Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Pseudomonas agarici" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pseudomonas agarici is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that causes drippy gill in mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus). It was first isolated in New Zealand. P. agarici could not be grouped based on 16S rRNA analysis, so it is designated incertae sedis in the genus Pseudomonas.
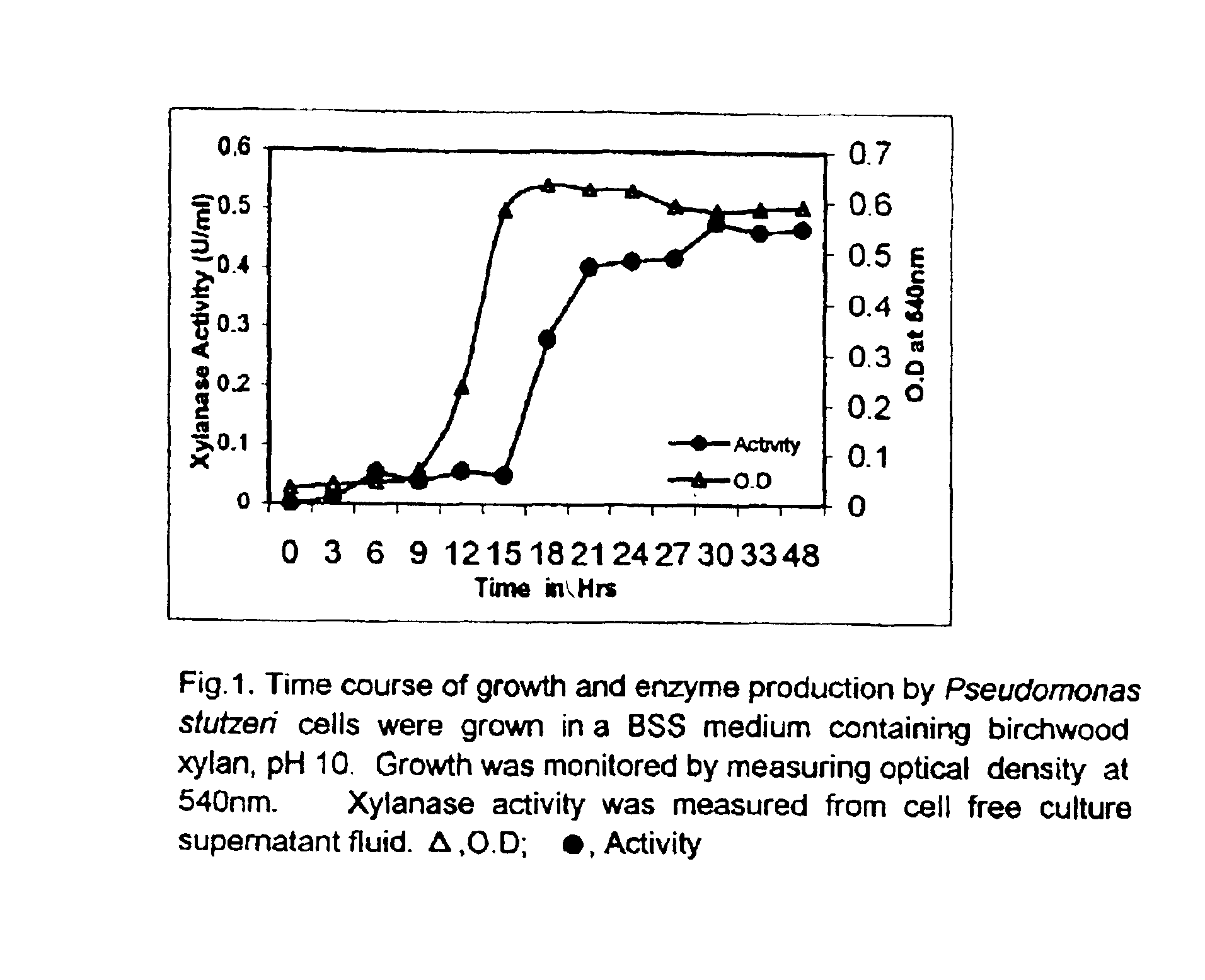
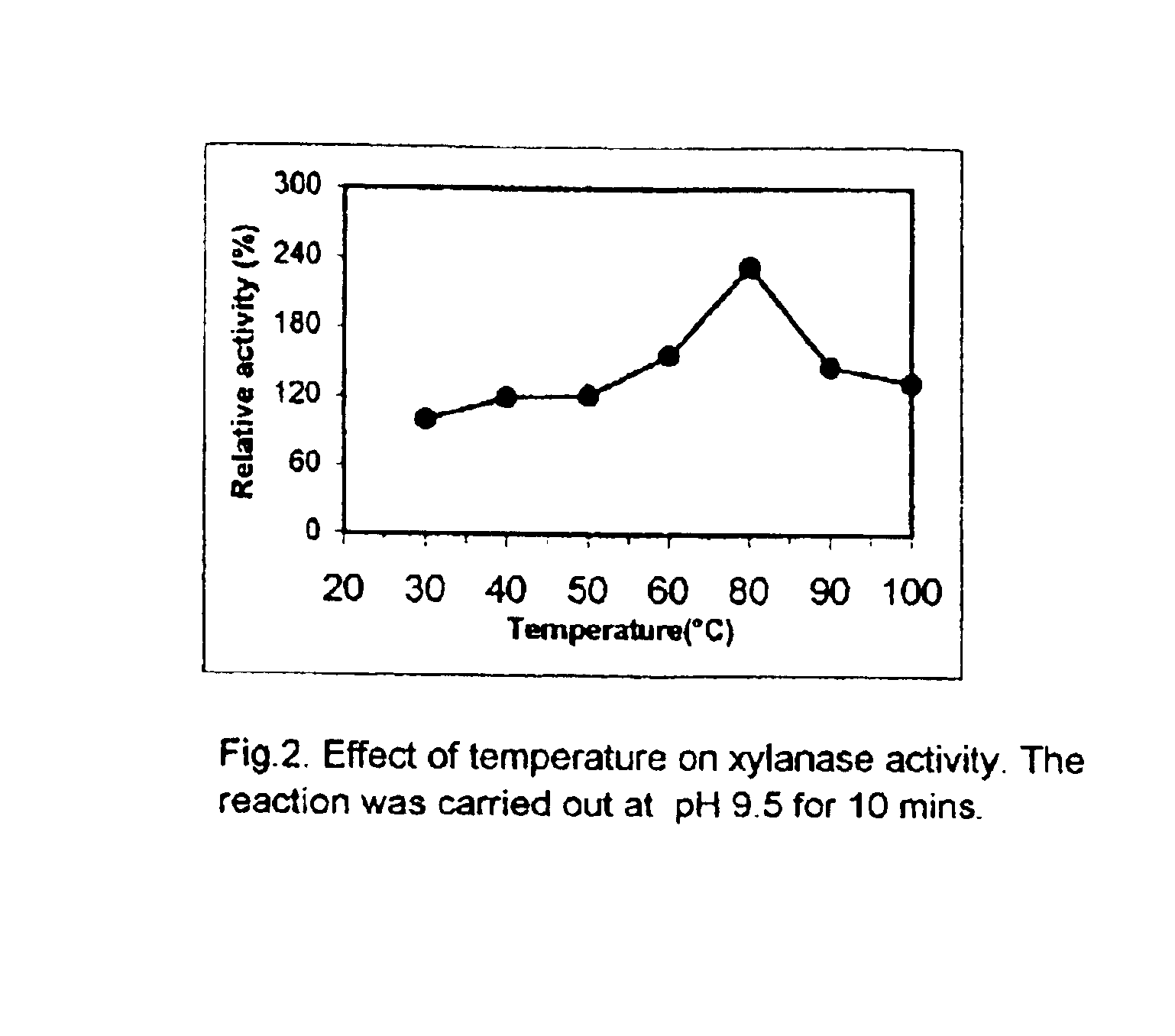
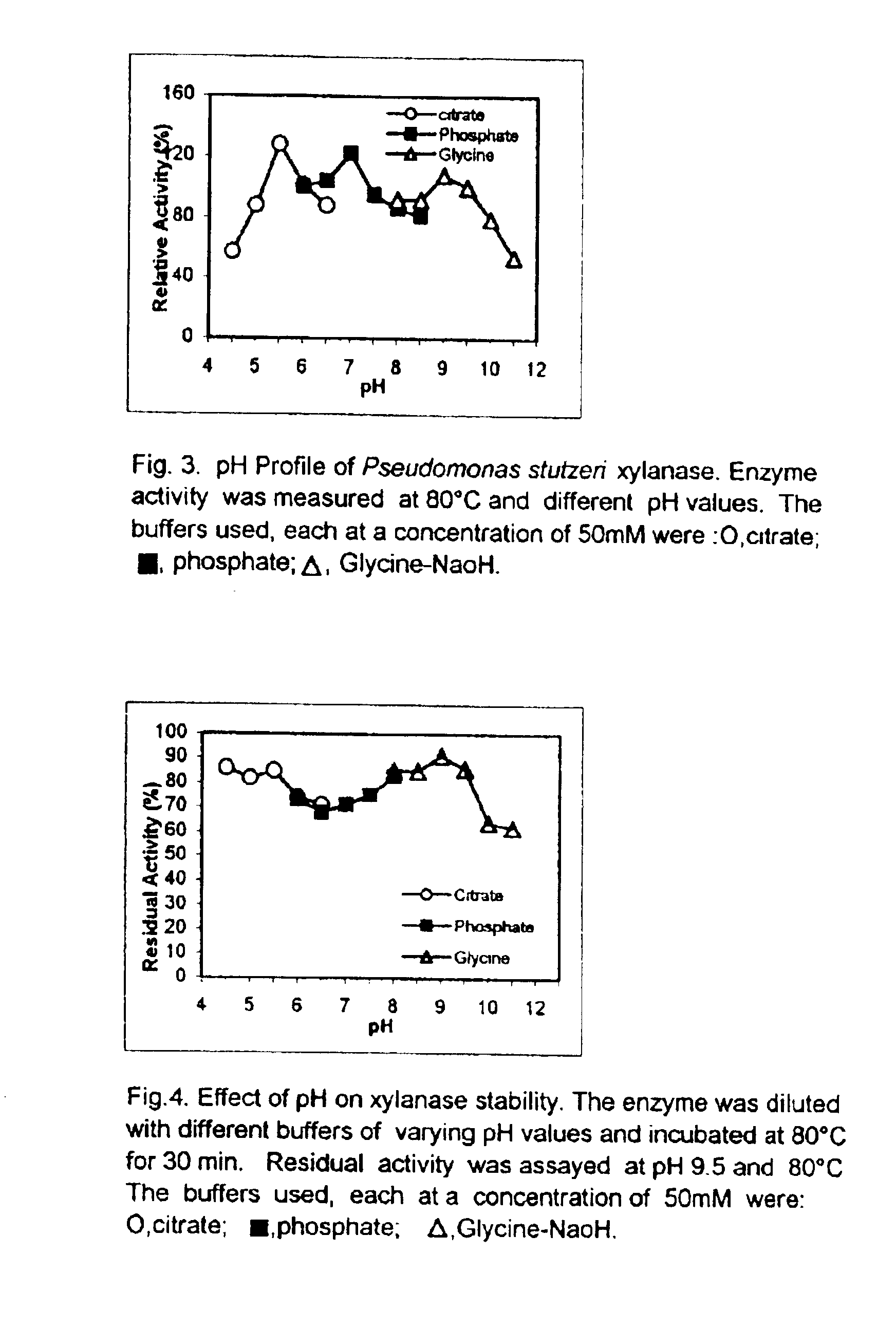
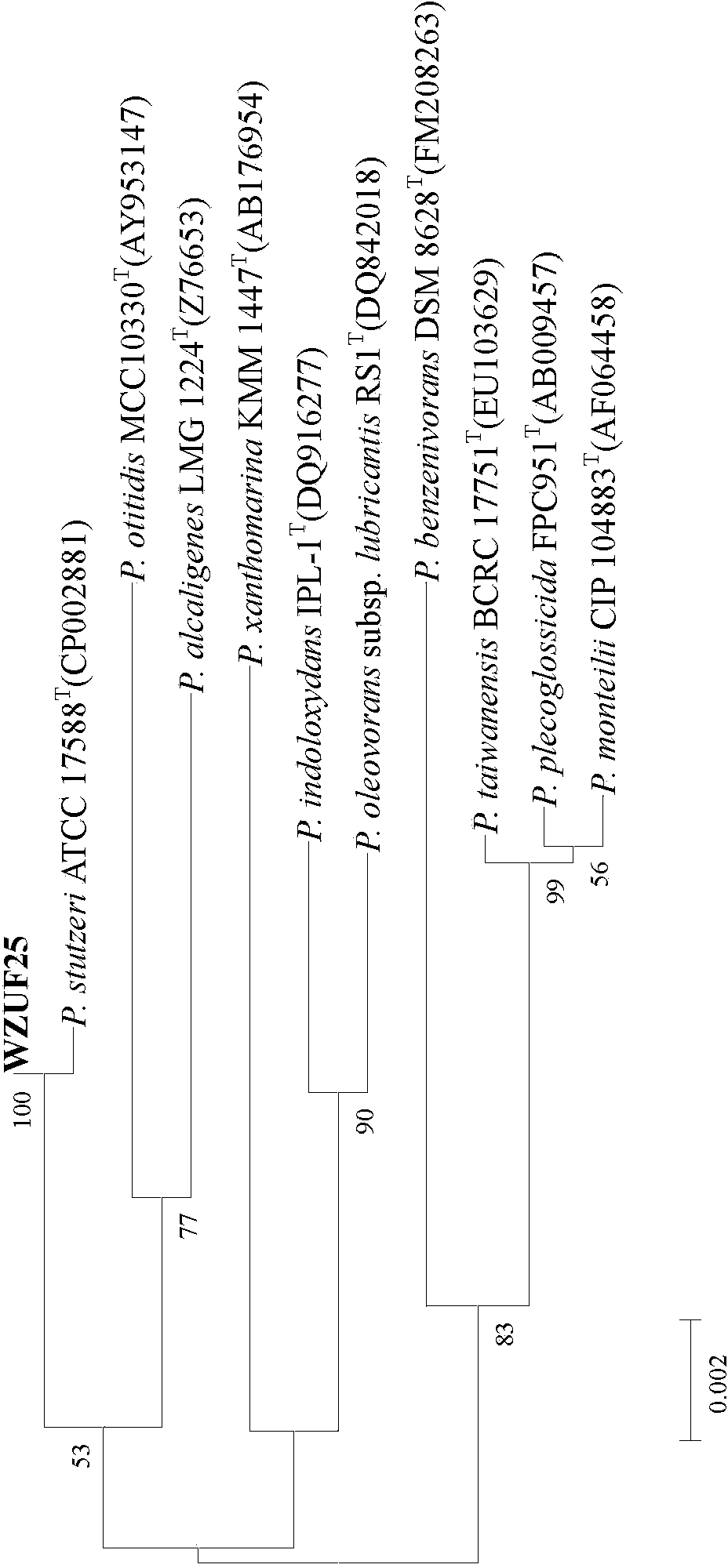
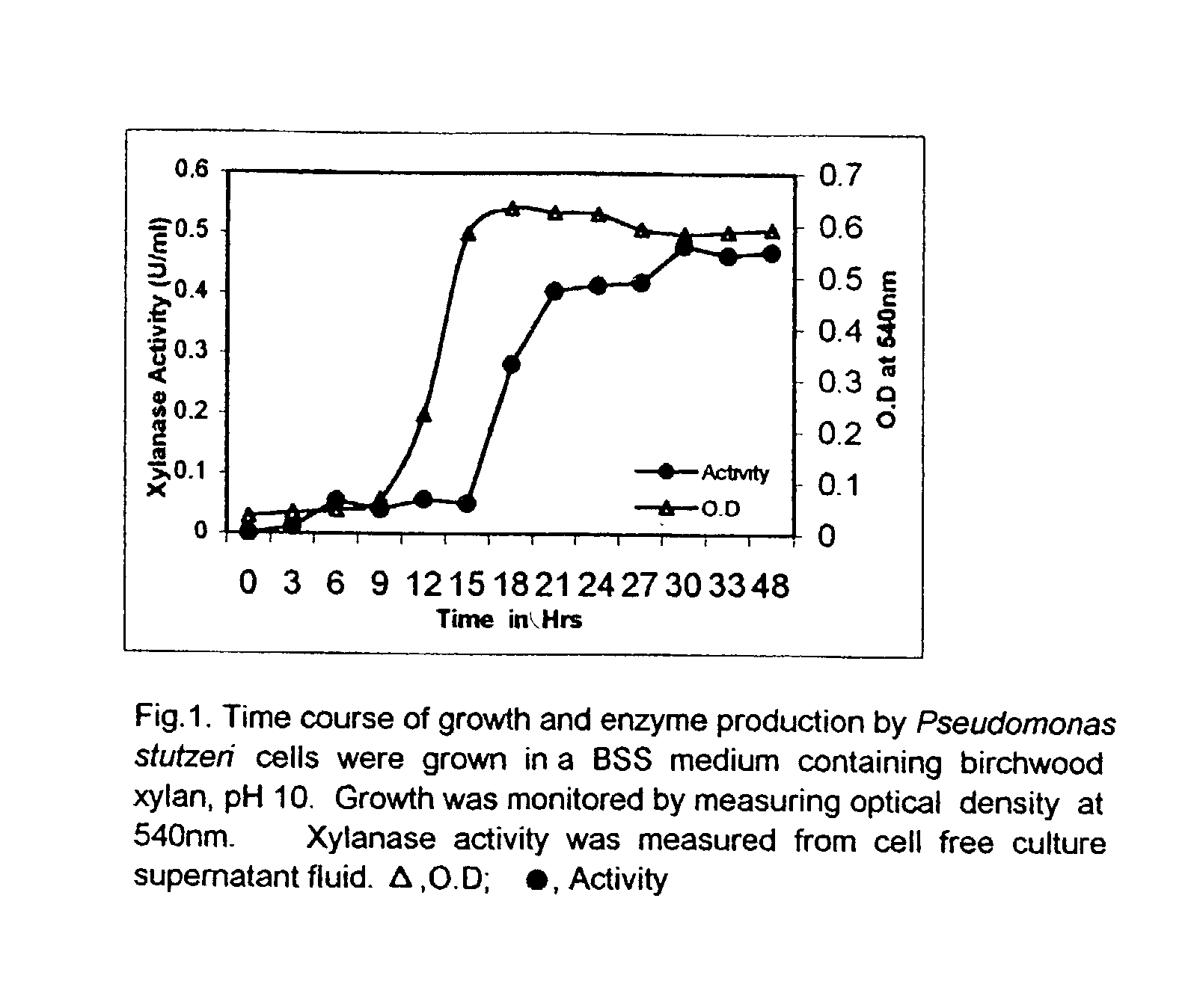
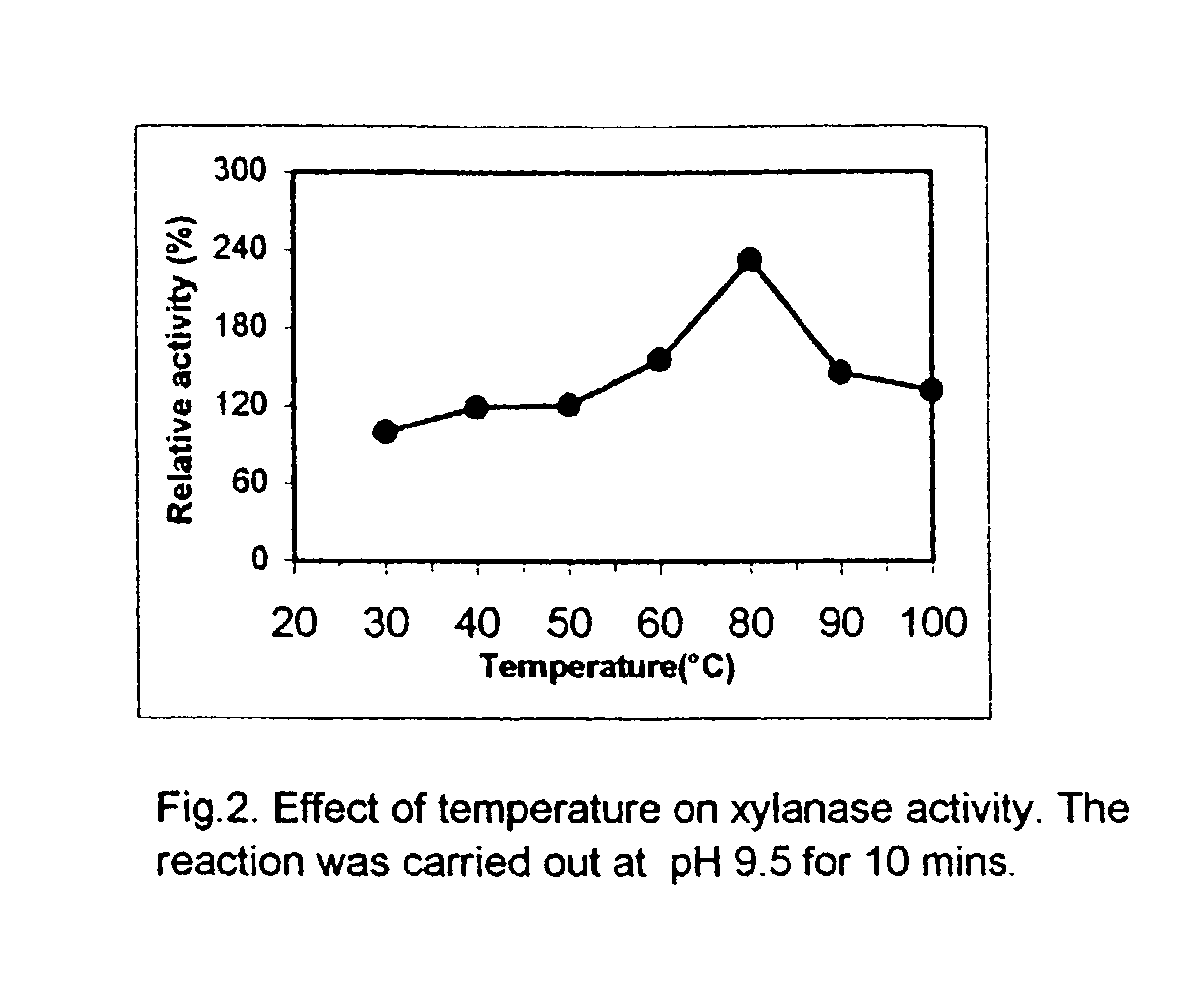
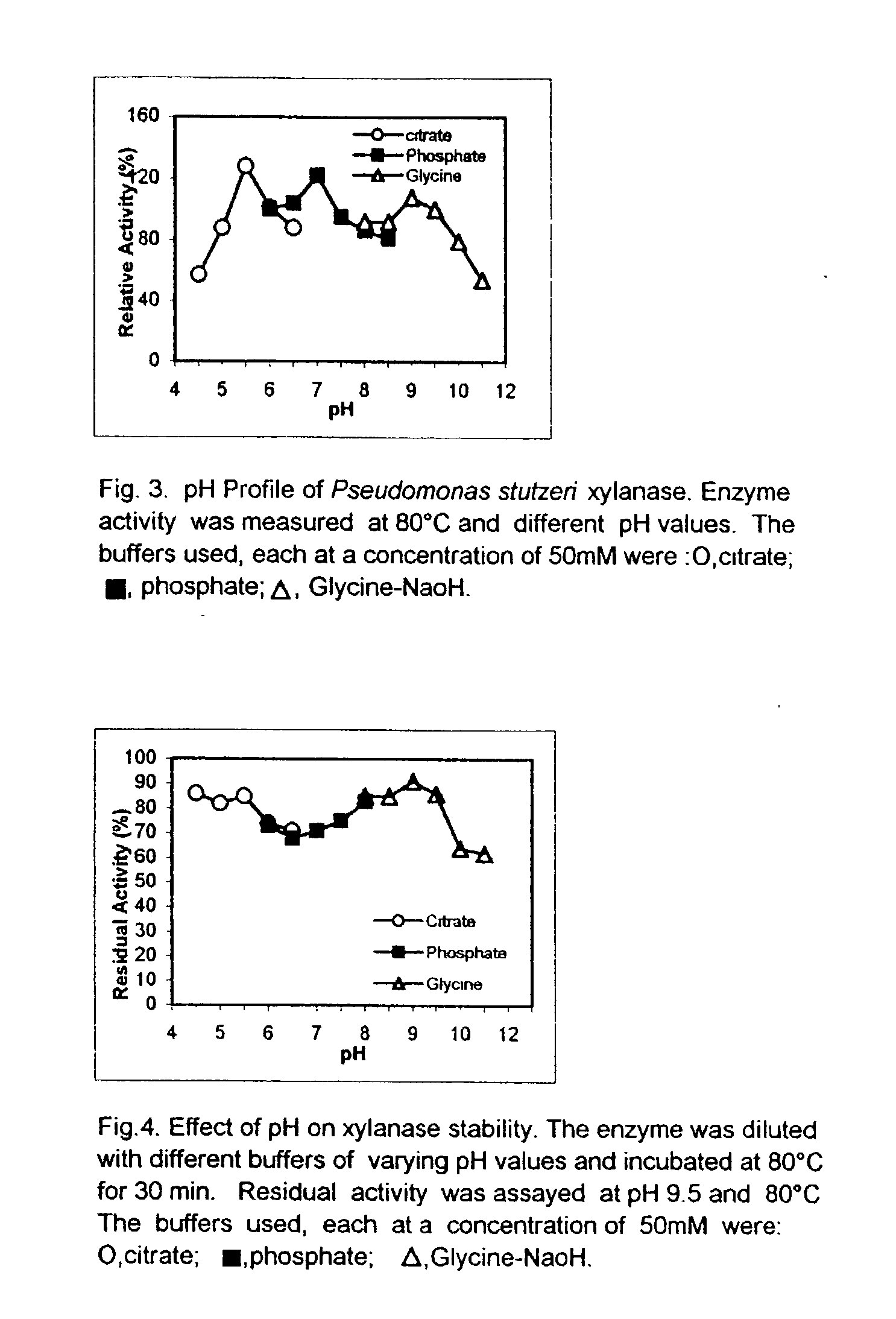
'Pseudomonas stutzeri' strain and process for preparation of xylanase
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Preparation method and application of pseudomonas chlororaphis for resisting disease and promoting growth
ActiveCN104017744AIncrease productionPowerful biological control functionBiocideBio-organic fraction processingMetaboliteMicrobial agent
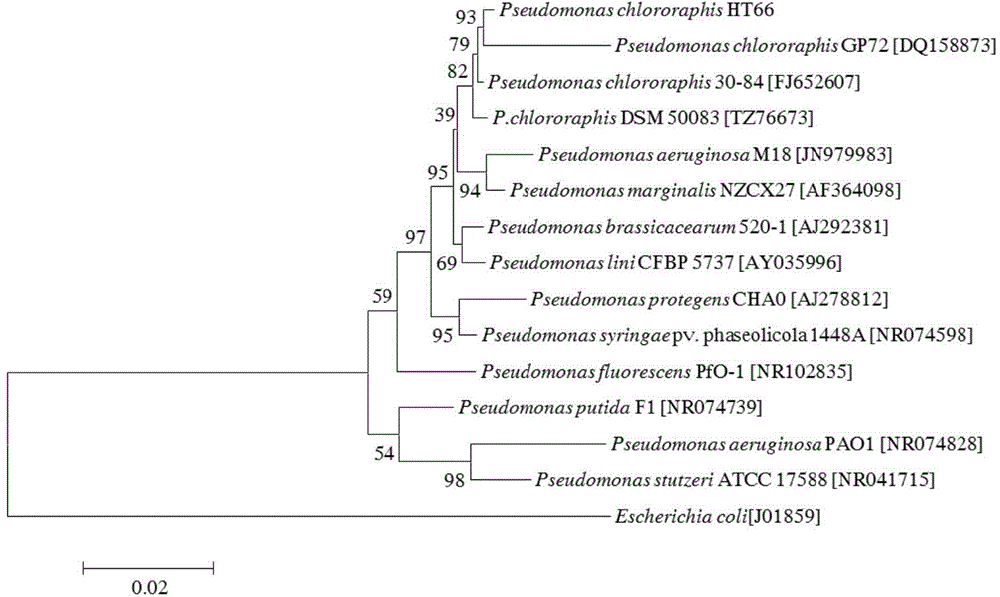
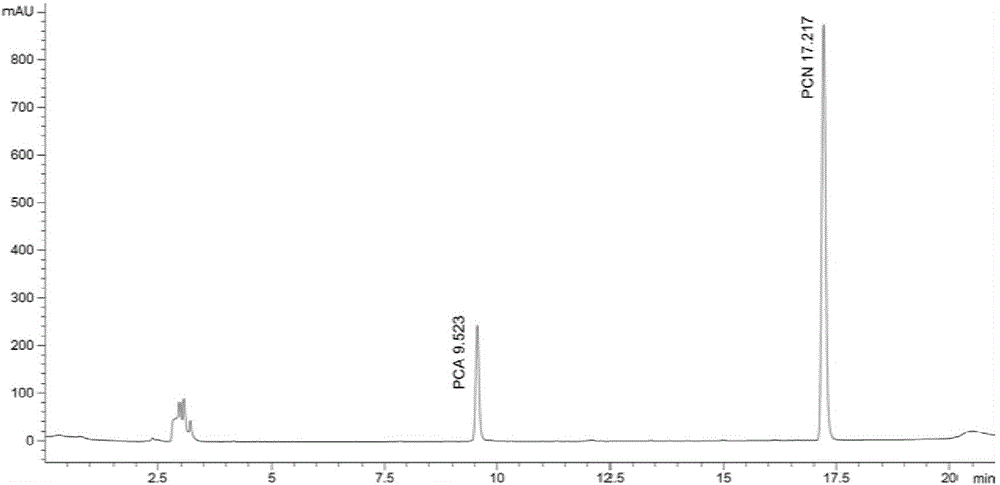
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of pseudomonas chlororaphis for resisting disease and promoting growth. A strain is pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66CCTCC No:M2013467. A main metabolite of the strain comprises phenazine-1-phenazine and phenazine-1 formamide. The strain is inoculated into a microorganism culture medium and is fermented to obtain a thallus with high concentration and the metabolite, and can be mixed with materials like powder active carbon, bentonite, swell soil, kaolin, diatomite, zeolite, calcium carbonate and the like to prepare a microbial agent; the quantity of viable organisms in a finished product is 1-8.5*10<9>cfu / mL. The tablet laboratory verifies that the pseudomonas chlororaphis has good control effect of pathogenic bacteria of rice sheath blight diseases, cotton fusarium wilt, gaeumannomyces graminis and watermelon fusarium wilt, and also has a good promotion function in the growth of a part of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Composite microbial inoculum for preparing biological bacterial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a microbiological composite bacterial inoculum and a preparation method thereof, in particular to the microbiological composite bacterial inoculum used for preparing a biological bacterial fertilizer. The microbiological composite bacterial inoculum is prepared by culturing Rhodop seudanonas palustris, Candida utilis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis and Streptomyces microflavus var. lactosus which are disclosed in a culture catalogue of the China Center for General Microbiology Culture Collection (CGMCC), wherein the serial number of the Rhodop seudanonas palustris is 1.2352; the serial number of the Candida utilis is 2.1180; the serial number of the Lactobacillus acidophilus is 1.1854; the serial number of the Bacillus subtilis is 1.1630; the serial number of the Streptomyces microflavus var. lactosus is 4.0891; and the weight ratio of the Rhodop seudanonas palustris to the Candida utilis to the Lactobacillus acidophilus to the Bacillus subtilis is 1:0.5:0.5:0.1. When used for preparing the biological bacterial fertilizer, the composite bacterial inoculum can effectively decompose and release crude fibers and other nutrient components in straws and livestock manure; and the prepared biological organic fertilizer can condition the soil, increase the activity rate of microorganisms in the soil, avoid soil hardening, improve the permeability of the soil, play a role in production increasing, and effectively solve the problem of the area source pollution of agricultural wastes in rural areas.
Owner:于和军
Gene engineering bacterial strain used for producing phenazine-1-methanamide and its purpose
ActiveCN103642714AIncrease productionEffective biological controlBiocideBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyBacterial strain
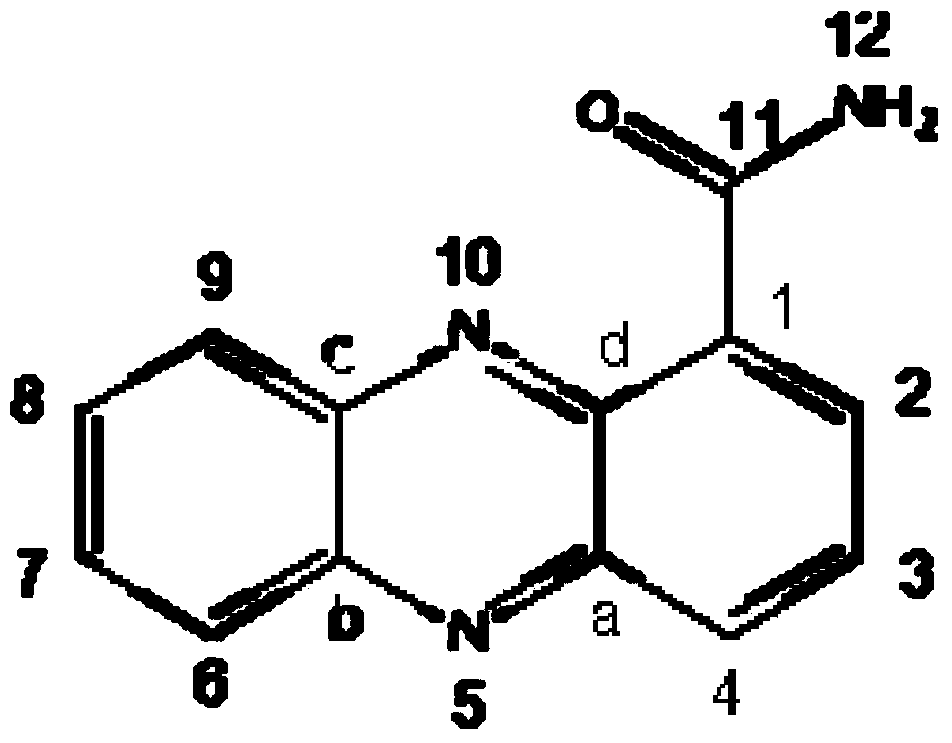
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterial strain used for producing phenazine-1-methanamide and its purpose; which is characterized in that knockout of psrA or rpeA gene in Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66(Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66) CCTCC NO: M 2013467 genome is carried out. According to the invention, a strain of Pseudomonas chlororaphis is performed with seed culture, fermentation, extraction, concentration and crystallization to obtain phenazine-1-methanamide with purity of more than 96%. After the deletion of psrA and rpeA gene in the bacterium genome, the fermentation output of phenazine-1-methanamide can reach as high as 1800ppm. The agar plate bacteriostasis tests found that phenazine-1-methanamide has obvious inhibition effect on common plant pathogenic fungi such as Rhizoctonia solani, fusarium oxysporum, pythium wltmum and Stevia Septoria, has good stability and activity, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Use of Novel Strains for Biological Control of Pink Rot Infections in Potato Tubers
ActiveUS20120076765A1Inhibition is effectiveEffective for suppression and controlBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBacterial strain
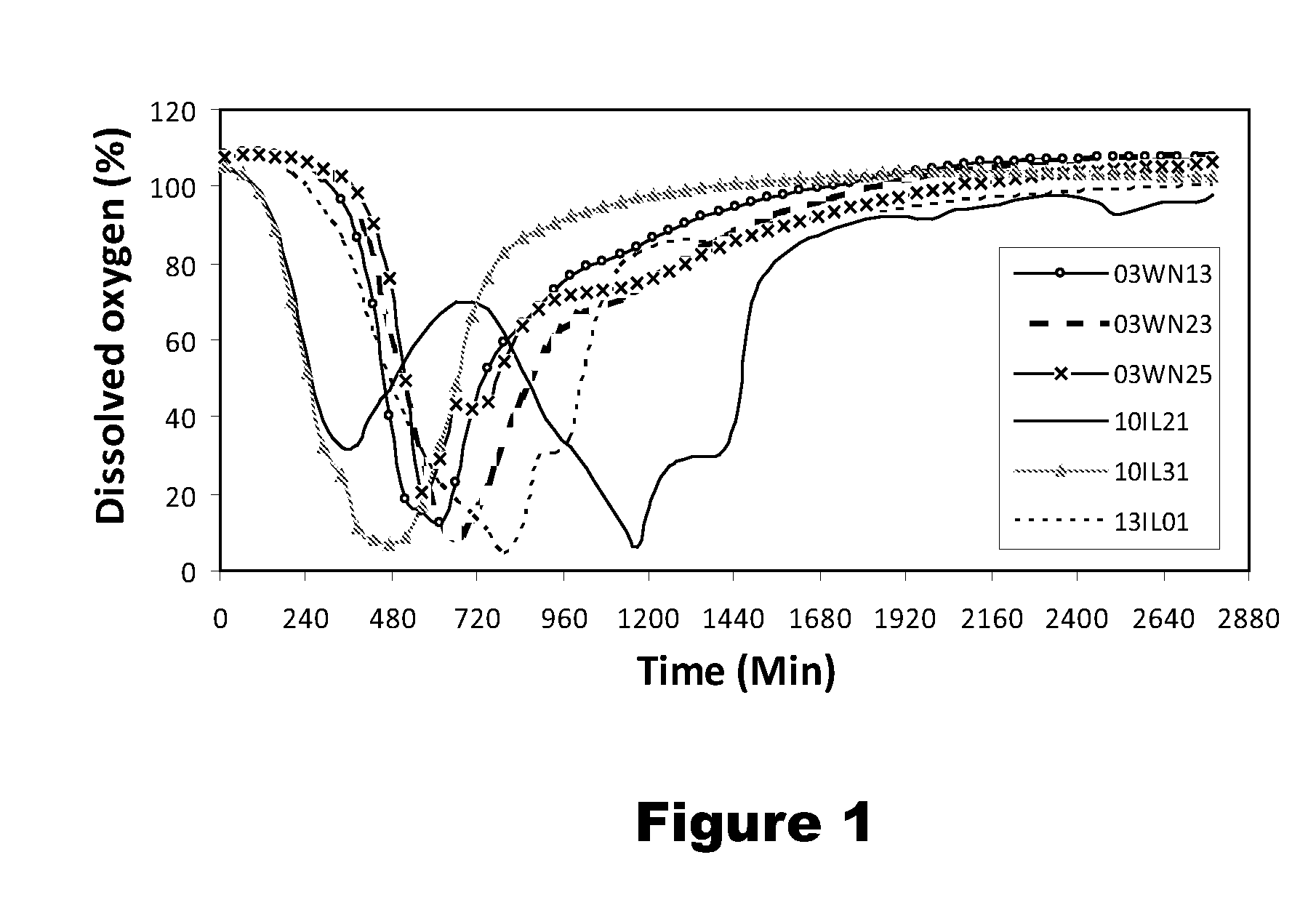
Six bacterial strains: Bacillus simplex strain 03WN13, Bacillus simplex strain 03WN23, Bacillus simplex strain 03WN25, Pseudomonas koreensis strain 10IL21, Pantoea agglomerans strain 10IL31, and Pseudomonas lini strain 13IL01, are superior antagonists of Phytophthora erythroseptica Pethybr., the causative agent of pink rot on potatoes. These bacterial strains are effective for suppression and control of pink rot on potatoes.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating crop fusarium disease and applications thereof
The invention provides pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating the crop fusarium disease and applications thereof. The preservation number of the pseudomonas chlororaphis is CGMCC No. 7729. The Pcho01 bacterium strain of the pseudomonas chlororaphis has a high effective antagonistic action, is capable of being applied to the preventing and treating wheat scab caused by fusarium, and the preventing and treating efficiency in the field is maintained above 60%. The Pcho01 bacterium strain also has a very good antagonistic action on botrytis cinerea, rice sheath blight fungus, bipolaris maydis, pythium wltmum, rhizopus, and pseudomonas solanacearum, and can be used to prevent and treat the diseases caused by those bacteria mentioned above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glycomimetic inhibitors of the PA-IL lectin, PA-IIL lectin or both the lectins from Pseudomonas
Compositions and methods are provided related to Pseudomonas bacteria. The compositions and methods may be used for diagnosis and therapy of medical conditions involving infection with Pseudomonas bacteria. Such infections include Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis. A compound useful in the present methods may be used in combination with a therapeutic agent or may be linked to a therapeutic agent. Pseudomonas bacteria may be inhibited by blocking colonization, inhibiting virulence factors, arresting growth or killing the bacteria.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
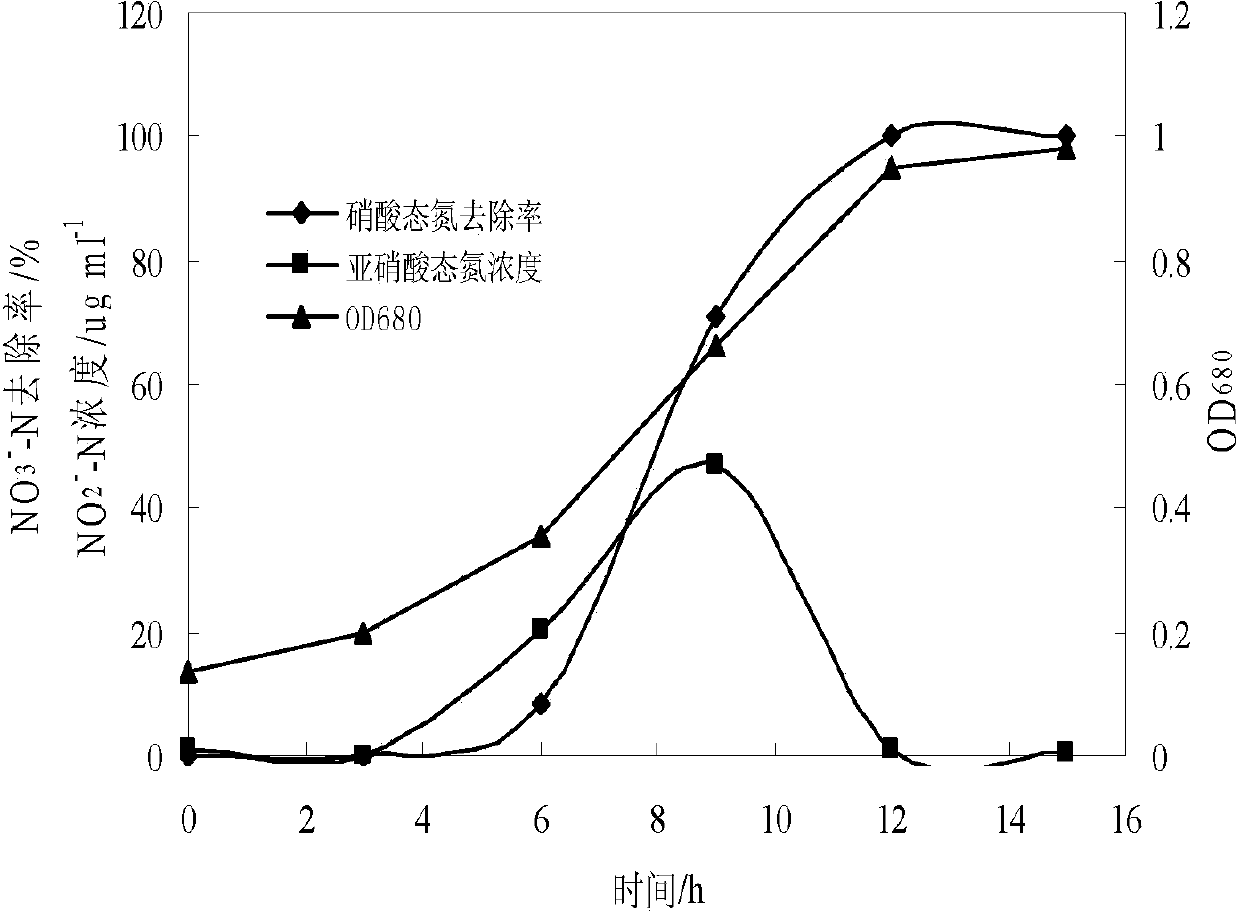
Pseudomonas stutzeri and its culture, immobilization and use
InactiveCN103497908AHigh removal rateWide pH rangeBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobiological cultureDenitrification
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Novel 'pseudomonas stutzeri' strain and process for preparation of xylanase
The present invention relates to a novel xylanase producing bacteria, Pseudomonas stutzeri deposited at the MCMRD, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa 403004, India and having the assession number MCMRD-AB-001 and also deposited at ______ having accession No. ______, and a process for production of thermophilic and alkalophilic extracellular enzyme xylanase using the said bacteria.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis CLP-7, and applications thereof
The invention discloses an acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 which is capable of preventing diseases and promoting growth, and can be used for biocontrol. The acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on 27th, October, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13204. The antibacterial spectrum of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is relatively large; the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of inhibiting growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, Ralstonia solanacearum, and Alternaria alternata Keissler; the antagonistic activity under acidic conditions is high, the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of producing siderophore, possesses protease and glucanase activity, and potassium releasing capacity. The results of biocontrol pot experiment show that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of preventing under acidic soil conditions, and promoting growth and chlorophyll synthesis of tobacco seedlings in acidic soil, so that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 and microorganism bacterium agents of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 can be used for preventing tobacco fungi and bacterial root and stem diseases under continuous cropping or acidic soil conditions effectively, and is high in application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Pseudomonas and purpose of pseudomonas
ActiveCN102876617AEasy to trainFast growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas stutzeriWastewater
The invention discloses pseudomonas with the preservation name being pseudomonas stutzeri SC221-M, the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation address is Wuhan university, Wuhan, China, the preservation date is July 11, 2012, and the preservation number is CCTCC No: M2012281. The invention simultaneously discloses a purpose of the pseudomonas used for purifying culture wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Taxus chinensis var. mairei rhizosphere high-efficient phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonas fluorescens and application thereof
InactiveCN101899409APromote growth and developmentImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentPhosphate
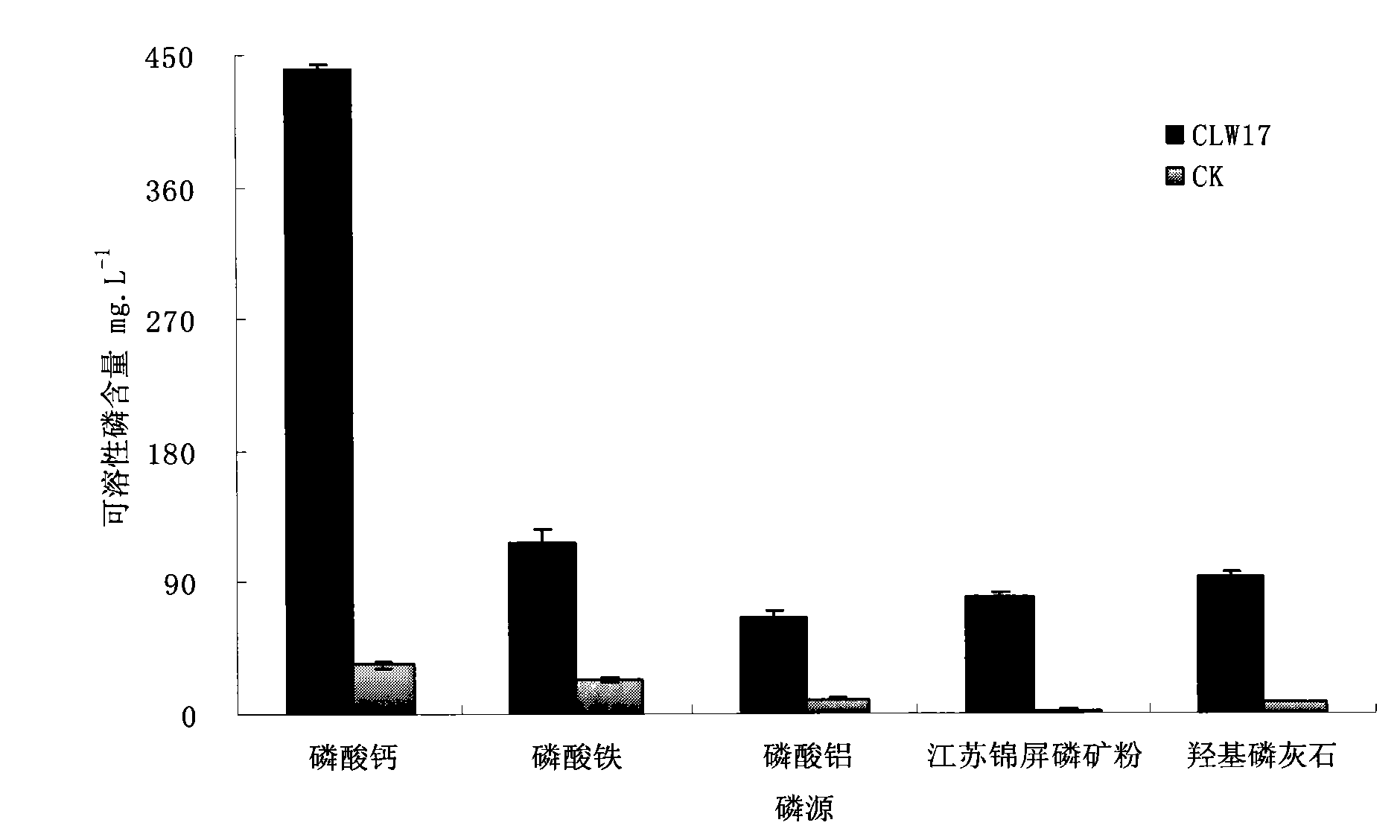
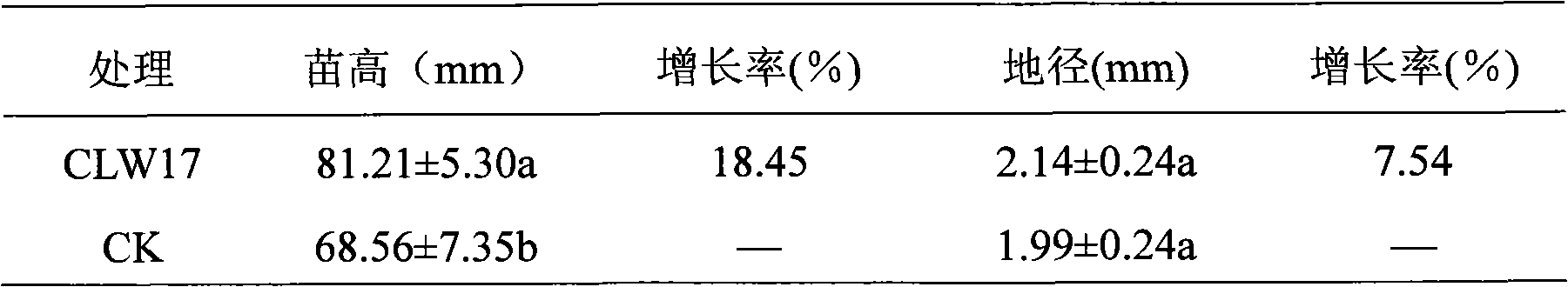
The invention discloses taxus chinensis var. mairei rhizosphere high-efficient phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonas fluorescens, which is classified and named as pseudomonas fluorescens CLW17 collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the collection number of CCTCC NO. M 2010158. The invention further discloses an application of the taxus chinensis var. mairei rhizosphere high-efficient phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonas fluorescens in promoting the growth of taxus chinensis var. mairei. A strain of the invention has very strong effect of dissolving insoluble phosphates of tricalcium phosphate, iron phosphate, aluminum phosphate, Jiangsu Jinping phosphate rock powder and hydroxylapatite under the situation of being cultured in a liquid shake flask; and the strain is produced into a microbial agent to be respectively inoculated in a cutting seedling and a seedling of the taxus chinensis var. mairei, and the results show that the microbial agent can significantly promote the growth and the development of the two. Therefore, the invention can provide excellent strain resources for special microbial fertilizers for developing the taxus chinensis var. mairei in the future.
Owner:长治学院
Medicago pseudomonas strain capable of producing ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase and application of medicago pseudomonas strain
ActiveCN102827793APromotes nutrient absorptionPromote growth and developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarboxylateRoot system
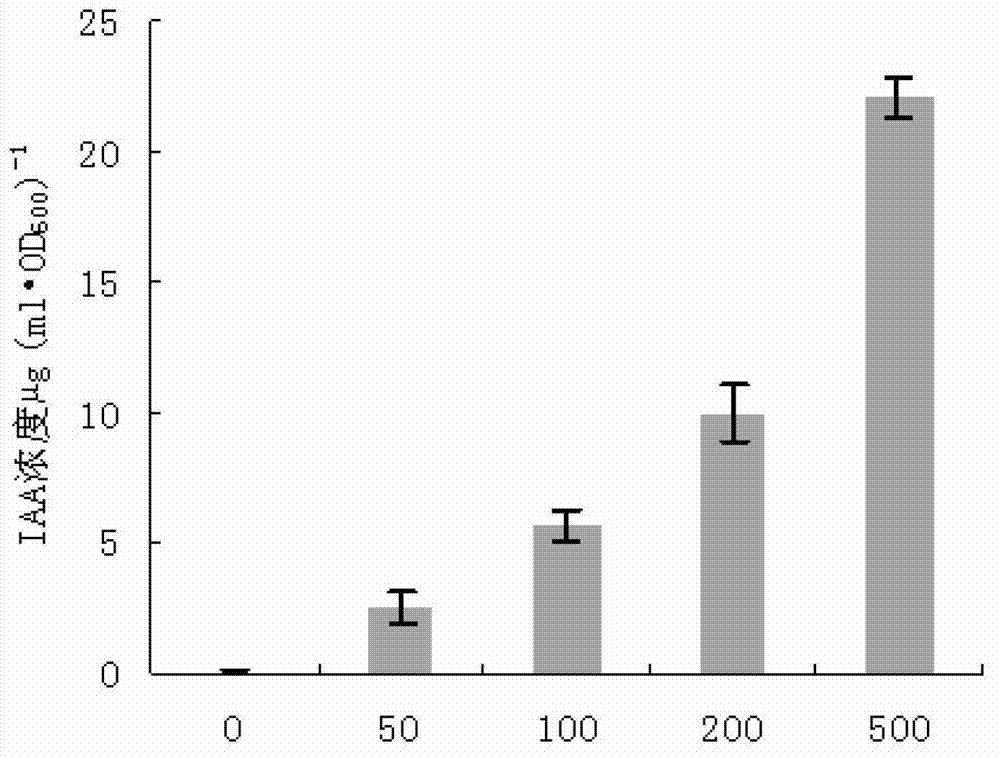
The invention discloses a medicago pseudomonas strain capable of producing ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase and application of the medicago pseudomonas strain, and relates to a medicago pseudomonas strain and application thereof. The pseudomonas (pseudomonas sp.) MJM-9 is preserved in the general microorganism center of the China microorganism culture preservation management committee in 26th July, 2012, and the preservation number of the pseudomonas MJM-9 is CGMCC NO.6294. The medicago pseudomonas strain containing the ACC deaminase is used as bacterial manure for growing crops. The medicago pseudomonas strain can generate the ACC deaminase, secrete auximone IAA (indole acetic acid), synthesize siderophores, reduce the concentration of ethylene inside a plant under the condition of environmental stress, promote the plant to grow fast, particularly promote growth and development of a root system of the plant, and increase utilization rate of fertilizers. Besides, when the strain is applied to agricultural production, growth of plants can be promoted, yield of crops can be increased, and stress resistance of the crops is improved.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Exopolysaccharide generated by pseudomonas, culture method and application
ActiveCN104232548AIncrease productionGood water solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to an exopolysaccharide generated by pseudomonas, a culture method and application. The pseudomonas sp. QL212 is preserved in common microbe center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on September 12, 2014, at the address of Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard No. 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and having the preservation number of CGMCC NO.9651. The curdlan synthesized by the pseudomonas sp. QL212 serves as the exopolysaccharide; through fermentation condition optimization, the yield of curdlan is up to 5.94 g / L which is higher than the production peak of the already known pseudomonas curdlan.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Korean pseudomonas and application thereof
InactiveCN105586303APromote degradationPhosphorus dissolving ability is strongBiocideBacteriaMicrobial agentRoot rot
The invention provides a Korean pseudomonas and application thereof. The Korean pseudomonas is identified as Korean pseudomonas CJ-361, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.12122. The Korean pseudomonas CJ-361 is obtained through separation from radix pseudostellariae rhizosphere soil by adopting a pseudomonas selectivity culture medium, an antagonistic experiment is performed on fusarium oxysporum and fusarium moniliforme separated to the radix pseudostellariae root lesion portion through an agar plate opposite culture method, and it is found that the Korean pseudomonas has the strong antagonism on the fusarium oxysporum and the fusarium moniliforme. Meanwhile, the invention provides the optimum culture medium for antagonistic bacterium growth, the optimum formula is 1 / 4LB+1 / 20MS (containing no ferric salt)+0.1 wt% brown sugar, and the fermented liquor has the obvious antagonistic effect. The antagonistic strain and the microbial agent thereof can effectively prevent and treat radix pseudostellariae root rot diseases, and the environment-friendly, ecological and safe biological prevention and control potential strain is provided for overcoming or relieving replantation diseases of radix pseudostellariae.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Compound microbial bacterium for aerobic fermentation stage
ActiveCN103667117AQuick breakdownFully rottenBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacillus licheniformisBiotechnology
The invention provides a compound microbial bacterium for an aerobic fermentation stage. The compound microbial bacterium for an aerobic fermentation stage is prepared by culturing, fermenting, drying and mixing Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, saccharomycete, 5406 actinomycete, Trichoderma viride, Aspergillus oryzae and pseudomonad respectively, wherein the compound microbial bacterium comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.7-1.2 parts of Bacillus licheniformis, 0.7-0.8 part of Bacillus subtilis, 1.1-1.2 parts of saccharomycete, 1.5-2.5 parts of 5406 actinomycete, 1-2 parts of Trichoderma viride, 1-2 parts of Aspergillus oryzae and 0.5-1 part of pseudomonad. The compound microbial bacterium for an aerobic fermentation stage has phosphate-solubilizing, potassium-solubilizing and nitrogen-fixing capabilities, and can quickly decompose organic substances, so that materials are thoroughly decomposed, and oxidation-resistant substances are generated through metabolism, thus generating a complex and stable ecological system; and the heating speed is high in the whole fermentation process, the temperature can be up to 50 DEG C or above within 1-2 days, and undesirable odor starts to disappear within 24 hours.
Owner:GUANGXI JINSUI ECOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
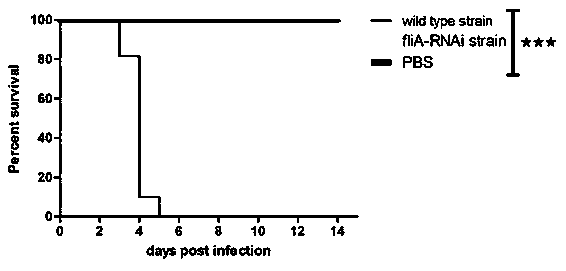
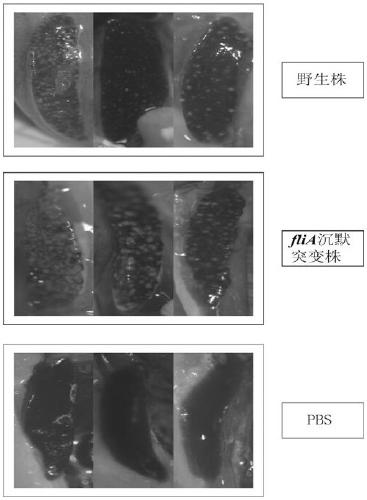
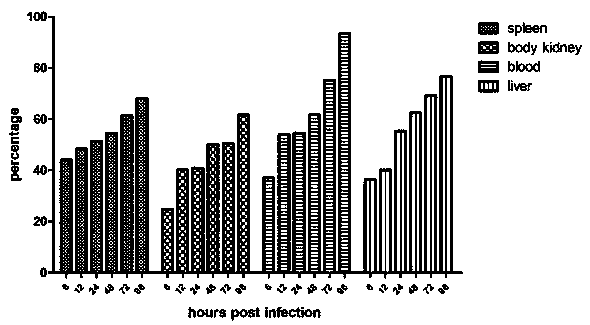
Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain
ActiveCN109706105AReduced toxicityReduce mortalityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMicrobiologyGene silencing
The invention provides a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain that is Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA-RNAi and deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 12th, 2018 with an accession number of CCTCC NO:M 2018770. The constructed Pseudomonas plecoglossicida fliA gene silenced strain has virulence significantly lower than that of a Pseudomonas plecoglossicida wild strain, time of death caused by same infection conditions is delayed, and the death rate is greatly reduced, thus laying a theoretical foundation for development of an attenuated Pseudomonasplecoglossicida vaccine.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Pseudomonas choloeaphtis and application
ActiveCN103602621AMake up for the deficiency of poor prevention effectGood control effectBiocideBacteriaPseudomonas cichoriiMicrobiology
The invention relates to pseudomonas choloeaphtis with a preservation number of CGMCC: 8431 and application thereof. Pseudomonas choloeaphtis can be further made into a biocontrol microbial inoculum for controlling wheat take-all disease with good control effect, and helps to make up the disadvantage of bad control effect of chemical agents. Because pseudomonas choloeaphtis strains can be colonized at the wheat rhizosphere, the inoculant has a relatively long lasting period, and the inoculant does not bring environmental problems and is beneficial to pollution-free production of wheat.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Antagonistic and growth-promoting pseudomonas producing ACC deaminase and application thereof
InactiveCN104818231APromote growthImprove stress resistancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideTriticeaeGrowth promoting
The invention relates to an antagonistic and growth-promoting pseudomonas FRBN3 producing ACC deaminase and an application thereof. The pseudomonas FRBN3 is obtained through separation on surface of watermelon roots from Hefei city, Anhui province and is named Pseudomonas guariconensis. The pseudomonas FRBN3 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center at Apr.14 2015 and is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.10715. The pseudomonas FRBN3 has an ACC deaminase activity and can highly produce siderophores. The pseudomonas FRBN3 has a certain inhibition effect on all of fusarium oxyspirum, fusarium graminearum, bipolaria maydis and fusarium oxgsporum. A liquid bacterial agent prepared from the pseudomonas FRBN3 can be applied in the field of promoting growth of plants and preventing and treating diseases. The liquid bacterial agent can be used in manners of being diluted with water to form spray for use, being blended with seeds or dipped with roots, or being irrigated on root soil.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pseudomonas strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105349463AThere is no ecological security riskCompliance with Biosafety RegulationsBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesSludge
The invention discloses a pseudomonas strain and application thereof. The strain is pseudomonas protegens IAS03, and is preserved in the China center for type culture collection on November 27th, 2015, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2015711. The strain is screened from pond bottom sludge and then a backwater body is used, so that ecological safety risks do not exist, and biological safety regulations are conformed. The strain has the specific antimicrobial function on aeromonas hydrophila and aeromonas sobria, has no inhibition effect on other bacteria and has no pathogenicity on fishes. Only one strain can be used for inhibiting aeromonas hydrophila and / or aeromonas sobria. Compared with traditional antibiotic and sterilizing agent prevention measures, the strain has the advantages of being safe, environmentally friendly and efficient. The strain can be developed into a microecological preparation to control aeromonas sobria and aeromonas hydrophila in the breeding environment and prevent hemorrhagic septicemia caused when the fishes are infected with aeromonas sobria and aeromonas hydrophila.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
1-strain pseudomonas mendocina and uses thereof
InactiveCN101270345AIncrease elasticityEasy to processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOctanoic AcidsStearic acid
The invention discloses pseudomonas mendocina and application thereof, and relates to pseudomonas mendocina NK-01 CCTCC M 208005, and a method for producing medium-and-long-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate which is the copolymer of 3-hydroxy hexanoate, 3-hydroxy octanoic acid, 3-hydroxy capric acid, Delta<7>-3-jalapinolic acid and 3-hydroxy stearic acid. In the method, Pseudomonas mendocina NK-01 CCTCC M 208005 is fermented in the culture medium of carbon source including glucose or treacle, or the mixture of glucose and treacle. The invention overwhelms the defects that long chain fatty acid needs to be added in the carbon source when long-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate, microbial growth is inhibited easily, the fermentation rate is low and the rate of production of fermentation products is low. By adopting the strain and the production process, a novel high elasticity biologic degradable material easy to be processed and shaped, namely the copolymer of 3-hydroxy hexanoate, 3-hydroxy octanoic acid, 3-hydroxy capric acid, Delta<7>-3-jalapinolic acid and 3-hydroxy stearic acid, can be produced. In addition, the fermentation conditions and the process enable large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
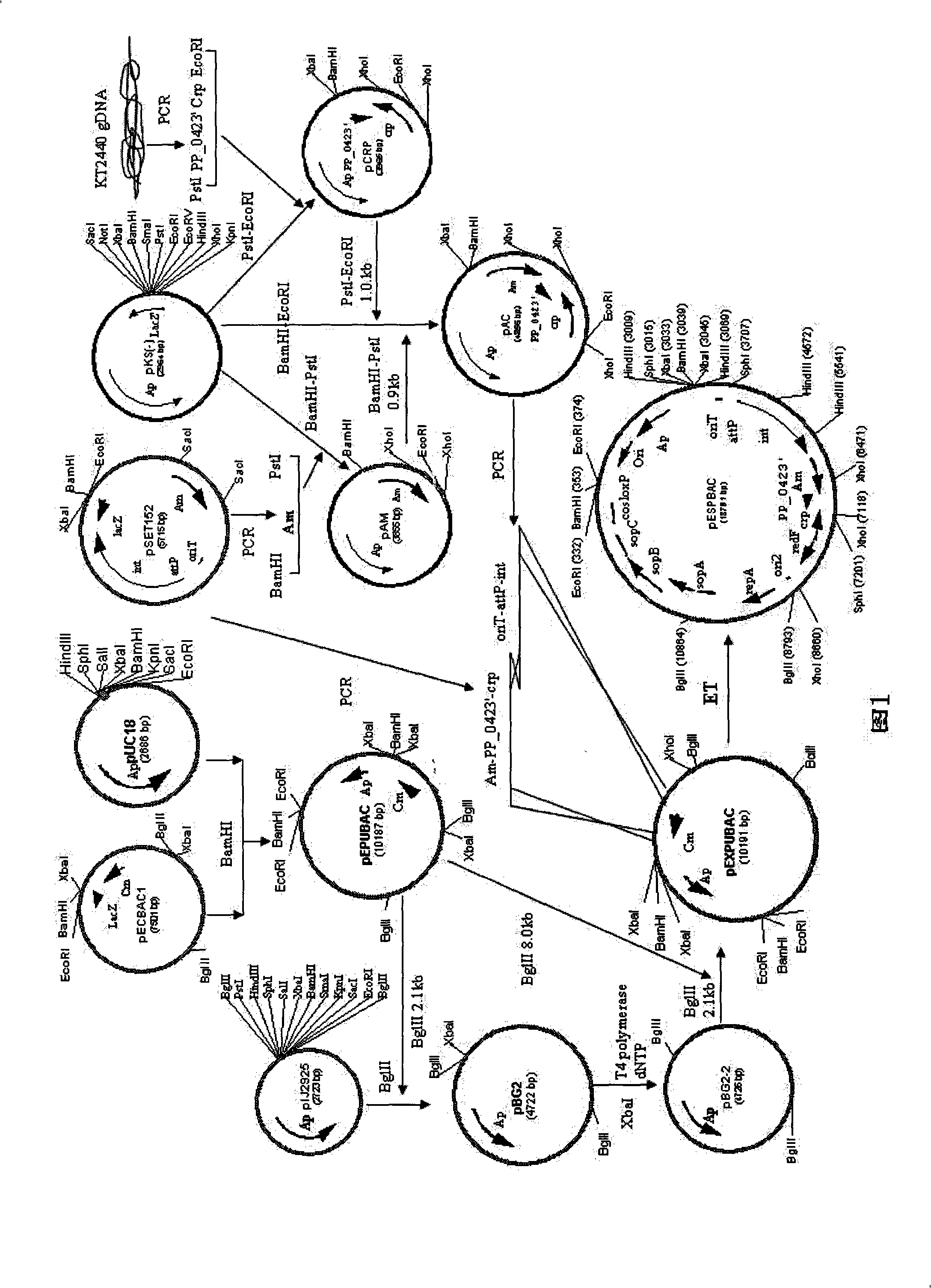
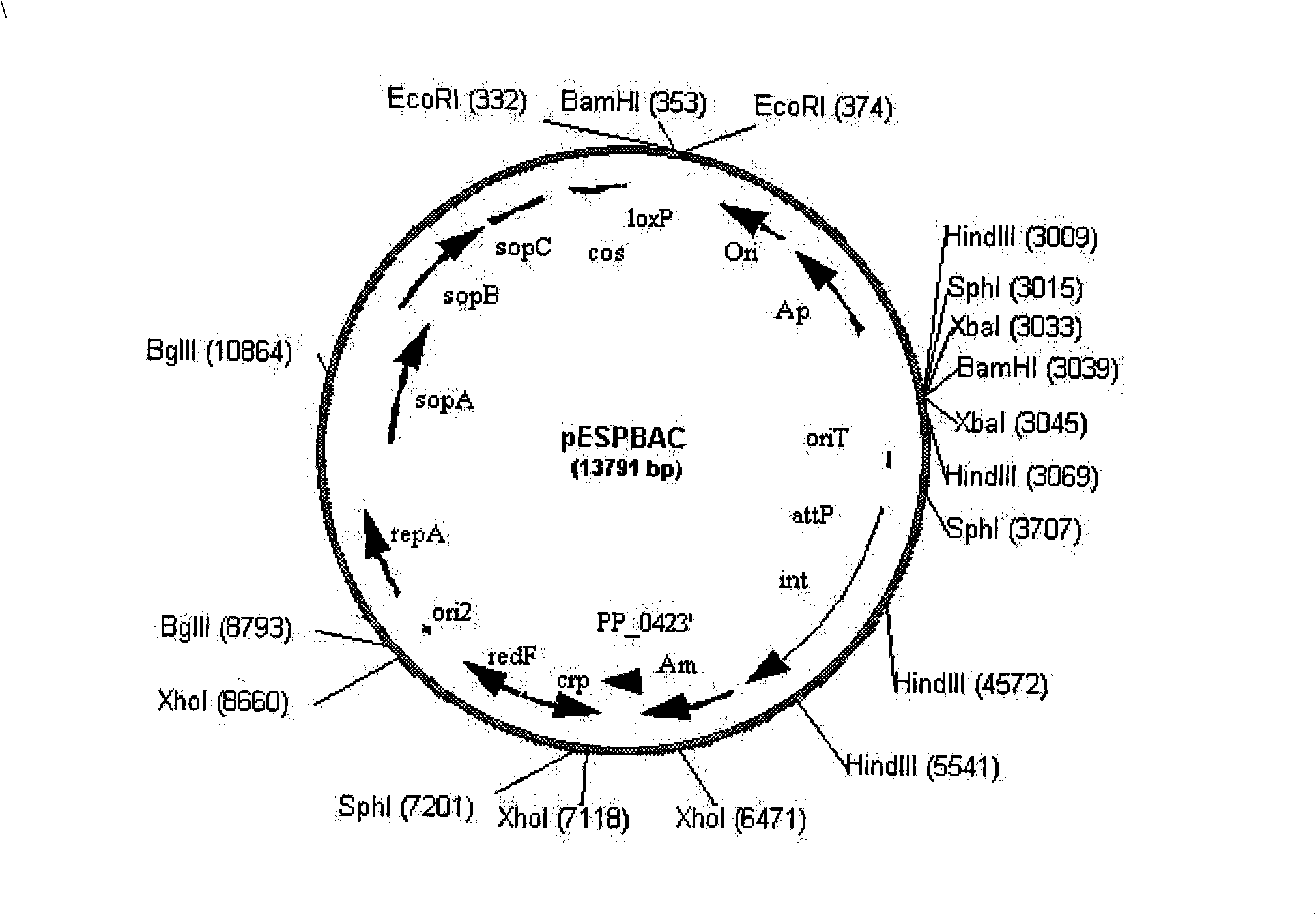
Bacillus coli-streptomycete-pseudomonas shuttling expressing BAC vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101302531AEfficient synthesisEffective optimizationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousIntegrases
The invention relate to a shuttle expression BAC vector among colon bacillus, streptomyces and pseudomonad, and a construction method thereof. The BAC vector contains a replicon of pUC18, a penbritin resistance gene, a conjugal transfer fragment oriT, an attP locus, an integrase gene int, an Am resistance gene, a 5' end of a PP_0423' gene of the pseudomonad, a crp gene of the pseudomonad, a redF gene of the BAT vector, duplicate field OriS, a repA gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC gene, a cos locus, and a loxP locus. The method starts from pECBAC1, effectively combines and optimizes a necessary original of heterologous expression, applies means such as gene clone and recombination engineering and so on, successfully constructs the shuttle expression BAC vector, and provides the convenience for biosynthetic gene clusters with the heterologous expression and high throughput screening.
Owner:广州冀源生物科技有限公司
Pseudomonas having antagonistic action against Xanthomonas oryzae and magnaporthe oryzae and application of pseudomonas
ActiveCN108998389AStrong antagonistic effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBacilli
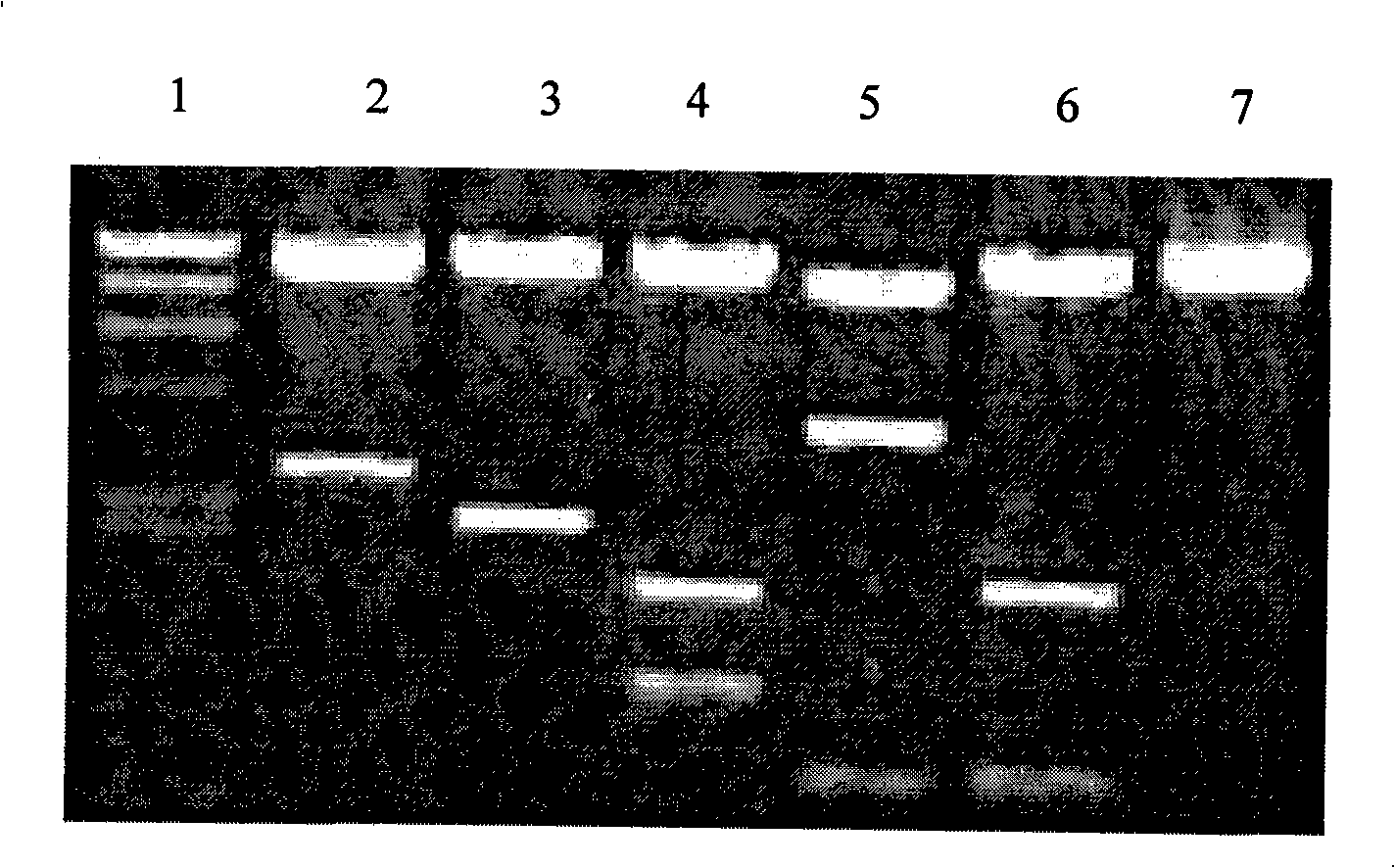
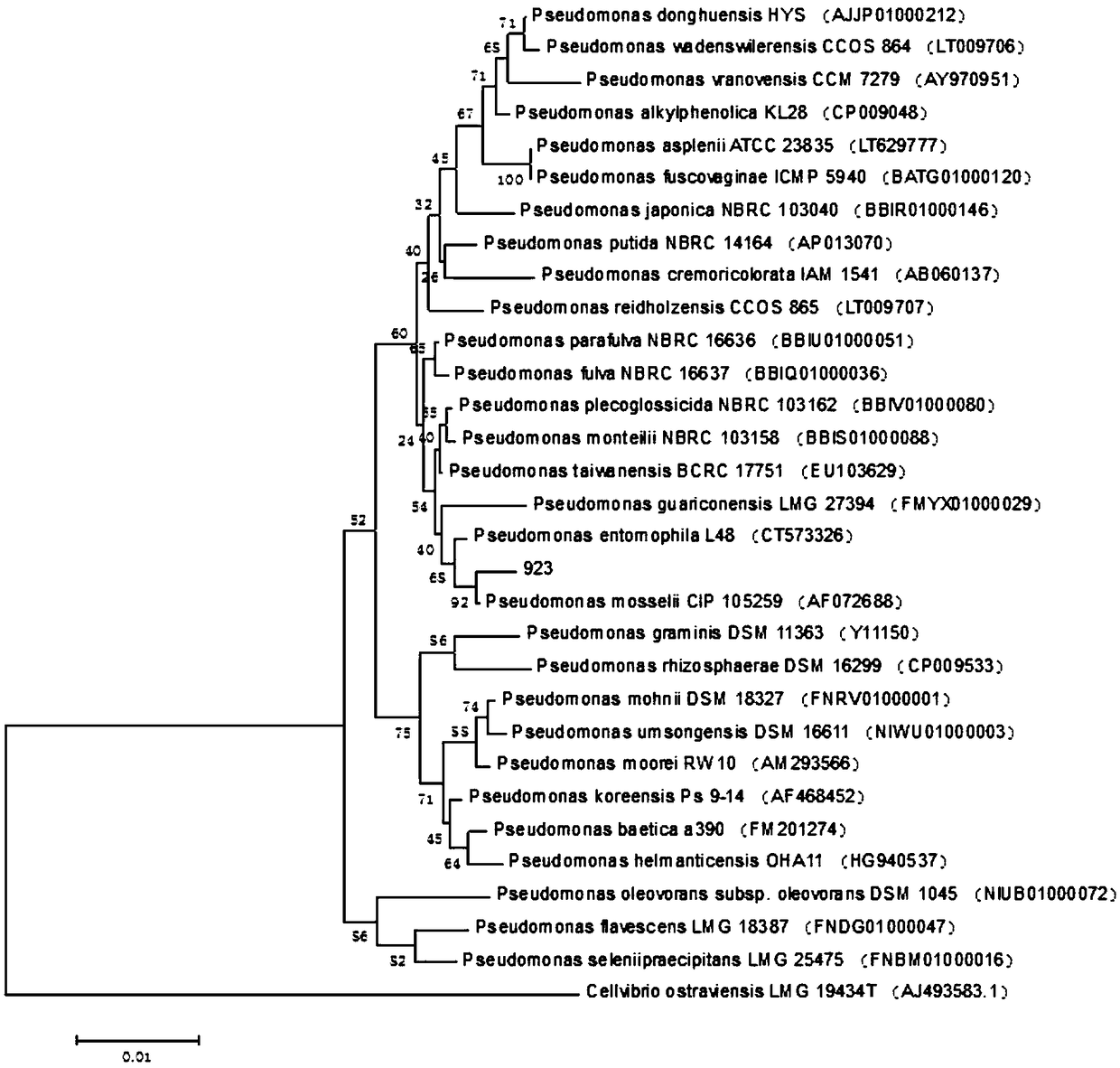
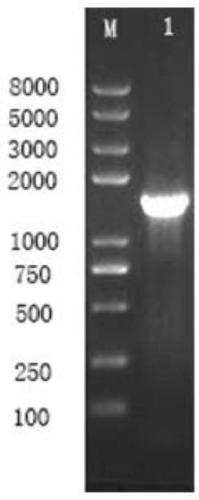
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to a strain of pseudomonas having significant antagonistic action against Xanthomonas oryzae and magnaporthe oryzae and application of the pseudomonas. The strain is isolated from rice rhizosphere soil of Fengxian District, Shanghai; the pseudomonas provided by the invention was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2018, the preservation name is Pseudomonas mosselii 923, and the preservation number is CCTCC No:M 2018252. The pseudomonas provided by the invention has a significant inhibitory effect on Xanthomonas oryzae, has relatively strong inhibitory capacity against other plant pathogenic bacteria and magnaporthe oryzae of Xanthomonas, and has biological control application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Pseudomonas strain for preventing and treating kiwifruit canker and application of pseudomonas strain
InactiveCN107083344ASignificant effect on ulcersEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaActinidiaScreening method
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a pseudomonas strain for preventing and treating kiwifruit canker and application of the pseudomonas strain. The Pseudomonas (pseudomonas sp.) strain provided by the invention has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2016556. The pseudomonas is obtained by separating and purifying collected kiwifruit twigs, a separation and screening method is simple, and the strain has very strong inhibition effect to pathogenic bacteria of kiwifruit bacterial canker and is capable of obviously inhibiting the growth of the pathogenic bacteria of the kiwifruit bacterial canker. The strain is separated from healthy plant tissues and is inoculated to the kiwifruit twigs, leaves are not abnormal, and a generated active metabolite has no obvious toxic effect to the plant tissues; the strain has stable property and remarkable effects on treating and preventing the kiwifruit canker and is easily wetted through spraying and beneficial to the environmental protection, and an environment-friendly, simple and effectively way is provided for the control and treatment of the kiwifruit canker.
Owner:四川省自然资源科学研究院
Pseudomonas for bacterial disease control and application
InactiveCN106978373AResidue reductionQuality assuranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBacterial disease
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and provides a pseudomonas for bacterial disease control and an application. A microorganism with bacteriostatic activity on phytopathogenic bacteria is separated from peanut foot rot soil; and a pseudomonas bacterium is determined according to 16S rRNA and a whole genome sequence. By adopting a bacteria solution root-irrigation method, tomato bacterial wilt can be effectively inhibited. The pseudomonas can be used for green biological control of the phytopathogenic bacteria.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for analyzing root domain soil microbial community structure of soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a root domain soil microbial community structure of a soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and treating a test sample, preparing a culture medium, performing microorganism isolation and enumeration, identifying dominant strains, testing the pH and the nutrition of soil, and processing data. By adopting the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant, the change of the soil microbial community structure with the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease is studied, relevant micro-ecology mechanisms of the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease can be studied for a first time, and great significance is achieved. The study of the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant shows that 9 dominant microorganisms, namely, 3 dominant bacteria including pseudomonas plecoglossicida, pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens and stenotrophomonas pavanii, 4 dominant bacteria including fusarium solani, fusarium oxysporum, penicillium canescens and penucillium, and 2 dominant actionmycetes including streptomyces scabiei and streptomyces cellulosae, massively exist at the root domain of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Pseudomonas putida and application thereof to promotion of growth of cercidiphyllum japonicum
ActiveCN105543152APromote degradationPromote germinationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDecompositionPseudomonas putida
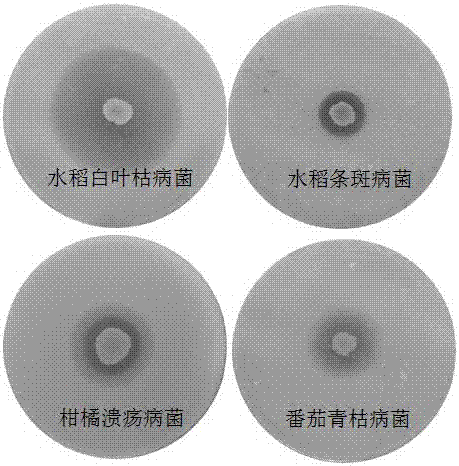
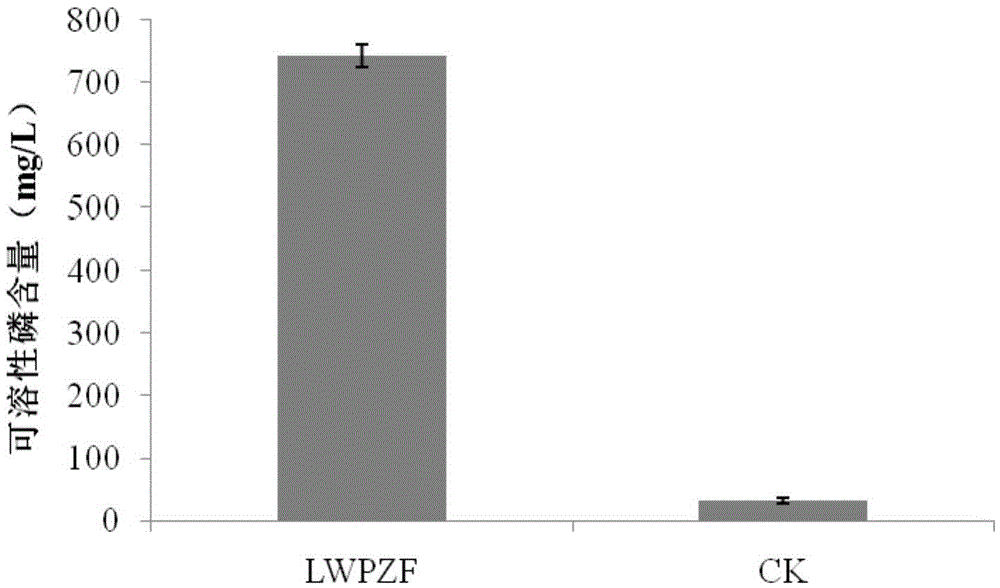
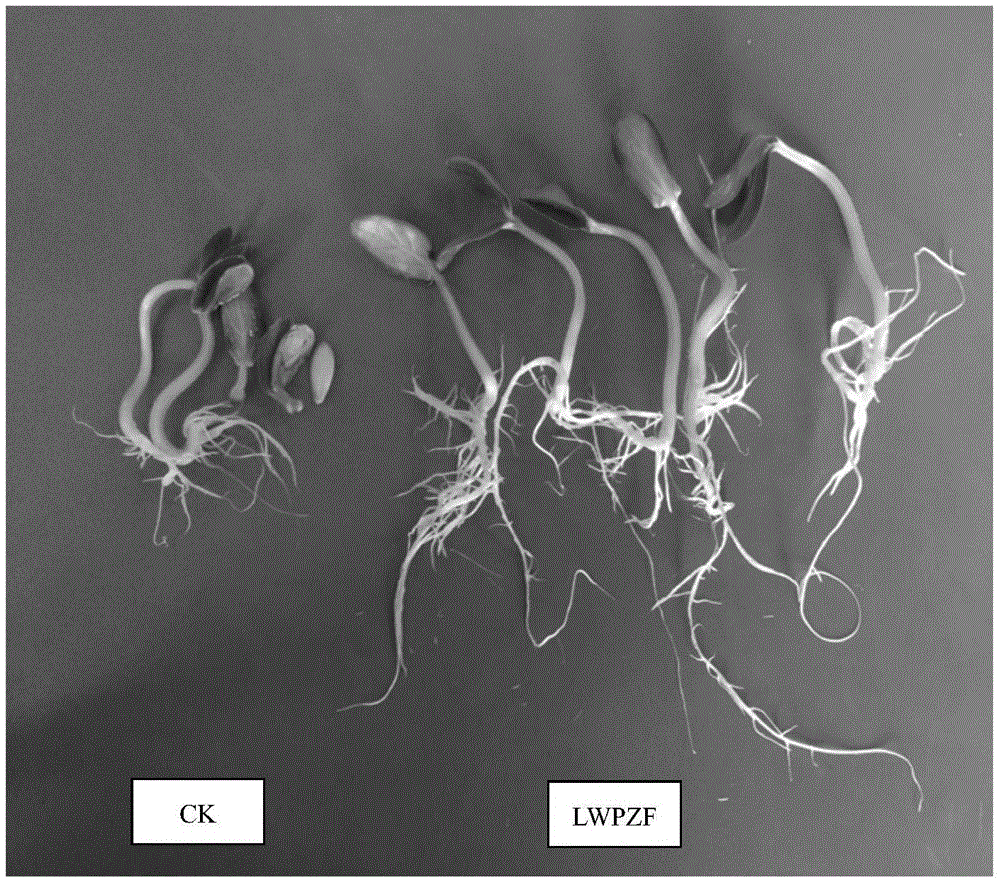
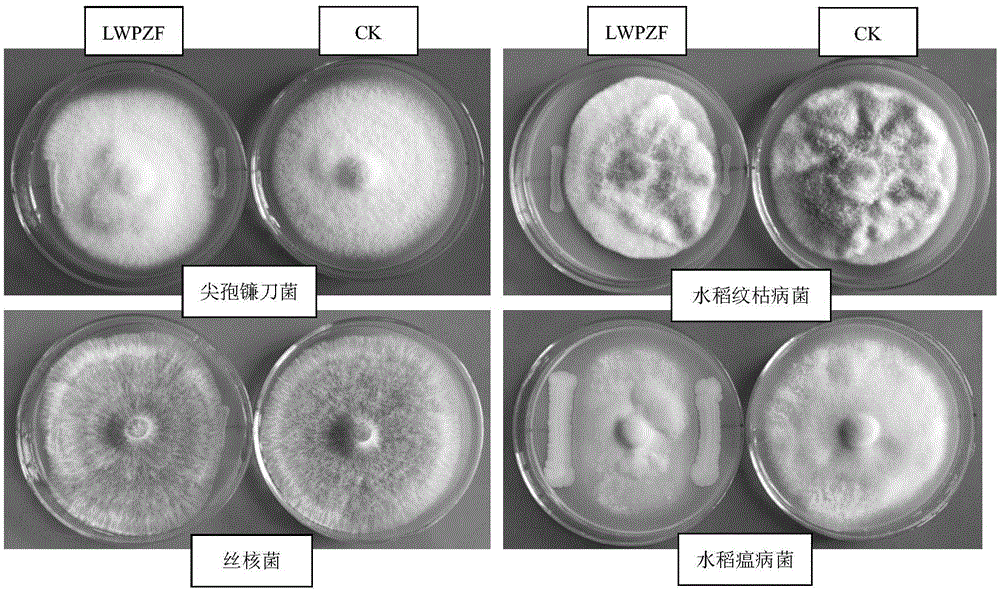
The invention discloses pseudomonas putida which is classified and named as pseudomonas putida, the strain number is LWPZF, the pseudomonas putida is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation serial number is CCTCC NO: M 2016008, and the preservation data is Jan 5th, 2016. The invention further discloses application of the pseudomonas putida to promotion of growth of cercidiphyllum japonicum. The LWPZF strain has high inorganic phosphorus decomposition capacity and growth hormone secretion capacity; germination of cucumber seeds can be obviously promoted; the LWPZF fungicide is inoculated with cercidiphyllum japonicum seedlings; it is proved by results that the fungicide can obviously promote growth of cercidiphyllum japonicum seedlings; meanwhile, the culture has a certain antagonistic effect on fusarium oxysporum, rhizoctonia solani, rhizoctonia, rice blast pathogen and other phytopathogen; therefore an excellent strain resource is provided for development of a biofertilizer special for cercidiphyllum japonicum.
Owner:长治学院
Bjerkandera sp. Gause 15 for controlling vegetable root diseases and preparation thereof
The invention provides bjerkandera sp. Gause 15 and a fungicide prepared from bjerkandera sp. Gause 15. Bjerkandera sp. Gause 15 is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), with collection number of CCTCC NO:M2015351. The fungicide is granular or is wettable powder. The fungicide prepared from bjerkandera sp. Gause 15 provided by the invention has obvious bacteriostatic activities towards Fusarium spp., Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc, Rhizoctonia cerealis Vander Hoeven and Pseudomonas solanacearum Smith. The granular fungicide or wettable powder prepared from the strain can be used for controlling tomato root rot, tomato damping off, tomato bacterial wilt, konjac root rot, konjac southern blight, green pepper root rot, green pepper bacterial wilt, green pepper damping off, watermelon root rot, watermelon bacterial wilt and watermelon damping off.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Human Anti-pseudomonas-aeruginosa antibodies derived from transgenic xenomouse
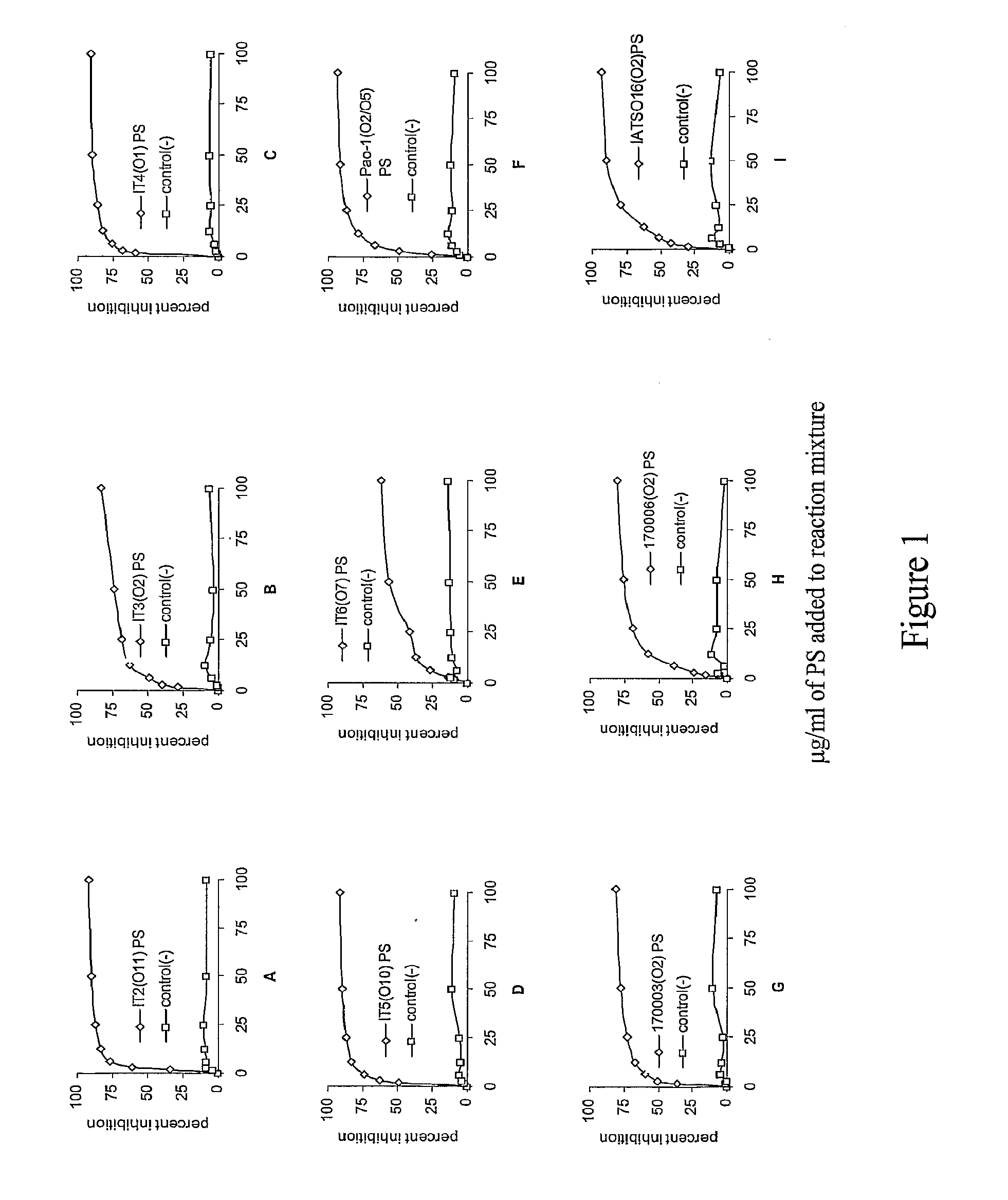
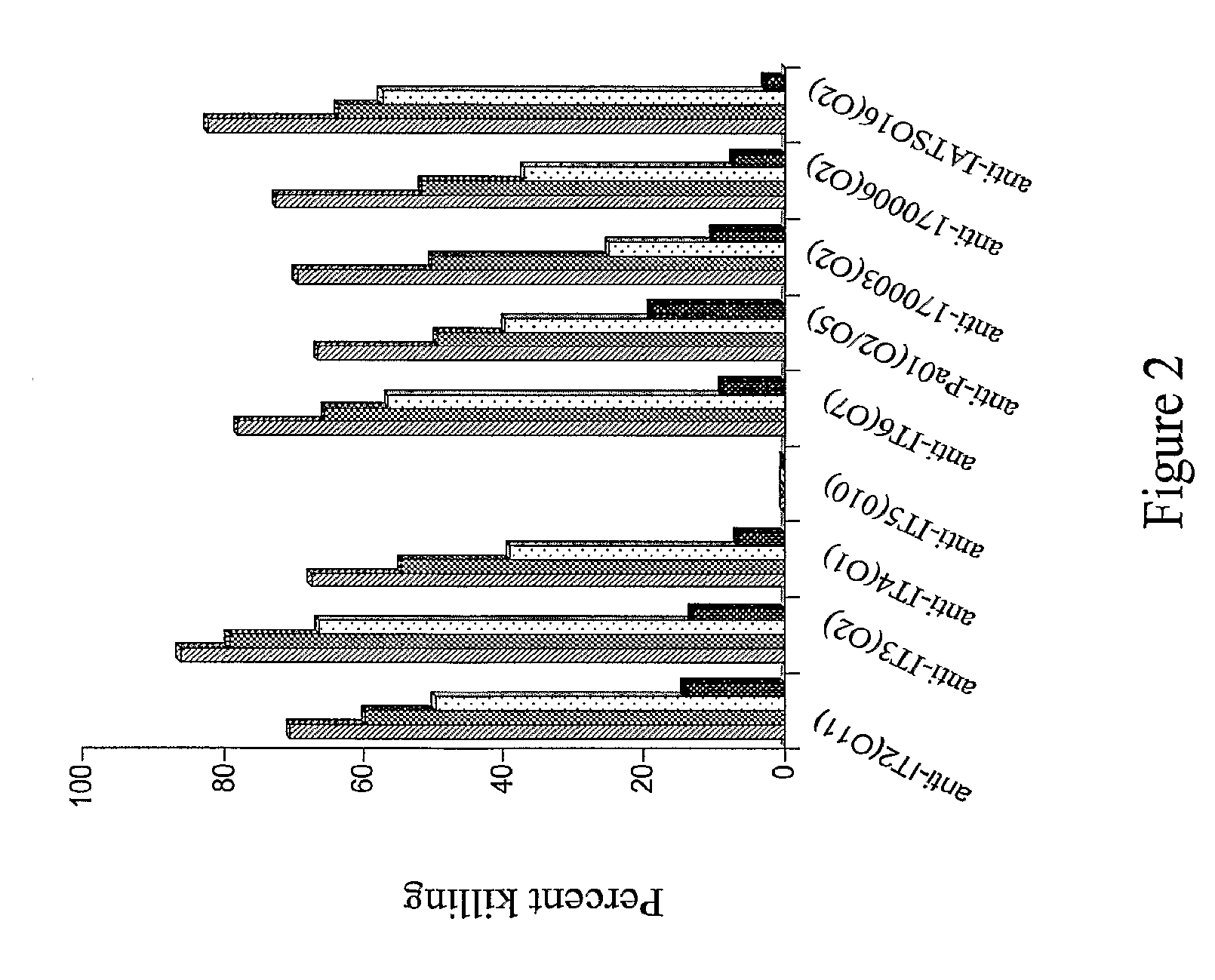
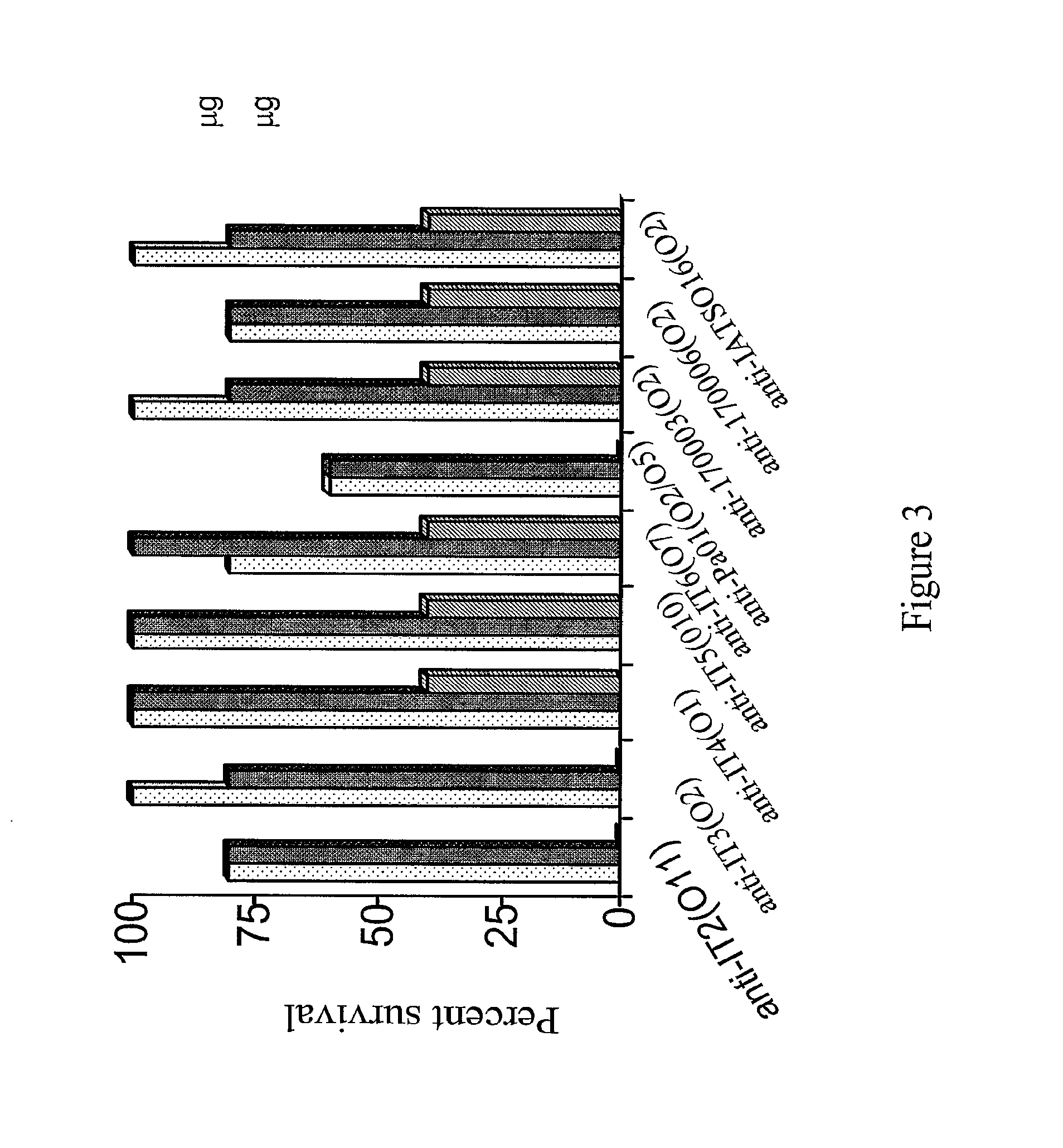
The invention described herein provides for human antibodies produced in non-human animals that specifically bind to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from strains Fisher Devlin (International Serogroups) It-2 (011), It-3 (02), It-4 (01), It-5 (010), It-6 (07), PA01 (05), 170003 (02), IATS016 (02 / 05), and 170006 (02). The invention further provides methods for making the antibodies in a non-human animal, expression of the antibodies in cell lines including hybridomas and recombinant host cell systems. Also provided are kits and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of treating or preventing pseudomonas infection by administering to a patient the pharmaceutical compositions described herein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
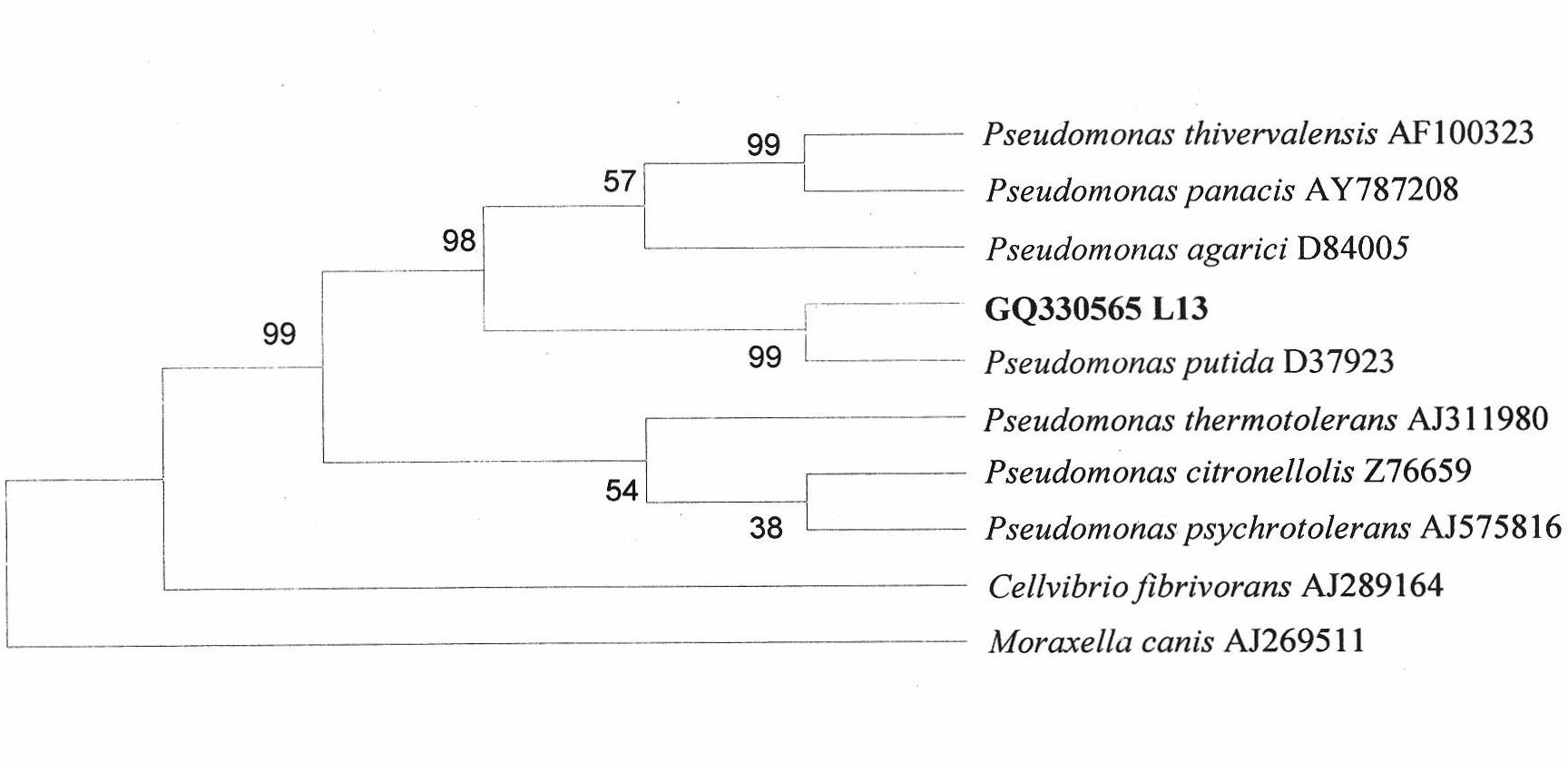
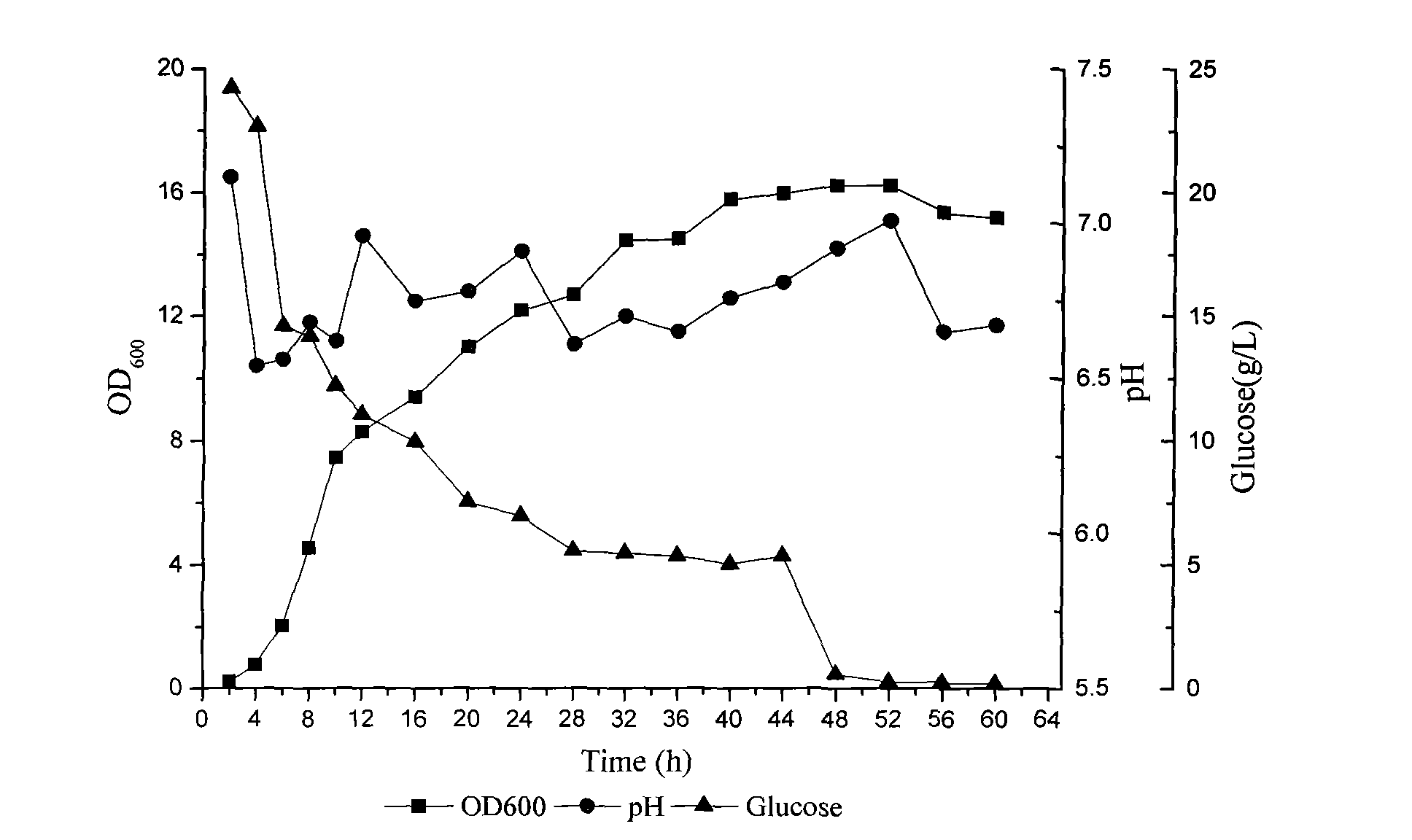
Phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 and fermentation process thereof
InactiveCN102649941APromote growthImprove micro-ecological environmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePseudomonas putida
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and particularly relates to the separation screening and fermentation cultivation of phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13. A phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 strain with the capacity of dissolving phosphorus is obtained through separation, and the preservation No. is CCTCC No.2010342. The fermentation process comprises the following steps of: (1) taking L13 bacterial strain slope seeds for streak cultivation on an LB (lysogeny broth) culture medium flat plate to obtain first-level seeds; (2) inoculating a first-level seed single bacterial colony into an LB culture medium shake flask to make OD (optical density) 600 be 2.0 to obtain second-level seeds; (3) inoculating the second-level seeds into a shake flask for fermentation cultivation to obtain the pseudomonas putida; or inoculating the second-level seeds into a fermentation tank so as to obtain the pseudomonas putida through optimized cultivation. The pseudomonas putida strain disclosed by the invention grows rapidly, the yield of the pseudomonas putida is high, and the viable count can reach more than 10 billions. The phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO (Pikovskaya') culture medium in which 1-3g / L of calcium phytate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 120-220mg / L, and the phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO culture medium in which 4-6g / L of tricalcium phosphate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 300-500mg / L.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST OF HUBEI PROVINCE +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com