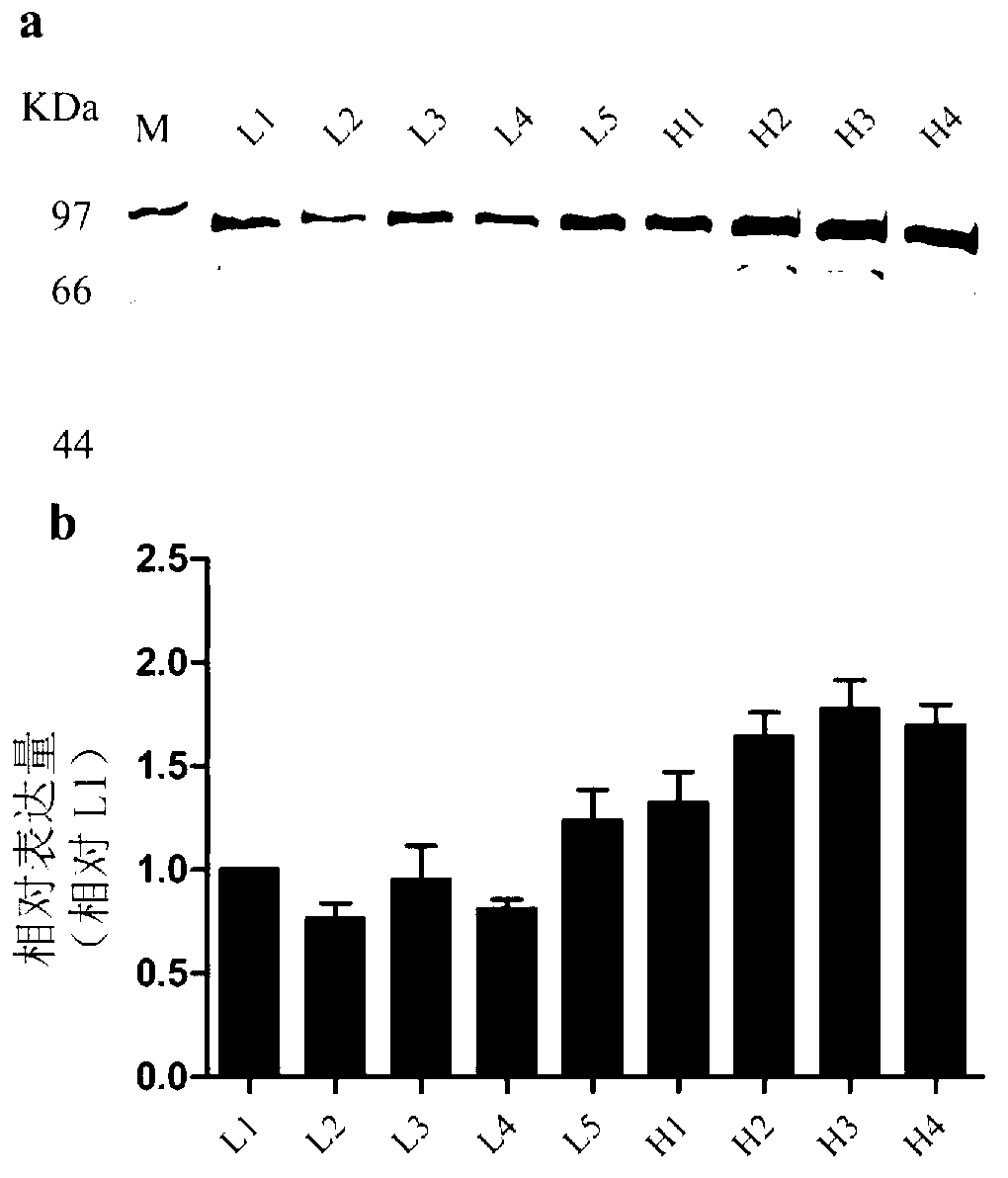
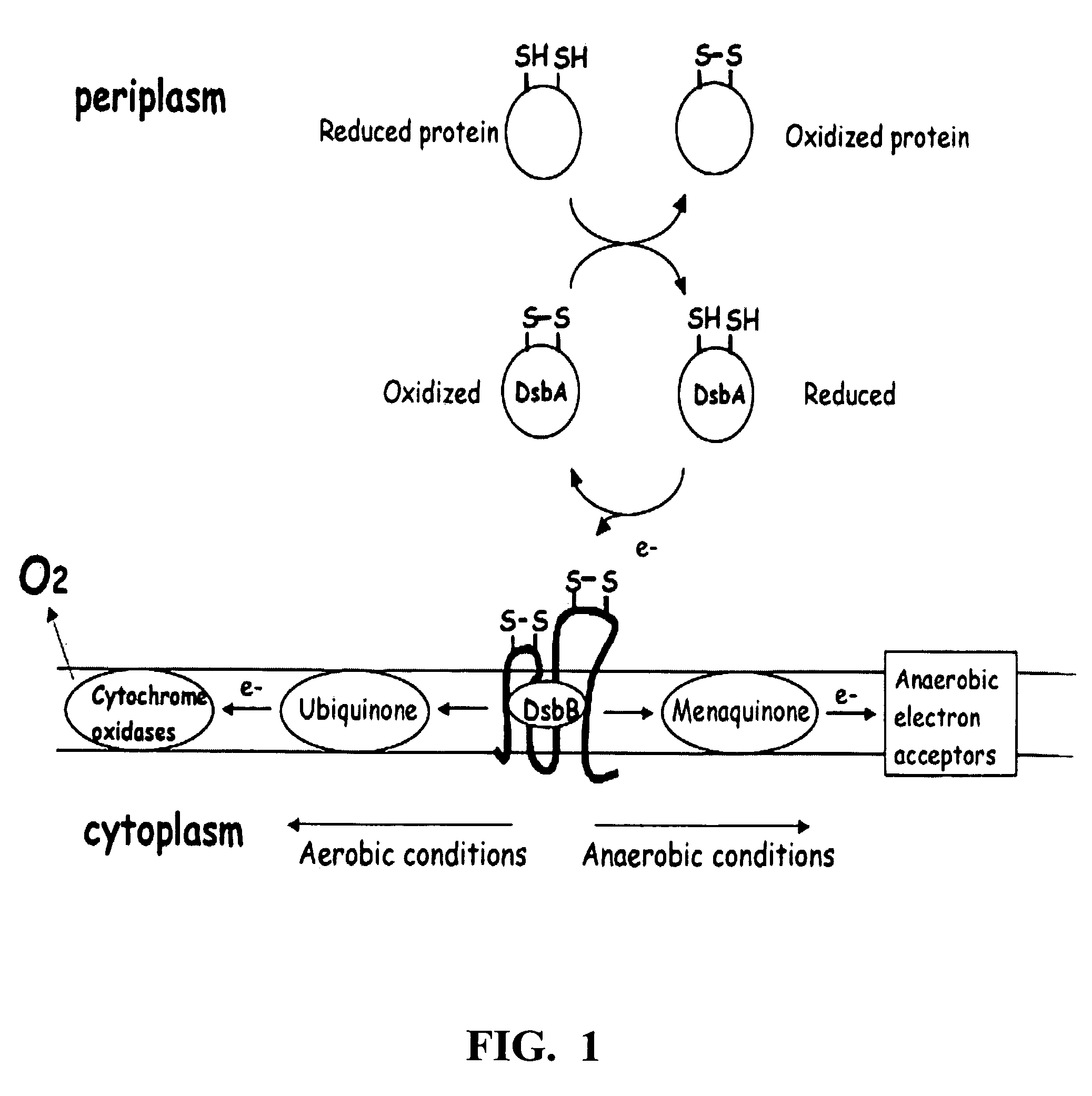
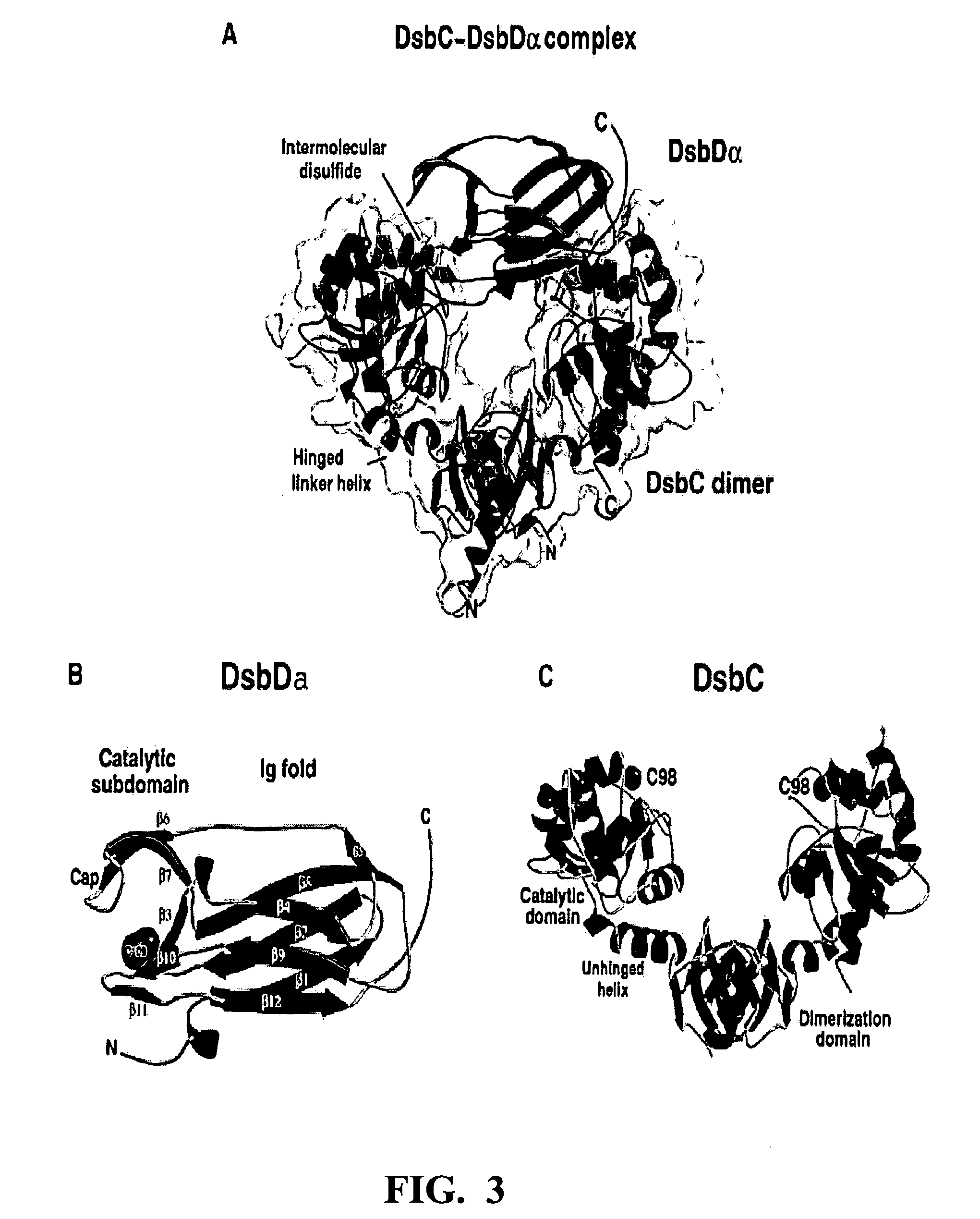
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Protein disulfide-isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
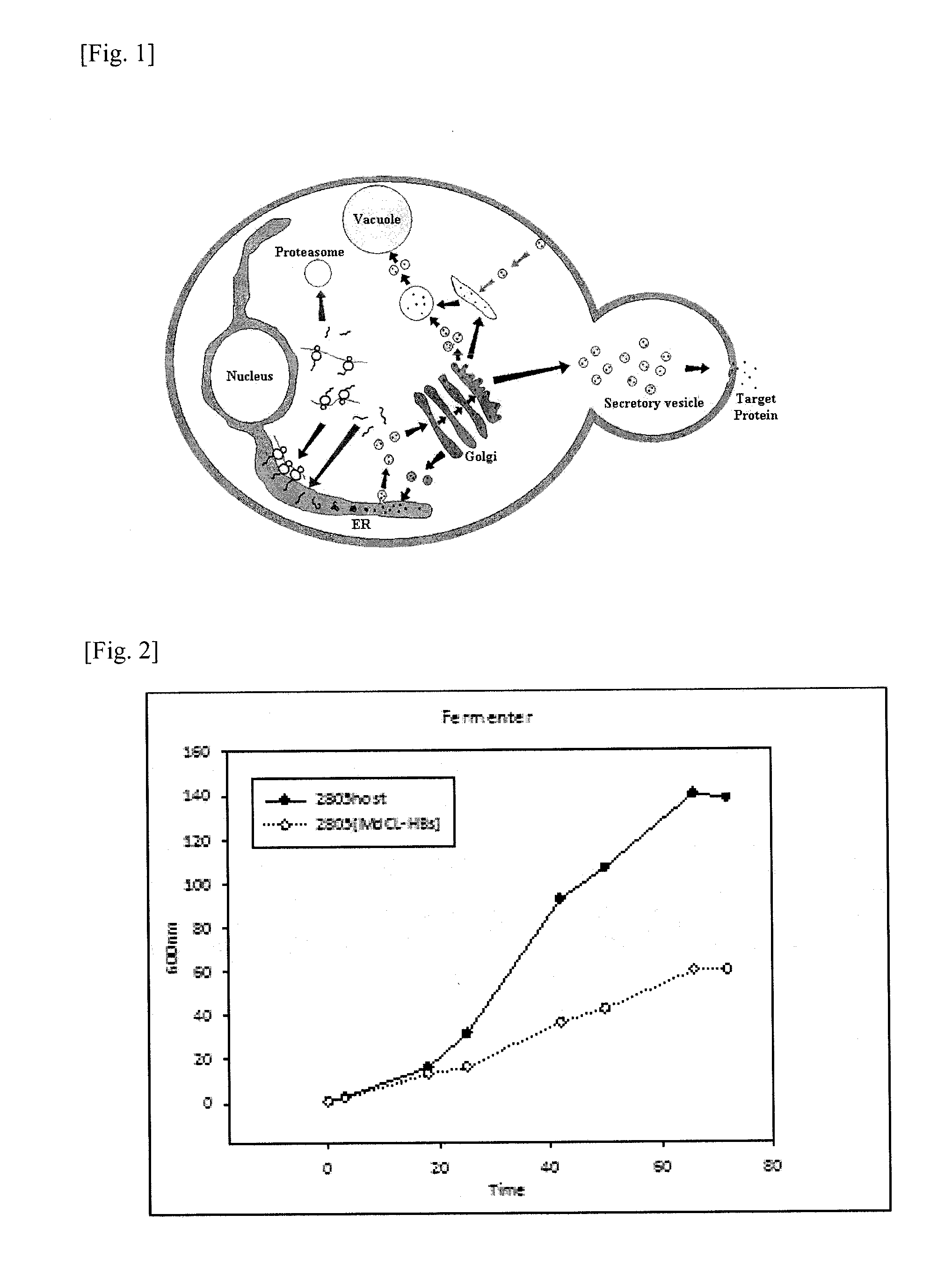
Protein disulfide isomerase, or PDI, is an enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotes and the periplasm of bacteria that catalyzes the formation and breakage of disulfide bonds between cysteine residues within proteins as they fold. This allows proteins to quickly find the correct arrangement of disulfide bonds in their fully folded state, and therefore the enzyme acts to catalyze protein folding.
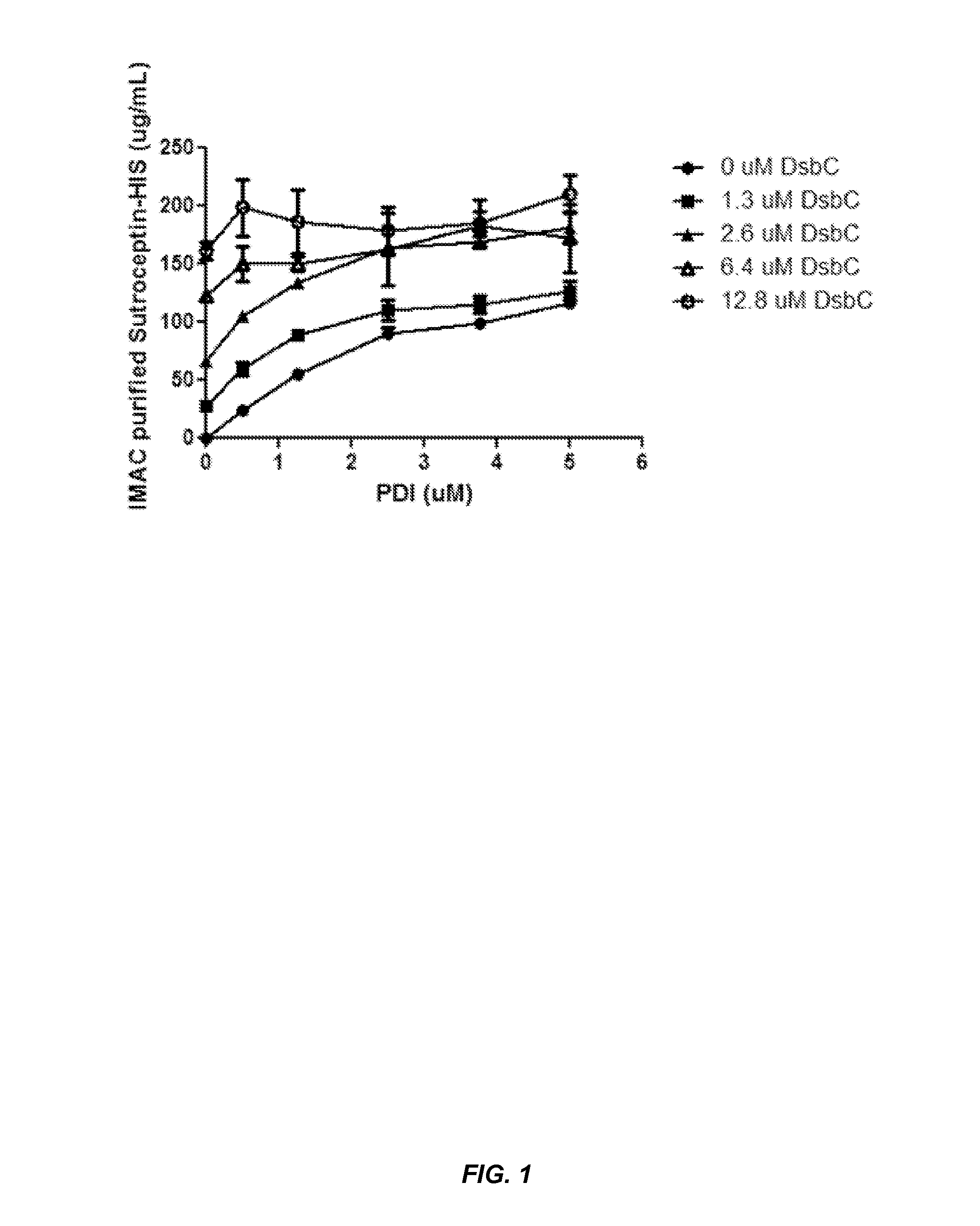
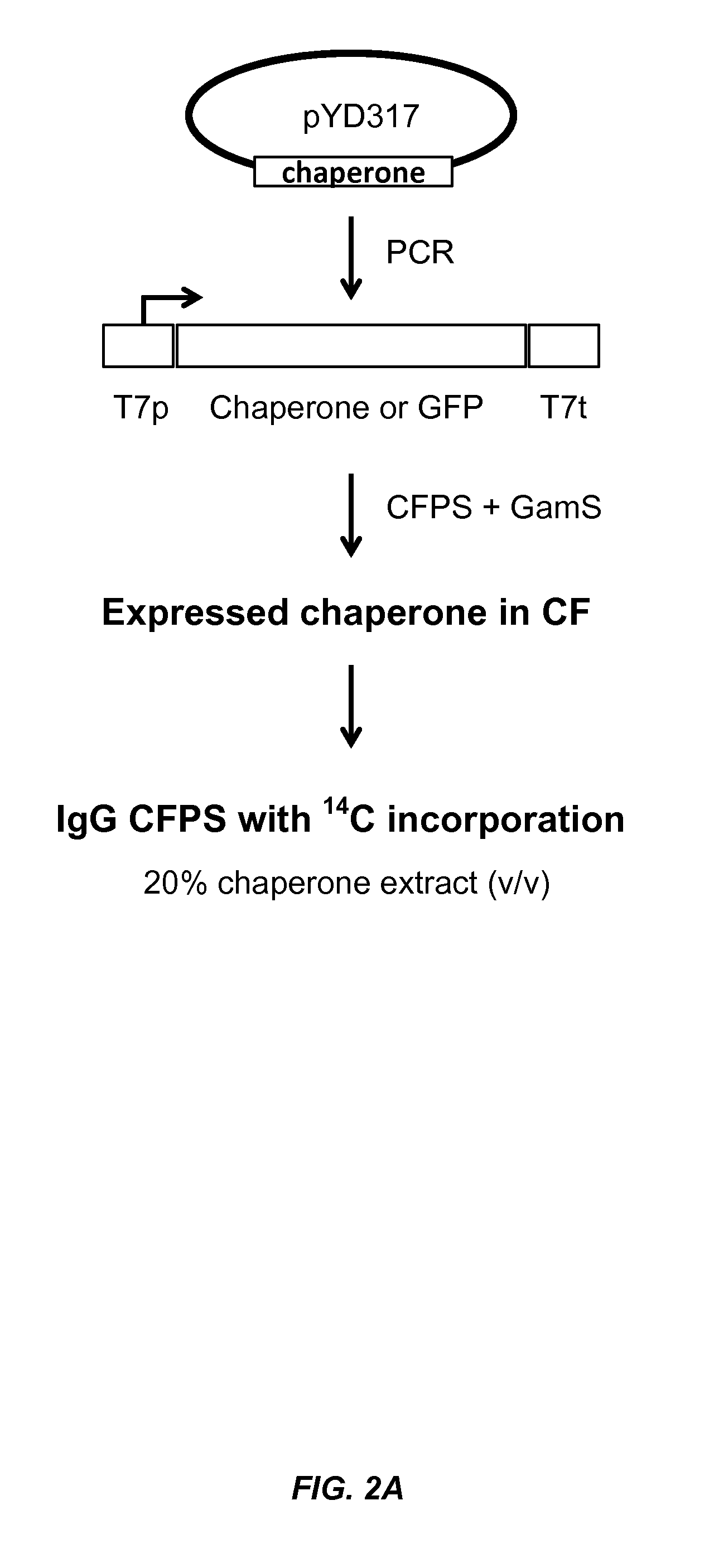
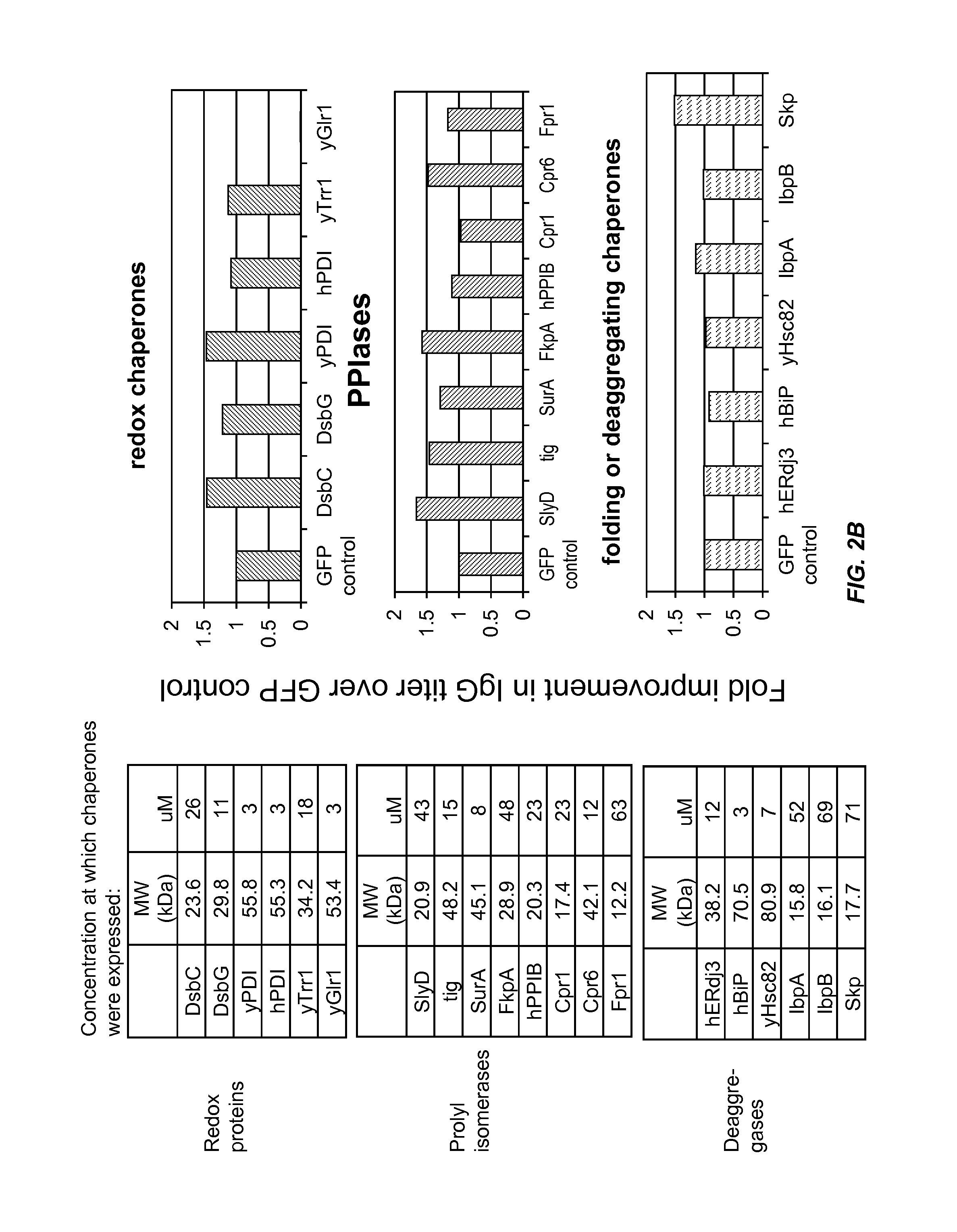
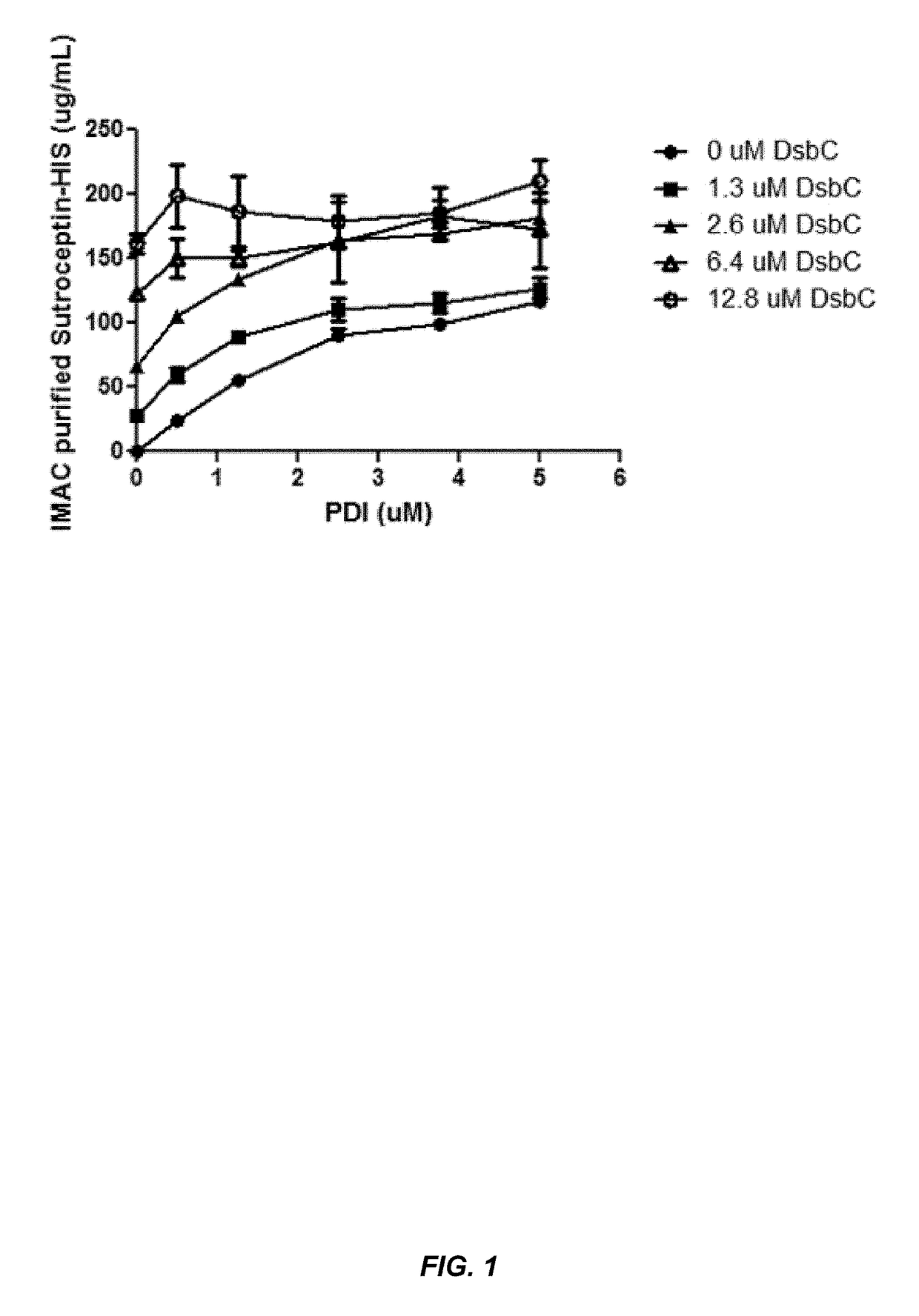
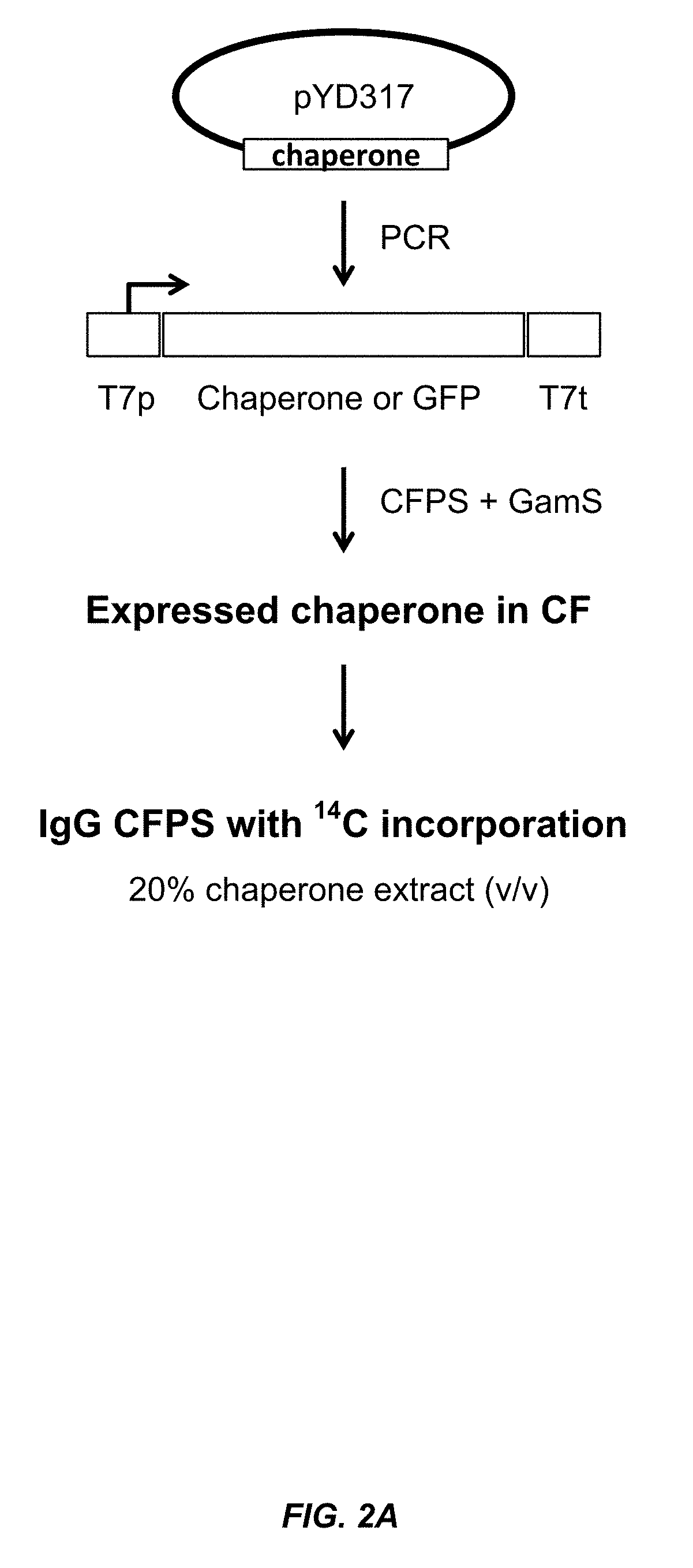
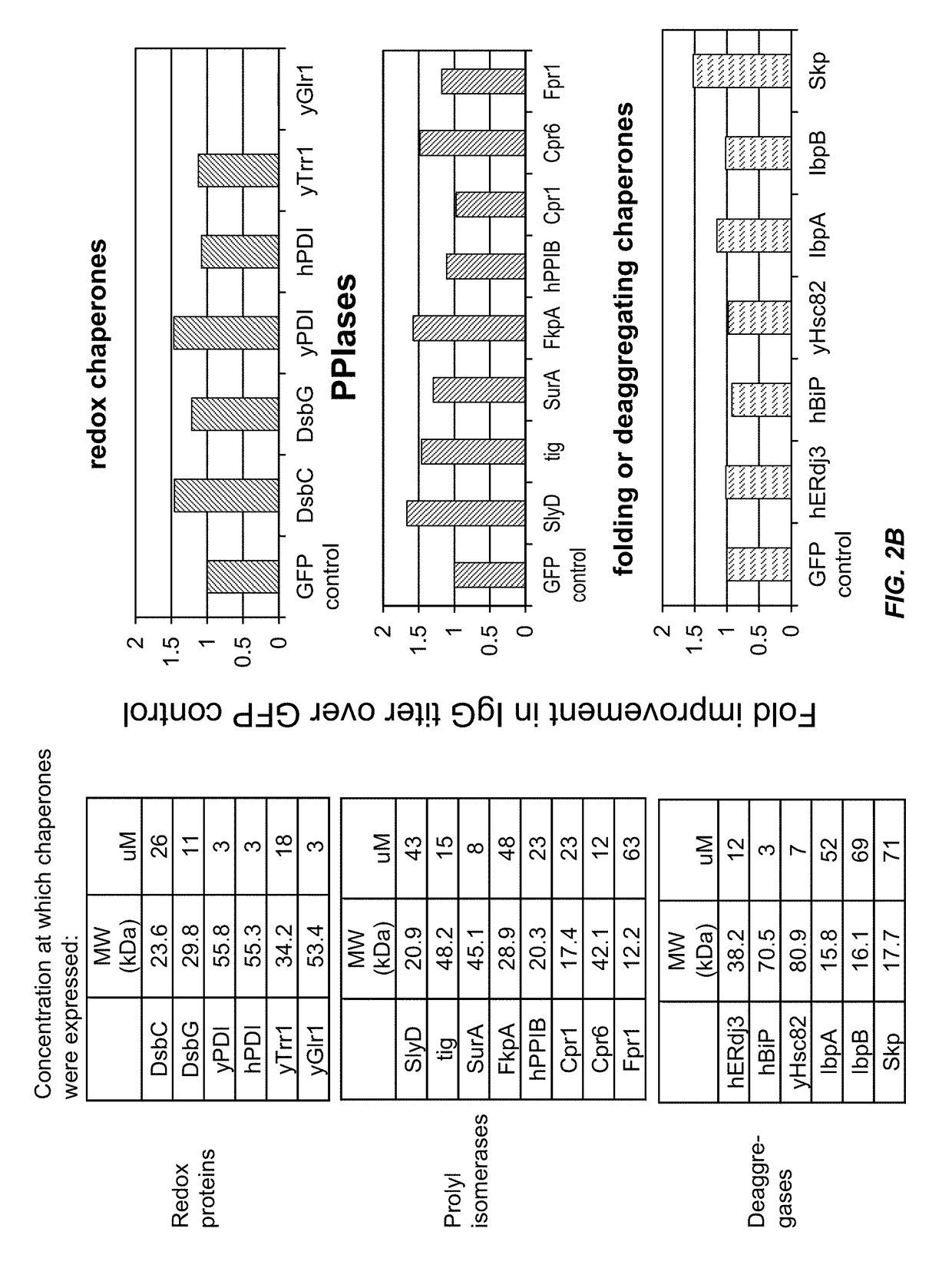
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101735336ASimple reaction conditionsQuick responseOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderDepolymerizationGlycan
The invention discloses a method for preparing oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan which is prepared by depolymerizing fucosylated glycosaminoglycan by a depolymerization method of peroxide catalyzed by a 4th period transition metal ion in an aqueous medium, and the preparation method has mild reaction condition, good reproducibility and stability, high pyrolysis selectivity and uniform and controllable product quality. The polysaccharide molecule number of the obtained oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan using GalNAc as a reducing end is not less than 80 percent, the weight average molecular weight is about 6, 000-20, 000Da, and the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) is 1.0-2.0.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
Methods for treating diseases through interruption of protein maturation, compounds that inhibit the function of molecular chaperones such as protein disulfide isomerases or interfere with glycosylation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising them, and screening methods for identifying therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20070015803A1Reduce inflammationInhibit functioningAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseMedicine
A method of treating an infectious disease caused by a pathogen comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of one or more compounds that inhibit the function of a molecular chaperone, wherein said compound is other than tizoxanide or nitazoxanide.
Owner:ROMARK LAB L C
Cloning, expression and application of eimeria tenella protein disulfide isomerase gene
InactiveCN101418309AGenetic material ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliEmoia loyaltiensis
The invention discloses an E.tenella protein disulfide linkage isomerase gene EtPDI (Clone ID is BW1-E06,and the Genbank accession number of is EF552214). The gene is connected with a procaryon expression vector pGEX-4T-2; a procaryon expression recombination plasmid pGEX-4T-EtPDI is constructed and is expressed in a colibacillus system; and most of the expressed recombining protein exists in a soluble form. The recombining protein 4T-EtPDI is purified to carry out SPS-PAGE and is transferred to a PVDF film; and antiserum of E.tenella oocyst oral immunized chicken is used as first resistance and goat anti-chicken IgG is used as second resistance to carry out Western-blot analysis, thereby indicating that the gene has certain antigen. The gene is used for preparing an anti-chicken coccidiosis drug and an anti-chicken coccidiosis vaccine.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101735336BSmall batch-to-batch varianceOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderDepolymerizationGlycan
The invention discloses a method for preparing oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan which is prepared by depolymerizing fucosylated glycosaminoglycan by a depolymerization method of peroxide catalyzed by a 4th period transition metal ion in an aqueous medium, and the preparation method has mild reaction condition, good reproducibility and stability, high pyrolysis selectivity and uniform and controllable product quality. The polysaccharide molecule number of the obtained oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan using GalNAc as a reducing end is not less than 80 percent, the weight averagemolecular weight is about 6, 000-20, 000Da, and the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) is 1.0-2.0.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
Method for a production of a recombinant protein using yeast co-expression system
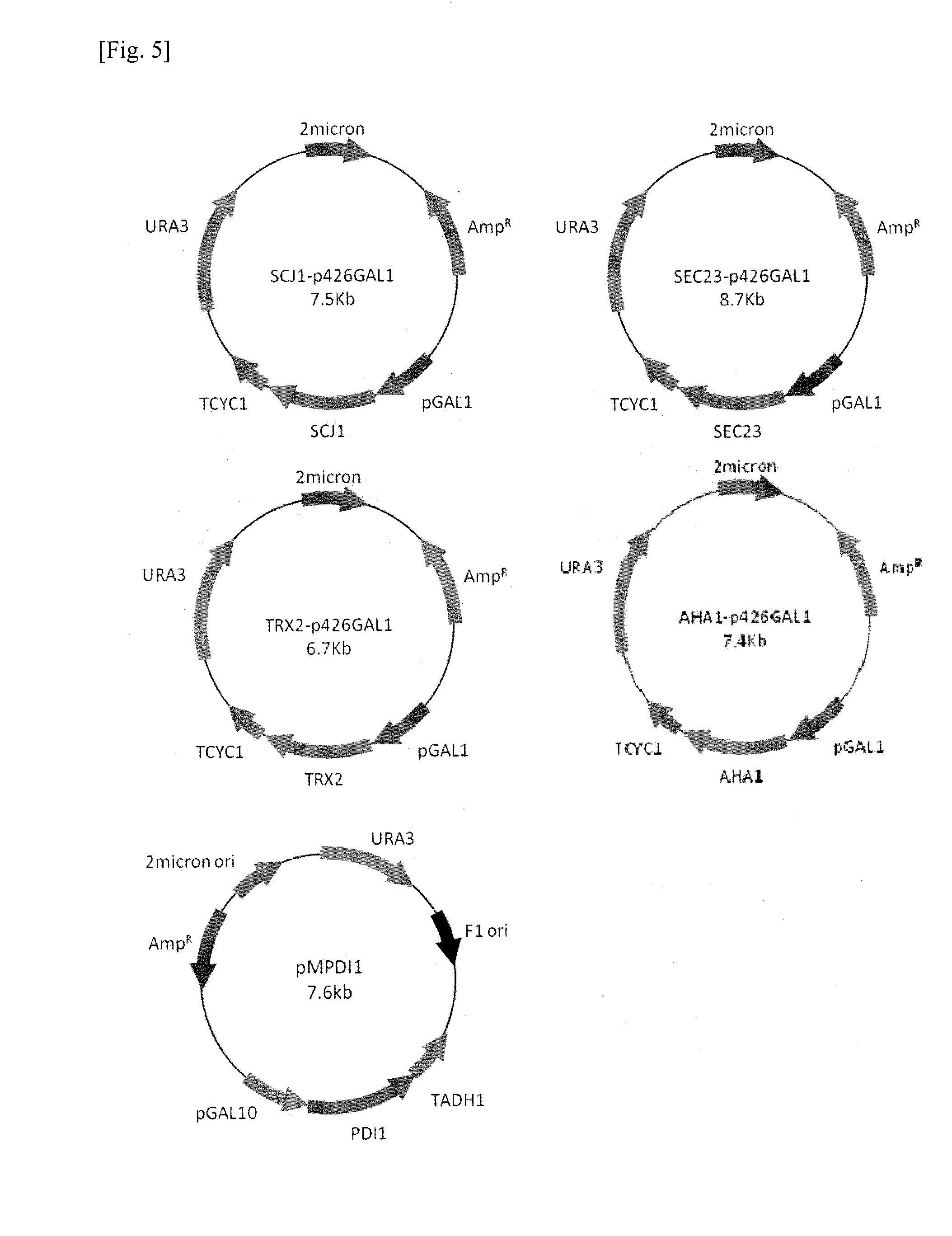
The present invention relates to a method for mass production of a recombinant protein comprising the step of culturing a yeast transformed with: a recombinant gene construct comprising a yeast promoter, a gene coding a signal sequence and a gene coding a target protein; and also with one or more genes coding folding accessory protein selected from the group consisting of PDI1 (protein disulfide isomerase 1), SEC23 (secretory 23), TRX2 (thioredoxin 2) AHA1 (activator of heat shock protein 90 ATPase), and SCJ1 (S. cerevisiae DnaJ) followed by culturing the transformed yeast.
Owner:MOGAM BIOTECH RES INST
Method for performing fusion expression on protein containing disulfide bond
ActiveCN102533839AHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisDisulfide bonding
The invention relates to a method for performing fusion expression on a protein containing a disulfide bond, in particular to a method for performing fusion expression on a recombinant protein, in particular a eukaryotic recombinant protein of which the activity is closely related with the forming of the (intrachain and interchain) disulfide bond in an eukaryotic host cell. An exogenous recombinant protein is expressed in a pichia pastoris expression system by a method for fusing human protein disulphide isomerase (hPDI) or a mutant of the hPDI. The method is suitable for expressing a eukaryotic exogenous protein of which protein activity or protein folding (comprising forms of a monomer, a dimmer or a polymer) are resistant to the disulphide bond. The protein expressed by the mode can be secreted out of a cell easily, and is high in yield, products cannot be gathered on a large scale and can be captured and purified easily, and the obtained target protein is uniform in N tail end, and high in activity. The recombinant protein expressed by the method can be industrially produced on a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI KAIYANG BIOTECH
Lactase mutator, secretory expression method and application thereof
ActiveCN101948854AIncrease relative enzyme activityIncrease secreted expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisLactase
The invention discloses a lactase mutator with optimized codon and high specific activity and a secretory expression method thereof. The lactase gene cloned in bifidobacterium animalis is optimized for codon of the gene and the GC content on condition that the amino acid sequence of the gene is not changed according to the preference of the codon of Pichia pastoris; the optimized lactase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2.After optimizing, 461 basic groups are changed; the percentage of GC% is lowered to 53.79% from 61.11%t; the enzymatic activity of the lactase is obviously increased after the codon is optimized. Moreover, the method shows that: since the lactase gene and protein disulfide isomerase are transformed into the Pichia pastoris cell, the relative activity of the lactase is obviously increased; and the secretory expression content of the lactase gene in the Pichia pastoris is obviously increased.
Owner:北京森根比亚生物工程技术有限公司
Expression system of fusion protein from human serum albumin and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
ActiveCN102766648AEasy to separateLow immunogenicityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisYeast
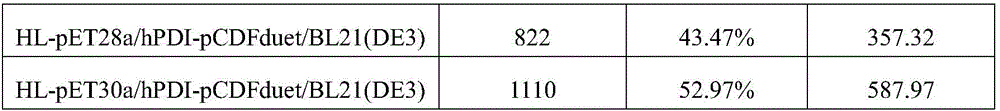
The invention discloses an expression system of fusion protein from human serum albumin and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. The expression system comprises a host cell and an expression vector transferred into the same. The expression vector comprises a first expression vector with an inserted fusion protein gene and a second expression vector with an inserted protein disulfide isomerase gene.The fusion protein gene comprises the human serum albumin and the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. The host cell is Pichia pastoris GS115. The co-expression host of PDI (protein disulfide isomerase) and IGH (immunoglobulin heavy) is established, and expression index of the IGH is evidently increased. The PDI is expressed intracellularly, the IGH secretory expression is subjected to extracellular secretory expression, and accordingly no newly generated other proteins occur when concentration of the IGH in collected medium supernate increases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Compounds and compounds for use in methods for treating diseases or conditions mediated by protein disulfide isomerase
The invention provides compounds of formula (I) that inhibit PDI, for use in methods to treat or prevent a disease or condition in a subject that would benefit by inhibition of PDI. Formula (I)
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Preparation method of recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor (haFGF) protein
ActiveCN103882047AEasy to prepareImprove product qualityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a recombinant protein in the field of gene engineering and in particular relates to a preparation method of a recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor (haFGF) protein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) designing primers according to the full-length sequence of the haFGF to obtain an original gene segment through cloning, and replacing a codon which exists in the original gene segment and is unfavourable to be expressed by escherichia coli, thus obtaining an optimized haFGF gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the optimized haFGF gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; cloning to obtain an original gene segment of a molecular chaperone PDI (protein disulfide isomerase), and replacing a codon which exists in the original gene segment and is unfavourable to be expressed by escherichia coli, thus obtaining an optimized PDI gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the optimized PDI gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; (2) linking and cloning the optimized haFGF gene, the optimized PDI gene, tag sequences and a protease cutting site sequence into a vector to obtain an efficient expression vector through construction; or firstly constructing standby vectors of part of the sequences, and then linking the remaining sequences on part of the sequences.
Owner:杨霞
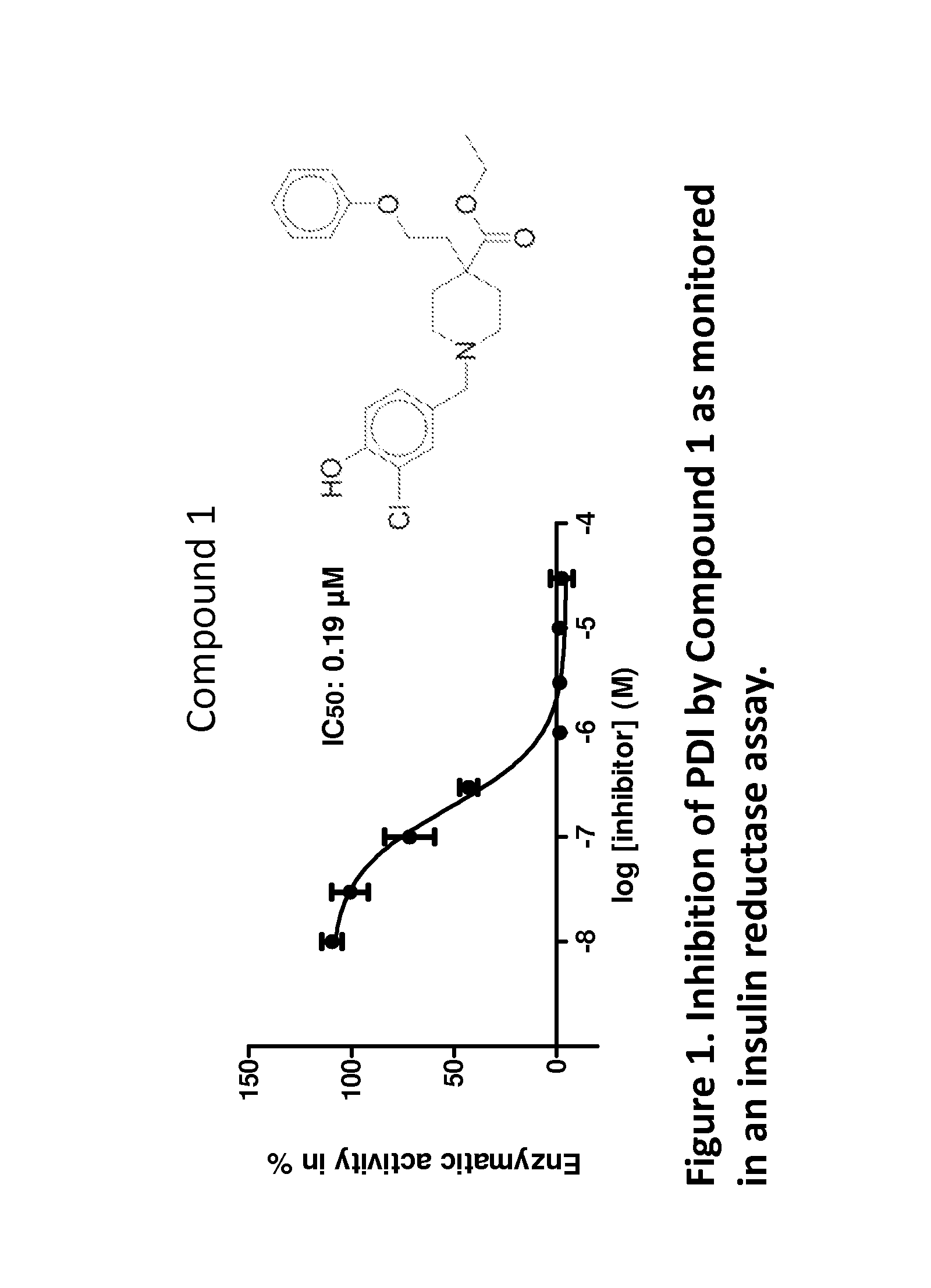
Small molecule oxidizers of pdi and their use
InactiveUS20180092908A1Improve stabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryChemical compoundNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention provides a method for treating or ameliorating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder in a subject in need thereof. The method includes, for example, administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound selected from:combinations thereof, or an N-oxide, crystalline form, hydrate thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention also provides a method for treating or ameliorating the effects of a condition associated with increased protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) activity and a method of modulating PDI activity in a cell. The present invention also provides compounds, salts, compositions and kits useful for the provided methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
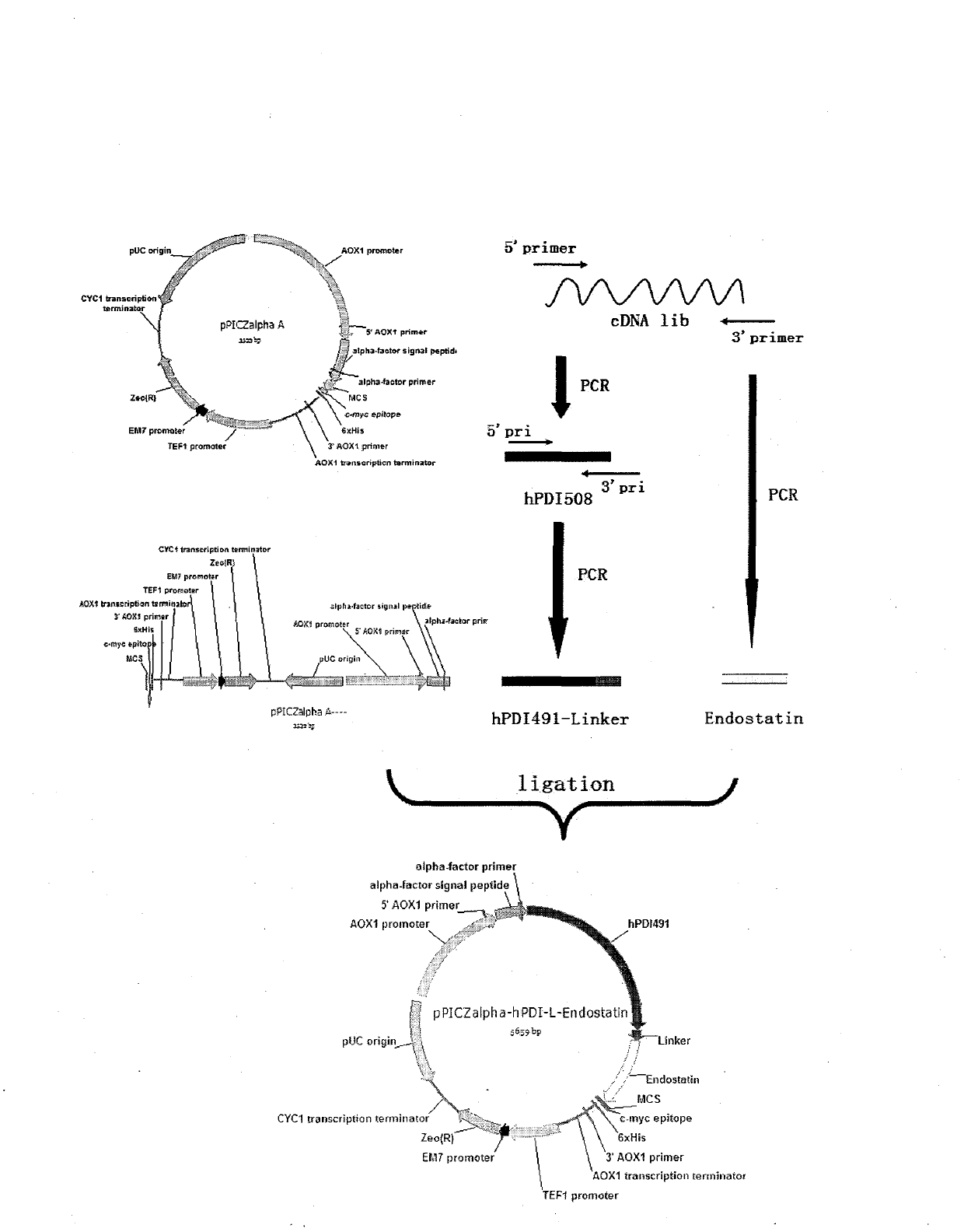
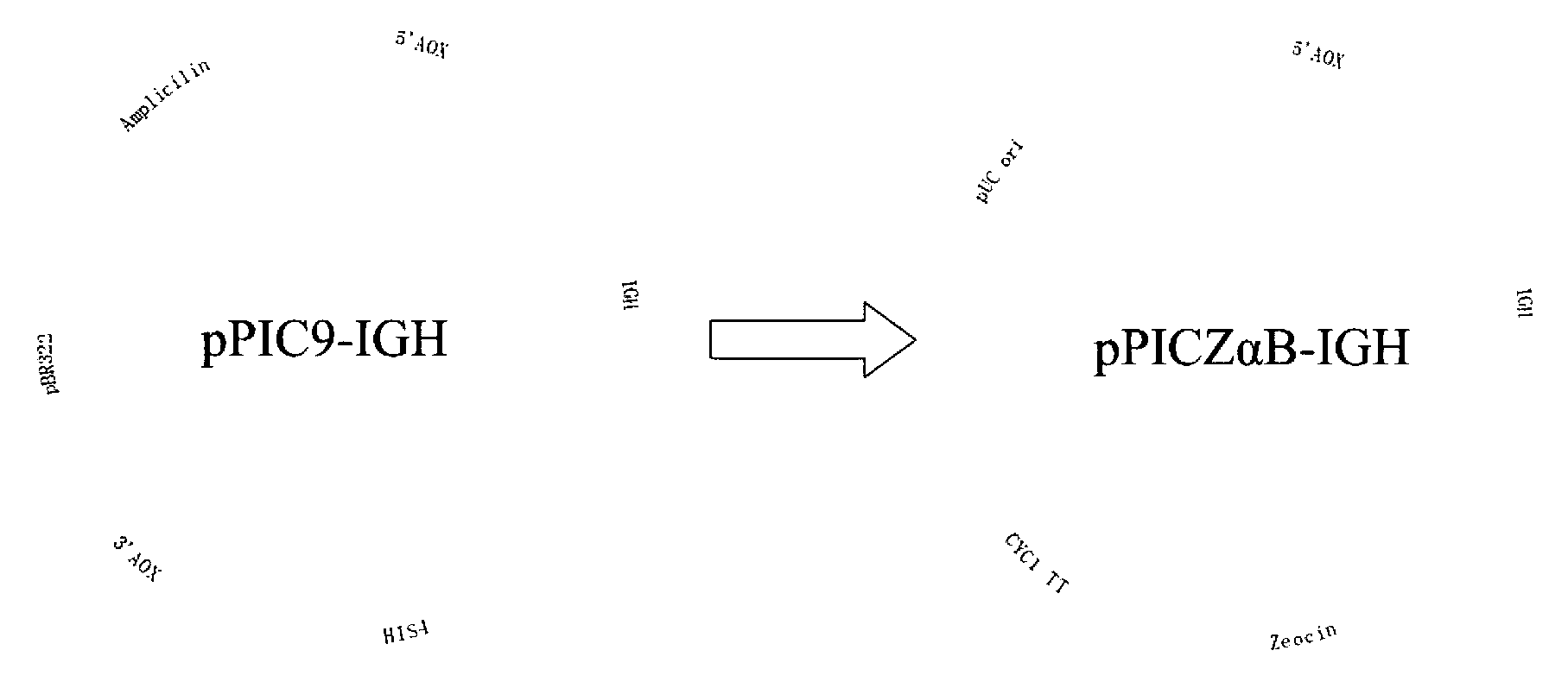
Expression of recombined human protein disulphide isomerase (hPDI491) with Pichia pastoris in secretion manner
ActiveCN102485890ABiologically activeMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyIsomeraseHuman proteins
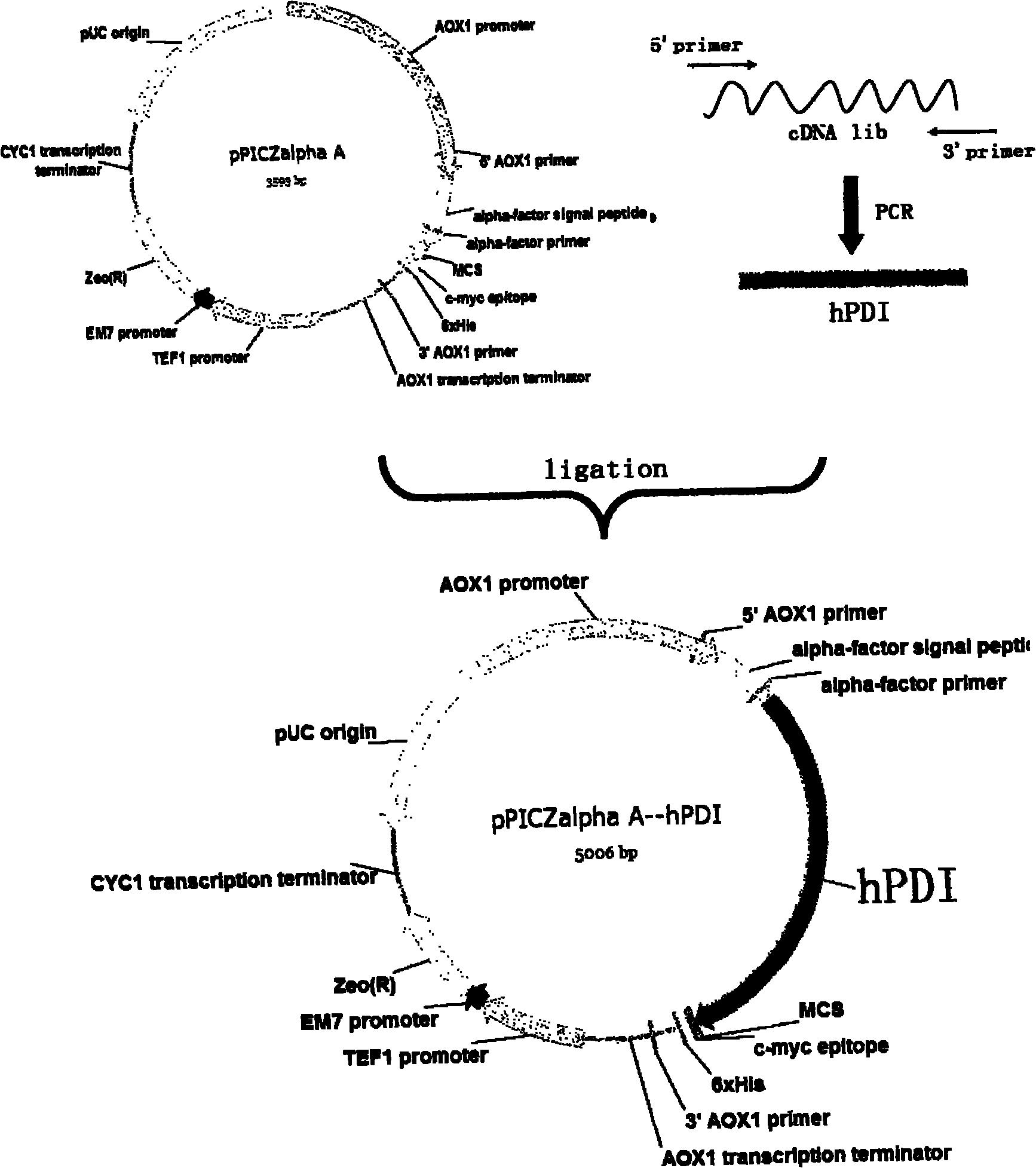
The invention which belongs to the biotechnological field concretely relates to recombined hPDI491, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. According to the invention, an RT-PCR process is applied to amplify to obtain hPDI491 cDNA, the hPDI491 cDNA is recombined with a Pichia pastoris expression vector pPICZalpha to obtain an expression plasmid pPICZalpha-hPDI, the pPICZalpha-hPDI is converted into Pichia pastoris X33, and high expression engineering strains are screened out. The expression of a large amount of the recombined hPDI491 in Pichia pastoris in secretion manner is realized. The purity of the engineering strains which are fermented, induction-expressed, and separation-purified is greater than 90%. Experiments proves that the hPDI491 has an in vitro correct folding promotion effect on other proteins.
Owner:张洁
Protein disulfide isomerase inhibiting anticancer agents
ActiveUS20150133514A1Favorable pharmacokinetic activityConfirmed promiseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHalogenHeteroatom
Protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors according to formula Iare described, wherein R1 is an aryl or cycloalkyl group, R2 is selected from the group consisting of CN, SO2CH3, NO2, CO2R3, CONHR3, NMe2, and CF3, R3 is selected from H or lower alkyl, R4 is H, halogen, CN, or COOH, and X and Y are C—H or heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, and S. The protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors can be used for the treatment of cancer in a subject.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method for preparing thrombolytic medicament Reteplase without inclusion-body renaturation in escherichia coli
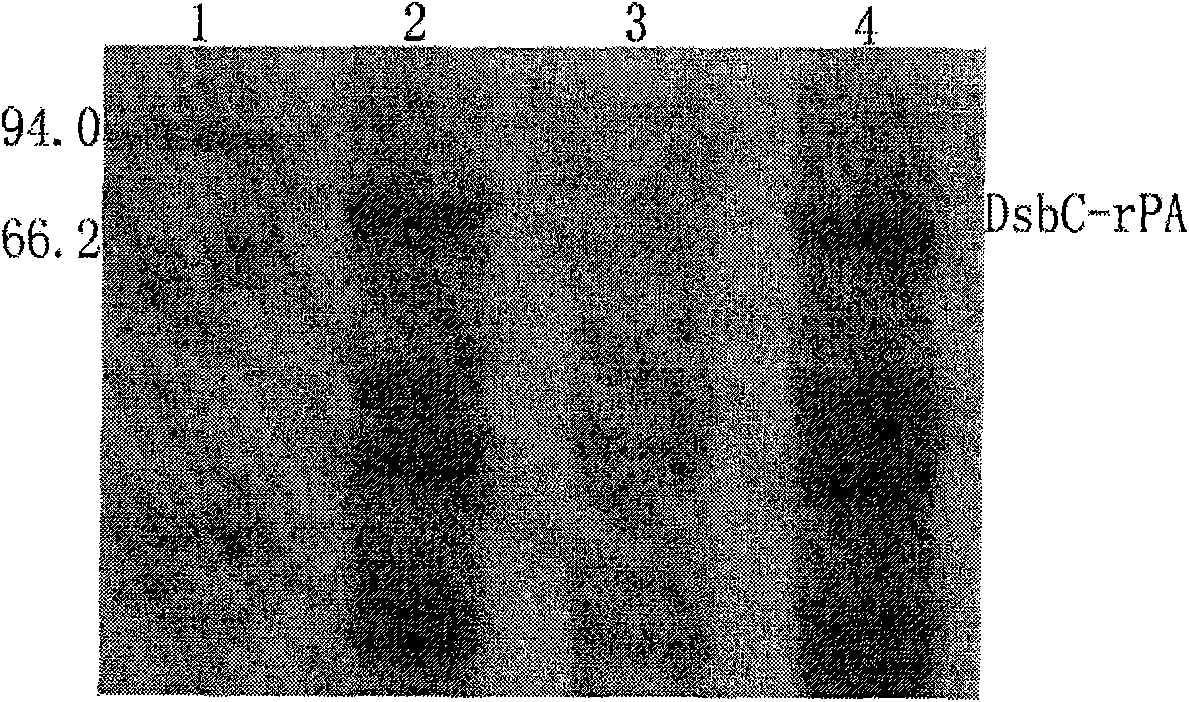
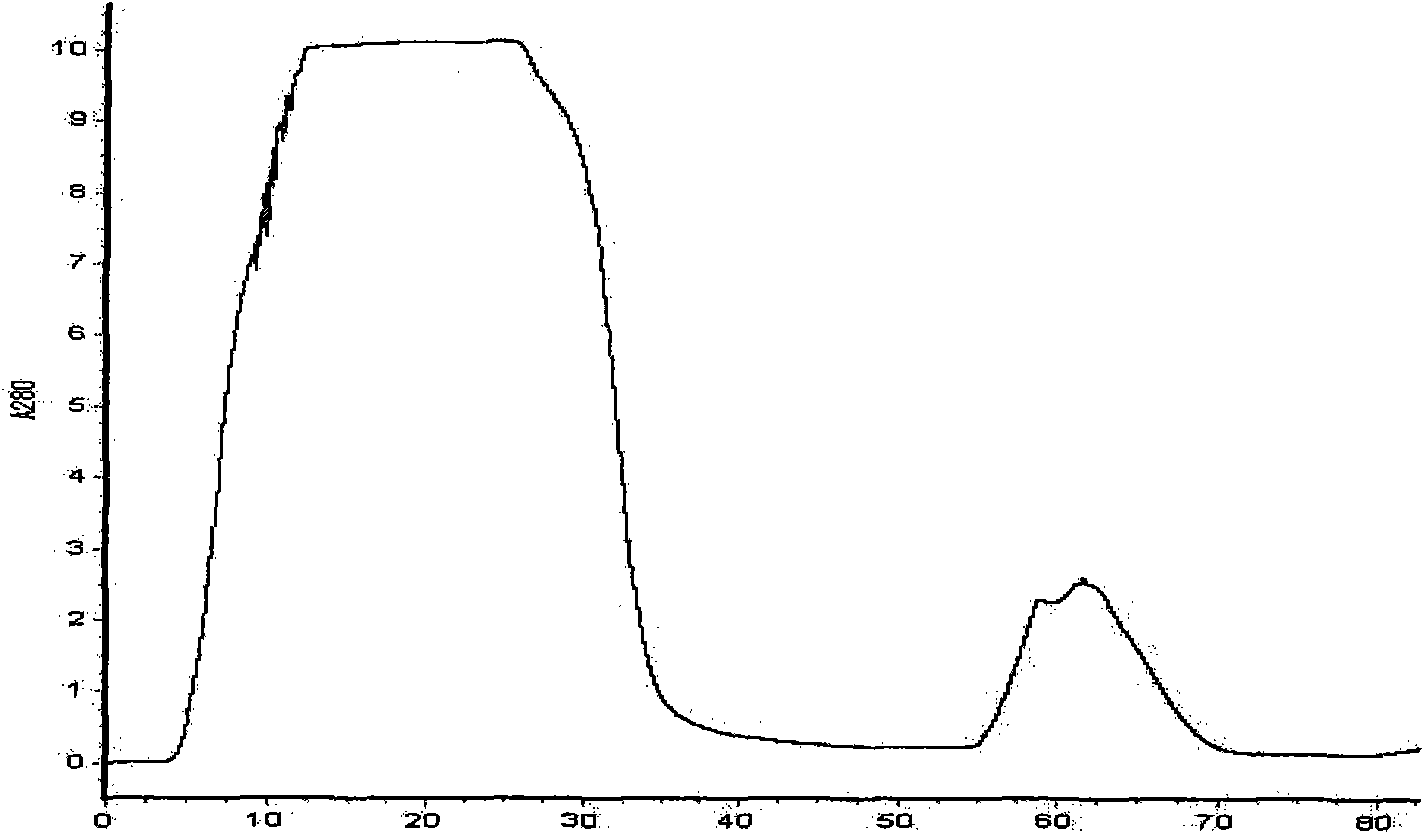
The invention relates to a method for preparing a thrombolytic medicament Reteplase (rPA) directly through an escherichia coli expression system without inclusion-body renaturation. A gene segment of the rPA is obtained through PCR amplification, and is cloned into a vector pET40b to construct a pET40b-rPA recombinant plasmid, and the rPA is made to perform fusion expression with the protein disulfide isomerase DsbC in the vector pET40b. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into the escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and induction expression conditions of IPTG and lactose are respectively established optimally. The obtained target fusion protein is mainly expressed by soluble components, and is purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography and processed by a Xa factor (or formic acid or thrombin) to form the high-purity rPA target protein. Fibrin plate method detection results show that the fusion protein DsbC-rPA obtained by the method and the rPA protein obtained by removing a label and purifying have obvious thrombolytic activity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
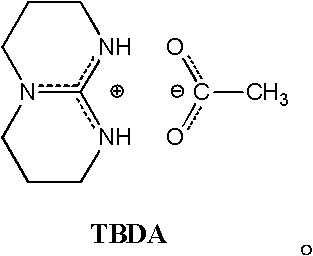
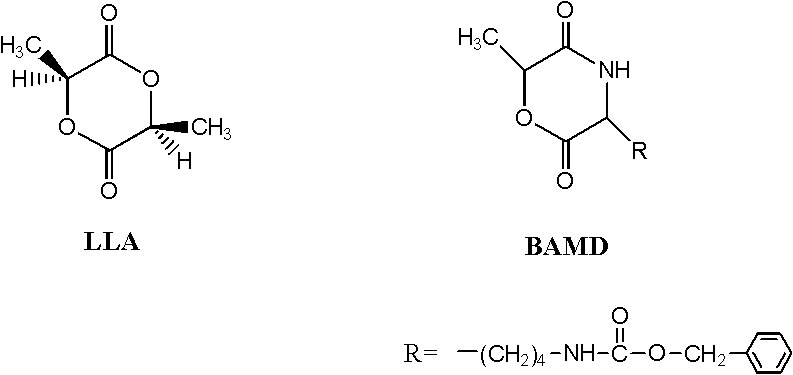
Process method for synthesizing lactic acid-lysine copolymer by catalytically opening loop and copolymerizing with acetic bicyclo-guanidine
ActiveCN102504227AGood compatibilityHigh biosecurityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPolymer scienceLactide
The invention discloses a process method for synthesizing a lactic acid-lysine copolymer by catalytically opening a loop and copolymerizing with acetic bicyclo-guanidine (the molar content of diaminocaproic acid is 1-5 percent). The lactic acid-lysine copolymer is synthesized by taking acetic bicyclo-guanidine as a catalyst, taking lactide and lysine morpholine diketone as monomers, performing body loop opening copolymerization and undergoing a phenmethyl carboxide removing action. The process method has characteristics that: the acetic bicyclo-guanidine serving as a catalyst is bionic organic guanidinium which is effective, nontoxic and free from metals; the monomer transformation ratio is high (more than or equal to 95 percent); the yield is over 93 percent; a product does not contain any metal or other toxic residue, and has high biological safety; the number average molecular weight is adjustable in the range of 1.5-2.8*10<4>, and the molecular weight distribution is narrow (PDI (Protein Disulfide Isomerase) is less than or equal to 1.30); the molar content of lysine in the copolymer is adjustable in the range of 1-5 percent; and the synthesized lactic acid-lysine copolymer isan amphiphilic functional group biodegradable polymer, is suitable for serving as targeted and controlled release medicament carriers, and can be applied on other aspects in the field of biological medical tissue engineering.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for increasing expression amount of pichia pastoris for secreting and expressing plectasin
InactiveCN107988289AHigh expressionCorrect spatial structureMicroorganism based processesPeptidesYeastEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for increasing expression amount of pichia pastoris for secreting and expressing plectasin. The method is characterized in that a pichia pastoris genome is used as a template, a PDI (protein disulfide isomerase) gene is amplified, a PDI segment is treated by BstBI and EcoRI double enzyme digestion, and is connected to a pPIC6aphlaA carrier segment which is also treated by the BstBI and EcoRI double enzyme digestion, and an expression carrier pPIC-PDI is formed; the PDI is expressed in a plectasin expression strain, three pairs of disulfide bonds of the plectasin are promoted to form a correct space structure, the plectasin is smoothly secreted and expressed out of cells, and the purpose of increasing the expression amount of plectasin is realized. The method has the advantage that the expression amount of plectasin is increased by 30%.
Owner:GUANGDONG HINAPHARM PHARMA CO LTD
Protein disulfide bond isomerase A3 and use of antibody thereof in liver cancer detection
InactiveCN101323876AImprove reliabilityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisWestern blotIsomerase
The invention verifies that protein disulfide isomerase A3 expression in the cancer tissues and adjacent tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma is different through screening the protein having differential expression in the cancer tissues and adjacent tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma and carrying out western blot experiment. The invention discloses the application of the protein disulfide isomerase A3 to the detection of liver cancer and / or susceptibility of liver cancer and the application of the antibody of the protein disulfide isomerase A3 to the detection of liver cancer and / or susceptibility of liver cancer. Therefore, as the potential marker of liver cancer, the protein disulfide isomerase A3 can serve as a marker of the prognosis molecule of liver cancer and a target molecule of clinical treatment.
Owner:上海中科新生命生物科技有限公司
Small molecule inhibitor of protein disulfide isomerase
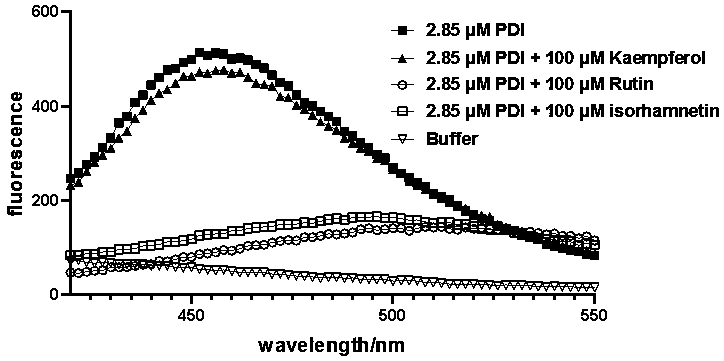
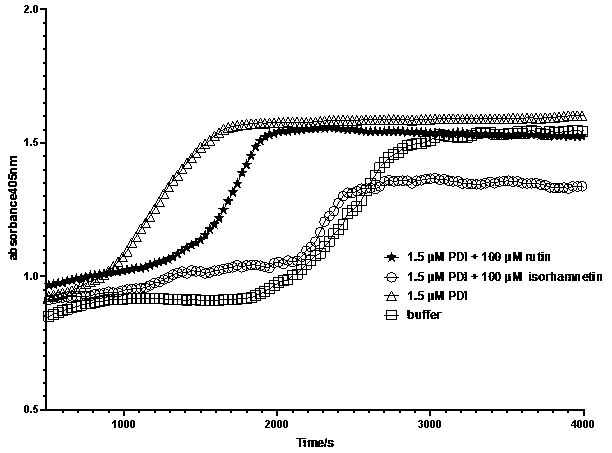
PendingCN110693874AInhibitor rutin inhibits reductive activityDelayed serum agglutinationOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderDisulfide bondingAntithrombotic treatment
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
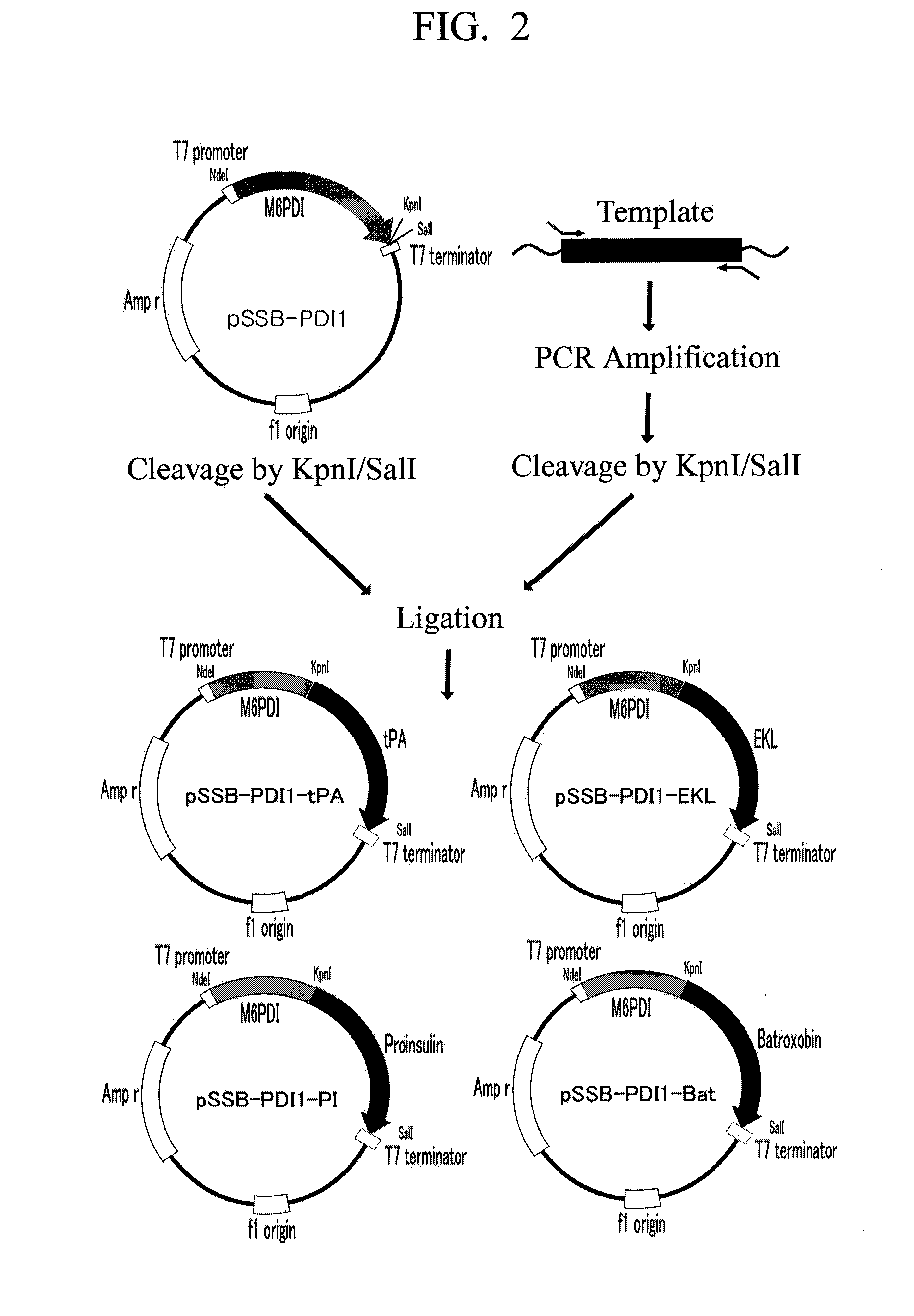
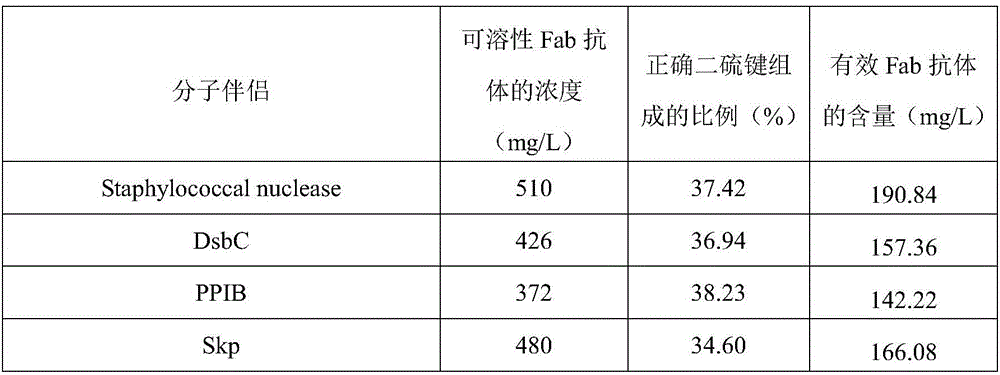
Method for preparing soluble and active recombinant proteins using pdi as a fusion partner
ActiveUS20090305351A1Improve expression rateIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesSolubilityProtein target
The present invention relates to a method for producing a recombinant protein capable of increasing expression rate of a target protein and also improving solubility and folding of the expressed target protein using a modified protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) as a fusion partner, and an expression vector containing the modified PDI gene as a fusion partner. The method for preparing a recombinant protein using a modified PDI as a fusion partner according to the present invention may solve the problems concerning a low yield and solubility and folding that conventional fusion partners have, and be widely used for protein drug and industrial protein production.
Owner:PNP BIOPHARM
Process for producing polypeptide having disulfide bond
InactiveUS7037684B2Increased correct disulfide bond formationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsA-DNAChemistry
The invention relates to a DNA that enables co-expression of a protein disulfide isomerase and a polypeptide having disulfide bonds. The invention further relates to a process of producing polypeptides using the DNA and a process of enhancing the efficiency of formation of correct disulfide bond in an expression system of a gene recombinant polypeptide having disulfide bonds.
Owner:ITOHAM FOODS +1
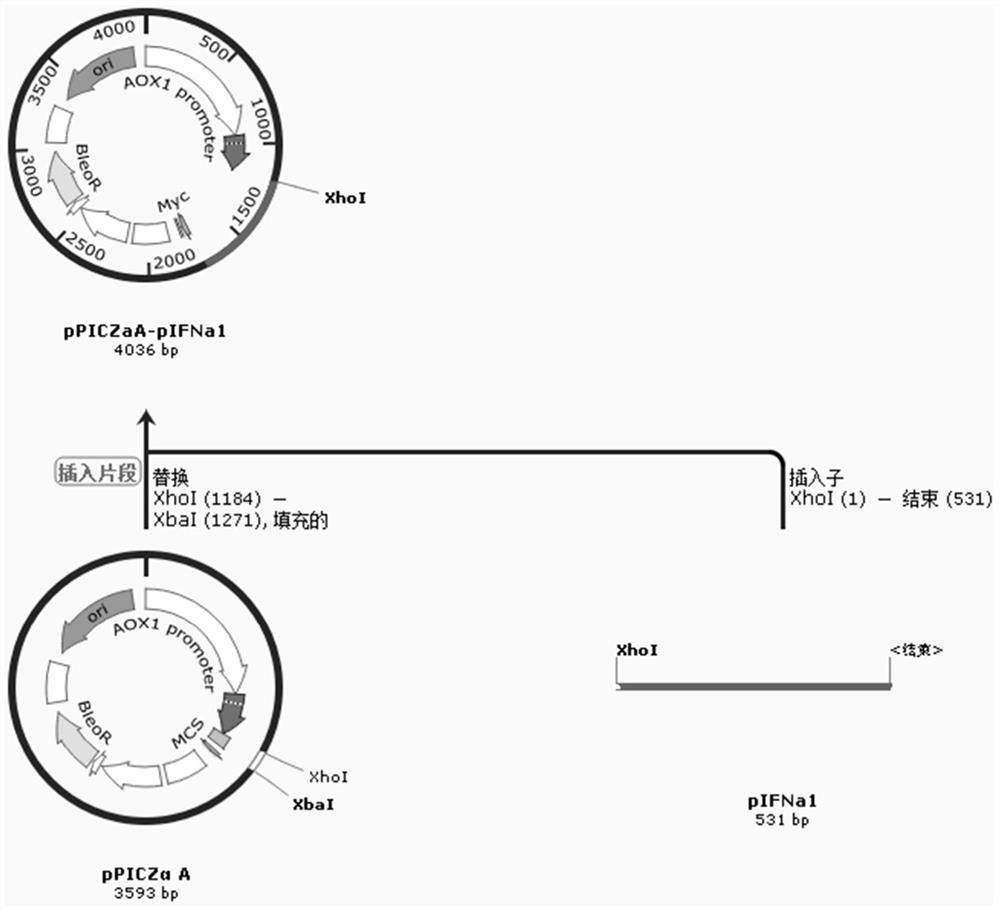
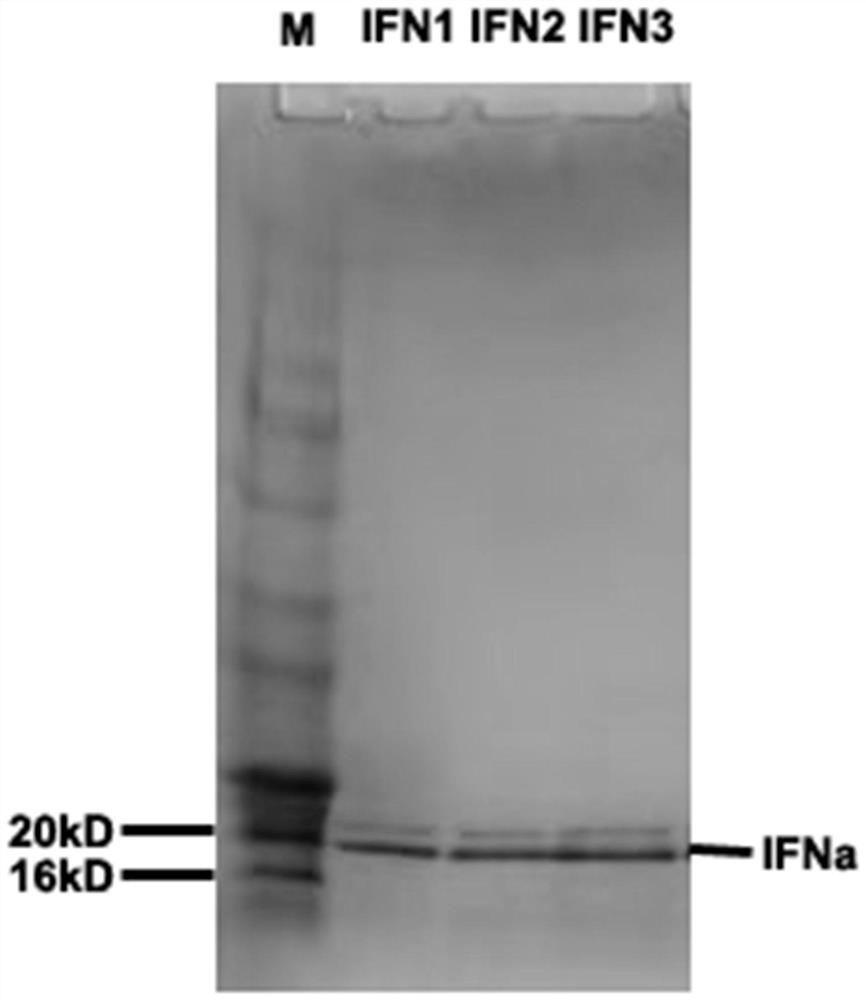
Pichia pastoris for efficiently expressing recombinant porcine alpha1 interferon through auxiliary secretion
ActiveCN111925952AReduce accumulationImprove the level ofFungiStable introduction of DNAPichia pastorisYeast Proteins
The invention discloses pichia pastoris for efficiently expressing recombinant porcine alpha1 interferon through auxiliary secretion. The pichia pastoris comprises a recombinant porcine alpha1 interferon gene segment with a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and a protein disulfide isomerase PDI gene segment with a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2; a multi-copy recombinant porcine alpha1 interferon gene segment and a DNA segment for inserting and expressing yeast protein disulfide isomerase are integrated in pichia pastoris; the auxiliary protein is folded in yeast cells, so that accumulation of interferon in cells is reduced, the amount of the porcine alpha 1 interferon secreted out of the cells is increased, the expression quantity of the porcine interferon alpha 1 reaches 1.43 g / L and is improved by 40% or above compared with that of a bacterial strain only integrating an interferon expression cassette, the level of producing the porcine interferon alpha 1 through thallus fermentation is remarkably improved, and the production performance of a high-copy bacterial strain is effectively exerted.
Owner:GUANGDONG HINAPHARM PHARMA CO LTD
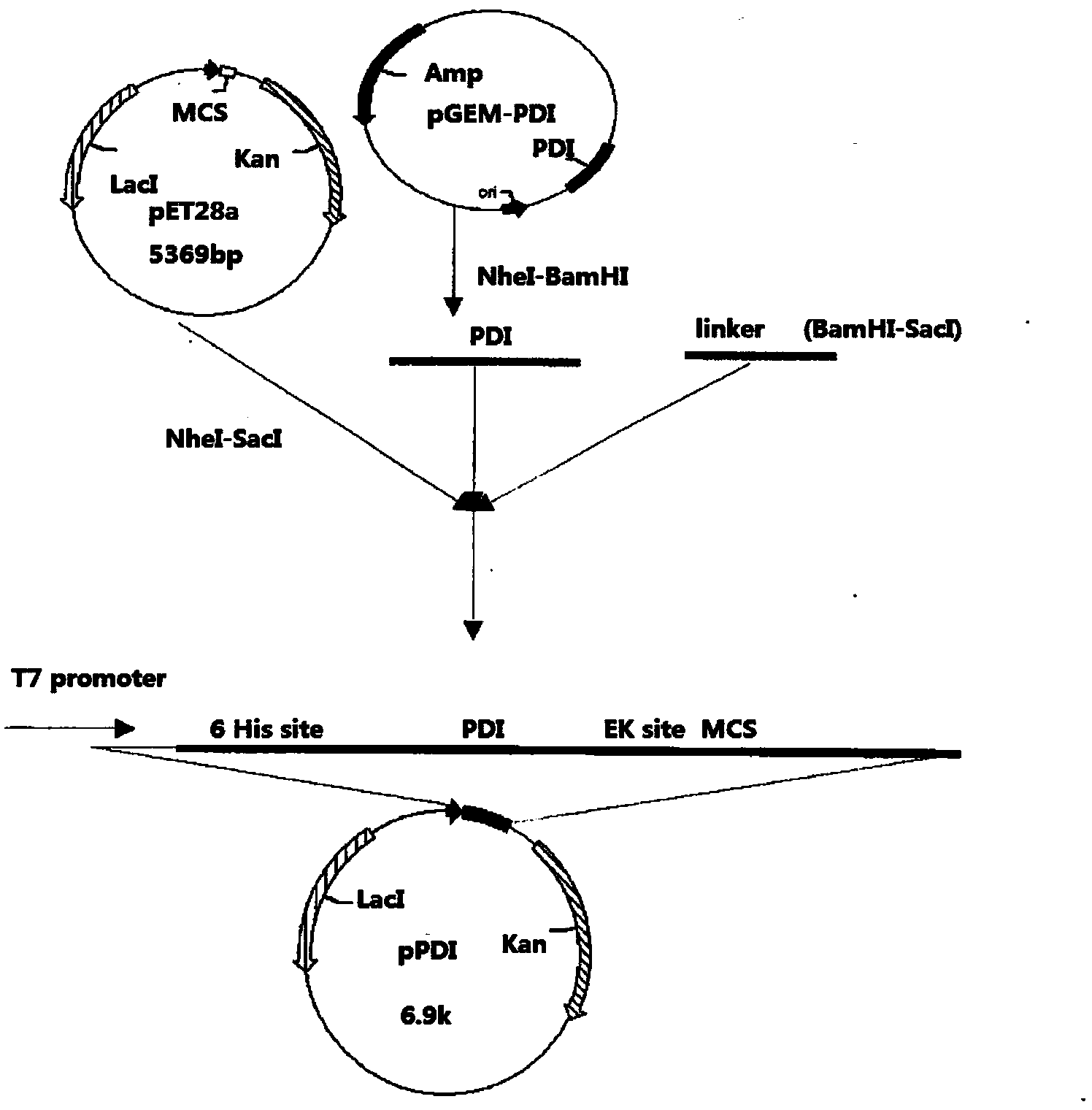
Pronuclei fusion expression vector and application thereof
The invention provides a pronuclei fusion expression vector which comprises a nucleotide fragment. The nucleotide fragment is composed of a promoter, a gene for coding a PDI (Protein Disulfide Isomerase) parasporal protein, and a joining region which are serially connected, wherein the joining region contains an enterokinase cleavage site and a multiple cloning site. The pronuclei fusion expression vector is capable of efficiently expressing an exogenous gene in a form of a fusion protein, is good in solubility of an expression product, simple in purification, and has natural bioactivity of the exogenous gene. The pronuclei fusion expression vector is suitable for mass production of a recombinant protein, is suitable for research and production of a genetic engineering product and a biological agent, and can also be used for researching a protein function and conformation relationship.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Hybridoma cell, monoclonal antibody generated by hybridoma cell and application of monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN103966173AWith bi-directional inhibitory functionInhibition formationMicroorganism based processesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesThrombus
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and discloses a hybridoma cell, a monoclonal antibody generated by the hybridoma cell and application of the monoclonal antibody. The collection number of the hybridoma cell is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.9153. The hybridoma cell and the monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell are prepared from a member of the optimized PDI (protein disulfide isomerase) protein family as antigen protein; the hybridoma cell can stably generate the monoclonal antibody resistant to protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the monoclonal antibody has a two-way inhibition function, can inhibit thrombogenesis and blood clotting reaction, and can be applied to preparation of drugs for treating thrombotic diseases and clotting diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for producing glucose oxidase
The invention discloses a method for producing glucose oxidase. The invention firstly provides a recombinant bacterium, which is obtained by introducing a coding gene of glucose oxidase and a coding gene of a molecular chaperone into a starting bacterium. The molecular chaperone can be concretely protein disulfide isomerase and / or tuberculosis immune globulin. The invention also discloses the method for producing the glucose oxidase. The method comprises the following steps of culturing the recombinant bacterium to obtain the glucose oxidase. The invention also discloses application of the molecular chaperone in promoting microbial expression glucose oxidase. The method for producing the glucose oxidase provided by the invention has significance on secretory expression and industrial production of the enhanced glucose oxidase.
Owner:福建力多利生物科技有限公司
Recombinant engineered Escherichia coli for expressing anti-TNF antibody Fab fragment
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to recombinant engineered Escherichia coli that converts a recombinant expression vector, and the recombinant expression vector comprises genes for expressing anti-TNF antibody Fab fragment and genes for expressing protein disulfide isomerase. By expressing the ant-TNF Fab fragment with the recombinant engineered Escherichia coli, it is possible to significantly improve correct formation of disulfide bonds at the premise of significantly improving periplasmic space expression quantity.
Owner:BEIJING TRI PRIME GENE PHARMA CO LTD
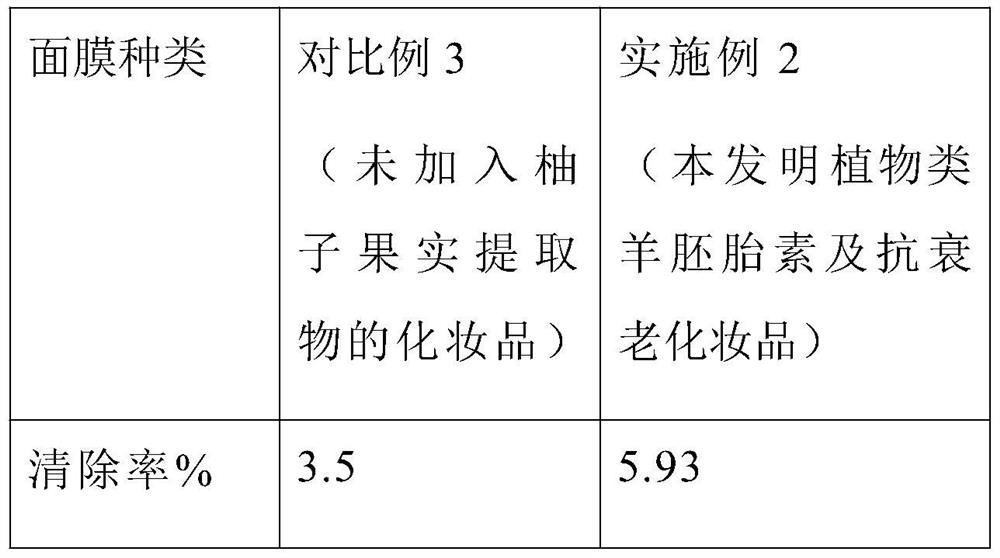
Extraction method of plant sheep embryo extract and preparation of anti-aging cosmetic
InactiveCN112353743AHas an anti-aging effectImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDisulphide bondsProtein
The invention discloses an extraction method for a plant sheep embryo extract and preparation of anti-aging cosmetics. The product is prepared from sheep placenta, modified bioactive peptide, grapefruit fruit extract, paraffin, protein disulfide isomerase, a surfactant, a humectant, a preservative, propylene glycol and deionized water. Wherein the modified bioactive peptide is obtained by converting partial connected peptide bonds in the bioactive peptide into isopeptide bonds through reaction. According to the invention, the bioactive peptide in the sheep placenta is extracted and modified, so that the stability of the bioactive peptide is enhanced, the antioxidant and anti-aging effects of the bioactive peptide are enhanced, and the grapefruit fruit extract is added to enhance the auxiliary anti-aging effect. The plant sheep embryo extract and the anti-aging cosmetic disclosed by the invention can generate an anti-aging effect on the basis of cleaning the skin, so that the anti-agingeffect on the skin is achieved while the skin is cleaned.
Owner:周慧青
Expression system of fusion protein from human serum albumin and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
ActiveCN102766648BEasy to separateLow immunogenicityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisHuman albumin
The invention discloses an expression system of fusion protein from human serum albumin and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. The expression system comprises a host cell and an expression vector transferred into the same. The expression vector comprises a first expression vector with an inserted fusion protein gene and a second expression vector with an inserted protein disulfide isomerase gene.The fusion protein gene comprises the human serum albumin and the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. The host cell is Pichia pastoris GS115. The co-expression host of PDI (protein disulfide isomerase) and IGH (immunoglobulin heavy) is established, and expression index of the IGH is evidently increased. The PDI is expressed intracellularly, the IGH secretory expression is subjected to extracellular secretory expression, and accordingly no newly generated other proteins occur when concentration of the IGH in collected medium supernate increases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Chimeric disintegrin domain
InactiveUS7754850B2High affinityFacilitate the proper folding of nascent recombinant CN disintegrin domainBiocideBacteriaADAMTS ProteinsIsomerase
This invention relates to methods of expressing eukaryotic proteins in prokaryotic hosts, particularly eukaryotic proteins that require formation of disulfide bridges for biological activity. Various approaches are used including fusion to thioredoxin, cytoplasmic expression of disulfide isomerases, deficiencies in thioredoxin and / or glutathione reductases, deficiencies in proteases, and the like. The method is applicable to express monomeric and dimeric forms of the eukaryotic protein with biological activity such as monomeric and dimeric forms of a disintegrin or a disintegrin domain. Included are the vectors, host cells expressing the proteins, the expressed proteins and methods of using the proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com