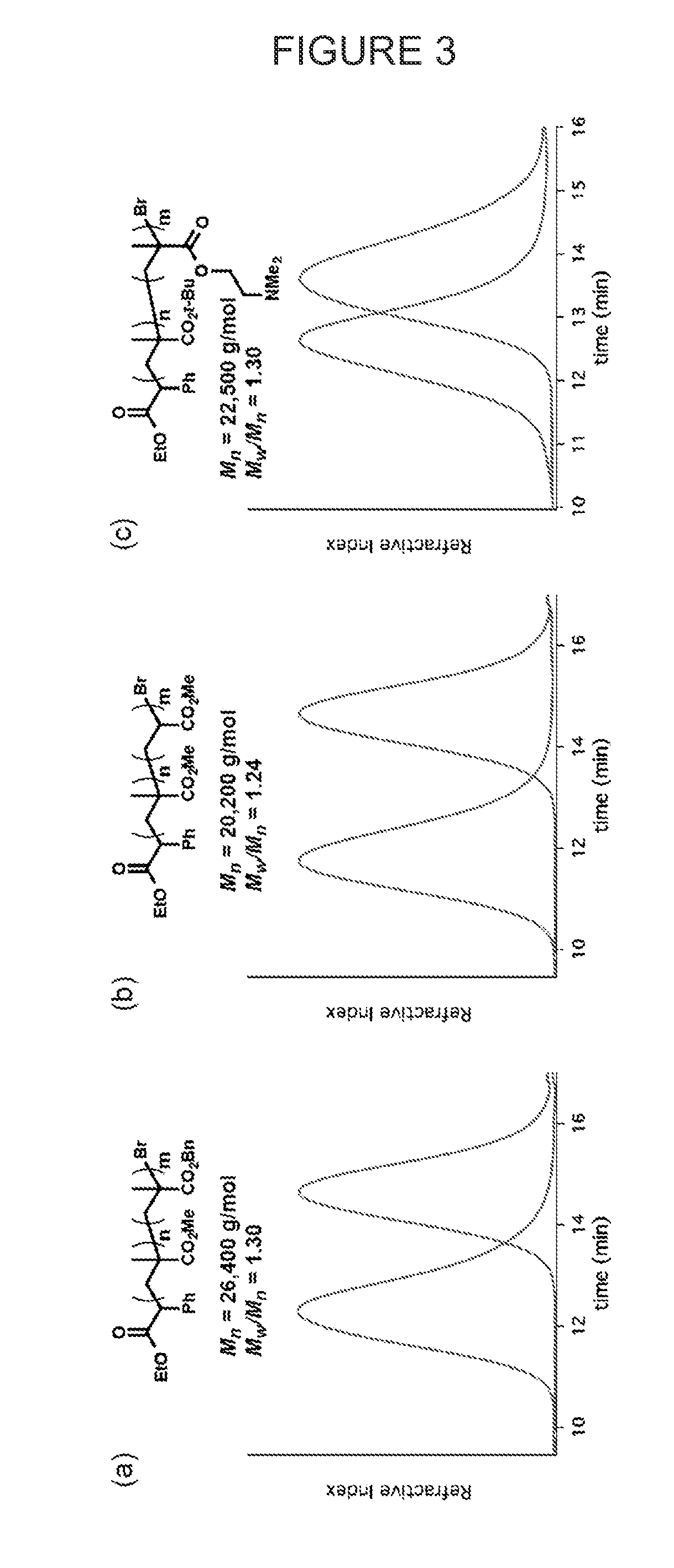
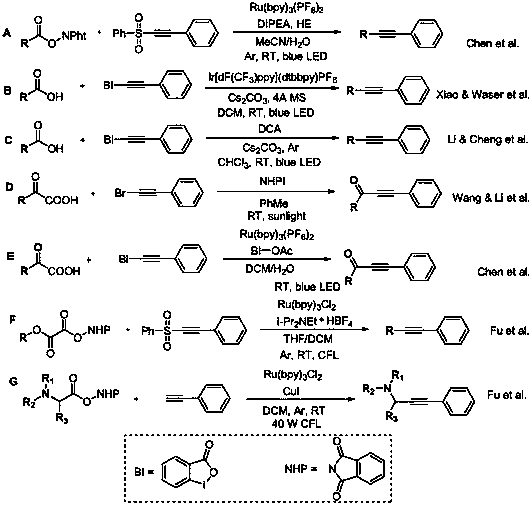
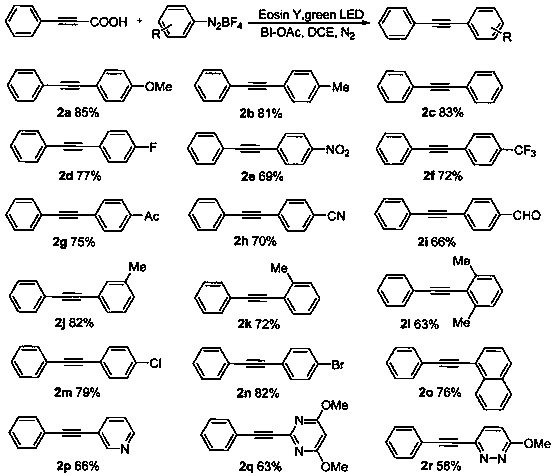
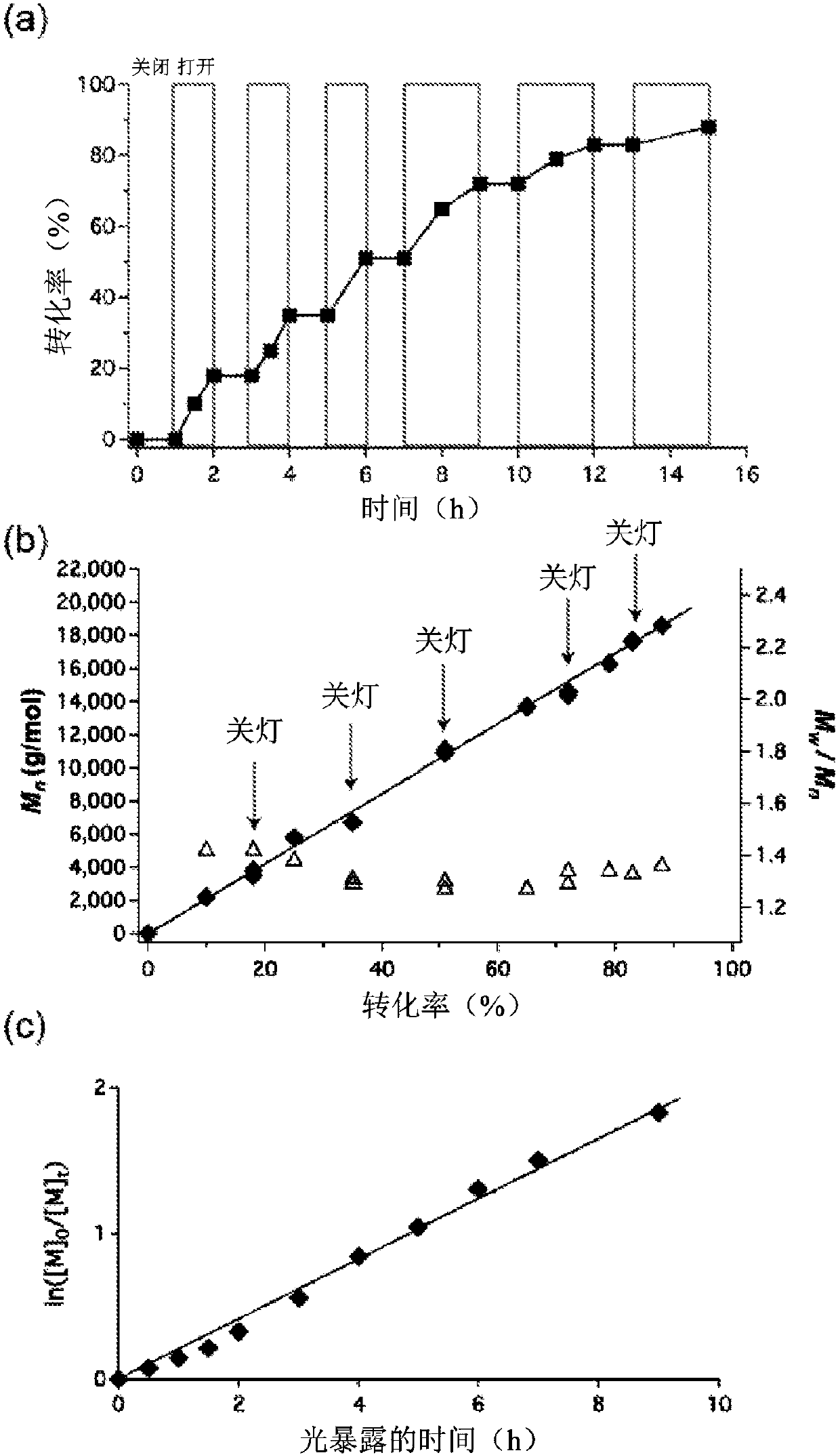
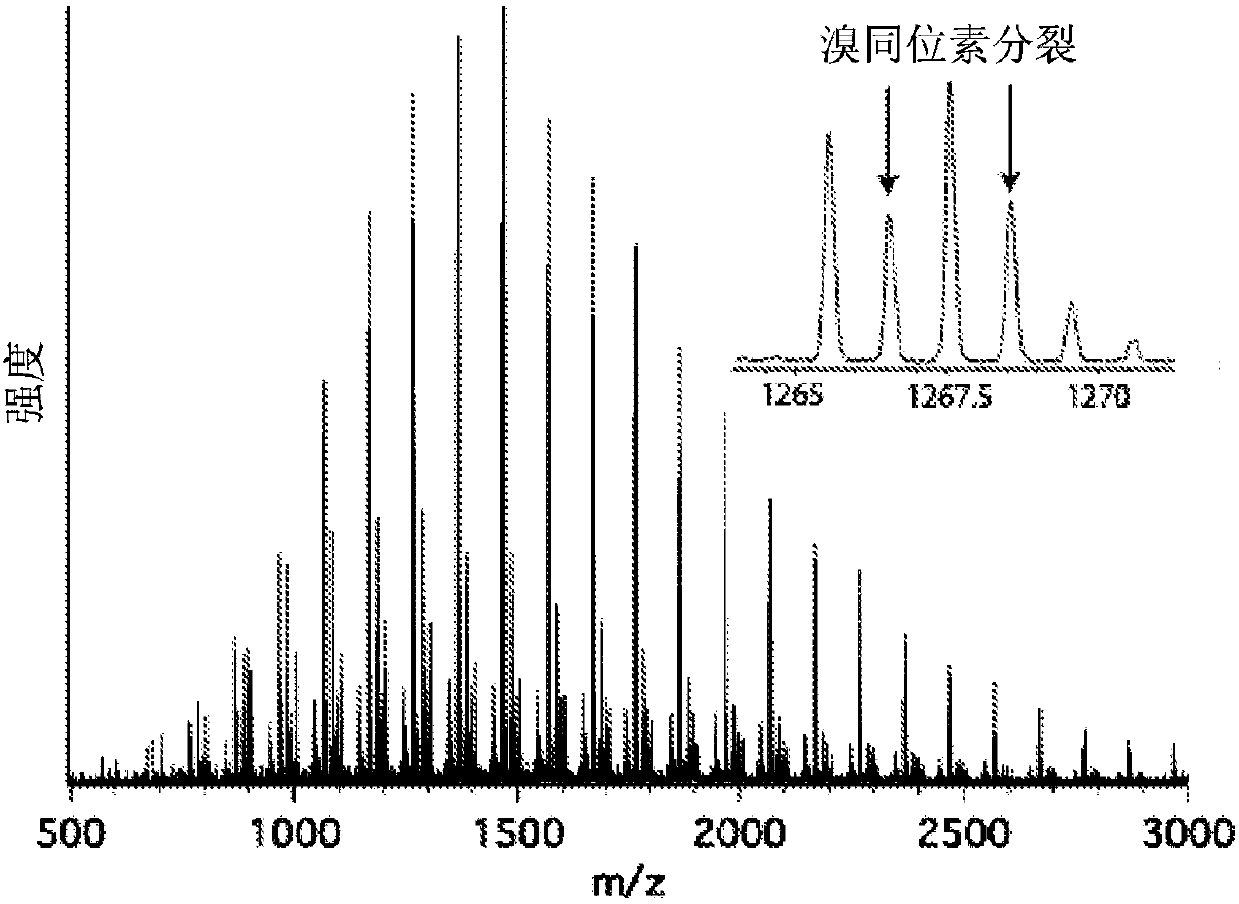
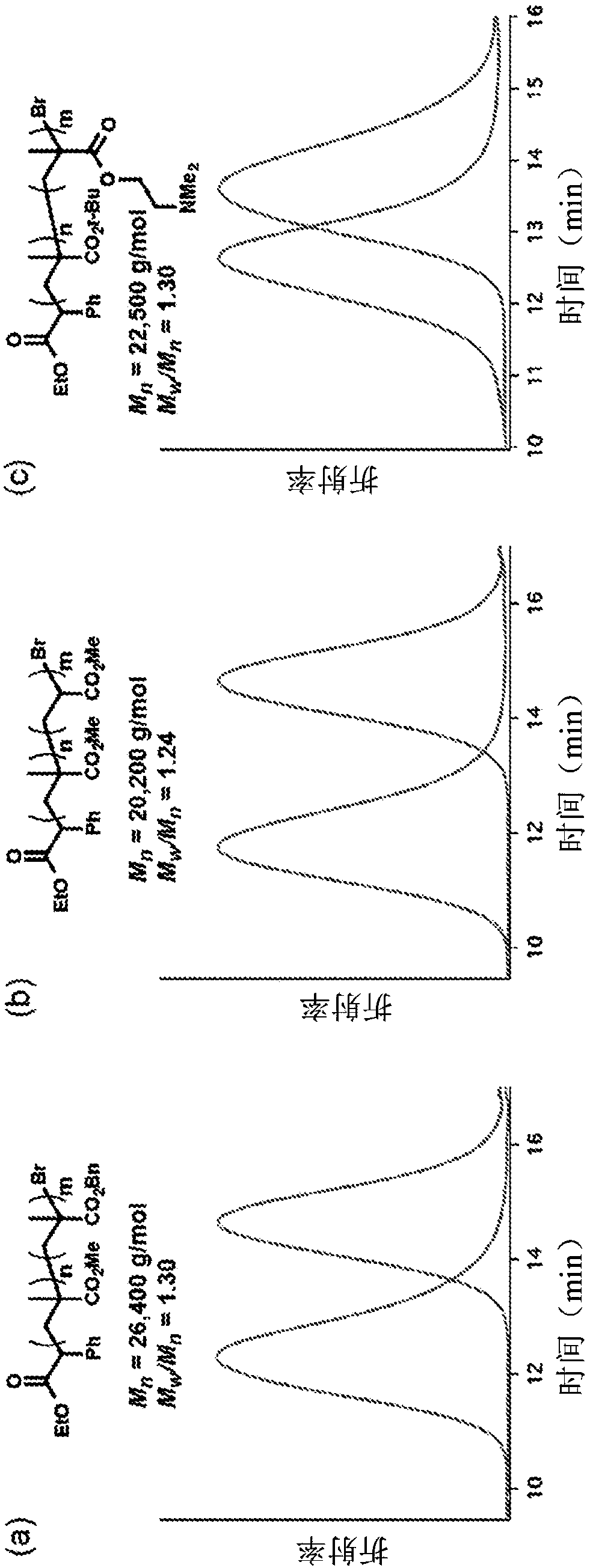
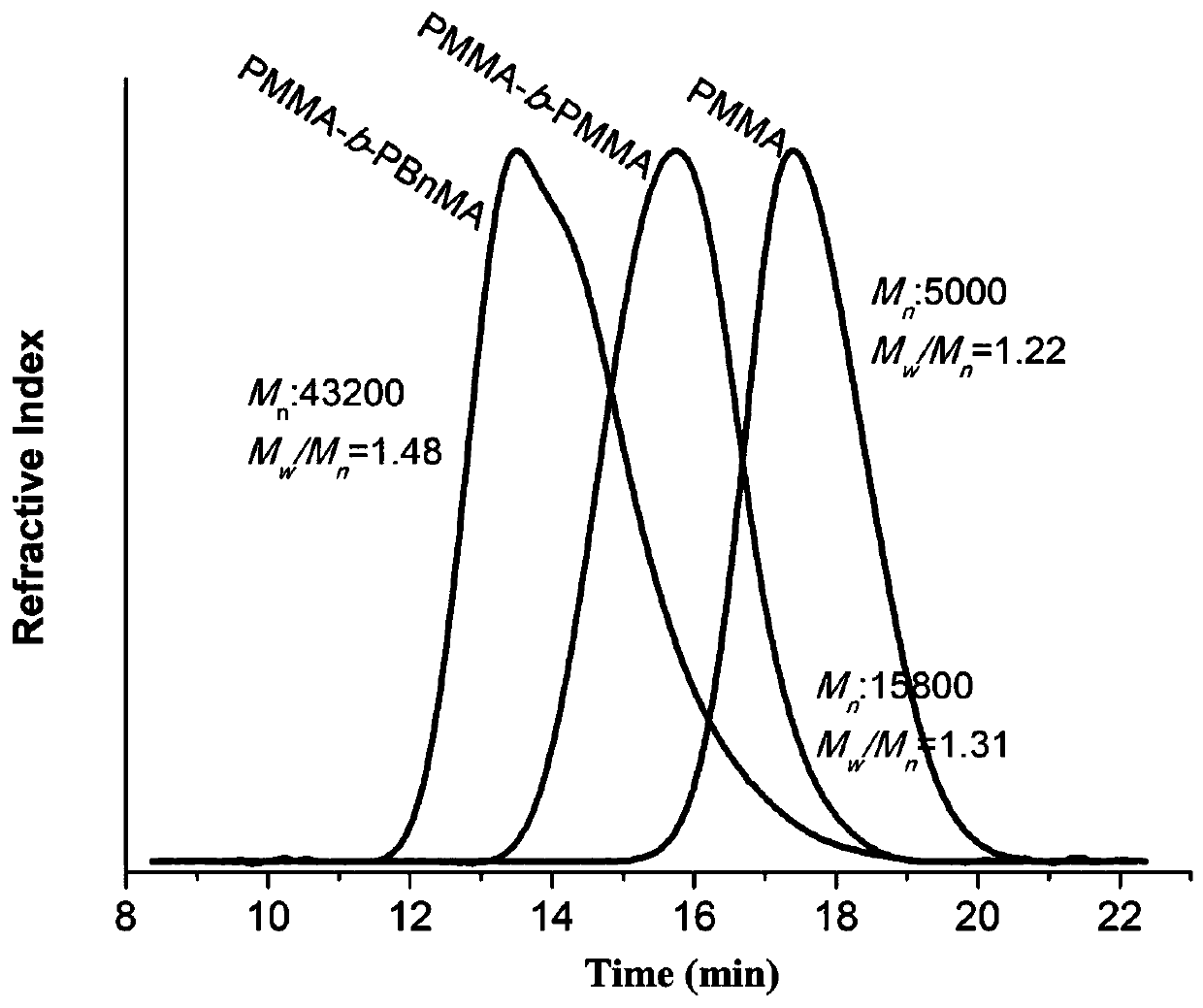
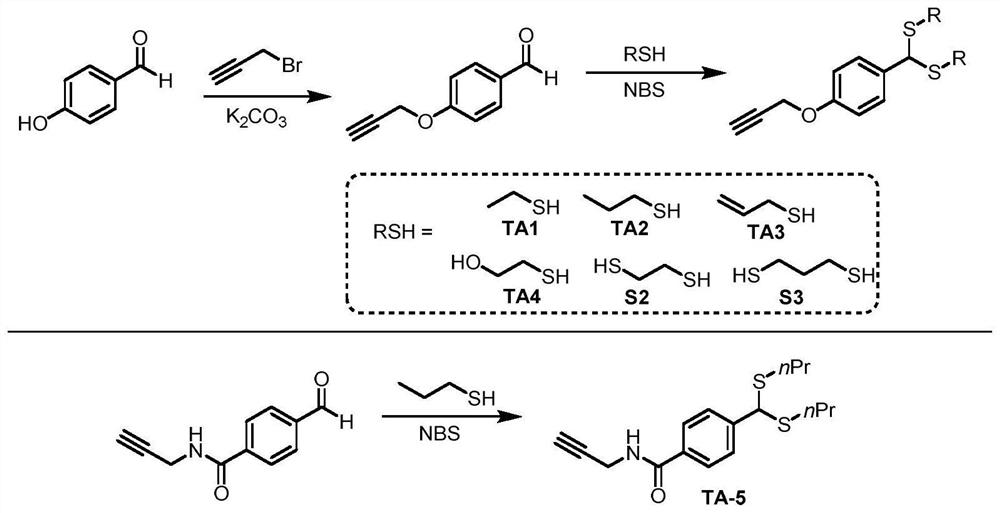
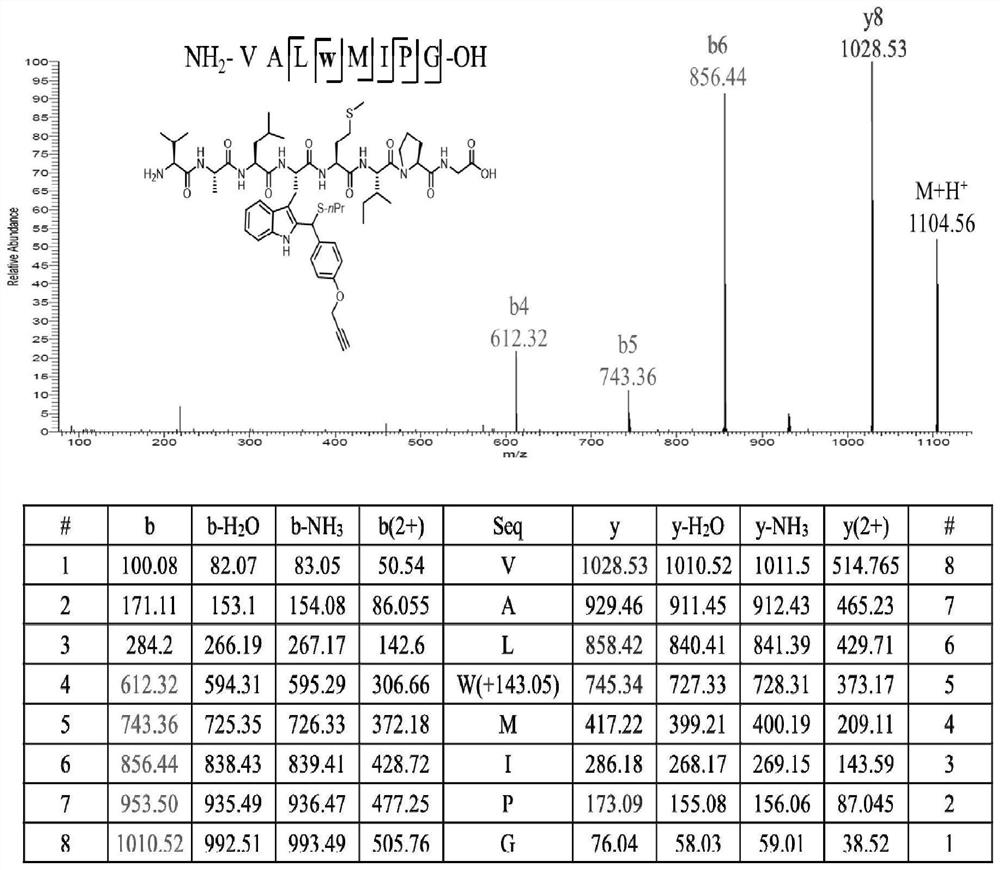
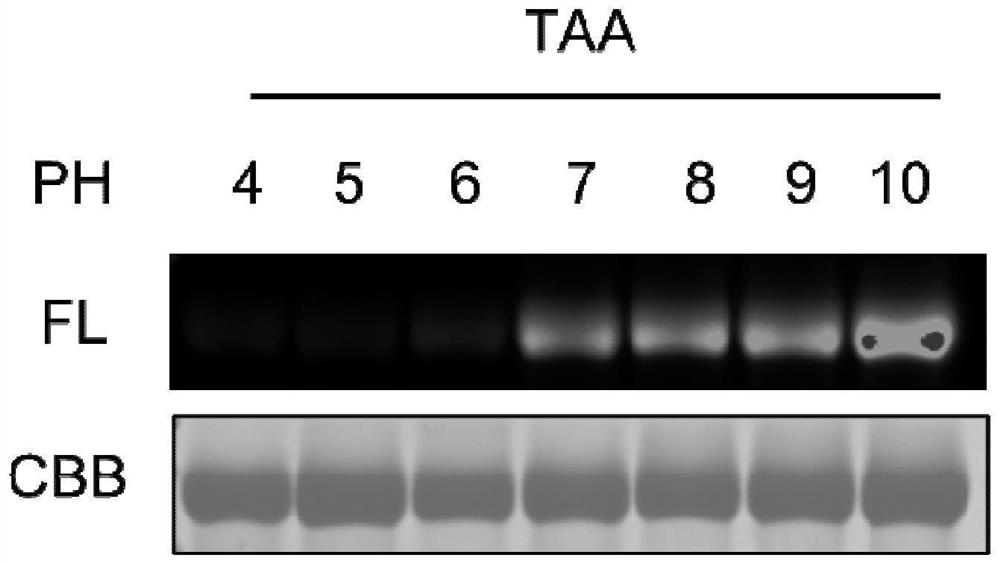
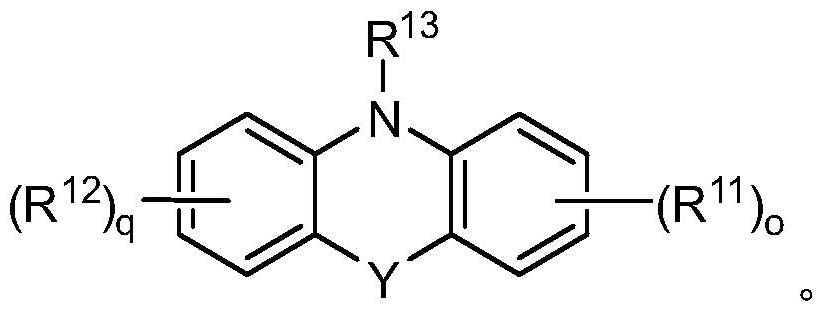
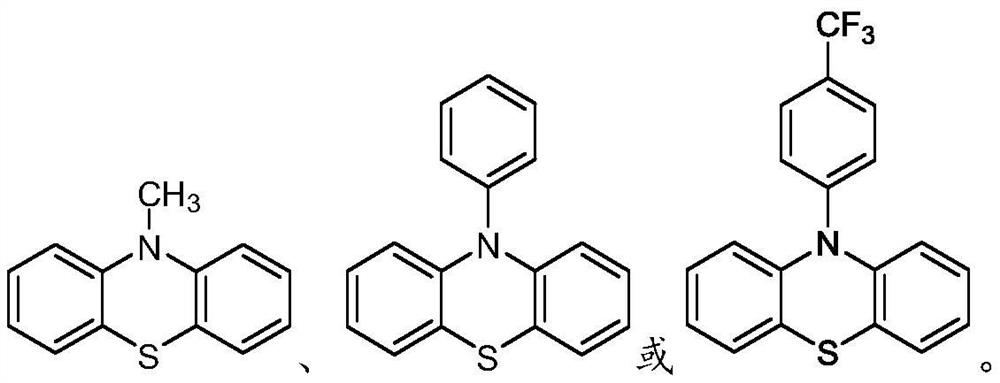
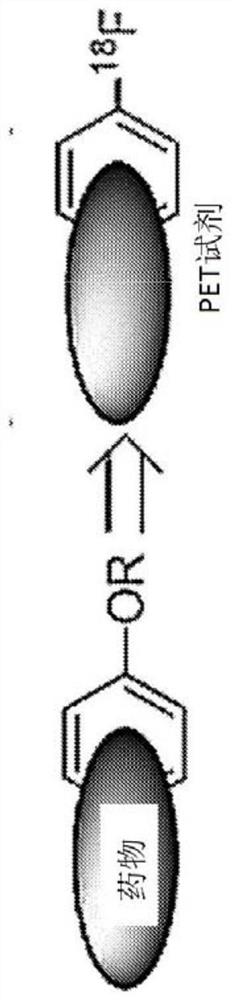
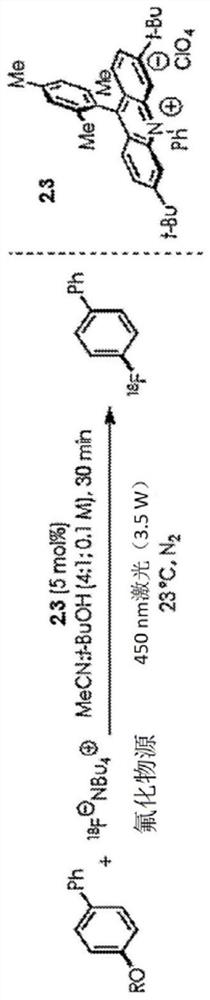
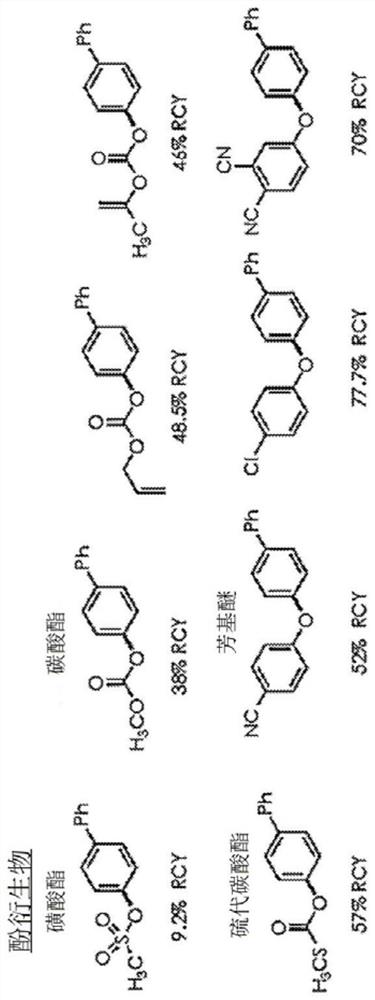
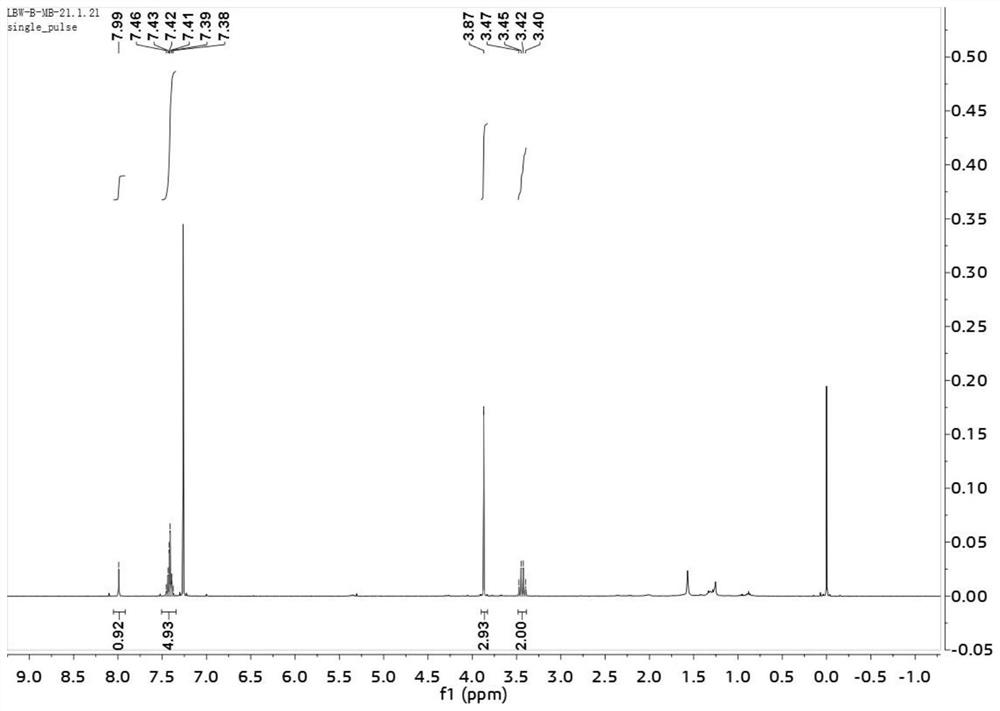
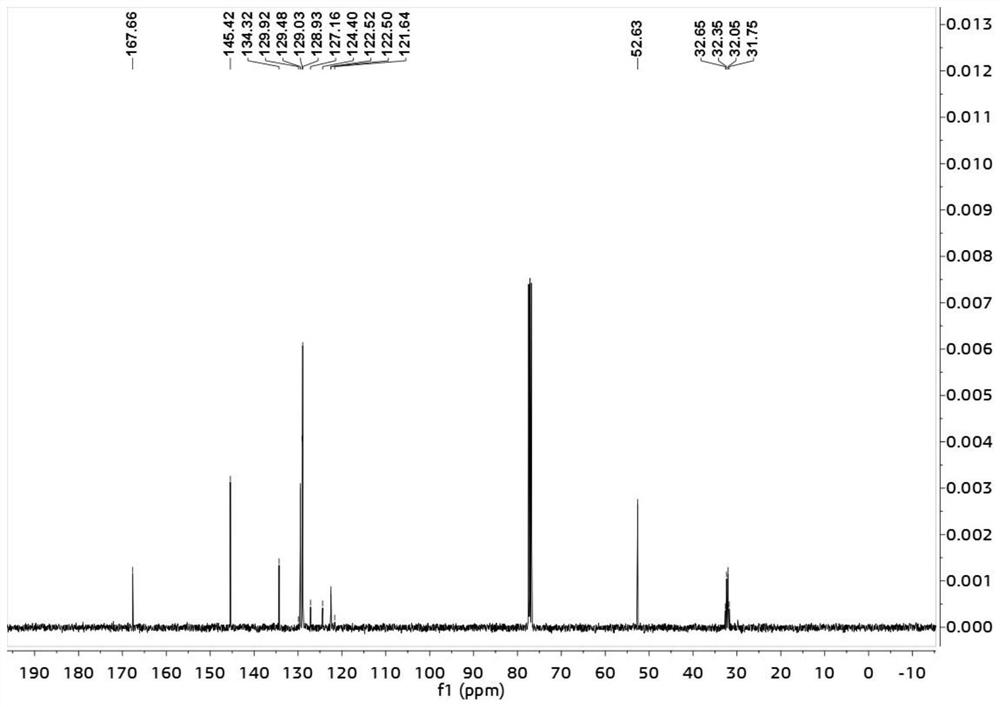
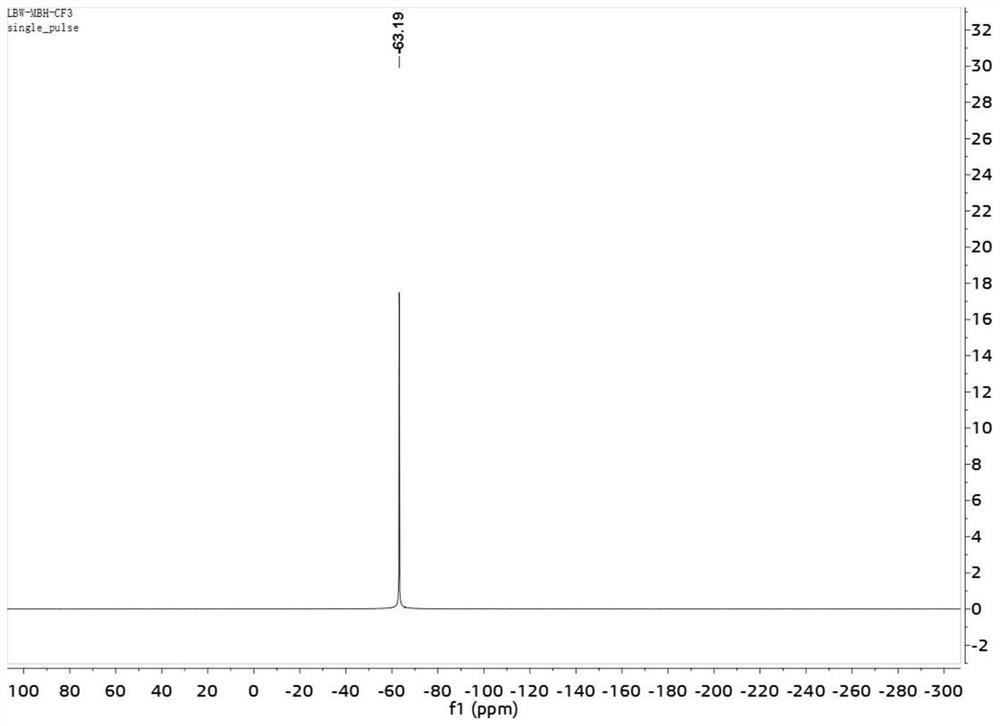
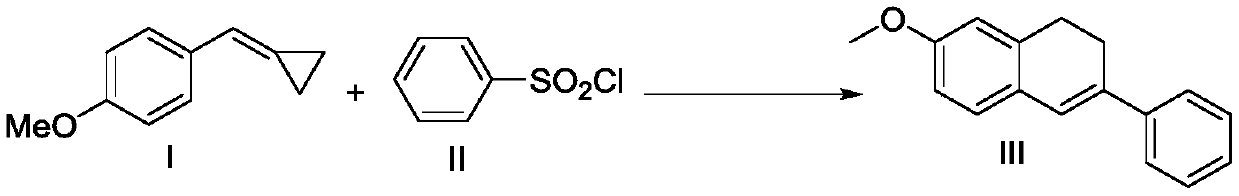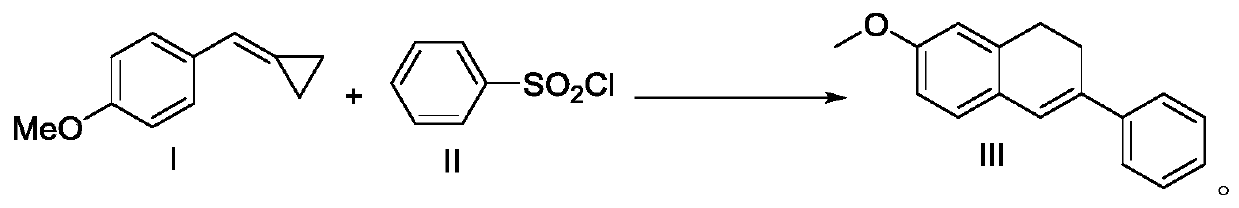Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Photoredox catalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of light to accelerate a chemical reaction via single-electron transfer events. This area is named as a combination of "photo-" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that would usually not react at all. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes, and semiconductors. While organic photoredox catalysts were dominant throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, soluble transition-metal complexes are more commonly used today.
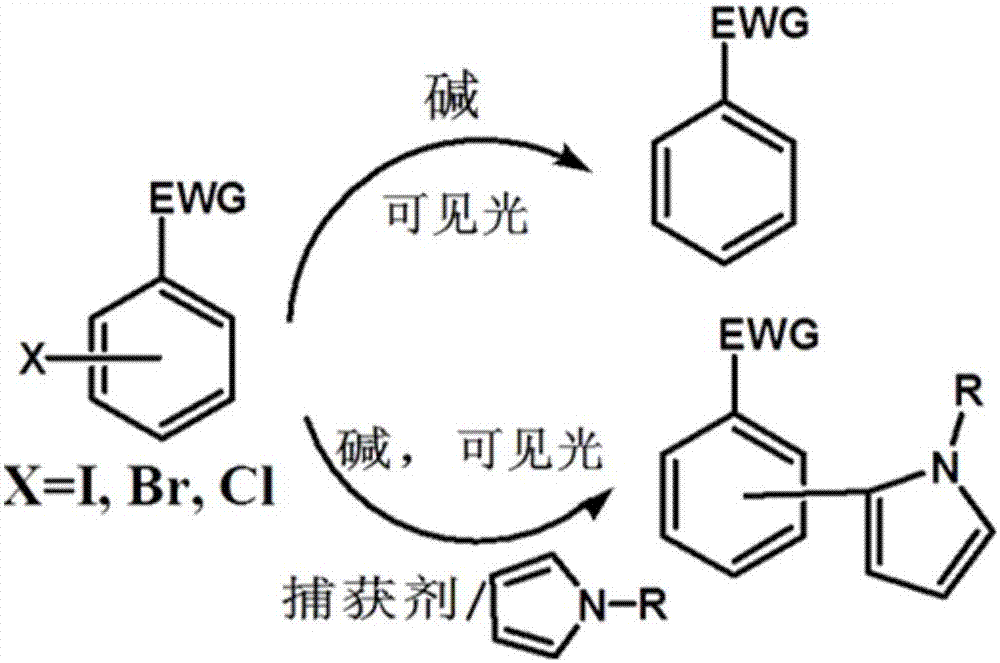
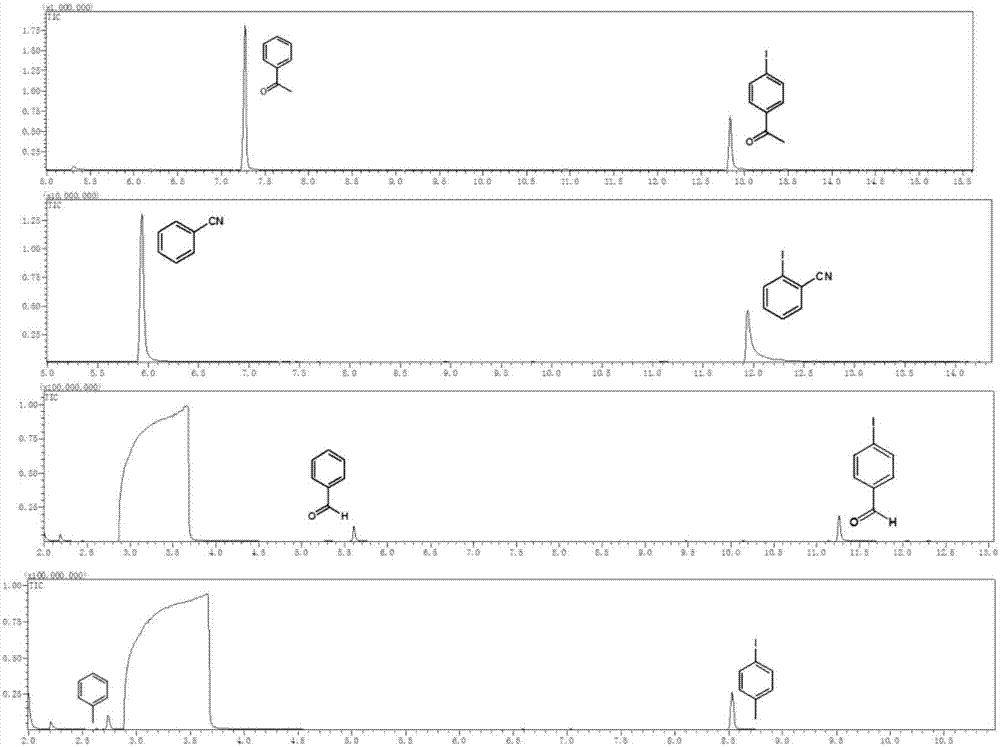
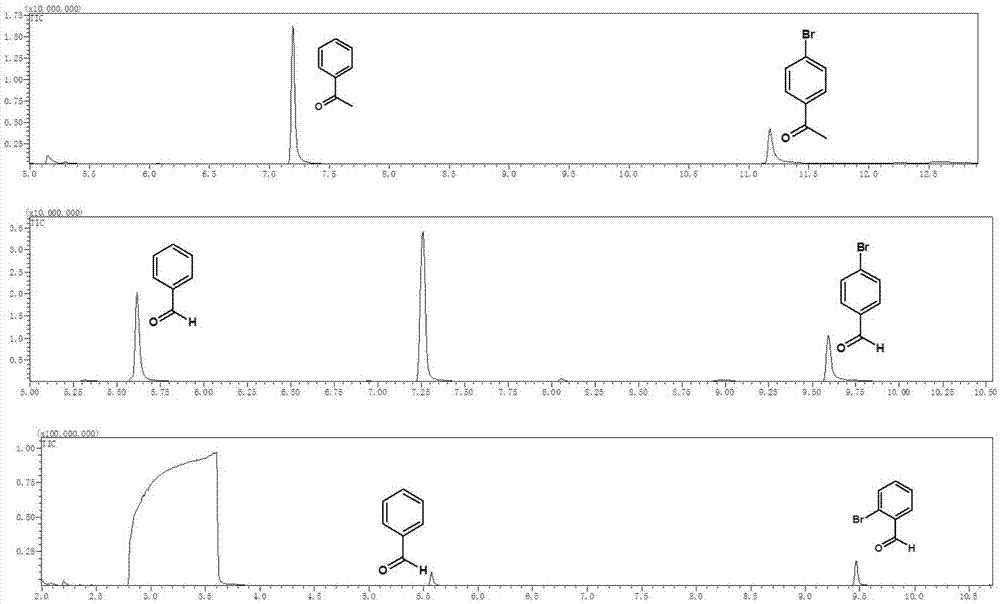
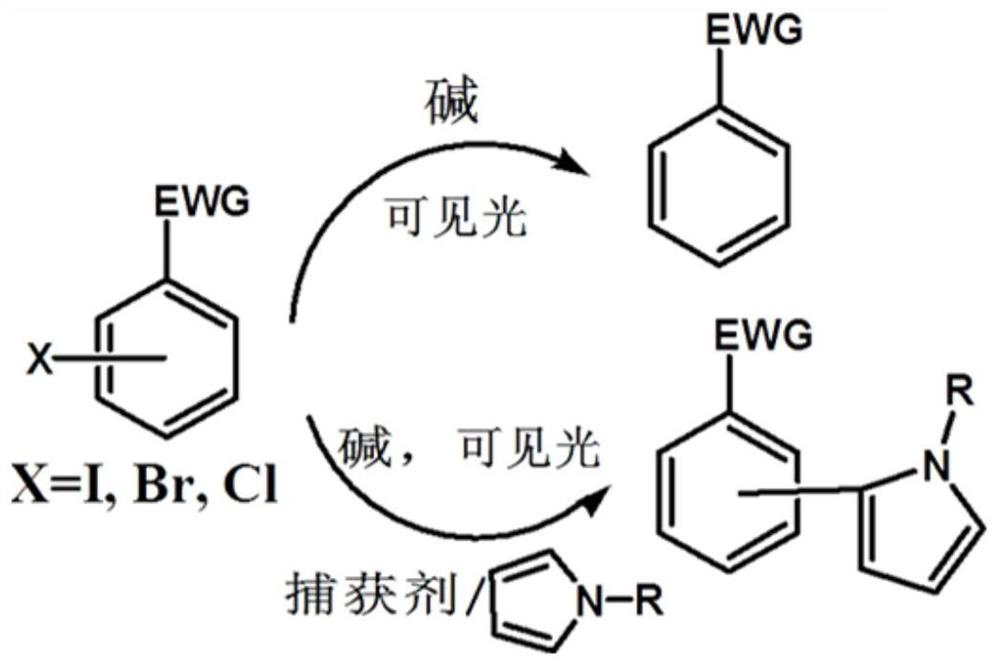
Visible light catalysis method for dehalogenation of aryl halide without need of photooxidation reduction catalyst
ActiveCN108002991AAchieve degradationPromote productionCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationOrganic synthesisPhotoredox catalysis
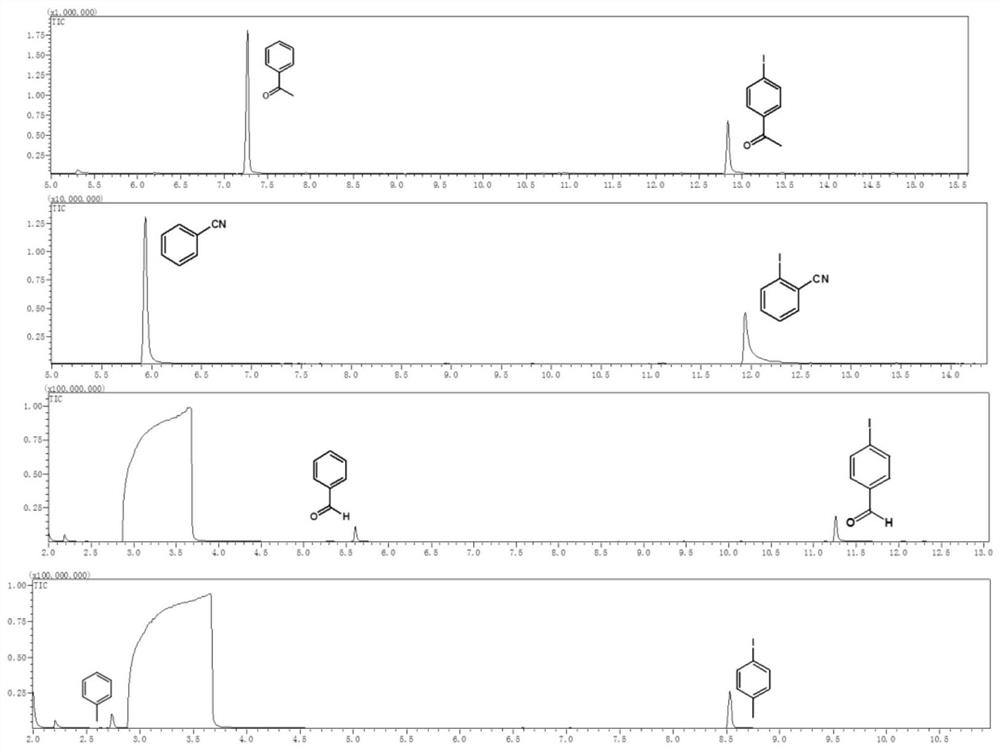
The invention discloses a visible light catalysis method for dehalogenation of aryl halide without the need of a photooxidation reduction catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of visible lightcatalysis organic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the aryl halide is weighed and placed in a reaction vessel, and a solvent is added; secondly, the reaction vessel isfilled with nitrogen for oxygen removal for 0-50 minutes, and alkali is added during the oxygen removal period; thirdly, the reaction vessel is sealed and placed over a light emitting diode with thewavelength of 400-500 nm and the power of 0.5-30 W for irradiation, and reacting is conducted for 3-48 hours at room temperature under the condition of stirring and then finished. By means of the method, the photooxidation reduction catalyst which is high in price or complex in synthesis is not needed, reacting can be achieved under the condition of the room temperature or under a mild condition,a reaction substrate is high in adaptability, and the reaction yield is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
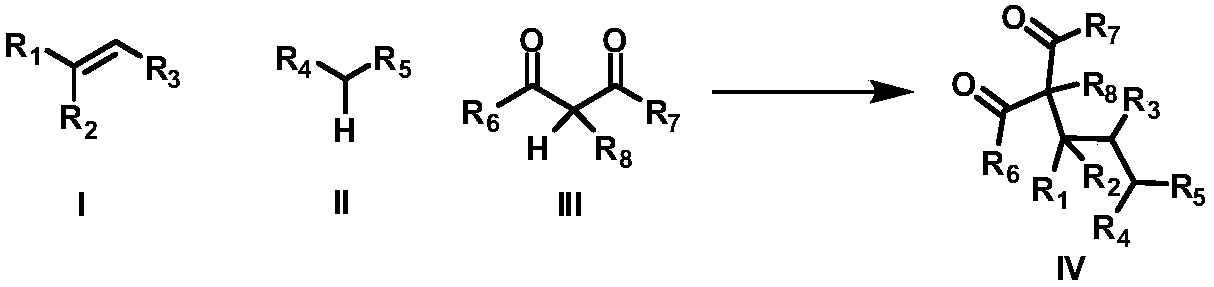
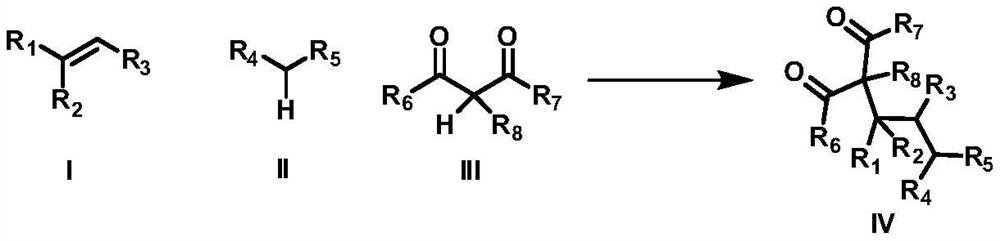
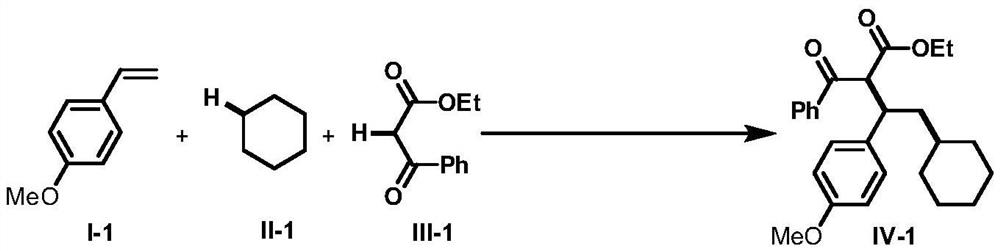
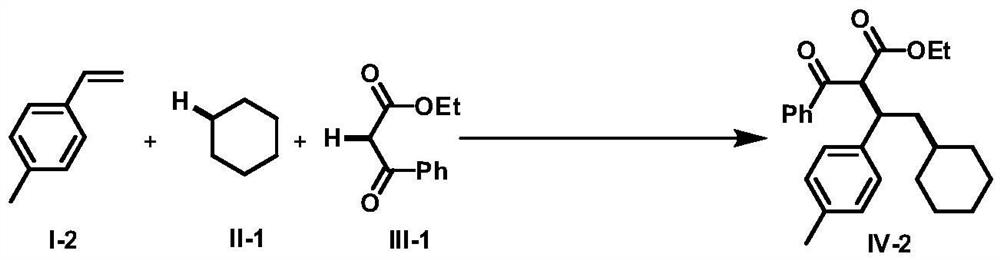
Intermolecular 1,2-dialkylation reaction method of olefine compound under photoredox/iron (II) catalytic system
ActiveCN108640839AMild reaction conditionsLow reaction temperatureCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPolyamine CompoundPhotoredox catalysis
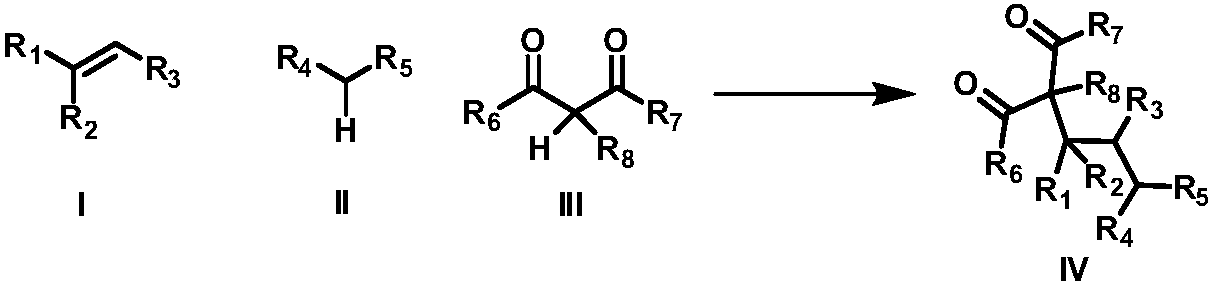
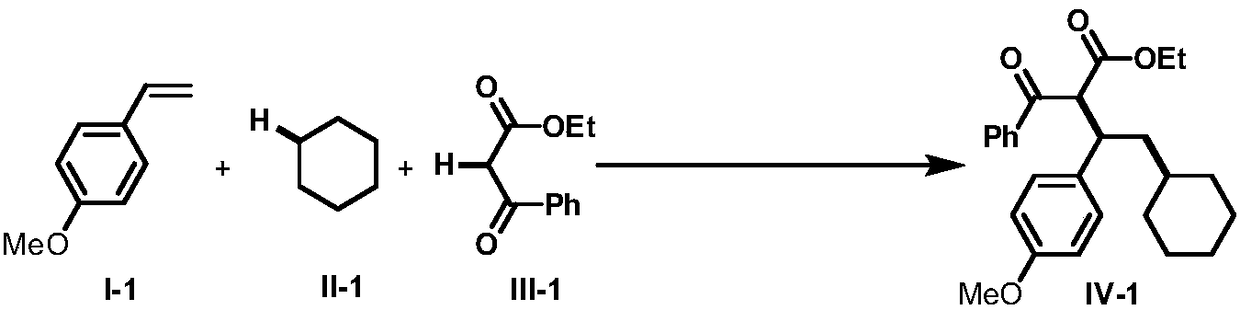
The invention discloses an intermolecular 1,2-dialkylation reaction method of an olefine compound under a photoredox / iron (II) catalytic system. According to the method, the olefine compound shown inI, a compound as shown in the formula II and a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound as shown in the formula III are subjected to intermolecular 1,2-dialkylation reaction of olefins under the photoredox catalysis / ferrous iron concerted catalytic system to obtain a series of compounds as shown in the formula IV. The method has the advantages that the technology is simple, reaction conditions are mild, the methodis environmentally friendly, the reaction substrates are wide in application range, and the yield is high.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
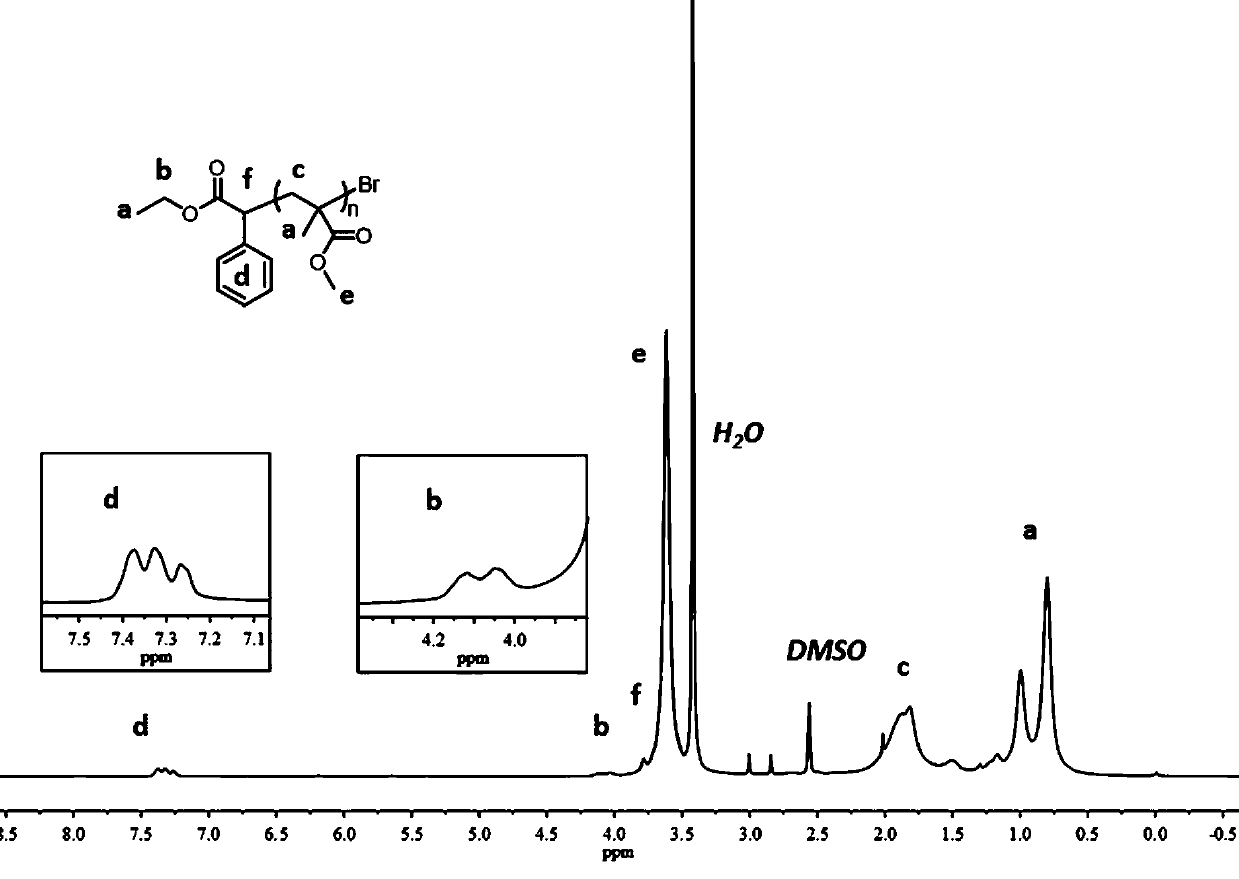
Using organic photoredox catalysts to achieve metal free photoregulated controlled radical polymerization
InactiveUS20170240660A1Efficient deactivationRapid reactivationRadical polymerizationPhotoredox catalysis
Disclosed are methods for controlled radical polymerization of acrylic monomers using an organic photoredox catalyst, where the polymerization is mediated, as well as regulated, by light.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Preparation method of aryl alkyne catalyzed by visible light
InactiveCN110386854AMild reaction conditionsImprove toleranceCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationArylPhotoredox catalysis
The invention discloses a simple and convenient method for directly synthesizing an aryl alkyne compound through photoredox catalysis. Aryl fluoroborate diazoate is used as an aryl free radical source, and different types of aryl alkyne are synthesized in situ through a decarboxylation process. A reaction has good functional group tolerability, and a simple domestic visible light source can be used for synthesizing the aryl alkyne of different functional groups under mild, neutral and transition-free metal reaction conditions.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
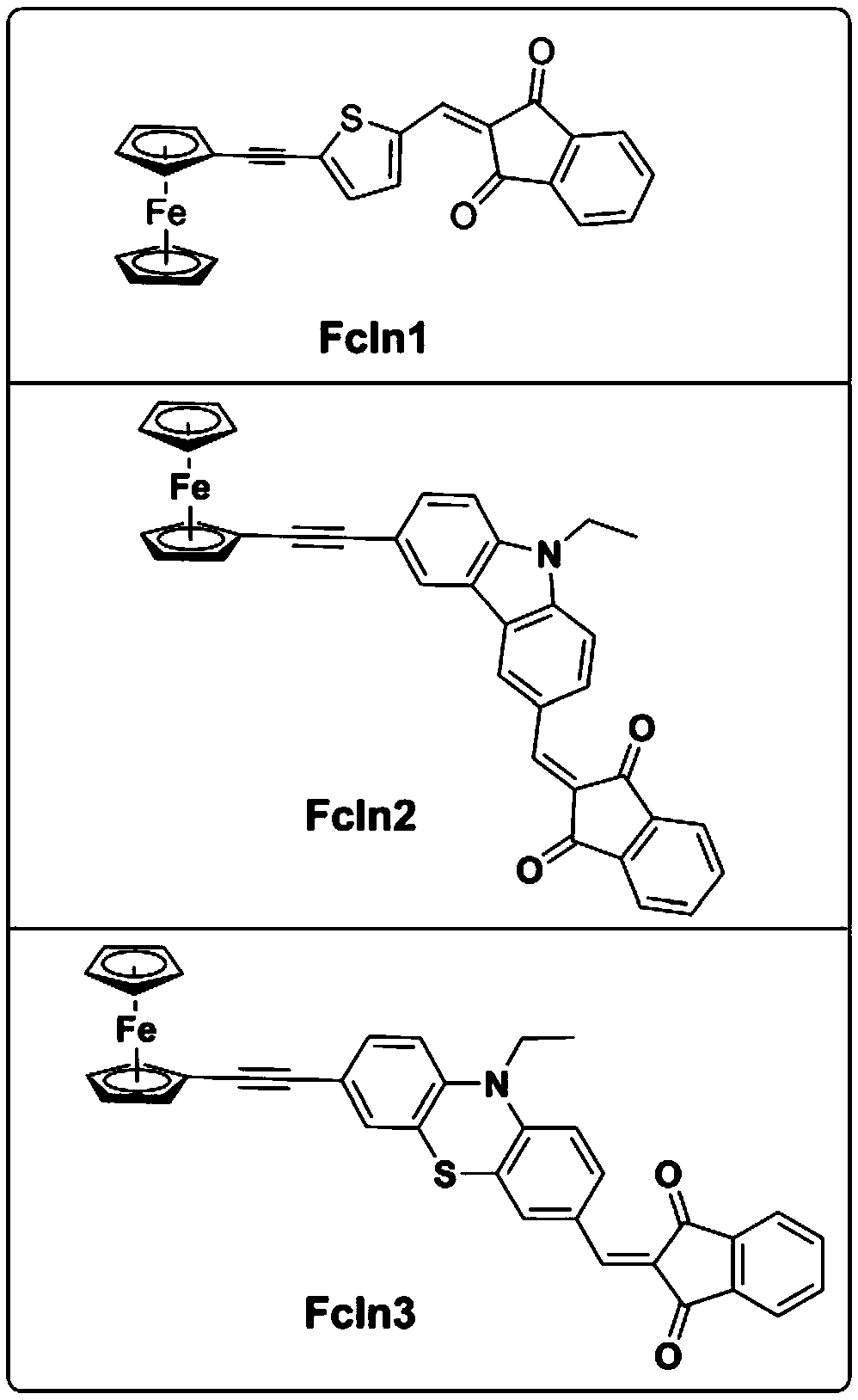
Ferrocene derivative used as photo-oxidation reduction catalyst in photo-polymerization and composition thereof
ActiveCN109232668AImprove redox performanceStrong absorption capacityMetallocenesPhotoredox catalysisElectron transfer
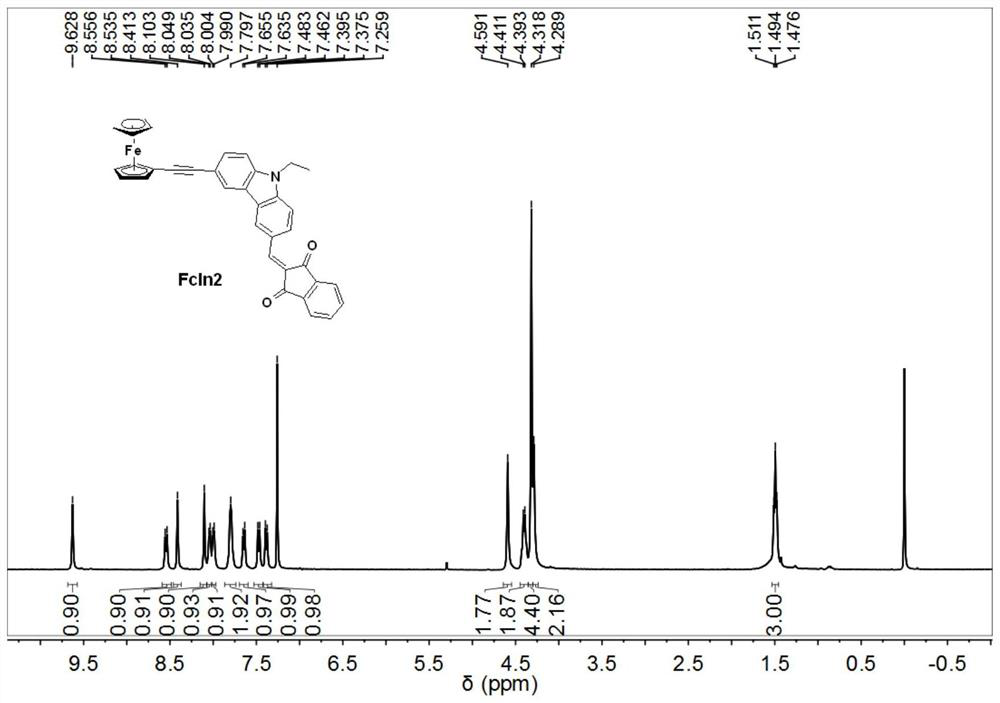
The present invention discloses a ferrocene derivative used as a photo-oxidation reduction catalyst in photo-polymerization and a composition thereof. The ferrocene derivative is obtained by connecting ferrocene and 1,3-indandione through a carbon-carbon triple bond / double bond and a conjugated bridged molecule; the ferrocene derivative has a D-Pi-A type molecular structure, and relatively strongintramolecular electron transfer ensures that the ferrocene derivative has strong absorption in blue-green regions, so that the ferrocene derivative is an effective photo-oxidation reduction catalyst;and a photo-initiation system formed by the ferrocene derivative, an onium salt photo-initiator and an amine compound can effectively induce free radical photo-polymerization under visible light LEDlight sources.
Owner:安庆北化大科技园有限公司
Method of preparing organic porous material through photo-induced electro transfer - reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization
The invention discloses a method of preparing an organic porous material through photo-induced electro transfer - reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT) in an oil / water / oil (O / W / O) double emulsion system. The method includes steps of: under stirring, dropwise adding an oil phase to a water phase, wherein the oil phase includes a polymerizable functional monomer, a crosslinker, a chain transfer reagent and a surfactant and a continuous phase is a water solution of a photo-redox catalyst; dropwise adding an organic solvent to a water phase, continuously stirring the mixture for a certain time to form an oil / water emulsion (O / W); dropwise adding the O / W emulsion to an organic solvent containing a surfactant and further stirring the mixture to prepare the O / W / Oemulsion; feeding nitrogen to displace oxygen, and performing light-irradiation polymerization reaction at room temperature to obtain the organic porous material. The organic porous material has a regular spherical structure, and contains large quantity of pores on surface and in interior.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
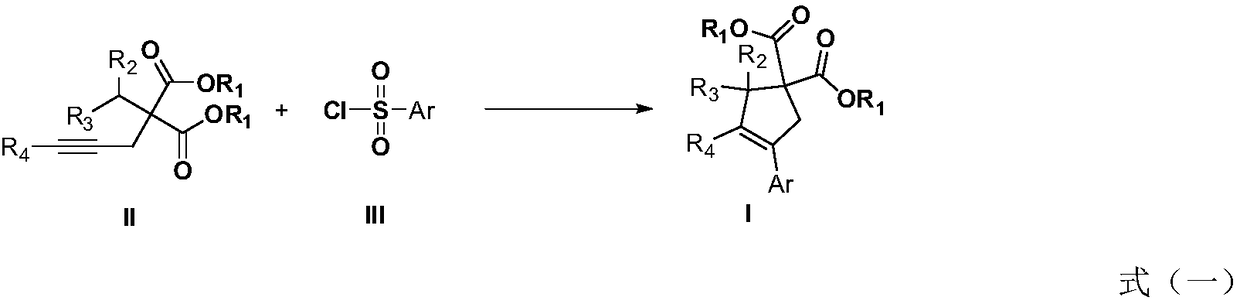
Method for performing C(sp3)-H functionalization cyclization reaction under photooxidation reduction catalytic system
InactiveCN108623467AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationArylSulfonyl chloride
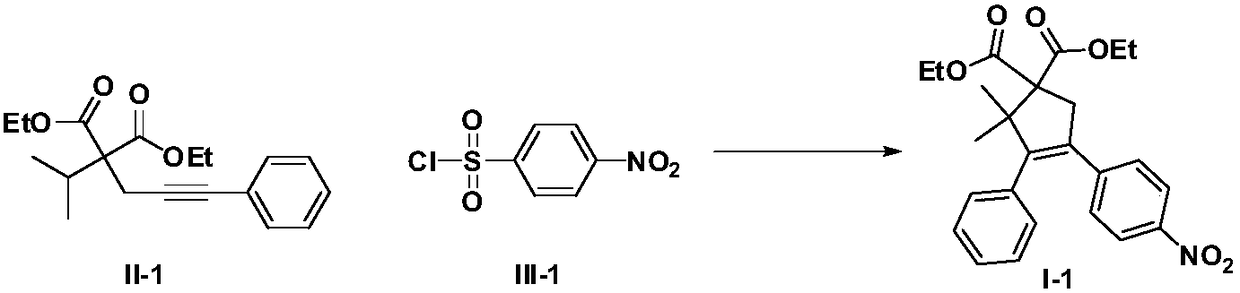
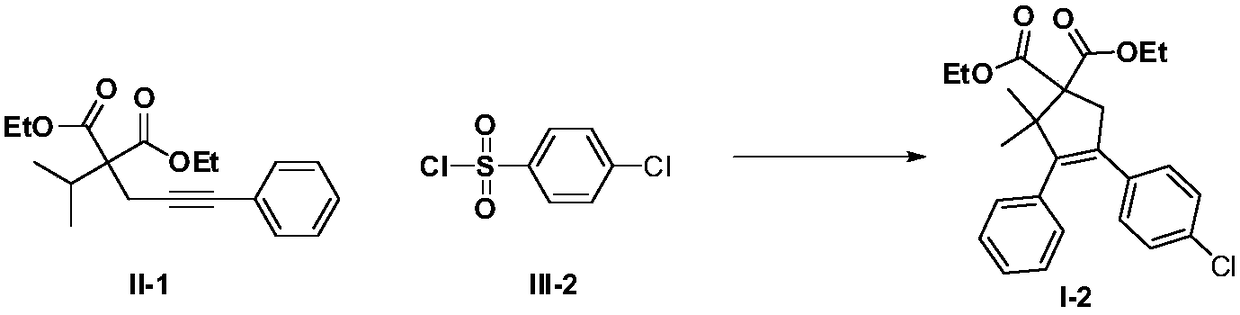
The invention discloses a method for performing C(sp3)-H functionalization cyclization reaction under a photooxidation reduction catalytic system. Under the photooxidation reduction catalytic system,aryl sulfonyl chloride as shown in a formula III which serves as a free radical donor and a 2-alkyl-2-propargyl malonate compound as shown in a formula II are subjected to oxidation quenching circulation mechanism to synthesize a series of five-memberred ring compounds as shown in a formula I. (The formulas are as shown in the description).
Owner:安徽古尔特科技有限公司
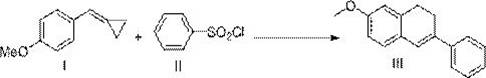
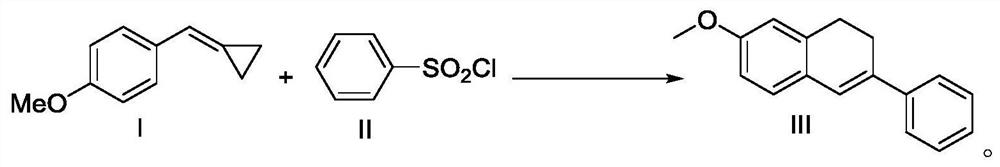
Preparation method of 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
ActiveCN109956854AConvenient sourceHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPhotoredox catalysisCyclopropane
The invention discloses a preparation method of 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene. 4-methoxyphenylmethylene cyclopropane and benzenesulfonyl chloride are used as raw materials to directly prepare the 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene. According to the method, the raw materials are easily available, compared with the prior art, the cost is remarkably reduced, and the process route is shortened. The technological condition of the method is a photo-oxidation reduction catalysis system, which has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simplicity, feasibility, high target product yield, catalyst recycling and low cost.
Owner:HUNAN FIRST NORMAL UNIV
Using organic photoredox catalysts to achieve metal free photoregulated controlled radical polymerization
Disclosed are meihods for controlled radical polymerization of acrylic monomers using an organic photoredox catalyst, where the polymerization is mediated, as well as regulated, by light.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Application of binaphthol derivatives in aspect of active free radical photopolymerization reaction
The invention discloses application of binaphthol derivatives in the aspect of active free radical photopolymerization reaction, and relates to the field of controllable active free radical polymerization catalyzed by organic photocatalysts, in particular to an organic catalytic system which takes 1, 1'-bi-2, 2'-naphthol derivatives as organic photocatalysts and generates activity-controllable free radical photopolymerization under visible light. According to the invention, a BINOL polymer is used as an organic photooxidation reduction catalyst, so that rapid reversible equilibrium between dormant species and an active chain can be achieved, the polymerization reaction has controllability, and a novel application method for the BINOL organic polymer in the organic photocatalytic active free radical polymerization is provided while a homopolymer and a block copolymer with characteristics of the controllable molecular weight and the low polydispersity can be prepared; and moreover, the organic catalytic system provided by the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency, low cost and easiness in operation, and the prepared polymer has the characteristics of the controllable molecular weight and the narrow polydispersity, and conforms to the production concept of environment-friendly green production.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
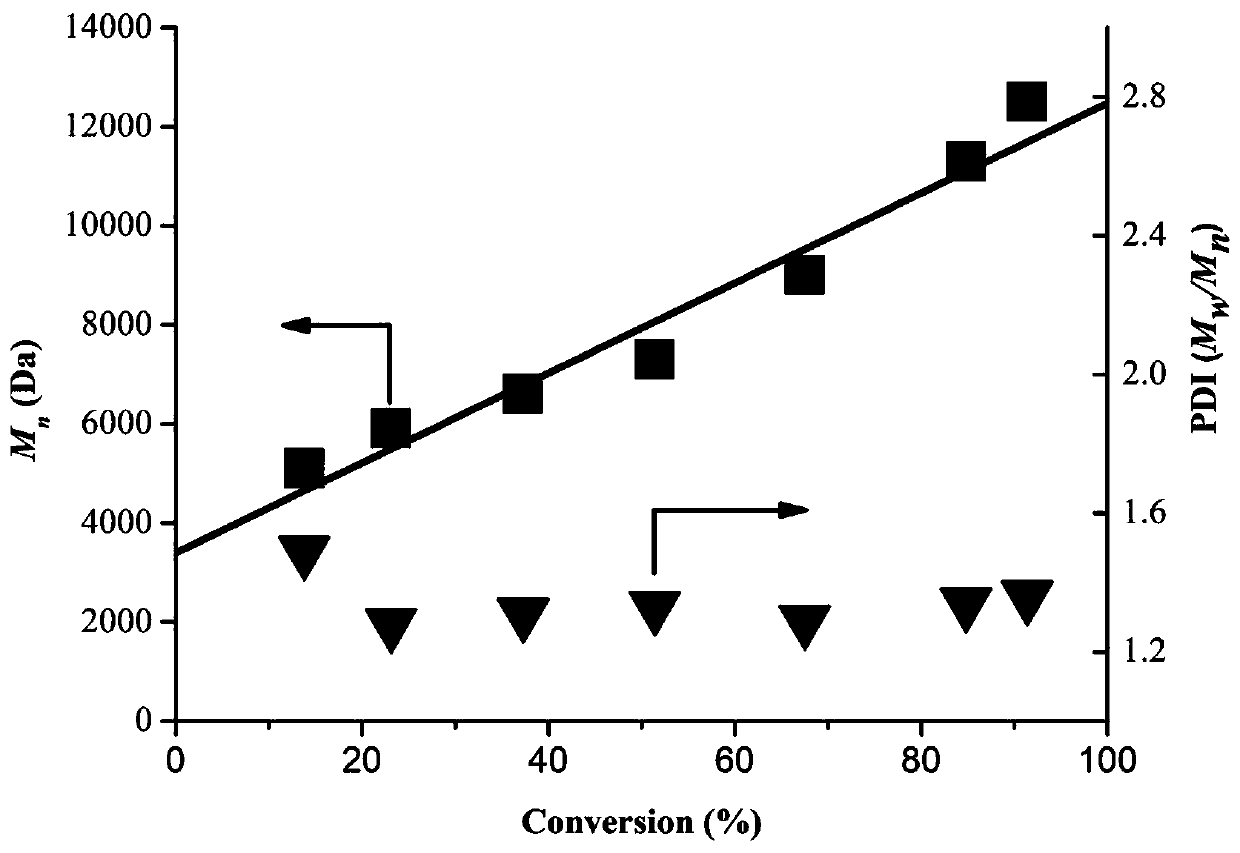
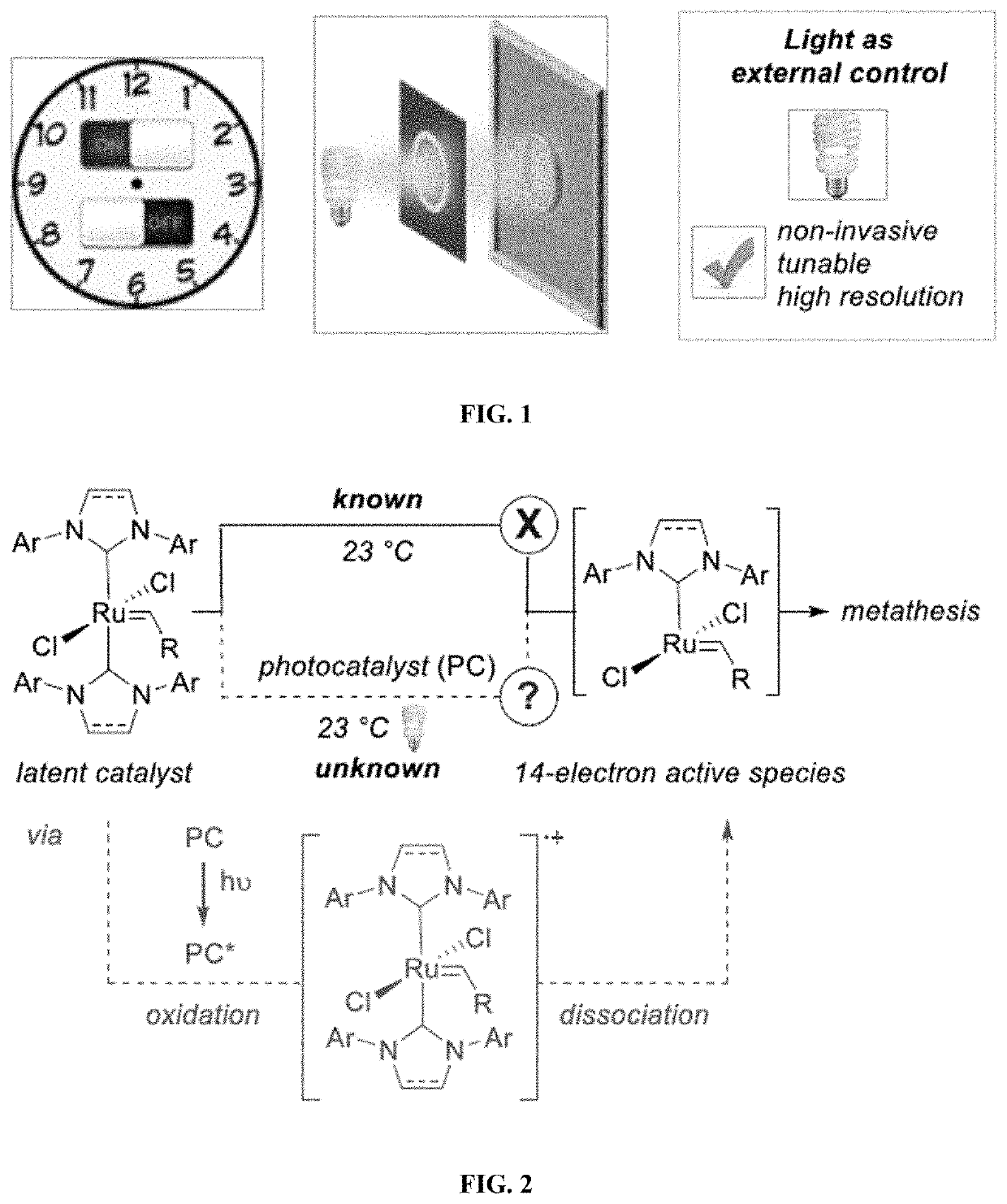
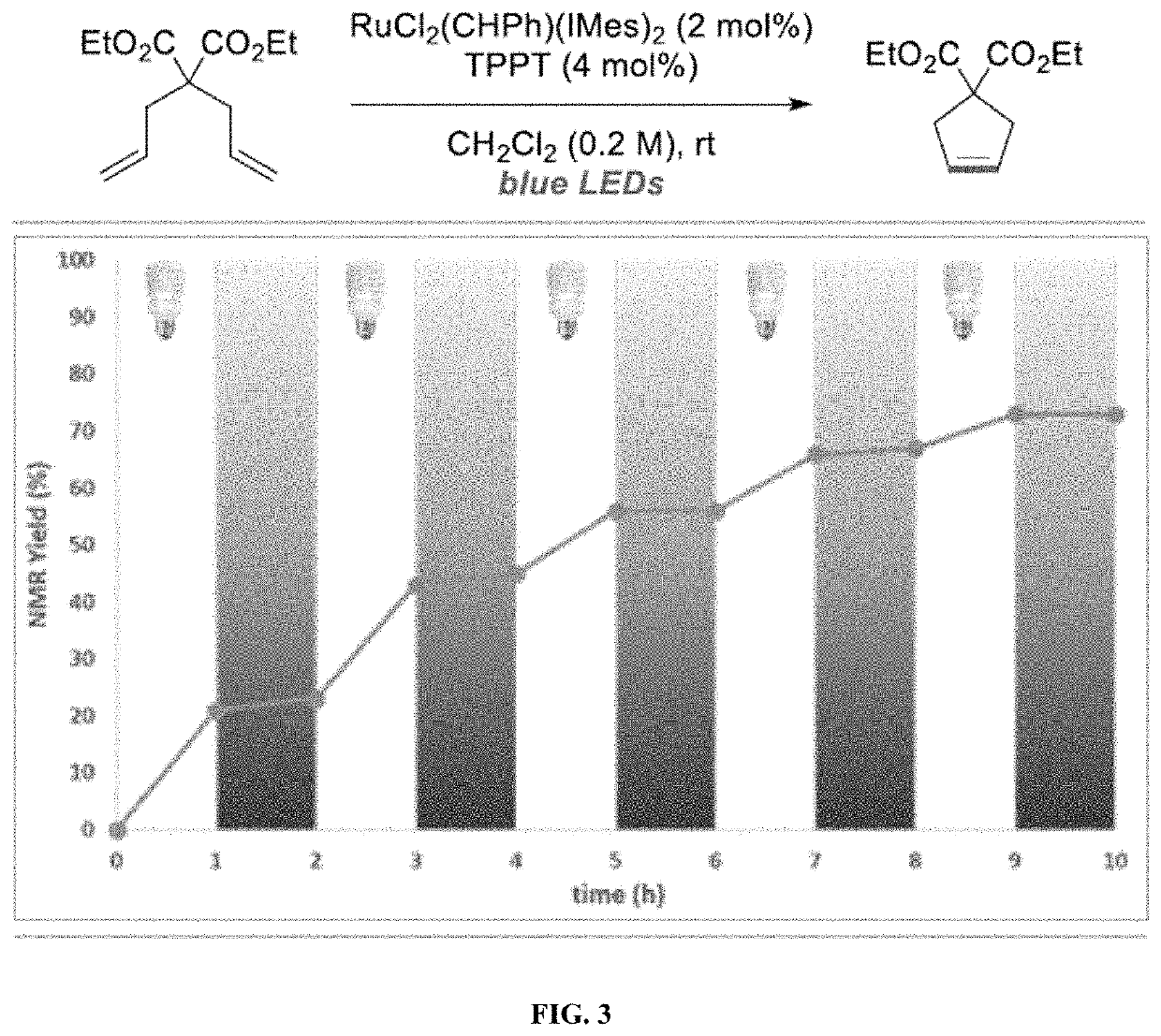
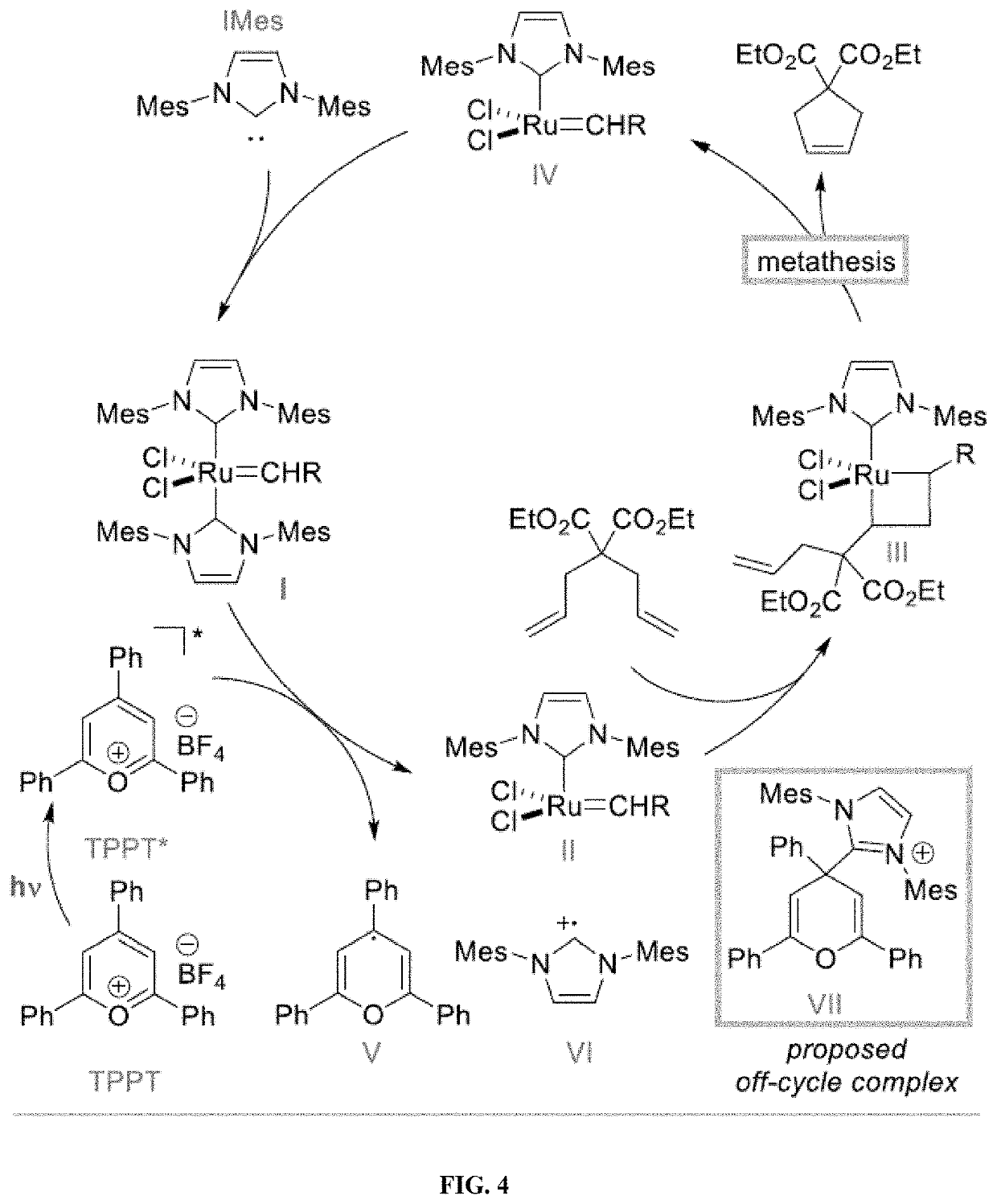
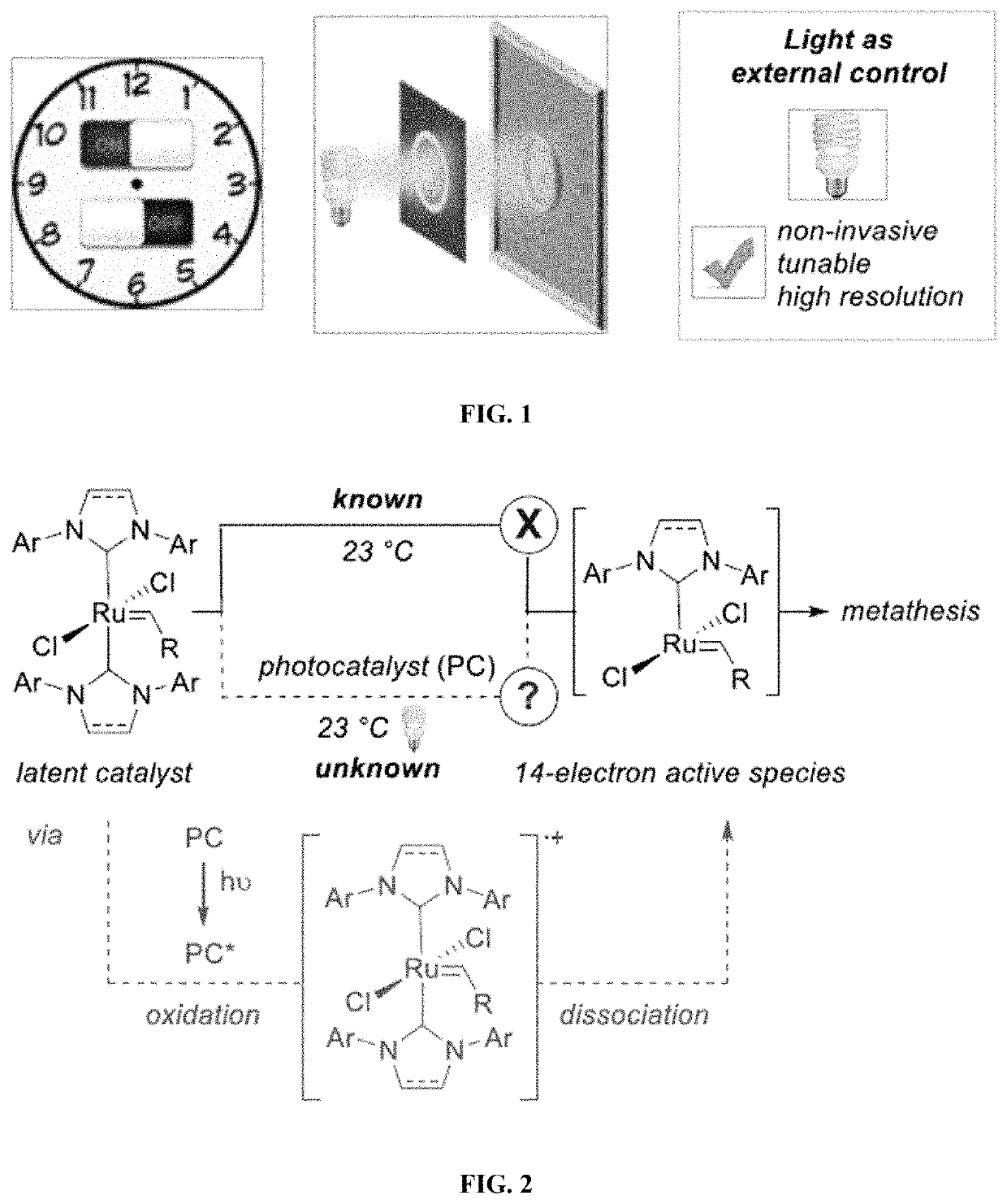
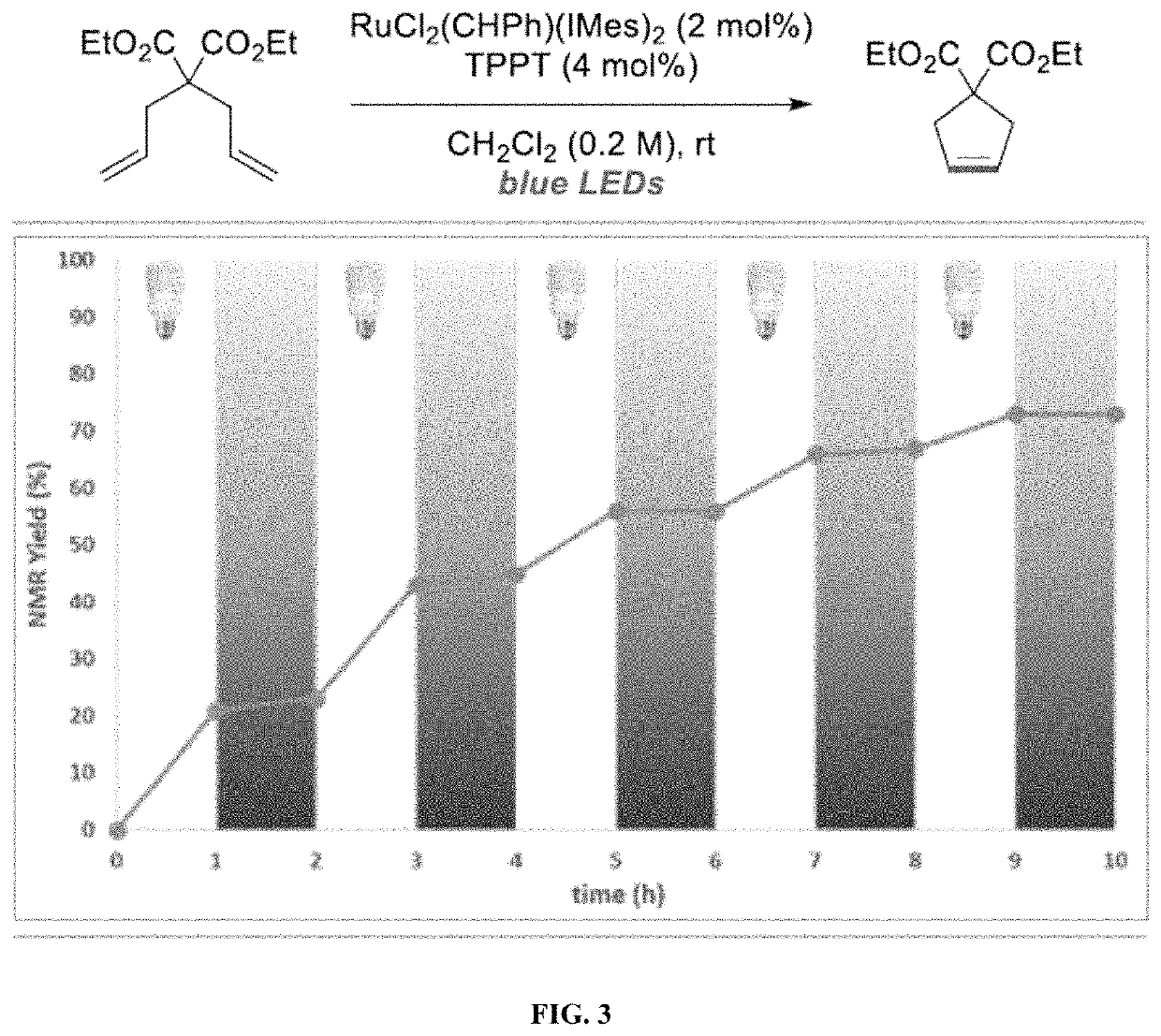
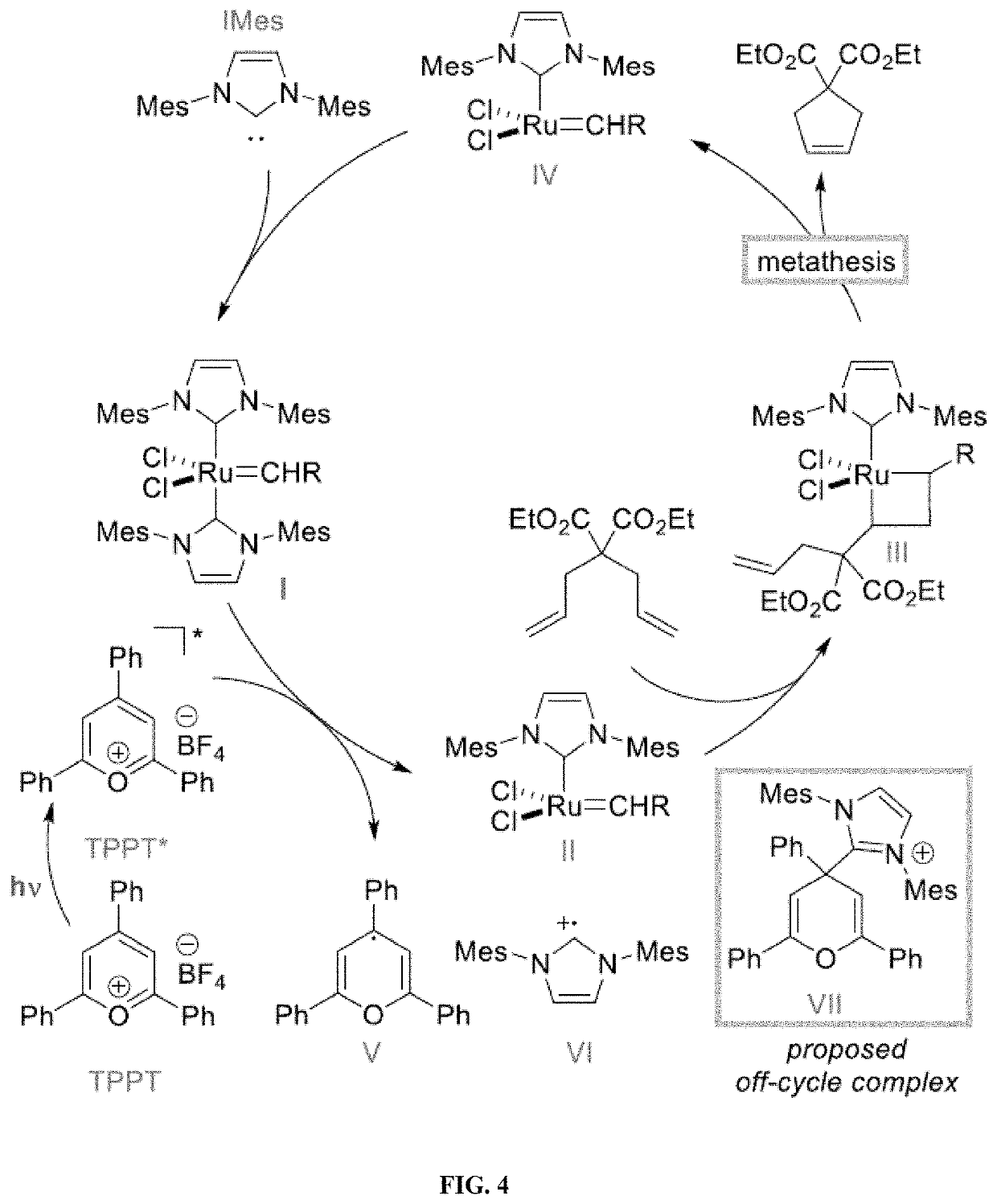
Compositions And Methods For Visible-Light-Controlled Ruthenium-Catalyzed Olefin Metathesis
ActiveUS20200108381A1Minimal reagent requirementReducing and even eliminating needRuthenium organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationPtru catalystRuthenium
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for metathesizing a first alkenyl or alkynyl group with a second alkenyl or alkynyl group, the composition comprising a ruthenium metathesis catalyst and a photoredox catalyst that is activated by visible light.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for realizing N-alpha site arylation of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring by photocatalysis
PendingCN114805107AImprove efficiencyAchieving direct arylationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationPtru catalystOrganic synthesis
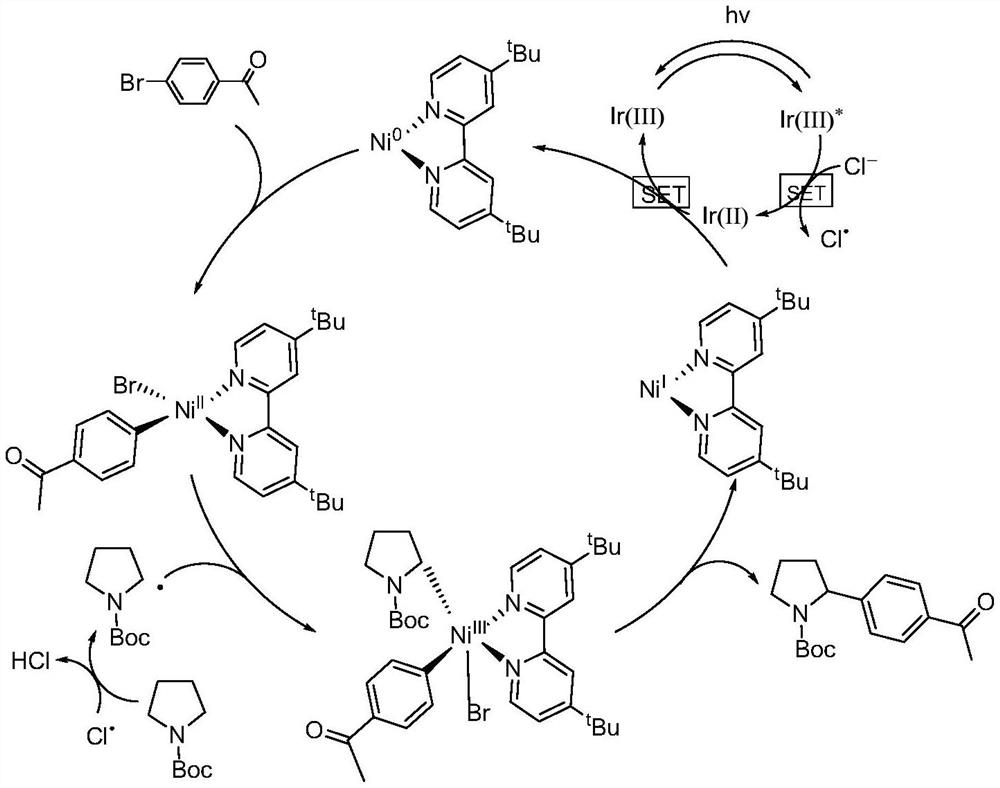
The invention discloses a method for realizing N-alpha site arylation of a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring by photocatalysis, relates to the technical field of catalytic synthesis, and in particular relates to a method for realizing N-alpha site arylation of the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring by photocatalysis under the condition of no additional HAT reagent. The method comprises the following steps: adding a brominated aromatic compound, a nitrogen-containing compound, Ir [dF (CF3) ppy] 2 (dtbbpy) PF6, nickel chloride, 4, 4-di-tertbutyl-2, 2-dipyridyl and alkali into a mixed solvent to obtain a reaction mixed solution, and performing light source irradiation at room temperature in an inert gas atmosphere to obtain the nitrogen heterocyclic ring N-alpha-position aryl compound. The coupling of C (sp3)-C (sp2) is completed under the condition that no HAT reagent is added, and the reaction is simple and convenient; and the cheap brominated aromatic compound and the photosensitizer are used, so that the economic and environment-friendly characteristics of the reaction are reflected. The method disclosed by the invention is very simple to operate, the raw materials are commercially available, the reaction can be realized at a higher yield by using a catalytic amount of a photooxidation reduction catalyst, and the method is high in atom economy and has wide substrate universality. The method is applied to the field of organic synthesis.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
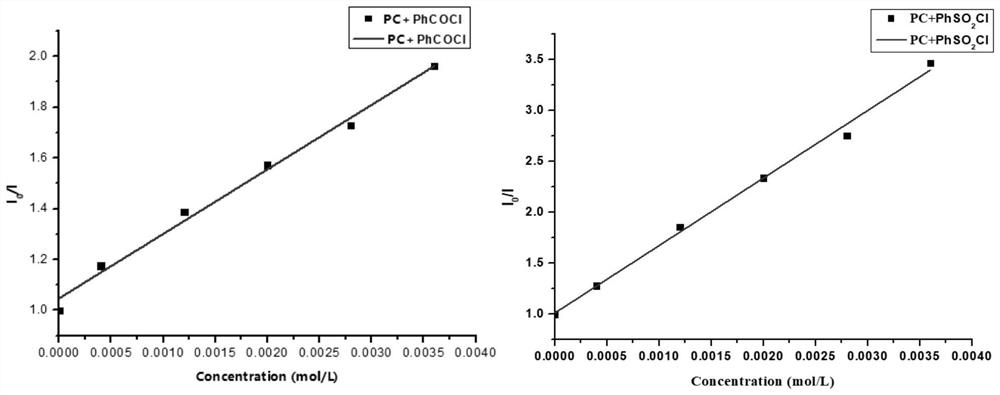
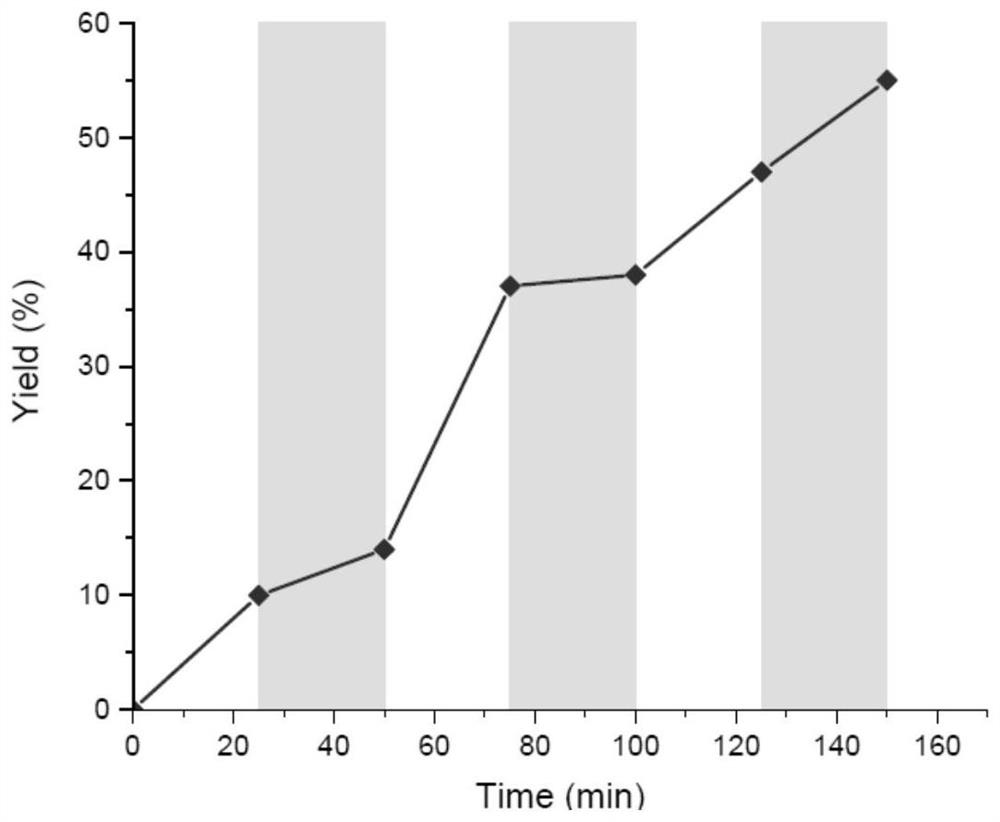
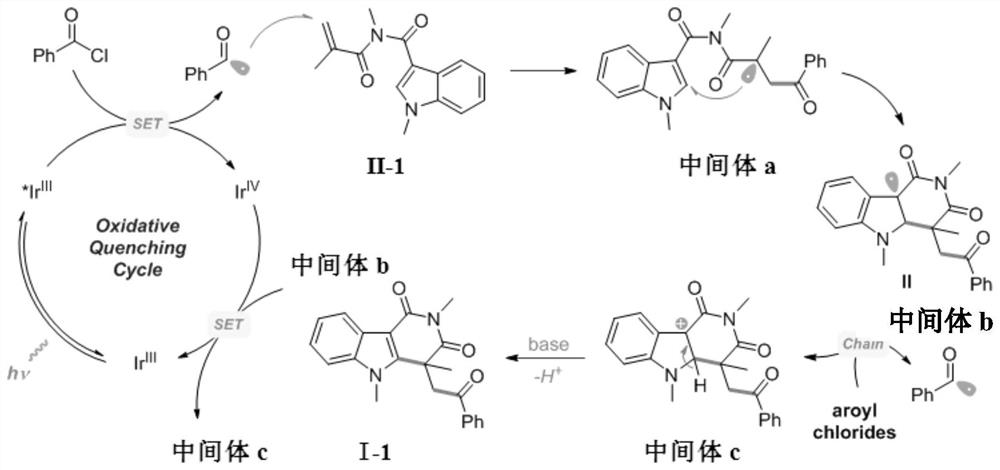
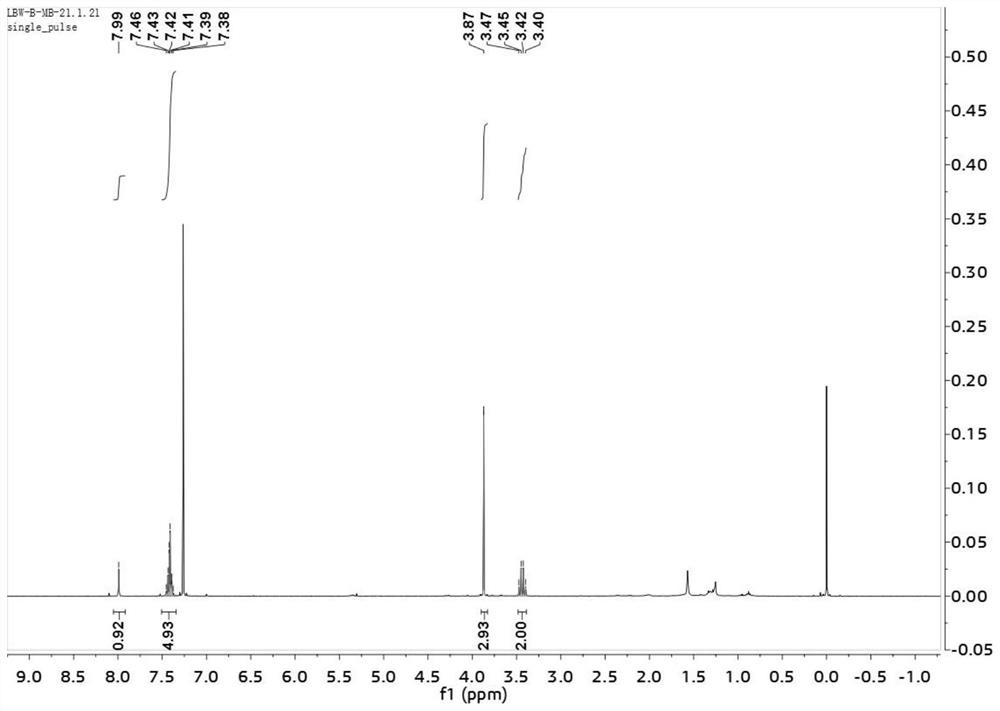
Method for preparing indolotetrahydropyridinedione and derivative thereof through photo-initiated free radical cascade reaction and product
PendingCN113861193AMultiple synthetic valuesOrganic chemistrySulfonyl chlorideSimple Organic Compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing indolotetrahydropyridinedione and derivative thereof through photo-initiated free radical cascade reaction and a product, and belongs to the technical field of organic compound preparation. The invention discloses the method for preparing indolo tetrahydropyridinedione and a derivative thereof by photo-initiated free radical cascade reaction. The method mainly comprises the following steps: carrying out illumination reaction on an indole derivative and any one of acyl chloride or sulfonyl chloride in the presence of alkali under the catalysis of facic-Ir (ppy) 3 to obtain the indolo tetrahydropyridinedione and the derivative. The method belongs to a photo-oxidation reduction catalytic tandem cyclization reaction between a Michael receptor and a free radical (wherein the free radical is derived from acyl chloride or sulfonyl chloride). According to the preparation method of the photo-initiated free radical tandem reaction, free radical sources are wide, and a simple solution is provided for simple synthesis of various indolo tetrahydropyridinedione derivatives through a free radical tandem strategy.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Trifluoromethyl allyl compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113200856AEasy to synthesizeImprove conversion rateEsterified saccharide compoundsPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesTrifluoromethylationPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a trifluoromethyl allyl compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, allyl alcohol is directly used as a raw material, CF3SO2Na is selected as a trifluoromethylation reagent, a metal-free and cheap photooxidation reduction catalyst is used, and under the catalysis of an organic photooxidation reduction agent, a byproduct SO2 generated in situ is reused as an activated C-OH bond, so that the reaction is carried out in an environment-friendly manner under a mild condition. The allyl alcohol used in the preparation method disclosed by the invention is a MoritA-Baylis-Hillman alcohol allyl alcohol raw material which is simple to synthesize and high in conversion rate, the applicable substrate range is wide, and the preparation cost is low. In addition, the preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in steps, and has the characteristics of convenience in operation, environment friendliness, excellent stereoselectivity and broad-spectrum functional group tolerance. The trifluoromethyl allyl compound provided by the invention is a general precursor for preparing related CF3 molecules, has potential pharmaceutical activity and biological activity, and can be widely applied to biological and pharmaceutical active molecules.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for modifying protein tryptophan residues
PendingCN114262356ASuitable for research applicationsLow toxicitySerum albuminPeptide preparation methodsPtru catalystTryptophan
The invention discloses a method for modifying protein tryptophan residues, which is used for chemically modifying the protein tryptophan residues through irradiation of visible light with proper wavelength in the presence of a photooxidation reduction catalyst by taking a thioacetal compound or a derivative thereof as a substrate. A nontoxic organic compound or a metal organic compound can be used as a catalyst, visible light is used as a light source, and the method is suitable for laboratory and industrial proteomics research and application.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAY LAB PINGSHAN TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE CENT +2
A kind of preparation method of 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
ActiveCN109956854BConvenient sourceHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystMeth-
The invention discloses a preparation method of 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene, which uses 4-methoxyphenylmethylenecyclopropane and benzenesulfonyl chloride as raw materials, The 7-methoxy-3-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene is directly prepared, and the source of raw materials is easy to obtain. Compared with the prior art, the cost is significantly reduced and the process route is shortened. The process condition of the present invention is a photoredox catalysis system, which has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simplicity, high target product yield, recyclable catalyst and low cost.
Owner:HUNAN FIRST NORMAL UNIV
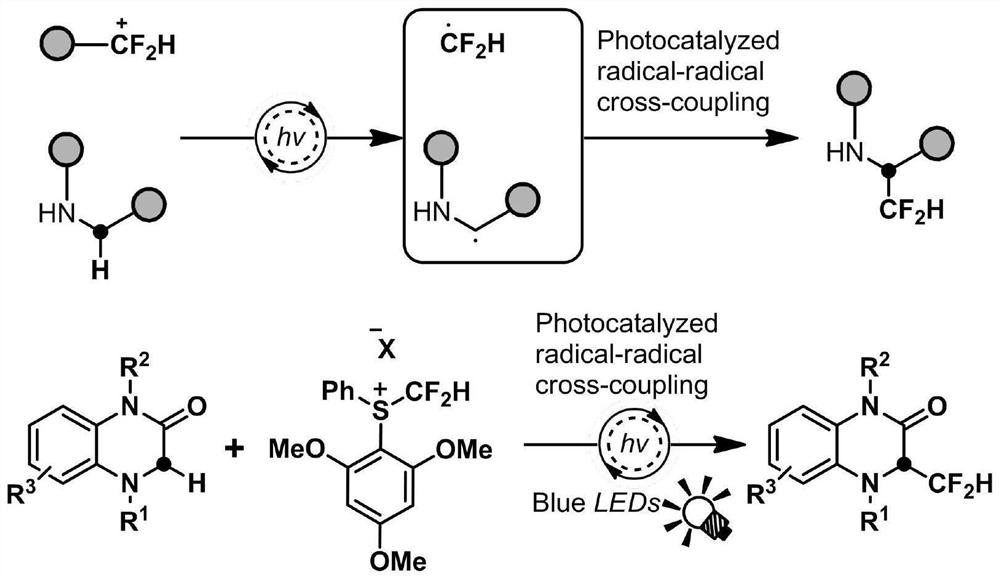
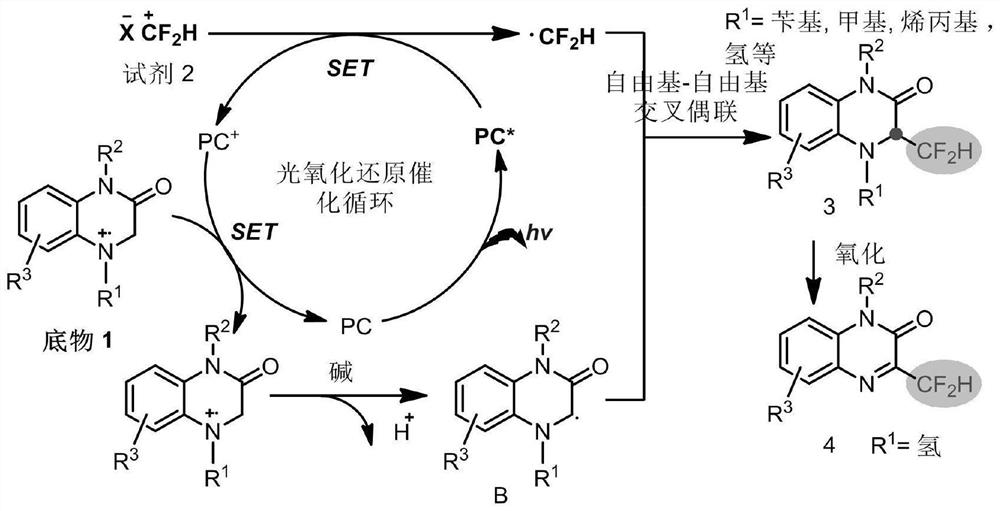
Difluoromethyl reaction method and application thereof
ActiveCN114685384AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugPhotoredox catalysis
The invention discloses a difluoromethyl reaction method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of medicine preparation. N heterocyclic rings, other amine compounds and a difluoromethyl reagent are adopted to react under the condition of photooxidation reduction catalysis, and construction of C (sp3)-CF2H is completed; the reaction under the photooxidation reduction catalysis condition is that a free radical cross-coupling reaction is carried out in a solvent containing alkali and a photocatalyst under the illumination condition with the wavelength of 350-550 nm, and the reaction time is 10 minutes to 72 hours. According to the method, the cross-coupling reaction of the C (sp3) free radical and the difluoromethyl free radical (. CF2H) is realized, so that the direct difluoromethyl functionalization reaction of C (sp3)-H is completed to construct the C (sp3)-CF2H building block, the method can be used for carrying out difluoromethyl functionalization on 3-site C of 1, 4-dihydroquinoxalinone in a wide range, and the method has the advantages of greenness, environmental protection, economy, convenience, high efficiency and good functional group compatibility.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Amines based on electron-rich fluoroaromatic hydrocarbons, and preparation method of amines
ActiveCN110294685AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationPhotoredox catalysisAmination
The invention provides amines based on electron-rich fluoroaromatic hydrocarbons, and a preparation method of the amines. The structure of the amines is as shown in a formula I. The invention also provides the preparation method of the amines based on the electron-rich fluoroaromatic hydrocarbons; the method concretely comprises the following steps: dissolving a compound a in an organic solvent together with a photosensitizer and a compound b at the temperature of 25 DEG C under the protection of argon, irradiating with blue light for 48-72h, reducing pressure and distilling, carrying out column chromatography, and leaching to obtain the amines. The preparation method provided by the application utilizes a photoredox catalytic principle mediated by visible light; compared with the traditional method, the method is more environmentally-friendly, milder in conditions and more suitable for amination of the electron-rich fluoroaromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Application of Binaphthol Derivatives in Living Radical Photopolymerization
ActiveCN110885388BReduce air sensitivityWell formedLiving free-radical polymerizationOrganocatalysis
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
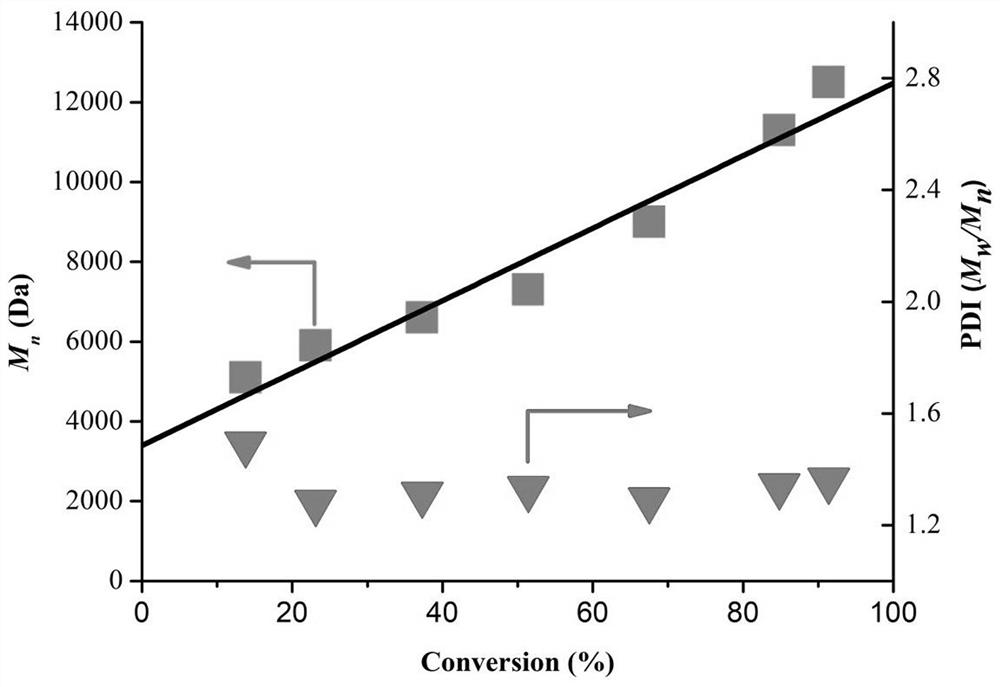
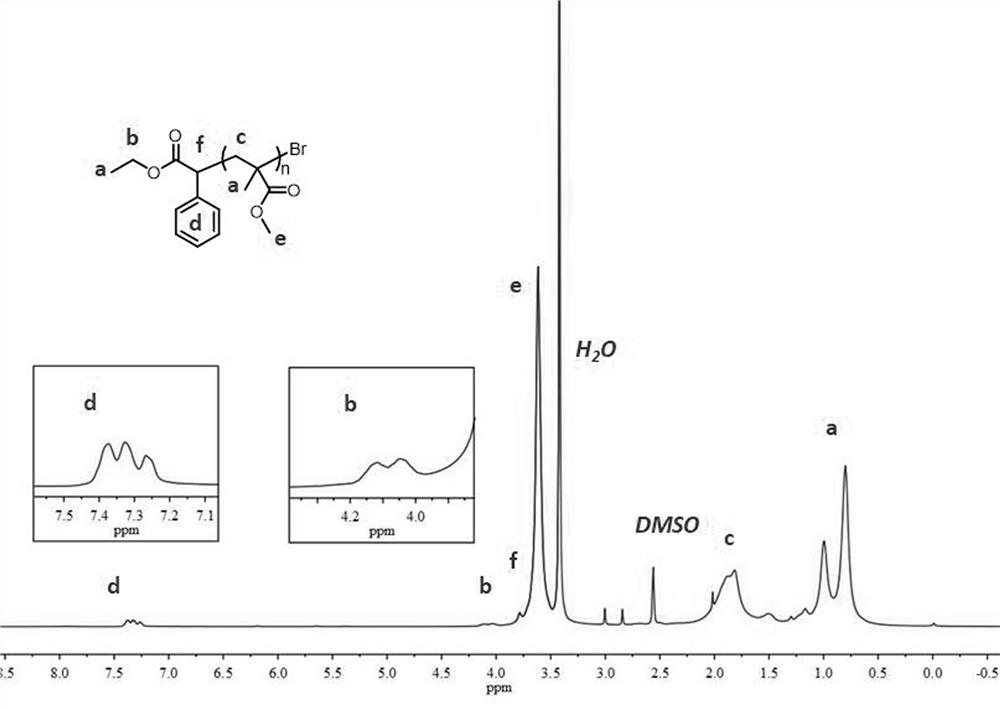
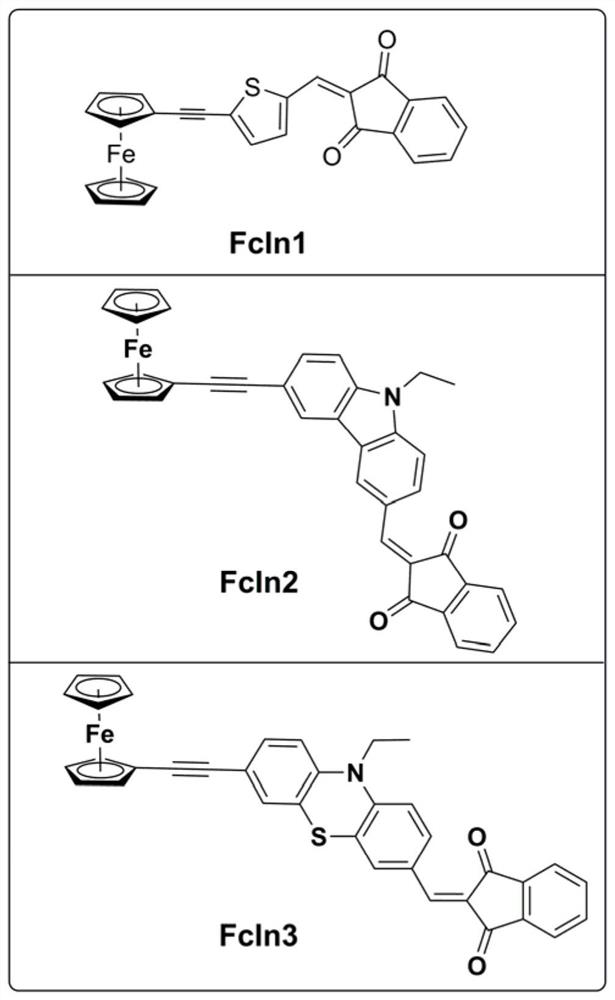
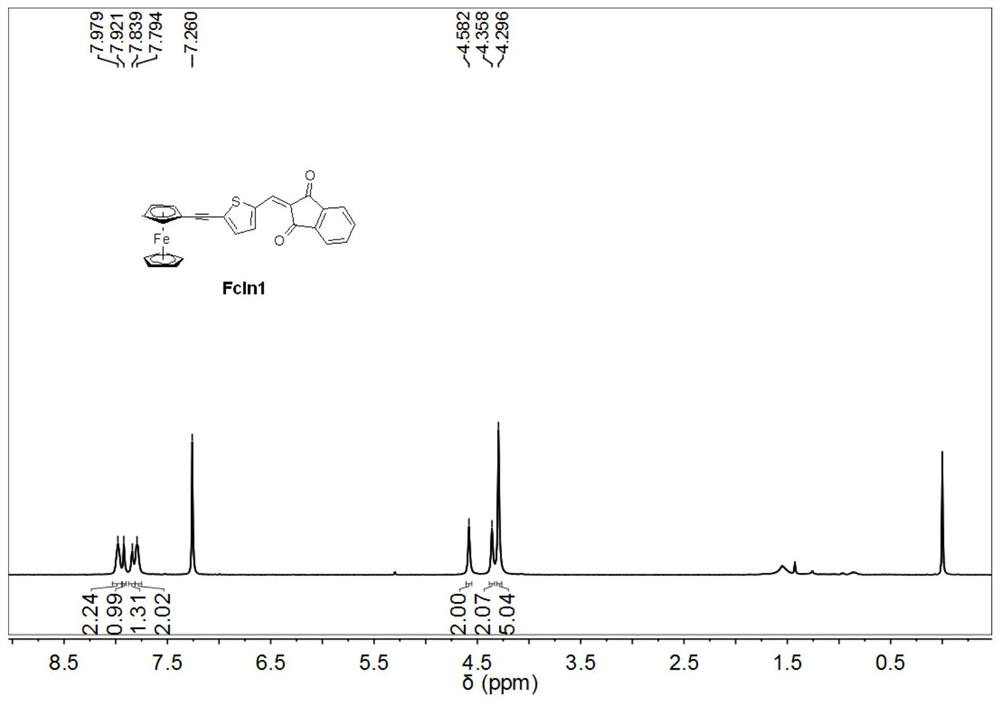
A kind of ferrocene derivative and composition thereof that can be used as photoredox catalyst in photopolymerization
ActiveCN109232668BImprove redox performanceStrong absorption capacityMetallocenesPtru catalystPhotoredox catalysis
The invention discloses a ferrocene derivative which can be used as a photoredox catalyst in photopolymerization and a composition thereof. The ferrocene derivative is a molecule bridged by a carbon-carbon triple bond / double bond and a conjugate It is obtained by connecting ferrocene and 1,3-indanedione. This type of ferrocene derivative has a molecular structure of D-π-A type, and its strong intramolecular electron transfer makes it have Strong absorption, is an effective photoredox catalyst; the photoinitiation system composed of ferrocene derivatives, onium salt photoinitiators and amine compounds can effectively initiate free radical light under visible light LED light source polymerization.
Owner:安庆北化大科技园有限公司
A visible light-catalyzed dehalogenation method of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons without photoredox catalyst
ActiveCN108002991BAchieve degradationPromote productionCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystOrganic synthesis
The invention discloses a visible light catalysis method for dehalogenation of aryl halide without the need of a photooxidation reduction catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of visible lightcatalysis organic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the aryl halide is weighed and placed in a reaction vessel, and a solvent is added; secondly, the reaction vessel isfilled with nitrogen for oxygen removal for 0-50 minutes, and alkali is added during the oxygen removal period; thirdly, the reaction vessel is sealed and placed over a light emitting diode with thewavelength of 400-500 nm and the power of 0.5-30 W for irradiation, and reacting is conducted for 3-48 hours at room temperature under the condition of stirring and then finished. By means of the method, the photooxidation reduction catalyst which is high in price or complex in synthesis is not needed, reacting can be achieved under the condition of the room temperature or under a mild condition,a reaction substrate is high in adaptability, and the reaction yield is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Additive Manufacturing Method Using Light-Tuned Radical Polymerization
ActiveCN107428092BAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresMethacrylateVinyl ether
A method for making a three-dimensional object, the method comprising: meth(acrylate), (meth)acrylamide, (meth)acrylonitrile, styrene, acrylonitrile, vinyl acetate, vinyl carbazole, at least one of vinylpyridine, vinyl ether, vinyl chloride monomer, polyfunctional monomer, and polyfunctional prepolymer combined with an organic photoredox catalyst to provide a reaction mixture; depositing the reaction mixture; by irradiating with a light source the reaction mixture polymerizes the monomer; and repeats the deposition step until the three-dimensional object is formed.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Direct aromatic carbon-oxygen and carbon-hydrogen bond functionalization via organic photoredox catalysis
PendingCN114190073ACarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationCyanide compoundAcridine
The present invention generally relates to methods for preparing substituted aromatics via direct C-H, C-O, C-S or C-N bond conversion and methods for synthesizing isotopically labeled substituted aromatics via direct carbon-halogen bond conversion. The invention also relates to an anaerobic catalyst system comprising an acridinium photocatalyst and a nucleophile selected from the group consisting of halides, cyanides and isotopically labeled amines. This abstract is intended as a scanning tool for purposes of searching in the particular art and is not intended to be limiting of the present invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
A kind of trifluoromethyl propenyl compound and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113200856BEasy to synthesizeImprove conversion rateEsterified saccharide compoundsPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesTrifluoromethylationPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a trifluoromethylpropenyl compound, a preparation method and application thereof. The present invention directly uses allyl alcohol as raw material, selects CF 3 SO 2 Na is used as a trifluoromethylation reagent, using a metal-free and inexpensive photoredox catalyst, under the catalysis of an organic photoredox agent, the by-product SO is generated in situ 2 is repurposed to activate the C‑OH bond, allowing the reaction to occur in an environmentally friendly manner under mild conditions. The allyl alcohol used in the preparation method of the present invention is the MoritA-Baylis-Hillman alcohol allyl alcohol raw material with simple synthesis and high conversion rate, a wide range of applicable substrates, and low preparation cost; in addition, the preparation method of the present invention has simple steps, It has the characteristics of convenient operation, environmental protection, excellent stereoselectivity, and tolerance to broad-spectrum functional groups; the trifluoromethylpropenyl compound of the present invention is the preparation of related CF 3 Universal precursors of molecules with potential drug activity and biological activity can be widely used in biologically and pharmaceutically active molecules.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A kind of preparation method of 1,1-diaryl alkane derivative
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for visible-light-controlled ruthenium-catalyzed olefin metathesis
ActiveUS11331656B2Reducing and even eliminating needMinimal requirementRuthenium organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationPtru catalystRuthenium
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for metathesizing a first alkenyl or alkynyl group with a second alkenyl or alkynyl group, the composition comprising a ruthenium metathesis catalyst and a photoredox catalyst that is activated by visible light.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
A method for intermolecular 1,2-dialkylation of olefins under a photoredox/iron(ii) catalytic system
ActiveCN108640839BMild reaction conditionsLow reaction temperatureCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationCombinatorial chemistrySynergistic catalysis
The invention discloses an intermolecular 1,2-dialkylation reaction method of olefin compounds under a photoredox / iron (II) catalytic system. The method uses the olefin compound shown in I, the compound shown in the formula II, and the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound shown in the formula III, under the photoredox catalysis / ferrous iron synergistic catalytic system, through the intermolecular of the alkene. The 1,2-dialkylation reaction yields a series of compounds of formula IV. The method has the advantages of simple process, mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness, wide application range of reaction substrates and high yield.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Photo-oxidation reduction catalysis method
ActiveCN113387837AReduce manufacturing costCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAlcoholBond cleavage
The invention relates to the technical field of synthetic chemistry, in particular to a photo-oxidation reduction catalysis method. The photo-oxidation reduction catalysis method comprises the steps of providing a linear tertiary alcohol compound and a free radical capture reagent; and carrying out catalytic reaction on the linear tertiary alcohol compound and the free radical capture reagent under the condition of a photocatalyst. According to the novel alcohol-extended alkyl radical chemistry method provided by the invention, under the condition of a photocatalyst, linear tertiary alcohol induces carbon-carbon bond breakage through single-electron oxidation to generate alkyl radicals, and then the alkyl radicals are captured by a radical capture reagent to react to obtain various products; and according to the photo-oxidation reduction catalysis method, the production cost for preparing the capture product is remarkably reduced, and the designability and the application prospect of the product are greatly expanded.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAY LAB PINGSHAN TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE CENT
Method of additive manufacturing using photoregulated radical polymerization
ActiveCN107428092AAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresMethacrylateVinyl ether
A method of fabricating a three-dimensional object, the method comprising: combining at least one of a meth(acrylate), a (meth)acrylamide, a (meth)acrylonitrile, a styrene, an acrylonitrile, a vinyl acetate, a vinylcarbazole, a vinylpyridine, a vinyl ether, a vinyl chloride monomers, a polyfunctional monomer, and a polyfunctional prepolymer with an organic photoredox catalyst to provide a reaction mixture; depositing the reaction mixture; polymerizing the monomers by irradiating the reaction mixture with a light source; and repeating the depositing step until the three-dimensional object is formed.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
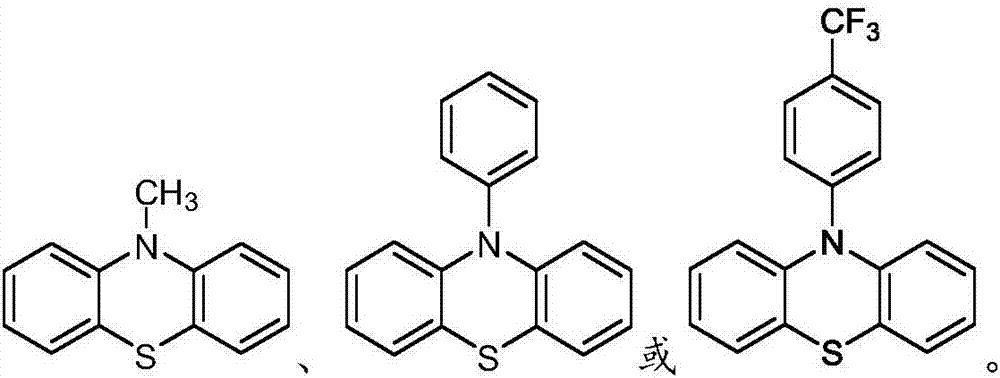
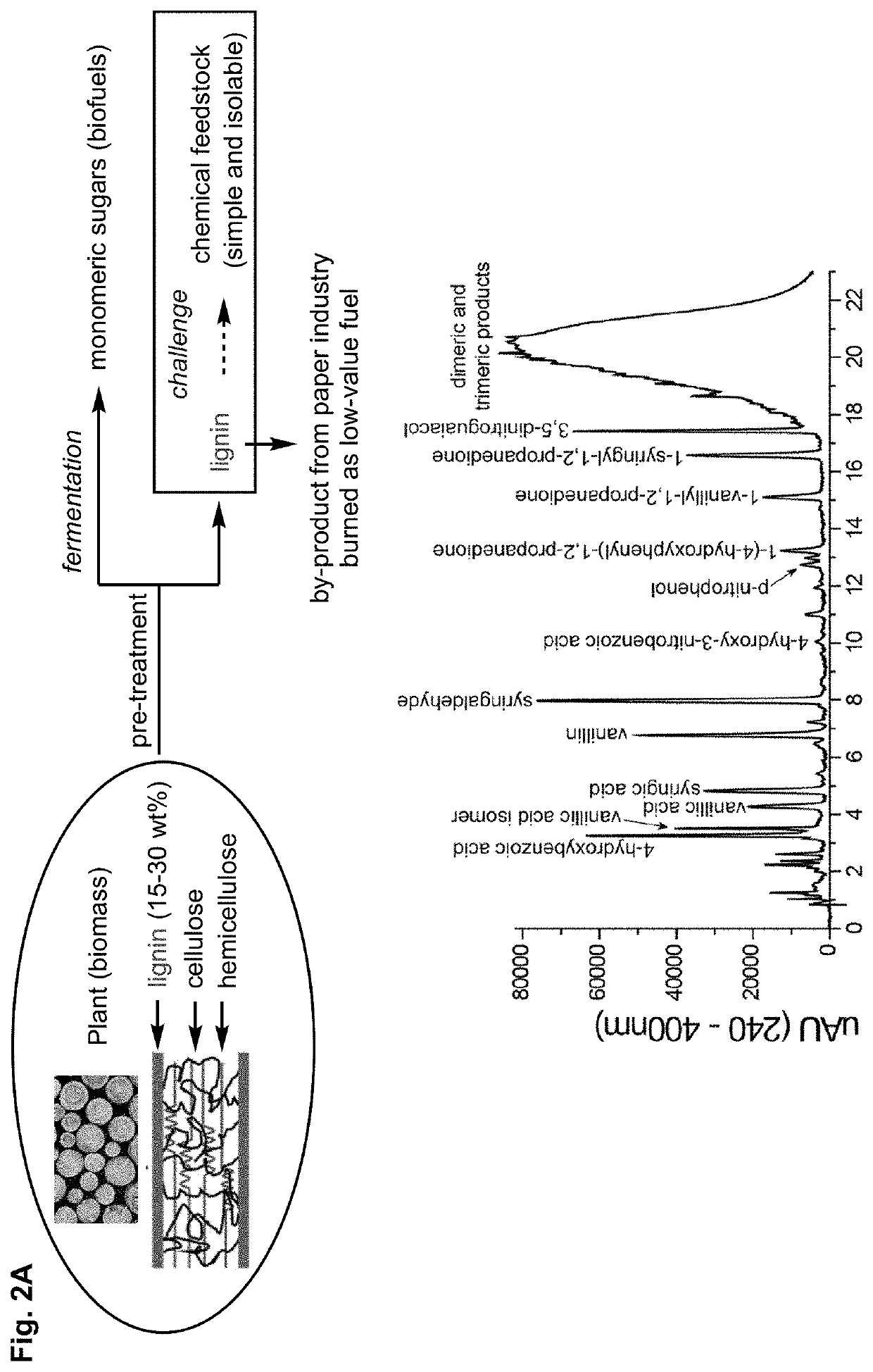
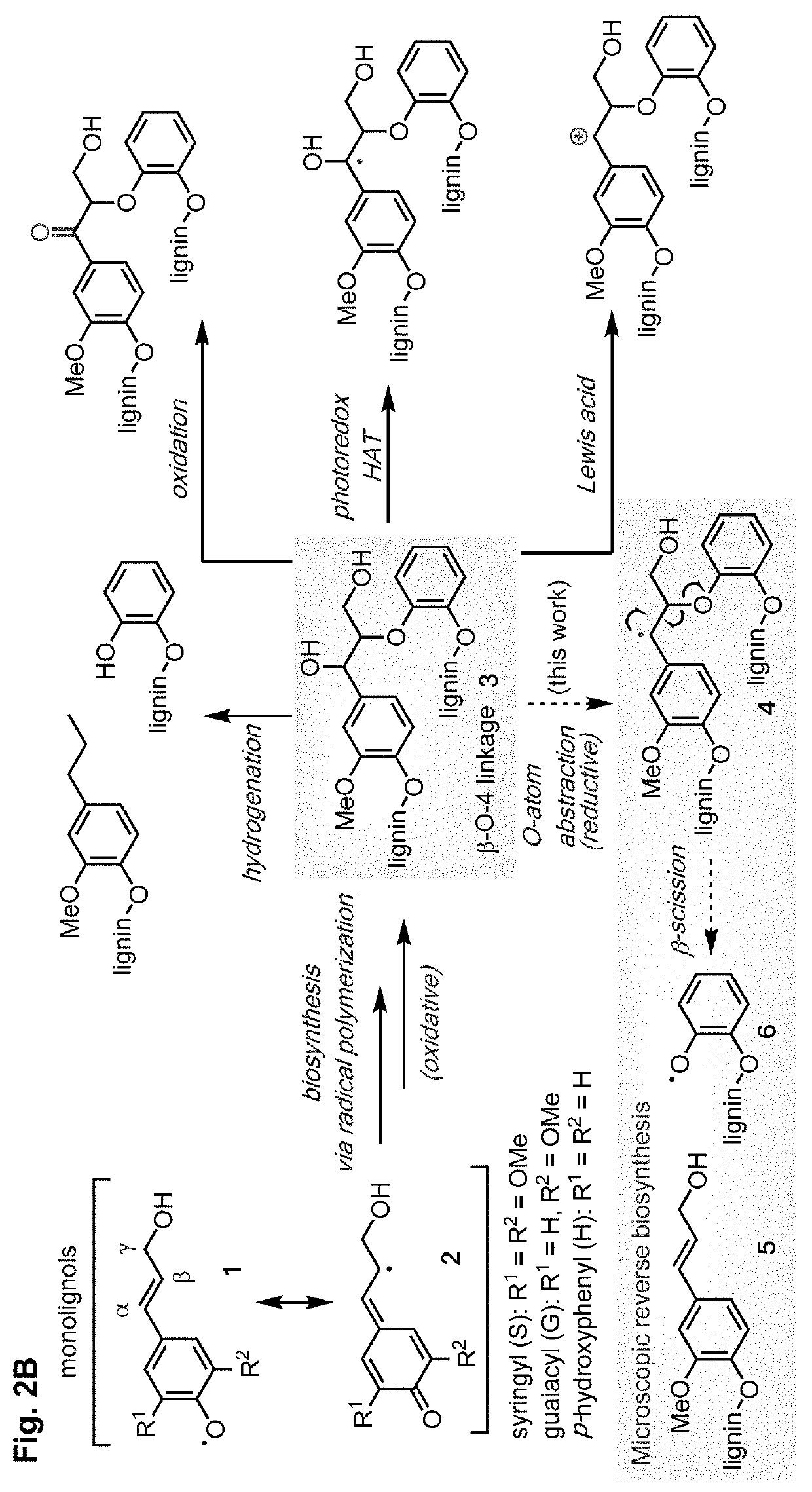
Depolymerization and valorization of a biopolymer
PendingUS20220324895A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLignin derivativesElectrochemical cellPhoto irradiation
A method of depolymerizing a biopolymer in a biomass is presented, the method comprising the step of contacting the biopolymer with a reaction system comprising at least one catalyst, at least one electron source, and at least one solvent. A second method of depolymerizing a biopolymer in a biomass is presented, the method comprising the step of contacting the biopolymer with an electrochemical cell comprising at least one catalyst, at least one solvent, at least one electrolyte, an anode, and a cathode. A third method of depolymerizing a biopolymer is presented, the method comprising the steps of providing a biopolymer; adding a photoredox-active functional group to the biopolymer to form a modified biopolymer; and irradiating the modified biopolymer with light in the presence of a reaction mixture; said mixture comprising a photoredox catalyst.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com