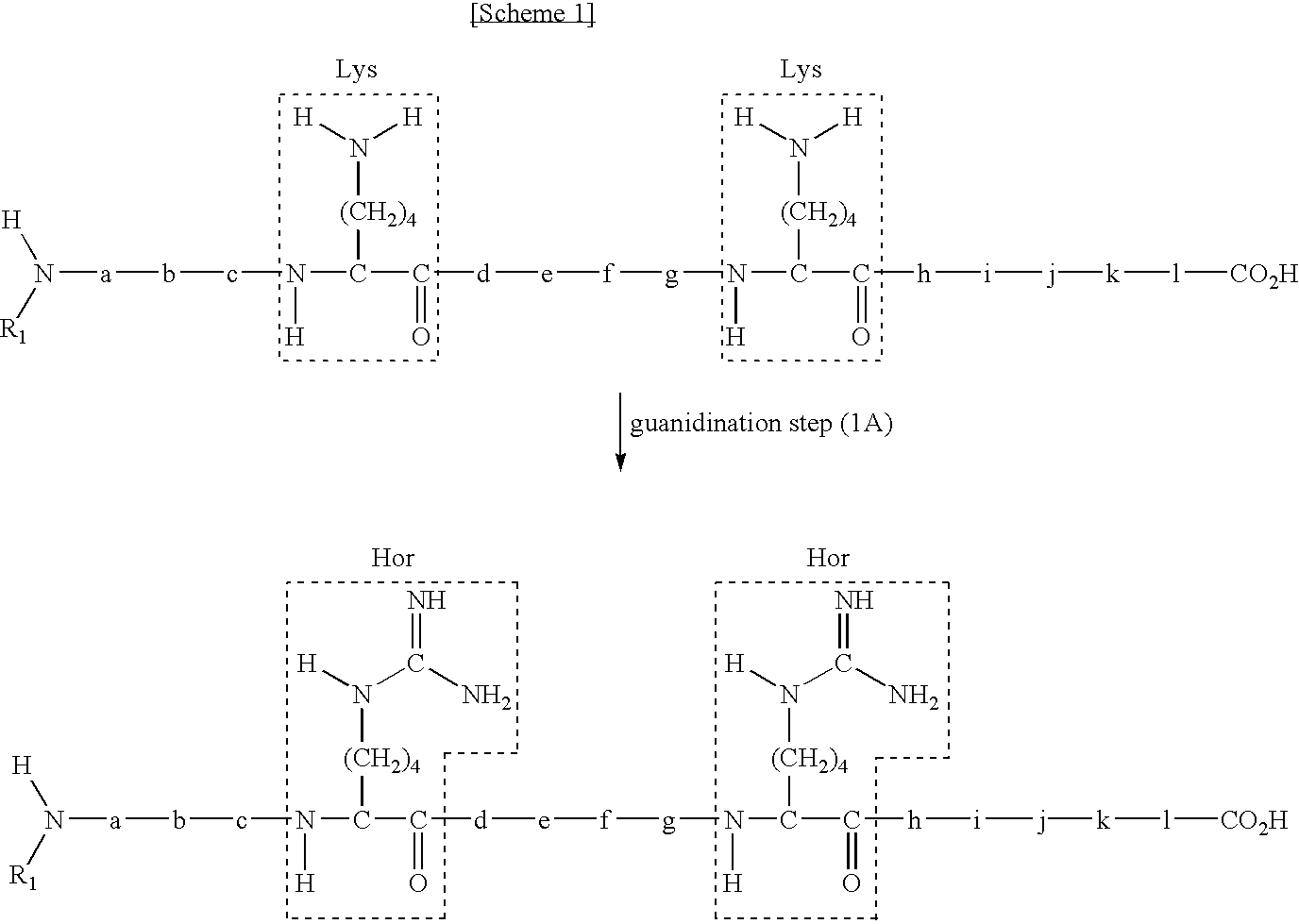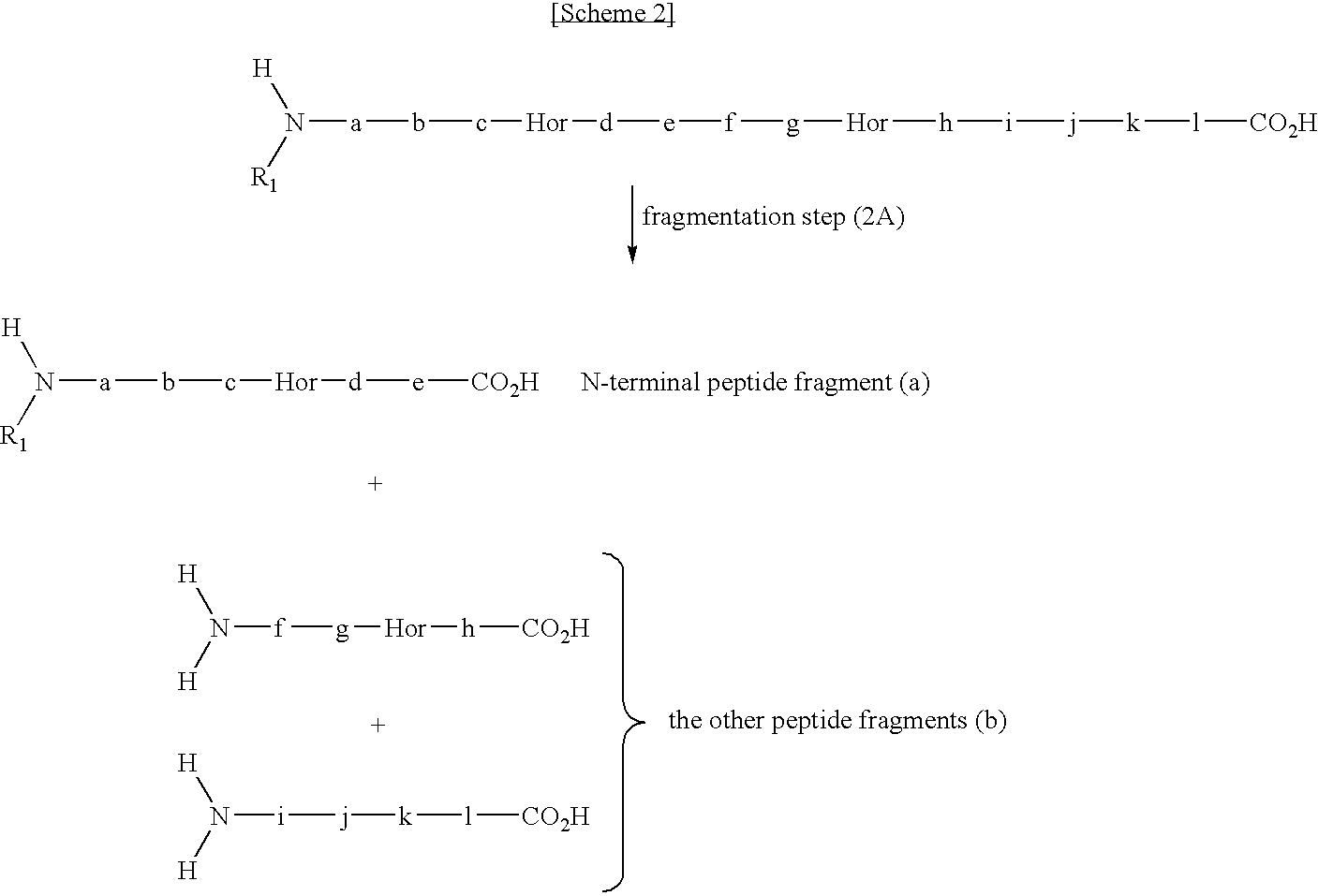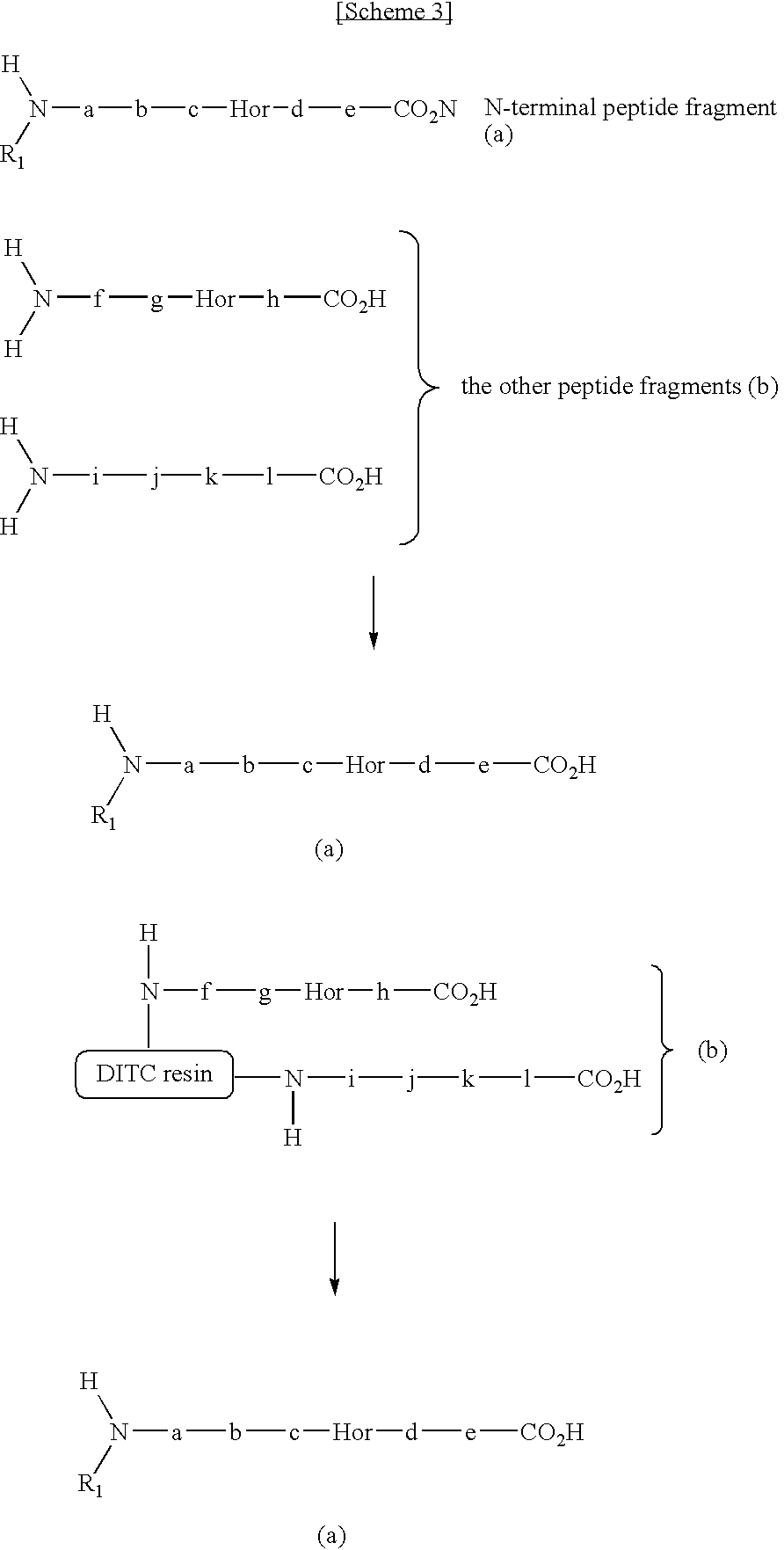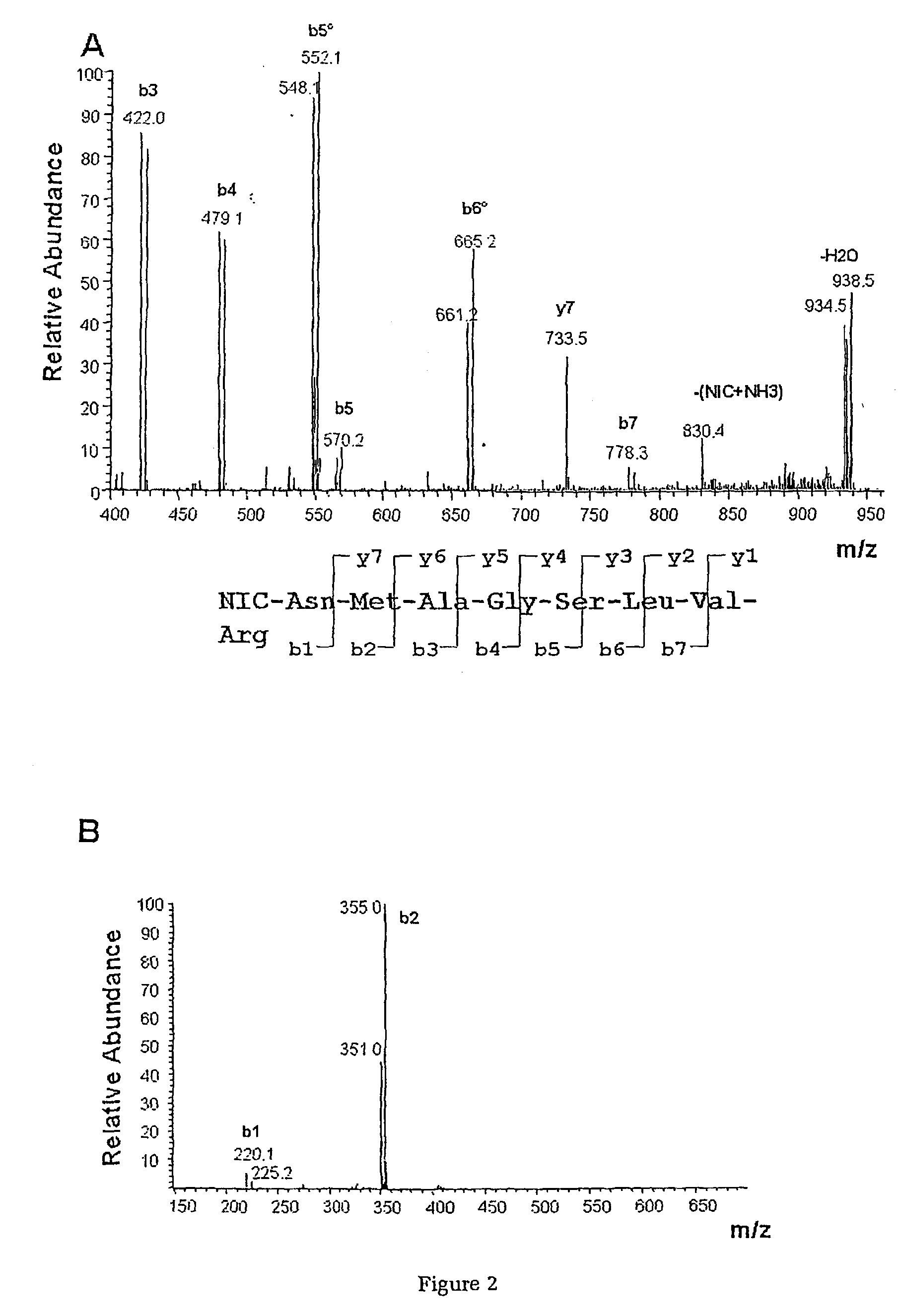Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Protein Cleavage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
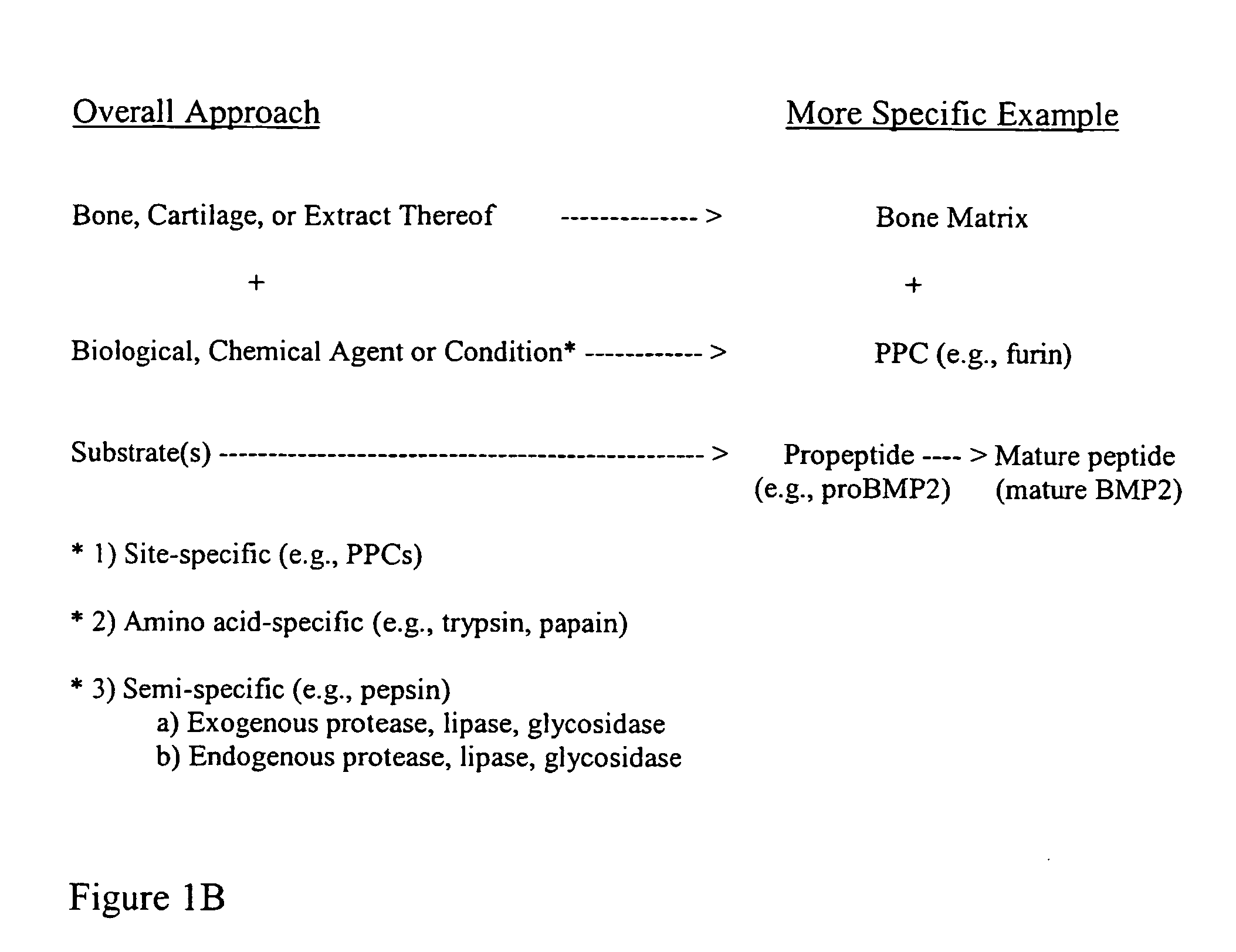
Protein Cleavage. Protein Cleavage involves hydrolysis by proteolytic enzymes of specific peptide bond(s), forming smaller polypeptides in the target protein during maturation or modification of functional activity.
Bone matrix compositions and methods
ActiveUS20070154563A1Good osteoinductivityHigh activityHydrolysed protein ingredientsBone implantOsteoblastLine of therapy
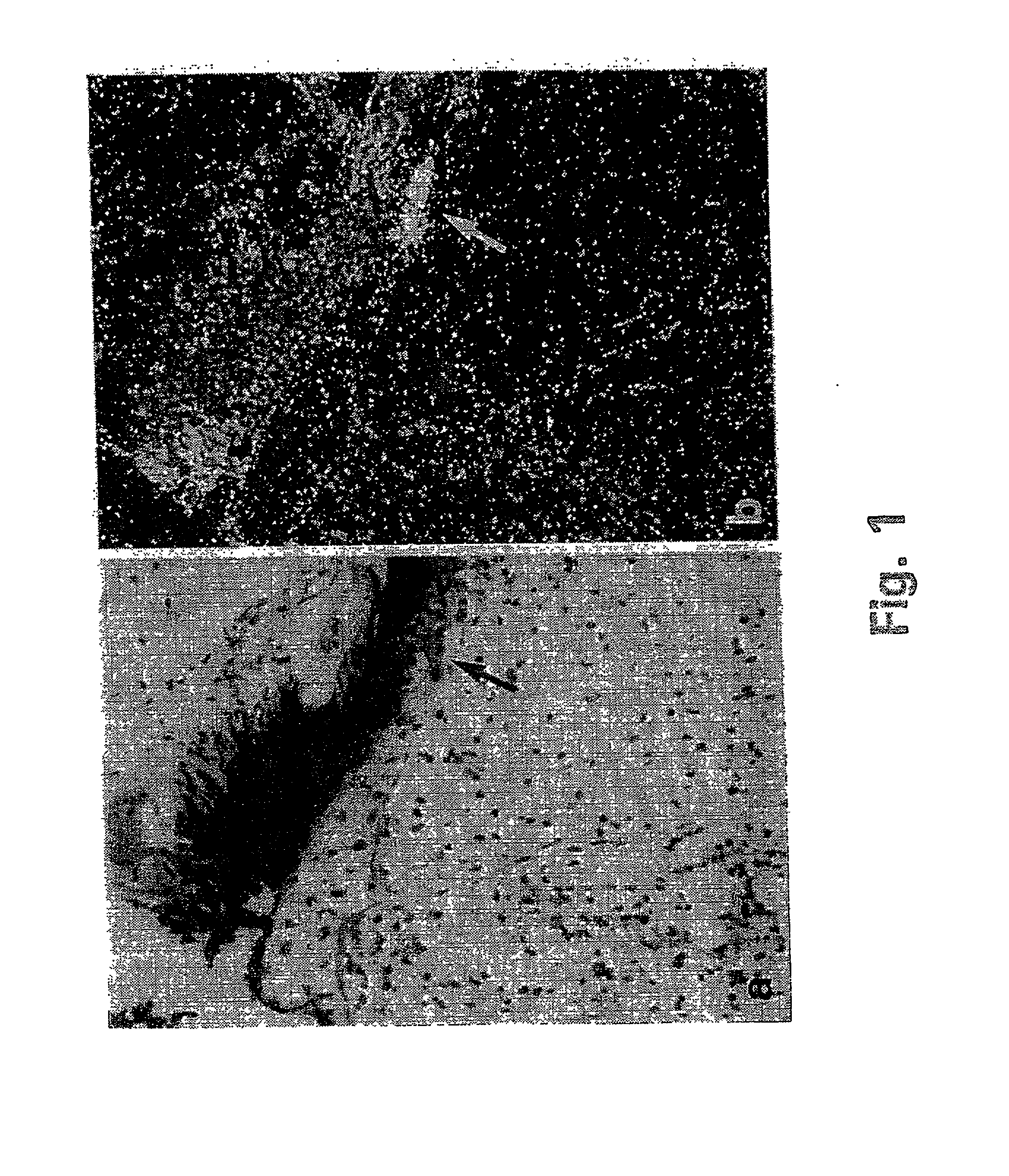
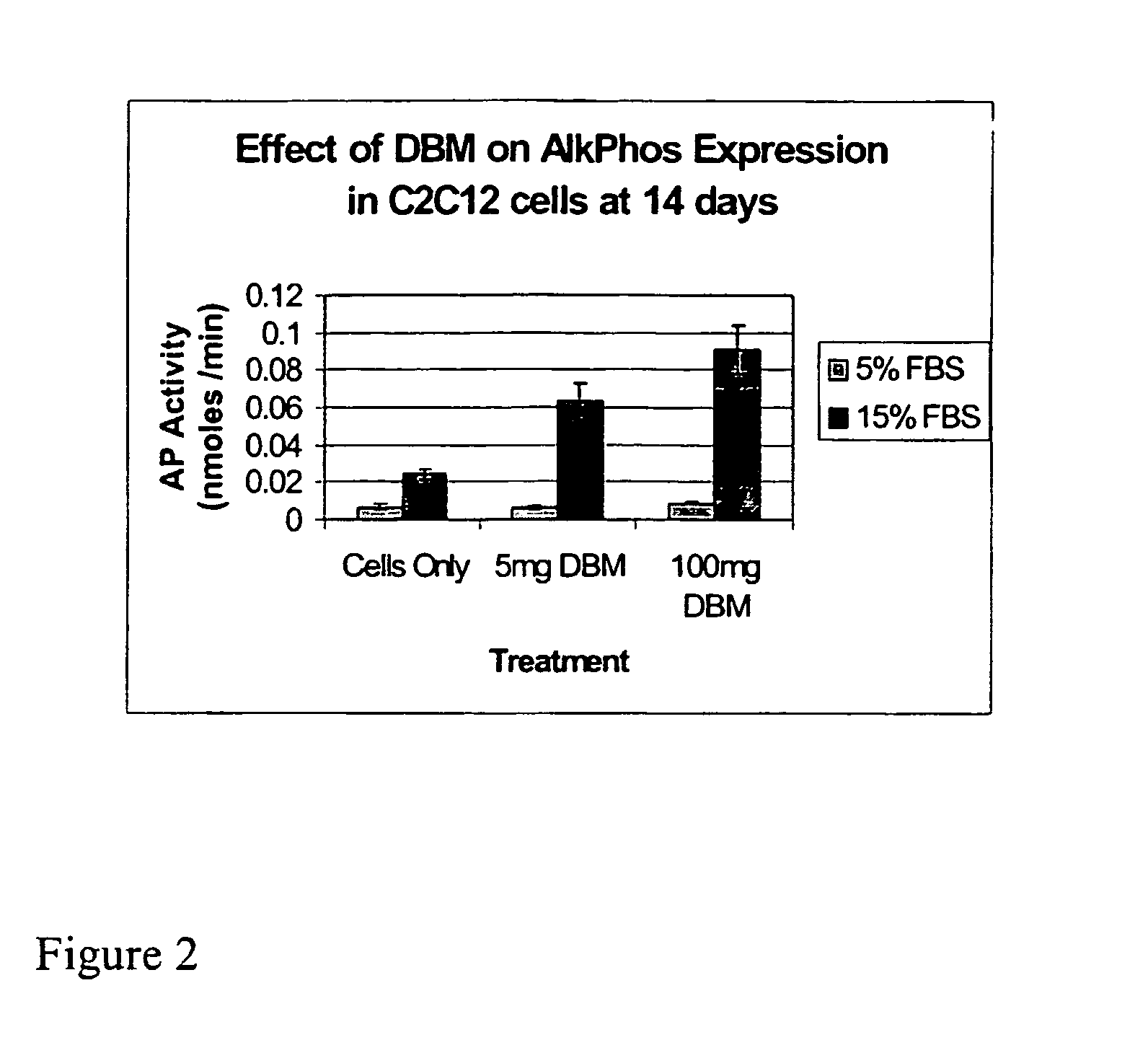
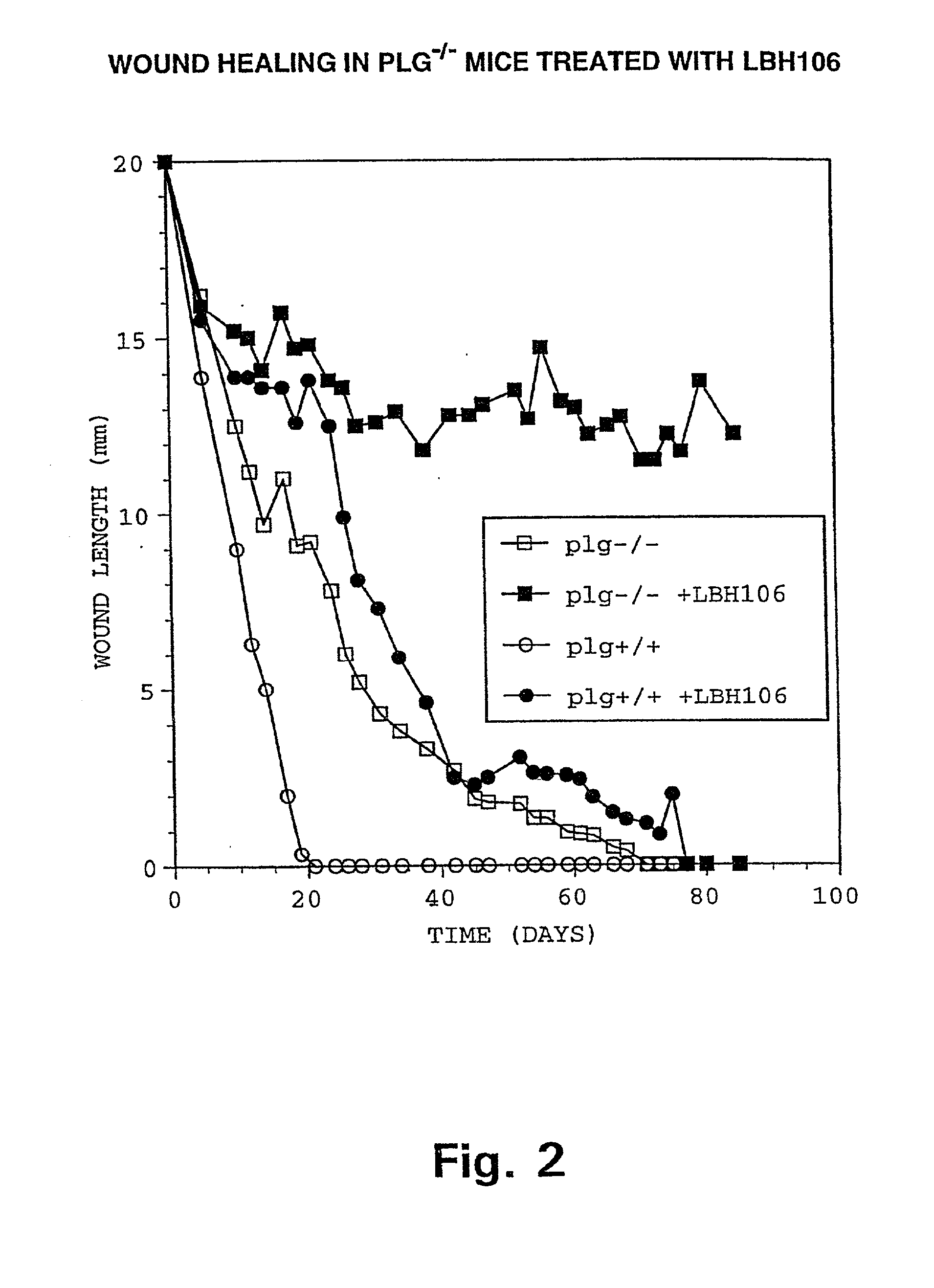
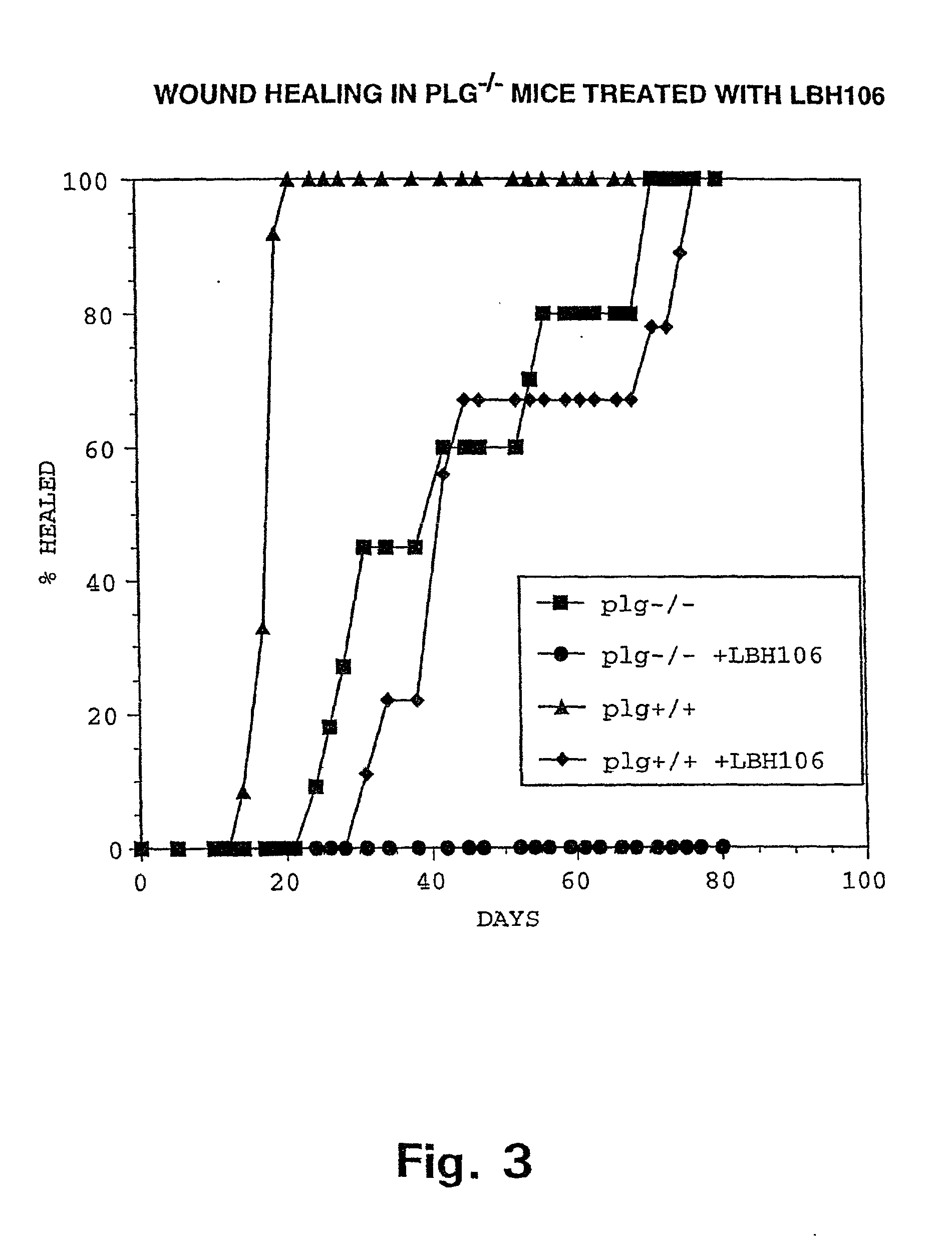
The present invention provides methods of improving the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of a bone matrix, e.g., a dermineralized bone matrix (DBM), by exposing the bone matrix to one or more treatments or conditions. In preferred embodiments the bone matrix is derived from human bone. The treatment or condition may alter the structure of the bone matrix and / or cleave one or more specific proteins. Cleavage may generate peptides or protein fragments that have osteoinductive, osteogenic, or chondrogenic activity. Preferred treatments include collagenase and various other proteases. The invention further provides improved bone and cartilage matrix compositions that have been prepared according to the inventive methods and methods of treatment using the compositions. The invention further provides methods of preparing, testing, and using the improved bone matrix compositions. Ona assay comprises exposing relatively undifferentiated mesenchymal cells to a bone matrix composition and measuring expression of a marker characteristic of osteoblast or chondrocyte lineage(s). Increased expression of the marker relative to the level of the marker in cells that have been exposed to a control matrix (e.g., an inactivated or untreated matrix) indicates that the treatment or condition increased the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of the bone matrix. Suitable cells include C2C12 cells. A suitable marker is alkaline phosphatase. The inventive methods increase the osteogenic and / or chondrogenic activity of human DBM when tested using this assay system.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104988124AHigh growth titerHigh biological propertiesViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesViral MarkersChick embryos
The invention discloses a genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain rescue and application. A built Newcastle disease virus reverse genetic operating platform is utilized for enabling NP protein of a G7 strain to miss 18 amino acids and conducting mutation on F-protein cleavage loci, and the highly-weak virulence and high-virus titer genotype VII Newcastle disease virus marker vaccine strain MG7-NPdelta18+Fmut is rescued through screening. The microbial preservation serial number is CCTCC NO: V201505. The marker vaccine strain has the biological characteristics of high growth titer and low virulence in chick embryos and is genetically stable. The immune protection test result shows that the marker vaccine strain is good in immunogenicity, capable of inducing high-level protective antibodies, and capable of completely protecting immunized chicken, can be used for preventing and controlling a currently-popular genotype VII Newcastle disease virus and lays the foundation of identifying vaccine immunity and wild virus infection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for selectively collecting N-terminal peptide fragment of protein
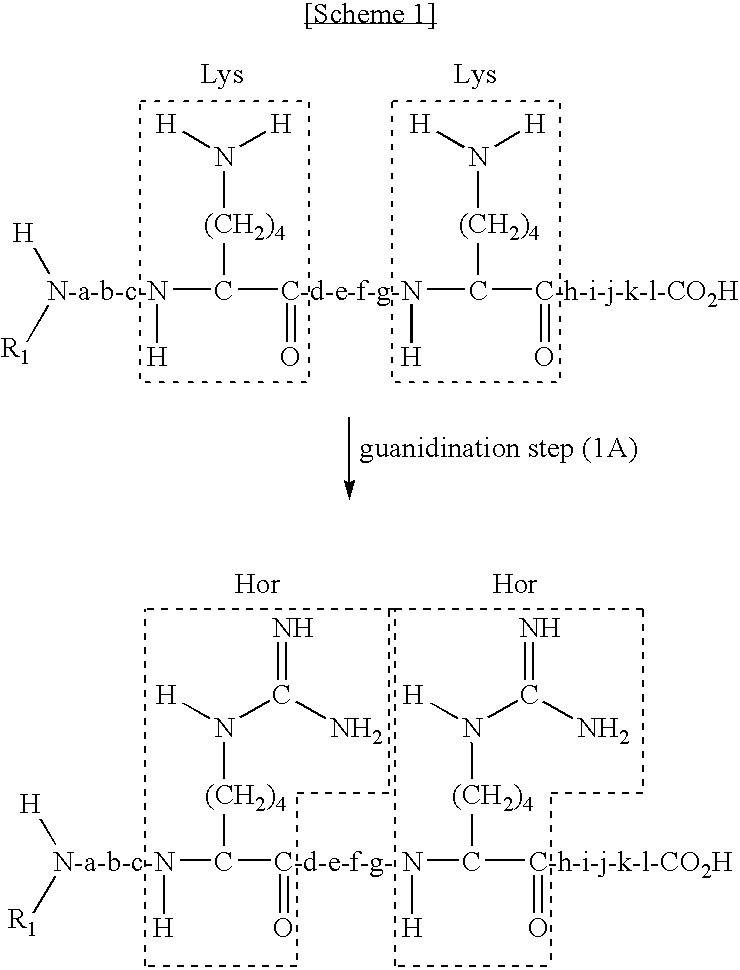
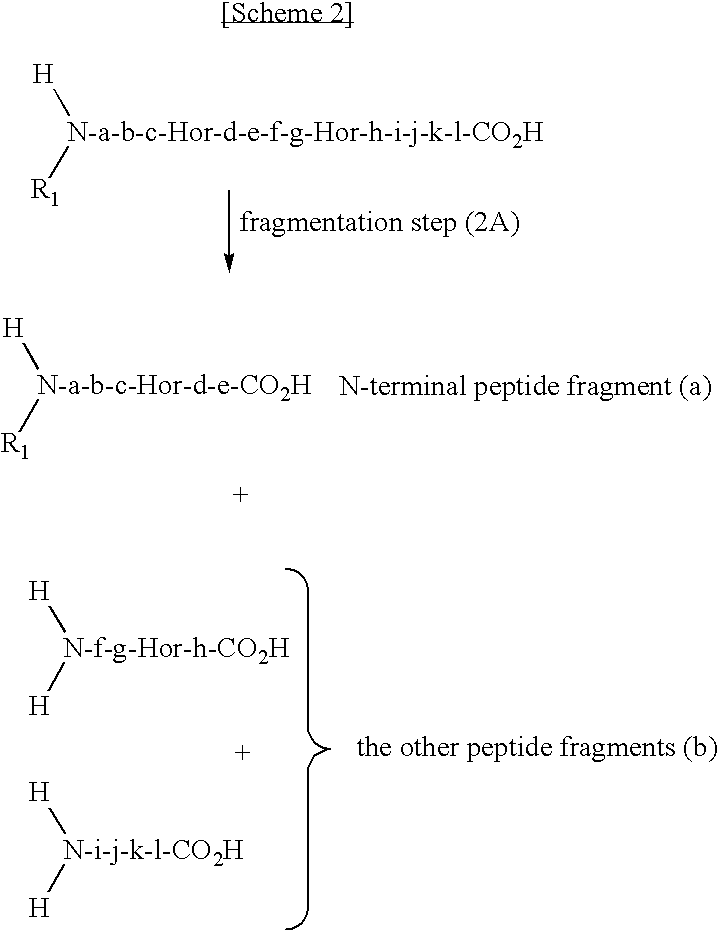
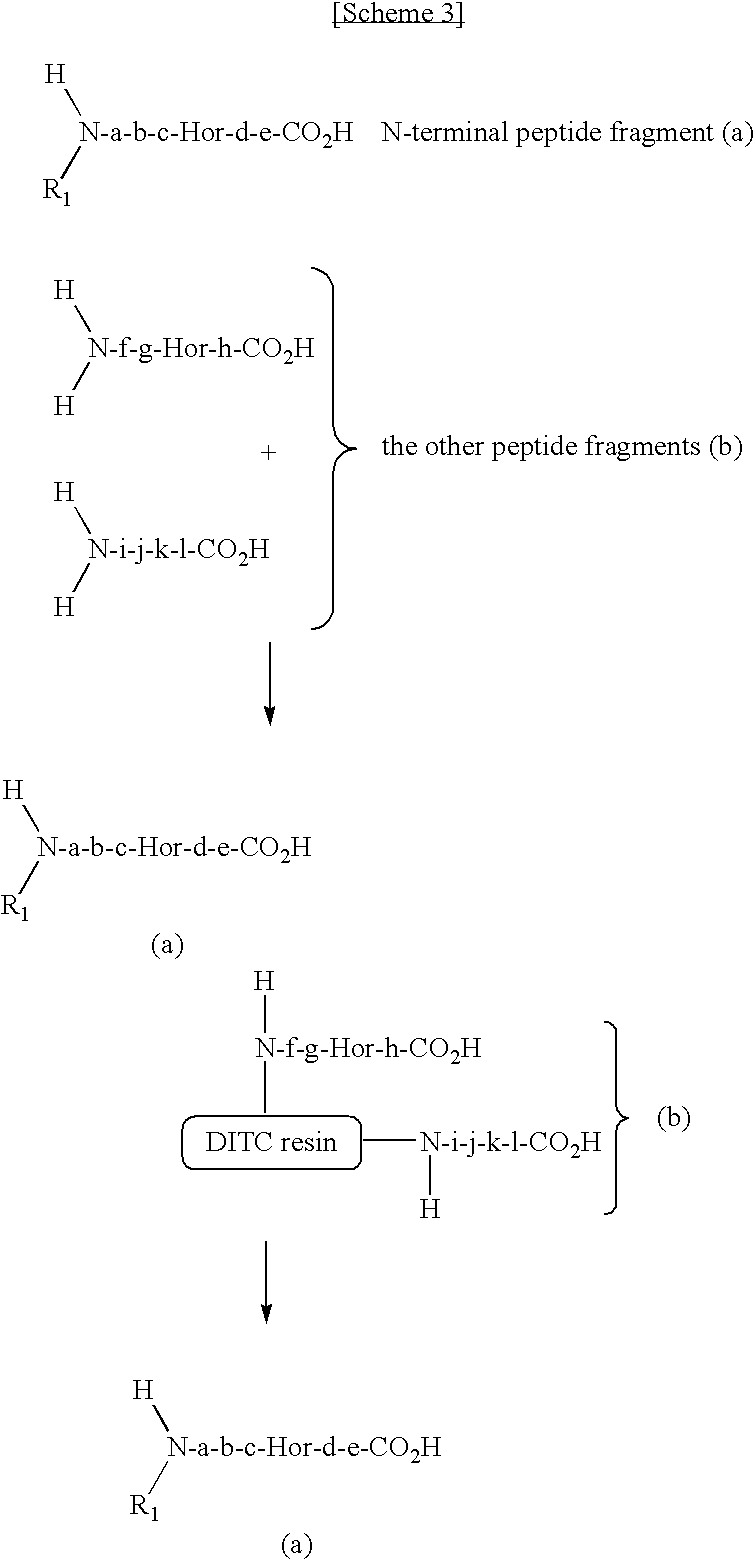
The present invention provides a method for selectively collecting the N-terminal peptide fragments of a protein of interest whether or not the protein of interest is modified on the N-terminus. A method for selectively collecting the N-terminal peptide fragment of a protein, comprising: a protection step (1) of protecting side chain-amino groups of amino acid residues containing side chain-amino groups of a protein of interest to obtain a protected protein protected on the side chain-amino groups; a fragmentation step (2) of cleaving the protected protein into one N-terminal peptide fragment (a) containing the N-terminus of the peptide of interest and one or more of peptide fragments (b) other than the N-terminal peptide fragment (a); and a separation step (3) of separating the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) from the other peptide fragments (b) by selectively eluting the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) based on the difference in their reactivity or affinity to substrate, wherein the selective elution is achieved either by allowing the other peptide fragments (b) to bind to the substrate while allowing the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) to elute, or by allowing the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) to bind to the substrate while allowing the other peptide fragments (b) to elute and subsequently eluting the bound N-terminal peptide fragment (a).
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
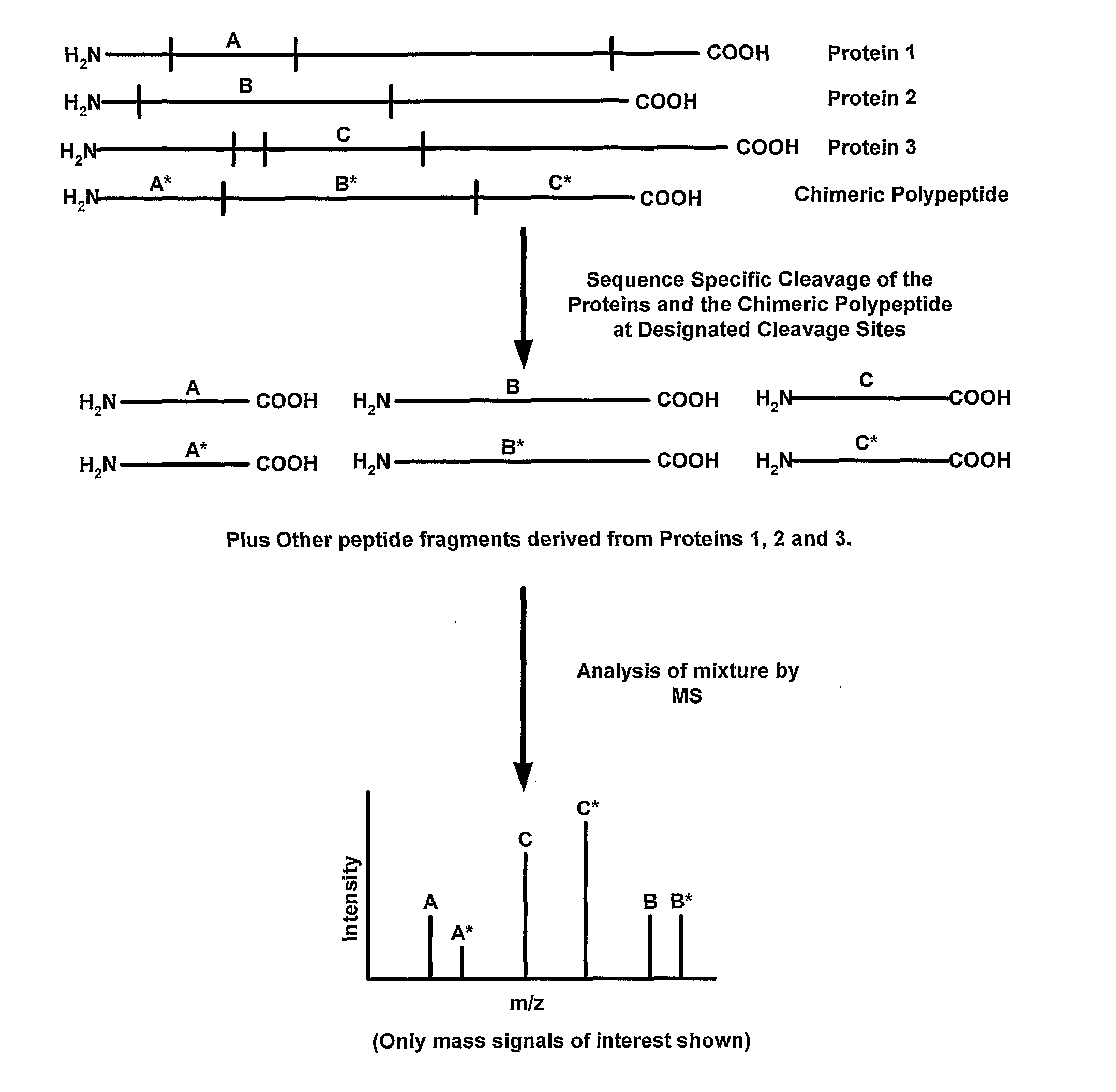
Methods For Making And Using Mass Tag Standards For Quantitative Proteomics
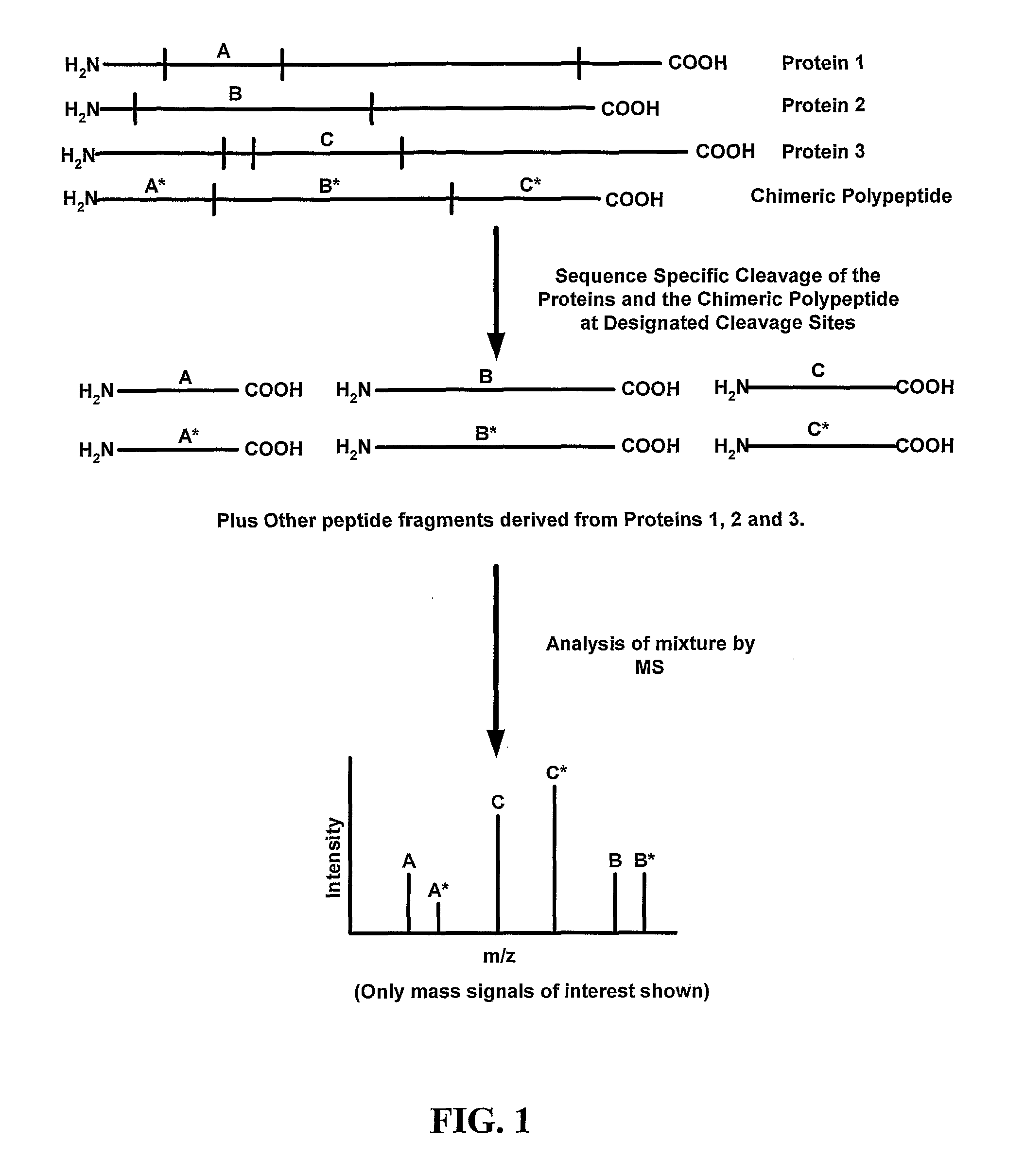
InactiveUS20080044857A1Efficient productionMonitor the efficiency of the protein cleavage stepPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesMass spectrometricTrypsin
Disclosed are methods for producing peptide standards for quantitative proteomics. In one disclosed embodiment, chimeric polypeptides that are a combination of mass tags for multiple proteins are expressed in a host cell that is grown on an isotopically-altered medium. The mass tags in the chimeric polypeptide are separated by specific cleavage sites (such as trypsin cleavage sites), and upon treatment with an appropriate protein cleavage agent (such as trypsin) the constituent peptide standards are released. Methods of mass spectrometric analysis that employ the disclosed chimeric polypeptides (or the peptide standards liberated therefrom) also are disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Inhibition of invasive remodelling
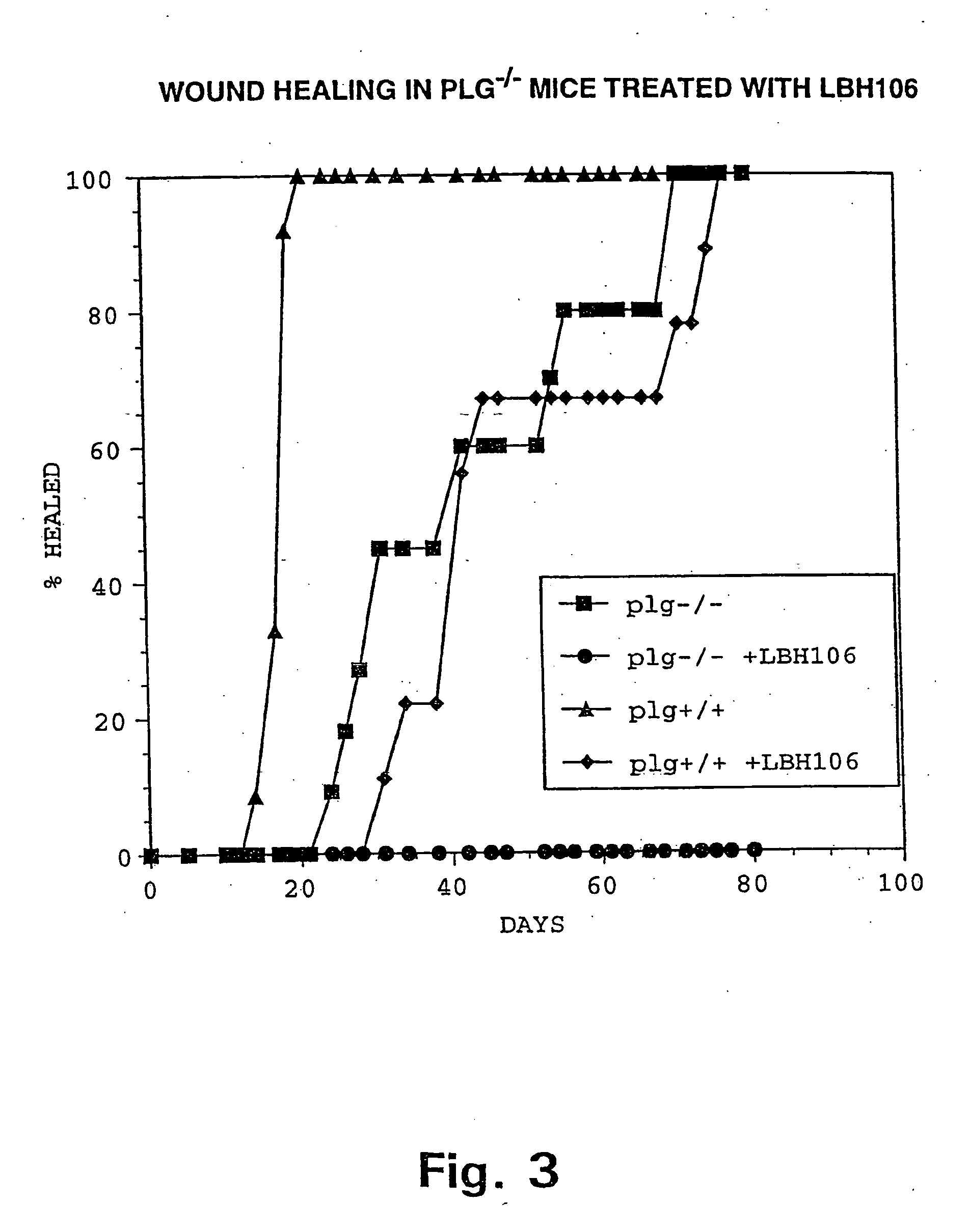
InactiveUS20020099004A1Blocks invasive tissue remodellingImprove survivalFibrinogenPeptide/protein ingredientsProteolytic enzymesCell biology
Owner:LUND LEIF ROGE +6
Soybean peptide for promoting lactobacillus proliferation and improving lactobacillus survivability as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103194512AHigh yieldModerate degree of denaturationMilk preparationFermentationSurvivabilityAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a soybean peptide for promoting lactobacillus proliferation and improving lactobacillus survivability as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of deep processing of soybean proteins. The preparation method comprises the following steps: extruding soybean protein at high temperature; damaging a tertiary structure for maintaining the protein through shearing and friction dual functions, thereby enabling the hydrophobic group of the soybean protein to spread; cutting the denatured protein into small molecule peptides by utilizing protease; and performing centrifugal separation, filtering, drying and the like to obtain the soybean peptide. The yield of the soybean peptide reaches up to 72%; and the soybean peptide is low in production cost and can be used for effectively promoting the proliferation of lactobacillus, shortening the fermentation time and improving the survivability of the lactobacillus in a storage period. In addition, the soybean peptide can be applied to fermented dairy products or other foods. Therefore, the soybean peptide is a health food ingredient with high quality.
Owner:广州合诚实业有限公司
Methods for assaying protein-protein interactions
The invention relates, in part, to methods for detecting, monitoring, measuring or assessing an interaction between at least two proteins. The invention also relates, in part, to methods for determining if a test compound, or a mix of compounds, modulates an interaction between at least two proteins. In some embodiments, determination is made possible via the use of two recombinant molecules, e.g., one of which contains a first protein cleavage site for a proteolytic molecules, and an activator of a gene. A second recombinant molecule may include a second protein and the proteolytic molecule. Various other formats are provided by the invention. In some embodiments, if the test compound binds to the first protein, a reaction is initiated whereby the activator is cleaved, and activates a reporter gene.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
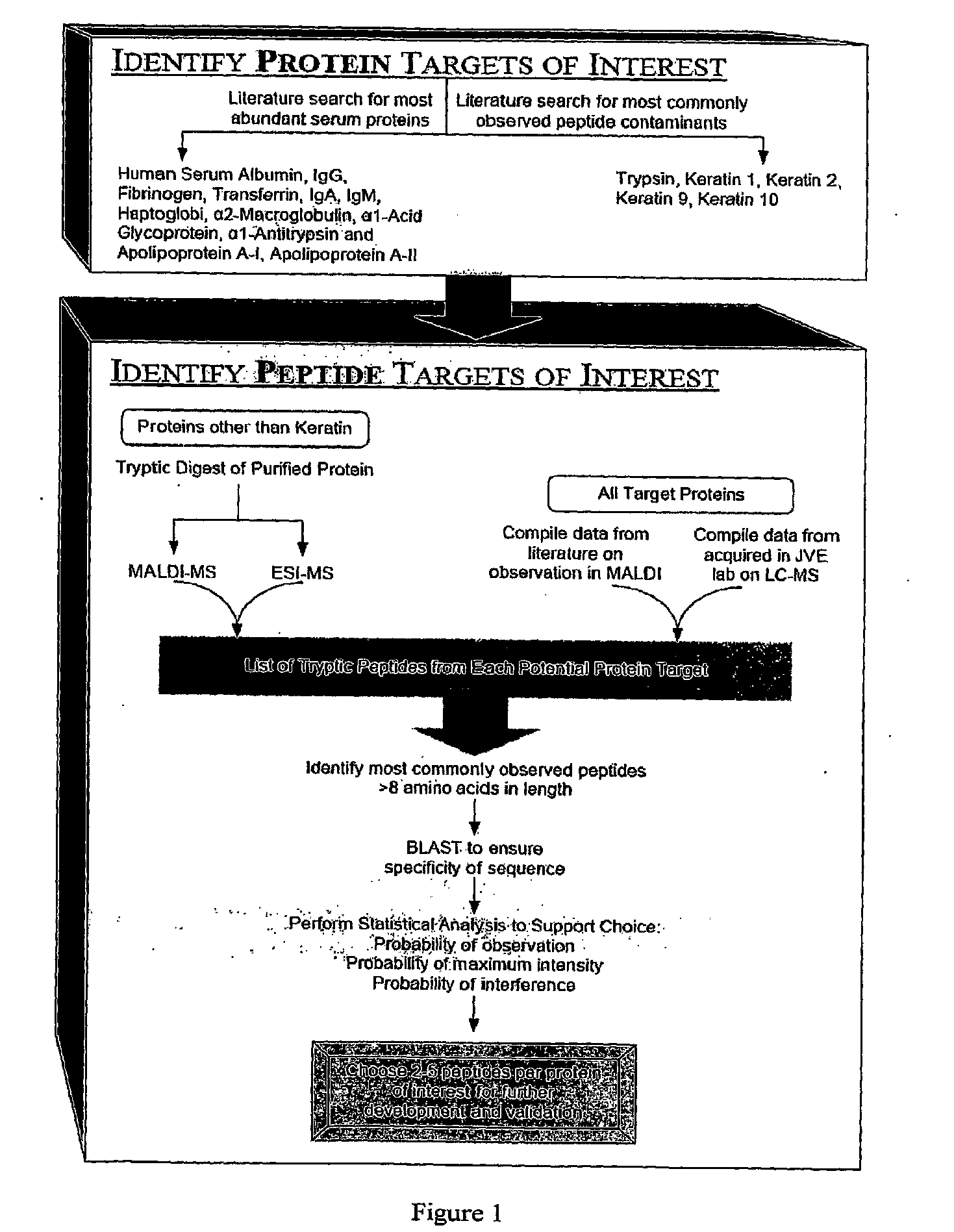
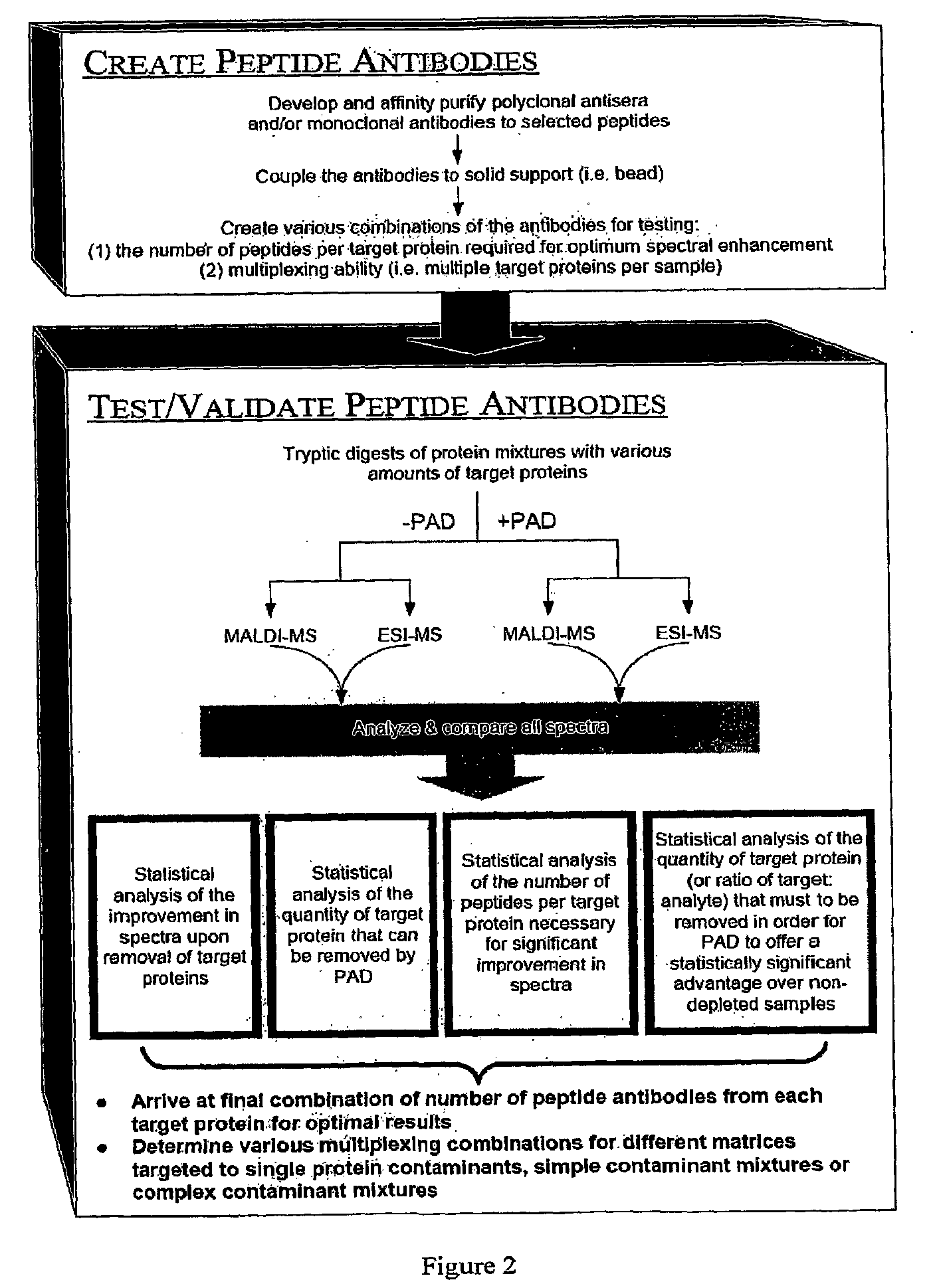
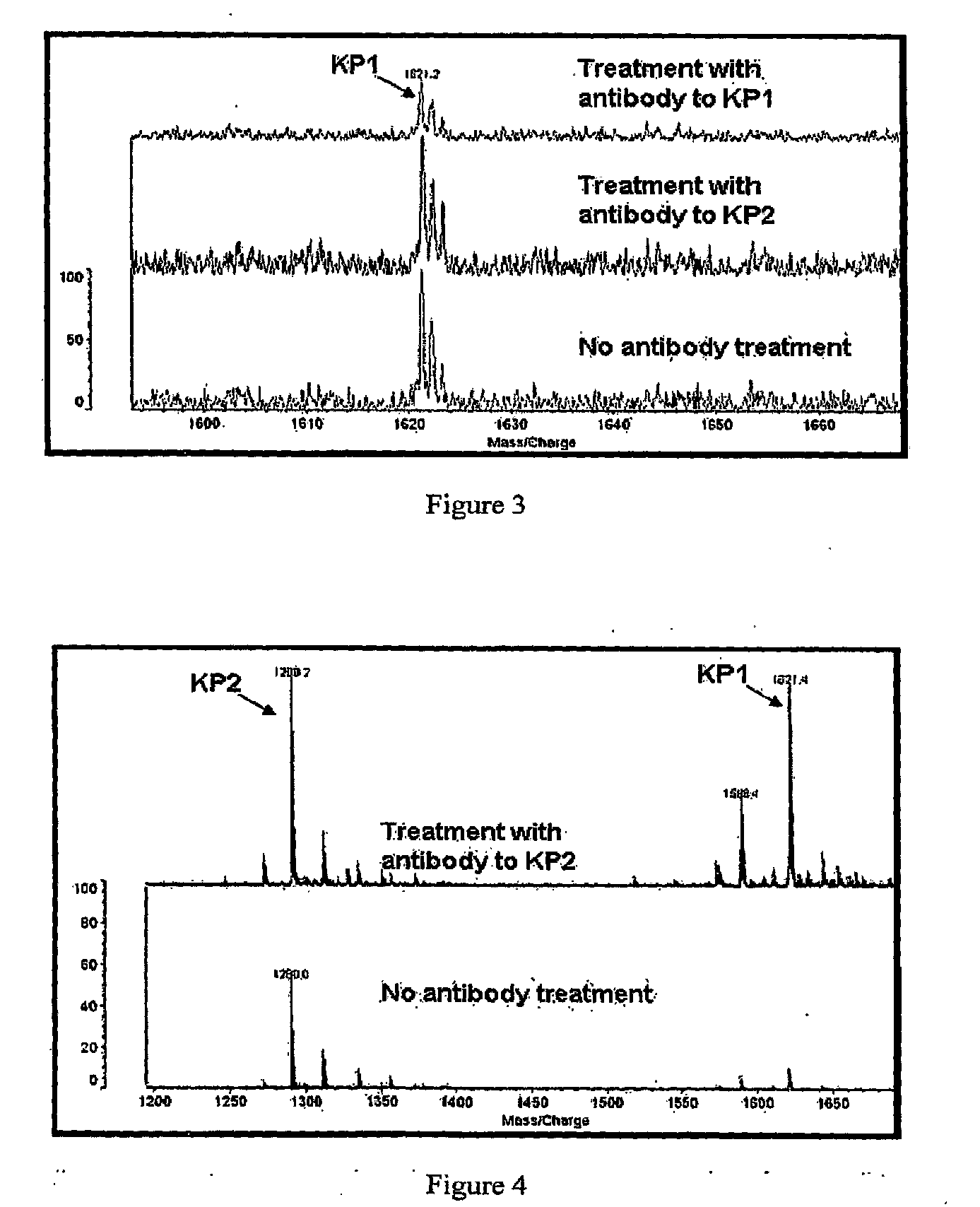
Peptide antibody depletion and its application to mass spectrometry sample preparation
ActiveUS20100047812A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsProtein targetMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
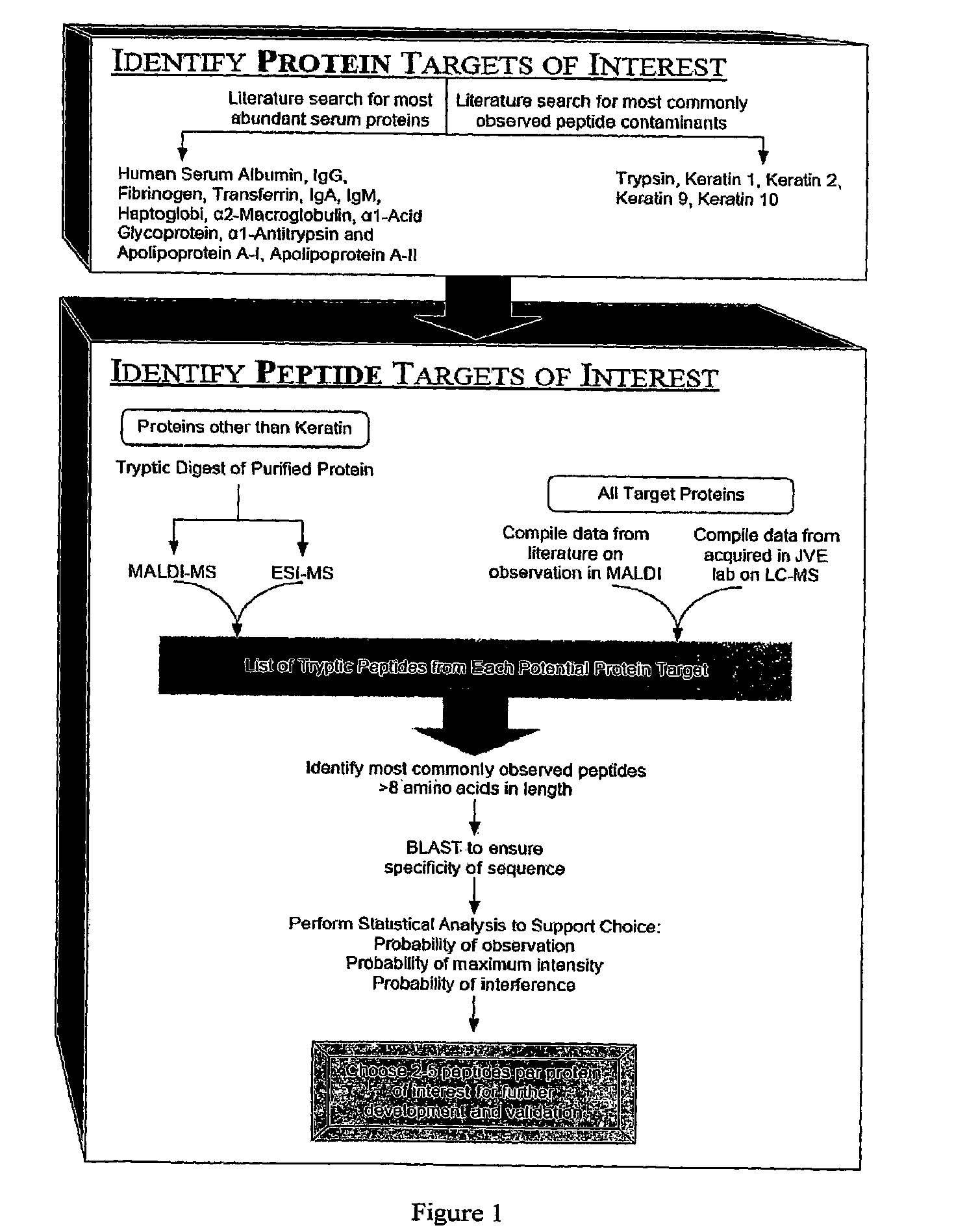
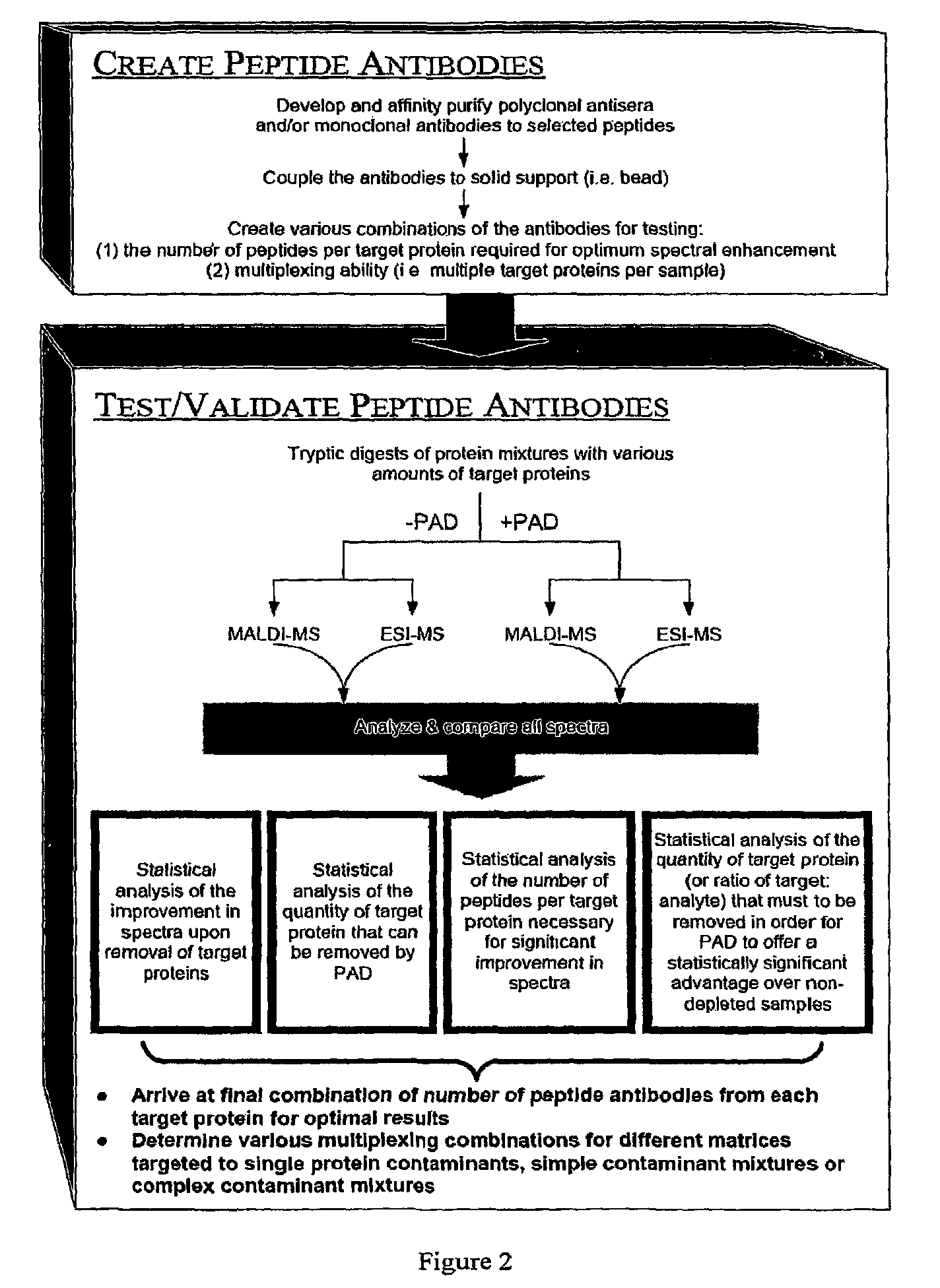
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for pre-processing a sample for mass spectral analysis, comprising cleaving proteins in the sample to peptides and immunodepleting highly abundant and / or well-ionizing and / or proteotypic peptides from the sample. Also described are methods for identifying well-ionizing peptides for use in this and other methods: analytic (diagnostic) methods using antibodies against highly ionizable peptides from a protein target of interest; and compositions kits and devices comprising antibodies of the invention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
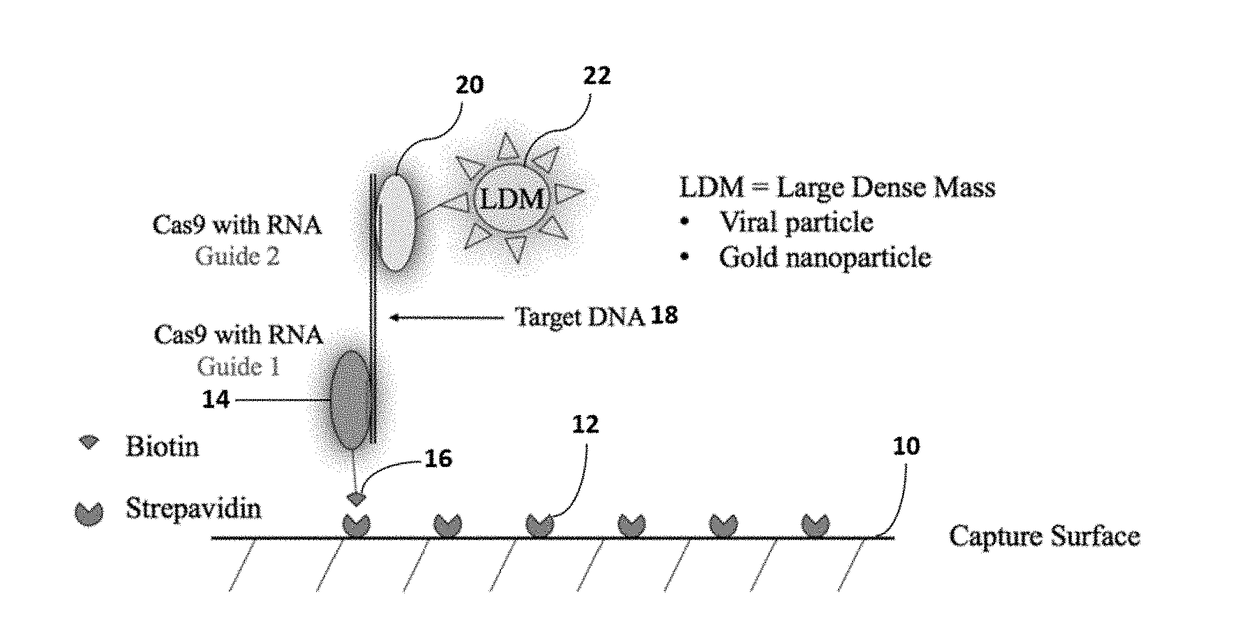
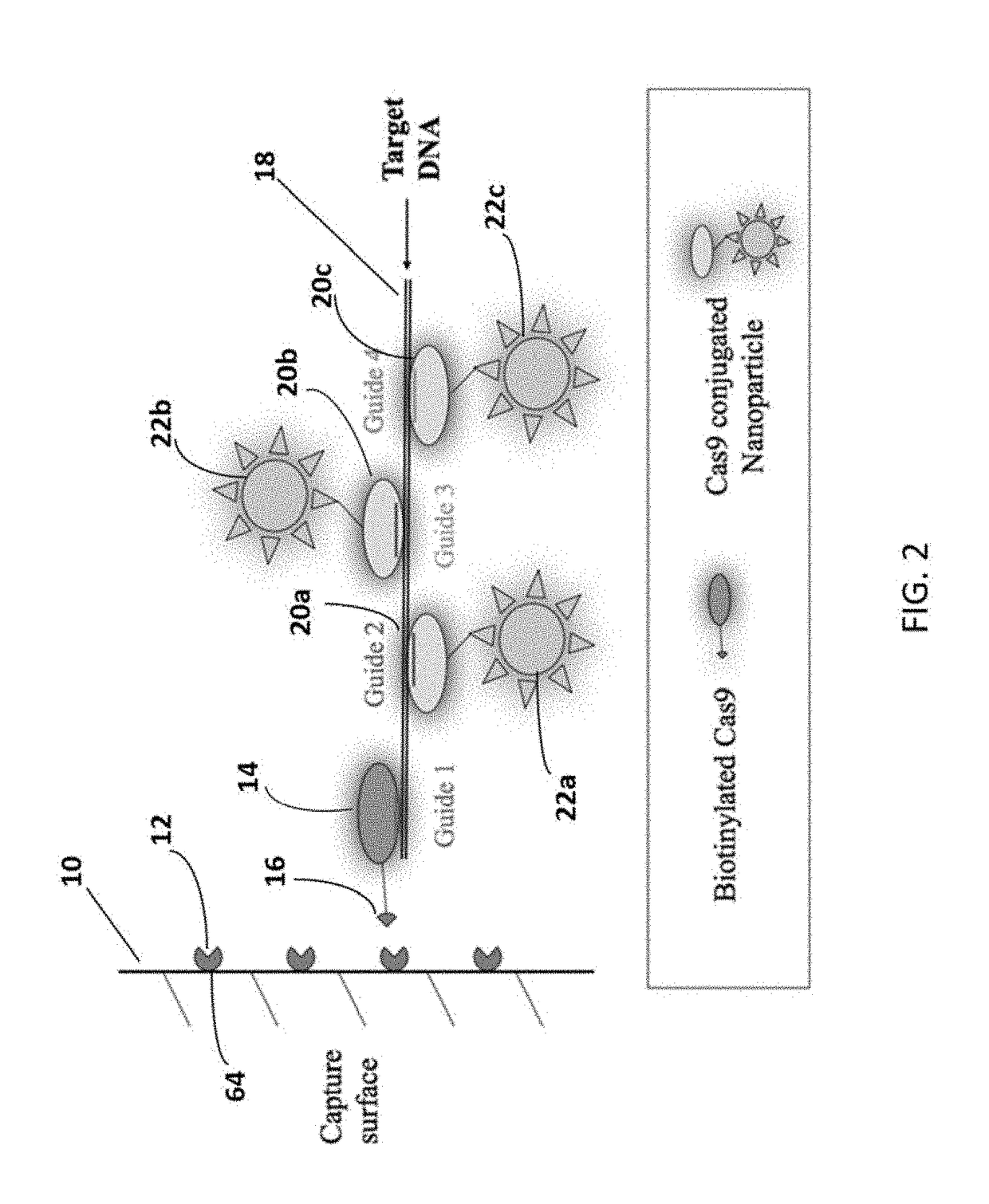
Method for isothermal DNA detection using a modified crispr/cas system and the apparatus for detection by surface acoustic waves for gene editing
InactiveUS20180334697A1Improve LODQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSingle electronAnalyte
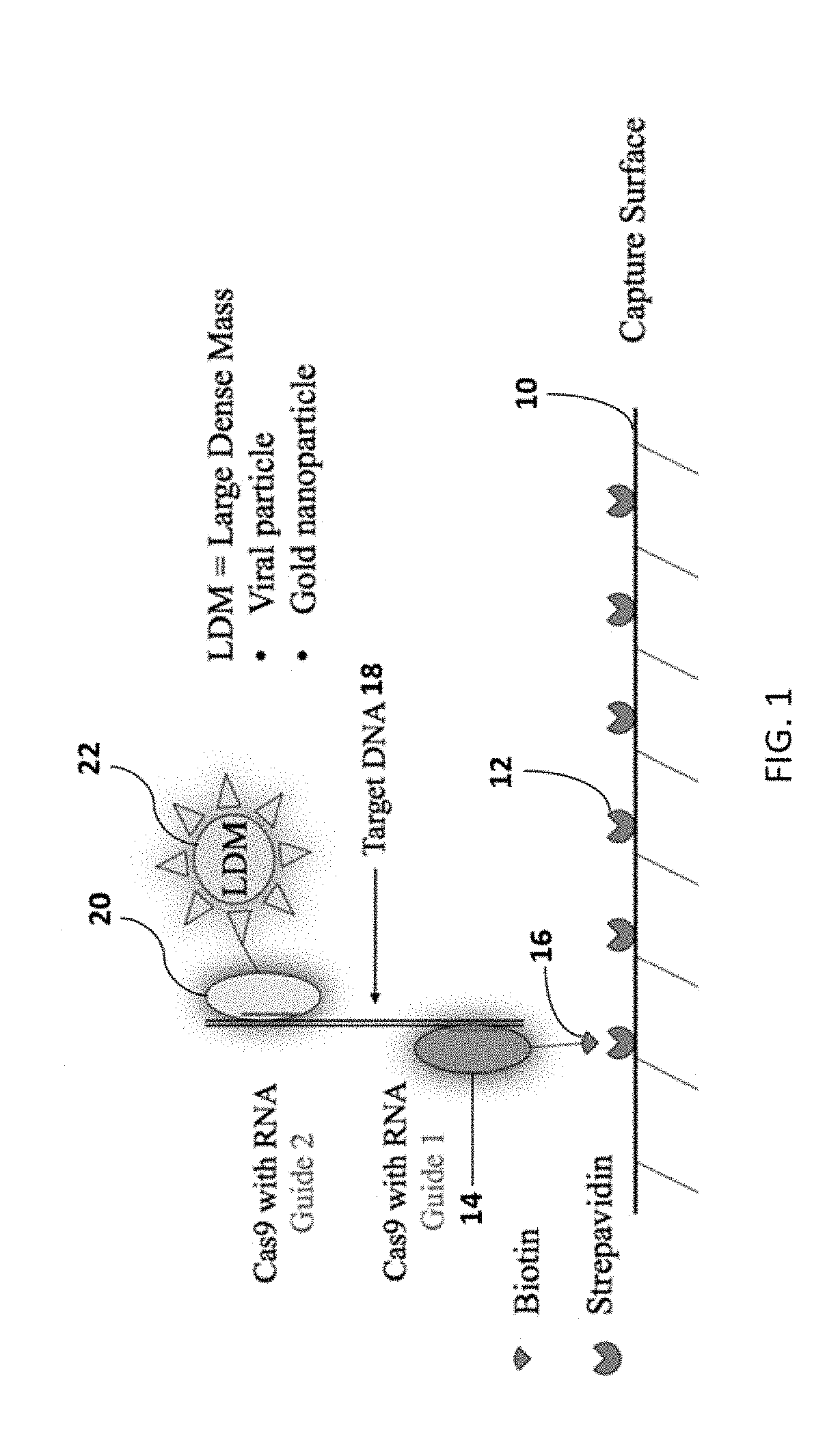
A method of reducing the limit of detection in a surface acoustic wave sensor (SAW) includes the steps of: attaching a plurality of DNA segments to a detection surface of a SAW; performing a CRISPR / Cas9 preparation of the DNA segments to cut and splice a selected protein into at least one of a plurality of the DNA segments; conjugating a nanoparticle to the selected protein; and measuring the number of DNA segments with conjugated nanoparticles using a surface acoustic wave sensor (SAW). The nanoparticle may be modified to form a single electron transistor (SET) which generates a detectable signal in response to RF or ultrasonic excitation which is indicative of binding of the corresponding nanoparticle to a selected target analyte.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
Method for designing peptides
InactiveUS20060240510A1Potent inhibitorImprove solubilityBacteriaSugar derivativesInteinRecombinant peptide
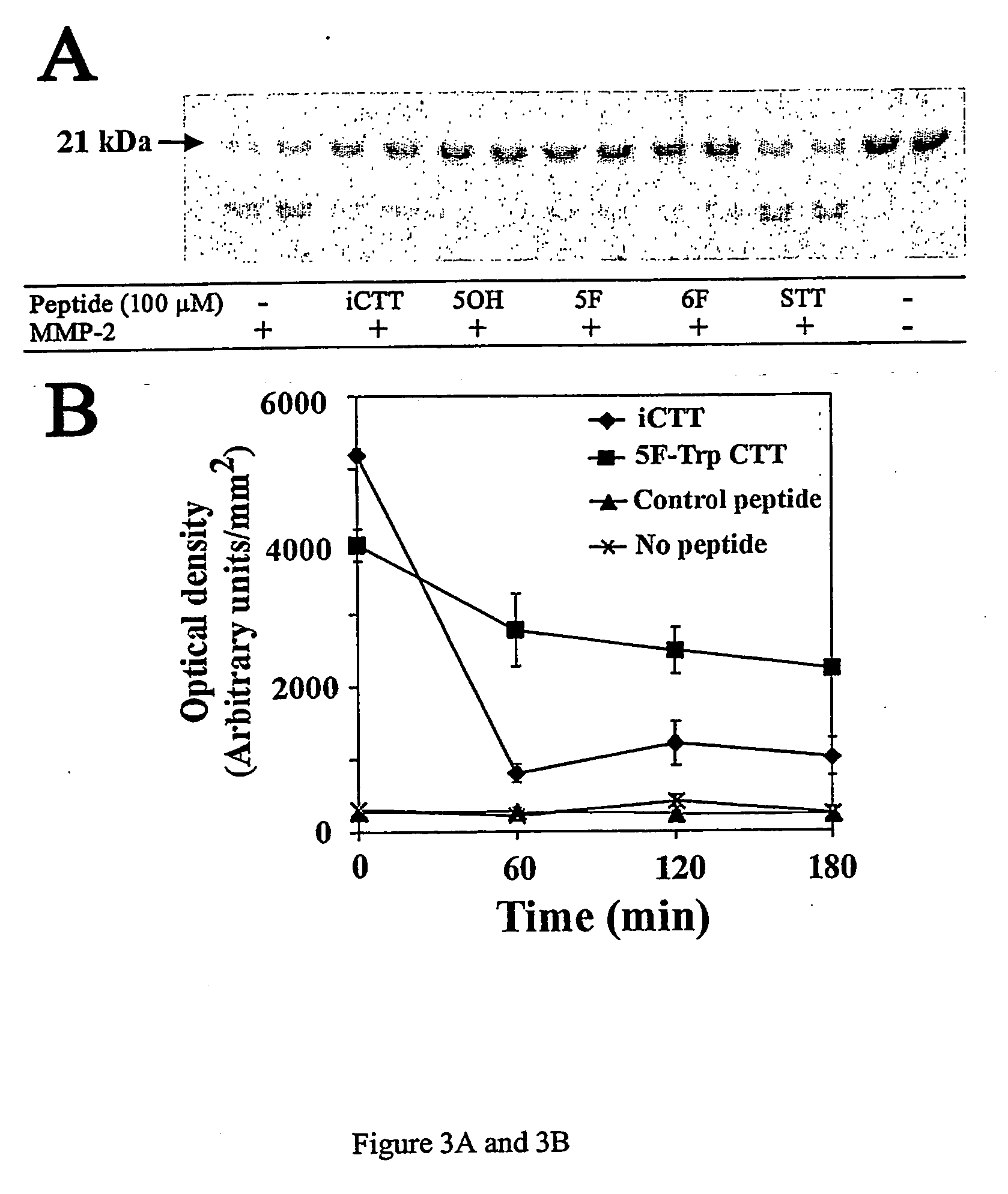
The present invention relates to genetic engineering and; in specific, to design, generation, and modification of recombinant peptides using a combination of phage display and intein-mediated protein cleavage reaction.
Owner:KARYON CTT
Macromolecule detection
InactiveUS20030175804A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptide preparation methodsAMINO BASELysine residue
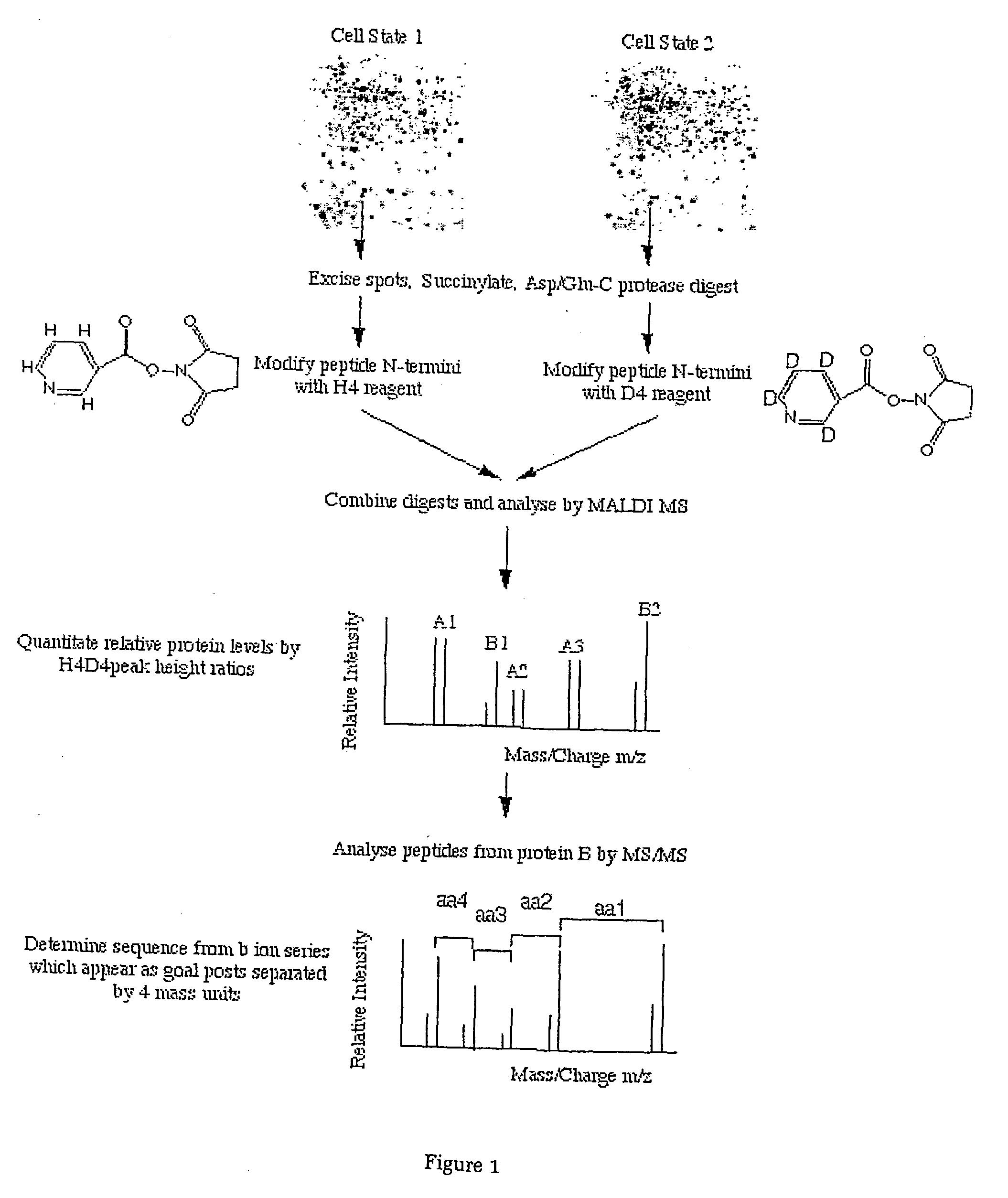
A method is provided of labelling a protein, which method comprises the steps of (a) treating the protein with a protecting agent so as to block epsilon amino acid groups present on lysines residues of the protein, (b) cleaving the protein into a peptide mixture; and (c) treating the peptide mixture with a labelled agent which binds to N-terminal amino acids of the peptides. The method may be used in differential expression detection methods for determining differences in protein expression.
Owner:PROTEOME SYST LTD
Method for immobilizing human source arginase-1 through surface display
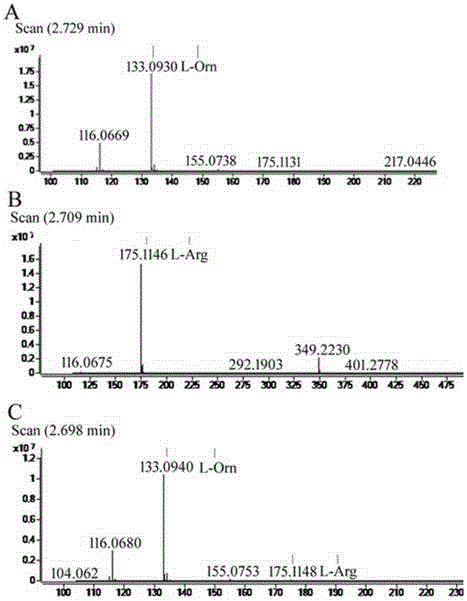
ActiveCN105713888AImmobilizationImprove display efficiencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionSurface displayL-Ornithine
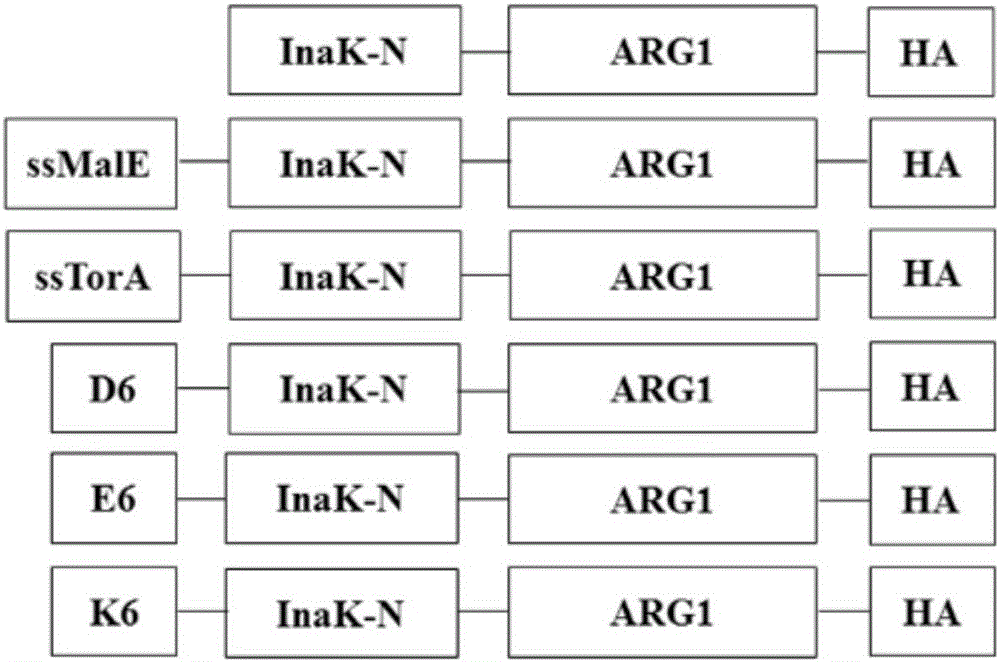
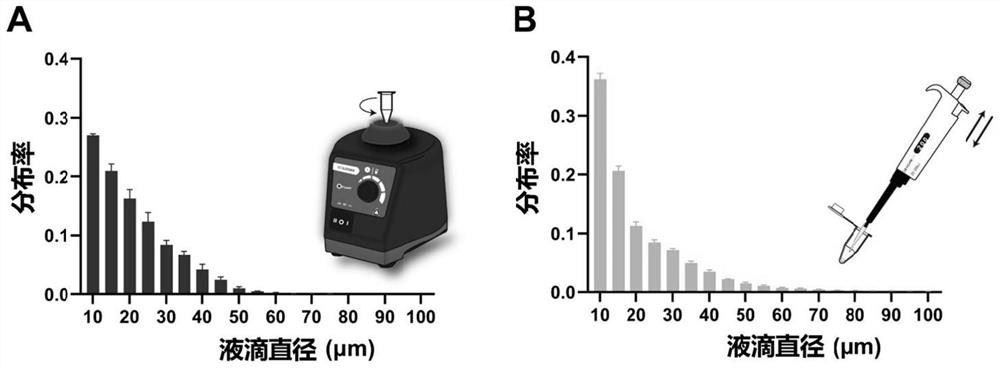
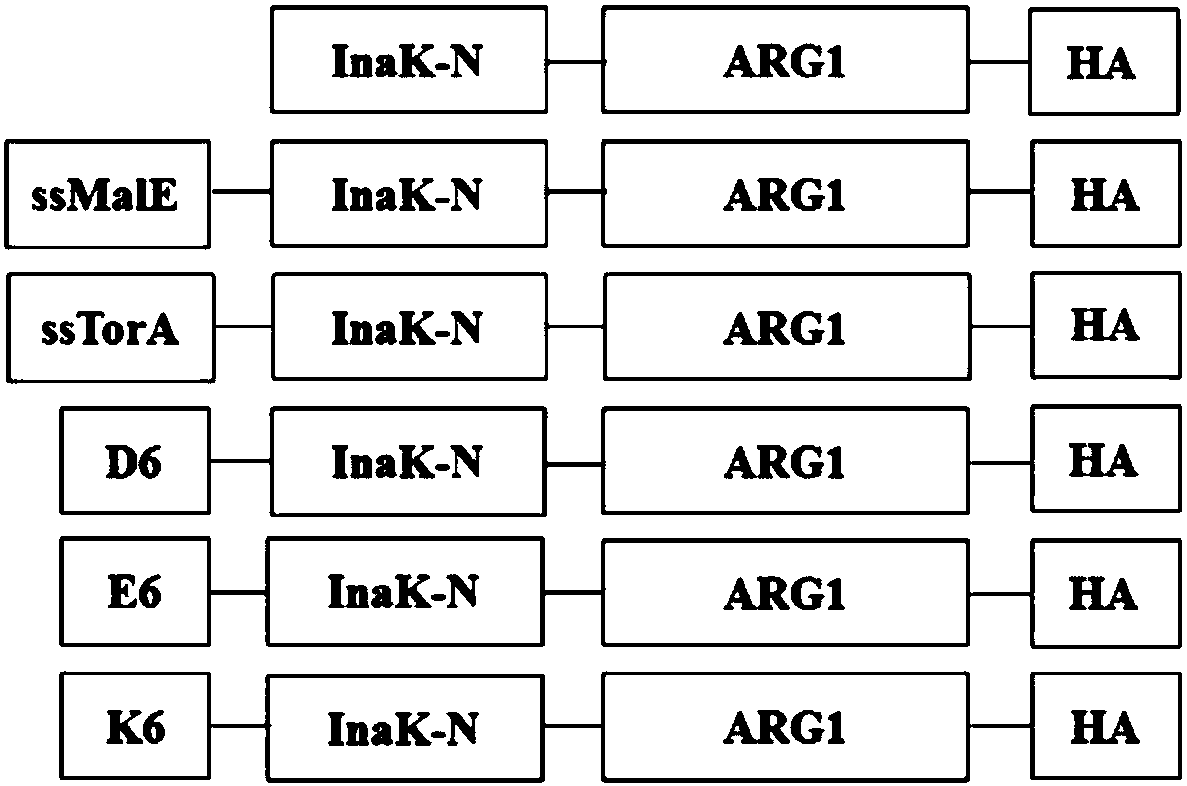
The invention discloses a method for immobilizing human source arginase-1 through surface display. The method comprises the steps of adding signal peptide and charged polypeptide to the amino terminal of a protein cleavage variant (InaK-N) formed on an ice core, fusing human source arginase-1 into the carboxyl terminal, and designing an HA label at the carboxyl terminal; constructing various recombinant plasmids to convert competent escherichia coli cells, so that different genetic engineering strains are obtained; conducting shake-flask culture on the strains; detecting the display efficiency and enzyme activity of human source arginase-1; selecting the strain with the highest enzyme activity for mass culture, conducting efficient L-arginine conversion, and synthesizing L-ornithine. Human source arginase-1 fused in the protein cleavage variant formed on the ice core is effectively displayed on the surface of an escherichia coli cell, so that human source arginase-1 is immobilized. Compared with an original ice core protein display system, the method has the advantage that the display efficiency and enzyme activity of human source arginase-1 are improved remarkably. Compared with a chitin immobilizing method, the method has the advantages that cost is reduced, process is shortened, and purification steps are simplified.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Peptide antibody depletion and its application to mass spectrometry sample preparation
ActiveUS8232066B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryNatural abundance
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for pre-processing a sample for mass spectral analysis, comprising cleaving proteins in the sample to peptides and immunodepleting highly abundant and / or well-ionizing and / or proteotypic peptides from the sample. Also described are methods for identifying well-ionizing peptides for use in this and other methods; analytic (diagnostic) methods using antibodies against highly ionizable peptides from a protein target of interest; and compositions kits and devices comprising antibodies of the invention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
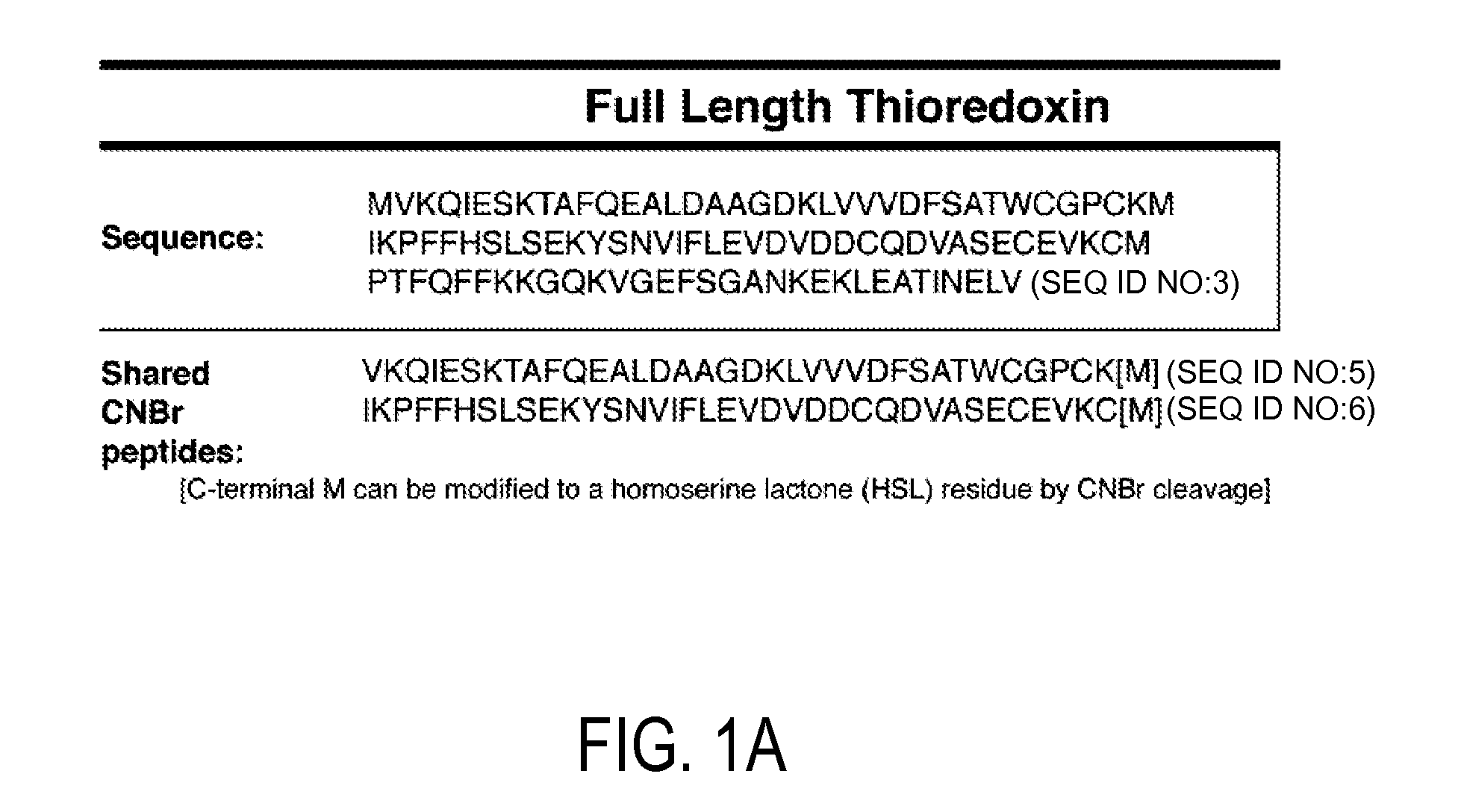
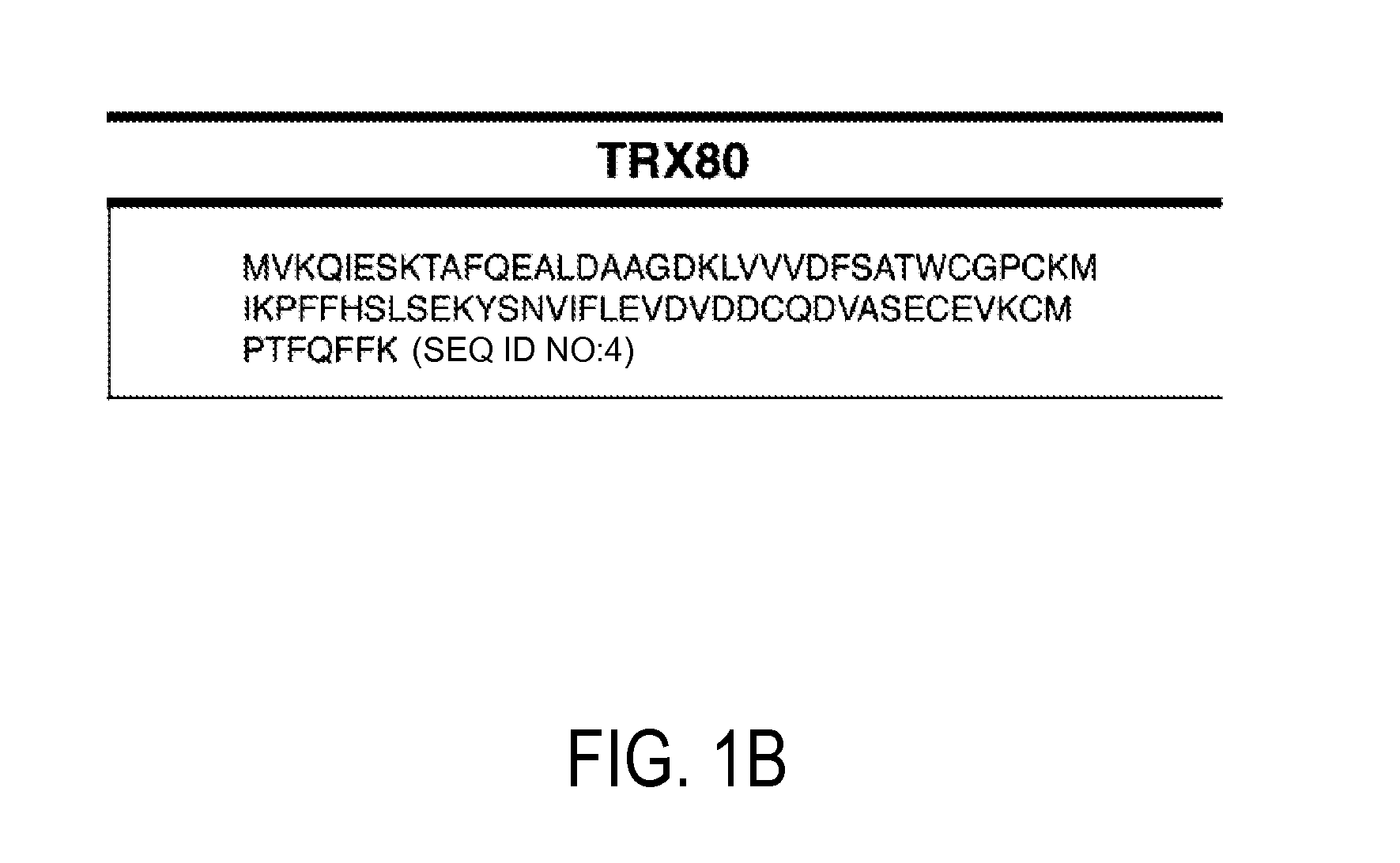
Detection and quantitation of full-length thioredoxin (TRX) and truncated thioredoxin (trx 80) in complex samples
ActiveUS20110143379A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSmall peptideADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for detecting a full-length protein and a truncated form (e.g., a naturally occurring cleavage product) thereof, in a sample, comprisingoptionally denaturing and reducing proteins in the sample,cleaving the proteins into smaller peptides, anddetecting a unique peptide identifier for the full-length protein and / or a unique peptide identifier for the truncated protein, in the sample.In one embodiment of the invention, the full-length protein is thioredoxin (TRX), and the truncated form thereof is its biologically active, C-terminal truncated, 10 kDa cleavage product, TRX 80.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and Materials for Use in Diagnosing Viral Myocarditis
InactiveUS20070292345A1Improvement in diagnostic techniqueSensitive highGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityEnteroviral infections
The invention consists of assay methods, assay kits and antibodies for detecting the polypeptide fragments of dystrophin protein cleavage by enteroviral protease 2A as a result of an enteroviral infection in the heart. The presence of dystrophin cleavage products in the myocytes or blood of a subject is diagnostic for enteroviral infection and myocarditis resulting therefrom.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and materials for use in diagnosing viral myocarditis
InactiveUS7867476B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnteroviral infectionsViral Myocarditis
The invention consists of assay methods, assay kits and antibodies for detecting the polypeptide fragments of dystrophin protein cleavage by enteroviral protease 2A as a result of an enteroviral infection in the heart. The presence of dystrophin cleavage products in the myocytes or blood of a subject is diagnostic for enteroviral infection and myocarditis resulting therefrom.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
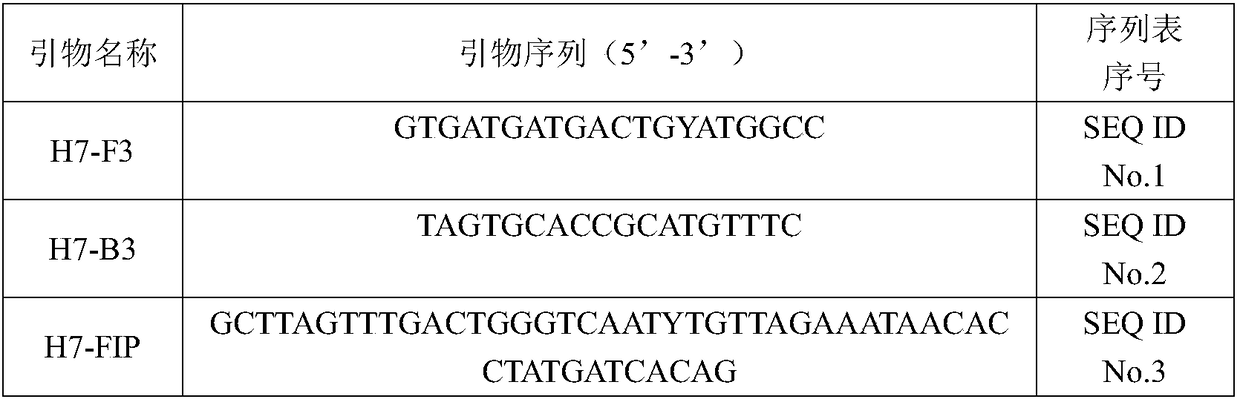
RT-LAMP detection primer group and kit for identifying H7 subtype HPAIV and LPAIV and application thereof
PendingCN108384897ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionTyping
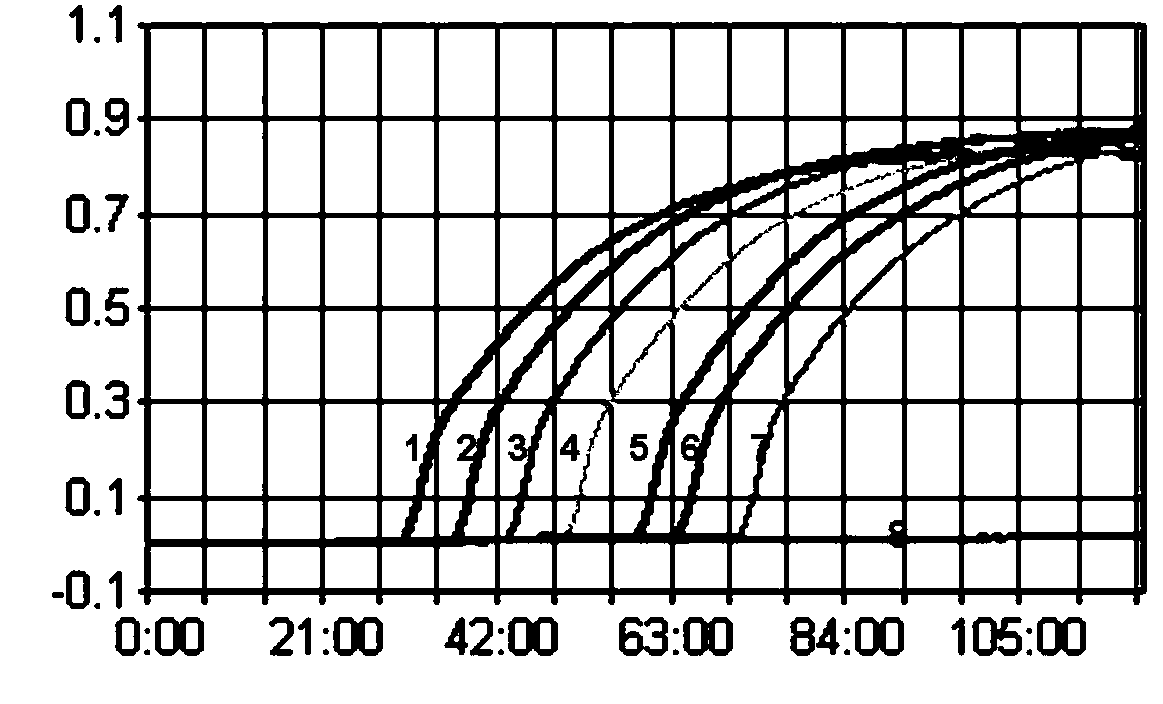
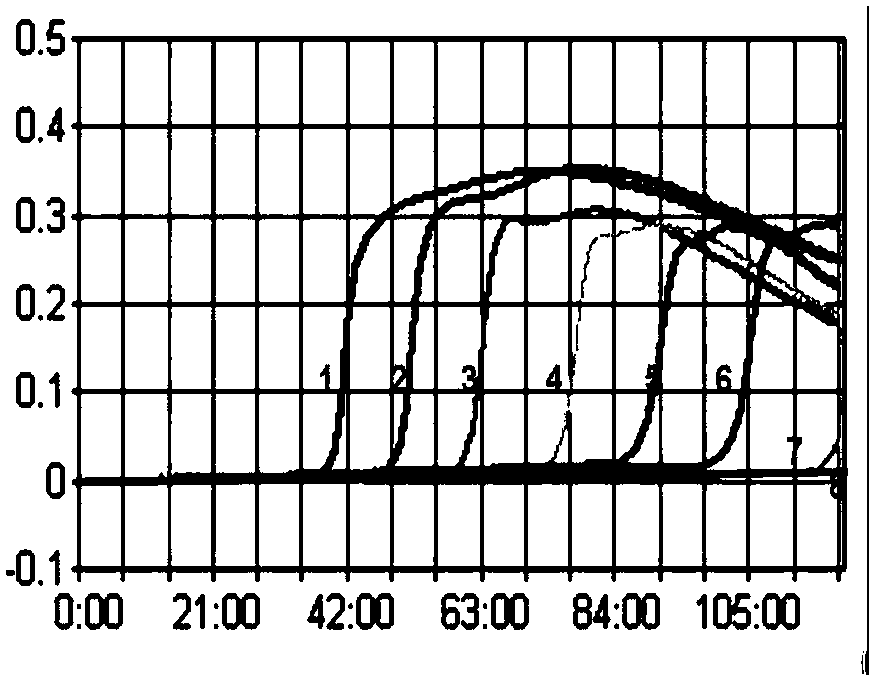
The invention belongs to the technical field of avian virus detection, and particularly relates to an RT-LAMP detection primer group and kit for identifying H7 subtype HPAIV and LPAIV and an application thereof. According to the RT-LAMP detection primer group and kit for identifying the H7 subtype HPAIV and LPAIV and the application thereof, an LAMP nucleic acid detection technology serves as a basis, amino acid sequences of an H7 subtype AIV HA protein cleavage sites are fully taken into account, two detection methods of universal LAMP and identification LAMP are specifically established. Theuniversal LAMP can simultaneously detect H7 subtype HPAIV and LPAIV, the identification LAMP can only detect H7 subtype LPAIV, and a new method for preliminary typing of H7 subtype AIV is provided. By optimizing each reaction condition, the detection method for H7 subtype avian influenza and H7 subtype attenuated strains is established, and the specificity and sensitivity experimental verifications are carried out on the detection method. By reacting for two hours at 62 DEG C in a turbidity meter, the H7 subtype avian influenza and the H7 subtype attenuated strains can be specifically identified and do not have cross reaction with other subtype avian influenza, and at least 10 copies of viral nucleic acids per microliter can be detected.
Owner:防城港市动物疫病预防控制中心
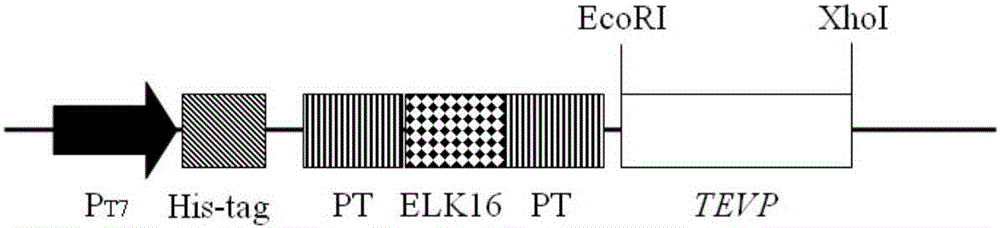
Tobacco etch virus protease active inclusion body as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105886489AFold preciselyHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorInclusion bodiesBiotechnology research
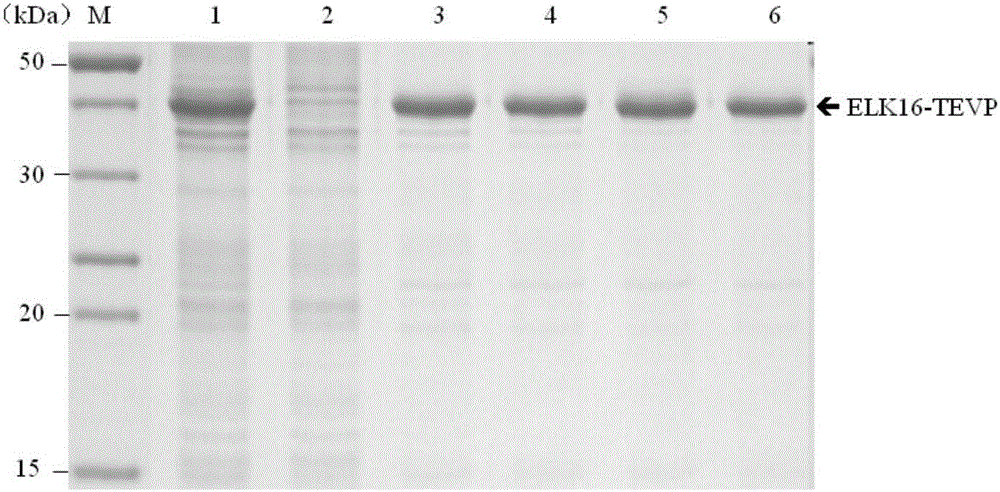
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology research, and particularly relates to a TEVP (Tobacco Etch Virus Protease) active inclusion body as well as a preparation method thereof and application thereof in the preparation of a recombinant protein. The TEVP active inclusion body consists of an ELK16 self-polymeric peptide and TEVP that are separated by two PT connectors. The preparation method of the TEVP active inclusion body comprises the steps of an expression vector construction, an active inclusion body expression and purification, recombinant protein cleavage and target protein recovery. Compared with existing TEVP, the TEVP active inclusion body proviced by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation, easiness for being removed from an end product, low cost and the like, and can be applied to prepare various recombinant proteins.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Rothia subtilisins, s8a family proteases, as therapeutic enzymes for application in gluten-intolerance disorders
ActiveUS20190040375A1Improve clinical symptomAlleviate symptomPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidasesPeptide bondCoeliac disease
There are gluten-degrading enzymes found in Rothia species bacteria that are subtilisins that belonging to the S8A family of serine protease family. The Rothia sp. derived subtilisin-like enzymes have the conserved catalytic triad composed of a Ser, His, and Asp residues that is characteristic of the serine protease family. The Rothia subtilisin enzymes are potent at cleaving proline-containing proteins, cleaving the second peptide bond after proline in the XPX1 motif, where X is any amino acid, P is proline and X1 is a hydrophobic amino acid, e.g. the XPQ motif, where Q is glutamine. Embodiments herein provide isolated enzyme compositions and formulations comprising subtilisins gluten-degrading enzyme from a Rothia species bacteria. Also provided herein are methods of treatment of celiac disease or a related disorder, treatment of gluten-containing foodstuff, degrading and / or detoxifying gluten comprising the subtilisins gluten-degrading enzyme and / or compositions.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
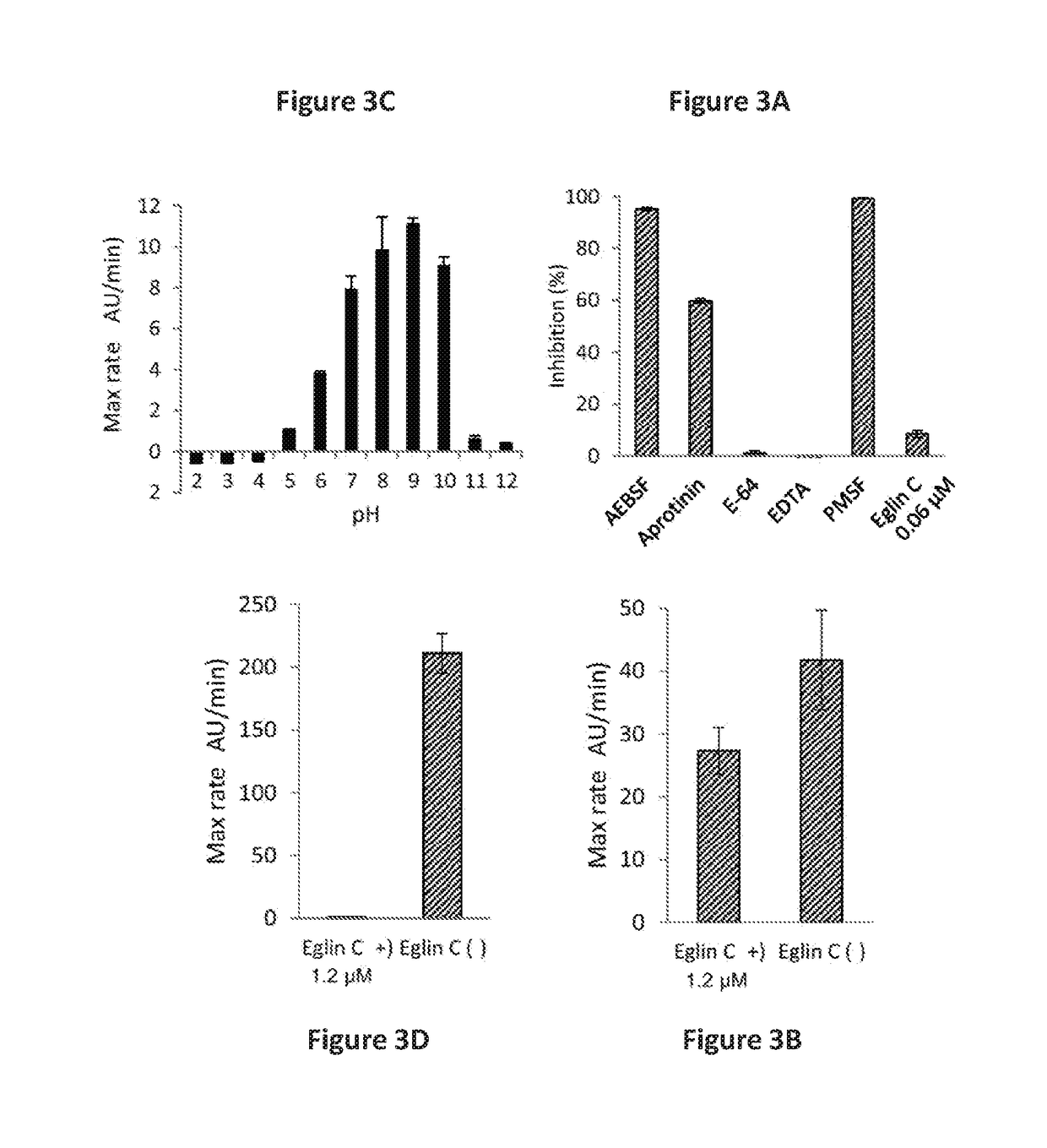
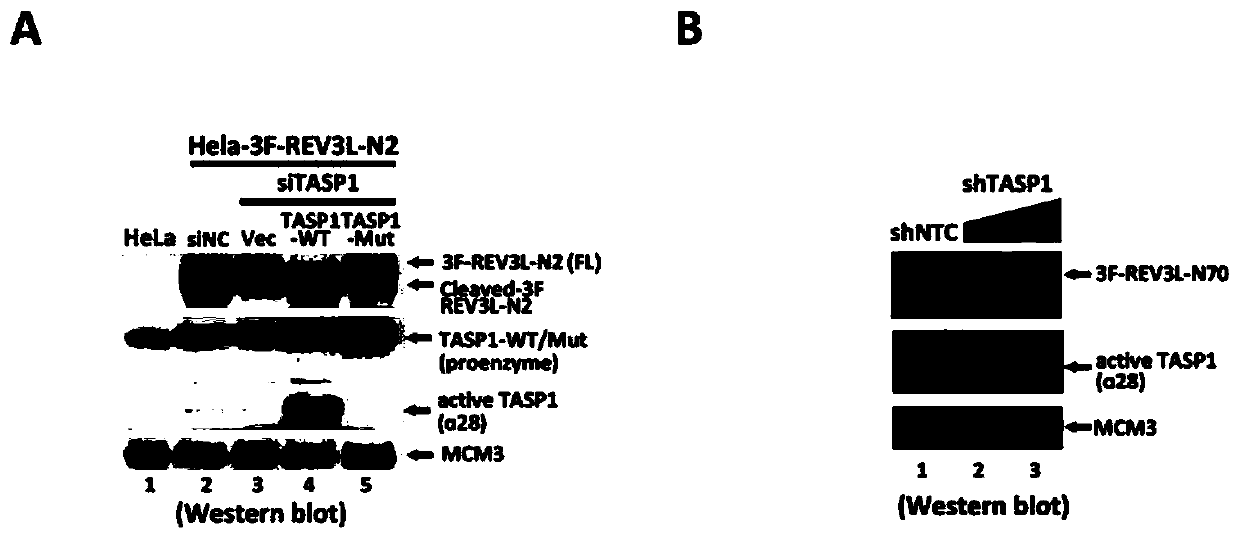
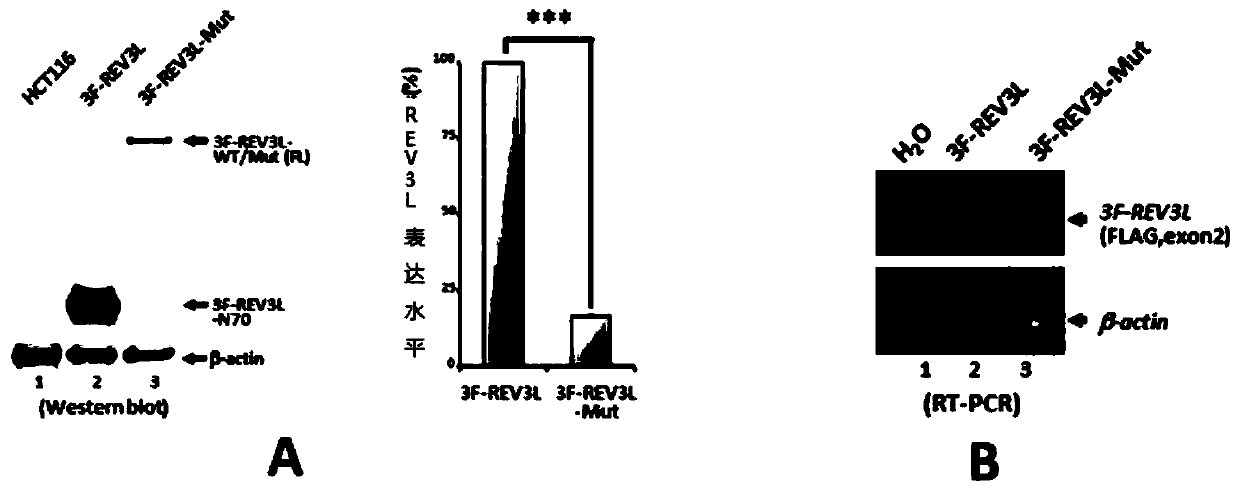
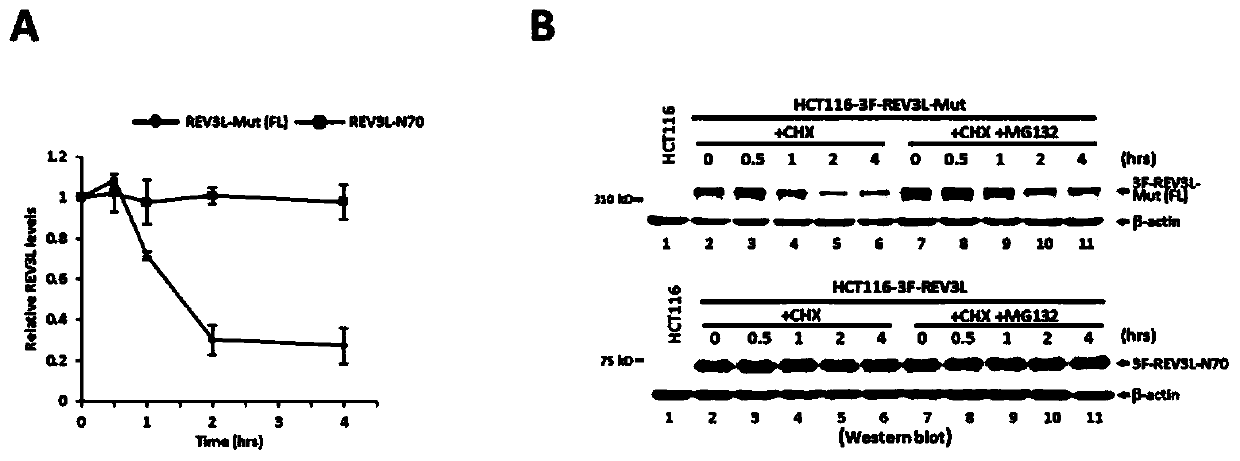
Human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof
InactiveCN111467493AIncreased sensitivityDelay drug resistanceHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseDrug target
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof. The invention discloses a drug for improvingsensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage and controlling drug resistance of tumor cells. The action target of the drug is obtained by a protease TASP1 mediated human REV3L protein position specific cleavage event. The inventor finds that the human REV3L protein has a TASP1 mediated sequence dependent protein cleavage event; polyubiquitination modification of REV3L protein and proteasome mediated degradation can be effectively promoted by interfering the REV3L protein cleavage event, so that low-fidelity cross-damage DNA synthesis activity in tumor cells is further reduced, DNA mutation inducedby DNA damage is reduced, sensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage is remarkably improved, and therefore, a new potential drug target is provided for enhancing the radiotherapy and chemotherapy effects of tumors and other diseases taking induction of DNA damage as a molecular basis and controlling generation of drug resistance.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
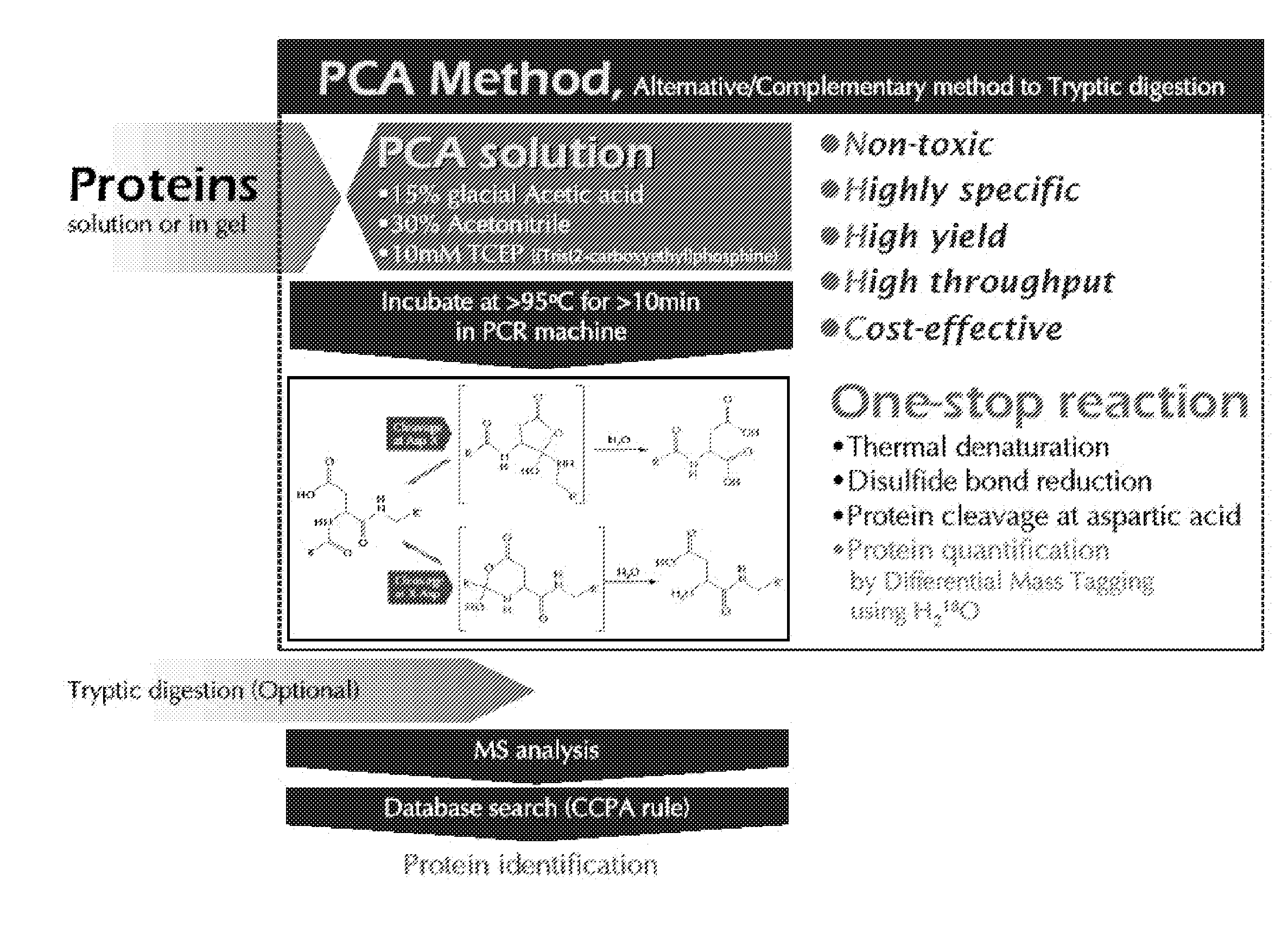
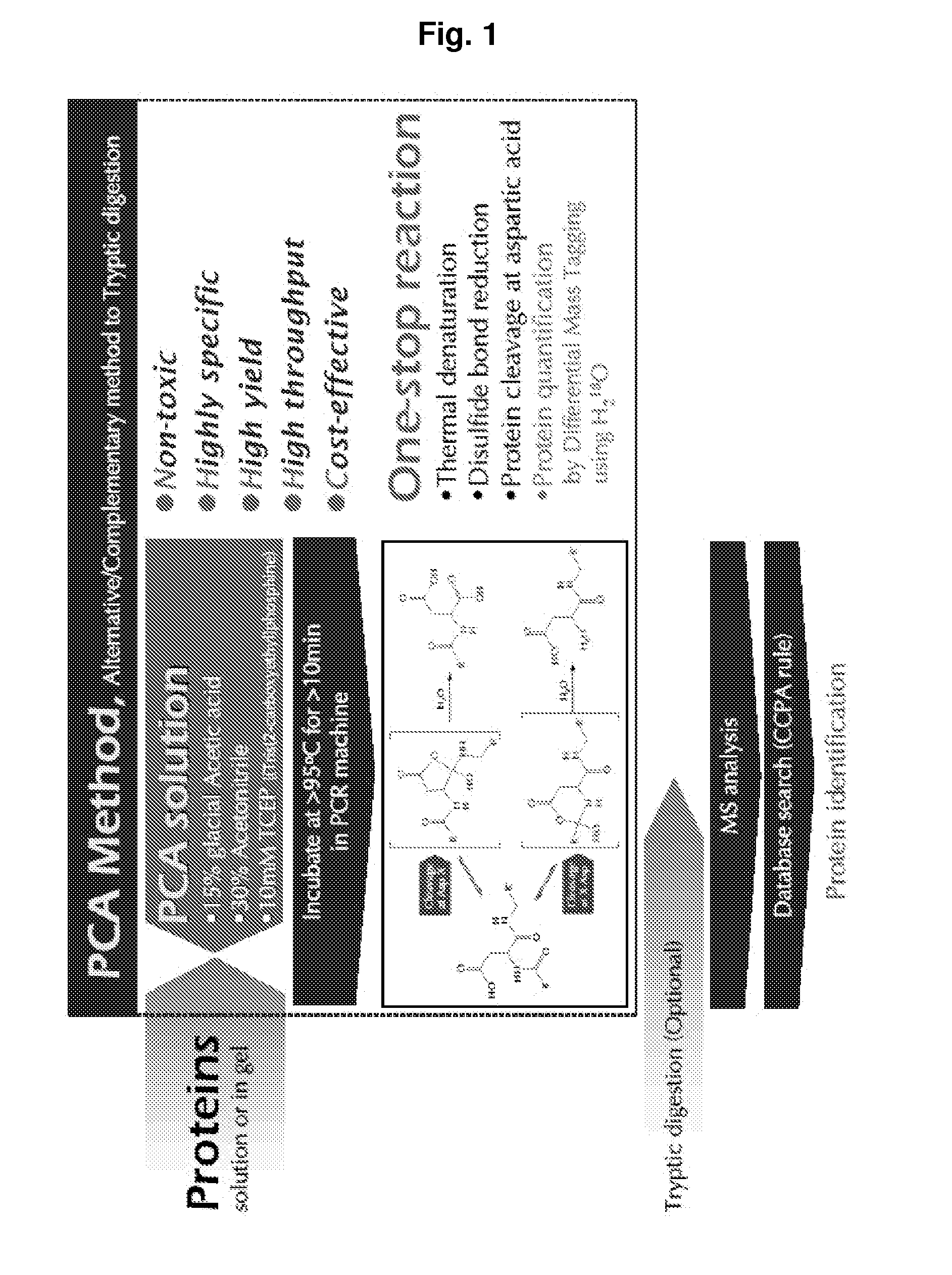
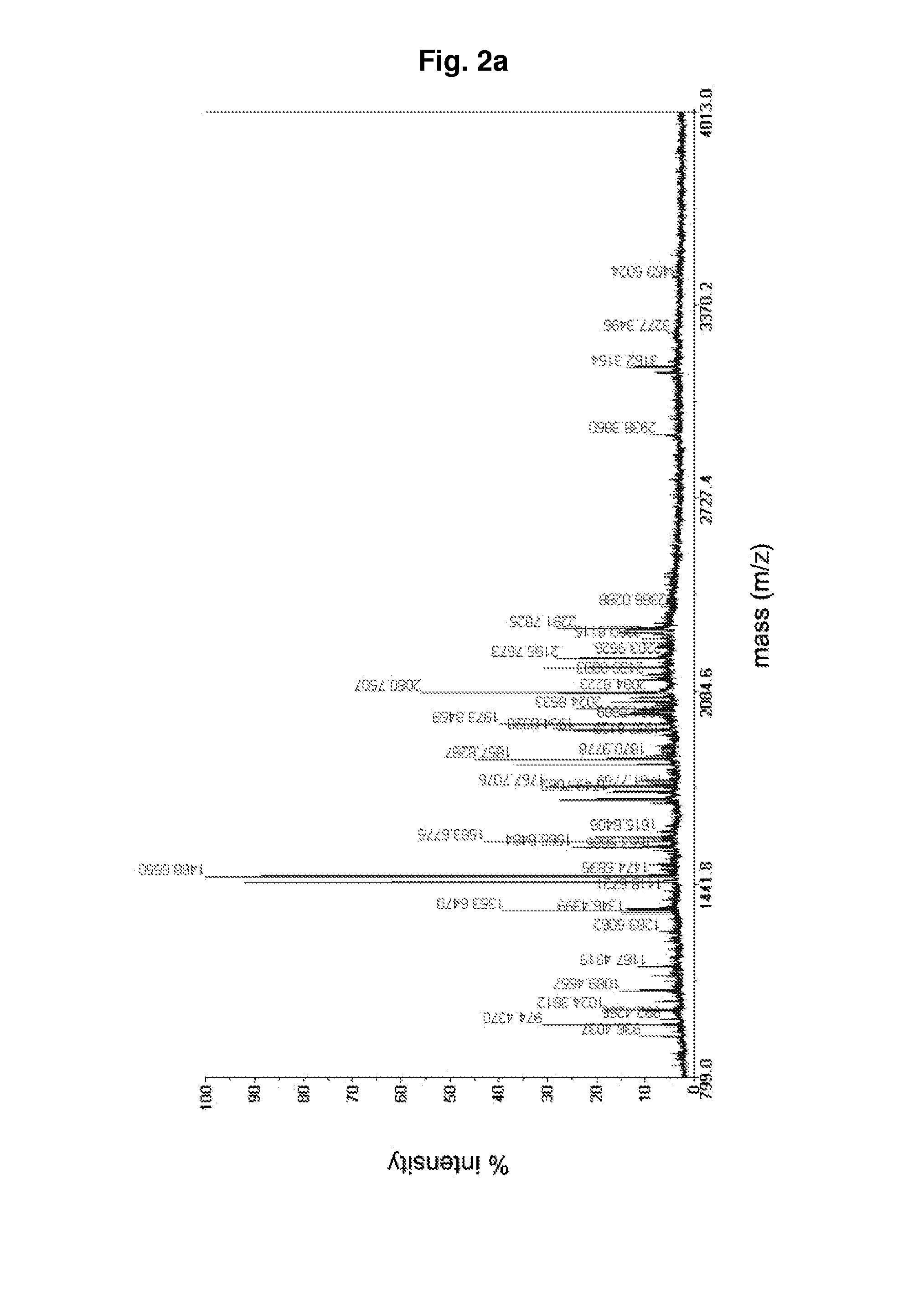
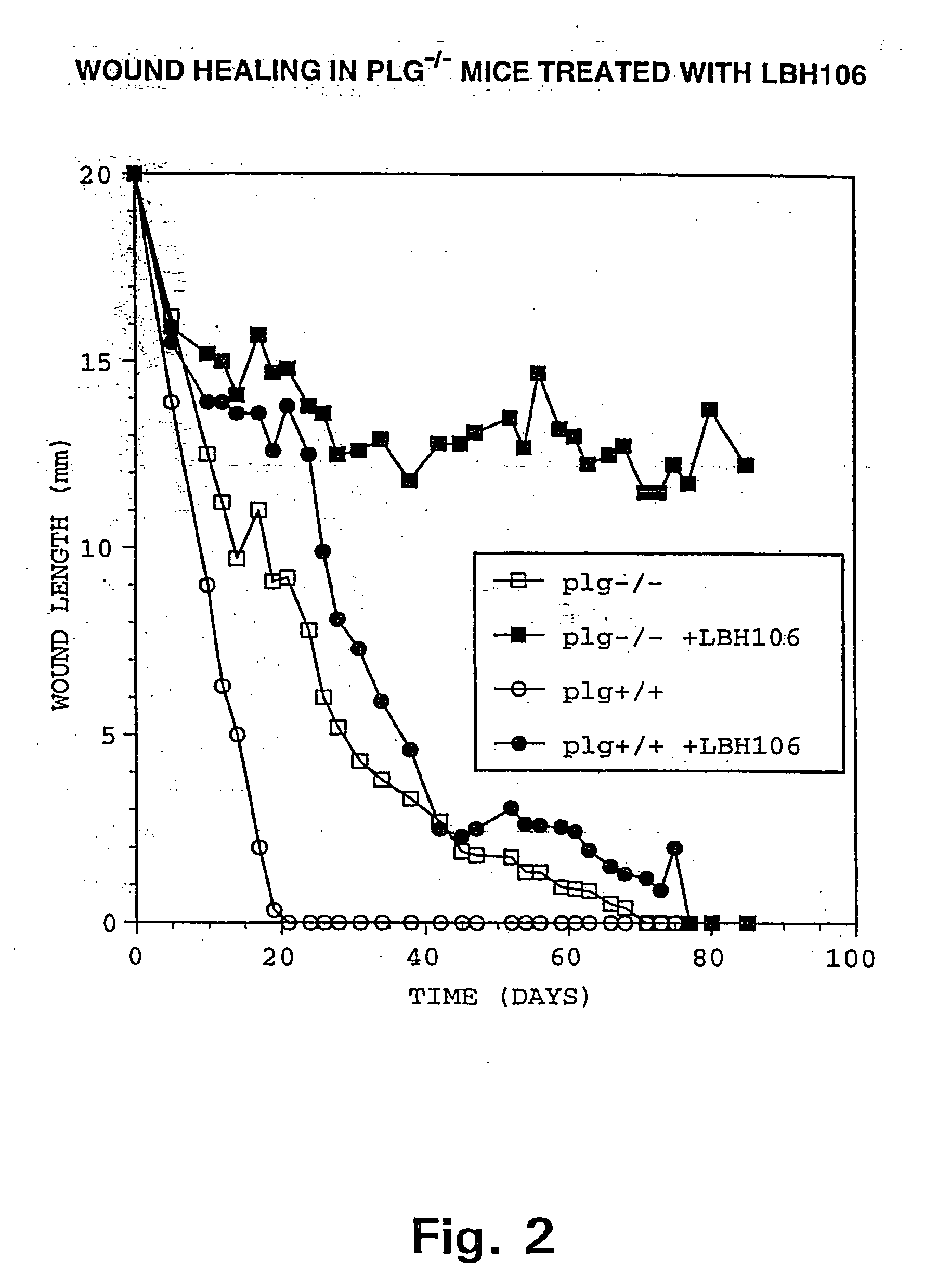
Protein Cleavage at Aspartic Acid Using Chemical Reagents
InactiveUS20080318262A1Reduce lossesSufficient informationInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryProteomics
The present invention relates to the methods of identifying and quantifying polypeptides in a given sample by mass spectrometric analysis. More specifically, the invention provides the methods for sample preparation for proteomic analysis: the methods for the fragmentation of proteins into peptides with the specific cleavage rule (cleavage at amino-terminal or carboxyl-terminal of aspartic acid), which are suitable for the analysis by mass spectrometry apparatus.
Owner:SIGMOL
Inhibition of invasive remodelling
InactiveUS20050137121A1Improve survivalIncrease delayBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiochemistryHydrolase
Owner:LUND LEIF +6
Method for selectively collecting N-terminal peptide fragment of protein
The present invention provides a method for selectively collecting the N-terminal peptide fragments of a protein of interest whether or not the protein of interest is modified on the N-terminus. A method for selectively collecting the N-terminal peptide fragment of a protein, comprising: a protection step (1) of protecting side chain-amino groups of amino acid residues containing side chain-amino groups of a protein of interest to obtain a protected protein protected on the side chain-amino groups; a fragmentation step (2) of cleaving the protected protein into one N-terminal peptide fragment (a) containing the N-terminus of the peptide of interest and one or more of peptide fragments (b) other than the N-terminal peptide fragment (a); and a separation step (3) of separating the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) from the other peptide fragments (b) by selectively eluting the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) based on the difference in their reactivity or affinity to substrate, wherein the selective elution is achieved either by allowing the other peptide fragments (b) to bind to the substrate while allowing the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) to elute, or by allowing the N-terminal peptide fragment (a) to bind to the substrate while allowing the other peptide fragments (b) to elute and subsequently eluting the bound N-terminal peptide fragment (a).
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Thiazole Inner Salt Compounds, and Preparation Methods and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20160137619A1Improve quality controlEquivalent activityBiocideCosmetic preparationsCross-linkThiazole
The present invention pertains to field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and relates to thiazole inner salt compounds, preparation methods and uses thereof. Specifically, the present invention relates to a compound of Formula I, hydrates or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compound of Formula I of the present invention is a potent cross-linking protein cleavage agent, has a stable structure, good physical and chemical properties, and good pharmacological activities, and is suitable for large scale production to obtain samples with stable, controllable and reliable quality, thereby being suitable for pharmaceutical development.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
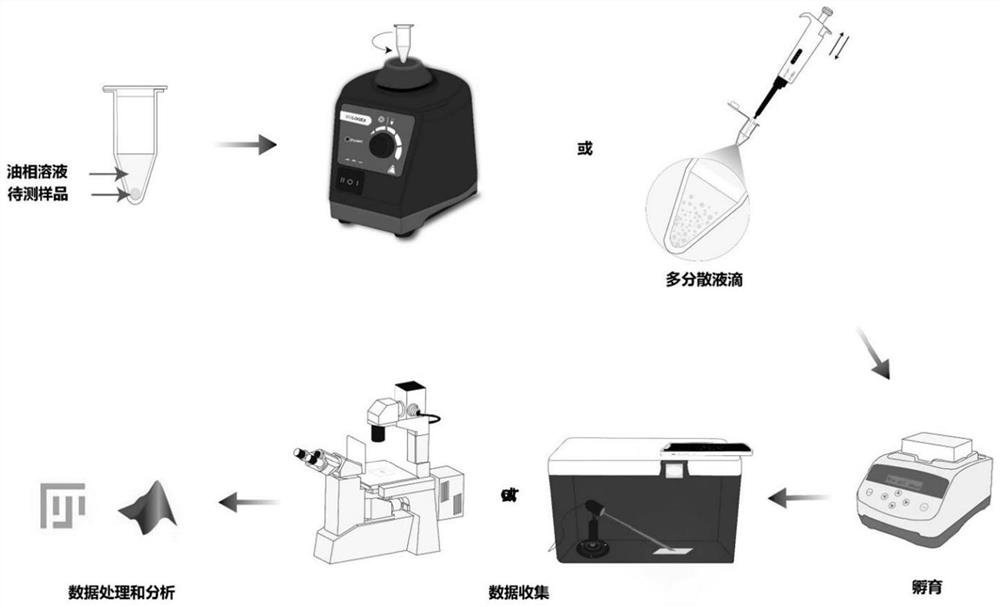
Polydispersion liquid drop digital nucleic acid detection method and application thereof
PendingCN114752657AReduce dependencyQuick splitMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionOil phase
The invention discloses a polydispersion liquid drop digital nucleic acid detection method and application thereof, and the method comprises the following steps: mixing an oil phase solution, a detection sample and a detection reagent, generating liquid drops through a simple method, incubating, and quantitatively detecting target nucleic acid molecules in the sample according to the number and volume of positive liquid drops. According to the method, the reaction reagent is quickly divided into independent liquid drops through simple dispersion operation, so that the requirements on the environment and instruments are reduced, and meanwhile, the demand quantity of the sample and the detection reagent is remarkably reduced. Moreover, through rapid emulsion segmentation, nucleic acid amplification carried out before reagent segmentation or Cas protein cleavage of a target is effectively avoided, the target nucleic acid concentration is calculated based on the droplet size, and the detection sensitivity can reach an aM level.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Series connection expression method from virus macrophage inflammatory protein IIN end 15 peptide
The genetic engineering tandem expression process of pentadecapeptide originated from virus macropage inflammatory protein II N terminal includes: synthesizing one gene segment including several pentadecapeptides connected through protein cleavage sequence gene by using virus macropage inflammatory protein II N terminal pentadecapeptided as target and in a eukaryotic expression system; adding limiting cleavage sites to the 5' and 3' terminals of the gene segment; connecting the gene segment to plasmid vector by means of gene recombination, converting saccaromycete to screen, express and purify target protein; cleaving the purified protein with protease, and separating and purifying to obtain target polypeptide. The polypeptide can antagonize CXCR4 pentadecapeptide, and has the function of preventing and treating AIDS and wide medicine application foreground.
Owner:广州法蕊仕药业科技有限公司
A method for immobilizing human arginase-1 by surface display
ActiveCN105713888BImmobilizationImprove display efficiencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionSurface displayL-Ornithine
The invention discloses a method for immobilizing human source arginase-1 through surface display. The method comprises the steps of adding signal peptide and charged polypeptide to the amino terminal of a protein cleavage variant (InaK-N) formed on an ice core, fusing human source arginase-1 into the carboxyl terminal, and designing an HA label at the carboxyl terminal; constructing various recombinant plasmids to convert competent escherichia coli cells, so that different genetic engineering strains are obtained; conducting shake-flask culture on the strains; detecting the display efficiency and enzyme activity of human source arginase-1; selecting the strain with the highest enzyme activity for mass culture, conducting efficient L-arginine conversion, and synthesizing L-ornithine. Human source arginase-1 fused in the protein cleavage variant formed on the ice core is effectively displayed on the surface of an escherichia coli cell, so that human source arginase-1 is immobilized. Compared with an original ice core protein display system, the method has the advantage that the display efficiency and enzyme activity of human source arginase-1 are improved remarkably. Compared with a chitin immobilizing method, the method has the advantages that cost is reduced, process is shortened, and purification steps are simplified.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
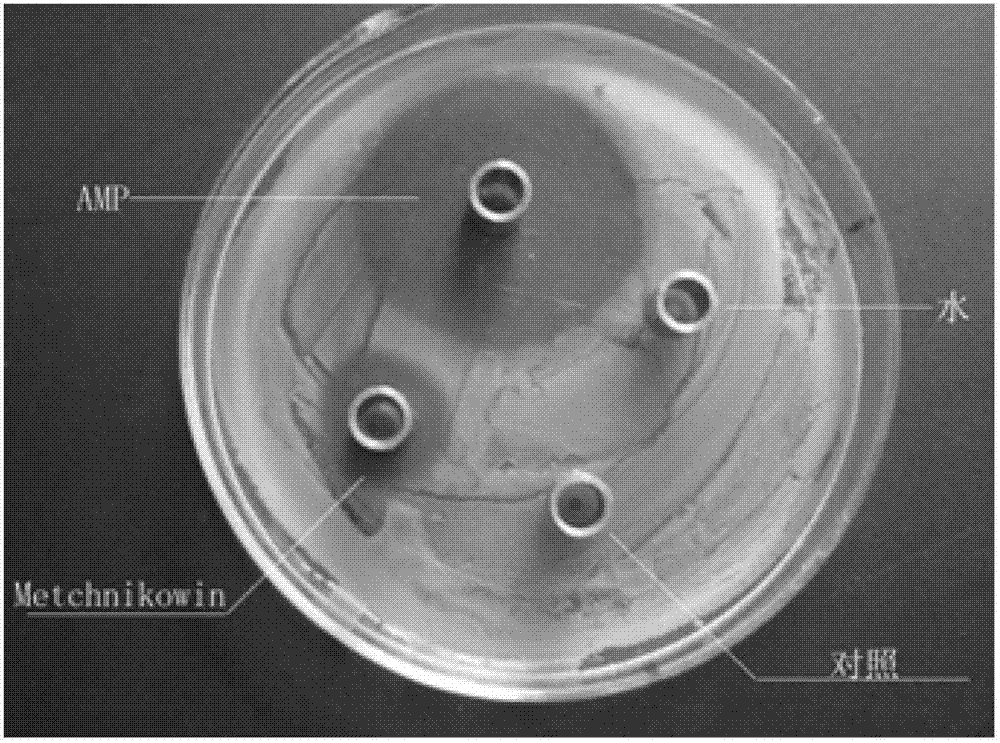
Construction method of colon bacillus genetic engineering strain for secretory expression of Metchnikowin antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN103088043ALow costEfficient and stable secretory expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCompetent cellCompanion animal
The invention discloses a construction method of a colon bacillus genetic engineering strain for secretory expression of antibacterial peptide Metchnikowin. The construction method comprises the steps of: genetically connecting a Metchnikowin antibacterial peptide gene, constructing a recombinant pET-22b plasmid, and transforming a colon bacillus BL21 competent cell. The construction method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the colon bacillus genetic engineering strain has efficient and stable secretory expression, and the protein cleavage is low in cost, and safe due to a downstream DP hydrolysis locus.
Owner:安徽希普生物科技有限公司
Thiazole inner salt compounds, and preparation methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190233383A1Improve quality controlEquivalent activity for breaking AGEsCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkThiazole
The present invention pertains to field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and relates to thiazole inner salt compounds, preparation methods and uses thereof. Specifically, the present invention relates to a compound of Formula I, hydrates or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compound of Formula I of the present invention is a potent cross-linking protein cleavage agent, has a stable structure, good physical and chemical properties, and good pharmacological activities, and is suitable for large scale production to obtain samples with stable, controllable and reliable quality, thereby being suitable for pharmaceutical development.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Rothia subtilisins, S8A family proteases, as therapeutic enzymes for application in gluten intolerance disorders
ActiveUS11124785B2Reduce productionReduction of toxic gluten oligopeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidasesGluten intoleranceDegradative enzyme
There are gluten-degrading enzymes found in Rothia species bacteria that are subtilisins that belonging to the S8A family of serine protease family. The Rothia sp. derived subtilisin-like enzymes have the conserved catalytic triad composed of a Ser, His, and Asp residues that is characteristic of the serine protease family. The Rothia subtilisin enzymes are potent at cleaving proline-containing proteins, cleaving the second peptide bond after proline in the XPX1 motif, where X is any amino acid, P is proline and X1 is a hydrophobic amino acid, e.g. the XPQ motif, where Q is glutamine. Embodiments herein provide isolated enzyme compositions and formulations comprising subtilisins gluten-degrading enzyme from a Rothia species bacteria. Also provided herein are methods of treatment of celiac disease or a related disorder, treatment of gluten-containing foodstuff, degrading and / or detoxifying gluten comprising the subtilisins gluten-degrading enzyme and / or compositions.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com