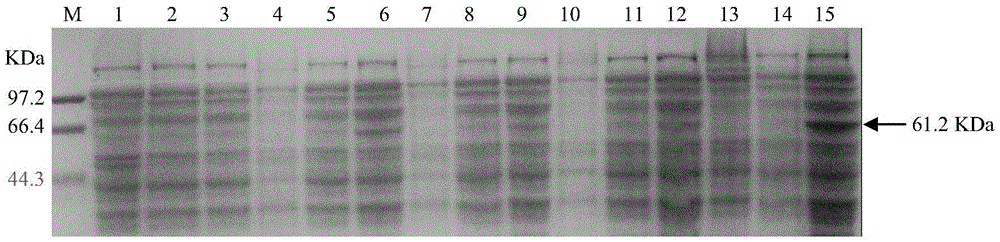
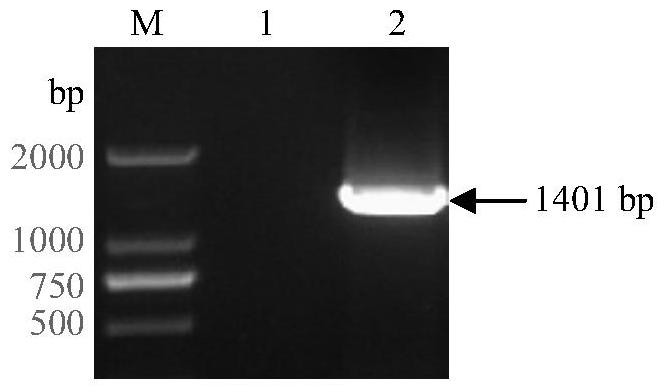
Soybean purple acid phosphatase GmPAP36 and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105647884AAchieve prokaryotic expressionHydrolasesFermentationCandidate Gene Association StudyPhytic acid
The invention provides soybean purple acid phosphatase GmPAP36 and an encoding gene and application thereof. A low-phosphorous induction soybean root system cDNA subtractive library is established based on the suppression subtractive hybridization technique, low-phosphorous stress inducible expression acid phosphatase candidate EST is selected from the subtractive library, and on this basis, an acid phosphatase candidate gene sequence is cloned and the expression difference of a candidate gene under the phytate phosphorus processing condition is analyzed with the real-time quantitative PCR technique; a gene prokaryotic expression vector is established to achieve gene prokaryotic expression; meanwhile, a gene eukaryotic expression vector is established, arabidopsis and soybean conversion is conducted to obtain transgenosis positive plants, the biological function of the gene GmPAP36 is analyzed, and functional genes are provided for efficient transgenosis breeding of plant phosphorus.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Methods of providing gene expression profiles for metastatic cancer phenotypes utilizing differentially expressed transcripts associated with circulating tumor cells
InactiveUS20070031876A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionCirculating cancer cellBiology
Methods of identifying the presence of differentially expressed transcripts associated with the presence of at least one circulating tumor cell in a biological sample of a cancer patient involves the use of suppression subtractive hybridization to identify differentially expressed transcripts present in biological samples of cancer patients not present in healthy patients, as well as differentially expressed transcripts present in biological samples of healthy patients and not present in the cancer patients. Utilizing these methods, a gene expression profile associated with a specific cancer phenotype can be constructed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers and application thereof
InactiveCN102676515AGood repeatabilityStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideRe engineering
The invention belongs to the field of crop genetic breeding, in particular 36 Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers. The 36 genome-specific molecular markers are obtained by the following steps: according to a nucleotide sequence of 18srRNA gene disclosed by National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI), designing primers in the sequence between two RsaI loci, removing homologous sequences between two genome DNA by using a suppression subtractive hybridization technology, enriching differential sequences, obtaining Lophopyrum elongatum specific DNA segments, sequencing the DNA segments, and redesigning primers according to sequences without homology with wheat. The markers can be used for identifying translocation lines in the process of transferring chromosome segments from Lophopyrum elongatum to wheat, can be used for linkage analysis of scab-resistant gene, and can serve as specific molecular markers for identifying chromatin of the Lophopyrum elongatum to be applied to scab-resistant and stress-resistant breeding of wheat.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
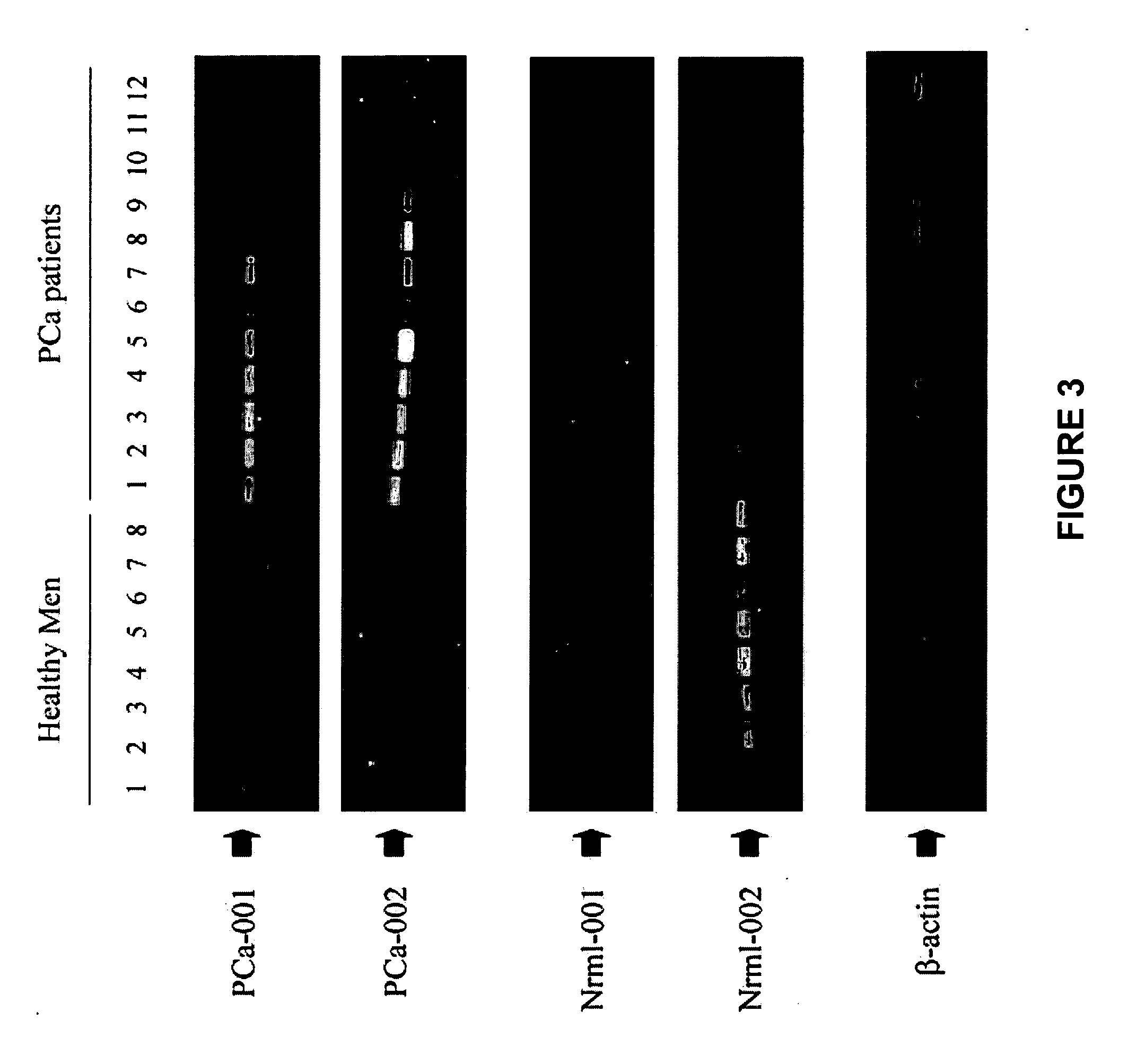
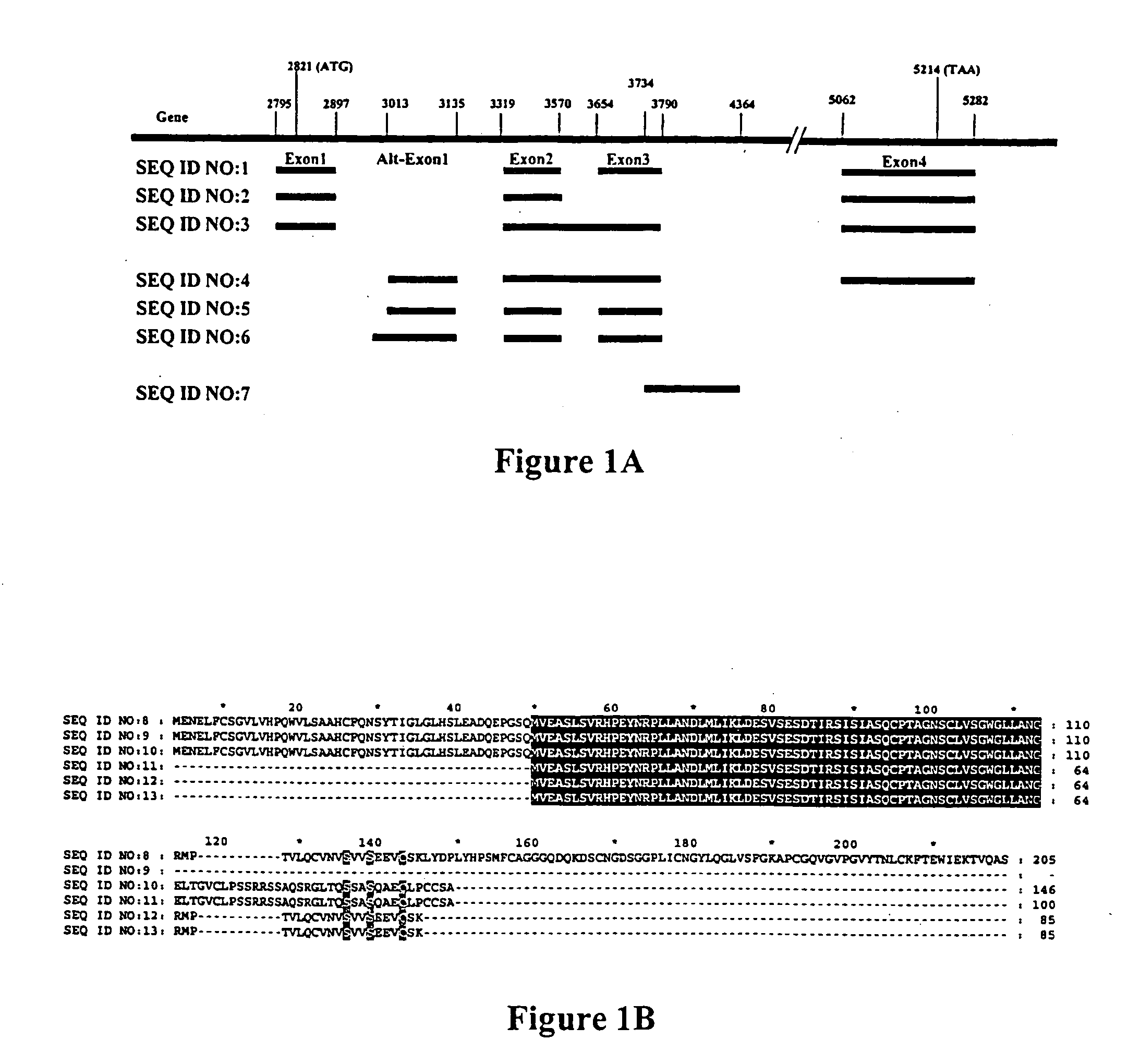
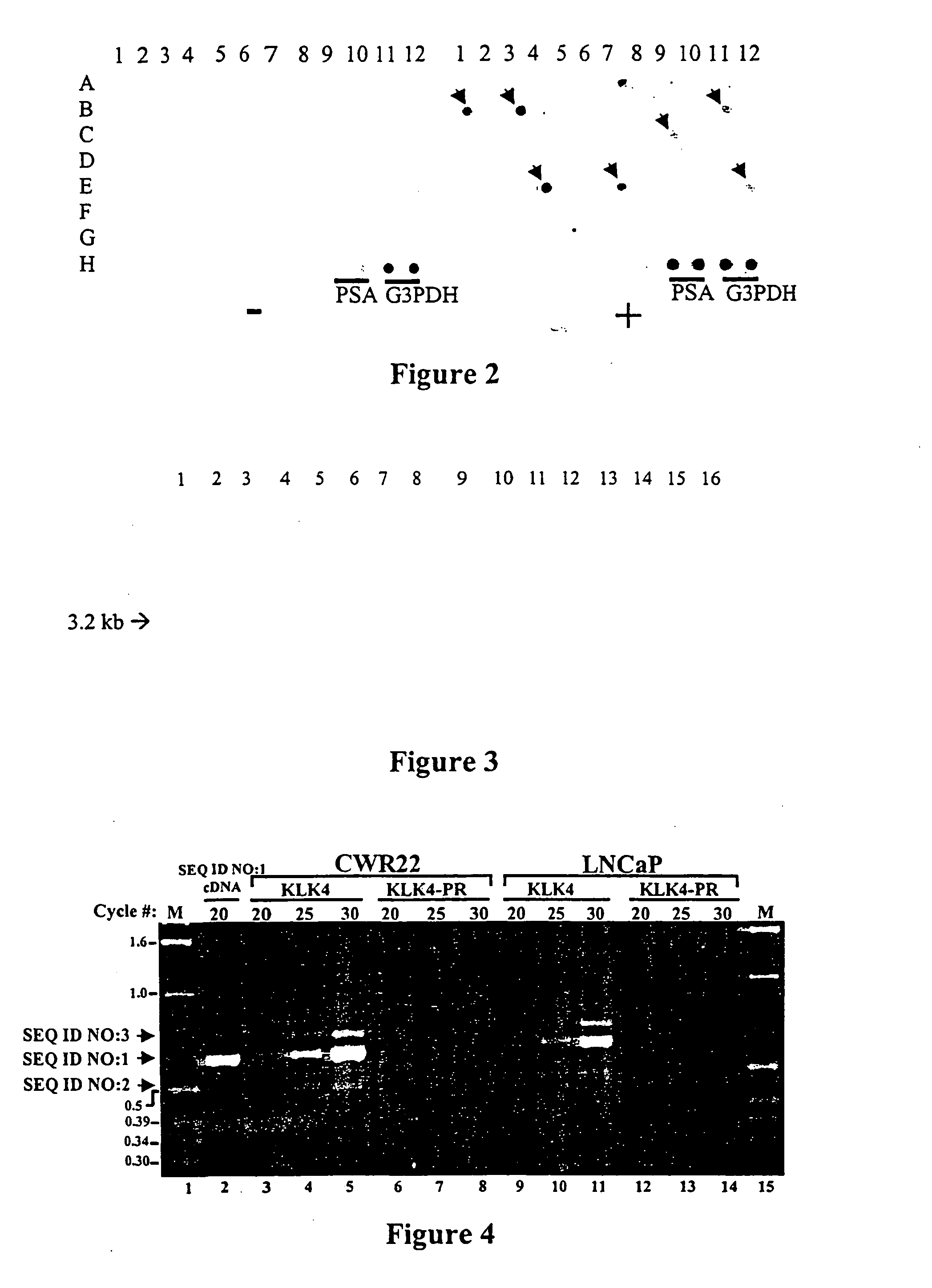
Differentially expressed genes in prostate cancer
SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, and SEQ ID NO: 3 encode an intracellular protein that is expressed in prostate epithelial cells in a hormone dependent manner. Encoded proteins SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 5, and SEQ ID NO: 6 have predominantly perinuclear, nuclear and predominantly nuclear location localization within a cell, respectively. In contemplated methods of detecting a neoplastic cell in a system, a predetermined amount of at least one of SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO:5, and SEQ ID NO: 6, or at least one of SEQ ID NO: 7, SEQ ID NO: 8, and SEQ ID NO: 9 is correlated with the presence of a neoplastic cell and detected within the system employing specific binding of a labeled probe. In a method of identifying differentially expressed genes, a tissue specific array of cDNA prepared by suppression subtractive hybridization is arranged on a solid phase. Two nucleic acid preparations are individually hybridized with the array, wherein the first and second nucleic acid preparations are prepared from treated and untreated target tissue. A comparison of the hybridization patterns reveals differentially expressed genes.
Owner:SAATCIOGLU FAHRI
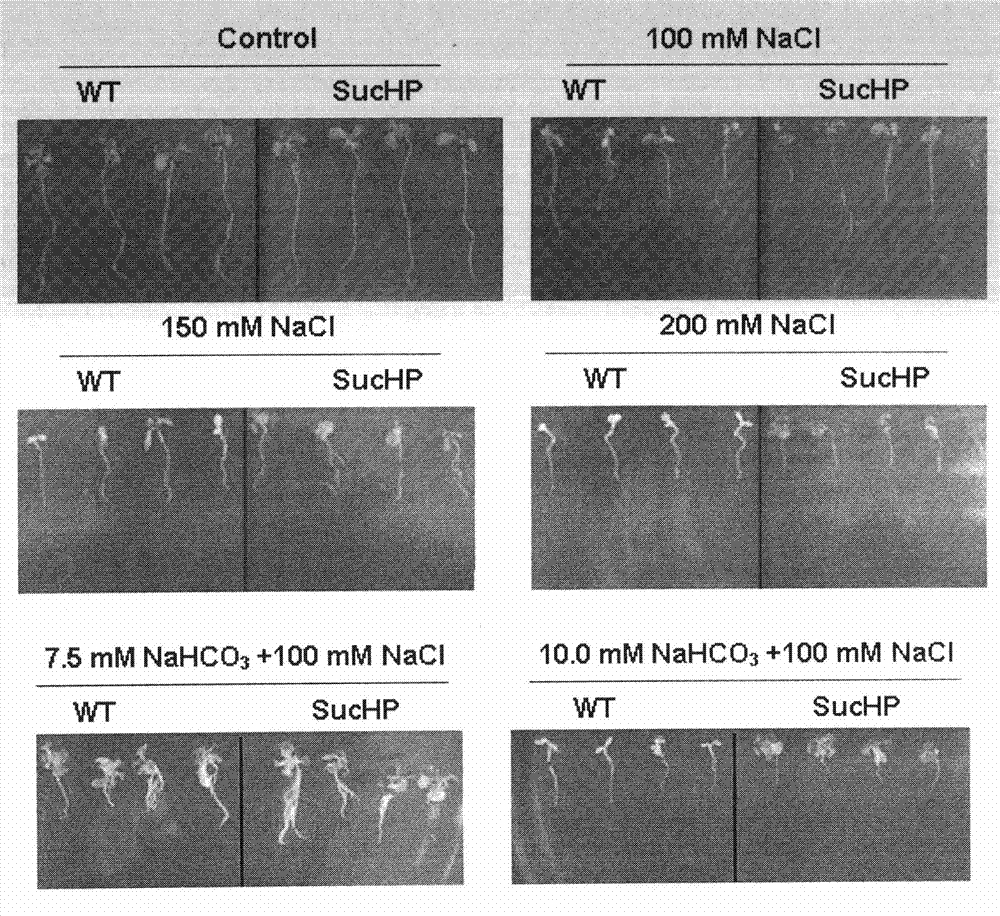
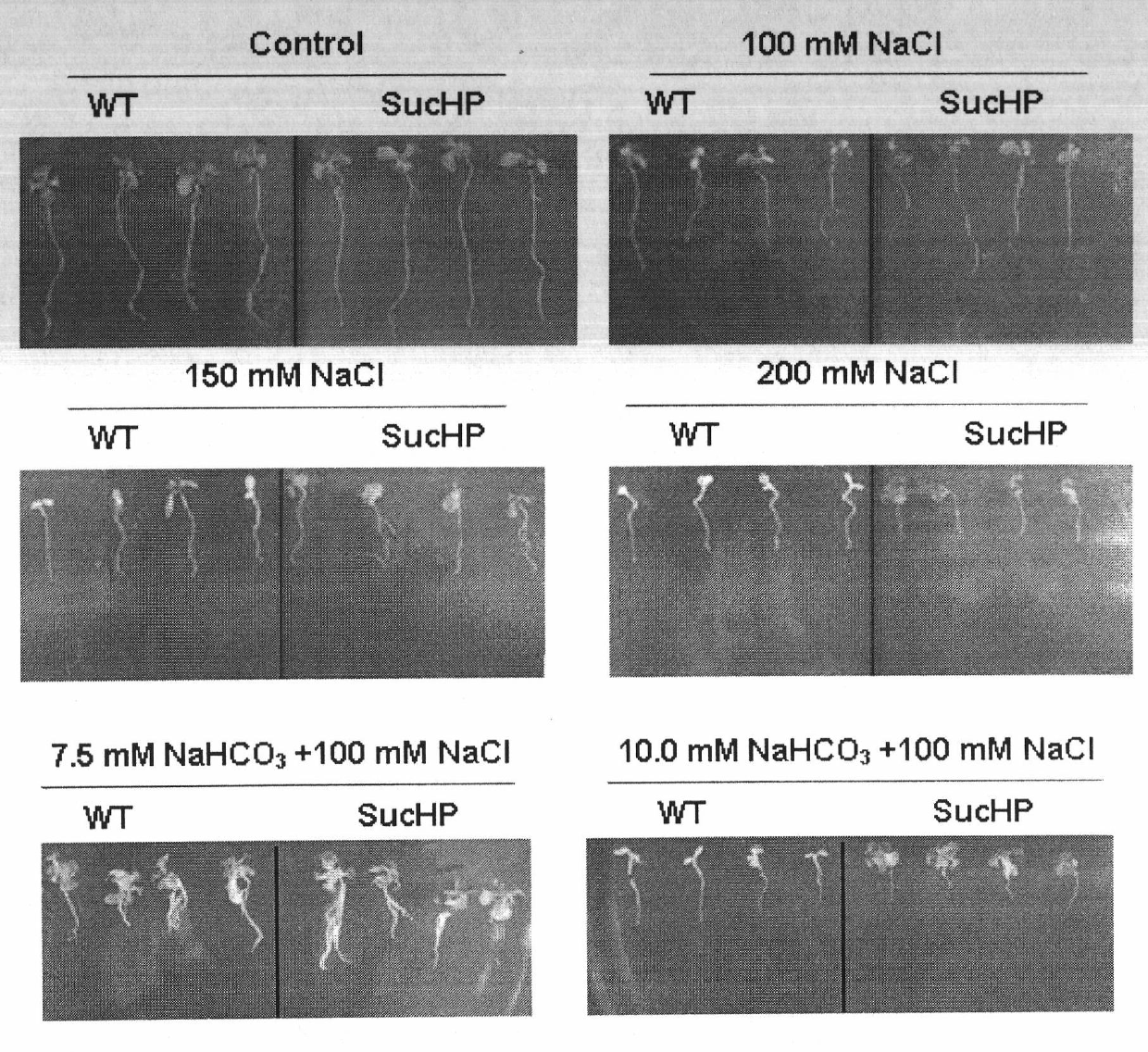
Plant high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance gene SucHP and application thereof
InactiveCN102002505AImprove salt and alkali resistanceHigh resistance to high pH saline alkaliPlant peptidesFermentationHigh densityNormal growth
The invention discloses a plant high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance gene SucHP and researches the expression of a high-pH saline and alkaline stress induction gene in a common seepweed herb seedling period by using suppression subtractive hybridization and high-density lattice film technology. The plant high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance gene SucHP can be prepared by the following steps of: firstly separating a gene of a coding tonoplast proton pump from common seepweed herbs; constructing a sense expression vector of the gene; and converting Arabidopsis. A transgenic plant has high high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance and can normally grow under the conditions of 100mM NaHCO3+200mM NaCl and 8.5 of pH. The plant high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance gene SucHP can be used for plant genetic transformation and increases plant saline and alkaline resistance.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Gene sequence correlated with cordycepin biological synthesis
The present invention relates to cordycepin biosynthesis relevant gene and its application. Seven cordycepin biosynthesis relevant genes are cloned by means of suppression and subduction hybridizing (SSH) technology. They are named separately as chcs1, chcs2, chcs3, chcs4, chcs5, chcs6 and chcs7 and have cDNA sequence lengths of 760bp, 774bp, 713bp, 823bp, 746bp, 763bp and 890bp separately. Through constituting high efficiency plant expression converting vector containing the said genes, it is possible to increase the copy quantity of biosynthesis gene inside thallus and to raise the content of cordycepin aweto expresses for meeting the requirement in developing medicine.
Owner:JONJEE HI TECH INDAL & COMML HLDG
Gene order relating to cordycepin biological synthesis
ActiveCN101423835AIncrease contentMeet the needs of pharmaceutical developmentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGene ordersBiosynthetic genes
The invention relates to cordycepin biosynthetic related genes and application thereof. By adopting a suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) technique, seven cordycepin biosynthetic related genes which are named as chcs1, chcs2, chcs3, chcs4, chcs5, chcs6 and chcs7 respectively are cloned, wherein the length of cDNA sequence of the chcs2 is 774bp. Through constructing an expression transformative vector of a high-efficiency plant containing the genes, means of biosynthetic gene copy amount in thalli is increased, and the content of cordycepin thalli for expressing cordycepin is improved, so as to meet requirement on medical development.
Owner:JONJEE HI TECH INDAL & COMML HLDG
Full length cDNA homogenizing subtractive hybridization method
InactiveCN101311266AImprove abatement efficiencyEfficient enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceFull length cdna
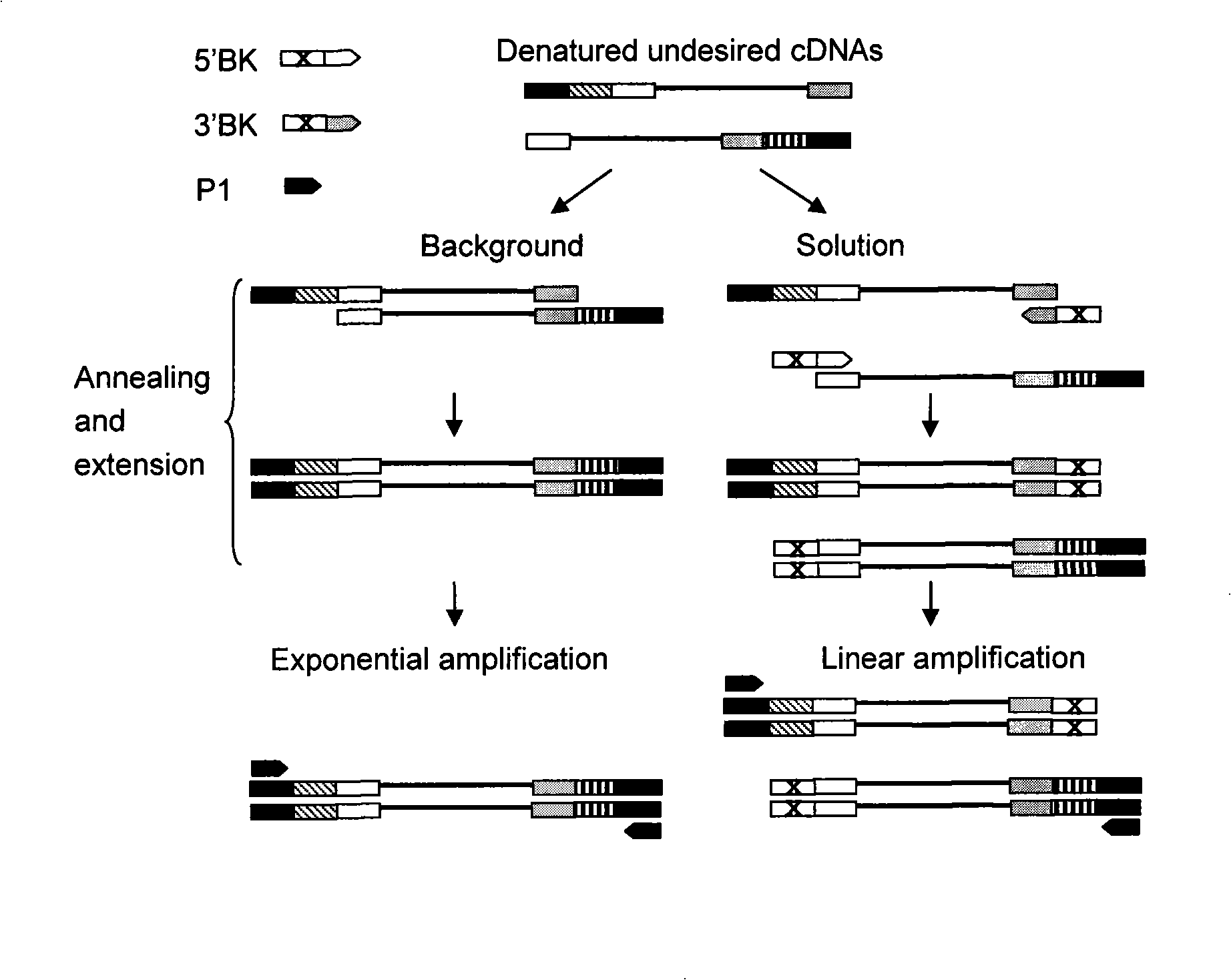
The invention provides a method for homogenization subtractive hybridization of full length cDNA. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) synthesizing a first chain cDNA; (2) synthesizing a double chain cDNA; (3) selective connection and primer extension; (4) subtractive hybridization; (5) PCR augmentation of cDNA of differential expression; wherein, the PCR products of the subtractive hybridization can be directly cloned to a vector so as to construct cDNA libraries, where differentially expressed genes are concentrated; the libraries can be utilized to analyze gene expression, prepare gene chips and be marked as probe which selects the differentially expressed genes from the existing libraries; in addition, if the subtractive efficiency is not high enough, the subtractive hybridization can repeat for the PCR products of subtractive hybridization to improve the homogenization and the subtractive efficiency. The method for homogenization subtractive hybridization of the full length cDNA (FNSH) creates the beneficial effects of high subtractive efficiency of differential genes, high efficiency of enriching differential expressed genes, high homogenization and gain of the full length cDNA.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method and applications of cDNA chip for detecting drug resistance level of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to trichlorphon and beta-cypermethrin
ActiveCN103614473ADelay drug resistanceMonitor resistance developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSubtraction hybridizationCypermethrin
The invention discloses a preparation method and applications of a cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) chip for detecting drug resistance level of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to trichlorphon and beta-cypermethrin. Upregulated drug resistance specificity expression gene segments of different resistant strains of bactrocera dorsalis can be obtained respectively by utilizing a forward suppression subtractive hybridization method, the related drug-resistant specificity expression genes are subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, 118 related resistance specificity gene segments of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to trichlorphon and 103 related resistance specificity gene segments of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to beta-cypermethrin can be obtained through purifying and recovering. The cDNA chip for detecting the resistance of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to trichlorphon and beta-cypermethrin can be constructed by taking the specific resistant target gene segments as DNA probes. The cDNA chip can simply and effectively realize the real-time detection on the drug resistance level of bactrocera dorsalis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Gene of containing 26S rRNA sequence from restoring line of cotton
This invention relates to a novel Gossypium hirsutum gene containing 26S rRNA sequence. The gene (GH18Rorf392) is obtained by: cloning EST sequence of cotton restorer through suppression subtractive hybridization method, designing primers according to the EST sequence, and performing 5'- and 3'-RACE to obtain full-length cDNA sequence. The gene comprises 26S rRNA sequence and 3'-end and a novel sequence at 5'-end. The gene is derived from Gossypium hirsutum restorer Y18R, and codes a protein of 392 amino acids. The gene can be used for studying fertility of cotton.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
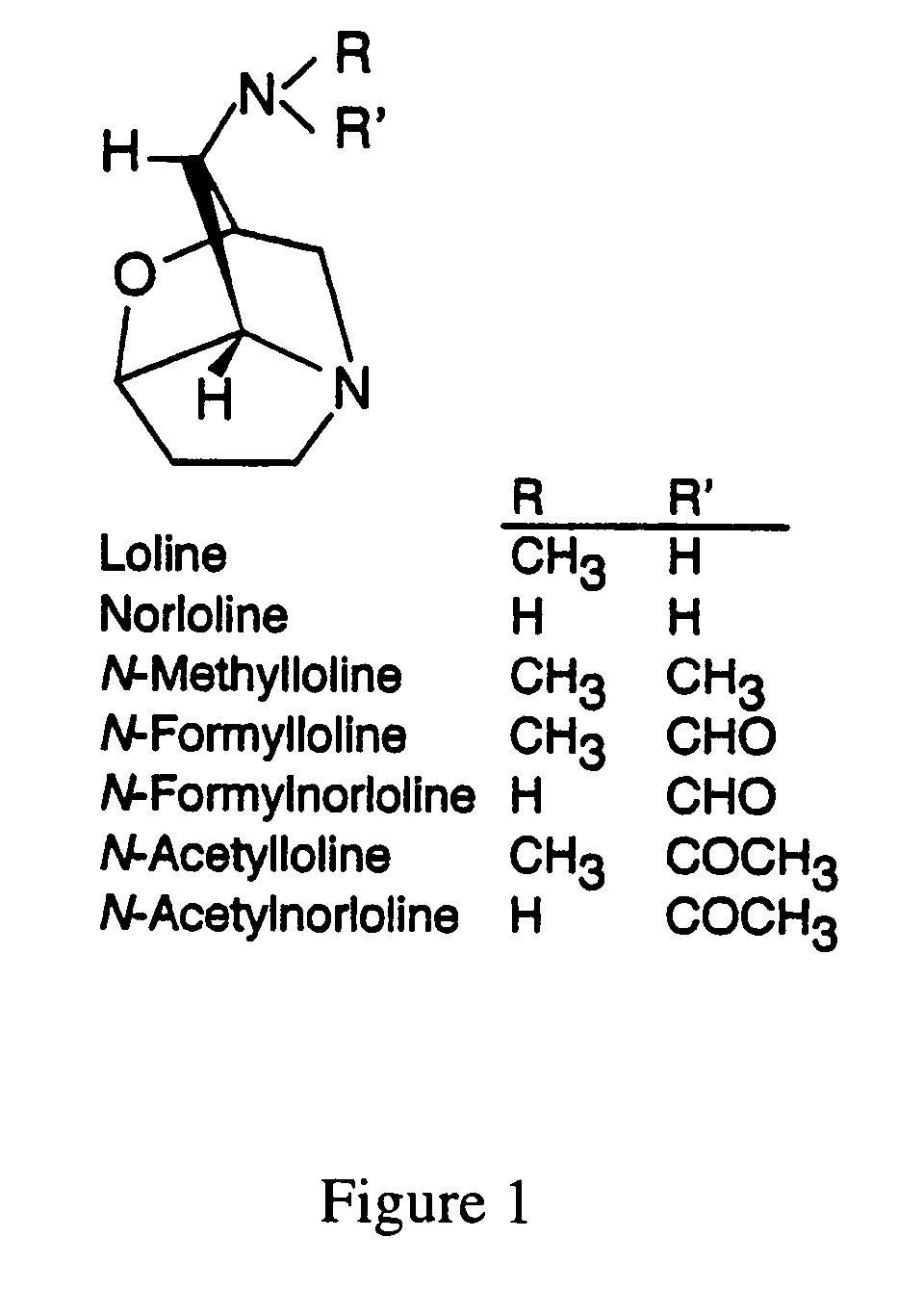
Loline alkaloid gene clusters of the fungal endophyte neotyphodium uncinatum
Loline alkaloids (LA), which are 1-aminopyrrolizidines with an oxygen bridge, are produced by Epichloë (anamorph=Neotyphodium) species, endophytes of grasses. LA are insecticidal, thus helping protect host plants from insect herbivory. Suppression subtractive hybridization PCR was used to isolate transcripts up-regulated during loline alkaloid production in cultures of Neotyphodium uncinatum. Subtracted cDNAs were cloned, and a λ-phage cDNA library from an LA-expressing N. uncinatum culture was screened with subtracted cDNA. In BLAST searches, several cDNAs identified had sequence similarities to aspartate kinases, and another with O-acetylhomoserine-(thiol)lyase. Differential expression of these two genes in LA-producing cultures of N. uncinatum was confirmed, and in a survey of 23 isolates from 21 Neotyphodium and Epichloë species these two genes strictly correlated with LA production. Two nucleic acid molecules encoding two loline alkaloid gene clusters have been identified.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Early light-inductive protein gene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101363024AImprove salt toleranceNormal growthPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
An early stage photoinduction protein gene and a preparation method relate to a protein gene and a preparation method, and solve the problem that the salt tolerance of salt tolerant transgenic plant obtained by the existing salt tolerant gene transformation is poor. The coded area sequence of the early stage photoinduction protein gene of the invention is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The amino acid sequence of the early stage photoinduction protein gene of the invention is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention adopts cDNA library technology and suppression subtractive hybridization technique, and carries out the EST analysis on the library clone; 5 and 3' part sequences of the gene are obtained by screening, and then the early stage photoinduction protein gene is obtained by splicing the 5 and 3' sequences. When the gene obtained by the invention is shifted to model plant tobacco, transgene tobacco can regularly grow on a culture medium containing 0.6% of NaCl, the grow situation and physiological index is obviously good compared with the contrast, and the salt tolerance is improved by over 50%.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Uranium-related gene segments of pokeweed and acquiring method and application
InactiveCN101792769ASolve the problem that pollution is difficult to accurately detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTotal rnaReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses uranium-related gene segments of pokeweed. The method for acquiring the gene segments comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA from root tissues of pokeweed in uranium tailings region and non-polluted contrast region, synthesizing a first chain and a second chain of cDNA by enzymatic reaction reverse transcription, carrying out suppression subtractive hybridization to separate gene segments with specific expression under heavy metal uranium stress, using the gene segments as probes and enabling the gene segments and RNA extracted from pokeweed in detected environment to hybridize, or using sequences of two ends of the gene segments with specific expression as primers to carry out reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to detect the cDNA of pokeweed in the detected environment. In the invention, gene with specific expression induced by uranium in pokeweed is used as a probe to detect uranium pollution, solving the problem of inaccurate detection of uranium pollution in surrounding environment of uranium-polluted areas.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Plant nutrition storage protein (GmVSPB) gene
A plant nutrition storage protein (GmVSPB) gene belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and is characterized in that soybean Dongnong50 cotyledonary node is used as a material in suppression subtractive hybridization of differential gene when induced by cytokinin 6-BA so as to obtain a regeneration-associated gene and carry out gene cloning; a plant is transformed by agrobacterium-mediated transformation, changes of the transgenic plant are observed, gene functions are preliminarily analyzed by a quantitative RT-PCR method, and the influence of the cytokinin on regeneration is researched; starting from the influence of cotyledonary node organogenesis regeneration binding hormone on expression of soybean regeneration pathway associated transcription factor gene, effects of regenerating gene in a regeneration system are analyzed, and a soybean plant nutrition storage protein (GmVSPB) gene (Seq ID No:1) is found out.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel milchgoat multiparous and monotocous ovary differential expression associated gene, screening method thereof, identification method thereof and functional analysis method thereof
InactiveCN101967484AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSubtractive Hybridization TechniquesOvarian tissue
The invention discloses a novel milchgoat multiparous and monotocous ovary differential expression gene, and a screening method thereof, an identification method thereof and a functional analysis method thereof. Xinong Saanen milchgoats are taken as experimental materials, the forward and reverse subtracted cDNA library of ovarian tissue in a milchgoat multiparous (3 goats) and monotocous anestrus is constructed by using suppression subtractive hybridization technology, differential expression gene fragments are screened, the differential expression gene is verified by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the gene structure and potential function are analyzed by bioinformatics.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Gene for expressing antibacterial peptide, antibacterial peptide and application
ActiveCN108300721AHas antibacterial activityHas bacteriolytic activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiNucleotide
The nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 is found in European eel for the first time, and antibacterial peptide with bacteriostatic activity is obtained through genetic engineering. Experiments prove that the antibacterial peptide can effectively inhibit the activity of staphylococcus aureus; the antibacterial function is realized. The inventor builds a suppression subtractive hybridization libraryof difference expression genes in tissues before and after the European eel infected with ibrio vulnificus by a suppression subtractive hybridization technology. From the library, people find that theoccurrence frequency of the gene is high; through bacteriostasis experiments, the condition that the gene has a pathogenic bacterium inhibition effect is found; the gene can be used as an antibioticsubstitute for controlling the pathogenic bacterium growth. The inventor expresses the gene through the genetic engineering; after the treatments of purification, GST label removing and the like are performed on the product, the effect that an extract has bacteriolysis activity is found.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Novel serine-threonine kinase gene
A novel gene having the consensus sequence of a serine-threonine kinase active site has been isolated by the suppression subtractive hybridization method which comprised of preparing a library of genes expressed specifically in fetal livers and isolating clones from this library at random. This gene presumably participates in cell growth control because it is highly expressed, especially in actively growing cells, and exhibits a significant homology with a vaccinia virus B1R kinase gene. Thus, it can be utilized as a target for developing cell growth inhibitors or antitumor agents.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Plant high-pH saline-alkaline tolerance gene SucHP and application thereof
InactiveCN102002505BImprove salt and alkali resistanceHigh resistance to high pH saline alkaliPlant peptidesFermentationHigh densityNormal growth
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Preparation method and applications of cDNA chip for detecting drug resistance level of bactrocera dorsalis resistant to trichlorphon and beta-cypermethrin
ActiveCN103614473BDelay drug resistanceMonitor resistance developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologySubtraction hybridization
The invention discloses a cDNA chip for detecting the resistance level of Bactrocera dorsalis against trichlorfon and beta-cypermethrin, a production method and application thereof. The present invention utilizes the forward suppressive subtractive hybridization (suppression subtractive hybridization, SSH) method to respectively obtain different resistant strains of Bacteralis dorsalis drug resistance-specific up-regulated expression gene fragments, and then PCR amplifies each drug resistance-related specific expression gene, purifies and recovers 118 specific gene fragments related to resistance to trichlorfon of Bactrocera dorsalis and 103 specific gene fragments related to resistance to beta-cypermethrin of Bactrocera dorsalis were obtained. Using the above-mentioned specific resistance target gene fragments as DNA probes, a cDNA chip for the detection of Bacteralis dorsalis resistance to trichlorfon and beta-cypermethrin was constructed. The cDNA chip of the invention can simply and effectively realize the real-time monitoring of the drug resistance level of Bactrocera dorsalis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Full length cDNA homogenizing subtractive hybridization method
InactiveCN101311266BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceFull length cdna
The invention provides a method for homogenization subtractive hybridization of full length cDNA. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) synthesizing a first chain cDNA; (2) synthesizing a double chain cDNA; (3) selective connection and primer extension; (4) subtractive hybridization; (5) PCR augmentation of cDNA of differential expression; wherein, the PCR products of the subtractive hybridization can be directly cloned to a vector so as to construct cDNA libraries, where differentially expressed genes are concentrated; the libraries can be utilized to analyze gene expression, prepare gene chips and be marked as probe which selects the differentially expressed genes from the existing libraries; in addition, if the subtractive efficiency is not high enough, the subtractive hybridization can repeat for the PCR products of subtractive hybridization to improve the homogenization and the subtractive efficiency. The method for homogenization subtractive hybridization of the full length cDNA (FNSH) creates the beneficial effects of high subtractive efficiency of differential genes, high efficiency of enriching differential expressed genes, high homogenization and gainof the full length cDNA.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for screening natural antisense transcripts related to human tumor
InactiveCN102827844BEfficient screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSequence analysisHuman tumor
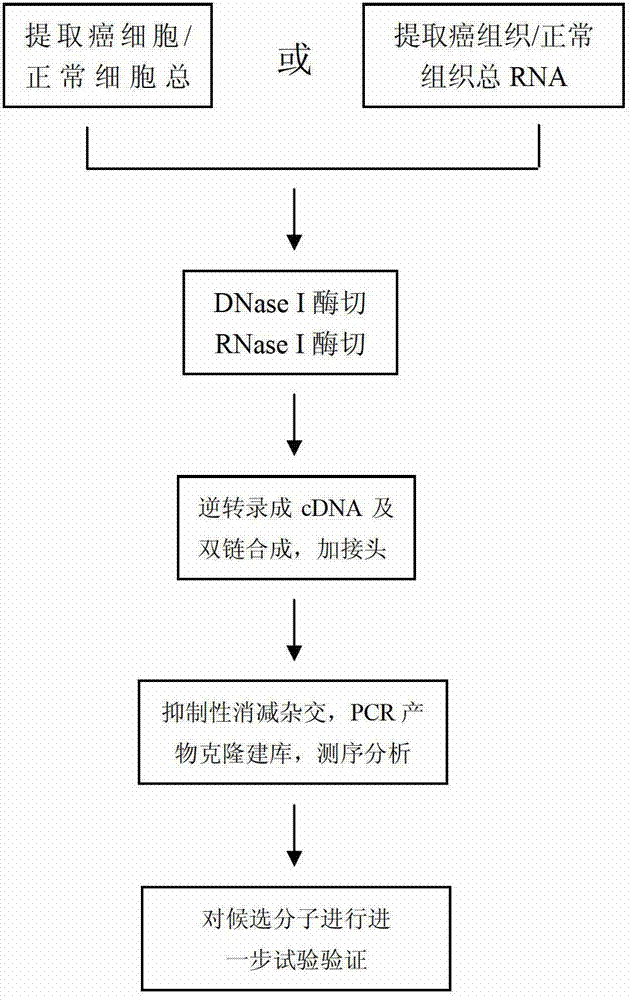
The invention provides a method for screening natural antisense transcripts related to the human tumor. The method comprises the following steps: extracting cancer cell / normal cell total RNA (ribonucleic acid); performing DNase I enzyme cutting and RNase I enzyme cutting; performing reverse transcription to obtain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), performing double-chain synthesis, and adding linkers; performing suppression subtractive hybridization, cloning the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product to establish a library, and performing sequencing analysis; and further performing experimental verification to candidate molecules and the like. After the method is applied and verified in normal cells and tumor cells, the method is proven to screen the natural antisense transcripts related to human tumor systematacially and rapidly.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Soybean purple acid phosphatase gmpap36, its coding gene and application
The invention provides soybean purple acid phosphatase GmPAP36 and an encoding gene and application thereof. A low-phosphorous induction soybean root system cDNA subtractive library is established based on the suppression subtractive hybridization technique, low-phosphorous stress inducible expression acid phosphatase candidate EST is selected from the subtractive library, and on this basis, an acid phosphatase candidate gene sequence is cloned and the expression difference of a candidate gene under the phytate phosphorus processing condition is analyzed with the real-time quantitative PCR technique; a gene prokaryotic expression vector is established to achieve gene prokaryotic expression; meanwhile, a gene eukaryotic expression vector is established, arabidopsis and soybean conversion is conducted to obtain transgenosis positive plants, the biological function of the gene GmPAP36 is analyzed, and functional genes are provided for efficient transgenosis breeding of plant phosphorus.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
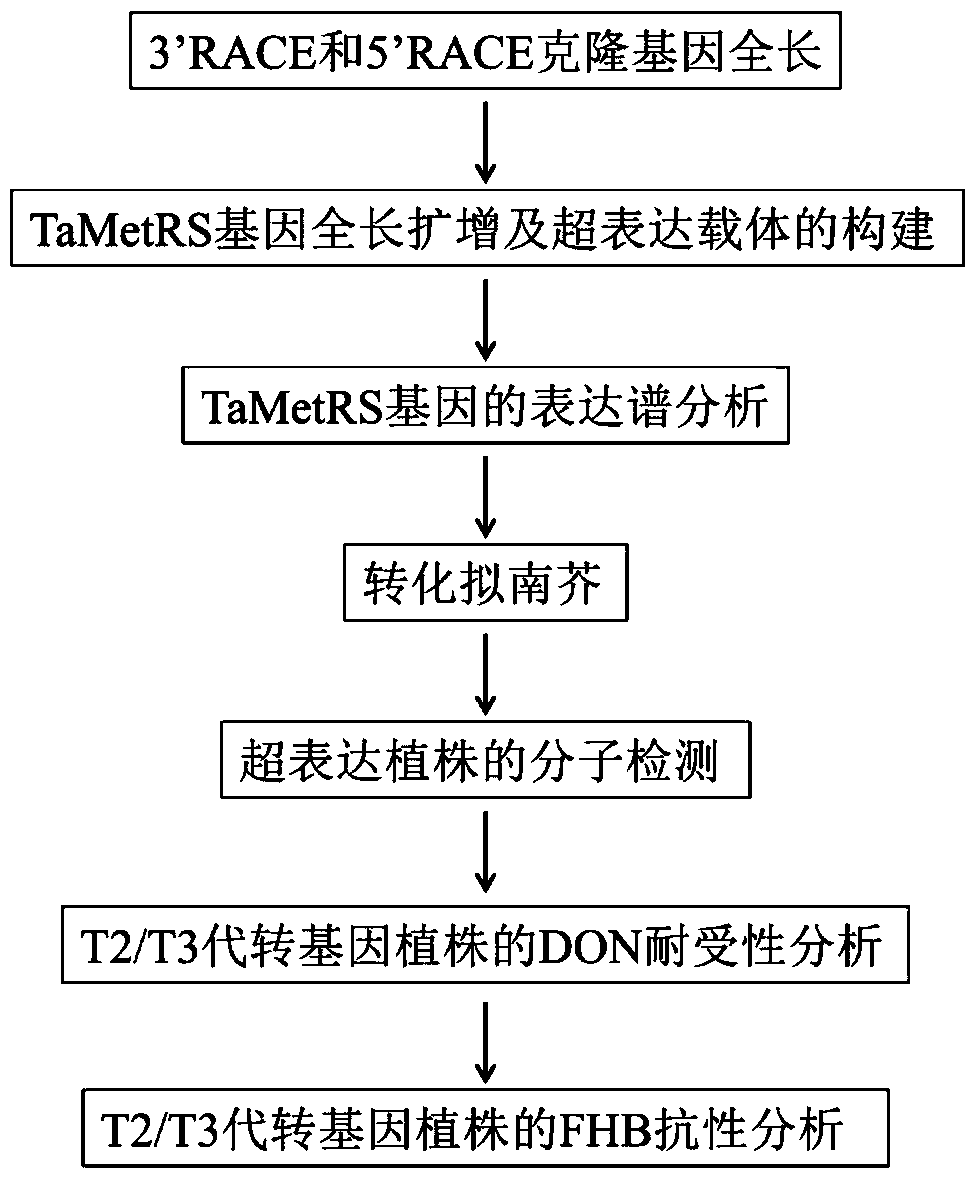
Using wheat genes to improve don and fhb resistance in Arabidopsis
ActiveCN106834337BImprove toleranceIncrease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and in particular relates to improvement of DON (deoxynivalenol) resistance and FHB (fusarium head blight) resistance of arabidopsis by utilizing wheat genes. A gene TaMetRS which is capable of improving DON resistance and gibberellic disease resistance of arabidopsis can be obtained through separation. By utilizing a method of screening a wheat suspension cell suppression subtractive hybridization cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) library and full length of RACE (rapid-amplification of complementary deoxyribonucleic acid ends) clone genes, a gene TaMetRS which is not induced by DON can be separated from a wheat variety. By utiizing an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated genetic transformation method, the gene is excessively expressed in arabidopsis, the resistance of the transgenic arabidopsis to the DON and the gibberellic diseases can be improved, and tests demonstrate novel application of the gene with a plant gibberellic disease resistance function. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is a sequence corresponding to a base at a site 1-2186 in SEQID NO:1, and 596 amino acids are encoded. The protein sequence encoded by the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers and application thereof
InactiveCN102676515BGood repeatabilityStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTriticeaeProtein translocation
The invention belongs to the field of crop genetic breeding, in particular 36 Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers. The 36 genome-specific molecular markers are obtained by the following steps: according to a nucleotide sequence of 18srRNA gene disclosed by National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI), designing primers in the sequence between two RsaI loci, removing homologous sequences between two genome DNA by using a suppression subtractive hybridization technology, enriching differential sequences, obtaining Lophopyrum elongatum specific DNA segments, sequencing the DNA segments, and redesigning primers according to sequences without homology with wheat. The markers can be used for identifying translocation lines in the process of transferring chromosome segments from Lophopyrum elongatum to wheat, can be used for linkage analysis of scab-resistant gene, and can serve as specific molecular markers for identifying chromatin of the Lophopyrum elongatum to be applied to scab-resistant and stress-resistant breeding of wheat.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com