Scintillation event position determination in a radiation particle detector
一种辐射粒子、探测器的技术,应用在核成像系统,单光子发射计算机断层摄影扫描器领域,能够解决恶化闪烁事件定位等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
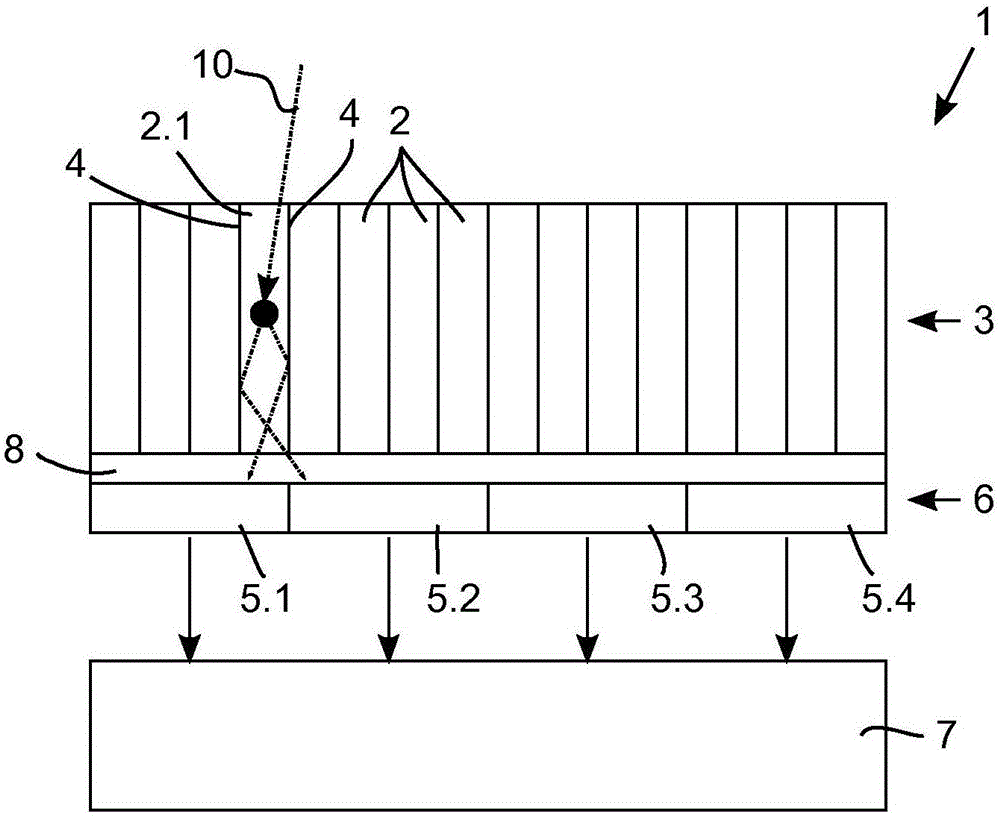
[0050] figure 1 A first embodiment of a radiation particle detector 1 for use in a nuclear imaging system (eg a high resolution PET scanner) is illustrated. The radiation particle detector 1 comprises a pixelated scintillator with a plurality of scintillator element locations, wherein the scintillator element locations are scintillator elements 2 . The material of the scintillator element 2 is chosen to provide a high stopping power of 511 keV gamma rays with a fast time delay of the scintillation burst. Some suitable scintillator materials are lutetium silicate (LSO), lutetium yttrium silicate (LYSO), and lanthanum bromide (LaBr). It should be appreciated that scintillator elements 2 made of other materials could be used instead. The structure of the scintillator material can be, for example, crystalline, polycrystalline or ceramic. The scintillator elements 2 are arranged in a scintillator layer 3 . In order to avoid light sharing between scintillator elements 2 , a refl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com