Method for increasing number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R height measurement satellites
A technology of sea surface reflection and satellite reception, which is applied in the field of satellite altimetry, can solve the problems affecting the coverage area of the antenna, and achieve the effect of improving work efficiency and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
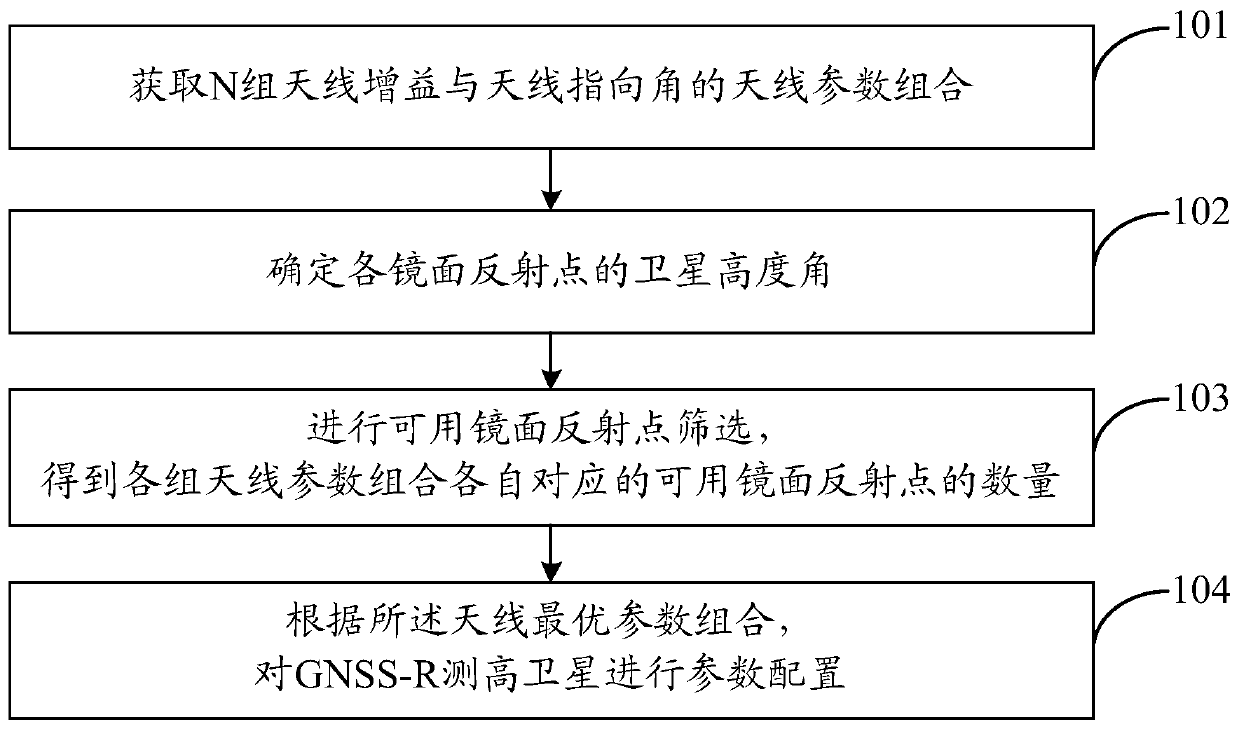
[0028] Such as figure 1 , in this embodiment, the method for increasing the number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R altimetry satellites includes:
[0029] Step 101, acquiring N sets of antenna parameter combinations of antenna gain and antenna directivity angle.
[0030] In this embodiment, the combination of antenna parameters refers to any combination of multiple antenna gains and multiple antenna directivity angles. Wherein, N>250000.
[0031] Step 102, obtaining the position information of all specular reflection points calculated and output by GPS satellite ephemeris and TDS-1 satellite ephemeris within 24 hours, and determining the satellite elevation angle of each specular reflection point.
[0032] In this embodiment, the data sources used are mainly as follows:
[0033] TDS-1 satellite data
[0034] Launched on July 8, 2014, the TDS-1 satellite is a technology verification satellite designed by the United Kingdom. The satellite carried eight ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] In this embodiment, the establishment process of the GNSS-R satellite-borne down-look antenna SNR model GSNASNRM can be as follows:
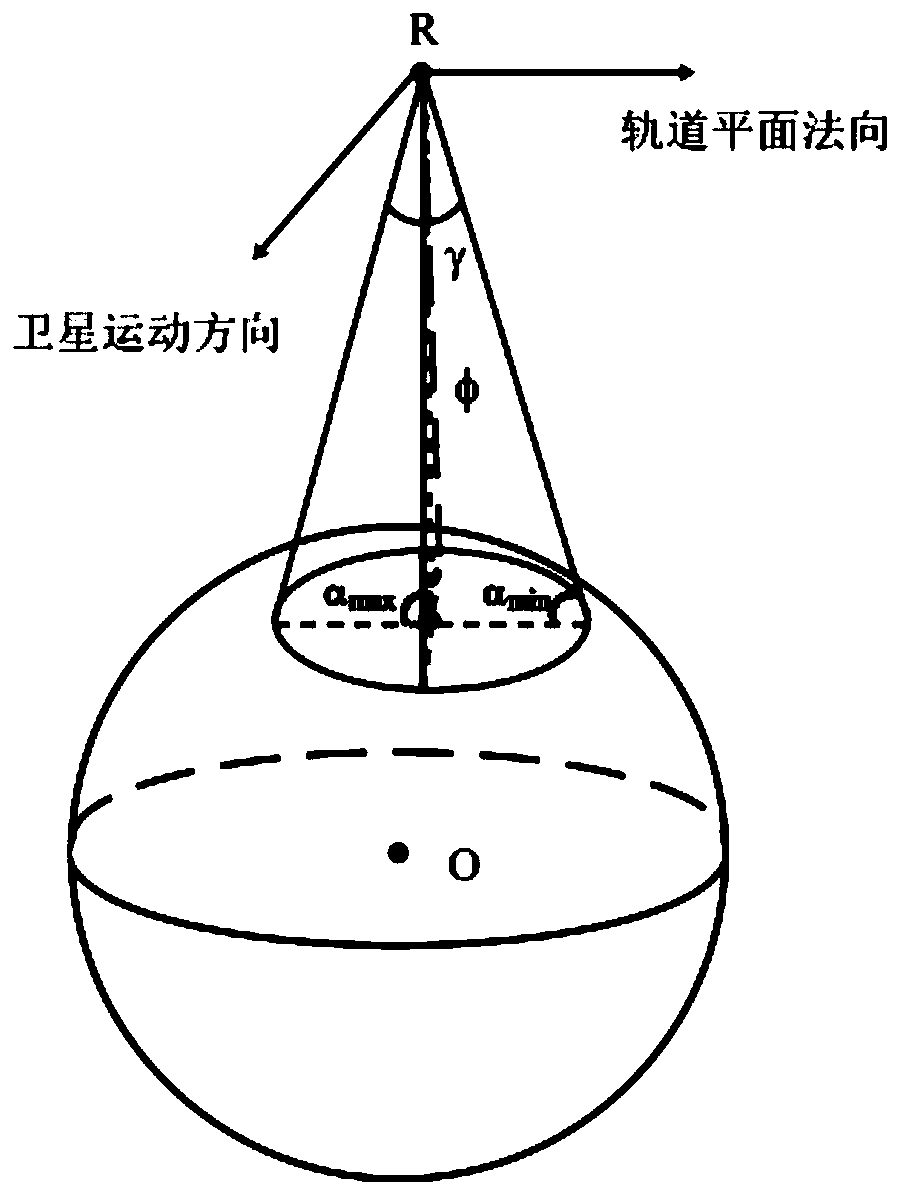
[0076] Such as Image 6 , according to the relative position of the GNSS-R altimetry satellite and the GNSS satellite, combined with the geometric theorem ( Figure 4 Point P is the mirror reflection point, and point O is the center of the earth), the following formula (3) can be obtained:
[0077]
[0078] Among them, R TP Indicates the distance from the GNSS satellite to the specular reflection point, R PR Indicates the distance from the GNSS-R altimetry satellite to the specular reflection point, R E is the radius of the earth, H T Indicates the height of the GNSS satellite, H R Indicates the altitude of the GNSS-R altimetry satellite.
[0079] Solving equation (3), we get:
[0080]
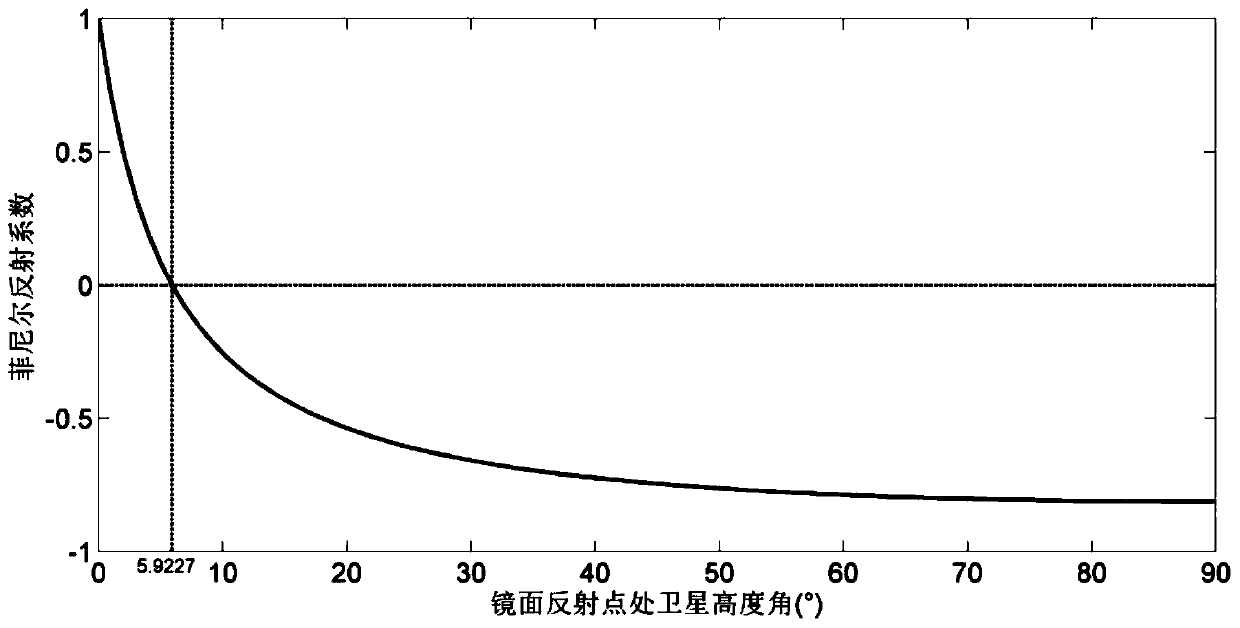
[0081] In order to more accurately evaluate the performance of the antenna's ability to receive signals, it is necessary to calculate the si...
Embodiment 3
[0097] On the basis of the above embodiments, the present invention also provides verification and simulation results of the method for increasing the number of sea surface reflection signals received by GNSS-R altimetry satellites.
[0098] Signal-to-noise ratio of received GNSS reflected signal
[0099] In this embodiment, TDS-1 satellite observation data is used to verify the reliability of GSNASNRM, so when calculating SNR, the parameter setting should be as consistent as possible with TDS-1. Among them, the orbit height of the GNSS-R altimetry satellite is set to 635km, the downward-looking antenna is set to point to the nadir with a gain of 13.3dBi, the frequency of the received signal is set to 1575.42MHz in the L1 band, the wavelength is 0.19m, and the antenna temperature is set to 300K , since the TDS-1 observation data has been despread by pseudo code, therefore, the noise bandwidth is set to 1000Hz. Such as Figure 7 , gives the relationship between the signal-to-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com