Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Photon distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging scene modeling method based on point cloud model
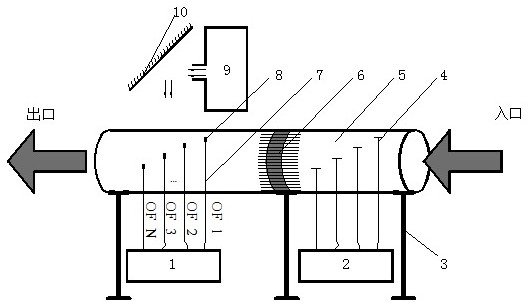
The invention discloses a laser non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging scene modeling method based on a point cloud model. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, setting non-visual-field scene space parameters, imaging system parameters and imaging index parameters, and determining a visible region of a specified scanning point-to-point cloud target; secondly, segmenting the visible region point cloud into a plurality of micro-point clouds by utilizing space voxels; detecting angular points to form micro-surface elements, estimating the region, the centroid and the surface normal of each micro-surface element, and establishing an energy transmission model of signals emitted from a laser through three times of diffuse reflection and received by a detector in combination with imaging system parameters to obtain echo energy and echo photon distribution histograms, and finally, setting different scanning points, and repeating the above steps to obtain a photon distribution histogram of multiple echo signals. The modeling method is advantaged in that the process that signals are emitted from a laser, subjected to three times of diffuse reflection of an intermediate surface and a point cloud target with three-dimensional characteristics and finally detected and counted is simulated for the first time.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
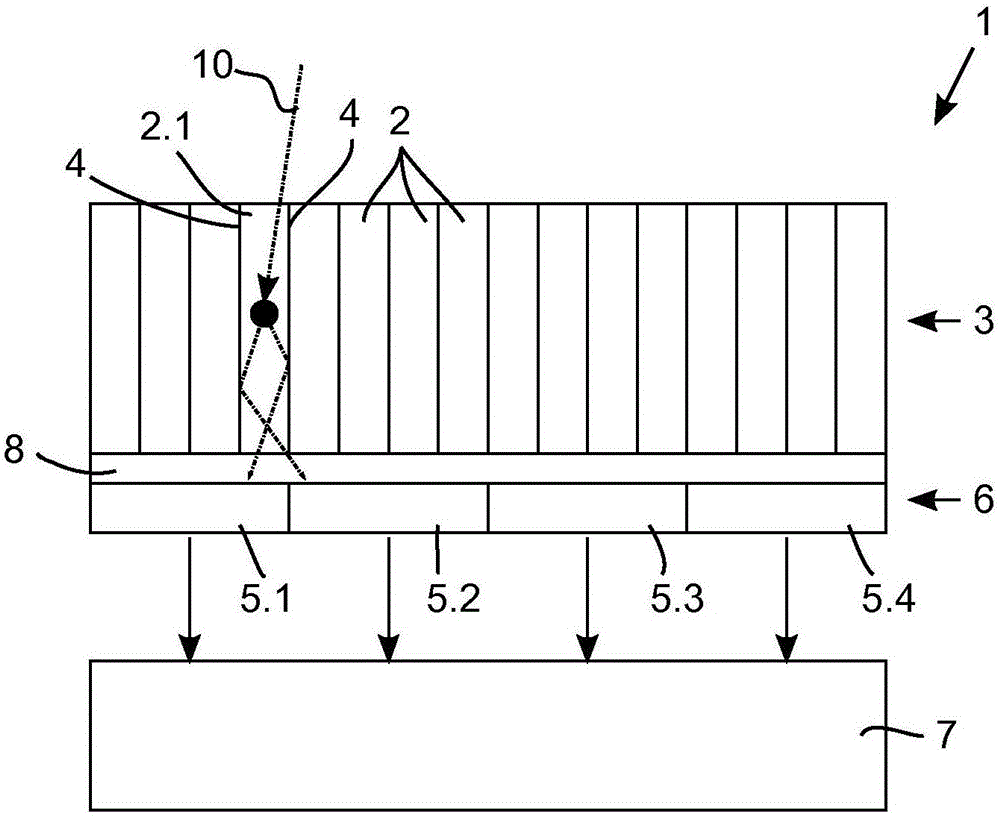
Scintillation event position determination in a radiation particle detector
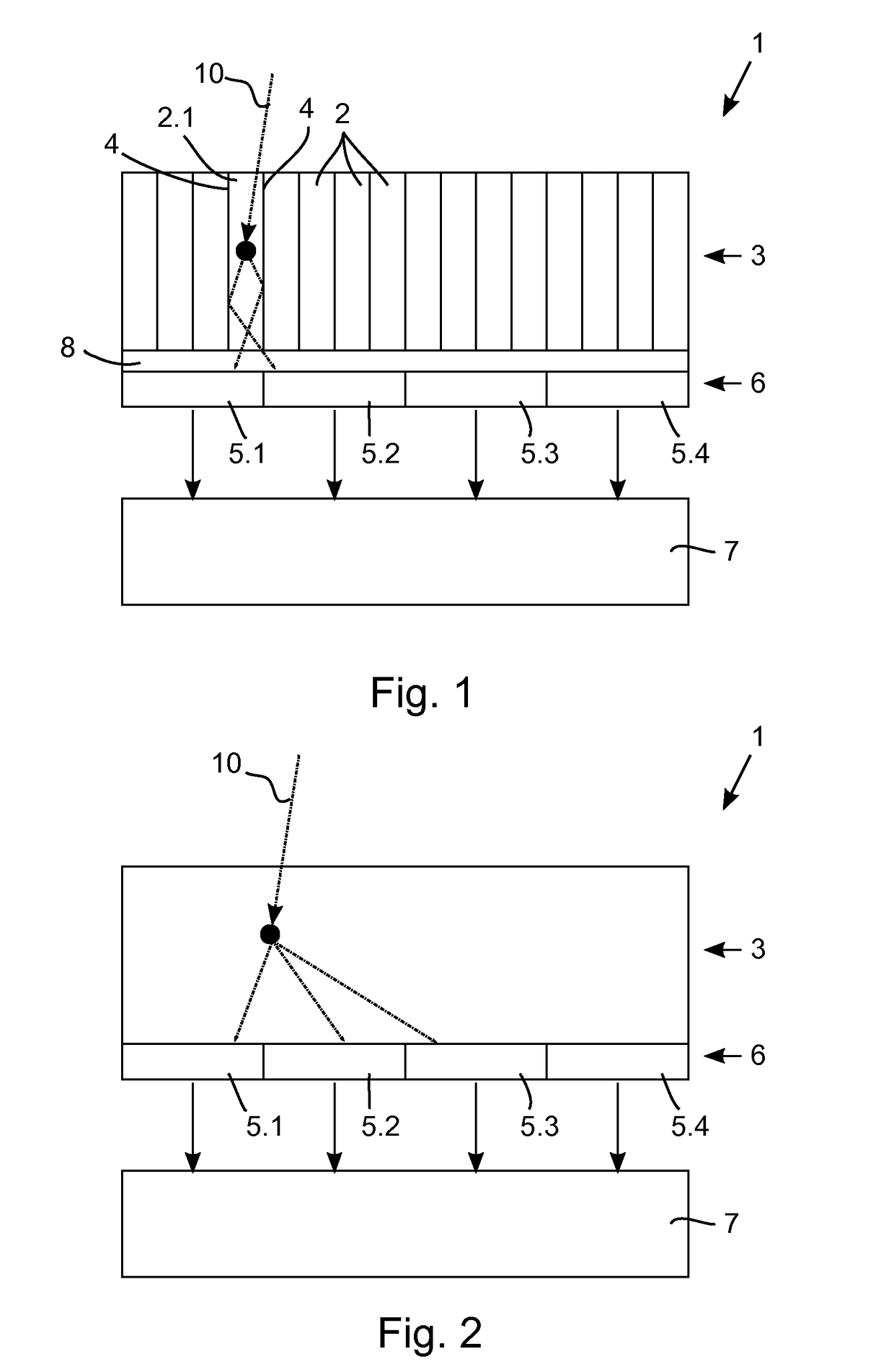
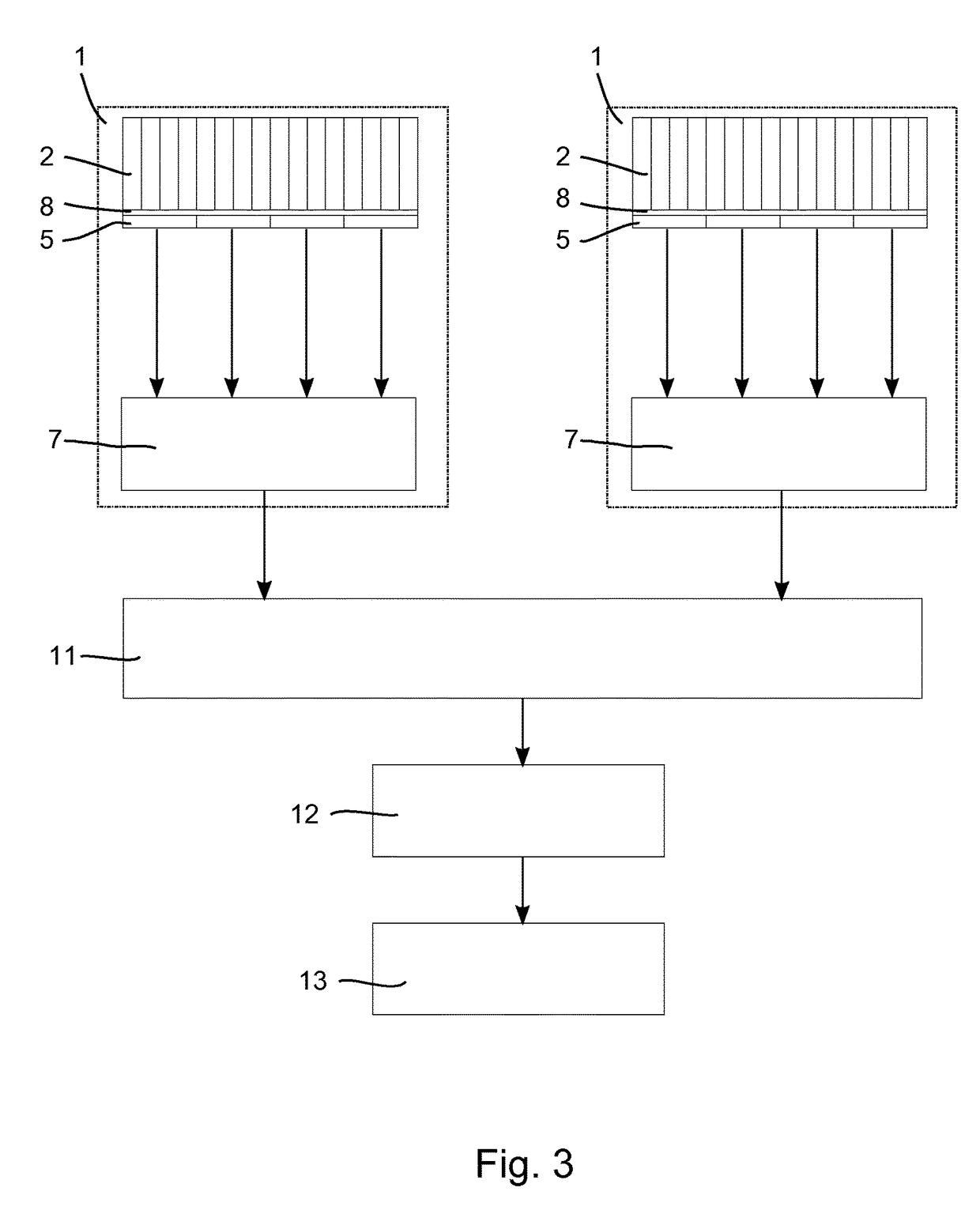
A method for determining the position of a scintillation event in a radiation particle detector with multiple scintillator element locations which are configured to emit a burst of photons responsive to a radiation particle being absorbed at the scintillator element location and with a plurality of photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) optically coupled to said scintillator element locations, comprising the steps of determining, for each of the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4), a triggering probability indicative of the probability of said photosensor (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) measuring a number of photons that exceeds a predetermined triggering threshold; measuring a photon distribution with the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) indicative of the number of photons incident on the individual photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4); calculating, for each of the scintillator element locations, a likelihood that a scintillation event with a predetermined energy value took place in said scintillator element location based on the measured photon distribution and the triggering probability of each of the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4); and identifying the scintillator element location having the maximum likelihood.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
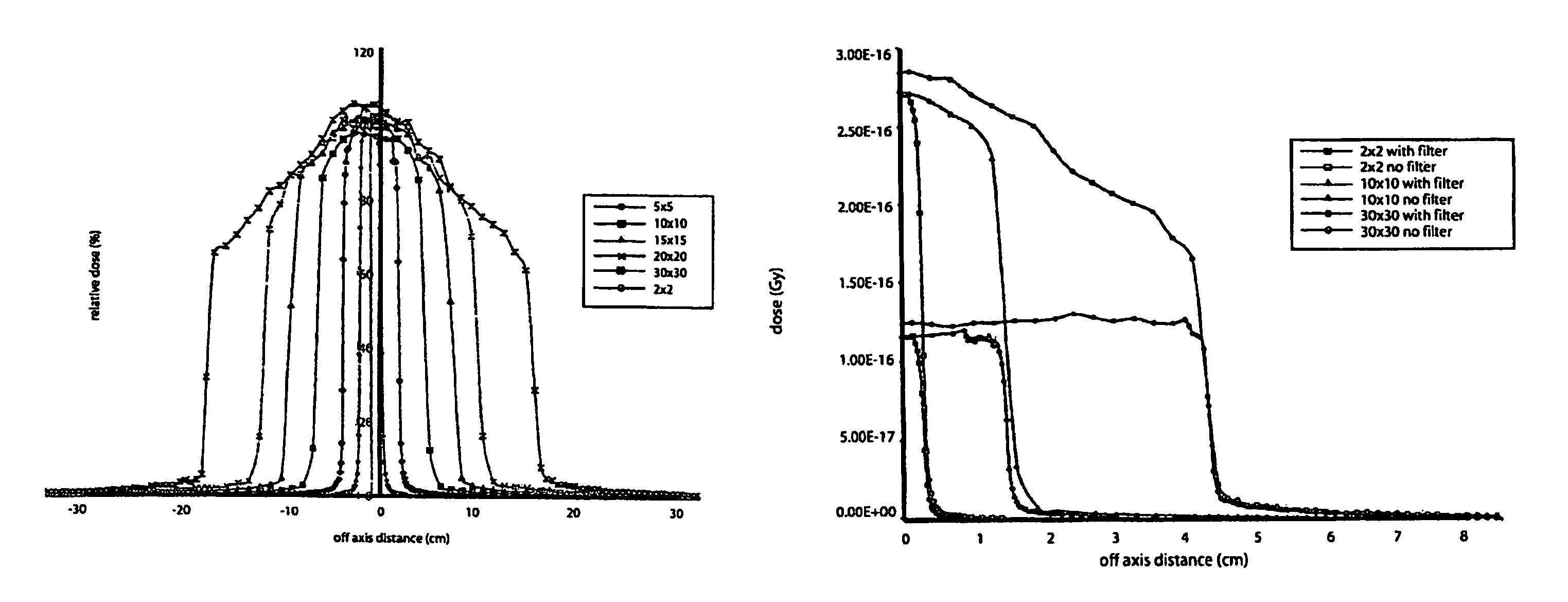
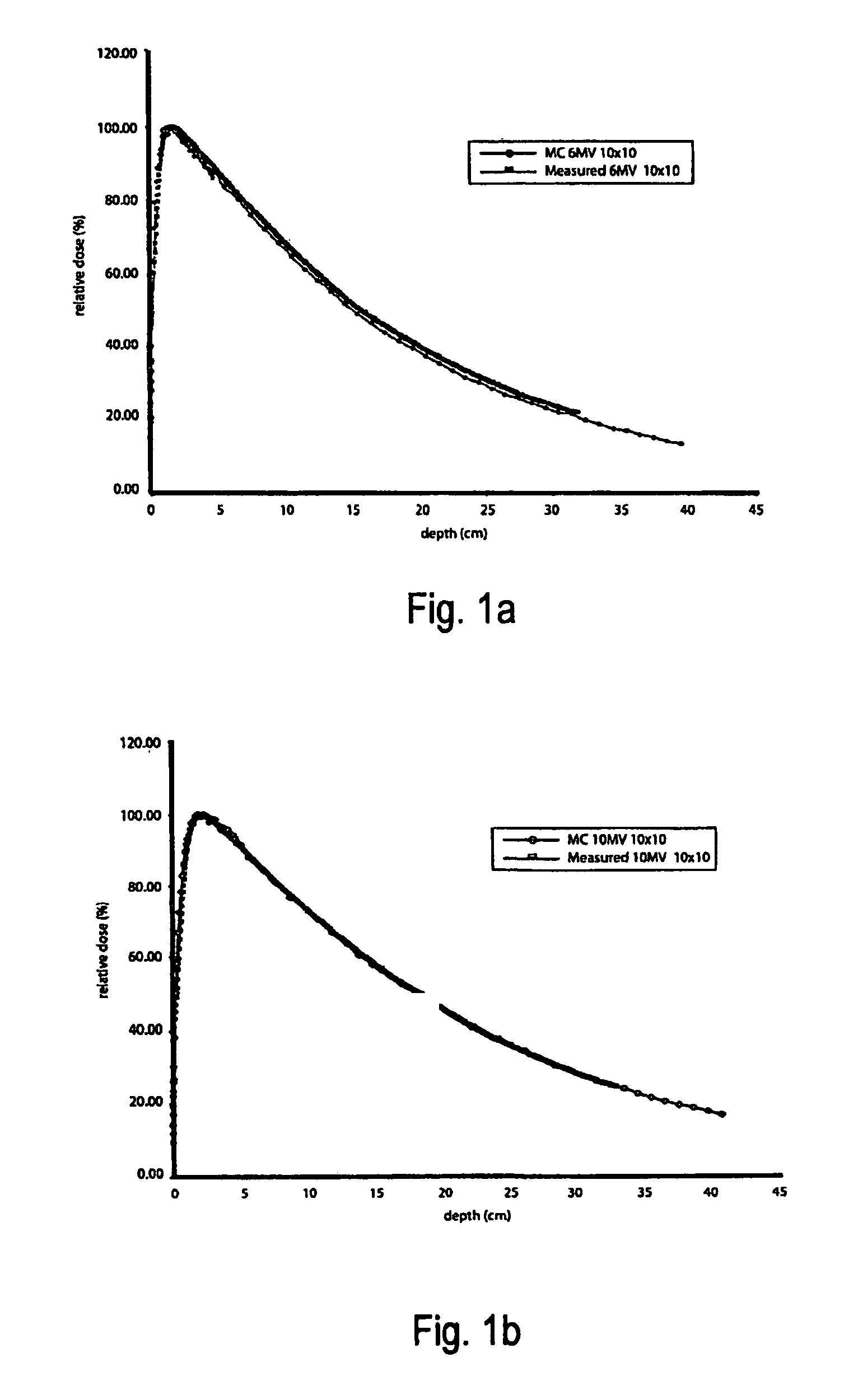
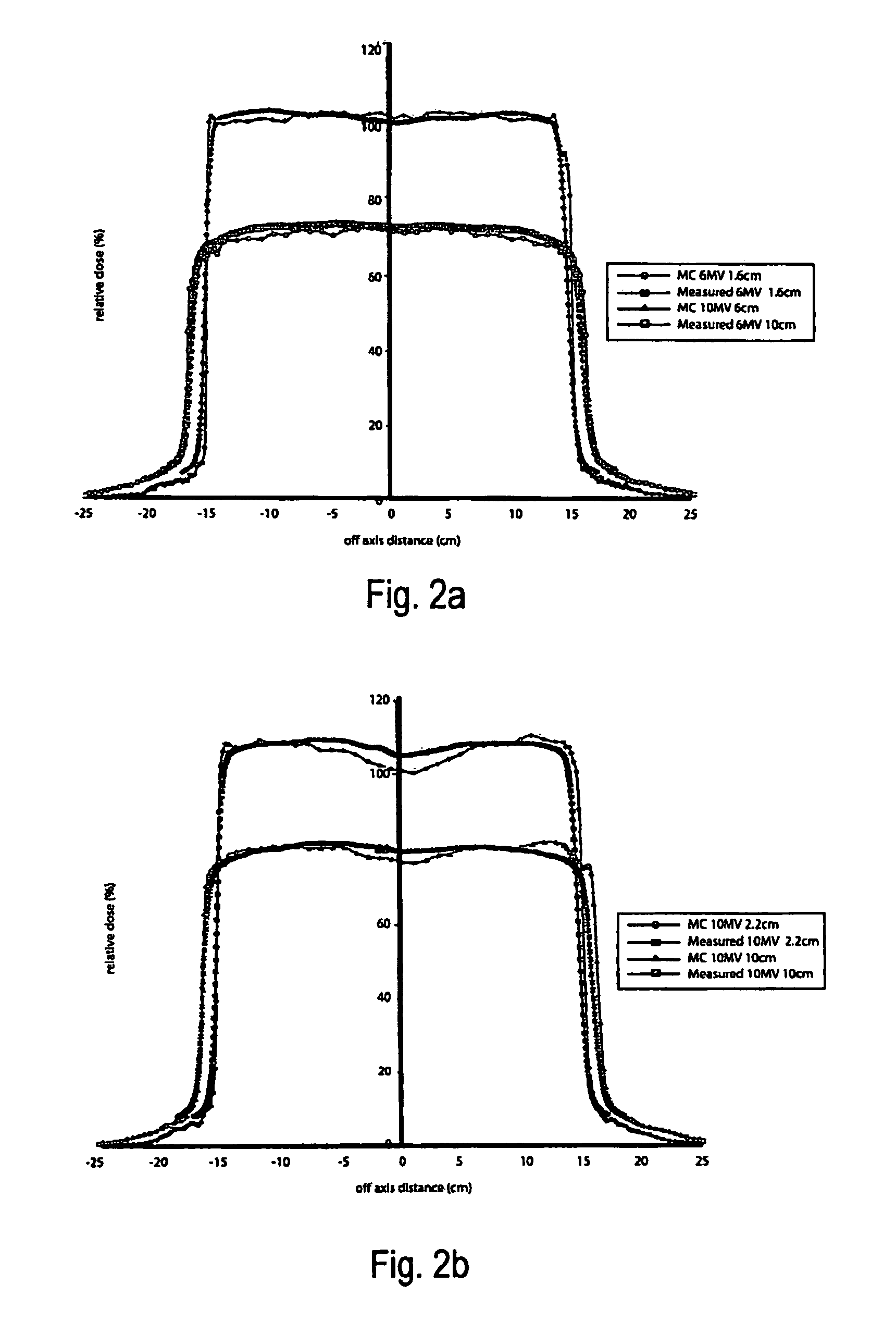
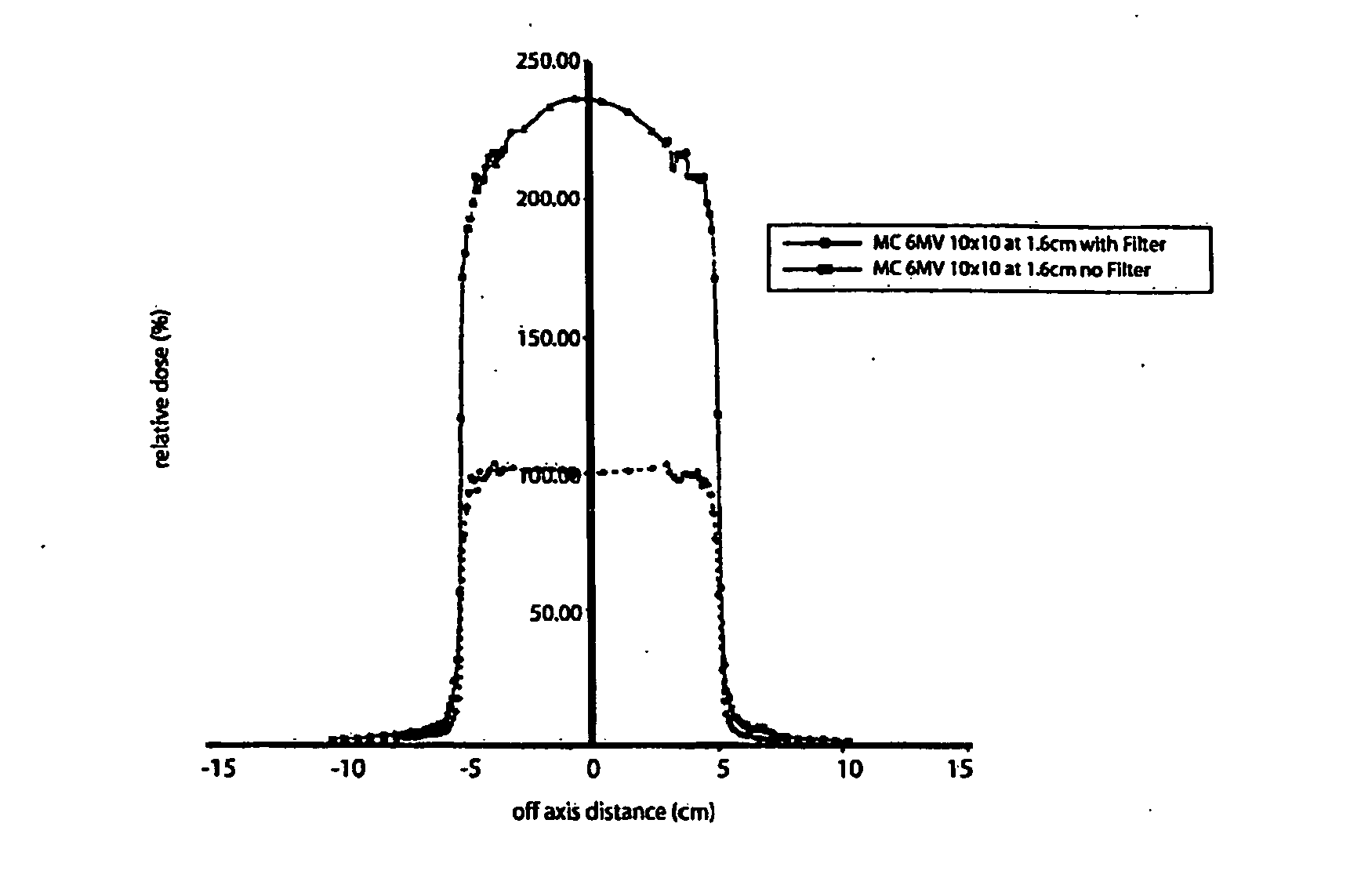
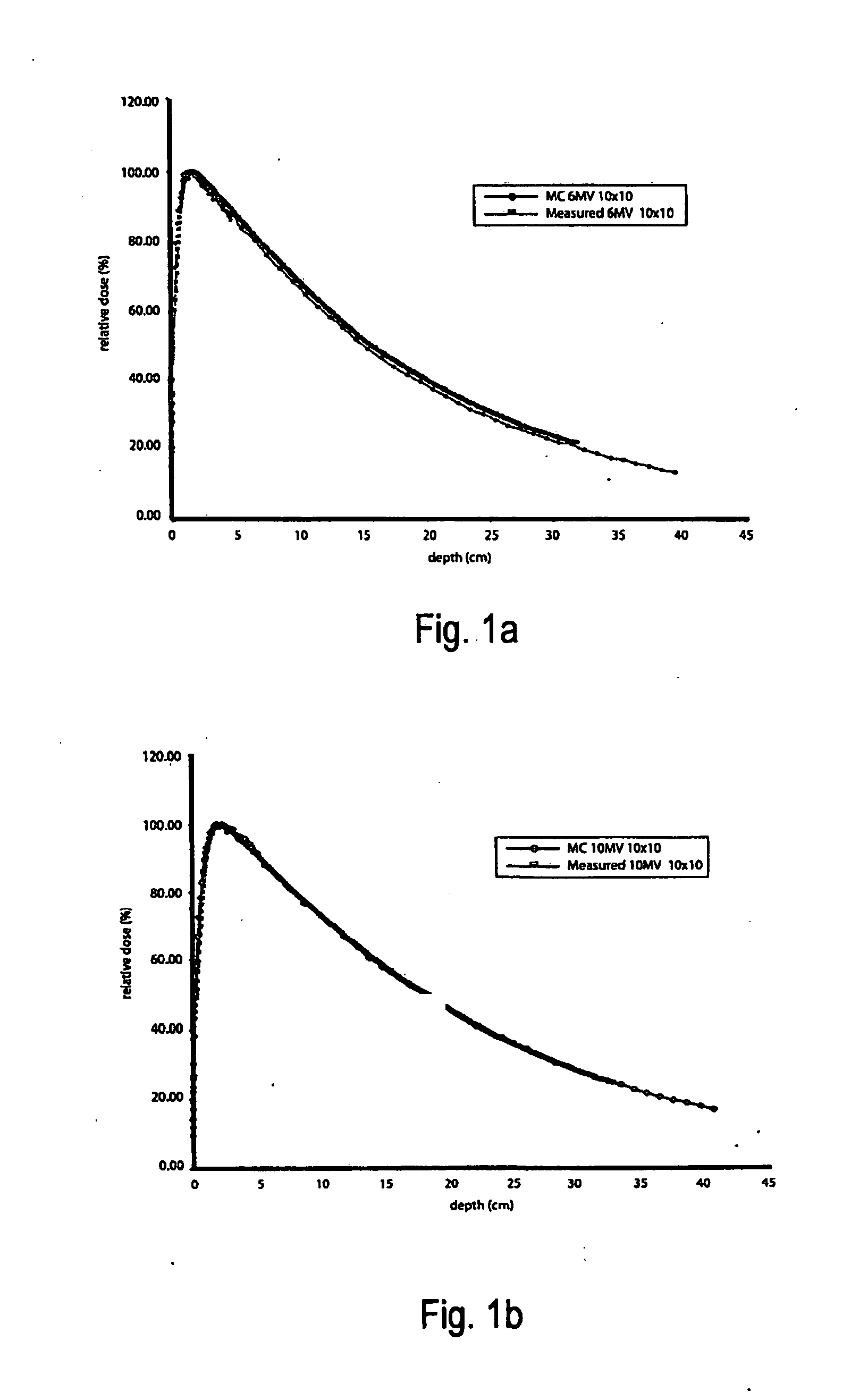
Unfiltered radiation therapy
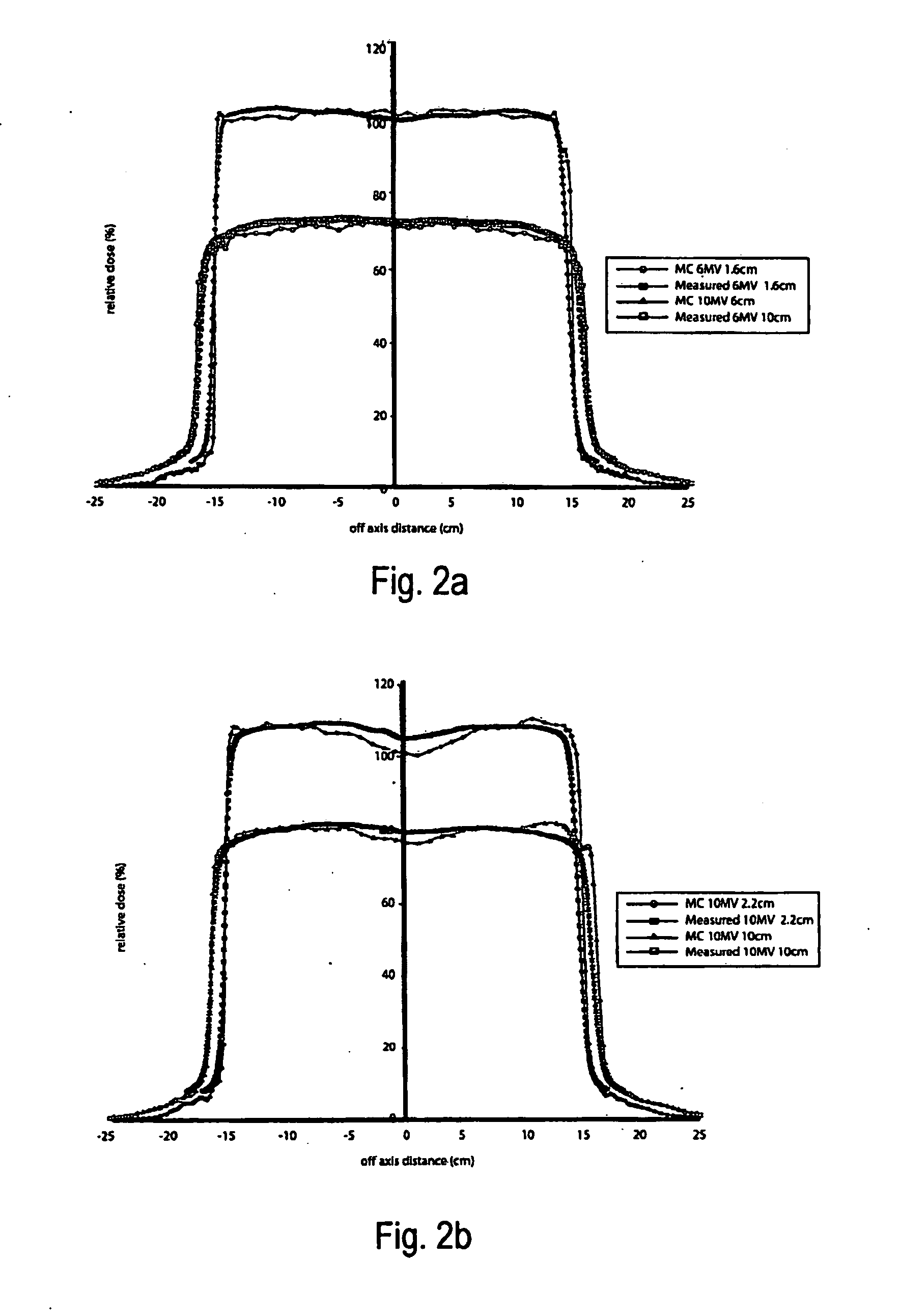
ActiveUS9370672B2Reduce doseIncrease dose rateRadiation/particle handlingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateUnfiltered
This is a new technique in IMRT and 3D conformal gamma radiation dose delivery using a linear accelerator with no flattening filter. The technique improves patient radiation therapy by reducing radiation scattered to surrounding normal tissue and reducing electron contamination. It increases dose rate to shorten treatment time. Linear accelerators have for decades come with a photon flattening filter to make the photon profile of planar fluence to make the dose distribution more uniform. These filters, however, resulted in fluence attenuation and contamination of the beam. Now in the age of techniques such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) the function of the flattening filter becomes redundant. The flattening filter now merely reduces the efficiency of the beam by reducing the fluence and increasing scattered radiation. Our technique involves removal of the flattening filter for complex treatments. It uses inverse planning along with multi-leaf collimators to shape the dose distribution.
Owner:TOLEDO THE UNIV OF
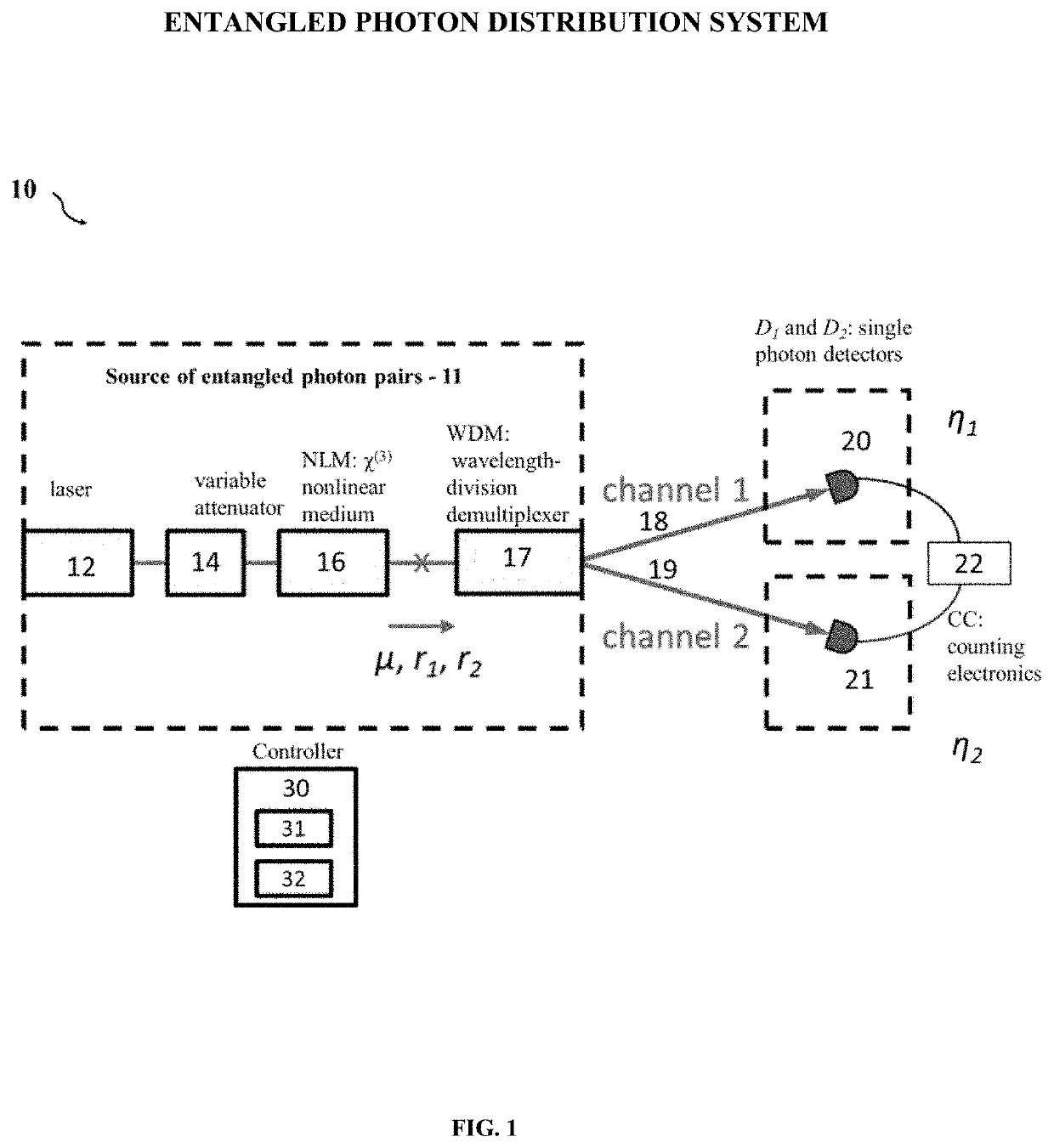
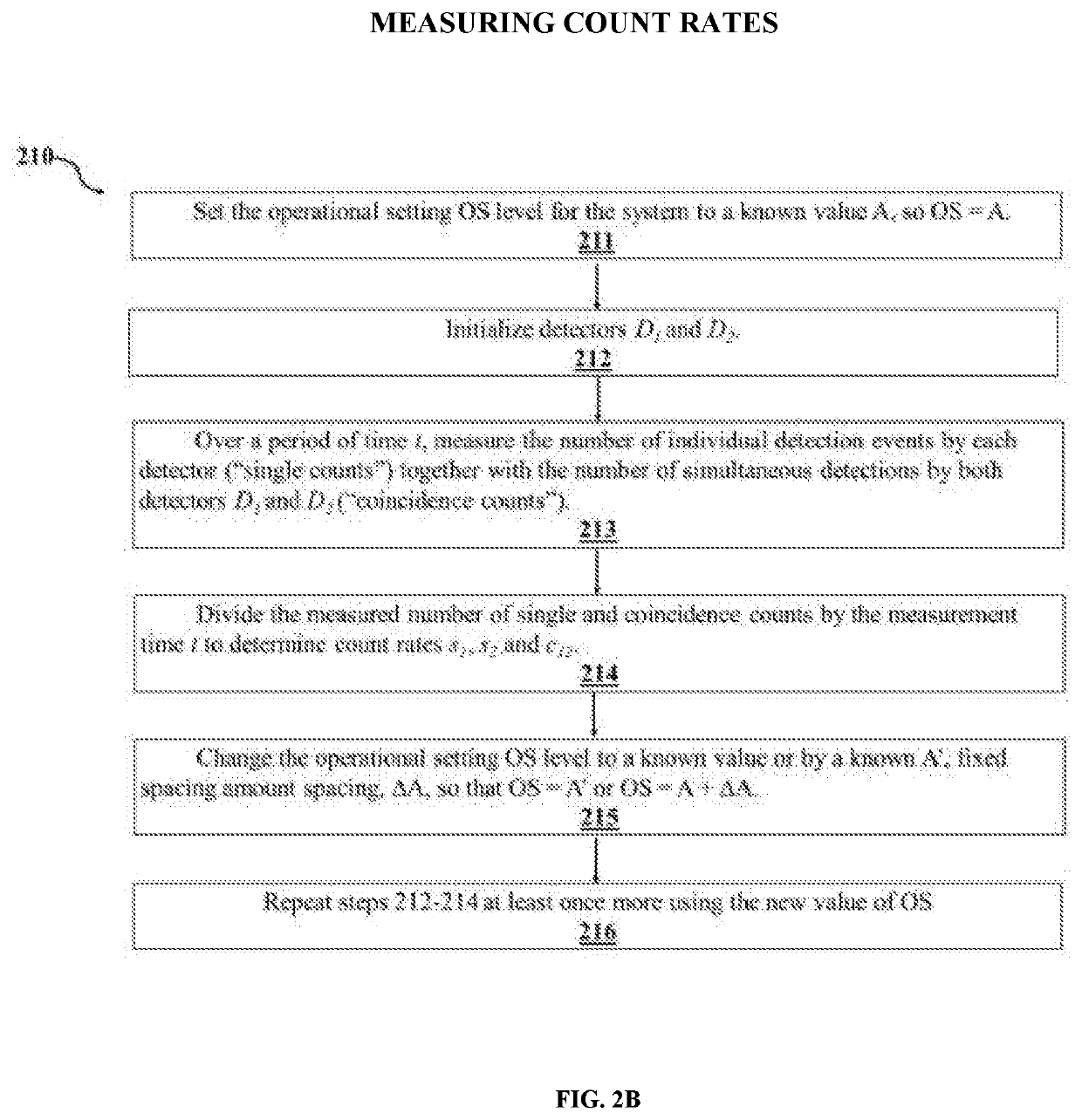
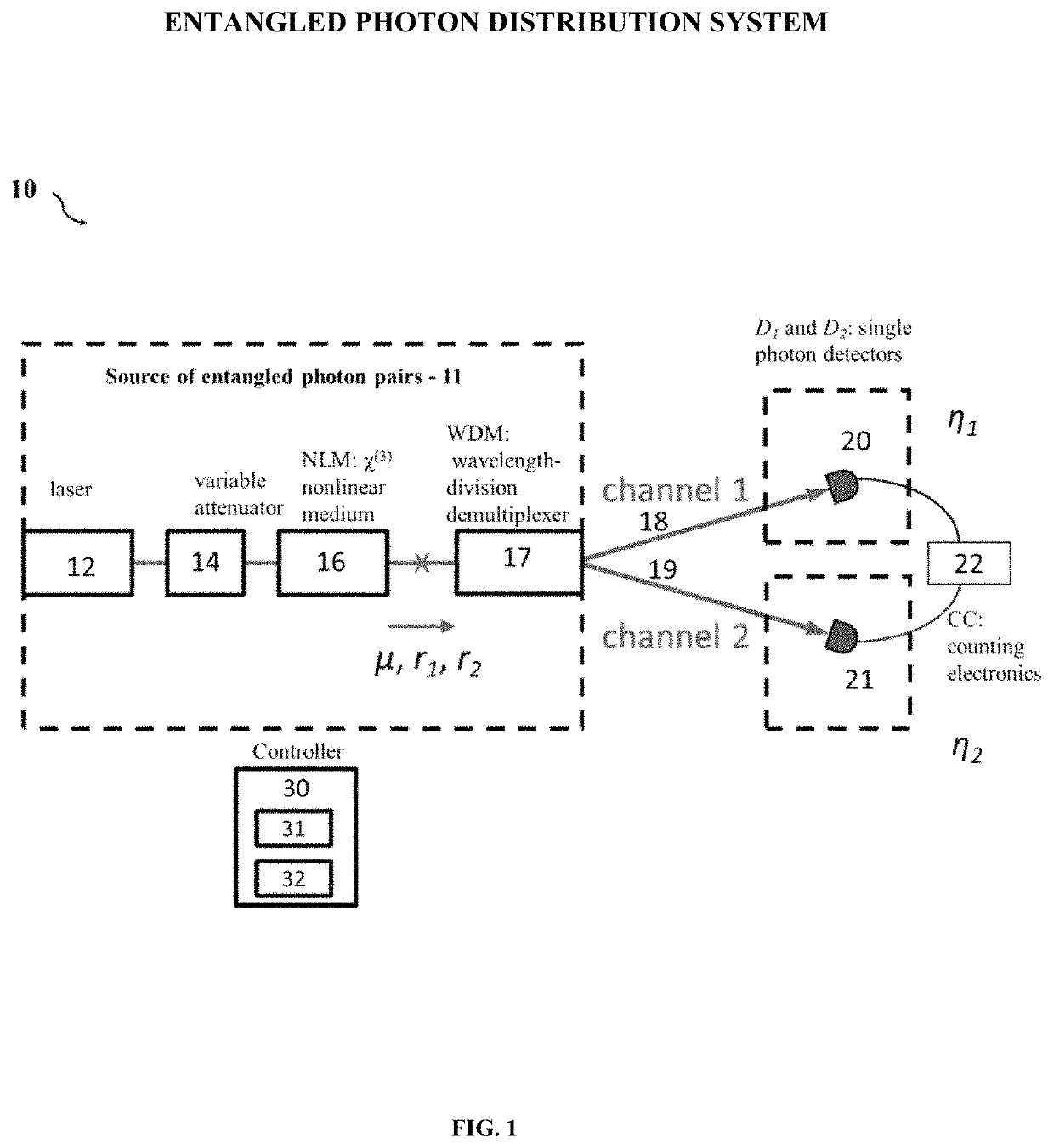
Methodology for in situ characterizing and calibrating an entangled photon distribution system
ActiveUS20190376820A1Accurate and fast measurementDisassemble and reassemble systemKey distribution for secure communicationLaser detailsCounting rateCoincidence
A novel methodology for characterizing and calibrating an entangled photon distribution system is disclosed. The entangled photon distribution system includes at least a source of entangled photon pairs, two photon detectors which detect photons among two channels and a controller. The methodology includes: for at least two different operational setting levels of the source of entangled photon pairs, measuring count rates for photons detected by the two photon detectors, individually and coincidently; fitting the measured individual and coincidence count rate data for the at least two different operational setting levels with theoretical models of detection probability; and determining operational parameters of the system from the fitting. The determined operational parameters of the system include the rate of generated entangled photon pairs by the source, the rates of Raman-scattered photons generated in the first and second channels, respectively, and the efficiency of the two photon detectors, respectively.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Unfiltered Radiation Therapy
ActiveUS20110033028A1Reduces efficiency of beamReduce the impactRadiation/particle handlingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateIntensity modulation
This is a new technique in IMRT and 3D conformal gamma radiation dose delivery using a linear accelerator with no flattening filter. The technique improves patient radiation therapy by reducing radiation scattered to surrounding normal tissue and reducing electron contamination. It increases dose rate to shorten treatment time. Linear accelerators have for decades come with a photon flattening filter to make the photon profile of planar fluence to make the dose distribution more uniform. These filters, however, resulted in fluence attenuation and contamination of the beam. Now in the age of techniques such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) the function of the flattening filter becomes redundant. The flattening filter now merely reduces the efficiency of the beam by reducing the fluence and increasing scattered radiation. Our technique involves removal of the flattening filter for complex treatments. It uses inverse planning along with multi-leaf collimators to shape the dose distribution.
Owner:TOLEDO THE UNIV OF
Scintillation event position determination in a radiation particle detector
ActiveUS20180059266A1Improve localizationReduce probabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorPhotoelectric sensor
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Microwave photon distributed radar imaging system and method
ActiveCN111505633ASimple structureImprove coherenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCarrier signalFrequency modulation
The invention discloses a distributed radar imaging system. The system comprises: a central station which is used for modulating the low-frequency narrow-band linear frequency modulation electric signal into n paths of optical carriers with different wavelengths, transmitting the echo optical signals to a transmitting station and (n-1) receiving stations through optical fibers with different timedelays, performing beam combination and parallel dechirping processing on the echo optical signals from the receiving stations, and performing analog-to-digital conversion, transmission phase delay compensation, frequency domain segmentation and three-dimensional imaging processing on the beam-combined dechirping signals; a transmitting station which converts the radio-over-fiber signals from thecentral station into high-frequency broadband linear frequency modulation electric signals to be transmitted; and the receiving stations which receive the target echo signal, modulate the radio-over-fiber signal from the central station, and transmit the radio-over-fiber signal back to the central station through an optical fiber. The invention further discloses a microwave photon distributed radar imaging method. Photon frequency multiplication, optical fiber radio frequency transmission and photon parallel dechirping processing technologies are applied to the distributed radar, three-dimensional imaging under a one-transmitting-multiple-receiving architecture is realized, the system complexity is reduced, and the system distribution capability and imaging performance are improved.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Scintillation event position determination in a radiation particle detector
ActiveUS9903960B1Reduce dead timeReduce the probability of eventsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorLocation determination
A method for determining the position of a scintillation event in a radiation particle detector with multiple scintillator element locations which are configured to emit a burst of photons responsive to a radiation particle being absorbed at the scintillator element location and with a plurality of photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) optically coupled to said scintillator element locations, comprising the steps of determining, for each of the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4), a triggering probability indicative of the probability of said photosensor (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) measuring a number of photons that exceeds a predetermined triggering threshold; measuring a photon distribution with the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4) indicative of the number of photons incident on the individual photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4); calculating, for each of the scintillator element locations, a likelihood that a scintillation event with a predetermined energy value took place in said scintillator element location based on the measured photon distribution and the triggering probability of each of the photosensors (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4); and identifying the scintillator element location having the maximum likelihood.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Progressive photon mapping method based on statistical model checking
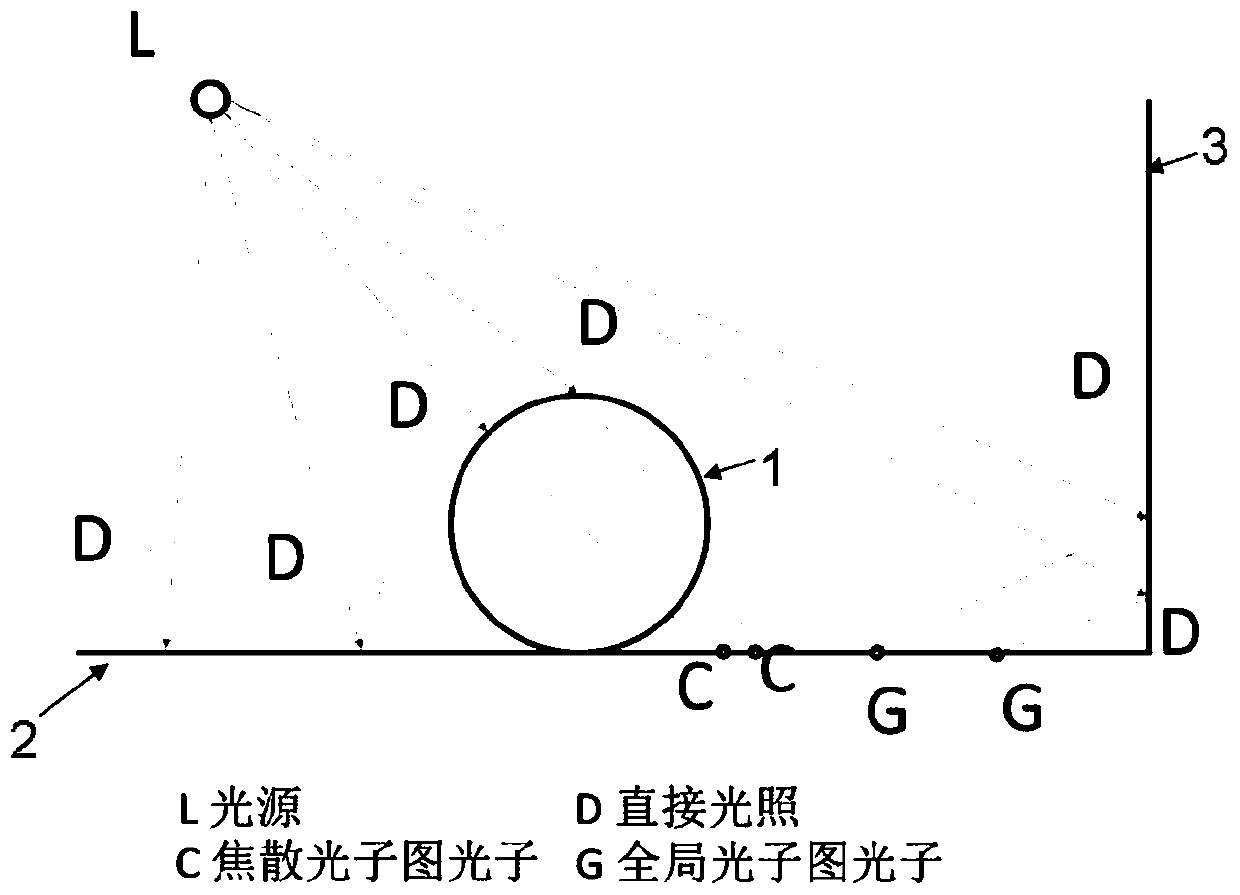
ActiveCN108961372AClear rendering resultsReduce biasImage renderingImage generationStatistical model checkingIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a progressive photon mapping method based on statistical model checking. The method comprises the steps of starting from a viewpoint to emit a ray to a pixel to be calculated on an imaging plane and intersect with a three-dimensional scene to be drawn, and if an intersection point with a diffuse reflection property is found on a tracking path, marking the intersection pointas a hit point; executing a photon step, wherein the photon step further comprises the sub-steps of 31) executing a photon tracking step; 32) for each hit point, executing photon collection processing; 33) if the current round current of the photon step does not need Chi-square detection, carrying out luminous flux accumulation, keeping the collection radius to be unchanged, if the current roundof the photon step needs Chi-square detection, carrying out quality evaluation on the photon distribution, then calculating the photon collection radius in the next round of the photon step accordingto the evaluated attributes of the photon distribution, and performing luminous flux accumulation on the current round of the photon step; and 34) if the photon collection radius is reduced, executingdistributed light tracking, generating a new hit point, then transferring to the step 31), otherwise, directly transferring to the step 31), and starting the new round of photon step iteration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Radiance calculation method with mixing of Kd-tree with Voronoi diagram
ActiveCN105118085AAccurate Radiance CalculationAccurate Radiance Estimation3D-image renderingViewpointsRadiance
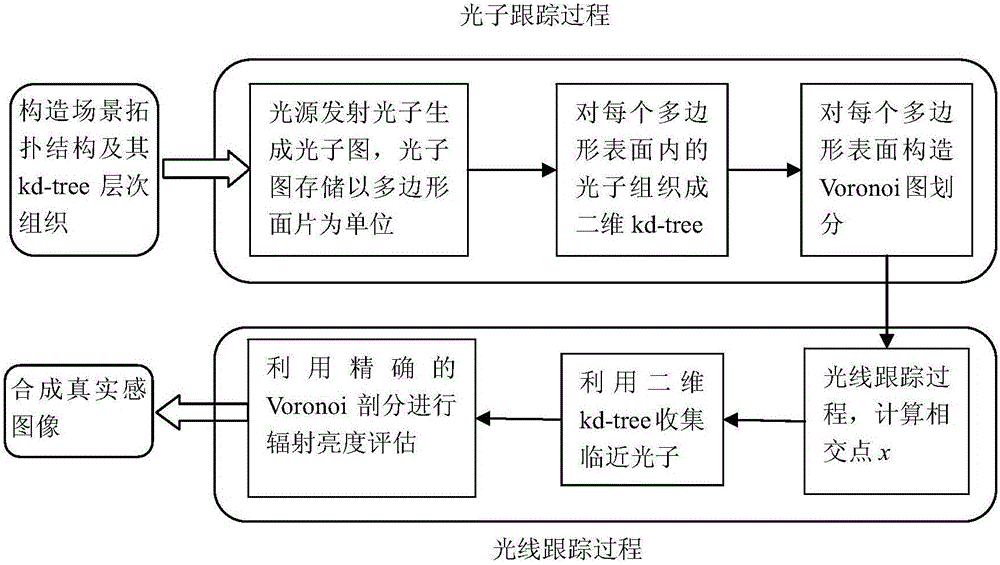
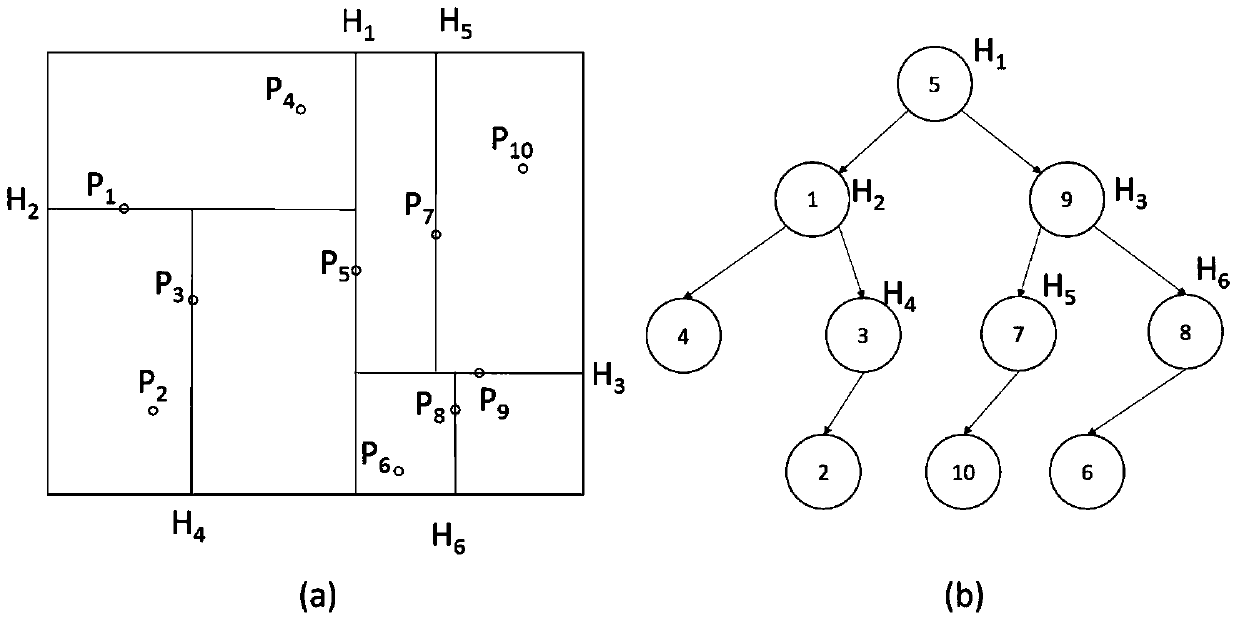
The invention relates to a radiance calculation method with the mixing of a Kd-tree with a Voronoi diagram. The method comprises the steps of (1) constructing a scene topology structure and a Kd-tree hierarchical organization, (2) storing generated a photon map with a polygon face as the unit, (3) carrying out traversal of each polygon of a three-dimensional scene surface, and collecting photos belonging to each polygon and forming a two-dimensional Kd-tree structure, (4) dividing each polygon surface construction Voronoi diagram and calculating the radiation flux density of a Voronoi unit, (5) calculating the intersection point x of a ray emitted from a viewpoint and a scene, (6) according to the polygon face to which the x belongs, collecting near photons by using the two-dimensional Kd-tree structure, (7) finding the precise area covered by the collected photos according to the Voronoi diagram division, and calculating the radiance of the x point. According to the method, the geometric features of local surface photon distribution can be utilized to carry out precise radiance kernel estimation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
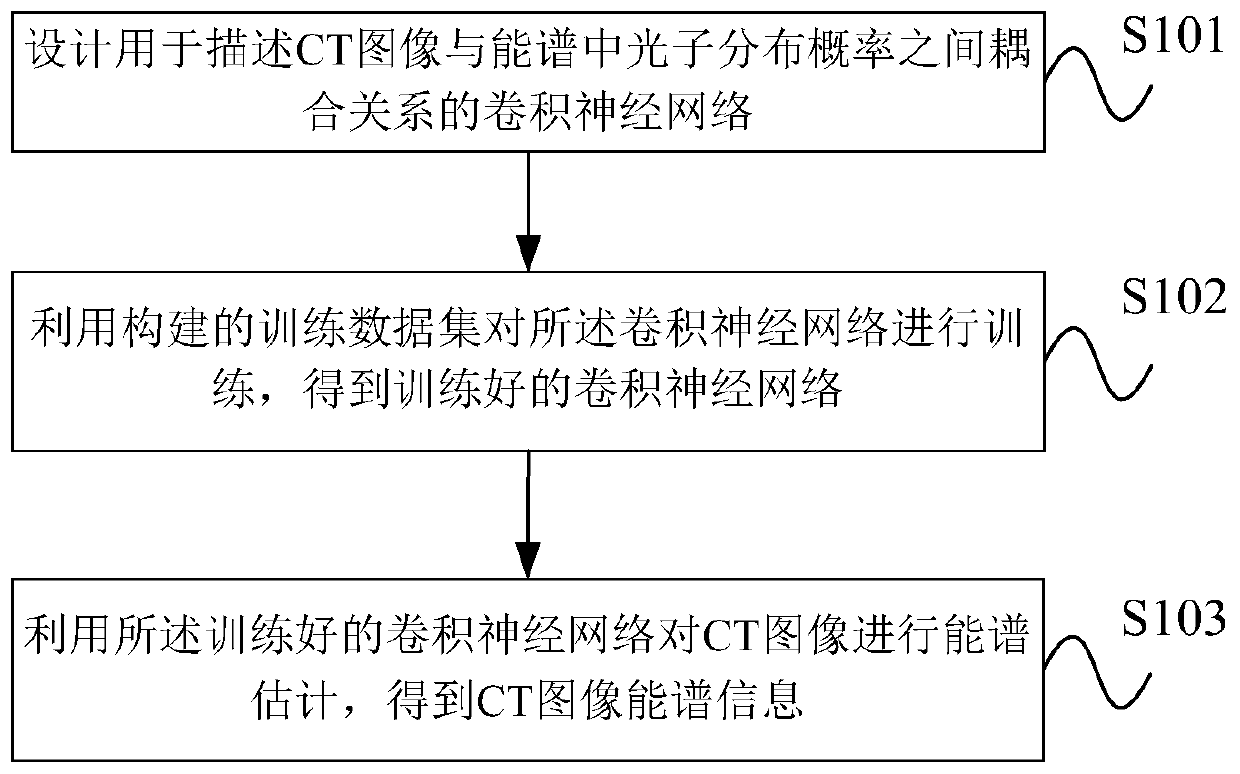
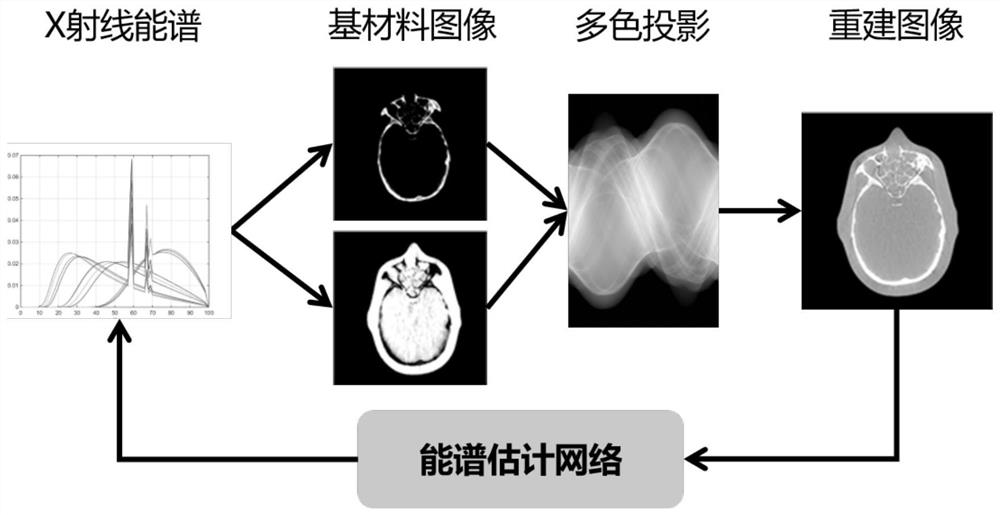
X-ray computed tomography energy spectrum estimation method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109916933AImprove work efficiencyPracticalX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setX-ray
The invention provides an X-ray computed tomography energy spectrum estimation method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, designing a convolutional neural network for describing a coupling relationship between a CT image and a photon distribution probability in an energy spectrum; step 2, training the convolutional neural network by using theconstructed training data set to obtain a trained convolutional neural network; and step 3, performing energy spectrum estimation on the CT image by using the trained convolutional neural network to obtain CT image energy spectrum information. The method is mainly used for estimating the X-ray energy spectrum information through the characteristics of the CT reconstructed image from the perspective of the image domain, does not need additional hardware or a special working process, can be directly applied to an existing CT scanning system, and is beneficial to improving the efficiency.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Detecting anomalies in annular materials of single and dual casing string environments
InactiveCN110546535ARadiation/particle handlingSeismology for water-loggingCasing stringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides an x-ray based cement evaluation tool for measurement of the density of material volumes within single, dual and multiple-casing wellbore environments, the tool including at least an internal length comprising a sonde section, wherein said sonde section further comprises an x-ray source; a radiation shield for radiation measuring detectors; sonde- dependent electronics; and a plurality of tool logic electronics and PSUs, wherein the tool uses x- rays to illuminate the formation surrounding a borehole and a plurality of detectors are used to directly measure the density of the cement annuli and any variations in density within. Detectors used to measure casing standoff such that other detector responses are compensated for tool stand-off and centralization; aplurality of reference detectors is used to monitor the output of the x-ray source, and a shortest-axial offset detector is configured to distribute incoming photons into energy classifications such that photoelectric measurements may be made.
Owner:菲利普蒂格 +1
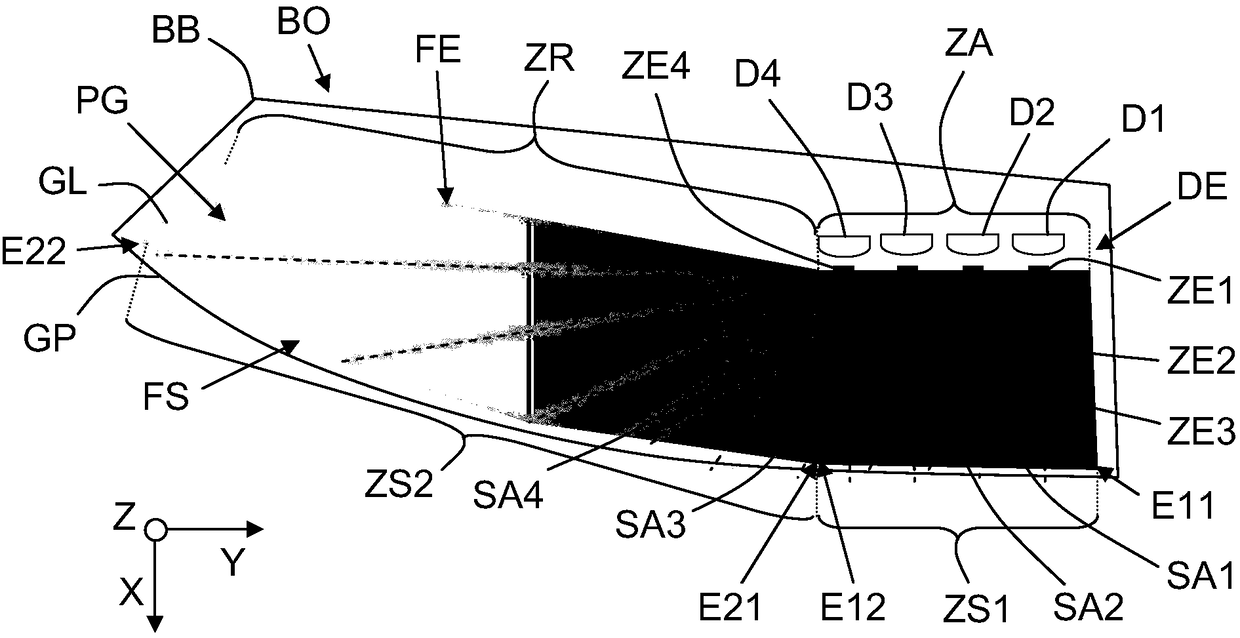
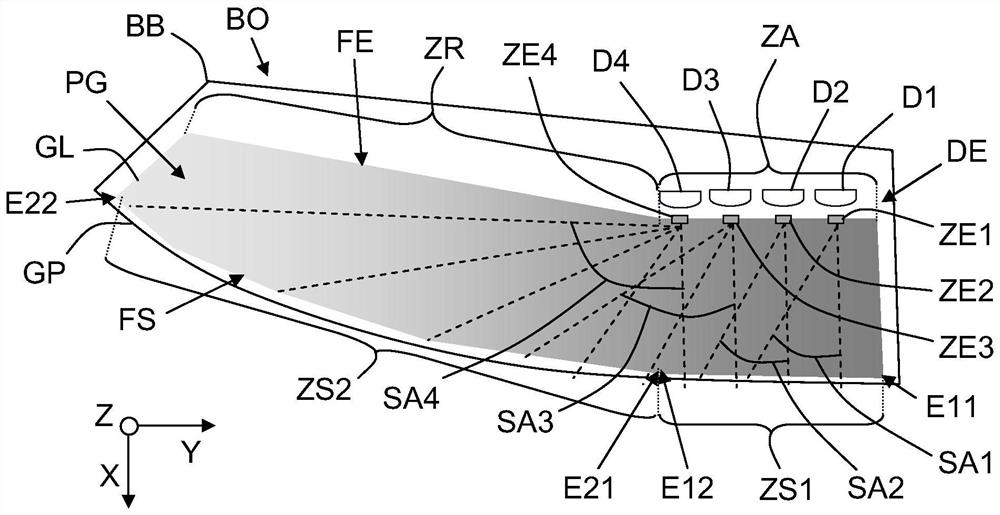
Lighting device with local photon supply area and photon distribution
The invention relates to a lighting device (DE), the lighting device includes electroluminescent diodes (D1-D4) and a flat light guide (GL), and the light guide includes a guiding unit (PG) arranged between an input surface (FE) and an output surface (FS). The input surface (FE) supplies photons to the guiding unit (PG), and the output surface (FS) sends the photons to the outside through guidance. The electroluminescent diodes (D1-D4) are all arranged to be opposite to input regions (ZE1-ZE4) defined in a supply region (ZA) of the input surface (FE), the supply region is opposite to the firstoutput region (ZS1) of the output surface (FS), the input region is configured to used for enabling received photons to be distributed in predefined angle sectors (SA1-SA4), so that luminous intensity decreasing progressively from a first output region (ZS1) is caused in a second output region (ZS2) of the output surface (FS), and the second output region is located beside the first output region(ZS1).
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA
Illumination device with photon localized supply area and distribution of photons
The invention relates to a lighting device (DE) comprising electroluminescent diodes (D1-D4) and a flat light guide (GL) comprising Between the guide part (PG). The input face (FE) supplies photons to the guide part (PG), and the output face (FS) sends the guided photons to the outside. Said electroluminescent diodes (D1-D4) are all arranged opposite respectively to an input zone (ZE1-ZE4) defined in a supply zone (ZA) of said input face (FE), said supply zone being in relation to said Opposite a first output zone (ZS1) of the output face (FS), said input zone being configured for distributing the received photons in a predefined angular sector (SA1-SA4) so that at said output face (FS) A decreasing luminous intensity from said first output zone (ZS1) is induced on a second output zone (ZS2), which is located next to said first output zone (ZS1).
Owner:PEZHO SITROEN AUTOMOBILS SA
An analysis method of solid-liquid two-phase flow in a magnetic fluid photocatalytic reactor
ActiveCN110054249BAvoid consumptionAvoid accumulationAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWater treatment parameter controlPhotocatalytic reactionPtru catalyst
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
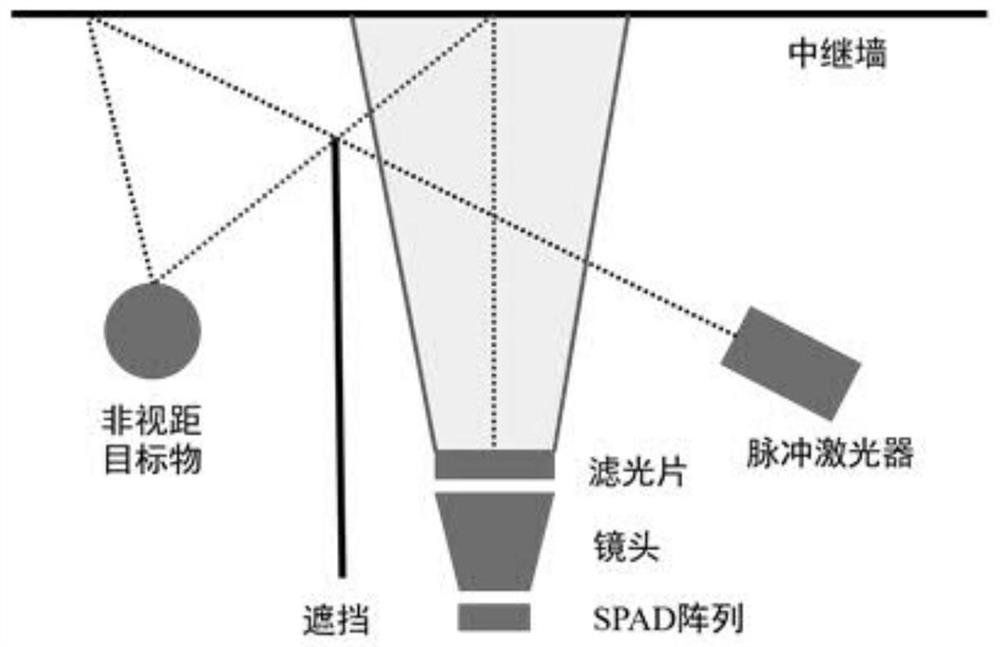
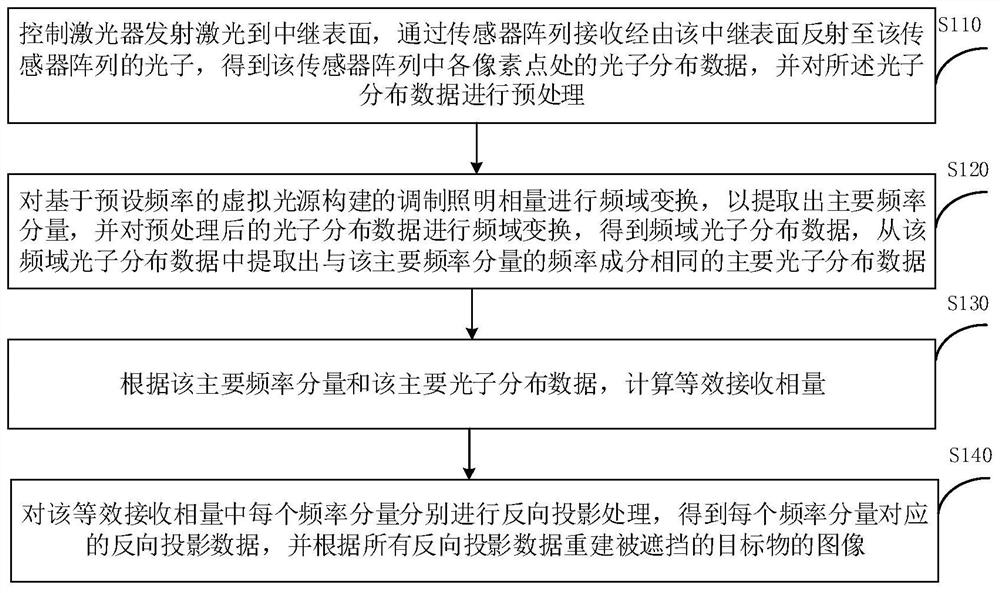
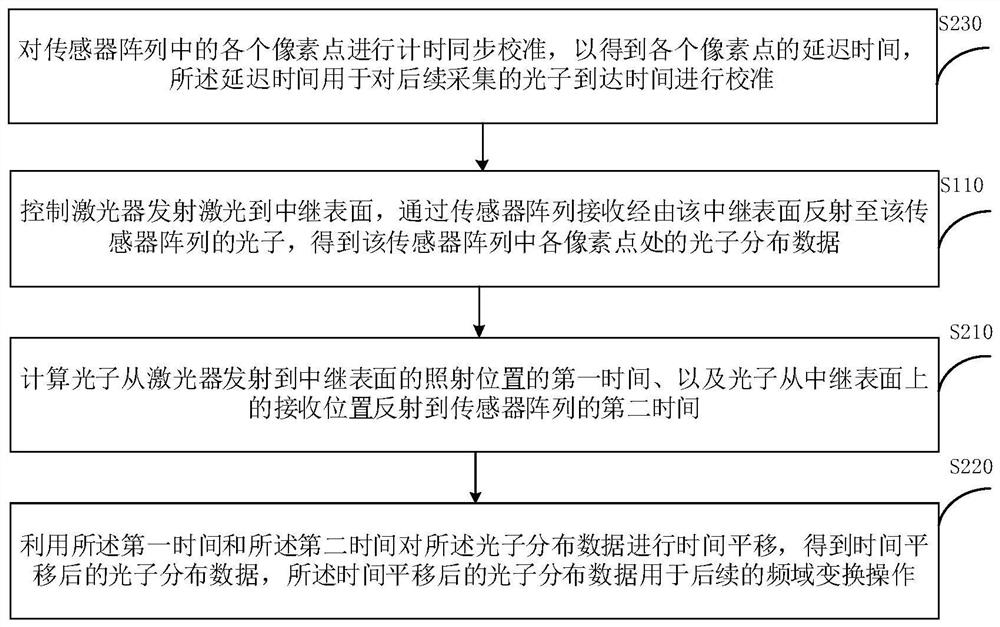
Non-line-of-sight image reconstruction method, device and system and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN113837969AFast non-line-of-sight imagingImage enhancementImage analysisSensor arrayGalvanometer
The embodiment of the invention provides a non-line-of-sight image reconstruction method, device and system and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: controlling a laser to emit laser to a relay surface, and receiving photons reflected to a sensor array through the relay surface through the sensor array, so as to obtain the photon distribution data of each pixel point; extracting a main frequency component from the preprocessed photon distribution data by using a modulation illumination phasor constructed by a virtual light source so as to obtain main photon distribution data; calculating an equivalent receiving phasor according to the main frequency component of the modulation illumination phasor and the main photon distribution data; and performing back projection on the equivalent receiving phasor to reconstruct an image of the shielded target object. According to the technical scheme of the invention, through a mode of reconstructing a scene based on a sensor array and a phasor field, galvanometer-free scanning and rapid parallel non-line-of-sight imaging can be realized.
Owner:宁波未感半导体科技有限公司
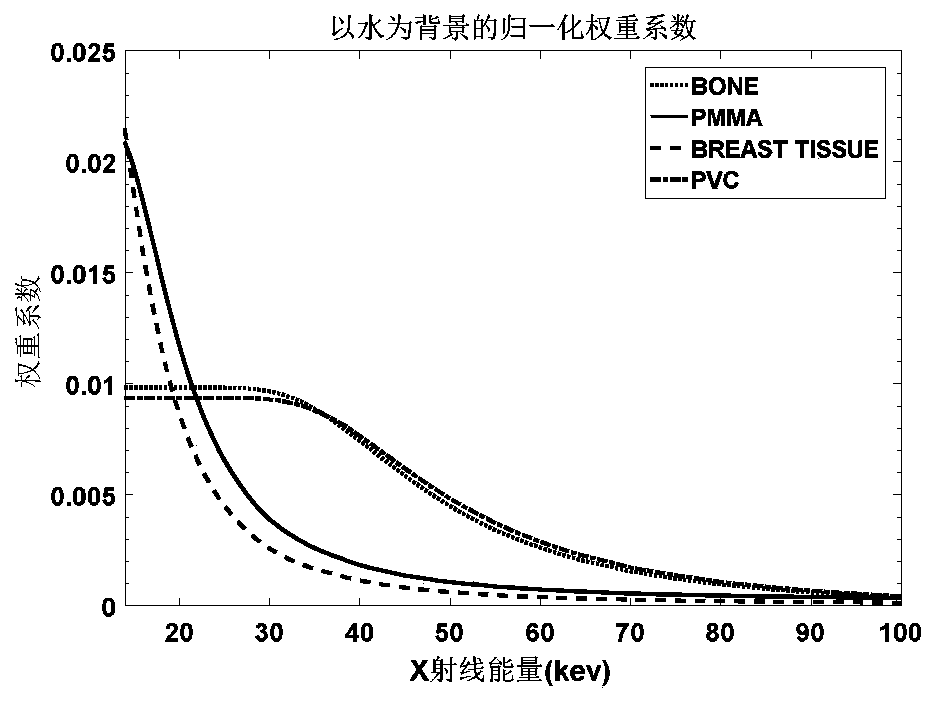
Material imaging weight determination method and device, medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN109801243ABig Imaging ContributionImprove image signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementWeight coefficientX-ray
The embodiment of the invention provides an imaging method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. The imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring signals and noise of electromagnetic wavespenetrating through a target material in a preset energy interval; constructing a signal-to-noise ratio function of the target material based on the signal and the noise; and maximizing a signal to noise ratio function and determining the weight coefficient of the target material. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, after energy weighting, the contribution of the low-energy interval to imaging is greater, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is improved, and the x-ray equivalent attenuation coefficient in the energy region is calculated by utilizing the acquired photon distribution information and the attenuation curve characteristics of photons in different materials, so that the calculation is more accurate.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Progressive Photon Mapping Method Employing Statistical Model Test
ActiveUS20210118222A1Increase speedIncreasing additional running timeImage renderingImage generationComputational physicsPhoton tracing
A progressive photon mapping method based on statistical test includes launching rays from the viewpoint to each pixel on the image plane and intersecting the three-dimensional scene to be rendered. If an intersection with diffuse surface is found on the tracing path, it is recorded as the hit point; a photon pass is performed: 31) performing photon tracing step; 32) performing photon collection processing for each hit point; 33) if the current iteration of photon pass does not need chi-square test, then performing flux accumulation and keeping the collection radius unchanged; if chi-square is required, evaluating the photon distribution quality; computing a collection radius according to the estimated photon distribution, and performing the flux accumulation in the current photon pass; 34) if the photon collection radius is reduced, then performing distributed ray tracing, generating new hit points, and go to 31), otherwise go to 31), start a new iteration of photon pass.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
X-ray computed tomography energy spectrum estimation method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109916933BImprove work efficiencyPracticalX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setAlgorithm
The invention provides a convolutional neural network-based X-ray computed tomography energy spectrum estimation method. The method comprises: step 1, designing a convolutional neural network for describing the coupling relationship between the CT image and the photon distribution probability in the energy spectrum; step 2, using the constructed training data set to train the convolutional neural network to obtain The trained convolutional neural network; step 3, using the trained convolutional neural network to estimate the power spectrum of the CT image to obtain CT image power spectrum information. This method mainly estimates X-ray energy spectrum information through the features of CT reconstruction images from the perspective of the image domain. It does not require additional hardware or a dedicated workflow, and can be directly applied to existing CT scanning systems, which is conducive to improving efficiency.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Microwave Photon Distributed Radar Imaging System and Method
ActiveCN111505633BSimple structureImprove coherenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCarrier signalWavelength
A distributed radar imaging system, comprising: a central station, which modulates n channels of optical carriers of different wavelengths with low-frequency narrow-band chirp electrical signals, and transmits them to a transmitting station and (n-1) receiving stations through optical fibers with different delays respectively, Perform beam combination and parallel deskewing processing on the echo optical signals from the receiving station, and perform analog-to-digital conversion, transmission phase delay compensation, frequency domain segmentation and three-dimensional imaging processing on the combined beam and deskewing signals; The optical radio frequency signal is converted into a high-frequency broadband linear frequency modulation electrical signal for transmission; the receiving station receives the target echo signal, modulates the optical radio frequency signal from the central station, and transmits it back to the central station through optical fiber. The invention also discloses a microwave photon distributed radar imaging method. The invention applies photon frequency doubling, optical fiber radio frequency transmission and photon parallel deskewing processing technology to distributed radar, realizes three-dimensional imaging under the architecture of one transmission and multiple reception, reduces system complexity, and improves system distribution capability and imaging performance.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
A kind of ultra-high power laser for communication and its preparation method
ActiveCN111600198BRequirements for Realizing Ultra-Large Optical Power OutputIncrease lateral photon densityOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionHigh power lasersMetallic electrode
The invention discloses an ultra-high-power laser for communication and a preparation method thereof. The laser includes a substrate on which a high-photon-density phase-shift grating structure layer is arranged. The second cladding layer, the active layer, the third cladding layer and the contact layer, the contact layer is covered with a p-metal electrode layer, and the lower surface of the substrate is plated with an n-metal electrode layer; the bottom grating structure and high photon density phase shift grating design are adopted, To increase the photon density and photon distribution uniformity to meet the ultra-large optical power output requirements of the laser optical power above 70mW in the silicon photonics integration scheme.
Owner:SHANXI YUANJIE SEMICONDUCTOR TECH CO LTD
Methodology for in situ characterizing and calibrating an entangled photon distribution system
ActiveUS11009375B2Accurate and fast measurementDisassemble and reassemble systemKey distribution for secure communicationLaser detailsCounting rateParticle physics
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Preparation method of double-layer film, quantum dot distributed photon illumination system and detection method of system
PendingCN110345422APromote absorptionFacilitated DiffusionElectric circuit arrangementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsQuantum dotLight head
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-layer film, a quantum dot distributed photon illumination system and a detection method of the system. The preparation method of the double-layer film comprises the following steps: preparing a bottom layer film; preparing an outer layer film; and performing synthesis. According to the quantum dot distributed photon illumination system, eachlamp holder comprises a left side plate, a right side plate and a base plate fixed between the left side plate and the right side plate; an included angle between the left side plate and the base plate, and an included angle between the right side plate and the base plate are obtuse angles or right angles; a main light source for enabling light rays to irradiate the double-layer film on a scattering plate is arranged on the upper surface of the base plate; and the scattering plate is fixedly arranged above the base plate. According to the detection method of the quantum dot distributed photonillumination system, the displayed wave property of light, irradiated on a reading surface, of the quantum dot distributed photon illumination system is detected. Quantum optics is used for creatingan illumination environment with main wave property display for a user; the photon distribution uniformity is improved; and the human eyes are protected. The quantum dot distributed photon illumination system is suitable for indoor illumination.
Construction method of medical linear accelerator photon source model function
ActiveCN113230549AFew modeling parametersModeling parameters are clearMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesParticle physicsRadiation field
The invention relates to the technical field of radiation dose measurement, provides a construction method of a medical linear accelerator photon source model function, and is used for calculating the dose of rays in a radiation treatment scheme. A source model of a treatment photon beam of the accelerator comprises two parts, namely a source model of original ray photons and a source model of scattered ray photons. Physical parameters in source model functions of the two parts are emission point position coordinates of particles, projection values of unit momentum vectors in the three-dimensional orthogonal direction and energy of the particles. The photon fluence information, the energy spectrum information and the photon unit momentum direction information on any phase space plane can be accurately calculated by utilizing the model function, the source model construction method and thought are suitable for construction of photon beam source models of various nominal energies of accelerators used in radiotherapy, and the method has the advantages of being few in modeling parameters, the physical significance of each parameter in the function is clear, the use is convenient, and the radiation field photon distribution information can be reproduced truthfully by using a mathematical analysis method.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method of Constructing Model Function of Photon Source of Medical Linear Accelerator
ActiveCN113230549BFew modeling parametersModeling parameters are clearMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNuclear engineeringRadiation field
The invention relates to the field of radiation dose measurement technology, and proposes a method for constructing a photon source model function of a medical linear accelerator, which is used for dose calculation of rays in a radiotherapy plan. The source model of the therapeutic photon beam of the accelerator includes primary ray photons and scattering The source model for line photons has two parts. The physical parameters in the source model function of these two parts are the position coordinates of the emission point of the particle, the projection value of the unit momentum vector in the three-dimensional orthogonal direction, and the energy of the particle. The model function can be used to accurately calculate the photon fluence information, energy spectrum information, and photon unit momentum direction information on any phase space plane. The source model construction method and ideas involved in the present invention are suitable for use in radiotherapy The construction of photon beam source models with various nominal energies of the accelerator has the advantages of less modeling parameters, clear physical meaning of each parameter in the function, easy to use, and the ability to faithfully reproduce the photon distribution information of the radiation field with mathematical analysis methods.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Single-photon ranging tracking and pointing and few-photon communication integrated receiving device and method
ActiveCN114142943AIncrease speedEasy to integratePhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic receiversMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention provides a single-photon distance measurement tracking and aiming and few-photon communication integrated receiving device and method, and the device comprises a single-photon detector, a fine aiming mechanism, and a terminal which comprises a distance measurement module, a communication module, and a fine aiming control module. The distance measuring module is used for demodulating the transmitting time of the transmitting optical signal and extracting the arrival time of the echo optical signal, and calculating the distance between the target transmitting end and the receiving end; the communication module is used for extracting communication information carried by photons in the echo optical signals and communicating with a target transmitting end; the fine aiming control module is used for acquiring distribution position differences of photons falling on the single-photon detector, and the fine aiming control module is in communication connection with the fine aiming mechanism. According to the receiving device, fine aiming, passive distance measurement and communication of a moving target are realized through the same single-photon detector, integration and miniaturization are improved, and high-precision tracking aiming, distance measurement and high-speed communication in an extreme scene are facilitated.
Owner:PURPLE MOUNTAIN LAB +1
Calculation method of radiance by mixing kd-tree and voronoi diagram
ActiveCN105118085BAccurate Radiance CalculationAccurate Radiance Estimation3D-image renderingViewpointsRadiance
The invention relates to a radiance calculation method with the mixing of a Kd-tree with a Voronoi diagram. The method comprises the steps of (1) constructing a scene topology structure and a Kd-tree hierarchical organization, (2) storing generated a photon map with a polygon face as the unit, (3) carrying out traversal of each polygon of a three-dimensional scene surface, and collecting photos belonging to each polygon and forming a two-dimensional Kd-tree structure, (4) dividing each polygon surface construction Voronoi diagram and calculating the radiation flux density of a Voronoi unit, (5) calculating the intersection point x of a ray emitted from a viewpoint and a scene, (6) according to the polygon face to which the x belongs, collecting near photons by using the two-dimensional Kd-tree structure, (7) finding the precise area covered by the collected photos according to the Voronoi diagram division, and calculating the radiance of the x point. According to the method, the geometric features of local surface photon distribution can be utilized to carry out precise radiance kernel estimation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Holographic radar three-dimensional imaging method and device based on TCSPC
InactiveCN113406664ASolve the problem of weak environmental awarenessGuaranteed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splittingPhoton counter
The invention provides a TCSPC-based holographic radar three-dimensional imaging method and device; the method comprises the steps: transmitting laser to a detection scene, enabling one laser beam to irradiate the detection scene after beam expansion and beam splitting, and enabling the other laser beam to serve as reference light to irradiate a detector; reflecting the laser irradiated to the detection scene by the scene and then is received by the detector as object light, wherein the object light interferes with the reference light at the detector; counting the photon distribution condition after interference by using a time correlation photon counter to generate a holographic time photon counting histogram; sequentially slicing the holographic time photon counting histogram according to different time to obtain holograms at different distances; reappearing the holograms at different distances in sequence to obtain distance slice holographic three-dimensional reconstruction results of the detected object at different distances; and analyzing, displaying or superposing distance slice results under different distances according to specific requirements to obtain an overall holographic three-dimensional reconstruction result. According to the invention, high-precision information measurement is ensured, and the ability of the automatic driving technology to perceive the surrounding environment is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A method and device for determining a gating signal
ActiveCN106236123BLow costRadiation diagnostic device controlTomographyCompanion animalDiagnostic system
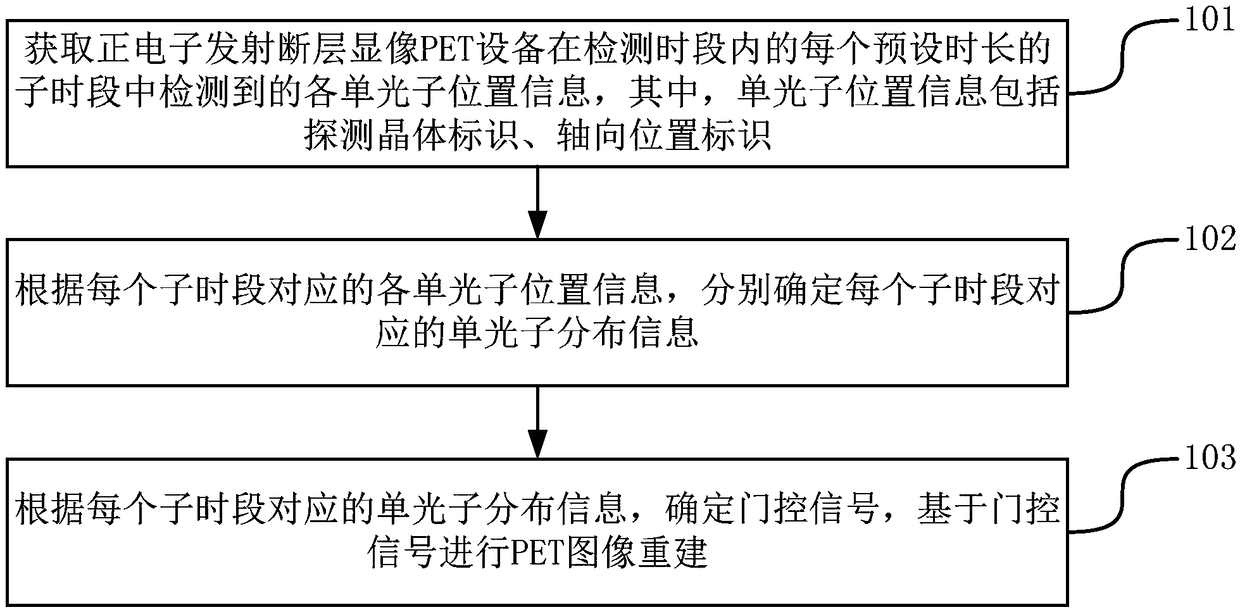
The invention belongs to the field of medicine and discloses a gating signal determination method and a gating signal determination device. The method includes: acquiring single photon position information detected in sub-periods of preset duration in a detection period by PET (positron emission tomography) equipment, wherein the single photon position information includes detection crystal identifiers and axial position identifiers; respectively determining single photon distribution information corresponding to each sub-period according to the single photon position information corresponding to each sub-period; determining gating signals according to the single photon distribution information corresponding to each sub-period, and performing PET image reconstruction on the basis of the gating signals. By adoption of the gating signal determination method and the gating signal determination device, diagnosis system cost can be reduced.
Owner:赛诺联合医疗科技(北京)有限公司
Method, device, medium and electronic equipment for determining material imaging weight
ActiveCN109801243BBig Imaging ContributionImprove image signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementAttenuation coefficientSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The embodiment of the invention provides an imaging method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. The imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring signals and noise of electromagnetic wavespenetrating through a target material in a preset energy interval; constructing a signal-to-noise ratio function of the target material based on the signal and the noise; and maximizing a signal to noise ratio function and determining the weight coefficient of the target material. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, after energy weighting, the contribution of the low-energy interval to imaging is greater, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is improved, and the x-ray equivalent attenuation coefficient in the energy region is calculated by utilizing the acquired photon distribution information and the attenuation curve characteristics of photons in different materials, so that the calculation is more accurate.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com