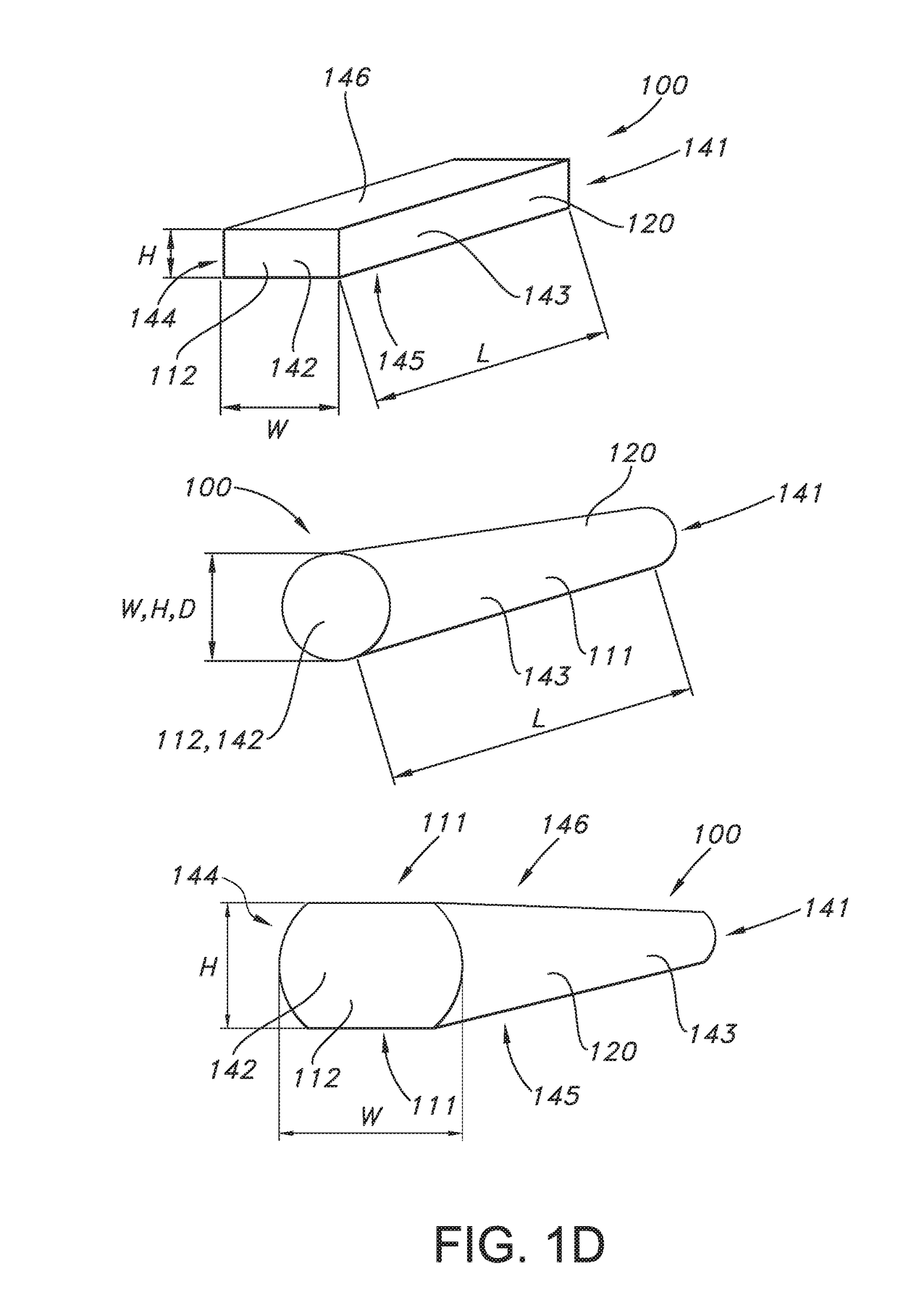
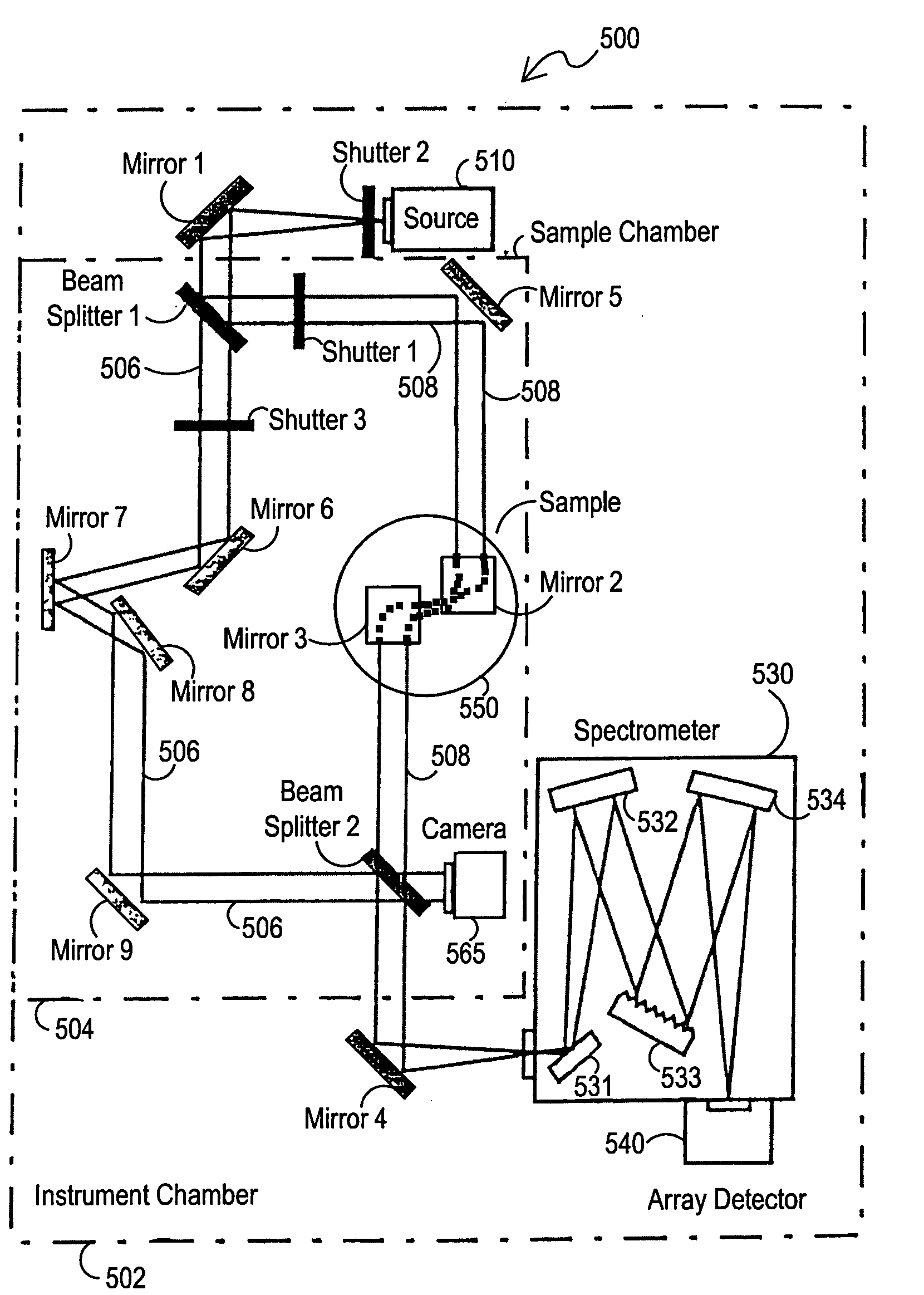
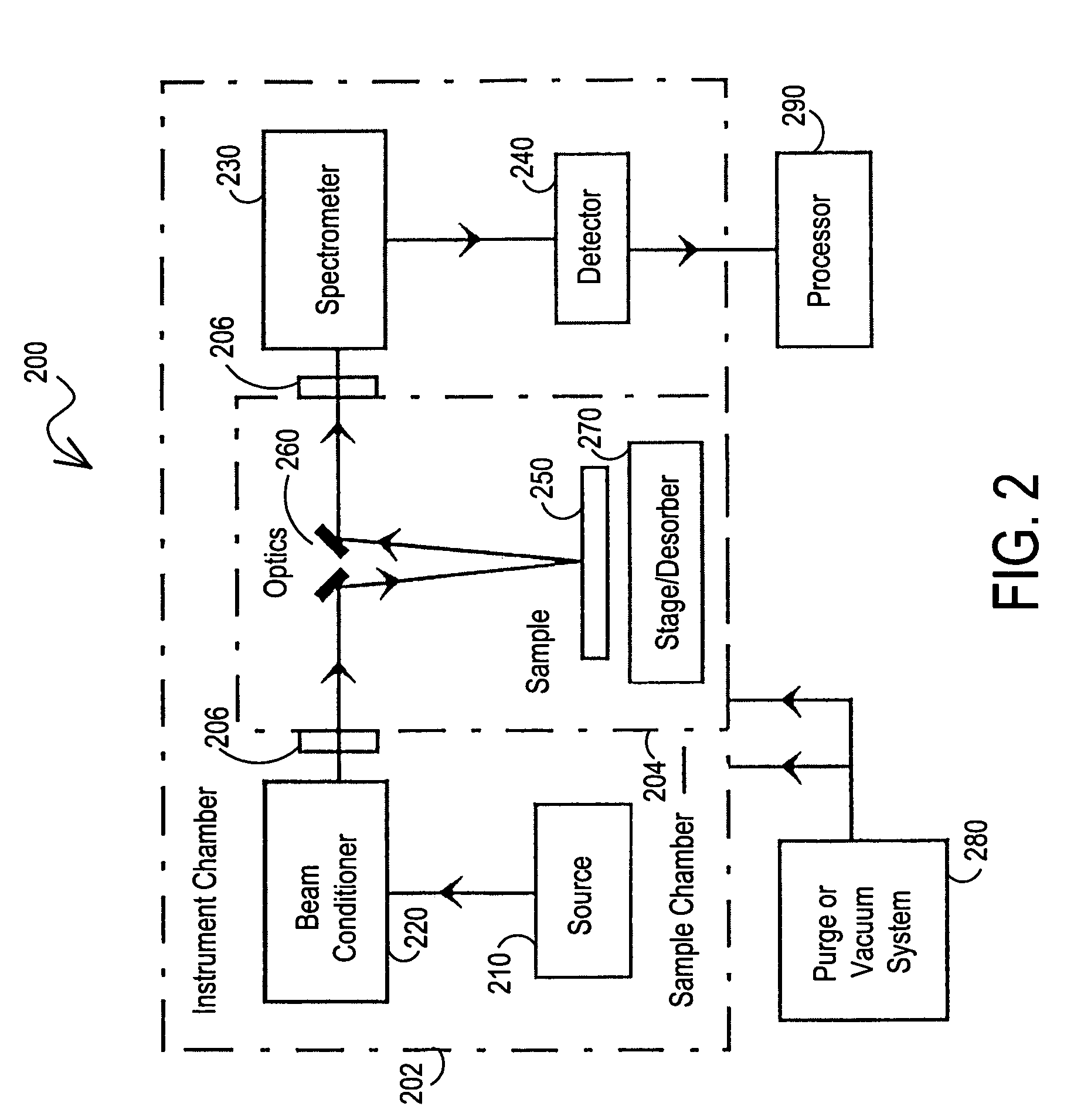
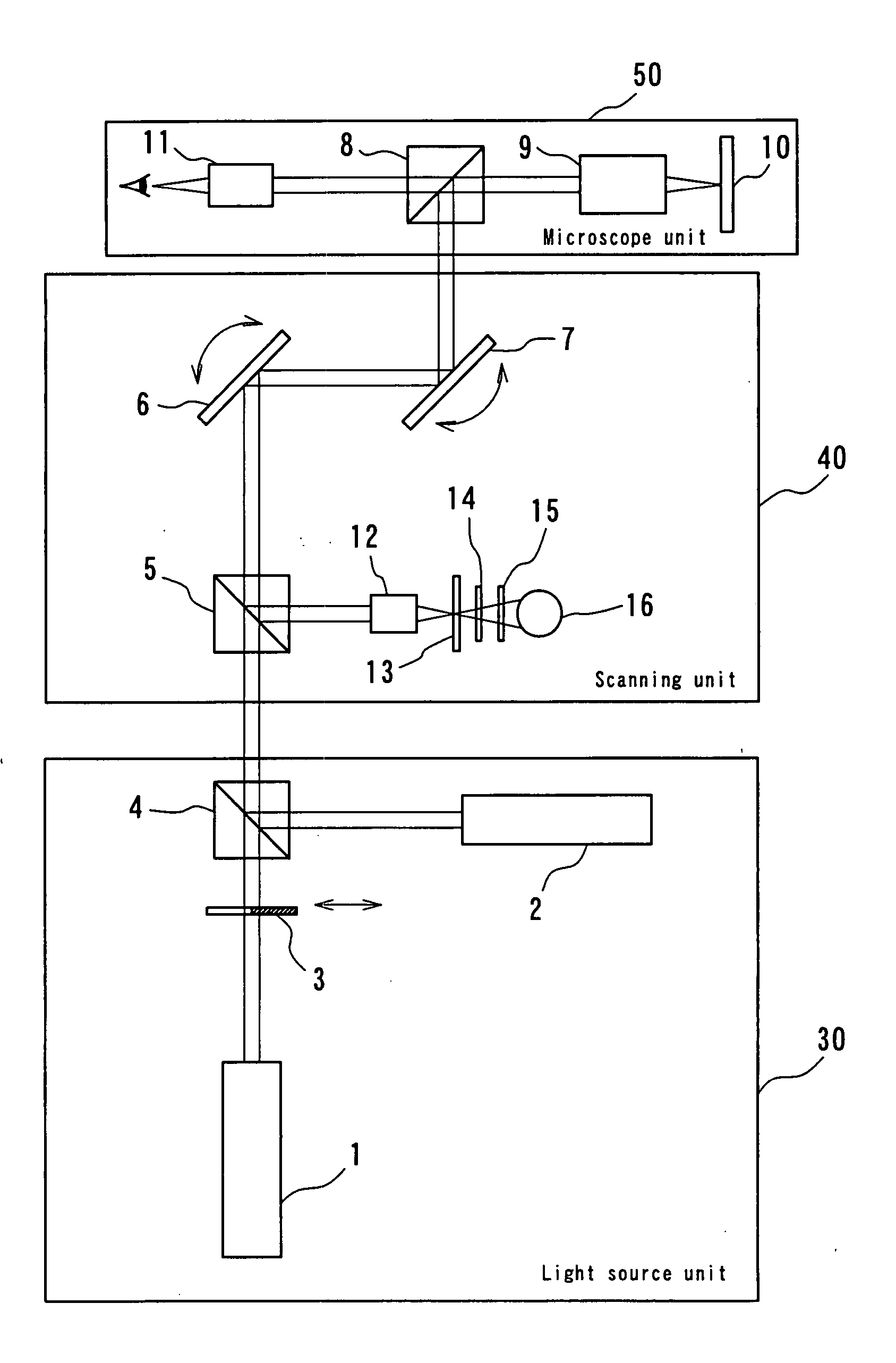
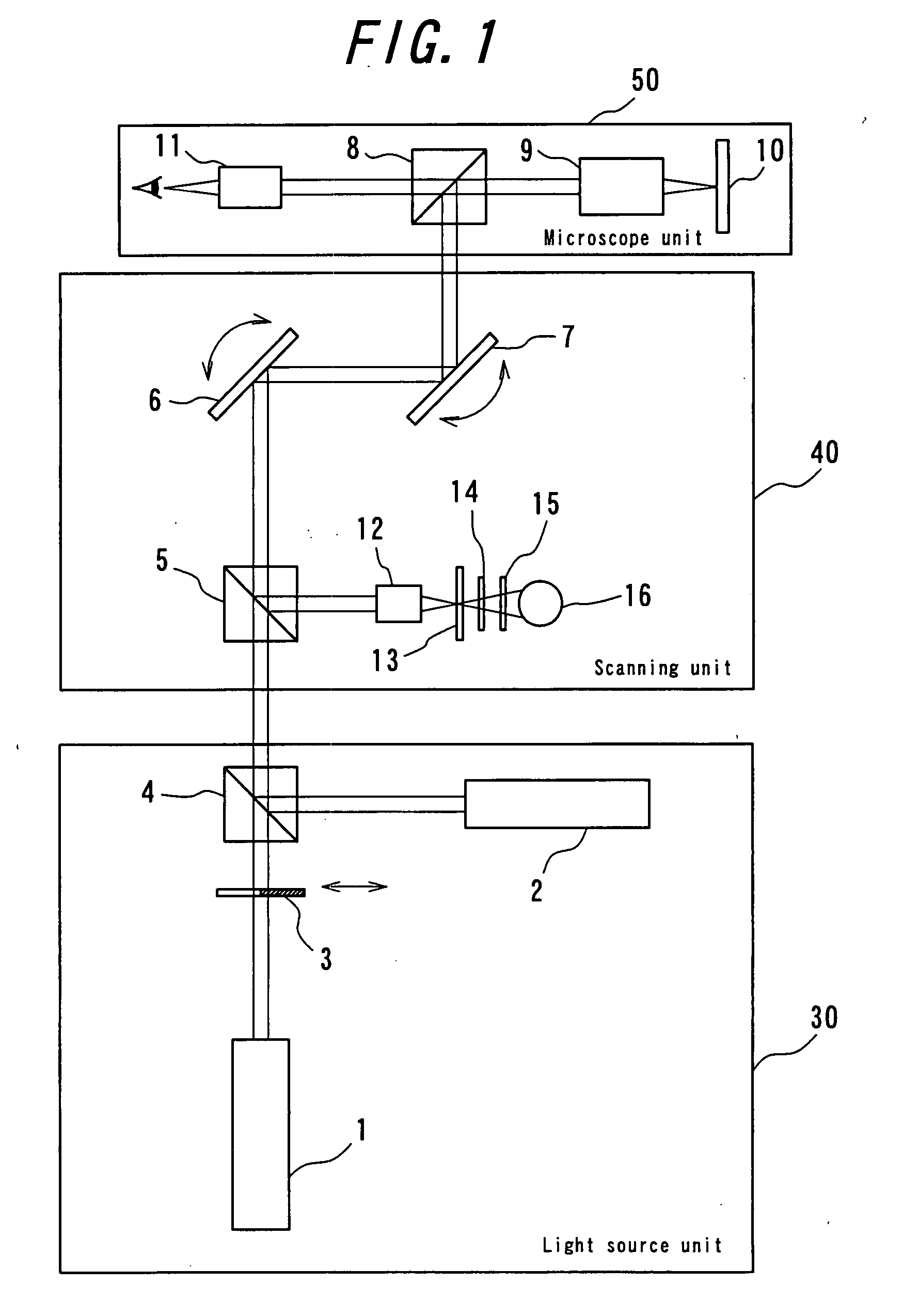
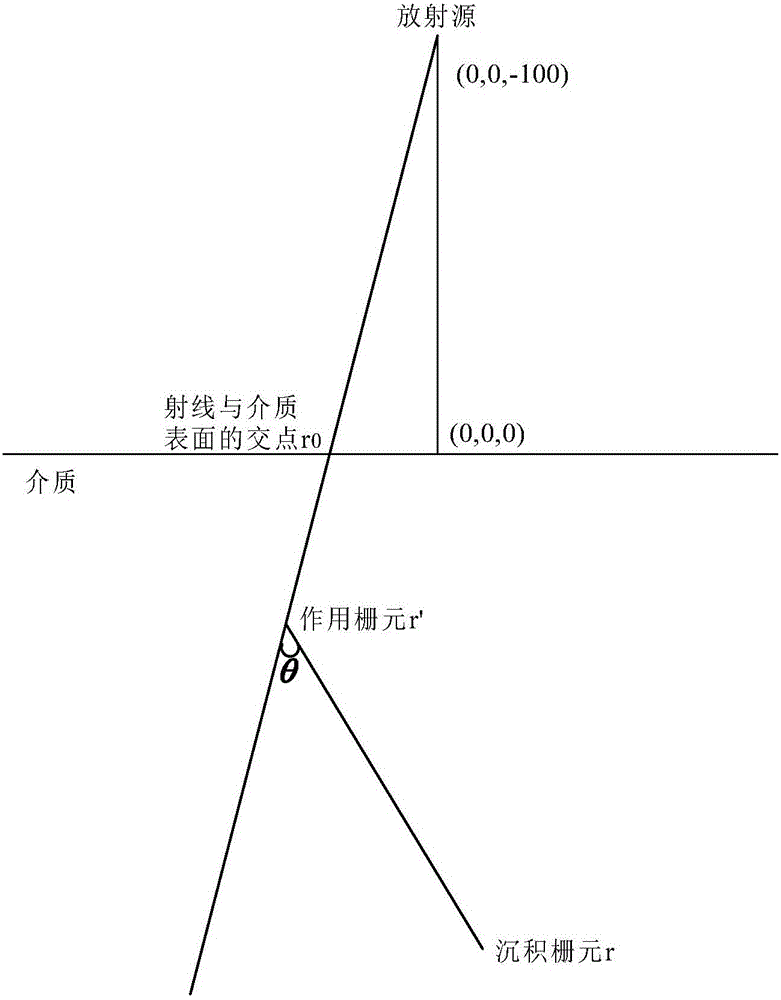
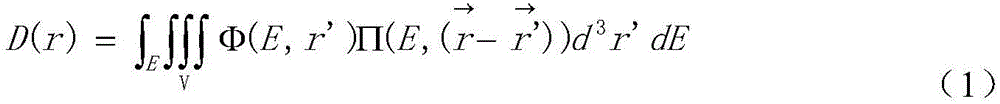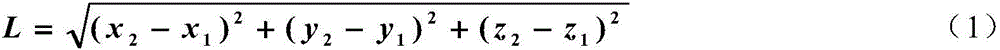Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Photon flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
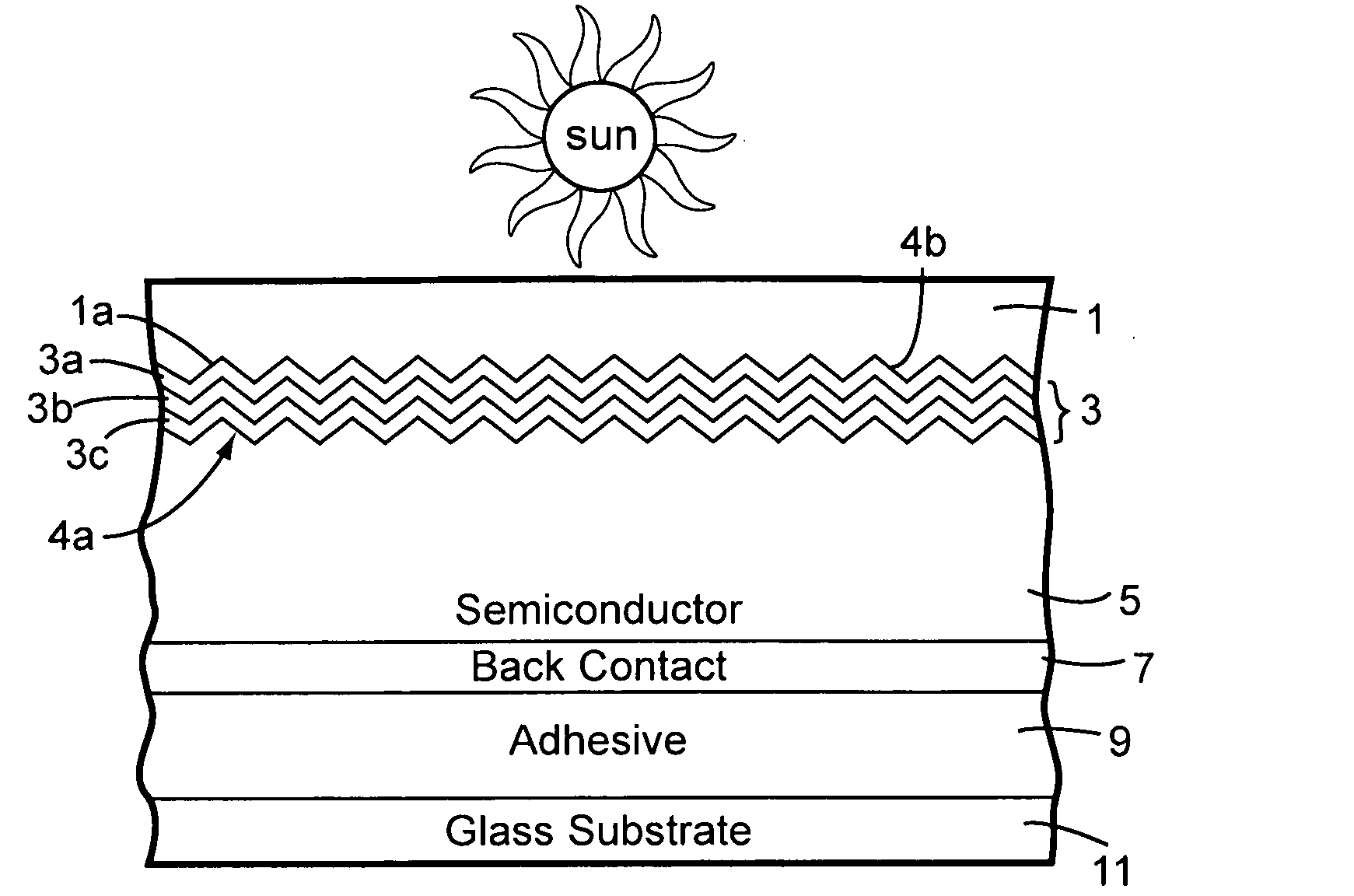
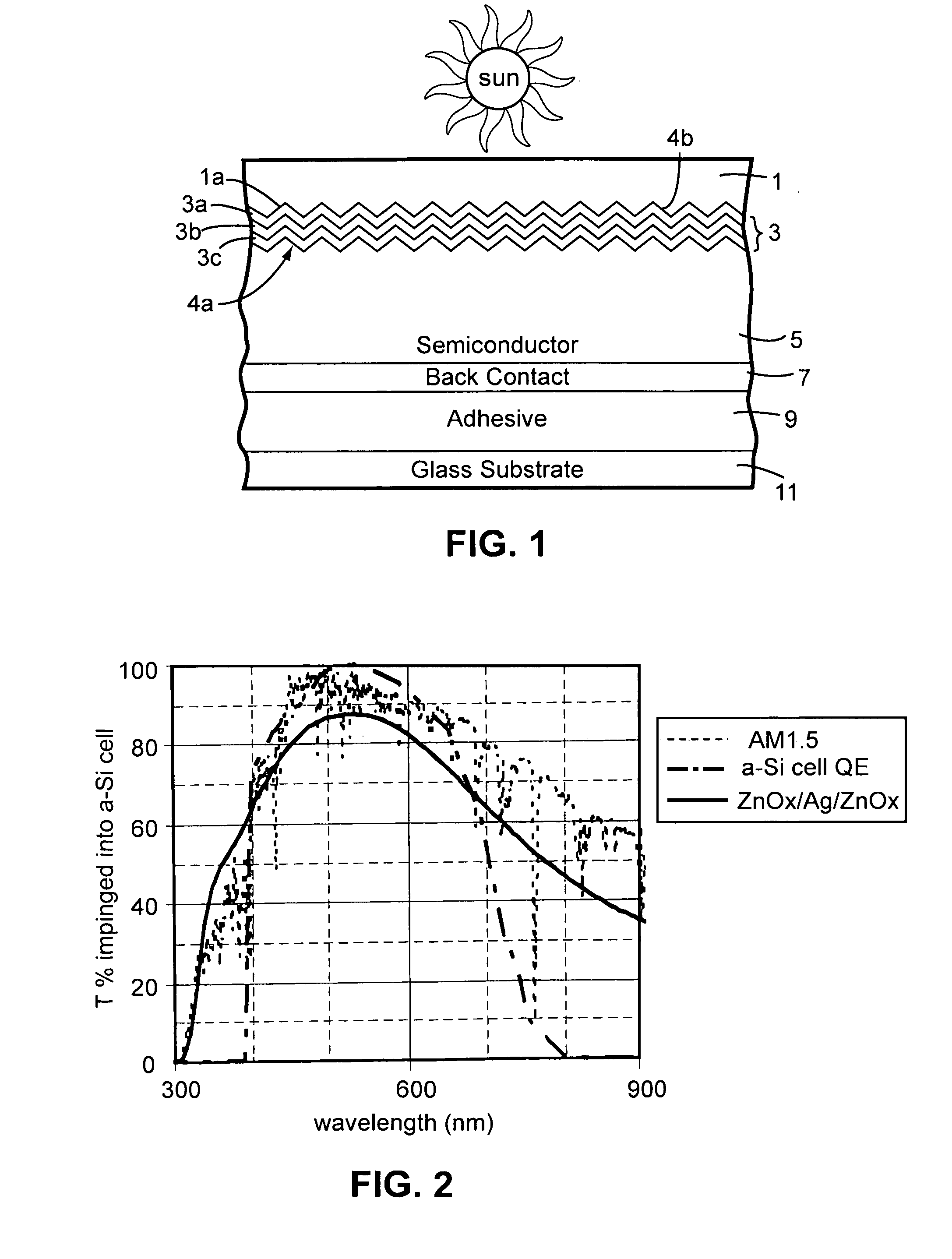
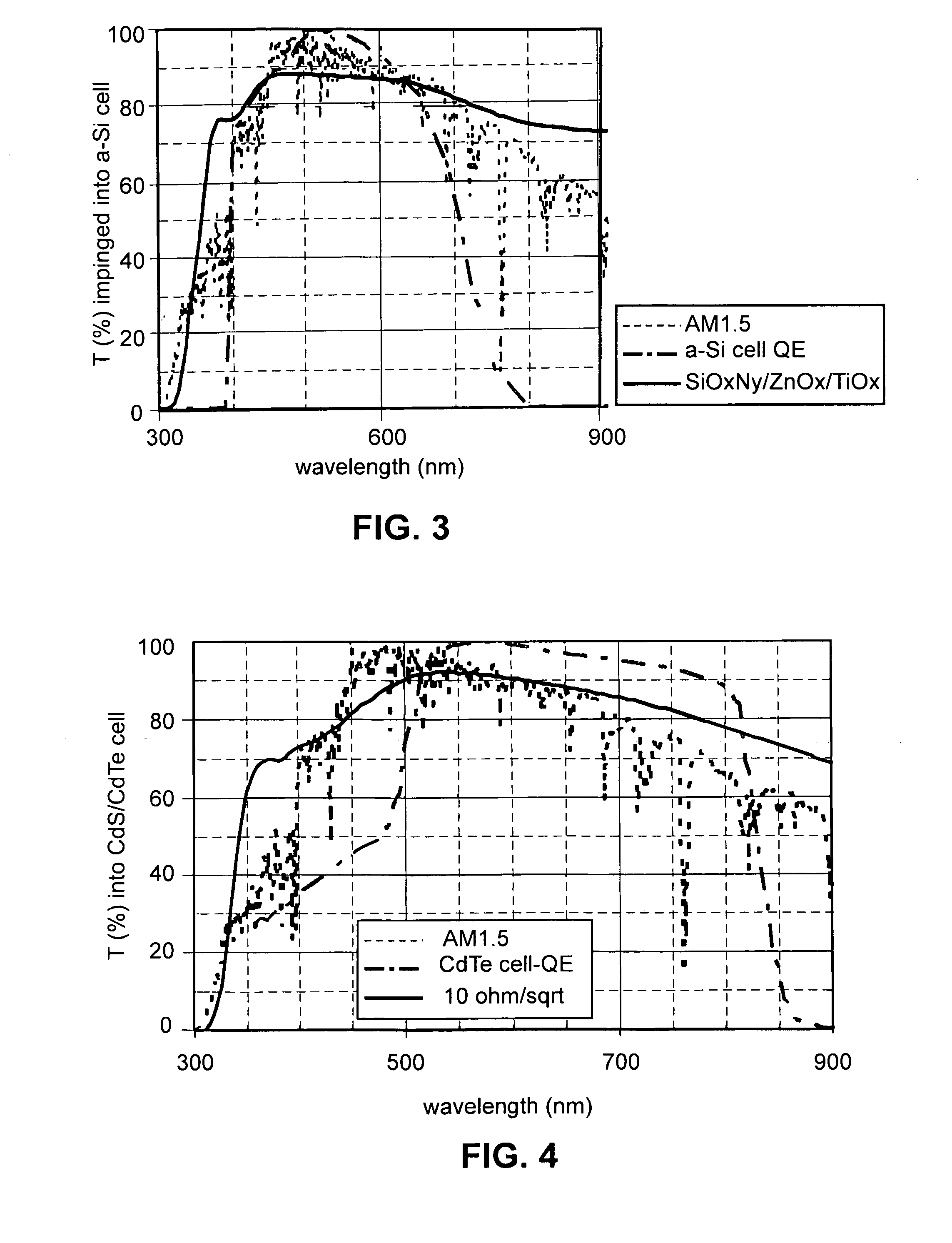
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080178932A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPeak valuePeak area
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) and / or QEx (photon flux of solar radiation) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode includes a transparent conductive layer of or including one or more of (i) titanium zinc oxide doped with aluminum and / or niobium, and / or (ii) titanium niobium oxide.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
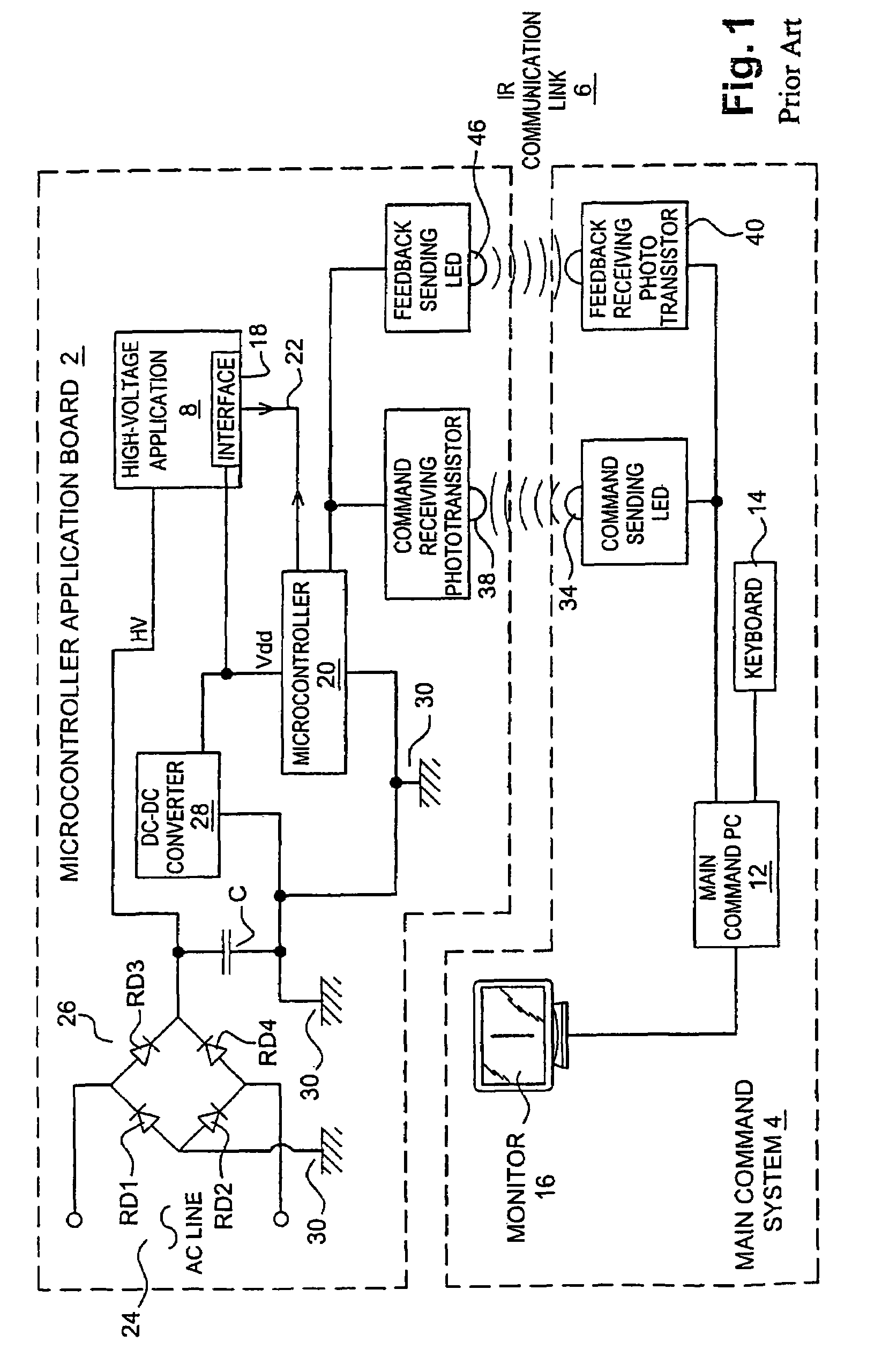
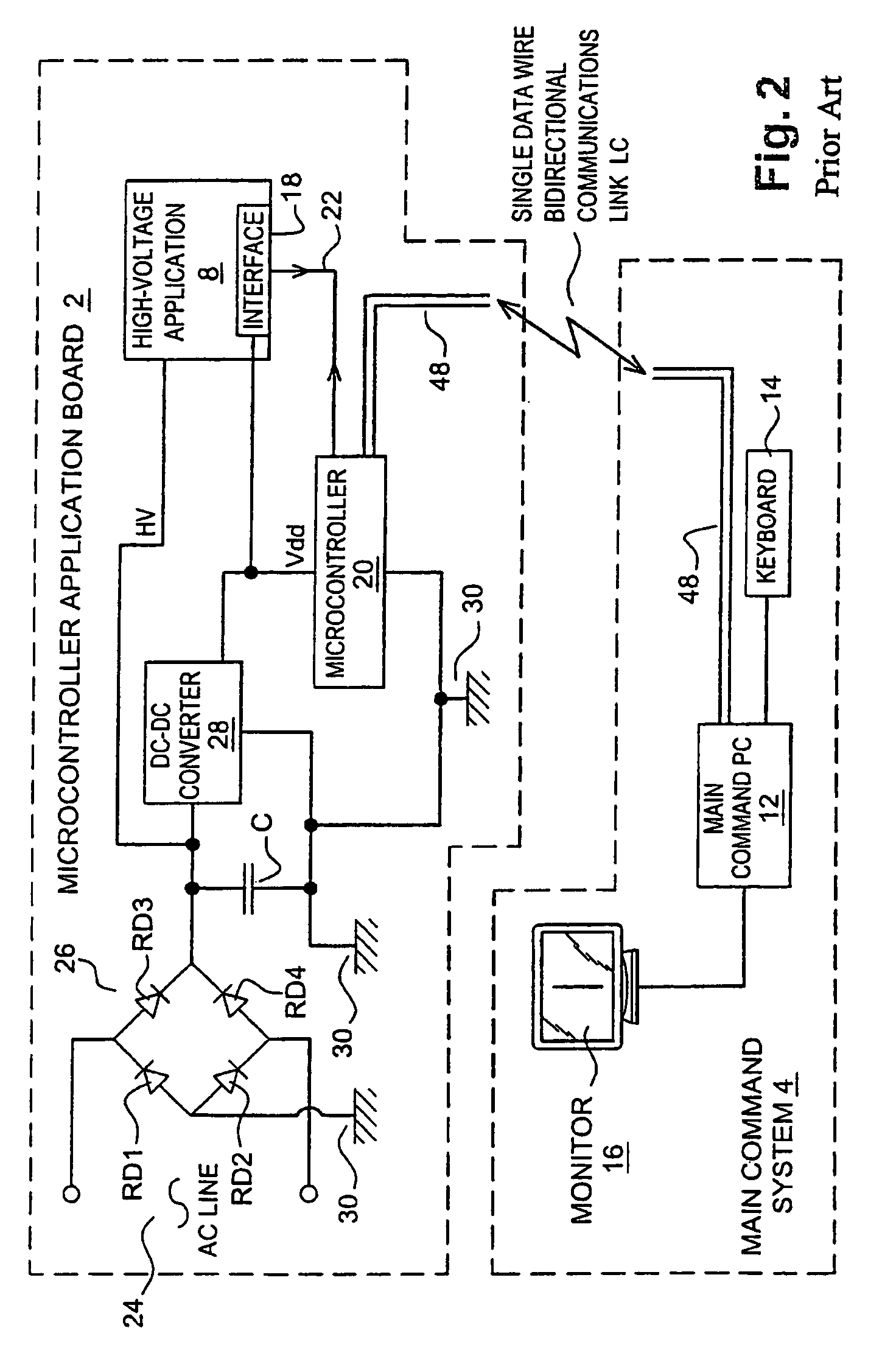
Optical coupling device and method for bidirectional data communication over a common signal line
ActiveUS7359640B2Optical radiation measurementWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal onOptical coupling
Optical coupling device operates over a bidirectional data link between at least first and second communicators, each communicating data along a common wire of the data link. The device includes at least first and second optical couplers, each including a photon flux source and a photon flux detector. The photon flux source of the first and second optical couplers, respectively, is commanded by the first and second communicator, respectively. The photon flux detector of the first and second optical coupler, respectively, produces a signal on the data link at the first and second communicator, respectively, in response to the photon flux source of the second and first optical coupler, respectively, from the second and first communicator, respectively. An inhibitor inhibits the photon flux source of the second and first optical coupler, respectively, in response to an activation of the photon flux source of the first and second optical coupler, respectively.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
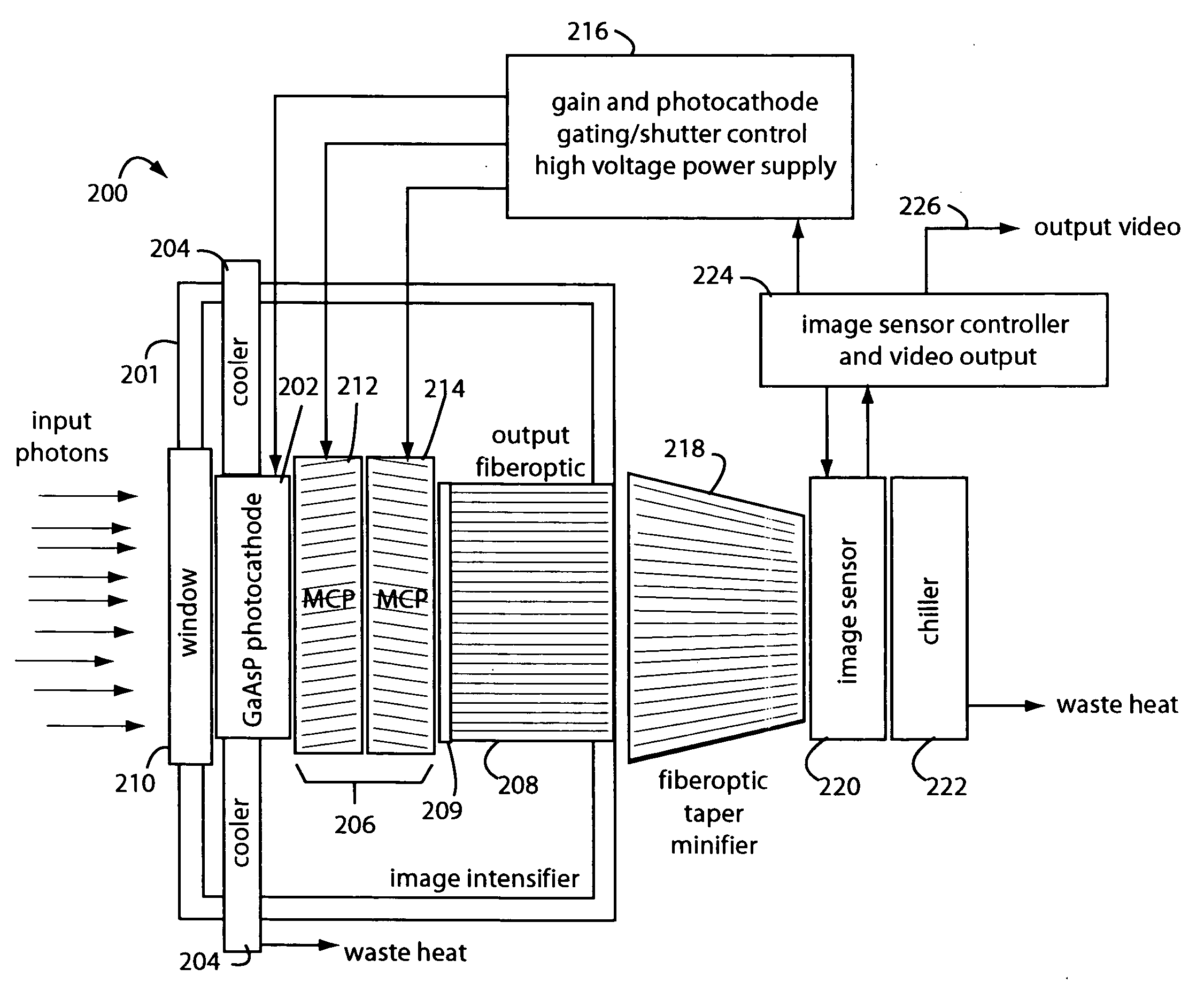
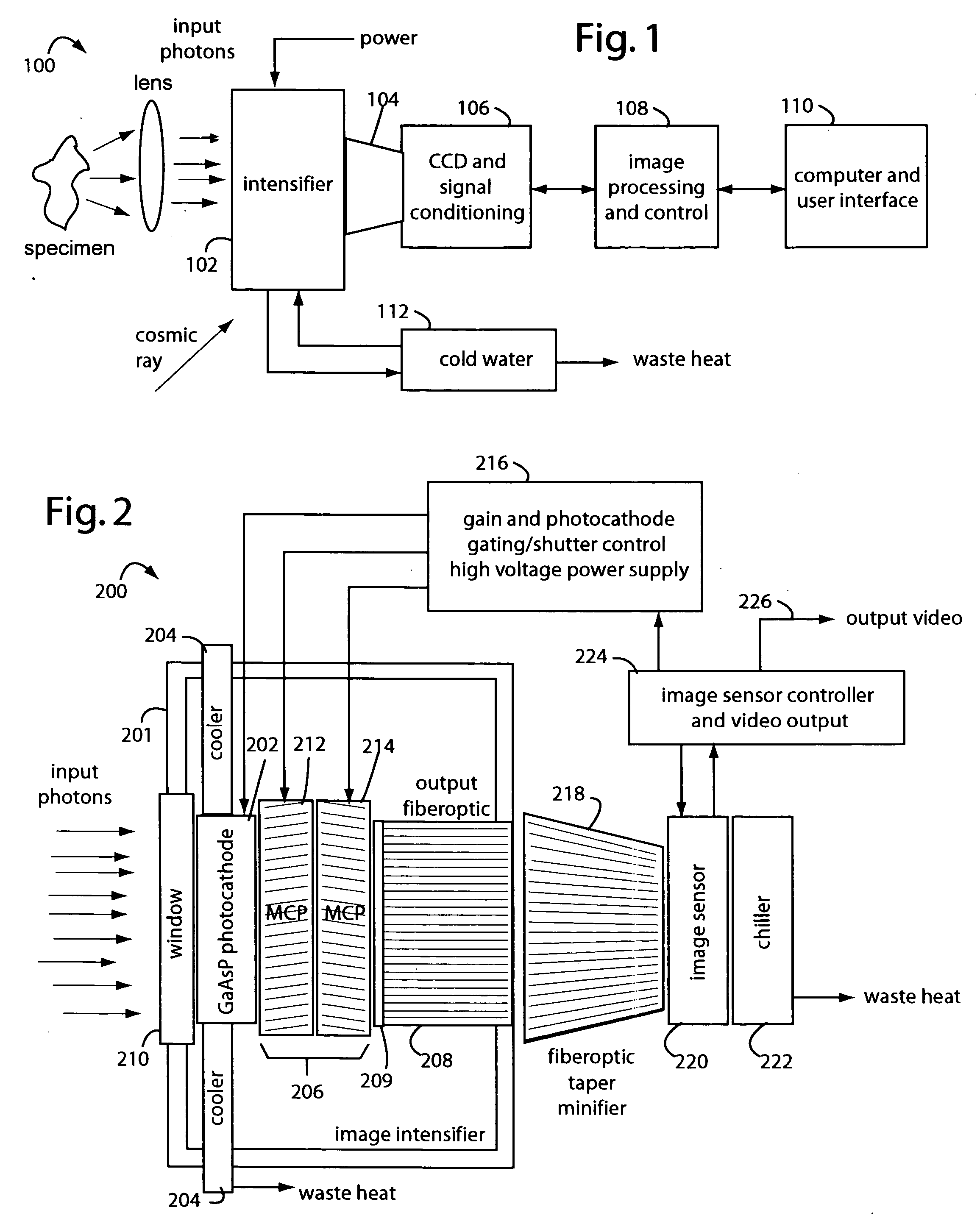
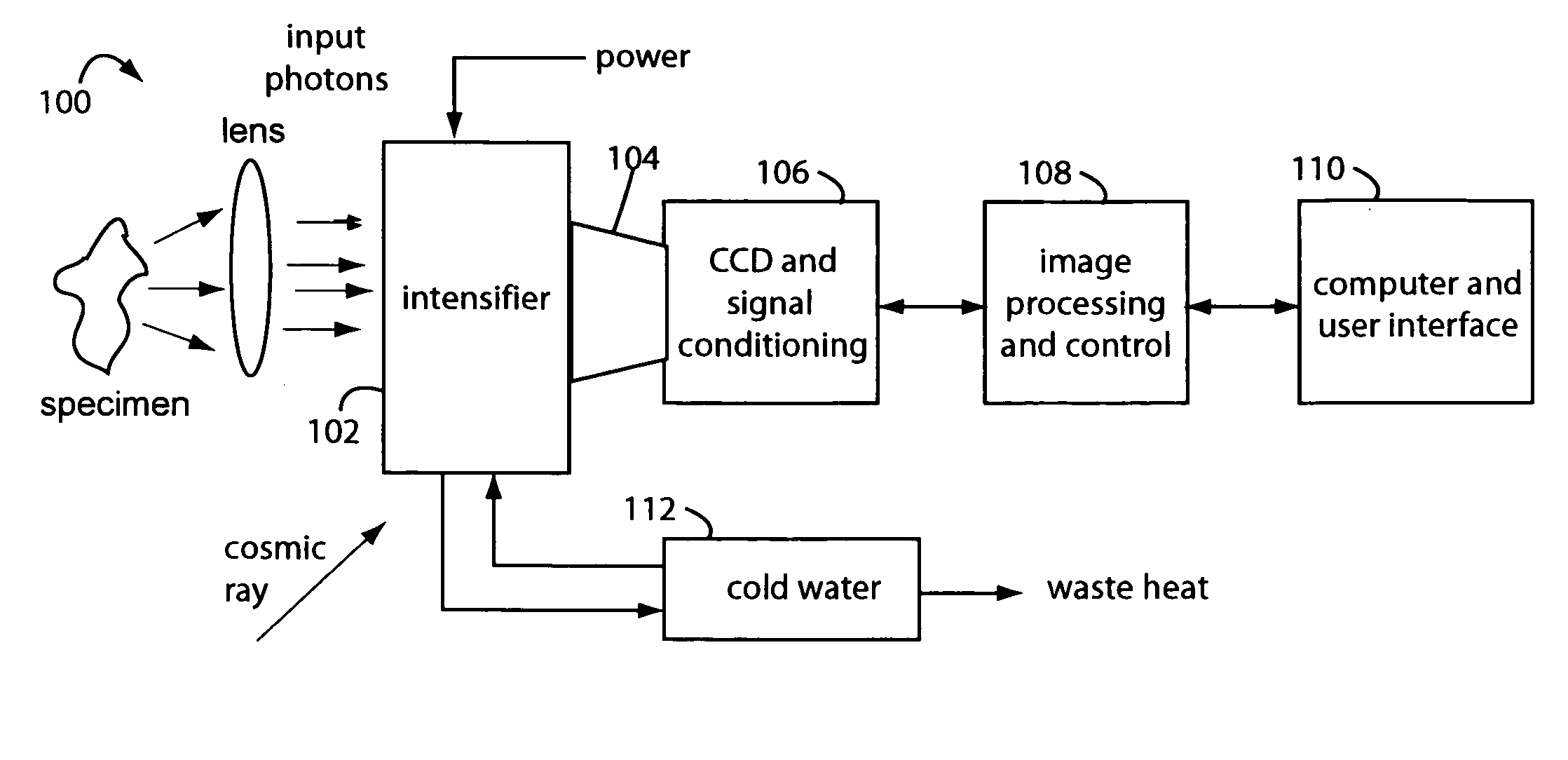
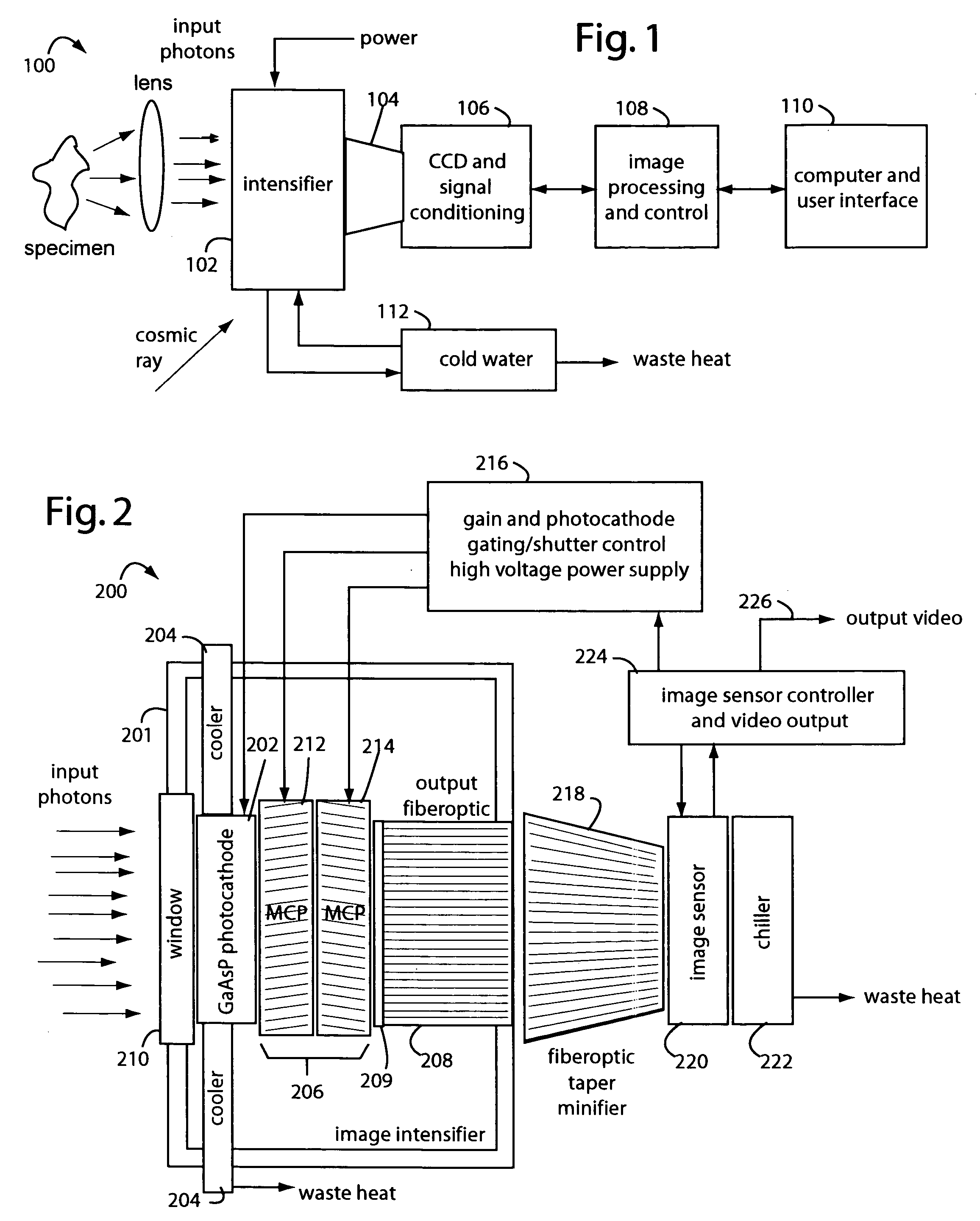
Low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera
ActiveUS20060081770A1Low backgroundZero effective read noiseSolid-state devicesMultiplier circuit arrangementsGallium arsenide phosphidePhotocathode
A low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera comprises a gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) photocathode in a high vacuum tube assembly behind a hermetic front seal to receive image photons. Such is cooled by a Peltier device to −20° C. to 0° C., and followed by a dual microchannel plate. The microchannels in each plate are oppositely longitudinally tilted away from the concentric to restrict positive ions that would otherwise contribute to the generation high brightness “scintillation” noise events at the output of the image. A phosphor-coated output fiberoptic conducts intensified light to an image sensor device. This too is chilled and produces a camera signal output. A high voltage power supply connected to the dual microchannel plate provides for gain control and photocathode gating and shuttering. A fiberoptic taper is used at the output of the image intensifier vacuum tube as a minifier between the internal output fiberoptic and the image sensor.
Owner:STANFORD PHOTONICS
Carbon monoxide (CO) microsir sensor system
InactiveUS20080173817A1Different in diameterDifferent in structureRadiation pyrometryAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDual sensorReservoir system
The present invention provides very small low cost apparatus and method for determining the concentration and / or hazard from a target gas by means of optically monitoring one or more sensors that responds to carbon monoxide. The apparatus comprises a photon source optically coupled to the sensor and the photon intensity passing through the sensor is quantified by one or more photodiode(s) in a system, so that the photon flux is a function of at least one sensor's response to the target gas, e.g., transmits light through the sensor to the photodiode. The photocurrent from the photodiode is converted to a sensor reading value proportional to the optical characteristics of the sensors and is loaded into a microprocessor or other logic circuit. In the microprocessor, the sensor readings may be differentiated to determine the rate of change of the sensor readings and the total photons absorbed value may be used to calculated the CO concentration.There are a number of methods to compute the CO hazard and these is subject of another patent to be filed. In addition, a preferred method to meet the BSI and European CO Standards is described using two sensor systems with two different sensors each having different sensitivity within one housing. The single housing dual sensor uses one LED and two photodiodes. The novel two sensors method to meet the European (BSI) CO standard is similar to the method developed to meet the Japanese standard.The major advantages of MICROSIR over SIR are: 1. Lower cost (estimates saving of US$1.25 per sensor, 2. Better controlled gas path therefore more accurate and more precision, 3. Better getter system therefore longer life (as shown by ammonia accelerated age tests), and 4. Better RESERVOIR SYSTEM THEREFORE BETTER humidity CONTROL AT BOTH LOW AND HIGH (as shown by sensor response curves).5. The MICROSIR Edgeview is faster and meets the Japanese standard for CO and the European Standard for CO enhanced smoke, 6. More easily automated as the board of alarms use surface mount and MICROSIR is a surface mount part that attaches over surface mounted optics after the soldering, 7. small size, and 8. approved UL recognized component.The MICROSIR device can also be used to detect the CO, which may be combined with temperature and smoke in a very small package. The detection of one or more indicators such as smoke and CO; increases the sensitivity of the other indicators. Combining signals produces an improved fire detector comprising a CO sensor and a smoke sensor in one unit. The smoke detection sensor may be either ionization or photoelectric either or both may be combined with the CO sensor to provide earlier warning to fire and reduce false alarms.
Owner:THE QUANTUM GROUP
Digitizer for a digital imaging system
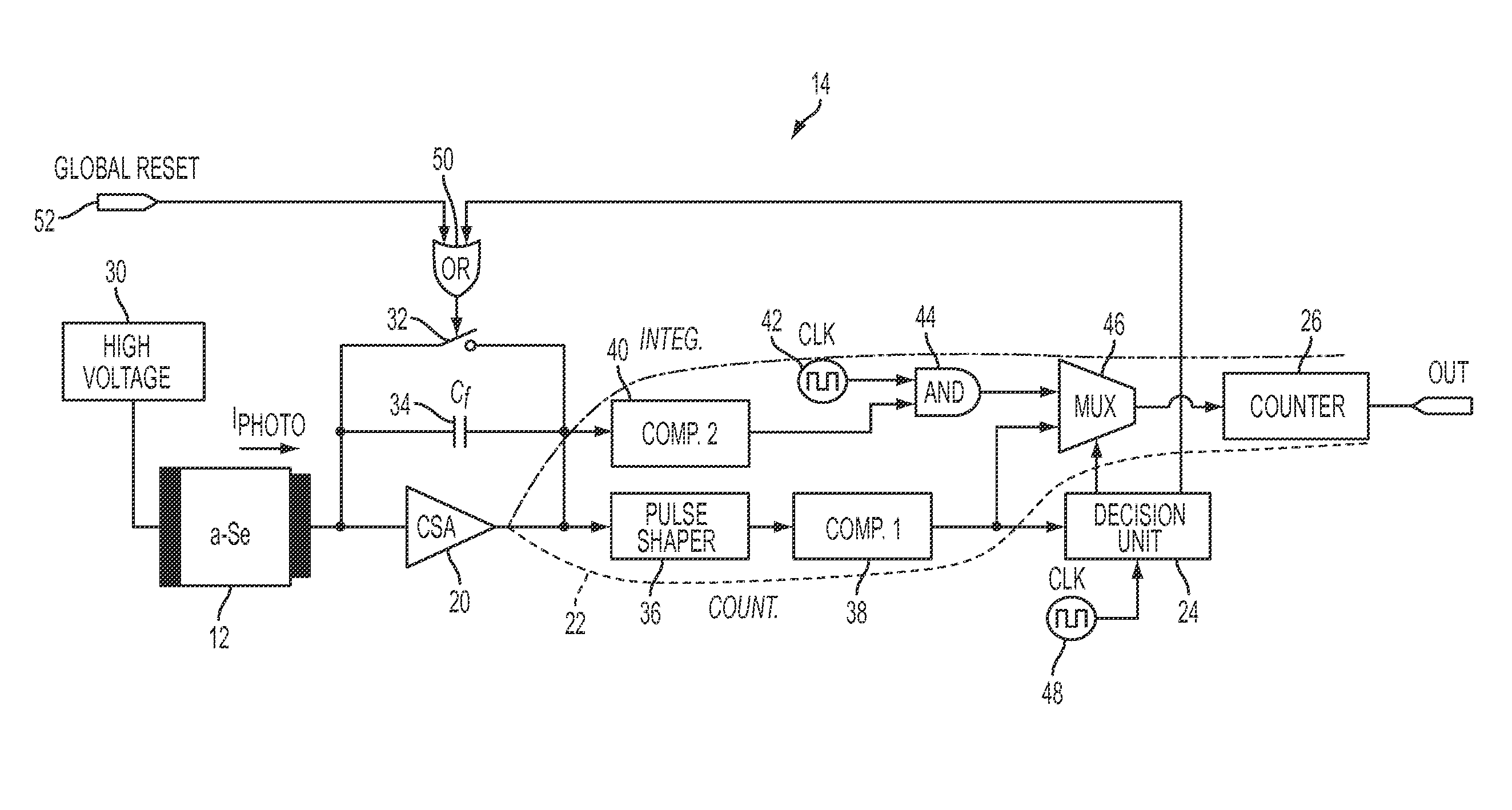
InactiveUS20100181491A1Excellent contrast ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsPhoton flux
The disclosure is directed at a method of digital imaging comprising sensing photons on at least one pixel within a pixel array of a radiation detector; counting the photons using photon counting to produce a digital signal representative of the sensed photons; monitoring a photon flux associated with the sensed photons; and using photon integration to produce a digital signal representative of the sensed photons when the photon flux is higher than a predetermined photon flux.
Owner:KARIM KARIM S +2
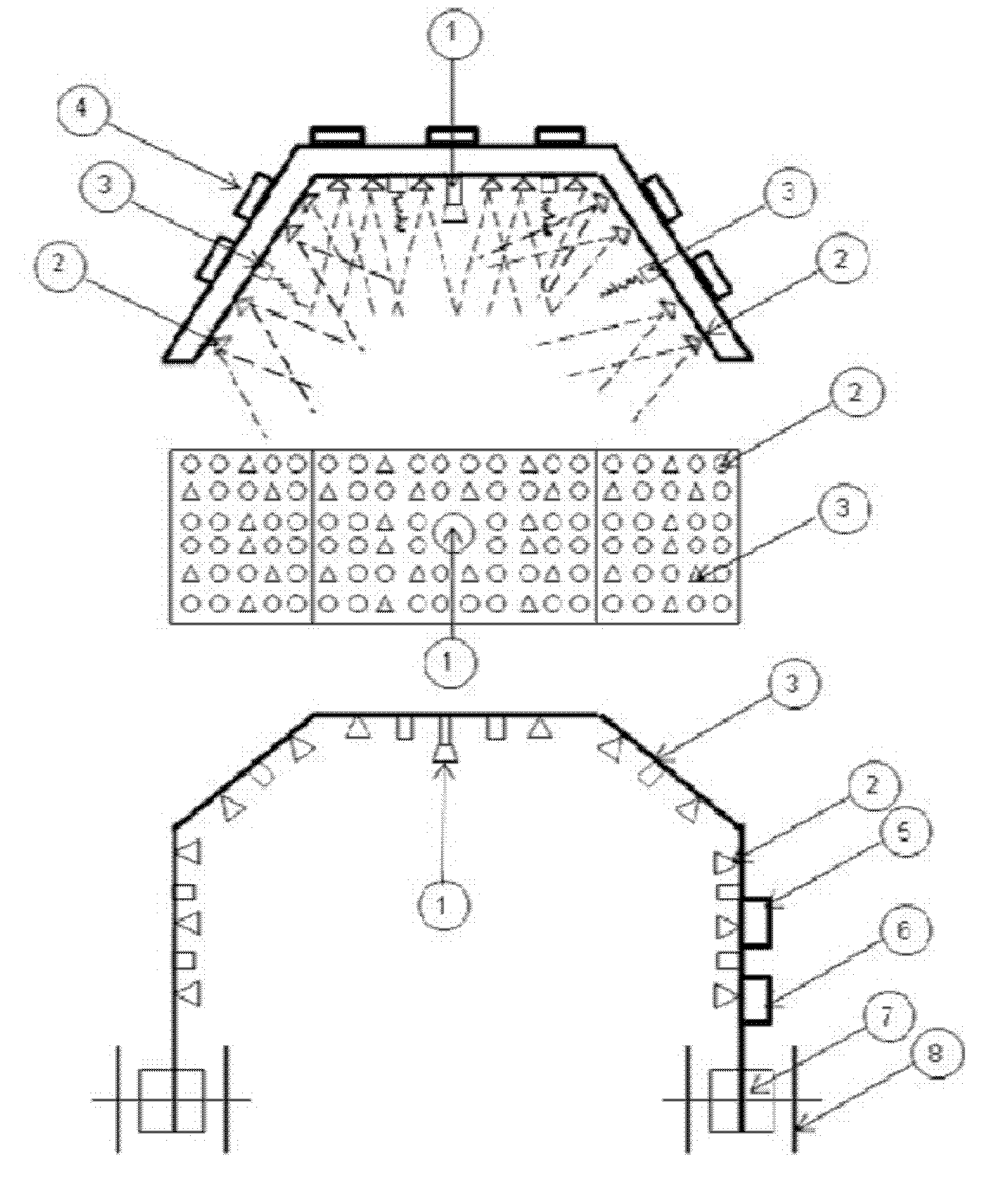
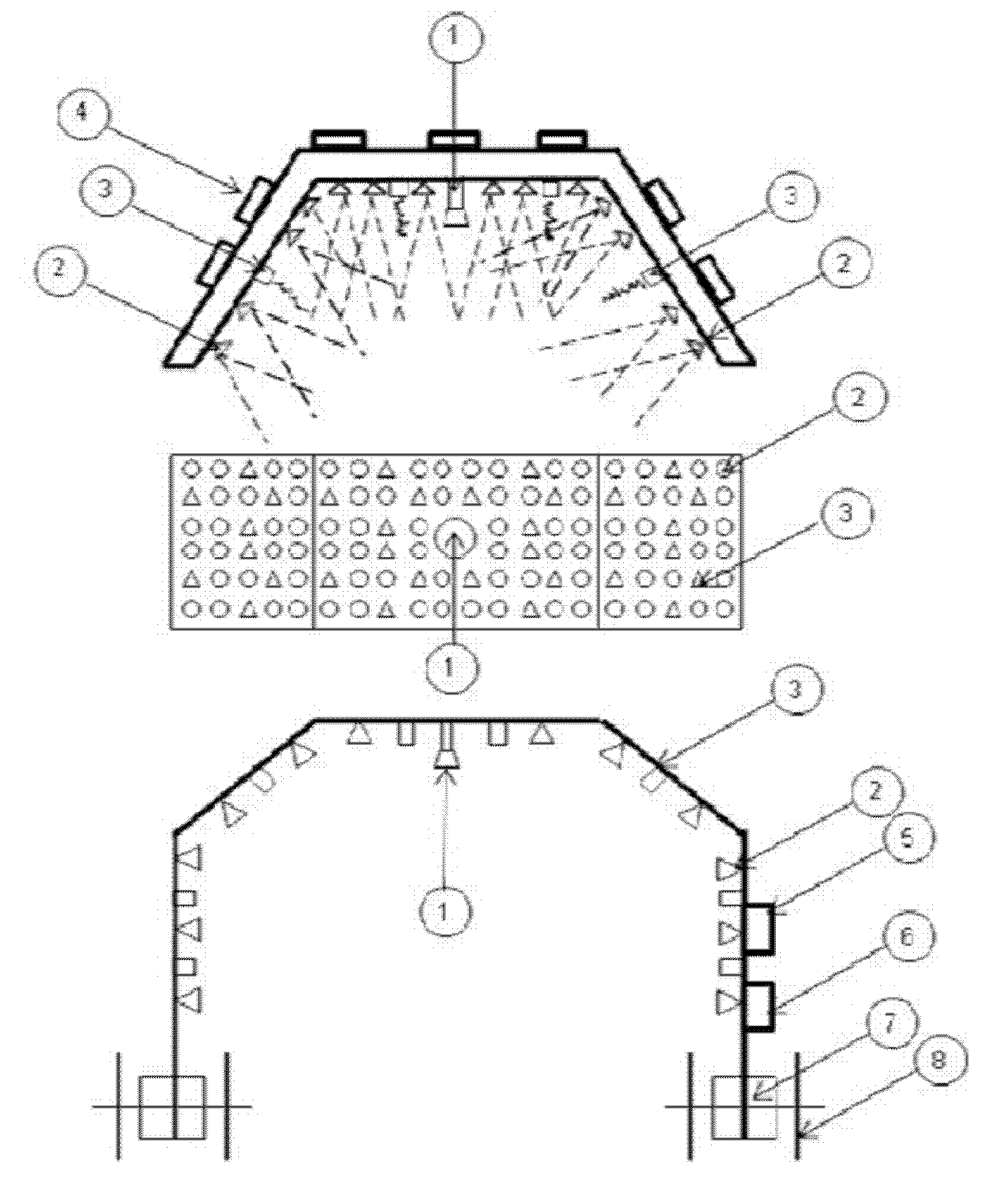
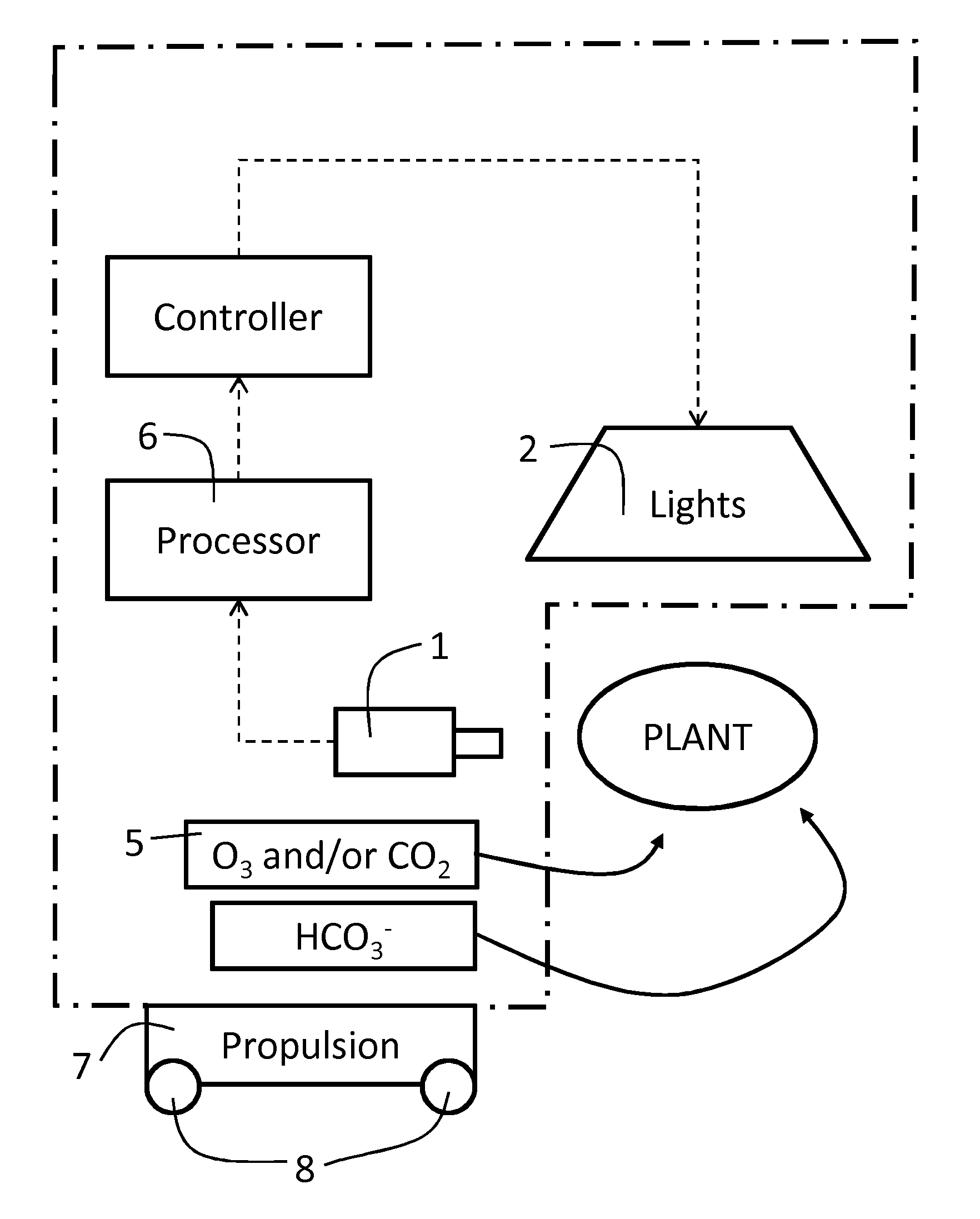
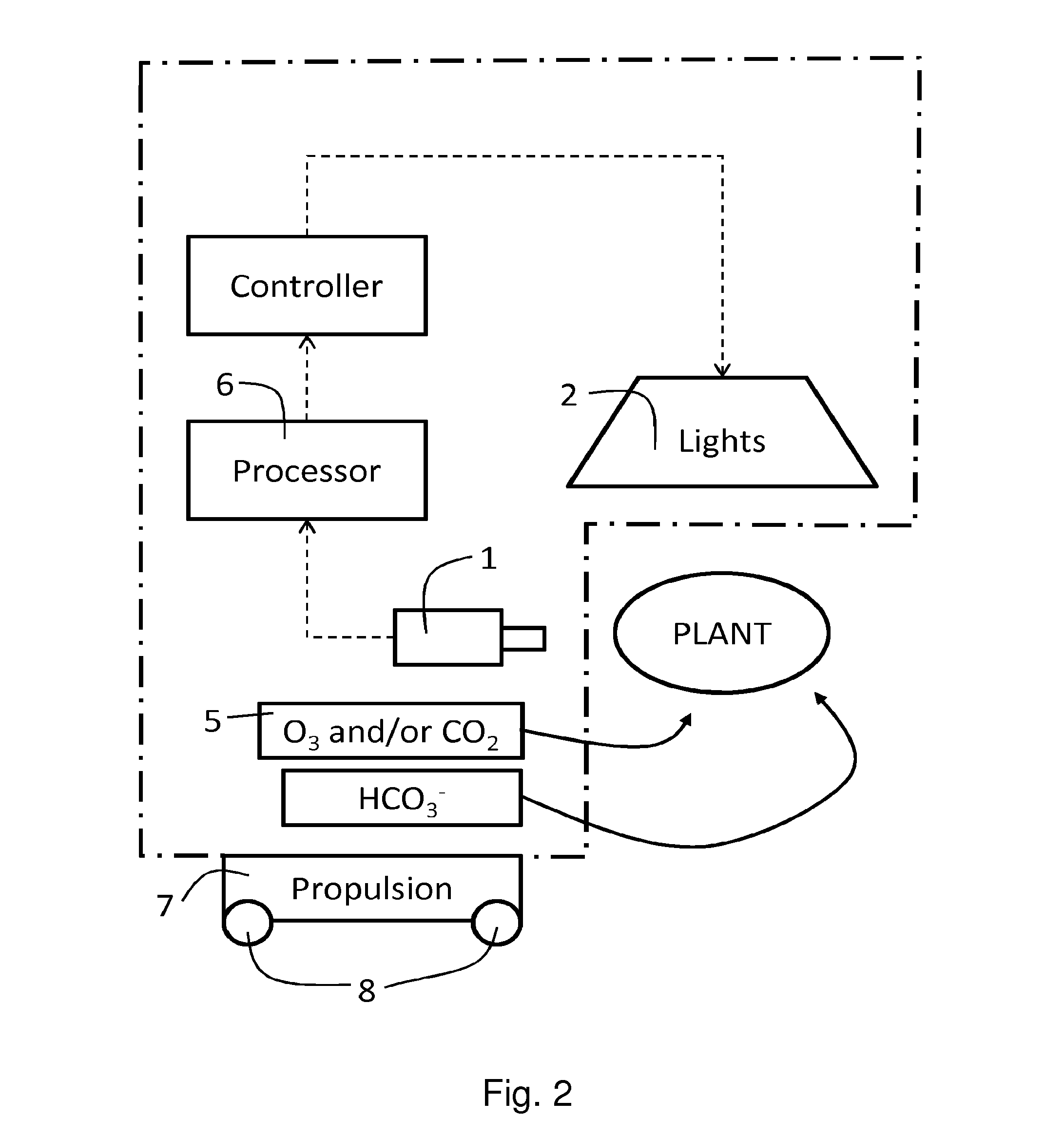
Method and apparatus for plant protection
InactiveUS20130255150A1Improve pathogen resistanceReduce infectionRoot feedersSaving energy measuresHigh intensityLength wave
A method of improving the growth and / or pathogen resistance of a plant, comprising the step of exposing at least part of the plant to a transient period of high intensity illumination providing a photon flux at the plant surface having at least one of the following characteristics: (a) a red photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square metre per second, and having a wavelength of between 600 and 700 nm; (b) a blue photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square metre per second, having a wavelength of between 420 and 480 nm. The Invention also provides apparatus for providing such conditions to growing plants.
Owner:KARPINSKI STANISLAW +1
Systems And Methods For Combined X-Ray Reflectometry And Photoelectron Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20190212281A1High measurement accuracyImprove throughputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationColor/spectral properties measurementsSemiconductor structureX-ray
Methods and systems for measuring structural and material characteristics of semiconductor structures based on combined x-ray reflectometry (XRR) and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) are presented herein. A combined XRR and XPS system includes an x-ray illumination source and x-ray illumination optics shared by both the XRR and XPS measurement subsystems. This increases throughput and measurement accuracy by simultaneously collecting XRR and XPS measurement data from the same area of the wafer. A combined XRR and XPS system improves measurement accuracy by employing XRR measurement data to improve measurements performed by the XPS subsystem, and vice-versa. In addition, a combined XRR and XPS system enables simultaneous analysis of both XRR and XPS measurement data to more accurately estimate values of one of more parameters of interest. In a further aspect, any of measurement spot size, photon flux, beam shape, beam diameter, and illumination energy are independently controlled.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Vacuum ultraviolet referencing reflectometer
ActiveUS20050002037A1Thin layerSmall featureSpectrum investigationPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterMetrology
A spectroscopy system is provided which operates in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum. More particularly, a system utilizing reflectometry techniques in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum is provided for use in metrology applications. To ensure accurate and repeatable measurement, the environment of the optical path is controlled to limit absorption effects of gases that may be present in the optical path. To account for absorption effects that may still occur, the length of the optical path is minimized. To further account for absorption effects, the reflectance data may be referenced to a relative standard. Referencing is particularly advantageous in the VUV reflectometer due to the low available photon flux and the sensitivity of recorded data to the composition of the gaseous medium contained with the optical path. Thus, errors that may be introduced by changes in the controlled environment may be reduced. In one exemplary embodiment, the VUV reflectometer may utilize a technique in which a beam splitter is utilized to create a sample beam and a reference beam to form the two arms of a near balanced Mach Zehnder interferometer. In another exemplary embodiment, the reference channel may be comprised of a Michelson interferometer.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
Lighting device with ceramic garnet
ActiveUS20170315433A1Low efficiencySimple processMechanical apparatusLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLutetiumEffect light
The invention provides a lighting device comprising a plurality of solid state light sources and an elongated ceramic body having a first face and a second face defining a length (L) of the elongated ceramic body, the elongated ceramic body comprising one or more radiation input faces and a radiation exit window, wherein the second face comprises the radiation exit window, wherein the plurality of solid state light sources are configured to provide blue light source light to the one or more radiation input faces and are configured to provide to at least one of the radiation input faces a photon flux of at least 1.0*1017 photons / (s·mm2), wherein the elongated ceramic body comprises a ceramic material configured to wavelength convert at least part of the blue light source light into at least converter light, wherein the ceramic material comprises an A3B5O12:Ce3+ ceramic material, wherein A comprises one or more of yttrium (Y), gadolinium (Gd) and lutetium (Lu), and wherein B comprises aluminum (Al).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Optical coupling device and method for bidirectional data communication over a common signal line
ActiveUS20050069326A1Optical radiation measurementWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal onBiological activation
Optical coupling device operates over a bidirectional data link between at least first and second communicators, each communicating data along a common wire of the data link. The device includes at least first and second optical couplers, each including a photon flux source and a photon flux detector. The photon flux source of the first and second optical couplers, respectively, is commanded by the first and second communicator, respectively. The photon flux detector of the first and second optical coupler, respectively, produces a signal on the data link at the first and second communicator, respectively, in response to the photon flux source of the second and first optical coupler, respectively, from the second and first communicator, respectively. An inhibitor inhibits the photon flux source of the second and first optical coupler, respectively, in response to an activation of the photon flux source of the first and second optical coupler, respectively.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Vacuum ultraviolet referencing reflectometer
ActiveUS7394551B2Change levelThin layerSpectrum investigationPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterMetrology
A spectroscopy system is provided which operates in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum. More particularly, a system utilizing reflectometry techniques in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum is provided for use in metrology applications. To ensure accurate and repeatable measurement, the environment of the optical path is controlled to limit absorption effects of gases that may be present in the optical path. To account for absorption effects that may still occur, the length of the optical path is minimized. To further account for absorption effects, the reflectance data may be referenced to a relative standard. Referencing is particularly advantageous in the VUV reflectometer due to the low available photon flux and the sensitivity of recorded data to the composition of the gaseous medium contained with the optical path. Thus, errors that may be introduced by changes in the controlled environment may be reduced. In one exemplary embodiment, the VUV reflectometer may utilize a technique in which a beam splitter is utilized to create a sample beam and a reference beam to form the two arms of a near balanced Mach Zehnder interferometer. In another exemplary embodiment, the reference channel may be comprised of a Michelson interferometer.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
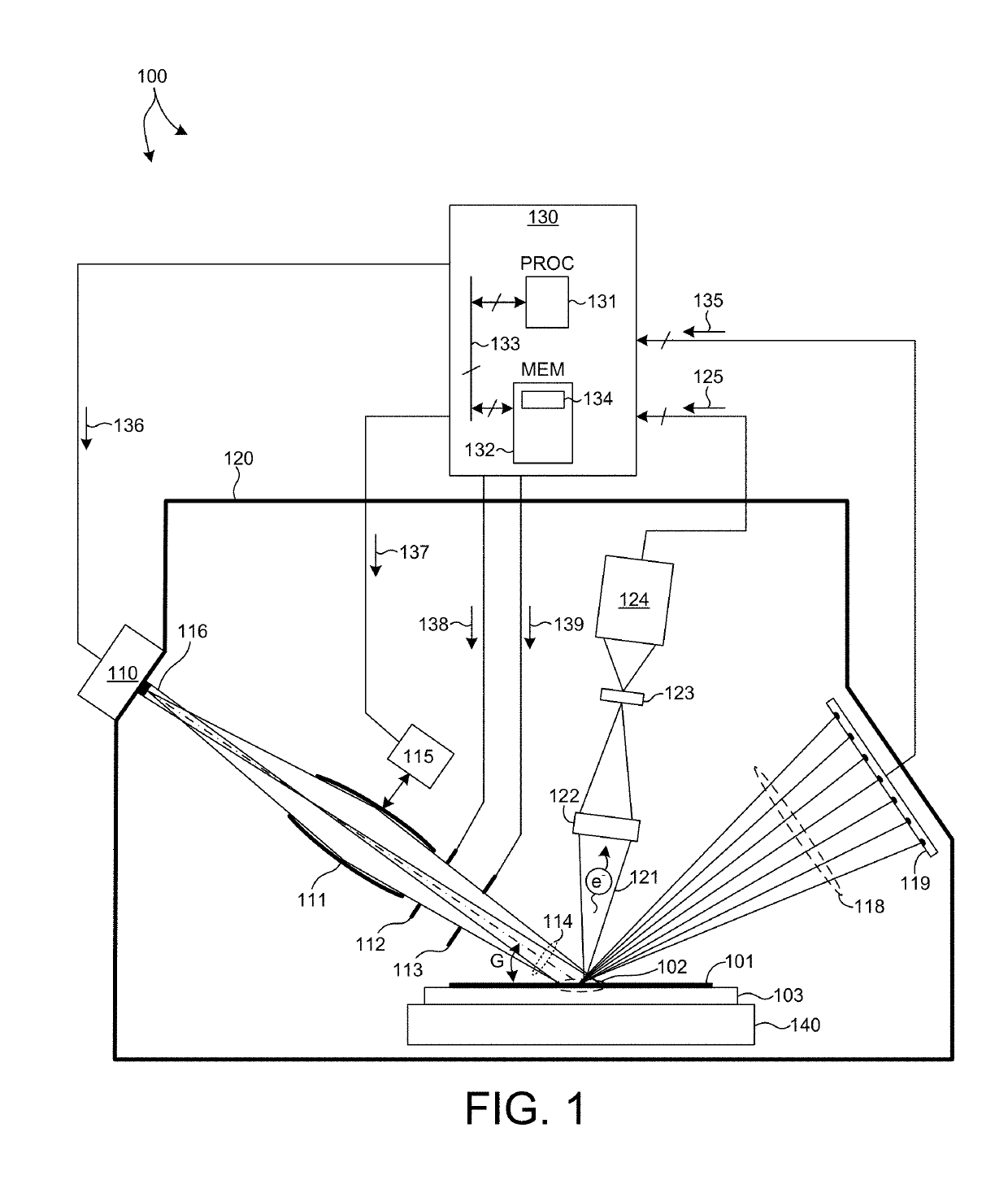
Super-Resolution Microscope
ActiveUS20070291353A1Improve reliabilitySimple and inexpensive arrangementLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansExcited stateFluorescence
[Task] To provide a super-resolution microscope whereby the light source of pump light and erase light can be selected easily and a super-resolution can be reliably achieved through a simple and inexpensive arrangement. [Solution of the Task] A super-resolution microscope includes an optical system (3, 4, 9) for combining a part of a first coherent light from a first light source (2) and a part of a second coherent light from a second light source (1) and focusing the coherent lights onto a sample (10), scanning means (6, 7) for scanning the coherent lights, and detecting means (16) for detecting an optical response signal from the sample (10). The microscope is configured so as to satisfy the following conditions: σ01Ipτ≦1, and 0.65(λe / λp)≦τσdipIe where λp is the wavelength of the first coherent light, λe is the wavelength of the second coherent light, τ is the excited lifetime in which the molecule is excited by the first coherent light from the ground state to the first electron-excited state, Ip is the maximum photon flux on the sample surface of the first coherent light, Ie is the maximum photon flux on the sample surface of the second coherent light, σ01, is the absorption cross-sectional area when the molecule is exited from the ground state to the first electron-excited state, and σdip is the fluorescence suppression cross-sectional area.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP +1
Two-dimensional radiation detector
InactiveUS6946660B2Improve efficiencyLower levelSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsAnode spot
A two-dimensional, pixellated, monolithic semiconductor radiation detector, in which each detector pixel is essentially a perpendicular mode detector. This is achieved by an arrangement of anode spots, one for each pixel located on the flux-exposed front surface of the detector substrate, surrounding by a cathode array preferably in the form of a network of lines, such that the field between the anodes and cathodes on this front surface has a major component in the direction parallel to the surface, and hence perpendicular to the incident photon flux. The conductivity of the substrate is high near this front surface, since this is where the highest level of absorption of photons takes place, and a significant photoconductive current is thus generated between cathodes and anodes. The conductivity is proportional to the incoming photon flux, and decays exponentially with depth into the detector. Since all of the conduction paths are in parallel to each other, the resultant conductance between each anode and its surrounding cathode is the summation of all those conductances.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
Ship reactor shielding design optimization method based on neural network and genetic algorithm
ActiveCN104933245AReduce time consumptionReduce programming difficultySpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkComputation process
The invention discloses a ship reactor shielding design optimization method based on a neural network and a genetic algorithm. A Monte Carlo method is used for simulating and calculating the reactor neutron and photon transport process; an MCNP (Monte Carlo N Particle Transport Code) program is used for carrying out simulation and calculation on a ship reactor layered shielding model; a neutron and photon flux after the reactor shielding is obtained; the total equivalent dose is worked out; a topological structure of a BP (Back Propagation) neural network is determined according to the input parameter number n1 and the output parameter number n2 of a sample; an adaptation degree function of the genetic algorithm is determined according to a reactor shielding problem objective; the recommended adaptation degree function is selected; and the strong optimization capacity of the genetic algorithm is used and is mutually coupled with the neural network to find the optimum shielding parameter. The ship reactor shielding design optimization method has the advantages that the high fitting capability of the neural network is used; the time consumption of the MCNP program in the particle transport process is reduced; the good optimization capacity of the genetic algorithm is used; and the optimum shielding parameter can be found in few iteration steps.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera
ActiveUS7129464B2Low backgroundZero effective read noiseMultiplier circuit arrangementsImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesGallium arsenide phosphidePhotocathode
A low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera comprises a gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) photocathode in a high vacuum tube assembly behind a hermetic front seal to receive image photons. Such is cooled by a Peltier device to −20° C. to 0° C., and followed by a dual microchannel plate. The microchannels in each plate are oppositely longitudinally tilted away from the concentric to restrict positive ions that would otherwise contribute to the generation high brightness “scintillation” noise events at the output of the image. A phosphor-coated output fiberoptic conducts intensified light to an image sensor device. This too is chilled and produces a camera signal output. A high voltage power supply connected to the dual microchannel plate provides for gain control and photocathode gating and shuttering. A fiberoptic taper is used at the output of the image intensifier vacuum tube as a minifier between the internal output fiberoptic and the image sensor.
Owner:STANFORD PHOTONICS
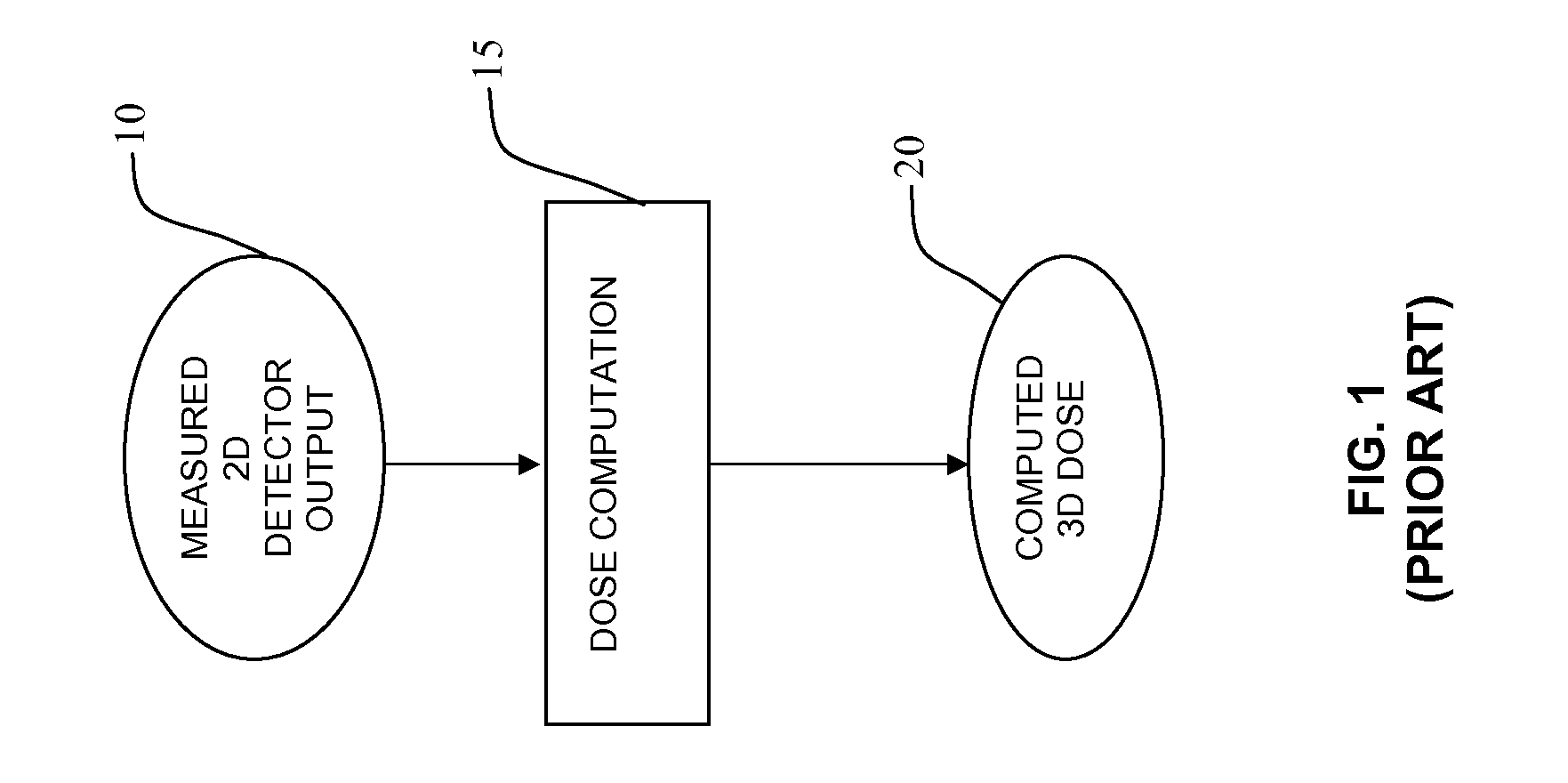
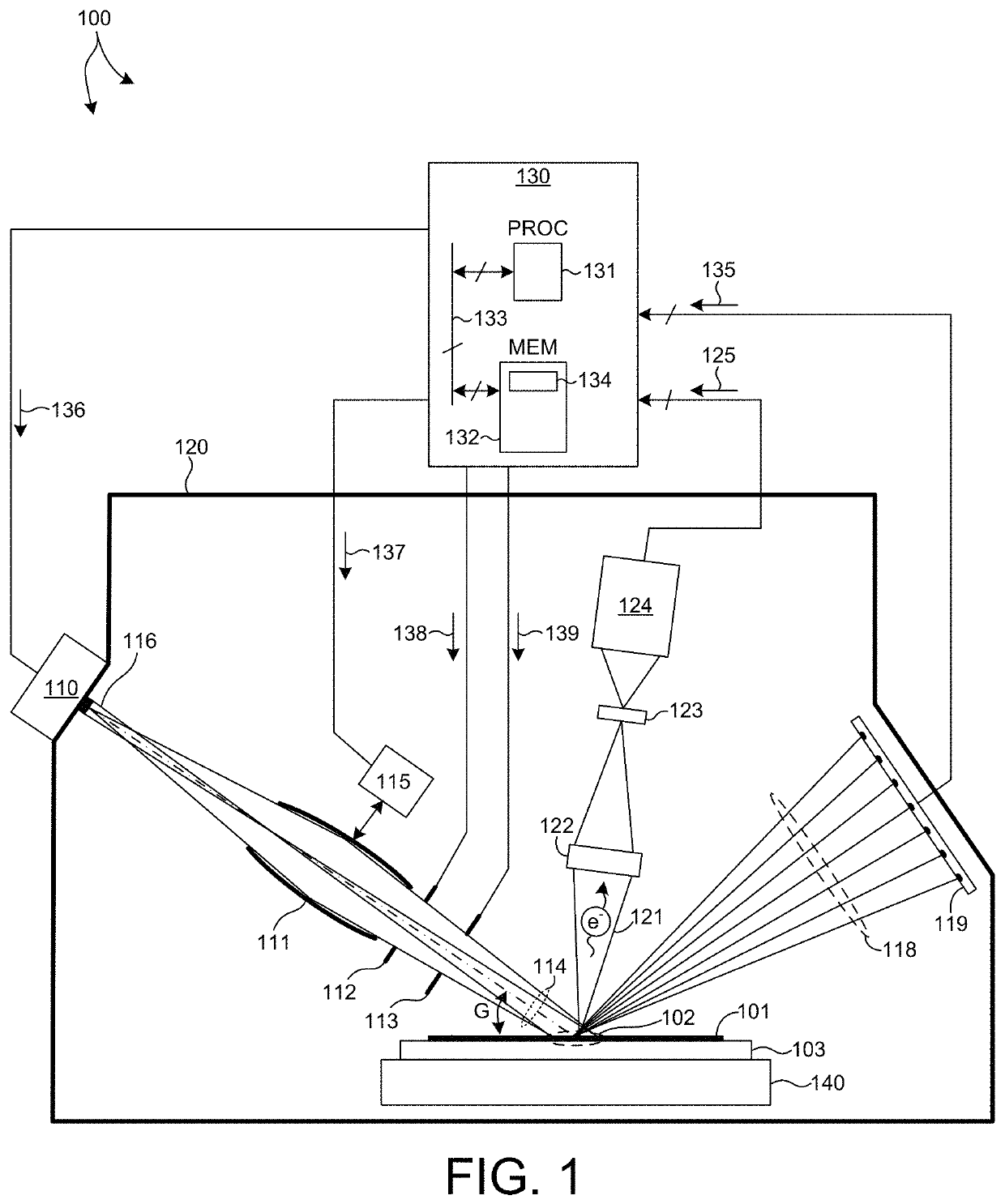
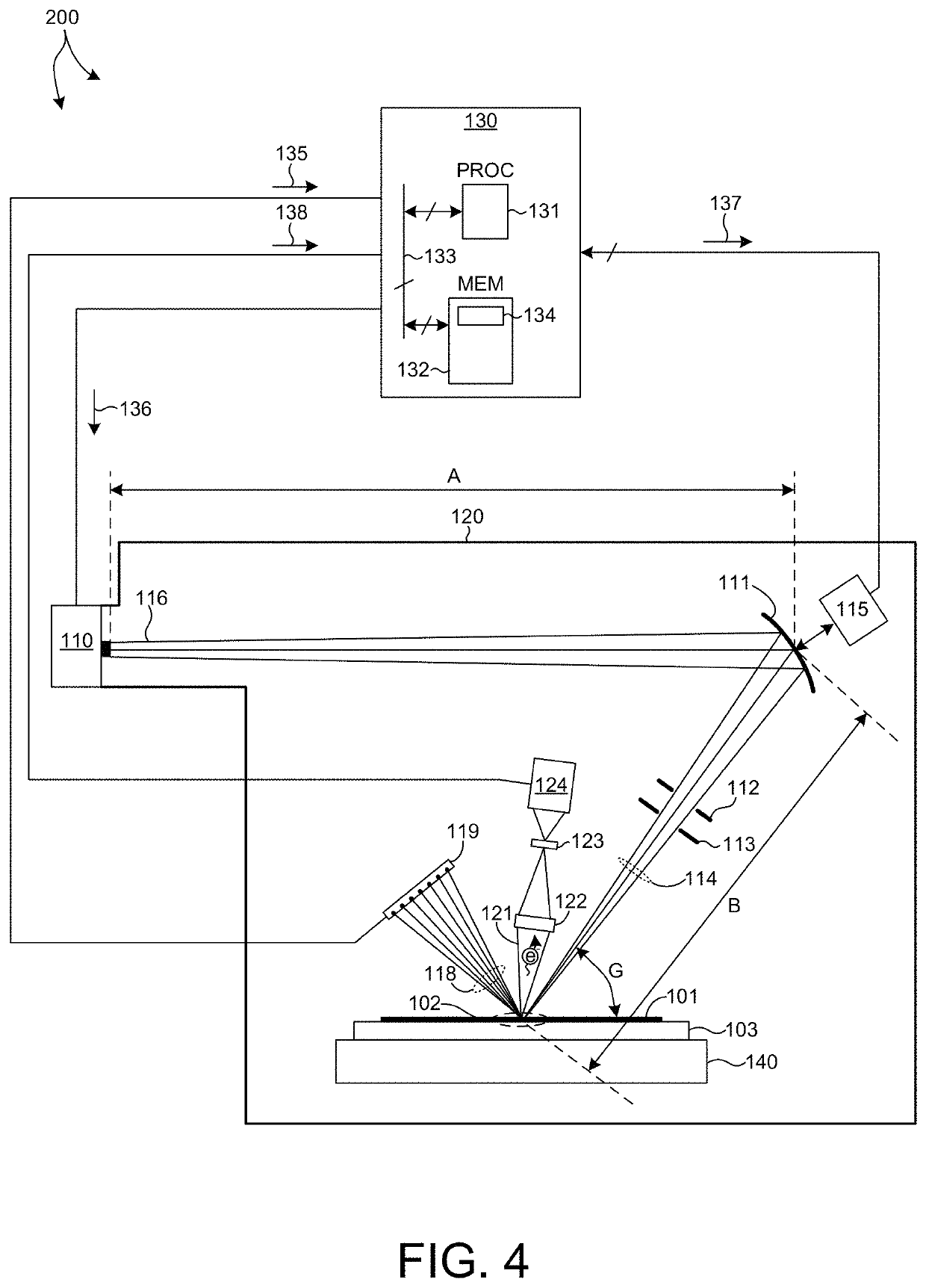
Device And Method For 3D Dose Tracking In Radiation Therapy
ActiveUS20120232324A1X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyConformal radiation therapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapy
The present invention relates to a device and method for verification of the quality of a radiation beam in conformal radiation therapy, and in particular for IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) applications. The actual 3D dose distribution in the patient is tracked during the course of the entire treatment by reconstructing the photon fluences from measured 2D detector responses during irradiation in conjunction with updated patient images.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Convolution and superposition dose calculation method based on Monte Carlo photon simulation
ActiveCN106199672AHigh precisionGuarantee the speed of analysis and calculationDosimetersCouplingComputational model
The invention discloses a convolution and superposition dose calculation method based on Monte Carlo photon simulation. The original analysis photon flux calculation is replaced by using Monte Carlo photon transportation on the basis of the conventional photon dose calculation model; and electron transportation is replaced by using the pre-calculated energy deposition nuclear so that time of simulation calculation can be greatly reduced in comparison with full space Monte Carlo photon-electron coupling transportation. Different calculation strategies can be used according to different calculation areas for further accelerating calculation speed; and convolution and superposition calculation is performed point by point as for the calculation points of the areas of interest, only a part of specific points are calculated as for calculation points of other areas and dose information of any point is obtained through the method of interpolation so that the calculation accuracy of the concerned areas of users can be guaranteed and calculation time can be reduced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated optical biosensor array including charge injection circuit and quantizer circuit
ActiveUS8969781B2Material analysis by optical meansMultiplier circuit arrangementsSensor arrayBiosensor array
An optical biosensor pixel for detecting the amount of light that is generated by the biosensing process and a biosensor array architecture that includes such biosensor pixels. The optical biosensor pixel includes a photodiode configured to convert an incident photon flux into a current. Additionally, the optical biosensor pixel includes an optical filter configured to select specific wavelengths and / or photon flux angles to reach the photodiode from a biological sample. The biosensor pixel further includes a trans-impedance amplifier coupled to the photodiode, where the trans-impedance amplifier is configured to convert the current into a voltage signal. Additionally, the biosensor pixel includes a 1-bit comparator coupled to the trans-impedance amplifier and a 1-bit digital-to-analog converter coupled to the 1-bit comparator, where the 1-bit digital-to-analog converter injects different levels of charge into an input of the trans-impedance amplifier at each cycle based on an output of the 1-bit comparator.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
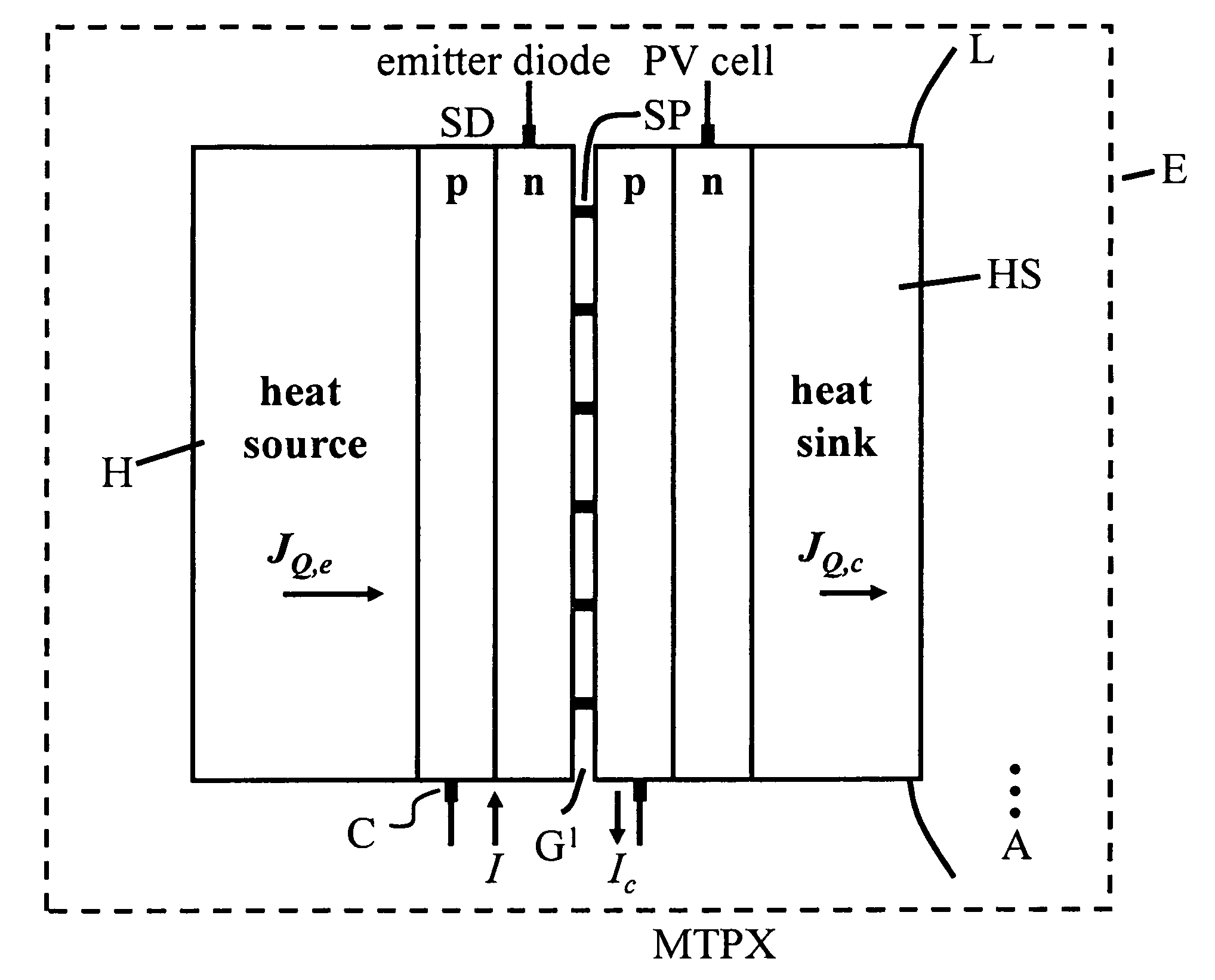
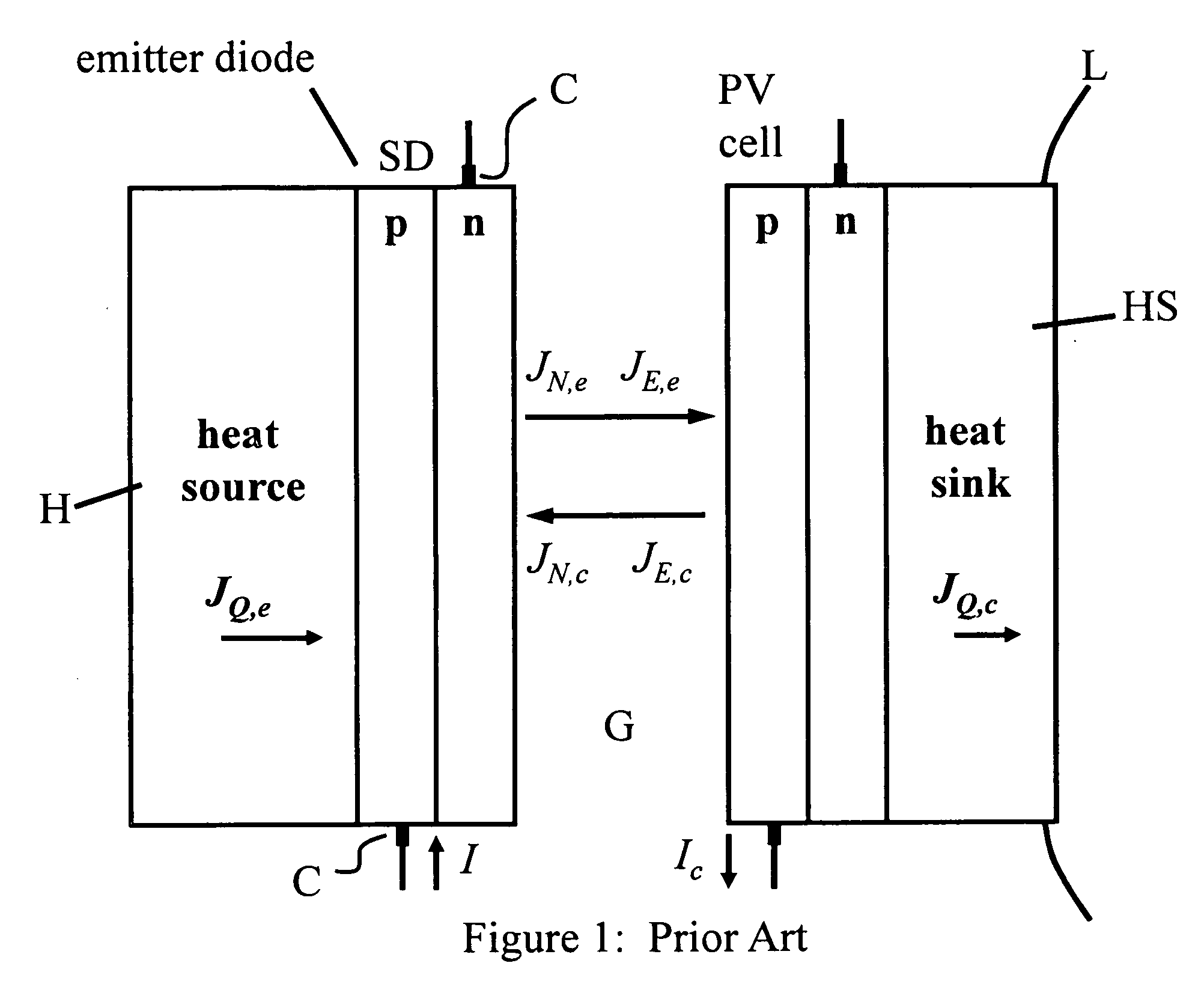
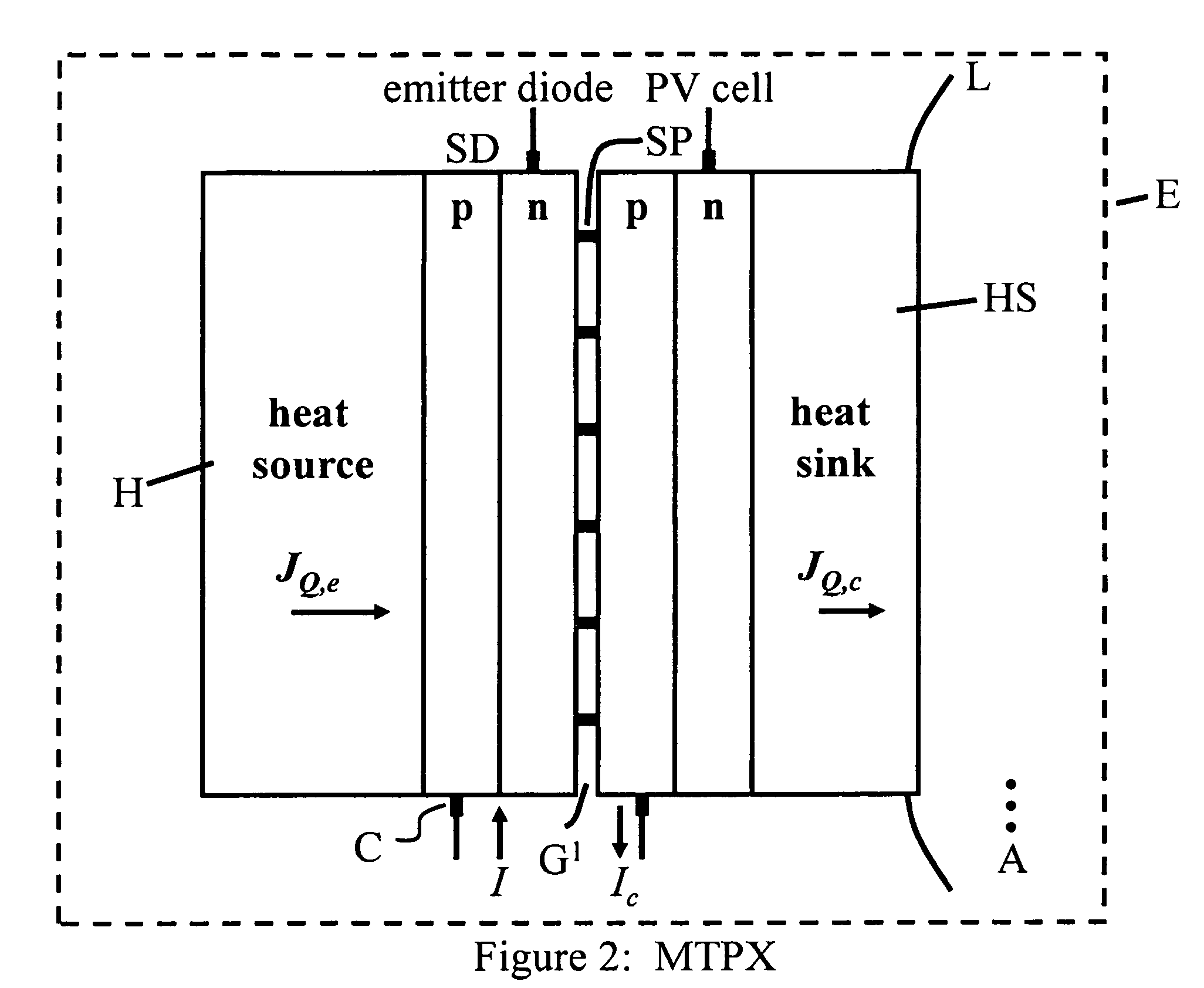
Method of and apparatus for improved thermophotonic generation of electricity
InactiveUS20090188549A1Efficient use ofImproved flow capturePV power plantsSemiconductor lasersElectricityEngineering
A thermophotonic method and generator of photovoltaic current wherein preferably a thermal source supplemented by photon flux as generated in an interposed semiconductor LED or the like is vacuum-spaced from a photovoltaic semiconductor surface by a gap of the order of submicrons / microns.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
Method for combining LED with homogeneous proportion of red blue light as well as module thereof
InactiveCN101251241AEasy to control automaticallyQuick installationPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsPlant factoryGreenhouse
The present invention discloses a light emitting diode combining method enabling uniform proportion between red light and blue light. Firstly, selecting single LED, an extra-bright circular lamp with a half-value angle of 7 degrees, a diameter of 5 mm and a wavelength of 636 nm is selected for the red light LED; an extra-bright circular lamp with a half-value angle of 7 degrees, a diameter of 5 mm and a wavelength of 459 nm is selected for the blue light LED; secondly, eight LEDs are arranged on each line and each row, and each red LED and each blue LED are evenly arranged at intervals, the surrounding of each LED are LEDs with the other color, the spacing between two adjacent LEDs is no more than 2.5 mm, 64 LEDs with the arranging manner form a 8x8 array to be arranged on a circuit board so as to be made into a light emitting diode combining module, and the module is used as a unit module which can be assembled or expanded longitudinally and / or transversely according to needs, and the uniformity of the distribution of the ratio R / B between the red light and blue light photons flux is not changed. The method is suitable for being used as light source for photosynthesis of plants in a greenhouse and being an illumination light source for plant factories. The method has the advantages of convenient mounting, replacing, assembly and expansion, and uniform distribution of R / B ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Green Alga Extract with High Astaxanthin Content and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080254056A1Increase productionIncrease concentrationBiocideCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientBetaxanthins
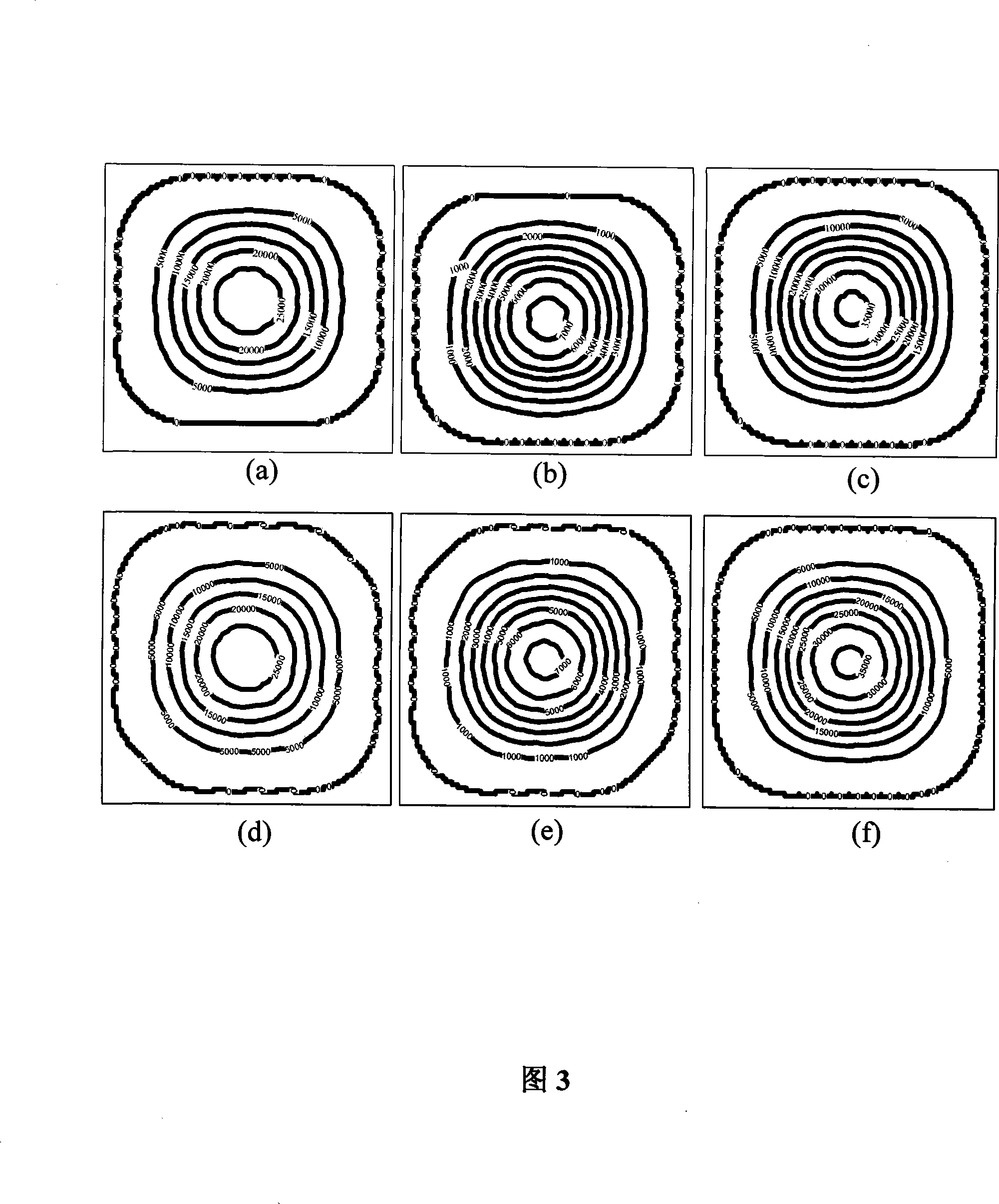
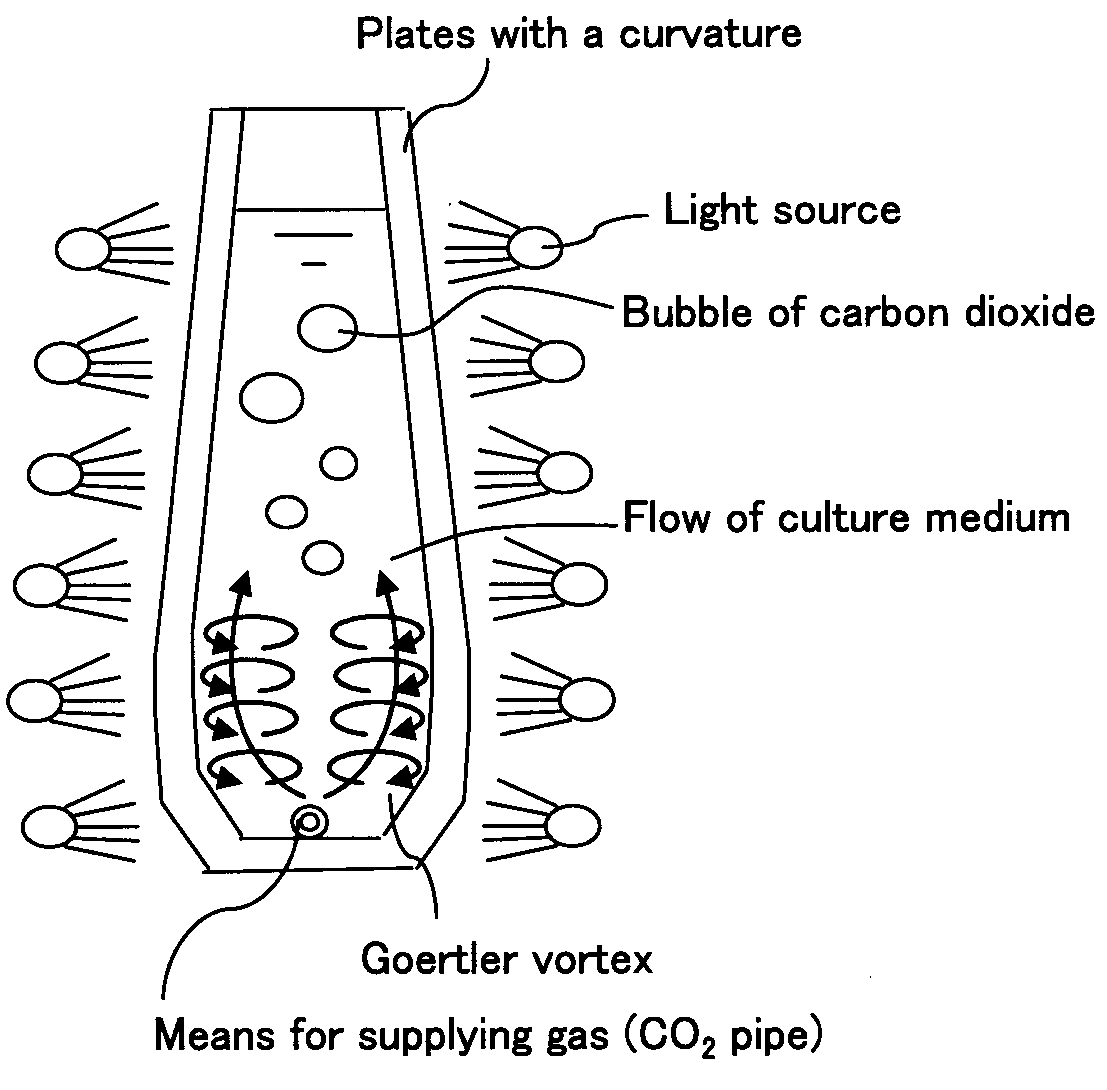
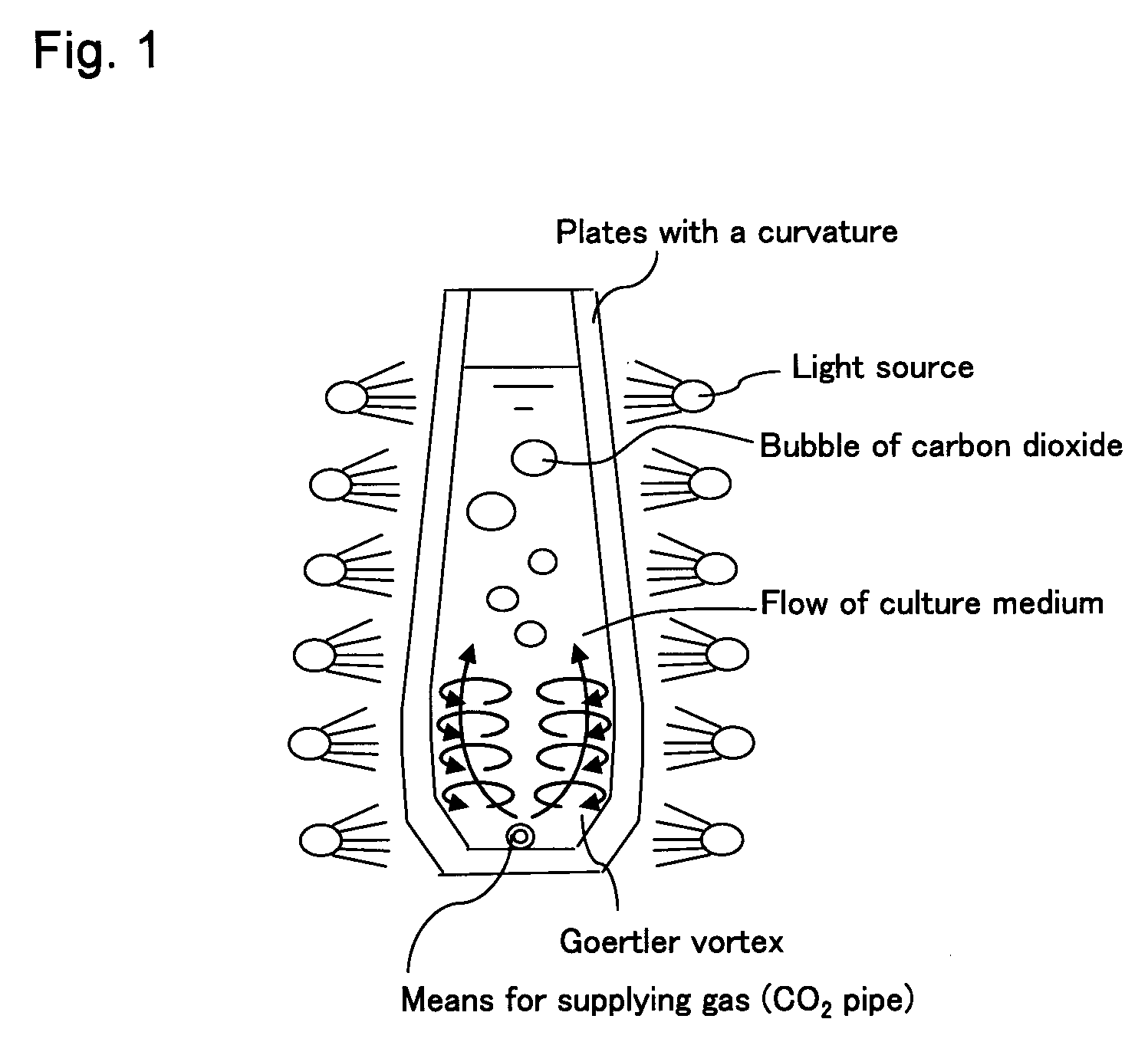
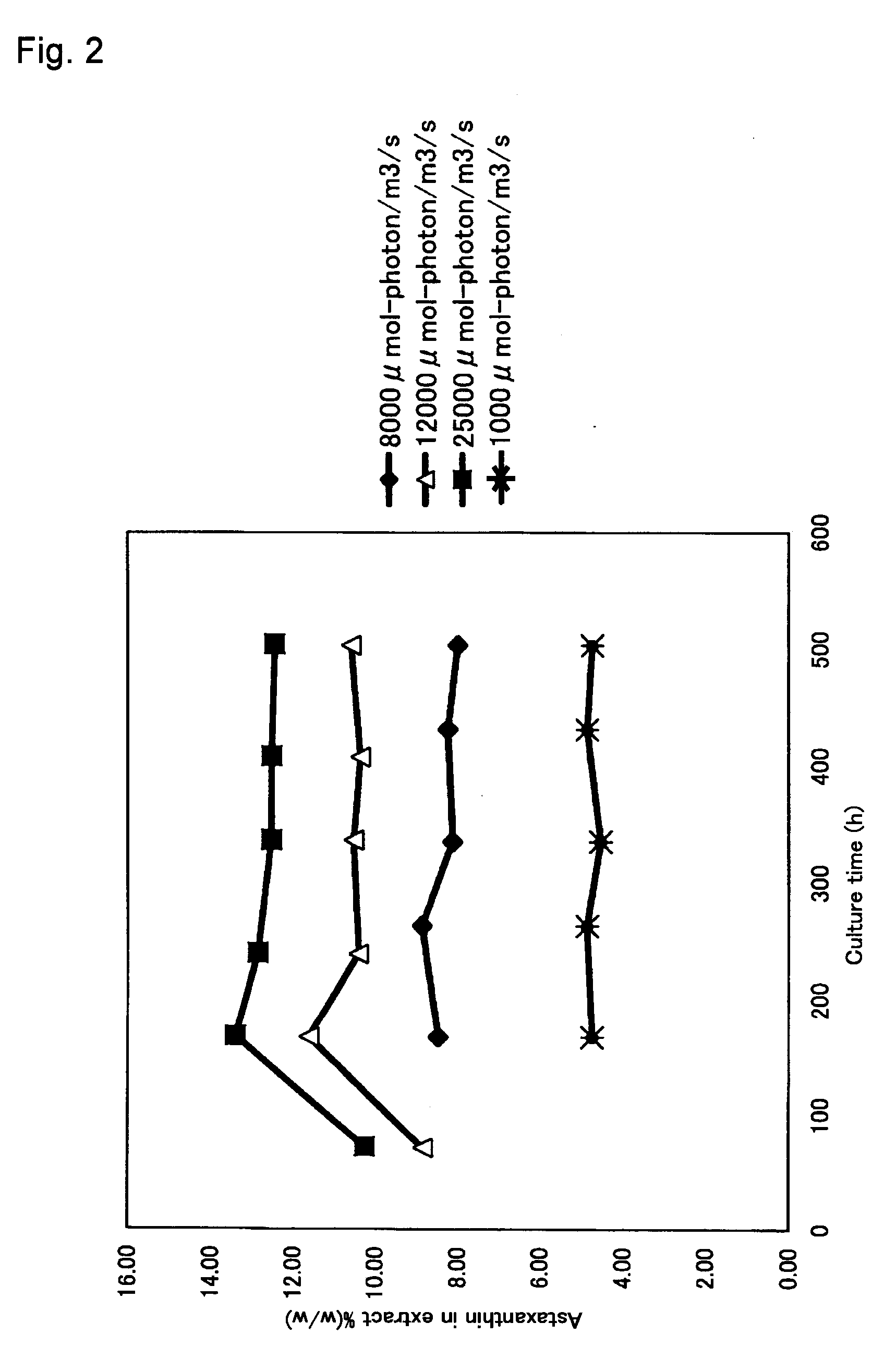
A green algal extract that contains astaxanthin at a concentration of 8 wt % or more can be obtained by cultivating an encysted green alga in a nutrient medium while supplying carbon dioxide and providing irradiation with light at a photosynthetically active photon flux input of 8000 μmol-photon / m3 / s or more, and extracting an oil component, which contains astaxanthin. A green alga that belongs to the genus Haematococcus is preferable.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
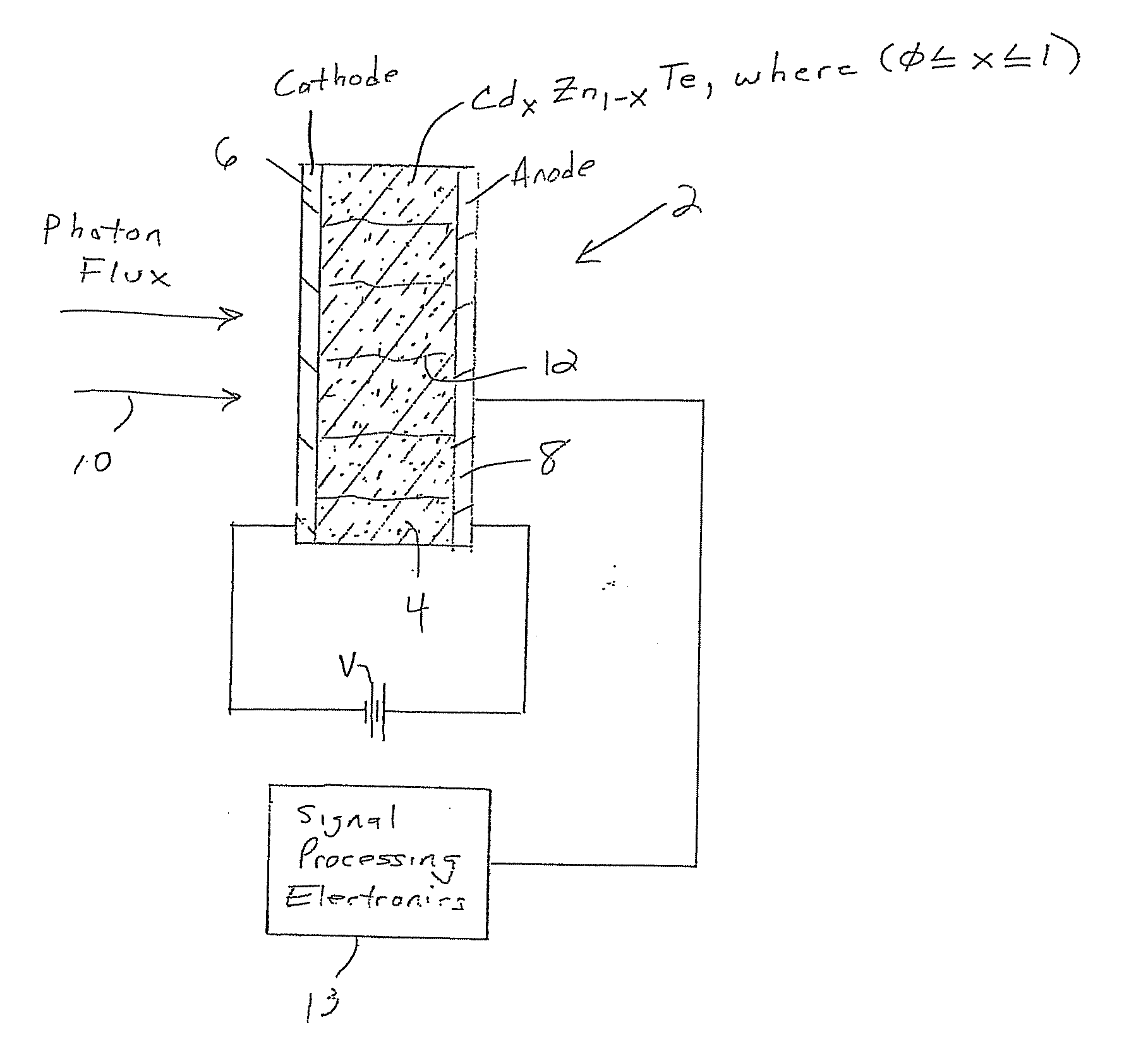
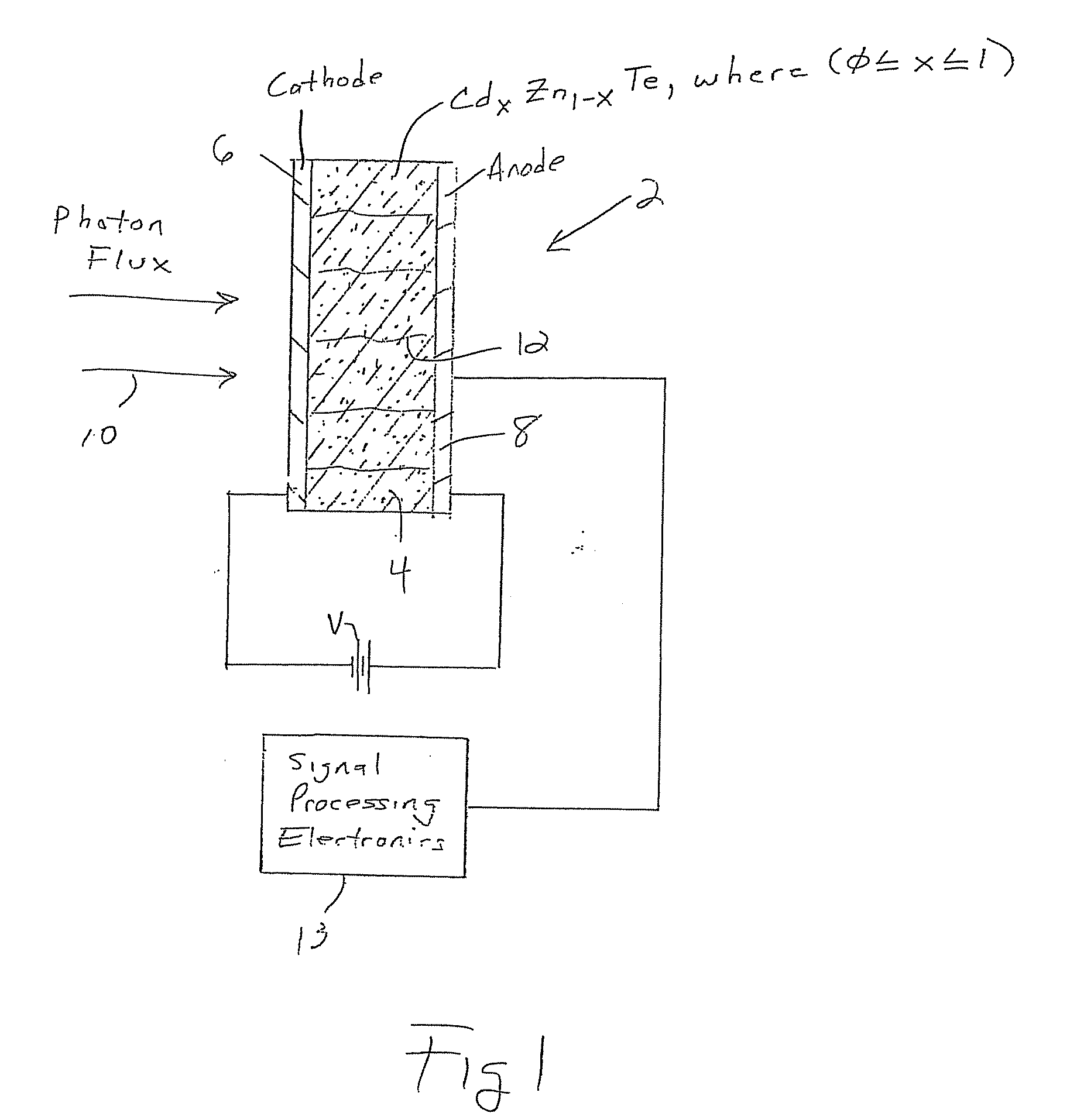
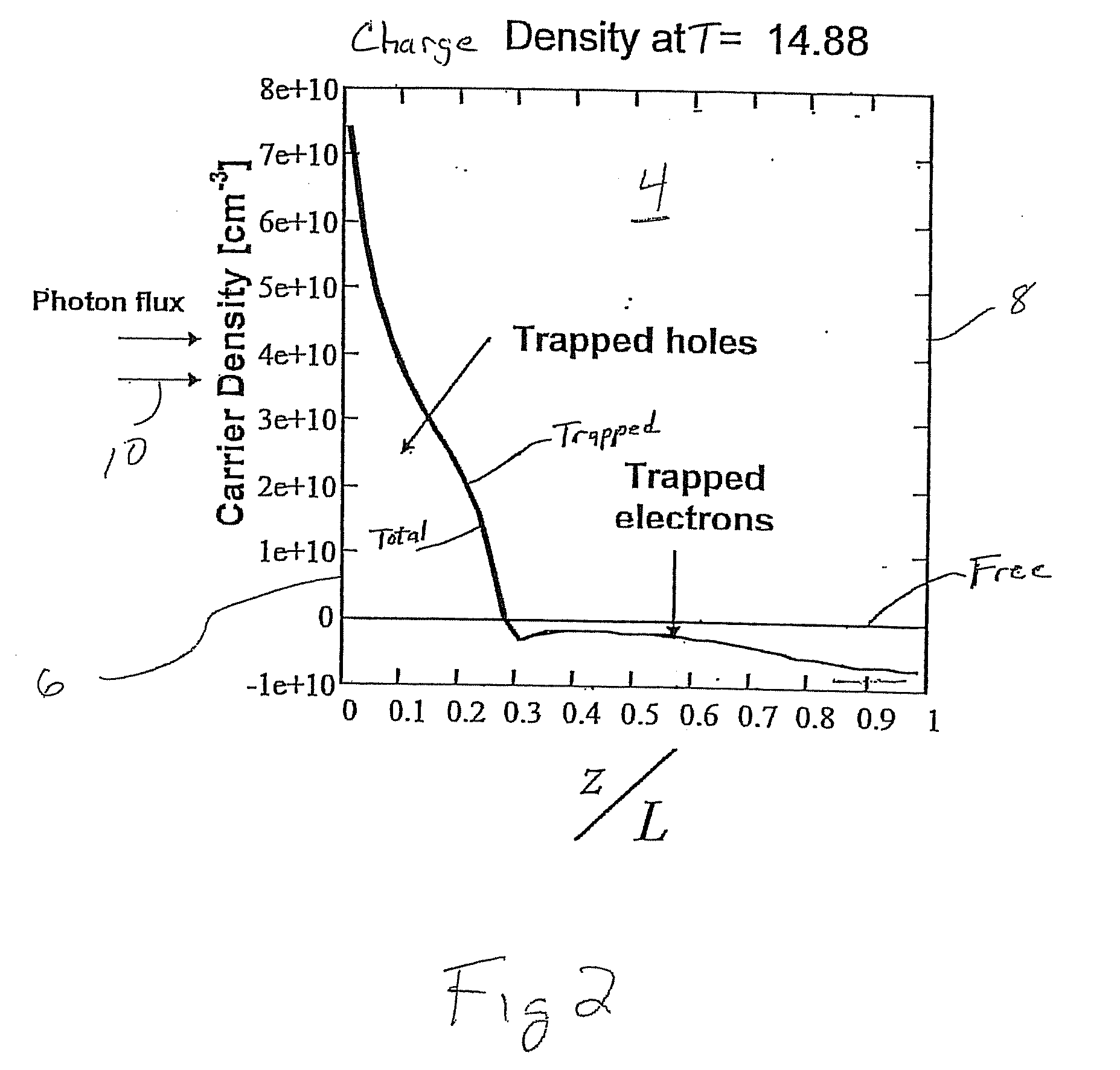
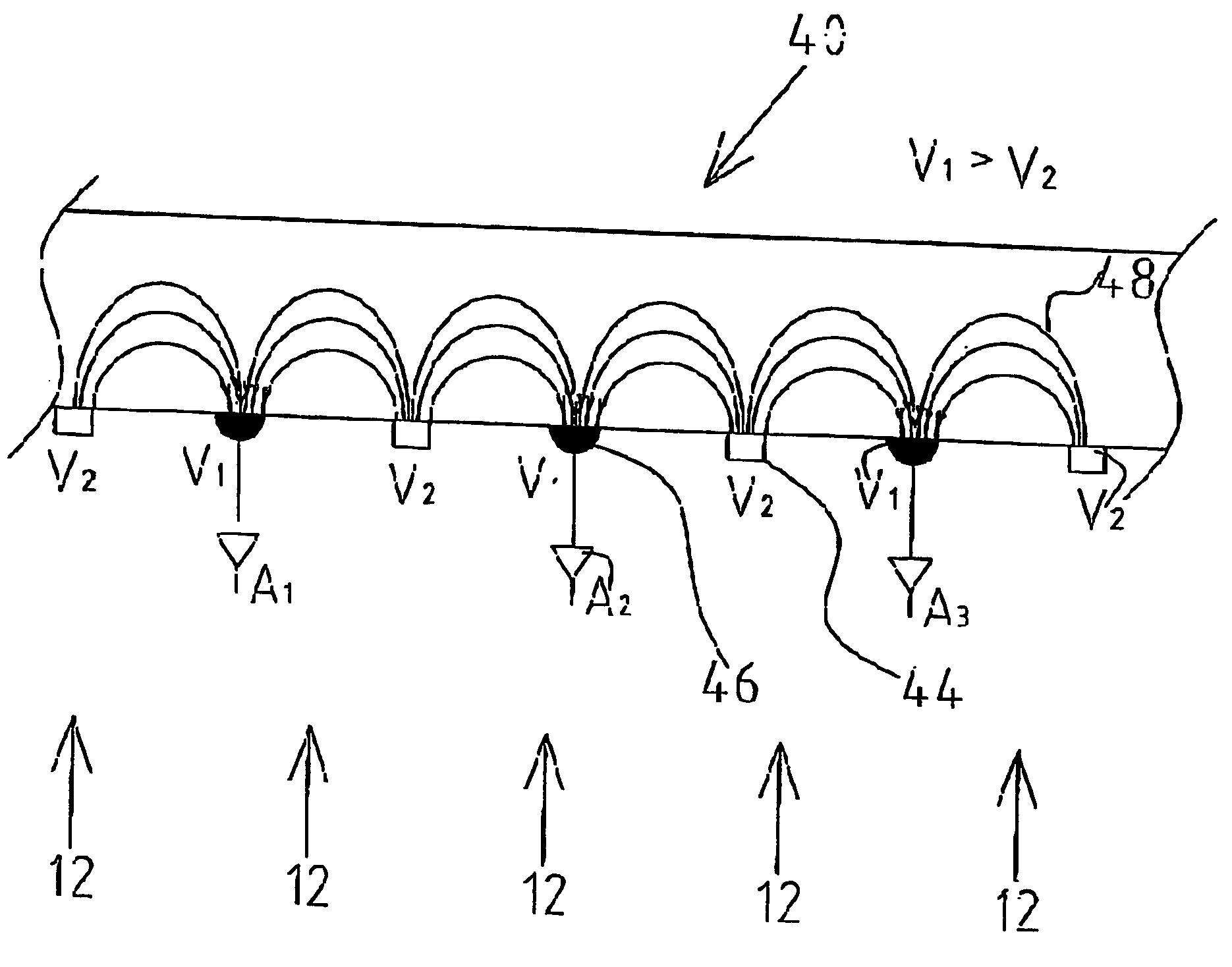
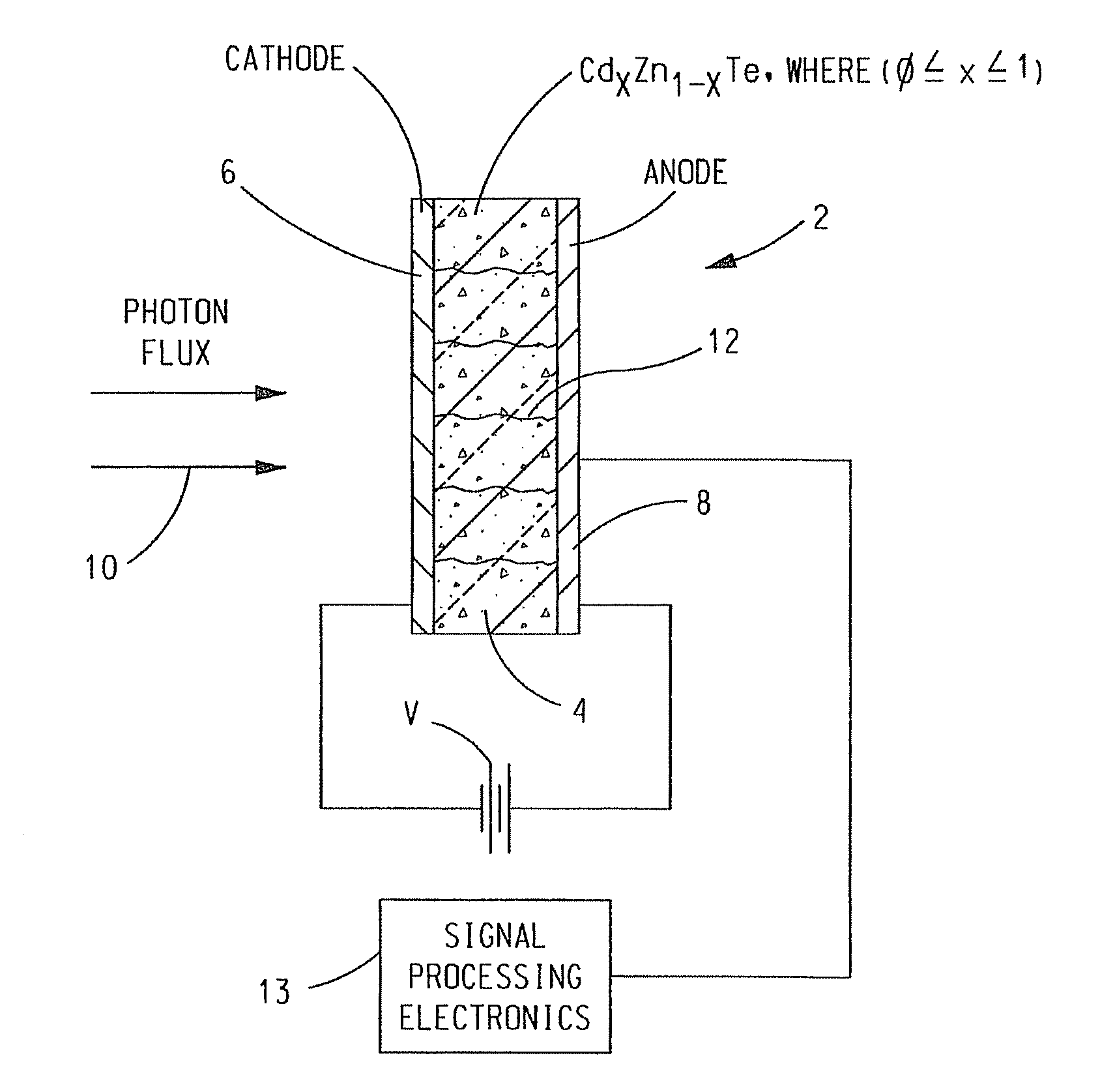
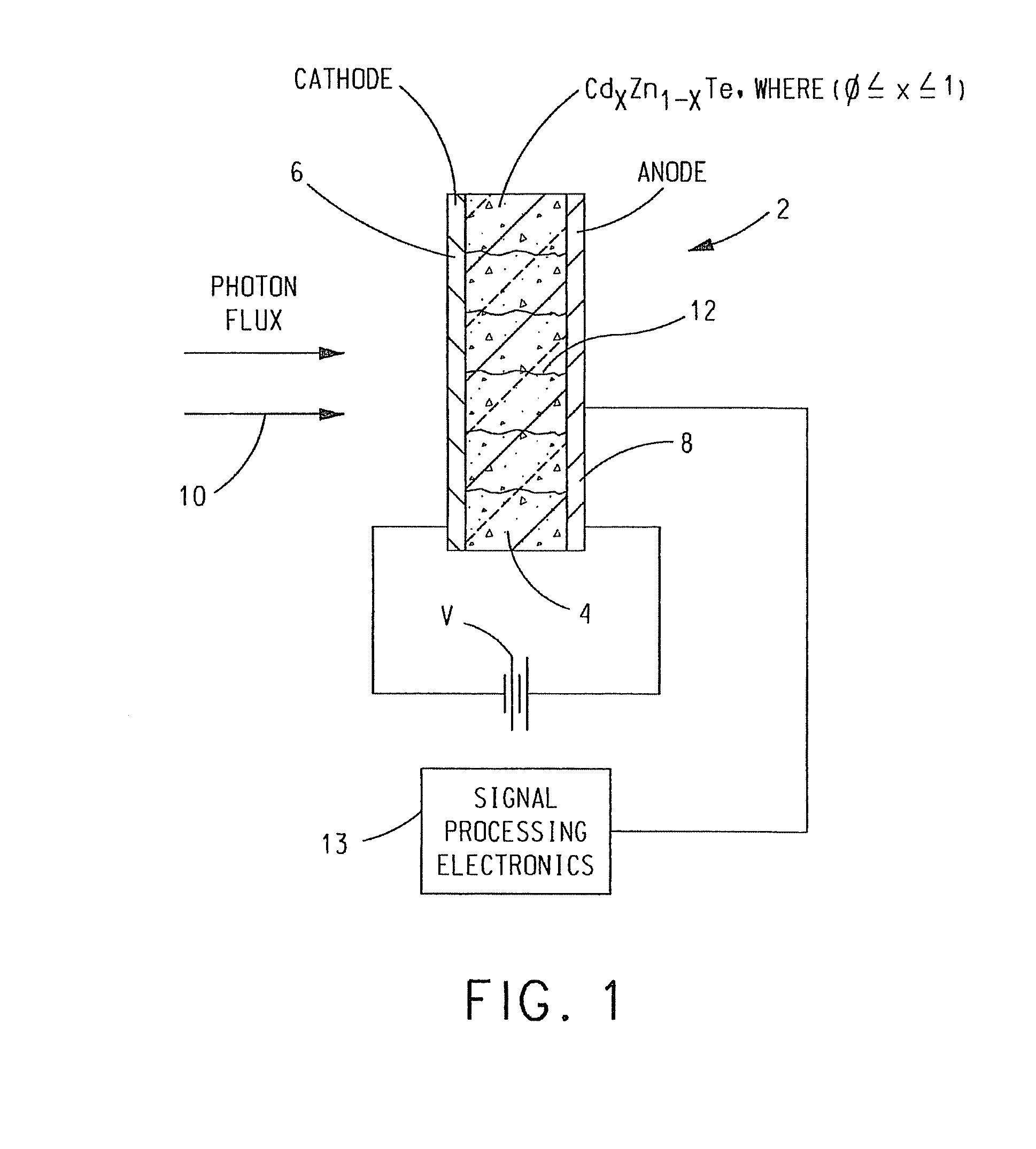
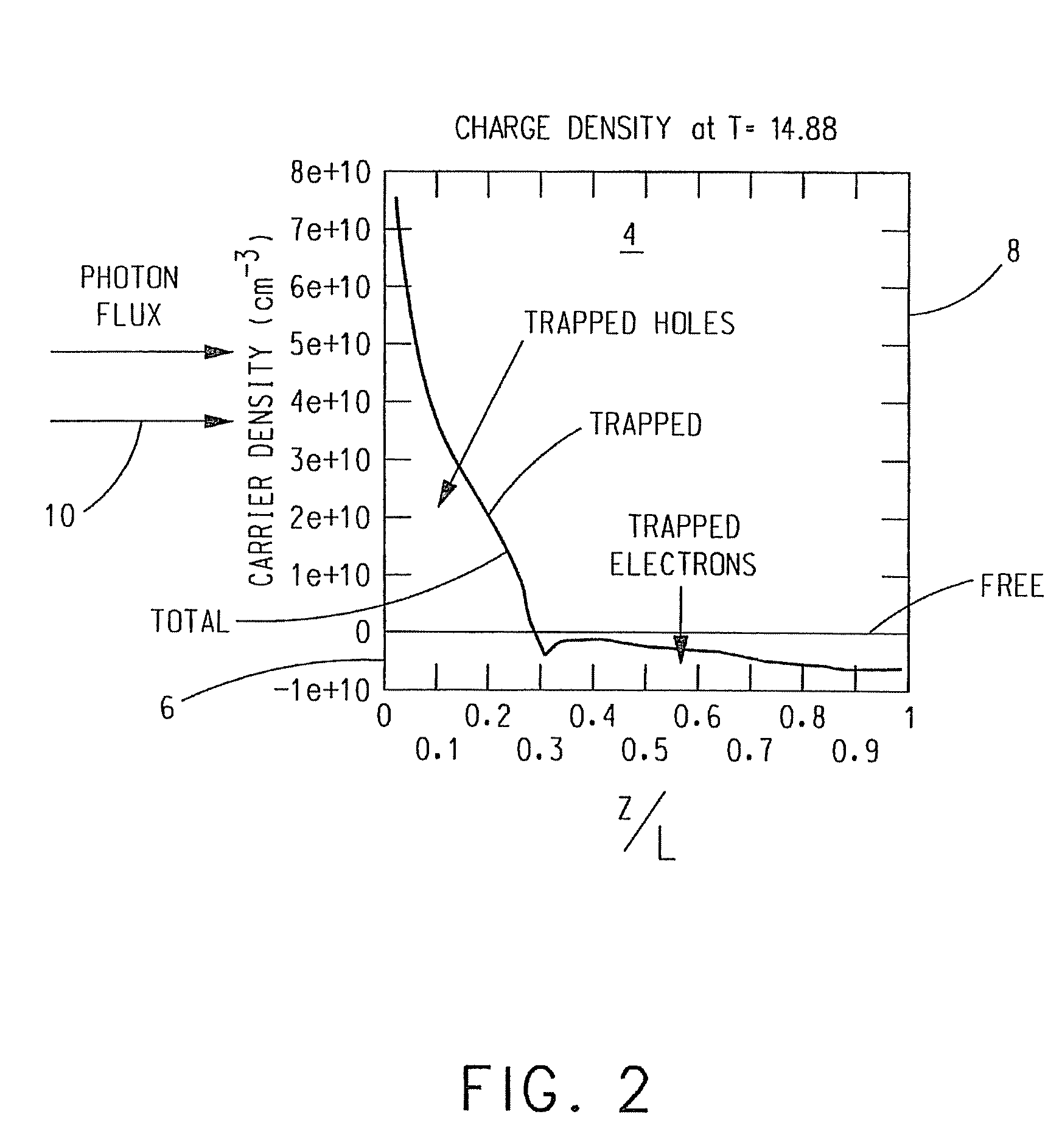
CdZnTe Device Using Constrained Design For High-Flux X-Ray Spectroscopic Imaging Applications
A CdZnTe photon counting detector includes a core material of Cd1-xZnxTe, where (0≦x<1), an anode terminal on one side of the core material and a cathode terminal on a side of the core material opposite the anode terminal. At least one of the following is selected in the design of the detector as a function of the maximum sustainable photon flux the core material is able to absorb in operation while avoiding polarization of the core material: electron lifetime-mobility product of the core material; de-trapping time of the core material; a value of a DC bias voltage applied between the anode and the cathode; a temperature of the core material in operation; a mean photon flux density to be absorbed by the core material in operation; and a thickness of the core material between the anode and the cathode.
Owner:PRODUCE
Two-dimensional radiation detector
InactiveUS20050242292A1Improve efficiencyLower levelElectric discharge tubesPhotometrySemiconductor radiation detectorsAnode spot
A two-dimensional, pixellated, monolithic semiconductor radiation detector, in which each detector pixel is essentially a perpendicular mode detector. This is achieved by an arrangement of anode spots, one for each pixel located on the flux-exposed front surface of the detector substrate, surrounding by a cathode array preferably in the form of a network of lines, such that the field between the anodes and cathodes on this front surface has a major component in the direction parallel to the surface, and hence perpendicular to the incident photon flux. The conductivity of the substrate is high near this front surface, since this is where the highest level of absorption of photons takes place, and a significant photoconductive current is thus generated between cathodes and anodes. The conductivity is proportional to the incoming photon flux, and decays exponentially with depth into the detector. Since all of the conduction paths are in parallel to each other, the resultant conductance between each anode and its surrounding cathode is the summation of all those conductances.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Method and apparatus for improving growth and/or pathogen resistance of a plant using transient high-intensity illumination
InactiveUS9131645B2Induce dormancyAccelerated deathSaving energy measuresHorticulture methodsHigh intensitySquare meter
A method of improving the growth and / or pathogen resistance of a plant, comprising the step of exposing at least part of the plant to a transient period of high intensity illumination providing a photon flux at the plant surface having at least one of the following characteristics: (a) a red photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square meter per second, and having a wavelength of between 600 and 700 nm; (b) a blue photon flux comprising at least 100 micromoles photons per square meter per second, having a wavelength of between 420 and 480 nm. The Invention also provides apparatus for providing such conditions to growing plants.
Owner:KARPINSKI STANISLAW +1
CdZnTe device using constrained design for high-flux x-ray spectroscopic imaging applications
A CdZnTe photon counting detector includes a core material of Cd1-xZnxTe, where (0≦x<1), an anode terminal on one side of the core material and a cathode terminal on a side of the core material opposite the anode terminal. At least one of the following is selected in the design of the detector as a function of the maximum sustainable photon flux the core material is able to absorb in operation while avoiding polarization of the core material: electron lifetime-mobility product of the core material; de-trapping time of the core material; a value of a DC bias voltage applied between the anode and the cathode; a temperature of the core material in operation; a mean photon flux density to be absorbed by the core material in operation; and a thickness of the core material between the anode and the cathode.
Owner:PRODUCE
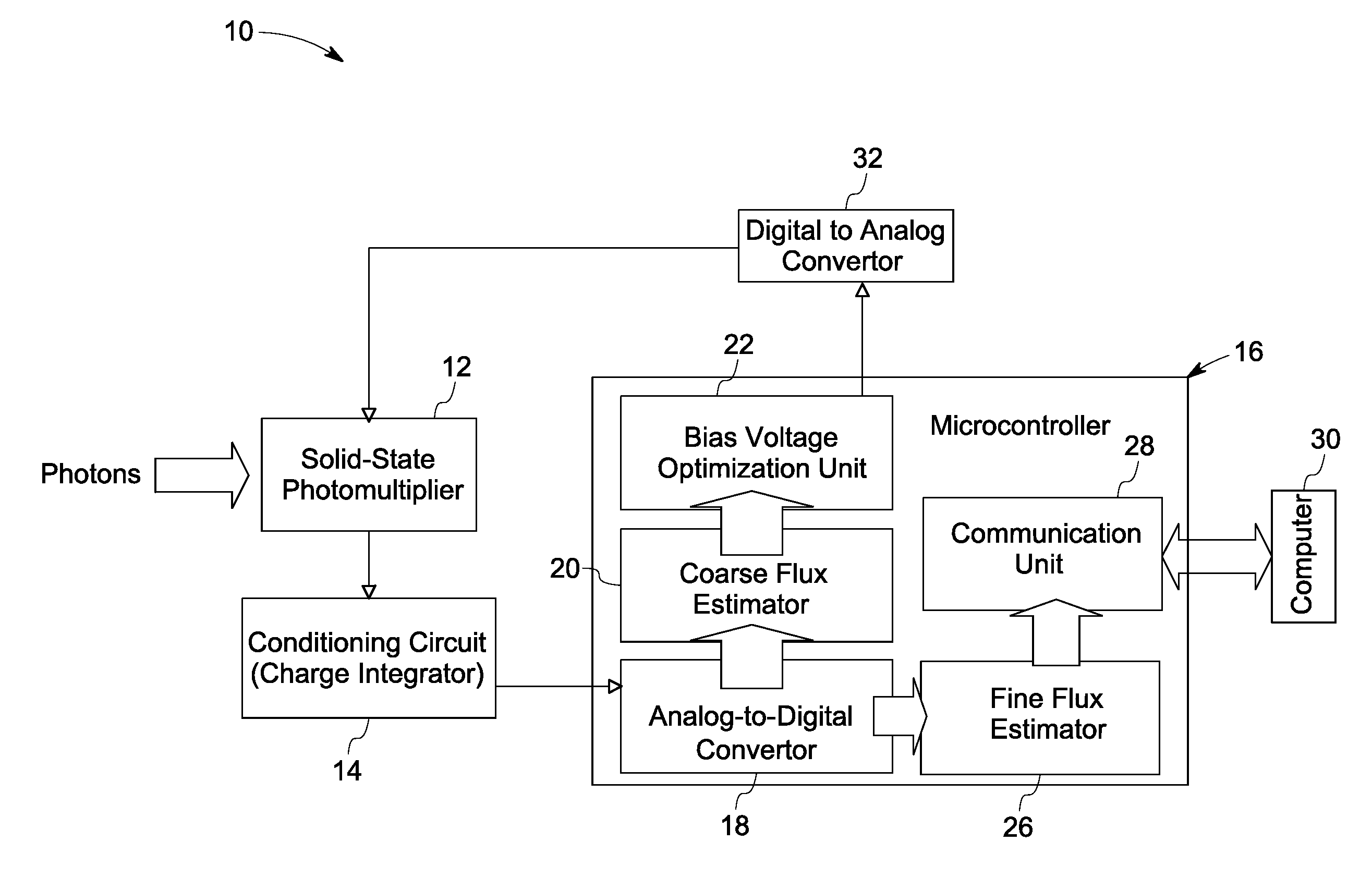
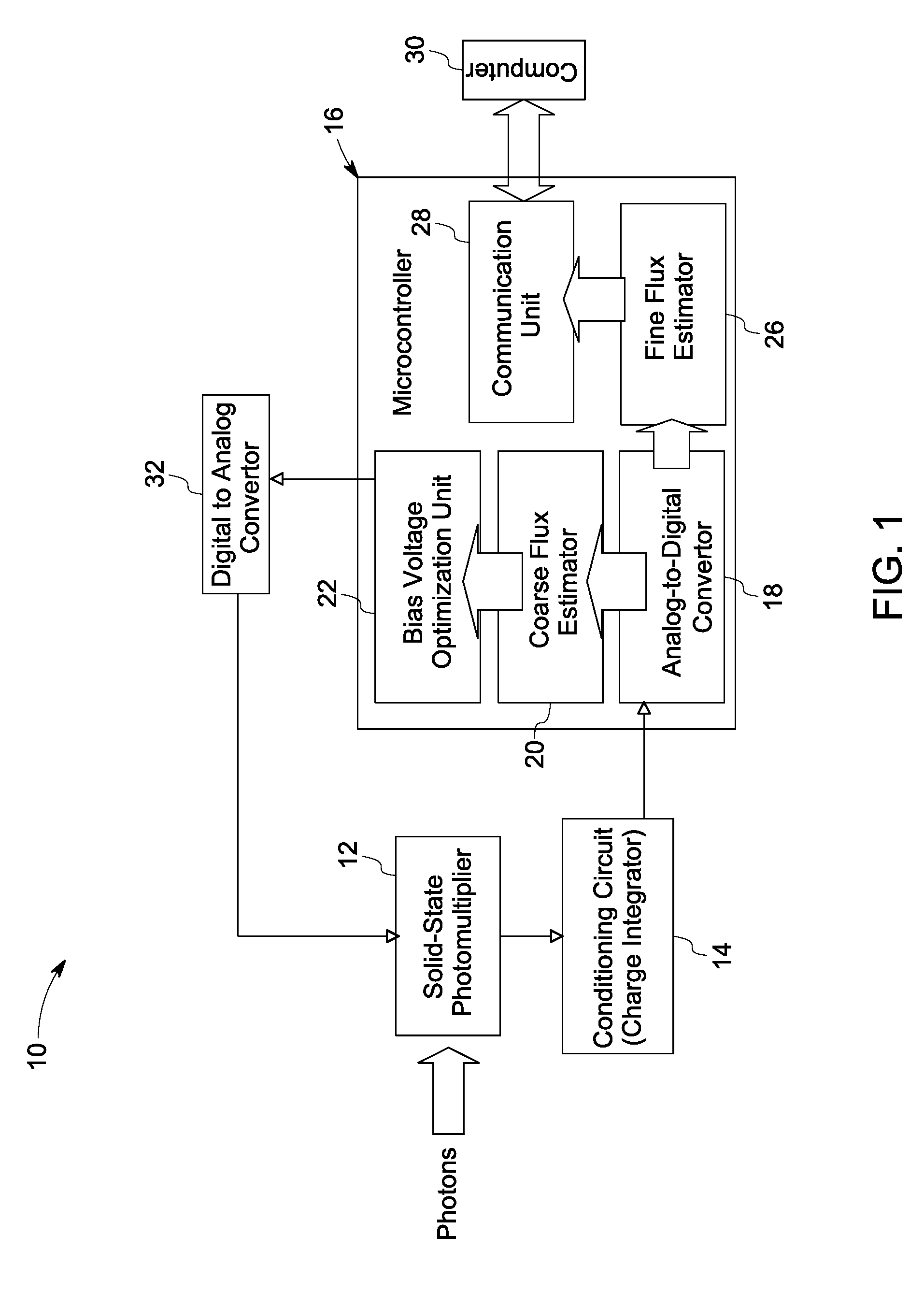
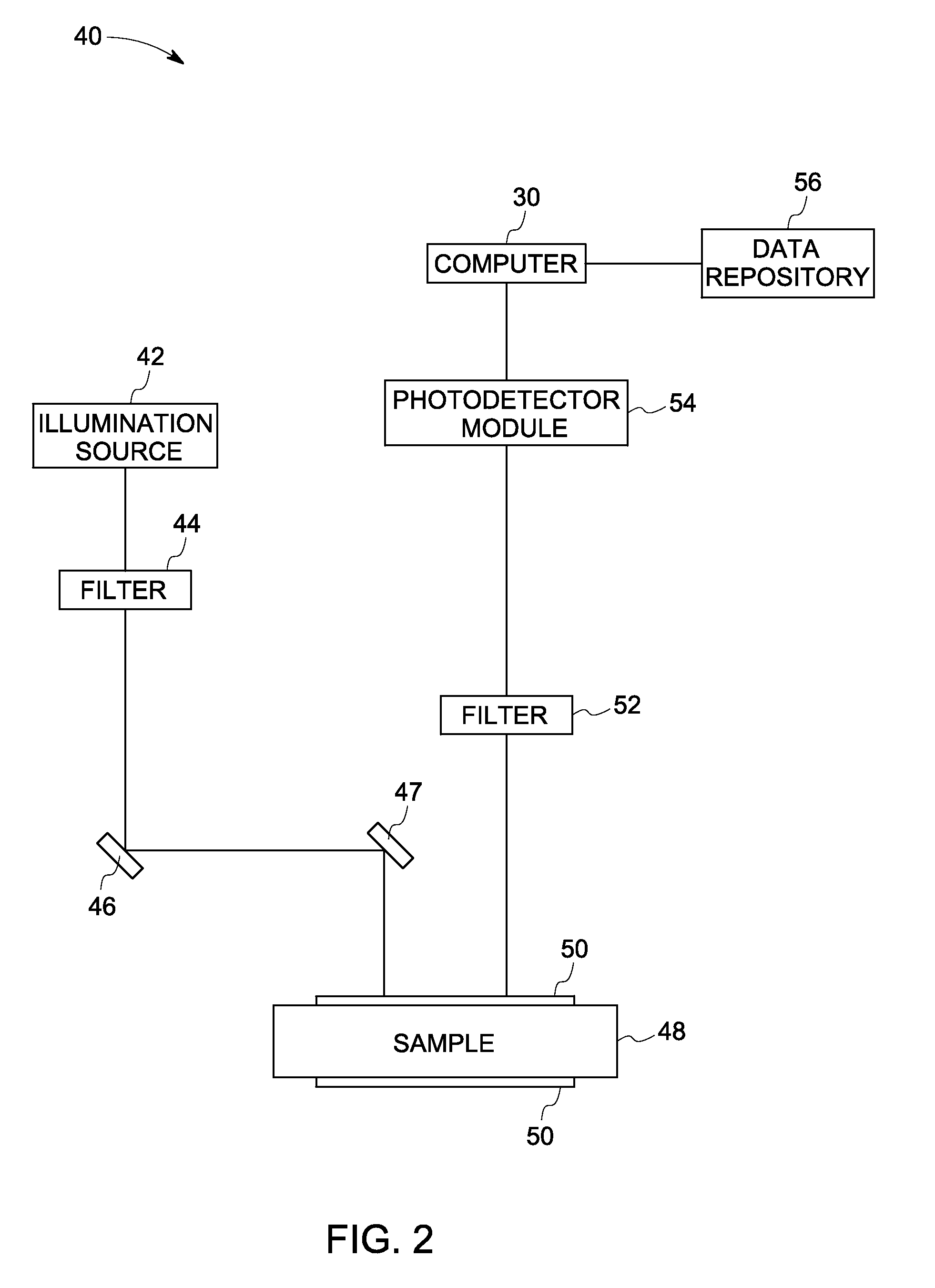
Solid-state photomultiplier module with improved signal-to-noise ratio
ActiveUS8222589B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Photomultiplier
A scanning imaging system is provided. The scanning imaging system comprises an illumination source for illuminating a sample with an excitation light, a filter to block emission light wavelengths from the illumination source. Further, the scanning imaging system comprises a SSPM module comprising a solid state photo multiplier to detect a photon flux and generate electrical signals based on impinging photons; a conditioning circuit to accumulate charge from the SSPM and a micro-controller to change a bias voltage applied to the SSPM to achieve a higher signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Carbon monoxide (CO) microsir sensor system
InactiveUS20110142719A1Different in diameterDifferent in structureAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptical propertyPhotocurrent
The present invention provides very small low cost apparatus and method for determining the concentration and / or hazard from a target gas by means of optically monitoring one or more sensors that responds to carbon monoxide. The apparatus comprises a photon source optically coupled to the sensor and the photon intensity passing through the sensor is quantified by one or more photodiode(s) in a system, so that the photon flux is a function of at least one sensor's response to the target gas, e.g., transmits light through the sensor to the photodiode. The photocurrent from the photodiode is converted to a sensor reading value proportional to the optical characteristics of the sensors and is loaded into a microprocessor or other logic circuit. In the microprocessor, the sensor readings may be differentiated to determine the rate of change of the sensor readings and the total photons absorbed value may be used to calculate the CO concentration.
Owner:THE QUANTUM GROUP
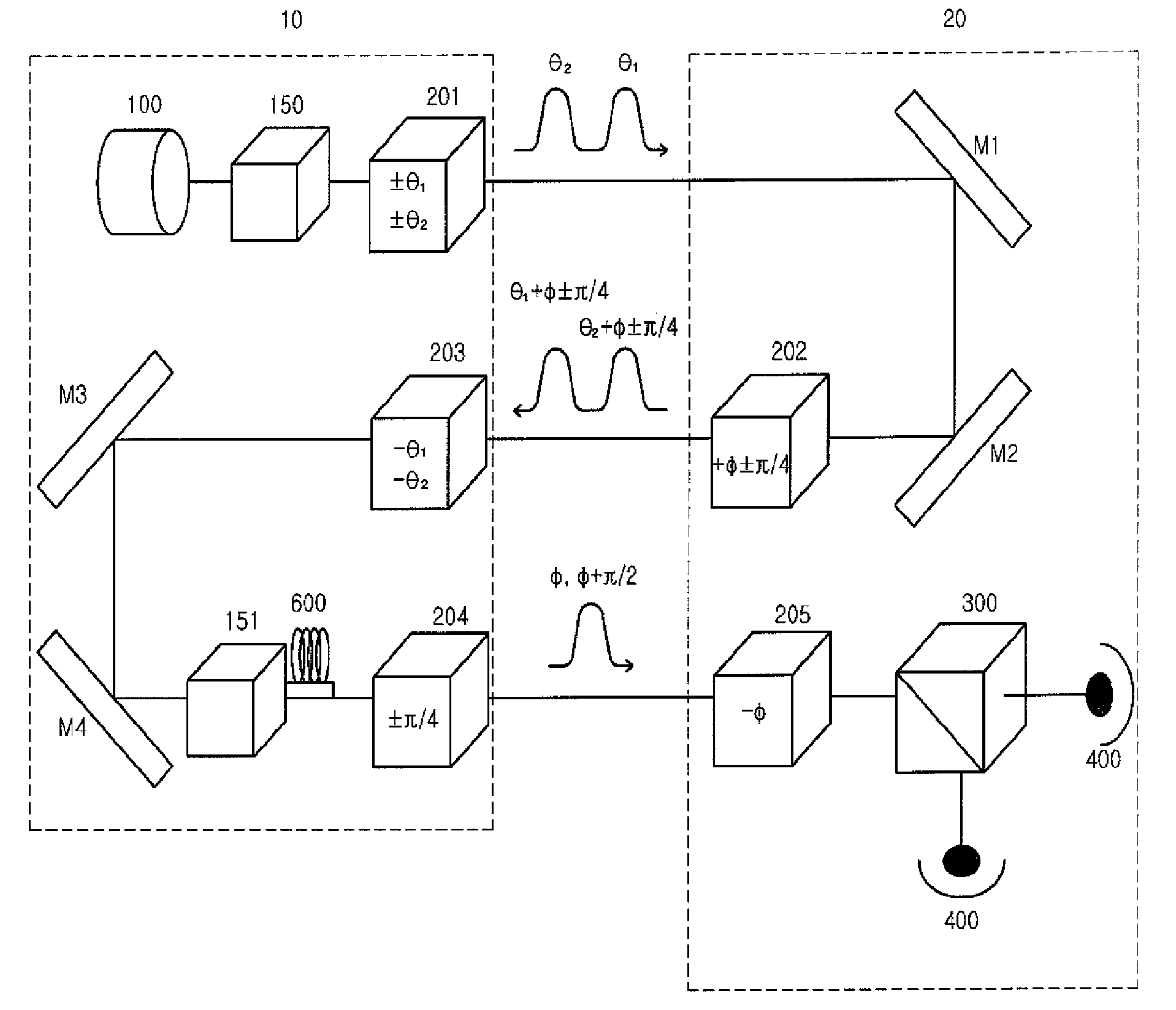
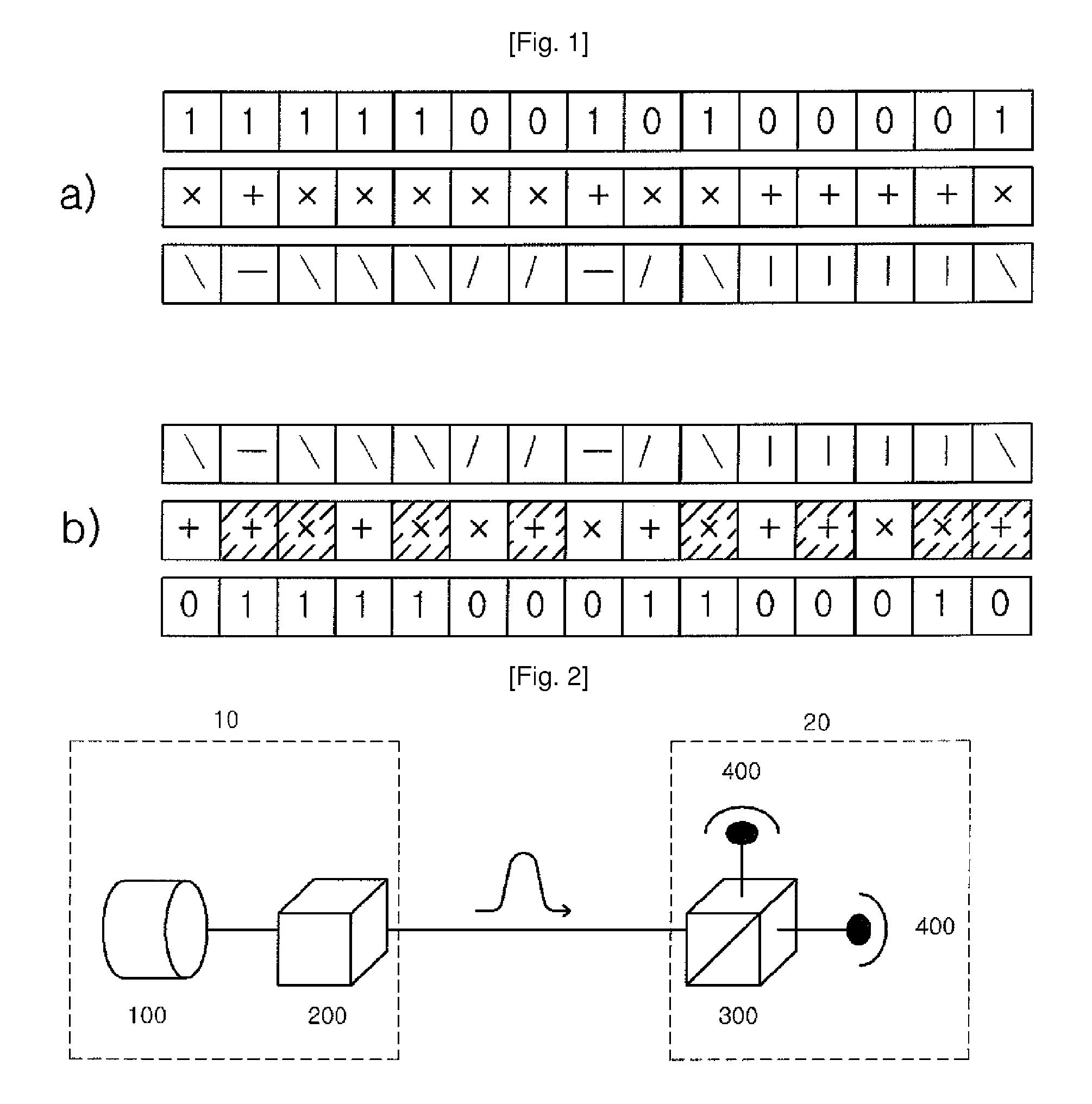
Method of quantum cryptography using blind photon polarization quibits with multiple stages
ActiveUS20090147955A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesThird partyPhoton polarization
A cryptography method using a quantum phenomenon, which performs a multi-staged polarization process between a transmitter and a receiver to prevent a third party from knowing the polarization value of a photon. A transmitter rotates a photon flux by arbitrary angle θ and transmits it to a receiver. The receiver rotates the received photon flux by arbitrary angle φ and transmits it to the transmitter. The transmitter rotates the received photon flux by the reverse angle −θ of an angle, by which the transmitter 10 rotated it, then rotates it by polarization corresponding to an information bit, and transmits it to the receiver which rotates the received photon flux by the reverse angle −φ of an angle, and measures the polarization of the photon flux corresponding to the information bit, and recovers the information bit transmitted by the transmitter. Cryptography information may be transmitted using a plurality of photon fluxes.
Owner:PAICHAI UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Systems and methods for combined x-ray reflectometry and photoelectron spectroscopy
ActiveUS10895541B2Improve accuracyImprove throughputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationColor/spectral properties measurementsSemiconductor structureQuantum electrodynamics
Methods and systems for measuring structural and material characteristics of semiconductor structures based on combined x-ray reflectometry (XRR) and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) are presented herein. A combined XRR and XPS system includes an x-ray illumination source and x-ray illumination optics shared by both the XRR and XPS measurement subsystems. This increases throughput and measurement accuracy by simultaneously collecting XRR and XPS measurement data from the same area of the wafer. A combined XRR and XPS system improves measurement accuracy by employing XRR measurement data to improve measurements performed by the XPS subsystem, and vice-versa. In addition, a combined XRR and XPS system enables simultaneous analysis of both XRR and XPS measurement data to more accurately estimate values of one of more parameters of interest. In a further aspect, any of measurement spot size, photon flux, beam shape, beam diameter, and illumination energy are independently controlled.
Owner:KLA CORP
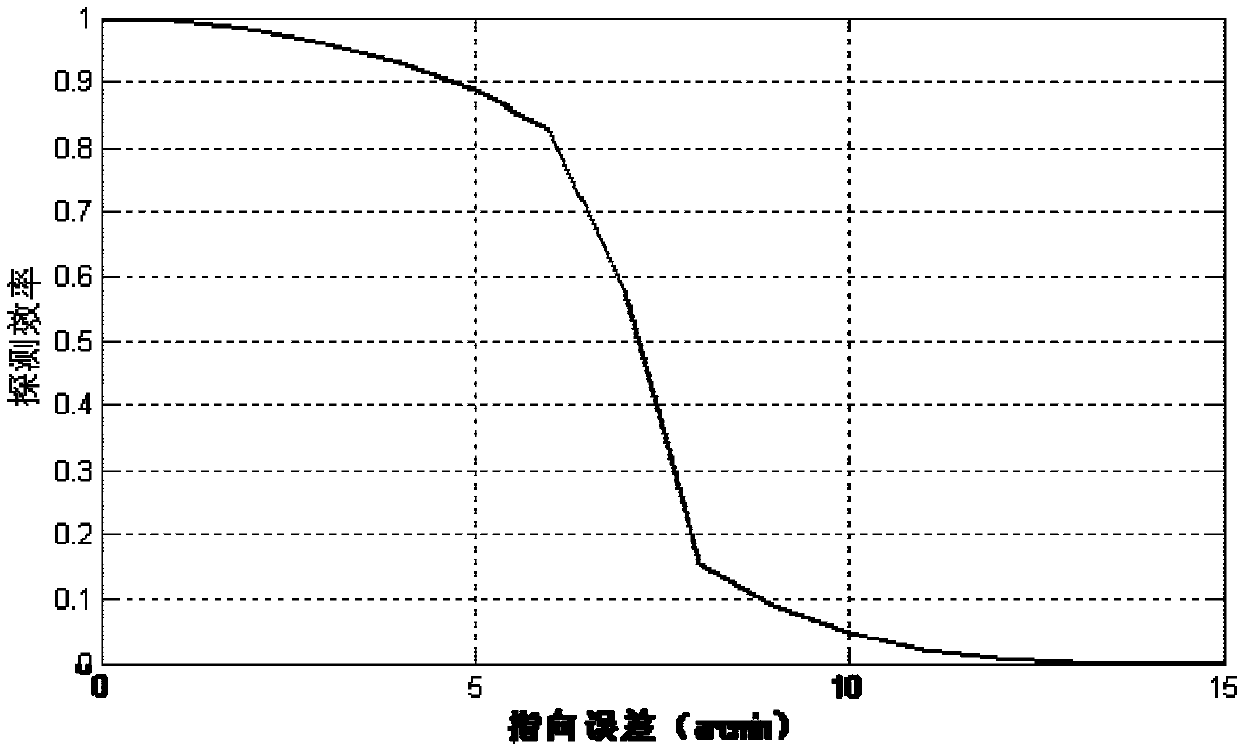
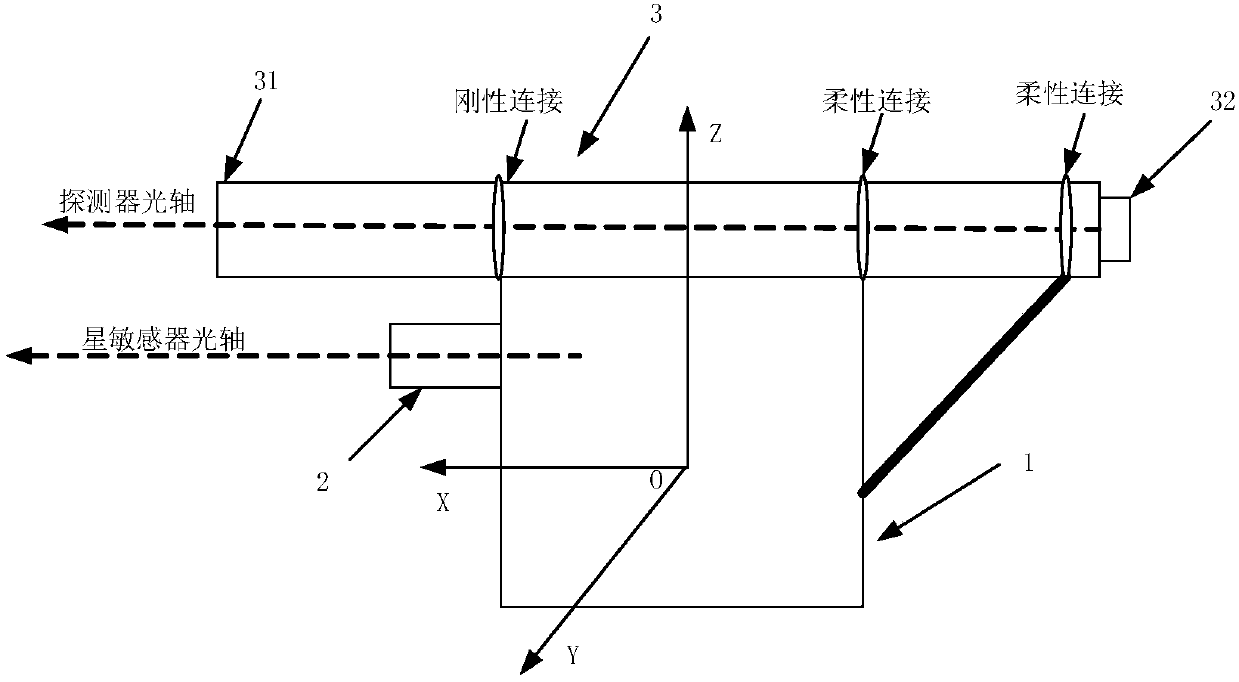
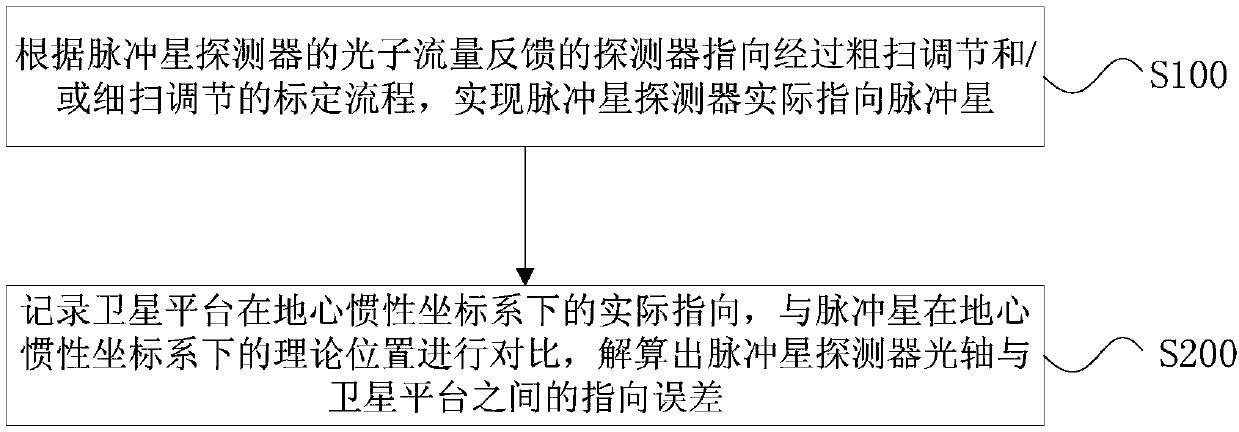
On orbit calibration method, processor and storage medium for pulsar detector pointing error
The invention discloses an on orbit calibration method, a processor and a storage medium for pulsar detector pointing error. The method comprises the steps that according to a calibration process of the pointing of the detector fed back by the photon flux of the pulsar detector adjusted by coarse scanning and / or fine scanning, the pulsar detector actually pointing to a pulsar is realized; an actual pointing of a satellite platform in geocentric inertial coordinate system is recorded and compared with a theoretical position of the pulsar in the geocentric inertial coordinate system, the pointing error between the optical axis of the pulsar detector and the satellite platform is solved. The pointing error provides a basis for automatic compensation of a next detection process, and the calibration method is completed on the satellite platform independently, ground intervention is not needed, and compared with ground calibration, the calibration method takes into account the effects of mechanics of the launching section and on orbit thermal shock, so that the calibration precision is high.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com