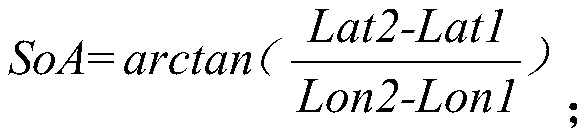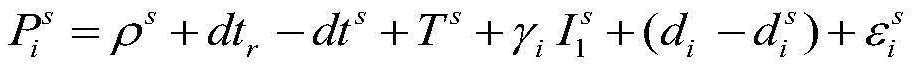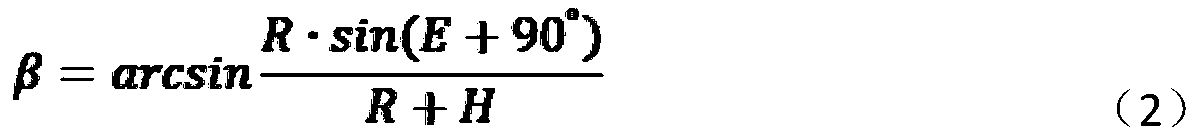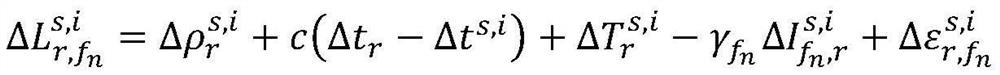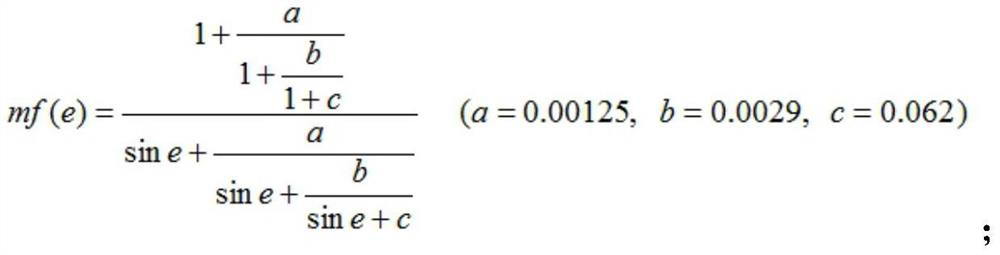Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Satellite altitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A geostationary satellite is an earth-orbiting satellite, placed at an altitude of approximately 35,800 kilometers (22,300 miles) directly over the equator, that revolves in the same direction the earth rotates (west to east). At this altitude, one orbit takes 24 hours, the same length of time as the earth requires to rotate once on its axis.
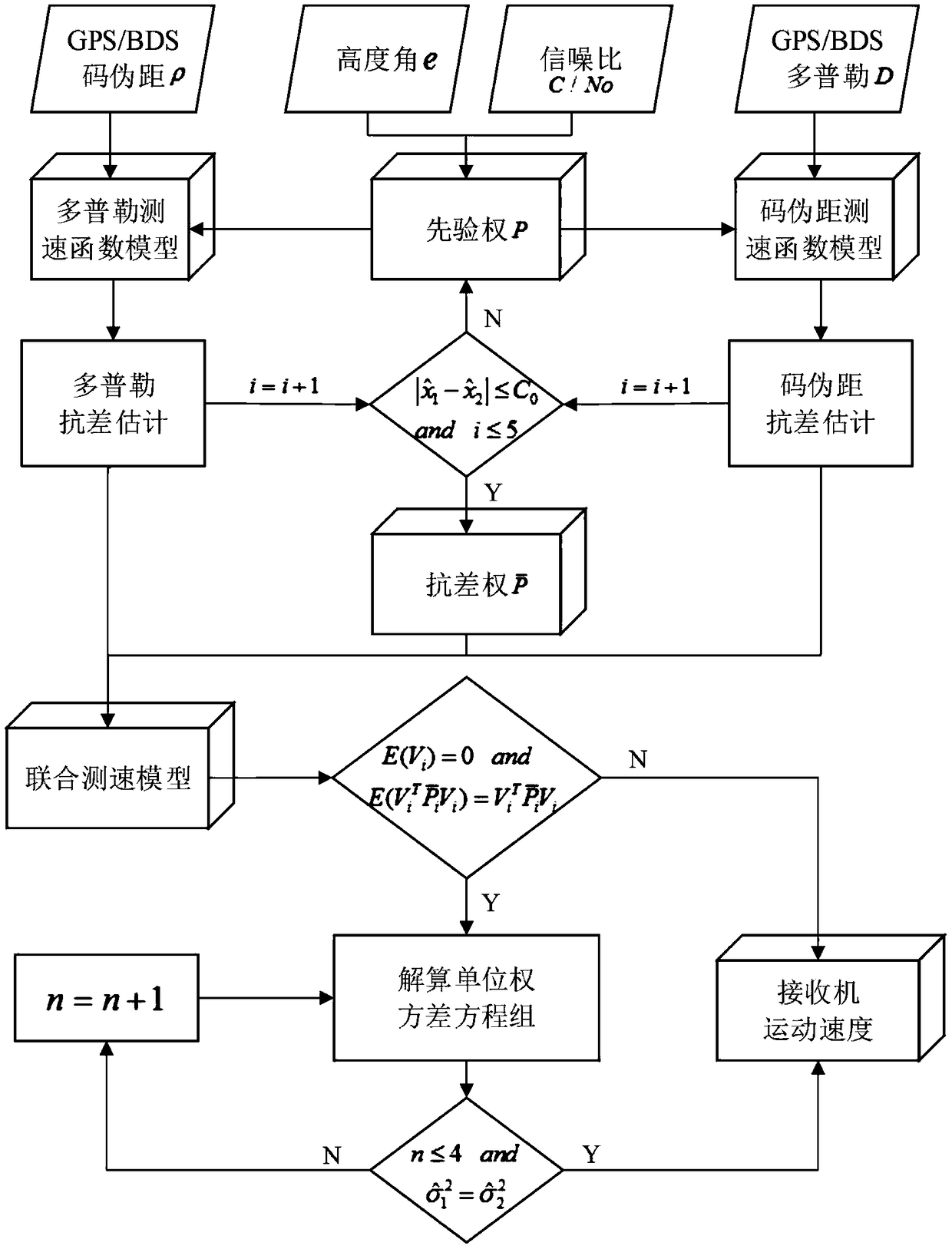
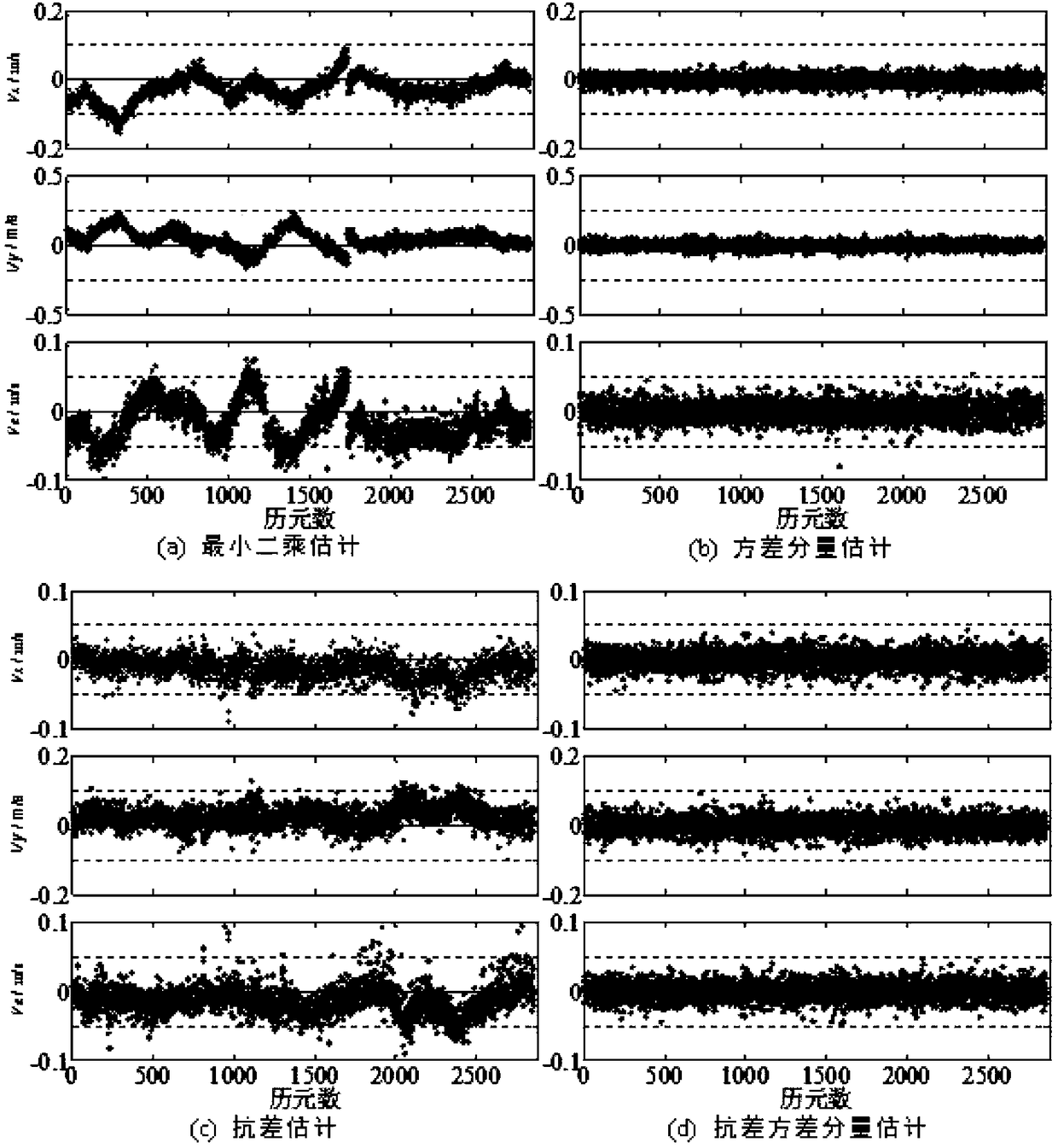
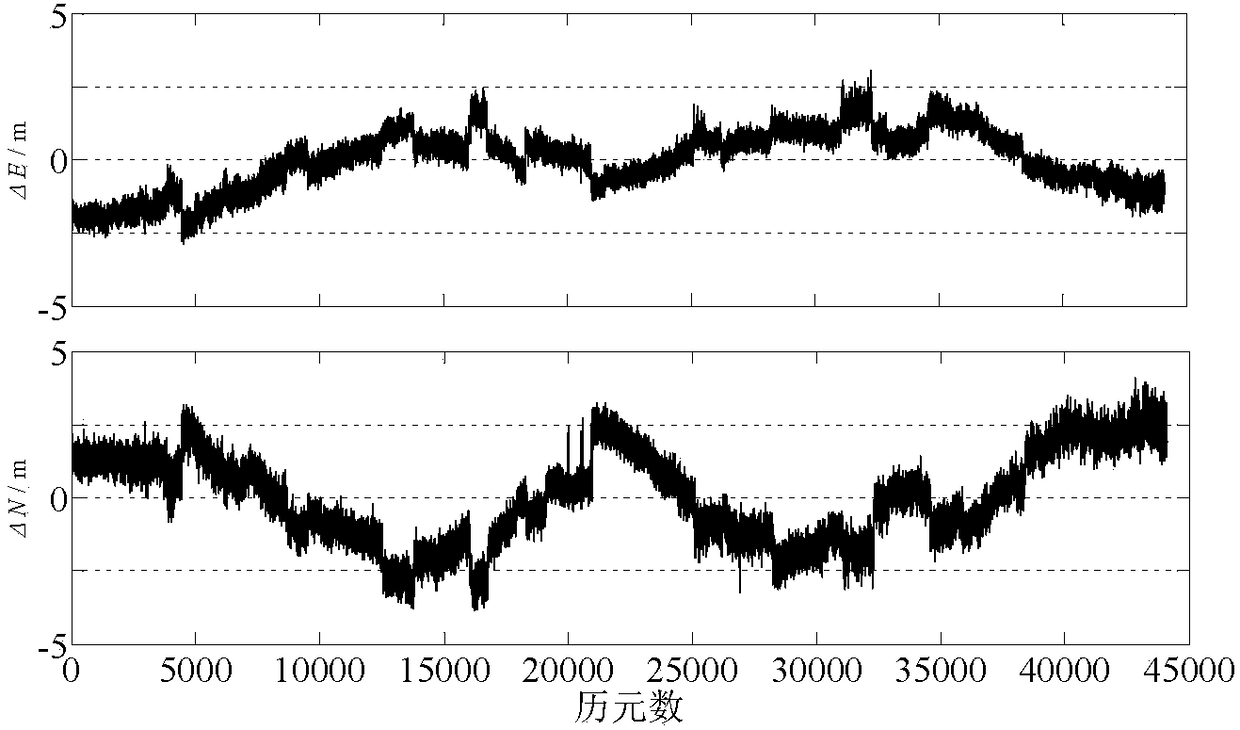
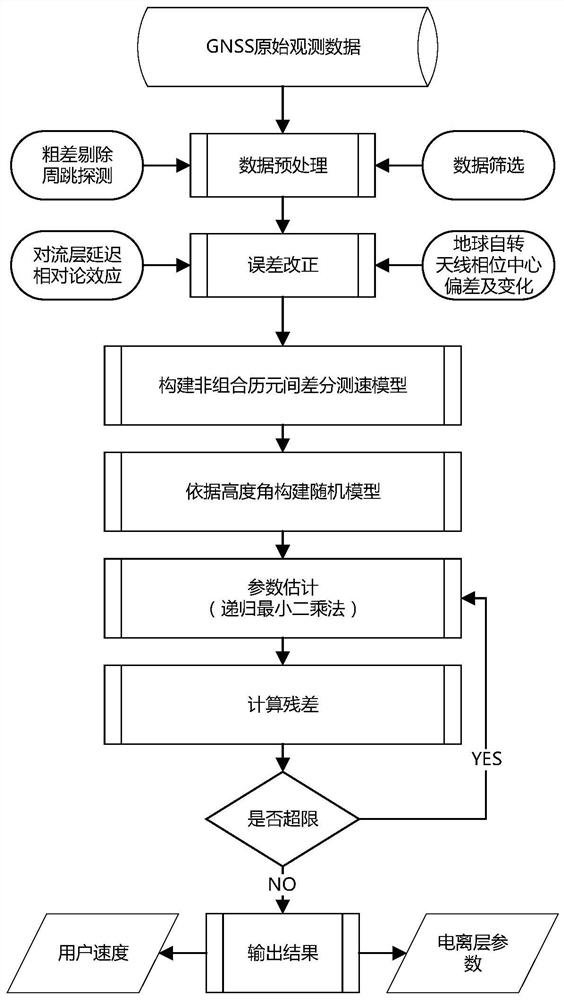
Code pseudo-range/Doppler combined speed measurement method based on robust variance assembly estimation and application thereof
ActiveCN109459778AImprove robustnessImprove stabilitySatellite radio beaconingEstimation methodsLeast squares
The invention discloses a code pseudo-range / Doppler combined speed measurement method based on robust variance assembly estimation, which comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively establishing a speed measurement function model and a random model by adopting observation information such as code pseudo-range, Doppler, carrier-to-noise ratio, satellite altitude angle and the like, then adopting a least square robust estimation method to obtain a robust random model capable of inhibiting the influence of gross error, and finally combining a speed measurement function model of code pseudo-range and Doppler with the robust random model to form a combined speed measurement model. According to the method, the limitation that the conventional single-frequency satellite receiver only uses single information to measure the speed can be broken through, the influence of observation gross error can be inhibited, and the robustness, the unbiased property and the stability of the combinedspeed measurement method can be obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
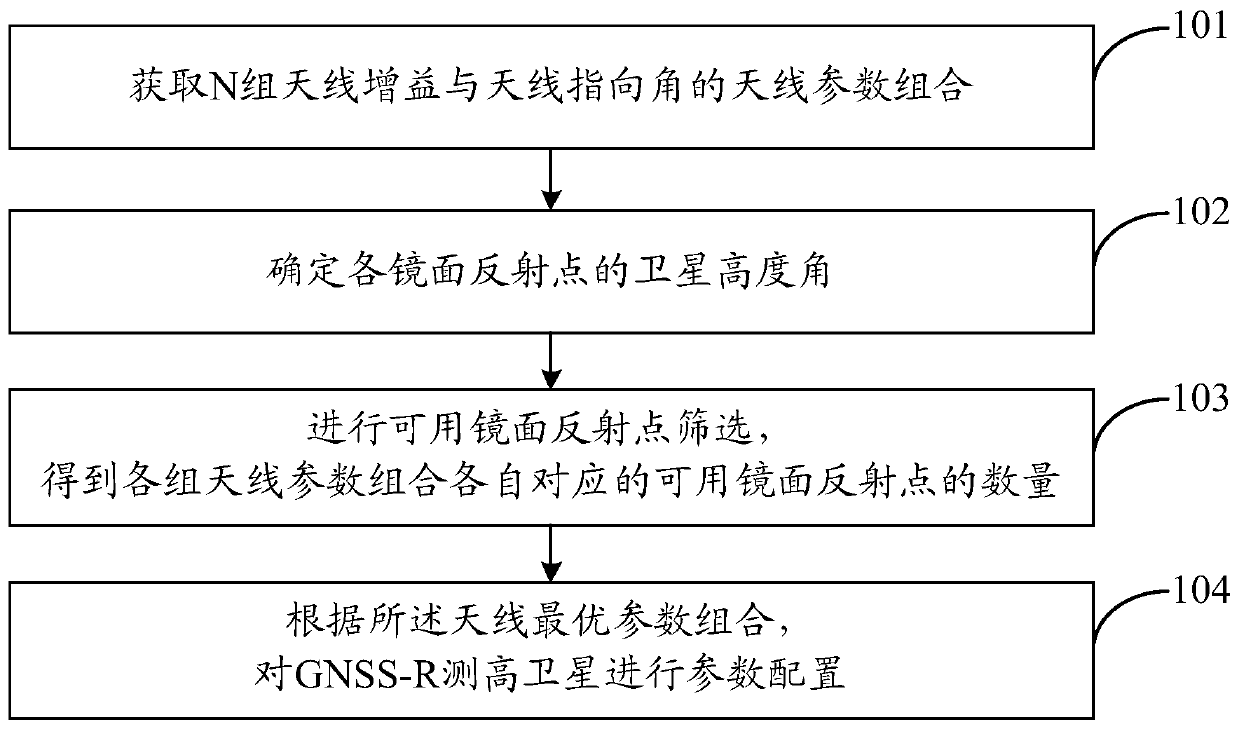
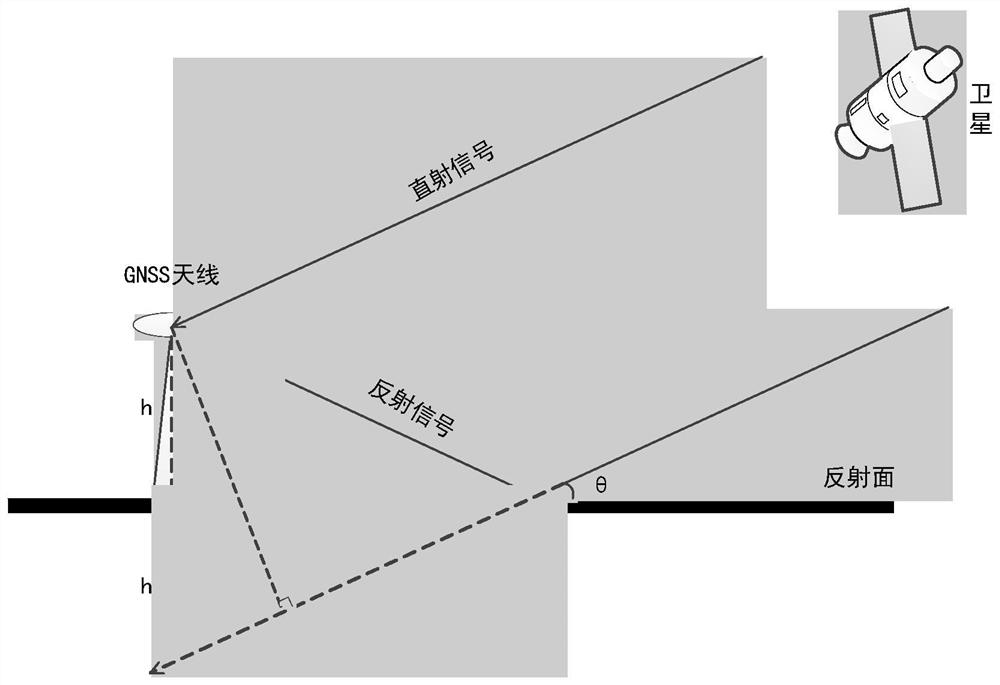
Method for increasing number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R height measurement satellites
ActiveCN110824510AImprove work efficiencyHigh working reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingMirror reflectionAntenna gain
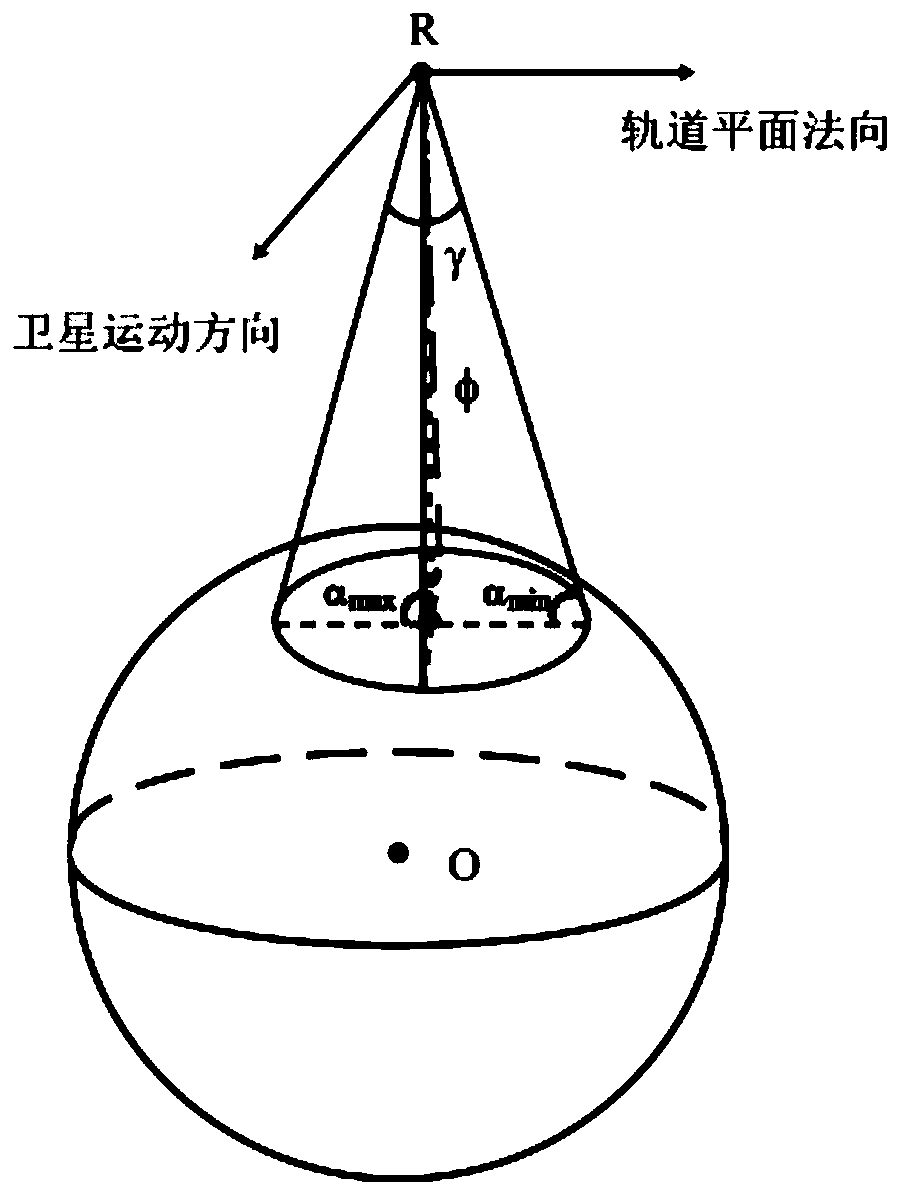
The invention discloses a method for increasing the number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R height measurement satellites. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining antenna parameter combinations of N groups of antenna gains and antenna pointing angles; acquiring position information of all mirror reflection points, and determining a satellite altitude angle of each mirror reflection point; under the condition of each group of antenna parameter combinations, screening available mirror reflection points according to the mirror reflection points, and obtaining the number of available mirror reflection points corresponding to each group of antenna parameter combinations; determining a group of antenna parameter combinations with the largest number of available mirror reflection points as an optimal antenna parameter combination; and according to the optimal antenna parameter combination, configuring parameters of the GNSS-R height measurement satellite to increase the number of sea surface reflection signals received by the GNSS-R height measurement satellite. According to the invention, the number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R height measurement satellites is increased.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Beidou IGSO/MEO satellite pseudo-range code deviation one-step modeling method
ActiveCN107544082AEliminate correctnessConvenient and effective connectionSatellite radio beaconingInteger ambiguityComputer science
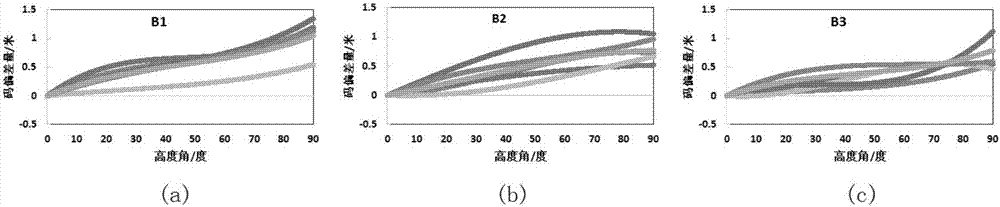
The present invention discloses a Beidou IGSO / MEO satellite pseudo-range code deviation one-step modeling method. An original phase observed value is subjected to cycle slip detection to determine whether a phase observed value in each frequency at a current epoch is set as a reference epoch or not, pseudo-range code deviation of a receiver is neglected based on an MP (Multi-Path) combination observed value, and each observation station MP combination observed value of each epoch is subjected to weighing according to a satellite elevation and then reference epochs with the same arc section aresubtracted from each observation station MP combination observed value of each epoch to accurately eliminate unknown integer ambiguity parameters so that the pseudo-range code deviation of a single satellite in each frequency is added into a same method equation to comprehensively solve a three-order polynomial correction model coefficient, the pseudo-range code deviation related to an elevatingangle of each satellite in each frequency is accurately corrected to an extreme, stability of a code-phase combination observed value of the Beidou satellite is improved, and the Beidou IGSO / MEO satellite pseudo-range code deviation one-step modeling method has an important meaning for shortening fuzziness convergence time.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
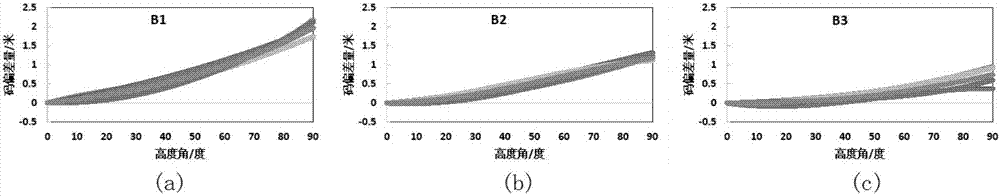
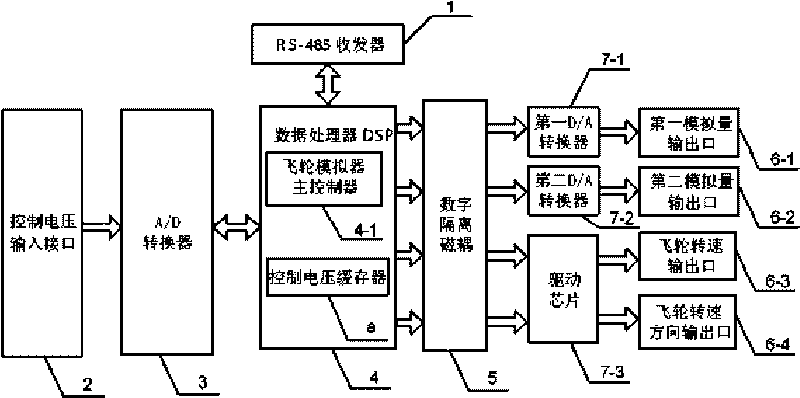
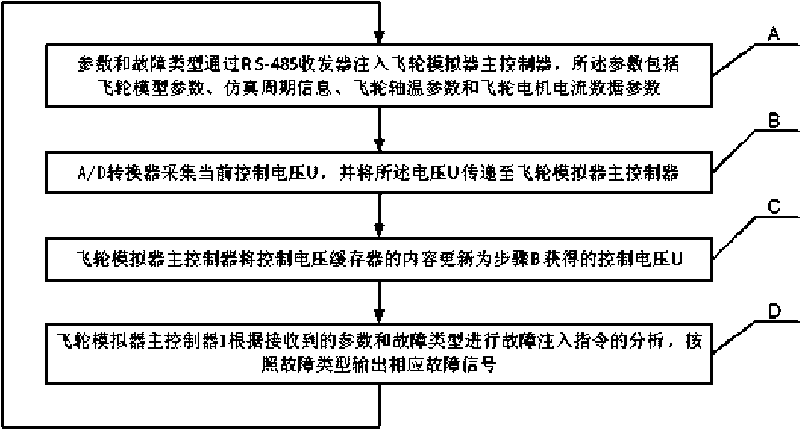
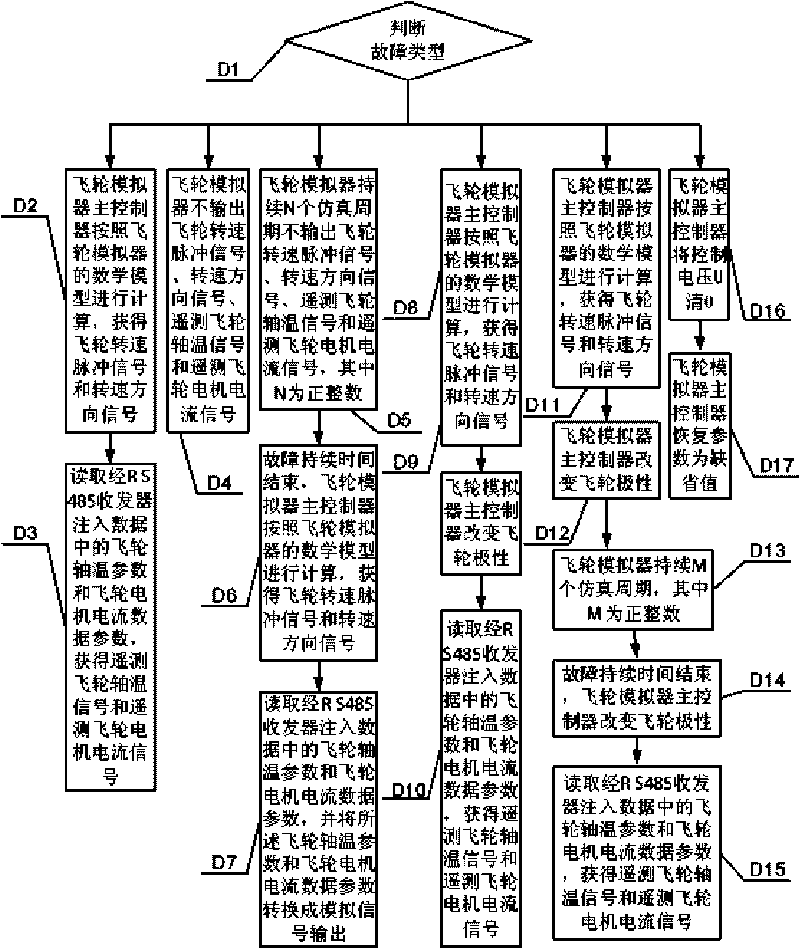
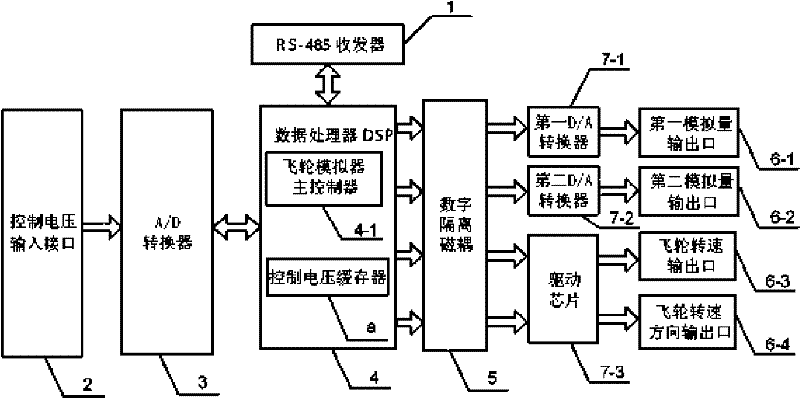
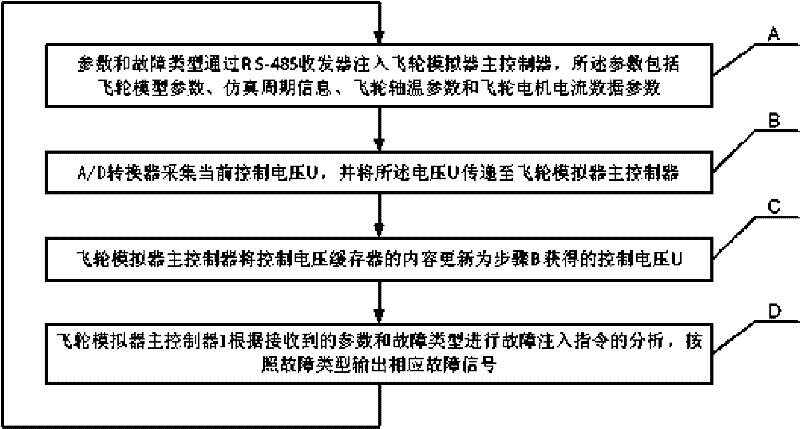
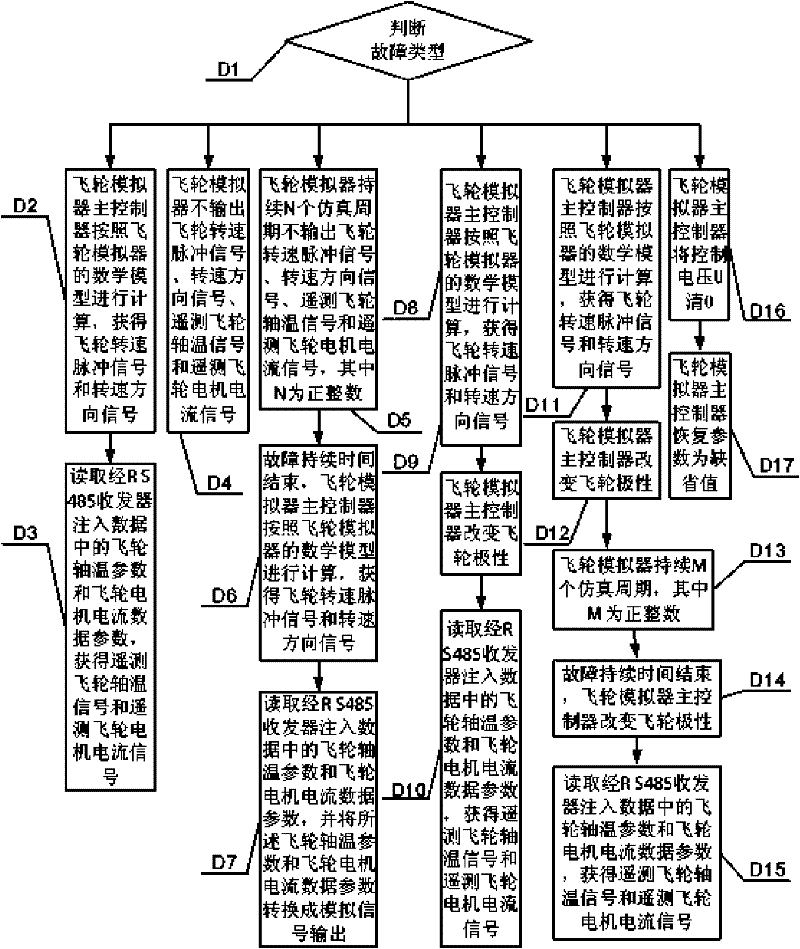
Flywheel simulator with fault simulating function and realizing method
The invention discloses a flywheel simulator with a fault simulating function and a realizing method and relates to a flywheel simulator and a fault simulation realizing method thereof. The flywheel simulator with the fault simulating function and the realizing method solve a problem that the flywheel simulator in the prior art does not support the fault simulating function. The flywheel simulator injects fault parameters into a digital signal processor DSP through a RS-485 receiver; the digital signal processor DSP acquires a control voltage signal through an A / D converter, then acquires the fault parameters corresponding to a given fault state from fault parameters by computing according to the injected fault parameters, sends the fault parameters to a D / A converter and a driving chip through a digital-isolation magnetic coupling, and finally acquires the four-channel signal output for simulating the fault. The output fault parameter comprises a flywheel rotating speed pulse, a rotating speed direction, a telemetering flywheel shaft temperature signal and a telemetering flywheel motor current signal. The flywheel simulator with the fault simulating function and the realizing method are applicable to the test and simulation of a satellite altitude control system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Binary diversity single-carrier transmission method based on self-adaptive cyclic prefix
InactiveCN104467944AEasy to adjustReduce complexityError preventionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsLow speedCyclic prefix
The invention relates to the field of satellite communication technologies and provides a binary diversity single-carrier transmission method based on a self-adaptive cyclic prefix. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a space segment provides information service forwarded based on processing through two co-orbital satellites, and a satellite receiver at an earth segment can synchronously receive signals of the two satellites to obtain space diversity gain; (2) inter-frame signal interference of a receiving end, which is brought by random perturbation of the satellites, is effectively resisted by utilizing a single-carrier transmission mechanism based on the cyclic prefix; (3) the satellite receiver carries out balancing and subsequent signal processing on the received signals, a specific statistical parameter is taken as an index, and the current length performance of the cyclic prefix is broadcasted to a satellite transmitting end in a manner of 1 bit; and (4) the satellite transmitting end adjusts the length of the cyclic prefix at the appointed step length according to feedback information. According to the method, when the satellite altitude is inaccurately known, lower complexity, low-speed feedback expenditure and higher transmission efficiency are achieved, and the signal diversity gain brought by binary transmission is obtained.
Owner:NO 61 INST OF GENERAL STAFF
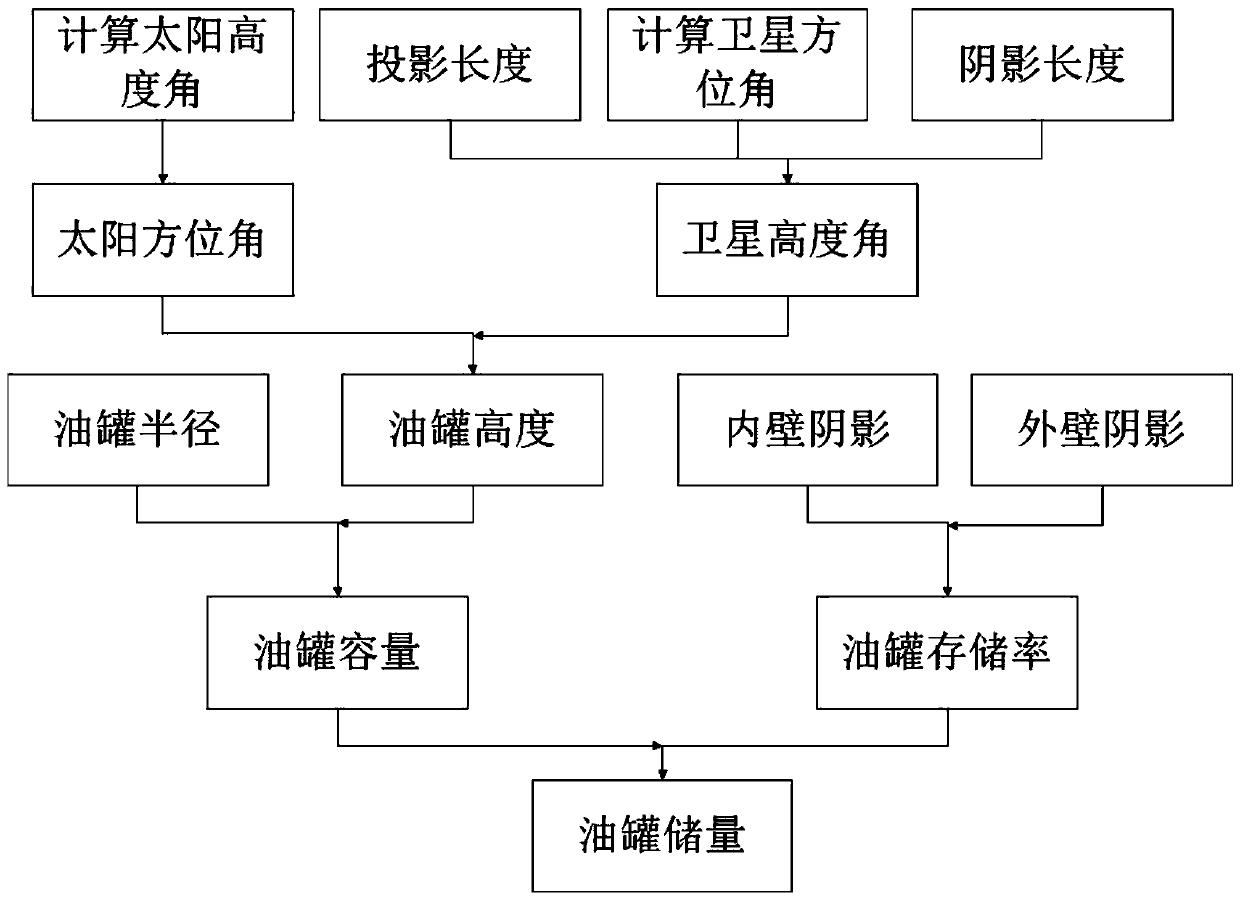
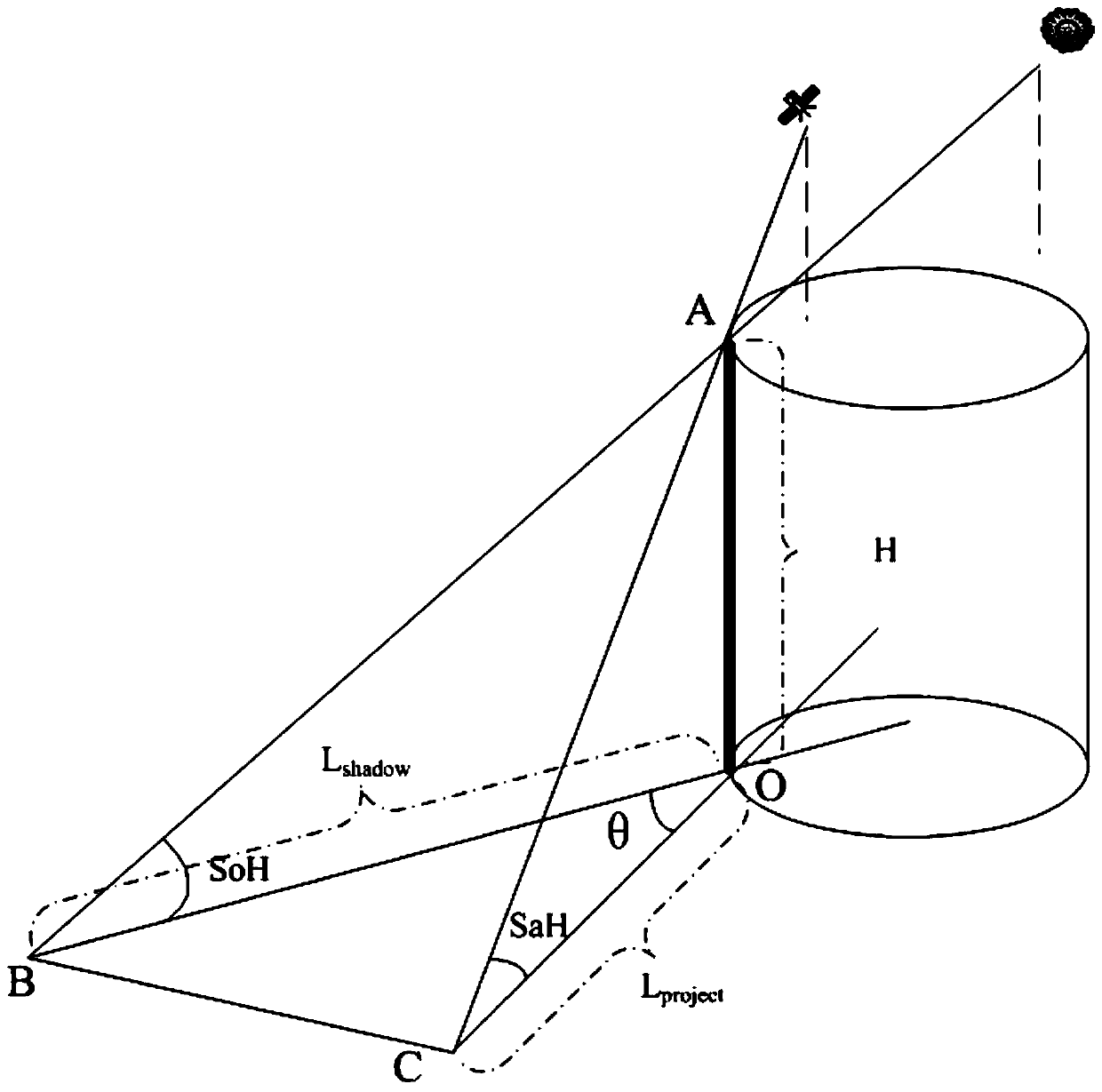
Oil tank storage capacity determination method and system based on remote sensing image characteristics
The invention discloses an oil tank storage capacity determination method and system based on remote sensing image characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) in a remote sensing image, calculating a solar azimuth by taking a sharp ground object near an oil tank as a reference; (2) determining an imaging date and a solar elevation angle of the remote sensing image according to asolar azimuth angle; (3) in the remote sensing image, calculating a satellite azimuth by taking the sharp ground object near the oil tank as the reference; (4) calculating a satellite elevation angleaccording to the shadow length, the projection length and the sun elevation angle of the sharp ground object near the oil tank; (5) selecting an oil tank needing to calculate the oil storage amount,and calculating the height of the oil tank by utilizing the tank top shadow length, the projection length, the solar altitude, the solar azimuth, the satellite altitude and the satellite azimuth; (6)calculating the oil tank capacity according to the oil tank height and the oil tank radius; (7) calculating the storage rate of the oil tank by using shadows on the inner wall and the outer wall of the oil tank; and (8) calculating the oil tank storage capacity by using the oil tank capacity and the oil tank storage rate.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Multi-path error correcting method based on height angle
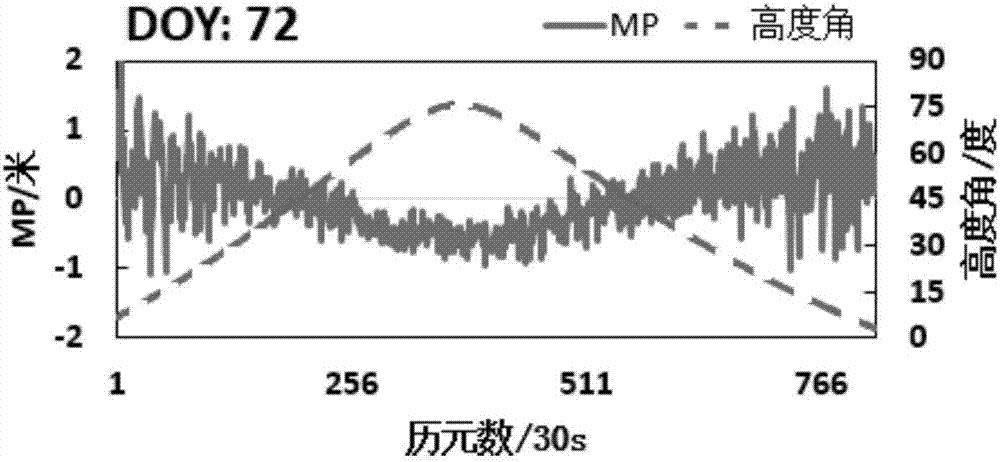
ActiveCN108957490AImprove efficiencyEasy to calculateSatellite radio beaconingEnvironmental effectInterference resistance
The invention discloses a multi-path error correcting method based on a satellite height angle. The method comprises the following steps of 1), in a positioning process of a multi-system combined pseudo-range single point, performing calculation by means of an observation file and an ephemeris file of each system; by means of relativity between a multi-path error and the satellite height angle, constructing a multi-path error calculation model by means of a trigonometric function of the height angle; 2), according to relativity between the multi-path error and an observed geographical environment, setting an environment influence factor for satisfying application in different conditions; and 3), correcting a pseudo-range observed value by means of the multi-path error obtained through calculation. The multi-path error correcting method has advantages of simple operation and high interference resistance. Compared with an existing double-frequency pseudo-range-carrier combined multi-patherror correcting method based on cycle slip detection, the multi-path error correcting method has an advantage of improving positioning precision by more than 30%.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Cruising ADCP data quality analysis and reprocessing system
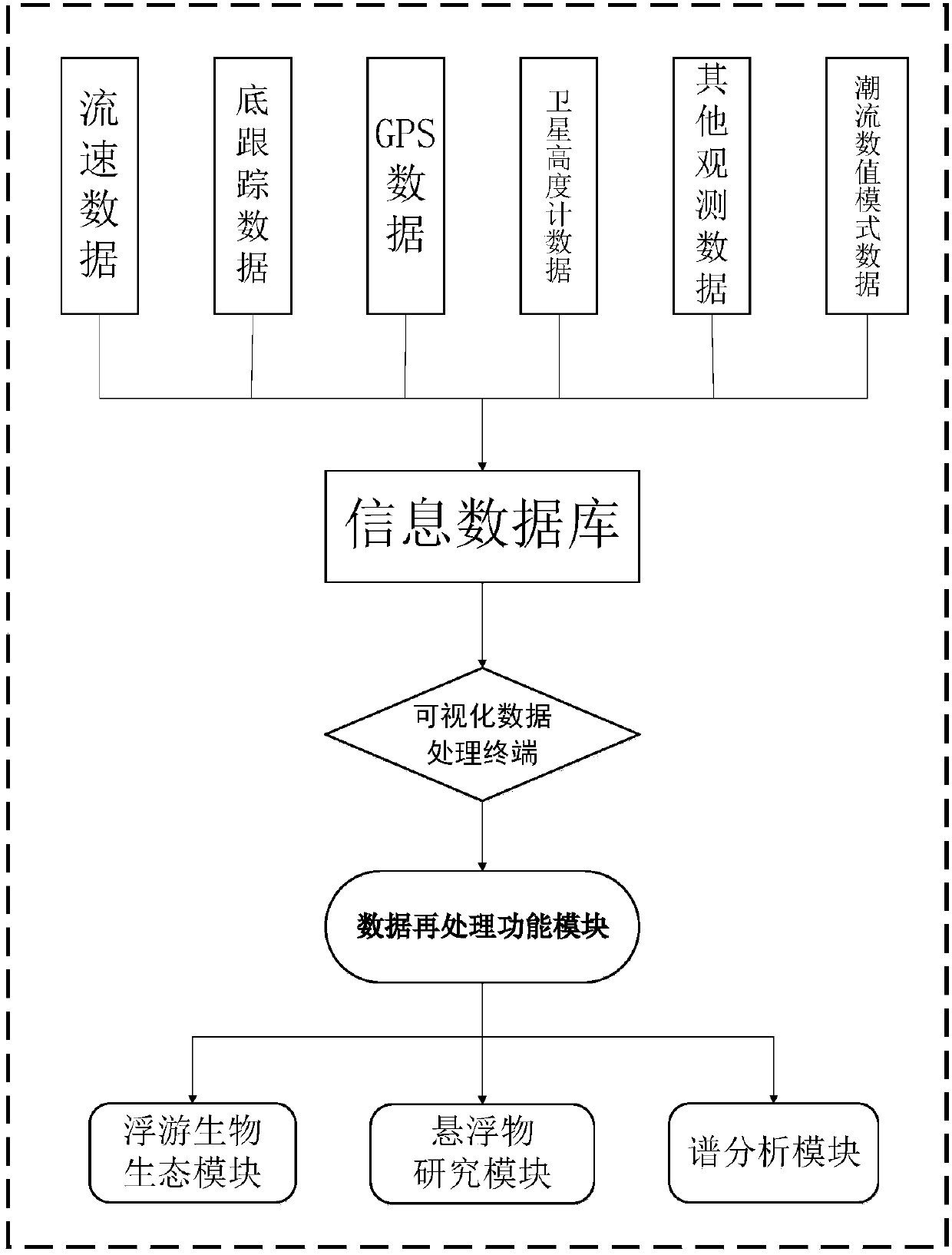
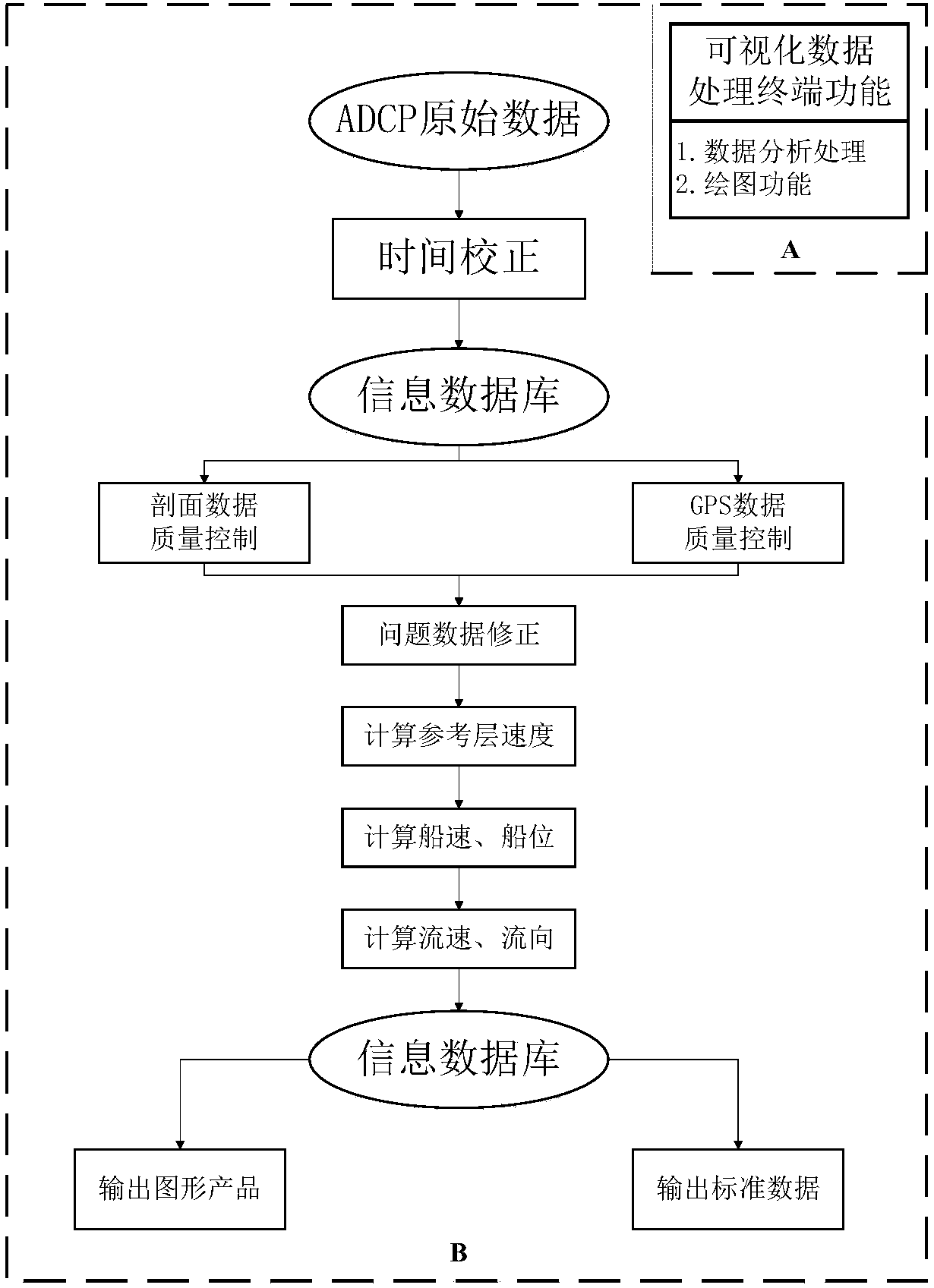
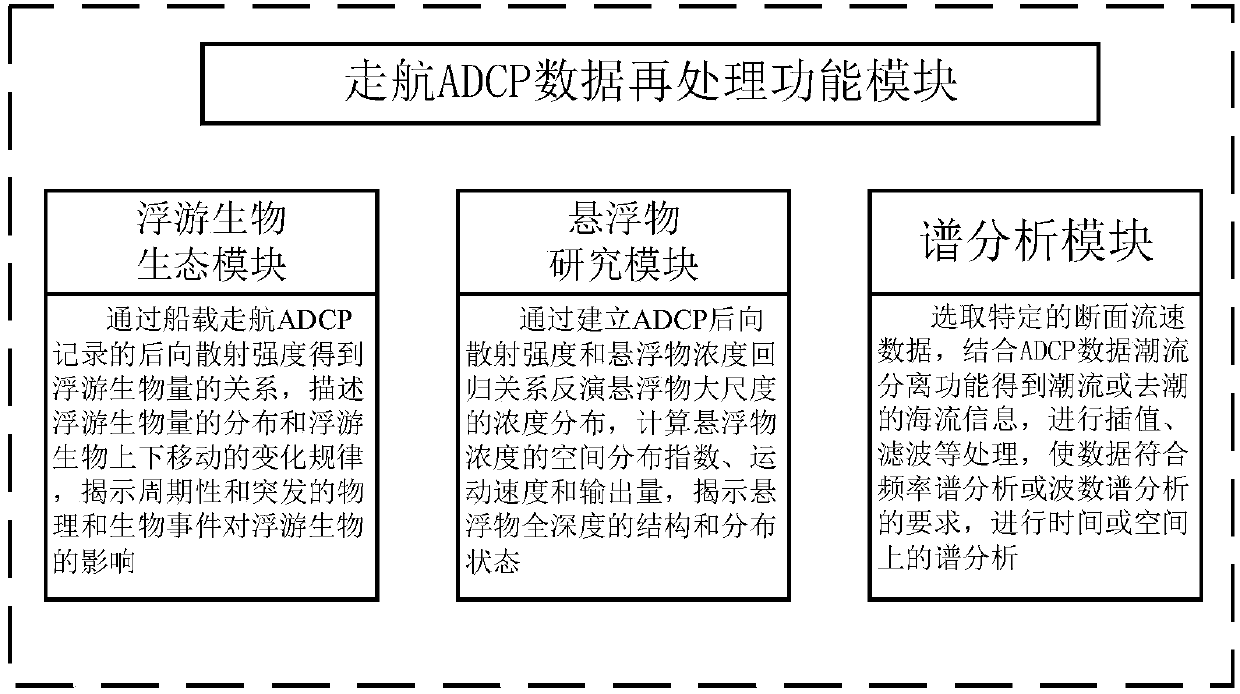
InactiveCN107895002AFacilitate quality analysisOverall clarityFluid speed measurementGeographical information databasesStream dataLongitude
The invention discloses a cruising ADCP data quality analysis and reprocessing system which consists of an information database, a visualized data processing terminal and a cruising ADCP data reprocessing function module. The information database stores flow speed data detected by a cruising ADCP, bottom tracking data, GPS longitude and latitude data, geostrophic flow data detected by an AVISO satellite altitude meter, other fixed-point flow speed observation data and high-resolution tidal stream data simulated in a global tide way. The visualized data processing terminal has data analysis anddrawing functions. The cruising ADCP data reprocessing function module comprises an ecological plankton module, a suspended matter research module and a spectral analysis module. The cruising ADCP data quality analysis and reprocessing system has the advantages of being visual, simple, clear, easy to operate and good in pertinence and can overcome the shortcomings of big difficulty, low efficiency, lots of errors and low data quality level of an existing cruising ADCP in data processing work.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
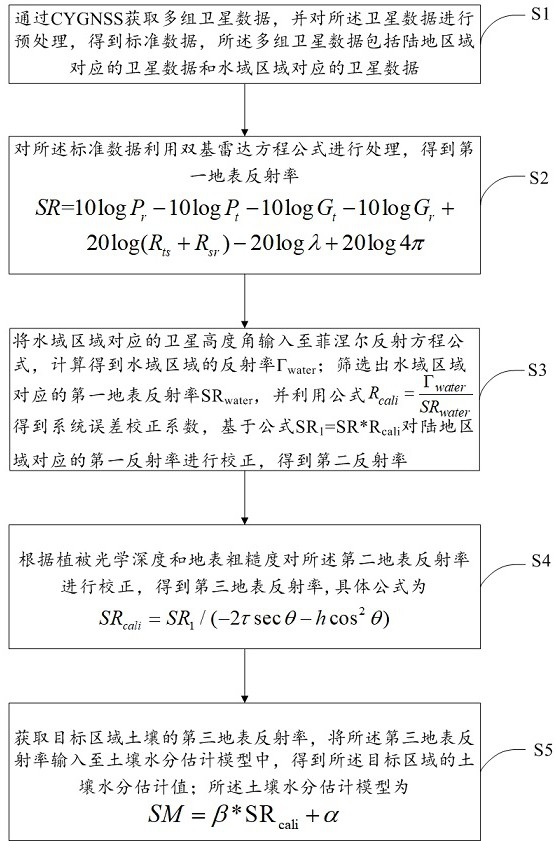
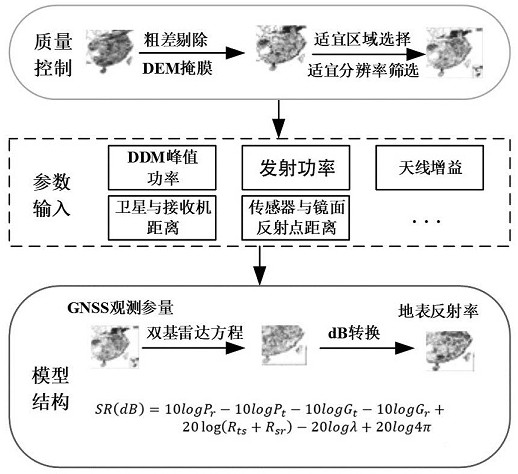
Satellite-borne GNSS-R high-precision soil moisture estimation method based on CYGNSS data
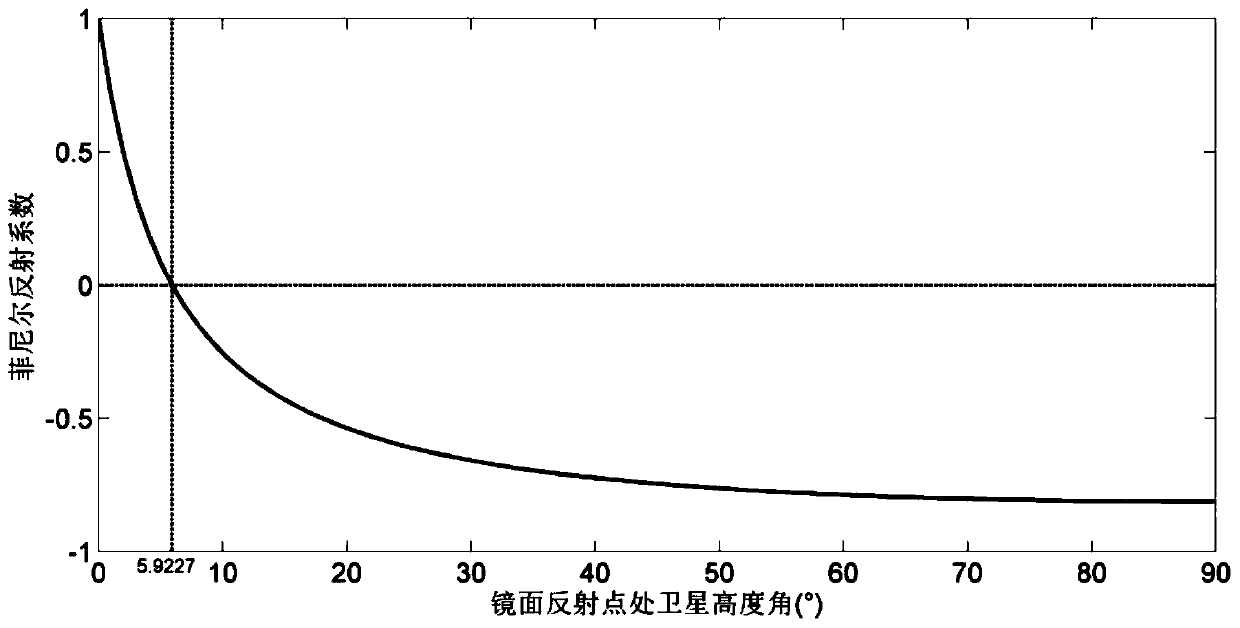
ActiveCN114371182AOptimizing Estimation ModelsImprove estimation accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEarth material testingSatellite dataRadar equation
The invention relates to a satellite-borne GNSS-R high-precision soil moisture estimation method based on CYGNSS data, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a plurality of groups of satellite data through CYGNSS, and carrying out the preprocessing of the data, and obtaining standard data; processing the standard data by using a bistatic radar equation to obtain a first surface reflectance; inputting a satellite elevation angle corresponding to the water area into a Fresnel reflection equation, and calculating to obtain a reflectivity gamma water; screening out a first surface reflectance SRwater of the water area, obtaining a system error correction coefficient by using a formula, and correcting the first reflectance of the land area based on a formula SR1 = SR * Rcali to obtain a second reflectance; correcting the second surface reflectance according to the vegetation optical depth and the surface roughness to obtain a third surface reflectance; acquiring a third surface reflectance of the soil in the target area, and inputting the third surface reflectance into the soil moisture estimation model to obtain a soil moisture estimation value of the target area; according to the invention, a method for correcting system errors, surface roughness and vegetation is provided through CYGNSS data, and the soil moisture estimation precision is improved.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
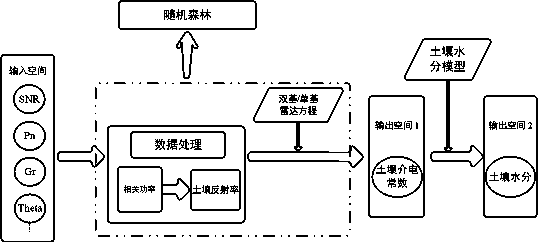
Method for predicting soil moisture by utilizing surface reflection signals and random forest regression algorithm
InactiveCN110795895ARealize large areaQuick forecastForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil typeSensing data
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil water content prediction and relates to a method for predicting soil moisture by utilizing surface reflection signals and a random forest regression algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: training and establishing a random forest algorithm model according to obtained surface reflectance and satellite elevation angles of different soil sample areas and soil humidity data of the sample areas; obtaining the soil type, the surface reflectance and the satellite elevation angle of the to-be-detected area, inputting the surface reflectance and the satellite elevation angle of the to-be-detected area into the random forest algorithm model, and obtaining the predicted soil humidity of the to-be-detected area. According to the method, through an all-weather, wide-coverage, continuous and stable signal source provided by a satellite, and in combination with a random forest algorithm in machine learning, relatively accurate soil humidity prediction can be carried out on a large area and an unknown area lacking remote sensing data.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-satellite combined inversion method for earth surface soil humidity based on GNSS-IR
ActiveCN112505068AFully reflectAccurate monitoringMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansLeast squares support vector machineEarth surface
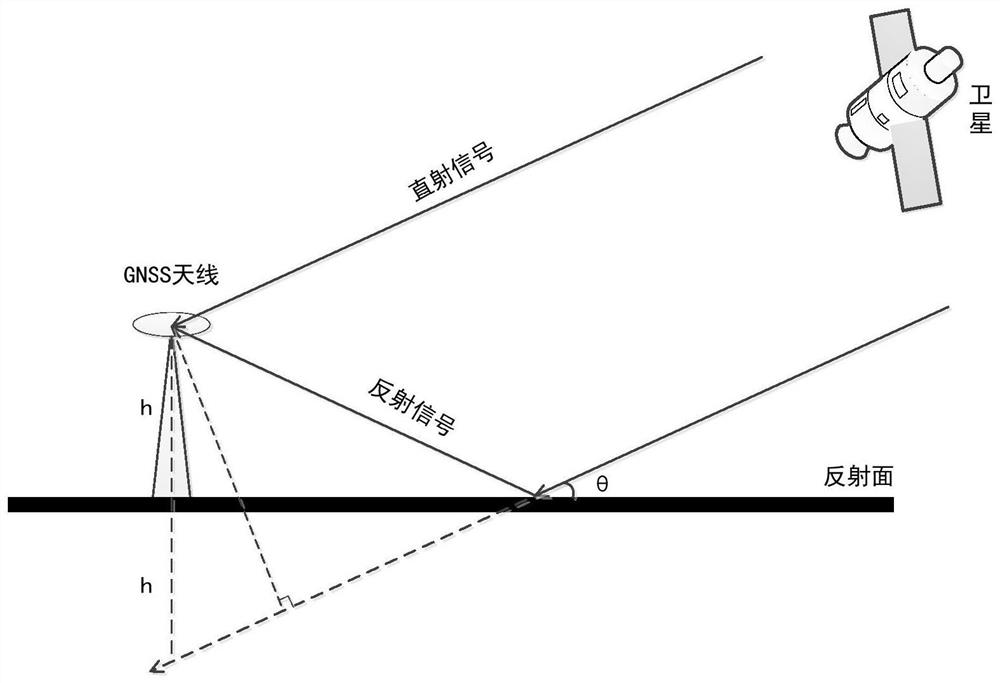
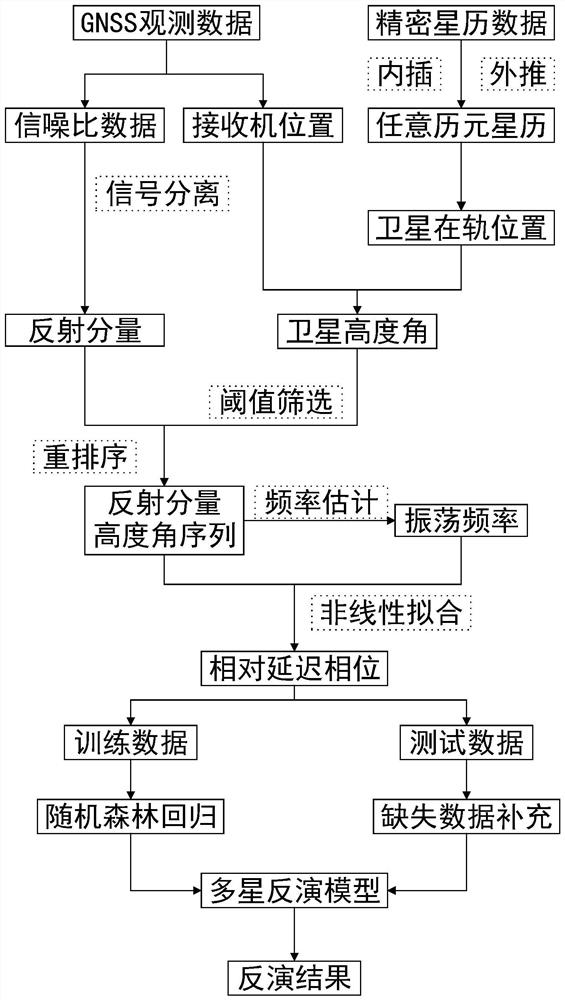
The invention discloses a multi-satellite combined inversion method for the earth surface soil humidity based on GNSS-IR, and belongs to the technical field of microwave remote sensing. The method comprises the steps of extracting a satellite altitude angle, an azimuth angle and a signal-to-noise ratio by adopting monitoring data of a measurement type GNSS receiver, and selecting multiple effective satellites through a space-time overlap ratio; separating reflected signals in the signal-to-noise ratios of the satellites by wavelet analysis, resampling the reflected signals with a low elevationangle, and obtaining the multipath delay phase of each satellite through nonlinear least square sine fitting; and finally, establishing a nonlinear relationship between the multipath delay phases ofthe multiple satellites and the soil humidity through a least square support vector machine to realize high-precision inversion of the soil humidity. The method is wide in application range and high in inversion precision, the defects of a traditional satellite reflection signal separation method can be effectively overcome, the problem that soil humidity information around a measurement station is difficult to comprehensively reflect only by adopting a single satellite is solved, and the problems in the prior art are solved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
GPS signal-to-noise ratio snow depth inversion method assisted by support vector machine
InactiveCN110927829ARainfall/precipitation gaugesSatellite radio beaconingFrequency spectrumSupervised learning
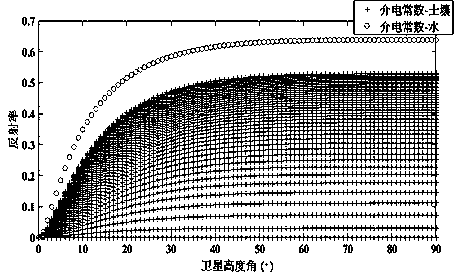
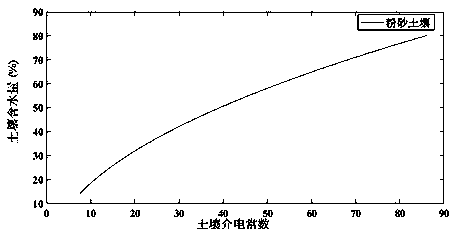
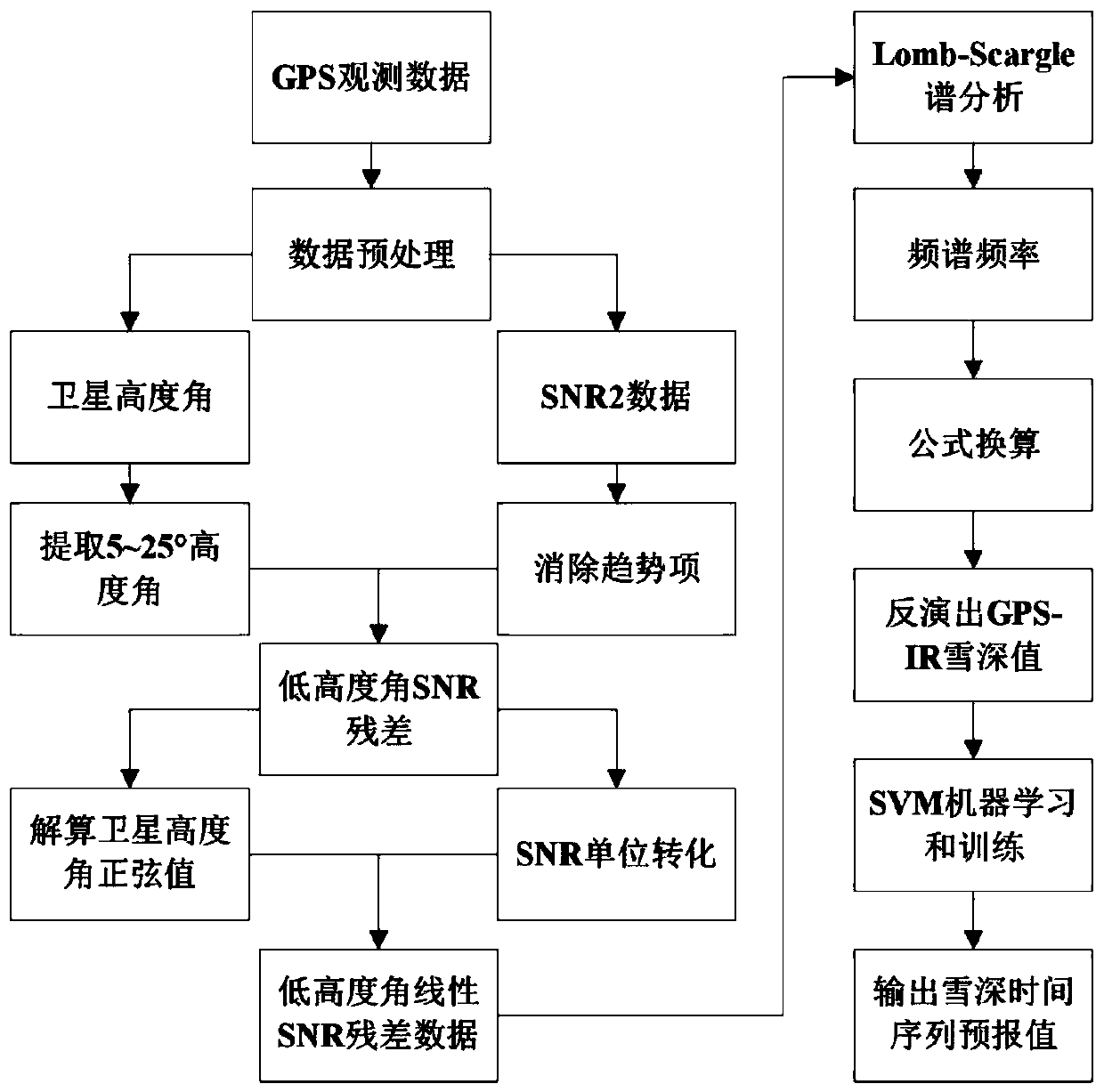
The invention discloses a GPS signal-to-noise ratio snow depth inversion method assisted by a support vector machine, and the method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the preprocessing of GPSdata through a quadratic term fitting method, and obtaining the direct reflection signals of all GPS satellites in batch; analyzing the direct reflection signal to separate out satellite altitude angle information and signal-to-noise ratio data of 5-25 degrees, and performing trend term and unit conversion on signal-to-noise ratio elimination to obtain low altitude angle linear signal-to-noise ratio residual data; performing Lomb-Scargle spectrum analysis on the low altitude angle linear signal-to-noise ratio residual error data to calculate a spectrum frequency, solving a difference value between a vertical distance of a receiver and an antenna height, and performing formula conversion to obtain snow depth inversion values of a plurality of satellites; and finally, screening out snow depth inversion values of the two groups of satellites by integrating GPS satellite observation quality and conditions, performing supervised learning and training on the snow depth inversion results of the two groups of satellites screened out by utilizing a support vector machine, and outputting a snow depth prediction value after machine learning.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Carrier phase epoch difference and Doppler observation fusion speed measurement method
The invention provides a carrier phase epoch difference and Doppler observation fusion speed measurement method. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: S1, obtaining original GNSS data containing carrier phases and Doppler observation values and an auxiliary product required by speed measurement data processing, performing screening and error correction on the obtained data, andsubstituting the corrected data into a carrier phase positioning equation; S2, differentiating the corrected observation equation among epochs to obtain a carrier phase inter-epoch differential velocity measurement equation, and combining the carrier phase inter-epoch differential velocity measurement equation with a Doppler velocity measurement equation to construct a velocity measurement equation fusing different observation values; S3, determining a corresponding random model by adopting a step-by-step weighting method according to satellite altitude angles and observation noise; and S4, linearizing the observation equation, solving velocity through a least square algorithm X=(BTPB)-1 (BTPL).
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
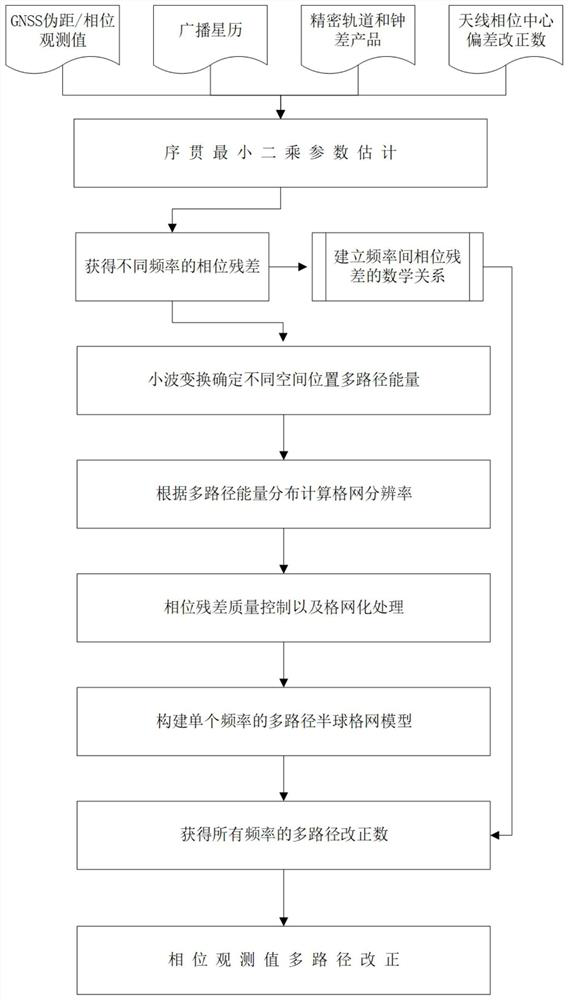
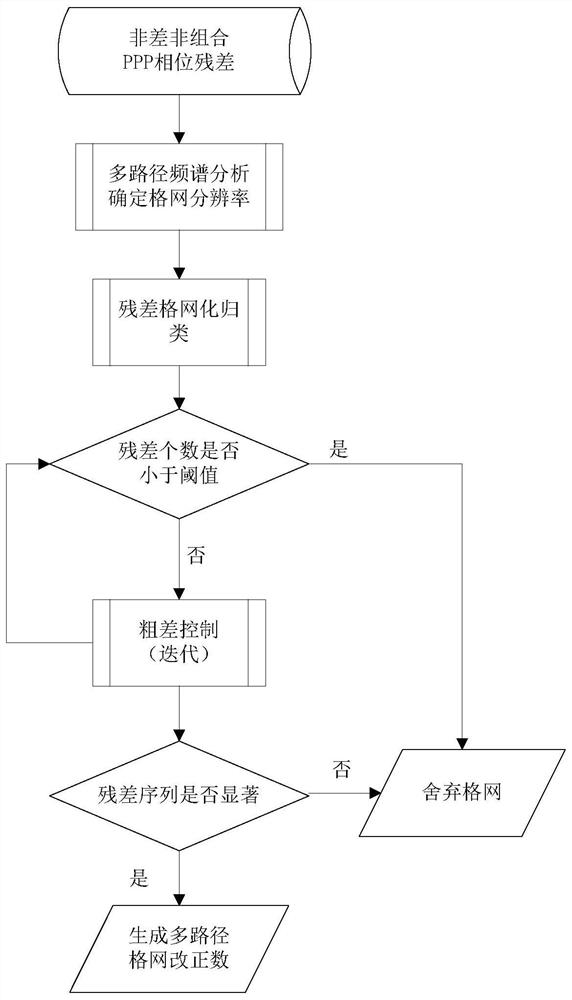
Phase multi-path extraction correction method based on non-difference and non-combination PPP model
ActiveCN112433240AAvoid the problem of not being able to handle multipath in the coordinate domainAvoid susceptibility to satellite orbital brakingSatellite radio beaconingICT adaptationAlgorithmWavelet transform analysis
The invention provides a phase multi-path correction method based on a non-difference and non-combination PPP model. According to GNSS original observation values, a non-difference non-combination PPPobservation equation is constructed, phase residual errors are calculated through a sequential least square algorithm, and coordinates serve as constant estimation in order to prevent multipath errors from being absorbed by coordinate parameters. And a mathematical relation between phase residuals of different frequencies is established, spatial distribution conditions of multiple paths of different frequency bands are analyzed by utilizing continuous wavelet transform, and an equal-arc-length hemispherical grid model considering spatial distribution characteristics of the multiple paths is constructed according to the spatial distribution conditions. A user searches a multi-path grid model according to a satellite altitude angle and an azimuth angle to obtain a multi-path correction number of a certain frequency, and calculates multi-path correction numbers of other frequencies according to a mathematical relationship of residual errors among the frequencies to correct multiple pathsin a phase observation value. According to the method, the multipath error is processed based on the observation value domain, only the phase multipath model of one frequency needs to be constructed,and the complexity of PPP data processing is greatly reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
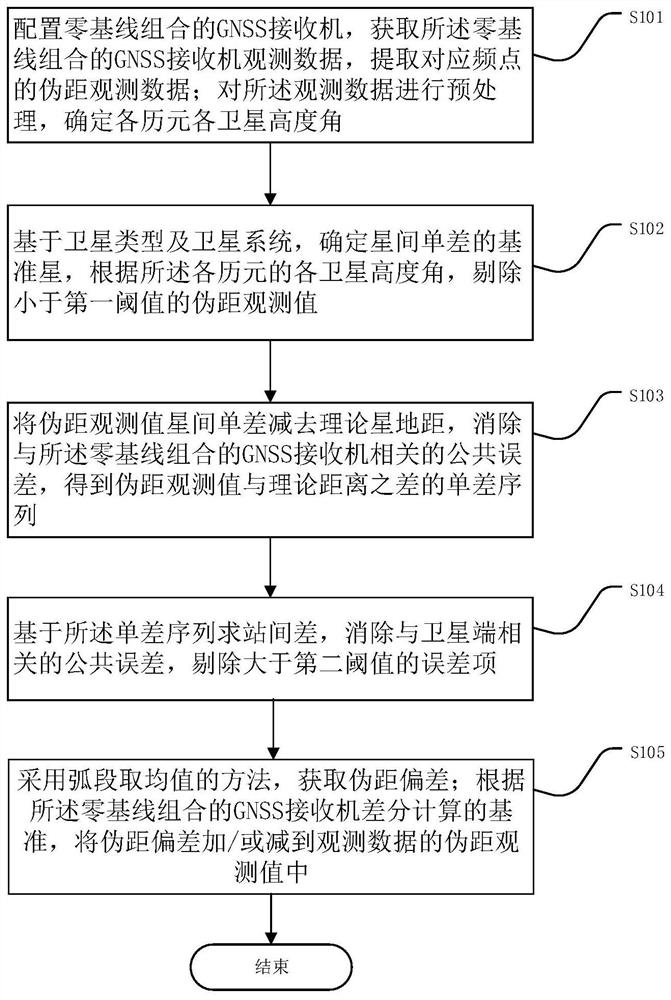
Pseudo-range deviation calculation and correction method and device based on receiver
PendingCN112462399AEffective extraction effectReliable extraction effectSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataEngineering
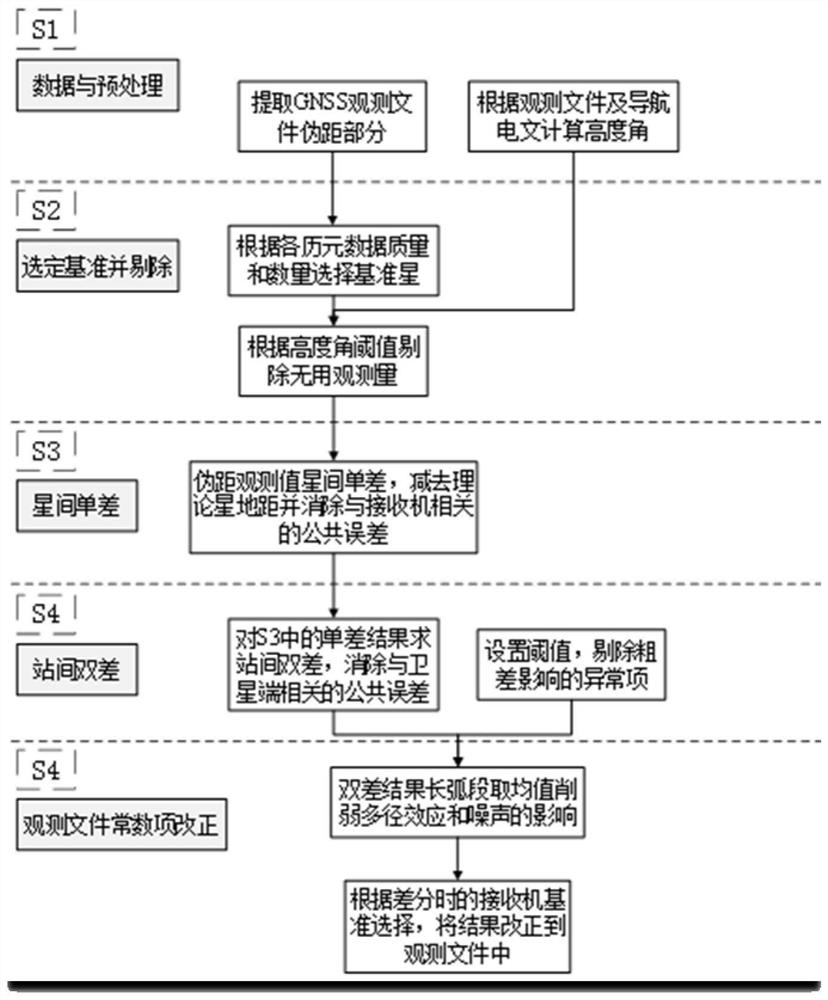
The invention provides a pseudo-range deviation calculation and correction method and device based on a receiver, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of observation data, and determining the altitude angles of all satellites of all epochs; determining a reference satellite of an inter-satellite single difference, and eliminating observation data smaller than a firstthreshold value according to each satellite altitude angle of each epoch; subtracting the theoretical satellite-ground distance from the inter-satellite single difference of the pseudo-range observation value, eliminating a common error related to the receiver, and obtaining a single difference sequence of the difference between the pseudo-range observation value and the theoretical distance; solving an inter-station difference based on the single difference sequence, eliminating a common error related to a satellite end, and eliminating an error term which does not meet a second threshold requirement; obtaining pseudo-range deviation by adopting a method of taking an average value of an arc section; and adding / or subtracting the pseudo-range deviation to the pseudo-range observation valueof the observation data according to the reference of receiver differential calculation. According to the scheme of the invention, the pseudo-range deviation can be effectively calculated, the precision of a positioning result is improved, and a reliable and efficient pseudo-range deviation extraction effect is obtained.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
GNSS random model building method considering troposphere residual delay
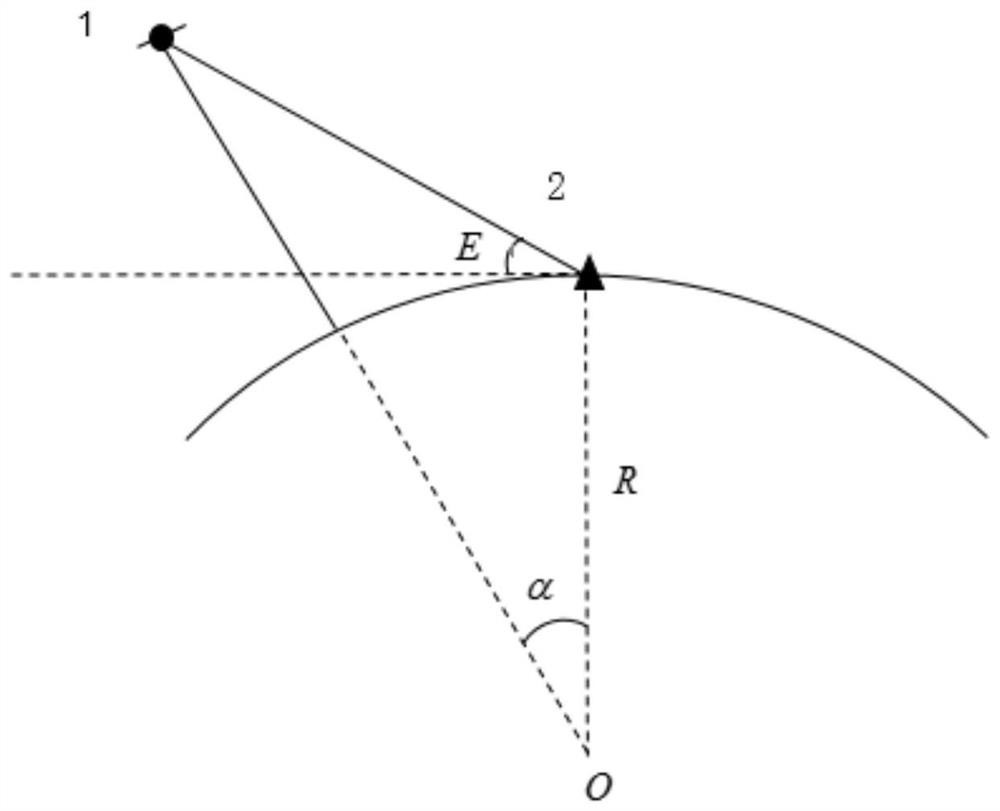
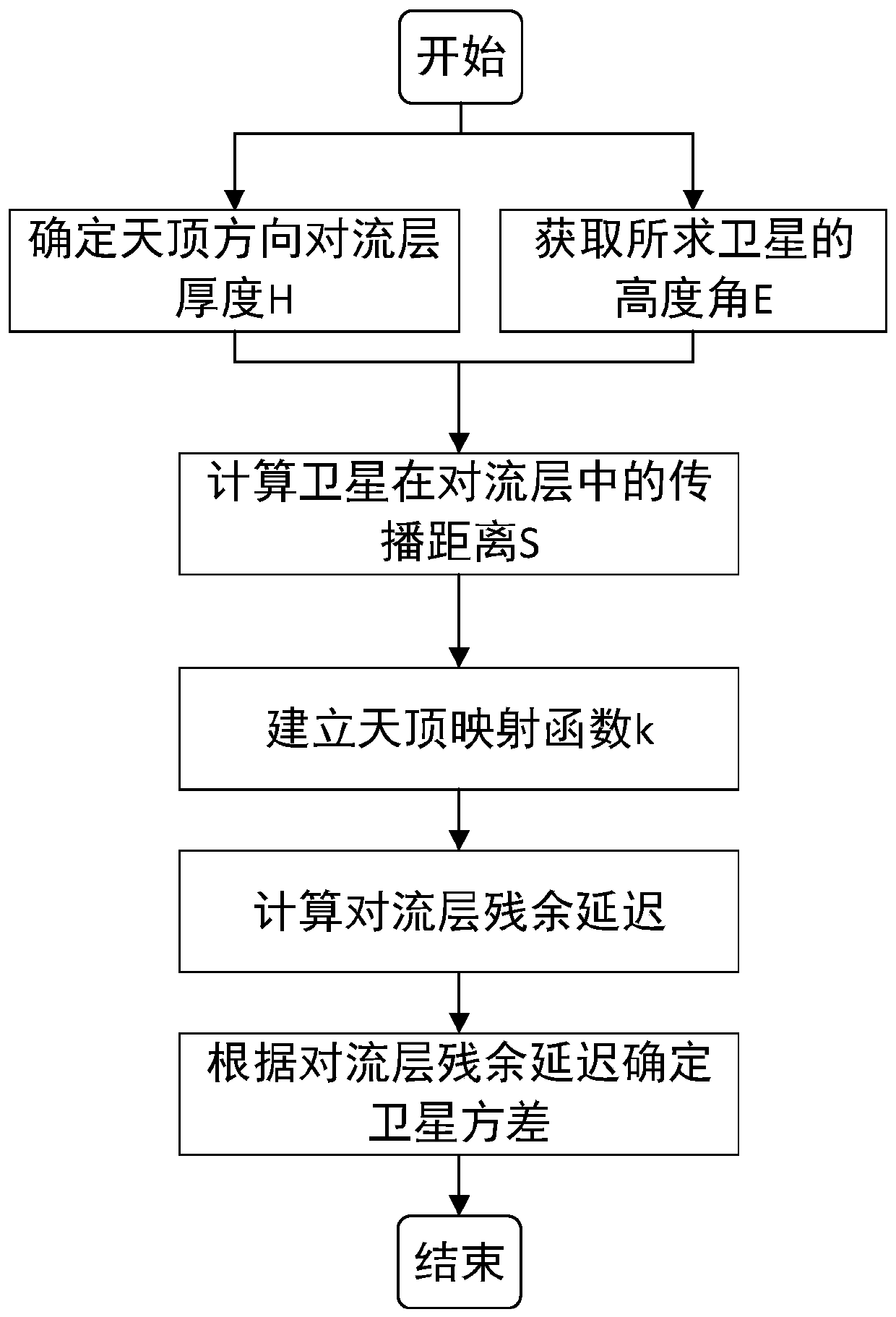
ActiveCN111273320ASolve problems that are difficult to characterize unmodeled errorsHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereElevation angle
The invention discloses a GNSS random model establishing method considering tropospheric residual delay, and belongs to the field of satellite navigation and positioning. The propagation distance of asatellite signal in the troposphere is calculated through a satellite elevation angle and zenith troposphere thickness; a zenith mapping function is given to calculate tropospheric residual delay, then tropospheric residual delay is brought into a random model to give a method for calculating satellite observation value variance, the characteristics of unmodeled errors are effectively reflected,and precision and reliability of precision single-point positioning can be improved. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) determining the troposphere thickness H in the zenith direction according to the position of an observation station, and obtaining a satellite elevation angle E; (2) calculating a propagation distance S of the satellite in a troposphere; (3) calculating aspecific value k of the zenith mapping function; (4) determining the tropospheric residual delay amount; and (5) determining the variance of the satellite according to the tropospheric residual delay.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Satellite orbit clock error correction coding method based on Beidou global short message communication
ActiveCN113267790AReduce precision lossHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingSatellite dataClock correction
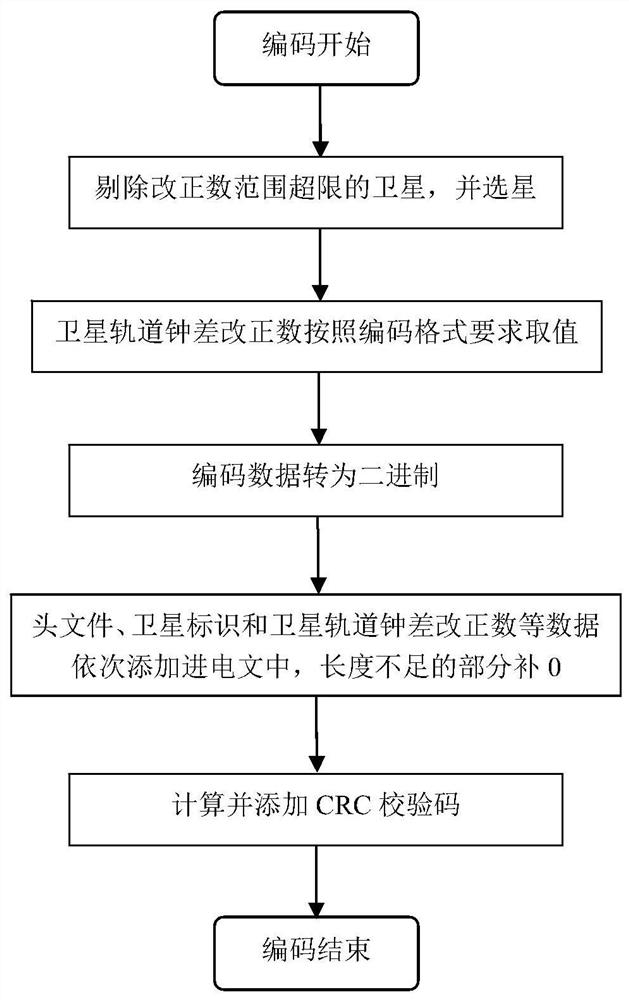
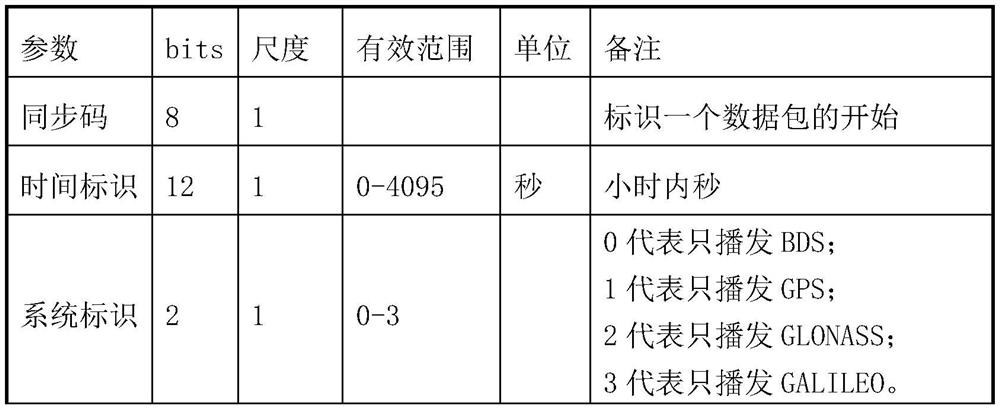
The invention provides a satellite orbit clock error correction coding method based on Beidou global short message communication, which aims at improving the real-time precision single-point positioning precision and convergence speed and takes the minimum space signal ranging error SISRE as the principle to realize coding within the limitation of Beidou global short message nodes. The method comprises: judging the satellite data according to the satellite orbit, the effective range of the clock error correction and the satellite elevation angle, and selecting a satellite; performing data processing and encoding of satellite orbital clock correction, including determining data lengths and encoding scales of satellite radial, normal and tangential orbital correction and clock correction according to a principle of minimum space signal range finding error SISRE, taking integers of the radial, normal and tangential orbital correction and clock correction of each satellite according to the encoding specified scale, and encoding the data length of the satellite orbital clock correction and the encoding scale of the satellite orbital clock correction; finally, converting the header file and the rounded satellite data into binary data; and sequentially adding information according to a sequence specified by a coding format, supplementing 0, and adding and calculating a CRC check code to form a complete telegraph text.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
GNSS-IR height measurement method suitable for navigation receiver
PendingCN113805208ASolve the difficulty of choosingAccurately reflectHeight/levelling measurementSatellite radio beaconingMoving averageFrequency spectrum
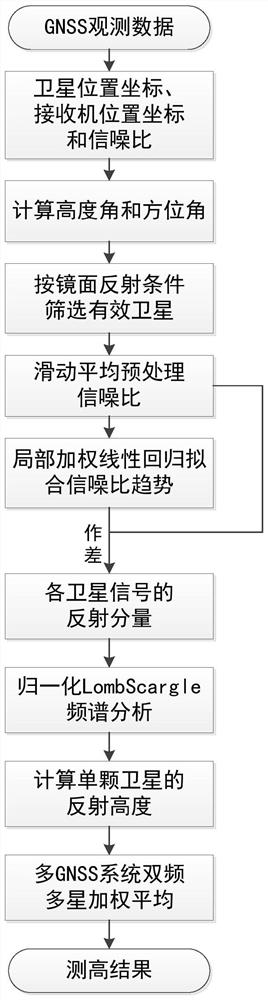
The invention discloses a GNSS-IR height measurement method suitable for a navigation receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a satellite in-orbit position coordinate, a signal-to-noise ratio and a user receiver position coordinate by using observation data of a common navigation type GNSS receiver, and calculating a satellite elevation angle and an azimuth angle according to original observed quantity; screening proper satellites according to space-time distribution of an observation scene, and preprocessing a signal-to-noise ratio time sequence by using a moving average method; separating reflection components in a signal-to-noise ratio of each satellite by using a local weighted regression method, performing spectral analysis on the signal-to-noise ratio sequence residual error based on elevation angle reordering, estimating the oscillation frequency of the signal-to-noise ratio of a reflection signal, and calculating the reflection height corresponding to a single satellite according to the oscillation frequency; and optimizing a measurement result of the reflection height through weighting. According to the GNSS-IR height measurement method, the application range is expanded, data resources of the navigation type receiver are fully utilized, the under-fitting problem of a traditional low-order polynomial method can be effectively solved, and the measurement precision and stability are improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Flywheel simulator with fault simulating function and realizing method
The invention discloses a flywheel simulator with a fault simulating function and a realizing method and relates to a flywheel simulator and a fault simulation realizing method thereof. The flywheel simulator with the fault simulating function and the realizing method solve a problem that the flywheel simulator in the prior art does not support the fault simulating function. The flywheel simulator injects fault parameters into a digital signal processor DSP through a RS-485 receiver; the digital signal processor DSP acquires a control voltage signal through an A / D converter, then acquires thefault parameters corresponding to a given fault state from fault parameters by computing according to the injected fault parameters, sends the fault parameters to a D / A converter and a driving chip through a digital-isolation magnetic coupling, and finally acquires the four-channel signal output for simulating the fault. The output fault parameter comprises a flywheel rotating speed pulse, a rotating speed direction, a telemetering flywheel shaft temperature signal and a telemetering flywheel motor current signal. The flywheel simulator with the fault simulating function and the realizing method are applicable to the test and simulation of a satellite altitude control system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
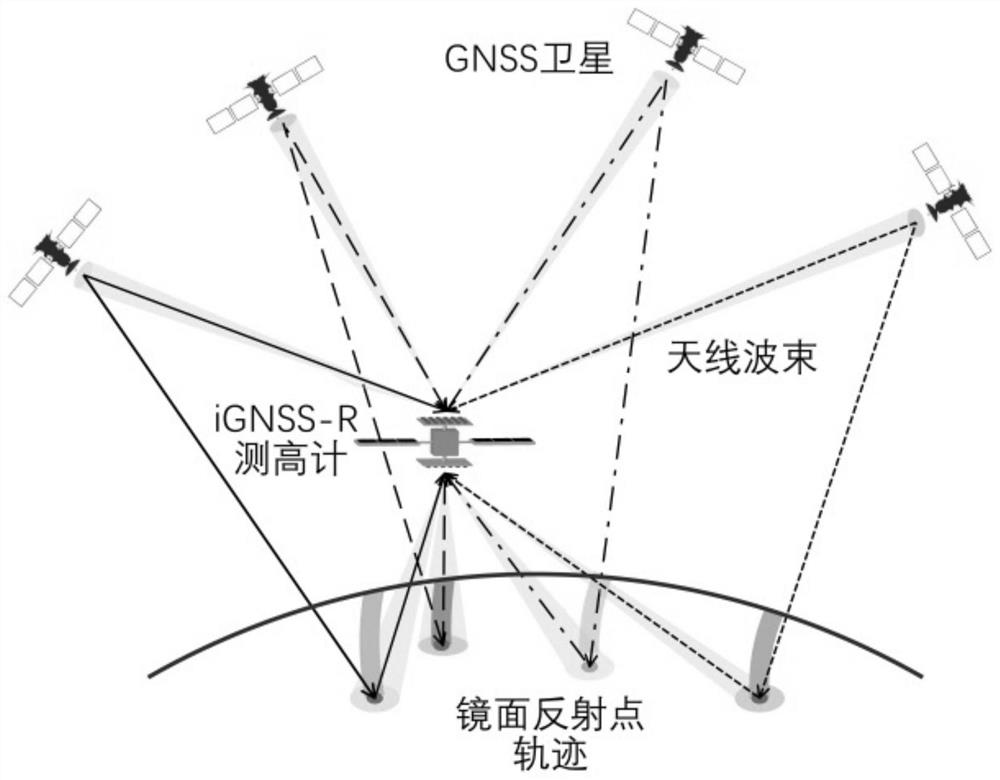
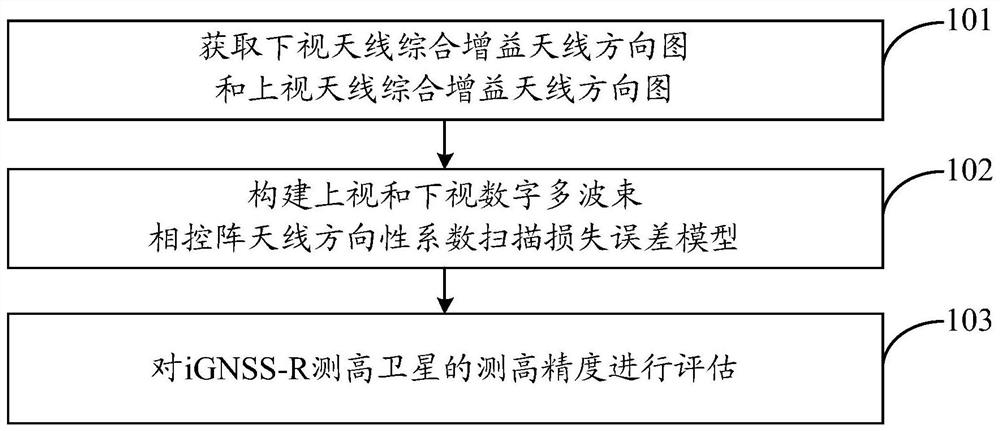
Satellite-borne iGNSS-R height measurement precision evaluation method
PendingCN112363185ASignificant scan lossIncrease Directivity CoefficientSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringSea-surface height
The invention discloses a satellite-borne iGNSS-R height measurement precision evaluation method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring comprehensive gain antenna directional diagrams of a downward-looking antenna and an upward-looking antenna; constructing an iGNSS-R height measurement satellite upward-looking and downward-looking digital multi-beam phased array antenna directivity coefficient scanning loss error model according to the acquired downward-looking and upward-looking antenna comprehensive gain antenna directional diagrams; and evaluating the height measurement precision ofthe iGNSS-R height measurement satellite according to the constructed scanning loss error model of the directivity coefficients of the upward-looking and downward-looking digital multi-beam phased array antennas of the iGNSS-R height measurement satellite. In order to improve the estimation precision of iGNSS-R sea surface height measurement, the directivity coefficient scanning loss error model suitable for a satellite-borne iGNSS-R sea surface height measurement scene is established for the first time, and directivity coefficient scanning losses of the up-looking digital multi-beam phased array antenna and the down-looking digital multi-beam phased array antenna at different satellite altitude angles are obtained; and by applying the model, the iGNSS-R height measurement precision is improved by more accurately estimating the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
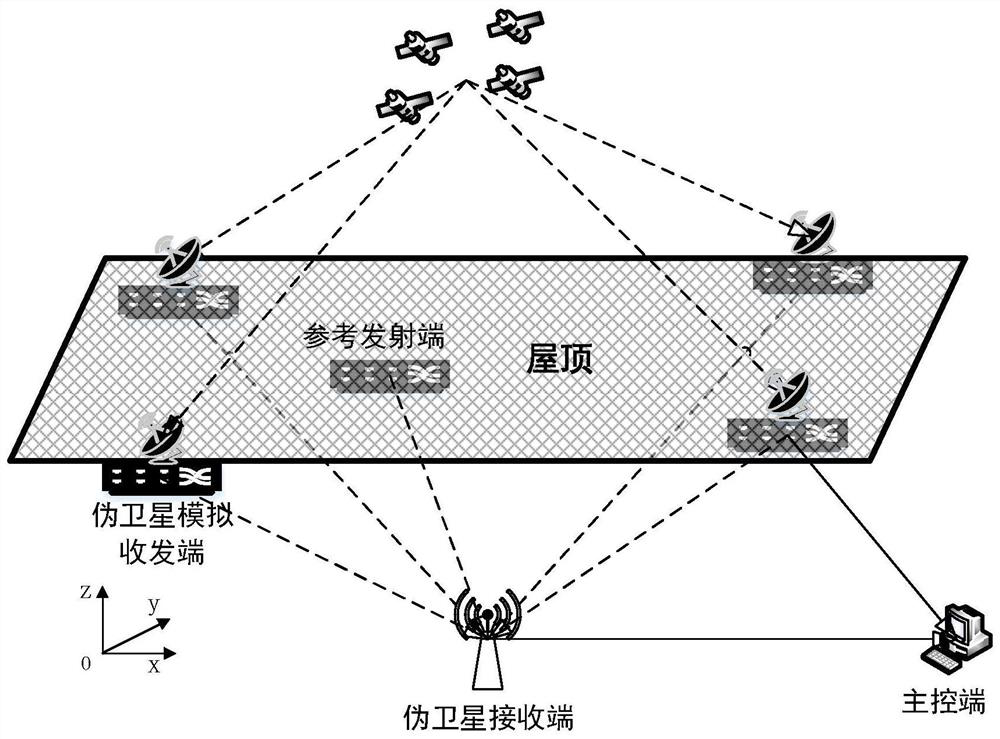
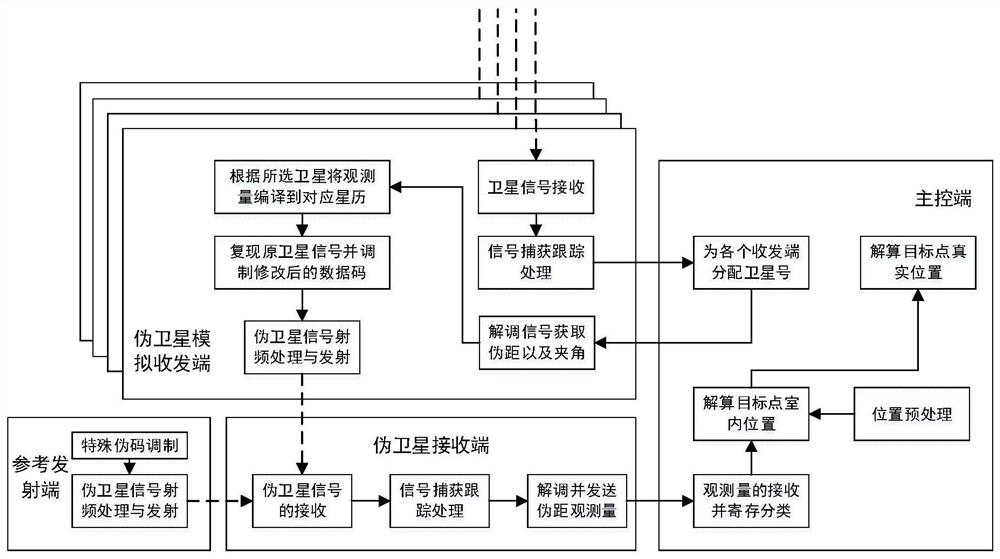
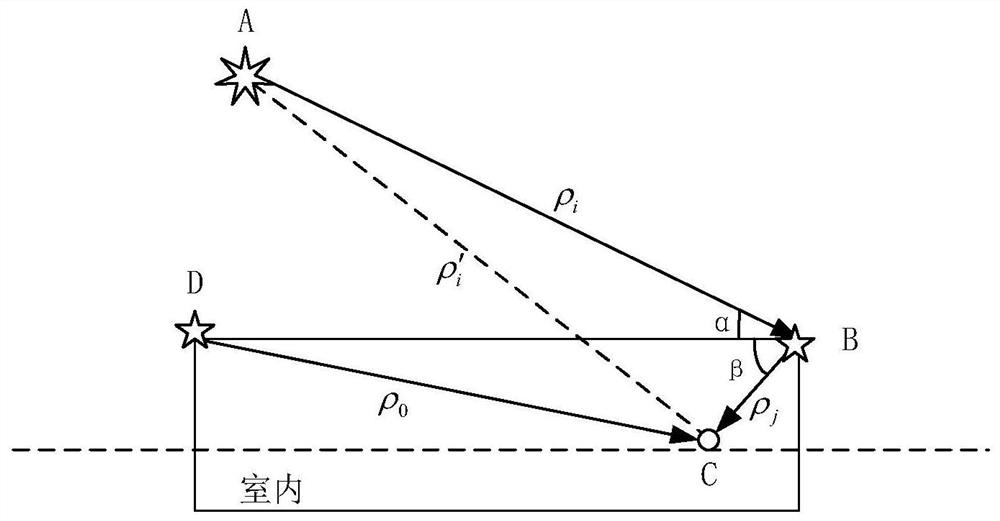
Indoor and outdoor seamless positioning method and system based on pseudo satellite technology
PendingCN113848573ASimple structureDoes not affect normal captureNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingSatellite technologyEngineering
The invention discloses an indoor and outdoor seamless positioning method and system based on a pseudo-satellite technology, and the method comprises the steps: changing a pseudo-satellite transmitting end into a receiving and transmitting system, receiving an external satellite signal during indoor positioning, enabling indoor positioning and outdoor positioning to be combined, and enabling the system to be additionally provided with a reference transmitting end; and obtaining the distance and the included angle with the indoor target, so that the outdoor position can be measured in an auxiliary manner. Flexible indoor and outdoor positioning switching can be realized, a pseudolite telegraph text is highly similar to that of a sky satellite, normal acquisition of a receiver is not affected, and no matter whether a positioning target is indoor or outdoor, the receiver can normally receive signals; a special receiver does not need to be additionally designed, indoor and outdoor modes do not need to be switched, the system technology is simple to realize, and the algorithm is easy to implement and high in controllability.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
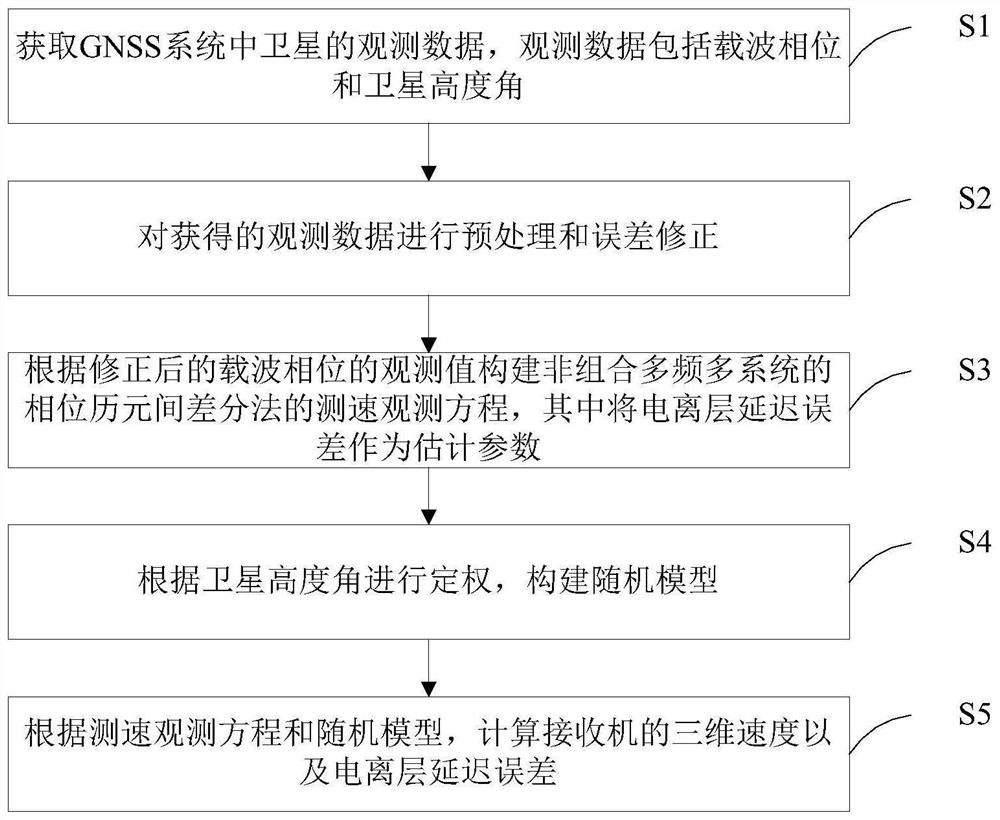
Differential velocity measurement method, system and device between non-combined carrier phase epochs and medium
PendingCN114002727ADelay error parameter reservedImplement speed estimatesSatellite radio beaconingElevation angleObservation data
The invention discloses a non-combined carrier phase epoch differential velocity measurement method, system and device and a medium, wherein the method comprises the steps: obtaining the observation data of a satellite, wherein the observation data comprise a carrier phase and a satellite elevation angle; carrying out preprocessing and error correction on the obtained observation data; constructing a velocity measurement observation equation of a phase epoch difference method of the non-combined multi-frequency multi-system according to the corrected observation value of the carrier phase, wherein an ionized layer delay error is used as an estimation parameter; performing weight determination according to the satellite elevation angle, and constructing a random model; and according to the velocity measurement observation equation and the random model, calculating the three-dimensional velocity and the ionosphere delay error of the receiver. Based on an original carrier phase observation value, ionosphere delay errors are parameterized, and speed estimation of a high-precision receiver is achieved in combination with a satellite elevation angle; meanwhile, ionosphere delay parameters are reserved, and observation data are provided for geophysical research, so that the method can be widely applied to the field of satellite measurement.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
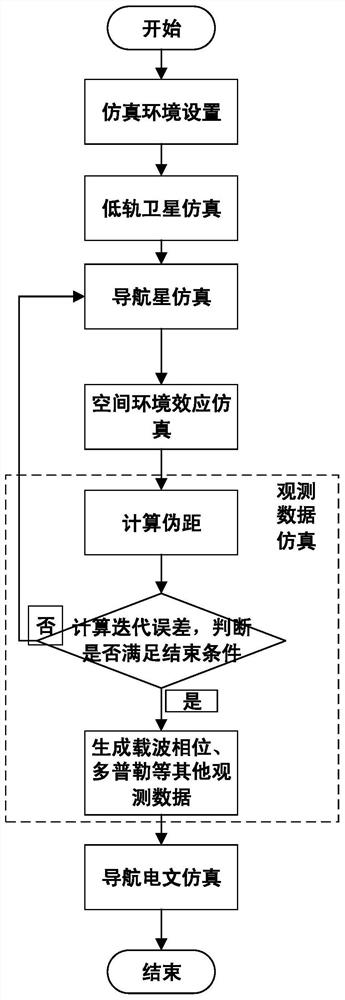
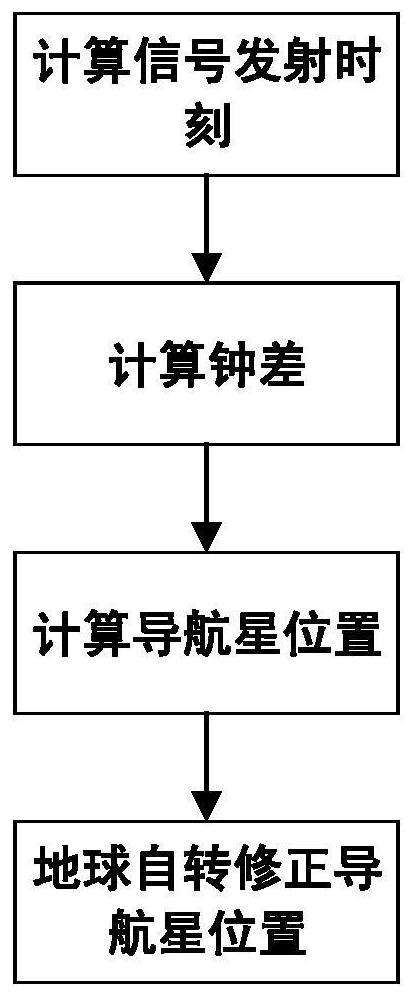
Satellite navigation signal simulation method for low-orbit satellite as terminal carrier
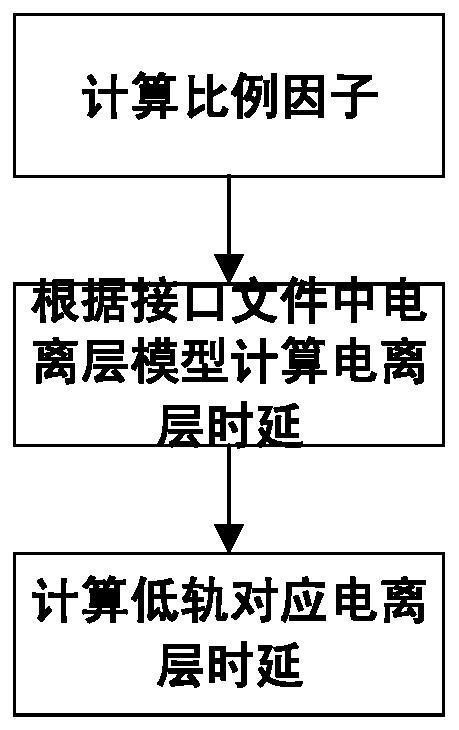
PendingCN112596077AAvoid situations that do not correspond to actual on-orbit statusSimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingIonosphereRemote sensing
The invention provides a satellite navigation signal simulation method for a low-orbit satellite as a terminal carrier, which comprises the steps of correspondingly improving a traditional ionospheremodel by considering the characteristics that the low-orbit satellite is positioned in the middle of an ionosphere and a navigation signal does not completely pass through the ionosphere on the basisof the traditional satellite signal simulation, and multiplying by a scaling factor highly correlated with the low-orbit satellite to obtain an ionosphere layer model suitable for the low orbit. Besides, the ionosphere model cannot completely represent the real ionosphere state, and only 60%-70% of real time delay can be corrected generally, so that the pseudo-range superimposed ionospheric erroris multiplied by a coefficient 1.3 to achieve a state closer to the actual state. When a navigation message is generated, ionosphere parameters are directly set. By means of the method, analogue simulation of satellite navigation signals received by the low-orbit satellite is achieved, and a testing tool is provided for a GNSS receiver carried by the low-orbit satellite and related systems.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
GNSS-IR soil humidity inversion method based on generalized continuation approximation
PendingCN114397425AEfficient and accurate extractionHelp to solveEarth material testingSatellite radio beaconingElevation angleObservation data
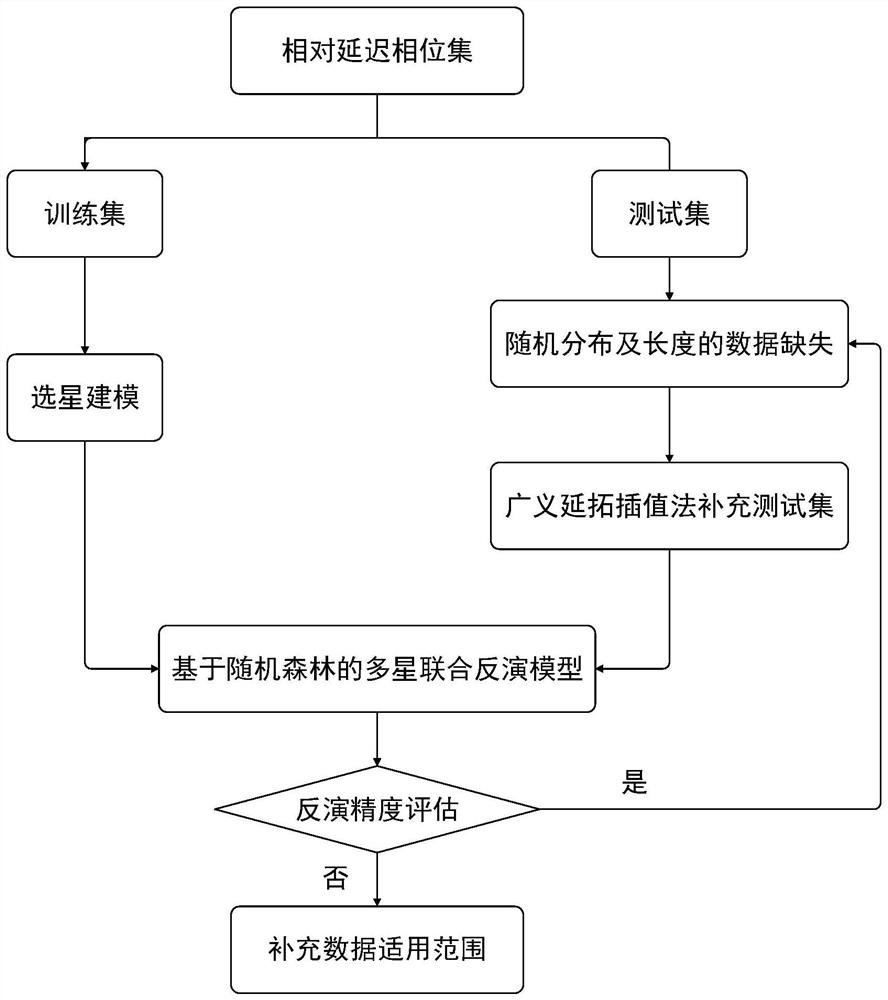
The invention discloses a GNSS-IR soil humidity inversion method based on generalized continuation approximation, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the interpolation and extrapolation of a precise ephemeris through employing the signal-to-noise ratio observation data of a measurement type GNSS receiver through a generalized continuation approximation model, so as to obtain the elevation angle of each satellite in each epoch; the signal-to-noise ratio of the reflected signal obtained through trend separation by the local weighted regression method is reordered about the sine value of the satellite elevation angle, then the normalized Lomb-Scargle spectrum peak value is subjected to generalized continuation interpolation approximation to obtain the oscillation frequency, and a corresponding relative delay phase is obtained through nonlinear least square sine fitting; a soil humidity inversion model is established through a random forest, and finally, missing relative delay phase data is supplemented by adopting a generalized continuation interpolation method to serve as inversion model input to predict soil humidity. The method can adapt to the missing condition of observation data with different lengths and distribution, can maintain high inversion precision, and solves the problems in the prior art.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
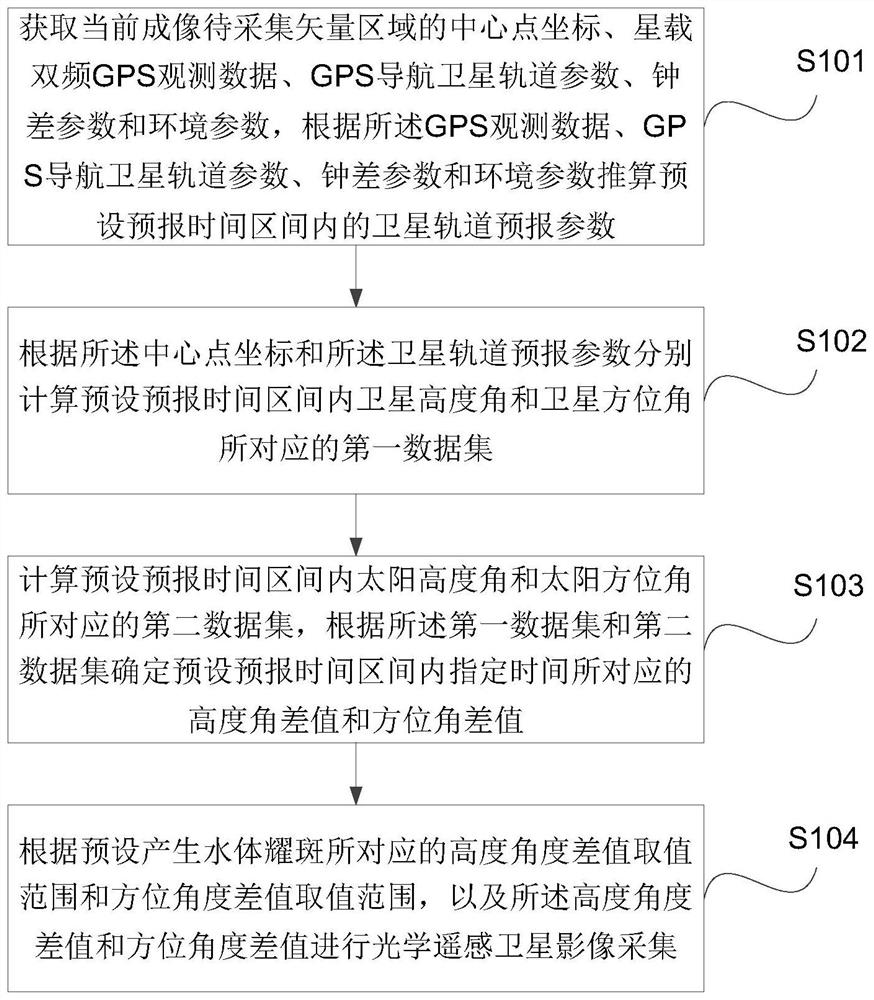
Method for avoiding optical remote sensing satellite image water flare and electronic equipment
The invention discloses a method for avoiding optical remote sensing satellite image water flareand electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the center point coordinate, satellite-borne dual-frequency GPS observation data, GPS navigation satellite orbit parameters, clock error parameters and environment parameters of a current imaging to-be-collected vector region, calculating satellite orbit forecasting parameters in a preset forecasting time interval, respectively calculating first data sets corresponding to a satellite elevation angle and a satellite azimuth angle according to the center point coordinates and the satellite orbit forecasting parameters, calculating a second data set corresponding to the solar elevation angle and the solar azimuth angle, and determining an elevation angle difference value and an azimuth angle difference value corresponding to specified time according to the first data set and the second data set, and performing optical remote sensing satellite image acquisition according to a preset height angle difference value range and an azimuth angle difference value range. The technical problem that in the prior art, the quality of a water body area of a collected remote sensing satellite image does not meet actual requirements is solved.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
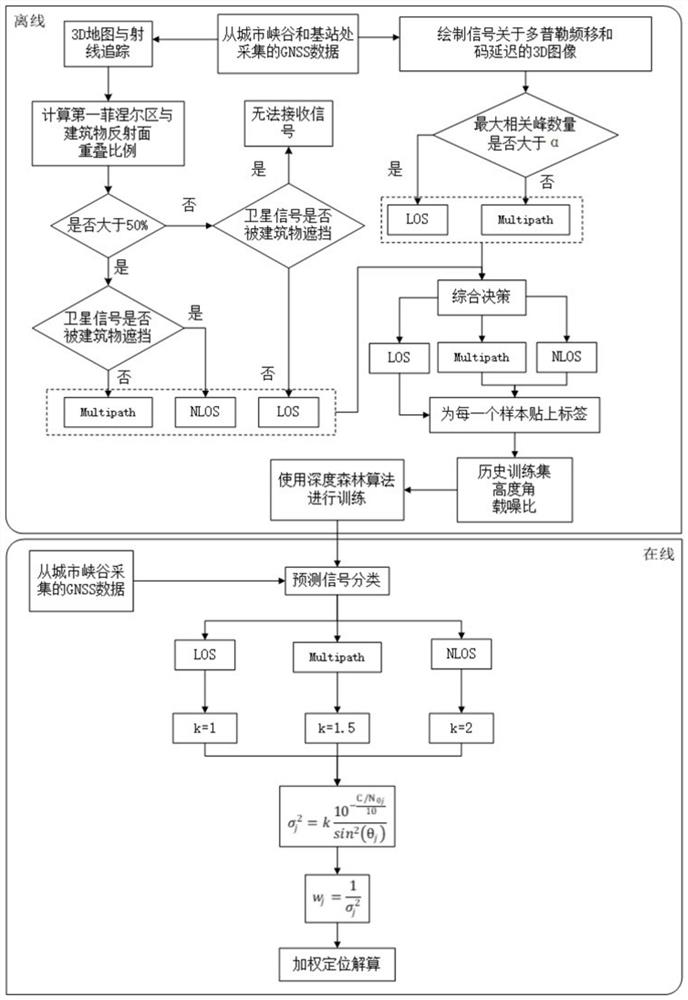
Weighted positioning method based on GNSS signal accurate classification in urban canyon
PendingCN113031031AImprove accuracyAchieve precise classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSatellite radio beaconingData setEngineering
The invention discloses a weighted positioning method based on GNSS signal accurate classification in an urban canyon, which belongs to the field of satellite positioning and navigation. The method comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a historical training data set, acquiring GNSS data from a base station and an urban canyon, calibrating a satellite signal receiving type by combining the GNSS data, forming a historical training data set by the carrier-to-noise ratio C / N0 of the satellite signal, the elevation angle theta of the satellite and the receiving type of the satellite signal, 2, mining the historical training data set by adopting a machine learning algorithm deep forest, and generating a satellite signal receiving type judgment rule, and 3, acquiring GNSS data from the urban canyon, predicting a satellite signal receiving type by using a depth forest, and performing positioning calculation in combination with weighted least squares. According to the method, precise classification of GNSS signal receiving types is realized, and the positioning precision is effectively improved by combining weighted positioning calculation considering the carrier-to-noise ratio, the satellite elevation angle and the signal receiving types.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
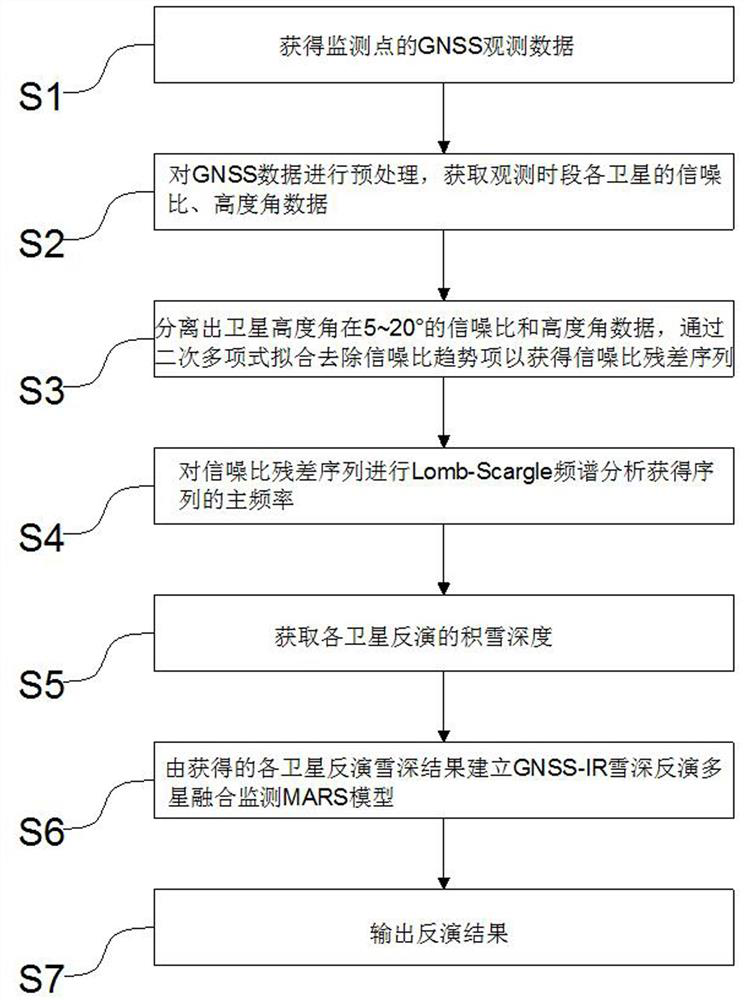
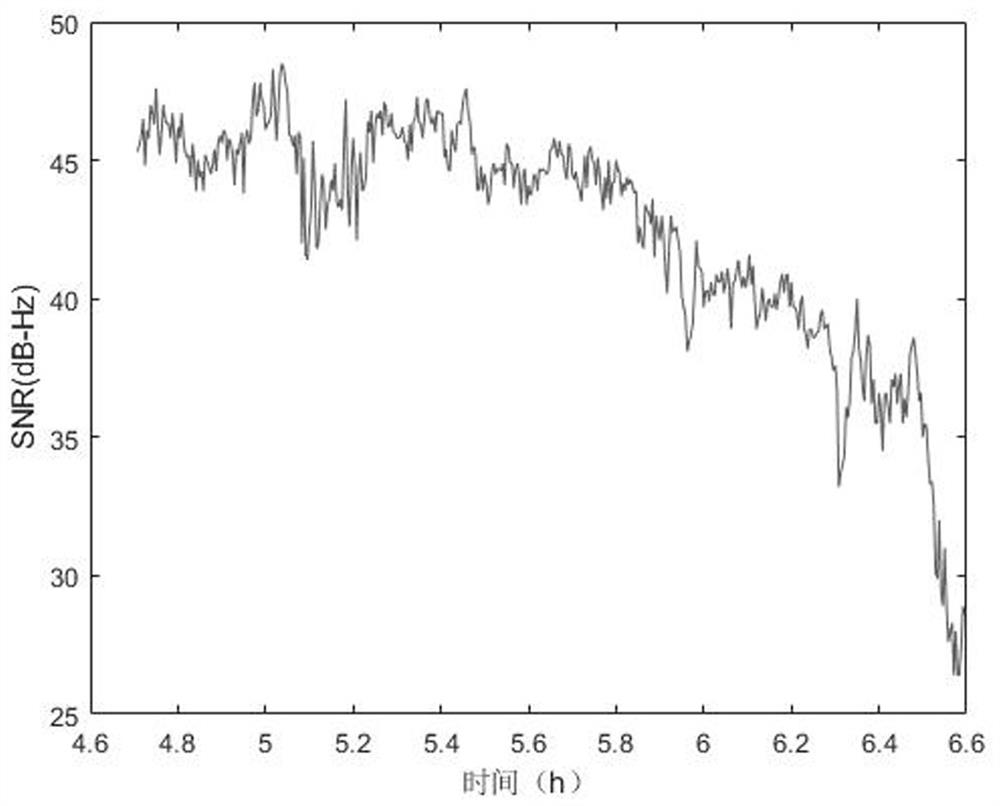
Accumulated snow depth inversion method based on multi-satellite data fusion
InactiveCN113959329AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionElectric/magnetic depth measurementSatellite radio beaconingSnowpackSatellite data
The invention relates to the technical field of accumulated snow depth monitoring, in particular to an accumulated snow depth inversion method based on multi-satellite data fusion, which comprises the following steps: acquiring GNSS observation data of a monitoring point; preprocessing the GNSS data, and acquiring the signal-to-noise ratio and elevation angle data of each satellite in the observation time period; separating signal-to-noise ratio and elevation angle data of a satellite elevation angle of 5-20 degrees, and removing a signal-to-noise ratio trend term through quadratic polynomial fitting to obtain a signal-to-noise ratio residual error sequence; carrying out lomb-Scargle spectrum analysis on the signal-to-noise ratio residual error sequence to obtain the main frequency of the sequence; acquiring the snow depth inverted by each satellite; establishing a GNSS-IR snow depth inversion multi-satellite fusion monitoring MARS model according to the obtained inversion snow depth result of each satellite; and outputting an inversion result. According to the method, the multi-satellite data fusion accumulated snow inversion model is established through the MARS theory, the inversion results of all satellites can be effectively integrated, data having great influence on the results are automatically eliminated, the optimal inversion satellite combination is obtained, and the reliability and precision of the inversion results are greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Dual-satellite diversity single-carrier transmission method with adaptive cyclic prefix
InactiveCN104467944BEasy to adjustReduce complexityError preventionRadio transmissionLow speedCyclic prefix
The invention relates to the field of satellite communication technologies and provides a binary diversity single-carrier transmission method based on a self-adaptive cyclic prefix. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a space segment provides information service forwarded based on processing through two co-orbital satellites, and a satellite receiver at an earth segment can synchronously receive signals of the two satellites to obtain space diversity gain; (2) inter-frame signal interference of a receiving end, which is brought by random perturbation of the satellites, is effectively resisted by utilizing a single-carrier transmission mechanism based on the cyclic prefix; (3) the satellite receiver carries out balancing and subsequent signal processing on the received signals, a specific statistical parameter is taken as an index, and the current length performance of the cyclic prefix is broadcasted to a satellite transmitting end in a manner of 1 bit; and (4) the satellite transmitting end adjusts the length of the cyclic prefix at the appointed step length according to feedback information. According to the method, when the satellite altitude is inaccurately known, lower complexity, low-speed feedback expenditure and higher transmission efficiency are achieved, and the signal diversity gain brought by binary transmission is obtained.
Owner:NO 61 INST OF GENERAL STAFF
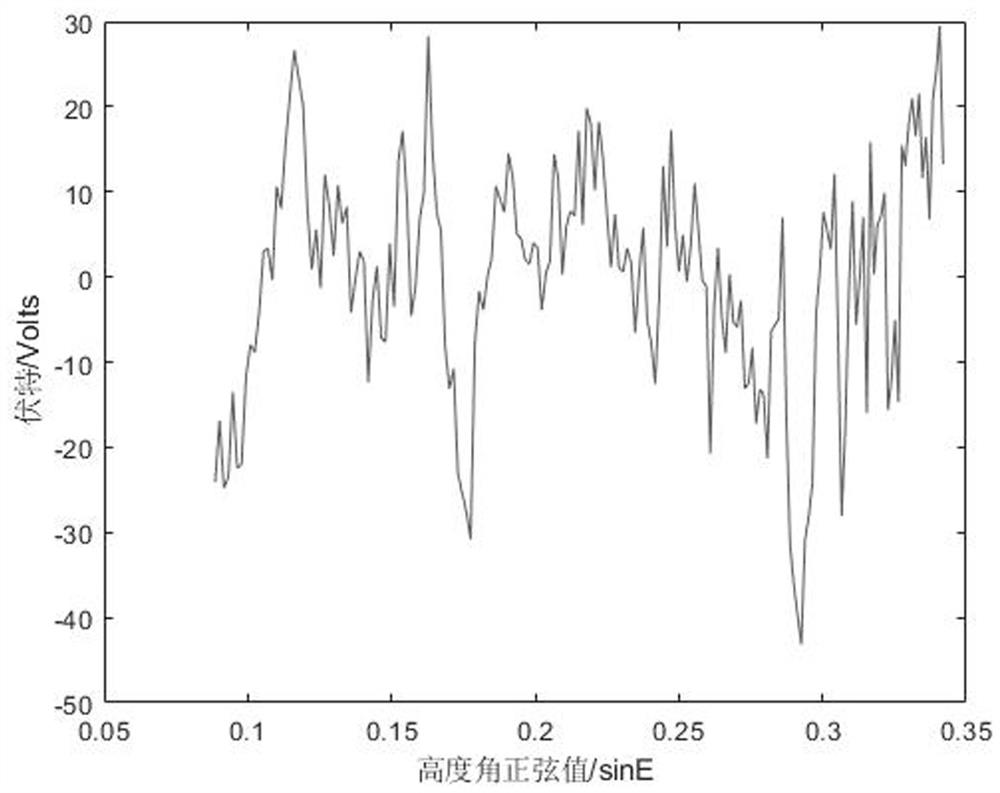
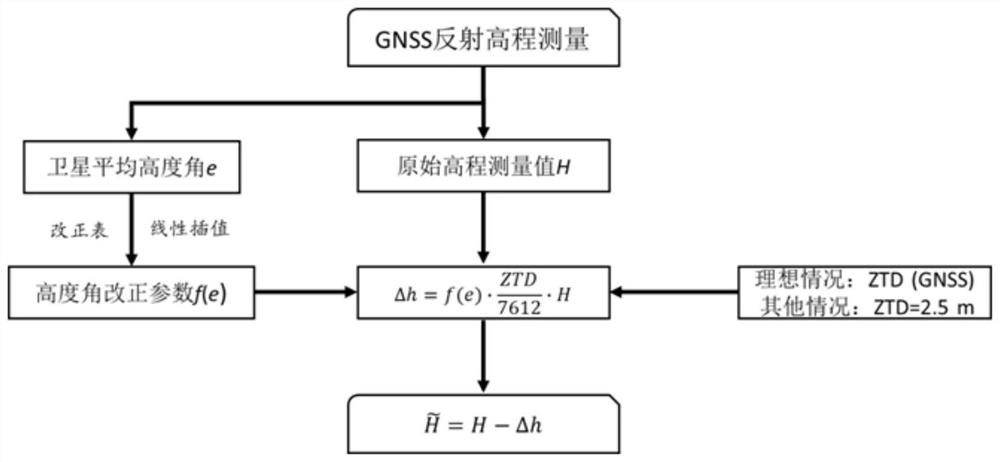
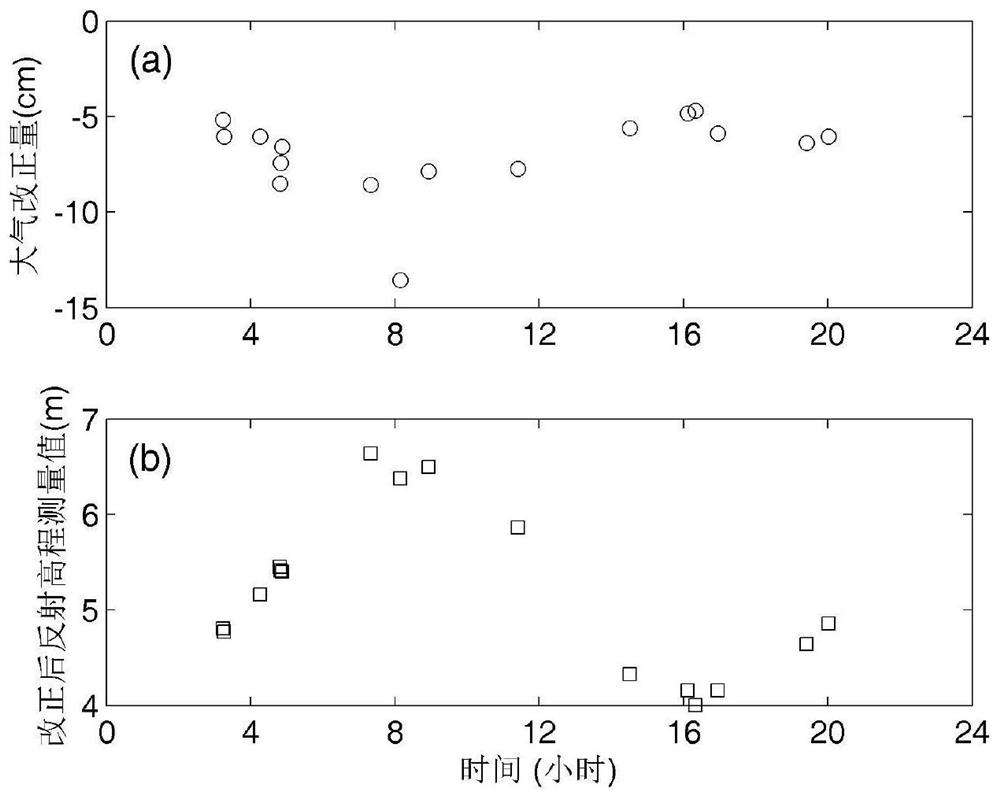
An Atmospheric Correction Method for GNSS Reflection Height Measurement
ActiveCN112130173BQuick correctionUniversalSatellite radio beaconingAtmospheric sciencesAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method for GNSS reflection height measurement, comprising the following steps: S1: establishing a satellite elevation angle parameter correction number table in GNSS reflection height measurement; S2: calculating the GNSS reflection height measurement satellite to be corrected The average elevation angle e and the original reflection elevation measurement value H; S3: according to the satellite average elevation angle e, in conjunction with the satellite elevation angle parameter correction number table in step S1, calculate the corresponding elevation angle parameter correction number f(e); S4: use Atmospheric correction formula calculates atmospheric correction amount; S5: Calculate the GNSS reflection elevation observation value after atmospheric correction according to the result obtained in step S4. The atmospheric correction method in the present invention aims at the elevation measurement error caused by the atmospheric delay of GNSS reflection measurement, which is convenient and fast to realize Atmospheric correction to improve the accuracy of GNSS reflection height measurement, and has a certain degree of universality.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
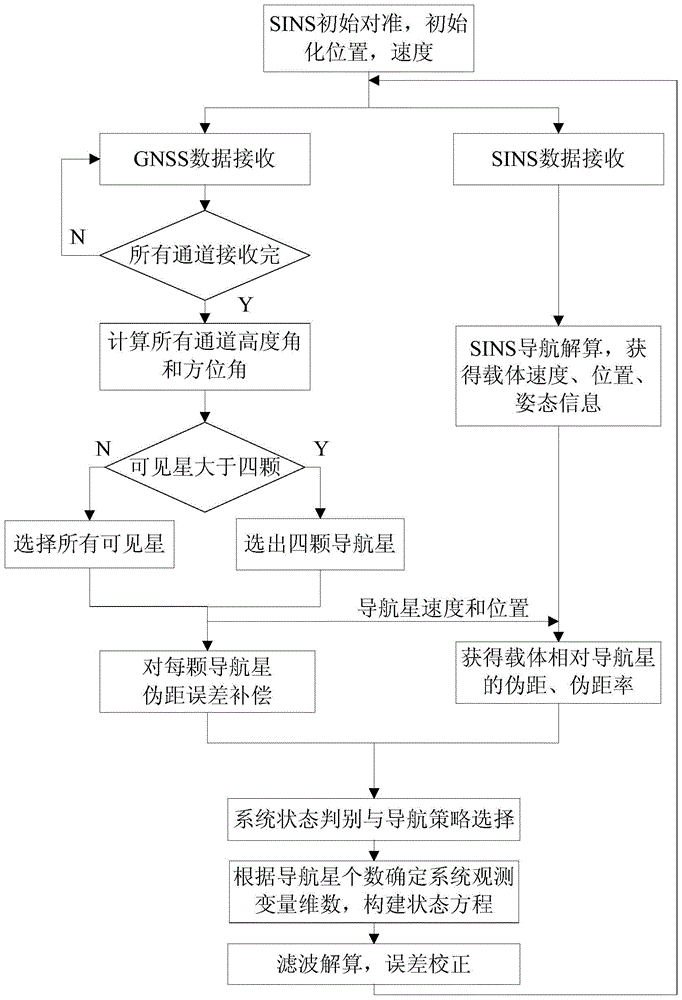
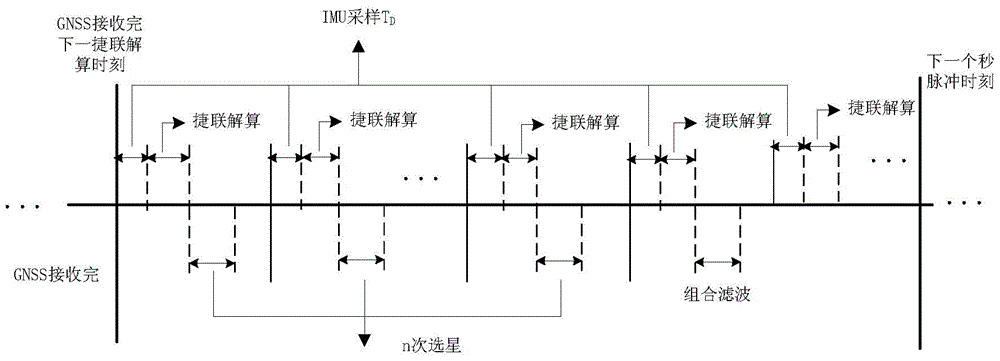
A Missile Inertial/Satellite Tight Integrated Navigation Method
ActiveCN104181572BWith independent operating status discriminationWith independent fault diagnosisNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteHysteresis
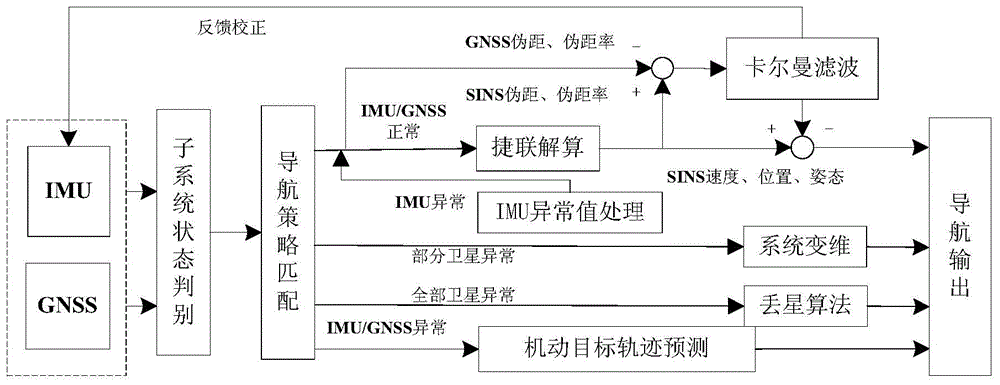
The invention discloses a missile-borne inertia / satellite tight combination navigation method. The method utilizes pseudo-range, pseudo-range rate information and inertial navigation output by a GNSS to calculate relative pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate difference of a satellite, filtering is carried out and the current system is corrected according to the filtering results. The method mainly comprises the following steps: carrying out SINS initialization; carrying out SINS navigation calculation; carrying out satellite altitude angle and azimuth angle calculation; carrying out navigational satellite selection; carrying out pseudorange measuring error compensation of the navigational satellite; carrying out calculation on pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate of a carrier with respect to each navigational satellite; carrying out system state judgment and navigation strategy selection; carrying out system state equation construction and system measurement equation construction; and carrying out filtering calculation, and for hysteresis error due to communication delay, correcting the system through an error compensation method based on state transition according to the filtering results. The method can realize inertia / satellite-based pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate seamless combination navigation; navigation accuracy and adaptability to complex environment are improved; and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com