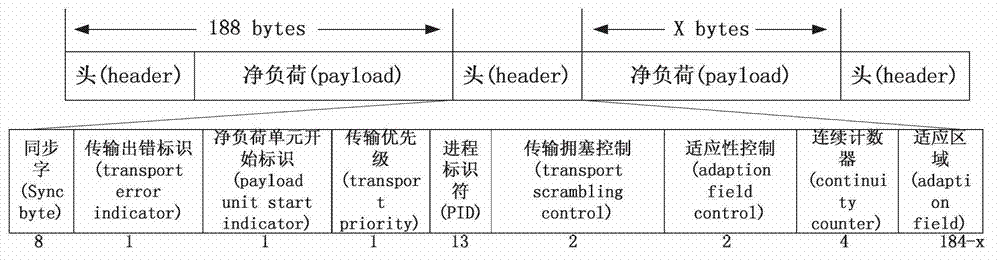
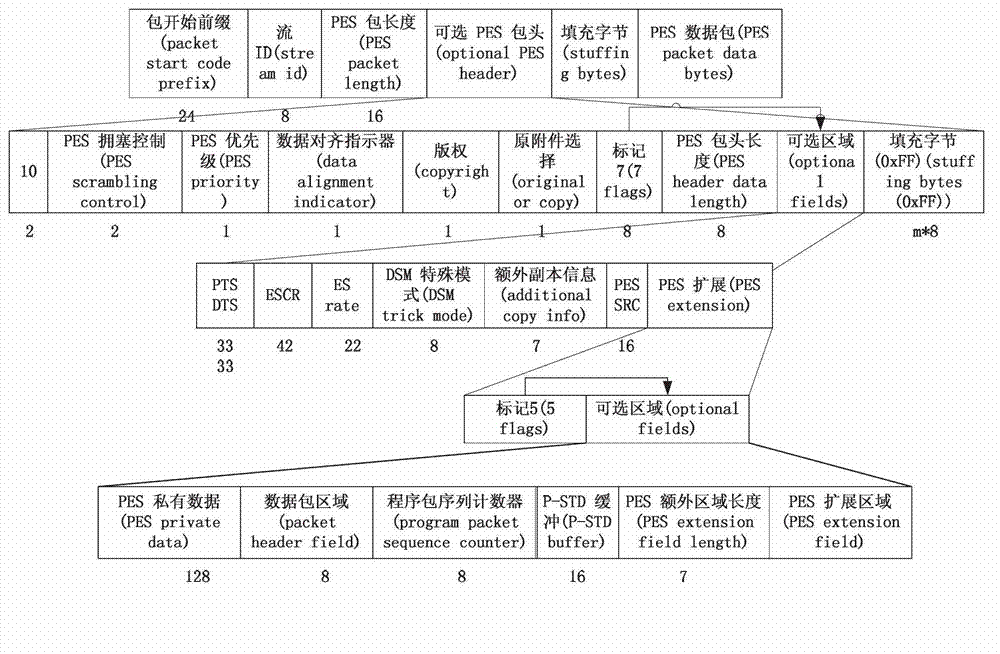
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
284 results about "Source-synchronous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
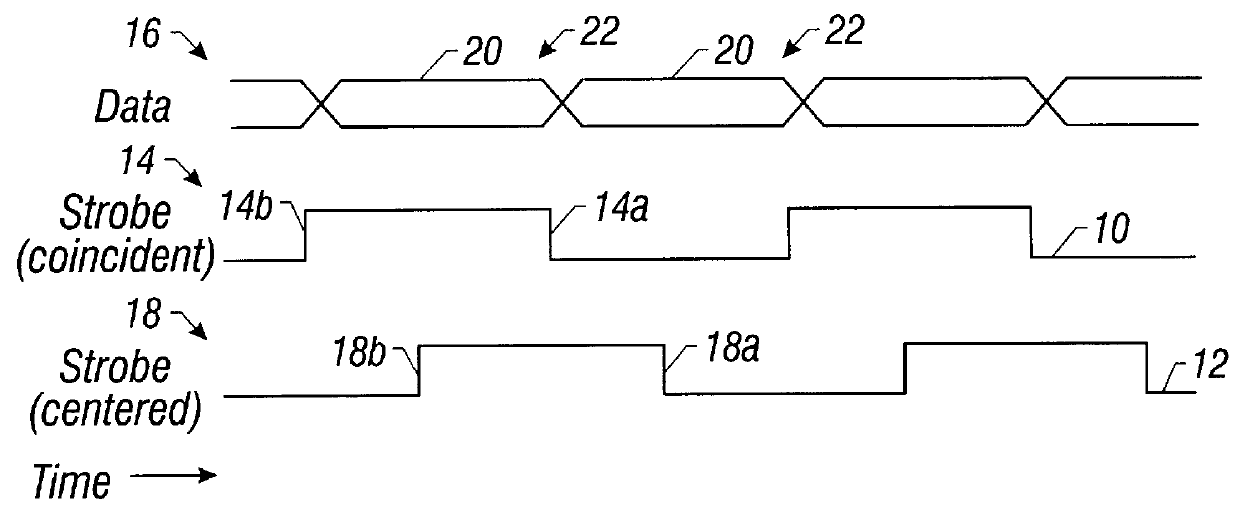
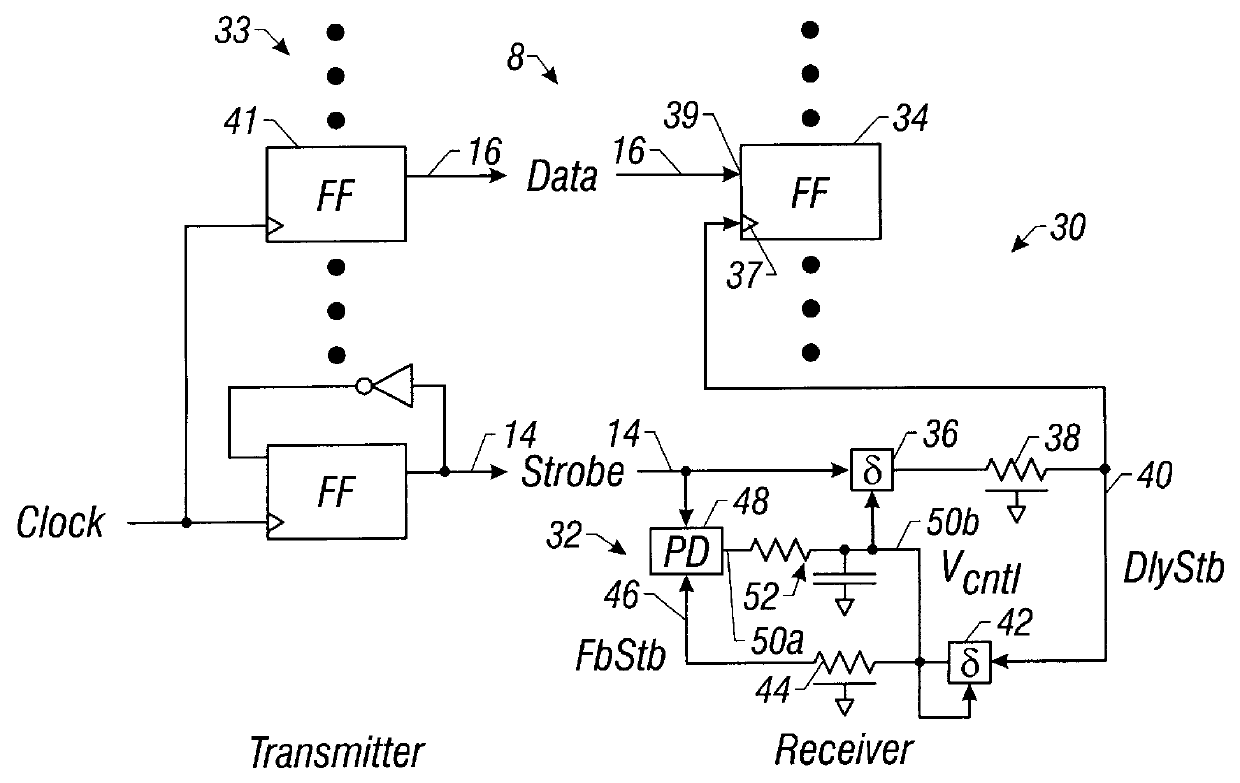
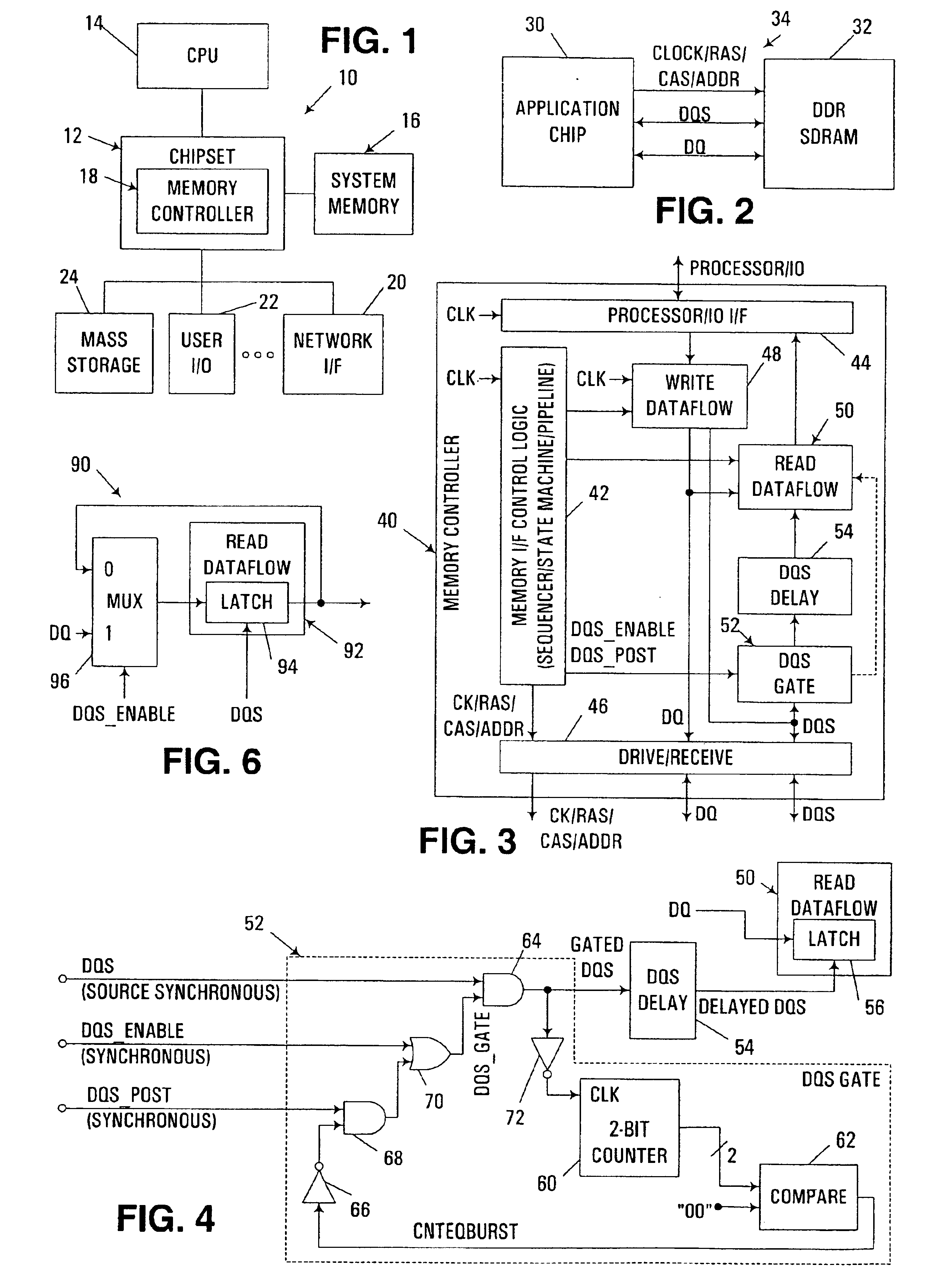
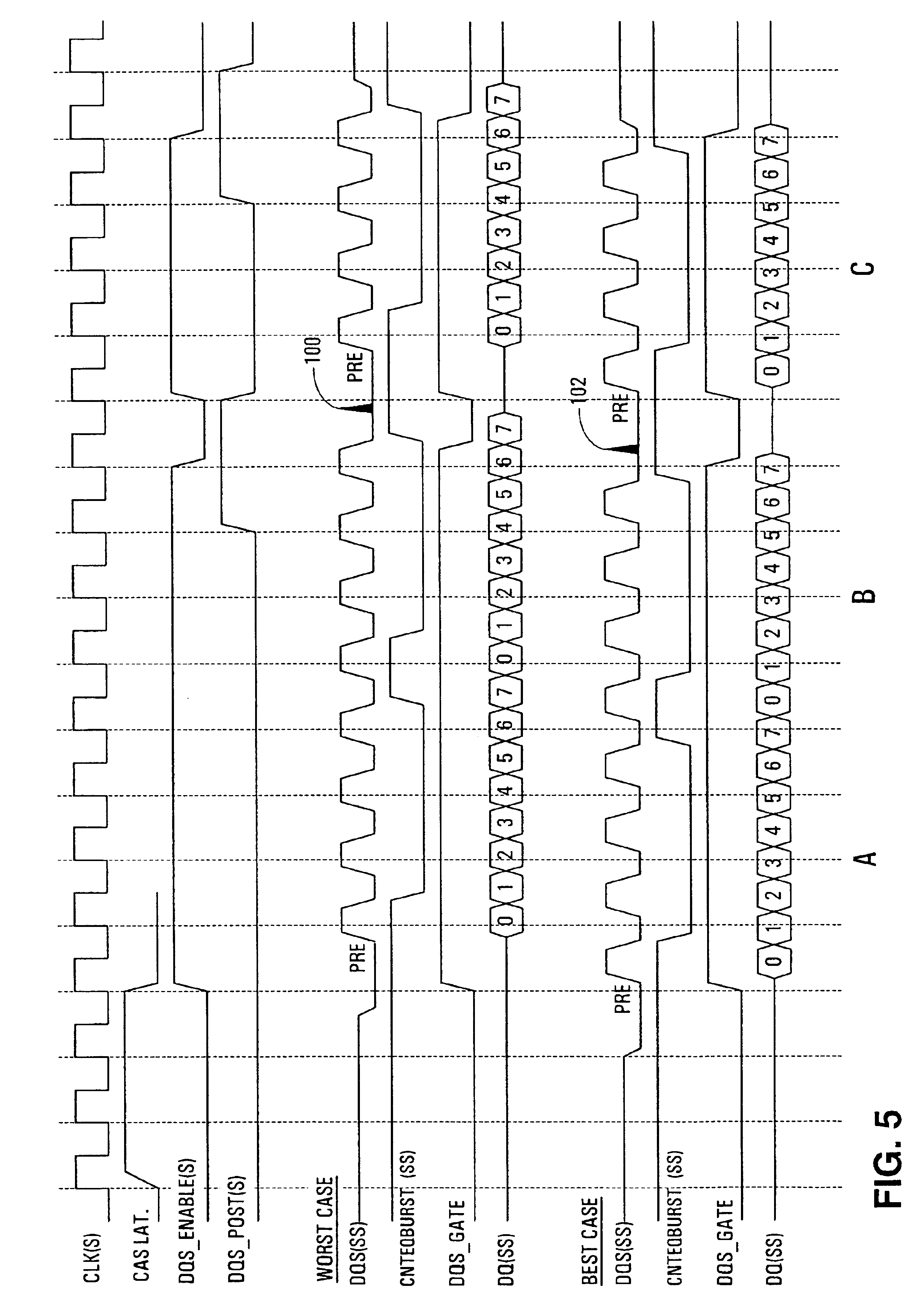
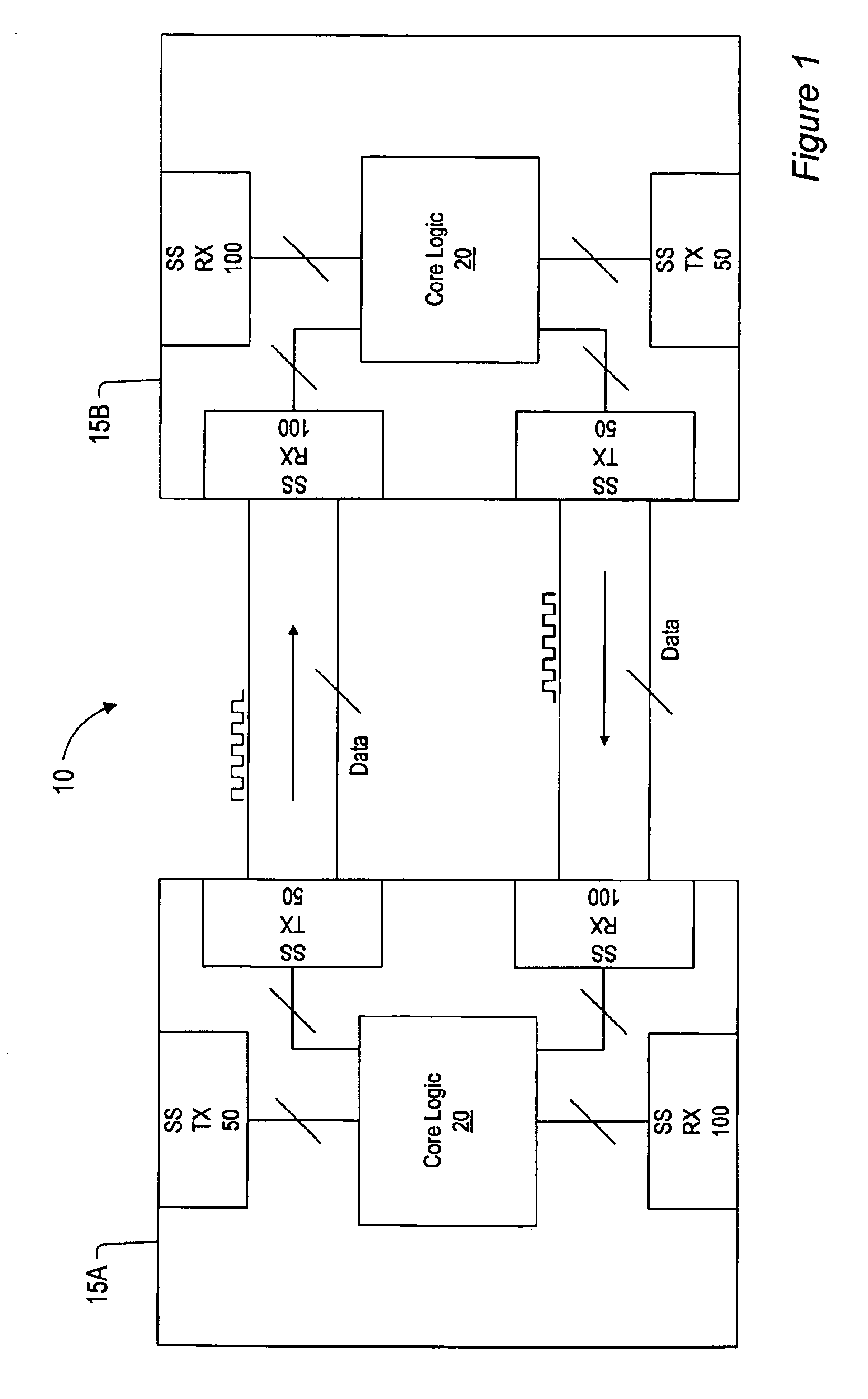
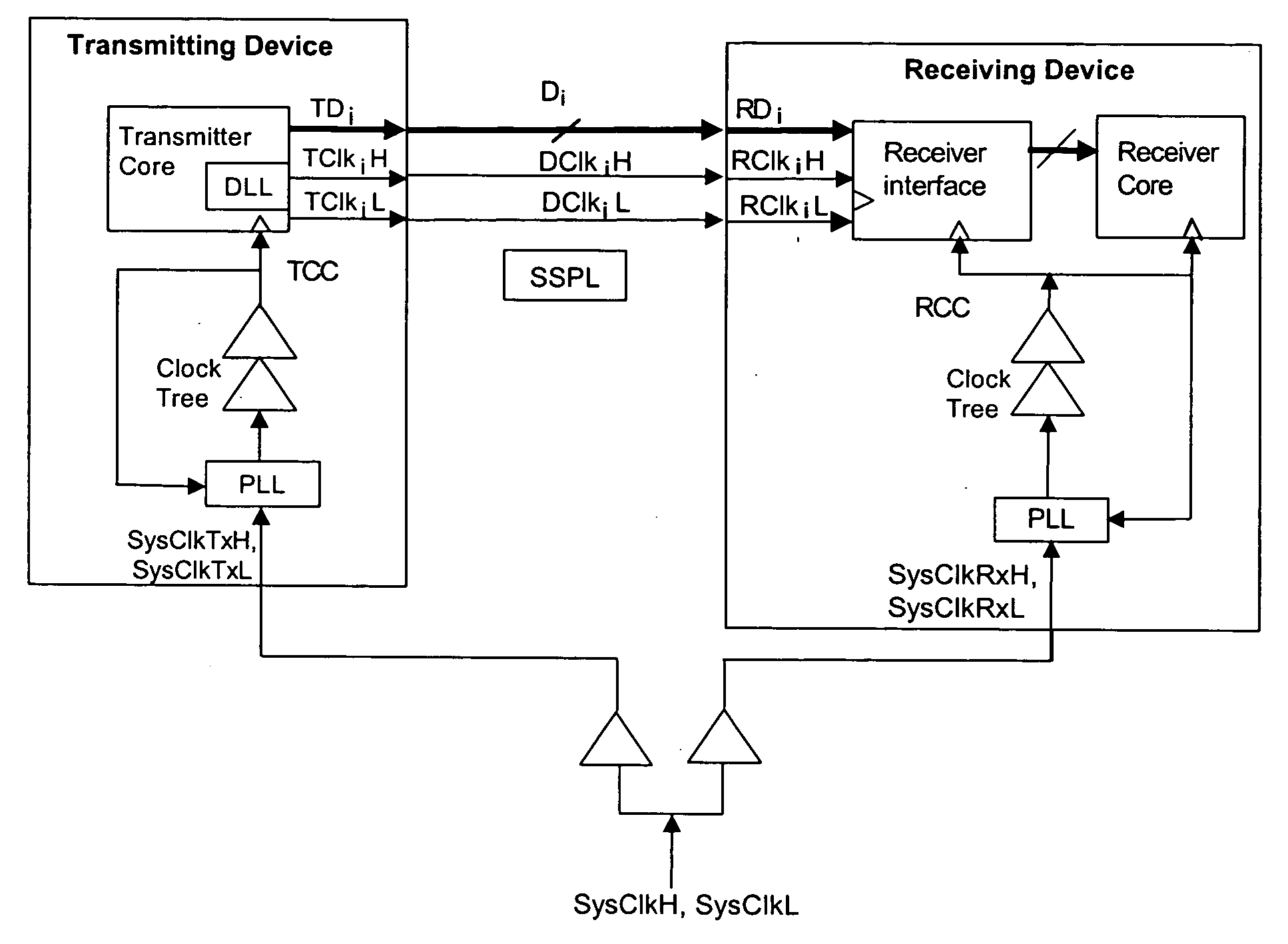
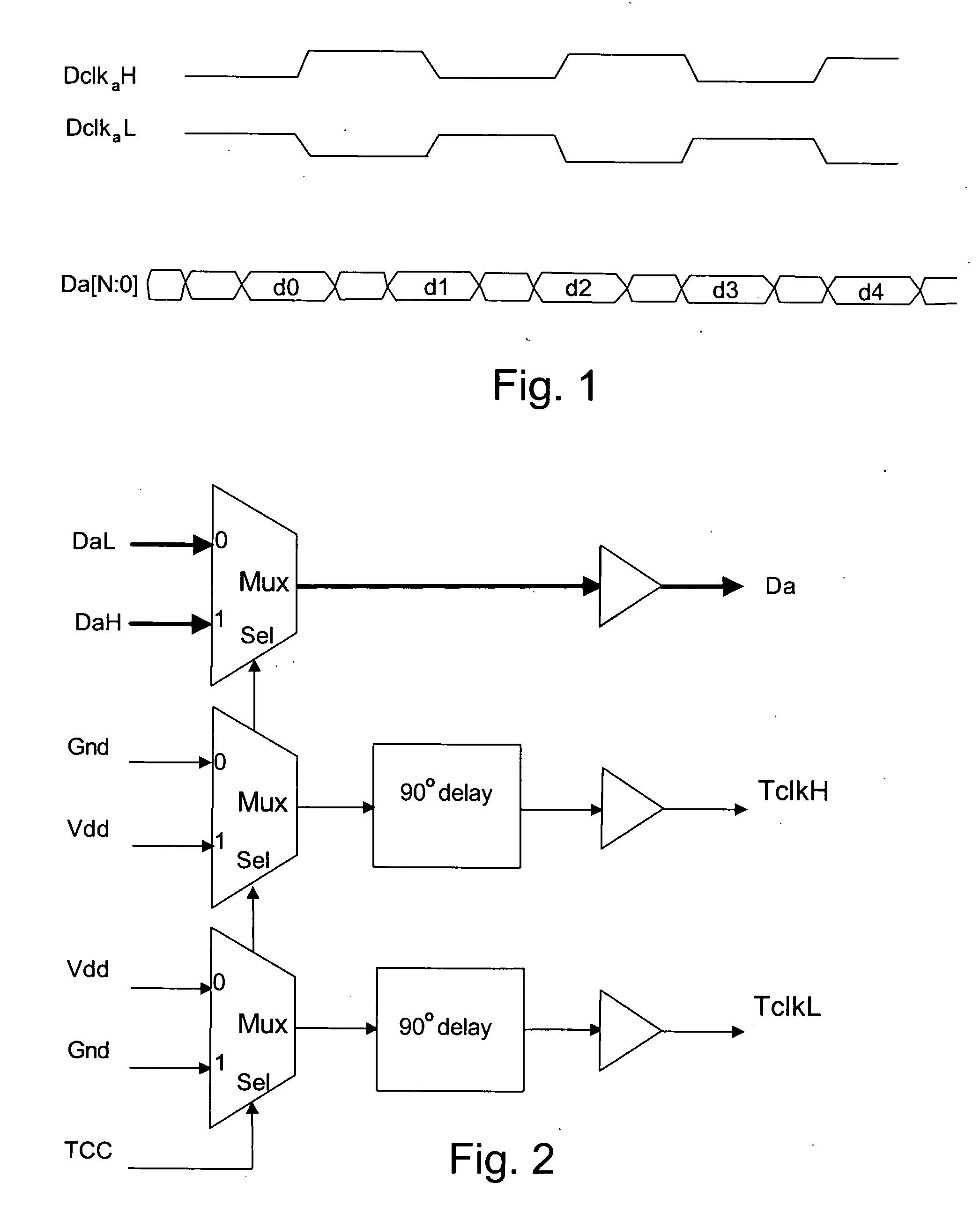
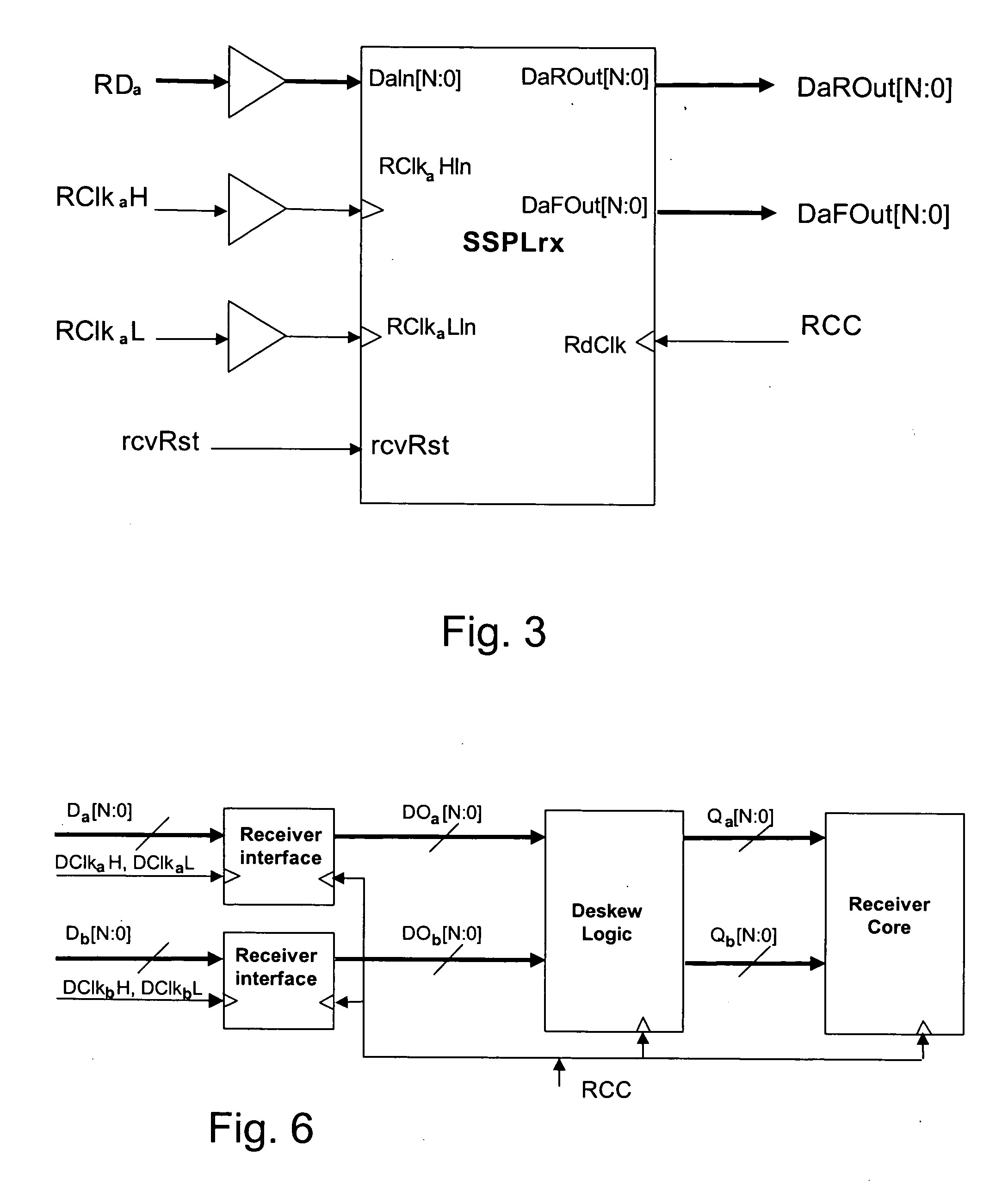
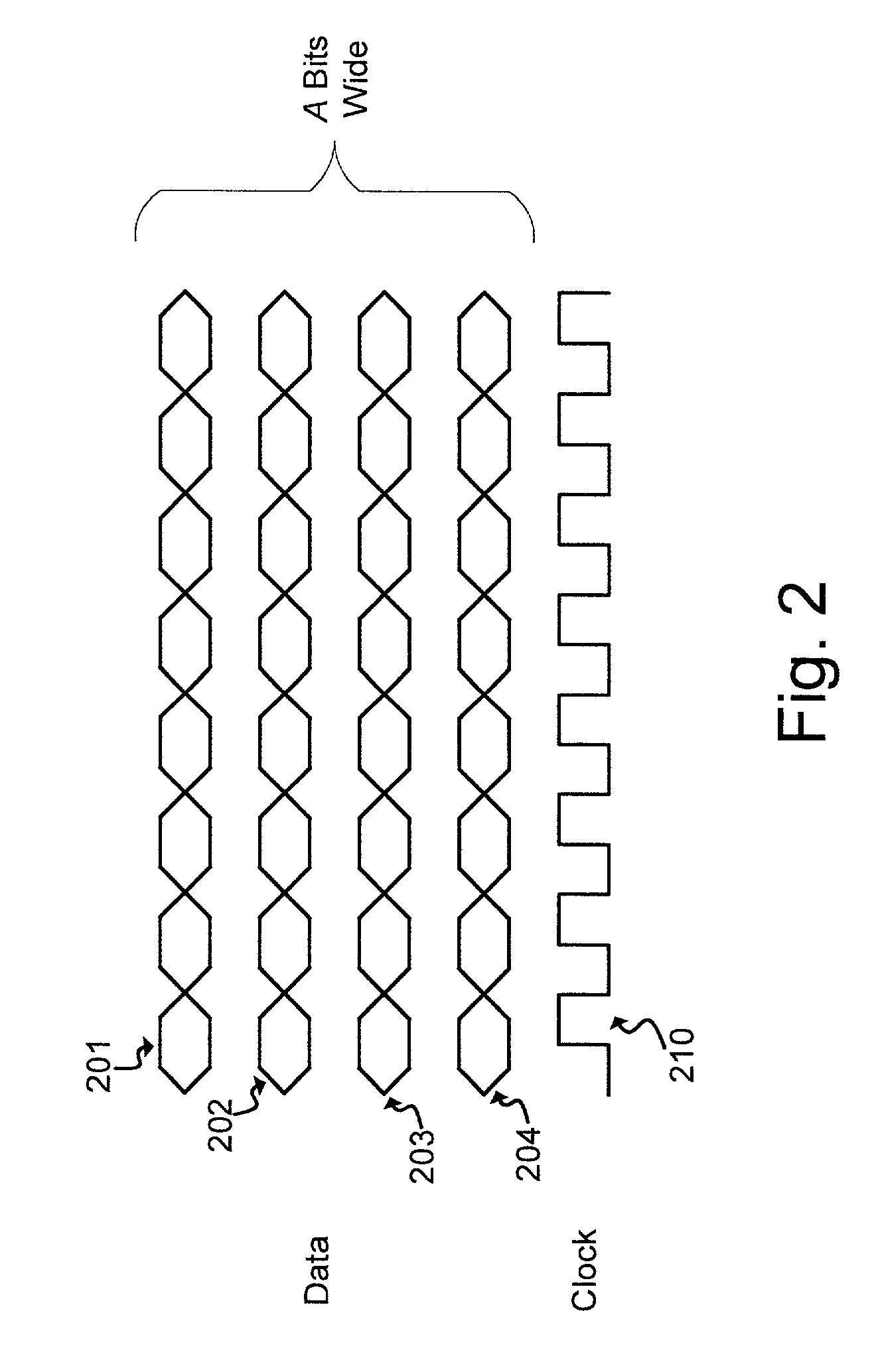
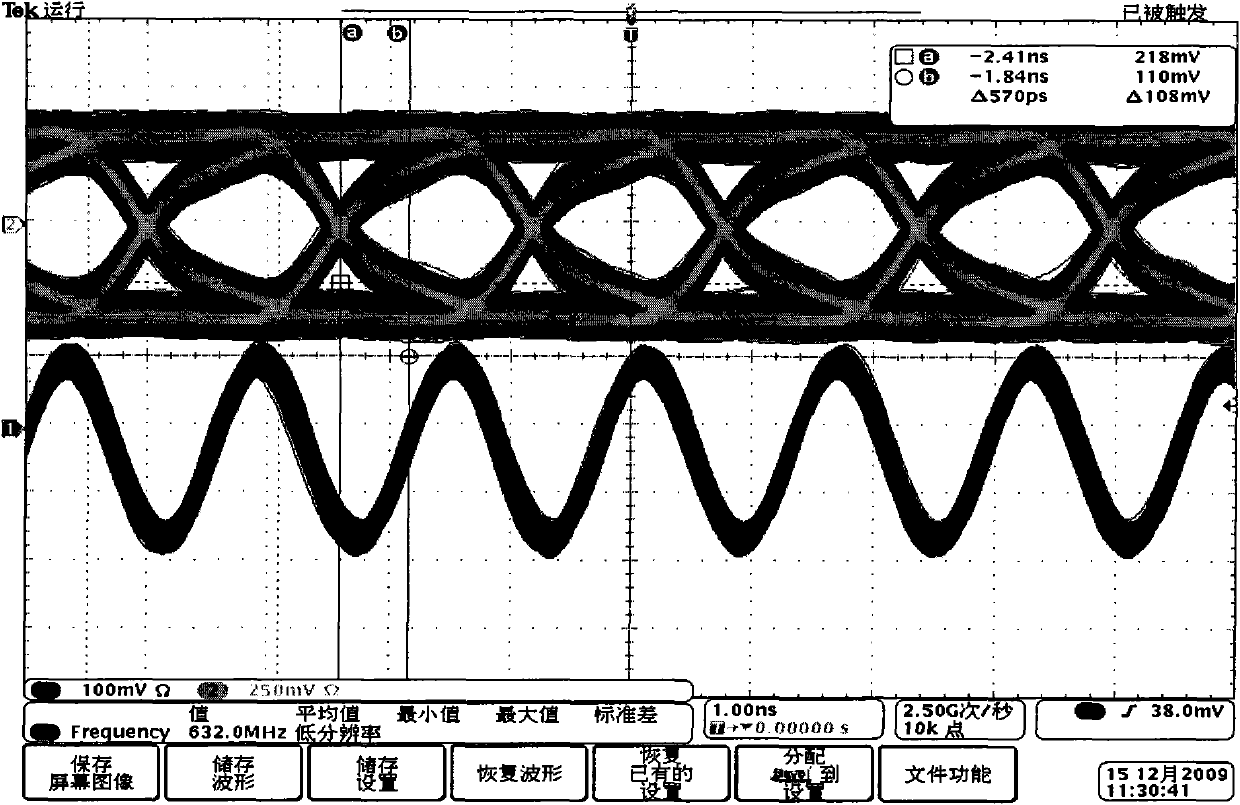
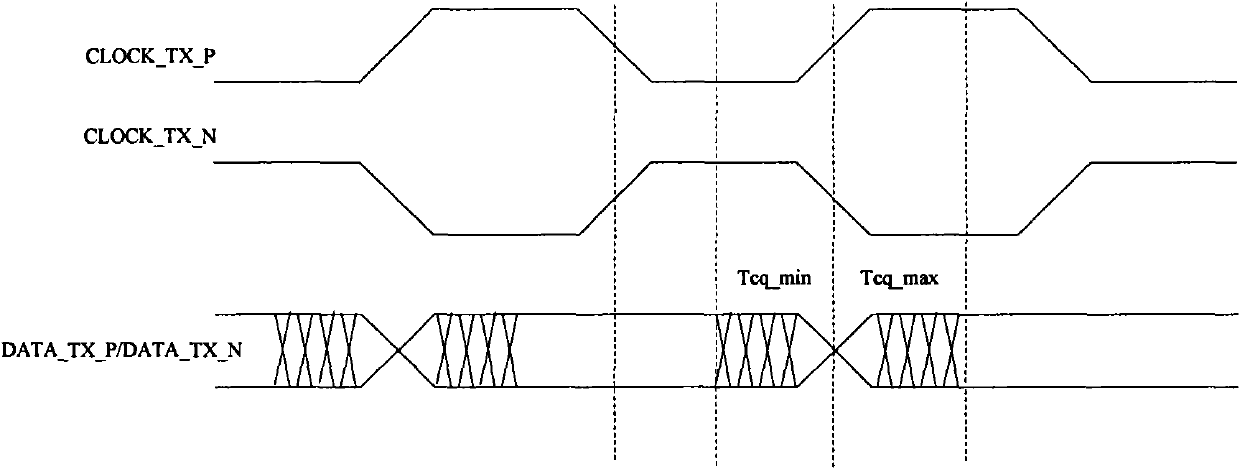
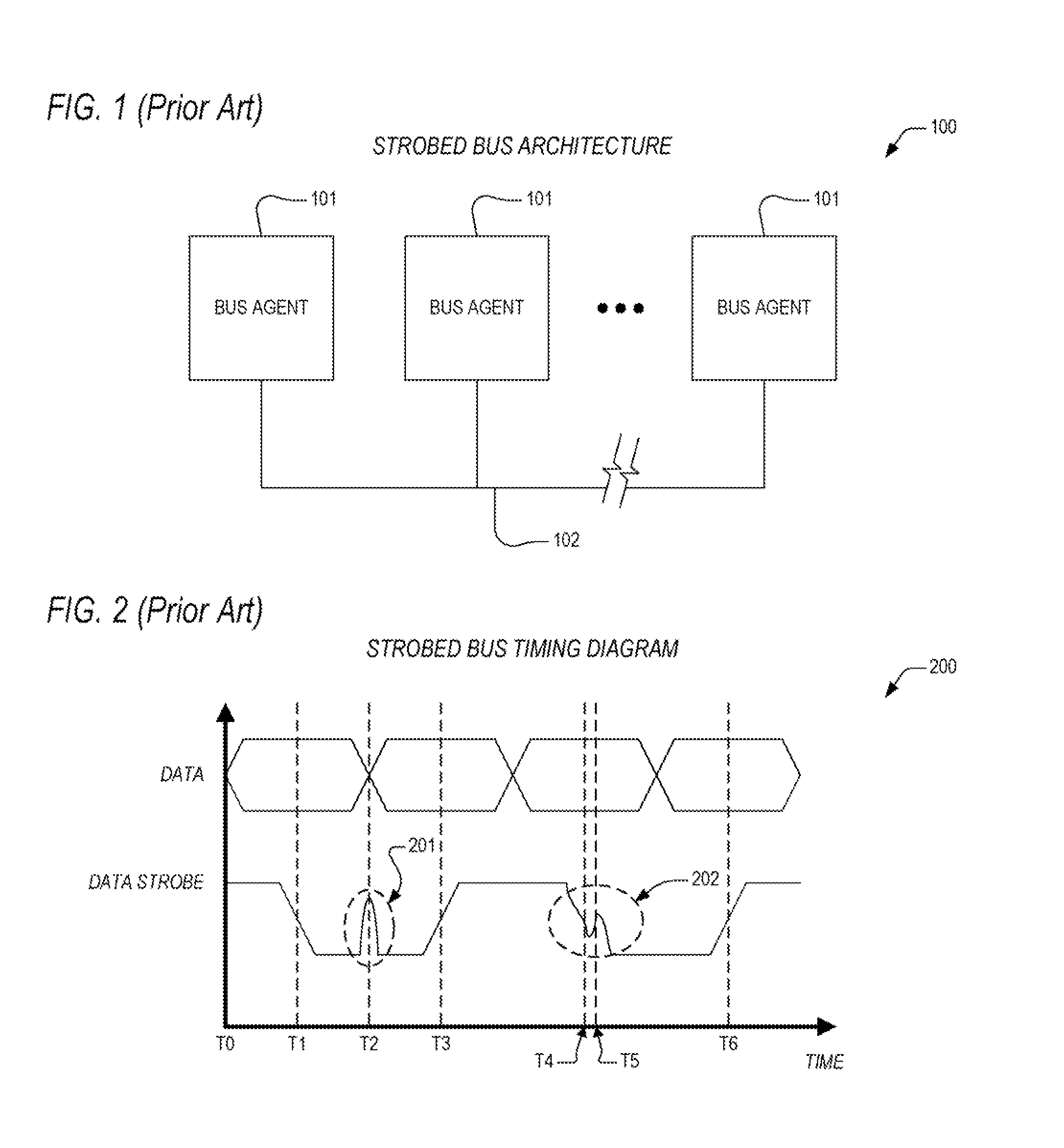
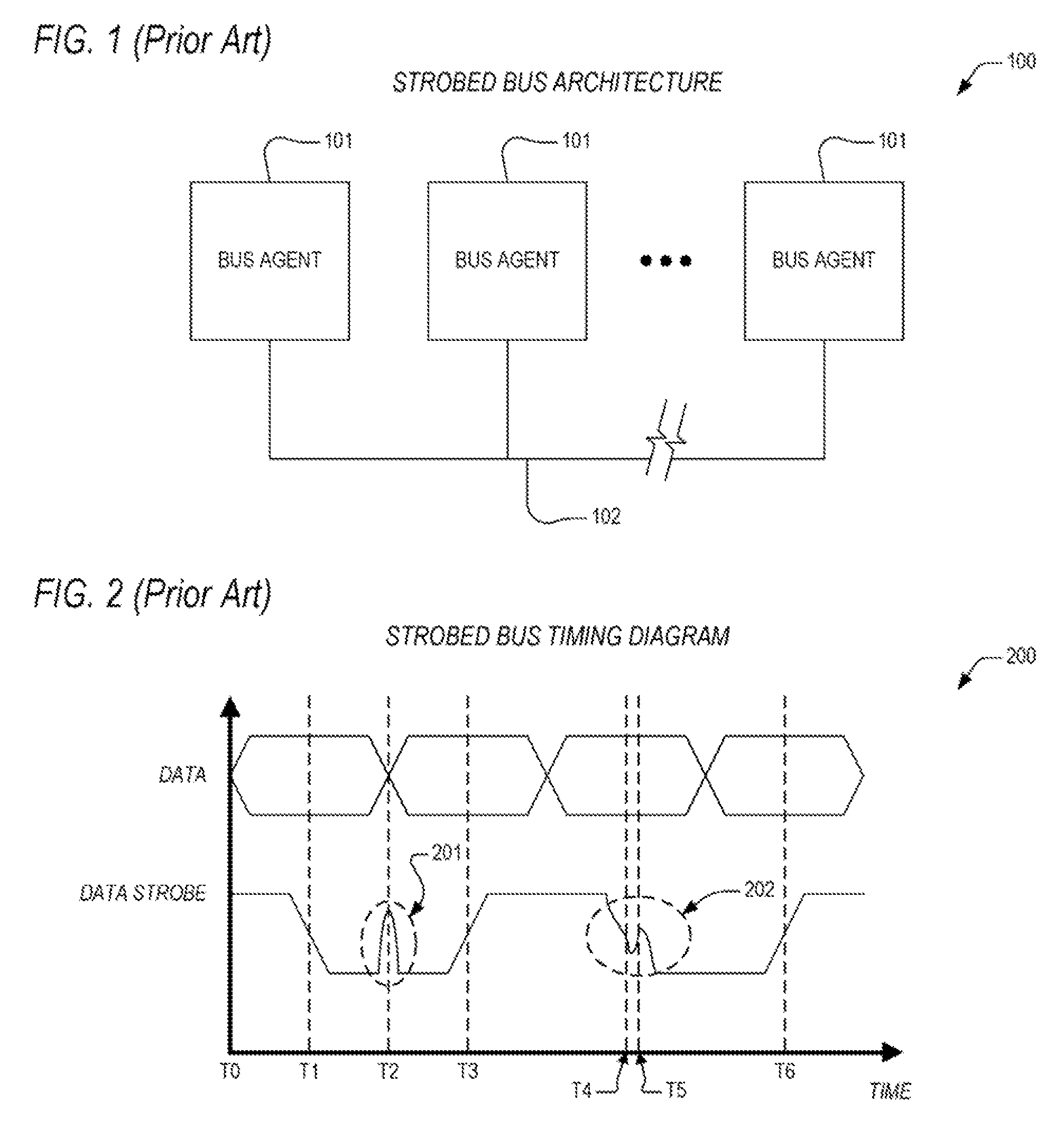
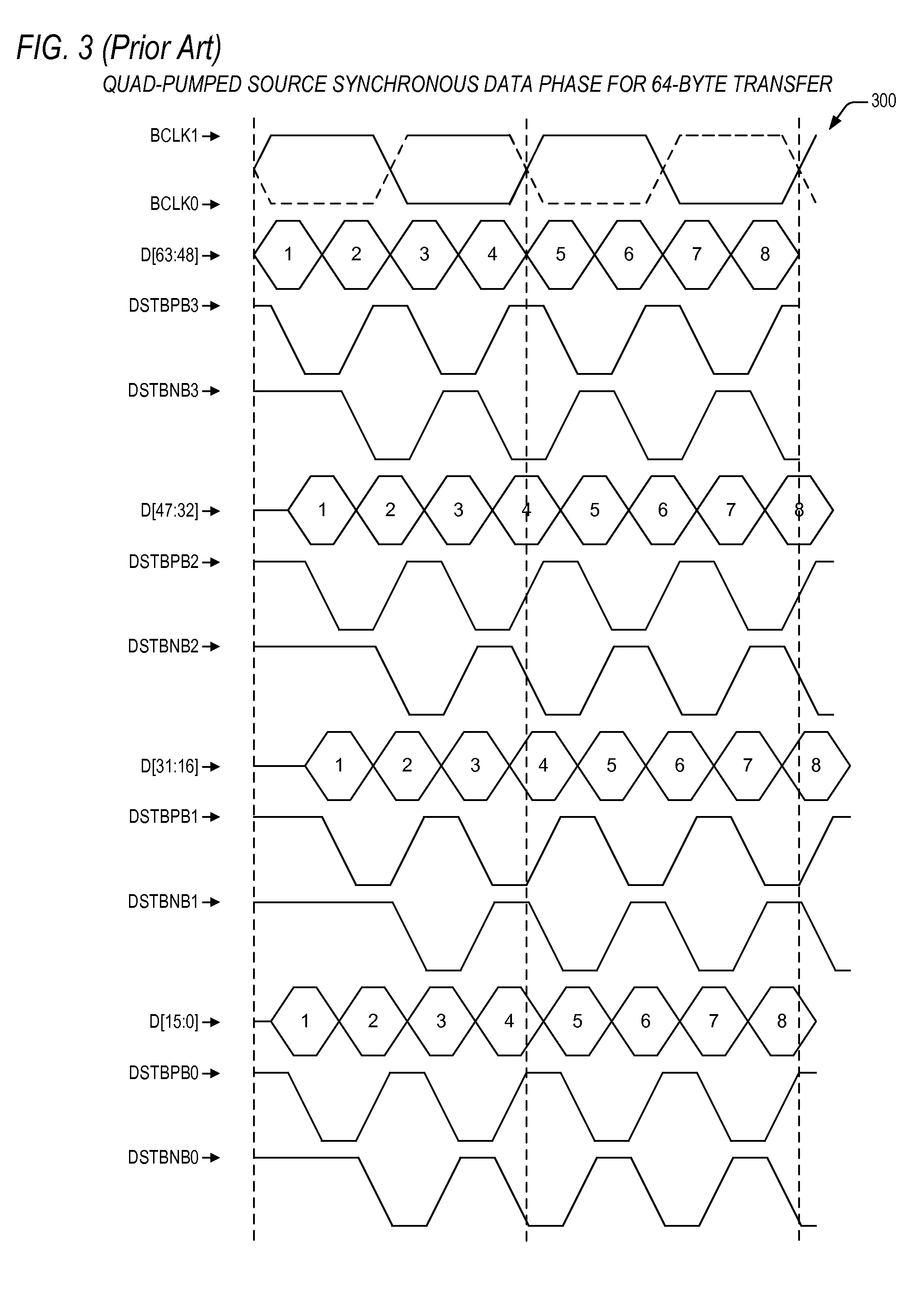
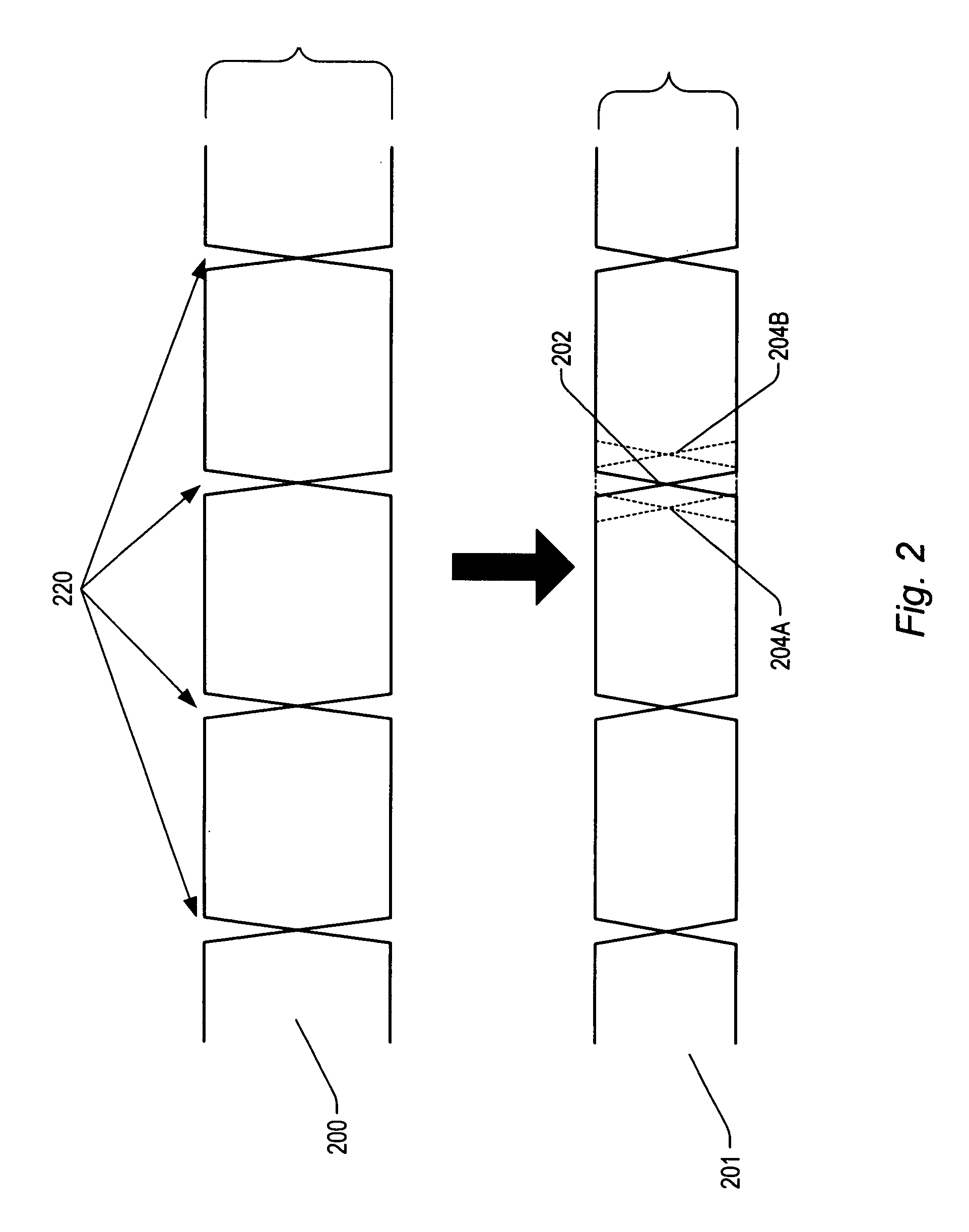
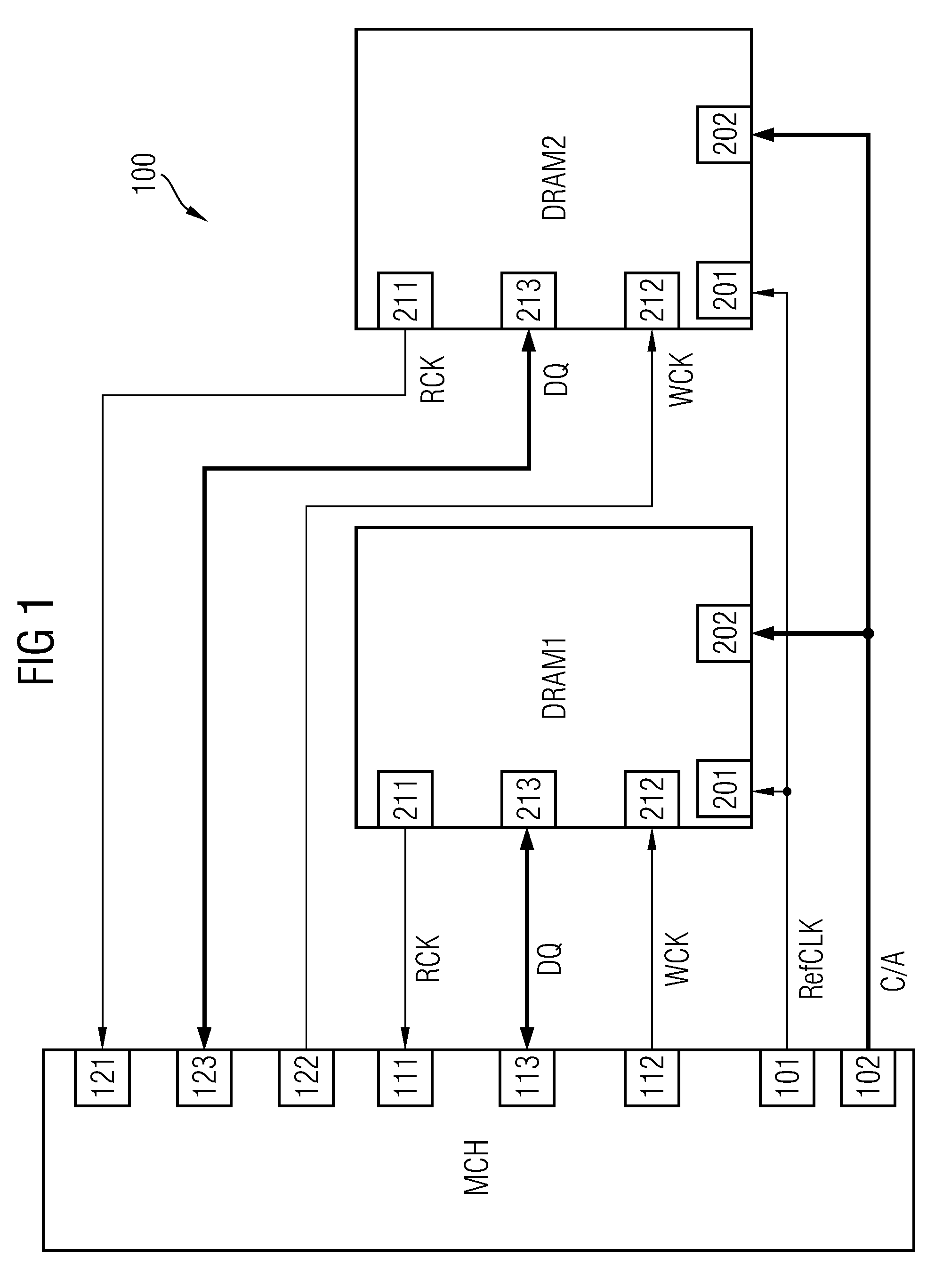
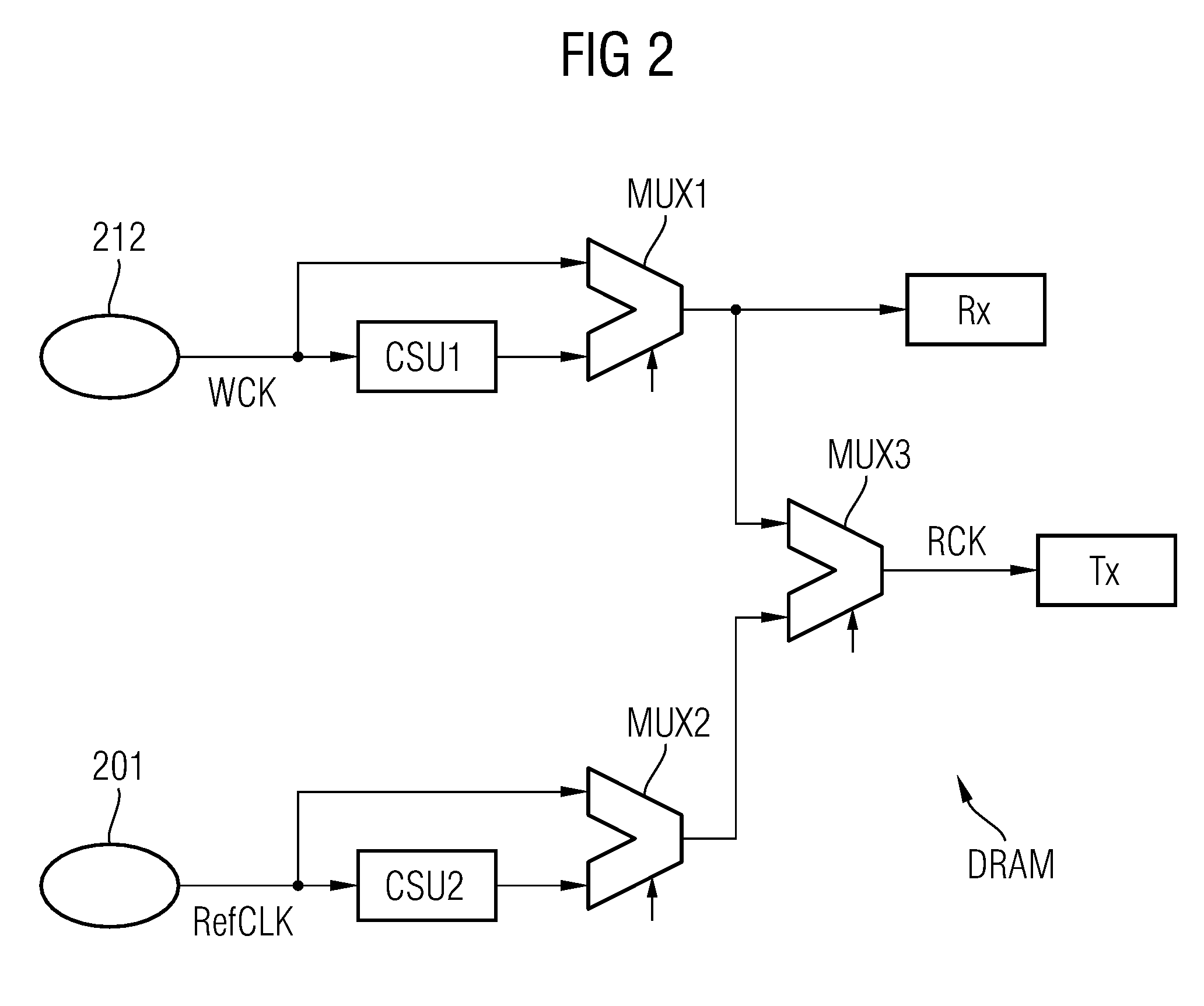
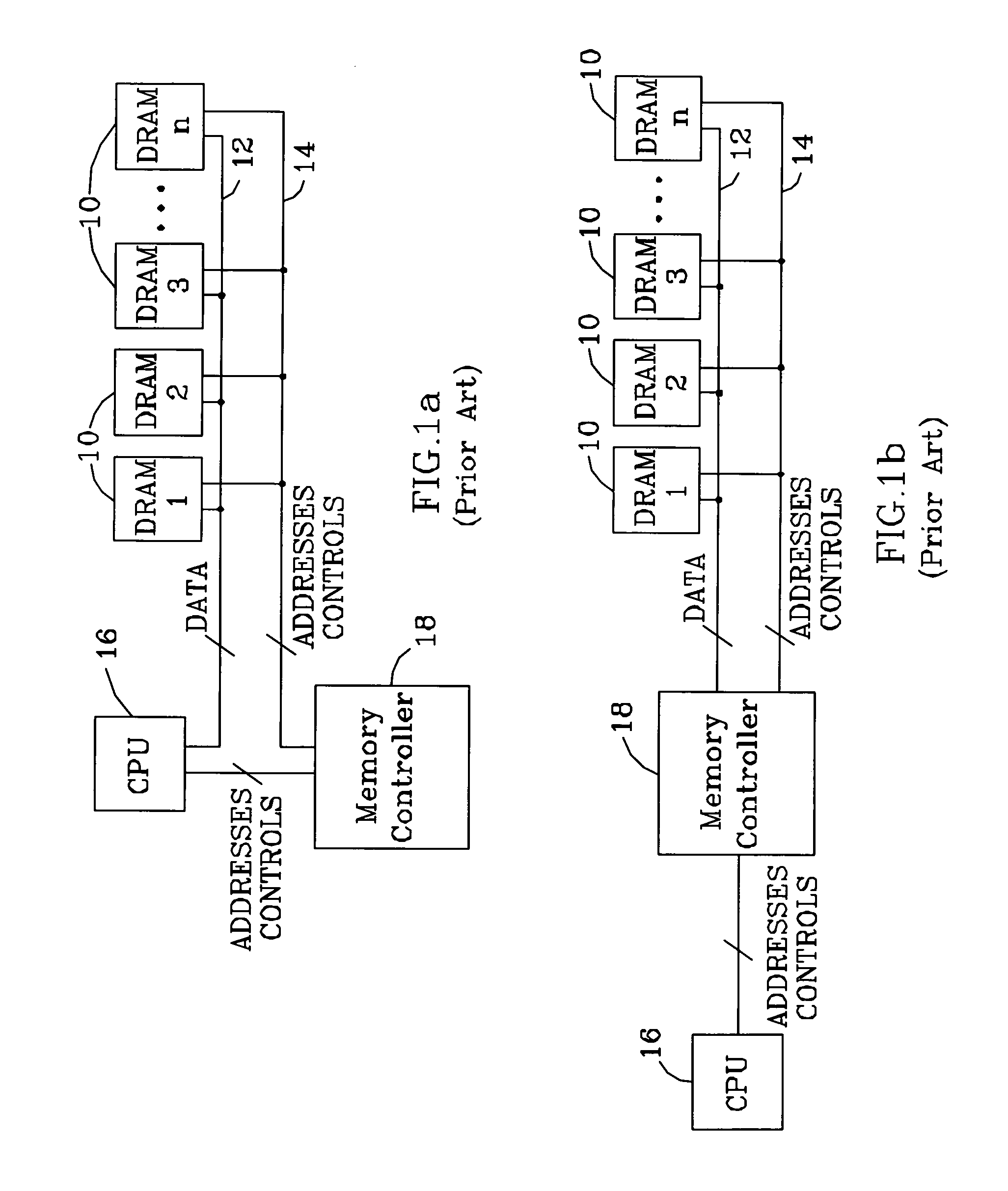
Source-Synchronous clocking refers to a technique used for timing symbols on a digital interface. Specifically, it refers to the technique of having the transmitting device send a clock signal along with the data signals. The timing of the unidirectional data signals is referenced to the clock (often called the strobe) sourced by the same device that generates those signals, and not to a global clock (i.e. generated by a bus master). Compared to other digital clocking topologies like system-synchronous clocks, where a global clock source is fed to all devices in the system, a source-synchronous clock topology can attain far higher speeds.
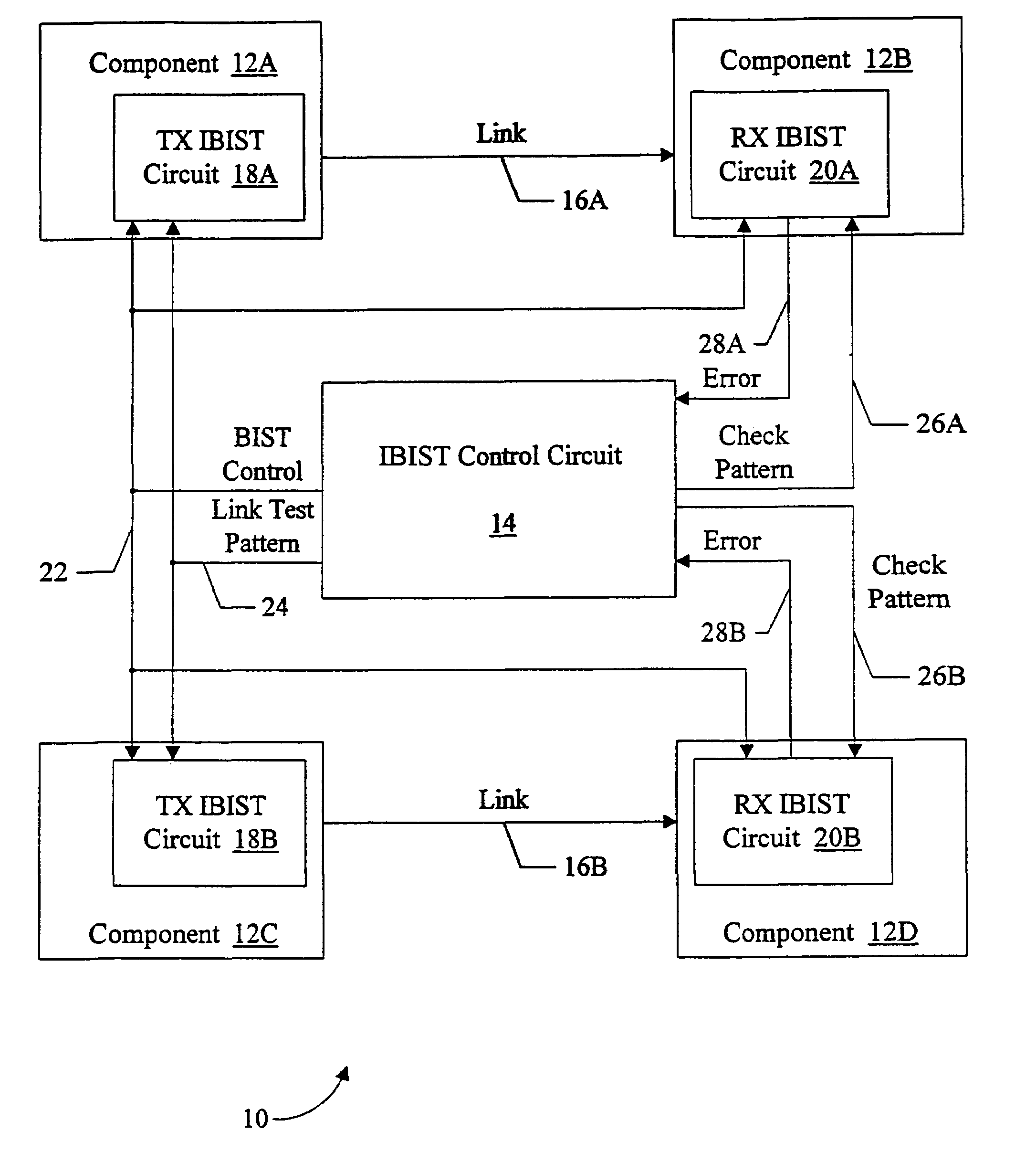
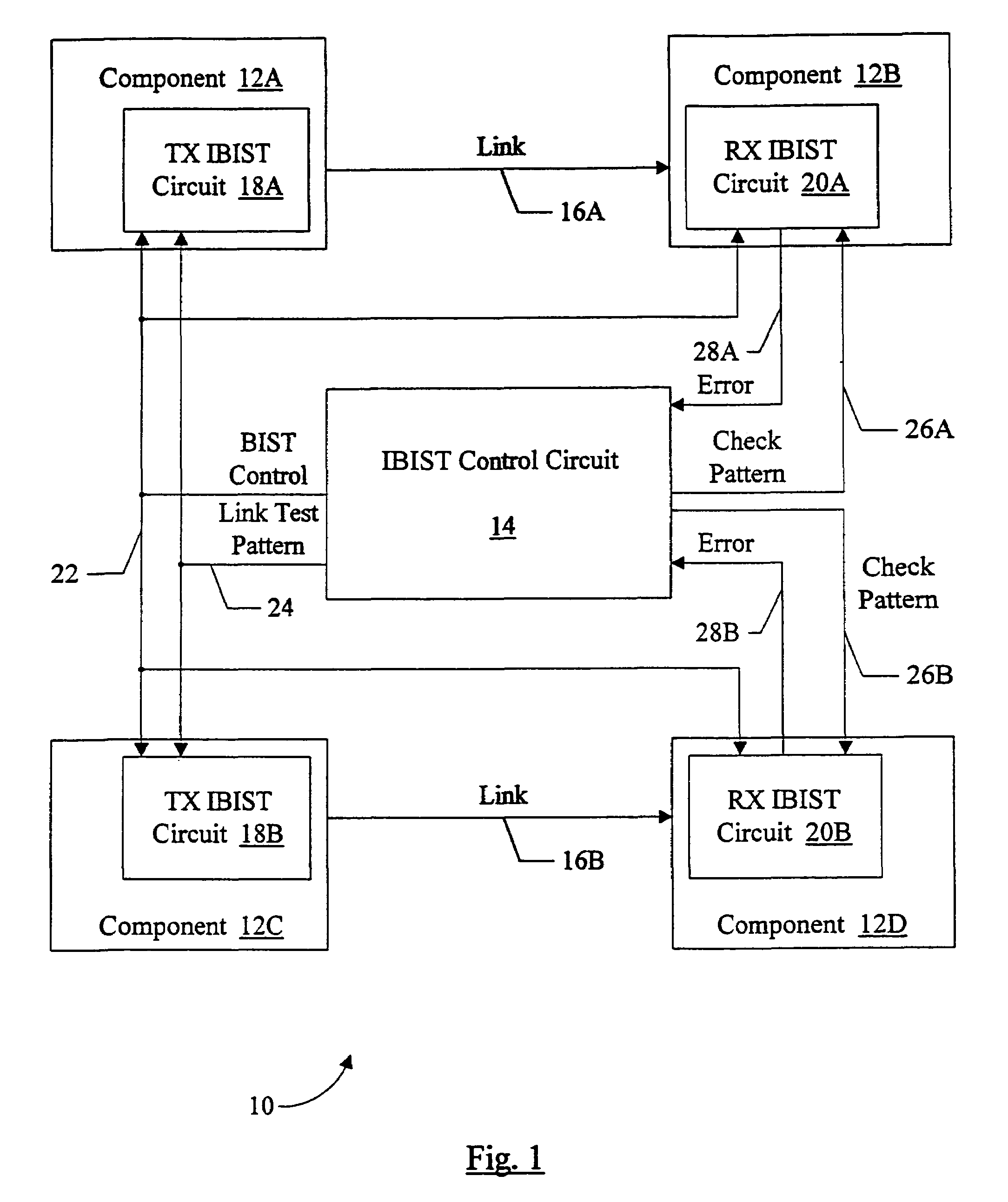
Source synchronous link integrity validation
InactiveUS6965648B1Flexible implementationCorrect operation testingElectronic circuit testingElectrical polaritySource-synchronous
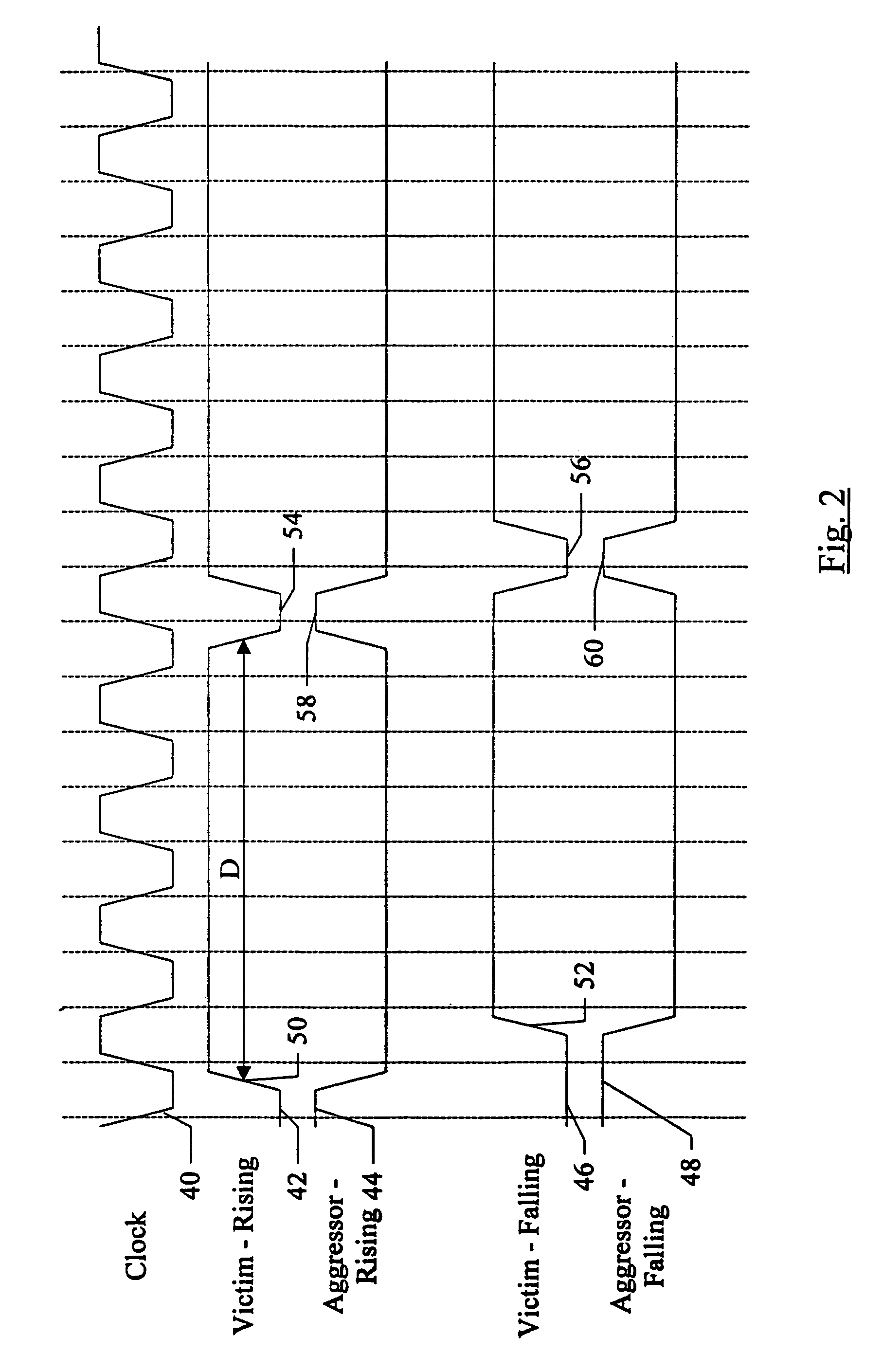
A system may perform interconnect BIST (IBIST) testing on source synchronous links. The system may perform, at normal operating frequency, a source synchronous link test that tests a victim line on the source synchronous link using a transition weave pattern. The transition weave pattern causes interaction between a data transition on the victim line, previous transitions on the victim line, and transitions on the other lines of the link (the “aggressor” lines). The interaction caused may be: (i) a first crossing pulse on the victim line; (ii) a second crossing pulse of the opposite polarity on each aggressor line concurrent with the first crossing pulse on the victim line; and (iii) a reflection in the opposite direction of the first transition of the first crossing pulse, wherein the reflection results from a previous transition on the victim line.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
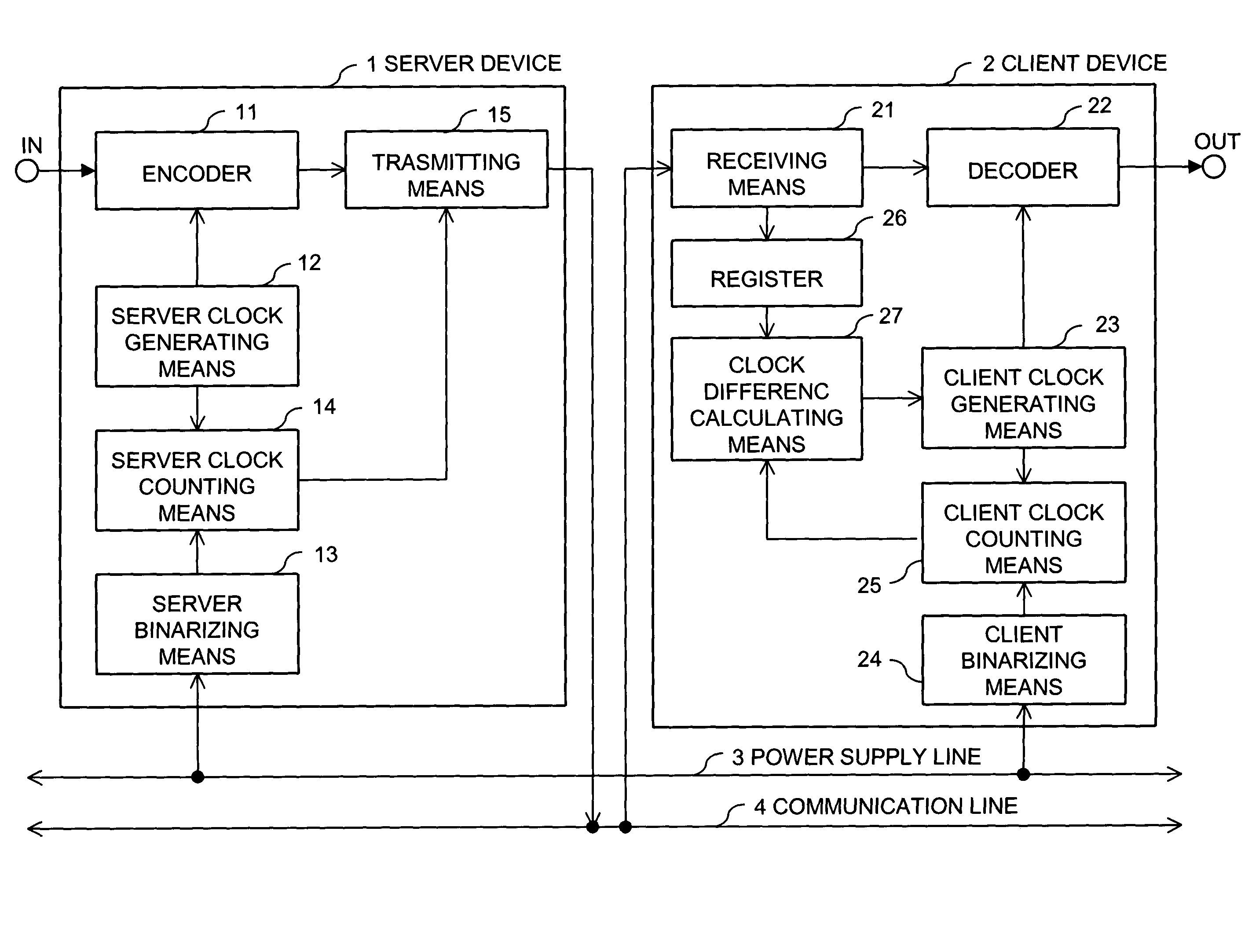
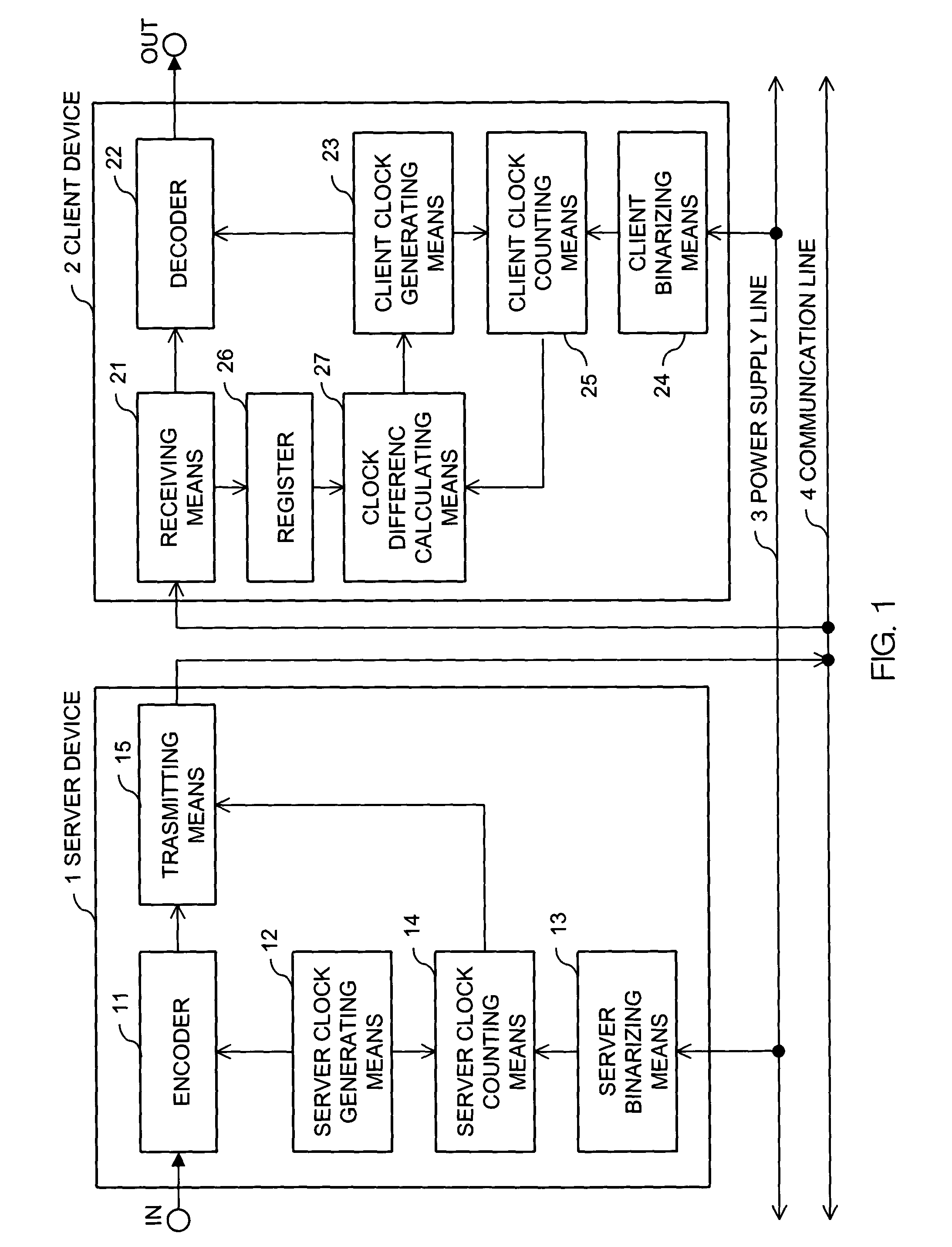
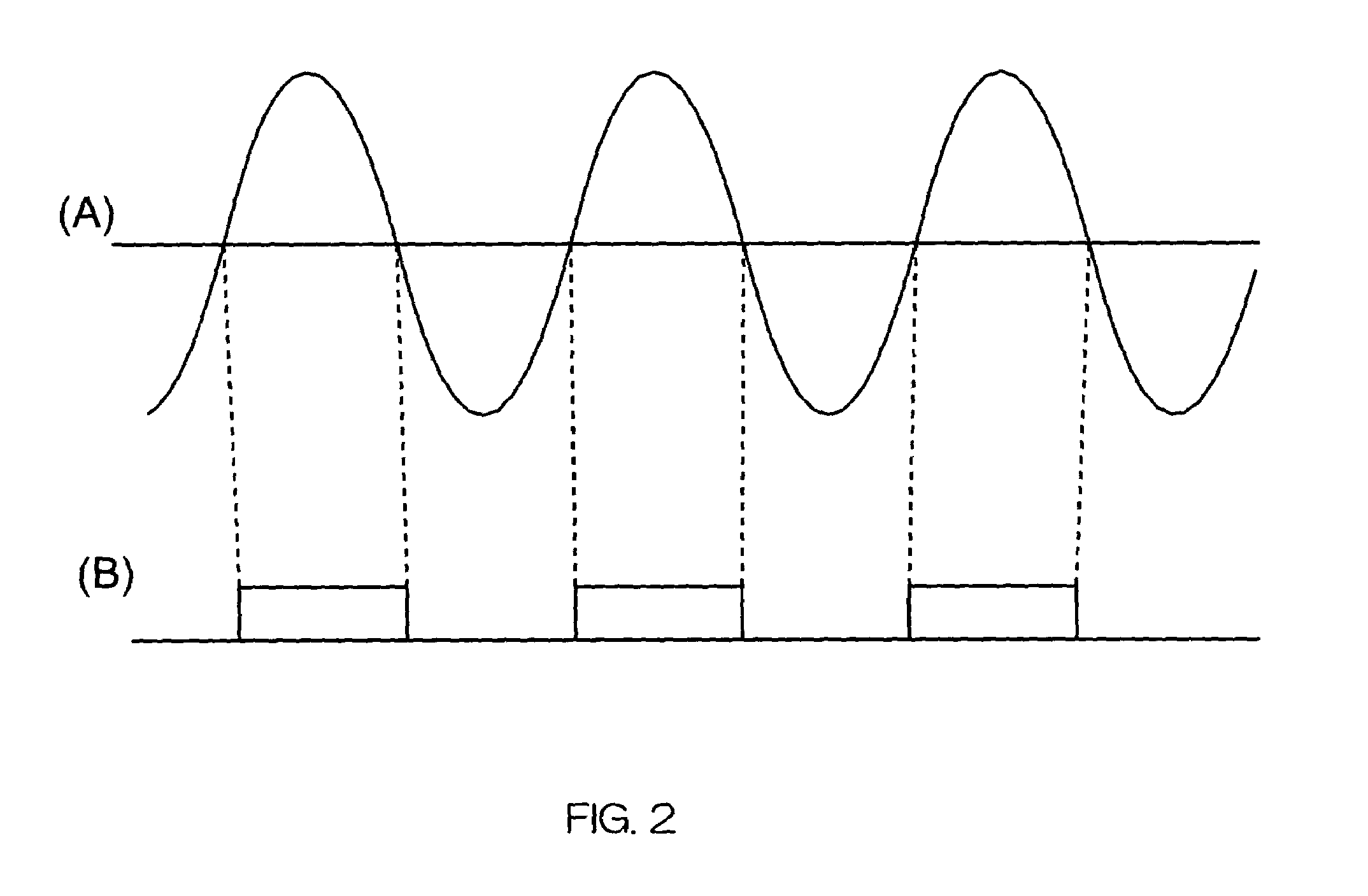
Synchronizing clock signals of server and client devices in a network system based on power source synchronous pulse signal
InactiveUS7263110B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData transmission timeNetworked system
In a network system, clock signals of a server device and a client device are synchronized with each other without having any influence of a change and a delay of the transmission time of data. Therefore, in the network system in which the client device receives and reproduces information transmitted from the server device, the server device counts the number of clock pulses of a server clock signal used to compress and encode information on the basis of a power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with a power source frequency. The server device outputs information showing the counted clock pulse number and the compressed and encoded information to the client device. The client device counts the number of clock pulses of a client clock signal used to decode and decompress the compressed and encoded information on the basis of the power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with the power source frequency. The client device conforms the frequency of the client clock signal to the frequency of the server clock signal on the basis of the clock difference between the clock pulse number received from the server device and the counted clock pulse number.
Owner:D & M HOLDINGS INC
Asynchronous memory using source synchronous transfer and system employing the same
A memory for storing data information and / or a controller for controlling read / write operations of the memory based on a source synchronous interface are provided. During the read / write operations, a command and an address are provided to the memory together with the first strobe signal. The memory may latch the command and address in response to the first strobe signal. During a read operation, the memory responds to a received second strobe signal to generate a third strobe signal. The memory outputs data from the memory and the third strobe signal, for example, so that the output data may be latched with the third strobe signal by the memory controller.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
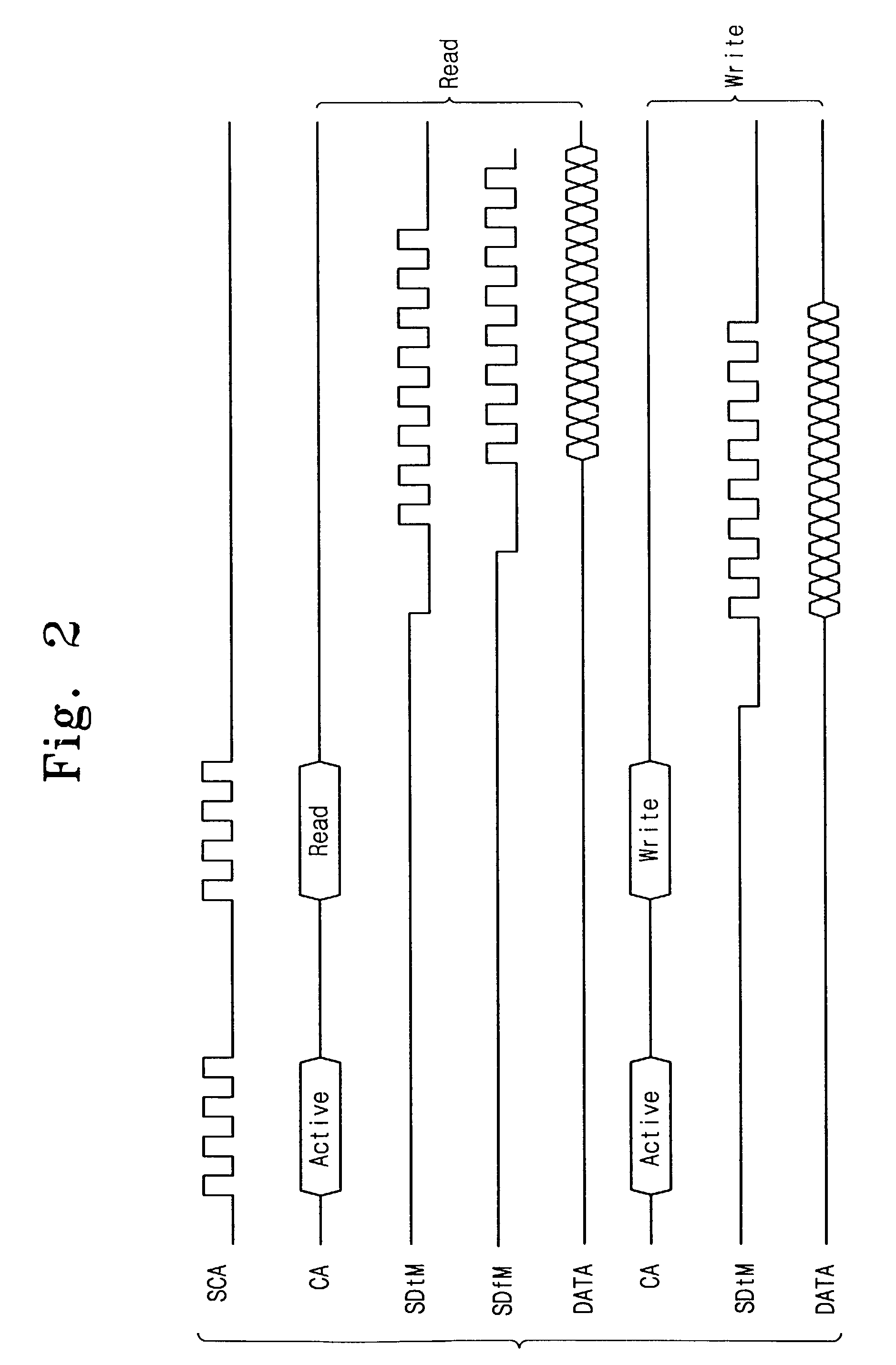
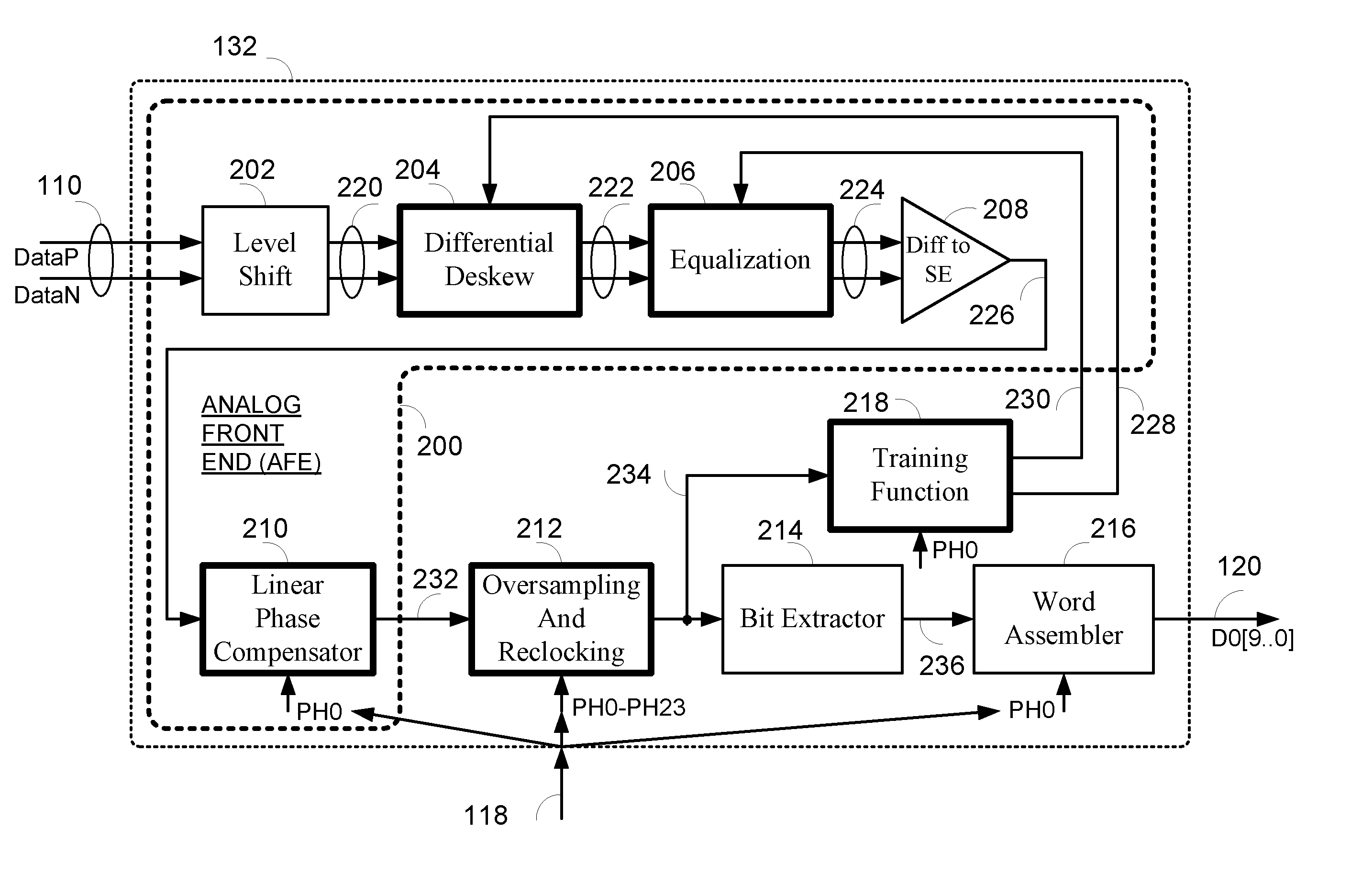
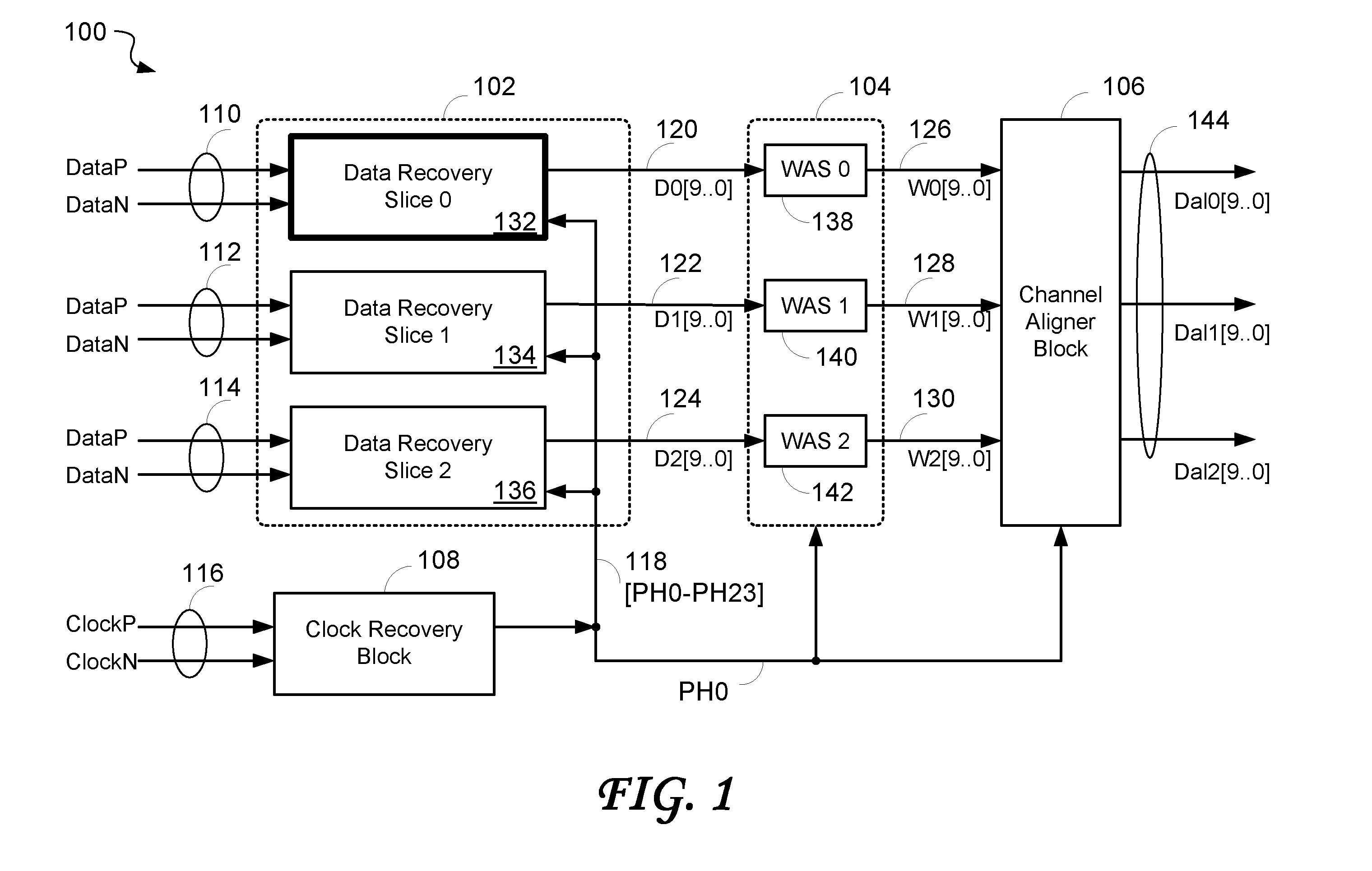
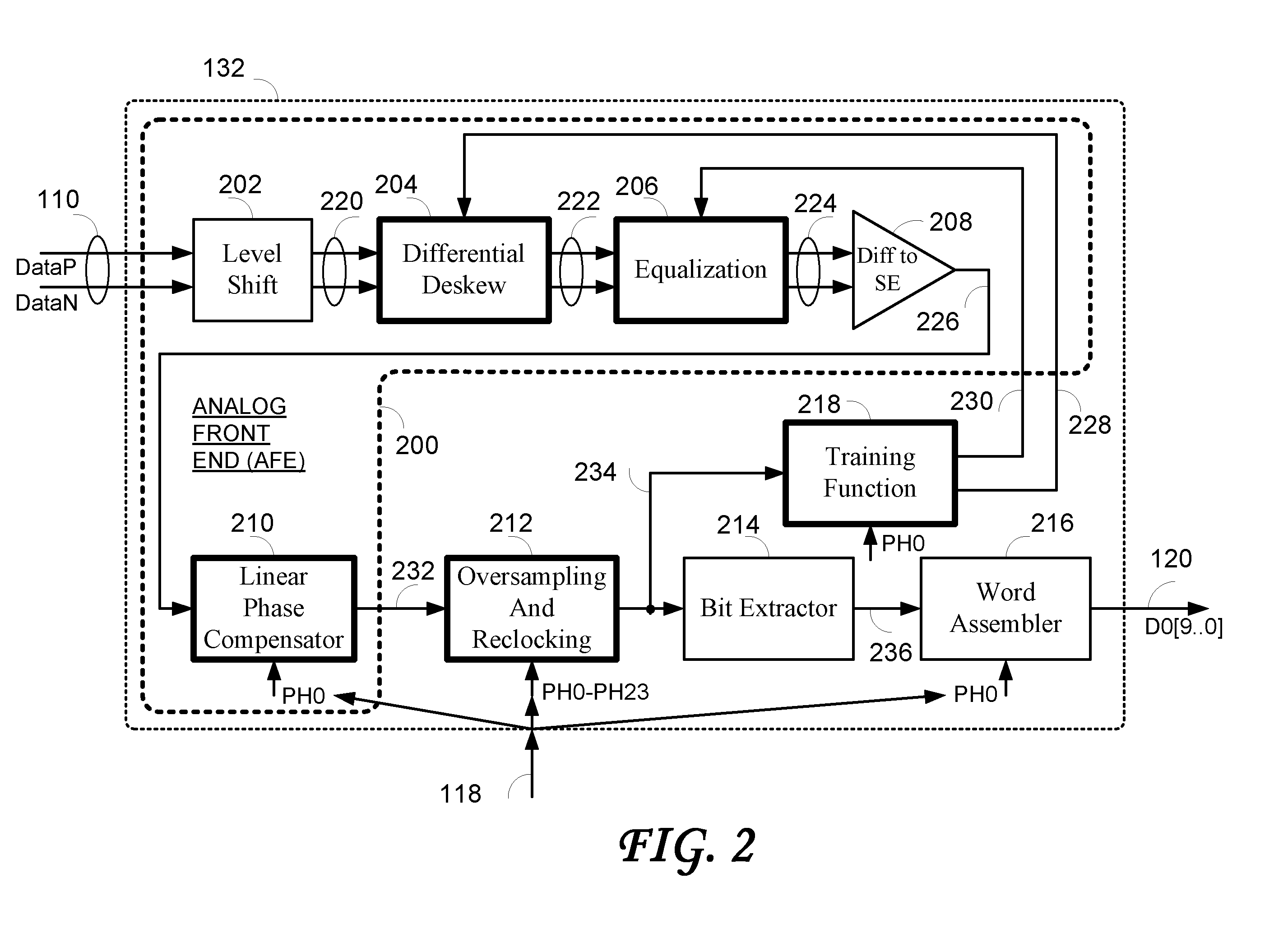
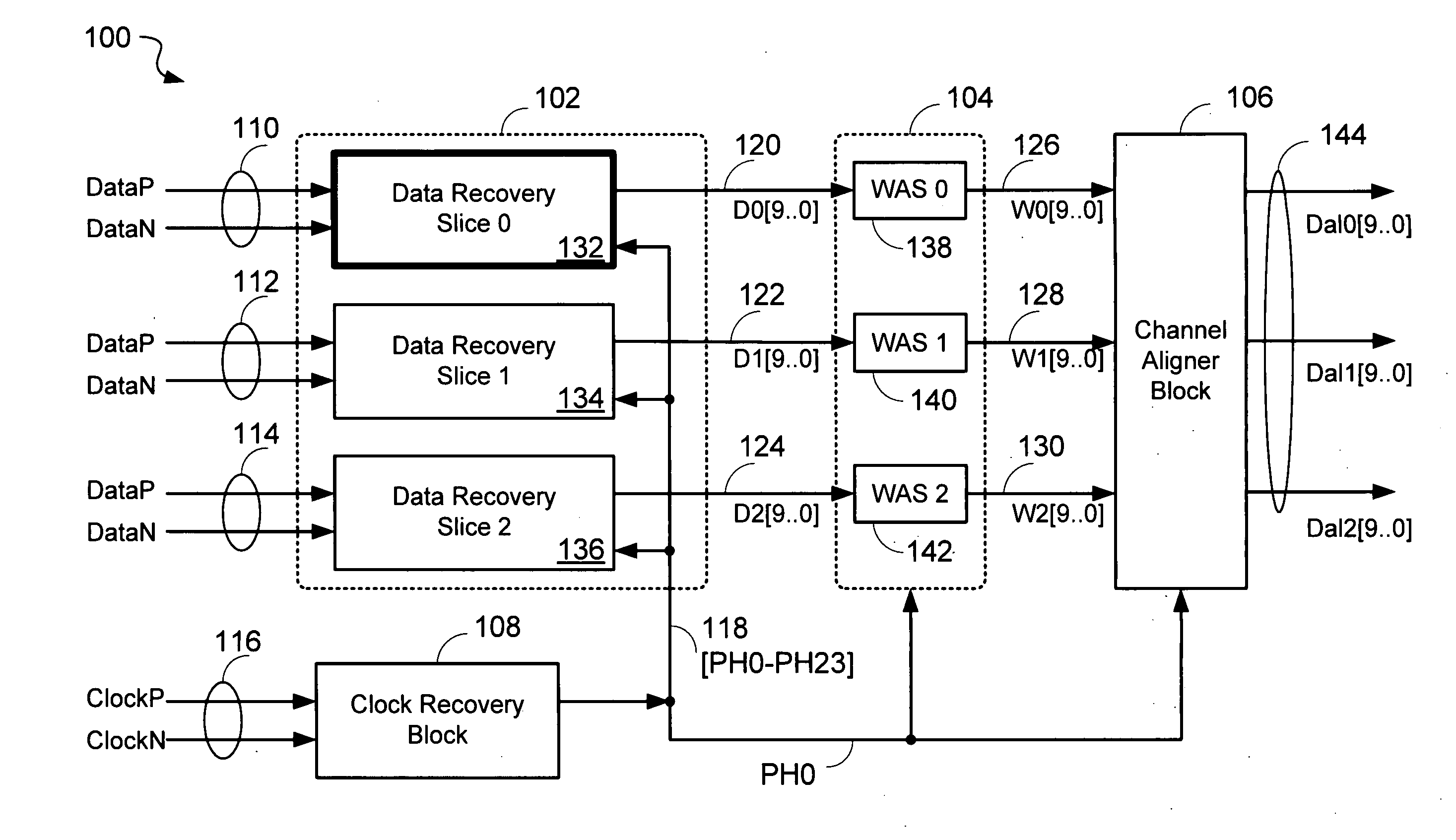
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
ActiveUS20070164802A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulator24-bitAnalog signal
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal. A corresponding method of deskewing a differential signal and a system and circuit therefor are also provided.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
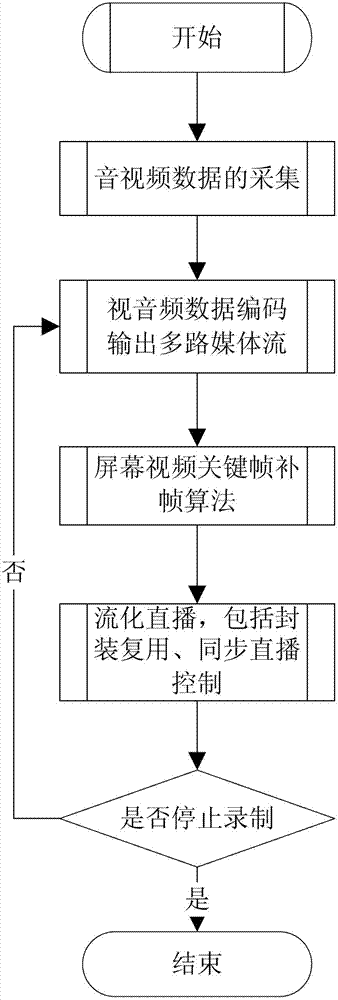
Multi-scene streaming media courseware recording and direct-broadcasting method
ActiveCN102821308ASupport synchronous controlRealize synchronous controlTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFile synchronizationComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a multi-scene streaming media courseware recording and direct-broadcasting method, which is characterized in that a recorded teacher camera video multimedia file is synchronized with a screen video multimedia file through a screen video key frame interpolation algorithm in recording; real-time video stream and real-time audio stream are coded to a transport stream (TS) file by synchronously encapsulating and multiplexing a video (PES) photoelectric scanning packet and an audio PES packet to be distributed to a web direct-broadcasting server, the teacher camera video and the screen video are synchronously broadcasted through the multi-video-source synchronous direct-broadcasting control. The method supports the windows / Linux cross-platform run and also supports the multi-source recording and stream direct-broadcasting technology of the teacher camera video, the teacher audio and the screen video, and the media courseware can be directly broadcasted while being recorded.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Timing control for input/output testability
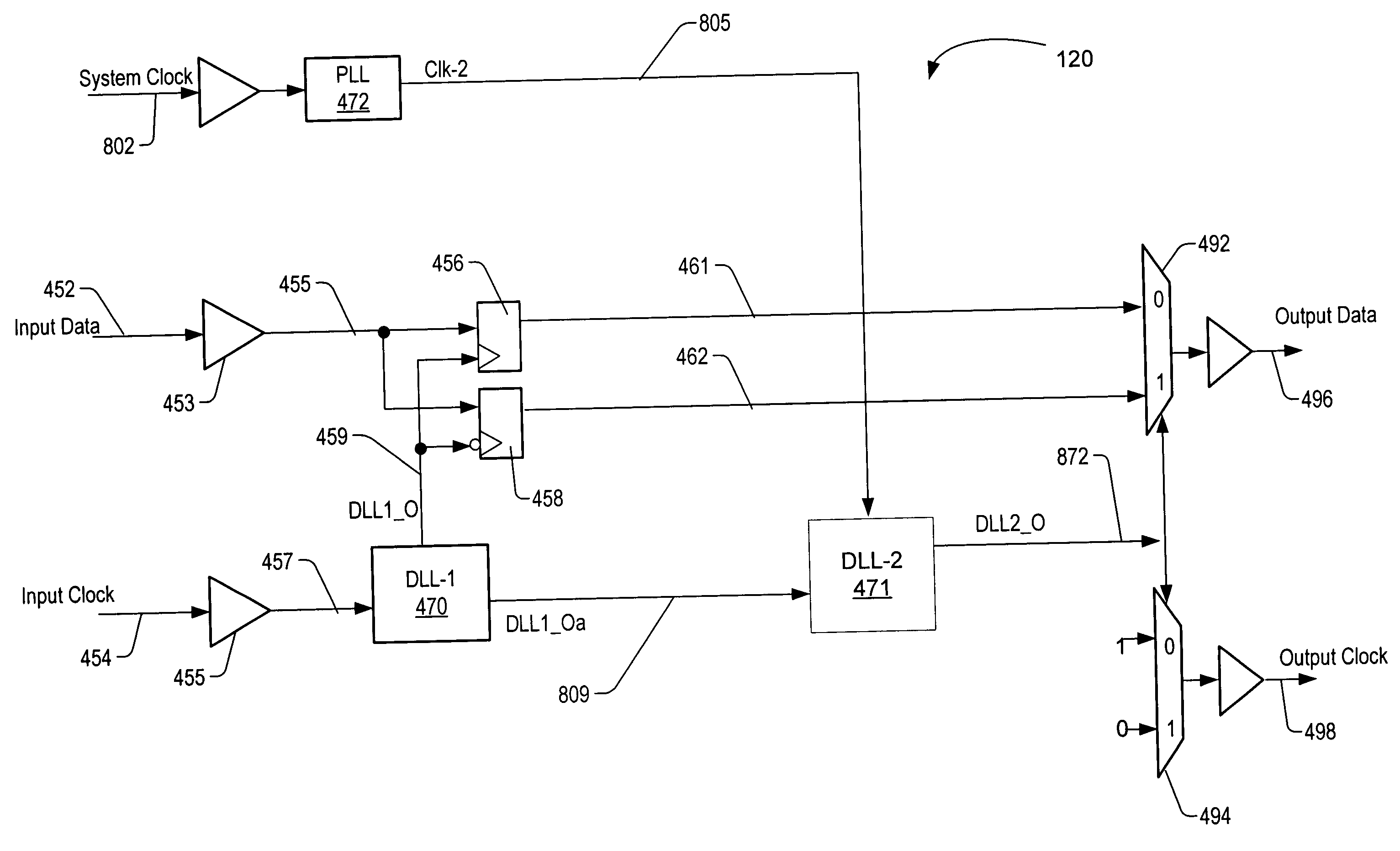
InactiveUS6085345AMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
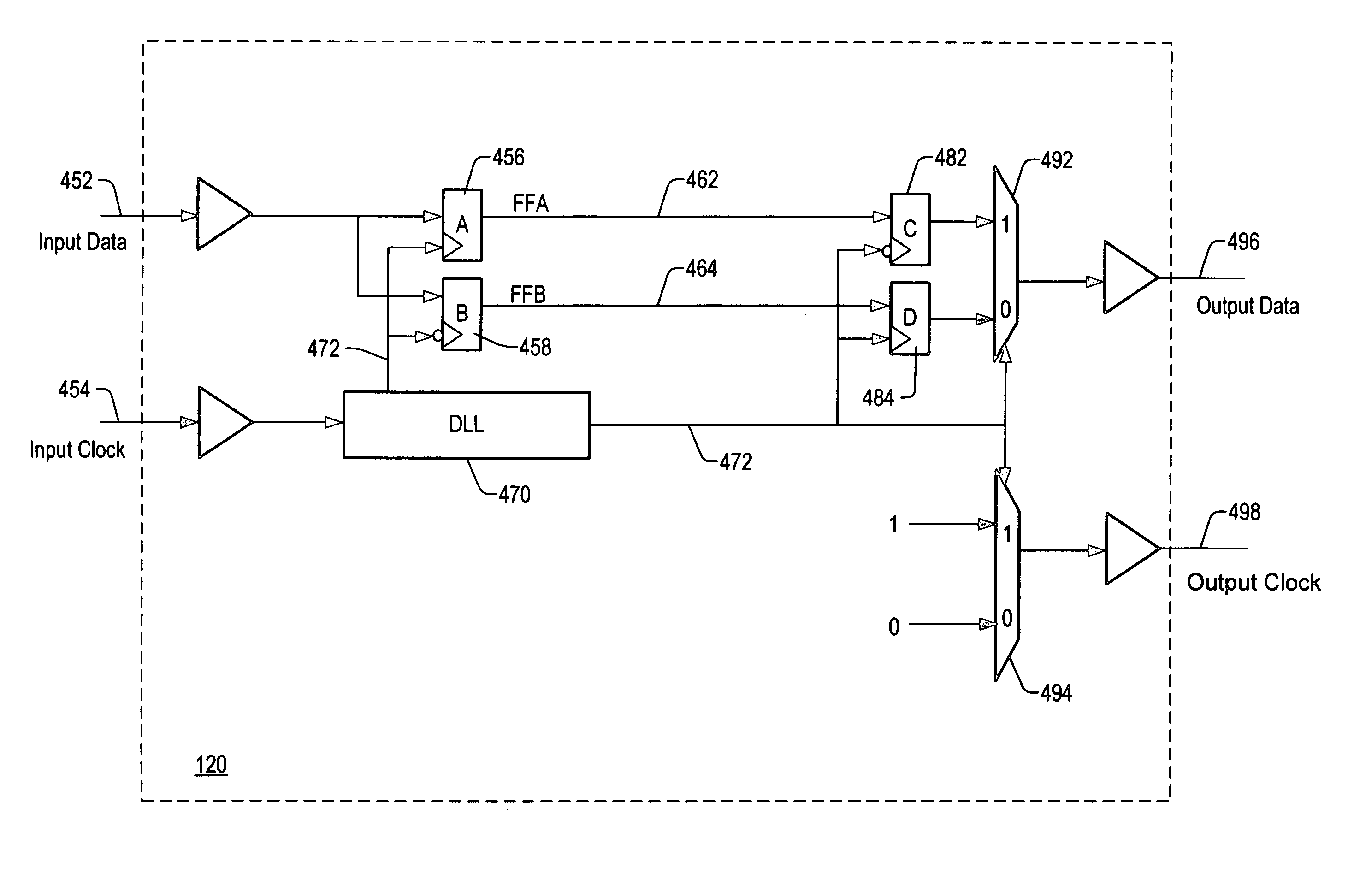
Circuitry added to chips that use source synchronous techniques reduces difficulties associated with testing the chips. The circuitry increases the ability to use source synchronous techniques for data transmission. The circuitry is implemented in a delayed-lock loop (DLL) in either a transmitter (driver) or a receiver. The DLL measures the phase difference between a strobe signal and a delayed strobe signal. The DLL can be externally controlled by a source selectable input which allows the delay of the delayed strobe signal to be varied to test Tsetup and Thold in the receiver without varying the timings of the strobe signal and the data signals supplied to the chips. A timing measurement circuit having the strobe signal, the delayed strobe signal, and reference signals as inputs may be used to calibrate the phase difference between the strobe signal and delayed strobe signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Data strobe gating for source synchronous communications interface
InactiveUS6940760B2Risk minimizationRead-only memoriesDigital storageCommunication interfaceCombined use
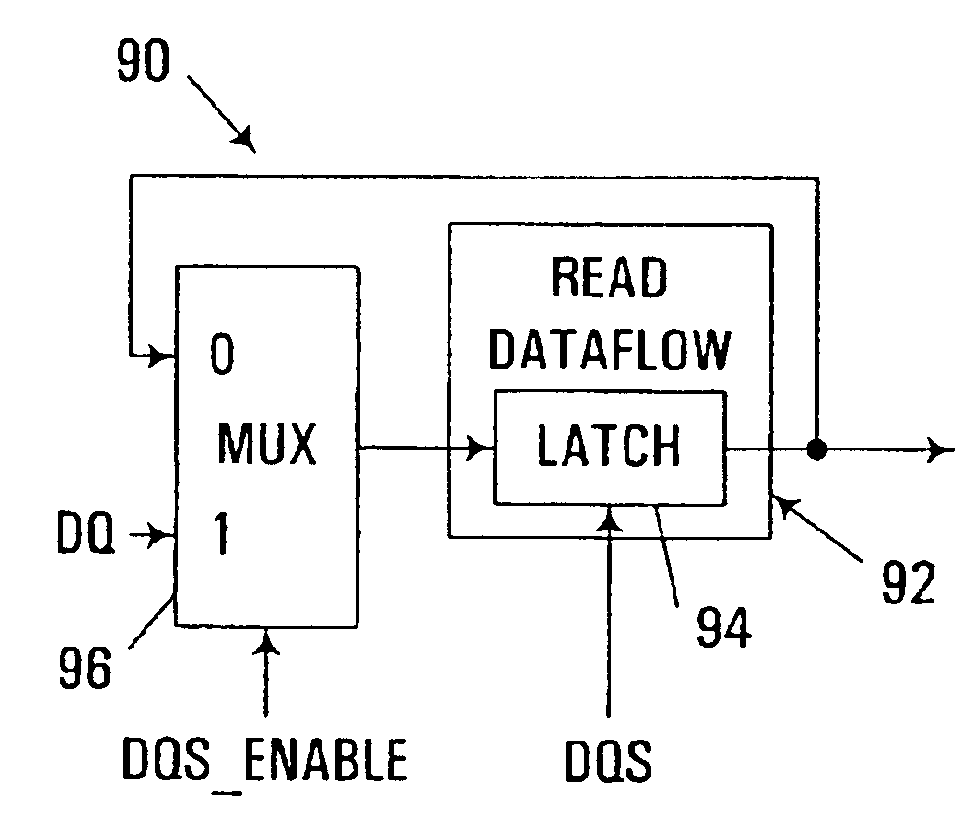
A circuit arrangement and method are used in connection with a data latch that is coupled to a data source over a source synchronous communications interface to disable the data latch from latching data whenever the data source is not driving the source synchronous data strobe signal. As such, when the data source is not driving the source synchronous data strobe signal, undesired and / or inadvertent latching by the data latch can be avoided. Moreover, in implementations where a data strobe signal line is bidirectional, and capable of being driven either by the data source or by another circuit used to access the data source (e.g., a memory controller), disabling data latching as described herein can minimize the risk of driver damage resulting from conflicting attempts to drive the data strobe signal line at both ends.
Owner:IBM CORP
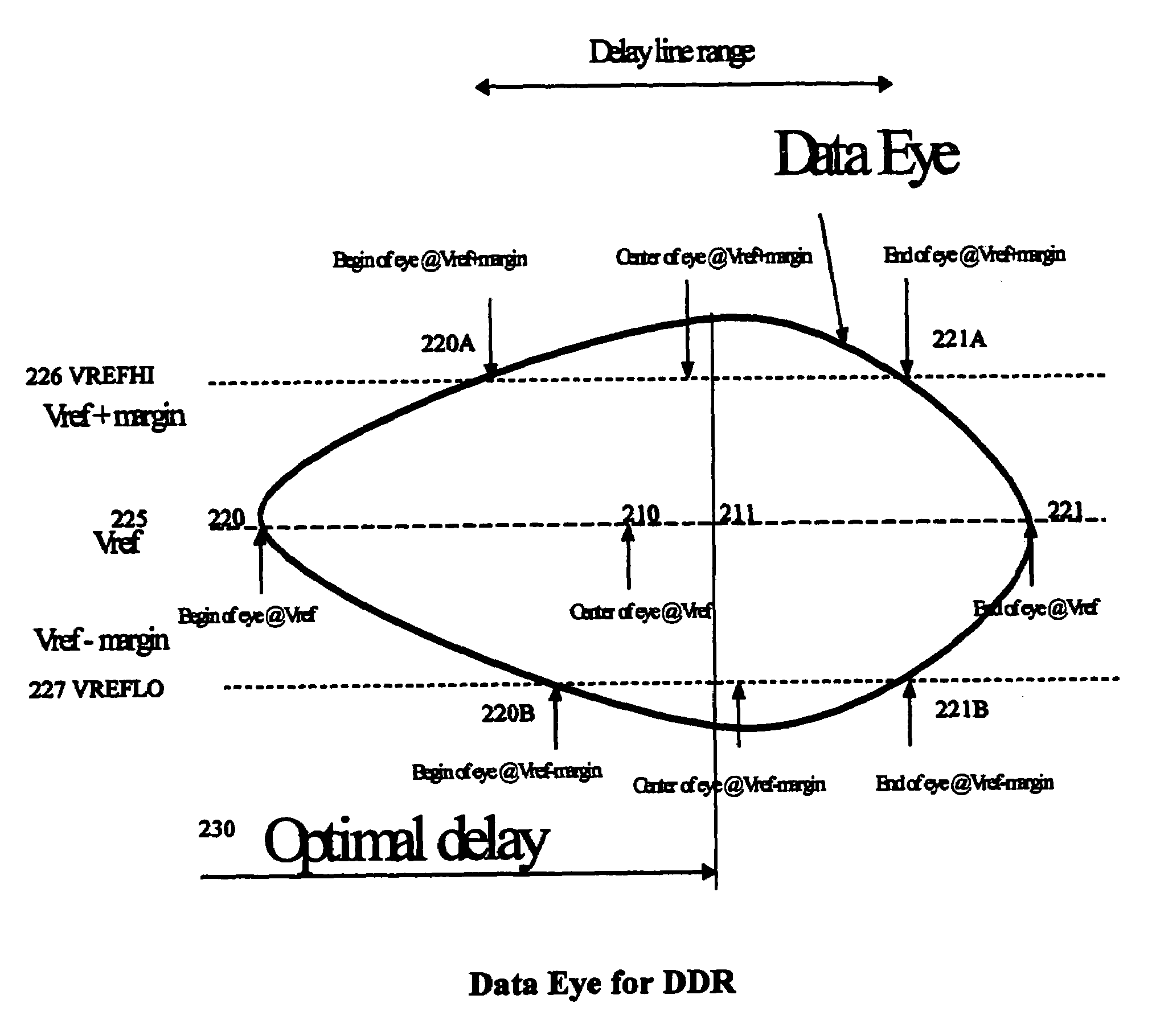
Two dimensional data eye centering for source synchronous data transfers
InactiveUS7036053B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionSource-synchronousSignal timing
A method for optimizing a source synchronous clock reference signal timing to capture data from a memory device (e.g., DDR SDRAM) includes conducting an iterative two-dimensional data eye search for optimizing the delay of the source synchronous clock reference signal (e.g., DQS). Embodiments of the present invention are directed to tuning the delay for each device for the optimal margin in two dimensions: maximize the distance from the data eye walls and maximize the noise margin on the interface. An iterative data eye search is performed while varying the DQS delay timing and noise margin.
Owner:INTEL CORP
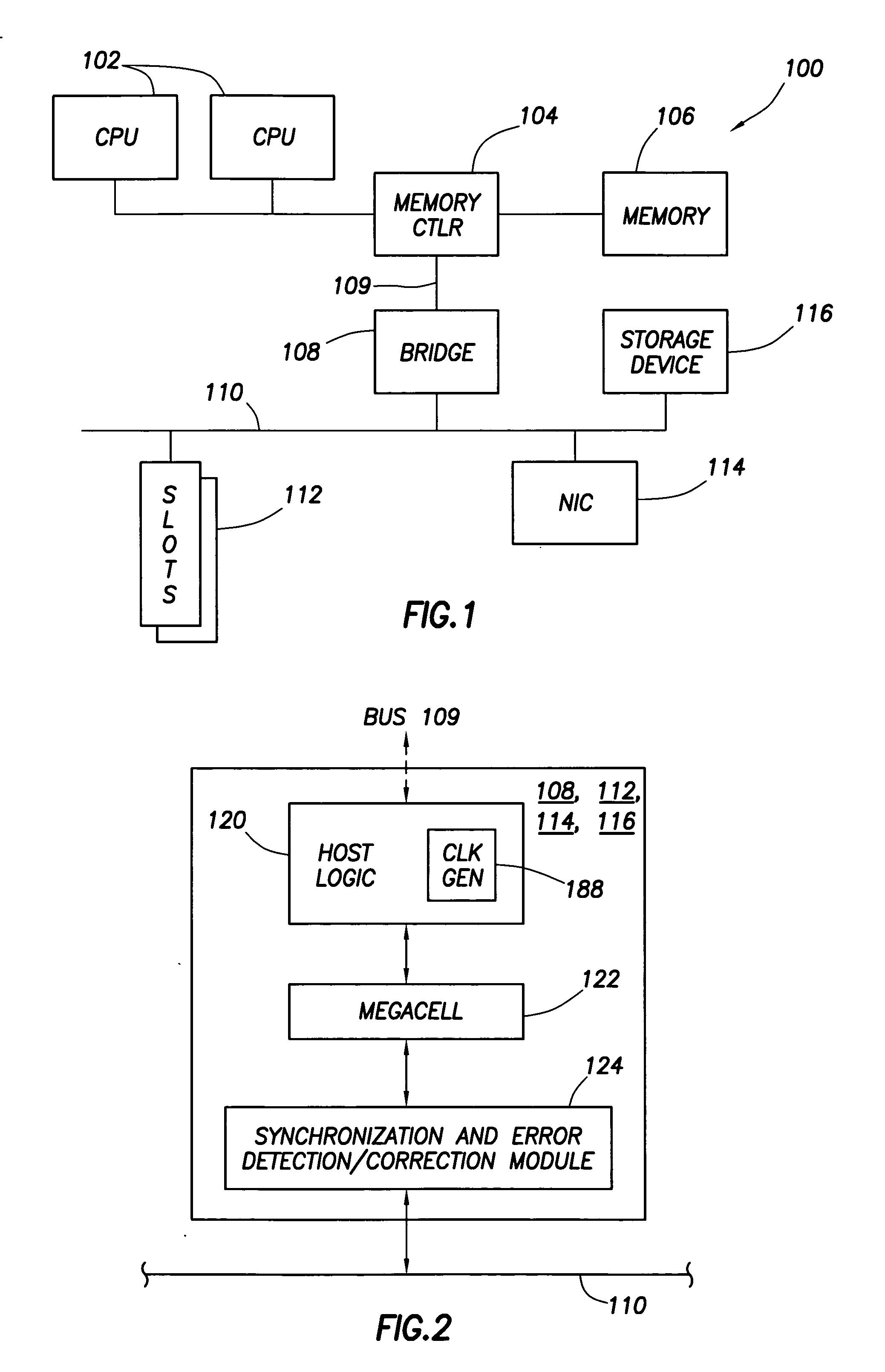
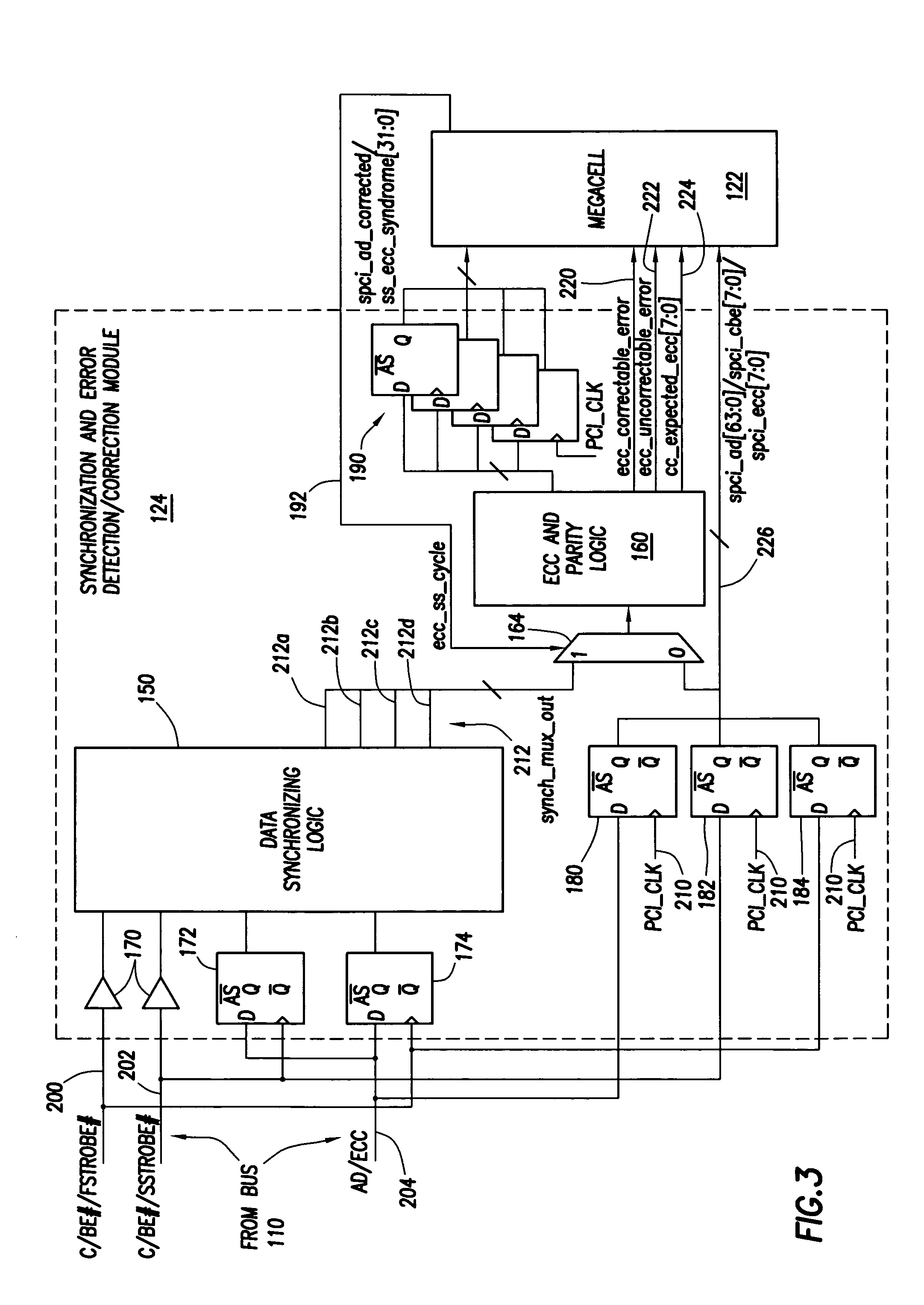
Bus device that concurrently synchronizes source synchronous data while performing error detection and correction
InactiveUS20050081129A1Synchronisation information channelsError detection/correctionData synchronizationSource-synchronous
A bus device comprises a clock generator that is adapted to generate a clock signal for internal use by the bus device, data synchronizing logic that is adapted to synchronize source synchronous data that the bus device receives from the bus to the bus device's clock signal, and error detection and correction logic coupled to the data synchronizing logic. The error detection and correction logic is adapted to detect and correct errors associated with the data received from the bus concurrently while the data synchronizing logic synchronizes source synchronous data received from the bus to the clock signal.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
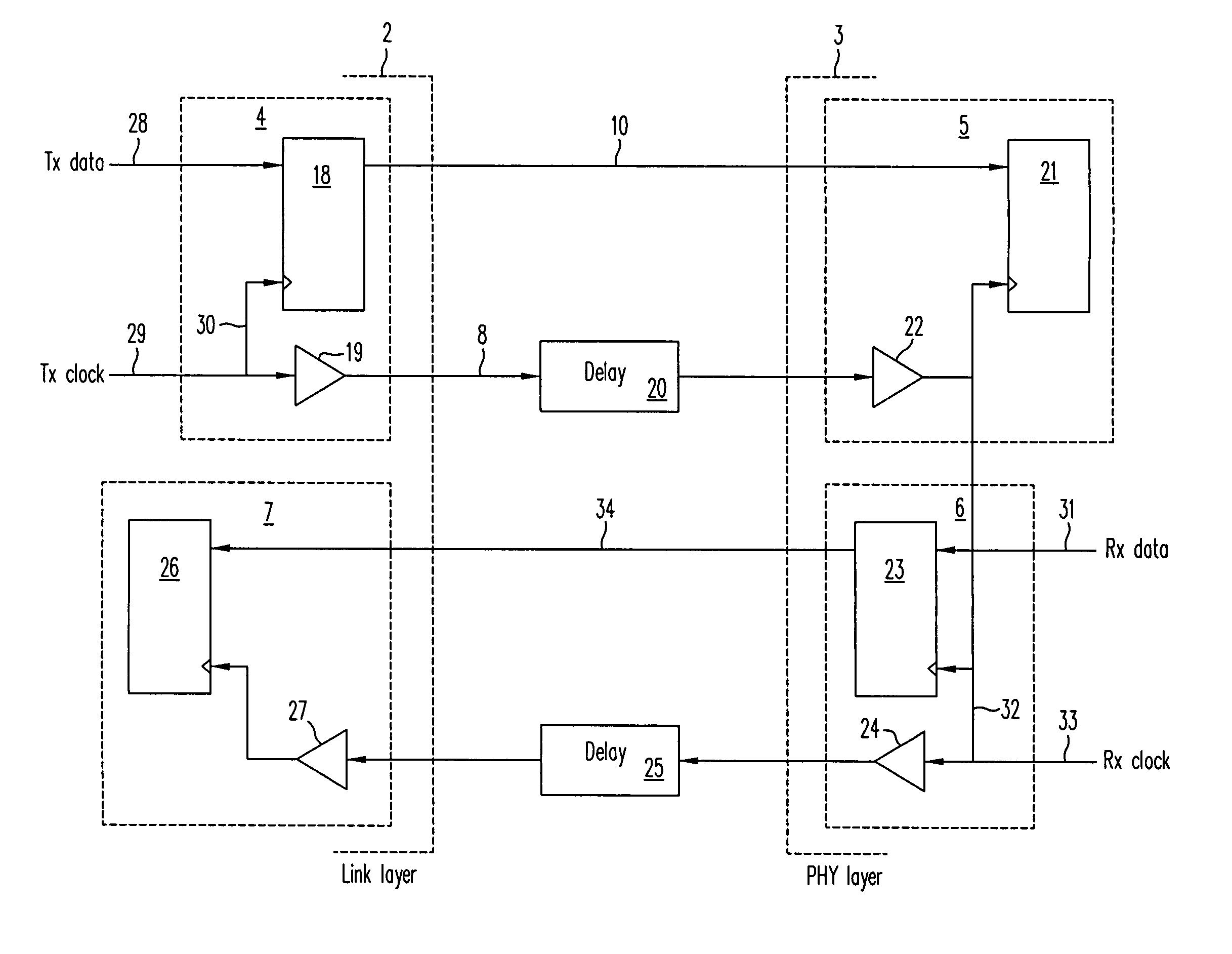
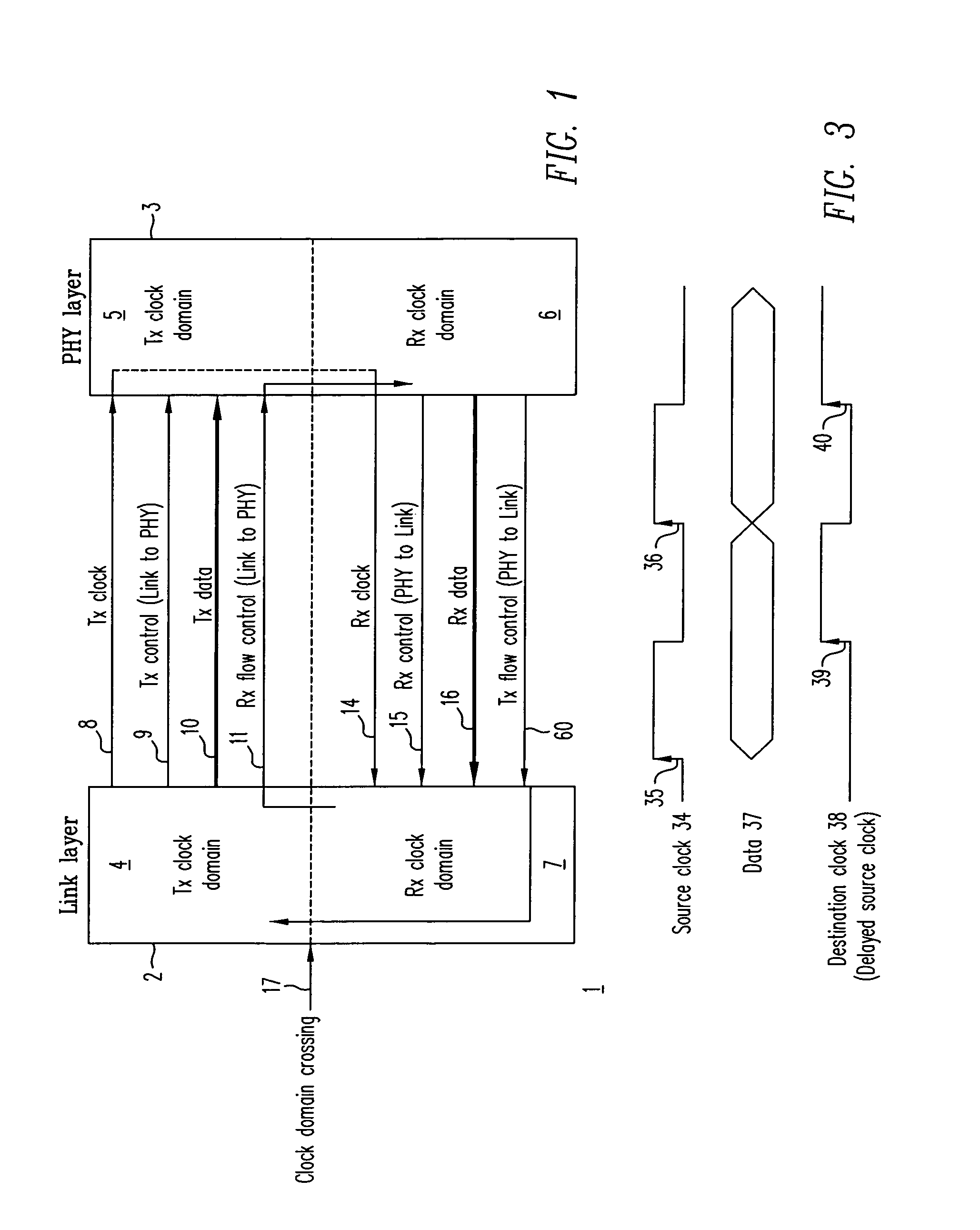
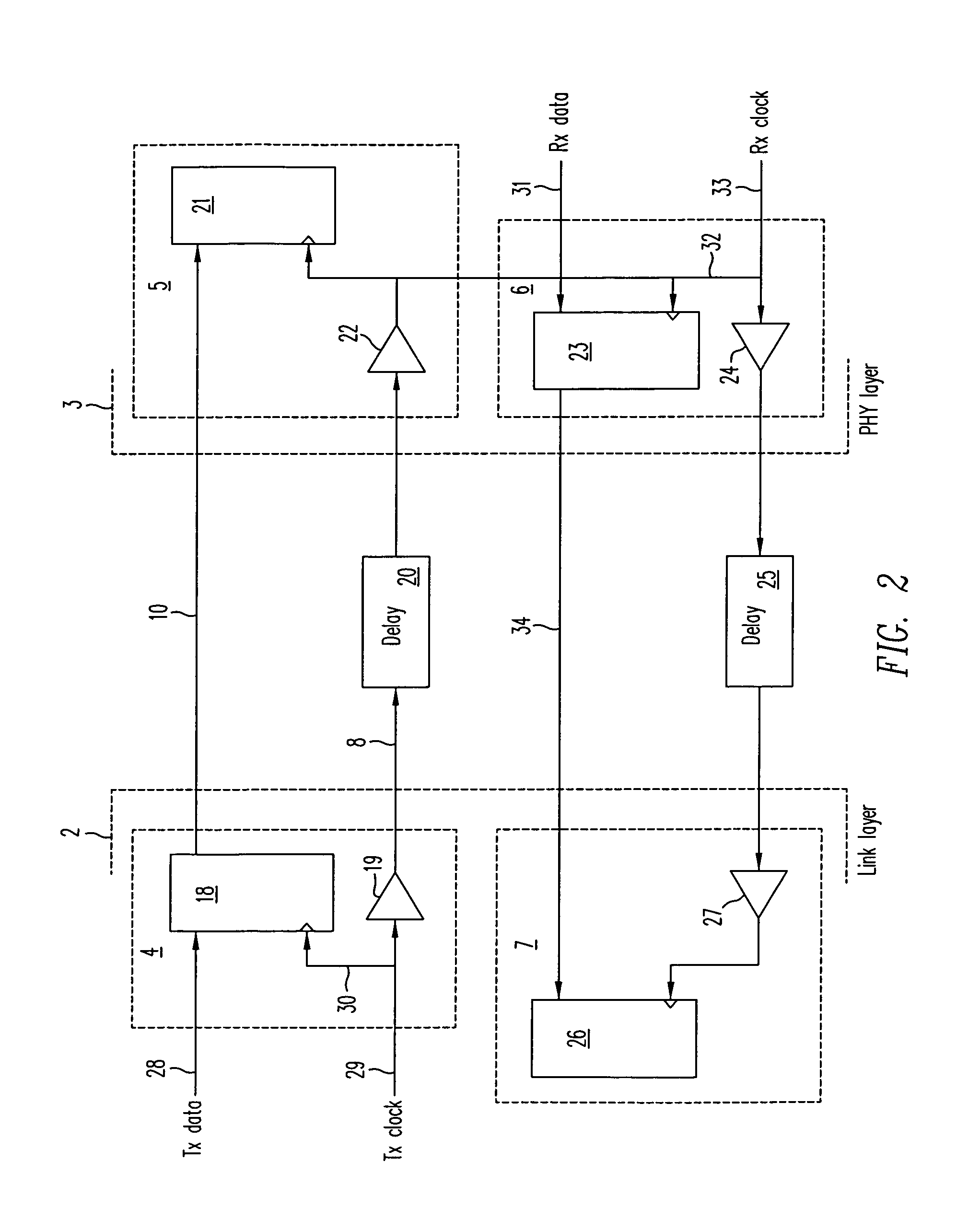
Method and system for source synchronous clocking
InactiveUS7110423B1Accurate recoveryEliminate needSynchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexProcessor registerData signal
A source synchronous clocking synchronizes data and clock signals transmitted between an ATM layer and a link layer. The source synchronous clocking includes a source clock domain in a first layer which includes a register having a first input for receiving a data signal, a second input for receiving a clock signal, and an output; and a buffer having an input for receiving the clock signal and an output, the buffer generating a delay that is substantially equivalent to a delay through the register. The source synchronous clocking further includes a destination clock domain in a second layer which includes a register having a first input and a second input, the first input of the register of the destination clock domain being coupled to the output of the register in the source clock domain.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
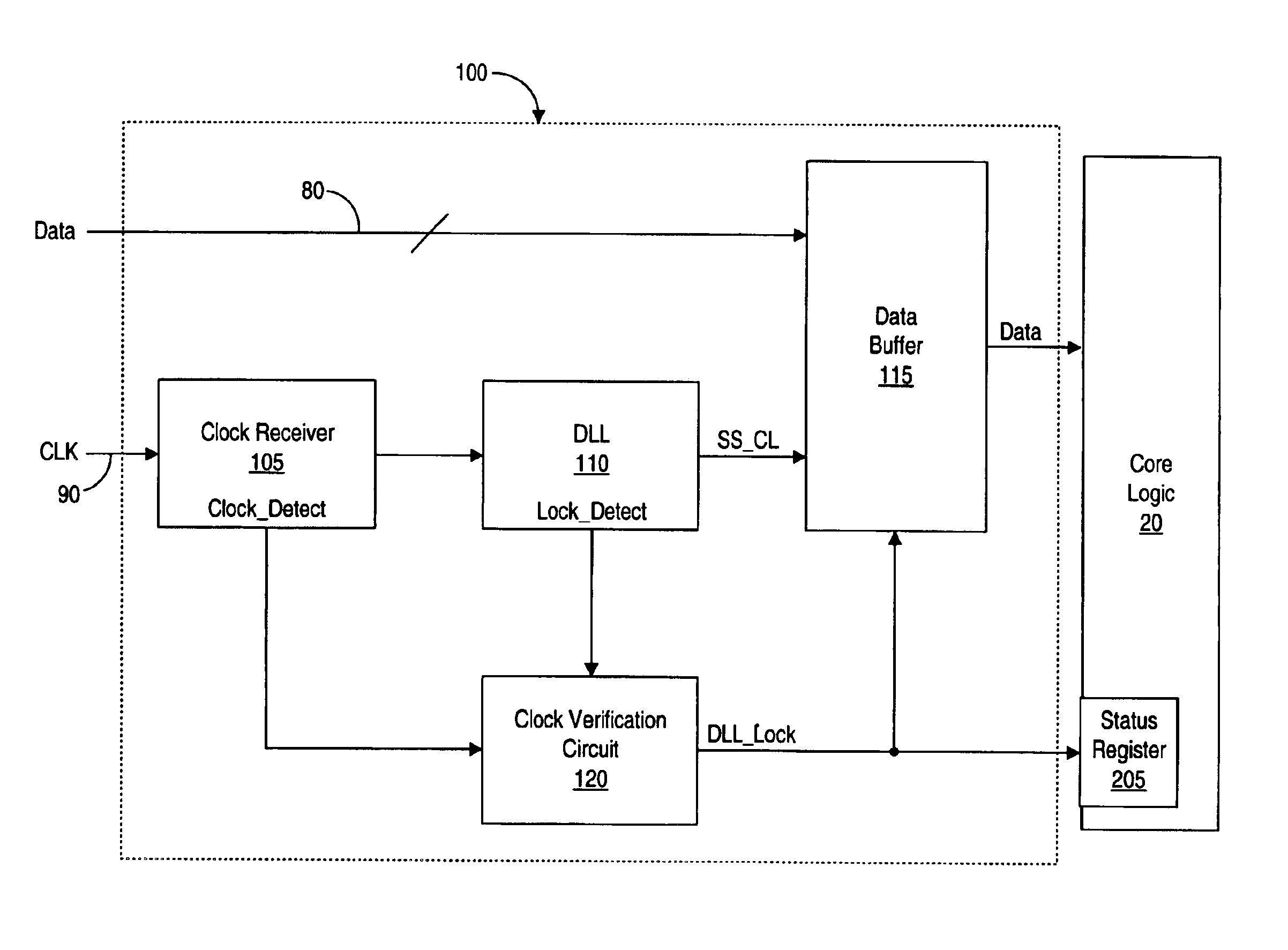
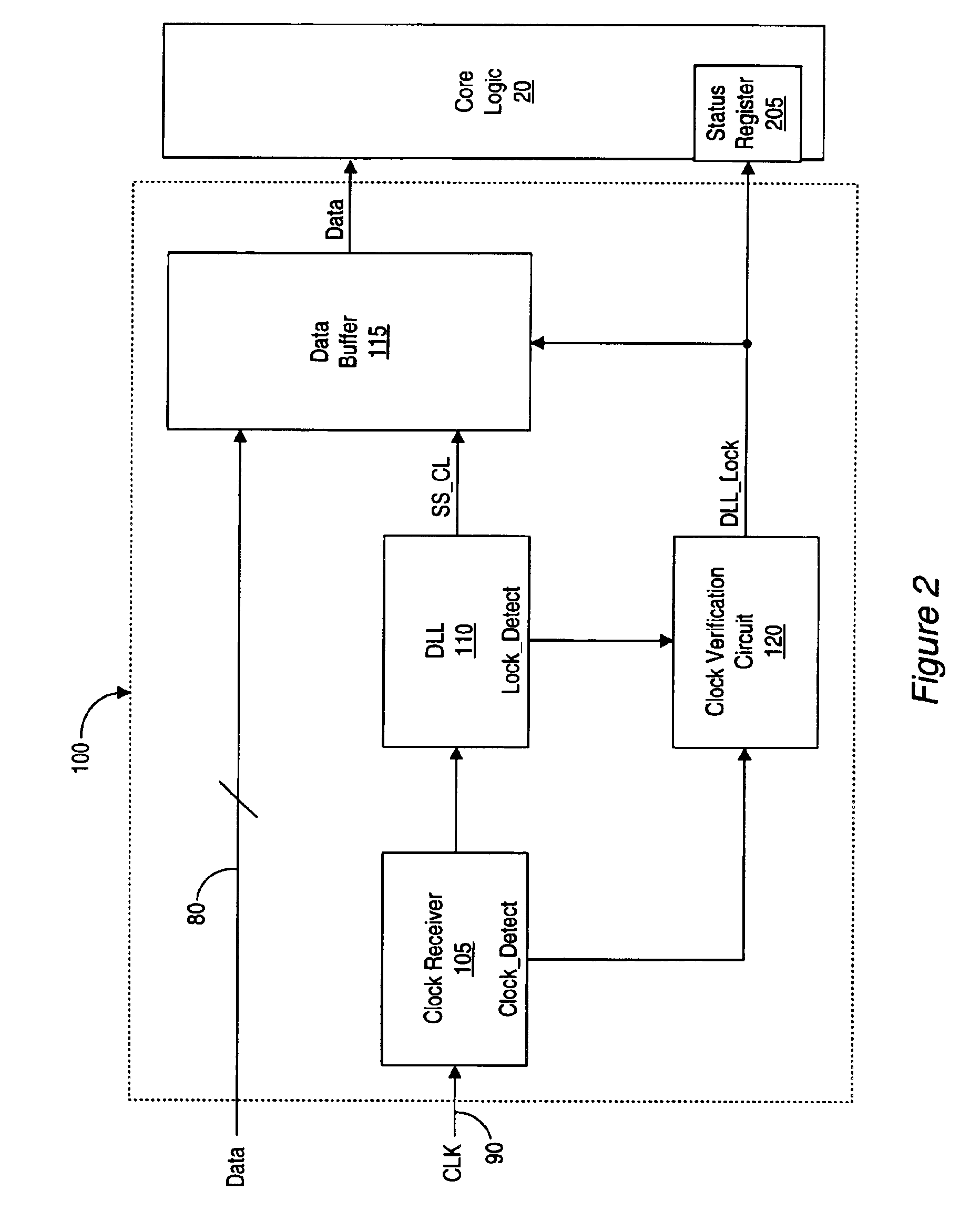
Source synchronous receiver link initialization and input floating control by clock detection and DLL lock detection
InactiveUS6937680B2Guaranteed uptimeSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlClock validationSource-synchronous
A method and apparatus for operating a source synchronous receiver. In one embodiment, a source synchronous receiver may include a clock receiver comprising a clock detector and a clock signal buffer. The clock detector may be configured to detect a first clock signal and assert a clock detect signal responsive to detecting the first clock signal. The clock buffer may receive the first clock signal and produce a second clock signal, which may be driven to a digital locked loop (DLL) circuit, where the second clock signal is regenerated and driven to a data buffer of the source synchronous receiver. The clock detect signal may be received by a clock verification circuit. The clock verification circuit may be configured to initiate a reset of the source synchronous receiver upon a failure to receive the clock detect signal. The resetting of the source synchronous receiver may be performed locally, and does not reset the core logic of the device in which it is implemented, nor any other source synchronous port on the device. Thus, other source synchronous ports on the device, as well as the core logic, may be able to continue operations as normal. The method and apparatus may include a source synchronous receiver that is hot-swappable.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Locking source synchronous selection pass receiver device and method
ActiveCN101079018AFix bugsWork around limitationsPulse automatic controlElectric digital data processingMultiplexerDelay-locked loop
The present invention provides a device of locking source synchronization gating receiver, including delay locking loop and gating receiver. The delay locking loop receives reference clock and generates selection vector signal and coding selection vector signal, the selection vector is used for selecting one of delay editions of the reference clock signal which are generated through the reference clock signal pass through certain periods. The selection vector subtracted by a value is used by Gray encode for indicating the first time period. All gating receivers connect with the delay locking loop. Each gating receiver receives the coding selection vector signal and corresponding gating signal, and locks the corresponding gating signal during the first time period after transforming the corresponding gating signal. The Gray code multiplexer selects one delay edition of corresponding gating signal to determine the first time period through the coding selection vector signal.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
ActiveUS20090290671A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationSignal quality24-bit
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
Method and apparatus for aligning data in a wide, high-speed, source synchronous parallel link
InactiveUS20050066142A1Limit jitter and wanderReduce depthChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsSource-synchronousComputer science
A source-synchronous parallel interface divides a wide data bus into clock-groups including a sub-group of the data lines and a clock line carrying a copy of the transmit clock. The traces in a clock-group are located physically close together to minimize skew between the signals carried on the traces of the clock-group. Deskew logic on the receiver compensates for skew between received clock-group signals.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
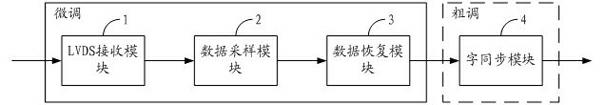
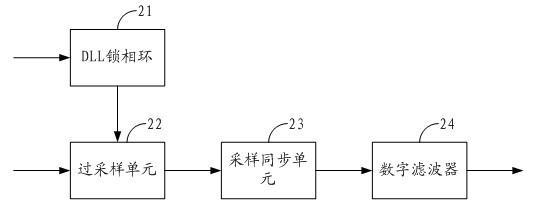
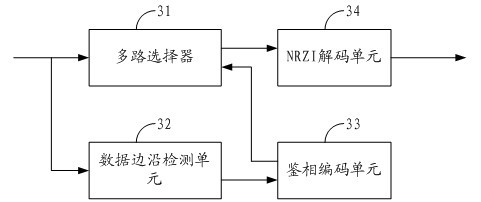
High-speed parallel interface circuit
The invention is suitable for the digital communication field, and provides a high-speed parallel interface circuit. The high-speed parallel interface circuit comprises a low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) receiving module, a data sampling module, a data restoring module and a word synchronization module, wherein the LVDS receiving module receives and shapes data; the data sampling module is connected with the LVDS receiving module and samples the data output by the LVDS receiving module under a plurality of phase clocks; the data restoring module is connected with the data sampling module, selects optimal sampling data from oversampling data output from the data sampling module and restores original data by non return to zero inverse (NRZI) decoding; and the word synchronization module is connected with the data restoring module and carries out shift adjustment to the data output by the data restoring module. In the high-speed parallel interface circuit, oversampling and word synchronization are combined to carry out accurate sampling restoration and synchronization to source-synchronous parallel data; and data in the center of an effective window can be dynamically and accurately sampled and restored in real time by dynamically synchronizing, filtering, discriminating phase, selecting the oversampling data and the like.
Owner:成都三零嘉微电子有限公司
Source synchronous transfer scheme for a high speed memory interface
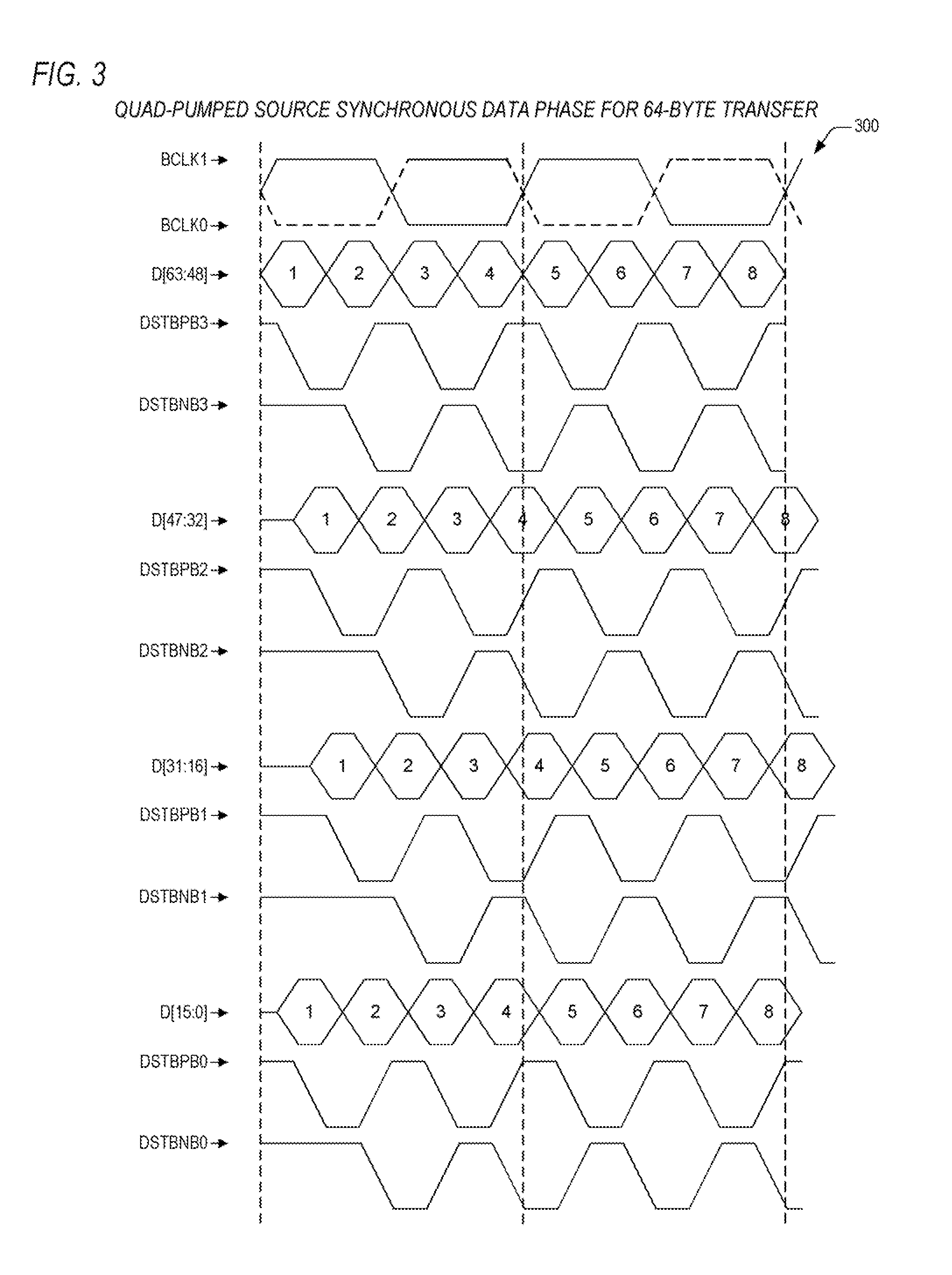
InactiveUS6199135B1Increase transfer rateReduce offsetData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsMultiplexingHigh speed memory
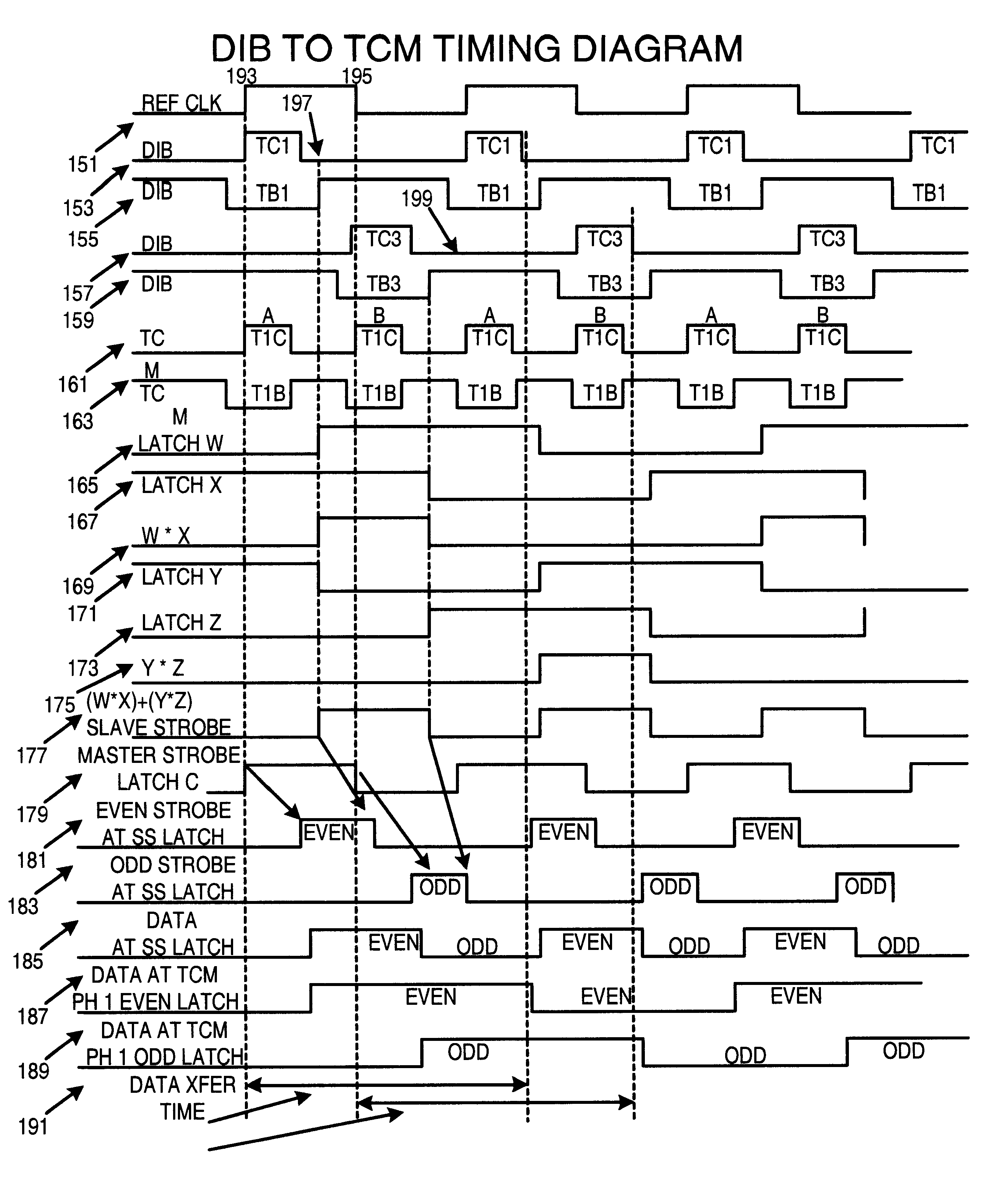
Data transfer scheme wherein data transfer rates can be effectively doubled with no increase in the clock speed of the interface. This is accomplished by allowing more than one data transfer to occur on a single clock cycle. This transfer scheme increases the transfer rate of the interface by multiplexing two data groups on the same interface. These data groups are transmitted from a source phase latch at approximately the same time as two strobe signals which have low skew with respect to the data. The master and slave strobe signals are logically combined to create an even latch enable signal and an odd latch enable signal that are used to latch and de-multiplex the multiplexed data groups at a receiving end of a pair of flow-though source synchronous latches.
Owner:CHARLES A JOHNSON
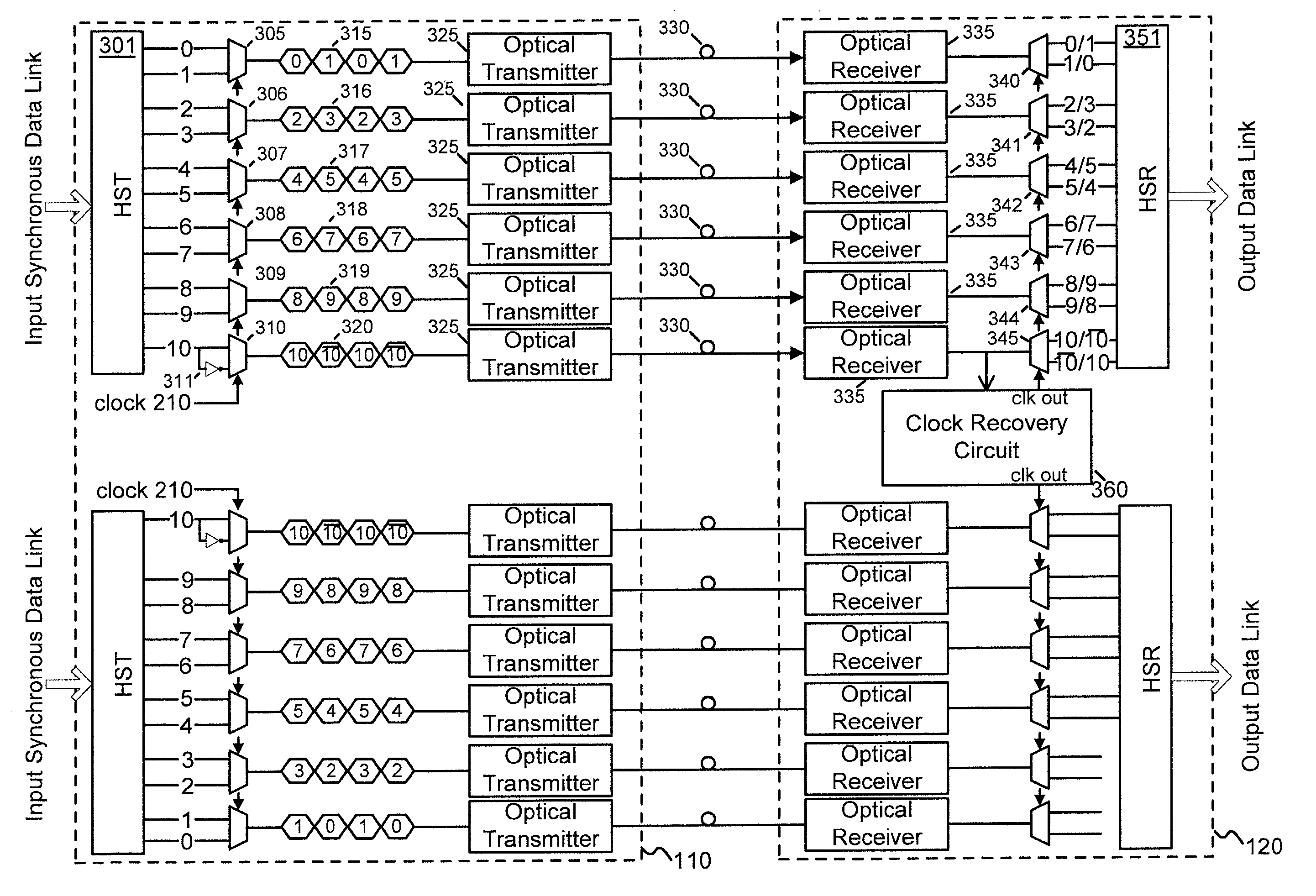
Source synchronous link with clock recovery and bit skew alignment
A high speed transmission system transfers data streams over a plurality of data links. Each data link may carry a number of bit streams. On the transmitting end, multiplexers serialize the bit streams, which are then transmitted to the receiving end. A clock signal is not transmitted over the optical link. Instead, an indication of the appropriate clock signal frequency and phase is embedded in the transmitted data. At the receiving end, a clock recovery circuit generates a clock signal of an appropriate frequency and phase based on the embedded indication. The new clock signal is used to sample and reconstruct the original data streams.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
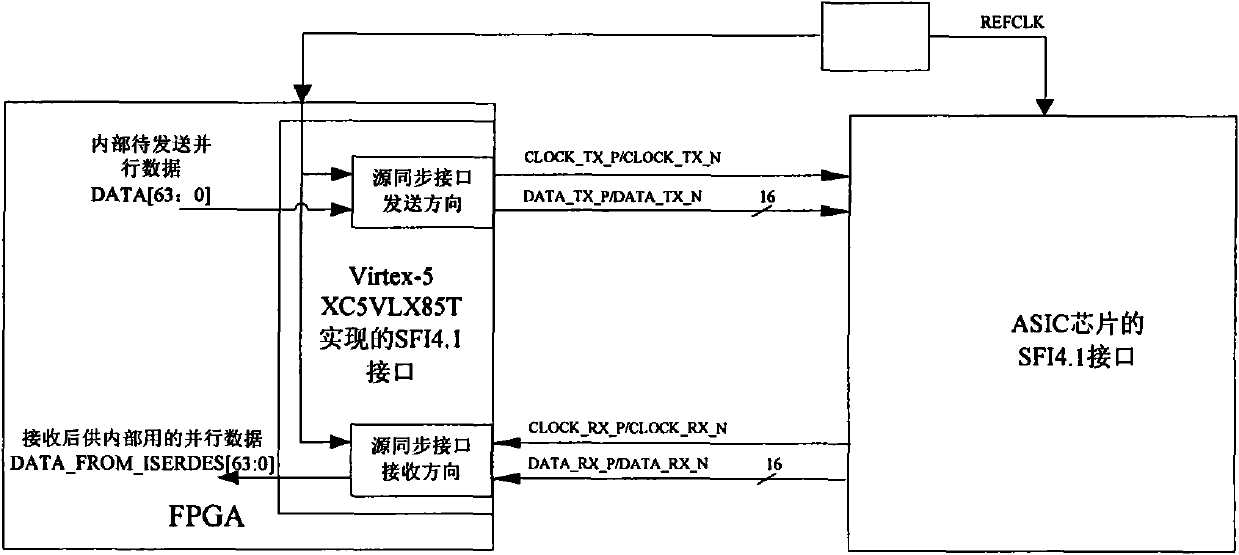
FPGA-based SFI4.1 device
ActiveCN101951313AEasy to handleIncrease flexibilitySynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFibre transmissionSource-synchronousData transmission
The invention relates to an FPGA-based SFI4.1 device, an FPGA is used in the device for realizing an SFI4.1 interface, the device is respectively connected with an FPGA device and an ASIC chip in an OTN system through the SFI4.1 interface, the ASIC chip and the FPGA device share a reference clock REFCLK, a transmitter clock in the data transmission direction further directly adopts the reference clock REFCLK, and a receiver clock in the receiving direction directly adopts a channel-associated clock for processing. The device can realize correct receiving and sending of high-speed source synchronous data in the FPGA device, realize resources adopting the FPGA device of the parallel interface (SFI4.1) between a serial-parallel converter and a framer disclosed by an OIF, facilitate the processing of signals of a 10G source synchronous parallel bus transmitted by adopting the SFI4.1 in the FPGA device, enhance the flexibility of processing ODU2 signals of the system in the practical use, further meet the actual requirements of the device and simultaneously provide technological accumulation for designing source synchronous interfaces in the future.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
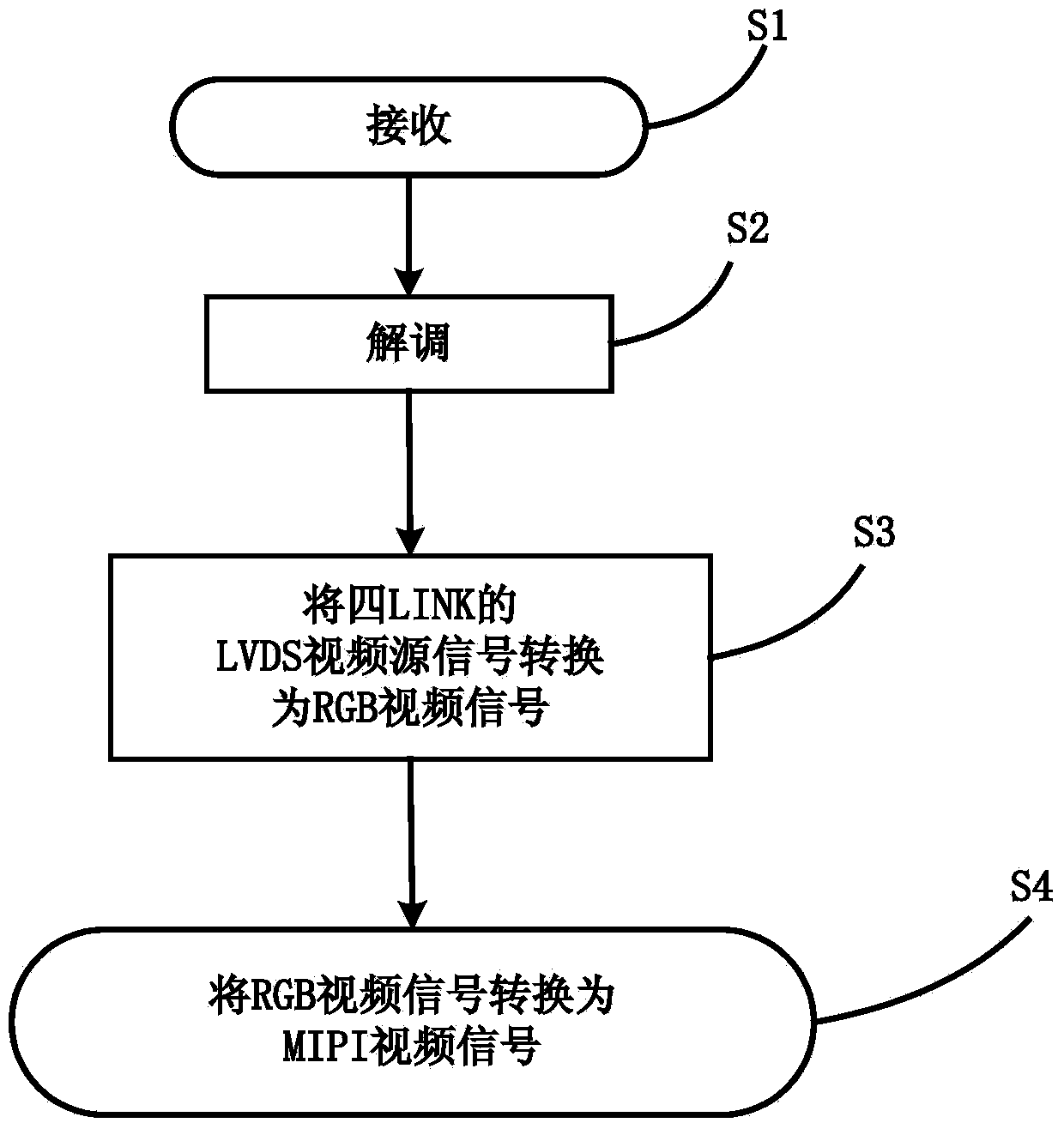
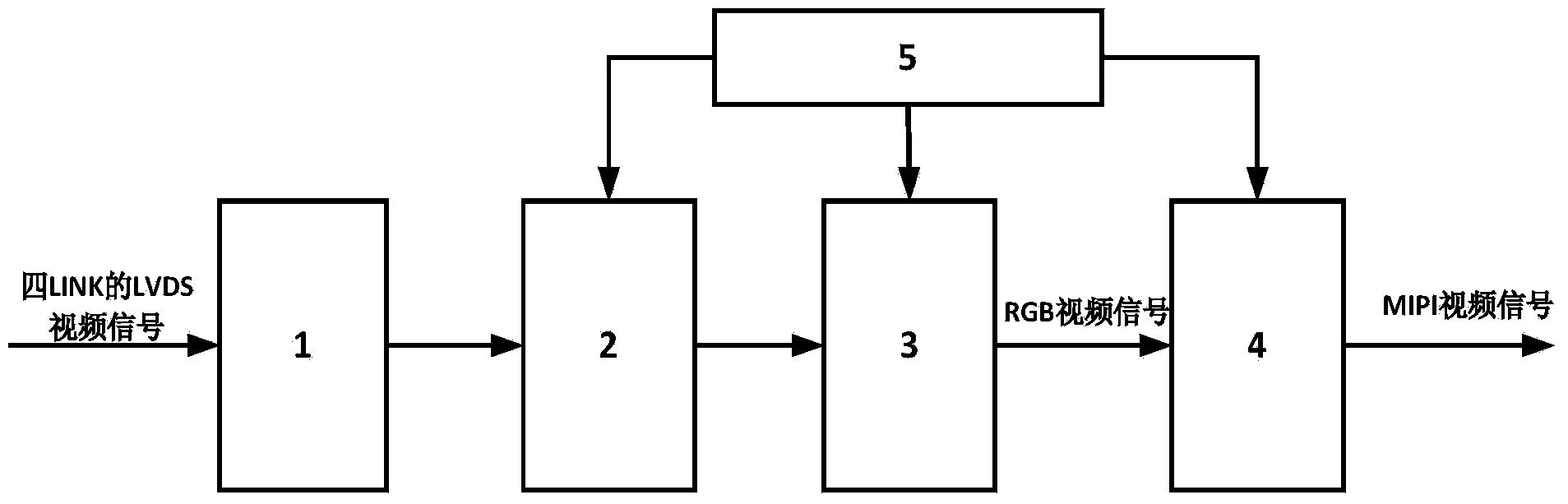
Method for switching four-LINK LVDS video signals into MIPI video signals
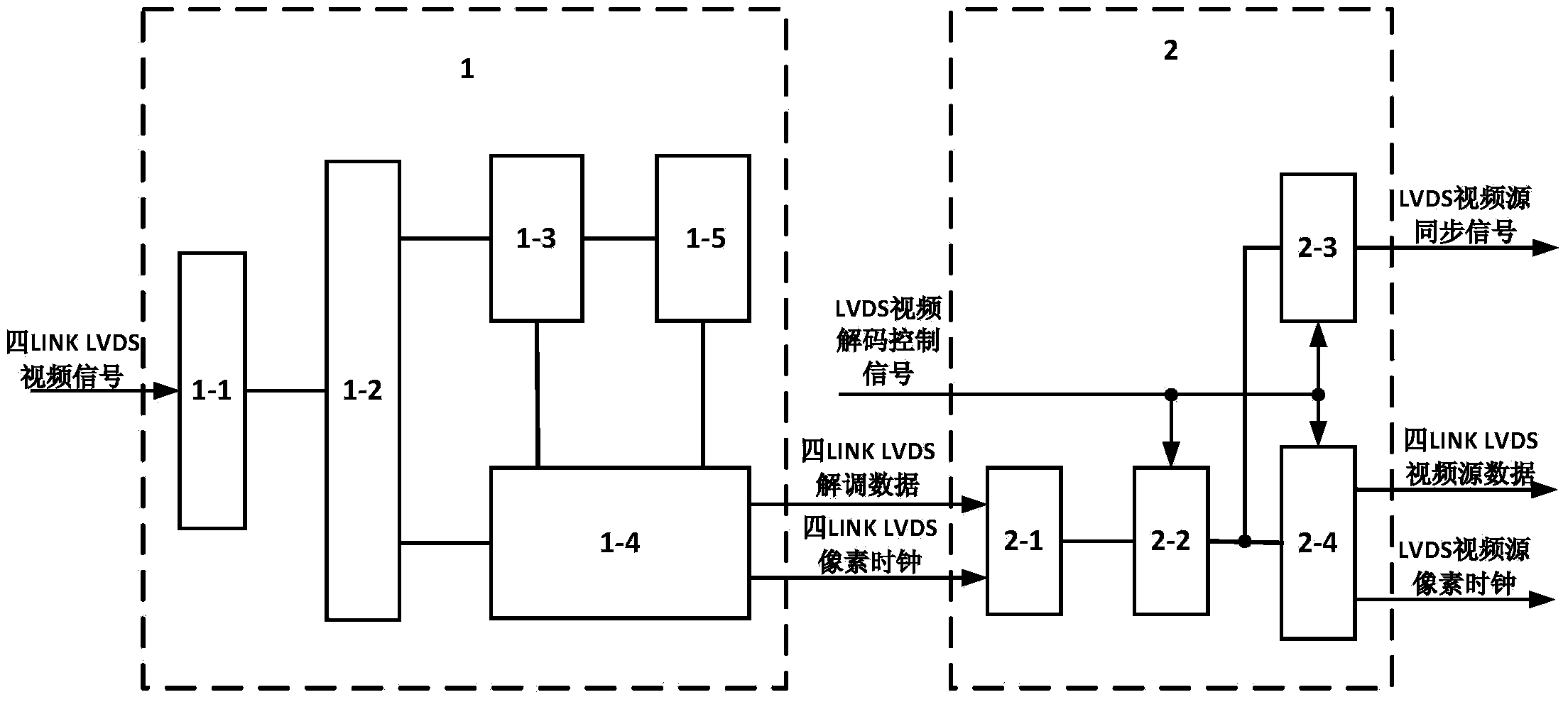
ActiveCN103475840AImprove matchSynchronization is easyStandards conversionPattern recognitionSource-synchronous
The invention discloses a method for switching four-LINK LVDS video signals into MIPI video signals. The method comprises the steps of respectively receiving and demodulating video signals of each link of four-LINK LVDS video signals so as to generate parallel demodulation data of four links and an LVDS pixel clock; conducting video decoding on the parallel demodulation data of the four links to generate LVDS video source signals of the four links, and switching the LVDS pixel clock into an LVDS video source pixel clock, wherein the LVDS video source signals of each link comprise LVDS video source data and LVDS video source synchronous signals; using the LVDS video source pixel clock to sample and cache the LVDS video source signals of the four links at the same time, and switching the LVDS video source signals into RGB video signals; switching the RGB video signals into MIPI video signals. The method has the advantages of being simple in operation, high in detection efficiency, and low in cost.
Owner:WUHAN JINGLI ELECTRONICS TECH
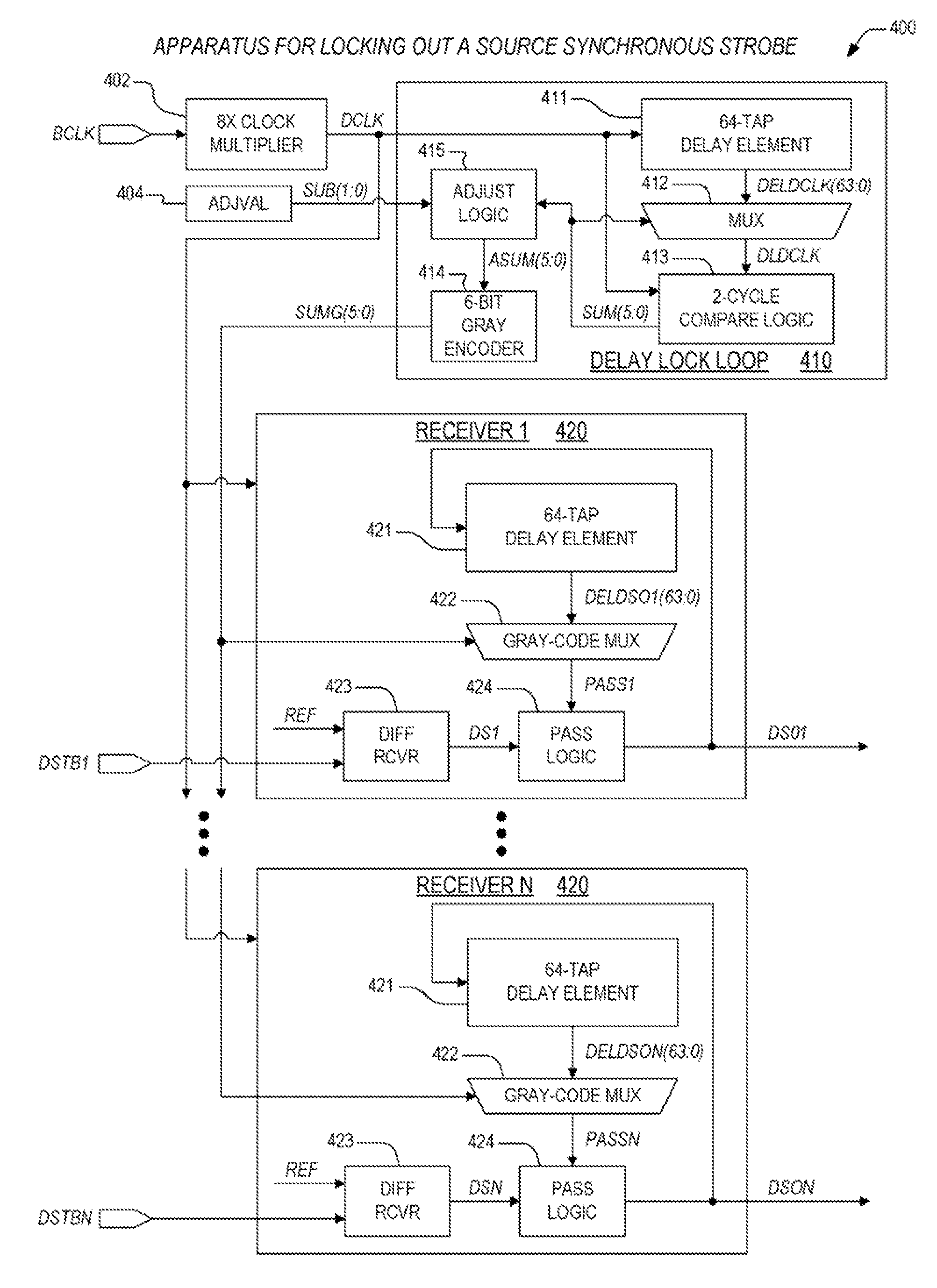
Encoded mechanism for source synchronous strobe lockout
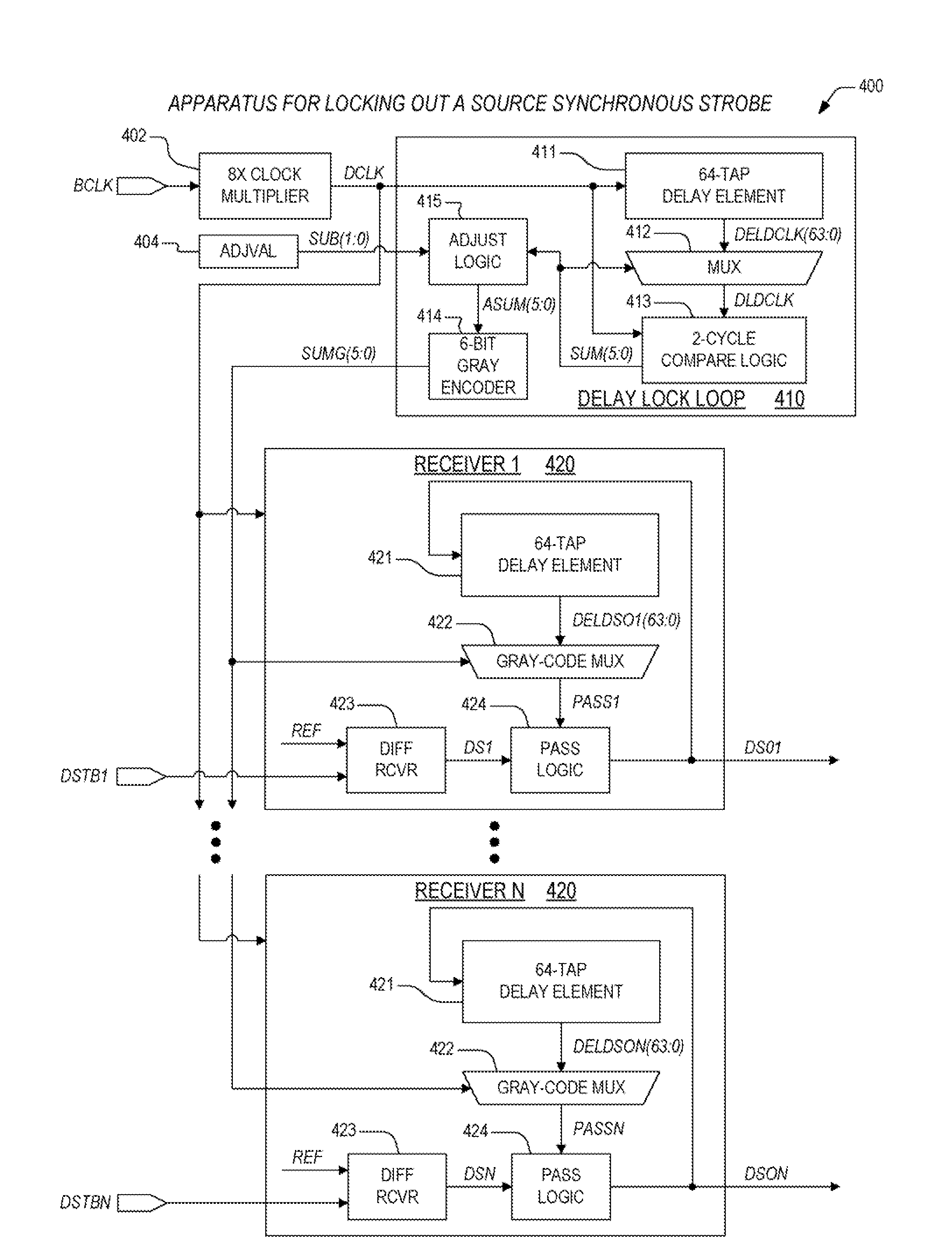
ActiveUS20080180147A1Good techniqueSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopSource-synchronous
An apparatus for locking out a source synchronous strobe receiver, including a delay-locked loop (DLL) and receivers. The DLL receives a reference clock, and generates a select vector and an encoded select vector. The select vector is employed to select a delayed version of the reference clock that lags the reference clock by a prescribed number of cycles. The select vector is reduced by an amount and is gray encoded to indicate the lockout time. The receivers are each coupled to the delay-locked loop. Each of the receivers receives the encoded select vector and a corresponding strobe, and locks out reception of the corresponding strobe for the lockout time following transition of the corresponding strobe. The encoded select vector is employed by a gray code mux therein to determine the lockout time by selecting a delayed version of the corresponding strobe.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Source synchronous I/O bus retimer
ActiveUS20050018760A1Improve signal integrityPulse transformerTime-division multiplexPhase differenceData signal
A device configured to recover and repeat source synchronous data. The device is configured to receive source synchronous data via a first interface and recover the received data utilizing a first clock signal which is generated to be approximately ninety degrees out of phase with the received clock signal. A second clock signal is generated to be in phase with the received source synchronous clock signal. The second clock signal is the utilized to select a newly generated clock signal and latched data for transmission in a source synchronous manner. The device is further configured to shift the phase of the generated first clock signal to be approximately ninety degrees out of phase with the received data signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
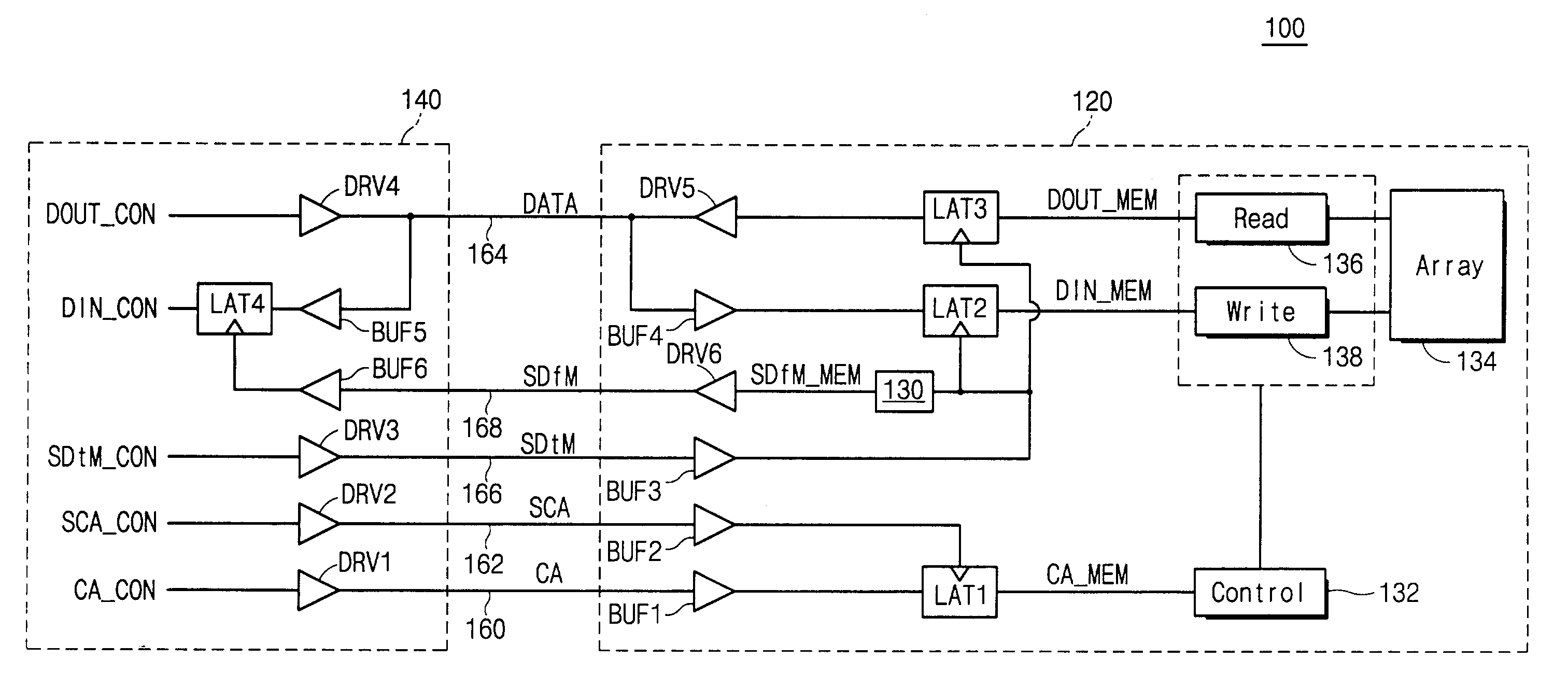
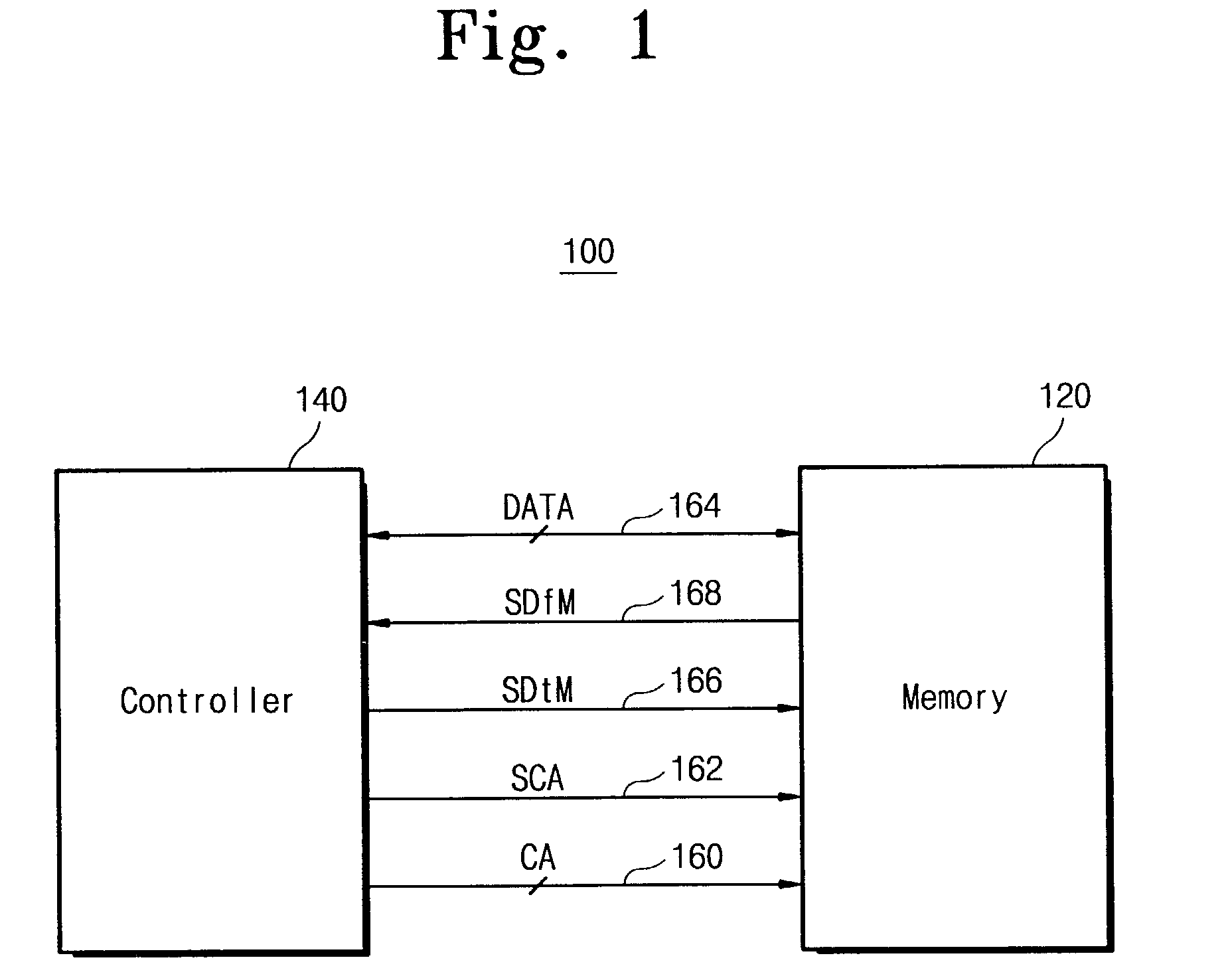
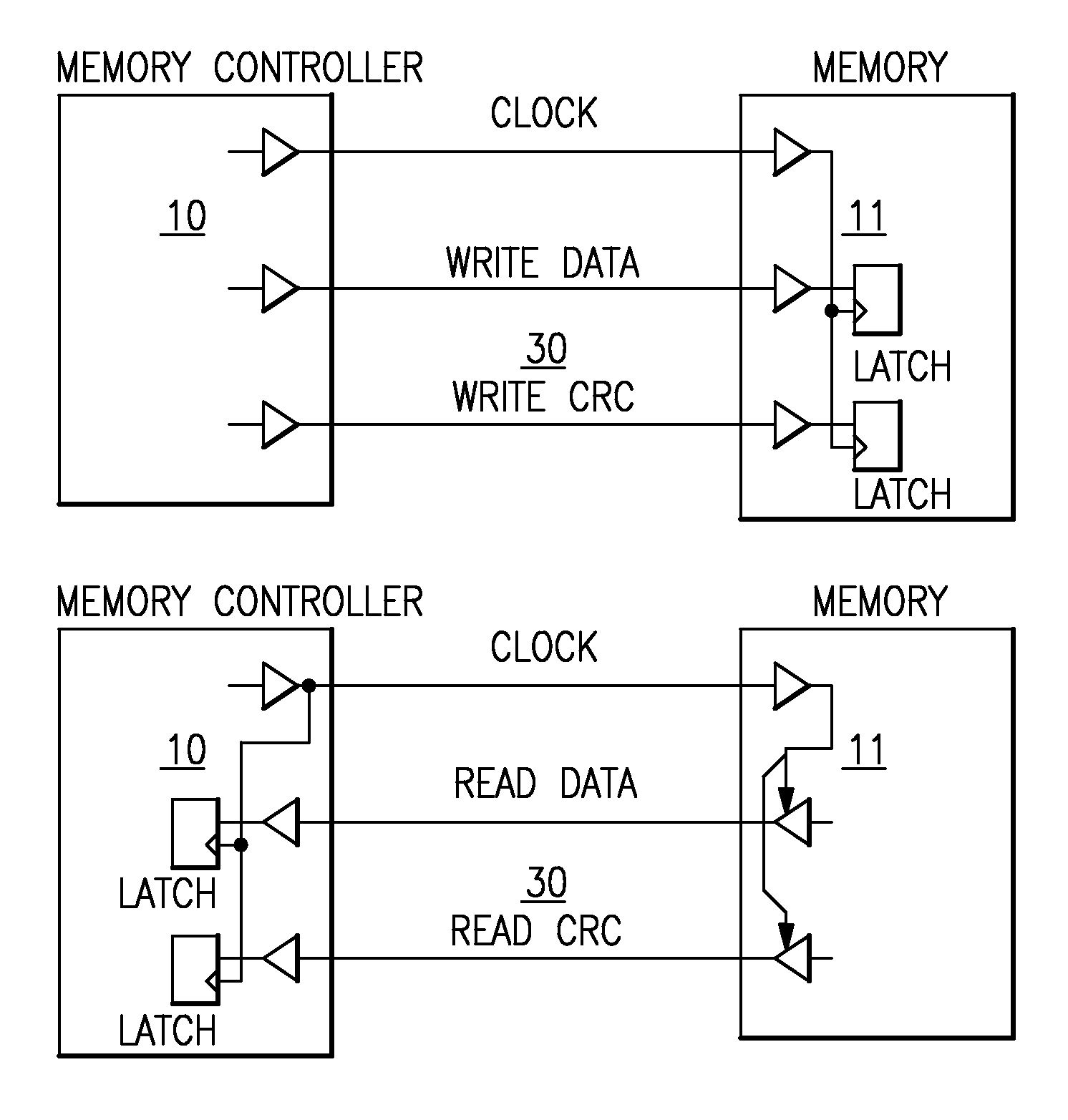
Synchronous memory having shared CRC and strobe pin
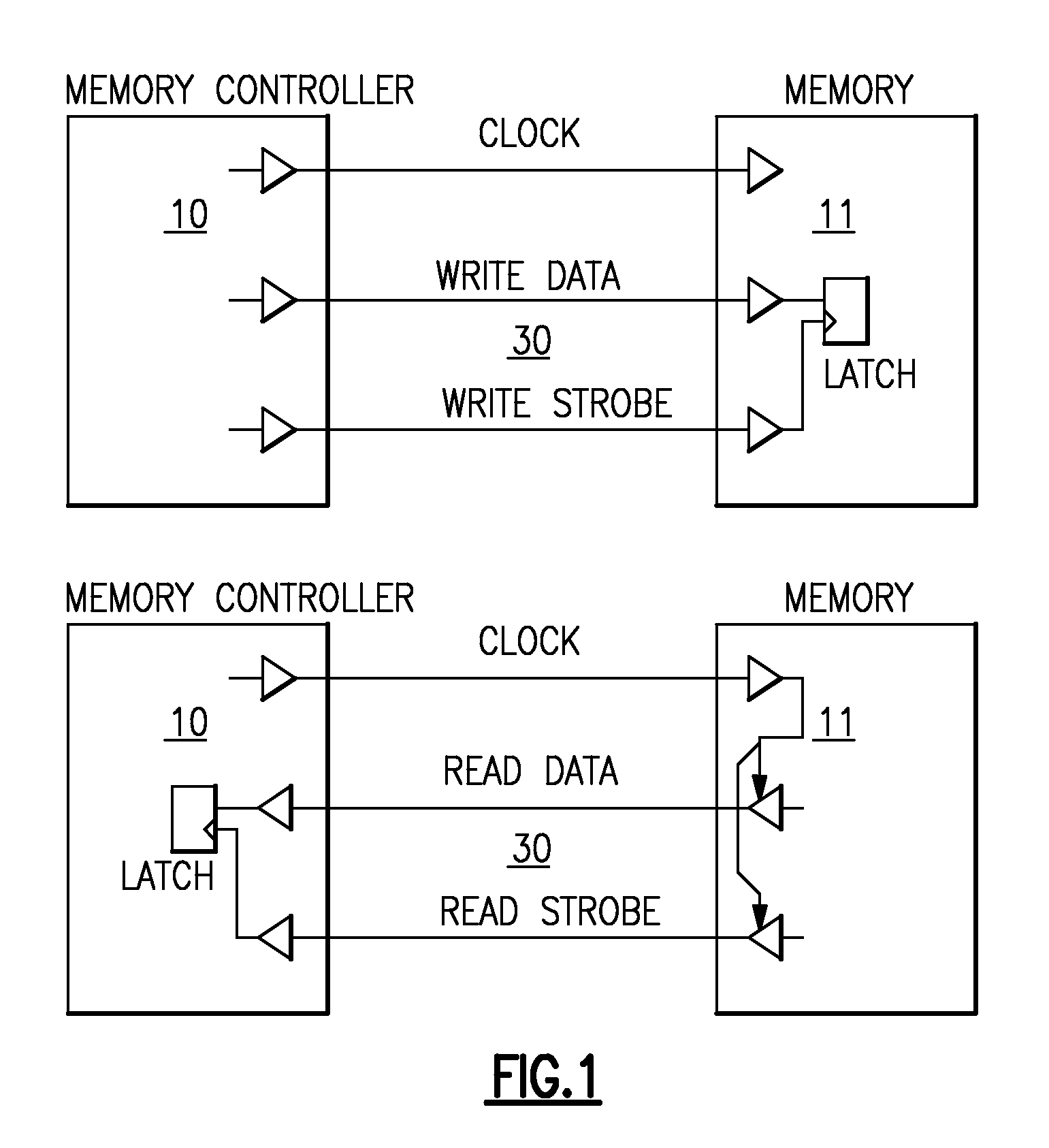
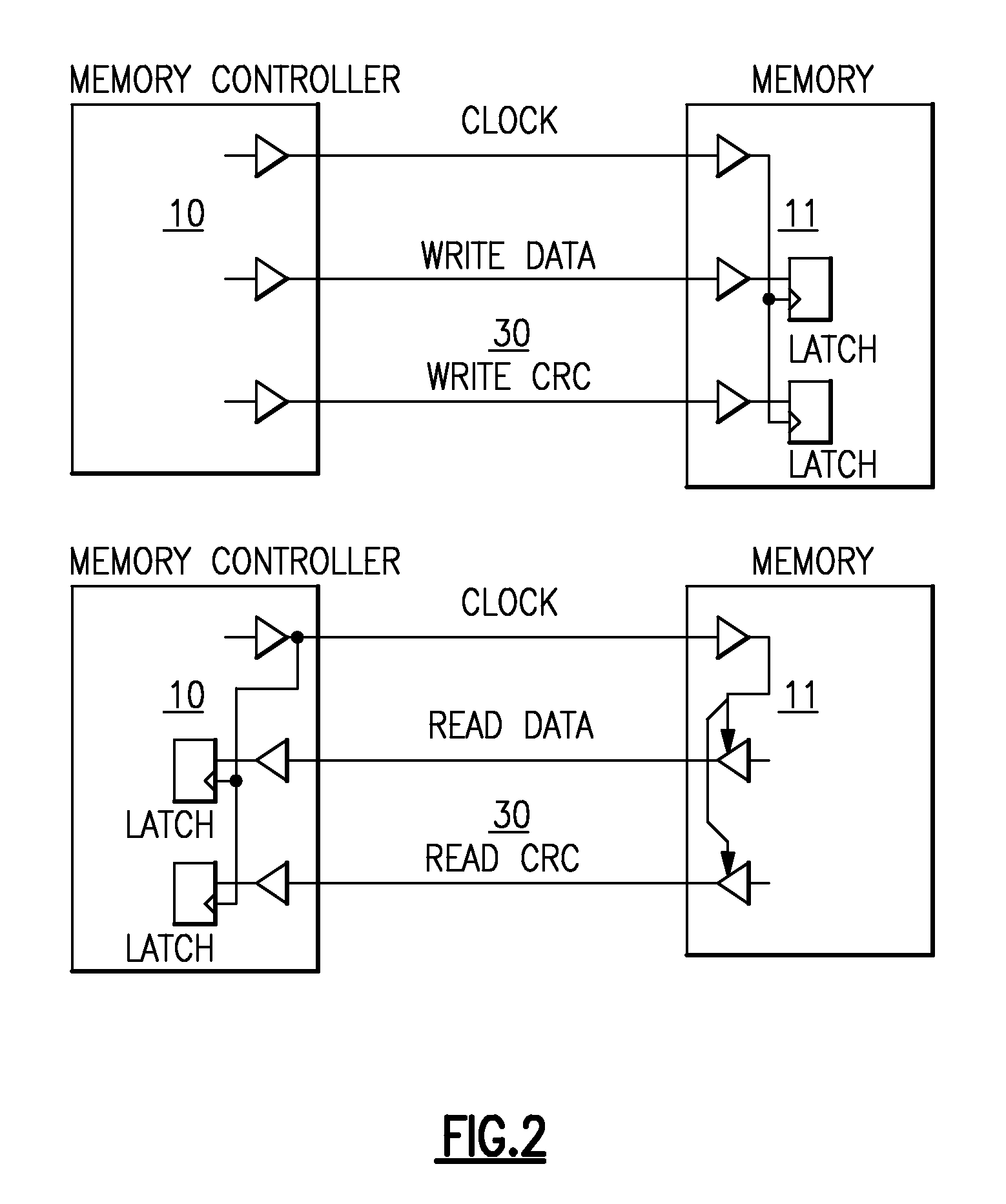
A memory system having a memory element chip (DRAM) and a memory controller chips having a plurality of drivers and receivers and latches for transferred data. For writes clocks, write data and write for CRC (cyclic redundancy checks) is transferred to the DRAM from the memory controller and latched for error checking. The reads are clocked and the read data is received and transferred to a read data latch with also receives a clocked read strobe for verification of data integrity from DRAM. Each chip has a bi-functional pin that acts as a shared CRC pin during write and acts as a shared strobe pin during READ. Data transfers with the CRC signal and DQS signal are transferred across two paths CRC0 / DQS and CRC1 / DQS1. One could also transfer the CRC signal across one path with only the CRC0 / DQS signal. Read operations have no CRC, and have no need for CRC because transfer errors during read can be detected by memory error correction coding (ECC). Write data provides source synchronous I / O data to said memory element chip needed for modem high speed memory communications.
Owner:IBM CORP
FPGA array processing board
InactiveCN101588175AIncrease storage capacityImprove memory depthDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingImaging processing
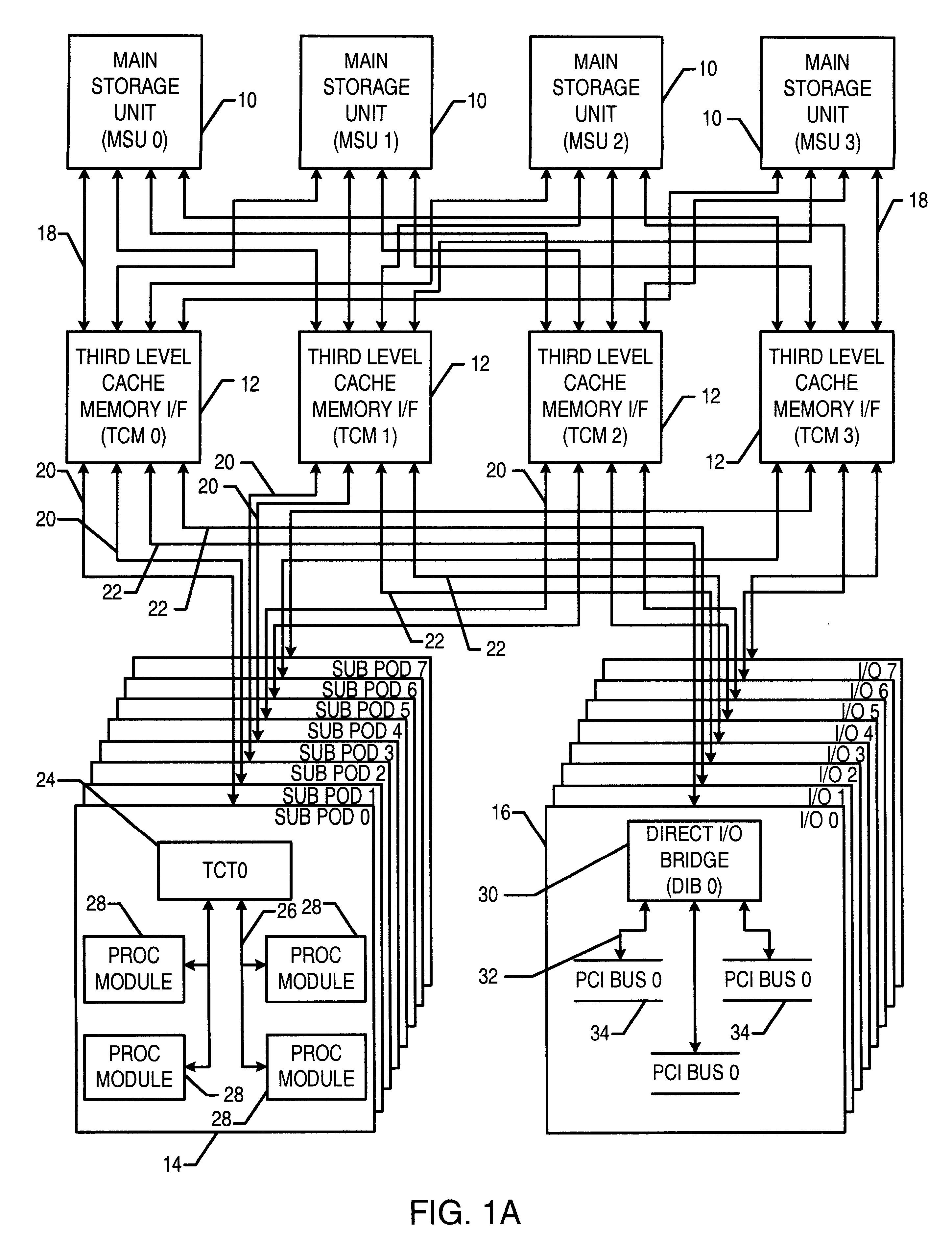
The invention relates to a FPGA signal processing board, belonging to the technical field of digital signal processing. The processing board comprises one power supply module, four FPGA processing sub modules, one FPGA transmit-receive module, one interconnect chip set module and one FPGA load application module, the FPGA processing sub module and the FPGA transmit-receive module are connected by full interconnect mode, the interconnect bandwidth between every two modules is as high as 1.6 B / s. The processing board can implement the external multiple high speed interfaces and load the DDR SDRAM with capacity of 4GB by PCI bus, Rapid IO bus and source synchronous interface, the storage bandwidth is as high as 10688 MB / s. the FPGA on the board has flexible configuring mode by adopting the DSP+CPLD+NAND configuring combination. The invention is suitable for the condition with harsh signal processing real time performance requirement, such as radar signal processing, image processing and communication base station and so on.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Double-pumped/quad-pumped variation mechanism for source synchronous strobe lockout
ActiveUS7543090B2Recording carrier detailsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopSource-synchronous
An apparatus for locking out a source synchronous strobe receiver, including a delay-locked loop (DLL) and receivers. The DLL receives a reference clock, and generates a select vector and an encoded select vector. The select vector is employed to select a delayed version of the reference clock that lags the reference clock by a prescribed number of cycles. The select vector is reduced by an amount and is gray encoded to indicate a first time. The receivers are each coupled to the delay-locked loop. Each of the receivers receives the encoded select vector and a corresponding strobe, and locks out reception of die corresponding strobe for a configurable lockout lime following transition of the corresponding strobe. The encoded select vector is employed by a gray code mux therein to determine the configurable lockout time by selecting a delayed version of the corresponding strobe.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
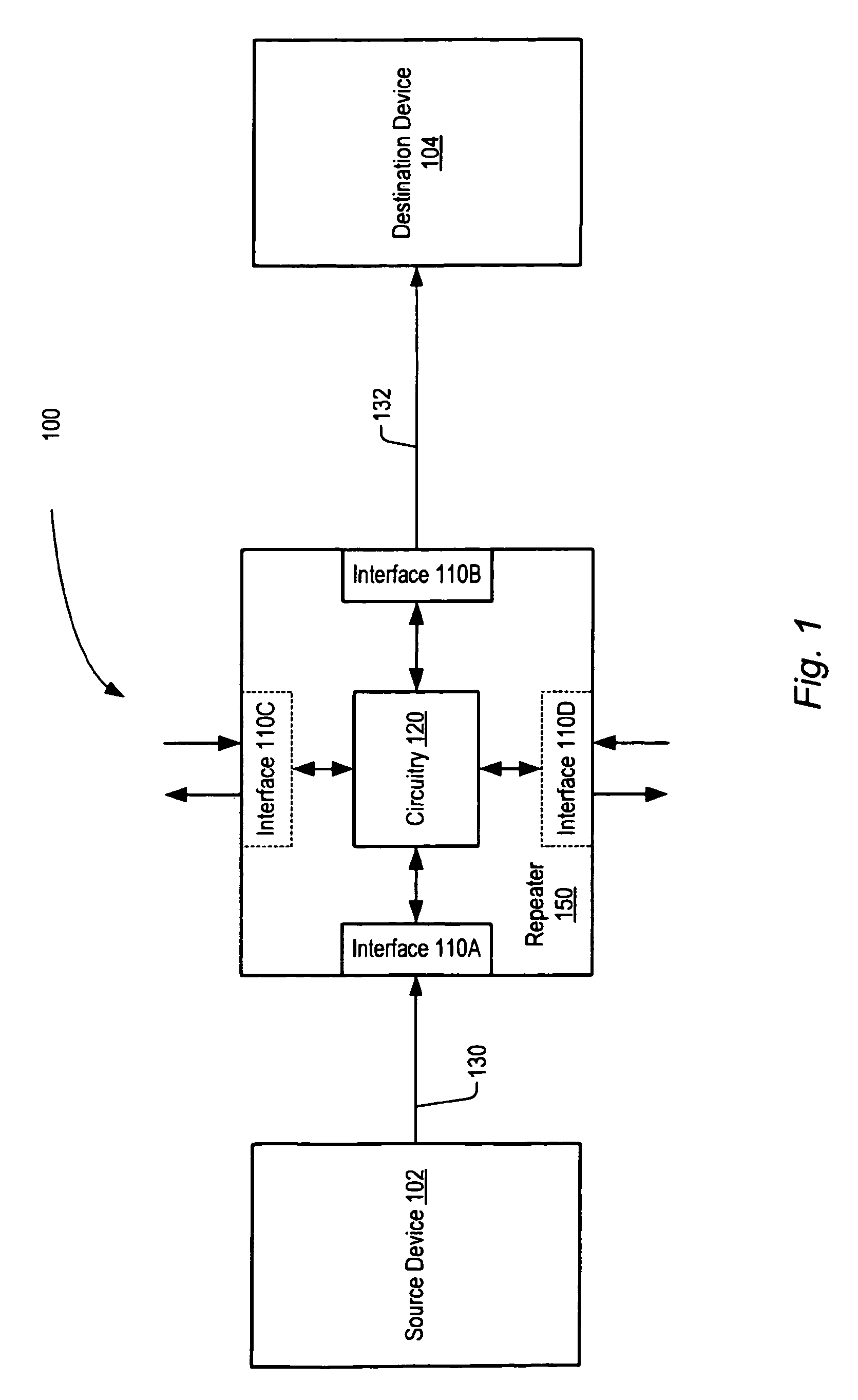
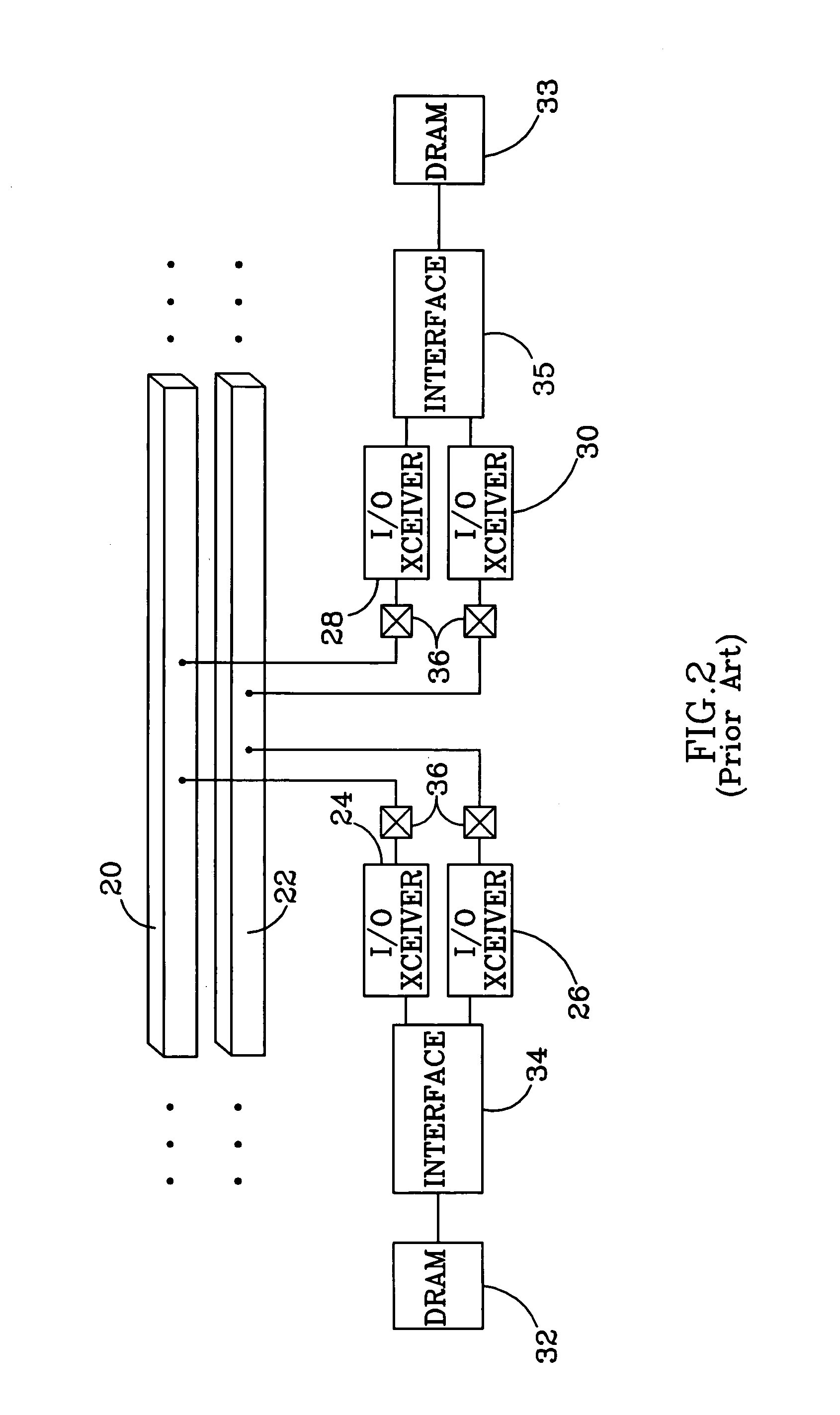
Source synchronous bus repeater
ActiveUS7139308B2Pulse transformerSynchronisation information channelsSource-synchronousSignal restoration
A device configured to recover and repeat source synchronous data. In one embodiment, the device is configured to receive source synchronous data via a first interface, recover the received data utilizing a corresponding received source synchronous clock signal, and transmit the recovered data and a corresponding clock signal in a source synchronous manner. In one embodiment, the device is configured to operate as a repeater without benefit of an internal clock signal. In addition, the device may be configured to remove data jitter and renew or restore amplitude to attenuated signals prior to retransmission.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
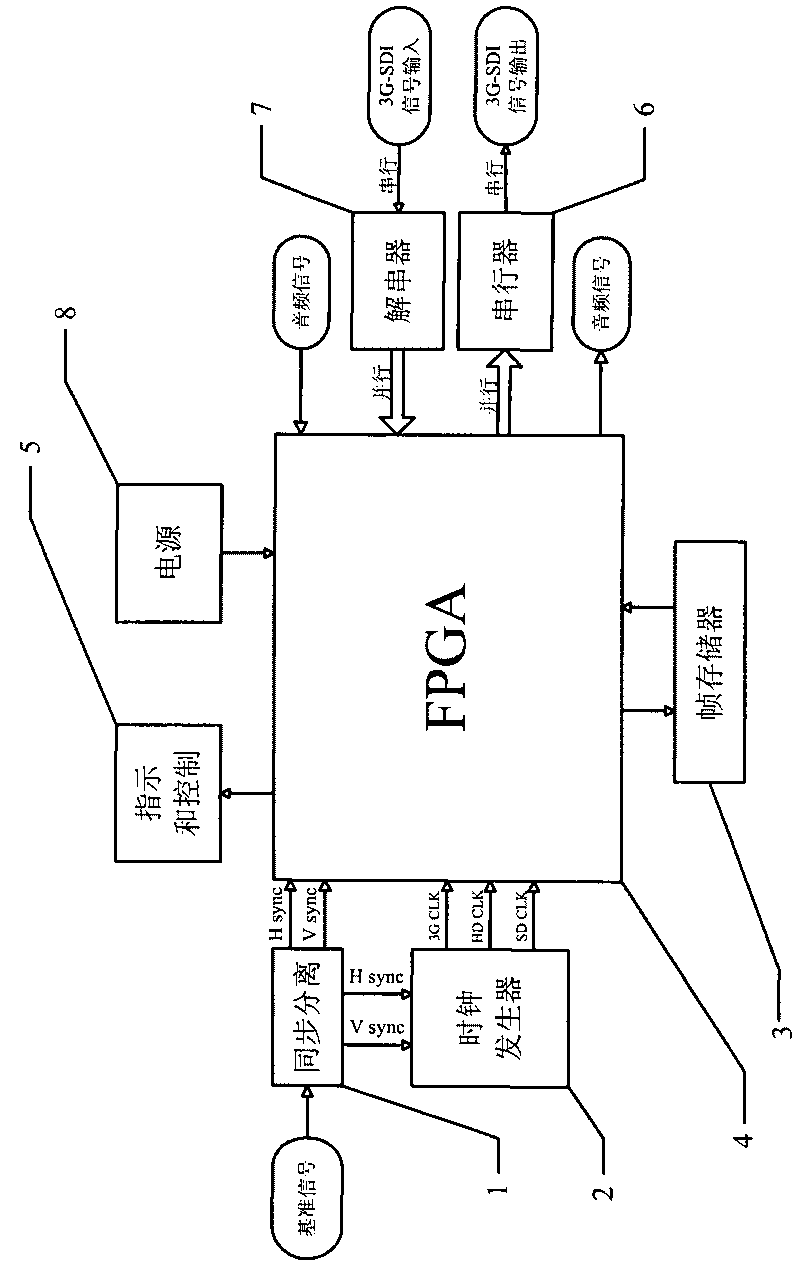
3G-SDI digital video frame synchronization system
InactiveCN101764921ARealize synchronous processingAccurate comparison of sync ratesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDistortionComputer science
The invention relates to a 3G-SDI digital video frame synchronization system comprising a synchronous separator (1), a clock generator (2), a frame storage (3), an FPGA chip (4), an indication and control unit (5), a serializer (6), a deserializer (7) and a power supply (8), wherein the synchronous separator (1) is connected with the FPGA chip (4) and the clock generator (2); and the frame storage (3), the indication and control unit (5), the serializer (6), the deserializer (7) and the power supply (8) are connected with the FPGA chip (4). The 3G-SDI digital video frame synchronization system overcomes the defect of time base errors or jitter caused by different signal sources or transmission paths at the signal transmission speed of 3 Gbps, and solves the problems of switching jitter, distortion, desynchronization, unstable station caption superposition, and the like of video images in a more precise and convenient way.
Owner:大连科迪视频技术有限公司
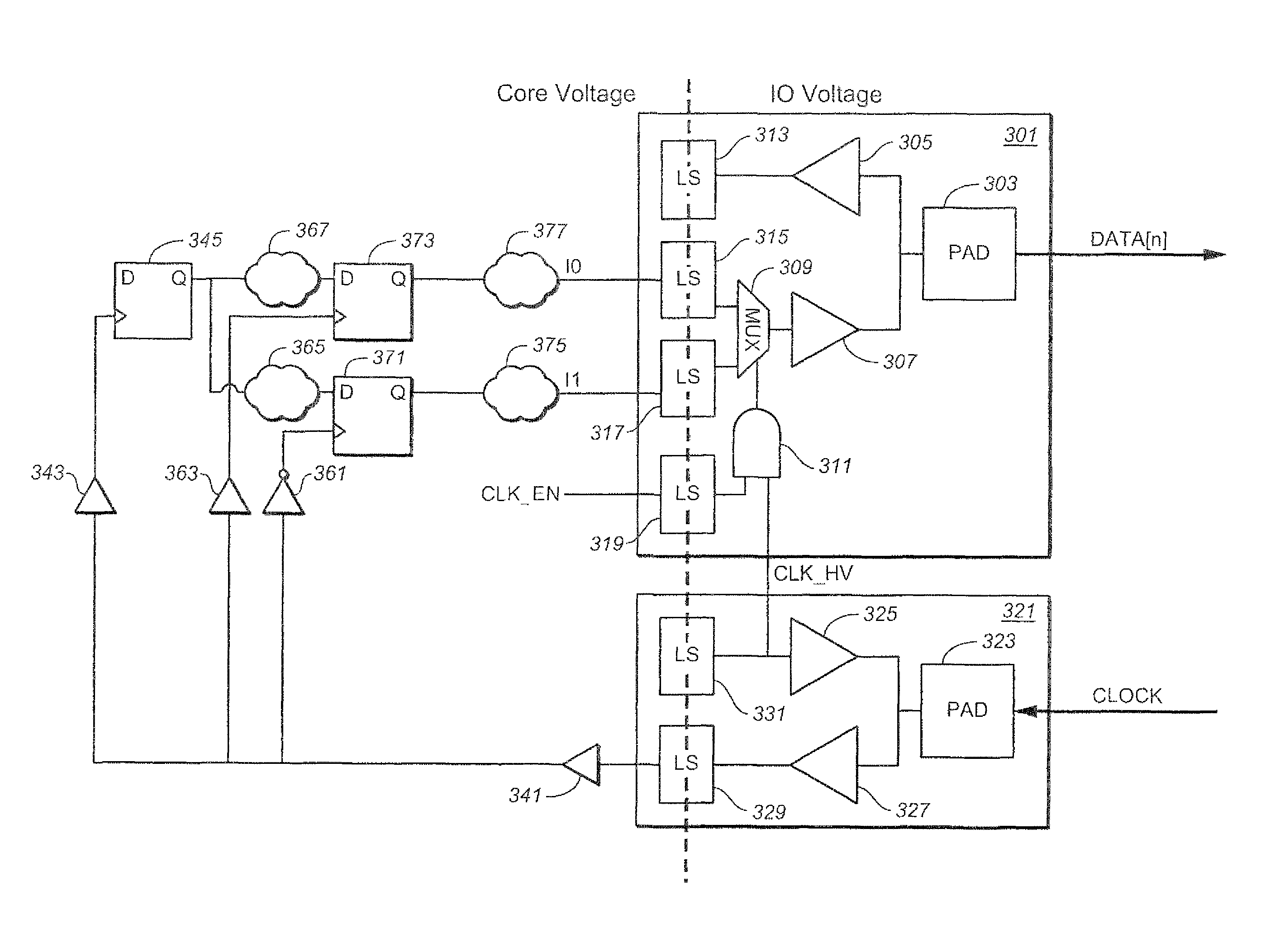
Enhancement of input/output for non source-synchronous interfaces
An interface for use of device whose core circuitry operates in one voltage domain, but exchanges signal with another device (or “host”) according a different voltage domain, and the use of such an interface for supplying data using a double data rate (DDR) transfer, is presented. One concrete example of this situation is a memory card, where the internal circuitry uses one voltage range for its core operating voltages, but exchanges signals with a host using different, input / output voltage range. According to a general set of aspects, the interface receives data signals from the device at the device's core operating voltage domain, individually level shifts these to the input / output voltage domain, and then combines them into a DDR signal for transfer to the host device, where a (non-level shifted) clock signal from the host device is used as the select signal to form the DDR data signal.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Memory device and memory system comprising a memory device and a memory control device
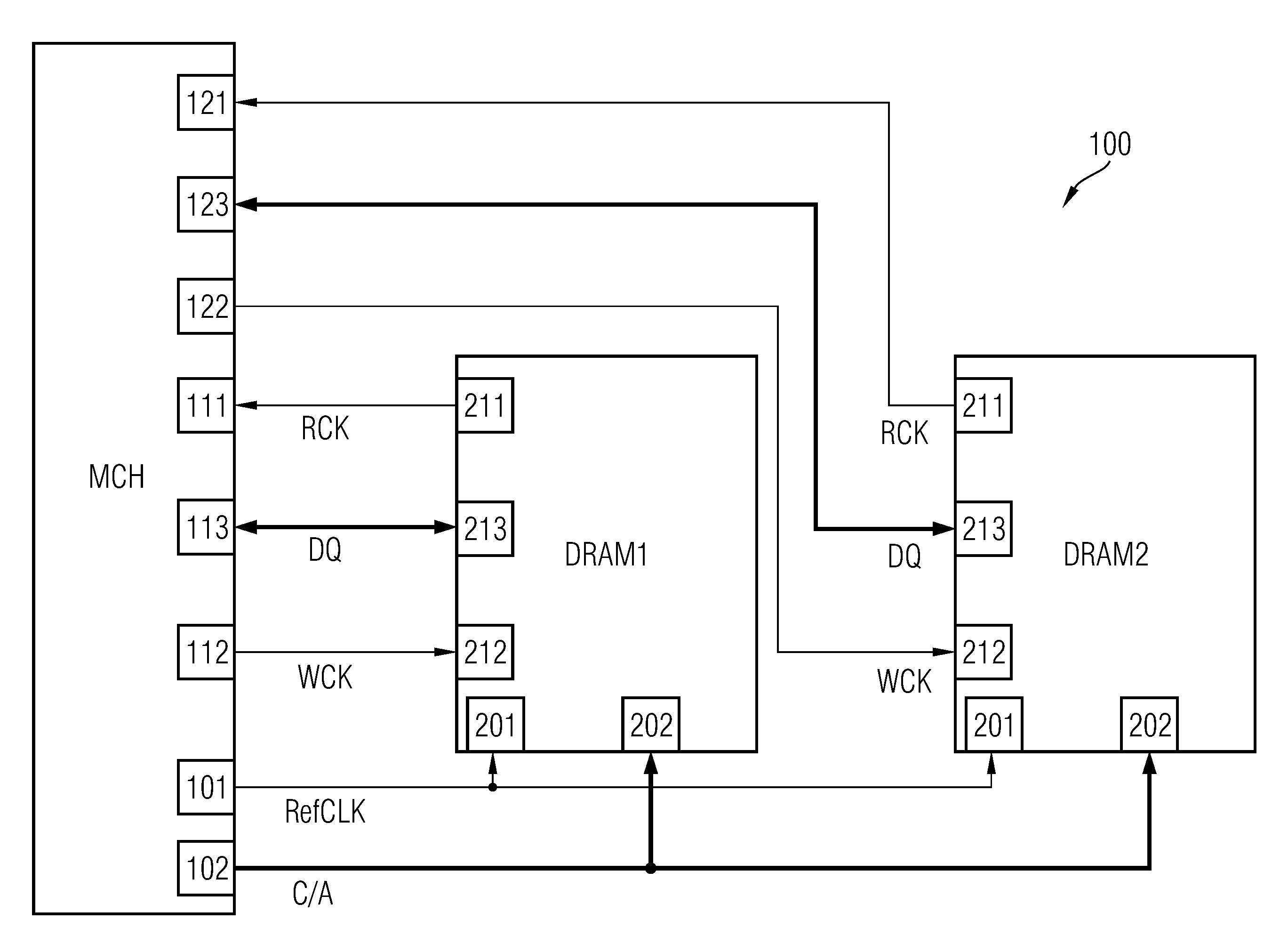
InactiveUS8031539B2Improve data transfer rateReduce power consumptionDigital storageElectric pulse generatorData signalSource-synchronous
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Data capture technique for high speed signaling
InactiveUS7418068B2Improve signal qualitySafely exchange setting parameterError preventionDigital data processing detailsData streamData rate
A data capture technique for high speed signaling to allow for optimal sampling of an asynchronous data stream. This technique allows for extremely high data rates and does not require that a clock be sent with the data as is done in source synchronous systems. The present invention also provides a hardware mechanism for automatically adjusting transmission delays for optimal two-bit simultaneous bi-directional (SiBiDi) signaling.
Owner:IBM CORP
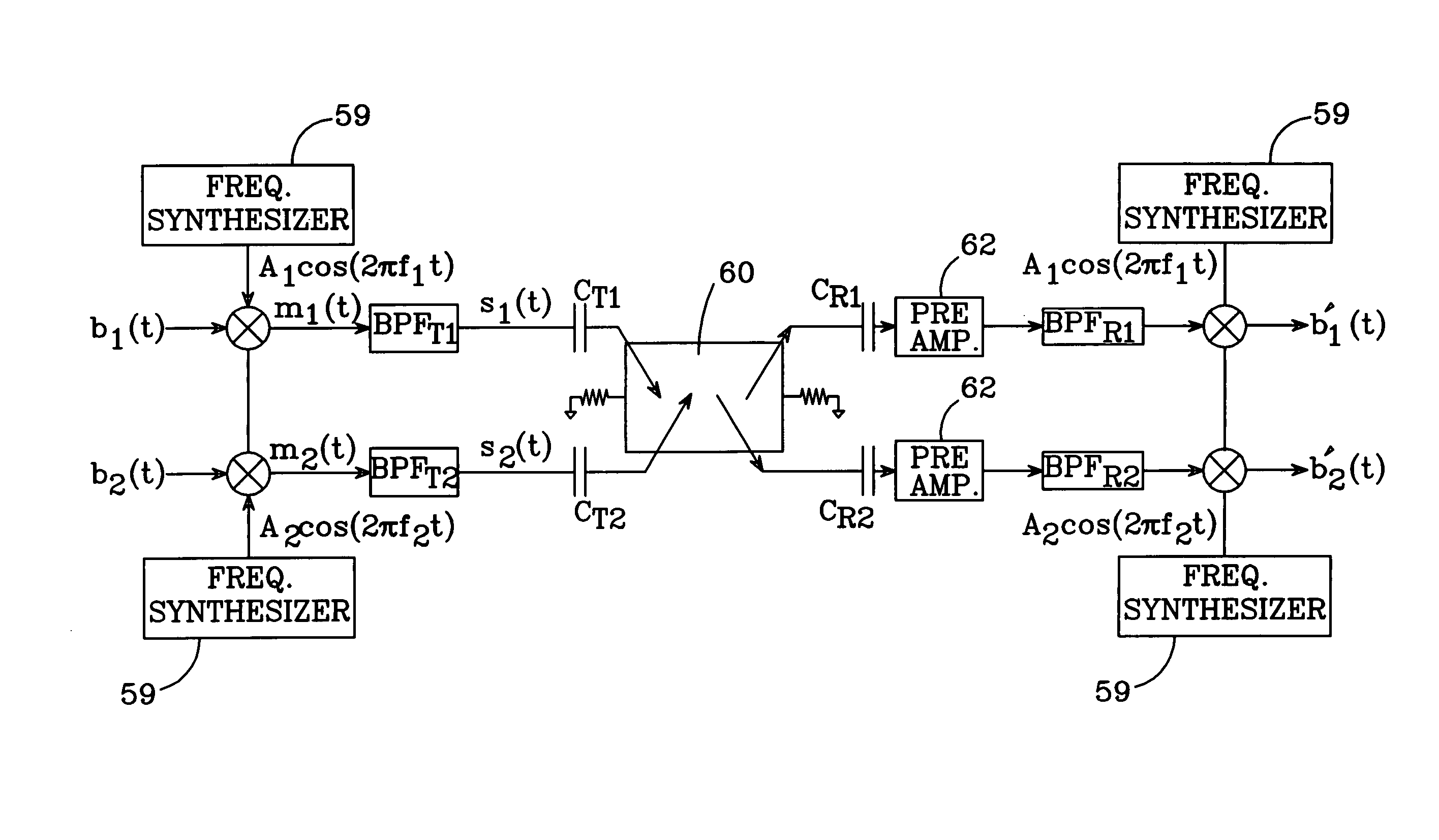
Source synchronous CDMA bus interface
InactiveUS7263148B2Eliminate featureEliminate rateModulated-carrier systemsNear-field systems using receiversCapacitanceHigh bandwidth
A wireless IC interconnect system and a source synchronous CDMA (SS-CDMA) bus interface facilitate interconnections between first and second IC locations. A signal conveyed using the wireless system is modulated and capacitively coupled to a transmission medium, and then capacitively coupled from the medium to a receiver which demodulates the modulated signal and provides the demodulated signal to the second IC location. Multiple signals can be conveyed simultaneously by modulating and demodulating them using multiple access algorithms such as CDMA and / or FDMA. The SS-CDMA bus interface utilizes source synchronous signaling and CDMA techniques to provide high bus concurrency and low channel latency. The interface is re-configurable, and provides multi-chip access in high-bandwidth multi-drop parallel interconnection applications. The interface employs spread spectrum multiple access schemes, which enable two or more data bits to be sent through the same channel simultaneously and successfully recovered at the receiver.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com